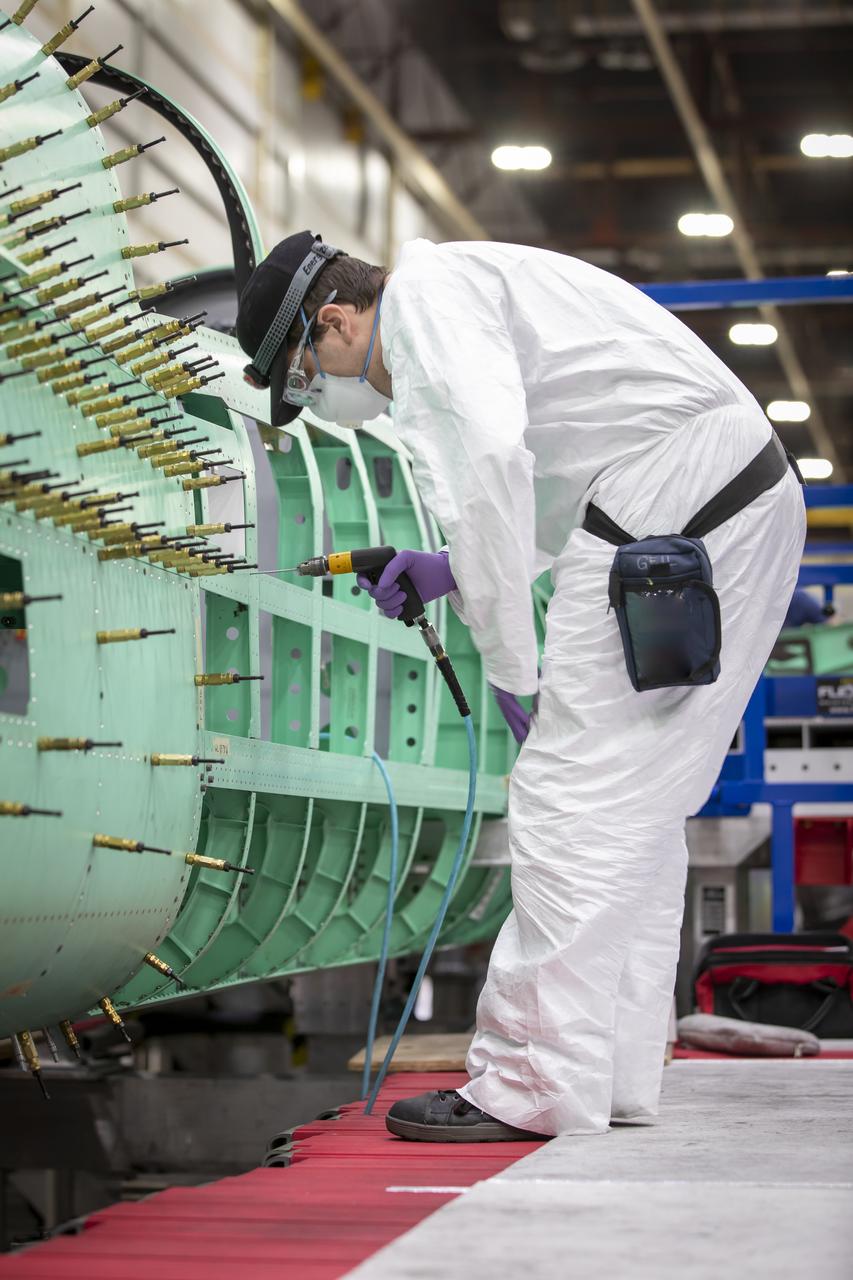

Event: SEG 210 Forebody A Lockheed Martin technician prepares to install the left fuselage skins onto the X-59. Once in the air, the aircraft, currently under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
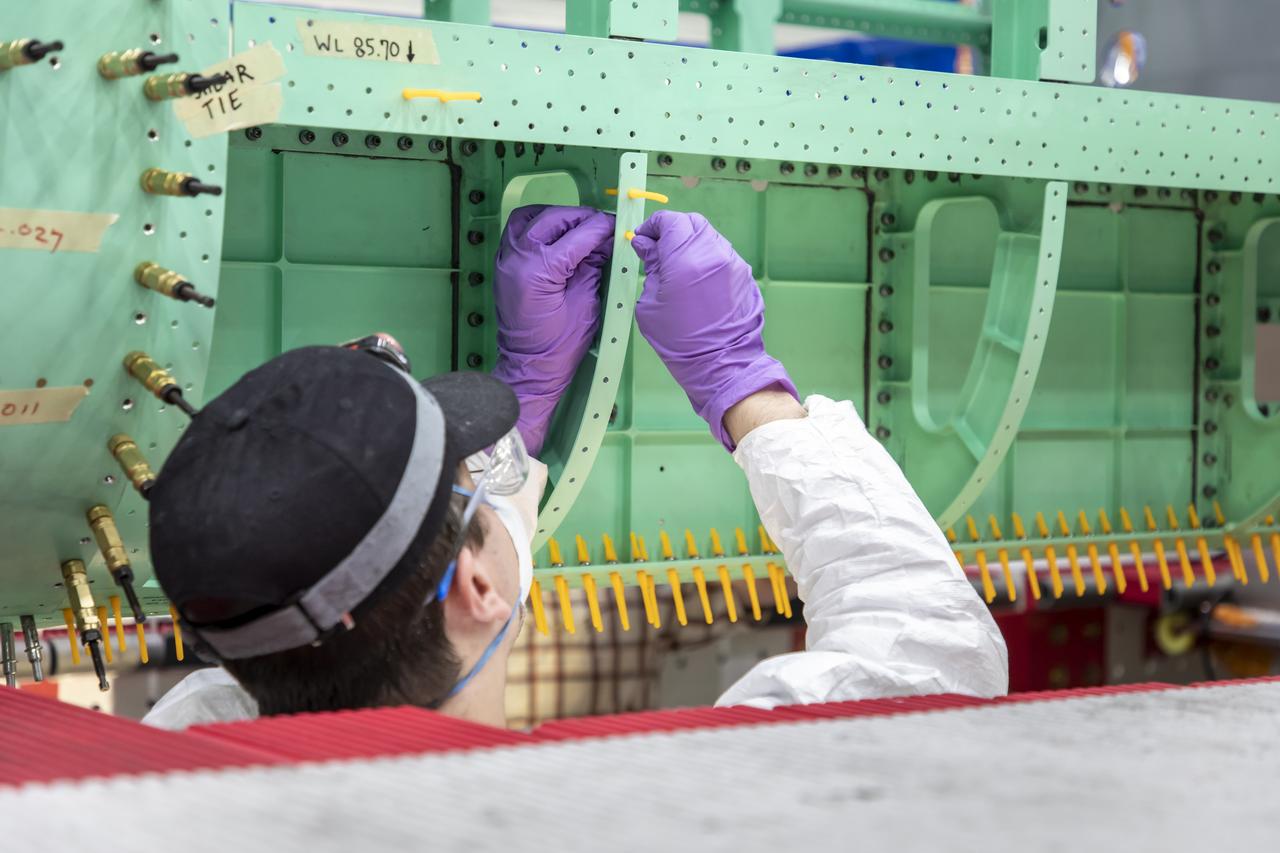

A Lockheed Martin technician prepares holes for installation of the fuselage panel on the X-59. The fuselage is the section of the aircraft that contains the cockpit. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

Event: Horizontal Stabilator Install The Low Boom Flight Demonstrator manufacturing team installed the horizontal stabilizers to the aircraft. These are used along with the flight control computers to keep the airplane flying safely and providing the pitch control so that the pilot can fly the missions envisioned for the X-59

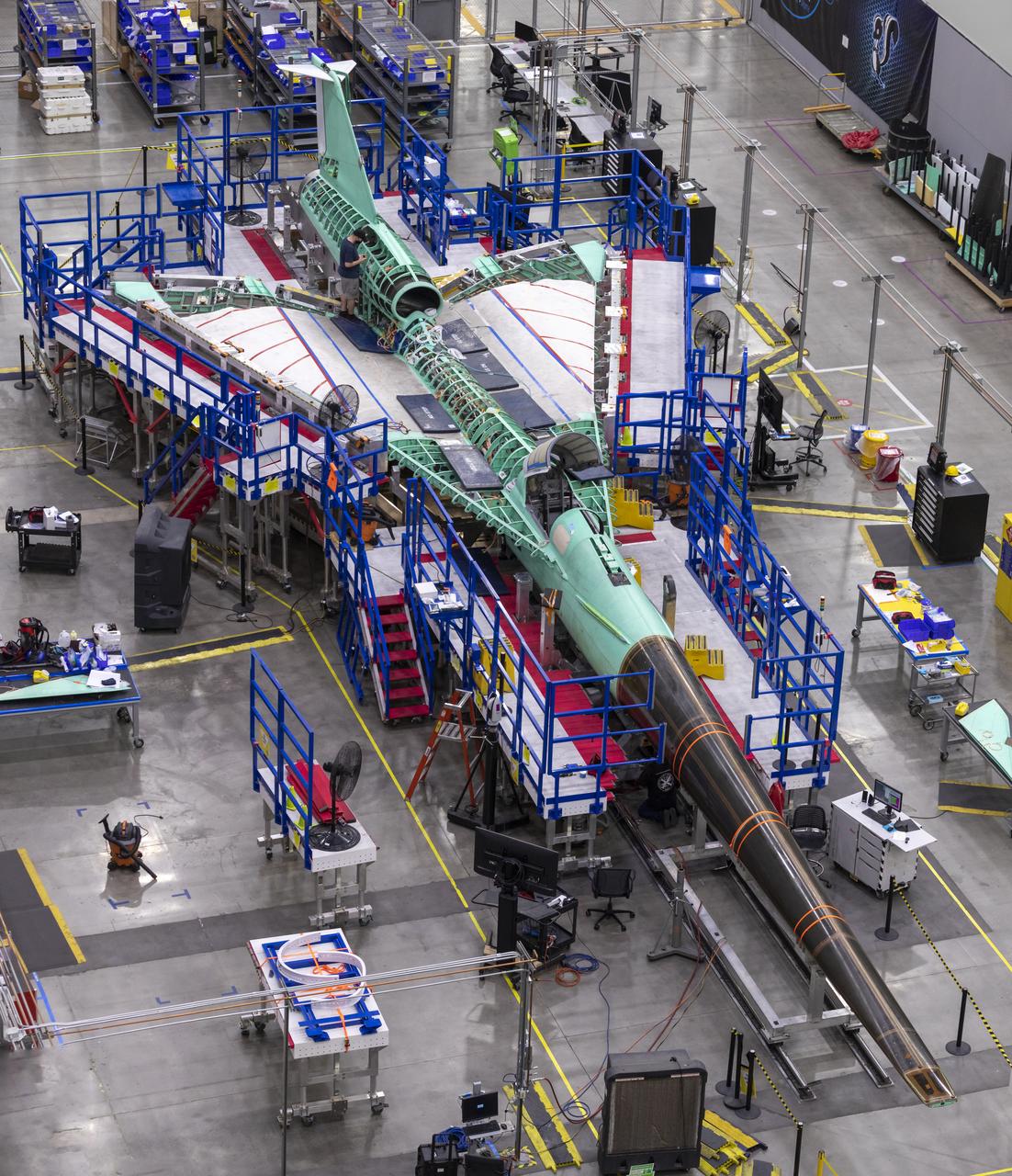
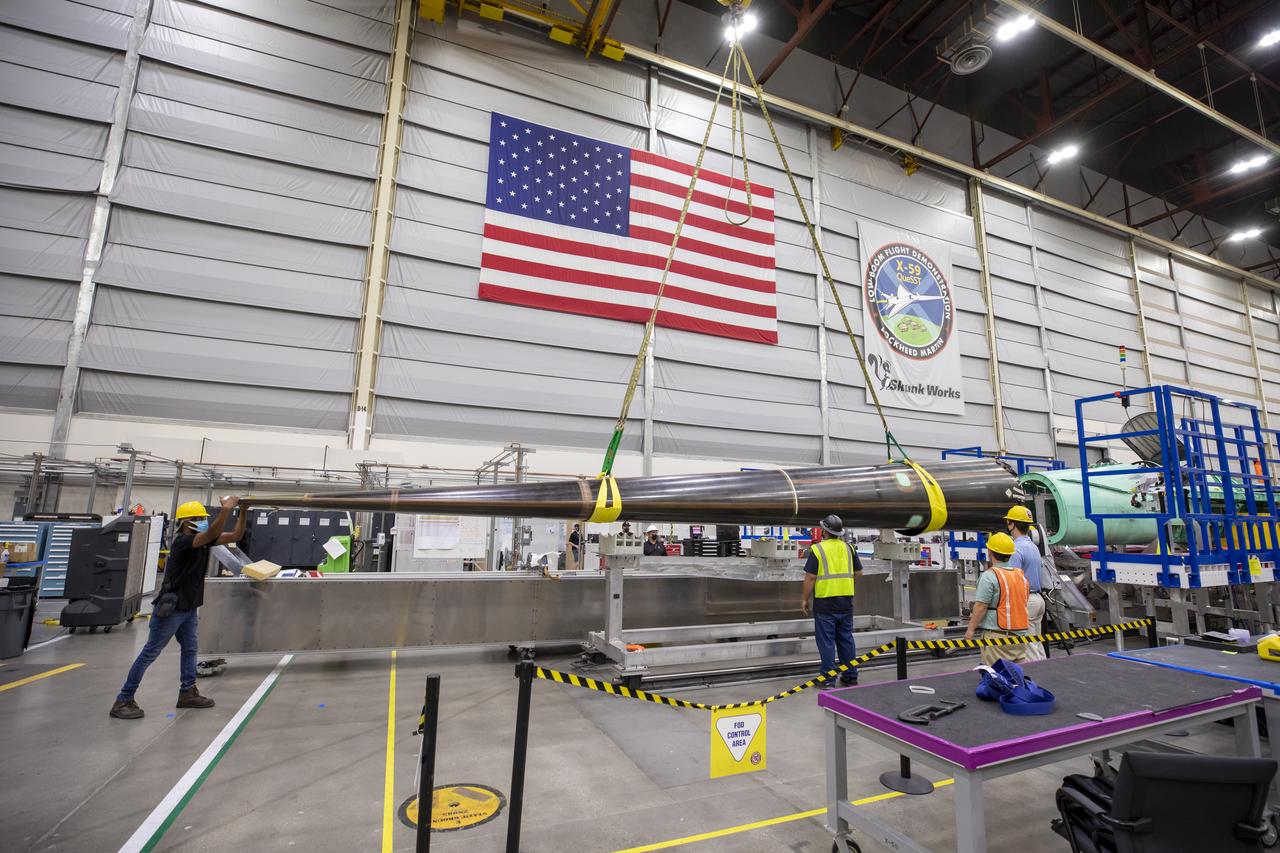
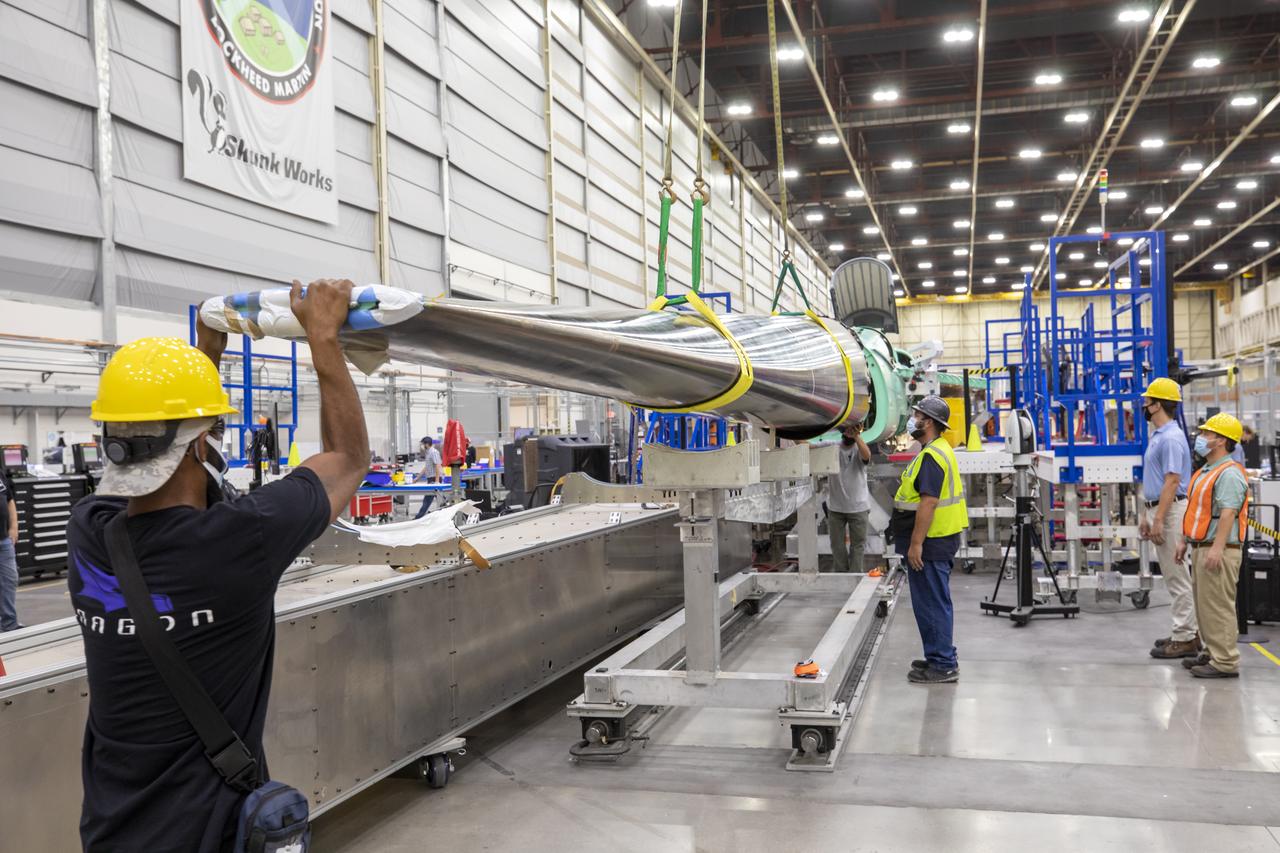
Here is an overhead view of the X-59 aircraft (left) prior to the installation of the General Electric F414 engine (center, located under the blue cover). After the engine is installed, the lower empennage (right), the last remaining major aircraft component, will be installed in preparation for integrated system checkouts. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the Quesst mission which plans to help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.

