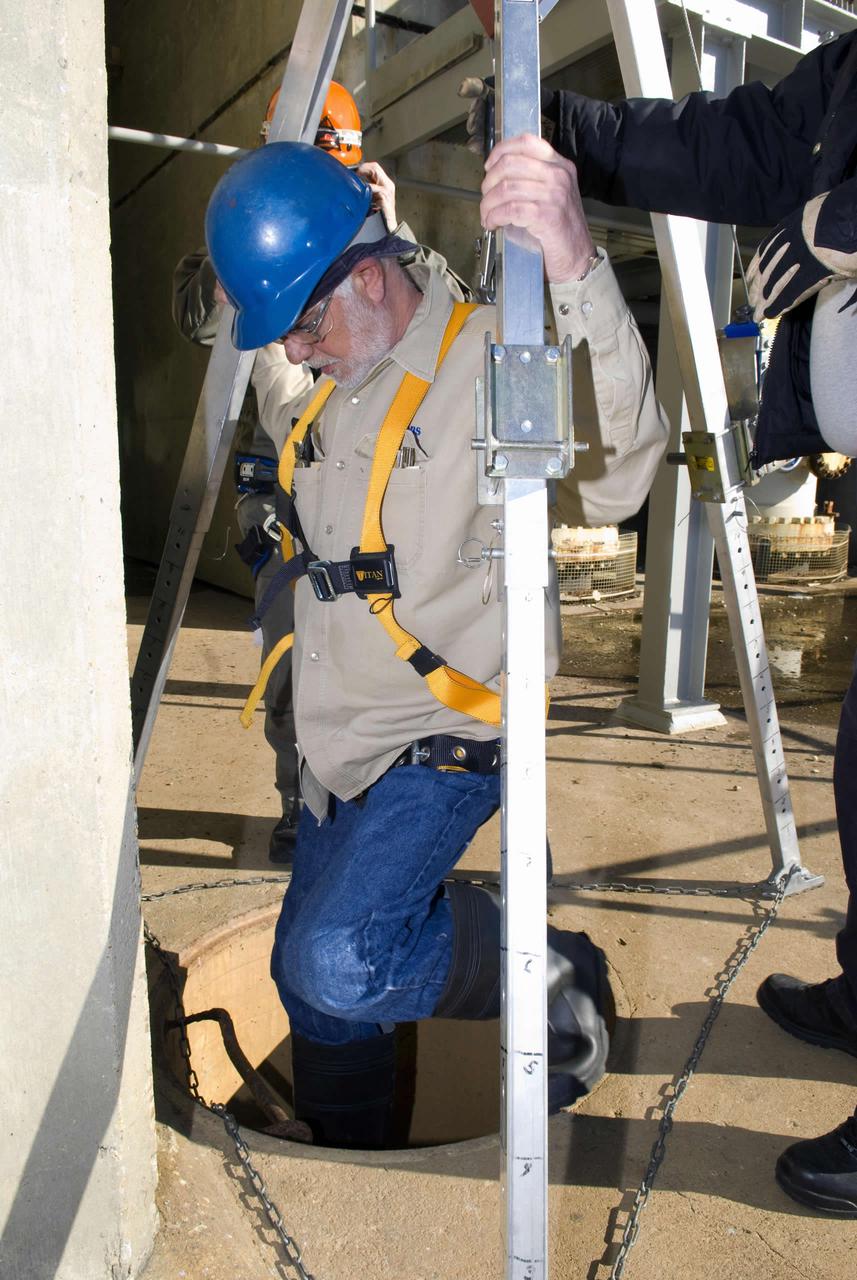

Robert Hayward of Jacobs FOSC descends beneath the B-1 Test Stand to perform maintenance.
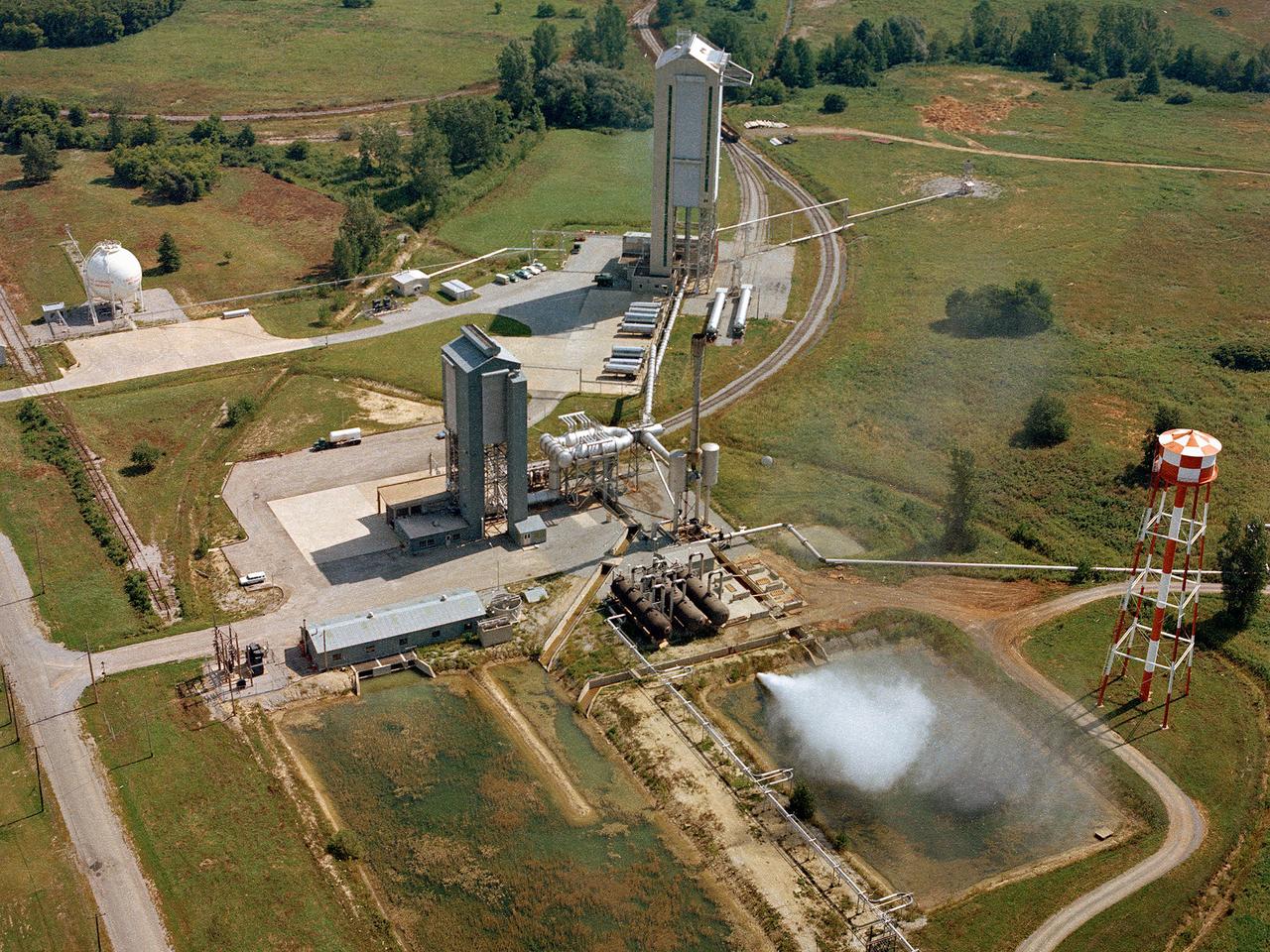

Operation of the High Energy Rocket Engine Research Facility (B-1), left, and Nuclear Rocket Dynamics and Control Facility (B-3) at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio. The test stands were constructed in the early 1960s to test full-scale liquid hydrogen fuel systems in simulated altitude conditions. Over the next decade each stand was used for two major series of liquid hydrogen rocket tests: the Nuclear Engine for Rocket Vehicle Application (NERVA) and the Centaur second-stage rocket program. The different components of these rocket engines could be studied under flight conditions and adjusted without having to fire the engine. Once the preliminary studies were complete, the entire engine could be fired in larger facilities. The test stands were vertical towers with cryogenic fuel and steam ejector systems. B-1 was 135 feet tall, and B-3 was 210 feet tall. Each test stand had several levels, a test section, and ground floor shop areas. The test stands relied on an array of support buildings to conduct their tests, including a control building, steam exhaust system, and fuel storage and pumping facilities. A large steam-powered altitude exhaust system reduced the pressure at the exhaust nozzle exit of each test stand. This allowed B-1 and B-3 to test turbopump performance in conditions that matched the altitudes of space.
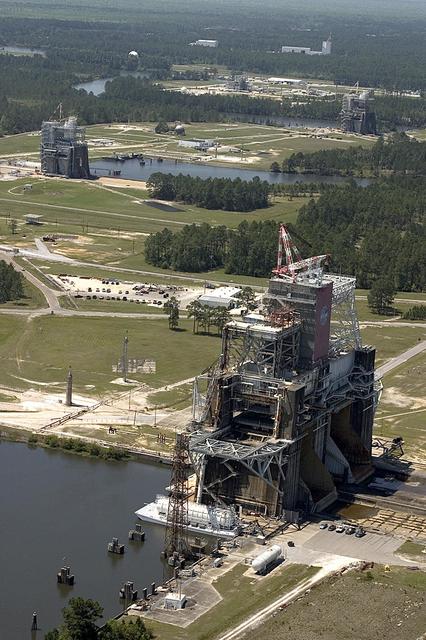

An aerial photo shows the B-1/B-2 Test Stand (foreground), A-2 Test Stand (middle) and A-1 Test Stand (back). The historic stands have been used to test engines used on every manned Apollo and space shuttle mission.
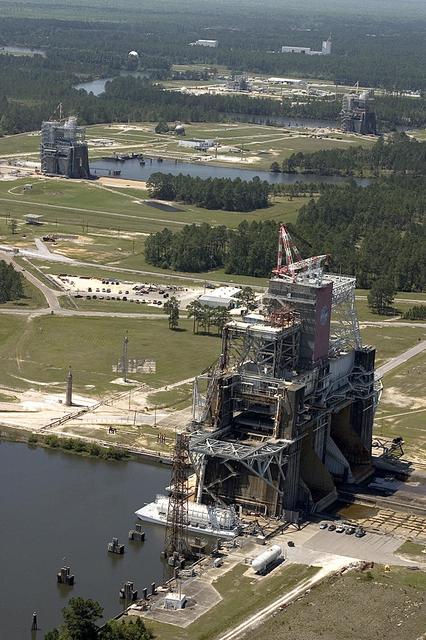

An aerial photo shows the B-1/B-2 Test Stand (foreground), A-2 Test Stand (middle) and A-1 Test Stand (back). The historic stands have been used to test engines used on every manned Apollo and space shuttle mission.

NASA engineers tested an Aerojet AJ26 rocket engine on the E-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on June 25, 2012, against the backdrop of the B-1/B-2 Test Stand. The engine will be used by Orbital Sciences Corporation to power commercial cargo flights to the International Space Station.
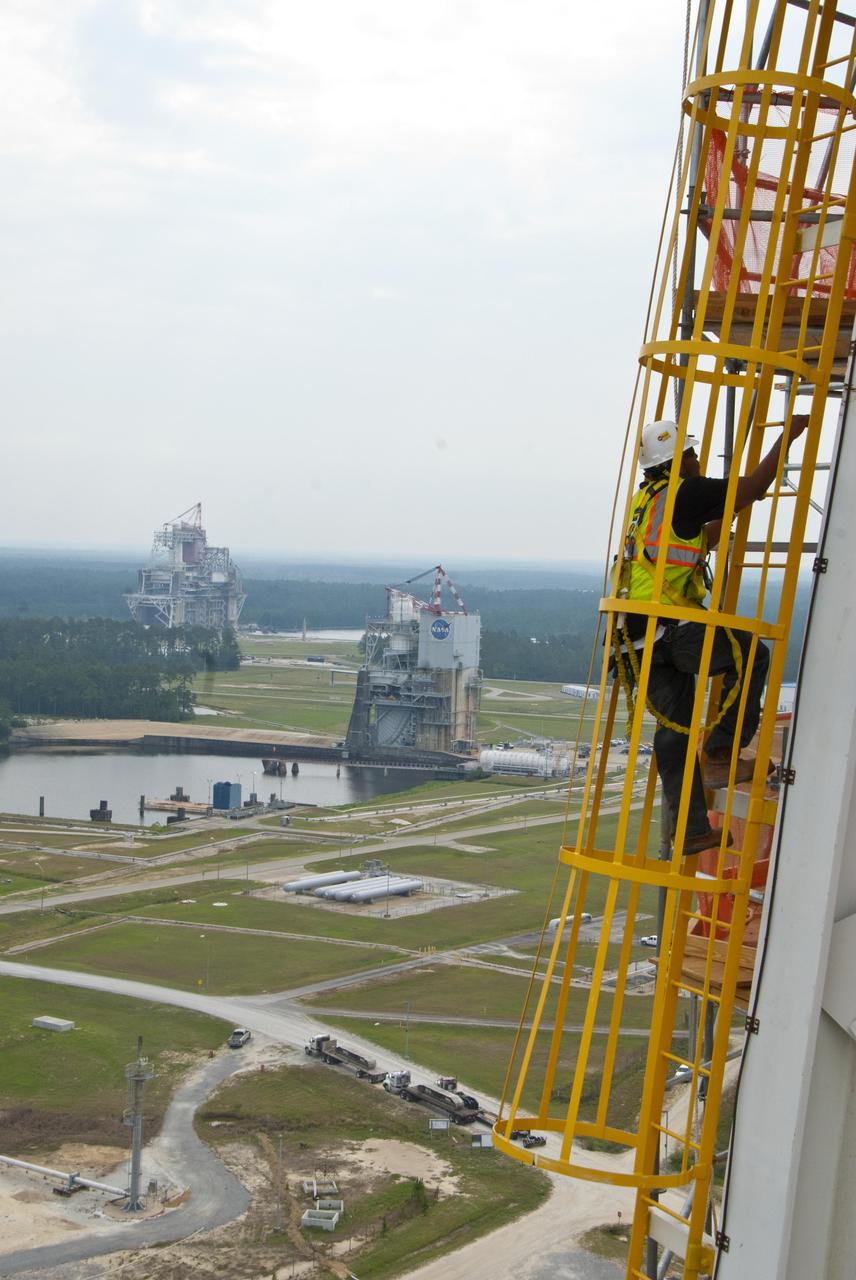

A tethered Stennis Space Center employee climbs an A-3 Test Stand ladder June 8, 2012, against the backdrop of the A-2 and B-1/B-2 stands. The new A-3 Test Stand will enable simulated high-altitude testing of next-generation rocket engines.
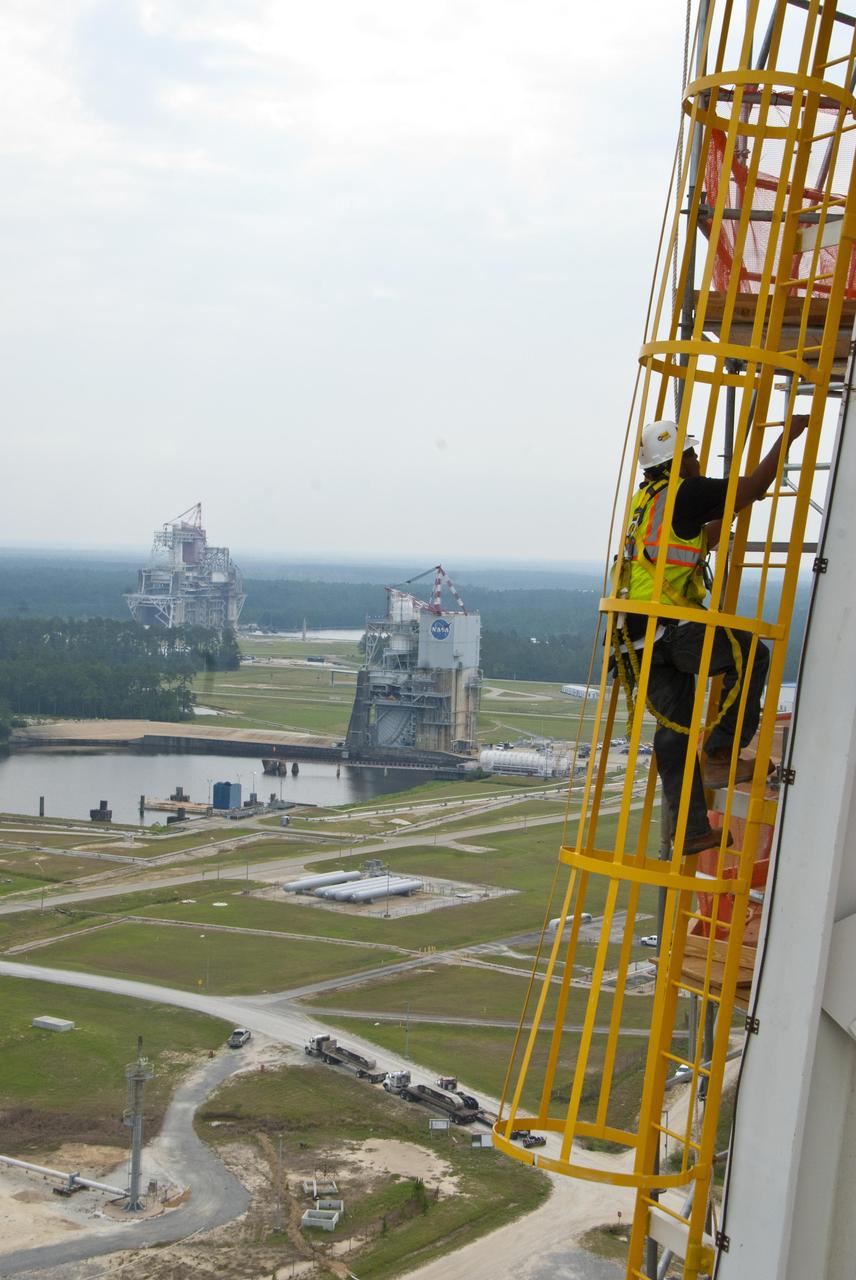

A tethered Stennis Space Center employee climbs an A-3 Test Stand ladded June 8, 2012, against the backdrop of the A-2 and B-1/B-2 stands. The new A-3 Test Stand will enable simulated high-altitude testing of next-generation rocket engines.
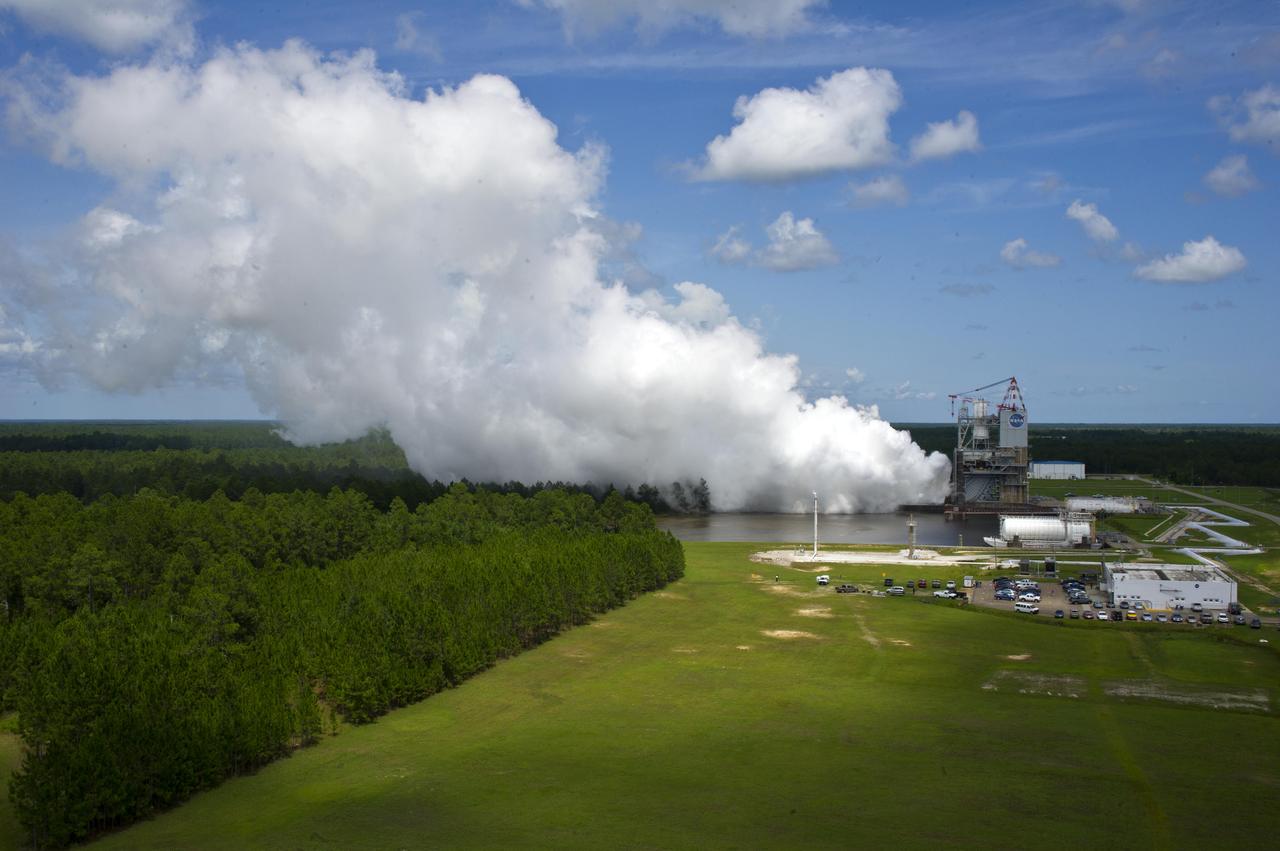

NASA's test of the J-2X rocket engine on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on July 13 was picture perfect in more ways than one. Not only did the test provide a breathtaking view from atop the nearby A-1 Test Stand, and with the center's B-1/B-2 Test Stand in the background, but it achieved its target of 550 seconds. The test continued a series of firings to gather critical data for engine development.
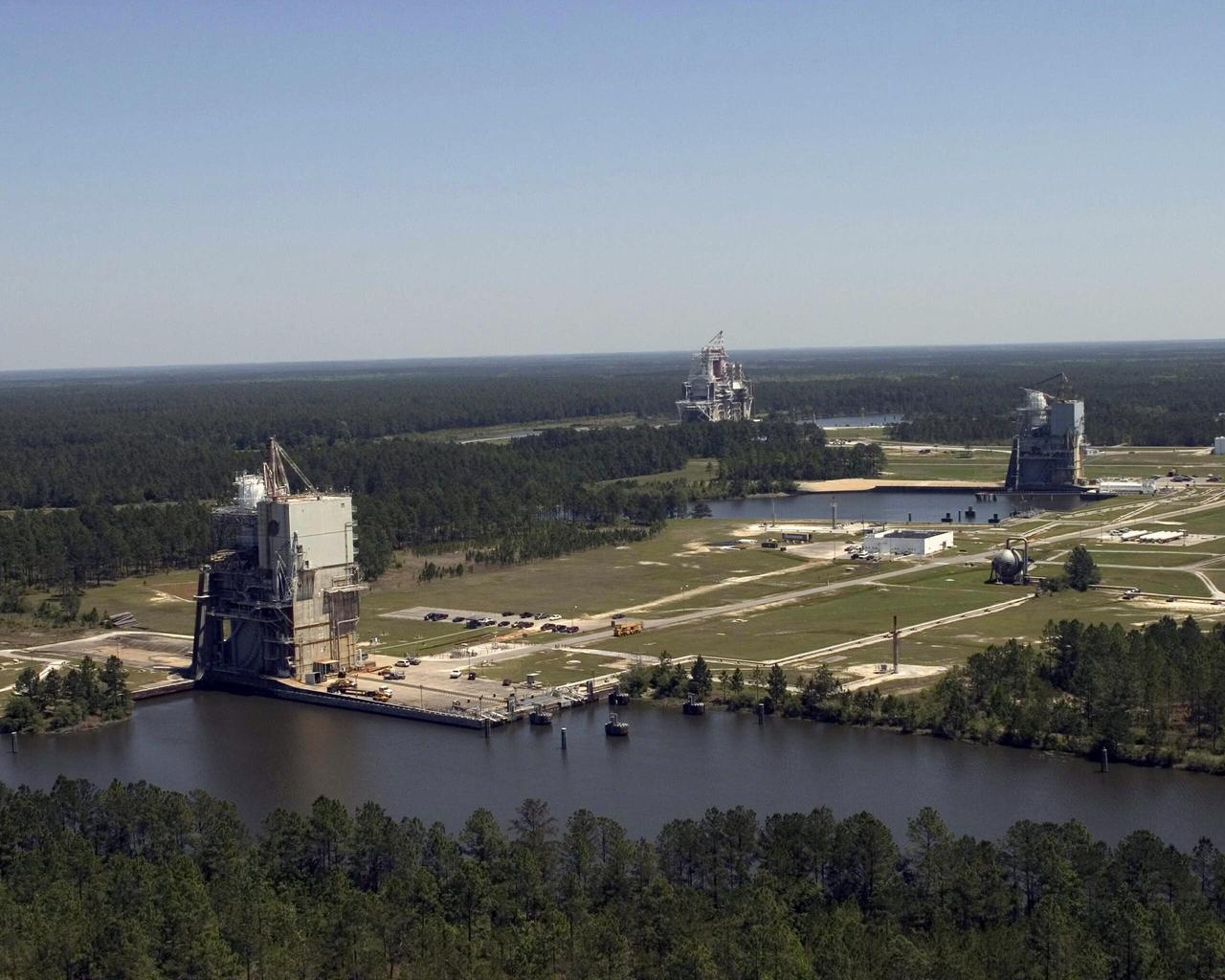

SSC's A-1, A-2 and B test stands were built in the early 1960s to test the first and second stages of the Apollo Saturn V rocket that safely transported Americans to the moon. The A-1 Stand (foreground) will soon test the J-2X engines that will power the rockets to take Americans back to the moon.
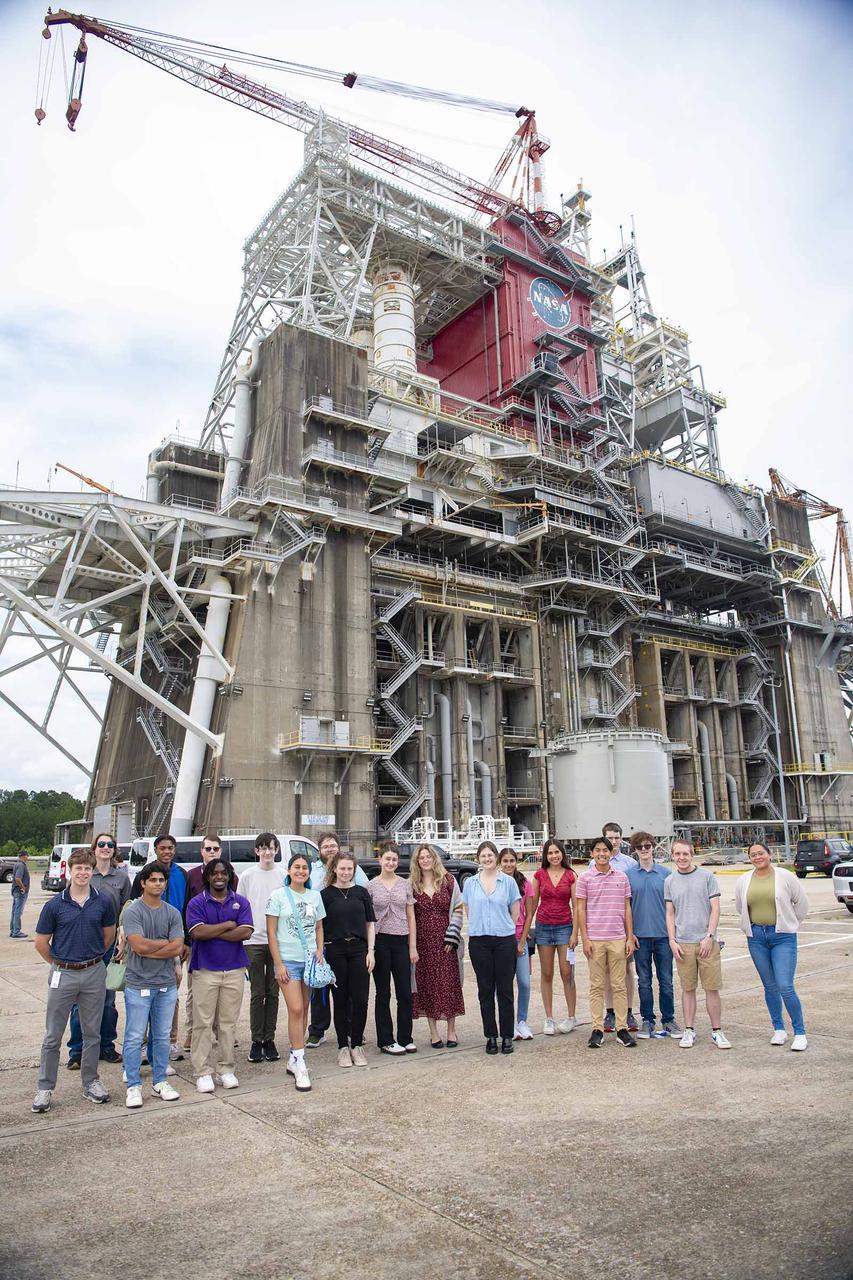

