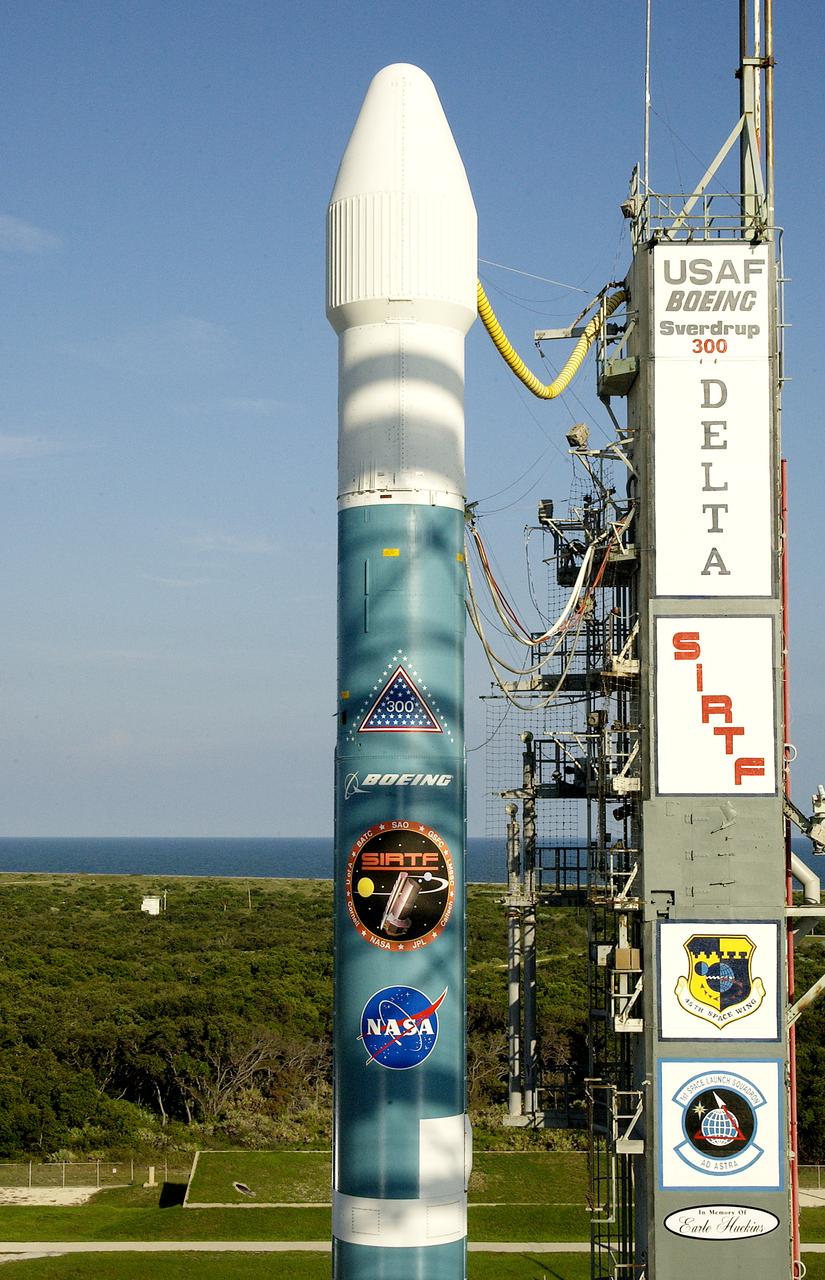
The mobile service tower is rolled back at Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, to reveal NASA's Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) ready for launch aboard a Delta II Heavy launch vehicle. Liftoff is scheduled for Aug. 25 at 1:35:39 a.m. EDT. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Consisting of a 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF will be the largest infrared telescope ever launched into space. It is the fourth and final element in NASA’s family of orbiting “Great Observatories.” Its highly sensitive instruments will give a unique view of the Universe and peer into regions of space that are hidden from optical telescopes.
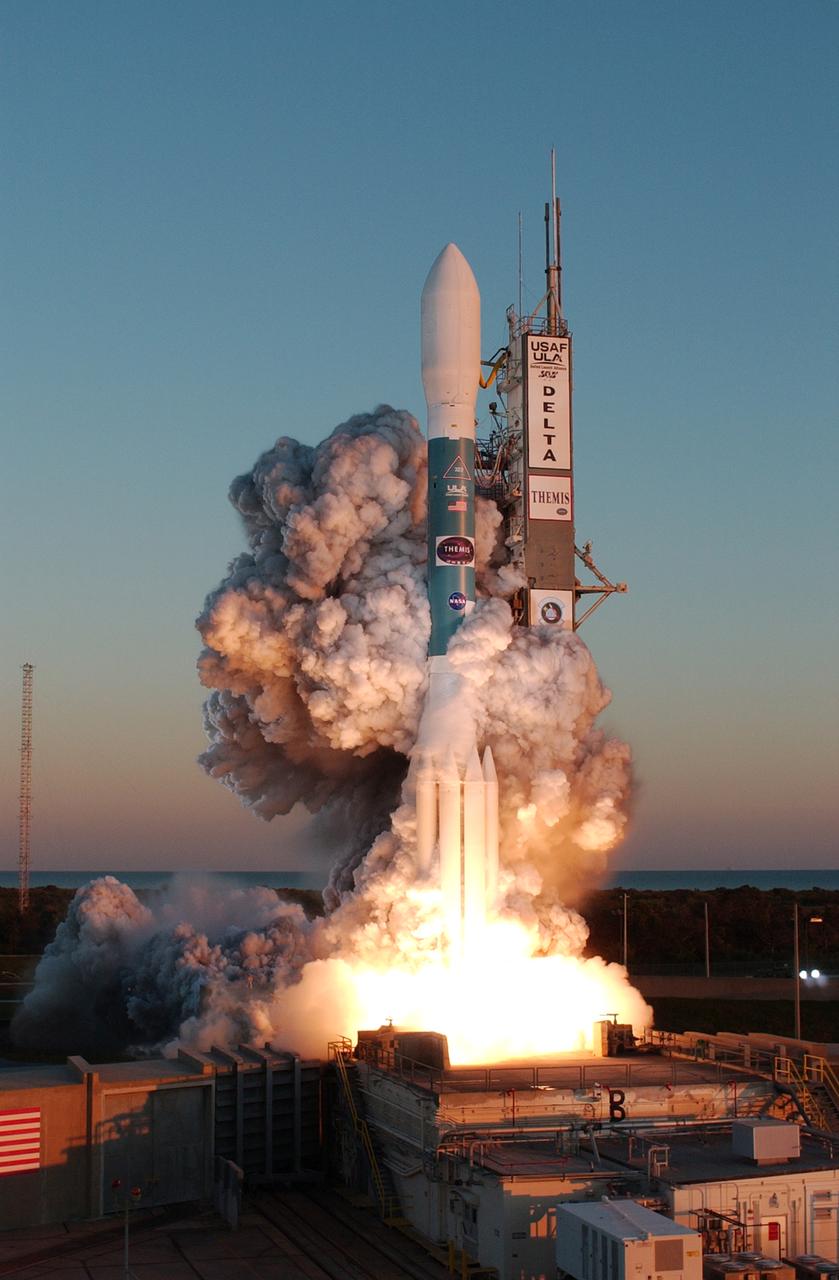

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, clouds of smoke form around the Delta II rocket with NASA's THEMIS spacecraft aboard as it blasts off Pad 17-B at 6:01 p.m. EST. THEMIS, an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms, consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA has ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color.
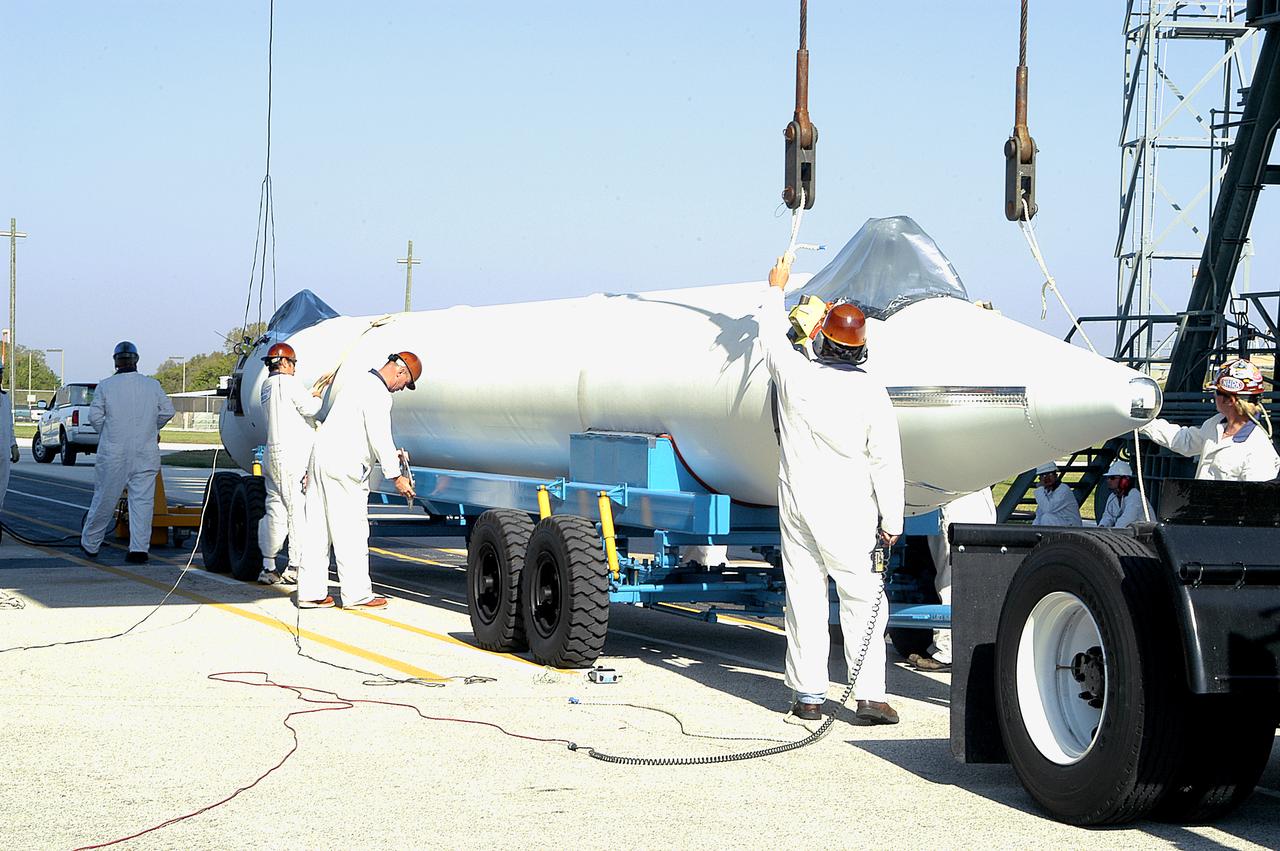

A booster rocket arrives at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. It is one of nine solid rocket boosters being erected and mated to the Delta II rocket for launch of the Space Infrared Telescope Facility. The second stage will later be hoisted atop the first stage. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is scheduled for launch April 15 at 4:34:07 a.m. EDT.
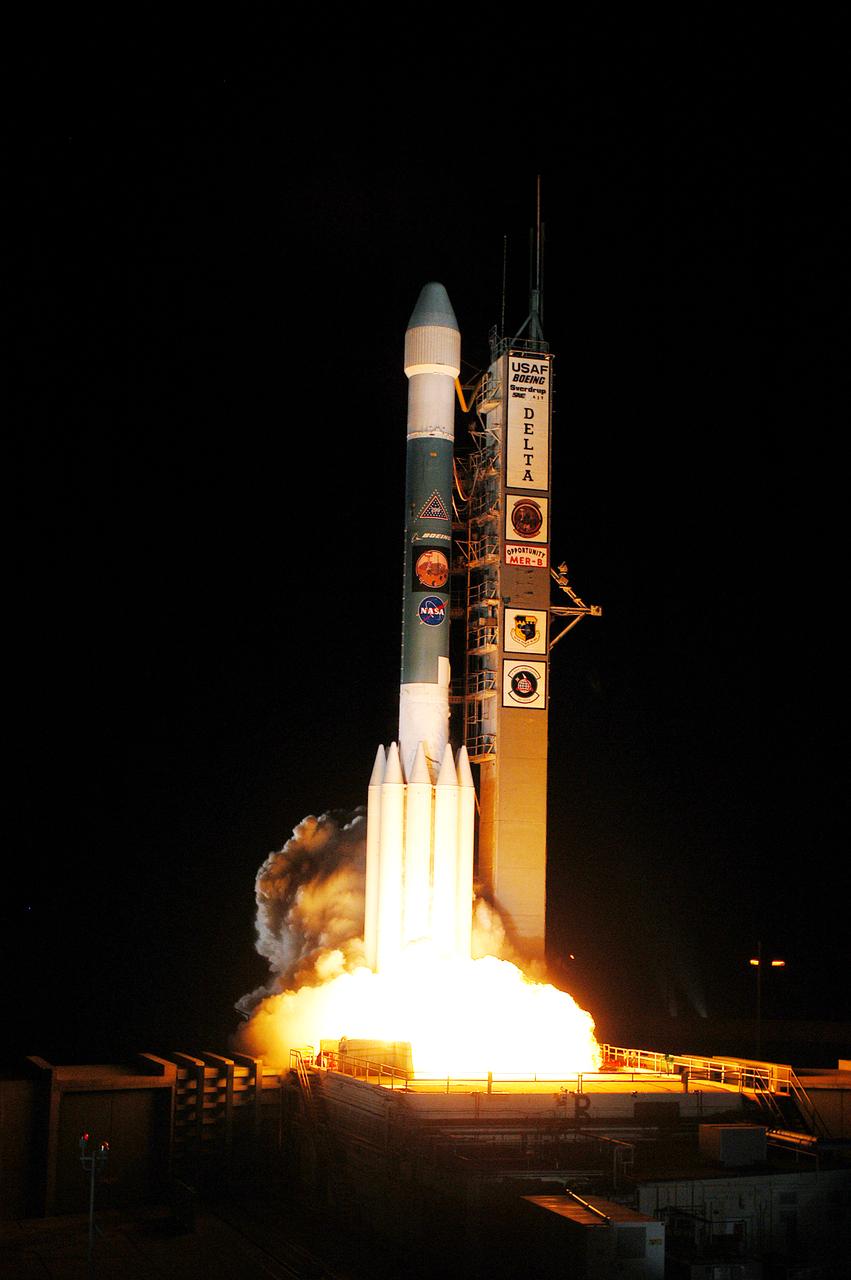

On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II Heavy launch vehicle carrying the rover "Opportunity" for the second Mars Exploration Rover mission launches at 11:18:15 p.m. EDT. Opportunity will reach Mars on Jan. 25, 2004. Together the two MER rovers, Spirit (launched June 10) and Opportunity, seek to determine the history of climate and water at two sites on Mars where conditions may once have been favorable to life. The rovers are identical. They will navigate themselves around obstacles as they drive across the Martian surface, traveling up to about 130 feet each Martian day. Each rover carries five scientific instruments including a panoramic camera and microscope, plus a rock abrasion tool that will grind away the outer surfaces of rocks to expose their interiors for examination. Each rover’s prime mission is planned to last three months on Mars.
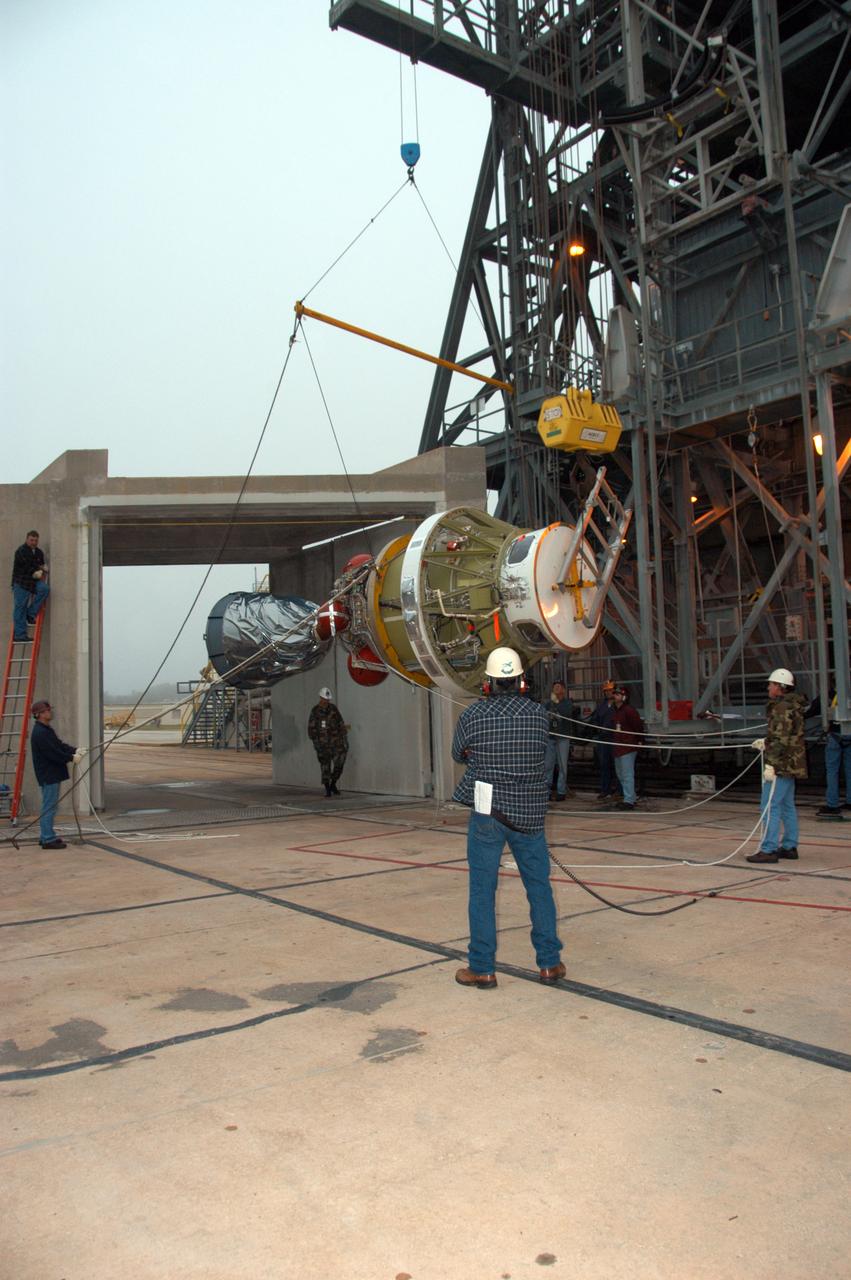

On Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers stand by while an overhead crane lifts the Delta II second stage to a vertical position. The second stage will be lifted into the mobile service tower and mated with the first stage already in place. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
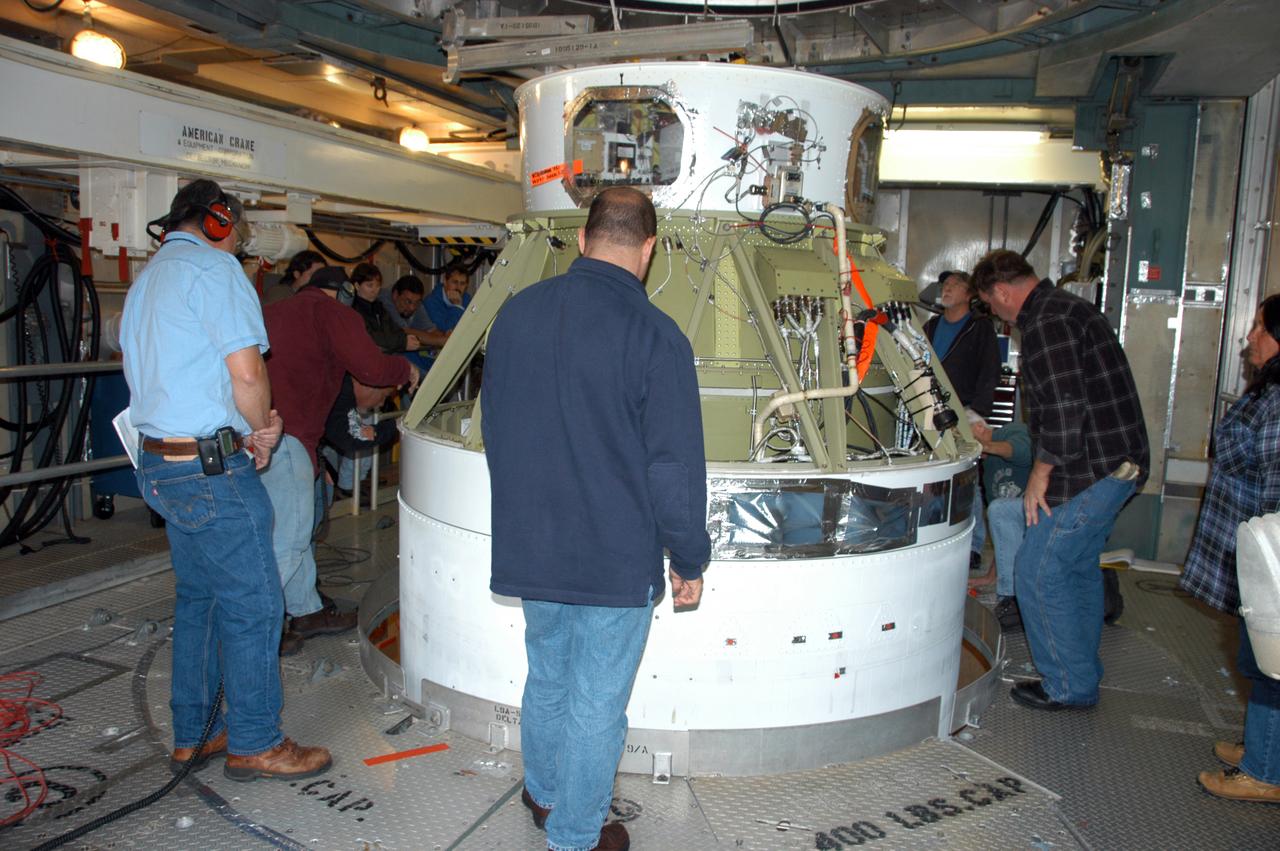

