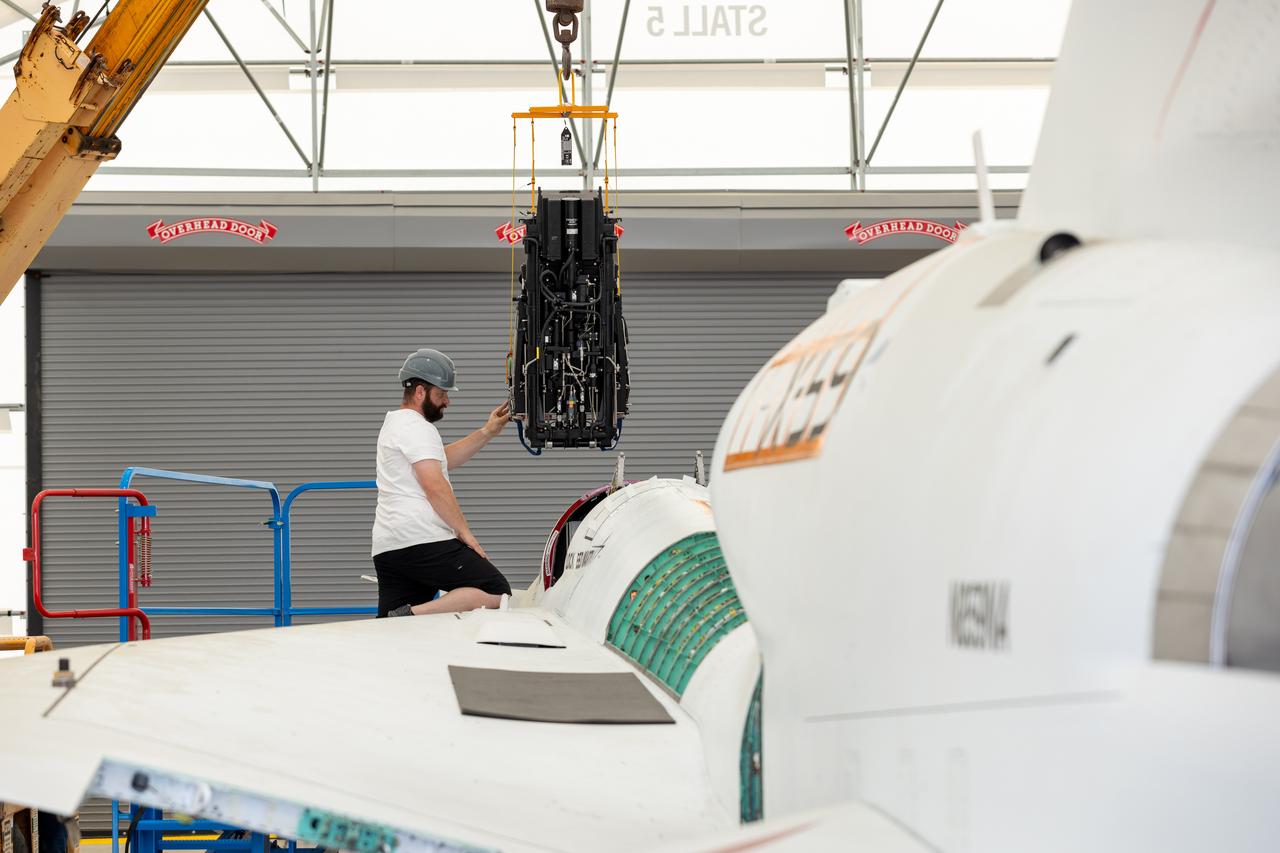

NASA Life Support Technician Mathew Sechler provides support as the X-59’s ejection seat is installed into the aircraft at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works’ facilities in Palmdale, California. Completion of the seat’s installation marks an integration milestone for the aircraft as it prepares for final ground tests.
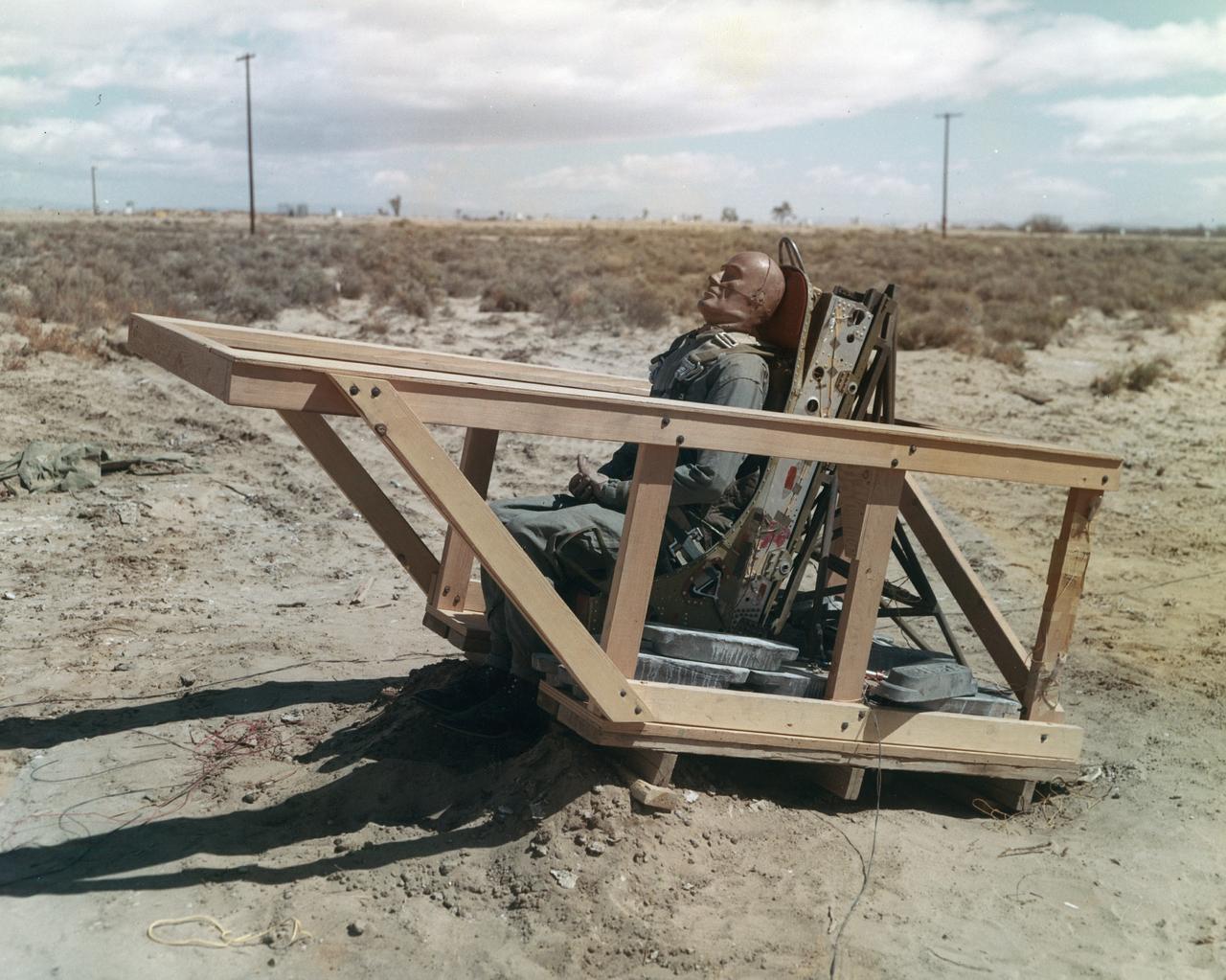

The M2-F1 was fitted with an ejection seat before the airtow flights began. The project selected the seat used in the T-37 as modified by the Weber Company to use a rocket rather than a ballistic charge for ejection. To test the ejection seat, the Flight Research Center's Dick Klein constructed a plywood mockup of the M2-F1's top deck and canopy. On the first firings, the test was unsuccessful, but on the final test the dummy in the seat landed safely. The M2-F1 ejection seat was later used in the two Lunar Landing Research Vehicles and the three Lunar Landing Training Vehicles. Three of them crashed, but in each case the pilot ejected from the vehicle successfully.
