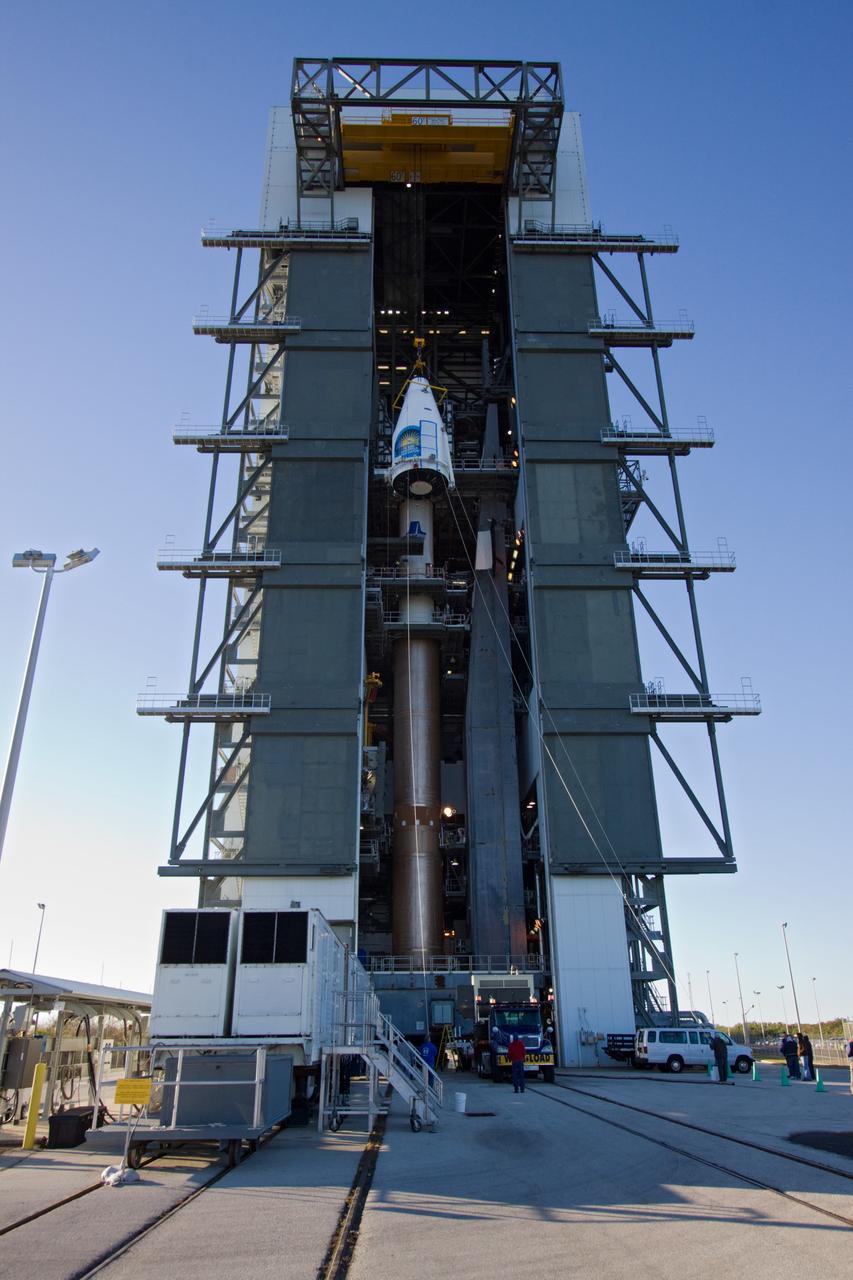

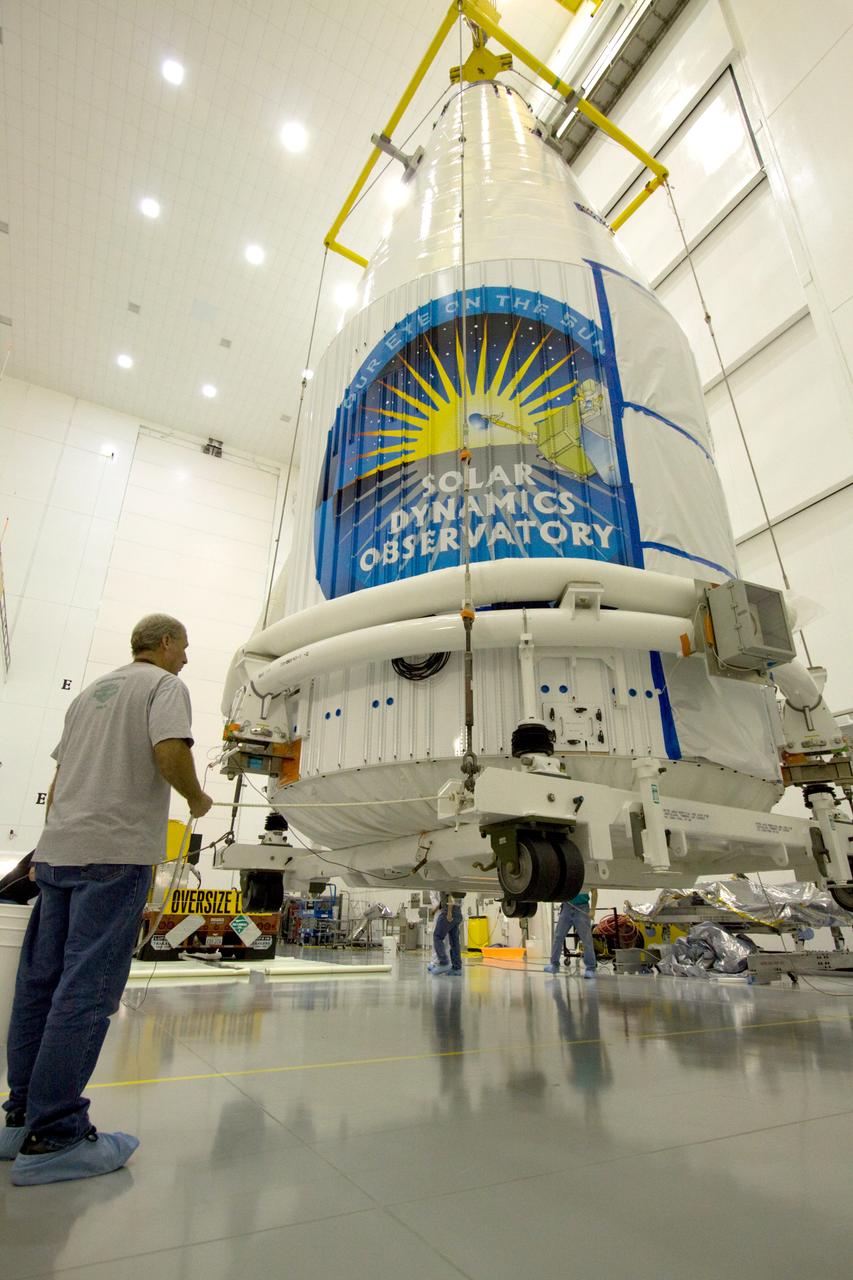
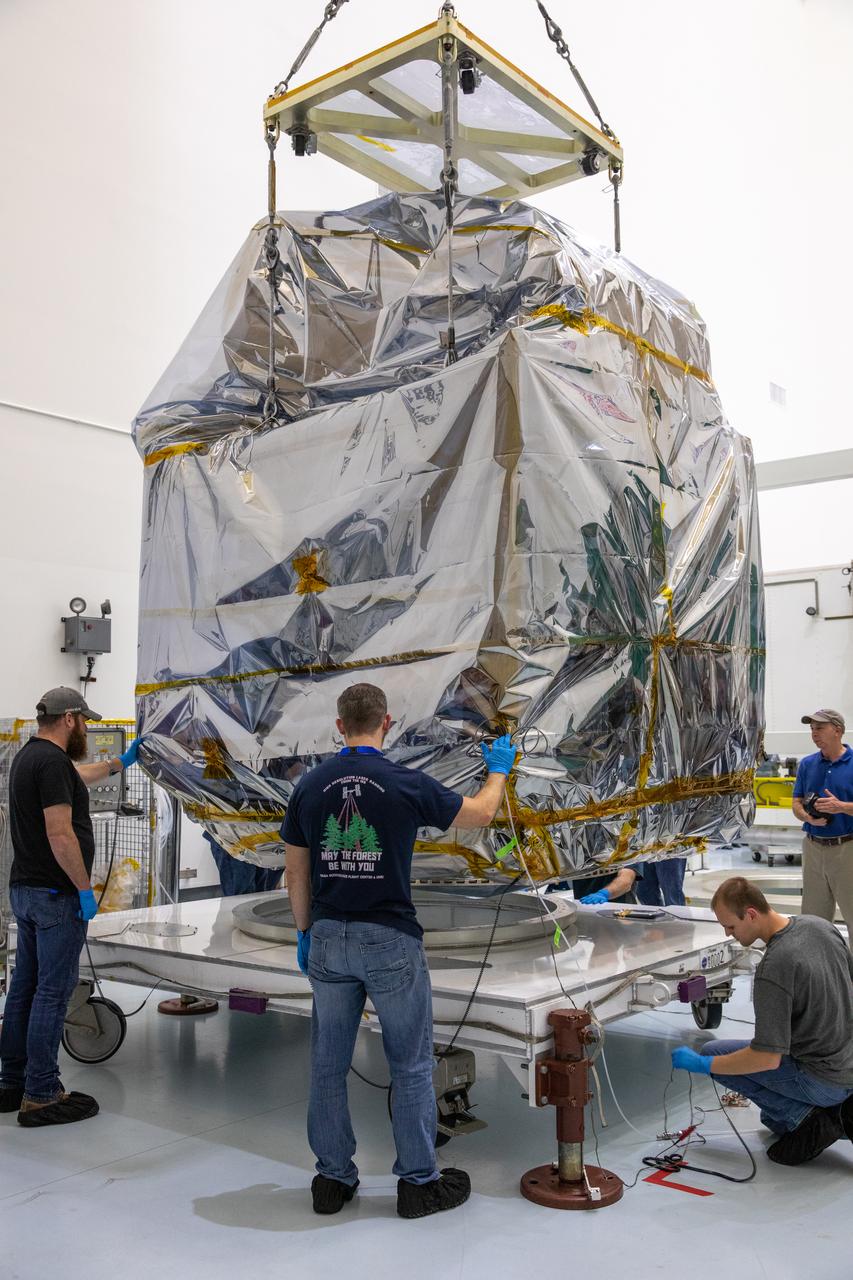
SDO MOVE FROM ASTROTECH TO PAD 41 - LIFT & MATE
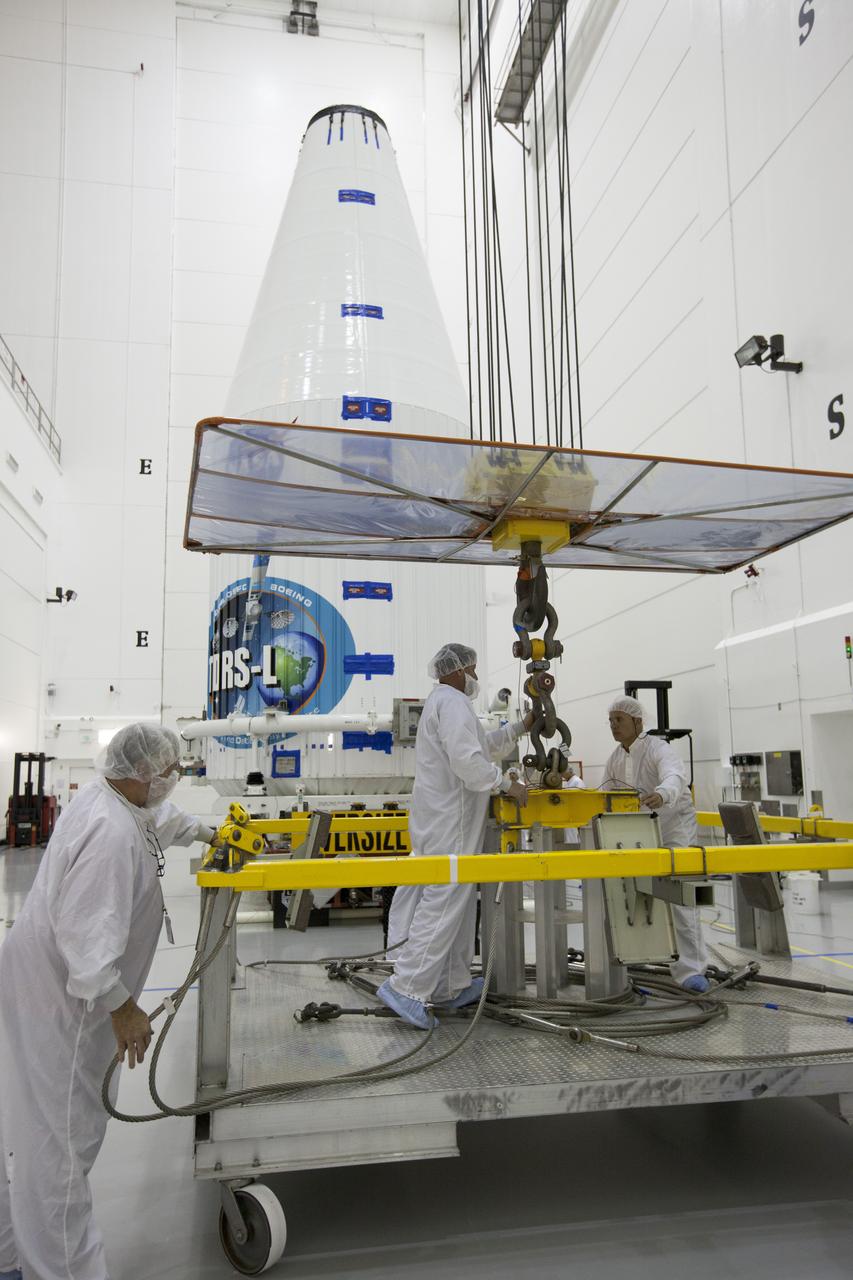

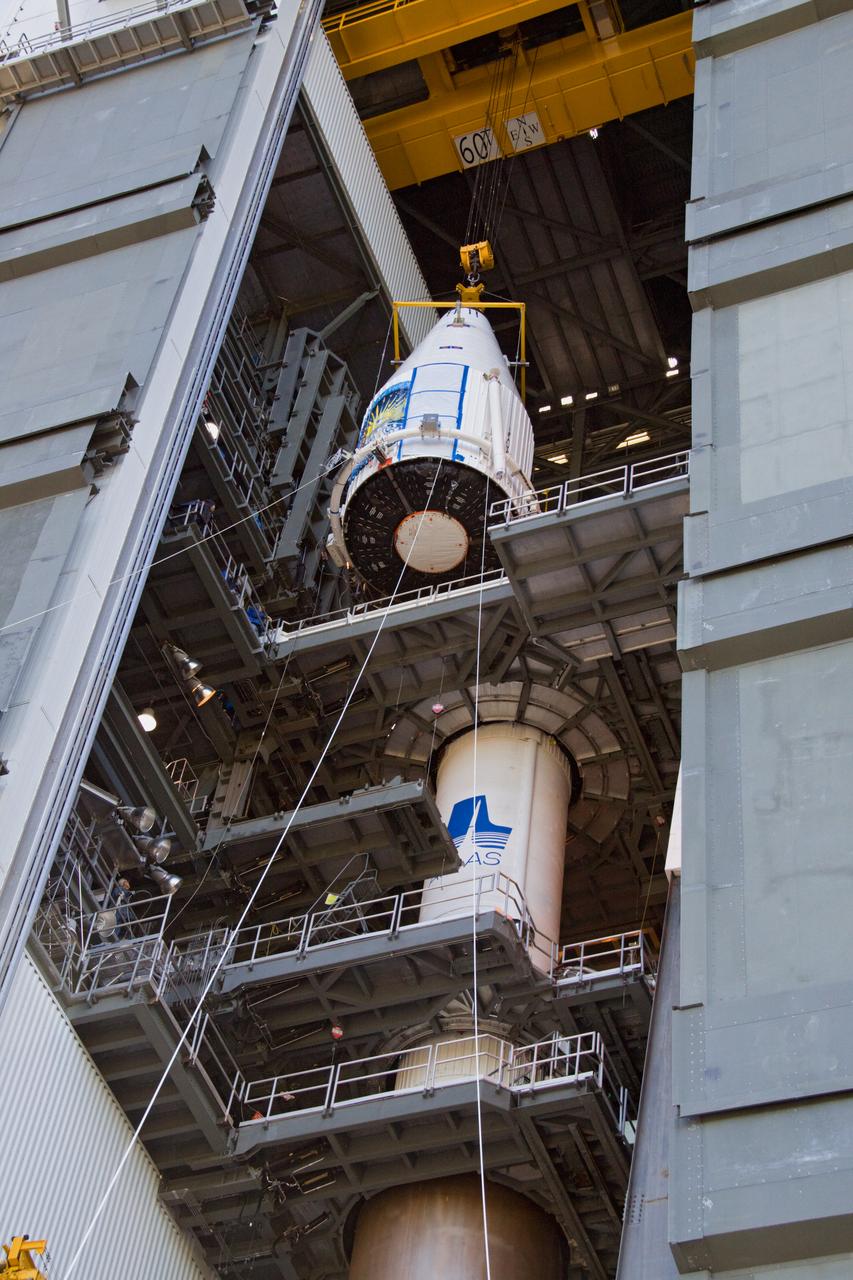
TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, a crane is disengaged from ground support equipment used to mount NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft on a transporter for its trip to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

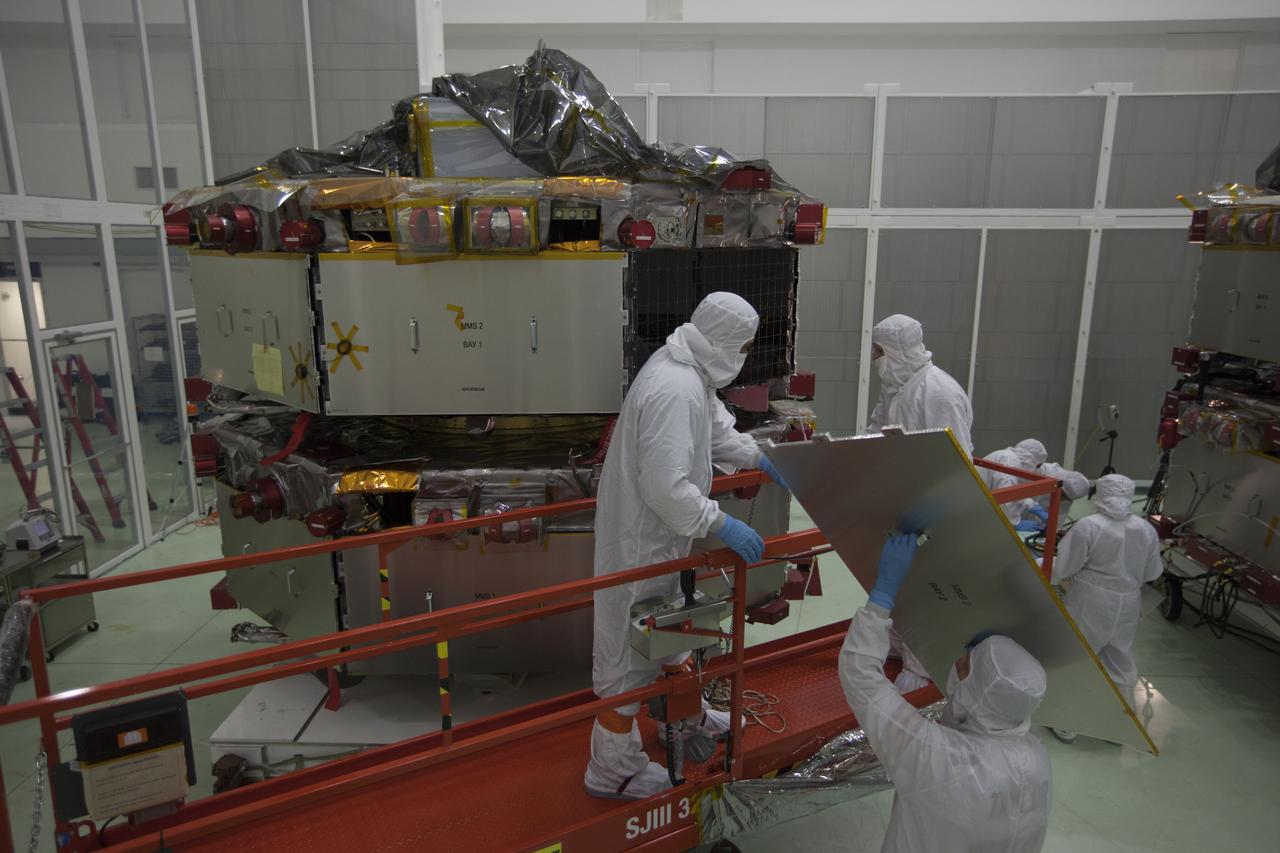
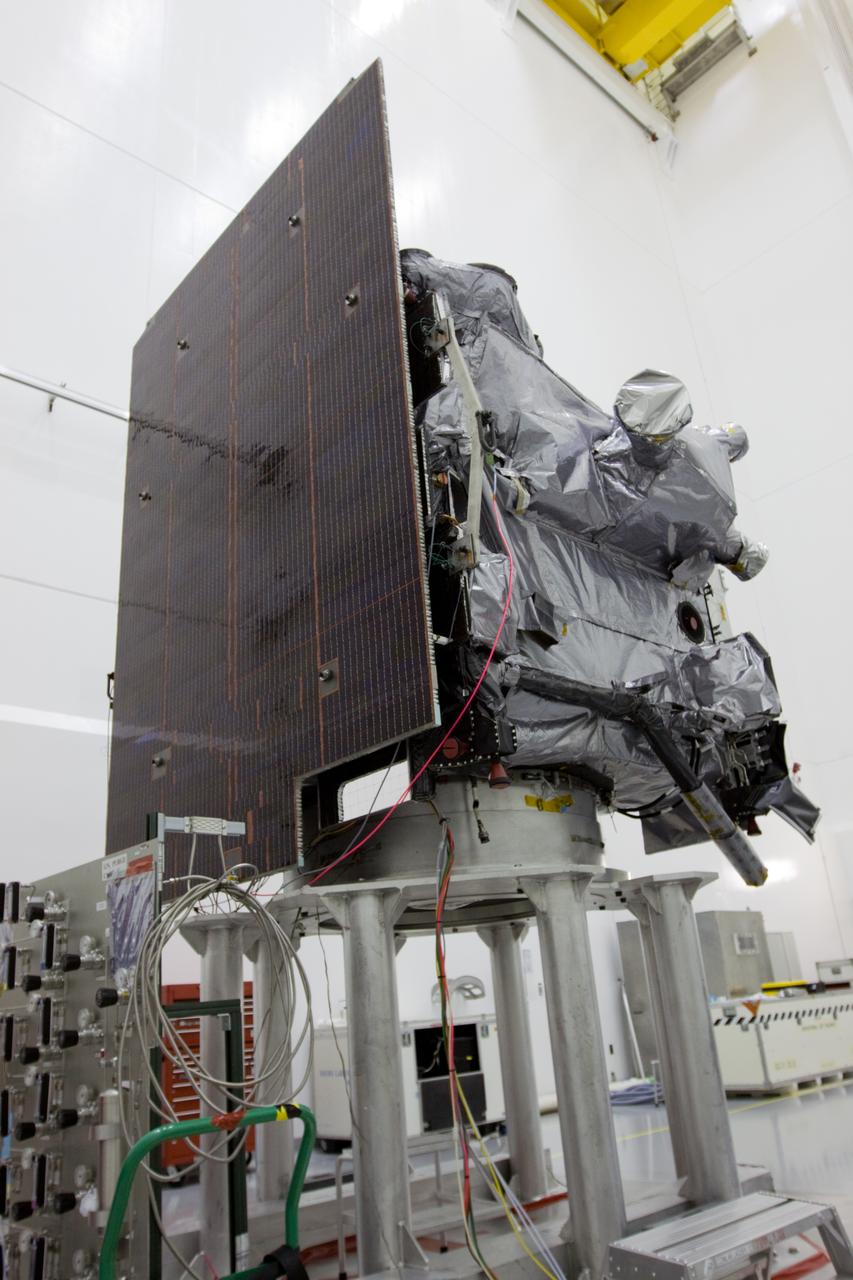
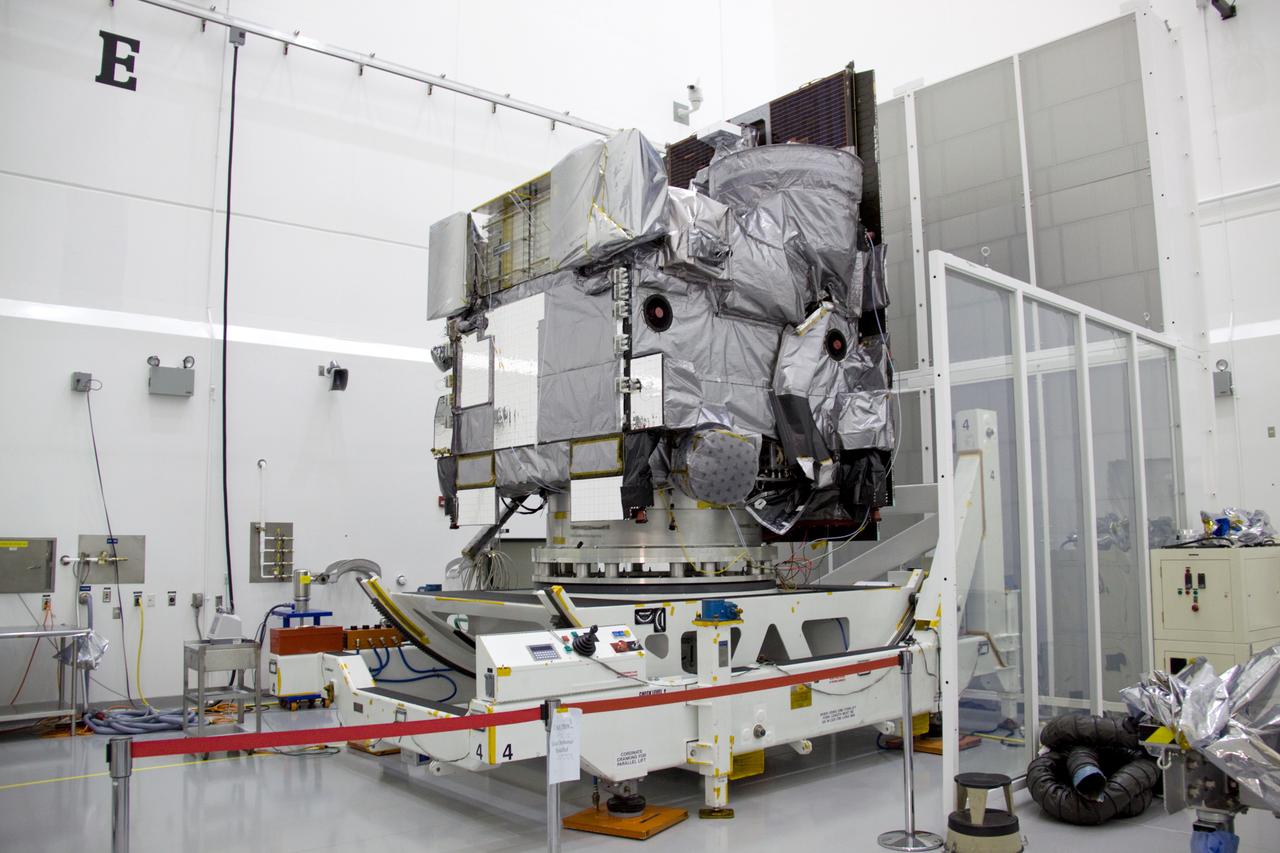
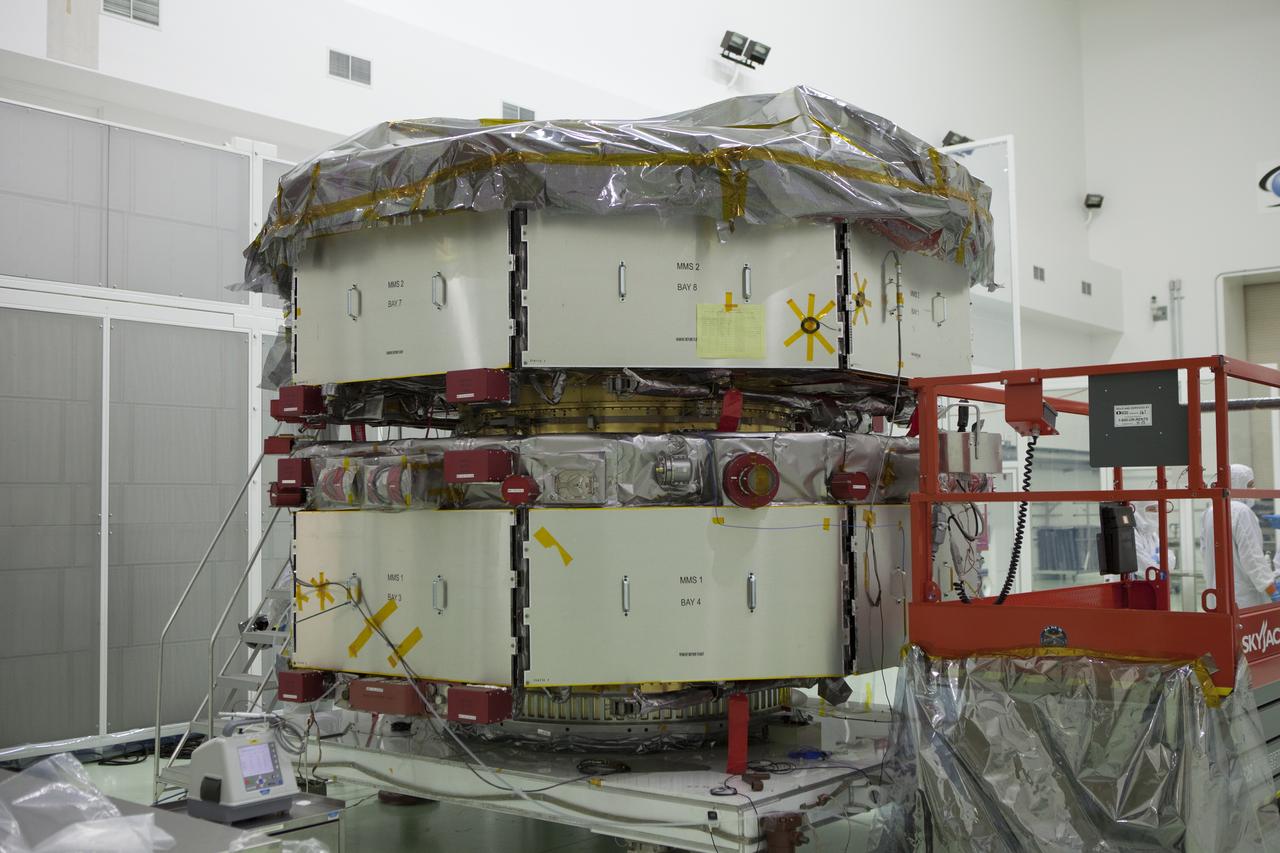
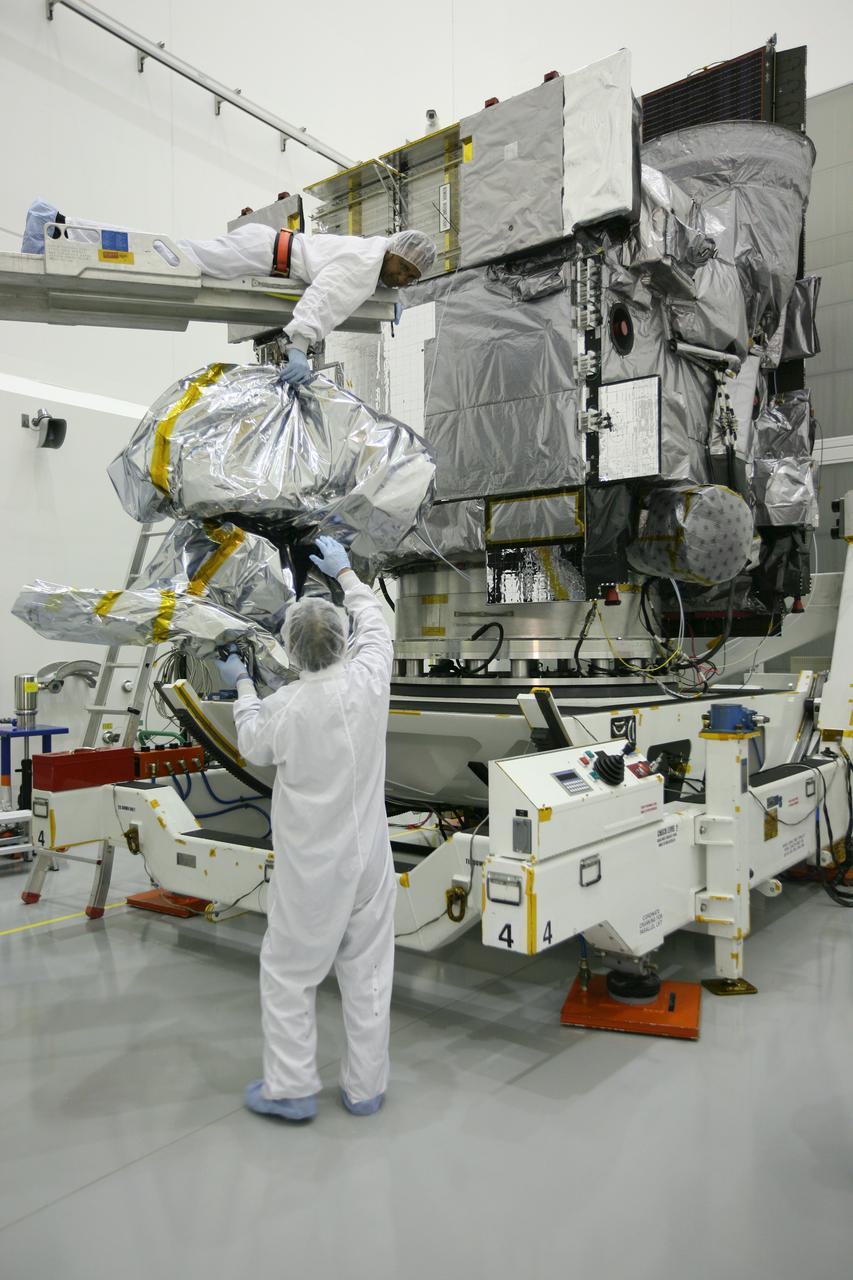
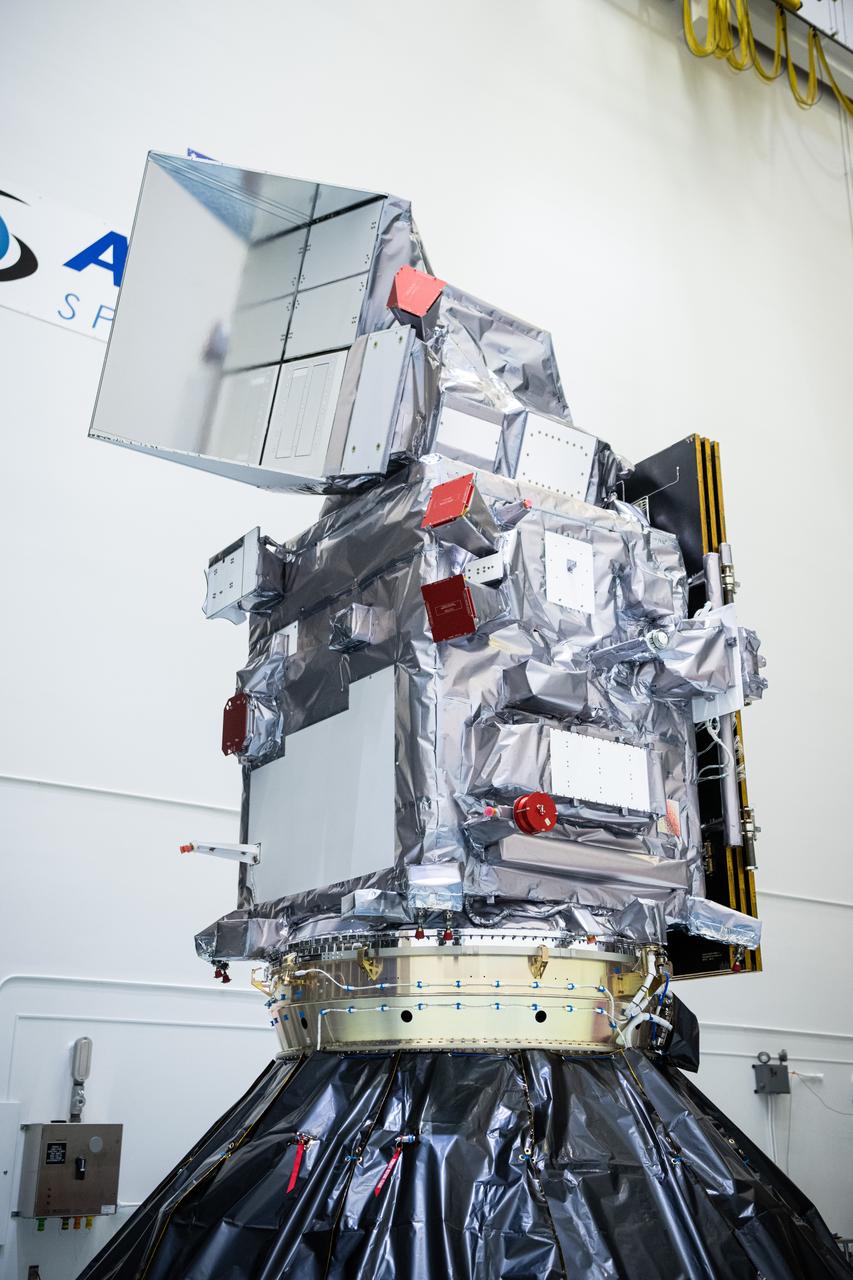
A plaque affixed to the side of a Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, observatory dedicates the mission to Richard “Richy” D’Antonio, now deceased, in grateful appreciation for his dedicated service to NASA’s MMS mission. MMS, led by a team from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission consisting of four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