Summer interns with the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory stand in front of the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) on July 10. NASA Stennis crews are preparing the B-2 side of the stand for future testing of NASA’s exploration upper stage. The more powerful second stage is expected to fly on NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis IV. The Naval Research Laboratory interns visited the stand during an afternoon tour of NASA Stennis. The Naval Research Laboratory is a tenant of the NASA Stennis federal city, where it provides advanced scientific capabilities required to bolster the nation’s position of global naval leadership.
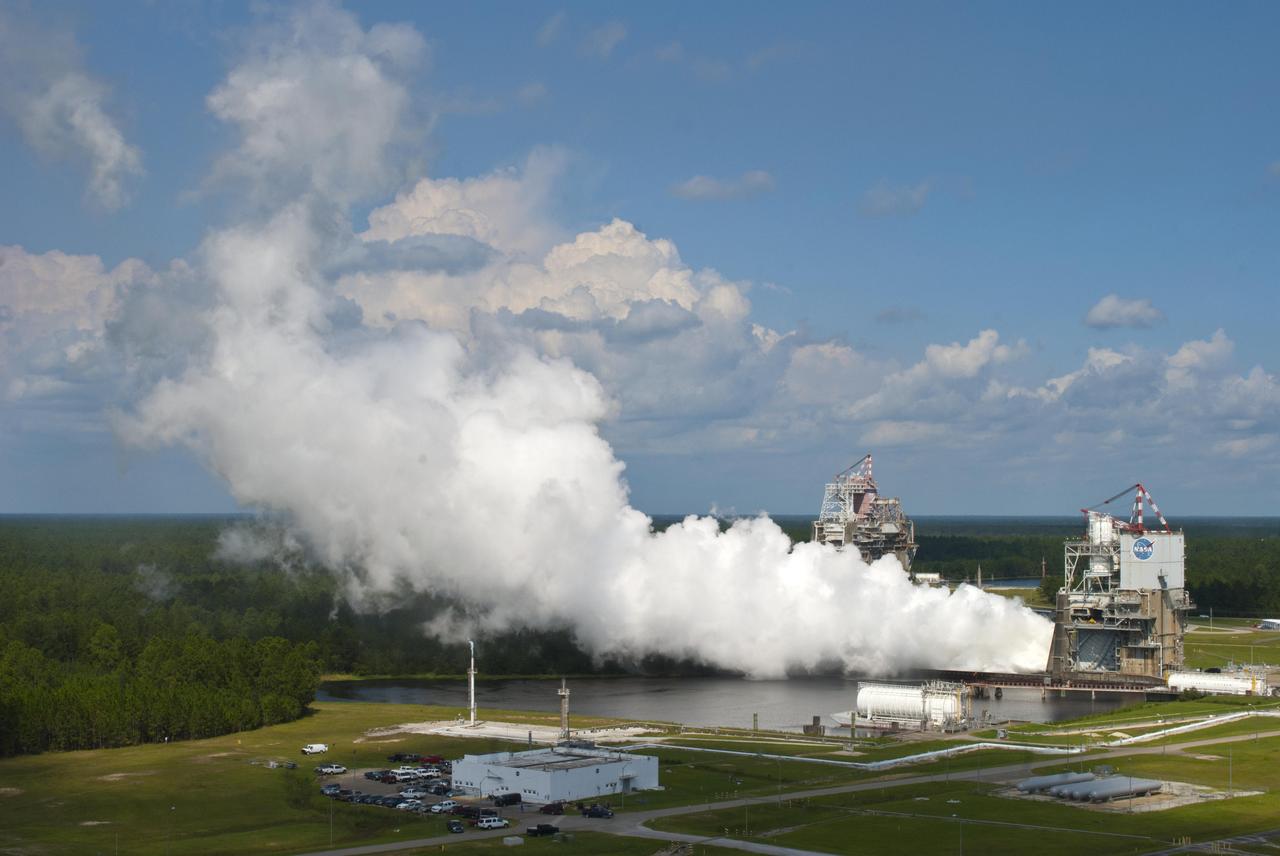

NASA engineers continued testing the next-generation J-2X rocket engine at Stennis Space Center with a 250-second test on Sept. 7. The test was the first conducted after the arrival of Hurricane Isaac forced closure of the Stennis facility for three days in late August. The est was conducted on the A-2 Test Stand at Stennis. The facility's B-1/B-2 Test Stand can be seen in the left background.
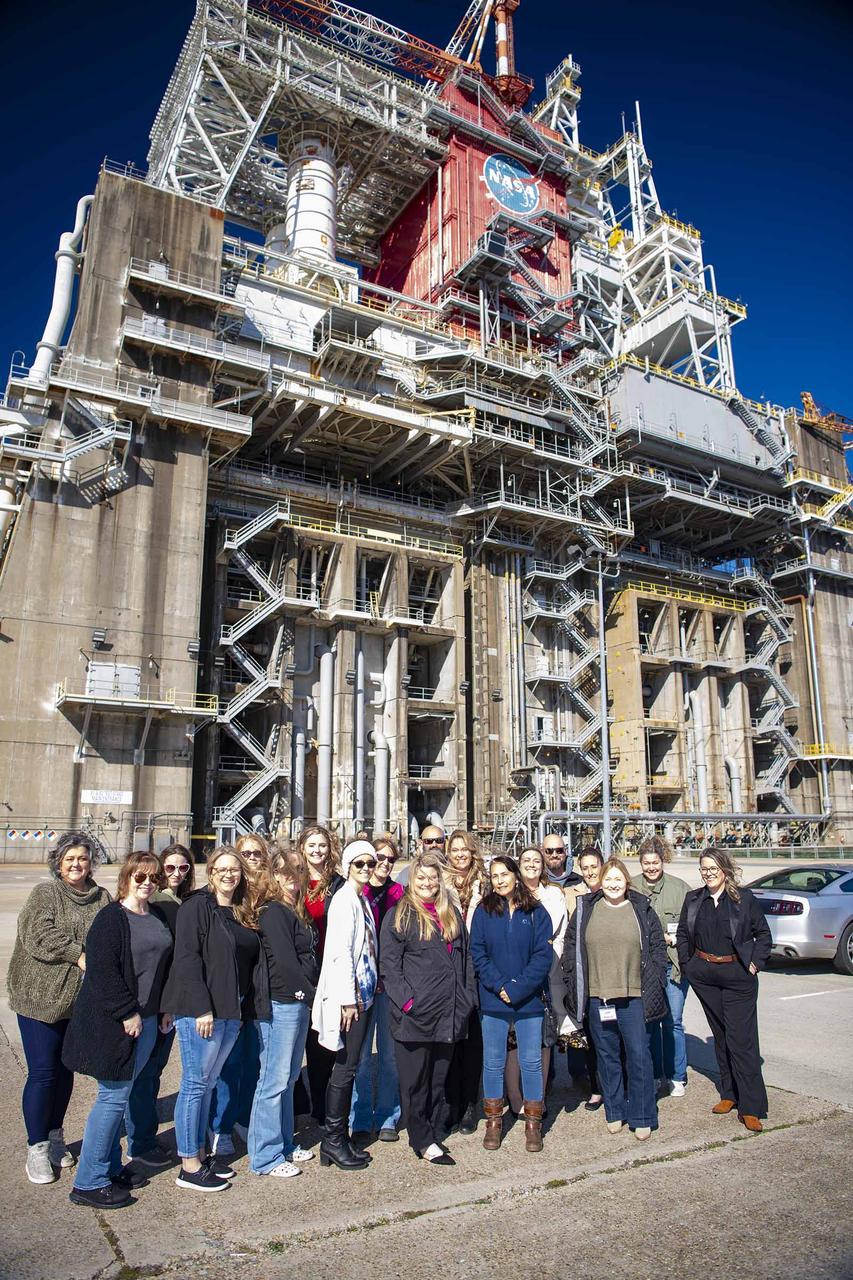

The Pearl River County Leadership Class visits the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) during a NASA Stennis tour on Feb. 20. NASA Stennis is at the front end of the critical path for the future of human deep space exploration through NASA’s Artemis campaign. The B-2 side of the Thad Cochran Test Stand is undergoing preparations for exploration upper stage testing. The upper stage is scheduled to undergo Green Run tests of its integrated systems before its first flight on the Artemis IV mission. The test series will culminate with a hot fire of the stage’s four RL10 engines, just as during an actual mission.
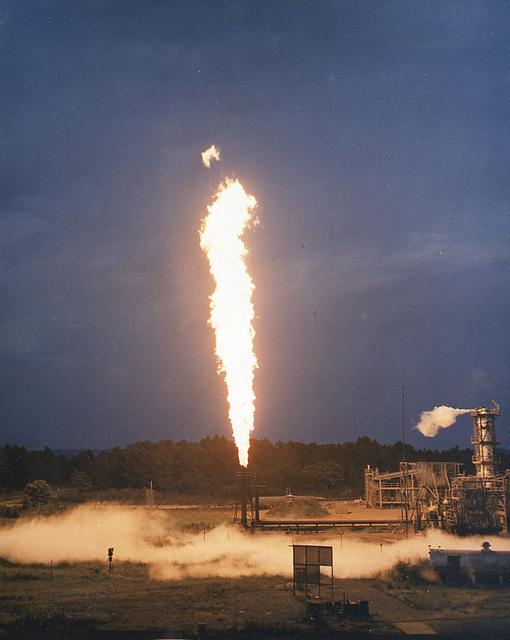

Marshall Space Flight Center's rocket development has always included component testing. Pictured here is a Cell 114-B burn stack. The C114-B is part of the gas generators used to test heat exchanges for the F-1 engine. On the initial firing of the C114-B the spark ignition would not light. The rocket propellant mixed with the liquid oxygen gelled creating a bomb. After several attempts at ignition, the spark ignited and blew up the stand. Subsequent testings were completed on newly constructed stands and no further mishaps were reported.
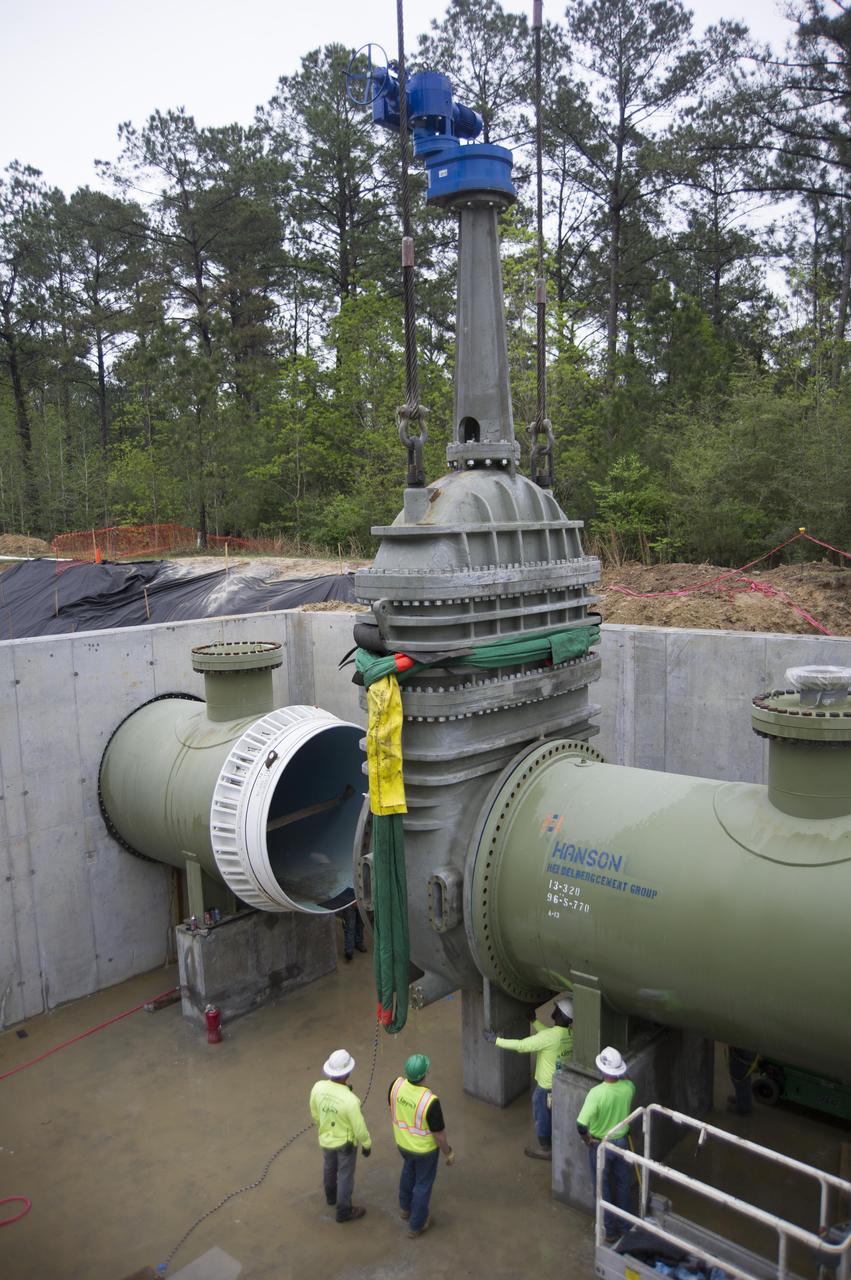

Stennis Space Center employees install a 96-inch valve during a recent upgrade of the high-pressure industrial water system that serves the site’s large rocket engine test stands. The upgraded system has a capacity to flow 335,000 gallons of water a minute, which is a critical element for testing. At Stennis, engines are anchored in place on large test stands and fired just as they are during an actual space flight. The fire and exhaust from the test is redirected out of the stand by a large flame trench. A water deluge system directs thousands of gallons of water needed to cool the exhaust. Water also must be available for fire suppression in the event of a mishap. The new system supports RS-25 engine testing on the A-1 Test Stand, as well as testing of the core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis.

Members of the Southeast U.S. Federal Laboratory Consortium for Technology Transfer gather at the base of the B-1/B-2 Test Stand during a Feb. 10 visit to John C. Stennis Space Center. The group visited Stennis to tour facilities and receive briefings on work at the rocket engine test site. They also visited the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center site and received a briefing on construction of the new science center. The FLC is a nationwide network of federal laboratories to facilitate technology transfers between federal agencies and commercial companies.
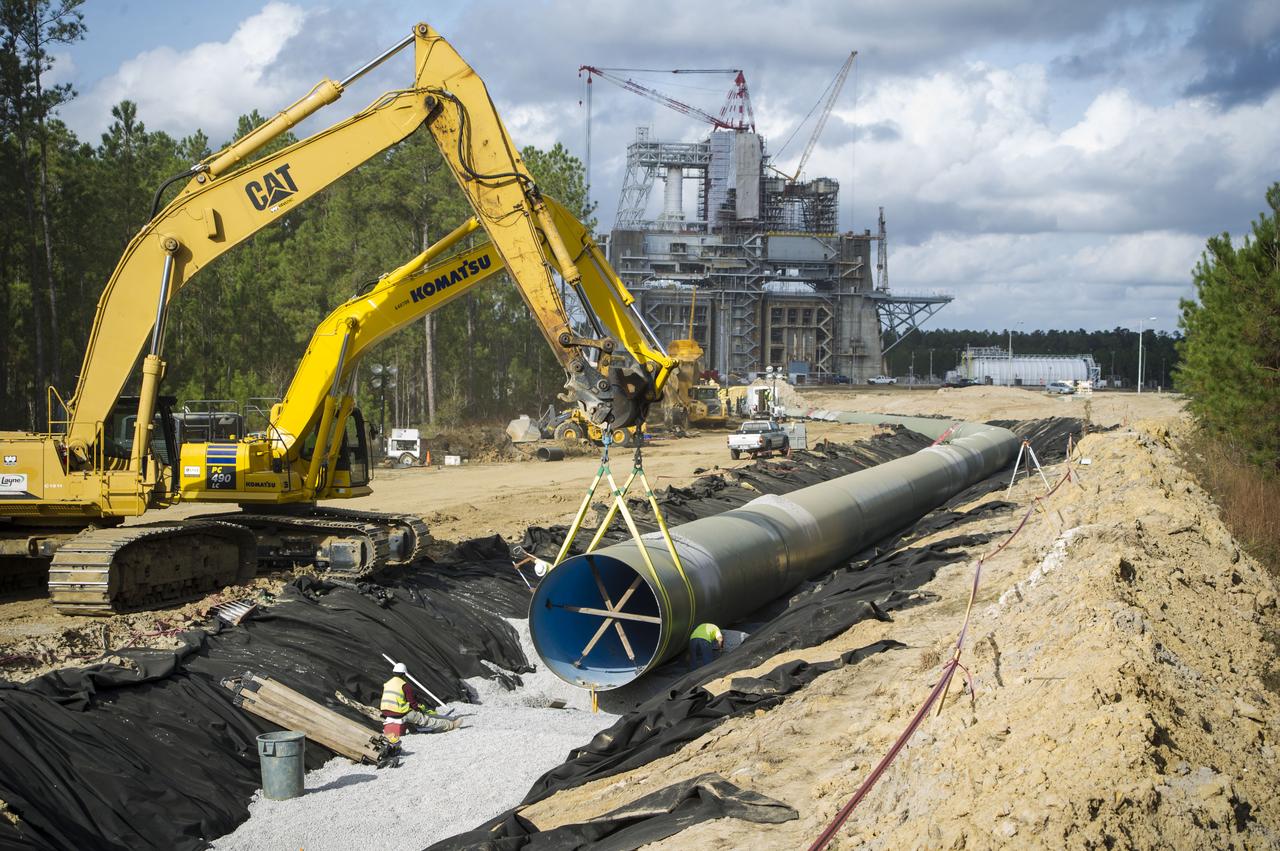

Water piping is installed near the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) at NASA’s Stennis Space Center in December 2014. The project to replace and upgrade the center’s high pressure industrial water system was a key milestone in preparations to test the SLS (Space Launch System) core stage ahead of the successful Artemis I launch.
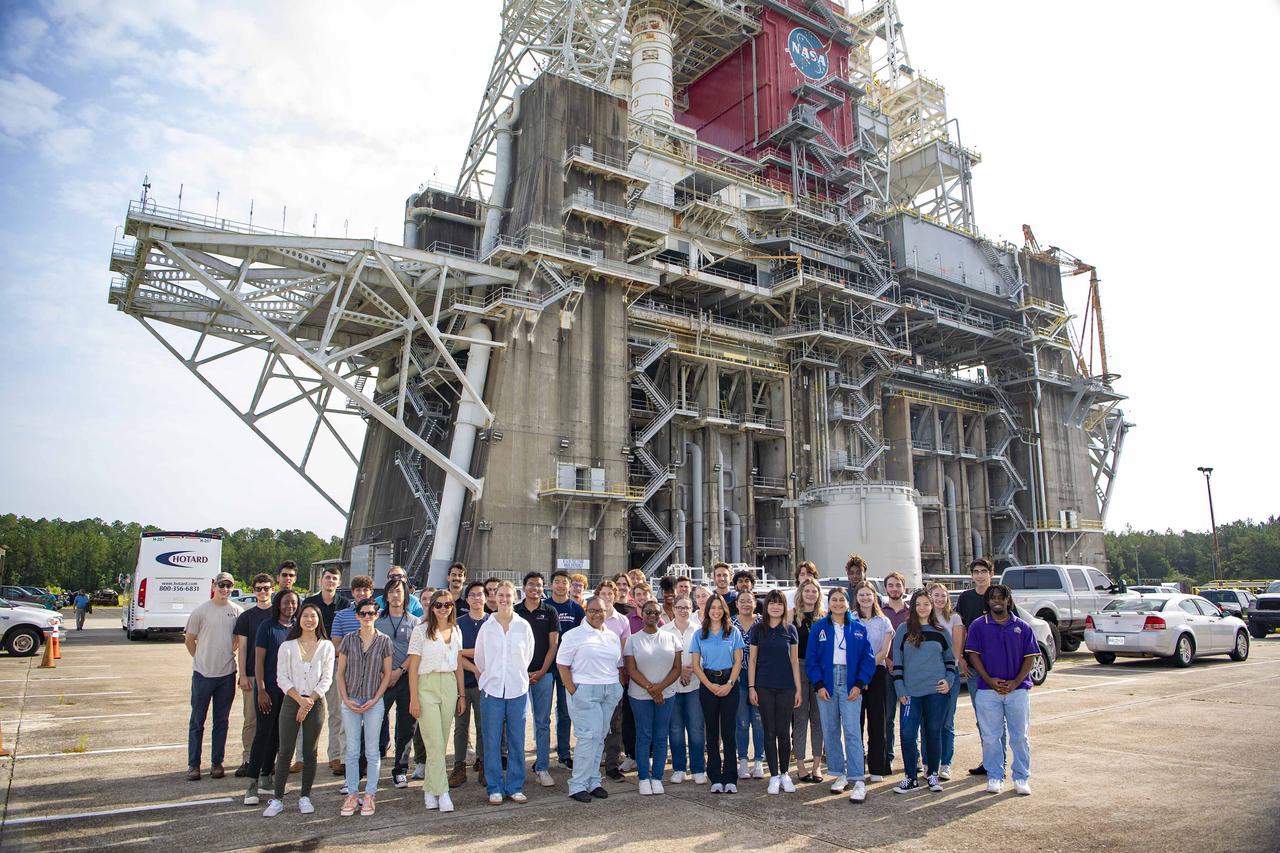

Interns at NASA Stennis visit the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) on July 25 during a test complex tour on National Intern Day. As NASA continues to progress with the Artemis campaign, students across the nation are invited to join the journey. NASA’s internships aim to inspire the Artemis Generation to pursue STEM careers across the nation.
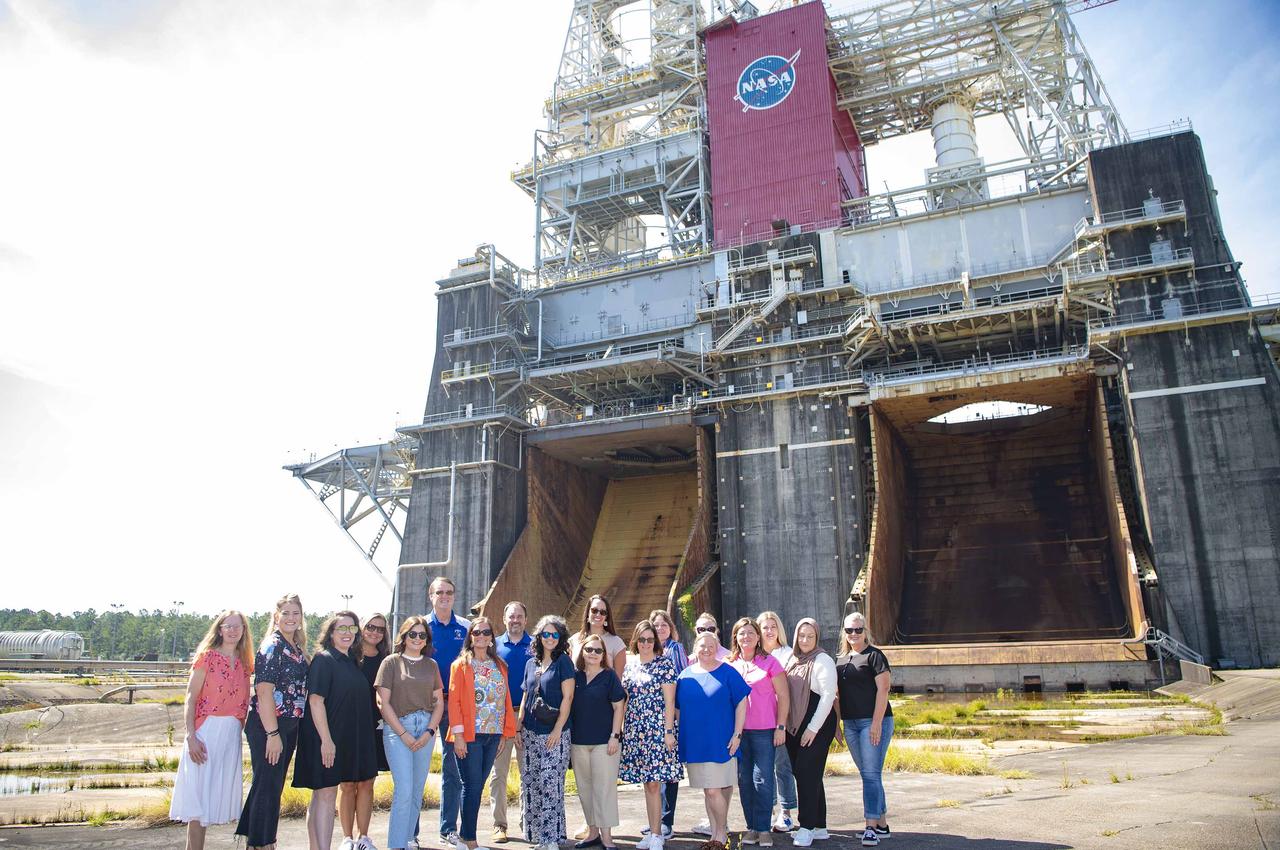

Pearl River County Elementary School leaders visit the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) during a NASA Stennis tour on July 15. The school leaders received an overview of work conducted at NASA Stennis, including how the south Mississippi site is contributing to NASA’s return to the Moon through the Artemis campaign by testing engines and stages to help power the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket.

Representatives of NASA’s Space Flight Awareness Program are shown at the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) on Sept. 25. The Space Flight Awareness program manager and working group had its annual meeting this year at NASA’s Stennis Space Center to review plans for 2025. NASA’s Space Flight Awareness Program recognizes outstanding job performances and contributions by civil servants and contract employees and focuses on excellence in quality and safety in support of human space flight.
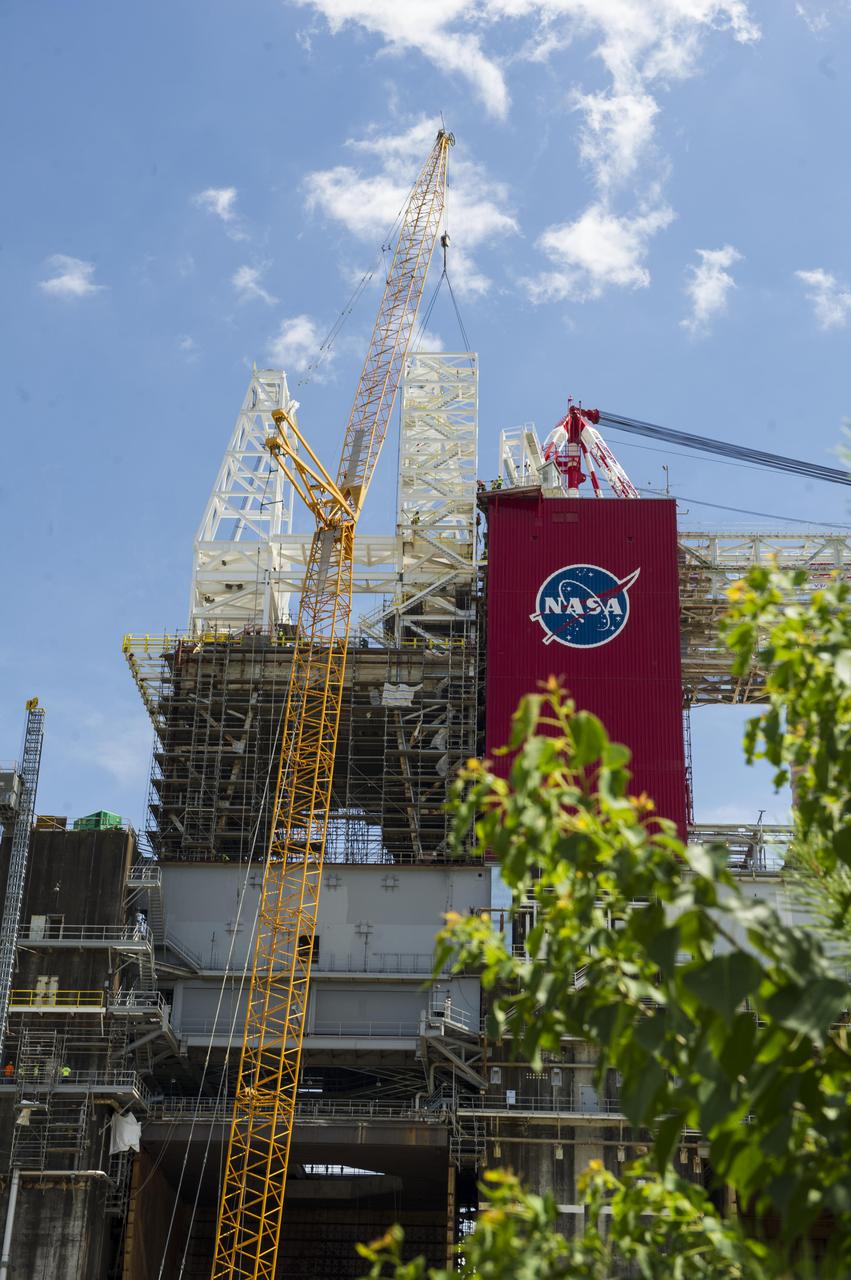

A structural steel section is lifted into place atop the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center as part of modification work to prepare for testing the core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System. The section is part of the Main Propulsion Test Article (MPTA) framework, which will support the SLS core stage for testing. The existing framework was installed on the stand in the late 1970s to test the shuttle MPTA. However, that framework had to be repositioned and modified to accommodate the larger SLS stage. About 1 million pounds of structural steel has been added, extending the framework about 100 feet higher and providing a new look to the Stennis skyline. Stennis will test the actual flight core stage for the first uncrewed SLS mission, Exploration Mission-1.
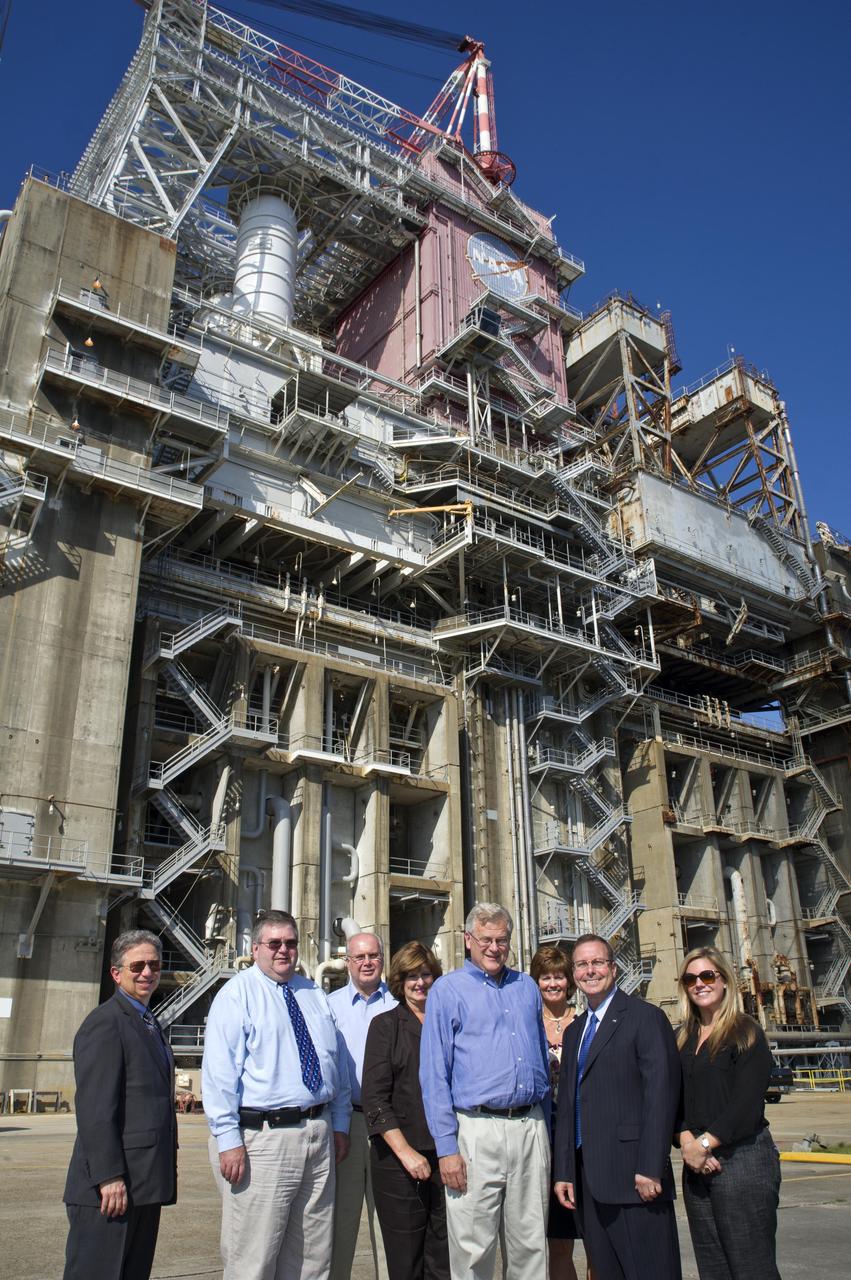

