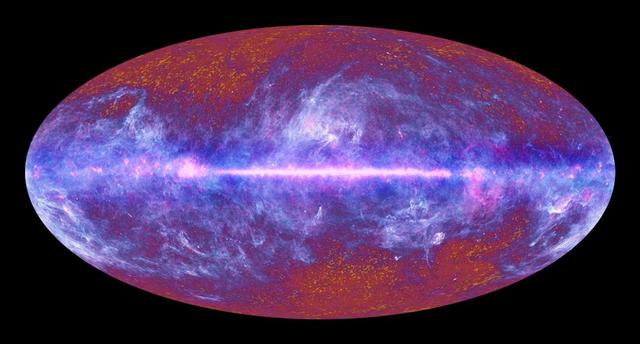
This image of the microwave sky was synthesized using data spanning the range of light frequencies detected by ESA Planck. A vast portion of the sky is dominated by the diffuse emission from gas and dust in our Milky Way galaxy.

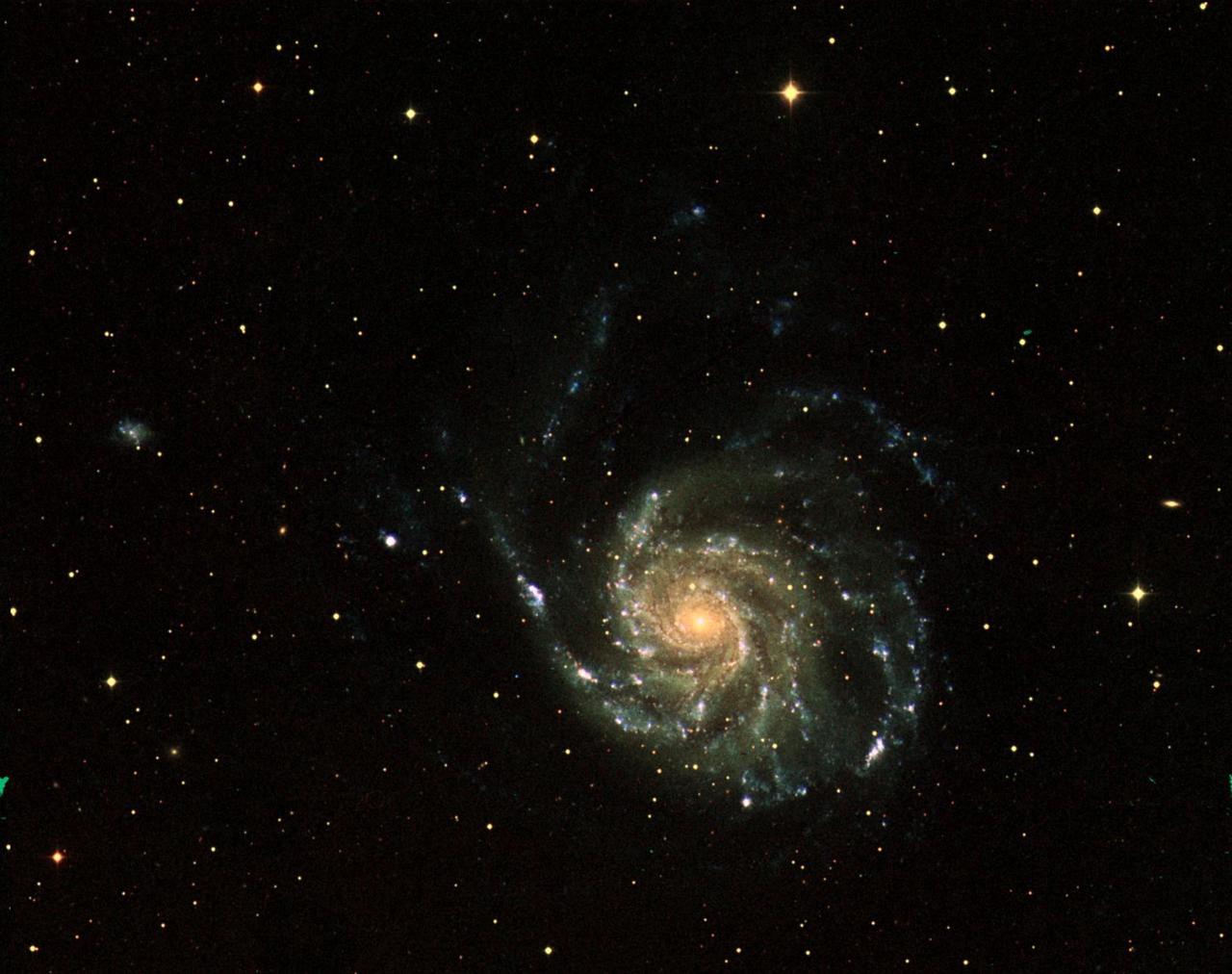
The image from NASA Hubble Telescope shows spiral arms and dust clouds in the nearby Whirlpool galaxy. Visible starlight and light from the emission of glowing hydrogen is seen, which is associated with the most luminous young stars in the spiral arms.

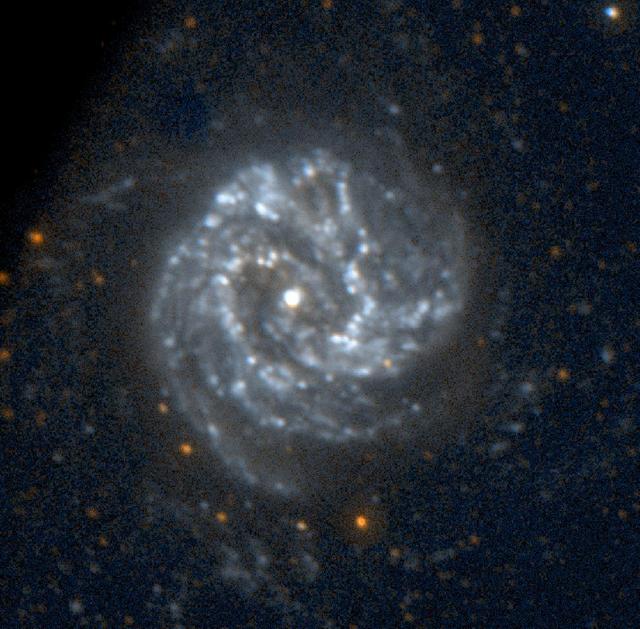
This three-color image of galaxy M101 was taken by NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer on June 20, 2003. The far ultraviolet emissions are shown in blue, the near ultraviolet emissions are green, and the red emissions, which were taken from NASA's Digital Sky Survey, represent visible light. This image combines short, medium, and long "exposure" pictures to best display the evolution of star formation in a spiral galaxy. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04630

This image of the active galaxy Centaurus A was taken by NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer on June 7, 2003. The galaxy is located 30 million light-years from Earth and is seen edge on, with a prominent dust lane across the major axis. In this image the near ultraviolet emission is represented as green, and the far ultraviolet emission as blue. The galaxy exhibits jets of high energy particles, which were traced by the X-ray emission and measured by NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. These X-ray emissions are seen as red in the image. Several regions of ultraviolet emission can be seen where the jets of high energy particles intersect with hydrogen clouds in the upper left corner of the image. The emission shown may be the result of recent star formation triggered by the compression of gas by the jet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04624
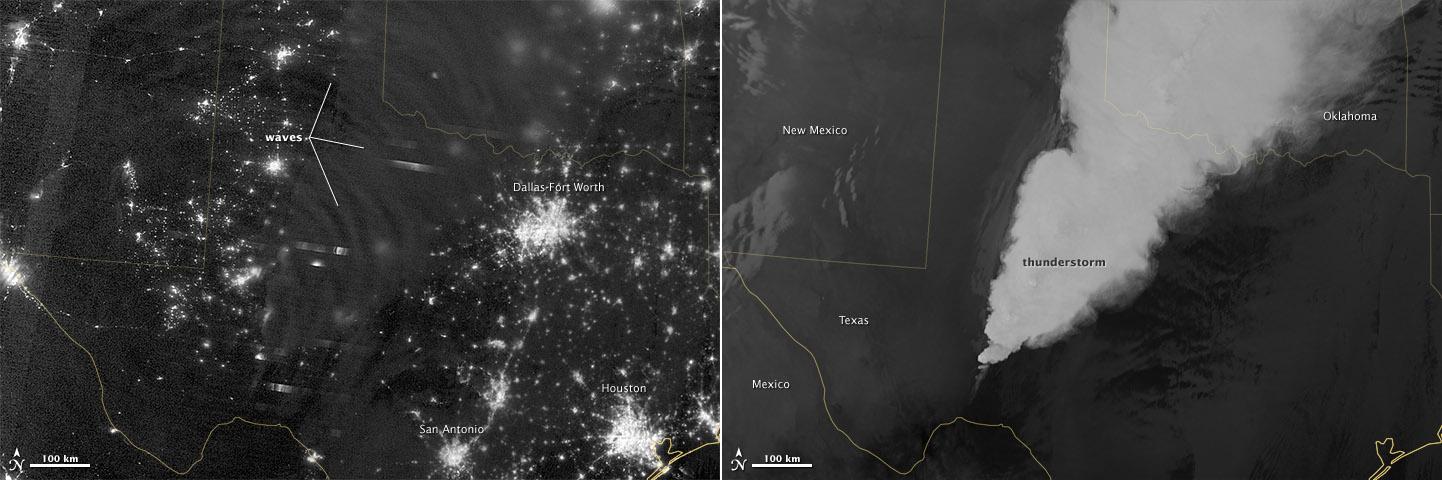
In April 2012, waves in Earth’s “airglow” spread across the nighttime skies of northern Texas like ripples in a pond. In this case, the waves were provoked by a massive thunderstorm. Airglow is a layer of nighttime light emissions caused by chemical reactions high in Earth’s atmosphere. A variety of reactions involving oxygen, sodium, ozone and nitrogen result in the production of a very faint amount of light. In fact, it’s approximately one billion times fainter than sunlight (~10-11 to 10-9 W·cm-2· sr-1). This chemiluminescence is similar to the chemical reactions that light up a glow stick or glow-in-the-dark silly putty. The “day-night band,” of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured these glowing ripples in the night sky on April 15, 2012 (top image). The day-night band detects lights over a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses highly sensitive electronics to observe low light signals. (The absolute minimum signals detectable are at the levels of nightglow emission.) The lower image shows the thunderstorm as observed by a thermal infrared band on VIIRS. This thermal band, which is sensitive only to heat emissions (cold clouds appear white), is not sensitive to the subtle visible-light wave structures seen by the day-night band. Technically speaking, airglow occurs at all times. During the day it is called “dayglow,” at twilight “twilightglow,” and at night “nightglow.” There are slightly different processes taking place in each case, but in the image above the source of light is nightglow. The strongest nightglow emissions are mostly constrained to a relatively thin layer of atmosphere between 85 and 95 kilometers (53 and 60 miles) above the Earth’s surface. Little emission occurs below this layer since there’s a higher concentration of molecules, allowing for dissipation of chemical energy via collisions rather than light production. Likewise, little emission occurs above that layer because the atmospheric density is so tenuous that there are too few light-emitting reactions to yield an appreciable amount of light. Suomi NPP is in orbit around Earth at 834 kilometers (about 518 miles), well above the nightglow layer. The day-night band imagery therefore contains signals from the direction upward emission of the nightglow layer and the reflection of the downward nightglow emissions by clouds and the Earth’s surface. The presence of these nightglow waves is a graphic visualization of the usually unseen energy transfer processes that occur continuously between the lower and upper atmosphere. While nightglow is a well-known phenomenon, it’s not typically considered by Earth-viewing meteorological sensors. In fact, scientists were surprised at Suomi NPP’s ability to detect it. During the satellite’s check-out procedure, this unanticipated source of visible light was thought to indicate a problem with the sensor until scientists realized that what they were seeing was the faintest of light in the darkness of night. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Aries Keck and Steve Miller. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79817" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space</a></b>
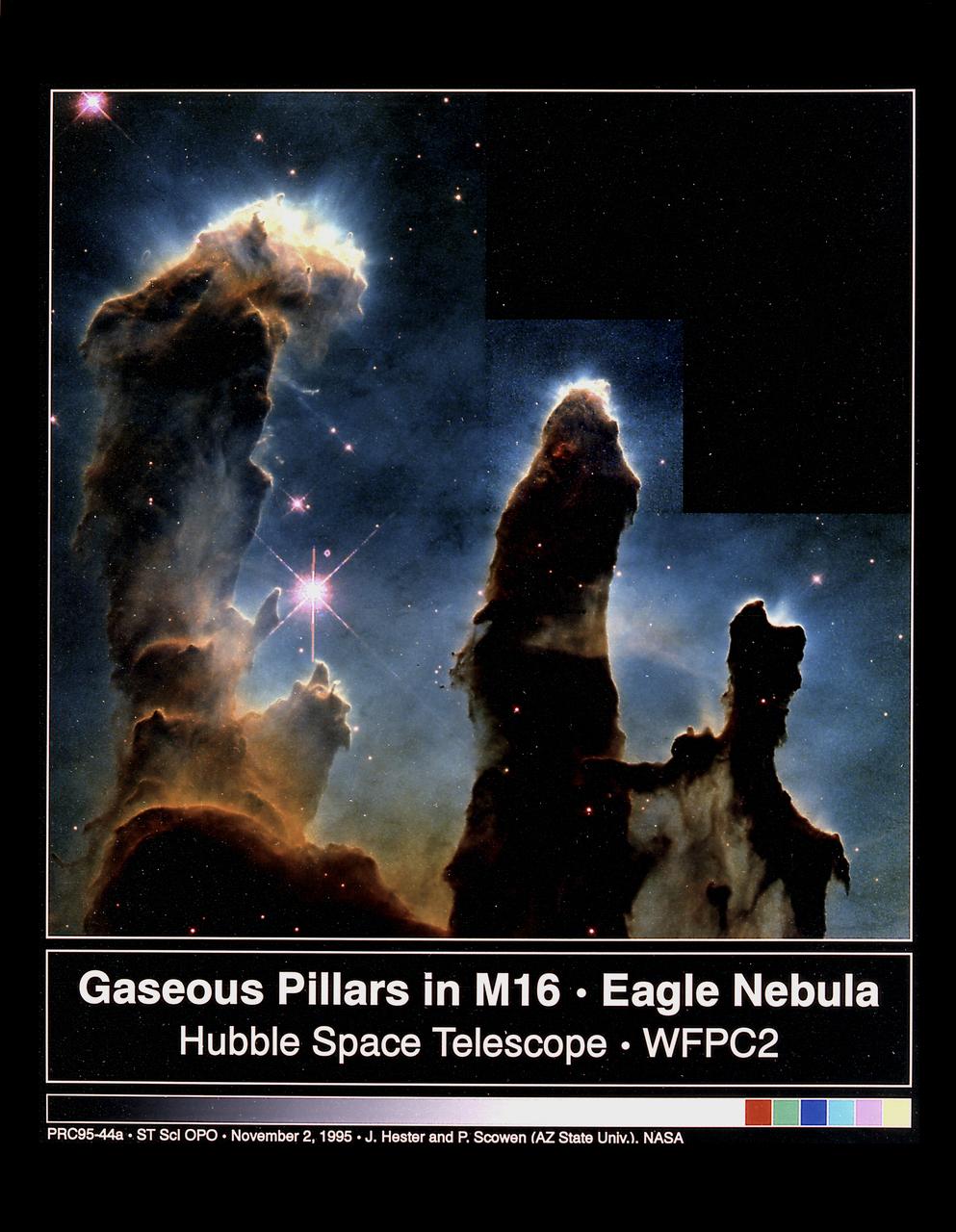
These eerie, dark, pillar-like structures are actually columns of cool interstellar hydrogen gas and dust that are also incubators for new stars. The pillars protrude from the interior wall of a dark molecular cloud like stalagmites from the floor of a cavern. They are part of the Eagle Nebula (also called M16), a nearby star-forming region 7,000 light-years away, in the constellation Serpens. The ultraviolet light from hot, massive, newborn stars is responsible for illuminating the convoluted surfaces of the columns and the ghostly streamers of gas boiling away from their surfaces, producing the dramatic visual effects that highlight the three-dimensional nature of the clouds. This image was taken on April 1, 1995 with the Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field Planetary Camera 2. The color image is constructed from three separate images taken in the light of emission from different types of atoms. Red shows emissions from singly-ionized sulfur atoms, green shows emissions from hydrogen, and blue shows light emitted by doubly-ionized oxygen atoms.

This image of the spiral galaxy Messier 83 was taken by NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer on June 7, 2003. Located 15 million light years from Earth and known as the Southern Pinwheel Galaxy, Messier 83 displays significant amounts of ultraviolet emissions far from the optically bright portion of the galaxy. It is also known to have an extended hydrogen disc that appears to radiate a faint ultraviolet emission. The red stars in the foreground of the image are Milky Way stars. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04629

Red and Green colors predominate in this view of the Aurora Australis photographed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-39) in May 1991 at the peak of the last geomagnetic maximum. The payload bay and tail of the shuttle can be seen on the left hand side of the picture. Auroras are caused when high-energy electrons pour down from the Earth's magnetosphere and collide with atoms. Red aurora occurs from 200 km to as high as 500 km altitude and is caused by the emission of 6300 Angstrom wavelength light from oxygen atoms. Green aurora occurs from about 100 km to 250 km altitude and is caused by the emission of 5577 Angstrom wavelength light from oxygen atoms. The light is emitted when the atoms return to their original unexcited state. At times of peaks in solar activity, there are more geomagnetic storms and this increases the auroral activity viewed on Earth and by astronauts from orbit.

STS099-355-024 (11-22 February 2000) -- Two separate atmospheric optical phenomena appear in this 35mm photograph captured from the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The thin greenish band above the horizon is airglow; radiation emitted by the atmosphere from a layer about 30-kilometers thick and about 100-kilometers' altitude. The predominant emission in airglow is the green 5577-Angstrom wavelength emission from atomic oxygen atoms, which is also the predominant emission from the aurora. A yellow-orange color is also seen in airglow, which is the emission of the 5800-Angstrom wavelength from sodium atoms. Airglow is always present in the atmosphere; it results from the recombination of molecules that have been broken apart by solar radiation during the day. But airglow is so faint that it can only be seen at night by looking "edge on" at the emission layer, such as the view that astronauts have in Earth orbit. The other phenomenon in the photo appears to be a faint, diffuse red aurora. Red aurora occur from about 200 kilometers to as high as 500 kilometers altitude only in the auroral zones at polar latitudes. They are caused by the emission of 6300- Angstrom wavelength light from oxygen atoms that have been raised to a higher energy level (excited) by collisions with energetic electrons pouring down from the Earth's magnetosphere. The light is emitted when the atoms return to their original unexcited state. With the red light so faint in this picture, scientists are led to believe that the flux density of incoming electrons was small. Also, since there is no green aurora below the red, that indicates that the energy of the incoming electrons was low - higher energy electrons would penetrate deeper into the atmosphere where the green aurora is energized.
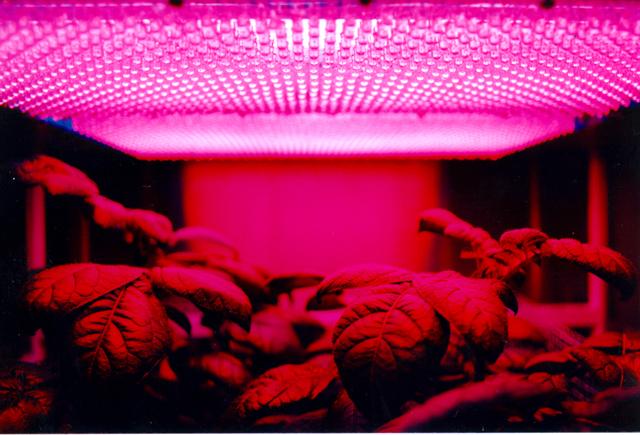

Astroculture is a suite of technologies used to produce and maintain a closed controlled environment for plant growth. The two most recent missions supported growth of potato, dwarf wheat, and mustard plants and provided scientists with the first opportunity to conduct true plant research in space. Light emitting diodes have particular usefulness for plant growth lighting because they emit a much smaller amount of radiant heat than do conventional lighting sources and because they have potential of directing a higher percentage of the emitted light onto plants surfaces. Furthermore, the high output LED's have emissions in the 600-700 nm waveband, which is of highest efficiency for photosynthesis by plants.
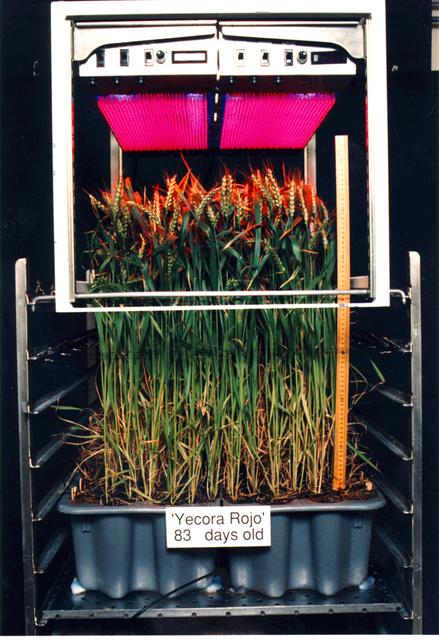

Astroculture is a suite of technologies used to produce and maintain a closed controlled environment for plant growth. The two most recent missions supported growth of potato, dwarf wheat, and mustard plants, and provided scientists with the first opportunity to conduct true plant research in space. Light emitting diodes have particular usefulness for plant growth lighting because they emit a much smaller amount of radiant heat than do conventional lighting sources and because they have potential of directing a higher percentage of the emitted light onto plants surfaces. Furthermore, the high output LED's have emissions in the 600-700 nm waveband, which is of highest efficiency for photosynthesis by plants.

iss064e035805 (Feb. 21, 2021) --- The International Space Station, pictured with Russia's ISS Progress 77 cargo craft attached to the Pirs docking compartment, orbits into a sunset 270 miles above the South Pacific. This long duration photograph also shows Earth's airglow (a faint emission of light in the upper atmosphere) and a starry night sky.
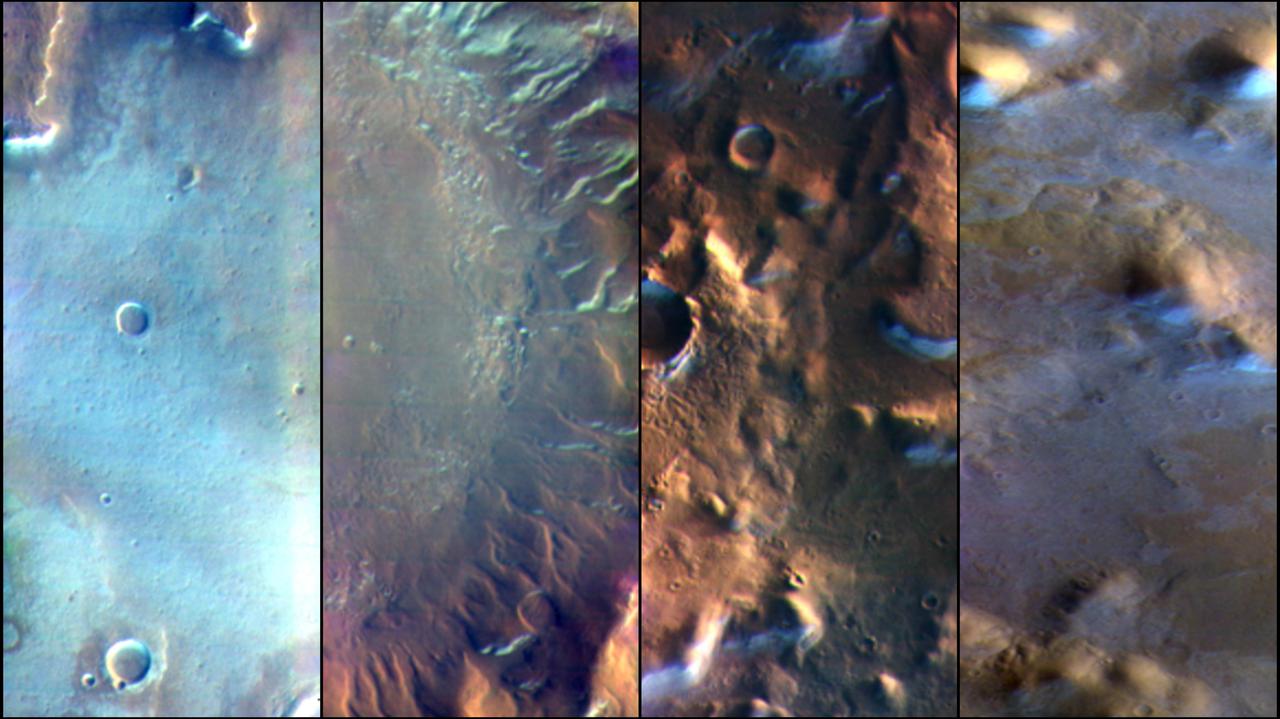

Martian surface frost, made up largely of carbon dioxide, appears blueish-white in these images from the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) camera aboard NASA's 2001 Odyssey orbiter. THEMIS takes images in both visible light perceptible to the human eye and heat-sensitive infrared. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25233

iss064e035804 (Feb. 21, 2021) --- The International Space Station, pictured with Russia's ISS Progress 77 cargo craft attached to the Pirs docking compartment, orbits into a sunset 270 miles above the South Pacific. This long duration photograph also shows Earth's airglow (a faint emission of light in the upper atmosphere) and a starry night sky.

iss064e035806 (Feb. 21, 2021) --- The International Space Station, pictured with Russia's ISS Progress 77 cargo craft attached to the Pirs docking compartment, orbits into a sunset 270 miles above the South Pacific. This long duration photograph also shows Earth's airglow (a faint emission of light in the upper atmosphere) and a starry night sky.

iss064e035808 (Feb. 21, 2021) --- The International Space Station, pictured with Russia's ISS Progress 77 cargo craft attached to the Pirs docking compartment, orbits into a sunset 265 miles above the South Pacific. This long duration photograph also shows Earth's airglow (a faint emission of light in the upper atmosphere) and a starry night sky.

iss064e035812 (Feb. 21, 2021) --- Russia's ISS Progress 77 cargo craft is pictured attached to the Pirs docking compartment as the International Space Station orbited 260 miles above the Gulf of Mexico off the southwest coast of Florida. This long duration photograph also shows the city lights of the Yucatan peninsula, Earth's airglow (a faint emission of light in the upper atmosphere), and a starry night sky.
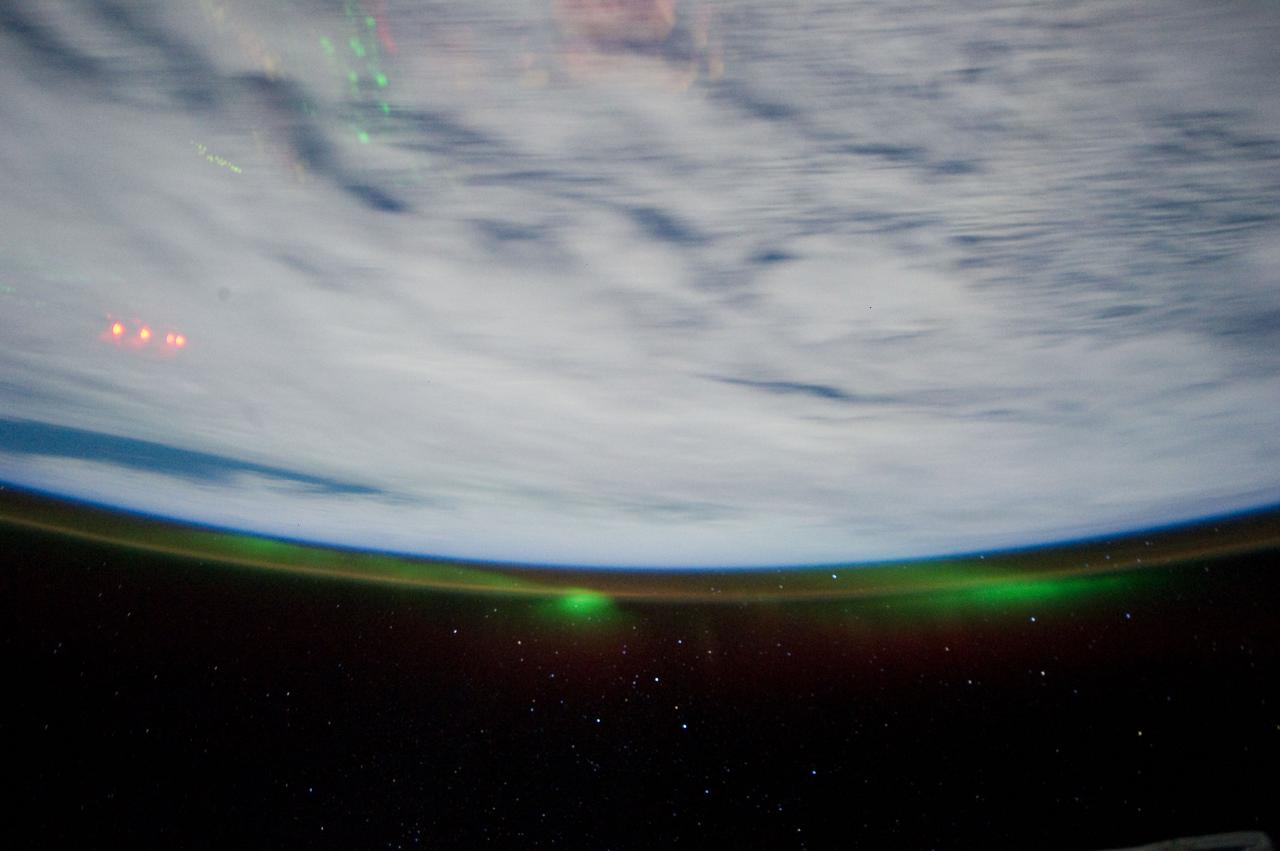

ISS028-E-017123 (16 July 2011) --- Separate atmospheric optical phenomena were captured in this electronic still photograph from the Inernational Space Station. The thin greenish band stretching along the Earth's horizon is airglow; light emitted by the atmosphere from a layer about 30 kilometers thick and about 100 kilometers in altitude. The predominant emission in airglow is the green 5577 Angstrom wavelength light from atomic oxygen atoms. Airglow is always and everywhere present in the atmosphere; it results from the recombination of molecules that have been broken apart by solar radiation during the day. But airglow is so faint that it can only be seen at night by looking "edge on" at the emission layer, such as the view astronauts and cosmonauts have in orbit. The second phenomenon is the appearnce of Aurora Australis.
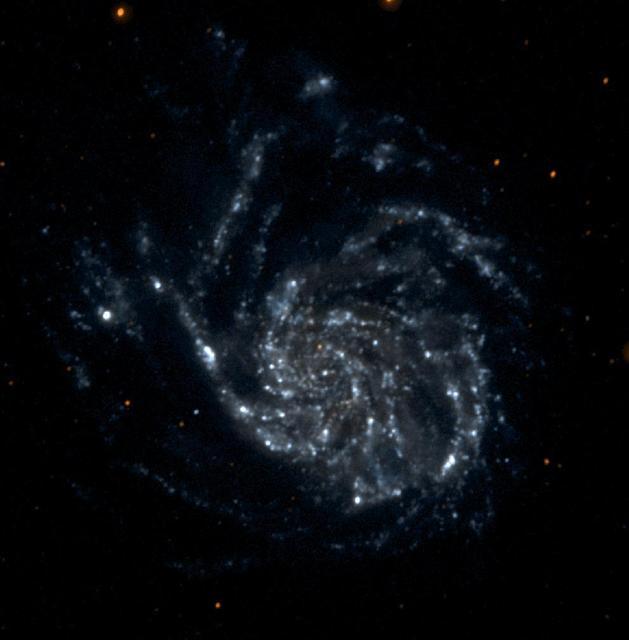