A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician inspects some of the wiring and sensors on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the first power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
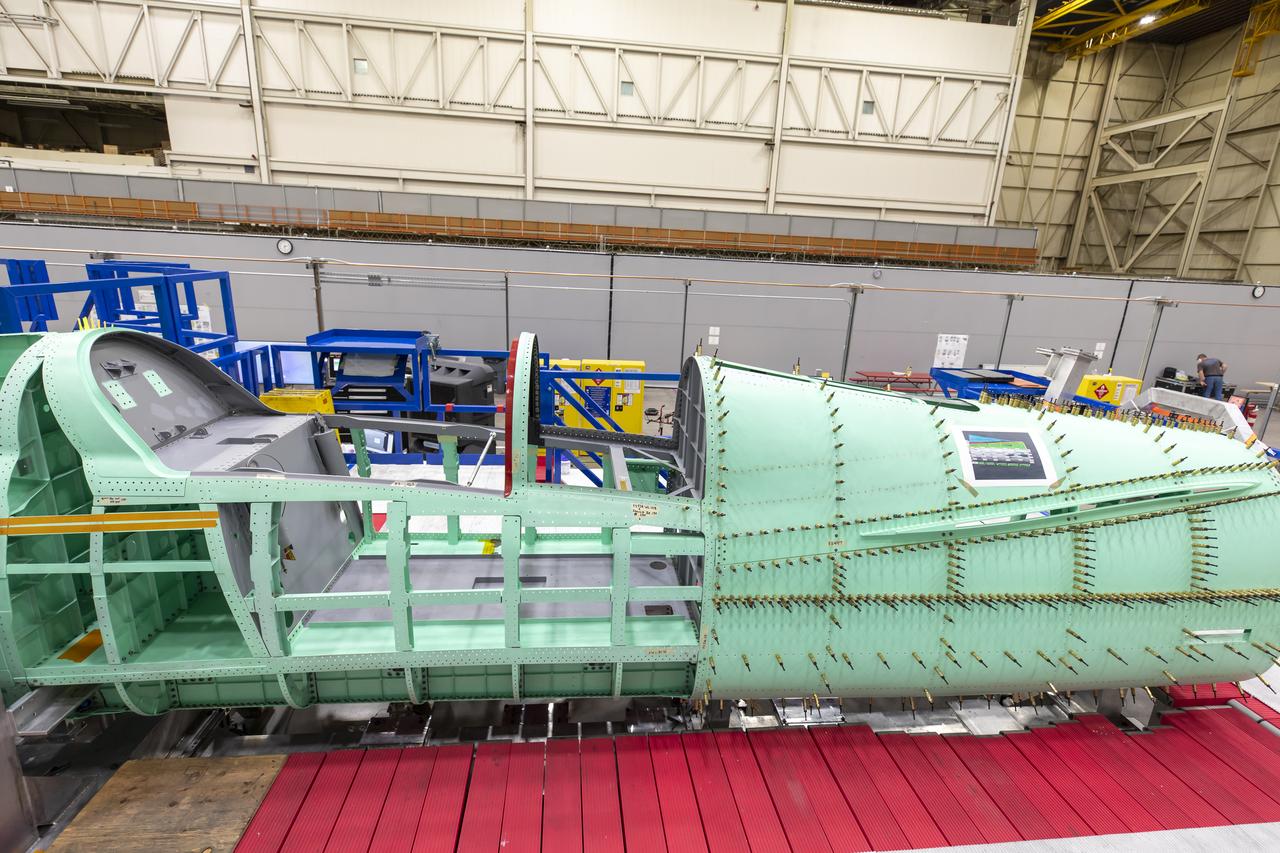
Event: SEG 210 Forebody A right side view of where the team is preparing the X-59 structure for installation of the forward fuselage, which contains the cockpit. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

Event: SEG 410 Main Wing A Lockheed Martin technician works on the installation of wiring on the trailing edge structure of the right side of the X-59’s wing. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
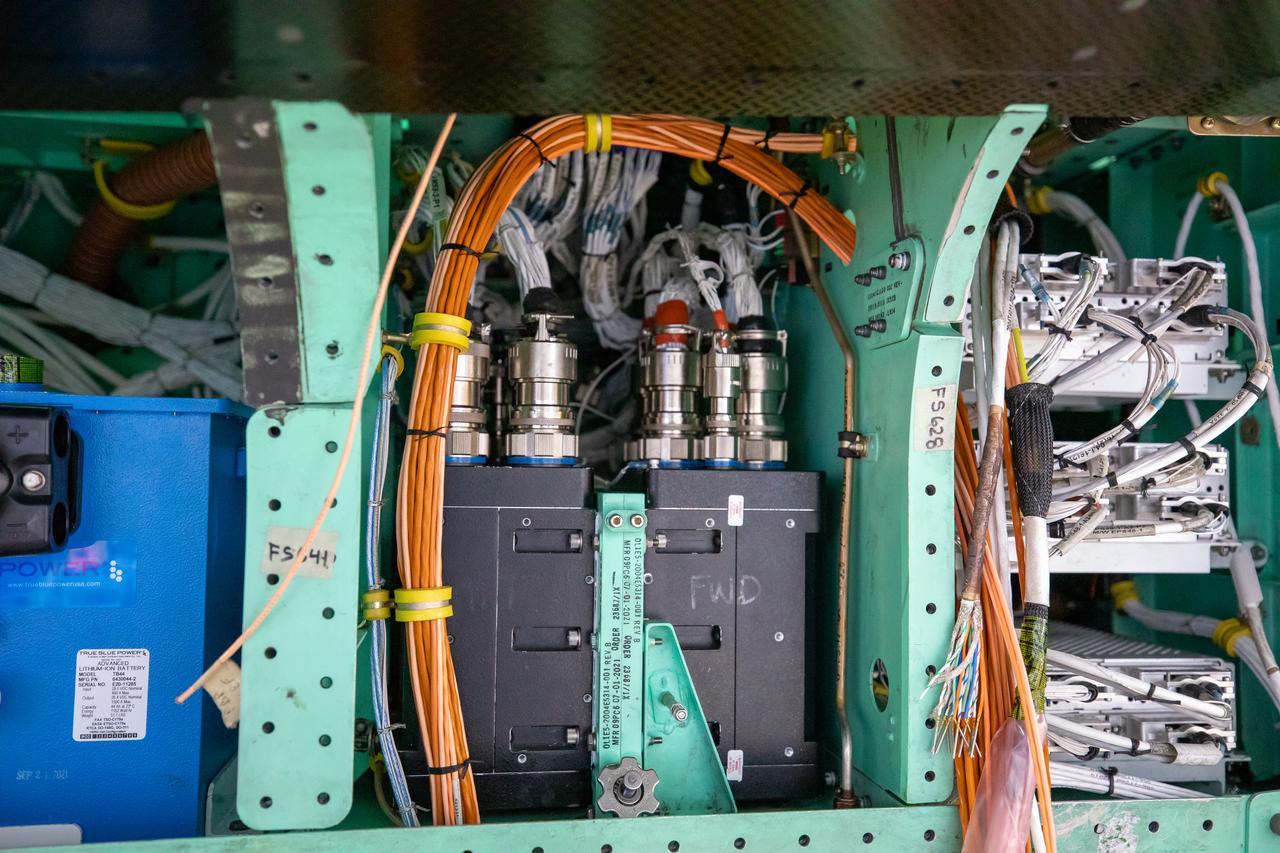
This is a closeup view of the inner workings of the X-59 aircraft. Visible are one the plane’s three lithium-ion batteries (blue box), electrical power system and other wiring components including the vehicle management systems computers (two black boxes) and the white wirings which assist in providing the power that is needed for the aircraft to function in flight. All of these components are essential to maintaining and monitoring the X-59 once it takes to the skies. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the Quesst mission which plans to help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.

A overhead view of the X-59 with its nose on. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The plane is under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
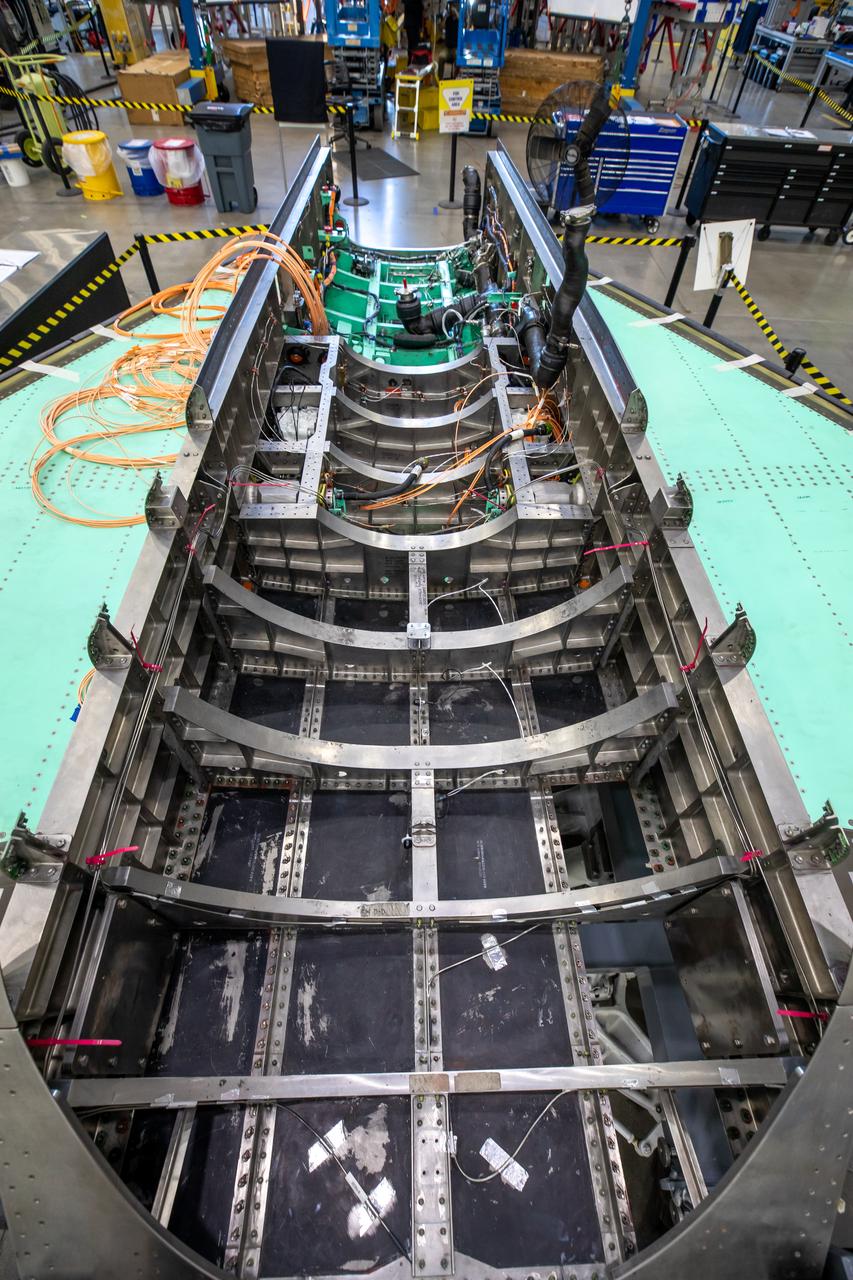
This image shows the X-59 aircraft’s lower empennage structure, or tail section of the plane, that was installed. The stabilators, the outer surfaces also seen in the photo, attach to the lower empennage and are used to help regulate the aircraft pitch which controls the up and down movement of the motion of the plane. The 13-foot engine will pack 22,000 pounds of propulsion and energy and power the X-plane to its planned cruising speed of Mach 1.4. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
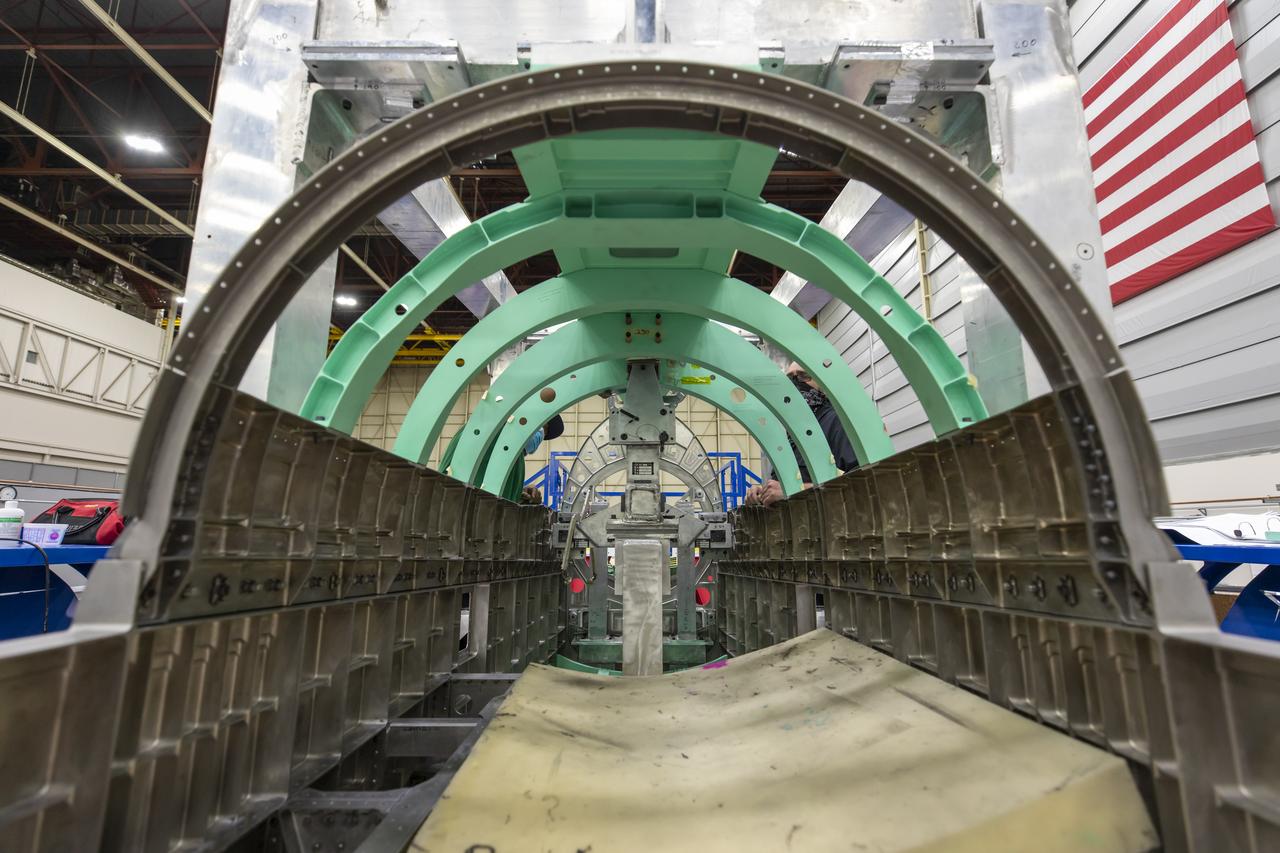

Event: SEG 510 Upper Empennage An inside peek at the X-59 gives us a view from the aft end looking at the engine bay. Later in the assembly process, the engine will be placed inside this section. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
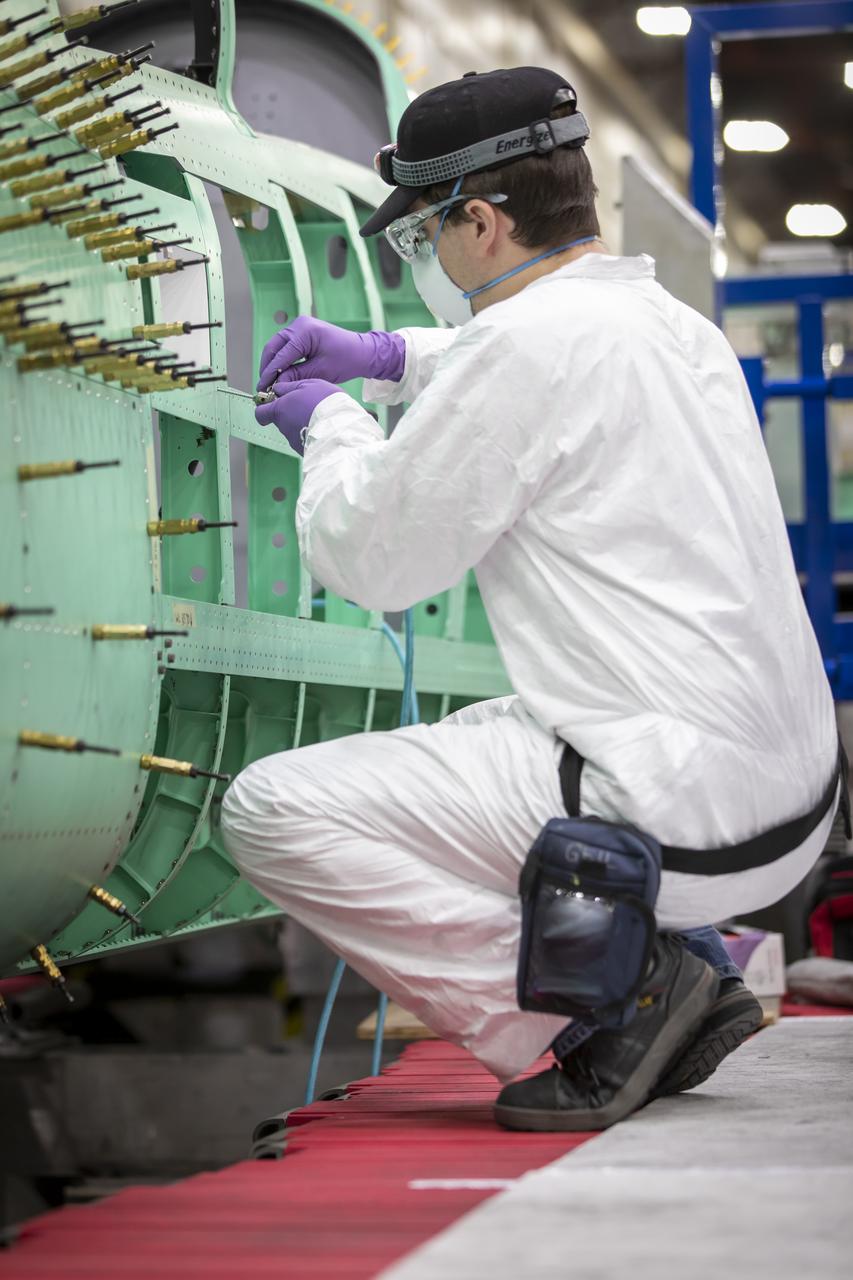

Event: SEG 210 Forebody A Lockheed Martin technician prepares to install the left fuselage skins onto the X-59. Once in the air, the aircraft, currently under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
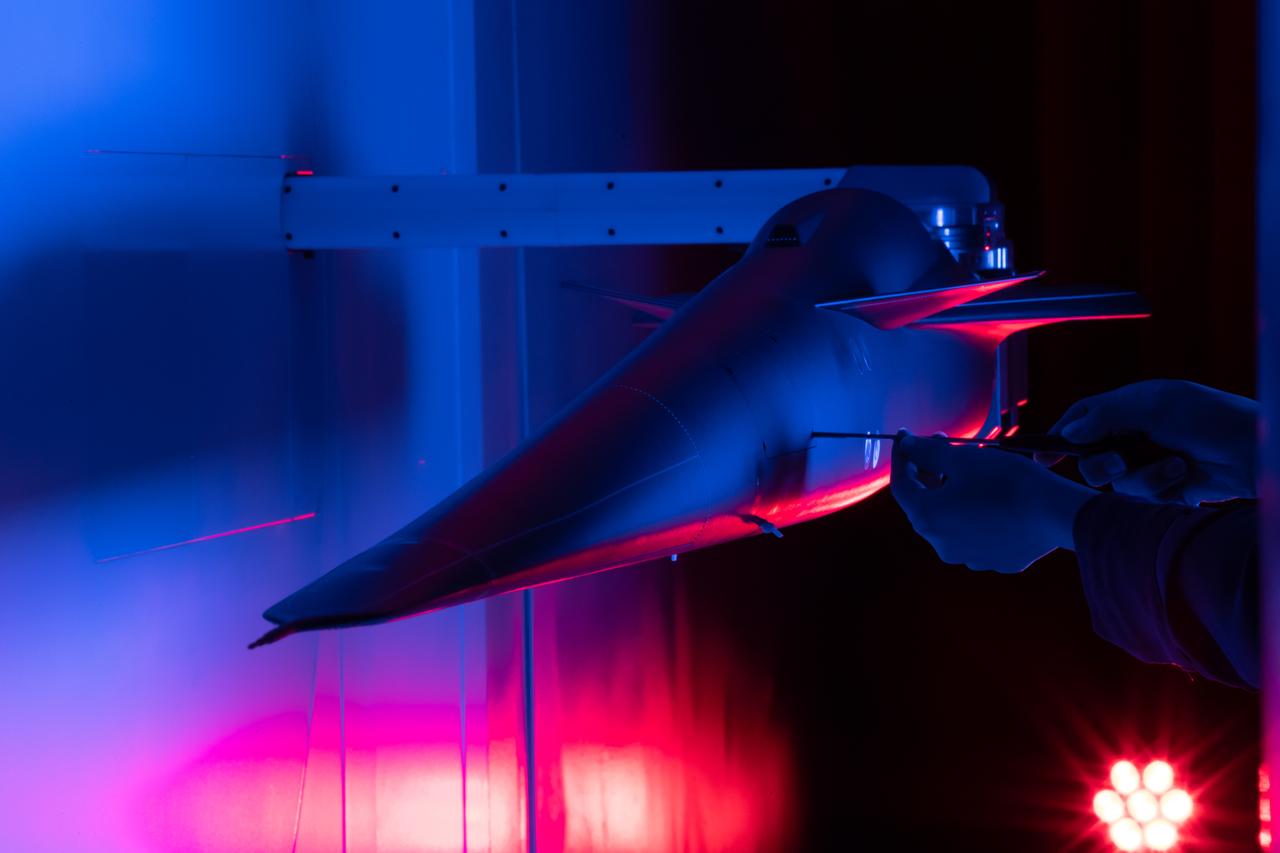

Event: Forebody and Nose - Windtunnel Testing A technician works on the X-59 model during testing in the low-speed wind tunnel at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. These tests gave the team measurements of wind flow angle around the aircraft’s nose and confirmed computer predictions made using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software tools. The data will be fed into the aircraft flight control system to tell the pilot the aircraft’s altitude, speed, and angle. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land.

