
NASA astronaut Andre Douglas collects soil samples during the first in a series of four simulated moonwalks in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Norther Arizona on May 13, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
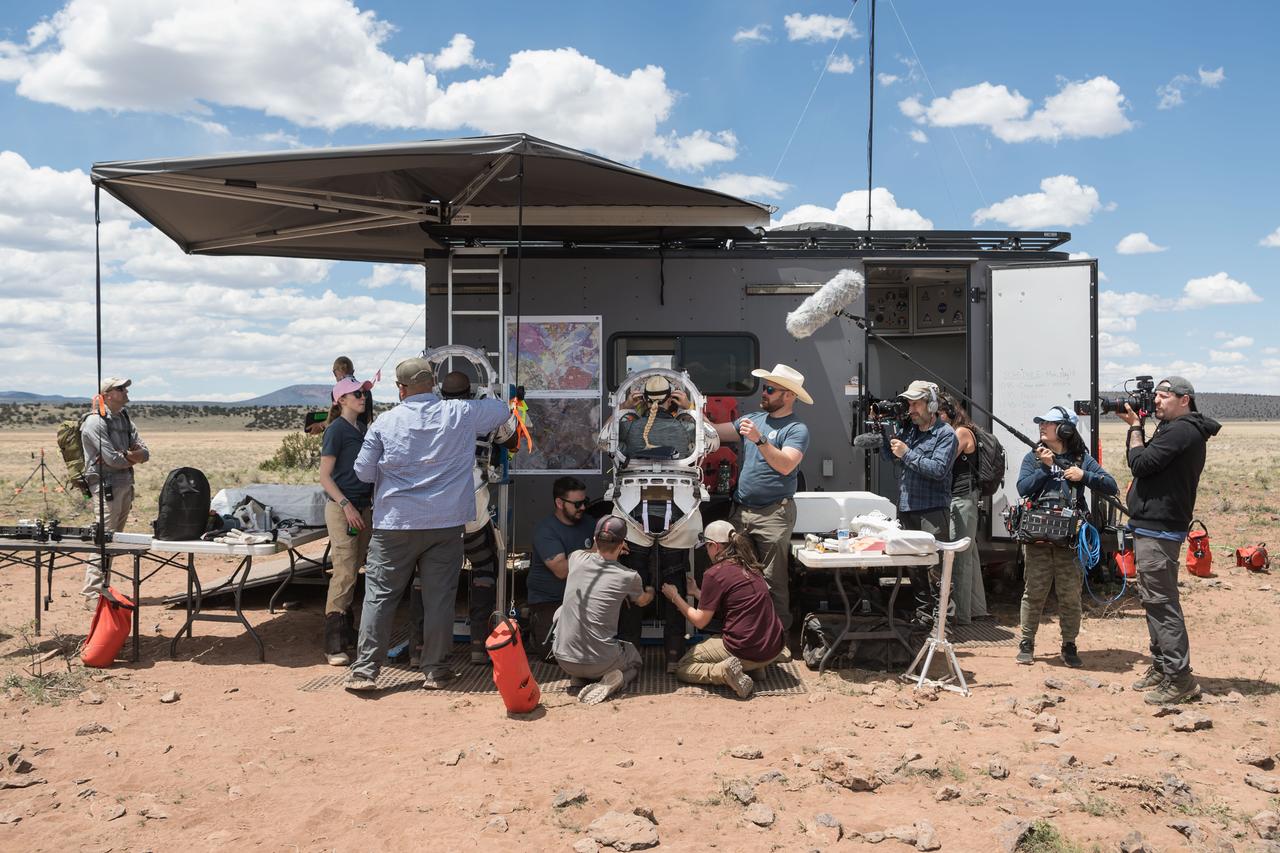

NASA engineering teams help NASA astronauts Andre Douglas (left) and Kate Rubins (right) get into their unpressurized mockup spacesuits before they perform the first of four simulated moonwalks north of Flagstaff, Arizona on May 13, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
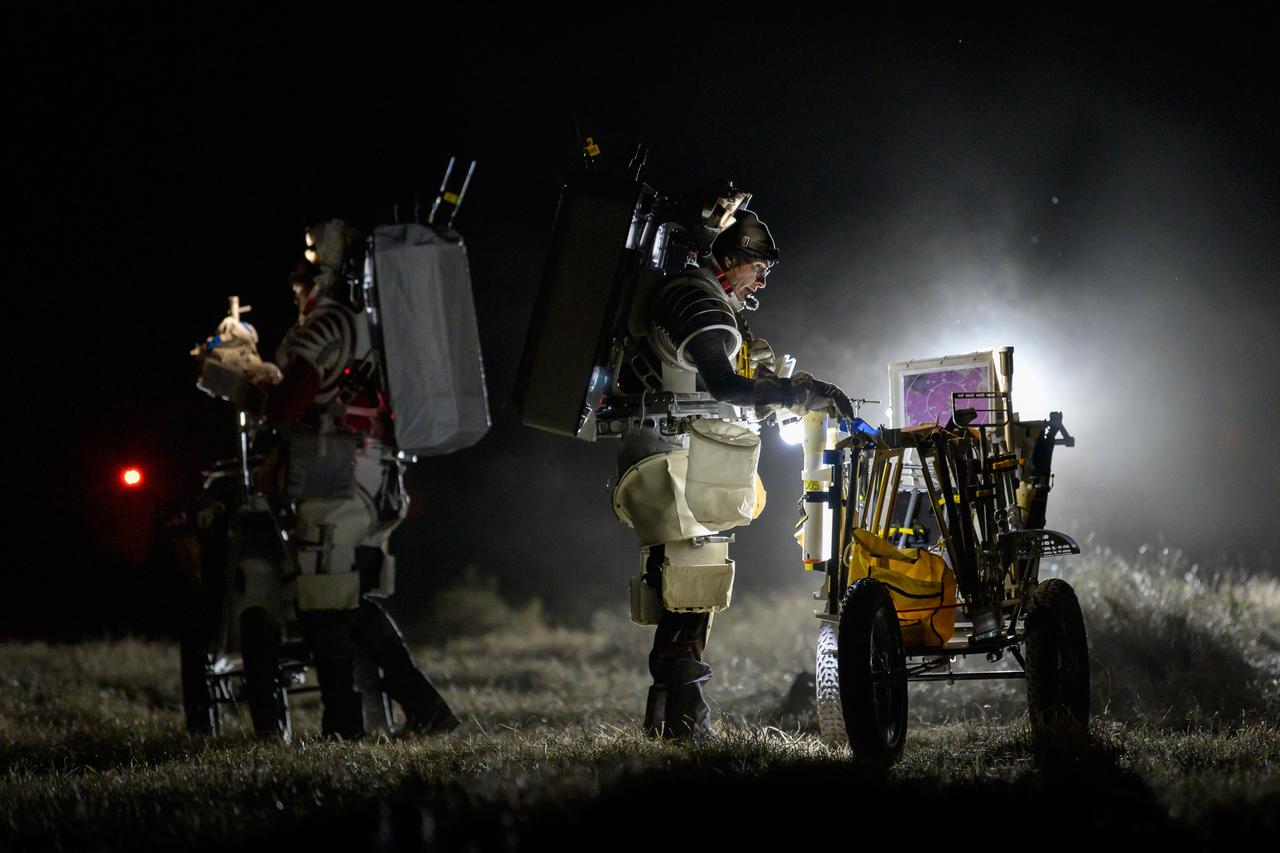

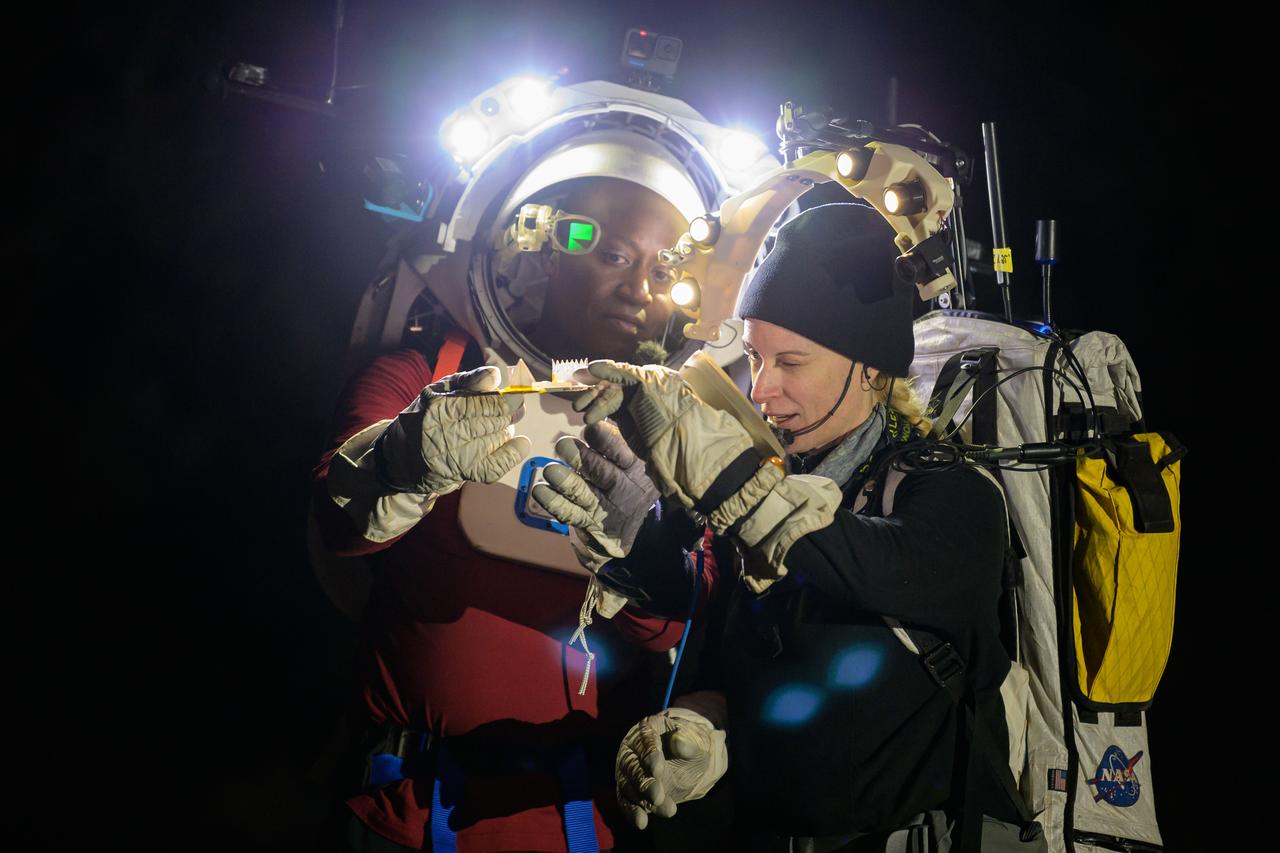
NASA astronaut Kate Rubins conducts a tool audit to ensure she has all of her tools while NASA astronaut Andre Douglas reviews procedures during a nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

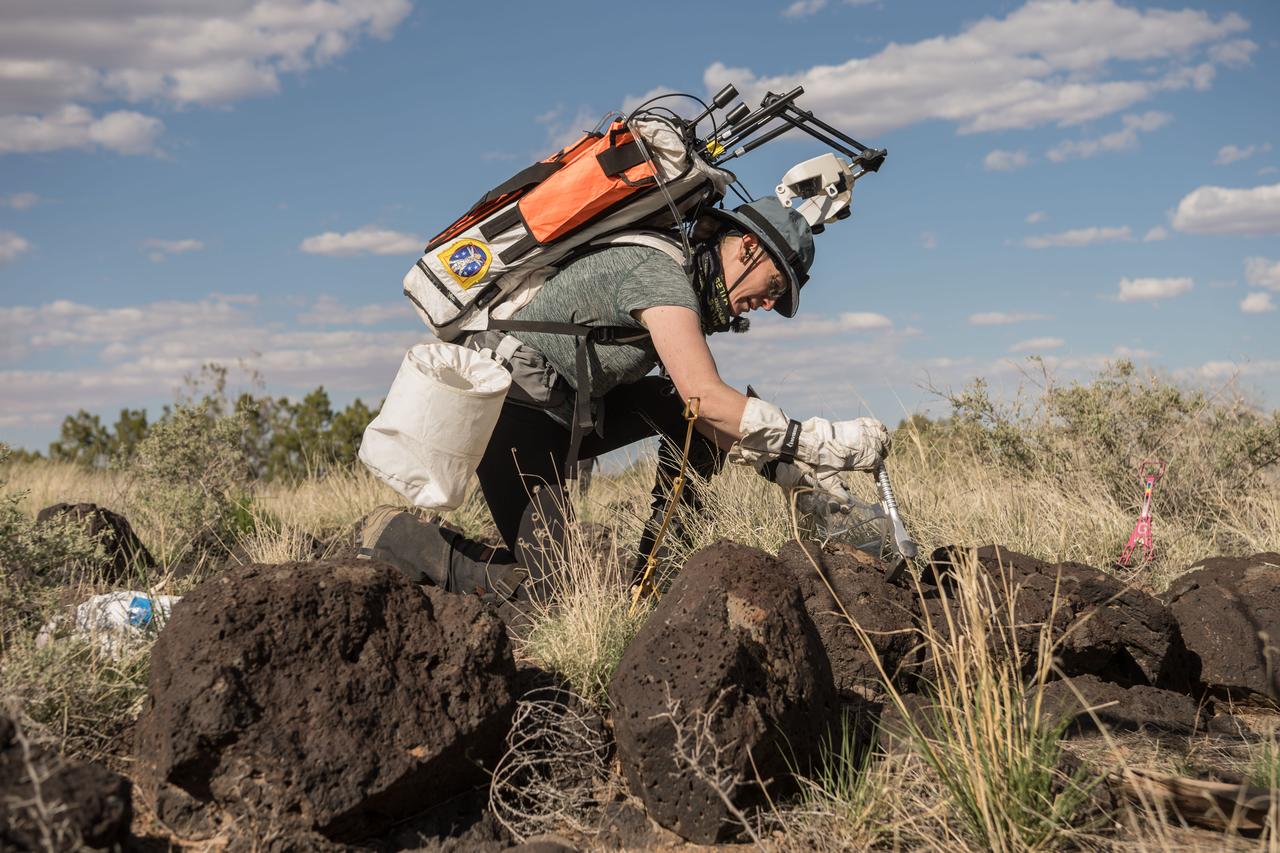
NASA astronaut Andre Douglas uses a hammer and chisel to break off a small sample during a¬¬ nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
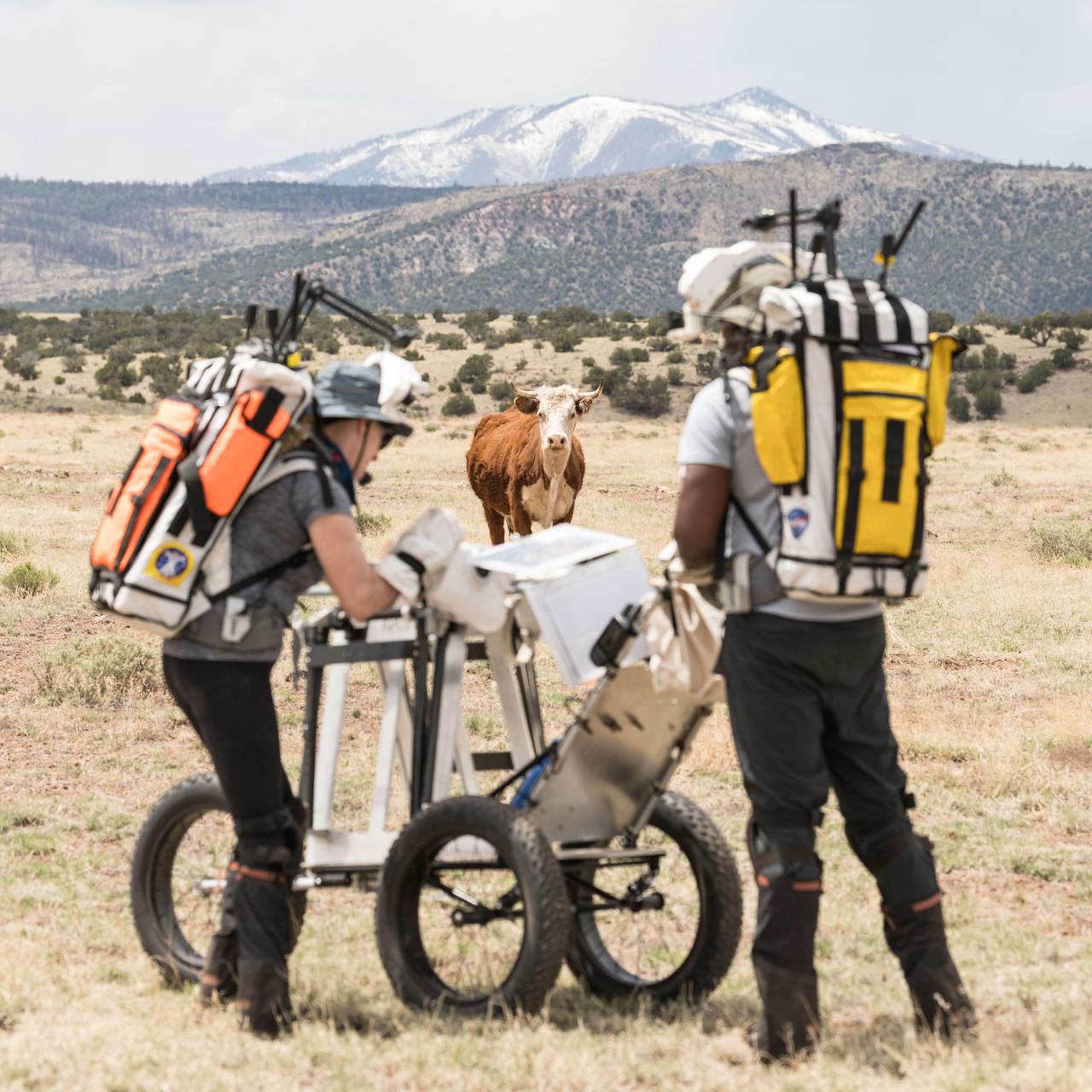

A curious cow watches as NASA astronauts Andre Douglas and Kate Rubins perform a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 14, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
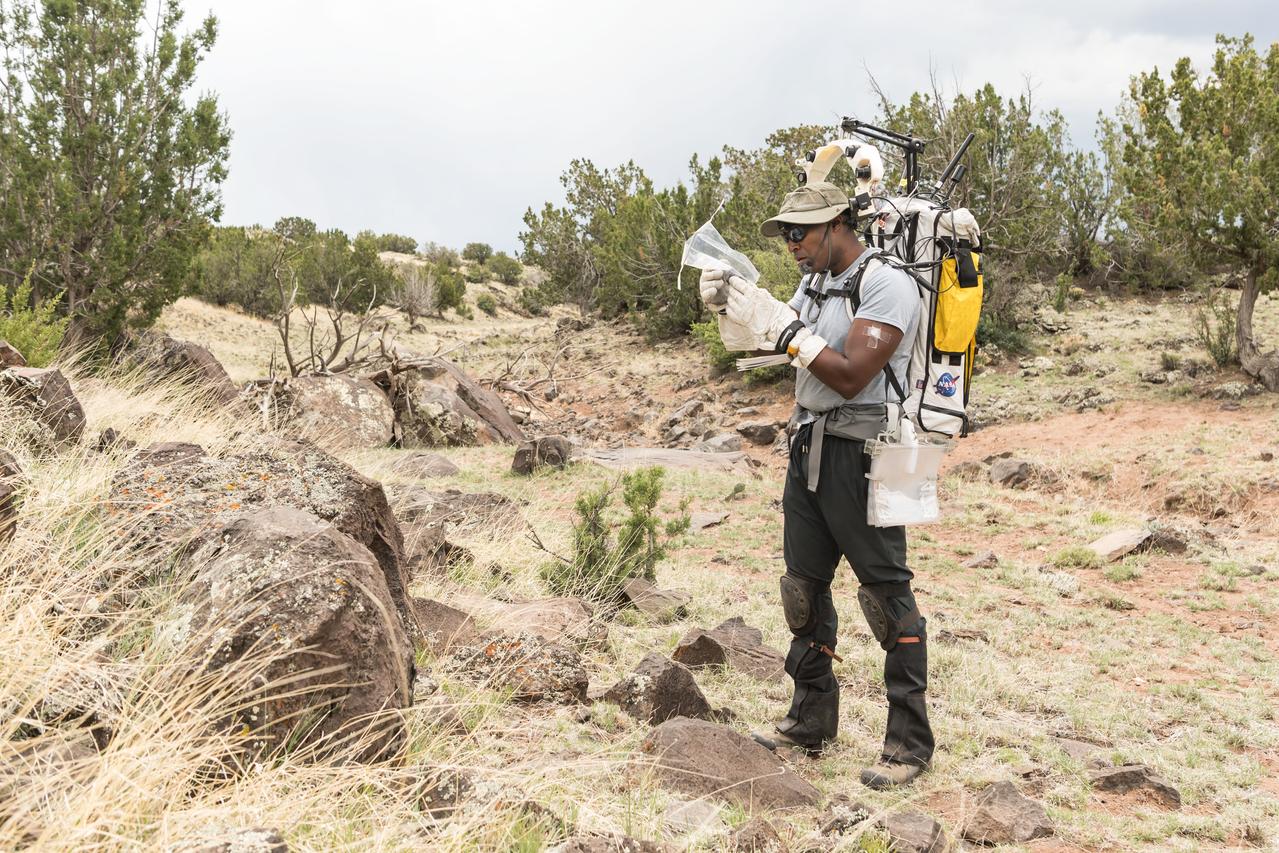

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas examines a geology sample he collected during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 14, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
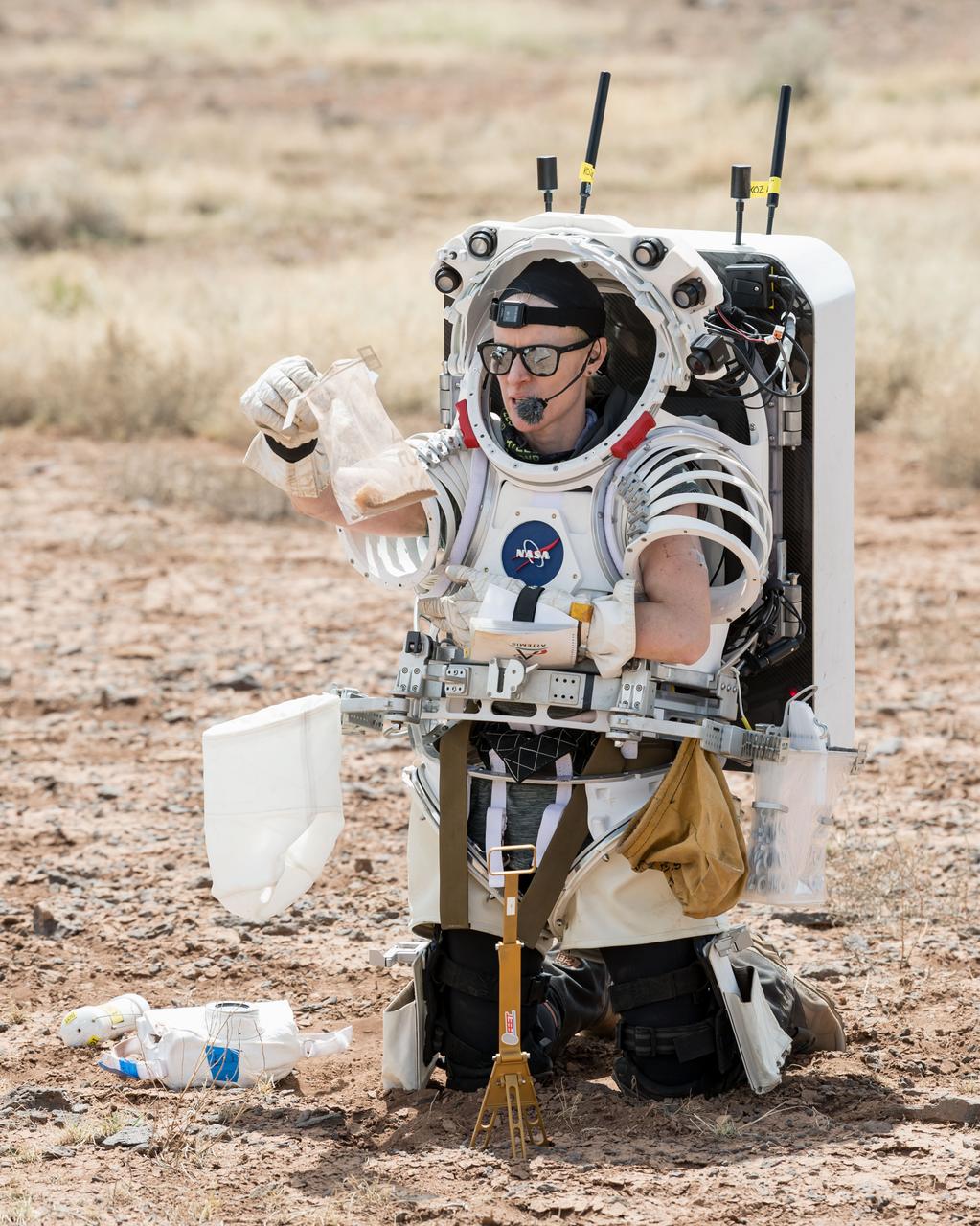

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins examines a geology sample she collected during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 13, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas uses a hammer to chip off a small rock sample to test equipment before the start of a week-long analog consisting of four simulated moonwalks and six advanced technology runs in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 12, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
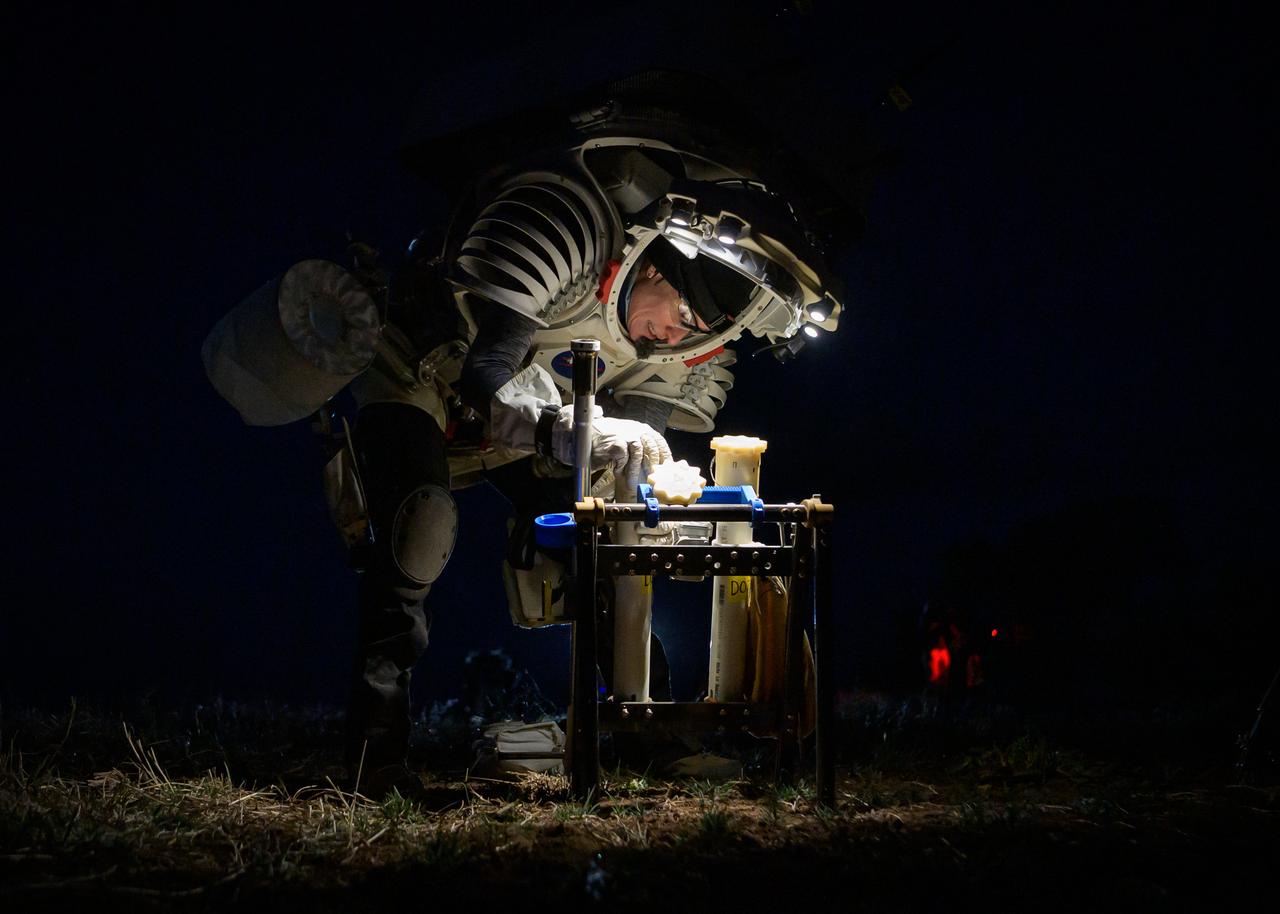

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins selects the geology tool needed during a nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
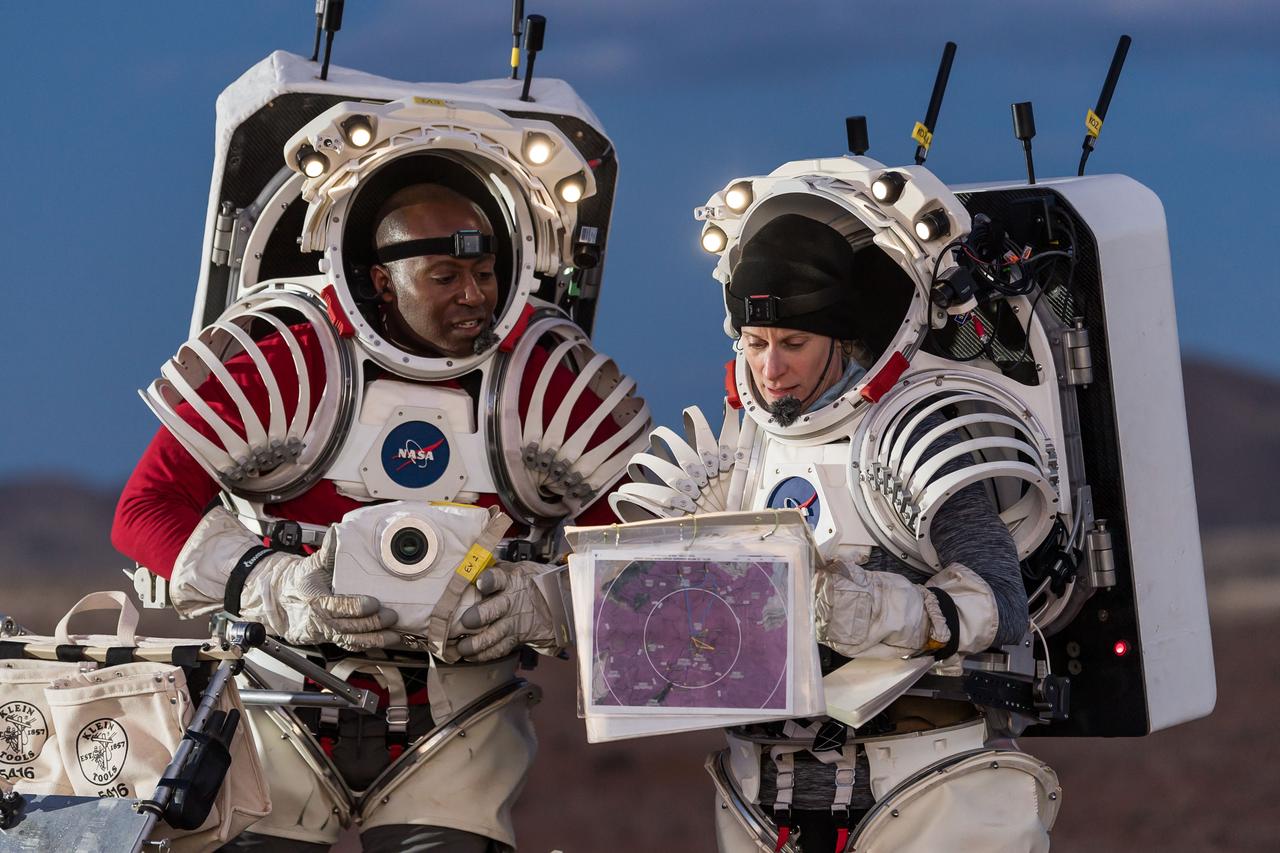

NASA astronauts Andre Douglas, left, and Kate Rubins review traverse plans during a¬¬ nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

The Joint Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Test Team and NASA astronauts Kate Rubins and Andre Douglas before the start of a week-long field test consisting of four simulated moonwalks and six advanced technology runs in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 13, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
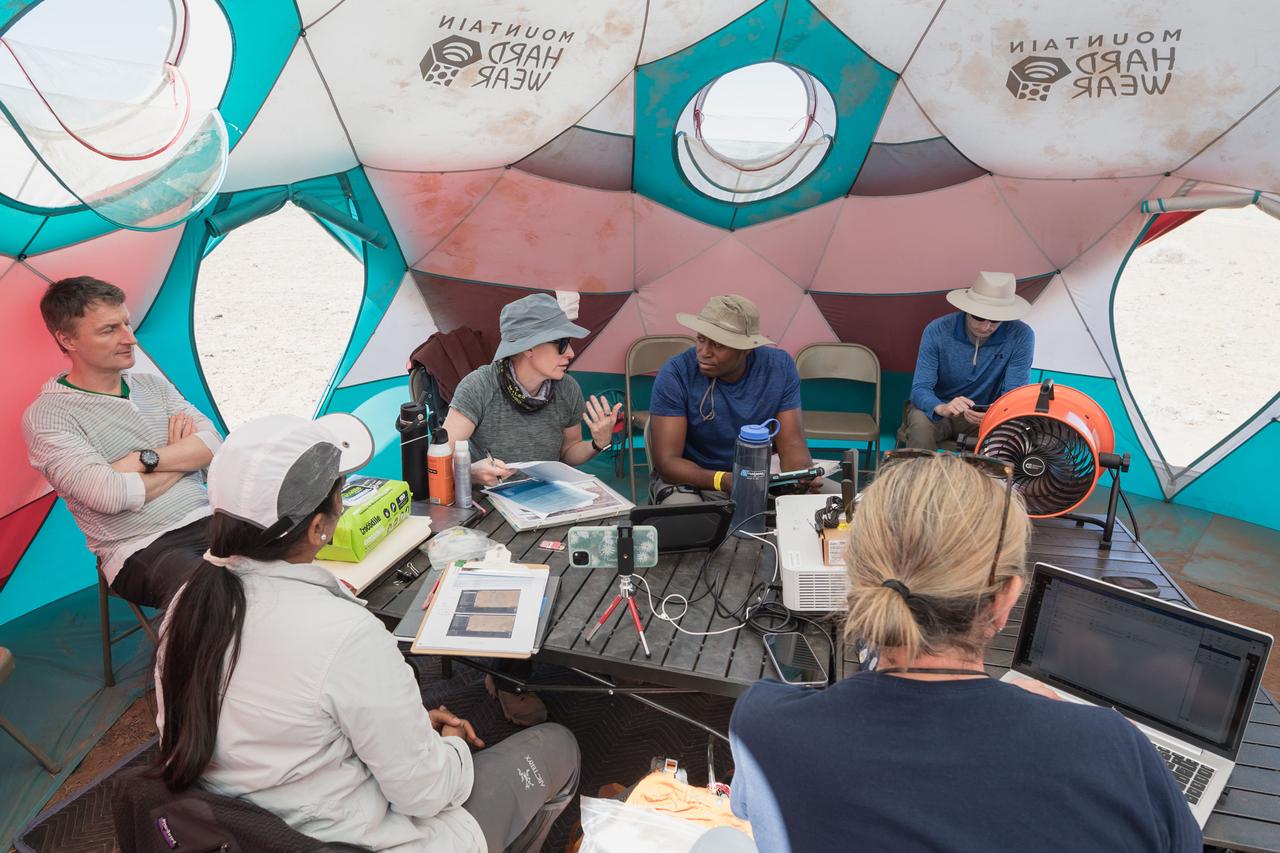

