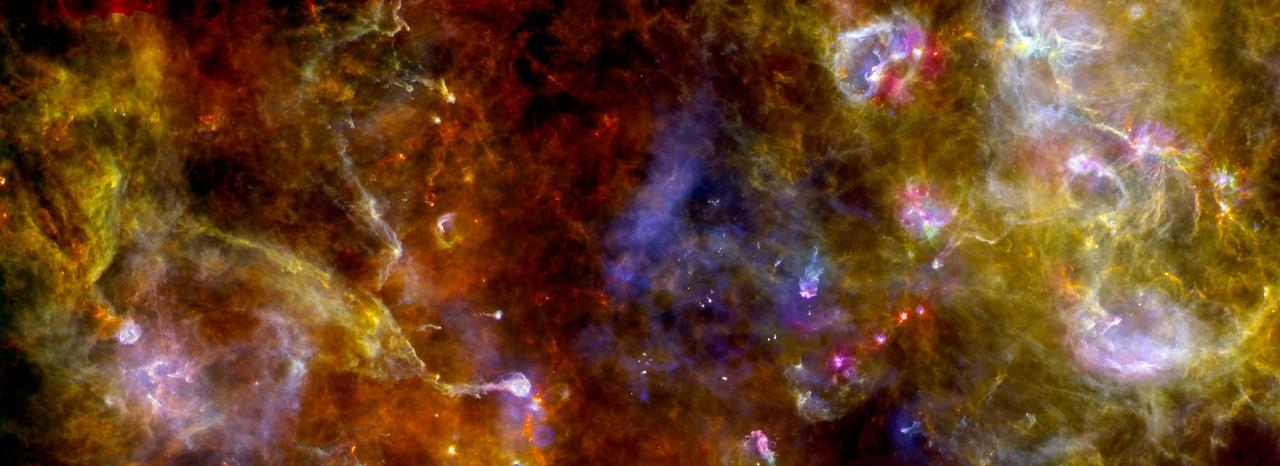

This new view of the Cygnus-X star-formation region by ESA Herschel Space Observatory highlights chaotic networks of dust and gas that point to sites of massive star formation.

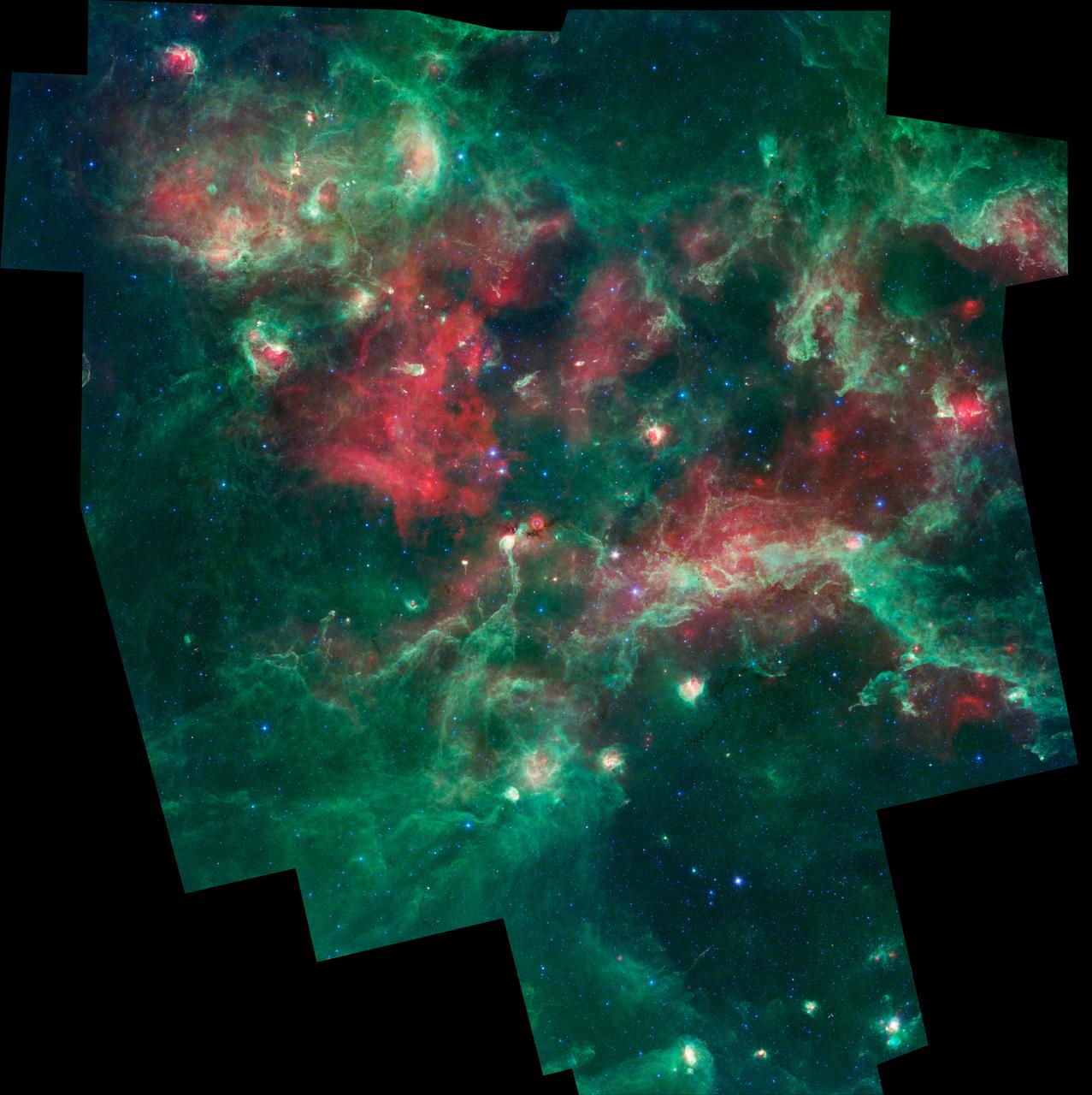
Cygnus X hosts many young stellar groupings. The combined outflows and ultraviolet radiation from the region's numerous massive stars have heated and pushed gas away from the clusters, producing cavities of hot, lower-density gas. In this 8-micron infrared image, ridges of denser gas mark the boundaries of the cavities. Bright spots within these ridges show where stars are forming today. Credit: NASA/IPAC/MSX To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/cygnus-cocoon.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/cygnus-cocoon.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

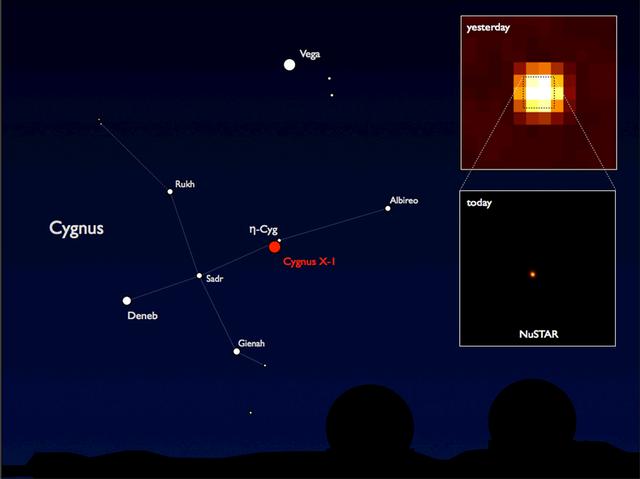
This image of the suspected Black Hole, Cygnus X-1, was the first object seen by the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-2/Einstein Observatory. According to the theories to date, one concept of a black hole is a star, perhaps 10 times more massive than the Sun, that has entered the last stages of stelar evolution. There is an explosion triggered by nuclear reactions after which the star's outer shell of lighter elements and gases is blown away into space and the heavier elements in the stellar core begin to collapse upon themselves. Once this collapse begins, the inexorable force of gravity continues to compact the material until it becomes so dense it is squeezed into a mere point and nothing can escape from its extreme gravitational field, not even light. The HEAO-2, the first imaging and largest x-ray telescope built to date, was capable of producing actual photographs of x-ray objects. Shortly after launch, the HEAO-2 was nicknamed the Einstein Observatory by its scientific experimenters in honor of the centernial of the birth of Albert Einstein, whose concepts of relativity and gravitation have influenced much of modern astrophysics, particularly x-ray astronomy.