Event: SEG 230 Nose - Craned Onto Tooling A close up of the X-59’s duckbill nose, which is a crucial part of its supersonic design shaping. The team prepares the nose for a fit check. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

Event: SEG 230 Nose - Craned Onto Tooling A close-up of the X-59’s duckbill nose, which is a crucial part of its supersonic design shaping. The team prepares the nose for a fit check. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
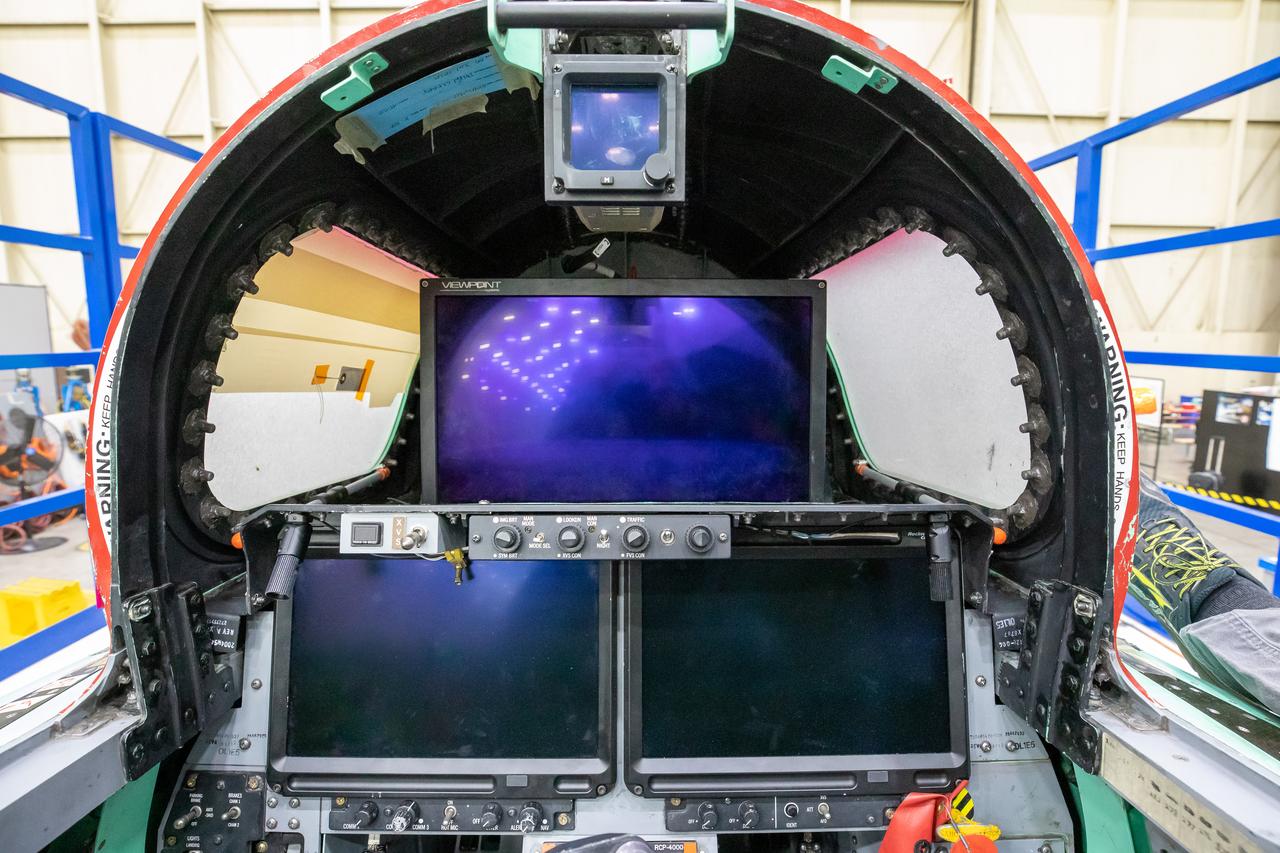

This image shows the forward view of the X-59’s cockpit with the canopy open. The aircraft will not have a forward-facing window and will use an eXternal Vision System (XVS) made up of a high definition 4K monitor (located in the center) and two monitors below to help the pilots safely fly through the skies.
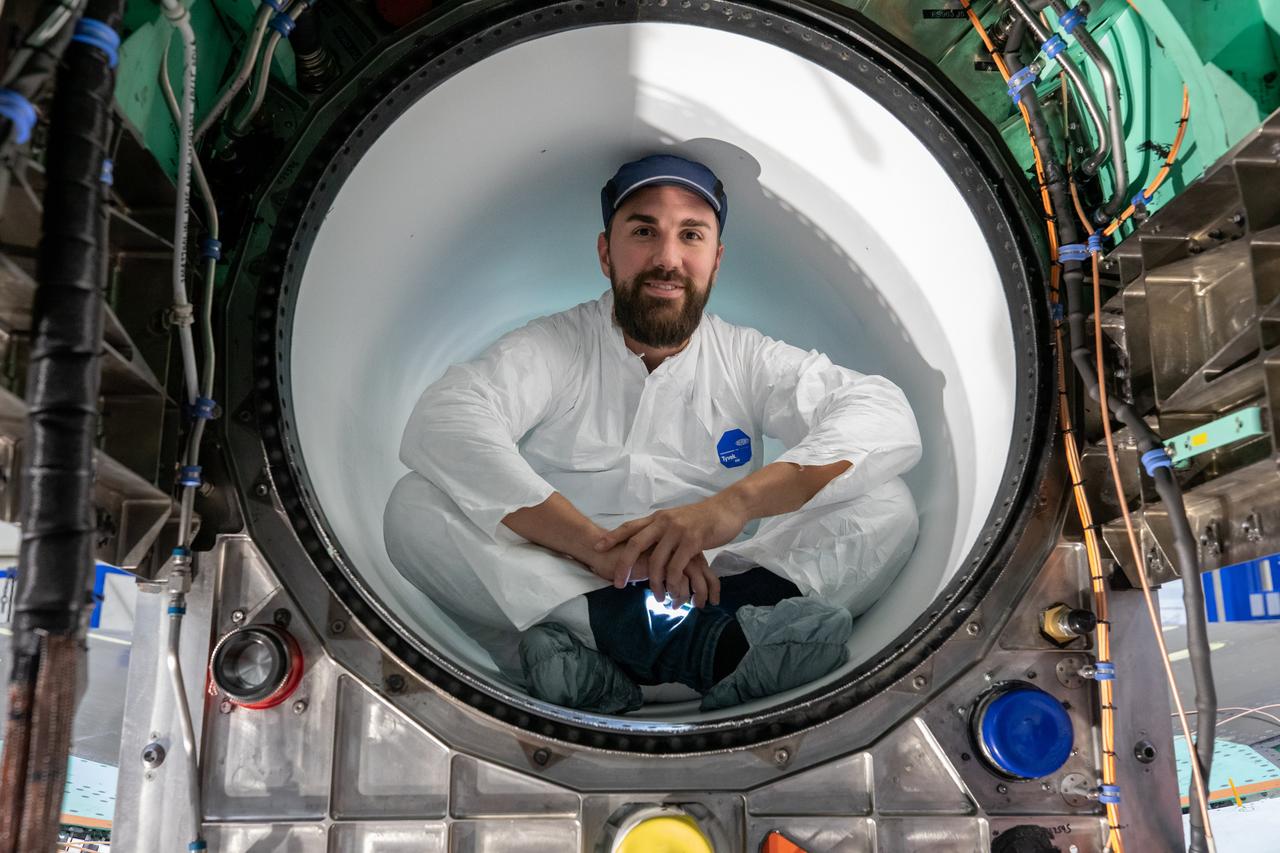

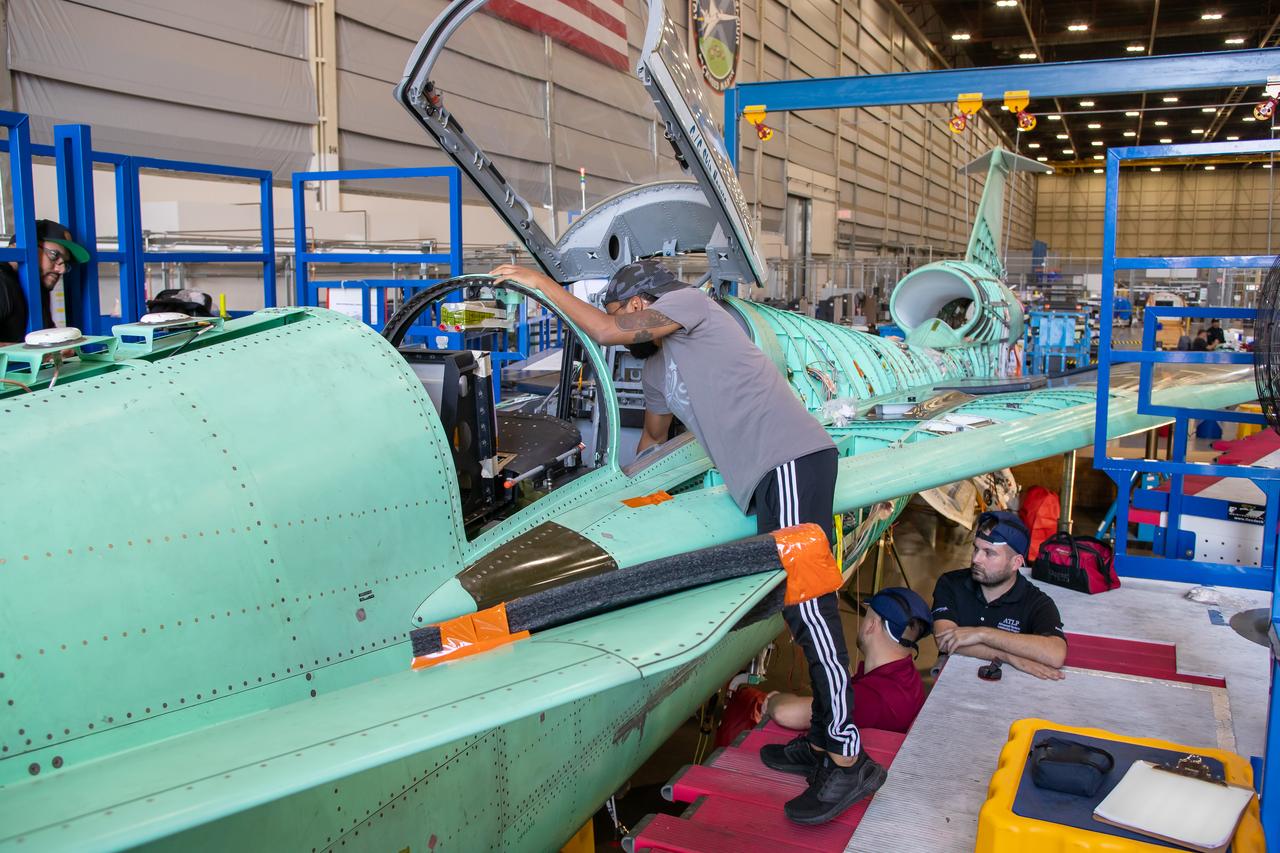
A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician takes a break for a photo. Note that the technician is wearing protective clean gear while sitting inside the X-59 engine inlet. Wearing this gear reduces the chance of any foreign objects from damaging the engine inlet.

Event: Horizontal Stabilator Install The Low Boom Flight Demonstrator manufacturing team installed the horizontal stabilizers to the aircraft. These are used along with the flight control computers to keep the airplane flying safely and providing the pitch control so that the pilot can fly the missions envisioned for the X-59.
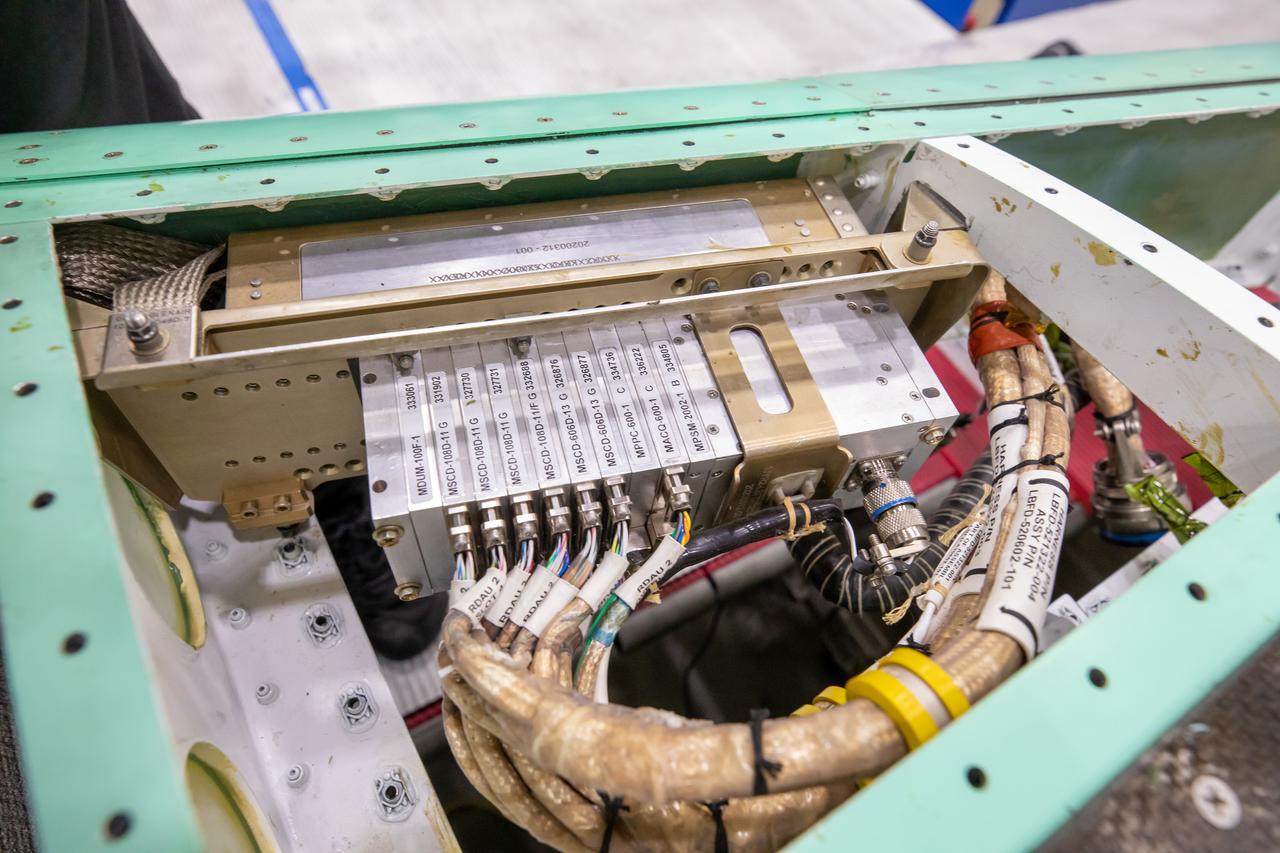
Here is a closeup of some of the X-59’s wiring and instrumentation system. Displayed here is the remote instrumentation encoder, which can be found in the wing of the aircraft. This encoder communicates with the plane’s other instrumentation systems like pressure and temperature sensors within the X-59.

Lockheed Martin technicians work to align and check the fastener holes on the X-59’s fuselage skin. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
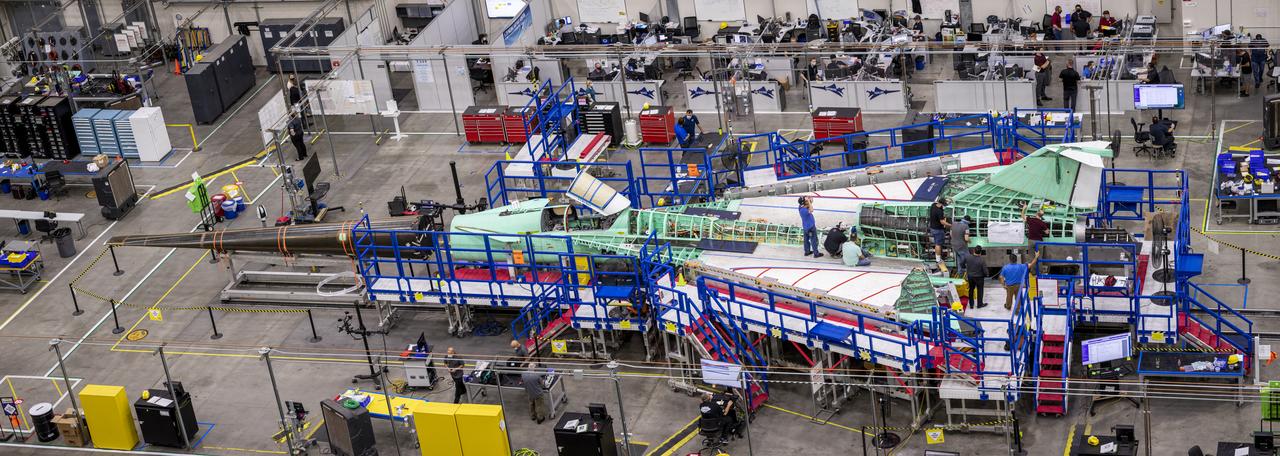

A panoramic side view of the left top of the X-59 supersonic plane with the tail on and the nose in the process of installation. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
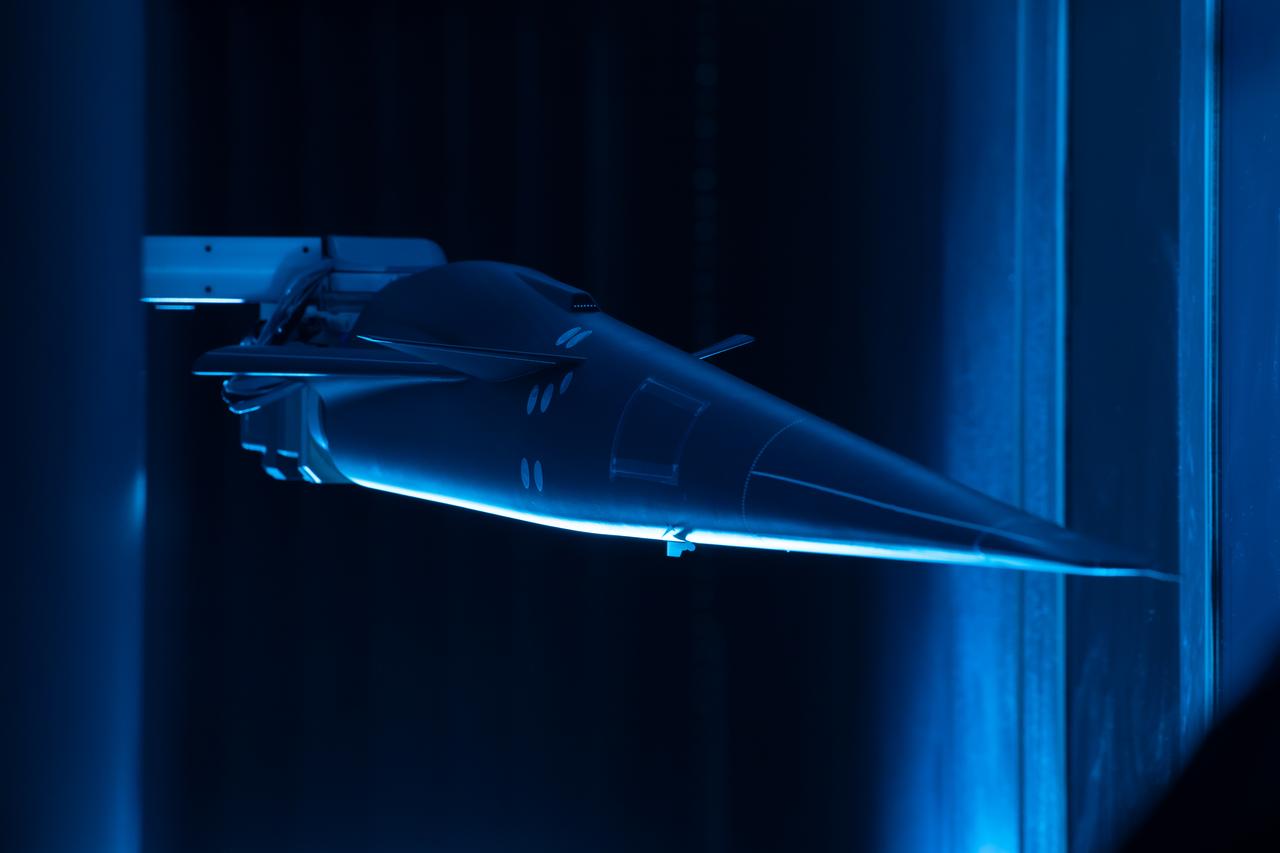