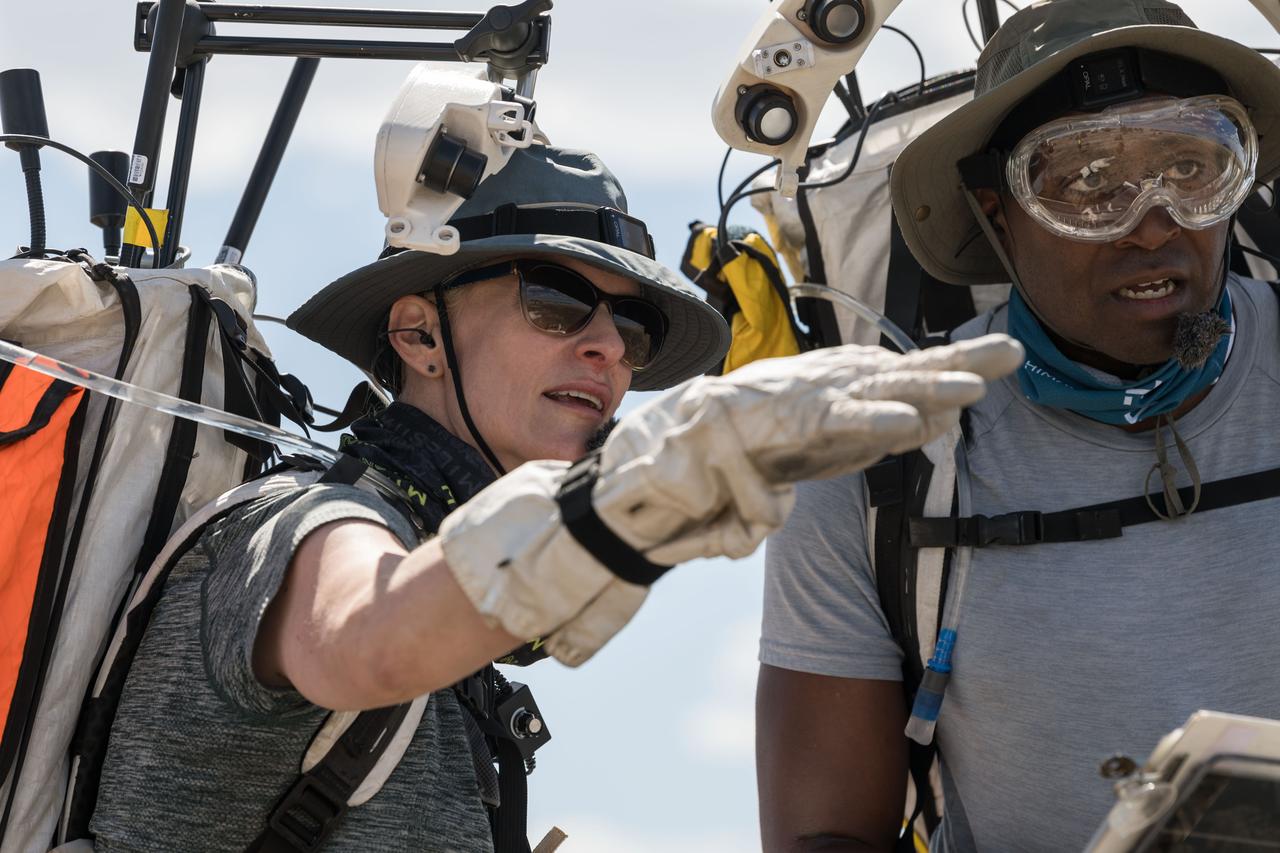
NASA astronauts Kate Rubins and Andre Douglas meet with teams to review test objectives and traverse plans before their first simulated moonwalk in a week-long field test consisting of four simulated moonwalks and six advanced technology runs in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 13, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
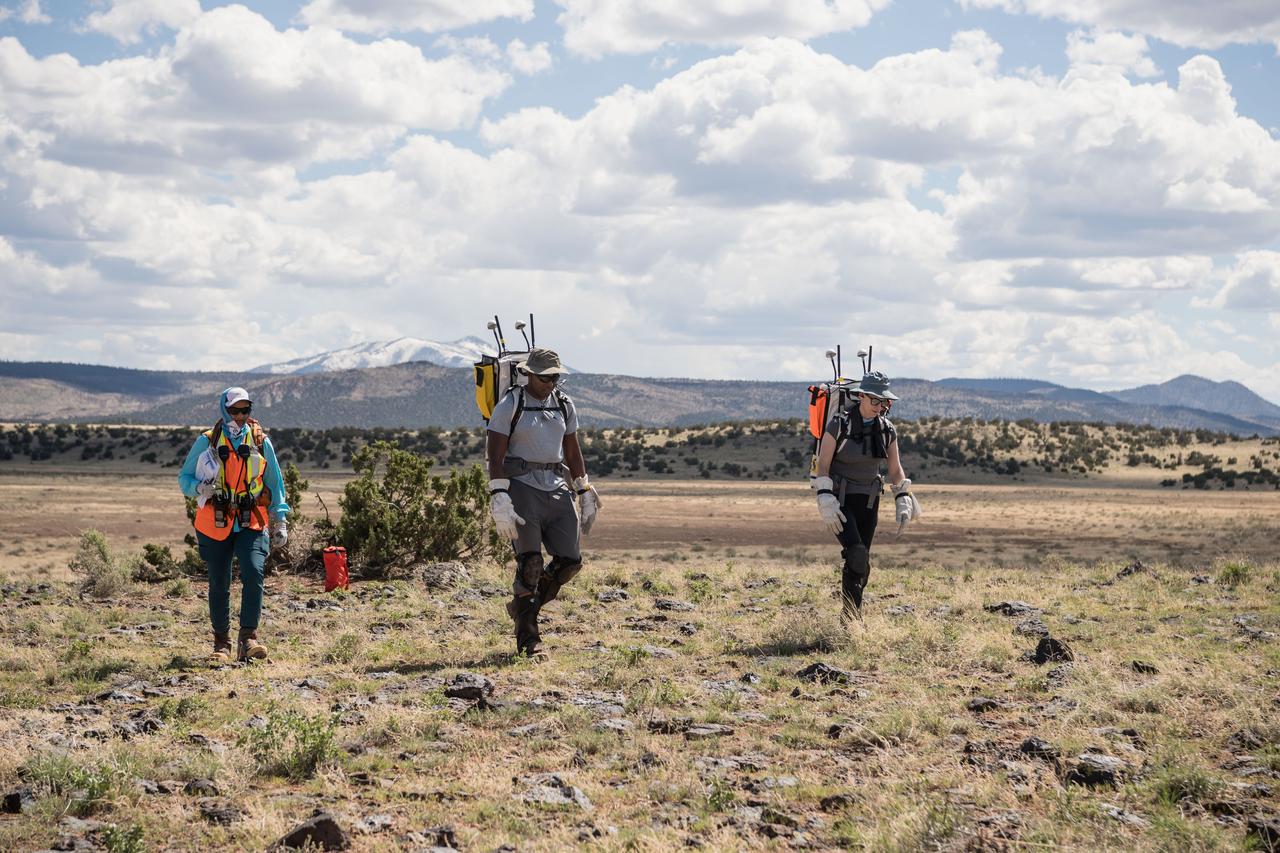

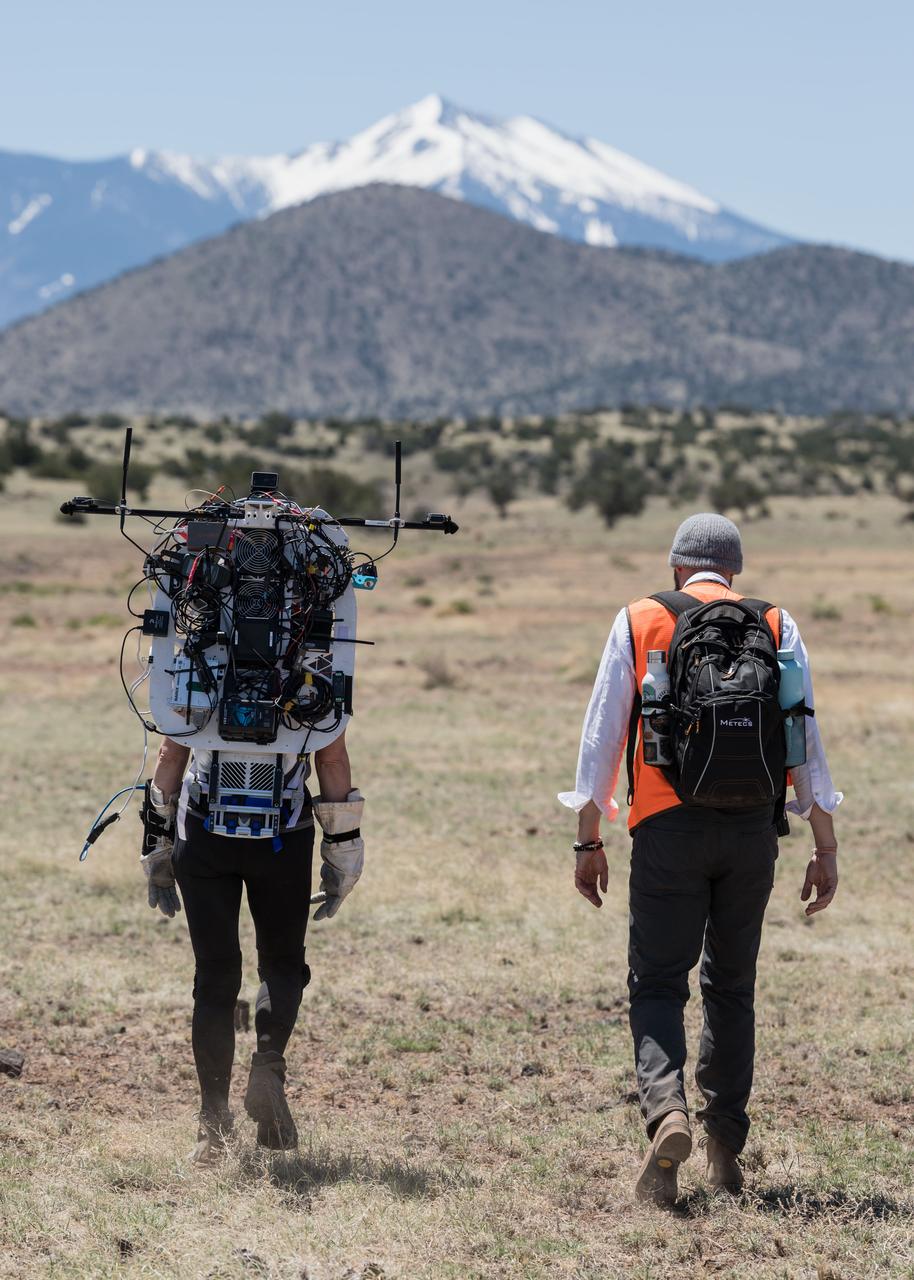
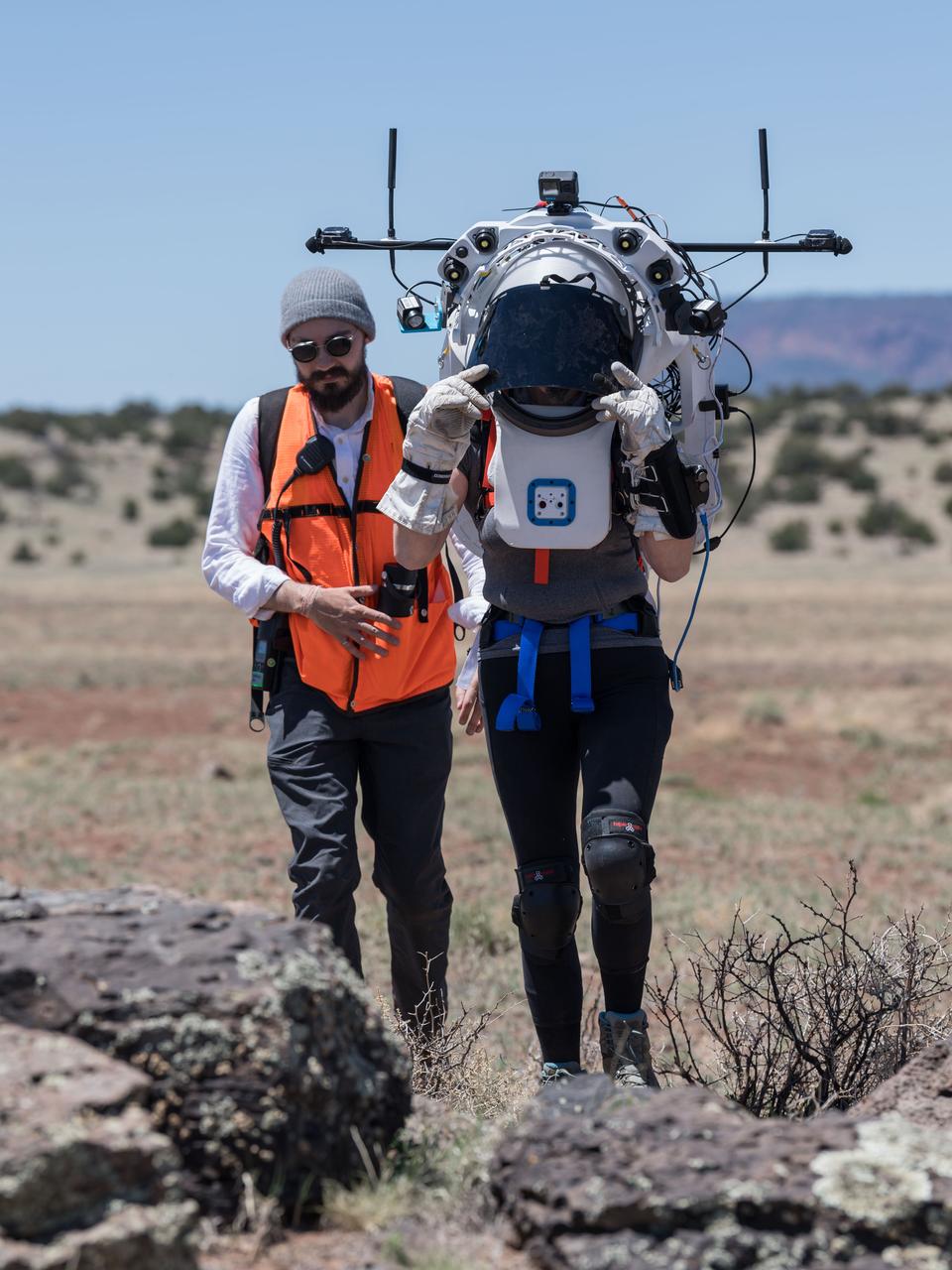
NASA astronauts Andre Douglas (middle) and Kate Rubins (right) walk through the desert during an engineering dry run before the start of a week-long field test consisting of four simulated moonwalks and six advanced technology runs in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 12, 2024. Image: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
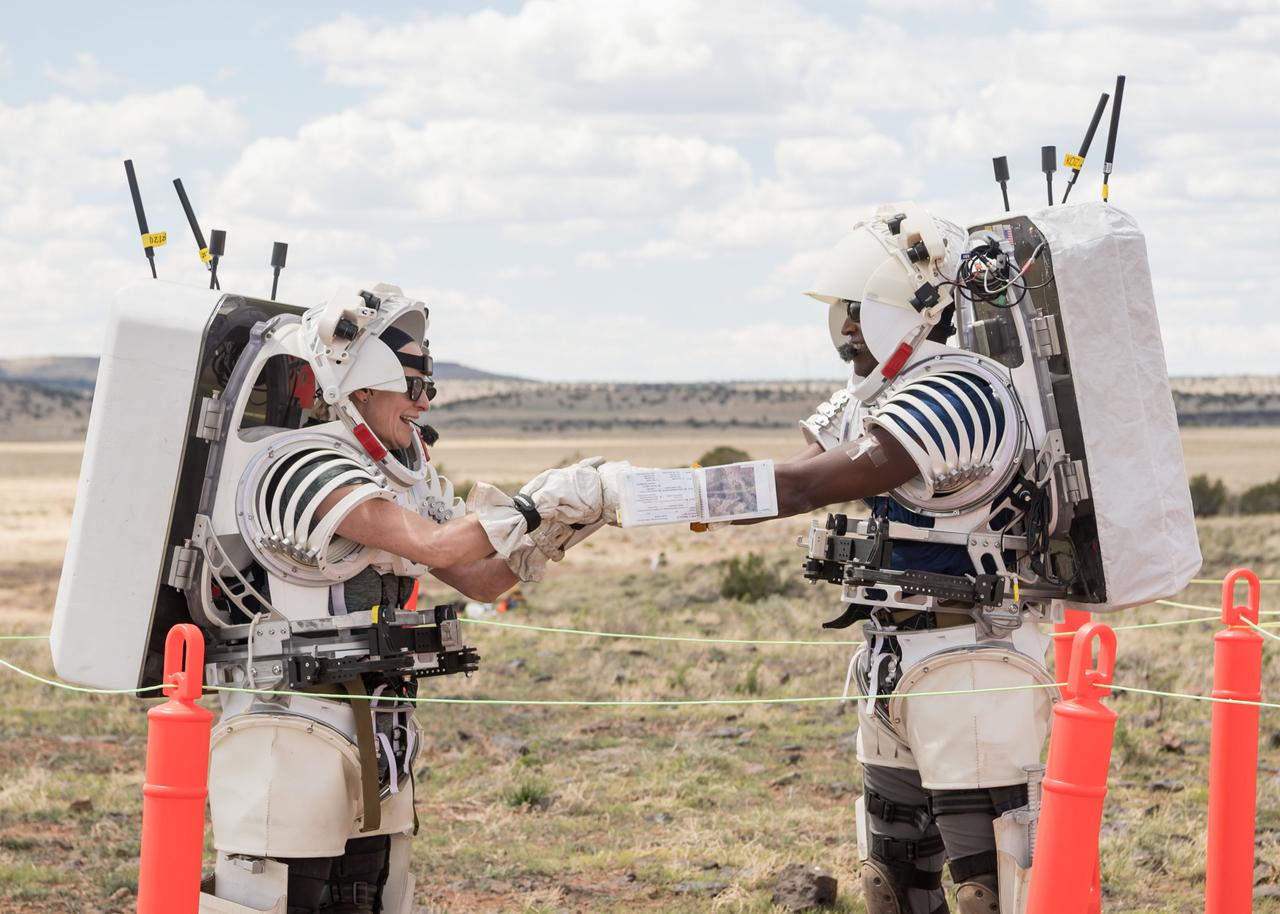

NASA astronauts Kate Rubins and Andre Douglas congratulate each other after the completion of the first simulated moonwalk in a week-long field test consisting of four simulated moonwalks and six advanced technology runs in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 13, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
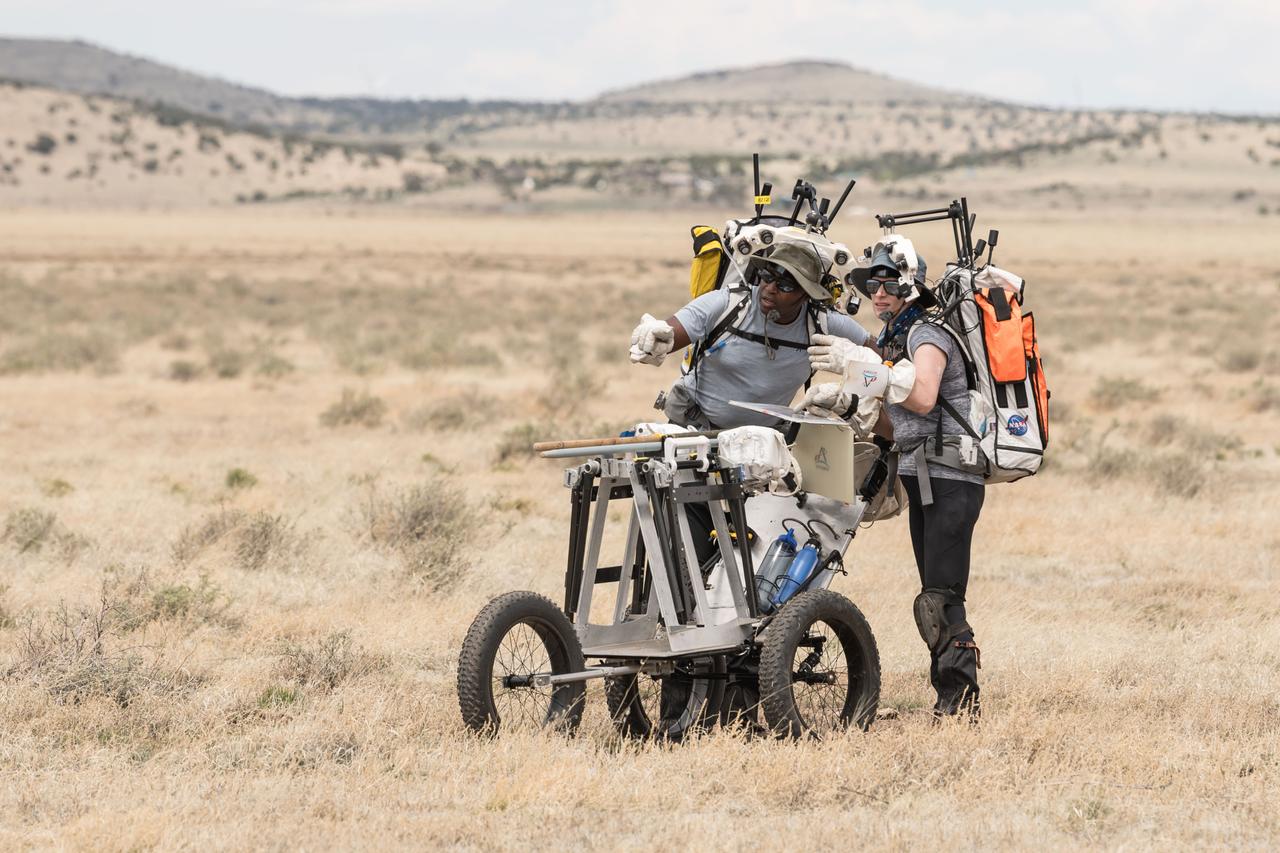

NASA astronauts Andre Douglas and Kate look ahead at their traverse during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 14, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
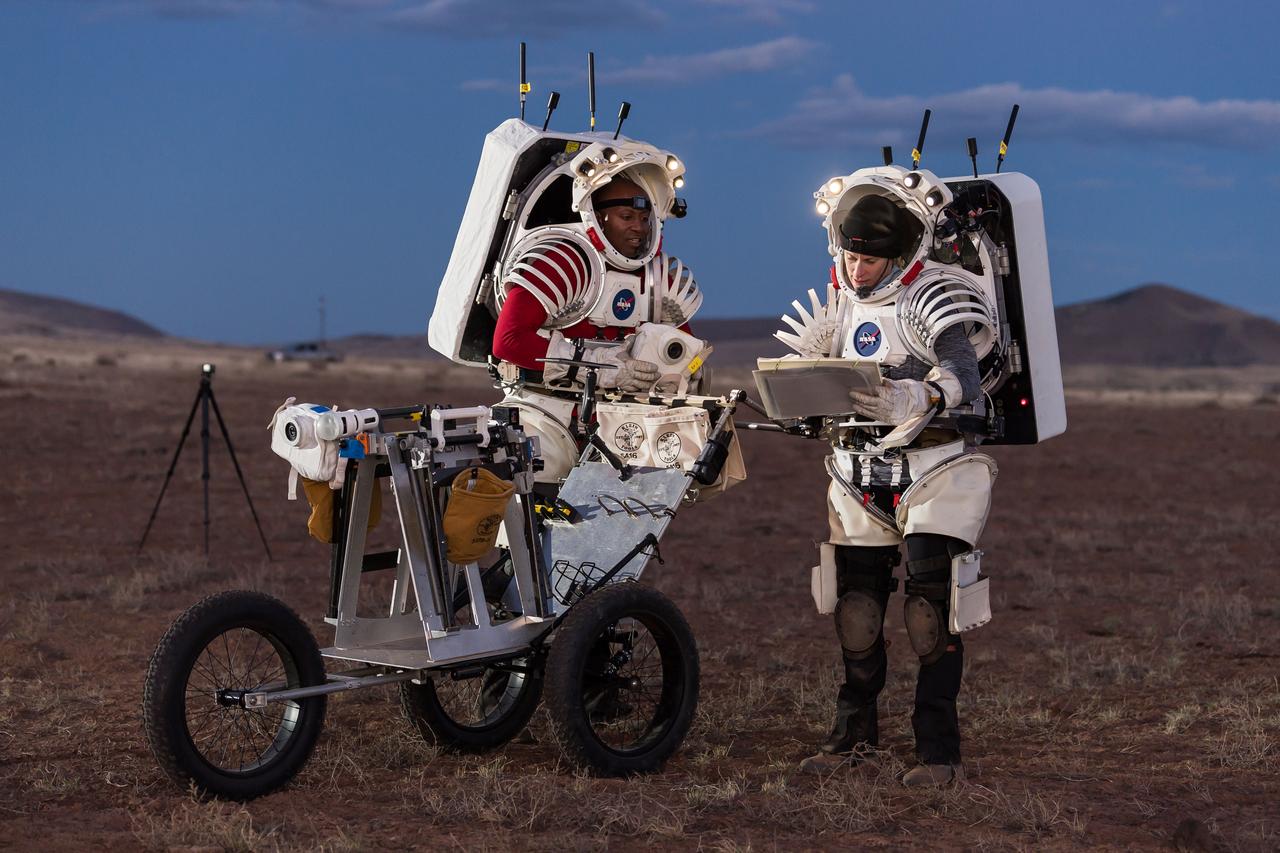

NASA astronauts Andre Douglas, left, and Kate Rubins review procedures during a nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas raises an American flag as NASA astronaut Kate Rubins looks on during their first simulated moonwalk in a week-long field test consisting of four simulated moonwalks and six advanced technology runs in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 13, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronauts Andre Douglas and Kate Rubins review procedures during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 14, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins closes a sample bag full of soil she collected during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 14, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
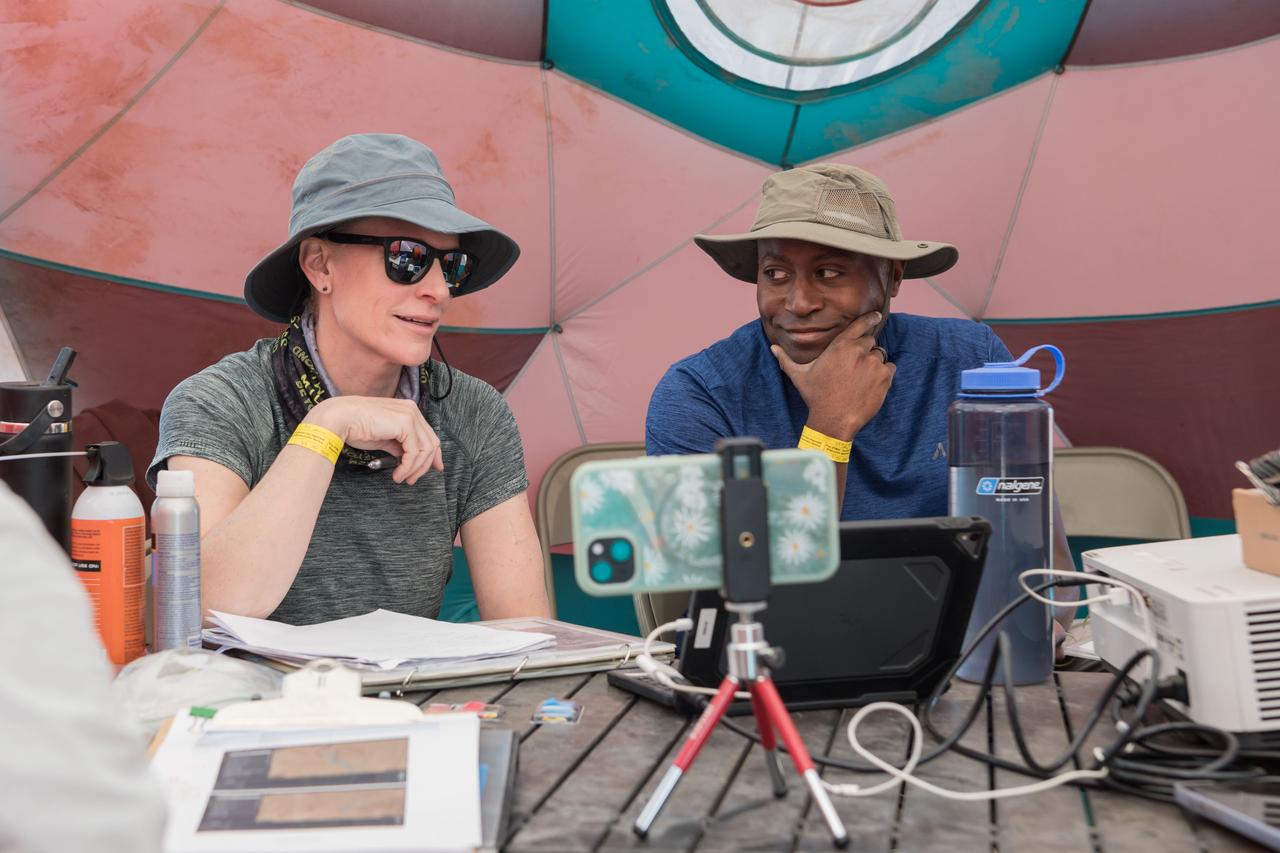

NASA astronauts Kate Rubins and Andre Douglas review test objectives and traverse plans before their first simulated moonwalk in a week-long field test consisting of four simulated moonwalks and six advanced technology runs in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 13, 2024 Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
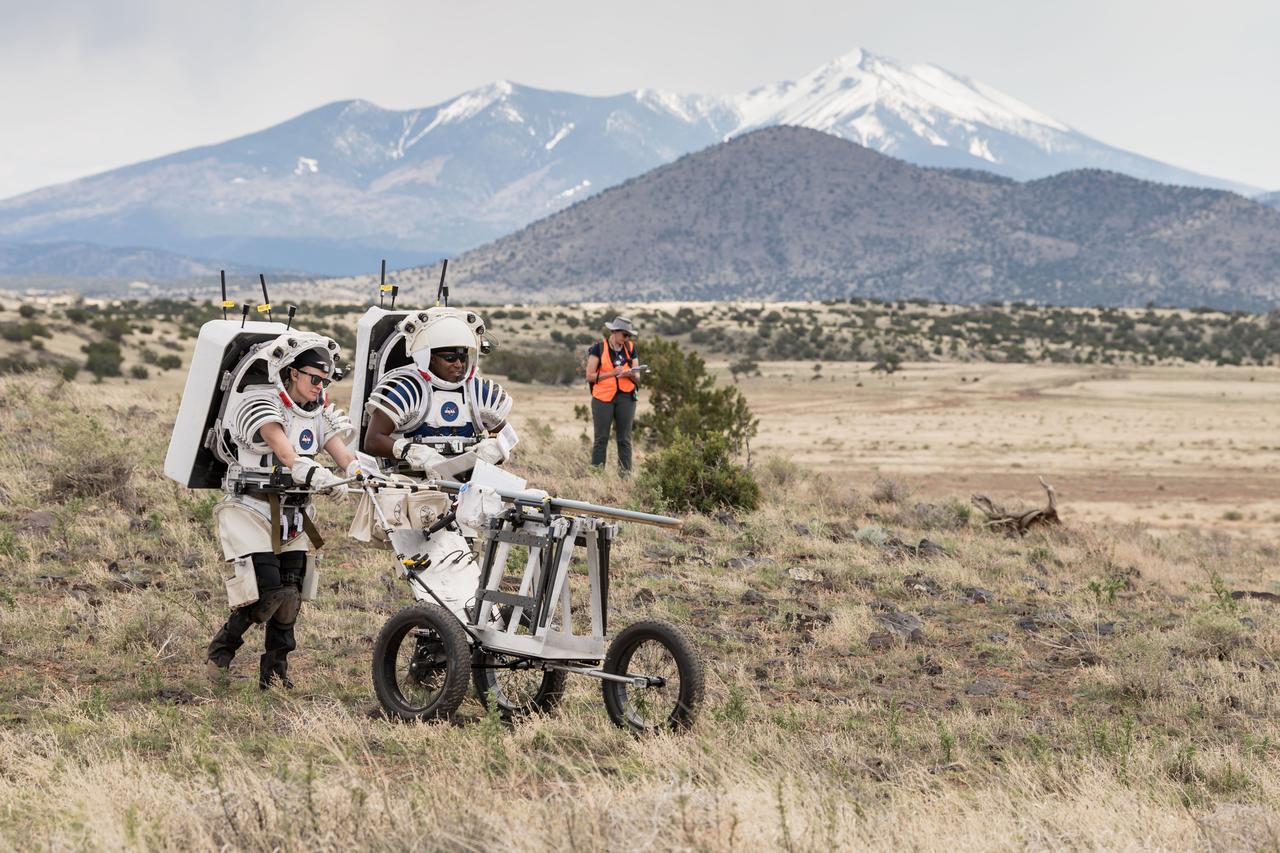

