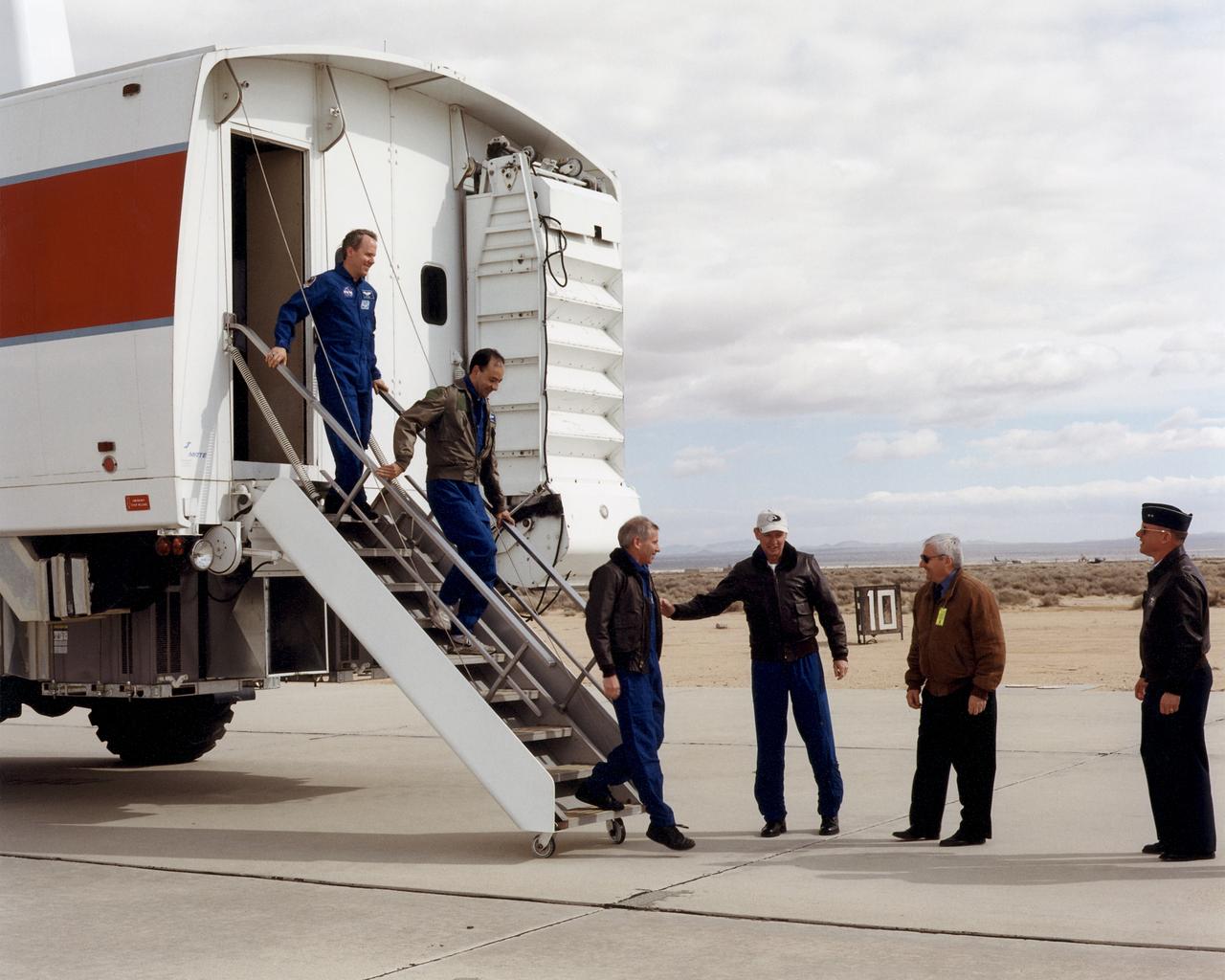

L to R: STS-98 Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Pilot Mark Polansky, and Commander Kenneth Cockrell greet STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy, Dryden Center Director Kevin Petersen, and AFFTC Commander Major General Richard Reynolds after landing on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base, California, where NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center is located.
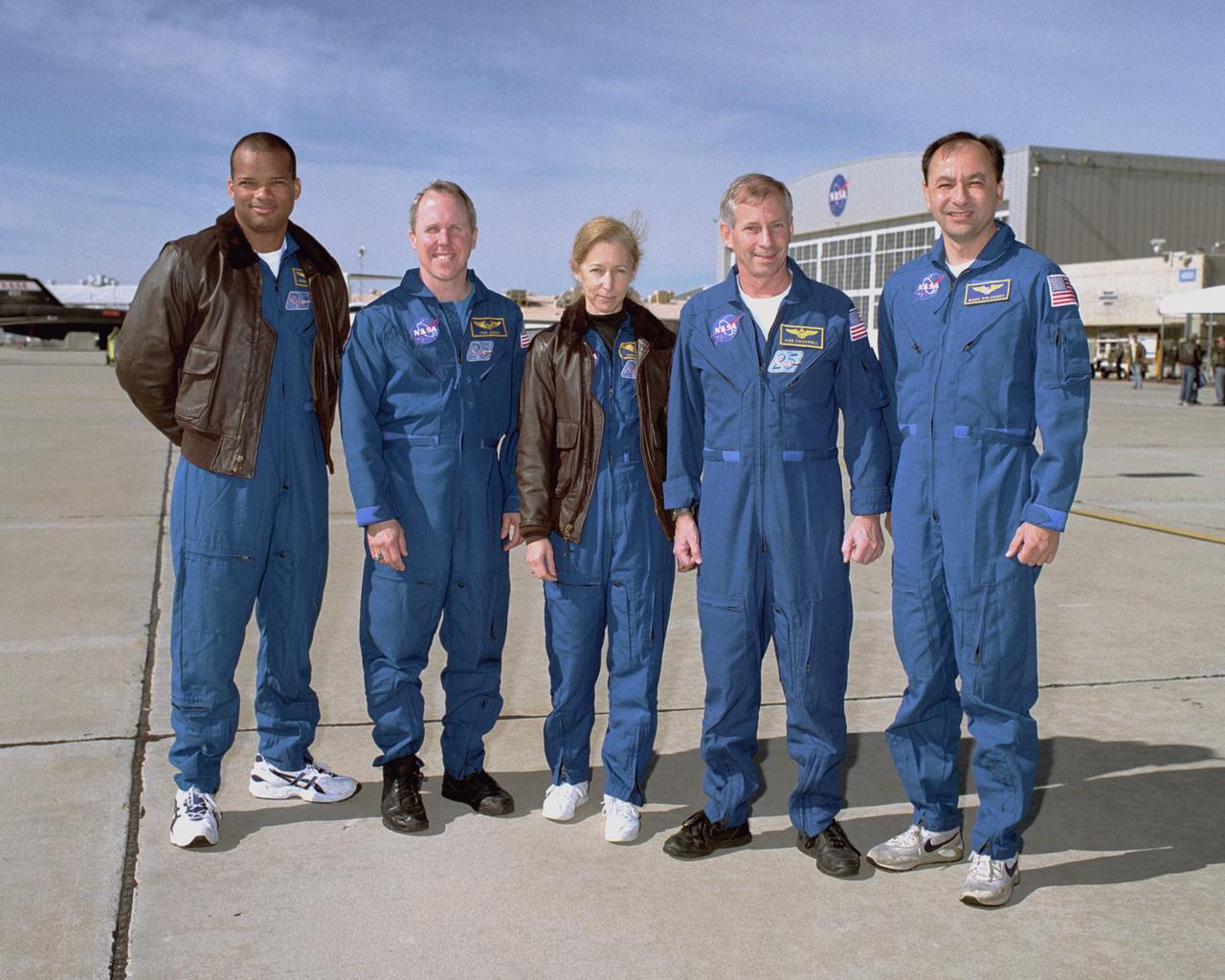

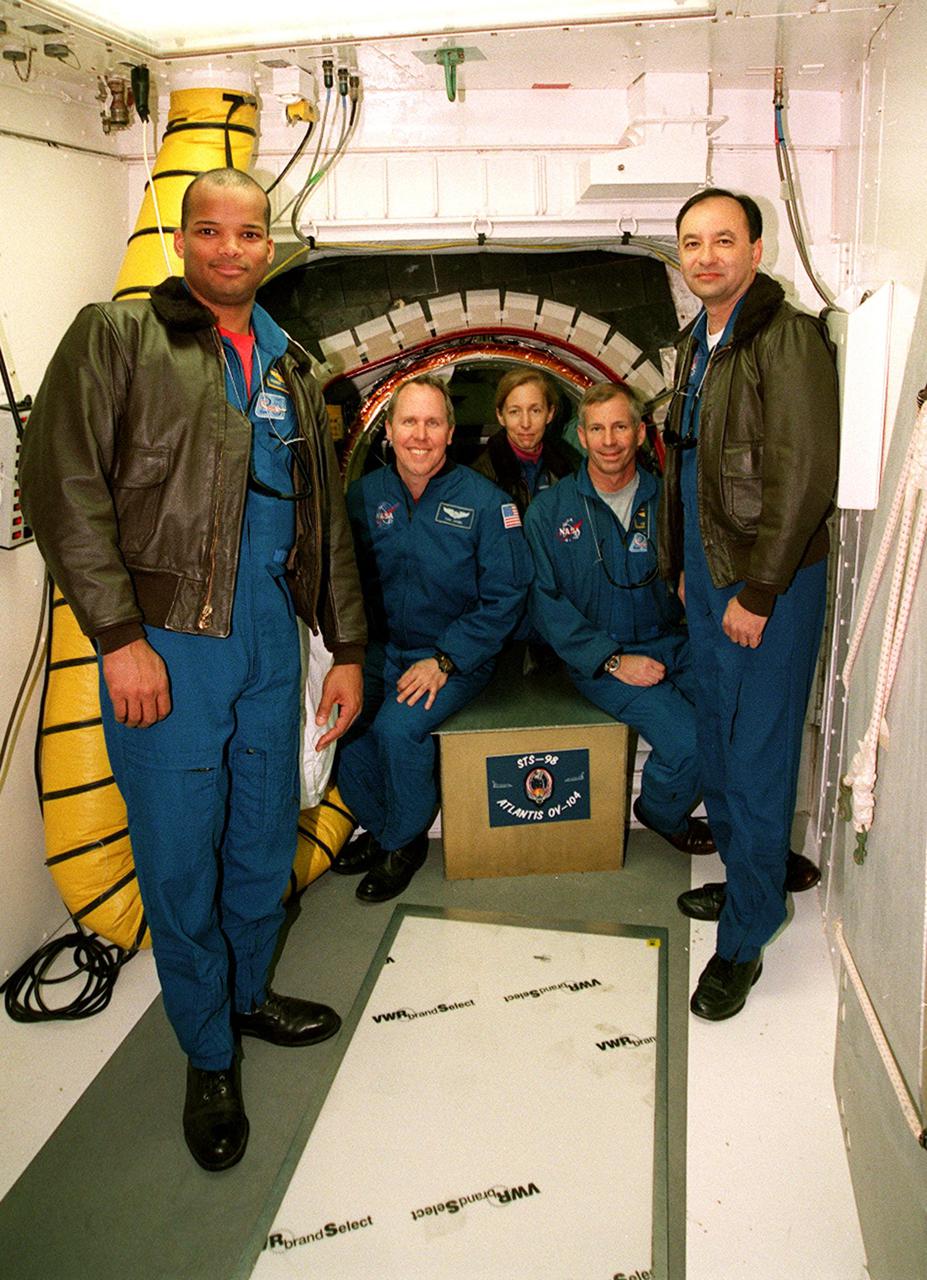
The crew of STS-98 poses for a group photo shortly before leaving NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center after a successful landing of the Space Shuttle Atlantis the day before. L to R: Mission Specialists Robert L. Curbeam, Thomas D. Jones, and Marsha S. Ivins, Commander Kenneth D. Cockrell, and Pilot Mark L. Polansky.
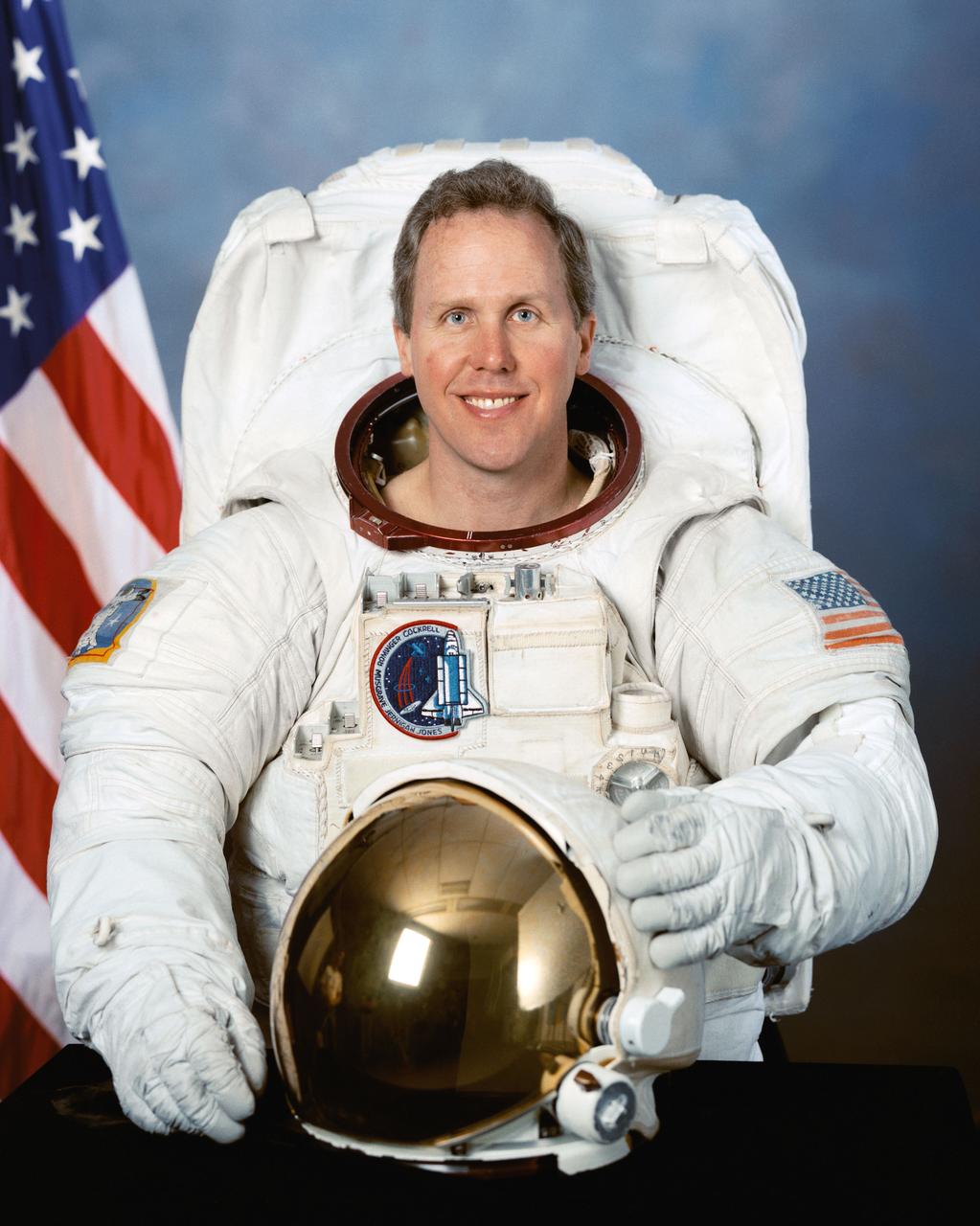

S97-06159 (3 April 1997) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist.
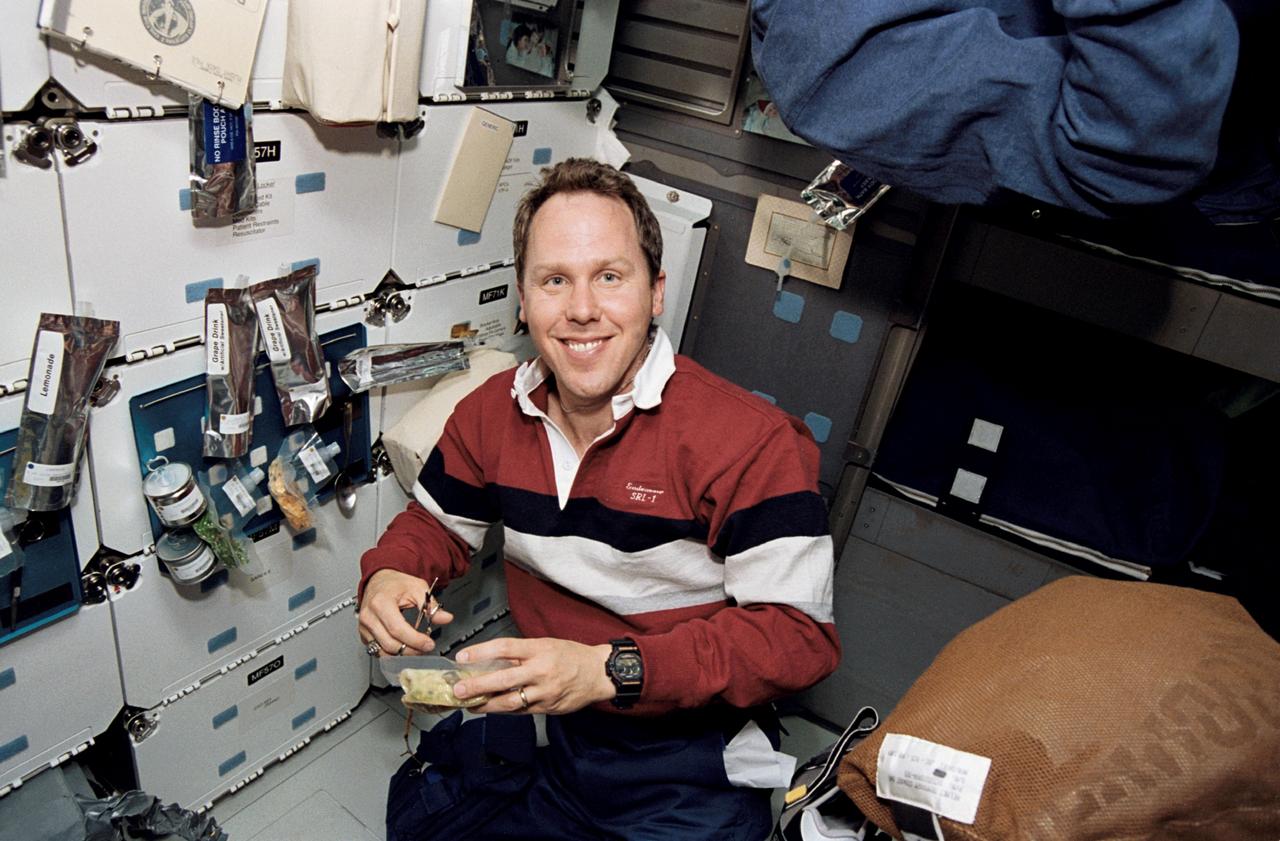

STS059-14-004 (9-20 April 1994) --- On the Space Shuttle Endeavour's middeck astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, cuts open a package of food as he prepares for mealtime. Jones was joined by five other NASA astronauts aboard Endeavour for the STS-59 mission.

S93-43108 (2 June 1993) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, takes a break during emergency bailout training at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Jones and five other NASA astronauts are scheduled to fly aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour next year.
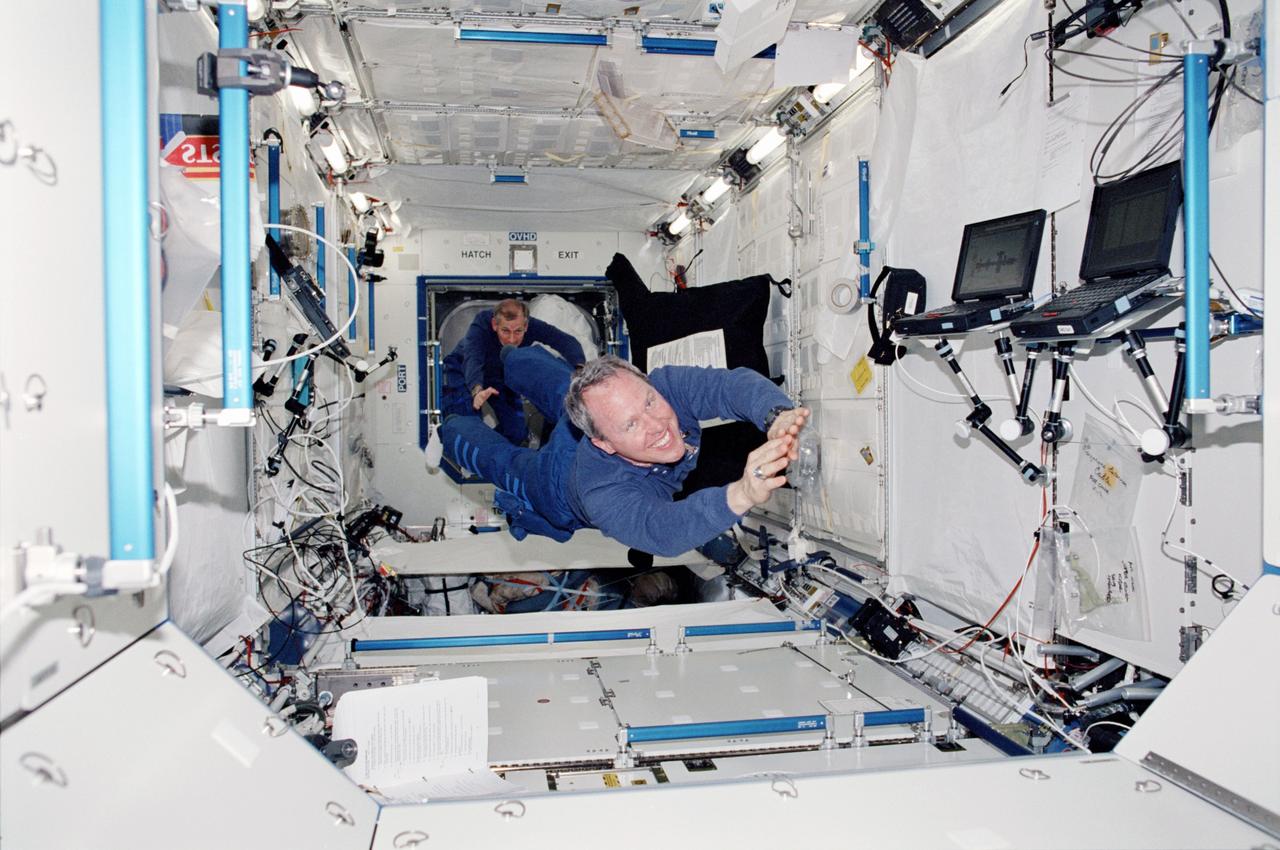

STS098-356-0026 (11 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones (foreground), mission specialist; and Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander, float in the newly installed Destiny laboratory aboard the International Space Station.
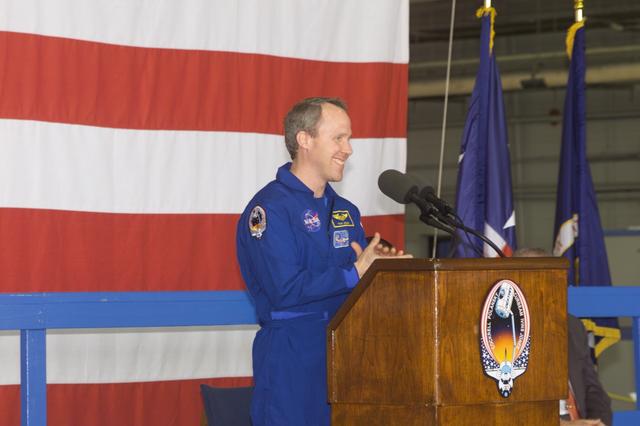

JSC2001-E-04808 (21 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, speaks to a crowd at the welcome home ceremony for the five STS-98 crew members.
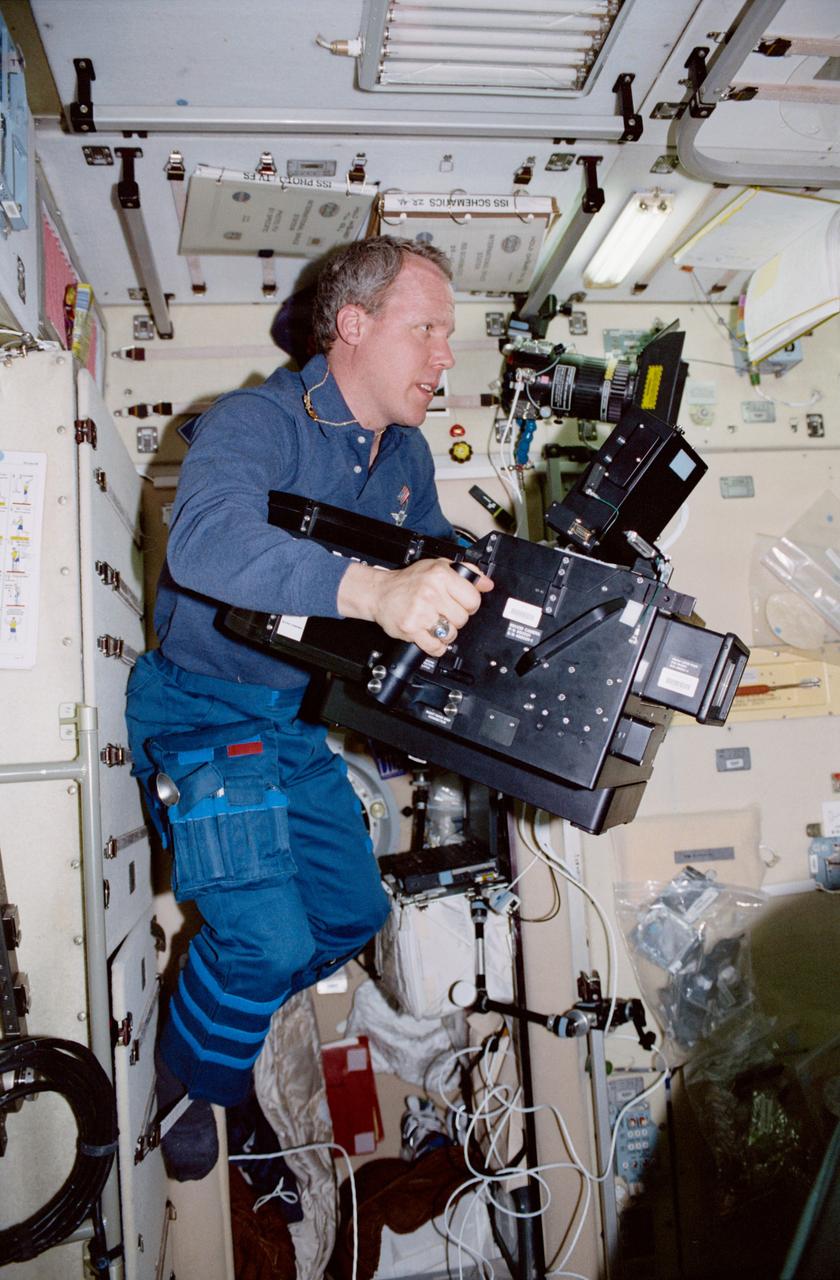

STS098-337-034 (7-20 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, is seen with an IMAX camera in the Zvezda service module of the International Space Station (ISS).
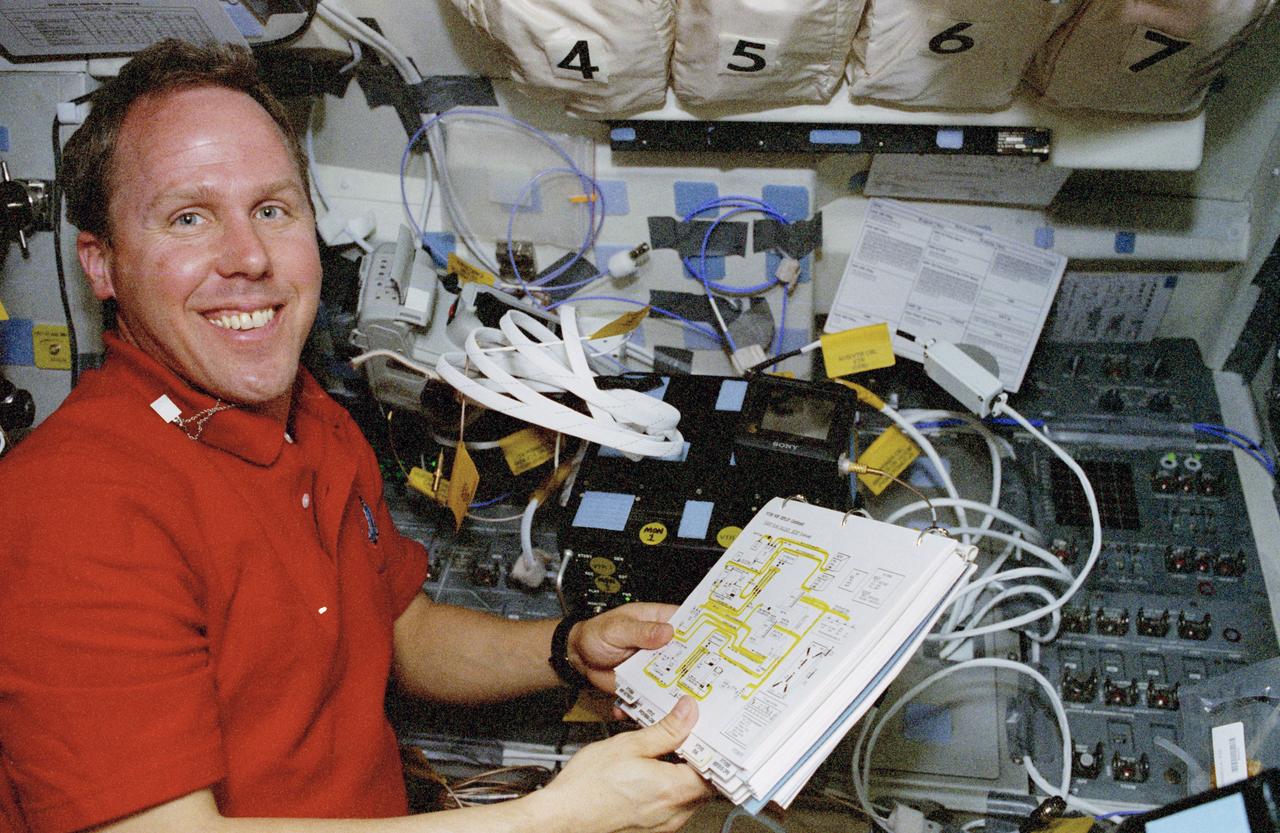

STS080-325-006 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, STS-80 mission specialist, looks over a photo-television checklist on the flight deck of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Columbia.
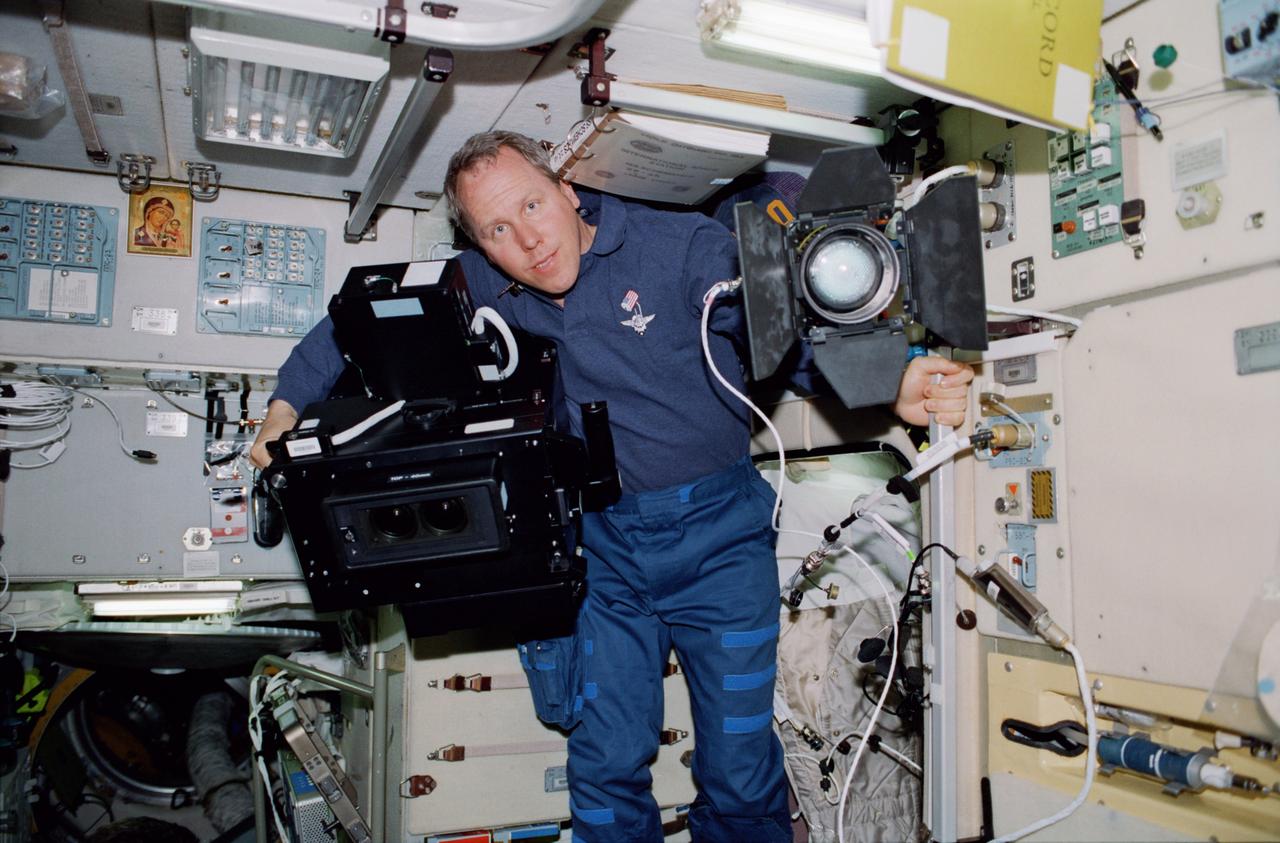

STS098-337-0026 (7-20 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, is seen with IMAX camera gear in the Zvezda service module of the International Space Station (ISS).
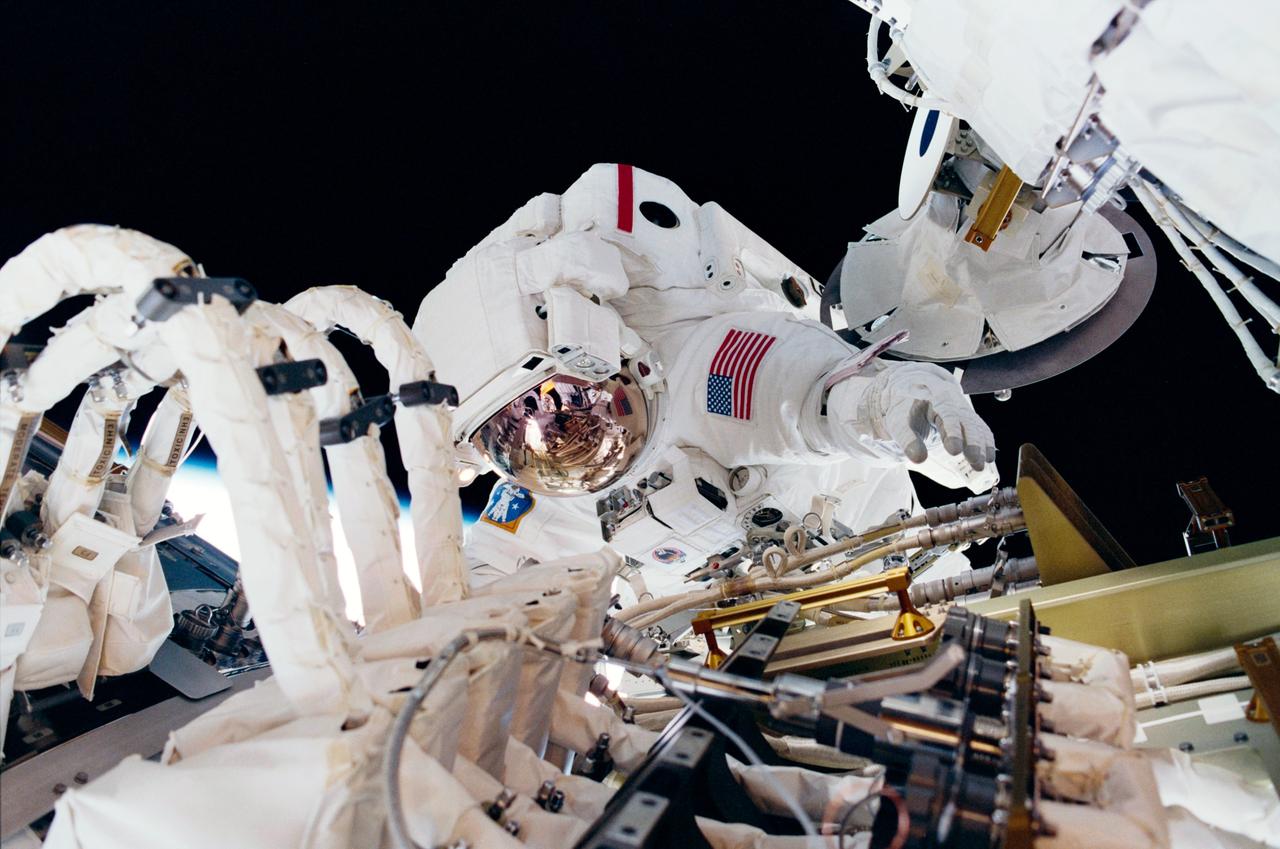

