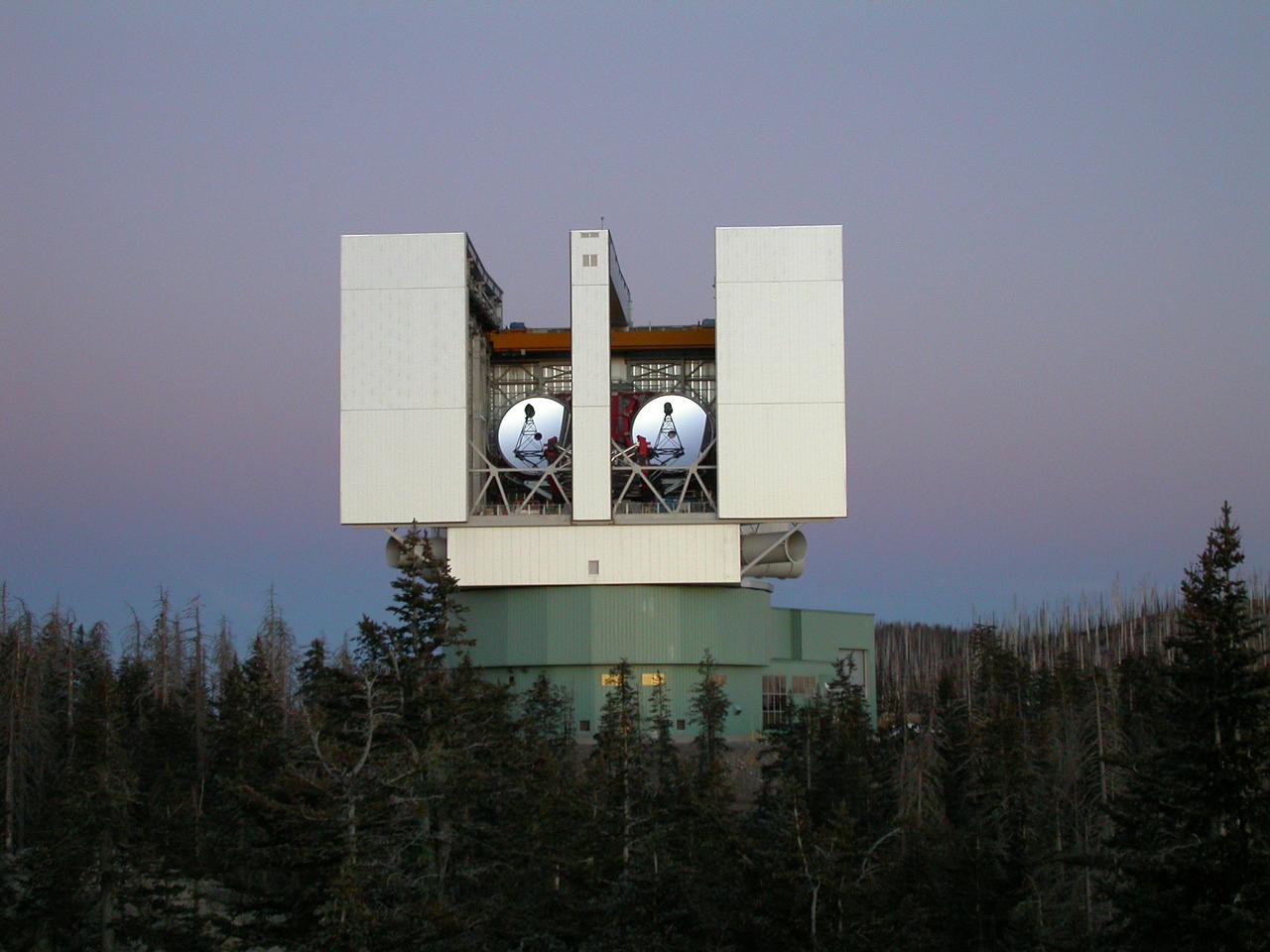

The Large Binocular Telescope Interferometer, or LBTI, is a ground-based instrument connecting two 8-meter class telescopes on Mount Graham in Arizona to form the largest single-mount telescope in the world. The interferometer is designed to detect and study stars and planets outside our solar system. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22354
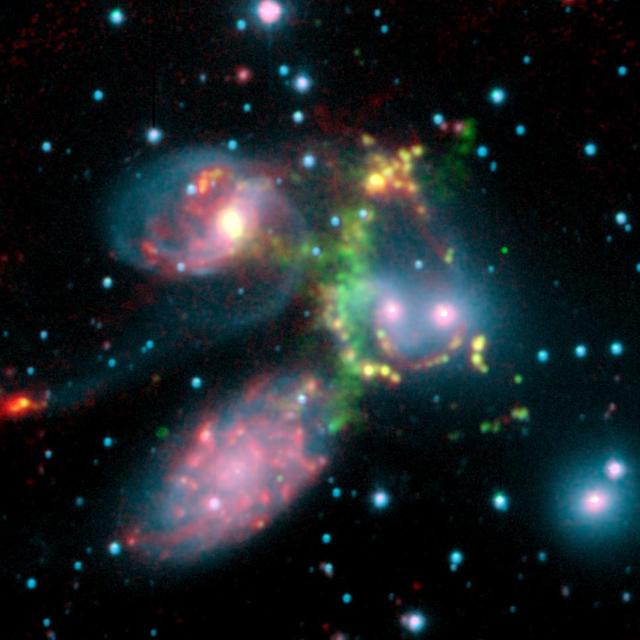

The false-color composite image of the Stephan’s Quintet galaxy cluster is made up of data from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope and a ground-based telescope in Spain.
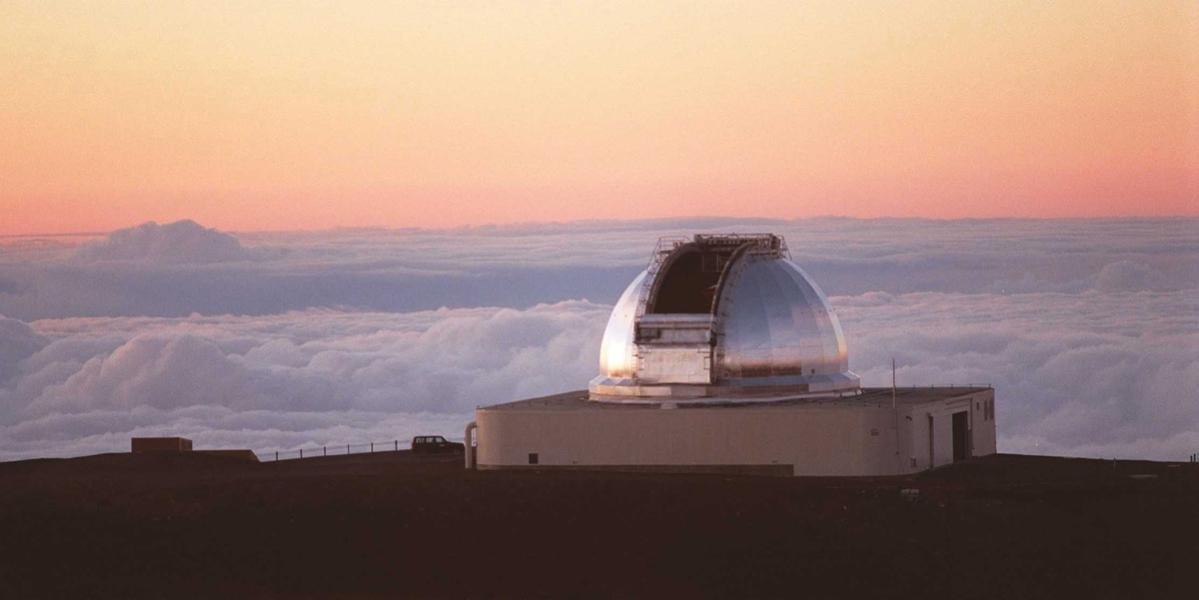

NASA Infrared Telescope Facility atop Mauna Kea, Hawaii. The IRTF is a venerable 30-year-old, 3-meter-diameter 10-foot telescope that ranks 40th among ground-based telescopes.
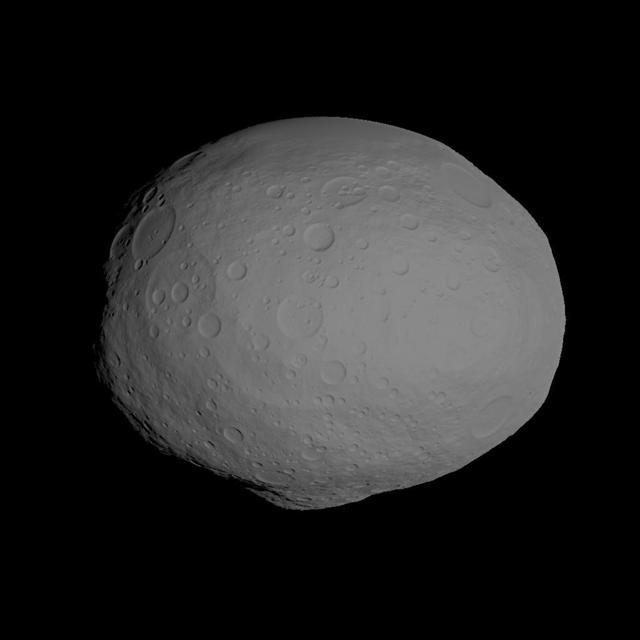

This image incorporates the best data on dimples and bulges of the protoplanet Vesta from ground-based telescopes and NASA Hubble Space Telescope. This model of Vesta uses scientists best guess to date of what the surface might look like.
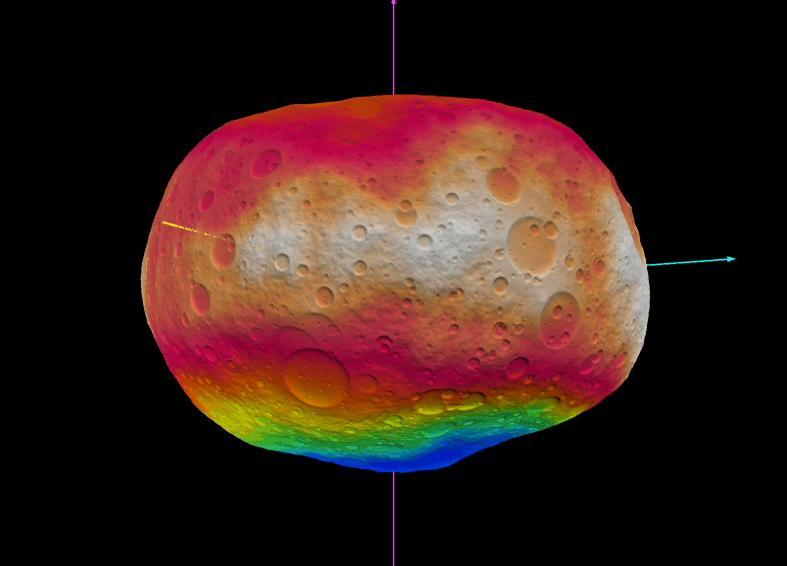
This image shows NASAS Dawn scientists best guess to date of what the surface of the protoplanet Vesta might look like; it incorporates the best data on dimples and bulges from ground-based telescopes and NASA Hubble Space Telescope.
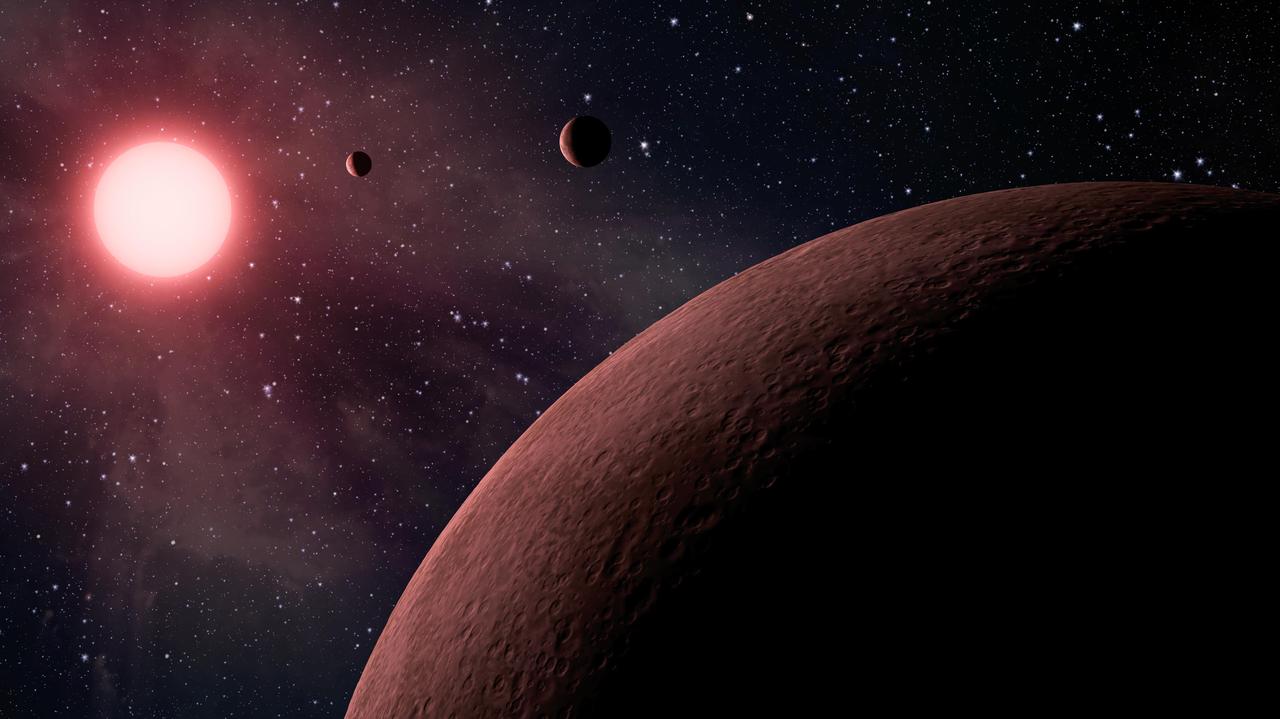

This artist concept, based on data from NASA Kepler mission and ground-based telescopes, depicts an itsy bitsy planetary system -- so compact, in fact, that it more like Jupiter and its moons than a star and its planets.

Using powerful ground-and space-based NASA telescopes, scientists have obtained a moving look at some of the wildest, weirdest weather in the solar system.

For the first time, two space-based telescopes have teamed up with ground-based observatories to observe a microlensing event, a magnification of the light of a distant star due to the gravitational effects of an unseen object in the foreground. In this case, the cause of the microlensing event was a brown dwarf, dubbed OGLE-2015-BLG-1319, orbiting a star. In terms of mass, brown dwarfs fall somewhere between the size of the largest planets and the smallest stars. Curiously, scientists have found that, for stars roughly the mass of our sun, less than 1 percent have a brown dwarf orbiting within 3 AU (1 AU is the distance between Earth and the sun). This newly discovered brown dwarf may fall in that distance range. This microlensing event was observed by ground-based telescopes looking for these uncommon events, and subsequently seen by NASA's Spitzer and Swift space telescopes. As the diagram shows, Spitzer and Swift offer additional vantage points for viewing this chance alignment. While Swift orbits close to Earth, and saw (blue diamonds) essentially the same change in light that the ground-based telescopes measured (grey markers), Spitzer's location much farther away from Earth gave it a very different perspective on the event (red circles). In particular, Spitzer's vantage point resulted in a time lag in the microlensing event it observed, compared to what was seen by Swift and the ground-based telescope. This offset allowed astronomers to determine the distance to OGLE-2015-BLG-1319 as well as its mass: around 30-65 times that of Jupiter. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21077
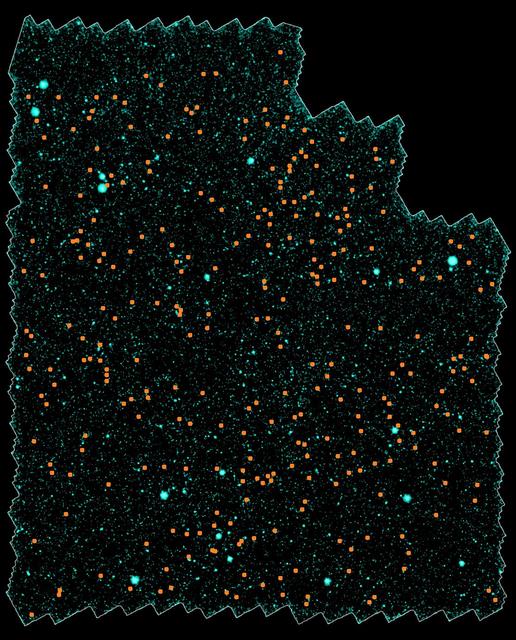

Astronomers have discovered nearly 300 galaxy clusters and groups, including almost 100 located 8 to 10 billion light-years away, using the space-based Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based Mayall 4-meter telescope.
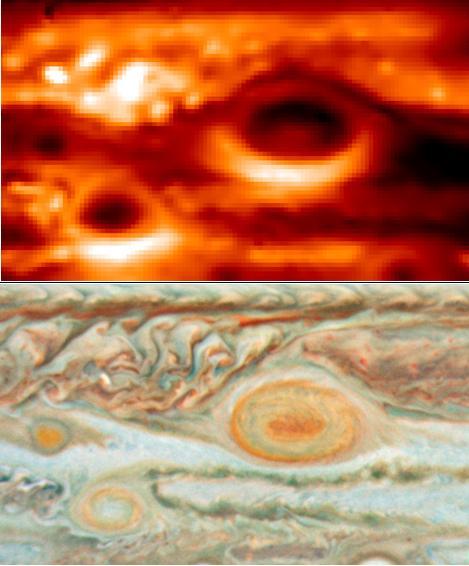
New thermal images from powerful ground-based telescopes show swirls of warmer air and cooler regions never seen before within Jupiter Great Red Spot.
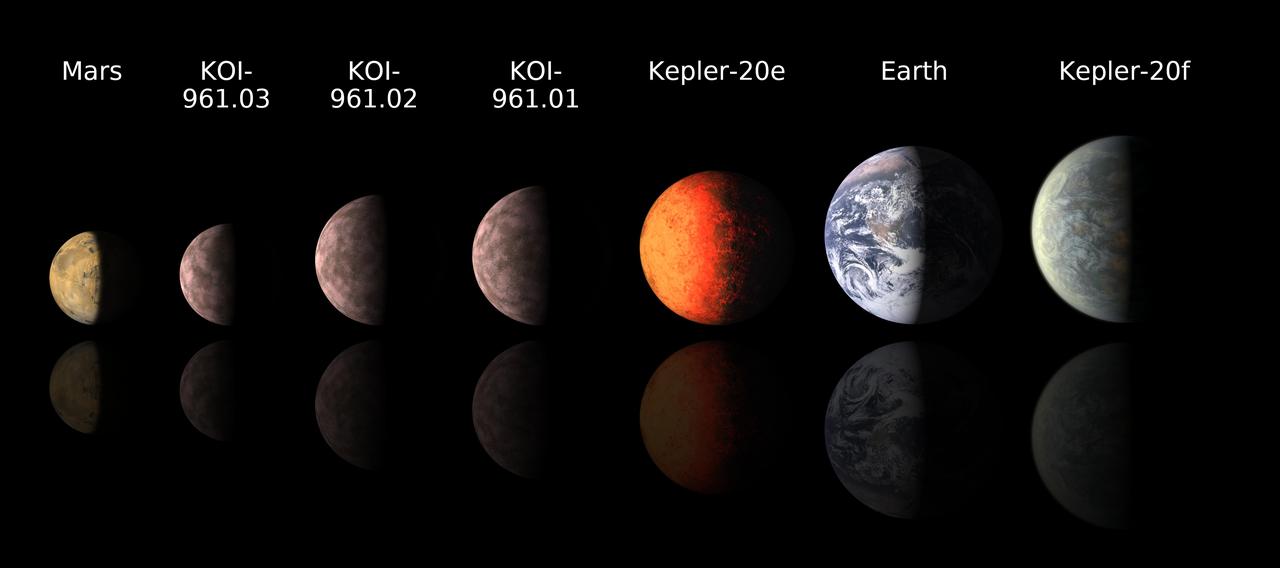
Astronomers using data from NASA Kepler mission and ground-based telescopes recently discovered the three smallest exoplanets known to circle another star, called KOI-961.01, KOI-961.02 and KOI-961.03.

This image shows the scientists best guess to date of what the surface of the protoplanet Vesta might look like from the south pole and incorporates the best data on dimples and bulges Vesta from ground-based telescopes and NASA Hubble Space Telescope.
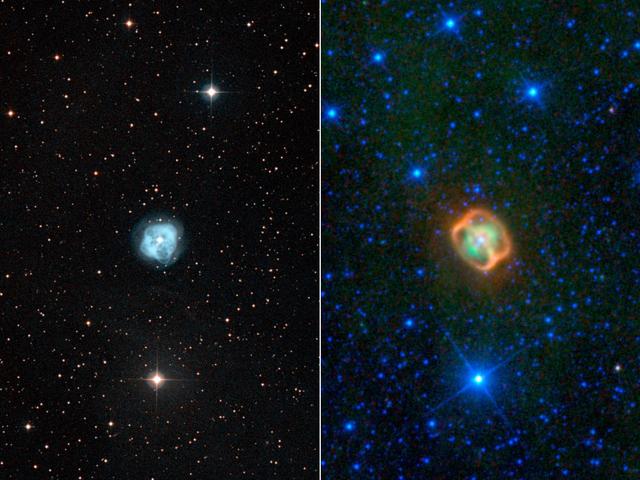

This image composite shows two views of a puffy, dying star, or planetary nebula, known as NGC 1514. At left is a view from a ground-based, visible-light telescope; the view on the right shows the object in infrared light from NASA WISE telescope.

The collection of red dots seen here show one of several very distant galaxy clusters discovered by combining ground-based optical data from the NOAO Kitt Peak National Observatory with infrared data from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.
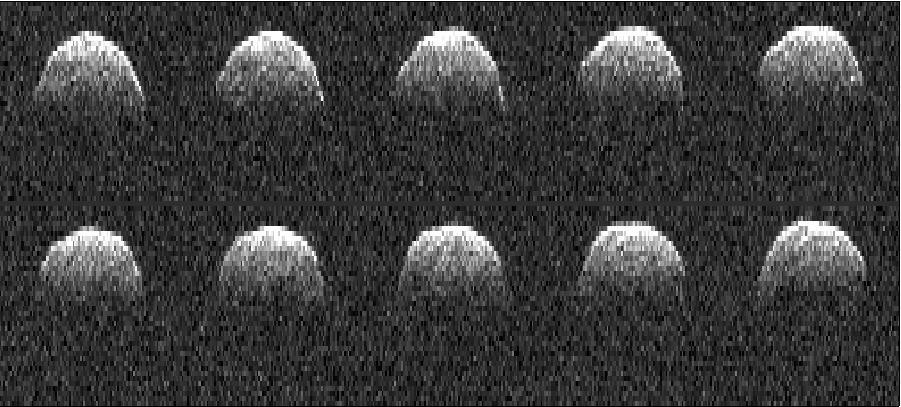

This radar image of asteroid 1999 RQ36 was obtained NASA Deep Space Network antenna in Goldstone, Calif. on Sept 23, 1999. NASA detects, tracks and characterizes asteroids and comets passing close to Earth using both ground- and space-based telescopes.