This single orbit exposure, ultraviolet color image of Messier 101 was taken by NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer on June 20, 2003. Messier 101 is a large spiral galaxy located 20 million light-years from Earth. This image is a short and medium "exposure" picture of the evolution of star formation in a spiral galaxy. The far ultraviolet emission detects the younger stars as concentrated in tight spiral arms, while the near ultraviolet emission, which traces stars living for more than 100 million years, displays the movement of the spiral pattern over a 100 million year period. The red stars in the foreground of the image are Milky Way stars. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04632

This is an x-ray image of the Crab Nebula taken with the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-2/Einstein Observatory. The image is demonstrated by a pulsar, which appears as a bright point due to its pulsed x-ray emissions. The strongest region of diffused emissions comes from just northwest of the pulsar, and corresponds closely to the region of brightest visible-light emission. The HEAO-2, the first imaging and largest x-ray telescope built to date, was capable of producing actual photographs of x-ray objects. Shortly after launch, the HEAO-2 was nicknamed the Einstein Observatory by its scientific experimenters in honor of the centernial of the birth of Albert Einstein, whose concepts of relativity and gravitation have influenced much of modern astrophysics, particularly x-ray astronomy. The HEAO-2, designed and developed by TRW, Inc. under the project management of the Marshall Space Flight Center, was launched aboard an Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle on November 13, 1978.
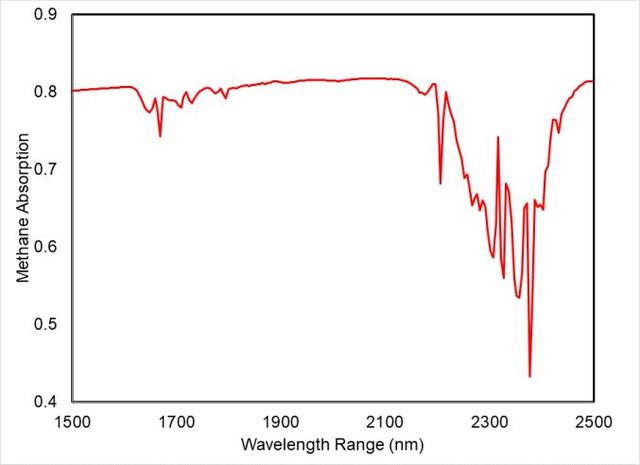
This spectral "fingerprint" of methane was produced from data taken during a September 2023 test at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California of a state-of-the-art imaging spectrometer that will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space. The instrument measures hundreds of wavelengths of light reflected by Earth's surface and absorbed by gases in the planet's atmosphere. Different compounds absorb different wavelengths of light, leaving a kind of spectral fingerprint that the imaging spectrometer can identify. These infrared fingerprints, invisible to the human eye, can pinpoint and quantify strong greenhouse gas emissions, and accelerate mitigation efforts. Before the imaging spectrometer was shipped from JPL to Planet Labs PBC in San Francisco, where it will be integrated into a Tanager satellite, there was a rare opportunity to use a sample of methane to test the completed instrument while it was in a vacuum chamber. The test was successful, and the imaging spectrometer produced this clear spectral fingerprint of methane (appearing as a red line in the graph). Designed and built by JPL, imaging spectrometer will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper organization to collect data on greenhouse gas point-source emissions. The information will help locate and quantify "super-emitters" – the small percentage of individual sources responsible for a significant fraction of methane and carbon dioxide emissions around the world. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26095
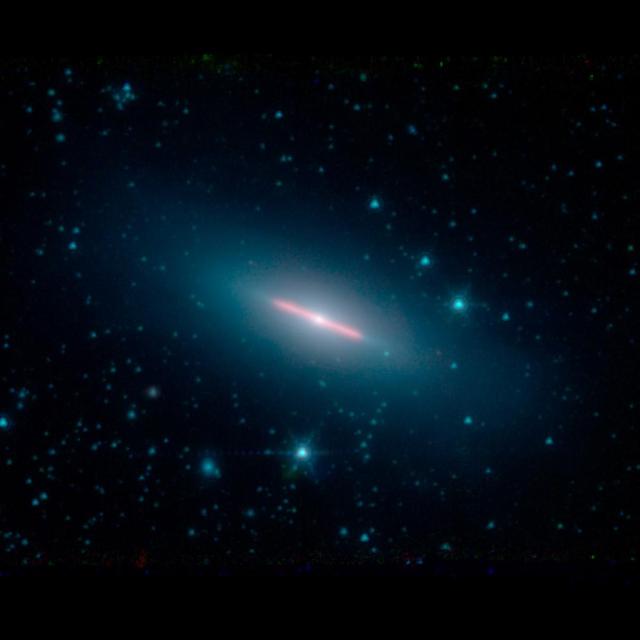

Galaxy NGC 5866 lies 44 million light-years from Earth and has a diameter of roughly 60,000 light-years — a little more than half the diameter of our own Milky Way galaxy. From our viewpoint, NGC 5866 is oriented almost exactly edge-on, yielding most of its structural features invisible. Spitzer detects infrared light, and the red color here corresponds to a wavelength typically emitted by dust. The clean edges of the dust emission from NGC 5866 indicate that there is a very flat ring or disk of dust circling the outer region of the galaxy. Spitzer took this image during its "cold" mission, which ended in 2009. The colors represent three infrared wavelengths captured by the Infrared Array Camera instrument. Blue light corresponds to a wavelength of 3.6 microns, produced mainly by stars; green corresponds to 4.5 microns, and red corresponds to 8 microns. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23129
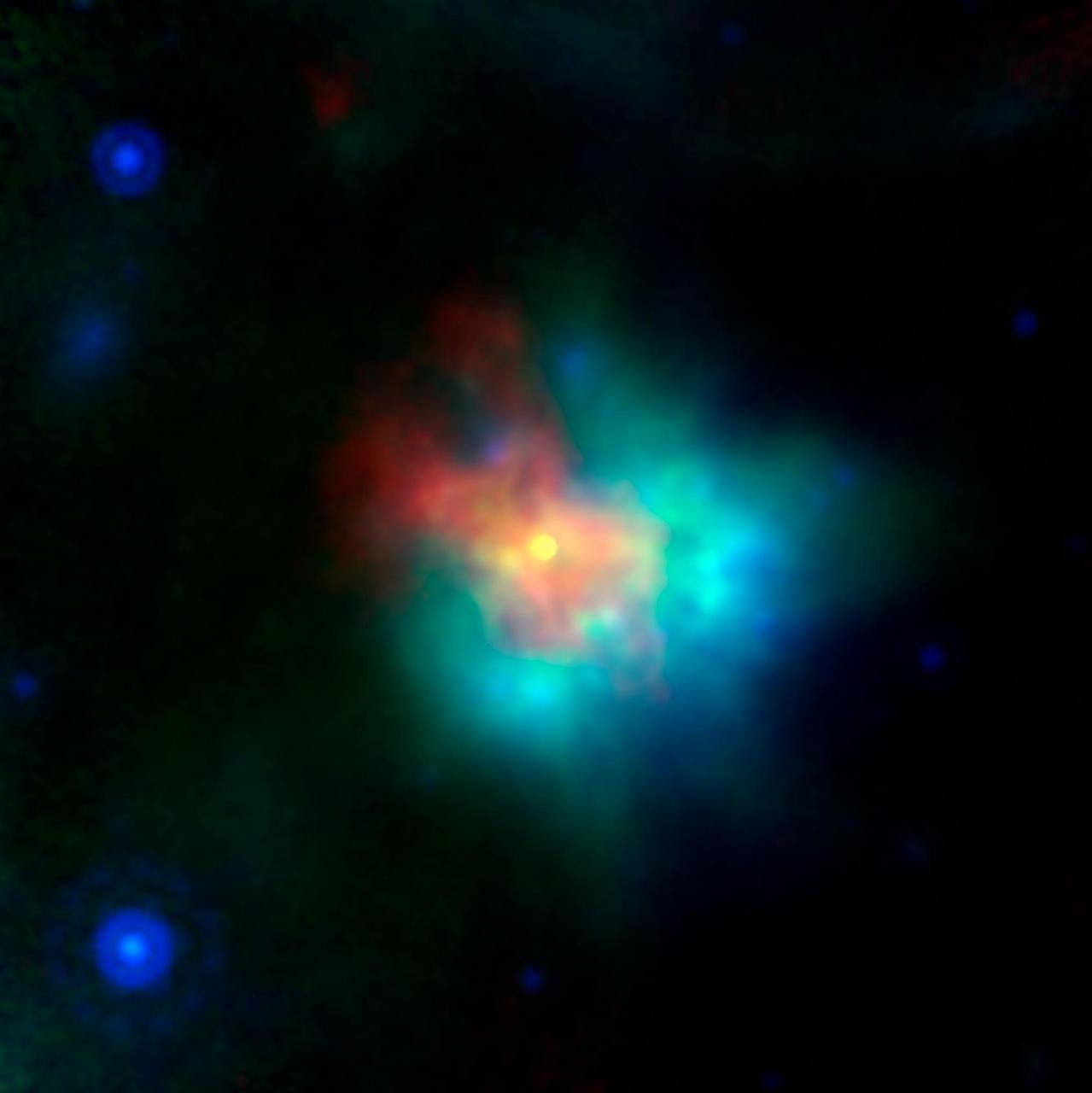

This image of supernova remnant G54.1+0.3 includes radio, infrared and X-ray light. The saturated yellow point at the center of the image indicates strong X-ray source at the center of the supernova remnant. This is an incredibly dense object called a neutron star, which can form as a star runs out of fuel to keep it inflated, and the unsupported material collapses down on to the star's core. G54.1+0.3 contains a special type of neutron star called a pulsar, which emits particularly bright radio and X-ray emissions. The blue and green emissions show the presence of dust, including silica. The red hues correspond to radio data from the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array; green corresponds to 70 µm wavelength infrared light from the European Space Agency's Herschel Space Observatory; blue corresponds to 24 µm wavelength infrared light from the Multiband Imaging Photometer (MIPS) instrument on NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope; yellow corresponds to X-ray data from the Chandra X-ray Observatory. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22569

Showcased at the centre of this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image is an emission-line star known as IRAS 12196-6300. Located just under 2300 light-years from Earth, this star displays prominent emission lines, meaning that the star’s light, dispersed into a spectrum, shows up as a rainbow of colours marked with a characteristic pattern of dark and bright lines. The characteristics of these lines, when compared to the “fingerprints” left by particular atoms and molecules, can be used to reveal IRAS 12196-6300’s chemical composition. Under 10 million years old and not yet burning hydrogen at its core, unlike the Sun, this star is still in its infancy. Further evidence of IRAS 12196-6300’s youth is provided by the presence of reflection nebulae. These hazy clouds, pictured floating above and below IRAS 12196-6300, are created when light from a star reflects off a high concentration of nearby dust, such as the dusty material still remaining from IRAS 12196-6300’s formation.

This movie shows the Martian moon Phobos as viewed in visible light by NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter on April 24, 2019. It was put together from 19 images taken 1 second apart by Odyssey's infrared camera, Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS). The apparent motion is due to progression of the camera's pointing during the observation. This was the third observation of Phobos by Mars Odyssey. While displayed here in visible-wavelength light, THEMIS also recorded thermal-infrared imagery in the same scan. The distance to Phobos from Odyssey during the observation was about 5,692 miles (9,160 kilometers). Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23207
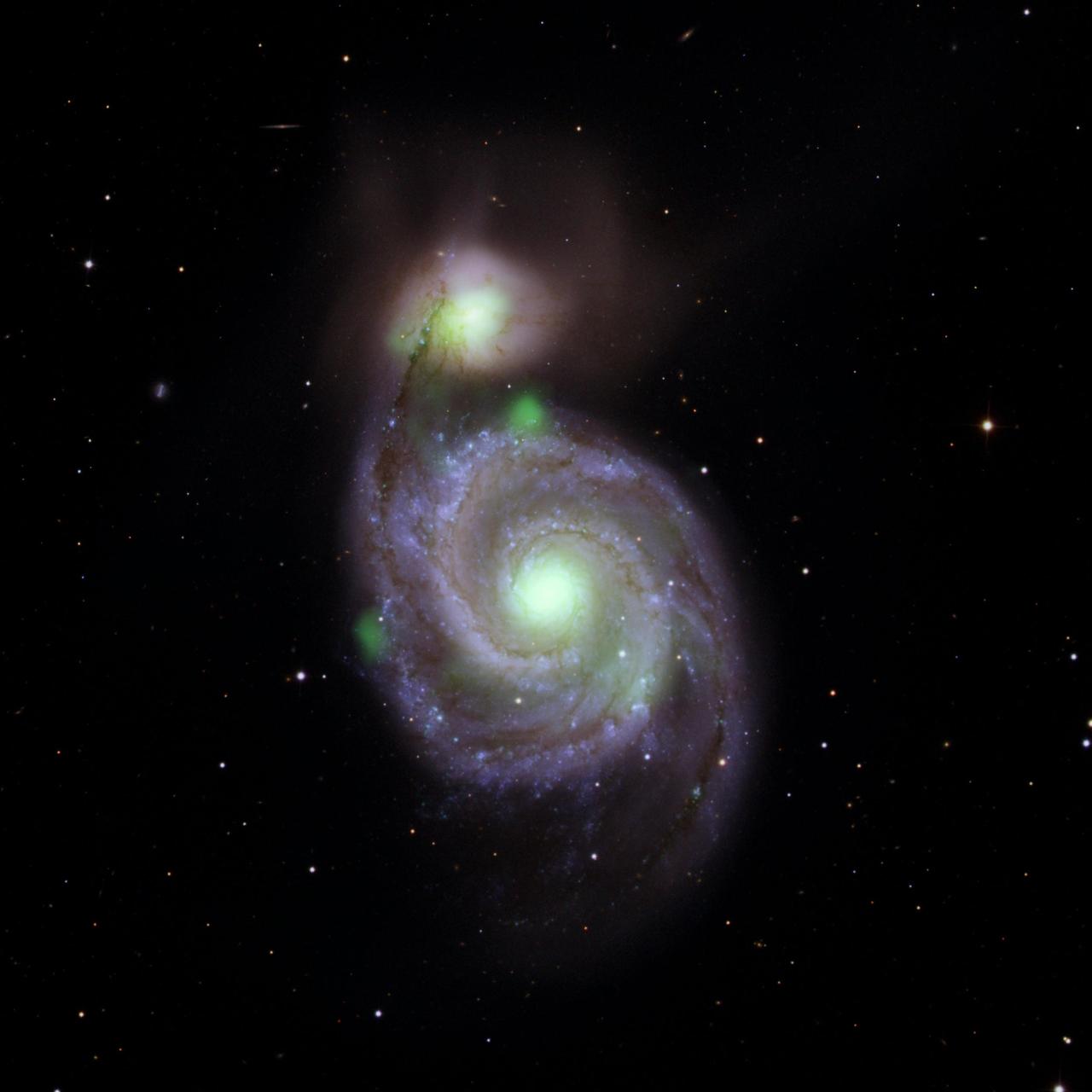

Bright green sources of high-energy X-ray light captured by NASA's NuSTAR mission are overlaid on an optical-light image of the Whirlpool galaxy (the spiral in the center of the image) and its companion galaxy, M51b (the bright greenish-white spot above the Whirlpool), taken by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. The bright green spots at the center of the Whirlpool and M51b are created by material surrounding supermassive black holes; additional X-ray sources in the vicinity contribute to the emission. The known ultraluminous neutron star is located on the left side of the Whirlpool. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23005
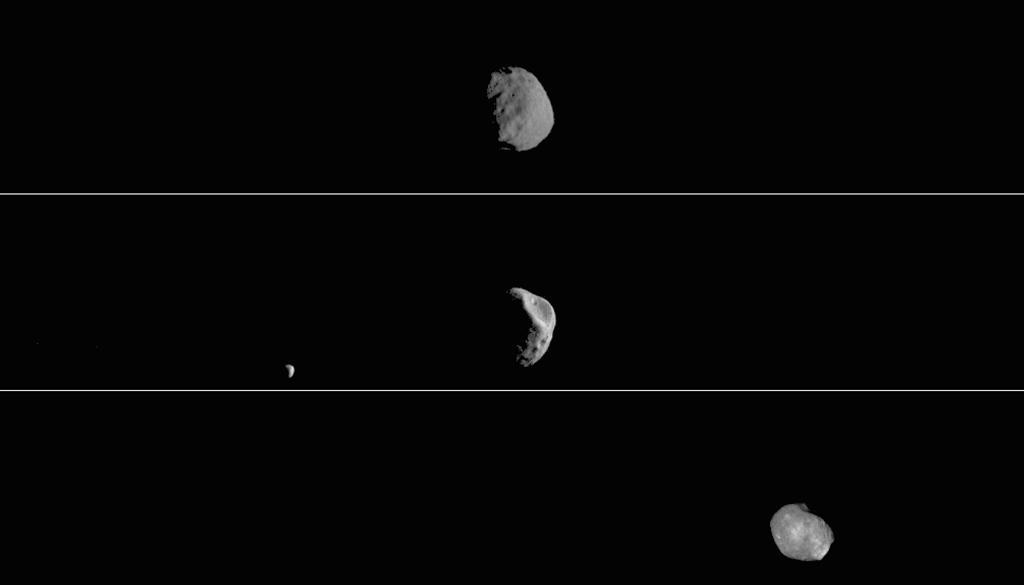

This movie shows three views of the Martian moon Phobos as viewed in visible light by NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter. The apparent motion is due to movement by Odyssey's infrared camera, Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), rather than movement by the moon. Each of the three panels is a series of images taken on different dates (from top to bottom): Sept. 29, 2017; Feb. 15, 2018; and April 24, 2019. Deimos, Mars' other moon, can also be seen in the second panel. While displayed here in visible-wavelength light, THEMIS also recorded thermal-infrared imagery in the same scan. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23208

Chandra X-Ray Observatory provided this composite X-ray (blue and green) and optical (red) image of the active galaxy NGC 1068 showing gas blowing away in a high-speed wind from the vicinity of a central supermassive black hole. Regions of intense star formation in the irner spiral arms of the galaxy are highlighted by both optical and x-ray emissions. A doughnut shaped cloud of cool gas and dust surrounding the black hole, known as the torus, appears as the elongated white spot . It has has a mass of about 5 million suns and is estimated to extend from within a few light years of the black hole out to about 300 light years.
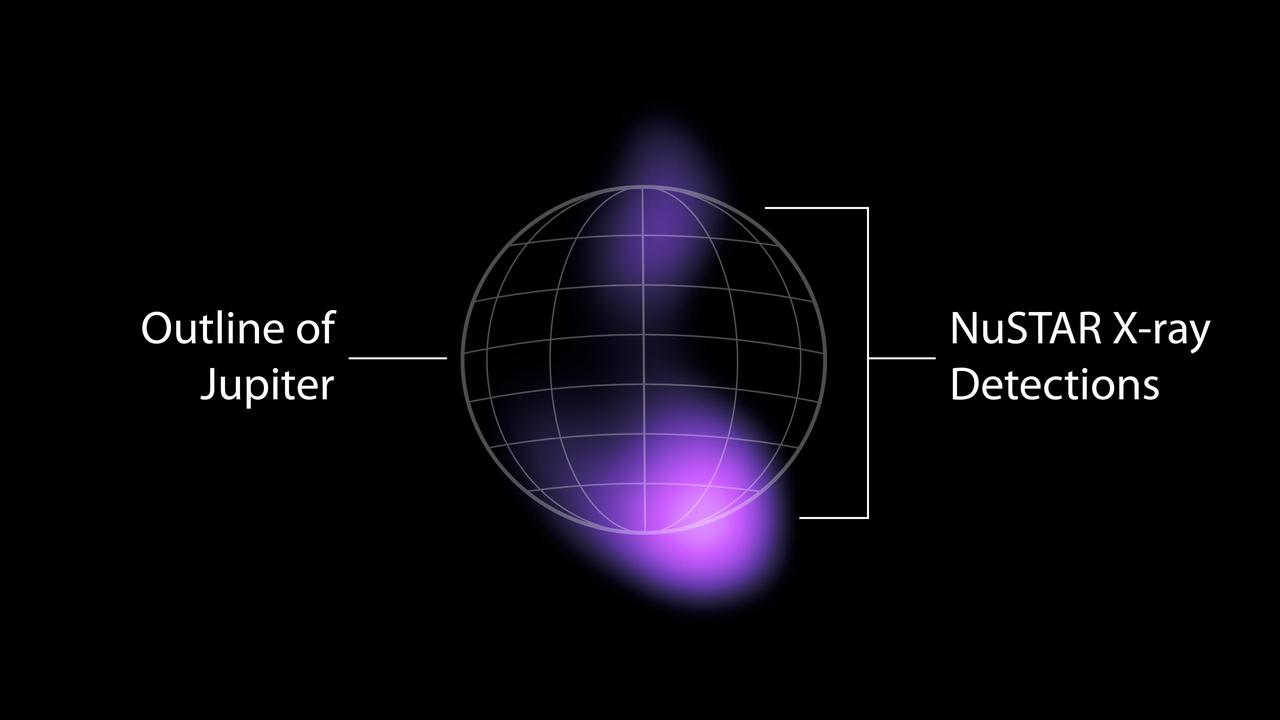
The areas where high-energy X-rays were detected by NASA's NuSTAR (Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array) from the auroras near Jupiter's north and south poles are shown in purple in this graphic. The emissions are the highest-energy light ever seen at Jupiter and the highest-energy light ever detected from a planet in our solar system other than Earth. The light comes from accelerated electrons colliding with the atmosphere. NuSTAR cannot pinpoint the source of the light with high precision, but can only find that it is coming from somewhere in the purple-colored regions. X-rays are a form of light, but with much higher energies and shorter wavelengths than the visible light human eyes can see. NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and the ESA (European Space Agency) XMM-Newton observatory have both studied X-rays from Jupiter's auroras – produced when volcanos on Jupiter's moon Io shower the planet with ions (atoms stripped of their electrons). Jupiter's powerful magnetic field accelerates the particles and funnels them toward the planet's poles, where they collide with its atmosphere and release energy in the form of light, including X-rays. Electrons from Io are also accelerated by the planet's magnetic field, according to observations by the Jovian Auroral Distributions Experiment (JADE) and Jupiter Energetic-particle Detector Instrument (JEDI) on NASA's Juno spacecraft, which arrived at Jupiter in 2016. Researchers suspected that those electrons should produce even higher-energy X-rays than those observed by Chandra and XMM-Newton, and the NuSTAR detections confirm that hypothesis. The high-energy X-rays are relatively faint, and required a week of NuSTAR observations to detect. Scientists have detected X-rays in Earth's auroras with even higher energies than what NuSTAR saw at Jupiter, but those emissions can only be spotted by small satellites or high-altitude balloons that get extremely close to the locations in the atmosphere that generate those X-rays. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25131
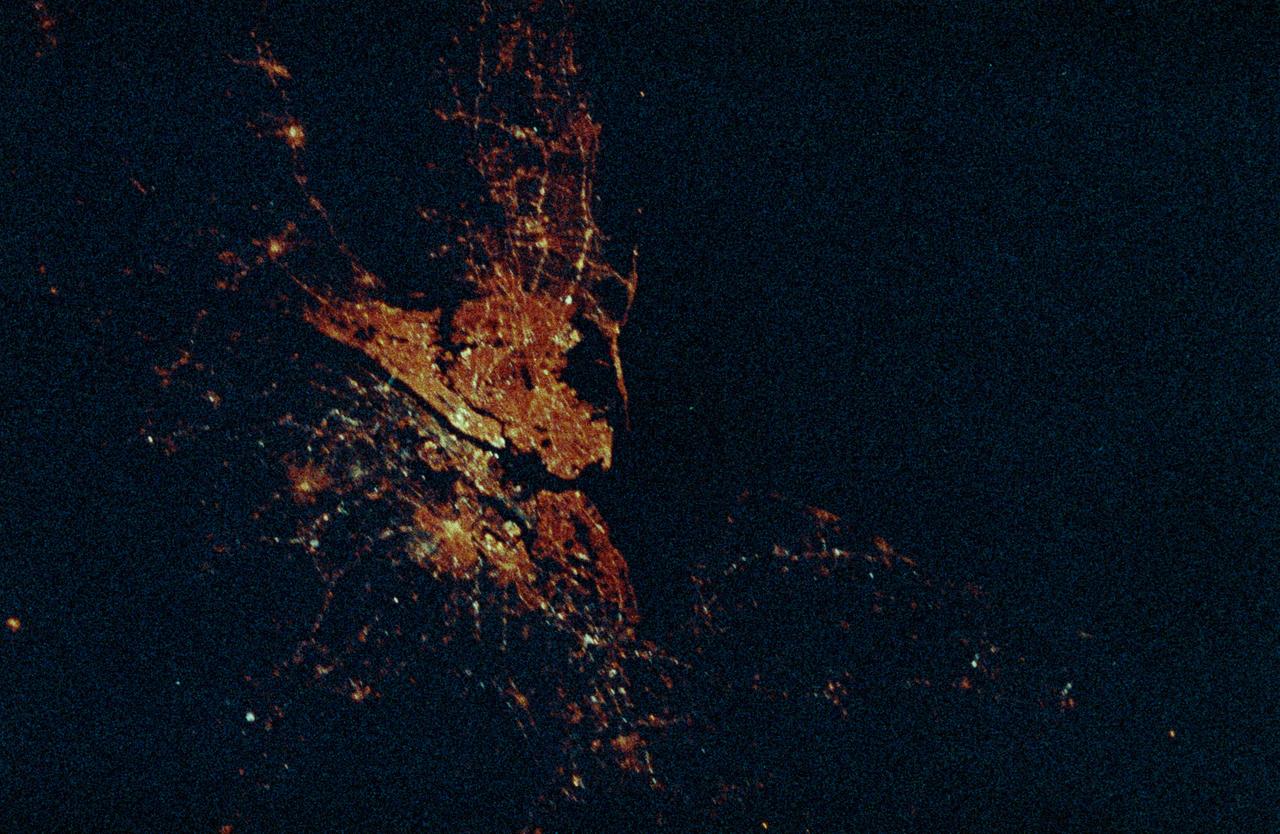

STS-36 Earth observation shows New York City, New York at night lit up along the Eastern seaboard of the United States and the Atlantic Ocean. The city lights designate the densely populated central city and the major highways surrounding it.
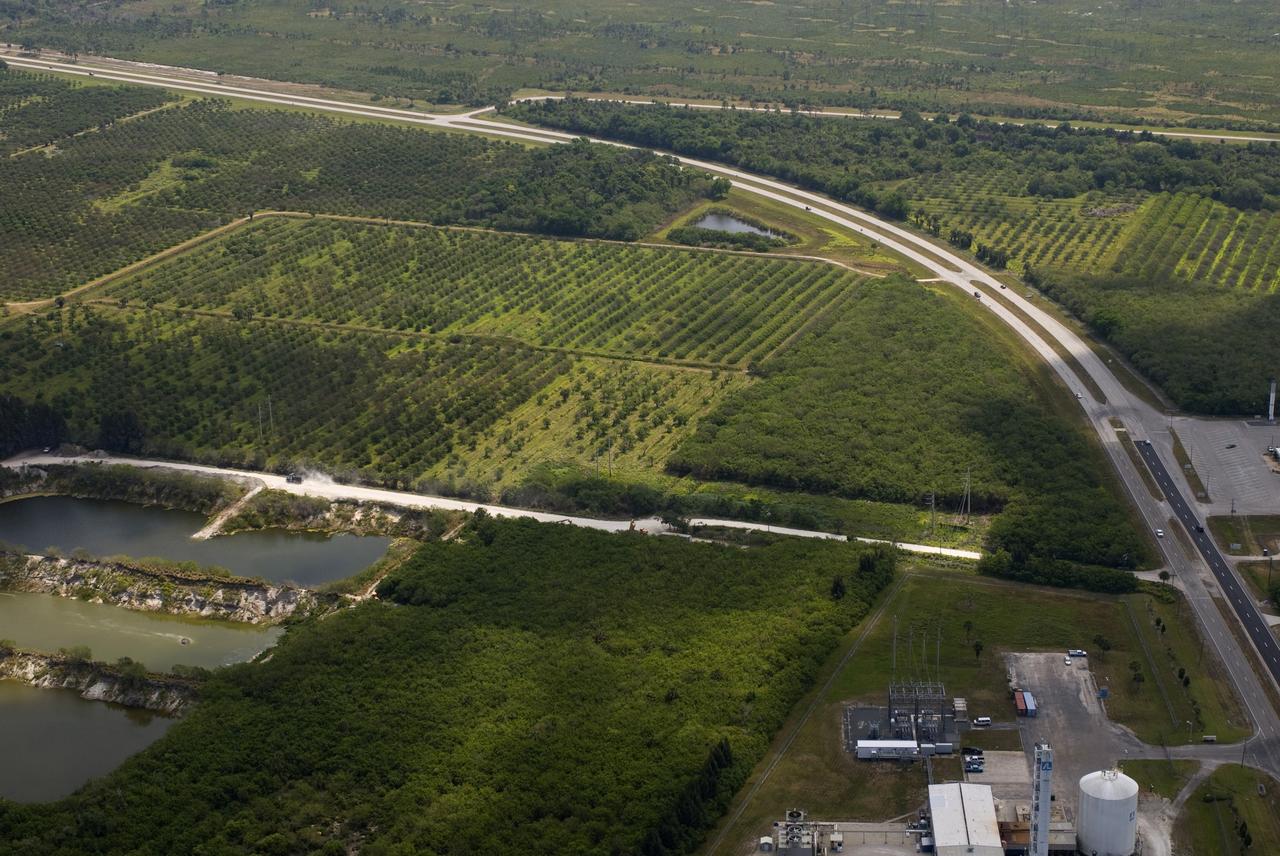