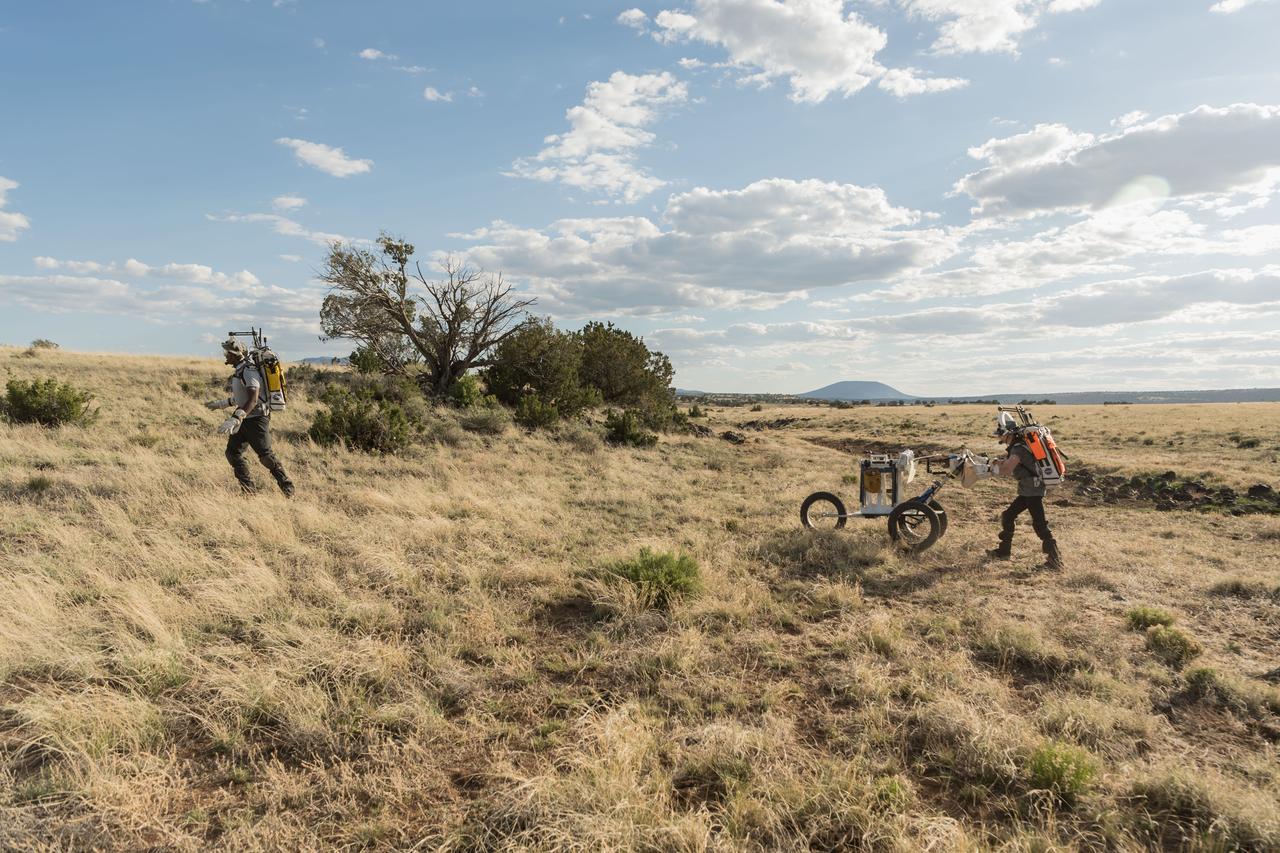
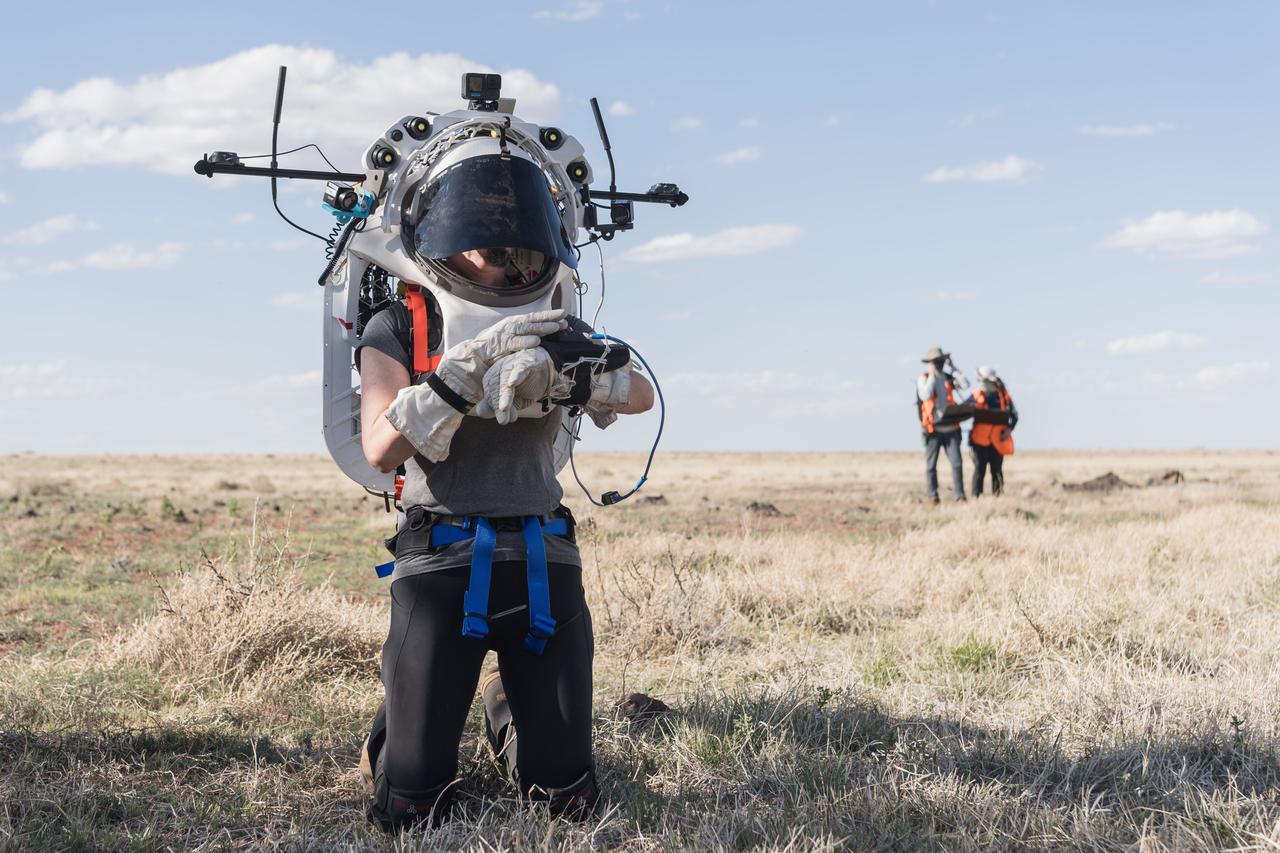
NASA astronauts Kate Rubins and Andre Douglas push a tool cart loaded with lunar tools through the San Francisco Volcanic Field north of Flagstaff, Arizona, as they practice moonwalking operations for Artemis III on May 13, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
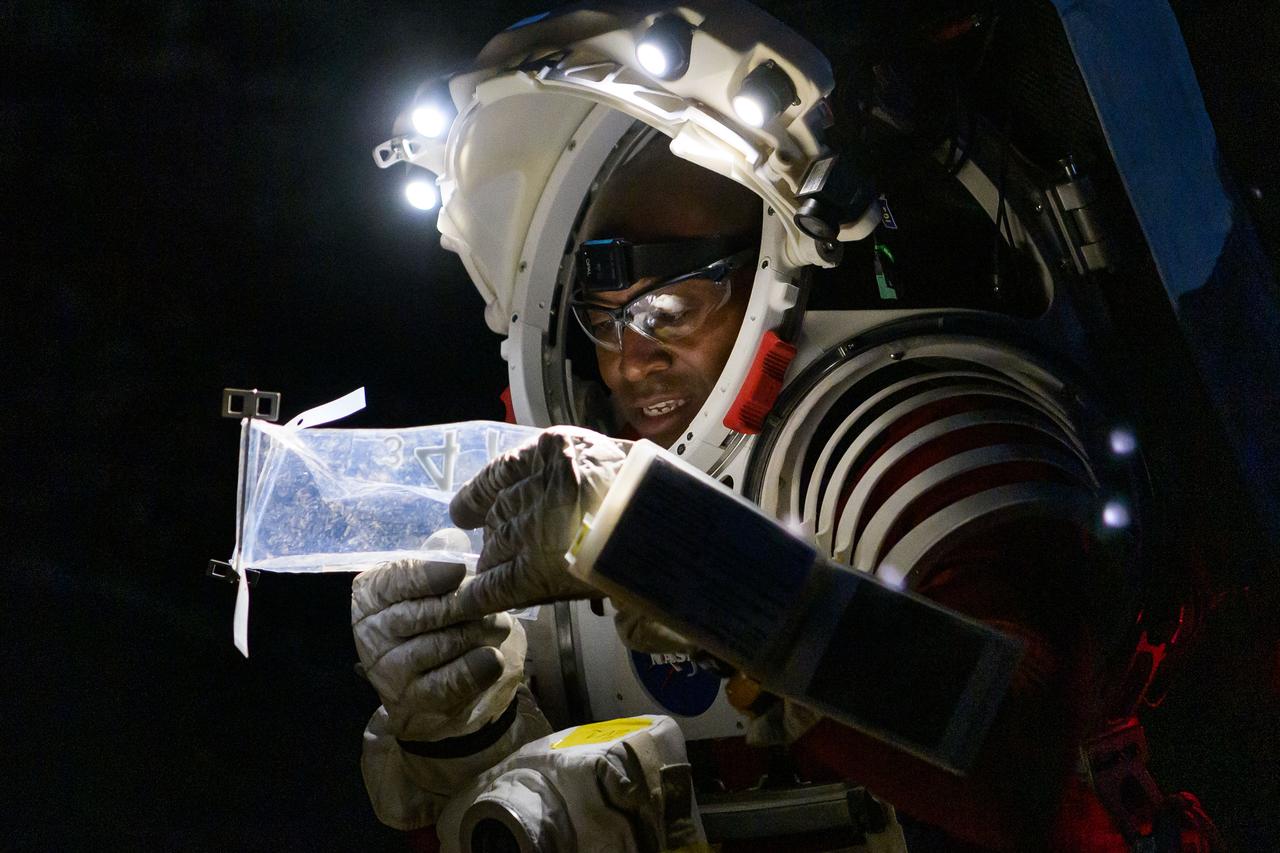

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas examines a geologic sample collected during a nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
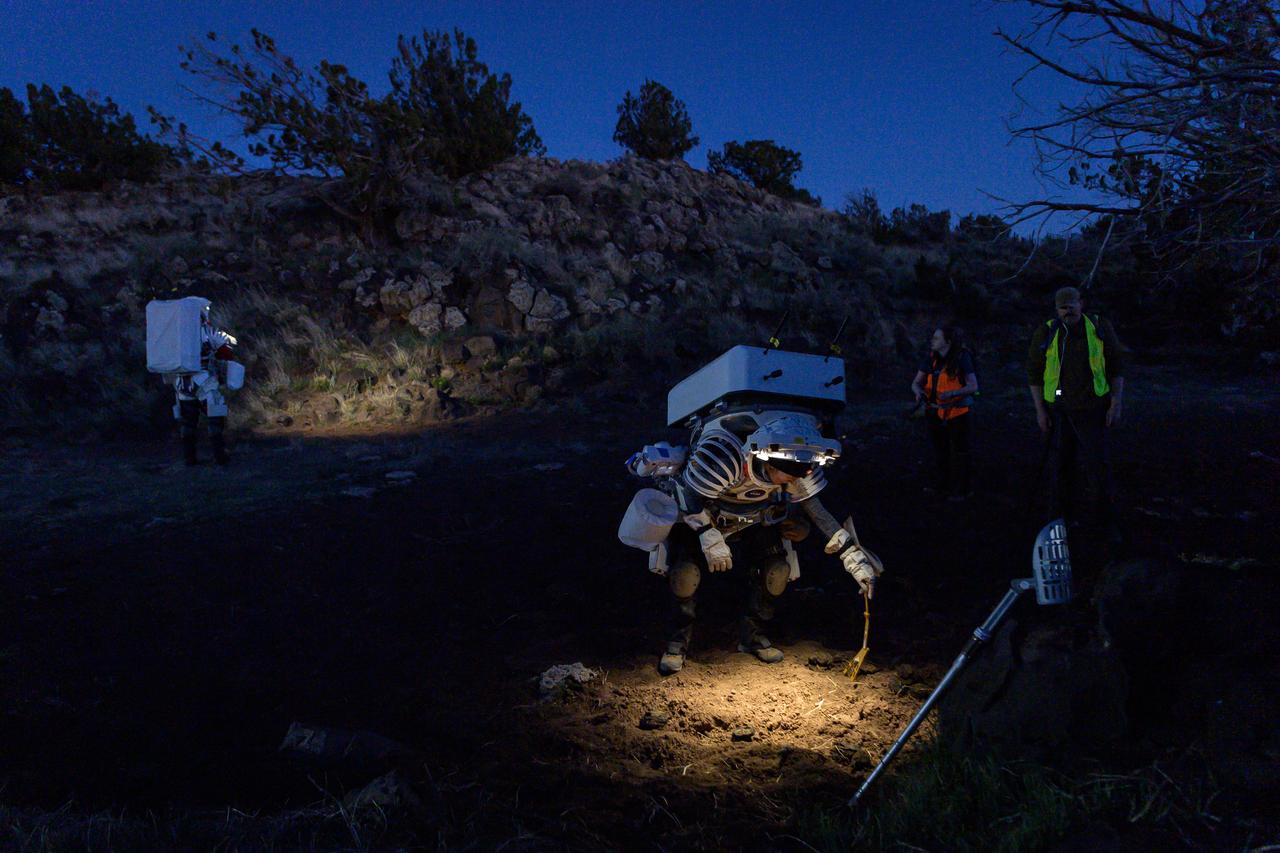

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins places a sample marker in the soil before collecting a sample during a nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. A sample marker provides a photographic reference point for science samples collected on the lunar surface. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
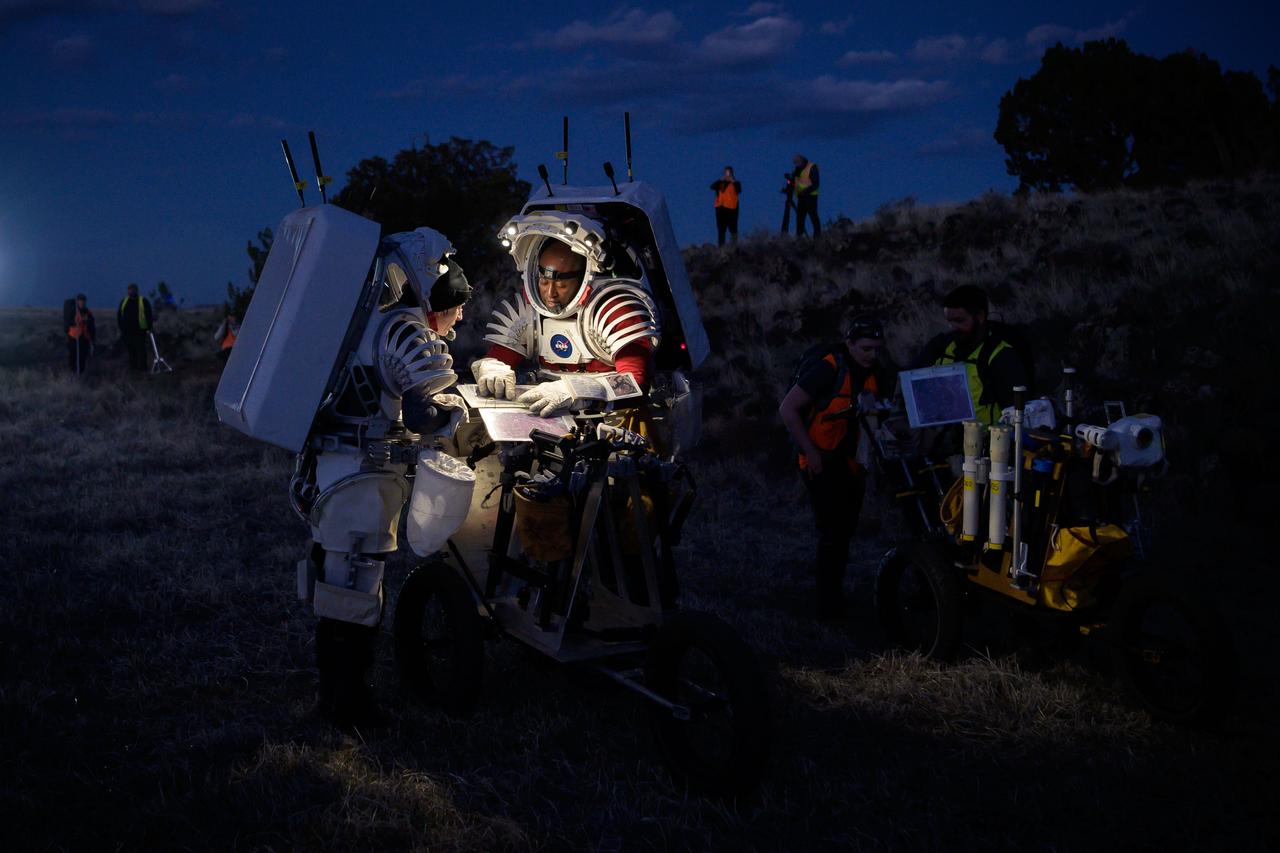

NASA astronauts Kate Rubins, left, and Andre Douglas look at a map that shows their traverse route during a nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
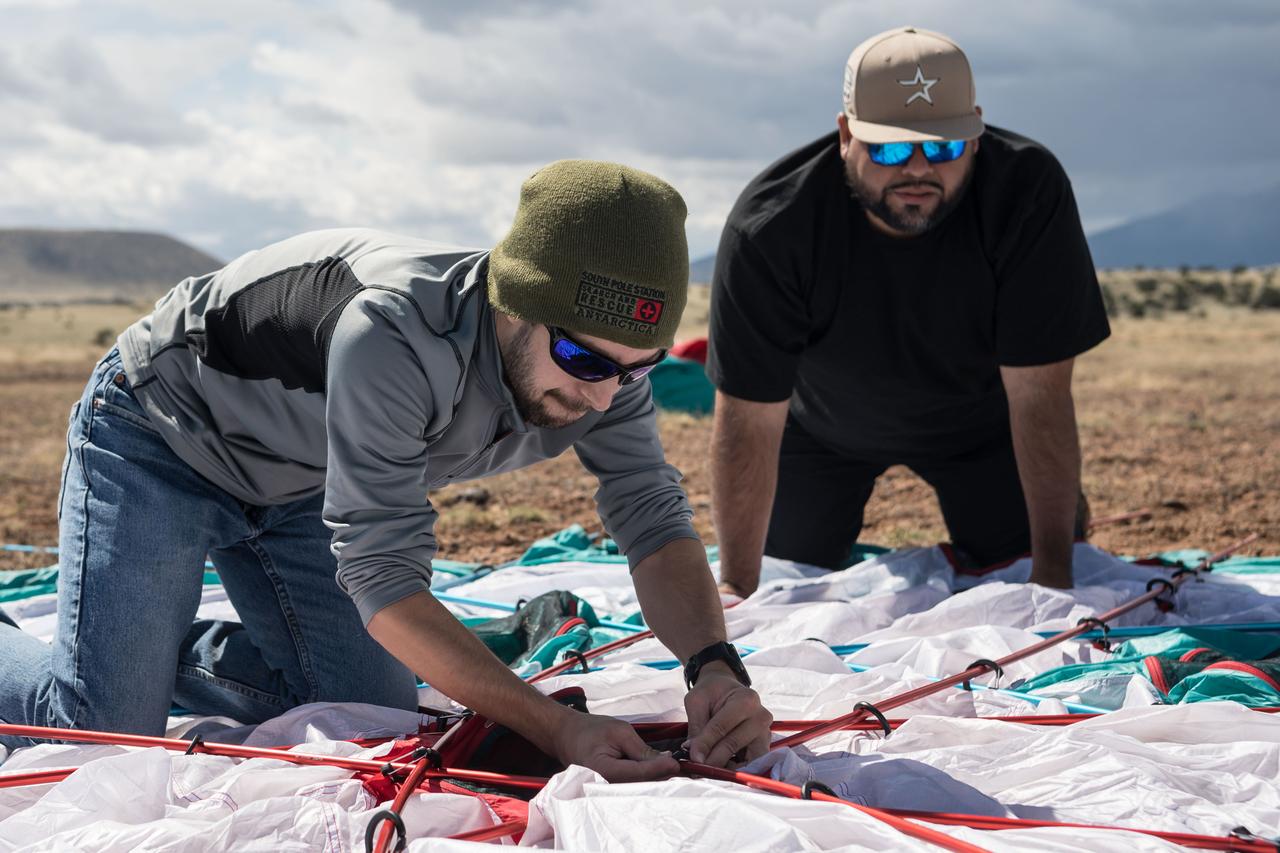

Spacesuit engineers Zach Tejral (left) and Joel Alvarado (right) work to set up the base camp for the Joint Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Test Team Field Test 5 in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 11, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins walks in the lunar-like landscape during a nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
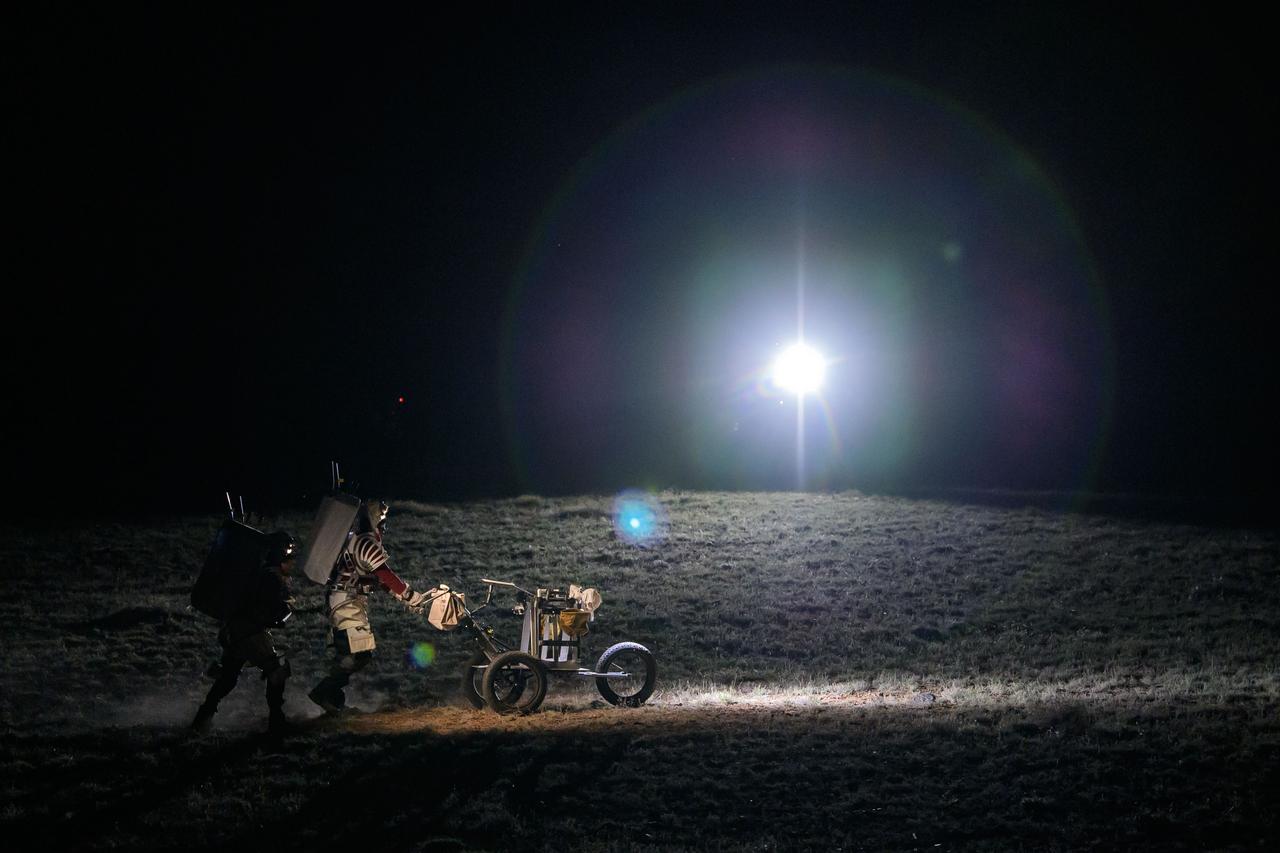

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas pushes a tool cart across the lunar-like landscape while NASA astronaut Kate Rubins follows close behind during a¬¬ nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
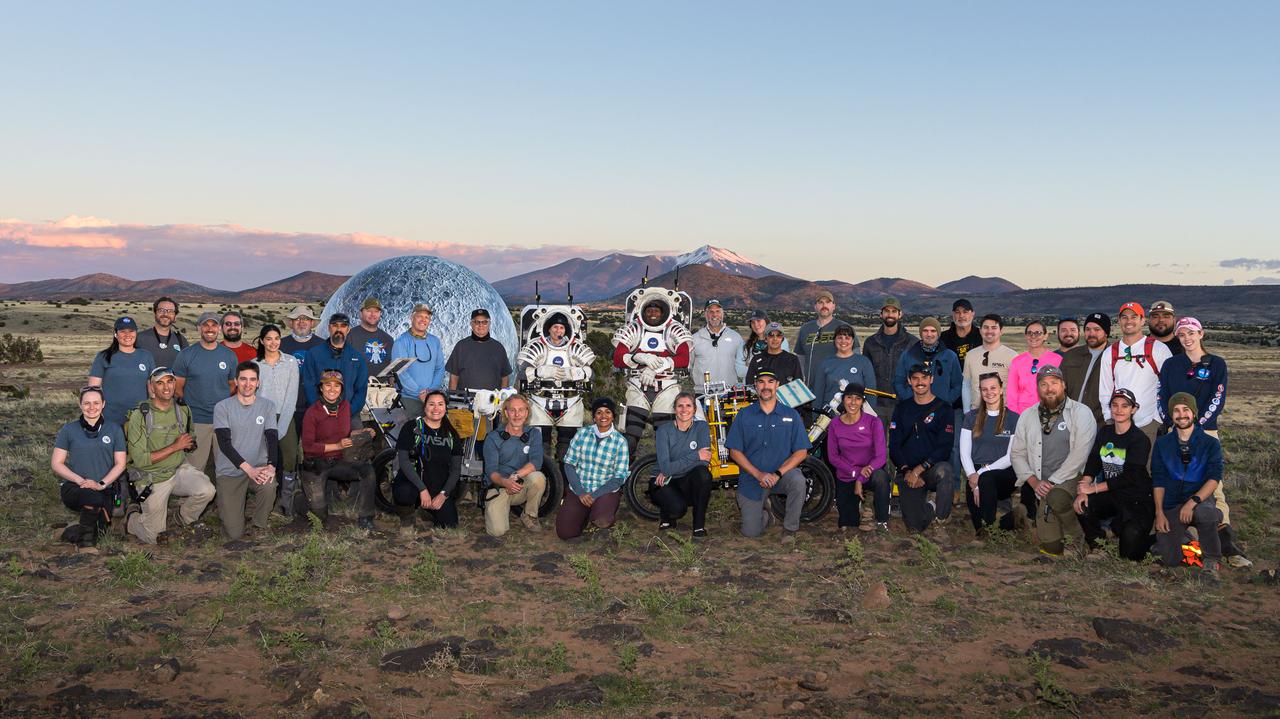

6. The Joint Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Test Team poses for a group photo in Northern Arizona after a week-long field test consisting of four simulated moonwalks and six advanced technology runs. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
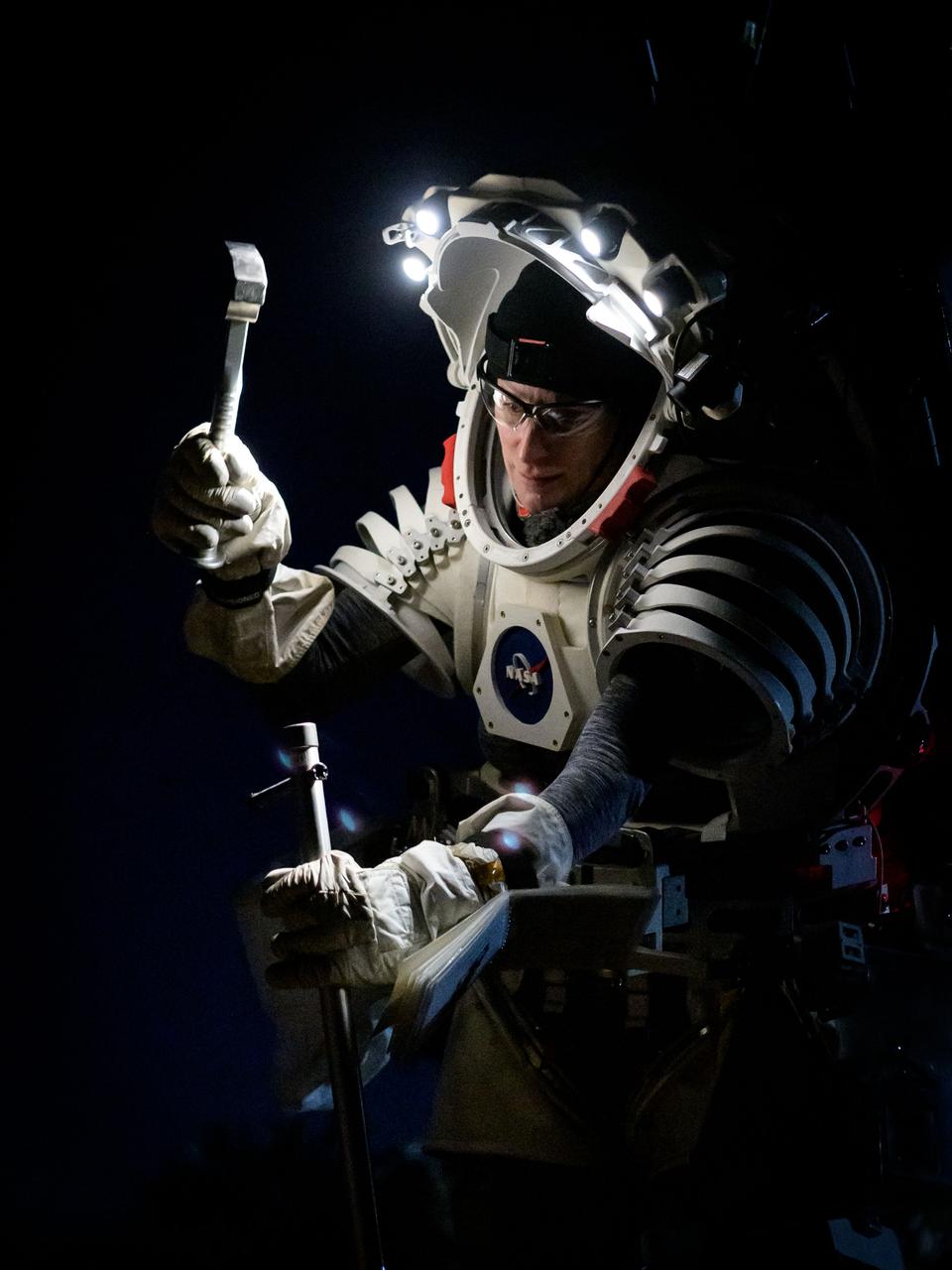

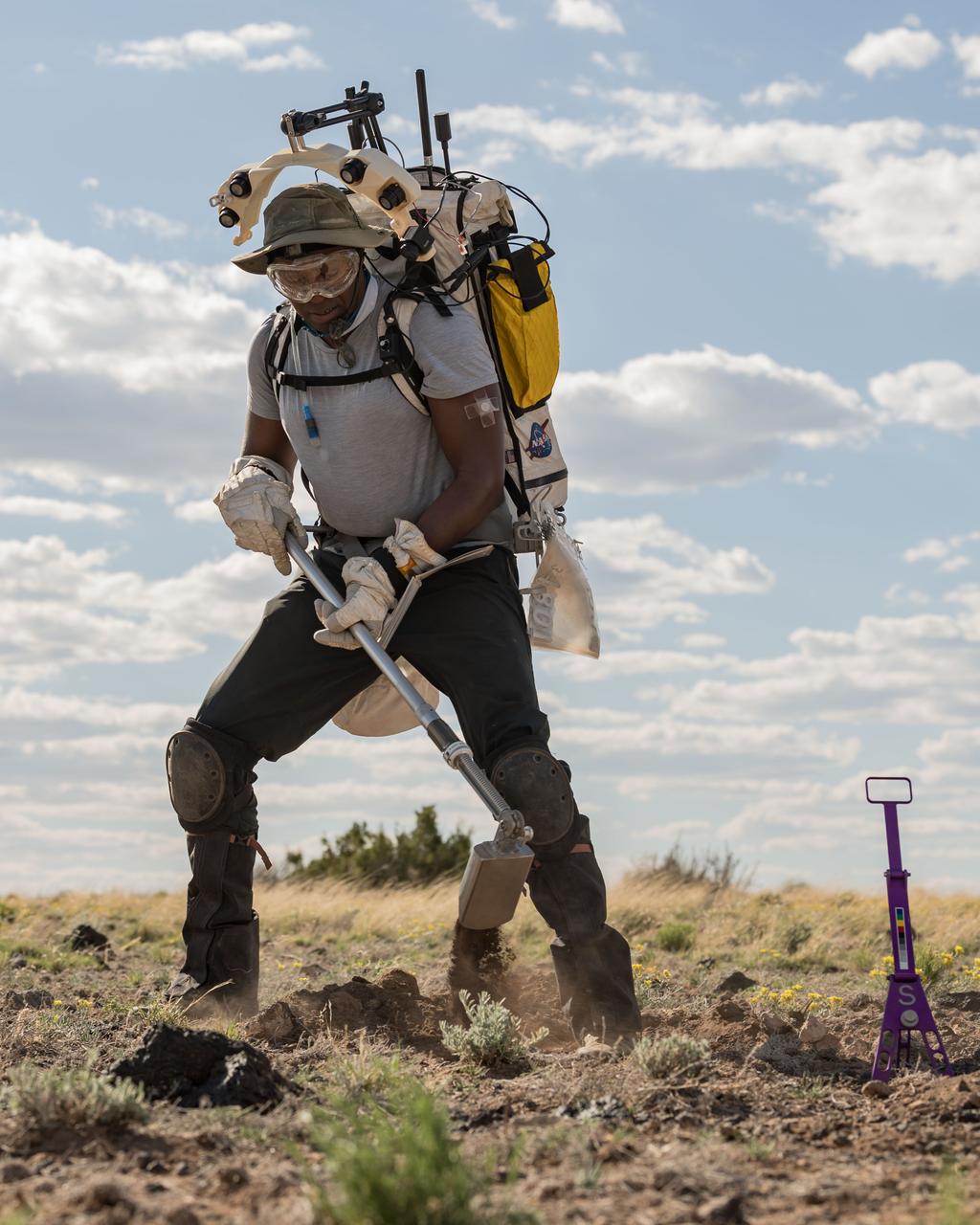
NASA astronaut Kate Rubins uses a hammer to get a drive tube into the ground to collect a pristine soil sample during a¬¬ nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. The drive tube is the key piece of hardware for preserving the integrity of samples from the Moon. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
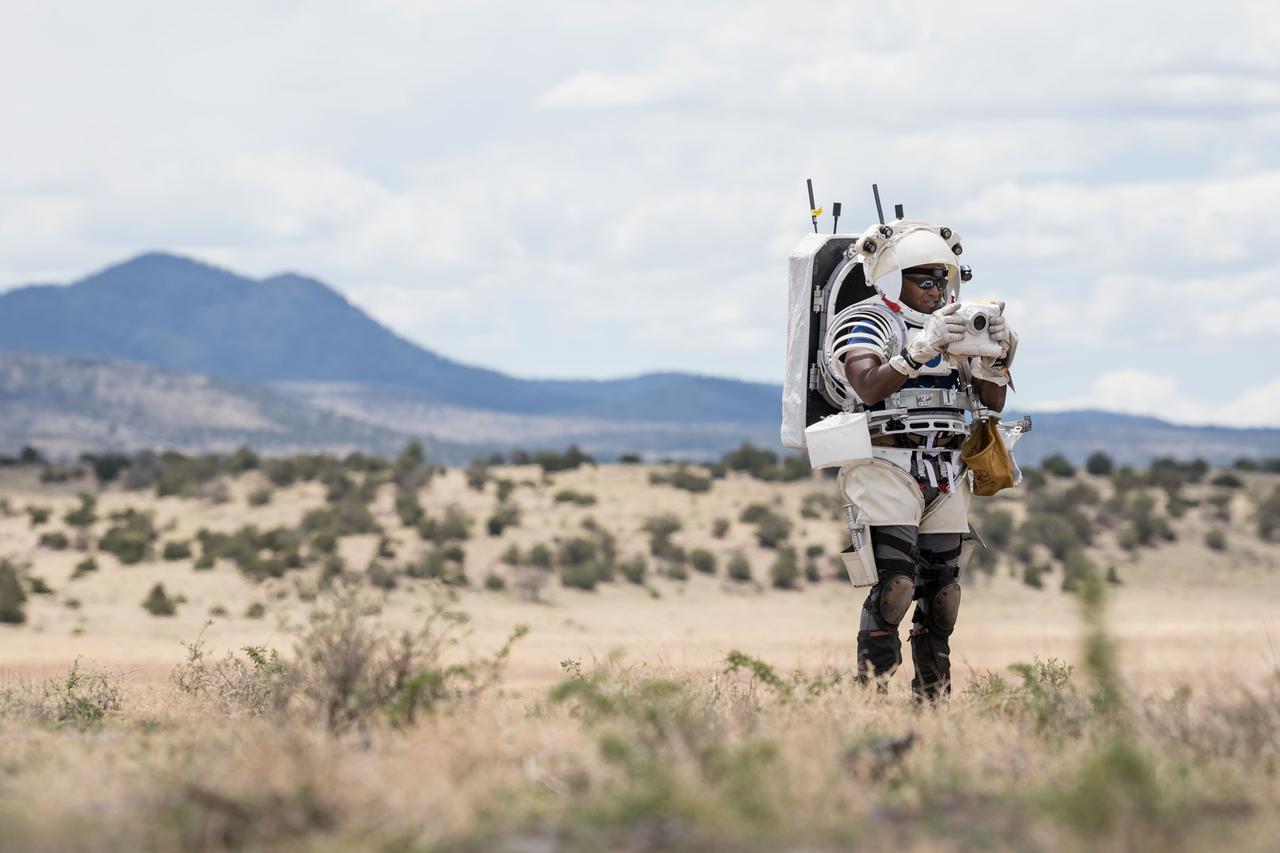