Inside the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II second stage is mated with the first stage. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

The first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket leaves for Launch Pad 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft, consisting of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. After the first stage is in the mobile service tower on the pad, nine solid rocket boosters will be placed around the base of the first stage and attached in sets of three. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.
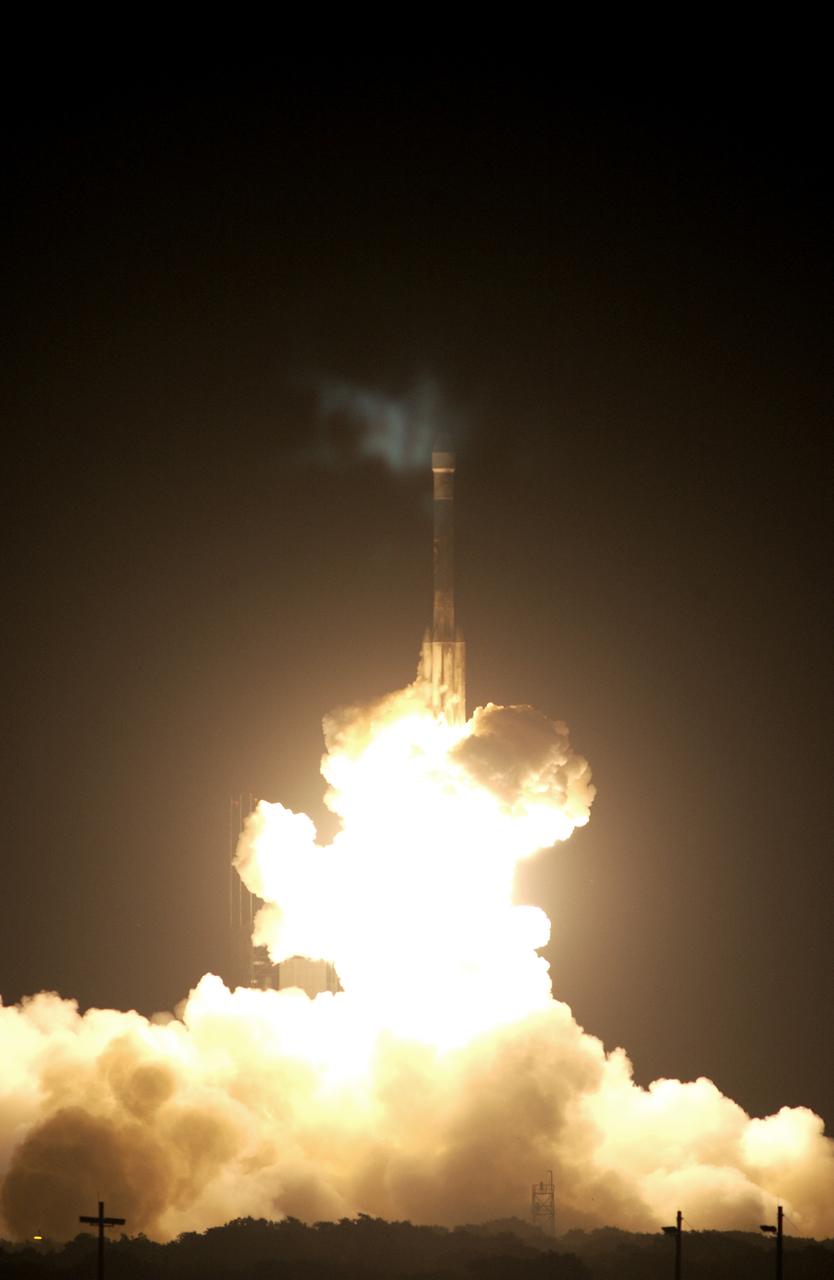

On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II Heavy launch vehicle carrying the rover "Opportunity" for the second Mars Exploration Rover mission launches at 11:18:15 p.m. EDT. Opportunity will reach Mars on Jan. 25, 2004. Together the two MER rovers, Spirit (launched June 10) and Opportunity, seek to determine the history of climate and water at two sites on Mars where conditions may once have been favorable to life. The rovers are identical. They will navigate themselves around obstacles as they drive across the Martian surface, traveling up to about 130 feet each Martian day. Each rover carries five scientific instruments including a panoramic camera and microscope, plus a rock abrasion tool that will grind away the outer surfaces of rocks to expose their interiors for examination. Each rover’s prime mission is planned to last three months on Mars.
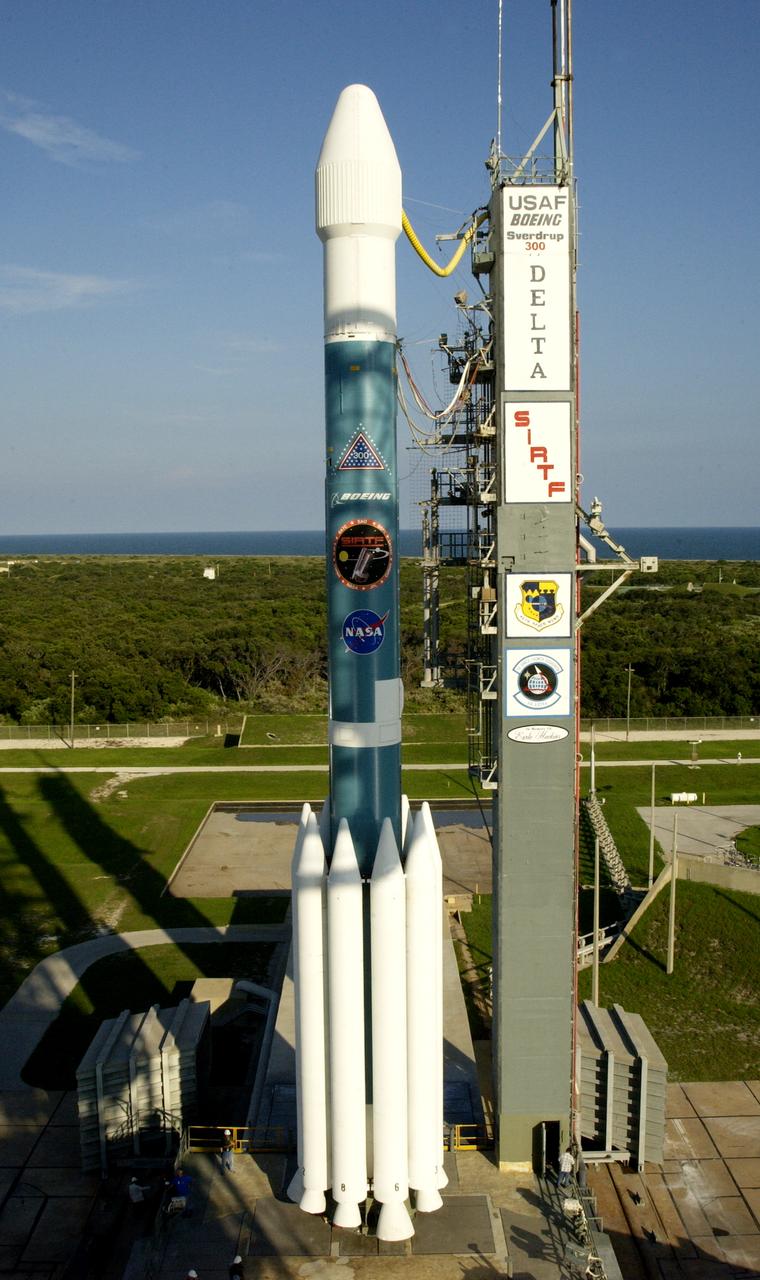

The mobile service tower is rolled back at Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, to reveal NASA's Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) ready for launch aboard a Delta II Heavy launch vehicle. Liftoff is scheduled for Aug. 25 at 1:35:39 a.m. EDT. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Consisting of a 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF will be the largest infrared telescope ever launched into space. It is the fourth and final element in NASA’s family of orbiting “Great Observatories.” Its highly sensitive instruments will give a unique view of the Universe and peer into regions of space that are hidden from optical telescopes.
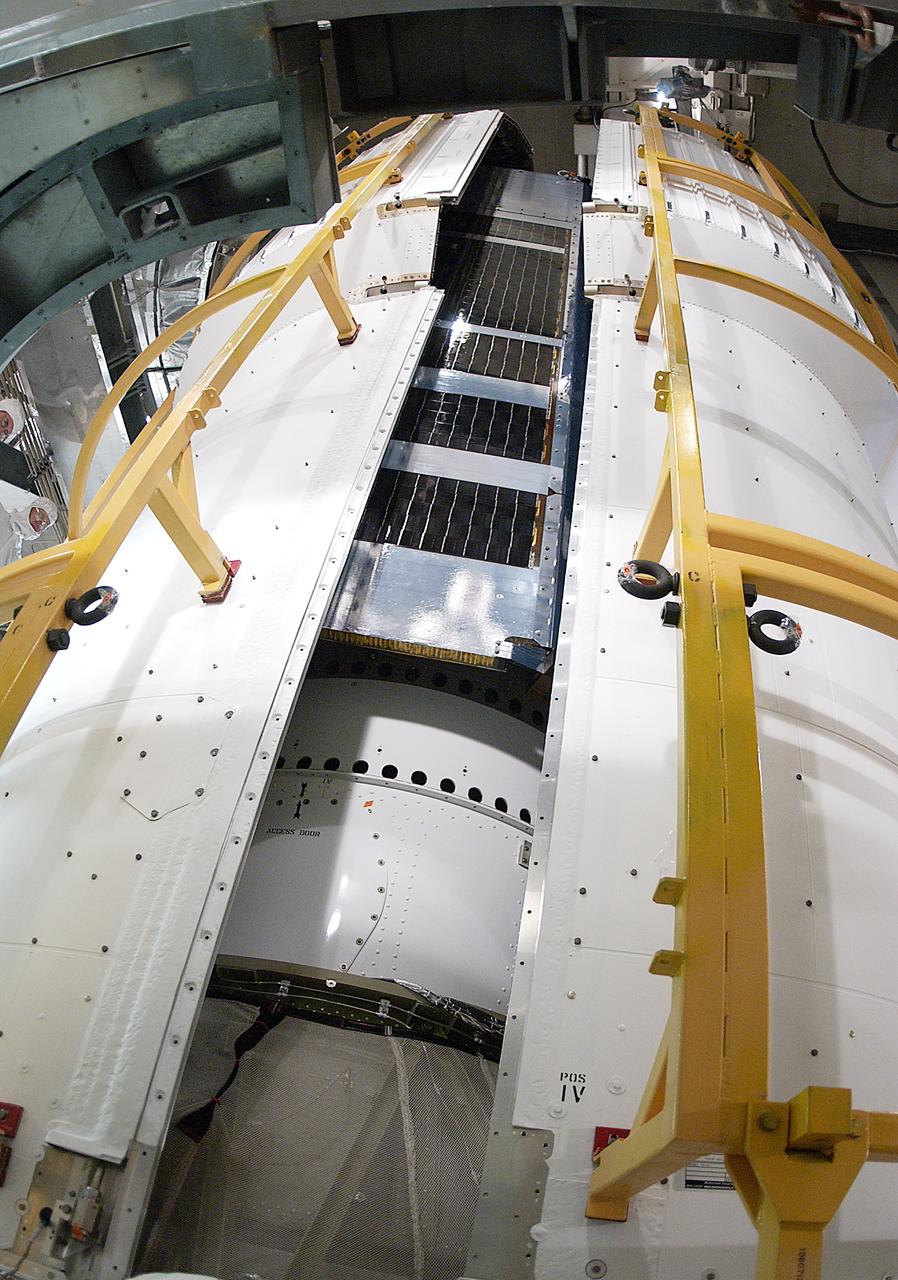

The two halves of the fairing move closer together around the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF). SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch April 18 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
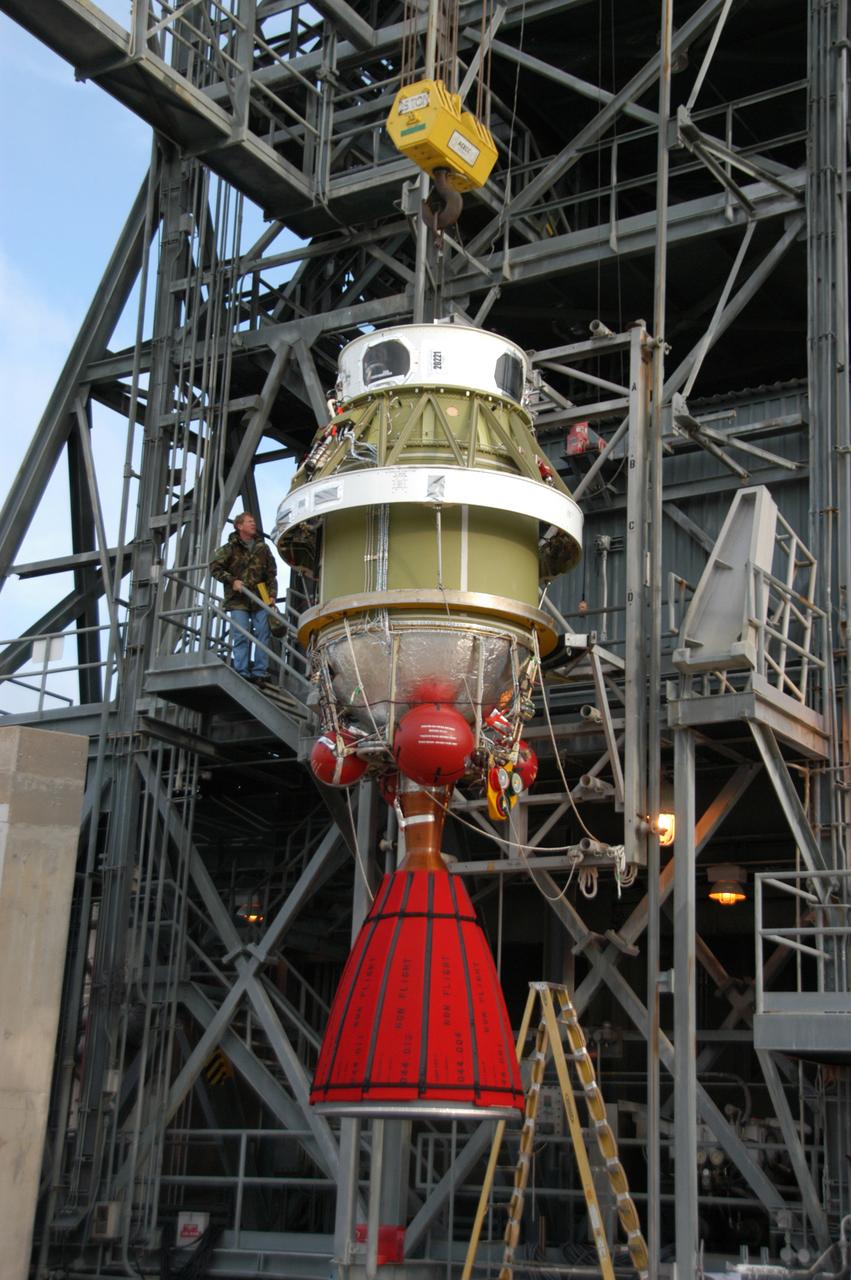

On Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II second stage is being lifted alongside the mobile service tower. Once inside, it will be mated with the first stage already in place. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is raised off its transporter to a vertical position. The rocket will then be lifted into the mobile service tower. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft, consisting of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. After the first stage is in the mobile service tower on the pad, nine solid rocket boosters will be placed around the base of the first stage and attached in sets of three. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.
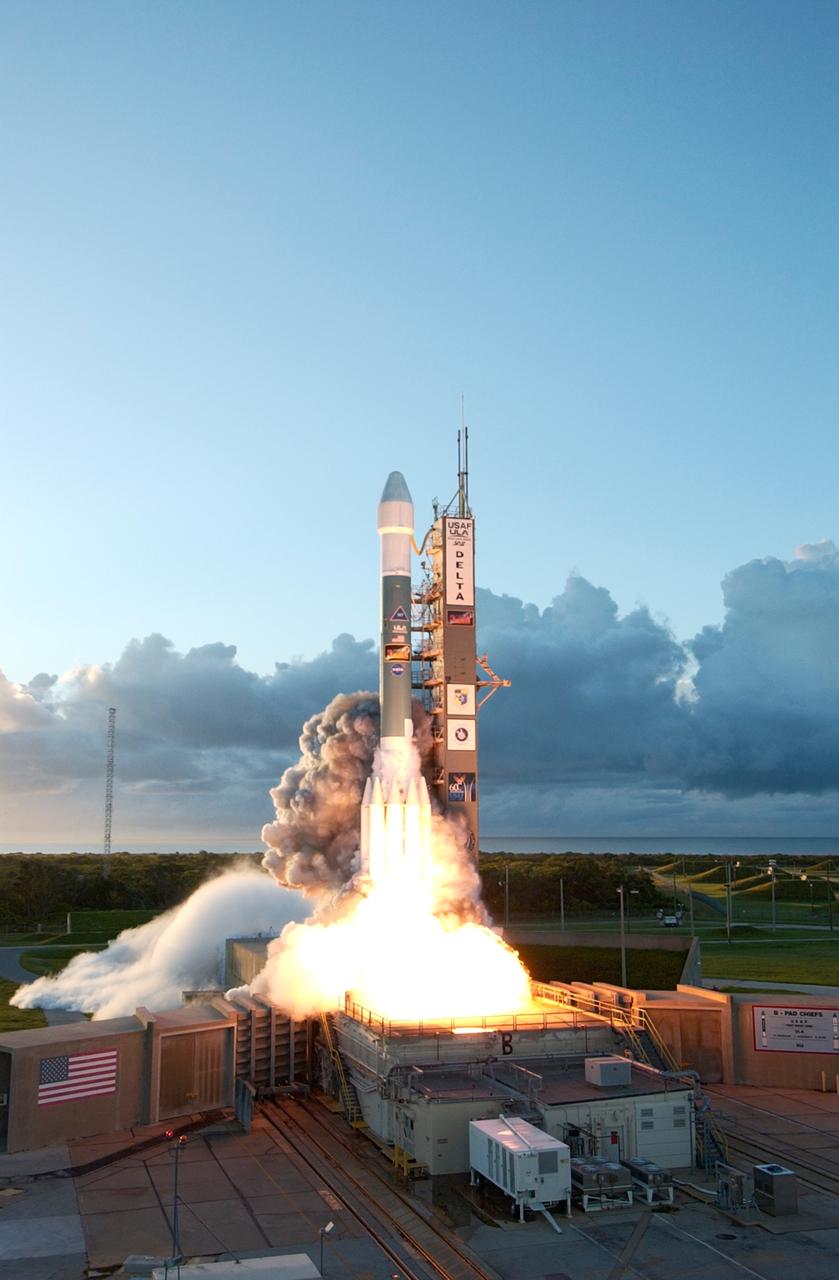

Against a backdrop of clouds on the horizon, the Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Dawn spacecraft rises from the smoke and fire on the launch pad to begin its 1.7-billion-mile journey through the inner solar system to study a pair of asteroids. Liftoff was at 7:34 a.m. EDT from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Dawn is the ninth mission in NASA's Discovery Program. The spacecraft will be the first to orbit two planetary bodies, asteroid Vesta and dwarf planet Ceres, during a single mission. Vesta and Ceres lie in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. It is also NASA's first purely scientific mission powered by three solar electric ion propulsion engines.
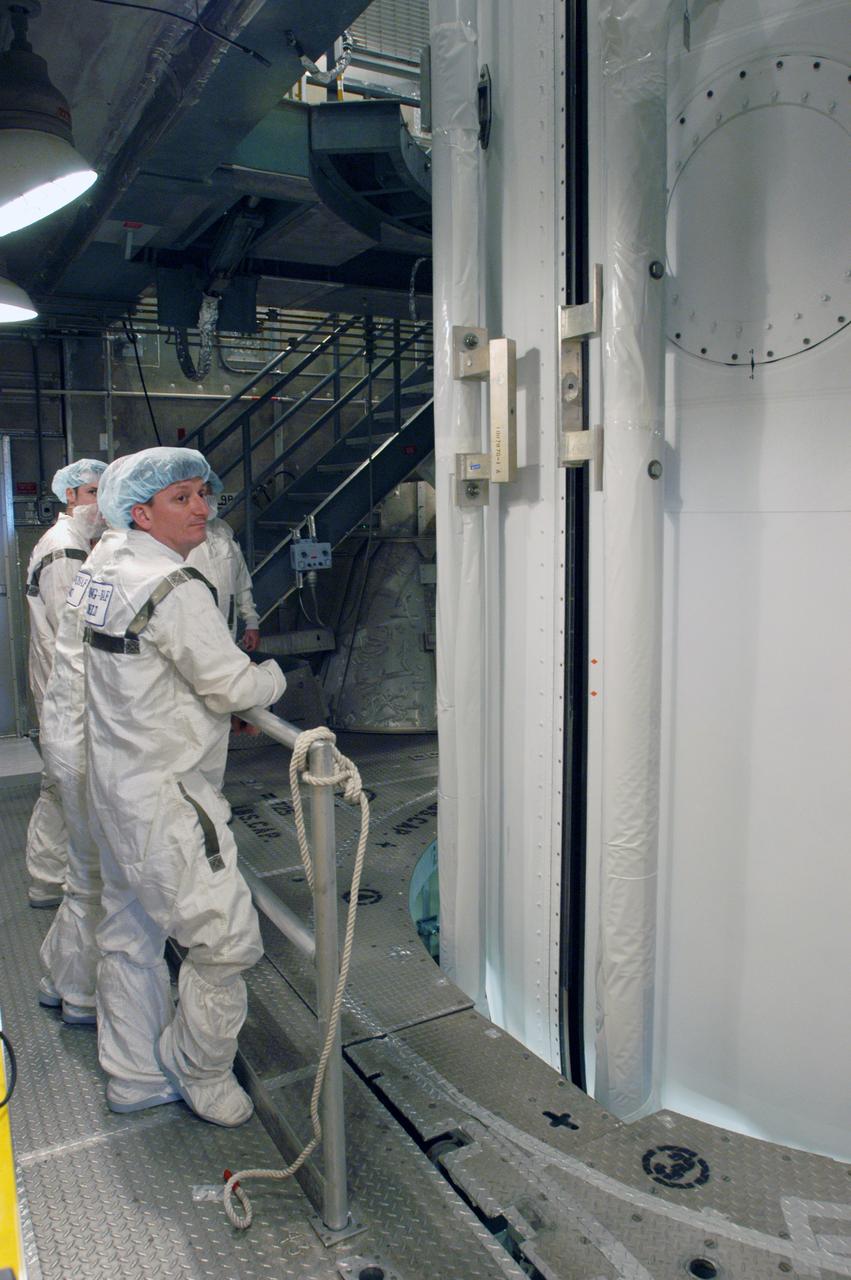