This artist's concept appeared on the Feb. 23, 2017 cover of the journal Nature announcing that the TRAPPIST-1 star, an ultra-cool dwarf, has seven Earth-size planets orbiting it. Any of these planets could have liquid water on them. Planets that are farther from the star are more likely to have significant amounts of ice, especially on the side that faces away from the star. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21421

The Galaxy Evolution Explorer specializes in surveying galaxies in ultraviolet light. Its telescope, 50 centimeters (19.7 inches) in diameter, has a field of view that is much wider than most ground-based and space-based telescopes. This field of view, nearly three times the diameter of the Moon, allowed the Galaxy Evolution Explorer to discover seemingly newborn galaxies in our local universe. The telescope surveyed thousands of galaxies before finding three-dozen of these newborns. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05979
This frame from a video details a system of seven planets orbiting TRAPPIST-1, an ultra-cool dwarf star. Spitzer was able to identify a total of seven rocky worlds, including three in the habitable zone where liquid water might be found. A study established the planets' size, distance from their sun and, for some of them, their approximate mass and density. It also established that some, if not all, of these planets are tidally locked, meaning one face of the planet permanently faces their sun. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. A video is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21427

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers add another base plate segment to the shrouded Space Infrared Telescope Facility. The base plate is being added for the canister. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
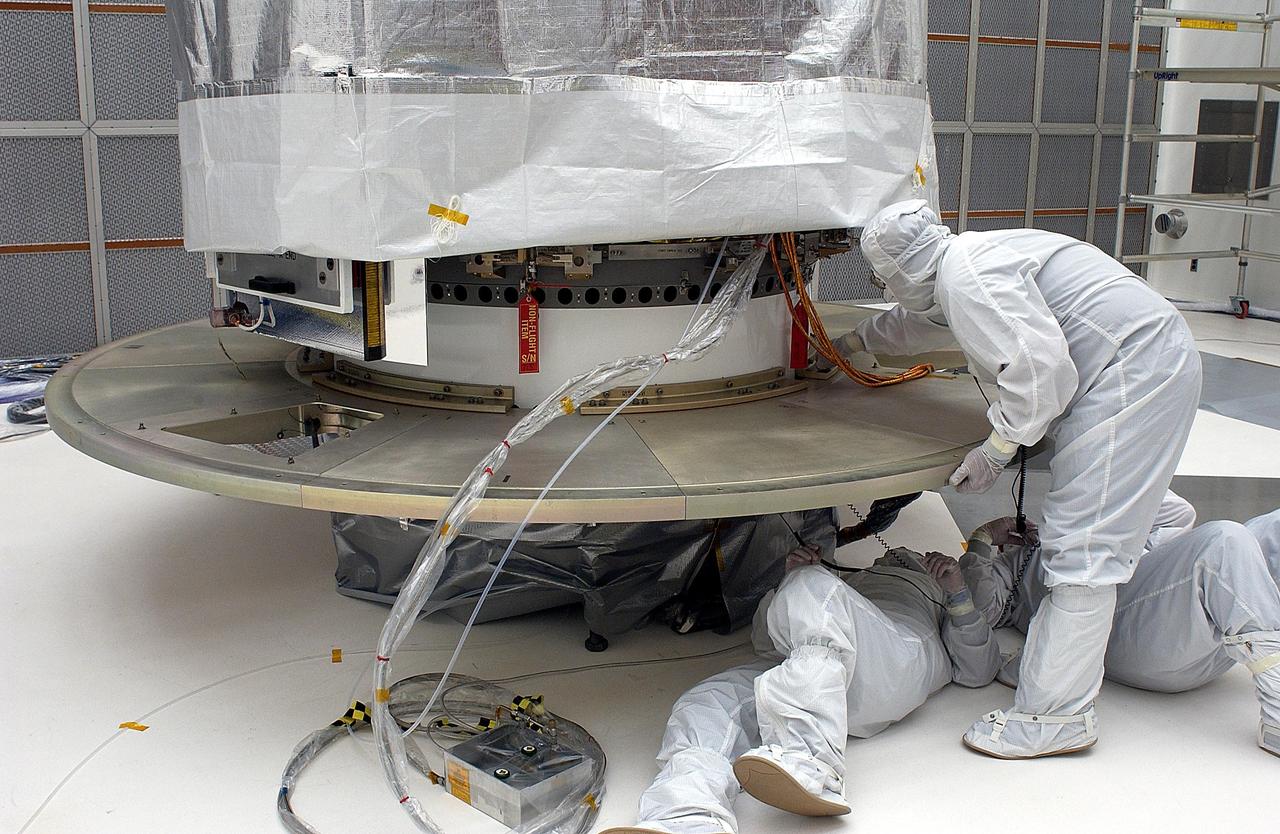

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers add another base plate segment to the shrouded Space Infrared Telescope Facility. The base plate is being added for the canister. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A worker carries a base plate segment to the shrouded Space Infrared Telescope Facility. The base plate is being added for the canister. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

This illustration shows the seven TRAPPIST-1 planets as they might look as viewed from Earth using a fictional, incredibly powerful telescope. The sizes and relative positions are correctly to scale: This is such a tiny planetary system that its sun, TRAPPIST-1, is not much bigger than our planet Jupiter, and all the planets are very close to the size of Earth. Their orbits all fall well within what, in our solar system, would be the orbital distance of our innermost planet, Mercury. With such small orbits, the TRAPPIST-1 planets complete a "year" in a matter of a few Earth days: 1.5 for the innermost planet, TRAPPIST-1b, and 20 for the outermost, TRAPPIST-1h. This particular arrangement of planets with a double-transit reflect an actual configuration of the system during the 21 days of observations made by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope in late 2016. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21429

This chart shows, on the top row, artist concepts of the seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 with their orbital periods, distances from their star, radii and masses as compared to those of Earth. On the bottom row, the same numbers are displayed for the bodies of our inner solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit their star extremely closely, with periods ranging from 1.5 to only about 20 days. This is much shorter than the period of Mercury, which orbits our sun in about 88 days. The artist concepts show what the TRAPPIST-1 planetary system may look like, based on available data about their diameters, masses and distances from the host star. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21425

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Infrared Telescope Facility is shrouded while workers install the base plate segments for the canister. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
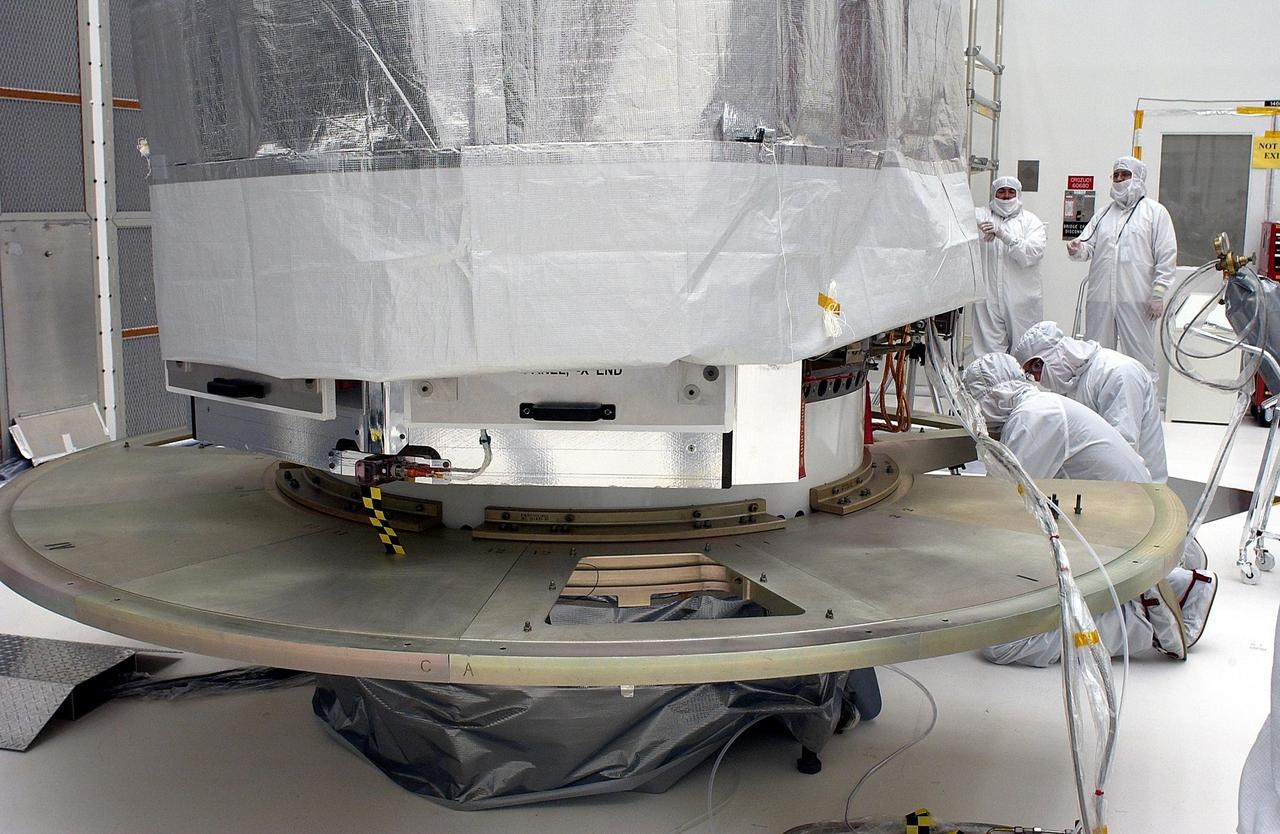

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Space Infrared Telescope Facility is shrouded while workers install the base plate segments for the canister. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

This artist's concept allows us to imagine what it would be like to stand on the surface of the exoplanet TRAPPIST-1f, located in the TRAPPIST-1 system in the constellation Aquarius. Because this planet is thought to be tidally locked to its star, meaning the same face of the planet is always pointed at the star, there would be a region called the terminator that perpetually divides day and night. If the night side is icy, the day side might give way to liquid water in the area where sufficient starlight hits the surface. One of the unusual features of TRAPPIST-1 planets is how close they are to each other -- so close that other planets could be visible in the sky from the surface of each one. In this view, the planets in the sky correspond to TRAPPIST1e (top left crescent), d (middle crescent) and c (bright dot to the lower right of the crescents). TRAPPIST-1e would appear about the same size as the moon and TRAPPIST1-c is on the far side of the star. The star itself, an ultra-cool dwarf, would appear about three times larger than our own sun does in Earth's skies. The TRAPPIST-1 system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21423

This illustration shows what the TRAPPIST-1 system might look like from a vantage point near planet TRAPPIST-1f (at right). The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. They are likely all tidally locked, meaning the same face of the planet is always pointed at the star, as the same side of our moon is always pointed at Earth. This creates a perpetual night side and perpetual day side on each planet. TRAPPIST-1b and c receive the most light from the star and would be the warmest. TRAPPIST-1e, f and g all orbit in the habitable zone, the area where liquid water is most likely to be detected. But any of the planets could potentially harbor liquid water, depending on their compositions. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21751

All seven planets discovered in orbit around the red dwarf star TRAPPIST-1 could easily fit inside the orbit of Mercury, the innermost planet of our solar system. In fact, they would have room to spare. TRAPPIST-1 also is only a fraction of the size of our sun; it isn't much larger than Jupiter. So the TRAPPIST-1 system's proportions look more like Jupiter and its moons than those of our solar system. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21428

The primary payload for Space Shuttle Mission STS-35, launched December 2, 1990, was the ASTRO-1 Observatory. Designed for round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-ray astronomy, ASTRO-1 featured a collection of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo- Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-ray Telescope (BBXRT). Ultraviolet telescopes mounted on Spacelab elements in cargo bay were to be operated in shifts by flight crew. Loss of both data display units (used for pointing telescopes and operating experiments) during mission impacted crew-aiming procedures and forced ground teams at Marshall Space Flight Center to aim ultraviolet telescopes with fine-tuning by flight crew. BBXRT, also mounted in cargo bay, was directed from outset by ground-based operators at Goddard Space Flight Center. This is the logo or emblem that was designed to represent the ASTRO-1 payload.

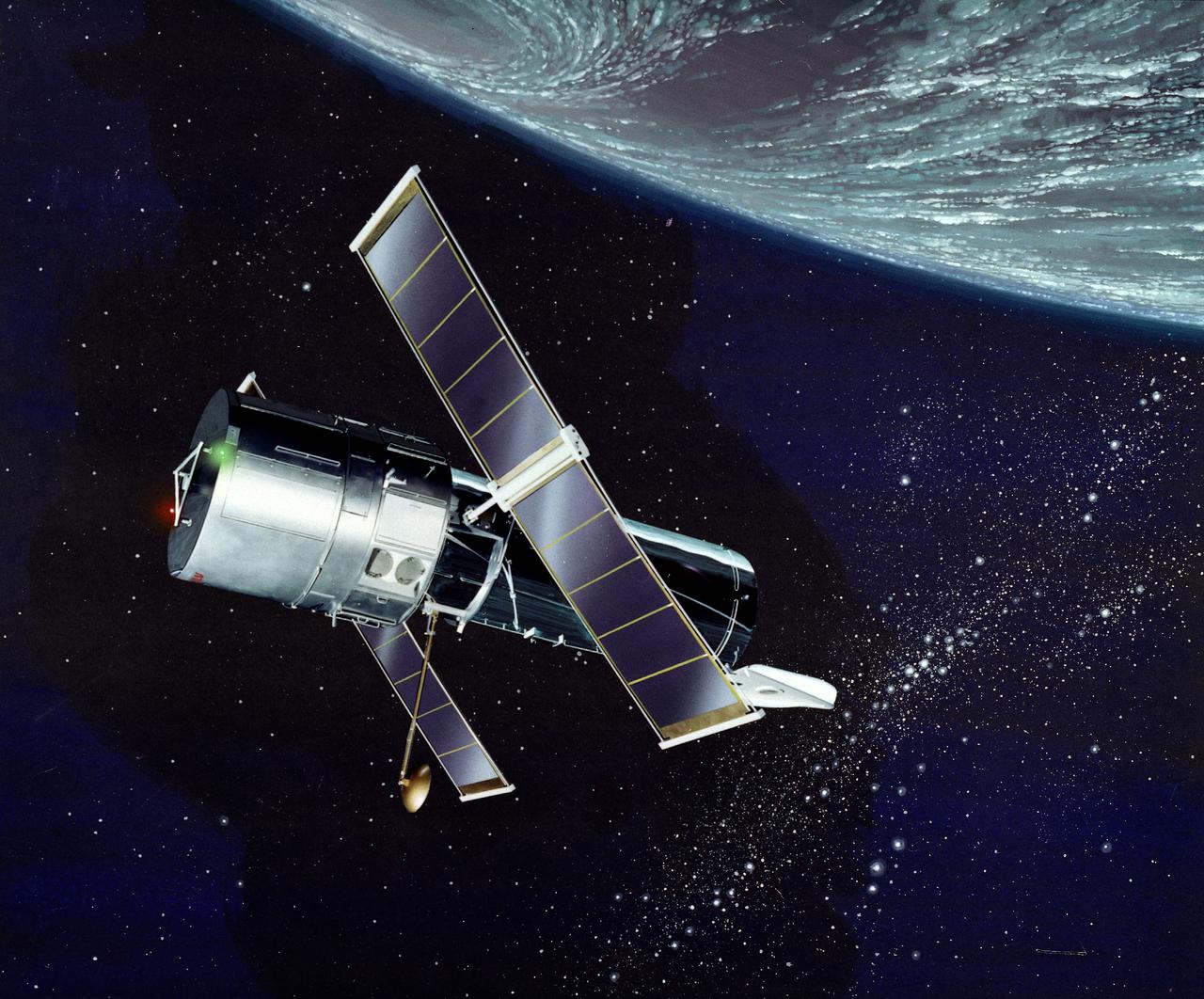
This is an artist's concept of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
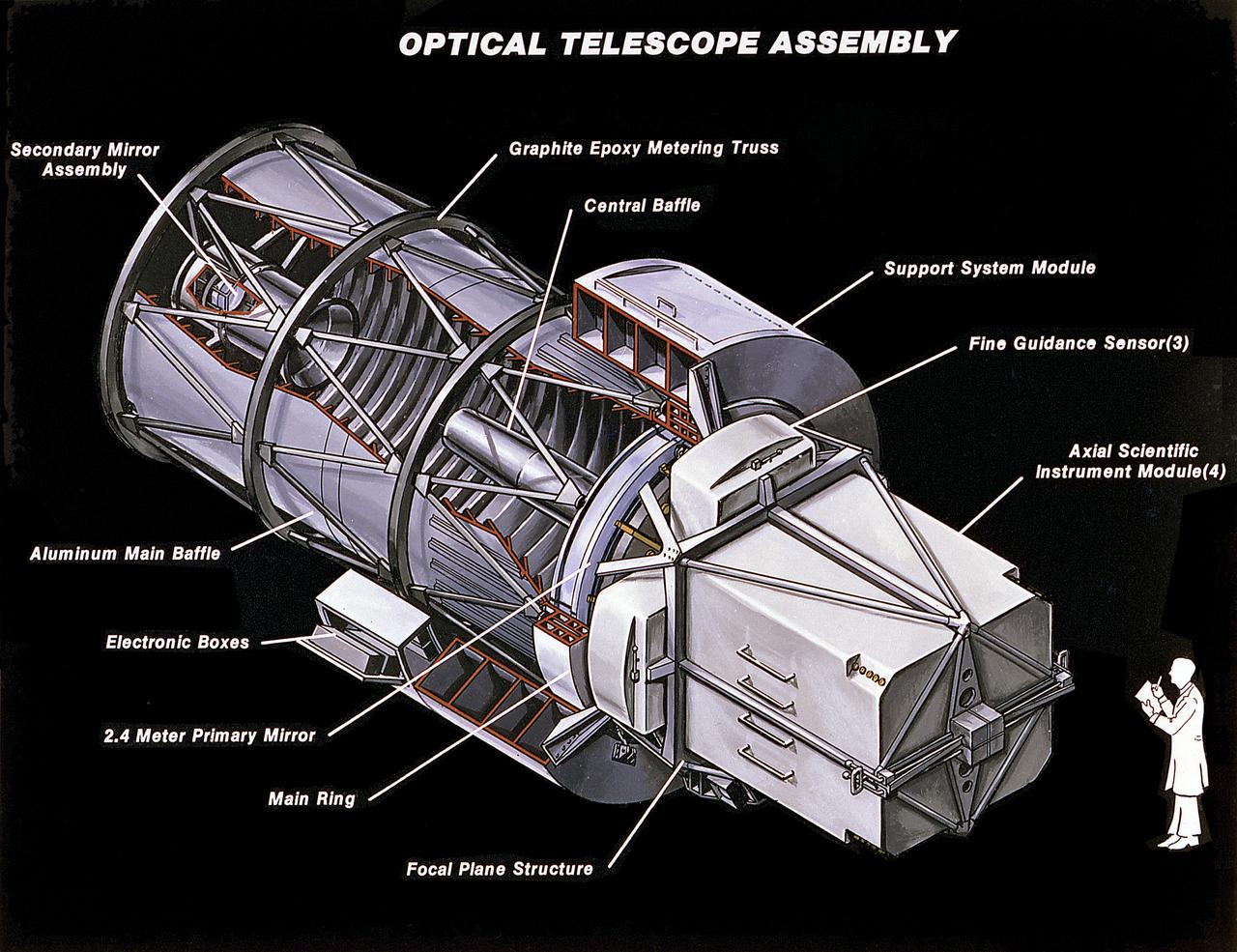
This image illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA). One of the three major elements of the HST, the OTA consists of two mirrors (a primary mirror and a secondary mirror), support trusses, and the focal plane structure. The mirrors collect and focus light from selected celestial objects and are housed near the center of the telescope. The primary mirror captures light from objects in space and focuses it toward the secondary mirror. The secondary mirror redirects the light to a focal plane where the Scientific Instruments are located. The primary mirror is 94.5 inches (2.4 meters) in diameter and the secondary mirror is 12.2 inches (0.3 meters) in diameter. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth Orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from the Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The spacecraft is 42.5 feet (13 meters) long and weighs 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

This illustration depicts a side view of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
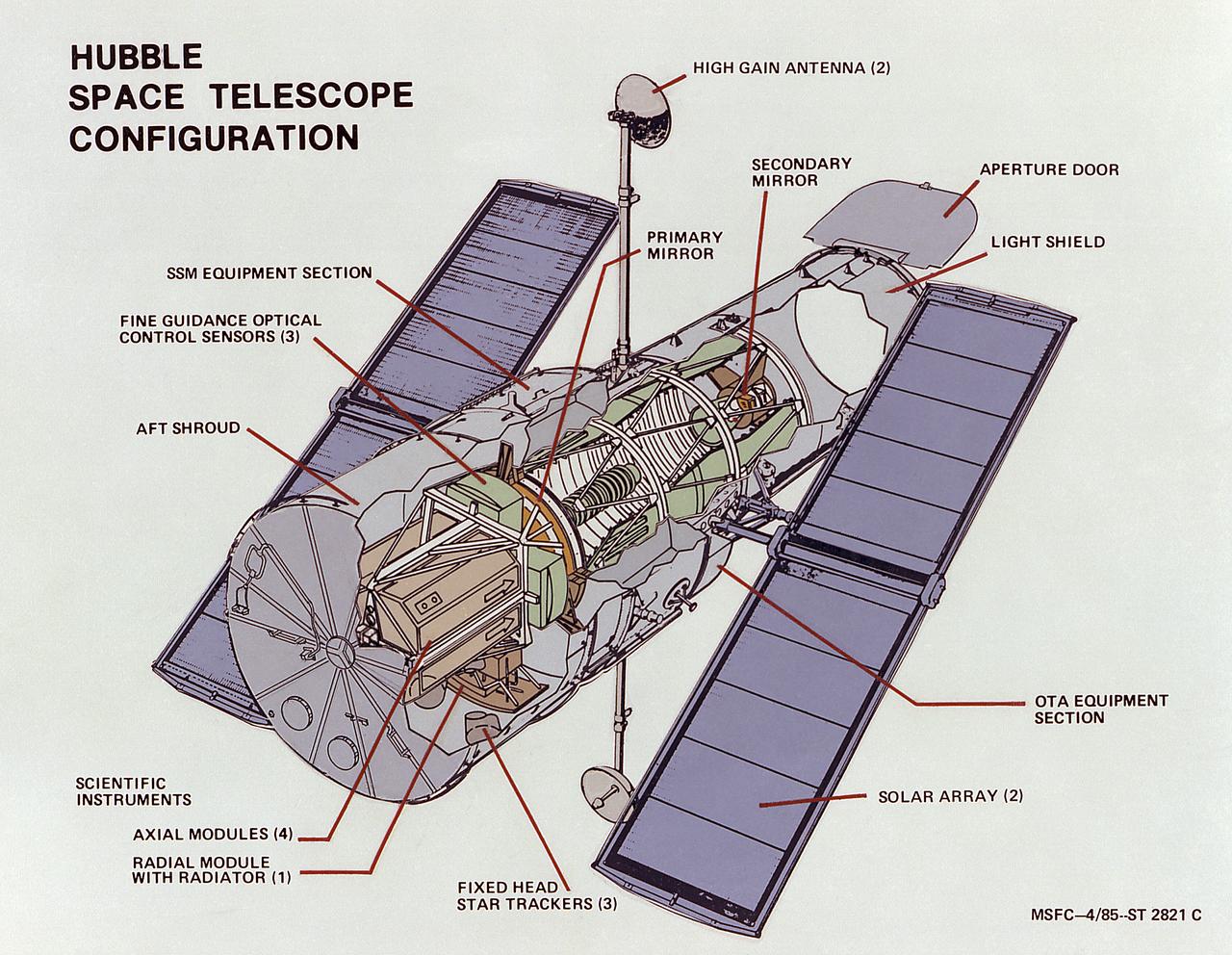
This image illustrates the overall Hubble Space Telescope (HST) configuration. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