STS098-330-007 (7-20 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, works near the International Space Station (ISS) during one of the three STS-98 sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA).
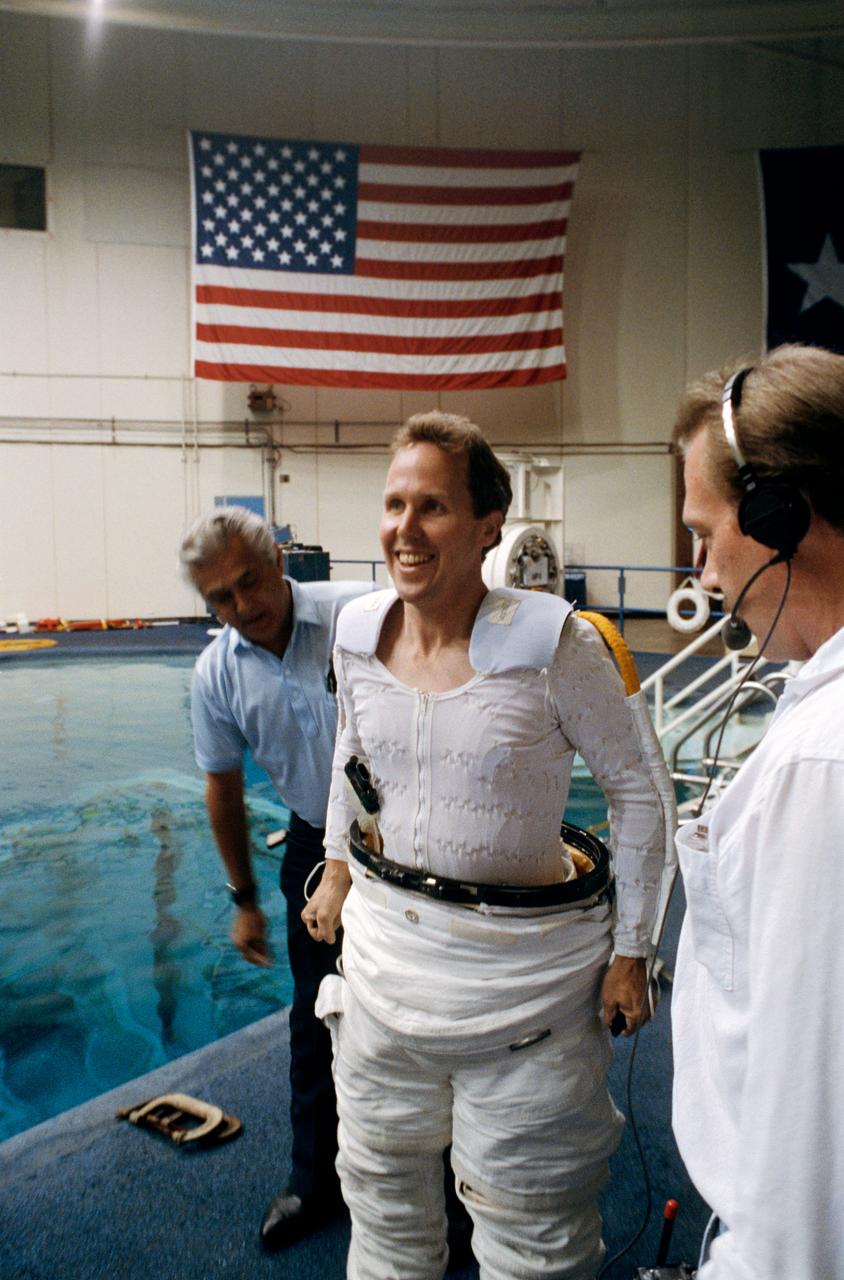

Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, dons a space suit prior to participating in contingency space walk simulations at the JSC Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF). Jones is assisted by Frank Hernandez (left) and suit technician Charles Hudson of Hamilton Standard. Jones suit is weighted to that he can achieve a neutrally buoyant state once under water. Extravehicular tasks are not planned for the STS-59 mission, but a number of chores are rehearsed in case of failure of remote systems to perform those jobs.
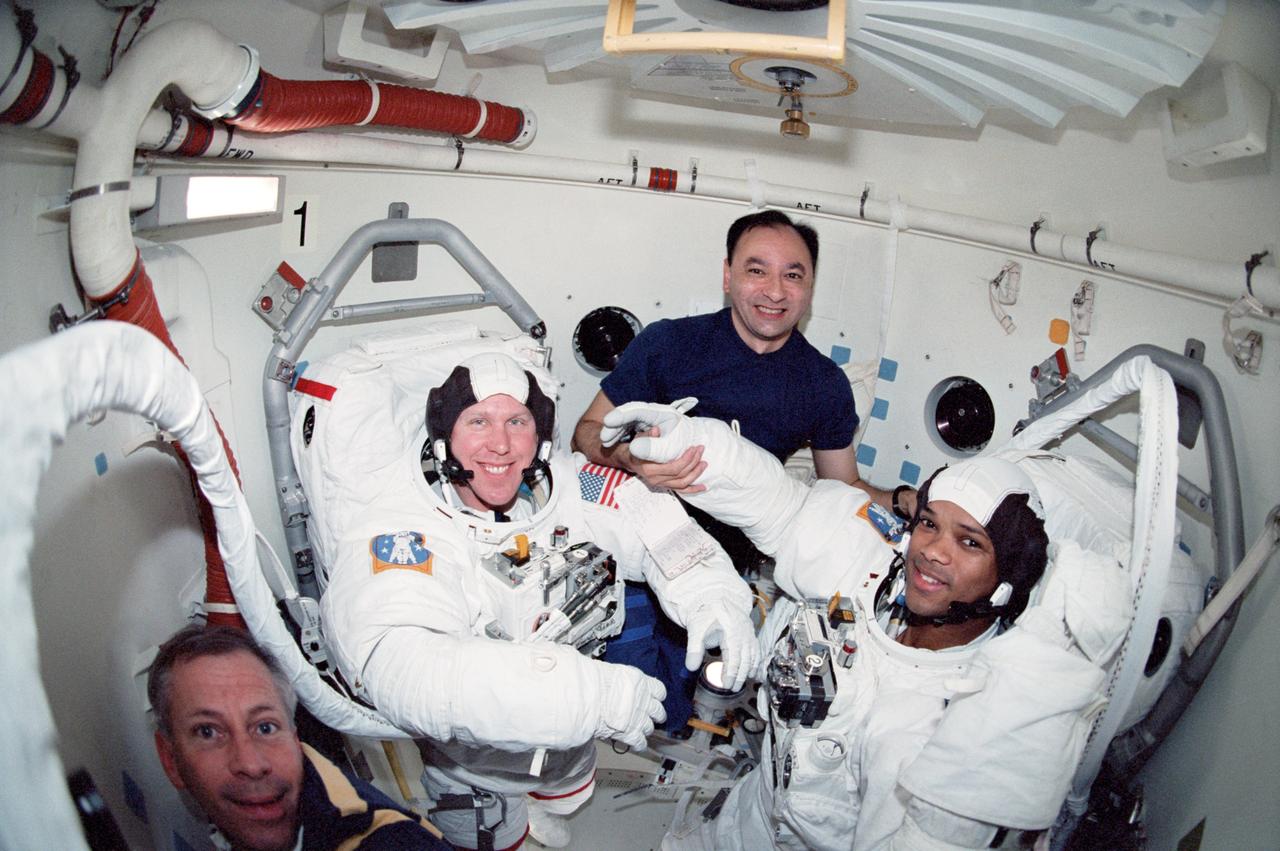

STS098-349-004 (7-20 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones (second left) and Robert L. Curbeam, both mission specialists, prepare for one of the three STS-98 sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell (lower left), mission commander, and Mark L. Polansky, mission specialist, assist Jones and Curbeam as they don their Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suits in the airlock of the Space Shuttle Atlantis.

SS98-E-5214 (14 February 2001) --- Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, STS-98 mission specialist, dons his extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) for the final of three space walks he shared with astonaut Thomas D. Jones on mission 5a. The scene was recorded with a digital still camera.

STS98-E-5223 (14 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, dons his extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) space garment in the airlock of the Space Shuttle Atlantis in this high-angle view photographed with a digital still camera. Jones was about to participate in the final of three space walks scheduled for the STS-98/5a mission.
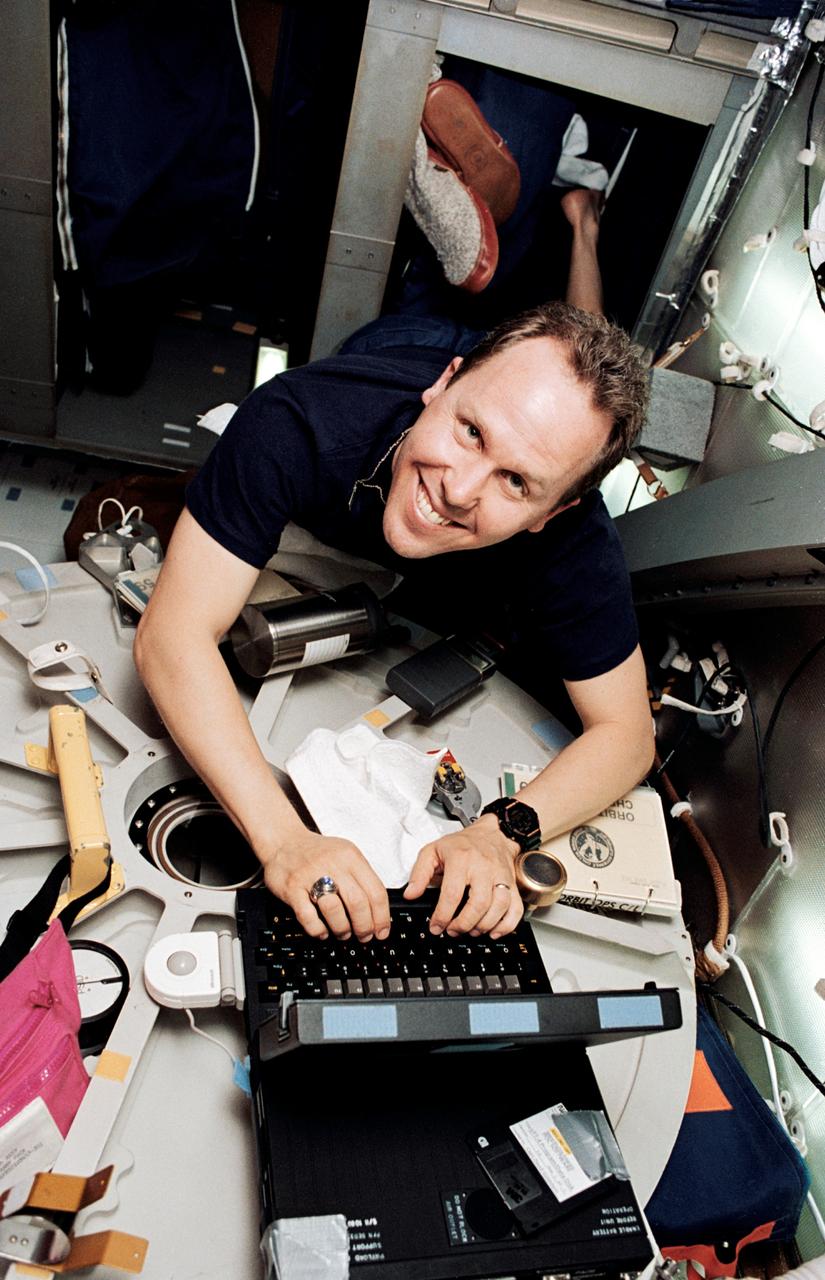

STS059-10-011 (9-20 April 1994) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones appears to have climbed out of bed right into his work in this onboard 35mm frame. Actually, Jones had anchored himself in the bunk facility while working on one of the onboard computers which transfered data to the ground via modem. The mission specialist was joined in space by five other NASA astronauts for a week and a half of support to the Space Radar Laboratory (SRL-1)/STS-59 mission.
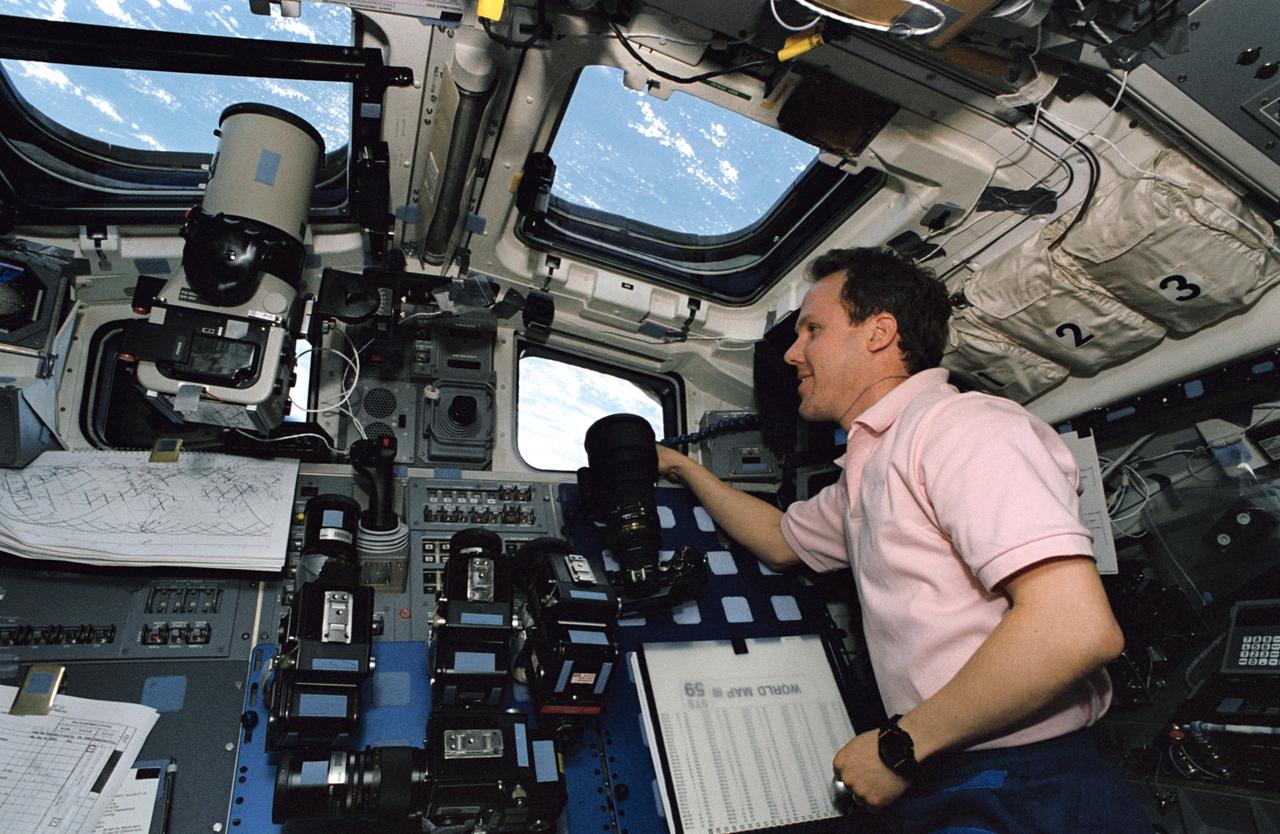

STS059-09-021 (9-20 April 1994) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, monitors a number of cameras fixed on targets of opportunity as the Space Shuttle Endeavour orbits Earth. Jones is one of six NASA astronauts supporting the week and half Space Radar Laboratory (SRL-1) mission. He has been assigned as payload commander for SRL-2, scheduled to fly later this year.
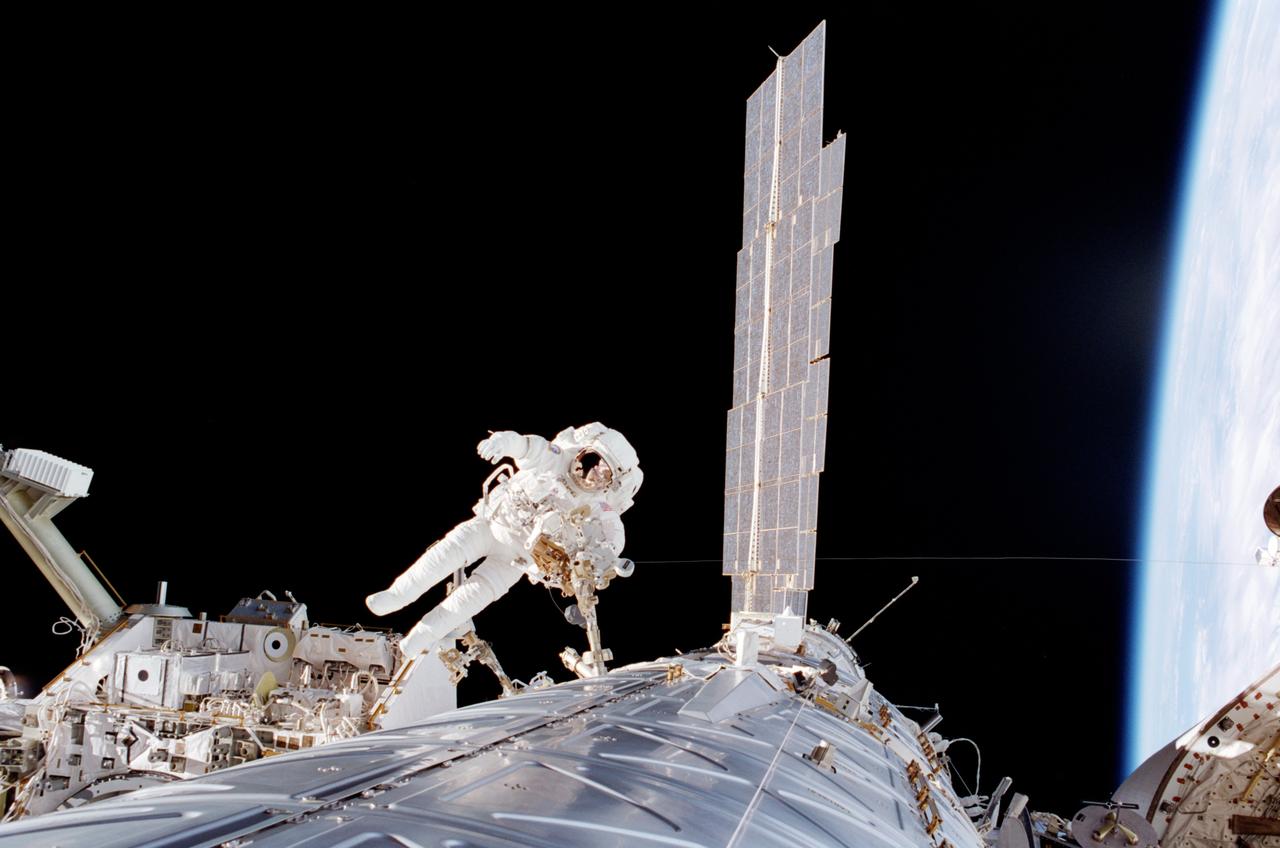

STS098-336-0026 (12 February 2001) --- Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, mission specialist, participates in the second of three STS-98 sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA). He was joined on all three space walks by astronaut Thomas D. Jones.
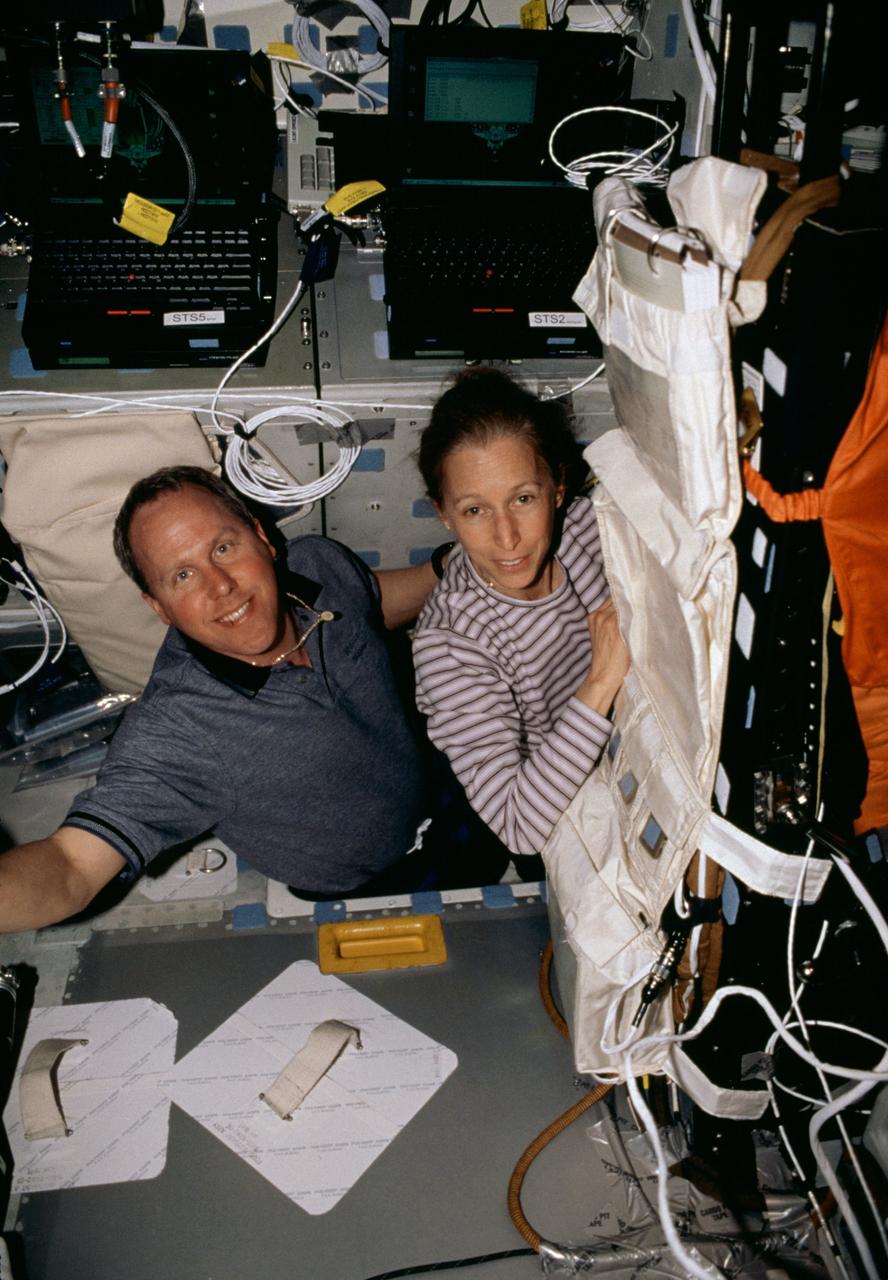

STS098-311-020 (7-20 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones and Marsha S. Ivins, both mission specialists, are photographed on the mid deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis near the Payload General Support Computers (PGSC).
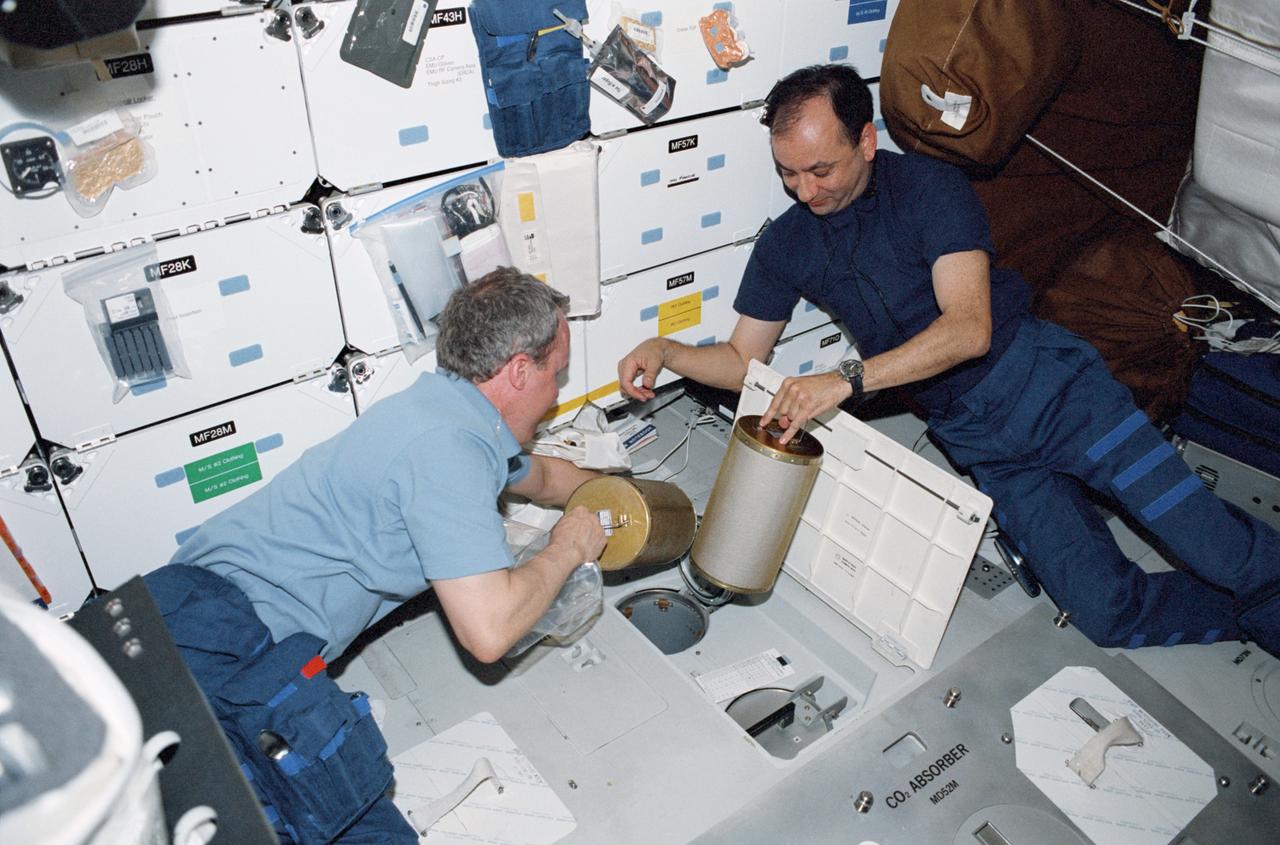

STS098-345-028 (7-20 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, and Mark L. Polansky, pilot, change out lithium hydroxide canisters on the mid deck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Atlantis.
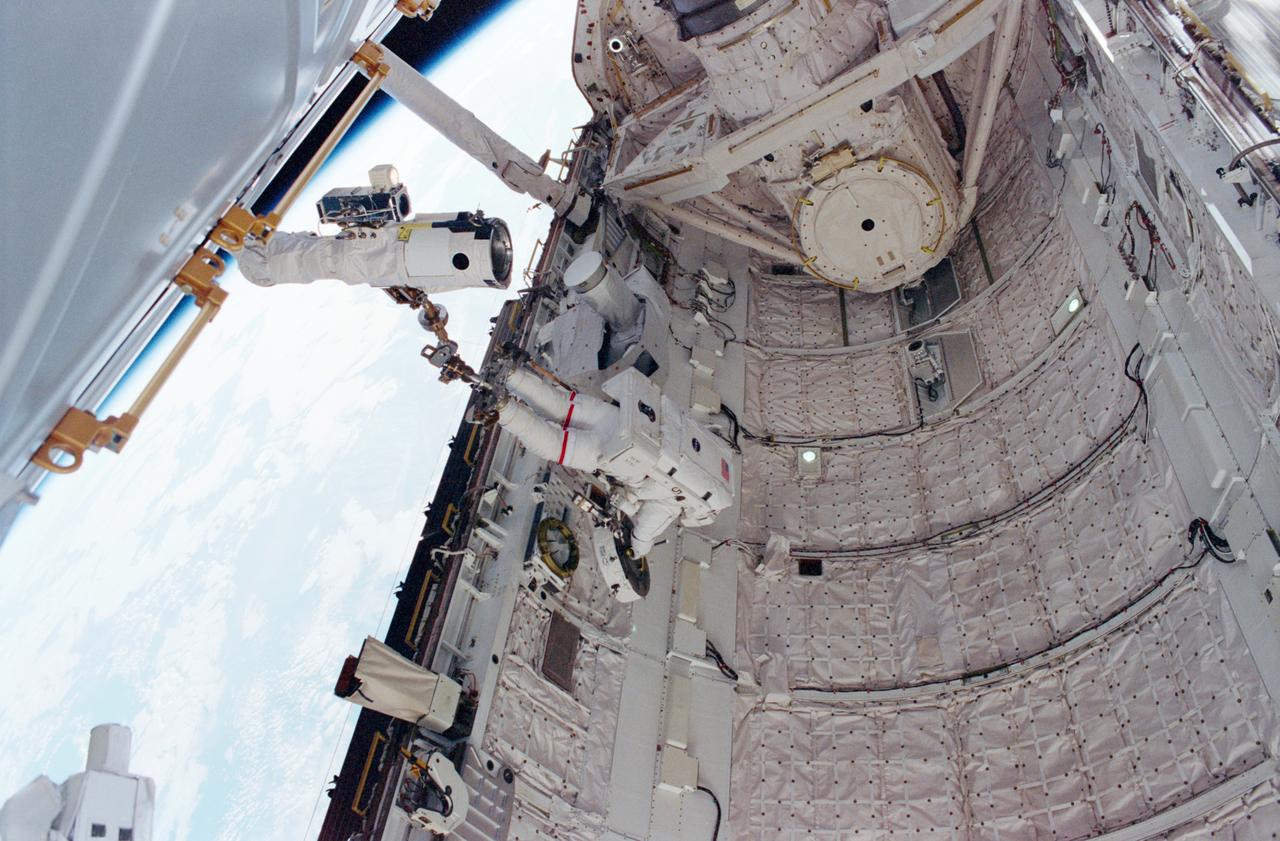

STS098-339-008 (7-20 February 2001) --- Anchored to a restraint device on the end of the shuttle’s remote manipulator system (RMS) robot arm, astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, works with the Power and Data Grapple Fixture (PDGF) in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Atlantis.

STS080-337-026 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, STS-80 mission specialist, uses the controls of the space shuttle Columbia's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) to conduct a test with the captured Wake Shield Facility (WSF) seen through window at frame center.
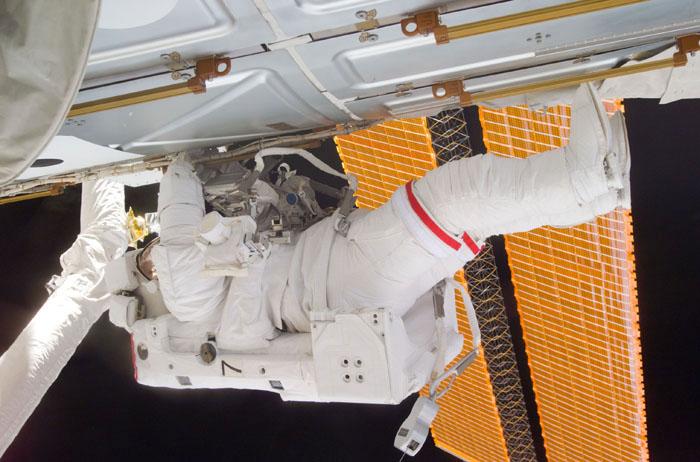
STS98-E-5229 (14 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, participates in the final of three STS-98/5a space walks to perform work on the International Space Station (ISS). The scene was photographed from the Space Shuttle Atlantis' crew cabin with a digital still camera.
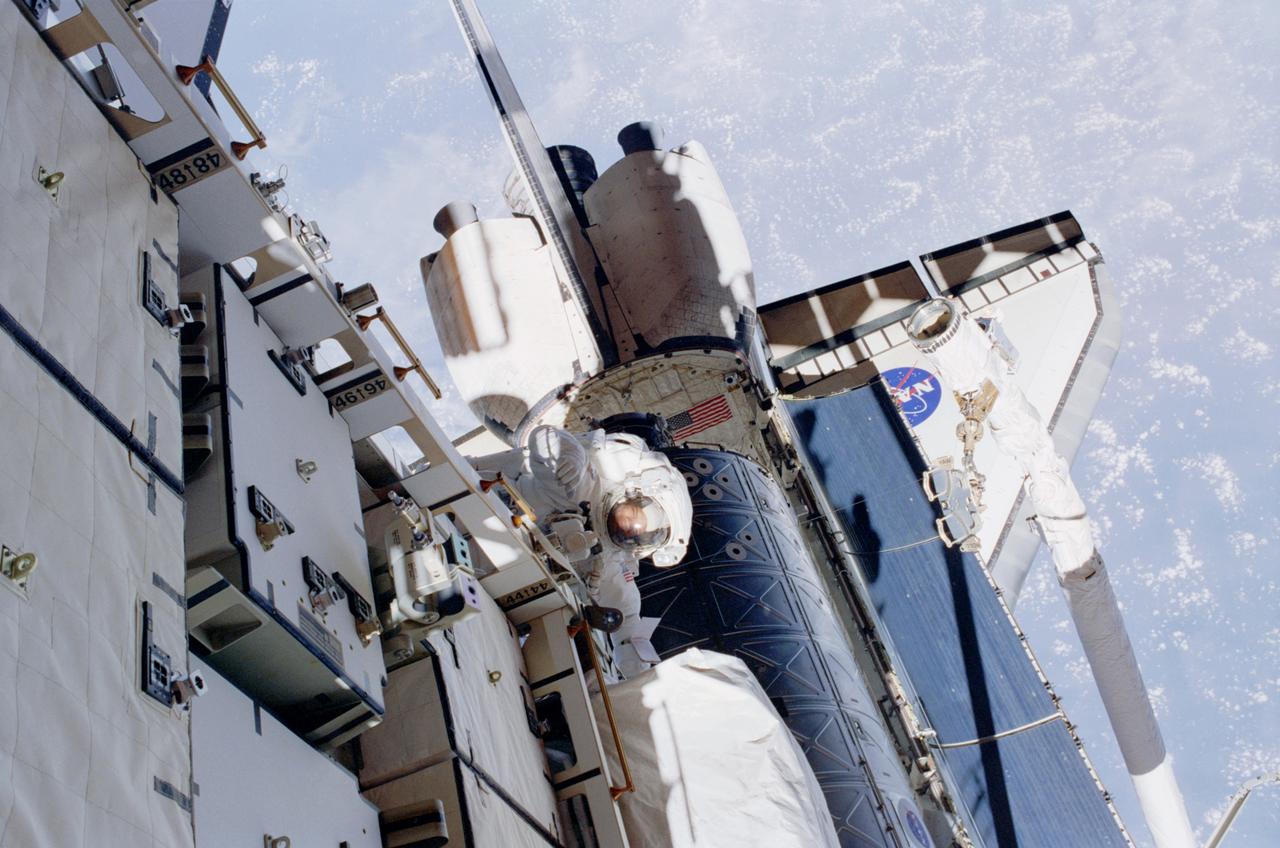

STS098-336-008 (7-20 February 2001) --- Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, mission specialist, is photographed by fellow space walker Thomas D. Jones, during one of the three STS-98 sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA).
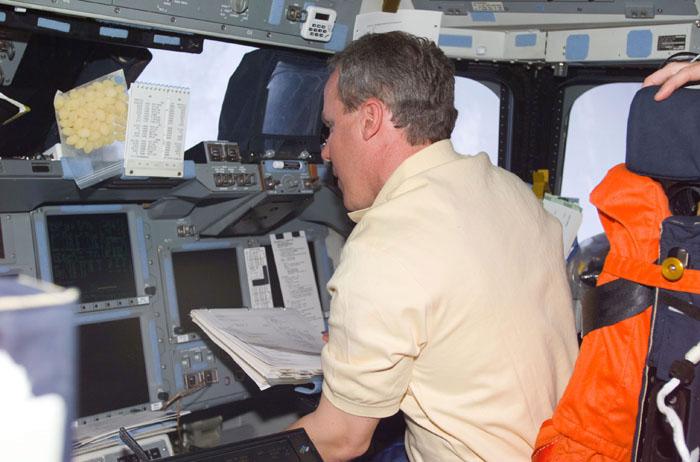