U.S. Rep. Alan Nunnelee, R-Miss., visited Stennis Space Center on Oct. 5, meeting with leaders and touring facilities to learn about ongoing work at the south Mississippi site. Joining Nunnelee during a stop at the B-1/B-2 Test Stand were: (l to r) Ken Human, Stennis associate director; Randy Galloway, director of the Stennis Engineering and Test Directorate; Ted Maness, chief of staff for Nunnelee; Nunnelee's wife, Toni; Nunnelee; Myron Webb, Stennis legislative affairs officer; Gilbrech; and Meyer Seligman, legislative director for Nunnelee. A Tupelo native, Nunnelee serves Mississipi's 1st Congressional District.
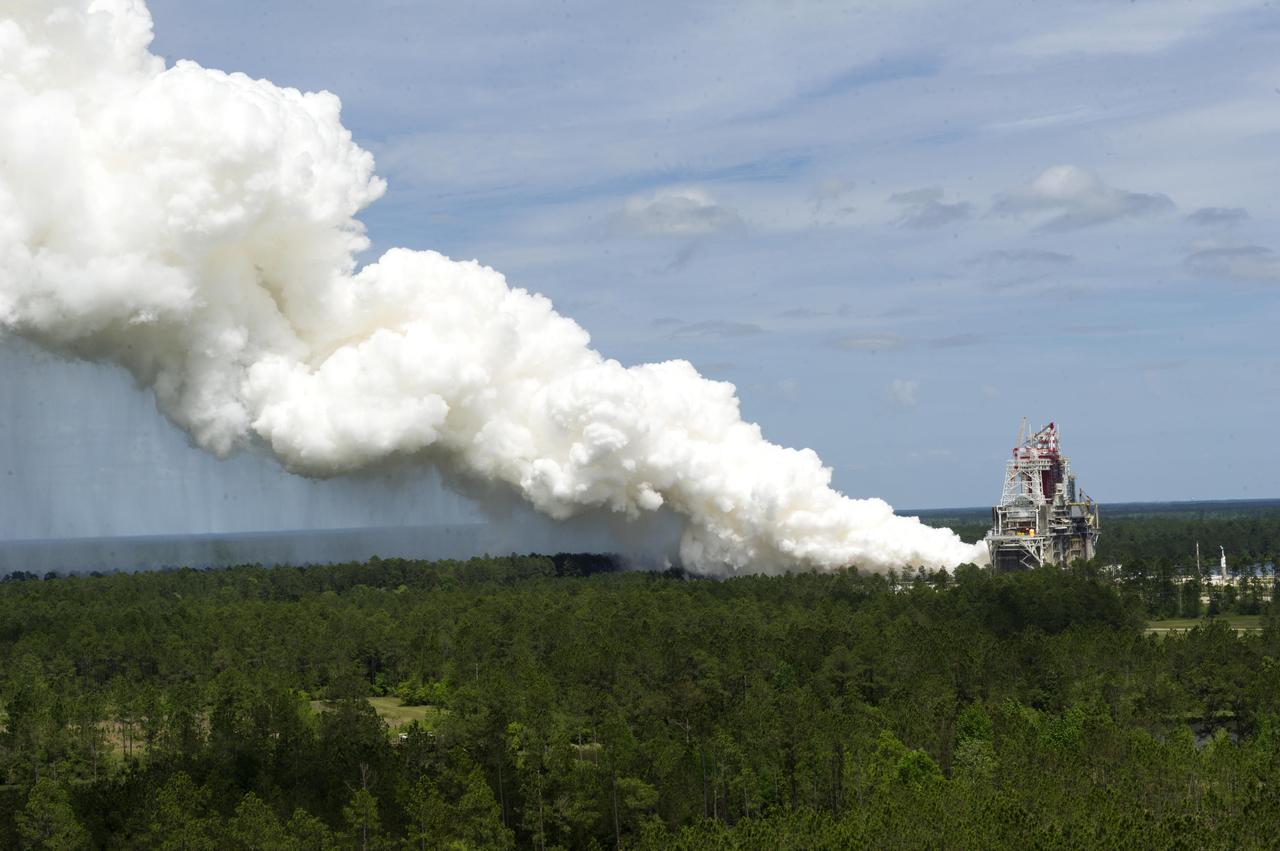

What better way to mark 50 years of rocket engine testing than with a rocket engine test? Stennis Space Center employees enjoyed a chance to view an RS-68 engine test at the B-1 Test Stand on April 19, almost 50 years to the day that the first test was conducted at the south Mississippi site in 1966. The test viewing was part of a weeklong celebration of the 50th year of rocket engine testing at Stennis. The first test at the site occurred April 23, 1966, with a 15-second firing of a Saturn V second stage prototype (S-II-C) on the A-2 Test Stand. The center subsequently tested Apollo rocket stages that carried humans to the moon and every main engine used to power 135 space shuttle missions. It currently tests engines for NASA’s new Space Launch System vehicle.
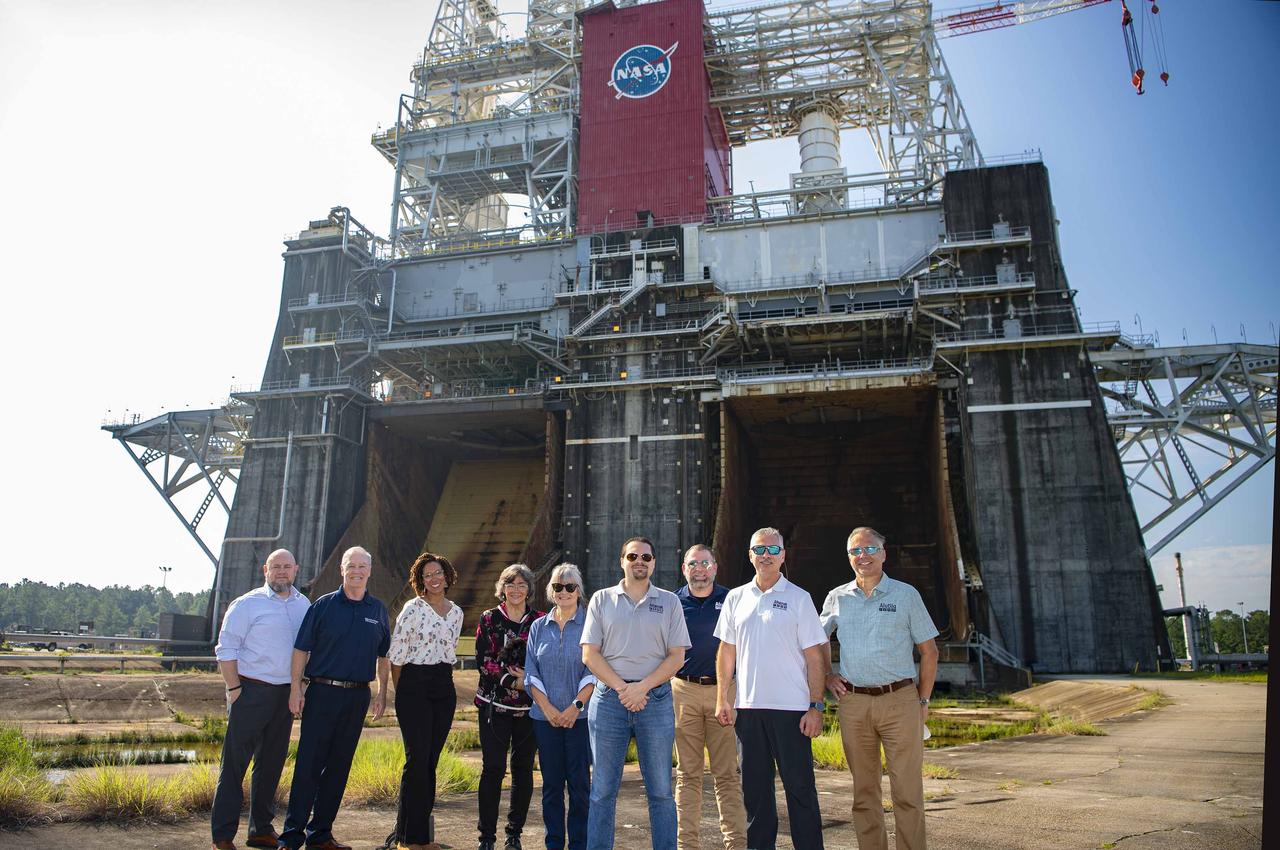

Afognak Native Corporation Board of Director members and Alutiiq, LLC executives stand at the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) during a visit to NASA’s Stennis Space Center on Sept. 19. The board members and executives visited the site to learn about laboratory services provided by Alutiiq Essential Services at NASA Stennis since 2020. Afognak is an Alaskan corporation focused on serving the needs of its native Alaskan people. Alutiiq, LLC operates as a subsidiary of the corporation to provide a variety of services to federal entities. Alutiiq Essential Services operates as a subsidiary of Alutiiq, LLC. Shown at the test stand during the Sept. 19 visit are, left to right: Ian Neumann, Alutiiq executive; John Monaccio, Alutiiq Essential Services president; Autumn Sellers, Alutiiq executive; Loretta Nelson, director; Marci Orth, director; Wade Hall, director; Shane Mendel, Alutiiq Essential Services program manager at NASA Stennis; Erik Olsen, director; Alan Hines, Alutiiq Essential Services executive.
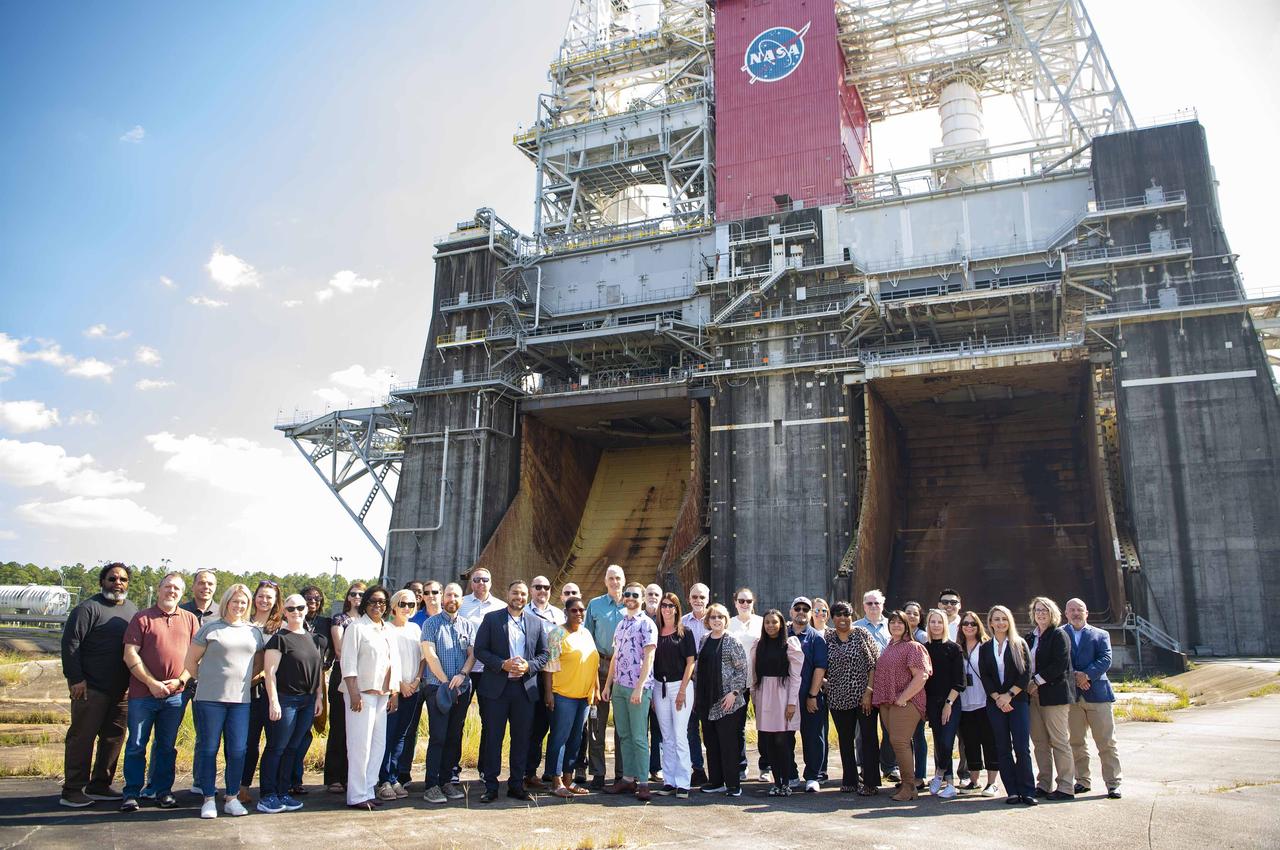

The NASA Office of the Chief Information Officer Integrated Design and Assurance Systems team are shown at the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) during a tour of NASA Stennis on Oct. 9. To accomplish NASA’s vision, the agency depends heavily on many things and information technology is key among them. Information technology capabilities enable NASA’s discoveries, allow sharing of mission data, improve workforce productivity, and increase mission quality, resilience, and cost-effectiveness. To enable success for NASA’s mission portfolio, the Office of the Chief Information Officer goals are to deliver great customer experiences; achieve consistent operational excellence; transform NASA through information and technology; and ensure proactive, resilient cybersecurity – all delivered by an exceptional team.
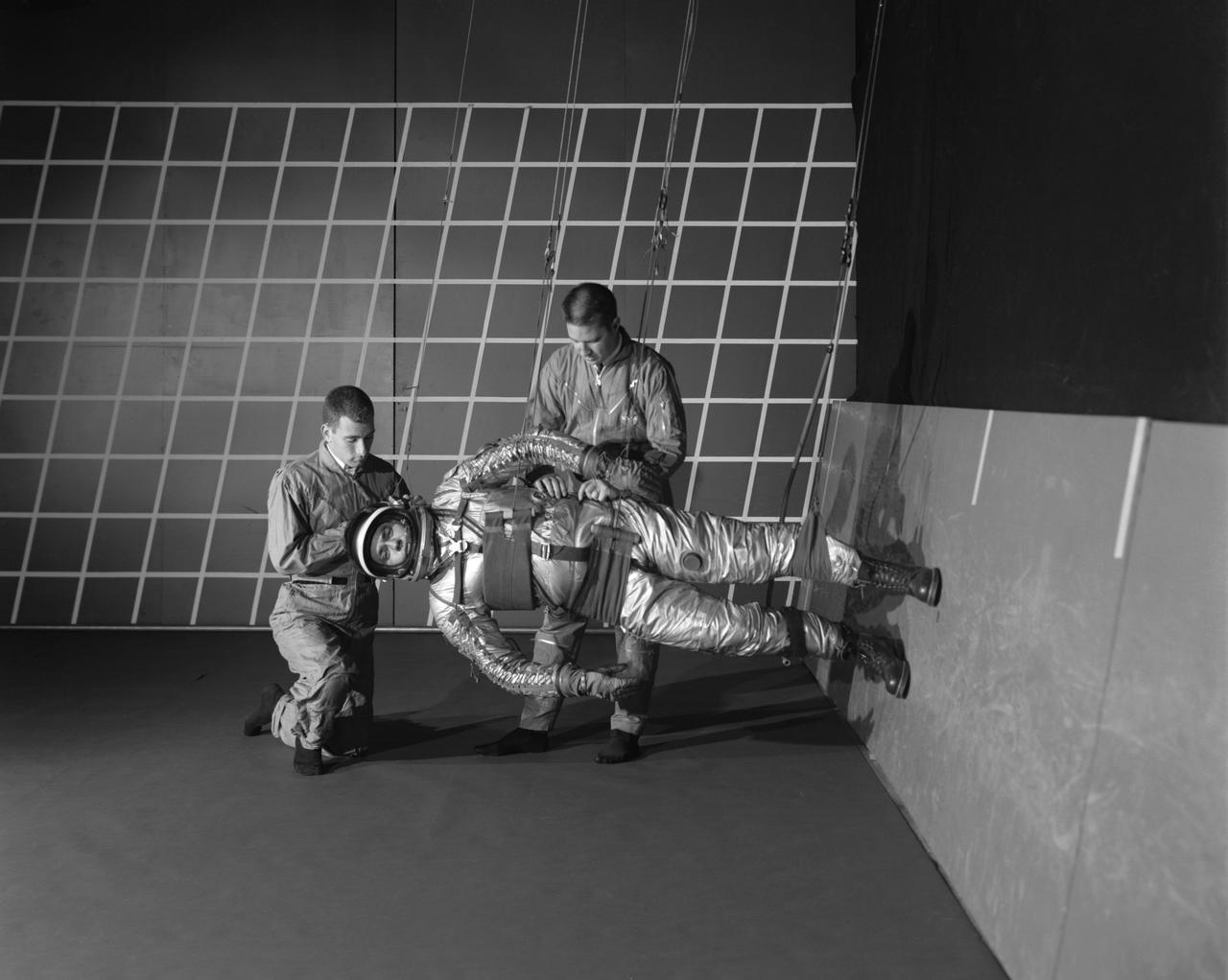

A test subject being suited up for studies on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located in the hangar at Langley Research Center. The initial version of this simulator was located inside the hangar. Later a larger version would be located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. Francis B. Smith wrote in his paper "Simulators For Manned Space Research," "I would like to conclude this talk with a discussion of a device for simulating lunar gravity which is very effective and yet which is so simple that its cost is in the order of a few thousand dollars at most, rather than hundreds of thousands. With a little ingenuity, one could almost build this type simulator in his backyard for children to play on. The principle is ...if a test subject is suspended in a sling so that his body axis makes an angle of 9 1/2 degrees with the horizontal and if he then "stands" on a platform perpendicular to his body axis, the component of the earth's gravity forcing him toward the platform is one times the sine of 9 1/2 degrees or approximately 1/6 of the earth's normal gravity field. That is, a 180 pound astronaut "standing" on the platform would exert a force of only 30 pounds - the same as if he were standing upright on the lunar surface." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308; Francis B. Smith, "Simulators For Manned Space Research," Paper for 1966 IEEE International Convention, New York, NY, March 21-25, 1966
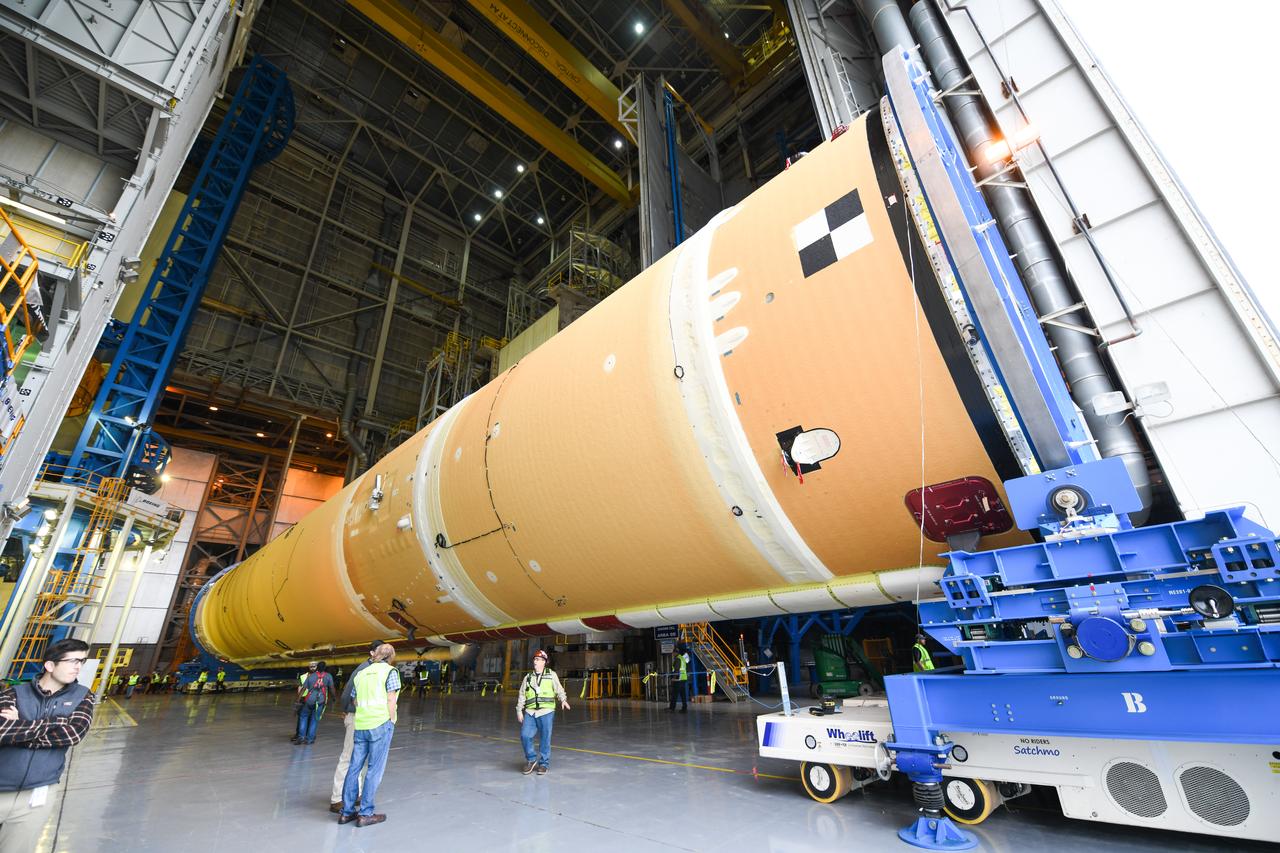

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
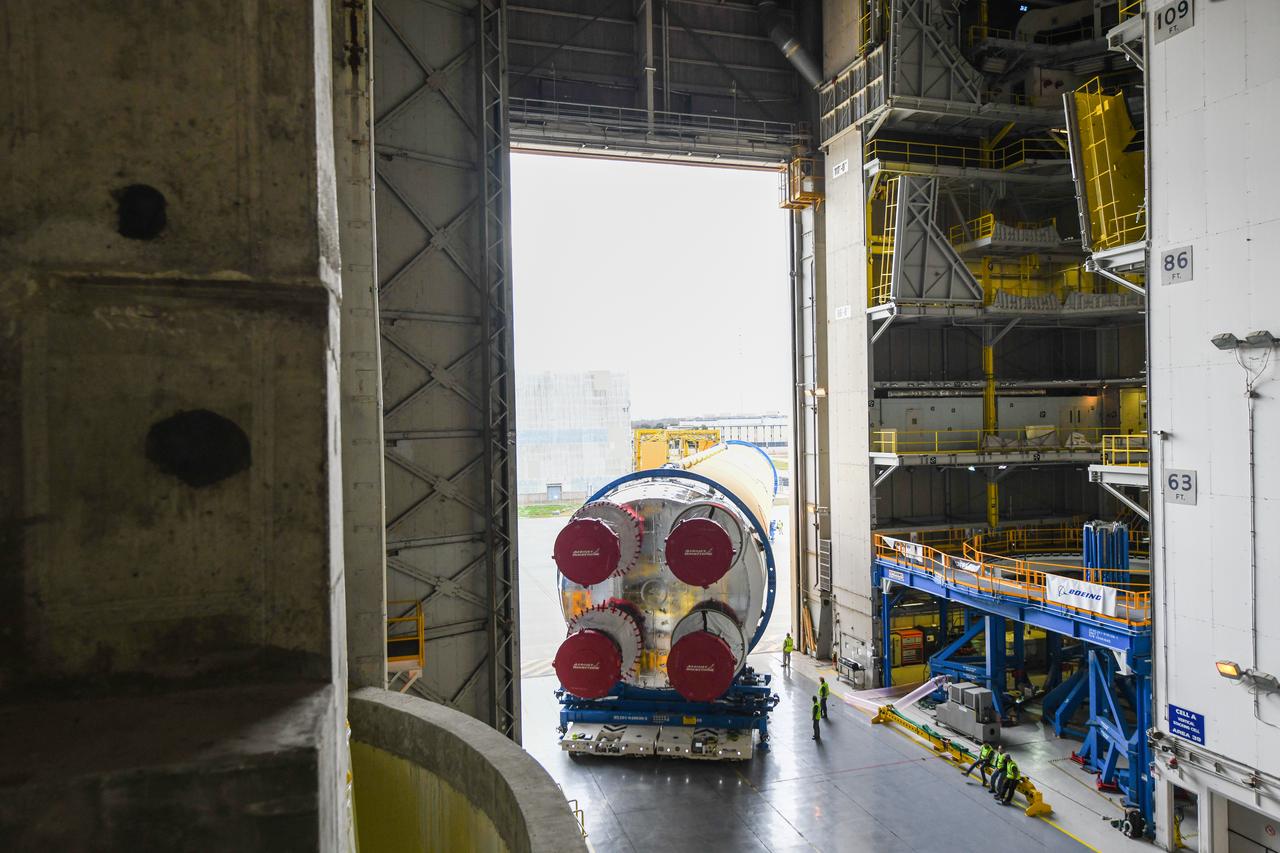

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
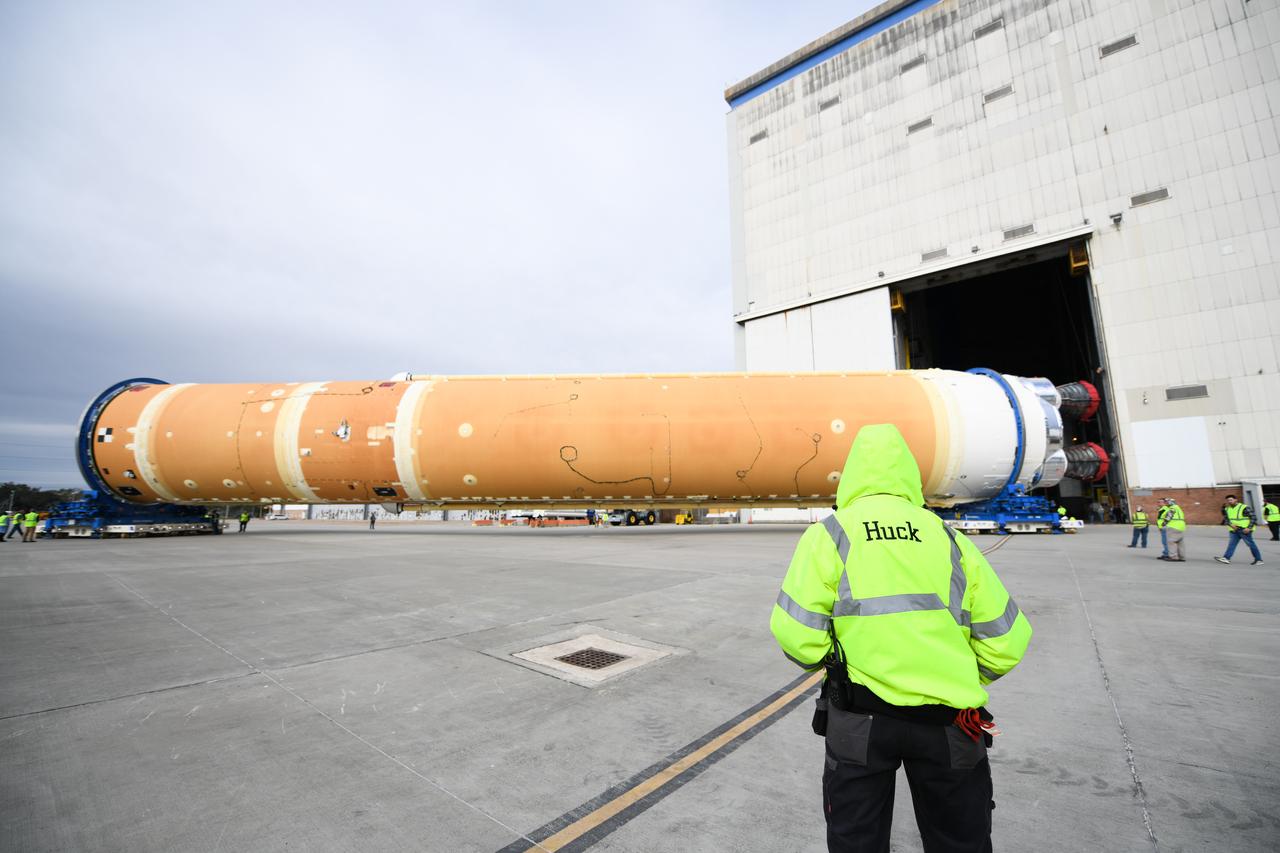