SDO MOVE FROM ASTROTECH TO PAD 41 - LIFT & MATE

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft is being encapsulated in its payload fairing in preparation for begin transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
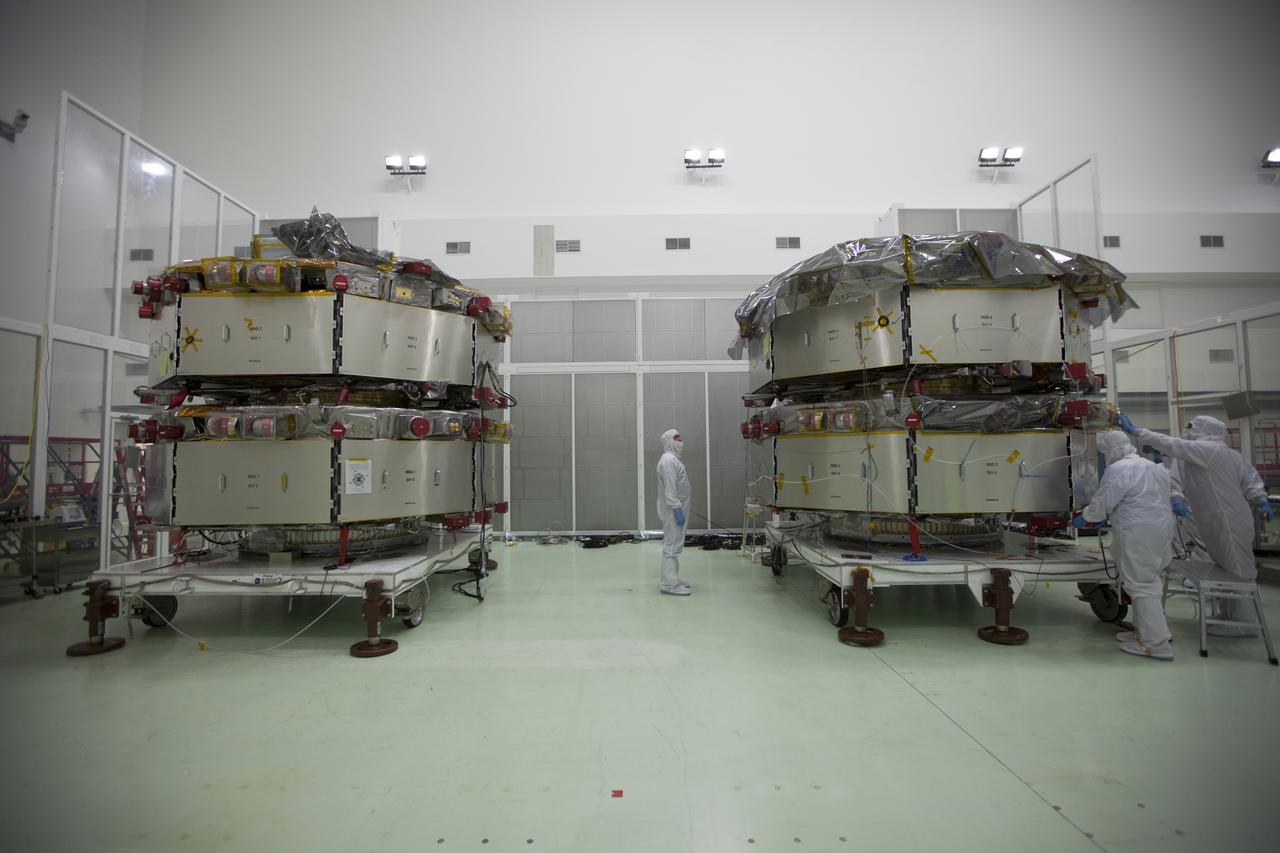

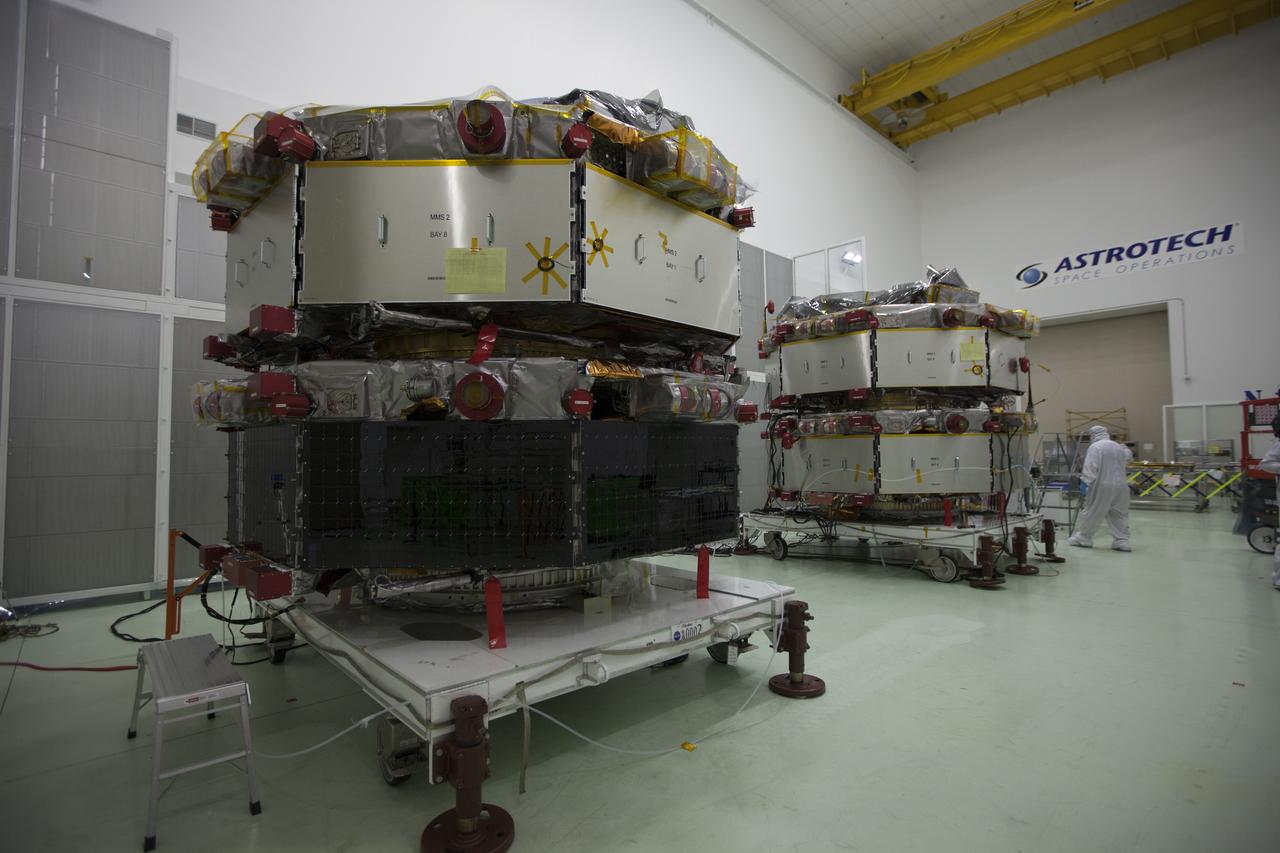
All four of the Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft have arrived in the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the upper deck arrived Nov. 12; the two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
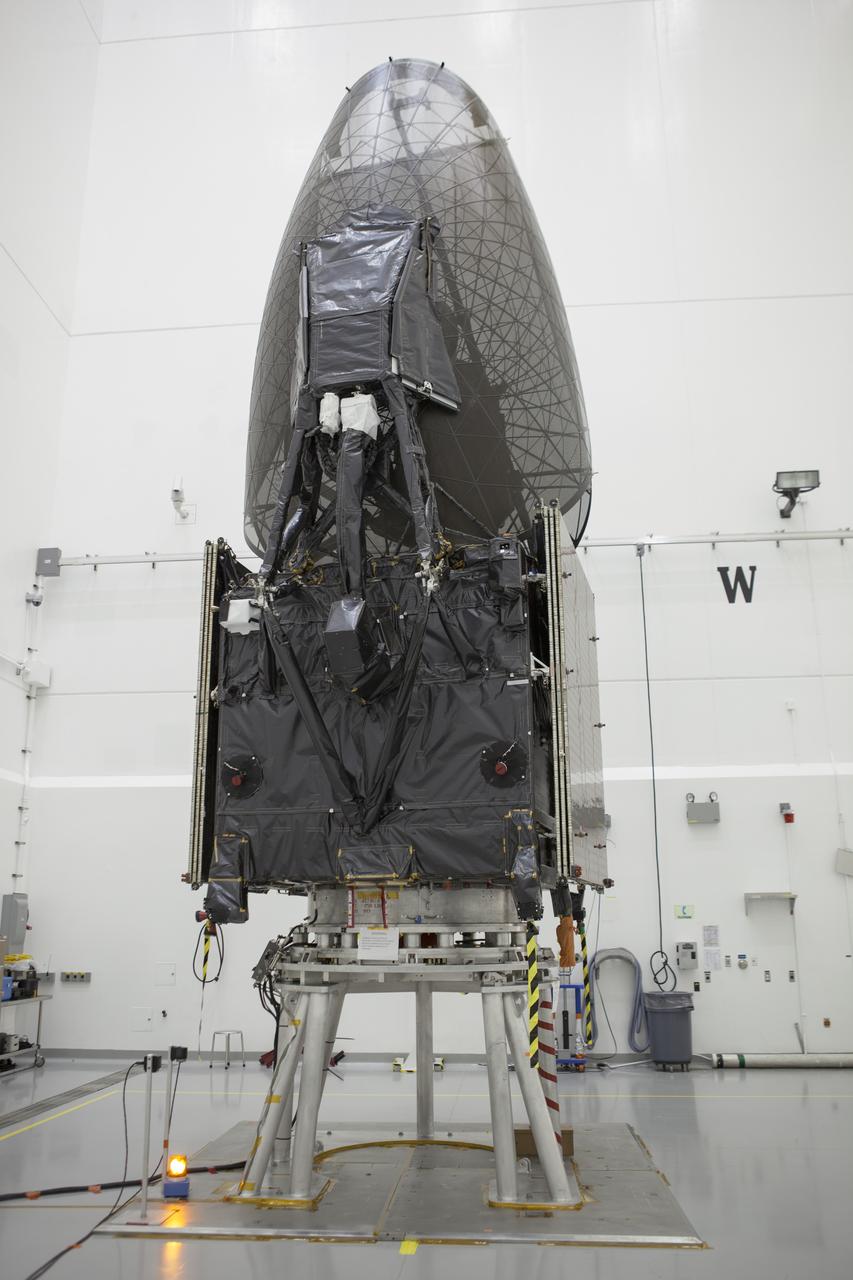

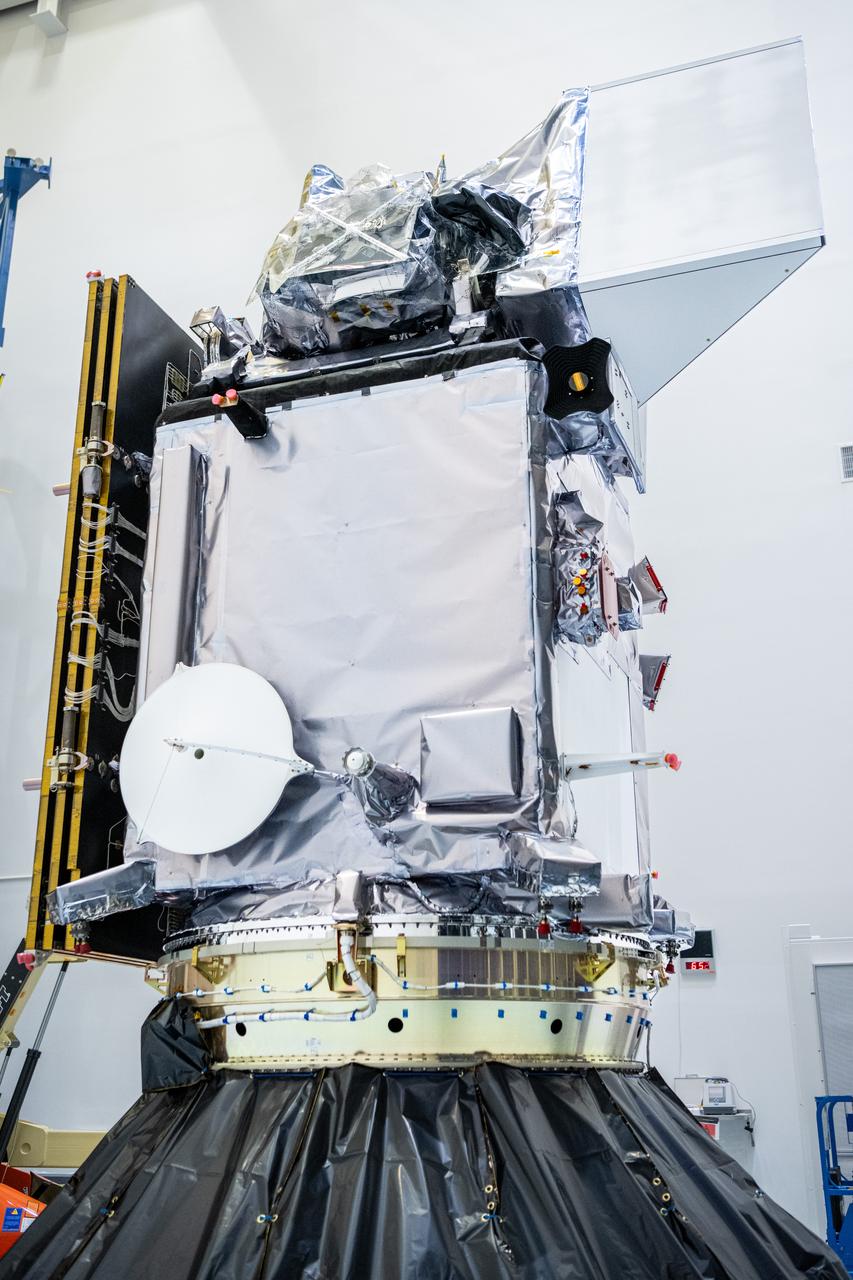
Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft is undergoing preflight processing.
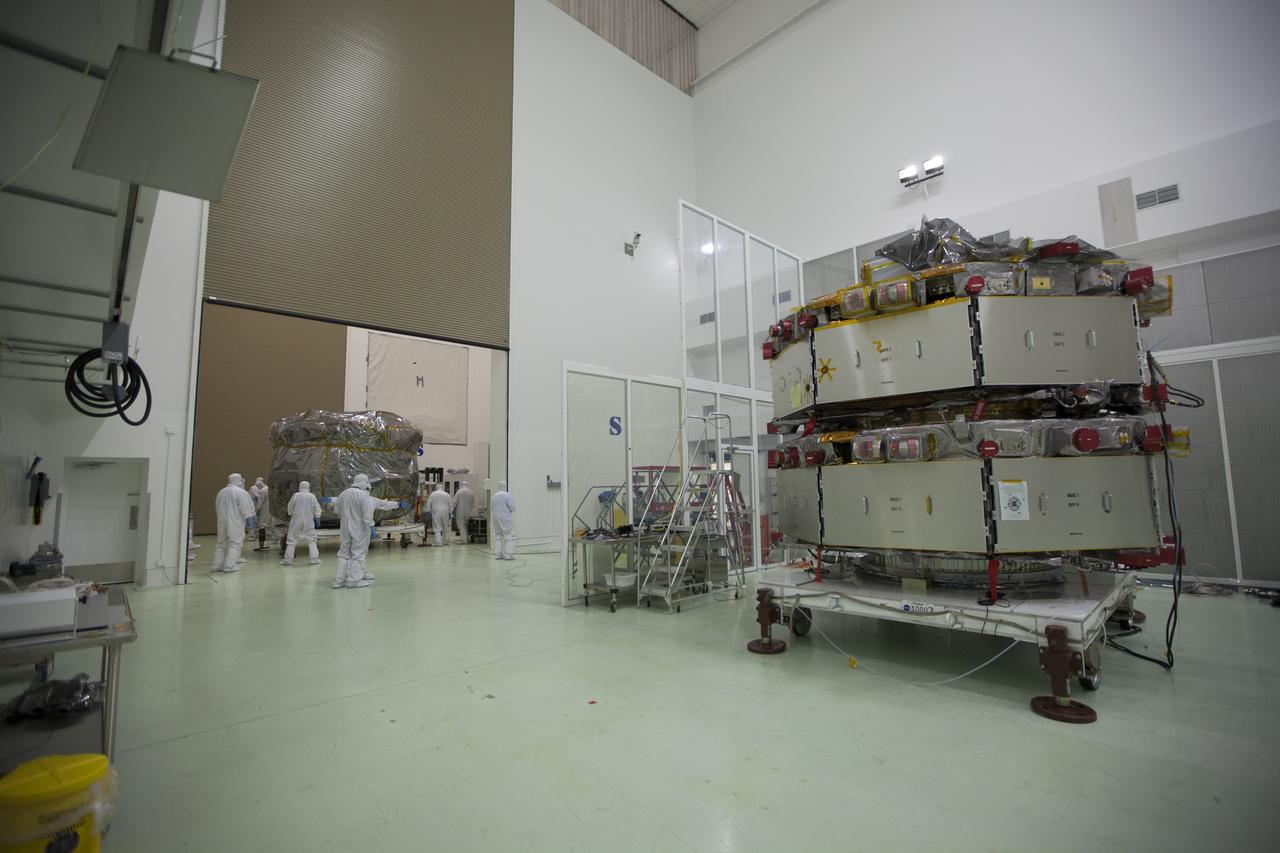

Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack arrive in the Building 1 airlock of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack, in the high bay uat right, arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
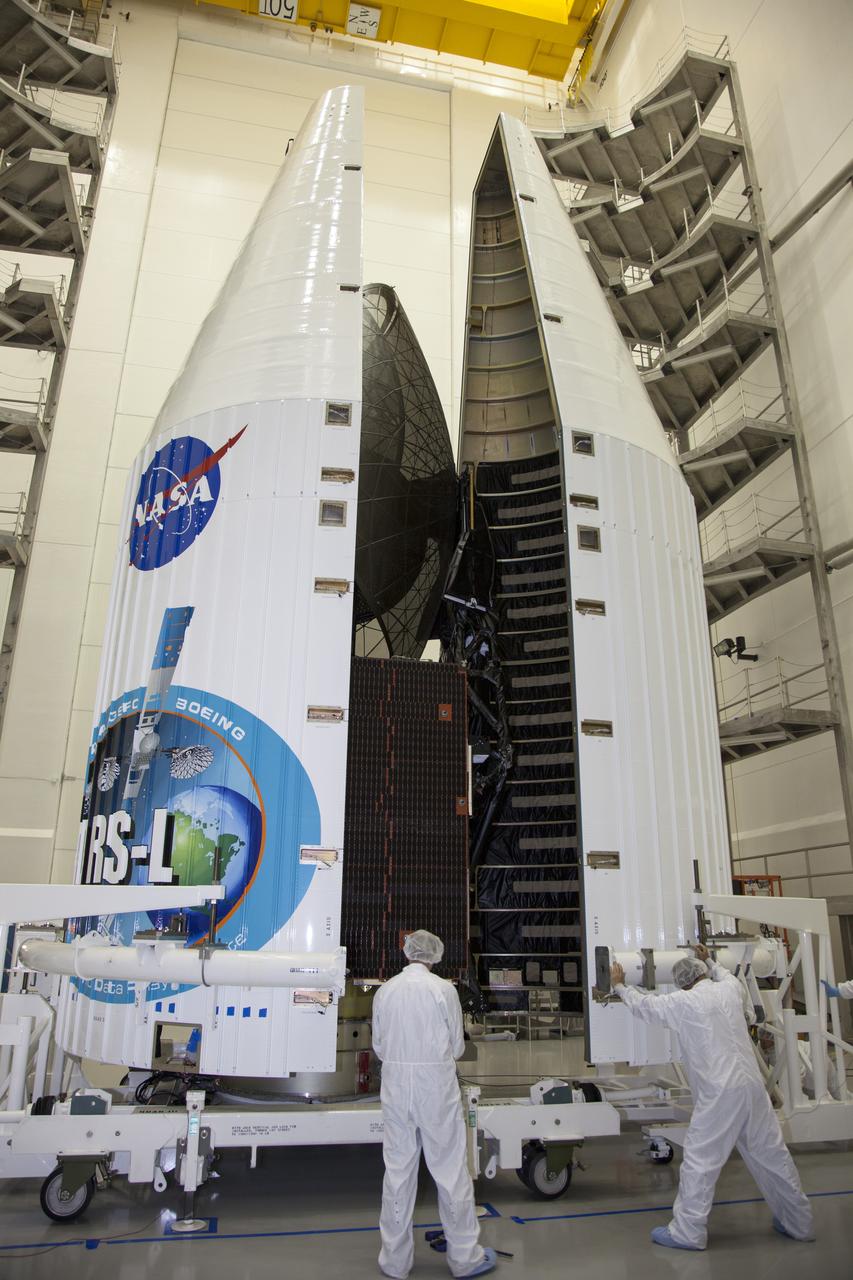

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, United Launch Alliance engineers and technicians encapsulate the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft in its payload fairing. TDRS-L will then be transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html

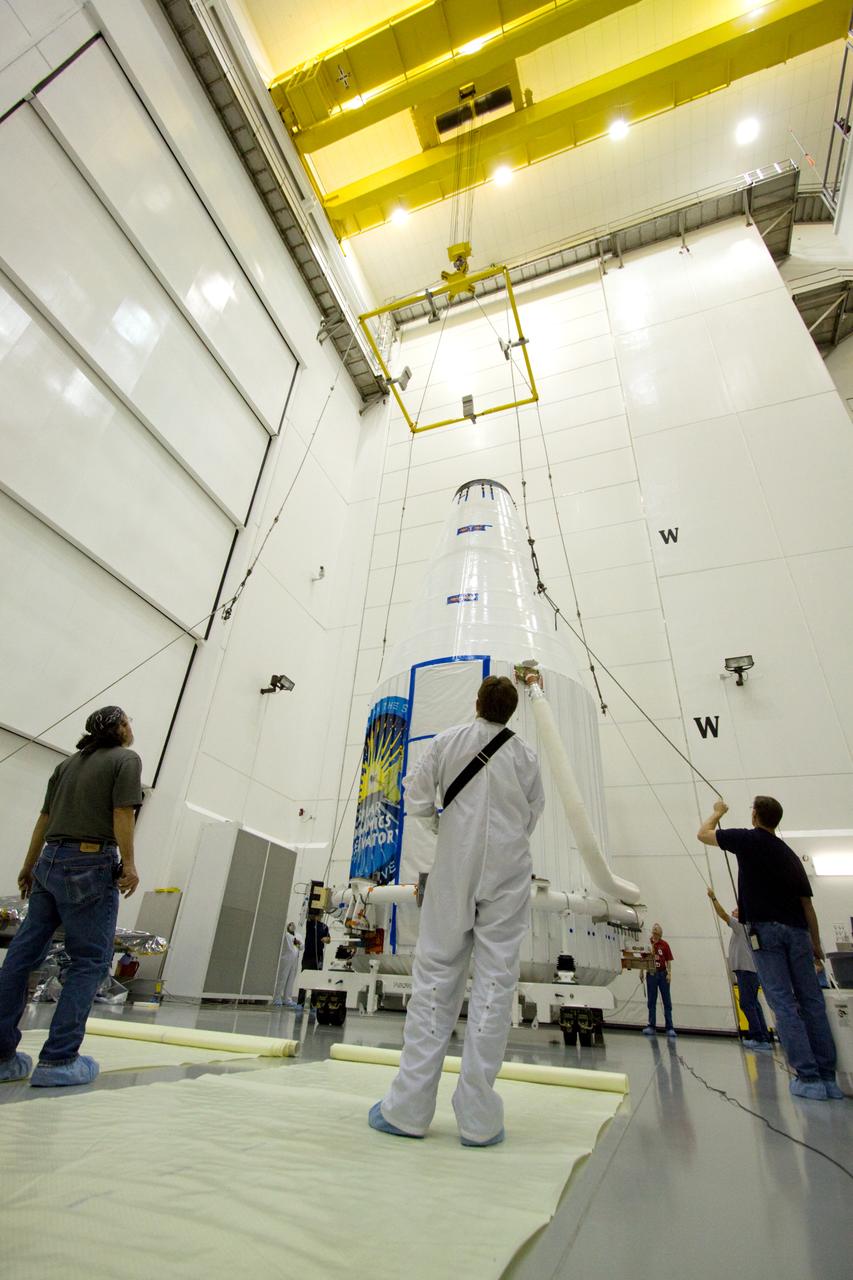
SDO MOVE TO TRANSPORTER

At Astrotech Space Operations, technicians conduct white light inspection of the THEMIS probes. They will also undergo black light inspection. White light inspection assures the telemetry is operating. Black light inspection uses UVA fluorescence to detect possible particulate microcontamination, minute cracks or fluid leaks. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

At Astrotech Space Operations, workers look over the integrated THEMIS spacecraft before spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

Workers monitor NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, wrapped in plastic and secured onto a portable work stand, as it travels between the airlock of Building 2 to the high bay of Building 1 at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is currently scheduled for January 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.

SDO MOVE TO TRANSPORTER
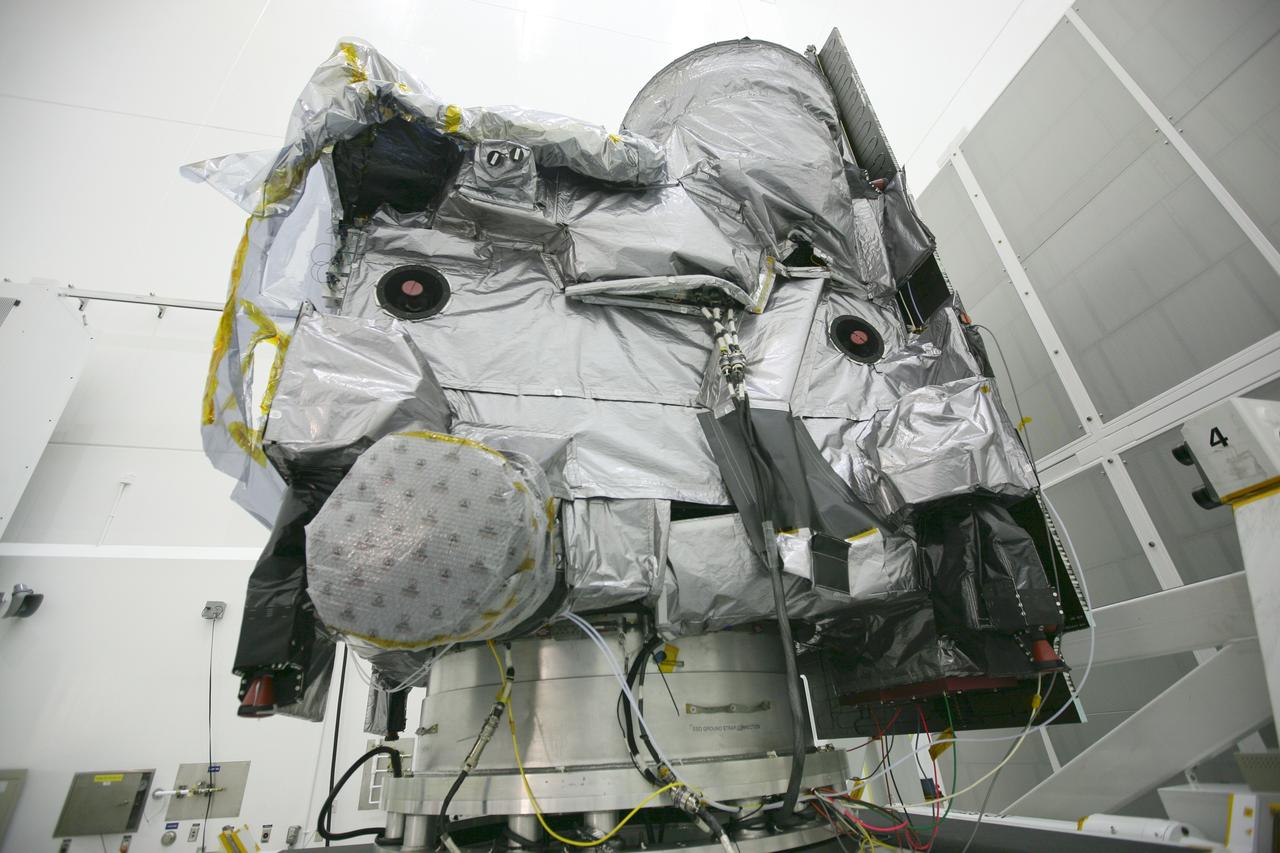

GOES-P UNBAGGING & ROTATION

The transport carrier containing NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft is offloaded at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023. PACE was shipped from the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and is targeted to launch on January 30, 2024, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web.
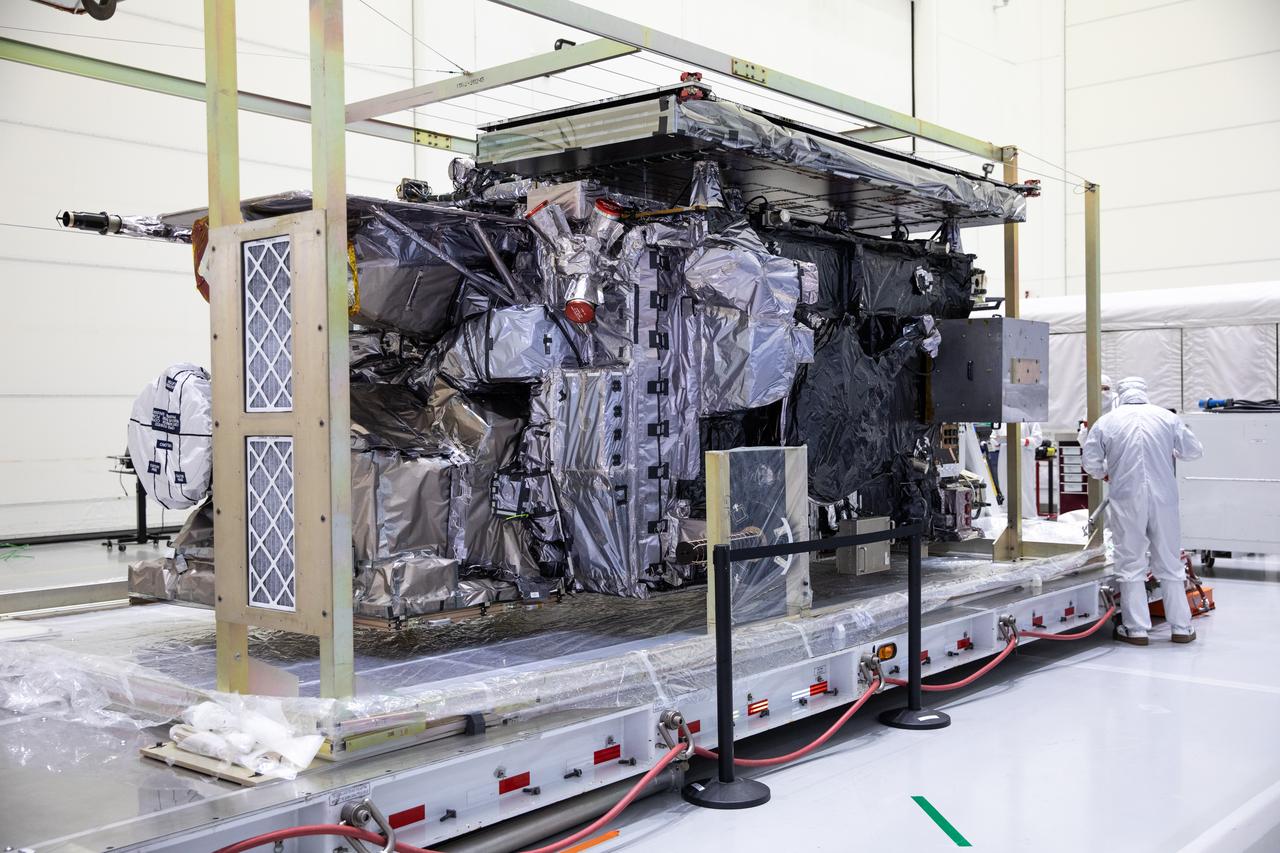

NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) is uncrated for prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the final in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
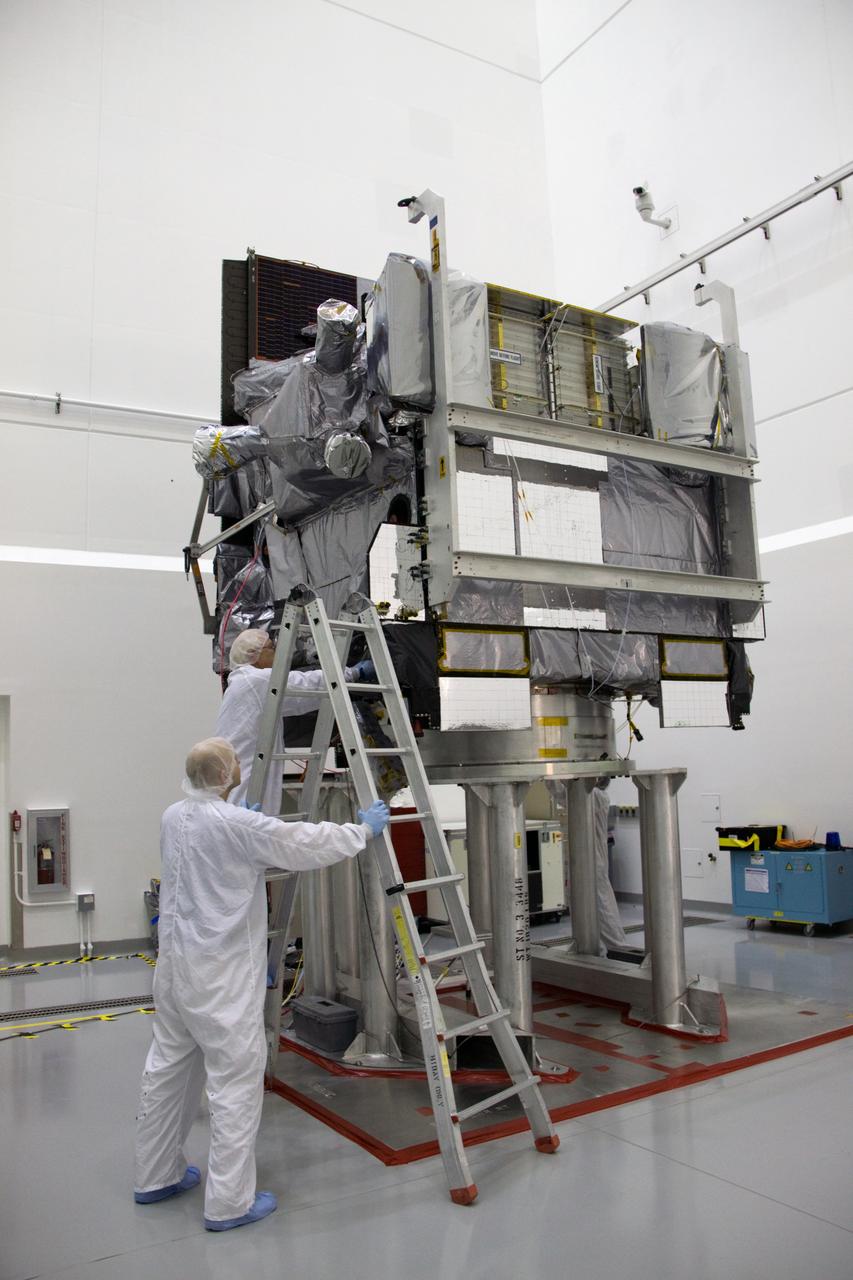

GOES-P MOVE TO FUELING STAND & MEDIA DAY
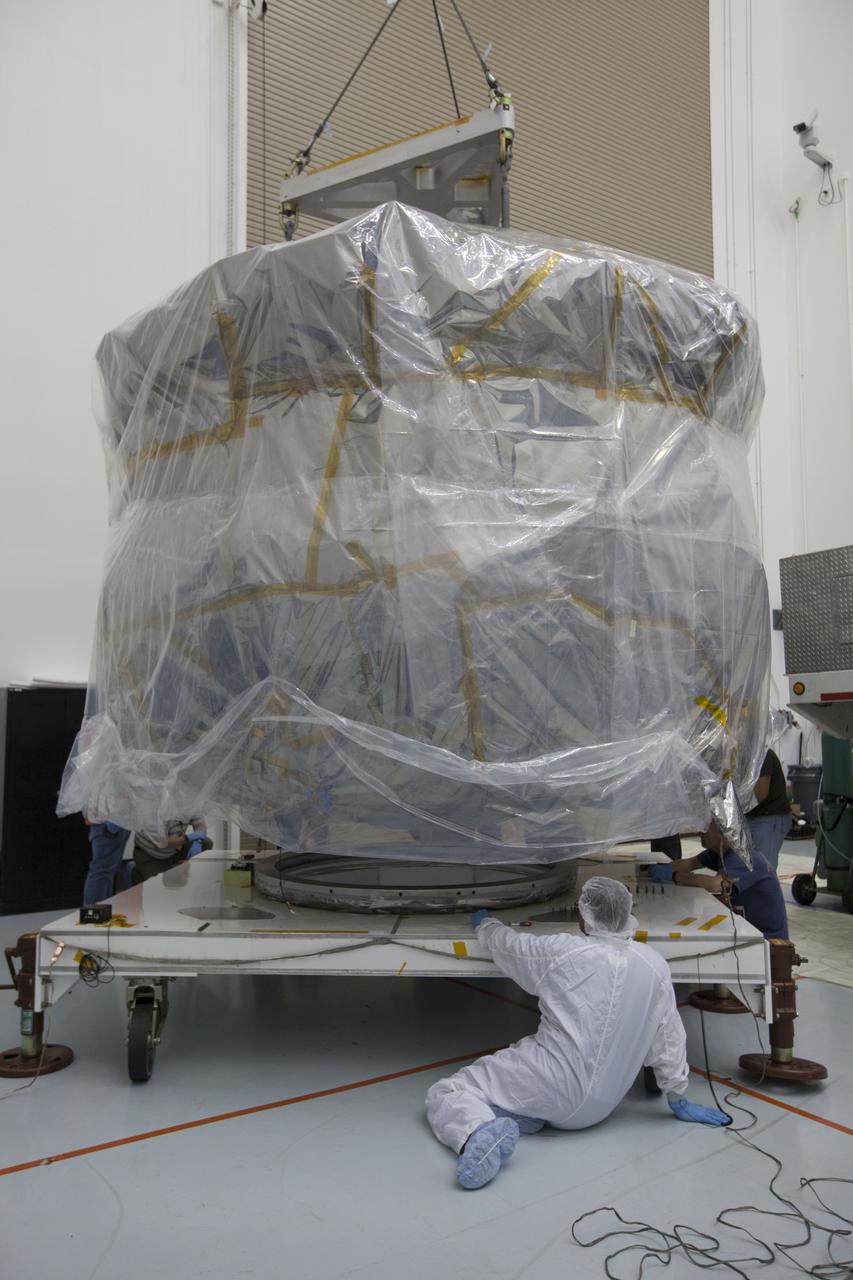

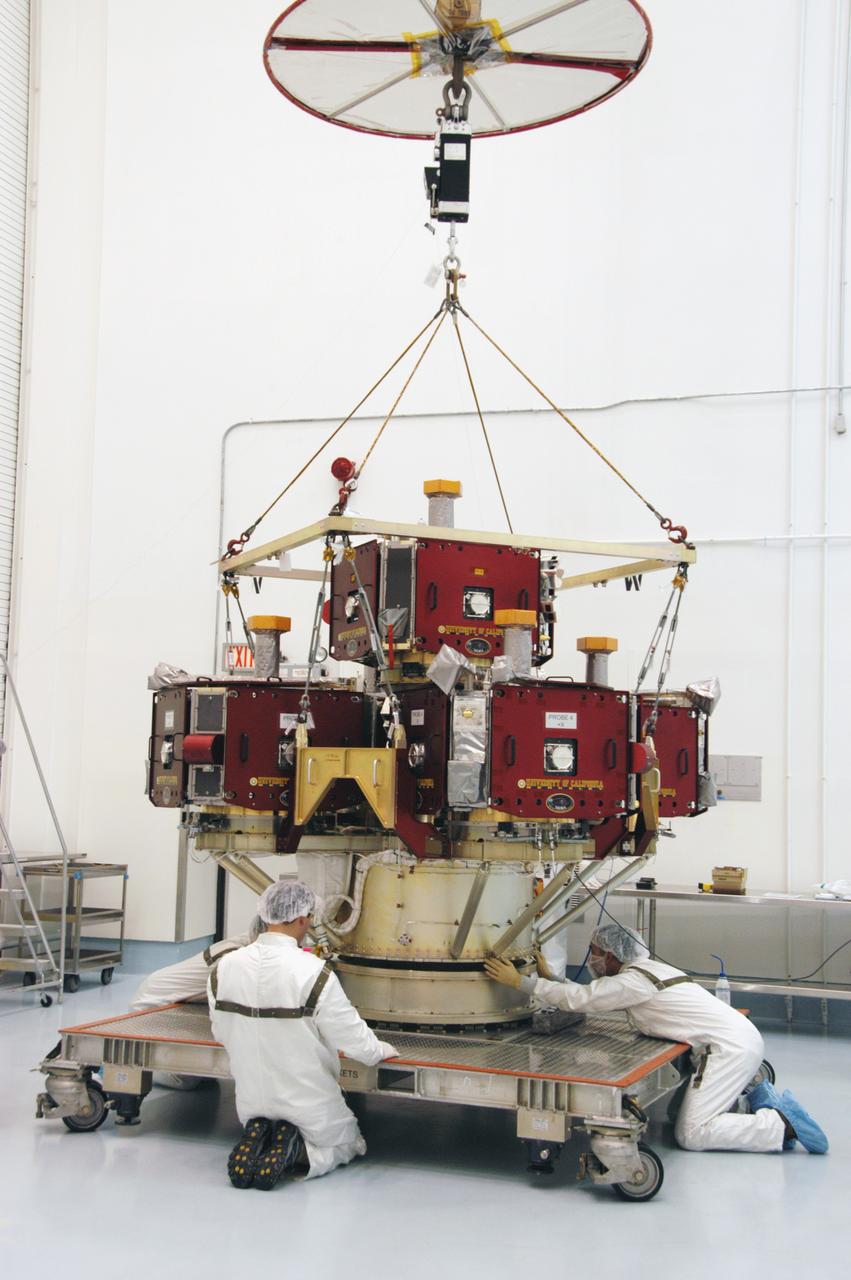
Two Magnetospheric Multiscale , or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are lowered onto a payload dolly in Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

Workers attach a crane to the protective shipping container to prepare to uncover the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS. They were delivered to the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

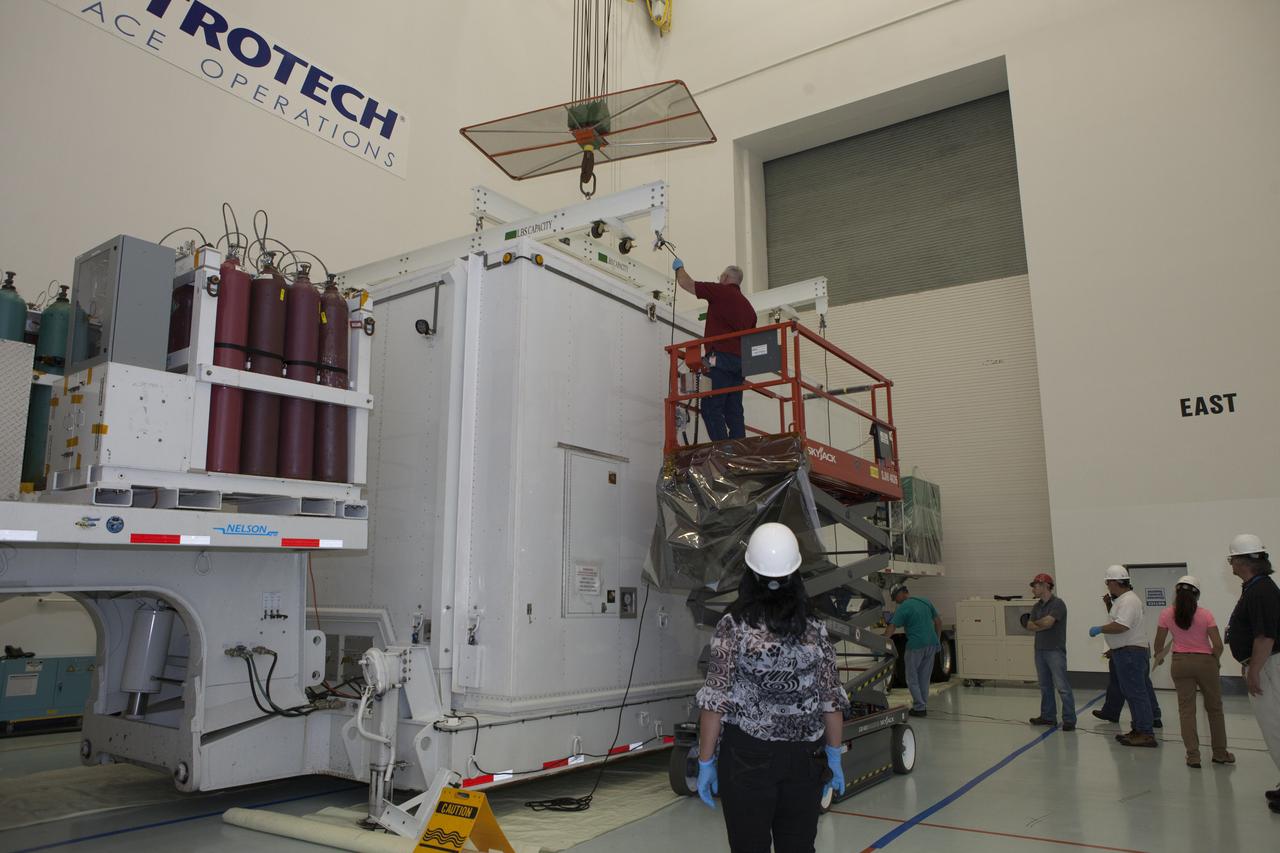
SDO MOVE FROM ASTROTECH TO PAD 41 - LIFT & MATE
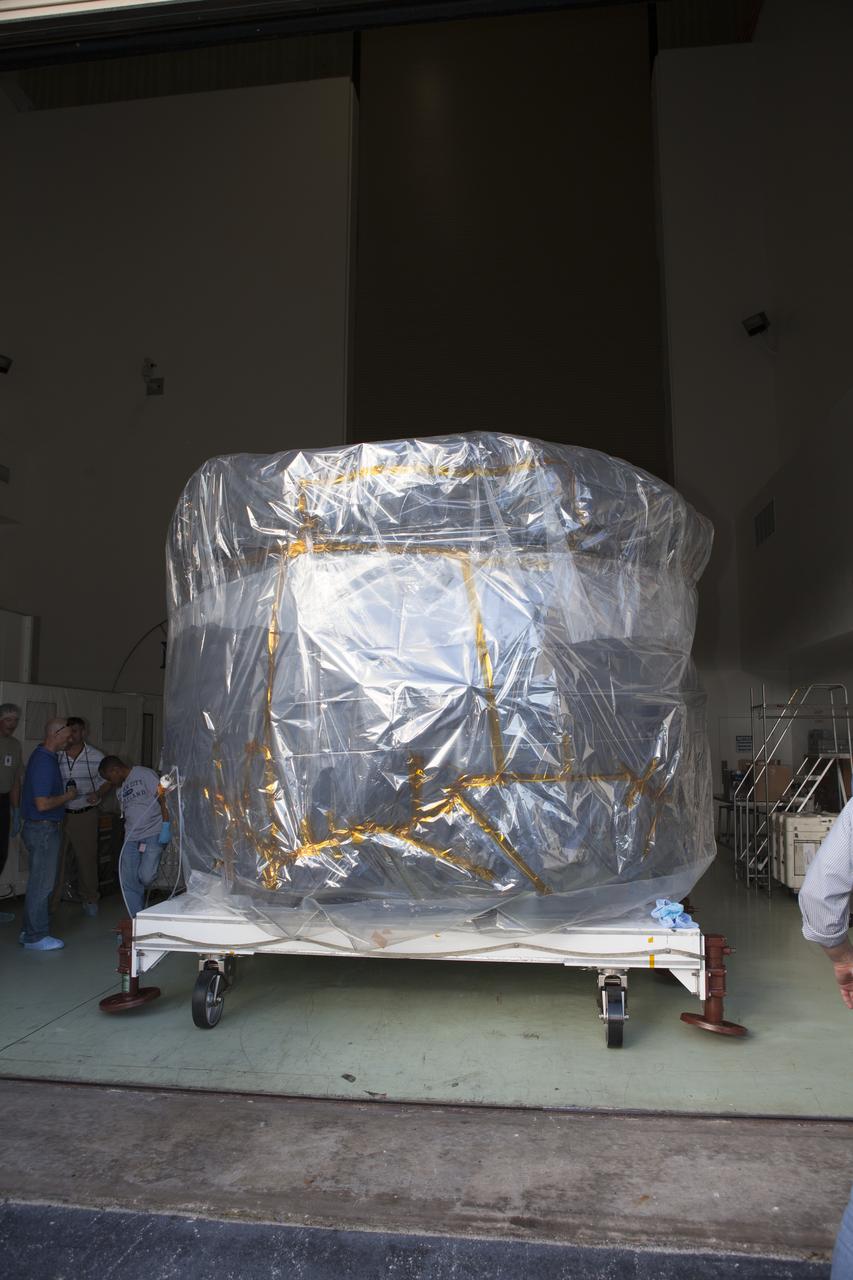

Two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, arrive in the Building 1 airlock at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

The mission insignia of NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) mission is pictured in front of the satellite in a vertical position on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft is uncrated for prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.

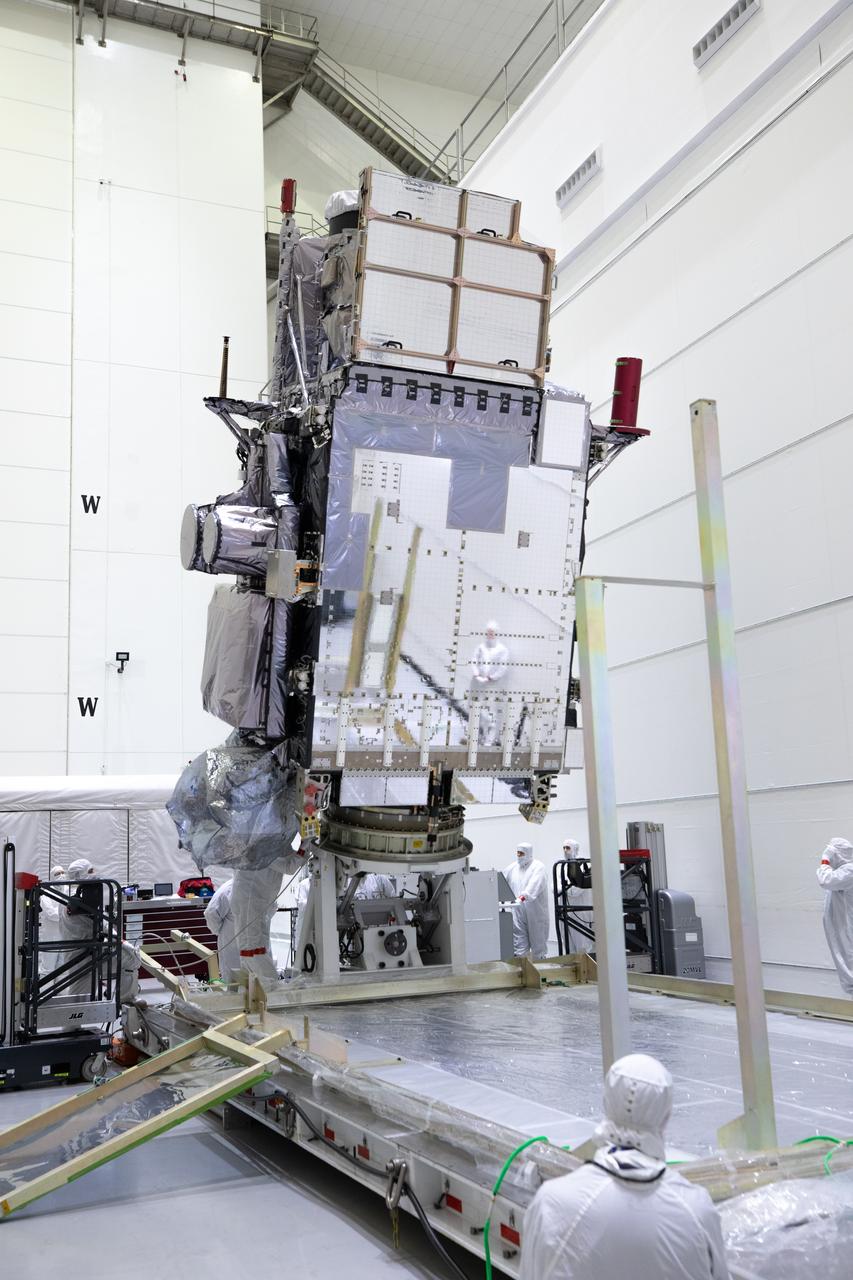
TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Members of the news media are given an up-close look at the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft undergoing preflight processing inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville. TDRS-L is being prepared for encapsulation inside its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
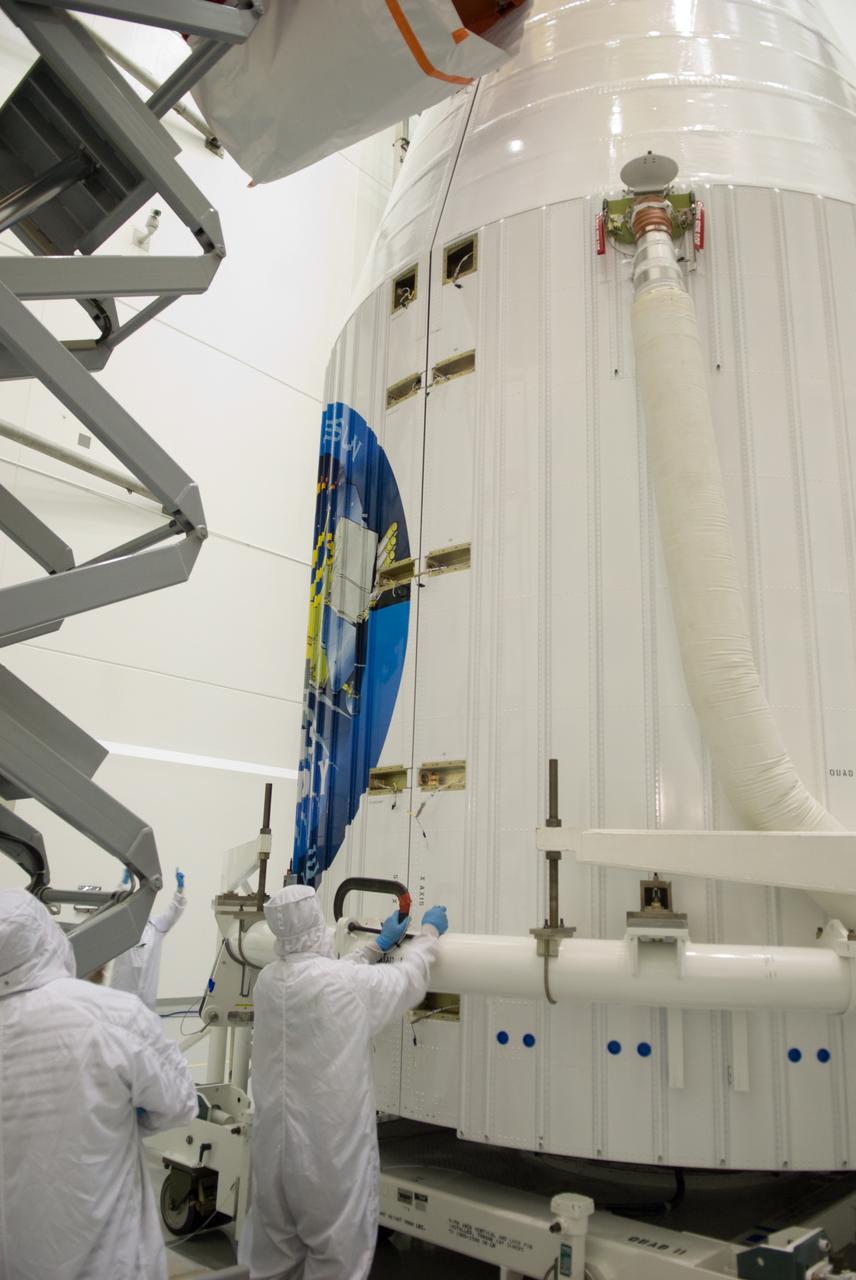

SDO - MEDIA DAY & FAIRING INSTALLATION
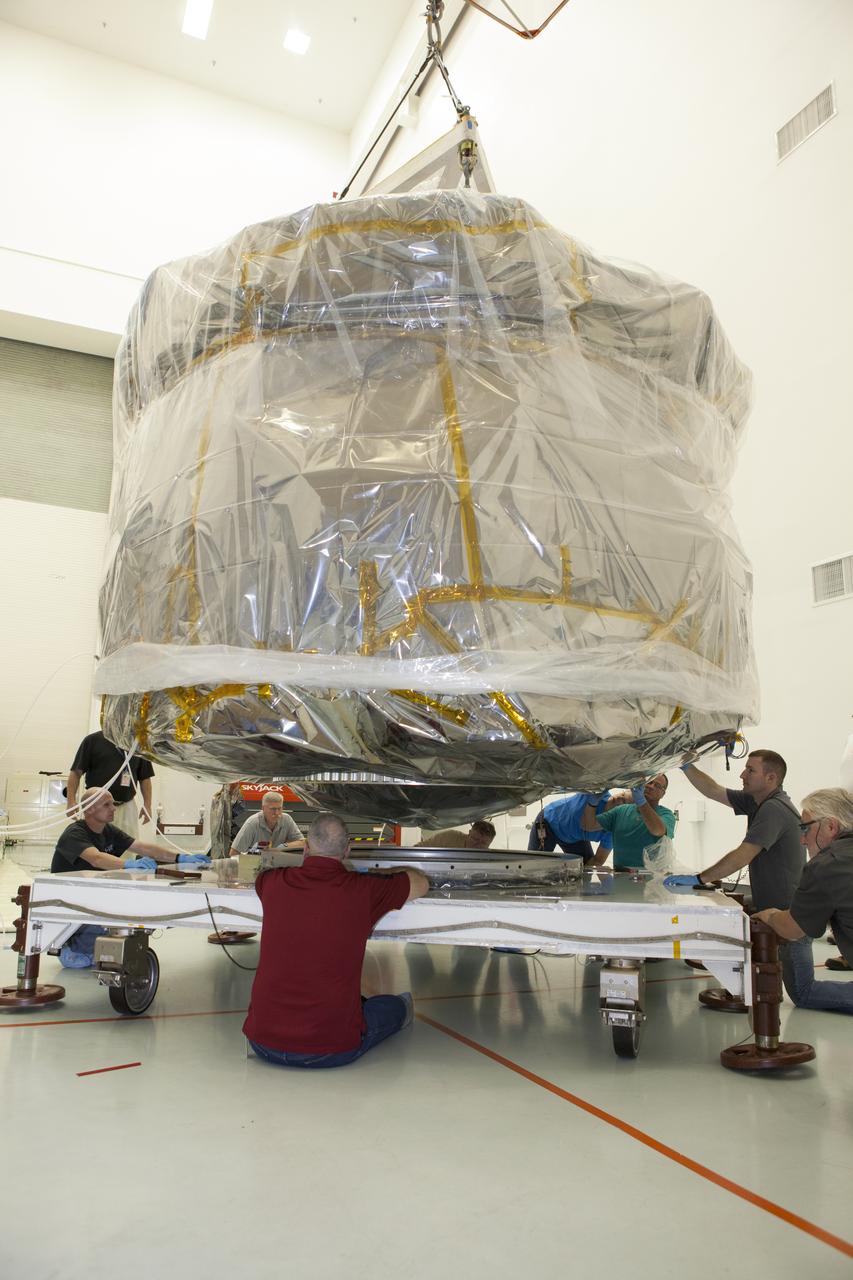

Workers position two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1 for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, onto a payload dolly in the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
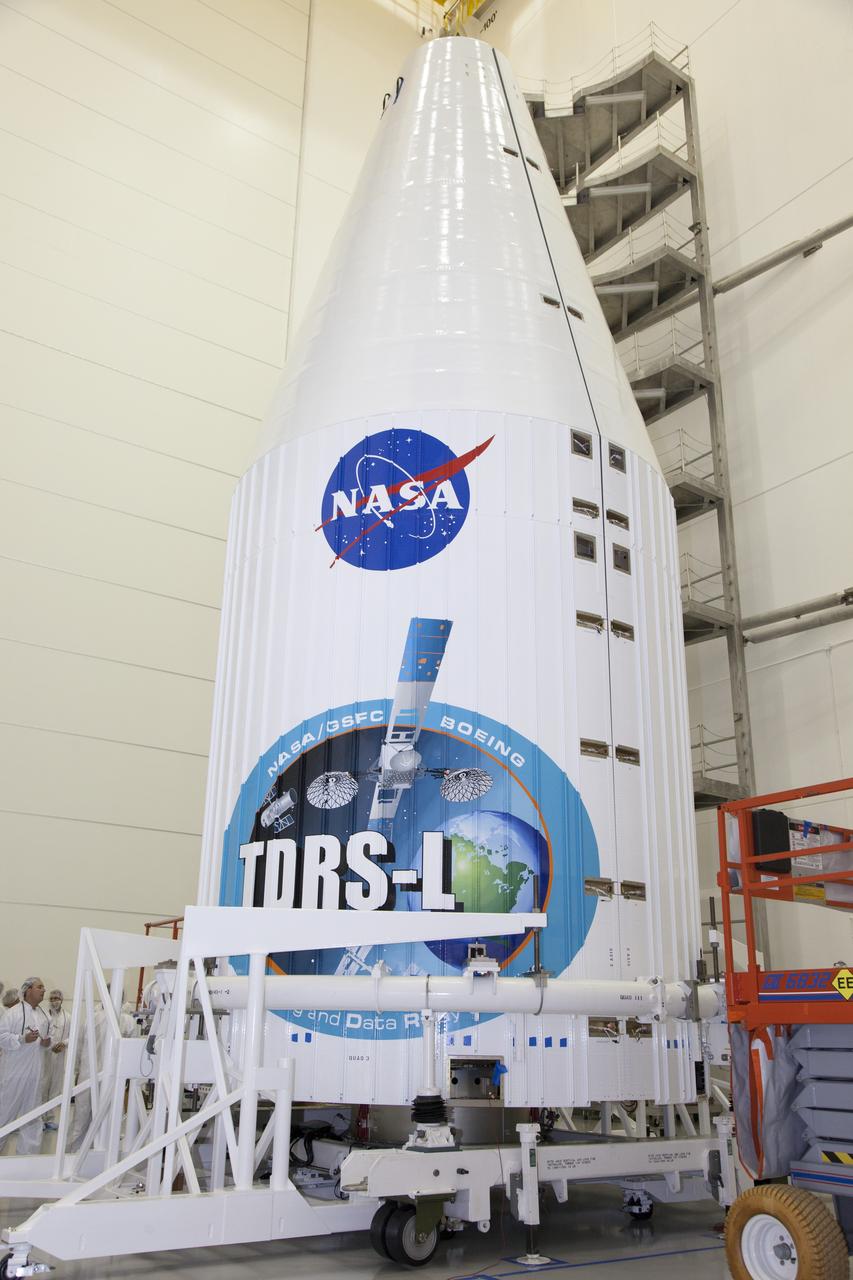