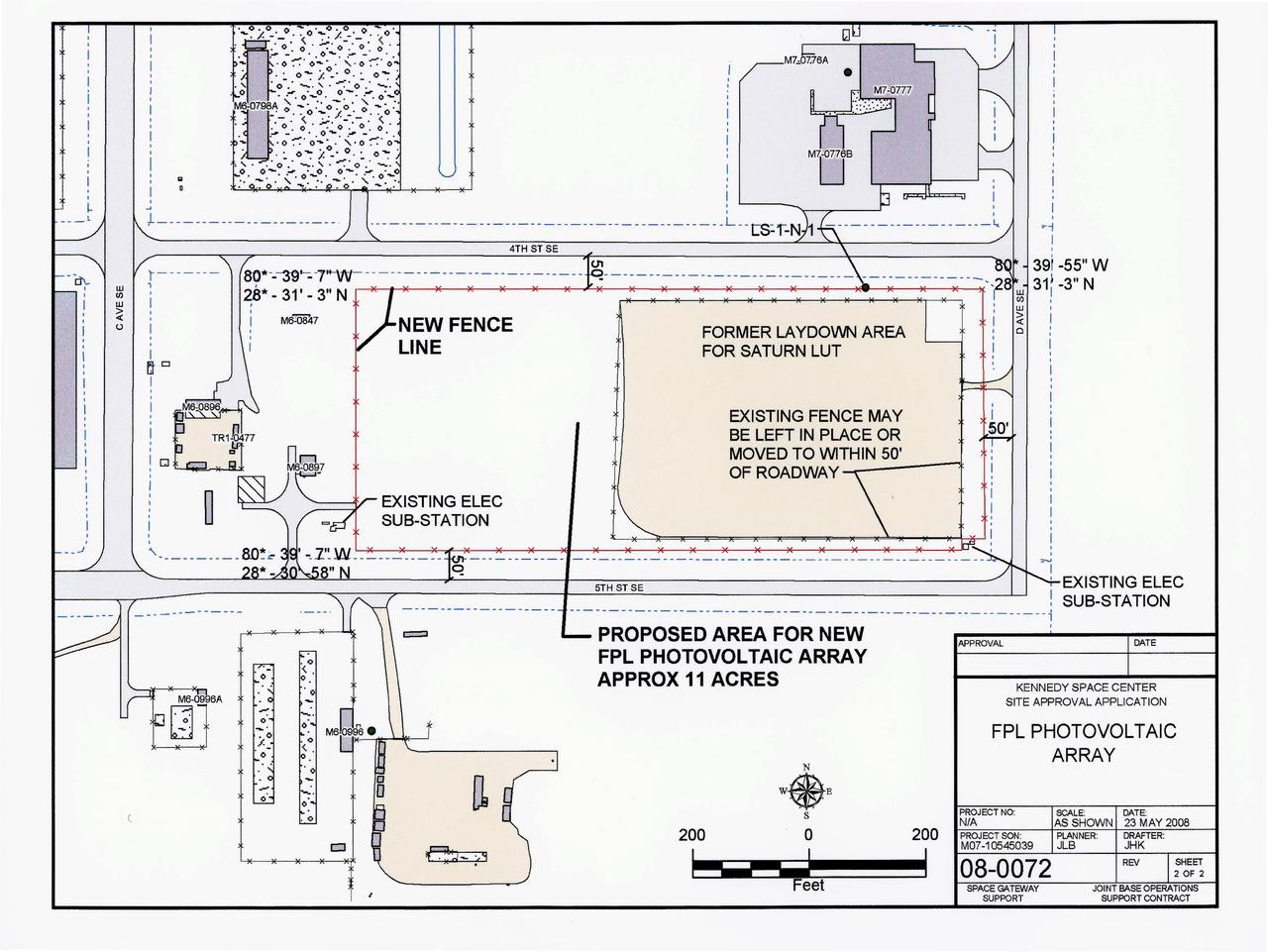
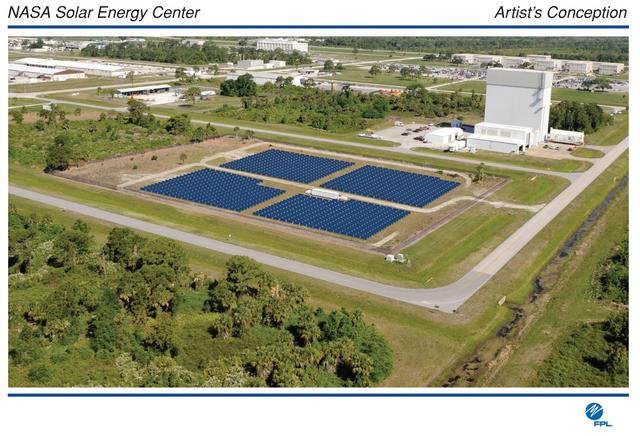
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This photo shows the area within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where a solar photovoltaic power generation system will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.
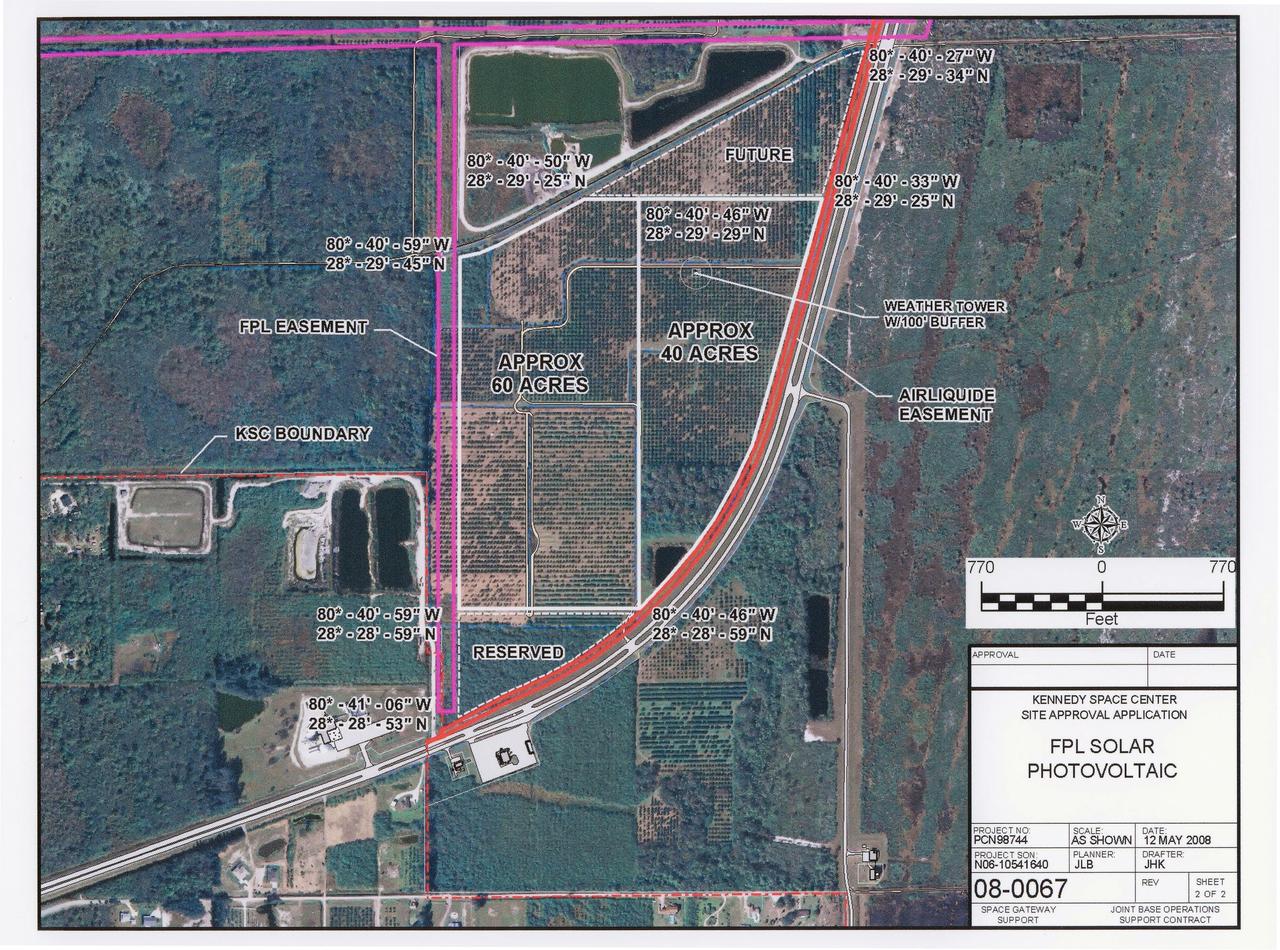
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This map shows the area within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where a solar photovoltaic power generation system will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.
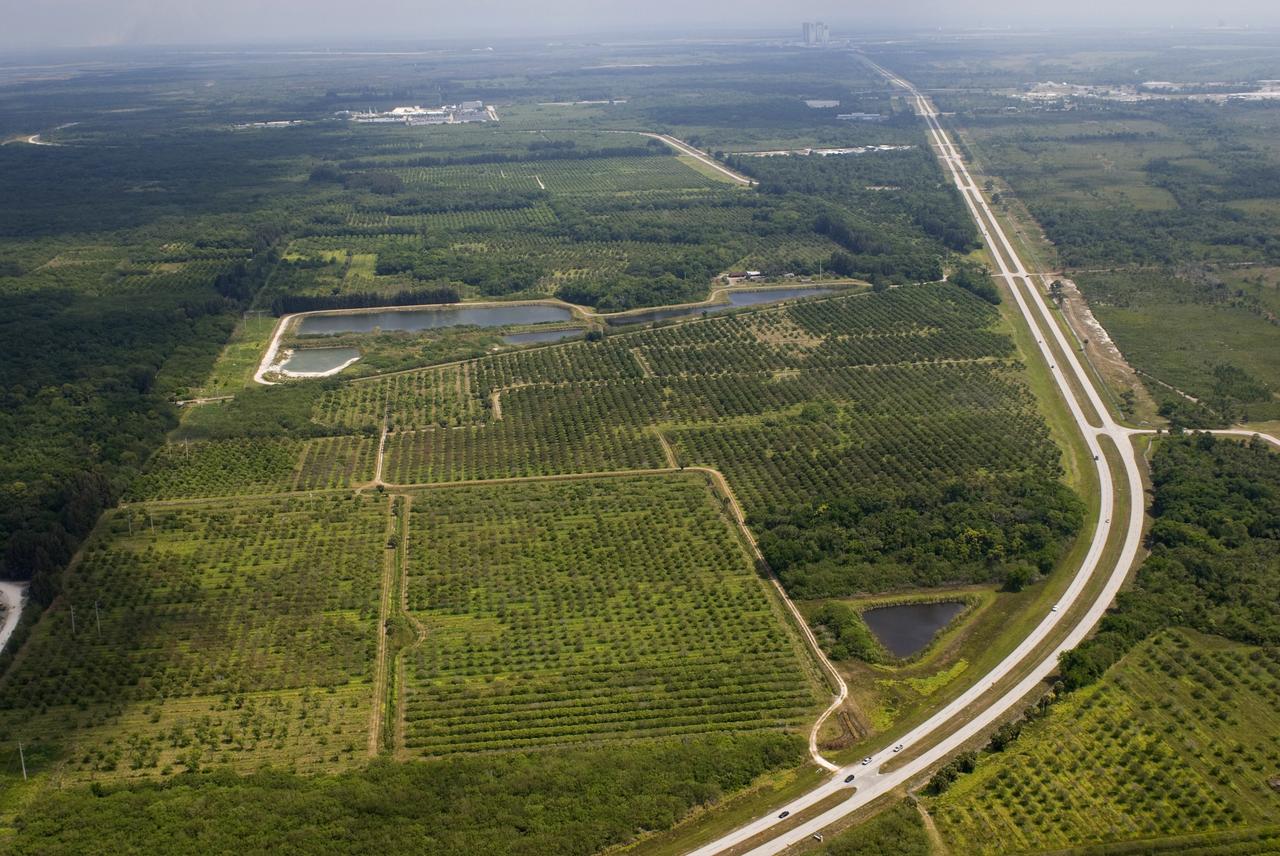

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This photo shows the area within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where a solar photovoltaic power generation system will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.
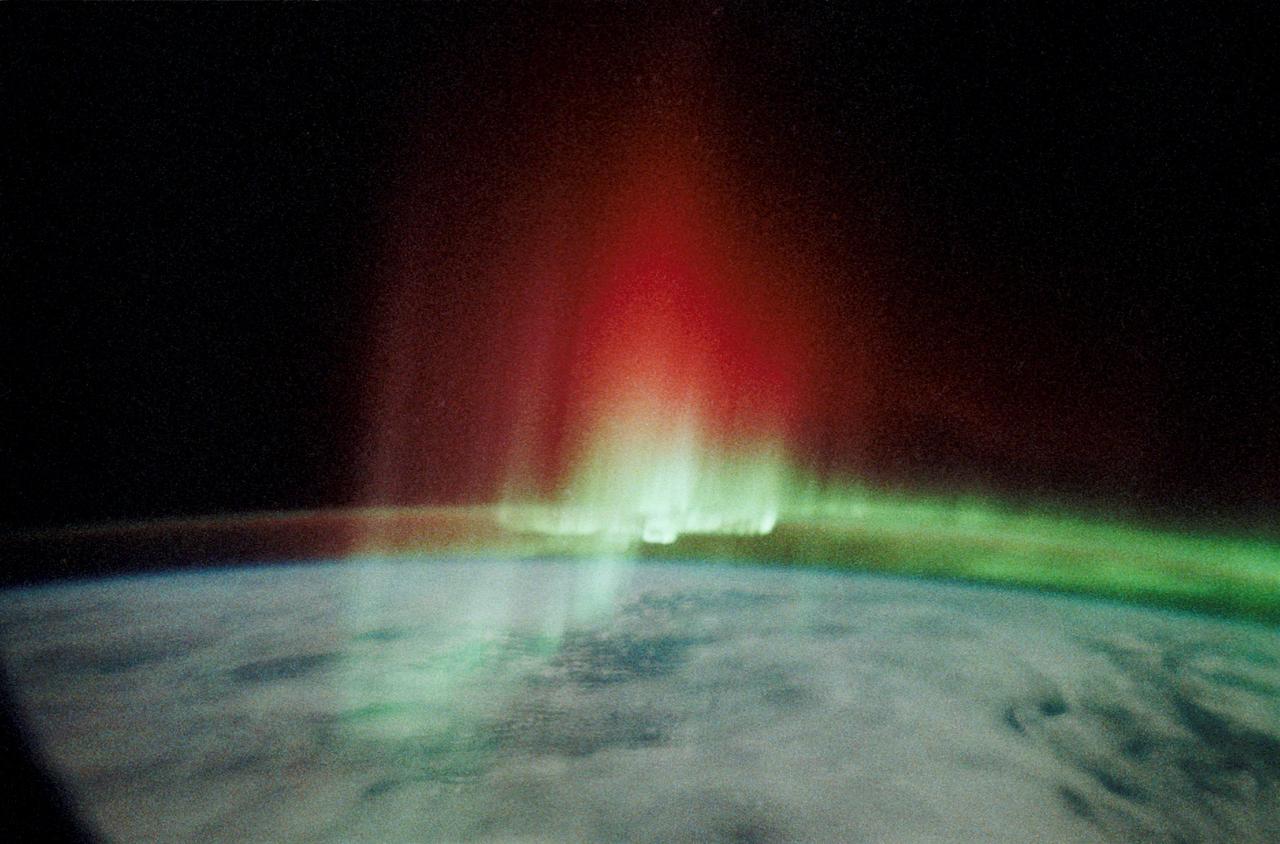

STS039-23-036 (28 April-6 May 1991) --- A 35mm frame of the Aurora Australis, also known as the Southern Lights, photographed from the Space Shuttle Discovery's flight deck by one of its seven crew members. One of the mission objectives was to measure the spectral and spatial characteristics of auroral emissions. While passing over the sunlit portion of Earth, the crew was able to take a number of photos of the various geographic points on the planet; much of the time on nightside passes was devoted to a thorough study and documentation of auroral displays.
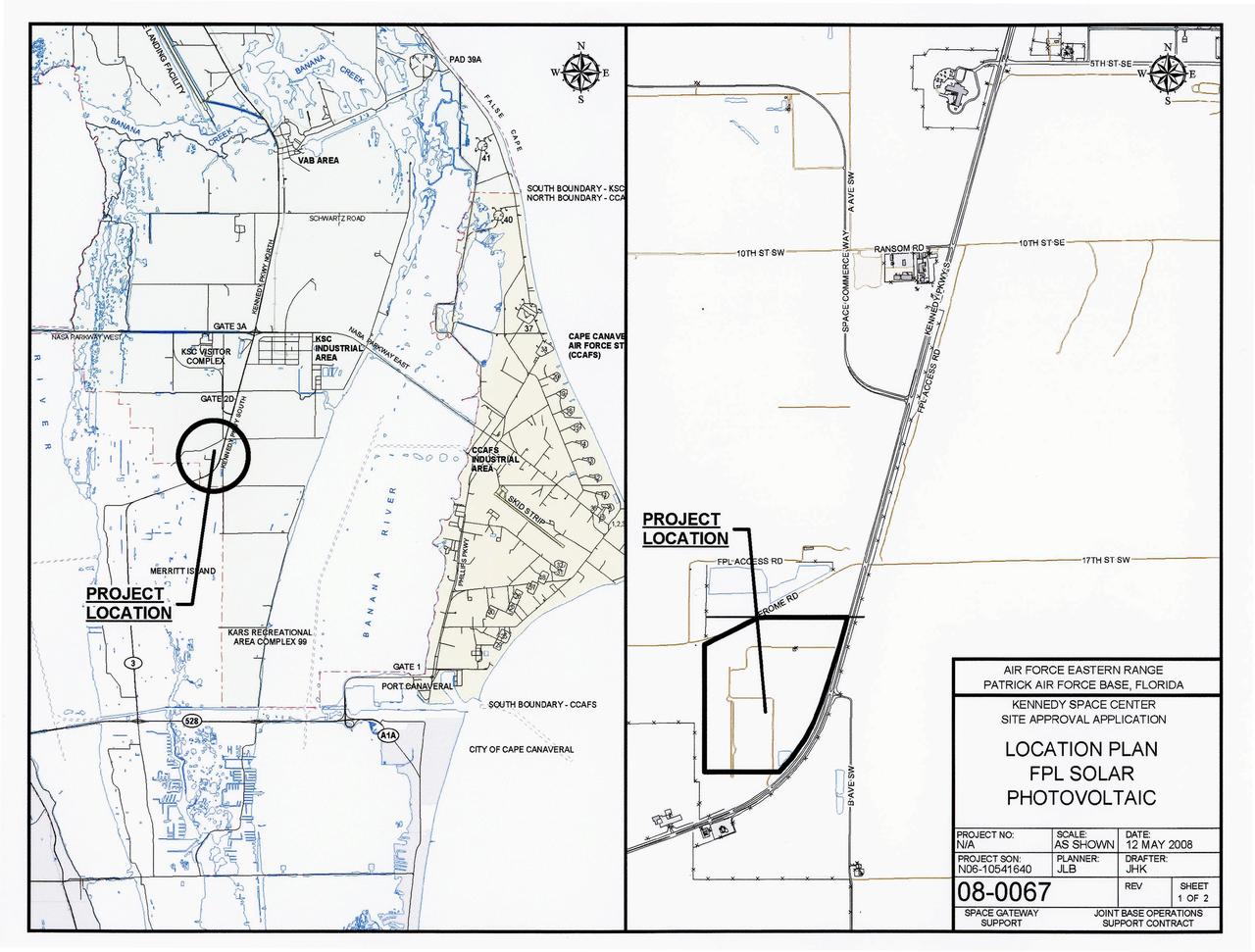
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This map shows the two sites within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where a solar photovoltaic power generation system will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.
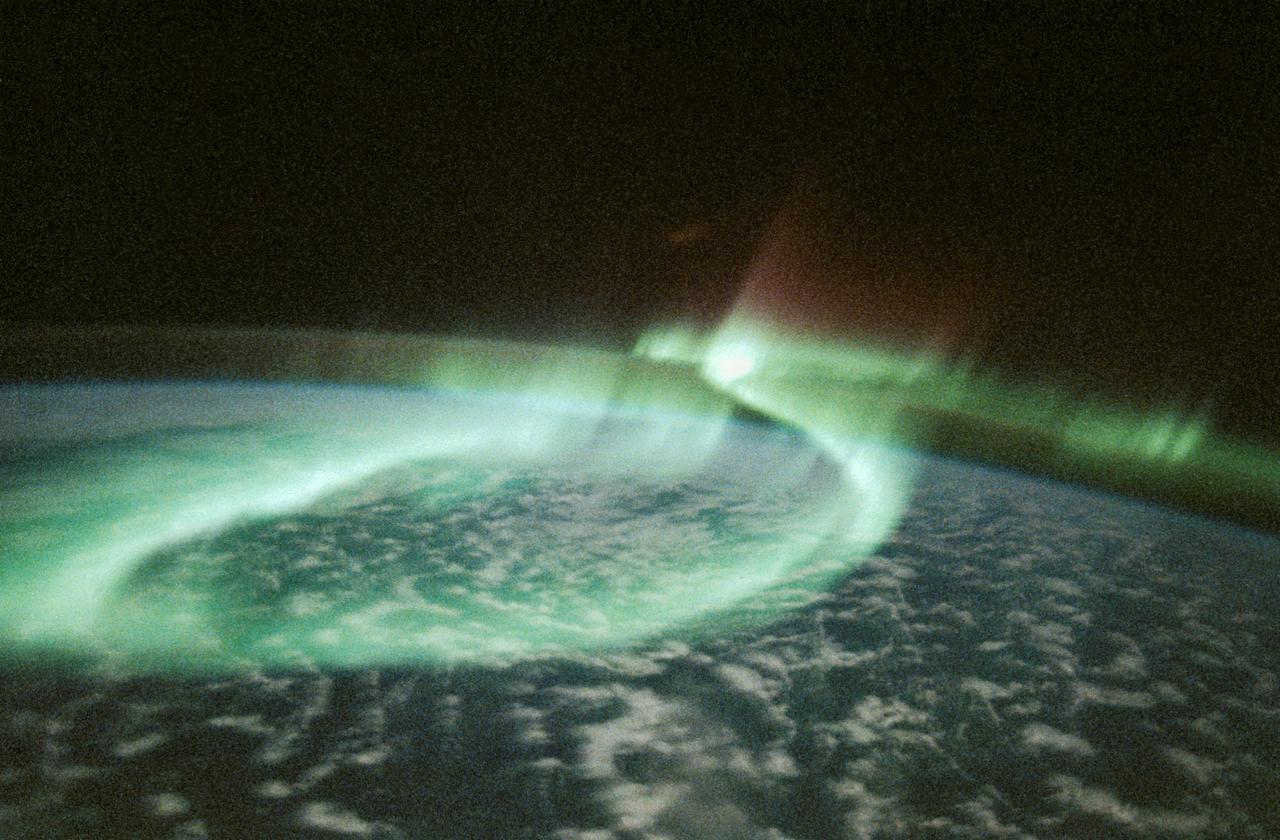

STS039-23-020 (28 April-6 May 1991) --- A 35mm frame of the Aurora Australis, also known as the Southern Lights, photographed from Space Shuttle Discovery's flight deck by one of its seven crew members. One of the mission objectives was to measure the spectral and spatial characteristics of auroral emissions. While passing over the sunlighted portion of Earth, the crew was able to take a number of photos of the various geographic points on the planet; much of the time on nightside passes was devoted to a thorough study and documentation of auroral displays.
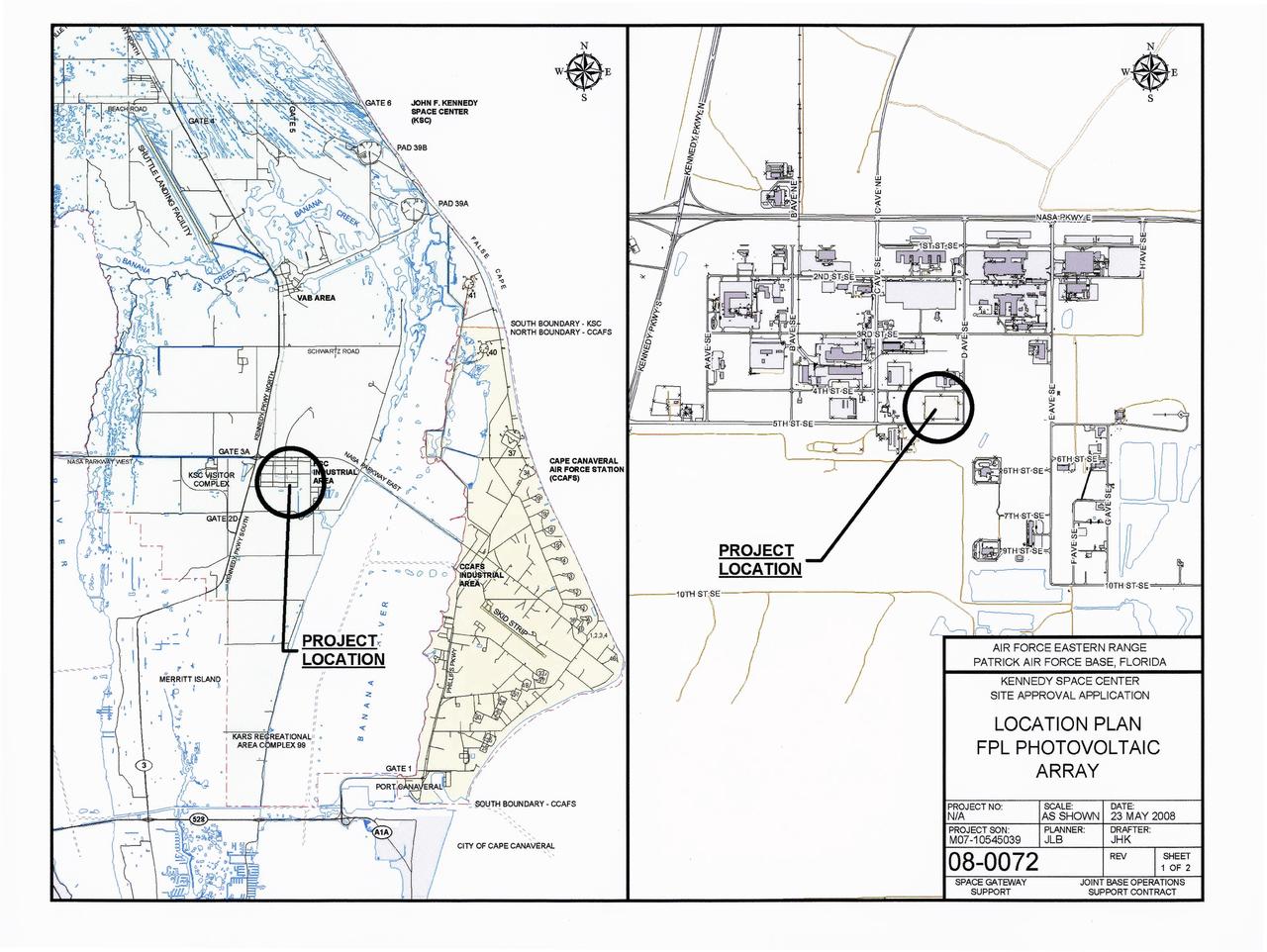
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This map shows the two sites within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where a solar photovoltaic power generation system will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.
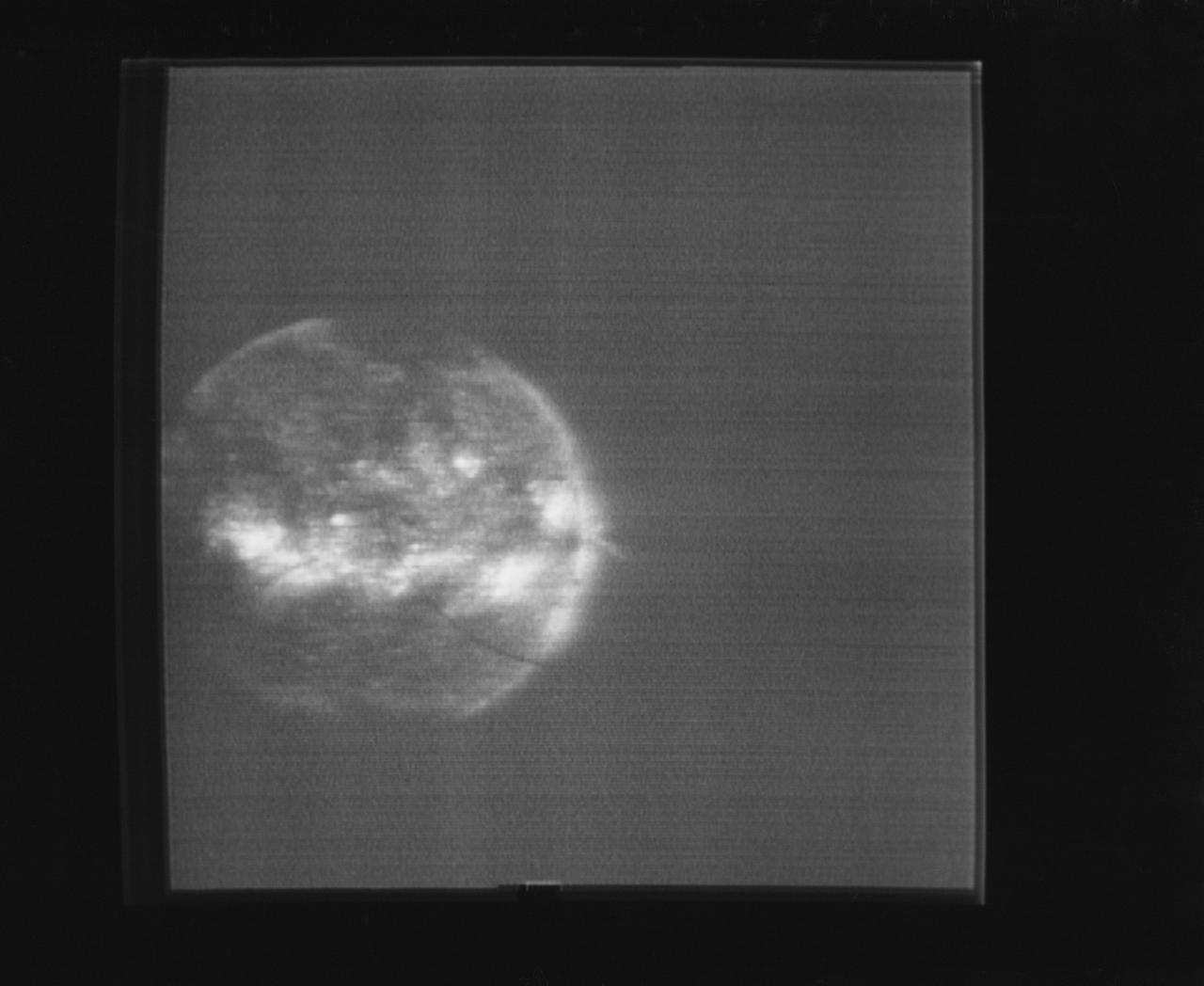
S74-15696 (1974) --- The solar disk photographed through the Skylab S082 Ultraviolet Spectrograph/Heliograph can be seen in this reproduction taken from a television tranmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The S082 experiment is located in the Apollo Telescope Mount. This spectroheliogram shows specific emission features greatly enhanced over photographs of the solar disk in white light. Photo credit: NASA
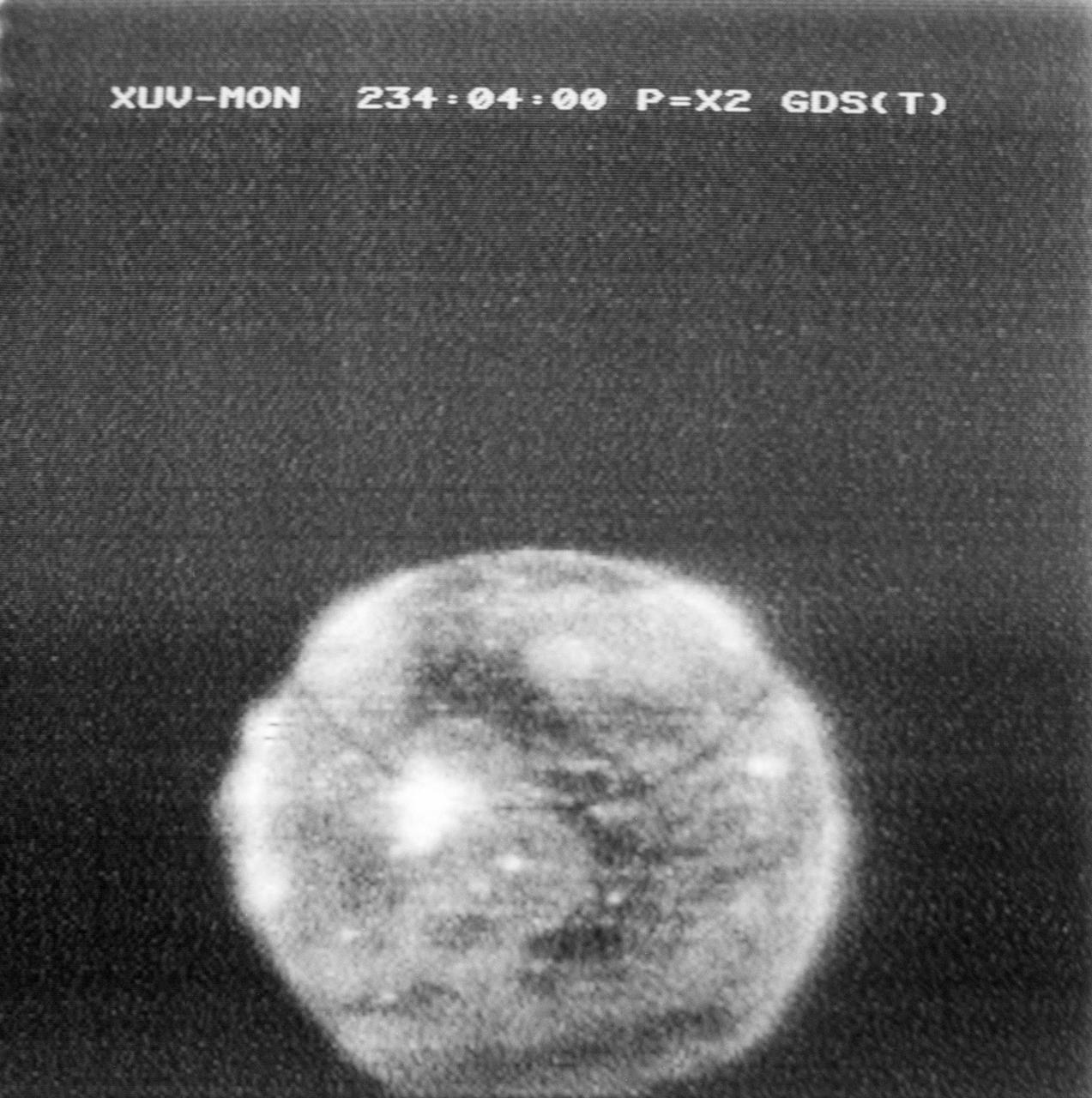
S73-32867 (21 Aug. 1973) --- The solar sphere viewed through the Skylab solar physics experiment (S082) Extreme Ultraviolet Spectroheliographis seen in this photographic reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The solar chromosphere and lower corona are much hotter than the surface of the sun characterized by the white light emissions. This image was recorded during the huge solar prominence which occurred on Aug. 21, 1973. Photo credit: NASA
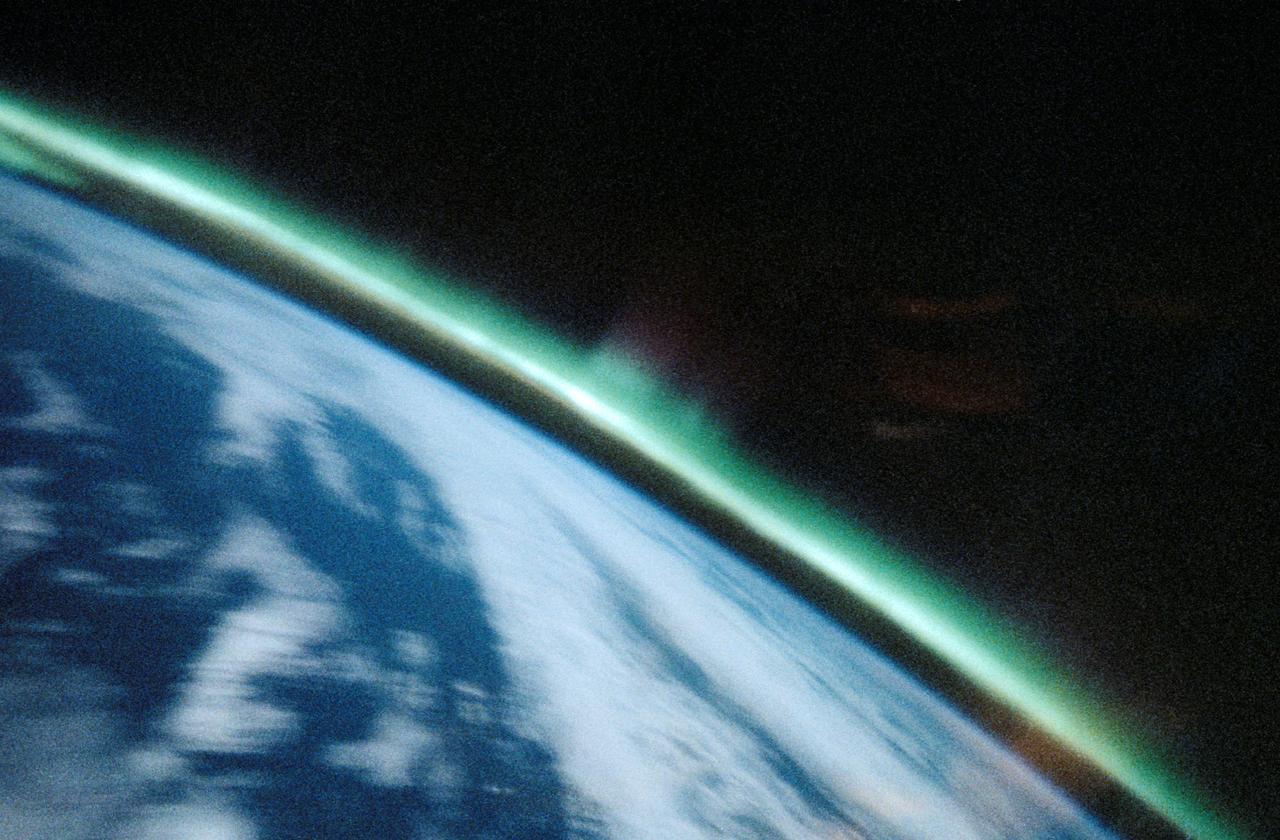