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
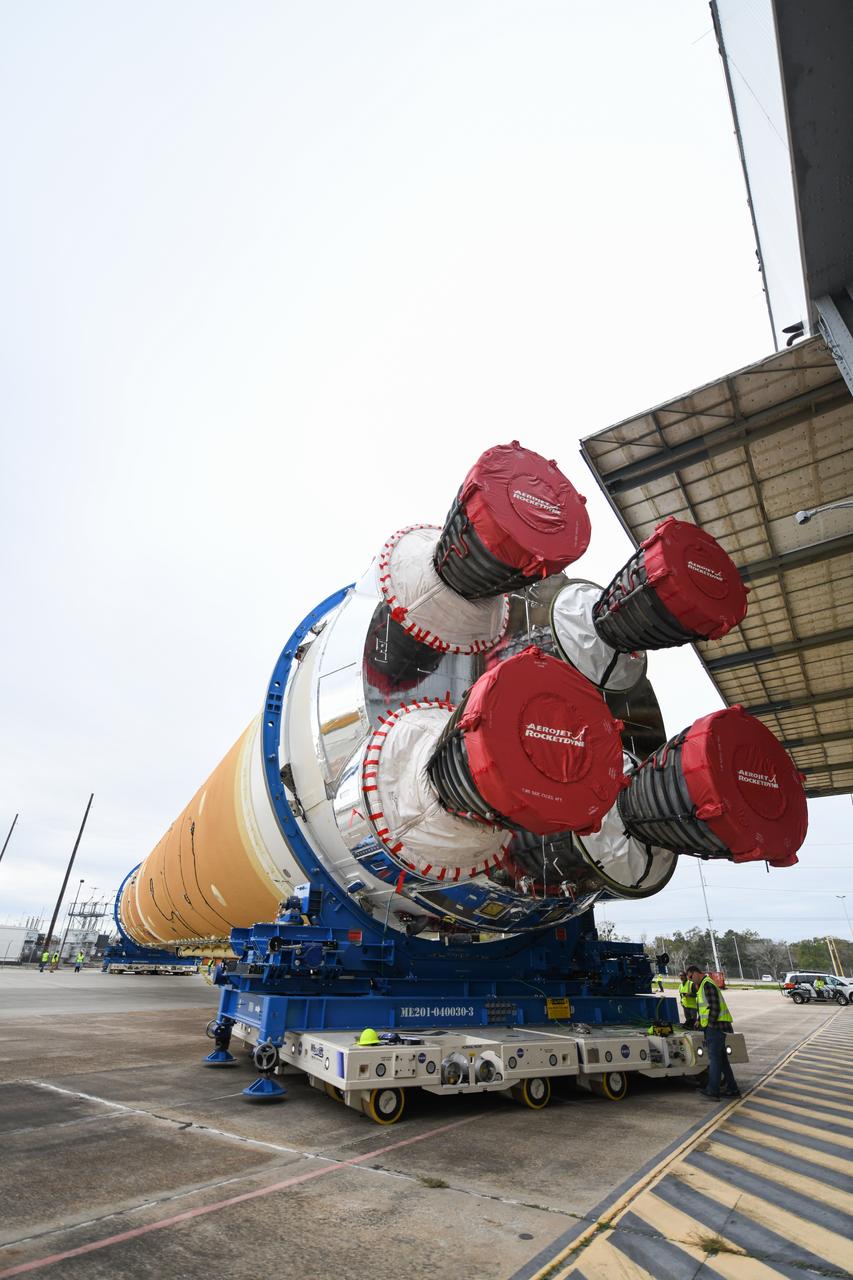

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
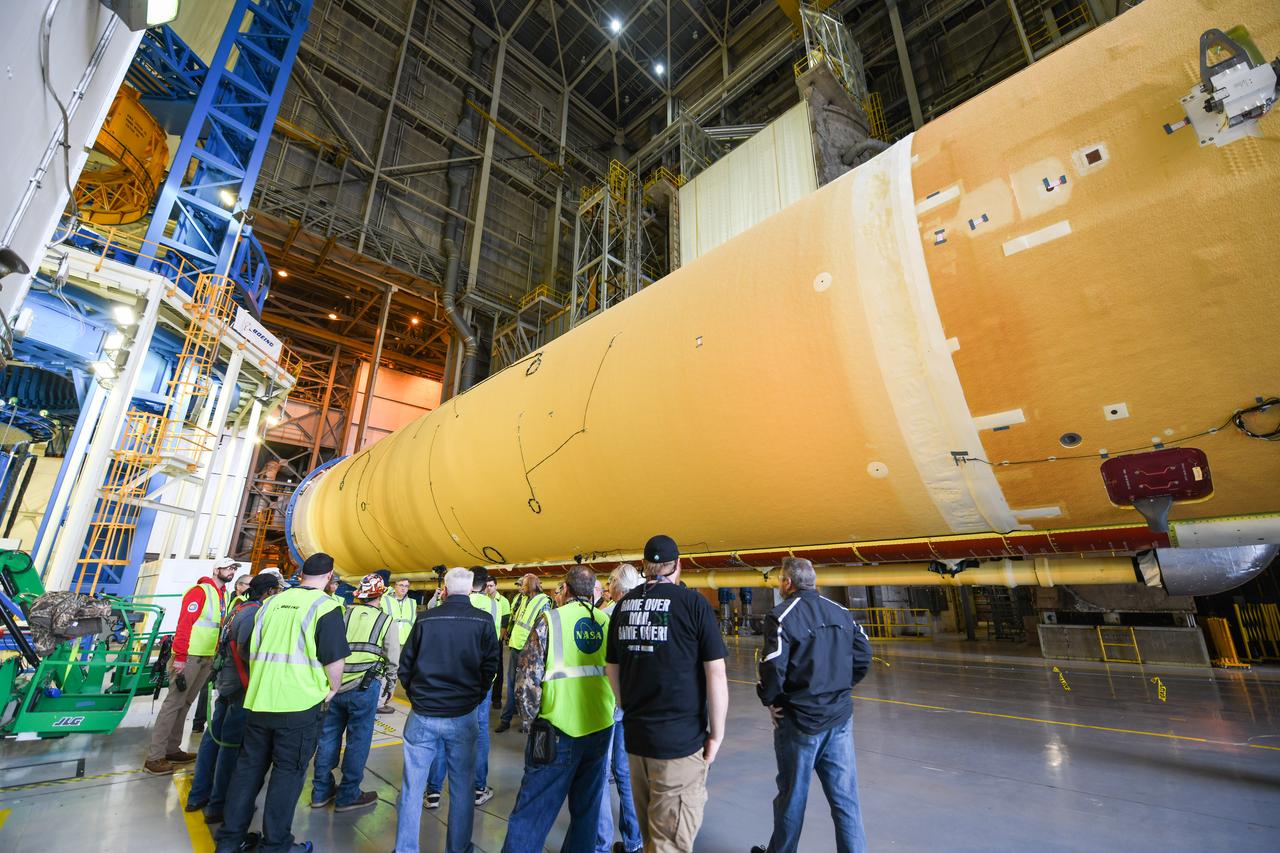

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
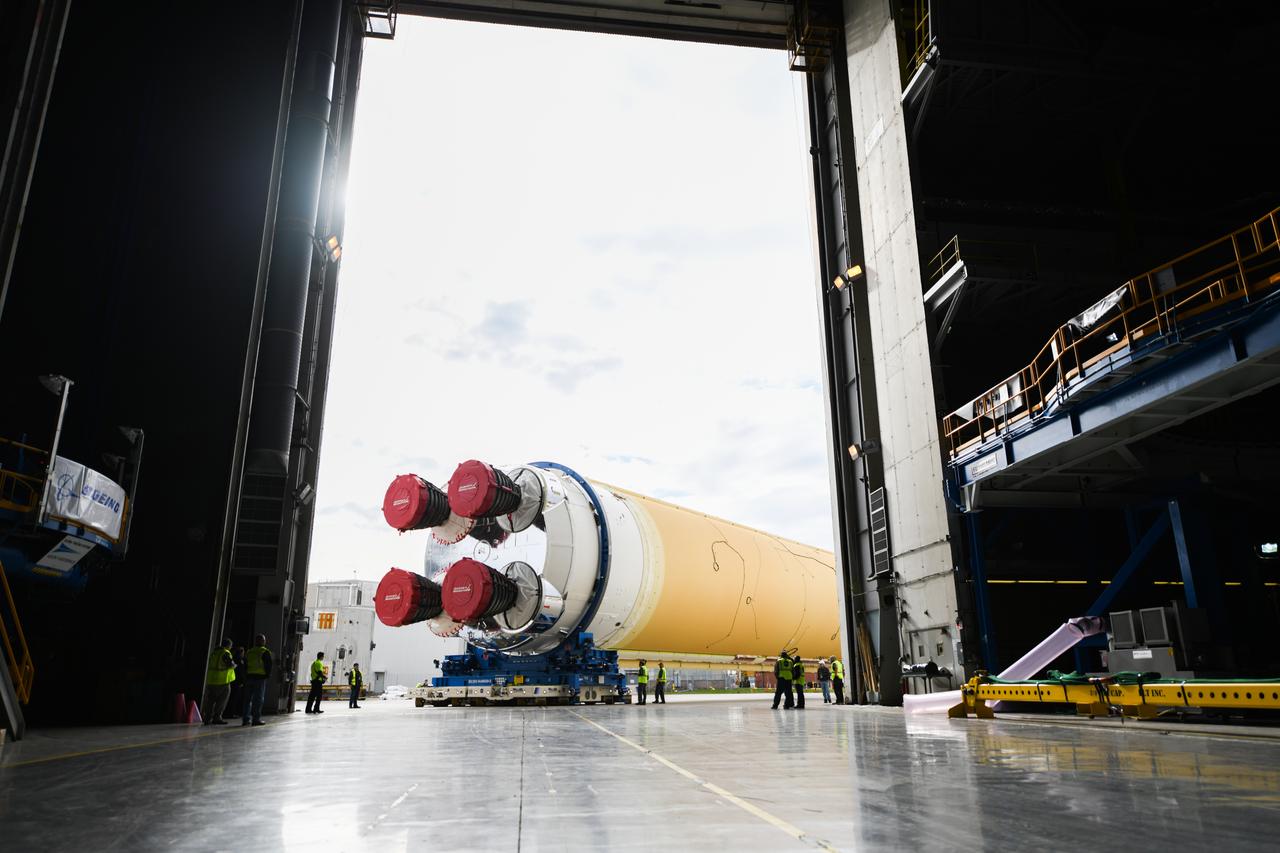

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
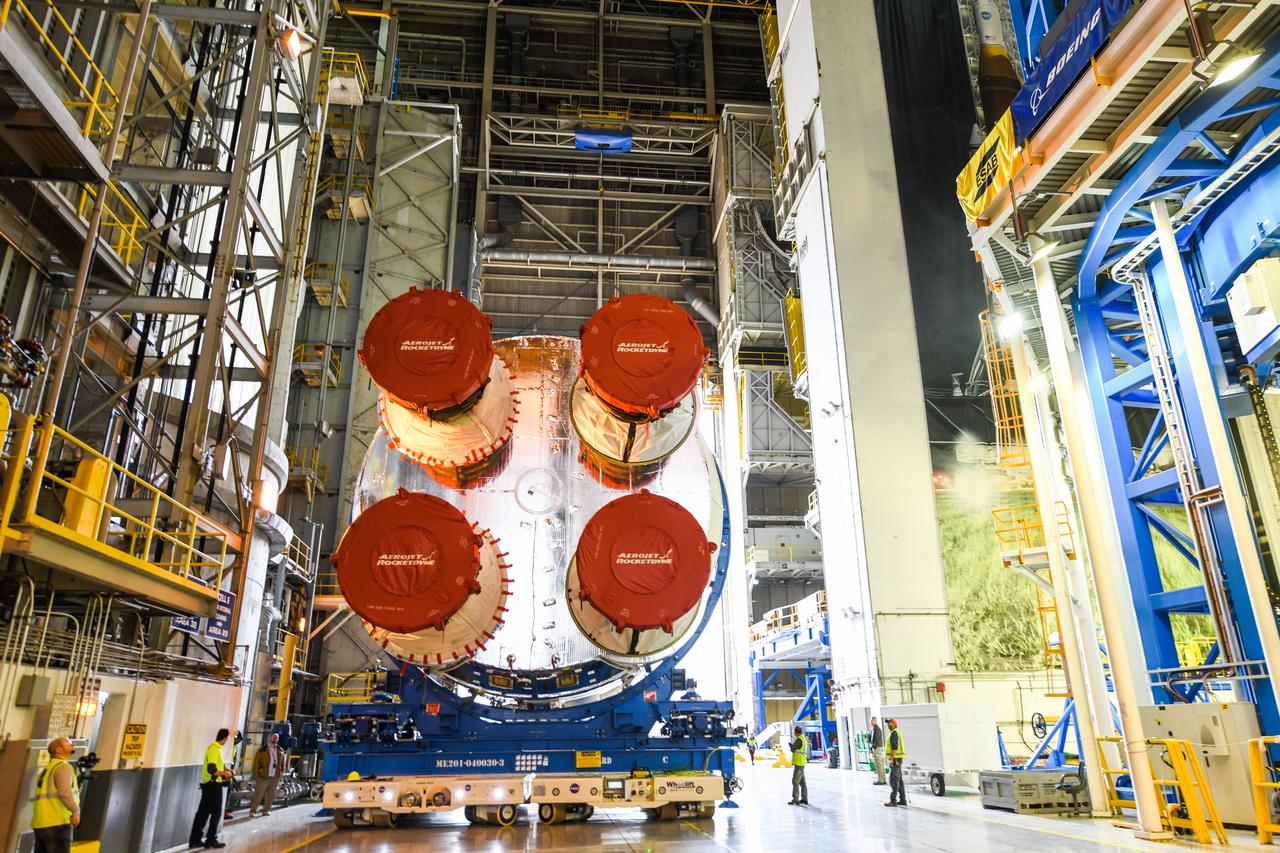
These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
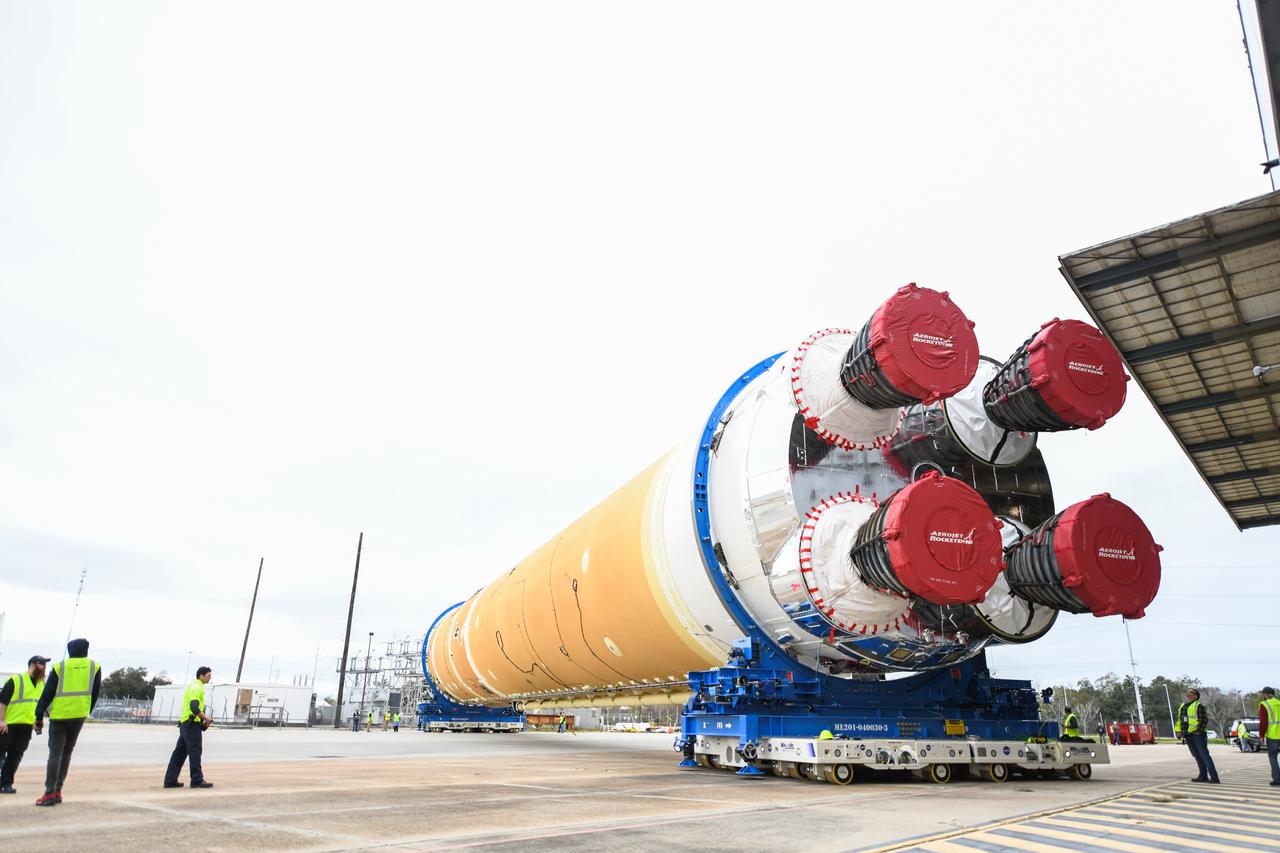

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
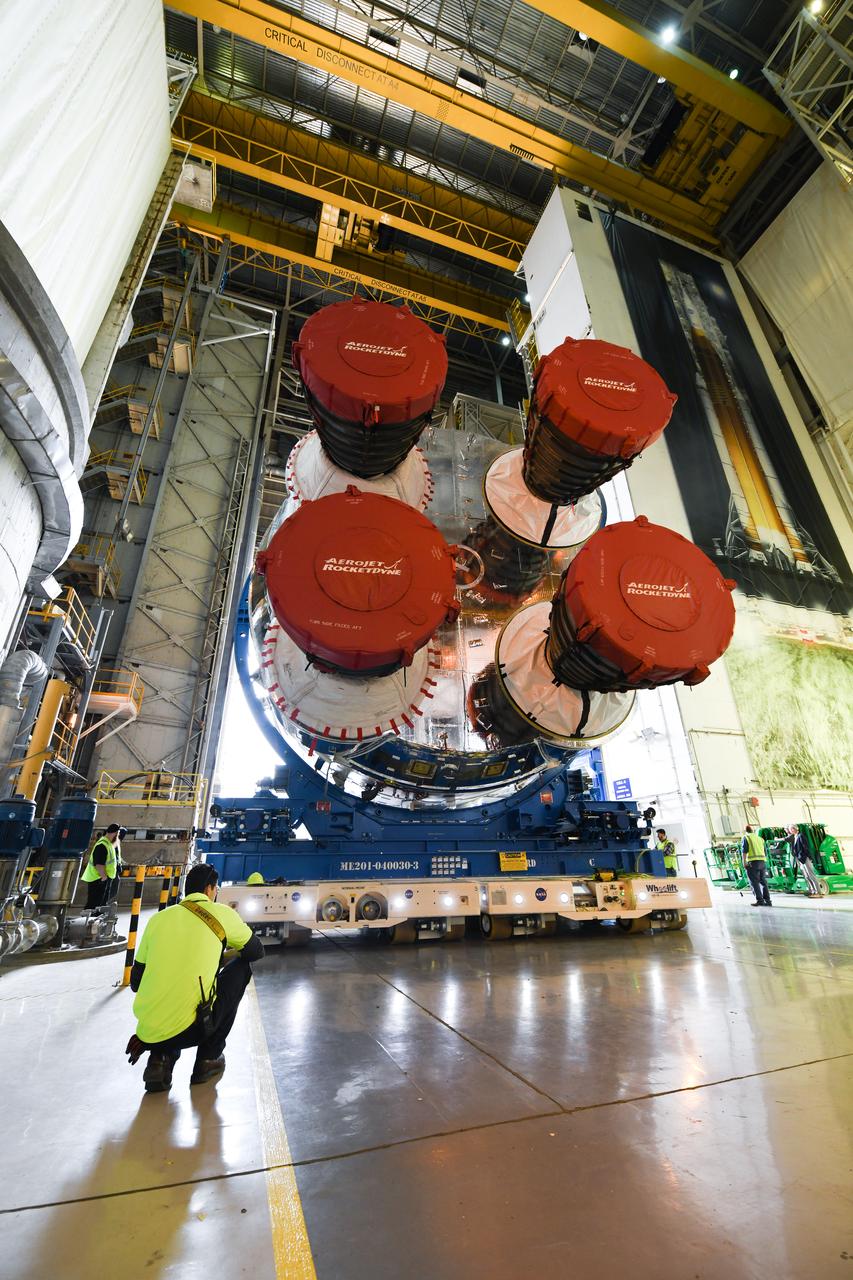

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
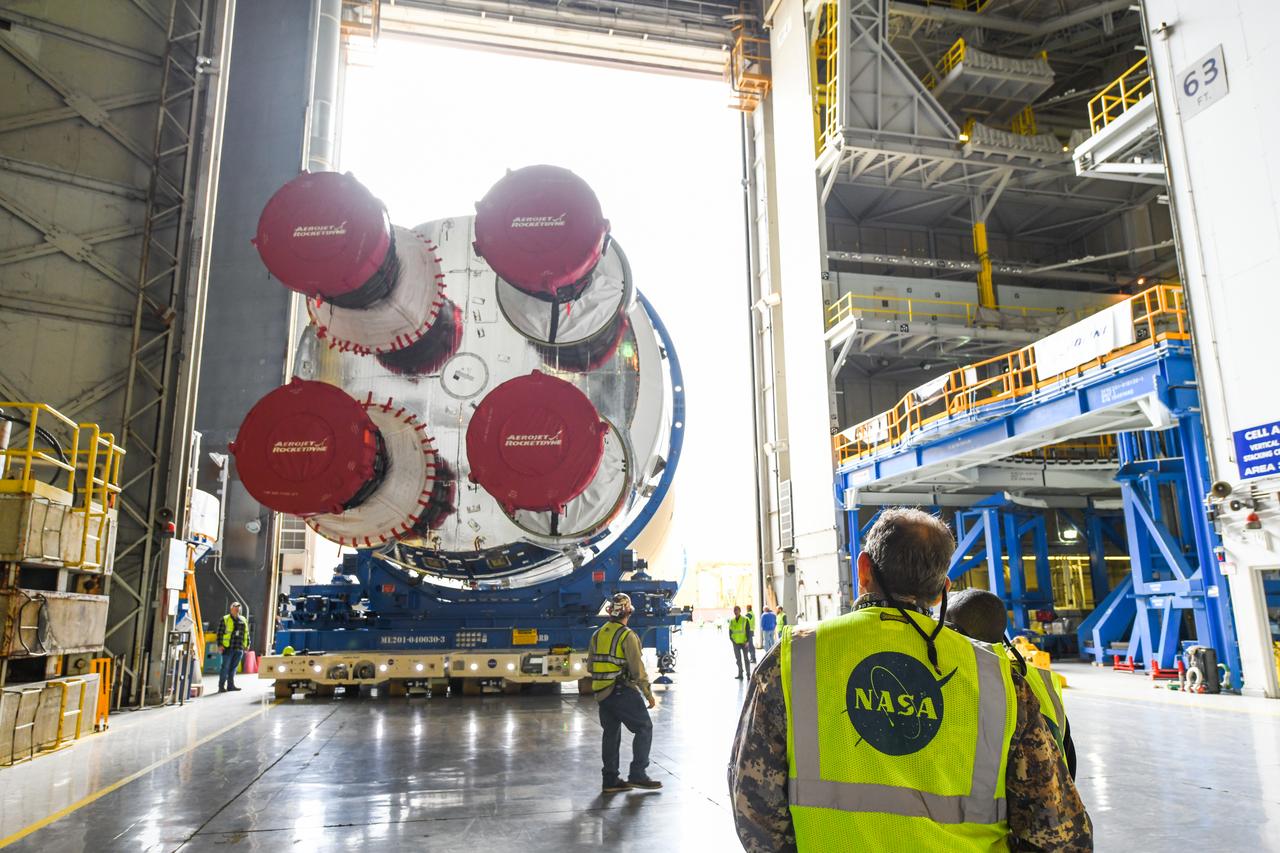

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
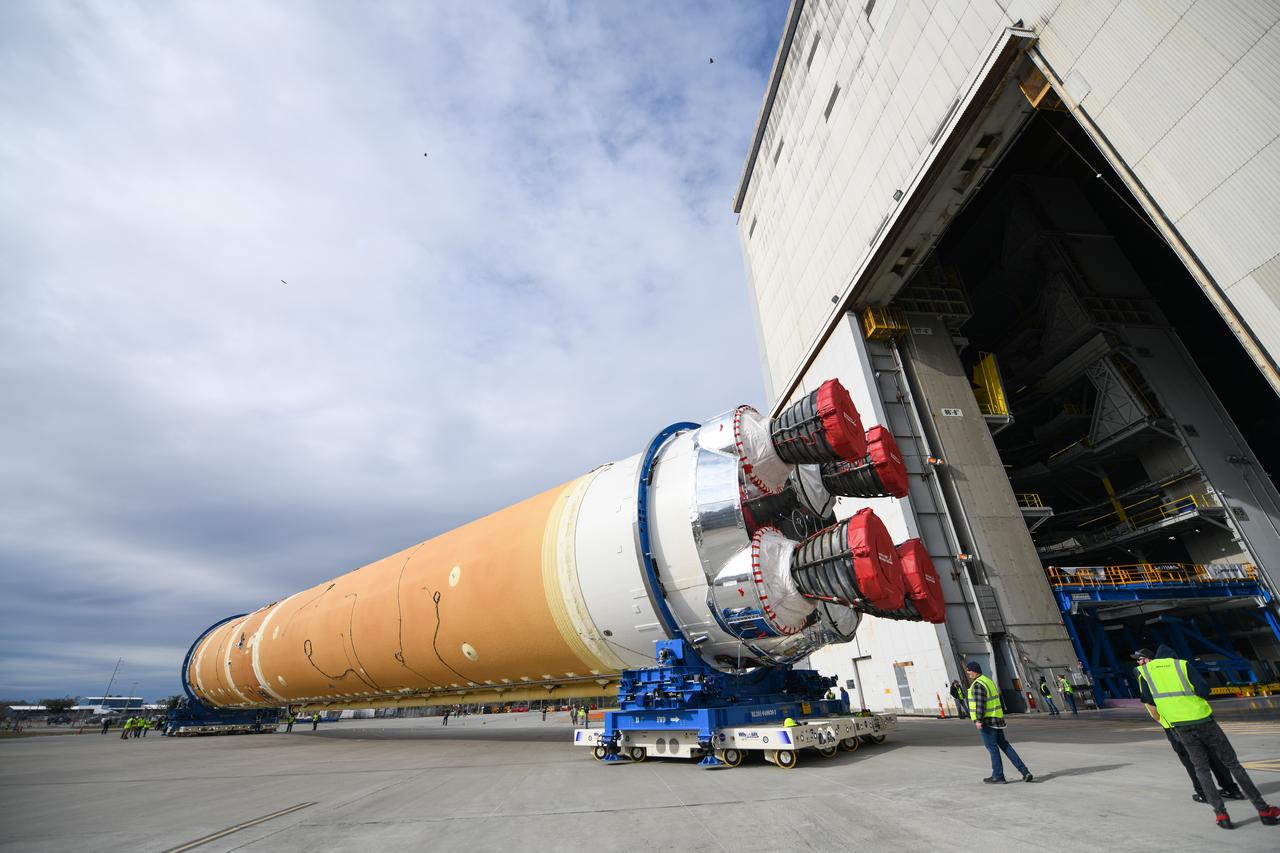

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
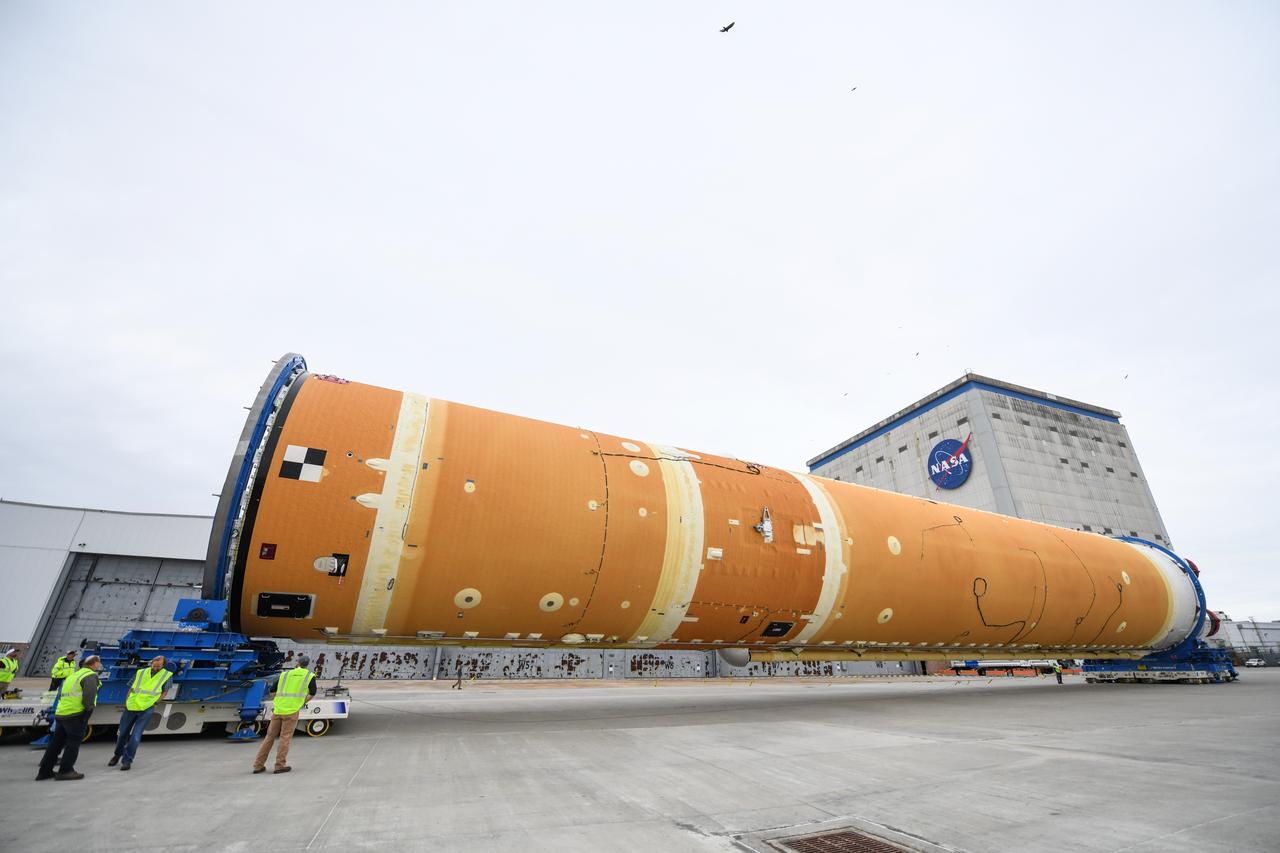