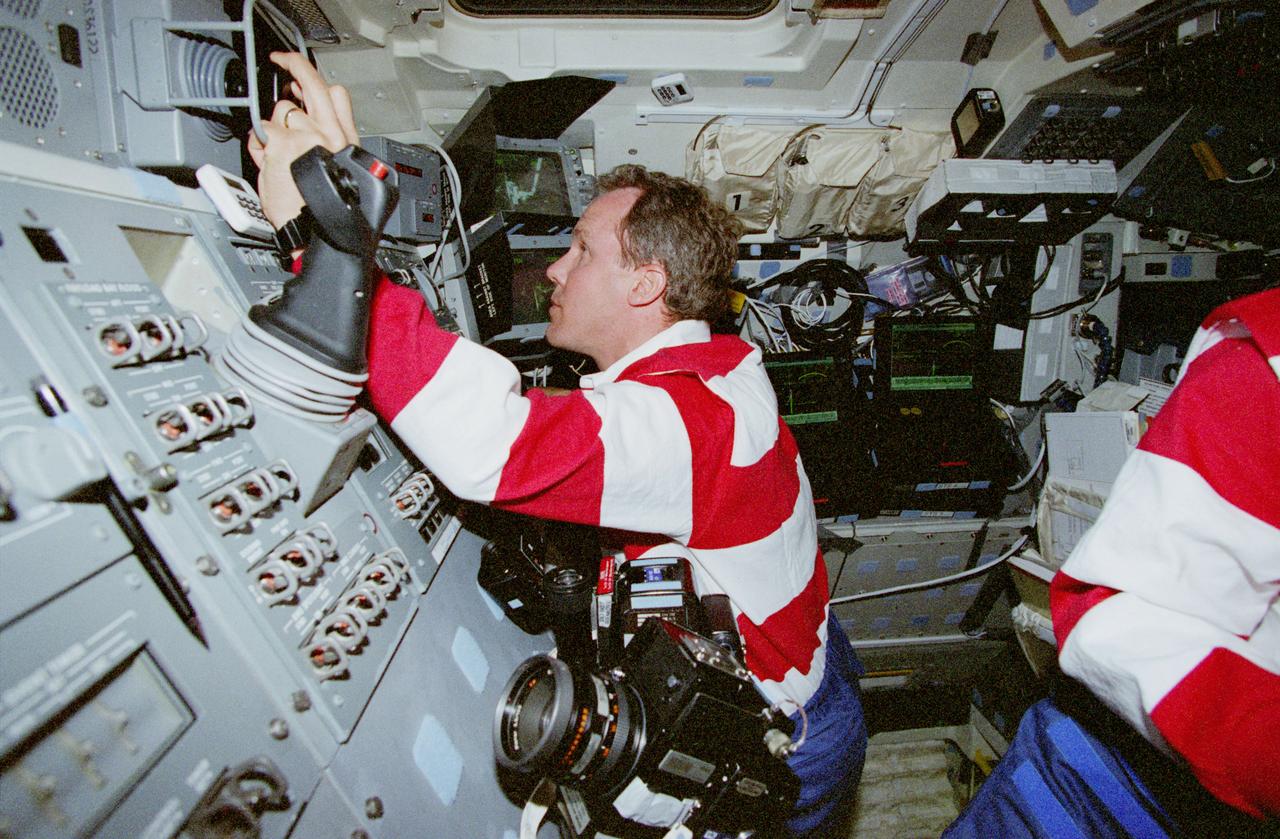
STS98-E-5027 (9 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, temporarily mans the pilot's station on the flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis during STS-98 Flight Day 2 maneuvers. The photograph was recorded with a digital still camera.
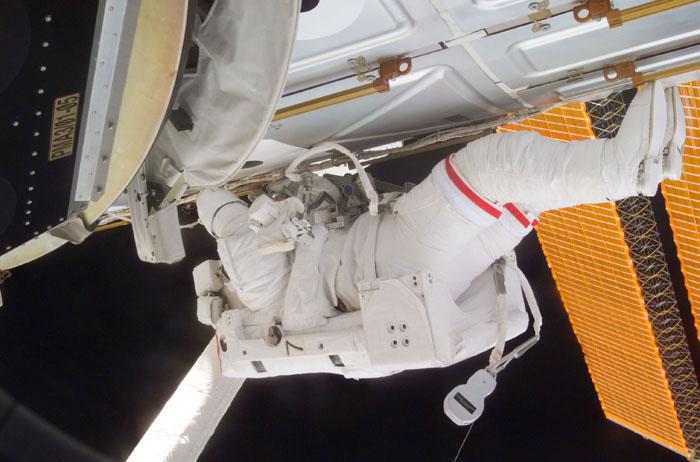

STS98-E-5230 (14 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, participates in the final of three STS-98/5a space walks to perform work on the International Space Station (ISS). The scene was photographed from the Space Shuttle Atlantis' crew cabin with a digital still camera.
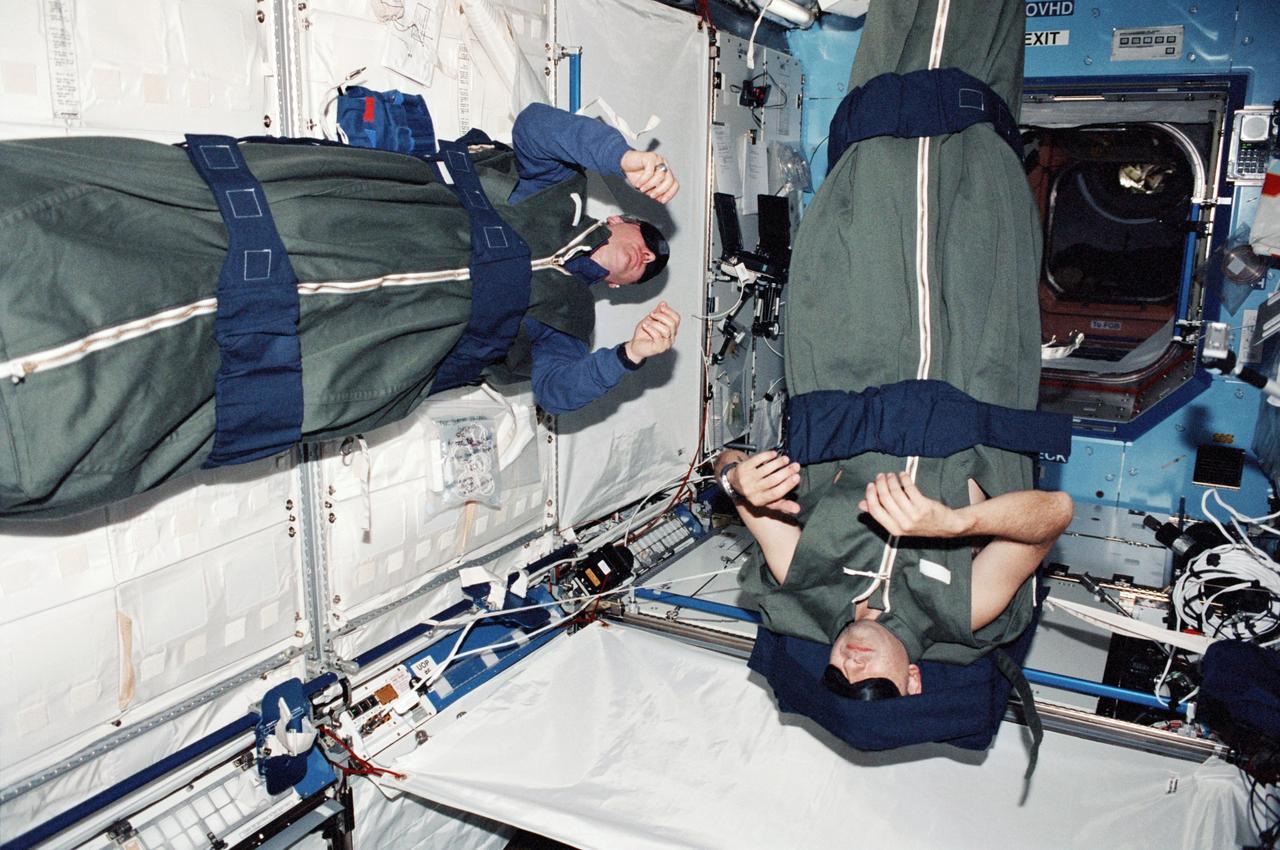

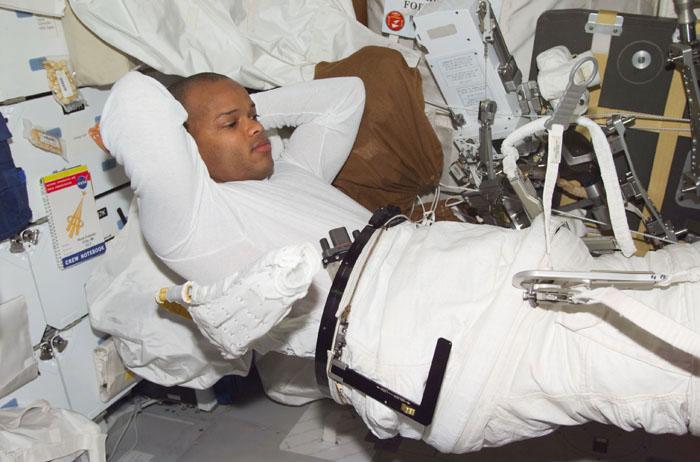
STS098-355-001 (7-20 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones and Mark L. Polansky, STS-98 mission specialists, are photographed during their sleep shift in the newly-attached Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS).
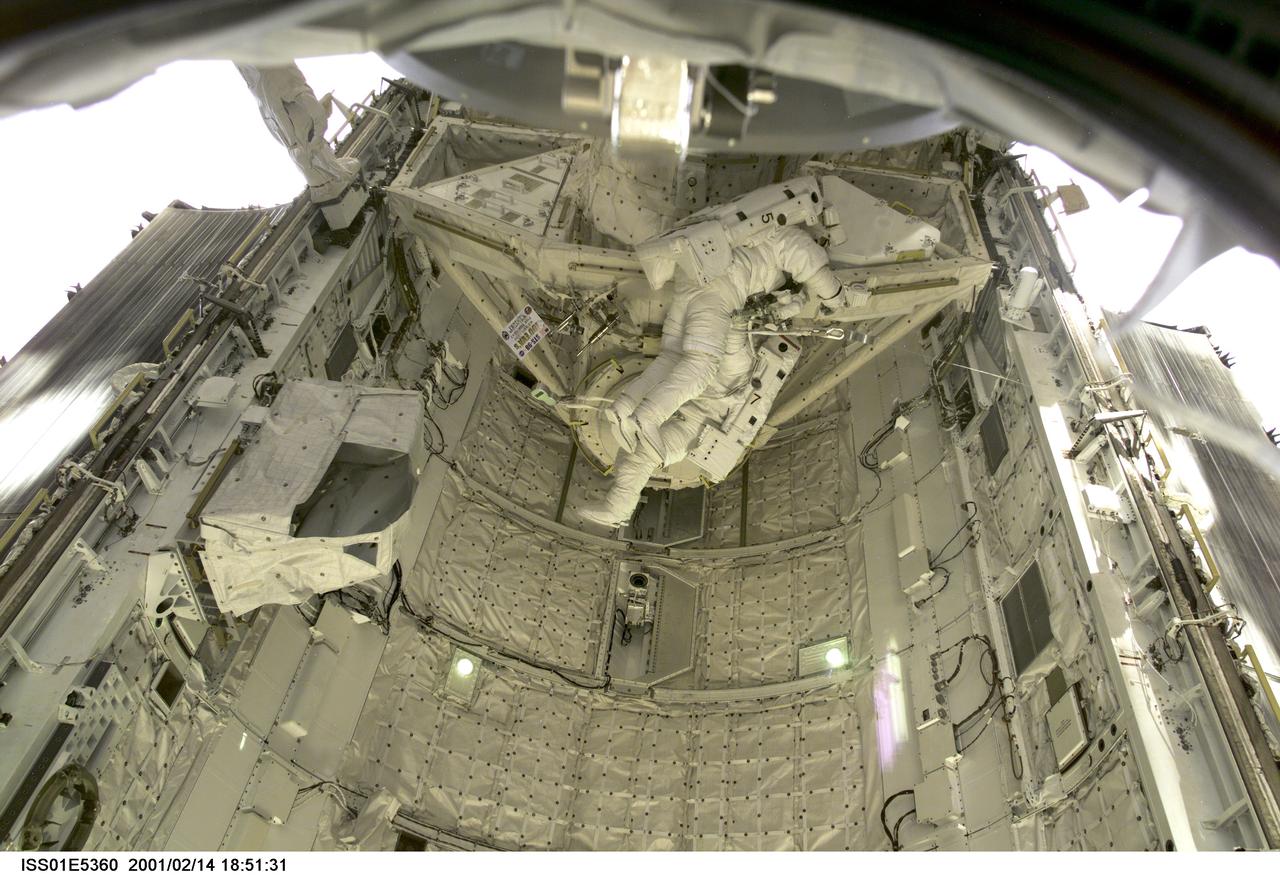

ISS01-E-5360 (14 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones (partially obscured) and Robert L. Curbeam, STS-98 mission specialists, are pictured in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Atlantis during their third space walk, as photographed with a digital still camera from the International Space Station's new Destiny laboratory.
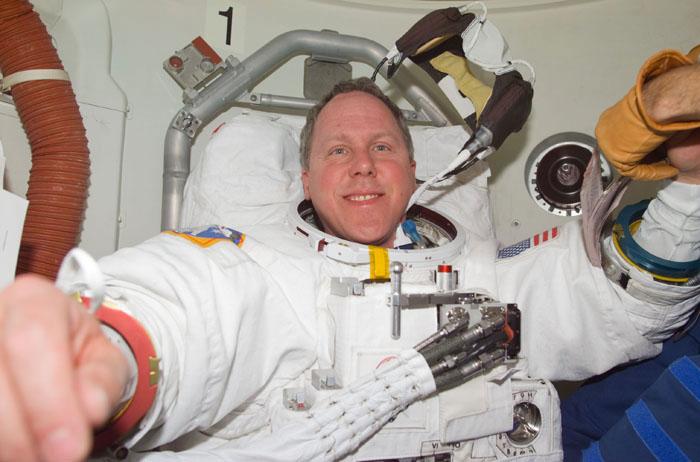

STS98-E-5176 (12 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, STS-98 mission specialist, dons his extravehicular mobility unit for the upcoming space walk on the International Space Station on February 12. This scene was recorded with a digital still camera.
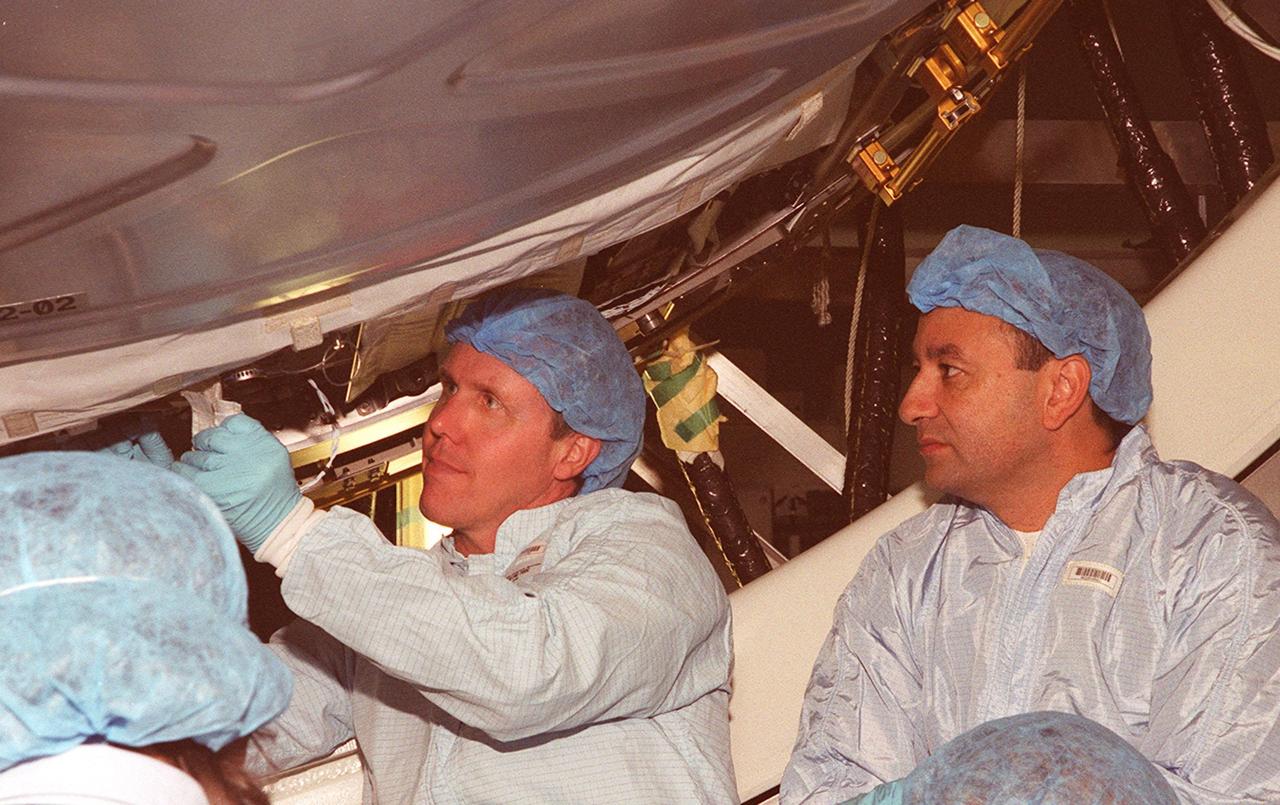

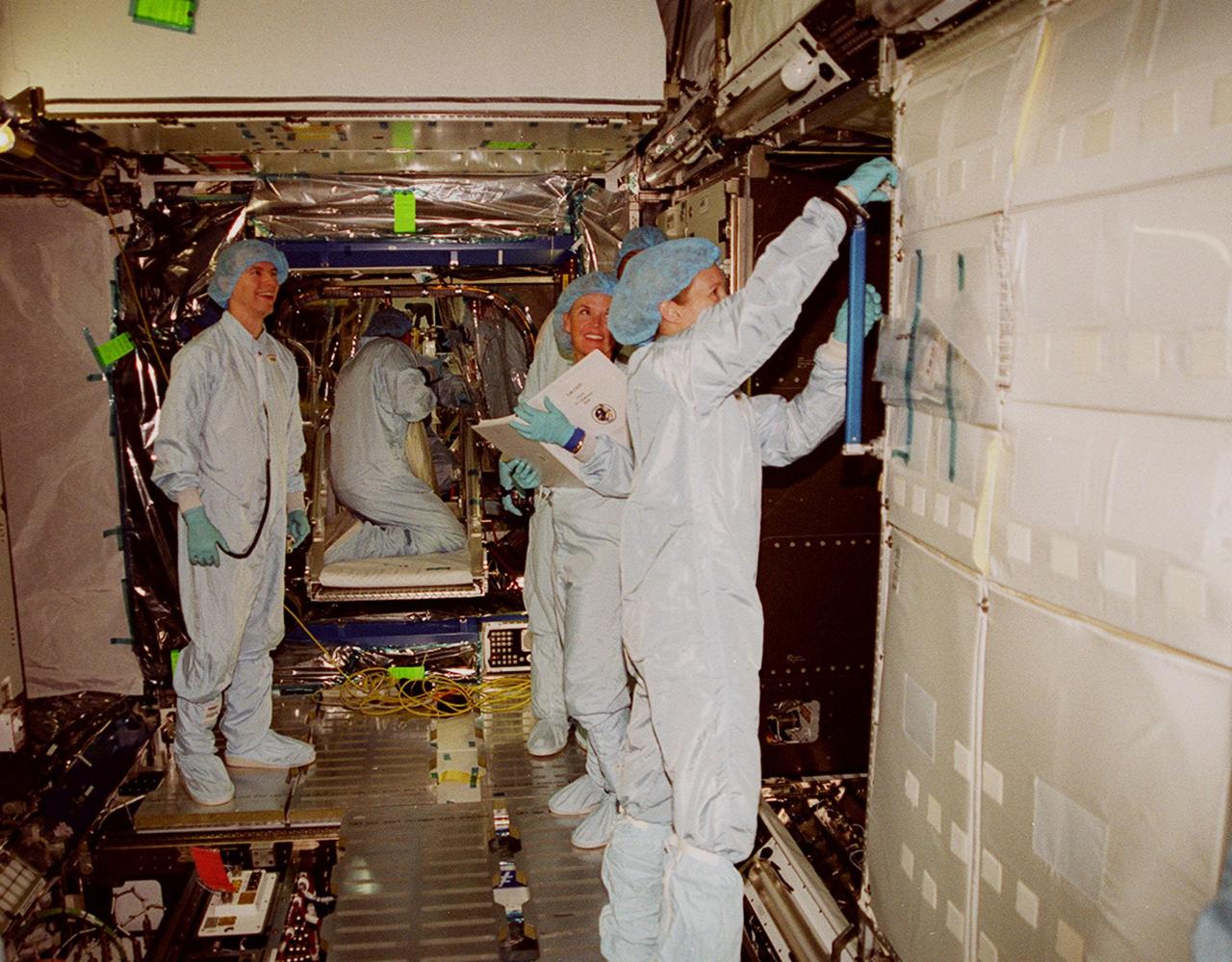
In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-98 Mission Specialist Thomas Jones works on a part of the U.S. Lab, Destiny. Watching at right is Pilot Mark Polansky. Jones and Polansky, along with other crew members, are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities to become familiar with equipment they will be handling during the mission. Others in the crew are Commander Ken Cockrell and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam and Marsha Ivins. The mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. With delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. The STS-98 launch is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001
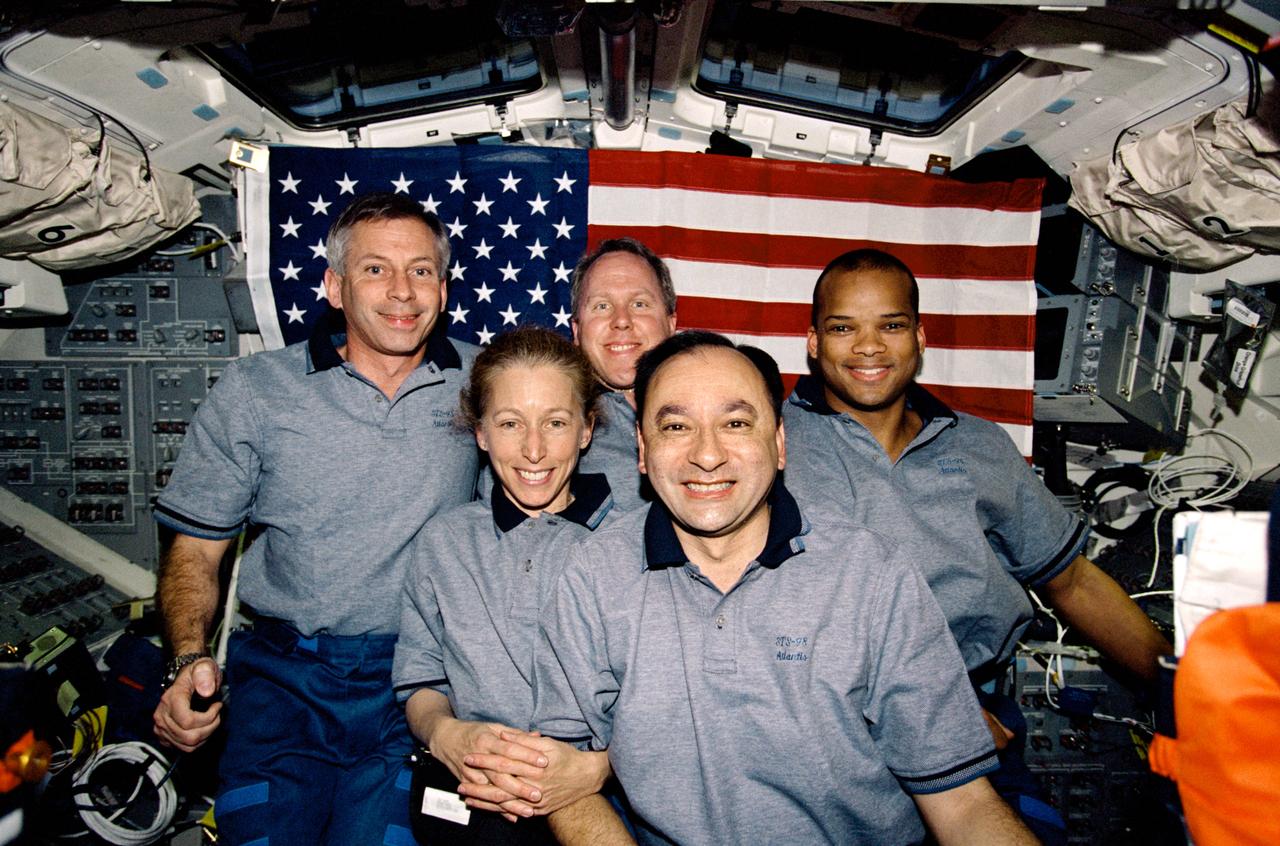

STS098-365-0034 (7-20 February 2001) --- The crew of the STS-98 mission poses for the traditional inflight portrait on the flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. From left are astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander; Marsha S. Ivins, mission specialist; Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist; Mark L. Polansky, pilot; and Robert L. Curbeam, mission specialist.

STS080-701-004 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- The STS-80 crew used a pre-set 70mm camera onboard the space shuttle Columbia's middeck to record its traditional inflight crew portrait. Back row, left to right, astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander; Tamara E. Jernigan, mission specialist; and Kent V. Rominger, pilot. Front row, astronauts Thomas D. Jones (left) and Story Musgrave, both mission specialists.
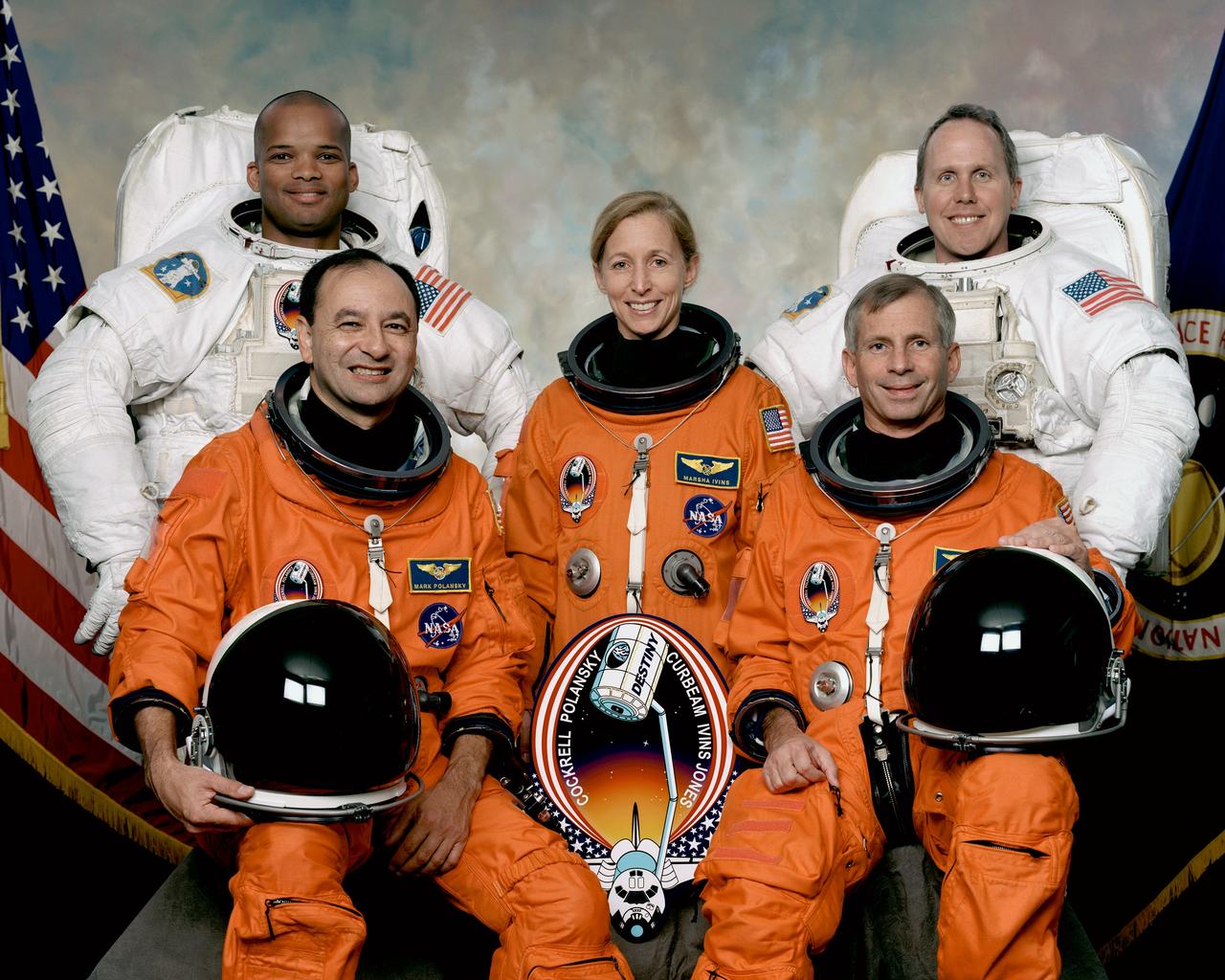

STS098-S-002 (December 2000) --- These five astronauts have been in training for the STS-98 mission, scheduled for launch aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis in January of 2001. The crew is composed of astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell (right front), mission commander; and Mark L. Polansky (left front), pilot; along with astronauts Marsha S. Ivins, Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., (left rear) and Thomas D. Jones (right rear), all mission specialists. Curbeam and Jones are the scheduled extravehicular activity (EVA) participants for the International Space Station's 5a mission.
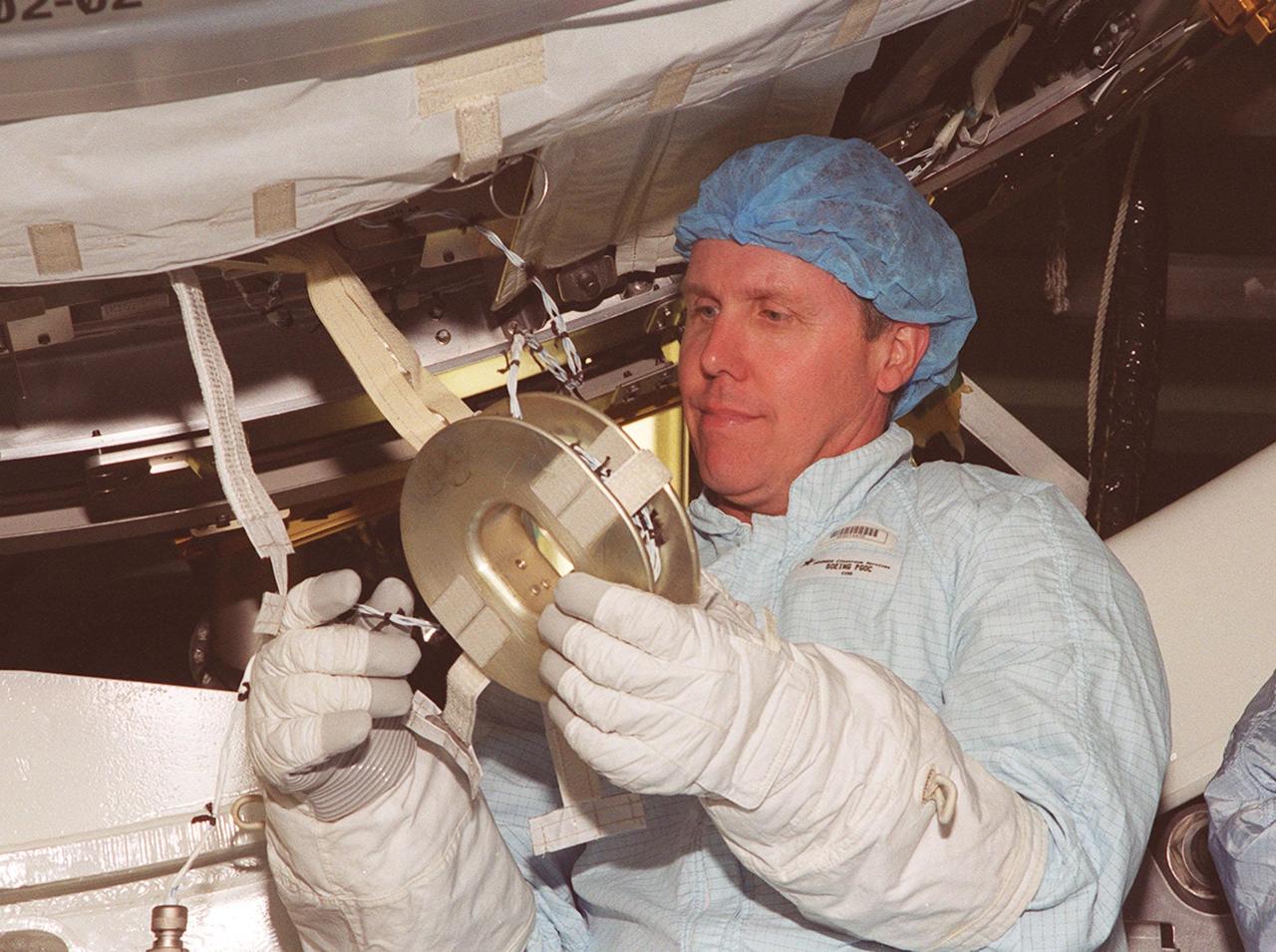

STS-98 Mission Specialist Thomas Jones practices handling a piece of equipment on the U.S. Lab, Destiny, while wearing the gloves he will wear in space. Jones and other crew members are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities to become familiar with equipment they will be handling during the mission. With launch scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001, the STS-98 mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated
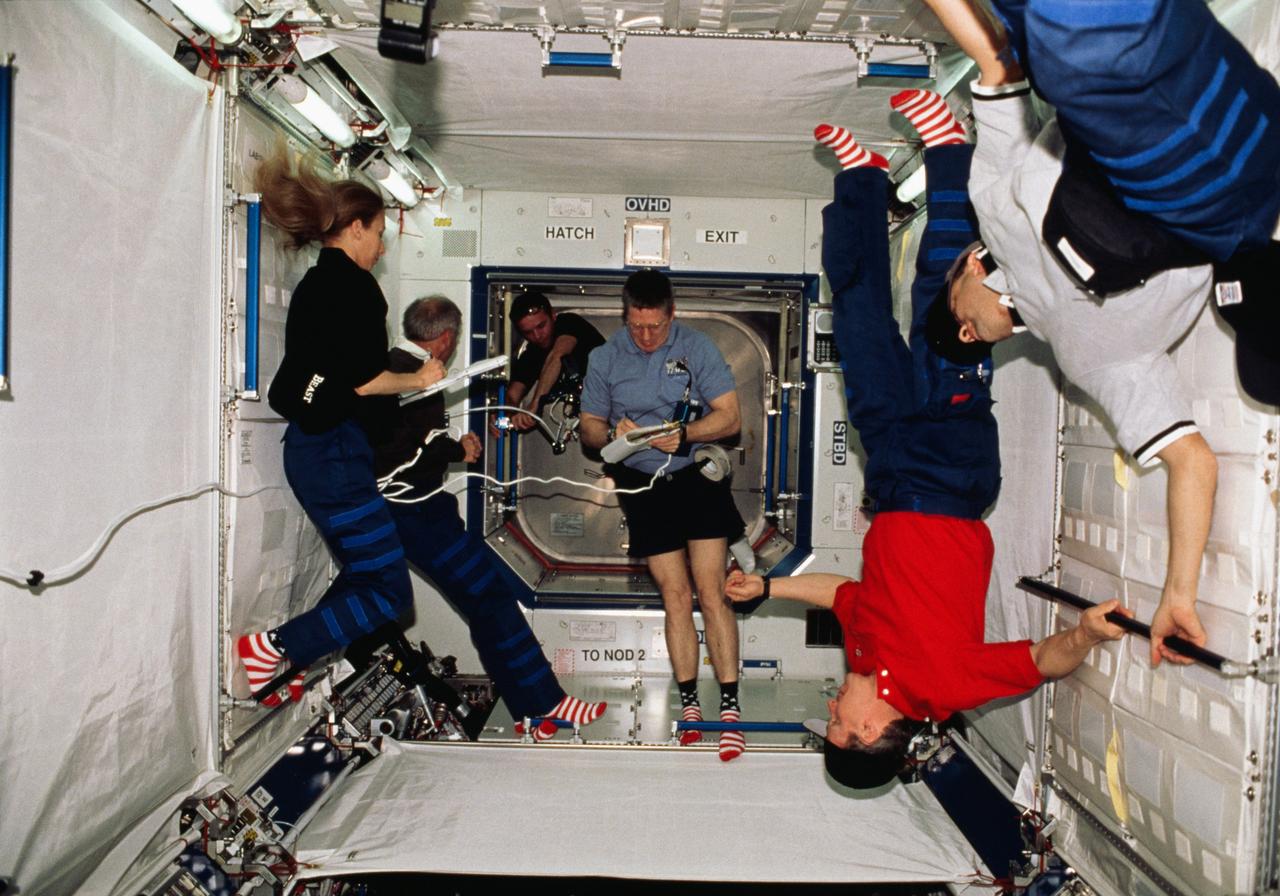

STS098-323-015 (7-20 February 2001) --- Astronauts and cosmonauts from the Expedition One and STS-98 crews are photographed in the newly-attached Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). From the left are Marsha S. Ivins, mission specialist; Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander; Yuri P. Gidzenko, Expedition One Soyuz commander; William M. (Bill) Shepherd, Expedition One mission commander; Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist; and Mark L. Polansky, pilot. Out of view are Robert L. Curbeam, mission specialist, and Sergei K. Krikalev, Expedition One flight engineer. Gidzenko and Krikalev represent Rosaviakosmos.
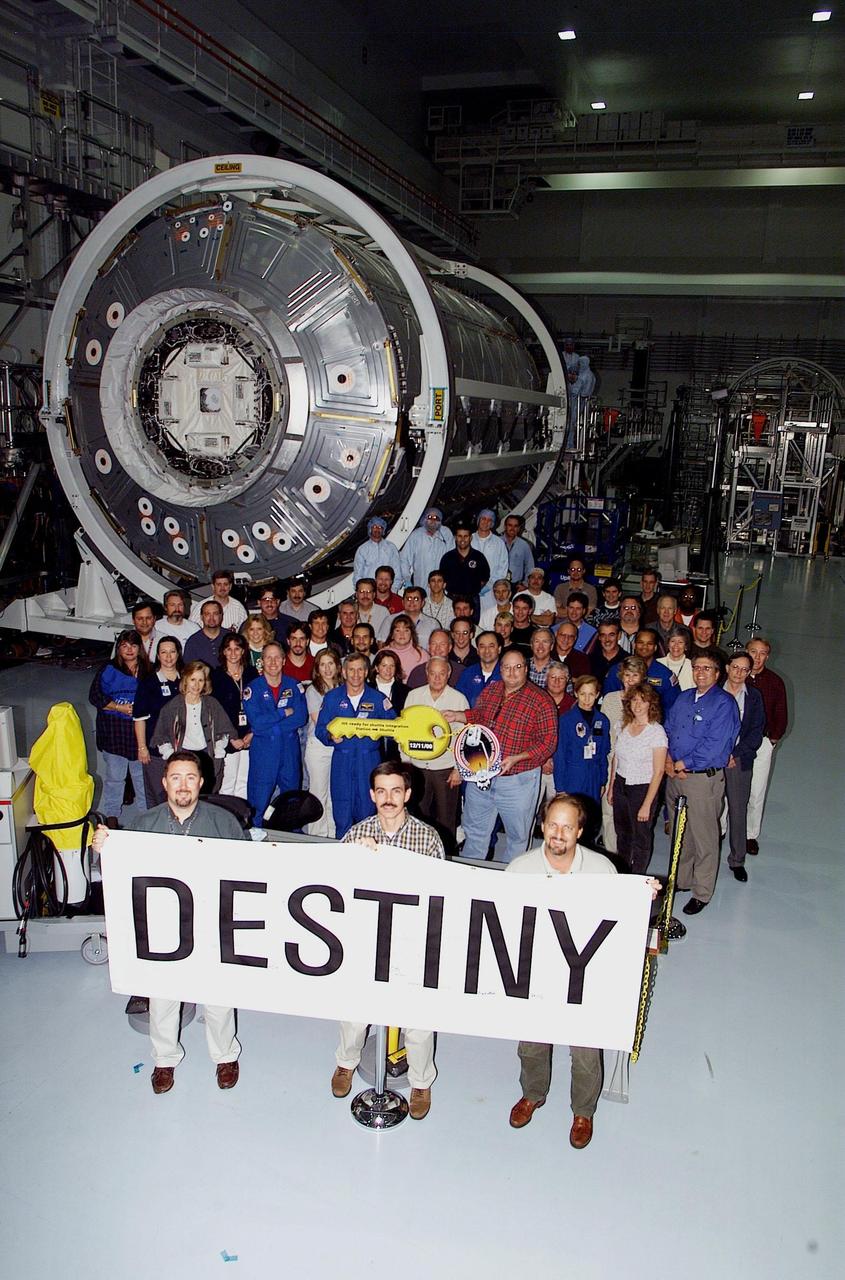

