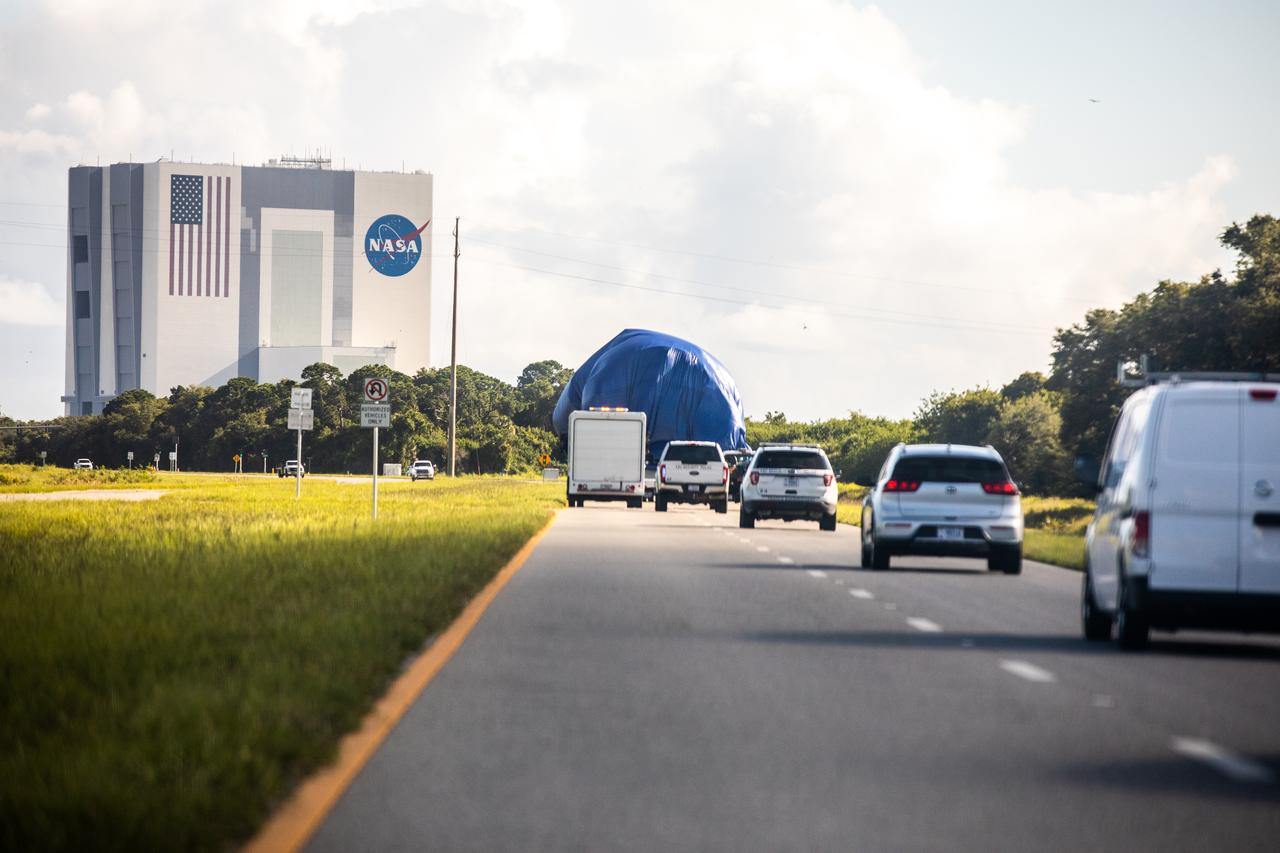

A flatbed truck, carrying the node structural test article (STA), is on its way to the Launch and Landing Facility from the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 20, 2020. In view is the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building. The Node STA was used to prove the manufacturing processes and procedures were robust for extended human spaceflight. Those same processes and procedures were then used to build Node 1, which Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana flew to the space station on STS 88. NASA has stored the node STA in the SSPF, and it is moving to a new location to allow for more space in the facility’s high bay to support the agency’s space exploration and commercialization efforts in low-Earth orbit.
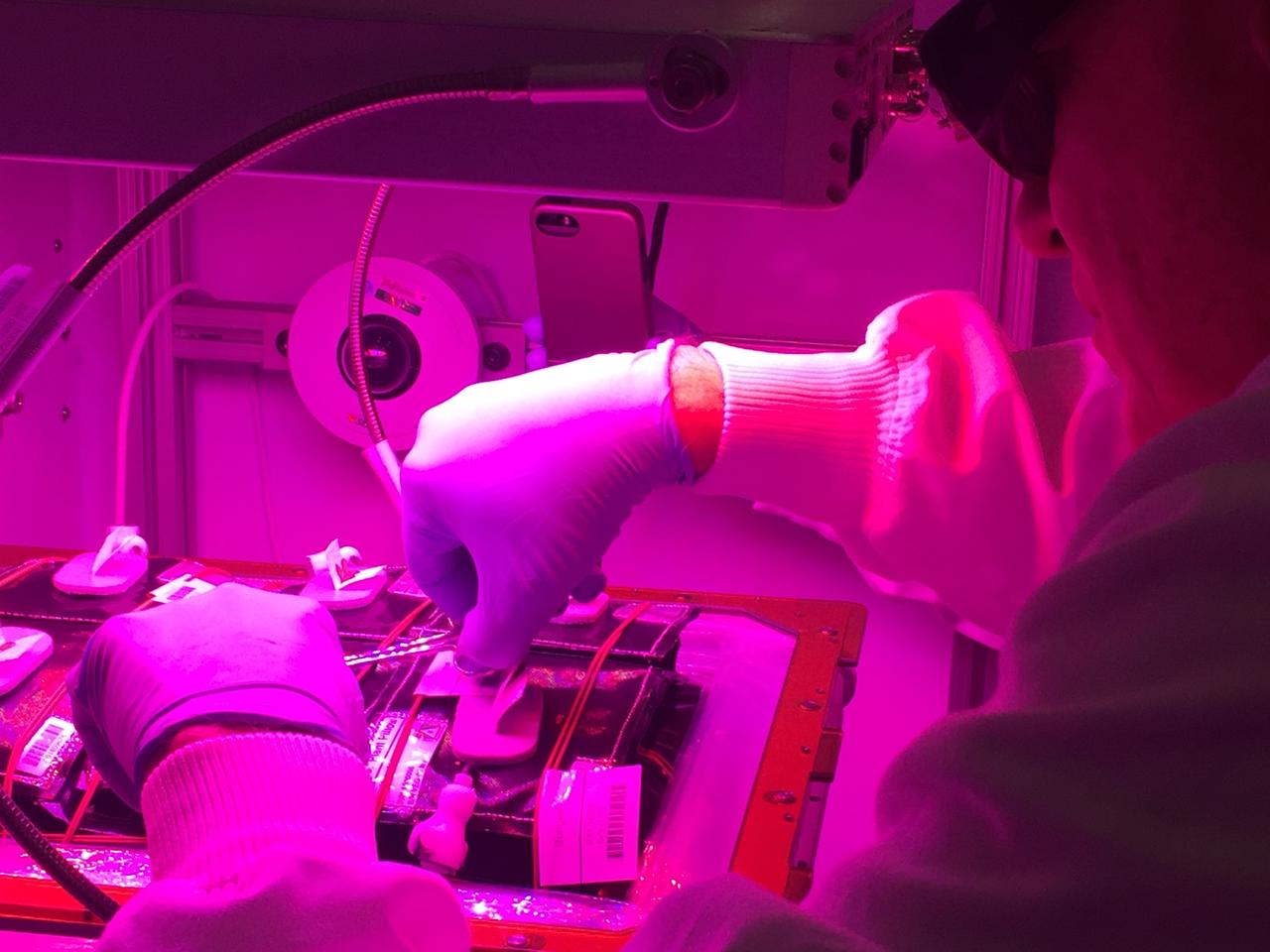

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
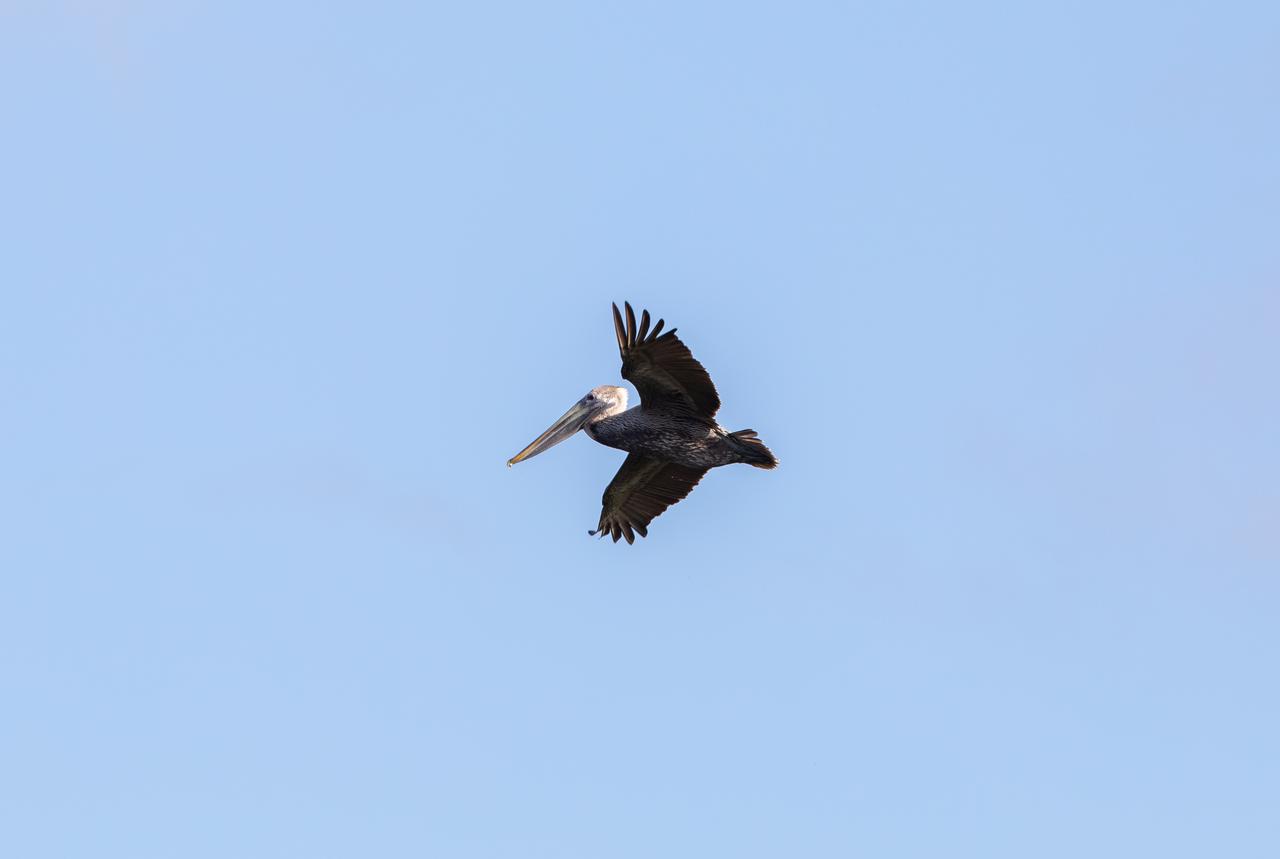