A bubbling cauldron of star birth is highlighted in this image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. Massive stars have blown bubbles, or cavities, in the dust and gas -- a violent process that triggers both the death and birth of stars.
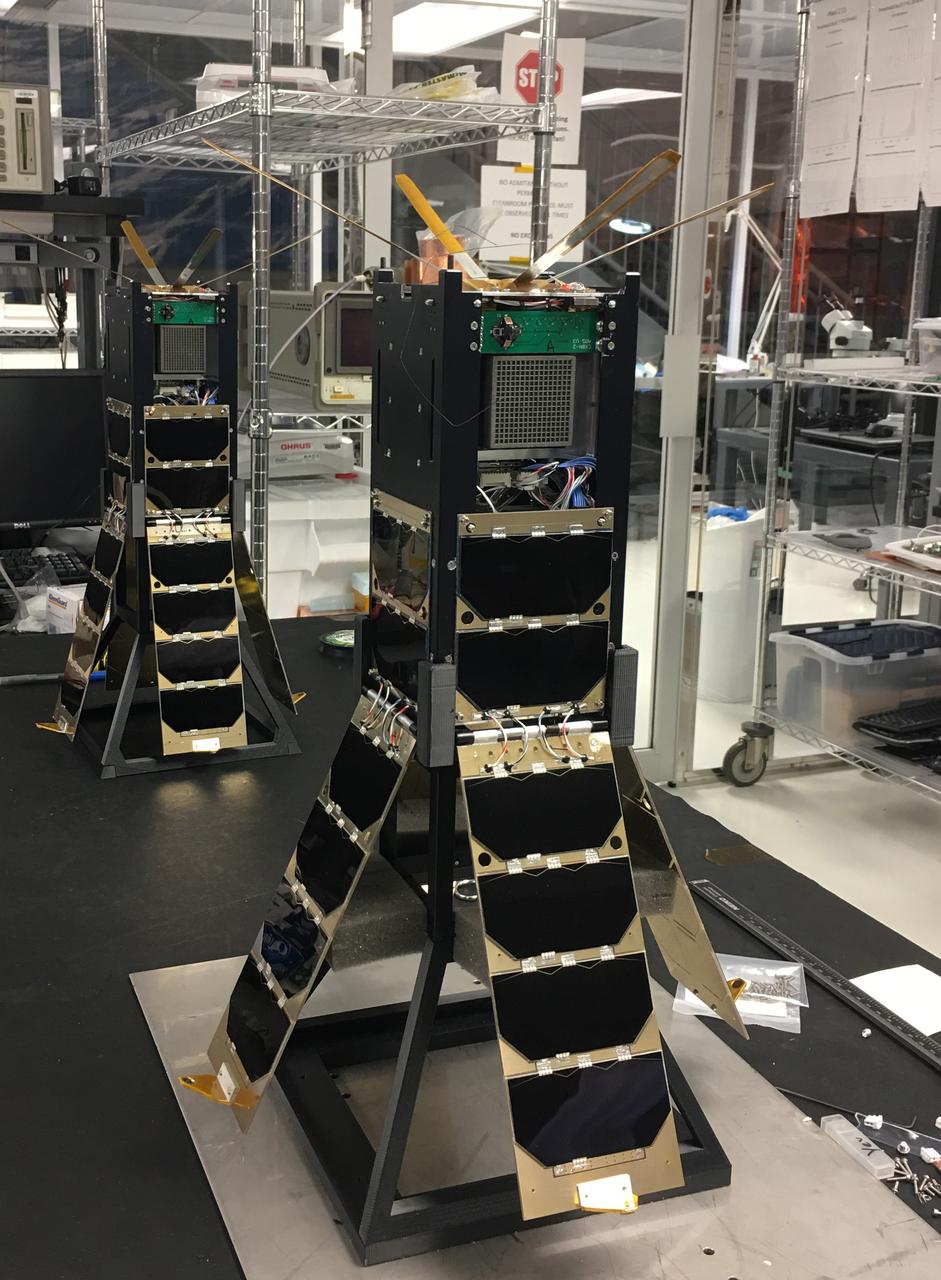

The Cosmic X-Ray Background NanoSat-2 (CXBN-2) CubeSat Mission developed by Morehead State University and its partners the Keldysh Institute (Moscow, Russia), the Maysville Community and Technical College (Morehead, KY) and KYSpace LLC (Lexington, KY) will increase the precision of measurements of the Cosmic X-Ray Background in the 30-50 keV range to a precision of <5%, thereby constraining models that attempt to explain the relative contribution of proposed sources lending insight into the underlying physics of the early universe. The mission addresses a fundamental science question that is central to our understanding of the structure, origin, and evolution of the universe by potentially lending insight into both the high-energy background radiation and into the evolution of primordial galaxies. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative NET April 18, 2017 ELaNa XVII mission on the seventh Orbital-ATK Cygnus Commercial Resupply Services (OA-7) to the International Space Station and deployed on tbd.
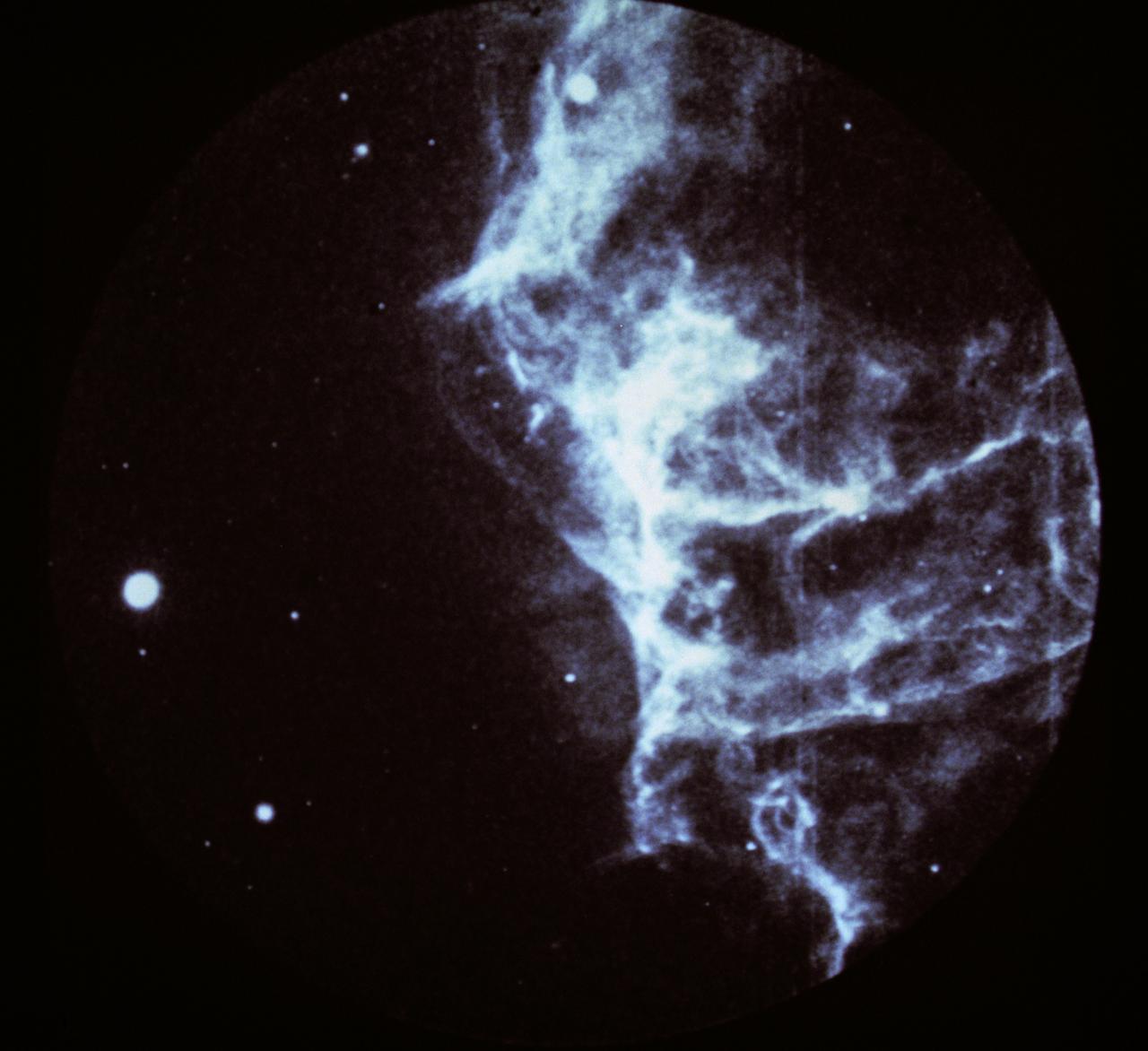
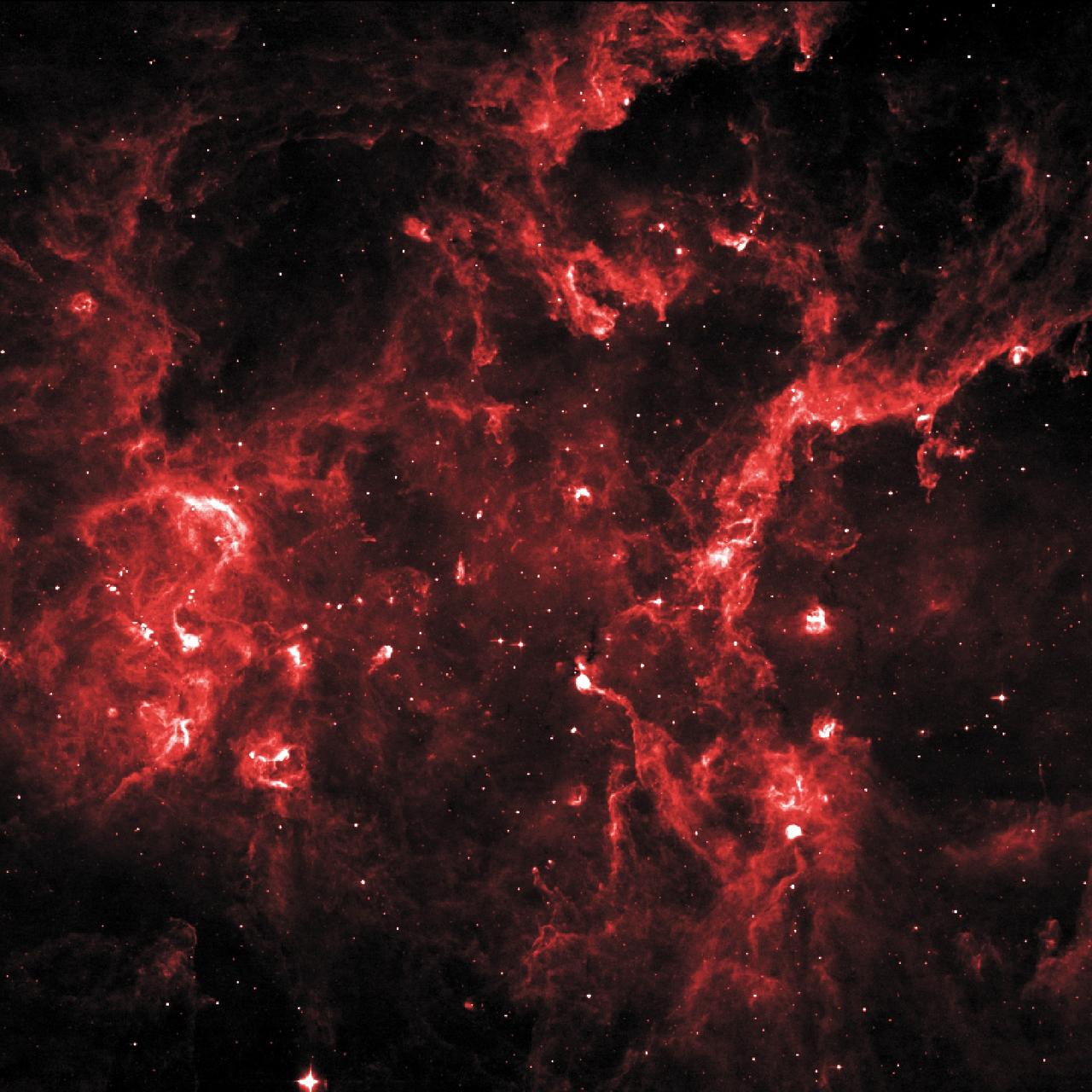
This image shows a part of the Cygnus loop supernova remnant, taken by the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT) on the Astro Observatory during the Astro-1 mission (STS-35) on December 5, 1990. Pictured is a portion of the huge Cygnus loop, an array of interstellar gas clouds that have been blasted by a 900,000 mile per hour shock wave from a prehistoric stellar explosion, which occurred about 20,000 years ago, known as supernova. With ultraviolet and x-rays, astronomers can see emissions from extremely hot gases, intense magnetic fields, and other high-energy phenomena that more faintly appear in visible and infrared light or in radio waves that are crucial to deepening the understanding of the universe. The Astro Observatory was designed to explore the universe by observing and measuring the ultraviolet radiation from celestial objects. Three instruments make up the Astro Observatory: The Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT), and the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimetry Experiment (WUPPE). The Marshall Space Flight Center had managment responsibilities for the Astro-1 mission. The Astro-1 Observatory was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia (STS-35) on December 2, 1990.