This artist's concept shows what the TRAPPIST-1 planetary system may look like, based on available data about the planets' diameters, masses and distances from the host star, as of February 2018. This image represents an updated version of PIA21422, which was created in 2017. The planets' appearances were re-imagined based on a 2018 study using additional observations from NASA's Spitzer and Kepler space telescopes, in addition to previous data from Spitzer, the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope and other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. The new analysis concludes that the seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all rocky, and some could contain significant amounts of water. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. The form that water would take on TRAPPIST-1 planets would depend on the amount of heat they receive from their star, which is a mere 9 percent as massive as our Sun. Planets closest to the star are more likely to host water in the form of atmospheric vapor, while those farther away may have water frozen on their surfaces as ice. TRAPPIST-1e is the rockiest planet of them all, but still is believed to have the potential to host some liquid water. In this illustration, the relative sizes of the planets and their host star, an ultracool dwarf, are all shown to scale. An annotated image is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22093
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope after being released into orbit, with the high gain anternas and solar arrays deployed and the aperture doors opened. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
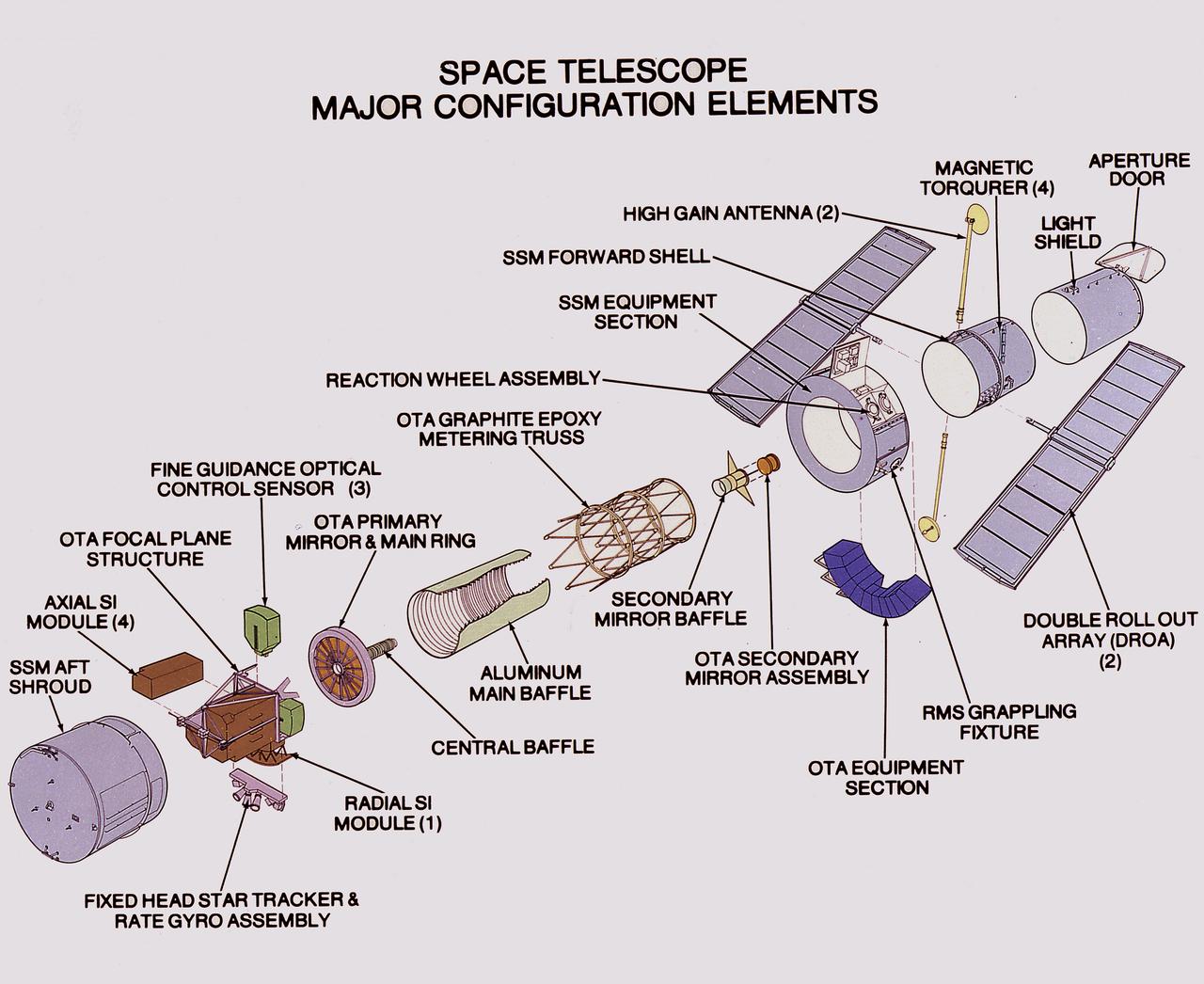
This illustration shows the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) major configuration elements. The spacecraft has three interacting systems: The Support System Module (SSM), an outer structure that houses the other systems and provides services such as power, communication, and control; The Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), which collects and concentrates the incoming light in the focal plane for use by the Scientific Instruments (SI); and five SIs. The SI Control and Data Handling (CDH) unit controls the five SI's, four that are housed in an aft section focal plane structure and one that is placed along the circumference of the spacecraft. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
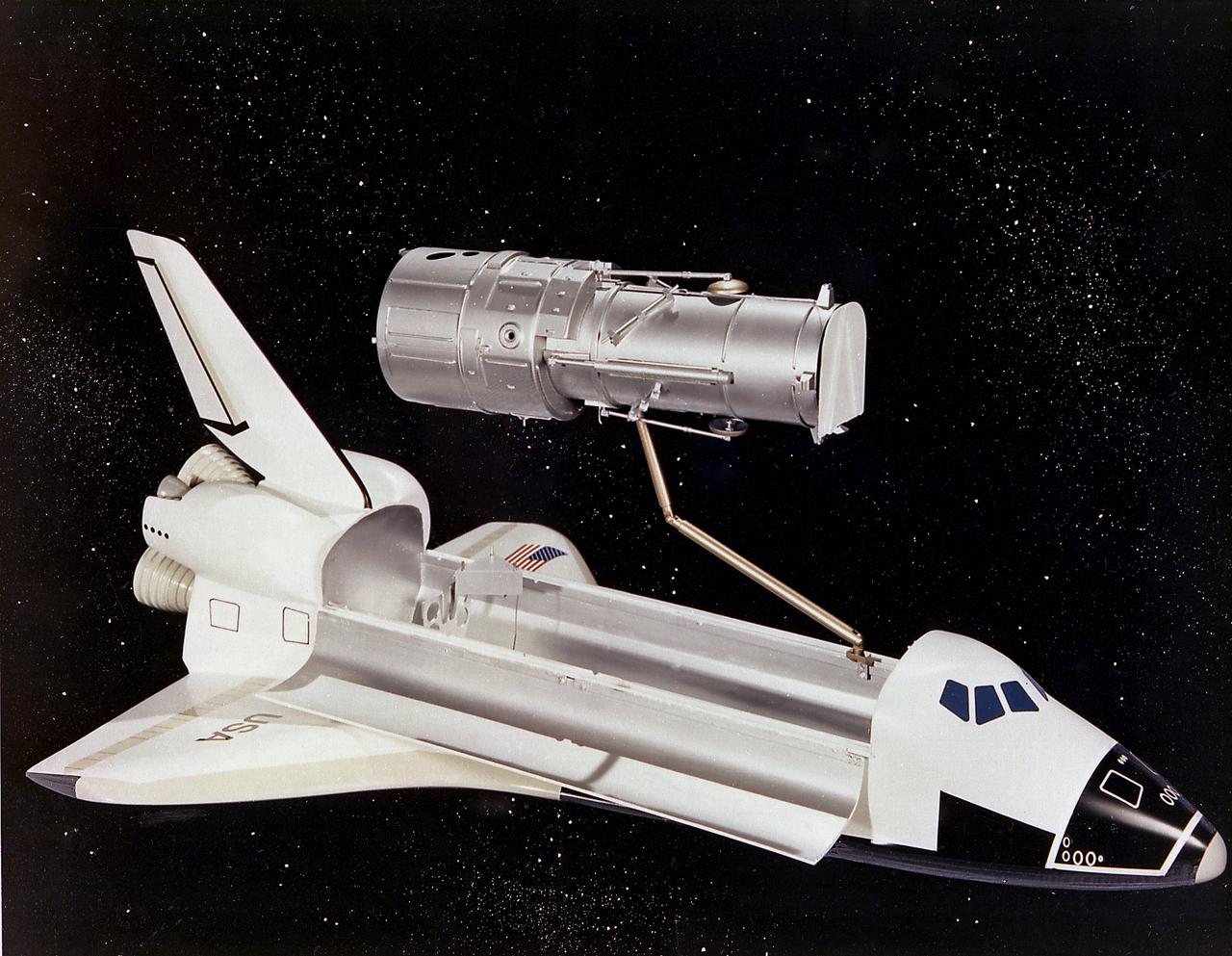
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being positioned for release from the Space Shuttle orbiter by the Remote Manipulator System (RMS). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13- meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
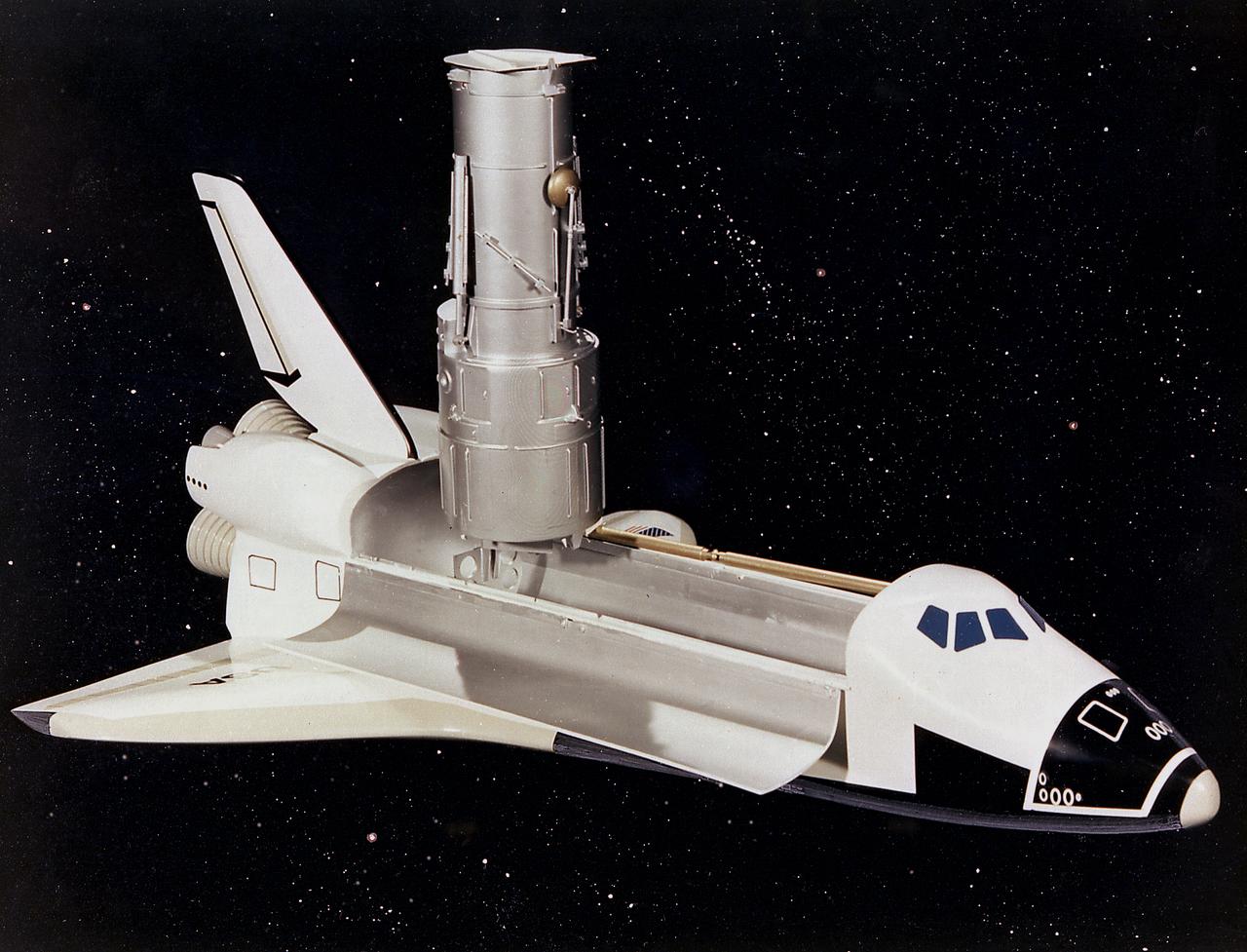
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being raised to a vertical position in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

This illustration depicts the design features of the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Support Systems Module (SSM). The SSM is one of the three major elements of the HST and encloses the other two elements, the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA) and the Scientific Instruments (SI's). The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The spacecraft is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). Two communication anternas, two solar array panels that collect energy for the HST, and storage bays for electronic gear are on the outside. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
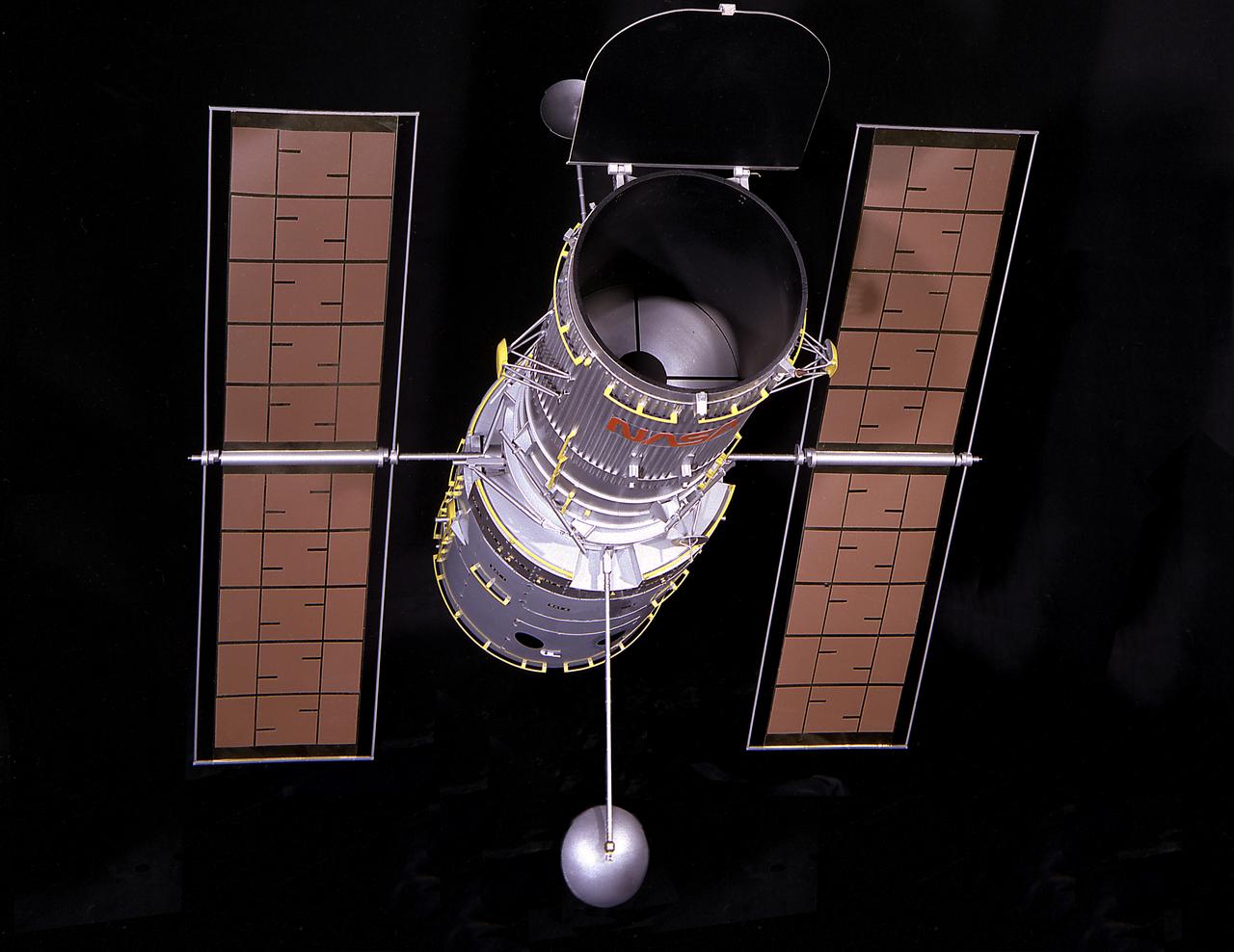
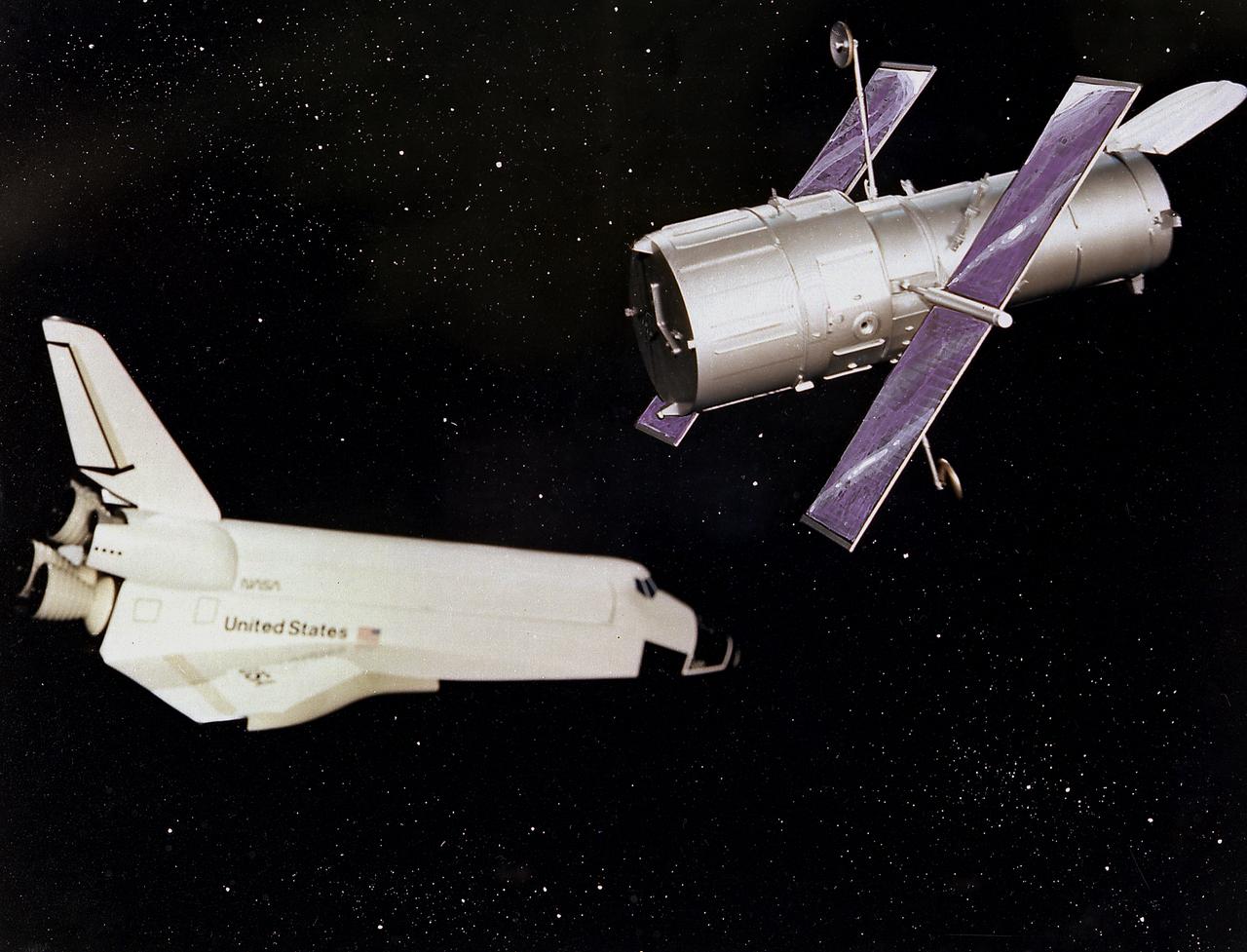
This is a photograph of a 1/15 scale model of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13- meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

Astronomers have discovered one of the most distant planets known, a gas giant about 13,000 light-years from Earth, called OGLE-2014-BLG-0124L. The planet was discovered using a technique called microlensing, and the help of NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment, or OGLE. In this artist's illustration, planets discovered with microlensing are shown in yellow. The farthest lies in the center of our galaxy, 25,000 light-years away. Most of the known exoplanets, numbering in the thousands, have been discovered by NASA's Kepler space telescope, which uses a different strategy called the transit method. Kepler's cone-shaped field of view is shown in pink/orange. Ground-based telescopes, which use the transit and other planet-hunting methods, have discovered many exoplanets close to home, as shown by the pink/orange circle around the sun. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19333
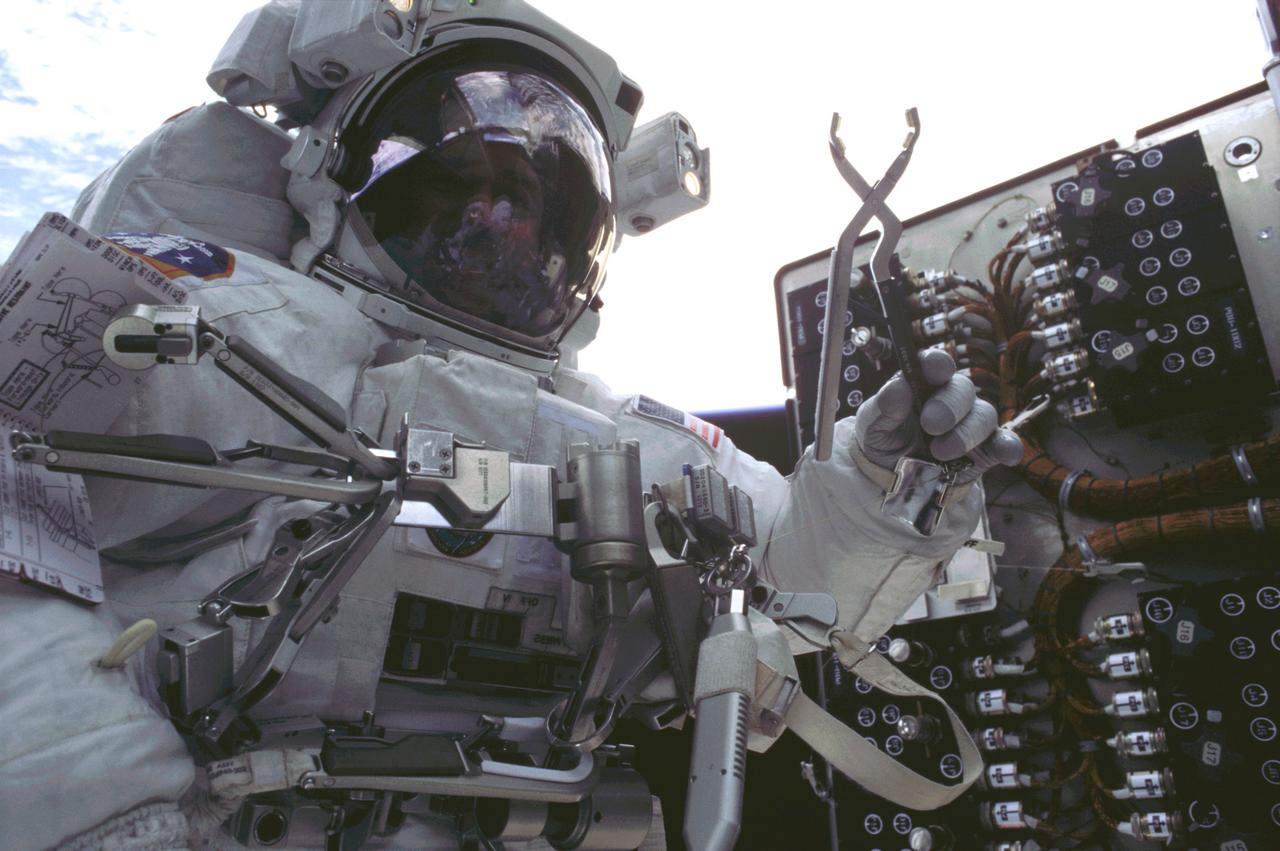

This is an onboard photo of Astronaut John M. Grunsfield, STS-109 payload commander, participating in the third of five spacewalks to perform work on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). On this particular walk, Grunsfield, joined by Astronaut Richard M. Lirnehan, turned off the telescope in order to replace its power control unit (PCU), the heart of the HST's power system. The telescope was captured and secured on a work stand in Columbia's payload bay using Columbia's robotic arm, where crew members completed system upgrades to the HST. Included in those upgrades were: replacement of the solar array panels; replacement of the power control unit (PCU); replacement of the Faint Object Camera (FOC) with a new advanced camera for Surveys (ACS); and installation of the experimental cooling system for the Hubble's Near-Infrared Camera and Multi-object Spectrometer (NICMOS), which had been dormant since January 1999 when its original coolant ran out. The Marshall Space Flight Center had the responsibility for the design, development, and construction of the HST, which is the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. Launched March 1, 2002 the STS-109 HST servicing mission lasted 10 days, 22 hours, and 11 minutes. It was the 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle Program.