STS039-25-006 (28 April-6 May 1991) --- A 35mm frame of the Aurora Australis, also known as the Southern Lights, photographed from the Space Shuttle Discovery's flight deck by one of its seven crew members. One of the mission objectives was to measure the spectral and spatial characteristics of auroral emissions. While passing over the sunlighted portion of Earth, the crew was able to take a number of photos of the various geographic points on the planet; much of the time on nightside passes was devoted to a thorough study and documentation of auroral displays.
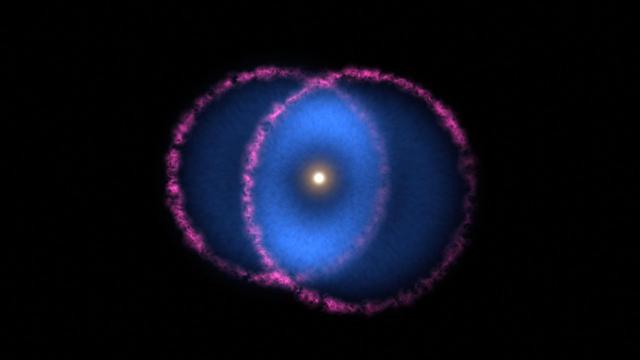
The Blue Ring Nebula is thought to be the product of two stars merging into one. The collision of the bodies ejected a cloud of hot debris into space. A disk of gas orbiting the larger star cut the cloud in half, creating two cones that are moving away from the star in opposite directions. The base of one cone is moving almost directly toward Earth, while the other is moving almost directly away. Magenta represents optical light from the shockwave at the front of the expanding debris cones, outlining the two cone bases at their widest points. Blue represents far-ultraviolet light (not visible to the human eye) and comes from gas behind the shockwave. As the gas expands and cools, it forms hydrogen molecules that interact with the interstellar medium and emit only far-ultraviolet light. These emissions are visible only where the cones overlap (as seen from Earth), forming the blue ring around the central star. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23868
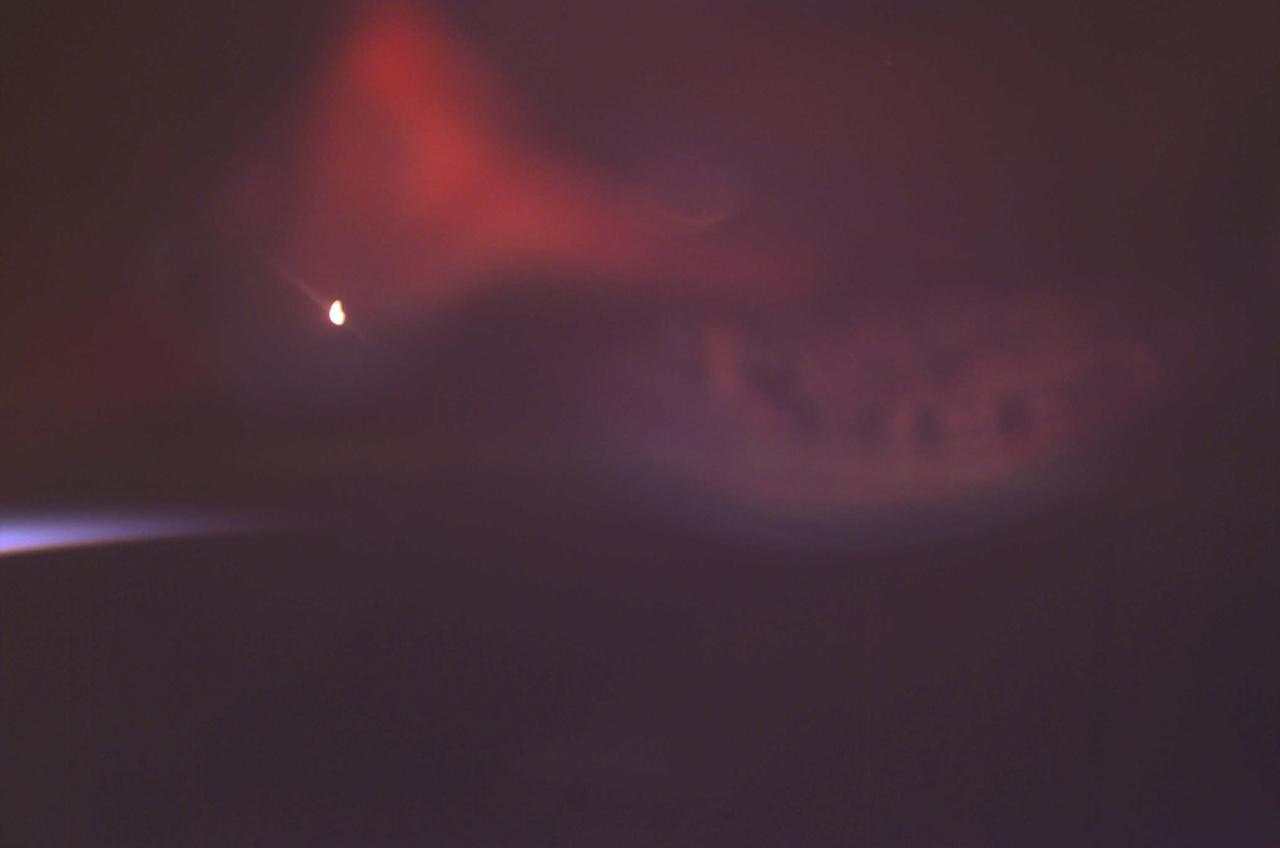
Auroras are caused when high-energy electrons pour down from the Earth's magnetosphere and collide with atoms. Red aurora, as captured here by a still digital camera aboard the International Space Station (ISS), occurs from 200 km to as high as 500 km altitude and is caused by the emission of 6300 Angstrom wavelength light from oxygen atoms. The light is emitted when the atoms return to their original unexcited state. The white spot in the image is from a light on inside of the ISS that is reflected off the inside of the window. The pale blue arch on the left side of the frame is sunlight reflecting off the atmospheric limb of the Earth. At times of peaks in solar activity, there are more geomagnetic storms and this increases the auroral activity viewed on Earth and by astronauts from orbit.
![This image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, shows the wispy filamentary structure of Henize 206, is a four-color composite mosaic created by combining data from an infrared array camera IRAC. The LMC is a small satellite galaxy gravitationally bound to our own Milky Way. Yet the gravitational effects are tearing the companion to shreds in a long-playing drama of 'intergalactic cannibalism.' These disruptions lead to a recurring cycle of star birth and star death. Astronomers are particularly interested in the LMC because its fractional content of heavy metals is two to five times lower than is seen in our solar neighborhood. [In this context, 'heavy elements' refer to those elements not present in the primordial universe. Such elements as carbon, oxygen and others are produced by nucleosynthesis and are ejected into the interstellar medium via mass loss by stars, including supernova explosions.] As such, the LMC provides a nearby cosmic laboratory that may resemble the distant universe in its chemical composition. The primary Spitzer image, showing the wispy filamentary structure of Henize 206, is a four-color composite mosaic created by combining data from an infrared array camera (IRAC) at near-infrared wavelengths and the mid-infrared data from a multiband imaging photometer (MIPS). Blue represents invisible infrared light at wavelengths of 3.6 and 4.5 microns. Note that most of the stars in the field of view radiate primarily at these short infrared wavelengths. Cyan denotes emission at 5.8 microns, green depicts the 8.0 micron light, and red is used to trace the thermal emission from dust at 24 microns. The separate instrument images are included as insets to the main composite. An inclined ring of emission dominates the central and upper regions of the image. This delineates a bubble of hot, x-ray emitting gas that was blown into space when a massive star died in a supernova explosion millions of years ago. The shock waves from that explosion impacted a cloud of nearby hydrogen gas, compressed it, and started a new generation of star formation. The death of one star led to the birth of many new stars. This is particularly evident in the MIPS inset, where the 24-micron emission peaks correspond to newly formed stars. The ultraviolet and visible-light photons from the new stars are absorbed by surrounding dust and re-radiated at longer infrared wavelengths, where it is detected by Spitzer. This emission nebula was cataloged by Karl Henize (HEN-eyes) while spending 1948-1951 in South Africa doing research for his Ph.D. dissertation at the University of Michigan. Henize later became a NASA astronaut and, at age 59, became the oldest rookie to fly on the Space Shuttle during an eight-day flight of the Challenger in 1985. He died just short of his 67th birthday in 1993 while attempting to climb the north face of Mount Everest, the world's highest peak. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05517](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA05517/PIA05517~medium.jpg)
This image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, shows the wispy filamentary structure of Henize 206, is a four-color composite mosaic created by combining data from an infrared array camera IRAC. The LMC is a small satellite galaxy gravitationally bound to our own Milky Way. Yet the gravitational effects are tearing the companion to shreds in a long-playing drama of 'intergalactic cannibalism.' These disruptions lead to a recurring cycle of star birth and star death. Astronomers are particularly interested in the LMC because its fractional content of heavy metals is two to five times lower than is seen in our solar neighborhood. [In this context, 'heavy elements' refer to those elements not present in the primordial universe. Such elements as carbon, oxygen and others are produced by nucleosynthesis and are ejected into the interstellar medium via mass loss by stars, including supernova explosions.] As such, the LMC provides a nearby cosmic laboratory that may resemble the distant universe in its chemical composition. The primary Spitzer image, showing the wispy filamentary structure of Henize 206, is a four-color composite mosaic created by combining data from an infrared array camera (IRAC) at near-infrared wavelengths and the mid-infrared data from a multiband imaging photometer (MIPS). Blue represents invisible infrared light at wavelengths of 3.6 and 4.5 microns. Note that most of the stars in the field of view radiate primarily at these short infrared wavelengths. Cyan denotes emission at 5.8 microns, green depicts the 8.0 micron light, and red is used to trace the thermal emission from dust at 24 microns. The separate instrument images are included as insets to the main composite. An inclined ring of emission dominates the central and upper regions of the image. This delineates a bubble of hot, x-ray emitting gas that was blown into space when a massive star died in a supernova explosion millions of years ago. The shock waves from that explosion impacted a cloud of nearby hydrogen gas, compressed it, and started a new generation of star formation. The death of one star led to the birth of many new stars. This is particularly evident in the MIPS inset, where the 24-micron emission peaks correspond to newly formed stars. The ultraviolet and visible-light photons from the new stars are absorbed by surrounding dust and re-radiated at longer infrared wavelengths, where it is detected by Spitzer. This emission nebula was cataloged by Karl Henize (HEN-eyes) while spending 1948-1951 in South Africa doing research for his Ph.D. dissertation at the University of Michigan. Henize later became a NASA astronaut and, at age 59, became the oldest rookie to fly on the Space Shuttle during an eight-day flight of the Challenger in 1985. He died just short of his 67th birthday in 1993 while attempting to climb the north face of Mount Everest, the world's highest peak. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05517

The data captured here is one of the outputs of a September 2023 test conducted at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory of a state-of-the-art imaging spectrometer instrument, which will measure the greenhouse gases methane and carbon dioxide from space. The instrument successfully detected the presence of methane (dark blue line near the top of the rainbow band), a greenhouse gas, in a sample cylinder. The rainbow band shown on a screen here is a measure of the intensity of a spectrum of light. Blue is low intensity and red is high intensity. Designed and built by JPL, imaging spectrometer will be part of an effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper organization to collect data on greenhouse gas point-source emissions. The information will help locate and quantify "super-emitters" – the small percentage of individual sources responsible for a significant fraction of methane and carbon dioxide emissions around the world. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26096
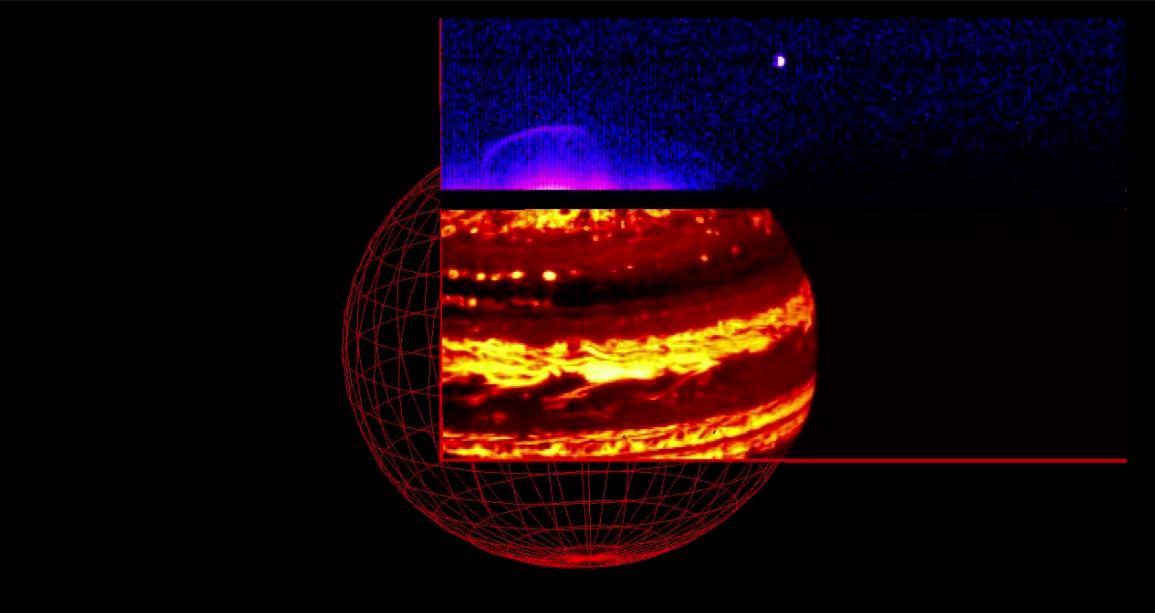
As NASA's Juno spacecraft approached Jupiter on Aug. 27, 2016, the Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument captured the planet's glow in infrared light. The video is composed of 580 images collected over a period of about nine hours while Jupiter completed nearly a full rotation on its axis. The video shows the two parts composing the JIRAM imager: the lower one, in a red color scale, is used for mapping the planet's thermal emission at wavelengths around 4.8 microns; the upper one, in a blue color scale, is used to map the auroras at wavelengths around 3.45 microns. In this case the exposure time of the imager was optimized to observe the planet's thermal emission. However, it is possible to see a faint aurora and Jupiter's moon Io approaching the planet. The Great Red Spot is also visible just south of the planet's equator. A movie is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21036
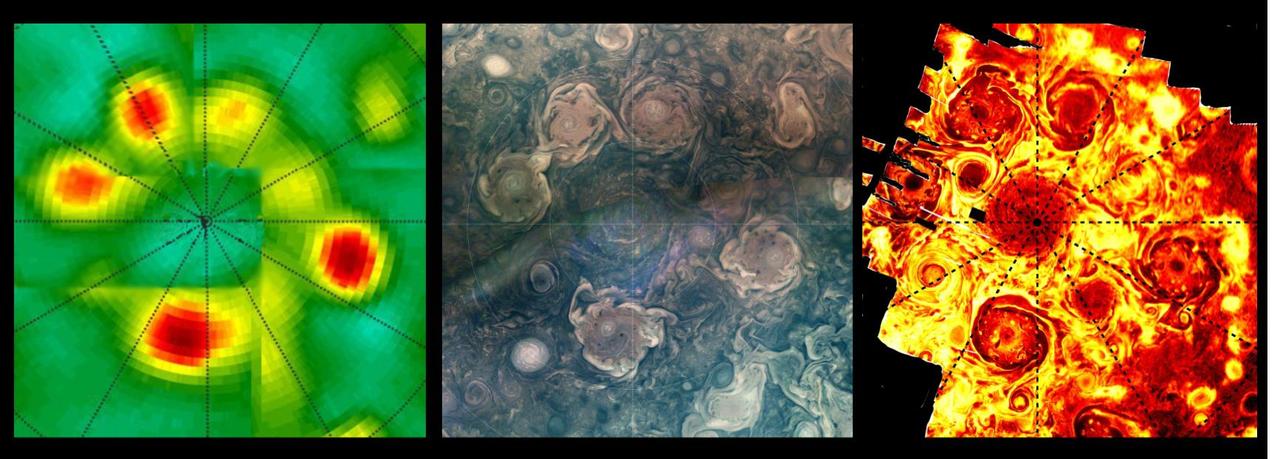
This composite shows views of Jupiter's northern polar cyclones in three different wavelengths of light – microwave, visible, and ultraviolet – as captured by NASA's Juno mission. These differing perspectives allowed Juno scientists to deduce that all Jovian polar cyclones are not created equal. The infrared image, on the far right, was derived from data collected by the spacecraft's Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument. The composite image at center was collected by the JunoCam visible-light imager. Though taken with separate instruments that record different wavelengths of light, both images depict Jupiter's northern polar storms as well defined and of similar size. The data on the left, collected by Juno's Microwave Radiometer (MWR), shows the polar storms in another light. MWR enables Juno to see deep into Jupiter by recording the planet's microwave emissions. In the MWR graphic, the polar storms at the 4 and 6 o'clock positions have bright microwave signatures, indicating they extend well beneath the cloud tops, at least 62 miles (100 kilometers) below. The size of those two storms is comparable to what's found in the visible light and infrared light images, but the other storms, as seen through MWR, have a notably reduced emissions intensity. Another disparity in the MWR graphic versus visible light and infrared can be seen in how the central cyclone is depicted by the data. In the infrared and visible light images, the central cyclone is evident; with MWR data, it all but disappears. This disparity indicates that the central cyclone's subsurface structure must be very different from the surrounding storms. JIRAM "sees" in infrared light not visible to the human eye. It captures the infrared glow from the heat of Jupiter's upper atmosphere, probing the top of the weather layer, and gaps in the clouds allow glimpses as deep as 30 to 45 miles (50 to 70 kilometers) below Jupiter's cloud tops. JunoCam's visible light images catch reflected sunlight, with a view that is very similar to what a human eye would see if a person could ride along with Juno. JunoCam's raw images are available for the public to peruse and process into image products at https://missionjuno.swri.edu/junocam/processing. Like JIRAM, the MWR instrument records the glow of Jupiter's atmosphere, but the brightness results from the temperature at depths below anything achievable with previous spacecraft or Earth-based observations. The MWR's six radio channels peer progressively deeper below the visible cloud tops, with a range from the top of the clouds (for the highest frequency channel) to 200 miles (320 kilometers) or more below (for the lowest frequency channel). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26295

Engineers in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in April 2023 examine the imaging spectrometer that will ride aboard the first of two satellites to be launched by the Carbon Mapper Coalition. The instrument will help researchers detect emissions of carbon dioxide and methane from sources on Earth's surface from space. The gold-colored component is the spectrometer, which was developed at JPL. It's designed to receive sunlight reflected from Earth and divide that light into hundreds of distinct colors in the near-infrared and visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. By analyzing the light's spectroscopic signature – the wavelengths that show up in the signal as well as those that do not – researchers can determine whether the instrument is observing greenhouse gas emissions and, if so, estimate their concentrations. The black portion at the base of the instrument is a telescope that captures light from Earth's surface and reflects it into the spectrometer. When released into the atmosphere, carbon dioxide and methane are the greenhouse gases most responsible for human-caused global warming. Both have unique spectral signatures that make them detectable from space via spectroscopy. The imaging spectrometer is JPL's contribution to the Carbon Mapper Coalition, a joint effort led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper that also includes Planet Labs PBC, the California Air Resources Board, Arizona State University, and the University of Arizona. Once the instrument is in orbit, researchers will use its measurements to identify the sources of carbon dioxide and methane plumes it detects. Identification of the origins of emissions is considered the first step towards mitigation. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25869

Hubble’s Spirograph In this classic Hubble image from 2000, the planetary nebula IC 418 glows like a multifaceted jewel with enigmatic patterns. IC 418 lies about 2,000 light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation Lepus. A planetary nebula represents the final stage in the evolution of a star similar to our sun. The star at the center of IC 418 was a red giant a few thousand years ago, but then ejected its outer layers into space to form the nebula, which has now expanded to a diameter of about 0.1 light-year. The stellar remnant at the center is the hot core of the red giant, from which ultraviolet radiation floods out into the surrounding gas, causing it to fluoresce. Over the next several thousand years, the nebula will gradually disperse into space, and then the star will cool and fade away for billions of years as a white dwarf. Our own sun is expected to undergo a similar fate, but fortunately, this will not occur until some 5 billion years from now. The Hubble image of IC 418 is shown with colors added to represent the different camera filters used that isolate light from various chemical elements. Red shows emission from ionized nitrogen (the coolest gas in the nebula, located furthest from the hot nucleus), green shows emission from hydrogen and blue traces the emission from ionized oxygen (the hottest gas, closest to the central star). The remarkable textures seen in the nebula are newly revealed by the Hubble Space Telescope, and their origin is still uncertain. Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2roofKS" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2roofKS</a> Credit: NASA and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA); Acknowledgment: Dr. Raghvendra Sahai (JPL) and Dr. Arsen R. Hajian (USNO)
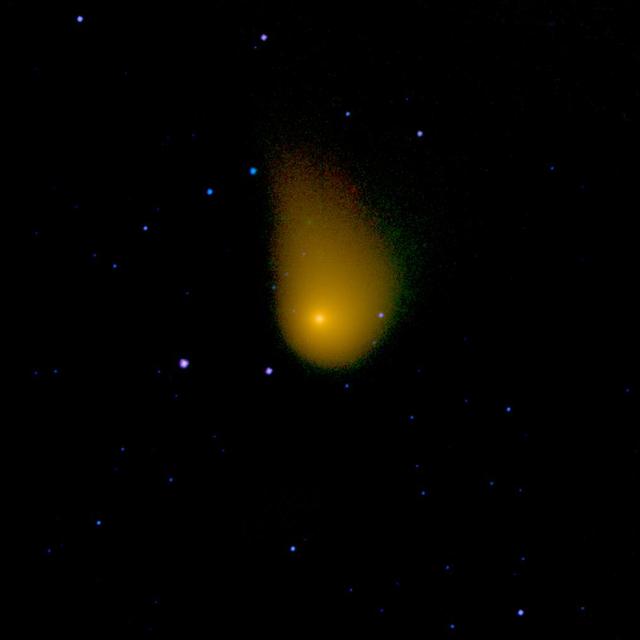
An infrared view from NASA's NEOWISE mission of the Oort cloud comet C/2006 W3 (Christensen). The spacecraft observed this comet on April 20th, 2010 as it traveled through the constellation Sagittarius. Comet Christensen was nearly 370 million miles (600 million kilometers) from Earth at the time. The image is half of a degree of the sky on each side. Infrared light with wavelengths of 3.4, 12 and 22 micron channels are mapped to blue, green, and red, respectively. The signal at these wavelengths is dominated primarily by the comet's dust thermal emission, giving it a golden hue. The WISE spacecraft was put into hibernation in 2011 upon completing its goal of surveying the entire sky in infrared light. WISE cataloged three quarters of a billion objects, including asteroids, stars and galaxies. In August 2013, NASA decided to reinstate the spacecraft on a mission to find and characterize more asteroids. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20118

Seen shortly after local Martian sunrise, clouds gather in the summit pit, or caldera, of Pavonis Mons, a giant volcano on Mars, in this image from the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) on NASA's Mars Odyssey orbiter. The clouds are mostly made of ice crystals. They appear blue in the image because the cloud particles scatter blue light more strongly than other colors. Pavonis Mons stands about nine miles (14 kilometers) high, and the caldera spans about 29 miles (47 kilometers) wide. This image was made by THEMIS through three of its visual-light filters plus a near-infrared filter, and it is approximately true in color. THEMIS and other instruments on Mars Odyssey have been studying Mars from orbit since 2001. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19675
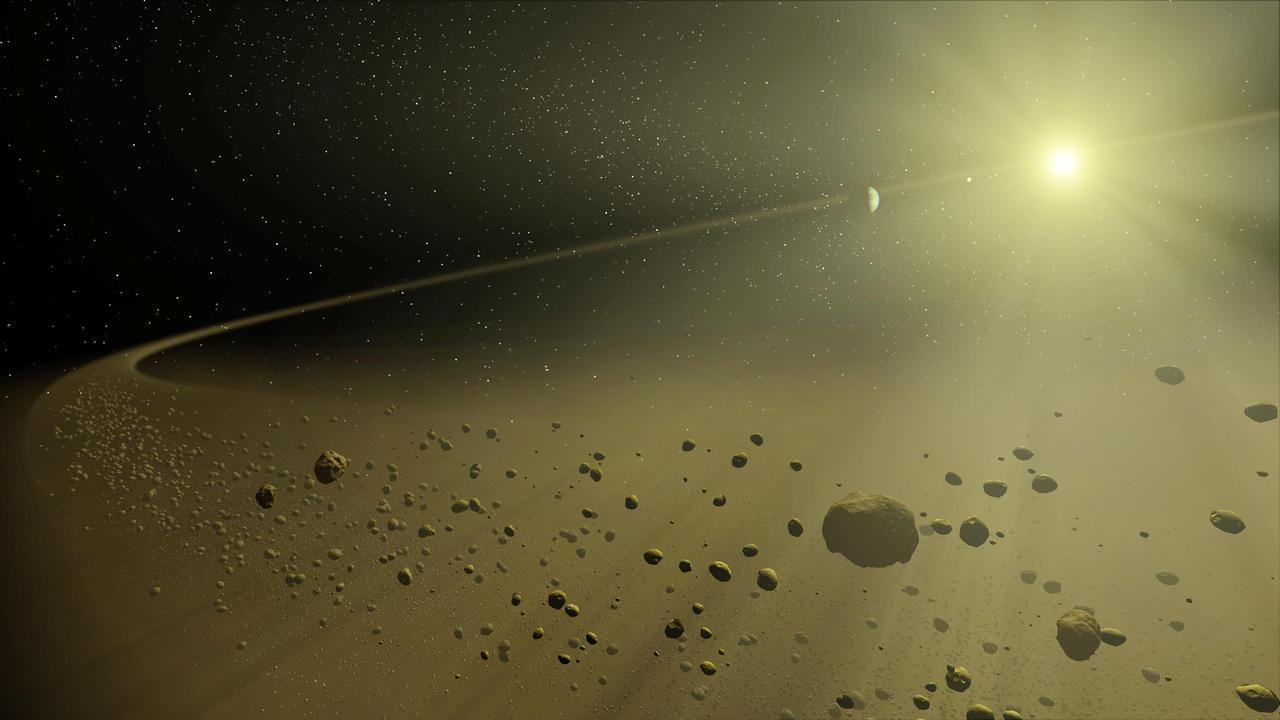