In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the two fairing segments come together around the THEMIS spacecraft. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. THEMIS is an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms. THEMIS consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the tantalizing mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color. Launch of THEMIS is scheduled for Feb. 15 aboard a Delta II rocket, with the launch service being conducted by the United Launch Alliance.
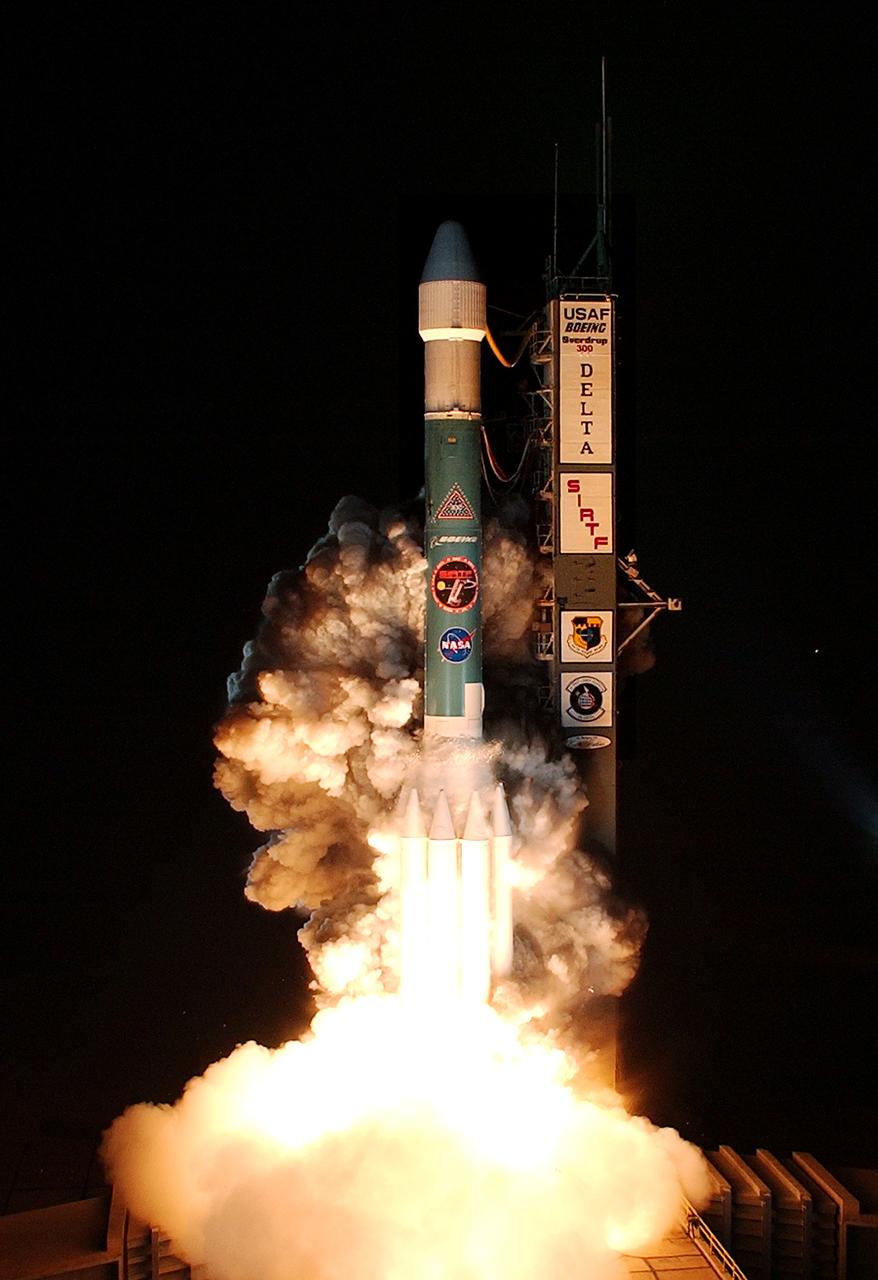

NASA's Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) lifts off from Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on Aug. 25 at 1:35:39 a.m. EDT. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Consisting of a 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF will be the largest infrared telescope ever launched into space. It is the fourth and final element in NASA’s family of orbiting “Great Observatories.” Its highly sensitive instruments will give a unique view of the Universe and peer into regions of space that are hidden from optical telescopes.
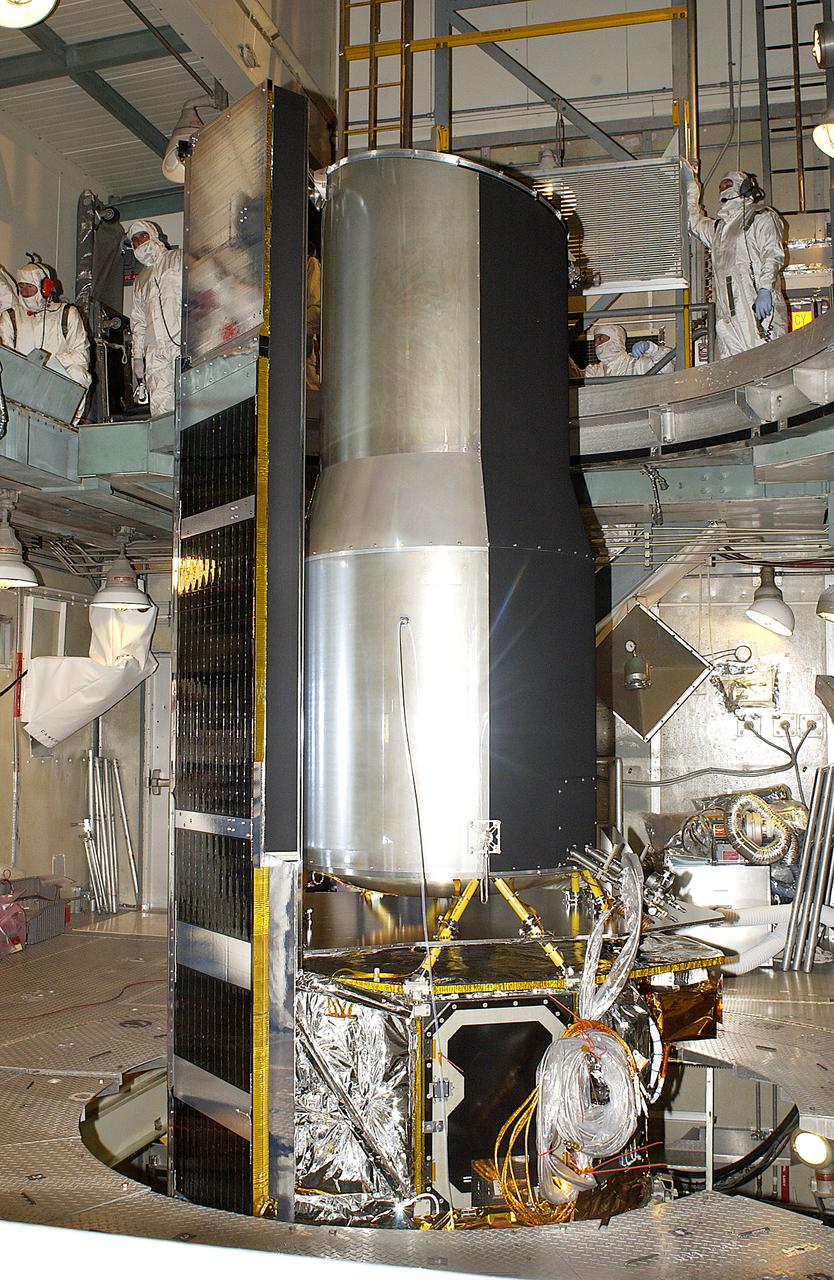

In the launch tower on Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) is ready for encapsulation. A fairing will be installed around the spacecraft to protect it during launch. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch April 18 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
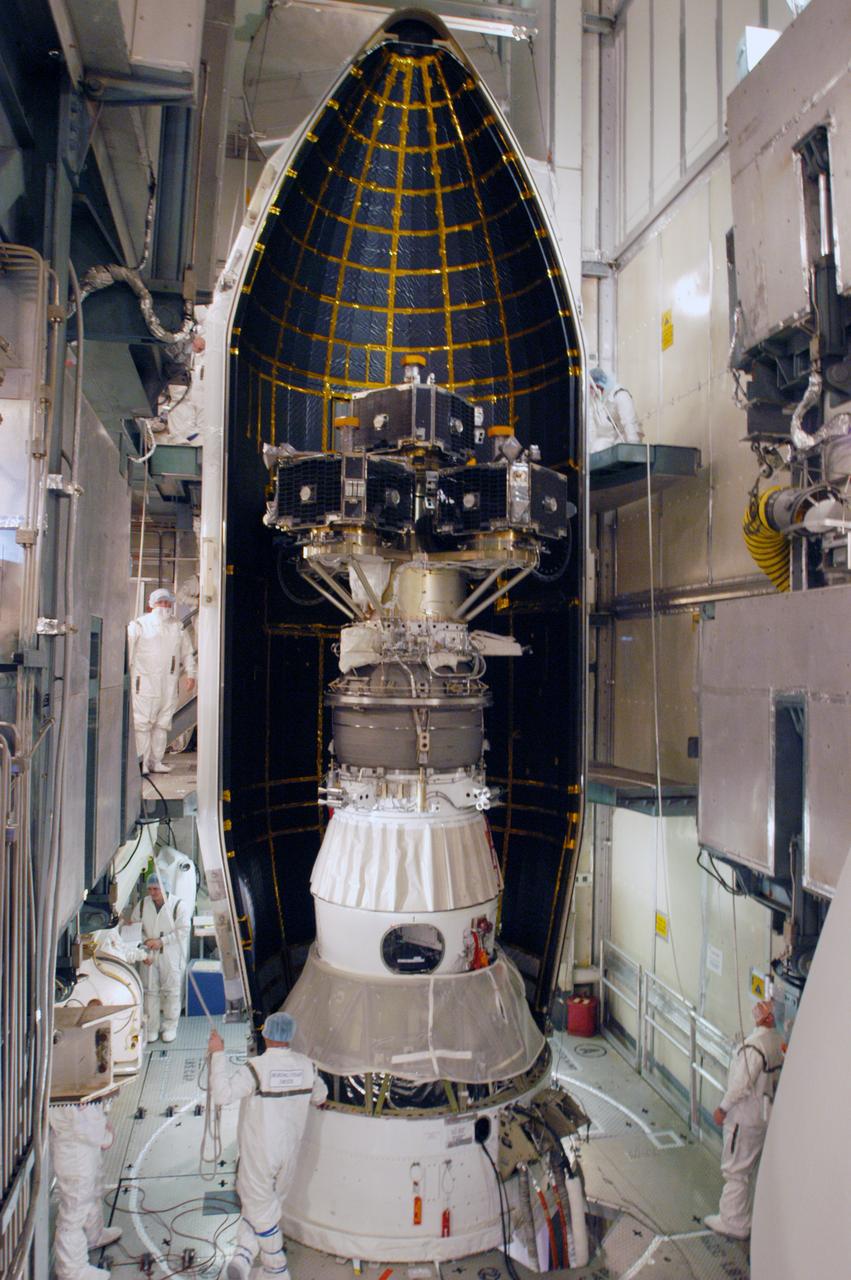

In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first half of the fairing is moved into place around the THEMIS spacecraft. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. THEMIS is an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms. THEMIS consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the tantalizing mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color. Launch of THEMIS is scheduled for Feb. 15 aboard a Delta II rocket, with the launch service being conducted by the United Launch Alliance.
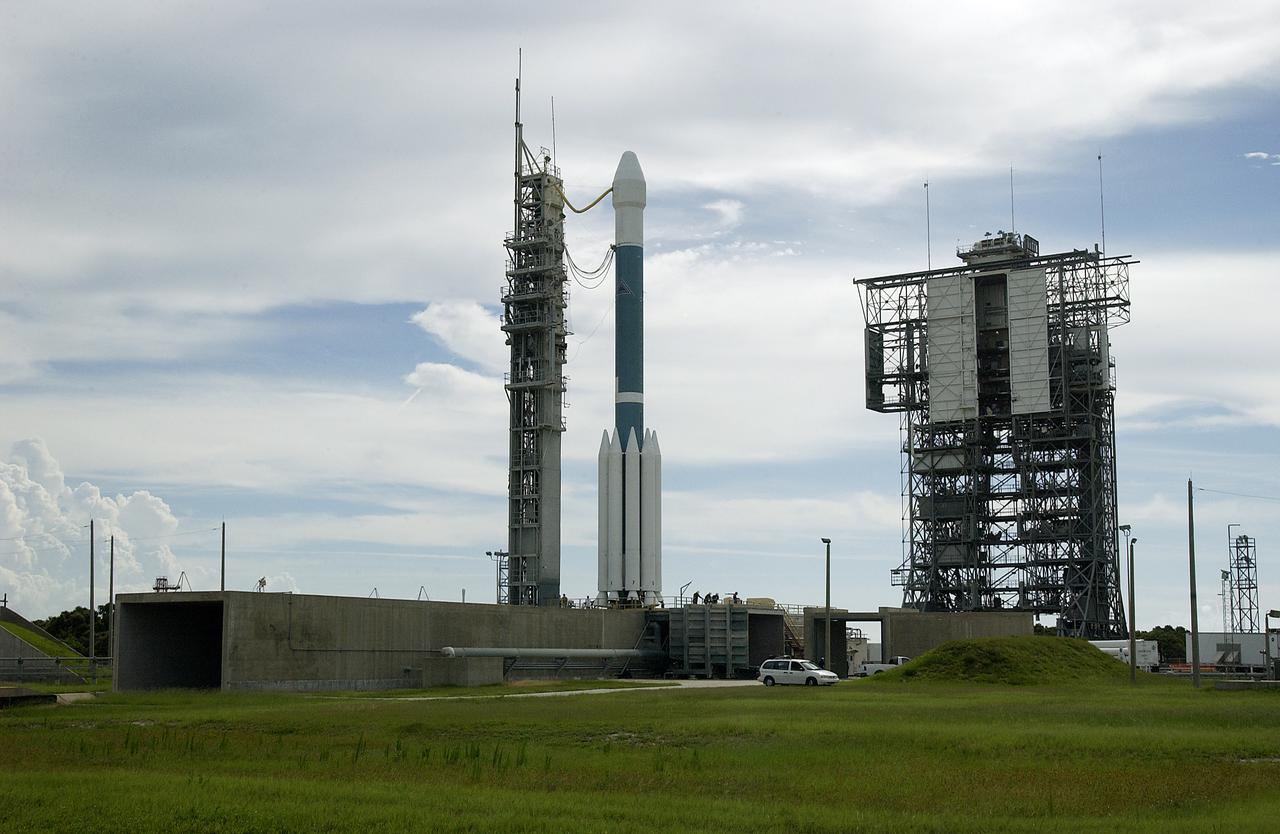

On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II Heavy launch vehicle carrying the rover "Opportunity" for the second Mars Exploration Rover mission is poised for launch after rollback of the Mobile Service Tower. Opportunity will reach Mars on Jan. 25, 2004. Together the two MER rovers, Spirit (launched June 10) and Opportunity, seek to determine the history of climate and water at two sites on Mars where conditions may once have been favorable to life. The rovers are identical. They will navigate themselves around obstacles as they drive across the Martian surface, traveling up to about 130 feet each Martian day. Each rover carries five scientific instruments including a panoramic camera and microscope, plus a rock abrasion tool that will grind away the outer surfaces of rocks to expose their interiors for examination. Each rover’s prime mission is planned to last three months on Mars.
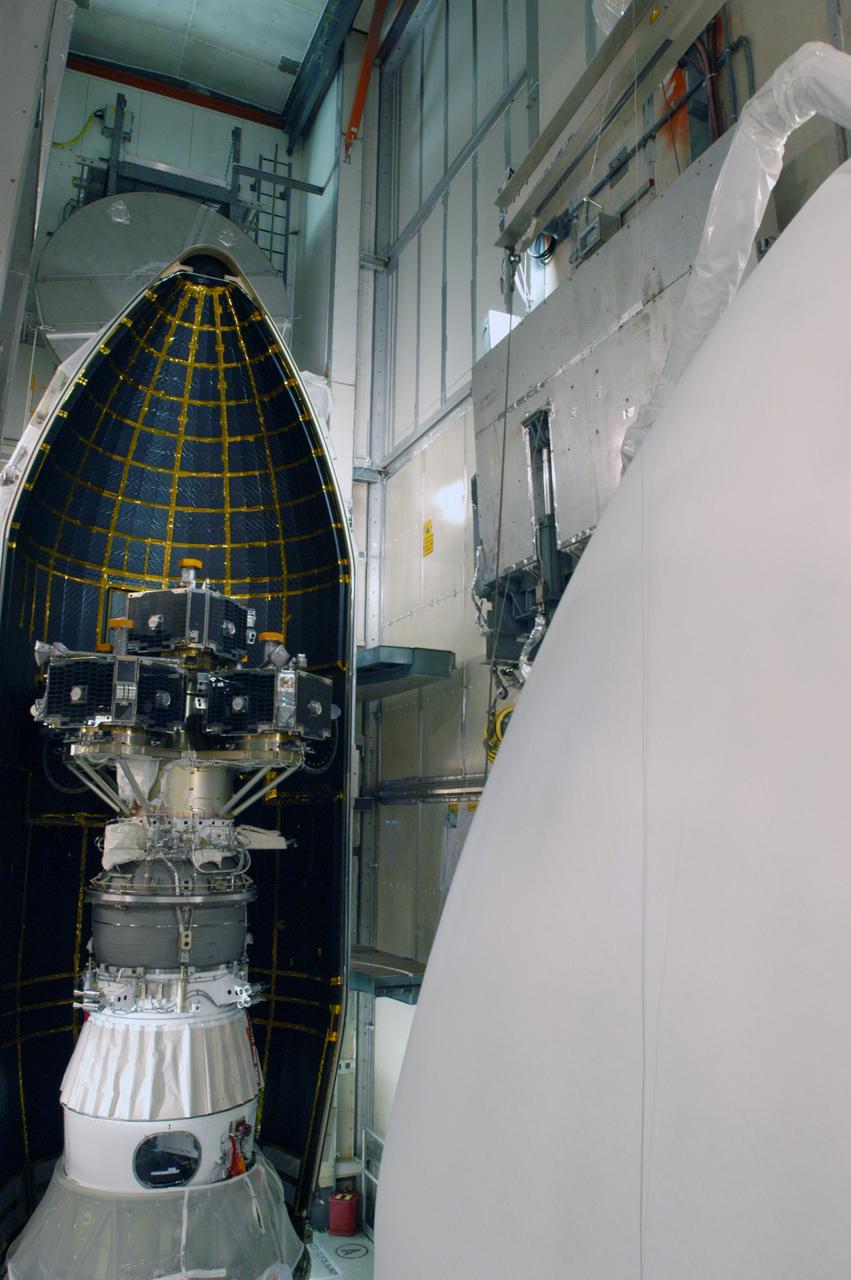
In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the second half of the fairing, at right, moves toward the waiting THEMIS spacecraft. The first half has already been put in place. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. THEMIS is an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms. THEMIS consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the tantalizing mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color. Launch of THEMIS is scheduled for Feb. 15 aboard a Delta II rocket, with the launch service being conducted by the United Launch Alliance.

