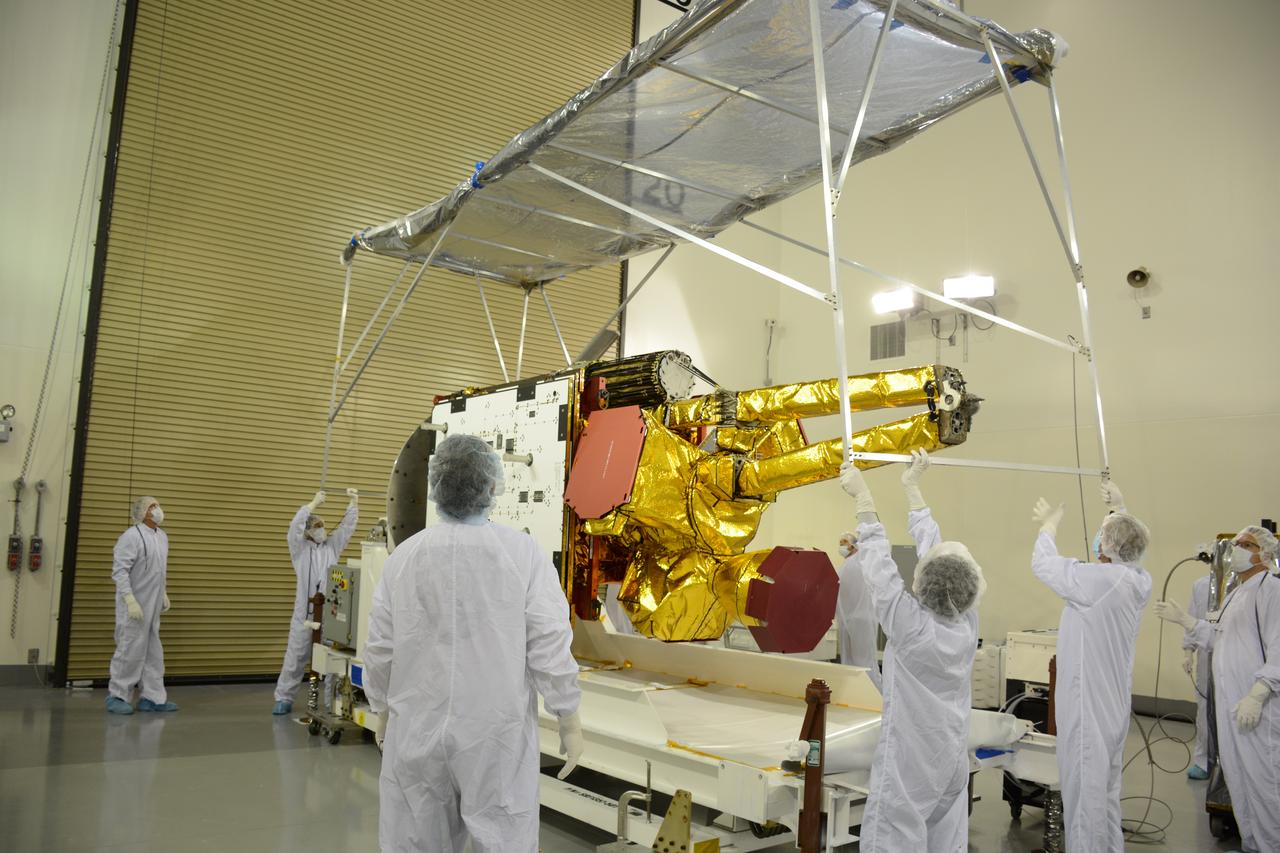

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians remove a protective covering from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
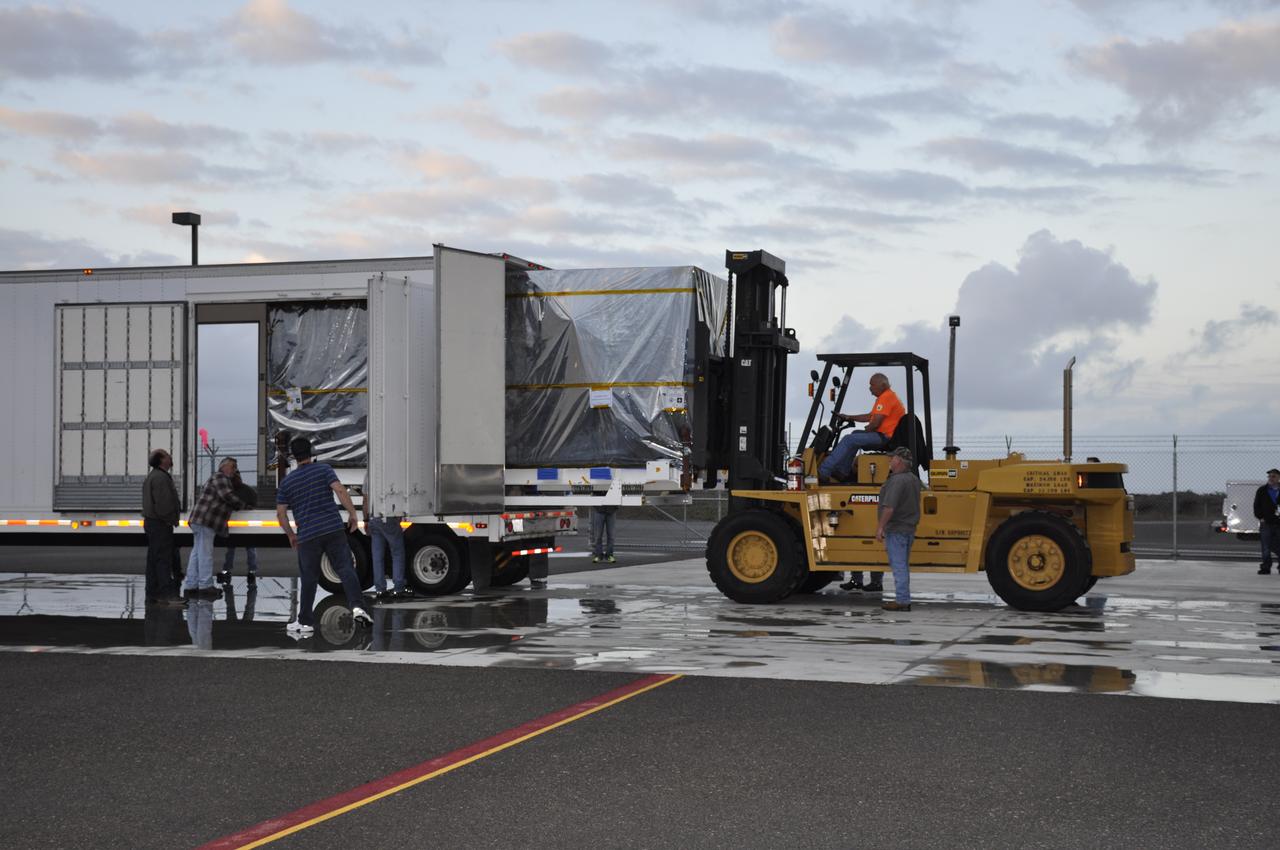

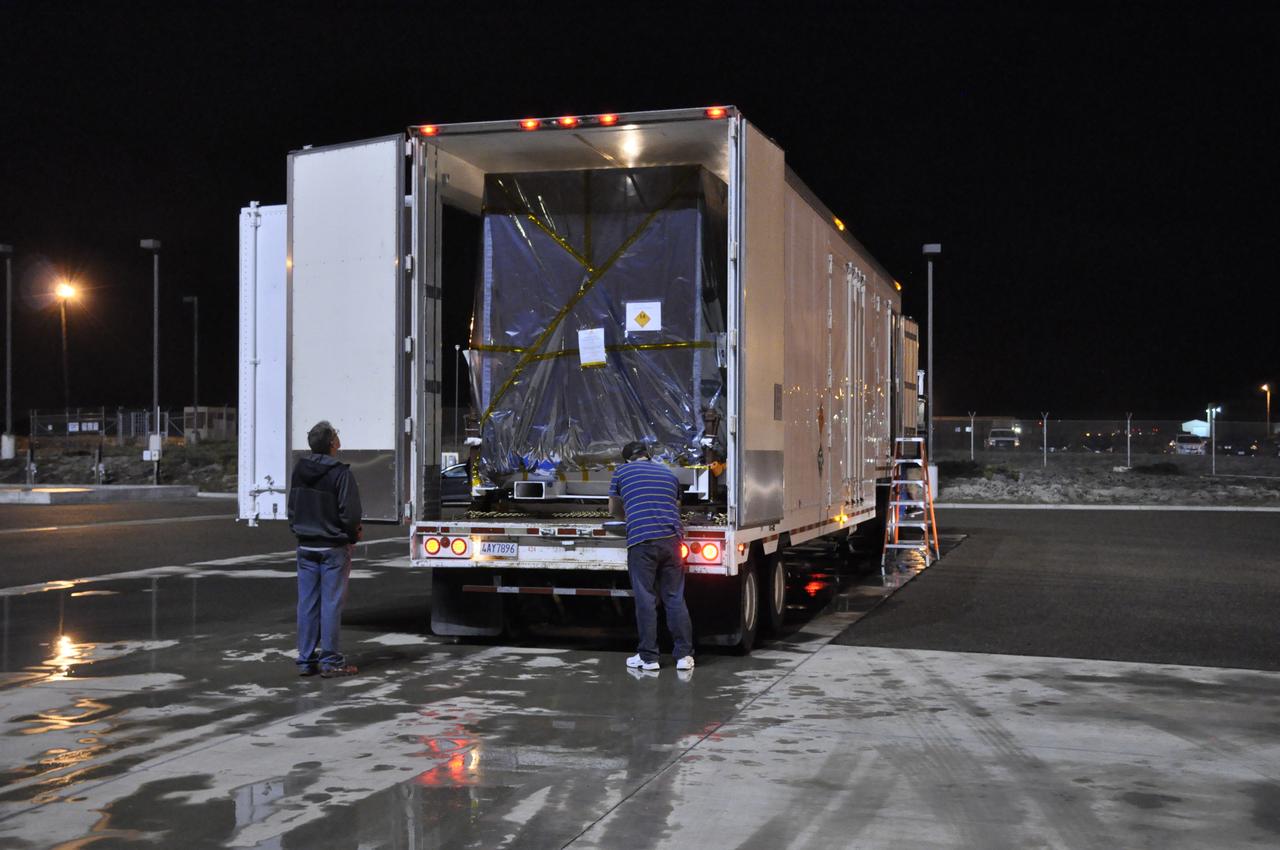
The transportation container protecting NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft is offloaded from the truck that delivered it from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, to the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California with the aid of a forklift. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
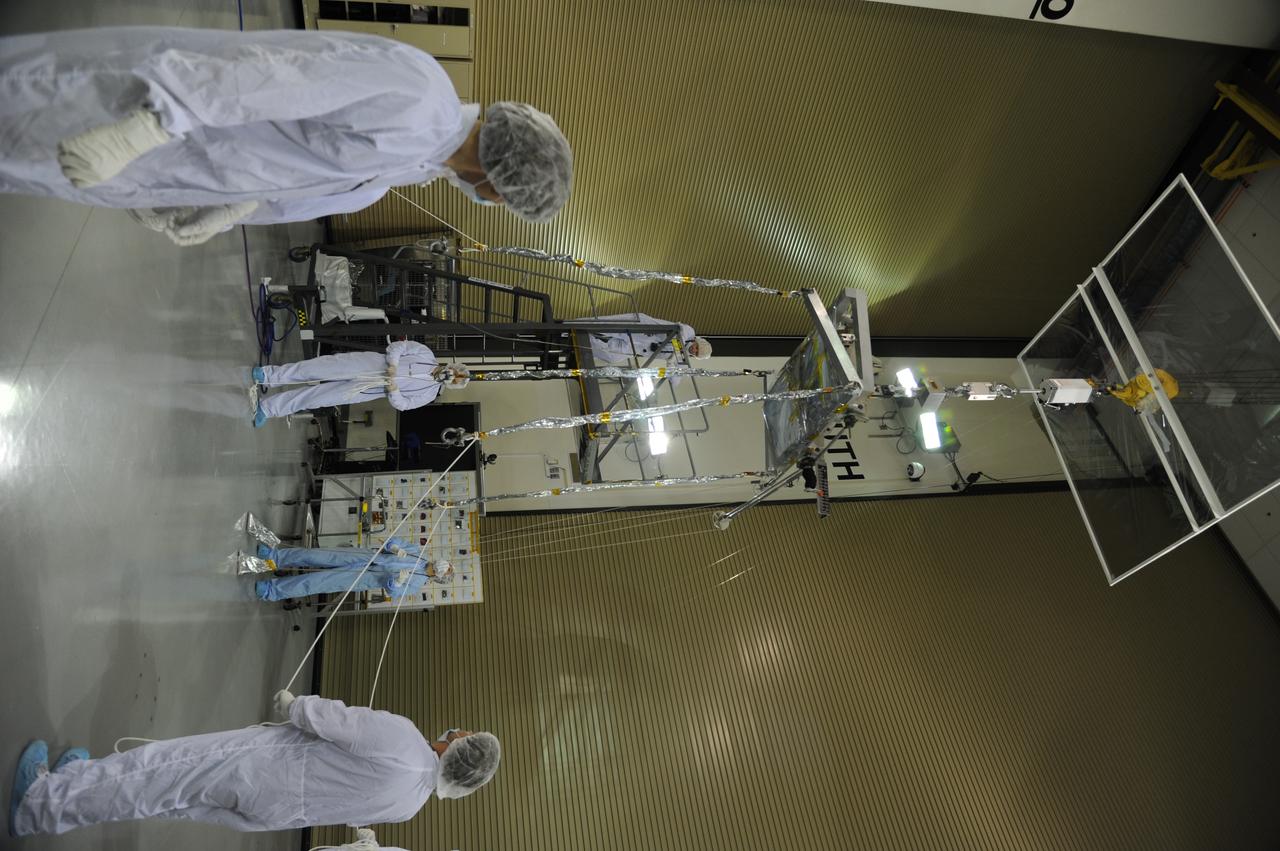

Operations are underway to weigh NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the clean room of the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The weighing of a spacecraft is standard procedure during prelaunch processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory that built the observatory and its radar instrument also is responsible for SMAP project management and mission operations. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

Preparations are underway to weigh NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the clean room of the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The weighing of a spacecraft is standard procedure during prelaunch processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory that built the observatory and its radar instrument also is responsible for SMAP project management and mission operations. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
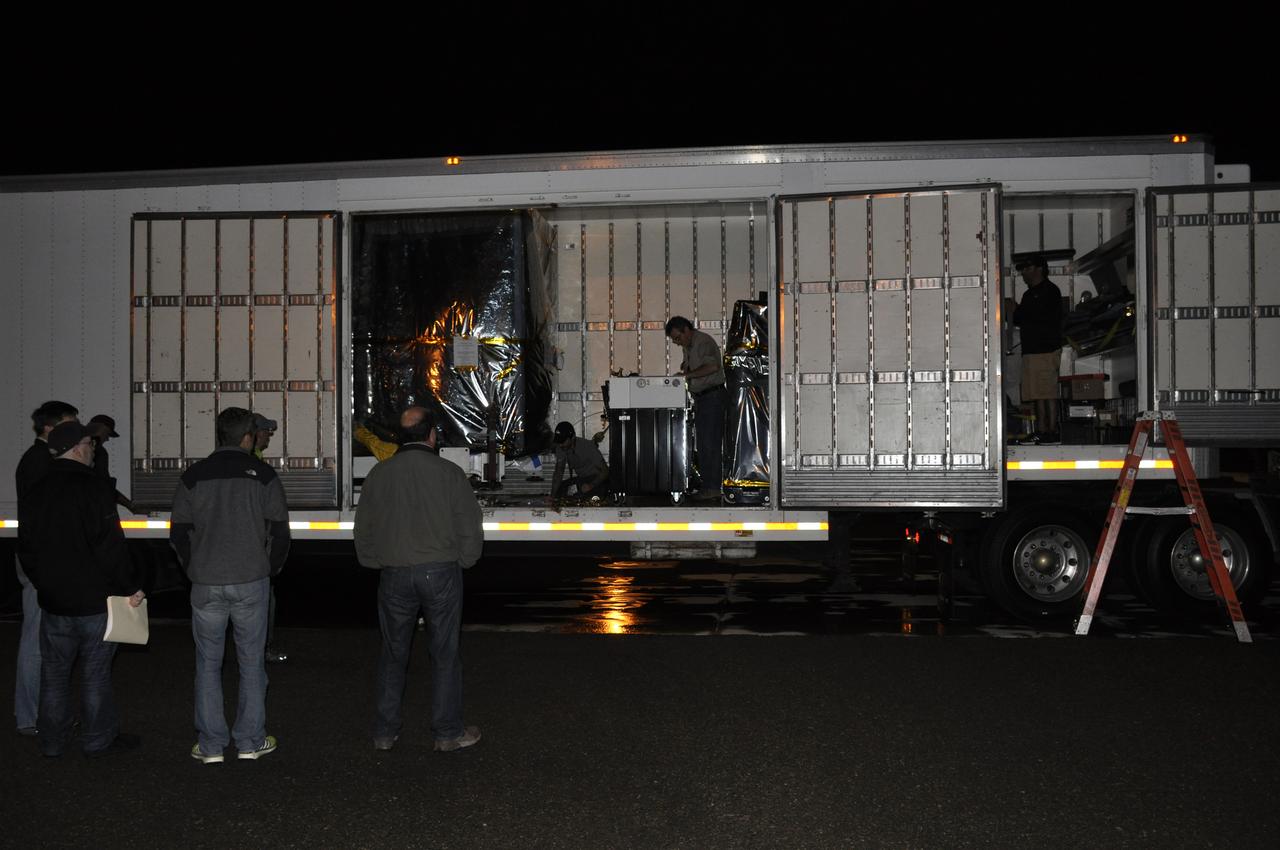