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers and the STS-98 crew gather for a ceremony that turns over the “key” for the U.S. Lab Destiny to NASA. Holding the key (left) is STS-98 Commander Ken Cockrell. To his left is Mission Specialist Thomas Jones; at right (in uniform) is Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins. Also in the group are Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. . Launch of mission STS-98 on Space Shuttle Atlantis is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001. The mission will carry the U.S. Lab Destiny to the International Space Station with five system racks and experiments already installed inside the module

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers and the STS-98 crew gather for a ceremony that turns over the “key” for the U.S. Lab Destiny to NASA. Holding the key (left) is STS-98 Commander Ken Cockrell. To his left is Mission Specialist Thomas Jones; at right (in uniform) is Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins. Also in the group are Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. . Launch of mission STS-98 on Space Shuttle Atlantis is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001. The mission will carry the U.S. Lab Destiny to the International Space Station with five system racks and experiments already installed inside the module
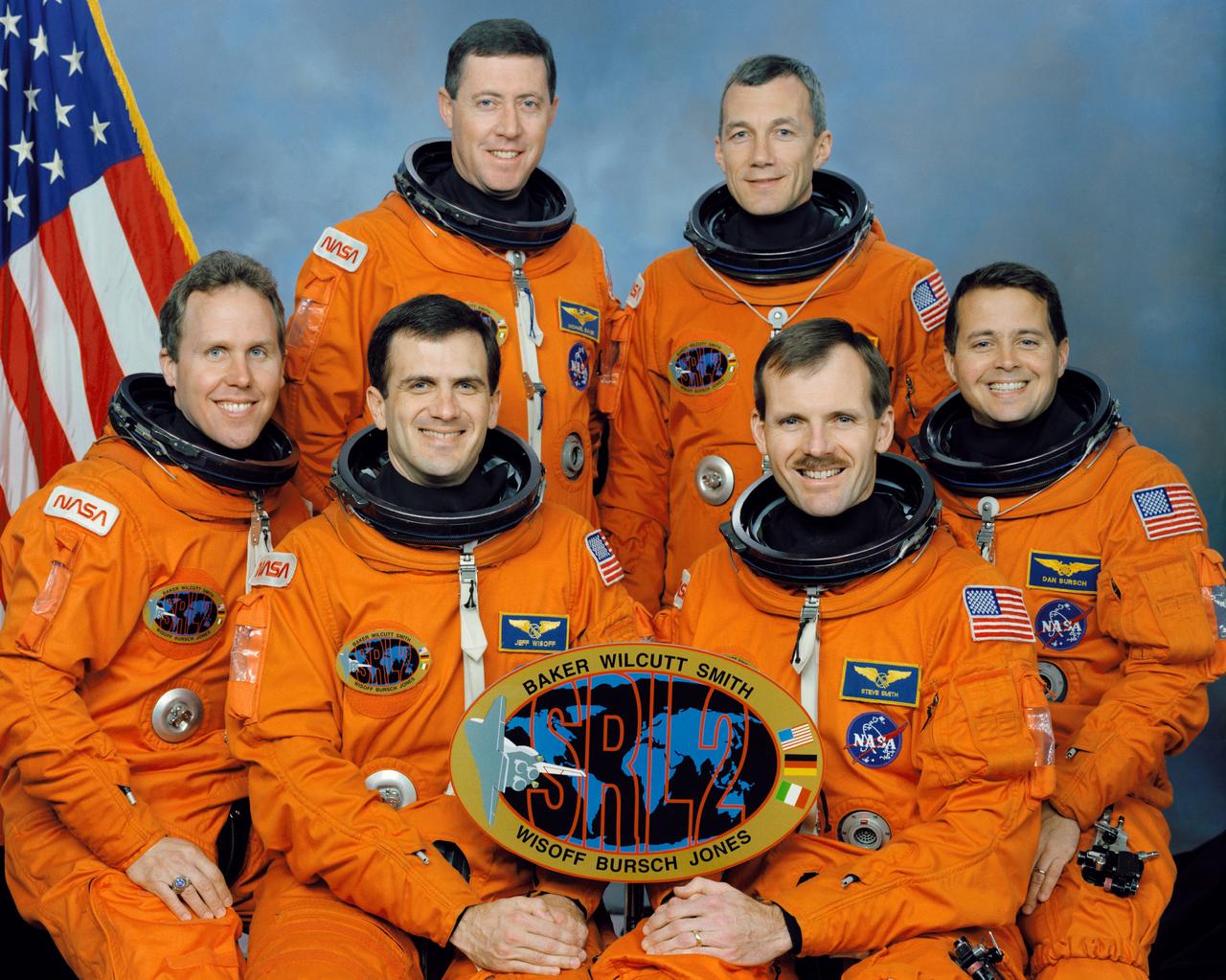

These six NASA astronauts composed the crew of the STS-68 mission that launched aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on September 30, 1994. Standing are, left to right, Michael A. Baker, mission commander; and Terrence W. Wilcutt, pilot. On the front row are, left to right, Thomas D. Jones, payload commander; and Peter J. K. (Jeff) Wisoff, Steven L. Smith, and Daniel W. Bursch, all mission specialists. STS-68 marked the second flight of the Space Radar Laboratory, part of NASA’s mission to planet Earth.
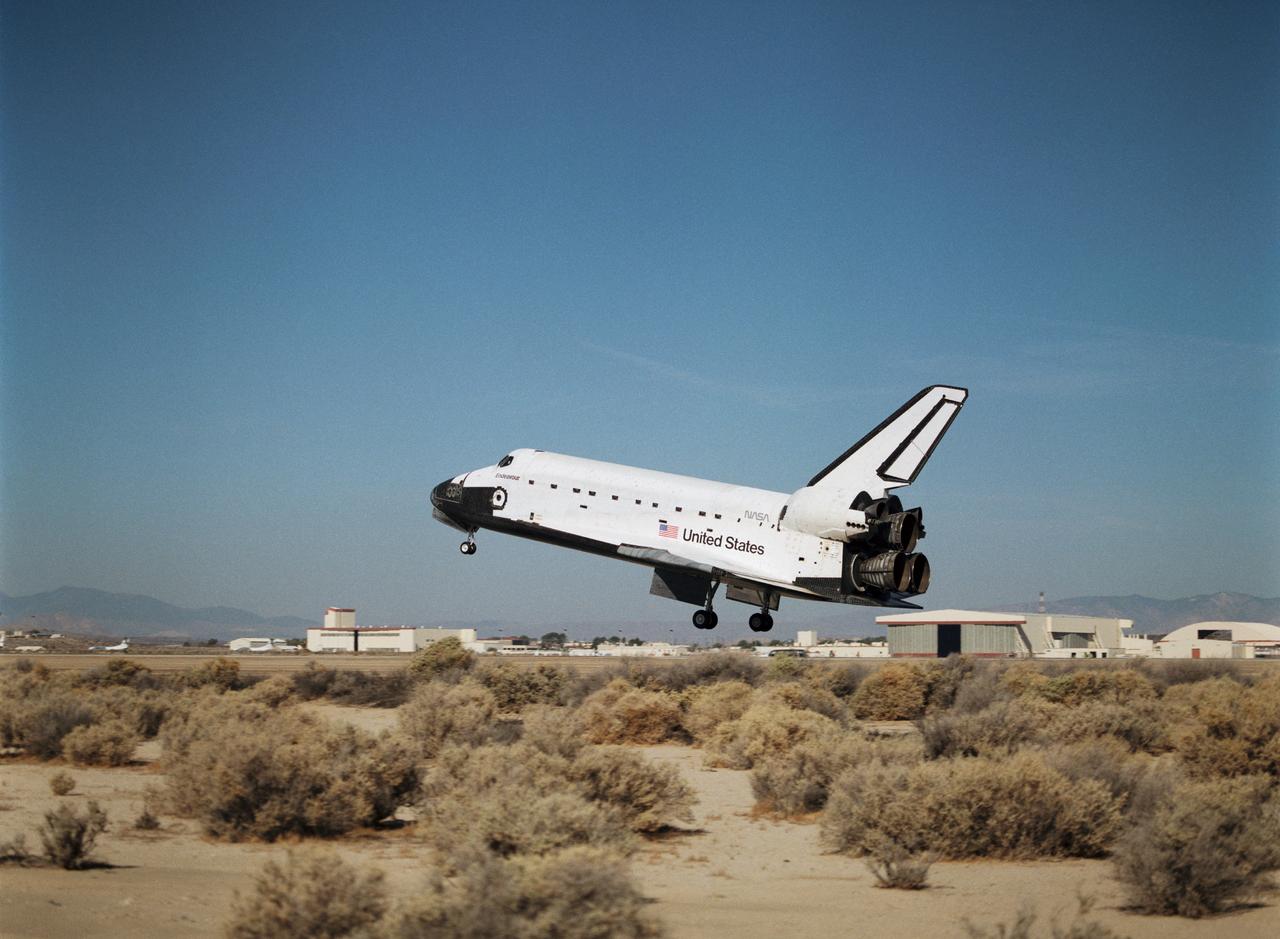

STS068-S-059 (11 October 1994) --- With its main landing gear not quite on the runway, the Space Shuttle Endeavour wraps up an eleven-day mission at Edwards Air Force Base, California. Landing occurred at 10:02 a.m. (PDT), October 11, 1994. Onboard were astronauts Michael A. Baker, mission commander; Terrence W. Wilcutt, pilot; Thomas D. Jones, payload commander; and Daniel W. Bursch, Peter J. K. (Jeff) Wisoff and Steven L. Smith, all mission specialists.
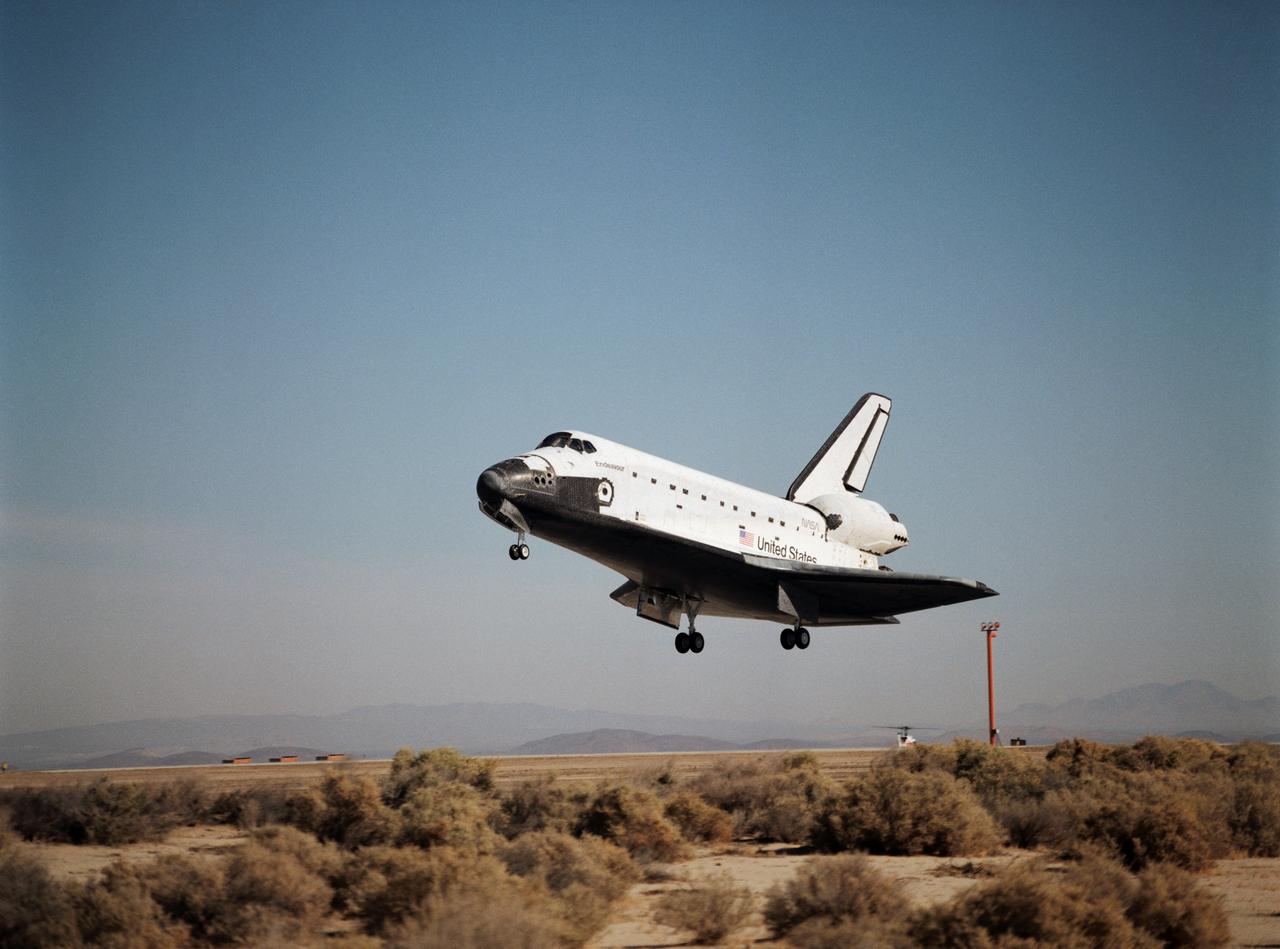

STS068-S-060 (11 October 1994) --- With its main landing gear not quite on the runway, the Space Shuttle Endeavour wraps up an eleven-day mission at Edwards Air Force Base, California. Landing occurred at 10:02 a.m. (PDT), October 11, 1994. Onboard were astronauts Michael A. Baker, mission commander; Terrence W. Wilcutt, pilot; Thomas D. Jones, payload commander; and Daniel W. Bursch, Peter J. K. (Jeff) Wisoff and Steven L. Smith, all mission specialists.

STS080-S-002 (August 1996) --- These five NASA astronauts are in training for the STS-80 mission, scheduled for launch aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia in the fall of this year. From the left are astronauts Kent V. Rominger, pilot; Tamara E. Jernigan, Story Musgrave and Thomas D. Jones, all mission specialists; and Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander.
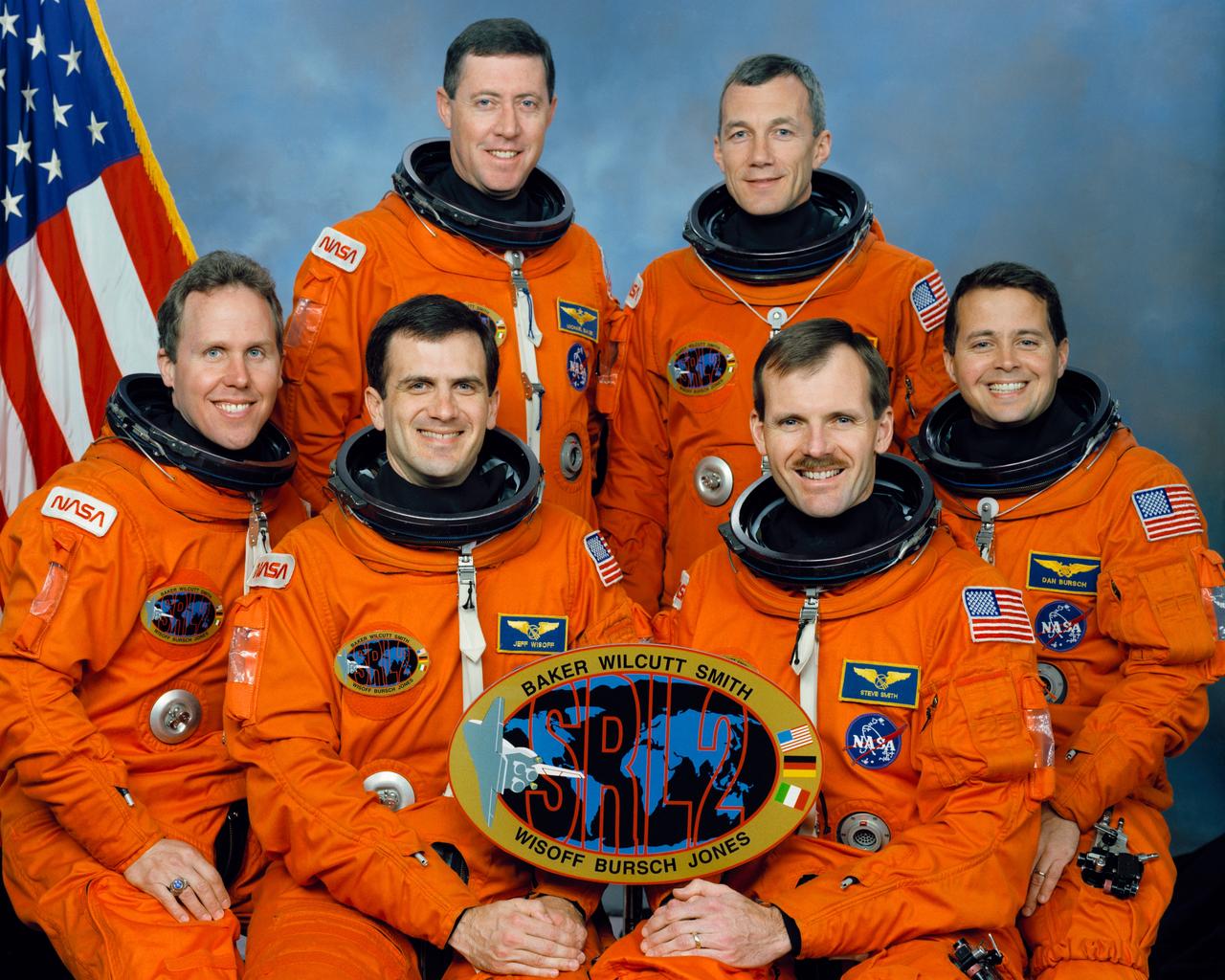

STS068-S-002 (March 1994) --- These six NASA astronauts are in training for the mission, scheduled for launch later this year. Standing are, left to right, Michael A. Baker, mission commander; and Terrence W. Wilcutt, pilot. On the front row are, left to right, Thomas D. Jones, payload commander; and Peter J. K. (Jeff) Wisoff, Steven L. Smith and Daniel W. Bursch, all mission specialists.
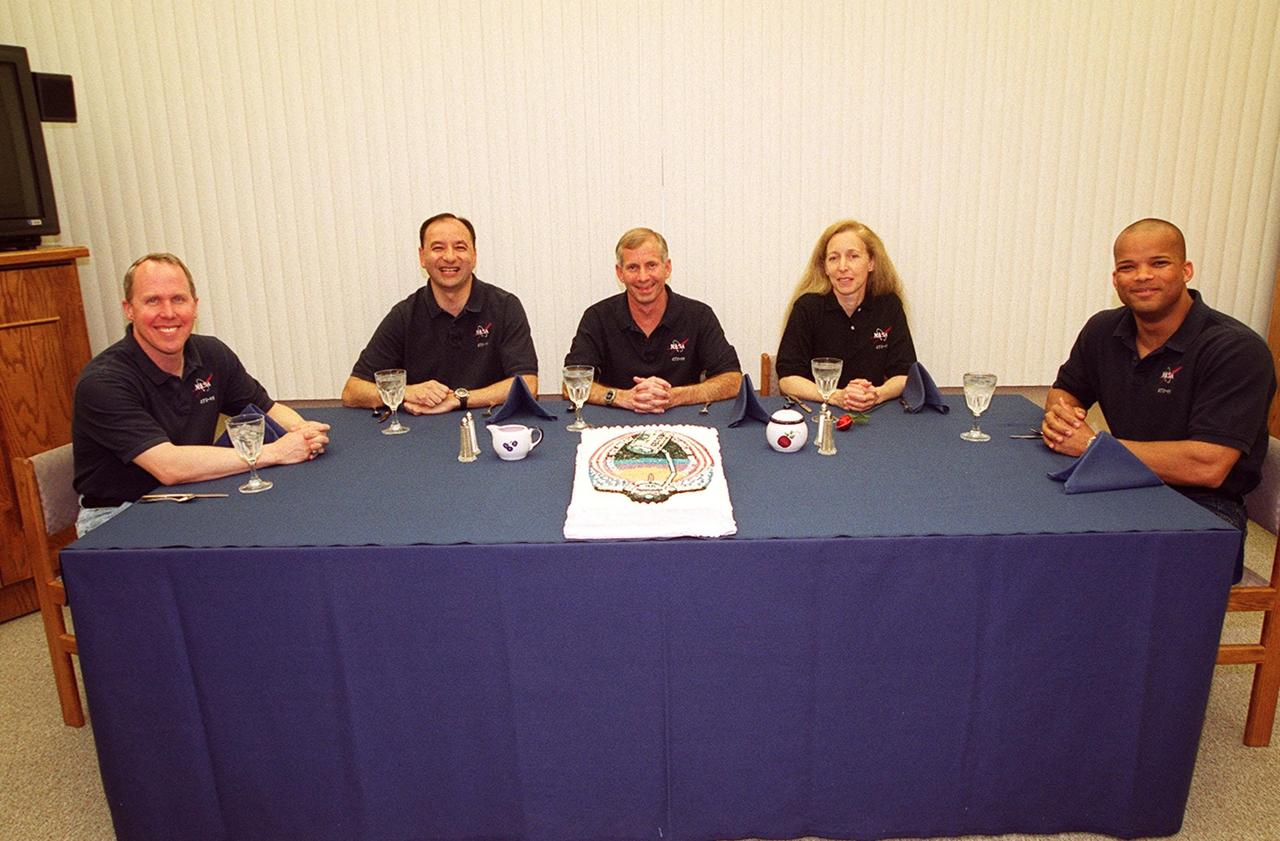

The STS-98 crew gathers around a table for a snack before getting ready for launch on Space Shuttle Atlantis. Seated left to right are Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Pilot Mark Polansky, Commander Ken Cockrell and Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks, by Curbeam and Jones, are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. Launch is targeted for 6:11 p.m. EST and the planned landing at KSC Feb. 18 about 1:39 p.m. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program
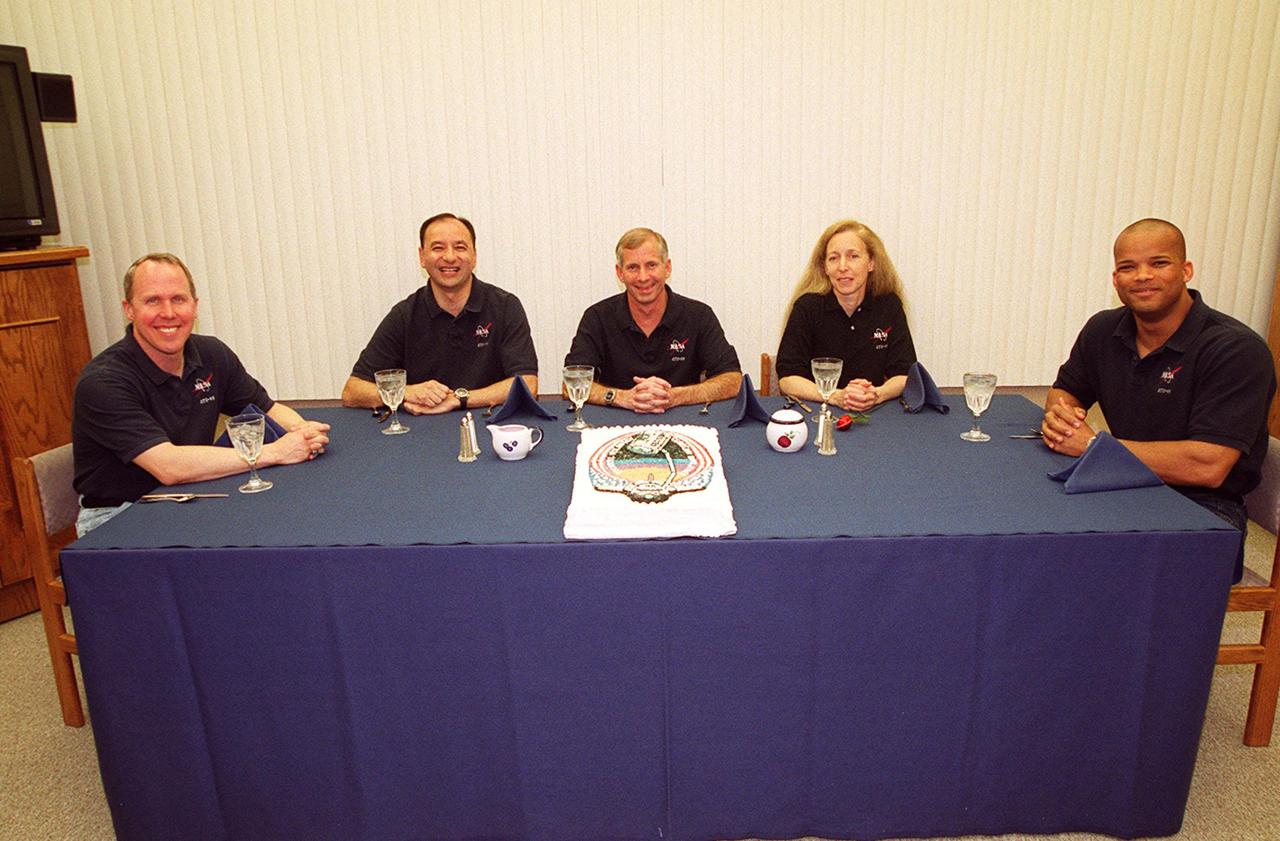

The STS-98 crew gathers around a table for a snack before getting ready for launch on Space Shuttle Atlantis. Seated left to right are Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Pilot Mark Polansky, Commander Ken Cockrell and Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks, by Curbeam and Jones, are required to complete the planned construction work during the 11-day mission. Launch is targeted for 6:11 p.m. EST and the planned landing at KSC Feb. 18 about 1:39 p.m. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program

STS-98 Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins waits in the White Room outside the entrance into Atlantis. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The other crew members are Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Commander Ken Cockrell and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
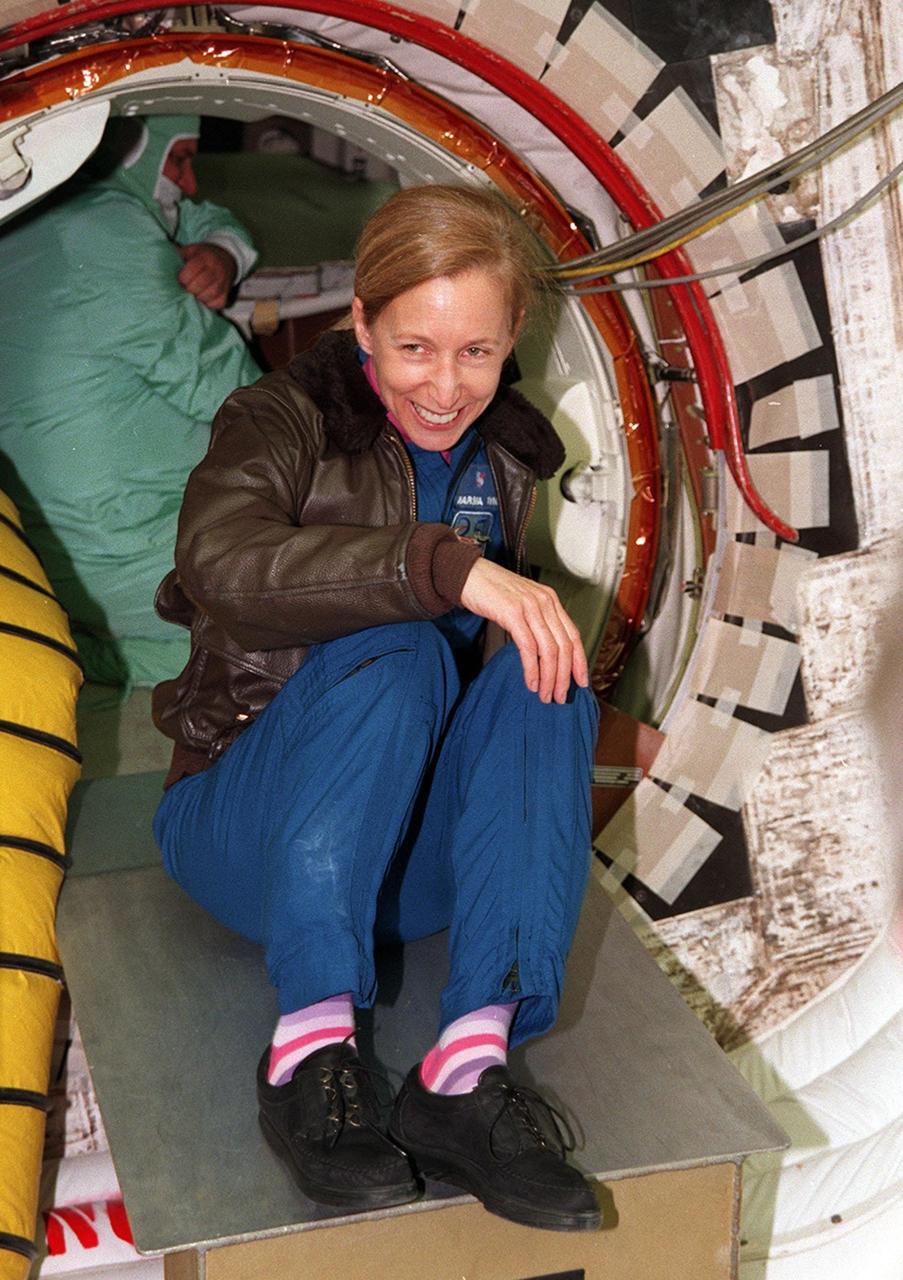

STS-98 Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins waits in the White Room outside the entrance into Atlantis. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. The other crew members are Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Commander Ken Cockrell and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
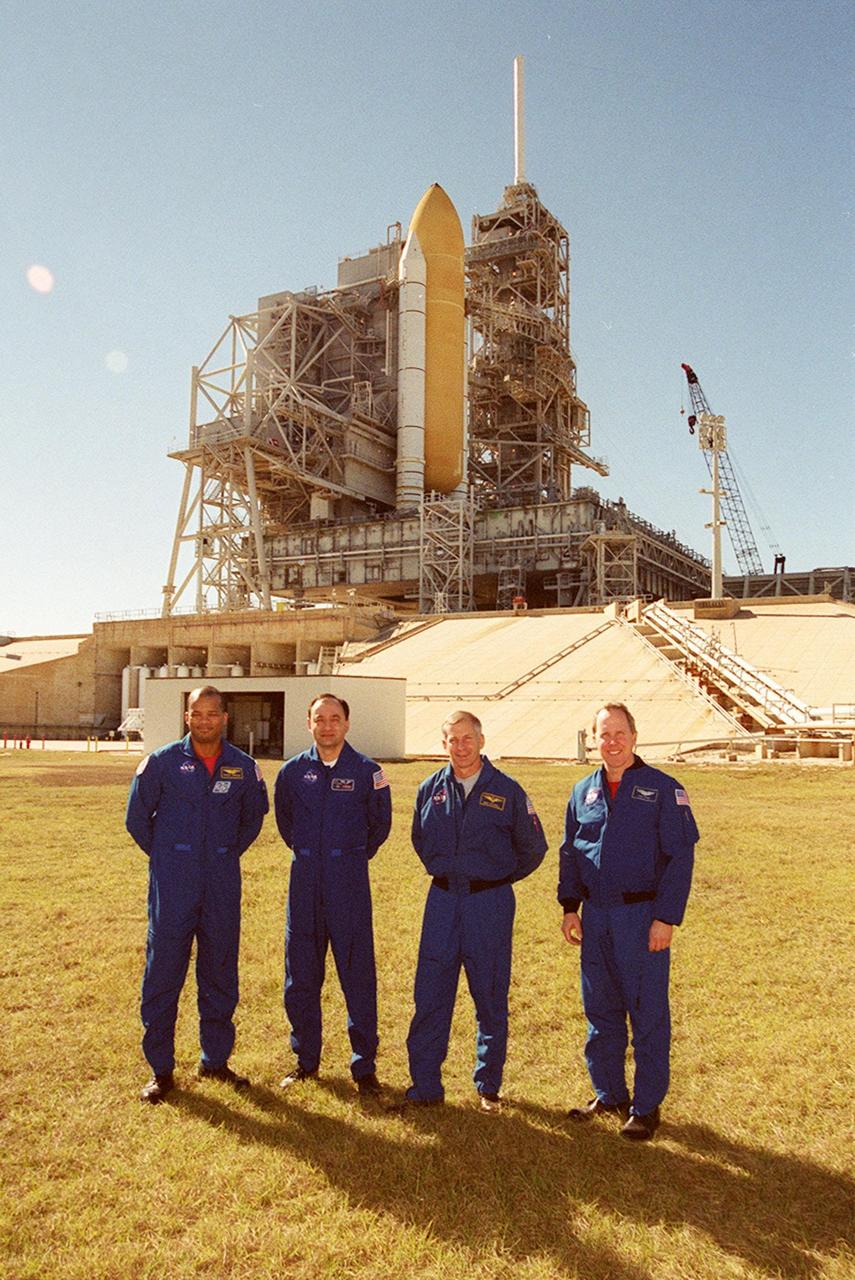

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Four members of the STS-98 crew pose for a photo at Launch Pad 39A. Standing, left to right, are Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam, Pilot Mark Polansky, Commander Ken Cockrell and Mission Specialist Thomas Jones. Not pictured is Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
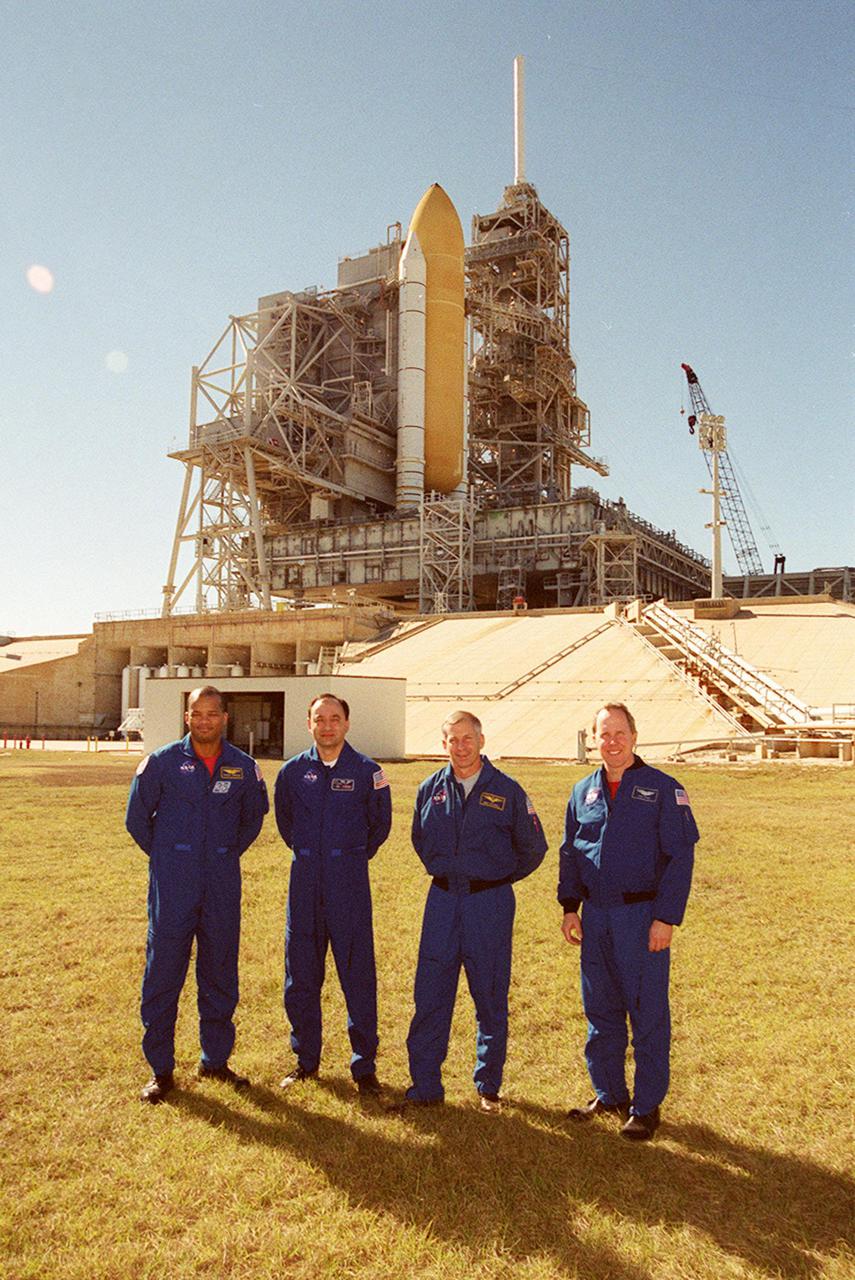