On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II Heavy launch vehicle carrying the rover "Opportunity" for the second Mars Exploration Rover mission is poised for launch after rollback of the Mobile Service Tower. Opportunity will reach Mars on Jan. 25, 2004. Together the two MER rovers, Spirit (launched June 10) and Opportunity, seek to determine the history of climate and water at two sites on Mars where conditions may once have been favorable to life. The rovers are identical. They will navigate themselves around obstacles as they drive across the Martian surface, traveling up to about 130 feet each Martian day. Each rover carries five scientific instruments including a panoramic camera and microscope, plus a rock abrasion tool that will grind away the outer surfaces of rocks to expose their interiors for examination. Each rover’s prime mission is planned to last three months on Mars.
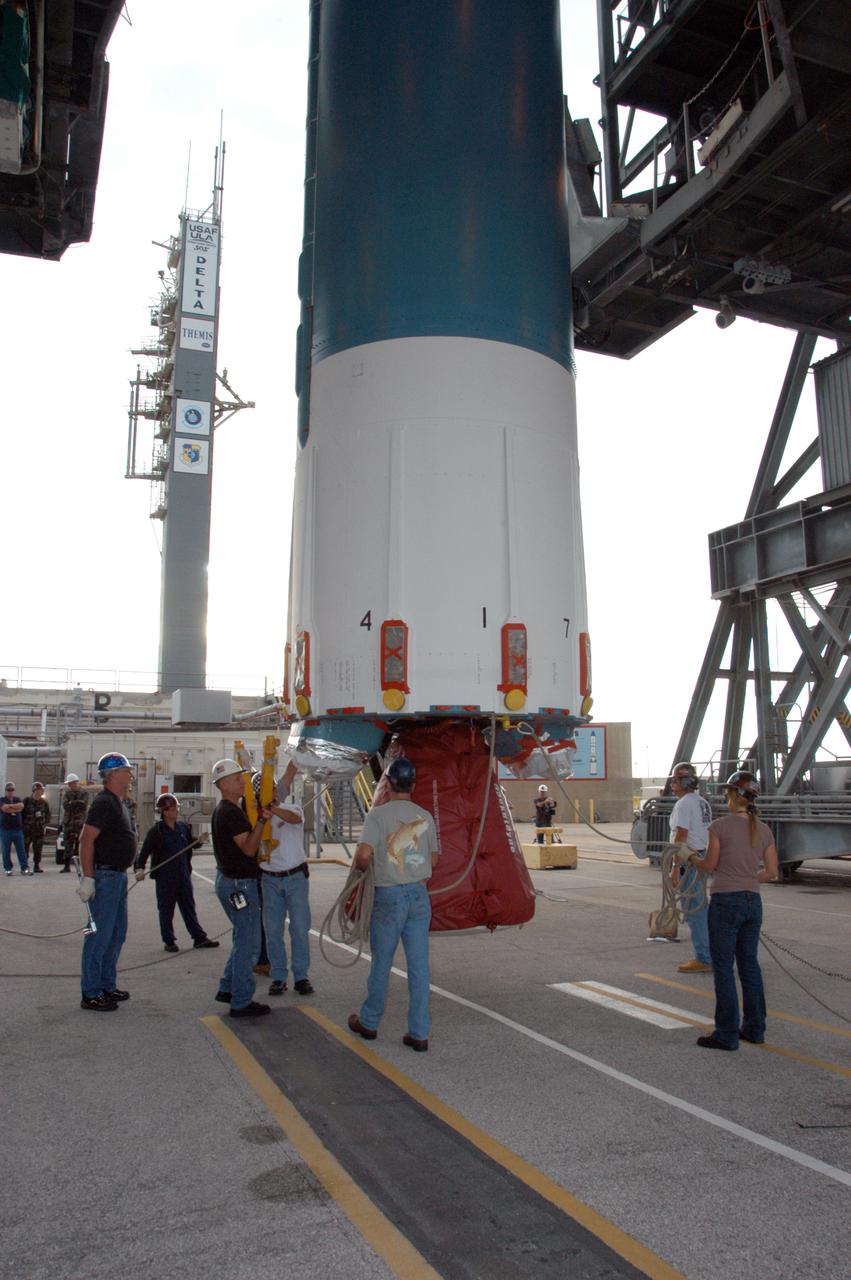

On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, workers check the lines attached to the lower end of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket before it is lifted into the mobile service tower. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft, consisting of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. After the first stage is in the mobile service tower on the pad, nine solid rocket boosters will be placed around the base of the first stage and attached in sets of three. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.
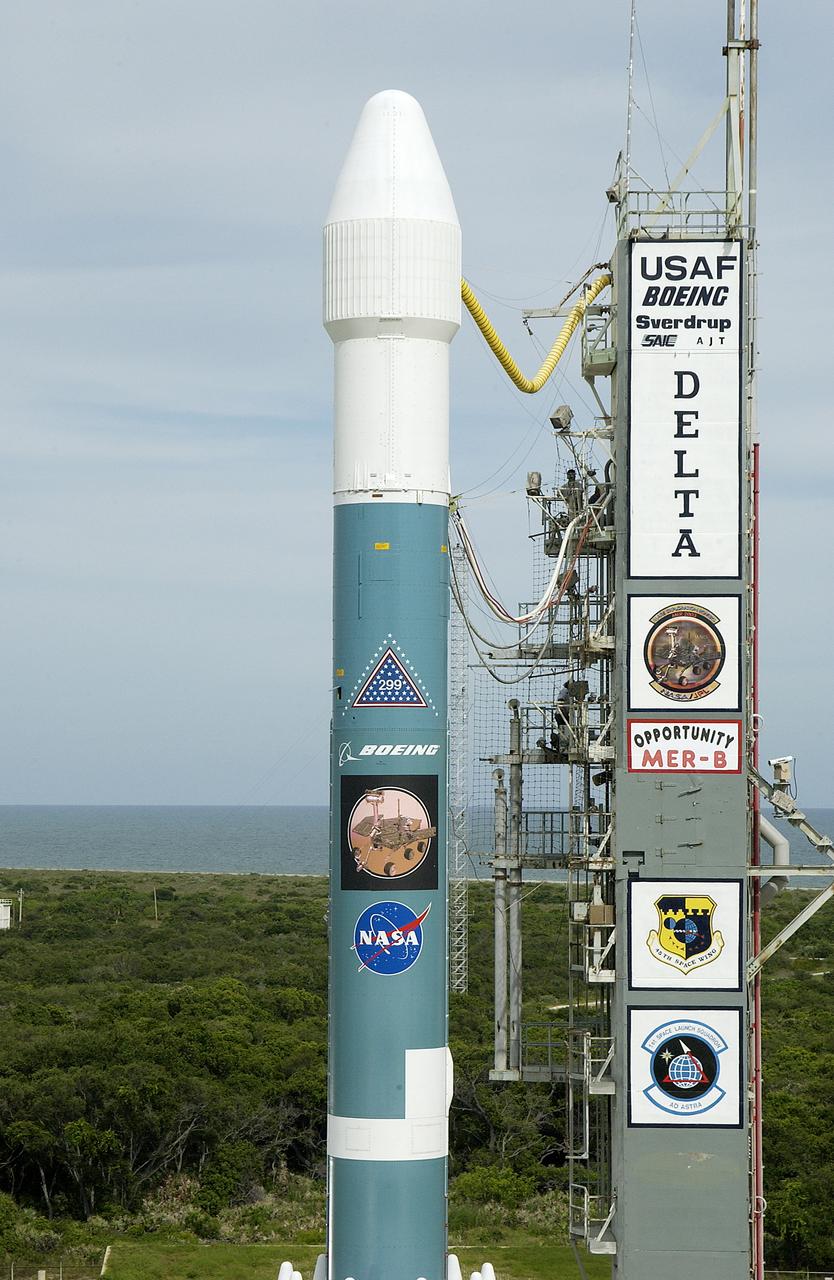
On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II Heavy launch vehicle carrying the rover "Opportunity" for the second Mars Exploration Rover mission is poised for launch after rollback of the Mobile Service Tower. Opportunity will reach Mars on Jan. 25, 2004. Together the two MER rovers, Spirit (launched June 10) and Opportunity, seek to determine the history of climate and water at two sites on Mars where conditions may once have been favorable to life. The rovers are identical. They will navigate themselves around obstacles as they drive across the Martian surface, traveling up to about 130 feet each Martian day. Each rover carries five scientific instruments including a panoramic camera and microscope, plus a rock abrasion tool that will grind away the outer surfaces of rocks to expose their interiors for examination. Each rover’s prime mission is planned to last three months on Mars.
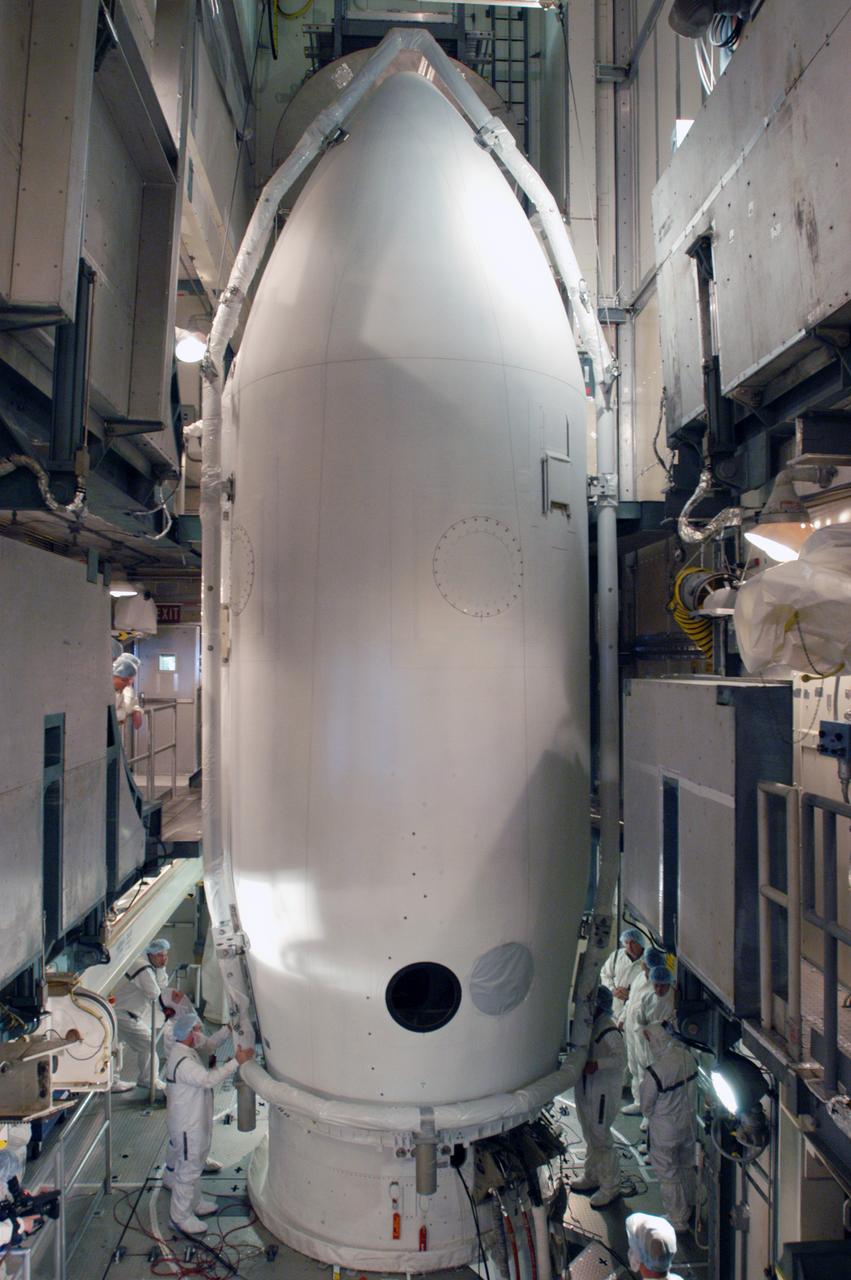

In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers prepare to join the two fairing segments around the THEMIS spacecraft. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. THEMIS is an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms. THEMIS consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the tantalizing mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color. Launch of THEMIS is scheduled for Feb. 15 aboard a Delta II rocket, with the launch service being conducted by the United Launch Alliance.
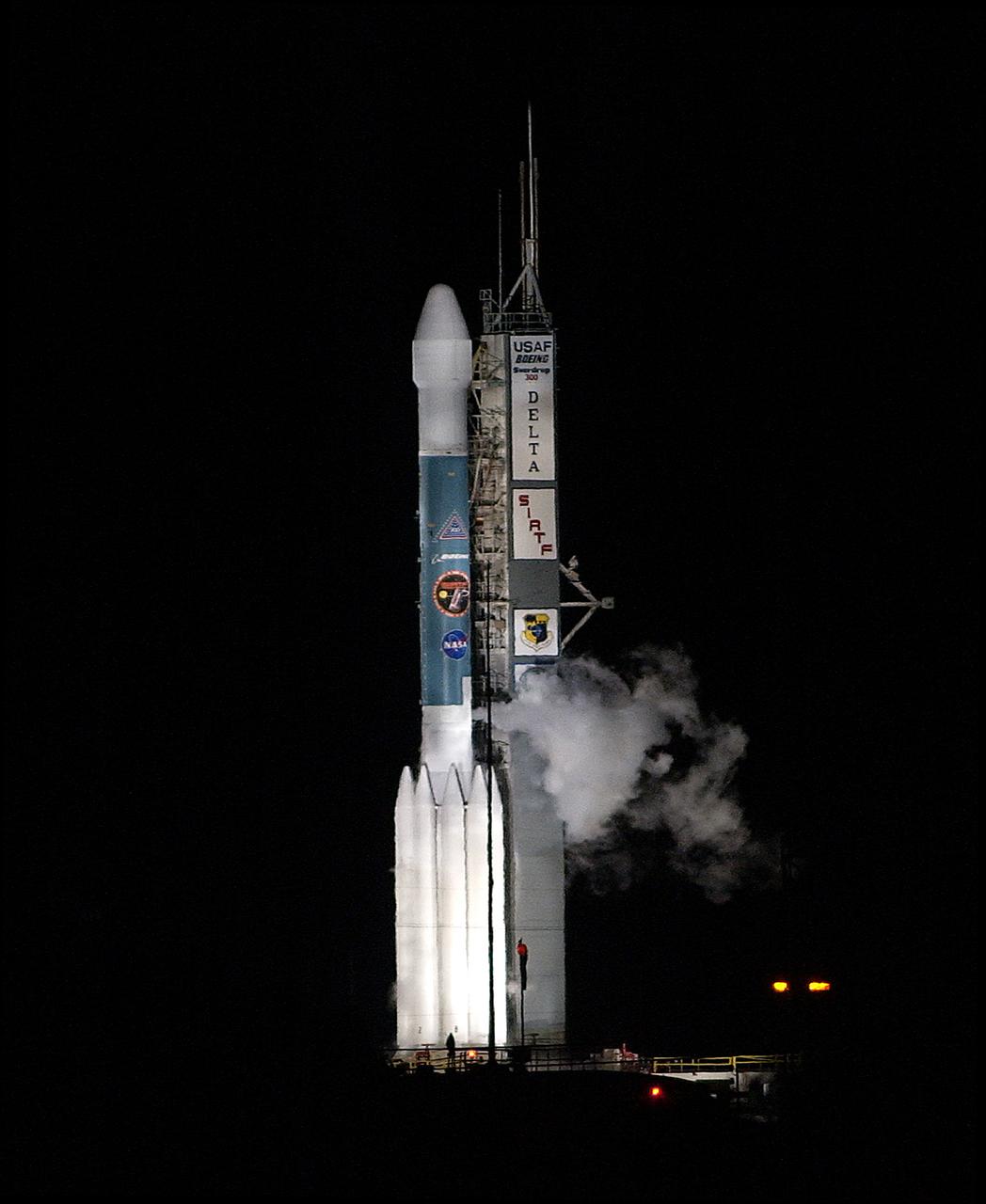

NASA's Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) is moments away from lift off from Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on Aug. 25. Launch is scheduled for 1:35:39 a.m. EDT. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Consisting of a 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF will be the largest infrared telescope ever launched into space. It is the fourth and final element in NASA’s family of orbiting “Great Observatories.” Its highly sensitive instruments will give a unique view of the Universe and peer into regions of space that are hidden from optical telescopes.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II rocket with NASA's THEMIS spacecraft aboard begins its ascent from Pad 17-B, in sight of the Atlantic Ocean, at 6:01 p.m. EST. THEMIS, an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms, consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA has ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color.
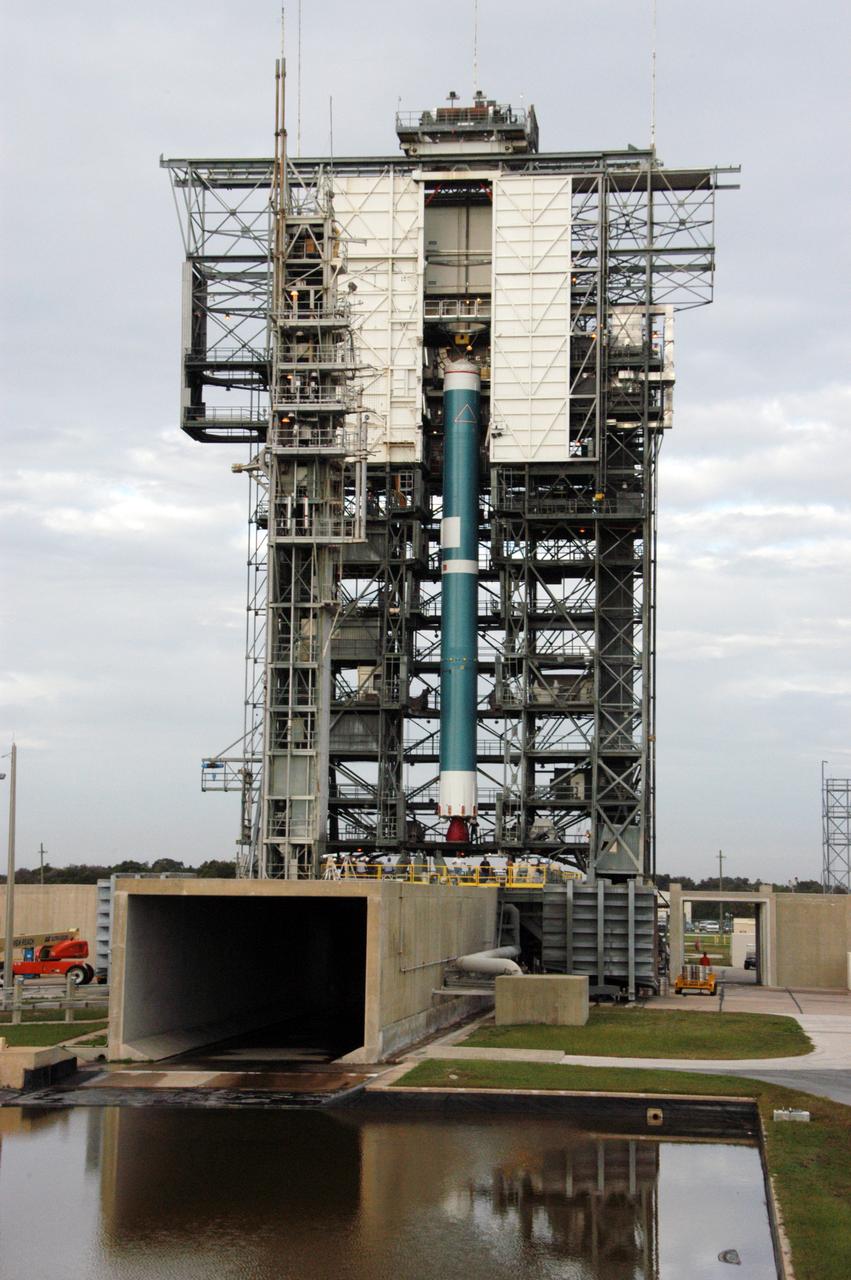

On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is moved inside the mobile service tower where nine solid rocket boosters will be attached in sets of three. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft, consisting of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.
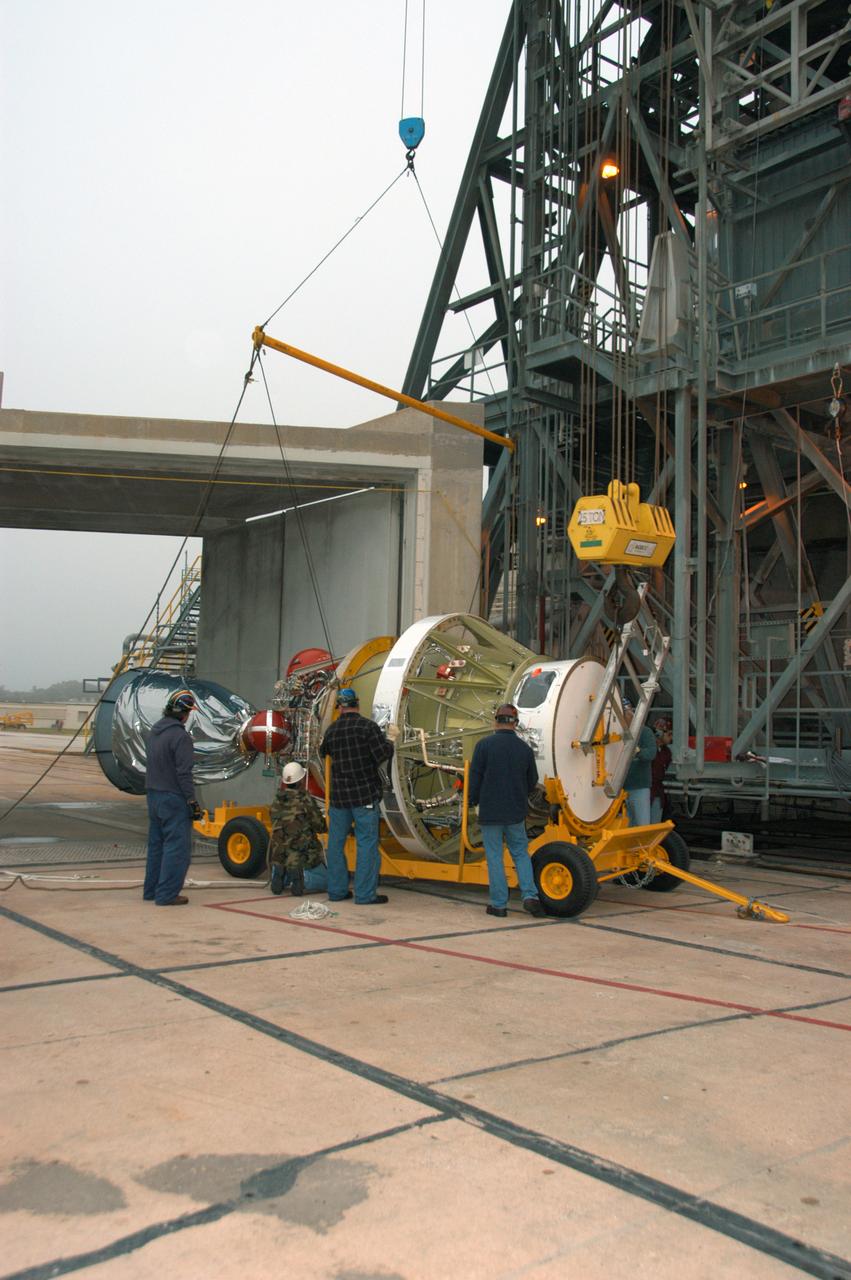

On Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers attach an overhead crane to the Delta II second stage in order to raise it to vertical. It will be lifted into the mobile service tower and mated with the first stage already in place. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

The Mobile Service Tower is ready to be rolled back at Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, to launch the Delta II Heavy launch vehicle carrying the rover "Opportunity" on the second Mars Exploration Rover mission. Opportunity will reach Mars on Jan. 25, 2004. Together the two MER rovers, Spirit (launched June 10) and Opportunity, seek to determine the history of climate and water at two sites on Mars where conditions may once have been favorable to life. The rovers are identical. They will navigate themselves around obstacles as they drive across the Martian surface, traveling up to about 130 feet each Martian day. Each rover carries five scientific instruments including a panoramic camera and microscope, plus a rock abrasion tool that will grind away the outer surfaces of rocks to expose their interiors for examination. Each rover’s prime mission is planned to last three months on Mars.
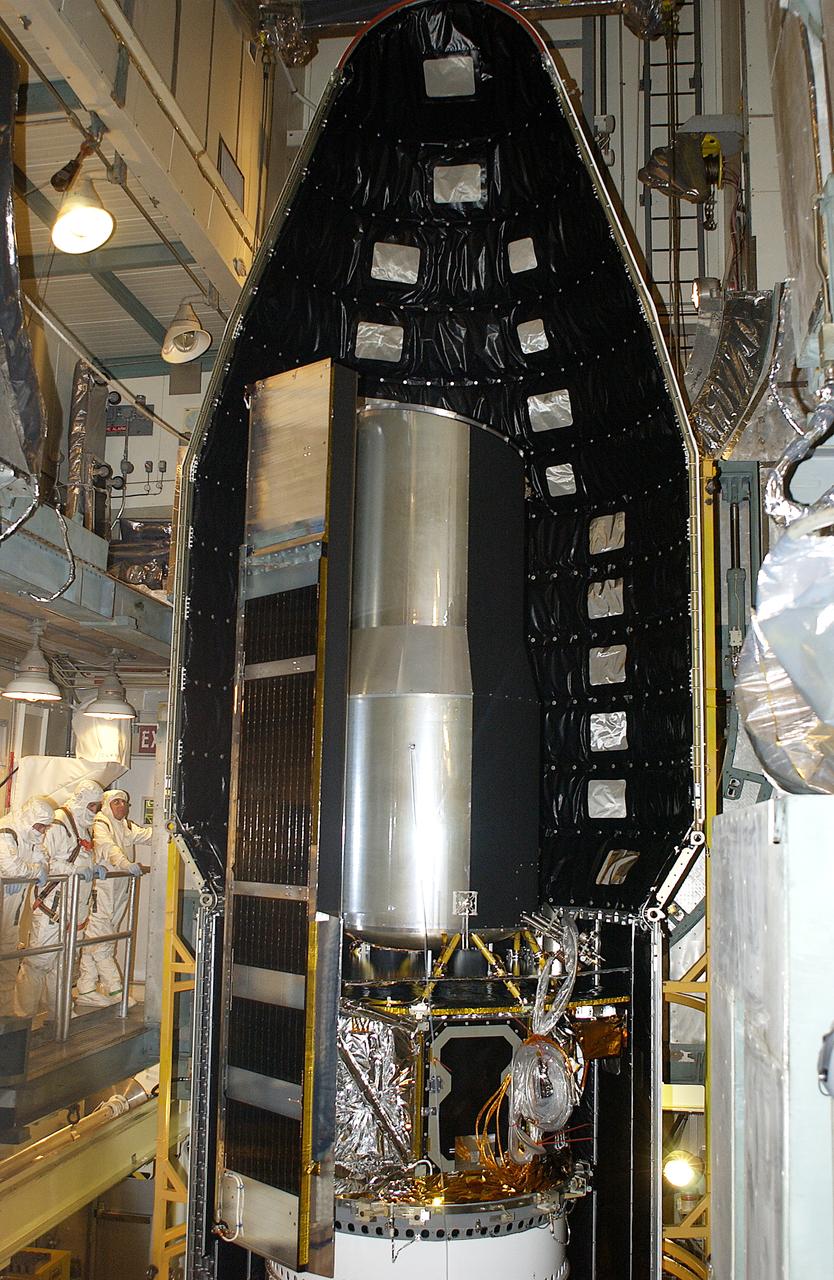

In the launch tower on Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first part of the fairing is seen in place around the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF). SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch April 18 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
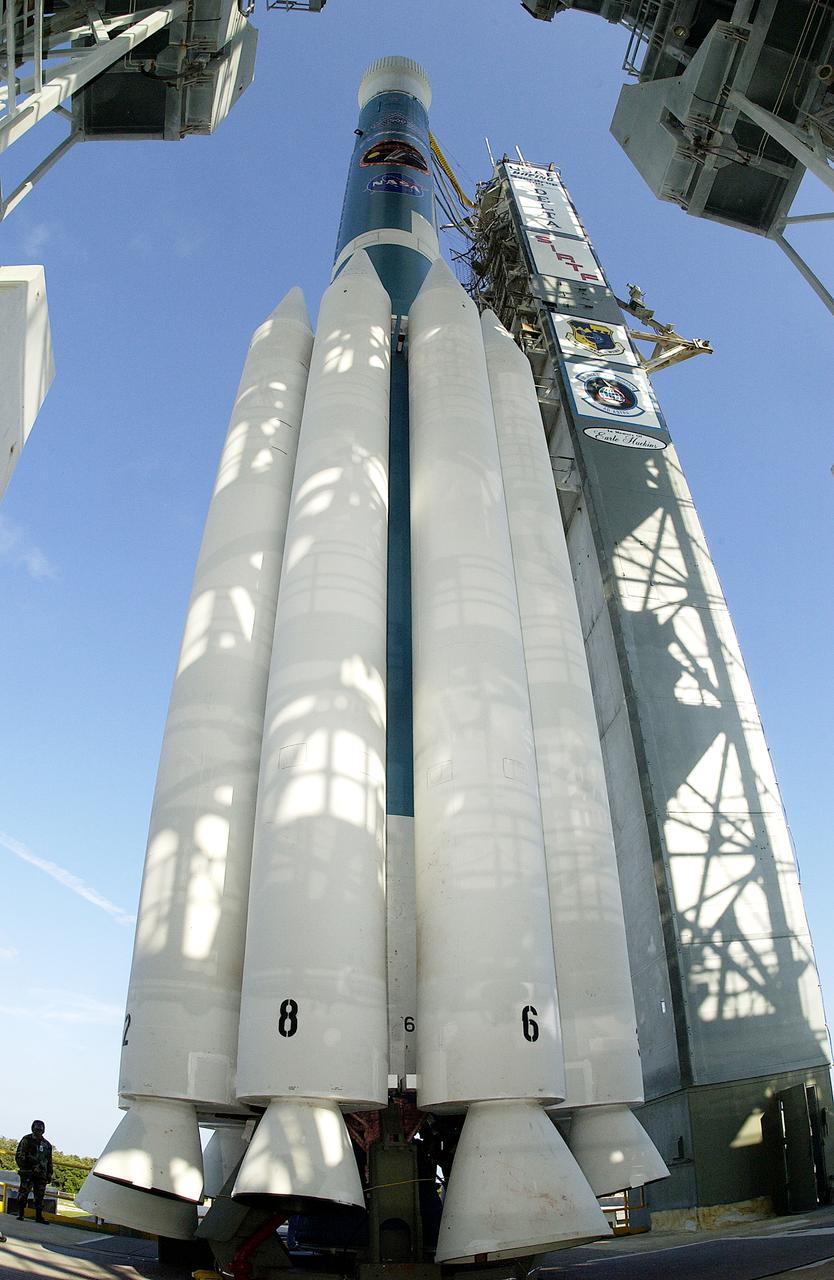

The mobile service tower is rolled back at Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, to reveal NASA's Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) ready for launch aboard a Delta II Heavy launch vehicle. Liftoff is scheduled for Aug. 25 at 1:35:39 a.m. EDT. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Consisting of a 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF will be the largest infrared telescope ever launched into space. It is the fourth and final element in NASA’s family of orbiting “Great Observatories.” Its highly sensitive instruments will give a unique view of the Universe and peer into regions of space that are hidden from optical telescopes.
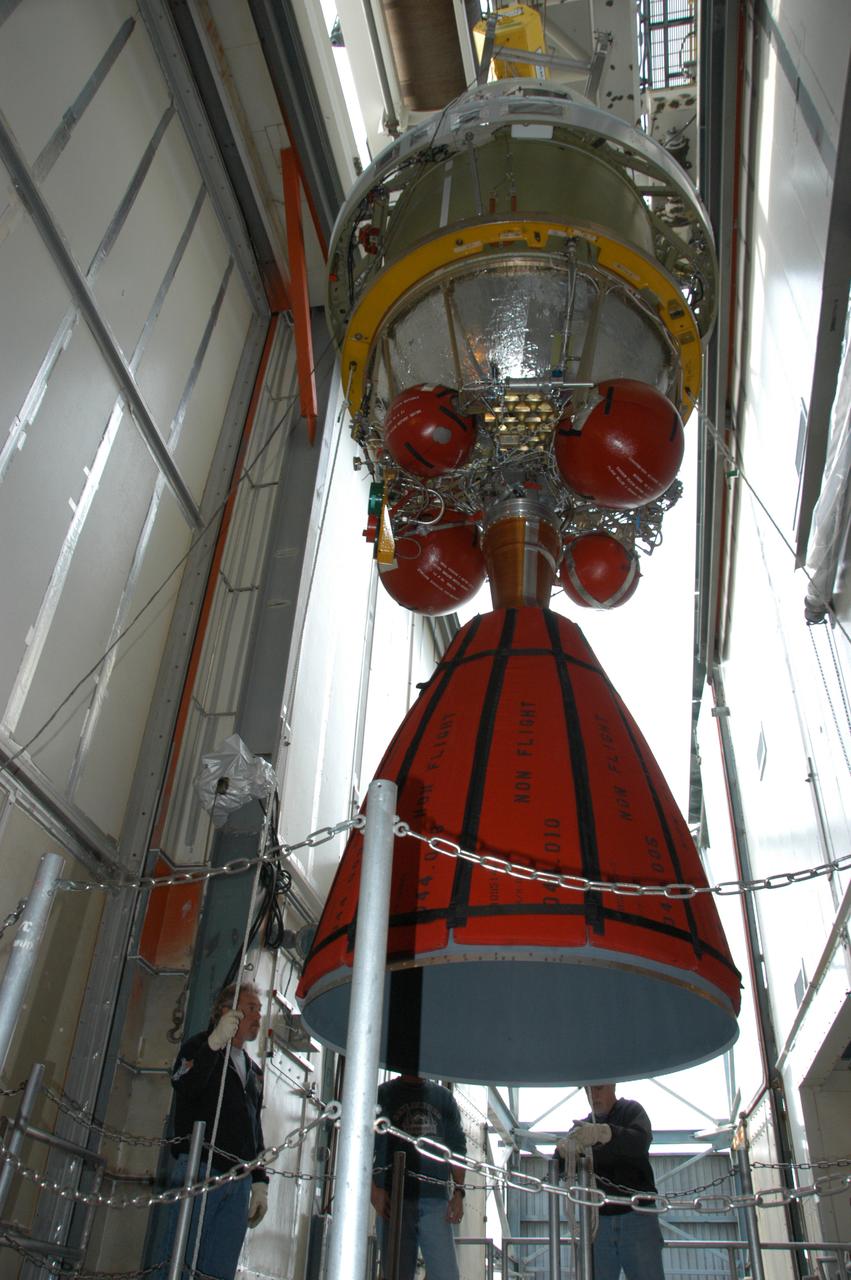

On Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II second stage is moved inside level 9 of the tower. It will be mated with the first stage already in place. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, clouds of smoke encompass the Delta II rocket with NASA's THEMIS spacecraft aboard as it blasts off Pad 17-B, in sight of the Atlantic Ocean, at 6:01 p.m. EST. THEMIS, an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms, consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA has ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color.
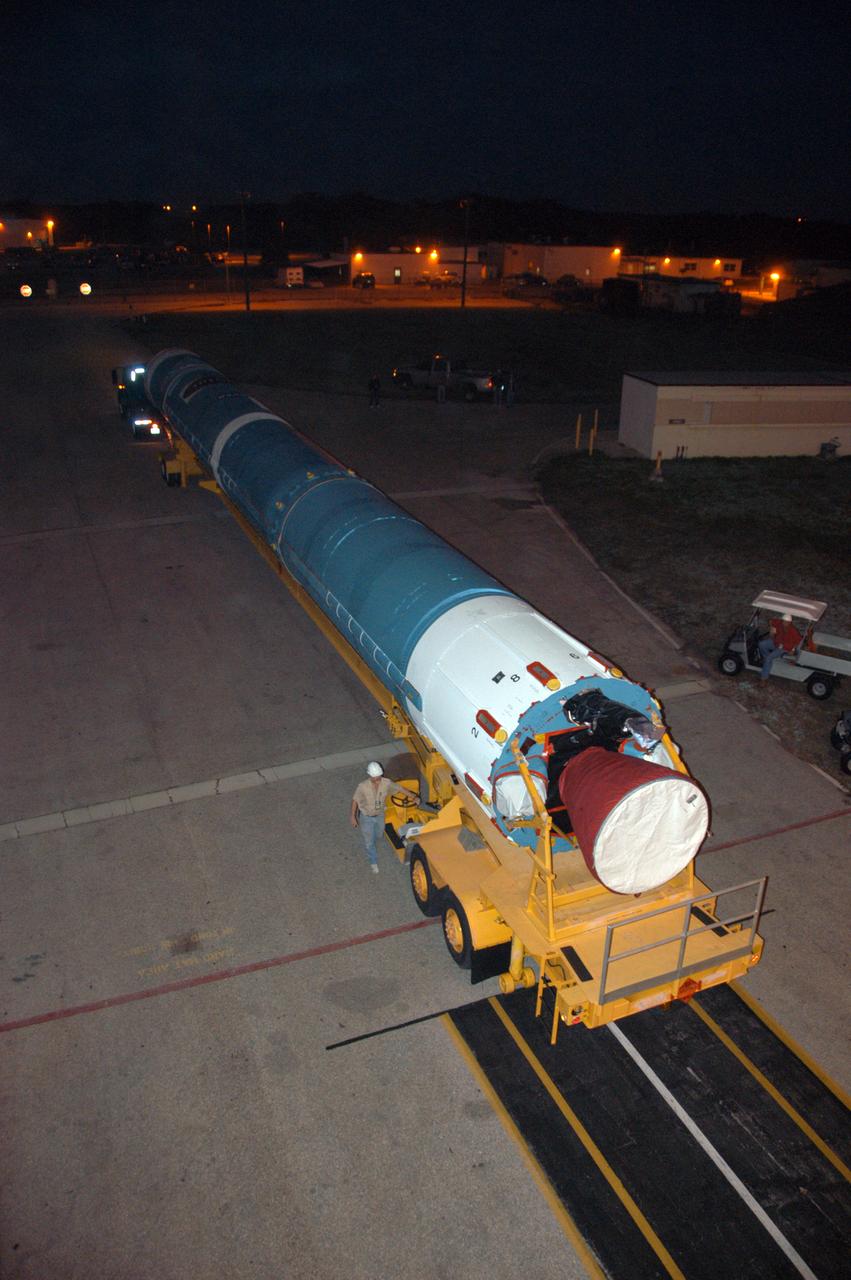

The first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is on its way to Launch Pad 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft, consisting of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. After the first stage is in the mobile service tower on the pad, nine solid rocket boosters will be placed around the base of the first stage and attached in sets of three. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.
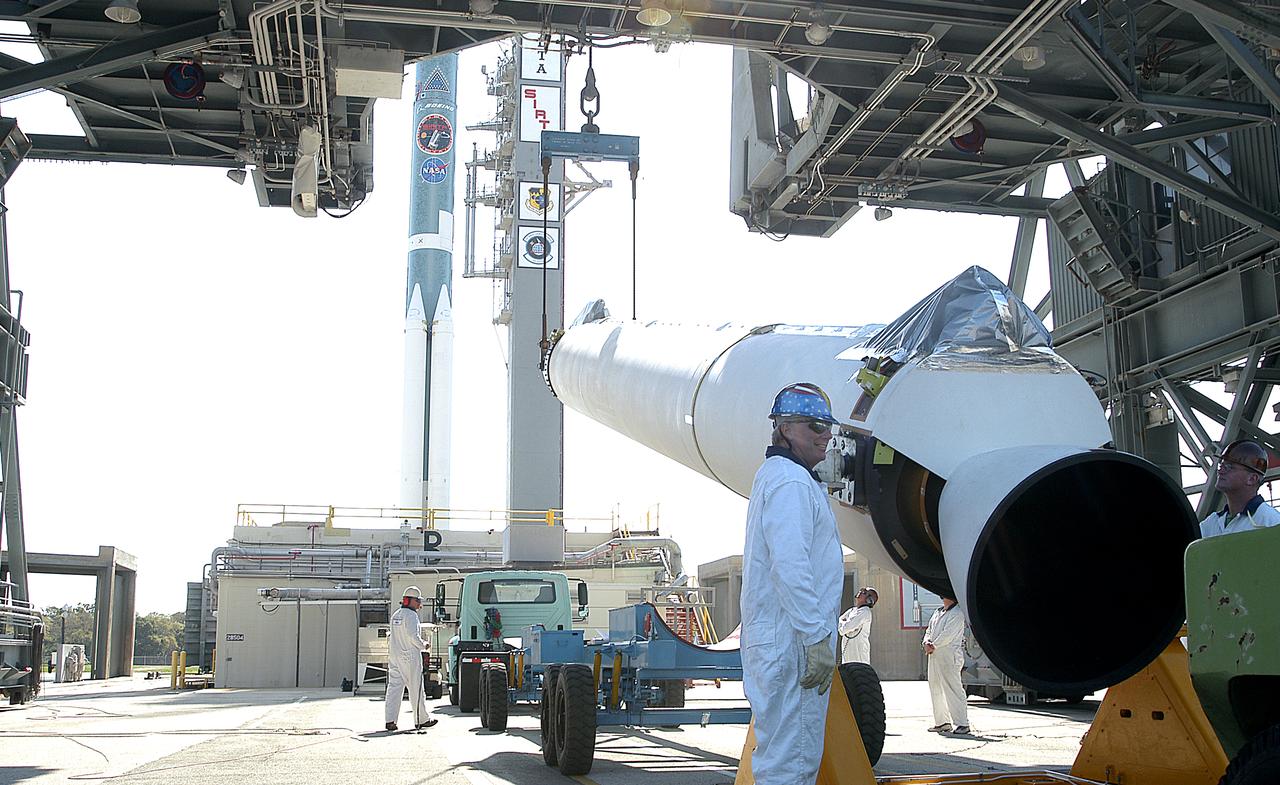

One of nine solid rocket boosters is lifted on Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for mating with the Delta II rocket in the background. The second stage will later be hoisted atop the first stage. The Delta rocket is the launch vehicle for the Space Infrared Telescope Facility. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is scheduled for launch April 15 at 4:34:07 a.m. EDT.
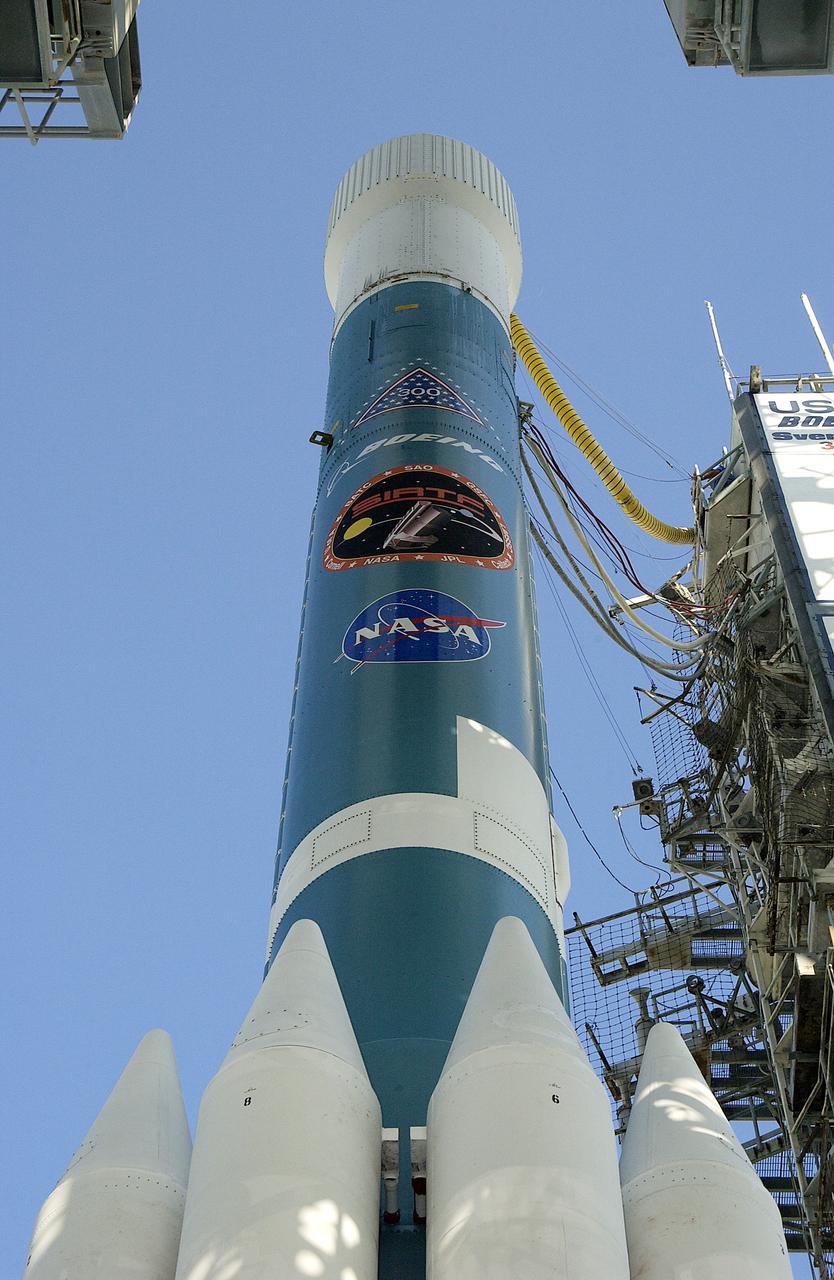

The mobile service tower is rolled back at Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, to reveal NASA's Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) ready for launch aboard a Delta II Heavy launch vehicle. Liftoff is scheduled for Aug. 25 at 1:35:39 a.m. EDT. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Consisting of a 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF will be the largest infrared telescope ever launched into space. It is the fourth and final element in NASA’s family of orbiting “Great Observatories.” Its highly sensitive instruments will give a unique view of the Universe and peer into regions of space that are hidden from optical telescopes.