Workers are standing by to assist with the offloading of NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft from the truck that delivered it from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, to the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians rotate NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft to begin processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

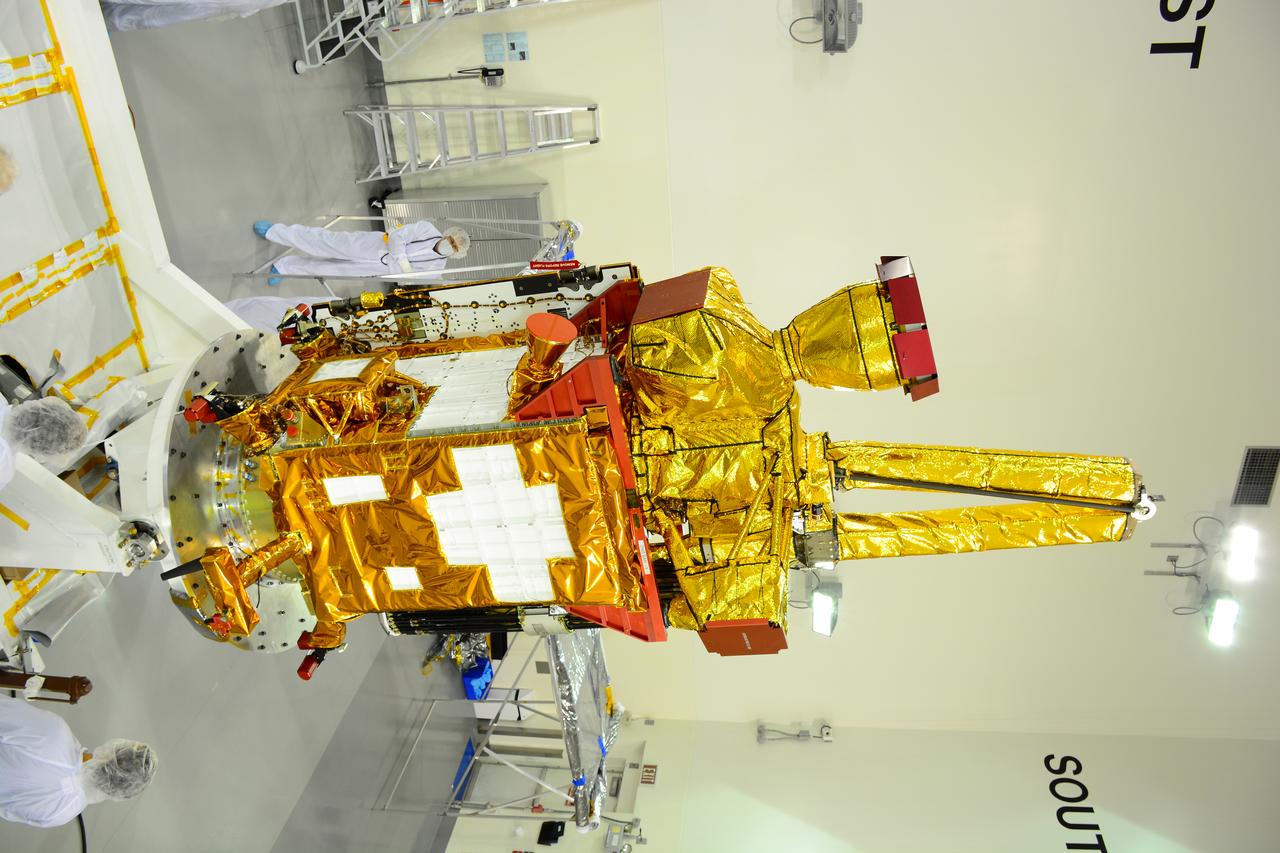
Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians remove a protective covering from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, an engineer inspects NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
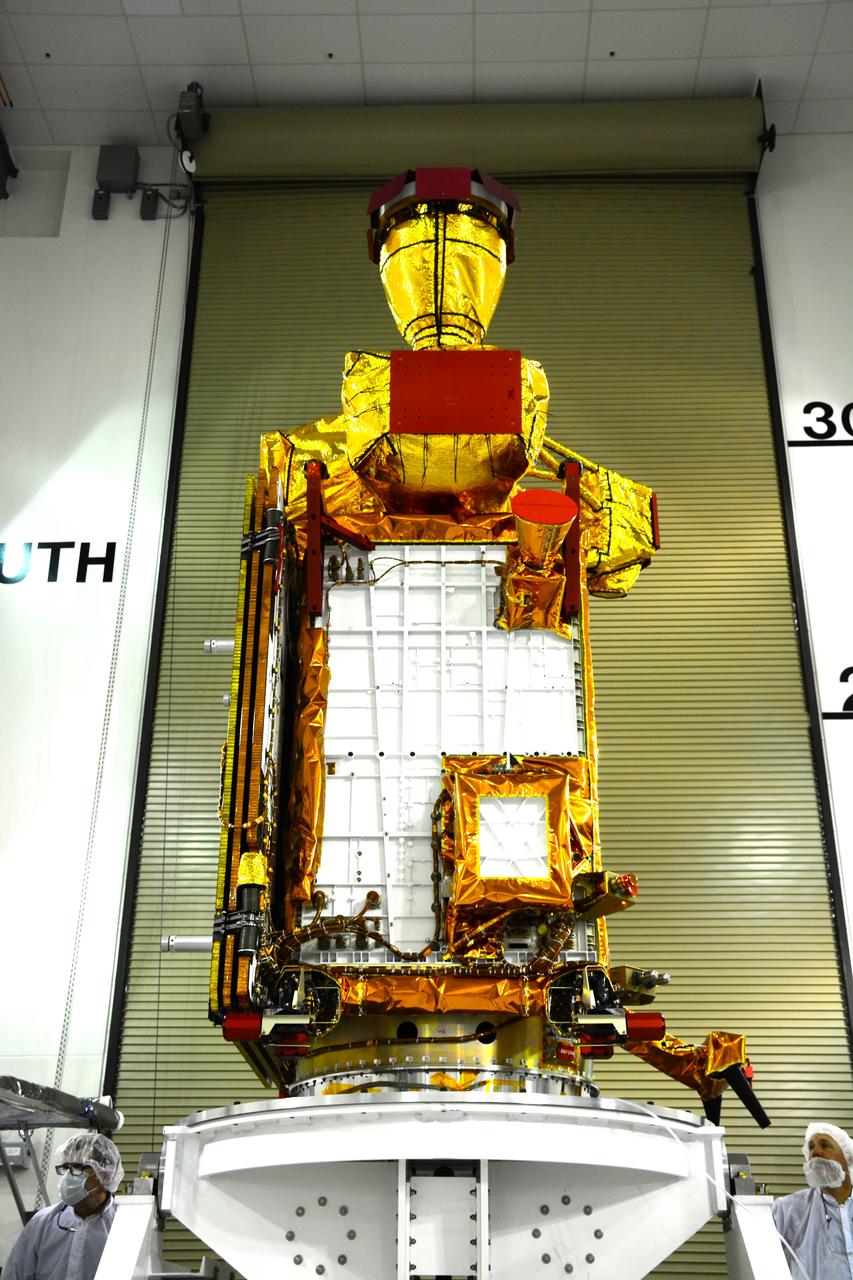
Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians rotate NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft to begin processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

Workers prepare to offload NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft from the truck that delivered it from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, to the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
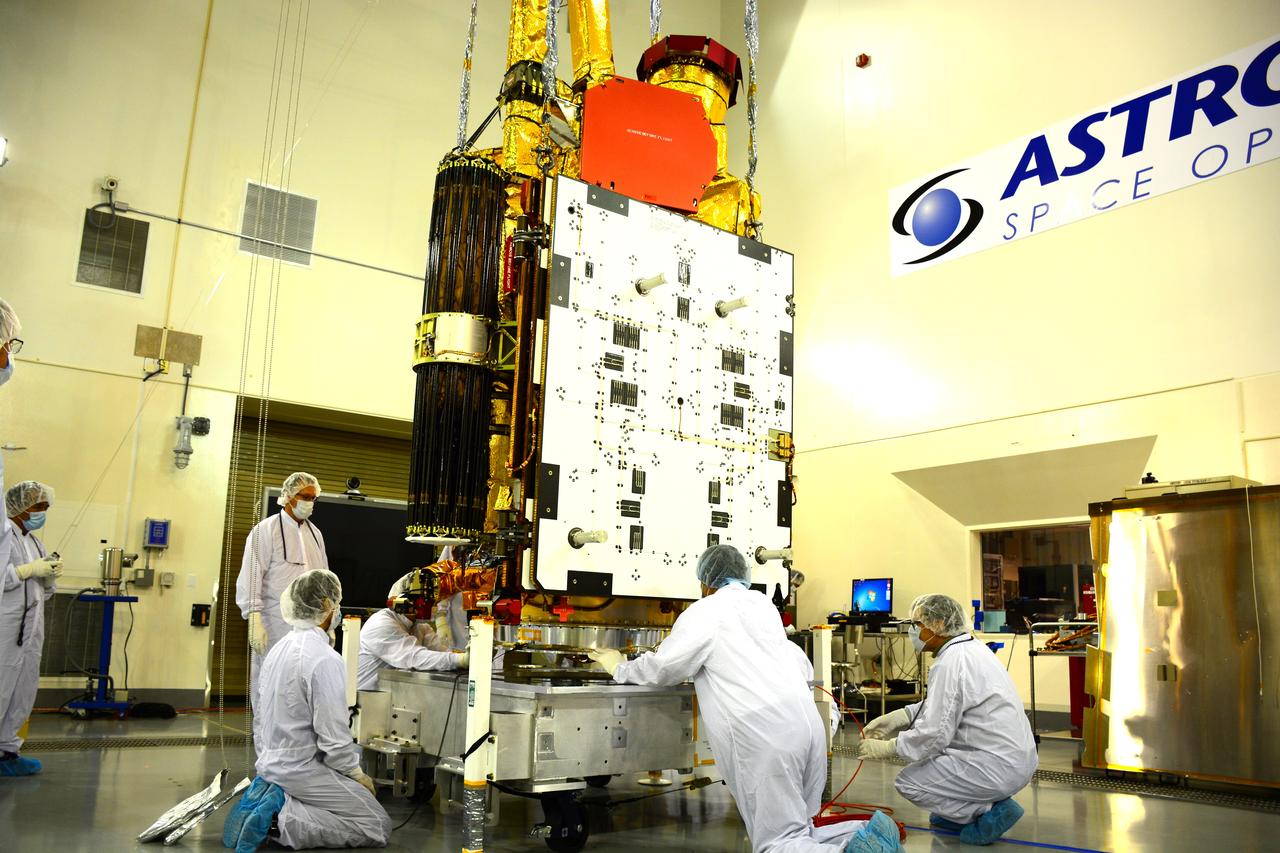

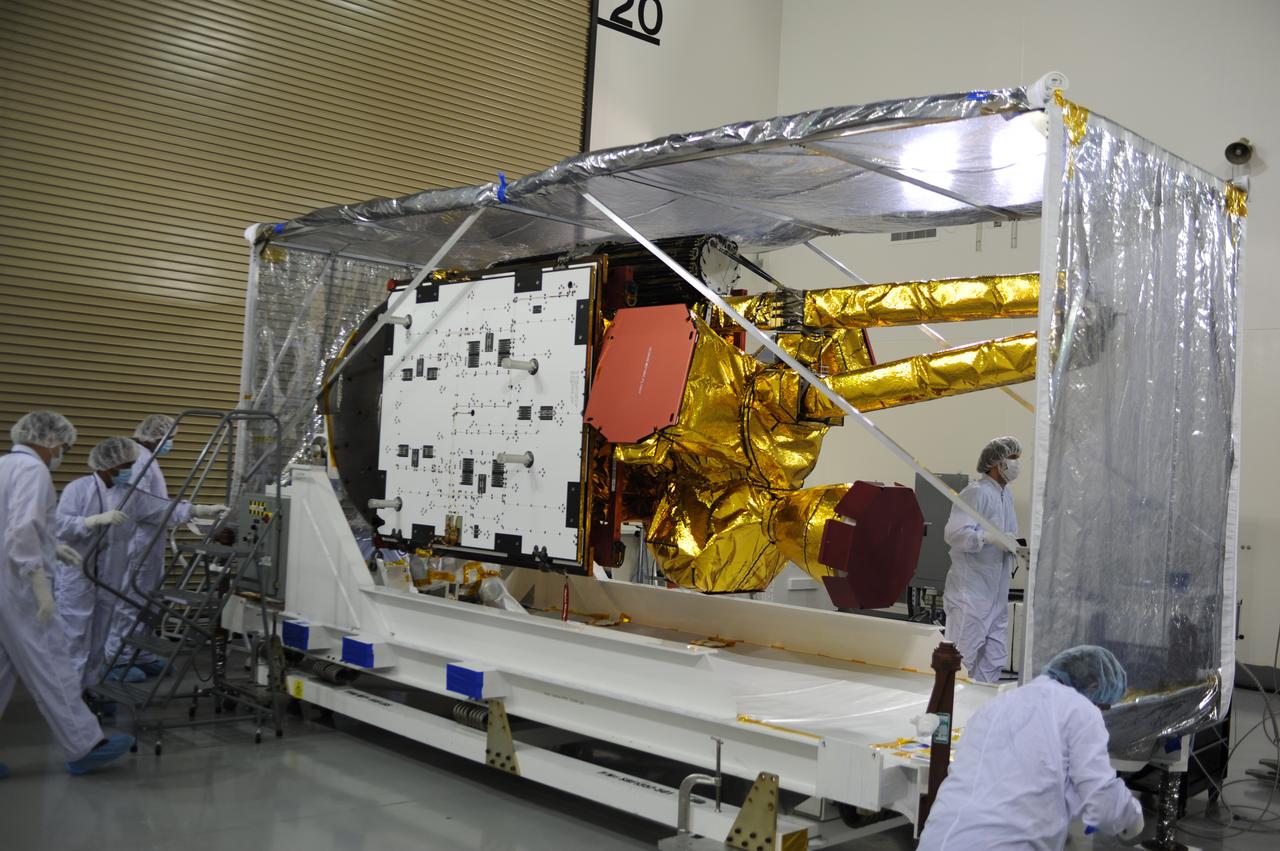
Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians mount NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft on a work platform. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
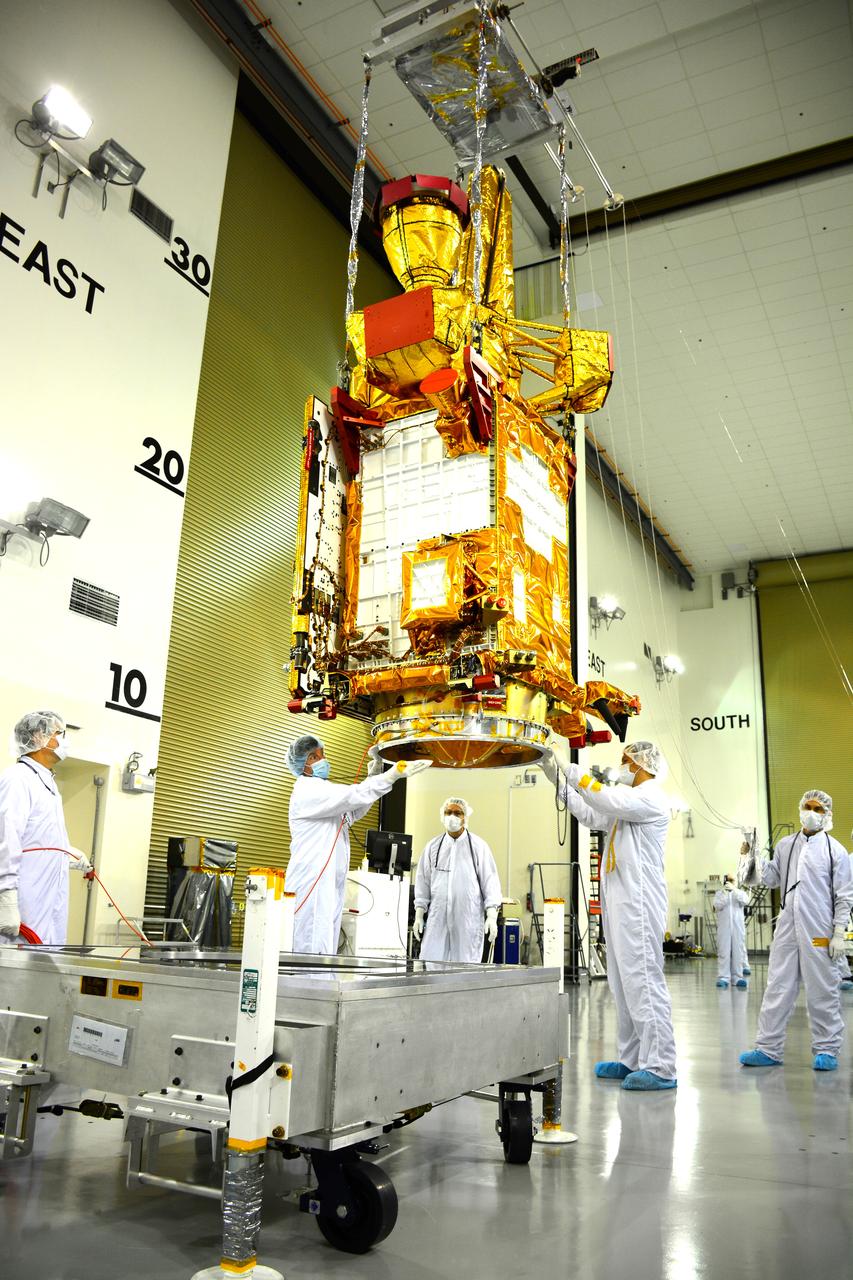