This artist's concept shows what the TRAPPIST-1 planetary system may look like, based on available data about the planets' diameters, masses and distances from the host star. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. They are likely all tidally locked, meaning the same face of the planet is always pointed at the star, as the same side of our moon is always pointed at Earth. This creates a perpetual night side and perpetual day side on each planet. TRAPPIST-1b and c receive the most light from the star and would be the warmest. TRAPPIST-1e, f and g all orbit in the habitable zone, the area where liquid water is most likely to be detected. But any of the planets could potentially harbor liquid water, depending on their compositions. In the imagined planets shown here, TRAPPIST-1b is shown as a larger analogue to Jupiter's moon Io. TRAPPIST-1d is depicted with a narrow band of water near the terminator, the divide between a hot, dry day and an ice-covered night side. TRAPPIST-1e and TRAPPIST-1f are both shown covered in water, but with progressively larger ice caps on the night side. TRAPPIST-1g is portrayed with an atmosphere like Neptune's, although it is still a rocky world. TRAPPIST-1h, the farthest from the star, would be the coldest. It is portrayed here as an icy world, similar to Jupiter's moon Europa, but the least is known about it. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21422
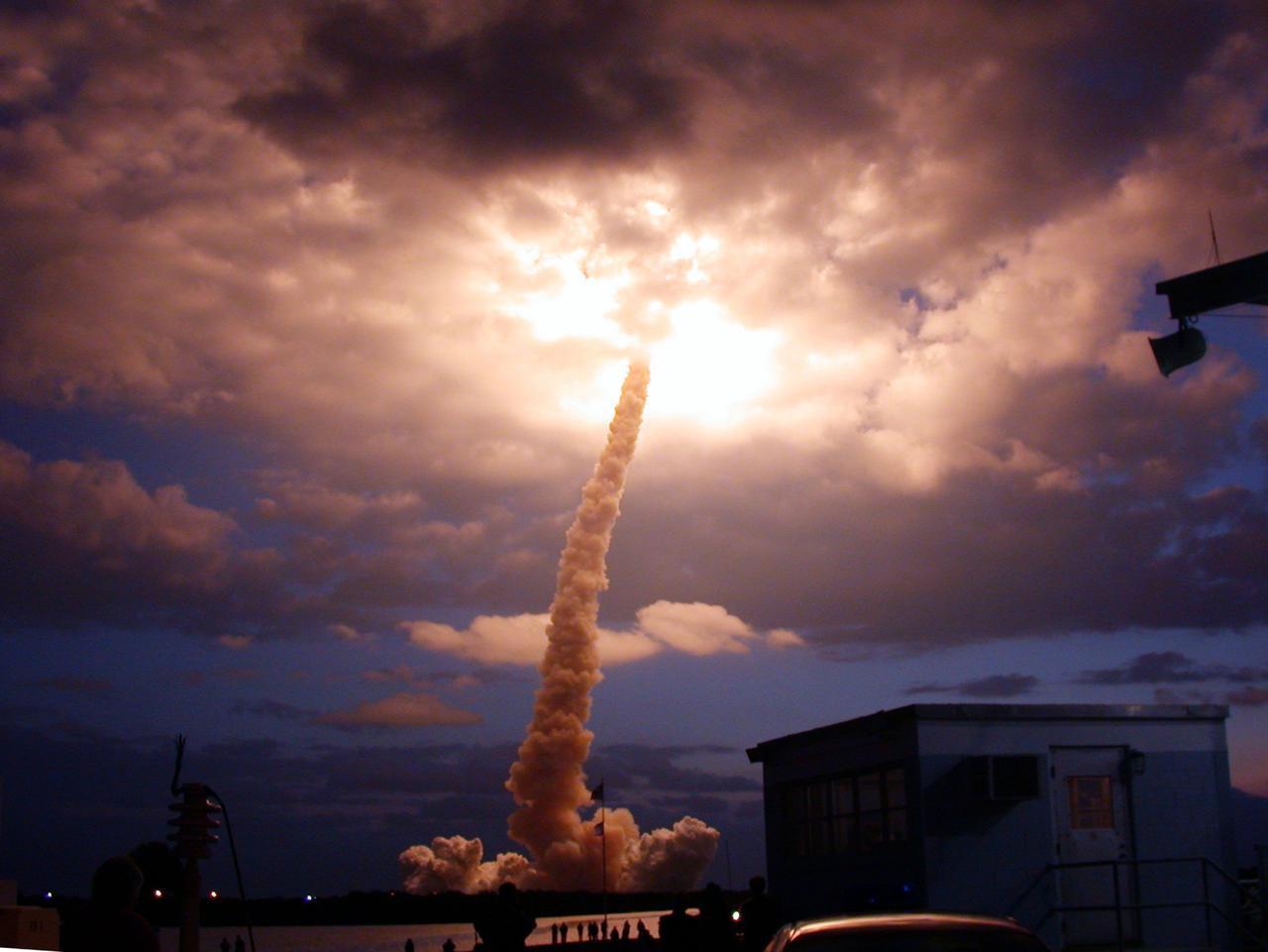

Carrying a crew of seven, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia soared through some pre-dawn clouds into the sky as it began its 27th flight, STS-109. Launched March 1, 2002, the goal of the mission was the maintenance and upgrade of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Marshall Space Flight Center had the responsibility for the design, development, and construction of the HST, which is the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. During the STS-109 mission, the telescope was captured and secured on a work stand in Columbia's payload bay using Columbia's robotic arm. Here four members of the crew performed five spacewalks completing system upgrades to the HST. Included in those upgrades were: replacement of the solar array panels; replacement of the power control unit (PCU); replacement of the Faint Object Camera (FOC) with a new advanced camera for Surveys (ACS); and installation of the experimental cooling system for the Hubble's Near-Infrared Camera and Multi-object Spectrometer (NICMOS), which had been dormant since January 1999 when it original coolant ran out. Lasting 10 days, 22 hours, and 11 minutes, the STS-109 mission was the 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle Program.

This is the insignia of the STS-109 Space Shuttle mission. Carrying a crew of seven, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia was launched with goals of maintenance and upgrades to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Marshall Space Flight Center had the responsibility for the design, development, and construction of the HST, which is the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. During the STS-109 mission, the telescope was captured and secured on a work stand in Columbia's payload bay using Columbia's robotic arm where four members of the crew performed five spacewalks completing system upgrades to the HST. Included in those upgrades were: The replacement of the solar array panels; replacement of the power control unit (PCU); replacement of the Faint Object Camera (FOC) with a new advanced camera for Surveys (ACS); and installation of the experimental cooling system for the Hubble's Near-Infrared Camera and Multi-object Spectrometer (NICMOS), which had been dormant since January 1999 when it original coolant ran out. Lasting 10 days, 22 hours, and 11 minutes, the STS-109 mission was the 27th flight of the Orbiter Columbia and the 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle Program.
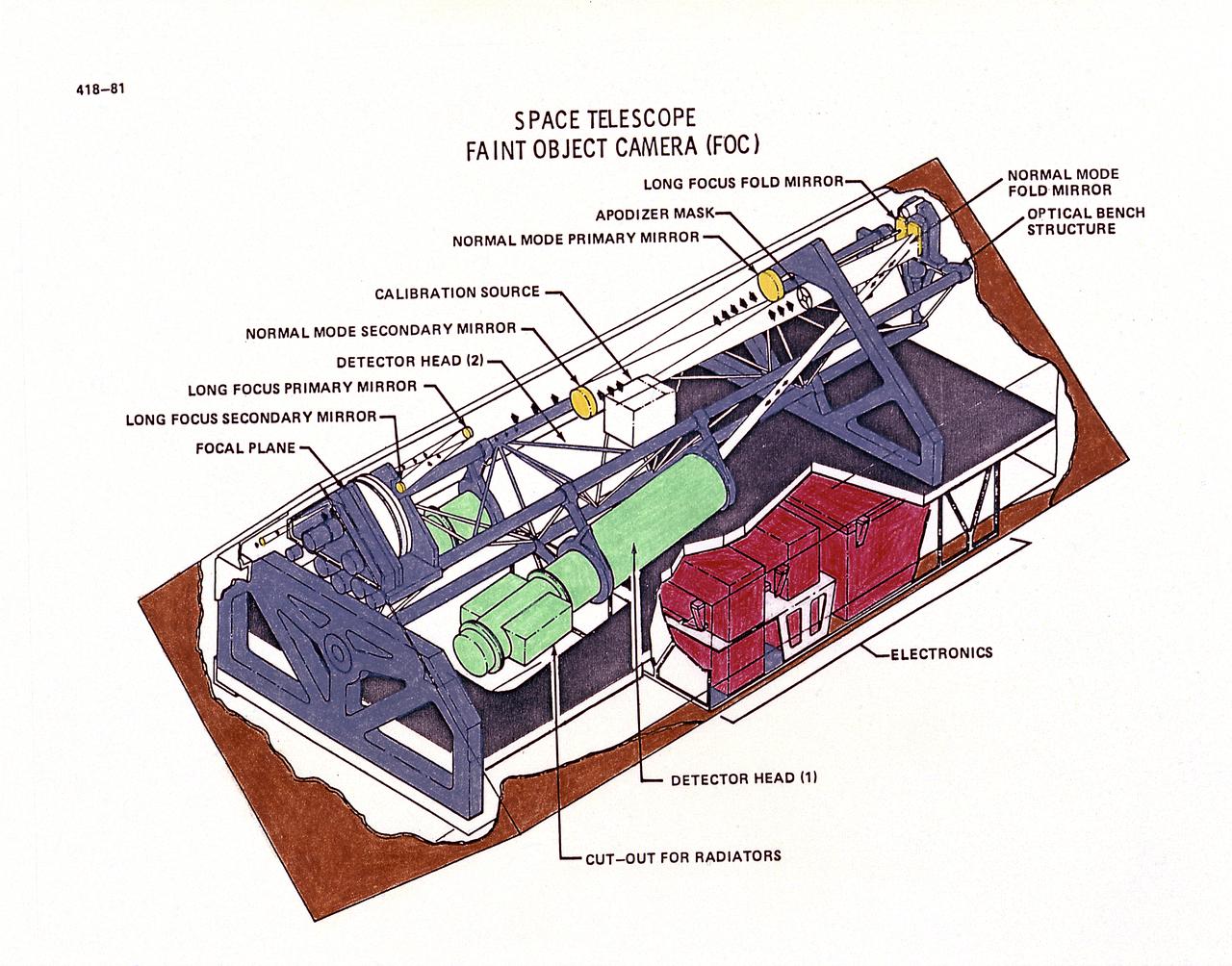
This drawing illustrates Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Faint Object Camera (FOC). The FOC reflects light down one of two optical pathways. The light enters a detector after passing through filters or through devices that can block out light from bright objects. Light from bright objects is blocked out to enable the FOC to see background images. The detector intensifies the image, then records it much like a television camera. For faint objects, images can be built up over long exposure times. The total image is translated into digital data, transmitted to Earth, and then reconstructed. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
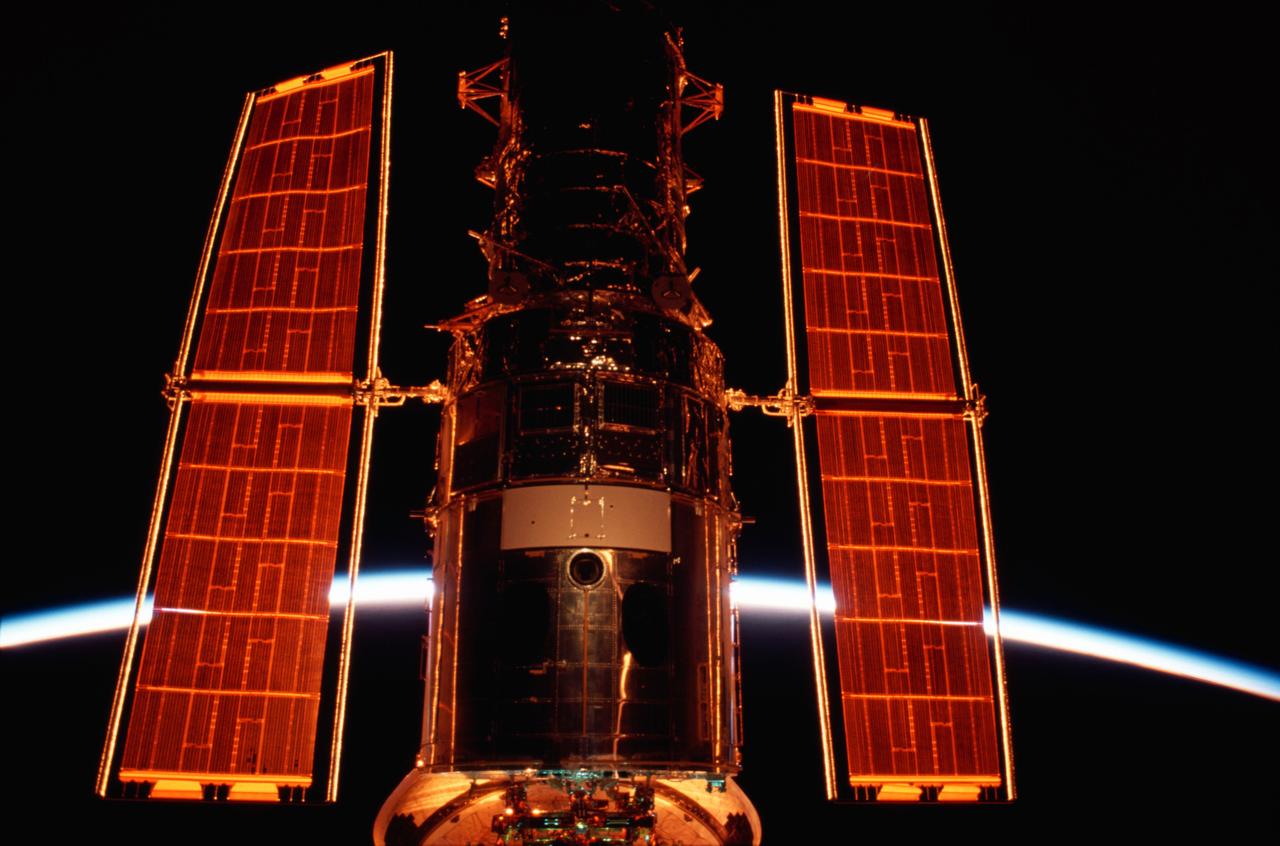

This is a photo of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST),in its origianl configuration, berthed in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Columbia during the STS-109 mission silhouetted against the airglow of the Earth's horizon. The telescope was captured and secured on a work stand in Columbia's payload bay using Columbia's robotic arm, where 4 of the 7-member crew performed 5 spacewalks completing system upgrades to the HST. Included in those upgrades were: replacement of the solar array panels; replacement of the power control unit (PCU); replacement of the Faint Object Camera (FOC) with a new advanced camera for Surveys (ACS); and installation of the experimental cooling system for the Hubble's Near-Infrared Camera and Multi-object Spectrometer (NICMOS), which had been dormant since January 1999 when its original coolant ran out. The Marshall Space Flight Center had the responsibility for the design, development, and construction of the the HST, which is the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. Launched March 1, 2002 the STS-109 HST servicing mission lasted 10 days, 22 hours, and 11 minutes. It was the 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle Program.
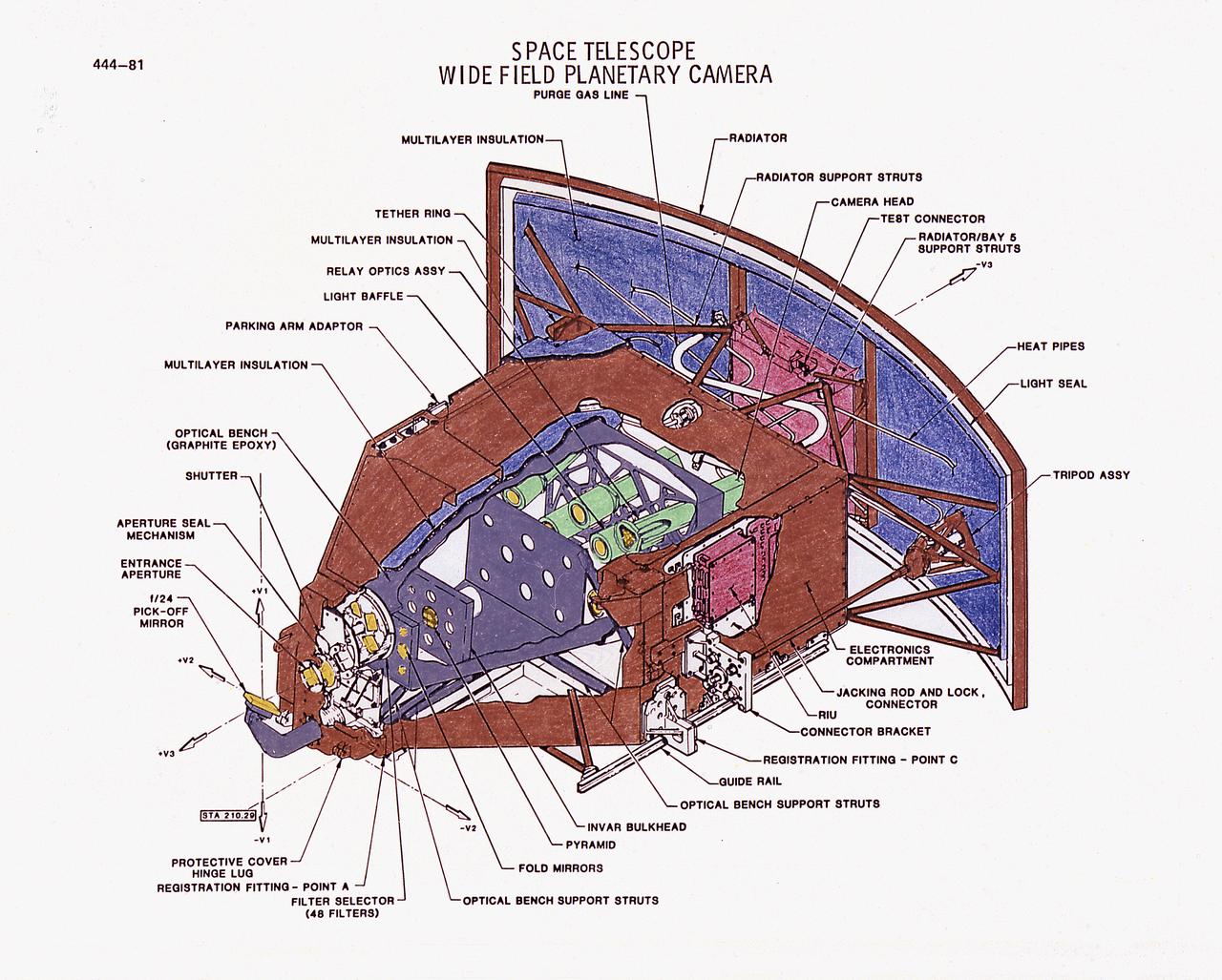
This illustration is a diagram of the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Wide Field Planetary Camera (WF/PC), one of the five Scientific Instruments. The WF/PC uses a four-sided pyramid mirror to split a light image into quarters. It then focuses each quadrant onto one of two sets of four sensors. The sensors are charge-coupled detectors and function as the electronic equivalent of extremely sensitive photographic plates. The WF/PC operates in two modes. The Wide-Field mode that will view 7.2-arcmin sections of the sky, and the Planetary mode that will look at narrower fields of view, such as planets or areas within other galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
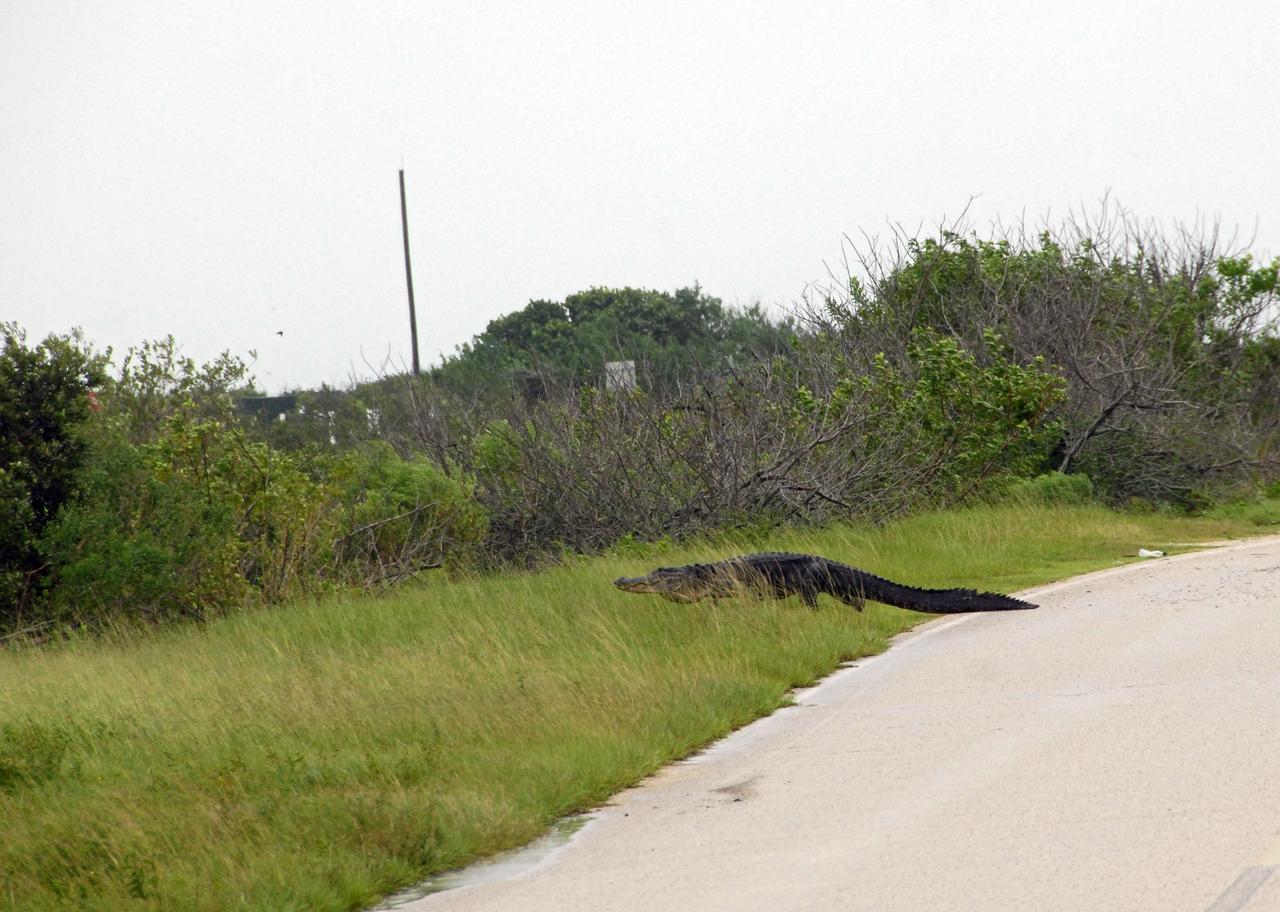

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An alligator seeks higher ground alongside a road at NASA's Kennedy Space Center during the onslaught of Tropical Storm Fay. The storm passed over the center Aug. 20 and then stalled offshore, bringing with it heavy rain and tropical storm force wind. Kennedy closed Aug. 19 because of Fay and reopened for normal operations Aug. 22. Based on initial assessments, there was no damage to space flight hardware, such as the space shuttles and Hubble Space Telescope equipment. Some facilities did sustain minor damage. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
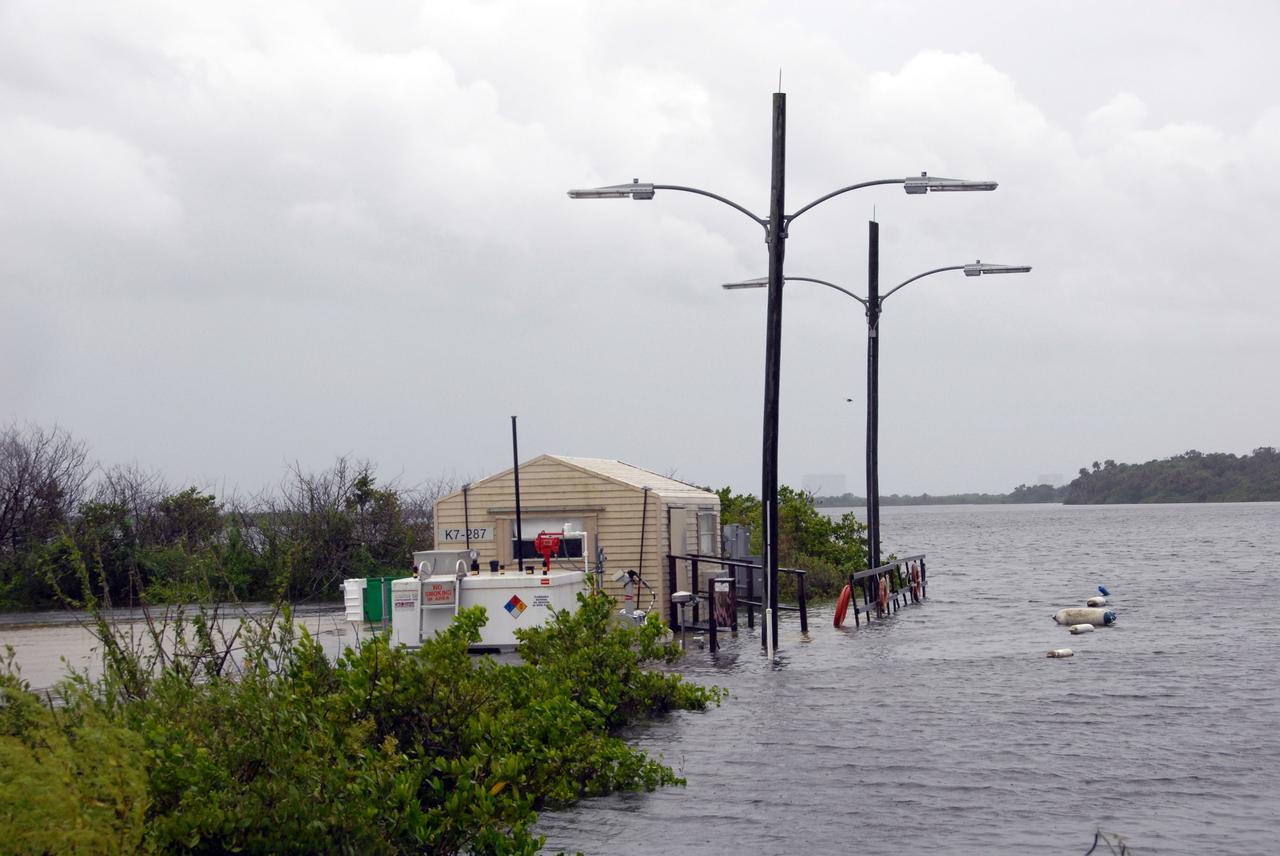