The first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket moves into place in front of at the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The rocket will be raised to a vertical position and lifted into the tower. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft, consisting of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. After the first stage is in the mobile service tower on the pad, nine solid rocket boosters will be placed around the base of the first stage and attached in sets of three. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.
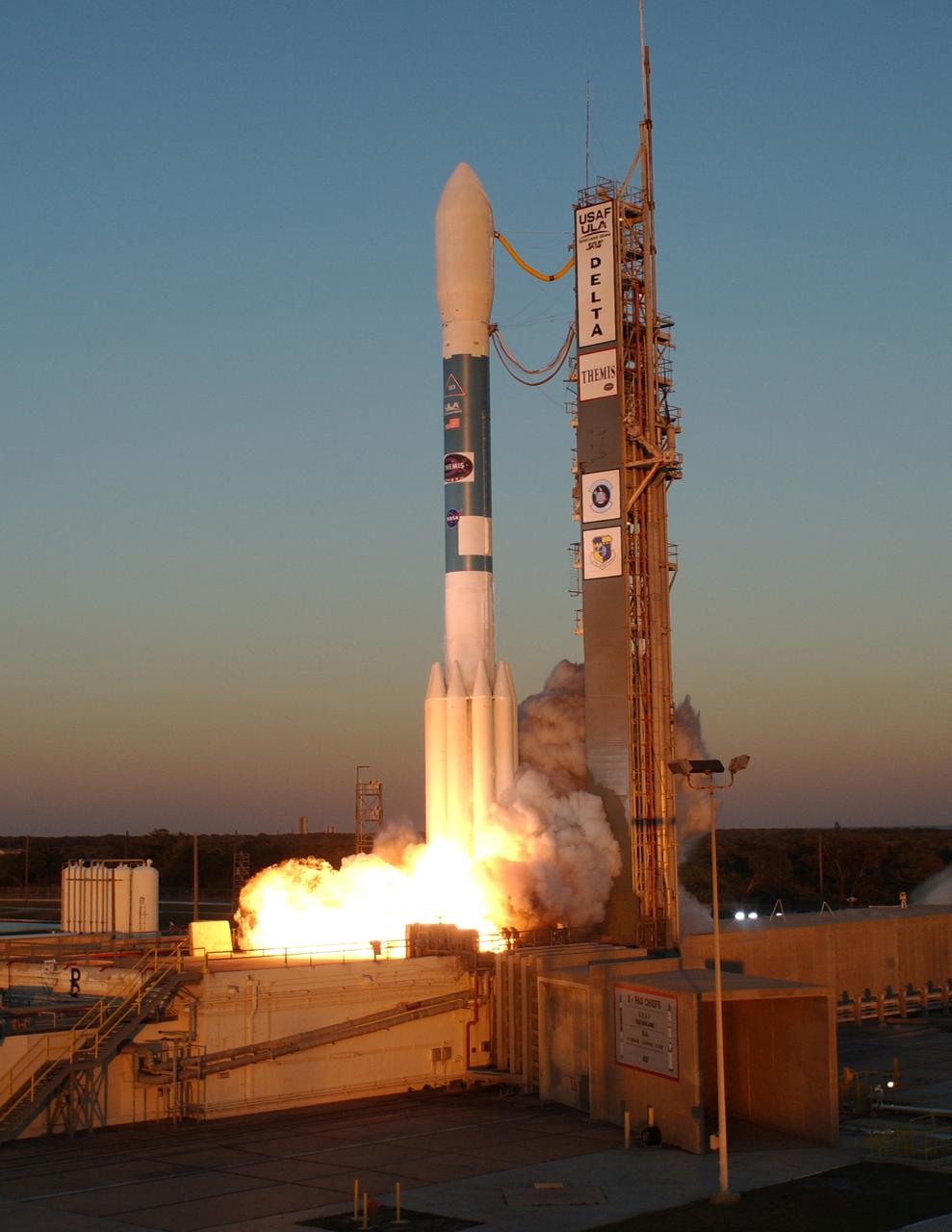

Amid billows of smoke, the Delta II rocket with NASA's THEMIS spacecraft aboard blasts off Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 6:01 p.m. EST. THEMIS, an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms, consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA has ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color.

In the launch tower on Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first part of the fairing is seen in place around the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF). SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch April 18 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
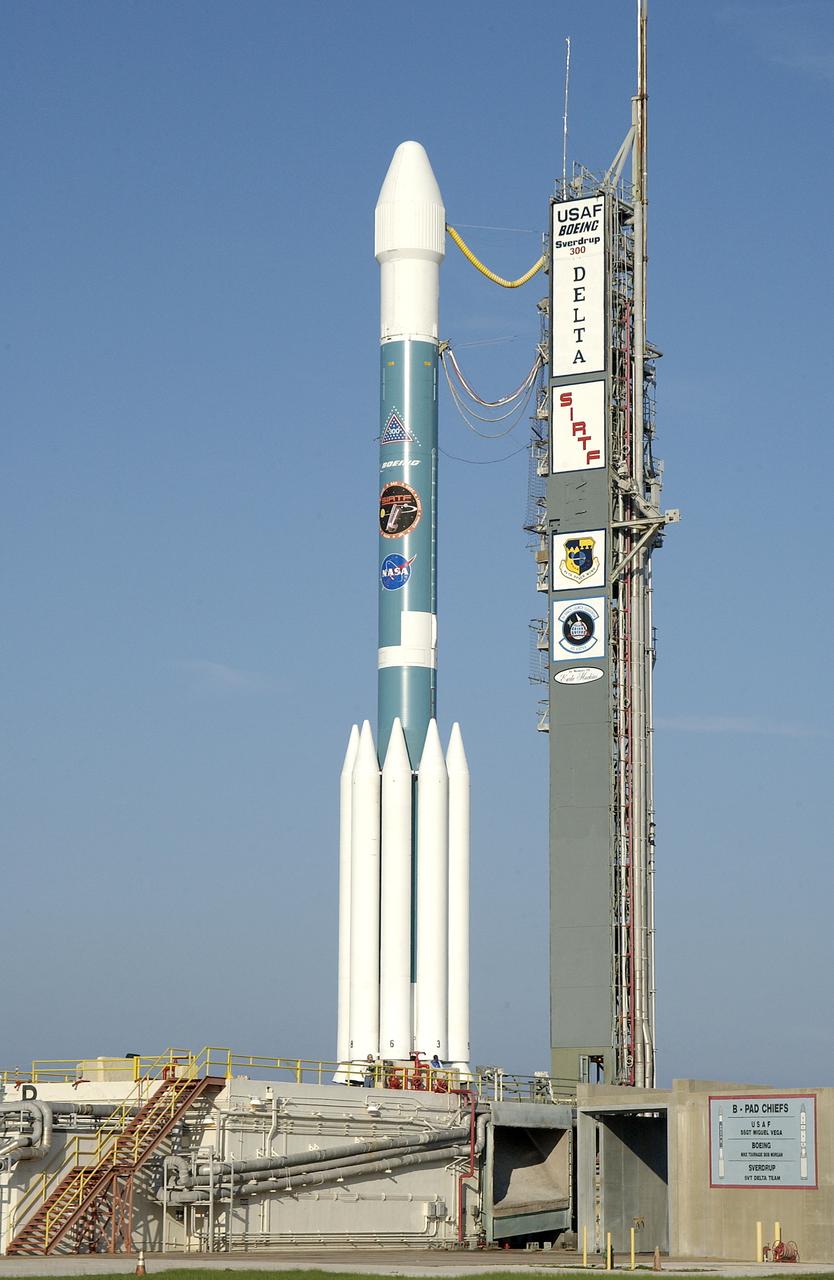

The mobile service tower is rolled back at Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, to reveal NASA's Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) ready for launch aboard a Delta II Heavy launch vehicle. Liftoff is scheduled for Aug. 25 at 1:35:39 a.m. EDT. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Consisting of a 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF will be the largest infrared telescope ever launched into space. It is the fourth and final element in NASA’s family of orbiting “Great Observatories.” Its highly sensitive instruments will give a unique view of the Universe and peer into regions of space that are hidden from optical telescopes.
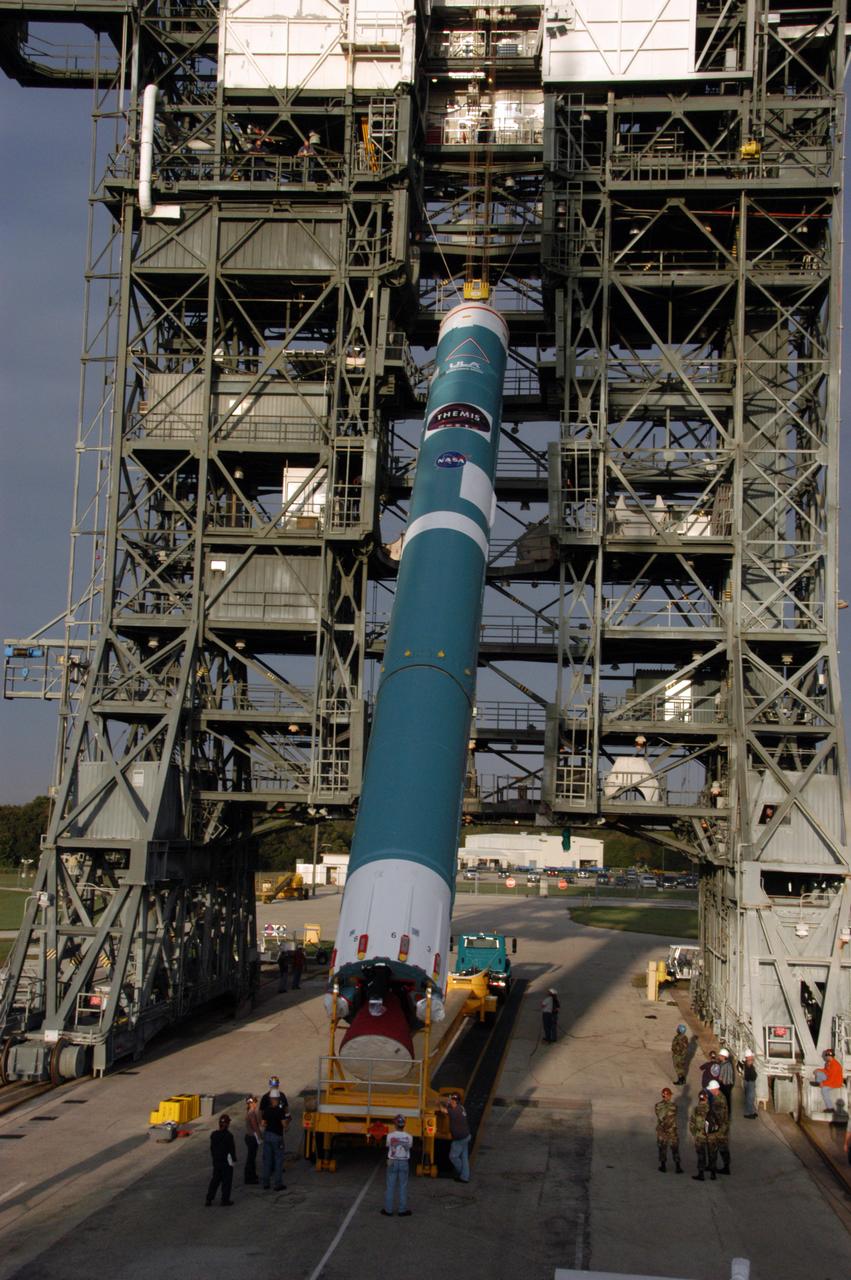

On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is raised off its transporter to a vertical position. The rocket will then be lifted into the mobile service tower. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft, consisting of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. After the first stage is in the tower on the pad, nine solid rocket boosters will be placed around the base of the first stage and attached in sets of three. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.

The first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket arrives at the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft, consisting of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. After the first stage is in the mobile service tower on the pad, nine solid rocket boosters will be placed around the base of the first stage and attached in sets of three. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.
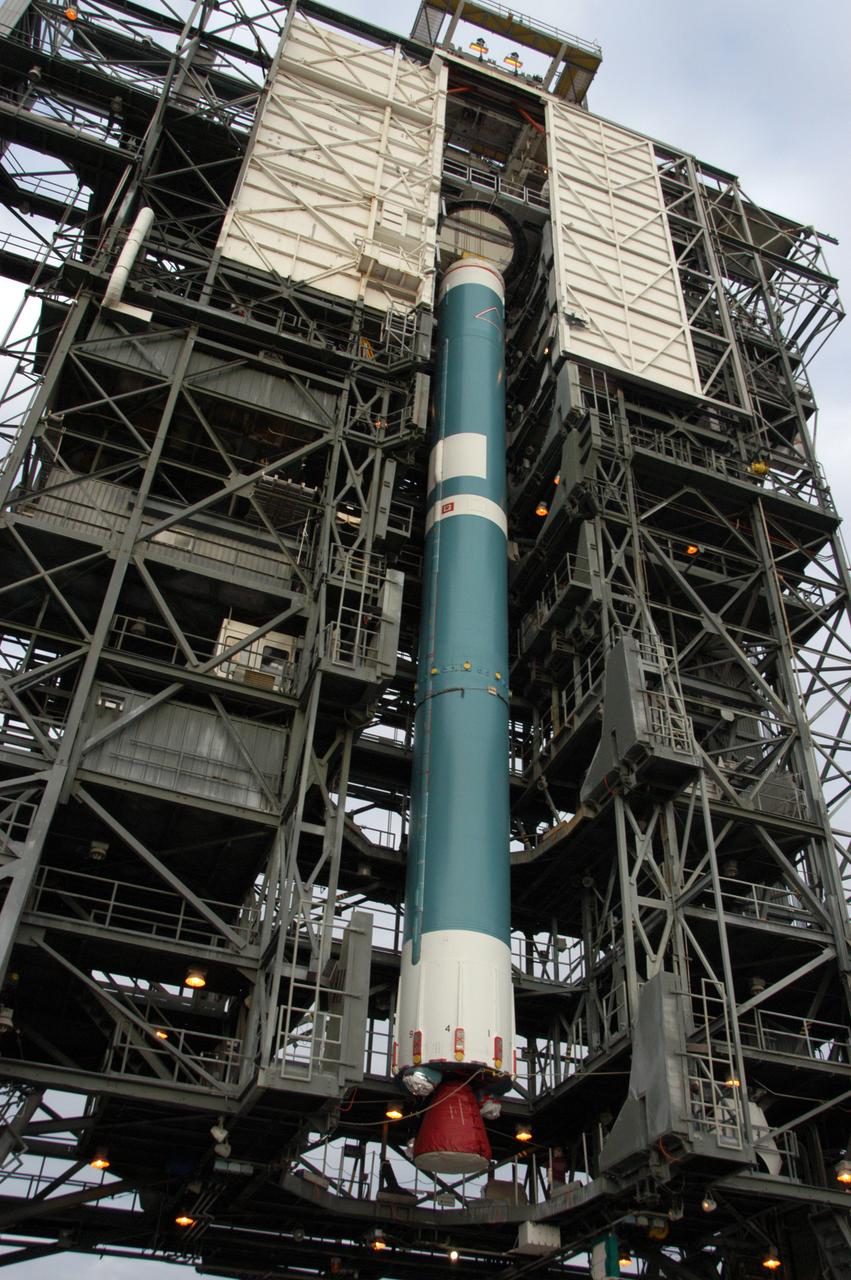

On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is lifted up into the mobile service tower. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft, consisting of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. After the first stage is in the tower on the pad, nine solid rocket boosters will be placed around the base of the first stage and attached in sets of three. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.
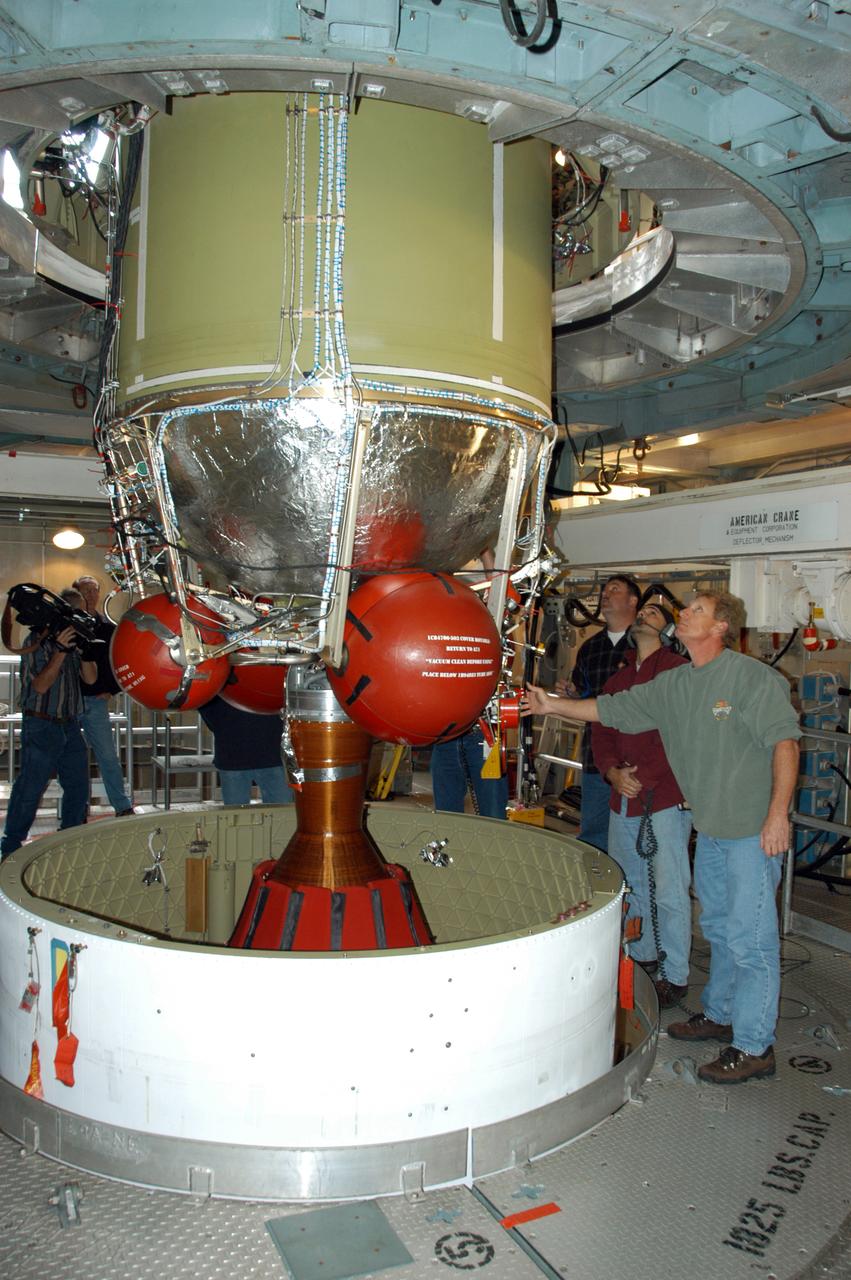

On Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II second stage is being lowered toward the Delta II first stage, already in place inside the mobile service tower. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
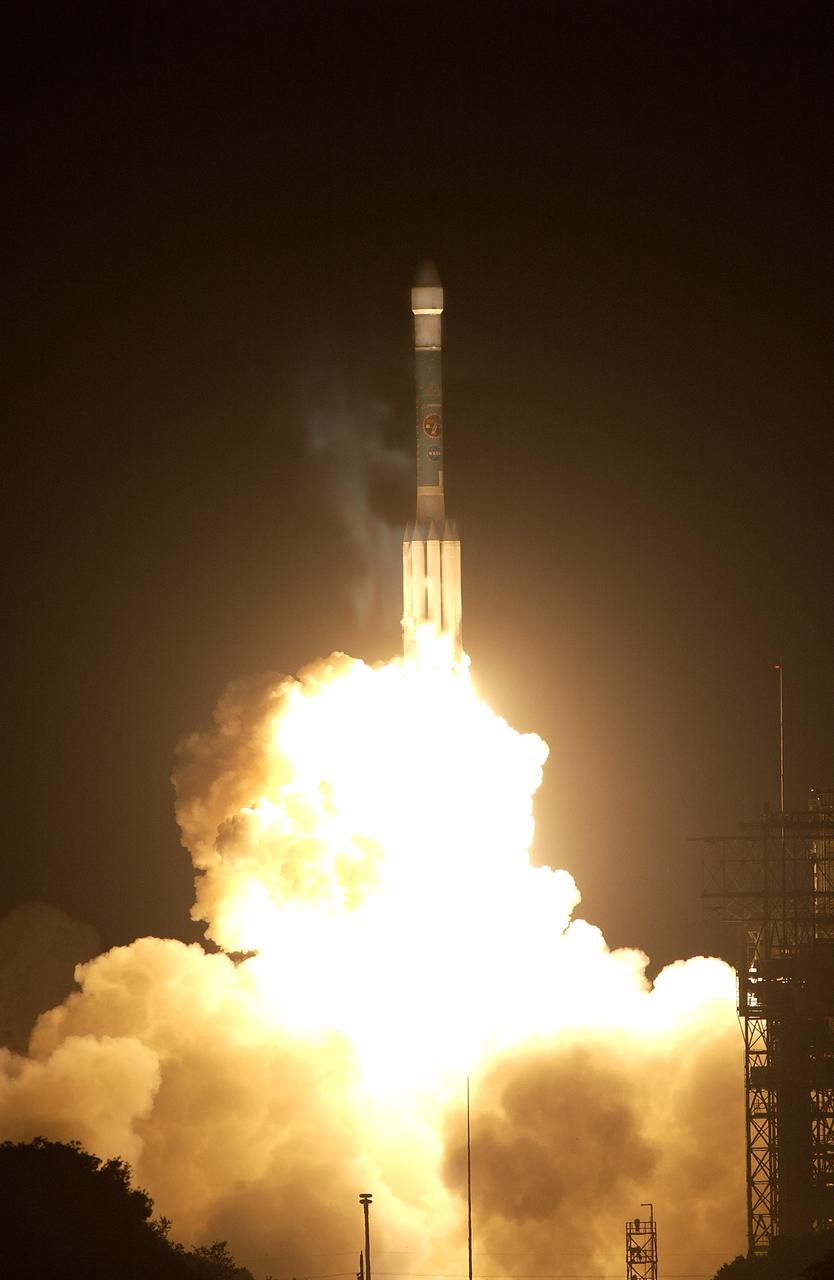

NASA's Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) lifts off from Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on Aug. 25 at 1:35:39 a.m. EDT. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Consisting of a 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF will be the largest infrared telescope ever launched into space. It is the fourth and final element in NASA’s family of orbiting “Great Observatories.” Its highly sensitive instruments will give a unique view of the Universe and peer into regions of space that are hidden from optical telescopes.