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Four members of the STS-98 crew pose for a photo at Launch Pad 39A. Standing, left to right, are Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam, Pilot Mark Polansky, Commander Ken Cockrell and Mission Specialist Thomas Jones. Not pictured is Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
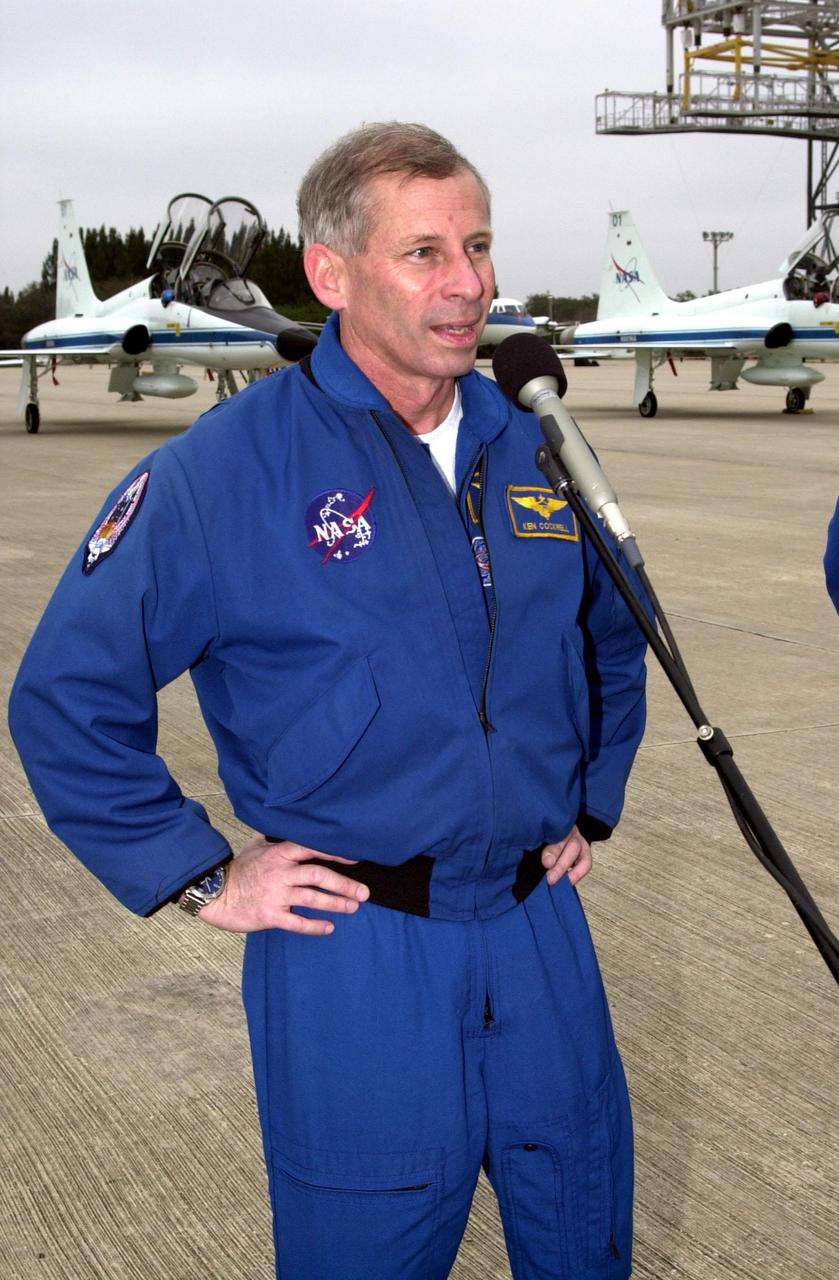

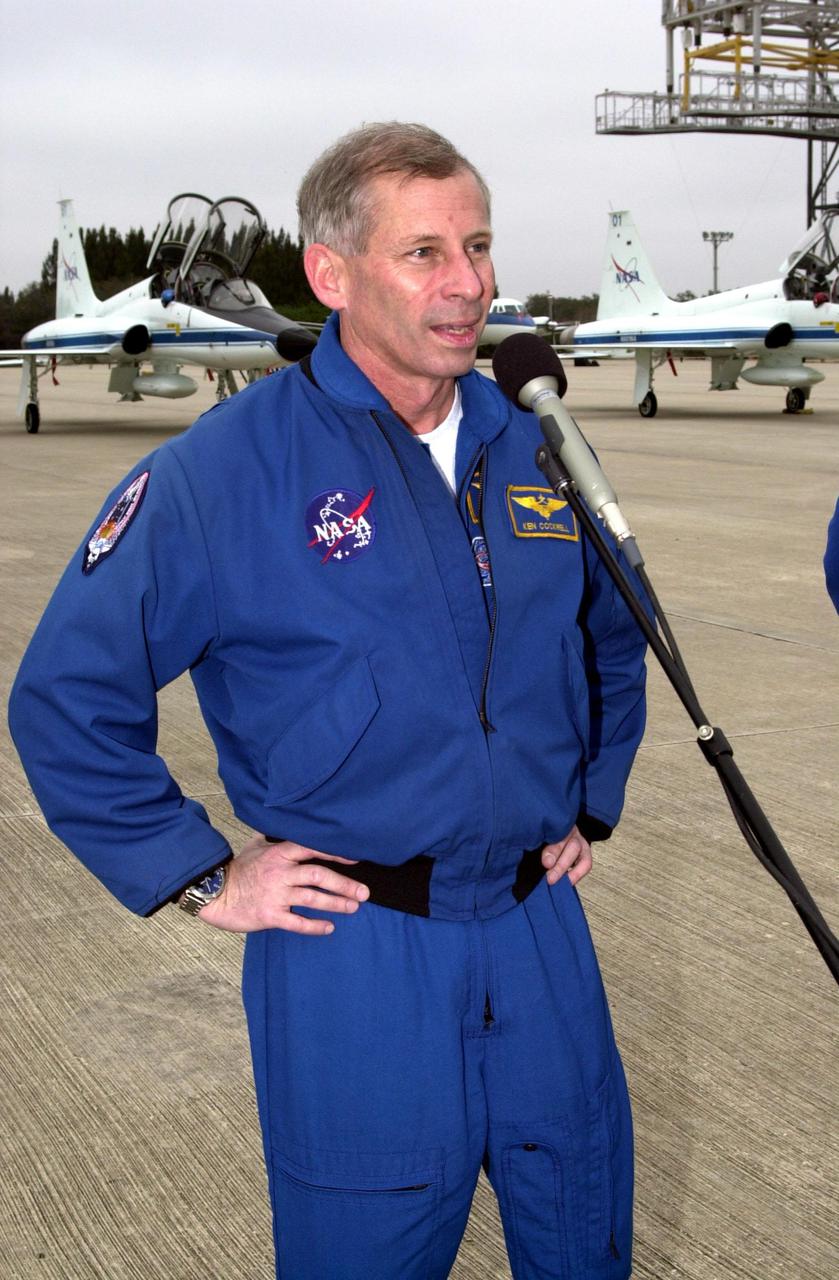
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-98 Mission Commander Kenneth Cockrell speaks to the media at the Shuttle Landing Facility after the crew's arrival Sunday to complete preparations for launch. The crew also includes Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Thomas Jones, Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam.; STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Feb. 7 at 6:11 p.m. EST
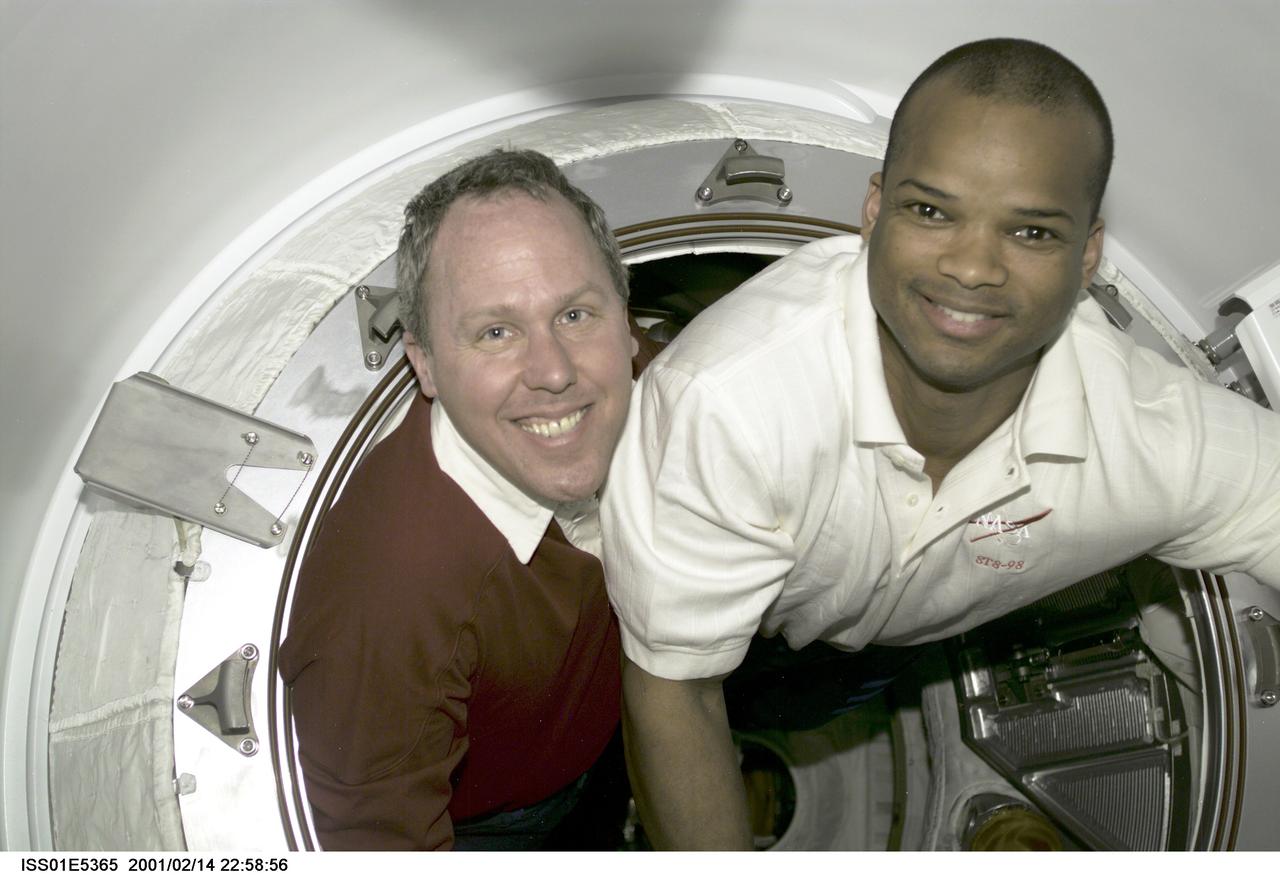

ISS01-E-5365 (14 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones (left) and Robert L. Curbeam, STS-98 mission specialists who will accomplish three lengthy space walks during the STS-98/5a mission, share space in a small hatch during break time. The scene was recorded with a digital still camera.
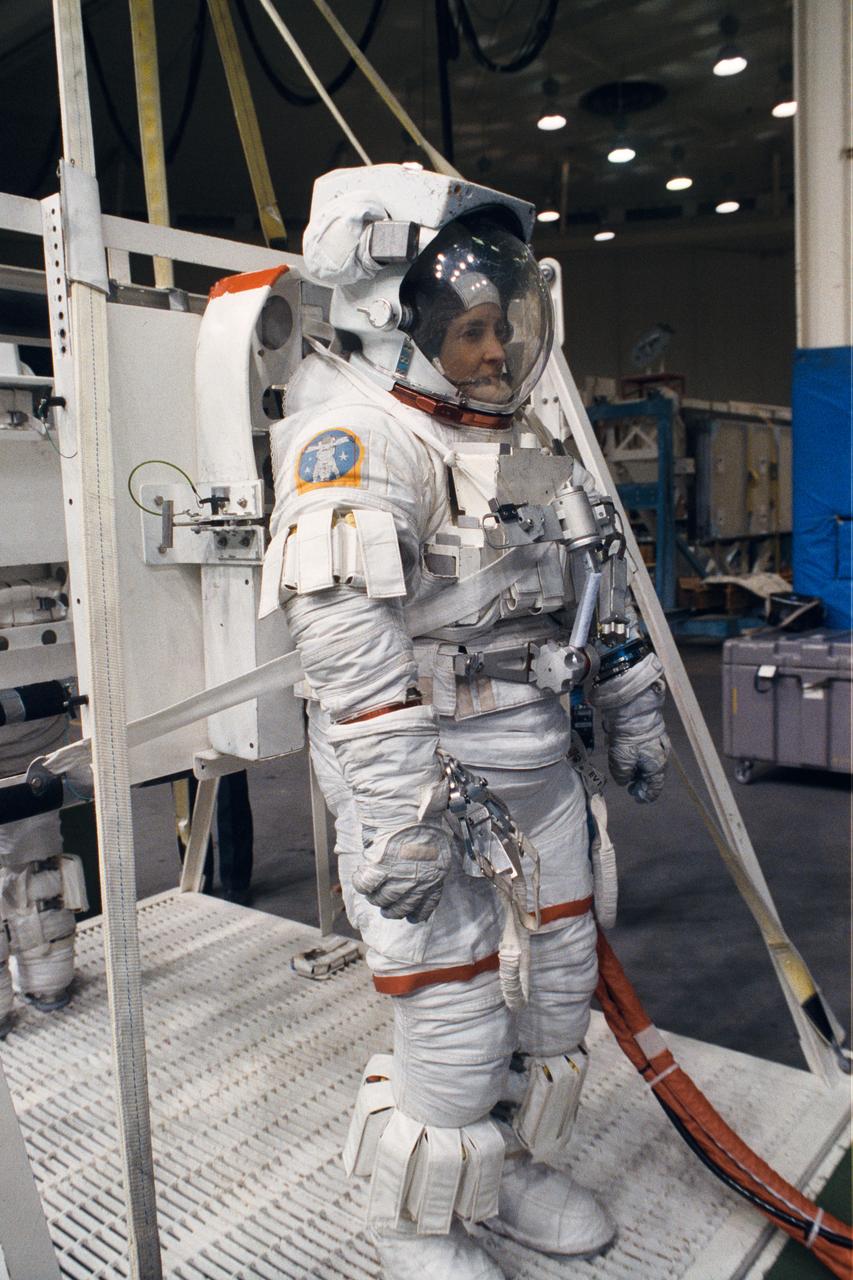

S93-41574 (17 Aug 1993) --- Astronaut Linda M. Godwin, payload commander, prepares to be submerged in a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Astronauts Godwin and Thomas D. Jones (out of frame at left), mission specialist, are using the WET-F to train for contingency space walks for their STS-59 Space Shuttle Endeavour mission next year. No space walks are planned for the flight.
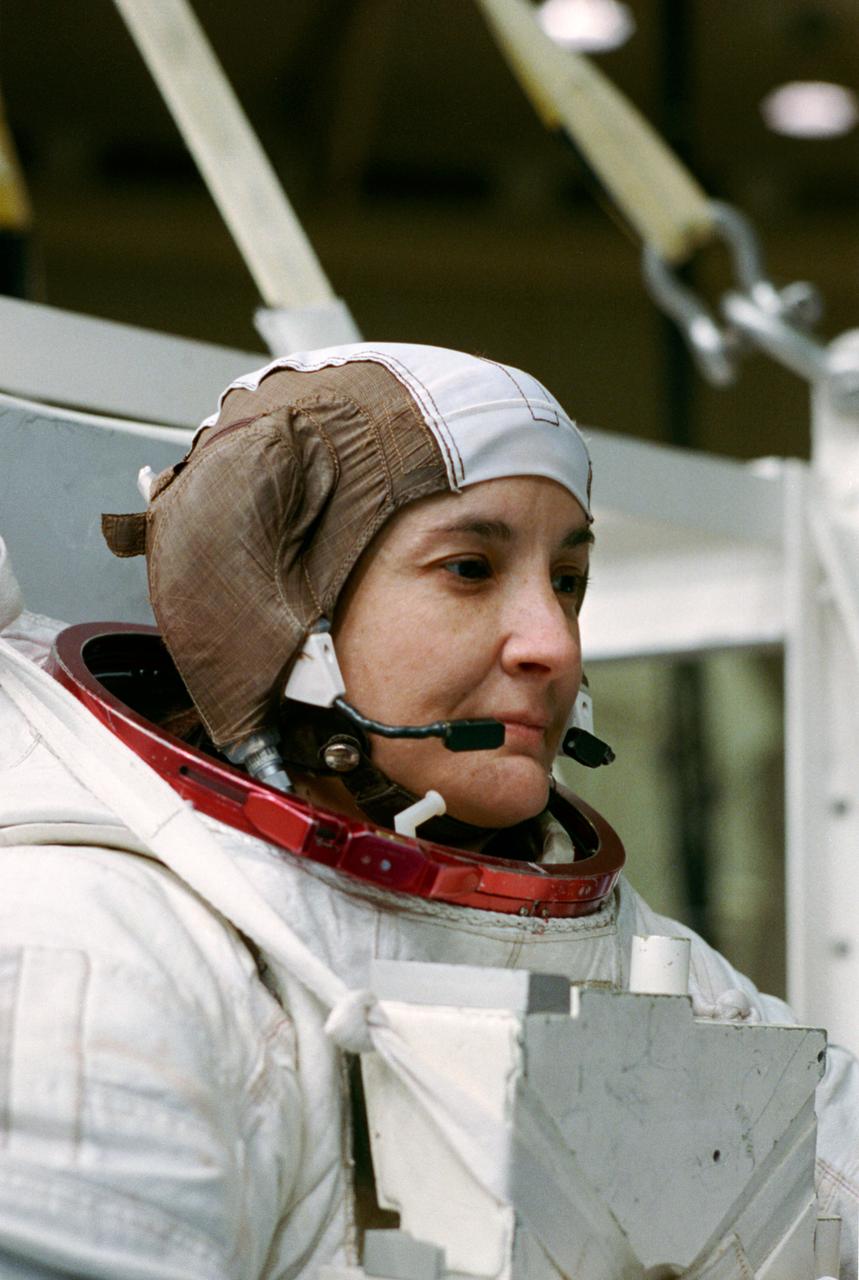

S93-41572 (17 Aug 1993) --- Astronaut Linda M. Godwin, payload commander, prepares to donn her helmet before being submerged in a 25-feet deep pool at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Astronauts Godwin and Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, are using the WET-F to train for contingency space walks for their Space Shuttle Endeavour mission next year. No space walks are planned for the flight.
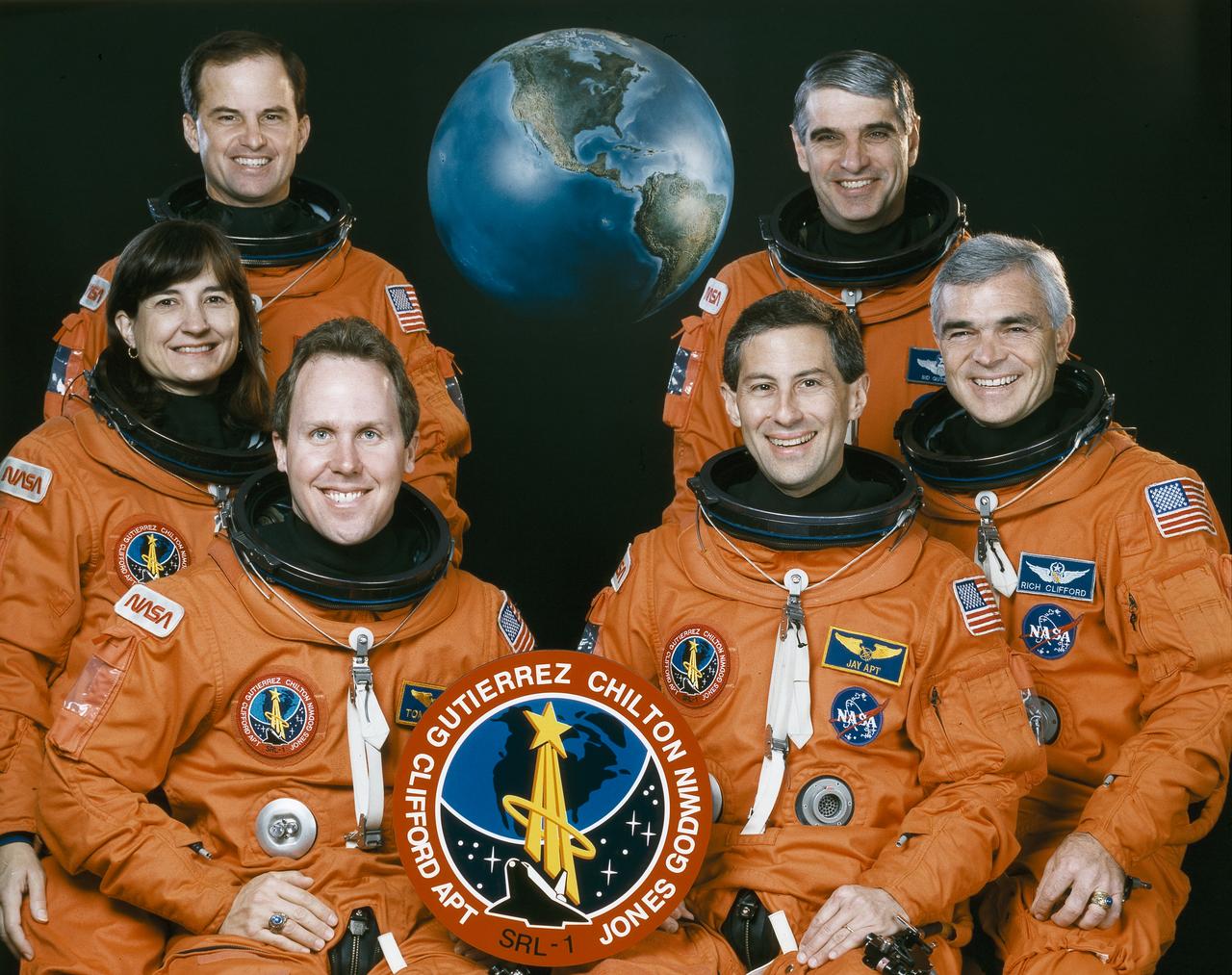

Astronauts included in the STS-59 crew portrait include (standing in rear, left to right) Kevin P. Chilton, pilot; and Sidney M. Gutierrez, commander. Seated left to right are Linda M. Godwin, payload commander; and mission specialists Thomas D. Jones, Jay Apt, and Michael R. Clifford. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on April 9, 1994 at 7:05:00 am (EDT), the STS-59 mission deployed the Space Radar Laboratory (SRL-1).

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-98 Mission Commander Kenneth Cockrell speaks to the media at the Shuttle Landing Facility after the crew's arrival Sunday to complete preparations for launch. The crew also includes Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Thomas Jones, Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam.; STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Feb. 7 at 6:11 p.m. EST

In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-98 Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins maneuvers a part of the U.S. Lab, Destiny. The crew is checking out equipment inside the lab as part of Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, becoming familiar with equipment it will be handling during the mission. Others in the crew are Commander Ken Cockrell, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam and Thomas Jones. The mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. With delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. The STS-98 launch is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001

S93-42727 (26 Aug 1993) --- The six astronauts in training for the STS-59 mission are given some onboard Earth observations tips by Justin Wilkinson (standing, foreground) of the Space Shuttle Earth Observations Project (SSEOP) group. Astronaut Sidney M. Gutierrez, mission commander, is at center on the left side of the table. Others, left to right, are astronauts Kevin P. Chilton, pilot; Jerome (Jay) Apt and Michael R.U. (Rich) Clifford, both mission specialists; Linda M. Godwin, payload commander; and Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist.

In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-98 Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins wields a tool on part of the U.S. Lab, Destiny. The crew is checking out equipment inside the lab as part of Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, becoming familiar with equipment it will be handling during the mission. Others in the crew are Commander Ken Cockrell, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam and Thomas Jones. The mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. With delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. The STS-98 launch is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001

In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-98 crew, sitting in front of the U.S. Lab, Destiny, listen to a trainer during Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities. Seen, left to right, are Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam and Marsha Ivins (with camera). The CEIT allows a crew to become familiar with equipment they will be handling during the mission. With launch scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001, the STS-98 mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated
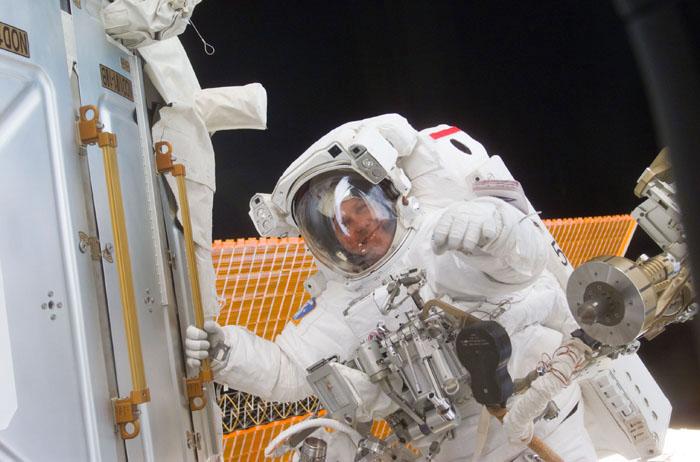

STS98-E-5194 (12 February 2001)--- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, STS-98 mission specialist, grabs a hand rail while working on the International Space Station (ISS) during the second of three scheduled space walks involving himself and astronaut Robert L. Curbeam and assisted by their STS-98 crew mates aboard the Atlantis. The scene was recorded with a digital still camera.

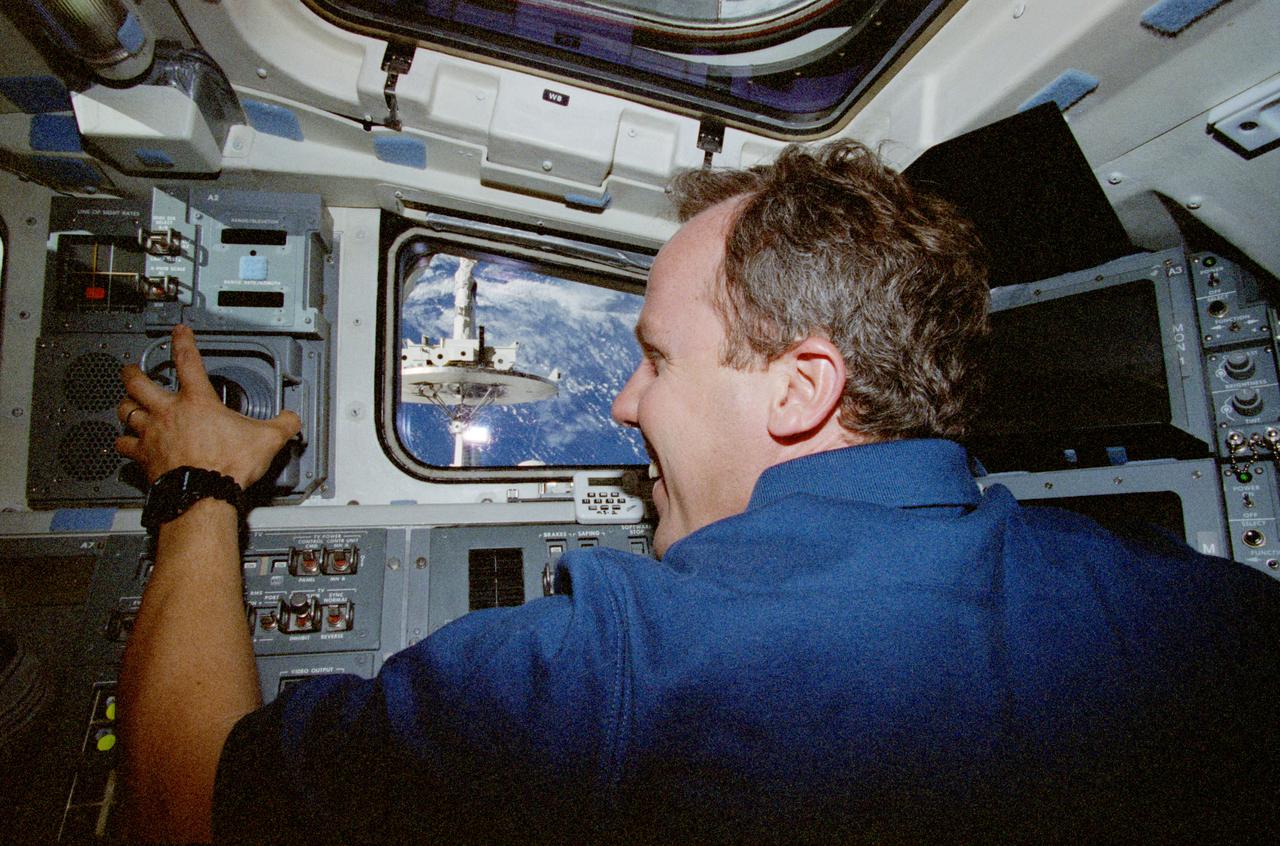
STS98-E-5035 (9 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, communicates on a radio during rendezvous operations between the Space Shuttle Atlantis and the International Space Station (ISS). Atlantis went on to dock with the station on schedule at 10:51 a.m. (CST), Feb. 9. A digital still camera was used to record the scene.
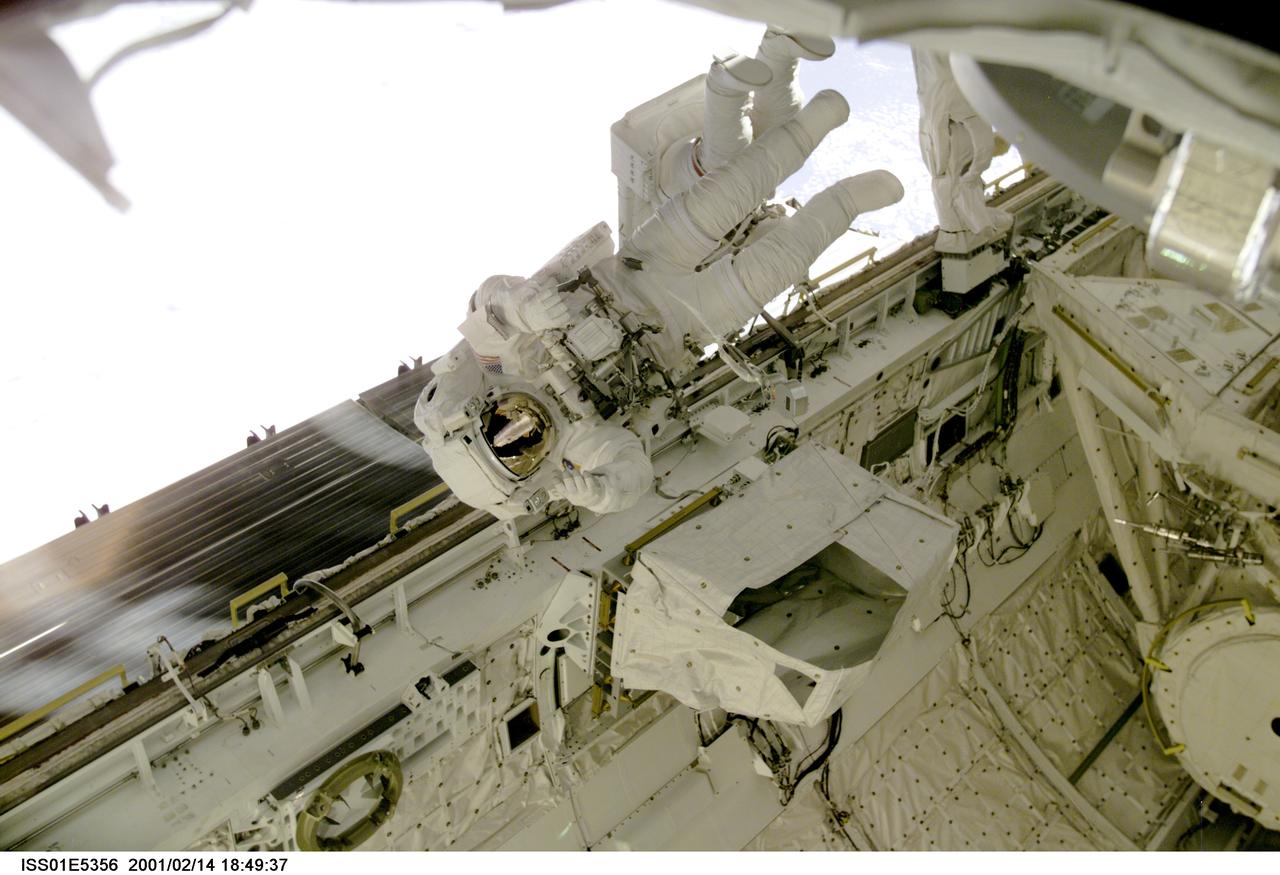

ISS01-E-5356 (14 February 2001) --- Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, STS-98 mission specialist, floats above the longerons of the cargo bay on the Space Shuttle Atlantis during the final of three STS-98/5a space walks. Partially obscured behind Curbeam is astronaut Thomas D. Jones, his colleague and partner for all three walks. The scene was recorded with a digital still camera.
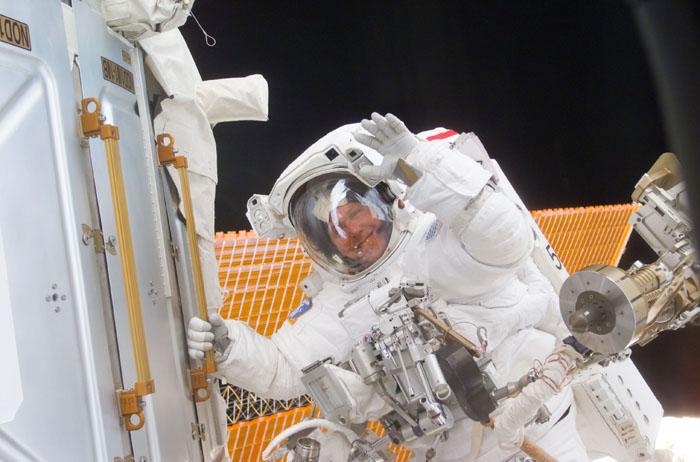

STS98-E-5195 (12 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, STS-98 mission specialist, waves at crew mates inside Atlantis' crew cabin while working on the International Space Station (ISS) during the second of three scheduled space walks involving himself and astronaut Robert L. Curbeam and assisted by their STS-98 astronauts aboard the Atlantis. The scene was recorded with a digital still camera.
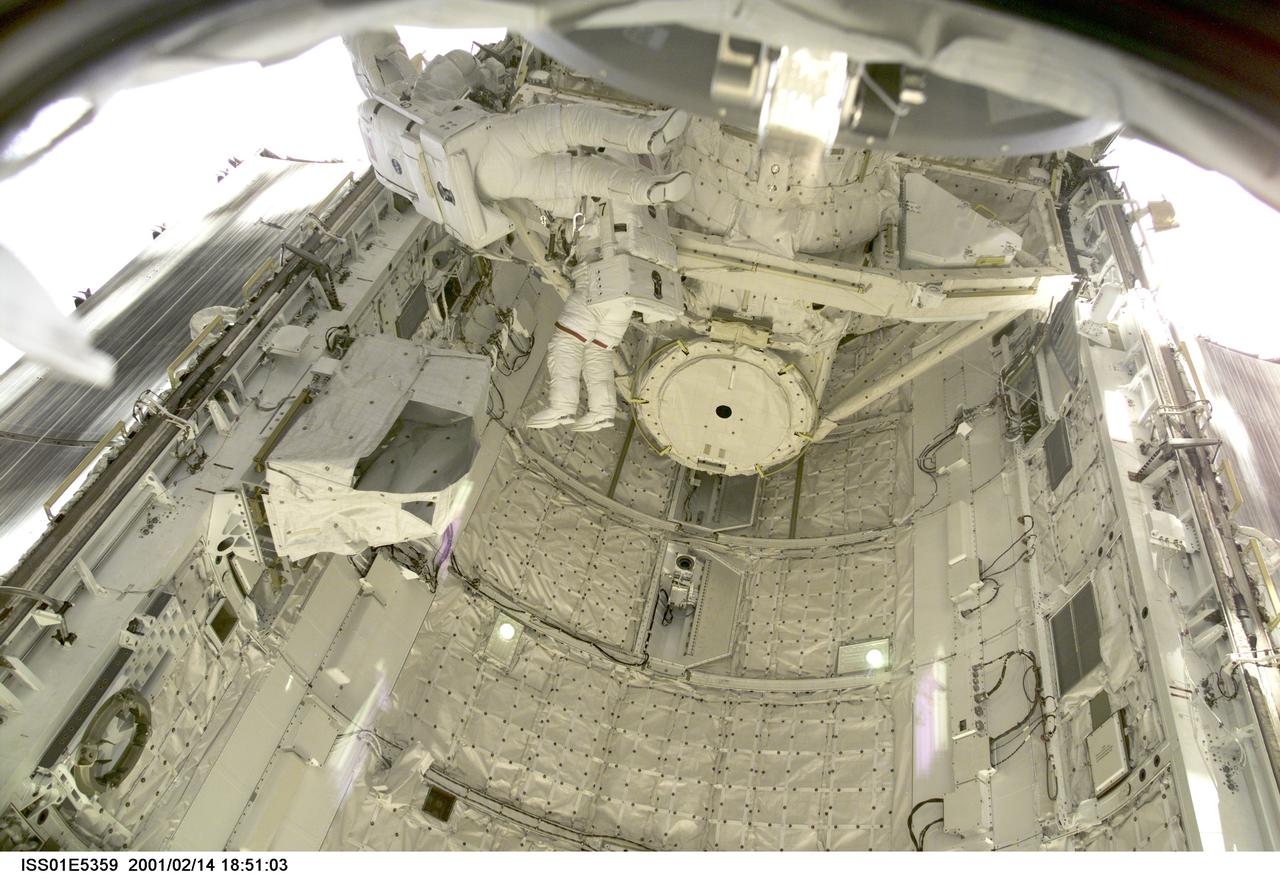
ISS01-E-5359 (14 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones (red stripes on suit pants)and Robert L. Curbeam, STS-98 mission specialists, are pictured in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Atlantis during their third space walk, as photographed with a digital still camera from the International Space Station's new Destiny laboratory.
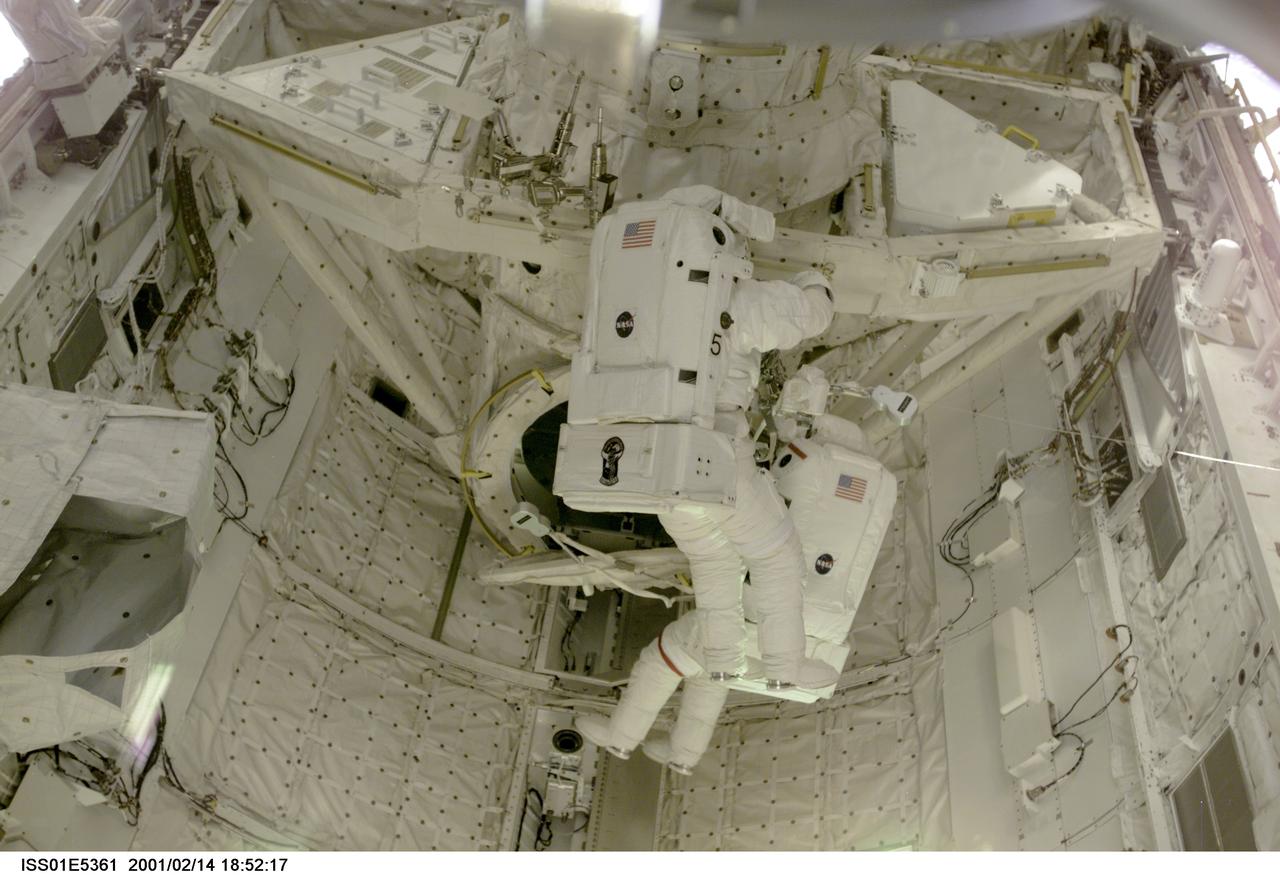

ISS01-E-5361 (14 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones (red stripes on suit) and Robert L. Curbeam, STS-98 mission specialists, are pictured in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Atlantis during their third space walk, as photographed with a digital still camera from the International Space Station's new Destiny laboratory.