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Due to Tropical Storm Fay, the ground is flooded on a road alongside the turn basin at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The storm passed over the center Aug. 20 and then stalled offshore, bringing with it heavy rain and tropical storm force wind. Kennedy closed Aug. 19 because of Fay and reopened for normal operations Aug. 22. Based on initial assessments, there was no damage to space flight hardware, such as the space shuttles and Hubble Space Telescope equipment. Some facilities did sustain minor damage. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
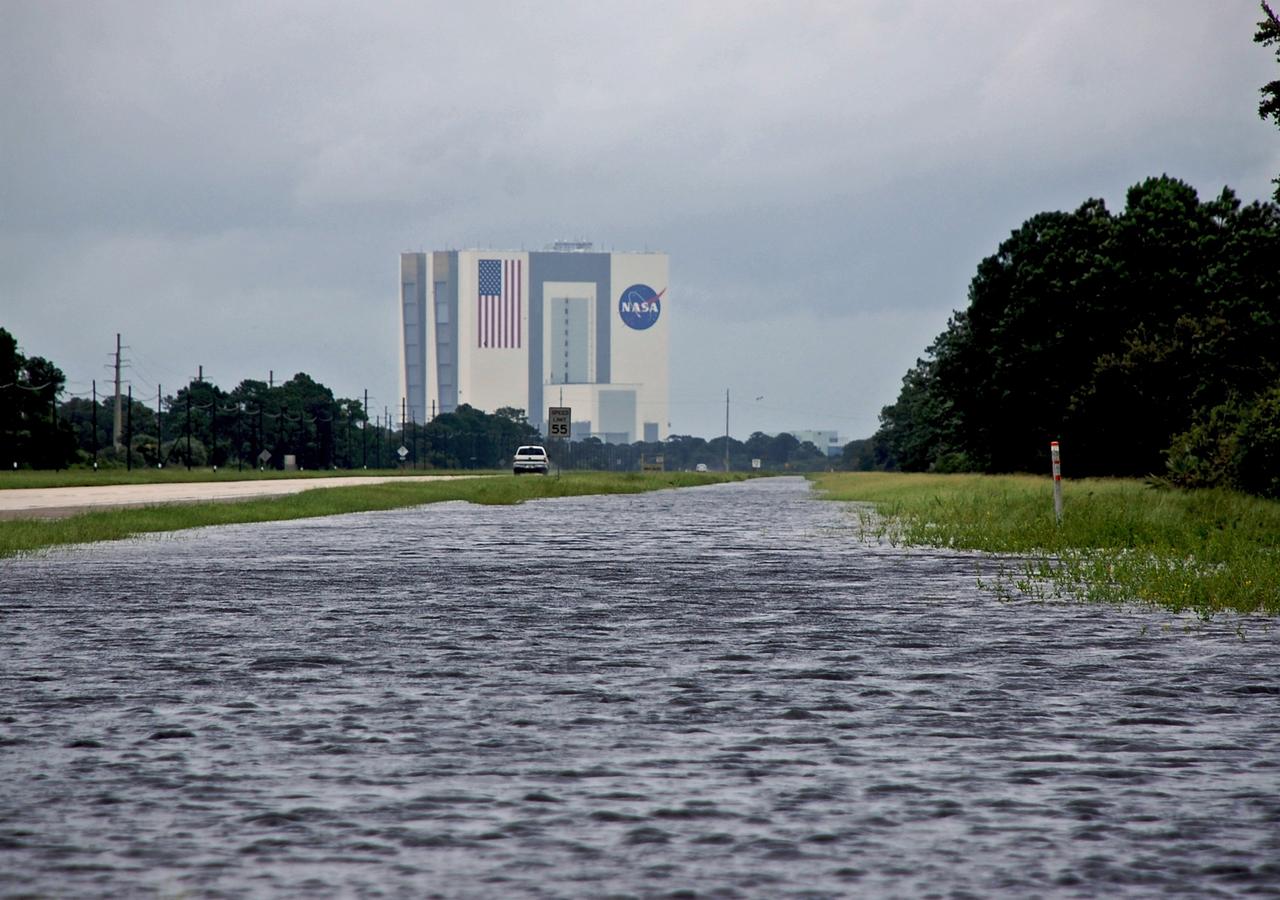

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Due to Tropical Storm Fay, the roadside canals and surrounding grounds are flooded at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. In the background is the Vehicle Assembly Building. The storm passed over the center Aug. 20 and then stalled offshore, bringing with it heavy rain and tropical storm force wind. Kennedy closed Aug. 19 because of Fay and reopened for normal operations Aug. 22. Based on initial assessments, there was no damage to space flight hardware, such as the space shuttles and Hubble Space Telescope equipment. Some facilities did sustain minor damage. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

The TRAPPIST-1 system contains a total of seven planets, all around the size of Earth. Three of them -- TRAPPIST-1e, f and g -- dwell in their star's so-called "habitable zone." The habitable zone, or Goldilocks zone, is a band around every star (shown here in green) where astronomers have calculated that temperatures are just right -- not too hot, not too cold -- for liquid water to pool on the surface of an Earth-like world. While TRAPPIST-1b, c and d are too close to be in the system's likely habitable zone, and TRAPPIST-1h is too far away, the planets' discoverers say more optimistic scenarios could allow any or all of the planets to harbor liquid water. In particular, the strikingly small orbits of these worlds make it likely that most, if not all of them, perpetually show the same face to their star, the way our moon always shows the same face to the Earth. This would result in an extreme range of temperatures from the day to night sides, allowing for situations not factored into the traditional habitable zone definition. The illustrations shown for the various planets depict a range of possible scenarios of what they could look like. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21424
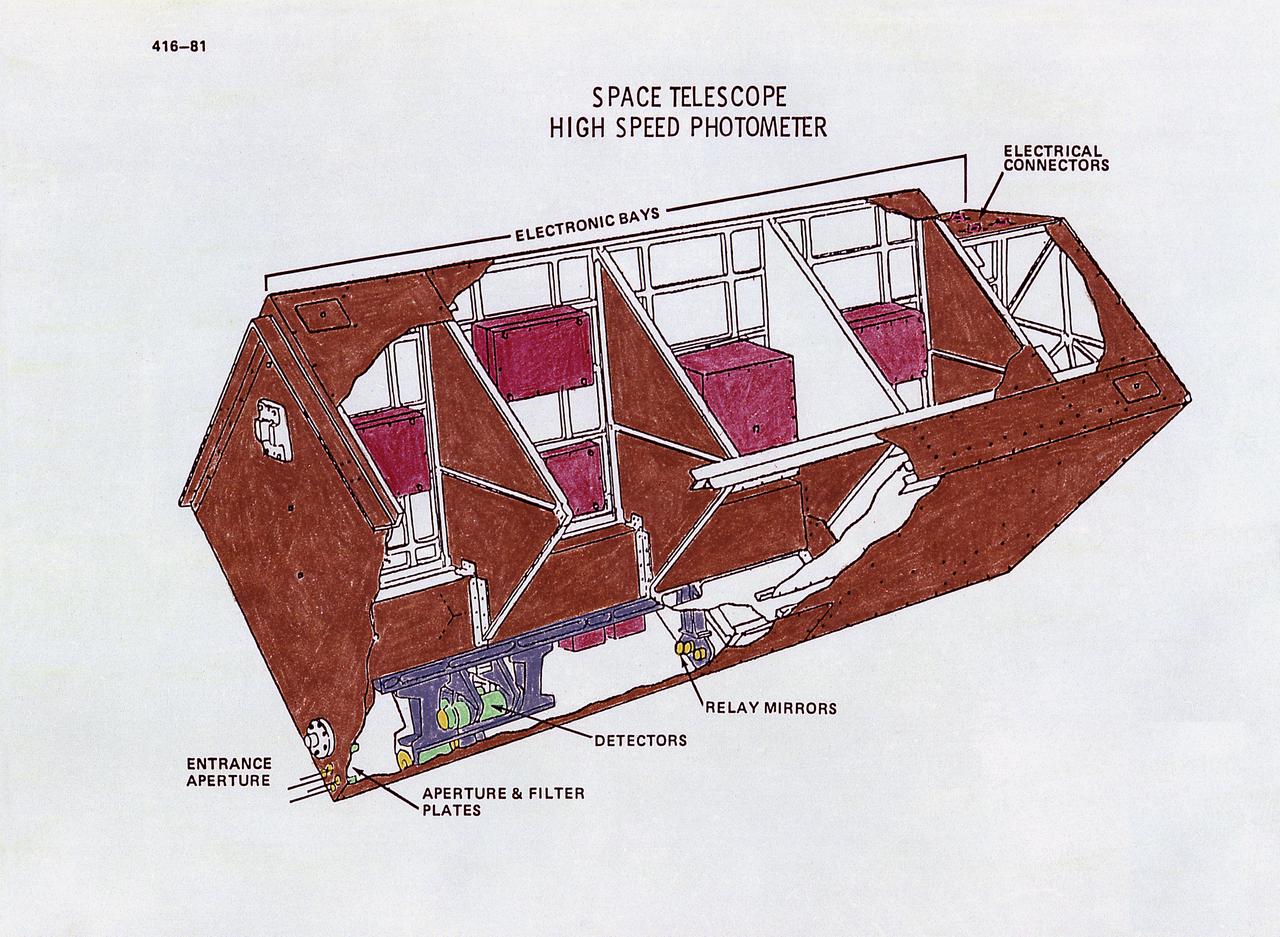
This drawing illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) High Speed Photometer (HSP). The HSP measures the intensity of starlight (brightness), which will help determine astronomical distances. Its principal use will be to measure extremely-rapid variations or pulses in light from celestial objects, such as pulsating stars. The HSP produces brightness readings. Light passes into one of four special signal-multiplying tubes that record the data. The HSP can measure energy fluctuations from objects that pulsate as rapidly as once every 10 microseconds. From HSP data, astronomers expect to learn much about such mysterious objects as pulsars, black holes, and quasars. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.

Caption: In this composite image, visible-light observations by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope are combined with infrared data from the ground-based Large Binocular Telescope in Arizona to assemble a dramatic view of the well-known Ring Nebula. Credit: NASA, ESA, C.R. Robert O’Dell (Vanderbilt University), G.J. Ferland (University of Kentucky), W.J. Henney and M. Peimbert (National Autonomous University of Mexico) Credit for Large Binocular Telescope data: David Thompson (University of Arizona) ---- The Ring Nebula's distinctive shape makes it a popular illustration for astronomy books. But new observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope of the glowing gas shroud around an old, dying, sun-like star reveal a new twist. "The nebula is not like a bagel, but rather, it's like a jelly doughnut, because it's filled with material in the middle," said C. Robert O'Dell of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn. He leads a research team that used Hubble and several ground-based telescopes to obtain the best view yet of the iconic nebula. The images show a more complex structure than astronomers once thought and have allowed them to construct the most precise 3-D model of the nebula. "With Hubble's detail, we see a completely different shape than what's been thought about historically for this classic nebula," O'Dell said. "The new Hubble observations show the nebula in much clearer detail, and we see things are not as simple as we previously thought." The Ring Nebula is about 2,000 light-years from Earth and measures roughly 1 light-year across. Located in the constellation Lyra, the nebula is a popular target for amateur astronomers. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14VAOMk" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14VAOMk</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This composite picture is a seamless blend of ultra-sharp NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) images combined with the wide view of the Mosaic Camera on the National Science Foundation's 0.9-meter telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory, part of the National Optical Astronomy Observatory, near Tucson, Ariz. Astronomers at the Space Telescope Science Institute assembled these images into a mosaic. The mosaic was then blended with a wider photograph taken by the Mosaic Camera. The image shows a fine web of filamentary "bicycle-spoke" features embedded in the colorful red and blue gas ring, which is one of the nearest planetary nebulae to Earth. Because the nebula is nearby, it appears as nearly one-half the diameter of the full Moon. This required HST astronomers to take several exposures with the Advanced Camera for Surveys to capture most of the Helix. HST views were then blended with a wider photo taken by the Mosaic Camera. The portrait offers a dizzying look down what is actually a trillion-mile-long tunnel of glowing gases. The fluorescing tube is pointed nearly directly at Earth, so it looks more like a bubble than a cylinder. A forest of thousands of comet-like filaments, embedded along the inner rim of the nebula, points back toward the central star, which is a small, super-hot white dwarf. The tentacles formed when a hot "stellar wind" of gas plowed into colder shells of dust and gas ejected previously by the doomed star. Ground-based telescopes have seen these comet-like filaments for decades, but never before in such detail. The filaments may actually lie in a disk encircling the hot star, like a collar. The radiant tie-die colors correspond to glowing oxygen (blue) and hydrogen and nitrogen (red). Valuable Hubble observing time became available during the November 2002 Leonid meteor storm. To protect the spacecraft, including HST's precise mirror, controllers turned the aft end into the direction of the meteor stream for about half a day. Fortunately, the Helix Nebula was almost exactly in the opposite direction of the meteor stream, so Hubble used nine orbits to photograph the nebula while it waited out the storm. To capture the sprawling nebula, Hubble had to take nine separate snapshots. Planetary nebulae like the Helix are sculpted late in a Sun-like star's life by a torrential gush of gases escaping from the dying star. They have nothing to do with planet formation, but got their name because they look like planetary disks when viewed through a small telescope. With higher magnification, the classic "donut-hole" in the middle of a planetary nebula can be resolved. Based on the nebula's distance of 650 light-years, its angular size corresponds to a huge ring with a diameter of nearly 3 light-years. That's approximately three-quarters of the distance between our Sun and the nearest star. The Helix Nebula is a popular target of amateur astronomers and can be seen with binoculars as a ghostly, greenish cloud in the constellation Aquarius. Larger amateur telescopes can resolve the ring-shaped nebula, but only the largest ground-based telescopes can resolve the radial streaks. After careful analysis, astronomers concluded the nebula really isn't a bubble, but is a cylinder that happens to be pointed toward Earth. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18164
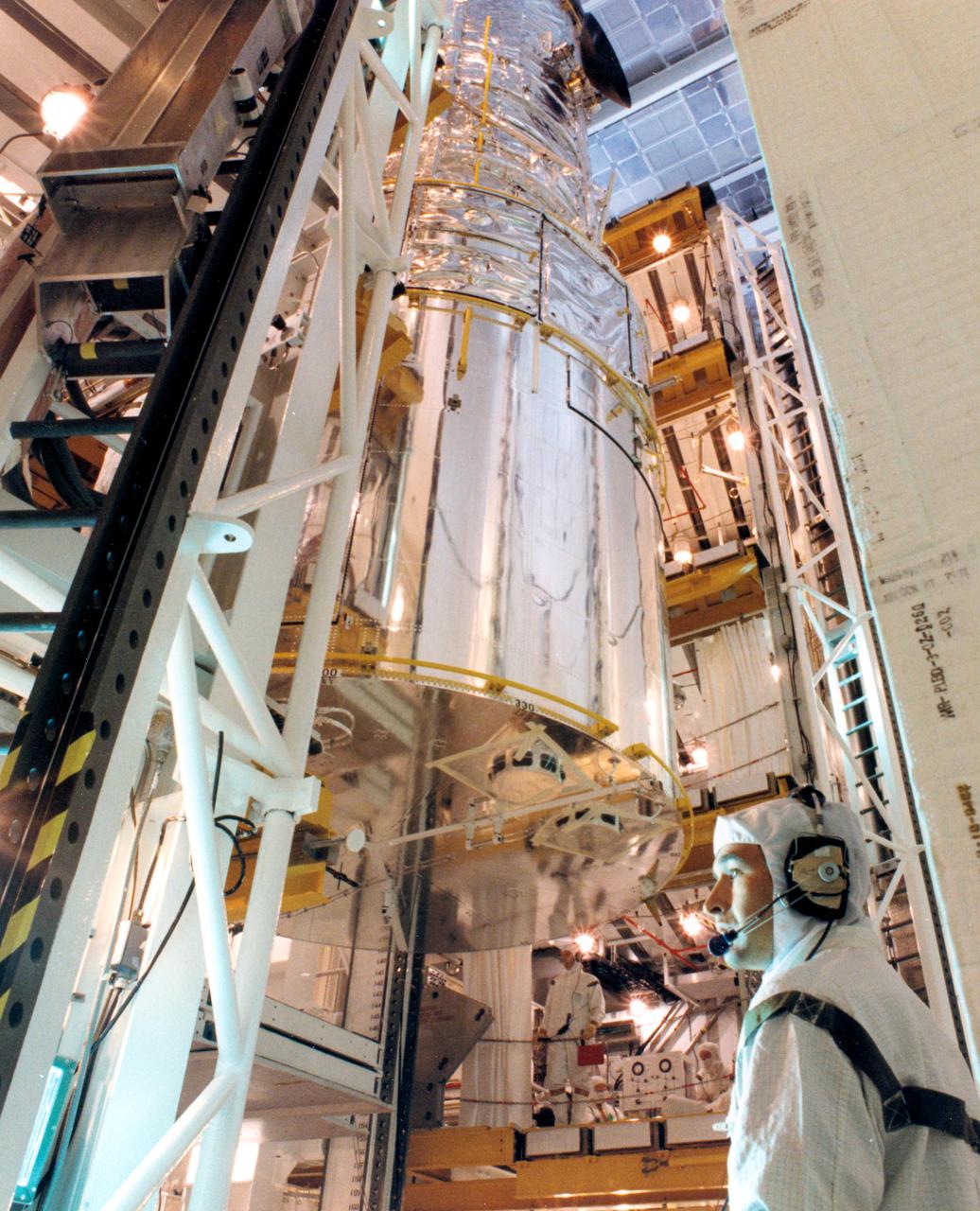
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The bus-size Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is carefully being transferred on March 29 from the surgically clean Payload Changeout Room at Launch Pad 39B into the cargo bay of the orbiter Discovery. The payload ground handling mechanism (left) is a device that extends the HST into the cargo bay (right), allowing workers to fasten it in place with four retention latches. Deployment of Hubble will occur during the five-day flight of Space Shuttle Mission STS-31, set for April 10. With HST, astronomers will be able to view 97 percent of the known universe, and will be able to get pictures unlimited and undistorted by the Earth's atmosphere. Compared with earth-based observatories, the HST will be able to view celestial objects that are 50 times fainter, provide images that are 10 times sharper, and see objects that are seven times farther away. .
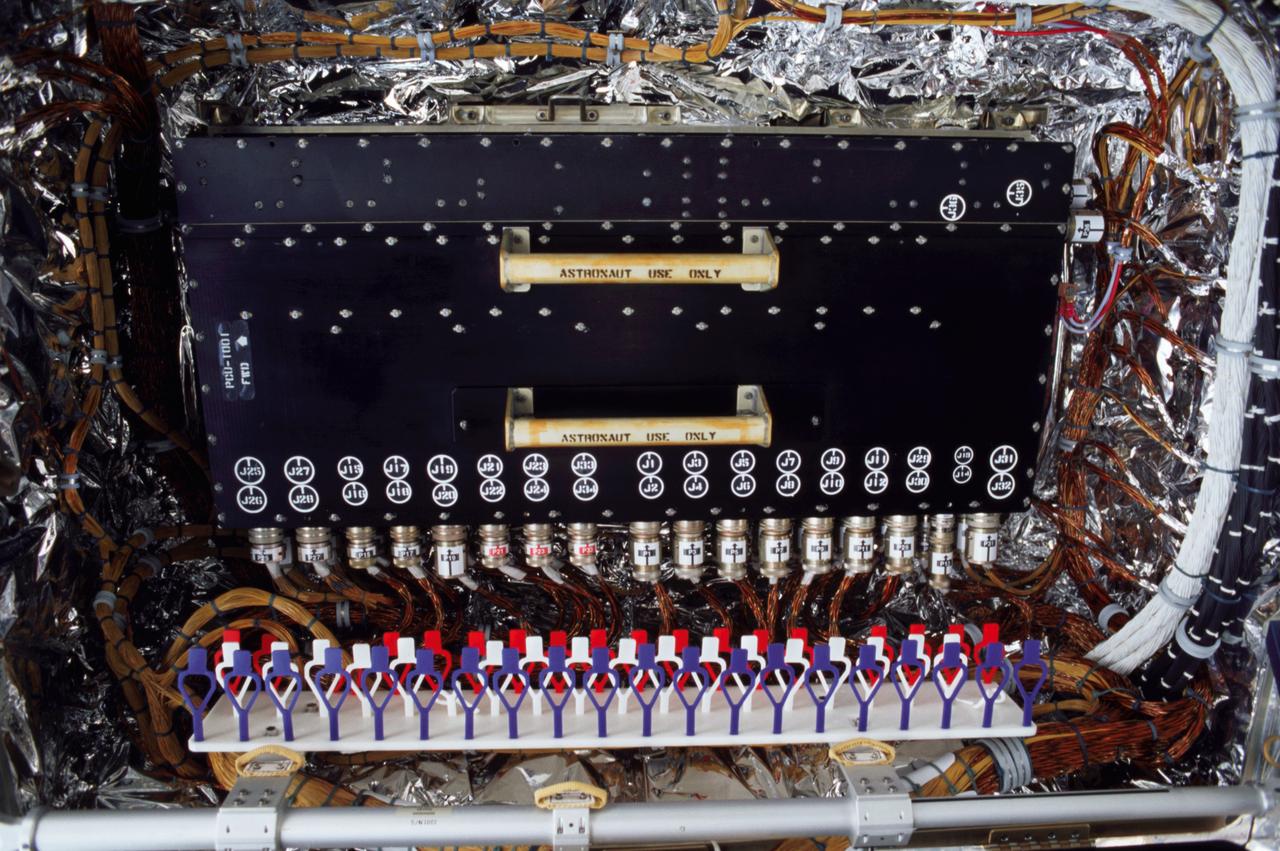
This is an onboard photo of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) power control unit (PCU), the heart of the HST's power system. STS-109 payload commander John M. Grunsfeld, joined by Astronaut Richard M. Lirnehan, turned off the telescope in order to replace its PCU while participating in the third of five spacewalks dedicated to servicing and upgrading the HST. Other upgrades performed were: replacement of the solar array panels; replacement of the Faint Object Camera (FOC) with a new advanced camera for Surveys (ACS); and installation of the experimental cooling system for the Hubble's Near-Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS), which had been dormant since January 1999 when its original coolant ran out. The telescope was captured and secured on a work stand in Columbia's payload bay using Columbia's robotic arm, where crew members completed the system upgrades. The Marshall Space Flight Center had the responsibility for the design, development, and construction of the HST, which is the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. Launched March 1, 2002 the STS-109 HST servicing mission lasted 10 days, 22 hours, and 11 minutes. It was the 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle Program.
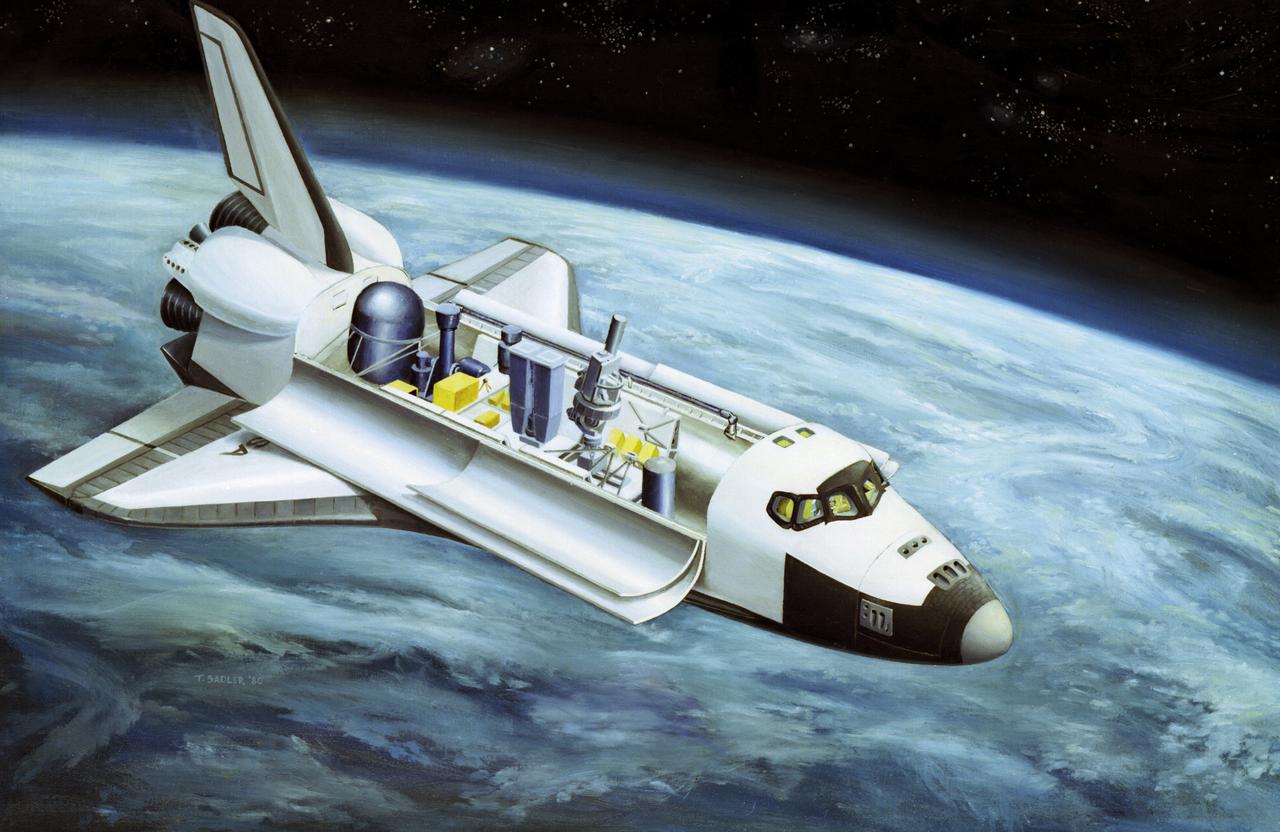
This illustration depicts the configuration of the Spacelab-2 in the cargo bay of the orbiter. Spacelab was a versatile laboratory carried in the Space Shuttle's cargo bay for scientific research flights. Each Spacelab mission had a unique design appropriate to the mission's goals. A number of Spacelab configurations could be assembled from pressurized habitation modules and exposed platforms called pallets. Spacelab-2 was the first pallet-only mission. One of the goals of the mission was to verify that the pallets' configuration was satisfactory for observations and research. Except for two biological experiments and an experiment that used ground-based instruments, the Spacelab-2 scientific instruments needed direct exposure to space. On the first pallet, three solar instruments and one atmospheric instrument were mounted on the Instrument Pointing System, which was being tested on its first flight. The second Spacelab pallet held a large double x-ray telescope and three plasma physics detectors. The last pallet supported an infrared telescope, a superfluid helium technology experiment, and a small plasma diagnostics satellite. The Spacelab-2 mission was designed to capitalize on the Shuttle-Spacelab capabilities, to launch and retrieve satellites, and to point several instruments independently with accuracy and stability. Spacelab-2 (STS-51F, 19th Shuttle mission) was launched aboard Space Shuttle Orbiter Challenger on July 29, 1985. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall management responsibilities of the Spacelab missions.
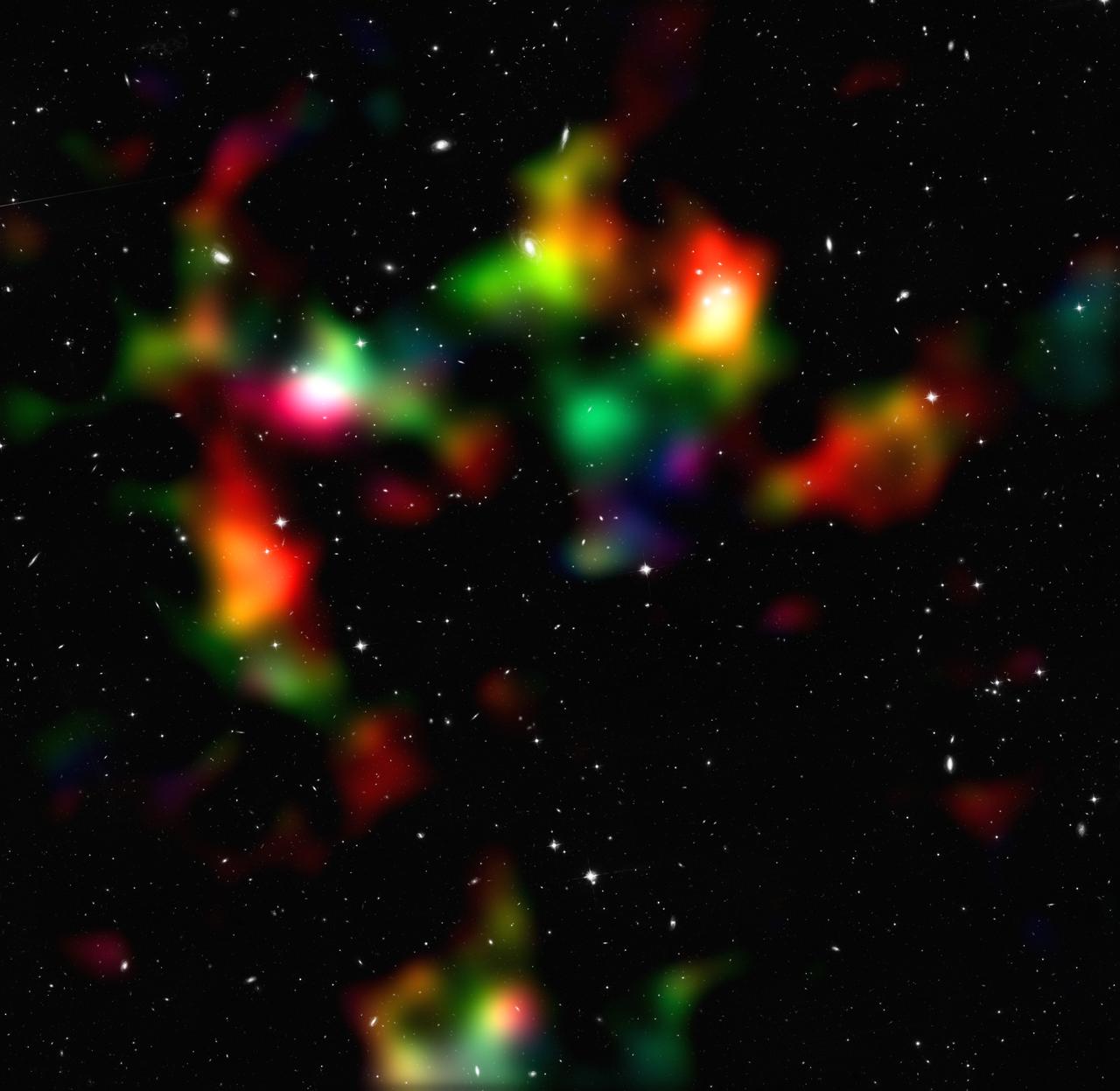