This artist concept depicts a distant hypothetical solar system, similar in age to our own. Looking inward from the system outer fringes, a ring of dusty debris can be seen, and within it, planets circling a star the size of our Sun. This debris is all that remains of the planet-forming disk from which the planets evolved. Planets are formed when dusty material in a large disk surrounding a young star clumps together. Leftover material is eventually blown out by solar wind or pushed out by gravitational interactions with planets. Billions of years later, only an outer disk of debris remains. These outer debris disks are too faint to be imaged by visible-light telescopes. They are washed out by the glare of the Sun. However, NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope can detect their heat, or excess thermal emission, in infrared light. This allows astronomers to study the aftermath of planet building in distant solar systems like our own. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07096
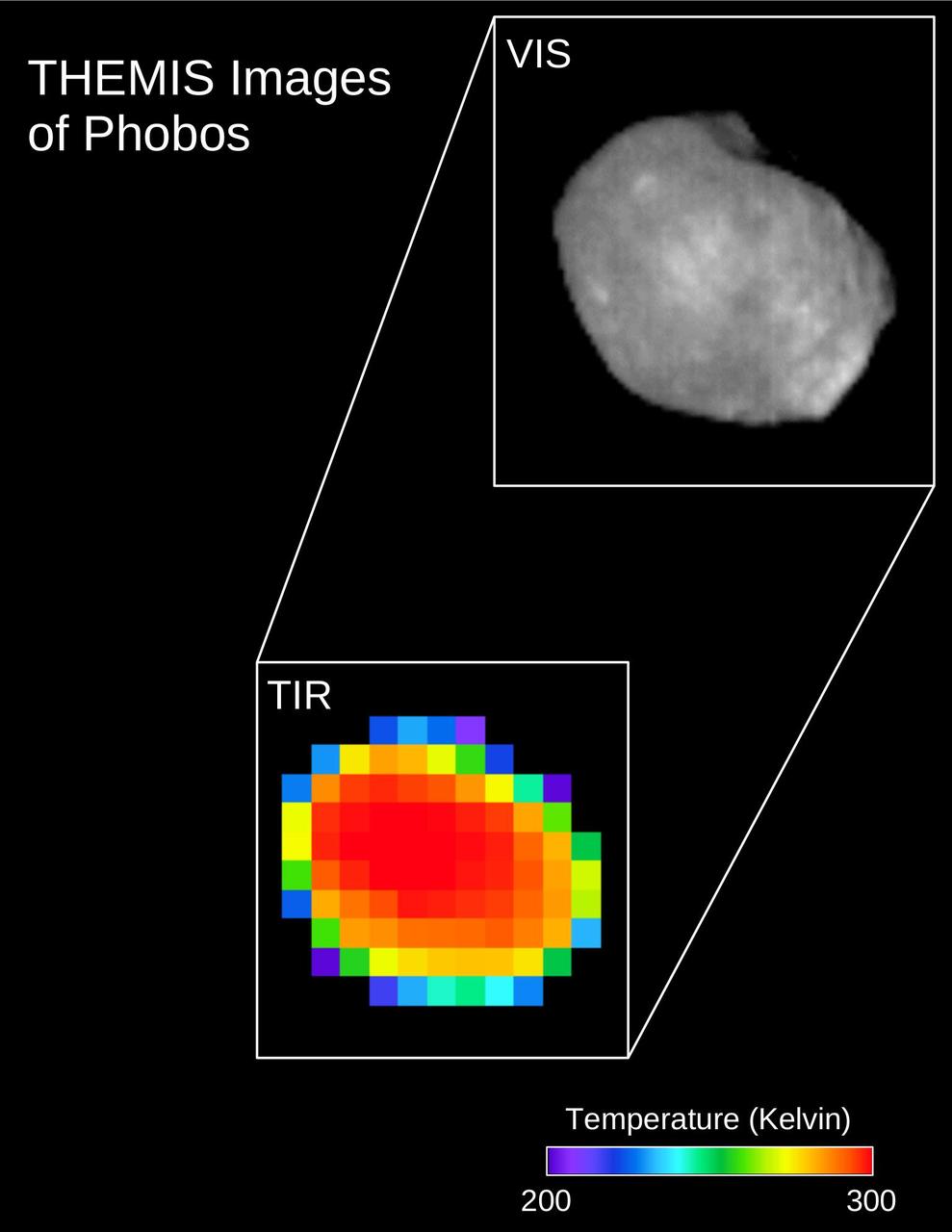
These are two views of the same observation of the Martian moon Phobos taken in both infrared and visible light by NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter using its infrared camera, Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS). The image was taken on April 24, 2019. The top view is what Phobos looked like in the visible light spectrum, as viewed by THEMIS. The bottom view is what it looks like in infrared, which reveals temperature differences. The warmest temperatures are in the center, and the coolest are on the outer edge. A scale bar is provided to reflect the temperatures, which range from 200 to 300 degrees Kelvin, or -100 degrees Fahrenheit (-73 Celsius) to 80 degrees Fahrenheit (27 Celsius). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23206
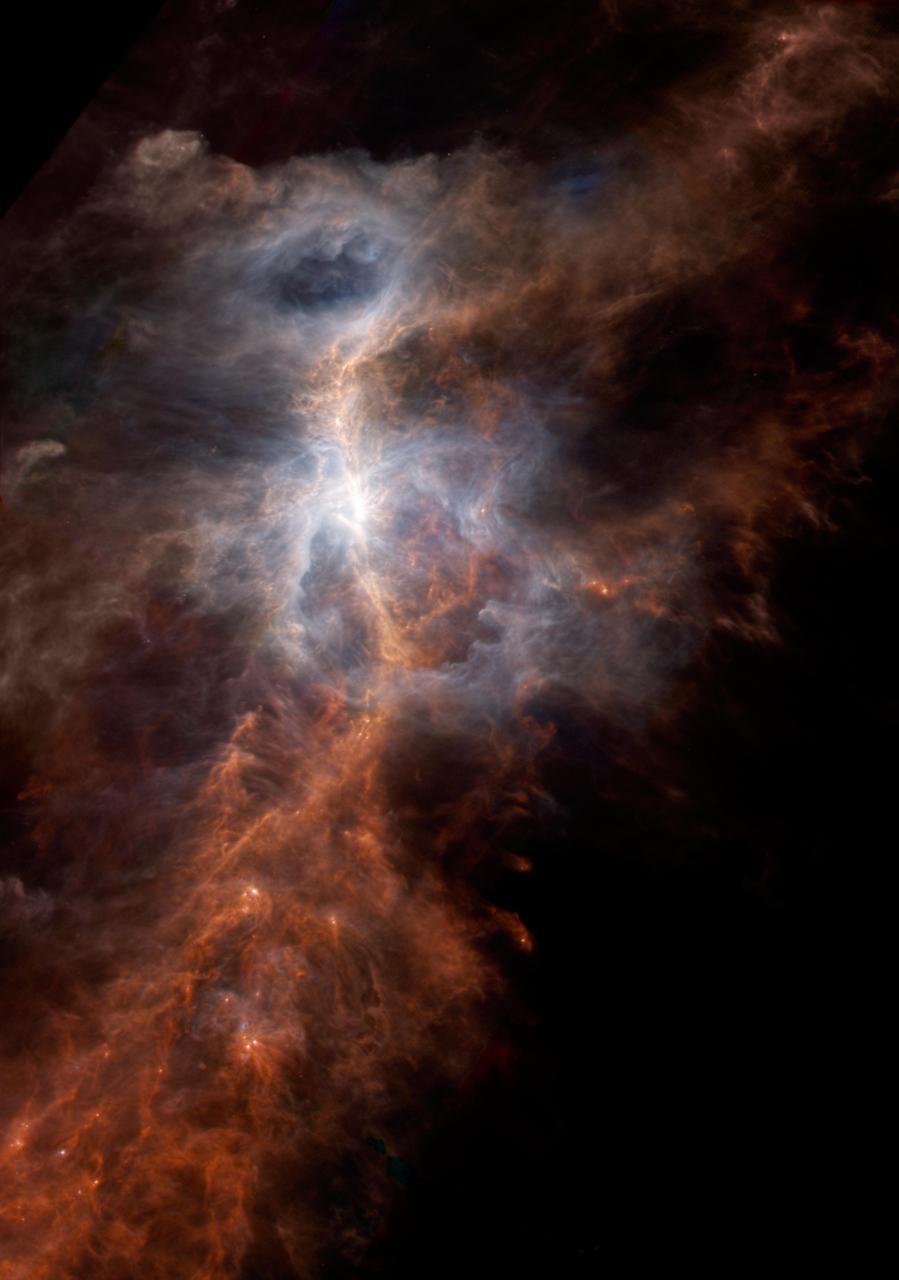

The dusty side of the Sword of Orion is illuminated in this striking infrared image from the European Space Agency's Hershel Space Observatory. This immense nebula is the closest large region of star formation, situated about 1,500 light years away in the constellation of Orion. The parts that are easily observed in visible light, known alternatively as the Orion Nebula or Messier 42, correspond to the light blue regions. This is the glow from the warmest dust, illuminated by clusters of hot stars that have only recently been born in this chaotic region. The red spine of material running from corner to corner reveals colder, denser filaments of dust and gas that are scattered throughout the Orion nebula. In visible light this would be a dark, opaque feature, hiding the reservoir of material from which stars have recently formed and will continue to form in the future. Herschel data from the PACS instrument observations, at wavelengths of 100 and 160 microns, is displayed in blue and green, respectively, while SPIRE 250-micron data is shown in red. Within the inset image, the emission from ionized carbon atoms (C+), overlaid in yellow, was isolated and mapped out from spectrographic data obtained by the HIFI instrument. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21073
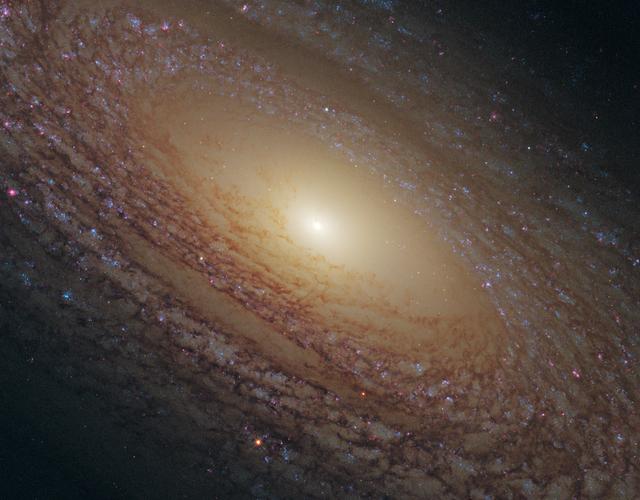

NASA image release Feb. 17, 2011 <b>To see a hd vidoe of this sprial galaxy go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5453173577/">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5453173577/</a></b> The Hubble Space Telescope revealed this majestic disk of stars and dust lanes in this view of the spiral galaxy NGC 2841. A bright cusp of starlight marks the galaxy's center. Spiraling outward are dust lanes that are silhouetted against the population of whitish middle-aged stars. Much younger blue stars trace the spiral arms. Notably missing are pinkish emission nebulae indicative of new star birth. It is likely that the radiation and supersonic winds from fiery, super-hot, young blue stars cleared out the remaining gas (which glows pink), and hence shut down further star formation in the regions in which they were born. NGC 2841 currently has a relatively low star formation rate compared to other spirals that are ablaze with emission nebulae. NGC 2841 lies 46 million light-years away in the constellation of Ursa Major (The Great Bear). This image was taken in 2010 through four different filters on Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3. Wavelengths range from ultraviolet light through visible light to near-infrared light. NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage (STScI/AURA)-ESA/Hubble Collaboration; Acknowledgment: M. Crockett and S. Kaviraj (Oxford University, UK), R. O’Connell (University of Virginia), B. Whitmore (STScI), and the WFC3 Scientific Oversight Committee <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This map shows the area within NASA's Kennedy Space Center where one of the two solar photovoltaic power generation systems will be built as the result of an agreement between NASA and Florida Power & Light. The agreement is part of a new initiative that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The major facility will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of electrical power, which can serve roughly 3,000 homes. A separate one-megawatt solar power facility will support the electrical needs of the center.
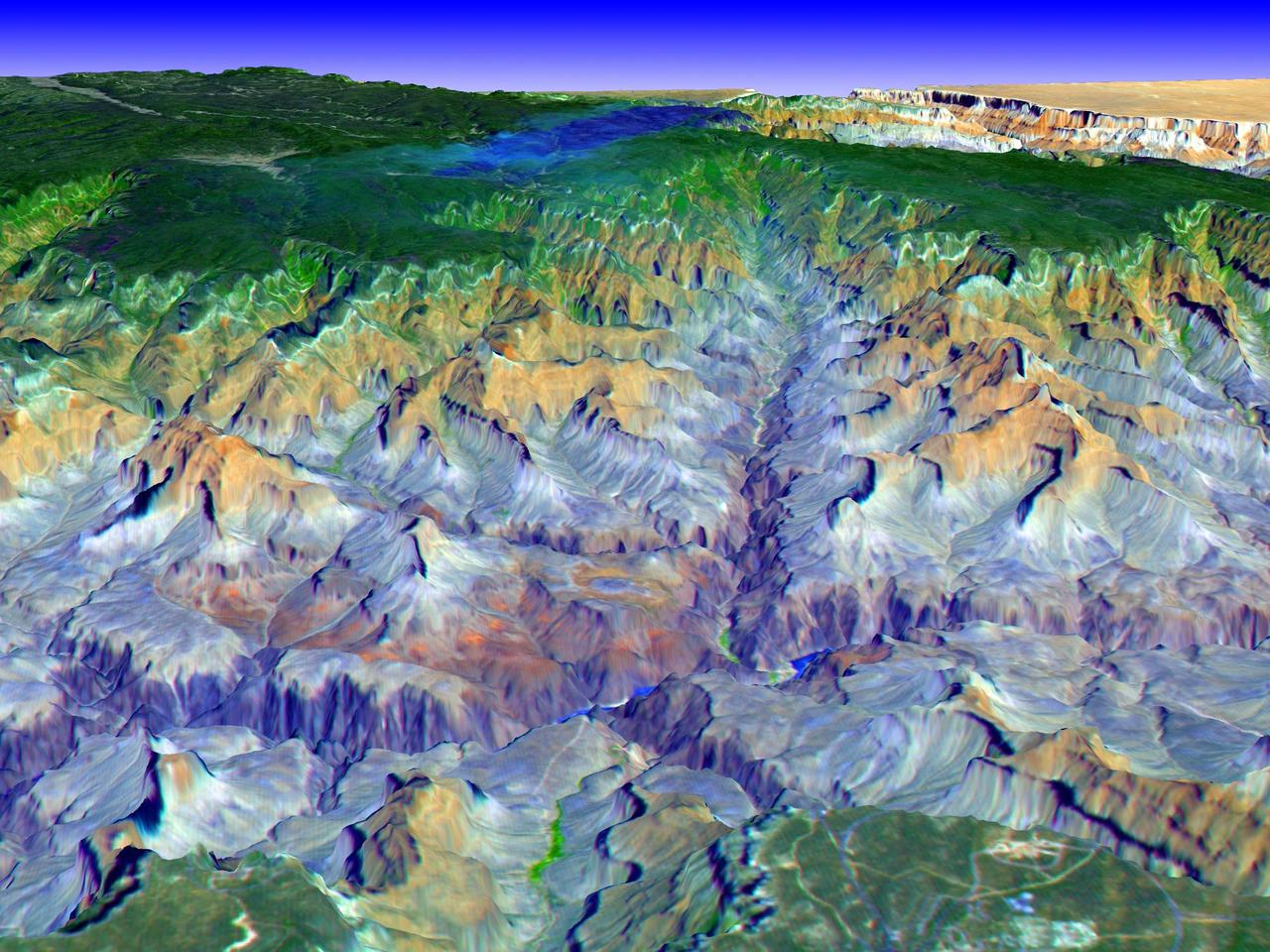
This simulated true color perspective view over the Grand Canyon was created from Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) data acquired on May 12, 2000. The Grand Canyon Village is in the lower foreground; the Bright Angel Trail crosses the Tonto Platform, before dropping down to the Colorado Village and then to the Phantom Ranch (green area across the river). Bright Angel Canyon and the North Rim dominate the view. At the top center of the image the dark blue area with light blue haze is an active forest fire. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01908

This new composite image of stellar cluster NGC 1333 combines X-rays from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory (pink); infrared data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope (red); and optical data from the Digitized Sky Survey and the National Optical Astronomical Observatories' Mayall 4-meter telescope on Kitt Peak near Tucson, Arizona. The Chandra data reveal 95 young stars glowing in X-ray light, 41 of which had not been seen previously using Spitzer because they lacked infrared emission from a surrounding disk. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19347
On Sept. 28, 2017, Manaro Voui volcano on Ambae island in Vanuatu began spewing ash in a moderate eruption, prompting authorities to order the evacuation of all 11,000 residents. This nighttime thermal infrared image from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER), acquired on Oct. 7, shows a hot spot (white) on the volcano's summit crater, but no large eruption. Cold clouds are dark gray, the warmer island is gray, and the ocean, (warmer than the island), is light gray. The image covers an area of 17 by 26 miles (27 by 42.4 kilometers), and is centered at 15.4 degrees south, 167.8 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22045
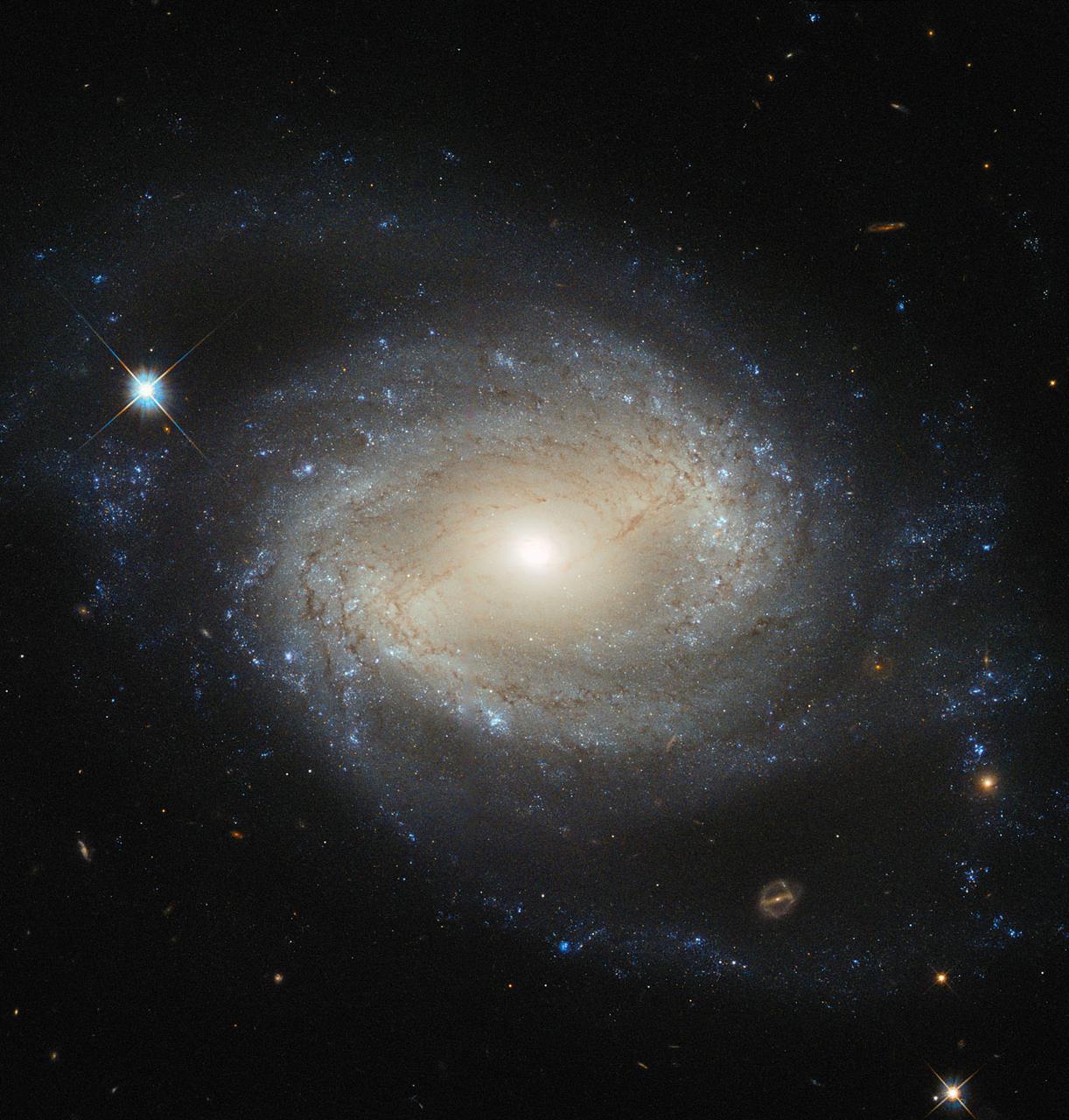

NGC 4639 is a beautiful example of a type of galaxy known as a barred spiral. It lies over 70 million light-years away in the constellation of Virgo and is one of about 1500 galaxies that make up the Virgo Cluster. In this image, taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, one can clearly see the bar running through the bright, round core of the galaxy. Bars are found in around two thirds of spiral galaxies, and are thought to be a natural phase in their evolution. The galaxy’s spiral arms are sprinkled with bright regions of active star formation. Each of these tiny jewels is actually several hundred light-years across and contains hundreds or thousands of newly formed stars. But NGC 4639 also conceals a dark secret in its core — a massive black hole that is consuming the surrounding gas. This is known as an active galactic nucleus (AGN), and is revealed by characteristic features in the spectrum of light from the galaxy and by X-rays produced close to the black hole as the hot gas plunges towards it. Most galaxies are thought to contain a black hole at the centre. NGC 4639 is in fact a very weak example of an AGN, demonstrating that AGNs exist over a large range of activity, from galaxies like NGC 4639 to distant quasars, where the parent galaxy is almost completely dominated by the emissions from the AGN.
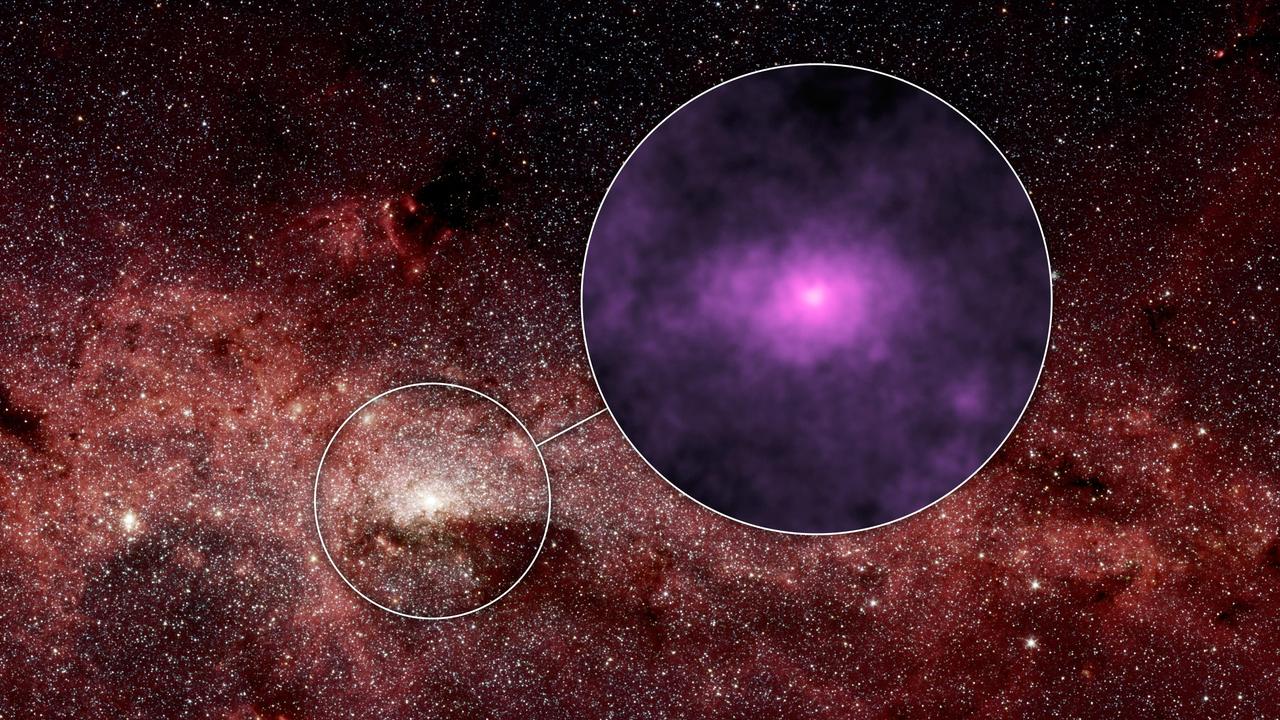
NASA's Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, has captured a new high-energy X-ray view (magenta, Figure 1) of the bustling center of our Milky Way galaxy. The smaller circle shows the area where the NuSTAR image was taken -- the very center of our galaxy, where a giant black hole resides. That region is enlarged to the right, in the larger circle, to show the NuSTAR data. The NuSTAR picture is one of the most detailed ever taken of the center of our galaxy in high-energy X-rays. The X-ray light, normally invisible to our eyes, has been assigned the color magenta. The brightest point of light near the center of the X-ray picture is coming from a spinning dead star, known as a pulsar, which is near the giant black hole. While the pulsar's X-ray emissions were known before, scientists were surprised to find more high-energy X-rays than predicted in the surrounding regions, seen here as the elliptical haze. Astronomers aren't sure what the sources of the extra X-rays are, but one possibility is a population of dead stars. The background picture was captured in infrared light by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. The NuSTAR image has an X-ray energy range of 20 to 40 kiloelectron volts. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19334
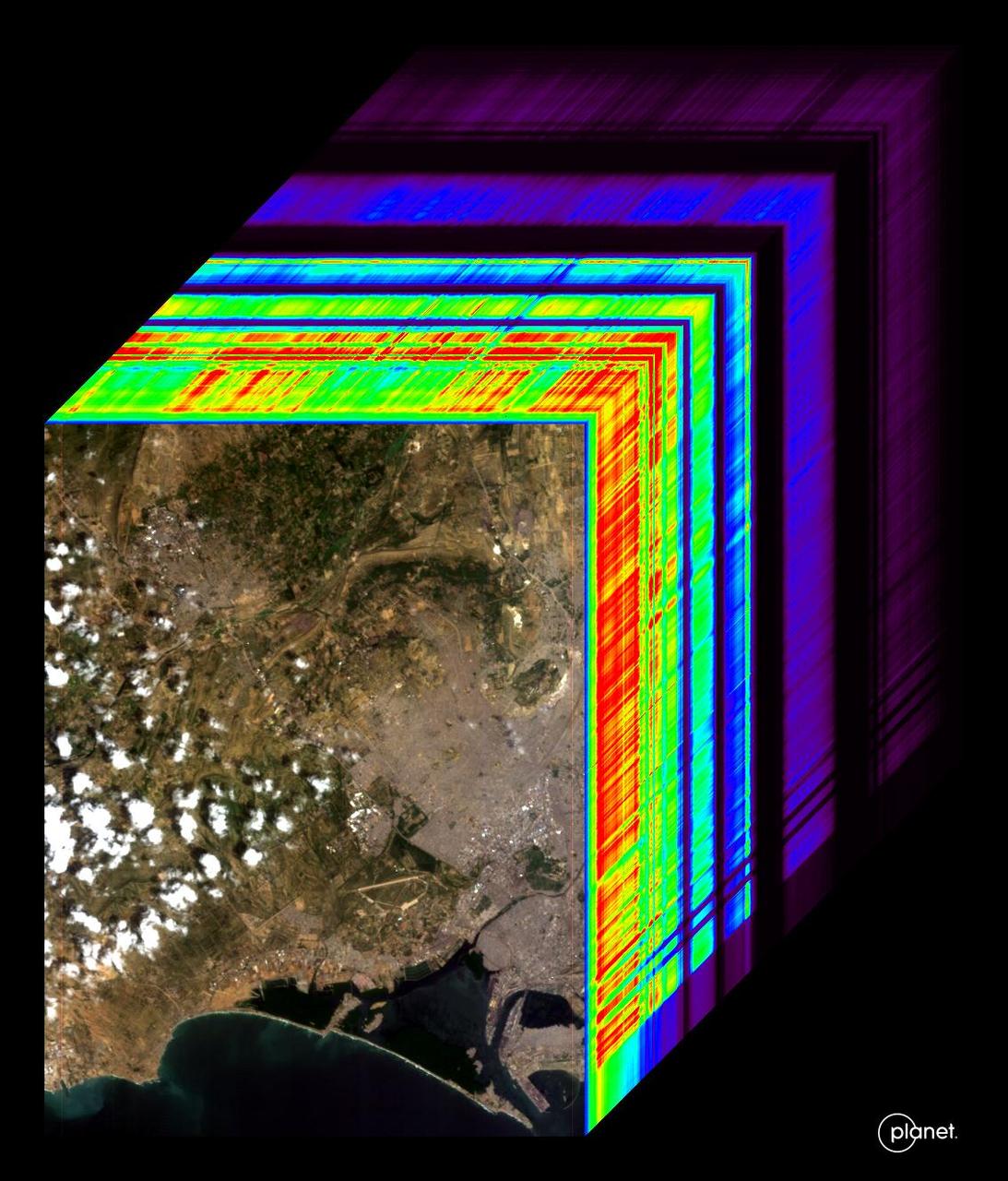
An imaging spectrometer designed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory captured its first data over Karachi, Pakistan, on Sept. 19, 2024. The instrument is aboard the Carbon Mapper Coalition's Tanager-1 satellite, which was built by Planet Labs PBC. An imaging spectrometer can measure hundreds of wavelengths of light that are reflected by Earth's surface. Different compounds in the planet's atmosphere and on the ground absorb different wavelengths of light, leaving spectral "fingerprints" that researchers can identify. The imaging spectrometer aboard Tanager-1 will enable the satellite to measure methane and carbon dioxide point-source emissions, down to the level of individual facilities and equipment, on a global scale. The image at the front of the cube shows a mix of information on land cover and water in the city and surrounding area, including exposed soil (brown), vegetation (green), and clouds. The rainbow colors extending through the main part of the cube are the wavelengths of light from corresponding spots in the front image. Tanager-1, which launched on Aug. 16, 2024, was developed as part of a philanthropically funded public-private coalition led by the nonprofit Carbon Mapper. Planet Labs and JPL are both members of the Carbon Mapper Coalition. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26412
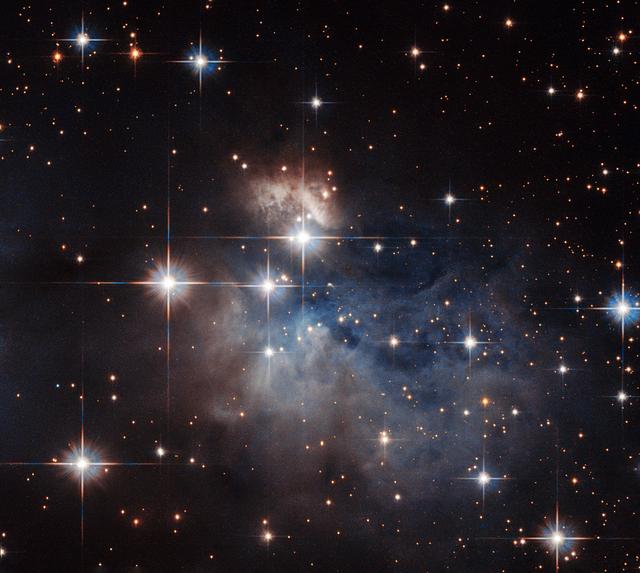