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians use a crane to move NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

Preparations are underway to weigh NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the clean room of the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The weighing of a spacecraft is standard procedure during prelaunch processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory that built the observatory and its radar instrument also is responsible for SMAP project management and mission operations. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
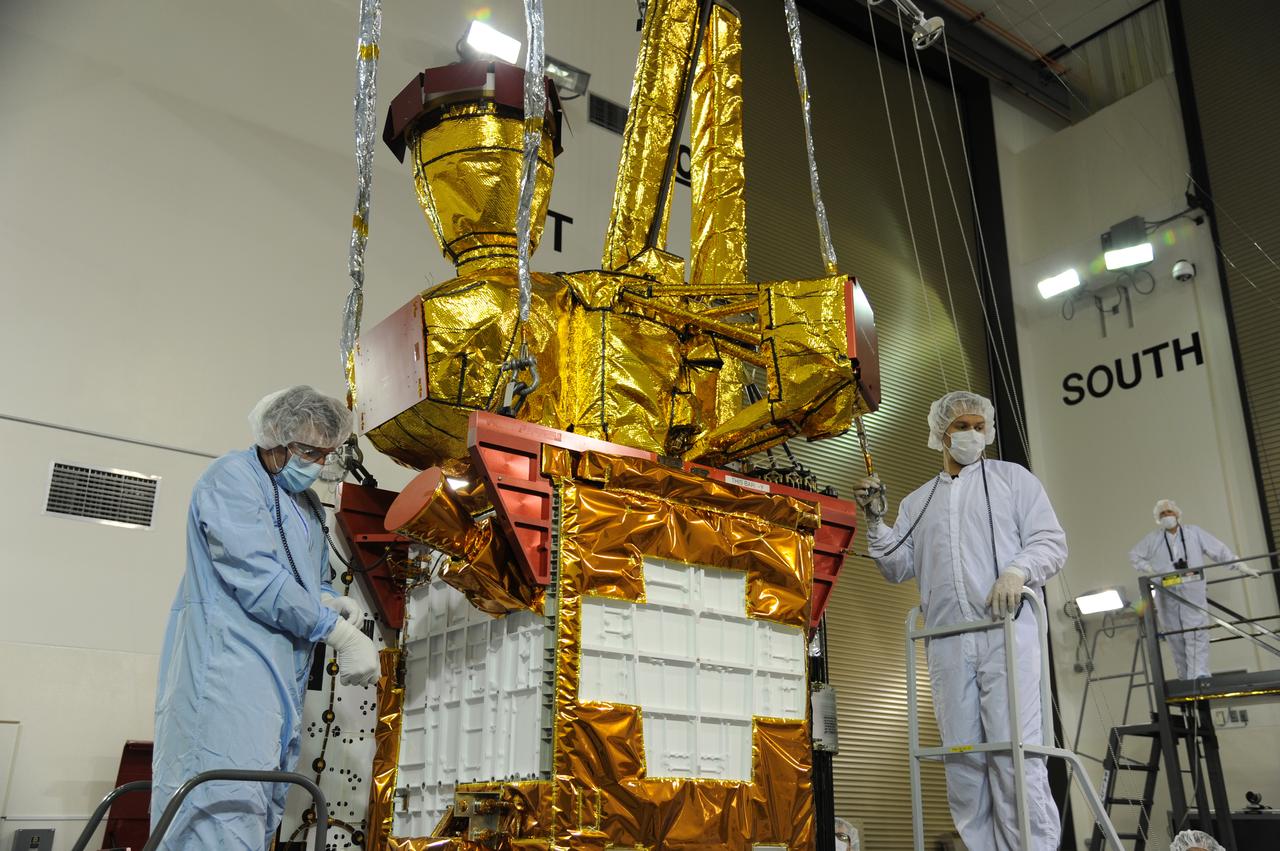

Operations are underway to weigh NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the clean room of the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The weighing of a spacecraft is standard procedure during prelaunch processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory that built the observatory and its radar instrument also is responsible for SMAP project management and mission operations. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
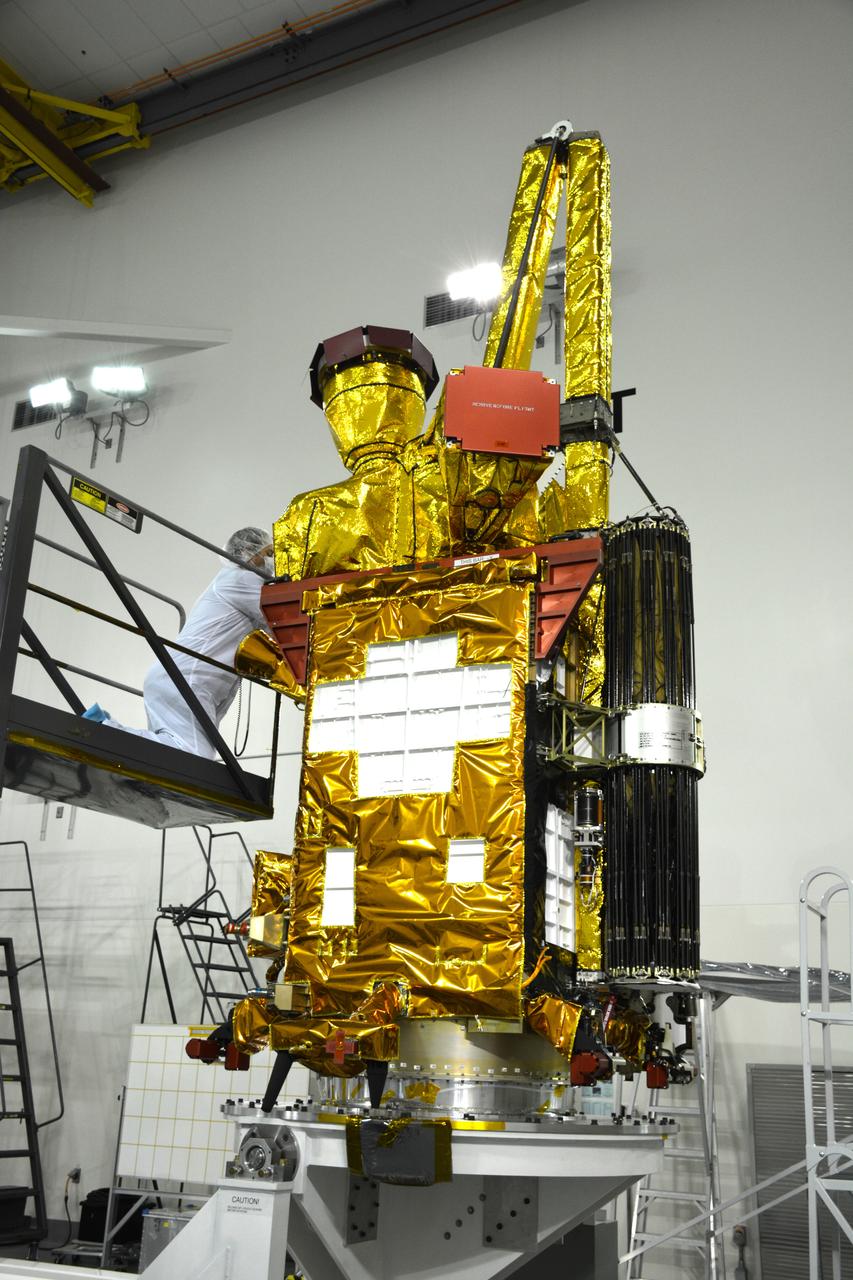

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians have rotated NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft to begin processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
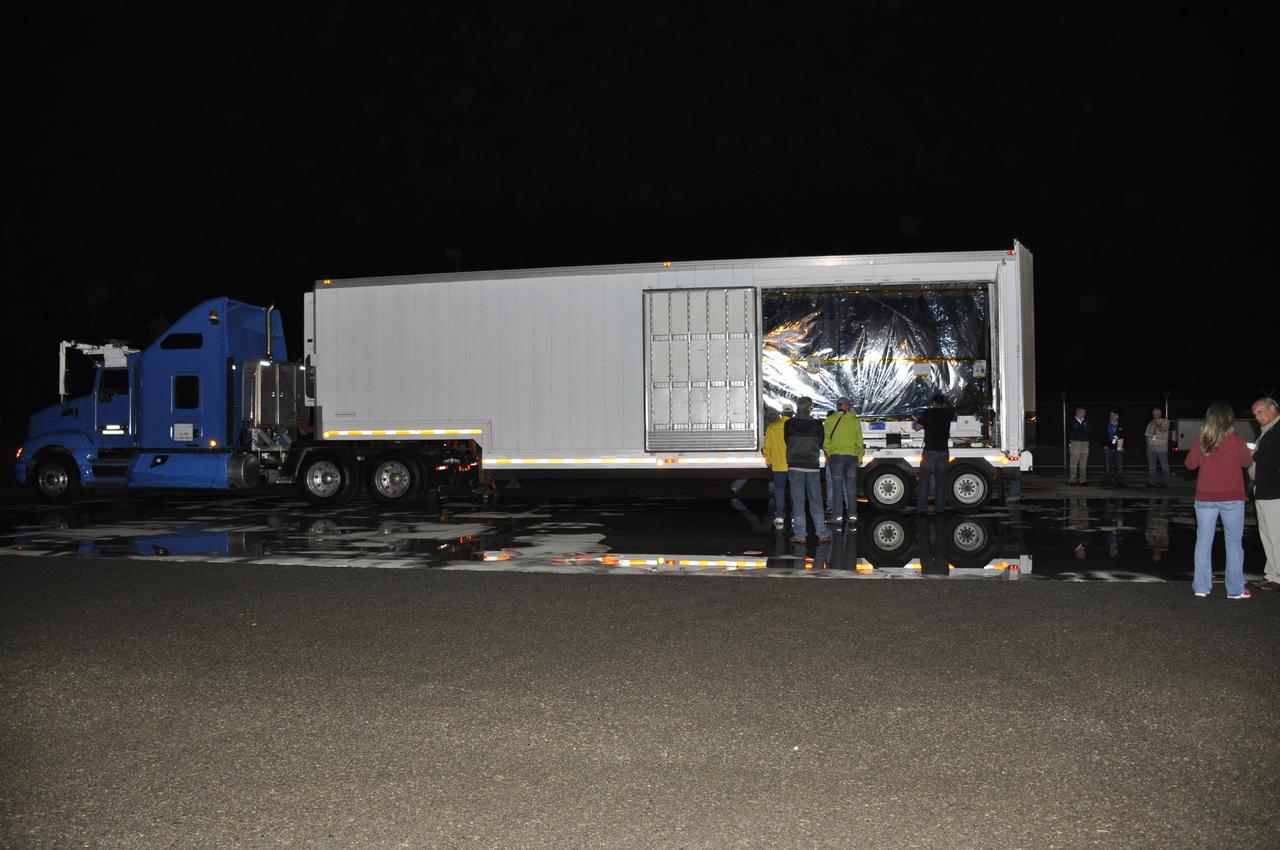

Operations are underway to offload NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft from the truck that delivered it from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, to the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
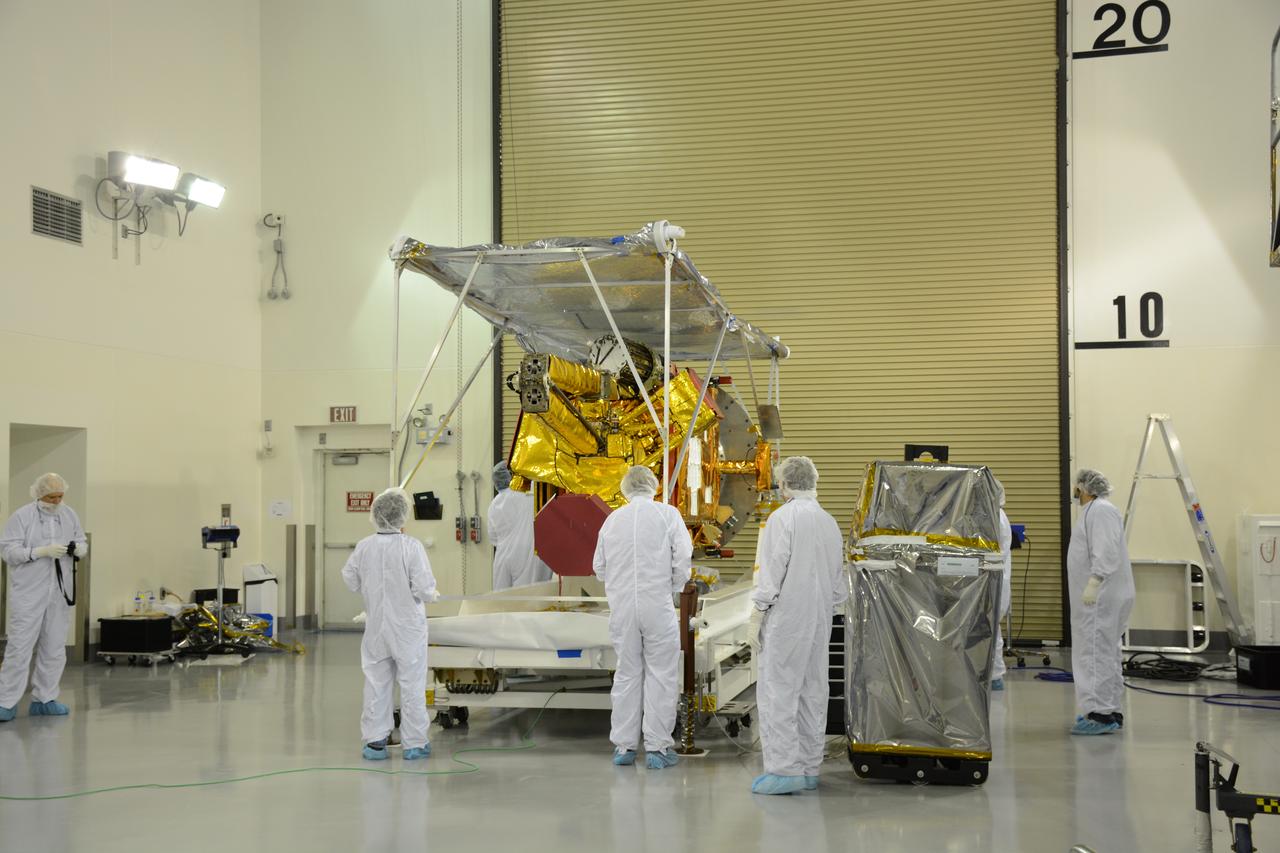