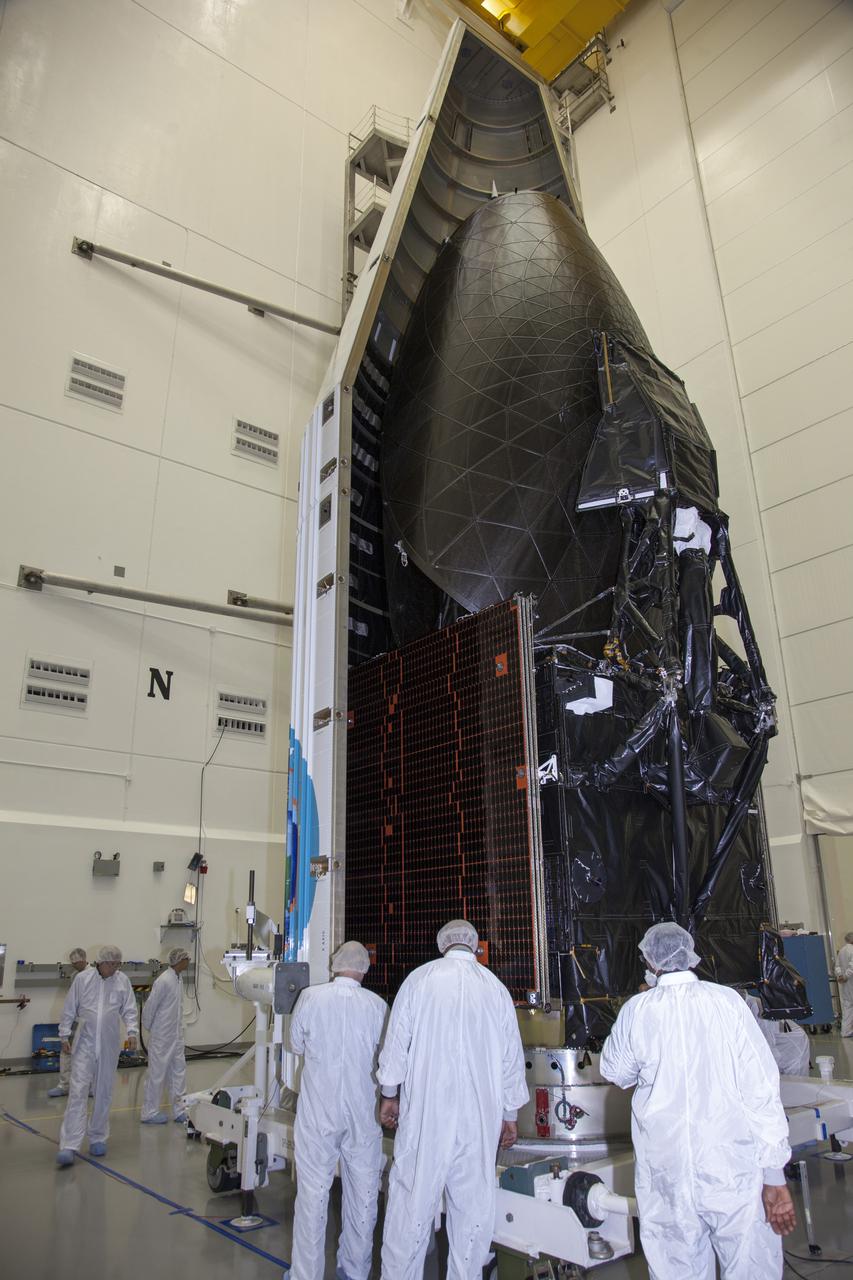
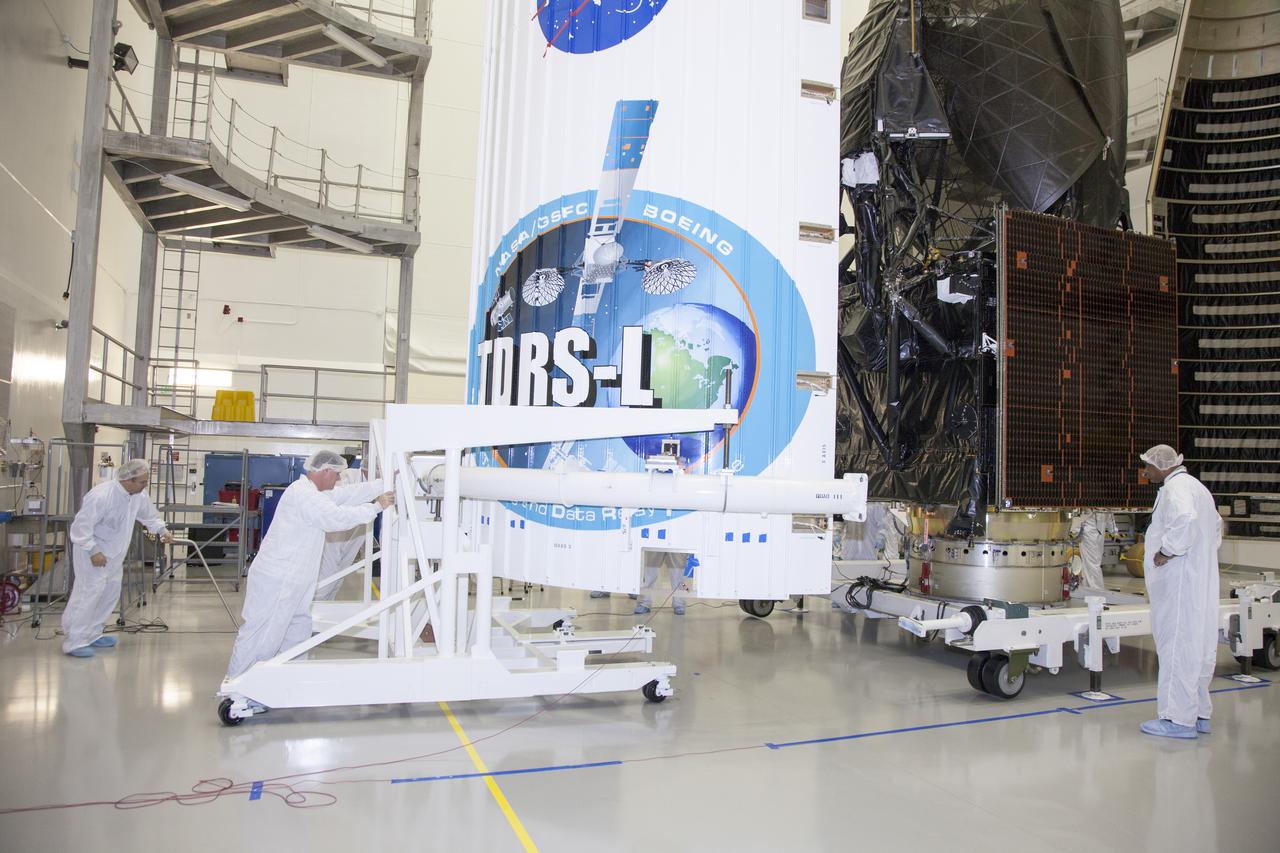
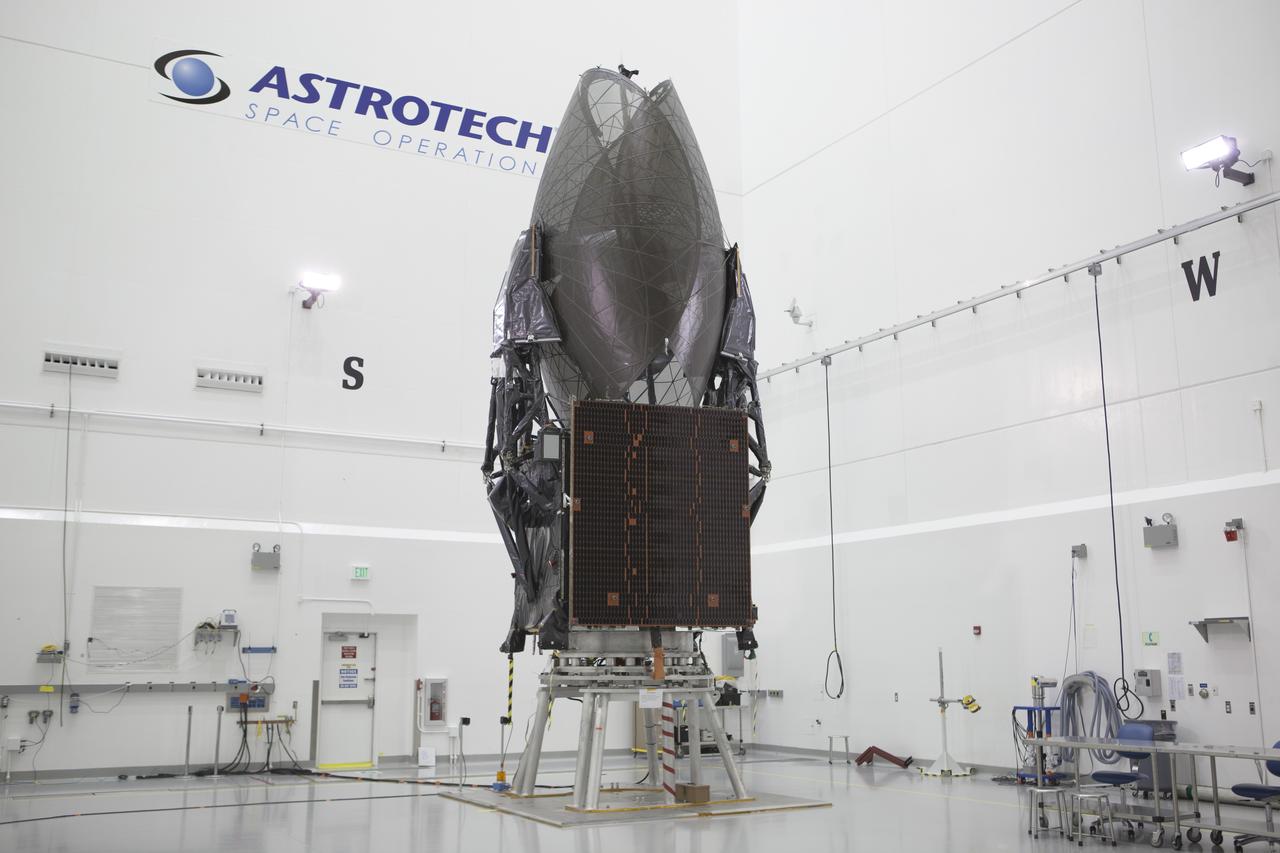
TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft has been encapsulated in its payload fairing. TDRS-L will then be transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
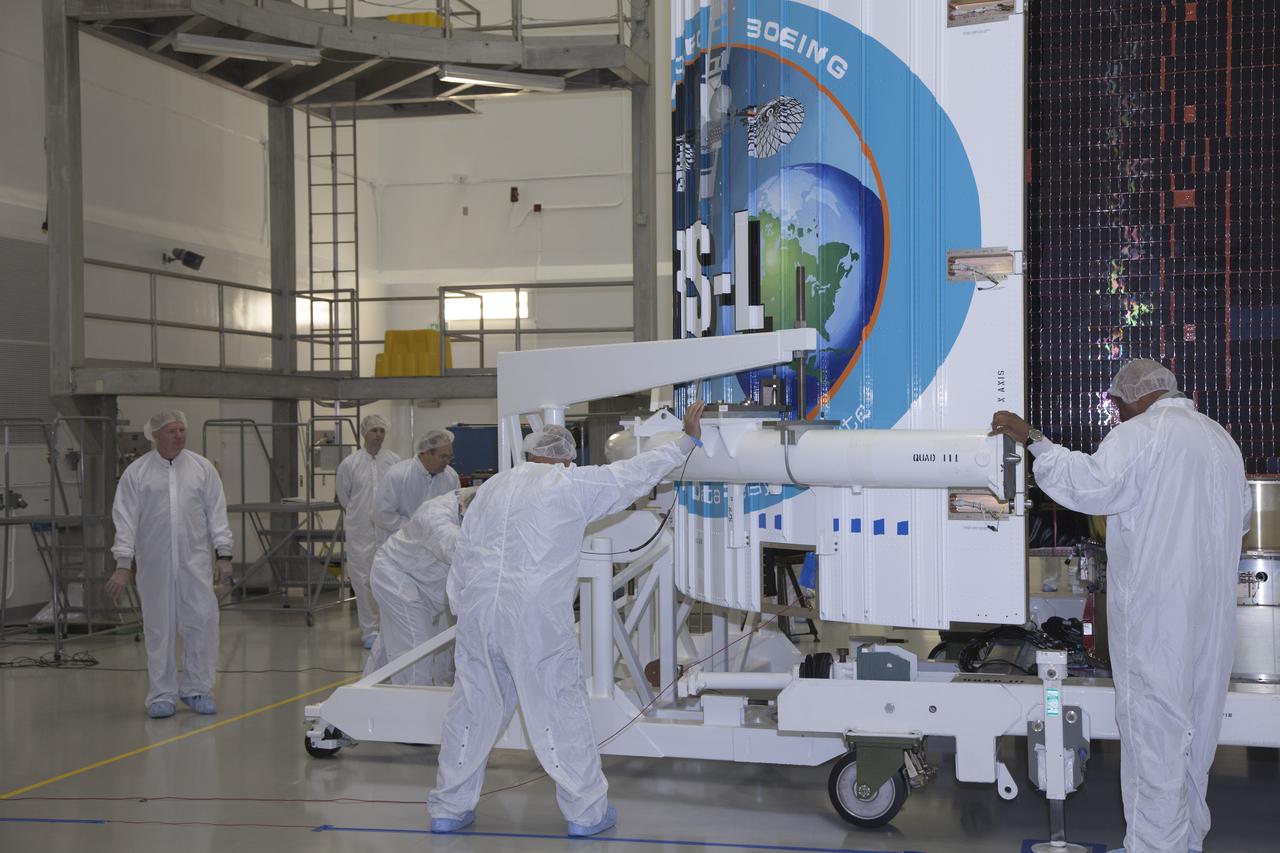

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, United Launch Alliance engineers and technicians encapsulate the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft in its payload fairing. TDRS-L will then be transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
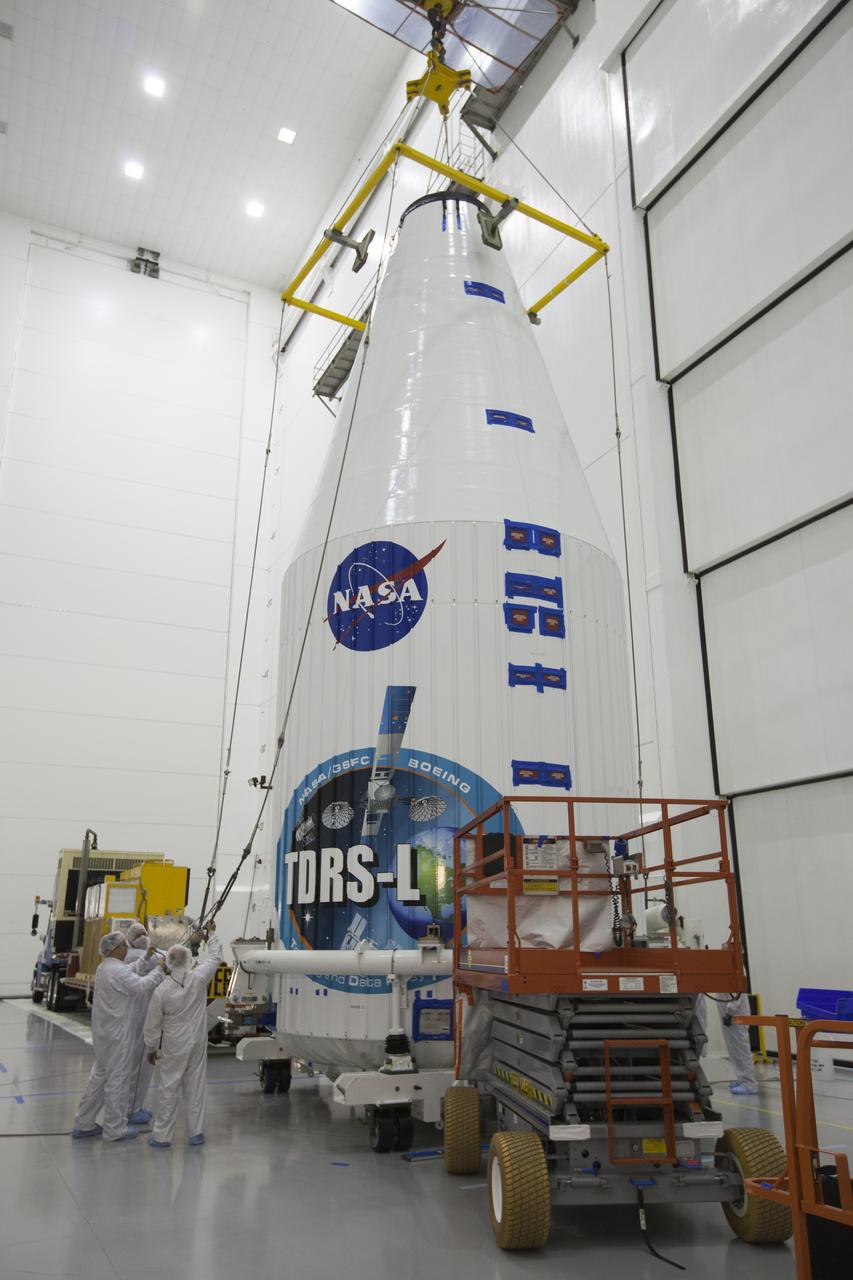

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft has been encapsulated in its payload fairing in preparation for begin transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
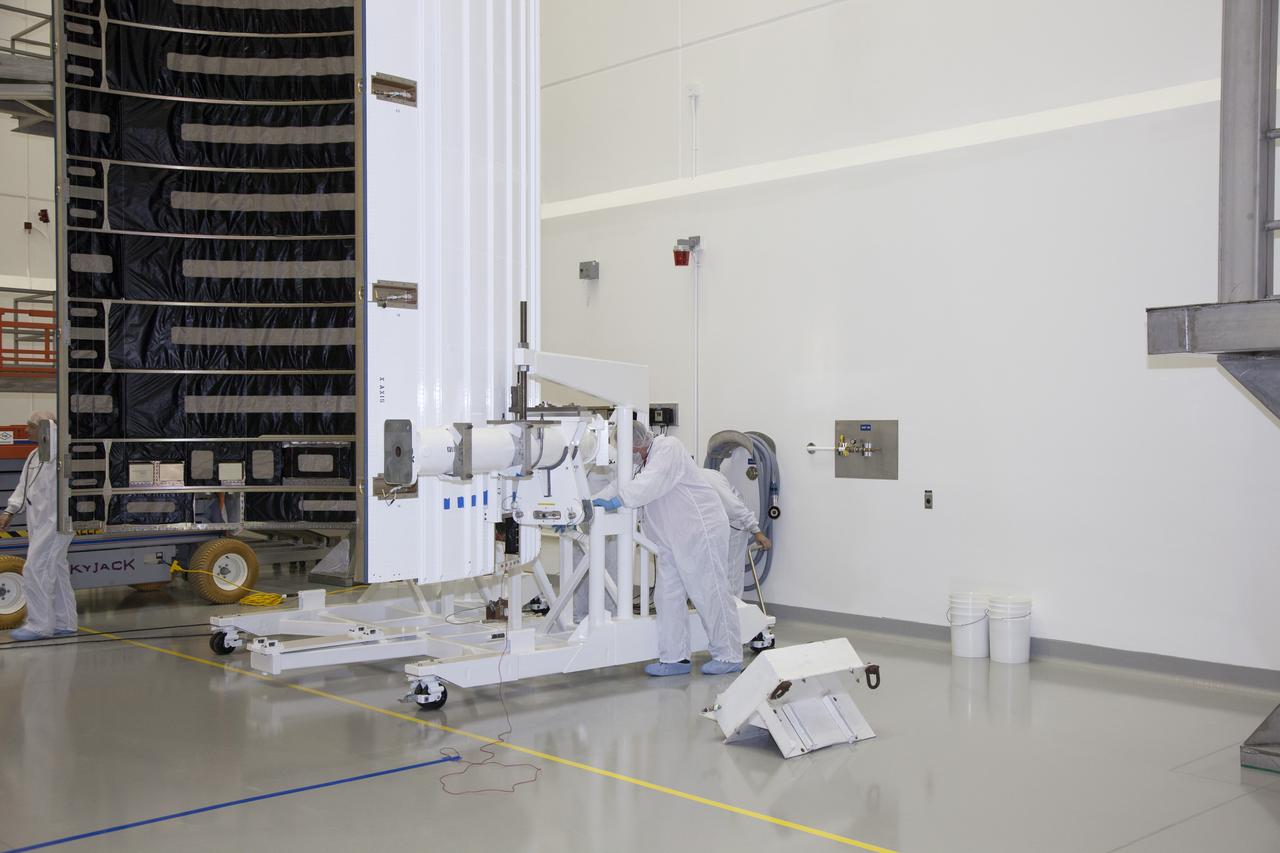

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft is being encapsulated in its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html

GOES-P MOVE TO FUELING STAND & MEDIA DAY

In the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech Space Operations, a technician observes one of the THEMIS probes as it undergoes solar array illumination telemetry testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.

Technicians remove the protective covering from the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, in Building 1 D high bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

SDO MOVE TO TRANSPORTER

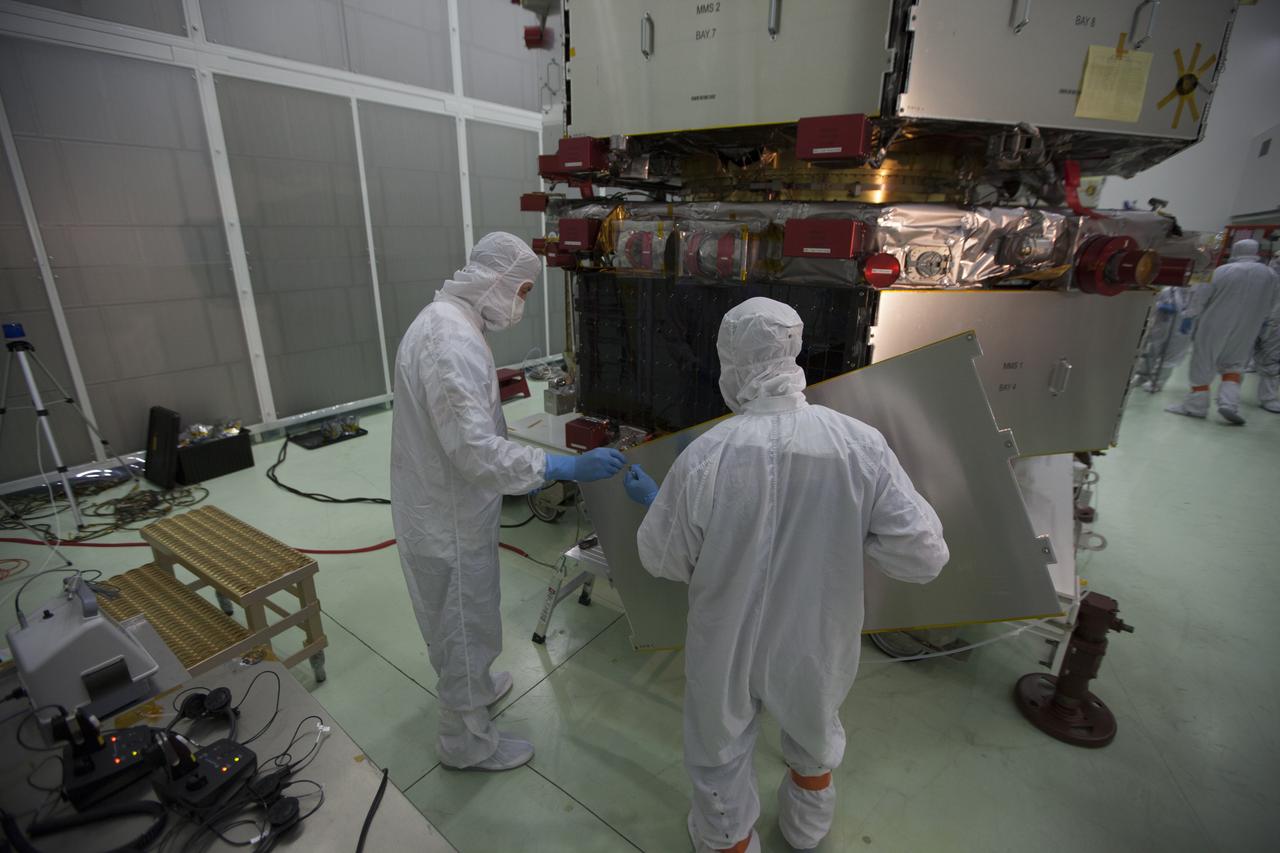
Technicians have removed most of the protective covering from the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, in Building 1 D high bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

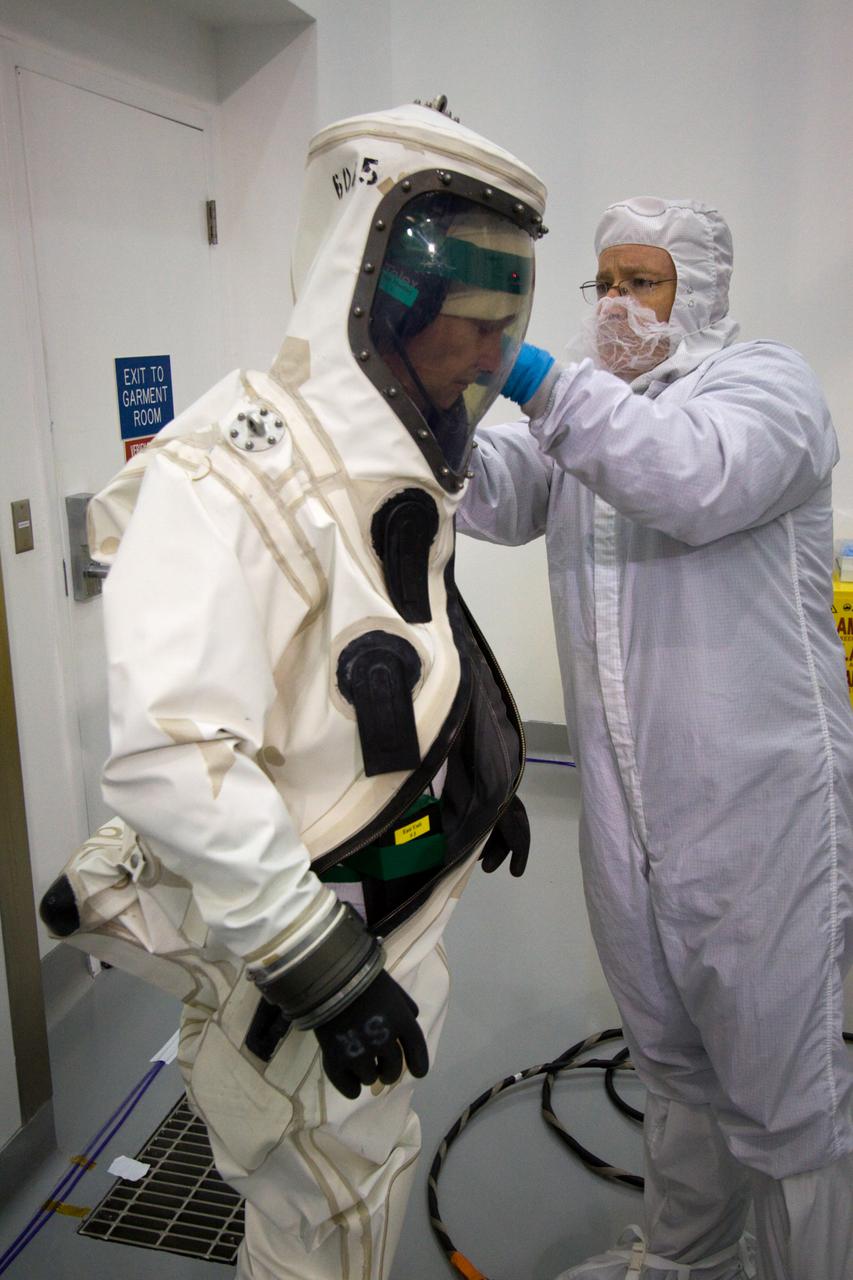
SDO FUELING PREPS FOR SATELLITE W/CREW
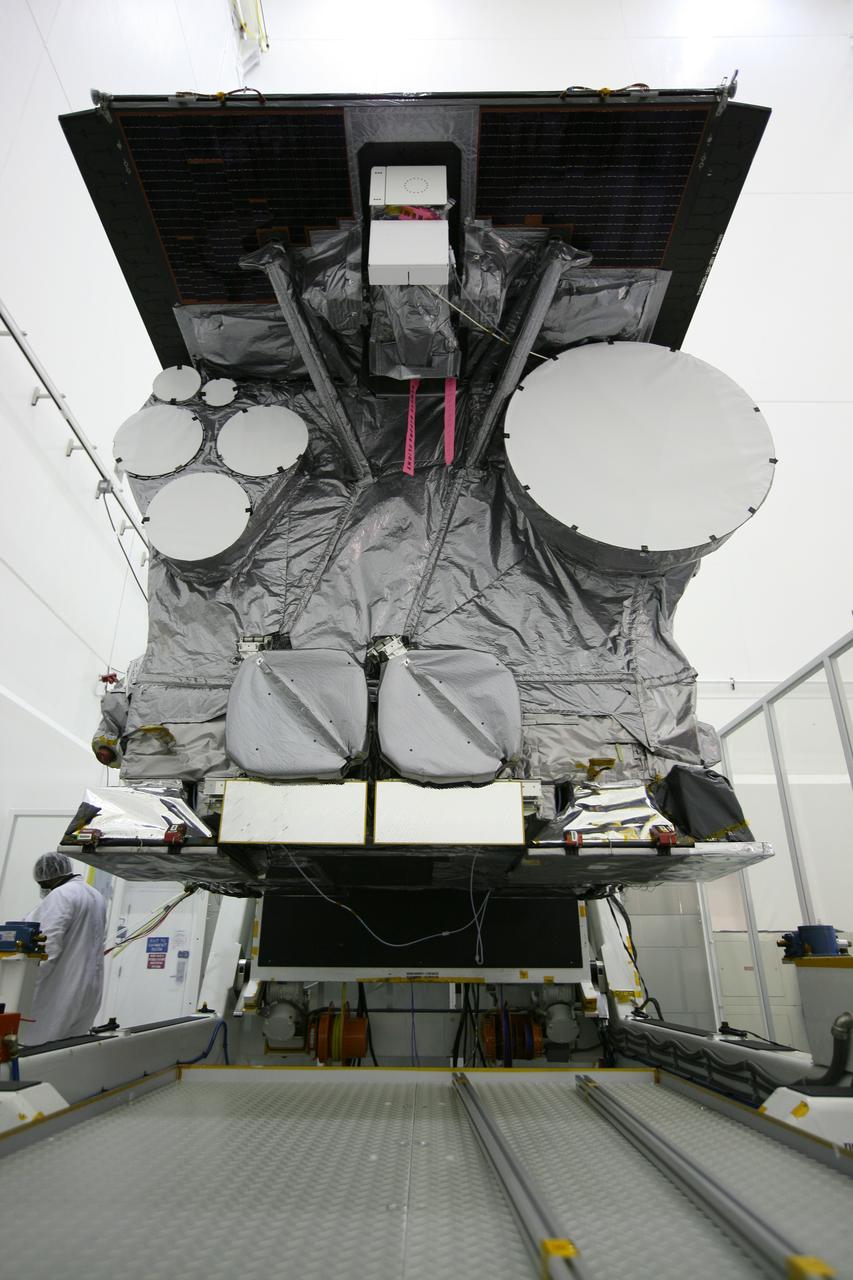