NASA/ESA Hubble Release Date: March 25, 2010 This image shows a smoothed reconstruction of the total (mostly dark) matter distribution in the COSMOS field, created from data taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope and ground-based telescopes. It was inferred from the weak gravitational lensing distortions that are imprinted onto the shapes of background galaxies. The colour coding indicates the distance of the foreground mass concentrations as gathered from the weak lensing effect. Structures shown in white, cyan, and green are typically closer to us than those indicated in orange and red. To improve the resolution of the map, data from galaxies both with and without redshift information were used. The new study presents the most comprehensive analysis of data from the COSMOS survey. The researchers have, for the first time ever, used Hubble and the natural "weak lenses" in space to characterise the accelerated expansion of the Universe. Credit: NASA, ESA, P. Simon (University of Bonn) and T. Schrabback (Leiden Observatory) To learn more abou this image go to: <a href="http://www.spacetelescope.org/news/html/heic1005.html" rel="nofollow">www.spacetelescope.org/news/html/heic1005.html</a> For more information about Goddard Space Flight Center go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html</a>

This chart shows, on the top row, artist concepts of the seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 with their orbital periods, distances from their star, radii, masses, densities and surface gravity as compared to those of Earth. These numbers are current as of February 2018. On the bottom row, the same numbers are displayed for the bodies of our inner solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit their star extremely closely, with periods ranging from 1.5 to only about 20 days. This is much shorter than the period of Mercury, which orbits our sun in about 88 days. The masses and densities of the TRAPPIST-1 planets were determined by careful measurements of slight variations in the timings of their orbits using extensive observations made by NASA's Spitzer and Kepler space telescopes, in combination with data from Hubble and a number of ground-based telescopes. These measurements are the most precise to date for any system of exoplanets. In this illustration, the relative sizes of the planets are all shown to scale. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22094

This is a Hubble Space Telescope composite image of a supernova explosion designated SN 2014J in the galaxy M82. At a distance of approximately 11.5 million light-years from Earth it is the closest supernova of its type discovered in the past few decades. The explosion is categorized as a Type Ia supernova, which is theorized to be triggered in binary systems consisting of a white dwarf and another star — which could be a second white dwarf, a star like our sun, or a giant star. Astronomers using a ground-based telescope discovered the explosion on January 21, 2014. This Hubble photograph was taken on January 31, as the supernova approached its peak brightness. The Hubble data are expected to help astronomers refine distance measurements to Type Ia supernovae. In addition, the observations could yield insights into what kind of stars were involved in the explosion. Hubble’s ultraviolet-light sensitivity will allow astronomers to probe the environment around the site of the supernova explosion and in the interstellar medium of the host galaxy. Because of their consistent peak brightness, Type Ia supernovae are among the best tools to measure distances in the universe. They were fundamental to the 1998 discovery of the mysterious acceleration of the expanding universe. A hypothesized repulsive force, called dark energy, is thought to cause the acceleration. Among the other major NASA space-based observatories used in the M82 viewing campaign are Spitzer Space Telescope, Chandra X-ray Observatory, Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR), Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, Swift Gamma Ray Burst Explorer, and the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA). Image Credit: NASA, ESA, A. Goobar (Stockholm University), and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The galaxy UGC 1382 has been revealed to be far larger and stranger than previously thought. Astronomers relied on a combination of ground-based and space telescopes to uncover the true nature of this "Frankenstein galaxy." The composite image shows the same galaxy as viewed with different instruments. The component images are also available. In the image at left, UGC 1382 appears to be a simple elliptical galaxy, based on optical data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS). But spiral arms emerged when astronomers incorporated ultraviolet data from the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) and deep optical data from SDSS, as seen in the middle image. Combining that with a view of low-density hydrogen gas (shown in green), detected at radio wavelengths by the Very Large Array, scientists discovered that UGC 1382 is a giant, and one of the largest isolated galaxies known. GALEX in particular was able detect very faint features because it operated from space, which is necessary for UV observations because ultraviolet light is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere. Astronomers also used Stripe 82 of SDSS, a small region of sky where SDSS imaged the sky 80 times longer than the original standard SDSS survey. This enabled optical detection of much fainter features as well. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20695
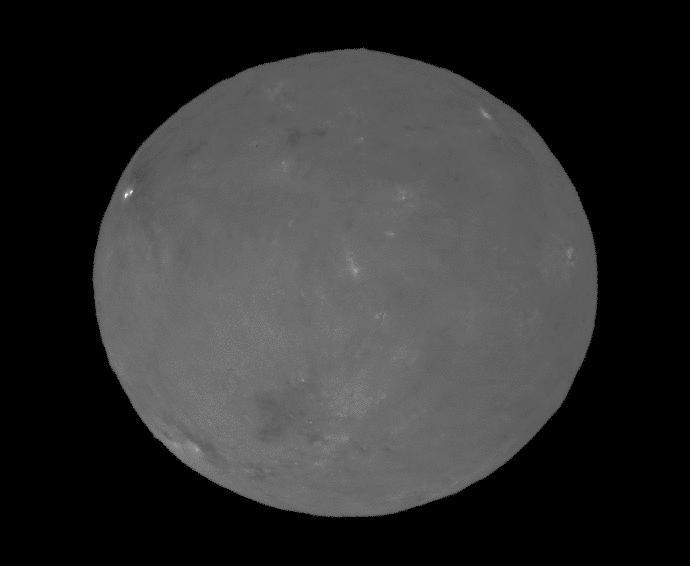

NASA's Dawn spacecraft successfully observed Ceres at opposition on April 29, 2017, taking images from a position exactly between the sun and Ceres' surface. Mission specialists had carefully maneuvered Dawn into a special orbit so that the spacecraft could view Occator Crater, which contains the brightest area of Ceres, from this new perspective. A movie shows these opposition images, with contrast enhanced to highlight brightness differences. The bright spots of Occator stand out particularly well on an otherwise relatively bland surface. Dawn took these images from an altitude of about 12,000 miles (20,000 kilometers). Based on data from ground-based telescopes and spacecraft that have previously viewed planetary bodies at opposition, scientists predicted that Ceres would appear brighter from this opposition configuration. This increase in brightness, or "surge," relates the size of the grains of material on the surface, as well as how porous those materials are. The science motivation for performing these observations is further explained in the March 2017 issue of the Dawn Journal blog. A movie can be viewed at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21405

To view a video of this story go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8448332724">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/8448332724</a> Working with astronomical image processors at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Md., renowned astro-photographer Robert Gendler has taken science data from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) archive and combined it with his own ground-based observations to assemble a photo illustration of the magnificent spiral galaxy M106. Gendler retrieved archival Hubble images of M106 to assemble a mosaic of the center of the galaxy. He then used his own and fellow astro-photographer Jay GaBany's observations of M106 to combine with the Hubble data in areas where there was less coverage, and finally, to fill in the holes and gaps where no Hubble data existed. The center of the galaxy is composed almost entirely of HST data taken by the Advanced Camera for Surveys, Wide Field Camera 3, and Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 detectors. The outer spiral arms are predominantly HST data colorized with ground-based data taken by Gendler's and GaBany's 12.5-inch and 20-inch telescopes, located at very dark remote sites in New Mexico. The image also reveals the optical component of the "anomalous arms" of M106, seen here as red, glowing hydrogen emission. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/m106.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/m106.html</a> Credit: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), R. Gendler (for the Hubble Heritage Team), and G. Bacon (STScI) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
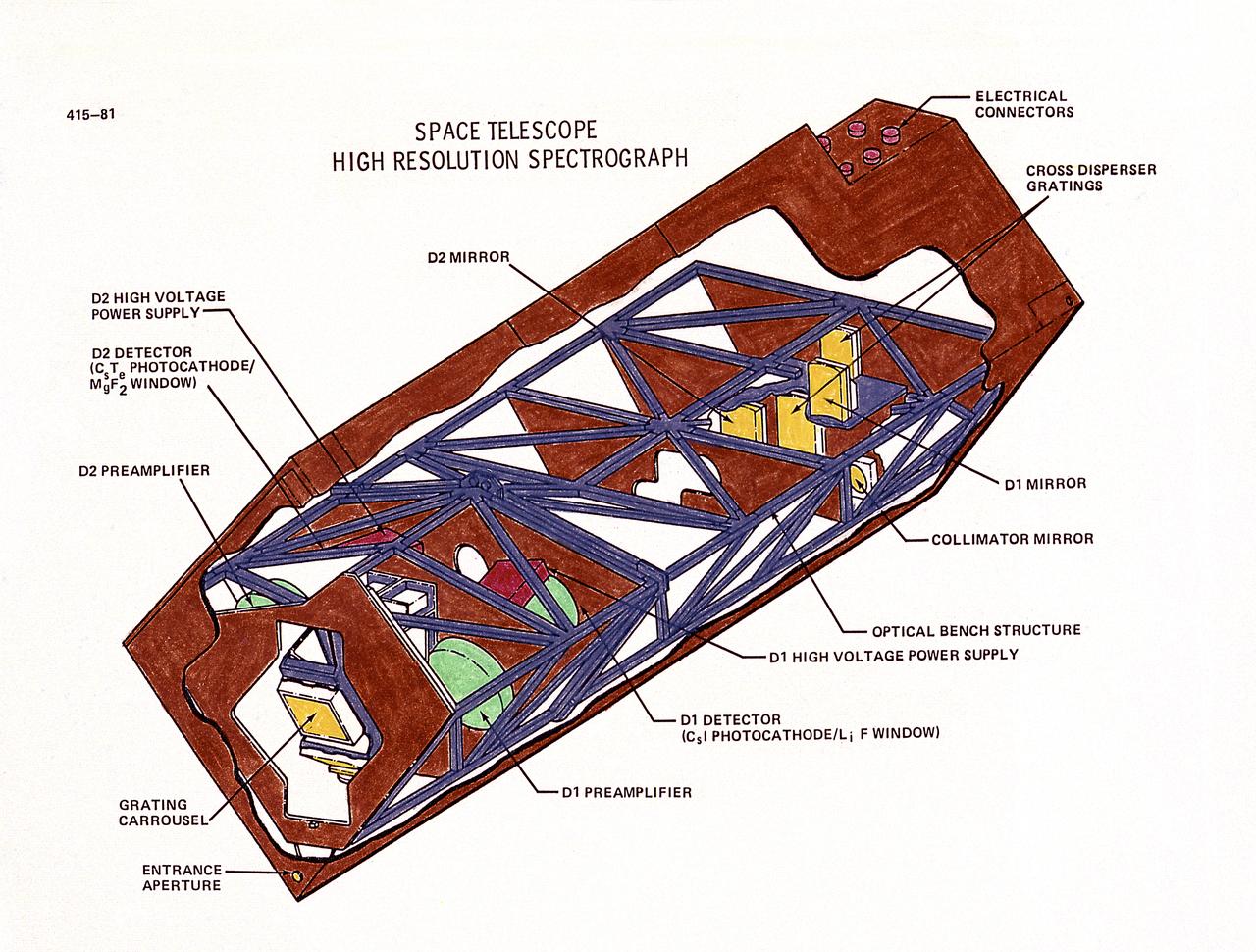
This drawing illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Goddard High-Resolution Spectrograph (GHRS). The HST's two spectrographs, the GHRS and the Faint Object Spectrograph (FOS), can detect a broader range of wavelengths than is possible from Earth because there is no atmosphere to absorb certain wavelengths. Scientists can determine the chemical composition, temperature, pressure, and turbulence of the stellar atmosphere producing the light, all from spectral data. The GHRS can detect fine details in the light from somewhat brighter objects but only ultraviolet light. Both spectrographs operate in essentially the same way. The incoming light passes through a small entrance aperture, then passes through filters and diffraction gratings, that work like prisms. The filter or grating used determines what range of wavelength will be examined and in what detail. Then the spectrograph detectors record the strength of each wavelength band and sends it back to Earth. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
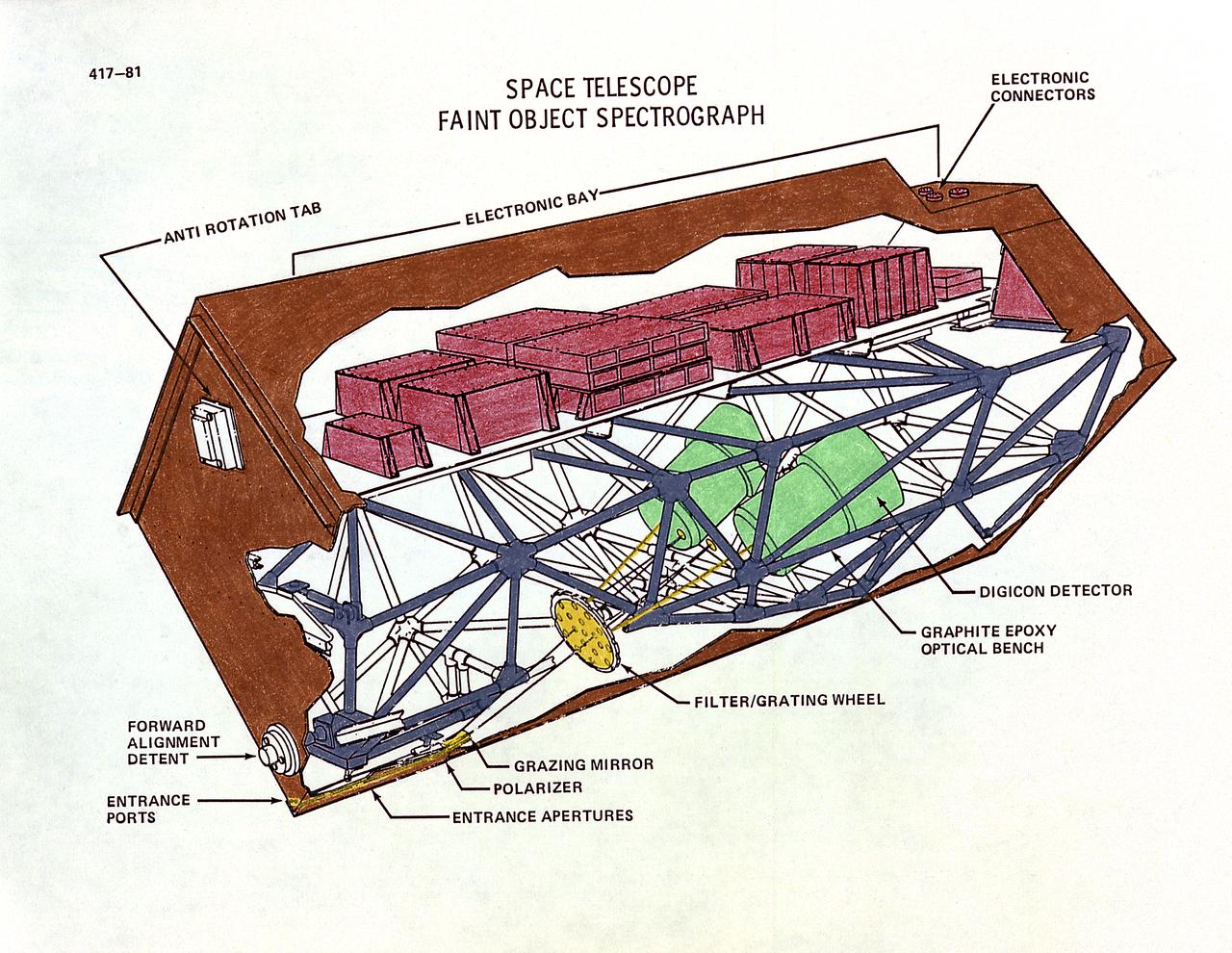
This drawing illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Faint Object Spectrograph (FOS). The HST's two spectrographs, the Goddard High-Resolution Spectrograph and the FOS, can detect a broader range of wavelengths than is possible from the Earth because there is no atmosphere to absorb certain wavelengths. Scientists can determine the chemical composition, temperature, pressure, and turbulence of the stellar atmosphere producing the light, all from spectral data. The FOC can detect detail in very faint objects, such as those at great distances, and light ranging from ultraviolet to red spectral bands. Both spectrographs operate in essentially the same way. The incoming light passes through a small entrance aperture, then passes through filters and diffraction gratings, that work like prisms. The filter or grating used determines what range of wavelength will be examined and in what detail. Then the spectrograph detectors record the strength of each wavelength band and sends it back to Earth. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
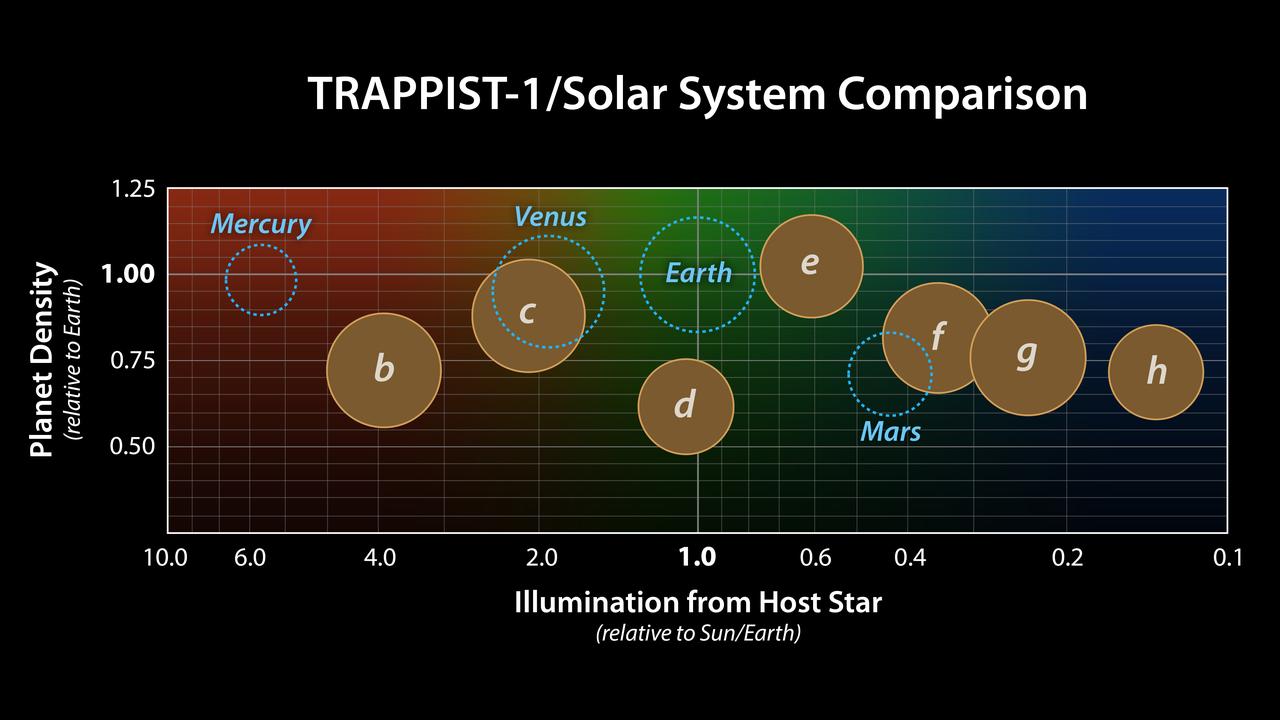
This graph presents known properties of the seven TRAPPIST-1 exoplanets (labeled b through h), showing how they stack up to the inner rocky worlds in our own solar system. The horizontal axis shows the level of illumination that each planet receives from its host star. TRAPPIST-1 is a mere 9 percent the mass of our Sun, and its temperature is much cooler. But because the TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit so closely to their star, they receive comparable levels of light and heat to Earth and its neighboring planets. The vertical axis shows the densities of the planets. Density, calculated based on a planet's mass and volume, is the first important step in understanding a planet's composition. The plot shows that the TRAPPIST-1 planet densities range from being similar to Earth and Venus at the upper end, down to values comparable to Mars at the lower end. The relative sizes of the planets are indicated by the circles. The masses and densities of the TRAPPIST-1 planets were determined by careful measurements of slight variations in the timings of their orbits using extensive observations made by NASA's Spitzer and Kepler space telescopes, in combination with data from Hubble and a number of ground-based telescopes. These measurements are the most precise to date for any system of exoplanets. By comparing these measurements with theoretical models of how planets form and evolve, researchers have determined that they are all rocky in overall composition. Estimates suggest the lower-density planets could have large quantities of water -- as much as 5 percent by mass for TRAPPIST-1d. Earth, in comparison, has only about 0.02 percent of its mass in the form of water. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22095