On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a crane (foreground) raises the first stage of a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket off its transporter to a vertical position. The rocket will then be lifted into the mobile service tower. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft, consisting of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. After the first stage is in the mobile service tower on the pad, nine solid rocket boosters will be placed around the base of the first stage and attached in sets of three. THEMIS is scheduled to launch aboard the Delta II at 6:07 p.m. EST on Feb. 15.
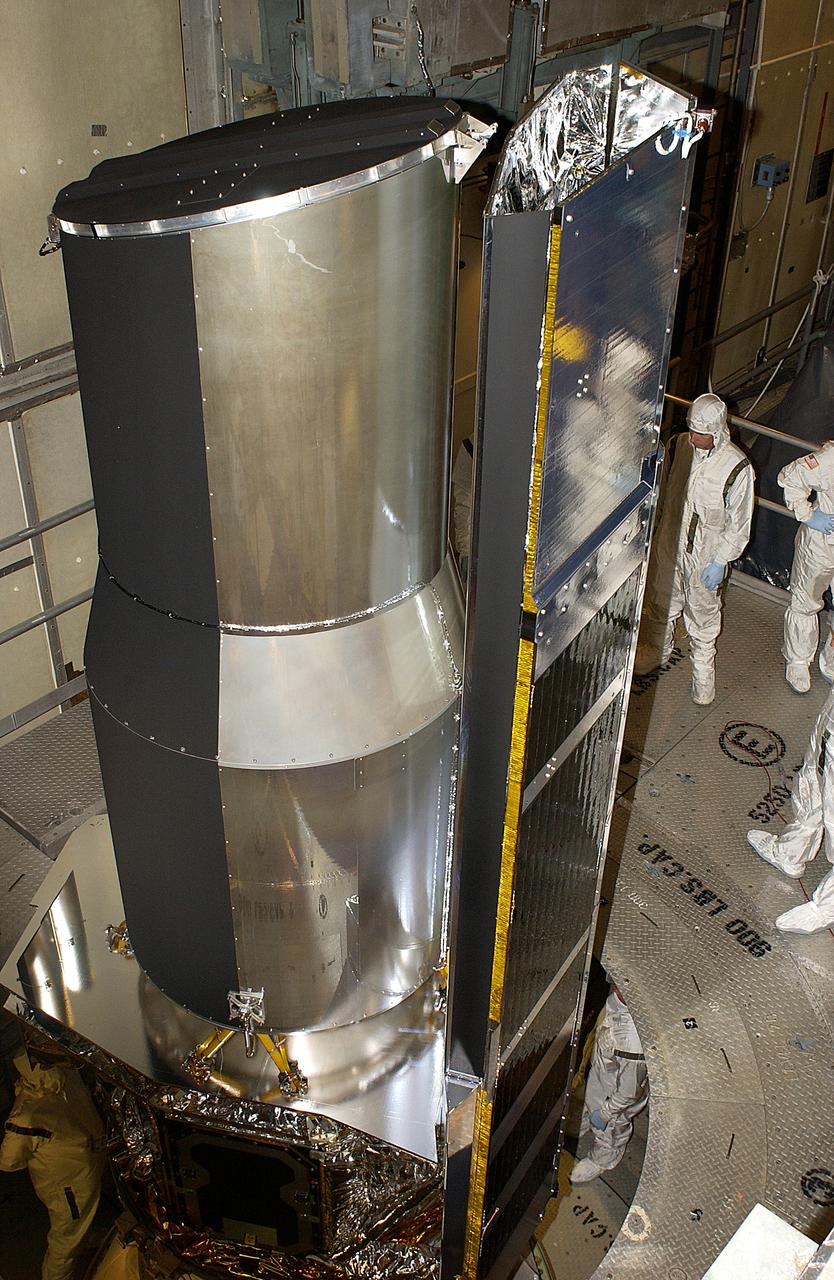

In the launch tower on Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) is lifted into position for installation of the fairing. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch April 18 aboard a Delta II rocket.
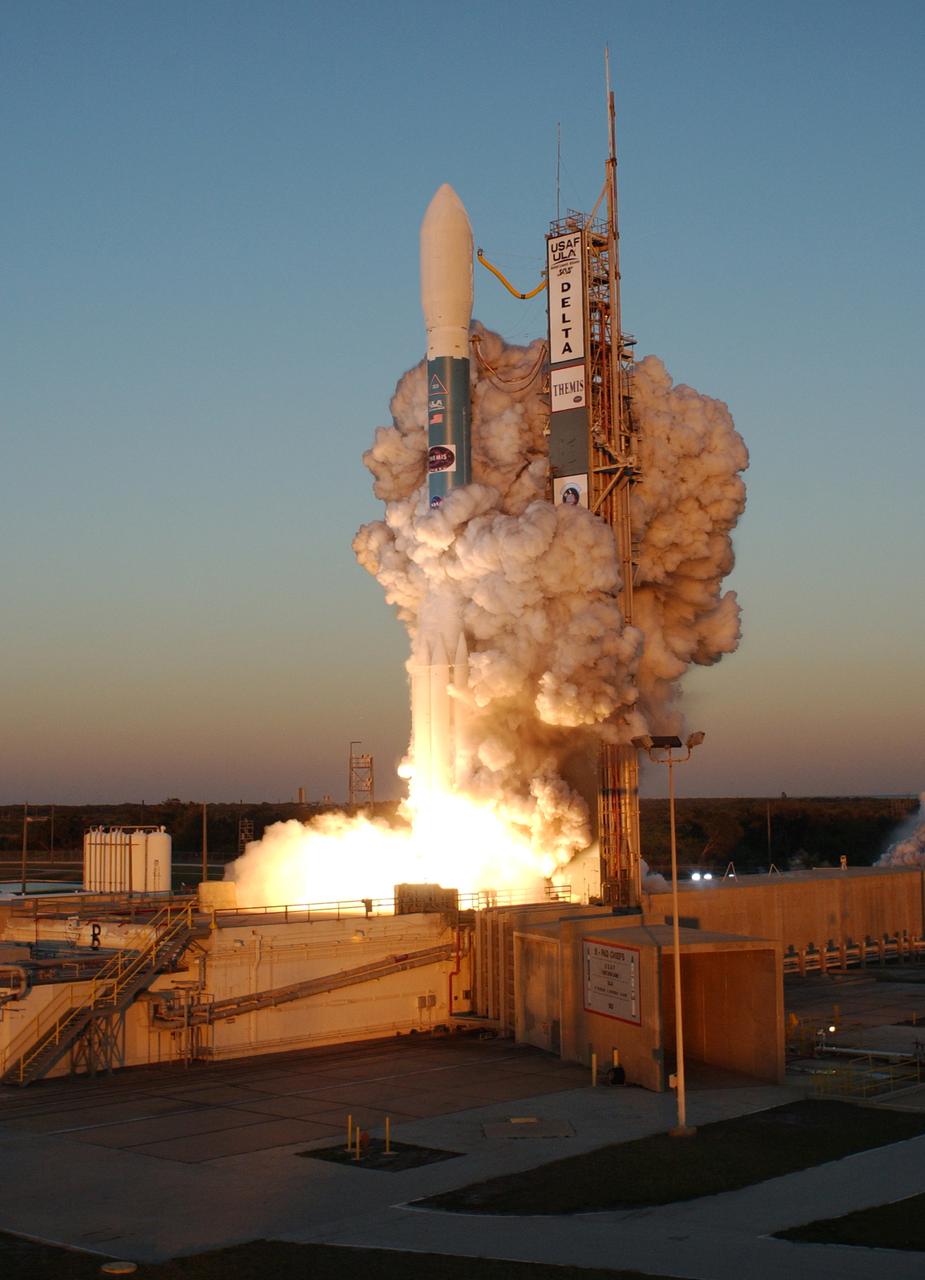

Clouds of smoke encompass the Delta II rocket with NASA's THEMIS spacecraft aboard as it blasts off Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 6:01 p.m. EST. THEMIS, an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms, consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA has ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color
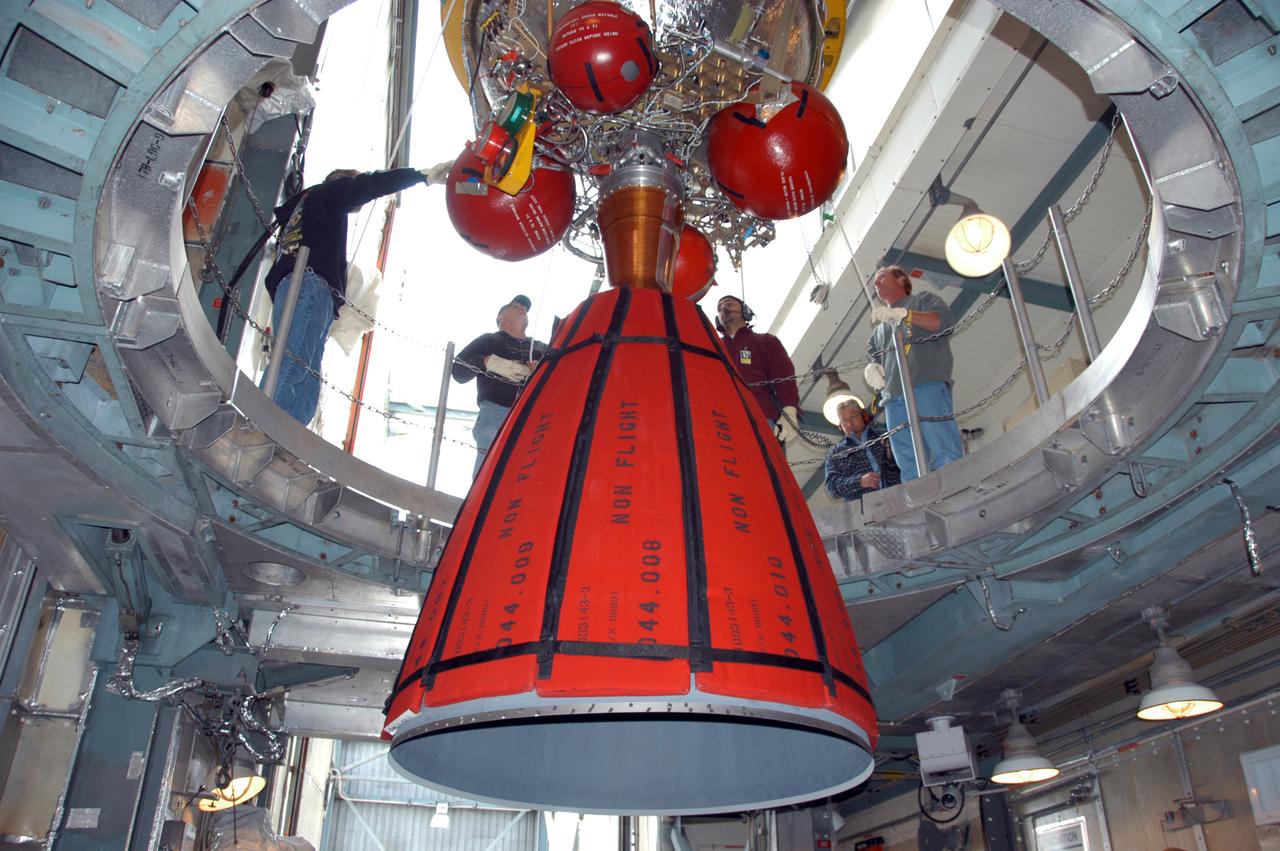
On Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II second stage is being lowered toward the Delta II first stage, already in place inside the mobile service tower. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
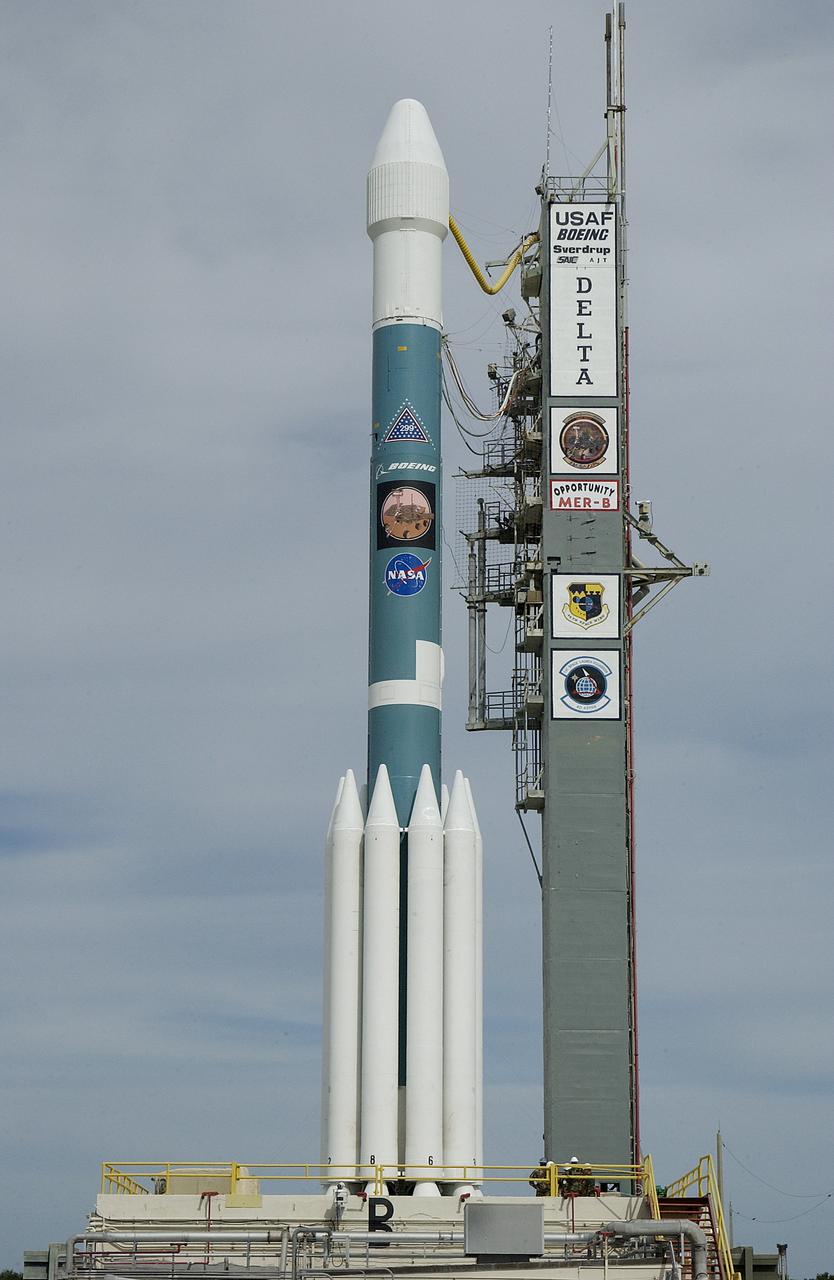

On Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II Heavy launch vehicle carrying the rover "Opportunity" for the second Mars Exploration Rover mission is poised for launch after rollback of the Mobile Service Tower. Opportunity will reach Mars on Jan. 25, 2004. Together the two MER rovers, Spirit (launched June 10) and Opportunity, seek to determine the history of climate and water at two sites on Mars where conditions may once have been favorable to life. The rovers are identical. They will navigate themselves around obstacles as they drive across the Martian surface, traveling up to about 130 feet each Martian day. Each rover carries five scientific instruments including a panoramic camera and microscope, plus a rock abrasion tool that will grind away the outer surfaces of rocks to expose their interiors for examination. Each rover’s prime mission is planned to last three months on Mars.
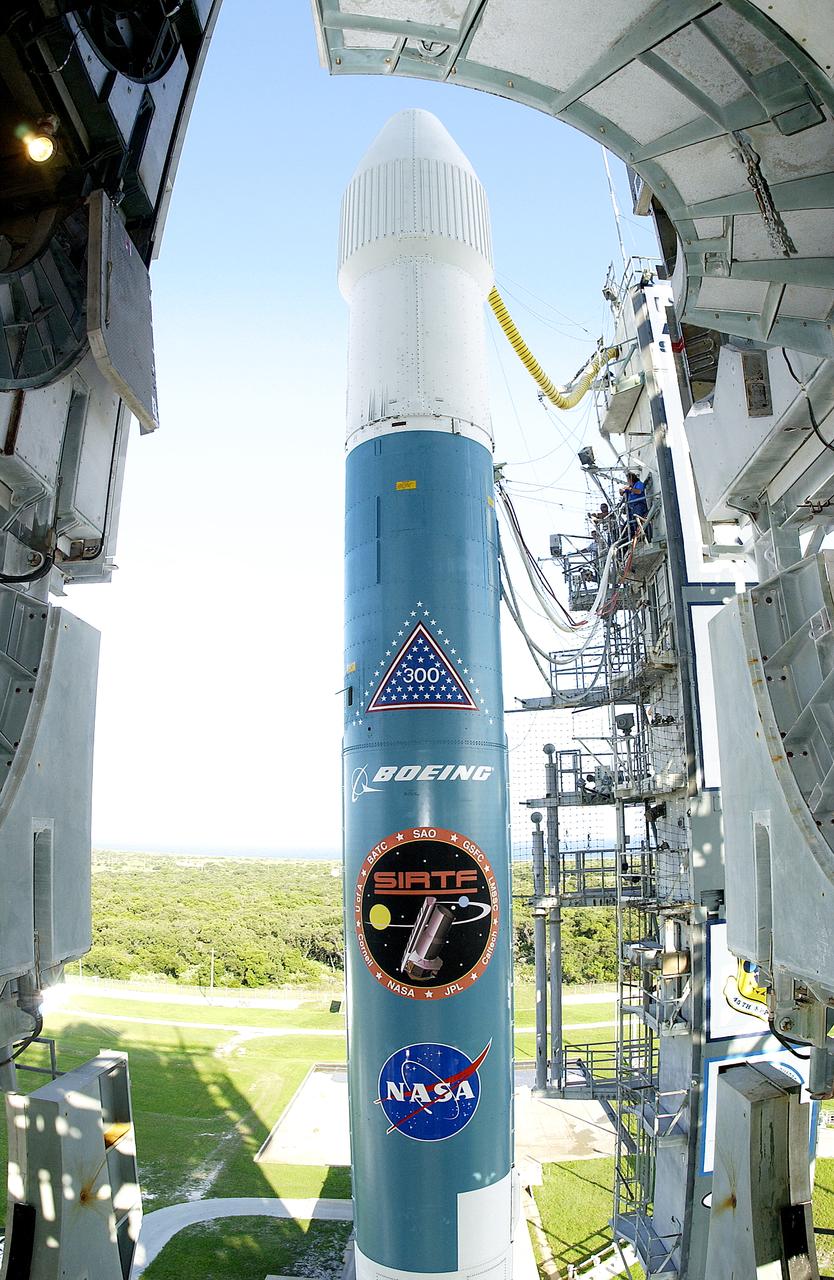