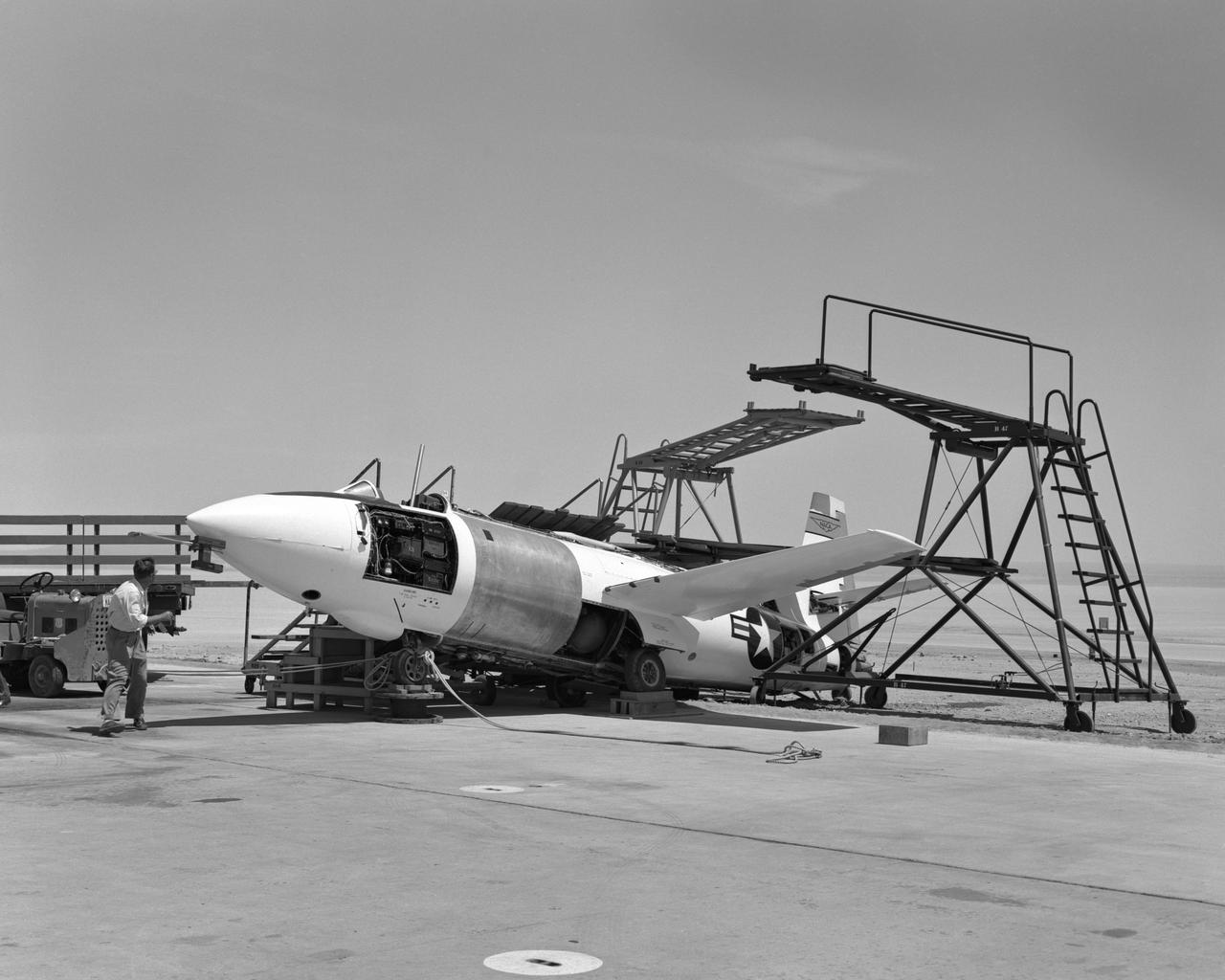

Bell X-1A ejection seat test setup
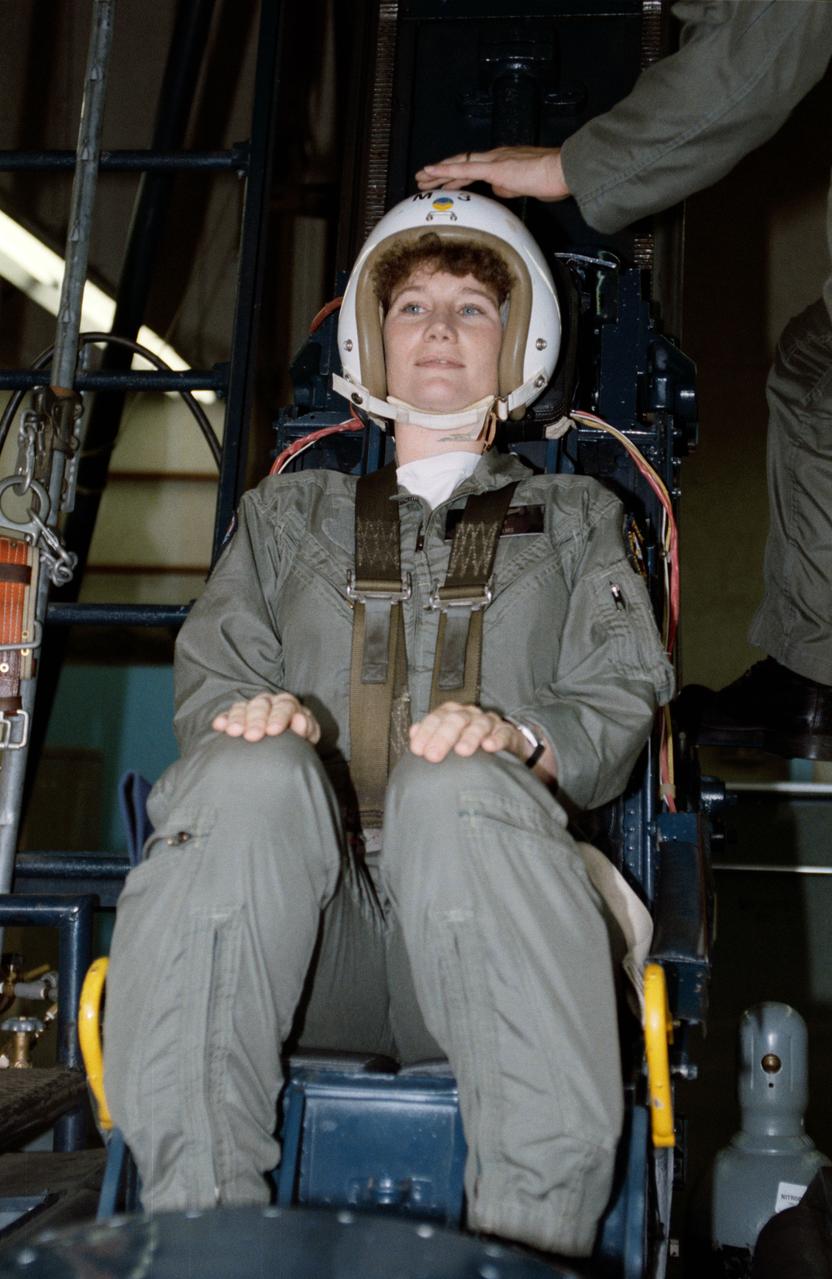

S90-45852 (29-31 July 1990) --- Susan J. Helms, one of 23 astronaut candidates who began a year's training and evaluation in July, participates in one of may sessions at a survival training course at Vance Air Force Base. This portion of the course is designed to familiarize the trainee with the "feel" of emergency ejection from a jet aircraft.