This frame from an animation shows Jupiter volcanic moon Io as seen by NASA Voyager and Galileo spacecraft (at left) and the pattern of heat flow from 242 active volcanoes (at right). The red and yellow areas are places where local heat flow is greatest -- the result of magma erupting from Io's molten interior onto the surface. The map is the result of analyzing decades of observations from spacecraft and ground-based telescopes. It shows Io's usual volcanic thermal emission, excluding the occasional massive but transient "outburst" eruption; in other words, this is what Io looks like most of the time. This heat flow map will be used to test models of interior heating. The map shows that areas of enhanced volcanic heat flow are not necessarily correlated with the number of volcanoes in a particular region and are poorly correlated with expected patterns of heat flow from current models of tidal heating -- something that is yet to be explained. This research is published in association with a 2015 paper in the journal Icarus by A. Davies et al., titled "Map of Io's Volcanic Heat Flow," (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2015.08.003.) http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19655

This composite NASA Hubble Space Telescope Image captures the positions of comet Siding Spring and Mars in a never-before-seen close passage of a comet by the Red Planet, which happened at 2:28 p.m. EDT October 19, 2014. The comet passed by Mars at approximately 87,000 miles (about one-third of the distance between Earth and the Moon). At that time, the comet and Mars were approximately 149 million miles from Earth. The comet image shown here is a composite of Hubble exposures taken between Oct. 18, 8:06 a.m. EDT to Oct. 19, 11:17 p.m. EDT. Hubble took a separate photograph of Mars at 10:37 p.m. EDT on Oct. 18. The Mars and comet images have been added together to create a single picture to illustrate the angular separation, or distance, between the comet and Mars at closest approach. The separation is approximately 1.5 arc minutes, or one-twentieth of the angular diameter of the full Moon. The background starfield in this composite image is synthesized from ground-based telescope data provided by the Palomar Digital Sky Survey, which has been reprocessed to approximate Hubble’s resolution. The solid icy comet nucleus is too small to be resolved in the Hubble picture. The comet’s bright coma, a diffuse cloud of dust enshrouding the nucleus, and a dusty tail, are clearly visible. This is a composite image because a single exposure of the stellar background, comet Siding Spring, and Mars would be problematic. Mars is actually 10,000 times brighter than the comet, and so could not be properly exposed to show detail in the Red Planet. The comet and Mars were also moving with respect to each other and so could not be imaged simultaneously in one exposure without one of the objects being motion blurred. Hubble had to be programmed to track on the comet and Mars separately in two different observations. The images were taken with Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3. Credit: NASA, ESA, PSI, JHU/APL, STScI/AURA Credit: NASA, ESA, PSI, JHU/APL, STScI/AURA

These images represent radar observations of asteroid 99942 Apophis on March 8, 9, and 10, 2021, as it made its last close approach before its 2029 Earth encounter that will see the object pass our planet by less than 20,000 miles (32,000 kilometers). The 70-meter radio antenna at the Deep Space Network's Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex near Barstow, California, and the 100-meter Green Bank Telescope in West Virginia used radar to precisely track Apophis' motion. At the time of these observations, Apophis was about 10.6 million miles (17 million kilometers) from Earth, and each pixel has a resolution of 127 feet (38.75 meters). These observations helped scientists of the Center for Near Earth Object Studies (CNEOS), managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, precisely determine the 1,100-feet-wide (340-meter-wide) asteroid's orbit around the Sun, ruling out any Earth impact threat for the next hundred years or more. As a result of these observations, Apophis was removed from the Sentry Impact Risk Table. The radar team will continue to analyze these observations to determine more information about Apophis' size, shape, and rate of spin. Relying on optical telescopes and ground-based radar to help characterize every near-Earth object's orbit to improve long-term hazard assessments, CNEOS computes high-precision orbits in support of NASA's Planetary Defense Coordination Office. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24168
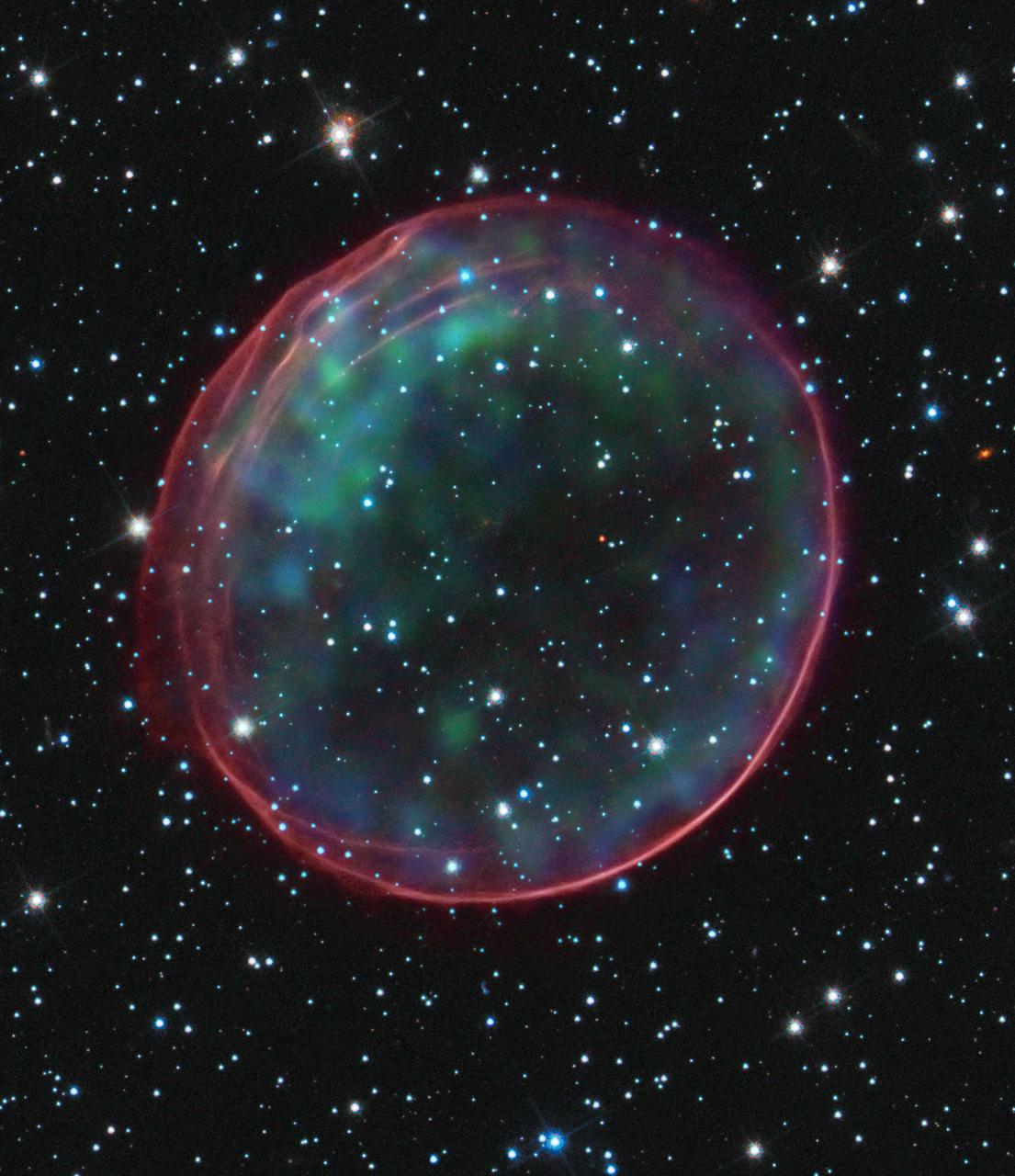

NASA image release January 11, 2012 Using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have solved a longstanding mystery on the type of star, or so-called progenitor, that caused a supernova in a nearby galaxy. The finding yields new observational data for pinpointing one of several scenarios that could trigger such outbursts. Based on previous observations from ground-based telescopes, astronomers knew that a kind of supernova called a Type Ia created a remnant named SNR 0509-67.5, which lies 170,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy. The type of system that leads to this kind of supernova explosion has long been a high importance problem with various proposed solutions but no decisive answer. All these solutions involve a white dwarf star that somehow increases in mass to the highest limit. Astronomers failed to find any companion star near the center of the remnant, and this rules out all but one solution, so the only remaining possibility is that this one Type Ia supernova came from a pair of white dwarfs in close orbit. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/supernova-source.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/supernova-sourc...</a> Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CXC, SAO, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), and J. Hughes (Rutgers University) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This close-up of the sunspot underneath the March 29, 2014, flare shows incredible detail. The image was captured by the G-band camera at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. This instrument can focus on only a small area at once, but provide very high resolution. Ground-based telescope data can be hindered by Earth's atmosphere, which blocks much of the sun's ultraviolet and X-ray light, and causes twinkling even in the light it does allow through. As it happens, the March 29 flare occurred at a time of day in New Mexico that often results in the best viewing times from the ground. Credit: Kevin Reardon (National Solar Observatory), Lucia Kleint (BAER Institute) -- On March 29, 2014 the sun released an X-class flare. It was observed by NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS; NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO; NASA's Reuven Ramaty High Energy Solar Spectroscopic Imager, or RHESSI; the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency's Hinode; and the National Solar Observatory's Dunn Solar Telescope located at Sacramento Peak in New Mexico. To have a record of such an intense flare from so many observatories is unprecedented. Such research can help scientists better understand what catalyst sets off these large explosions on the sun. Perhaps we may even some day be able to predict their onset and forewarn of the radio blackouts solar flares can cause near Earth - blackouts that can interfere with airplane, ship and military communications. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1kMDQbO</a> Join our Google+ Hangout on May 8 at 2:30pm EST: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1mwbBEZ</a> Credit: NASA Goddard <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
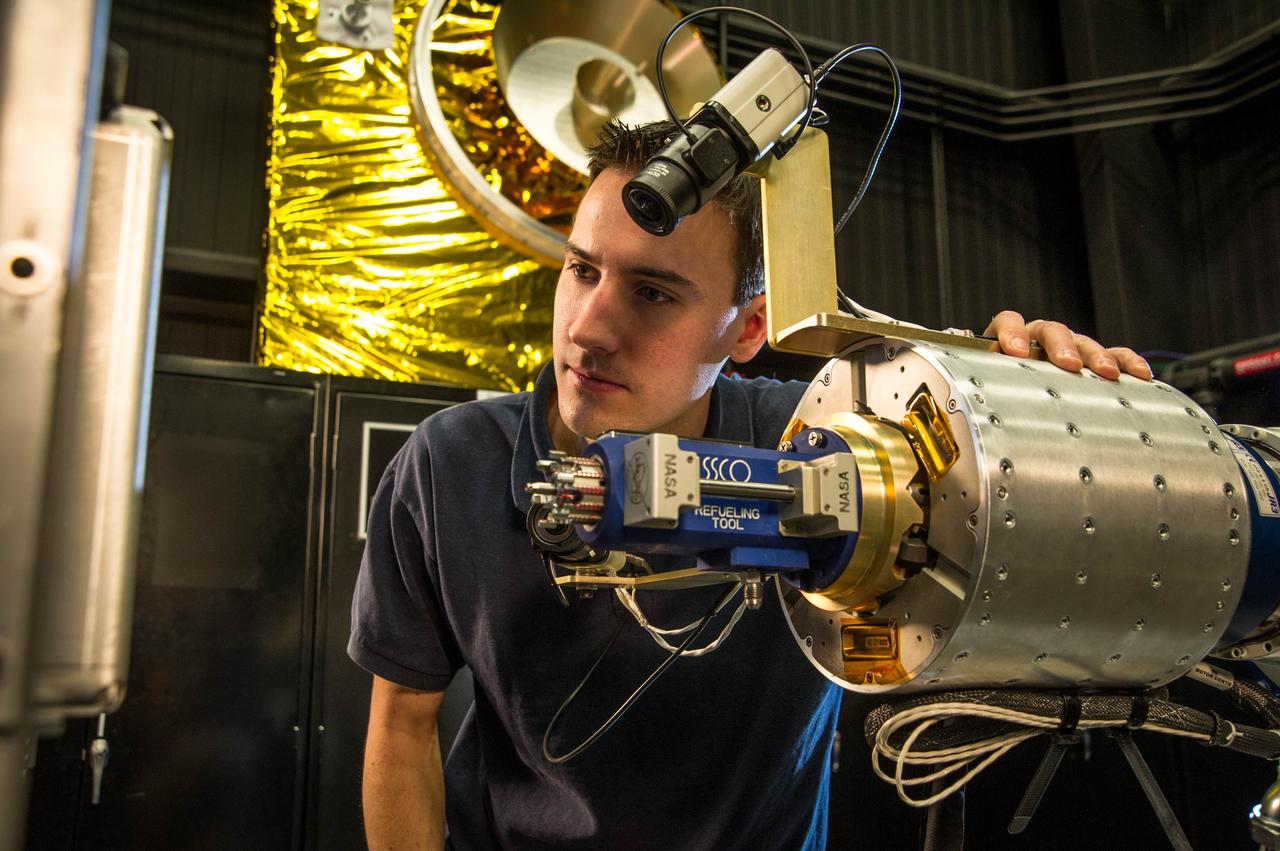
RROxiTT lead roboticist Alex Janas stands with the Oxidizer Nozzle Tool as he examines the work site. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn NASA has successfully concluded a remotely controlled test of new technologies that would empower future space robots to transfer hazardous oxidizer – a type of propellant – into the tanks of satellites in space today. Concurrently on the ground, NASA is incorporating results from this test and the Robotic Refueling Mission on the International Space Station to prepare for an upcoming ground-based test of a full-sized robotic servicer system that will perform tasks on a mock satellite client. Collectively, these efforts are part of an ongoing and aggressive technology development campaign to equip robots and humans with the tools and capabilities needed for spacecraft maintenance and repair, the assembly of large space telescopes, and extended human exploration. Read more here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-tests-new-robotic-refueling-technologies/#.UxeLyyRkLH4" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/nasa-tests-new-robotic-refue...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

In this illustration showing NEO Surveyor, NASA's next-generation near-Earth object hunter, the spacecraft floats in an infrared starfield containing stars, star clusters, gas, and dust. More than 100 asteroids can be seen as red dots, with some of them visible in a track that shows how they were captured at different times as they marched across the sky. This starfield was observed by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, during its primary all-sky survey in March 2010 before it was put into hibernation a year later. In December 2013, the space telescope was reactivated to search for more asteroids as the NEOWISE mission. NASA's NEO Surveyor will build upon the successes of NEOWISE as the first space mission built specifically to find large numbers of hazardous asteroids and comets. The space telescope will launch to a region of gravitational stability between the Earth and the Sun called the L1 Lagrange point, where the spacecraft will orbit during its five-year primary mission. From this location, the space telescope will view the solar system in infrared wavelengths &ndash light that is invisible to the human eye. Because those wavelengths are mostly blocked by Earth's atmosphere, larger ground-based observatories may miss near-Earth objects that NEO Surveyor will be able to spot from space by using its modest light-collecting aperture of nearly 20 inches (50 centimeters). NEO Surveyor's cutting-edge detectors are designed to observe two heat-sensitive infrared bands that were chosen specifically so the spacecraft can track the most challenging-to-find near-Earth objects, such as dark asteroids and comets that don't reflect much visible light. In the infrared wavelengths to which NEO Surveyor is sensitive, these objects glow as they are heated by sunlight. In addition, NEO Surveyor will be able to find asteroids that approach Earth from the direction of the Sun, as well as those that lead and trail our planet's orbit, where they are typically obscured by the glare of sunlight – objects known as Earth Trojans. The mission is tasked by NASA's Planetary Science Division within the Science Mission Directorate; program oversight is provided by the PDCO, which was established in 2016 to manage the agency's ongoing efforts in planetary defense. NASA's Planetary Missions Program Office at Marshall Space Flight Center provides program management for NEO Surveyor. The project is being developed by JPL and is led by survey director Amy Mainzer at the University of Arizona. Established aerospace and engineering companies have been contracted to build the spacecraft and its instrumentation, including Ball Aerospace , Space Dynamics Laboratory, and Teledyne. The Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics at the University of Colorado, Boulder will support operations, and IPAC-Caltech in Pasadena, California, is responsible for processing survey data and producing the mission's data products. Caltech manages JPL for NASA. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25253

NASA image release December 14, 2010 A delicate sphere of gas, photographed by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, floats serenely in the depths of space. The pristine shell, or bubble, is the result of gas that is being shocked by the expanding blast wave from a supernova. Called SNR 0509-67.5 (or SNR 0509 for short), the bubble is the visible remnant of a powerful stellar explosion in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a small galaxy about 160,000 light-years from Earth. Ripples in the shell's surface may be caused by either subtle variations in the density of the ambient interstellar gas, or possibly driven from the interior by pieces of the ejecta. The bubble-shaped shroud of gas is 23 light-years across and is expanding at more than 11 million miles per hour (5,000 kilometers per second). Astronomers have concluded that the explosion was one of an especially energetic and bright variety of supernovae. Known as Type Ia, such supernova events are thought to result from a white dwarf star in a binary system that robs its partner of material, takes on much more mass than it is able to handle, and eventually explodes. Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys observed the supernova remnant on Oct. 28, 2006 with a filter that isolates light from glowing hydrogen seen in the expanding shell. These observations were then combined with visible-light images of the surrounding star field that were imaged with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 on Nov. 4, 2010. With an age of about 400 years as seen from Earth, the supernova might have been visible to southern hemisphere observers around the year 1600, however, there are no known records of a "new star" in the direction of the LMC near that time. A more recent supernova in the LMC, SN 1987A, did catch the eye of Earth viewers and continues to be studied with ground- and space-based telescopes, including Hubble. For images and more information about SNR 0509, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2010/27" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2010/27</a> <a href="http://heritage.stsci.edu/2010/27" rel="nofollow">heritage.stsci.edu/2010/27</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b>Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: J. Hughes (Rutgers University)</b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: : <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?11530" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?11530</a>

This graph presents measured properties of the seven TRAPPIST-1 exoplanets (labeled b through h), showing how they stack up with one another as well as with Earth and the other inner rocky worlds in our own solar system. The relative sizes of the planets are indicated by the circles. All of the known TRAPPIST-1 planets are larger than Mars, with five of them within 15% of the diameter of Earth. The vertical axis shows the uncompressed densities of the planets. Density, calculated from a planet's mass and volume, is the first important step in understanding its composition. Uncompressed density takes into account that the larger a planet is, the more its own gravity will pack the planet's material together and increase its density. Uncompressed density, therefore, usually provides a better means of comparing the composition of planets. The plot shows that the uncompressed densities of the TRAPPIST-1 planets are similar to one another, suggesting they may have all have a similar composition. The four rocky planets in our own solar system show more variation in density compared to the seven TRAPPIST-1 planets. Mercury, for example, contains a much higher percentage of iron than the other three rocky planets and thus has a much higher uncompressed density. The horizontal axis shows the level of illumination that each planet receives from its host star. The TRAPPIST-1 star is a mere 9% the mass of our Sun, and its temperature is much cooler. But because the TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit so closely to their star, they receive comparable levels of light and heat to Earth and its neighboring planets. The corresponding "habitable zones" — regions where an Earth-like planet could potentially support liquid water on its surface — of the two planetary systems are indicated near the top of the plot. The the two zones do not line up exactly because the cooler TRAPPIST-1 star emitting more of its light in the form of infrared radiation that is more efficiently absorbed by an Earth-like atmosphere. Since it takes less illumination to reach the same temperatures, the habitable zone shifts farther away from the star. The masses and densities of the TRAPPIST-1 planets were determined by measurements of slight variations in the timings of their orbits using extensive observations made by NASA's Spitzer and Kepler space telescopes, in combination with data from Hubble and a number of ground-based telescopes. The latest analysis, which includes Spitzer's complete record of over 1,000 hours of TRAPPIST-1 observations, has reduced the uncertainties of the mass measurements to a mere 3-6%. These are among the most accurate measurements of planetary masses anywhere outside of our solar system. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24371

The Hubble Space Telescope has spotted a UFO — well, the UFO Galaxy, to be precise. NGC 2683 is a spiral galaxy seen almost edge-on, giving it the shape of a classic science fiction spaceship. This is why the astronomers at the Astronaut Memorial Planetarium and Observatory gave it this attention-grabbing nickname. While a bird’s eye view lets us see the detailed structure of a galaxy (such as this Hubble image of a barred spiral), a side-on view has its own perks. In particular, it gives astronomers a great opportunity to see the delicate dusty lanes of the spiral arms silhouetted against the golden haze of the galaxy’s core. In addition, brilliant clusters of young blue stars shine scattered throughout the disc, mapping the galaxy’s star-forming regions. Perhaps surprisingly, side-on views of galaxies like this one do not prevent astronomers from deducing their structures. Studies of the properties of the light coming from NGC 2683 suggest that this is a barred spiral galaxy, even though the angle we see it at does not let us see this directly. NGC 2683, discovered on 5 February 1788 by the famous astronomer William Herschel, lies in the Northern constellation of Lynx. A constellation named not because of its resemblance to the feline animal, but because it is fairly faint, requiring the “sensitive eyes of a cat” to discern it. And when you manage to get a look at it, you’ll find treasures like this, making it well worth the effort. This image is produced from two adjacent fields observed in visible and infrared light by Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys. A narrow strip which appears slightly blurred and crosses most the image horizontally is a result of a gap between Hubble’s detectors. This strip has been patched using images from observations of the galaxy made by ground-based telescopes, which show significantly less detail. The field of view is approximately 6.5 by 3.3 arcminutes. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This planetary nebula's simple, graceful appearance is thought to be due to perspective: our view from Earth looking straight into what is actually a barrel-shaped cloud of gas shrugged off by a dying central star. Hot blue gas near the energizing central star gives way to progressively cooler green and yellow gas at greater distances with the coolest red gas along the outer boundary. Credit: NASA/Hubble Heritage Team ---- The Ring Nebula's distinctive shape makes it a popular illustration for astronomy books. But new observations by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope of the glowing gas shroud around an old, dying, sun-like star reveal a new twist. "The nebula is not like a bagel, but rather, it's like a jelly doughnut, because it's filled with material in the middle," said C. Robert O'Dell of Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn. He leads a research team that used Hubble and several ground-based telescopes to obtain the best view yet of the iconic nebula. The images show a more complex structure than astronomers once thought and have allowed them to construct the most precise 3-D model of the nebula. "With Hubble's detail, we see a completely different shape than what's been thought about historically for this classic nebula," O'Dell said. "The new Hubble observations show the nebula in much clearer detail, and we see things are not as simple as we previously thought." The Ring Nebula is about 2,000 light-years from Earth and measures roughly 1 light-year across. Located in the constellation Lyra, the nebula is a popular target for amateur astronomers. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14VAOMk" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14VAOMk</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building, Rainer Goercke shakes hands with Norman Jatz in front of the Spacelab Module MD001 as they prepare to close it for the last time before shipment to the National Air and Space Museum in Washington, DC. Goercke and Jatz have been on the Spacelab program since 1979 and were part of the team that first unloaded the module at KSC. Goercke is the only remaining European representative from the German-based Spacelab contractor, ERNO, and Jatz is a mechanical engineering lead from Boeing. Spacelab was designed by the European Space Agency (ESA) for the Space Shuttle program. It first flew on STS-9 in November 1983 and its final flight was the STS-90 Neurolab mission in April 1998. The sister module will travel home and be placed on display in Europe. The Spacelab concept of modular experiment racks in a pressurized shirt-sleeve environment made it highly user-friendly and accessible. Numerous experiments conceived by hundreds of scientists on the ground were conducted by flight crews in orbit. Spacelab modules served as on-orbit homes for everything from squirrel monkeys to plant seeds. They supported astronomical as well as Earth observations, for servicing the Hubble Space Telescope and for research preparatory to the International Space Station. One of the greatest benefits afforded by the Spacelab missions was the opportunity to fly a mission more than once, with the second or third flight building on the experiences and data gathered from its predecessors
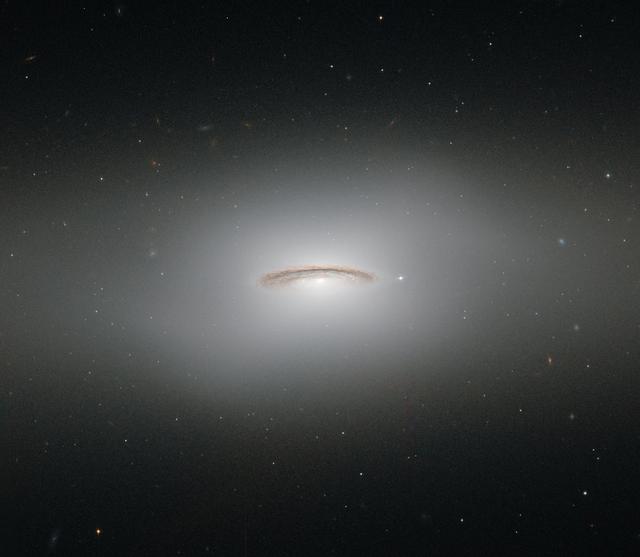