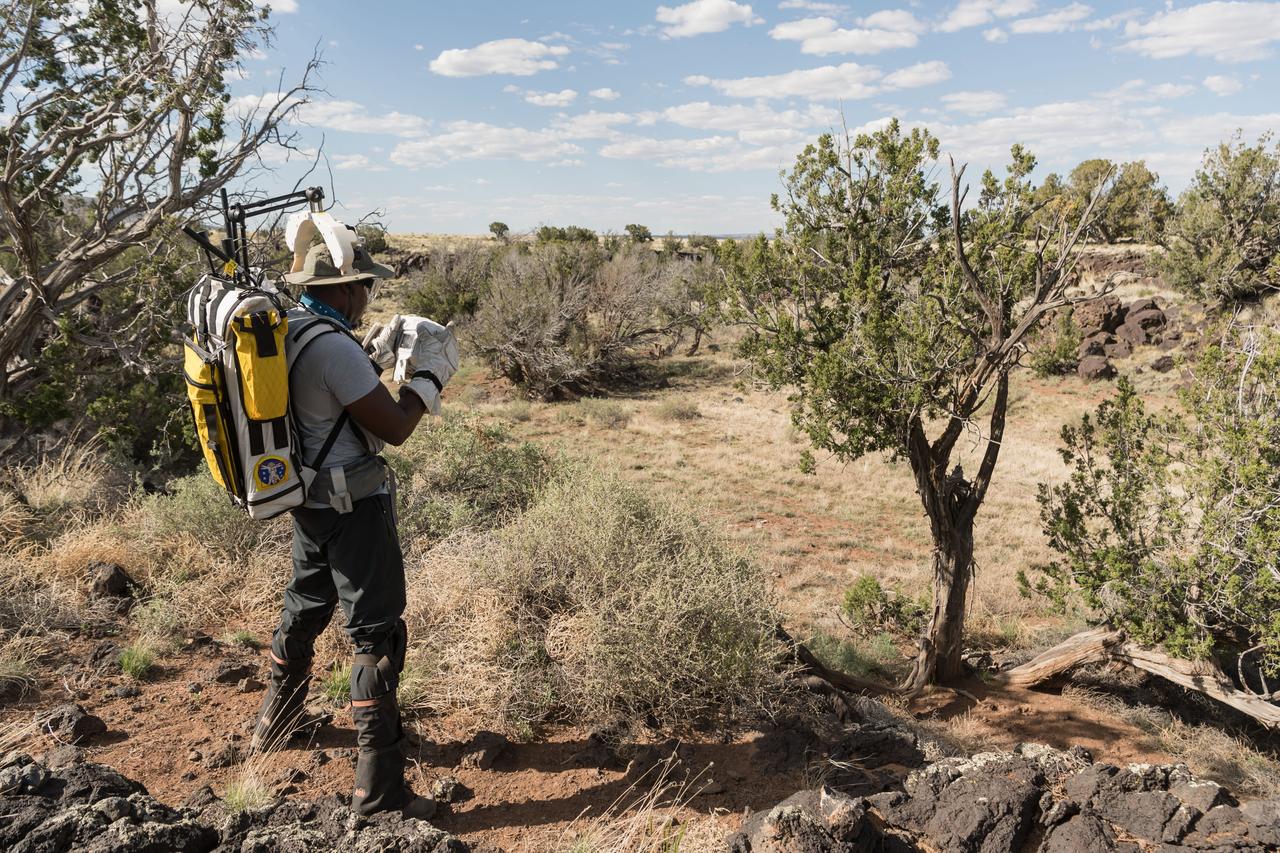
NASA astronaut Andre Douglas takes a picture of the lunar-like landscape during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 13, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
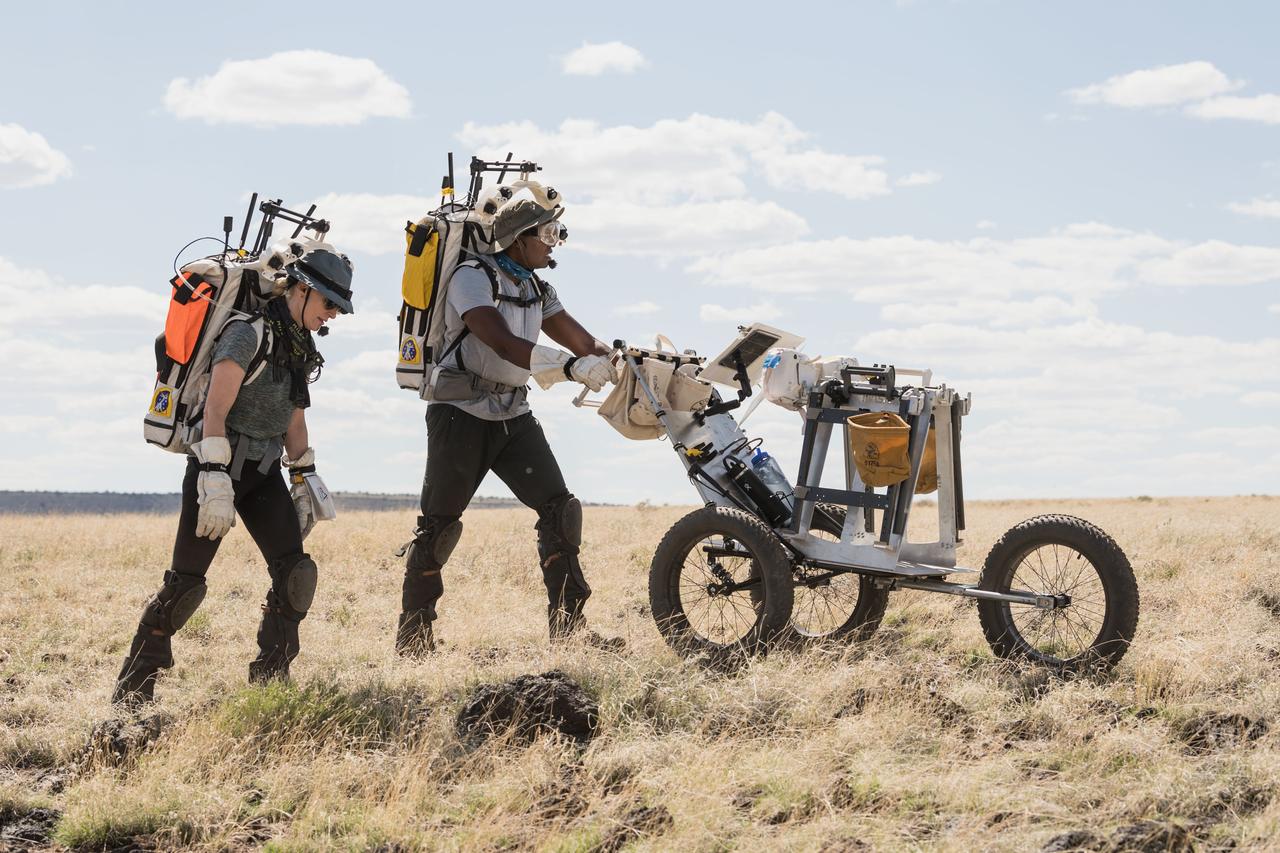

NASA astronauts Kate Rubins and Andre Douglas walk through the lunar-like landscape during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
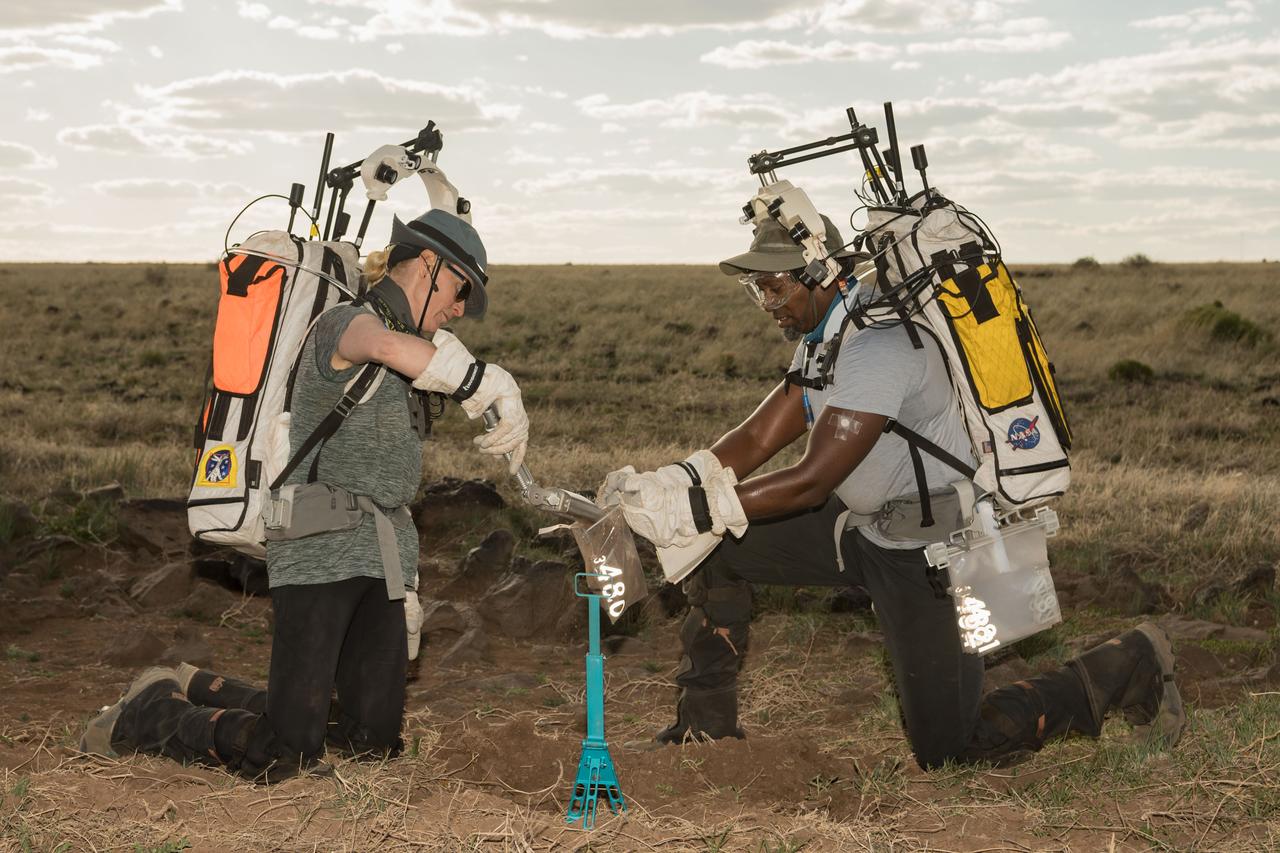

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas holds open a sample bag for NASA astronaut Kate Rubins as she pours some geology samples into it during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas uses a rake to pour “lunar” samples into a sample bag during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas leads the way while NASA astronaut Kate Rubins follows behind with a lunar tool cart during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronauts Kate Rubins and Andre Douglas look ahead at their traverse during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

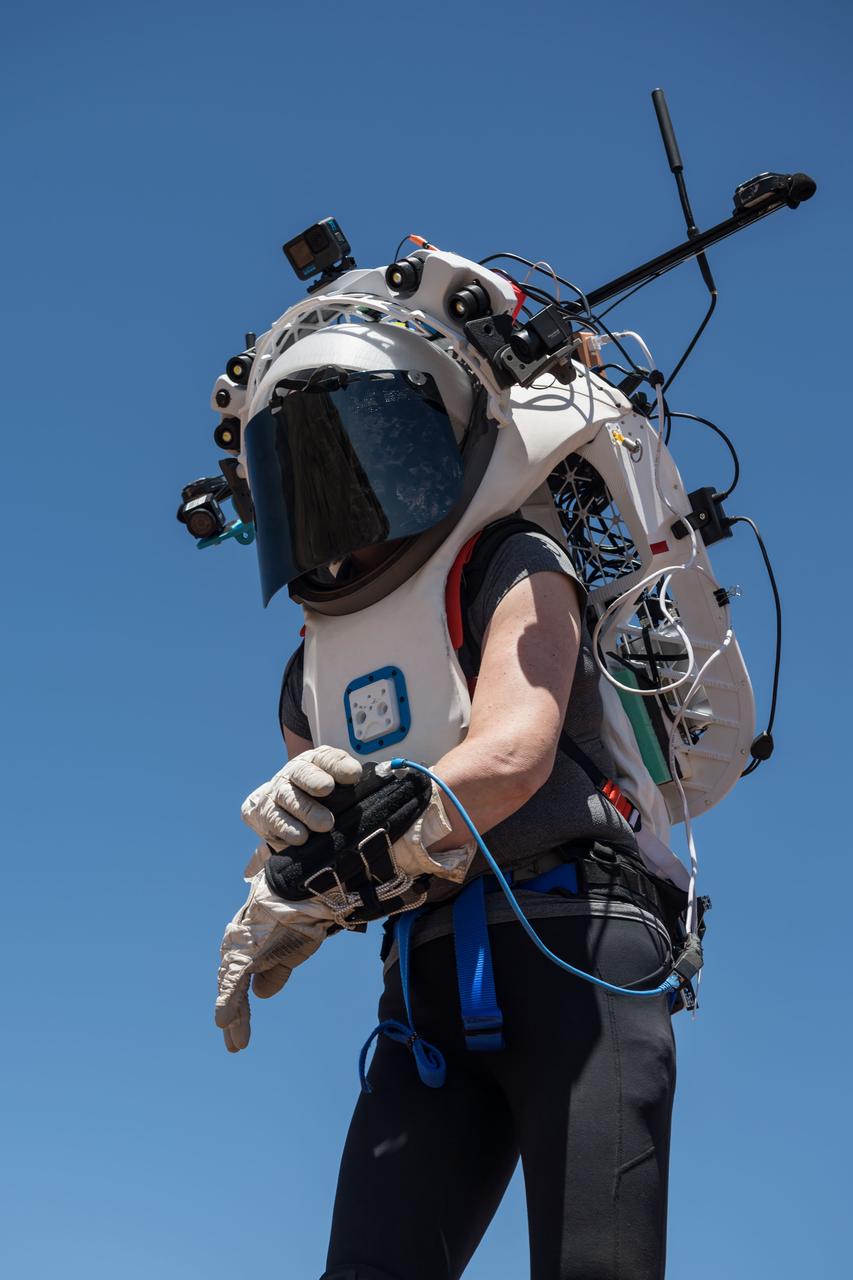
NASA astronauts Andre Douglas and Kate Rubins during a nighttime advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. Douglas is wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins uses a chisel to collect a small geologic sample during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

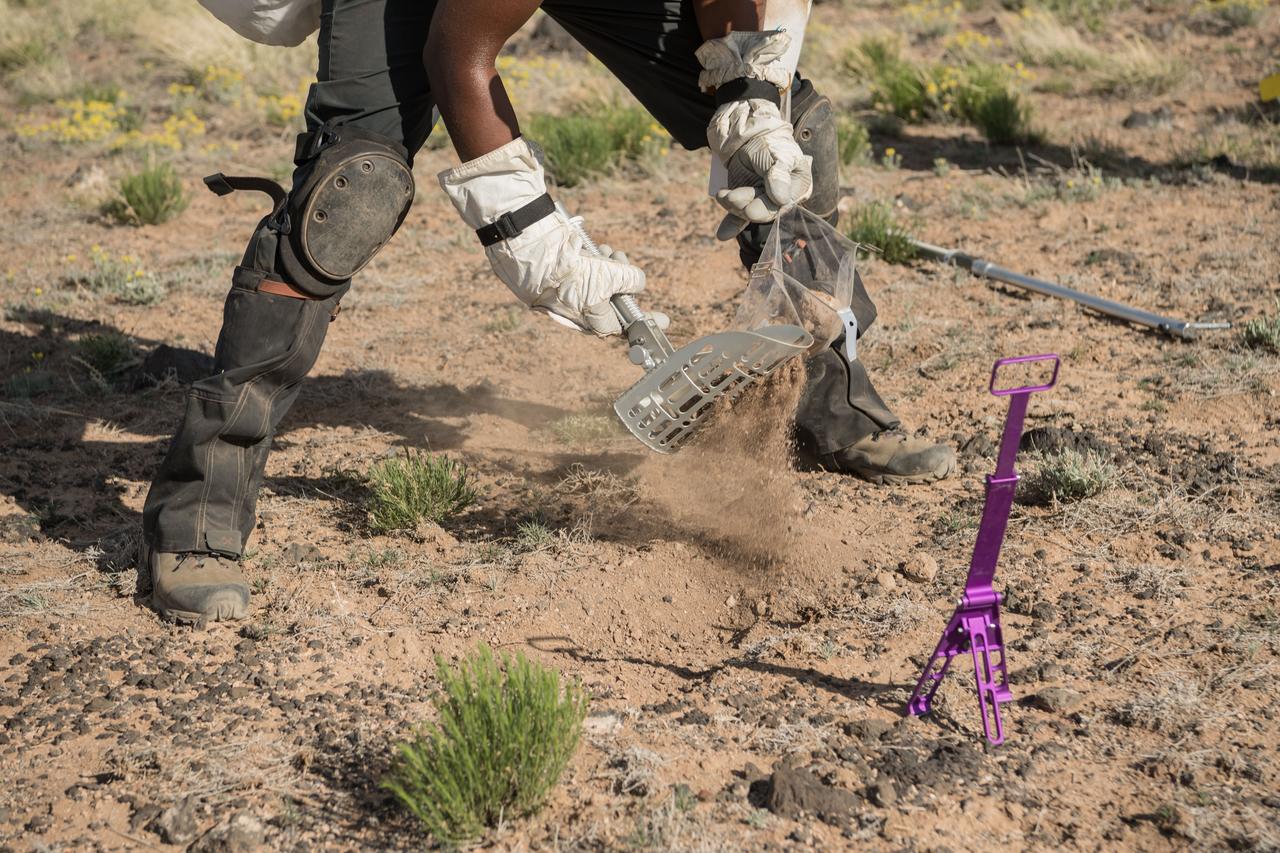
NASA astronaut Andre Douglas uses a scoop to dig into the ground to collect geologic samples during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas takes a picture of the surrounding lunar-like landscape during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
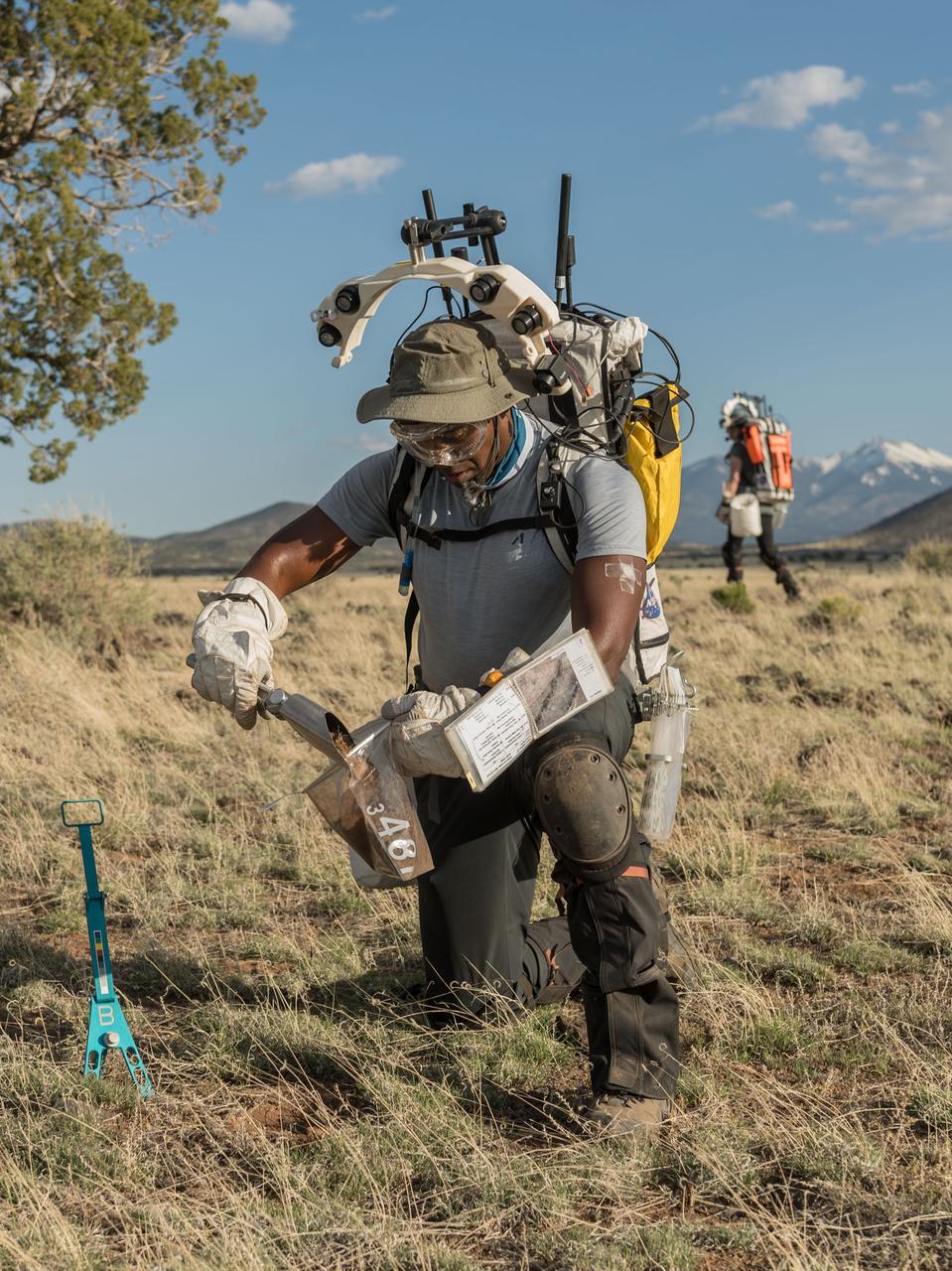

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas pours a scoopful of geologic samples into a sample bag during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins uses the hand controller on her wrist to display information while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
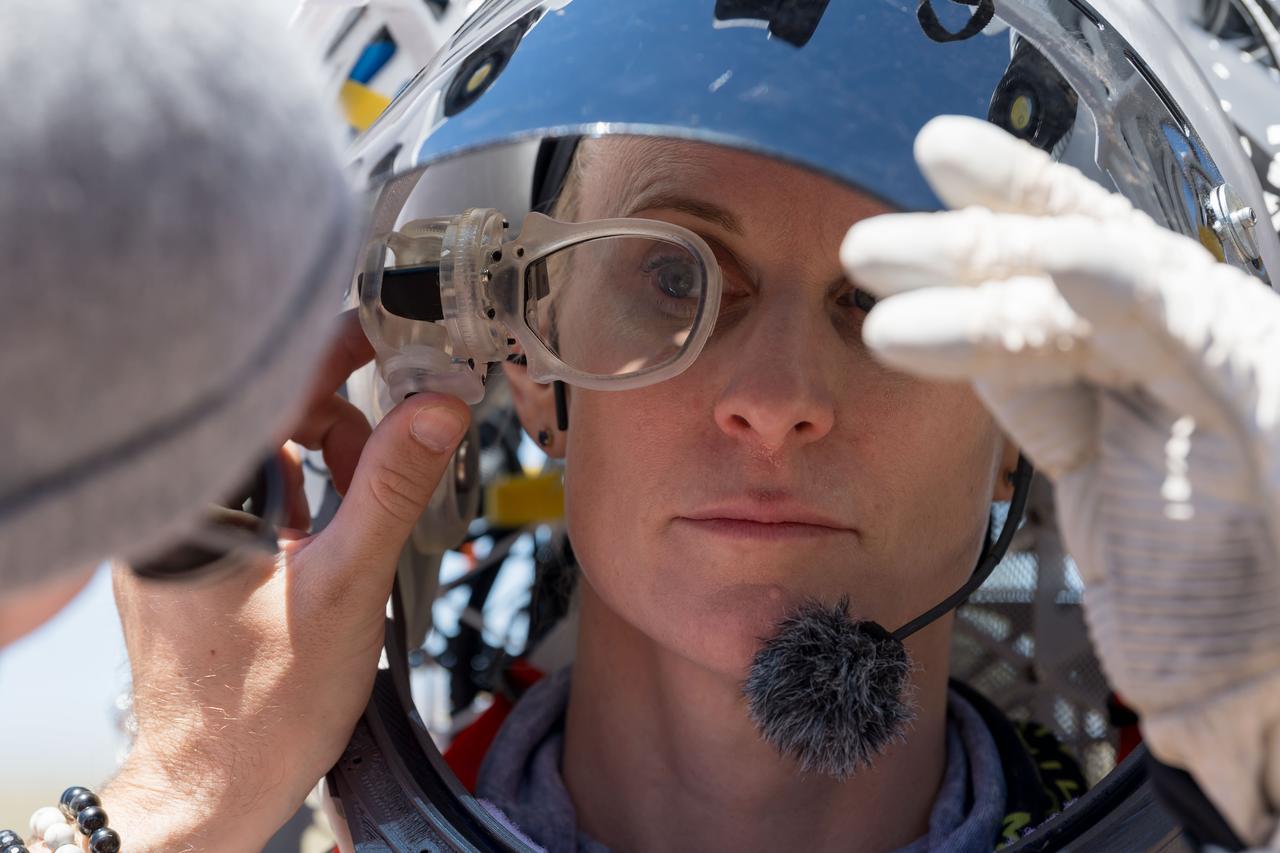

An engineer helps NASA astronaut Kate Rubins adjust the lens on the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display she’s wearing during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins walks through the lunar-like landscape wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
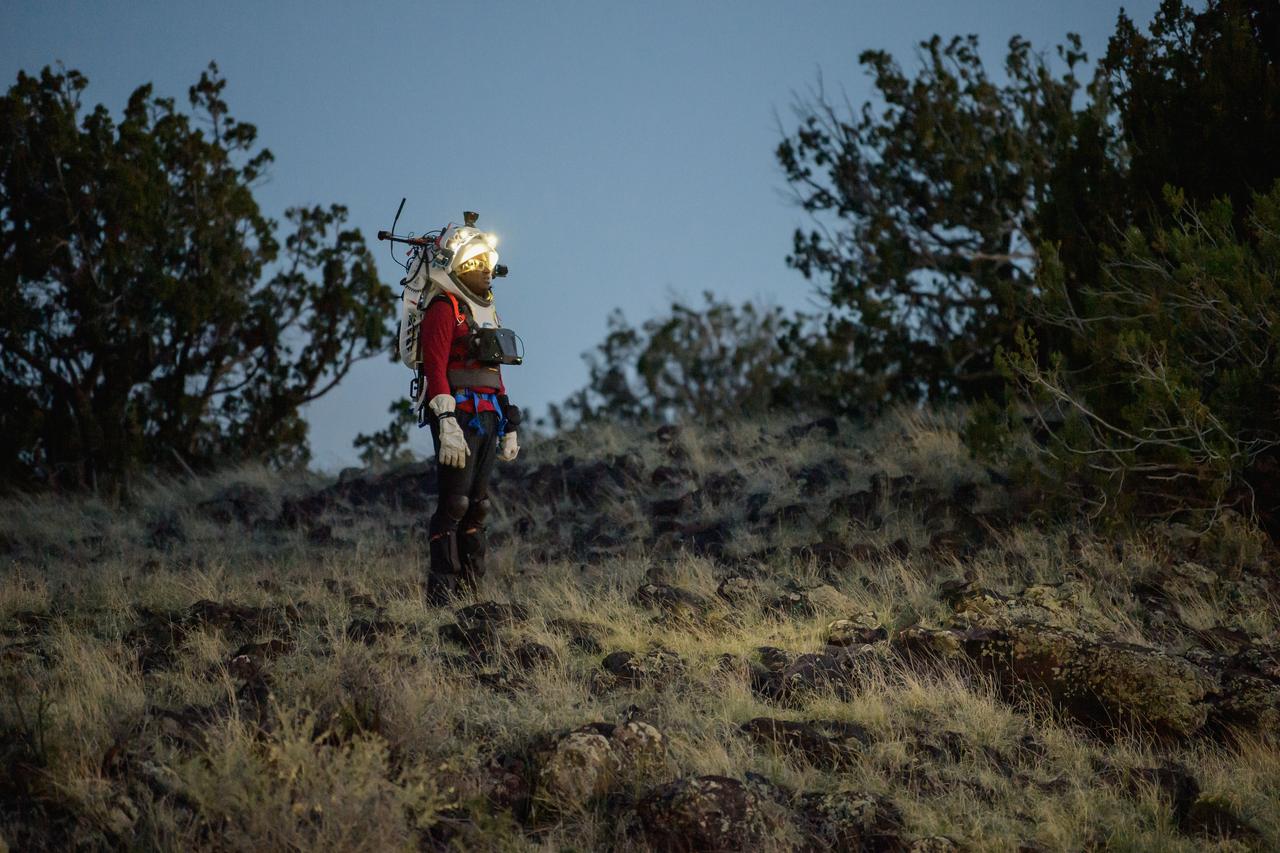

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas views the lunar-like landscape at dusk while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins walks through the lunar-like landscape wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins uses the hand controller on her wrist to display information while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
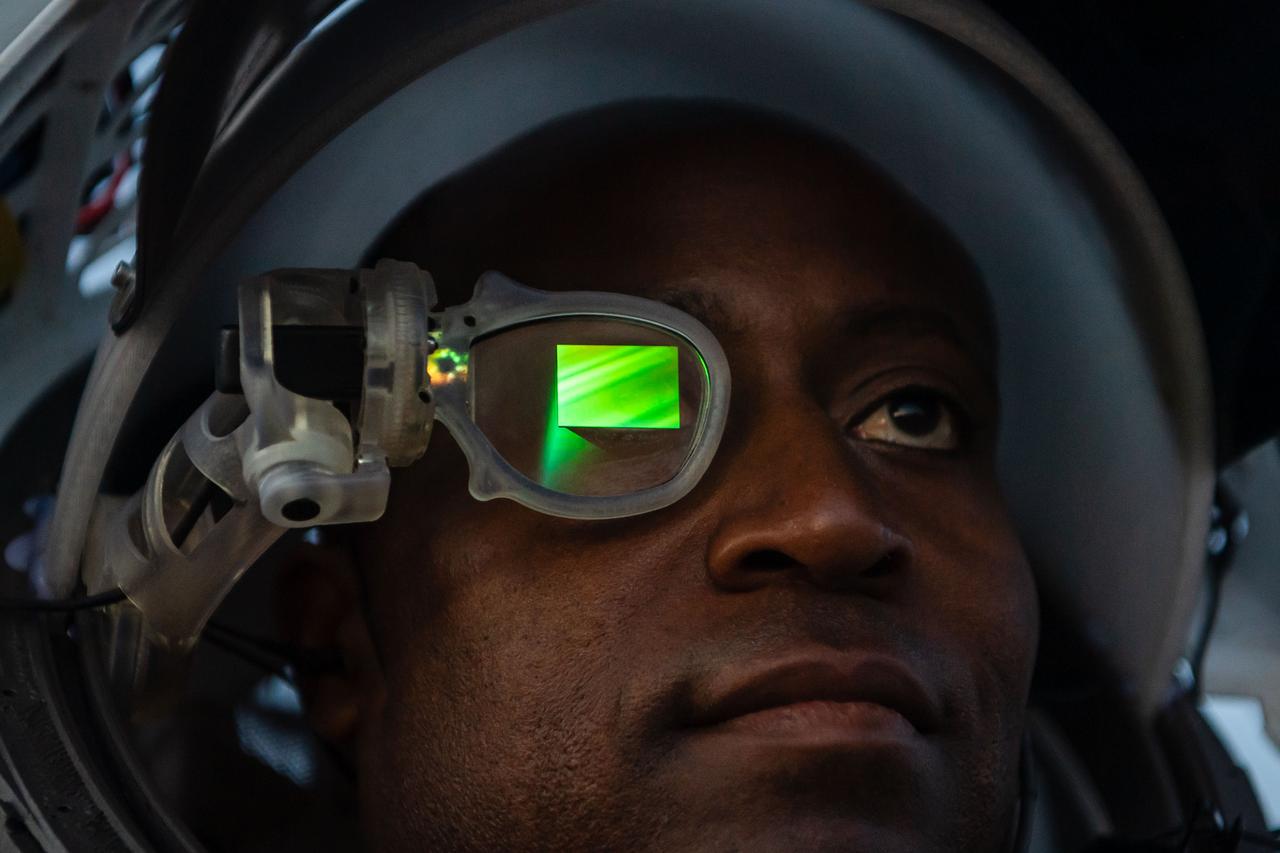