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians remove a protective covering from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
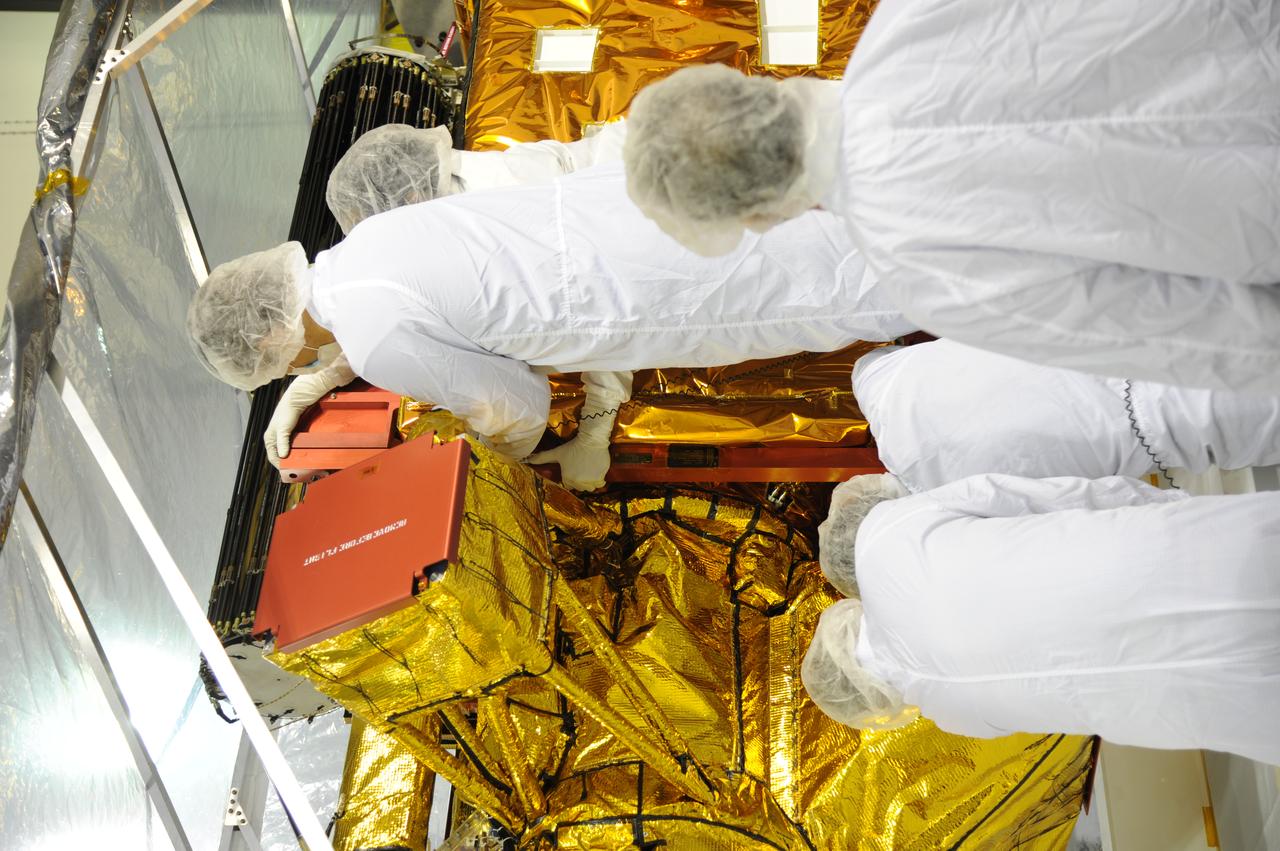

Workers inspect instrument and optics covers on NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during a post-shipment inspection. The spacecraft was delivered to the launch site today from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
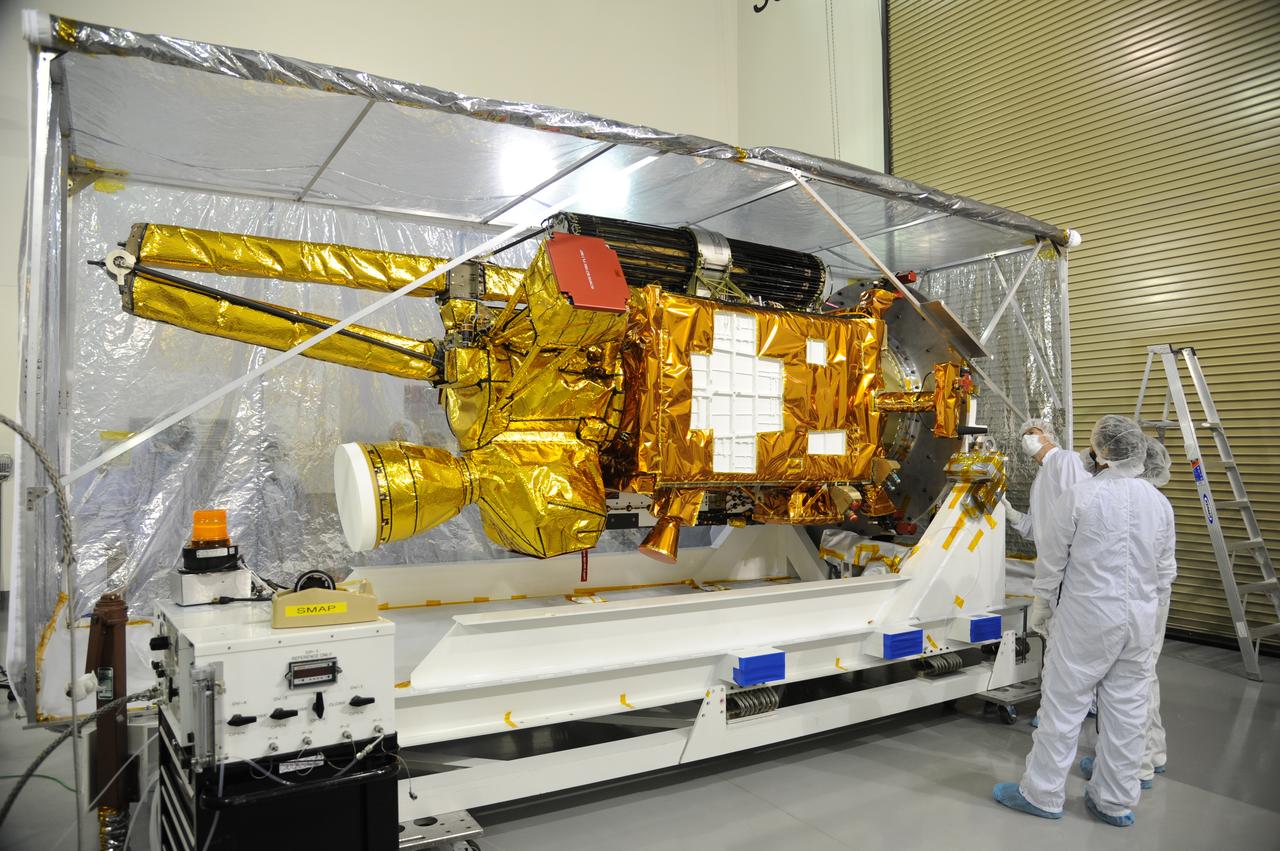

NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft comes into view as the protective covering is removed in the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during a post-shipment inspection. The covering protected the spacecraft from static-charge buildup and contamination while it was in transit from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
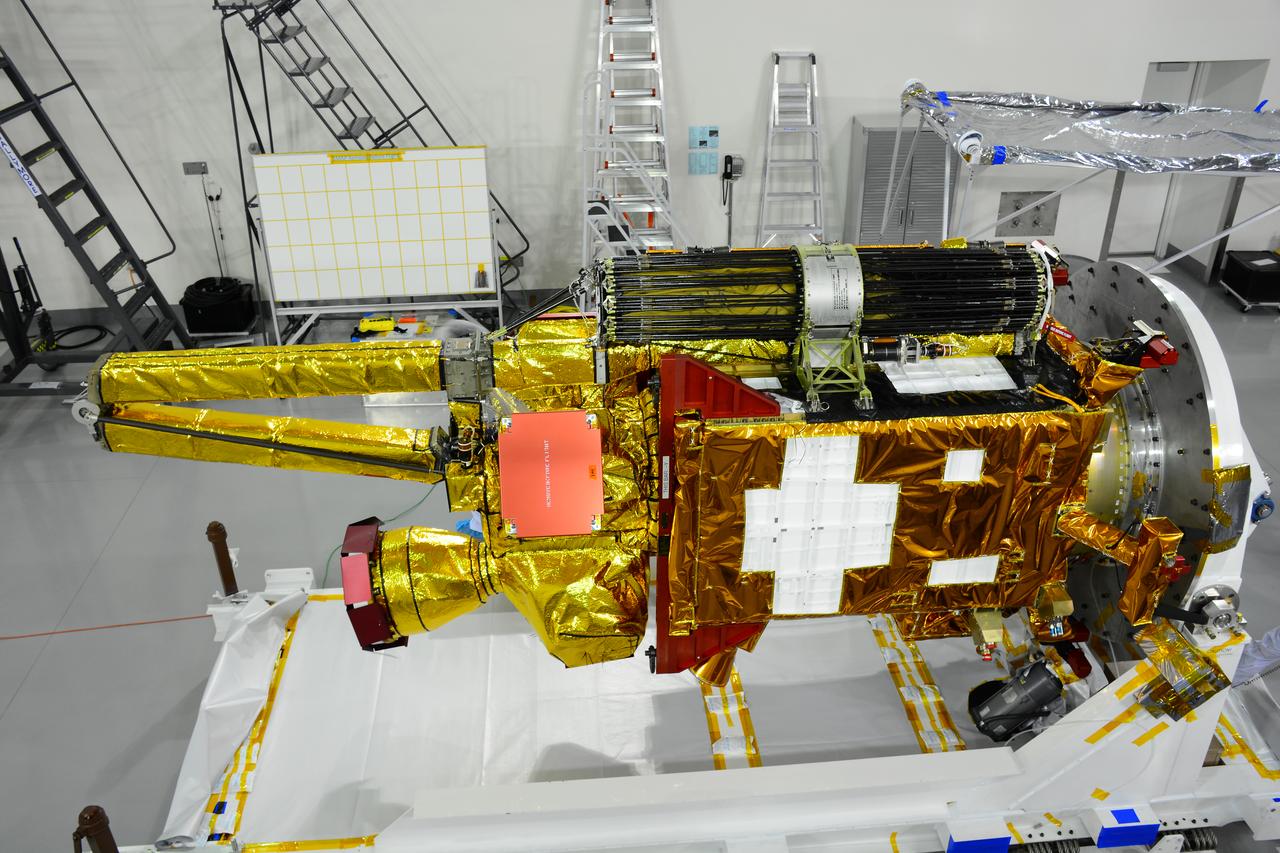

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, processing has begun on NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
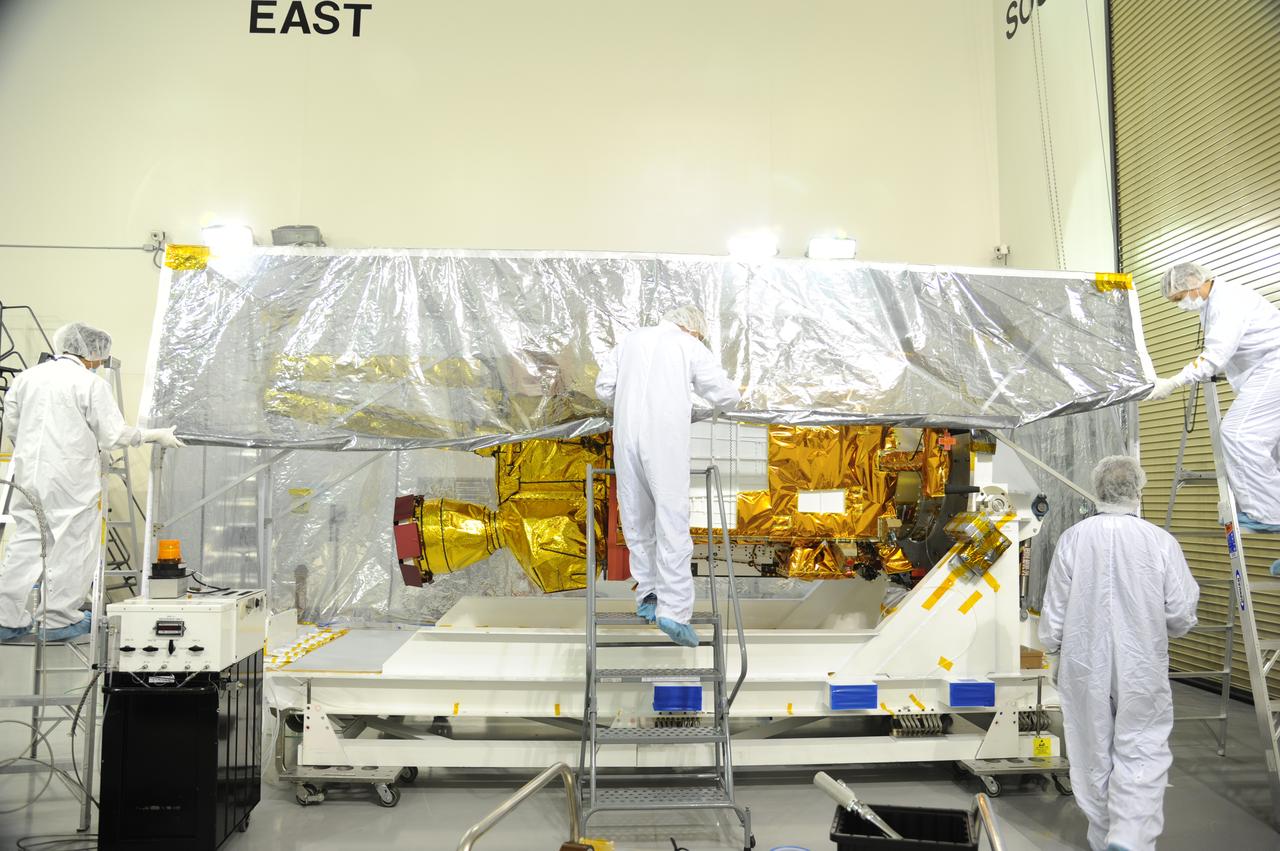

Workers replace the protective covering around NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft following the spacecraft's post-shipment inspection in the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The covering protected the spacecraft from static-charge buildup and contamination while it was in transit from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

Operations are underway to weigh NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the clean room of the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The weighing of a spacecraft is standard procedure during prelaunch processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory that built the observatory and its radar instrument also is responsible for SMAP project management and mission operations. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
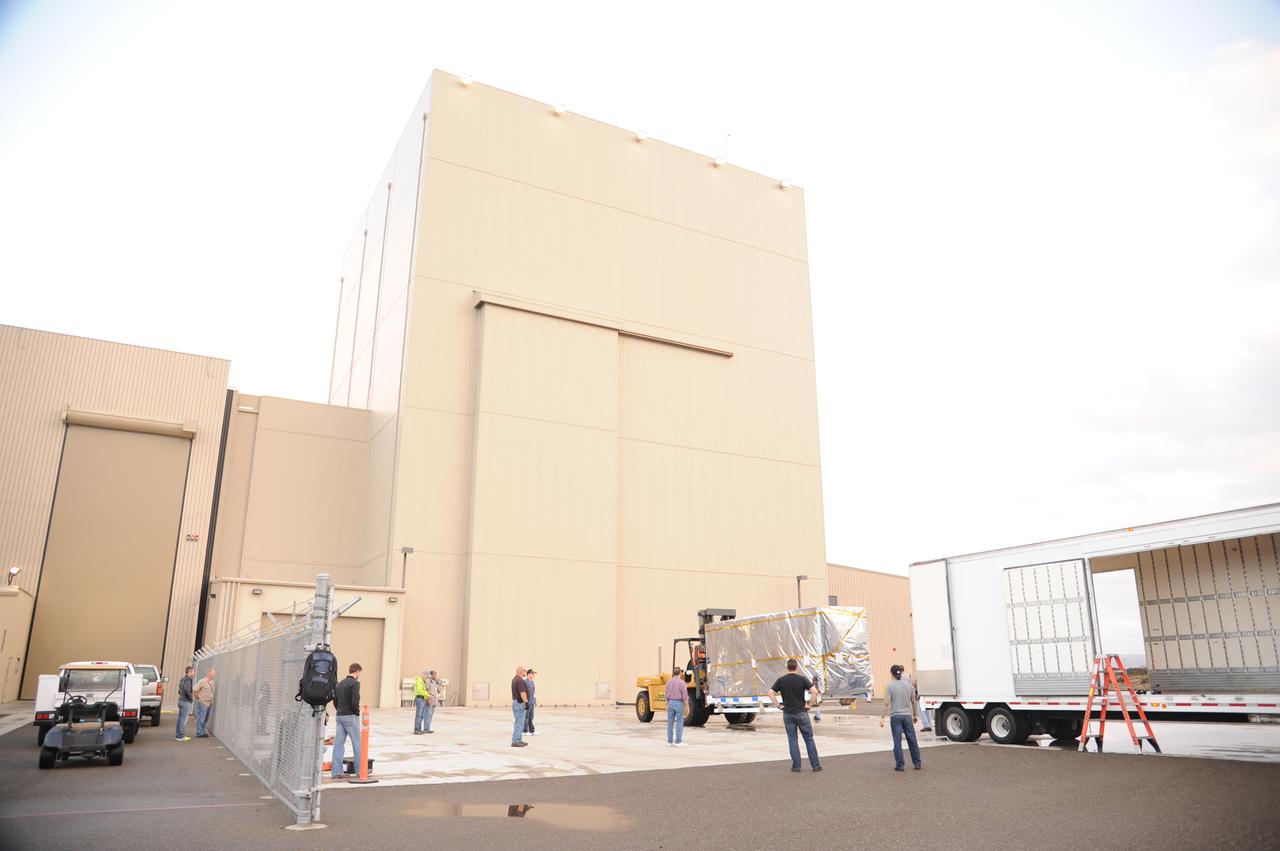

NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft, enclosed in a transportation container, is offloaded from the truck on which it traveled from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, to the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
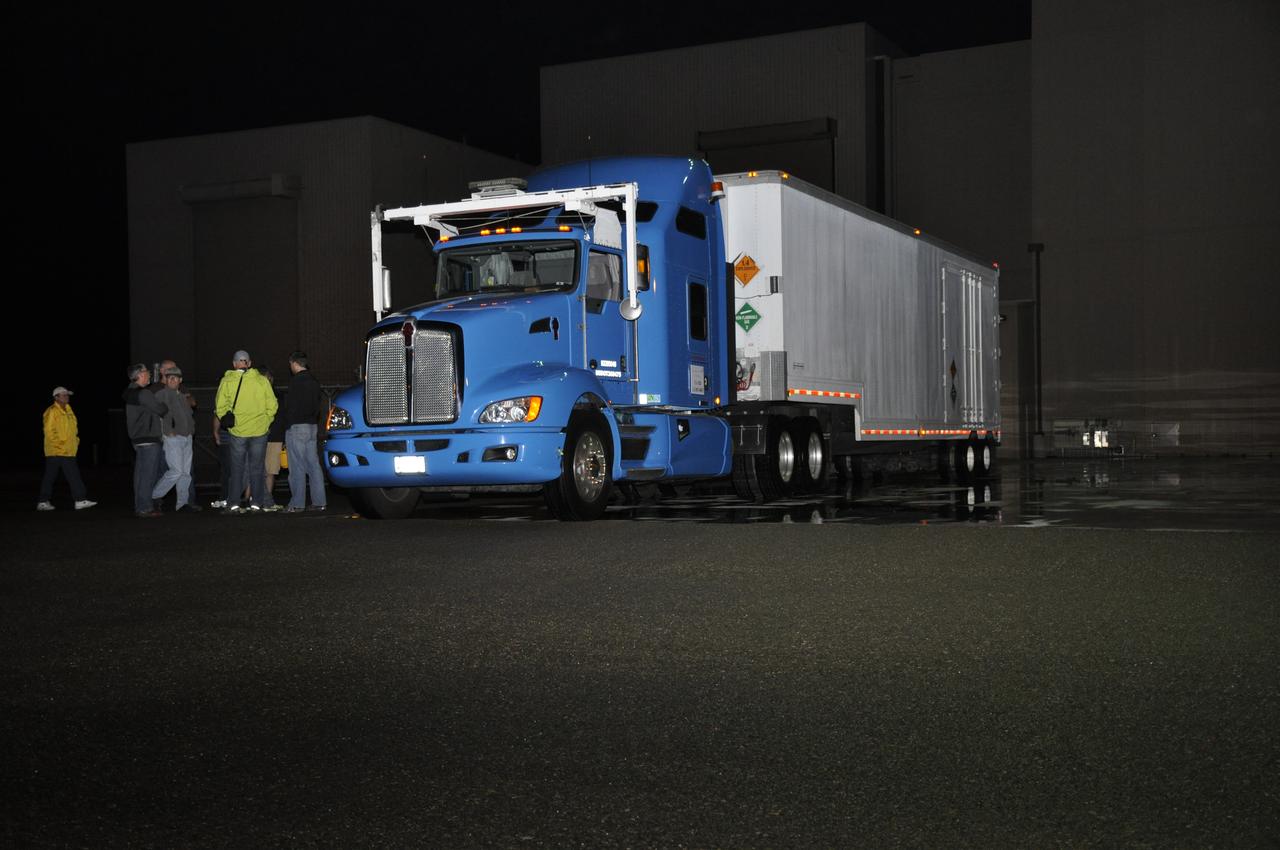

The truck transporting NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft arrives at the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
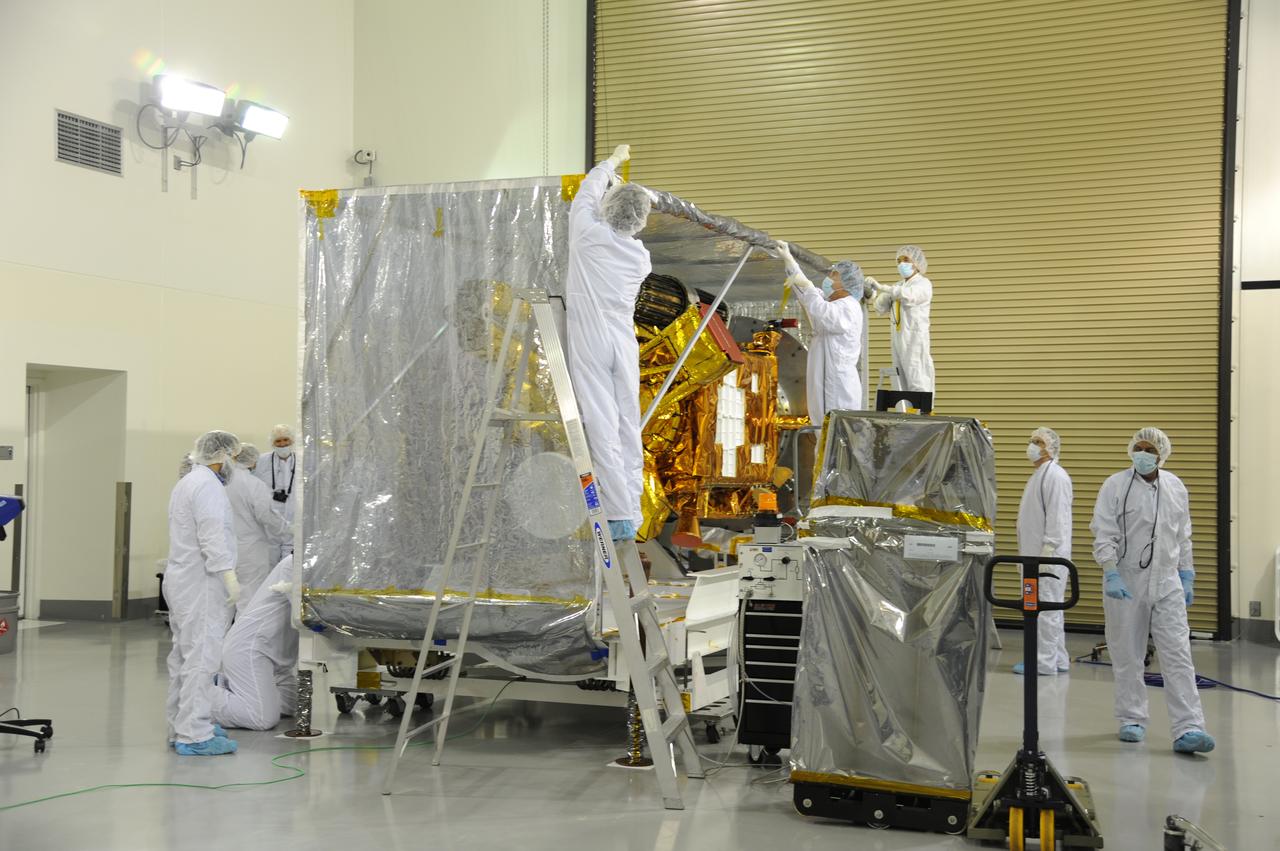

Workers remove the protective covering from around NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during a post-shipment inspection. The covering protected the spacecraft from static-charge buildup and contamination while it was in transit from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians use a crane to move NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
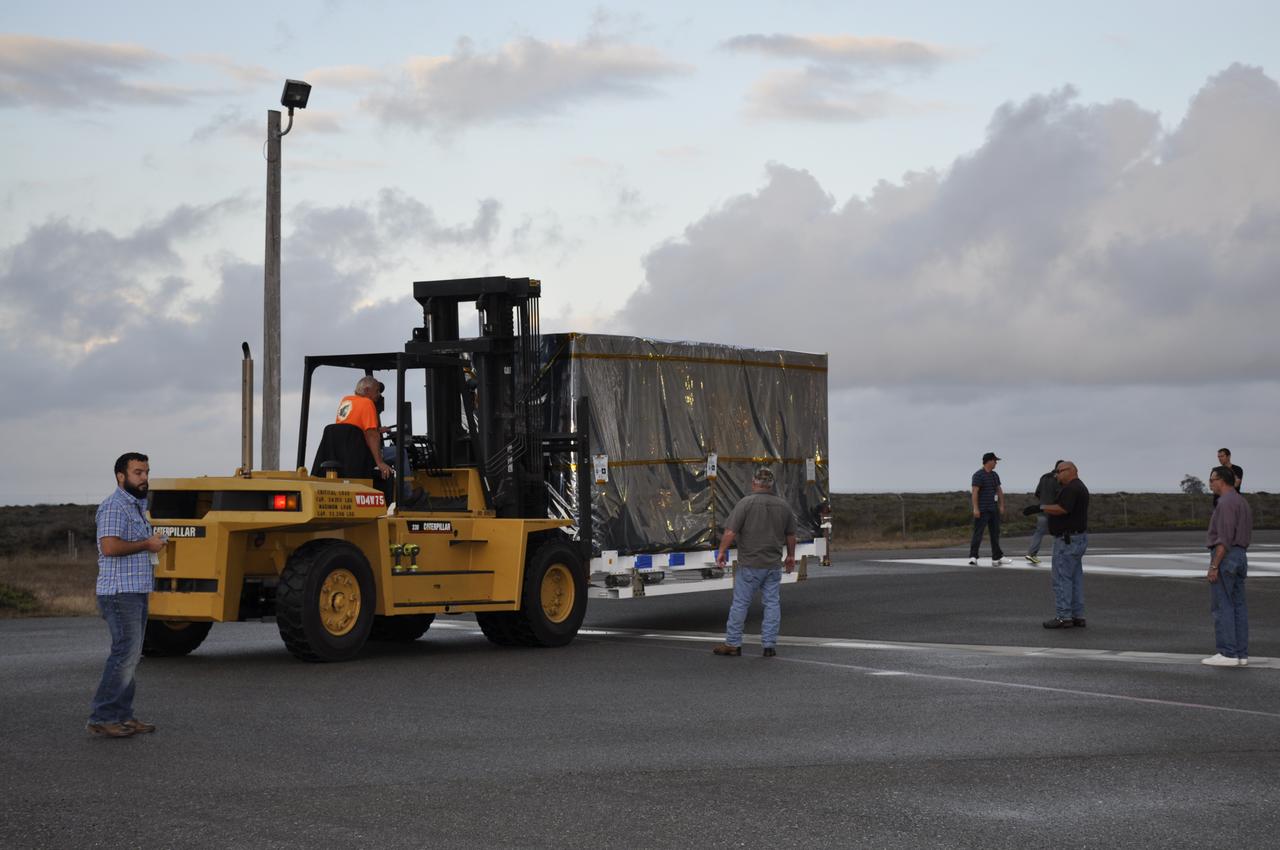

Workers push the pallet supporting the transportation container protecting NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft into the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
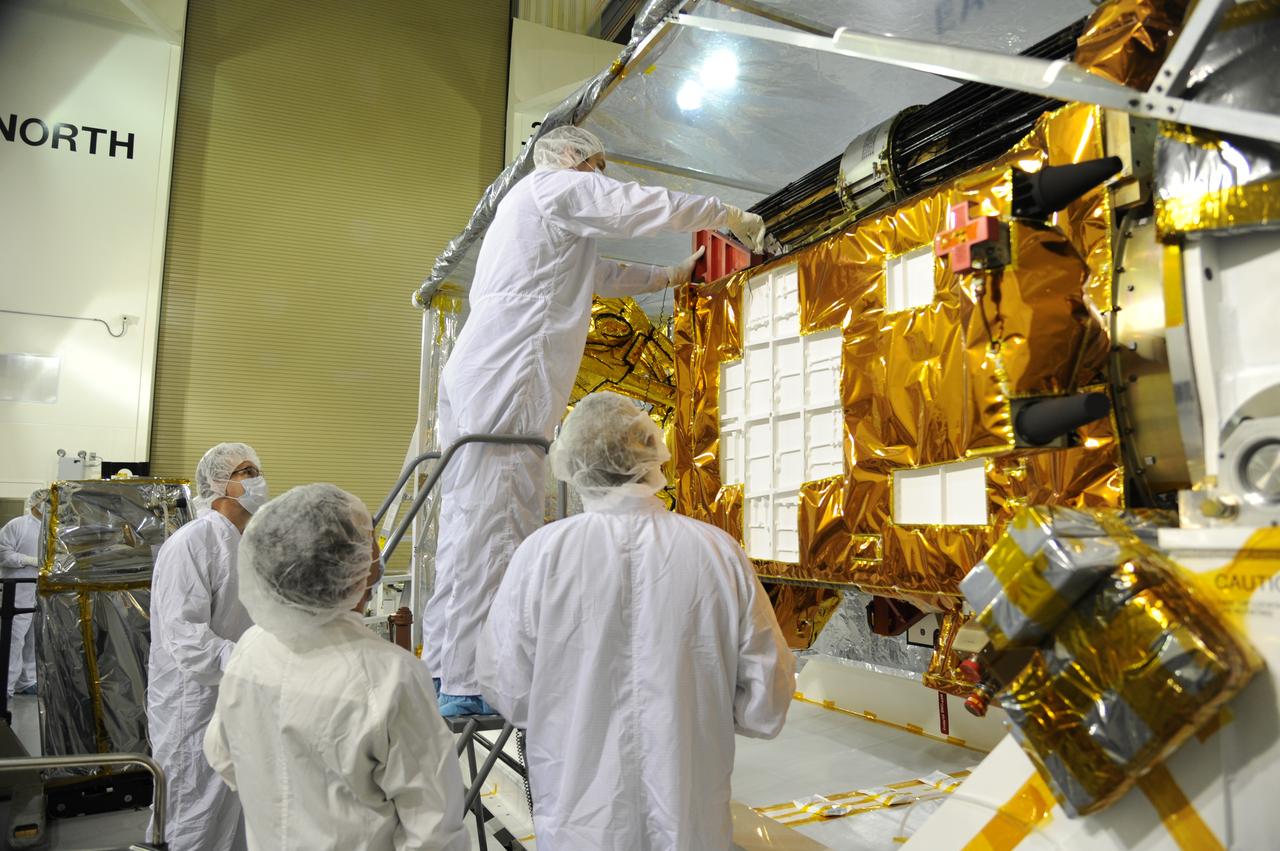