Showcased at the center of this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image is an emission-line star known as IRAS 12196-6300. Located just under 2,300 light-years from Earth, this star displays prominent emission lines, meaning that the star’s light, dispersed into a spectrum, shows up as a rainbow of colors marked with a characteristic pattern of dark and bright lines. The characteristics of these lines, when compared to the “fingerprints” left by particular atoms and molecules, can be used to reveal IRAS 12196-6300’s chemical composition. Under 10 million years old and not yet burning hydrogen at its core, unlike the sun, this star is still in its infancy. Further evidence of IRAS 12196-6300’s youth is provided by the presence of reflection nebulae. These hazy clouds, pictured floating above and below IRAS 12196-6300, are created when light from a star reflects off a high concentration of nearby dust, such as the dusty material still remaining from IRAS 12196-6300’s formation. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Hidden behind a shroud of dust in the constellation Cygnus is an exceptionally bright source of radio emission called DR21. Visible light images reveal no trace of what is happening in this region because of heavy dust obscuration. In fact, visible light is attenuated in DR21 by a factor of more than 10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000, 000,000,000,000 (ten thousand trillion heptillion). New images from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope allow us to peek behind the cosmic veil and pinpoint one of the most massive natal stars yet seen in our Milky Way galaxy. The never-before-seen star is 100,000 times as bright as the Sun. Also revealed for the first time is a powerful outflow of hot gas emanating from this star and bursting through a giant molecular cloud. This image shows a 24-micron image mosaic, obtained with the Multiband Imaging Photometer aboard Spitzer (MIPS). This image maps the cooler infrared emission from interstellar dust found throughout the interstellar medium. The DR21 complex is clearly seen near the center of the strip, which covers about twice the area of the IRAC image. Perhaps the most fascinating feature in this image is a long and shadowy linear filament extending towards the 10 o'clock position of DR21. This jet of cold and dense gas, nearly 50 light-years in extent, appears in silhouette against a warmer background. This filament is too long and massive to be a stellar jet and may have formed from a pre-existing molecular cloud core sculpted by DR21's strong winds. Regardless of its true nature, this jet and the numerous other arcs and wisps of cool dust signify the interstellar turbulence normally unseen by the human eye. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05733
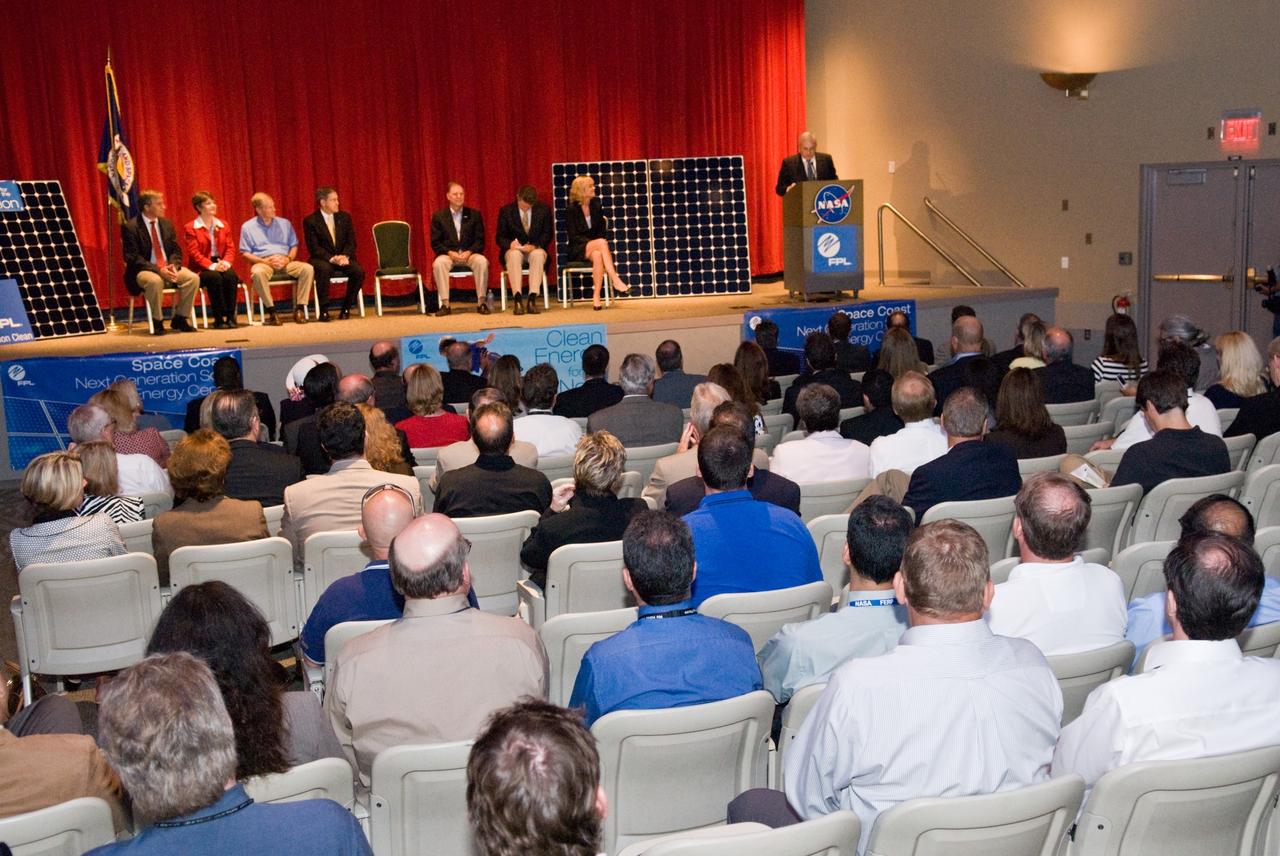

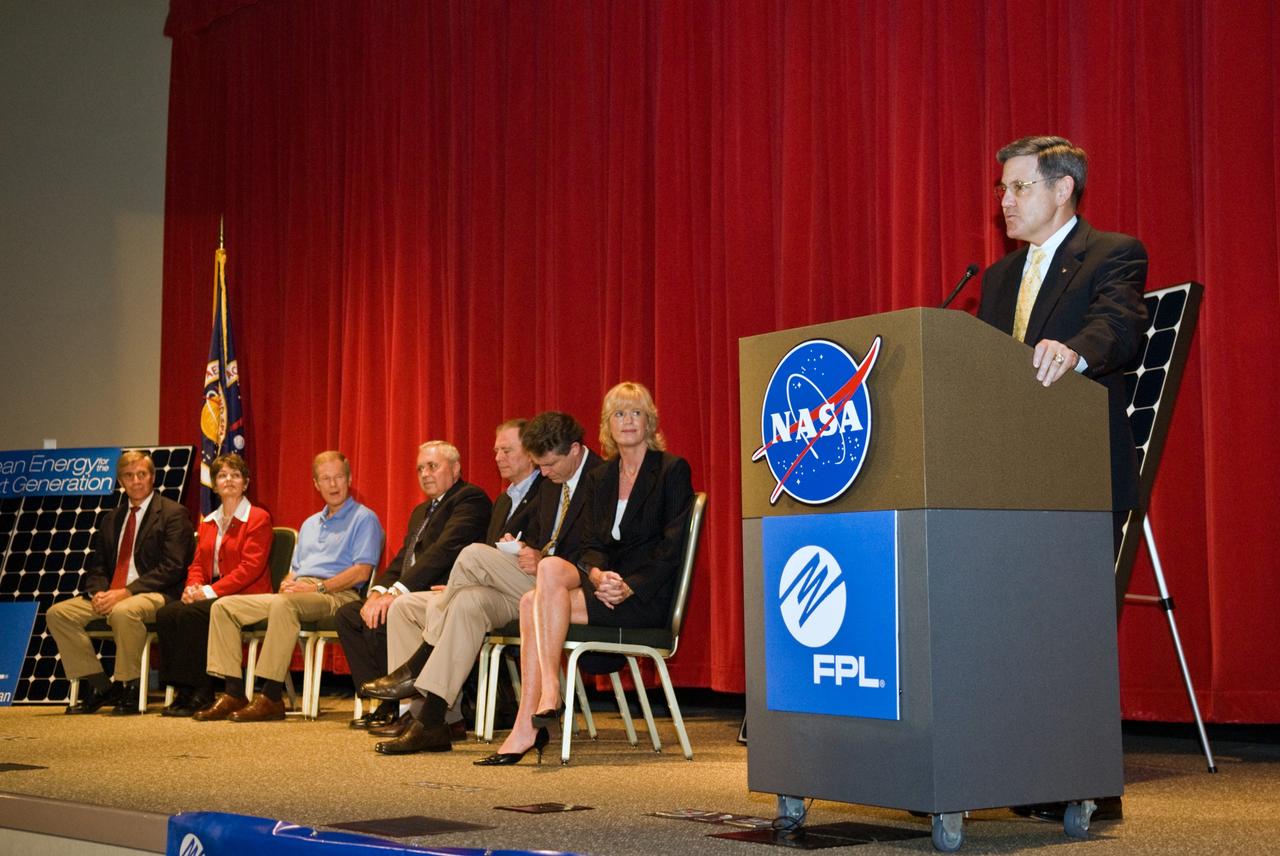
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Armando Olivera, president and CEO of Florida Power & Light, or FPL, speaks to guests at the groundbreaking ceremony for the joint NASA and FPL solar power project at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Others on the stage are, from left, Ed Smeloff with SunPower Corporation, Florida Rep. Suzanne Kosmas, Sen. Bill Nelson, Center Director Bob Cabana, Florida Rep. Bill Posey, Eric Draper, deputy director of Audubon of Florida, and Pam Rauch, vice president of External Affairs for FPL. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
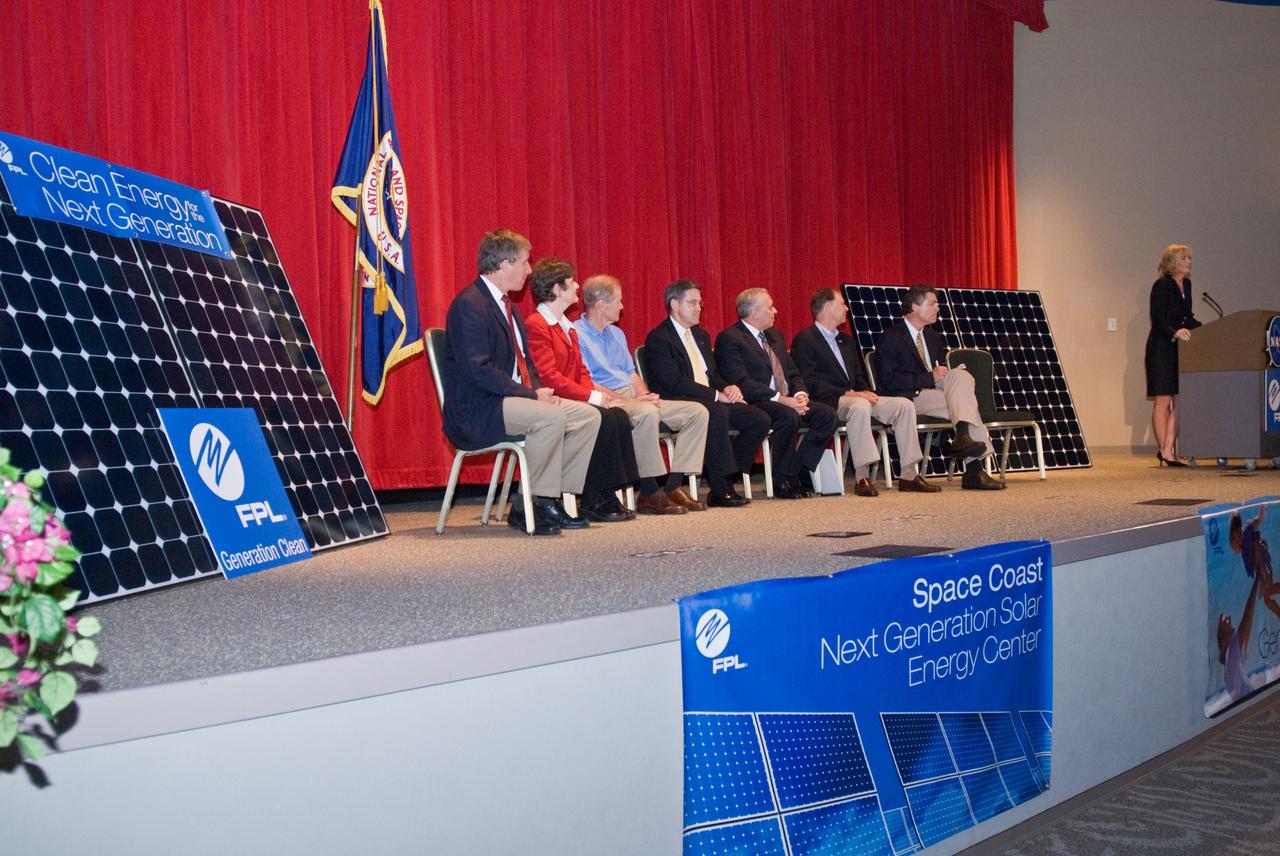

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Pam Rauch, vice president of External Affairs for Florida Power & Light, or FPL, speaks to guests at the groundbreaking ceremony for the joint NASA and FPL solar power project at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Others on the stage are Ed Smeloff with SunPower Corporation, Florida Rep. Suzanne Kosmas, Sen. Bill Nelson, Center Director Bob Cabana, Armando Olivera, president and CEO of FPL, Florida Rep. Bill Posey and Eric Draper, deputy director of Audubon of Florida. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
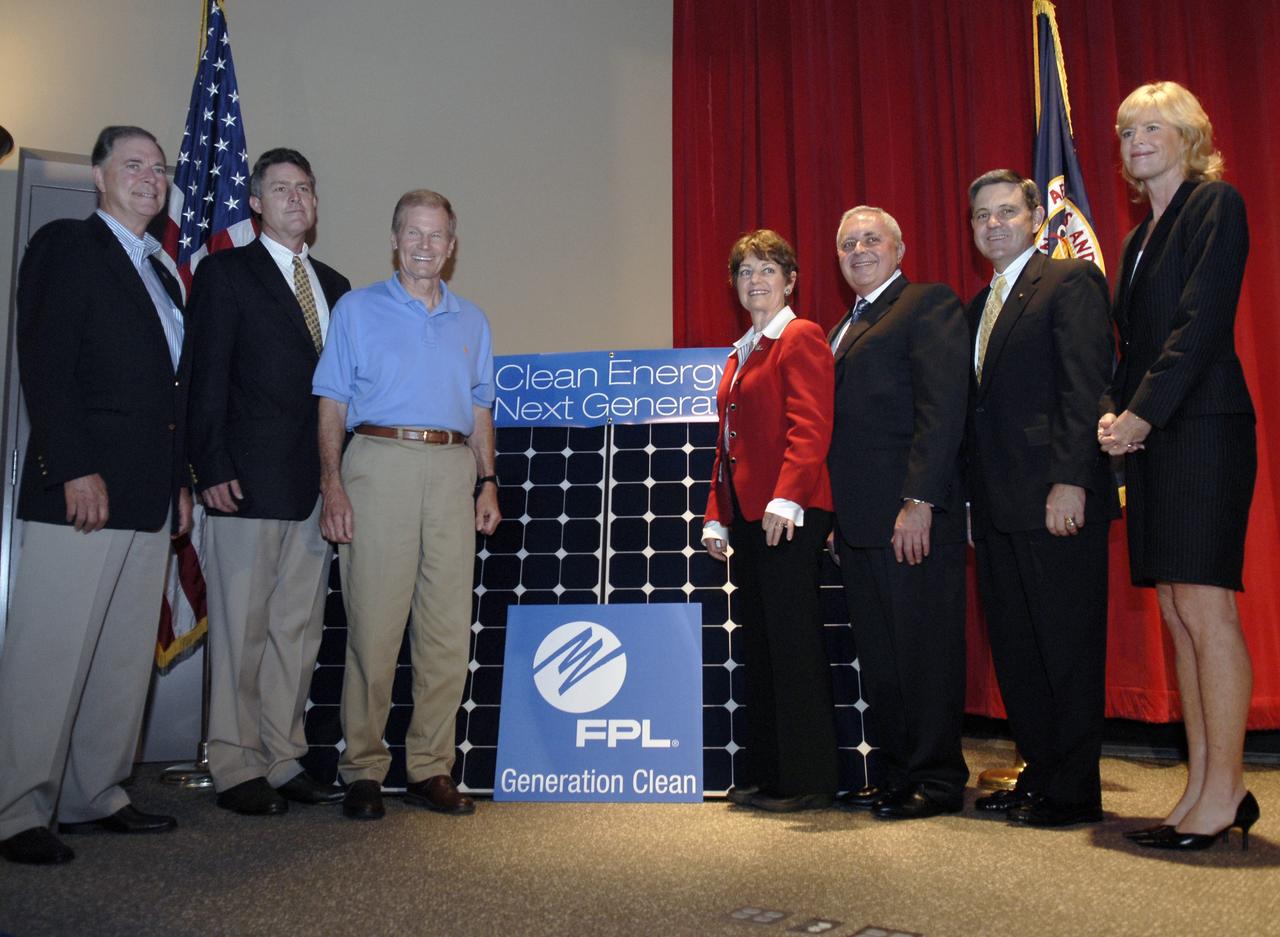

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Gathering on stage for the groundbreaking ceremony for the joint NASA and Florida Power & Light, or FPL, solar power project at NASA's Kennedy Space Center are Florida Rep. Bill Posey, Eric Draper, deputy director of Audubon of Florida, Sen. Bill Nelson, Florida Rep. Suzanne Kosmas, Armando Olivera, president and CEO of FPL, Center Director Bob Cabana and Pam Rauch, vice president of External Affairs for FPL. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
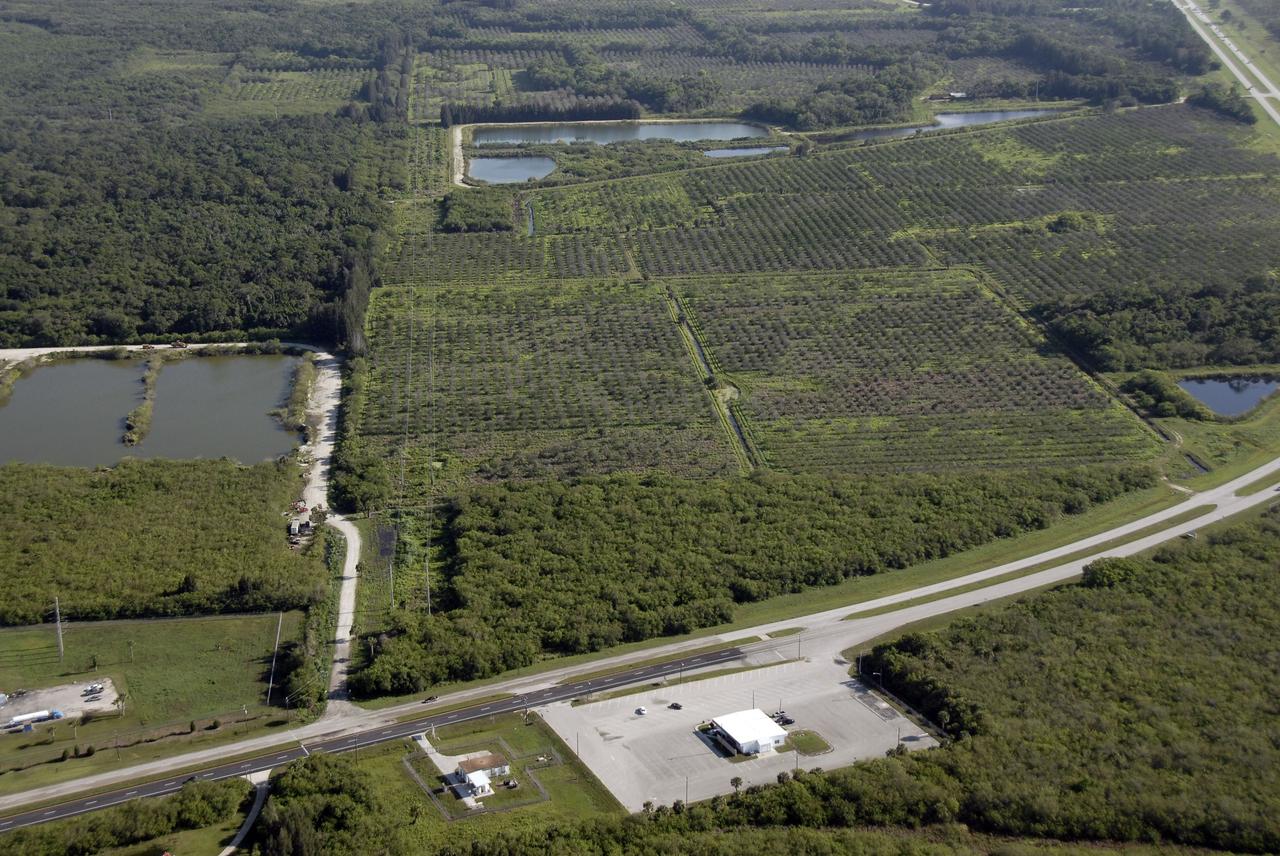

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the site on S.R. 3 on NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where a solar power system will be built. The solar power systems are being constructed by NASA and Florida Power & Light Company as part of a public-private partnership that promotes a clean-energy future. A groundbreaking ceremony took place on May 27 at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One, which will be built on the pictured location, will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
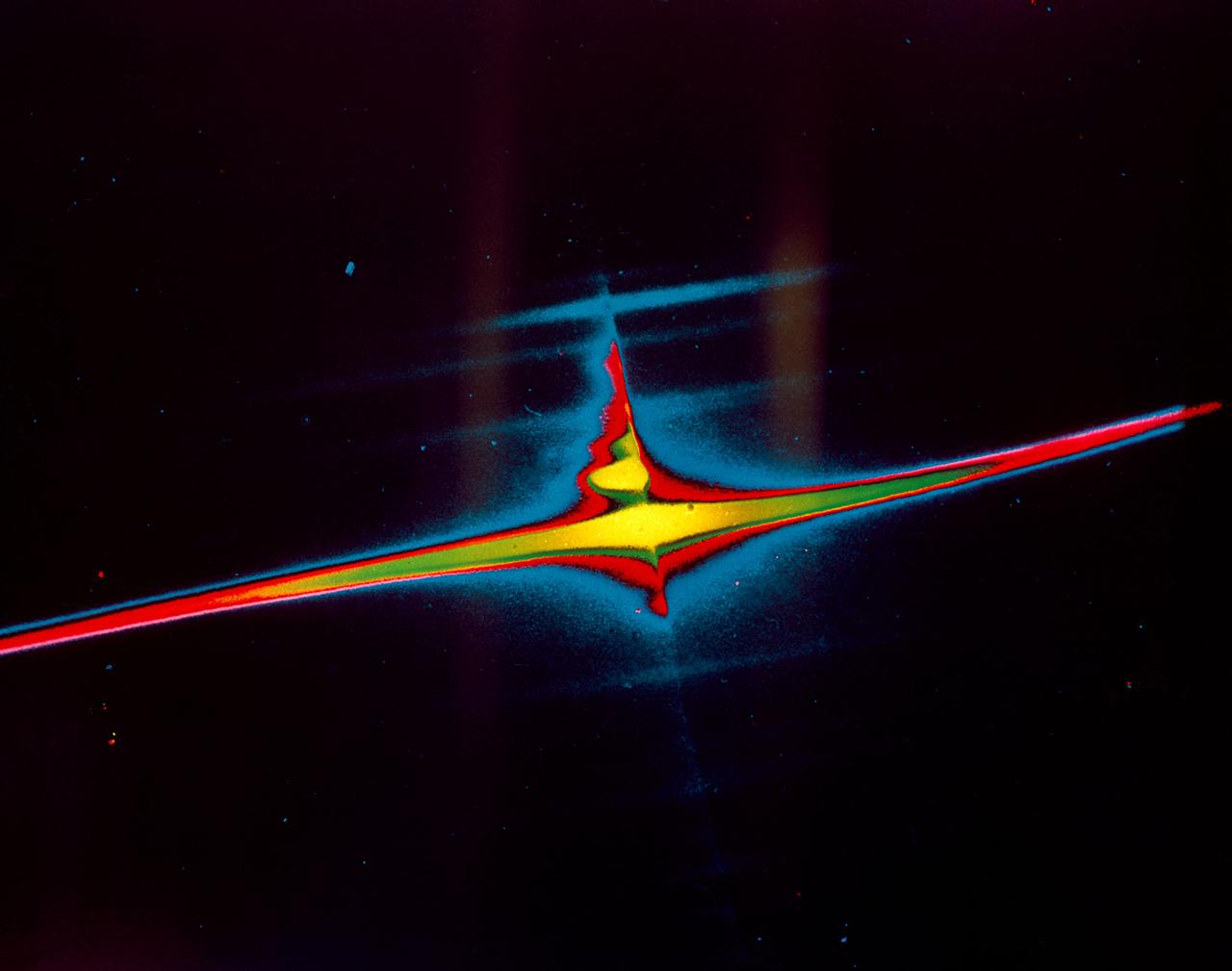
S72-40820 (21 April 1972) --- A color enhancement of a photograph taken on ultra-violet light showing the spectrum of the upper atmosphere of Earth and geocorona. The bright horizontal line is far ultra-violet emission (1216 angstrom) of hydrogen extending 10 degrees (40,000 miles) either side of Earth. The knobby vertical line shows several ultra-violet emissions from Earth's sunlit atmosphere, each "lump" being produced by one type gas (oxygen, nitrogen, helium, etc.). The spectral dispersion is about 10 angstrom per millimeter on this enlargement. The UV camera/spectrograph was operated on the lunar surface by astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission. It was designed and built at the Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, D.C. While astronauts Young and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands region of the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Center Director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bob Cabana addresses guests at the groundbreaking ceremony for the joint NASA and Florida Power & Light, or FPL, solar power project at Kennedy. Others on the stage are (from left) Ed Smeloff with SunPower Corporation, Florida Rep. Suzanne Kosmas, Sen. Bill Nelson, Armando Olivera, president and CEO of FPL, Florida Rep. Bill Posey, Eric Draper, deputy director of Audubon of Florida, and Pam Rauch, vice president of External Affairs for FPL. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
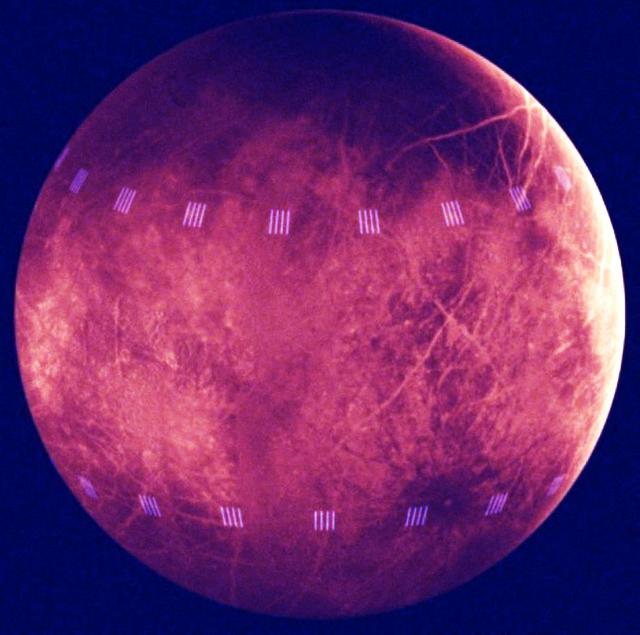
This image is a simulation of how NASA's Europa Clipper will understand which areas of the Jovian moon Europa are warm and active by studying the moon's thermal emissions. Scientists based this image on a model of data from NASA's Galileo mission and data from an instrument on NASA's Cassini mission that studied warm regions of Saturn's moon Enceladus where jets of water ice and organic chemicals spray out from vents in the icy surface. Europa Clipper's Europa Thermal Emission Imaging System, or E-THEMIS, will take both daytime and nighttime observations of Europa. The light pink vertical stripes simulate the warm vents seen on the surface of Enceladus, if they were viewed on Europa in the night. If Europa has warm spots like Enceladus, E-THEMIS is expected to detect such areas on Europa, even from a distance. Europa Clipper will get as close as 16 miles (25 kilometers) from the moon's surface, resulting in observations at much higher resolution. Europa Clipper's three main science objectives are to determine the thickness of the moon's icy shell and its interactions with the ocean below, to investigate its composition, and to characterize its geology. The mission's detailed exploration of Europa will help scientists better understand the astrobiological potential for habitable worlds beyond our planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26105

An expanded view of comet C/2006 W3 (Christensen) is shown here. The WISE spacecraft observed this comet on April 20th, 2010 as it traveled through the constellation Sagittarius. Comet Christensen was nearly 370 million miles (600 million kilometers) from Earth at the time. The extent of the dust, about a tenth of a degree across in this image, is about 2/3rds the diameter of the sun. The red contours show the signal from the gas emission observed by the WISE spacecraft in the 4.6 micron wavelength channel, which contains carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) emission lines. The strength of the 4.6 micron signal indicates over half a metric ton per second of CO or CO2 was emitted from this comet at the time of the observations. The WISE spacecraft was put into hibernation in 2011 upon completing its goal of surveying the entire sky in infrared light. WISE cataloged three quarters of a billion objects, including asteroids, stars and galaxies. In August 2013, NASA decided to reinstate the spacecraft on a mission to find and characterize more asteroids. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20119