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas wears AR (Augmented Reality) display technology during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The monocular lens consists of a pico-projector and waveguide optical element to focus an image for crew to see their real world overlaid with digital information. These unique near-eye form factors may be used to improve the usability and minimally impact the complex biomechanics of working in a pressurized suit environment. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
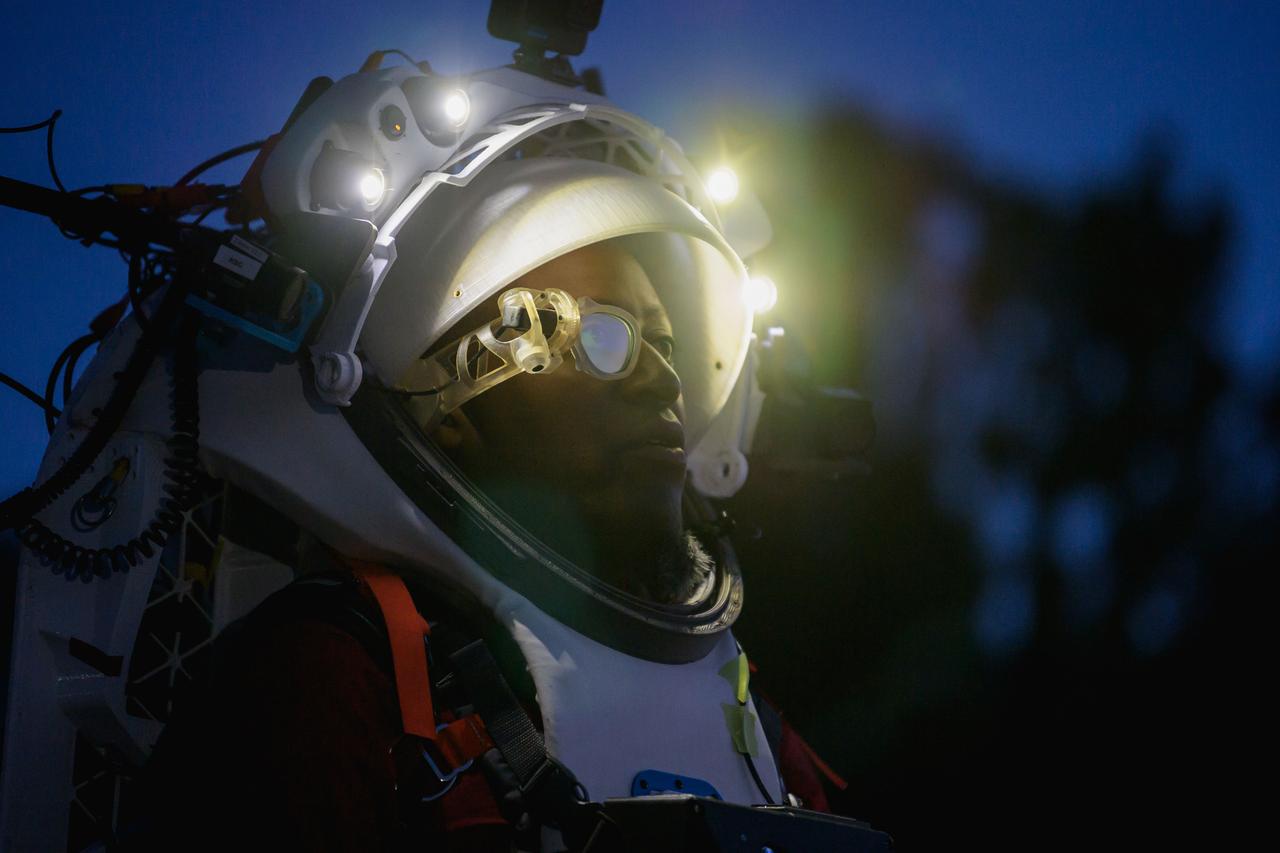

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas wears AR (Augmented Reality) display technology during a nighttime advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The monocular lens consists of a pico-projector and waveguide optical element to focus an image for crew to see their real world overlaid with digital information. These unique near-eye form factors may be used to improve the usability and minimally impact the complex biomechanics of working in a pressurized suit environment. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

Engineers help NASA astronaut Andre Douglas adjust the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display he’s wearing during a nighttime advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins opens the sun visor on the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display she’s wearing during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
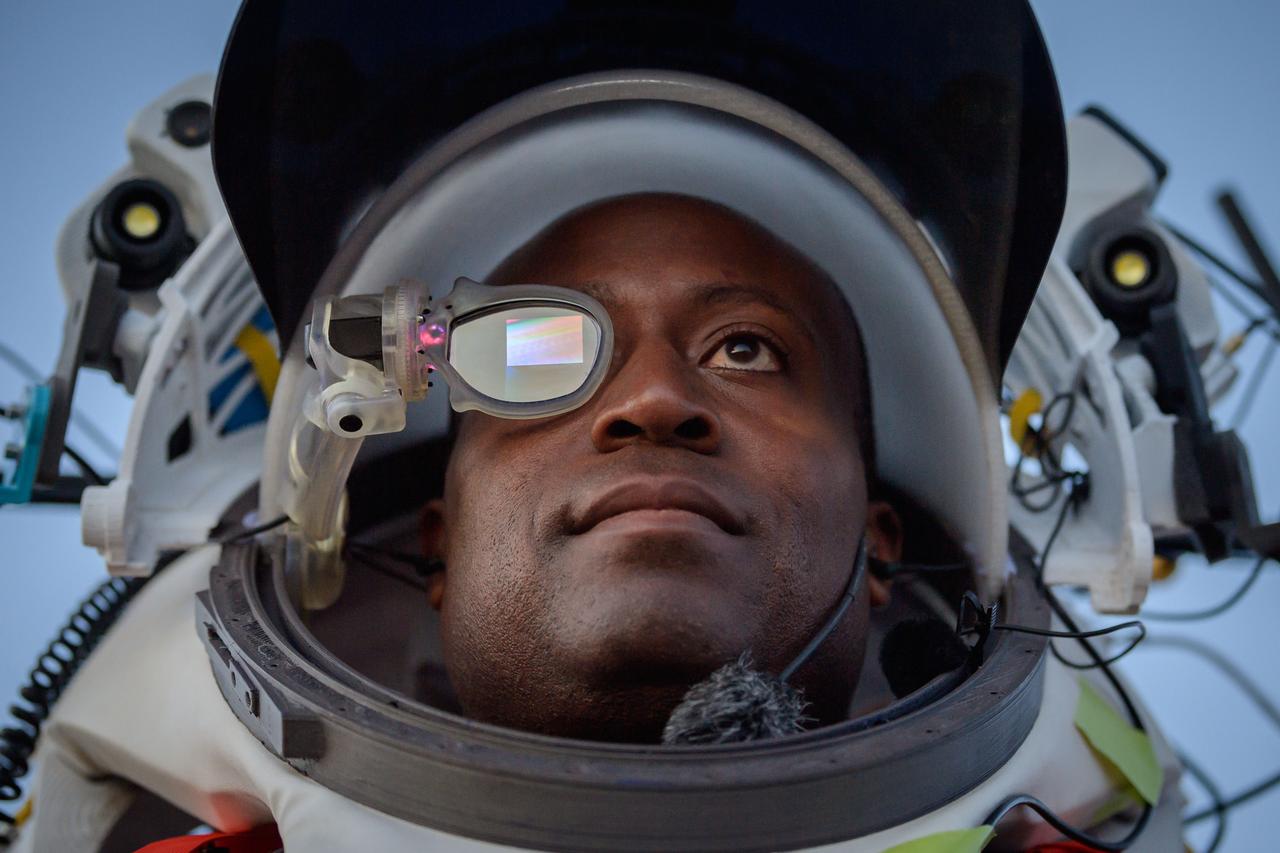

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas wears AR (Augmented Reality) display technology during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The monocular lens consists of a pico-projector and waveguide optical element to focus an image for crew to see their real world overlaid with digital information. These unique near-eye form factors may be used to improve the usability and minimally impact the complex biomechanics of working in a pressurized suit environment. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

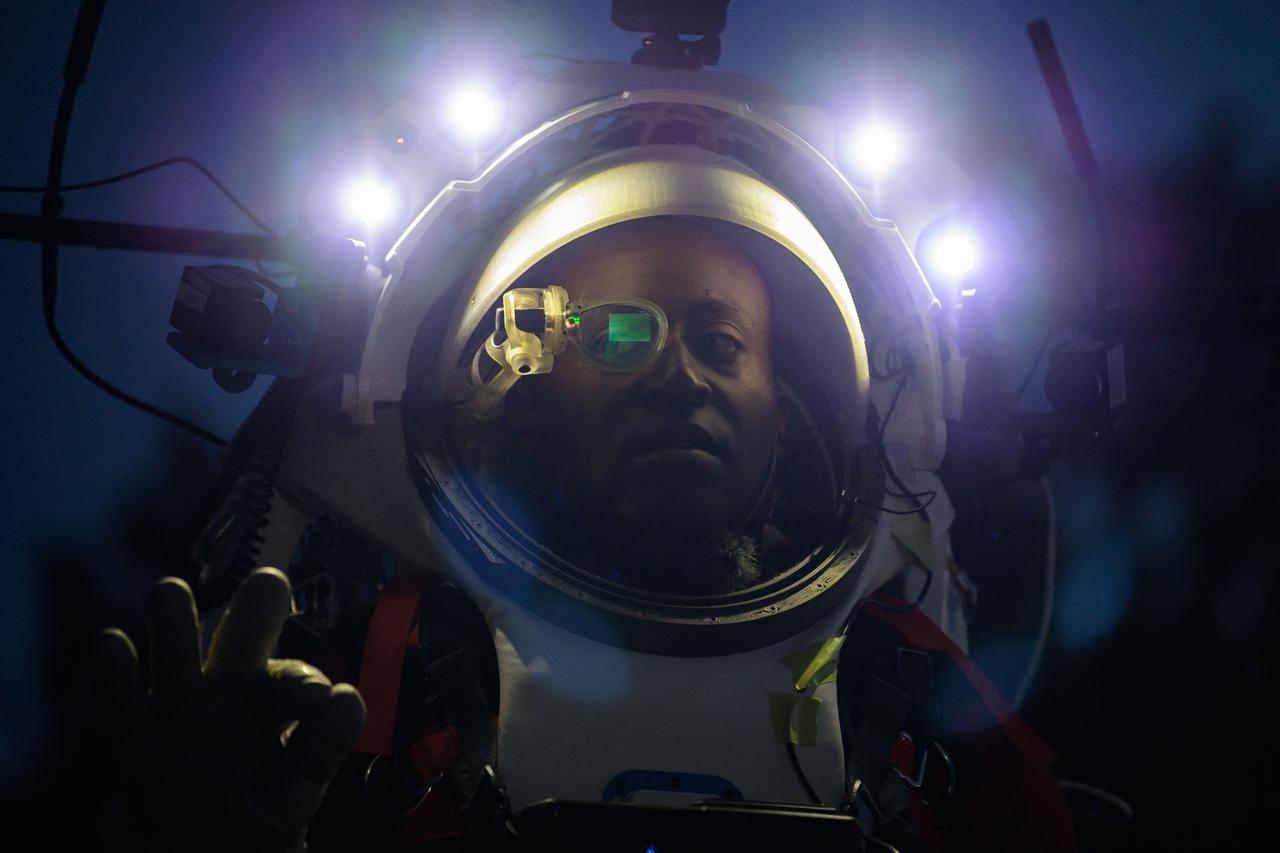
NASA astronaut Andre Douglas wears the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during a nighttime advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
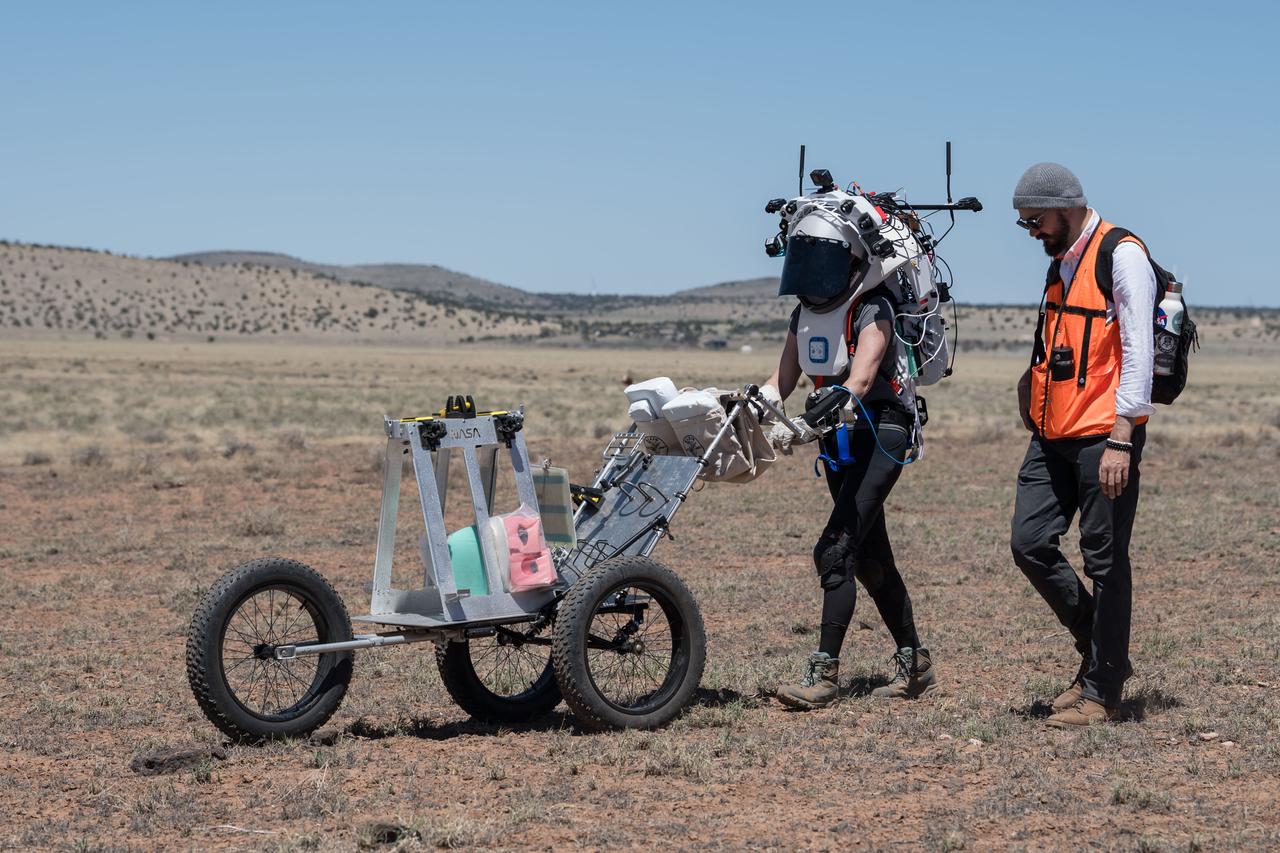

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins pushes a cart through the lunar-like landscape while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

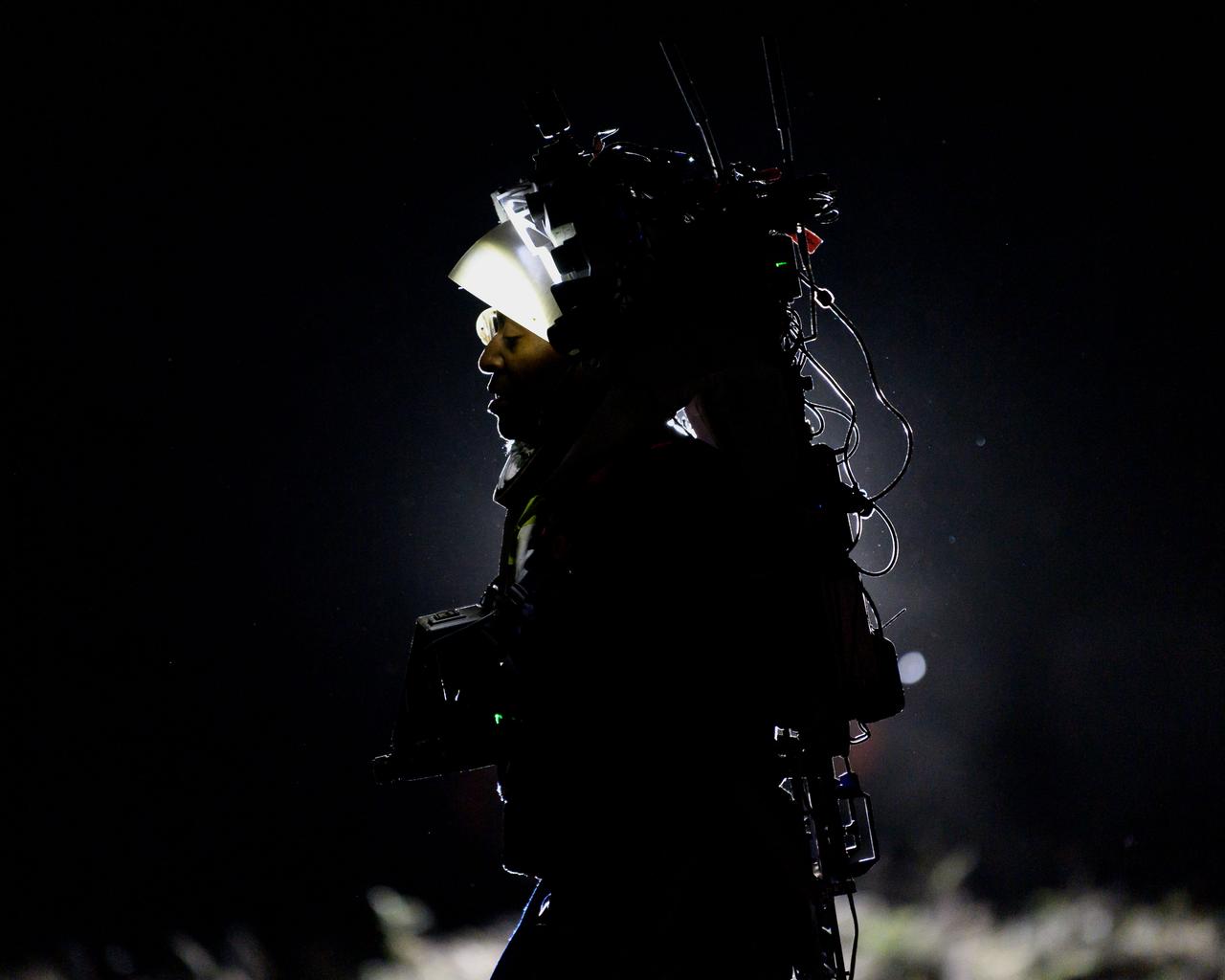
NASA astronaut Andre Douglas wears AR (Augmented Reality) display technology during a nighttime advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The monocular lens consists of a pico-projector and waveguide optical element to focus an image for crew to see their real world overlaid with digital information. These unique near-eye form factors may be used to improve the usability and minimally impact the complex biomechanics of working in a pressurized suit environment. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
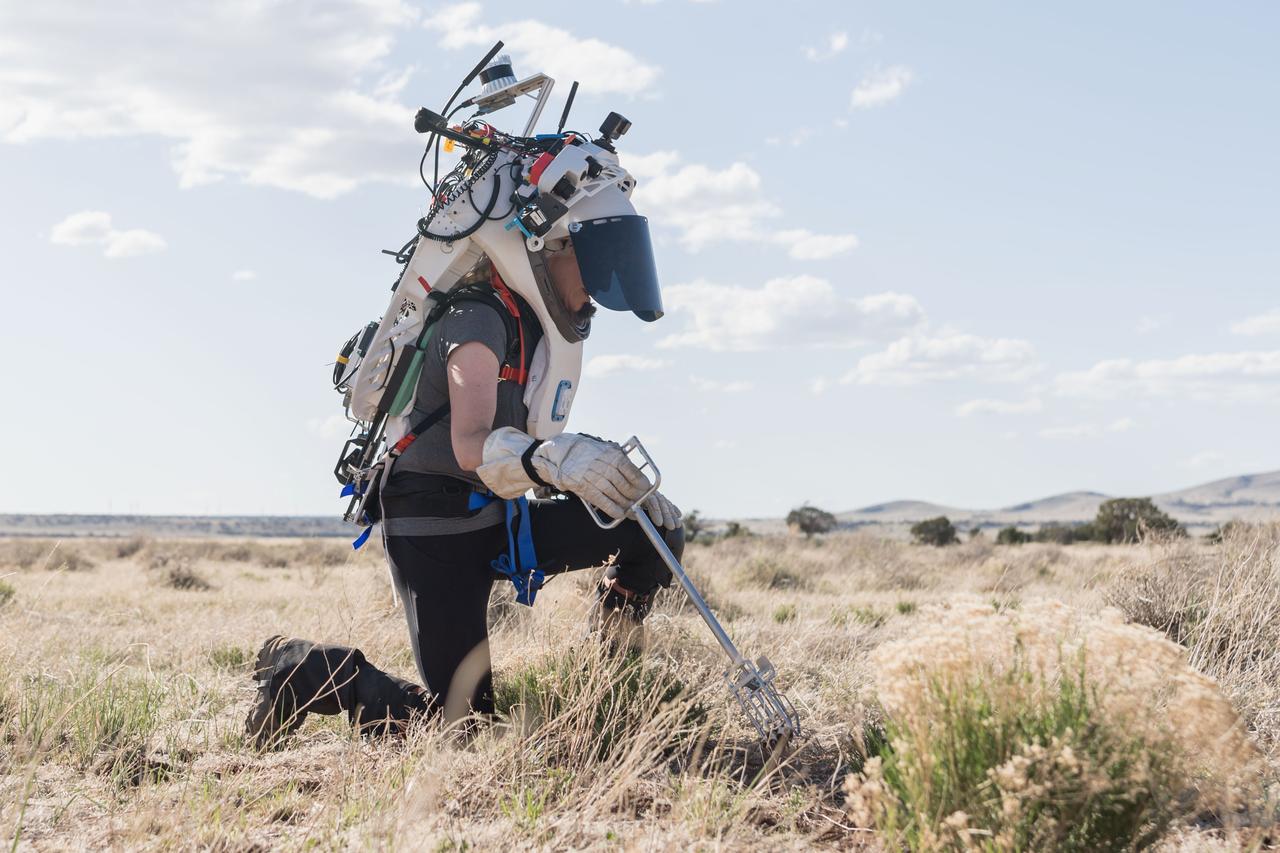

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins uses tongs to collect geologic samples while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
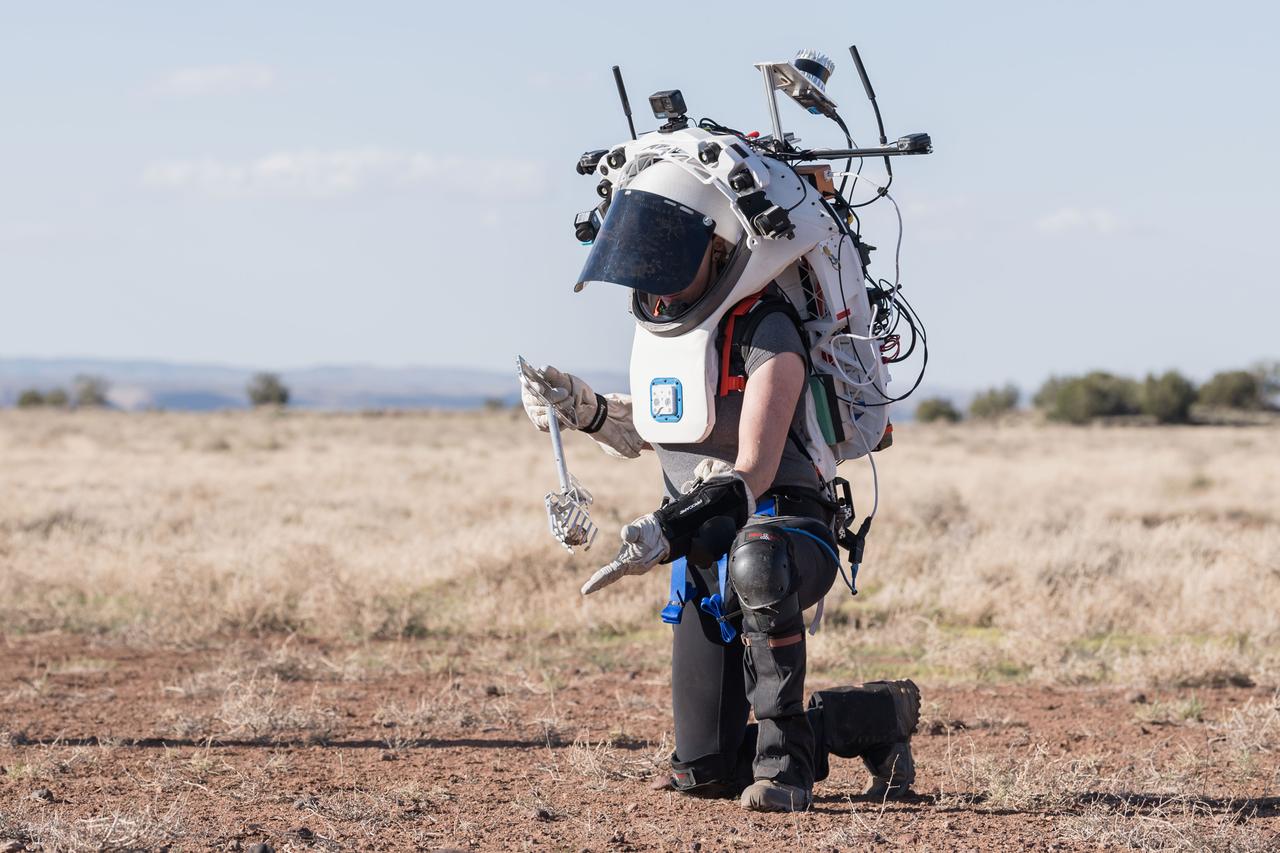

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins uses tongs to pick up a geologic sample while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
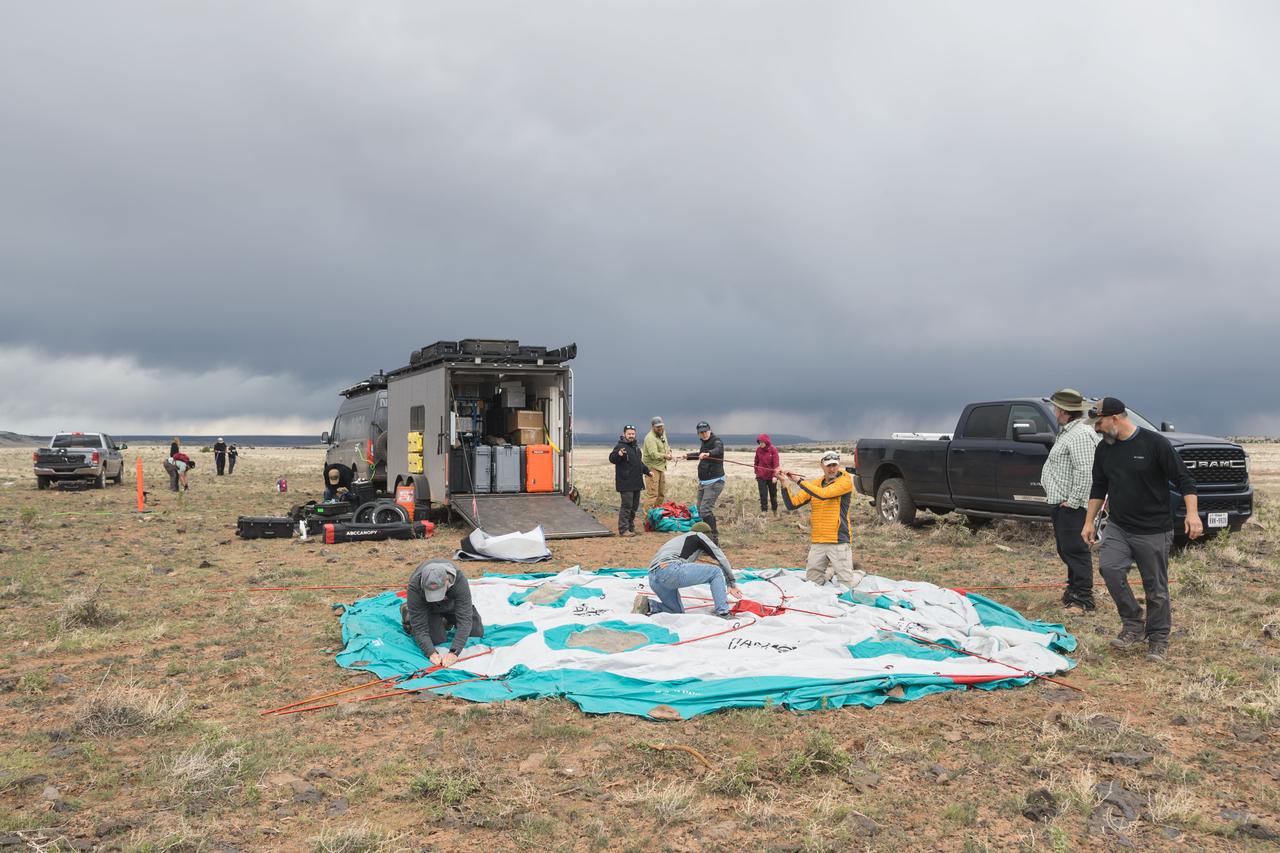

NASA teams work to set up the base camp for the Joint Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Test Team Field Test 5 (JETT5) in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 11, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

Engineers Juan Busto (left) and Mike Miller (right) work to install the communications network for the base camp during the Joint Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Test Team Field Test 5 (JETT5) in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 11, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
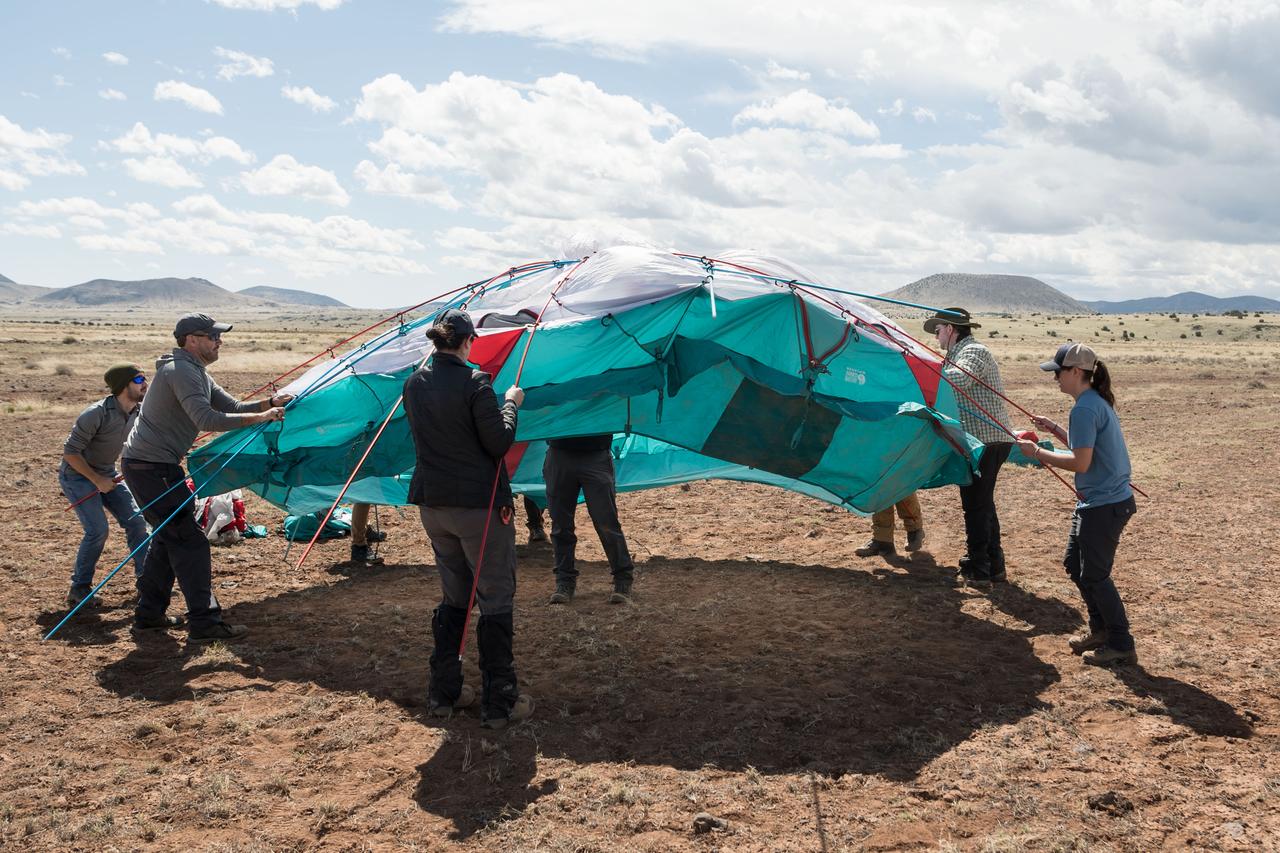

NASA teams work to set up a one of many tents that will serve as the base camp for the Joint Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Test Team Field Test 5 (JETT5) in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 11, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA teams work to set up the base camp for the Joint Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Test Team Field Test 5 (JETT5) in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 11, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
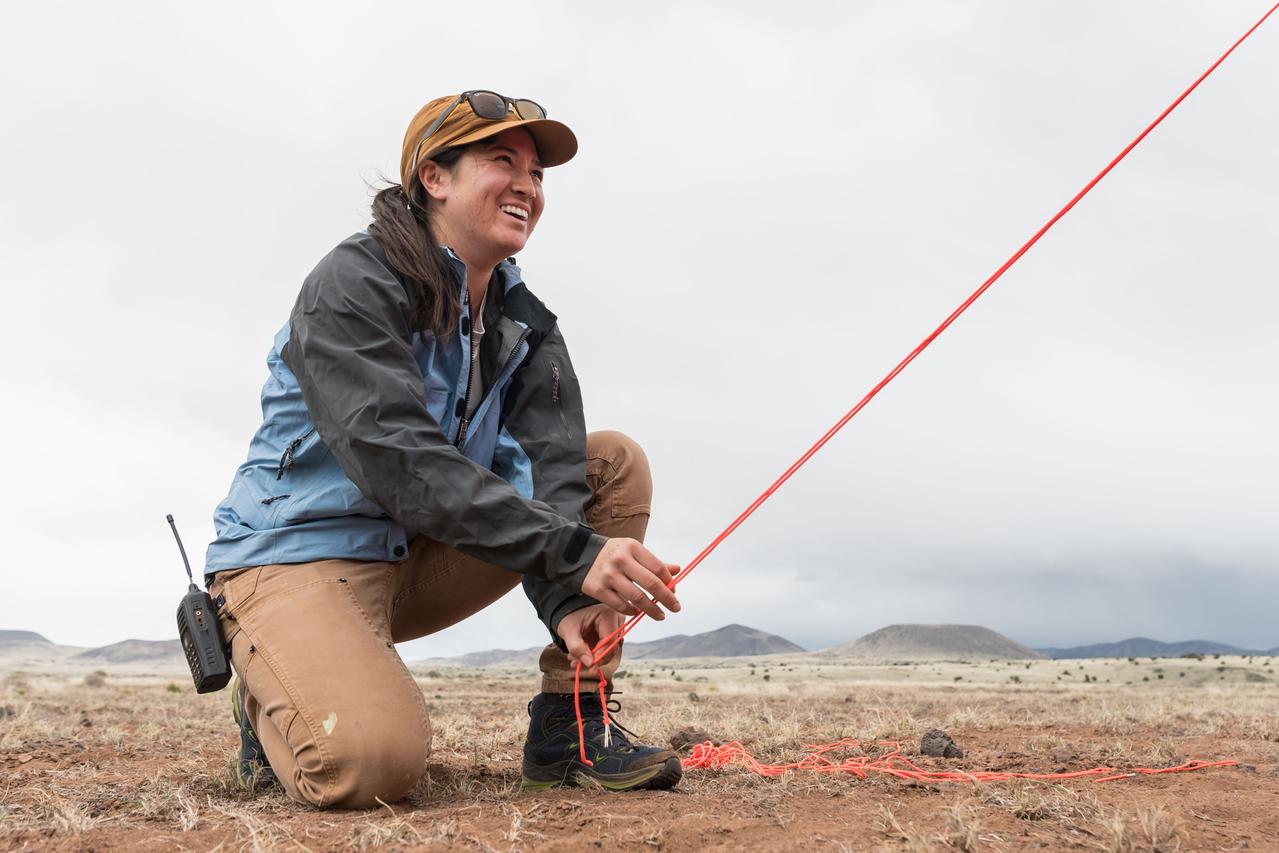