Workers prepare to inspect instrument and optics covers on NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during a post-shipment inspection. The spacecraft was delivered to the launch site today from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
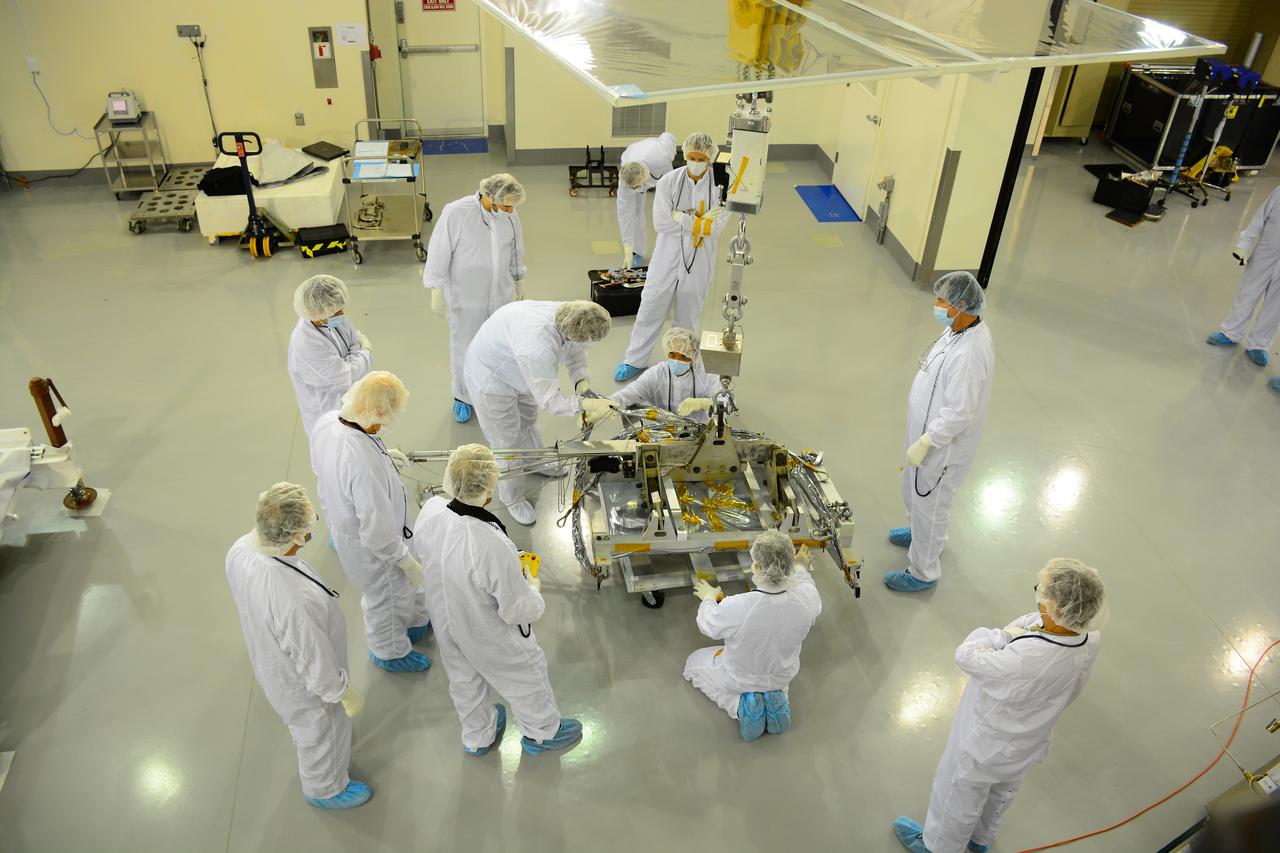

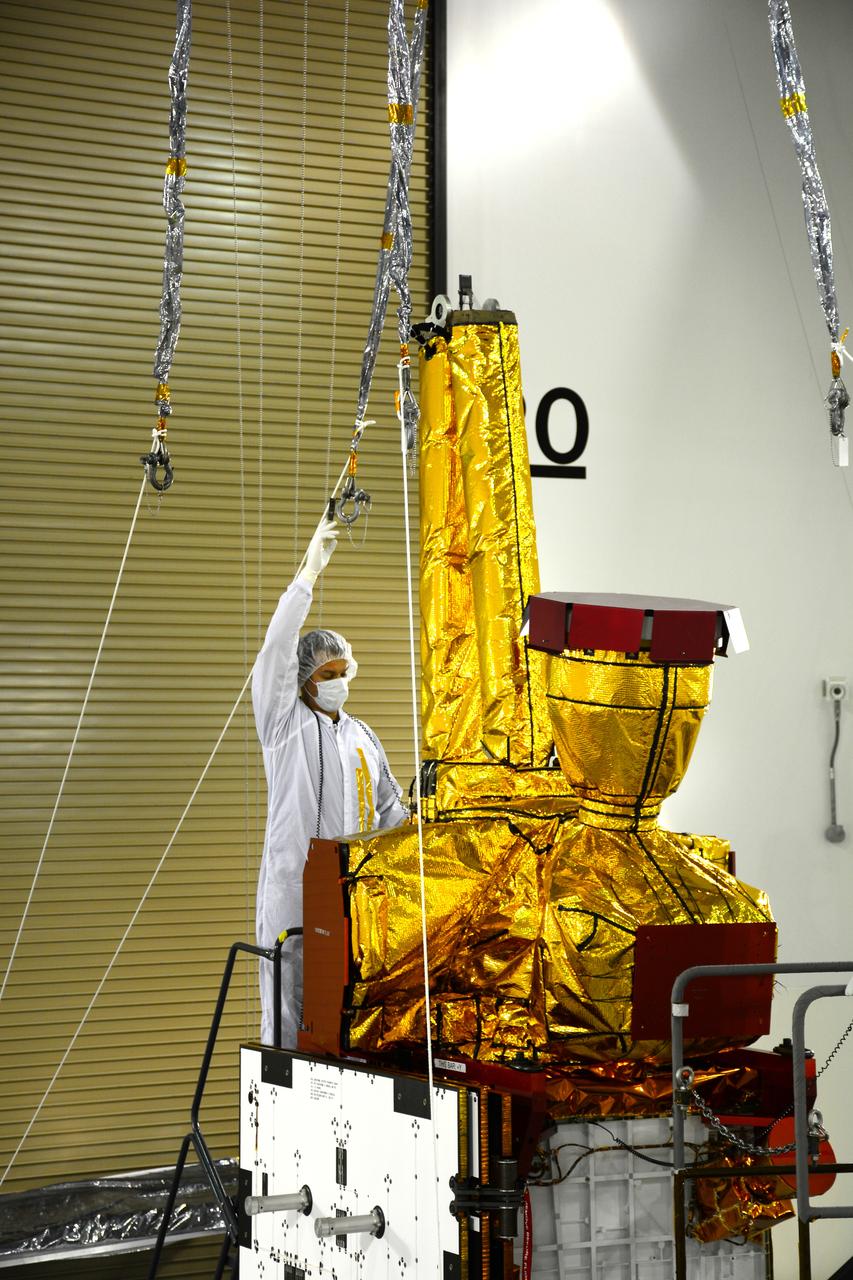
Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians prepare a component of NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft for a lift by a crane. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
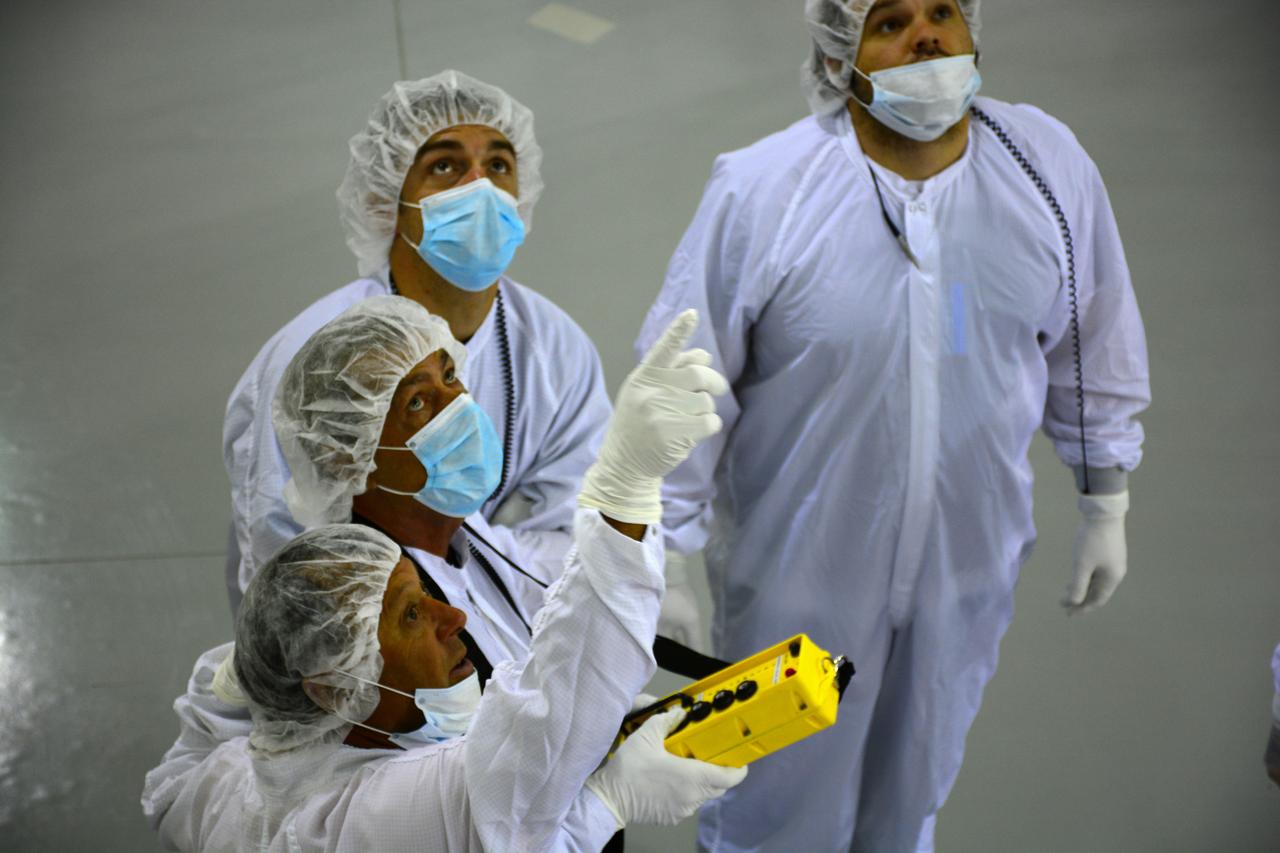

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians wearing protective garb, monitor operations as a crane lifts a component of NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians inspect NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
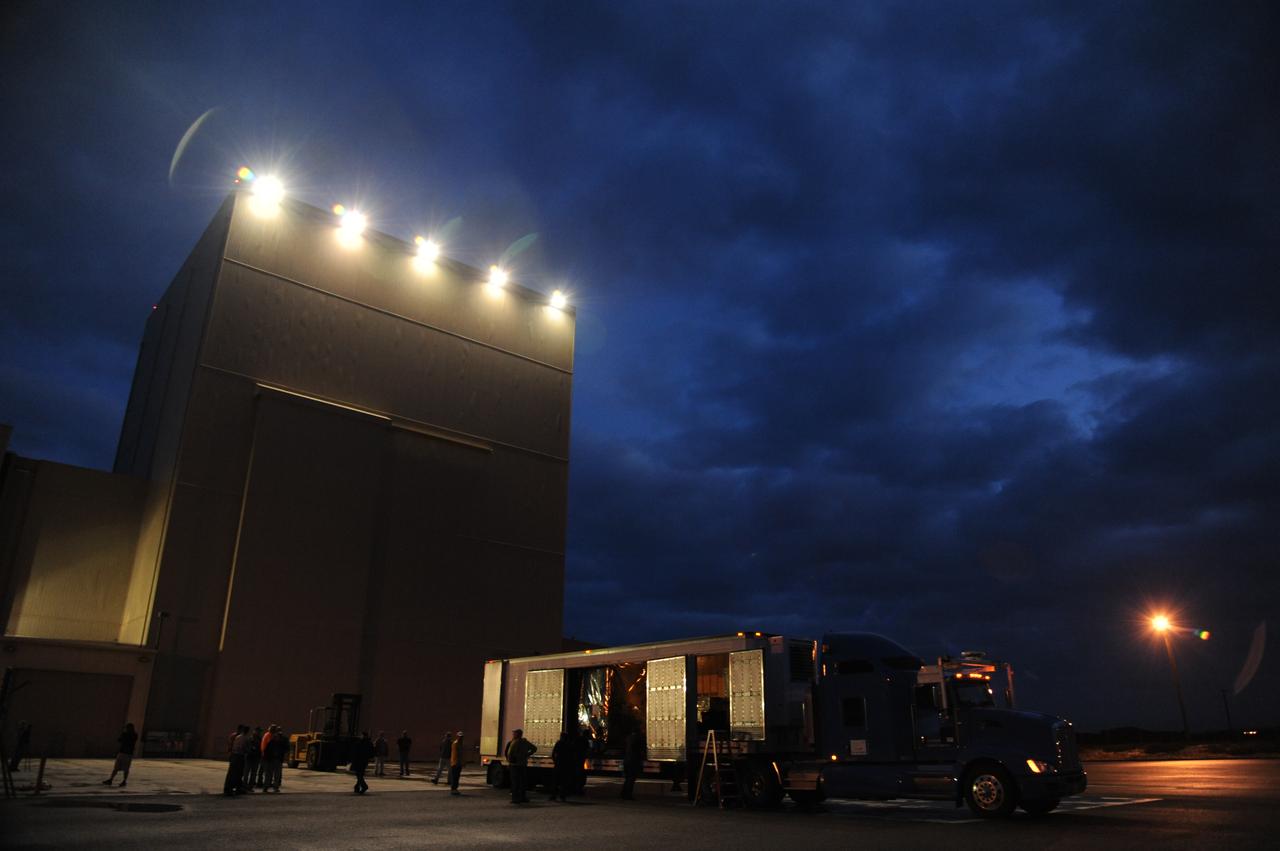

NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft is delivered by truck from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, to the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
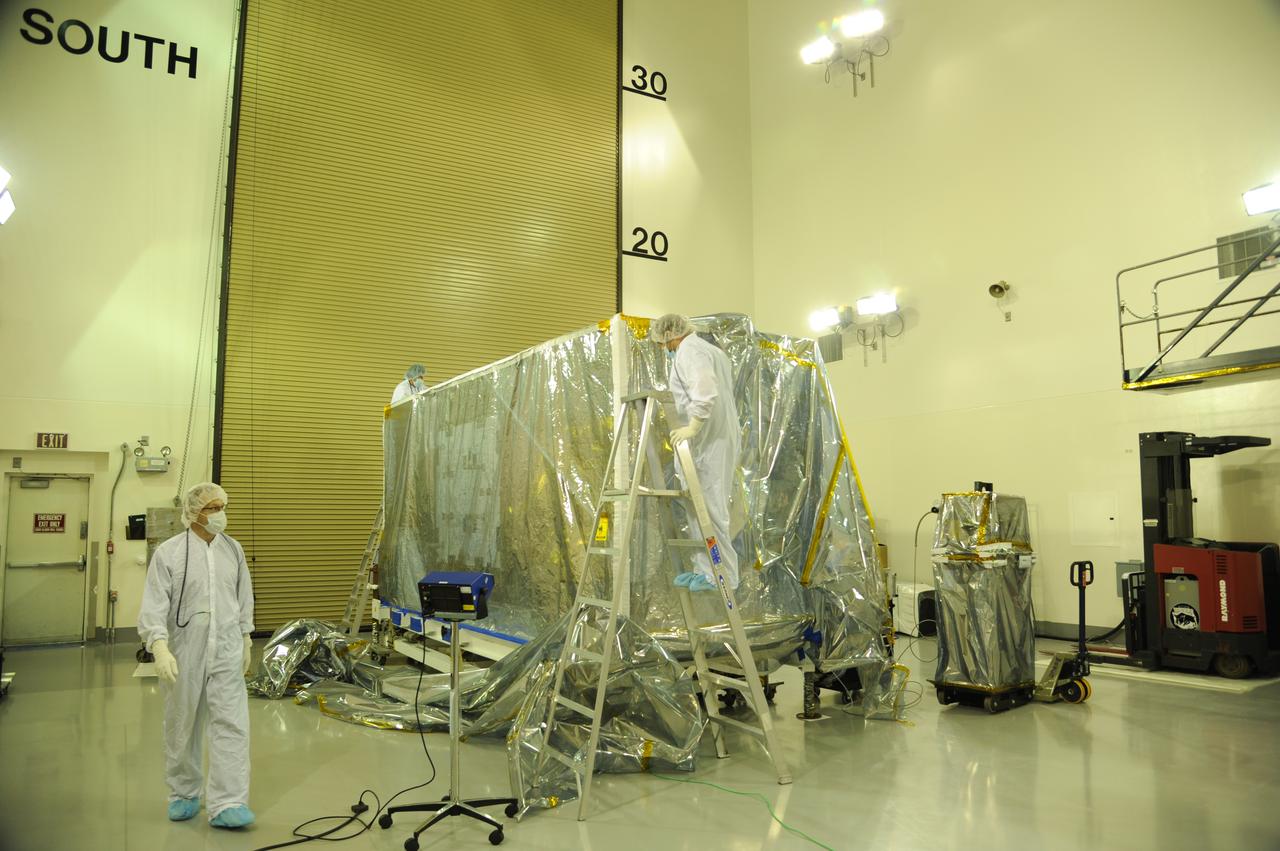