GOES-P UNBAGGING & ROTATION

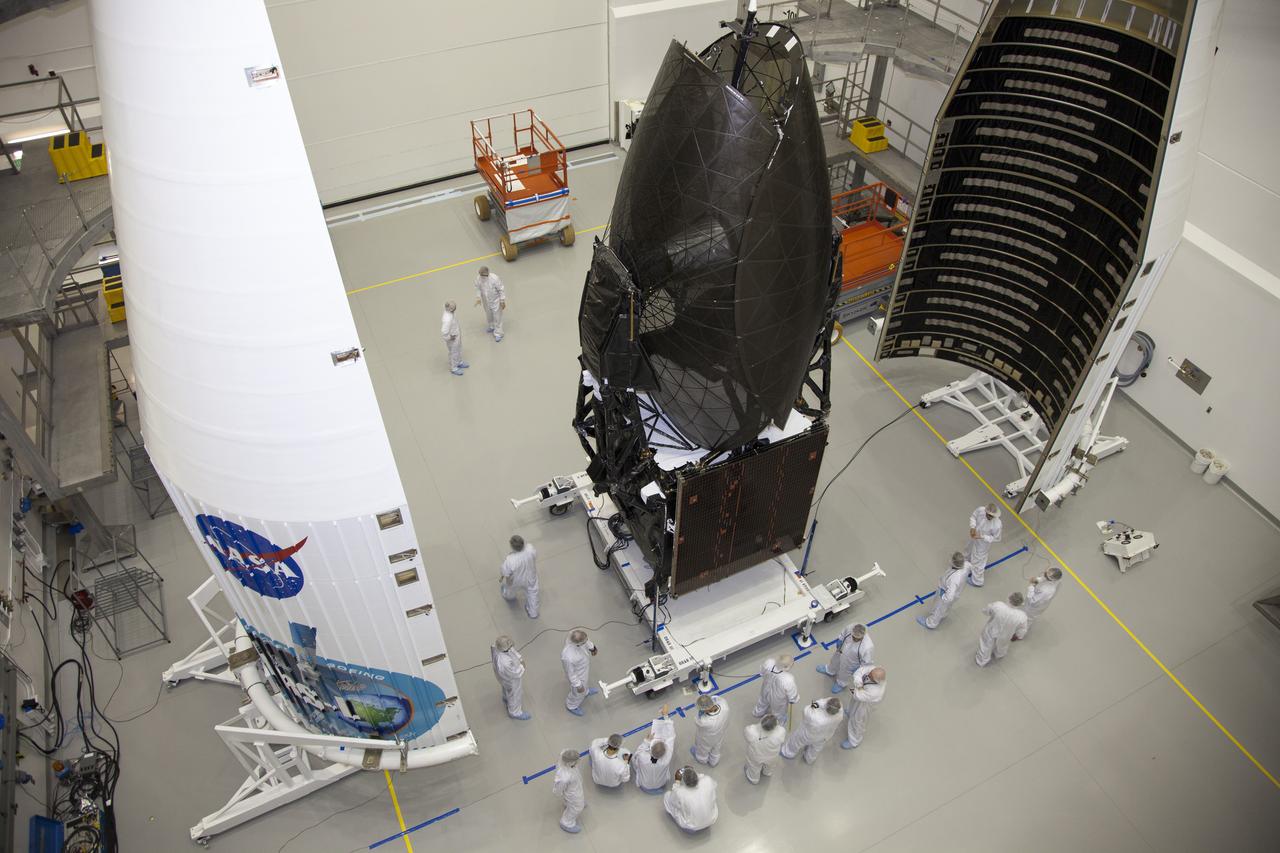
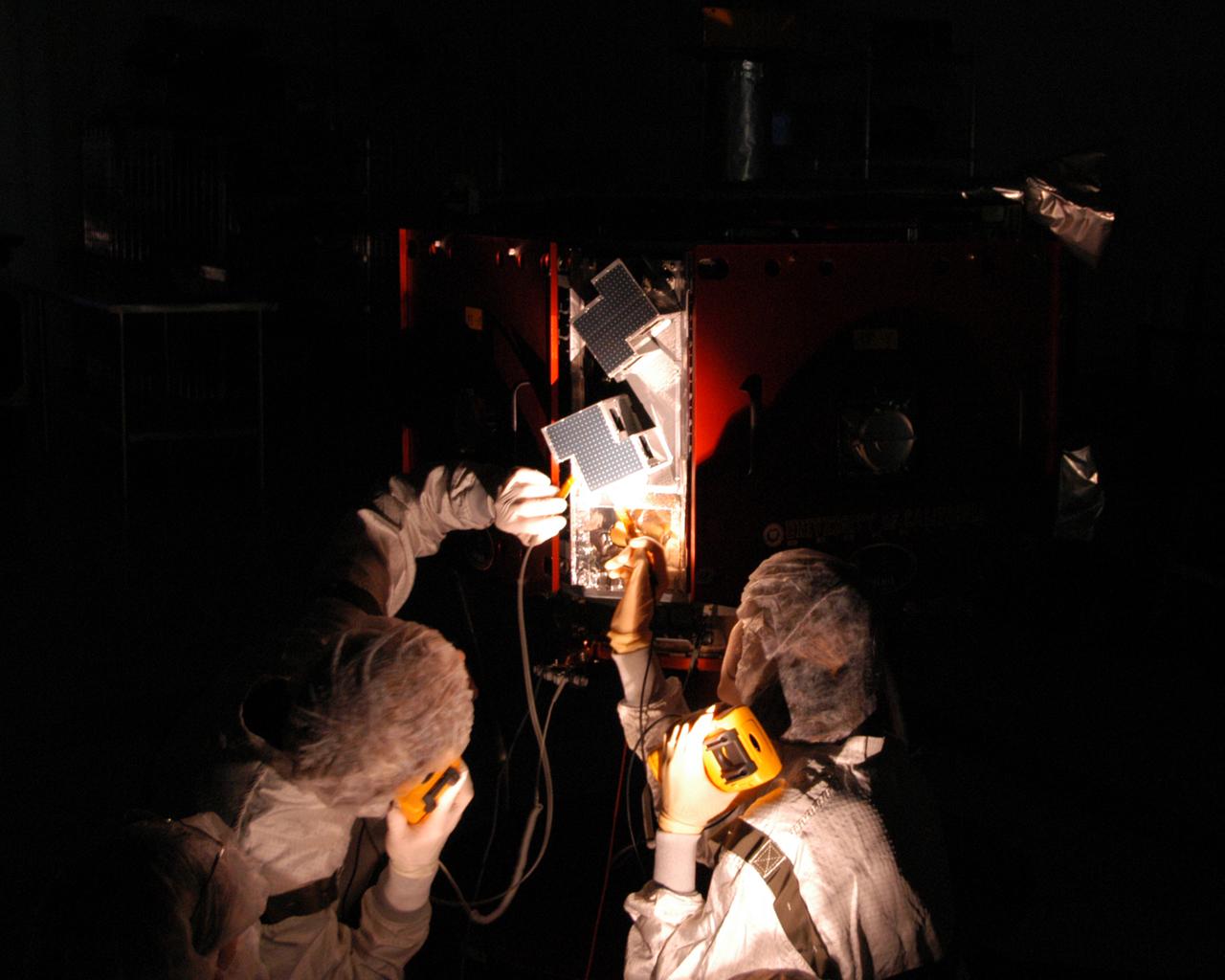
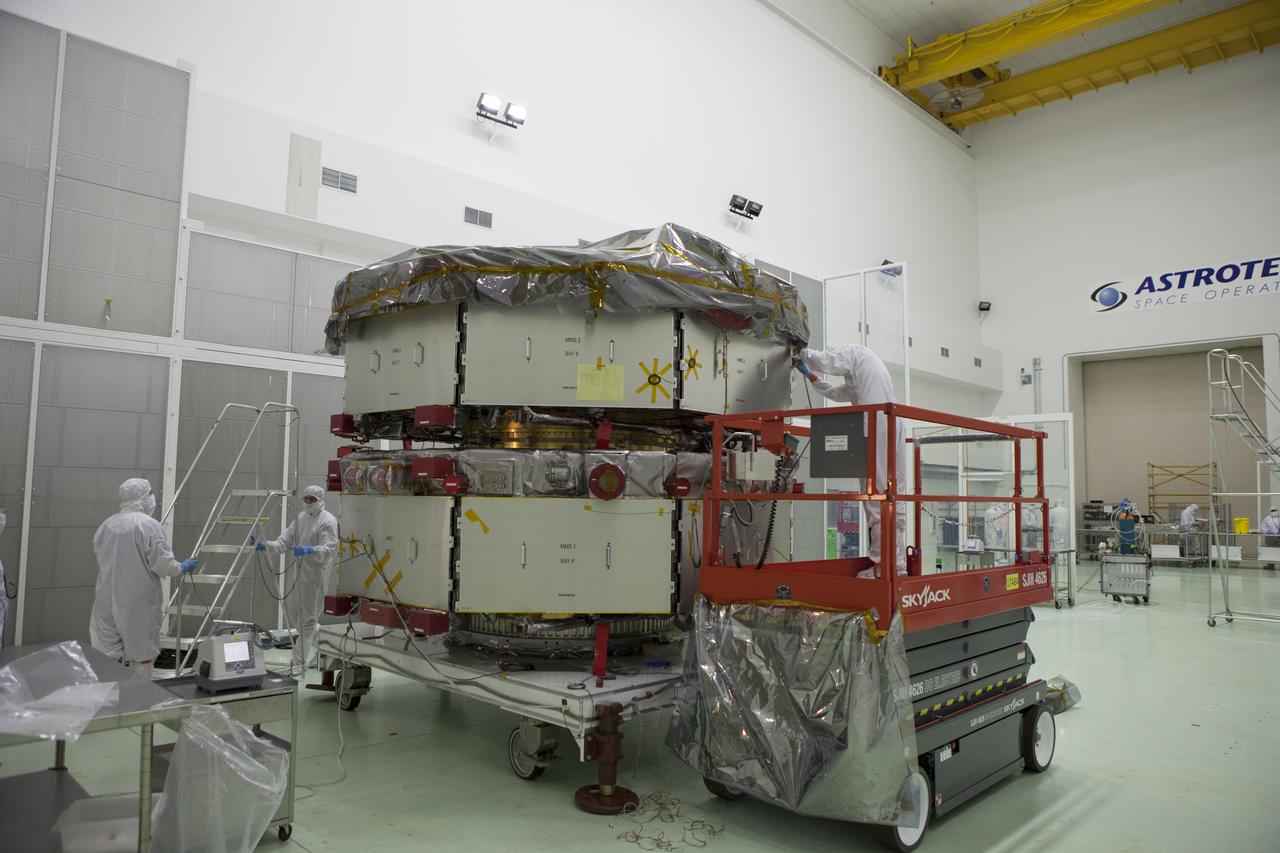
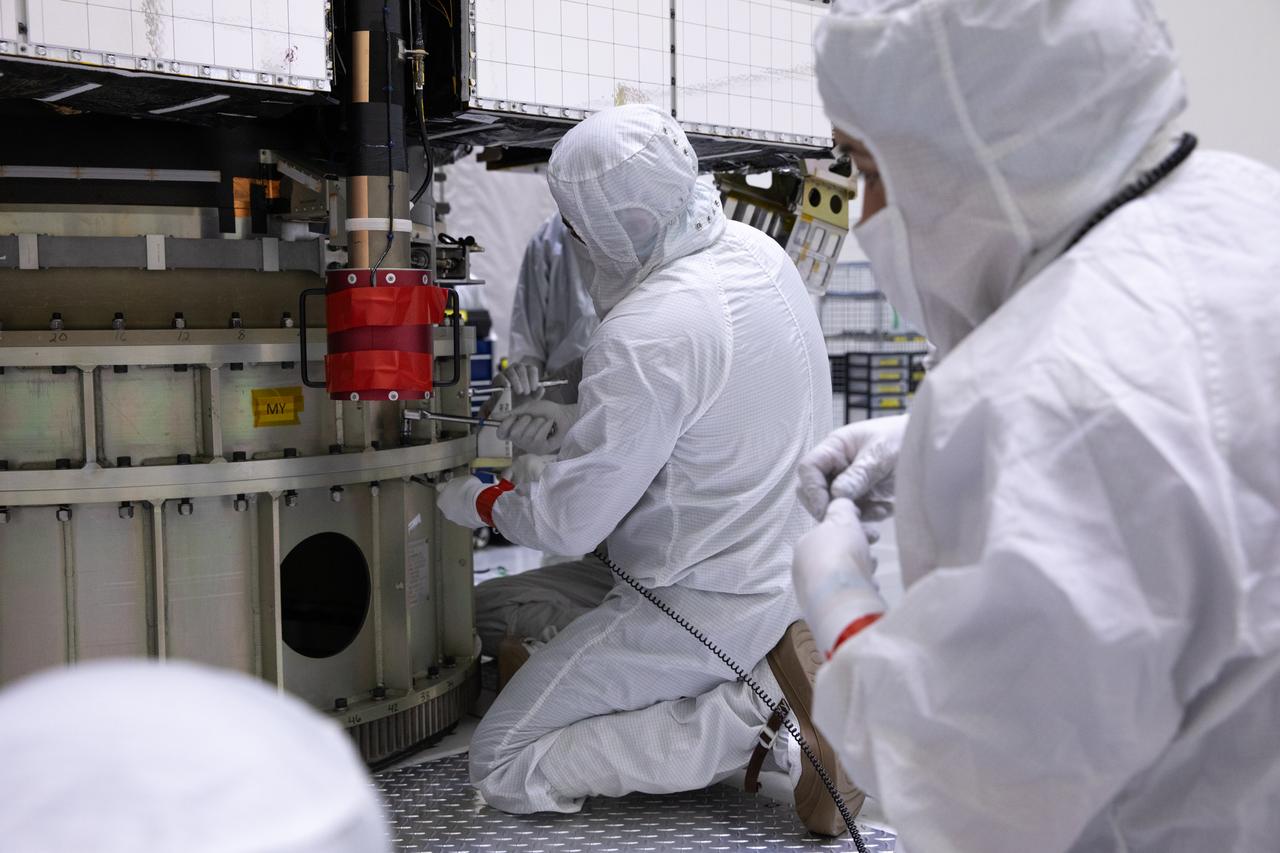
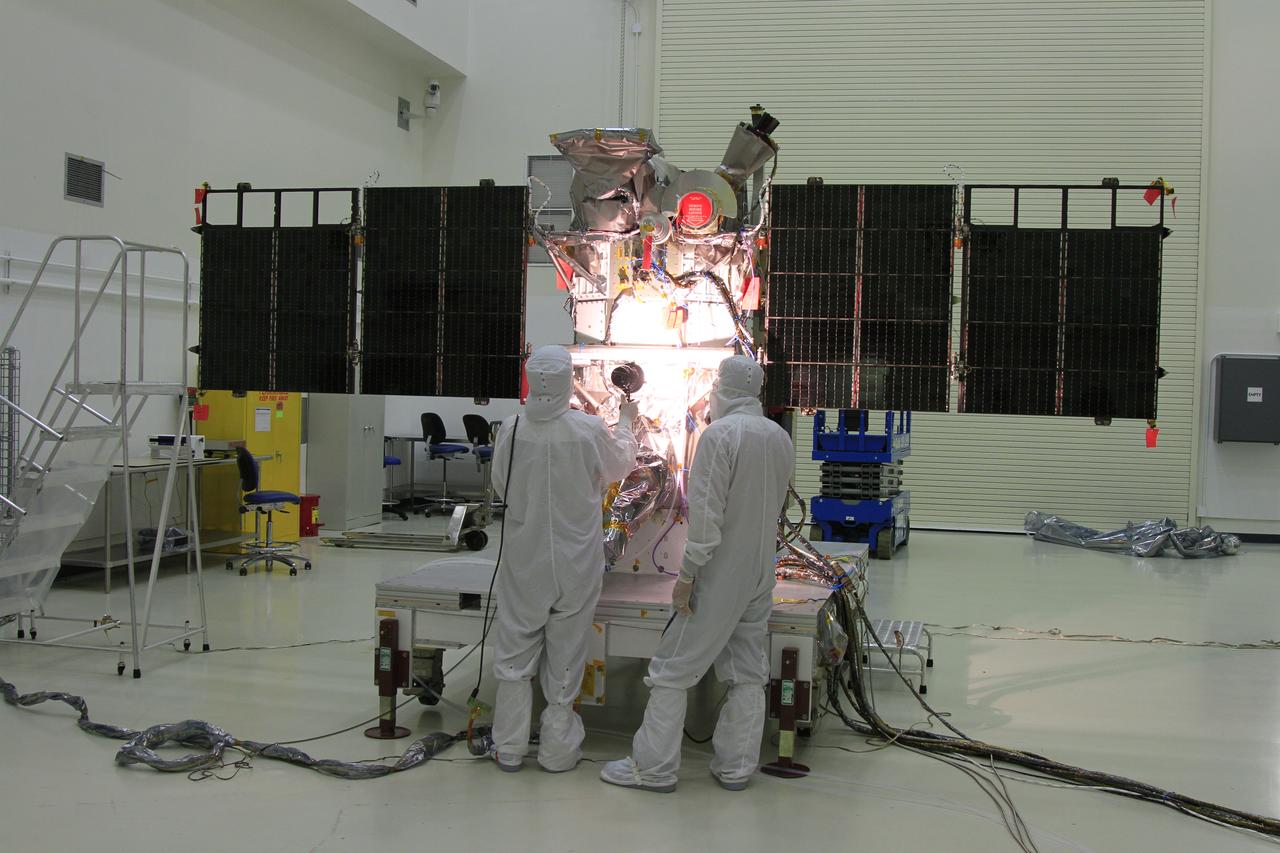
Workers inspect the solar arrays on the Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, observatories in the Building 1 D high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the upper deck arrived Nov. 12; the two comprising the lower stack arrived Oct. 29. MMS, led by a team from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission consisting of four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
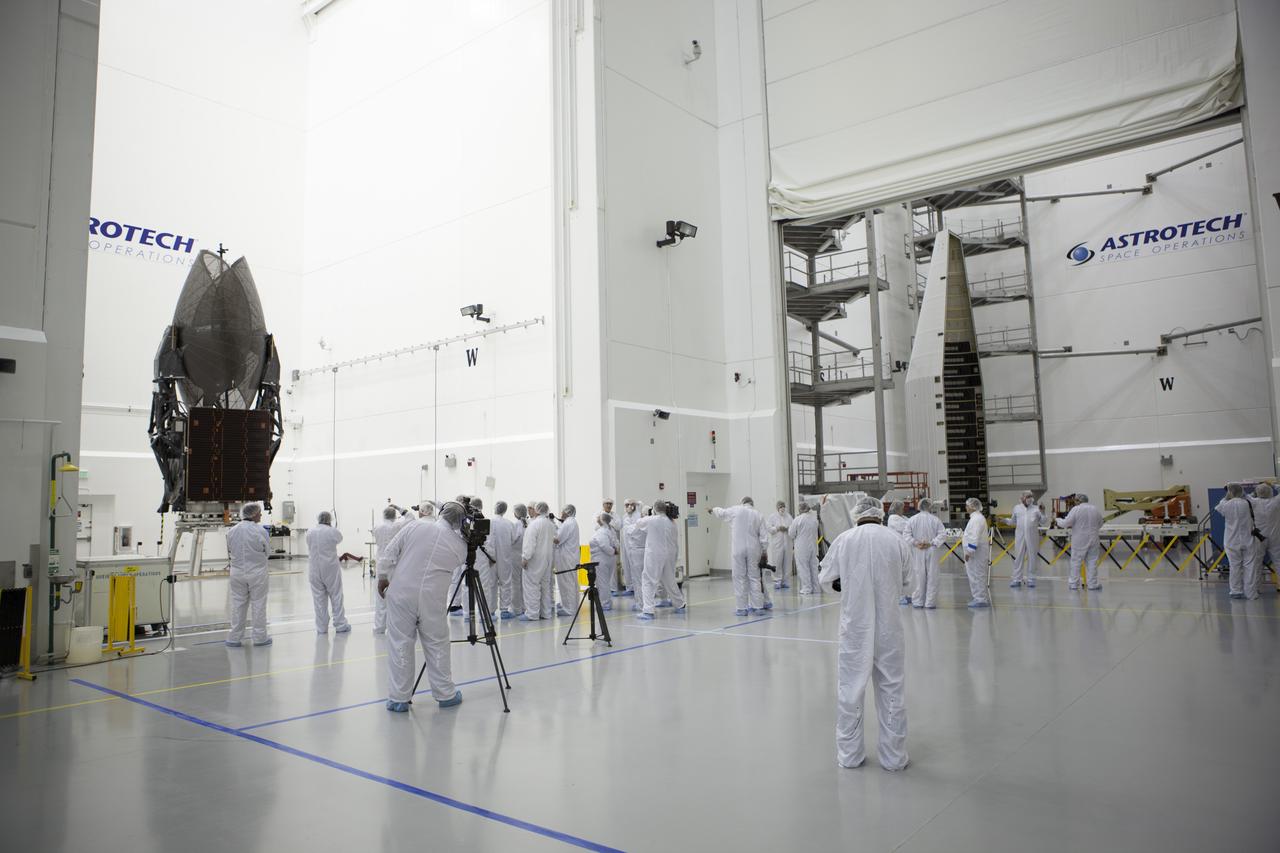

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Members of the news media are given an up-close look at the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft undergoing preflight processing inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville. TDRS-L is being prepared for encapsulation inside its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html

In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, technicians dressed in "bunny suits," or clean-room attire, begin working on the Dawn spacecraft. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.
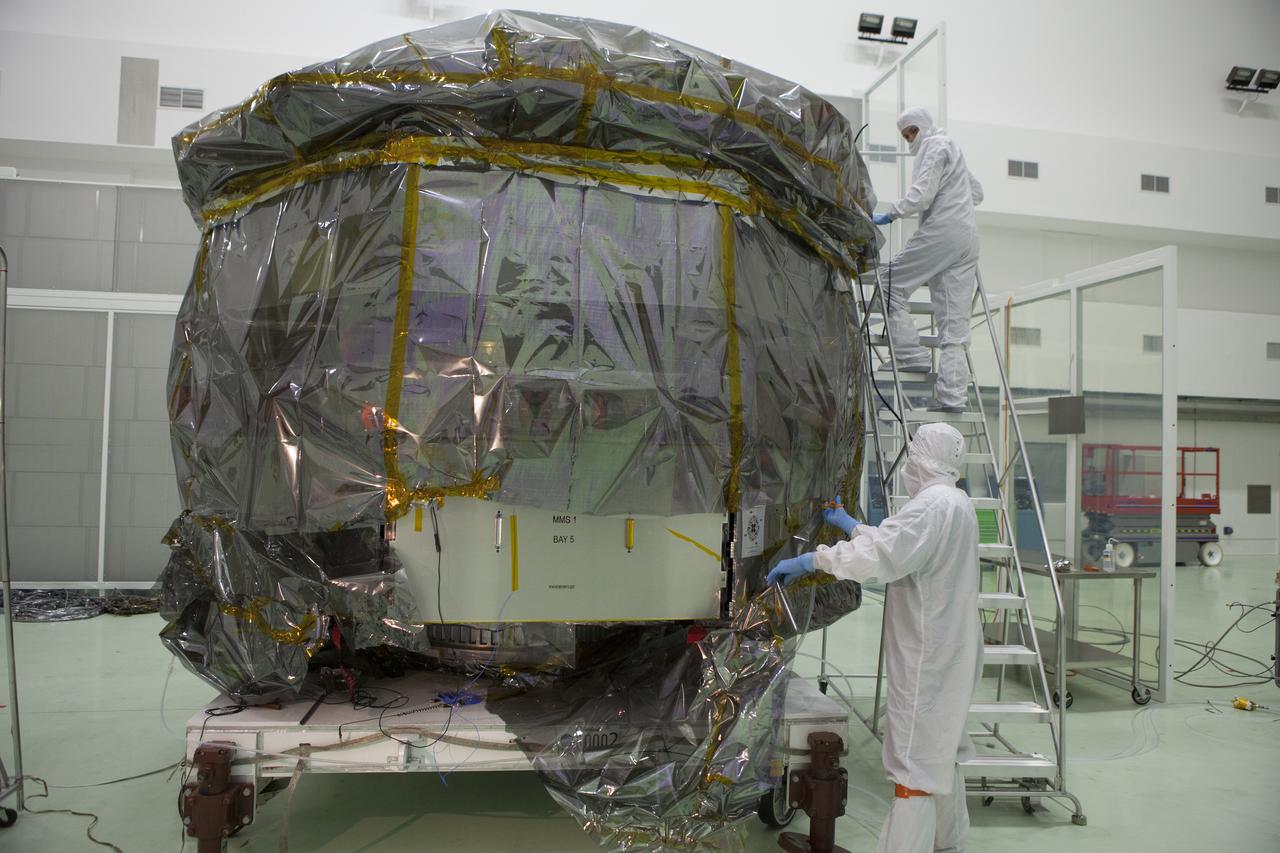

Technicians begin to remove the protective covering from the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, in Building 1 D high bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, has been uncovered and is ready for processing in the high bay of Building 1 at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is currently scheduled for January 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.

The airlock door opens at Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center, for ingress of the protective shipping container enclosing the Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
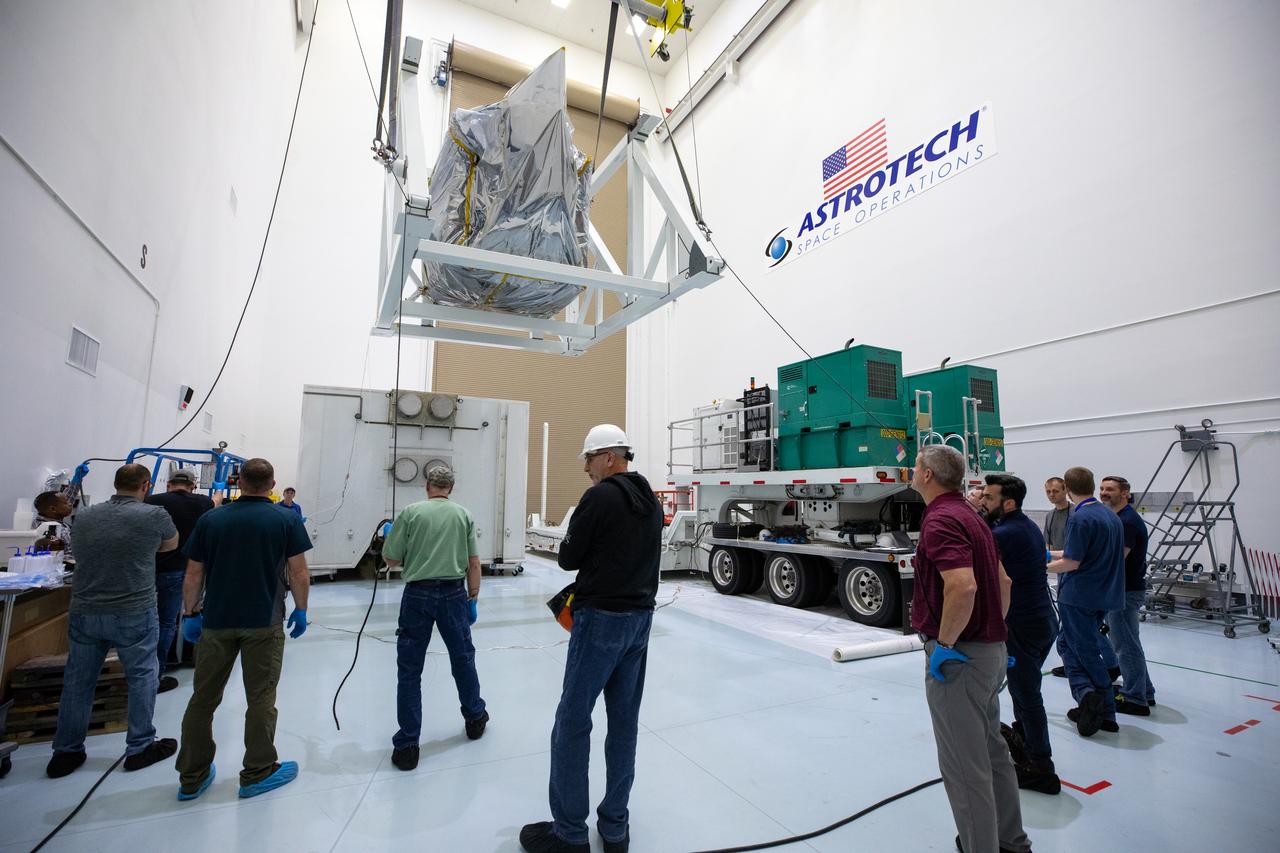

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft after being uncrated on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.

Workers inspect the solar arrays on the Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, observatories in the Building 1 D high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the upper deck arrived Nov. 12; the two comprising the lower stack arrived Oct. 29. MMS, led by a team from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission consisting of four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
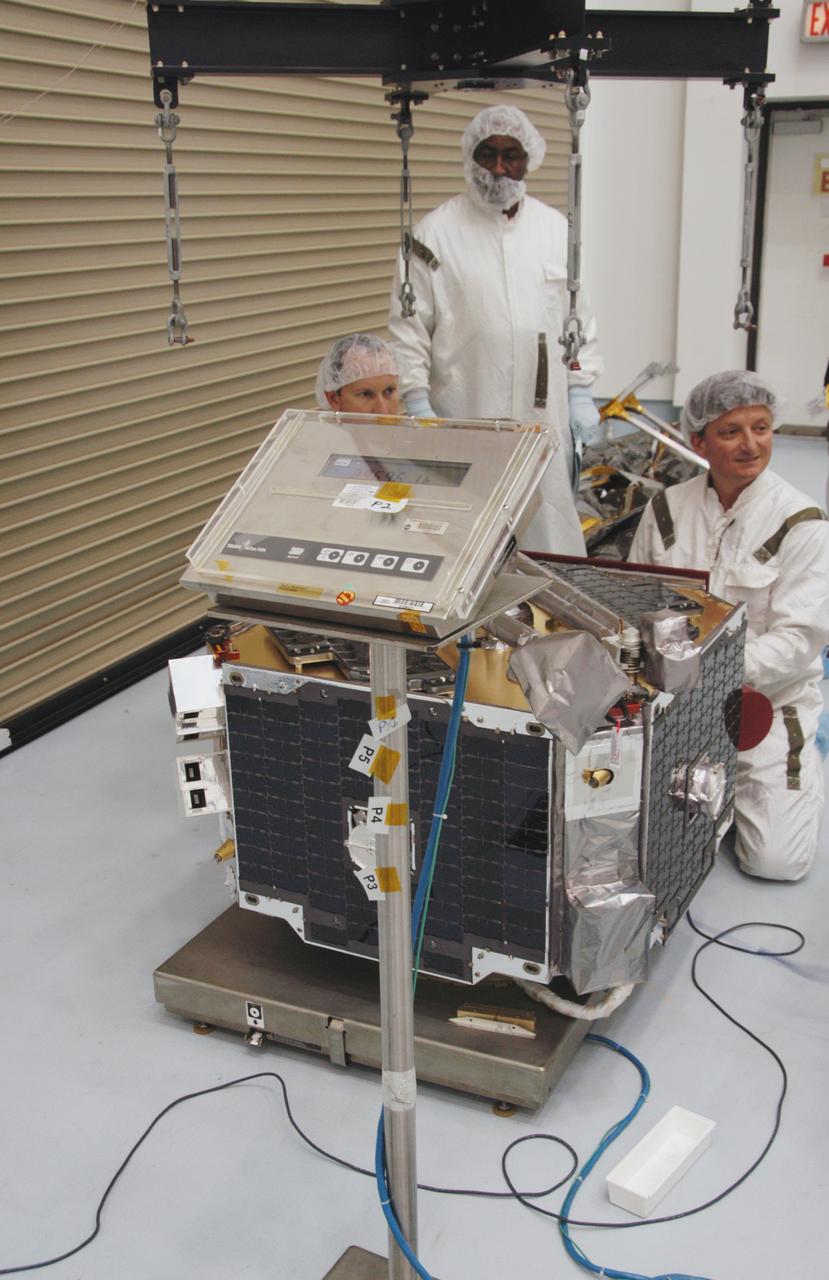

At Astrotech Space Operations, technicians weigh one of the THEMIS probes. Next the probe will be installed on a probe carrier, along with is four mates, and then undergo spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

At Astrotech Space Operations, one of the five THEMIS probes is lifted from a scale. It will be moved to a probe carrier for installation, along with its four mates, and then undergo spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
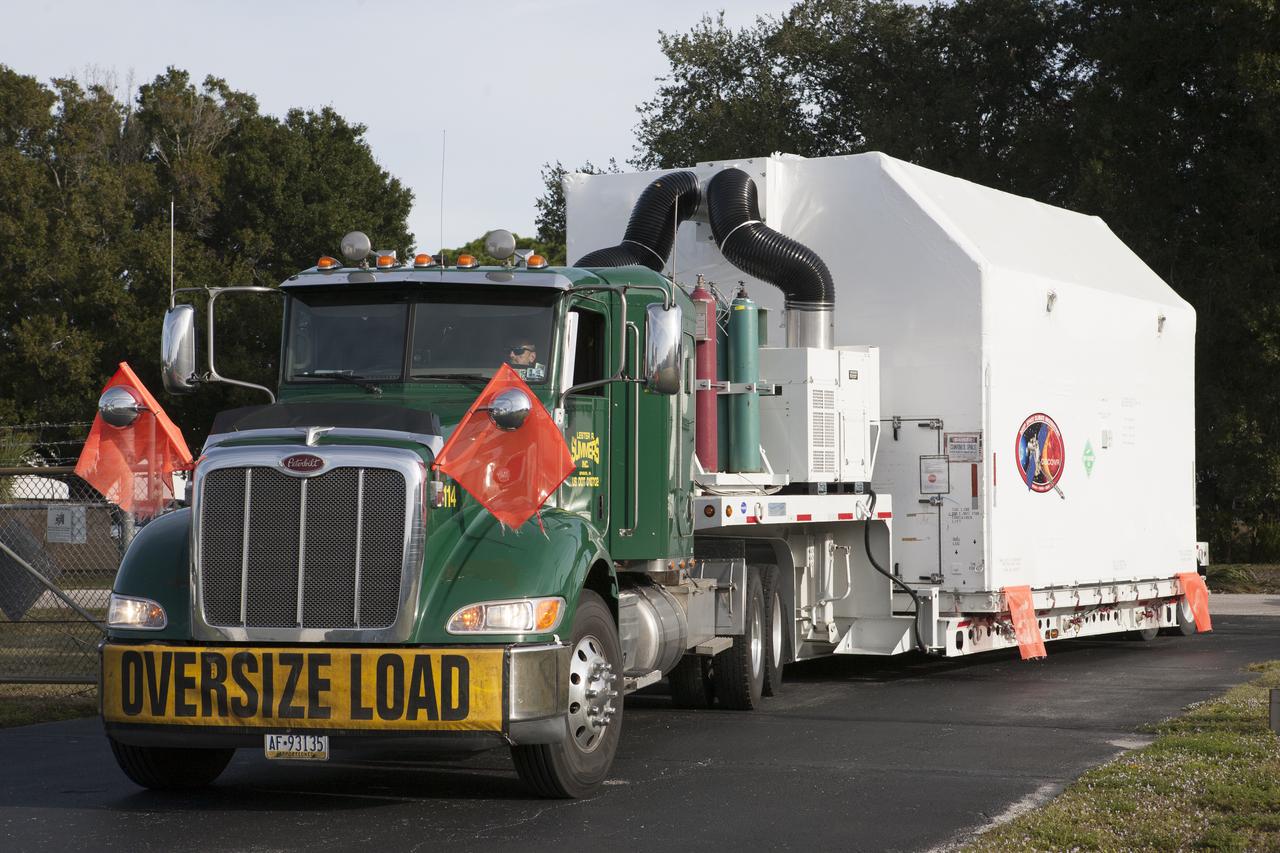

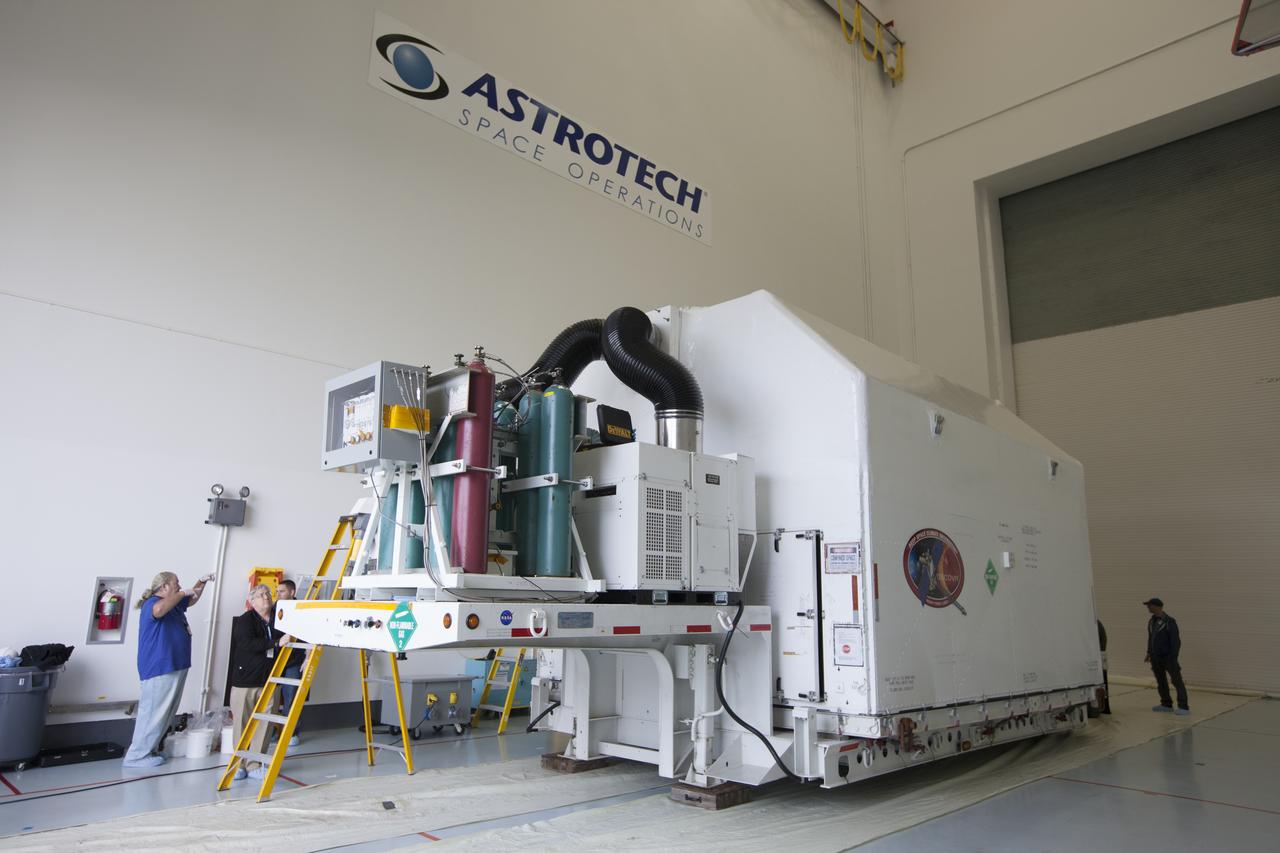
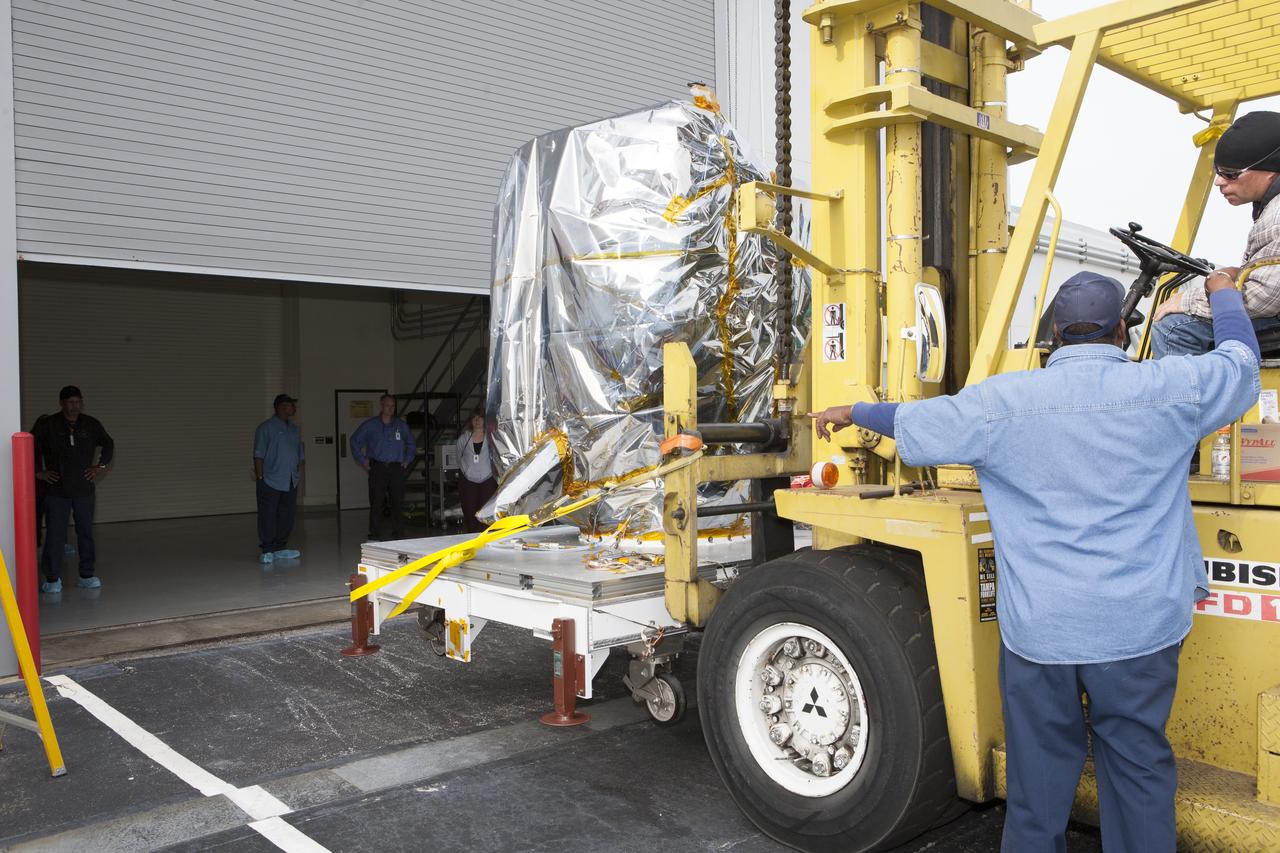
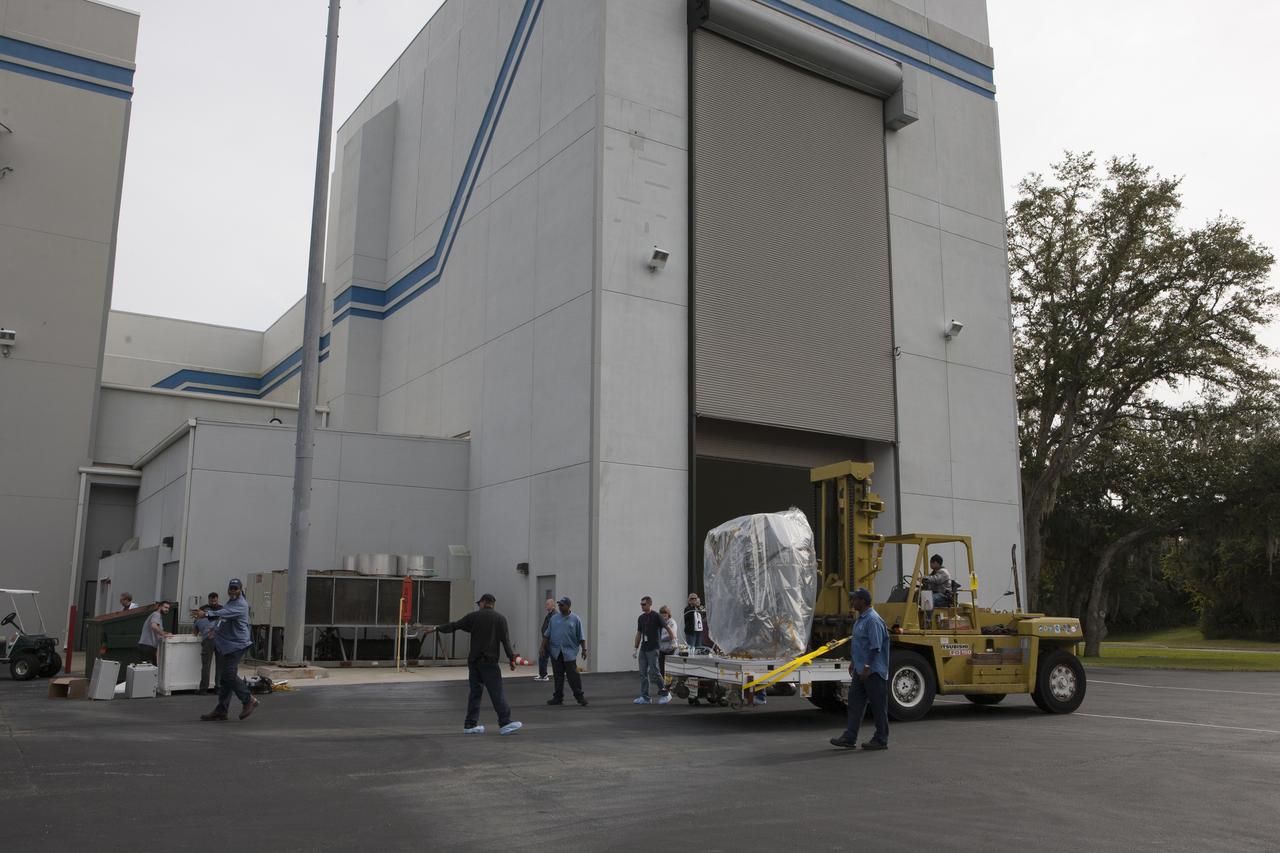
NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, enclosed in a protective shipping container, is delivered by truck to the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is currently scheduled for January 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.