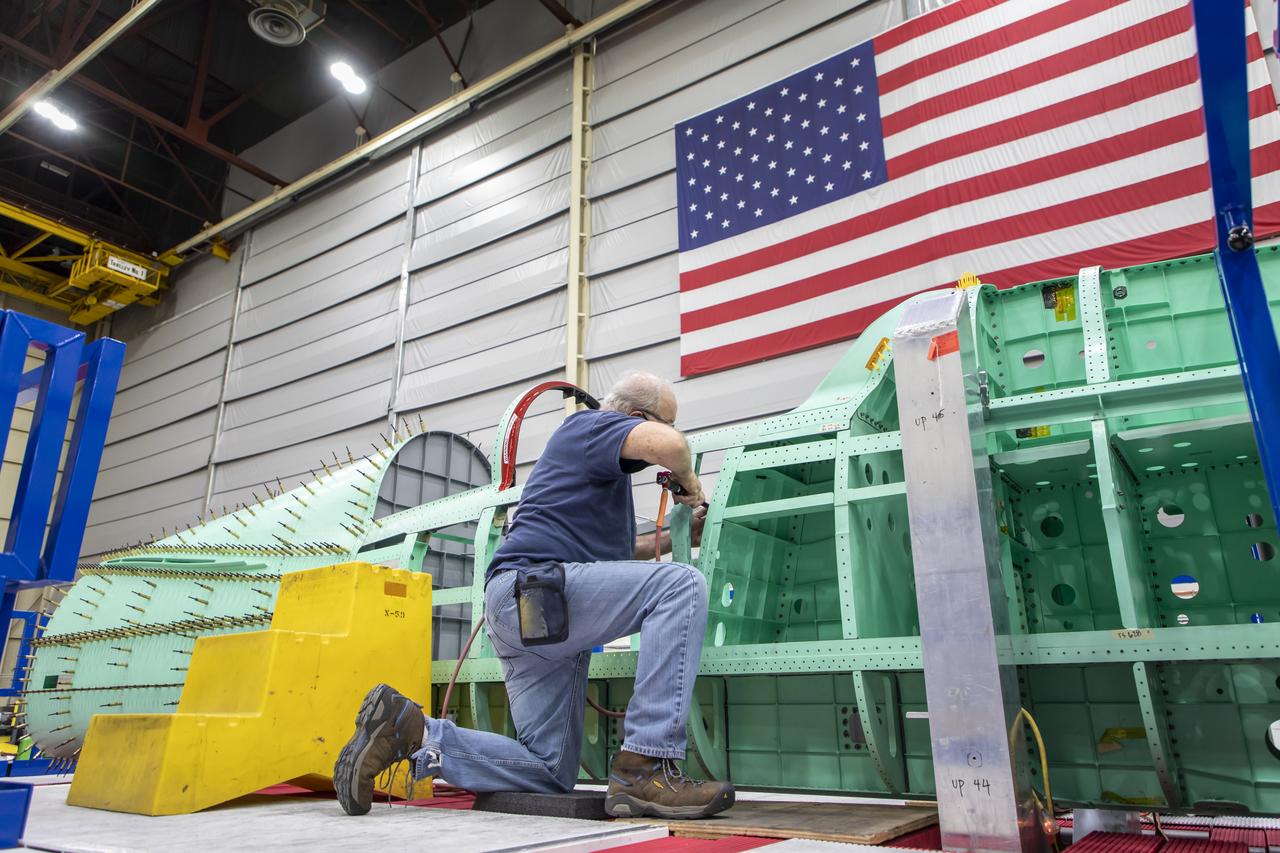

Event: SEG 210 Forebody A Lockheed Martin technician works on the ejection seat support structure and once complete, the ejection seat rails will be installed on the X-59 airplane. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
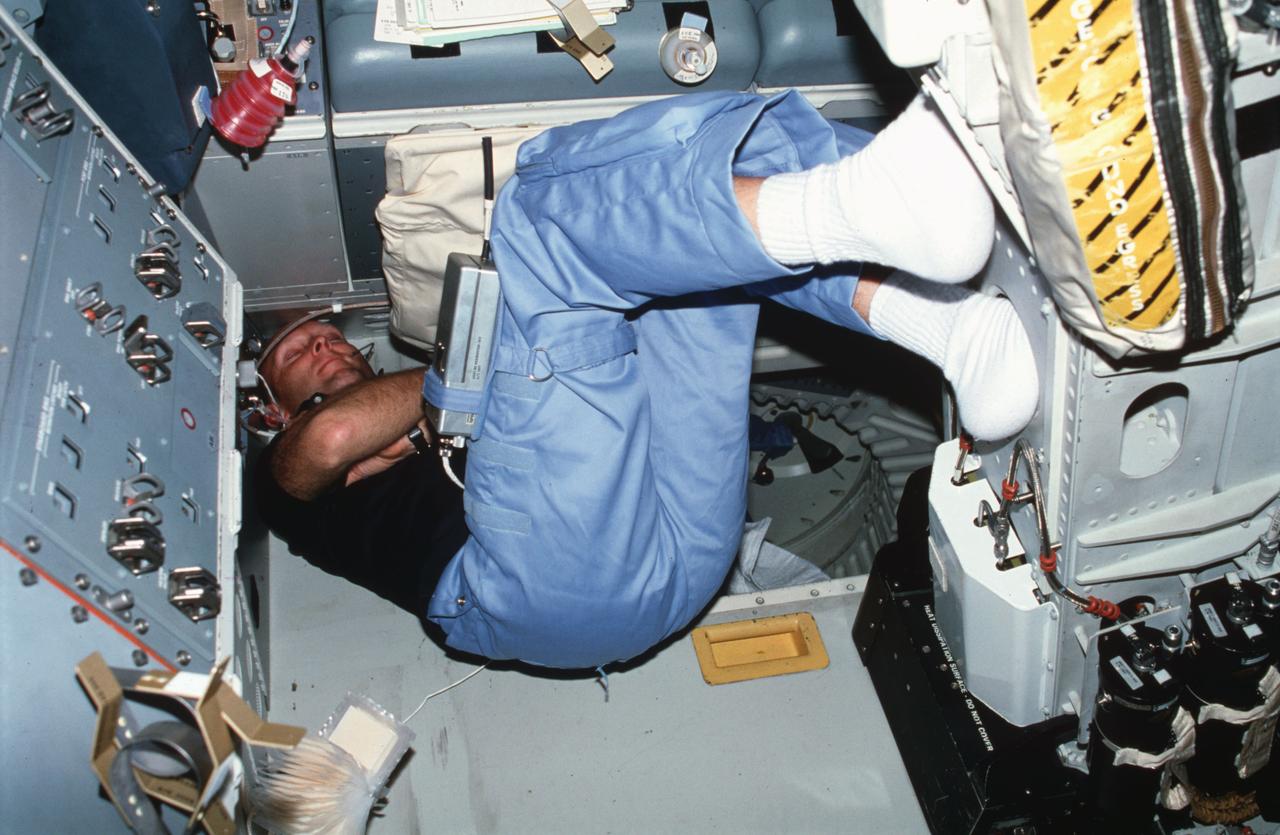
STS003-22-113 (24 March 1982) --- Astronaut Gordon Fullerton, STS-3 pilot, wearing communication kit assembly mini-headset (HDST), sleeps on aft flight deck resting his back against the floor and his feet against commander's ejection seat (S1) back. On-orbit station control panel A8 and payload station panel L15 appear above Fullerton. Special clips for holding notebooks open and beverage containers are velcroed on various panels. Photo credit: NASA
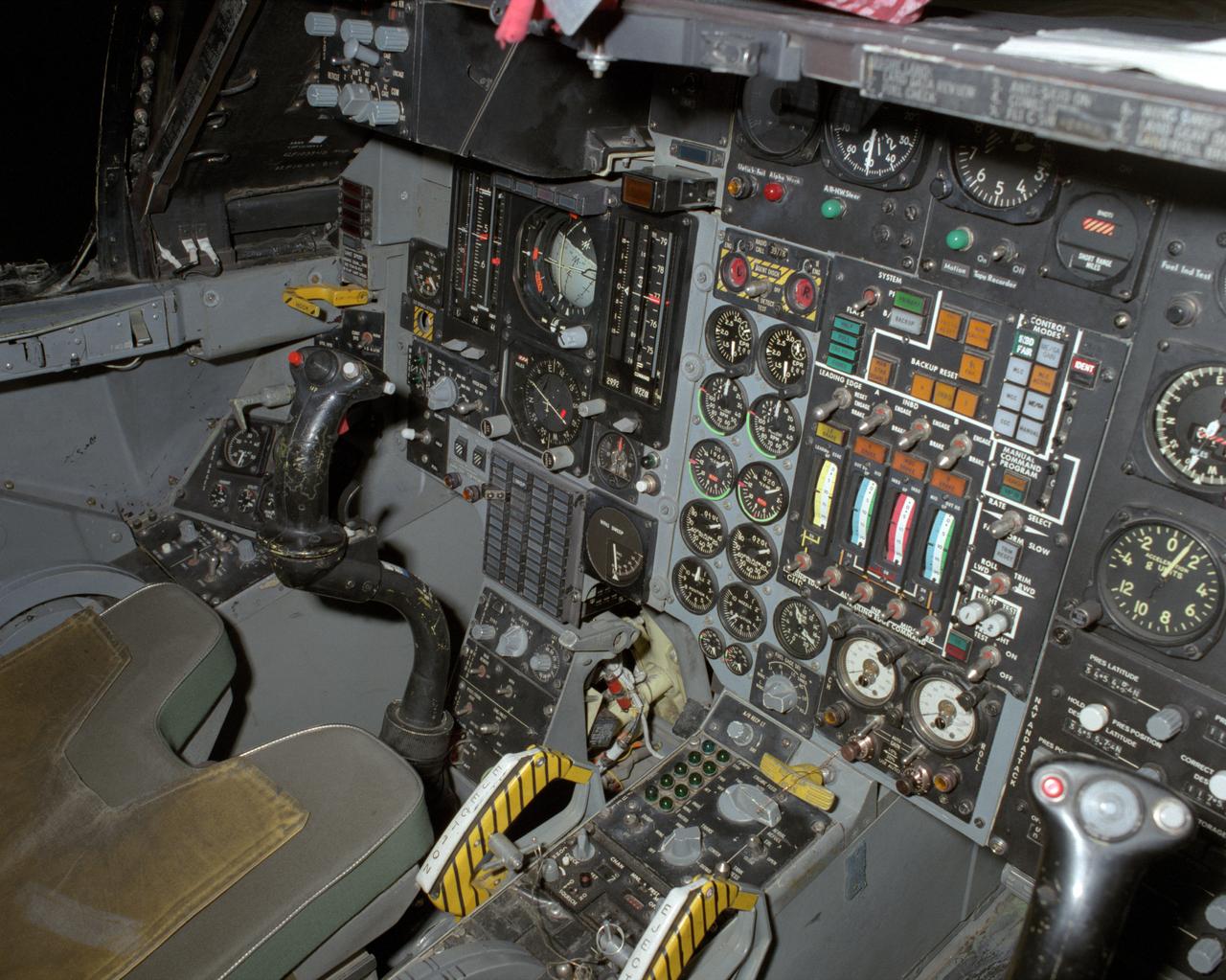

View of the left cockpit and pilot's seat of the F-111 MAW aircraft. Unlike most fighter aircraft of the time, the F-111 had side-by-side seating. The pilot sat on the left side, and the weapons systems officer on the right. Both had control sticks to fly the aircraft. The two yellow and black striped handles would be used in an emergency to eject the entire F-111 cockpit. The F-111 also did not have ejection seats, but used a capsule.