Preparations are underway to remove the protective covering from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during a post-shipment inspection. The covering protects the spacecraft from static-charge buildup and contamination. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

Operations are underway to weigh NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft in the clean room of the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The weighing of a spacecraft is standard procedure during prelaunch processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory that built the observatory and its radar instrument also is responsible for SMAP project management and mission operations. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
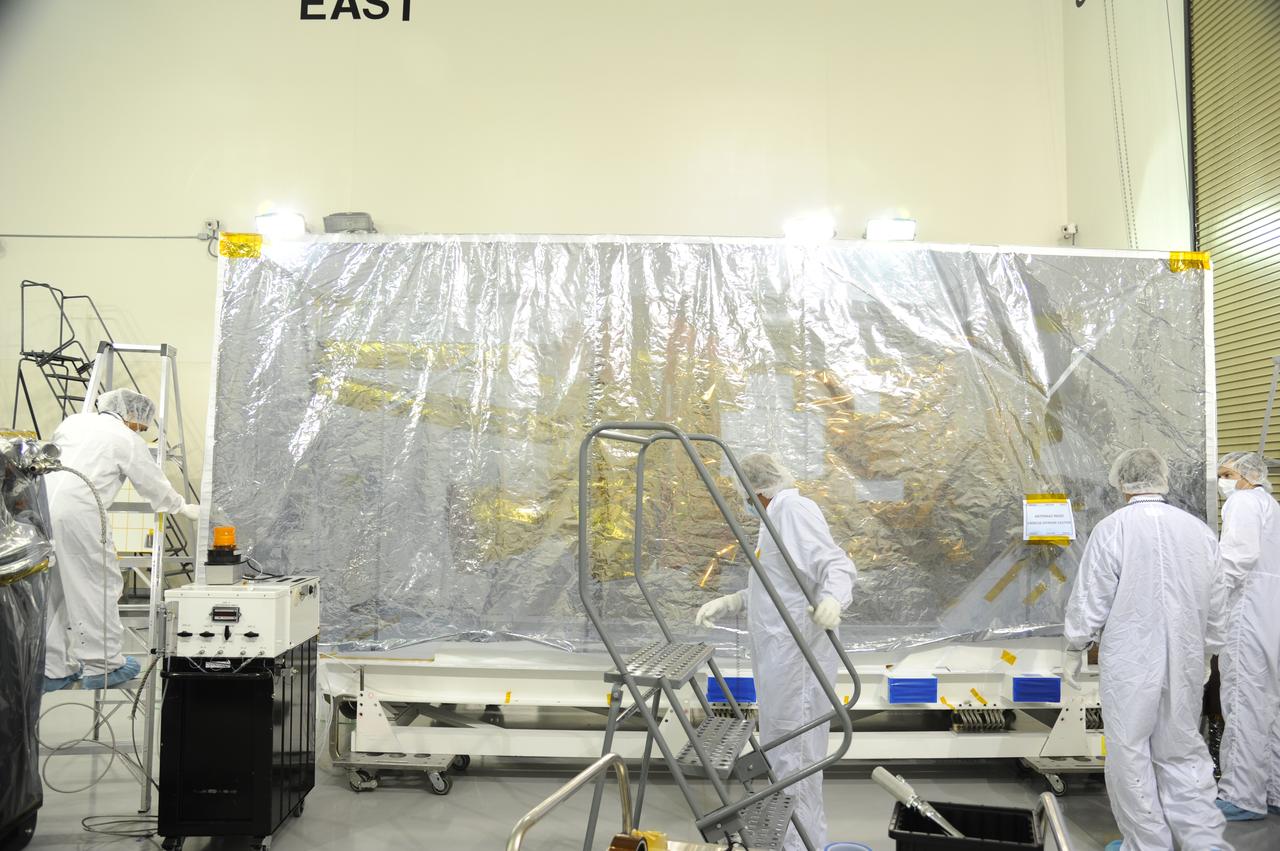

The protective covering has been replaced around NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft following the spacecraft's post-shipment inspection in the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The covering will protect the spacecraft from static-charge buildup and contamination while it awaits further processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
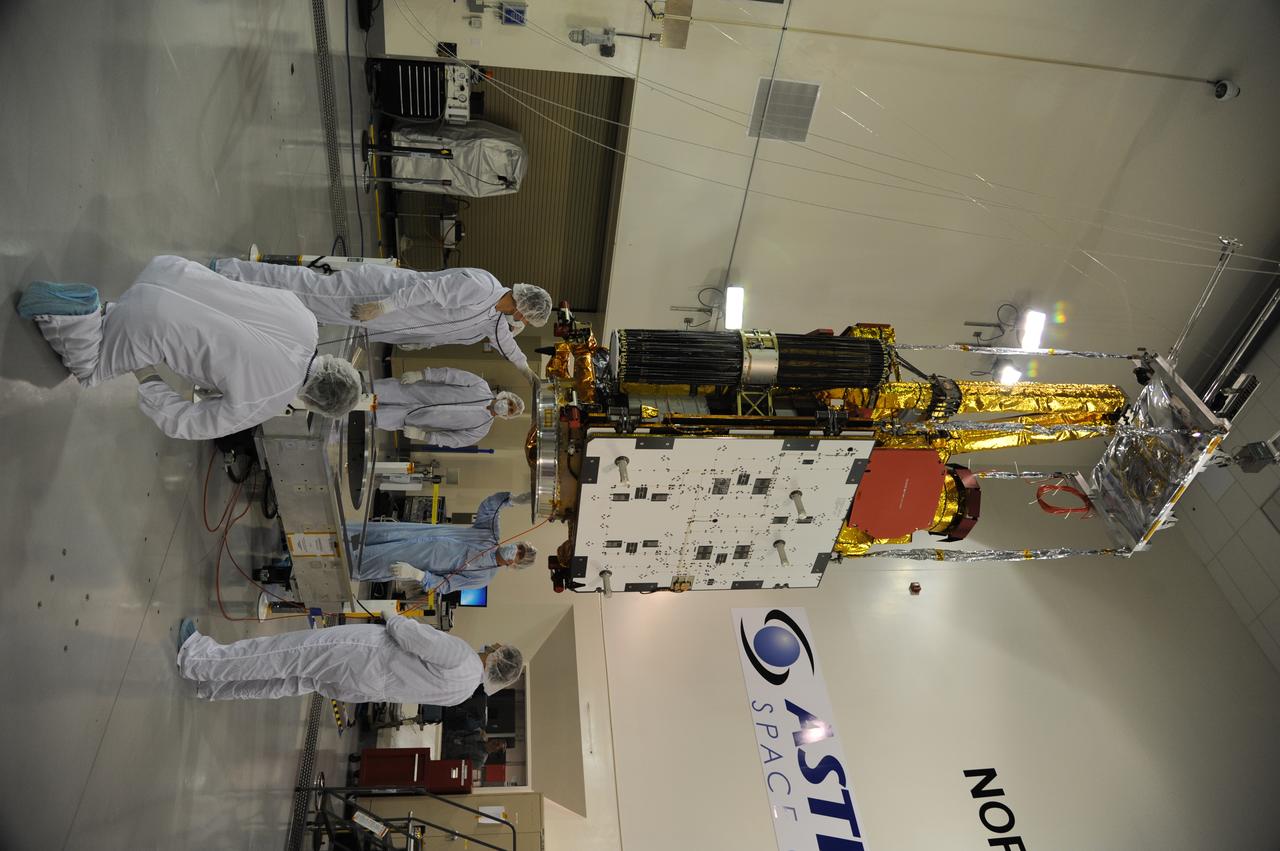

NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft is lifted from its workstand in the clean room of the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during operations to determine its weight. The weighing of a spacecraft is standard procedure during prelaunch processing. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory that built the observatory and its radar instrument also is responsible for SMAP project management and mission operations. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
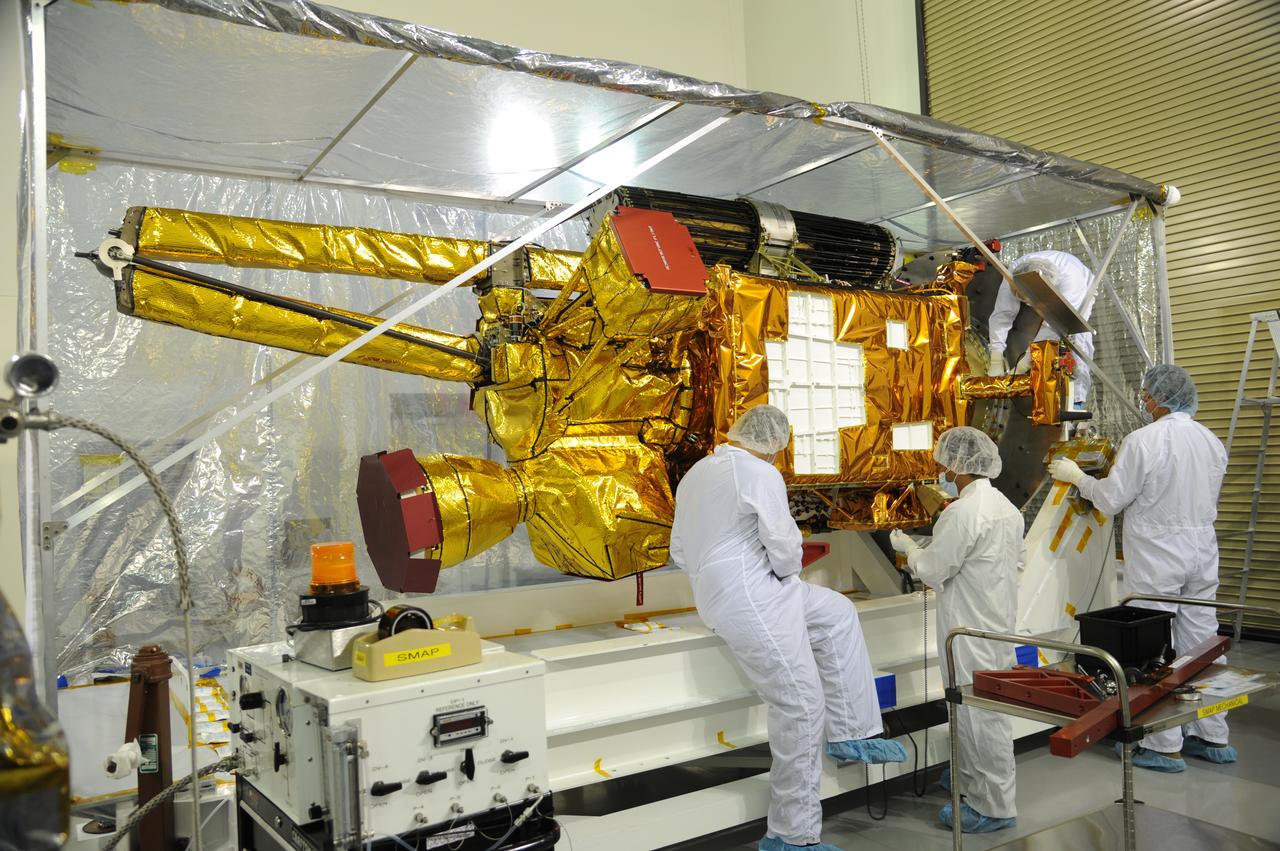

Workers inspect NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft after its protective covering is removed in the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during a post-shipment inspection. The covering protected the spacecraft from static-charge buildup and contamination while it was in transit from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
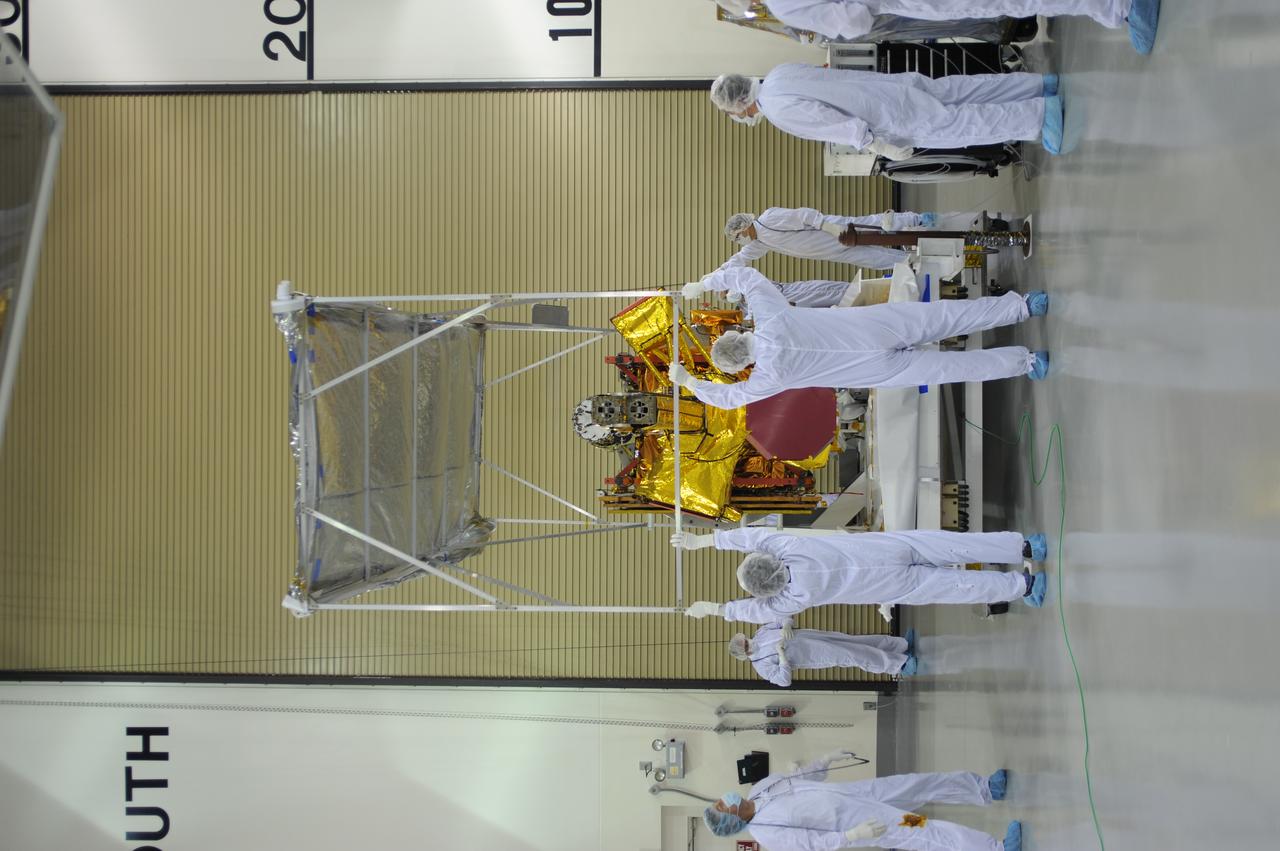