Test deputy field manager Angela Garcia ties down a tent that will serve as the base camp for the Joint Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Test Team Field Test 5 (JETT5) in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 11, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA teams work to set up one of many tents that will serve as the base camp for the (JETT5) Joint Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Test Team Field Test 5 in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 11, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

Spacesuit engineers Sheldon Stockfleth and Christine Jerome work to set up the base camp for the Joint Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Test Team Field Test 5 (JETT5) in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 11, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins takes a picture of a geologic sample during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
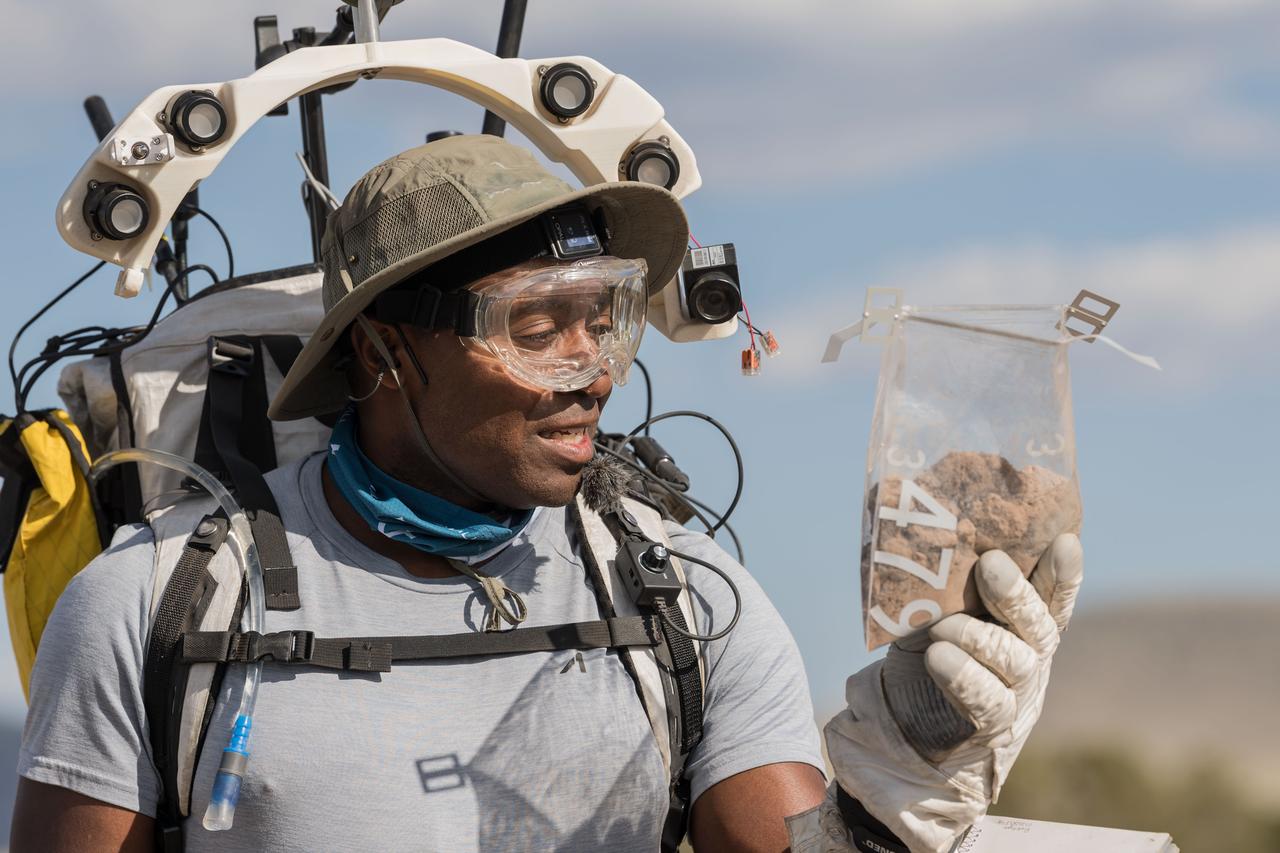

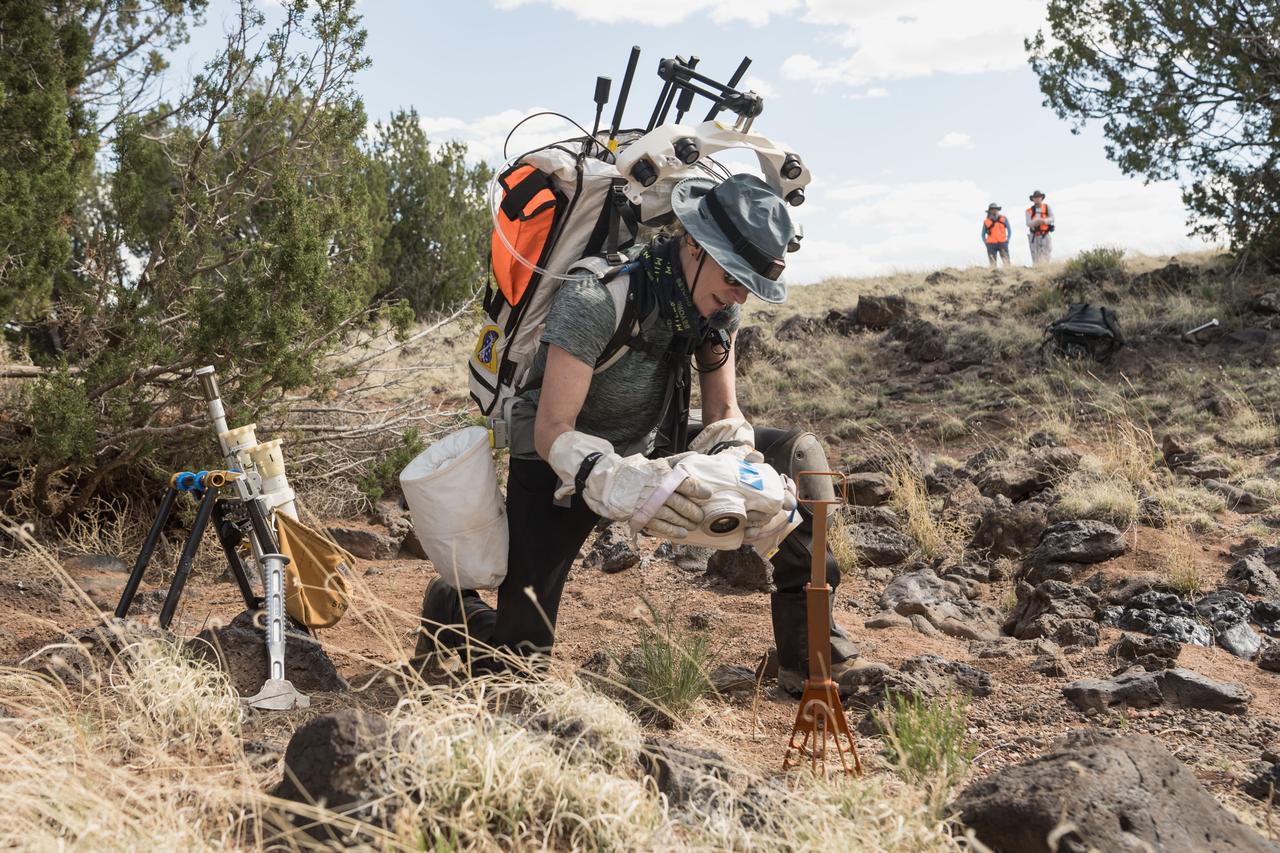
NASA astronaut Andre Douglas takes a closer look at the geologic samples he collected during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
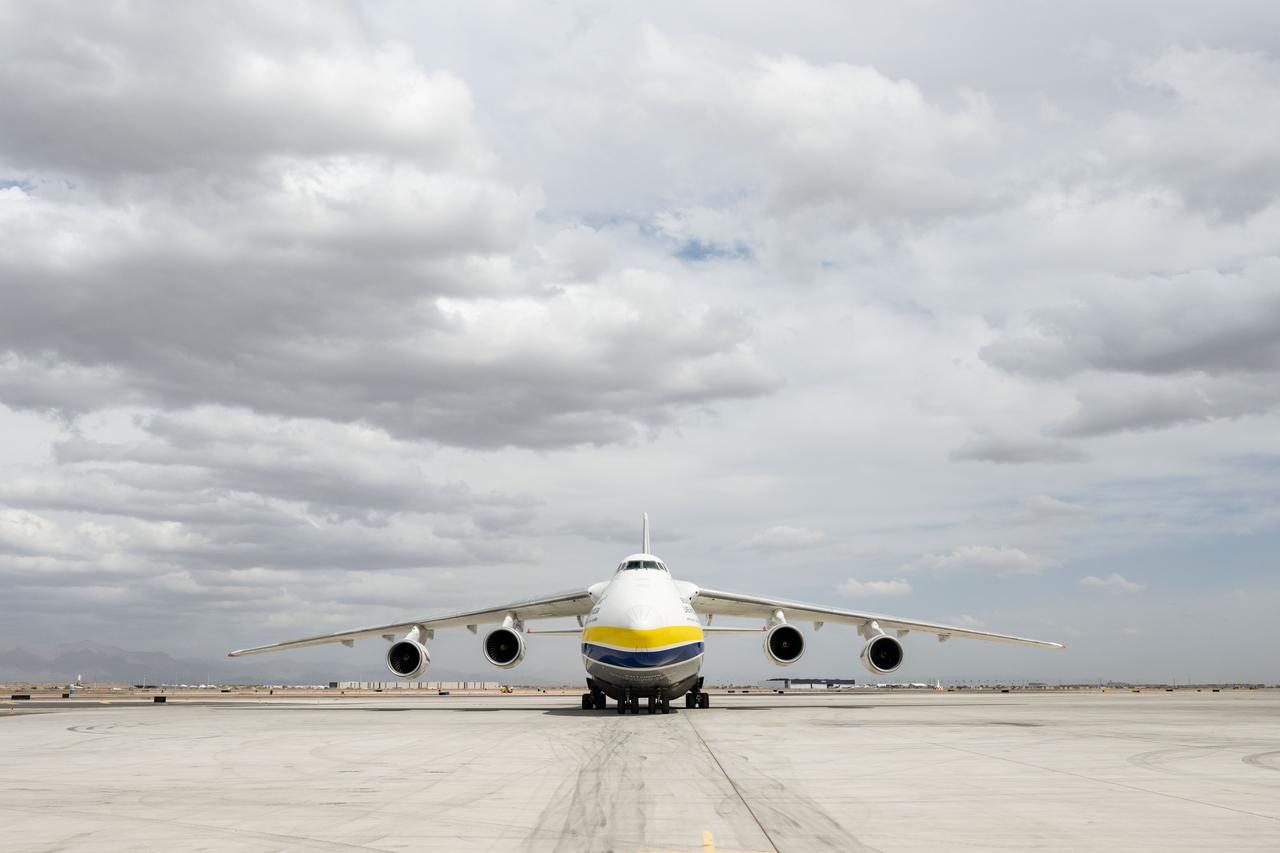

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
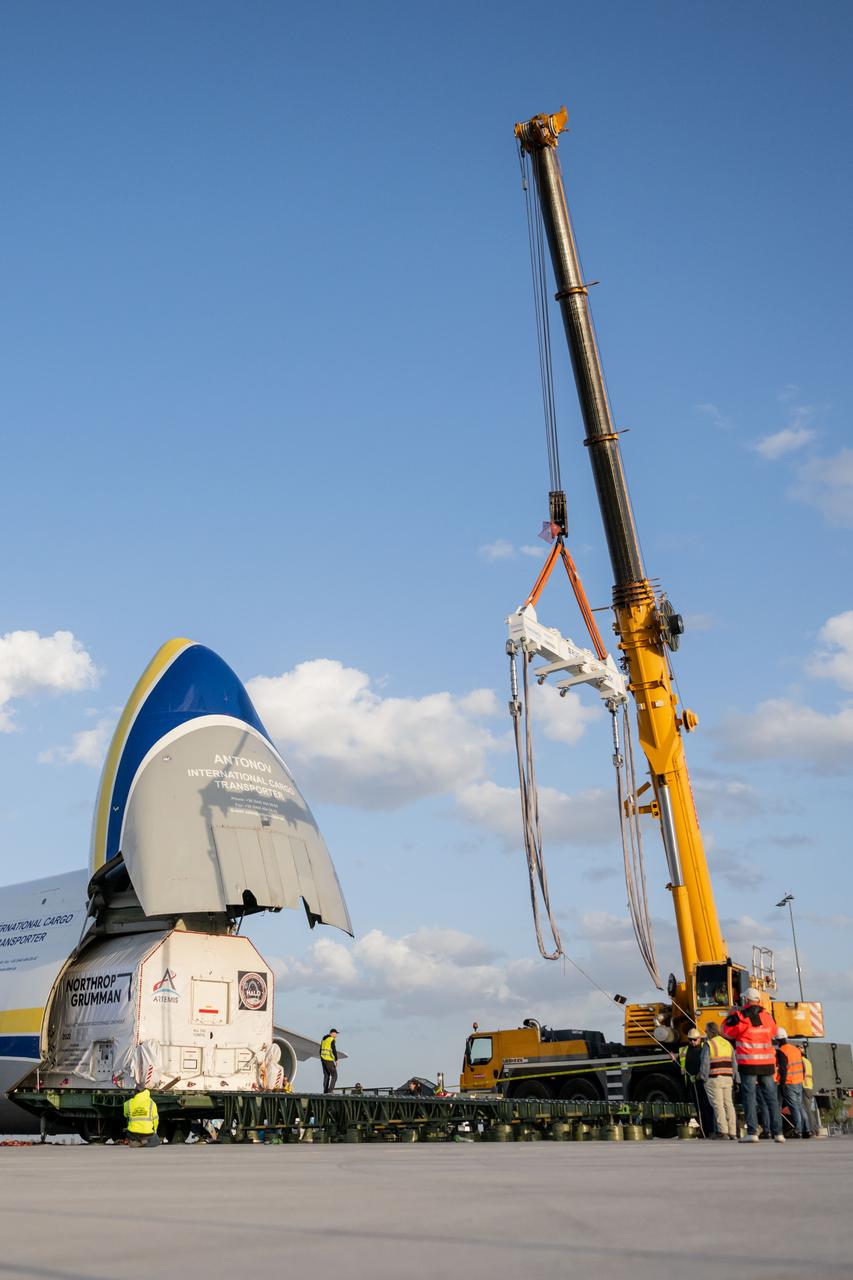

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
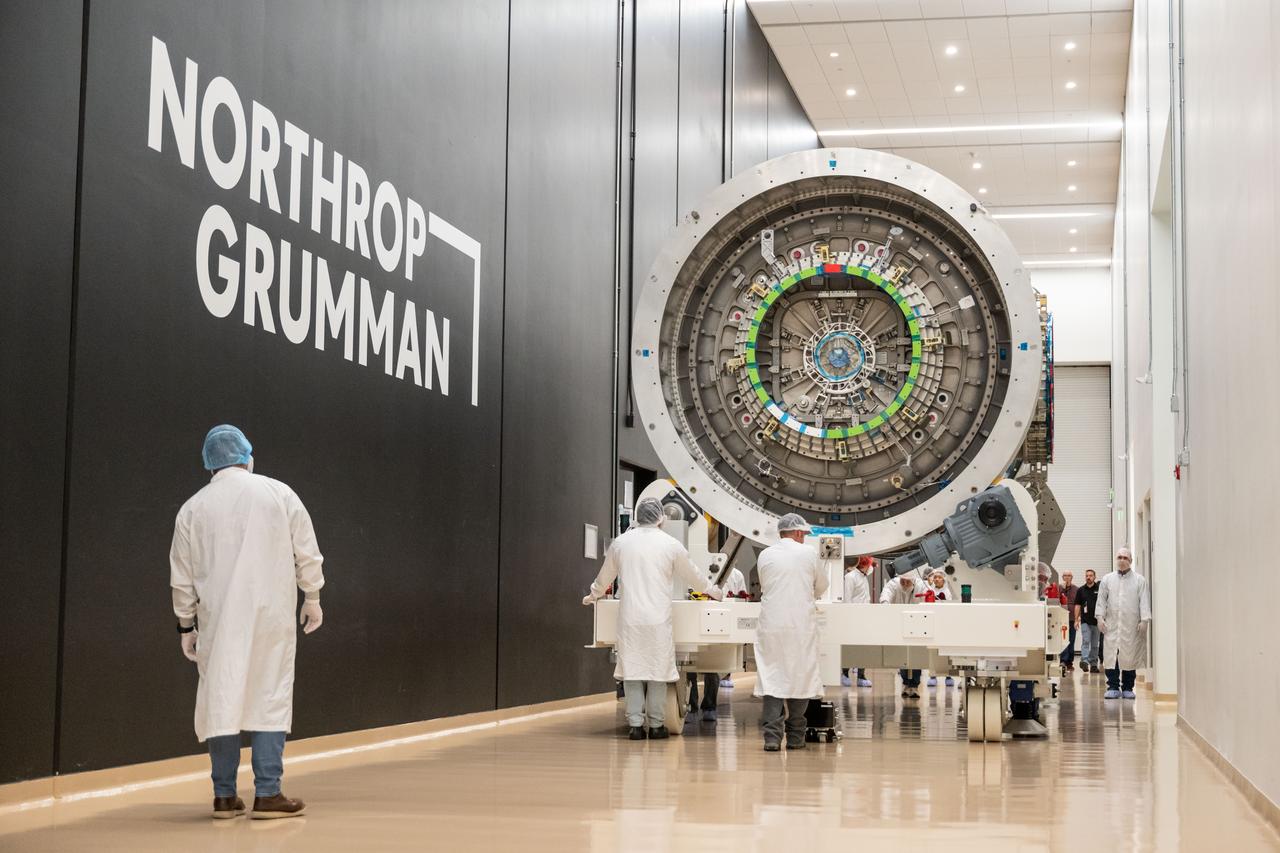

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams guide Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) down a hallway. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
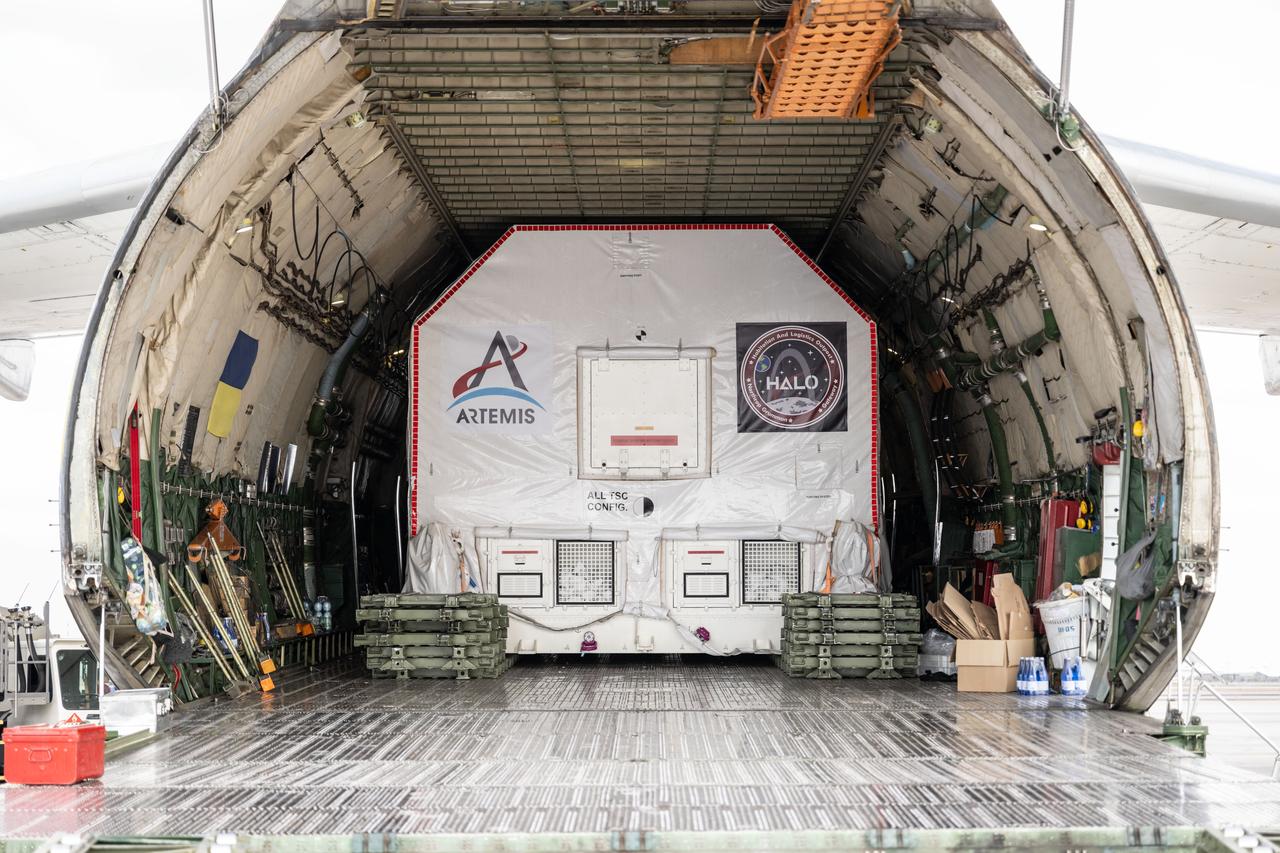

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
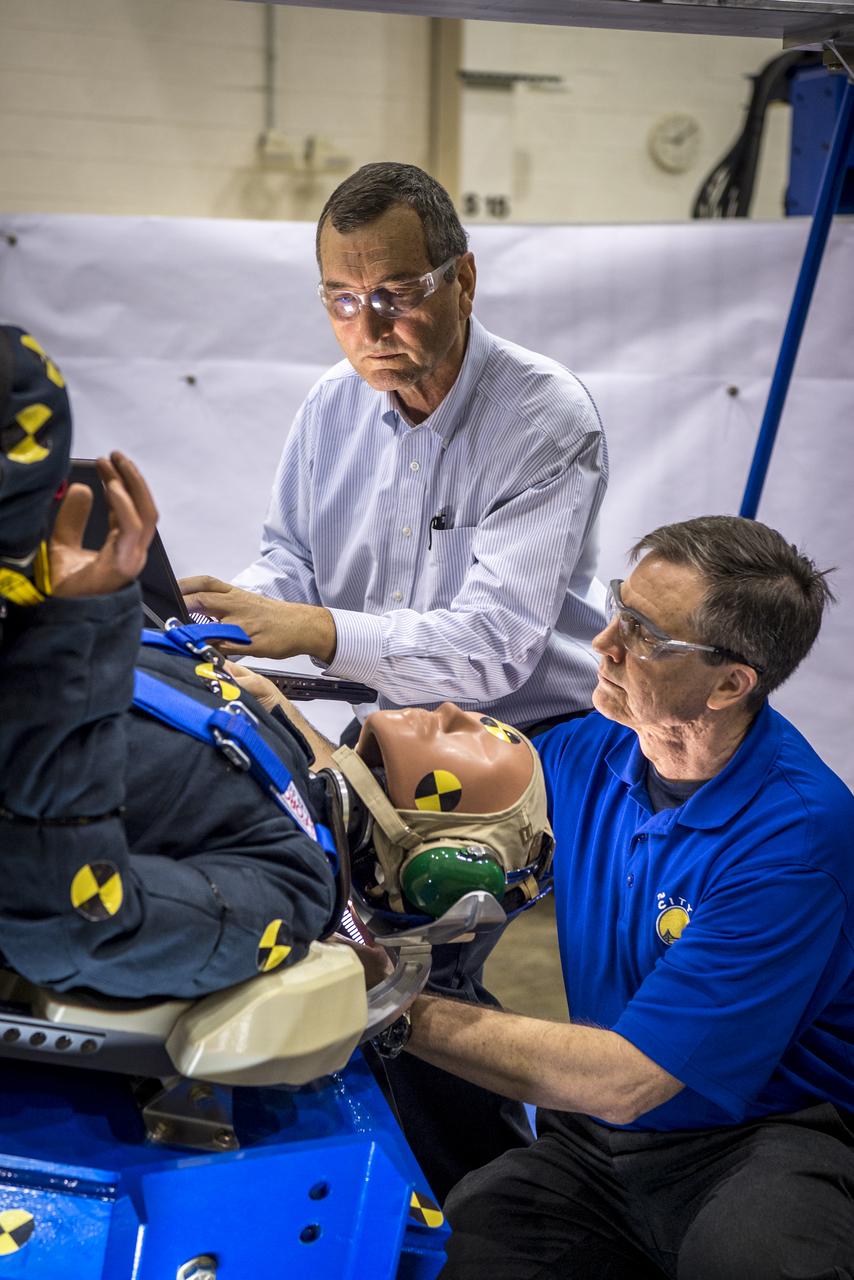
Engineers working with Boeing's CST-100 Starliner test the spacecraft's seat design in Mesa, Arizona, focusing on how the spacecraft seats would protect an astronaut's head, neck and spine during the 240-mile descent from the International Space Station. The company incorporated test dummies for a detailed analysis of impacts on a crew returning to earth. The human-sized dummies were equipped with sensitive instrumentation and secured in the seats for 30 drop tests at varying heights, angles, velocities and seat orientations in order to mimic actual landing conditions. High-speed cameras captured the footage for further analysis. The Starliner spacecraft is being developed in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program.
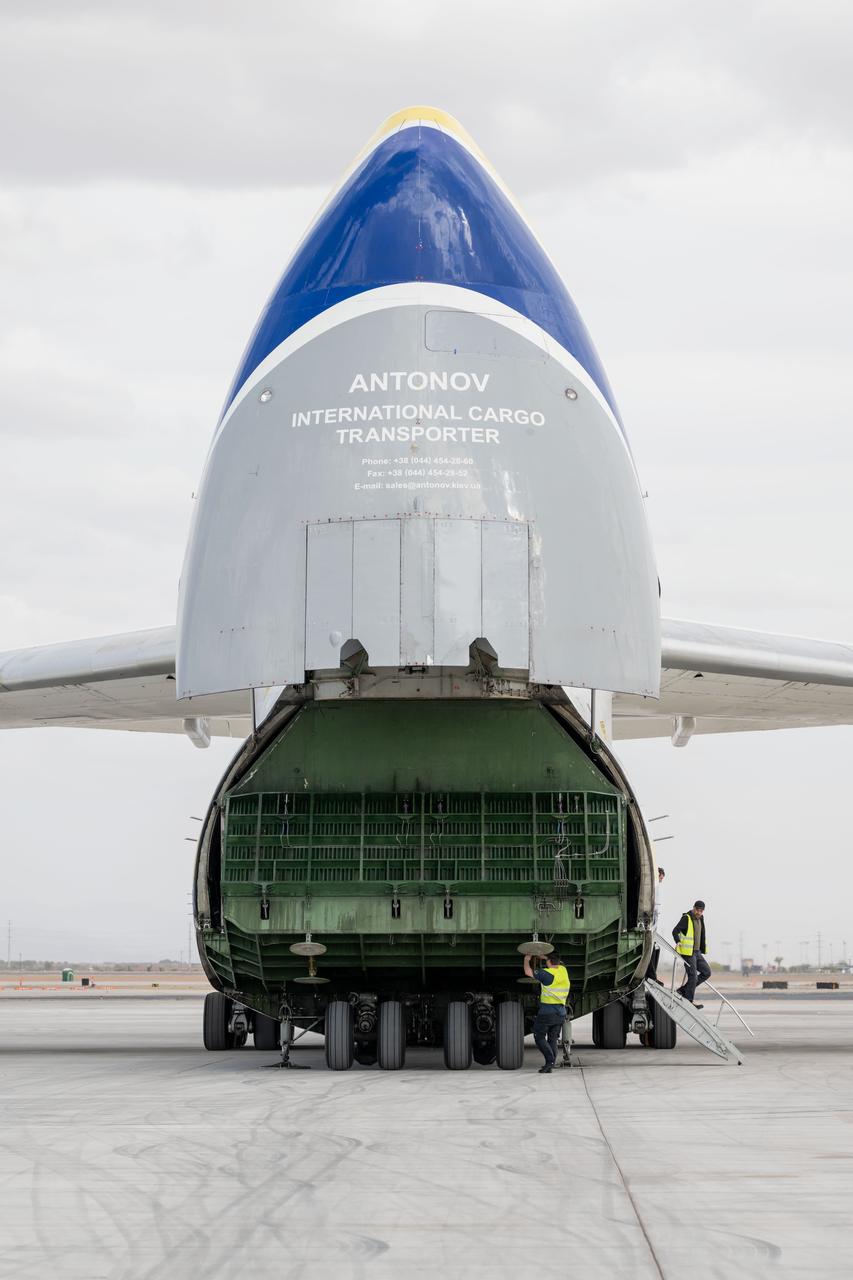

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
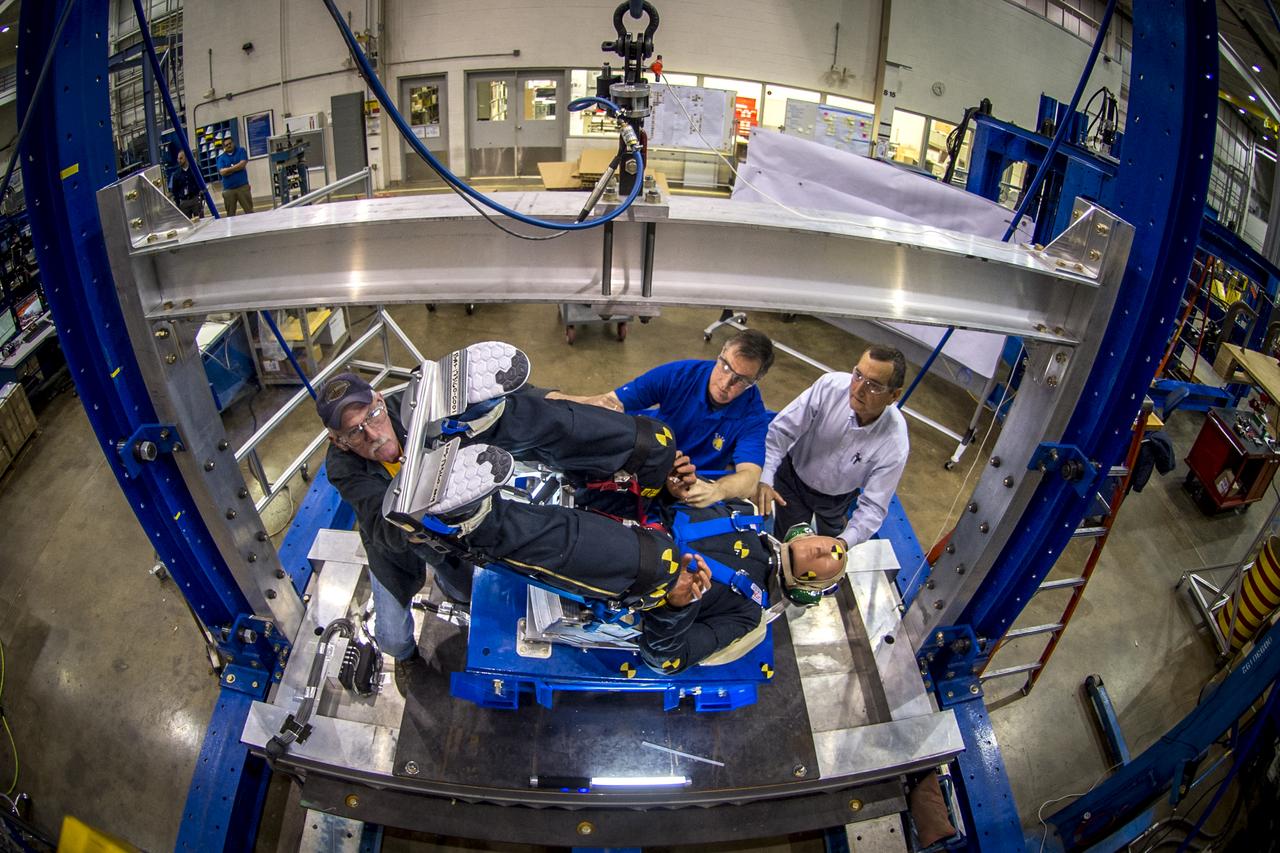

Engineers working with Boeing's CST-100 Starliner test the spacecraft's seat design in Mesa, Arizona, focusing on how the spacecraft seats would protect an astronaut's head, neck and spine during the 240-mile descent from the International Space Station. The company incorporated test dummies for a detailed analysis of impacts on a crew returning to earth. The human-sized dummies were equipped with sensitive instrumentation and secured in the seats for 30 drop tests at varying heights, angles, velocities and seat orientations in order to mimic actual landing conditions. High-speed cameras captured the footage for further analysis. The Starliner spacecraft is being developed in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program.