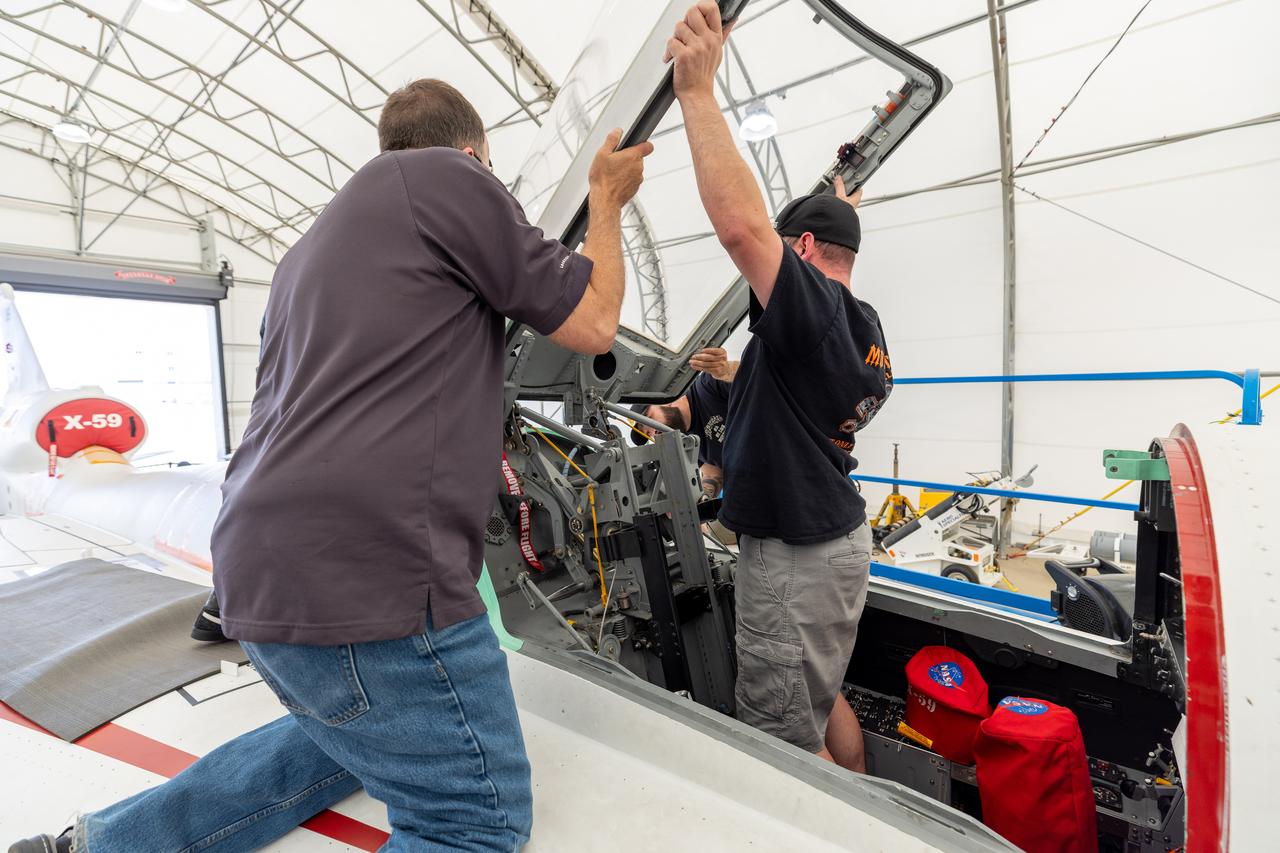

Lockheed Martin technicians temporarily remove the canopy from the X-59 in preparation for final installation of the ejection seat into the aircraft.