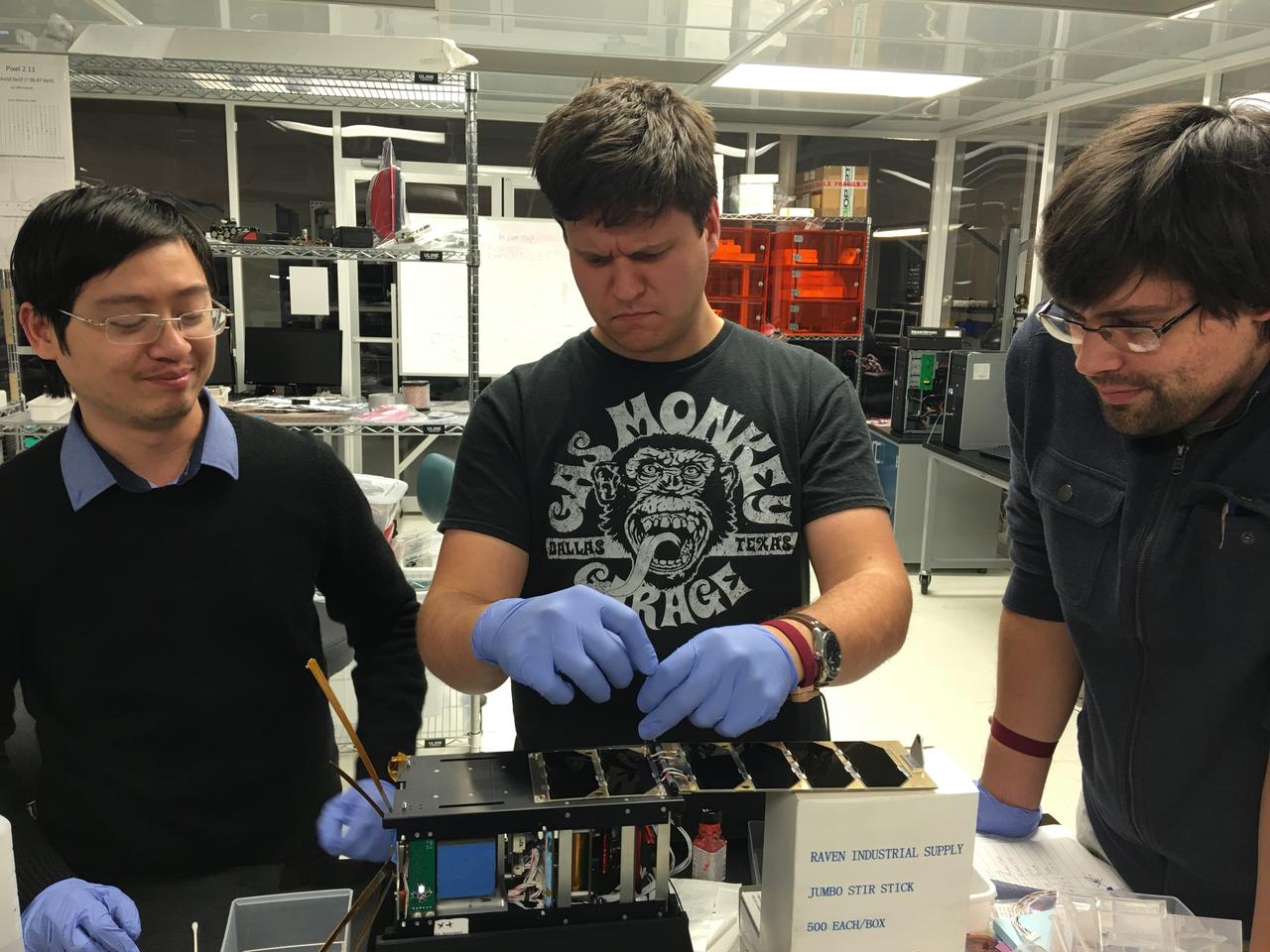
CXBN-2 Integration Team in the Morehead State University Spacecraft Integration and Assembly Facility. Left to right: Kein Dant, Yevgeniy Byleborodov, and Nate Richard. The Cosmic X-Ray Background NanoSat-2 (CXBN-2) CubeSat Mission developed by Morehead State University and its partners the Keldysh Institute (Moscow, Russia), the Maysville Community and Technical College (Morehead, KY) and KYSpace LLC (Lexington, KY) will increase the precision of measurements of the Cosmic X-Ray Background in the 30-50 keV range to a precision of <5%, thereby constraining models that attempt to explain the relative contribution of proposed sources lending insight into the underlying physics of the early universe. The mission addresses a fundamental science question that is central to our understanding of the structure, origin, and evolution of the universe by potentially lending insight into both the high-energy background radiation and into the evolution of primordial galaxies. Launched by NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative NET April 18, 2017 ELaNa XVII mission on the seventh Orbital-ATK Cygnus Commercial Resupply Services (OA-7) to the International Space Station and deployed on tbd.
converted PNM file