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
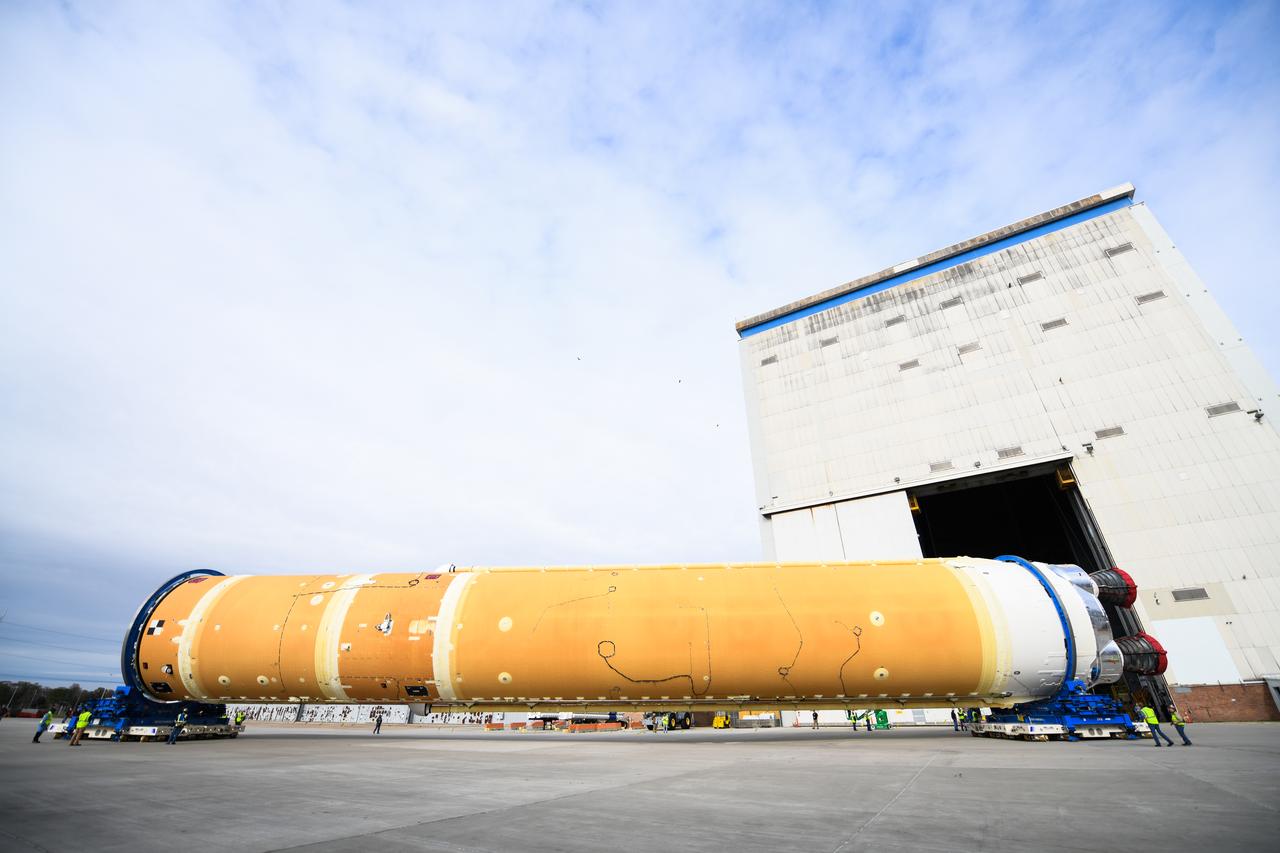

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
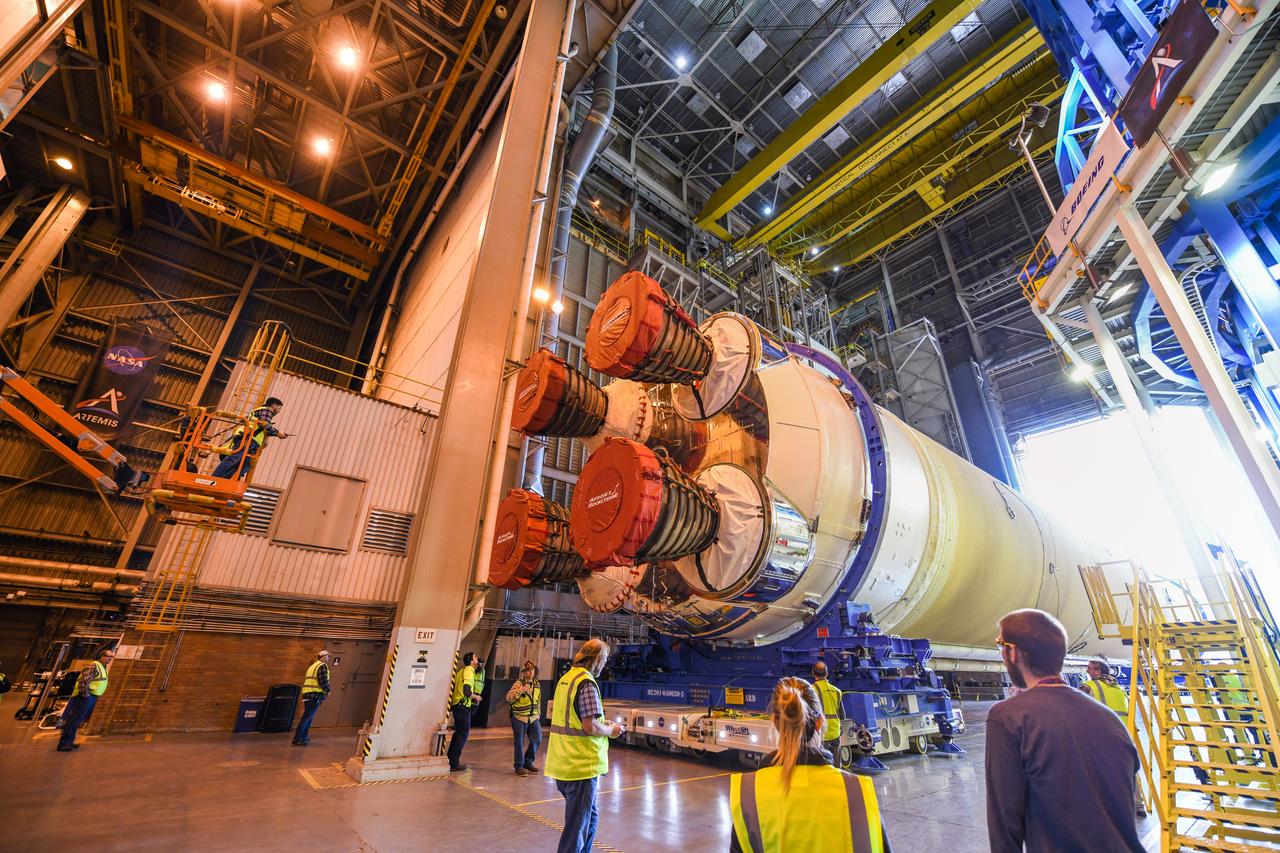

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
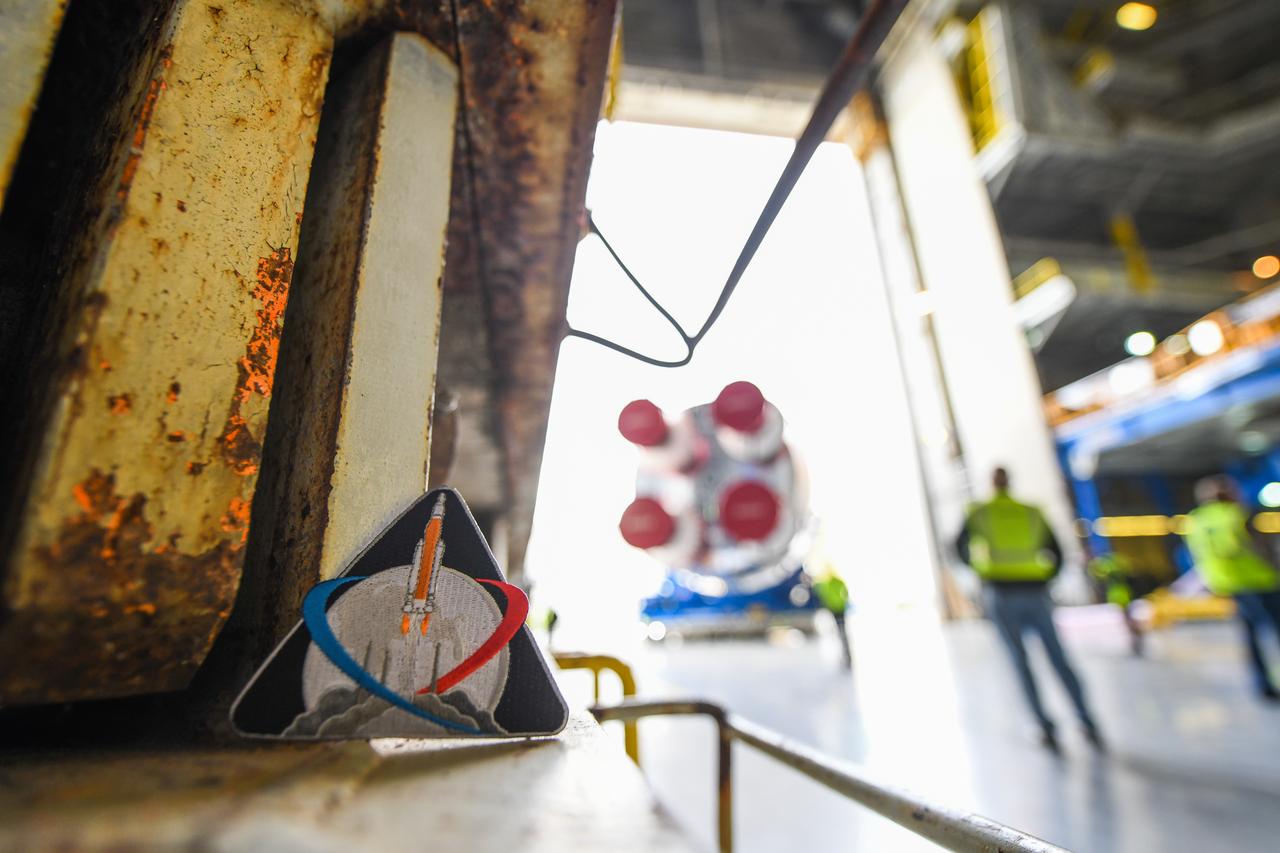

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
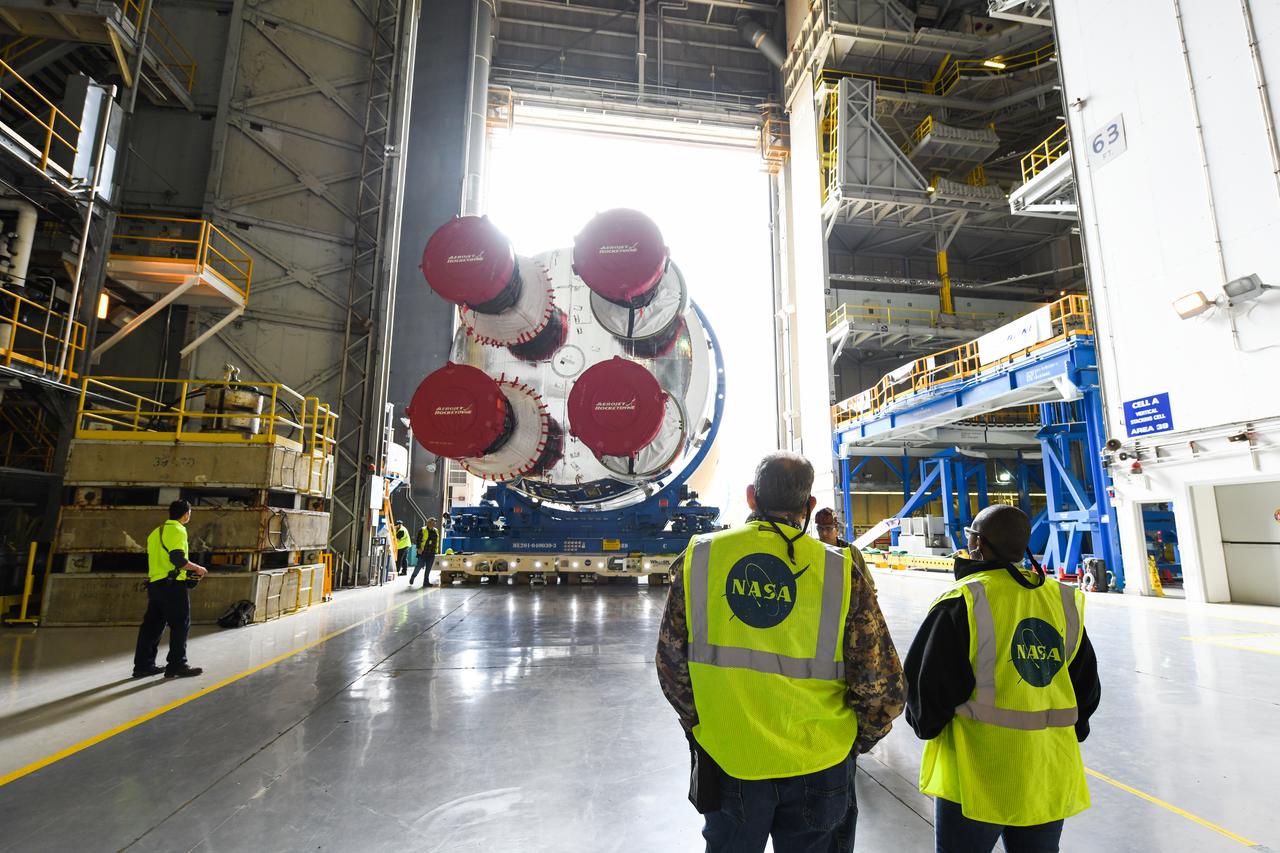

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
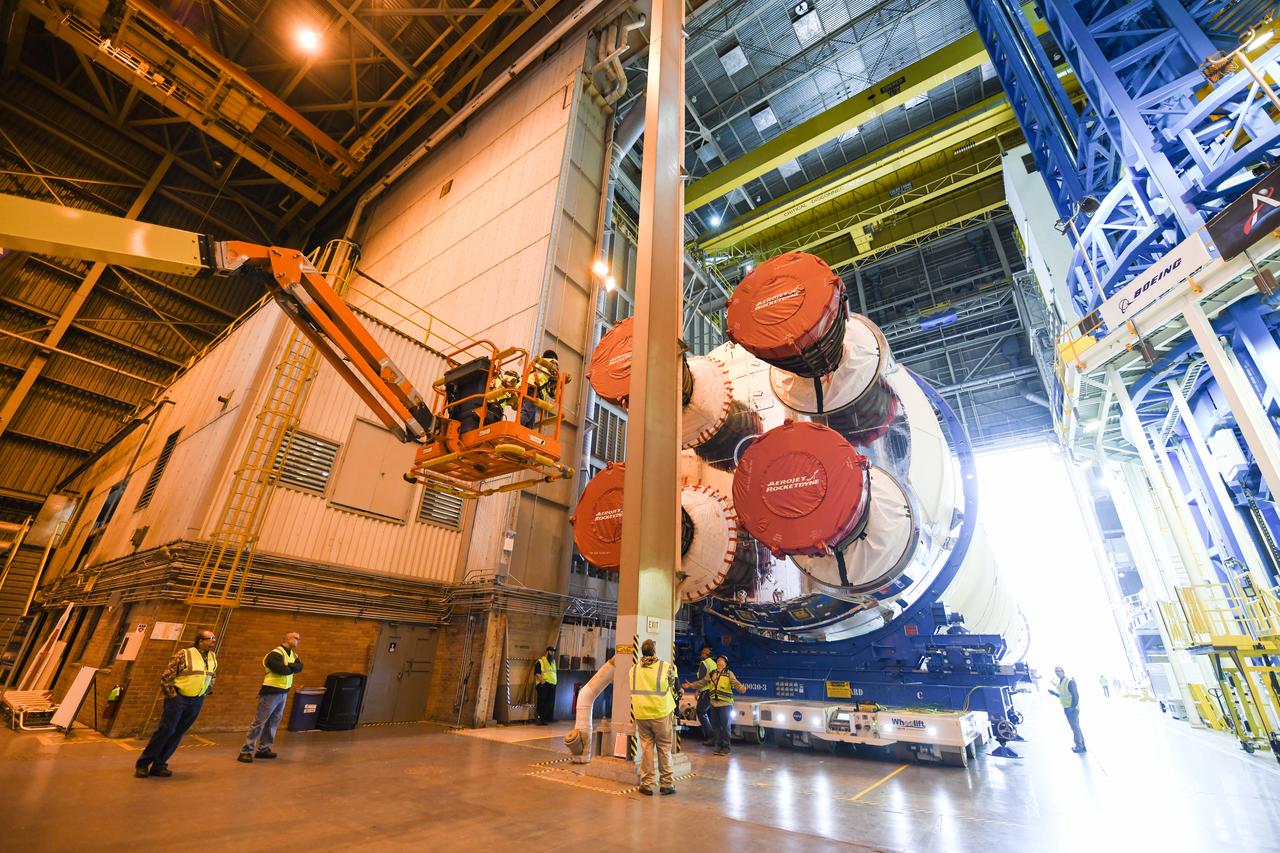

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
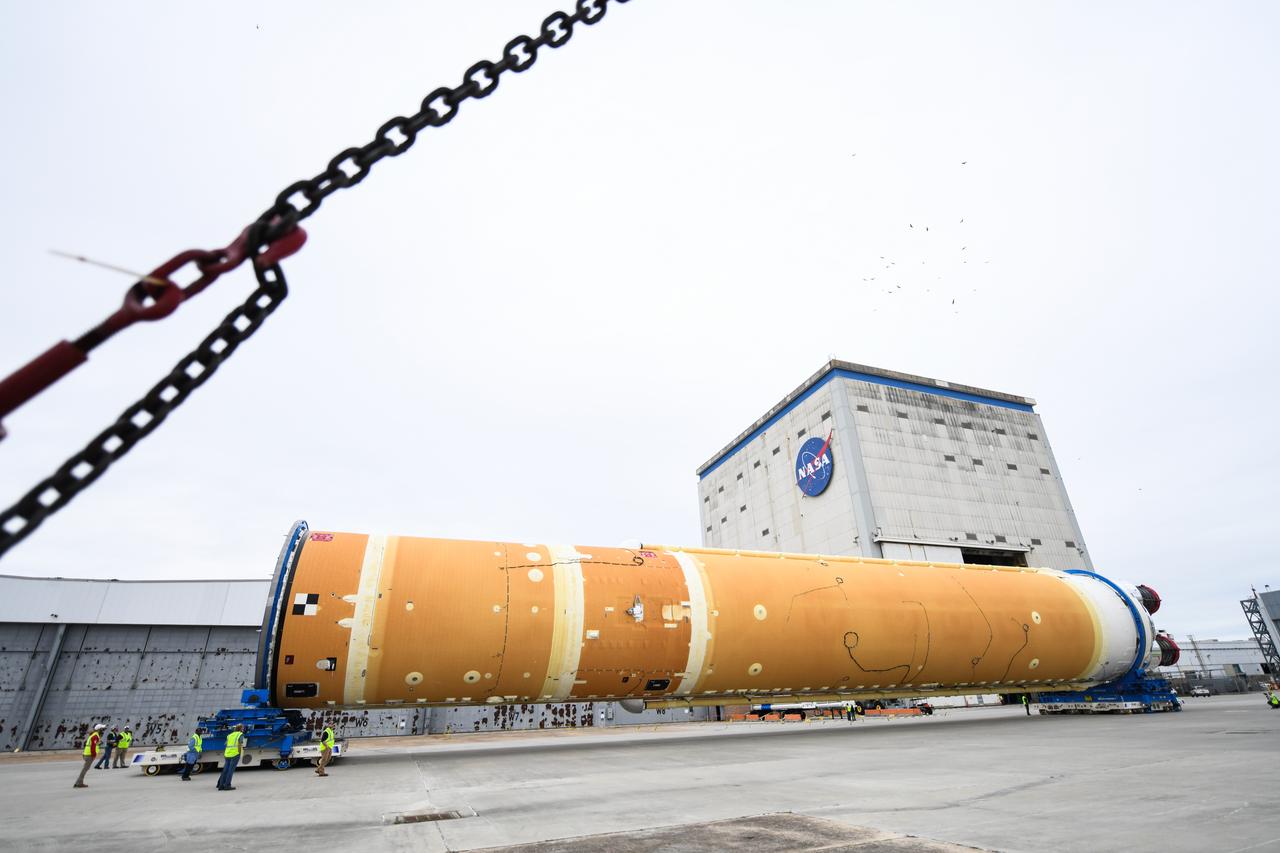

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
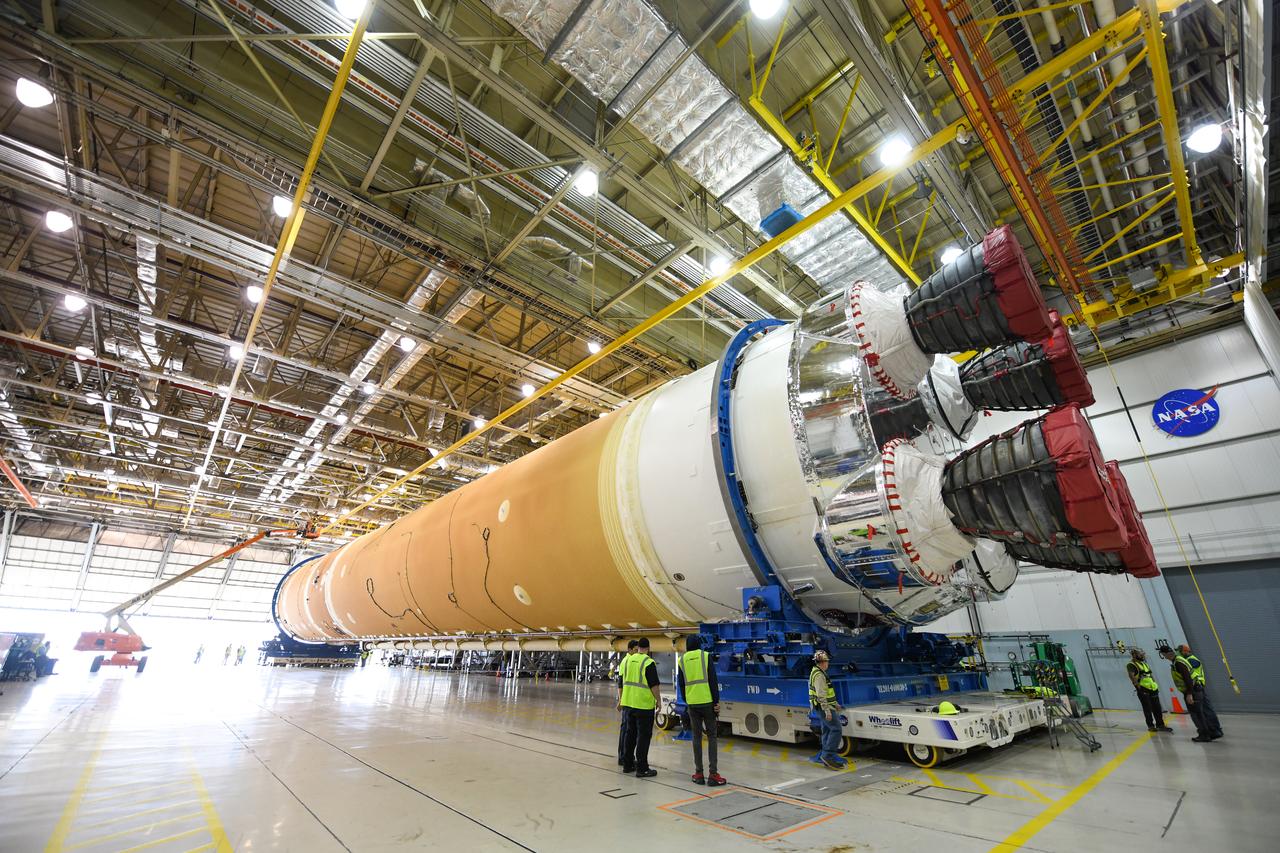

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
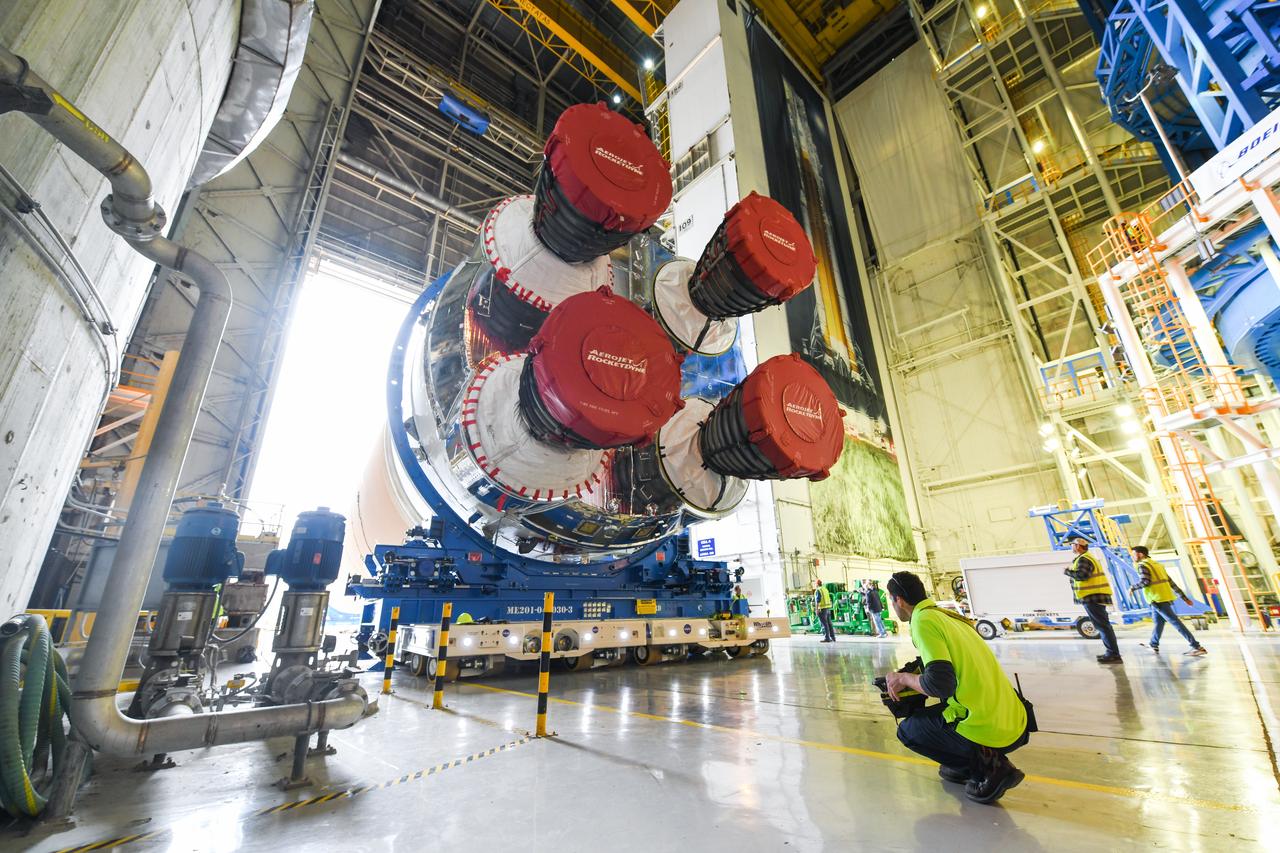

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
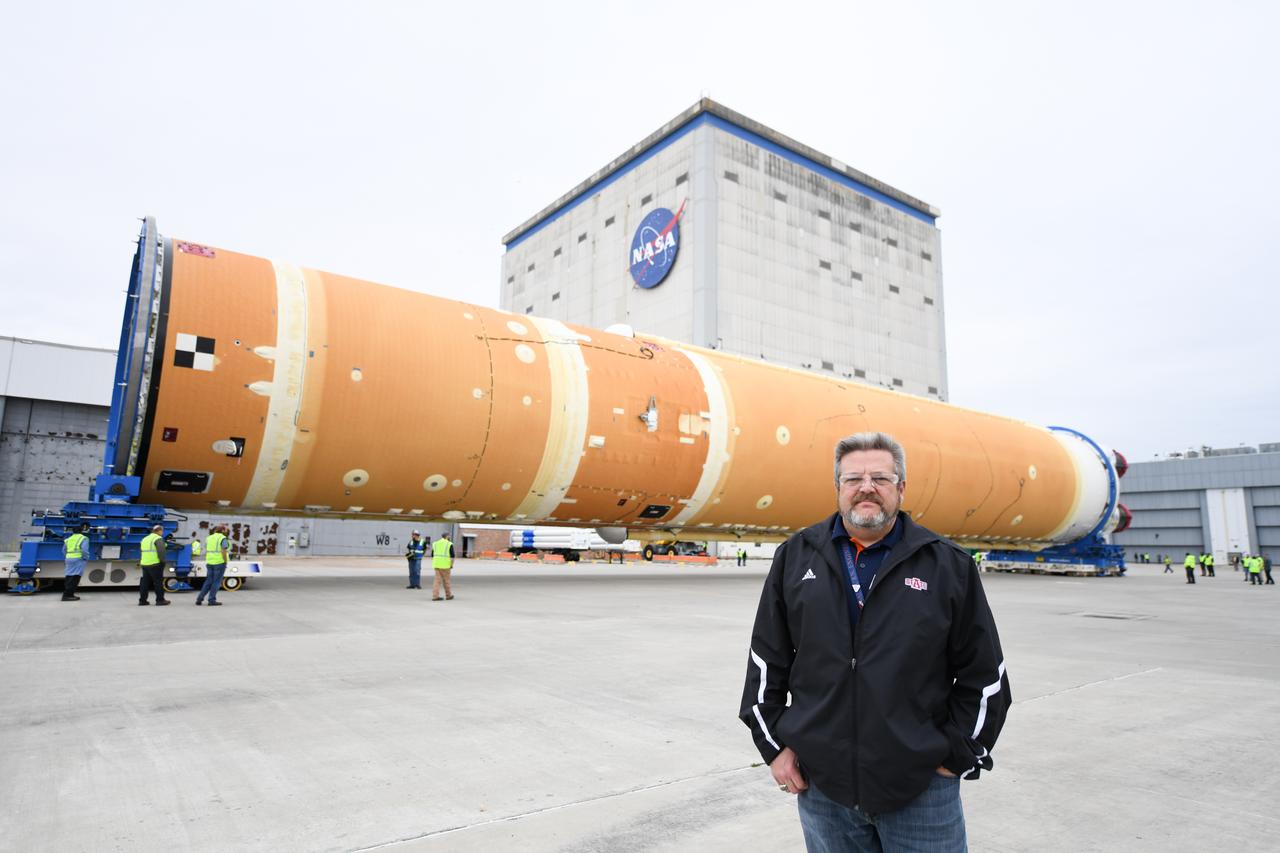