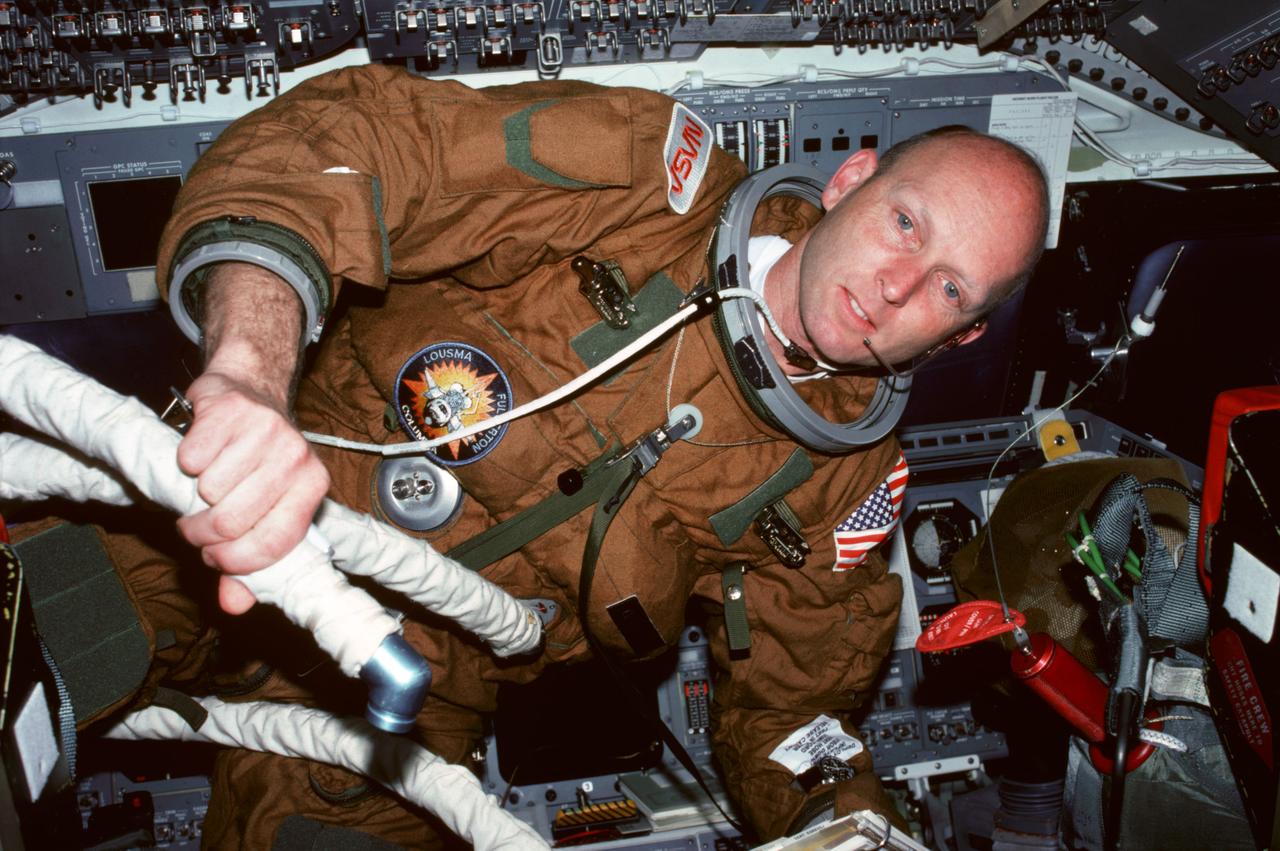

STS003-31-290 (30 March 1982) --- Astronaut Gordon Fullerton, STS-3 pilot, wearing communications kit assembly (ASSY) mini-headset (HDST) and ejection escape suit (EES), holds flexible hose attached to his EES vent hose fitting and second hose for commander's EES while behind pilots ejection seat (S2) seat back on the aft flight deck. Forward flight deck control panels are visible in the background. Photo credit: NASA
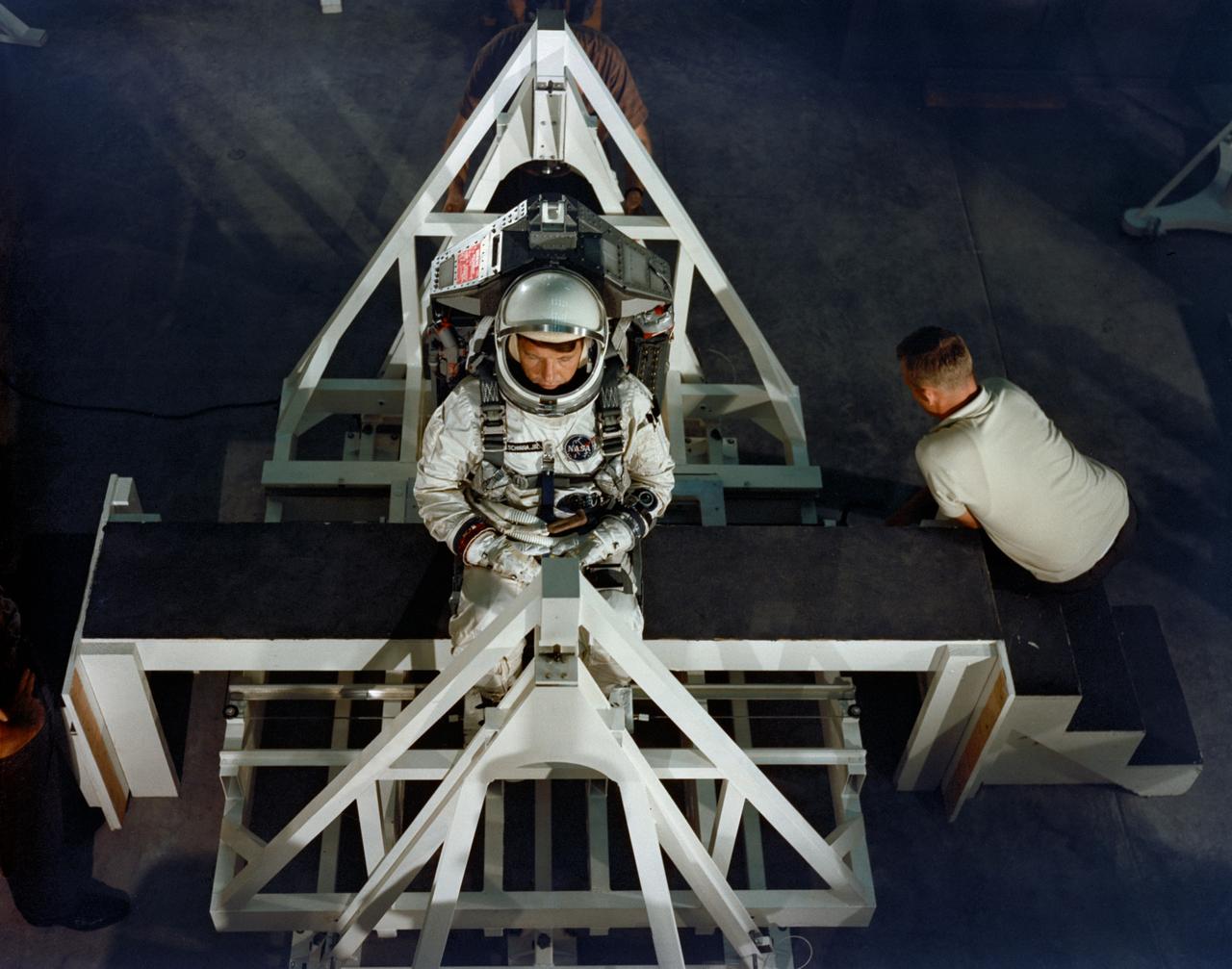
S65-54319 (22 Sept. 1965) --- Astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr., command pilot of the Gemini-6 prime crew, undergoes weight and balance tests in the Pyrotechnic Installation Building, Merritt Island, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
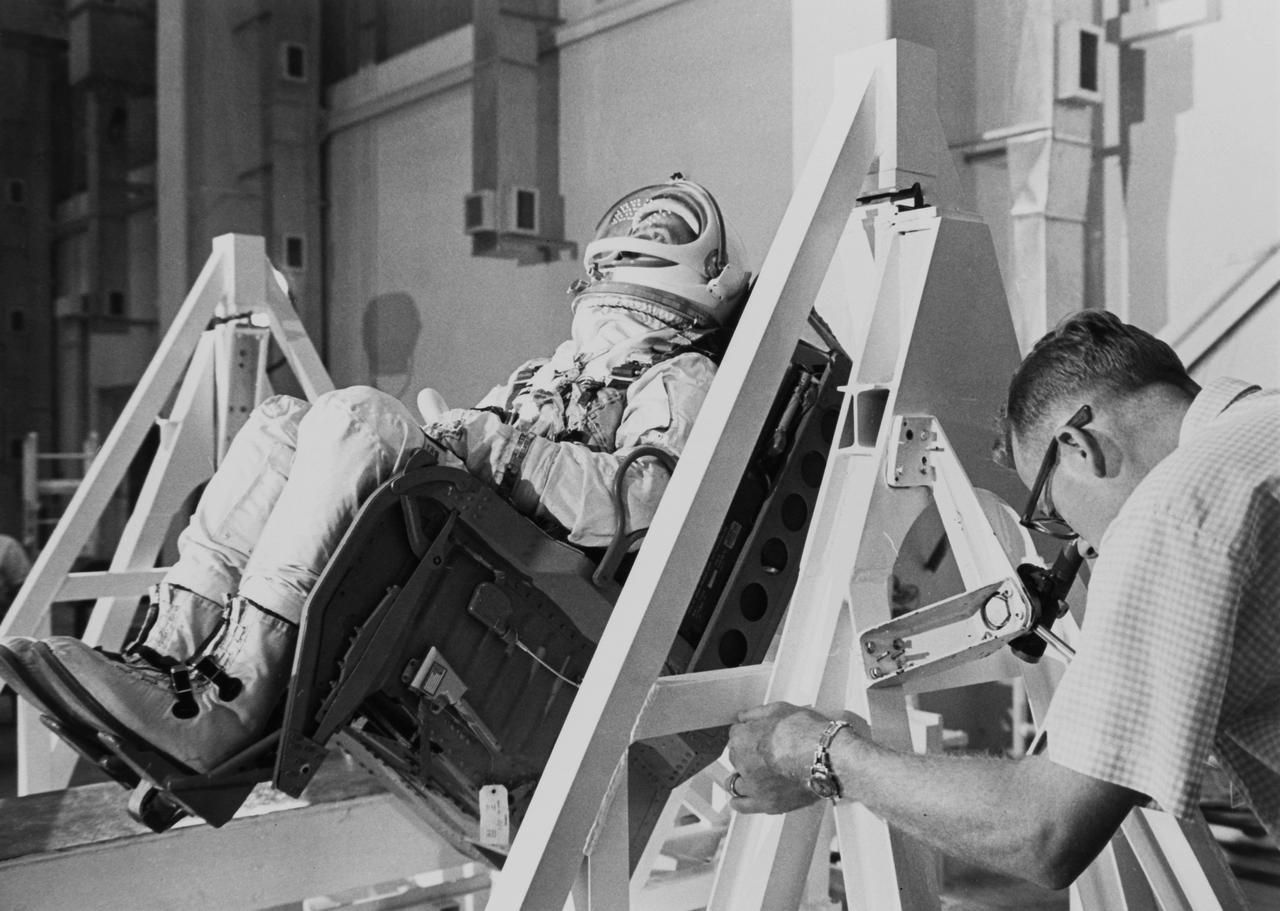

S65-19585 (21 May 1965) --- Astronaut James A. McDivitt, command pilot for the Gemini-Titan 4 prime crew, participates in a weight and balance test during a wet mock simulation exercise at Cape Kennedy, Florida. The two-man Gemini-4 mission, scheduled no earlier than June 3, 1965, will orbit Earth 62 times in four days. Astronaut Edward H. White II (out of frame) is the GT-4 prime crew pilot.