STS080-330-023 (19 Nov.-7 Dec. 1996) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, STS-80 mission specialist, operates the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) controls during operations with the Wake Shield Facility (WSF). When this picture was taken, the part time free-flying WSF was in the grasp of the RMS' end effector, as evidenced by the scene on the space shuttle Columbia's aft flight deck monitor in upper right.
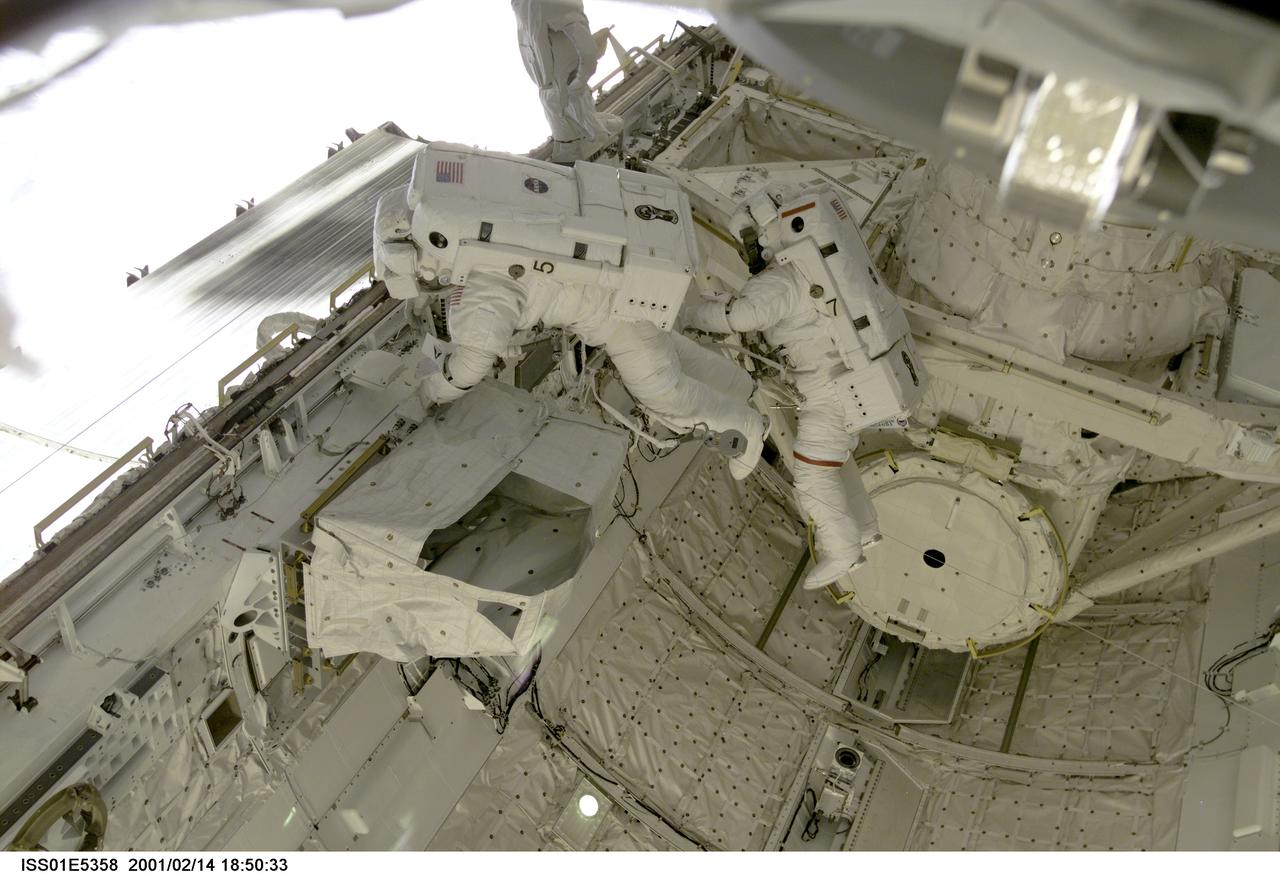
ISS01-E-5358 (14 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones (red stripes on suit) and Robert L. Curbeam, STS-98 mission specialists, are pictured in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Atlantis during their third space walk, as photographed with a digital still camera from the International Space Station's new Destiny laboratory.
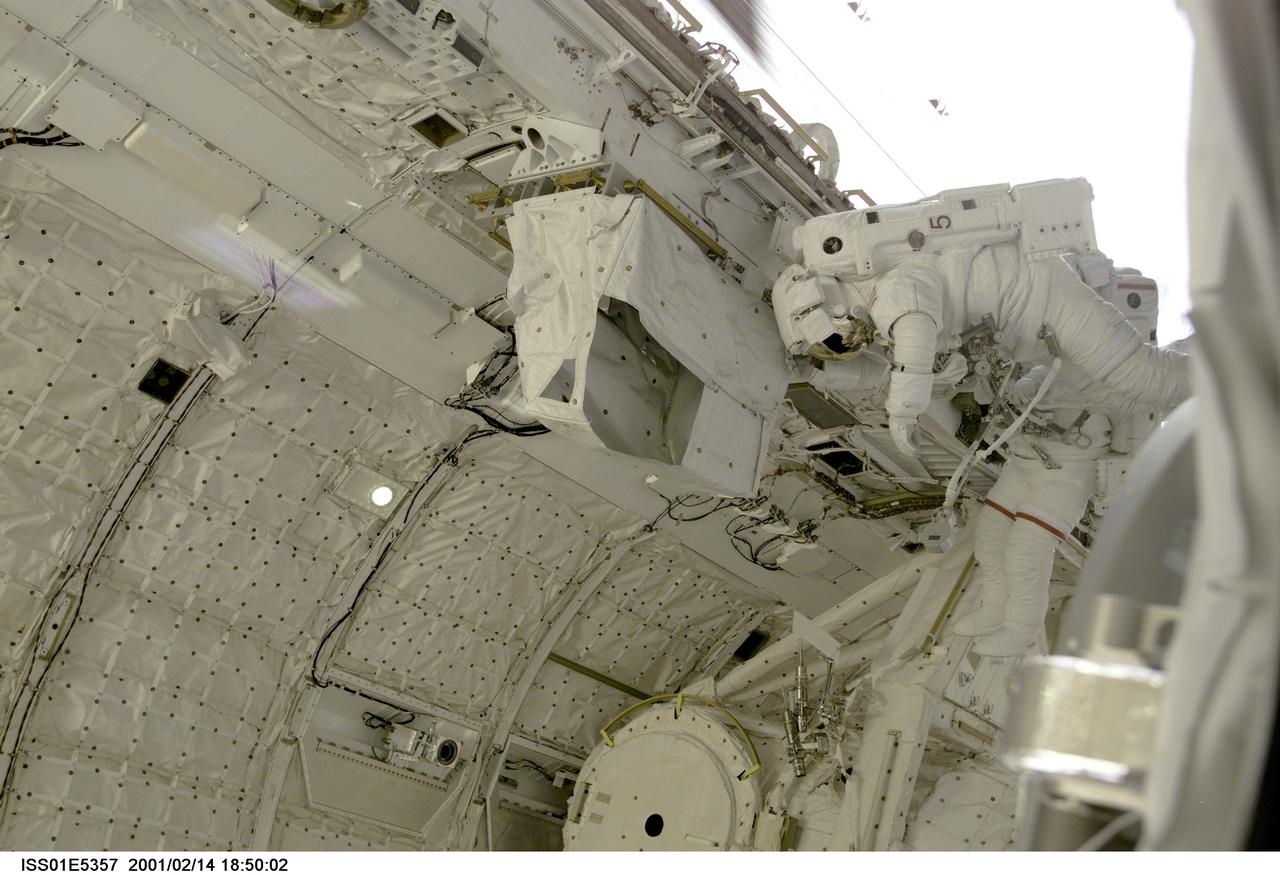

ISS01-E-5357 (14 February 2001) --- Astronauts Thomas D. Jones (red stripes on suit pants)and Robert L. Curbeam, STS-98 mission specialists, are pictured in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Atlantis during their third space walk, as photographed with a digital still camera from the International Space Station's new Destiny laboratory.
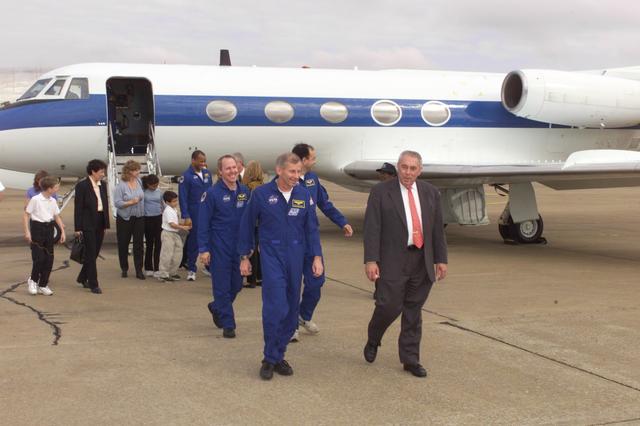

JSC2001-E-04805 (21 February 2001) --- JSC director George W.S. Abbey talks with the STS-98 crew members following the arrival of the Gulfstream Aircraft which transported the astronauts from their landing at Dryden Flight Research Center (DFRC) in Edwards, California. Pictured along side Mr. Abbey is astronaut Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander. Behind him (from the left distant background) are astronauts Robert L. Curbeam and Thomas D. Jones (both mission specialists) and Mark L. Polansky, pilot. Astronaut Marsha S. Ivins, mission specialist, is out of the frame.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Sitting in the entrance to the orbiter Atlantis are (left to right) STS-98 Mission Specialists Thomas Jones and Marsha Ivins and Commander Ken Cockrell. Below them is the mission patch just placed there by Cockrell. Standing at left is Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam and at right Pilot Mark Polansky. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
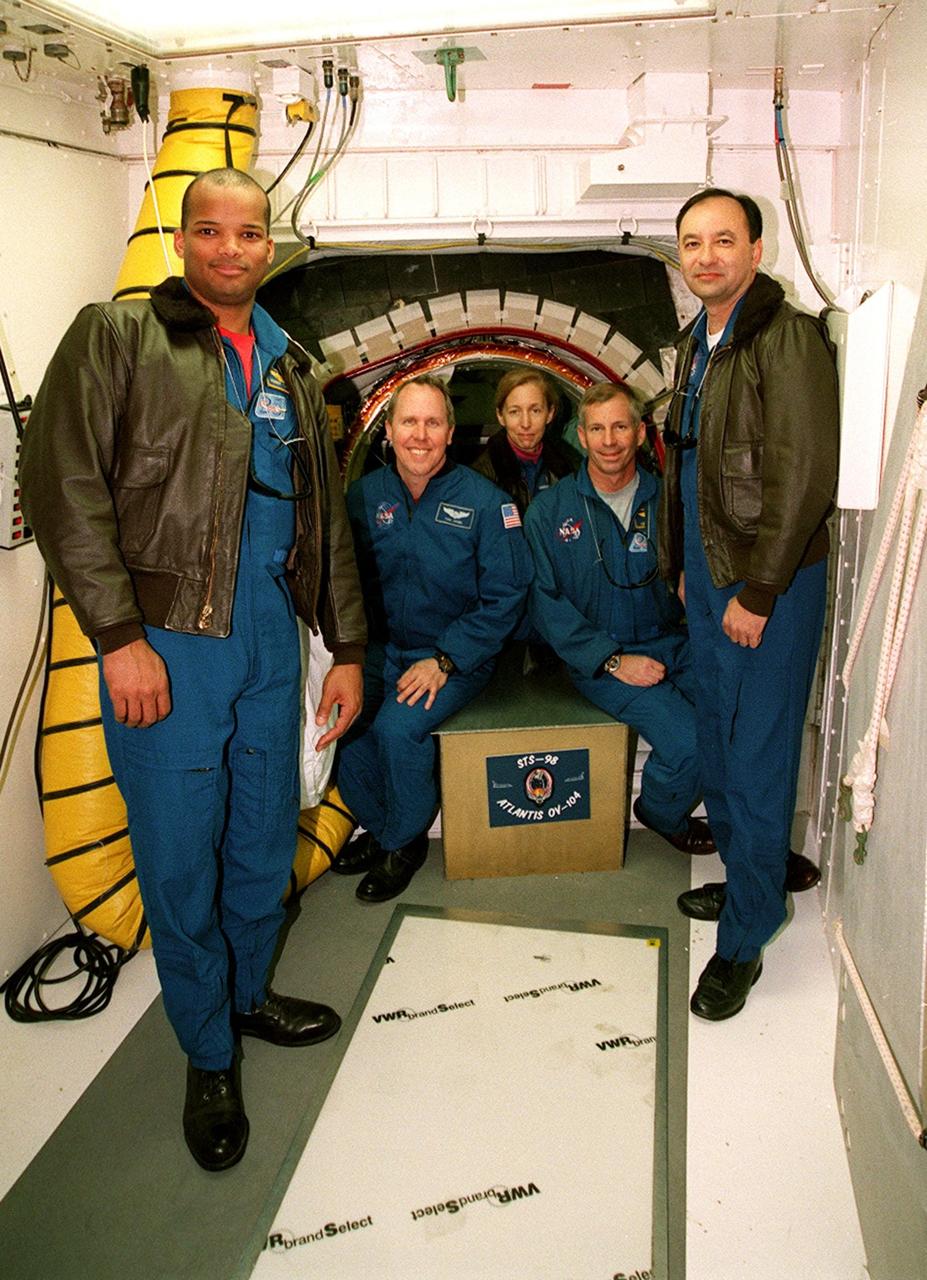

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Sitting in the entrance to the orbiter Atlantis are (left to right) STS-98 Mission Specialists Thomas Jones and Marsha Ivins and Commander Ken Cockrell. Below them is the mission patch just placed there by Cockrell. Standing at left is Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam and at right Pilot Mark Polansky. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
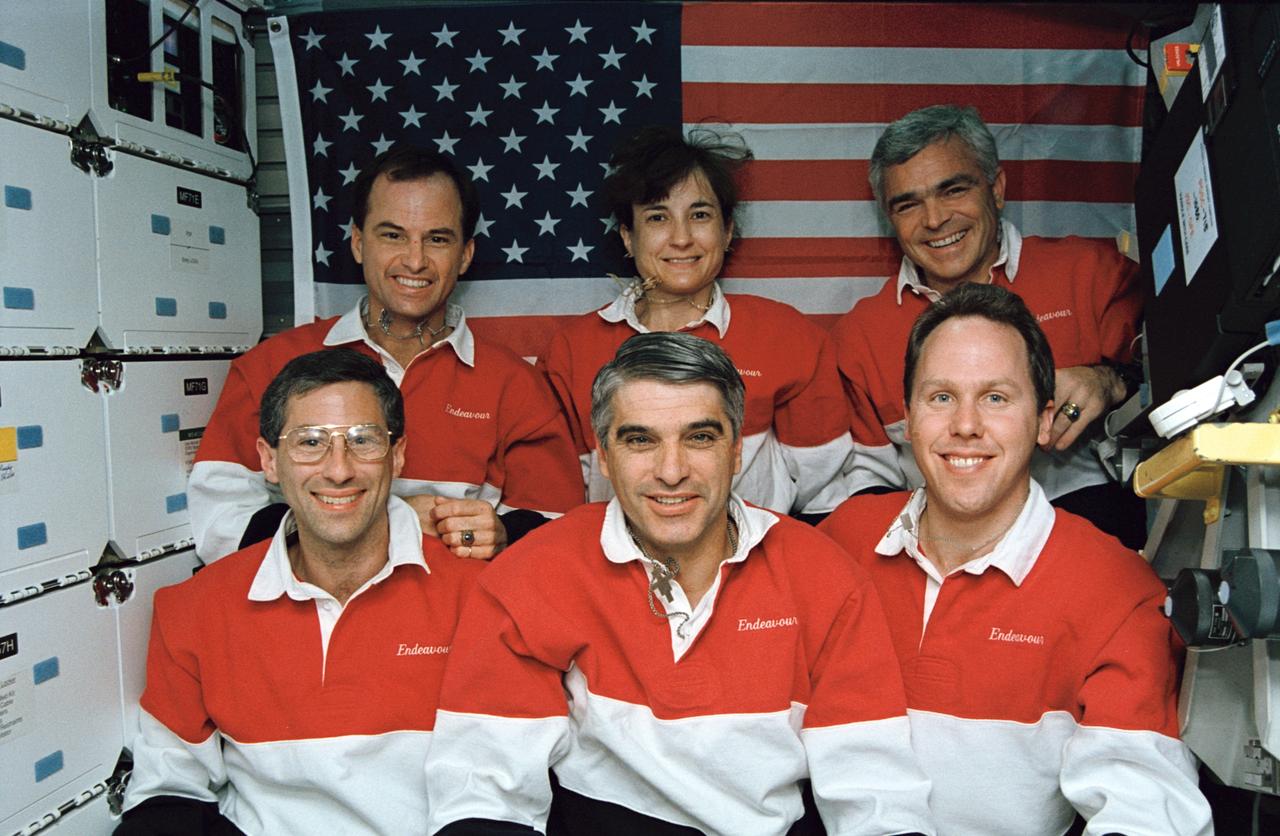

STS059-44-004 (9-20 April 1994) --- This middeck scene aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour caught all six STS-59 crew members in a rare group shot. Astronaut Sidney M. Gutierrez, mission commander (front center) is flanked by astronauts Jerome (Jay) Apt and Thomas D. Jones, both mission specialists. On the back row are (left to right) astronaut Kevin P. Chilton, pilot; Linda M. Godwin, payload commander; and Michael R. (Rich) Clifford, mission specialist. Most of the week and a half was divided into two work shifts for the crew members.
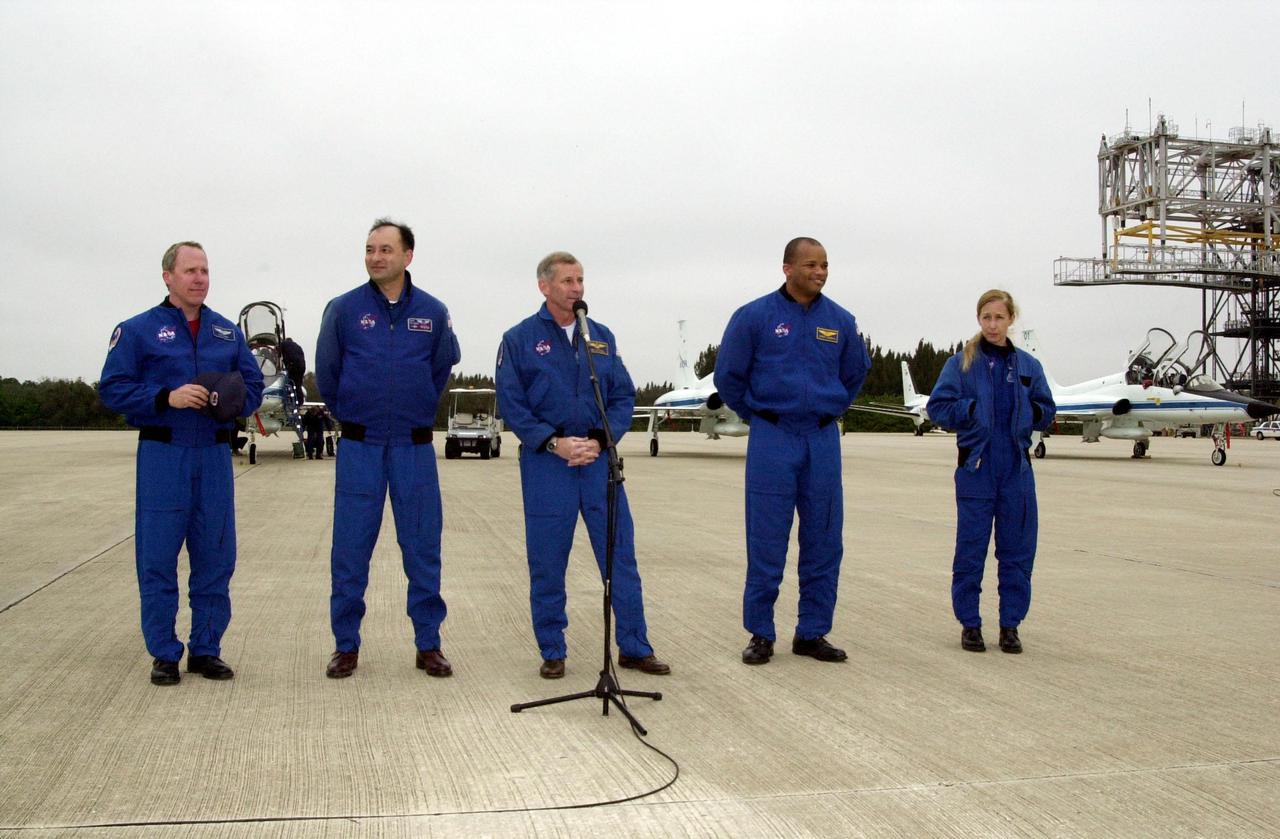

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-98 Mission Commander Kenneth Cockrell (center at microphone) speaks to the media at the Shuttle Landing Facility after the crew's arrival Sunday to complete preparations for launch.; The crew also includes, from left to right, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam and Marsha Ivins. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Feb. 7 at 6:11 p.m. EST
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-98 crew talks to the press at a briefing at Launch Pad 39A. With the microphone is Commander Ken Cockrell, who discusses the EVAs on the mission. The other crew members are (left to right) Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, [Cockrell], and Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam. They are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/KSC01padig014/KSC01padig014~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-98 crew talks to the press at a briefing at Launch Pad 39A. With the microphone is Commander Ken Cockrell, who discusses the EVAs on the mission. The other crew members are (left to right) Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, [Cockrell], and Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam. They are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
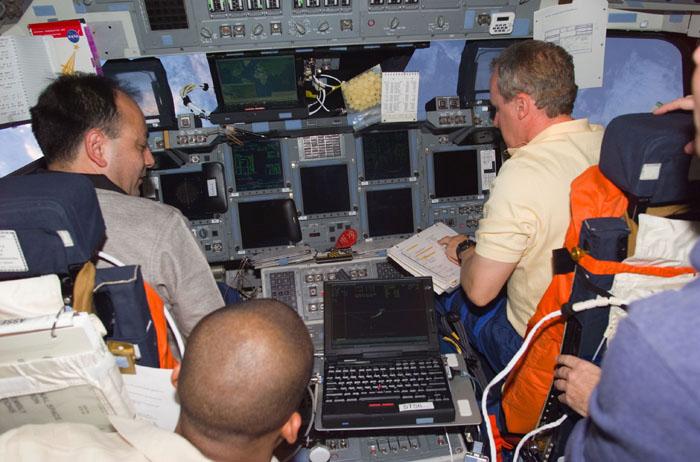

STS98-E-5030 (9 February 2001) --- Three members of the STS-98 crew prepare for rendezvous with the International Space Station (ISS). Astronaut Thomas D. Jones (right), mission specialist, temporarily mans the pilot's station on the flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. Astronaut Mark L. Polansky, left, sits at the commander's station for this maneuver. At lower left is Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, mission specialist. Astronaut Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander, is just out of frame at right. The photograph was recorded with a digital still camera.
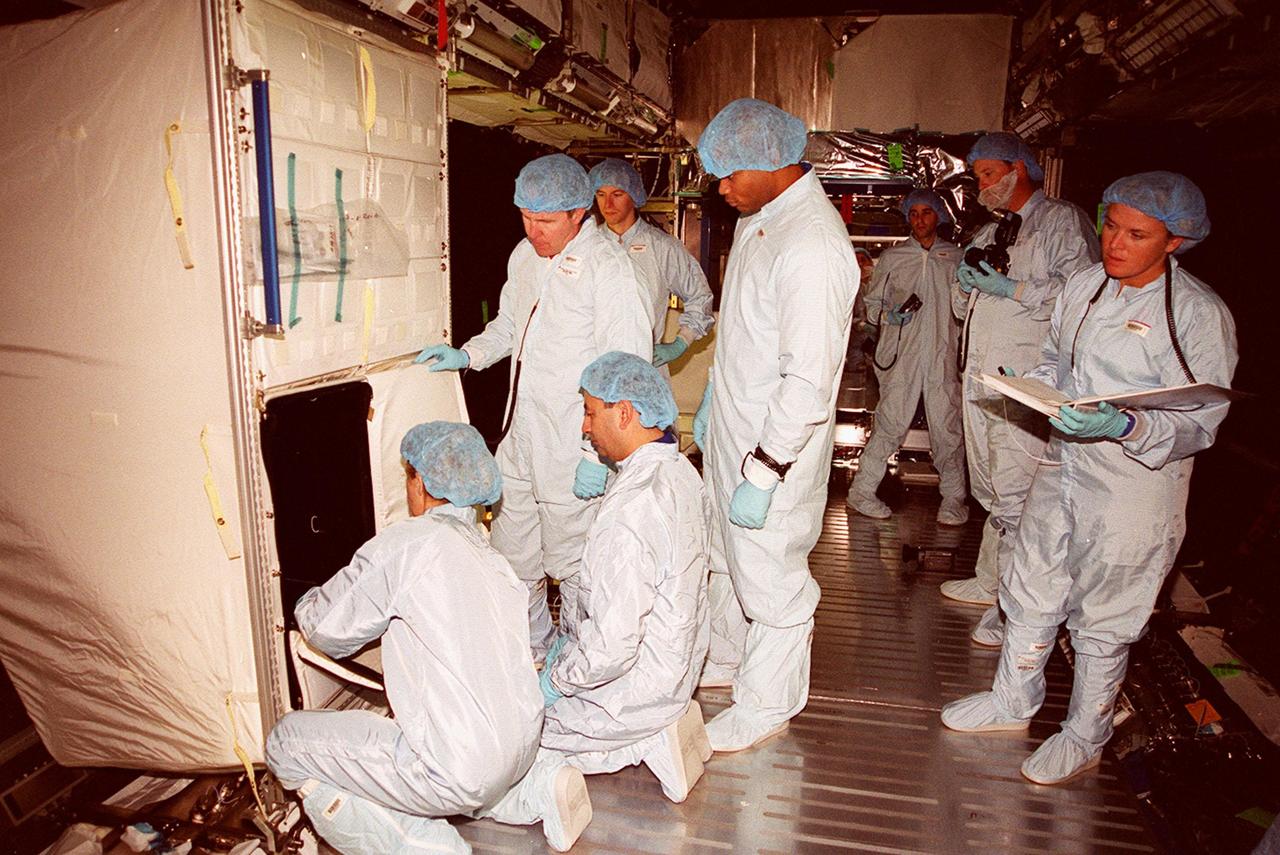

Inside the U.S. Lab, Destiny, members of the STS-98 crew work with technicians (in the background) to learn more about the equipment in the module. They are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities. At left, back to camera, is Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins. Standing are Mission Specialists Thomas Jones (left) and Robert Curbeam (right). Other crew members not seen are Commander Ken Cockrell and Pilot Mark Polansky. The mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. With delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. The STS-98 launch is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-98 crew talks to the press at a briefing at Launch Pad 39A. With the microphone is Commander Ken Cockrell, who discusses the EVAs on the mission. The other crew members are (left to right) Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, [Cockrell], and Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam. They are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01padig014/01padig014~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-98 crew talks to the press at a briefing at Launch Pad 39A. With the microphone is Commander Ken Cockrell, who discusses the EVAs on the mission. The other crew members are (left to right) Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, [Cockrell], and Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam. They are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
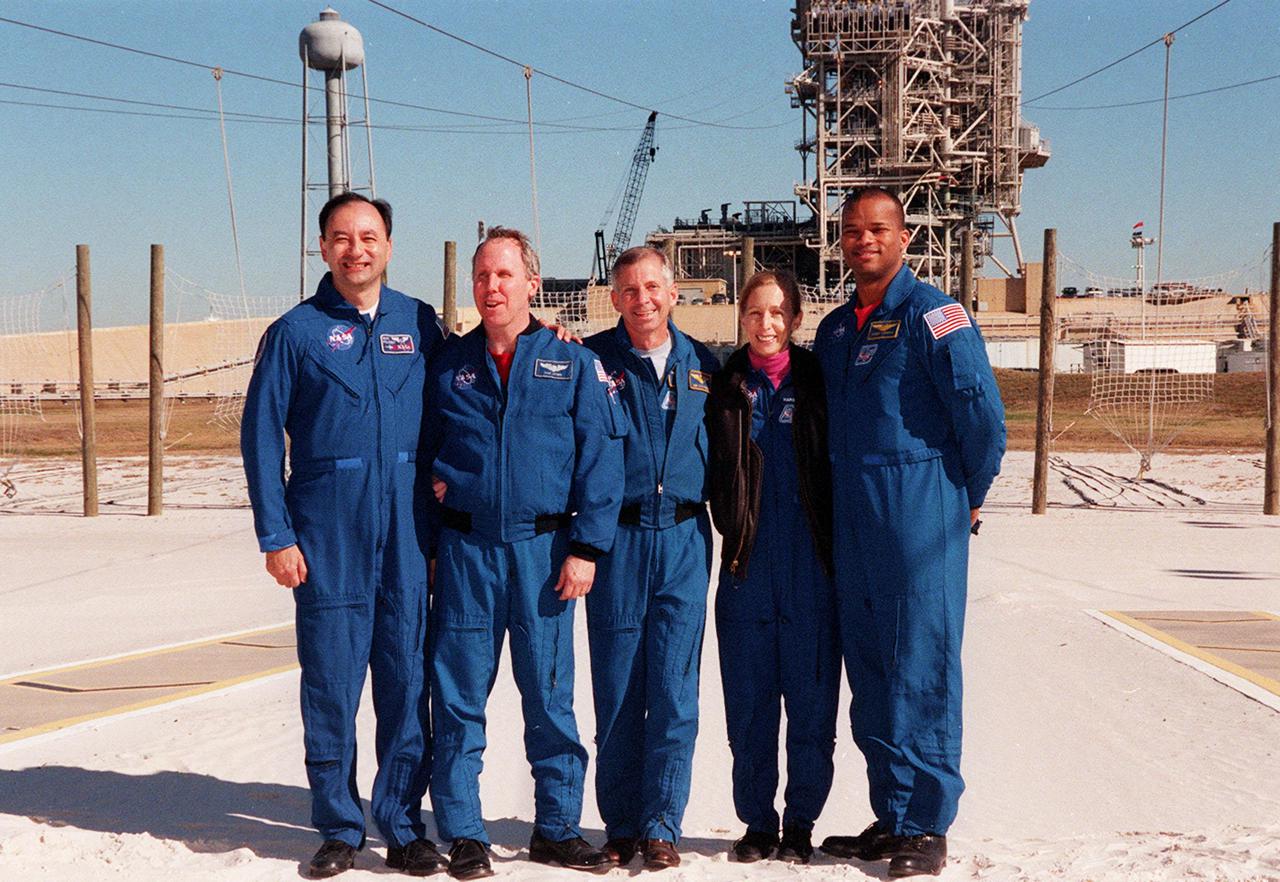

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA -- After a media briefing at Launch Pad 39A, the STS-98 crew poses in the slidewire basket landing zone. Standing, left to right, are Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Commander Ken Cockrell and Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam. All are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
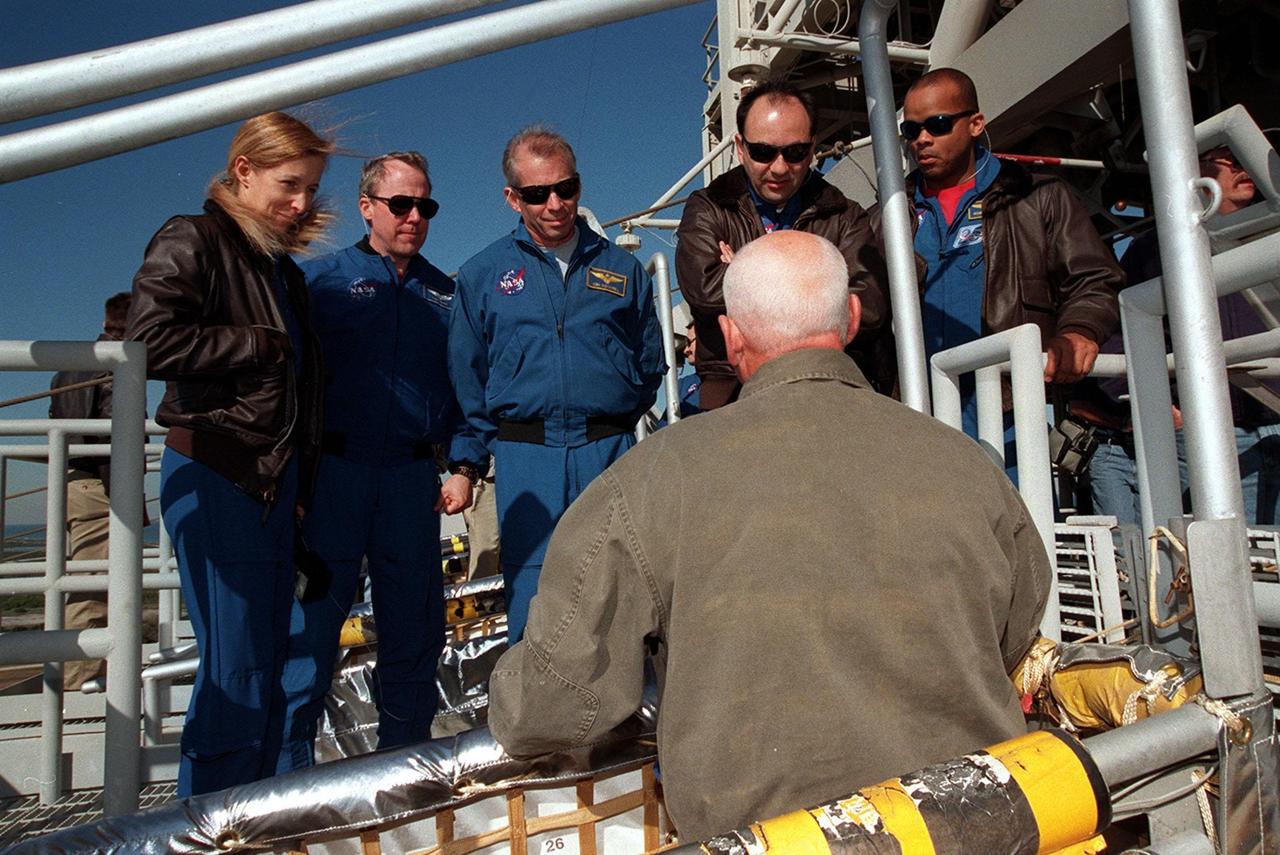