The mobile service tower is rolled back at Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, to reveal NASA's Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) ready for launch aboard a Delta II Heavy launch vehicle. Liftoff is scheduled for Aug. 25 at 1:35:39 a.m. EDT. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Consisting of a 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF will be the largest infrared telescope ever launched into space. It is the fourth and final element in NASA’s family of orbiting “Great Observatories.” Its highly sensitive instruments will give a unique view of the Universe and peer into regions of space that are hidden from optical telescopes.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, clouds of smoke envelop the Delta II rocket with NASA's THEMIS spacecraft aboard as it blasts off Pad 17-B at 6:01 p.m. EST. THEMIS, an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms, consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA has ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color.
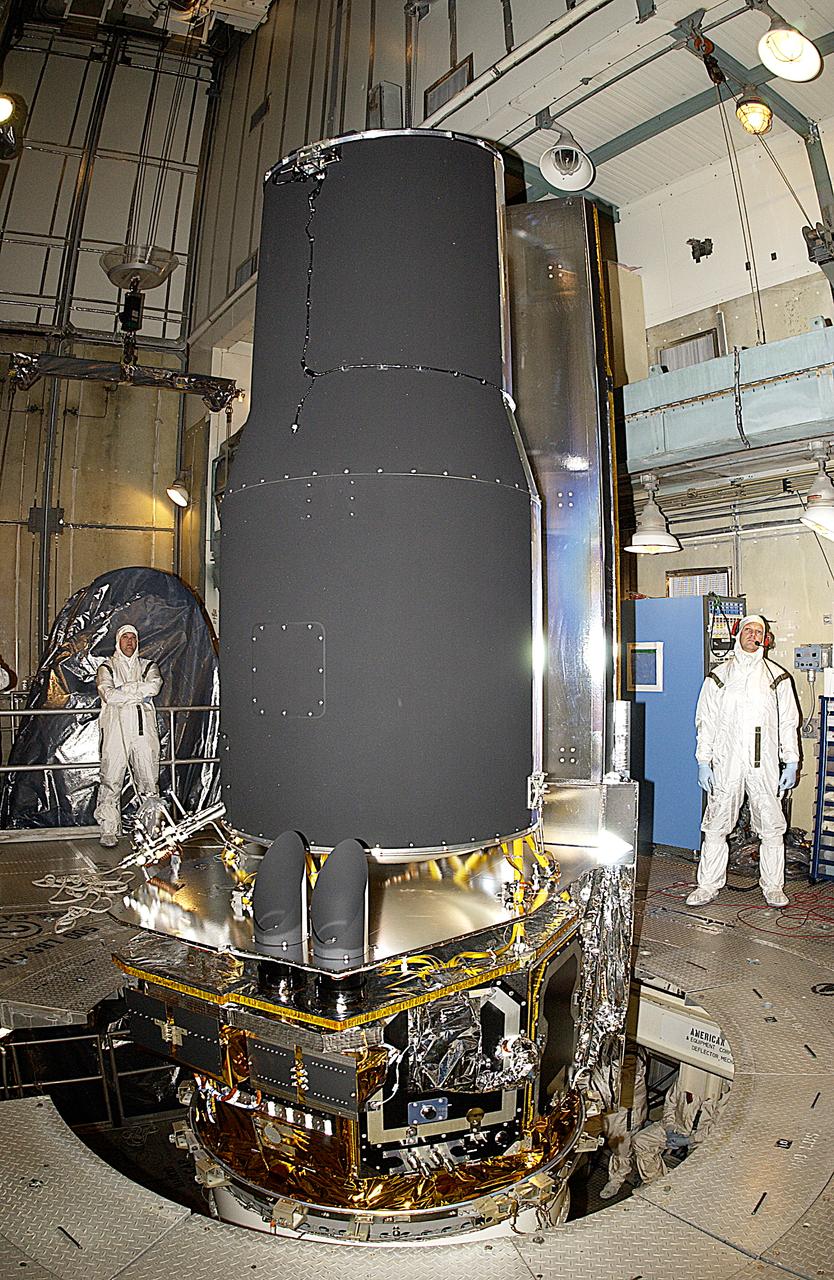

In the launch tower on Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) is lifted into position for installation of the fairing. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch April 18 aboard a Delta II rocket.
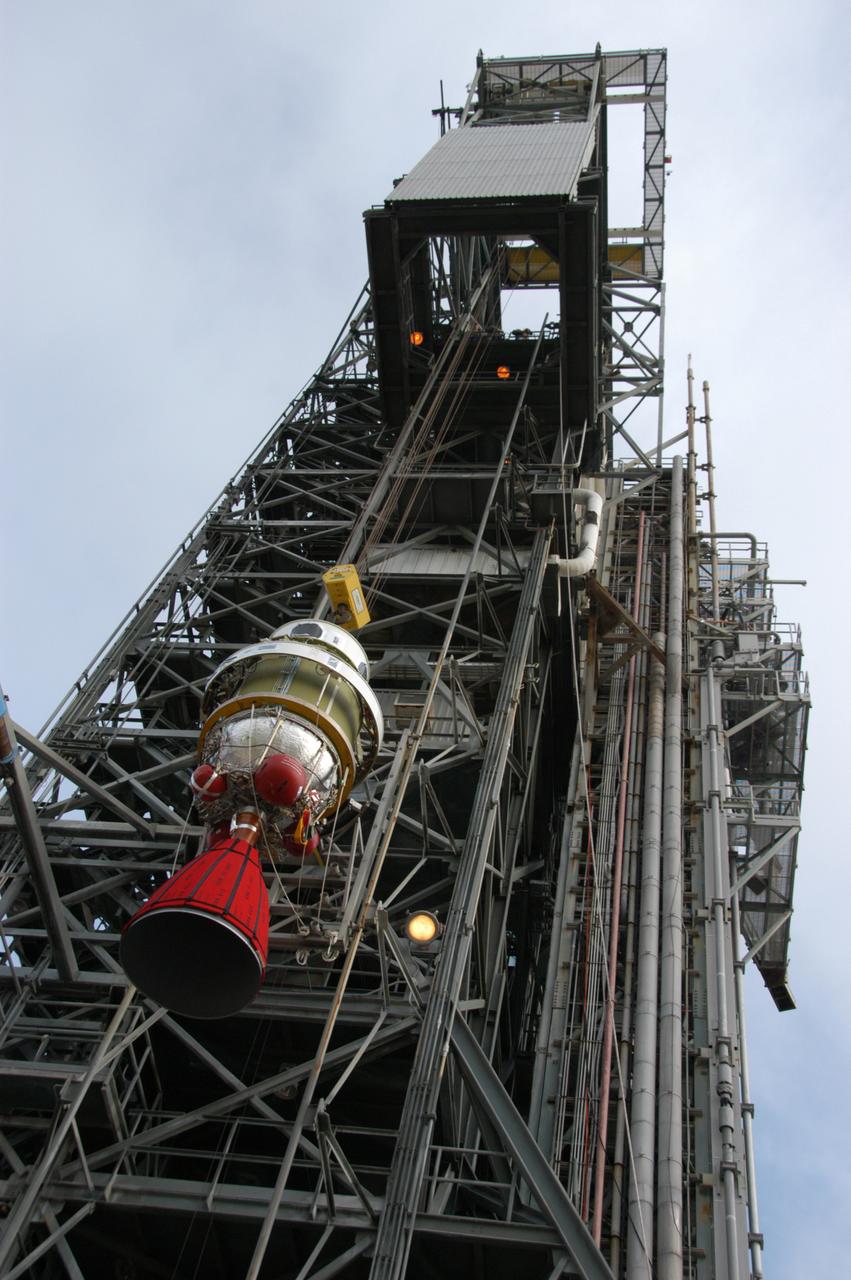

On Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II second stage is being lifted alongside the mobile service tower. Once inside, it will be mated with the first stage already in place. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
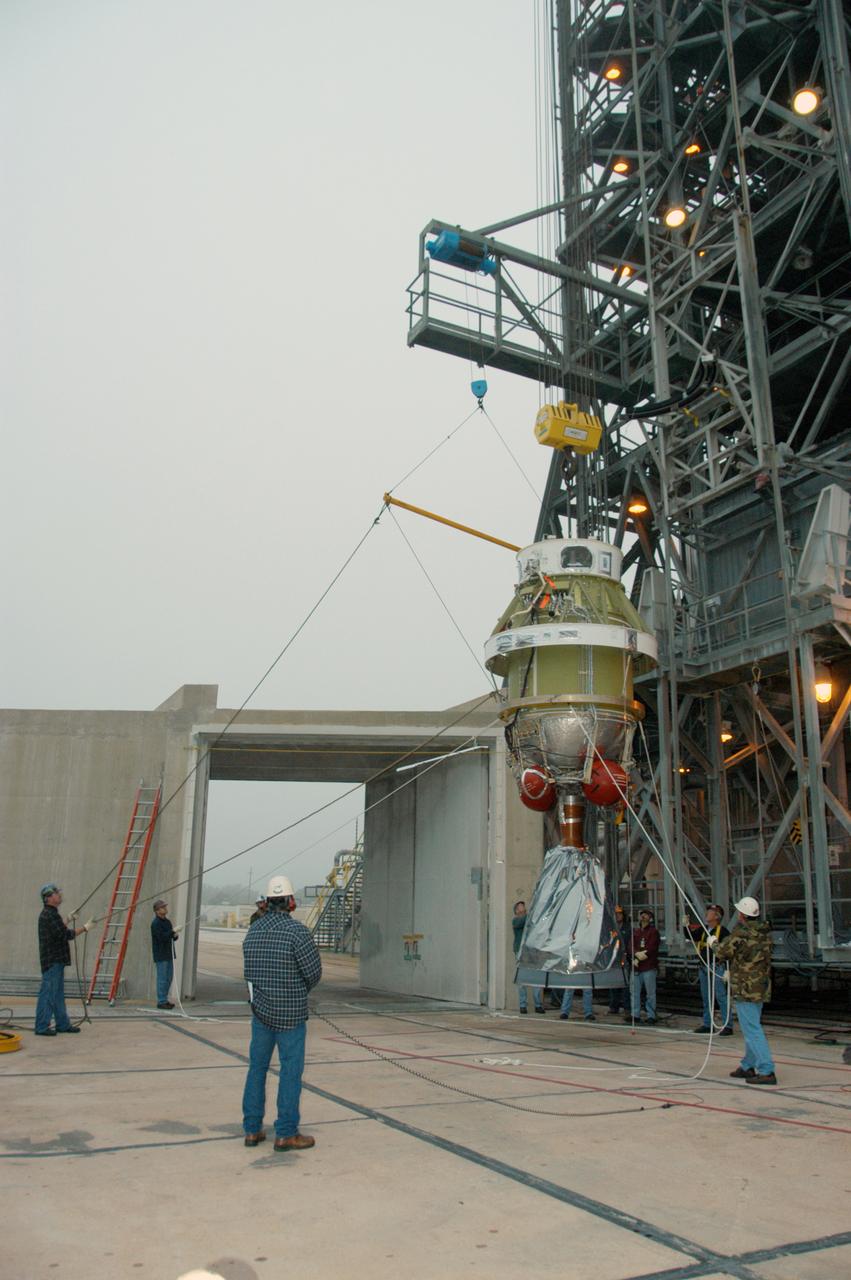

On Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II second stage is lifted toward the mobile service tower. Once inside, it will be mated with the first stage already in place. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
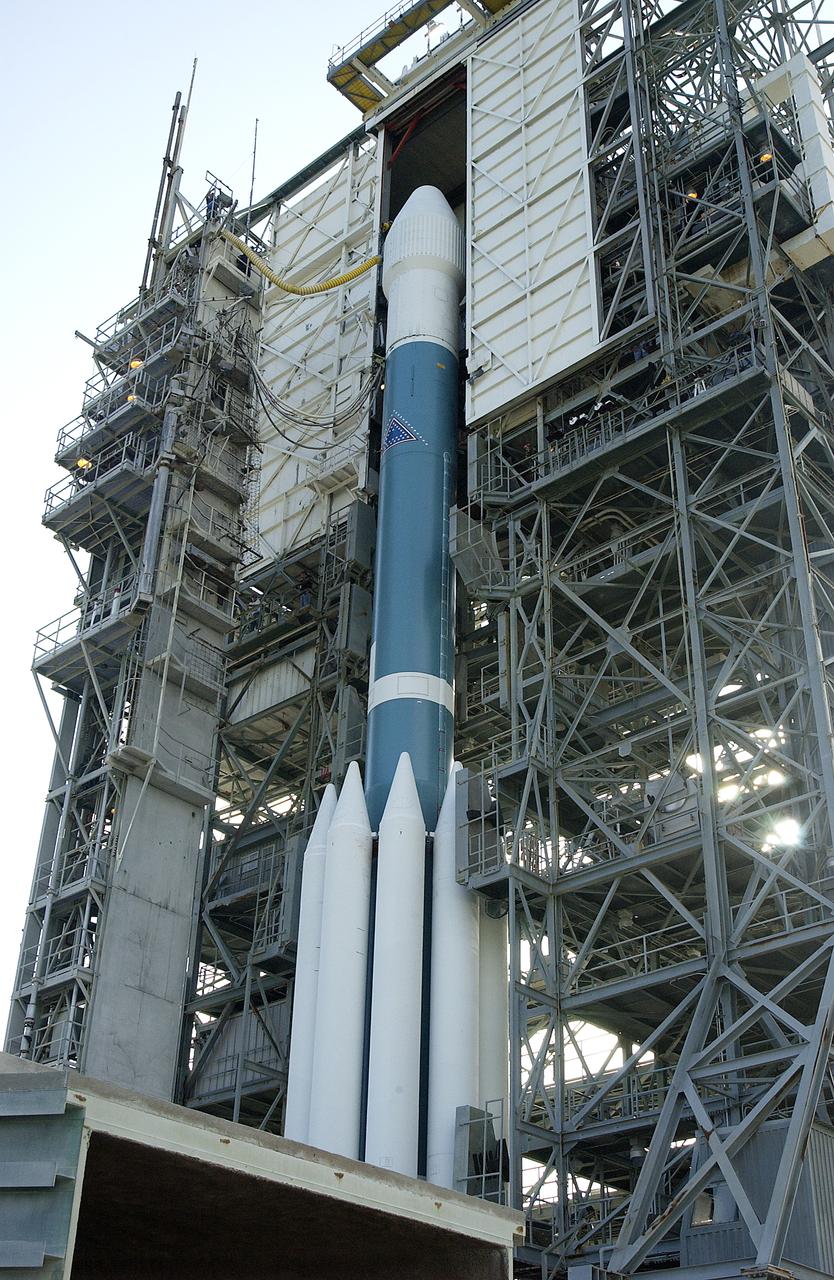

The mobile service tower is rolled back at Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, to reveal NASA's Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF) ready for launch aboard a Delta II Heavy launch vehicle. Liftoff is scheduled for Aug. 25 at 1:35:39 a.m. EDT. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Consisting of a 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF will be the largest infrared telescope ever launched into space. It is the fourth and final element in NASA’s family of orbiting “Great Observatories.” Its highly sensitive instruments will give a unique view of the Universe and peer into regions of space that are hidden from optical telescopes.
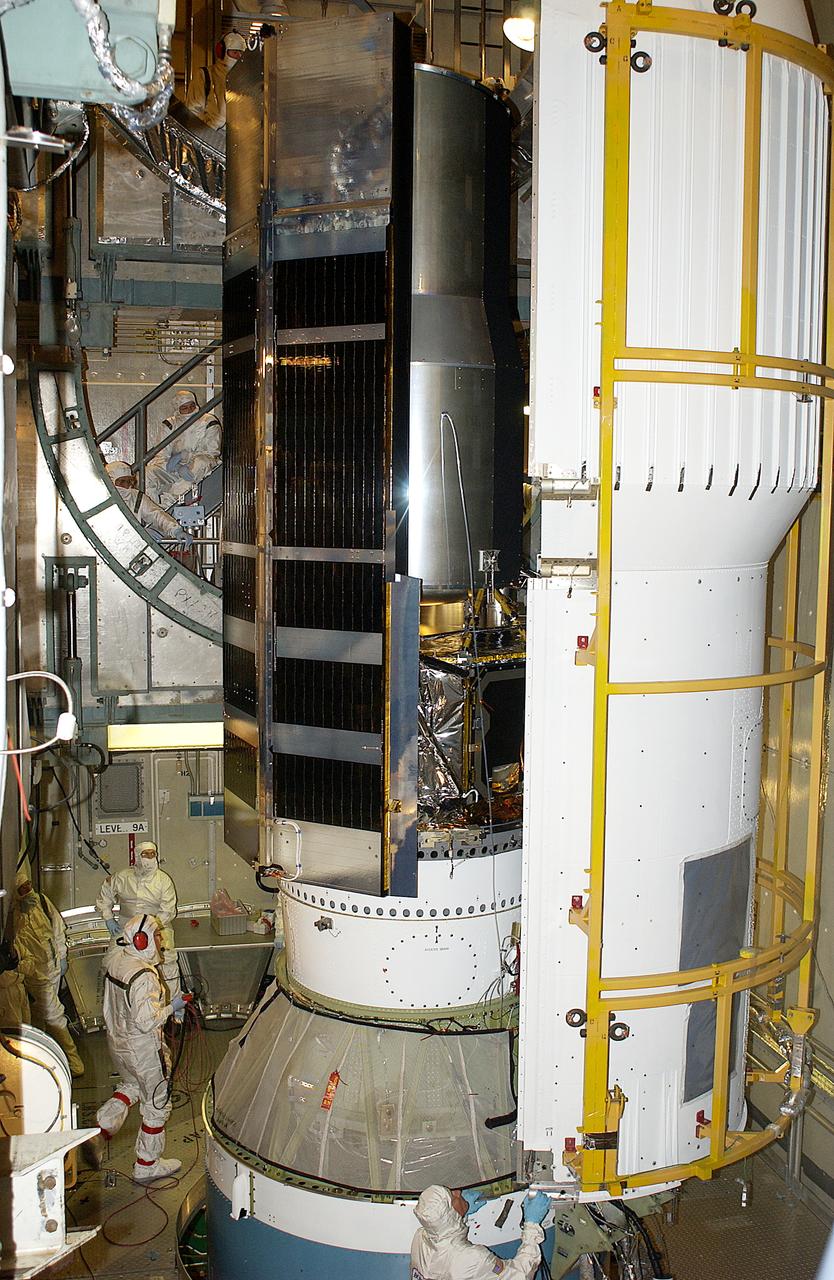

In the launch tower on Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first part of the fairing is place around the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF). The fairing protects the spacecraft during launch. SIRTF will obtain images and spectra by detecting the infrared energy, or heat, radiated by objects in space. Most of this infrared radiation is blocked by the Earth's atmosphere and cannot be observed from the ground. Consisting of an 0.85-meter telescope and three cryogenically cooled science instruments, SIRTF is one of NASA's largest infrared telescopes to be launched. SIRTF is currently scheduled for launch April 18 aboard a Delta II rocket from Launch Complex 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
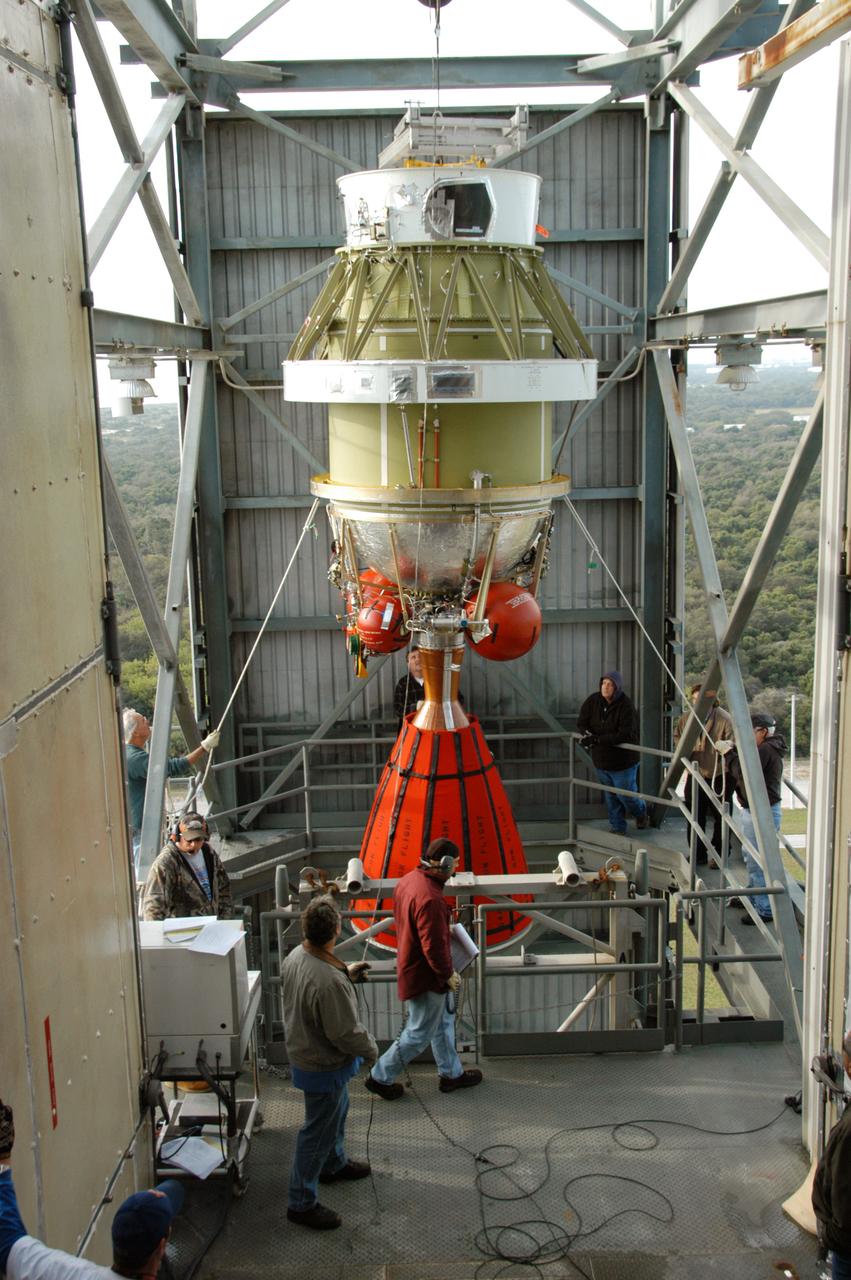

On Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Delta II second stage arrives at level 9 of the tower. The second stage will be moved inside and mated with the first stage already in place. The Delta II is the launch vehicle for the THEMIS spacecraft THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the first half of the fairing is in place around the THEMIS spacecraft and workers turn to wait for the second half. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. THEMIS is an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms. THEMIS consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the tantalizing mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color. Launch of THEMIS is scheduled for Feb. 15 aboard a Delta II rocket, with the launch service being conducted by the United Launch Alliance.