A pelican soars above a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2021. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, along with 25 mammal, 117 fish, and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
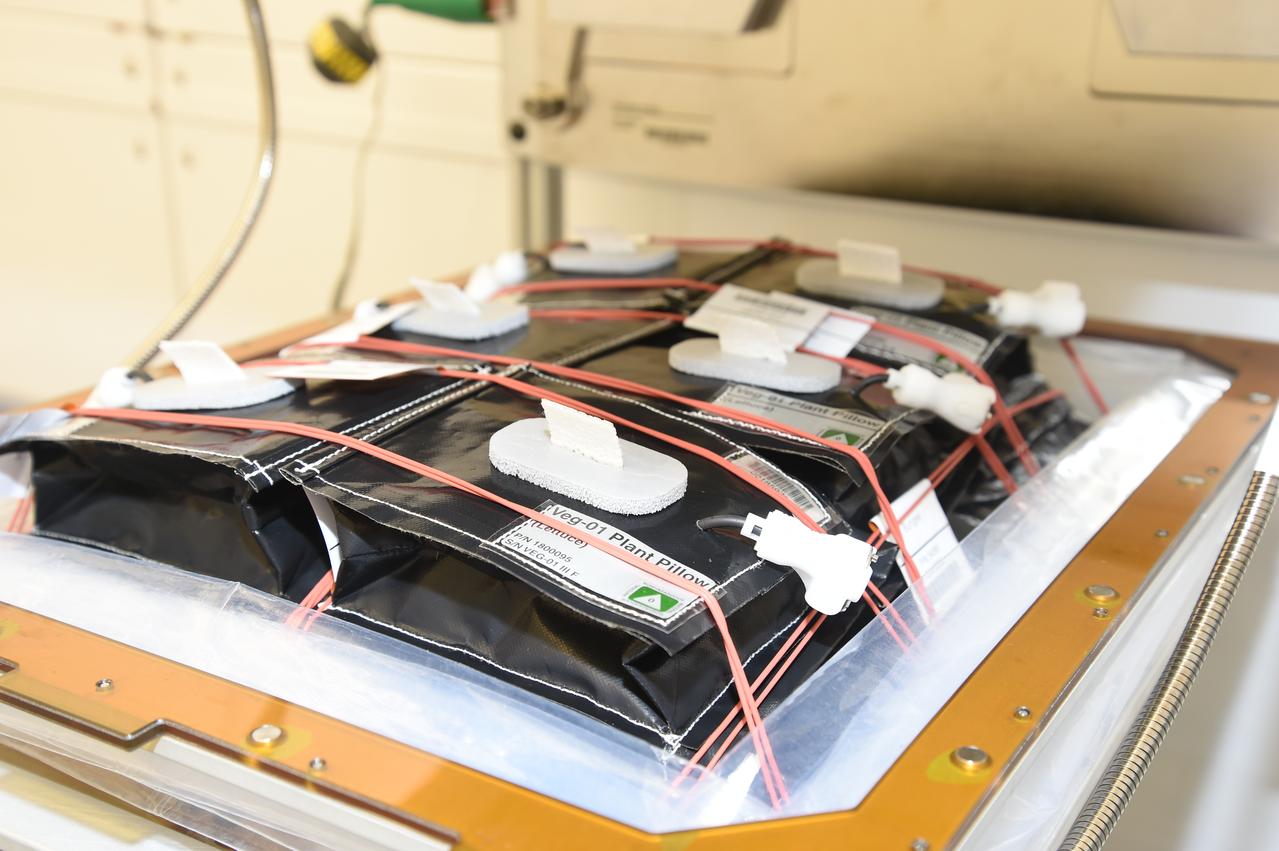

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
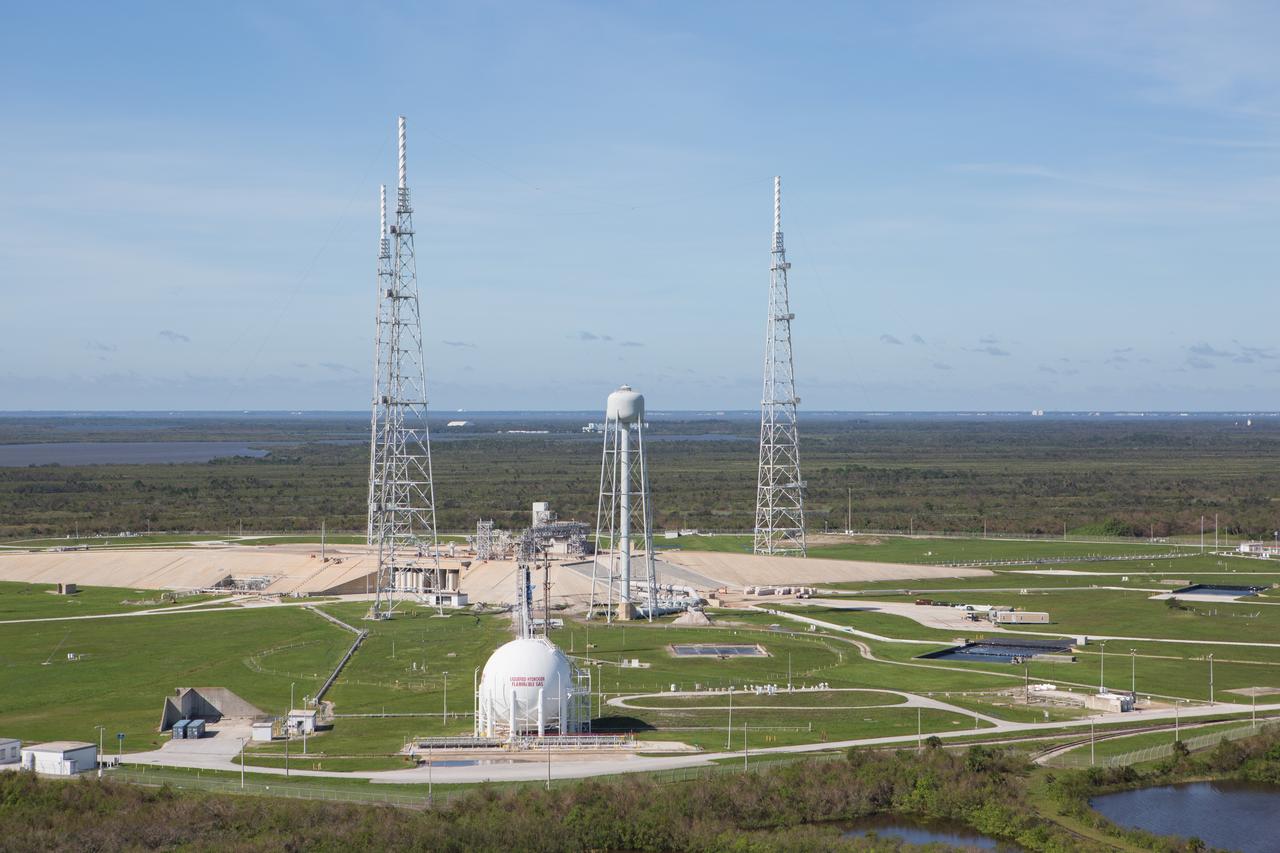

Launch Complex 39B is seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Matthew as the storm passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. Officials determined that the center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm’s onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed

Standing atop the mobile launcher, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft can be seen at Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 18, 2022. The Artemis I stack was carried from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the pad – a 4.2-mile journey that took nearly 11 hours to complete – by the agency’s crawler-transporter 2 for a wet dress rehearsal ahead of the uncrewed launch. Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.

In this close-up view inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the base of the Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage pathfinder can be seen as it is lowered into High Bay 3 on Oct. 16, 2019. The 212-foot-long core stage pathfinder arrived on NASA's Pegasus Barge at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Sept. 27, 2019. The Pegasus Barge made its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The pathfinder is being used by Exploration Ground Systems and its contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy through at least the month of October before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
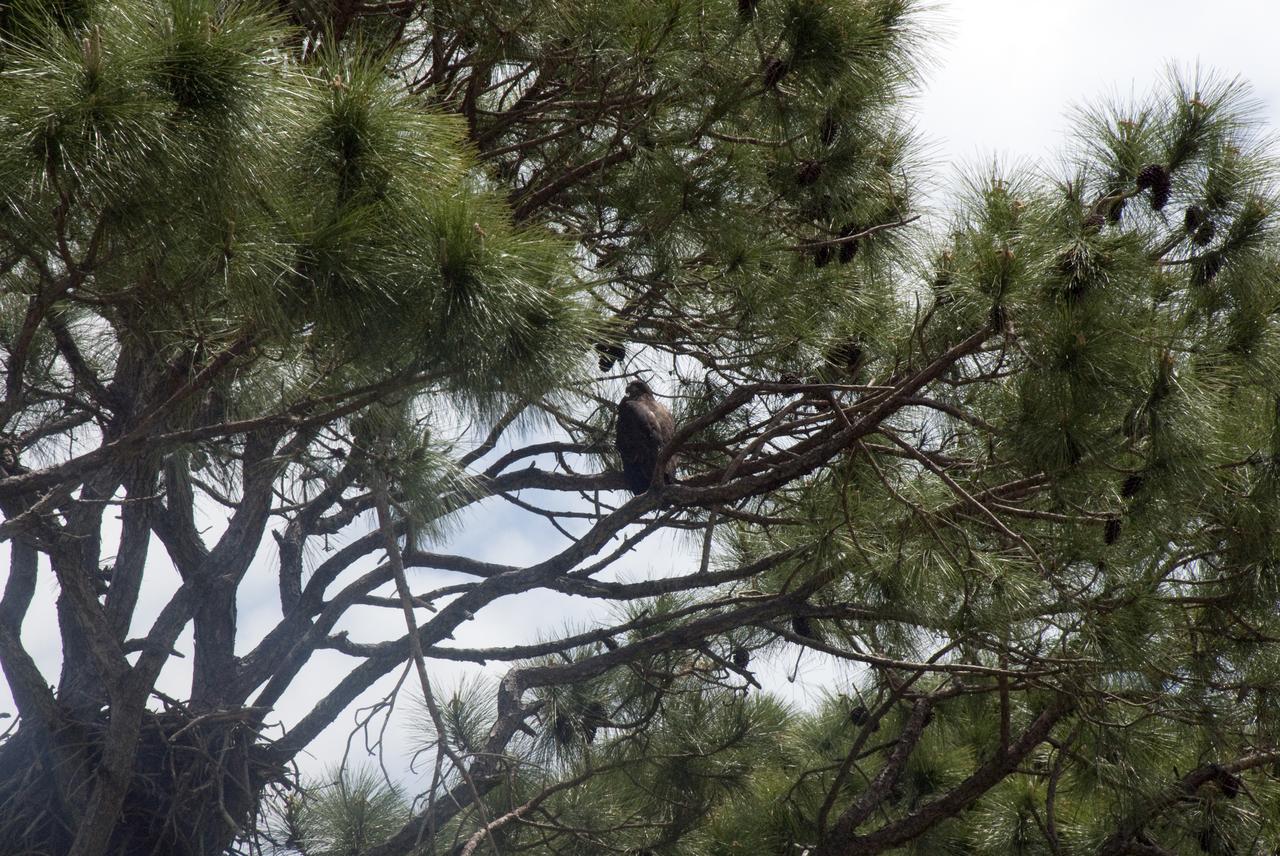

KSC WILDLIFE - BABY EAGLE AT REST ON SR3 - BABY OSPREYS AT PRESS SITE
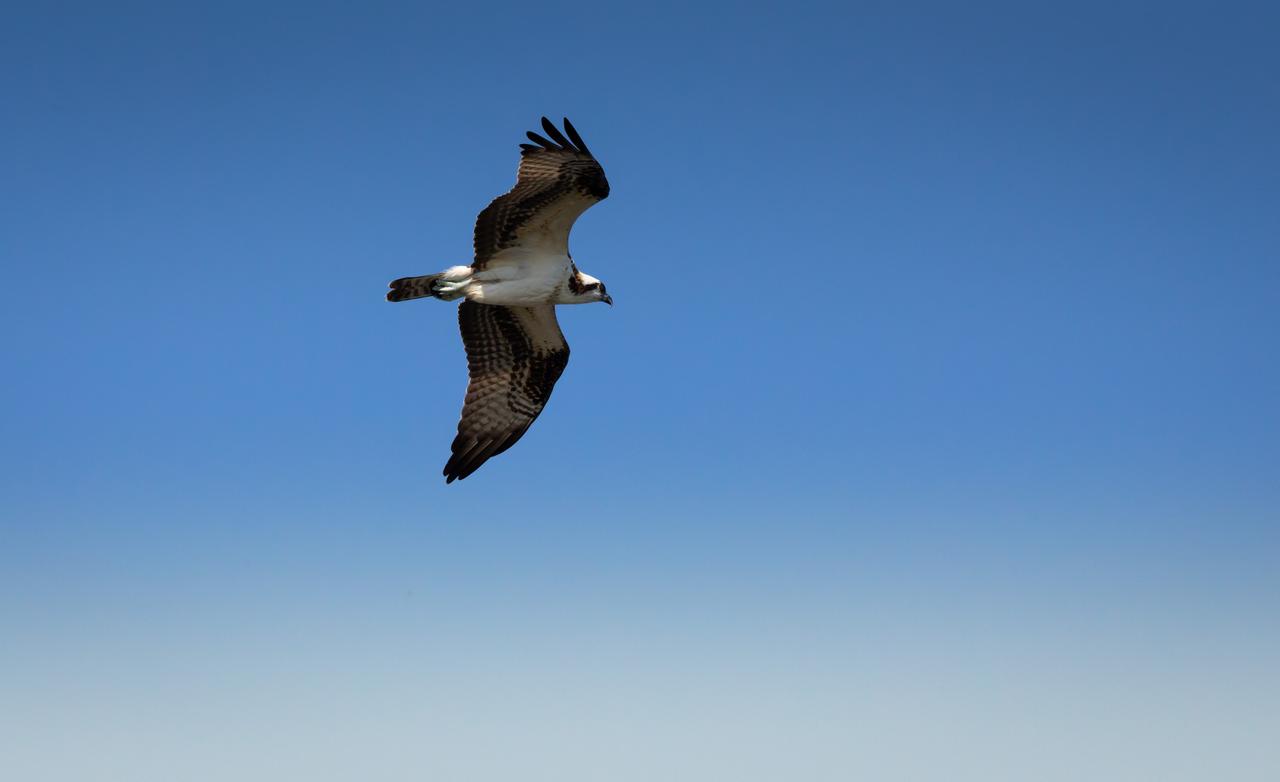

An osprey soars above NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
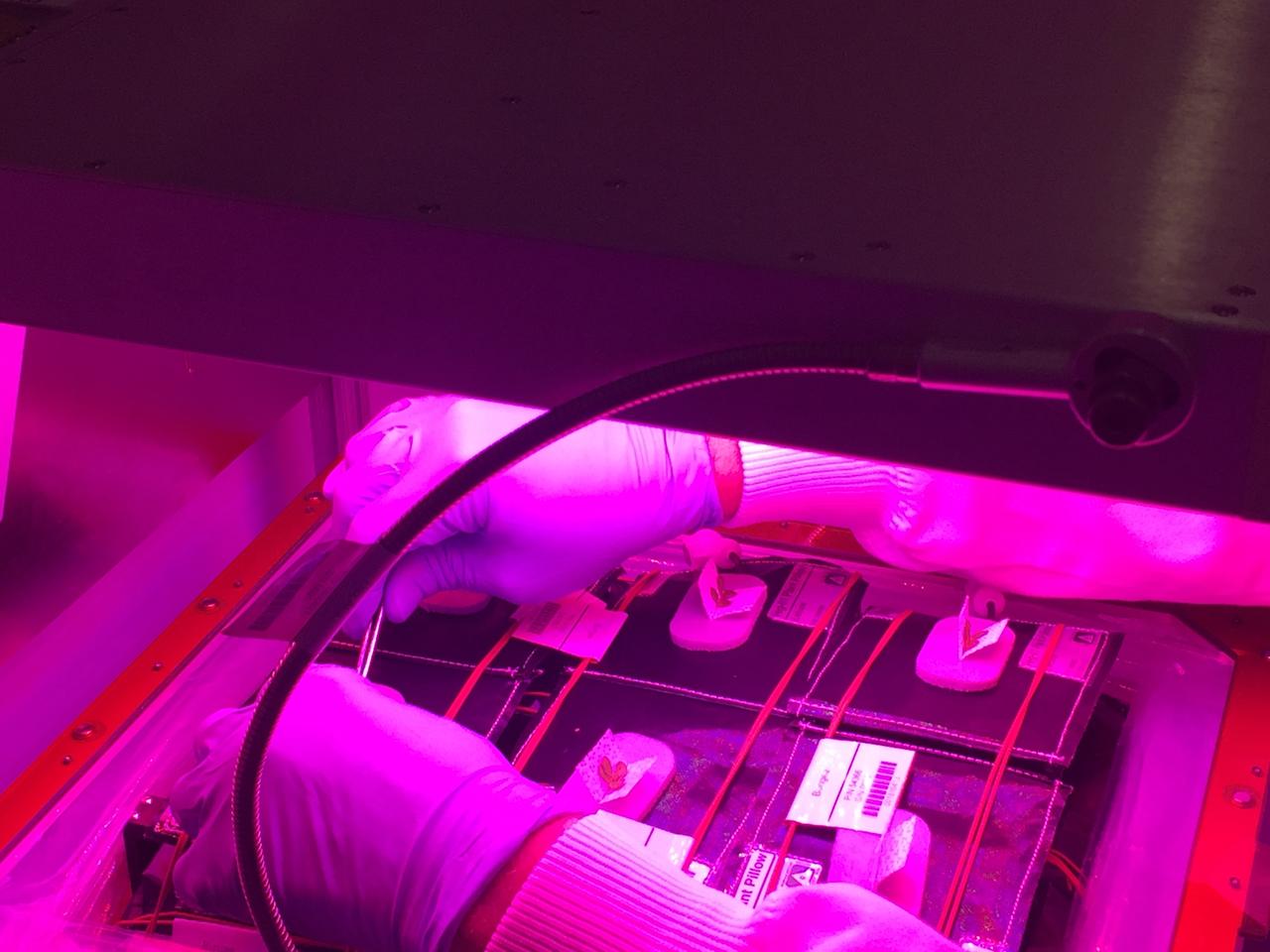

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
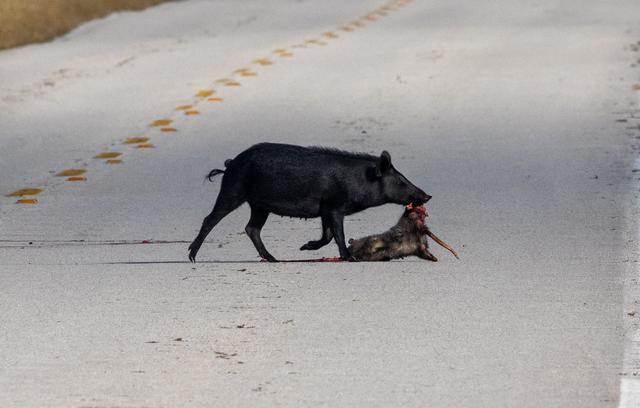

A wild pig is spotted with its prey on a roadway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2021. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
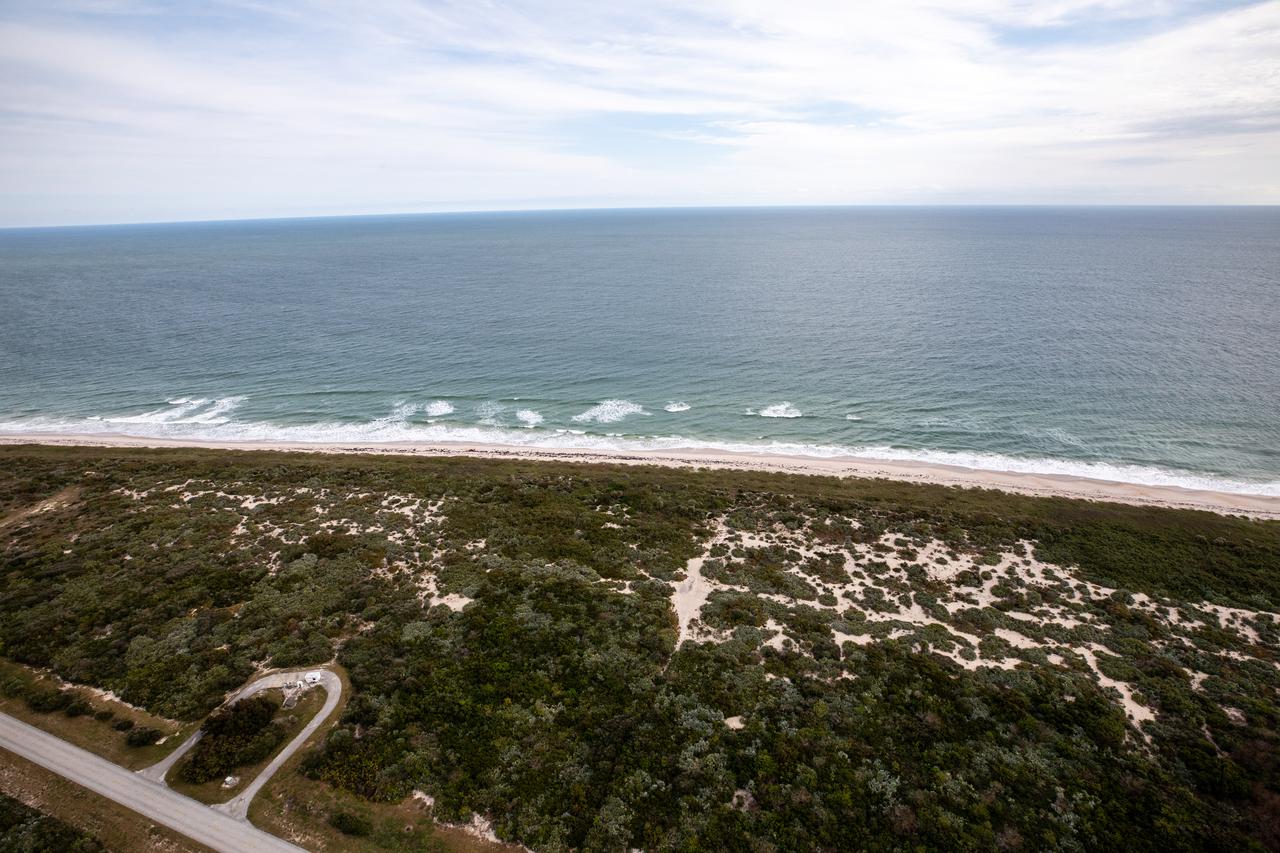

An aerial view of the Atlantic Ocean coastline and dunes along NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 13, 2021.
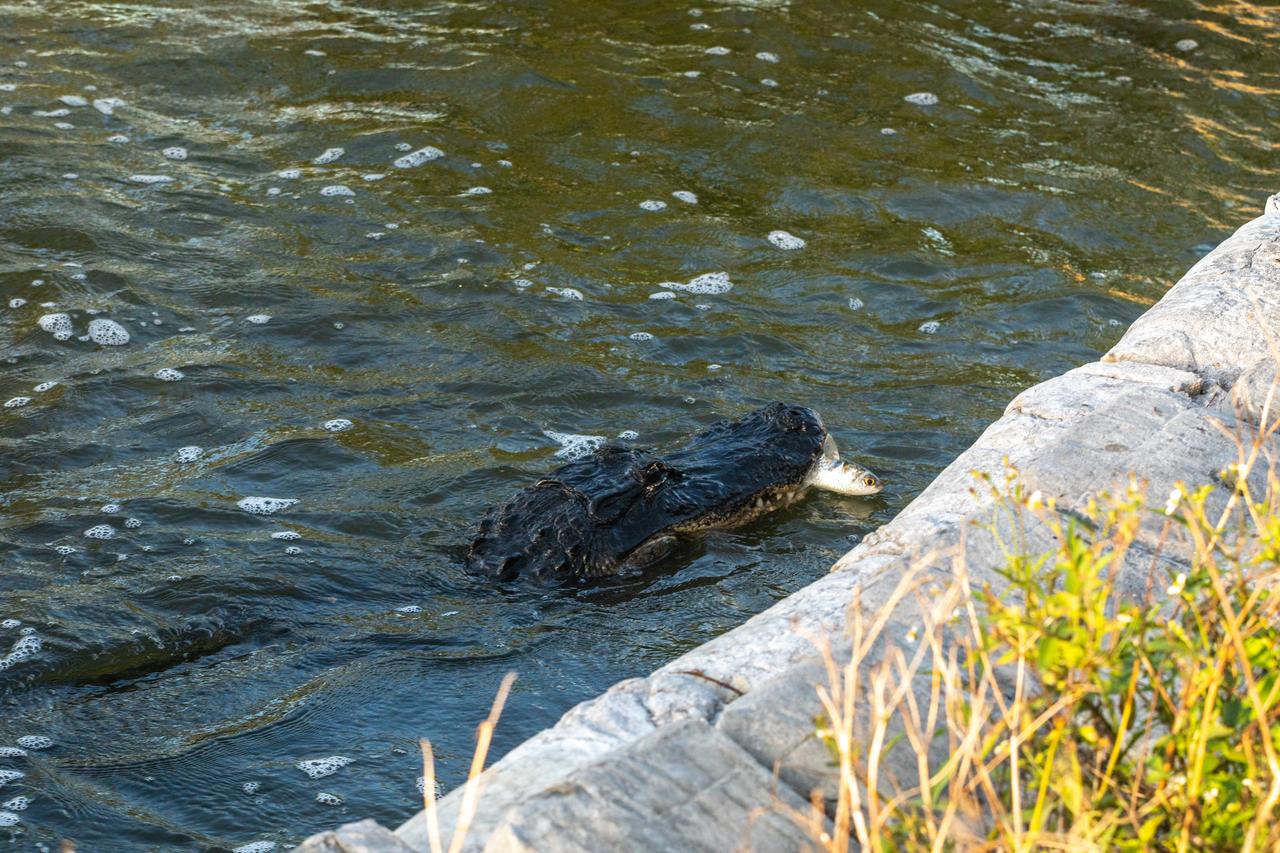

Kennedy Space Center shares boundaries with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge on Florida’s Atlantic coast. Alligators can be found in many areas of the refuge. They are important top predators that help keep populations of smaller animals under control. They also create habitat for other wildlife in the marsh by digging holes that hold water during the dry season.
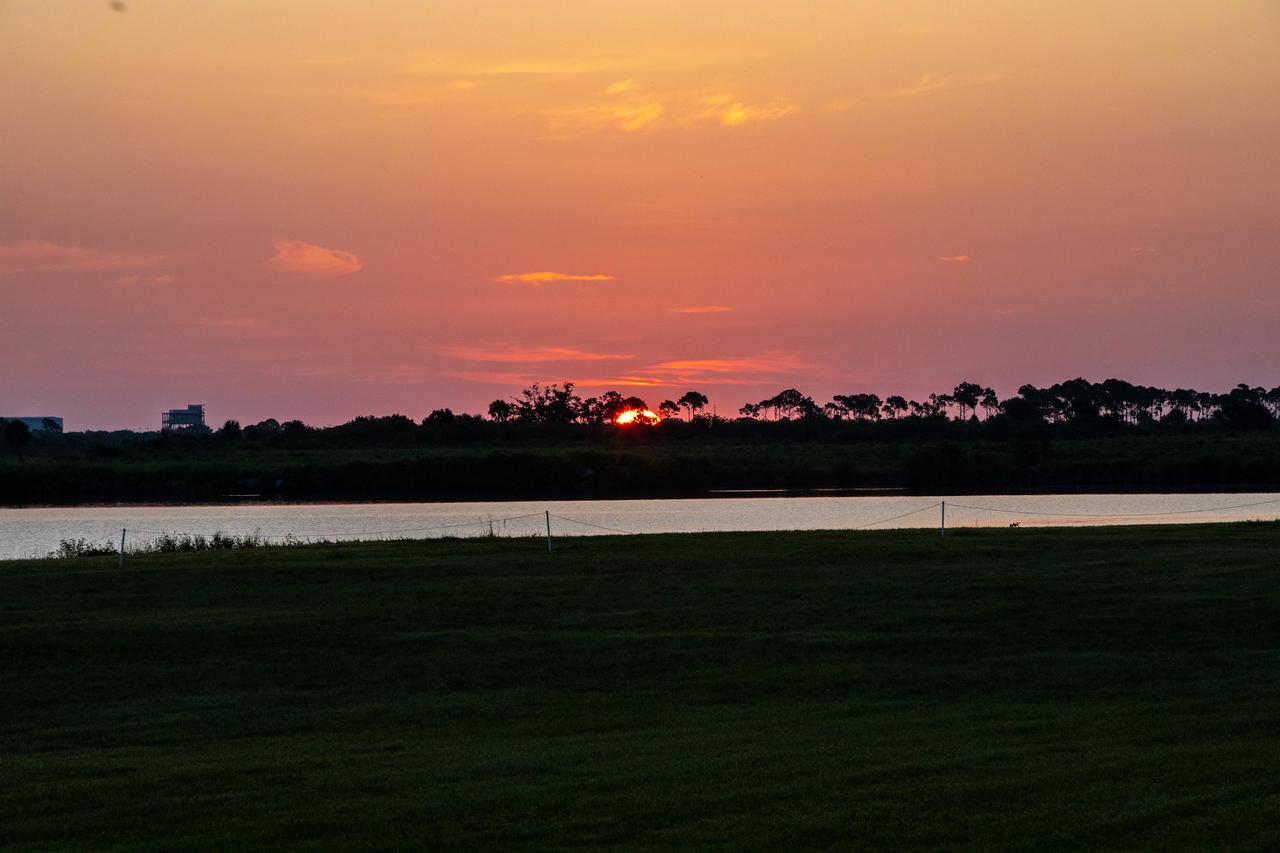

The Sun just begins to rise over NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 15, 2020. A multi-user spaceport, Kennedy has partnerships with both government and commercial entities, providing the facilities and infrastructure necessary for venturing to space.
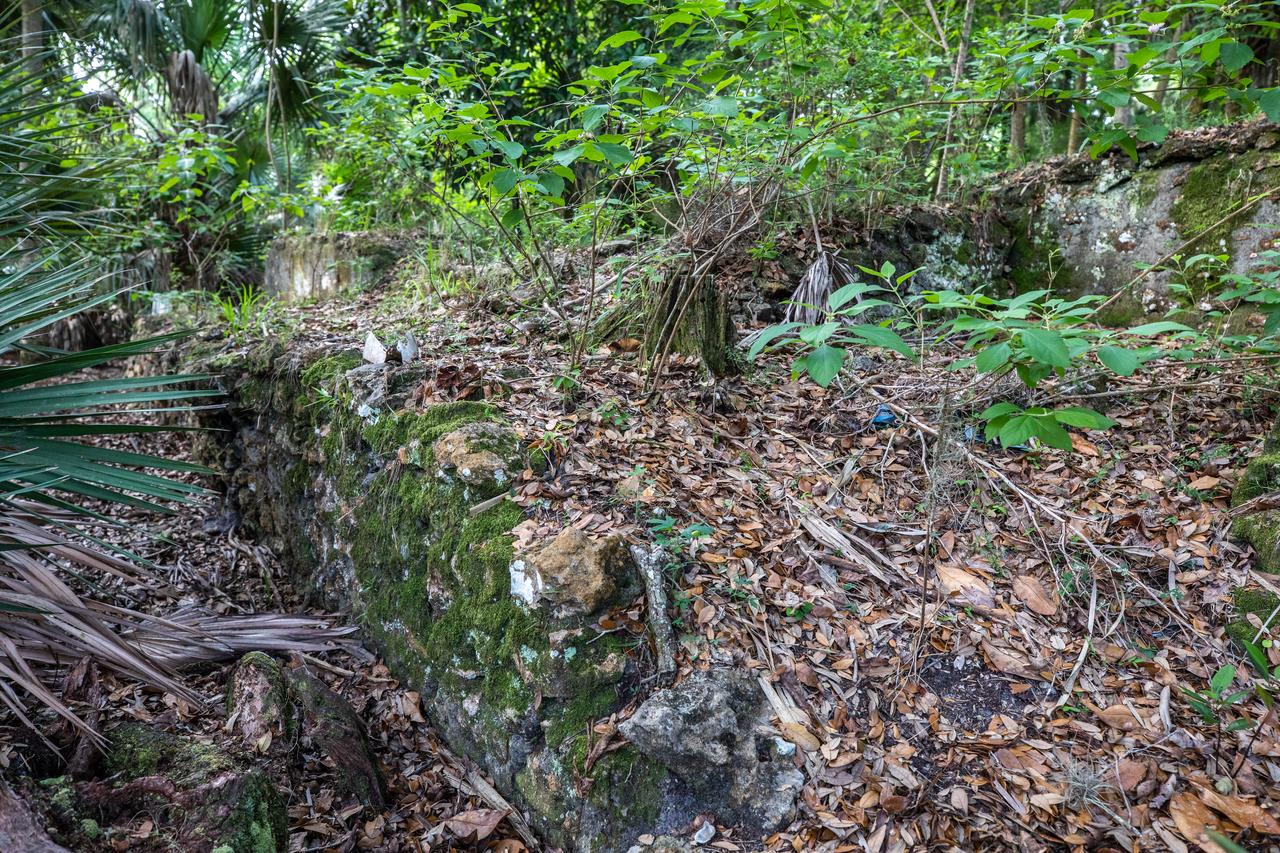

Archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill are revealed through the oak hammock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.

Twin rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) that will power Artemis missions to the Moon have arrived at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The two motor segments, each comprised of five segments, arrived at Kennedy’s Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on June 15, 2020, by train from a Northrop Grumman manufacturing facility in Promontory, Utah. The booster segments will remain in the RPSF for inspection prior to processing until it’s time to move them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. This is the first piece of flight hardware to arrive at Kennedy by train for the Artemis program, but NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) can expect to receive additional hardware soon, including the Launch Vehicle Service Adapter and the rocket’s core stage. NASA is working toward an Artemis I launch date in 2021, keeping the program moving at the best possible pace toward the earliest possible opportunity.
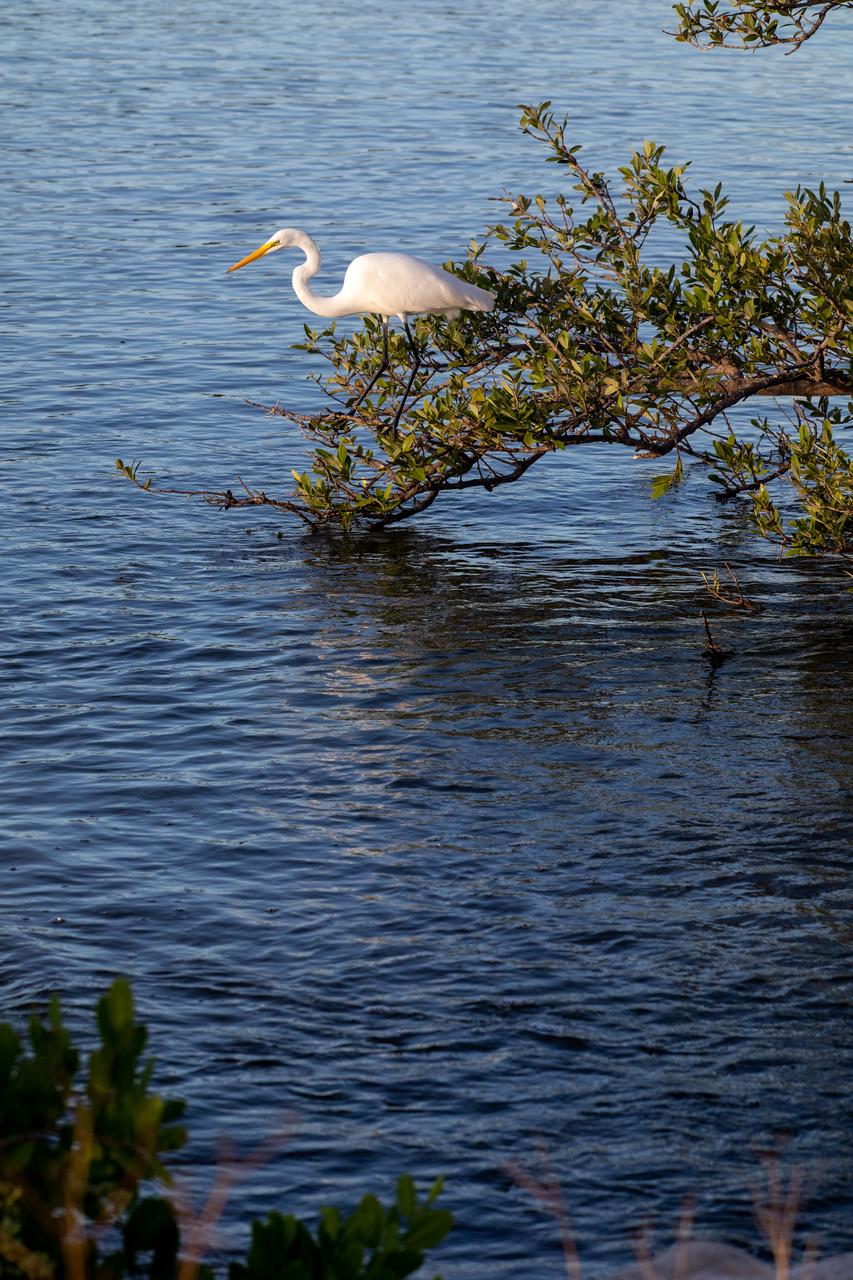

Kennedy Space Center shares boundaries with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge on Florida’s Atlantic coast. The refuge's coastal location, tropic-like climate, and wide variety of habitat types contribute to a diverse bird population. More than 350 species have been identified on the refuge.
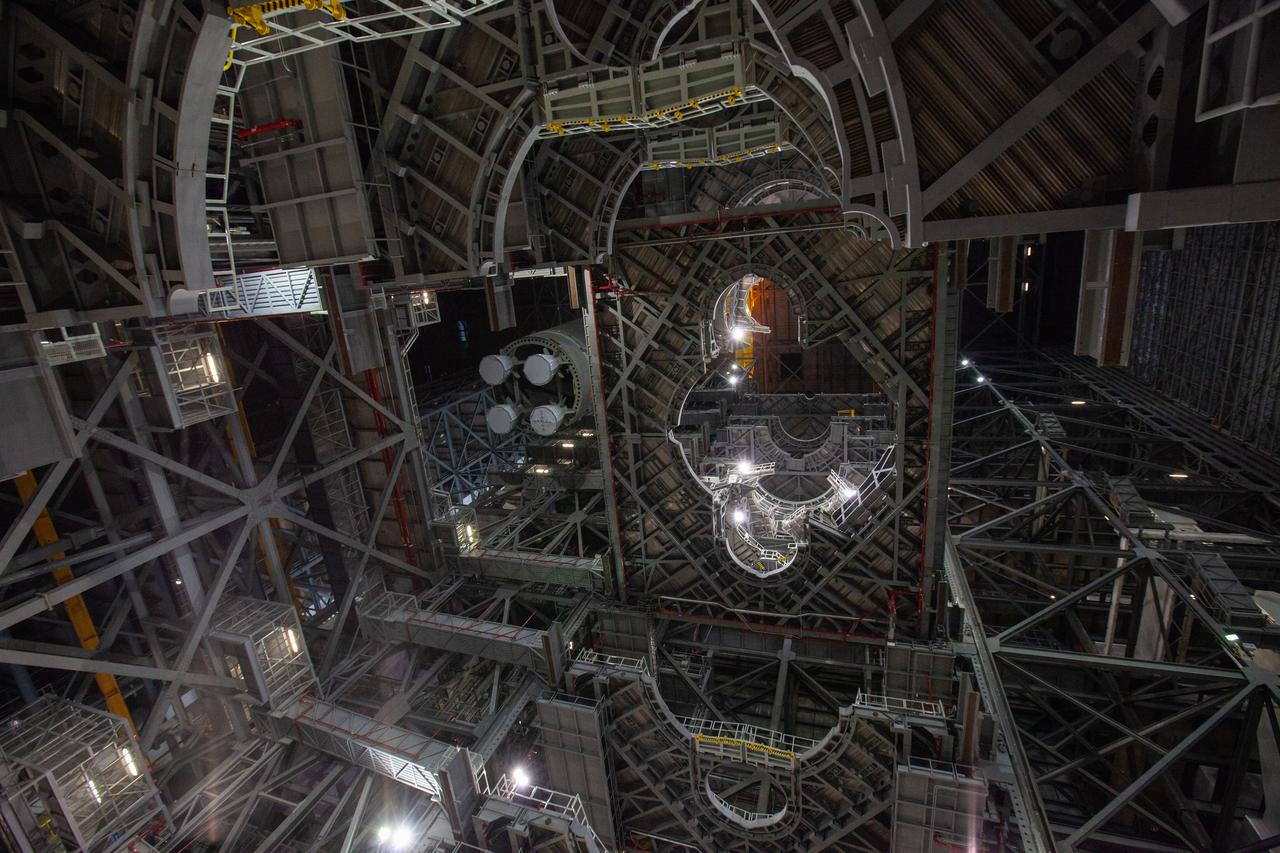

In this view looking up inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage pathfinder into High Bay 3 on Oct. 16, 2019. The 212-foot-long core stage pathfinder arrived on NASA's Pegasus Barge at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Sept. 27, 2019. The Pegasus Barge made its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The pathfinder is being used by Exploration Ground Systems and its contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy through at least the month of October before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
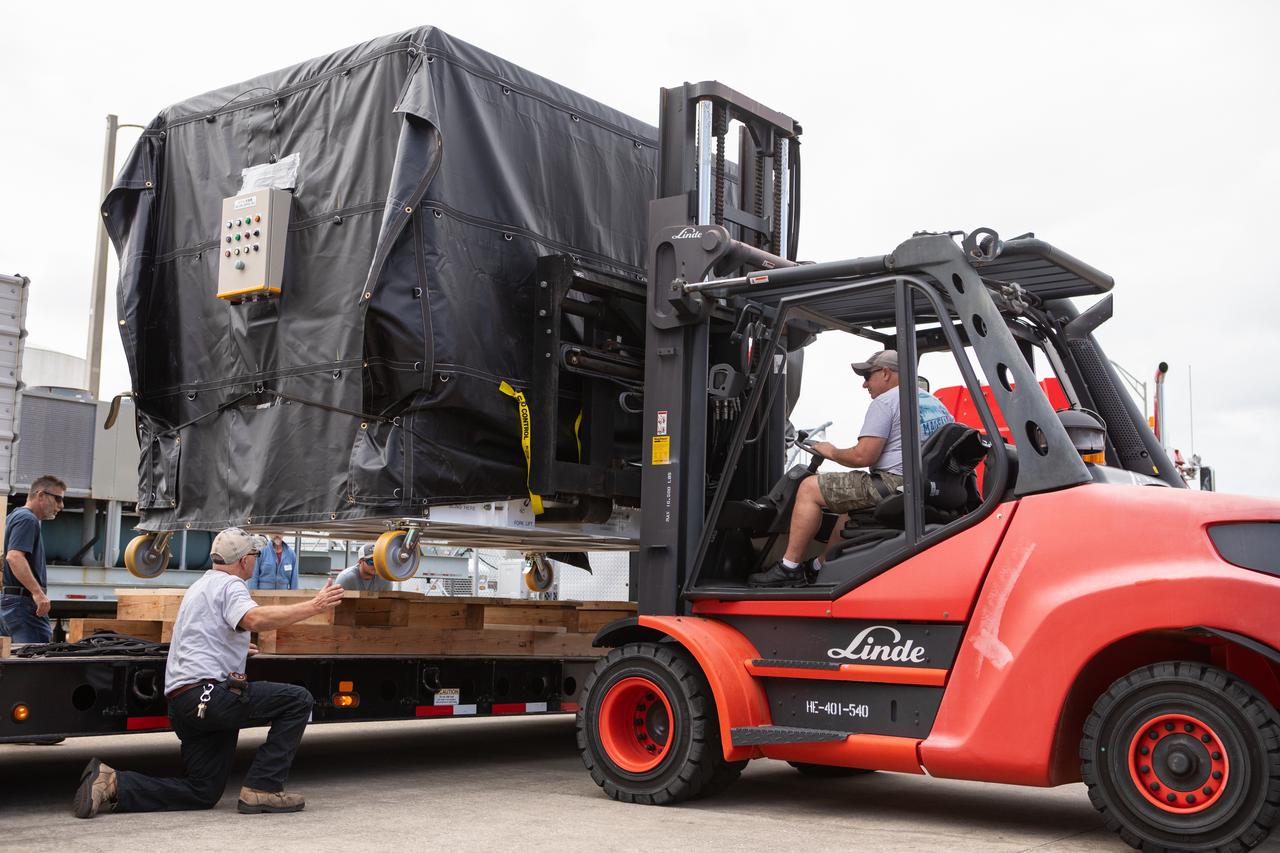

The Hyperspectral Imager Suite (HISUI), a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) payload, is lifted off of its transporter in its shipping container at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 25, 2019. The payload will be packed inside the external trunk of the SpaceX Dragon cargo module at Launch Complex 39A. HISUI will be delivered to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA in December 2019. HISUI is a spaceborne hyperspectral Earth Imaging System with a reflective telescope and two grating spectrometers.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
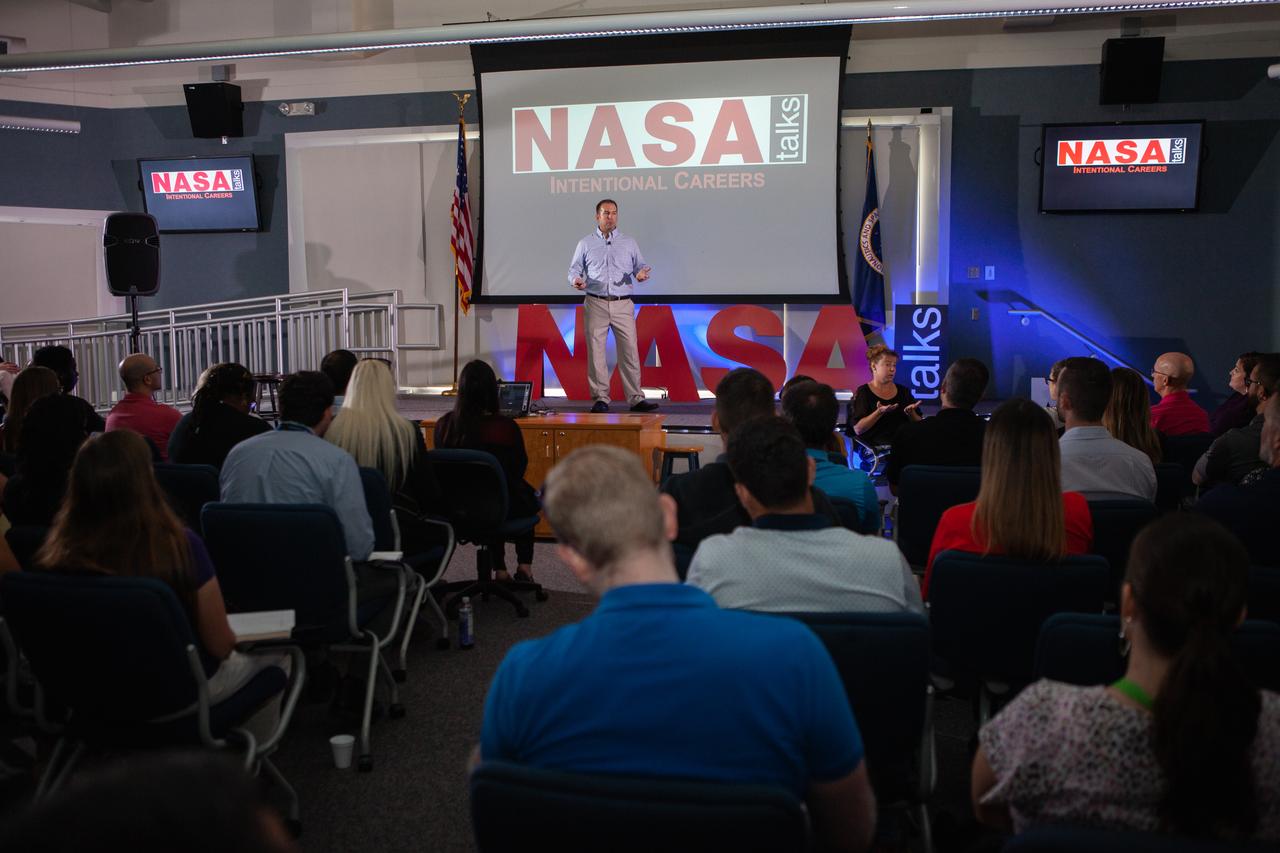

Kennedy Space Center’s Dave Grau addresses co-workers inside the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute on Oct. 17, 2019, during the third in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this third session was customers, and additional speakers included Kennedy employees Ryan Richards and Mike Williams, with a skill-building section on active listening and negotiating by Tim Bass.
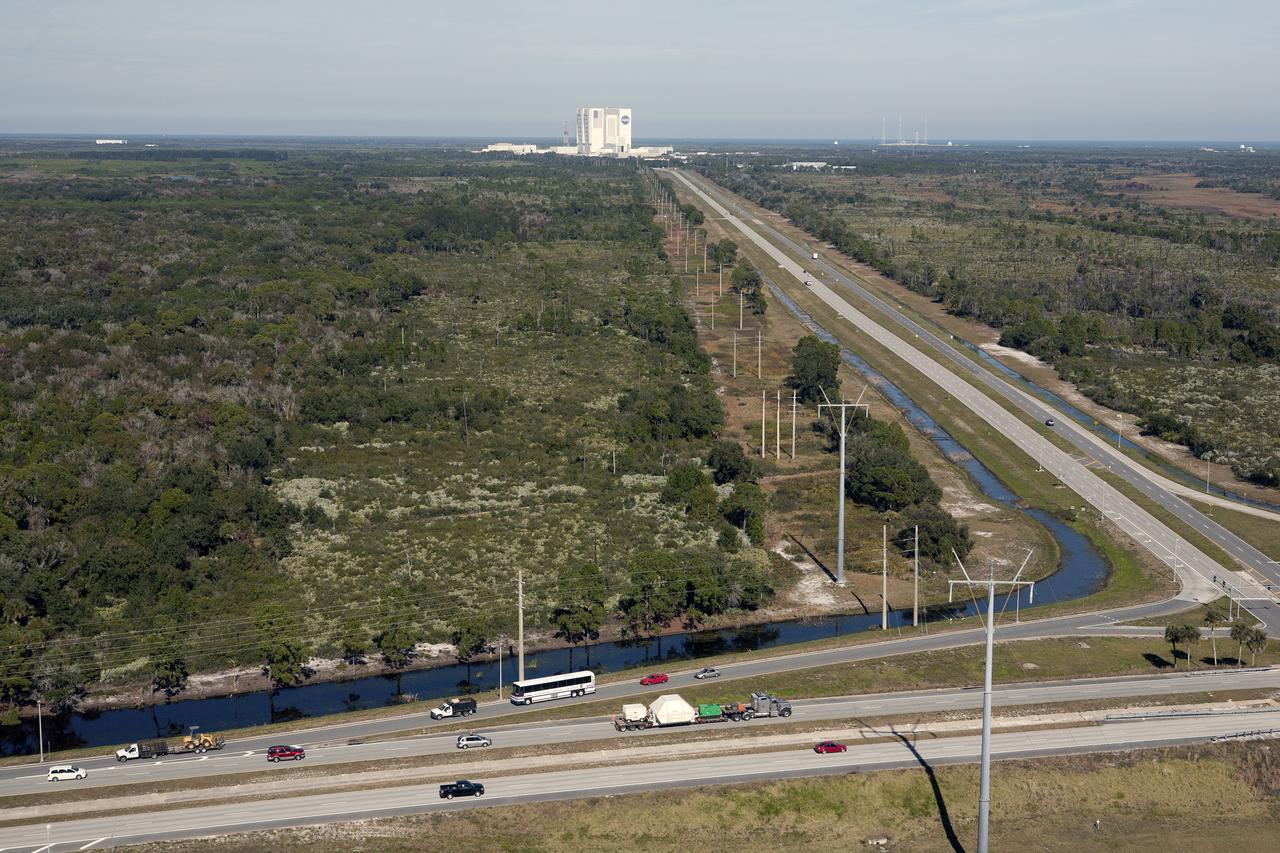

Aerial of Orion Returns to KSC after Successful Mission
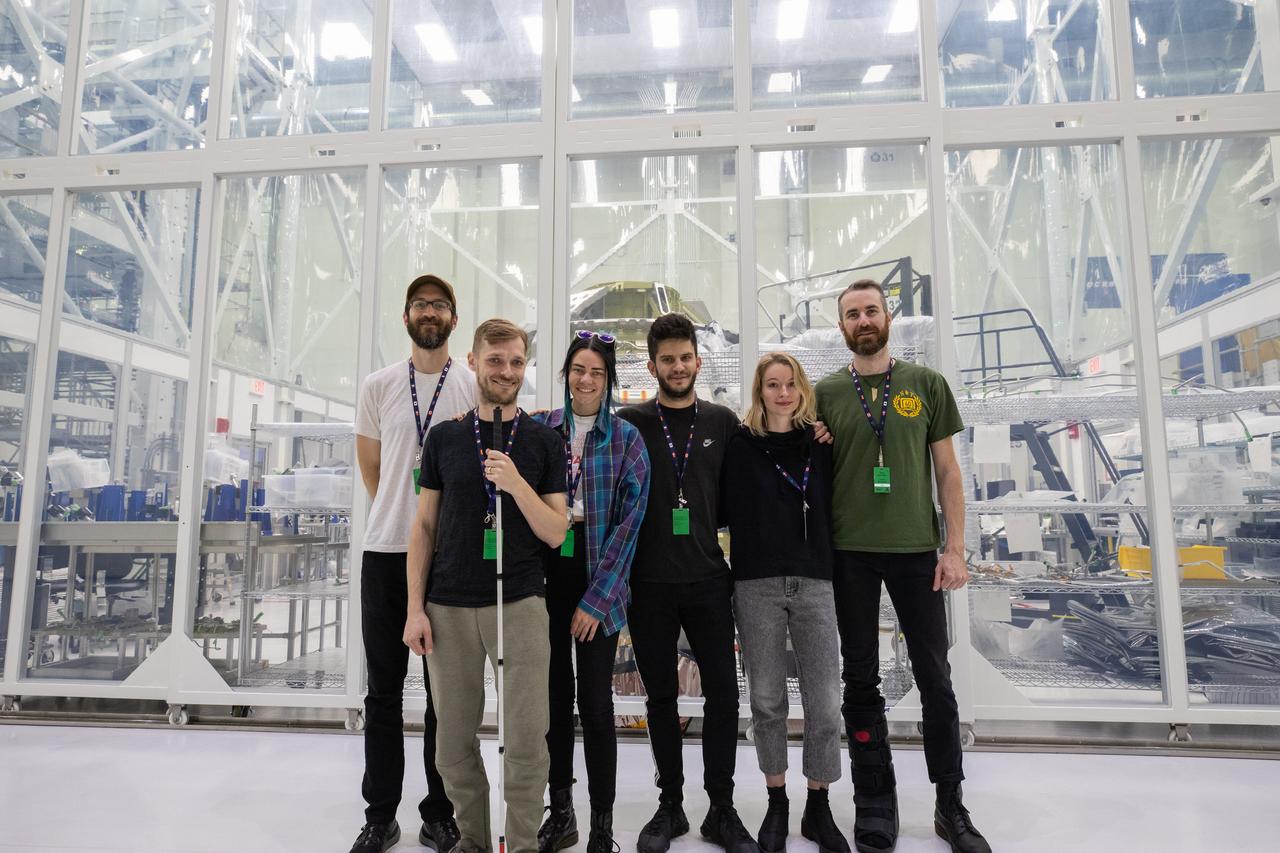