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
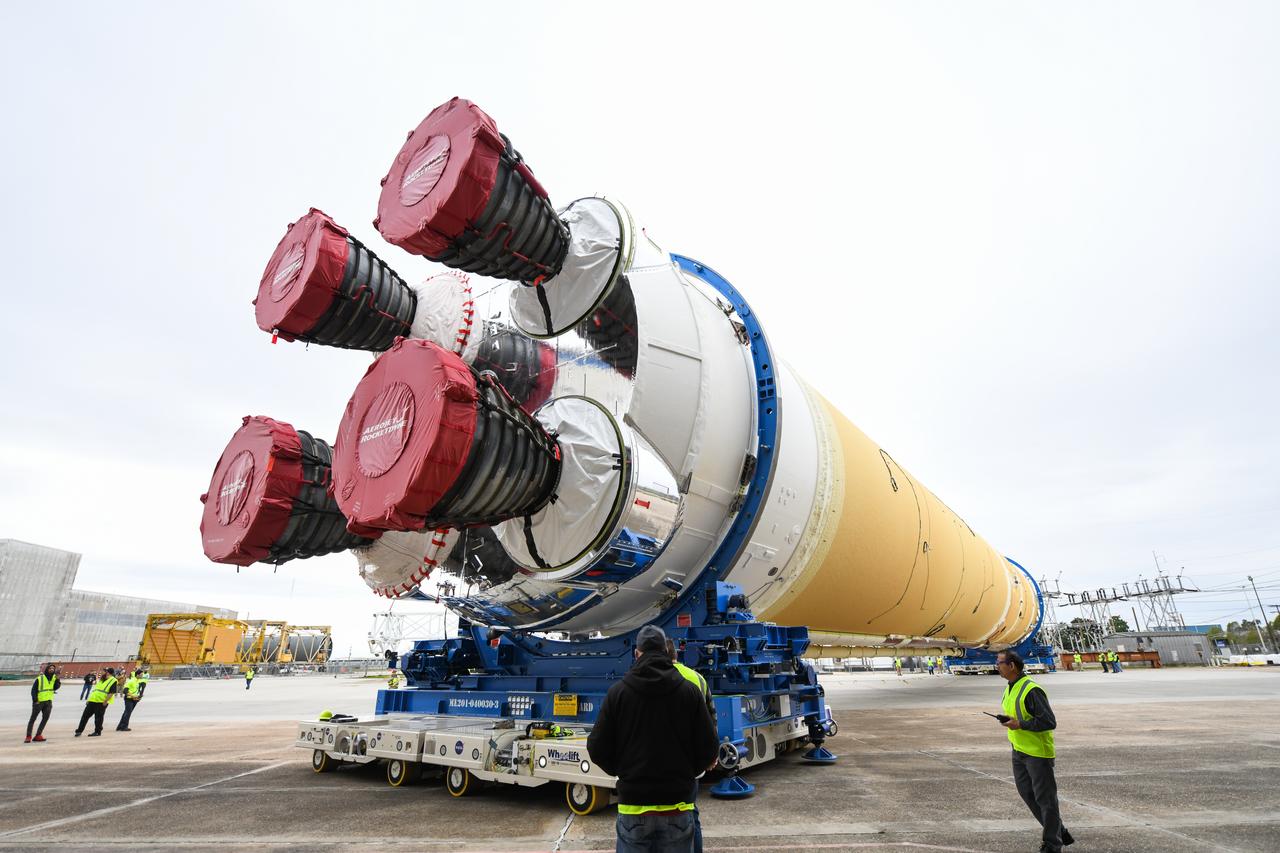

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
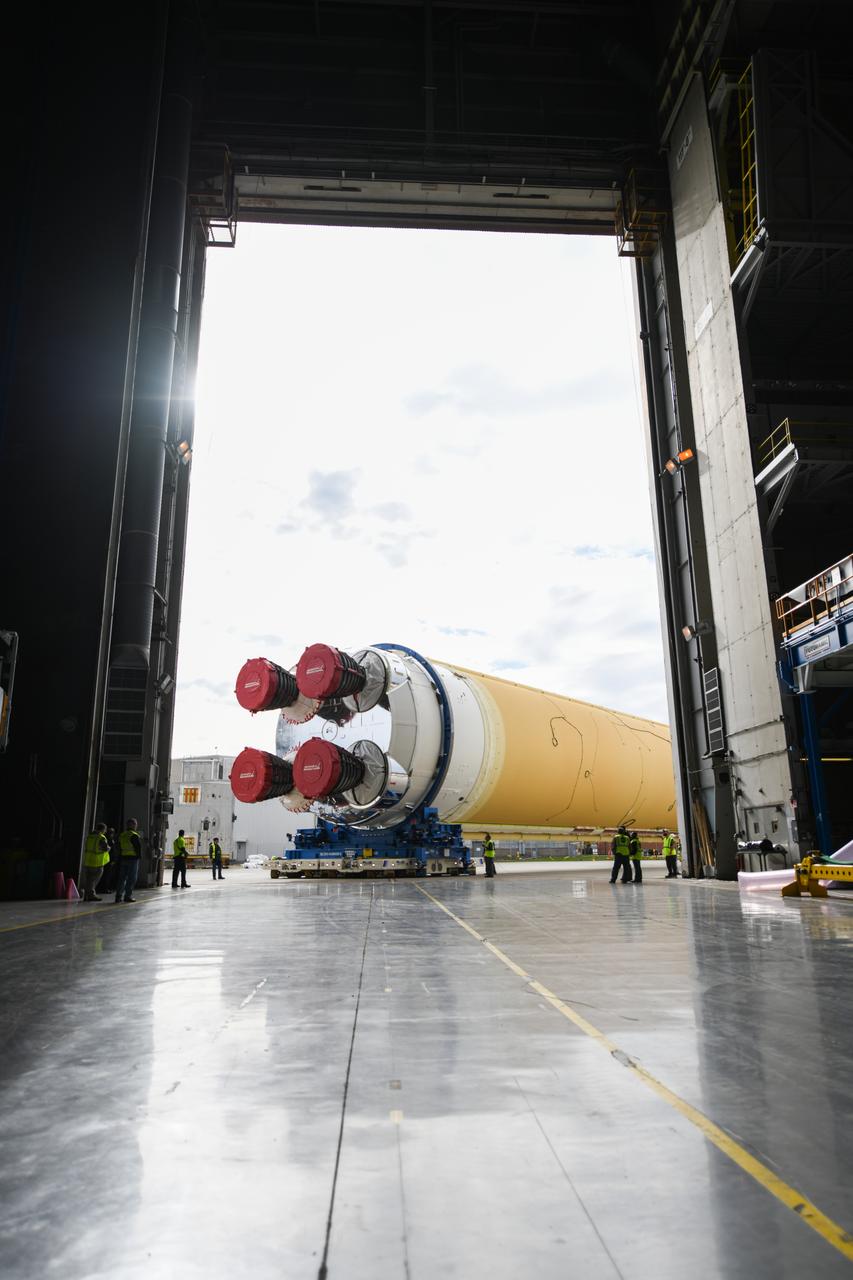

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
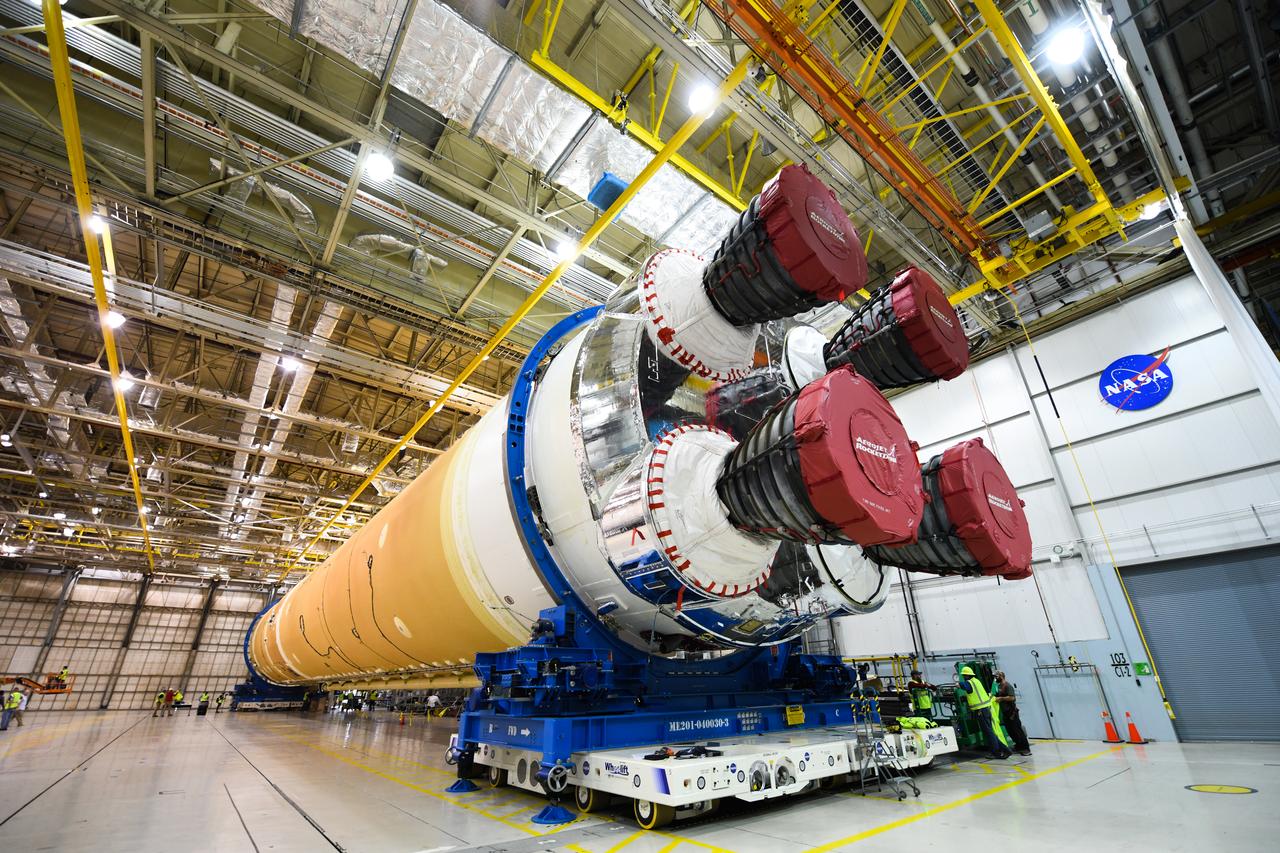

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
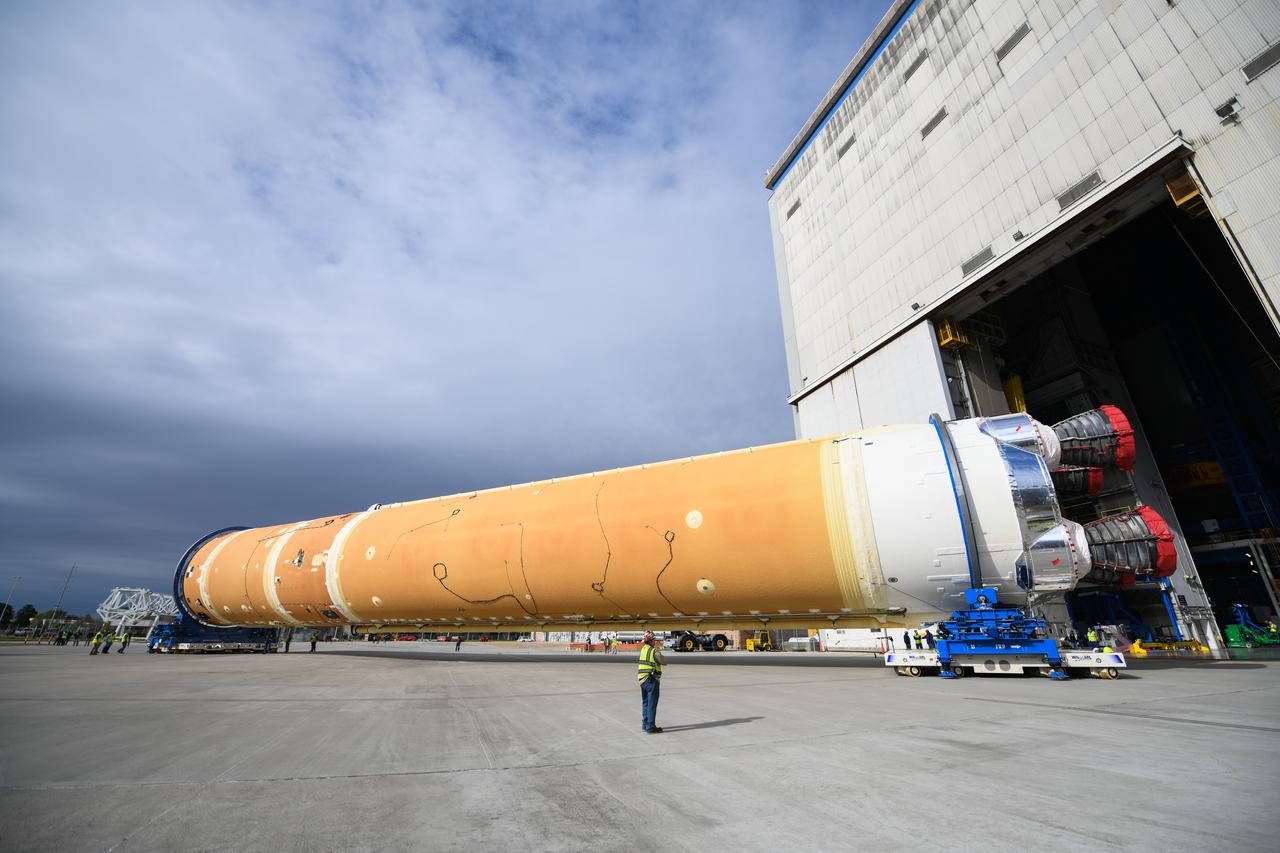

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
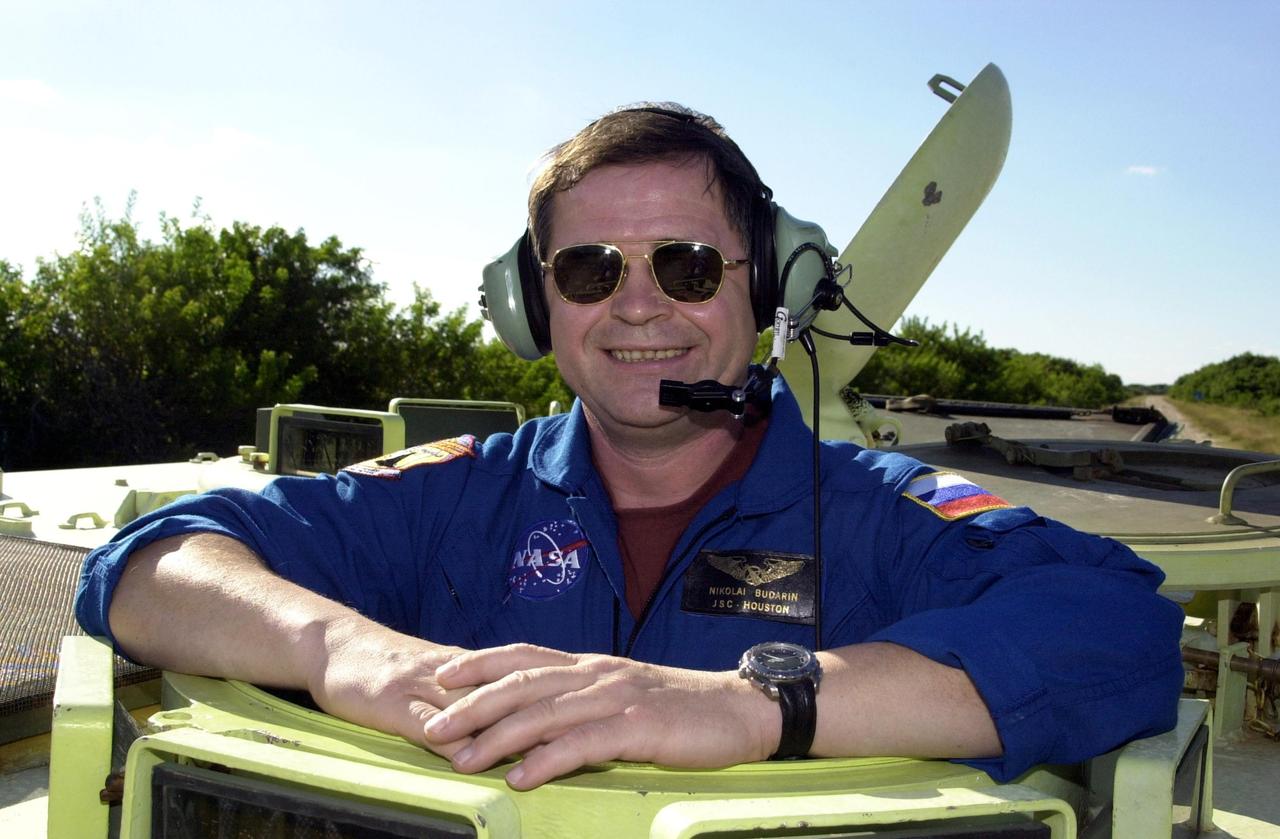

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Expedition 6 crew member Nikolai Budarin stands ready for a practice drive in an M-113 armored personnel carrier during emergency egress training at the pad, one of the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities in preparation for launch. The TCDT also includes a simulated launch countdown. The Expedition 6 crew will travel on Space Shuttle Endeavour to the International Space Station to replace Expedition 5, returning to Earth after 4 months. The primary payloads on mission STS-113 are the first port truss segment, P1, and the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) Cart B. Once delivered, the P1 truss will remain stowed until flight 12A.1 in 2003 when it will be attached to the central truss segment, S0, on the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for Nov. 10, 2002.
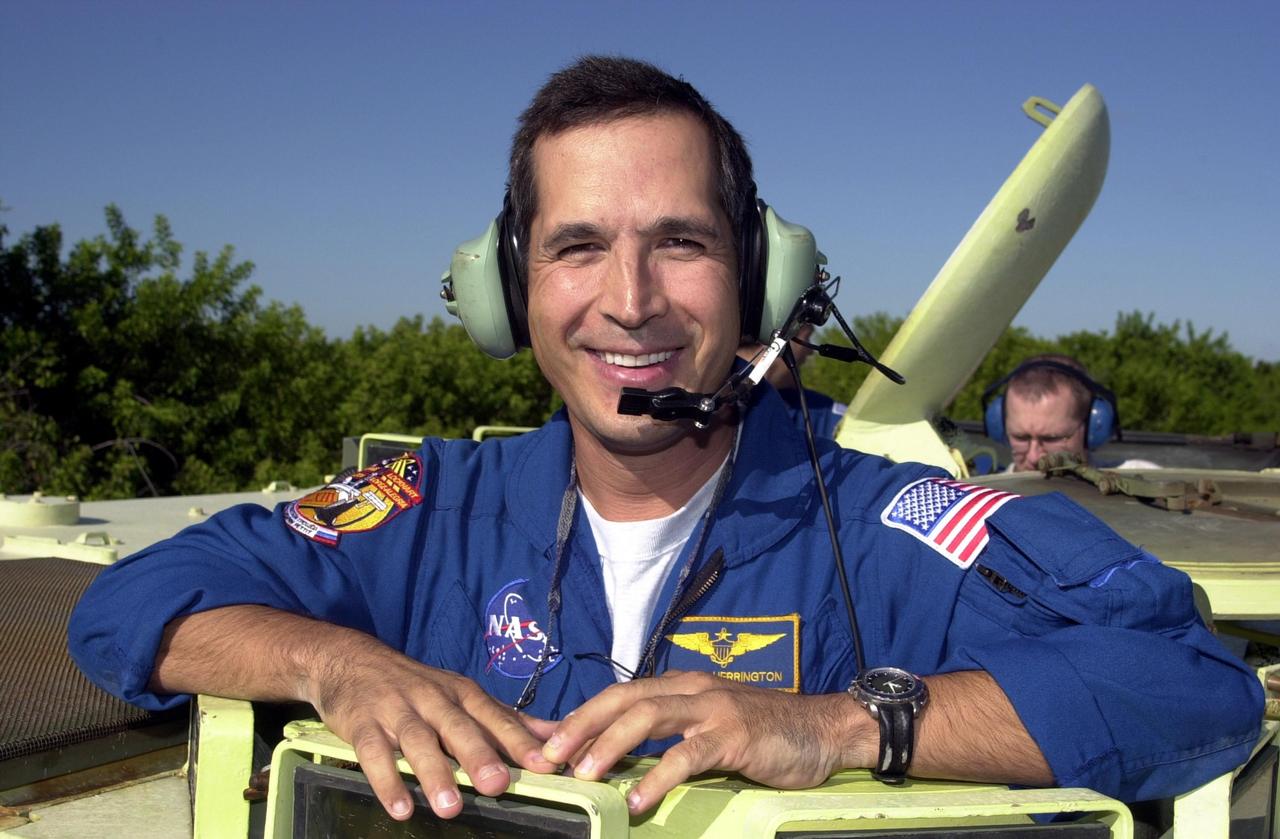

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-113 Mission Specialist John Herrington stands inside an M-113 armored personnel carrier that he is about to drive as part of emergency egress training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. He and the rest of the crew are preparing for the mission aboard Space Shuttle Endeavour, which is scheduled to launch Nov. 10. The TCDT includes a simulated launch countdown. The primary payloads on mission STS-113 are the first port truss segment, P1, and the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) Cart B. Once delivered, the P1 truss will remain stowed until flight 12A.1 in 2003 when it will be attached to the central truss segment, S0, on the Space Station. Also onboard Space Shuttle Endeavour will be the Expedition 6 crew who will replace Expedition 5, returning to Earth after 4 months.
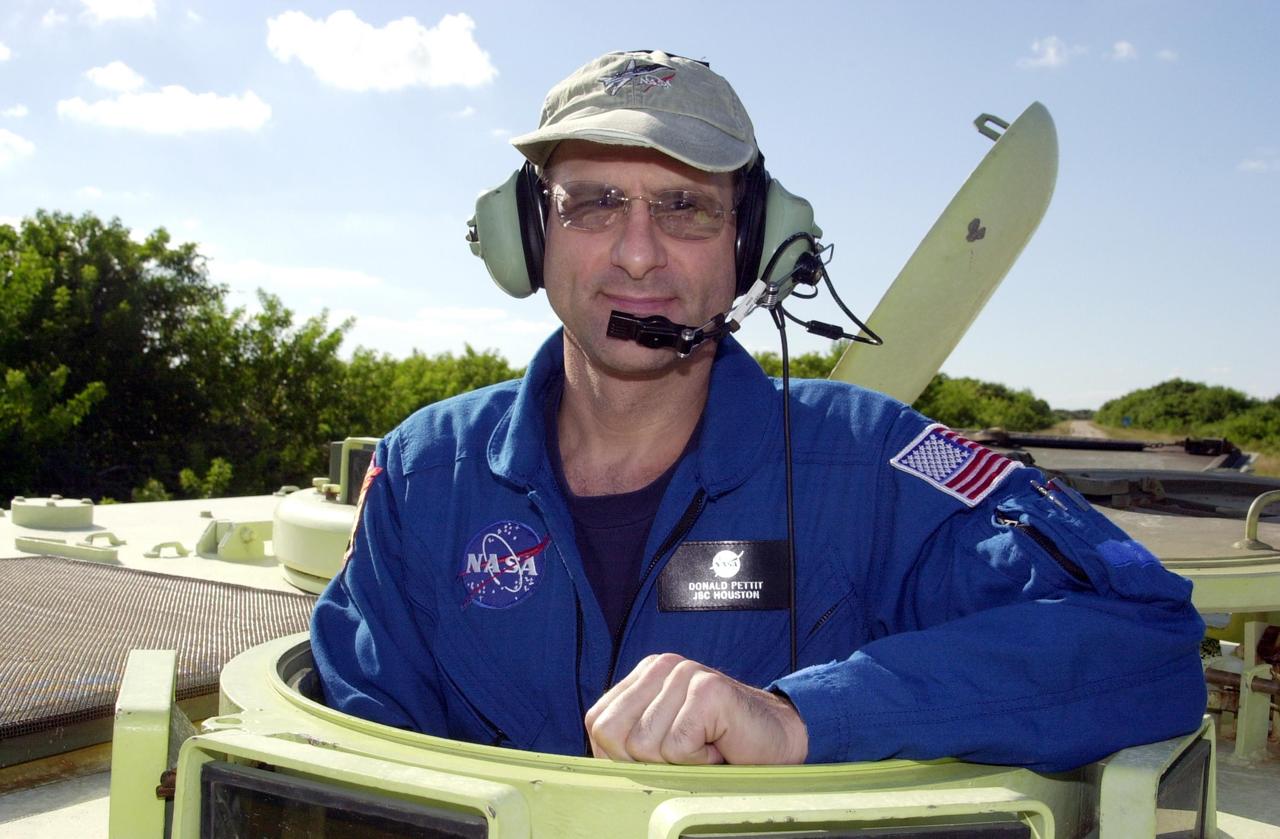

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During emergency egress training at the pad, Expedition 6 crew member Donald Pettit stands inside an M-113 armored personnel carrier before his practice drive. The training is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities in preparation for launch. The TCDT also includes a simulated launch countdown. The Expedition 6 crew will travel on Space Shuttle Endeavour to the International Space Station to replace Expedition 5, returning to Earth after 4 months. The primary payloads on mission STS-113 are the first port truss segment, P1, and the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) Cart B. Once delivered, the P1 truss will remain stowed until flight 12A.1 in 2003 when it will be attached to the central truss segment, S0, on the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for Nov. 10, 2002.
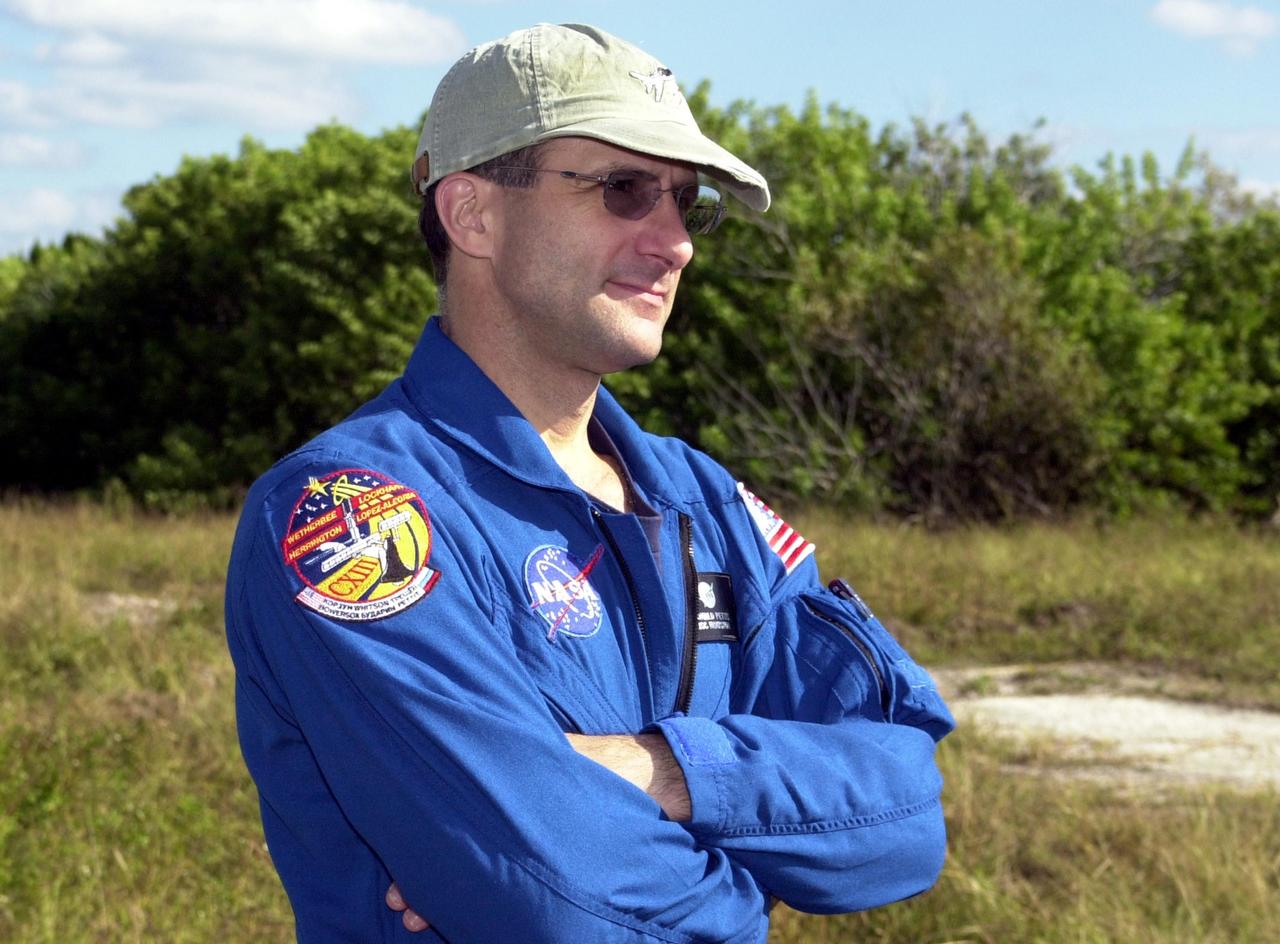