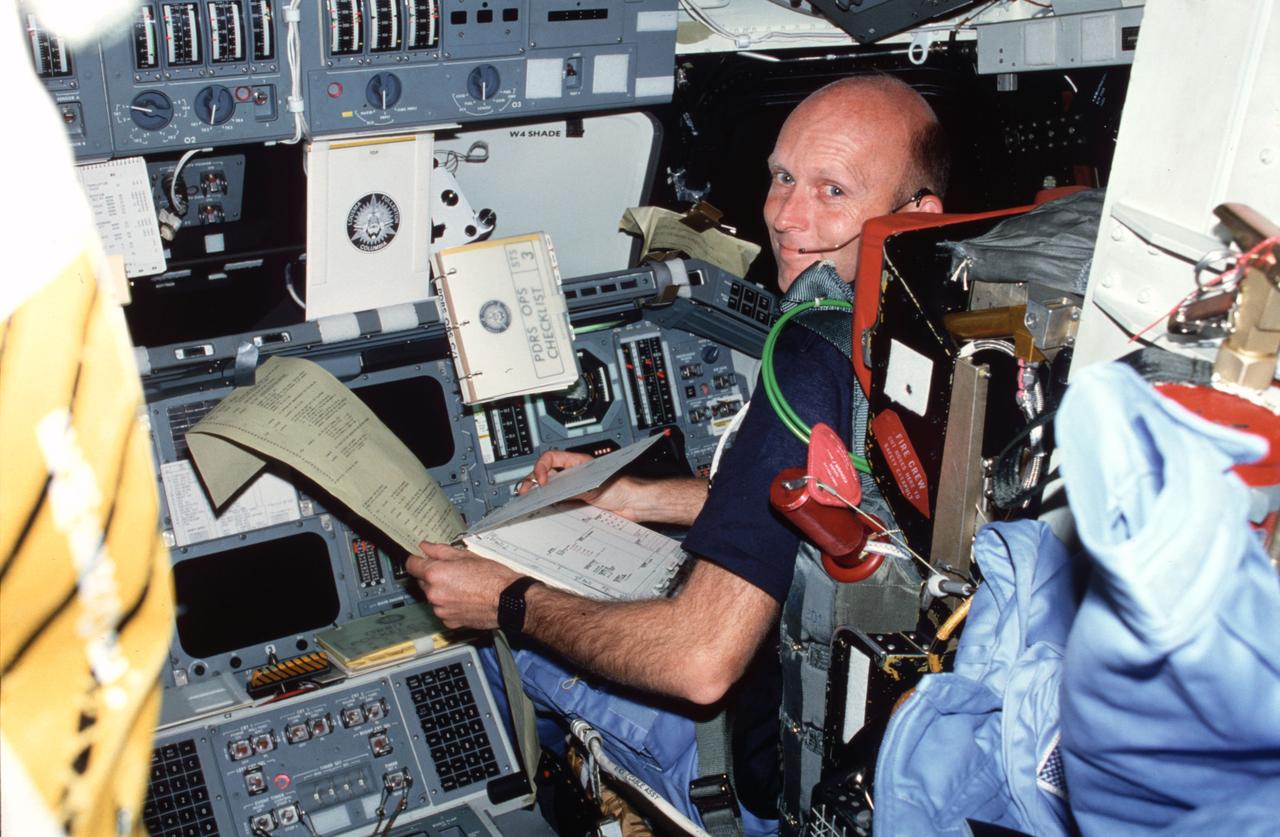

STS003-23-180 (22-30 March 1982) --- Astronaut Gordon Fullerton, STS-3 pilot, wearing communications kit assembly (ASSY) mini-headset (HDST), reviews flight data file (FDF) checklist and text and graphics system (TAGS) printout (ticker tape) while in pilots ejection seat (S2). Pilot station control panels F4, F7, F8, O3, window shade, and portable oxygen system (POS) assy appear in view. Photo credit: NASA
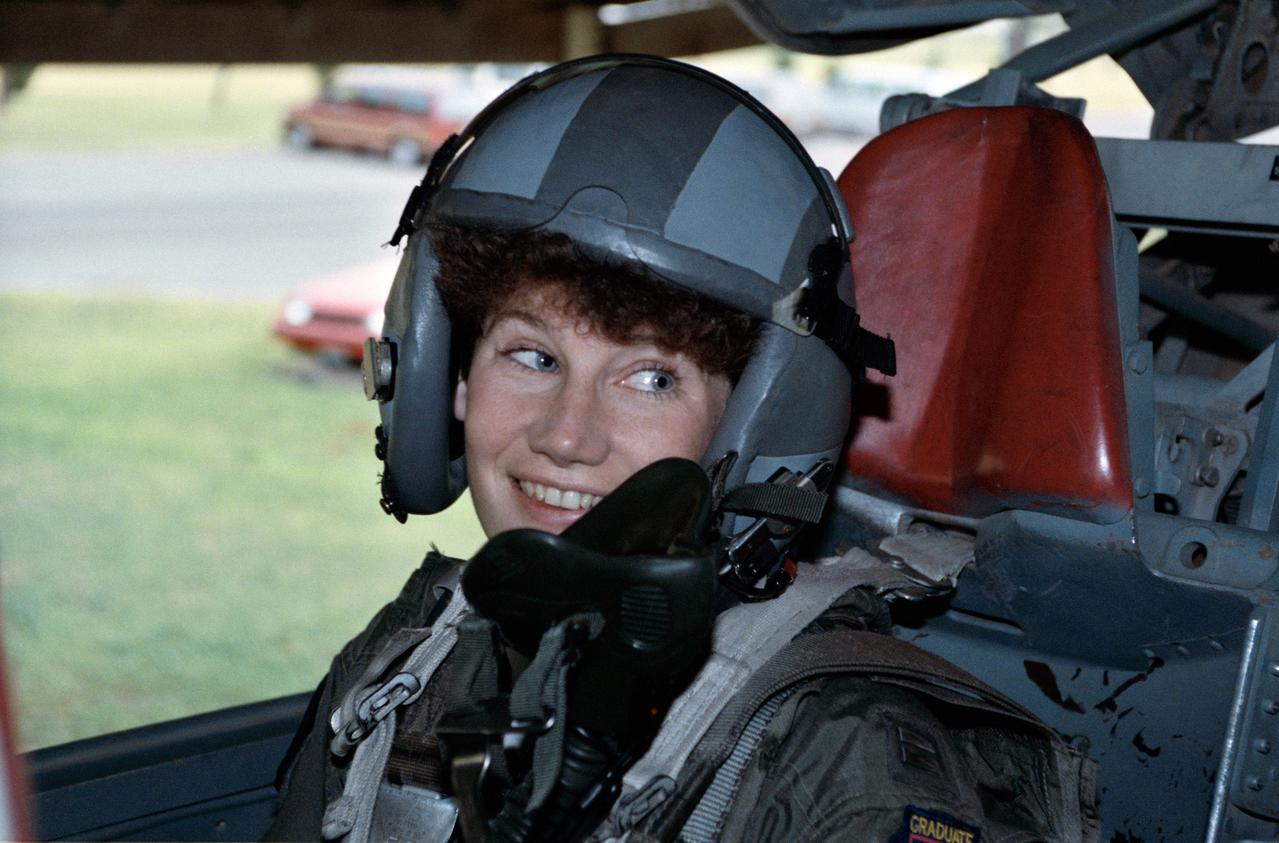

S90-45896 (29-31 July 1990) --- Susan J. Helms, one of the 23 astronaut candidates who began a year's training and evaluation program in July, participates in one of themany sessions at a survival training course at Vance Air Force Base. This portion of the course is designed to familiarize the trainee with procedures to follow in preparation for ejection from a jet aircraft.