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the site in the Industrial Area of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where a solar power system will be built. The solar power systems are being constructed by NASA and Florida Power & Light Company as part of a public-private partnership that promotes a clean-energy future. A groundbreaking ceremony took place on May 27 at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second, which will be built on the pictured location, is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This is a rendering of one of two proposed solar power systems that NASA and Florida Power & Light Company are beginning to construct on NASA's Kennedy Space Center as part of a public-private partnership that promotes a clean-energy future. A groundbreaking ceremony took place on May 27 at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo courtesy of FPL
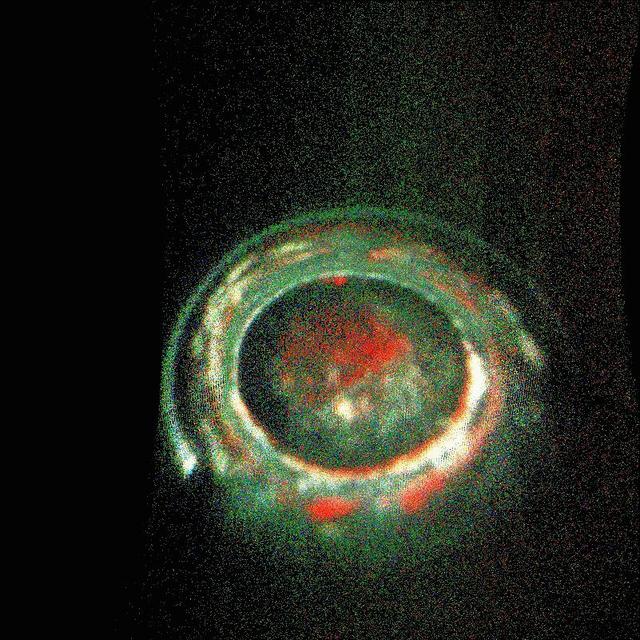
The complexity and richness of Jupiter's "southern lights" (also known as auroras) are on display in this animation of false-color maps from NASA's Juno spacecraft. Auroras result when energetic electrons from the magnetosphere crash into the molecular hydrogen in the Jovian upper atmosphere. The data for this animation were obtained by Juno's Ultraviolet Spectrograph. The images are centered on the south pole and extend to latitudes of 50 degrees south. Each frame of the animation includes data from 30 consecutive Juno spins (about 15 minutes), just after the spacecraft's fifth close approach to Jupiter on February 2, 2017. The eight frames of the animation cover the period from 13:40 to 15:40 UTC at Juno. During that time, the spacecraft was receding from 35,000 miles to 153,900 miles (56,300 kilometers to 247,600 kilometers) above the aurora; this large change in distance accounts for the increasing fuzziness of the features. Jupiter's prime meridian is toward the bottom, and longitudes increase counterclockwise from there. The sun was located near the bottom at the start of the animation, but was off to the right by the end of the two-hour period. The red coloring of some of the features indicates that those emissions came from deeper in Jupiter's atmosphere; green and white indicate emissions from higher up in the atmosphere. Animations are available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21643
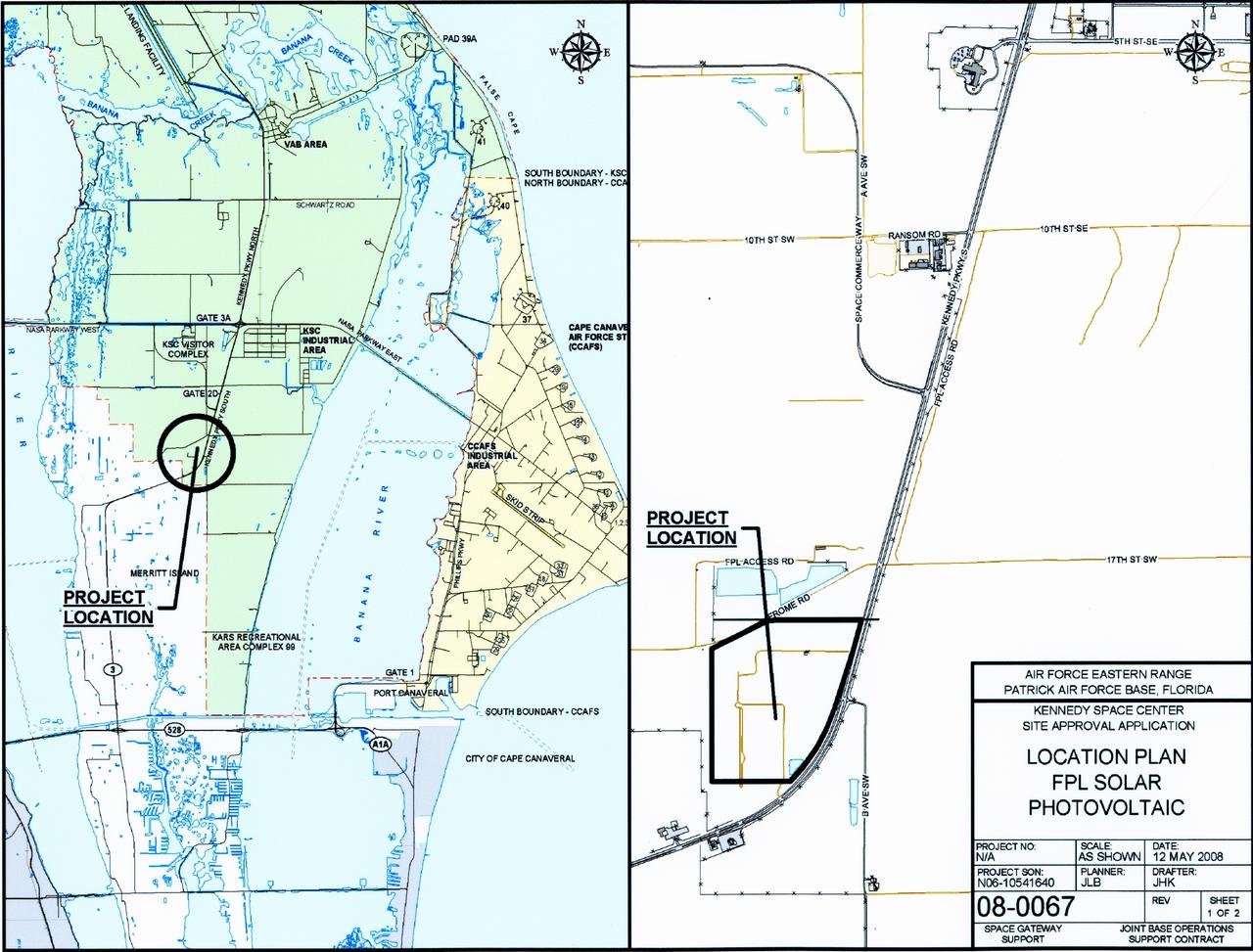
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – These maps show one of the locations of the proposed solar power systems that NASA and Florida Power & Light Company are beginning to construct on NASA's Kennedy Space Center as part of a public-private partnership that promotes a clean-energy future. A groundbreaking ceremony took place on May 27 at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. FPL, Florida's largest electric utility, will build and maintain two solar photovoltaic power generation systems at Kennedy. One will produce an estimated 10 megawatts of emissions-free power for FPL customers, which is enough energy to serve roughly 1,100 homes. The second is a one-megawatt solar power facility that will provide renewable energy directly to Kennedy. The FPL facilities at NASA will help provide Florida residents and America's space program with new sources of clean energy that will cut reliance on fossil fuels and improve the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The one megawatt facility also will help NASA meet its goal for use of power generated from renewable energy. Photo courtesy of FPL
![In celebration of the International Year of Astronomy 2009, NASA's Great Observatories -- the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory -- have produced a matched trio of images of the central region of our Milky Way galaxy. Each image shows the telescope's different wavelength view of the galactic center region, illustrating the unique science each observatory conducts. In this spectacular image, observations using infrared light and X-ray light see through the obscuring dust and reveal the intense activity near the galactic core. Note that the center of the galaxy is located within the bright white region to the right of and just below the middle of the image. The entire image width covers about one-half a degree, about the same angular width as the full moon. Spitzer's infrared-light observations provide a detailed and spectacular view of the galactic center region [Figure 1 (top frame of poster)]. The swirling core of our galaxy harbors hundreds of thousands of stars that cannot be seen in visible light. These stars heat the nearby gas and dust. These dusty clouds glow in infrared light and reveal their often dramatic shapes. Some of these clouds harbor stellar nurseries that are forming new generations of stars. Like the downtown of a large city, the center of our galaxy is a crowded, active, and vibrant place. Although best known for its visible-light images, Hubble also observes over a limited range of infrared light [Figure 2 (middle frame of poster)]. The galactic center is marked by the bright patch in the lower right. Along the left side are large arcs of warm gas that have been heated by clusters of bright massive stars. In addition, Hubble uncovered many more massive stars across the region. Winds and radiation from these stars create the complex structures seen in the gas throughout the image.This sweeping panorama is one of the sharpest infrared pictures ever made of the galactic center region. X-rays detected by Chandra expose a wealth of exotic objects and high-energy features [Figure 3 (bottom frame of poster)]. In this image, pink represents lower energy X-rays and blue indicates higher energy. Hundreds of small dots show emission from material around black holes and other dense stellar objects. A supermassive black hole -- some four million times more massive than the Sun -- resides within the bright region in the lower right. The diffuse X-ray light comes from gas heated to millions of degrees by outflows from the supermassive black hole, winds from giant stars, and stellar explosions. This central region is the most energetic place in our galaxy. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12348](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA12348/PIA12348~medium.jpg)
In celebration of the International Year of Astronomy 2009, NASA's Great Observatories -- the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Chandra X-ray Observatory -- have produced a matched trio of images of the central region of our Milky Way galaxy. Each image shows the telescope's different wavelength view of the galactic center region, illustrating the unique science each observatory conducts. In this spectacular image, observations using infrared light and X-ray light see through the obscuring dust and reveal the intense activity near the galactic core. Note that the center of the galaxy is located within the bright white region to the right of and just below the middle of the image. The entire image width covers about one-half a degree, about the same angular width as the full moon. Spitzer's infrared-light observations provide a detailed and spectacular view of the galactic center region [Figure 1 (top frame of poster)]. The swirling core of our galaxy harbors hundreds of thousands of stars that cannot be seen in visible light. These stars heat the nearby gas and dust. These dusty clouds glow in infrared light and reveal their often dramatic shapes. Some of these clouds harbor stellar nurseries that are forming new generations of stars. Like the downtown of a large city, the center of our galaxy is a crowded, active, and vibrant place. Although best known for its visible-light images, Hubble also observes over a limited range of infrared light [Figure 2 (middle frame of poster)]. The galactic center is marked by the bright patch in the lower right. Along the left side are large arcs of warm gas that have been heated by clusters of bright massive stars. In addition, Hubble uncovered many more massive stars across the region. Winds and radiation from these stars create the complex structures seen in the gas throughout the image.This sweeping panorama is one of the sharpest infrared pictures ever made of the galactic center region. X-rays detected by Chandra expose a wealth of exotic objects and high-energy features [Figure 3 (bottom frame of poster)]. In this image, pink represents lower energy X-rays and blue indicates higher energy. Hundreds of small dots show emission from material around black holes and other dense stellar objects. A supermassive black hole -- some four million times more massive than the Sun -- resides within the bright region in the lower right. The diffuse X-ray light comes from gas heated to millions of degrees by outflows from the supermassive black hole, winds from giant stars, and stellar explosions. This central region is the most energetic place in our galaxy. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA12348

This majestic false-color image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows the "mountains" where stars are born. Dubbed "Mountains of Creation" by Spitzer scientists, these towering pillars of cool gas and dust are illuminated at their tips with light from warm embryonic stars. The new infrared picture is reminiscent of Hubble's iconic visible-light image of the Eagle Nebula, which also features a star-forming region, or nebula, that is being sculpted into pillars by radiation and winds from hot, massive stars. The pillars in the Spitzer image are part of a region called W5, in the Cassiopeia constellation 7,000 light-years away and 50 light-years across. They are more than 10 times in the size of those in the Eagle Nebula (shown to scale here). The Spitzer's view differs from Hubble's because infrared light penetrates dust, whereas visible light is blocked by it. In the Spitzer image, hundreds of forming stars (white/yellow) can seen for the first time inside the central pillar, and dozens inside the tall pillar to the left. Scientists believe these star clusters were triggered into existence by radiation and winds from an "initiator" star more than 10 times the mass of our Sun. This star is not pictured, but the finger-like pillars "point" toward its location above the image frame. The Spitzer picture also reveals stars (blue) a bit older than the ones in the pillar tips in the evacuated areas between the clouds. Scientists believe these stars were born around the same time as the massive initiator star not pictured. A third group of young stars occupies the bright area below the central pillar. It is not known whether these stars formed in a related or separate event. Some of the blue dots are foreground stars that are not members of this nebula. The red color in the Spitzer image represents organic molecules known as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. These building blocks of life are often found in star-forming clouds of gas and dust. Like small dust grains, they are heated by the light from the young stars, then emit energy in infrared wavelengths. This image was taken by the infrared array camera on Spitzer. It is a 4-color composite of infrared light, showing emissions from wavelengths of 3.6 microns (blue), 4.5 microns (green), 5.8 microns (orange), and 8.0 microns (red). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03096
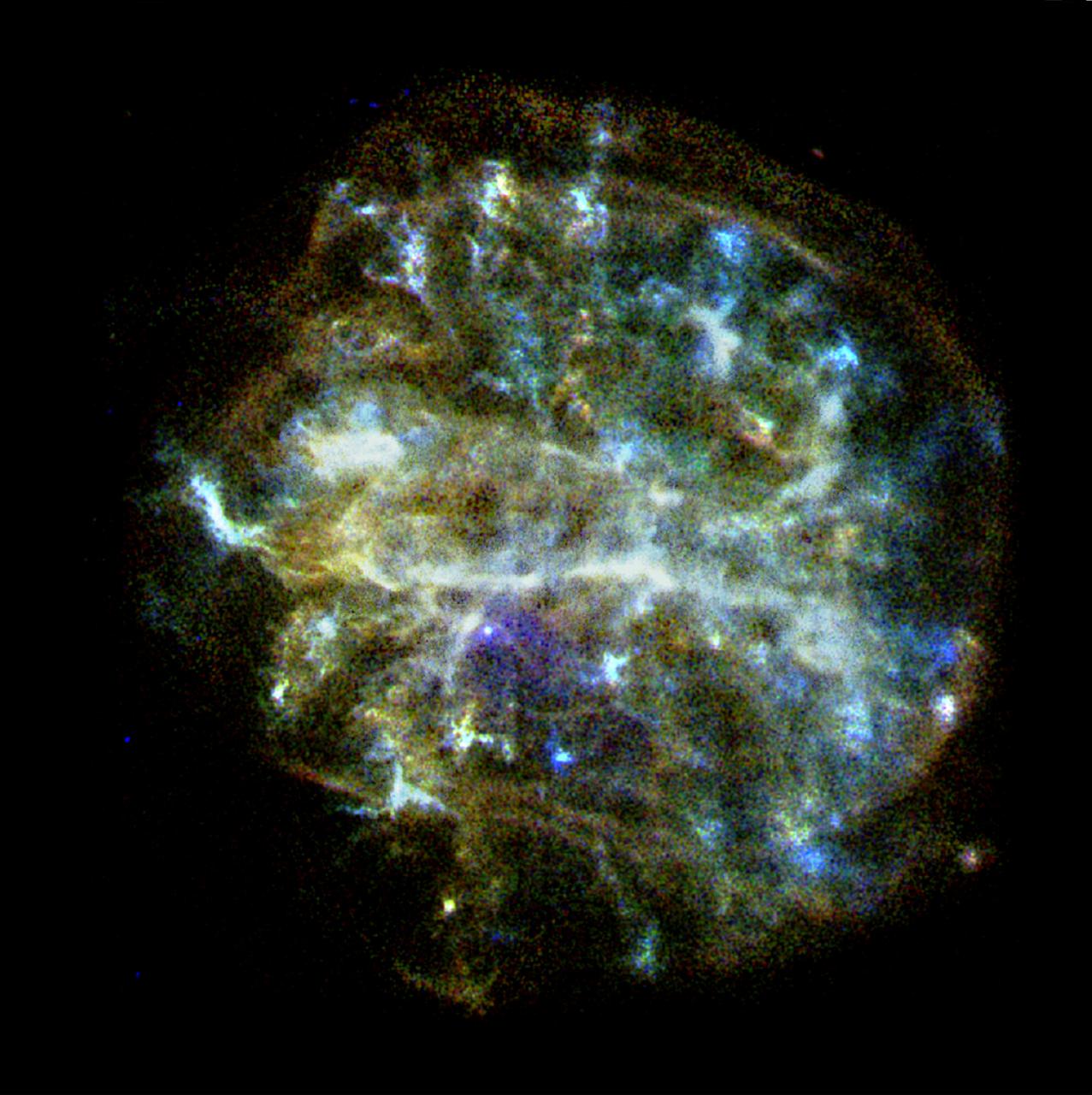
The Chandra X-Ray Observatory has captured this spectacular image of G292.0+1.8, a young, oxygen-rich supernova remnant with a pulsar at its center surrounded by outflowing material. This image shows a rapidly expanding shell of gas that is 36 light-years across and contains large amounts of elements such as oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon and sulfur. Embedded in this cloud of multimillion-degree gas is a key piece of evidence linking neutron stars and supernovae produced by the collapse of massive stars. With an age estimated at 1,600 years, G292.0+1.8 is one of three known oxygen-rich supernovae in our galaxy. These supernovae are of great interest to astronomers because they are one of the primary sources of the heavy elements necessary to form planets and people. Scattered through the image are bluish knots of emissions containing material that is highly enriched in newly created oxygen, neon, and magnesium produced deep within the original star and ejected by the supernova explosion.
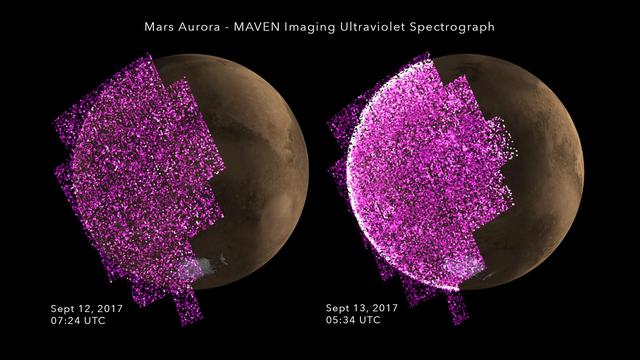
These images show the sudden appearance of a bright aurora on Mars during a solar storm in September 2017. The purple-white color scheme shows the intensity of ultraviolet light seen on Mars' night side before (left) and during (right) the event. A simulated image of Mars for the same time and orientation has been added, with the dayside crescent visible on the right. The auroral emission appears brightest at the edges of the planet where the line of sight passes along the length of the glowing atmosphere layer. The data are from observations by the Imaging Ultraviolet Spectrograph instrument (IUVS) on NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution orbiter, or MAVEN. Note that, unlike auroras on Earth, the Martian aurora is not concentrated at the planet's polar regions. This is because Mars has no strong magnetic field like Earth's to concentrate the aurora near the poles. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21855

The Soberanes fire, in Central California near Big Sur, had grown to more than 67,000 acres when the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra spacecraft captured this image on Aug. 6, 2016. More than 4,800 personnel are battling the blaze, which is now 50 percent contained. The fire has destroyed 57 homes and 11 outbuildings and caused one fatality. Evacuation orders are still in effect for a number of nearby communities. The fire was caused by an illegal unattended campfire. Vegetation is depicted in red colors; burned areas are dark grey; clouds are white; smoke and ash are light grey. Yellow indicates active fires, detected on ASTER's thermal infrared channels. The image covers an area of 19 by 26 miles (30 by 42 kilometers), and is located at 36.4 degrees north, 121.8 degrees west. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20725

Astronomers have discovered a vast cloud of high-energy particles called a wind nebula around a rare ultra-magnetic neutron star, or magnetar, for the first time. The find offers a unique window into the properties, environment and outburst history of magnetars, which are the strongest magnets in the universe. A neutron star is the crushed core of a massive star that ran out of fuel, collapsed under its own weight, and exploded as a supernova. Each one compresses the equivalent mass of half a million Earths into a ball just 12 miles (20 kilometers) across, or about the length of New York's Manhattan Island. Neutron stars are most commonly found as pulsars, which produce radio, visible light, X-rays and gamma rays at various locations in their surrounding magnetic fields. When a pulsar spins these regions in our direction, astronomers detect pulses of emission, hence the name. Credit: ESA/XMM-Newton/Younes et al. 2016

Phobos and Deimos, the moons of Mars, are seen by the Mars Odyssey orbiter's Thermal Emission Imaging System, or THEMIS, camera. The images were taken in visible-wavelength light. THEMIS also recorded thermal-infrared imagery in the same scan. The apparent motion is due to progression of the camera's pointing during the 17-second span of the February 15, 2018, observation, not from motion of the two moons. This was the second observation of Phobos by Mars Odyssey; the first was on September 29, 2017. Researchers have been using THEMIS to examine Mars since early 2002, but the maneuver turning the orbiter around to point the camera at Phobos was developed only recently. The distance to Phobos from Odyssey during the observation was about 3,489 miles (5,615 kilometers). The distance to Deimos from Odyssey during the observation was about 12,222 miles (19,670 kilometers). An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22248
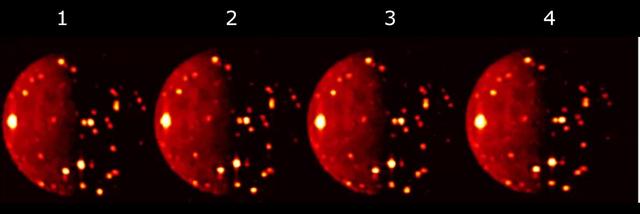
Data used to generate this composite image of volcanic activity on the Jovian moon Io was obtained by the JIRAM (Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper) instrument aboard NASA's Juno spacecraft during a flyby of the moon on Oct. 16, 2021. JIRAM took the four images over a short time interval to observe volcanic activity on the moon from different view angles. JIRAM data collected over time could provide information on changes to Io's surface, including the number of active volcanoes or variations in their intensity. JIRAM "sees" infrared light not visible to the human eye. In this composite image, the measurements of thermal emission radiated from the planet were in the infrared wavelength of around 5 microns. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25886

The Thomas fire, west of Los Angeles, continues to advance to the west and north and is threatening a number of coastal communities, including Santa Barbara. It is now the fifth largest wildfire in modern California history. According to CAL FIRE, as of midday Dec. 11, the fire had consumed more than 230,000 acres and was 15 percent contained. The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite captured this image on Dec. 10. The image depicts vegetation in red, smoke in light brown, burned areas in dark grey, and active fires in yellow, as detected by the thermal infrared bands. The image covers an area of 14.3 by 19.6 miles (23 by 31.5 kilometers), and is located at 34.5 degrees north, 119.4 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22122

NASA's ASTER (Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer)captured these images of Guatemala's Fuego volcano on Nov. 24, following a recent eruption. The main image shows the lava flows on the flanks of Fuego (upper left corner) in light gray. Vegetation is shown in red, clouds in white, and city and fields in dark gray. A thick ash plume rising from the peak of the volcano and more diffuse ash clouds over the southern part of the scene are also visible. The thermal infrared composite highlights the ash clouds in orange, with a dark orange cloud over the summit where the ash is thickest. White areas are relatively warmer; Fuego's summit is bright white at the active crater. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22820
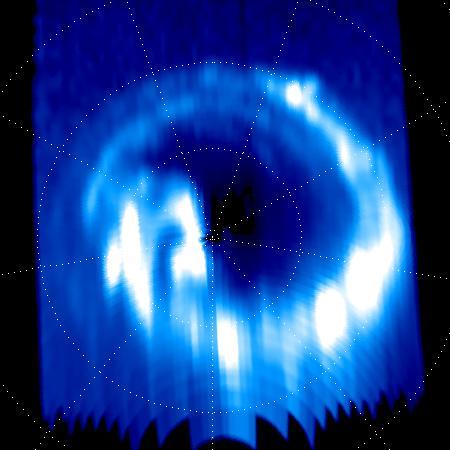
On Sept. 14, 2017, one day before making its final plunge into Saturn's atmosphere, NASA's Cassini spacecraft used its Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrograph, or UVIS, instrument to capture this final view of ultraviolet auroral emissions in the planet's north polar region. The view is centered on the north pole of Saturn, with lines of latitude visible for 80, 70 and 60 degrees. Lines of longitude are spaced 40 degrees apart. The planet's day side is at bottom, while the night side is at top. A sequence of images from this observation has also been assembled into a movie sequence. The last image in the movie was taken about an hour before the still image, which was the actual final UVIS auroral image. Auroral emissions are generated by charged particles traveling along the invisible lines of Saturn's magnetic field. These particles precipitate into the atmosphere, releasing light when they strike gas molecules there. Several individual auroral structures are visible here, despite that this UVIS view was acquired at a fairly large distance from the planet (about 424,000 miles or 683,000 kilometers). Each of these features is connected to a particular phenomenon in Saturn's magnetosphere. For instance, it is possible to identify auroral signatures here that are related to the injection of hot plasma from the dayside magnetosphere, as well as auroral features associated with a change in the magnetic field's shape on the magnetosphere's night side. Several possible scenarios have been postulated over the years to explain Saturn's changing auroral emissions, but researchers are still far from a complete understanding of this complicated puzzle. Researchers will continue to analyze the hundreds of image sequences UVIS obtained of Saturn's auroras during Cassini's 13-year mission, with many new discoveries likely to be made. This image and movie sequence were produced by the Laboratory for Planetary and Atmospheric Physics (LPAP) of the STAR Institute of the University of Liege in Belgium, in collaboration with the UVIS Team. The animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21899
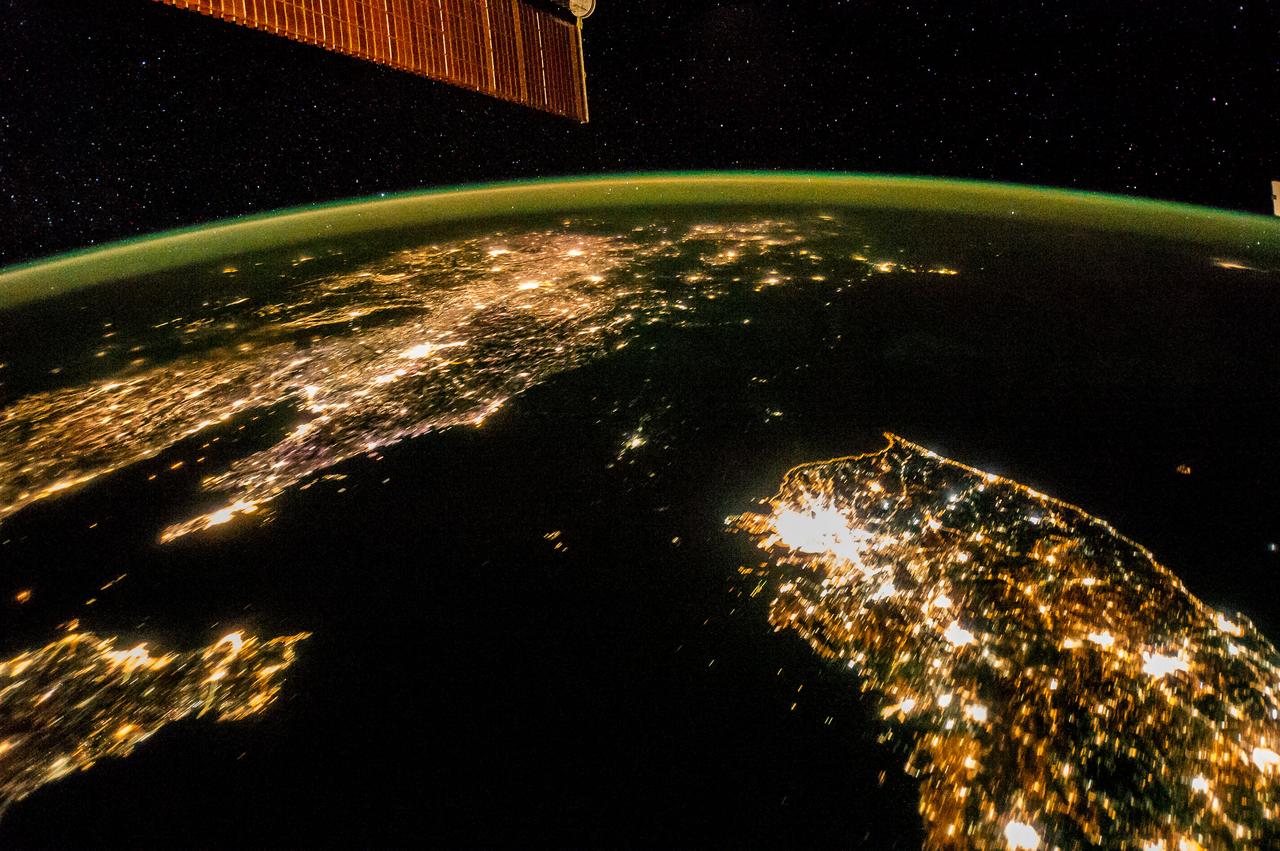

ISS038-E-038300 (30 Jan. 2014) --- Flying over East Asia, an Expedition 38 crew member on the International Space Station took this night image of the Korean Peninsula. Unlike daylight images, city lights at night illustrate dramatically the relative economic importance of cities, as gauged by relative size. In this north-looking view, it is immediately obvious that greater Seoul is a major city and that the port of Gunsan is minor by comparison. There are 25.6 million people in the Seoul metropolitan area-more than half of South Korea's citizens-while Gunsan's population is 280,000. North Korea is almost completely dark compared to neighboring South Korea and China. The darkened land appears as if it were a patch of water joining the Yellow Sea to the Sea of Japan. The capital city, Pyongyang, appears like a small island, despite a population of 3.26 million (as of 2008). The light emission from Pyongyang is equivalent to the smaller towns in South Korea. Coastlines are often very apparent in night imagery, as shown by South Korea's eastern shoreline. But the coast of North Korea is difficult to detect. These differences are illustrated in per capita power consumption in the two countries, with South Korea at 10,162 kilowatt hours and North Korea at 739 kilowatt hours.

This most distant x-ray cluster of galaxies yet has been found by astronomers using Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO). Approximately 10 billion light-years from Earth, the cluster 3C294 is 40 percent farther than the next most distant x-ray galaxy cluster. The existence of such a faraway cluster is important for understanding how the universe evolved. CXO's image reveals an hourglass-shaped region of x-ray emissions centered on the previously known central radio source (seen in this image as the blue central object) that extends outward for 60,000 light- years. The vast clouds of hot gas that surround such galaxies in clusters are thought to be heated by collapse toward the center of the cluster. Until CXO, x-ray telescopes have not had the needed sensitivity to identify such distant clusters of galaxies. Galaxy clusters are the largest gravitationally bound structures in the universe. The intensity of the x-rays in this CXO image of 3C294 is shown as red for low energy x-rays, green for intermediate, and blue for the most energetic x-rays. (Photo credit: NASA/loA/A. Fabian et al)
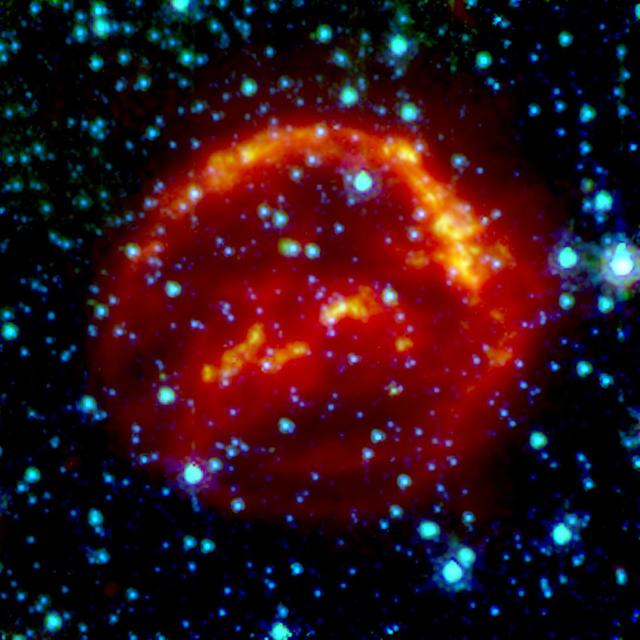

This Spitzer false-color image is a composite of data from the 24 micron channel of Spitzer's multiband imaging photometer (red), and three channels of its infrared array camera: 8 micron (yellow), 5.6 micron (blue), and 4.8 micron (green). Stars are most prominent in the two shorter wavelengths, causing them to show up as turquoise. The supernova remnant is most prominent at 24 microns, arising from dust that has been heated by the supernova shock wave, and re-radiated in the infrared. The 8 micron data shows infrared emission from regions closely associated with the optically emitting regions. These are the densest regions being encountered by the shock wave, and probably arose from condensations in the surrounding material that was lost by the supernova star before it exploded. The composite above (PIA06908, PIA06909, and PIA06910) represent views of Kepler's supernova remnant taken in X-rays, visible light, and infrared radiation. Each top panel in the composite above shows the entire remnant. Each color in the composite represents a different region of the electromagnetic spectrum, from X-rays to infrared light. The X-ray and infrared data cannot be seen with the human eye. Astronomers have color-coded those data so they can be seen in these images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06910
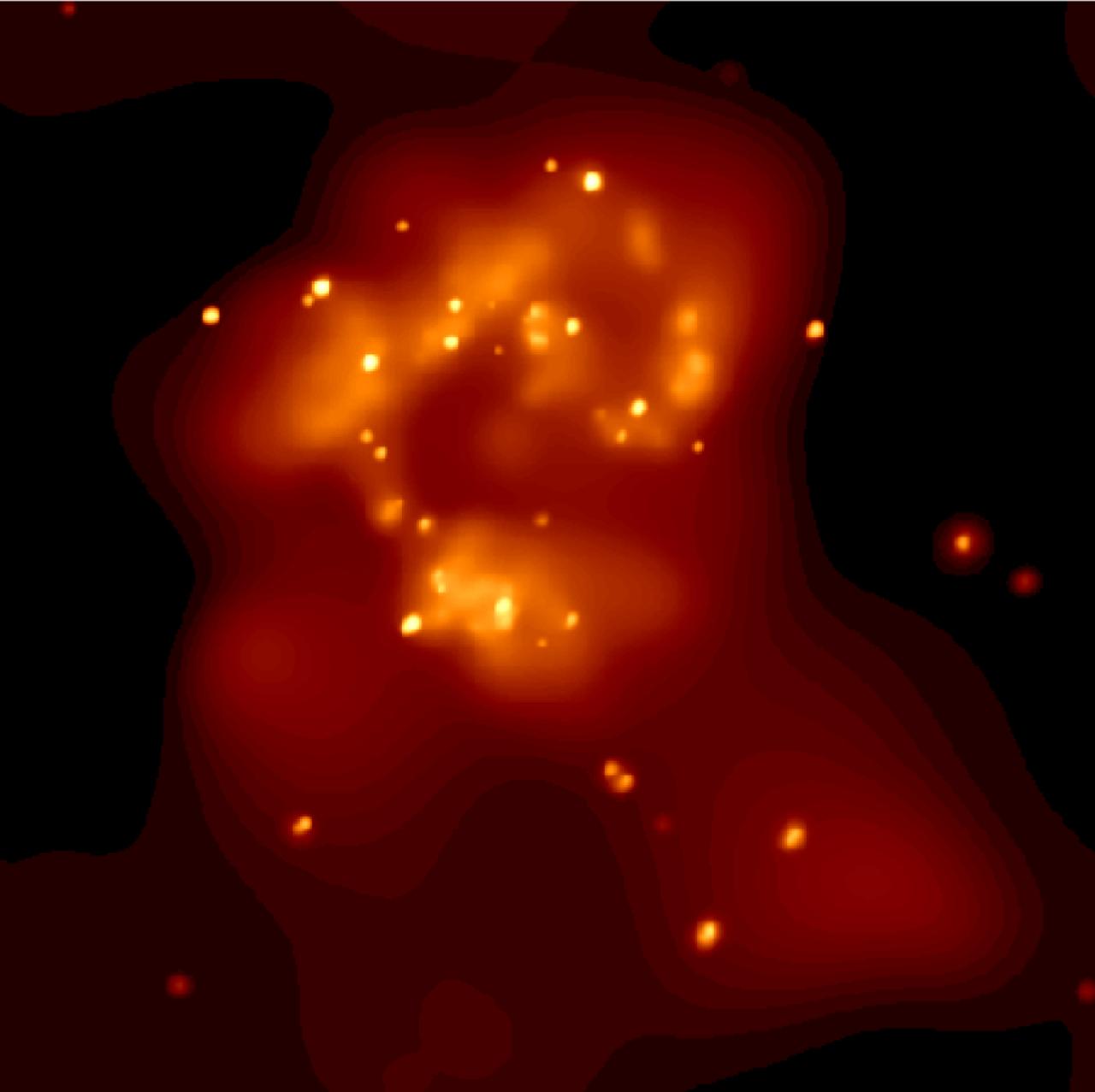
This Chandra image shows the central regions of two colliding galaxies known collectively as the Antennae (NGC-4038/4039). The dozens of bright pointy-like sources are neutron stars or black holes pulling gas off nearby stars. The bright fuzzy patches are multimillion degree gas superbubbles, thousands of light years in diameter that were produced by the accumulated power of thousands of supernovae. The remaining glow of x-ray emission could be due to many faint x-ray sources or to clouds of hot gas in the galaxies. About 60 million light years from Earth in the constellation Corvus, the Antennae Galaxies got their nickname from the wispy anntennae-like streams of gas as seen by optical telescopes. These ongoing wisps are believed to have been produced approximately 100 million years ago by the collision between the galaxies. Although it is rare for stars to hit each other during a galactic collision, clouds of dust and gas do collide. Compression of these clouds can lead to the rebirth of millions of stars, and a few million years later, to thousands of supernovae.