Teams transport NASA's encapsulated Psyche spacecraft from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville to Launch Pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Oct. 6, 2023. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket. Liftoff is targeted for 10:16 a.m. EDT Thursday, Oct. 12. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA's Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.

The solar arrays on the Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, observatories are uncovered for an inspection in the Building 1 D high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the upper deck arrived Nov. 12; the two comprising the lower stack arrived Oct. 29. MMS, led by a team from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission consisting of four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
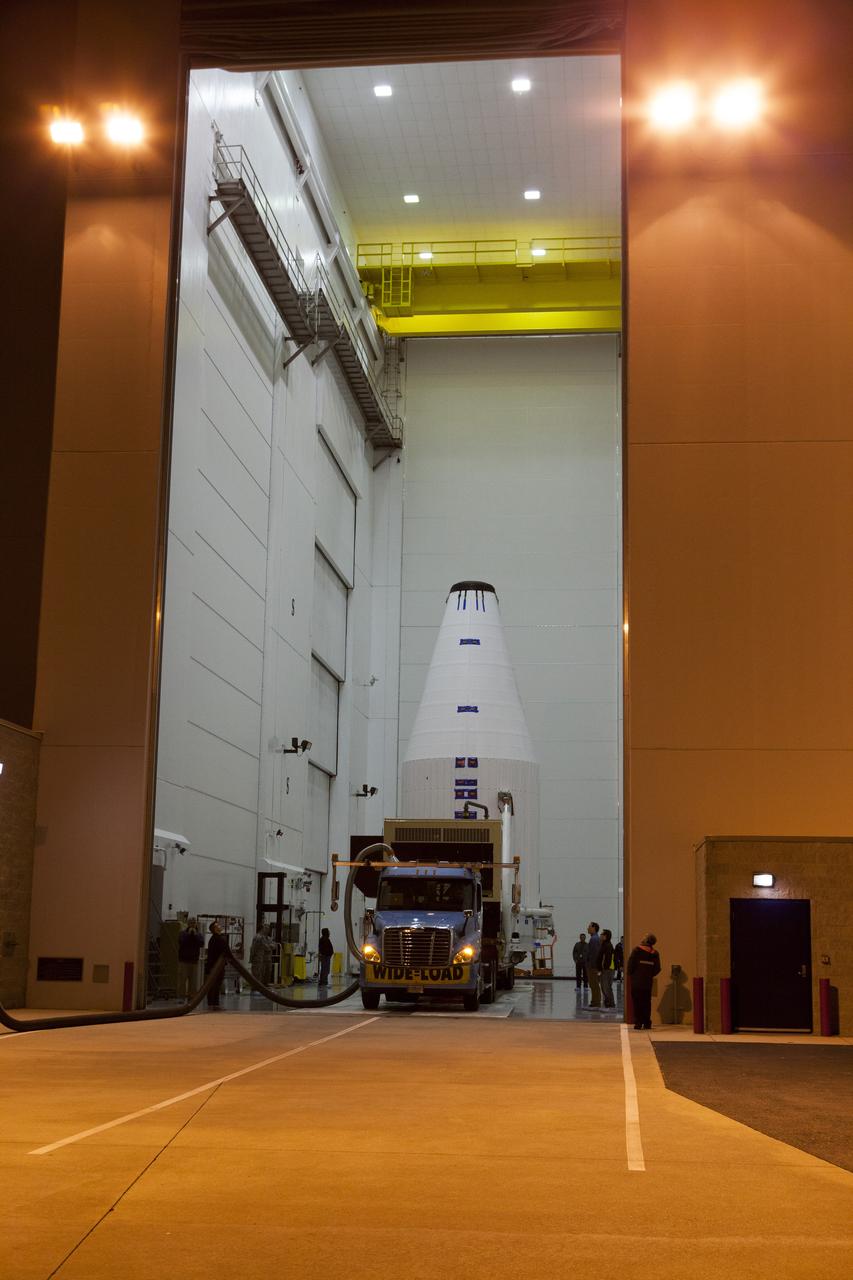

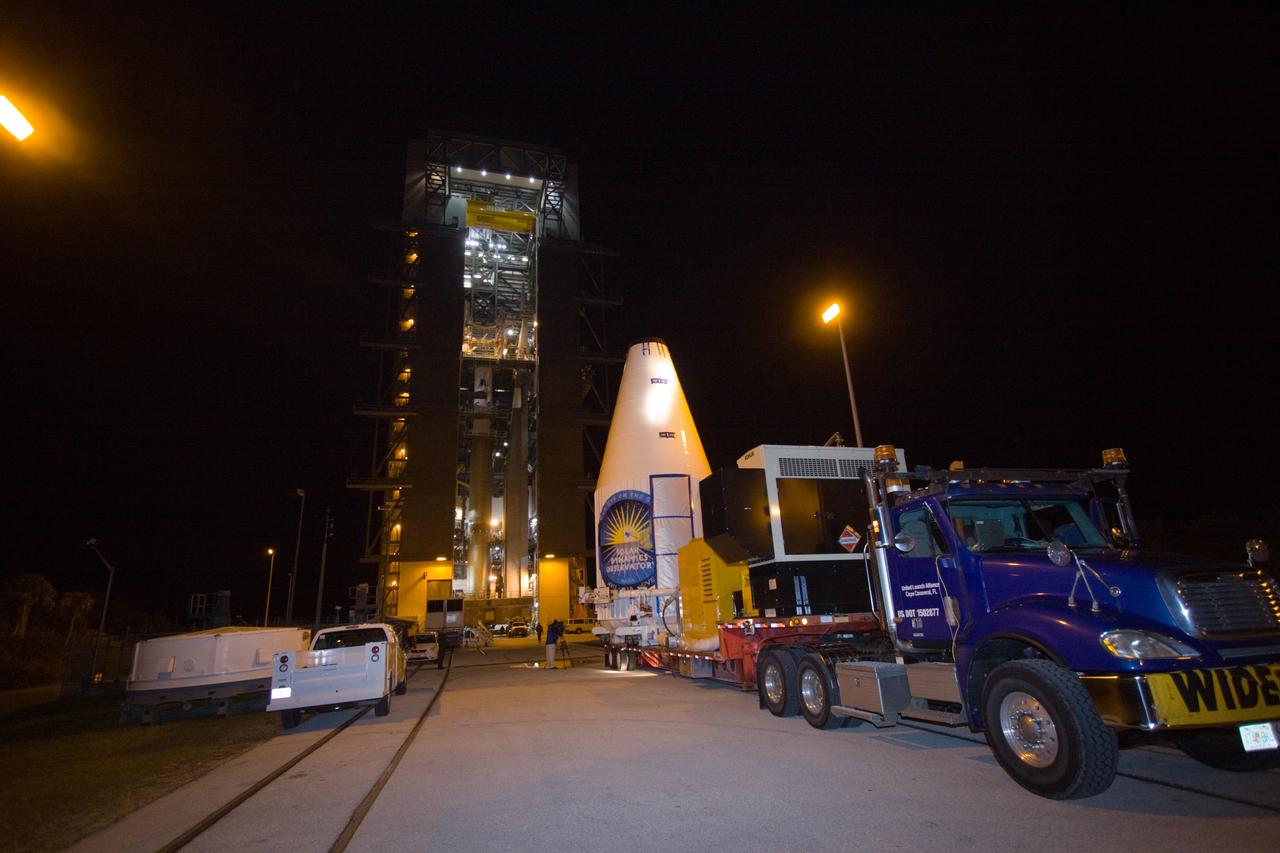
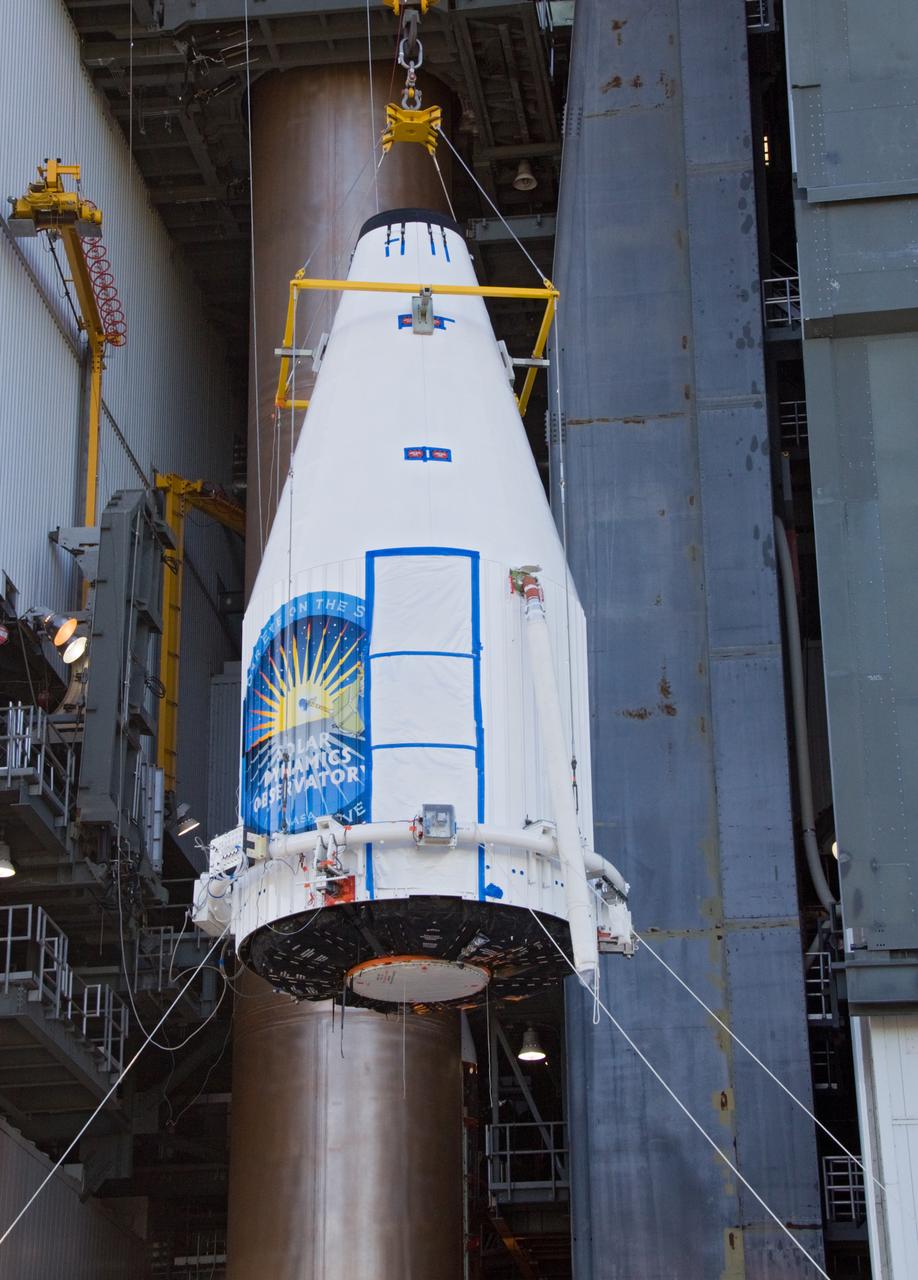
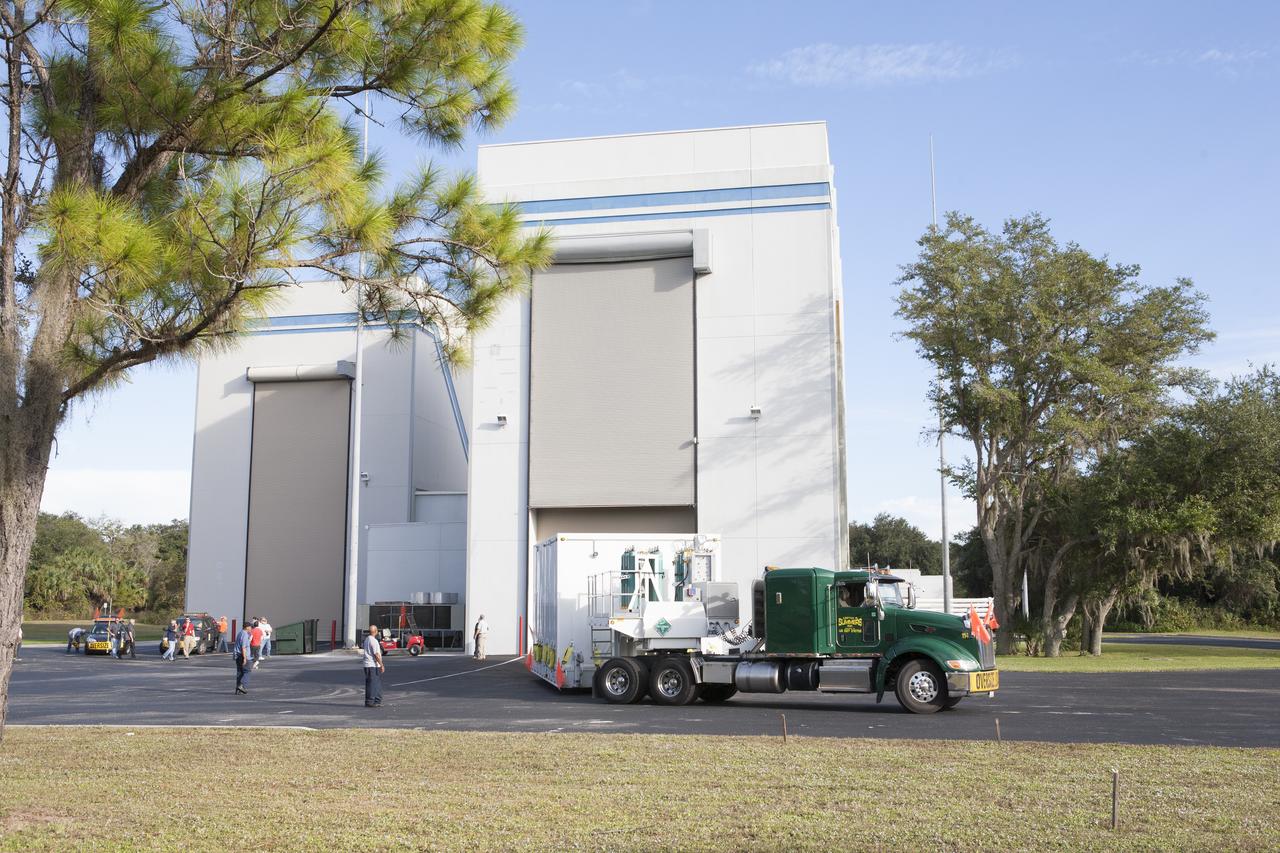
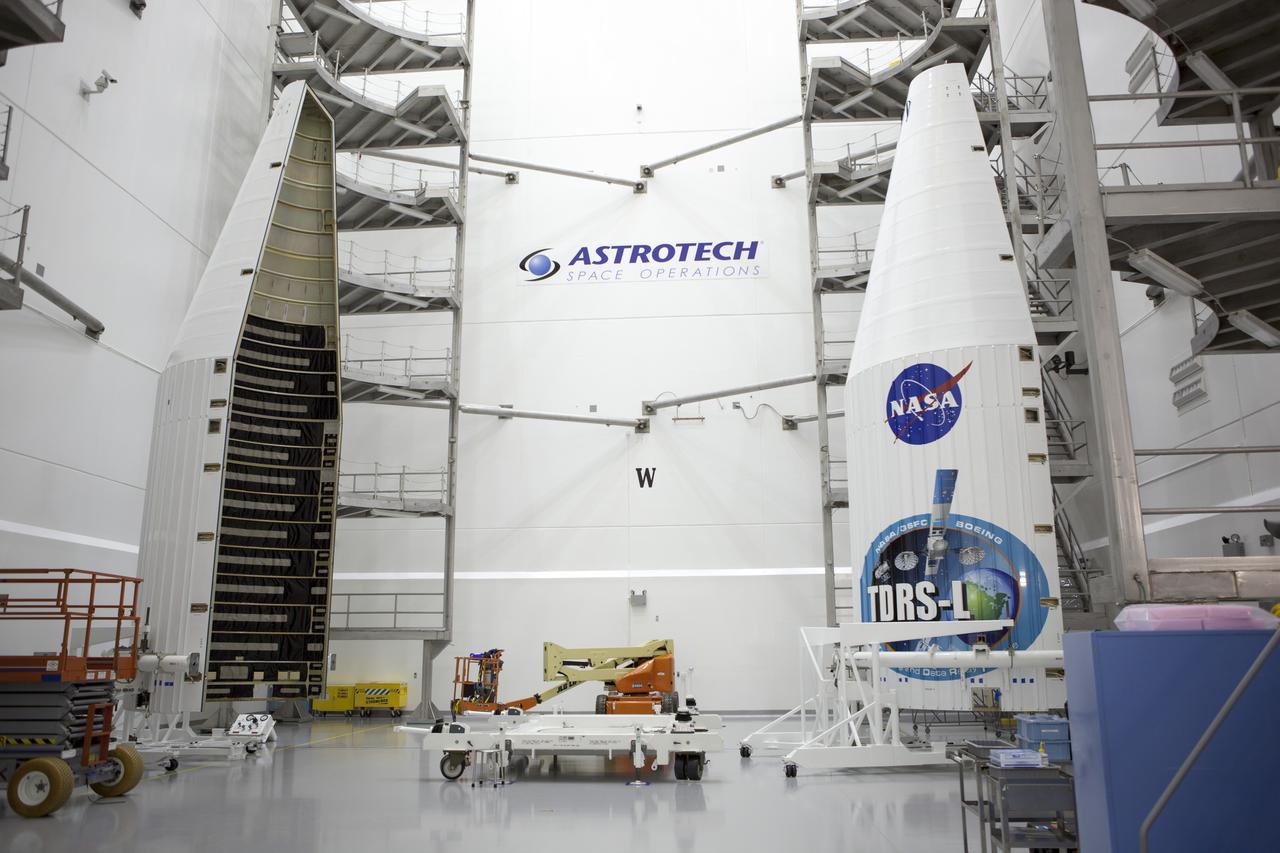
TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft has been mounted on a transporter for its trip from the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

SDO FUELING PREPS FOR SATELLITE W/CREW
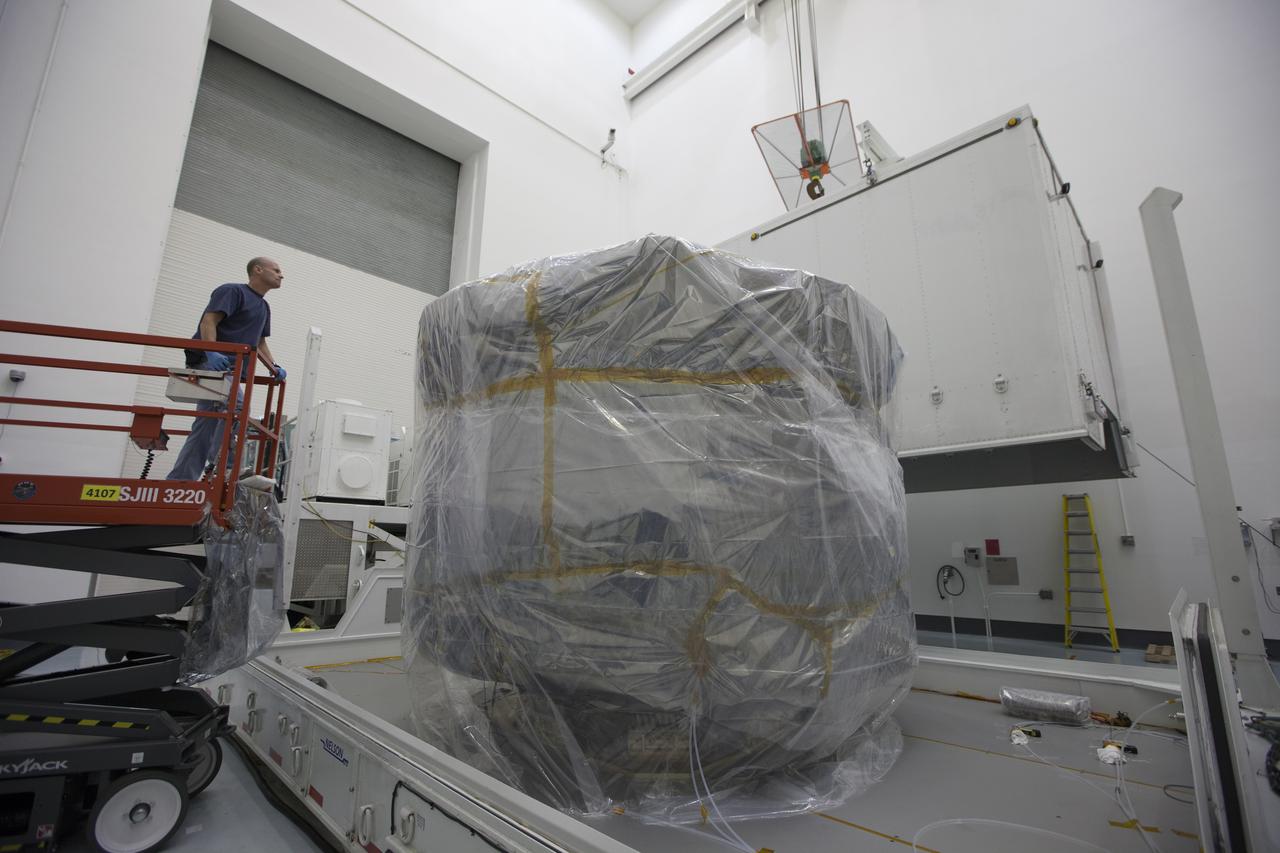

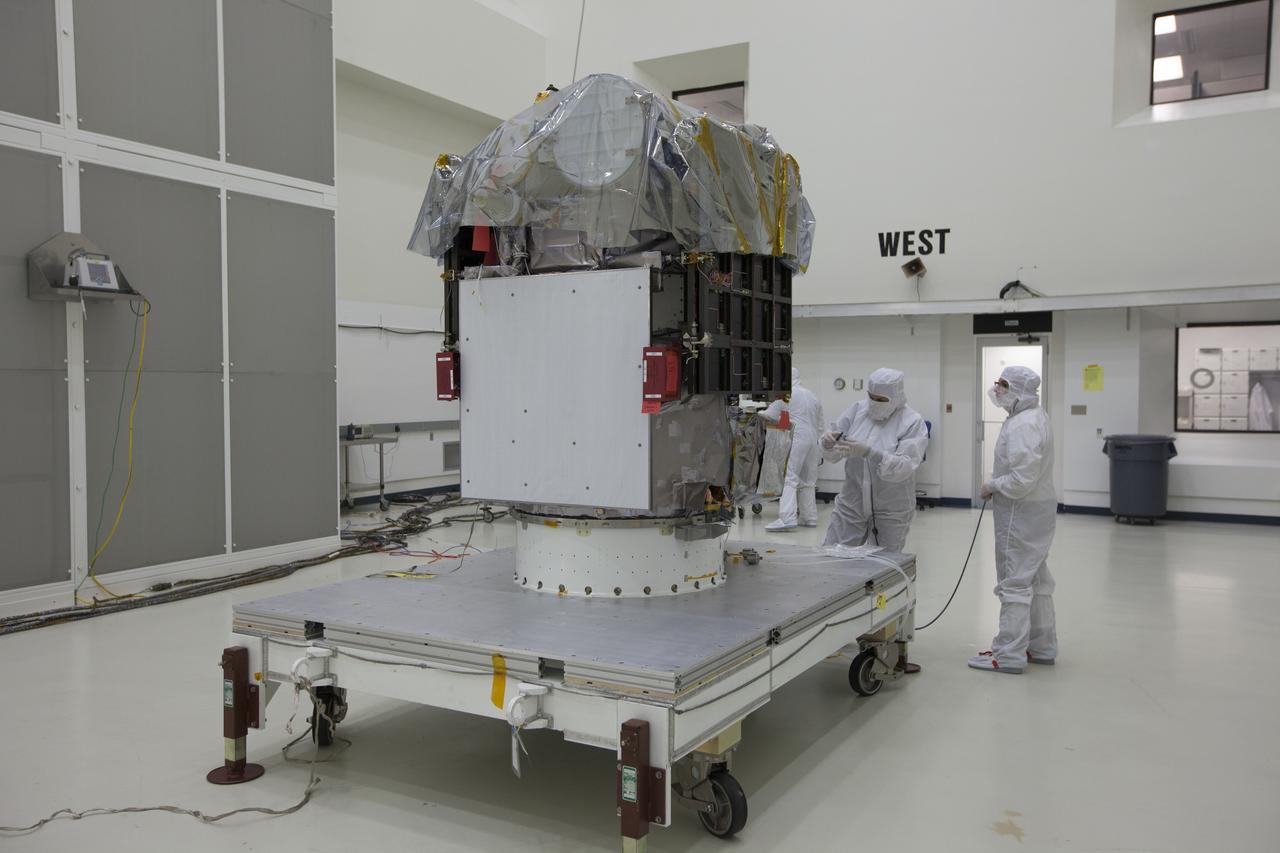
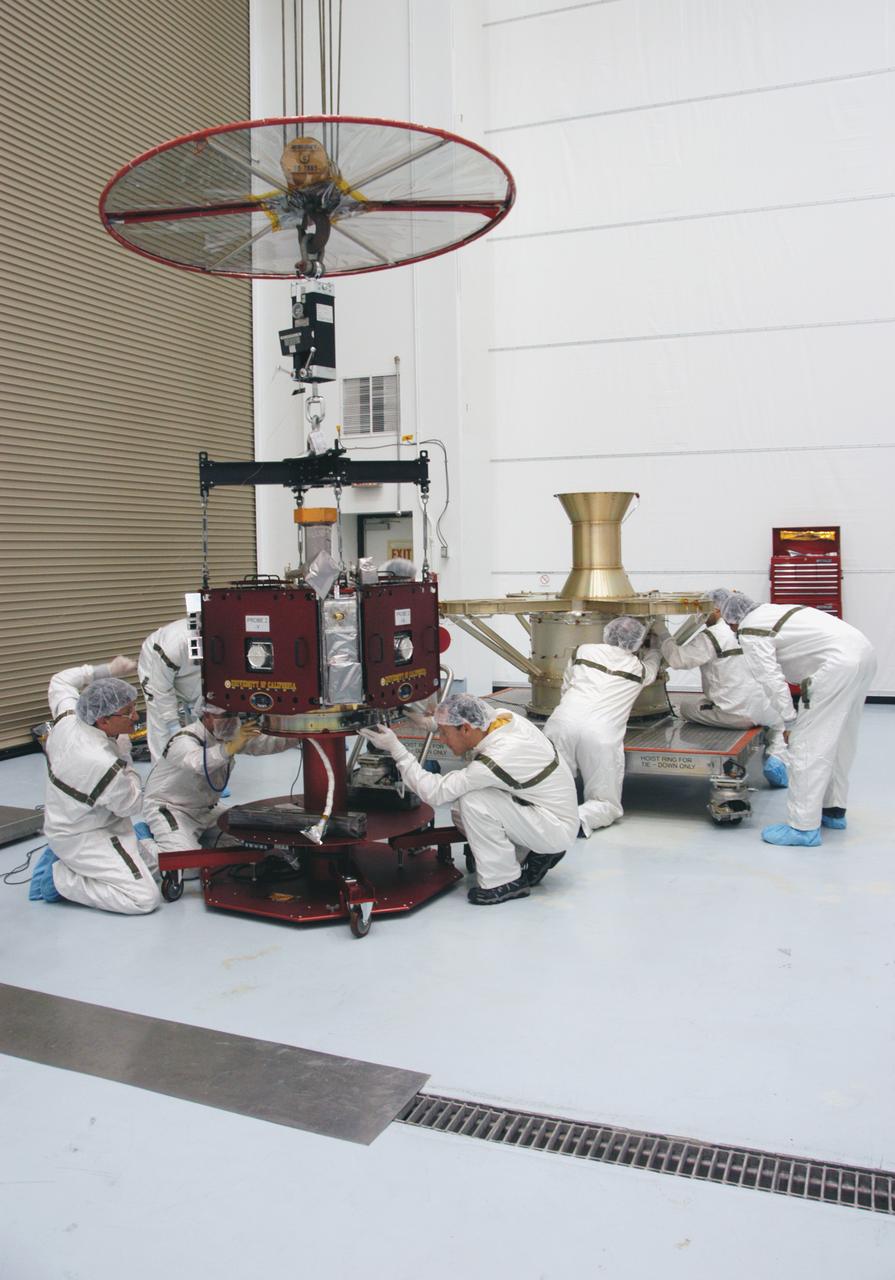
The protective shipping container is removed from around the upper stack of the Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft in Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

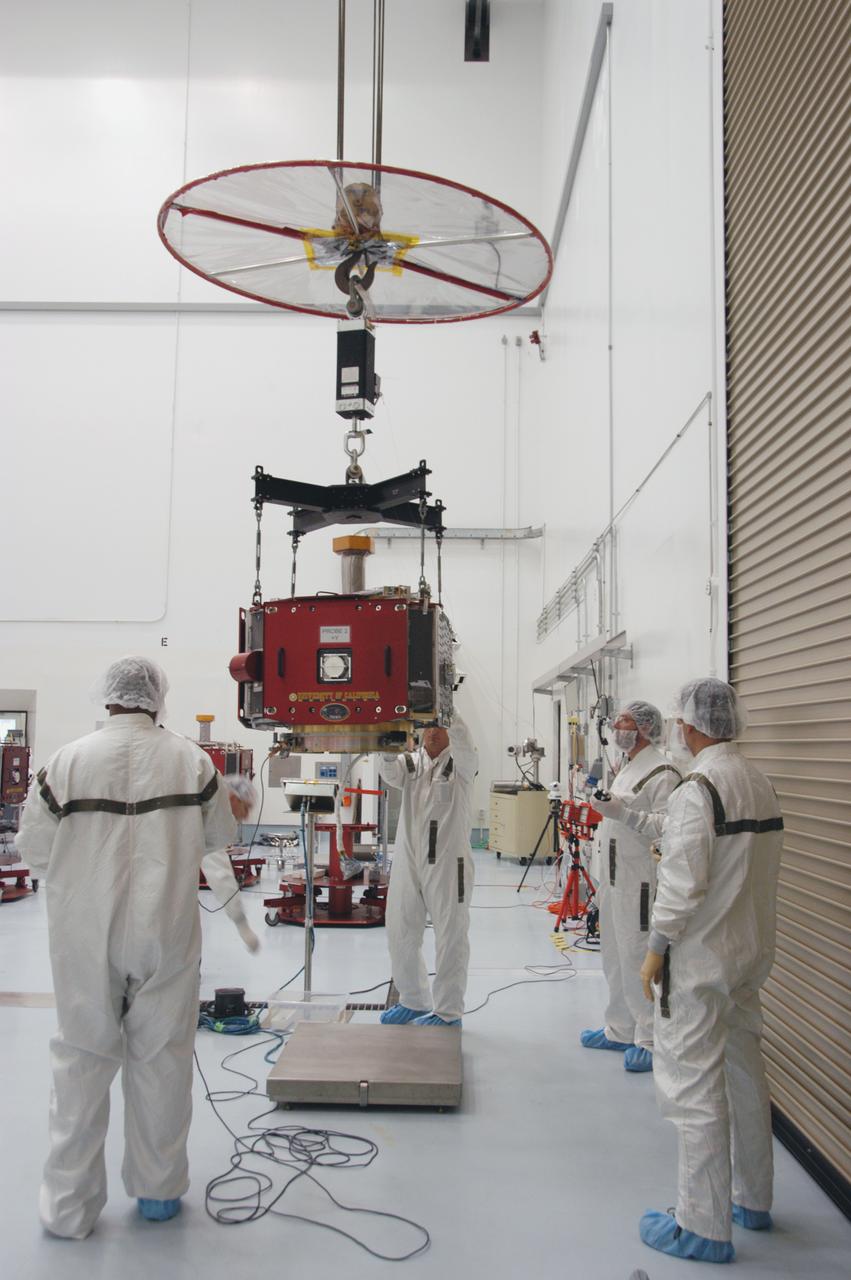
At Astrotech Space Operations, technicians guide one of the THEMIS probes into position on the probe carrier. When all five probes are in place, the carrier will undergo spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

In clean room C of Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, a worker wears a "bunny suit," or clean-room attire, next to the Dawn spacecraft, which will be unbagged and undergo further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C.