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) at Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert, Arizona, on April 4, 2025, shortly after its arrival from Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy.
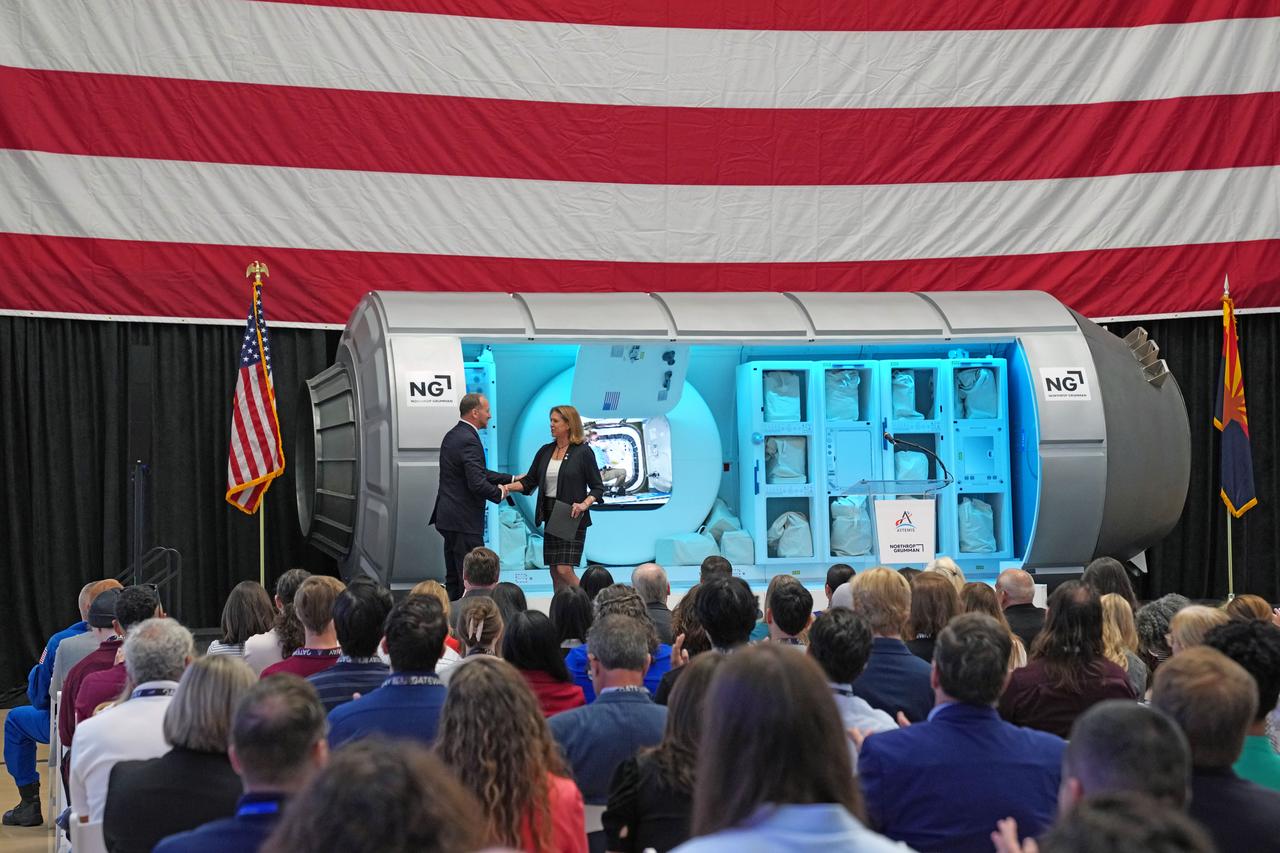

Dr. Lori Glaze, acting associate administrator for NASA’s Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, and Dr. Jon B. Olansen, Gateway Program manager, on stage during an April 24, 2025, event at Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert, Arizona, commemorating HALO’s arrival in the United States.
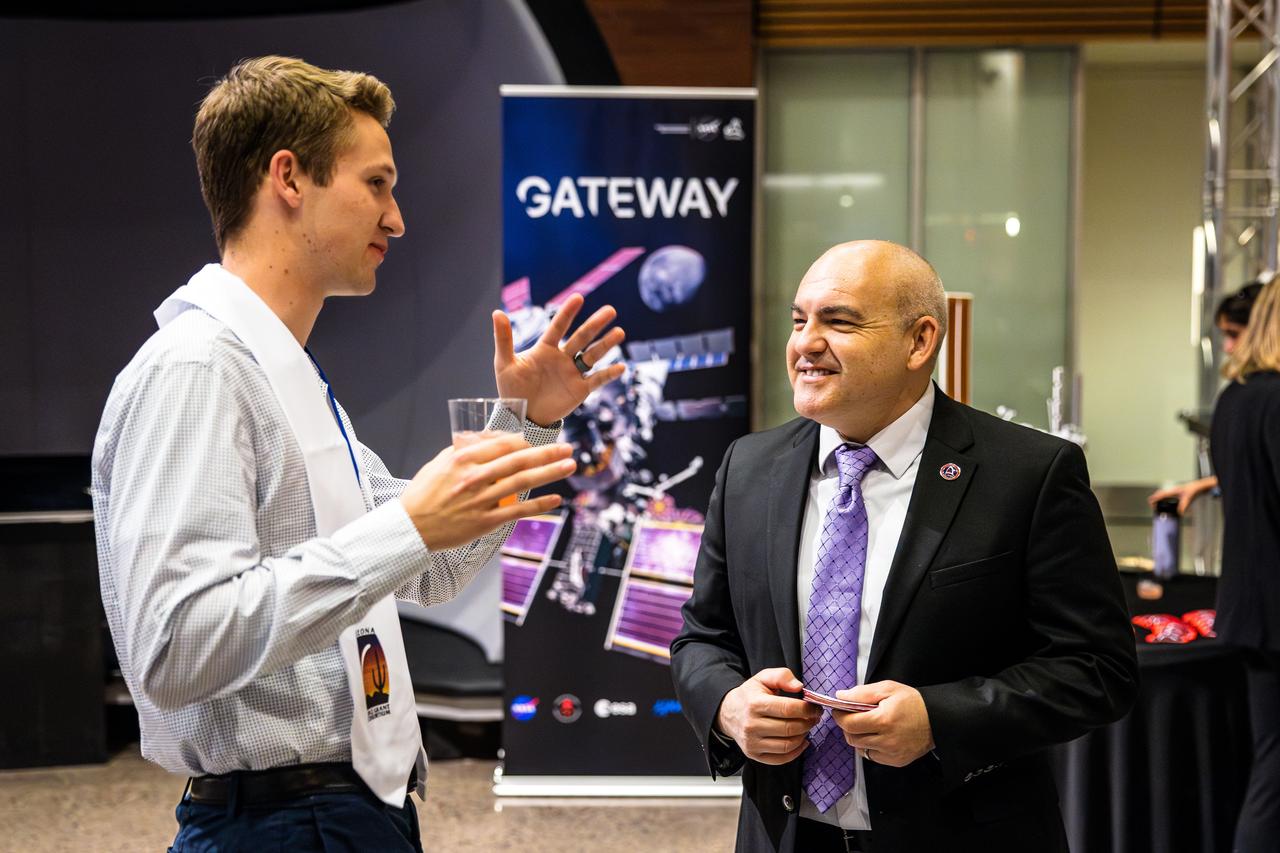

Carlos Garcia-Galan, deputy manager of NASA’s Gateway Program, talks with college students about NASA internship opportunities after delivering a keynote address on Gateway, Artemis, and the next era of human space exploration at the 2025 Arizona NASA Space Grant Consortium Statewide Student Research Symposium, held April 18, 2025, at Arizona State University.
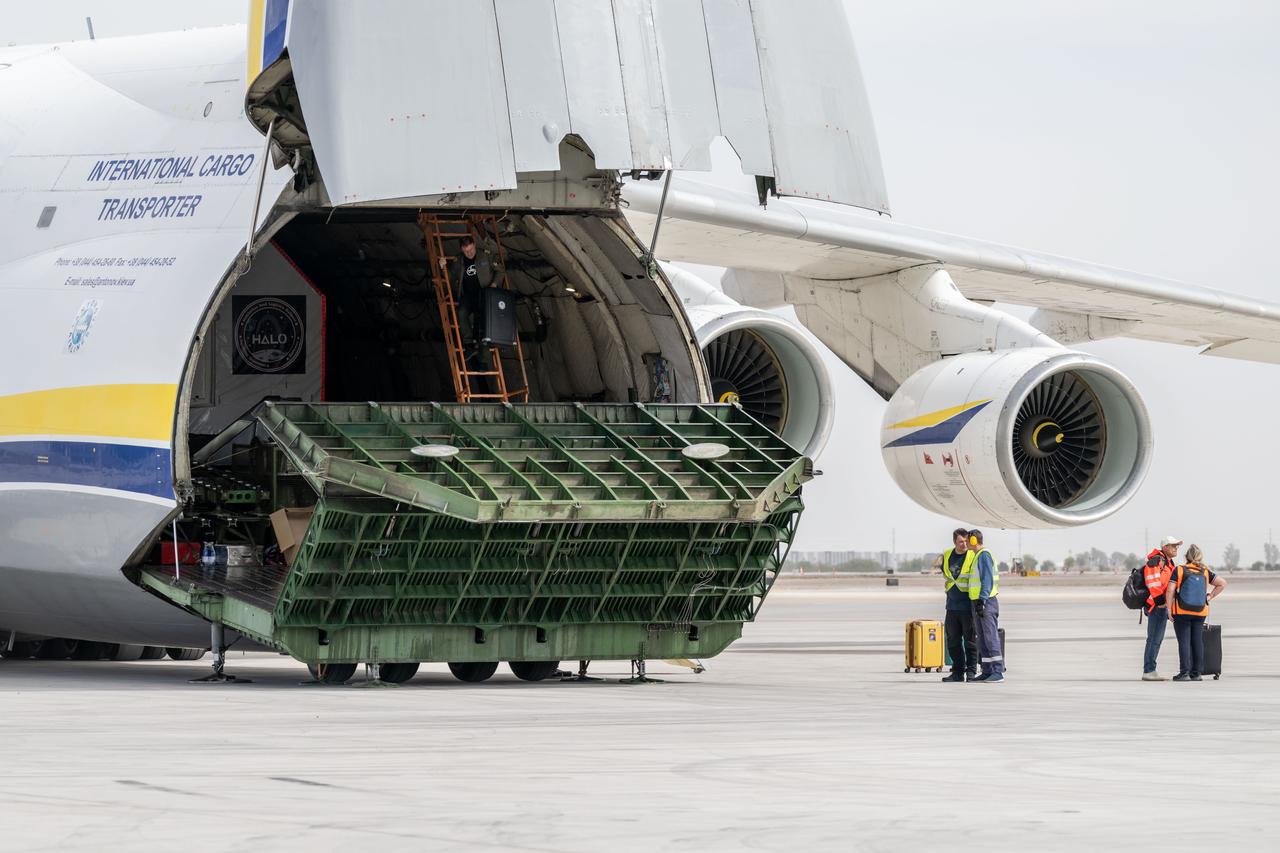

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
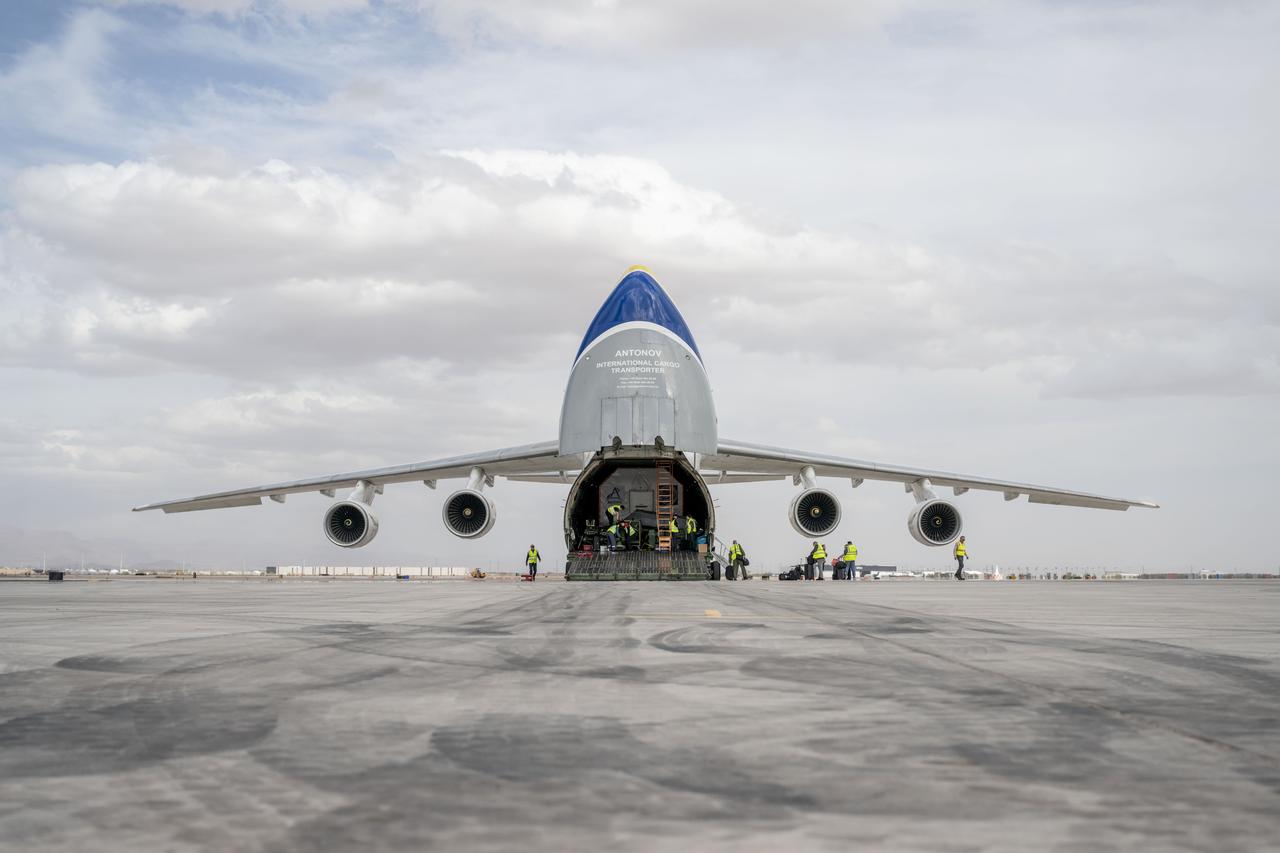

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
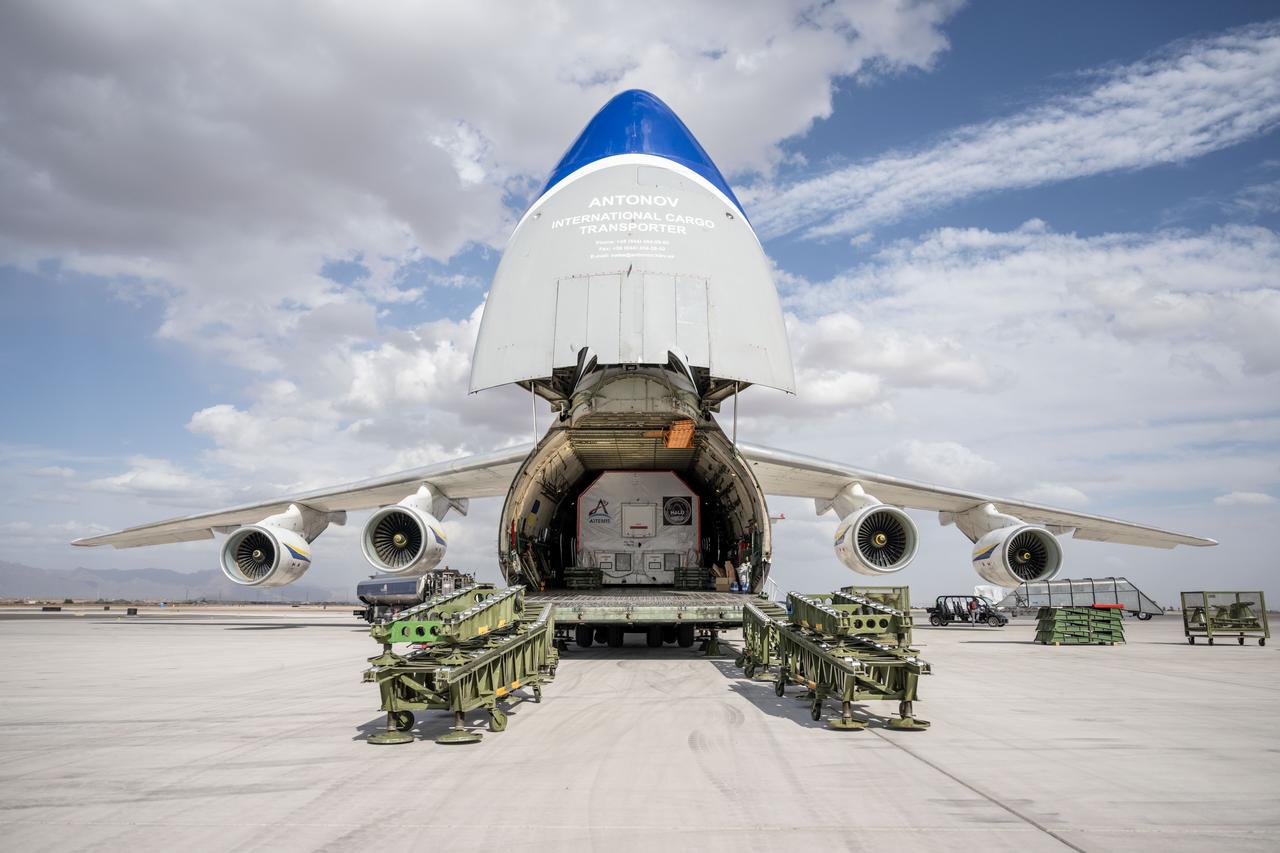

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
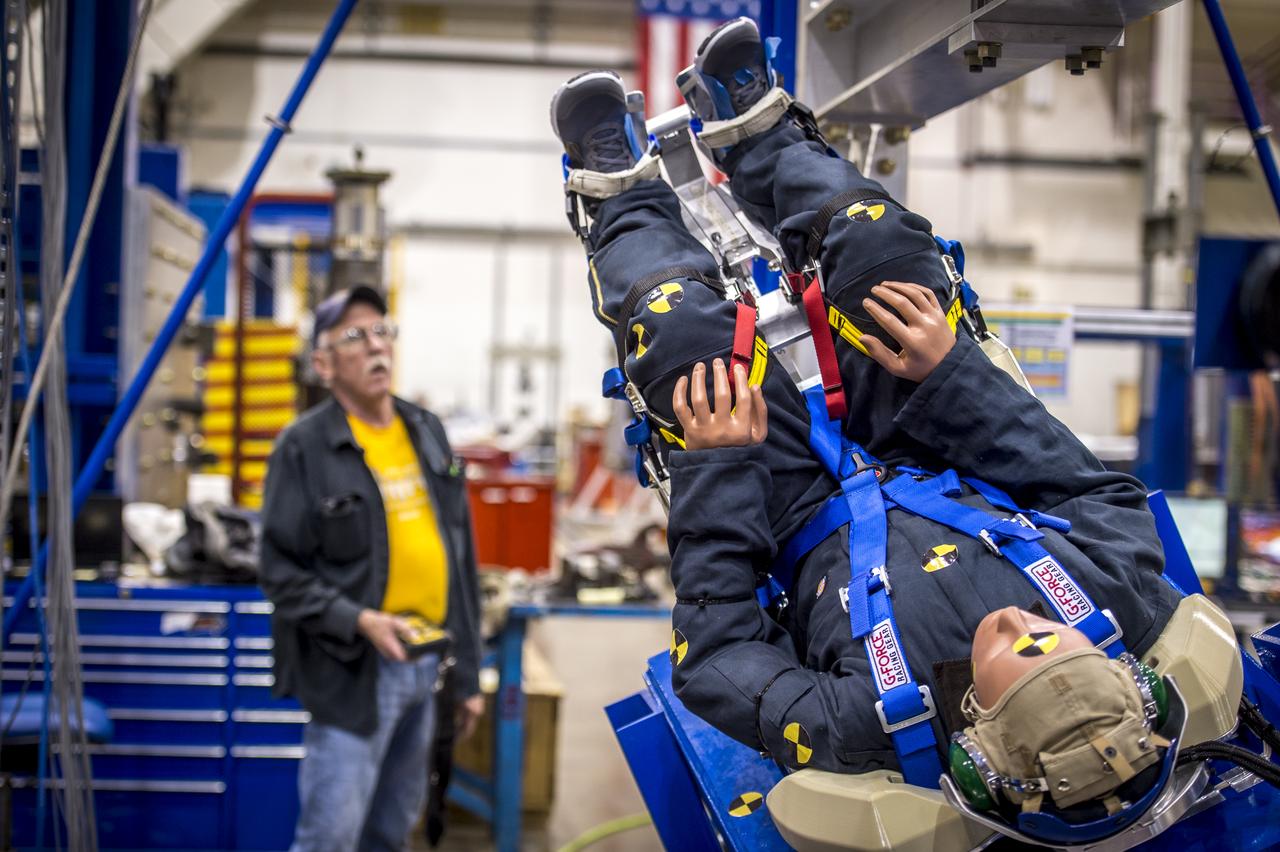

Engineers working with Boeing's CST-100 Starliner test the spacecraft's seat design in Mesa, Arizona, focusing on how the spacecraft seats would protect an astronaut's head, neck and spine during the 240-mile descent from the International Space Station. The company incorporated test dummies for a detailed analysis of impacts on a crew returning to earth. The human-sized dummies were equipped with sensitive instrumentation and secured in the seats for 30 drop tests at varying heights, angles, velocities and seat orientations in order to mimic actual landing conditions. High-speed cameras captured the footage for further analysis. The Starliner spacecraft is being developed in partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program.
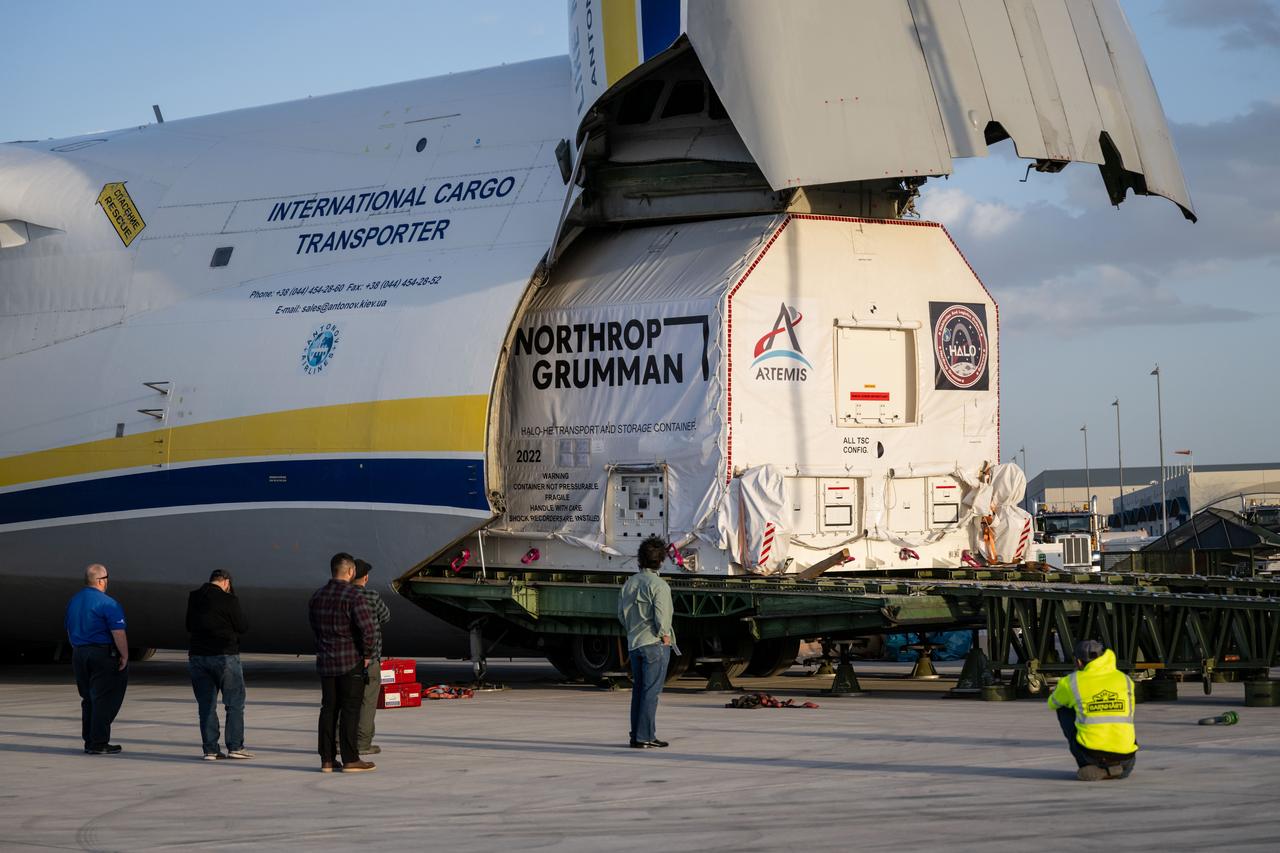

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) at Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert, Arizona, on April 4, 2025, shortly after its arrival from Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy.

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams remove Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
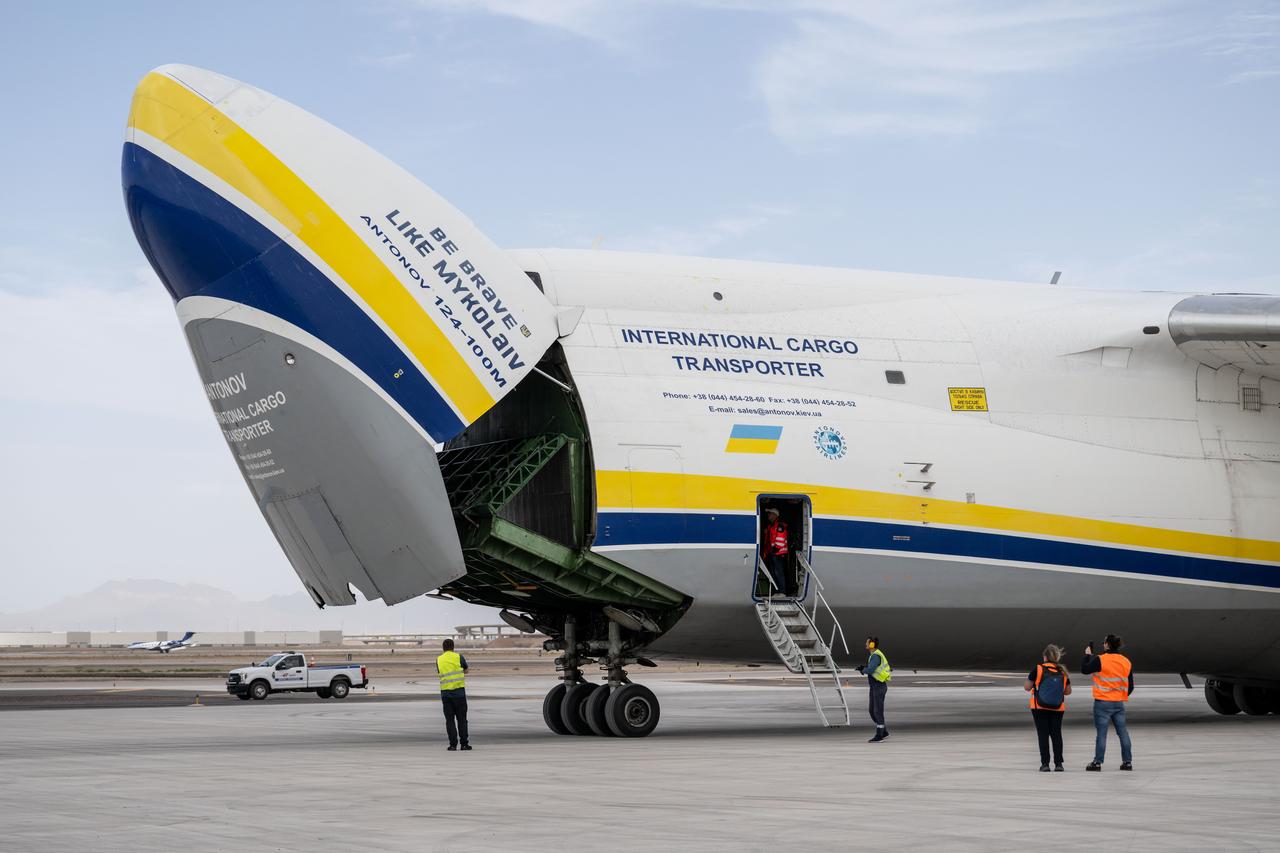

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
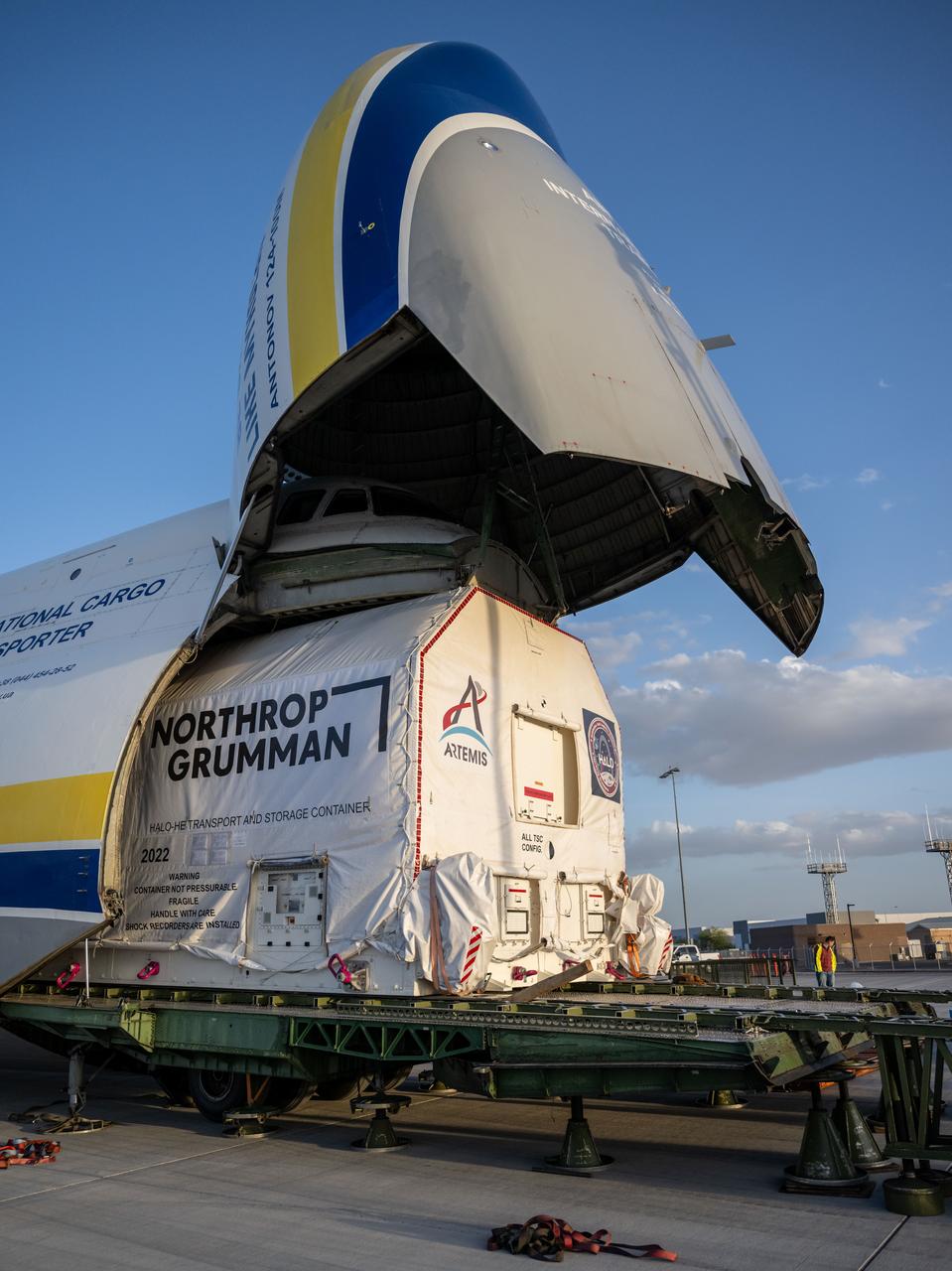

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams begin removing Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
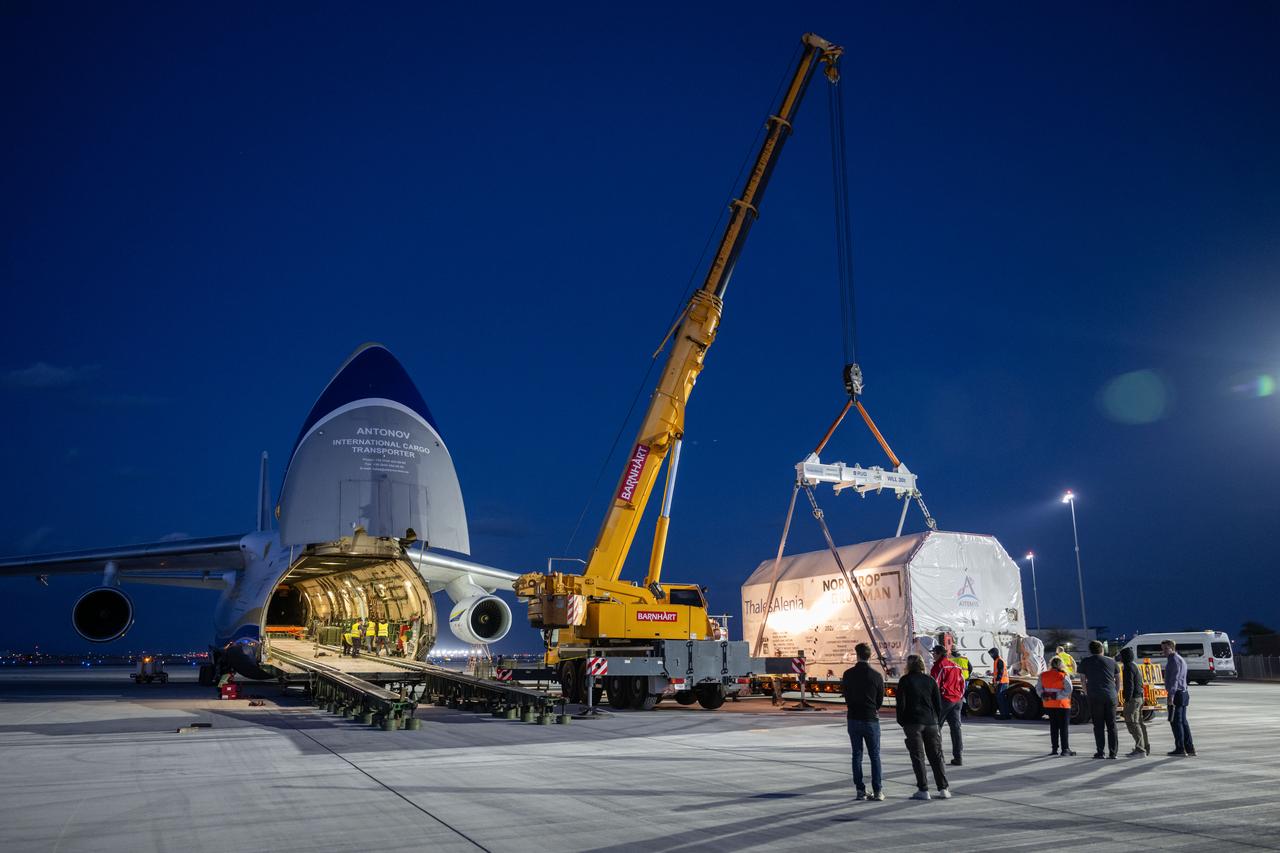