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians remove a protective covering from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
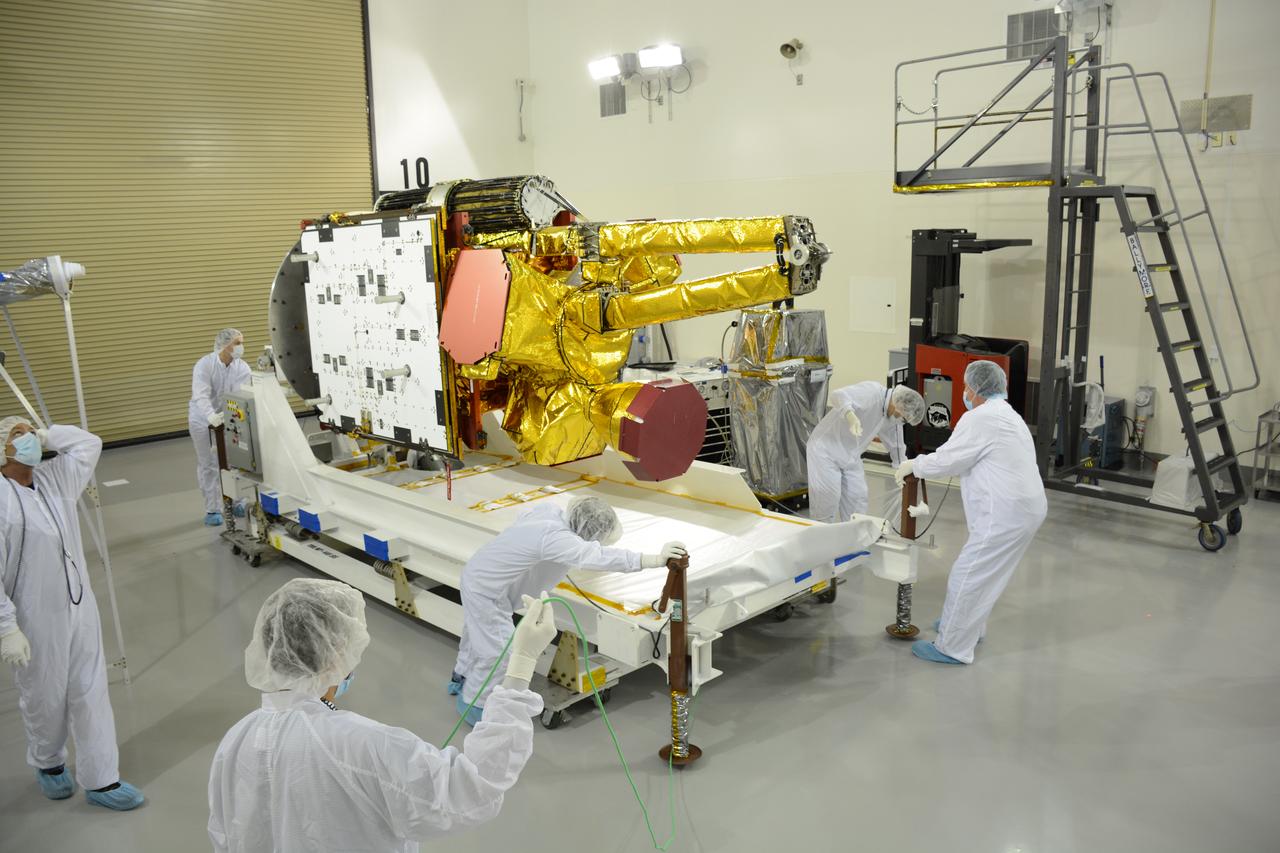

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians begin processing of NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
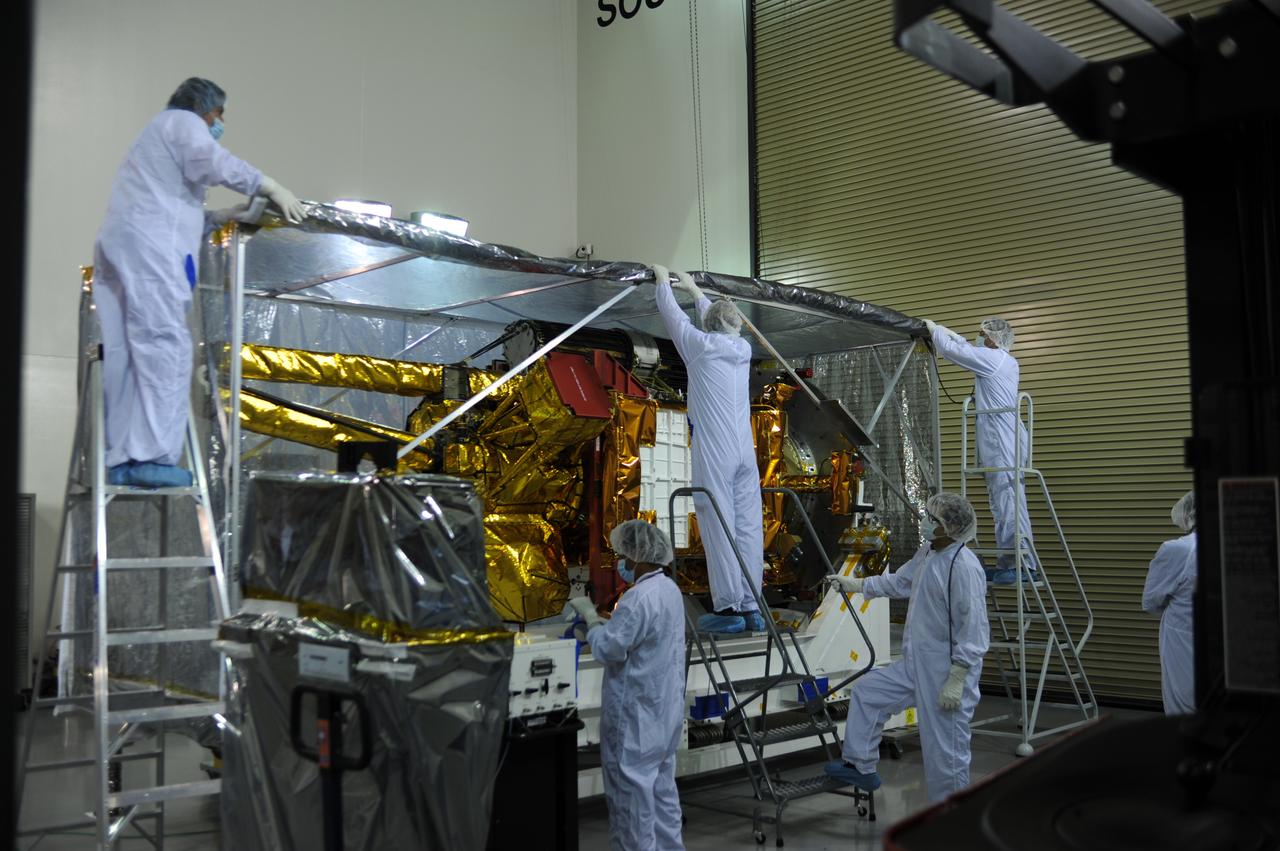

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians remove a protective covering from NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.

NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft is delivered by truck to the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
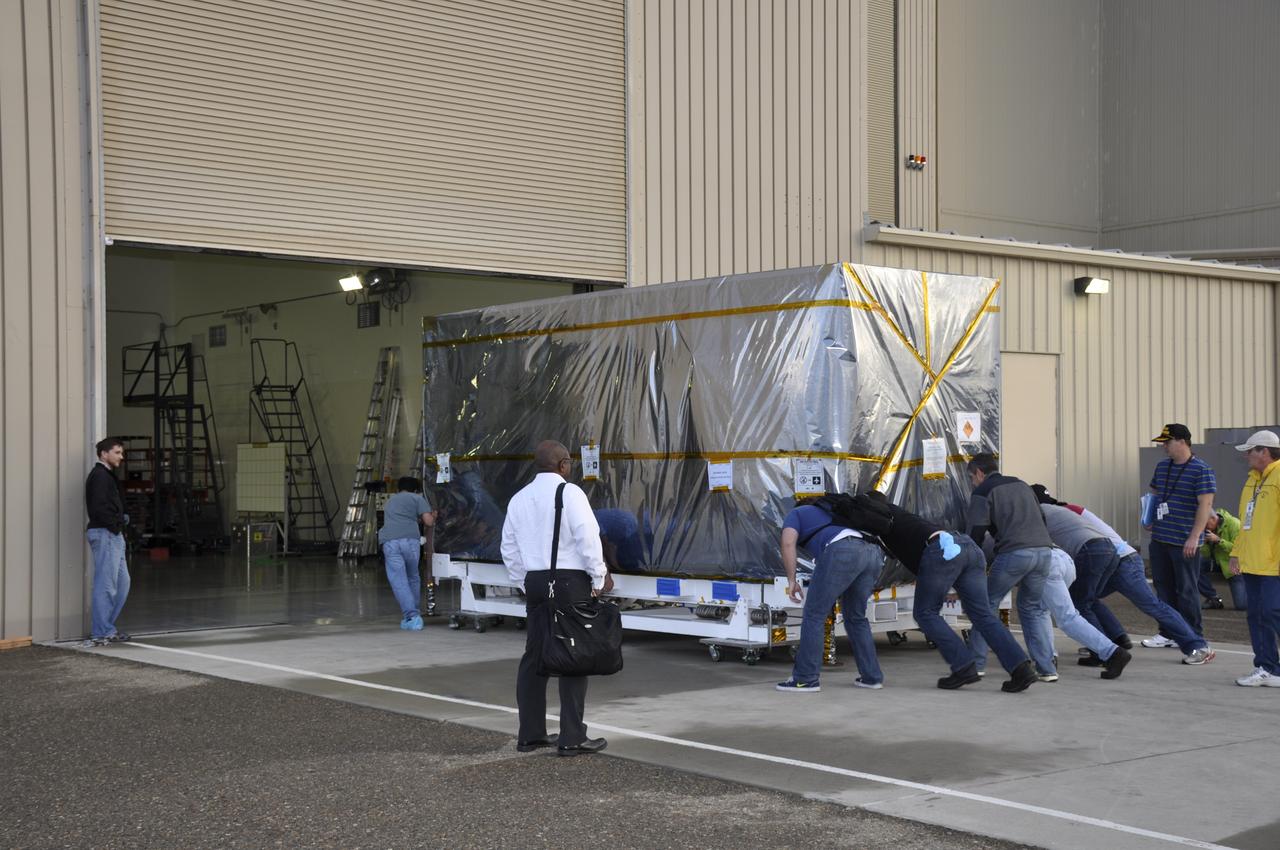

Workers push the pallet supporting the transportation container protecting NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft into the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
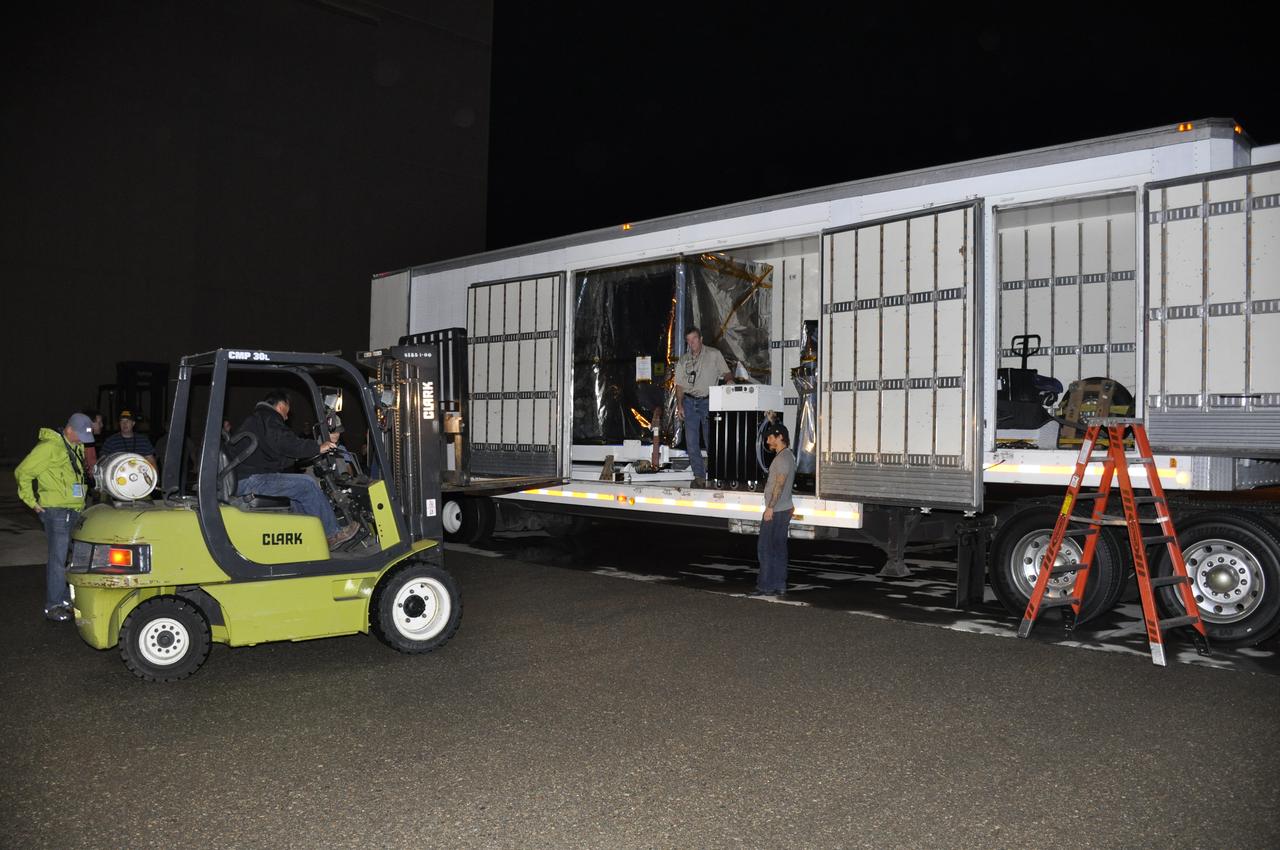

A forklift is moved into place to assist with the offloading of NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft from the truck that delivered it from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, to the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.
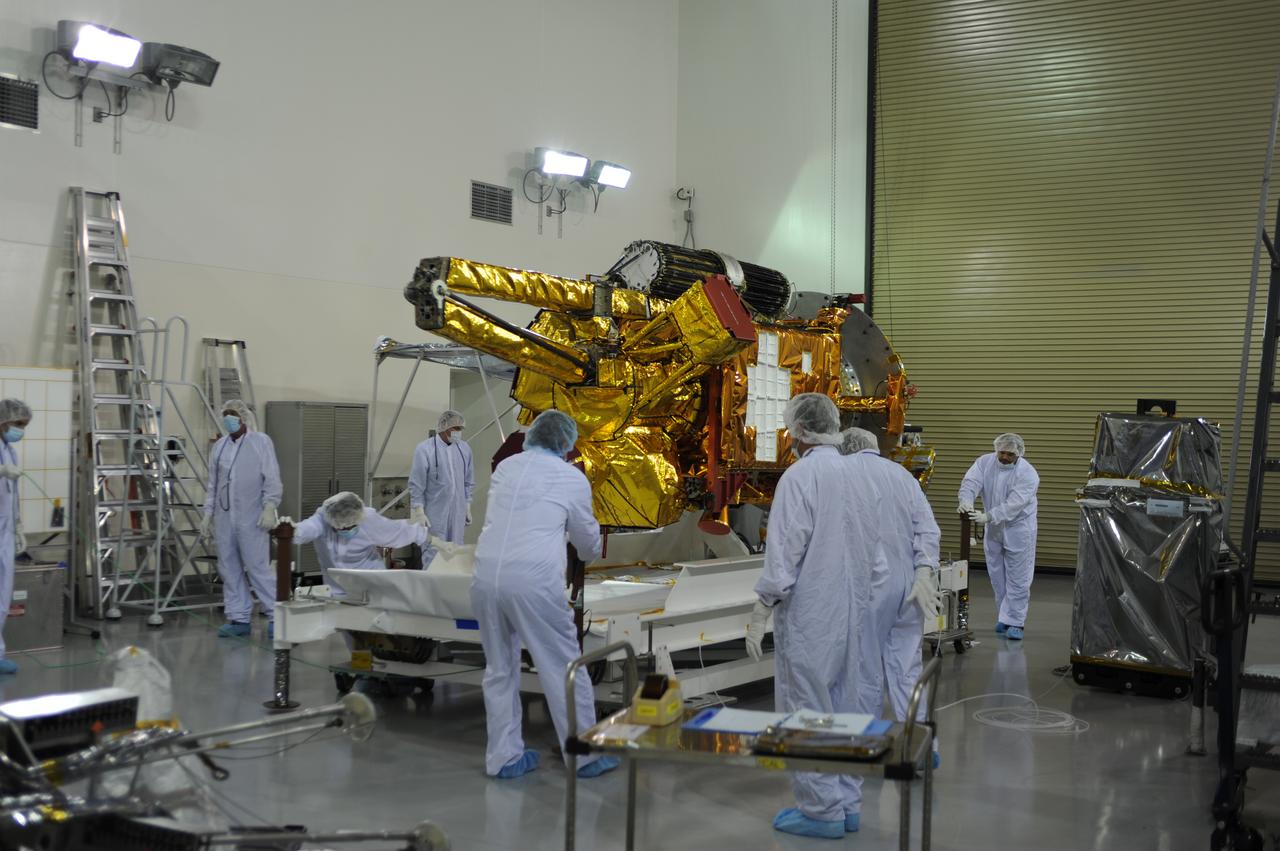

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, engineers and technicians begin processing of NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive, or SMAP, spacecraft. SMAP will launch on a Delta II 7320 configuration vehicle featuring a United Launch Alliance first stage booster powered by an Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-27A main engine and three Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, strap-on solid rocket motors. Once on station in Earth orbit, SMAP will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. SMAP data also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch from Space Launch Complex 2 is targeted for Jan. 29, 2015.