Event: Forebody and Nose - Windtunnel Testing A model of the X-59 forebody is shown in the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works’ wind tunnel in Palmdale, California. These tests gave the team measurements of wind flow angle around the aircraft’s nose and confirmed computer predictions made using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software tools. The data will be fed into the aircraft flight control system to tell the pilot the aircraft’s altitude, speed and angle. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land.
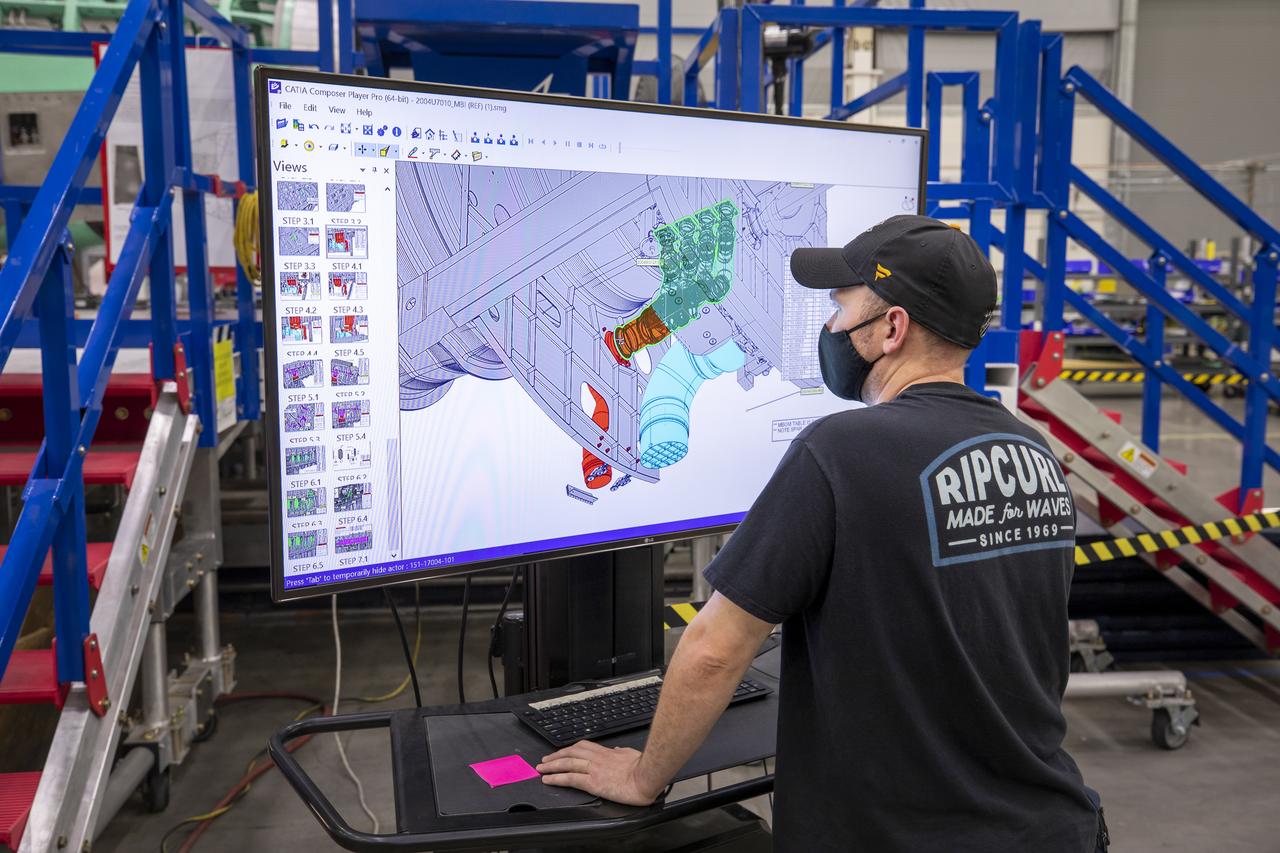

A Lockheed Martin technician looks at the connector installation on the cad model of the X-59 airplane. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
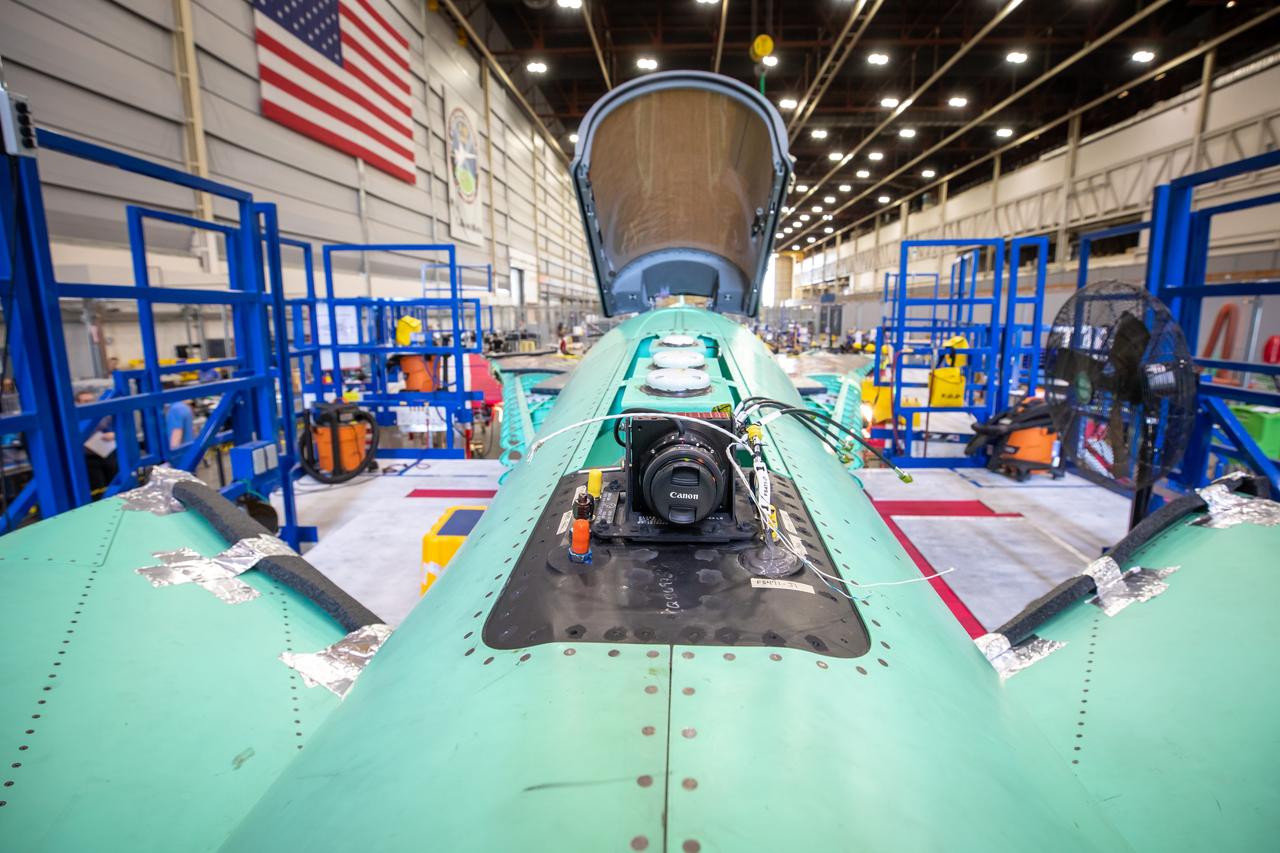

Event: Horizontal Stabilator Install A close up of the camera from the X-59’s eXternal Vision System. This camera is on the top of the X-59, but there will also be one on the belly of the aircraft. This visuals from this camera will be displayed on a 4K monitor for the pilot. As part of the supersonic shaping technology, the X-plane will not have a forward-facing window in the cockpit.
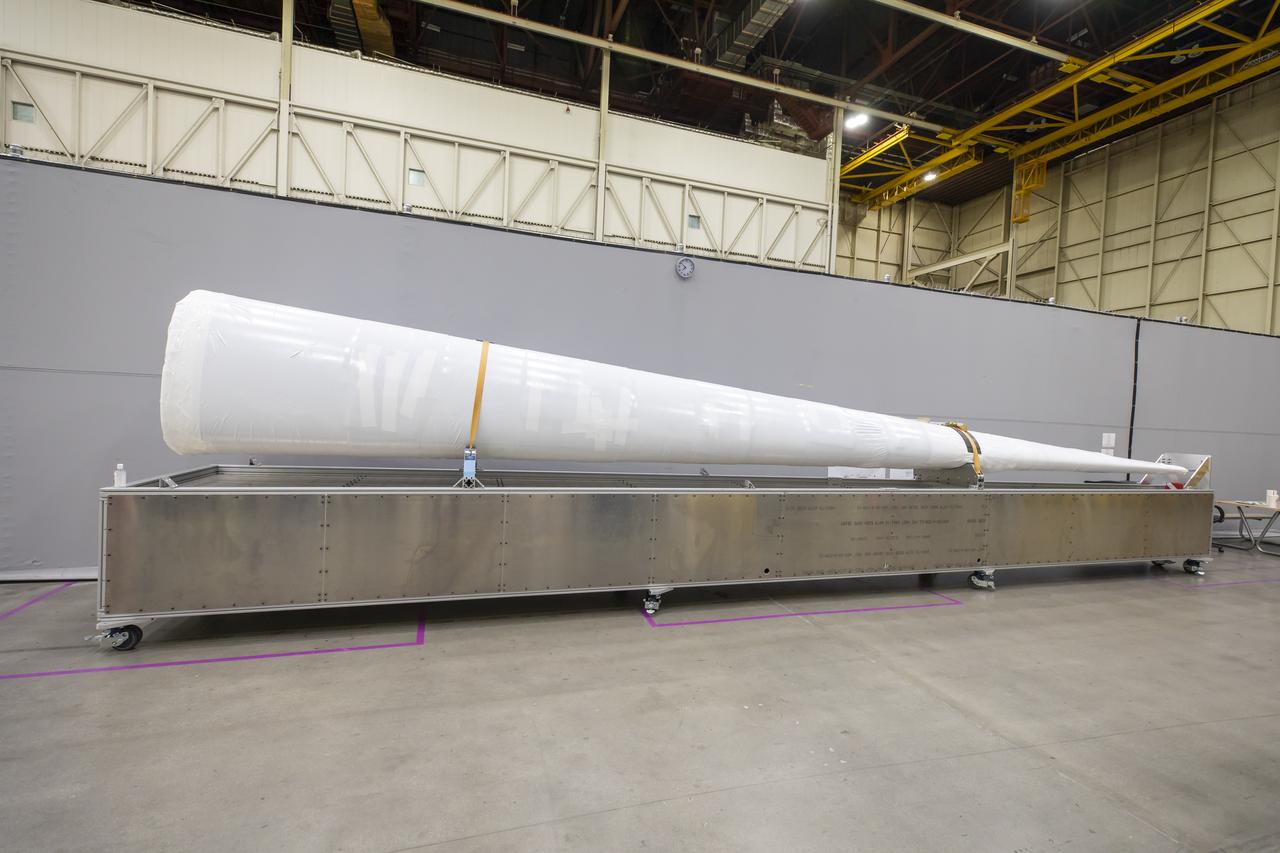

Event: SEG 230 Nose The X-59’s nose is wrapped up safely and rests on a dolly before the team temporarily attaches it to the aircraft for fit checks at Lockheed Martin in Palmdale, California. The full length of the X-plane’s nose is 38-feet – making up one third of the plane’s full length. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, once in the air will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
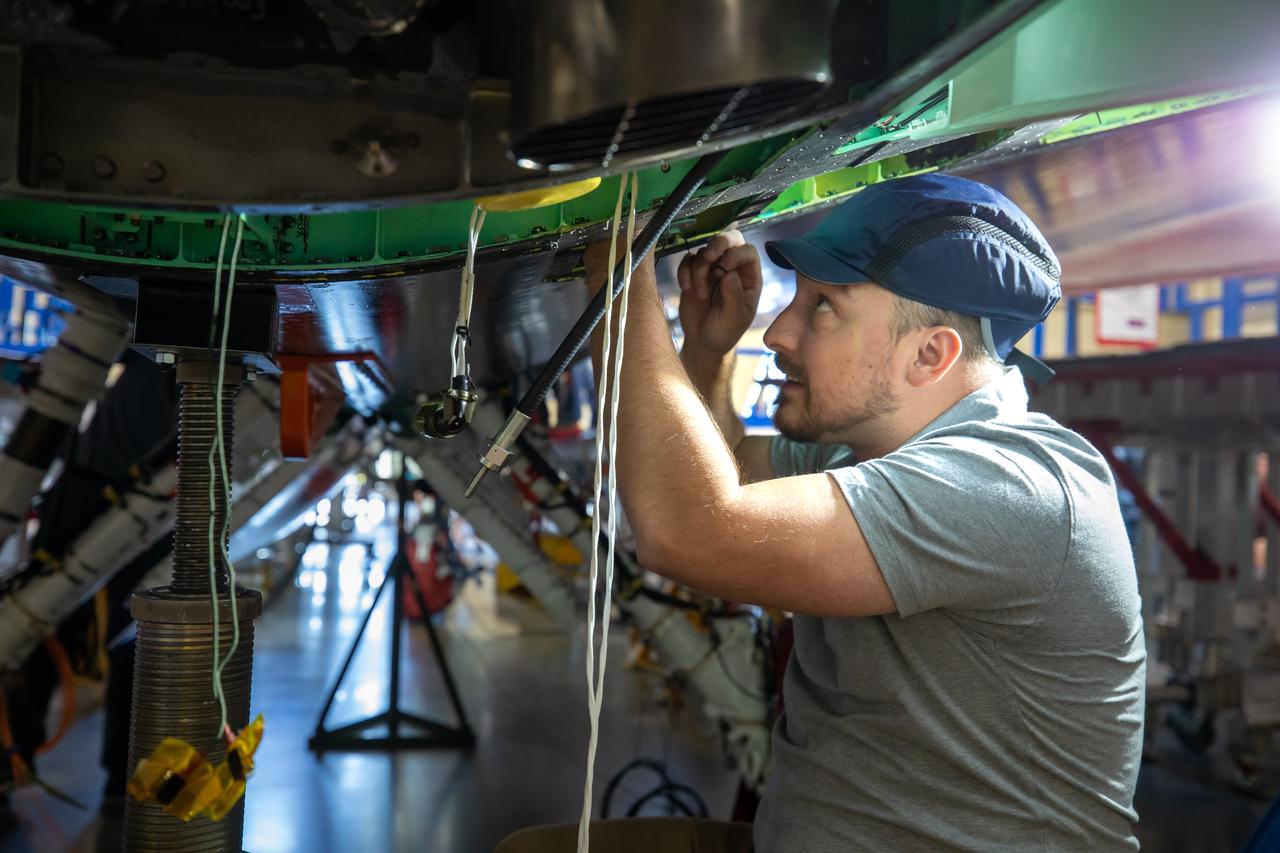

A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician works to complete wiring on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
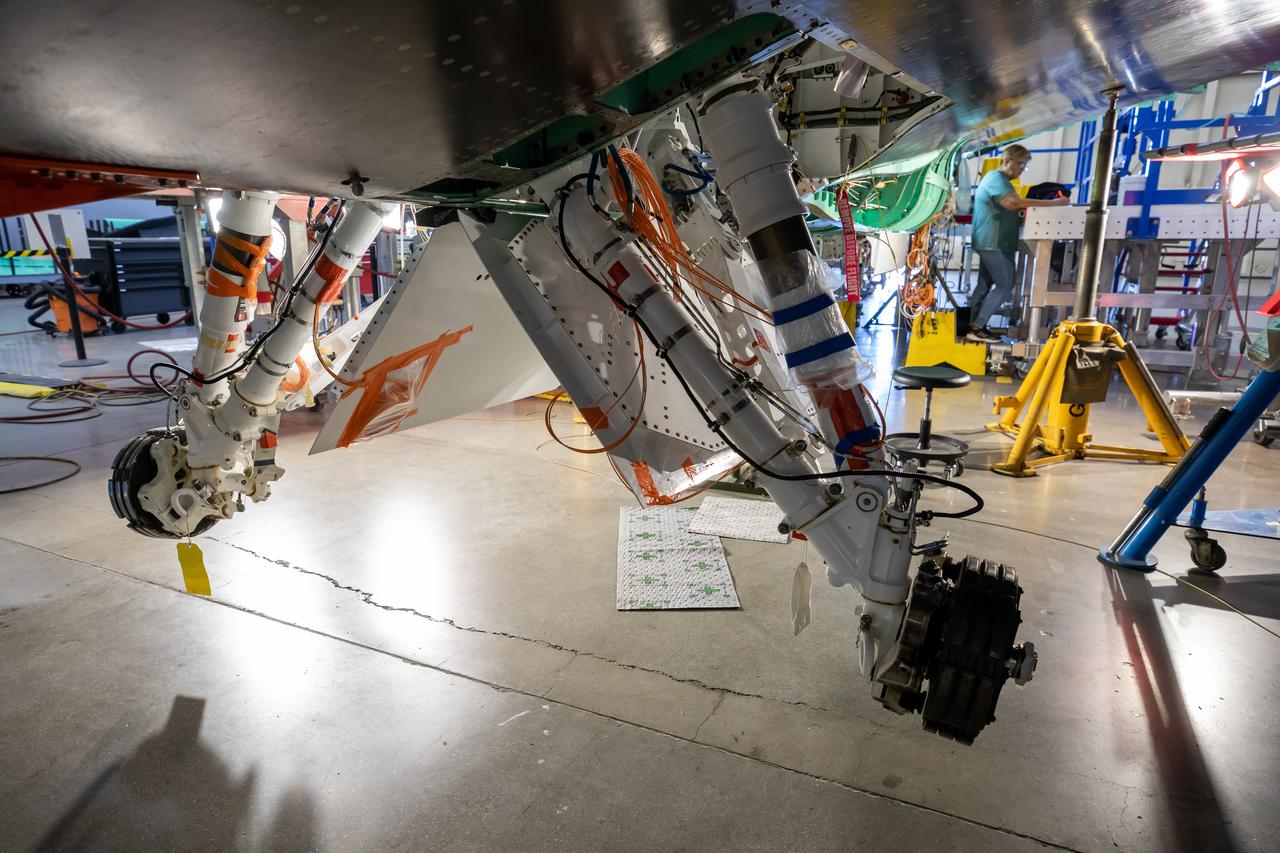