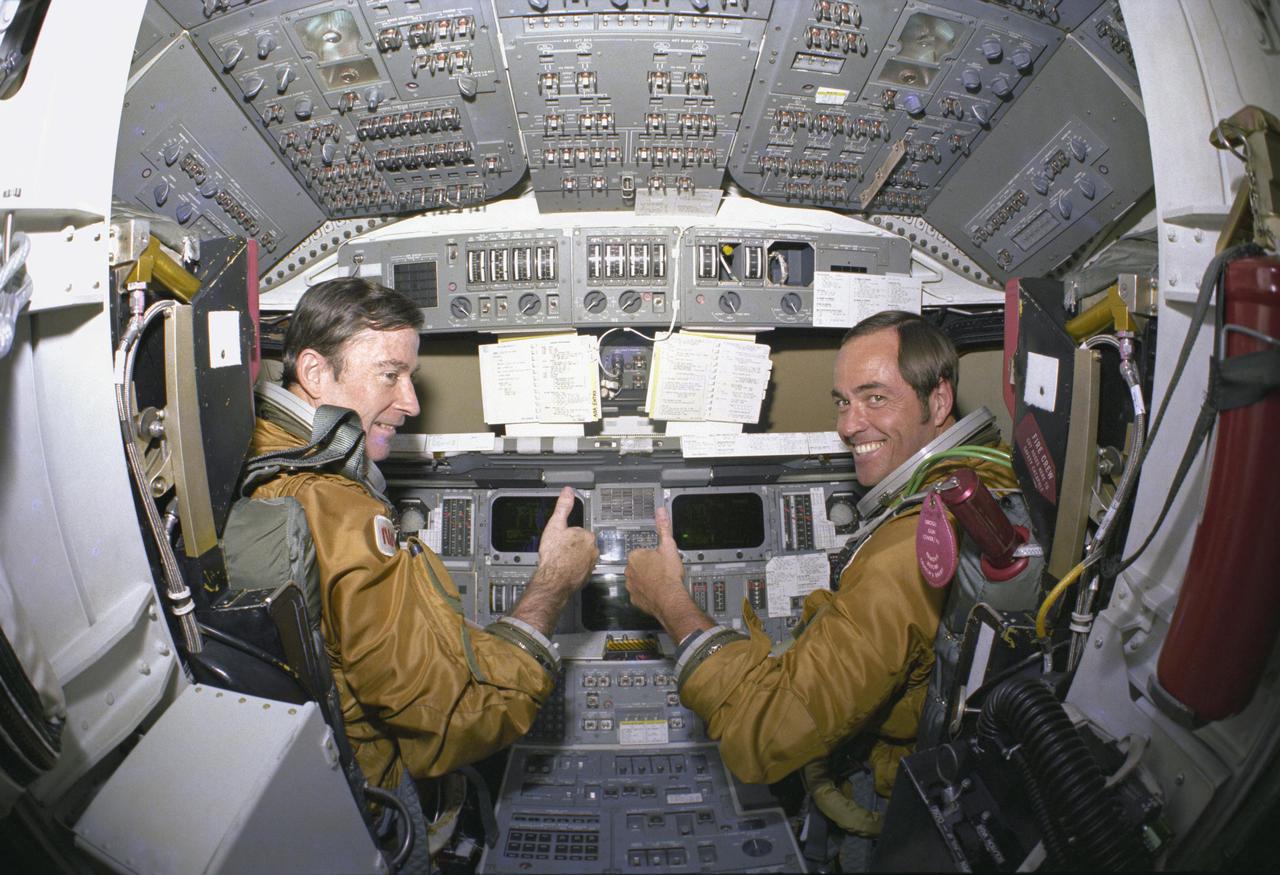

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Prime crew astronauts for the first space shuttle mission, Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen, take a break from their intensive training schedule to pose for pictures in the flight deck of the orbiter Columbia. The Space Shuttle is controlled and most payloads are handled from the flight deck. Looking forward, the ship’s commander is seated on the left and the pilot on the right. Shown are the TV-like displays, and duplicate sets of conventional-looking hand controllers, pedals, levers and switches with which either astronaut can fly the craft alone. The two-man crew are wearing their ejection escape suits which will be worn only during the orbital flight test program and then only during the launch and landing phases of the mission.

The X-1E research aircraft provides a striking view at the entrance of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The X-1E, one of the three original X-1 aircraft modified with a raised cockpit canopy and an ejection seat, was flown at the facility between 1953 and 1958 to investigate speeds at twice that of sound, and also to evaluate a thin wing designed for high-speed flight. The Dryden complex was originally established in 1946 as a small high-speed flight station to support the X-1 program. The X-1 was the first aircraft to fly at supersonic speeds. The main administrative building is to the rear of the X-1E and is the center of a research installation that has grown to more than 450 government employees and nearly 400 civilian contractors. Located on the northwest "shore" of Rogers Dry Lake, the Dryden Center was built around the original administrative-hangar building constructed in 1954 at a cost of $3.8 million. Since then many additional support and operational facilities have been built including a number of unique test facilities such as the Thermalstructures Research Facility, Flow Visualization Facility, and the newest addition, the Integrated Test Facility.
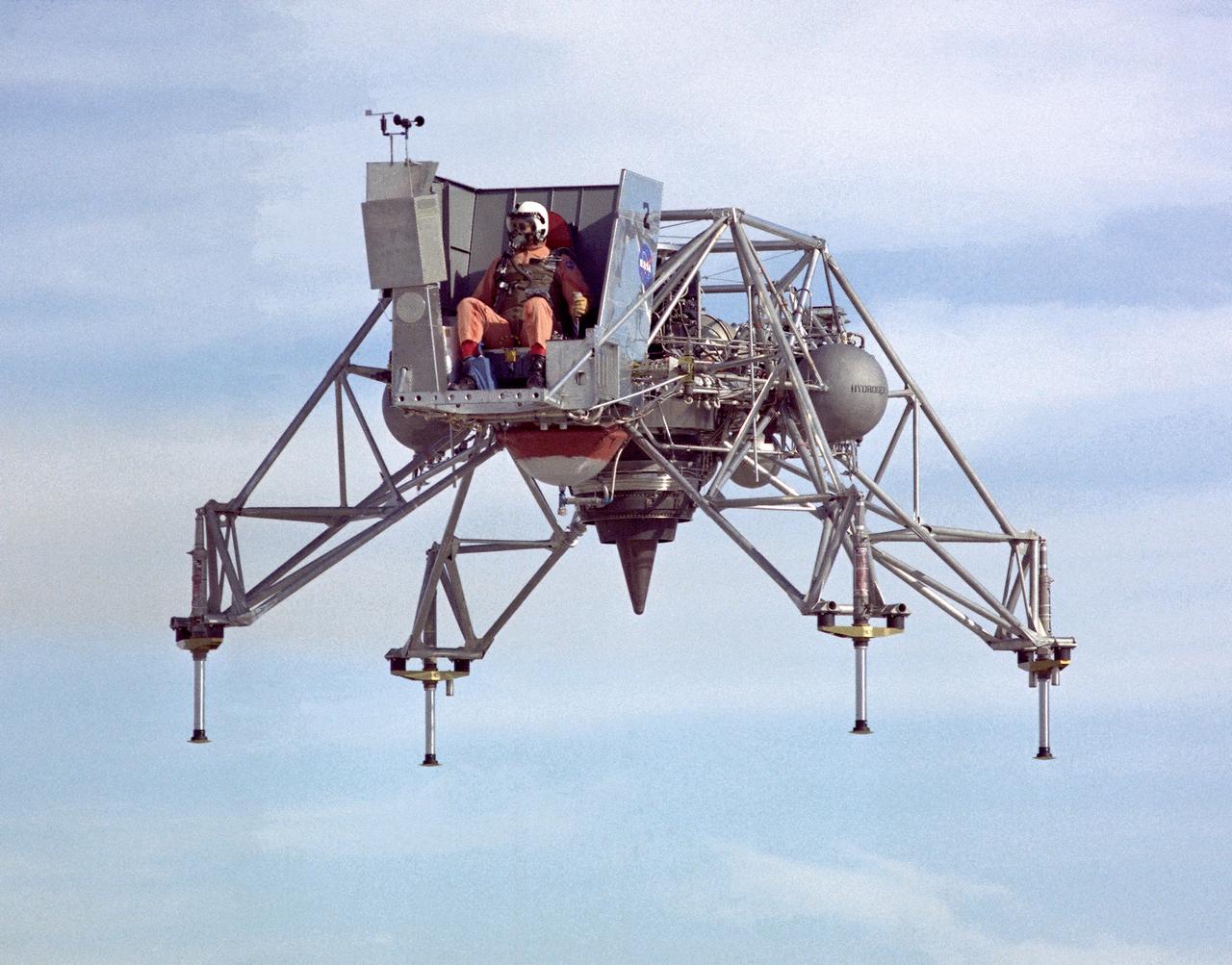
In this 1967 NASA Flight Reserch Center photograph the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) is viewed from the front. This photograph provideds a good view of the pilot’s platform with the restrictive cockpit view like that of he real Lunar Module (LM) When Apollo planning was underway in 1960, NASA was looking for a simulator to profile the descent to the Moon's surface. Three concepts surfaced: an electronic simulator, a tethered device, and the ambitious Dryden contribution, a free-flying vehicle. All three became serious projects, but eventually the NASA Flight Research Center’s (FRC) Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) became the most significant one. After conceptual planning and meetings with engineers from Bell Aerosystems Company, Buffalo, N.Y., NASA FRC issued a $3.6 million production contract awarded in 1963, for delivery of the first of two vehicles for flight