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Expedition 6 crew member Donald Pettit stands ready for a practice drive in an M-113 armored personnel carrier during emergency egress training at the pad, one of the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities in preparation for launch. The TCDT also includes a simulated launch countdown. The Expedition 6 crew will travel on Space Shuttle Endeavour to the International Space Station to replace Expedition 5, returning to Earth after 4 months. The primary payloads on mission STS-113 are the first port truss segment, P1, and the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) Cart B. Once delivered, the P1 truss will remain stowed until flight 12A.1 in 2003 when it will be attached to the central truss segment, S0, on the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for Nov. 10, 2002.
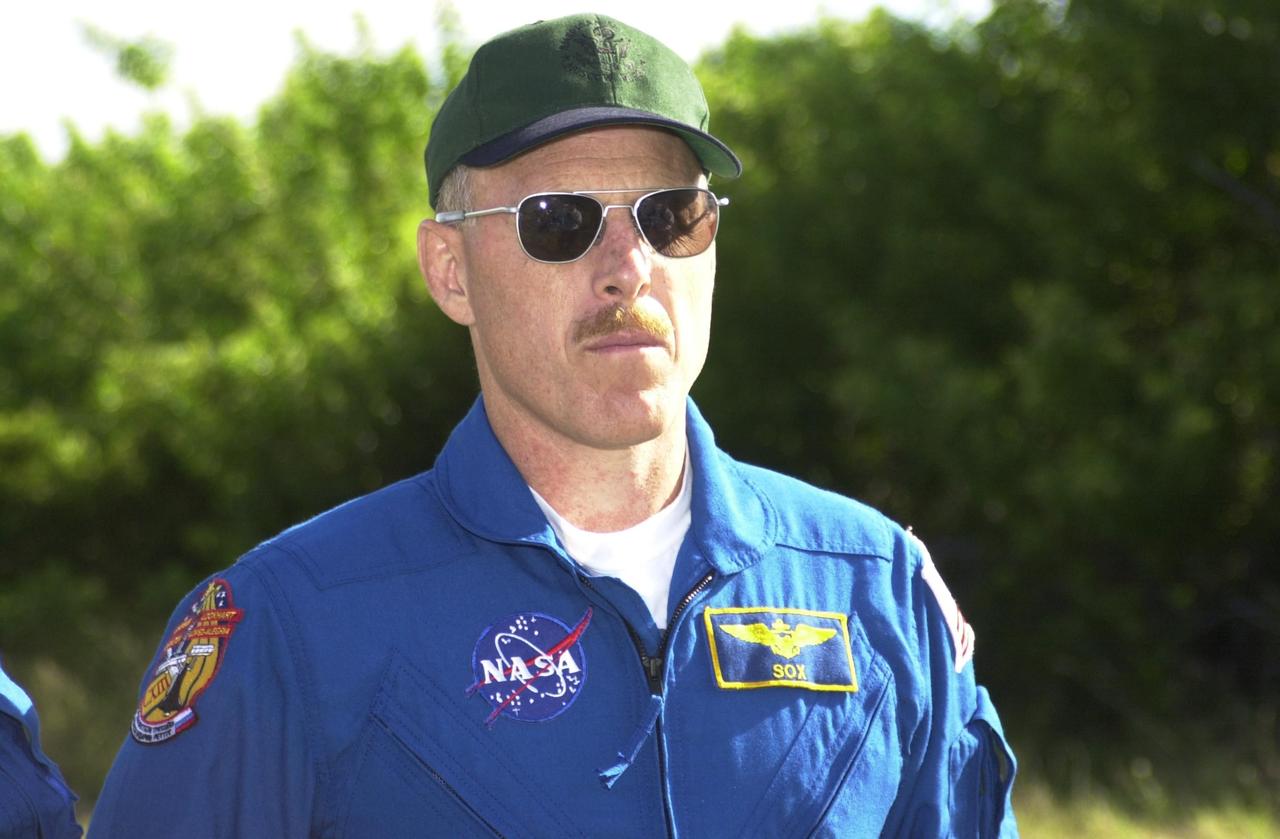

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Expedition 6 Commander Ken Bowersox stands ready for a practice drive in an M-113 armored personnel carrier during emergency egress training at the pad, one of the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities in preparation for launch. The TCDT also includes a simulated launch countdown. The Expedition 6 crew will travel on Space Shuttle Endeavour to the International Space Station to replace Expedition 5, returning to Earth after 4 months. The primary payloads on mission STS-113 are the first port truss segment, P1, and the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) Cart B. Once delivered, the P1 truss will remain stowed until flight 12A.1 in 2003 when it will be attached to the central truss segment, S0, on the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for Nov. 10, 2002.
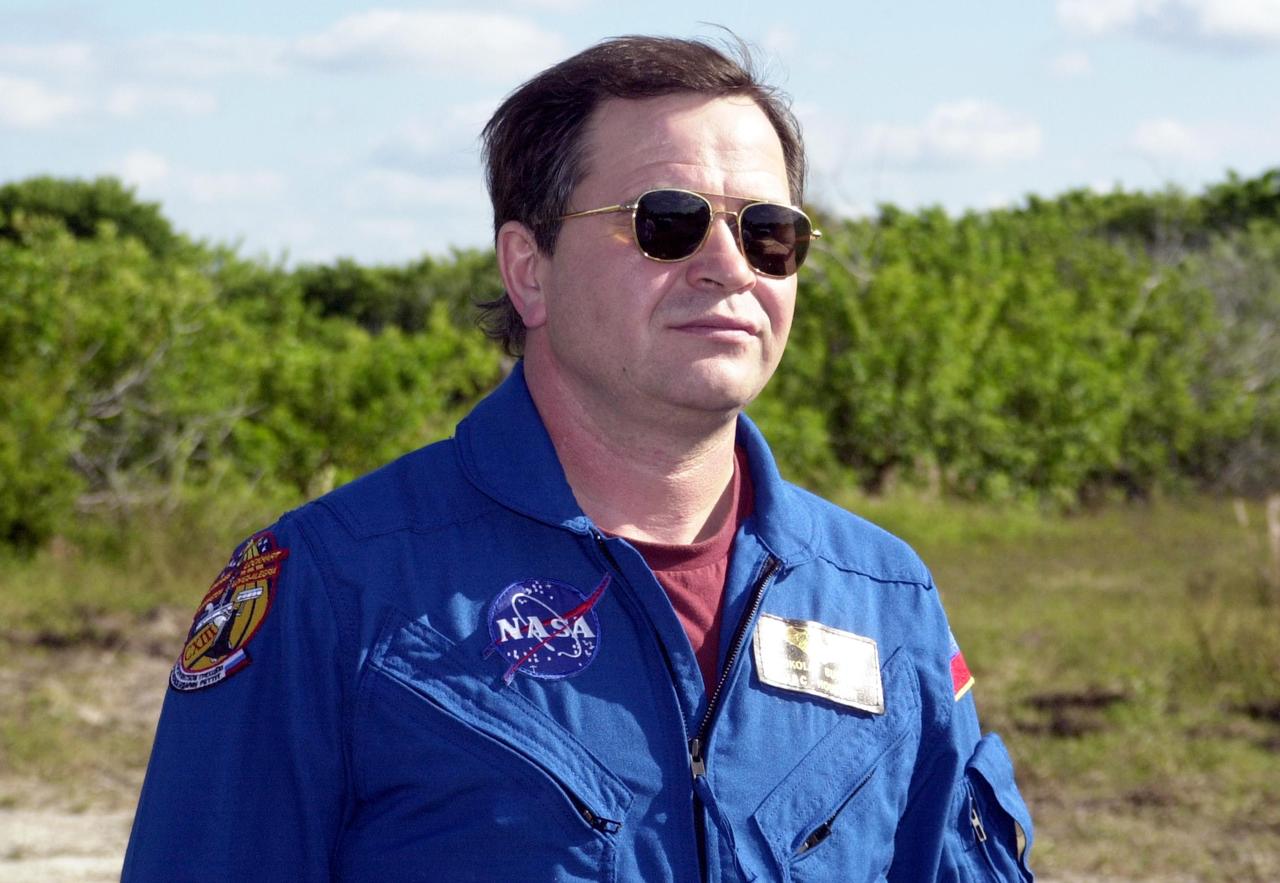

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Expedition 6 crew member Nikolai Budarin stands ready for a practice drive in an M-113 armored personnel carrier during emergency egress training at the pad, one of the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities in preparation for launch. The TCDT also includes a simulated launch countdown. The Expedition 6 crew will travel on Space Shuttle Endeavour to the International Space Station to replace Expedition 5, returning to Earth after 4 months. The primary payloads on mission STS-113 are the first port truss segment, P1, and the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) Cart B. Once delivered, the P1 truss will remain stowed until flight 12A.1 in 2003 when it will be attached to the central truss segment, S0, on the Space Station. Launch is scheduled for Nov. 10, 2002.
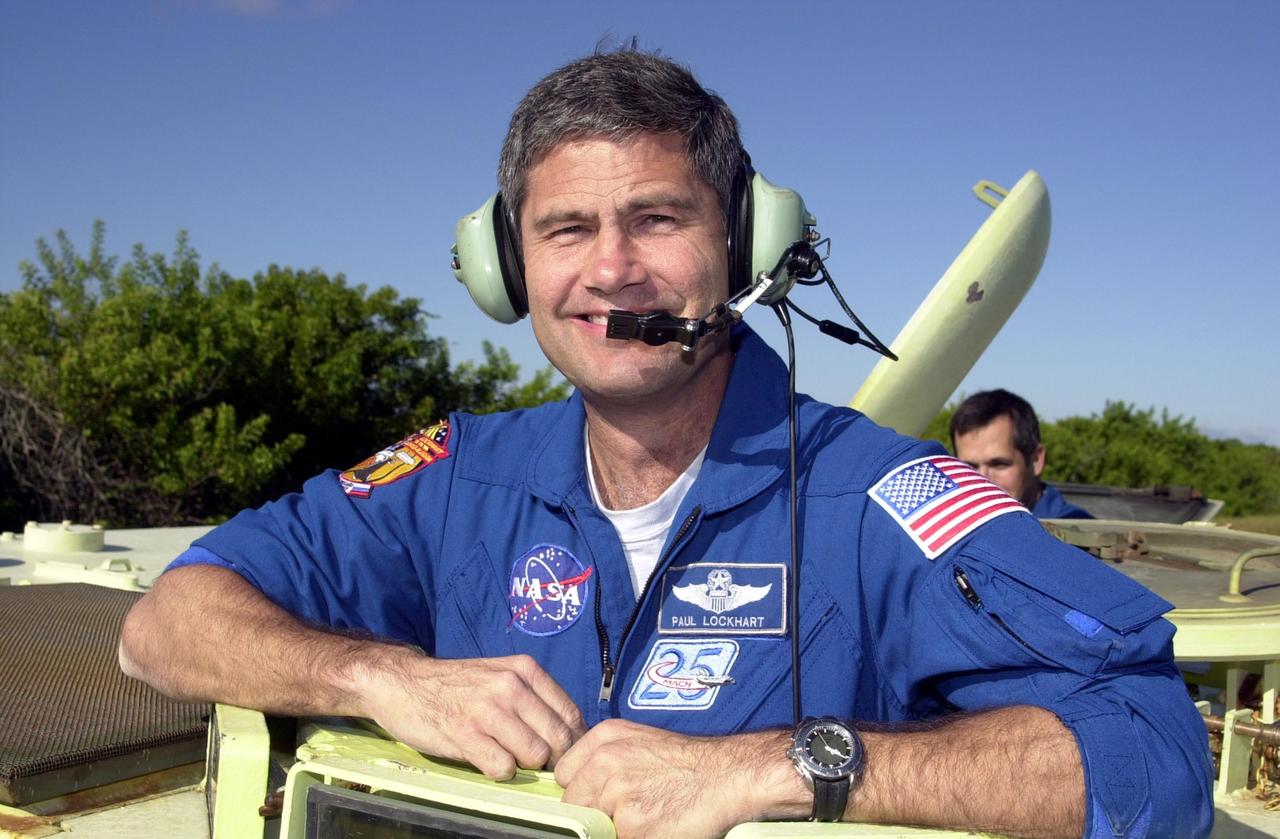

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-113 Pilot Paul Lockhart stands inside an M-113 armored personnel carrier he is about to drive, part of emergency egress training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. He and the rest of the crew are preparing for the mission aboard Space Shuttle Endeavour, which is scheduled to launch Nov. 10. The TCDT includes a simulated launch countdown. The primary payloads on mission STS-113 are the first port truss segment, P1, and the Crew and Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) Cart B. Once delivered, the P1 truss will remain stowed until flight 12A.1 in 2003 when it will be attached to the central truss segment, S0, on the Space Station. Also onboard Space Shuttle Endeavour will be the Expedition 6 crew who will replace Expedition 5, returning to Earth after 4 months.
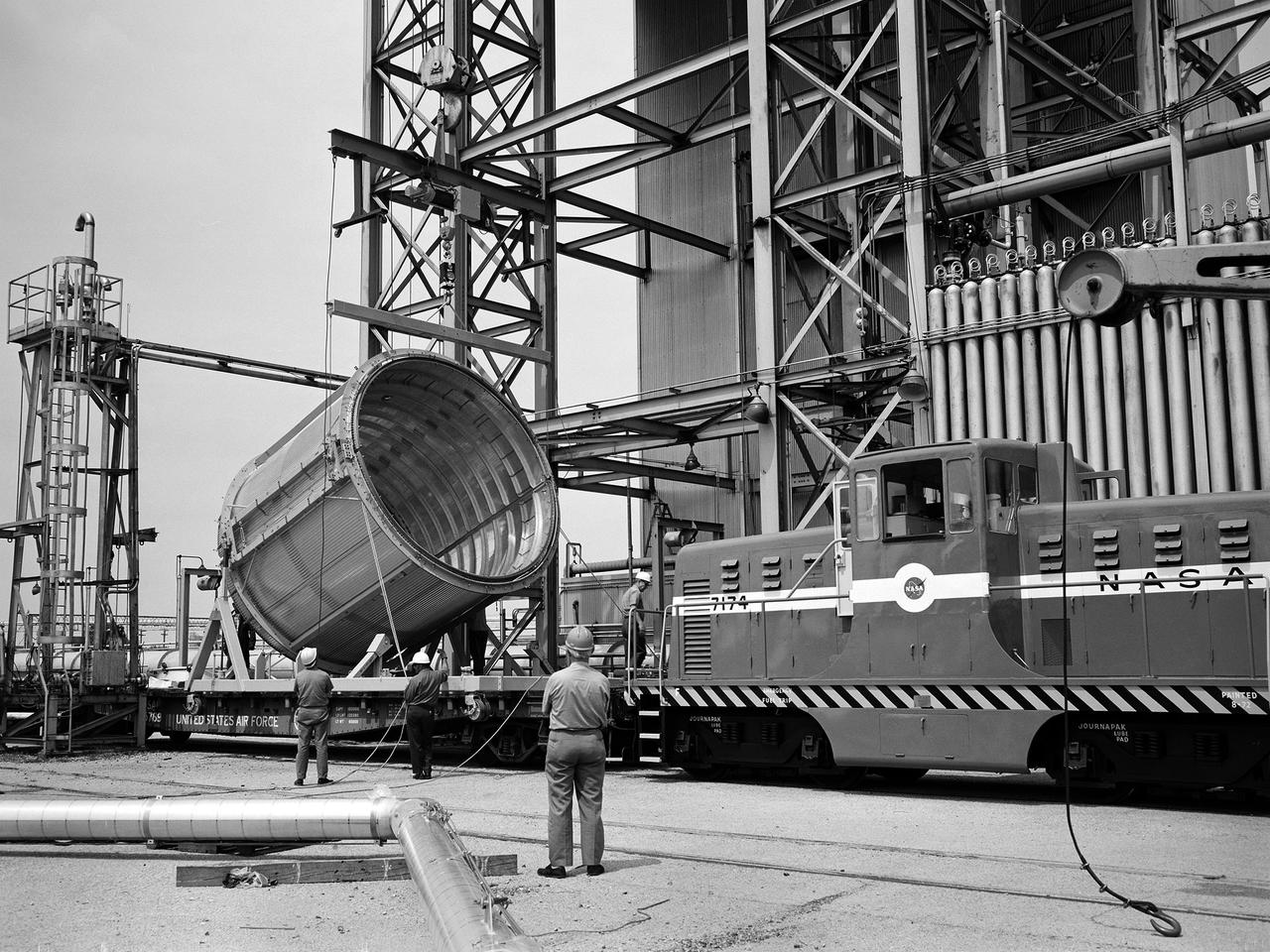

A section of the Centaur Standard Shroud transported to Nuclear Rocket Dynamics and Control Facility, or B-3 Test Stand, at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station. B-3 was built in the early 1960s to test full-scale liquid hydrogen fuel systems in simulated altitude conditions. The facility was used in 1972, however, for testing of the Centaur Standard Shroud’s ejection system. In the late 1960s NASA engineers were planning the ambitious new Viking mission to send two rover vehicles to the surface of Mars. The Viking rovers were the heaviest payloads ever attempted and were over three times the weight of Atlas-Centaur’s previous heaviest payload. Consequently, NASA engineers selected the more powerful the Titan III rocket booster to mate with the Centaur. Concurrently, General Dynamics was in the process of introducing a new Centaur model for Titan—the D-1T. The biggest change for the D-1T was a completely new shroud designed by Lockheed, called the Centaur Standard Shroud. The shroud, its insulation, the Centaur ground-hold purge system, and the hydrogen tank venting system were all studied in B-3. After more than two years of preparations, the tests were run between April and July 1973. The tests determined the ultimate flight loads on two axes, established the Centaur’s load sharing, the level of propellant boiloff during launch holds, and the vent system capacity. The Centaur Standard Shroud performed flawlessly during the August 20 and September 9, 1975 launches of Viking 1 and 2.
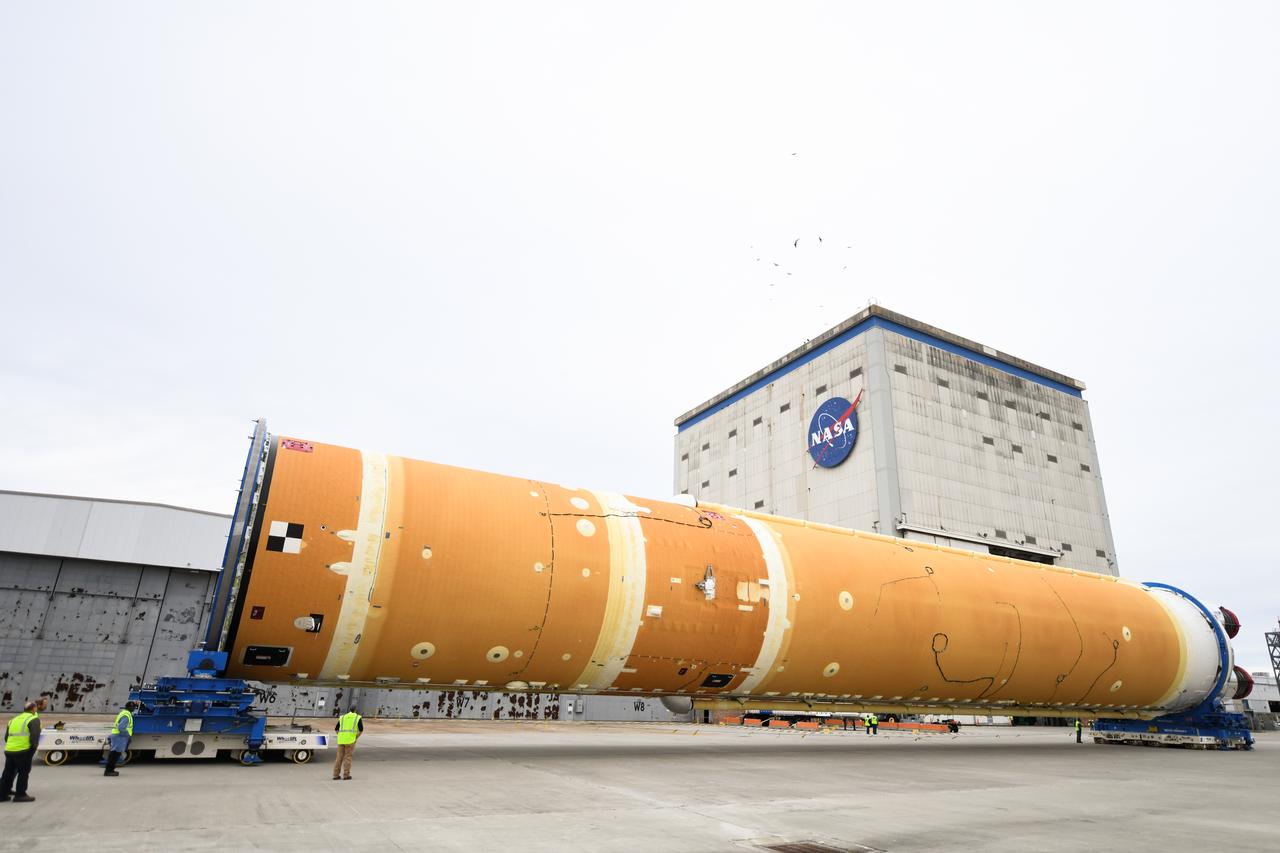

These images show how teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the core stage, complete with all four RS-25 engines, for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to Building 110 for final shipping preparations on Jan. 1. The SLS core stage includes state-of-the-art avionics, propulsion systems and two colossal propellant tanks that collectively hold 733,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen to power its four RS-25 engines. The completed stage, which will provide more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help power the first Artemis mission to the Moon, will be shipped via the agency’s Pegasus barge from Michoud to NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, later this month. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I.
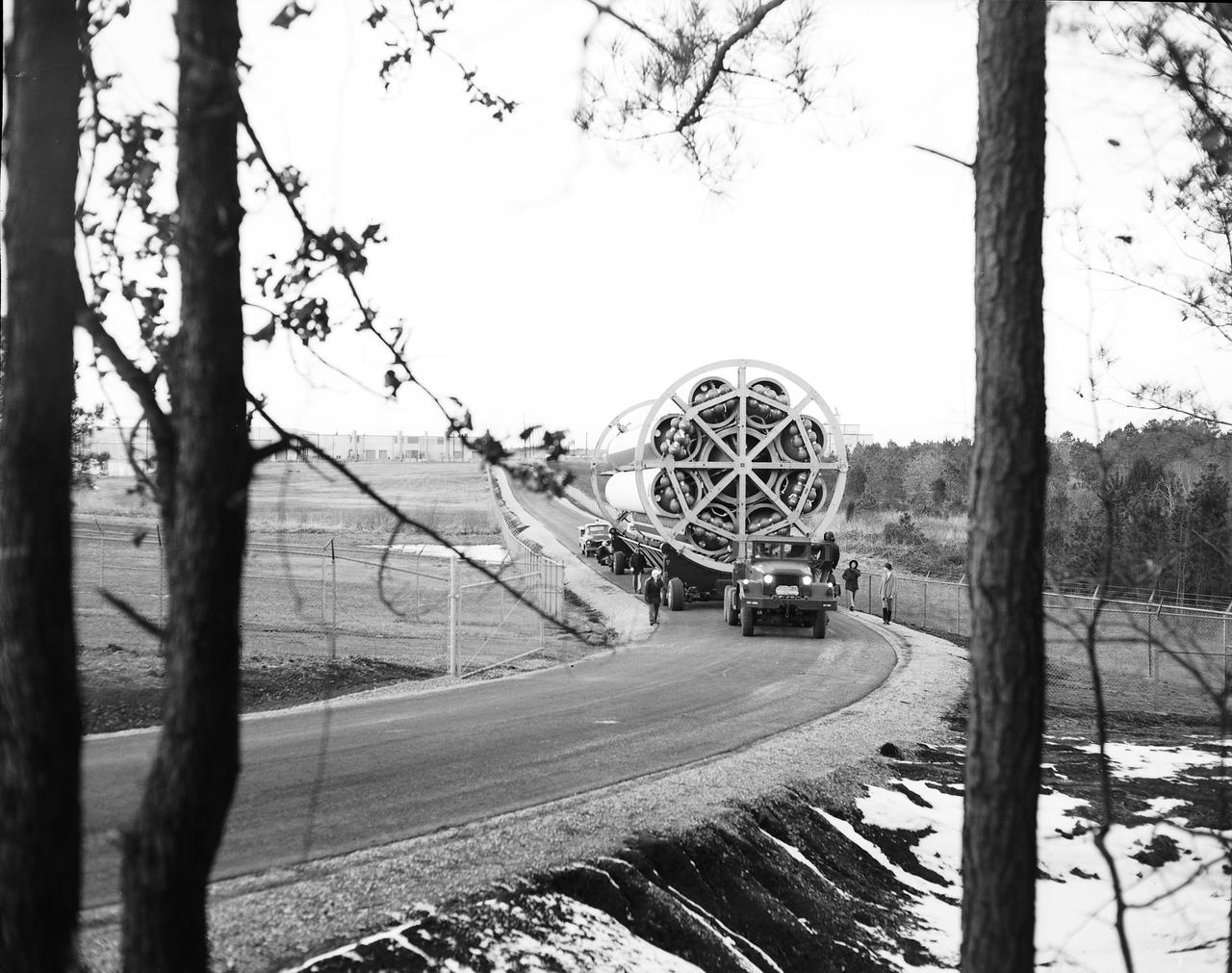

This photograph shows the Saturn-I first stage (S-1 stage) being transported to the test stand for a static test firing at the Marshall Space Flight Center. Soon after NASA began operations in October 1958, it was evident that sending people and substantial equipment beyond the Earth's gravitational field would require launch vehicles with weight-lifting capabilities far beyond any developed to that time. In early 1959, NASA accepted the proposal of Dr. Wernher von Braun for a multistage rocket, with a number of engines clustered in one or more of the stages to provide a large total thrust. The initiation of the Saturn launch vehicle program ultimately led to the study and preliminary plarning of many different configurations and resulted in production of three Saturn launch vehicles, the Saturn-I, Saturn I-B, and Saturn V. The Saturn family of launch vehicles began with the Saturn-I, a two-stage vehicle originally designated C-1. The research and development program was planned in two phases, or blocks: one for first stage development (Block I) and the second for both first and second stage development (Block-II). Saturn I had a low-earth-orbit payload capability of approximately 25,000 pounds. The design of the first stage (S-1 stage) used a cluster of propellant tanks containing liquid oxygen (LOX) and kerosene (RP-1), and eight H-1 engines, yielding a total thrust of 1,500,000 pounds. Of the ten Saturn-Is planned, the first eight were designed and built at the Marshall Space Flight Center, and the remaining two were built by the Chrysler Corporation.
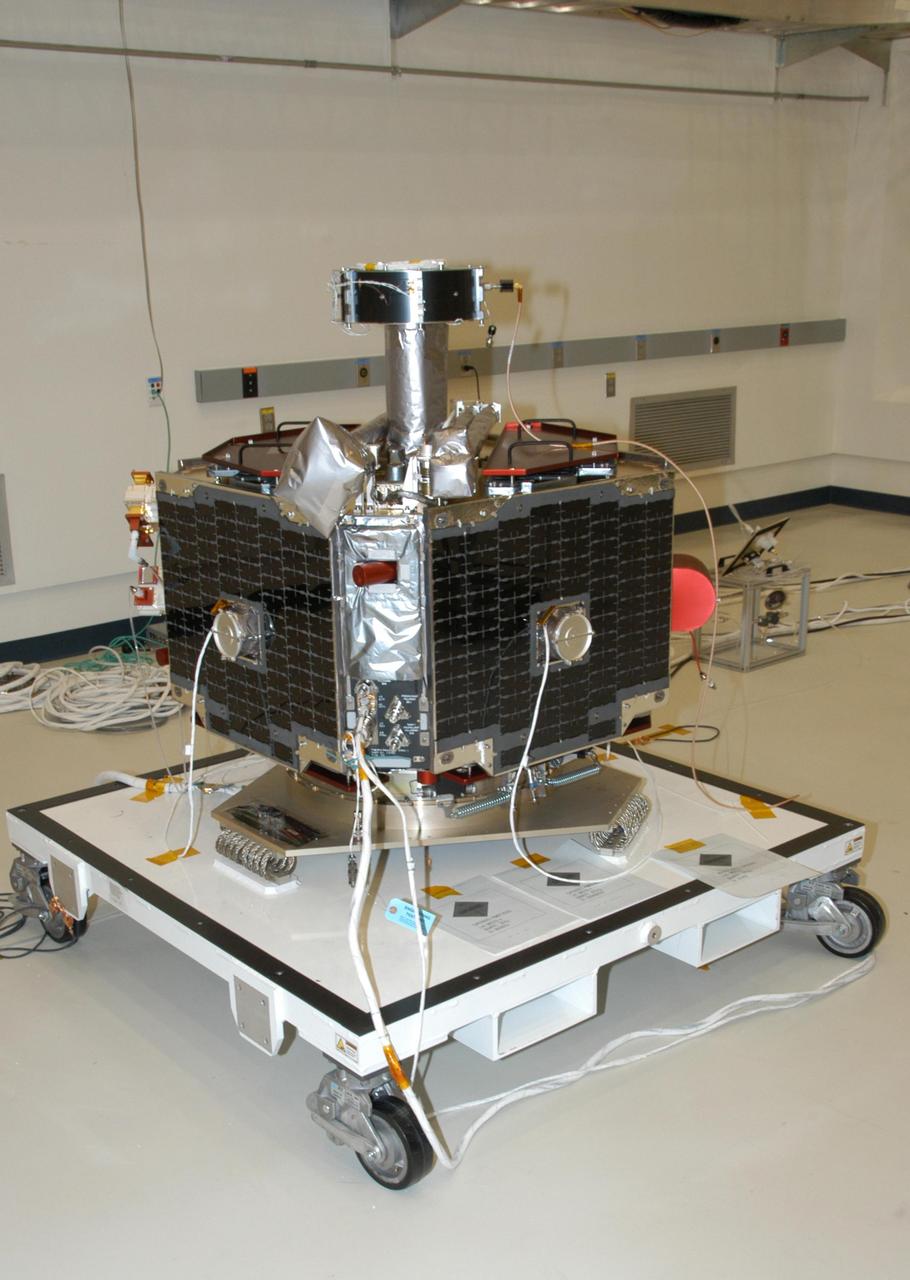
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., one of the five THEMIS probes is ready to be covered for its move to the hazardous processing facility. There it will be placed on a stand in preparation for fueling operations. Once fueling is complete, each probe will be weighed and individually mated to the payload carrier before pyrotechnics are installed. The fully integrated THEMIS payload is then ready for spin-balance testing and weighing. The final milestone is mating THEMIS to its upper stage booster. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. These lights are the visible manifestations of invisible energy releases, called geomagnetic substorms, in near-Earth space. THEMIS will not only seek to answer where and when substorms start, but will also provide clues as to how and why these space storms create havoc on satellites, terrestrial power grids, and communication systems. THEMIS will be transported to Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on February 1 for mating to the Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 15. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
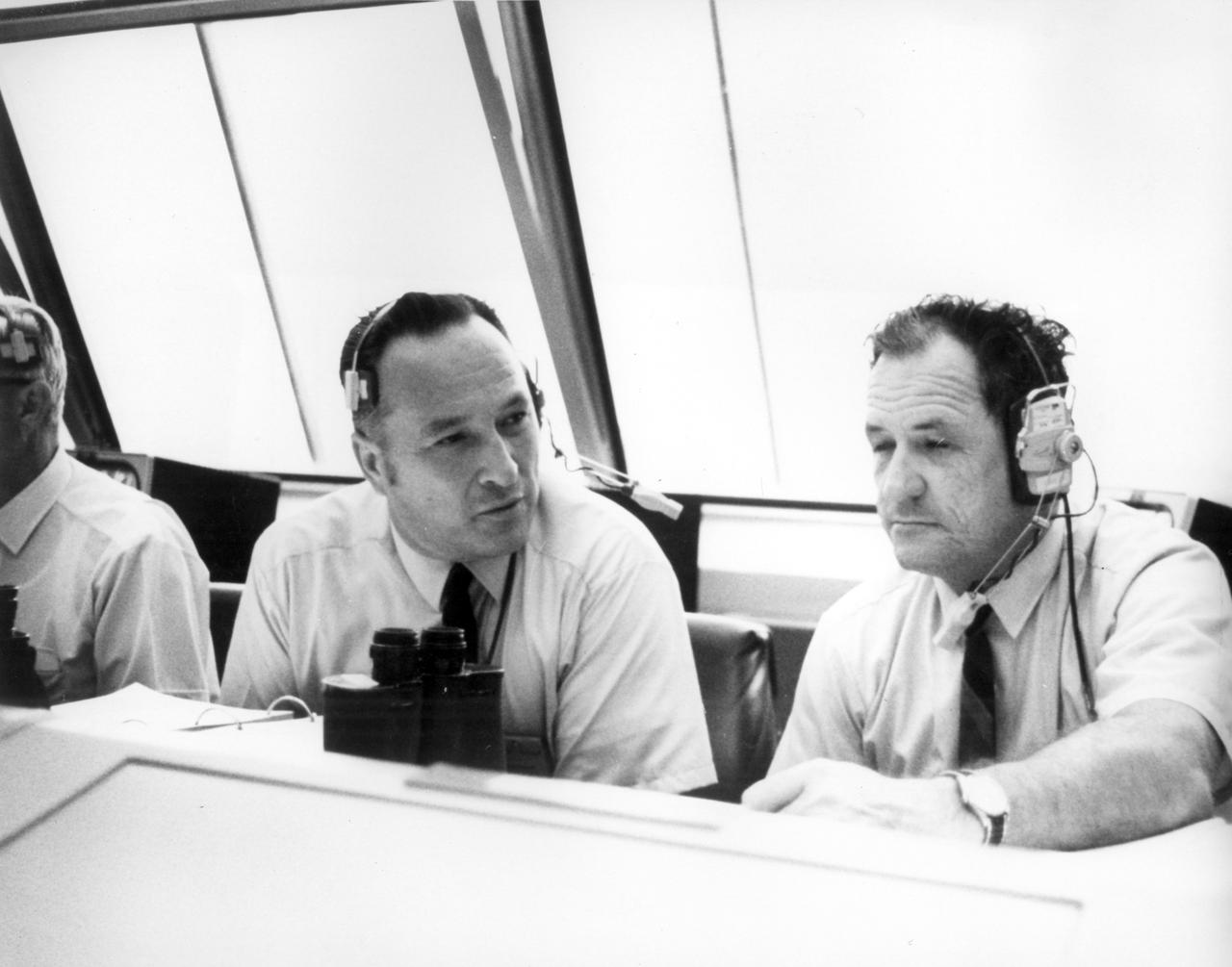