This image, taken with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 on board the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, shows the globular cluster Terzan 1. Lying around 20 000 light-years from us in the constellation of Scorpius (The Scorpion), it is one of about 150 globular clusters belonging to our galaxy, the Milky Way. Typical globular clusters are collections of around a hundred thousand stars, held together by their mutual gravitational attraction in a spherical shape a few hundred light-years across. It is thought that every galaxy has a population of globular clusters. Some, like the Milky Way, have a few hundred, while giant elliptical galaxies can have several thousand. They contain some of the oldest stars in a galaxy, hence the reddish colours of the stars in this image — the bright blue ones are foreground stars, not part of the cluster. The ages of the stars in the globular cluster tell us that they were formed during the early stages of galaxy formation! Studying them can also help us to understand how galaxies formed. Terzan 1, like many globular clusters, is a source of X-rays. It is likely that these X-rays come from binary star systems that contain a dense neutron star and a normal star. The neutron star drags material from the companion star, causing a burst of X-ray emission. The system then enters a quiescent phase in which the neutron star cools, giving off X-ray emission with different characteristics, before enough material from the companion builds up to trigger another outburst.
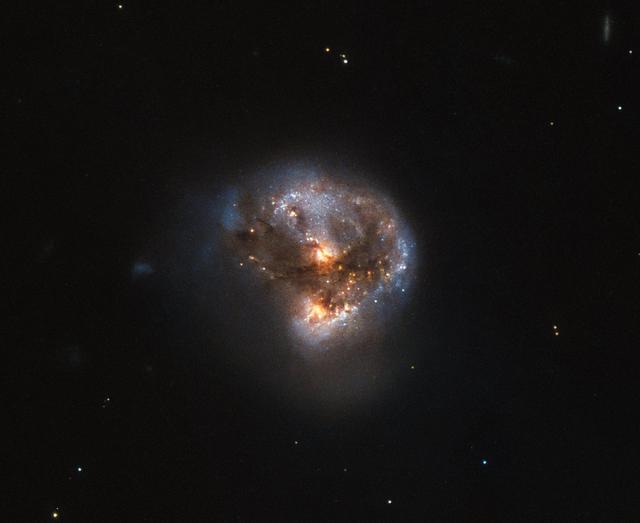

This galaxy has a far more exciting and futuristic classification than most — it hosts a megamaser. Megamasers are intensely bright, around 100 million times brighter than the masers found in galaxies like the Milky Way. The entire galaxy essentially acts as an astronomical laser that beams out microwave emission rather than visible light (hence the ‘m’ replacing the ‘l’). A megamaser is a process that involves some components within the galaxy (like gas) that is in the right physical condition to cause the amplification of light (in this case, microwaves). But there are other parts of the galaxy (like stars for example) that aren’t part of the maser process. This megamaser galaxy is named IRAS 16399-0937 and is located over 370 million light-years from Earth. This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image belies the galaxy’s energetic nature, instead painting it as a beautiful and serene cosmic rosebud. The image comprises observations captured across various wavelengths by two of Hubble’s instruments: the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), and the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS). NICMOS’s superb sensitivity, resolution, and field of view gave astronomers the unique opportunity to observe the structure of IRAS 16399-0937 in detail. They found it hosts a double nucleus — the galaxy’s core is thought to be formed of two separate cores in the process of merging. The two components, named IRAS 16399N and IRAS 16399S for the northern and southern parts respectively, sit over 11,000 light-years apart. However, they are both buried deep within the same swirl of cosmic gas and dust and are interacting, giving the galaxy its peculiar structure. The nuclei are very different. IRAS 16399S appears to be a starburst region, where new stars are forming at an incredible rate. IRAS 16399N, however, is something known as a LINER nucleus (Low Ionization Nuclear Emission Region), which is a region whose emission mostly stems from weakly-ionized or neutral atoms of particular gases. The northern nucleus also hosts a black hole with some 100 million times the mass of the sun! Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt (geckzilla) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
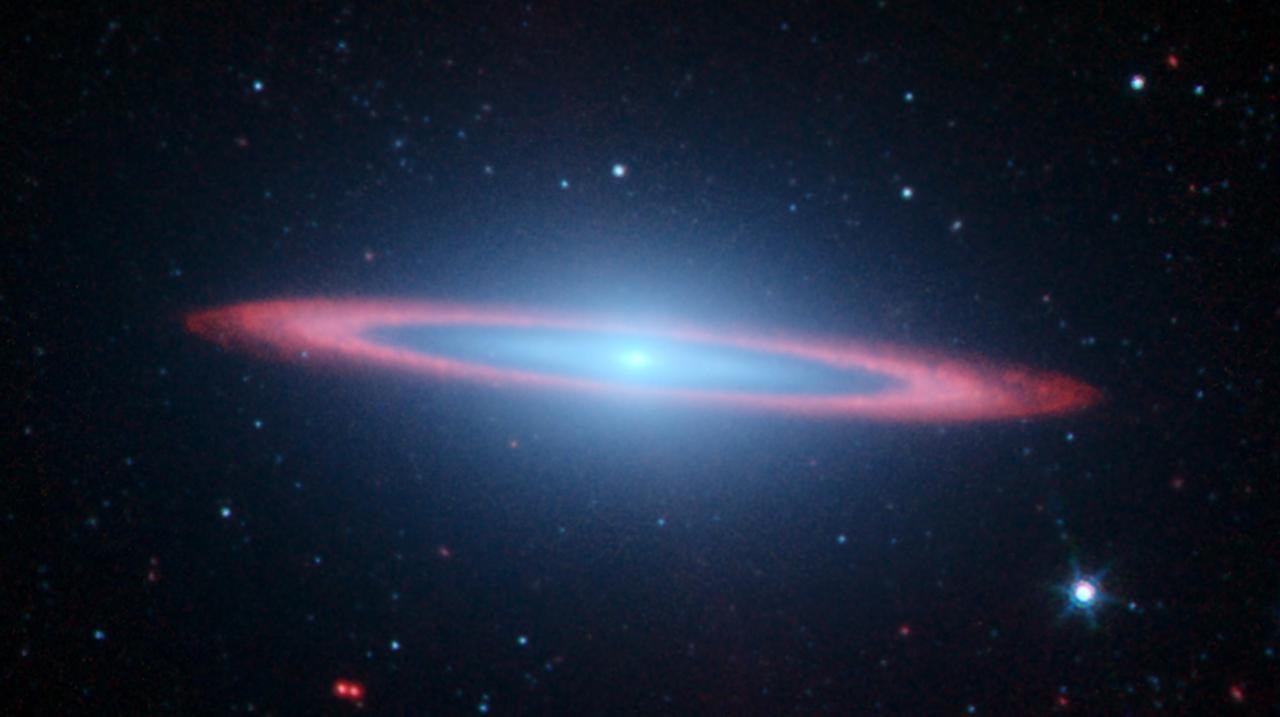

NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope set its infrared eyes on one of the most famous objects in the sky, Messier 104, also called the Sombrero galaxy. In this striking infrared picture, Spitzer sees an exciting new view of a galaxy that in visible light has been likened to a "sombrero," but here looks more like a "bulls-eye." Recent observations using Spitzer's infrared array camera uncovered the bright, smooth ring of dust circling the galaxy, seen in red. In visible light, because this galaxy is seen nearly edge-on, only the near rim of dust can be clearly seen in silhouette. Spitzer's full view shows the disk is warped, which is often the result of a gravitational encounter with another galaxy, and clumpy areas spotted in the far edges of the ring indicate young star-forming regions. Spitzer's infrared view of the starlight from this galaxy, seen in blue, can pierce through obscuring murky dust that dominates in visible light. As a result, the full extent of the bulge of stars and an otherwise hidden disk of stars within the dust ring are easily seen. The Sombrero galaxy is located some 28 million light years away. Viewed from Earth, it is just six degrees south of its equatorial plane. Spitzer detected infrared emission not only from the ring, but from the center of the galaxy too, where there is a huge black hole, believed to be a billion times more massive than our Sun. This picture is composed of four images taken at 3.6 (blue), 4.5 (green), 5.8 (orange), and 8.0 (red) microns. The contribution from starlight (measured at 3.6 microns) has been subtracted from the 5.8 and 8-micron images to enhance the visibility of the dust features. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA07899
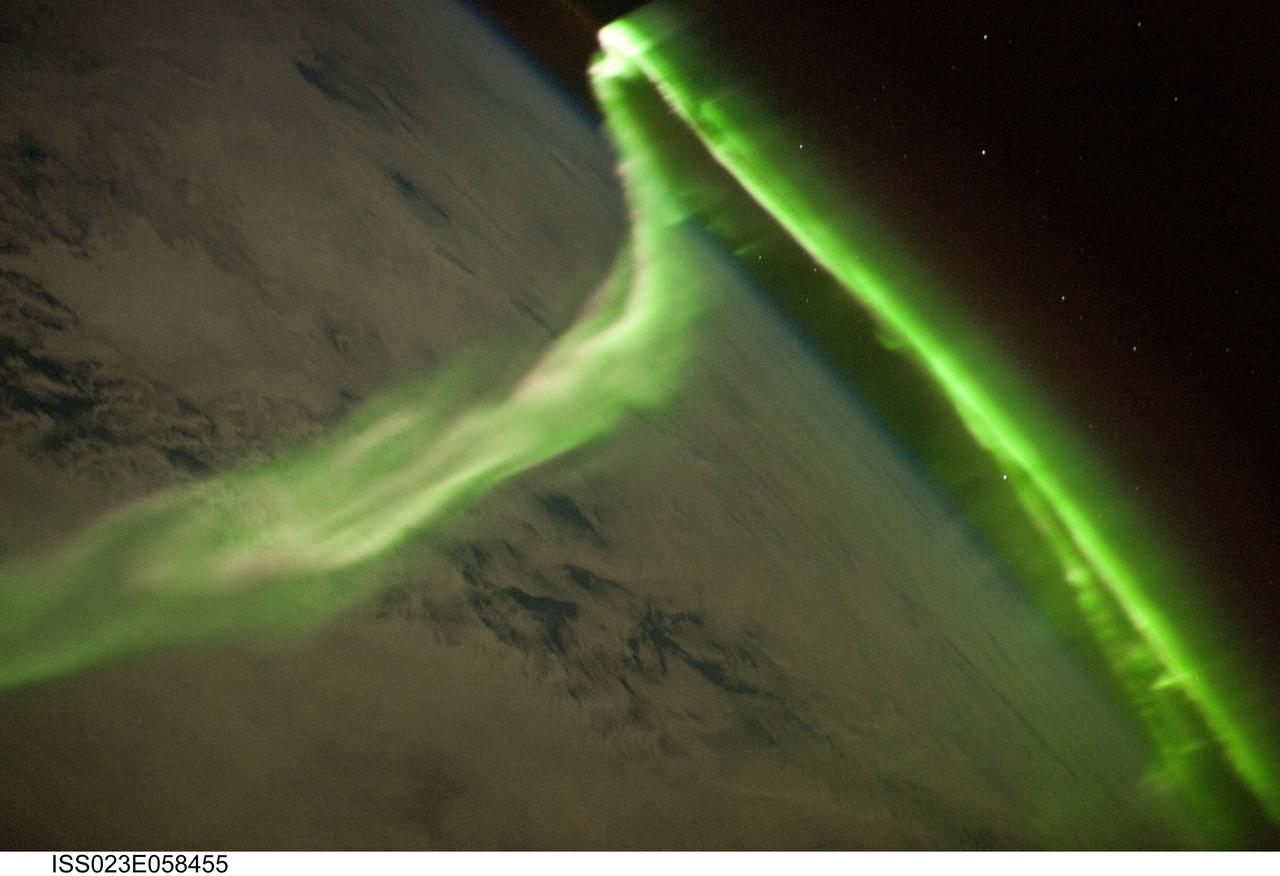

ISS023-E-058455 (29 May 2010) --- Aurora Australis is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 23 crew member on the International Space Station. Among the views of Earth afforded crew members aboard the ISS, surely one of the most spectacular is of the aurora. These ever-shifting displays of colored ribbons, curtains, rays, and spots are most visible near the North (Aurora Borealis) and South (Aurora Australis) Poles as charged particles streaming from the sun (the solar wind) interact with Earth’s magnetic field, resulting in collisions with atoms of oxygen and nitrogen in the upper atmosphere. The atoms are excited by these collisions, and typically emit photons as a means of returning to their original energy state. The photons form the aurora that we see. The most commonly observed color of aurora is green, caused by photons (light) emitted by excited oxygen atoms at wavelengths centered at 0.558 micrometers, or millionths of a meter. Visible light is reflected from healthy (green) plant leaves at approximately the same wavelength. Red auroras are generated by light emitted at a longer wavelength (0.630 micrometers), and other colors such as blue and purple are also sometimes observed. While auroras are generally only visible close to the poles, severe magnetic storms impacting Earth’s magnetic field can shift them towards the equator. This striking aurora image was taken during a geomagnetic storm that was most likely caused by a coronal mass ejection from the sun on May 24, 2010. The ISS was located over the Southern Indian Ocean at an altitude of 350 kilometers, with the observer most likely looking towards Antarctica (not visible) and the South Pole. The aurora has a sinuous ribbon shape that separates into discrete spots near the lower right corner of the image. While the dominant coloration of the aurora is green, there are faint suggestions of red photon emission as well (light fuscia tones at center left). Dense cloud cover is dimly visible below the aurora. The curvature of Earth’s horizon, or limb, is clearly visible as is the faint blue line of the upper atmosphere directly above at top center. Several stars appear as bright pinpoints against the blackness of space at top right.
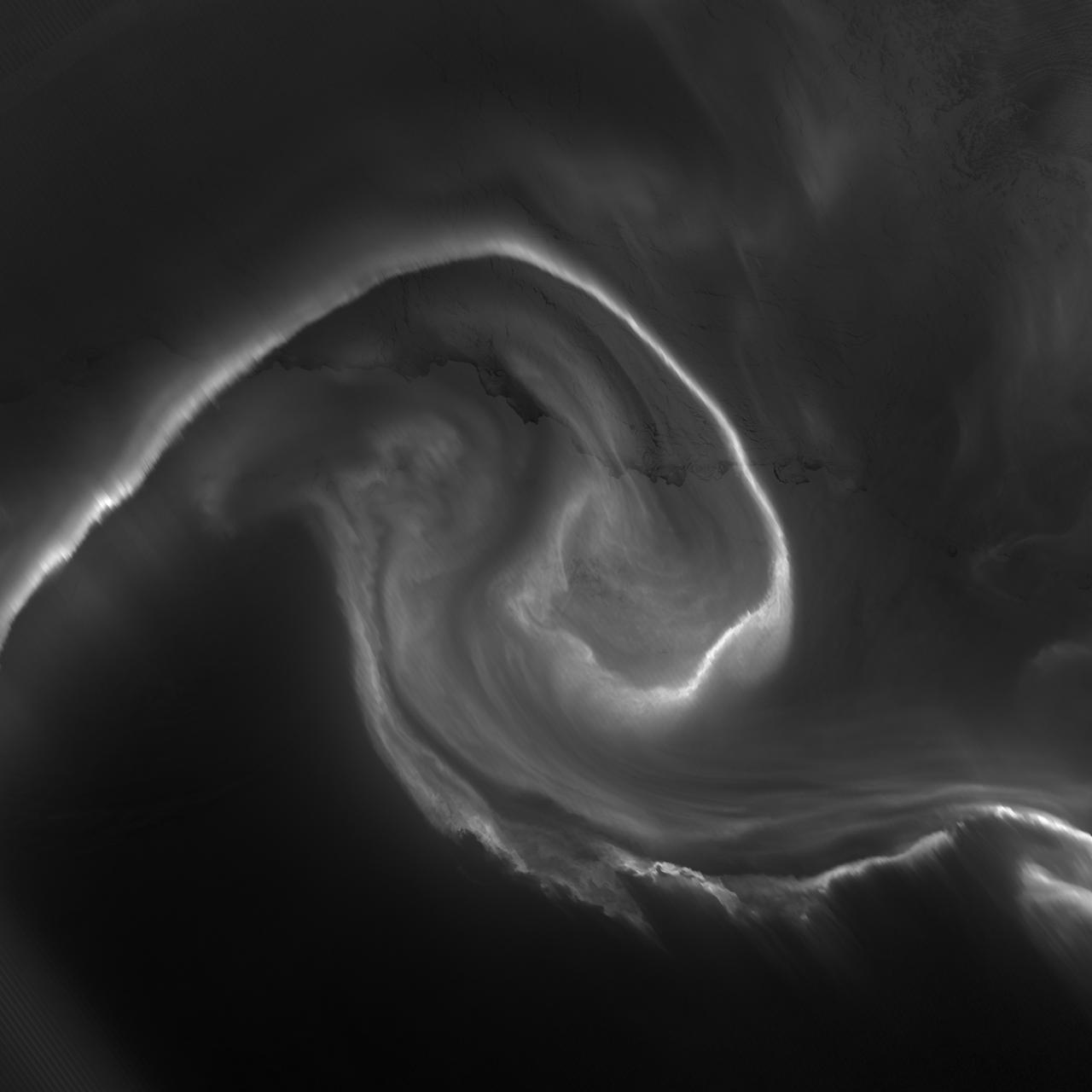
NASA acquired July 15, 2012 On July 15, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of the aurora australis, or “southern lights,” over Antartica’s Queen Maud Land and the Princess Ragnhild Coast. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as city lights, auroras, wildfires, and reflected moonlight. In the case of the image above, the sensor detected the visible auroral light emissions as energetic particles rained down from Earth’s magnetosphere and into the gases of the upper atmosphere. The slightly jagged appearance of the auroral lines is a function of the rapid dance of the energetic particles at the same time that the satellite is moving and the VIIRS sensor is scanning. The yellow box in the top image depicts the area shown in the lower close-up image. Light from the aurora was bright enough to illuminate the ice edge between the ice shelf and the Southern Ocean. At the time, Antarctica was locked in midwinter darkness and the Moon was a waning crescent that provided little light. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79750" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope has captured these infrared images of a nearby spiral galaxy that resembles our own Milky Way. The targeted galaxy, known as NGC 7331 and sometimes referred to as our galaxy's twin, is found in the constellation Pegasus at a distance of 50 million light-years. This inclined galaxy was discovered in 1784 by William Herschel, who also discovered infrared light. The evolution of this galaxy is a story that depends significantly on the amount and distribution of gas and dust, the locations and rates of star formation, and on how the energy from star formation is recycled by the local environment. The new Spitzer images are allowing astronomers to "read" this story by dissecting the galaxy into its separate components. The image, measuring 12.6 by 8.2 arcminutes, was obtained by Spitzer's infrared array camera. It is a four-color composite of invisible light, showing emissions from wavelengths of 3.6 microns (blue), 4.5 microns (green), 5.8 microns (yellow) and 8.0 microns (red). These wavelengths are roughly 10 times longer than those seen by the human eye. The infrared light seen in this image originates from two very different sources. At shorter wavelengths (3.6 to 4.5 microns), the light comes mainly from stars, particularly ones that are older and cooler than our Sun. This starlight fades at longer wavelengths (5.8 to 8.0 microns), where instead we see the glow from clouds of interstellar dust. This dust consists mainly of a variety of carbon-based organic molecules known collectively as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Wherever these compounds are found, there will also be dust granules and gas, which provide a reservoir of raw materials for future star formation. One feature that stands out in the Spitzer image is the ring of actively forming stars that surrounds the galaxy center (yellow). This ring, with a radius of nearly 20,000 light-years, is invisible at shorter wavelengths, yet has been detected at sub-millimeter and radio wavelengths. It is made up in large part of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Spitzer measurements suggest that the ring contains enough gas to produce four billion stars like the Sun. Three other galaxies are seen below NGC 7331, all about 10 times farther away. From left to right are NGC 7336, NGC 7335 and NGC 7337. The blue dots scattered throughout the images are foreground stars in the Milky Way; the red ones are galaxies that are even more distant. The Spitzer observations of NGC 7331 are part of a large 500-hour science project, known as the Spitzer Infrared Nearby Galaxy Survey, which will comprehensively study 75 nearby galaxies with infrared imaging and spectroscopy. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06322

A cluster of newborn stars herald their birth in this interstellar Valentine Day commemorative picture obtained with NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. These bright young stars are found in a rosebud-shaped and rose-colored nebulosity known as NGC 7129. The star cluster and its associated nebula are located at a distance of 3300 light-years in the constellation Cepheus. A recent census of the cluster reveals the presence of 130 young stars. The stars formed from a massive cloud of gas and dust that contains enough raw materials to create a thousand Sun-like stars. In a process that astronomers still poorly understand, fragments of this molecular cloud became so cold and dense that they collapsed into stars. Most stars in our Milky Way galaxy are thought to form in such clusters. The Spitzer Space Telescope image was obtained with an infrared array camera that is sensitive to invisible infrared light at wavelengths that are about ten times longer than visible light. In this four-color composite, emission at 3.6 microns is depicted in blue, 4.5 microns in green, 5.8 microns in orange, and 8.0 microns in red. The image covers a region that is about one quarter the size of the full moon. As in any nursery, mayhem reigns. Within the astronomically brief period of a million years, the stars have managed to blow a large, irregular bubble in the molecular cloud that once enveloped them like a cocoon. The rosy pink hue is produced by glowing dust grains on the surface of the bubble being heated by the intense light from the embedded young stars. Upon absorbing ultraviolet and visible-light photons produced by the stars, the surrounding dust grains are heated and re-emit the energy at the longer infrared wavelengths observed by Spitzer. The reddish colors trace the distribution of molecular material thought to be rich in hydrocarbons. The cold molecular cloud outside the bubble is mostly invisible in these images. However, three very young stars near the center of the image are sending jets of supersonic gas into the cloud. The impact of these jets heats molecules of carbon monoxide in the cloud, producing the intricate green nebulosity that forms the stem of the rosebud. Not all stars are formed in clusters. Away from the main nebula and its young cluster are two smaller nebulae, to the left and bottom of the central 'rosebud,'each containing a stellar nursery with only a few young stars. Astronomers believe that our own Sun may have formed billions of years ago in a cluster similar to NGC 7129. Once the radiation from new cluster stars destroys the surrounding placental material, the stars begin to slowly drift apart. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05266
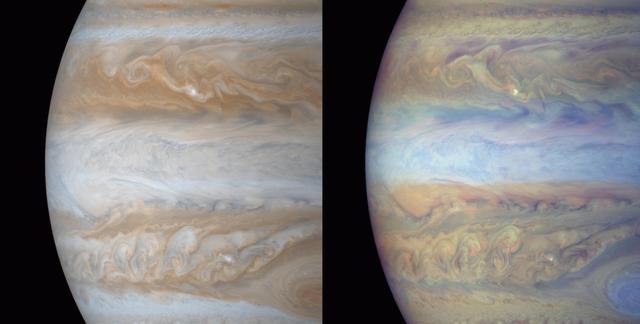
These color composite frames of the mid-section of Jupiter were of narrow angle images acquired on December 31, 2000, a day after Cassini's closest approach to the planet. The smallest features in these frames are roughly ~ 60 kilometers. The left is natural color, composited to yield the color that Jupiter would have if seen by the naked eye. The right frame is composed of 3 images: two were taken through narrow band filters centered on regions of the spectrum where the gaseous methane in Jupiter's atmosphere absorbs light, and the third was taken in a red continuum region of the spectrum, where Jupiter has no absorptions. The combination yields an image whose colors denote the height of the clouds. Red regions are deep water clouds, bright blue regions are high haze (like the blue covering the Great Red Spot). Small, intensely bright white spots are energetic lightning storms which have penetrated high into the atmosphere where there is no opportunity for absorption of light: these high cloud systems reflect all light equally. The darkest blue regions -- for example, the long linear regions which border the northern part of the equatorial zone, are the very deep "hot spots', seen in earlier images, from which Jovian thermal emission is free to escape to space. This is the first time that global images of Jupiter in all the methane and attendant continuum filters have been acquired by a spacecraft. From images like these, the stratigraphy of Jupiter's dynamic atmosphere will be determined. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA02877

This video shows the SPHEREx observatory's field of view as it scans across a section of the sky, observing the universe in 102 colors, or wavelengths of light. Taken in April 2025, just weeks after the spacecraft's launch, the images show a region inside the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy near the Milky Way. The wavelengths seen by NASA's SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) are in the infrared range, which is invisible to the human eye; the infrared wavelengths are represented here by visible light colors. While most telescopes use color filters that block one wavelength at a time, SPHEREx's filters gradually transition through a range of wavelengths, creating the rainbow gradients seen in this video. The telescope takes overlapping images so that every section of the sky is imaged 102 times, each time in a different wavelength. The color filters sit on top of two arrays, each with three detectors, that observe the sky simultaneously. In the video, one array's view moves from purple to green, followed by the second array's view (of the same section of sky), which changes from yellow to red. The images are looped four times. SPHEREx will repeat this scanning motion each day for two years, gradually compiling a map of the entire sky. Every day, it will take about 600 exposures, each of which is made up of six images, one from each of the six detectors. Combining those images, scientists can see the total emission from the observed section of the sky or look at an individual wavelength. Observing individual wavelengths of light from cosmic sources is called spectroscopy. This technique can be used to reveal the composition of objects, because chemical elements and molecules leave a unique signature in the colors they absorb and emit. This is made apparent in the images' lower right quadrant, where a collection of dust appears only in the red and orange wavelengths. This indicates the presence of a particular molecule that radiates in specific wavelengths and not others. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26351

Release date: July 1, 2008 SN 1006 Supernova Remnant (Hubble) A delicate ribbon of gas floats eerily in our galaxy. A contrail from an alien spaceship? A jet from a black-hole? Actually this image, taken by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, is a very thin section of a supernova remnant caused by a stellar explosion that occurred more than 1,000 years ago. On or around May 1, 1006 A.D., observers from Africa to Europe to the Far East witnessed and recorded the arrival of light from what is now called SN 1006, a tremendous supernova explosion caused by the final death throes of a white dwarf star nearly 7,000 light-years away. The supernova was probably the brightest star ever seen by humans, and surpassed Venus as the brightest object in the night time sky, only to be surpassed by the moon. It was visible even during the day for weeks, and remained visible to the naked eye for at least two and a half years before fading away. It wasn't until the mid-1960s that radio astronomers first detected a nearly circular ring of material at the recorded position of the supernova. The ring was almost 30 arcminutes across, the same angular diameter as the full moon. The size of the remnant implied that the blast wave from the supernova had expanded at nearly 20 million miles per hour over the nearly 1,000 years since the explosion occurred. In 1976, the first detection of exceedingly faint optical emission of the supernova remnant was reported, but only for a filament located on the northwest edge of the radio ring. A tiny portion of this filament is revealed in detail by the Hubble observation. The twisting ribbon of light seen by Hubble corresponds to locations where the expanding blast wave from the supernova is now sweeping into very tenuous surrounding gas. The hydrogen gas heated by this fast shock wave emits radiation in visible light. Hence, the optical emission provides astronomers with a detailed "snapshot" of the actual position and geometry of the shock front at any given time. Bright edges within the ribbon correspond to places where the shock wave is seen exactly edge on to our line of sight. Today we know that SN 1006 has a diameter of nearly 60 light-years, and it is still expanding at roughly 6 million miles per hour. Even at this tremendous speed, however, it takes observations typically separated by years to see significant outward motion of the shock wave against the grid of background stars. In the Hubble image as displayed, the supernova would have occurred far off the lower right corner of the image, and the motion would be toward the upper left. SN 1006 resides within our Milky Way Galaxy. Located more than 14 degrees off the plane of the galaxy's disk, there is relatively little confusion with other foreground and background objects in the field when trying to study this object. In the Hubble image, many background galaxies (orange extended objects) far off in the distant universe can be seen dotting the image. Most of the white dots are foreground or background stars in our Milky Way galaxy. This image is a composite of hydrogen-light observations taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys in February 2006 and Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 observations in blue, yellow-green, and near-infrared light taken in April 2008. The supernova remnant, visible only in the hydrogen-light filter was assigned a red hue in the Heritage color image. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: W. Blair (Johns Hopkins University) To learn more about the Hubble Space Telescope go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/main/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>