A plaque affixed to the side of a Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, observatory dedicates the mission to Dr. John William Klein, now deceased, who served the MMS team as the standing review board chairman. MMS, led by a team from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission consisting of four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
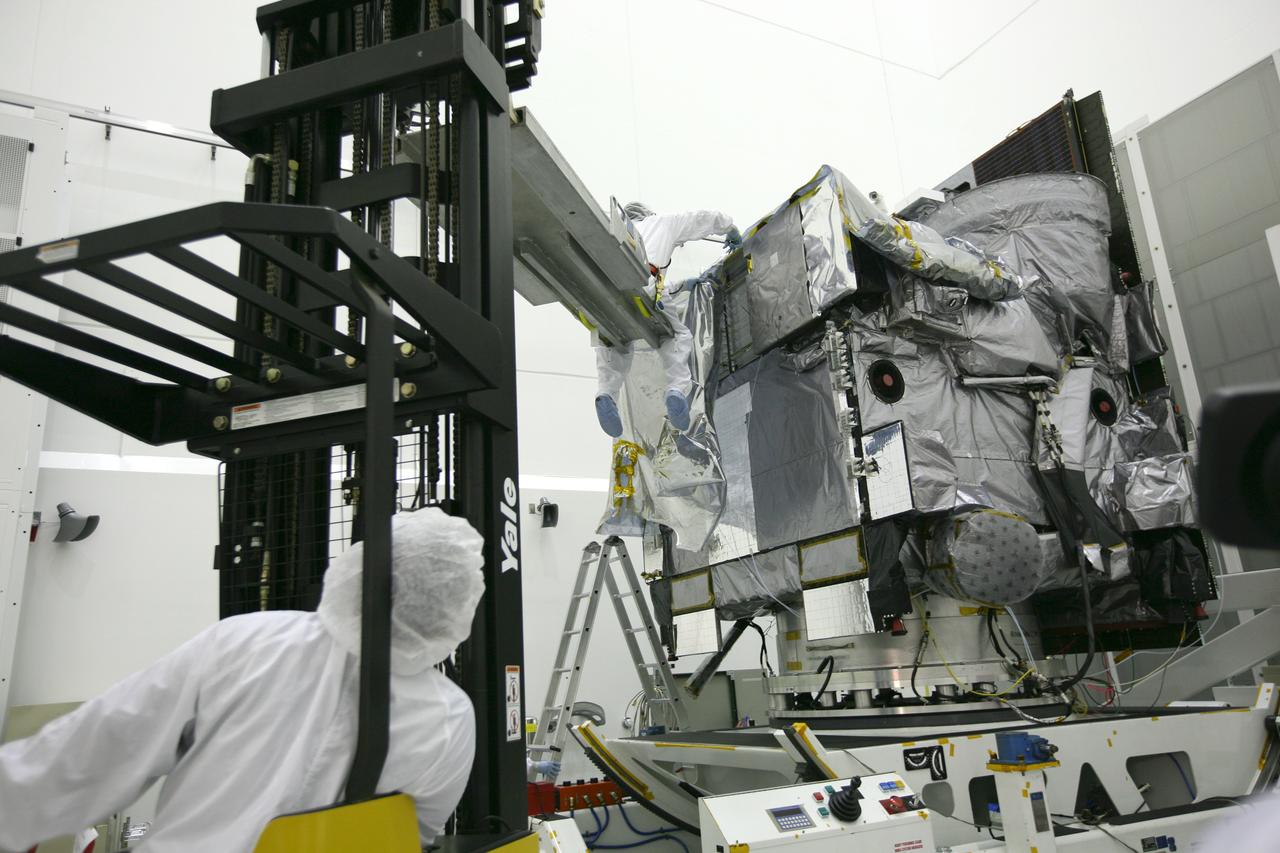

GOES-P UNBAGGING & ROTATION
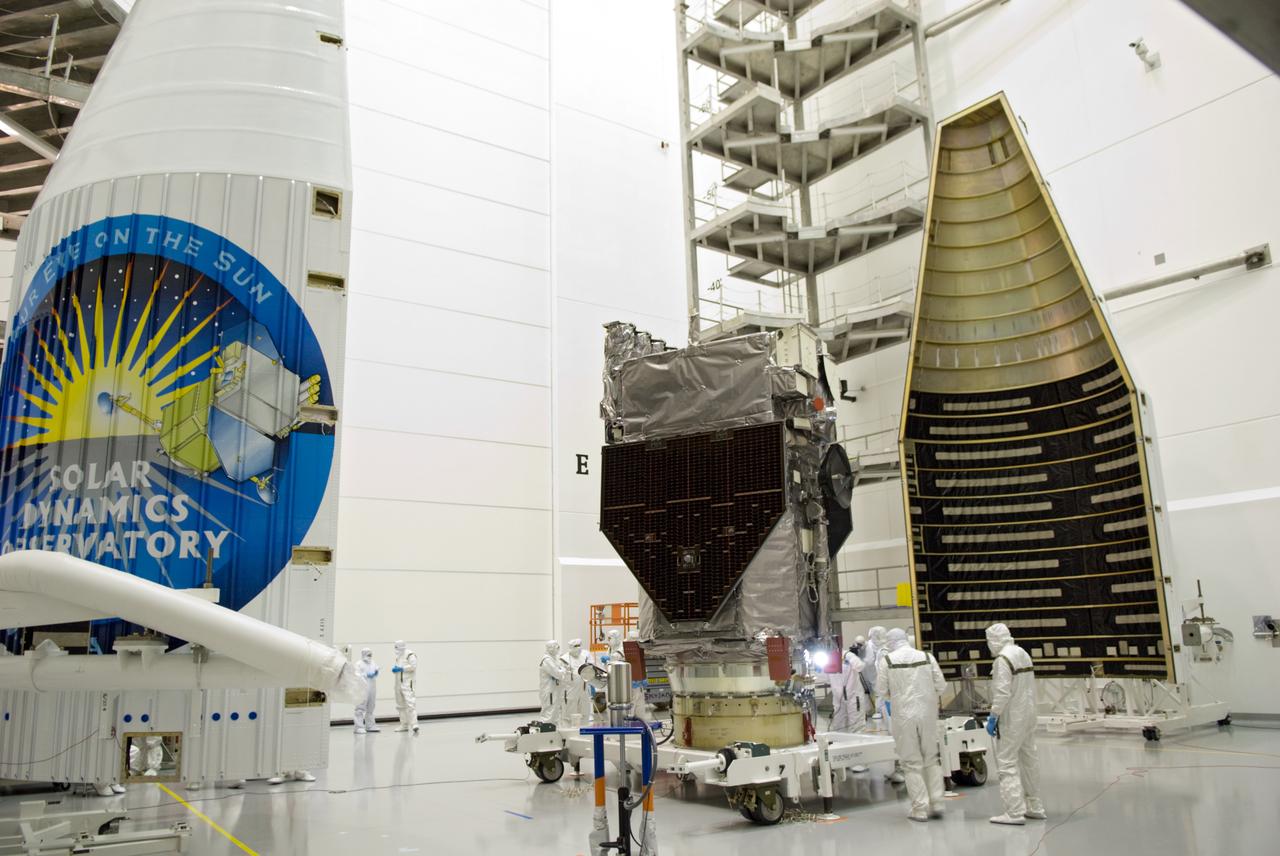

SDO - MEDIA DAY & FAIRING INSTALLATION
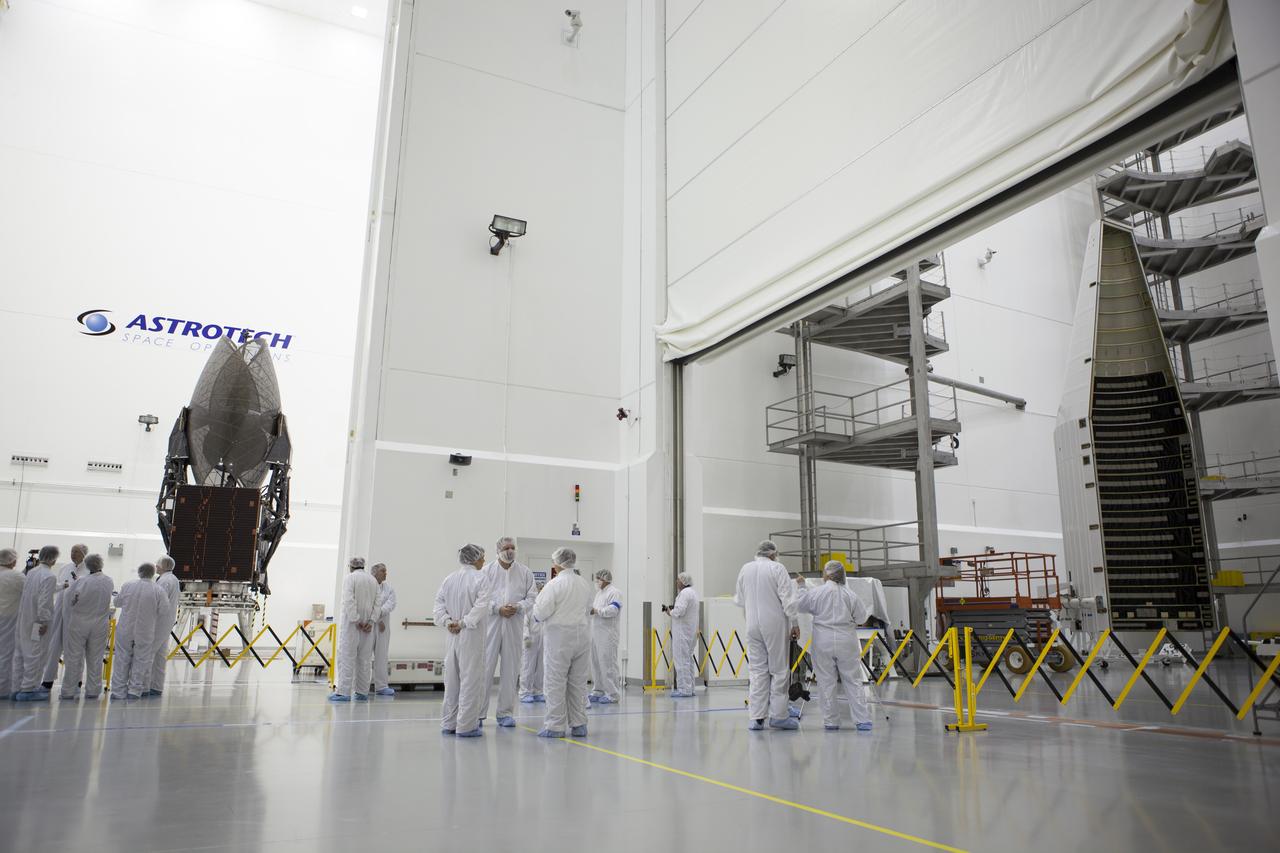

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Members of the news media are given an up-close look at the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft undergoing preflight processing inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville. TDRS-L is being prepared for encapsulation inside its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
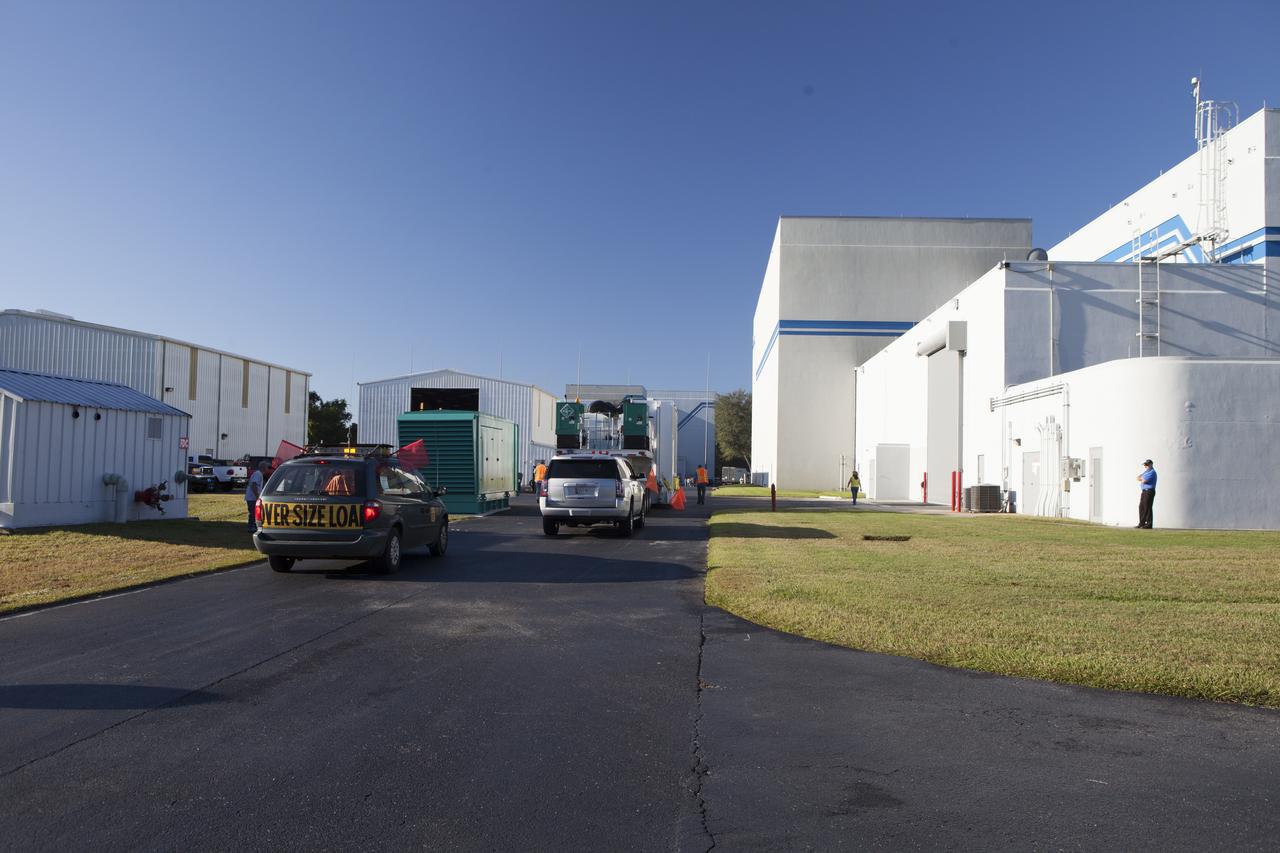

The Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft, enclosed in a protective shipping container, arrive at Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, United Launch Alliance engineers and technicians encapsulate the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft in its payload fairing. TDRS-L will then be transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
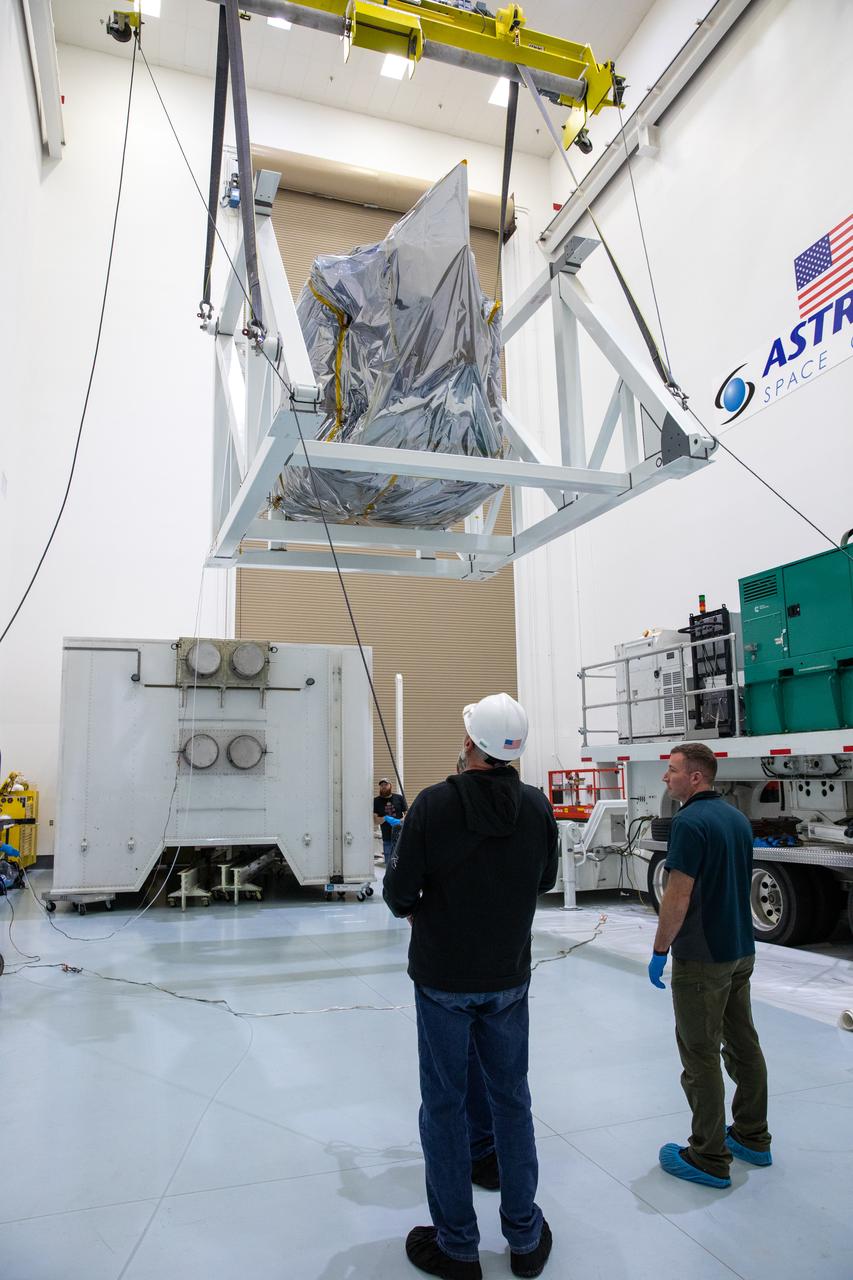

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft after being uncrated on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.

Preparations are underway to remove a protective shipping container from around NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is currently scheduled for January 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.

Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

GOES-P MOVE TO FUELING STAND & MEDIA DAY

SDO MOVE FROM ASTROTECH TO PAD 41 - LIFT & MATE

GOES-P MOVE TO FUELING STAND & MEDIA DAY
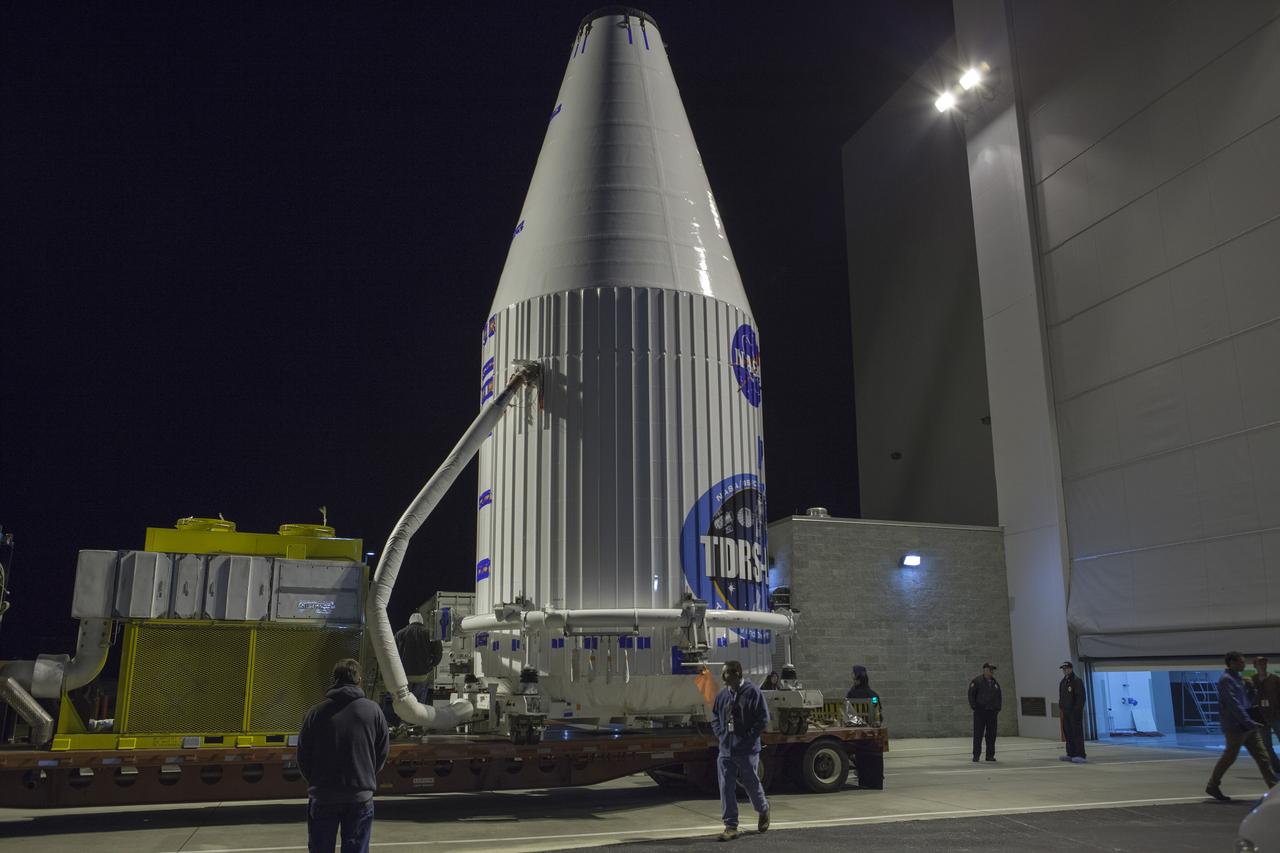

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft begins it trip from the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

SDO FUELING PREPS FOR SATELLITE W/CREW
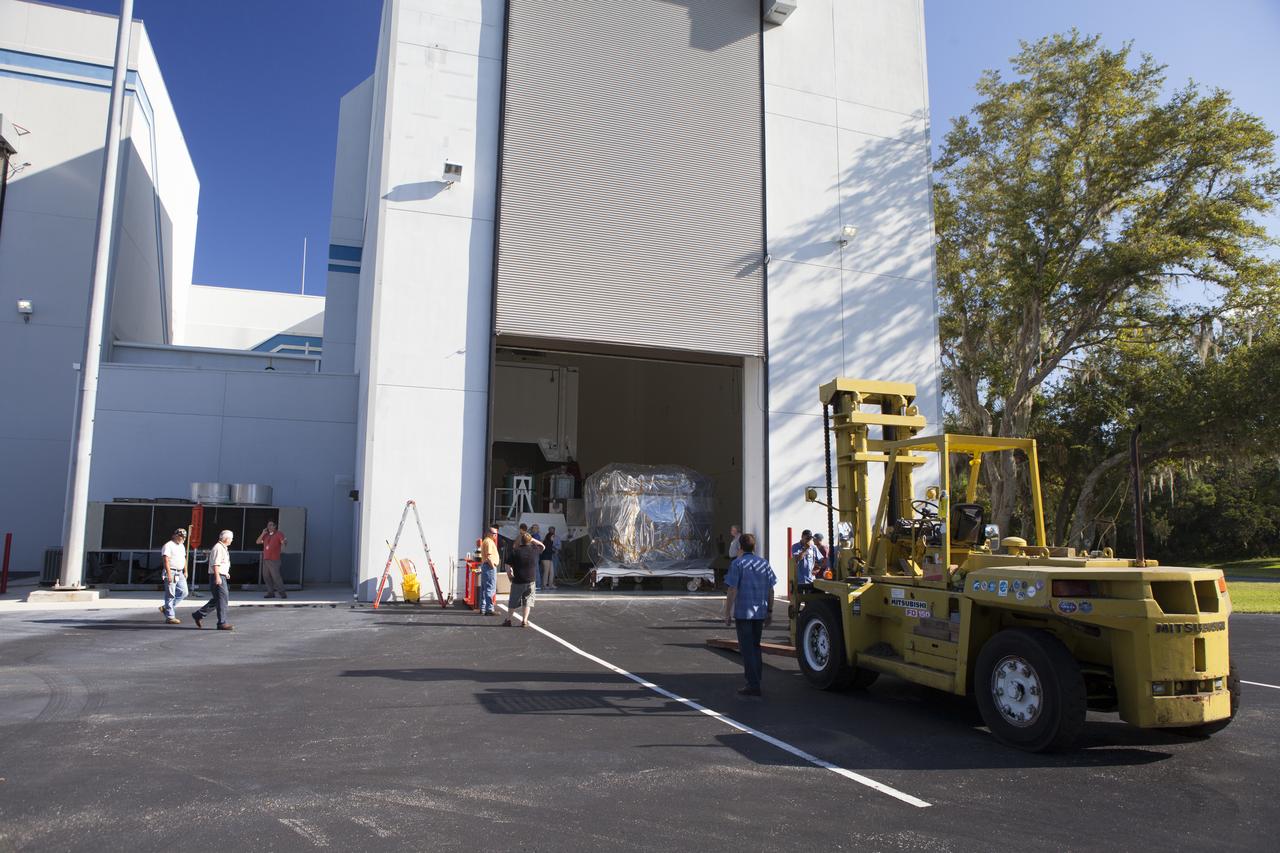

Preparations are underway to tow two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, from the Building 2 south encapsulation bay to the Building 1 high bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
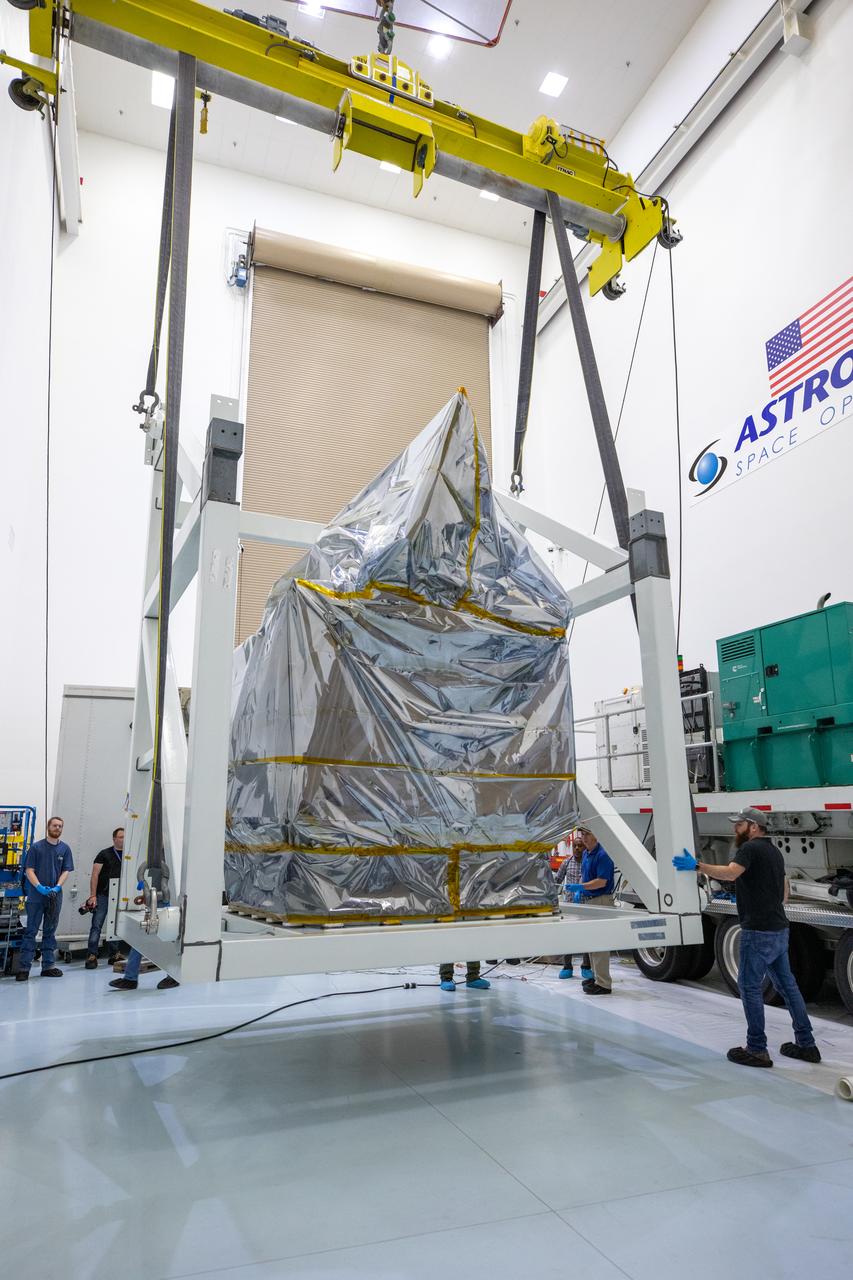

Technicians monitor movement as a crane hoists NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft after being uncrated on Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2023, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web. PACE will be encapsulated for launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.

Most of the protective covering has been removed from the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, two of the observatories for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory, or MMS, inside Building 1 D high bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

Two Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft, enclosed in a protective shipping container, are delivered by truck to the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission, or MMS, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. These two spacecraft comprise the mission's upper stack. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
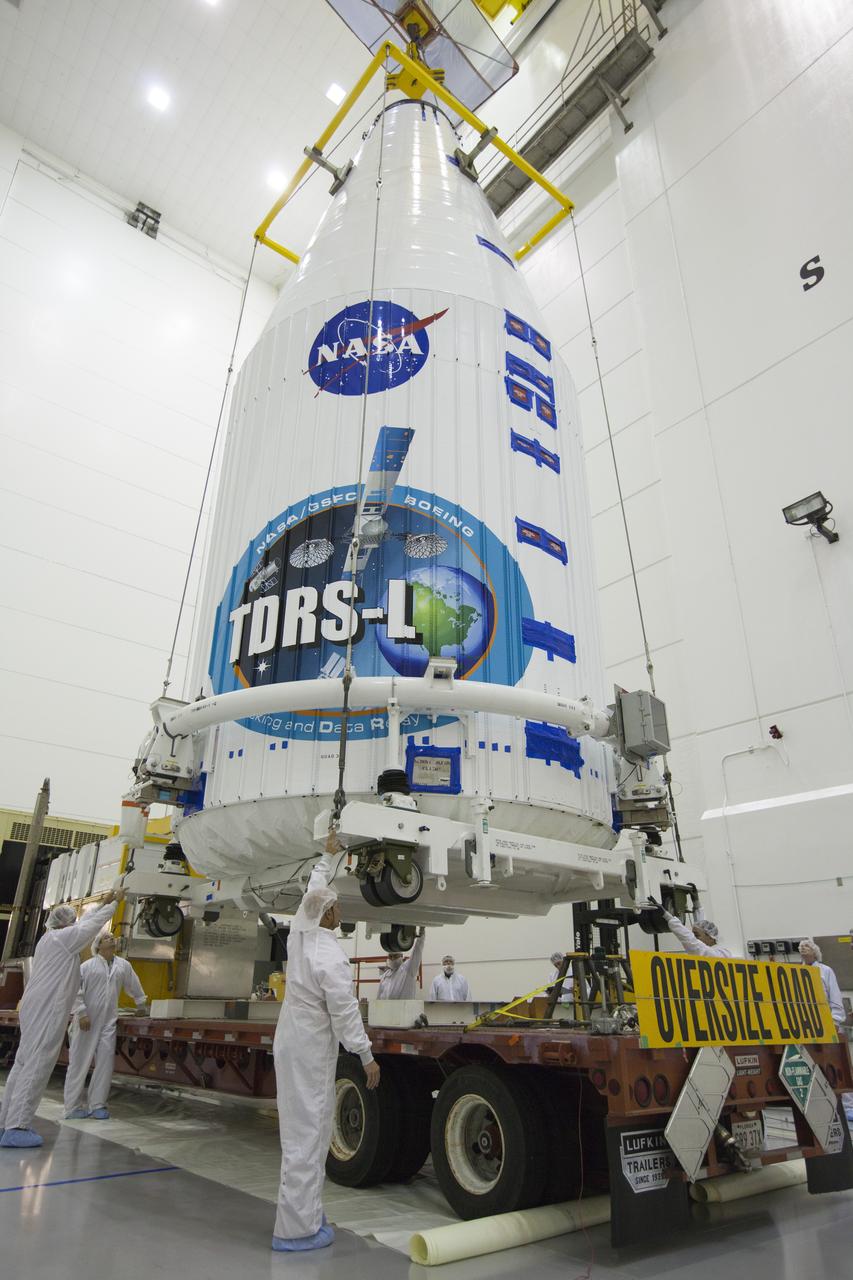

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft has been encapsulated in its payload fairing. It is being lifted by crane for mounting on a transporter for its trip to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

GOES-P UNBAGGING & ROTATION

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft is being encapsulated in its payload fairing in preparation for begin transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html

Workers conduct a light test on the solar arrays on NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, in the Building 1 high bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is targeted for early 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.

NOAA’s newly arrived Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, wrapped in plastic and secured onto a portable work stand, is delivered to the high bay of Building 1 at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is currently scheduled for January 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.

NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, wrapped in plastic and secured onto a portable work stand, makes a short trek from the airlock of Building 2 to the high bay of Building 1 at the Astrotech payload processing facility.

NASA and SpaceX technicians connect NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft to the payload adapter on Friday, Jan. 26, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6.

Technicians prepare to rotate NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) vertical after being uncrated on Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.

NASA and SpaceX technicians connect NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft to the payload adapter on Friday, Jan. 26, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6.