Lee B. James (left), manager of the Saturn Program at the Marshall Space flight Center (MSFC), talks with Isom Pigell in the firing room 1 of the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) control center during the countdown demonstration test for the Apollo 11 mission. The Apollo 11 mission, the first lunar landing mission, launched from the KSC in Florida via the MSFC developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
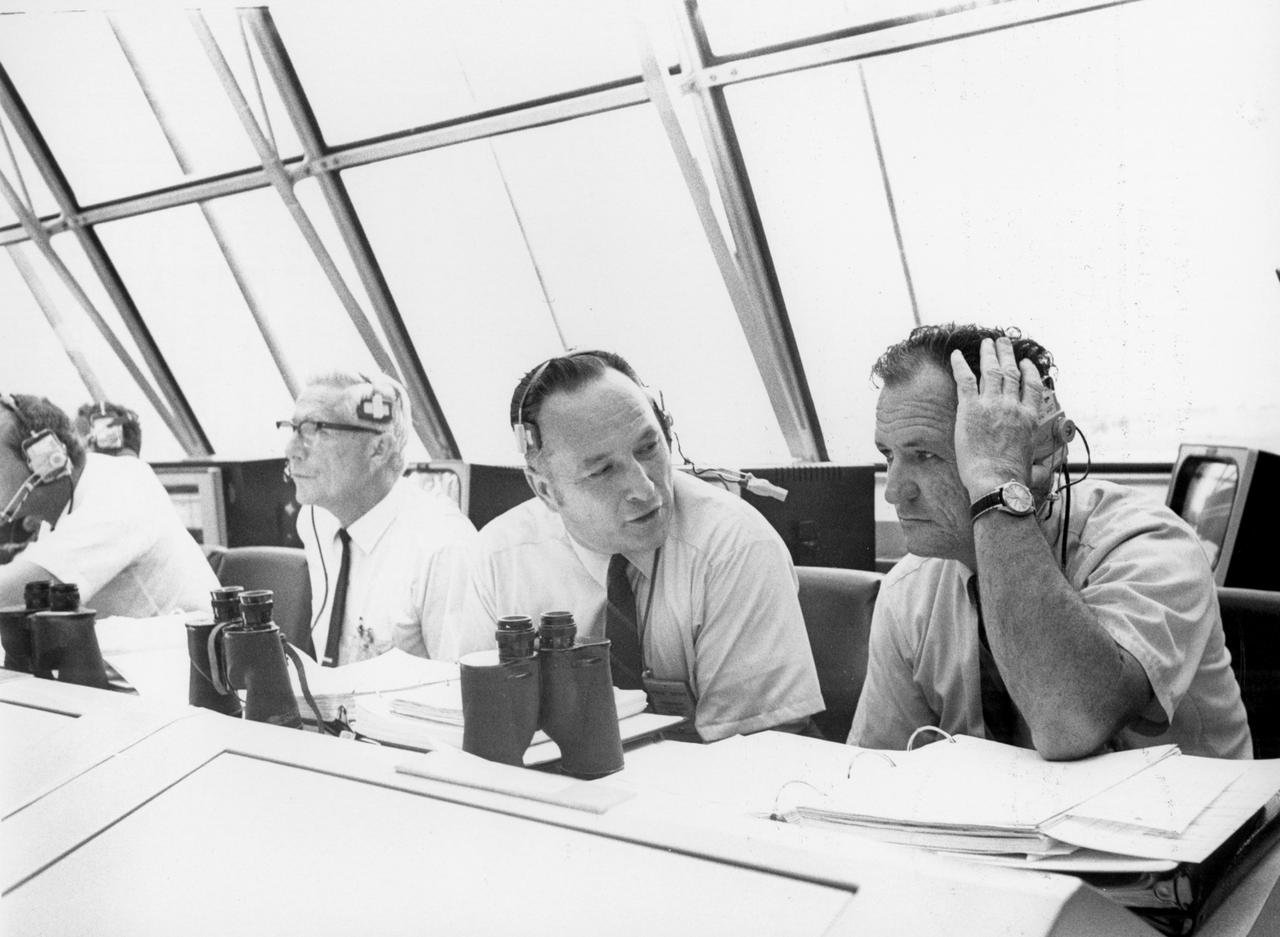

Lee B. James (left), manager of the Saturn Program at the Marshall Space flight Center (MSFC), talks with Isom Pigell in the firing room 1 of the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) control center during the countdown demonstration test for the Apollo 11 mission. At left is Dr. Hans C. Gruen of KSC. The Apollo 11 mission, the first lunar landing mission, launched from the KSC in Florida via the MSFC developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
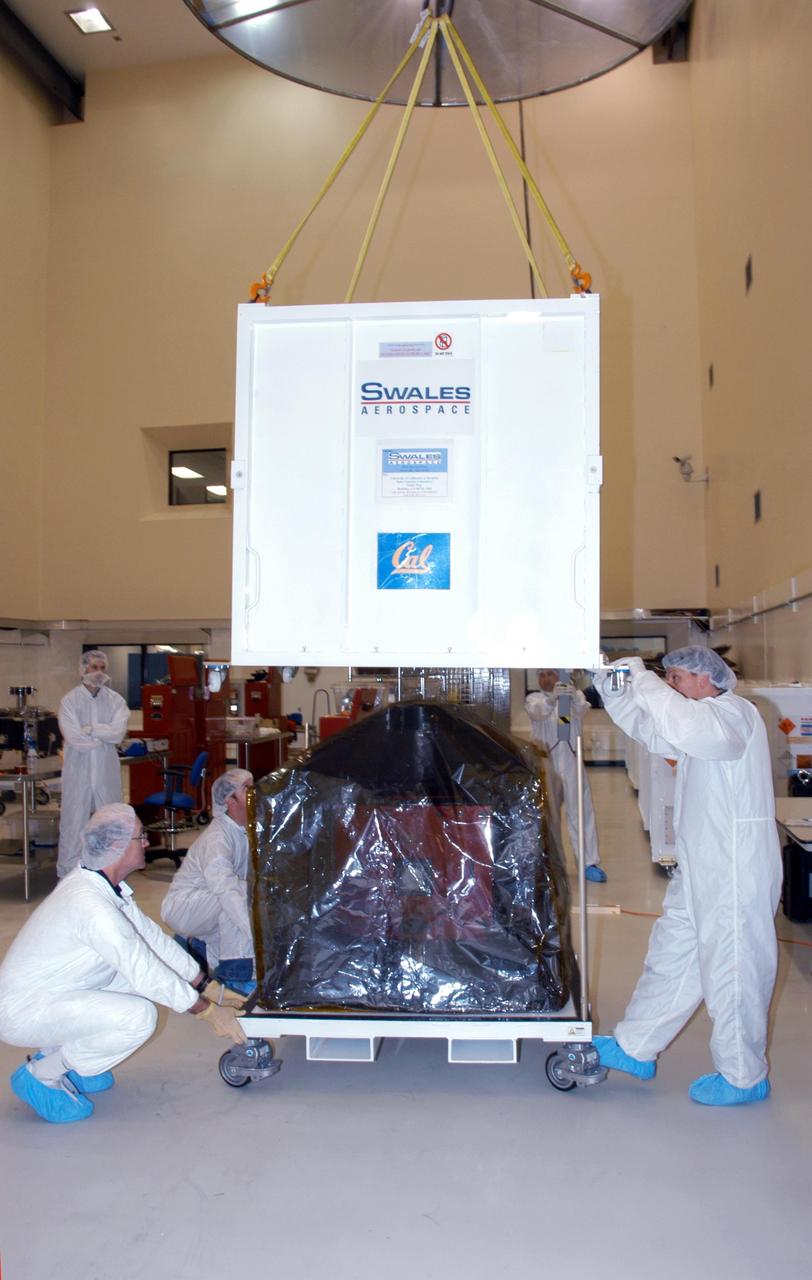

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians help lower a shipping container over one of the five THEMIS probes for its move to the hazardous processing facility. There it will be placed on a stand in preparation for fueling operations. Once fueling is complete, each probe will be weighed and individually mated to the payload carrier before pyrotechnics are installed. The fully integrated THEMIS payload is then ready for spin-balance testing and weighing. The final milestone is mating THEMIS to its upper stage booster. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. These lights are the visible manifestations of invisible energy releases, called geomagnetic substorms, in near-Earth space. THEMIS will not only seek to answer where and when substorms start, but will also provide clues as to how and why these space storms create havoc on satellites, terrestrial power grids, and communication systems. THEMIS will be transported to Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on February 1 for mating to the Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 15. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
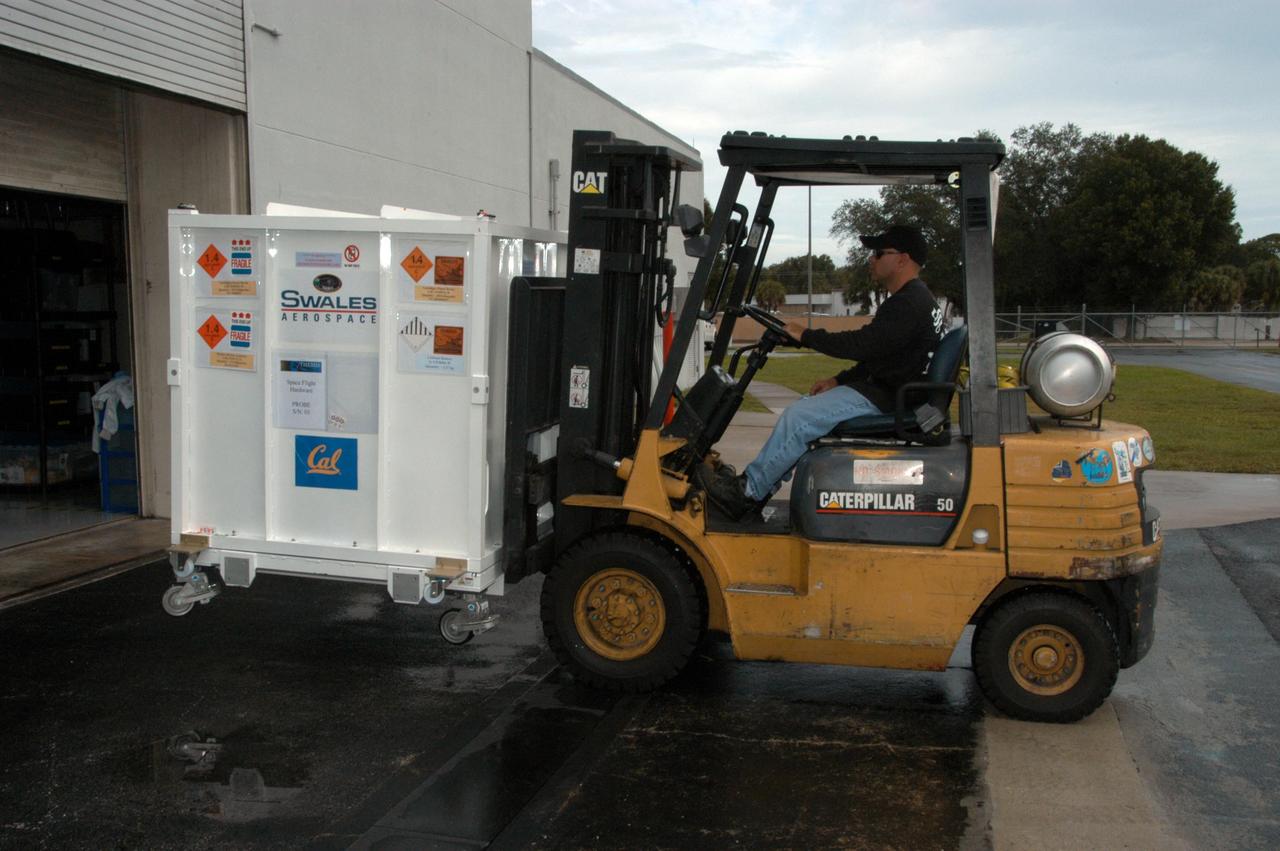

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., one of the five THEMIS probes is moved out of the facility and will be transported to the hazardous processing facility. There the probes will be placed on a stand in preparation for fueling operations. Once fueling is complete, each probe will be weighed and individually mated to the payload carrier before pyrotechnics are installed. The fully integrated THEMIS payload is then ready for spin-balance testing and weighing. The final milestone is mating THEMIS to its upper stage booster. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. These lights are the visible manifestations of invisible energy releases, called geomagnetic substorms, in near-Earth space. THEMIS will not only seek to answer where and when substorms start, but will also provide clues as to how and why these space storms create havoc on satellites, terrestrial power grids, and communication systems. THEMIS will be transported to Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on February 1 for mating to the Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 15. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians are preparing one of five THEMIS probes to be secured inside a shipping container (behind it). The probes are being moved to the hazardous processing facility where they will be placed on a stand in preparation for fueling operations. Once fueling is complete, each probe will be weighed and individually mated to the payload carrier before pyrotechnics are installed. The fully integrated THEMIS payload is then ready for spin-balance testing and weighing. The final milestone is mating THEMIS to its upper stage booster. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. These lights are the visible manifestations of invisible energy releases, called geomagnetic substorms, in near-Earth space. THEMIS will not only seek to answer where and when substorms start, but will also provide clues as to how and why these space storms create havoc on satellites, terrestrial power grids, and communication systems. THEMIS will be transported to Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on February 1 for mating to the Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 15. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
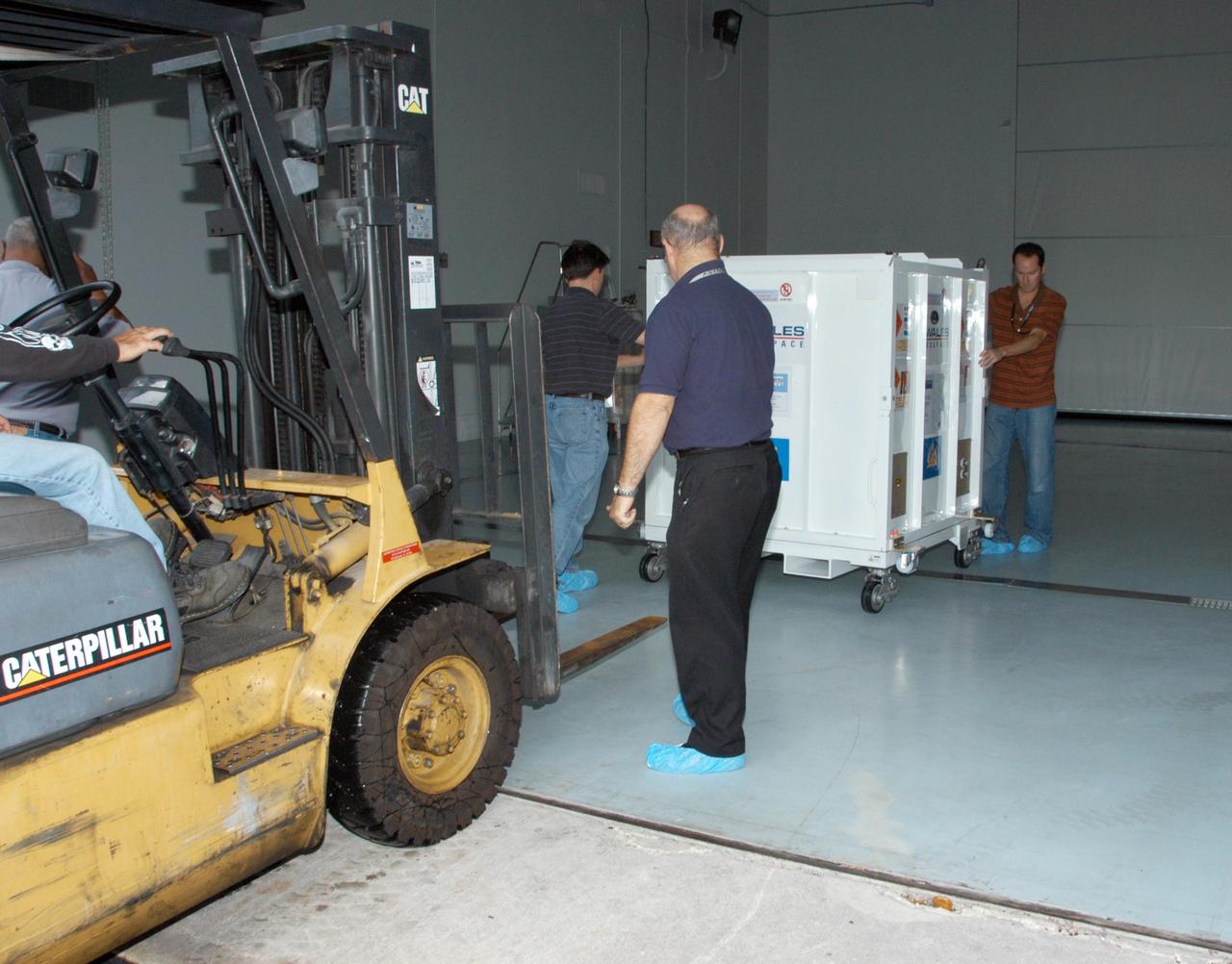

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- One of the five THEMIS probes arrives at the hazardous processing facility after leaving Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla. At the facility, the probes will be placed on a stand in preparation for fueling operations. Once fueling is complete, each probe will be weighed and individually mated to the payload carrier before pyrotechnics are installed. The fully integrated THEMIS payload is then ready for spin-balance testing and weighing. The final milestone is mating THEMIS to its upper stage booster. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. These lights are the visible manifestations of invisible energy releases, called geomagnetic substorms, in near-Earth space. THEMIS will not only seek to answer where and when substorms start, but will also provide clues as to how and why these space storms create havoc on satellites, terrestrial power grids, and communication systems. THEMIS will be transported to Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on February 1 for mating to the Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 15. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
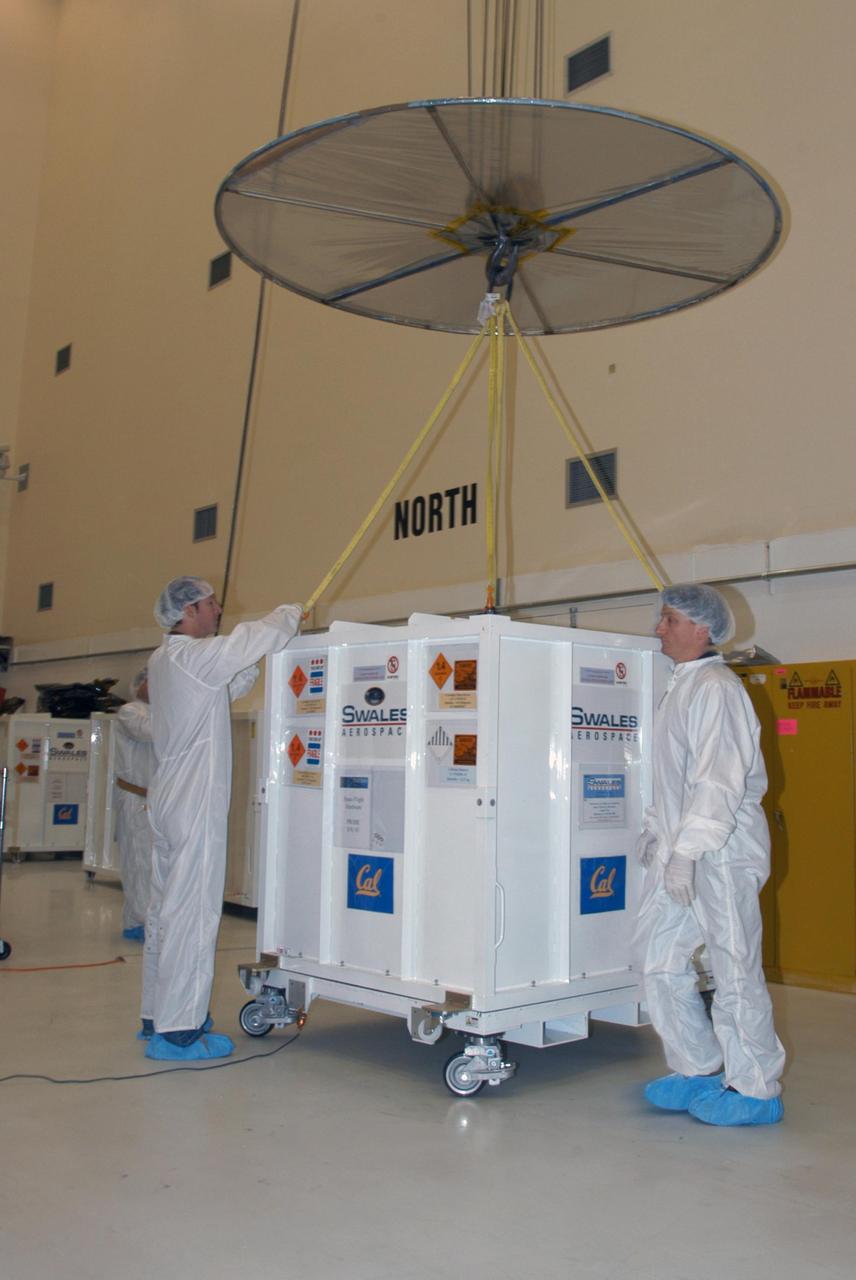

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., technicians release the overhead crane from the shipping container placed around one of the five THEMIS probes for its move to the hazardous processing facility. There the probes will be placed on a stand in preparation for fueling operations. Once fueling is complete, each probe will be weighed and individually mated to the payload carrier before pyrotechnics are installed. The fully integrated THEMIS payload is then ready for spin-balance testing and weighing. The final milestone is mating THEMIS to its upper stage booster. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. These lights are the visible manifestations of invisible energy releases, called geomagnetic substorms, in near-Earth space. THEMIS will not only seek to answer where and when substorms start, but will also provide clues as to how and why these space storms create havoc on satellites, terrestrial power grids, and communication systems. THEMIS will be transported to Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on February 1 for mating to the Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 15. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
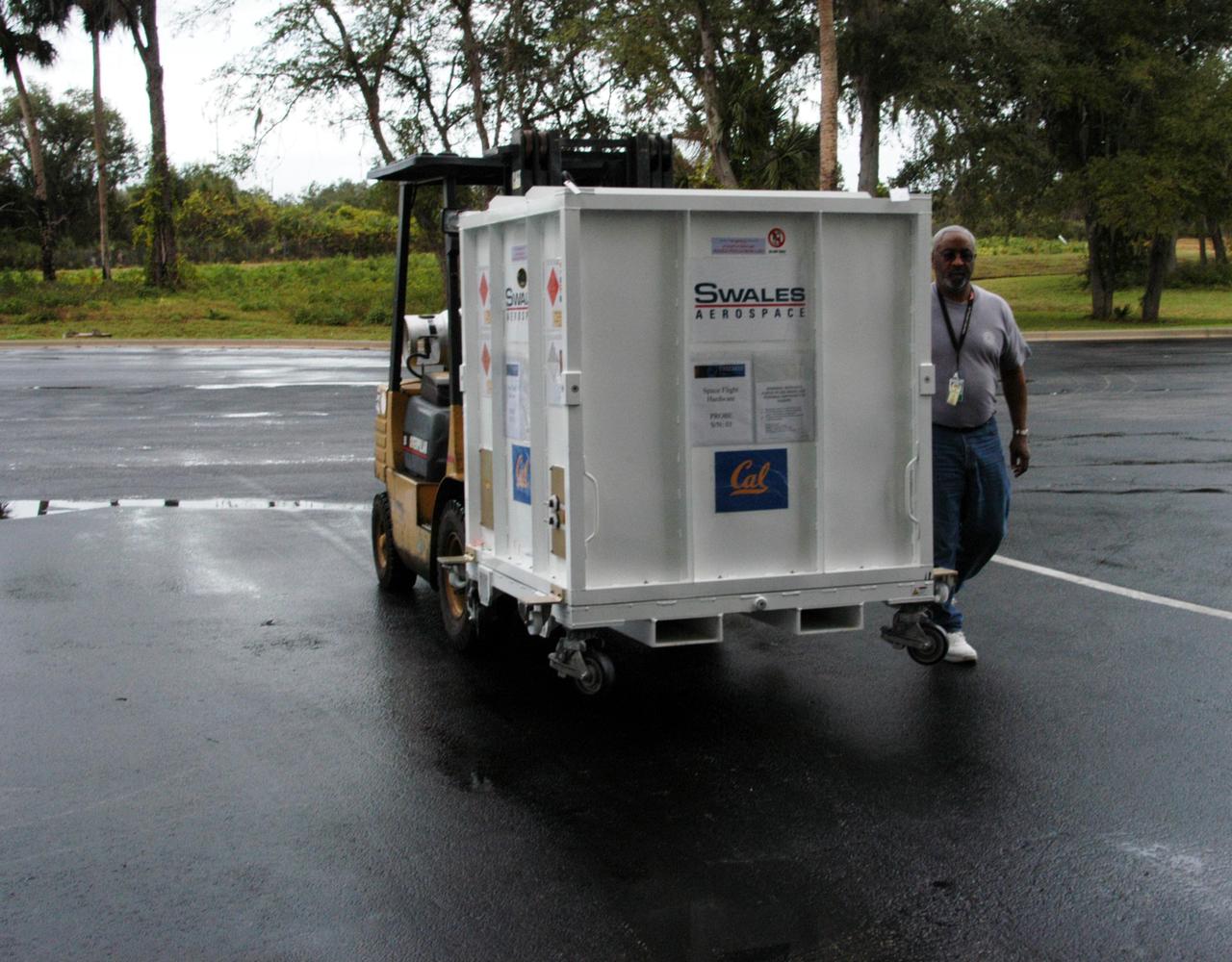

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- One of the five THEMIS probes is being transported from Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., to the hazardous processing facility. There the probes will be placed on a stand in preparation for fueling operations. Once fueling is complete, each probe will be weighed and individually mated to the payload carrier before pyrotechnics are installed. The fully integrated THEMIS payload is then ready for spin-balance testing and weighing. The final milestone is mating THEMIS to its upper stage booster. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. These lights are the visible manifestations of invisible energy releases, called geomagnetic substorms, in near-Earth space. THEMIS will not only seek to answer where and when substorms start, but will also provide clues as to how and why these space storms create havoc on satellites, terrestrial power grids, and communication systems. THEMIS will be transported to Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on February 1 for mating to the Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Feb. 15. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton