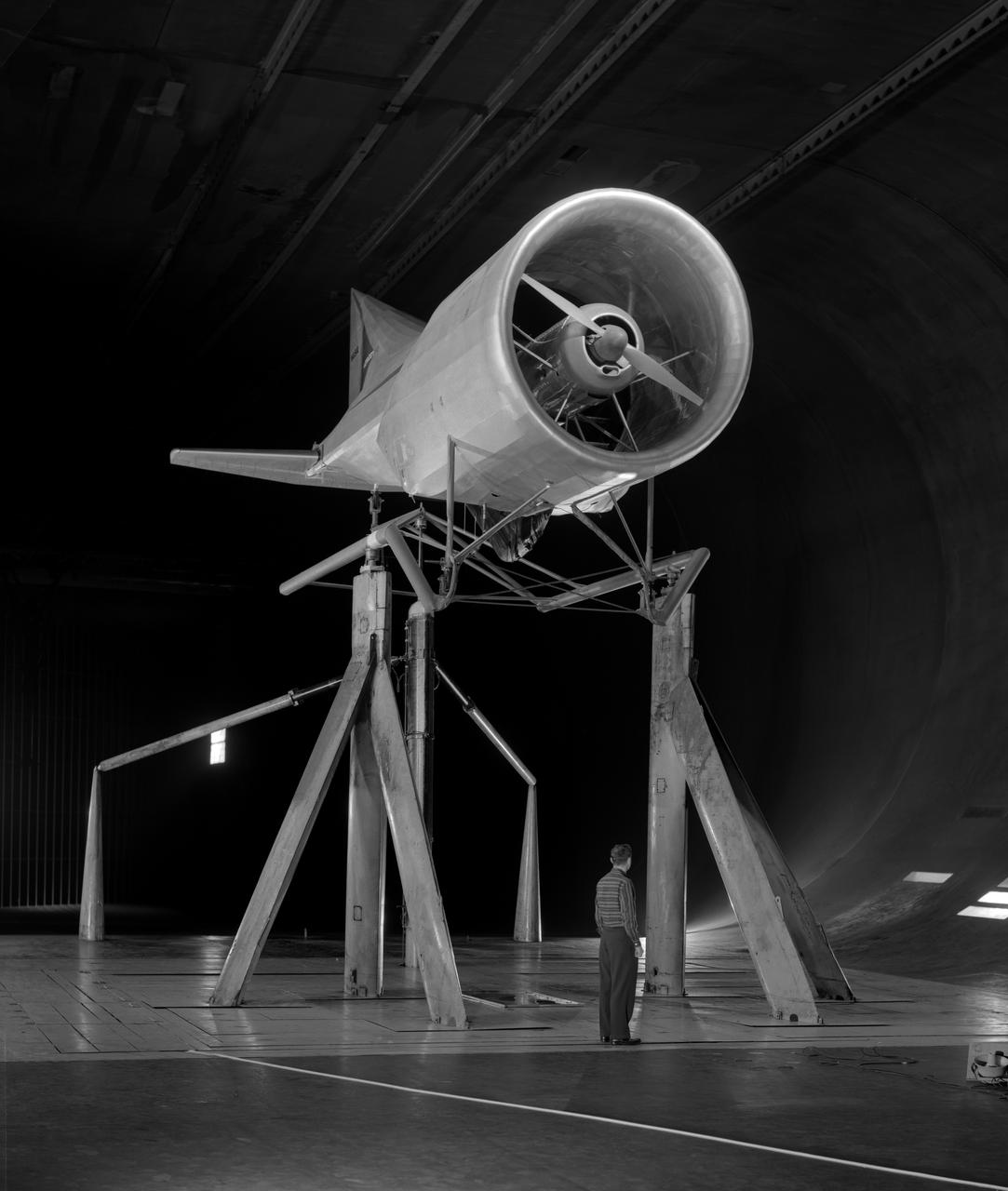

Collins Aerodyne VTOL Vertical take off and landing model in the 40x80 foot wind tunnel at NASA's Ames Research Center. Designed by Alexander Lippisch.
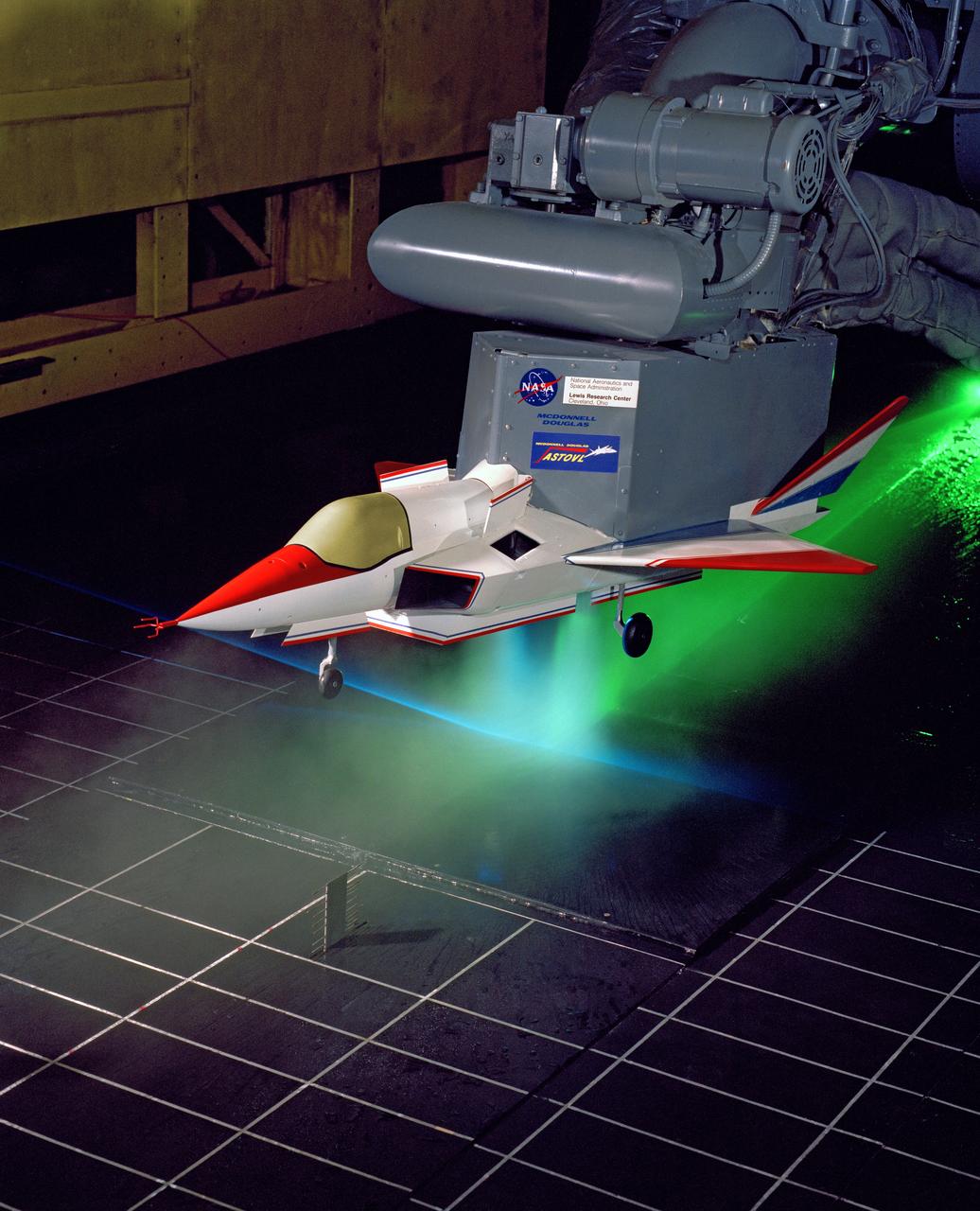
Supersonic Short Take Off Vertical Landing Hot Gas Ingestion Model Testing in the 9x15-foot Low Speed Wind Tunnel, LSWT
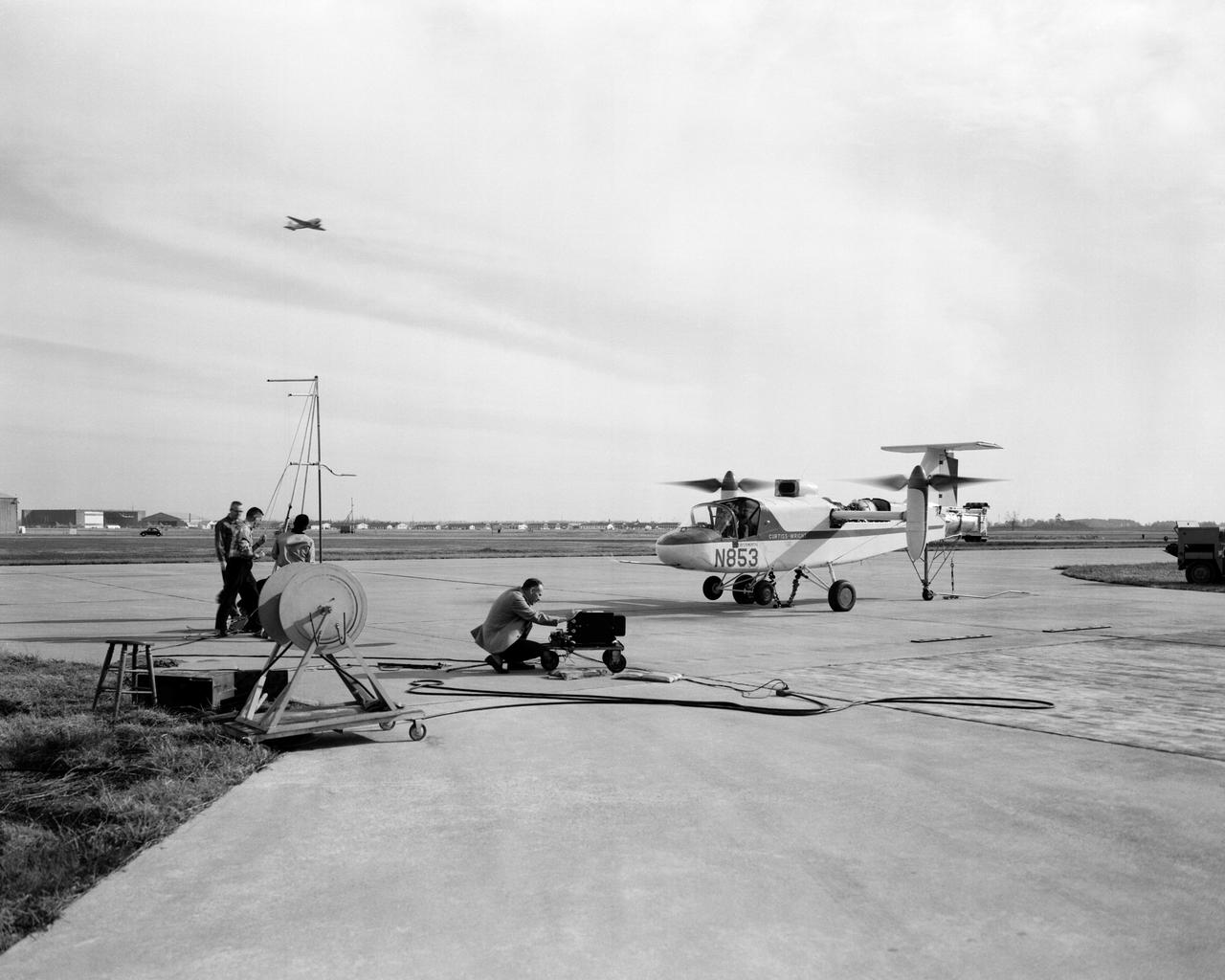

Curtiss-Wright X-100 (VTOL) Vertical Take-Off Transport.
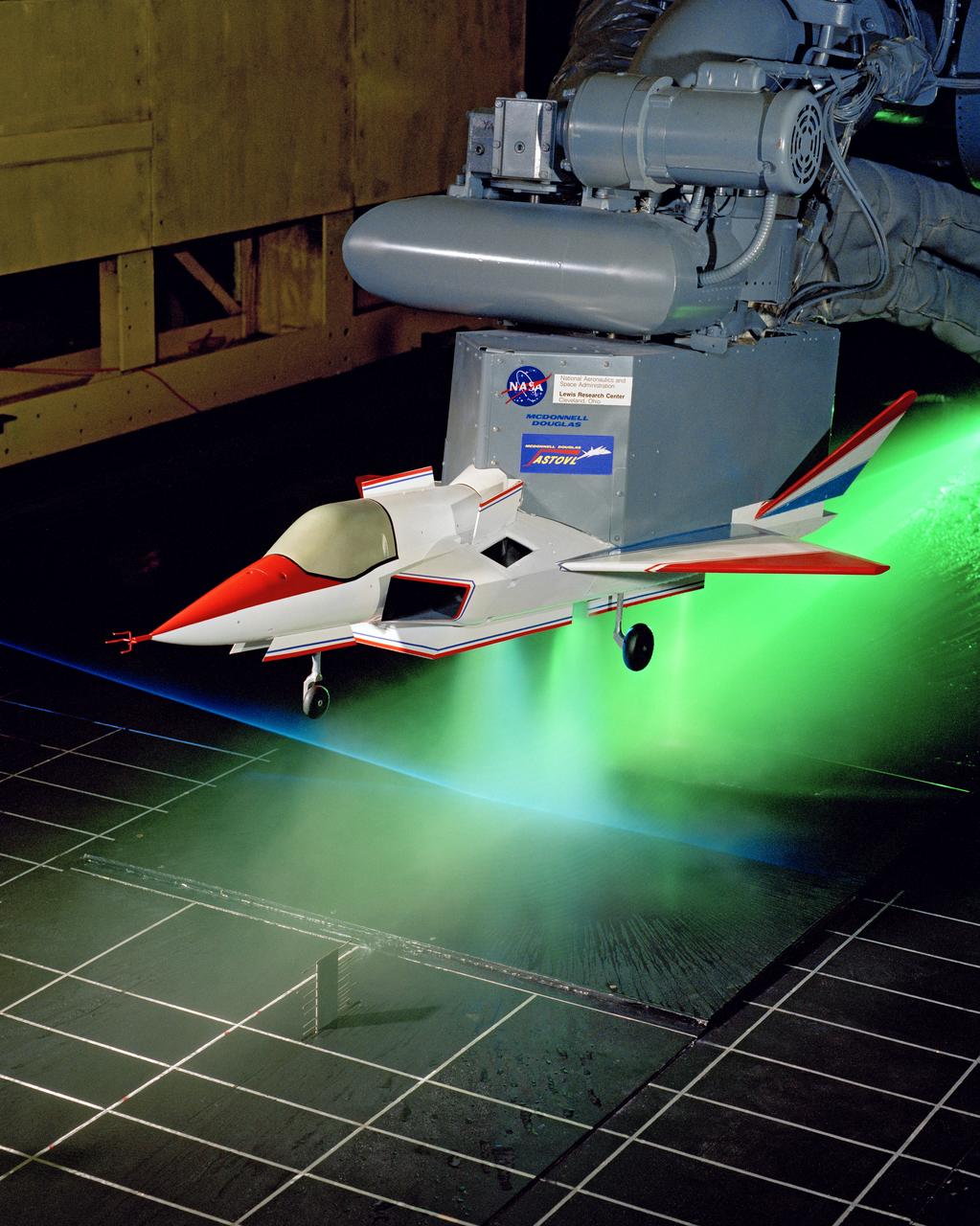

SUPERSONIC SHORT TAKE OFF Vertical LANDING HOT GAS INGESTION MODEL 9X15 WIND TUNNEL
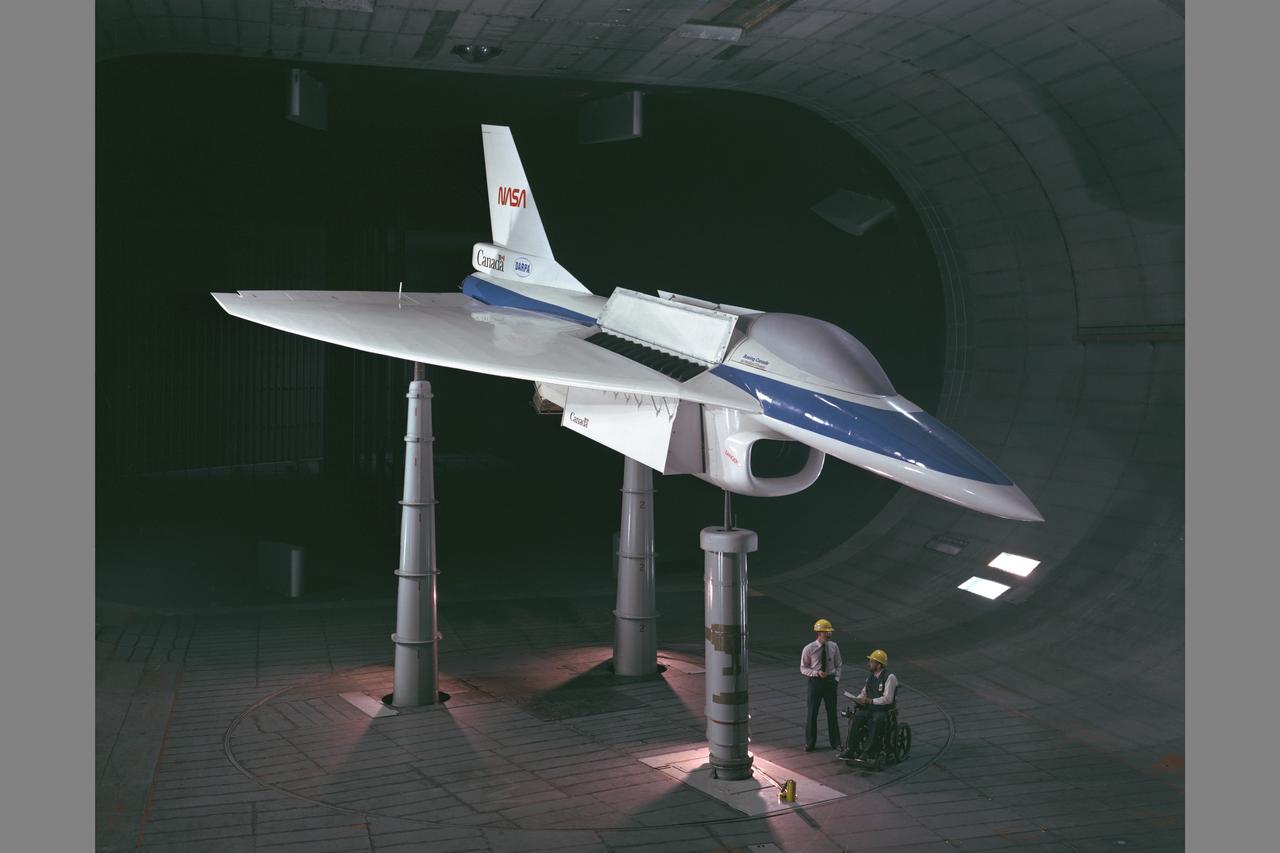

E-7 STOVL fighter model testing in Ames 40x80ft Subsonic wind tunnel. Investigating Supersonic Short Take-off and Vertical Landing (STOVL) technology.
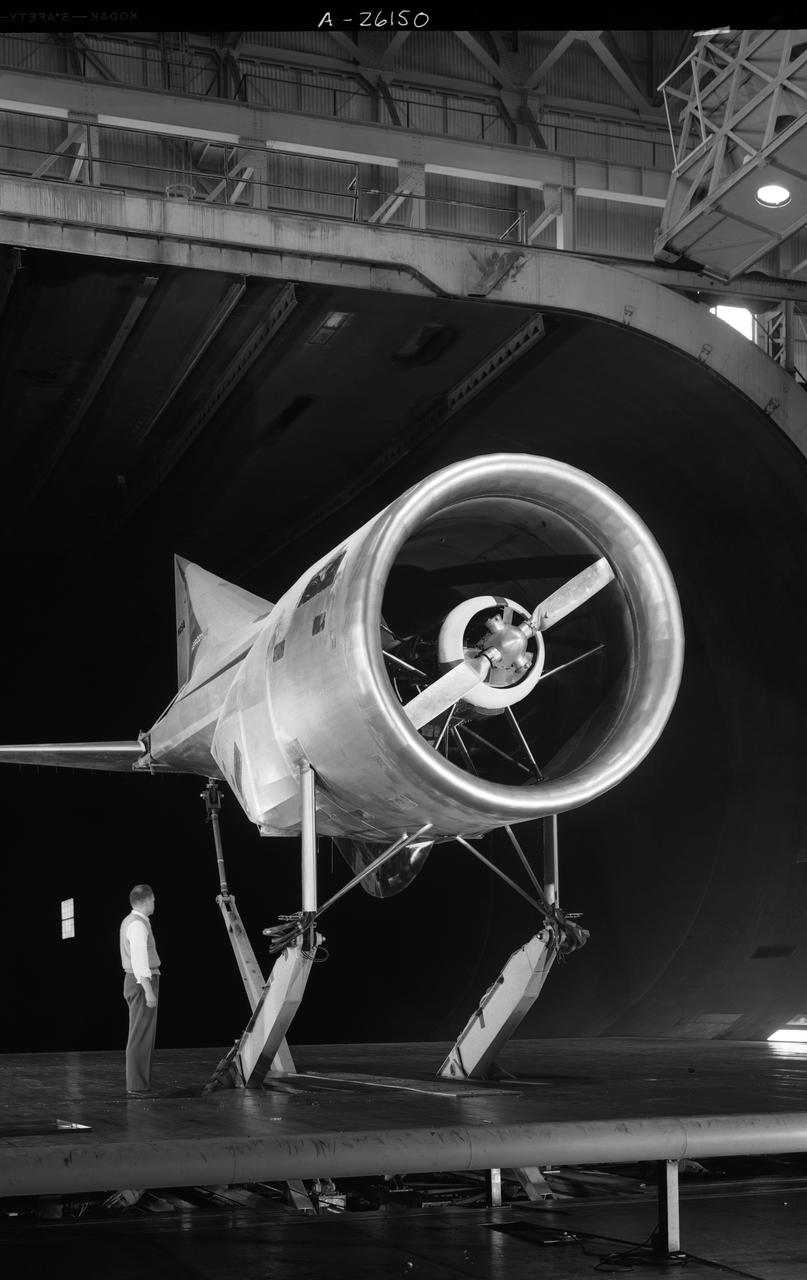

Collins Aerodyne vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft investigations. Ground plane support system. 3/4 front view. Dave Koening (from Collins Aerodyne) in photo. Mounted on variable height struts, ground board system, zero degree angle of attack. 01/11/1960

Vertol VZ-2 (Model 76): Arriving at Langley from Edwards Air Force Base, California, this Vertol VZ-2 underwent almost a year and a half of flight research before going back to the manufacturer for rework. The VZ-2 was used to investigate Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL).
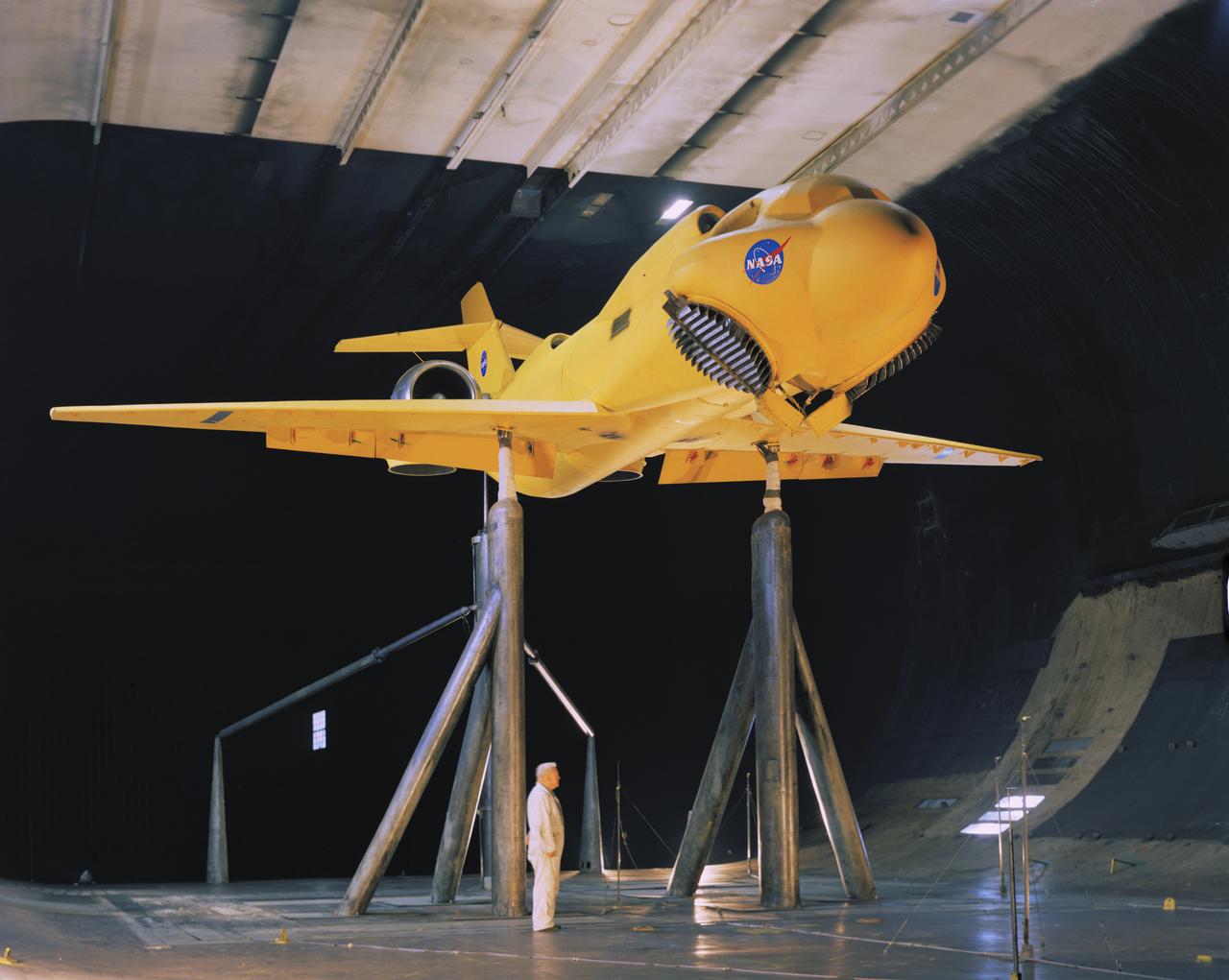

3/4 front view of McDonnell-Douglas Large-Scale lift fan, vertical and/or short take-off and landing (V/STOL), transport model. Francis Malerick in photograph. The McDonnell Douglas DC-9 (initially known as the Douglas DC-9) is a twin-engine, single-aisle jet airliner.
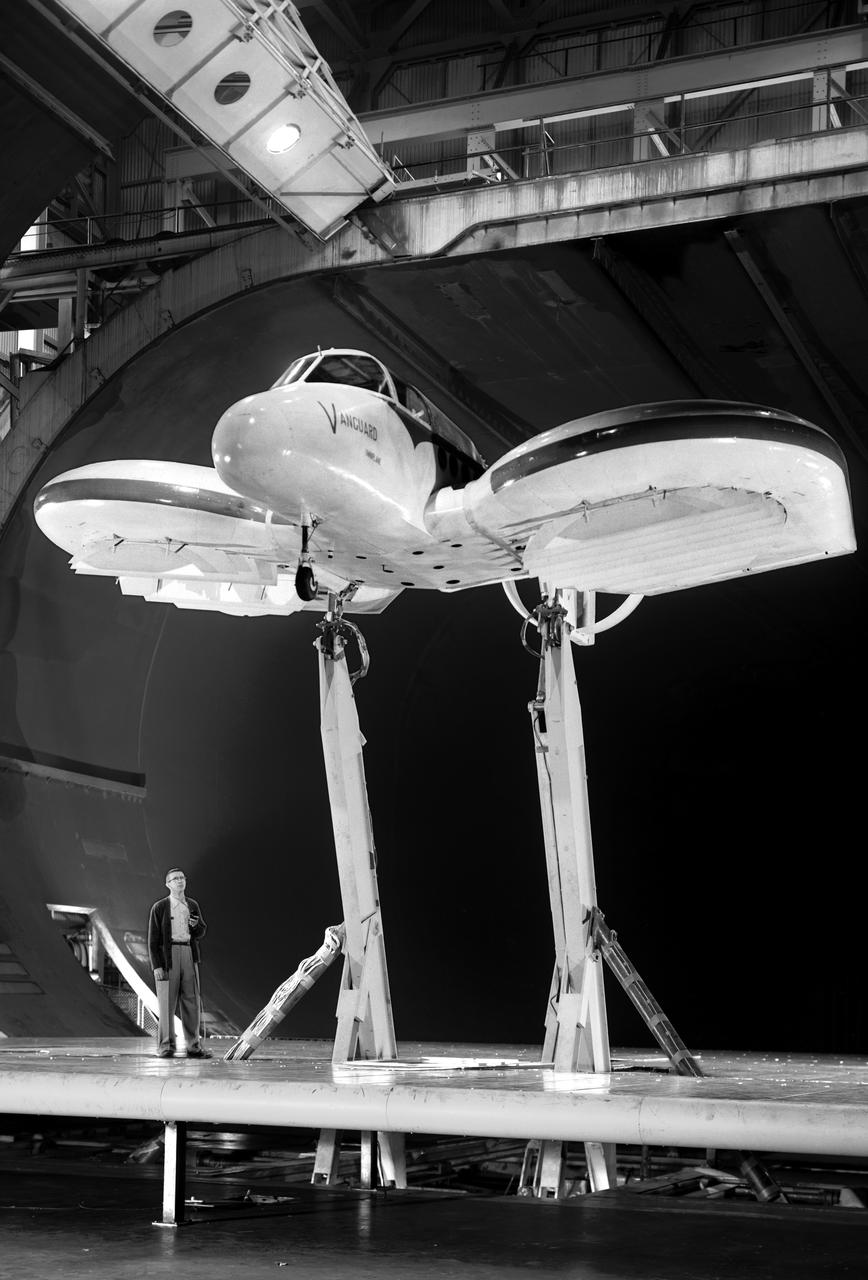

Vanguard 2C vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) airplane, wind tunnel test. Front view from below, model 14 1/2 feet high disk off. Nasa Ames engineer Ralph Maki in photo. Variable height struts and ground plane, low pressure ratio, fan in wing. 02/01/1960.
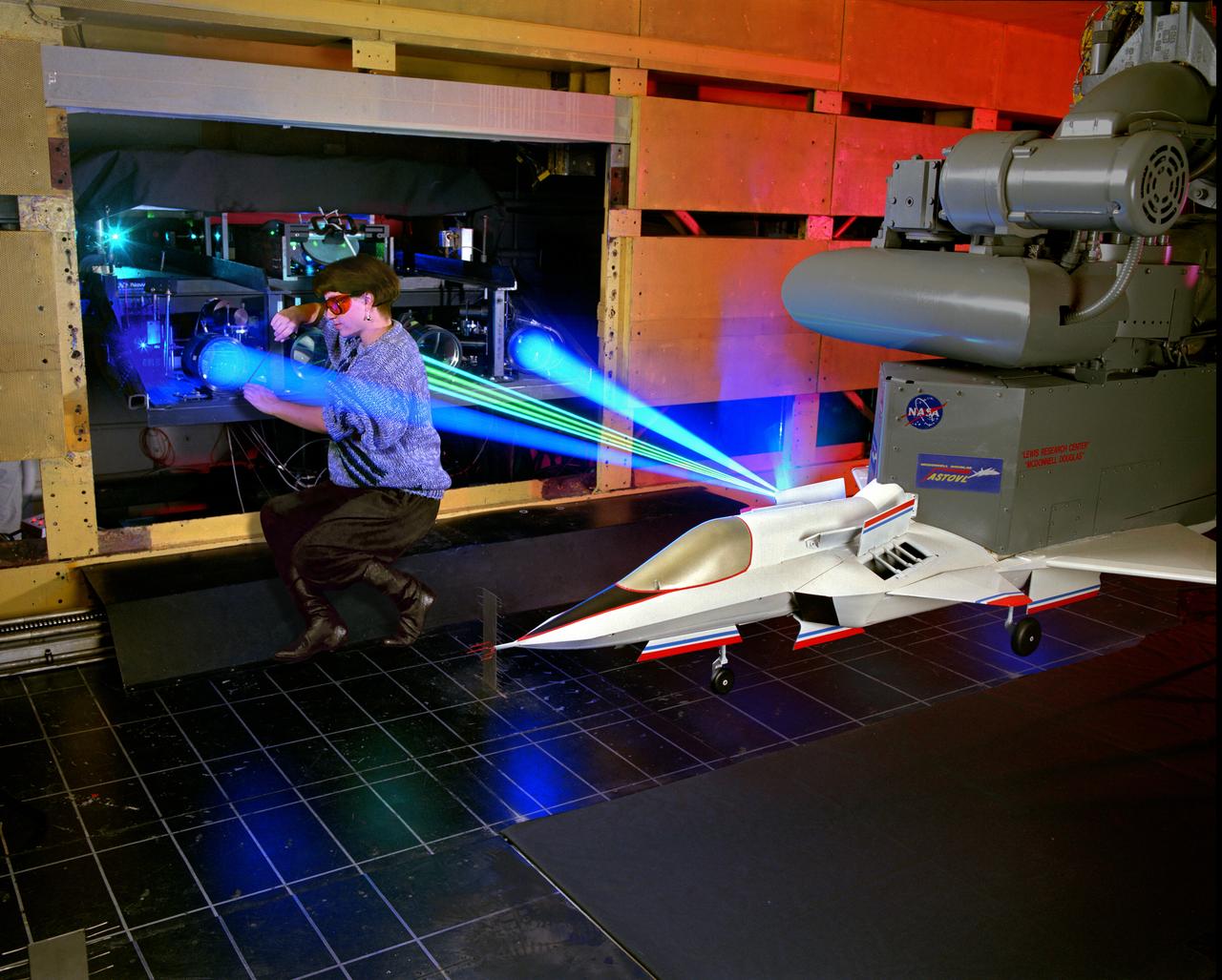

The 9x15 low speed tunnel tests take off and landing of aircraft. The laser velocimetry system for flow measurement show here, with the color blue and green lasers, measures engine exhaust that comes back up from the ground. The STOVL model n the 9x15 low speed wind tunnel, building 39, is similar to the British Harrier aircraft.
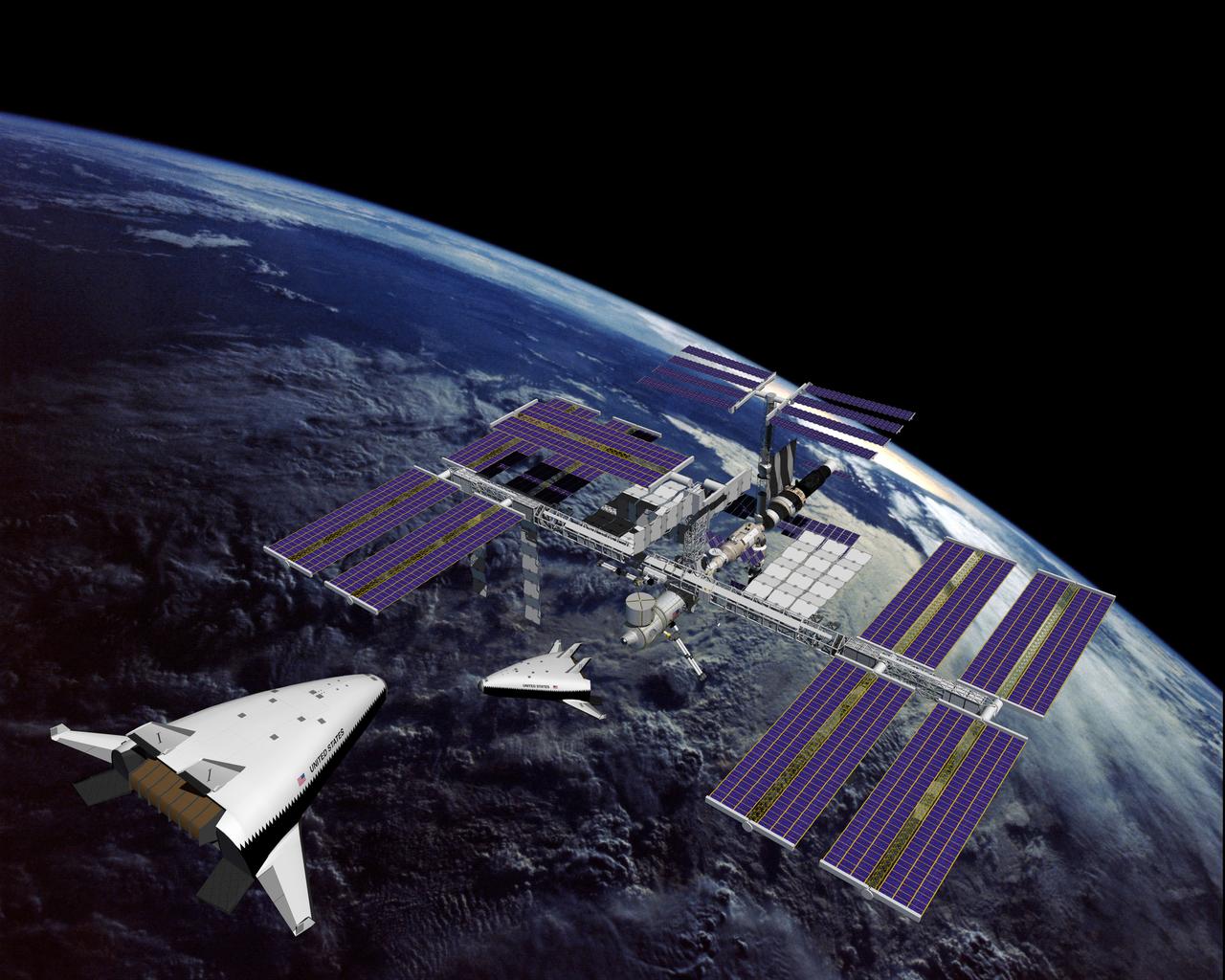

This is an artist's concept of the completely operational International Space Station being approached by an X-33 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV). The X-33 program was designed to pave the way to a full-scale, commercially developed RLV as the flagship technology demonstrator for technologies that would lower the cost of access to space. It is unpiloted, taking off vertically like a rocket, reaching an altitude of up to 60 miles and speeds between Mach 13 and 15, and landing horizontally like an airplane. The X-33 program was cancelled in 2001.
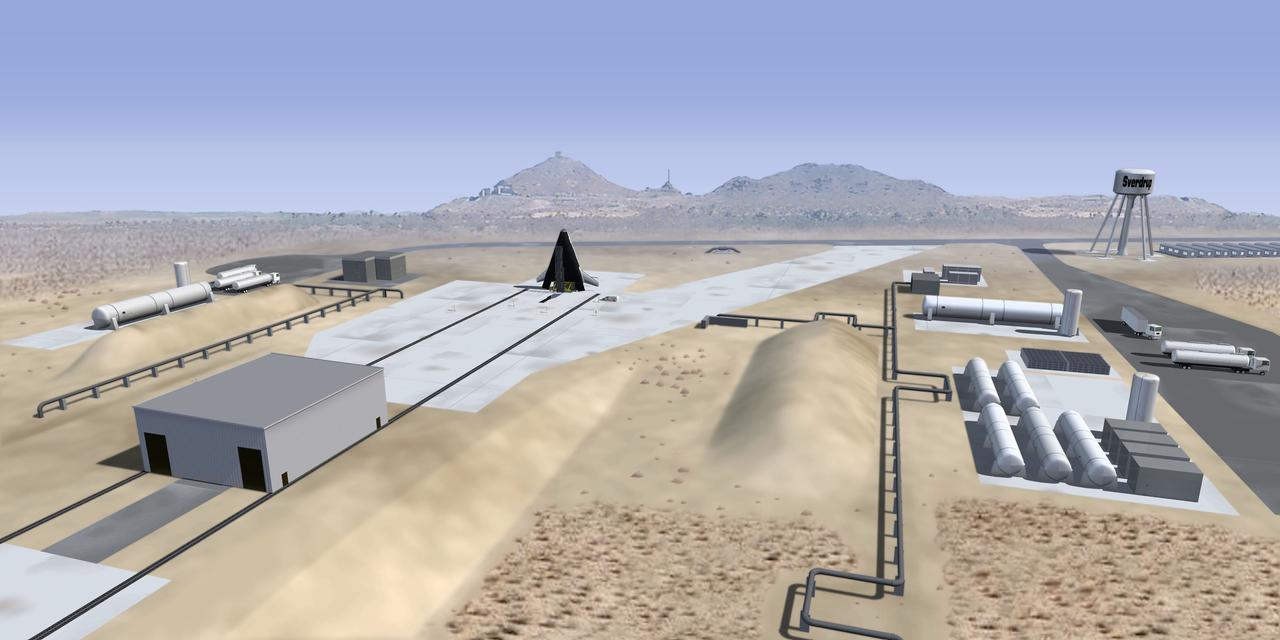

This is an artist's interpretation of a future launch complex for third generation propulsion reusable launch vehicles such as the X-33. The X-33 is a sub-scale technology demonstrator prototype of a Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV), with a vertical take off / horizontal landing (lifting body) concept, which was manufactured and named as the Venture Star by Lockheed Martin. The X-33 program was cancelled in 2001.
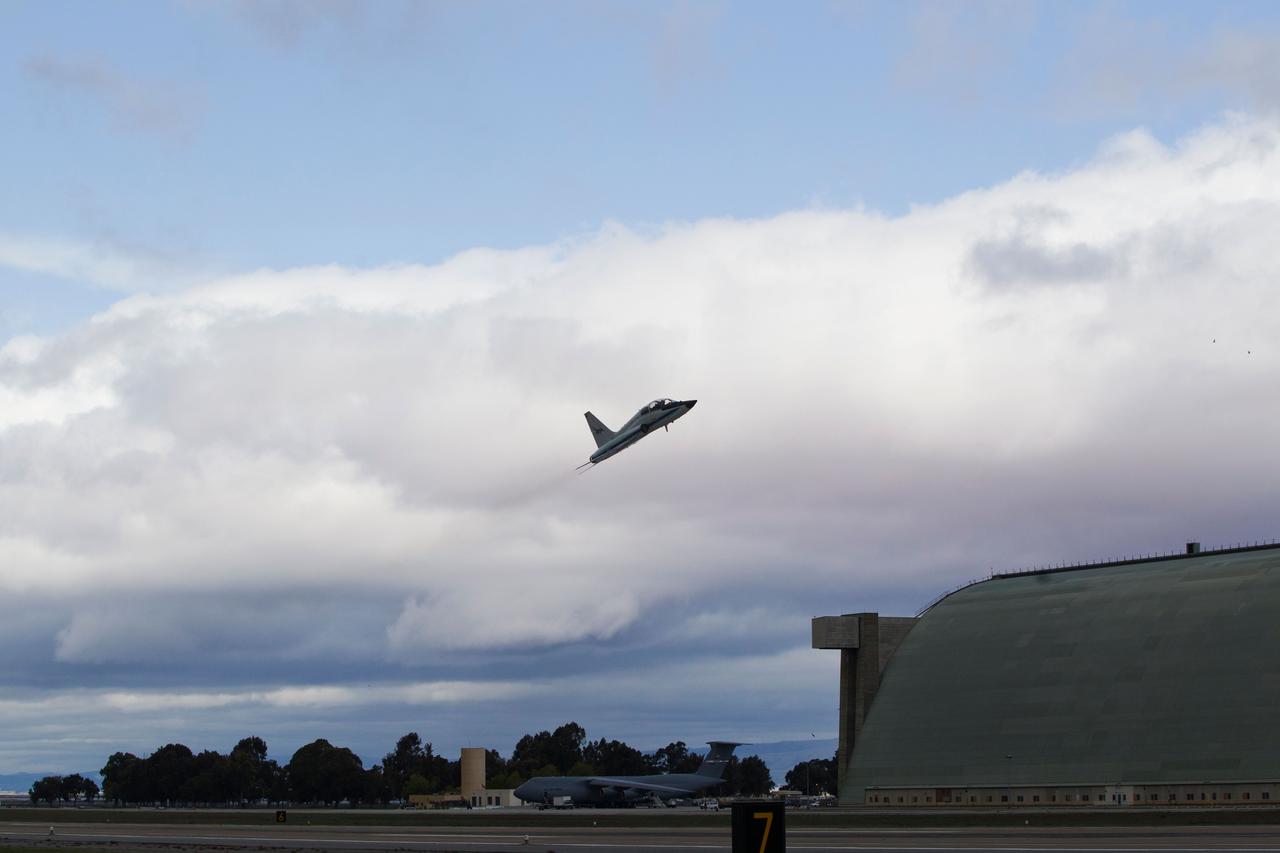

JSC2011-E-040205 (2 March 2011) --- A NASA T-38 jet trainer piloted by astronaut Chris Ferguson, STS-135 commander, takes off from Moffett Field in California for a flight home to Houston after Ferguson and his crew trained in the Vertical Motion Simulator (VMS) at NASA's Ames Research Center in Mountain View, March 2, 2011. Photo credit: NASA Photo/Houston Chronicle, Smiley N. Pool
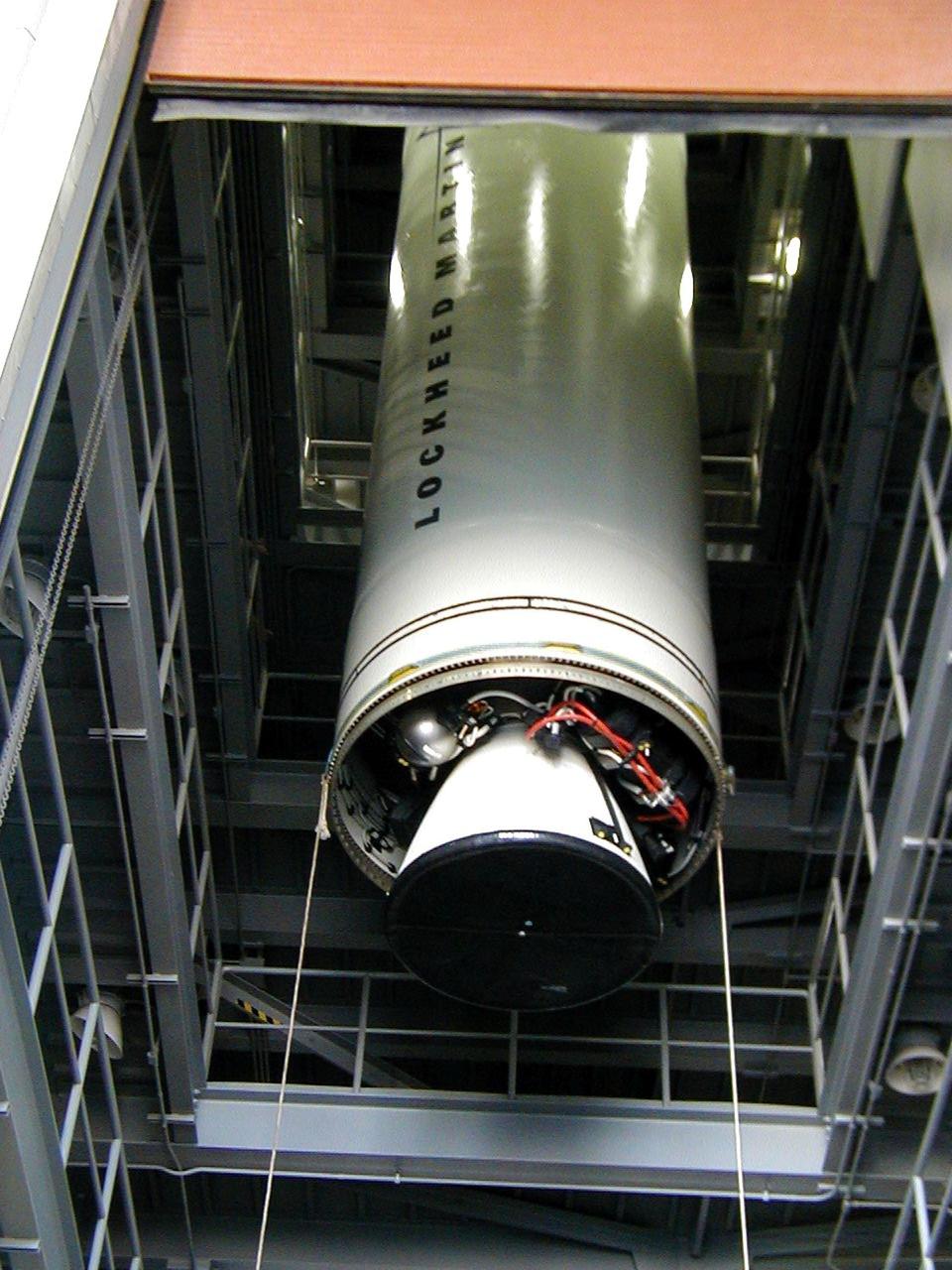

KODIAK ISLAND, Alaska -- Castor 120, the first stage of the Athena 1 launch vehicle, is lifted into a vertical position at Kodiak Island, Alaska, as preparations to launch Kodiak Star proceed. The first orbital launch to take place from Alaska's Kodiak Launch Complex, Kodiak Star is scheduled to lift off on a Lockheed Martin Athena I launch vehicle on Sept. 17 during a two-hour window that extends from 5:00 to 7:00 p.m. ADT. The payloads aboard include the Starshine 3, sponsored by NASA, and the PICOSat, PCSat and Sapphire, sponsored by the Department of Defense (DoD) Space Test Program.
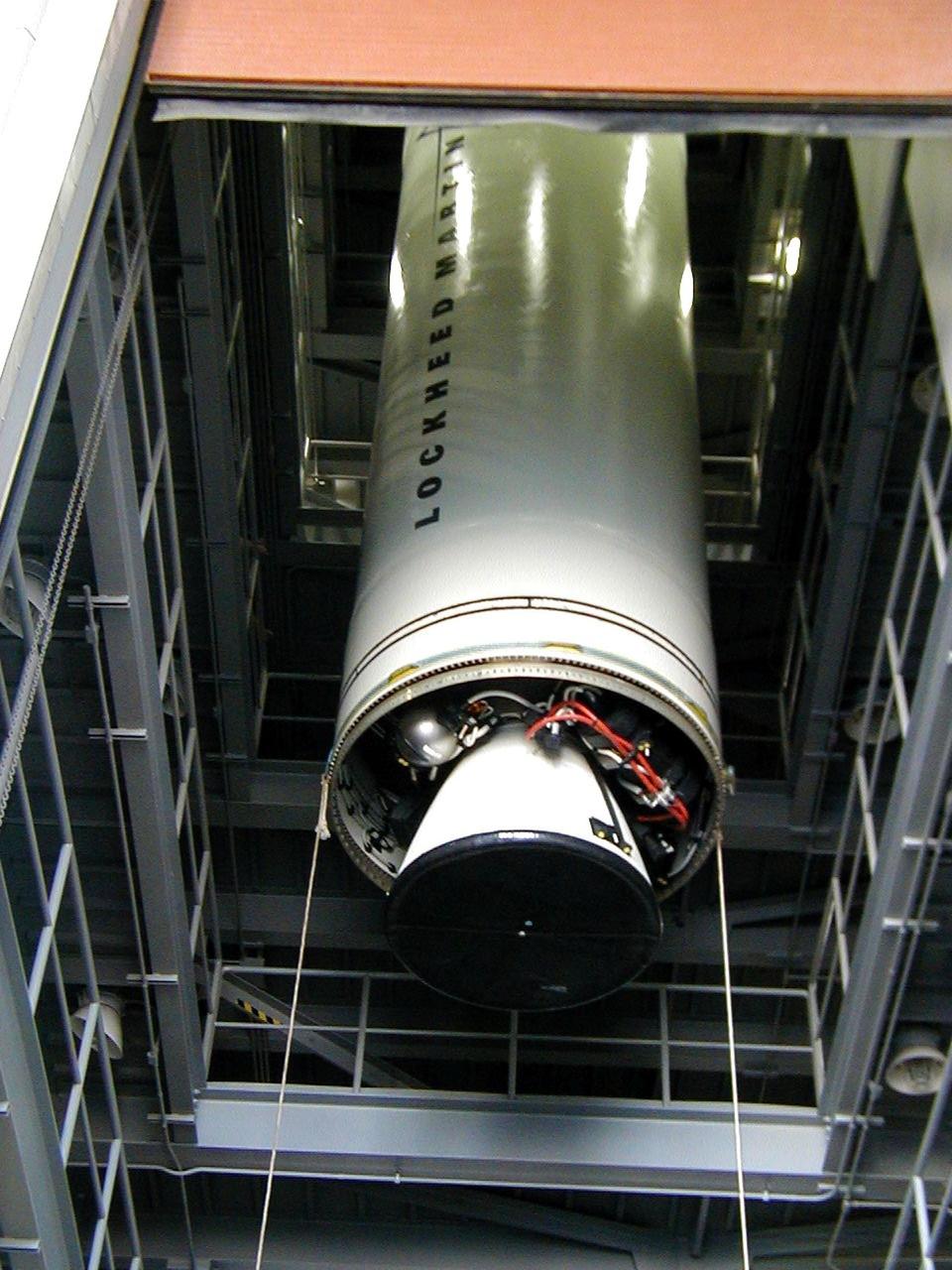

KODIAK ISLAND, Alaska -- Castor 120, the first stage of the Athena 1 launch vehicle, is lifted into a vertical position at Kodiak Island, Alaska, as preparations to launch Kodiak Star proceed. The first orbital launch to take place from Alaska's Kodiak Launch Complex, Kodiak Star is scheduled to lift off on a Lockheed Martin Athena I launch vehicle on Sept. 17 during a two-hour window that extends from 5:00 to 7:00 p.m. ADT. The payloads aboard include the Starshine 3, sponsored by NASA, and the PICOSat, PCSat and Sapphire, sponsored by the Department of Defense (DoD) Space Test Program.
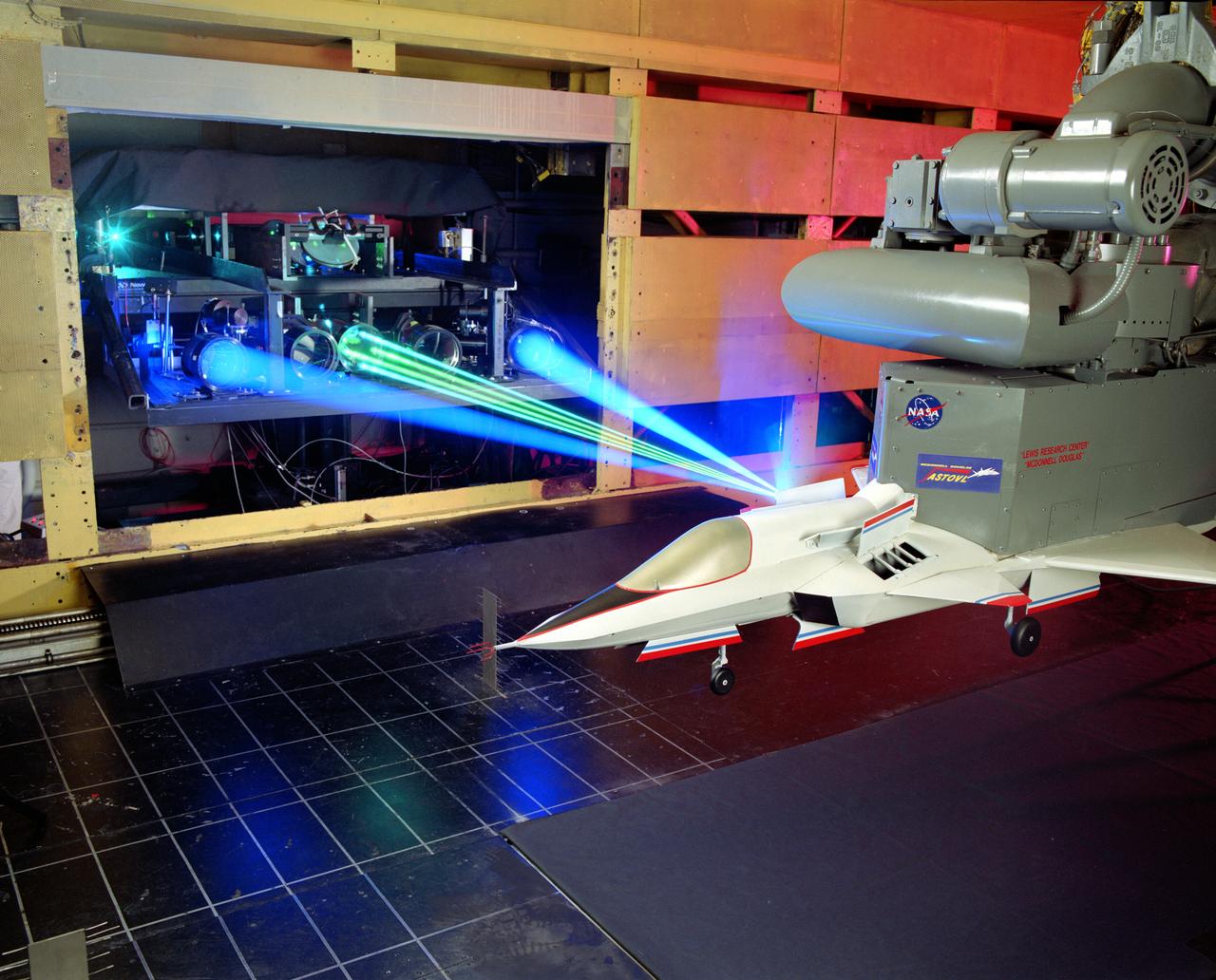

The 9x15 low speed tunnel tests take off and landing of aircraft. The laser velocimetry system for flow measurement show here, with the color blue and green lasers, measures engine exhaust that comes back up from the ground. The STOVL model n the 9x15 low speed wind tunnel, building 39, is similar to the British Harrier aircraft.
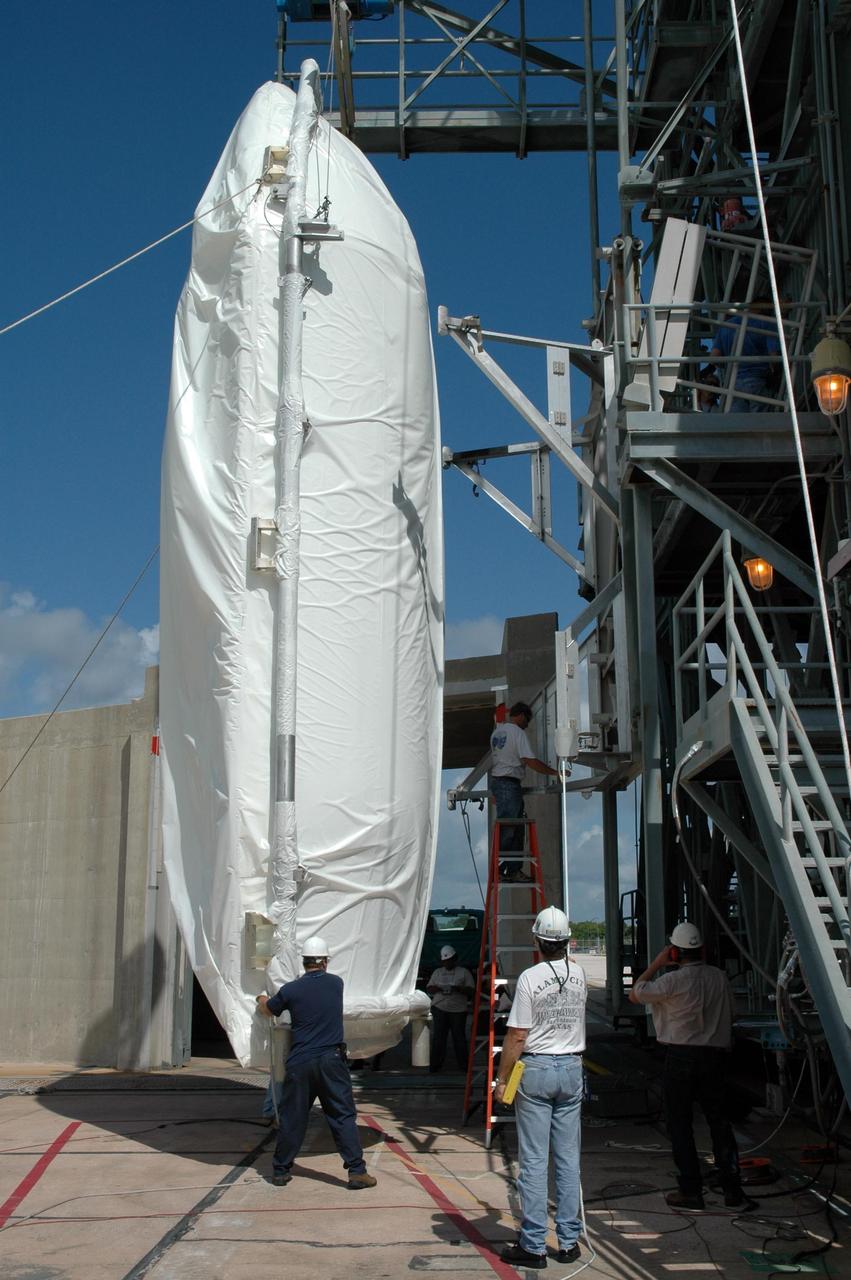

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Shrouded with a protective cover, half of the payload fairing for the STEREO spacecraft has been raised to a vertical position in front of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The fairing will be lifted into the clean room in the tower and later installed around the spacecraft for protection during launch. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. STEREO, which stands for Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, comprises two spacecraft. The STEREO mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-dimension. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. STEREO is expected to lift off aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket in August 2006. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
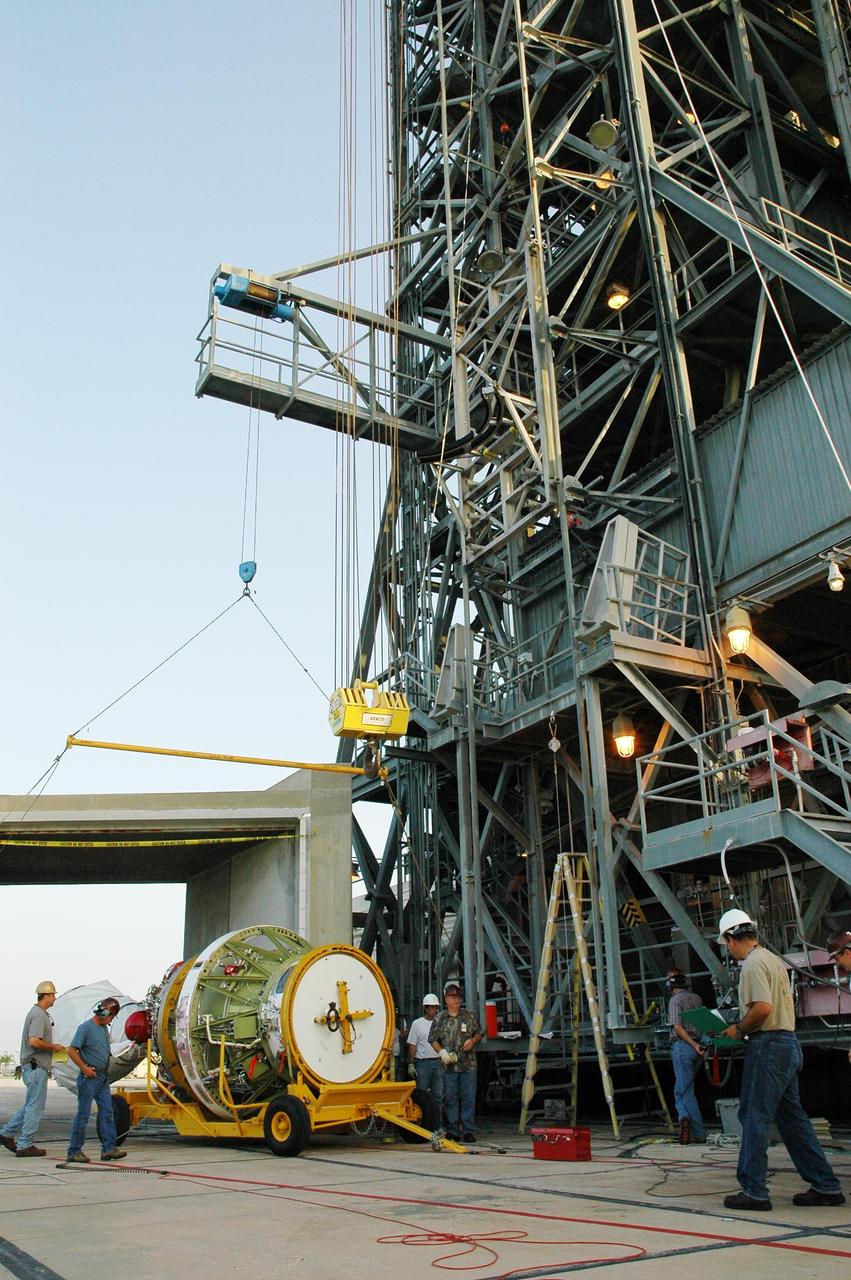

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After its return to Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second stage of the Boeing Delta II launch vehicle for the STEREO spacecraft is being prepared to be raised to vertical. The stage has been returned to the pad after being tested for leaks in the High-Pressure Test Facility; no leak was observed. The stage will again be lifted into the mobile service tower and remated with the Delta first stage. STEREO stands for Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory and comprises two spacecraft. The STEREO mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-dimension. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. STEREO is expected to lift off on Aug. 31. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
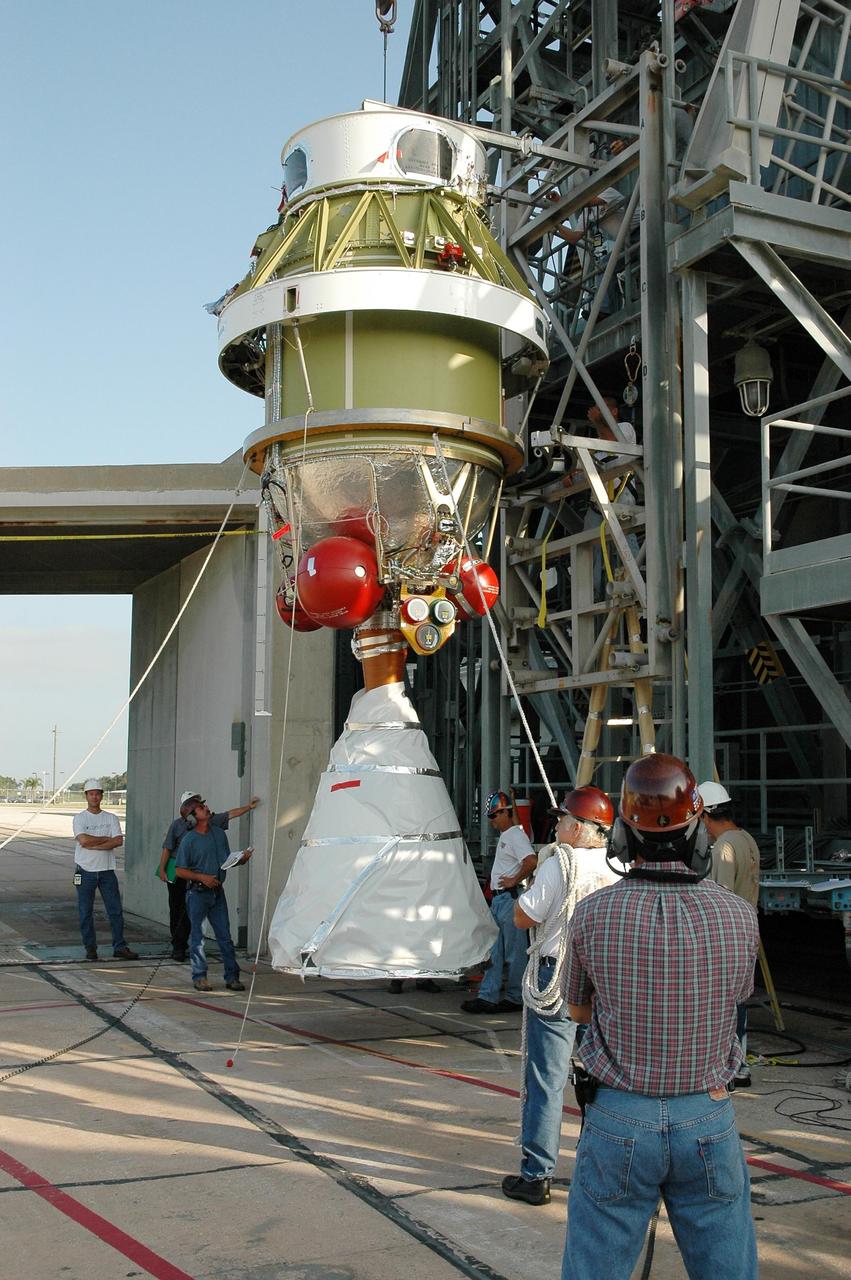

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the now-vertical second stage of the Boeing Delta II launch vehicle for the STEREO spacecraft is ready for lifting into the mobile service tower. There it will be remated with the Delta first stage. The stage has been returned to the pad after being tested for leaks in the High-Pressure Test Facility; no leak was observed. STEREO stands for Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory and comprises two spacecraft. The STEREO mission is the first to take measurements of the sun and solar wind in 3-dimension. This new view will improve our understanding of space weather and its impact on the Earth. STEREO is expected to lift off on Aug. 31. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In front of the mobile service tower on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Lockheed Martin Atlas V Centaur stage is raised off the transporter. Once vertical, the Centaur, the second stage of the launch vehicle for the New Horizons spacecraft, will be lifted up the tower and mated with the waiting first stage, seen at left. New Horizons will make the first reconnaissance of Pluto and its moon, Charon - a "double planet" and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. As it approaches Pluto, the spacecraft will look for ultraviolet emission from Pluto's atmosphere and make the best global maps of Pluto and Charon in green, blue, red and a special wavelength that is sensitive to methane frost on the surface. It will also take spectral maps in the near infrared, telling the science team about Pluto's and Charon's surface compositions and locations and temperatures of these materials. When the spacecraft is closest to Pluto or its moon, it will take close-up pictures in both visible and near-infrared wavelengths. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and Charon in July 2015.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- After being rotated from a horizontal to vertical position, the canister that contains the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, is lowered onto a transportation vehicle in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
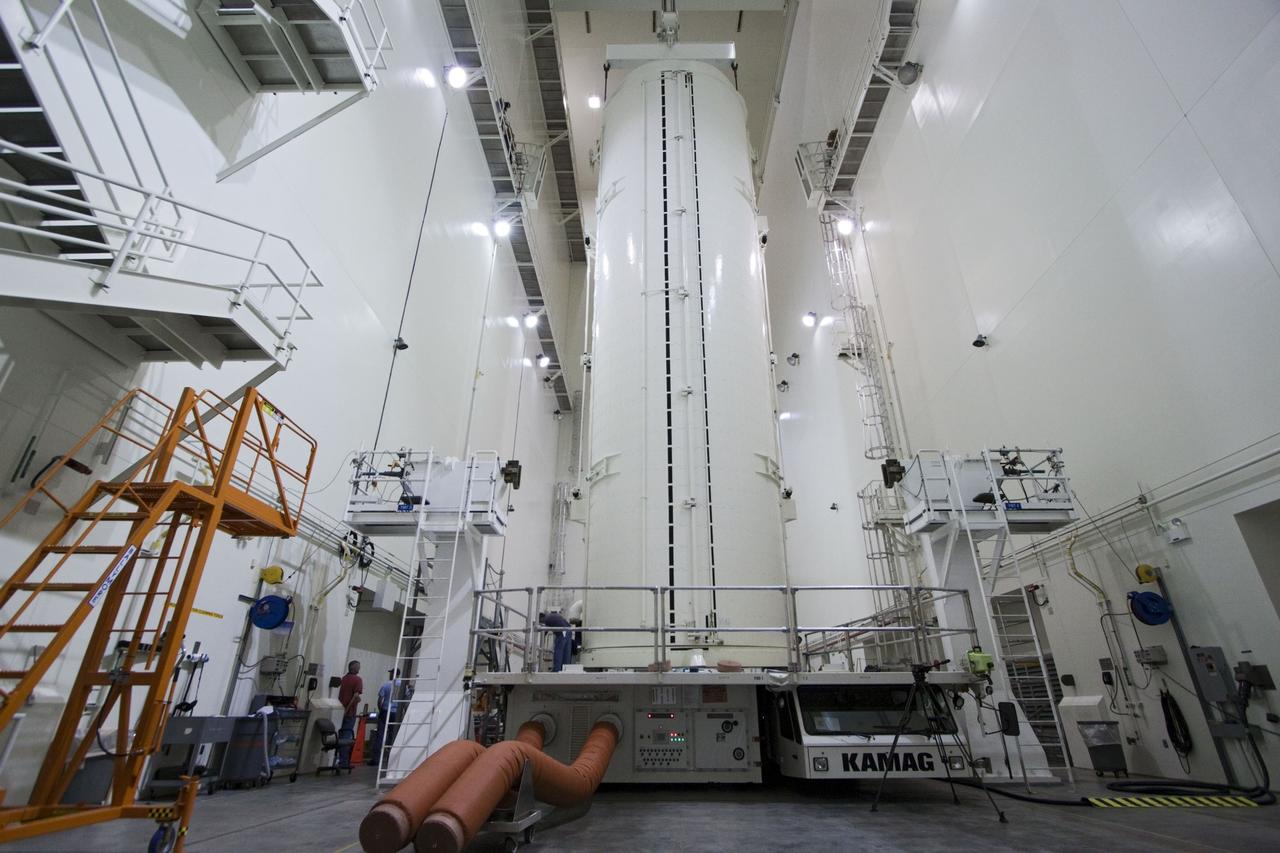

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- After being rotated from a horizontal to vertical position, the canister that contains the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, has been lowered onto a transportation vehicle in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
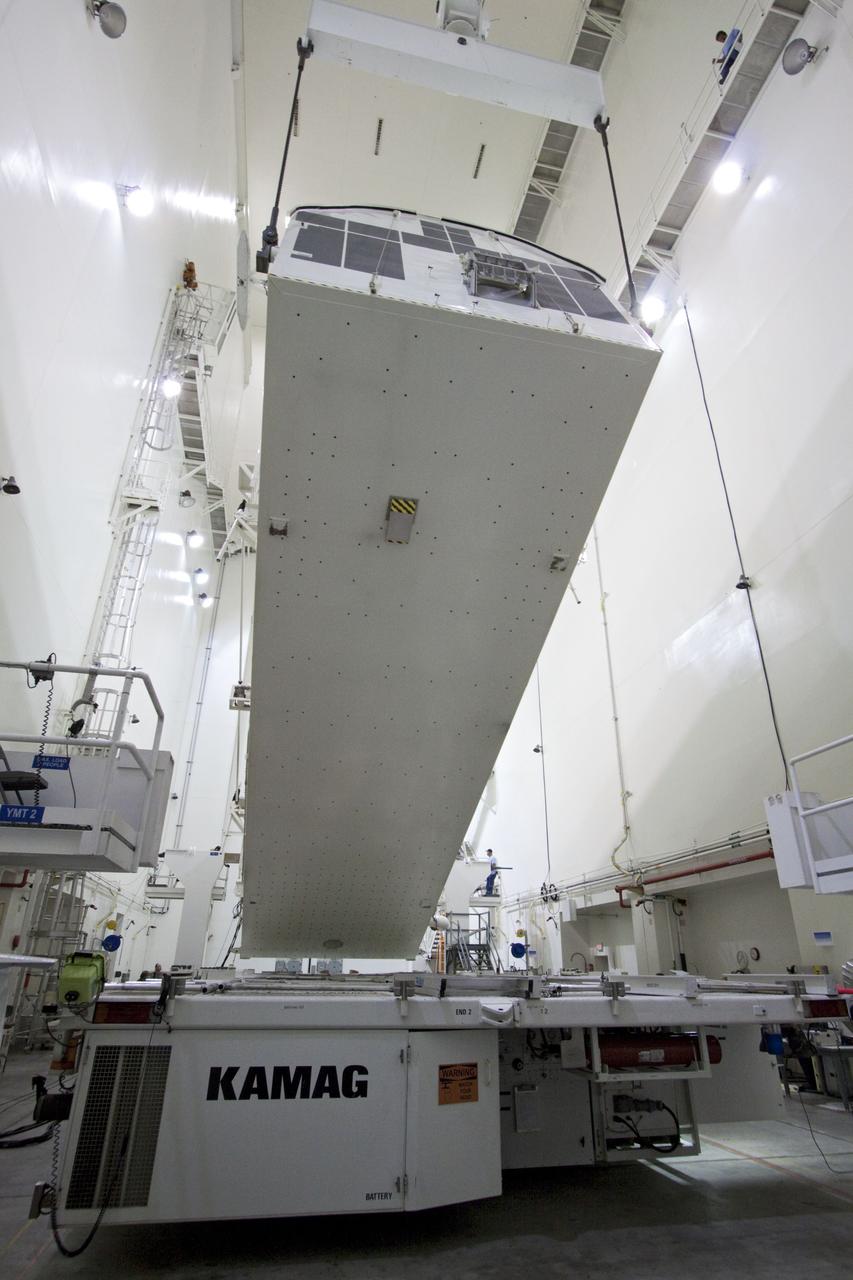

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers monitor the progress of a canister, carrying the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, as it is rotated from a horizontal to vertical position in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
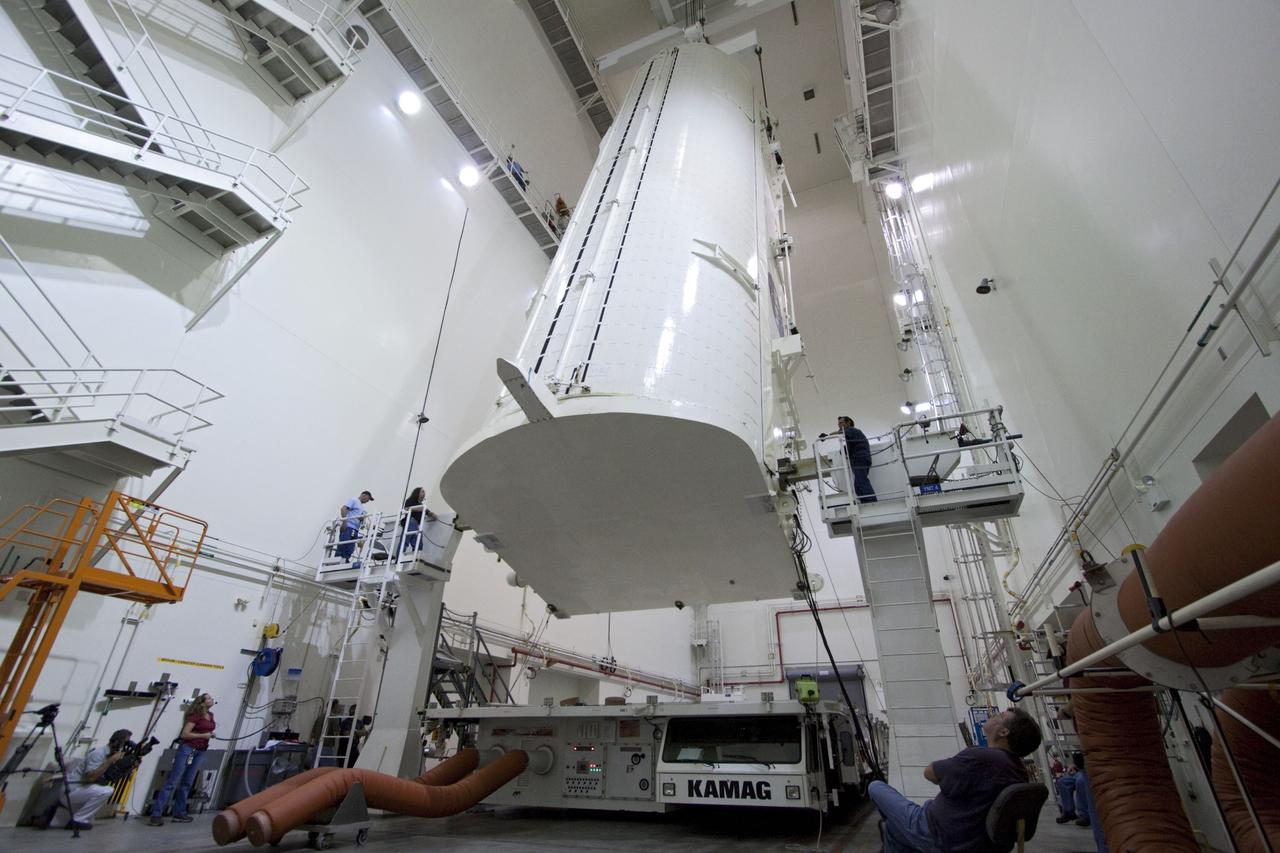

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers monitor the progress of a canister, carrying the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, as it is rotated from a horizontal to vertical position in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
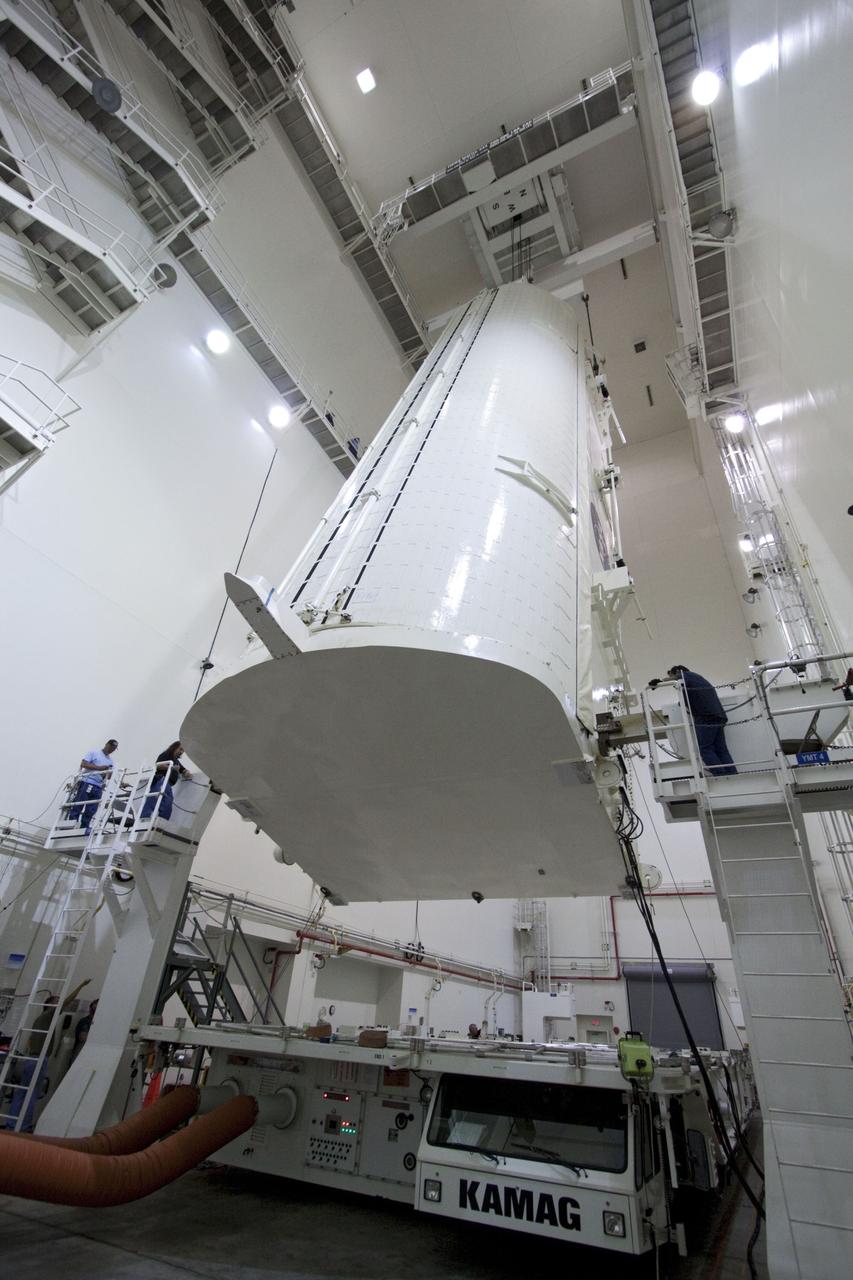

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers monitor the progress of a canister, carrying the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, as it is rotated from a horizontal to vertical position in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane slowly lifts shuttle Atlantis off its transporter. The spacecraft then will be positioned vertically in a high bay where it will be attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters already on the mobile launcher platform. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are expected to launch in mid-July, taking with them the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
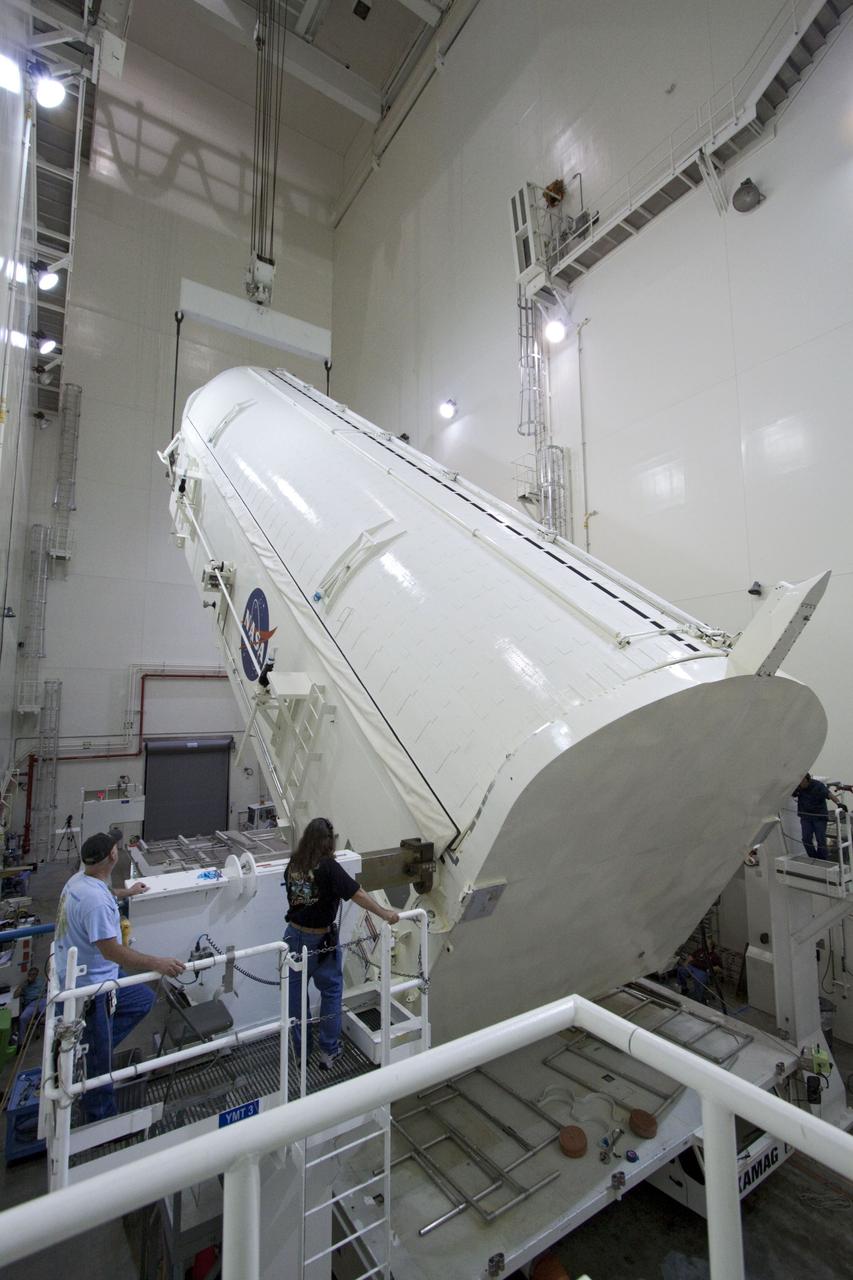

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers monitor the progress of a canister, carrying the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, as it is rotated from a horizontal to vertical position in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
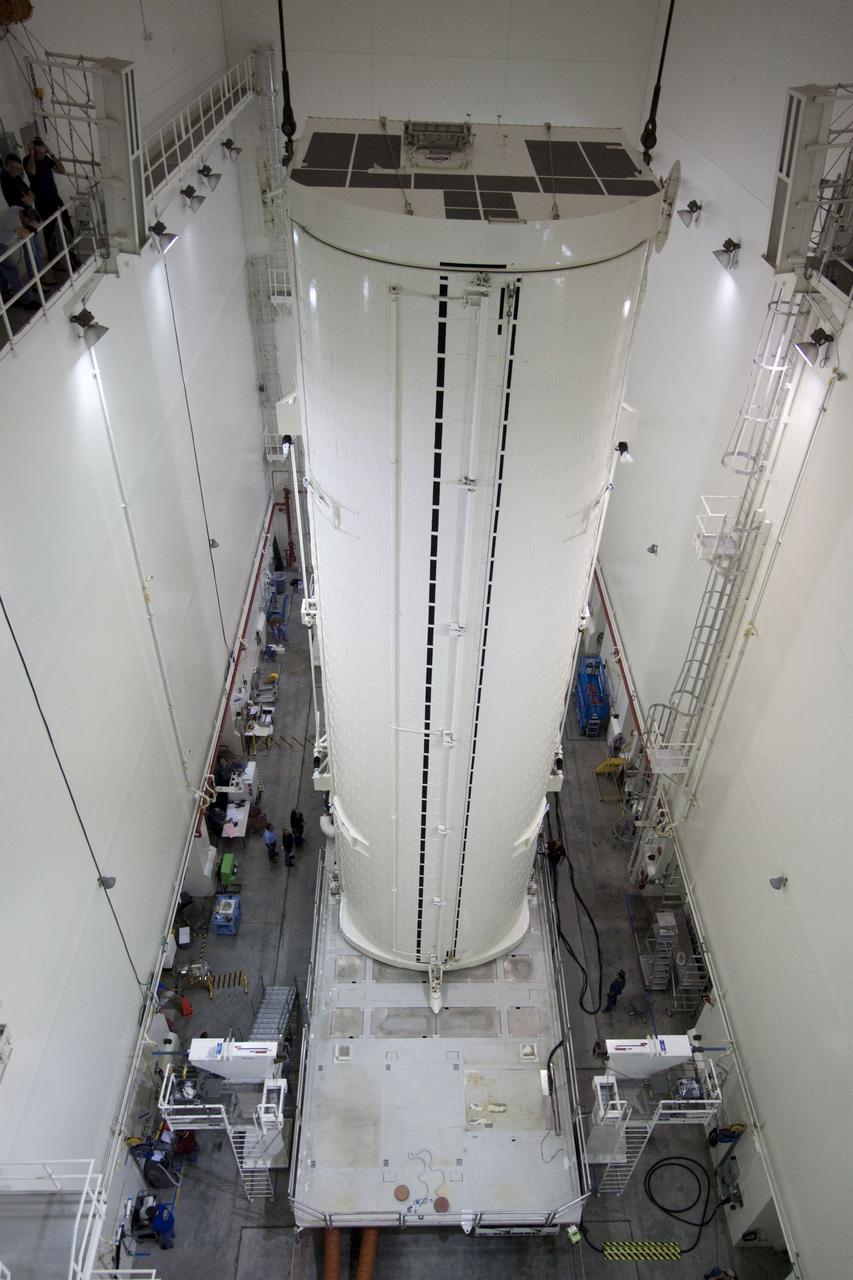

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- After being rotated from a horizontal to vertical position, the canister that contains the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, has been lowered onto a transportation vehicle in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
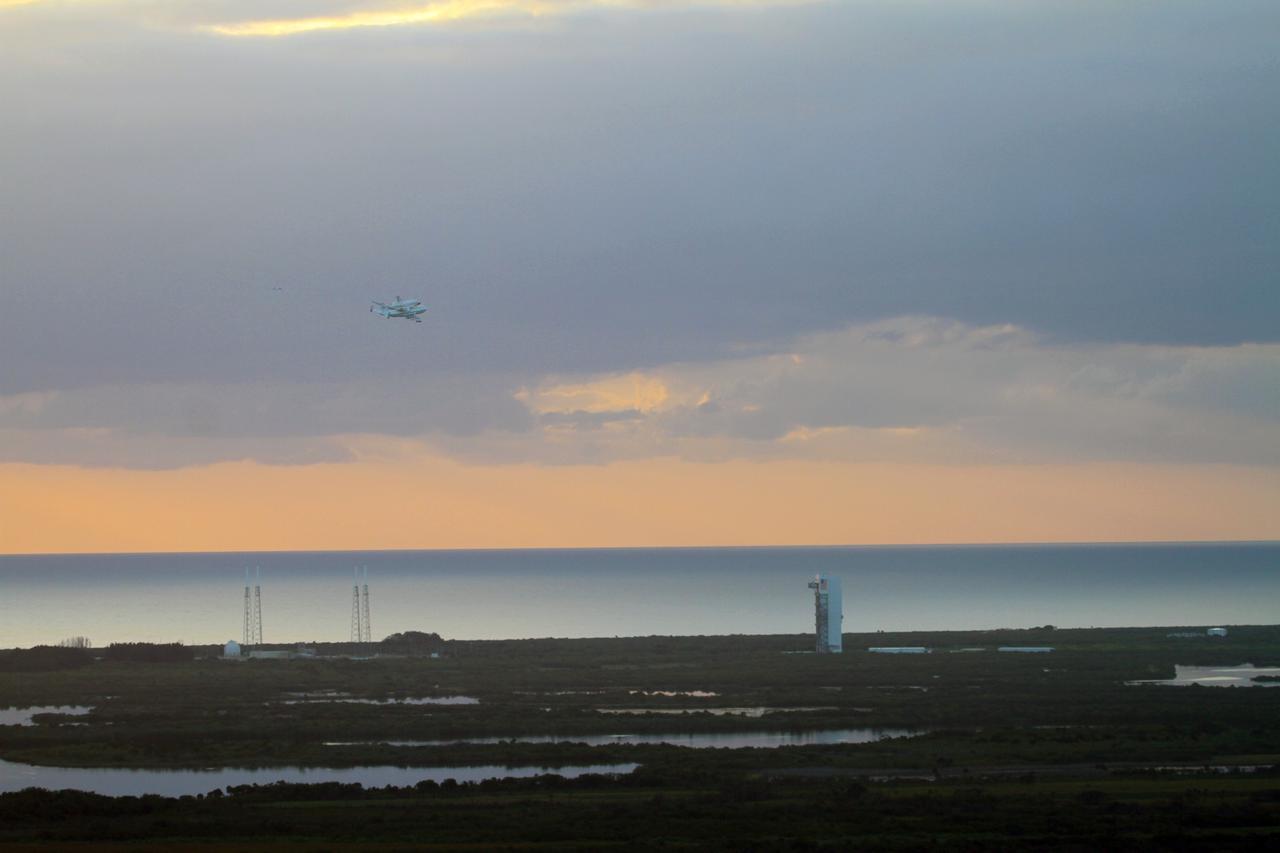

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft transporting space shuttle Discovery flies over the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station after taking off from Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility at 7 a.m. EDT. The duo are heading south to fly over Brevard County’s beach communities, offering residents the opportunity to see the shuttle before it leaves the Space Coast for the last time. The aircraft, known as an SCA, is a Boeing 747 jet, originally manufactured for commercial use, which was modified by NASA to transport the shuttles between destinations on Earth. This SCA, designated NASA 905, is assigned to the remaining ferry missions, delivering the shuttles to their permanent public display sites. NASA 905 is scheduled to ferry Discovery to the Washington Dulles International Airport in Virginia on April 17, after which the shuttle will be placed on display in the Smithsonian's National Air and Space Museum Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center. For more information on the SCA, visit http://www.nasa.gov/centers/dryden/news/FactSheets/FS-013-DFRC.html. For more information on shuttle transition and retirement activities, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Lorne Mathre
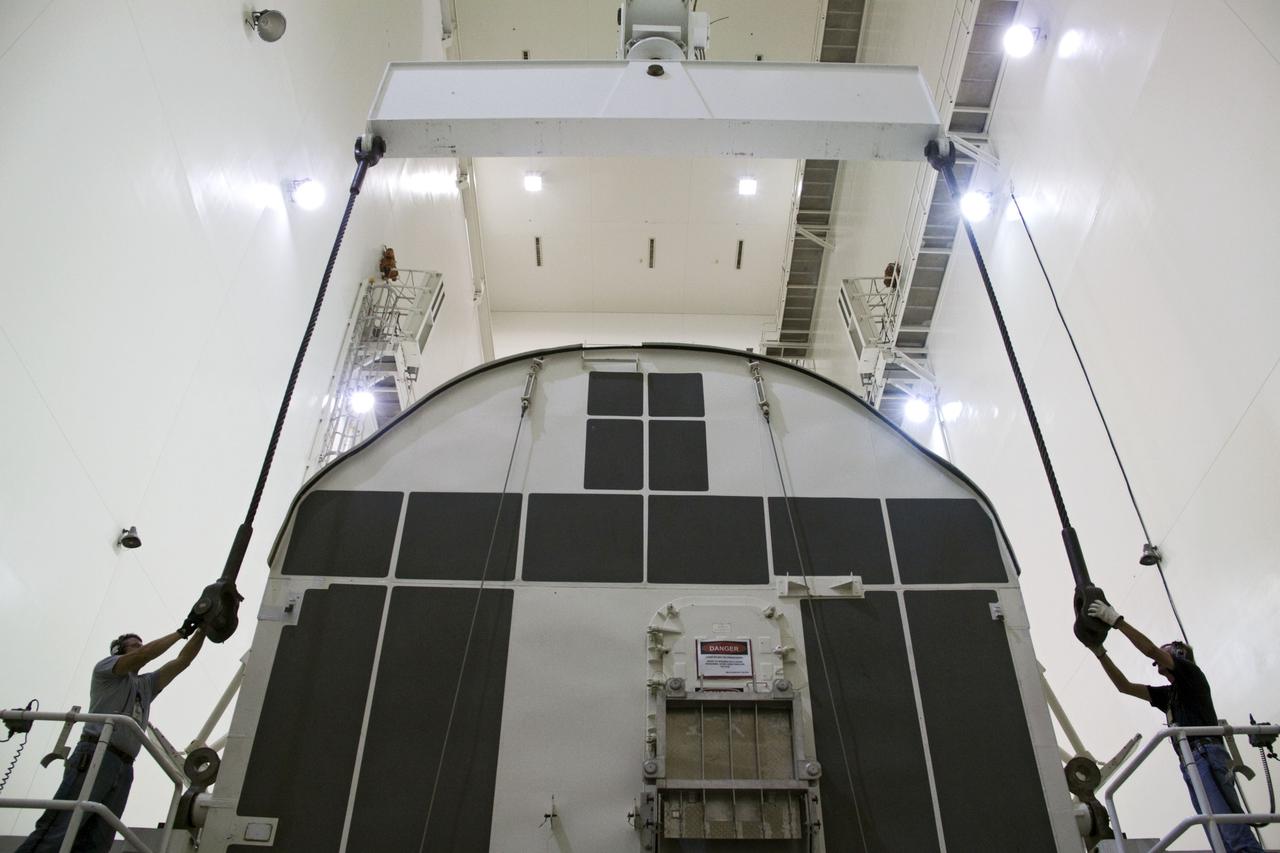

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers prepare a canister, carrying the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, to be rotated from a horizontal to vertical position in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Despite the incline, space shuttle Atlantis remains on a level plane as it rolls off Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. First motion was at 6:48 a.m. EDT. The crawler-transporter underneath the mobile launcher platform maintains the level plane through a leveling system designed to keep the top of the space shuttle vehicle vertical. This system also provides the leveling operations required to negotiate the 5-percent ramp leading to the launch pads. Atlantis is rolling back to the Vehicle Assembly Building to await launch on its STS-125 mission to repair NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Atlantis' targeted launch on Oct. 14 was delayed when a system that transfers science data from the orbiting observatory to Earth malfunctioned on Sept. 27. The new target launch date is under review. The space shuttle is mounted on a Mobile Launcher Platform and will be delivered to the Vehicle Assembly Building atop a crawler transporter. traveling slower than 1 mph during the 3.4-mile journey. The rollback is expected to take approximately six hours. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
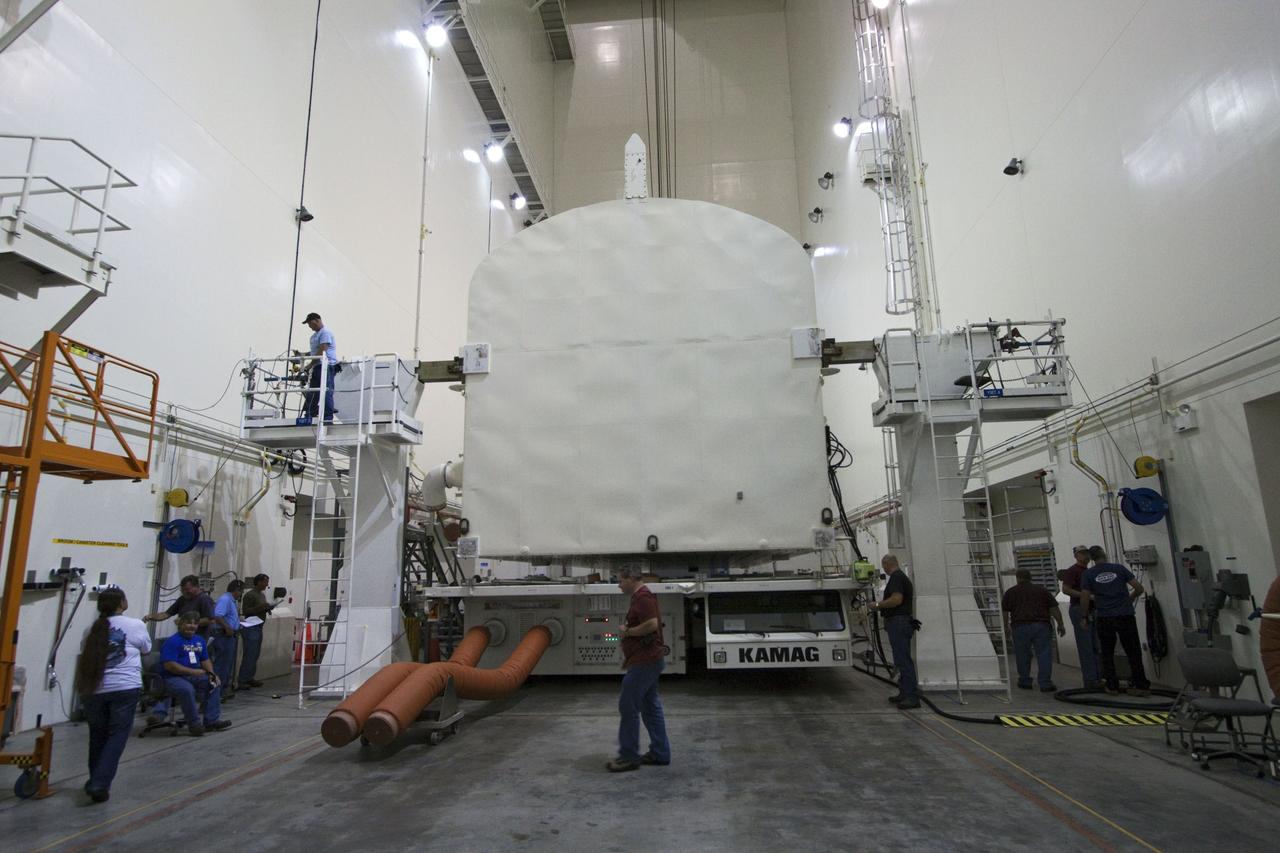

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A canister, carrying the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, will be rotated from a horizontal to vertical position in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
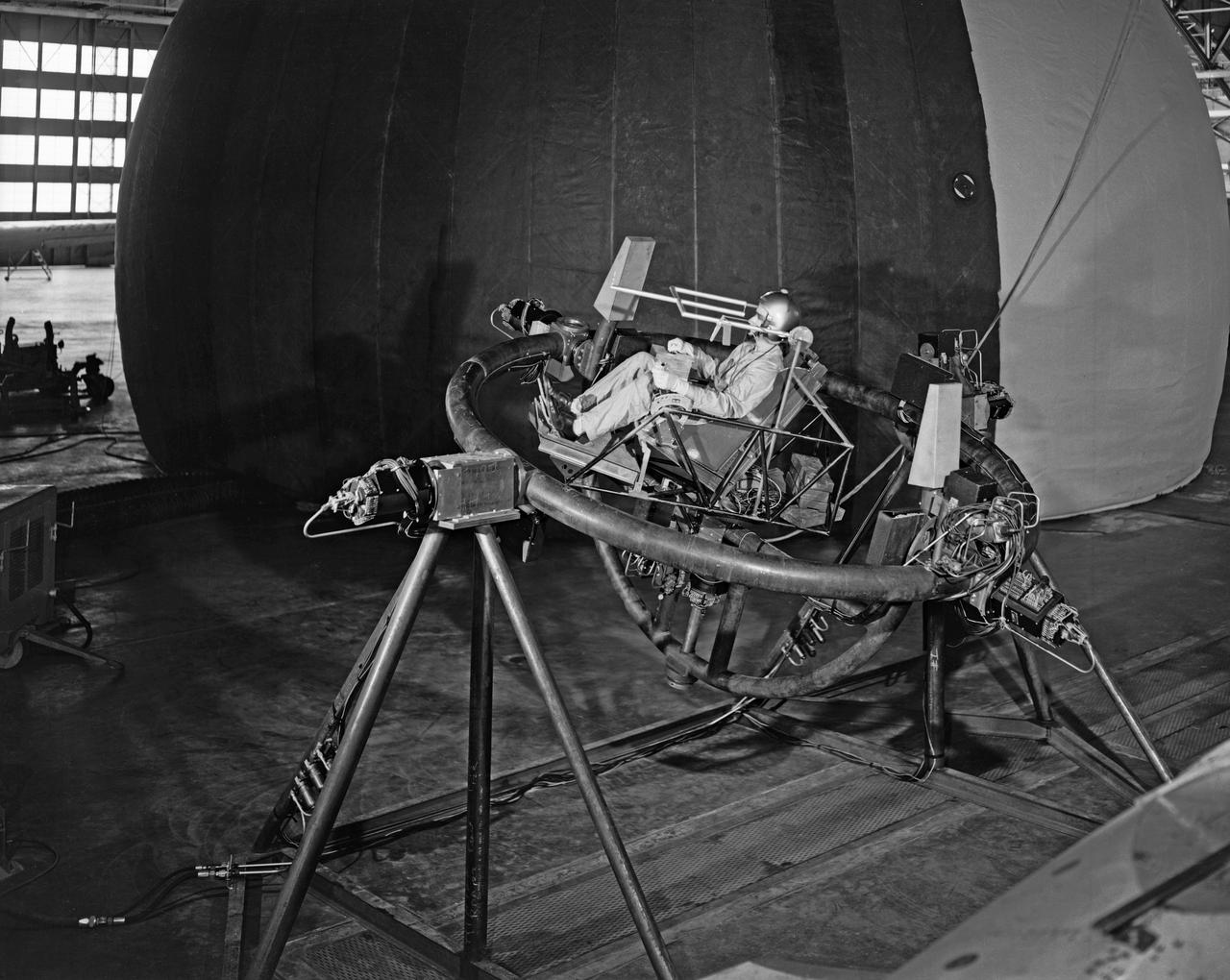
Lunar Take Off Simulator: This simulator is used by scientists at the Langley Research Center ... to help determine human ability to control a lunar launch vehicle in vertical alignment during takeoff from the moon for rendezvous with a lunar satellite vehicle on the return trip to earth. The three-axis chair, a concept which allows the pilot to sit upright during launch, gives the navigator angular motion (pitch, role, and yaw) cues as he operates the vehicle through a sidearm control system. The sight apparatus in front of the pilot's face enables him to align the vehicle on a course toward a chosen star, which will be followed as a guidance reference during the lunar launch. The pilot's right hand controls angular motions, while his left hand manipulates the thrust lever. The simulator is designed for operation inside an artificial planetarium, where a star field will be projected against the ceiling during "flights". The tests are part of an extensive NASA program at Langley in the study of problems relating to a manned lunar mission. (From a NASA Langley, photo release caption.)
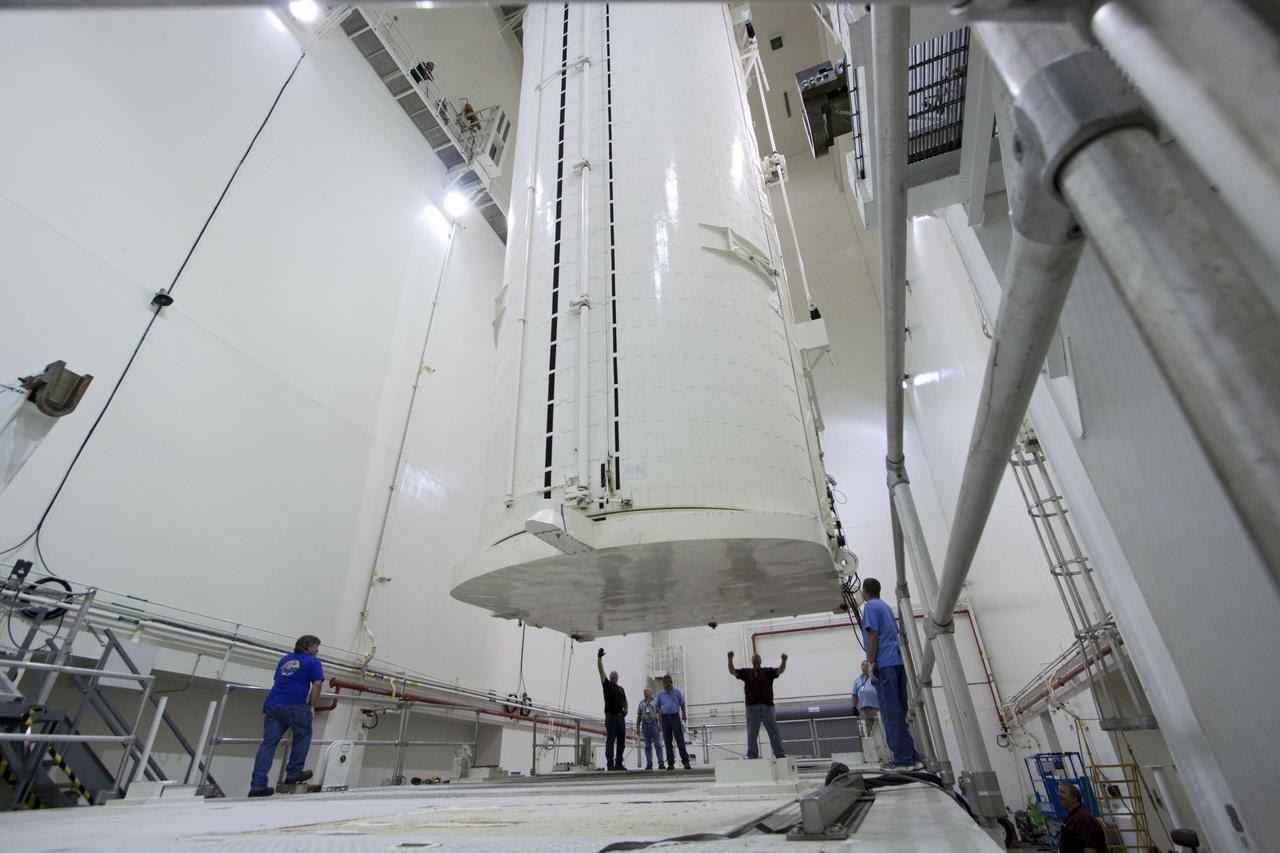

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- After being rotated from a horizontal to vertical position, the canister that contains the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, is lowered onto a transportation vehicle in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
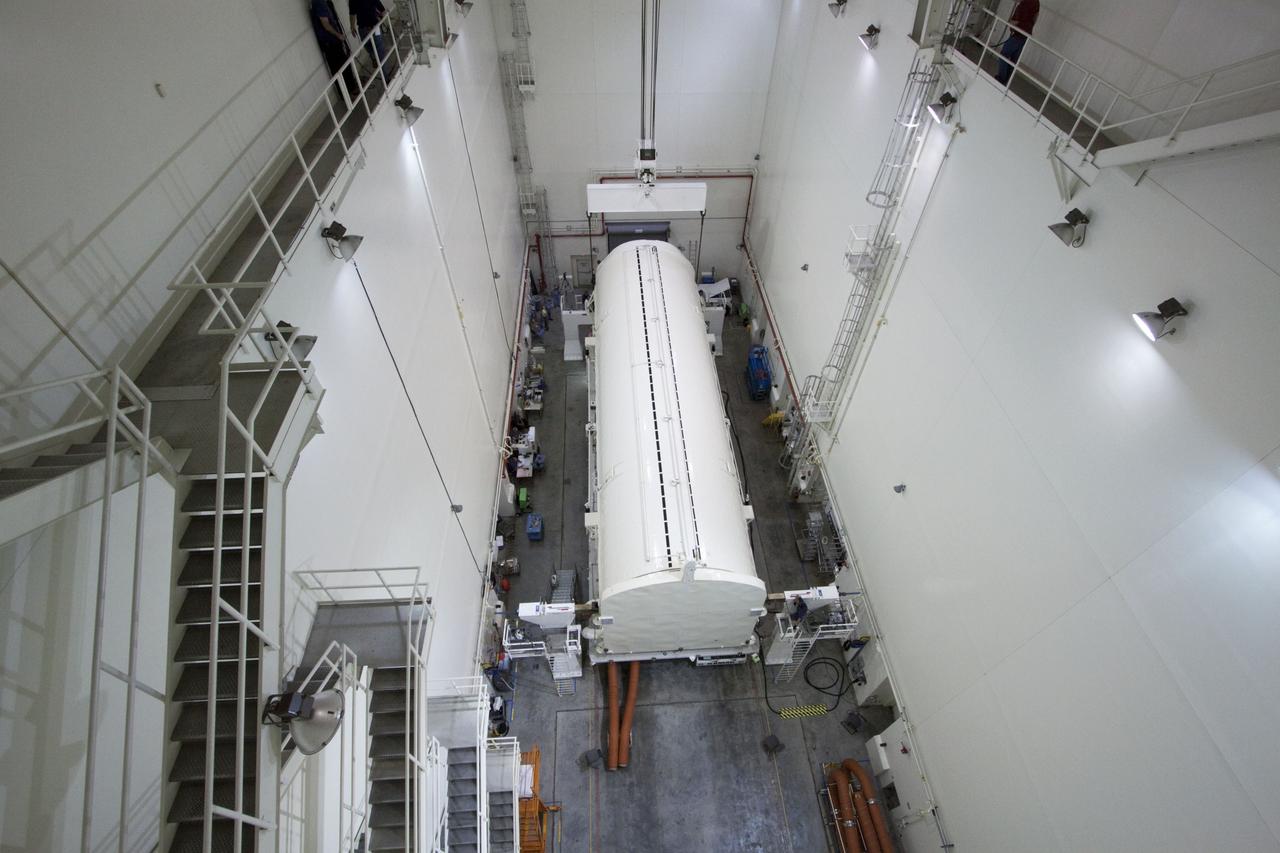

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers prepare a canister, carrying the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, to be rotated from a horizontal to vertical position in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media photograph shuttle Atlantis as an overhead crane slowly lifts it off its transporter. The spacecraft will be positioned vertically in a high bay where it will be attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters already on the mobile launcher platform. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are expected to launch in mid-July, taking with them the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
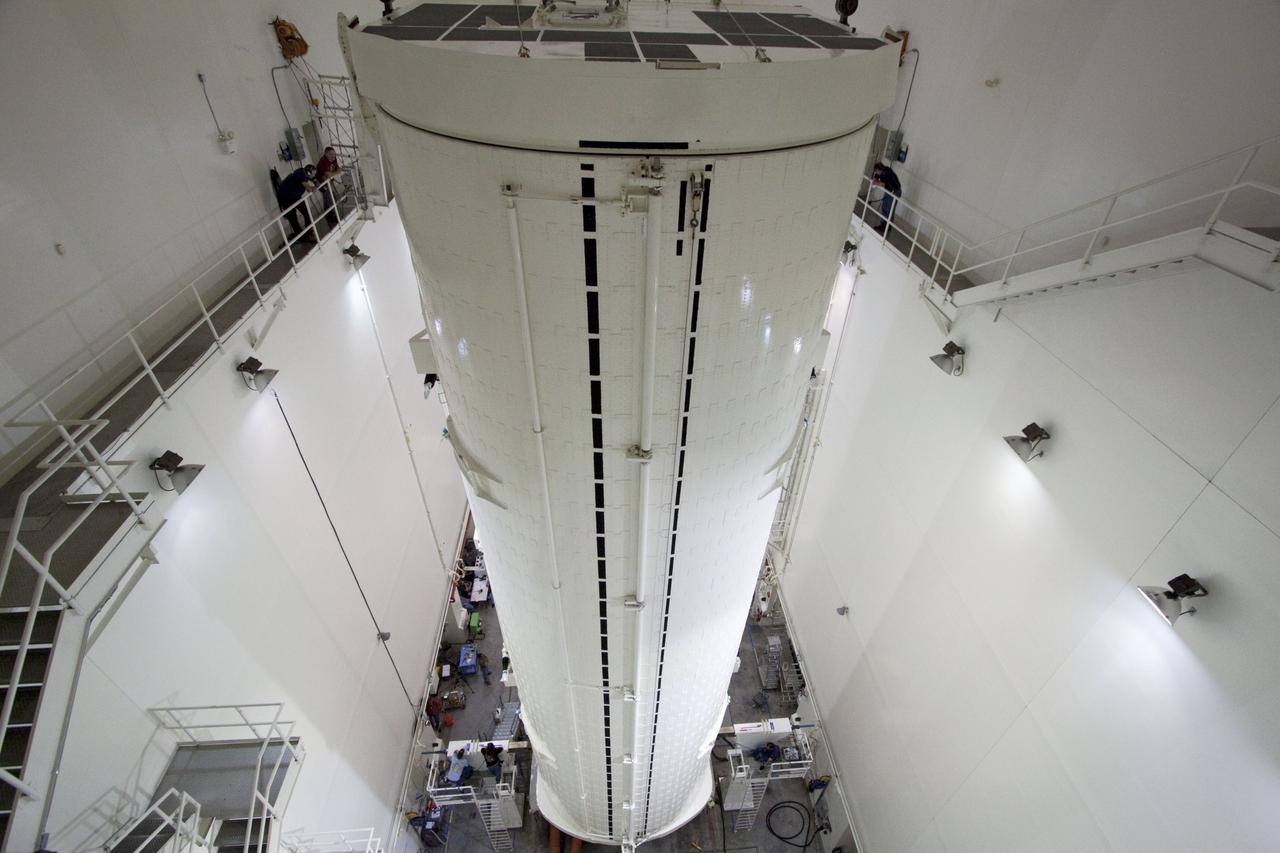

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- After being rotated from a horizontal to vertical position, the canister that contains the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, will be lowered onto a transportation vehicle in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
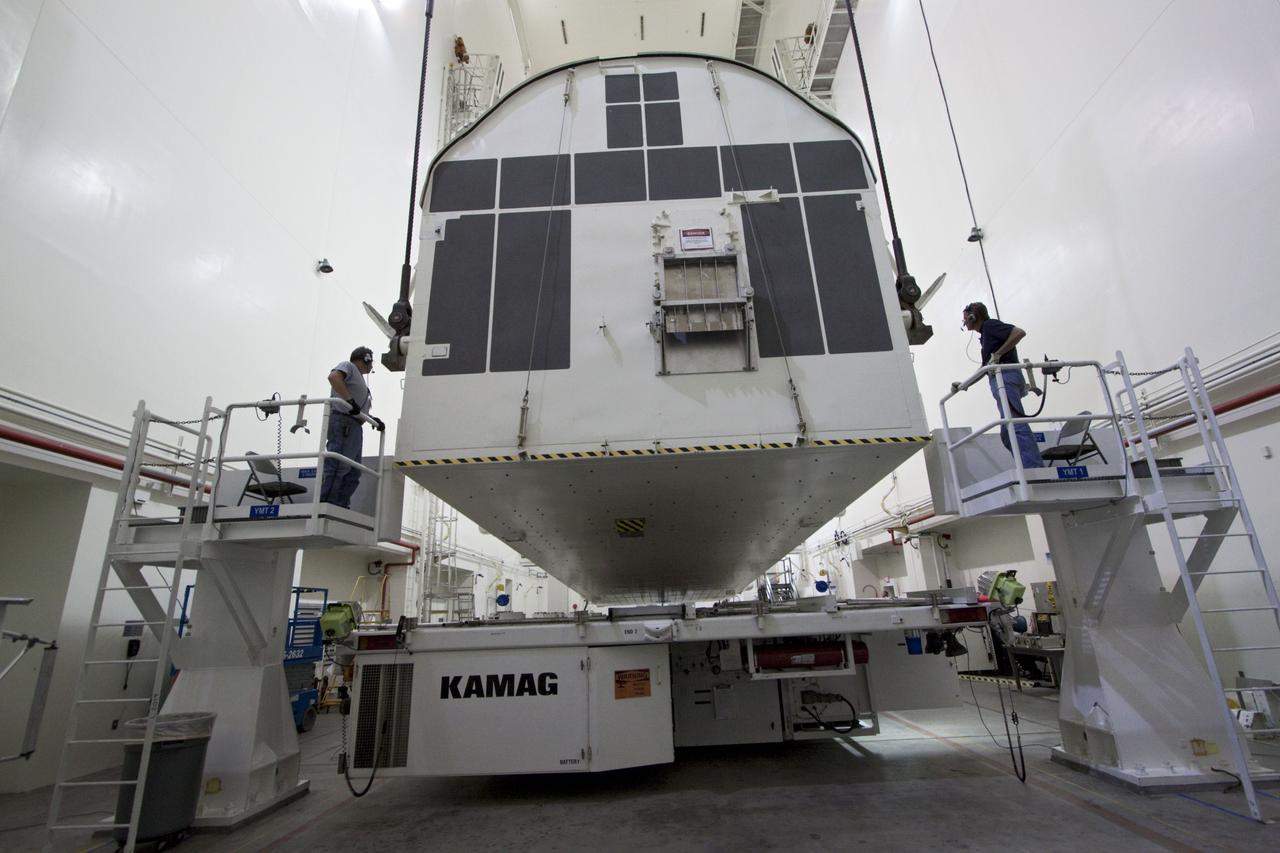

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers monitor the progress of a canister, carrying the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module, or MPLM, for the STS-135 mission, as it is rotated from a horizontal to vertical position in the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandra Magnus and Rex Walheim are targeted to lift off on space shuttle Atlantis July 8, taking with them the MPLM packed with supplies, logistics and spare parts to the International Space Station. The STS-135 mission also will fly a system to investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing spacecraft and return a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
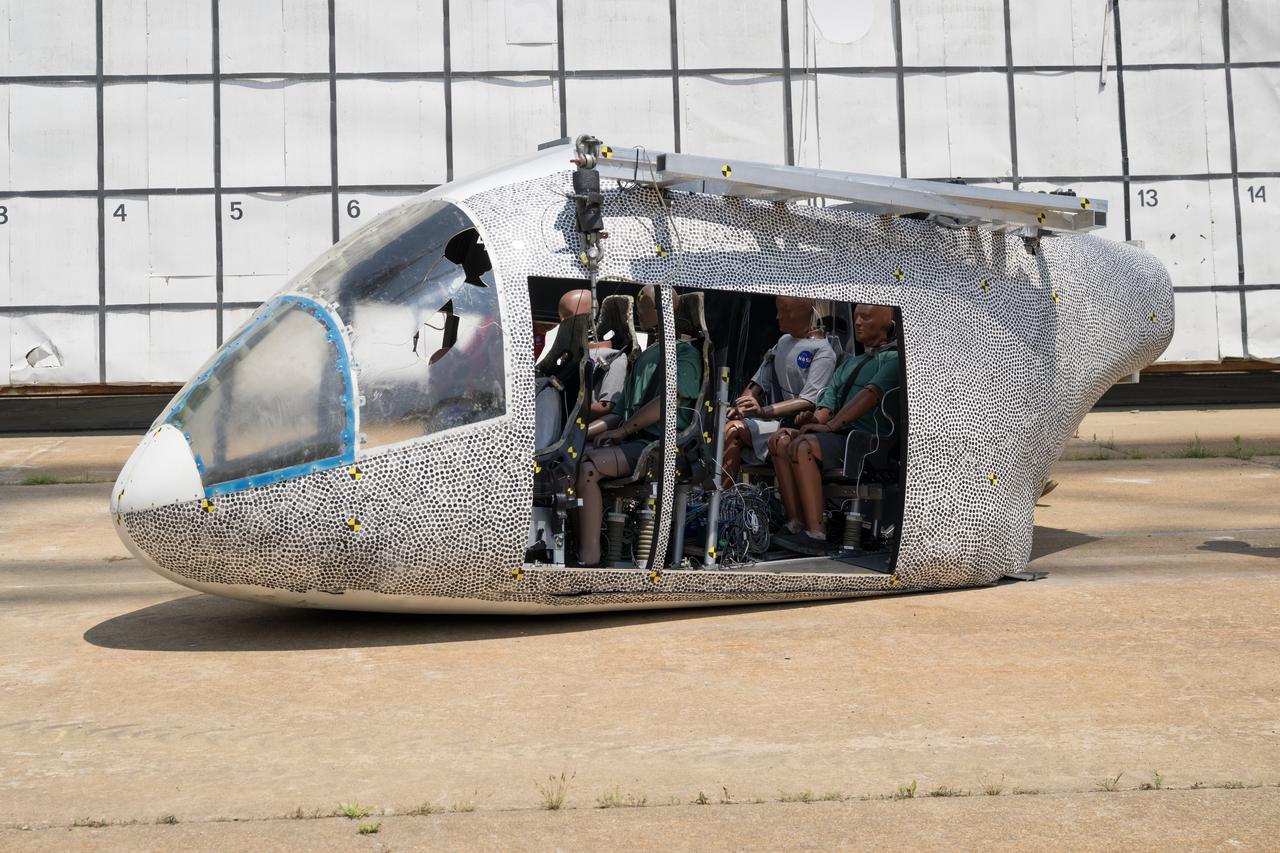

An aircraft body modeled after an air taxi with weighted test dummies inside is shown after a drop test at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. The test was completed June 26 at Langley’s Landing and Impact Research Facility. The aircraft was dropped from a tall steel structure, known as a gantry, after being hoisted about 35 feet in the air by cables. NASA researchers are investigating aircraft materials that best absorb impact forces in a crash.
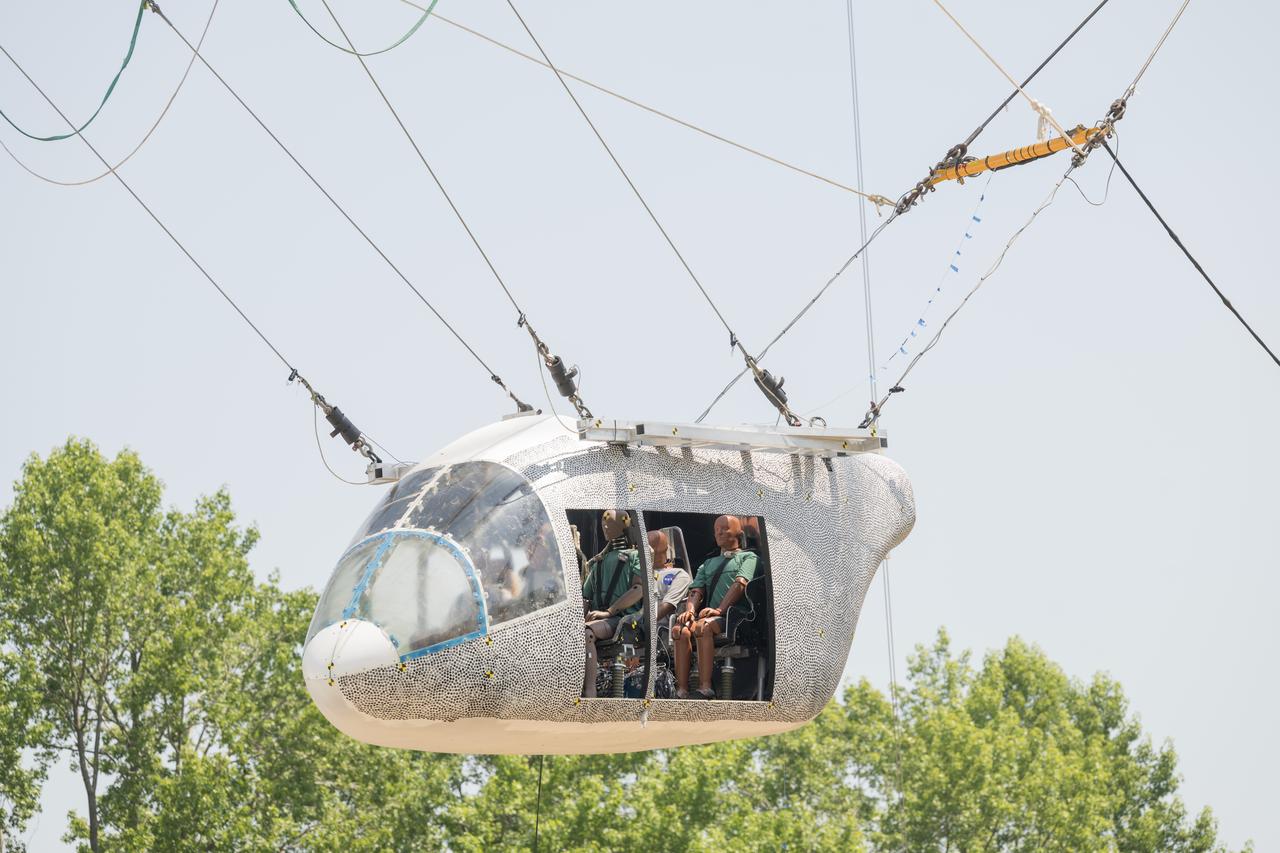

An aircraft body modeled after an air taxi with weighted test dummies inside is hoisted about 35 feet in the air by cables at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. The aircraft was dropped from a tall steel structure, known as a gantry, on June 26 at Langley’s Landing and Impact Research Facility. NASA researchers are investigating aircraft materials that best absorb impact forces in a crash.
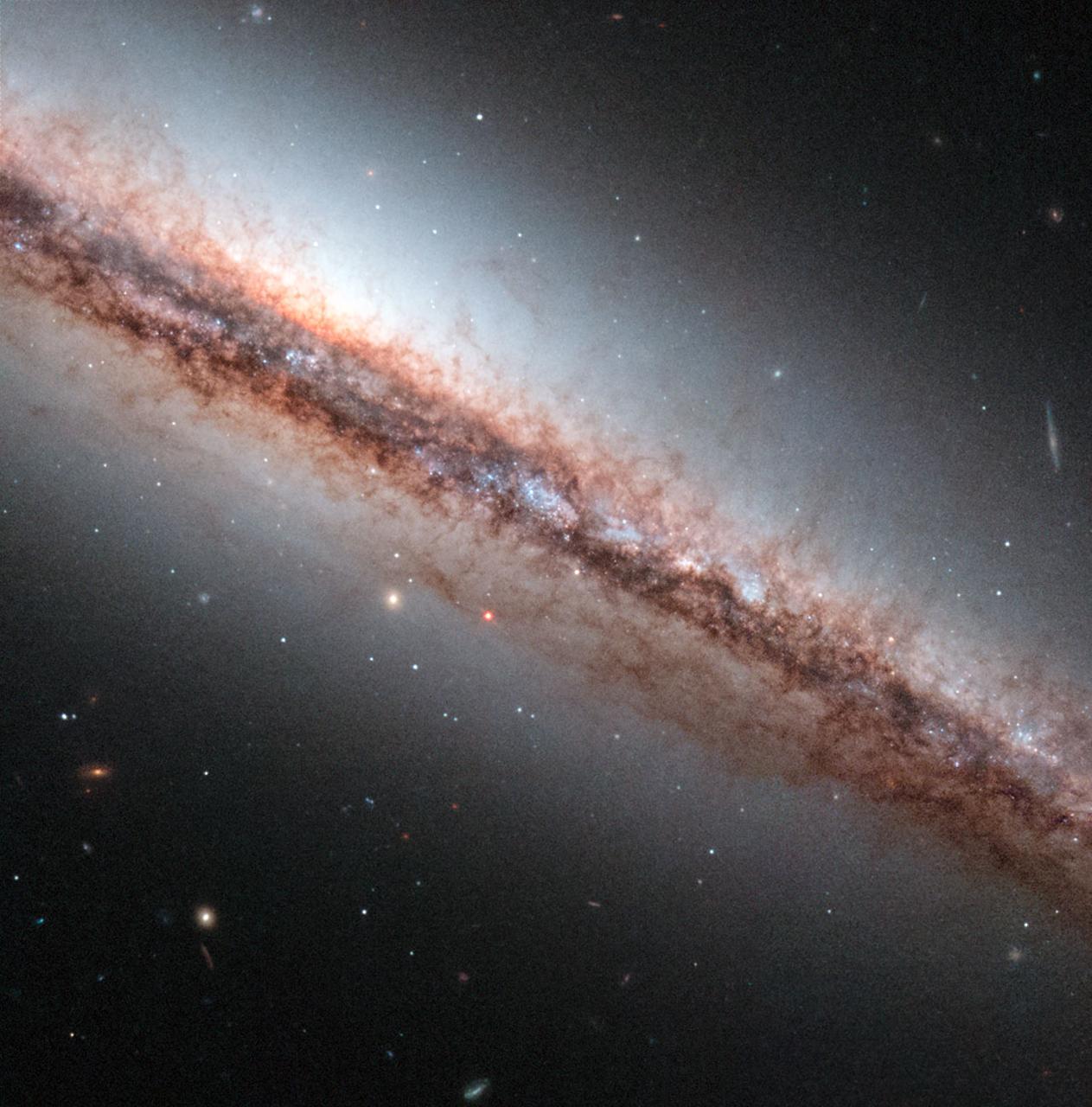

In this image the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope takes a close look at the spiral galaxy NGC 4217, located 60 million light-years away from Earth. The galaxy is seen almost perfectly edge on and is a perfect candidate for studying the nature of extraplanar dust structures — the patterns of gas and dust above and below the plane on the galaxy, seen here as brown wisps coming off NGC 4217. These tentacle-like filaments are visible in the Hubble image only because the contrast with their surroundings is so high. This implies that the structures are denser than their surroundings. The image shows dozens of dust structures some of which reach as far as 7,000 light-years away from the central plane. Typically the structures have a length of about 1,000 light-years and are about 400 light-years in width. Some of the dust filaments are round or irregular clouds, others are vertical columns, loop-like structures or vertical cones. These structures can help astronomers to identify the mechanisms responsible for the ejection of gas and dust from the galactic plane of spiral galaxies and reveal information on the transport of the interstellar medium to large distances away from galactic disks. The properties of the observed dust structures in NGC 4217 suggest that the gas and dust were driven out of the mid-plane of the galaxy by powerful stellar winds resulting from supernovae — explosions that mark the deaths of massive stars. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: R. Schoofs <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>