The Quesst team has repurposed the landing gear from an F-16 Fighting Falcon aircraft and is working on adjusting the fit onto the X-59 airplane. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
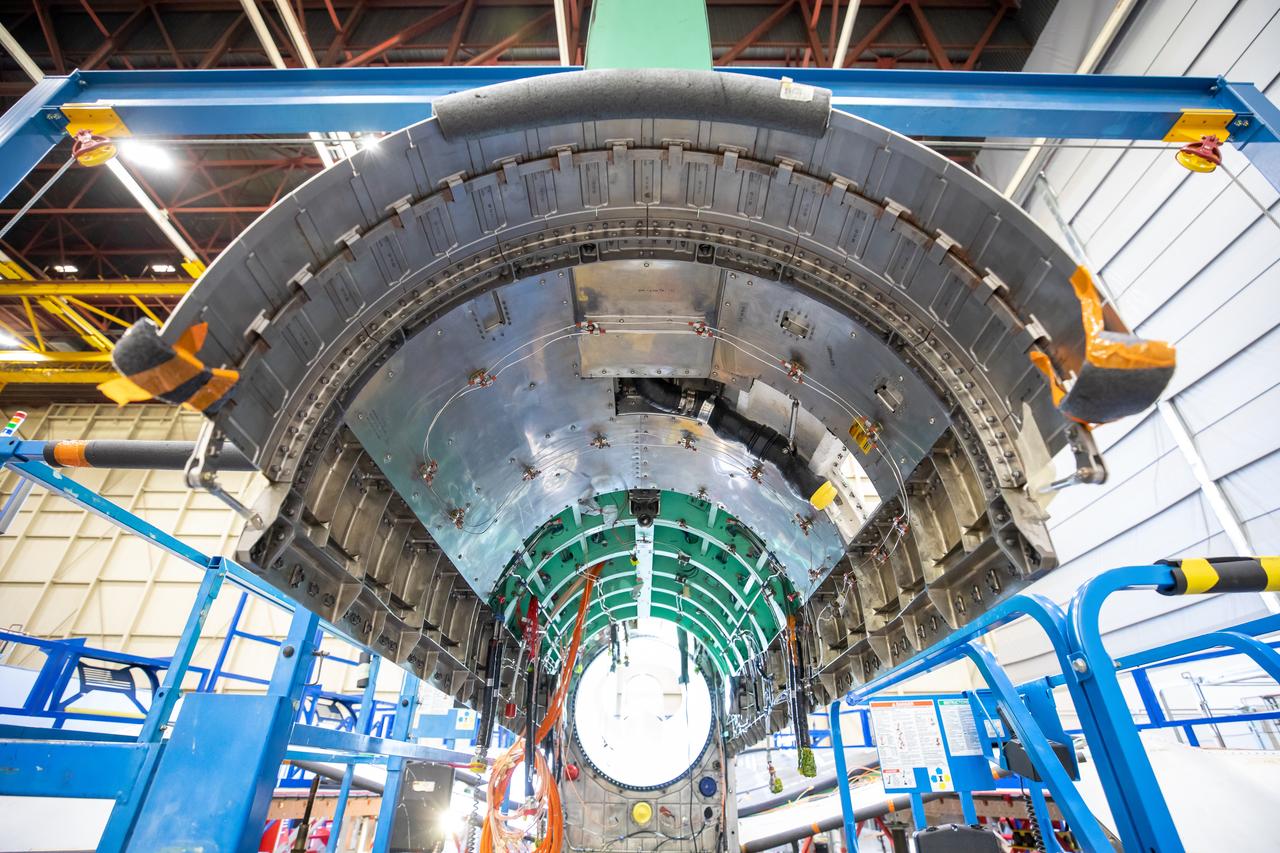

The upper empennage, or tail section of the plane, and engine bay is surrounded by a blue gantry that is used to assist with ground installation and removal of the X-59’s lower empennage and engine. Once fully assembled, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
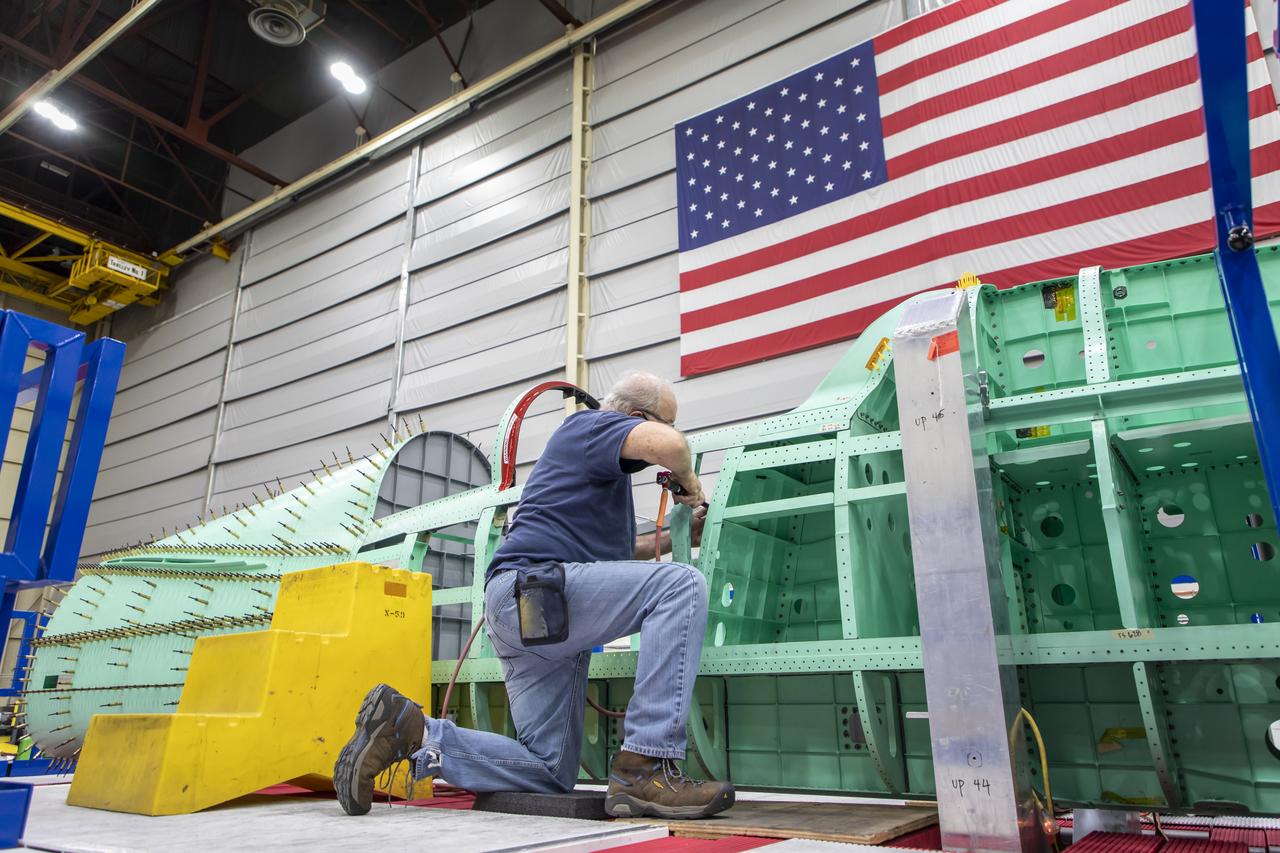

Event: SEG 210 Forebody A Lockheed Martin technician works on the ejection seat support structure and once complete, the ejection seat rails will be installed on the X-59 airplane. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
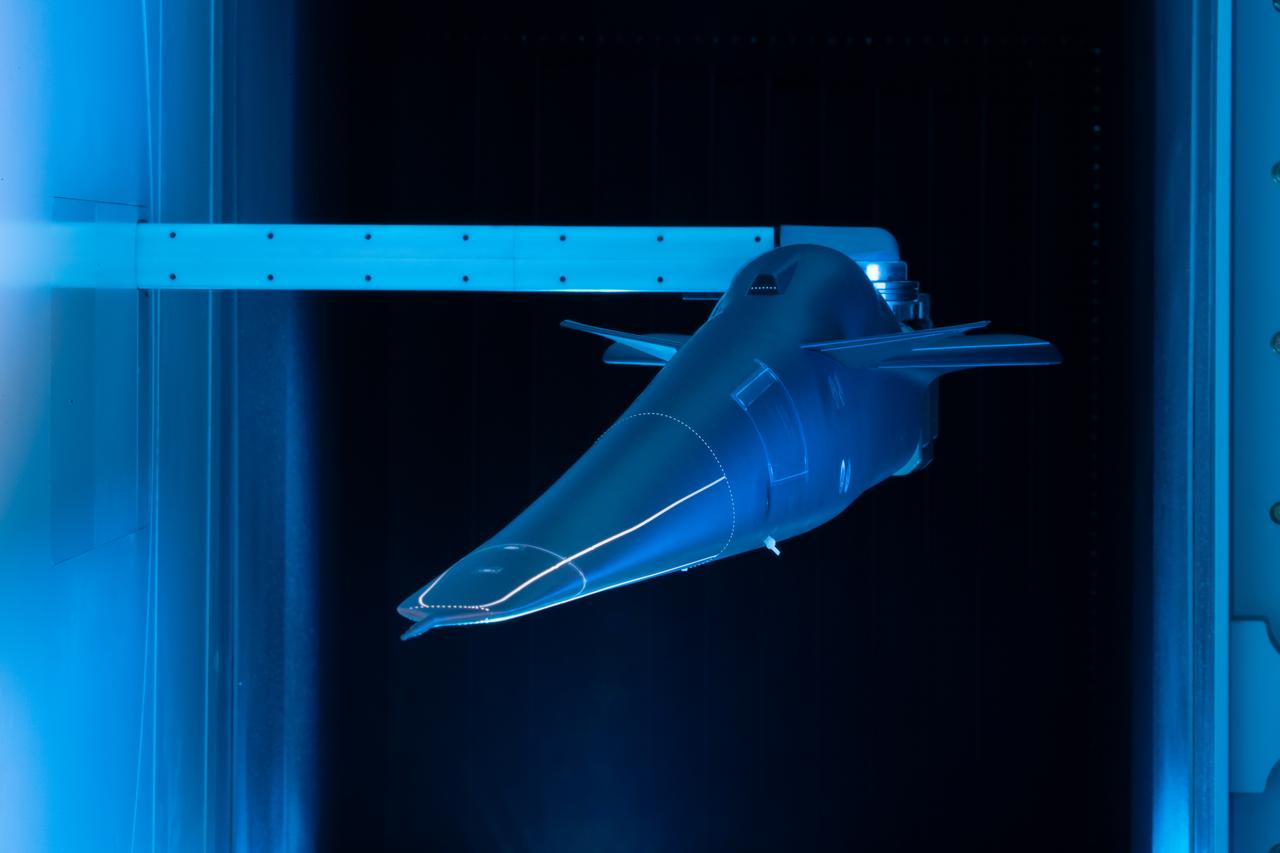

Event: Forebody and Nose - Windtunnel Testing A model of the X-59 forebody is shown in the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works’ wind tunnel in Palmdale, California. These tests gave the team measurements of wind flow angle around the aircraft’s nose and confirmed computer predictions made using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software tools. The data will be fed into the aircraft flight control system to tell the pilot the aircraft’s altitude, speed and angle. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land.
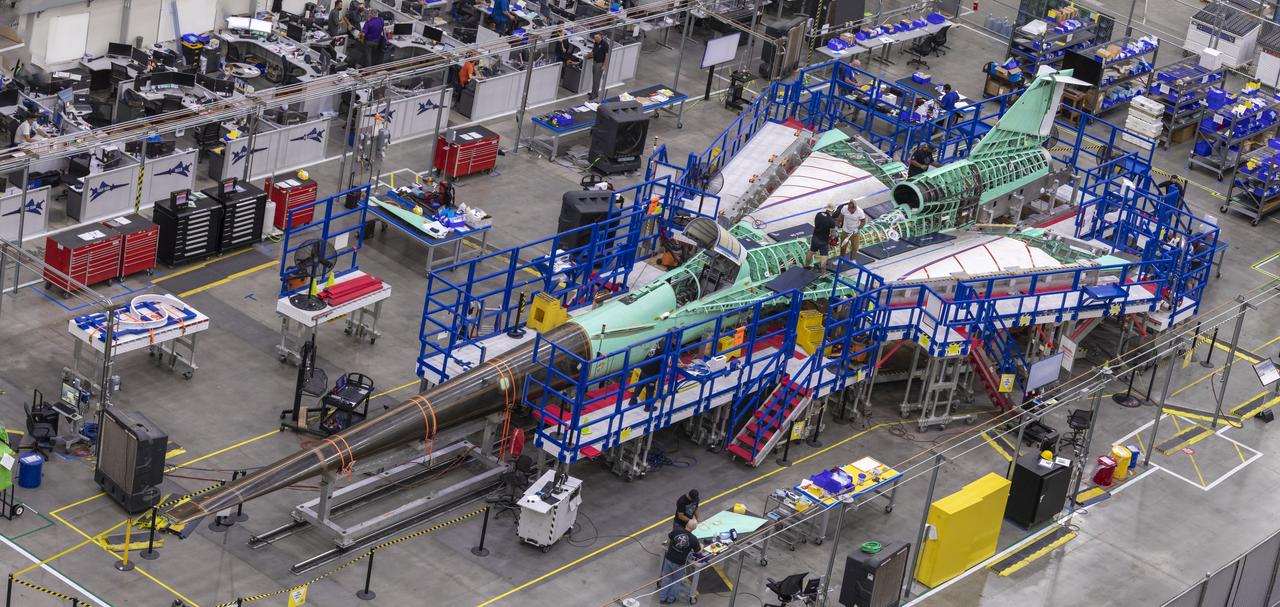

Event: Manufacturing Area From Above A overhead view of the X-59 with its nose on. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

Event: Horizontal Stabilator Install The Low Boom Flight Demonstrator manufacturing team installed the horizontal stabilizers to the aircraft. These are used along with the flight control computers to keep the airplane flying safely and providing the pitch control so that the pilot can fly the missions envisioned for the X-59.
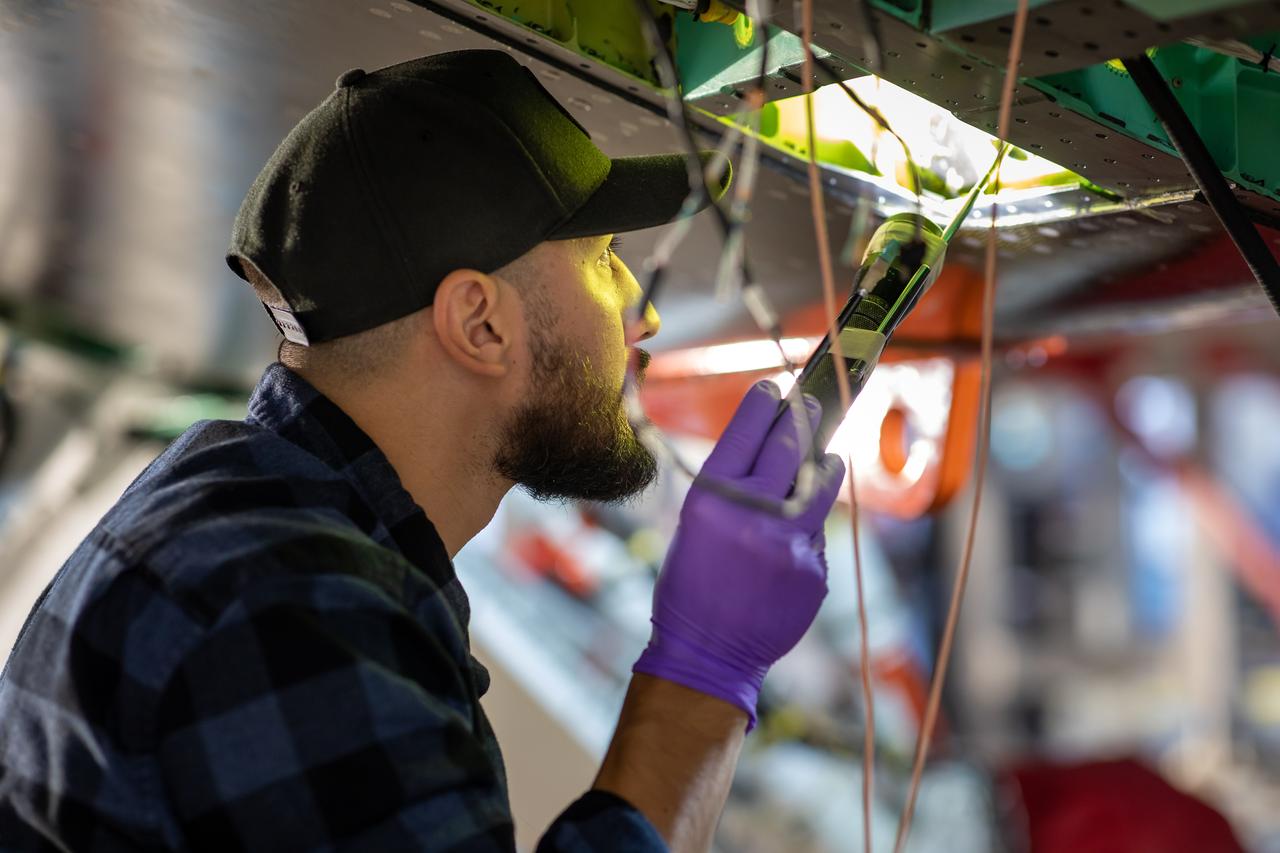

A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician inspects some of the wiring and sensors on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the first power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.

Here is an image of the X-59’s 13-foot General Electric F414 engine as the team prepares for a fit check. Making sure components, like the aircraft’s hydraulic lines, which help control functions like brakes or landing gear, and wiring of the engine, fit properly is essential to the aircraft’s safety. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
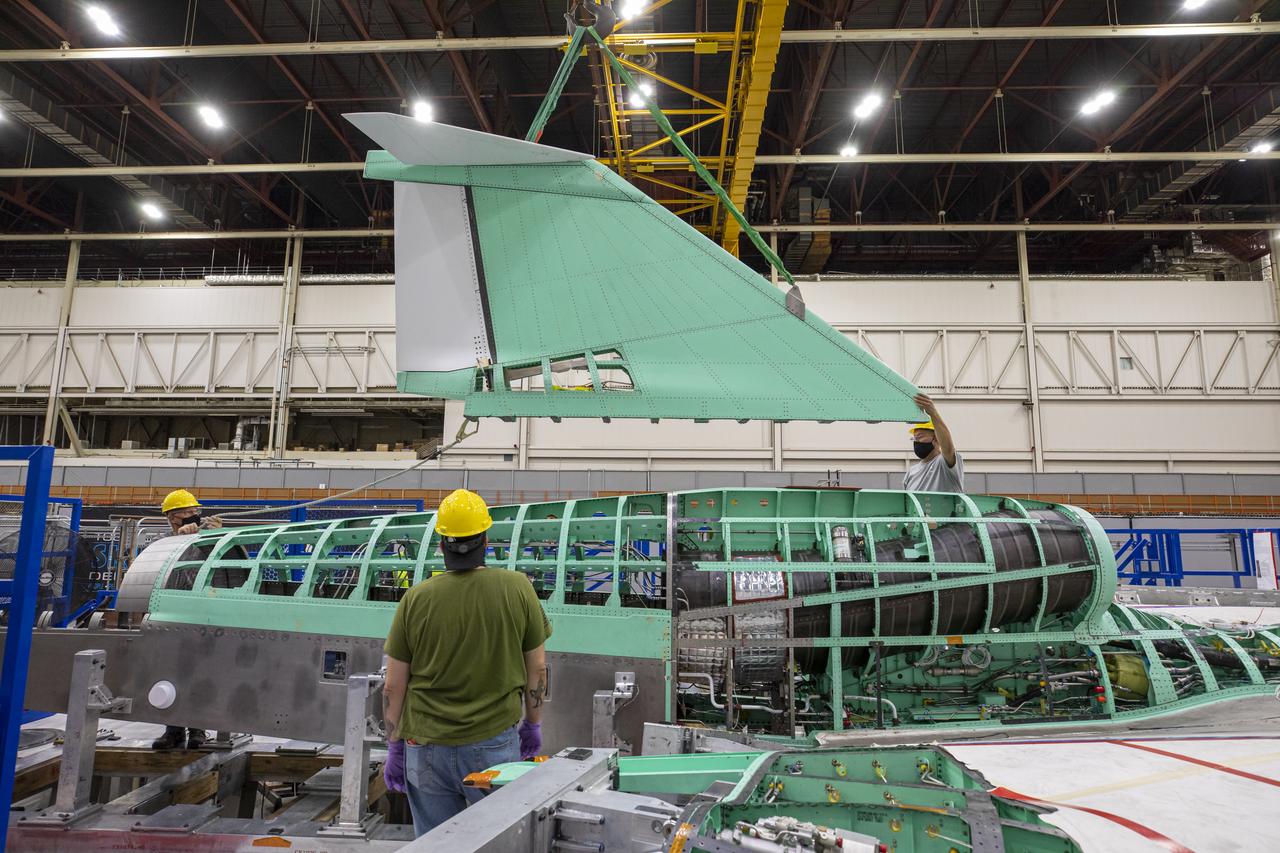