studies. Built of tubular aluminum alloy like a giant four-legged bedstead, the vehicle was to simulate a lunar landing profile from around 1500 feet to the Moon’s surface. The LLRV had a turbofan engine mounted vertically in a gimbal, with 4200 pounds of thrust. The engine, lifted the vehicle up to the test altitude and was then throttled back to support five-sixths of the vehicle's weight, thus simulating the reduced gravity of the Moon. Two lift rockets with thrust that could be varied from 100 to 500 pounds handled the LLRV's rate of descent and horizontal translations. Sixteen smaller rockets, mounted in pairs, gave the pilot control in pitch, yaw, and roll.. The pilot’s platform extended forward between two legs while an electronics platform, similarly located, extended rearward. The pilot had a zero-zero ejection seat that would then lift him away to safety. The two LLRVs were shipped from Bell to the FRC in April 1964, with program emphasis on vehicle No. 1. The first flight, Oct. 30, 1964, NASA research pilot Joe Walker flew it three times for a total of just under 60 seconds
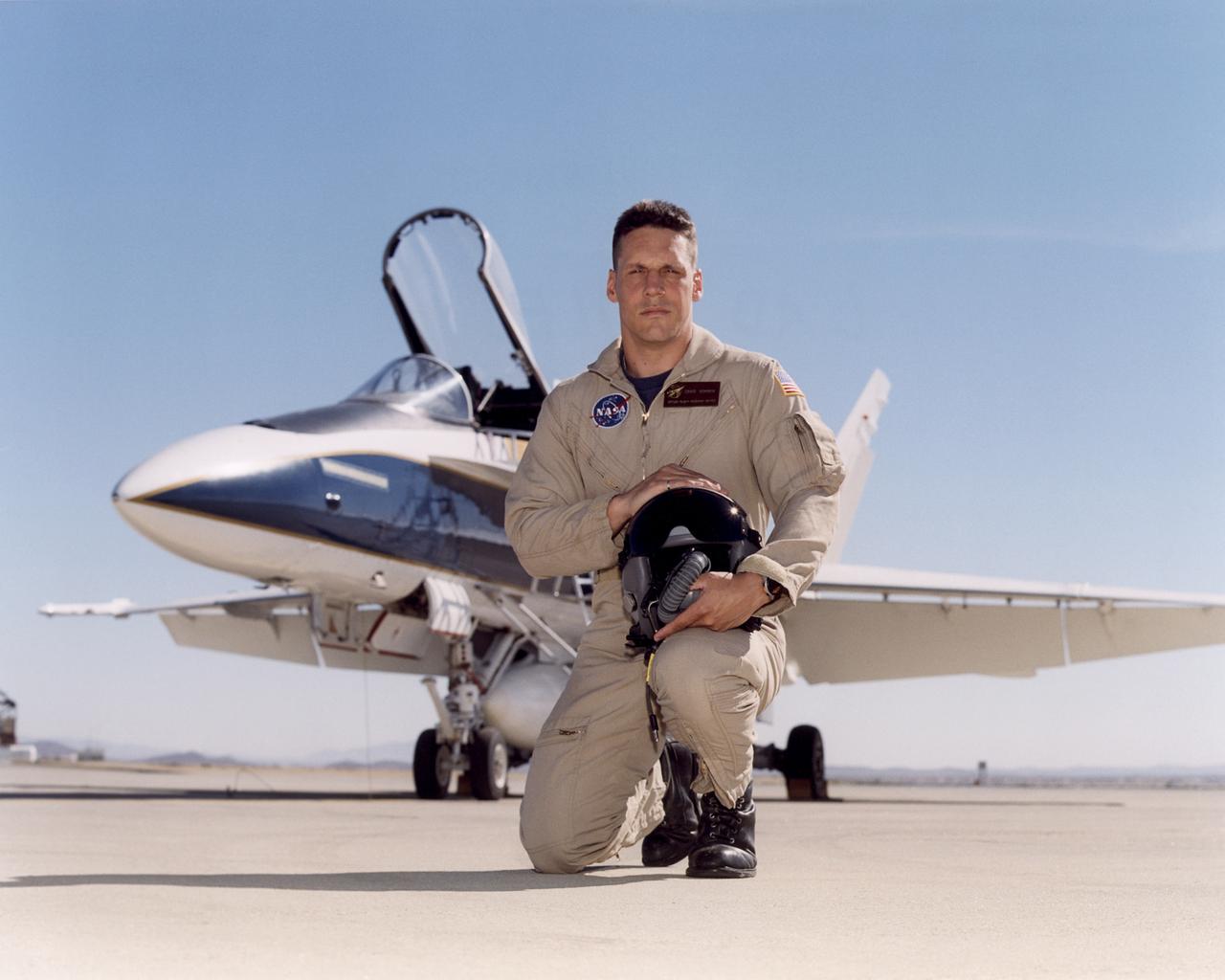

Craig R. Bomben became a pilot in the Flight Crew Branch of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif., in June 2001. His flying duties include a variety of research and support activities while piloting the F/A-18, DC-8, T-34C and King Air aircraft. He has more than 17 years and 3,800 hours of military and civilian flight experience in over 50 different aircraft types. Bomben came to NASA Dryden from a U.S. Navy assignment to the Personnel Exchange Program, Canada. He served as a test pilot in the Canadian Armed Forces located in Cold Lake, Alberta. He participated in numerous developmental programs to include CT-133 airborne ejection seat testing, F/A-18 weapons flutter testing and F/A-18 night vision goggles integration. Bomben performed U.S. Navy fleet service in 1995 as a strike-fighter department head. He completed two overseas deployments onboard the USS George Washington and USS Stennis. As a combat strike leader, he headed numerous multi-national missions over Iraq in support of Operation Southern Watch. Bomben graduated from the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School in 1992 and was subsequently assigned to the Naval Weapons Test Squadron at Pt. Mugu, Calif. During this tour he developed the F-14D bombsight and worked on various other F-14D and F/A-18 weapon systems developmental programs. Bomben is a 1985 graduate of Washington State University with a bachelor of science degree in electrical engineering. He graduated from naval flight training in 1987 and was recognized as a Commodore List graduate. His first assignment was to Naval Air Station Pensacola, Fla., where he was an instructor in the T-2B Buckeye. When selected to fly the F/A-18 in 1989, he joined a fleet squadron and deployed aboard the USS Forrestal. Bomben is married to the former Aissa Asuncion. They live in Lancaster, Calif., with their 3 children.