Workers conduct a light test on the solar arrays on NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, in the Building 1 high bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is targeted for early 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, members of the news media are given an opportunity for an up-close look at the payload fairing that will encapsulate the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Members of the news media are given an opportunity for an up-close look at the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft undergoing preflight processing inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville. TDRS-L is being prepared for encapsulation inside its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
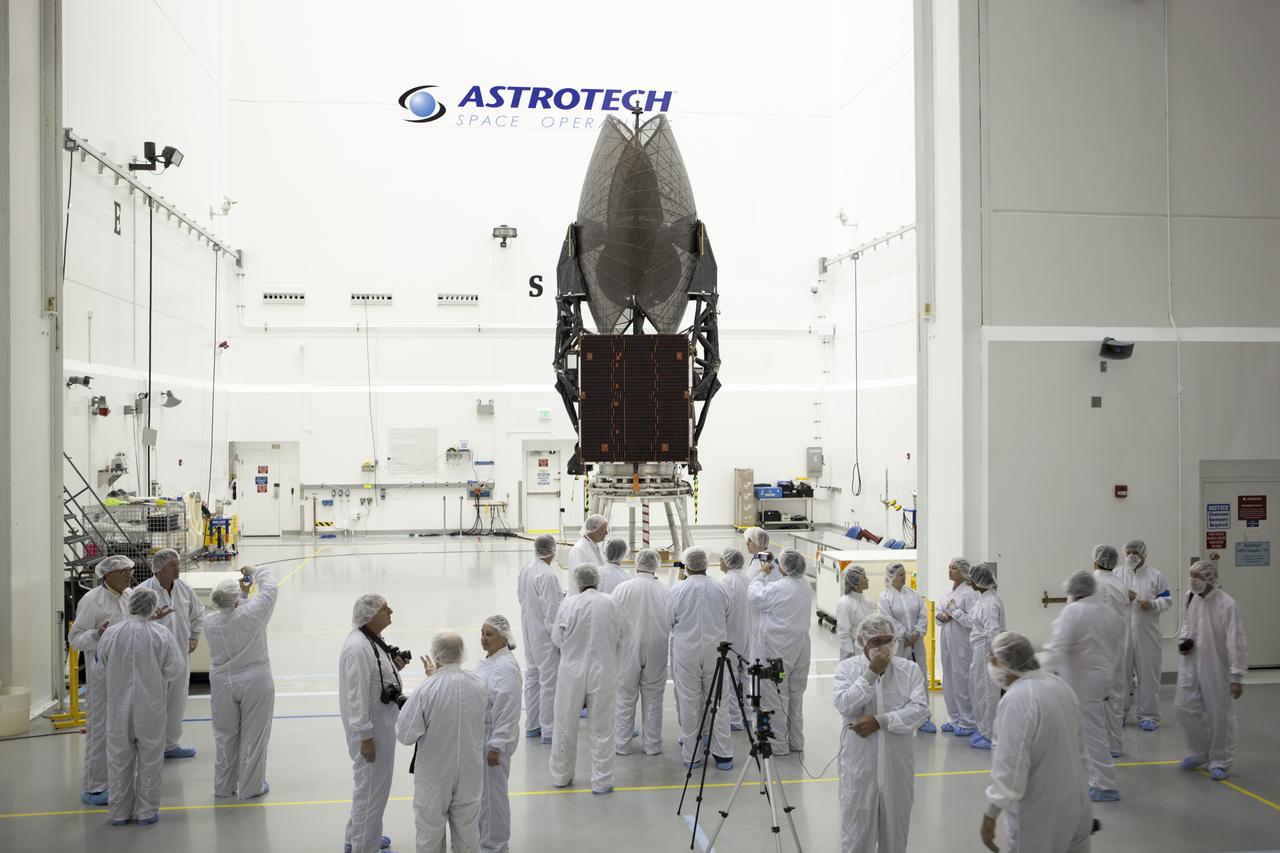

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Members of the news media are given an up-close look at the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft undergoing preflight processing inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville. TDRS-L is being prepared for encapsulation inside its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html

In the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech Space Operations, workers attach an overhead crane to the integrated THEMIS spacecraft. The carrier is being moved to a spin table for spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

At Astrotech Space Operations, technicians adjust connections of the overhead crane on one of the THEMIS probes. The probe and its other four mates will be lifted and installed on the probe carrier in the background. The probes will then undergo spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
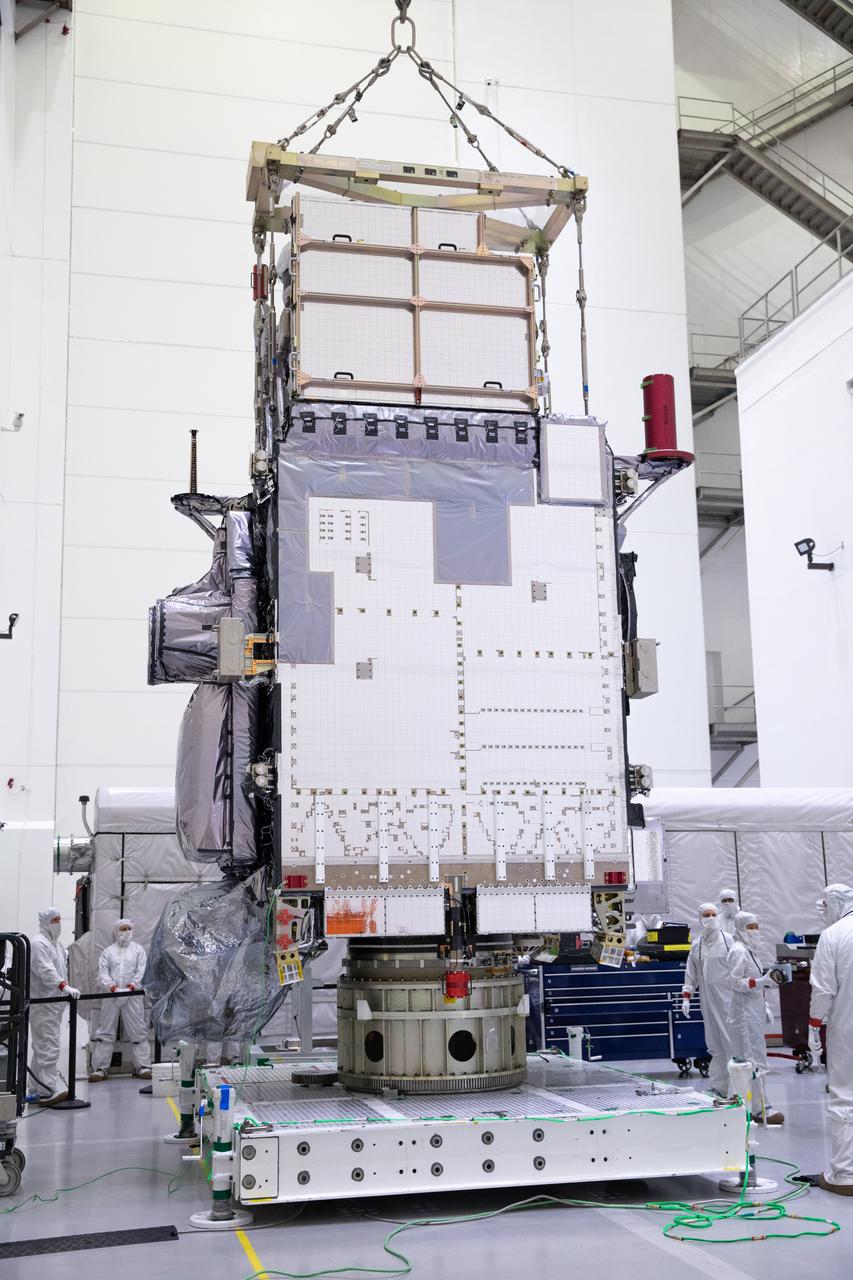
Technicians monitor movement and guide NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) as a crane hoists it on to a spacecraft dolly in a high bay at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Part of a collaborative NOAA and NASA program, GOES-U is the fourth in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. Data from the GOES satellite constellation – consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft – enables forecasters to predict, observe, and track local weather events that affect public safety like thunderstorms, hurricanes, and wildfires.
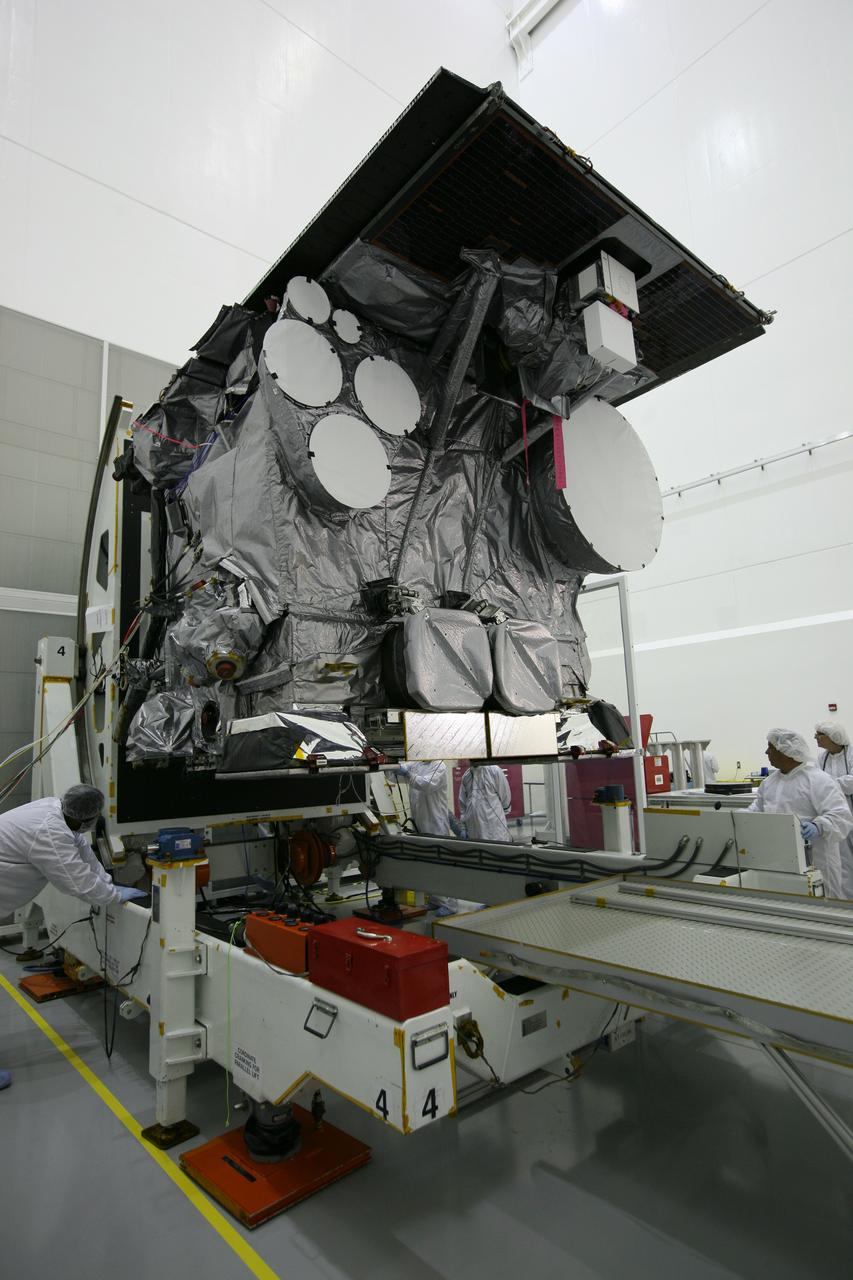

GOES-P UNBAGGING & ROTATION
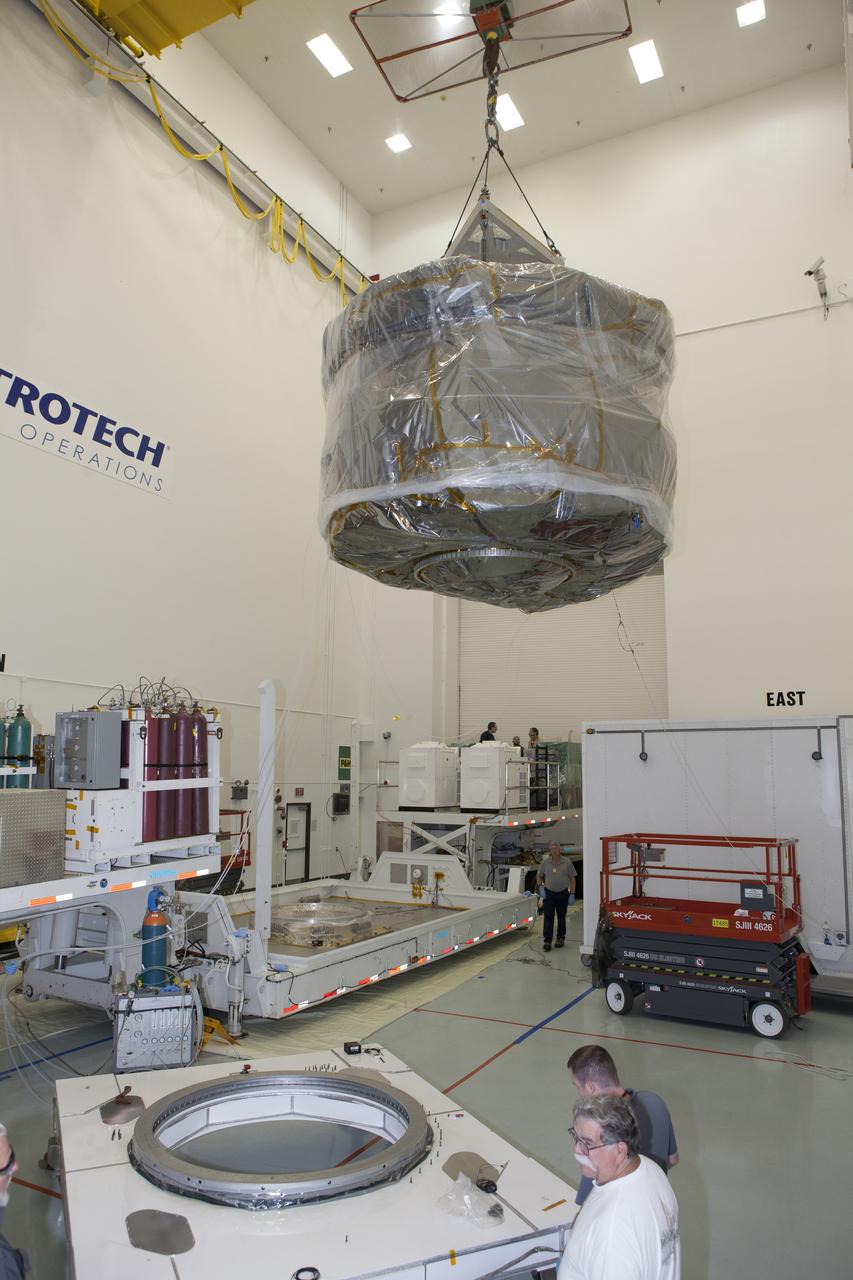

Two of the observatories, the lower stack, mini-stack number 1, for NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale Observatory are suspended over a payload dolly during uncrating operations in the Building 2 south encapsulation bay at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The MMS upper stack, mini-stack number 2, is scheduled to arrive in about two weeks. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
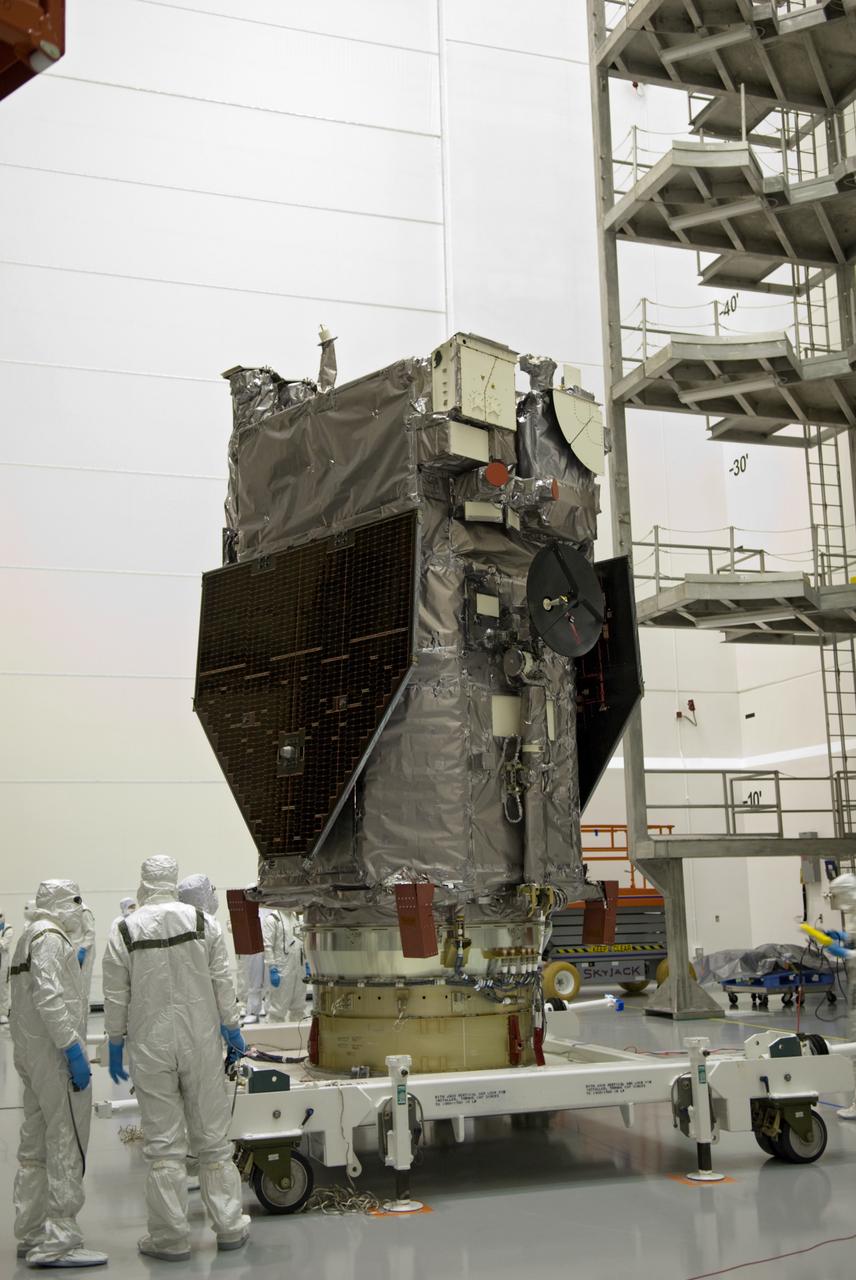

SDO - MEDIA DAY & FAIRING INSTALLATION
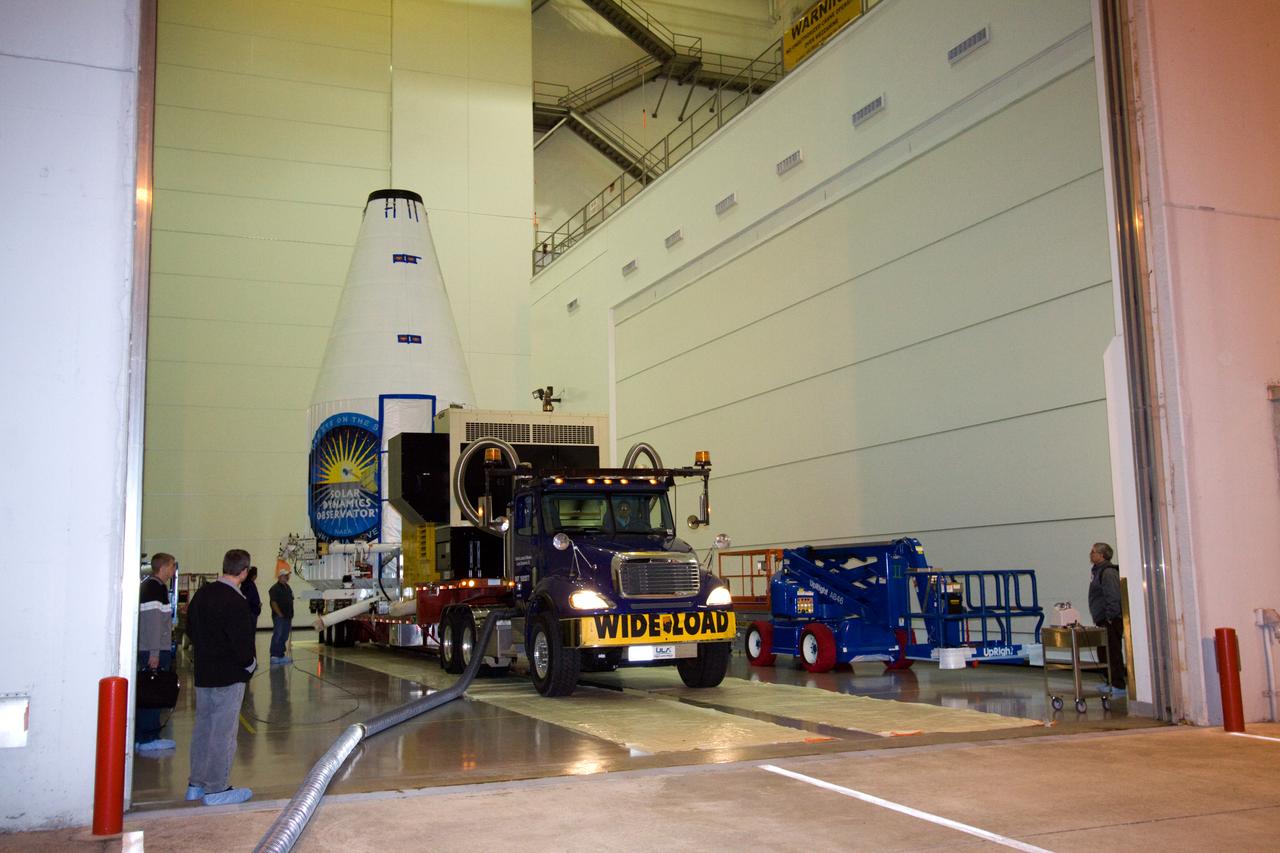

SDO MOVE FROM ASTROTECH TO PAD 41 - LIFT & MATE
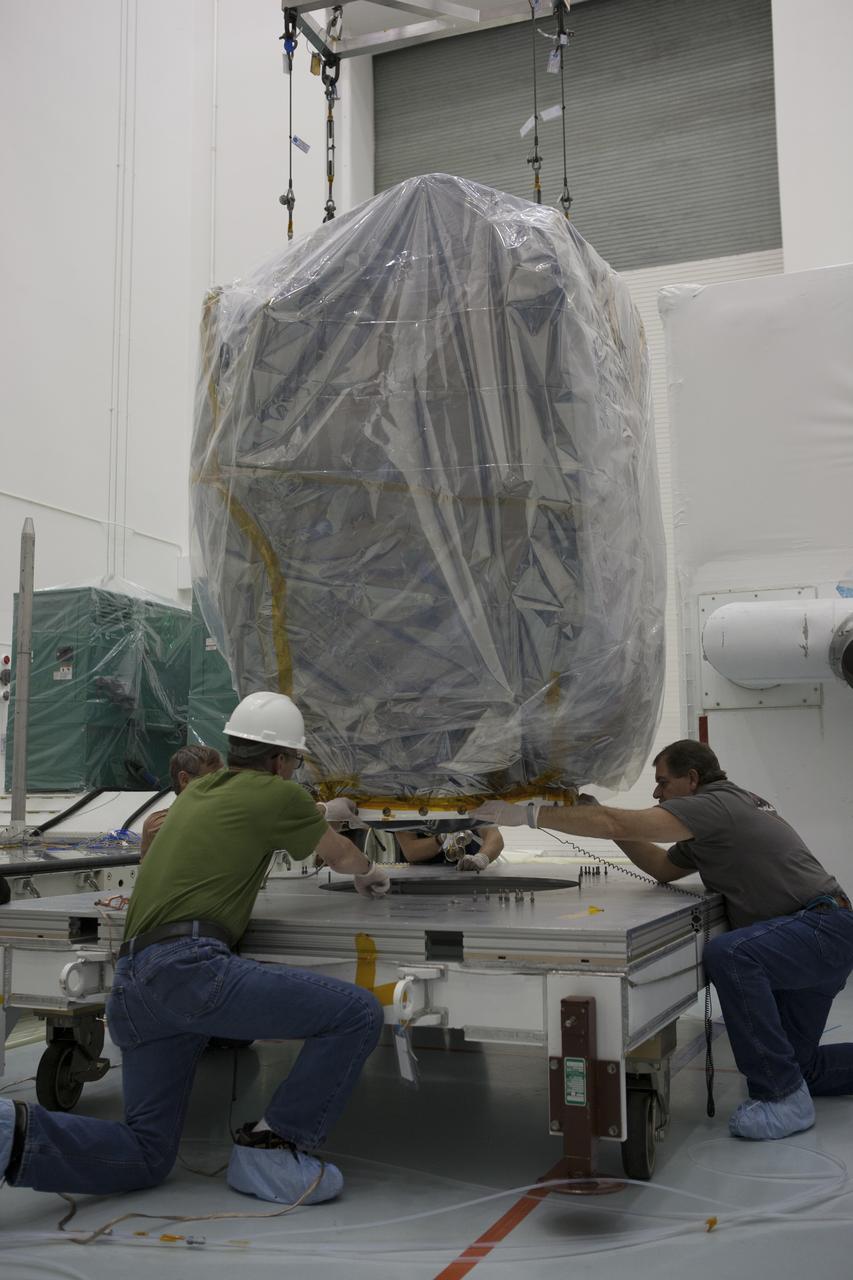

Workers align NOAA’s Deep Space Climate Observatory spacecraft, or DSCOVR, wrapped in plastic, onto a portable work stand at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. DSCOVR is a partnership between NOAA, NASA and the U.S. Air Force. DSCOVR will maintain the nation's real-time solar wind monitoring capabilities which are critical to the accuracy and lead time of NOAA's space weather alerts and forecasts. Launch is currently scheduled for January 2015 aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 v 1.1 launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
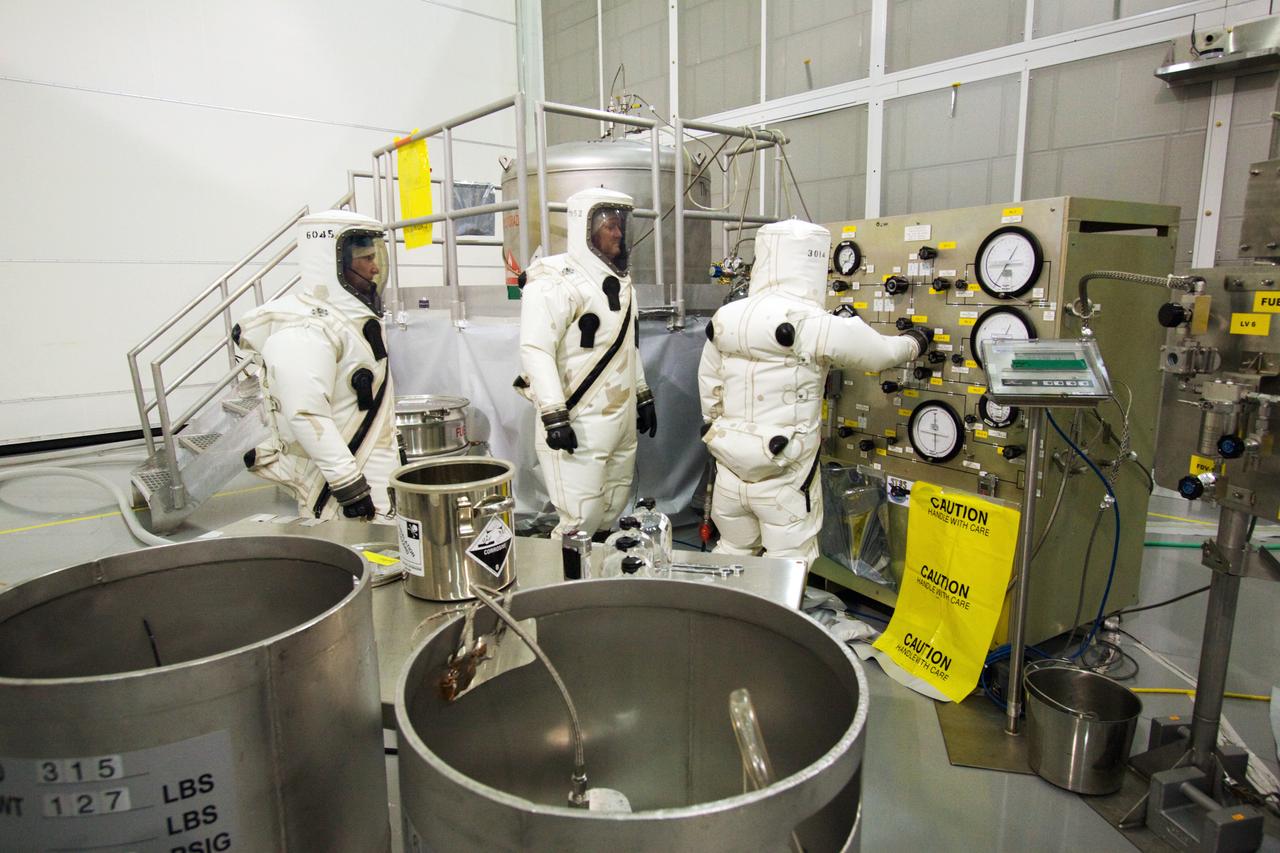

SDO FUELING PREPS FOR SATELLITE W/CREW

NASA and SpaceX technicians safely encapsulate NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft in SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings on Wednesday, Jan. 30, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fairing halves protect the spacecraft from aerodynamic pressure and heating during the ascent phase of launch. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6, 2024.
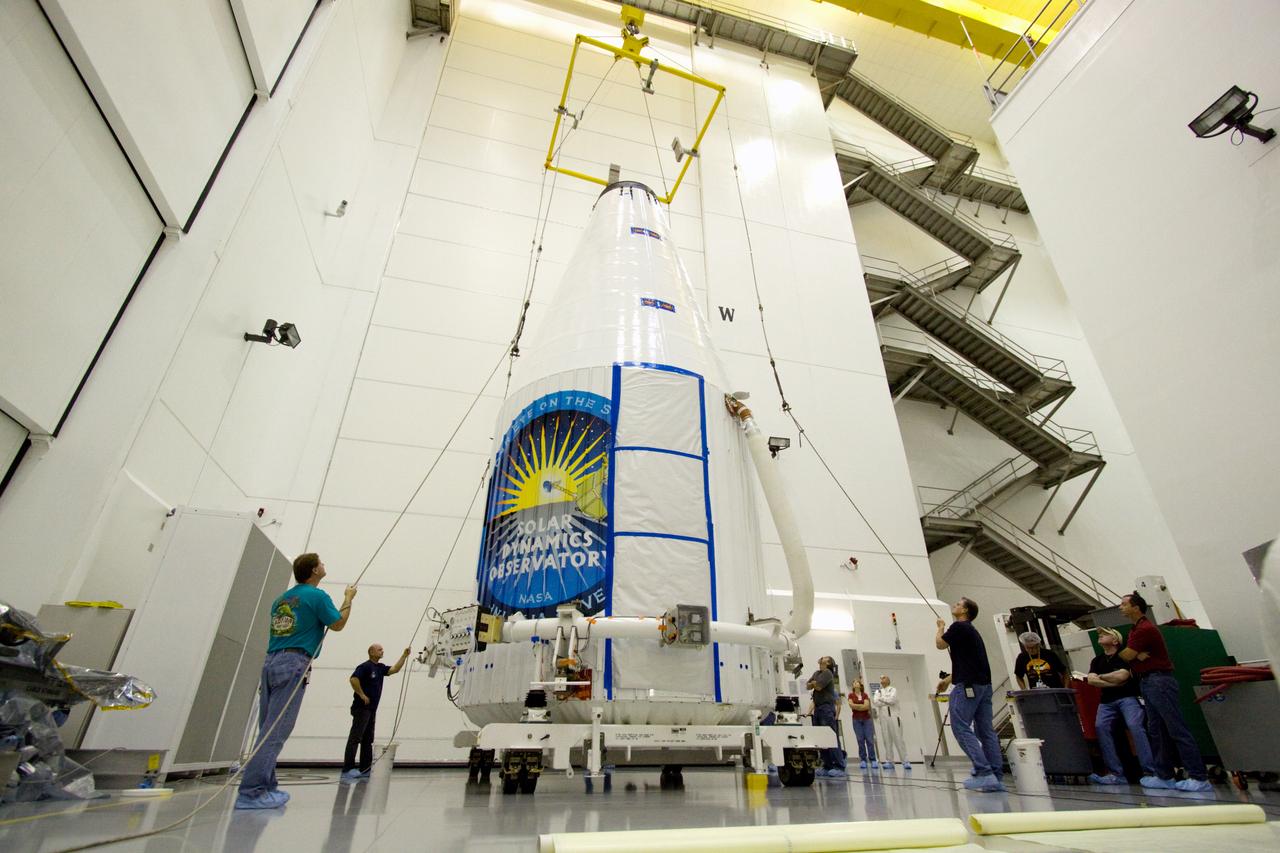

SDO MOVE TO TRANSPORTER

In Astrotech's Payload Processing Facility, an overhead crane lifts the Dawn spacecraft from its transporter. Dawn will be moved into clean room C for unbagging and further processing. Dawn's mission is to explore two of the asteroid belt's most intriguing and dissimilar occupants: asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The Dawn mission is managed by JPL, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington, D.C
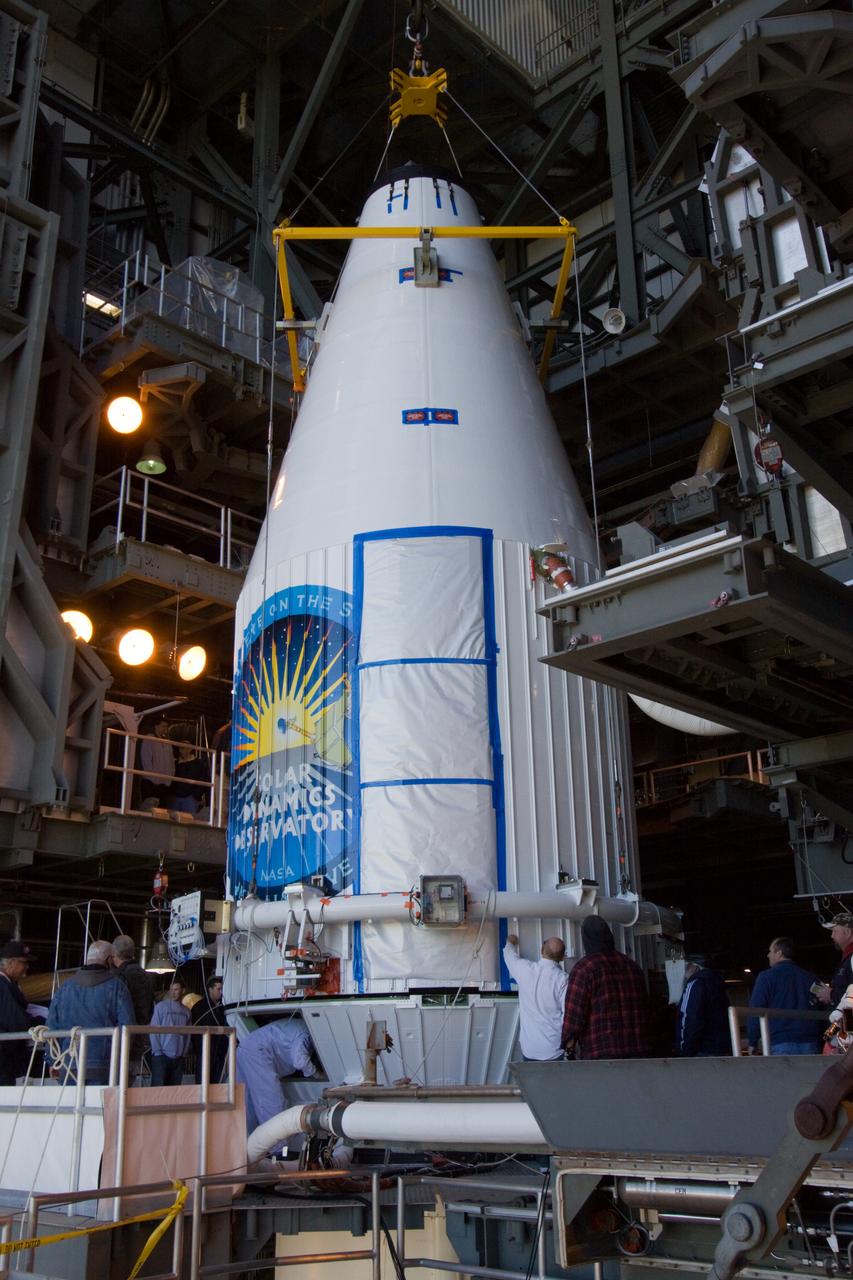

SDO MOVE FROM ASTROTECH TO PAD 41 - LIFT & MATE