Event: SEG 570 Vertical Tail Assembly - Final Install Lockheed Martin technicians work on a fit check and installation of the vertical tail onto the X-59 aircraft. The plane is under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
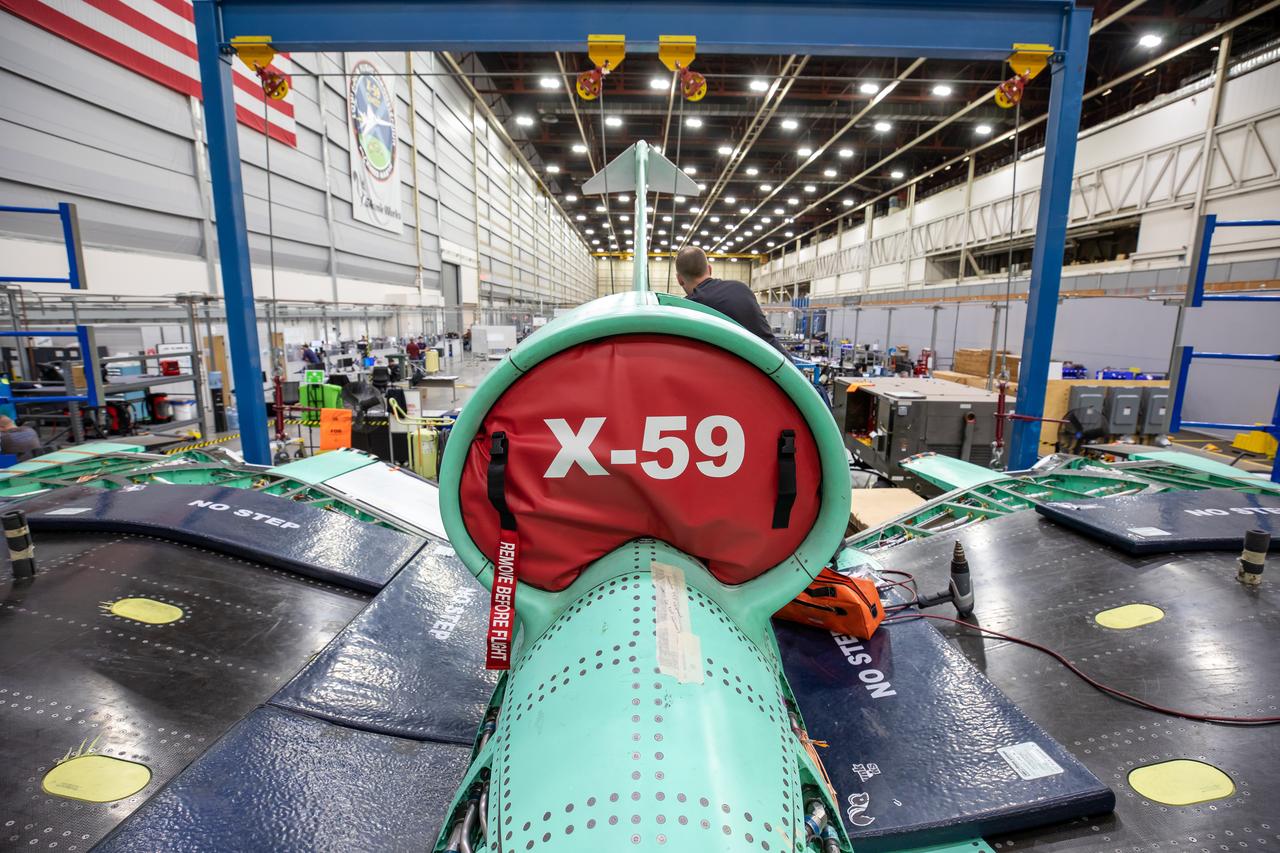

This is an image of the X-59 inlet with a safety covering. The inlet’s purpose is to adjust air speeds before they pass through the aircraft’s engine. The purpose of the covering is to protect the inlet and engine from foreign objects.
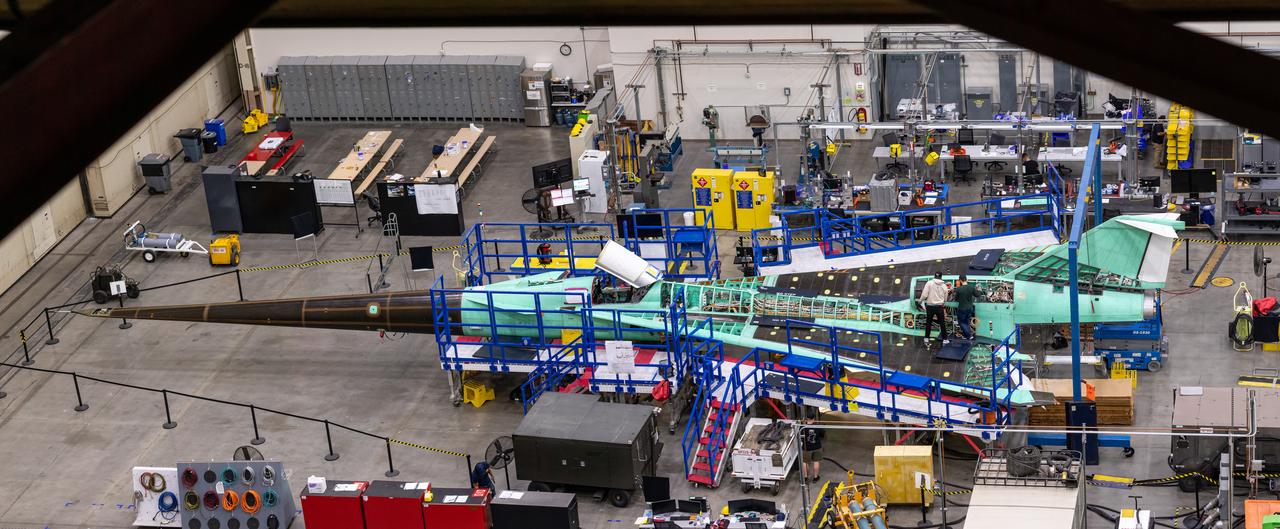

This is an overhead view of the X-59 aircraft at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The nose was installed, and the plane awaits engine installation. Technicians continue to wire the aircraft as the team preforms several system checkouts to ensure the safety of the aircraft. The X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
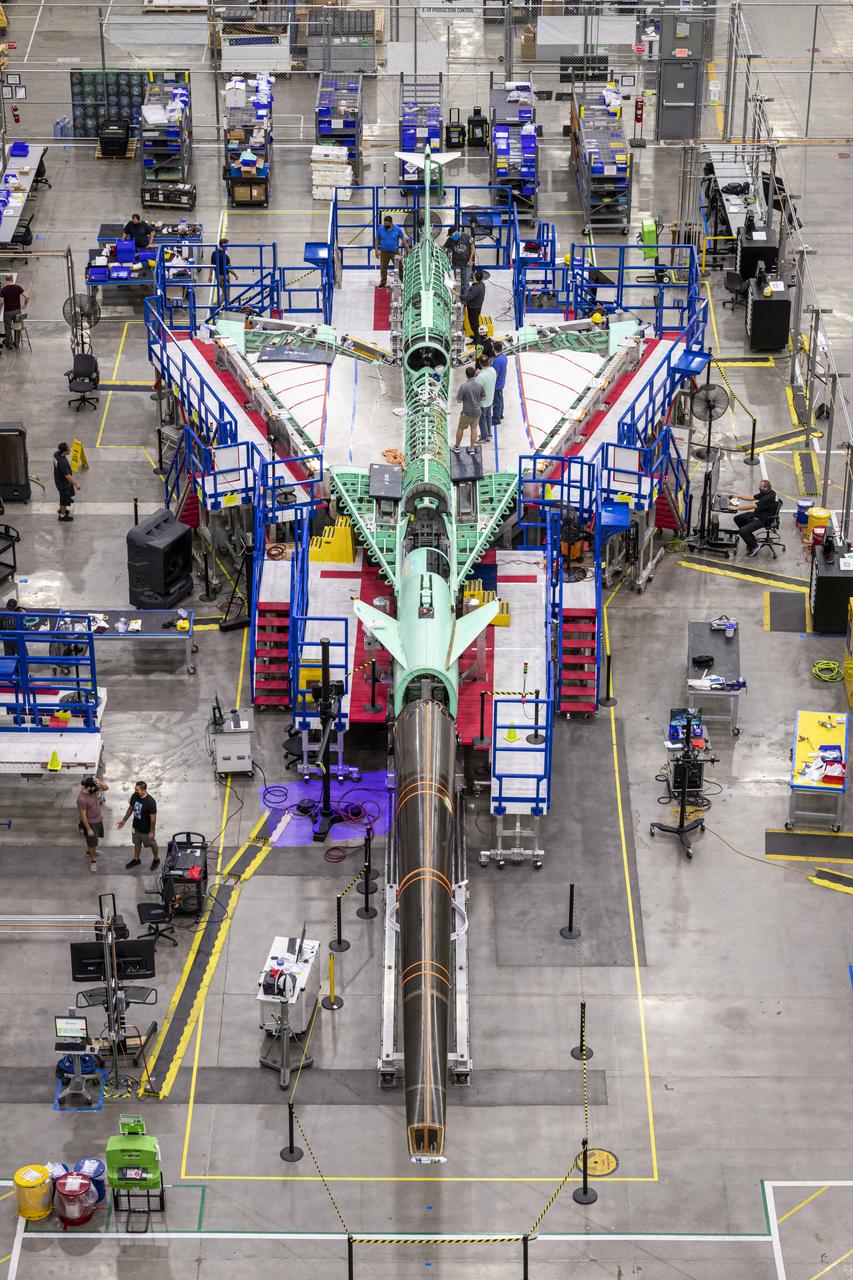

An overhead view of the X-59 supersonic plane with the tail on and the nose in the process of installation. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

Event: Horizontal Stabilator Install The Low Boom Flight Demonstrator manufacturing team installed the horizontal stabilizers to the aircraft. These are used along with the flight control computers to keep the airplane flying safely and providing the pitch control so that the pilot can fly the missions envisioned for the X-59.
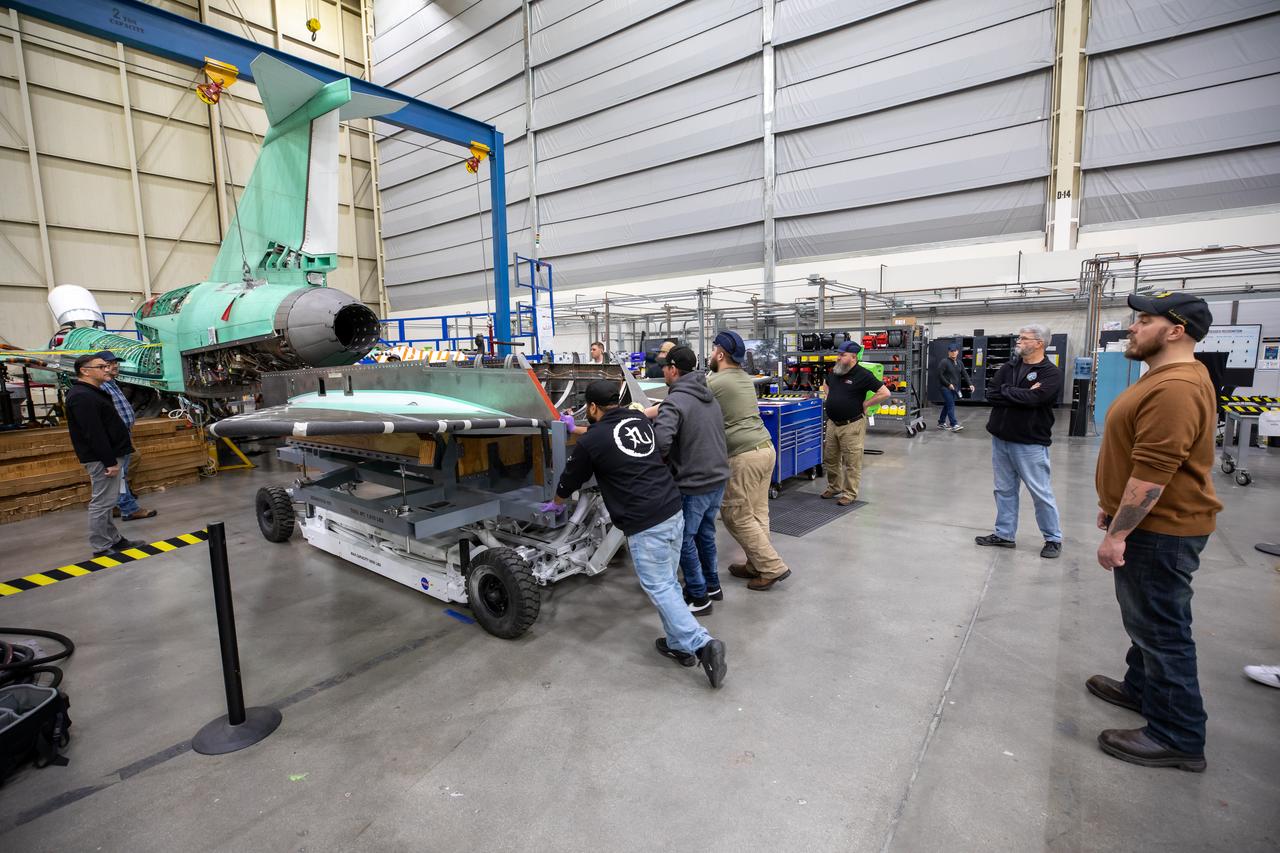

The X-59 team at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, load the lower empennage - the tail section - into place. The surfaces used to control the tilt of the airplane are called stabilators and are connected to the lower empennage. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which could help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
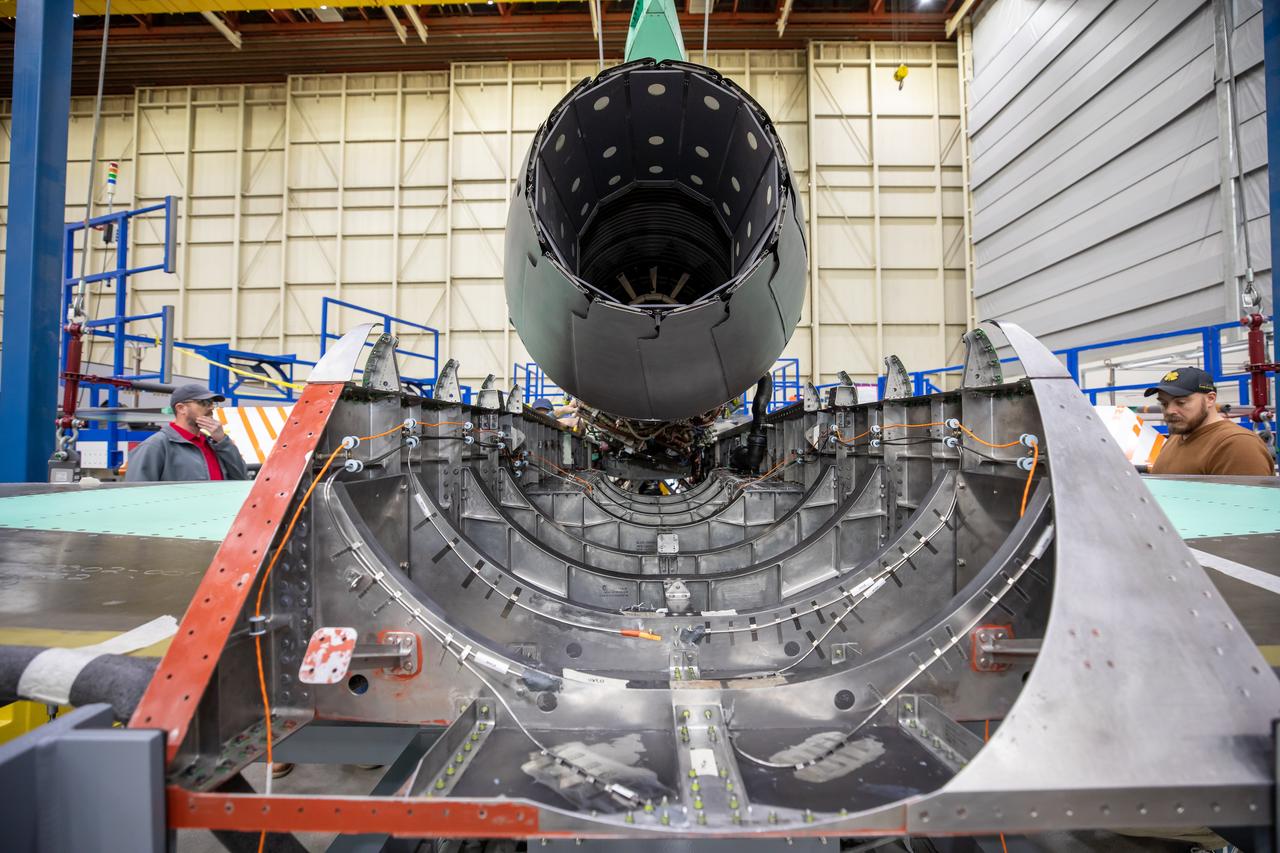

Here is a close-up of the GE F414 engine, from the aft deck or rear, before the tail section of the X-59 is lifted into place and attached to the aircraft. The aft deck helps control the shockwaves at the end of the aircraft and reduce the noise of a sonic boom to more of a sonic thump.