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
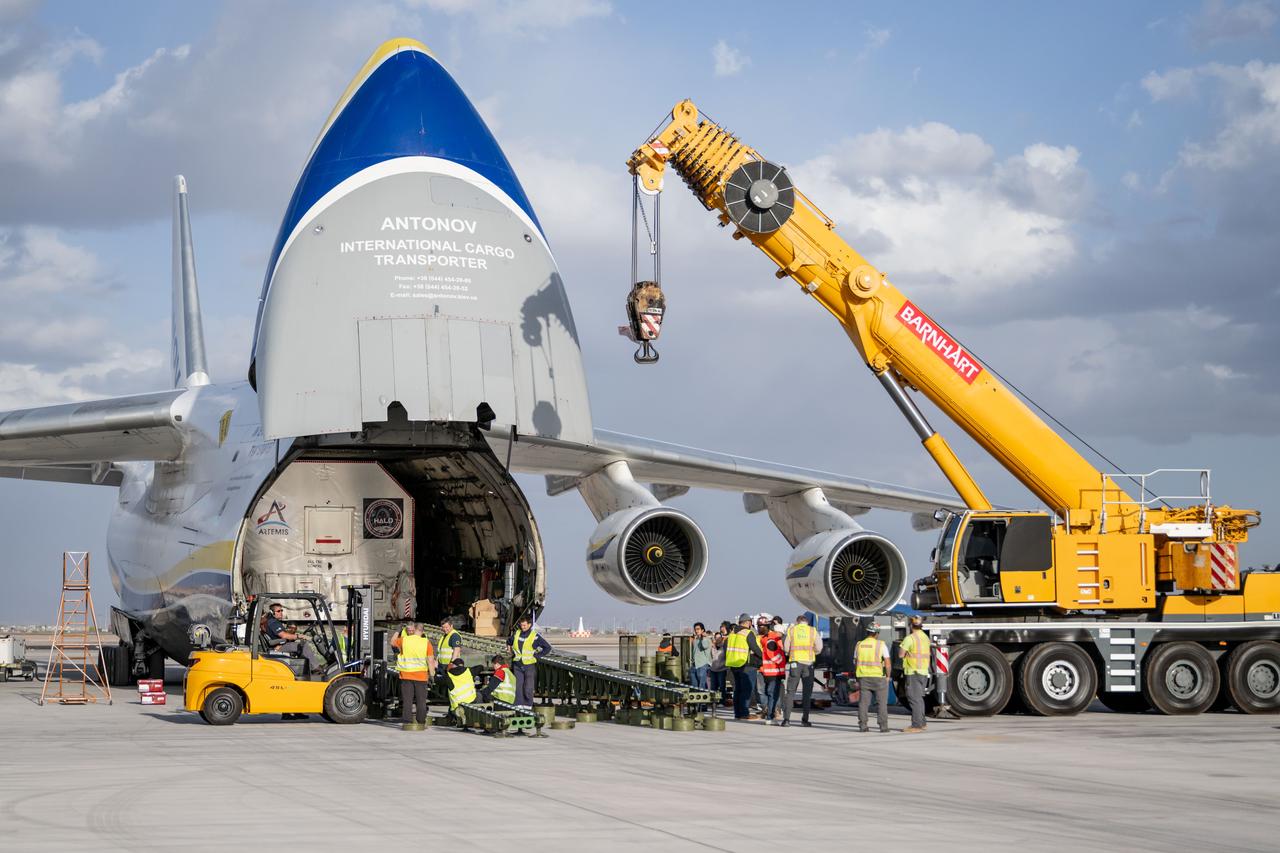

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
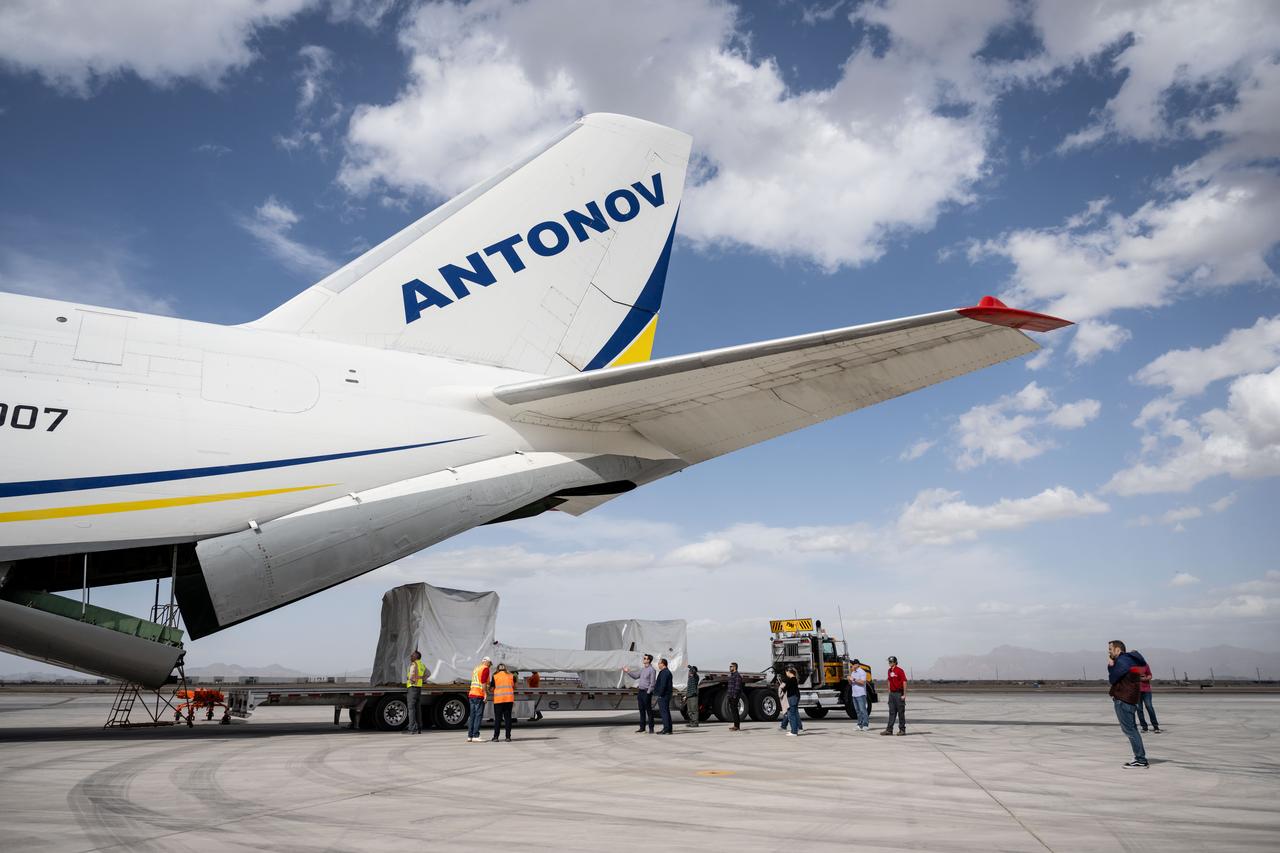

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams remove Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
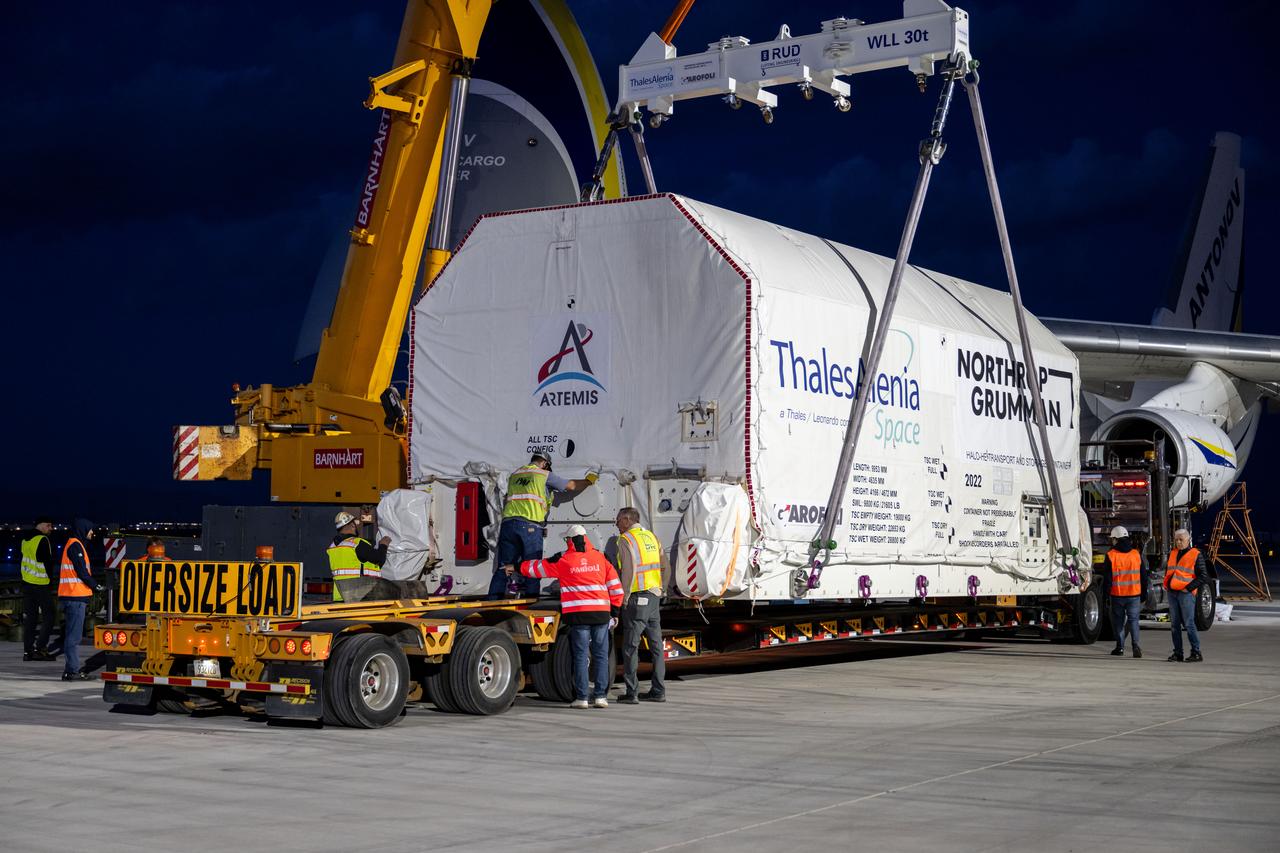

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
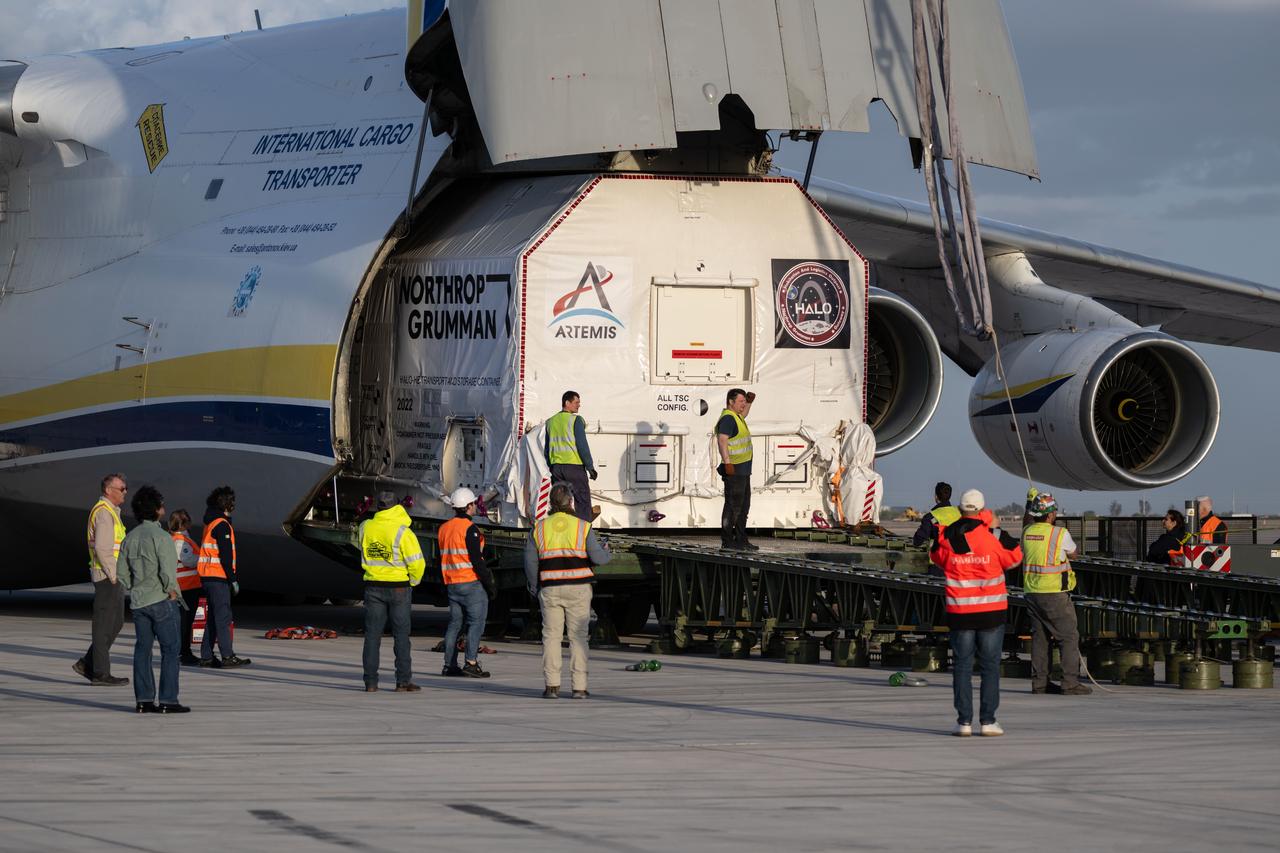

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
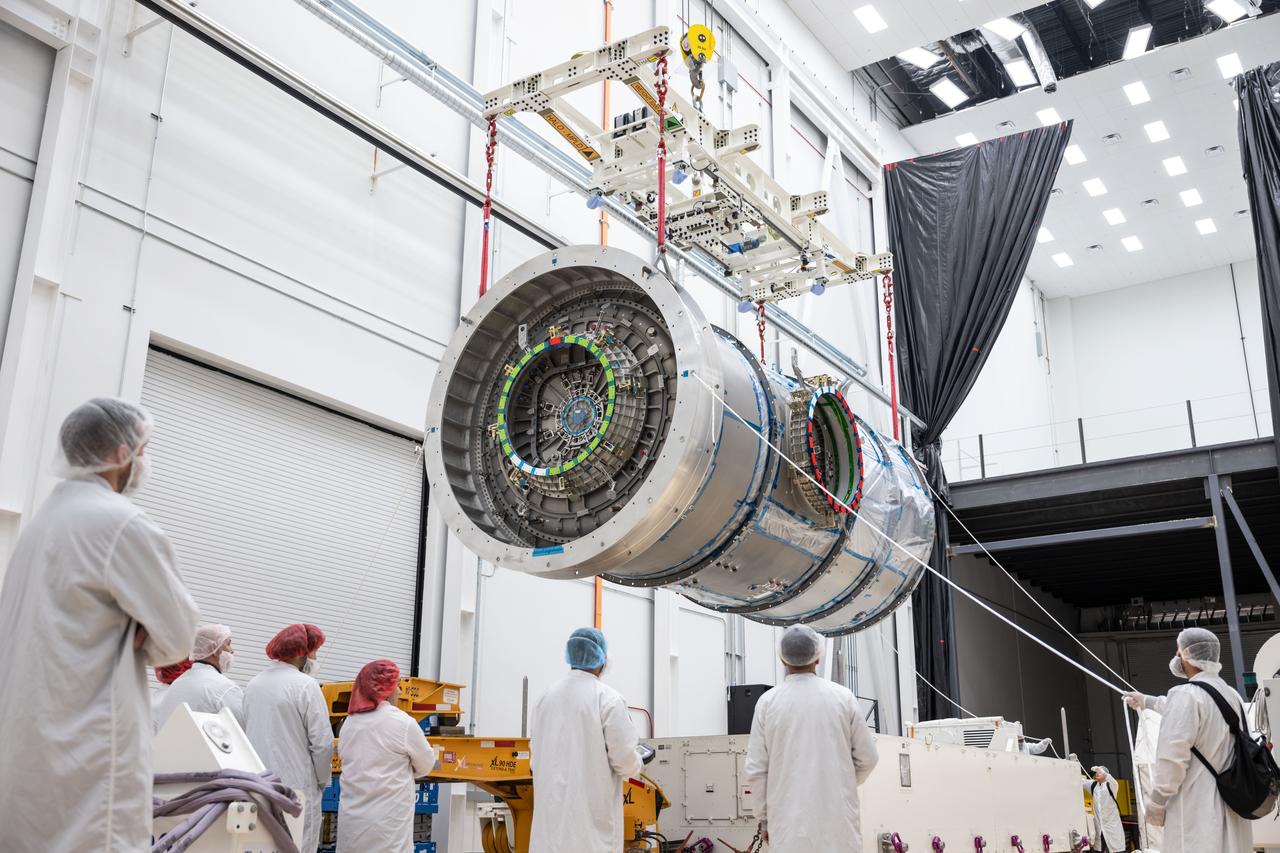

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams remove Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
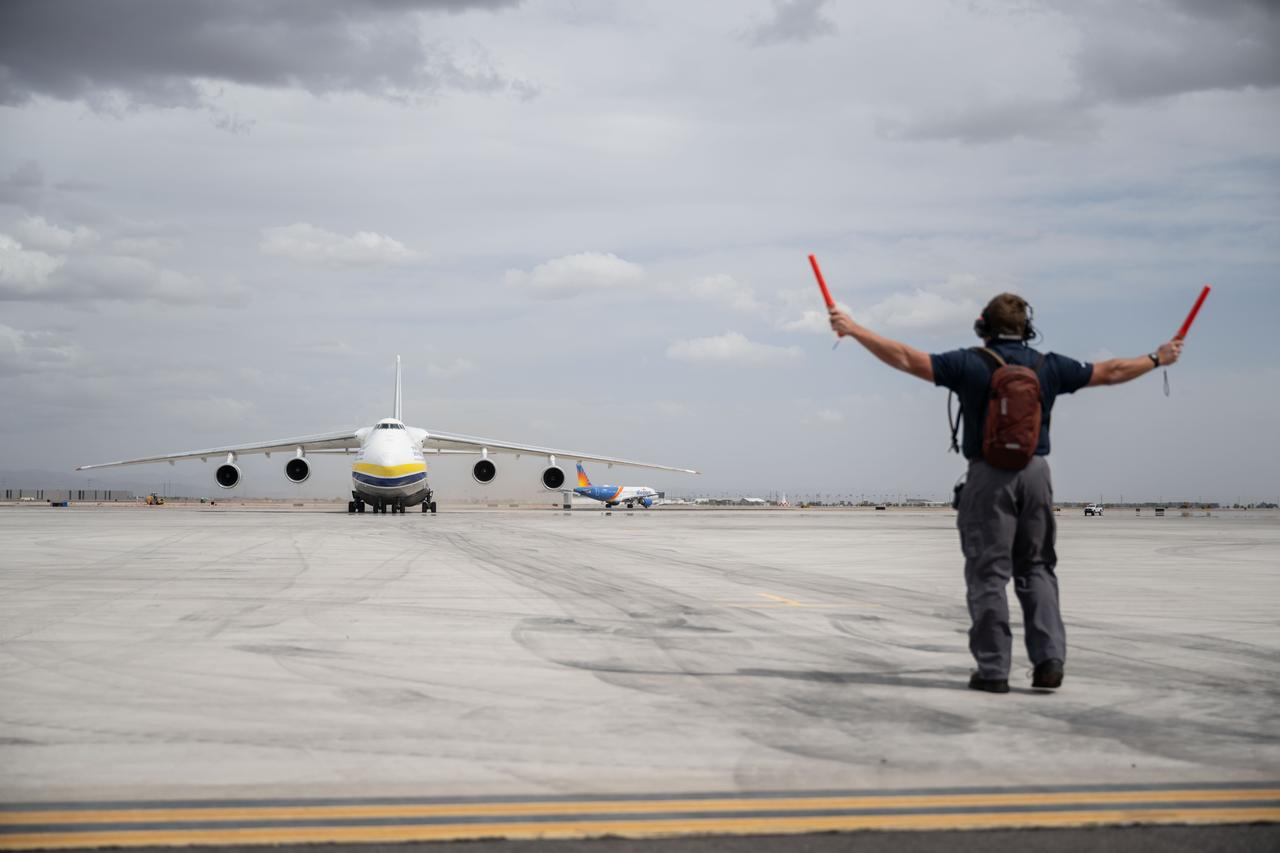

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
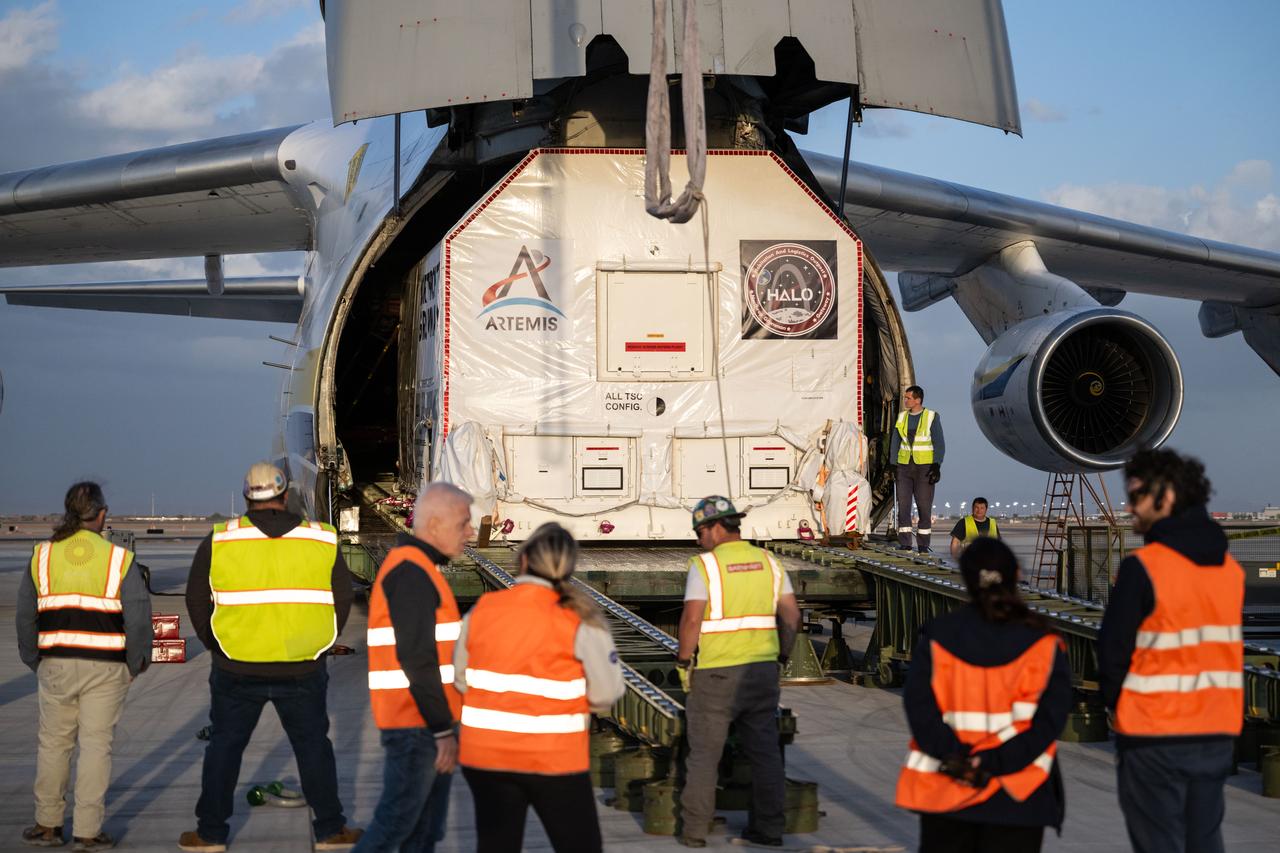

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams begin removing Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
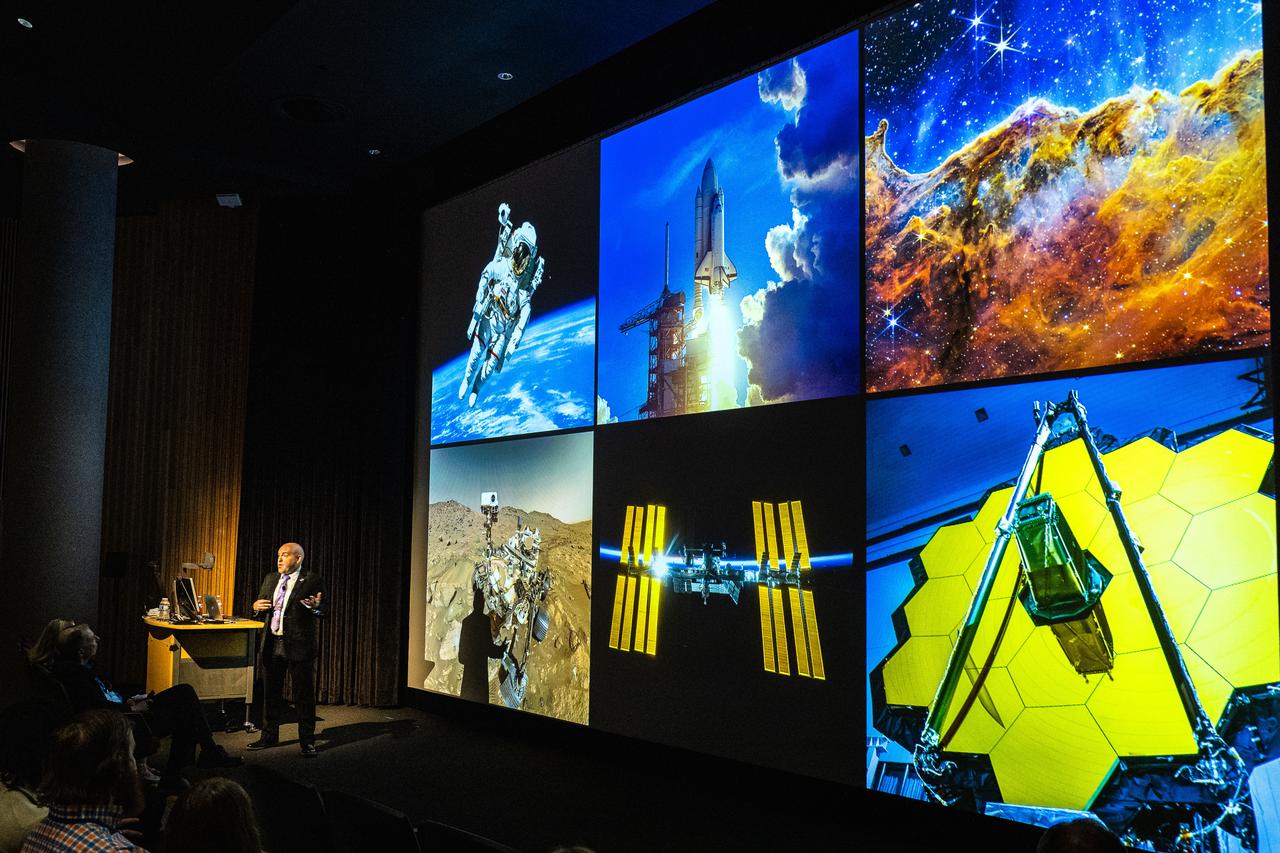

Carlos Garcia-Galan, deputy manager of NASA’s Gateway Program, delivers a keynote address on Gateway, Artemis, and the next era of human space exploration at the 2025 Arizona NASA Space Grant Consortium Statewide Student Research Symposium, held April 18, 2025, at Arizona State University.
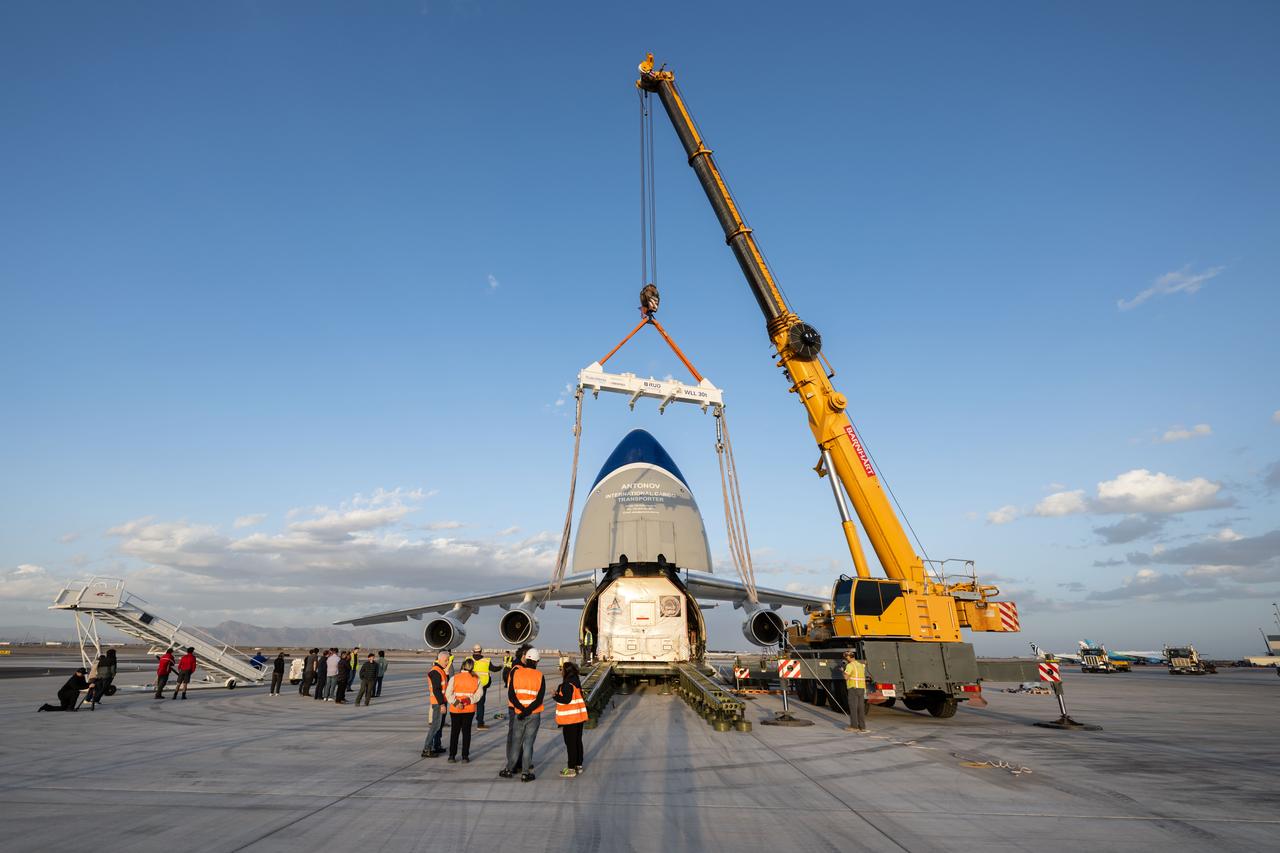

Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) arrives in Mesa, Arizona, after traveling from Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. Delivered by cargo aircraft to Phoenix-Mesa Gateway Airport, HALO will be transported to Northrop Grumman’s facility in Gilbert for final outfitting.
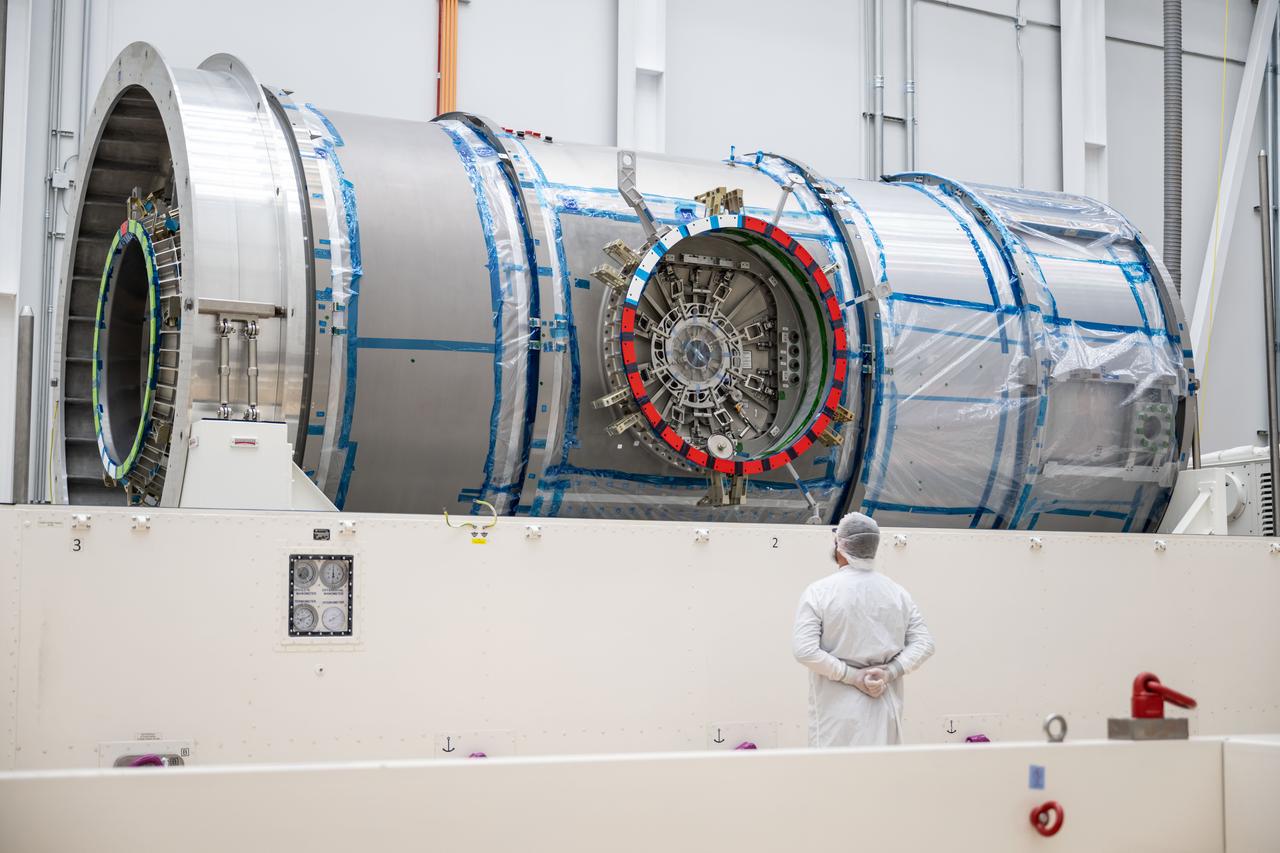

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams begin removing Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.