This neat little galaxy is known as NGC 4526. Its dark lanes of dust and bright diffuse glow make the galaxy appear to hang like a halo in the emptiness of space in this image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope. Although this image paints a picture of serenity, the galaxy is anything but. It is one of the brightest lenticular galaxies known, a category that lies somewhere between spirals and ellipticals. It has hosted two known supernova explosions, one in 1969 and another in 1994, and is known to have a colossal supermassive black hole at its center that has the mass of 450 million suns. NGC 4526 is part of the Virgo cluster of galaxies. Ground-based observations of galaxies in this cluster have revealed that a quarter of these galaxies seem to have rapidly rotating disks of gas at their centers. The most spectacular of these is this galaxy, NGC 4526, and its spinning disk of gas, dust, and stars reaches out uniquely far from its heart, spanning some seven percent of the galaxy's entire radius. This disk is moving incredibly fast, spinning at more than 250 kilometers per second. The dynamics of this quickly whirling region were actually used to infer the mass of NGC 4526’s central black hole — a technique that had not been used before to constrain a galaxy’s central black hole. This image was taken with Hubble's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 and the Advanced Camera for Surveys. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt

This image captures swirling cloud belts and tumultuous vortices within Jupiter's northern hemisphere. NASA's Juno spacecraft took this color-enhanced image at 10:23 p.m. PDT on May 23, 2018 (1:23 a.m. EDT on May 24), as the spacecraft performed its 13th close flyby of Jupiter. At the time, Juno was about 9,600 miles (15,500 kilometers) from the planet's cloud tops, above a northern latitude of 56 degrees. The region seen here is somewhat chaotic and turbulent, given the various swirling cloud formations. In general, the darker cloud material is deeper in Jupiter's atmosphere, while bright cloud material is high. The bright clouds are most likely ammonia or ammonia and water, mixed with a sprinkling of unknown chemical ingredients. A bright oval at bottom center stands out in the scene. This feature appears uniformly white in ground-based telescope observations. However, with JunoCam we can observe the fine-scale structure within this weather system, including additional structures within it. There is not significant motion apparent in the interior of this feature; like the Great Red Spot, its winds probably slows down greatly toward the center. Citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran created this image using data from the spacecraft's JunoCam imager. The view is a composite of several separate JunoCam images that were re-projected, blended, and healed. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22424
Data from NASA's Galileo spacecraft were used to produce this false-color composite of Jupiter's northern aurora on the night side of the planet. The height of the aurora, the thickness of the auroral arc, and the small-scale structure are revealed for the first time. Images in Galileo's red, green, and clear filters are displayed in red, green, and blue respectively. The smallest resolved features are tens of kilometers in size, which is a ten-fold improvement over Hubble Space Telescope images and a hundred-fold improvement over ground-based images. The glow is caused by electrically charged particles impinging on the atmosphere from above. The particles travel along Jupiter's magnetic field lines, which are nearly vertical at this latitude. The auroral arc marks the boundary between the "closed" field lines that are attached to the planet at both ends and the "open" field lines that extend out into interplanetary space. At the boundary the particles have been accelerated over the greatest distances, and the glow is especially intense. The latitude-longitude lines refer to altitudes where the pressure is 1 bar. The image shows that the auroral emissions originate about 500 kilometers (about 310 miles) above this surface. The colored background is light scattered from Jupiter's bright crescent, which is out of view to the right. North is at the top. The images are centered at 57 degrees north and 184 degrees west and were taken on April 2, 1997 at a range of 1.7 million kilometers (1.05 million miles) by Galileo's Solid State Imaging (SSI) system. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00603
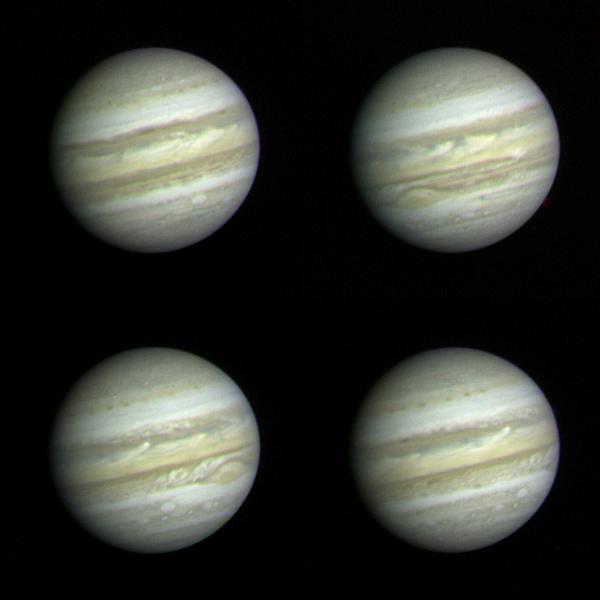

These Jupiter photographs are part of a set taken by NASA Voyager 1 on December 10 and 11, 1978 from a distance of 83 million km 52 million miles or more than half the distance from the Earth to the sun. At this range, Voyager 1 is able to record more detail on the giant planet than the very best ground-based telescopes. The highest resolution ever obtained on the Jovian disk was recorded by Pioneer 11 four years ago. Voyager, however, has longer focal-length optics than Pioneer, and while nearly three months from encounter (~ March 1979) was able to achieve higher resolution than that obtained by Pioneer only 24 hours from its encounter on 3 December 1974. Jupiter's colorful and turbulent atmosphere is evident in these photographs. The entire visible surface of the planet is made up of multiple layers of clouds, composed primarily of ammonia ice crystals colored by small amounts of materials of unknown composition. The Great Red Spot, seen to the lower left of 2 and lower right of 3, is now recovering from a period of relative inconspicuousness. An atmospheric system larger than the Earth and more than 100 years old, the Great Red Spot remains a mystery and a challenge to Voyager instruments. A bright convective cloud (center of and right of center in 4) displays a plume which has been swept westward (to the left) by local currents in the planet's equatorial wind system. Below and to the left and right of the Great Red Spot are a pair of white oval clouds; a third can be seen in 1. All three were formed almost 40 years ago and are the second oldest class of discrete features identified in the Jovian atmosphere. Each of the pictures was produced from blue, green, and orange originals in JPL's Image Processing Laboratory. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00454

Cassini has sighted Prometheus and Pandora, the two F-ring-shepherding moons whose unpredictable orbits both fascinate scientists and wreak havoc on the F ring. Prometheus (102 kilometers, or 63 miles across) is visible left of center in the image, inside the F ring. Pandora (84 kilometers, or 52 miles across) appears above center, outside the ring. The dark shadow cast by the planet stretches more than halfway across the A ring, the outermost main ring. The mottled pattern appearing in the dark regions of the image is 'noise' in the signal recorded by the camera system, which has subsequently been magnified by the image processing. The F ring is a narrow, ribbon-like structure, with a width seen in this geometry equivalent to a few kilometers. The two small, irregularly shaped moons exert a gravitational influence on particles that make up the F ring, confining it and possibly leading to the formation of clumps, strands and other structures observed there. Pandora prevents the F ring from spreading outward and Prometheus prevents it from spreading inward. However, their interaction with the ring is complex and not fully understood. The shepherds are also known to be responsible for many of the observed structures in Saturn's A ring. The moons, which were discovered in images returned by the Voyager 1 spacecraft in 1980, are in chaotic orbits--their orbits can change unpredictably when the moons get very close to each other. This strange behavior was first noticed in ground-based and Hubble Space Telescope observations in 1995, when the rings were seen nearly edge-on from Earth and the usual glare of the rings was reduced, making the satellites more readily visible than usual. The positions of both satellites at that time were different than expected based on Voyager data. One of the goals for the Cassini-Huygens mission is to derive more precise orbits for Prometheus and Pandora. Seeing how their orbits change over the duration of the mission will help to determine their masses, which in turn will help constrain models of their interiors and provide a more complete understanding of their effect on the rings. This narrow angle camera image was snapped through the broadband green spectral filter, centered at 568 nanometers, on March 10, 2004, when the spacecraft was 55.5 million kilometers (34.5 million miles) from the planet. Image scale is approximately 333 kilometers (207 miles) per pixel. Contrast has been greatly enhanced, and the image has been magnified to aid visibility of the moons as well as structure in the rings. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05387

Caption: Artist's view of night sky from a hypothetical planet within a young Milky Way-like galaxy 10 billion years ago, the sky are ablaze with star birth. Pink clouds of gas harbor newborn stars, and bluish-white, young star clusters litter the landscape. Image Credit: NASA/ESA/Z. Levay (STScI) More info: In one of the most comprehensive multi-observatory galaxy surveys yet, astronomers find that galaxies like our Milky Way underwent a stellar “baby boom,” churning out stars at a prodigious rate, about 30 times faster than today. Our sun, however, is a late “boomer.” The Milky Way’s star-birthing frenzy peaked 10 billion years ago, but our sun was late for the party, not forming until roughly 5 billion years ago. By that time the star formation rate in our galaxy had plunged to a trickle. Missing the party, however, may not have been so bad. The sun’s late appearance may actually have fostered the growth of our solar system’s planets. Elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were more abundant later in the star-forming boom as more massive stars ended their lives early and enriched the galaxy with material that served as the building blocks of planets and even life on Earth. Astronomers don’t have baby pictures of our Milky Way’s formative years to trace the history of stellar growth so they studied galaxies similar in mass to our Milky Way, found in deep surveys of the universe. The farther into the universe astronomers look, the further back in time they are seeing, because starlight from long ago is just arriving at Earth now. From those surveys, stretching back in time more than 10 billion years, researchers assembled an album of images containing nearly 2,000 snapshots of Milky Way-like galaxies. The new census provides the most complete picture yet of how galaxies like the Milky Way grew over the past 10 billion years into today’s majestic spiral galaxies. The multi-wavelength study spans ultraviolet to far-infrared light, combining observations from NASA’s Hubble and Spitzer space telescopes, the European Space Agency’s Herschel Space Observatory, and ground-based telescopes, including the Magellan Baade Telescope at the Las Campanas Observatory in Chile. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/our-sun-came-late-to-the-milky-way-s-star-birth-party/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/our-sun-came-late-to-the-mil...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Two's company, but three might not always be a crowd — at least in space. Astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, and a trick of nature, have confirmed the existence of a planet orbiting two stars in the system OGLE-2007-BLG-349, located 8,000 light-years away towards the center of our galaxy. The planet orbits roughly 300 million miles from the stellar duo, about the distance from the asteroid belt to our sun. It completes an orbit around both stars roughly every seven years. The two red dwarf stars are a mere 7 million miles apart, or 14 times the diameter of the moon's orbit around Earth. The Hubble observations represent the first time such a three-body system has been confirmed using the gravitational microlensing technique. Gravitational microlensing occurs when the gravity of a foreground star bends and amplifies the light of a background star that momentarily aligns with it. The particular character of the light magnification can reveal clues to the nature of the foreground star and any associated planets. The three objects were discovered in 2007 by an international collaboration of five different groups: Microlensing Observations in Astrophysics (MOA), the Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment (OGLE), the Microlensing Follow-up Network (MicroFUN), the Probing Lensing Anomalies Network (PLANET), and the Robonet Collaboration. These ground-based observations uncovered a star and a planet, but a detailed analysis also revealed a third body that astronomers could not definitively identify. Image caption: This artist's illustration shows a gas giant planet circling a pair of red dwarf stars in the system OGLE-2007-BLG-349, located 8,000 light-years away. The Saturn-mass planet orbits roughly 300 million miles from the stellar duo. The two red dwarf stars are 7 million miles apart. Credit: NASA, ESA, and G. Bacon (STScI) Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2dcfMns" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2dcfMns</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
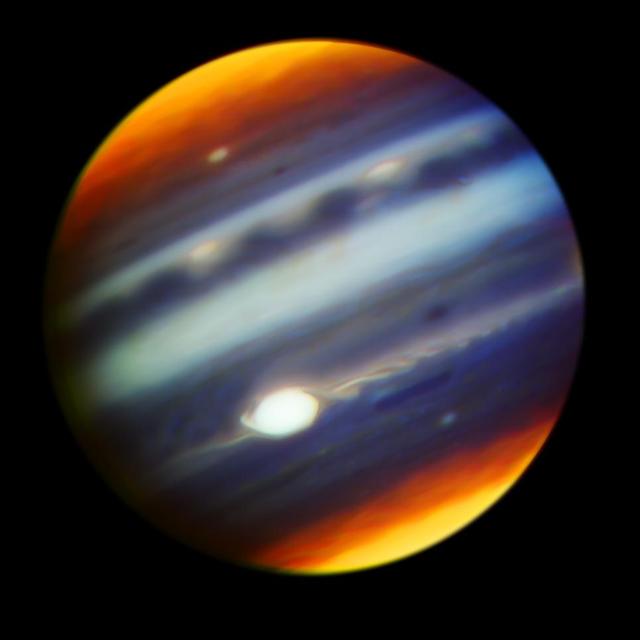

This composite, false-color infrared image of Jupiter reveals haze particles over a range of altitudes, as seen in reflected sunlight. It was taken using the Gemini North Telescope's Near-InfraRed Imager (NIRI) on May 18, 2017, in collaboration with the investigation of Jupiter by NASA's Juno mission. Juno completed its sixth close approach to Jupiter a few hours after this observation. The multiple filters corresponding to each color used in the image cover wavelengths between 1.69 microns and 2.275 microns. Jupiter's Great Red Spot (GRS) appears as the brightest (white) region at these wavelengths, which are primarily sensitive to high-altitude clouds and hazes near and above the top of Jupiter's convective region. The GRS is one of the highest-altitude features in Jupiter's atmosphere. Narrow spiral streaks that appear to lead into it or out of it from surrounding regions probably represent atmospheric features being stretched by the intense winds within the GRS, such as the hook-like structure on its western edge (left side). Some are being swept off its eastern edge (right side) and into an extensive wave-like flow pattern, and there is even a trace of flow from its northern edge. Other features near the GRS include the dark block and dark oval to the south and the north of the eastern flow pattern, respectively, indicating a lower density of cloud and haze particles in those locations. Both are long-lived cyclonic circulations, rotating clockwise -- in the opposite direction as the counterclockwise rotation of the GRS. A prominent wave pattern is evident north of the equator, along with two bright ovals, which are anticyclones that appeared in January 2017. Both the wave pattern and the ovals may be associated with an impressive upsurge in stormy activity that has been observed in these latitudes this year. Another bright anticyclonic oval is seen further north. The Juno spacecraft may pass over these ovals, as well as the Great Red Spot, during its close approach to Jupiter on July 10, 2017, Pacific Time (July 11, Universal Time). High hazes are evident over both polar regions with much spatial structure not previously been seen quite so clearly in ground-based images The filters used for observations combined into this image admit infrared light centered on the following infrared wavelengths (and presented here in these colors): 1.69 microns (blue), 2.045 microns (cyan), 2.169 microns (green), 2.124 microns https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21713

As Cassini nears its rendezvous with Saturn, new detail in the banded clouds of the planet's atmosphere are becoming visible. Cassini began the journey to the ringed world of Saturn nearly seven years ago and is now less than two months away from orbit insertion on June 30. Cassini’s narrow-angle camera took this image on April 16, 2004, when the spacecraft was 38.5 million kilometers (23.9 million miles) from Saturn. Dark regions are generally areas free of high clouds, and bright areas are places with high, thick clouds which shield the view of the darker areas below. A dark spot is visible at the south pole, which is remarkable to scientists because it is so small and centered. The spot could be affected by Saturn's magnetic field, which is nearly aligned with the planet's rotation axis, unlike the magnetic fields of Jupiter and Earth. From south to north, other notable features are the two white spots just above the dark spot toward the right, and the large dark oblong-shaped feature that extends across the middle. The darker band beneath the oblong-shaped feature has begun to show a lacy pattern of lighter-colored, high altitude clouds, indicative of turbulent atmospheric conditions. The cloud bands move at different speeds, and their irregularities may be due to either the different motions between them or to disturbances below the visible cloud layer. Such disturbances might be powered by the planet's internal heat; Saturn radiates more energy than it receives from the Sun. The moon Mimas (396 kilometers, 245 miles across) is visible to the left of the south pole. Saturn currently has 31 known moons. Since launch, 13 new moons have been discovered by ground-based telescopes. Cassini will get a closer look and may discover new moons, perhaps embedded within the planet’s magnificent rings. This image was taken using a filter sensitive to light near 727 nanometers, one of the near-infrared absorption bands of methane gas, which is one of the ingredients in Saturn's atmosphere. The image scale is approximately 231 kilometers (144 miles) per pixel. Contrast has been enhanced to aid visibility of features in the atmosphere. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05391
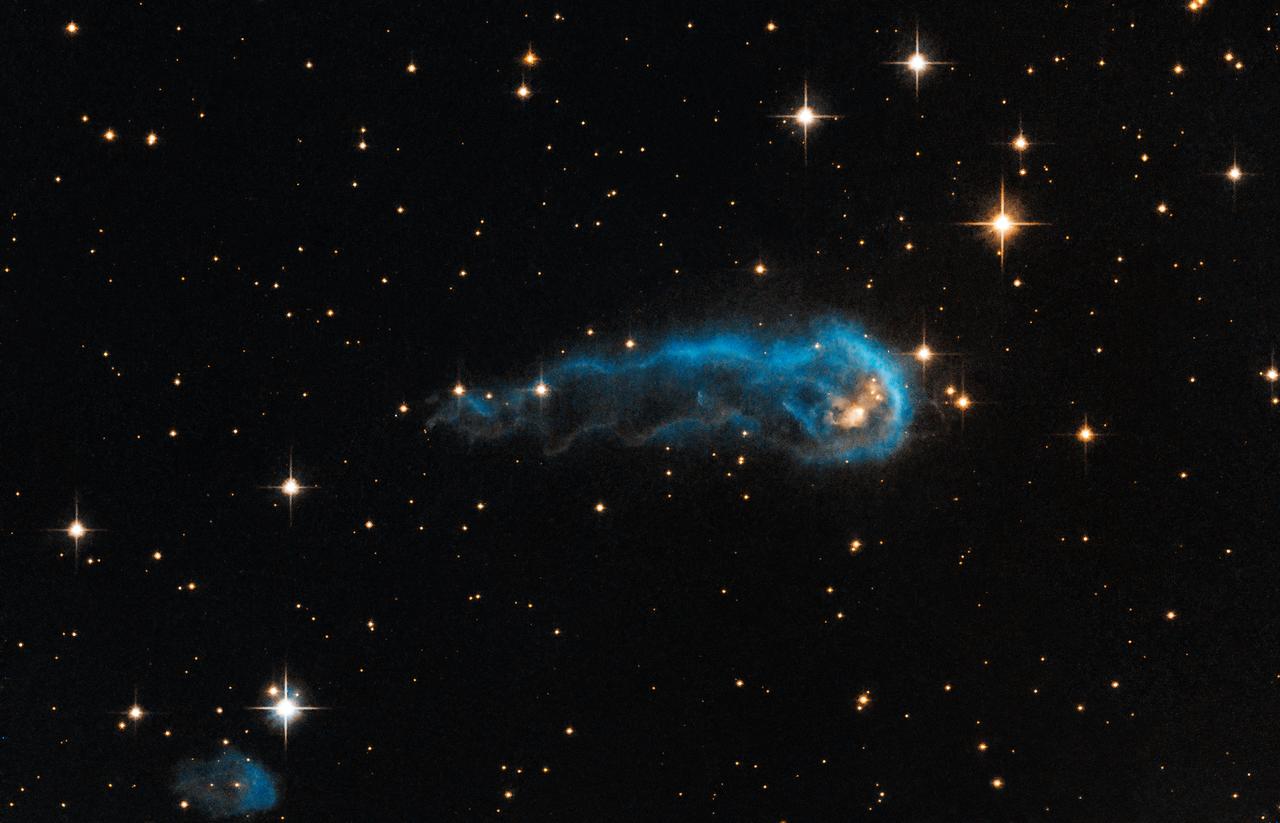
This light-year-long knot of interstellar gas and dust resembles a caterpillar on its way to a feast. But the meat of the story is not only what this cosmic caterpillar eats for lunch, but also what's eating it. Harsh winds from extremely bright stars are blasting ultraviolet radiation at this "wanna-be" star and sculpting the gas and dust into its long shape. The culprits are 65 of the hottest, brightest known stars, classified as O-type stars, located 15 light-years away from the knot, towards the right edge of the image. These stars, along with 500 less bright, but still highly luminous B-type stars make up what is called the Cygnus OB2 association. Collectively, the association is thought to have a mass more than 30,000 times that of our sun. The caterpillar-shaped knot, called IRAS 20324+4057, is a protostar in a very early evolutionary stage. It is still in the process of collecting material from an envelope of gas surrounding it. However, that envelope is being eroded by the radiation from Cygnus OB2. Protostars in this region should eventually become young stars with final masses about one to ten times that of our sun, but if the eroding radiation from the nearby bright stars destroys the gas envelope before the protostars finish collecting mass, their final masses may be reduced. Spectroscopic observations of the central star within IRAS 20324+4057 show that it is still collecting material quite heavily from its outer envelope, hoping to bulk up in mass. Only time will tell if the formed star will be a "heavy-weight" or a "light-weight" with respect to its mass. This image of IRAS 20324+4057 is a composite of Hubble Advanced Camera for Surveys data taken in green and infrared light in 2006, and ground-based hydrogen data from the Isaac Newton Telescope in 2003. The object lies 4,500 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This stunning new image from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows part of the sky in the constellation of Canes Venatici (The Hunting Dogs). Although this region of the sky is not home to any stellar heavyweights, being mostly filled with stars of average brightness, it does contain five Messier objects and numerous intriguing galaxies — including NGC 5195, a small barred spiral galaxy considered to be one of the most beautiful galaxies visible, and its nearby interacting partner the Whirlpool Galaxy (heic0506a). The quirky Sunflower Galaxy is another notable galaxy in this constellation, and is one of the largest and brightest edge-on galaxies in our skies. Joining this host of characters is spiral galaxy NGC 4244, nicknamed the Silver Needle Galaxy, shown in this new image from Hubble. This galaxy spans some 65,000 light-years and lies around 13.5 million light-years away. It appears as a wafer-thin streak across the sky, with loosely wound spiral arms hidden from view as we observe the galaxy from the side. It is part of a group of galaxies known as the M94 Group. Numerous bright clumps of gas can be seen scattered across its length, along with dark dust lanes surrounding the galaxy’s core. NGC 4244 also has a bright star cluster at its center. Although we can make out the galaxy’s bright central region and star-spattered arms, we cannot see any more intricate structure due to the galaxy’s position; from Earth, we see it stretched out as a flattened streak across the sky. A number of different observations were pieced together to form this mosaic, and gaps in Hubble’s coverage have been filled in using ground-based data. The Hubble observations were taken as part of the Galaxy Halos, Outer disks, Substructure, Thick disks and Star clusters (GHOSTS) survey, which is scanning nearby galaxies to explore how they and their stars formed to get a more complete view of the history of the Universe. European Space Agency Credit: NASA & ESA, Acknowledgement: Roelof de Jong <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>