NASA test pilot, Nils Larson, inspects the X-59 cockpit displays and lighting system during system checkouts. The External Vision System (XVS) is displayed on the top screen, and the avionics flight displays, which can show navigation information or aircraft status, are shown on the bottom two screens.
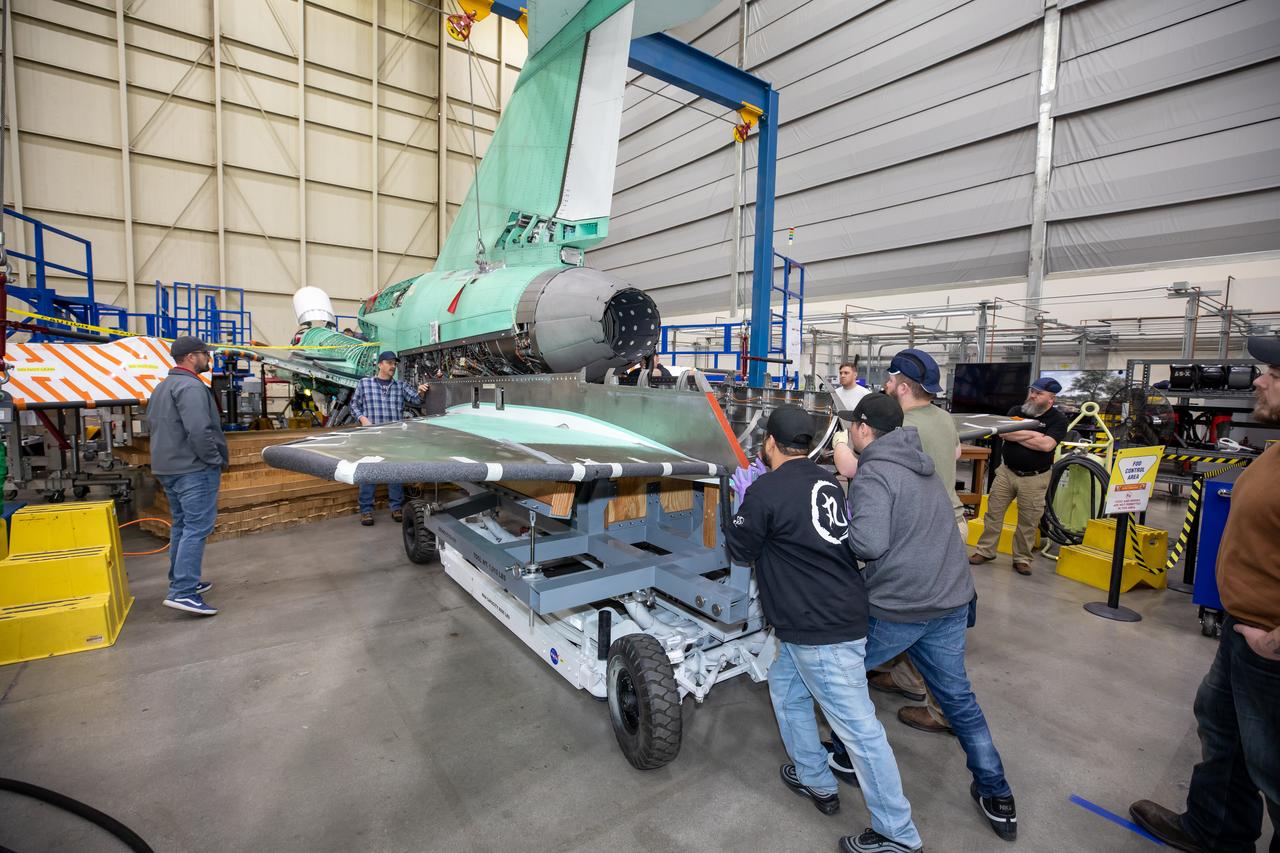

The X-59 team at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, load the lower empennage - the tail section - into place. The surfaces used to control the tilt of the airplane are called stabilators and are connected to the lower empennage. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which could help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
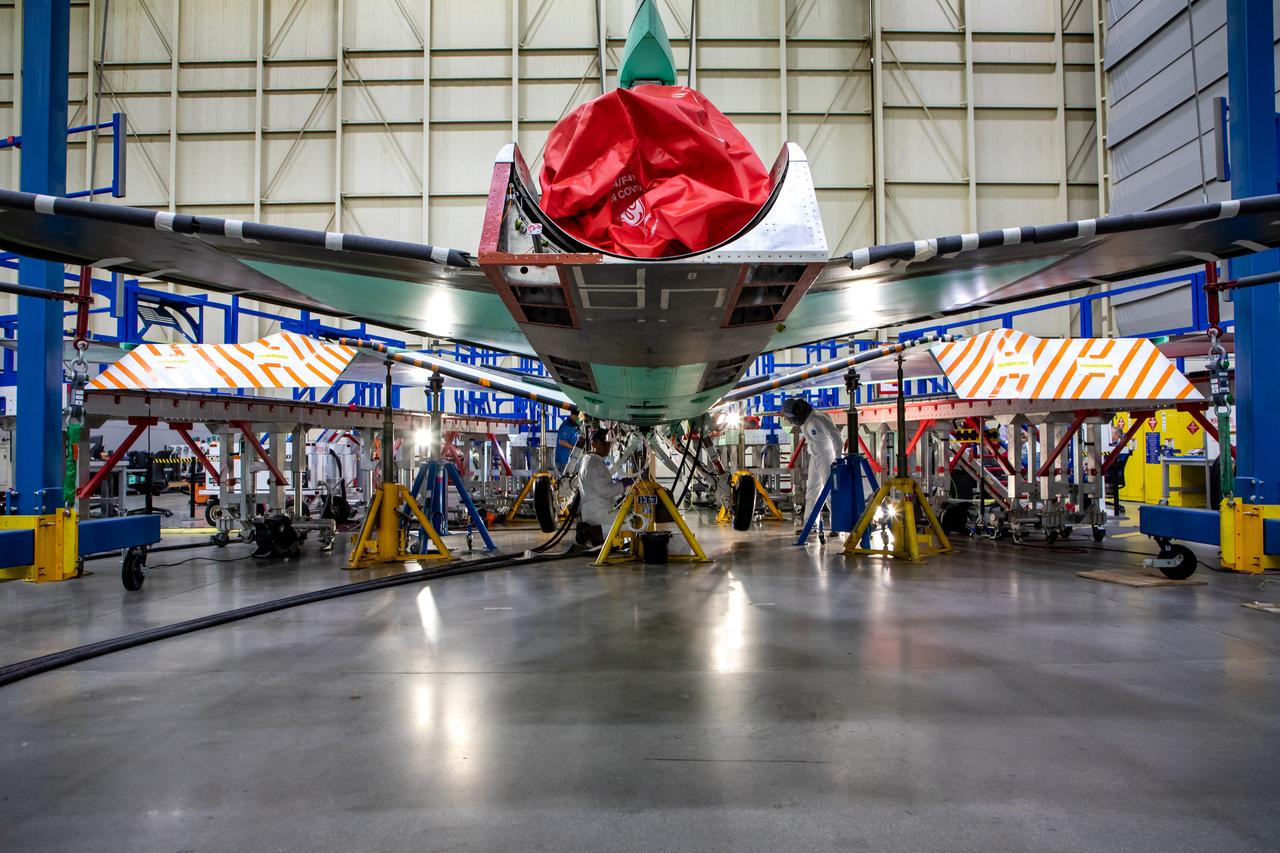

Technicians perform landing gear checkout testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. These tests make sure that all the parts of X-59’s landing gear and doors are working in the correct order. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which could help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
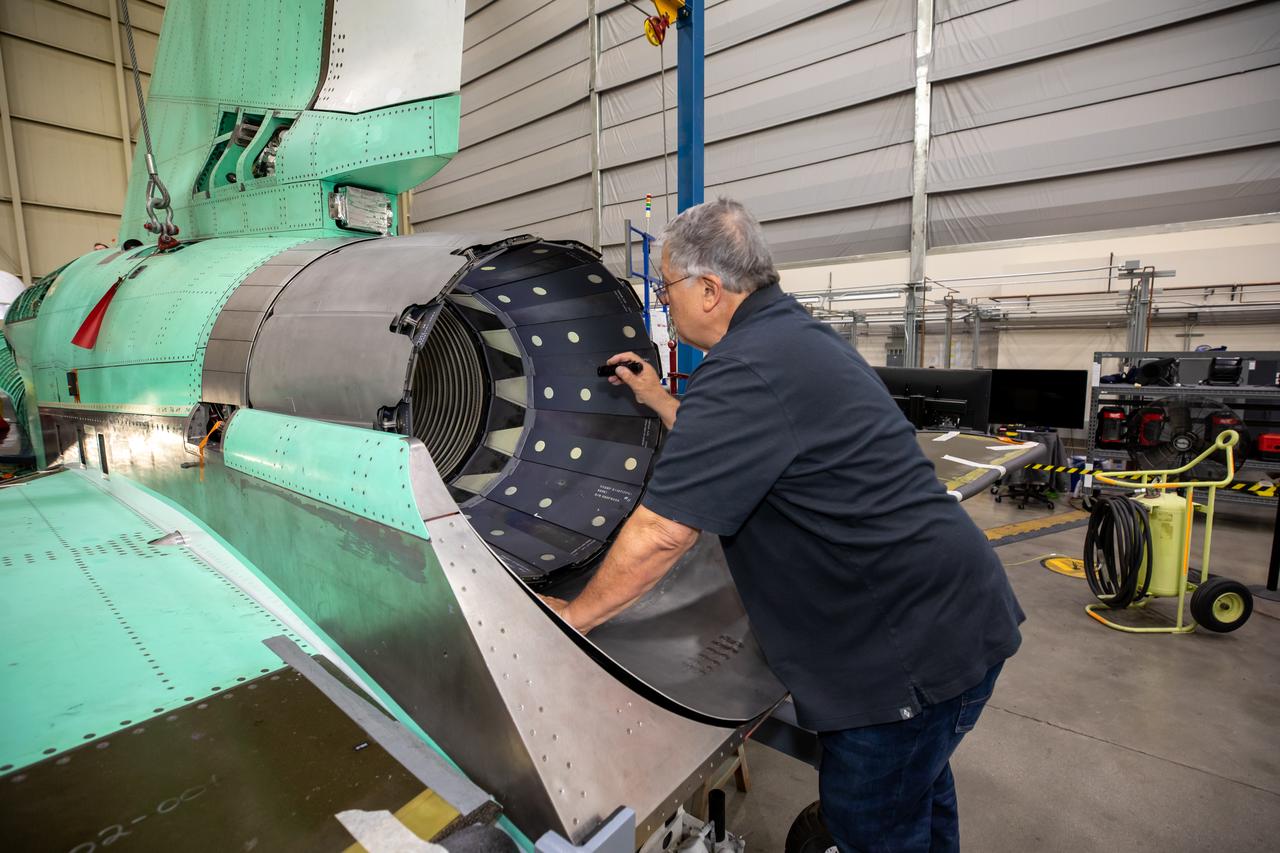

A quality inspector inspects the GE F-414 engine nozzle after installation at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Once the aircraft and ground testing are complete, the X-59 will undergo flight testing, which will demonstrate the plane’s ability to fly supersonic - faster than the speed of sound - while reducing the loud sonic boom. This could enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
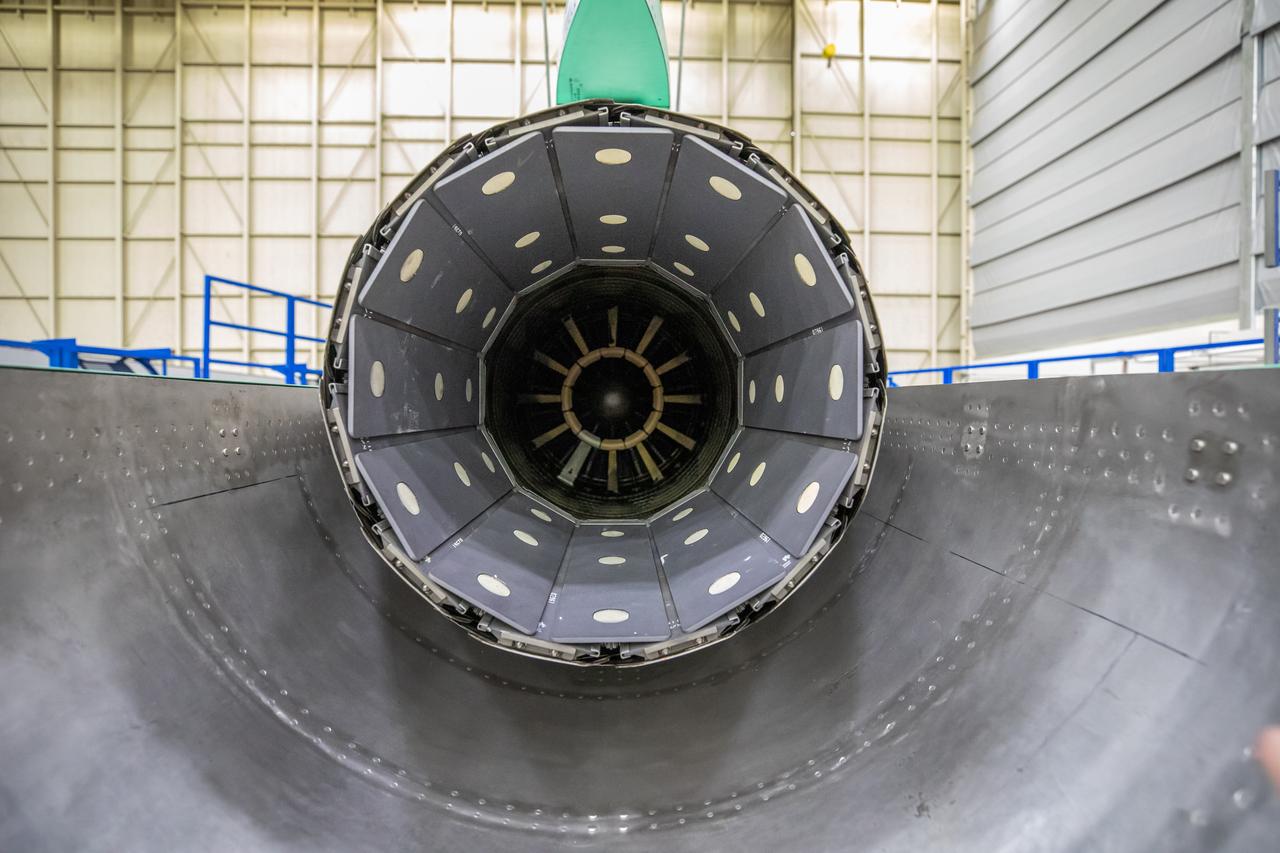

A look at the X-59’s engine nozzle, where the thrust -the force that moves the aircraft- will exit. Once complete, the X-59 is designed to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom. The Quesst mission could help change the rules for commercial supersonic air travel over land.
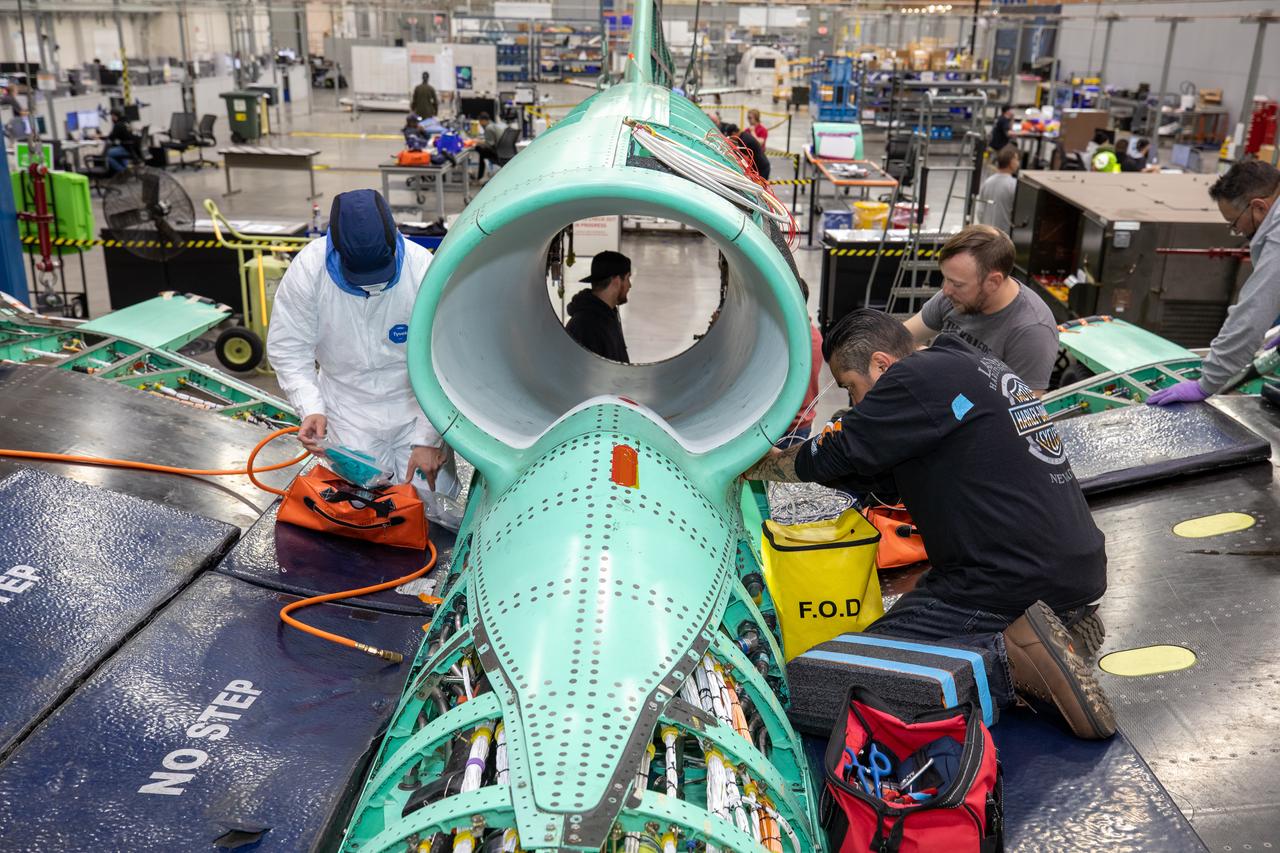

The X-59 team working on the aircraft’s wiring around the engine inlet prior to the engine being installed. Once complete, the X-59 is designed to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom. The Quesst mission could help change the rules for commercial supersonic air travel over land.
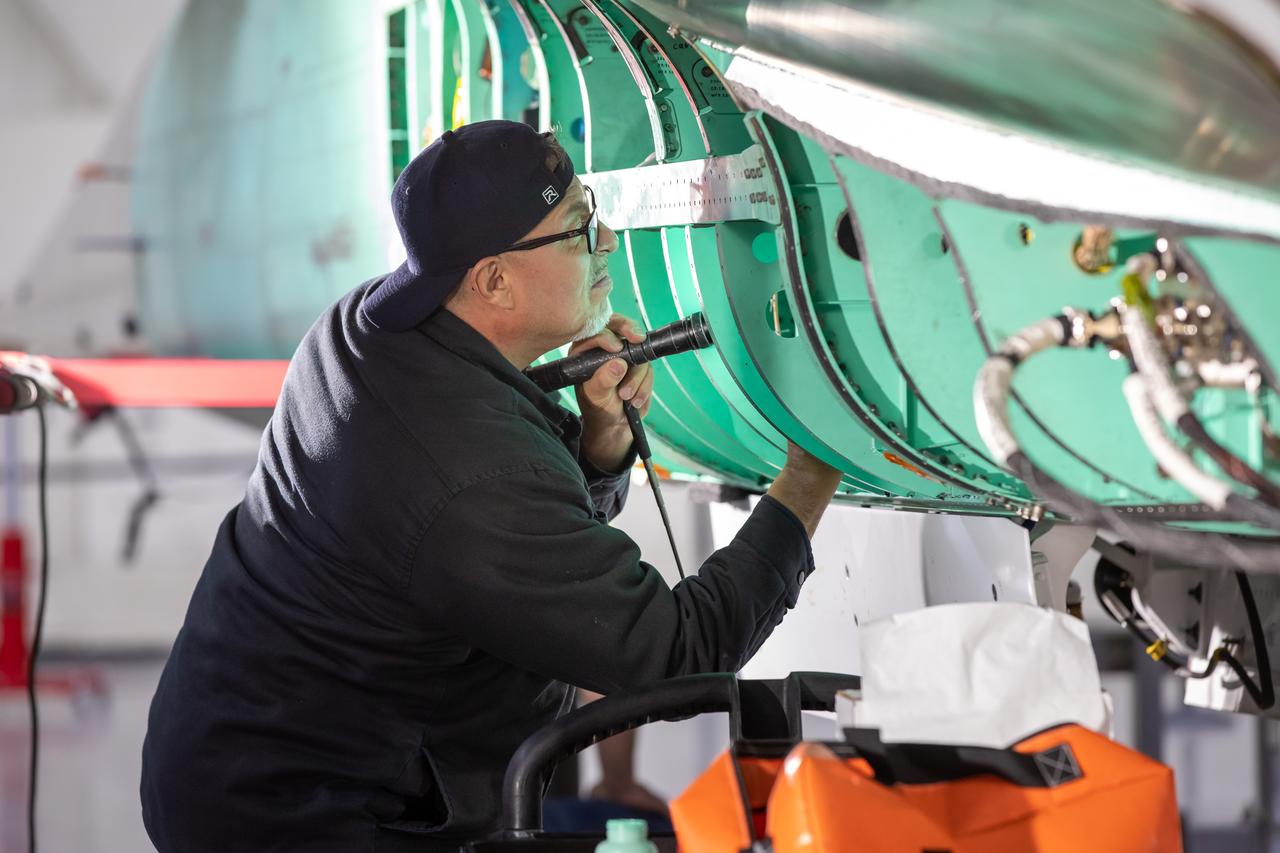