The STS-98 crew listens to instructions on use of the slidewire basket, part of emergency egress equipment from the launch pad. At the 195-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure are Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Thomas Jones, Commander Ken Cockrell, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown at the pad. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
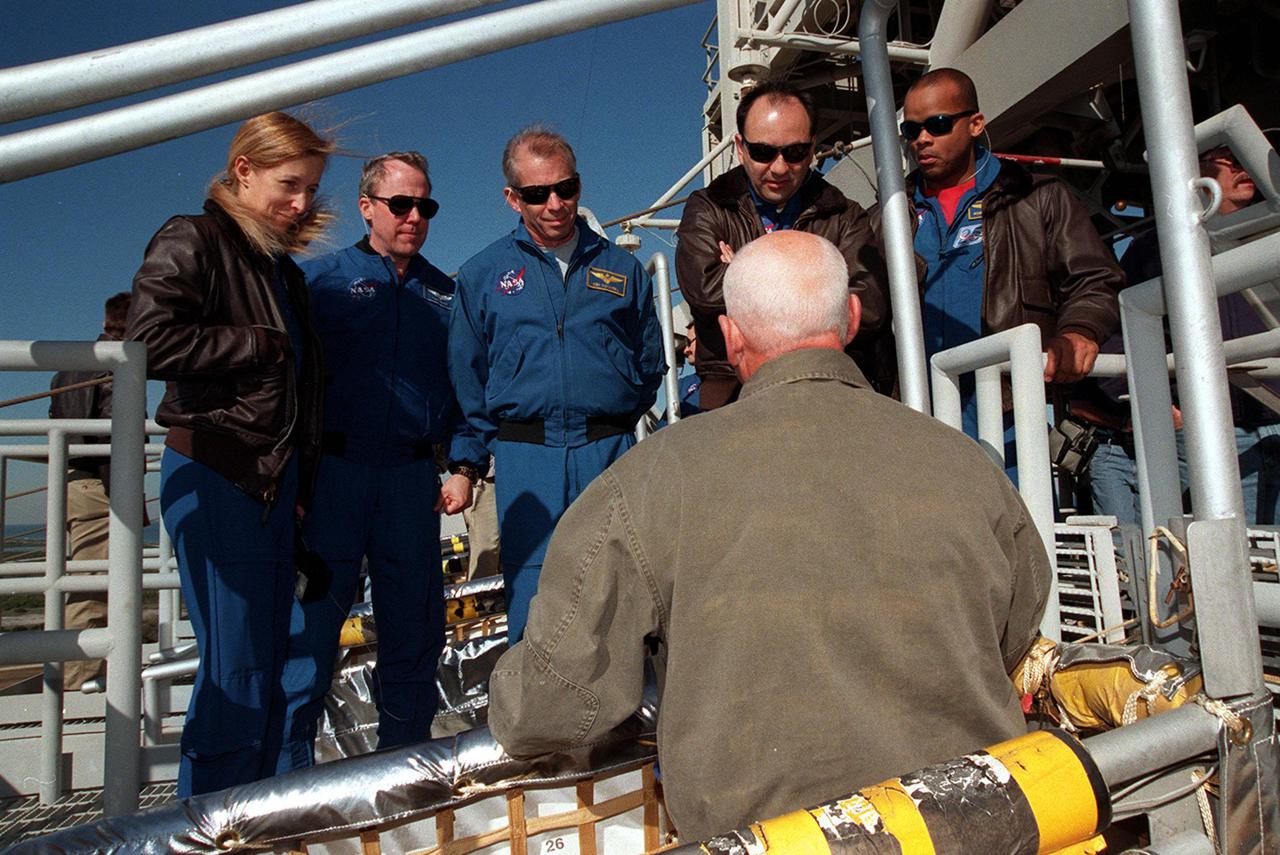

The STS-98 crew listens to instructions on use of the slidewire basket, part of emergency egress equipment from the launch pad. At the 195-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure are Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Thomas Jones, Commander Ken Cockrell, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown at the pad. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-98 Commander Ken Cockrell answers a question from the media during a briefing at Launch Pad 39A. Other crew members present are Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, [Cockrell], and Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam. All are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/01pp0044/01pp0044~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-98 Commander Ken Cockrell answers a question from the media during a briefing at Launch Pad 39A. Other crew members present are Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, [Cockrell], and Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam. All are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
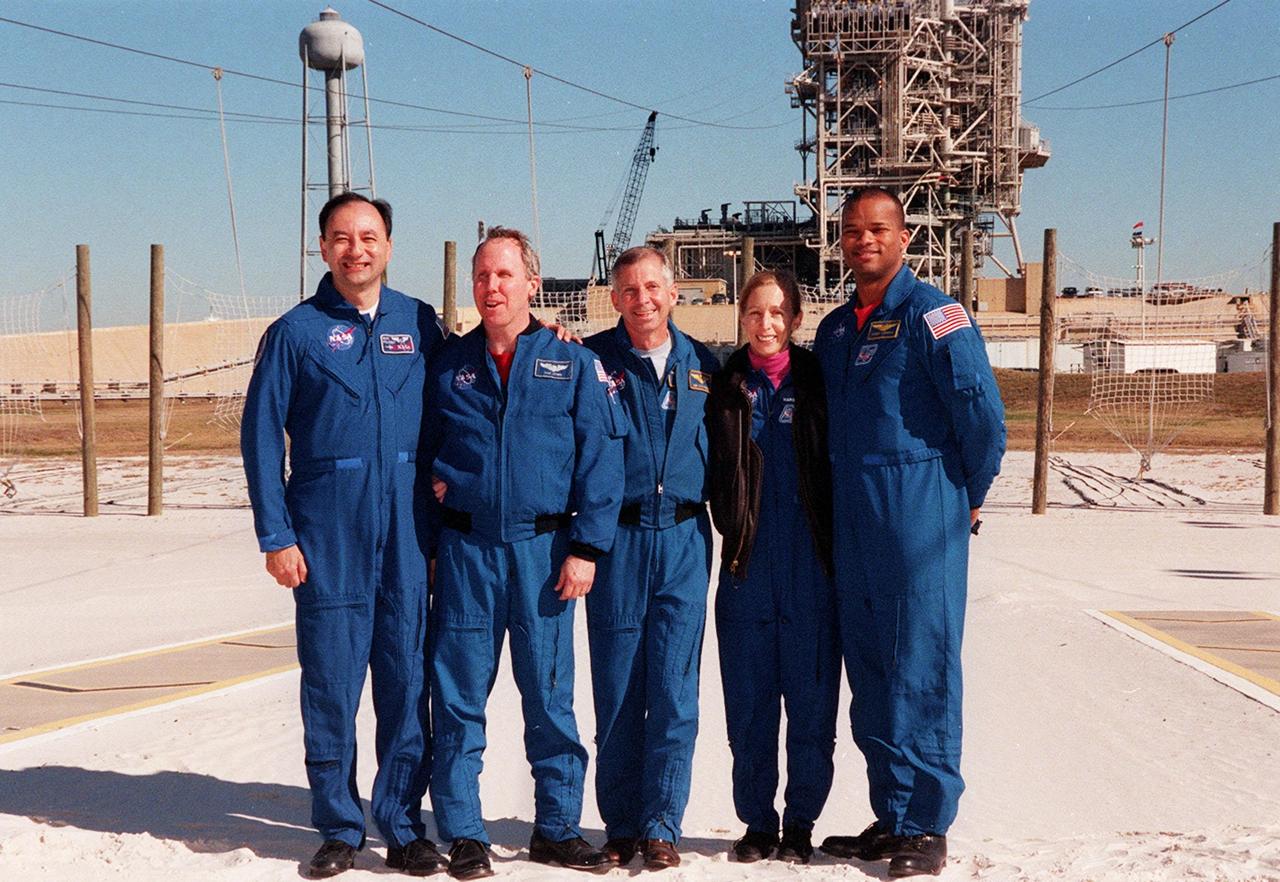

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA -- After a media briefing at Launch Pad 39A, the STS-98 crew poses in the slidewire basket landing zone. Standing, left to right, are Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Commander Ken Cockrell and Mission Specialists Marsha Ivins and Robert Curbeam. All are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include emergency egress training and a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m
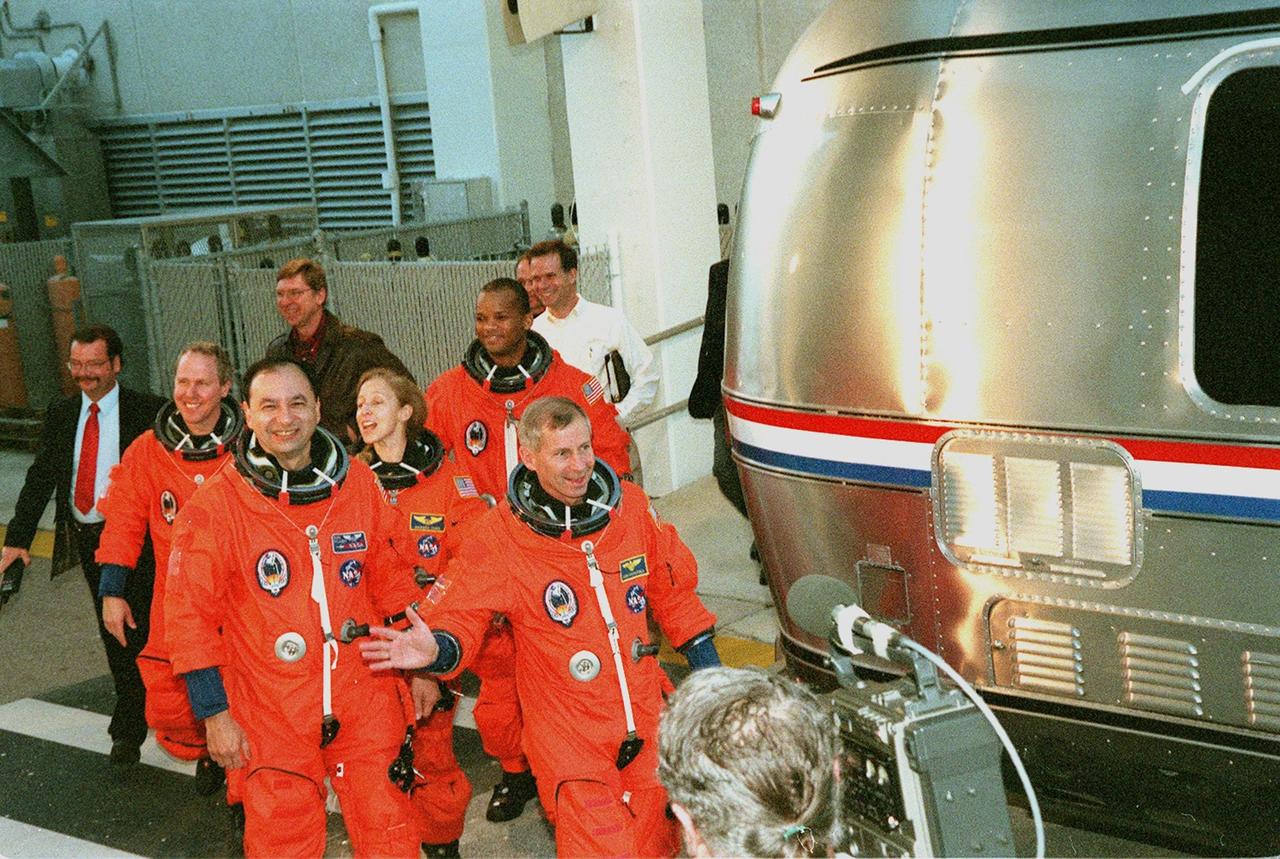

The STS-98 crew wave to onlookers as they walk out of the Operations and Checkout Building dressed for a simulated launch countdown at Launch Pad 39A. From left to right, they are Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialists Marsh Ivins and Robert Curbeam, being led by Commander Ken Cockrell. The crew is taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which include the countdown and emergency egress training at the pad. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m. EST
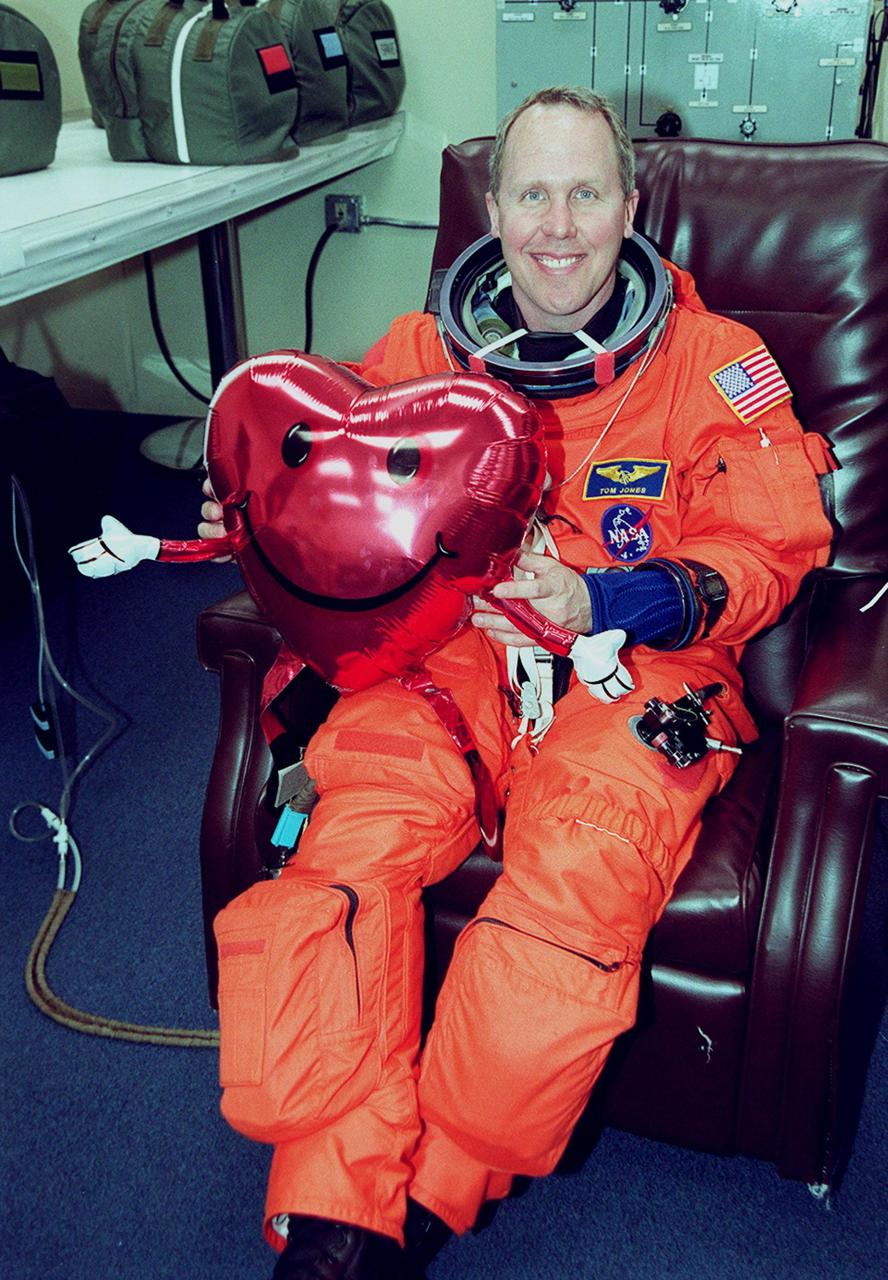

While donning his launch and entry suit, STS-98 Mission Specialist Thomas Jones holds a reminder that the crew will be in space on Valentine’s Day during the 11-day mission. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks, by Curbeam and Jones, are required to complete the planned construction work during the mission. Launch is targeted for 6:11 p.m. EST and the planned landing at KSC Feb. 18 about 1:39 p.m. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program
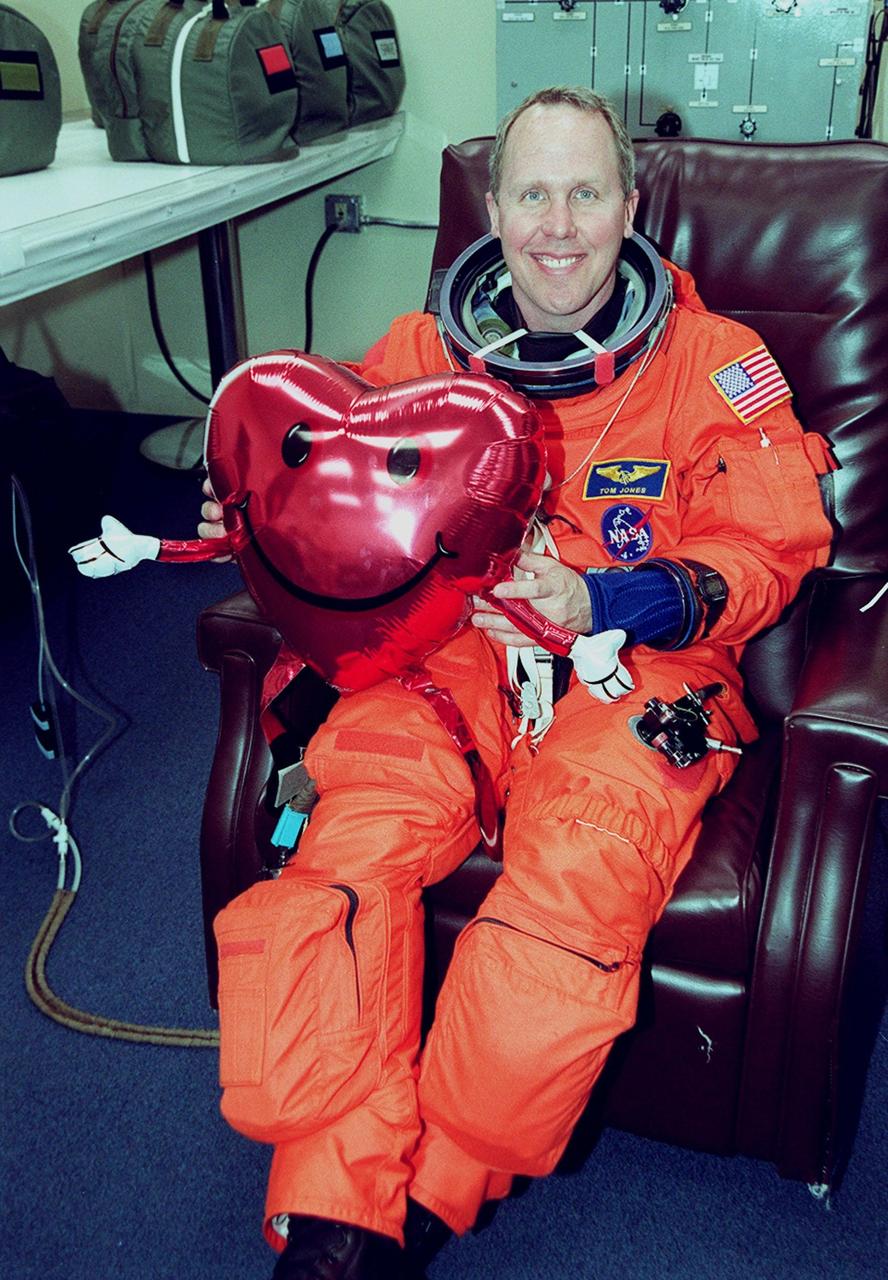

While donning his launch and entry suit, STS-98 Mission Specialist Thomas Jones holds a reminder that the crew will be in space on Valentine’s Day during the 11-day mission. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station. Atlantis is carrying the U.S. Laboratory Destiny, a key module in the growth of the Space Station. Destiny will be attached to the Unity node on the Space Station using the Shuttle’s robotic arm. Three spacewalks, by Curbeam and Jones, are required to complete the planned construction work during the mission. Launch is targeted for 6:11 p.m. EST and the planned landing at KSC Feb. 18 about 1:39 p.m. This mission marks the seventh Shuttle flight to the Space Station, the 23rd flight of Atlantis and the 102nd flight overall in NASA’s Space Shuttle program
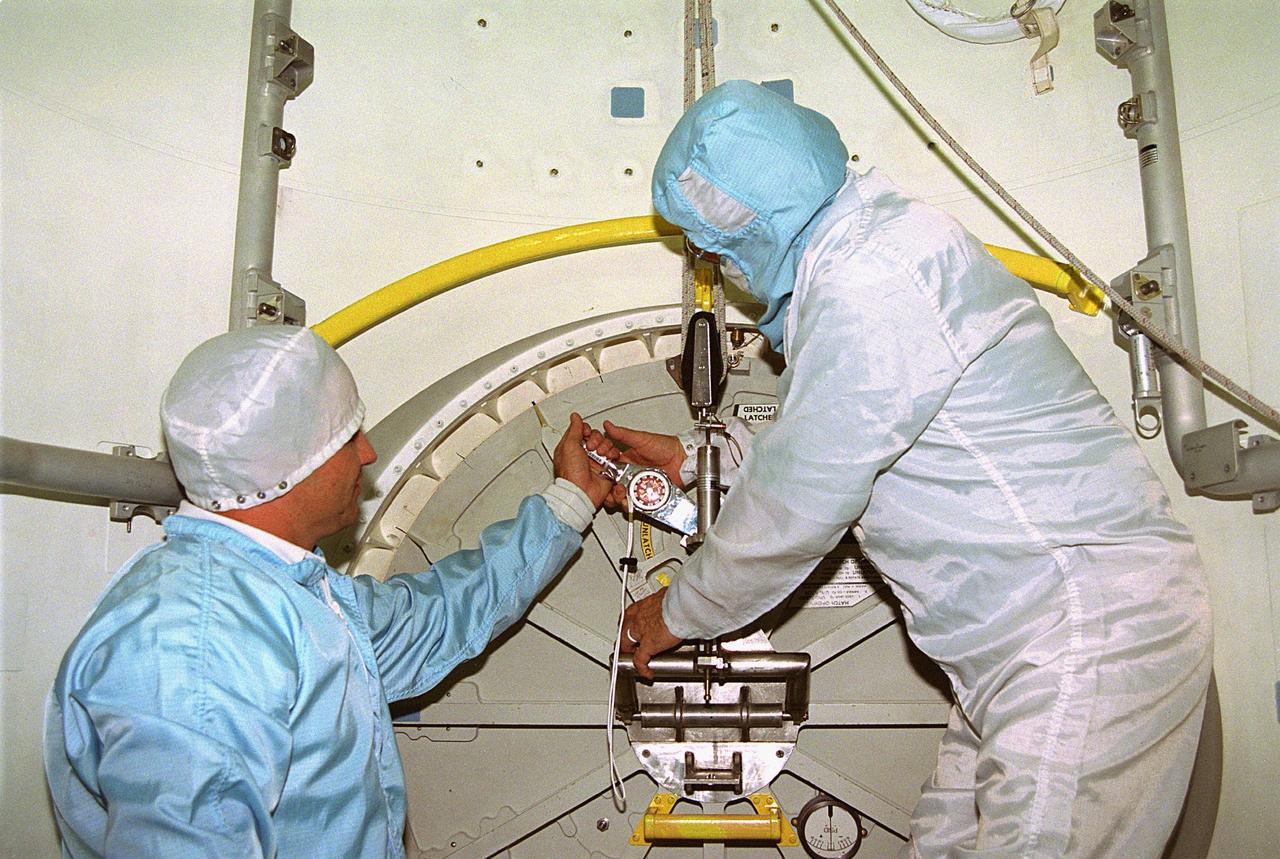

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 1, United Space Alliance (USA) technicians Dave Lawrence, at left, and James Cullop troubleshoot the orbiter Columbia’s outer hatch of the airlock, which failed to open during the recent STS-80 Space Shuttle mission. Mission Specialists Tamara E. Jernigan and Thomas D. Jones did not perform the mission’s planned two extravehicular activities (EVAs) or spacewalks because the hatch would not open on orbit. The spacewalks were to be part of the continuing series of EVA Development Flight Tests to evaluate equipment and procedures and to build spacewalking experience in preparation for the International Space Station.
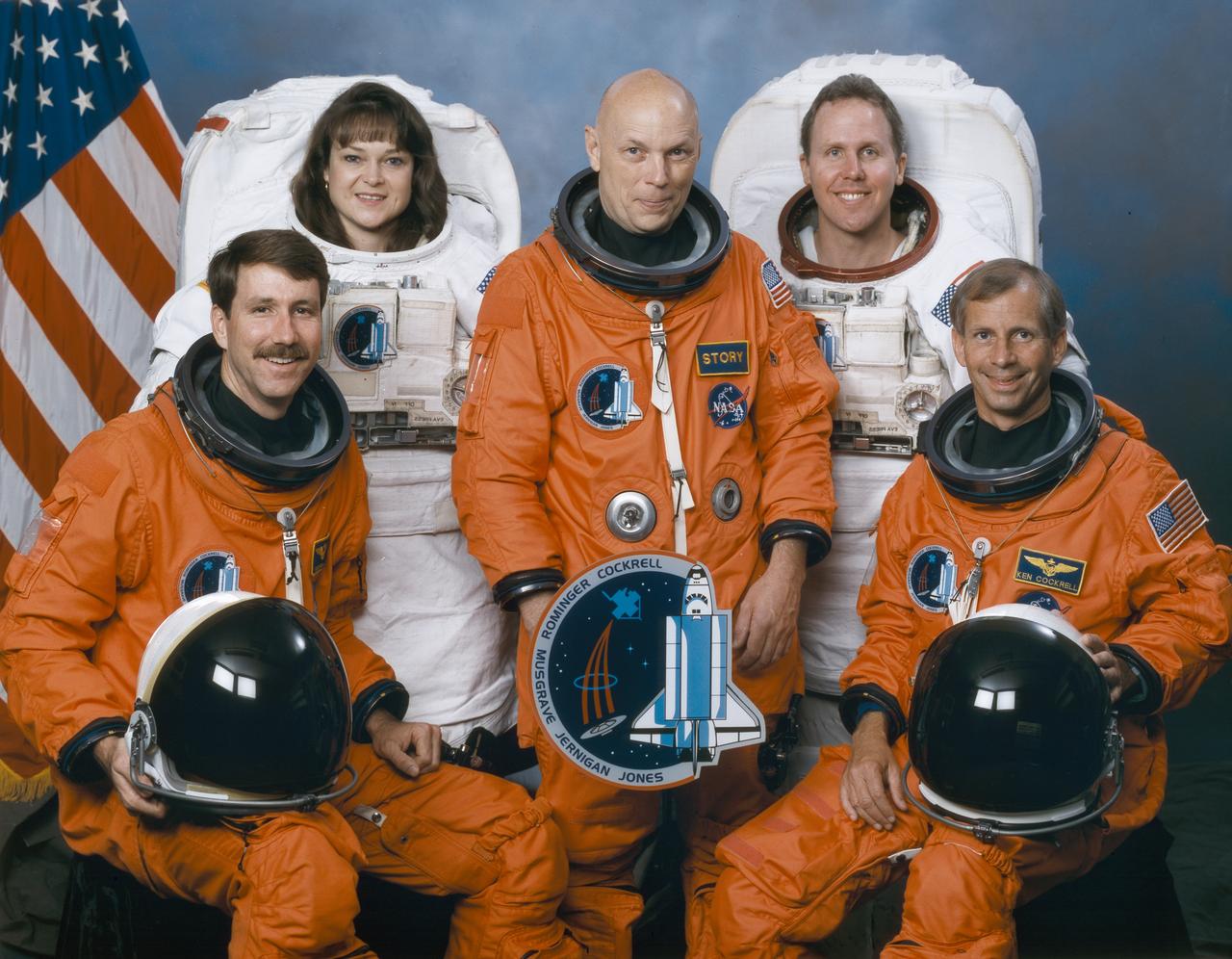

The crew assigned to the STS-79 mission included (seated left to right) Kent V. Rominger, pilot; and Kenneth D. Cockrell, commander. Standing (left to right) are mission specialists Tamara E. Jernigan, F. Story Musgrave, and Thomas D. Jones. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on November 19, 1996 at 2:55:47 pm (EST), the STS-80 mission marked the final flight of 1996. The crew successfully deployed and operated the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer-Shuttle Pallet Satellite II (ORFEUS-SPAS II), and deployed and retrieved the Wake Shield Facility-3 (WSF-3).
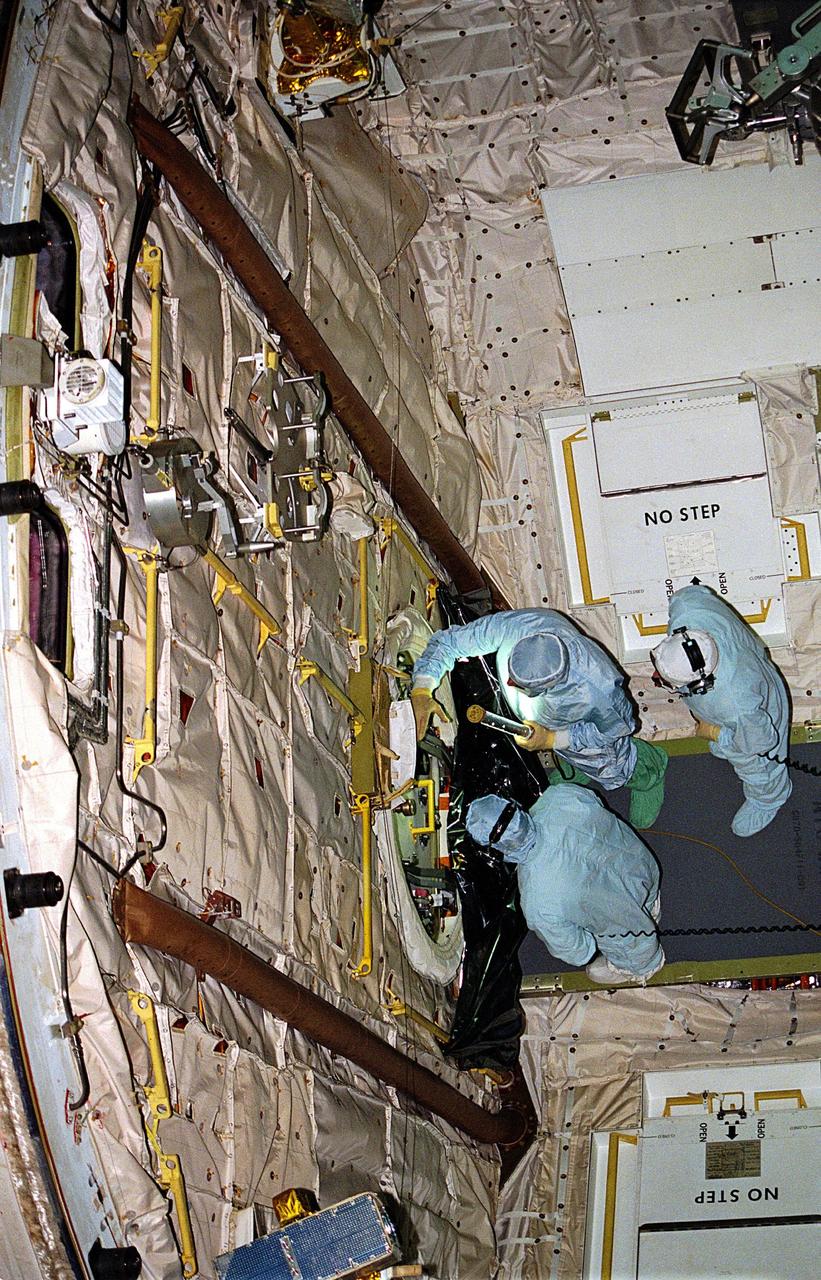

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance (USA) technicians in Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 1 troubleshoot the orbiter Columbia’s outer hatch of the airlock, which failed to open during the recent STS-80 Space Shuttle mission. Mission Specialists Tamara E. Jernigan and Thomas D. Jones did not perform the mission’s planned two extravehicular activities (EVAs) or spacewalks because the hatch would not open on orbit. The spacewalks were to be part of the continuing series of EVA Development Flight Tests to evaluate equipment and procedures and to build spacewalking experience in preparation for the International Space Station.
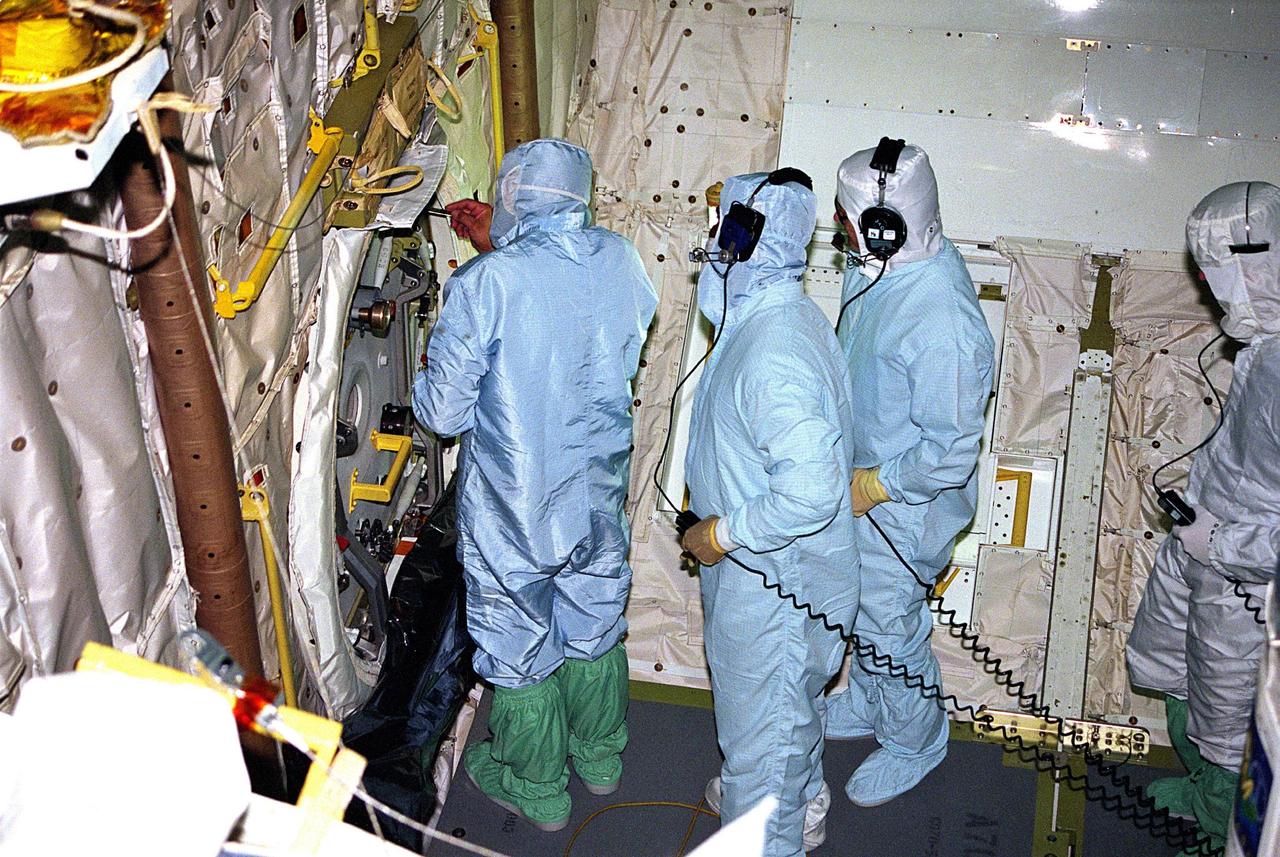