A quality inspector checks NASA’s X-59 aircraft during the construction phase. The X-59 was built in Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Once the aircraft and ground testing are complete, the X-59 will undergo flight testing, which will demonstrate the plane’s ability to fly supersonic - faster than the speed of sound - while reducing the loud sonic boom. This could enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
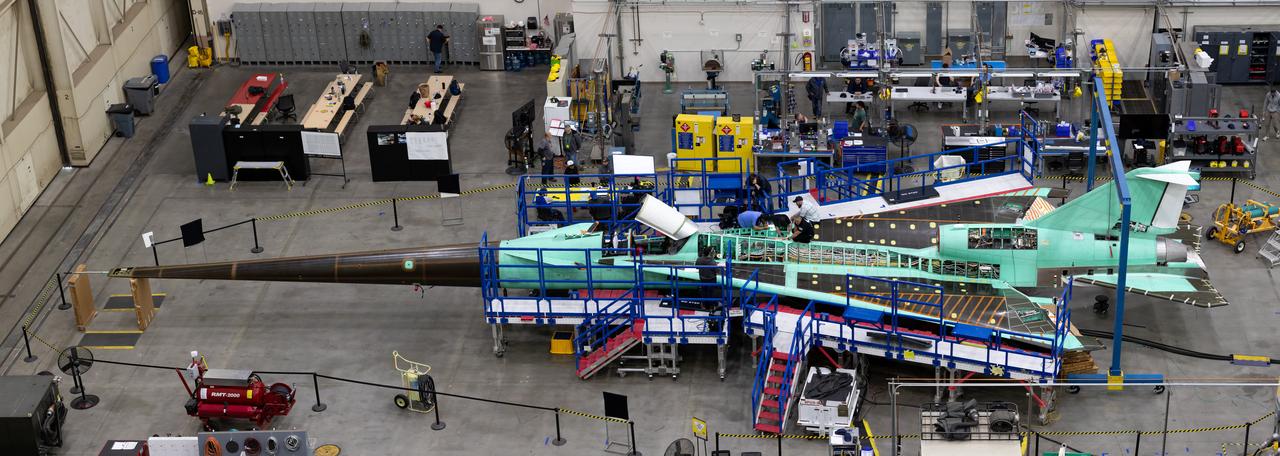

An overhead view of the X-59 during assembly in spring 2023. Assembly took place at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Once complete, the X-59 is designed to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom. The Quesst mission could help change the rules for commercial supersonic air travel over land.
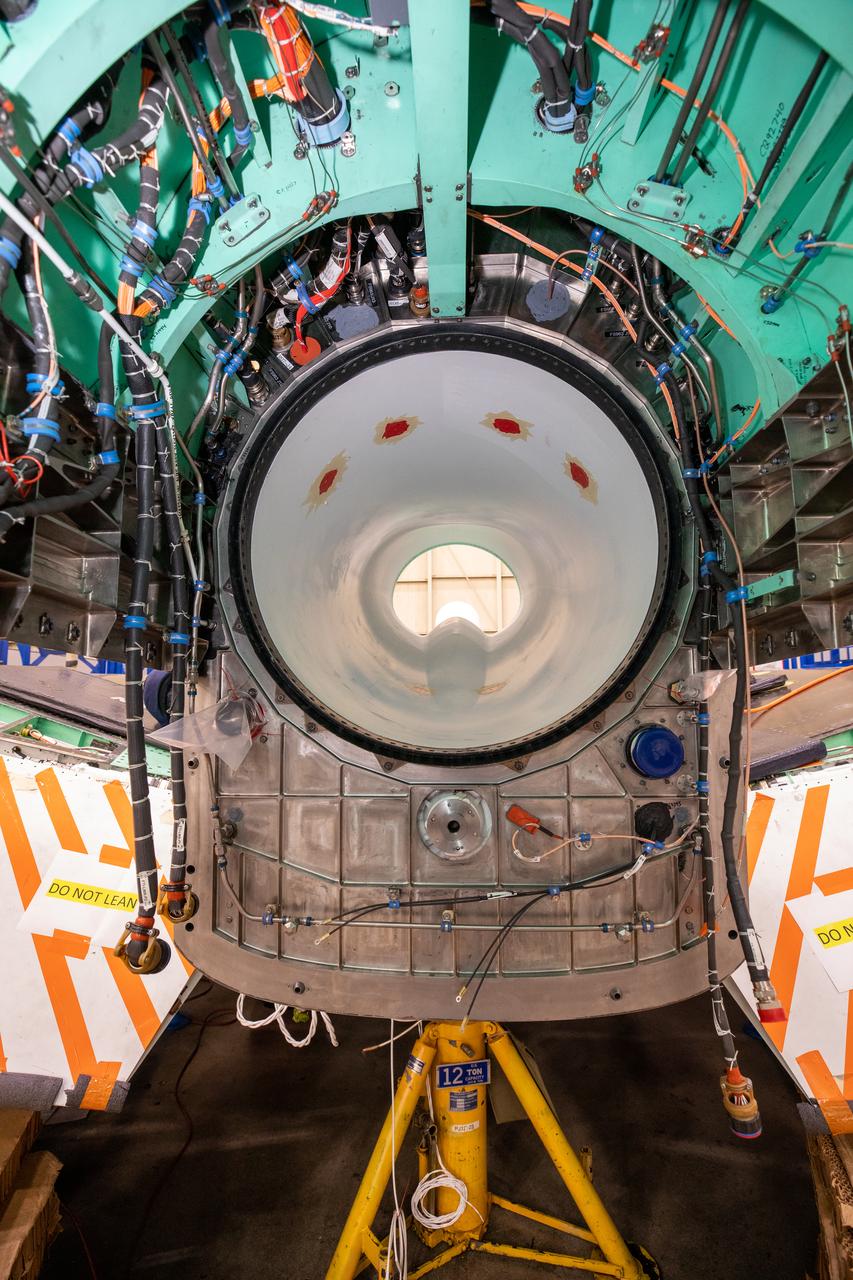

This image shows the X-59’s engine inlet from the aft view, which is the rear of the airplane, looking forward. Once the aircraft and ground testing are complete, the X-59 will undergo flight testing, which will demonstrate the plane’s ability to fly supersonic - faster than the speed of sound - while reducing the loud sonic boom. This could enable commercial supersonic air travel over land again.
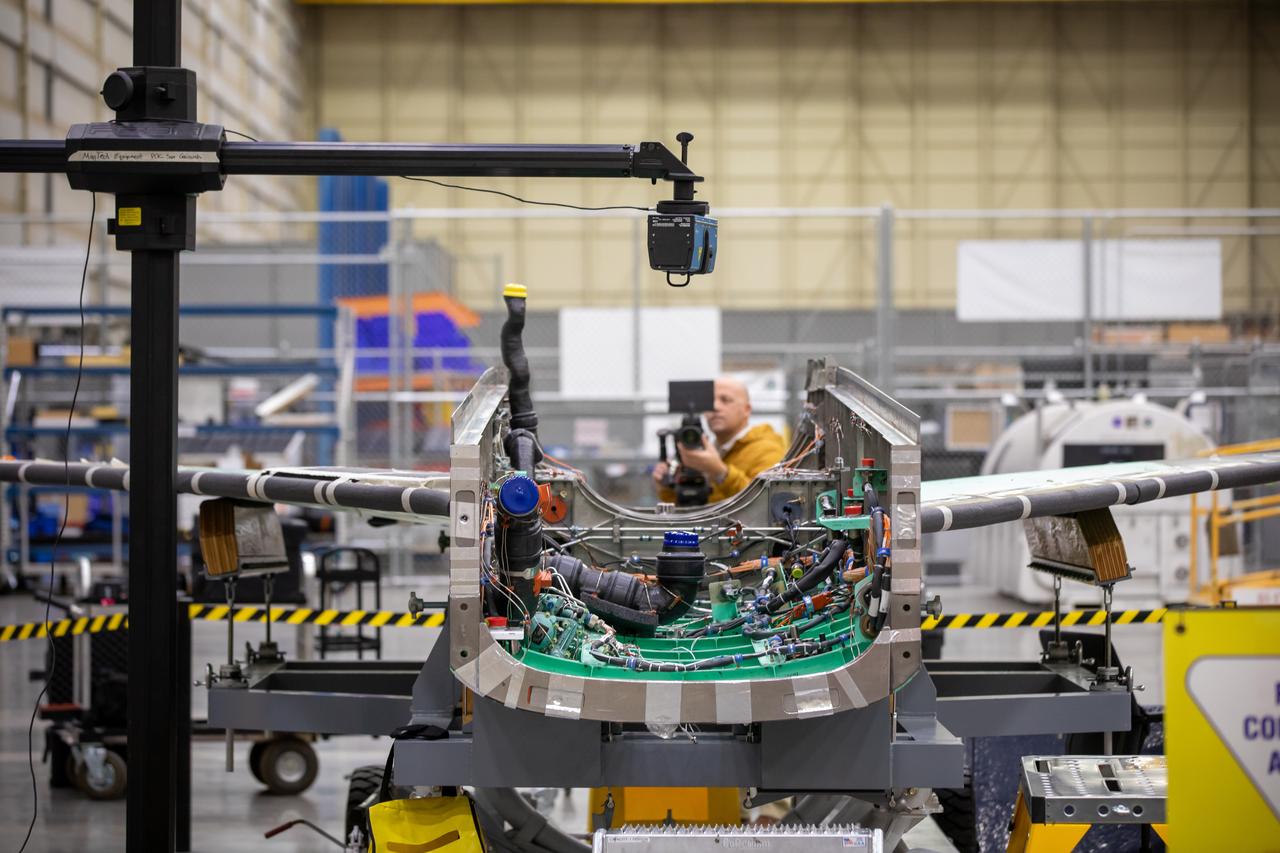

A laser scans the inside of the X-59 aircraft’s lower engine bay at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. These scans can help identify potential hardware or wiring interferences prior to the final installation of the engine and lower tail.
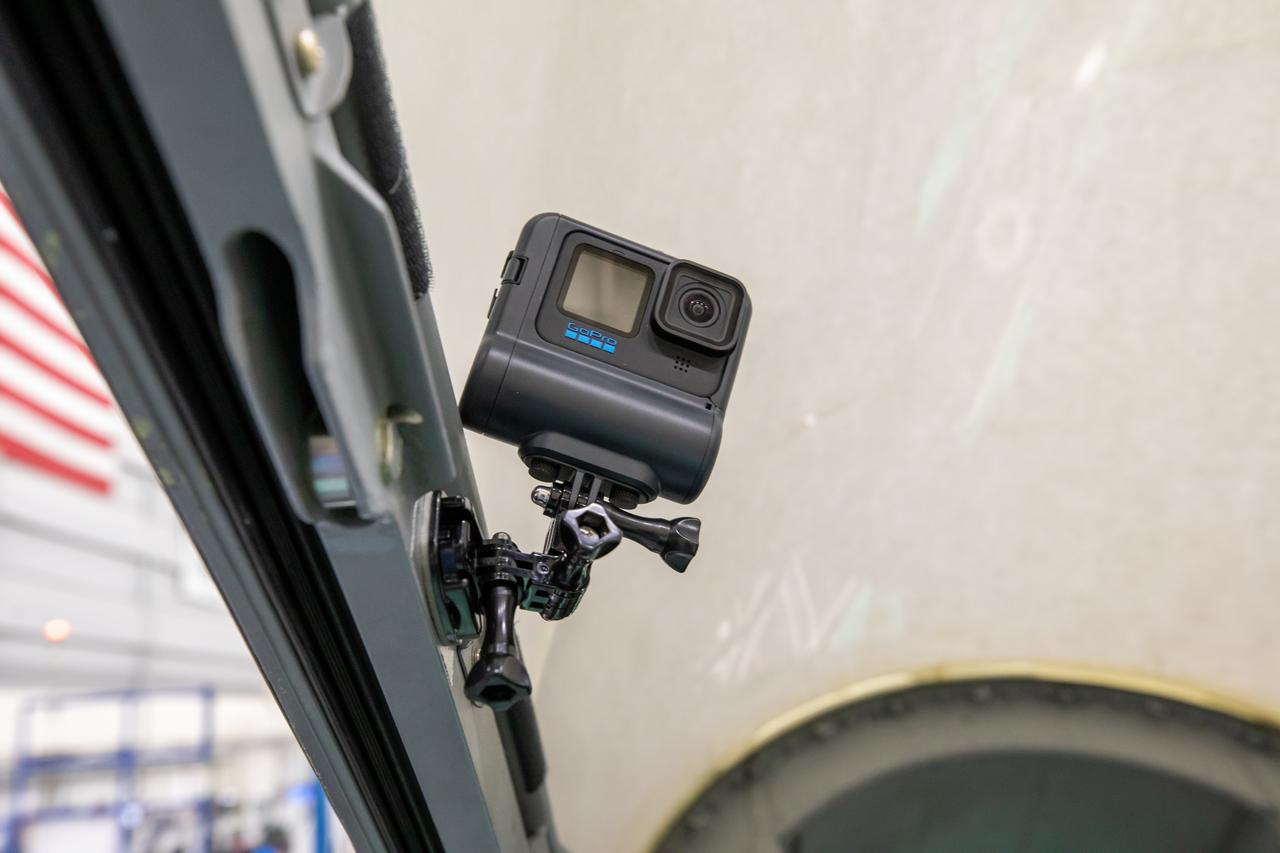

A Go-Pro is mounted on the inside of the X-59’s cockpit to capture the pilots activities during flight.
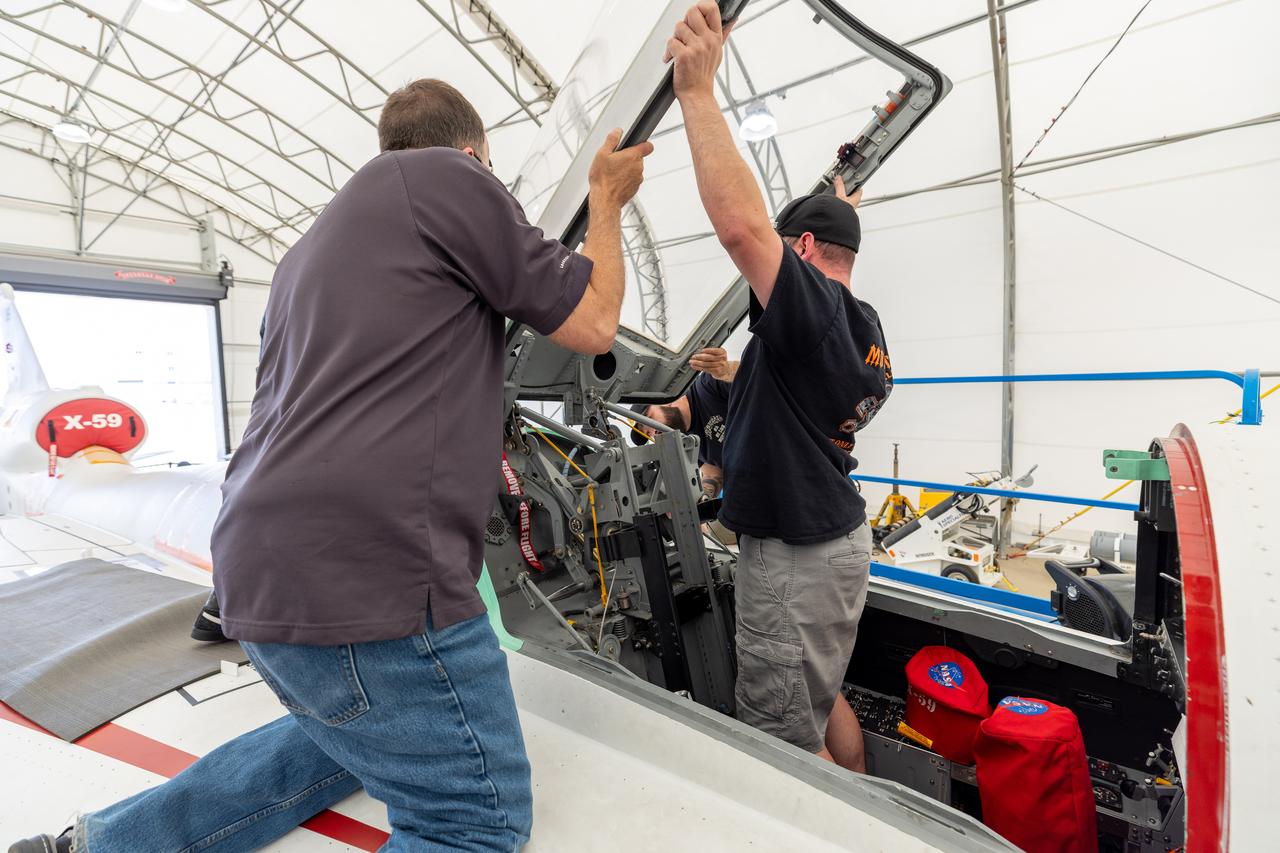

Lockheed Martin technicians temporarily remove the canopy from the X-59 in preparation for final installation of the ejection seat into the aircraft.
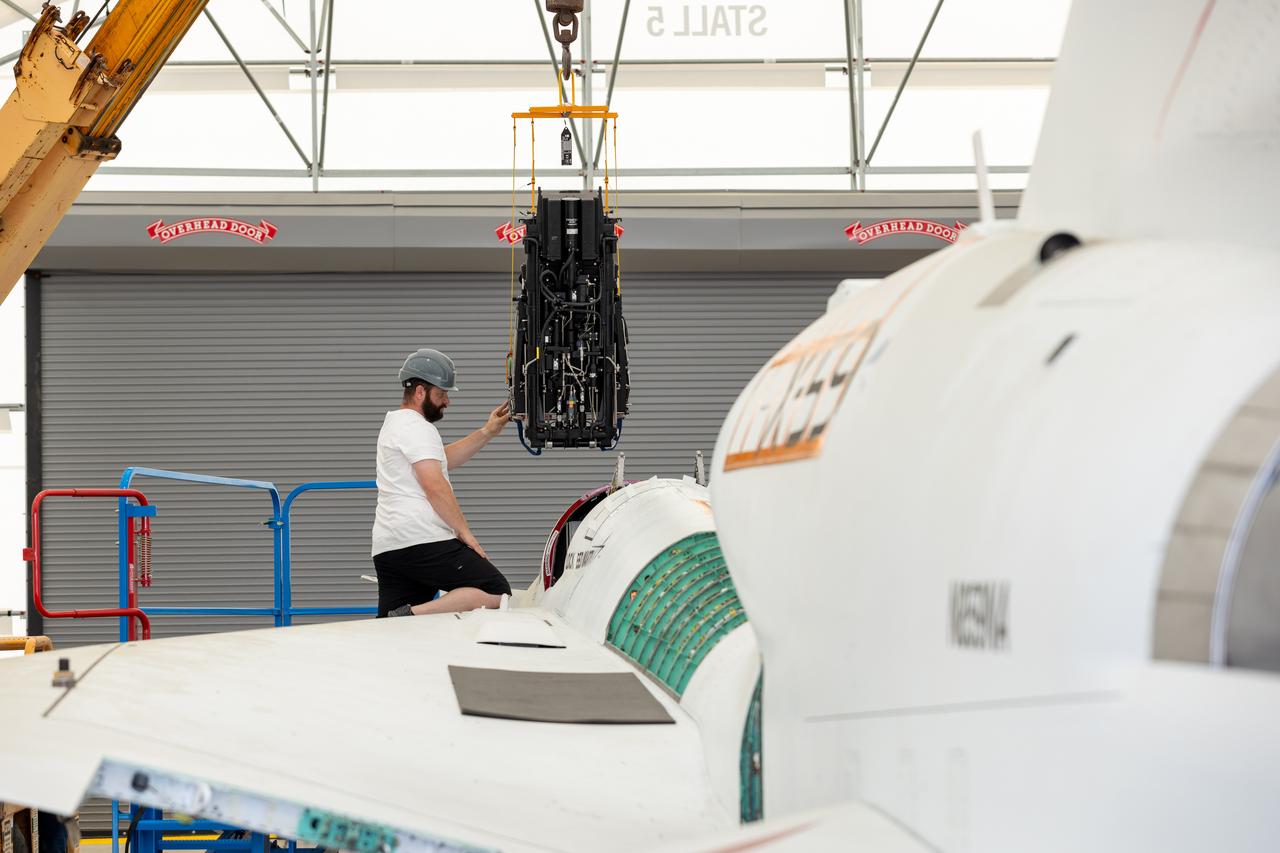

NASA Life Support Technician Mathew Sechler provides support as the X-59’s ejection seat is installed into the aircraft at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works’ facilities in Palmdale, California. Completion of the seat’s installation marks an integration milestone for the aircraft as it prepares for final ground tests.