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance (USA) technicians in Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 1 troubleshoot the orbiter Columbia’s outer hatch of the airlock, which failed to open during the recent STS-80 Space Shuttle mission. Mission Specialists Tamara E. Jernigan and Thomas D. Jones did not perform the mission’s planned two extravehicular activities (EVAs) or spacewalks because the hatch would not open on orbit. The spacewalks were to be part of the continuing series of EVA Development Flight Tests to evaluate equipment and procedures and to build spacewalking experience in preparation for the International Space Station.
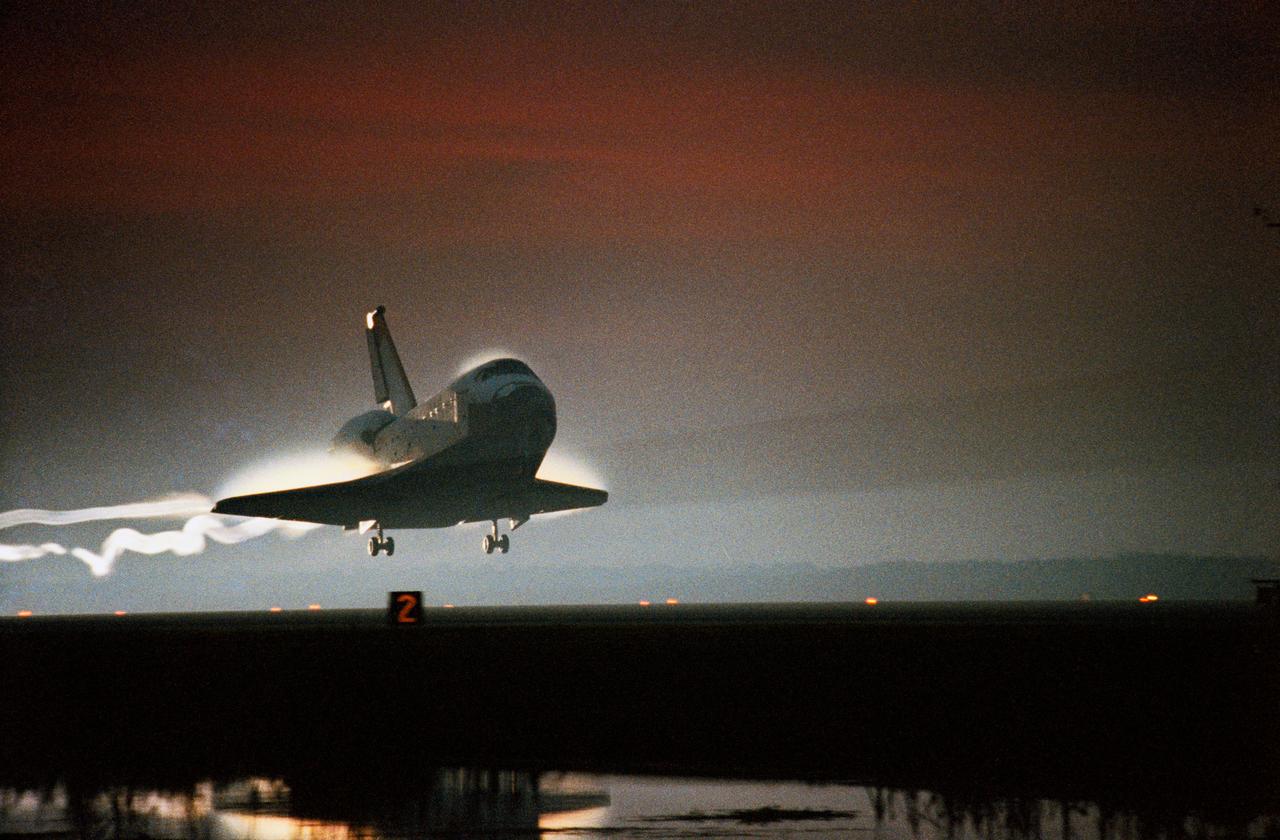

STS080-S-008 (7 Dec. 1996) --- Just prior to dawn, the space shuttle Columbia heads for a landing on Runway 33 at the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) to successfully complete a 17-day mission. Landing occurred just before dawn, at 6:49 a.m. (EST). The landing is the 33rd at KSC for the Space Transportation System (STS). Crew members aboard were astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission commander; and Kent V. Rominger, pilot; along with Story Musgrave, Tamara E. Jernigan and Thomas D. Jones, all mission specialists.
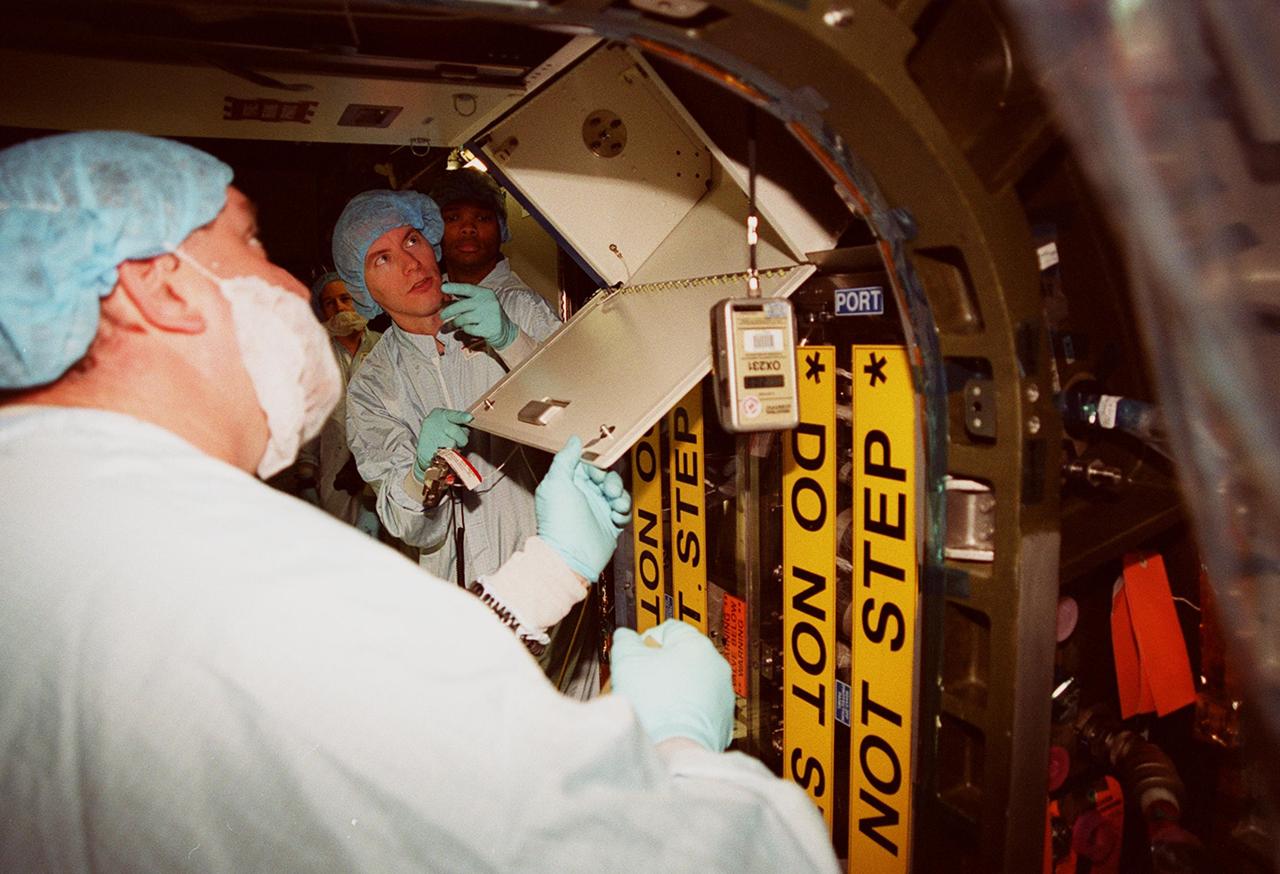
In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-98 crew check out components inside the U.S. Lab, Destiny, under the watchful eye of trainers. The crew comprises Commander Ken Cockrell, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam, Thomas Jones and Marsha Ivins. They are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, becoming familiar with equipment they will be handling during the mission. The mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. With delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. The STS-98 launch is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001
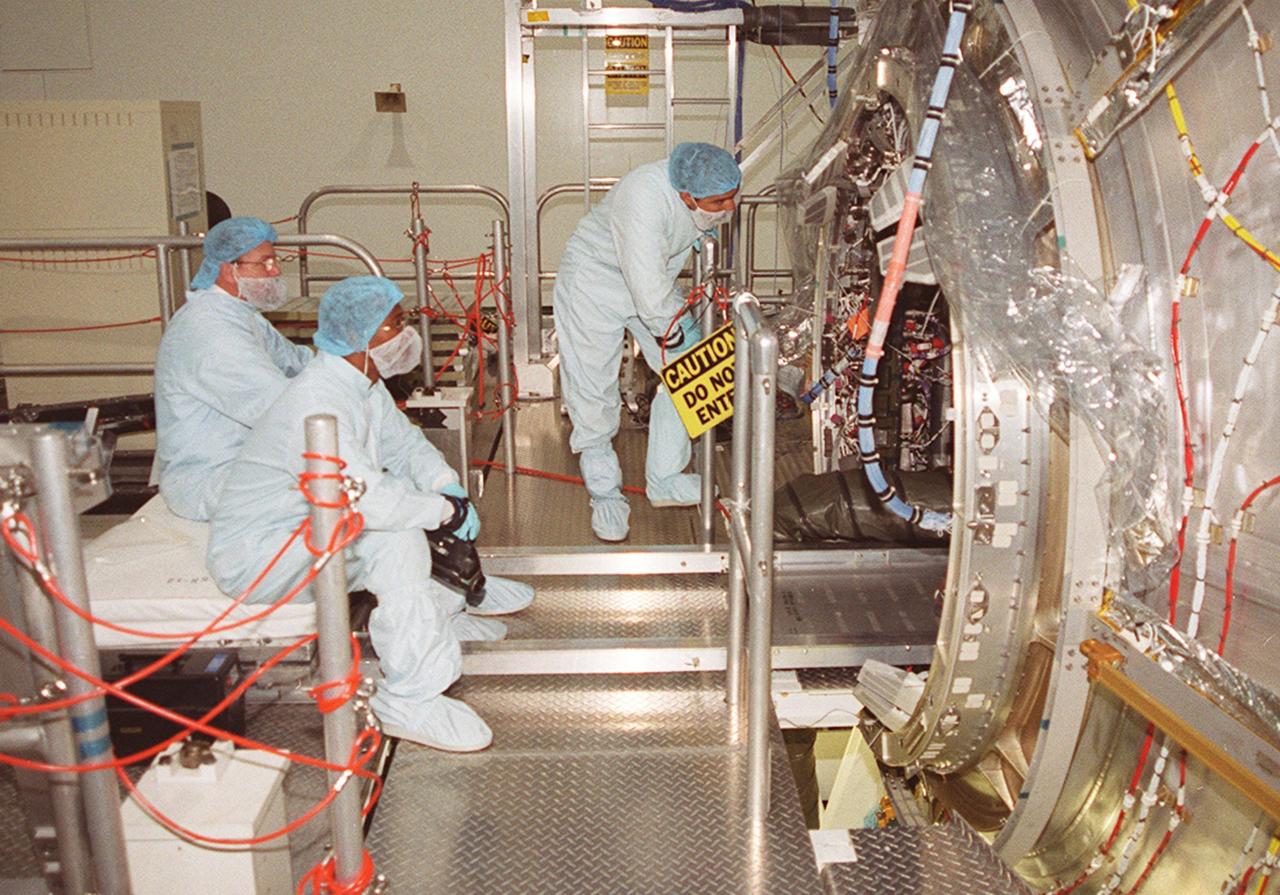

In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers at left watch while members of the STS-98 crew check out equipment inside the U.S. Lab, Destiny (at right). The crew comprises Commander Ken Cockrell, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam, Thomas Jones and Marsha Ivins. They are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, becoming familiar with equipment they will be handling during the mission. The mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. With delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. The STS-98 launch is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001
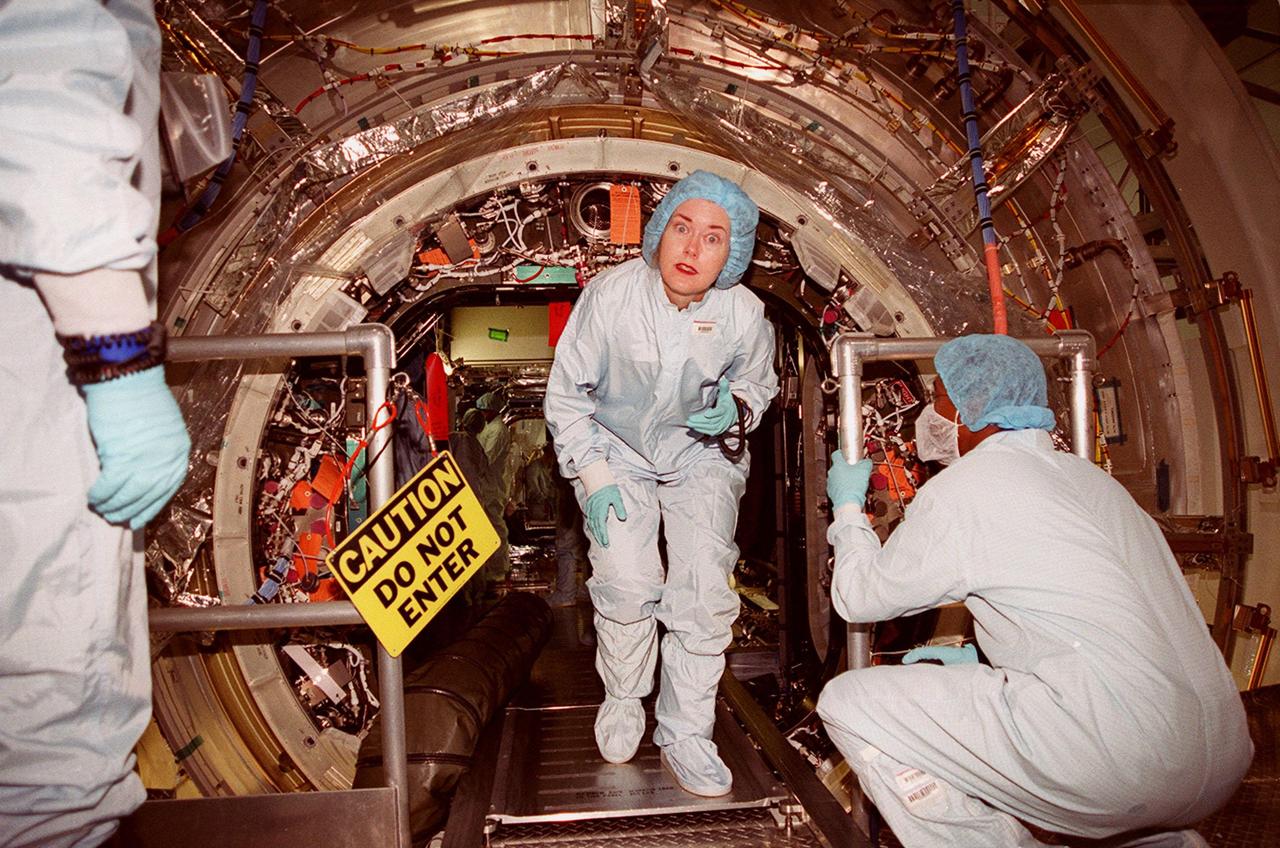

In the Space Station Processing Facility, a worker is surprised by the camera as she exits the U.S. Lab, Destiny. Inside the lab is the STS-98 crew, which is taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, becoming familiar with equipment it will be handling during the mission. The crew comprises Commander Ken Cockrell, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam, Thomas Jones and Marsha Ivins. The mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. With delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. The STS-98 launch is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001
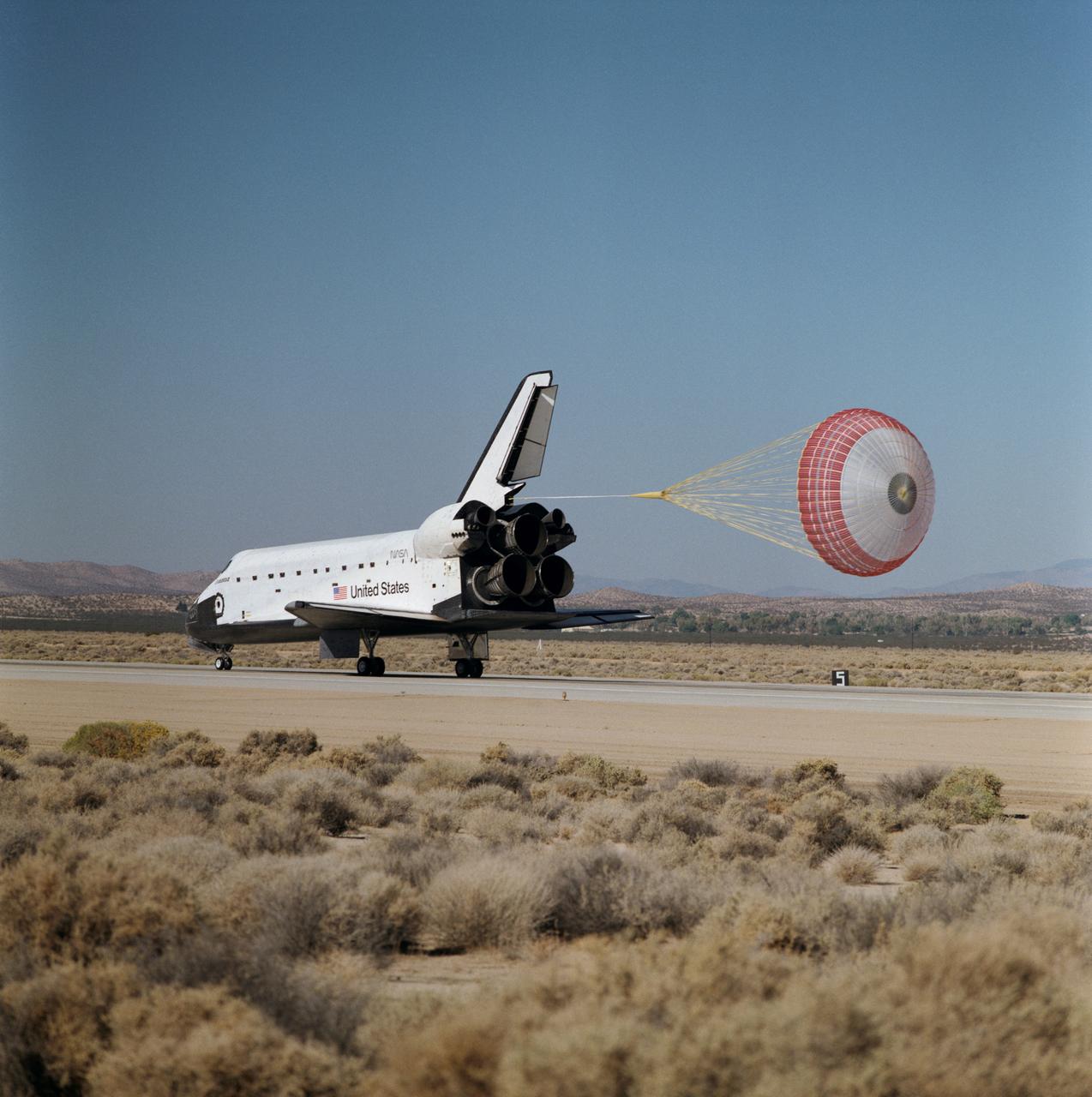

STS068-S-061 (11 October 1994) --- The drag chute system, one of 13 Detailed Test Objectives (DTO) for STS-68, is deployed as the Space Shuttle Endeavour completes an eleven-day mission at Edwards Air Force Base, California. Landing occurred at 10:02 a.m. (PDT), October 11, 1994. Onboard were astronauts Michael A. Baker, mission commander; Terrence W. Wilcutt, pilot; Thomas D. Jones, payload commander; and Daniel W. Bursch, Peter J. K. (Jeff) Wisoff and Steven L. Smith, all mission specialists.
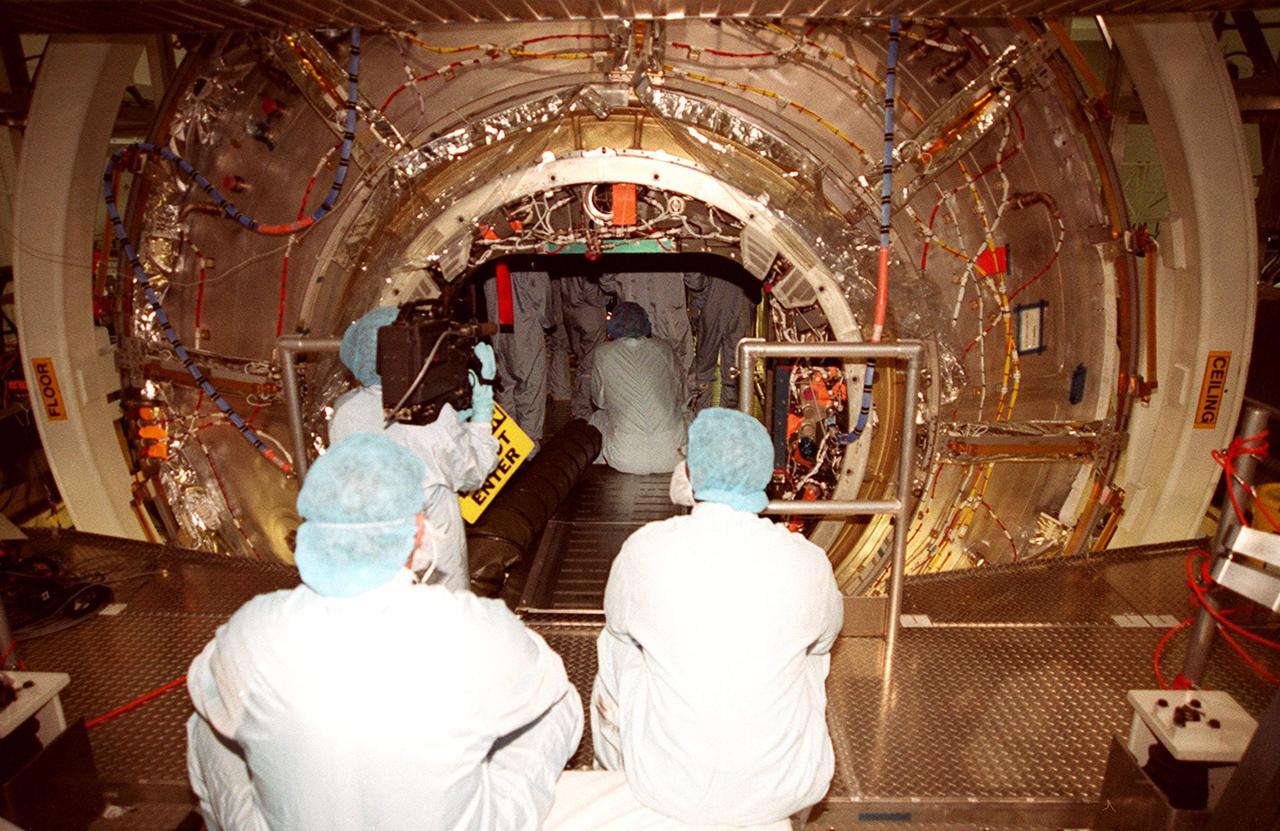

In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers in the foreground watch and wait while members of the STS-98 crew check out the U.S. Lab, Destiny in the background. The crew comprises Commander Ken Cockrell, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam, Thomas Jones and Marsha Ivins. They are taking part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, becoming familiar with equipment they will be handling during the mission. The mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. With delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. The STS-98 launch is scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001
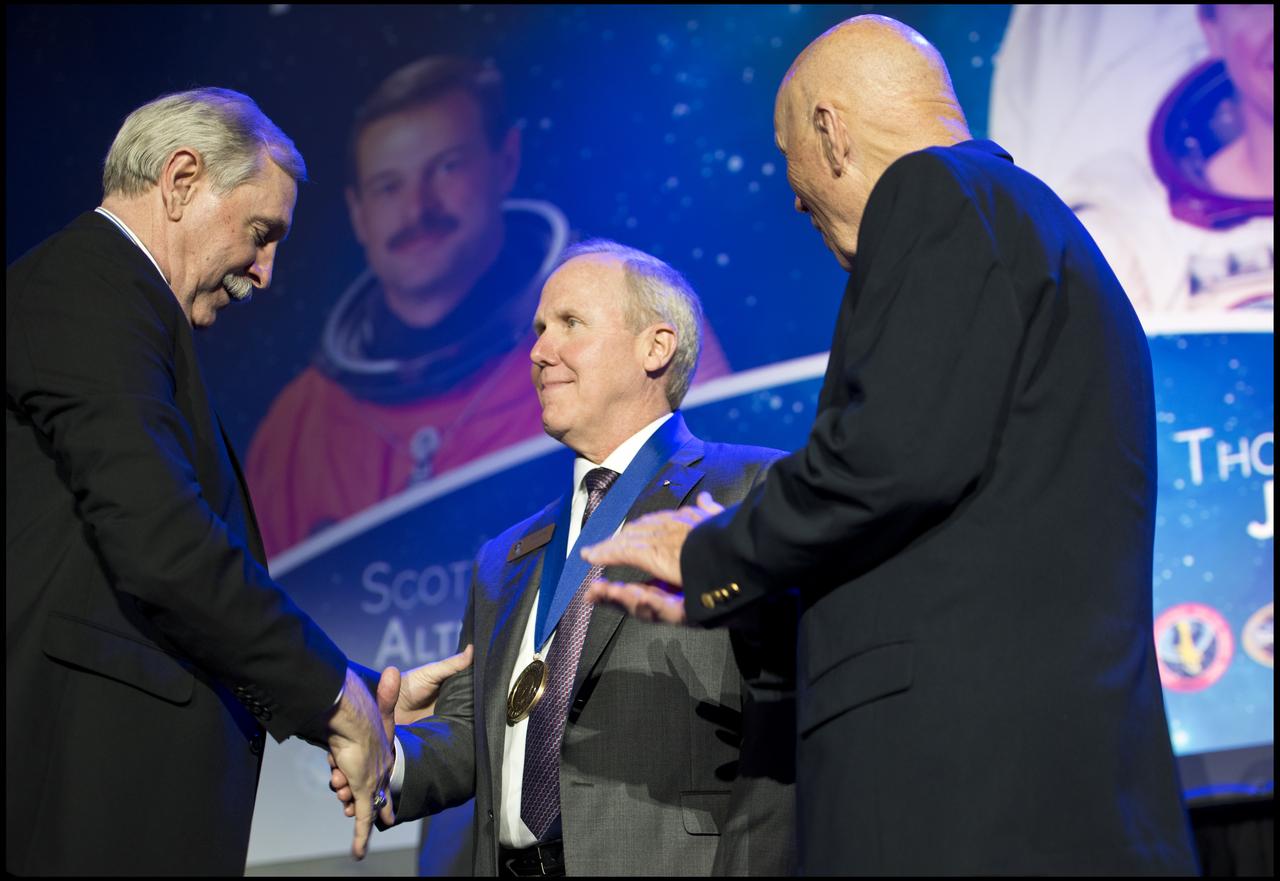

Thomas D. Jones, Ph.D., in the center, is inducted into the Astronaut Hall of Fame (AHOF) during a ceremony inside the Space Shuttle Atlantis attraction at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. At left, Hall of Famer Curt Brown, board chairman, Astronaut Scholarship Foundation (ASF), inducts Jones into the Hall of Fame Class of 2018. At right is Hall of Famer Storey Musgrave, who spoke on Jones behalf during the ceremony. Also inducted was retired astronaut Scott D. Altman. Inductees into the Hall of Fame are selected by a committee of Hall of Fame astronauts, former NASA officials, flight directors, historians and journalists. The process is administered by the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. To be eligible, an astronaut must have made his or her first flight at least 17 years before the induction. Candidates must be a U.S. citizen and a NASA-trained commander, pilot or mission specialist who has orbited the earth at least once. Including Altman and Jones, 97 astronauts have been inducted into the AHOF.
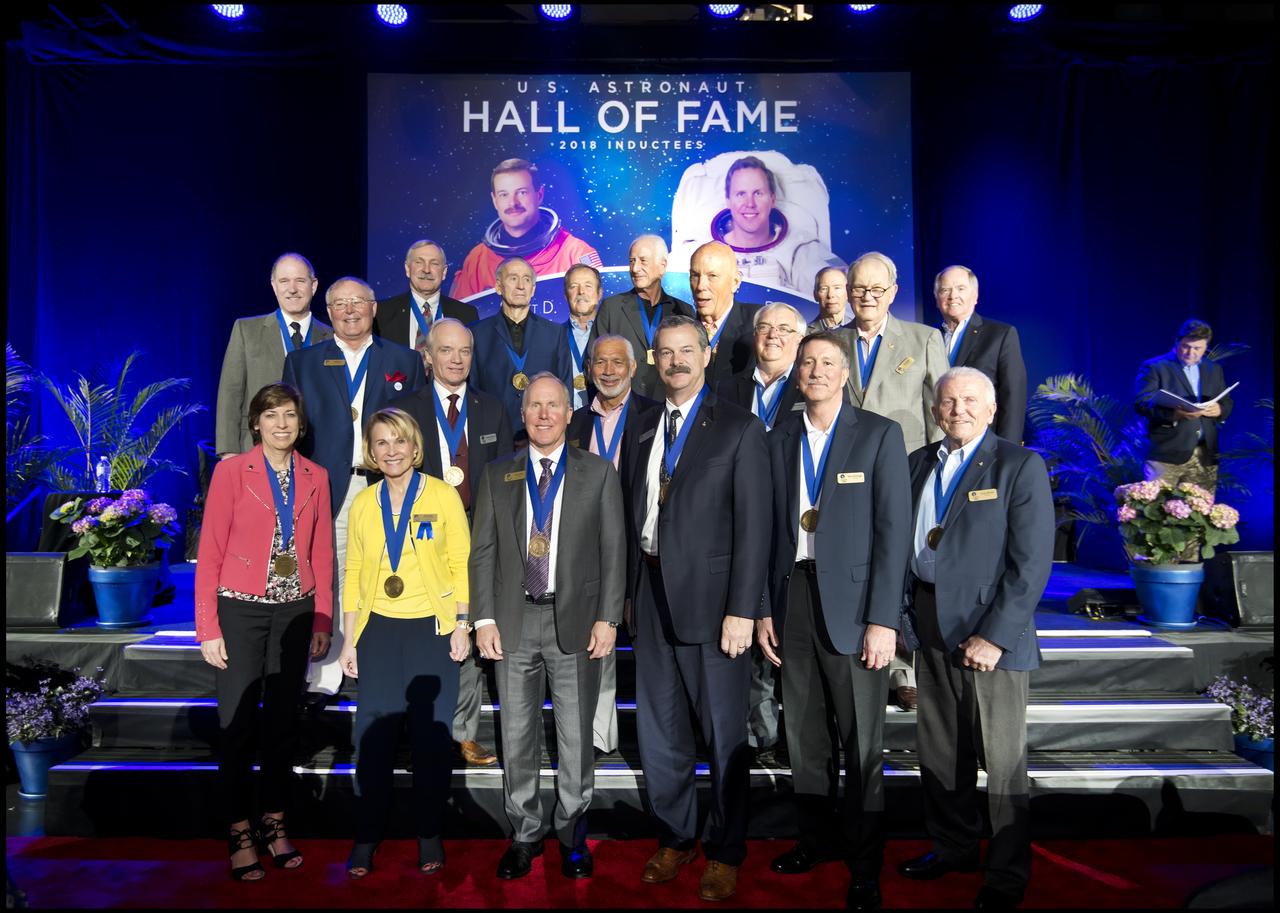

Former astronauts and space explorers, Thomas D. Jones, Ph.D., and Scott D. Altman, front row, center, left and right, respectively, were inducted into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame Class of 2018 during a ceremony inside the Space Shuttle Atlantis attraction at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. They are standing with previous Hall of Famers, including, Curt Brown, back row, far left, chairman of the board, Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. Brown performed the induction ceremony. Also in the group is former astronaut and NASA administrator Charlie Bolden, in the center, behind Jones and Altman. In the back row, second from left is John Grunsfeld, who spoke on behalf of Altman during the ceremony. Directly behind Altman is Storey Musgrave, who spoke on behalf of Jones during the ceremony. Inductees into the Hall of Fame are selected by a committee of Hall of Fame astronauts, former NASA officials, flight directors, historians and journalists. The process is administered by the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. To be eligible, an astronaut must have made his or her first flight at least 17 years before the induction. Candidates must be a U.S. citizen and a NASA-trained commander, pilot or mission specialist who has orbited the earth at least once. Including Altman and Jones, 97 astronauts have been inducted into the AHOF.

Former astronauts and space explorers Scott D. Altman, at left, and Thomas D. Jones, Ph.D., are inducted into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame Class of 2018 during a ceremony inside the Space Shuttle Atlantis attraction at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. They unveiled their plaques, which will be placed in Hall of Fame at the visitor complex. At far right is Master of Ceremonies, John Zarella, former CNN space correspondent. Inductees into the Hall of Fame are selected by a committee of Hall of Fame astronauts, former NASA officials, flight directors, historians and journalists. The process is administered by the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. To be eligible, an astronaut must have made his or her first flight at least 17 years before the induction. Candidates must be a U.S. citizen and a NASA-trained commander, pilot or mission specialist who has orbited the earth at least once. Including Altman and Jones, 97 astronauts have been inducted into the AHOF.

Former astronauts and space explorers Scott D. Altman, at left, and Thomas D. Jones, Ph.D., are inducted into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame Class of 2018 during a ceremony inside the Space Shuttle Atlantis attraction at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. They unveiled their plaques, which will be placed in the Hall of Fame at the visitor complex. At far right is Master of Ceremonies, John Zarella, former CNN space correspondent. Inductees into the Hall of Fame are selected by a committee of Hall of Fame astronauts, former NASA officials, flight directors, historians and journalists. The process is administered by the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. To be eligible, an astronaut must have made his or her first flight at least 17 years before the induction. Candidates must be a U.S. citizen and a NASA-trained commander, pilot or mission specialist who has orbited the earth at least once. Including Altman and Jones, 97 astronauts have been inducted into the AHOF.

Kelvin Manning, associate director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, welcomes guests to the 2018 U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame (AHOF) Induction inside the Space Shuttle Atlantis attraction at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex (KSCVC). Two veteran space explorers were inducted into the Hall of Fame Class of 2018. They are Scott D. Altman and Thomas D. Jones, Ph.D. Inductees into the Hall of Fame are selected by a committee of Hall of Fame astronauts, former NASA officials, flight directors, historians and journalists. The process is administered by the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. To be eligible, an astronaut must have made his or her first flight at least 17 years before the induction. Candidates must be a U.S. citizen and a NASA-trained commander, pilot or mission specialist who has orbited the earth at least once. Including Altman and Jones, 97 astronauts have been inducted into the AHOF.
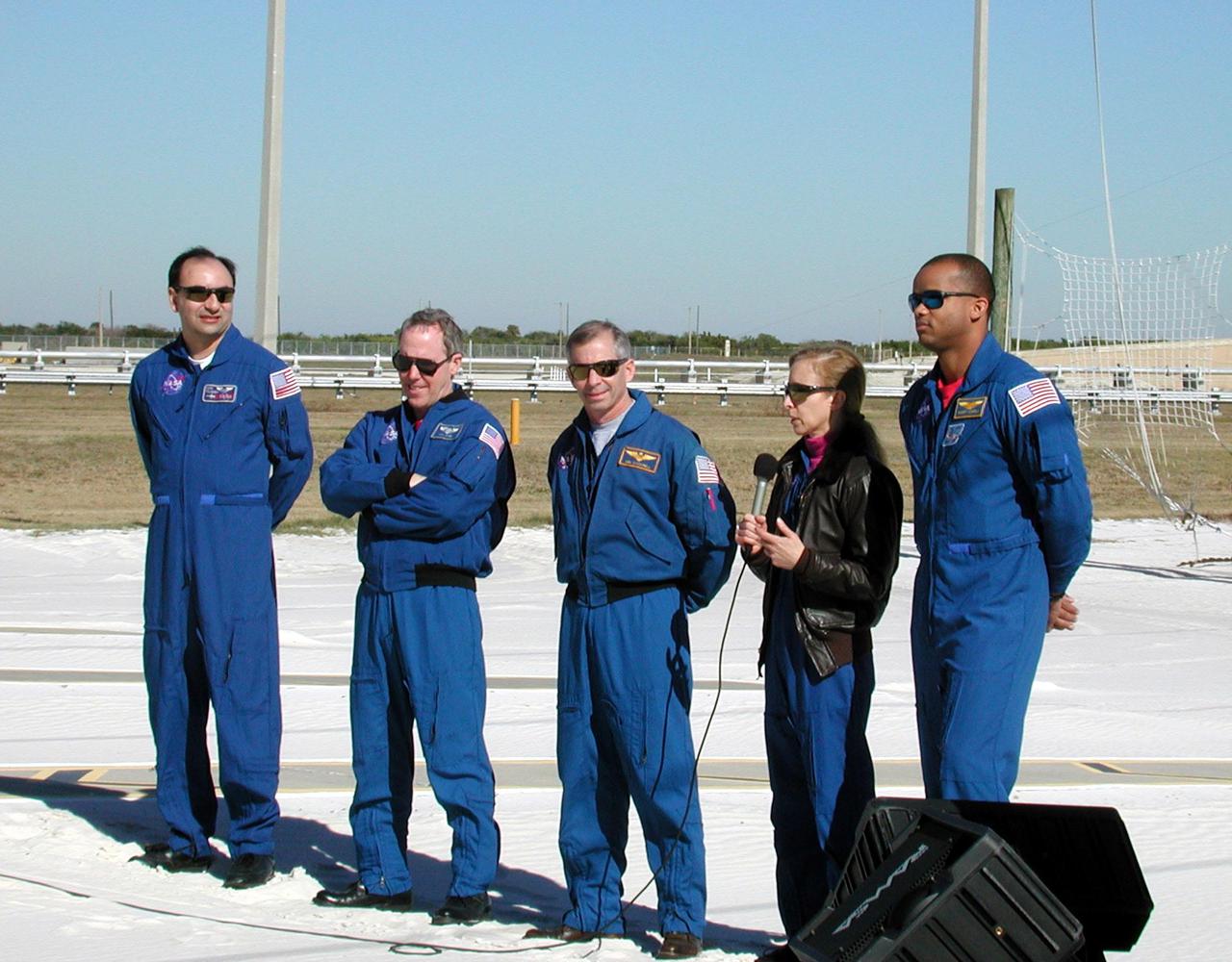

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-98 crew talks to the press at a briefing at Launch Pad 39A. With the microphone is Mission Specialist Marsha Ivins, who discusses her role in the mission using the robotic arm to move the payload into position. The other crew members are (left to right) Pilot Mark Polansky, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Commander Ken Cockrell and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam (far right). They are at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m