The rock band X Ambassadors is photographed in front of NASA’s Artemis II Orion crew module inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. X Ambassadors visited Kennedy on Oct. 21, 2019, and had the opportunity to tour areas around the multi-user spaceport such as the O&C, Launch Complex 39B and Swamp Works. The title of the band’s latest album, Orion, led them to an up-close look at the spacecraft that will take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before.
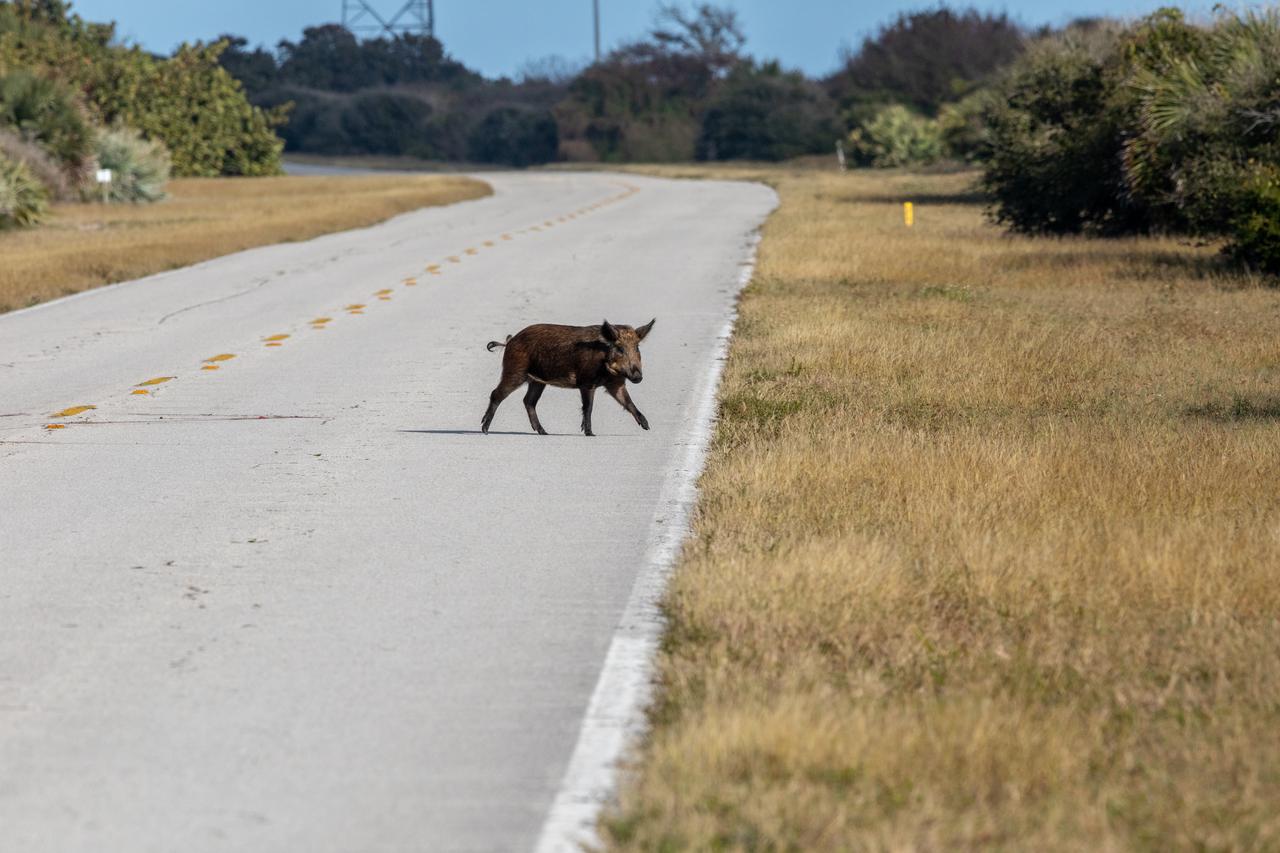

A wild pig crosses a roadway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2021. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.

A full Moon is in view from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 14, 2022. The Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft, atop the mobile launcher, are being prepared for a wet dress rehearsal to practice timelines and procedures for launch. The first in an increasingly complex series of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and using the Moon as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
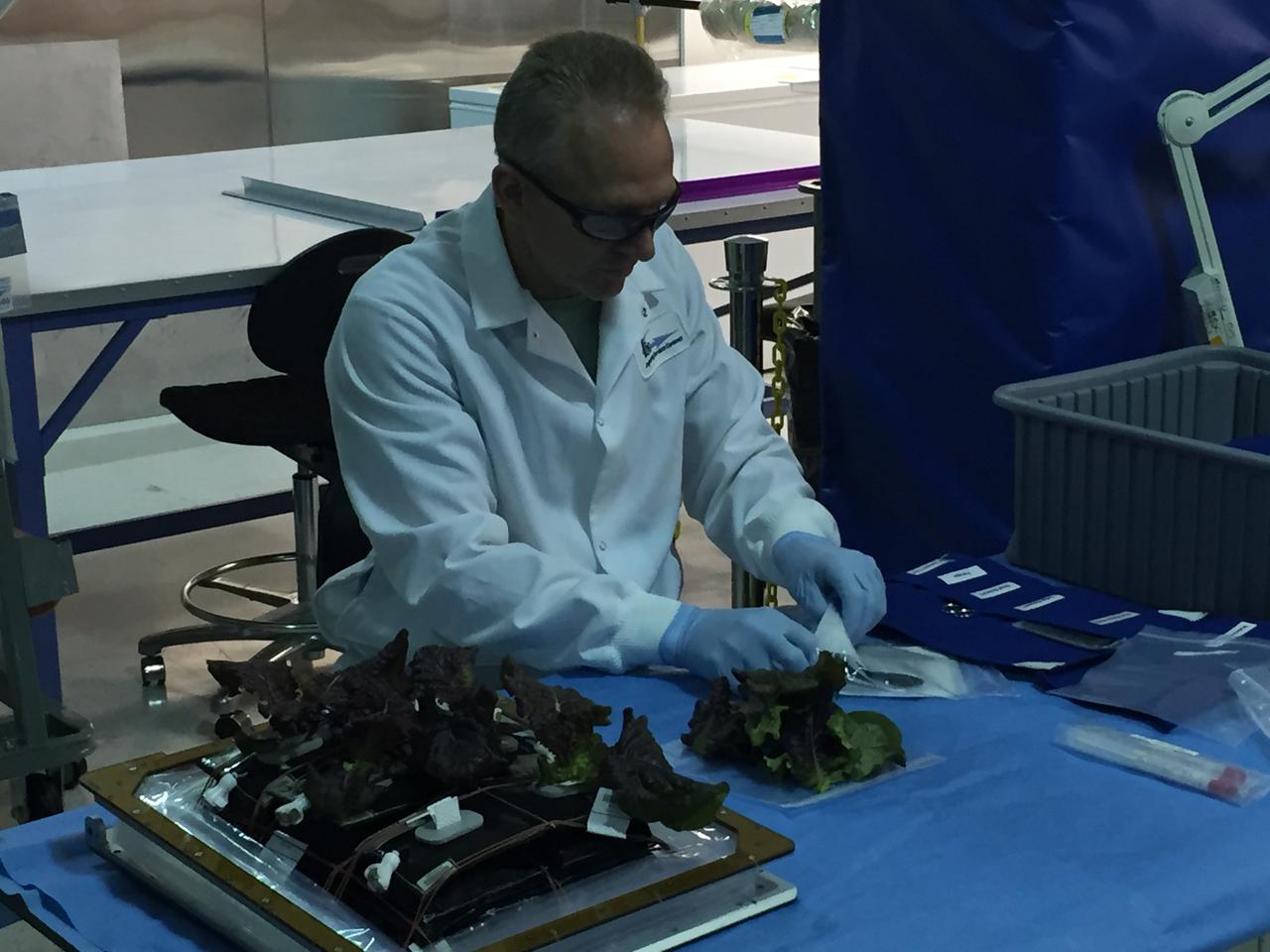

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
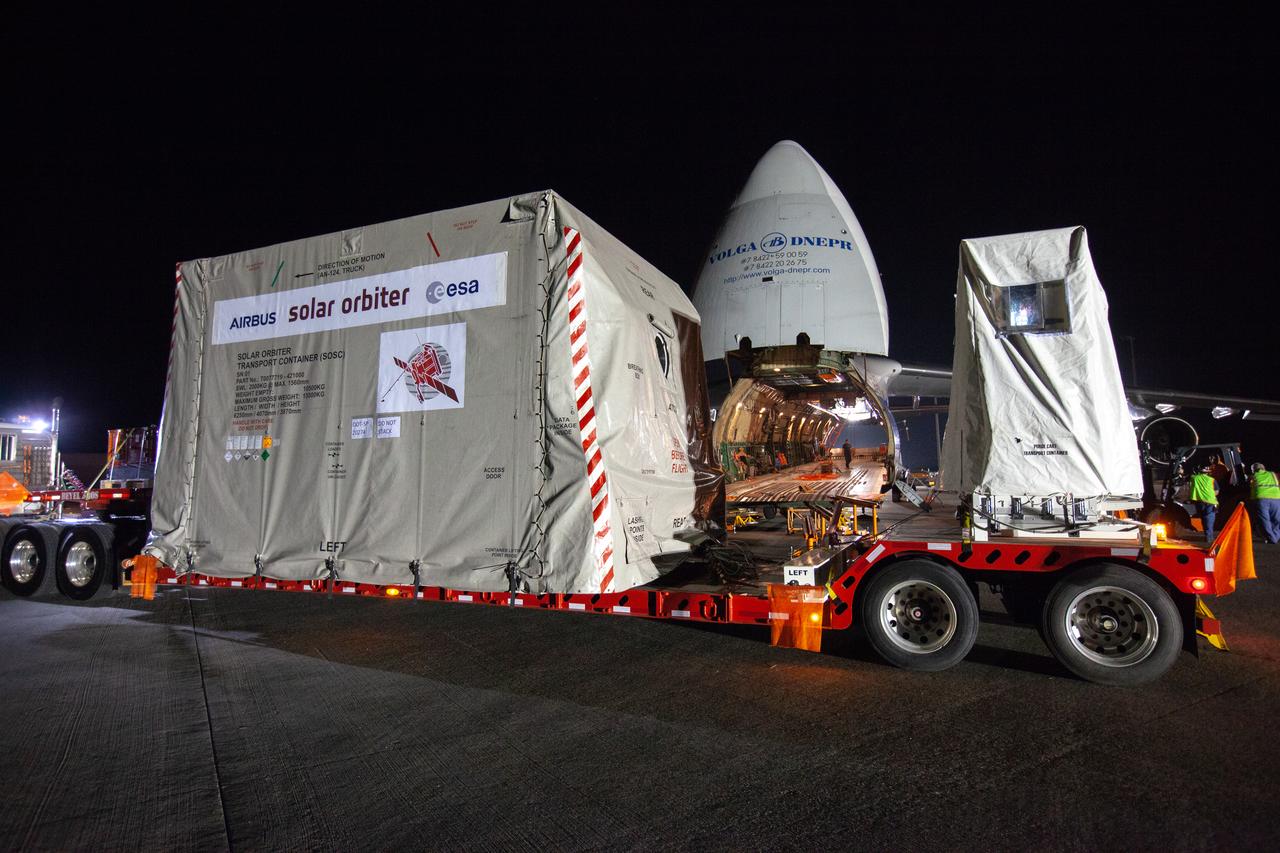

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is placed on a truck for transportation from the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in nearby Titusville on Nov. 1, 2019. The spacecraft was delivered to the Florida spaceport aboard an Antonov An-124 cargo plane from Munich, Germany. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
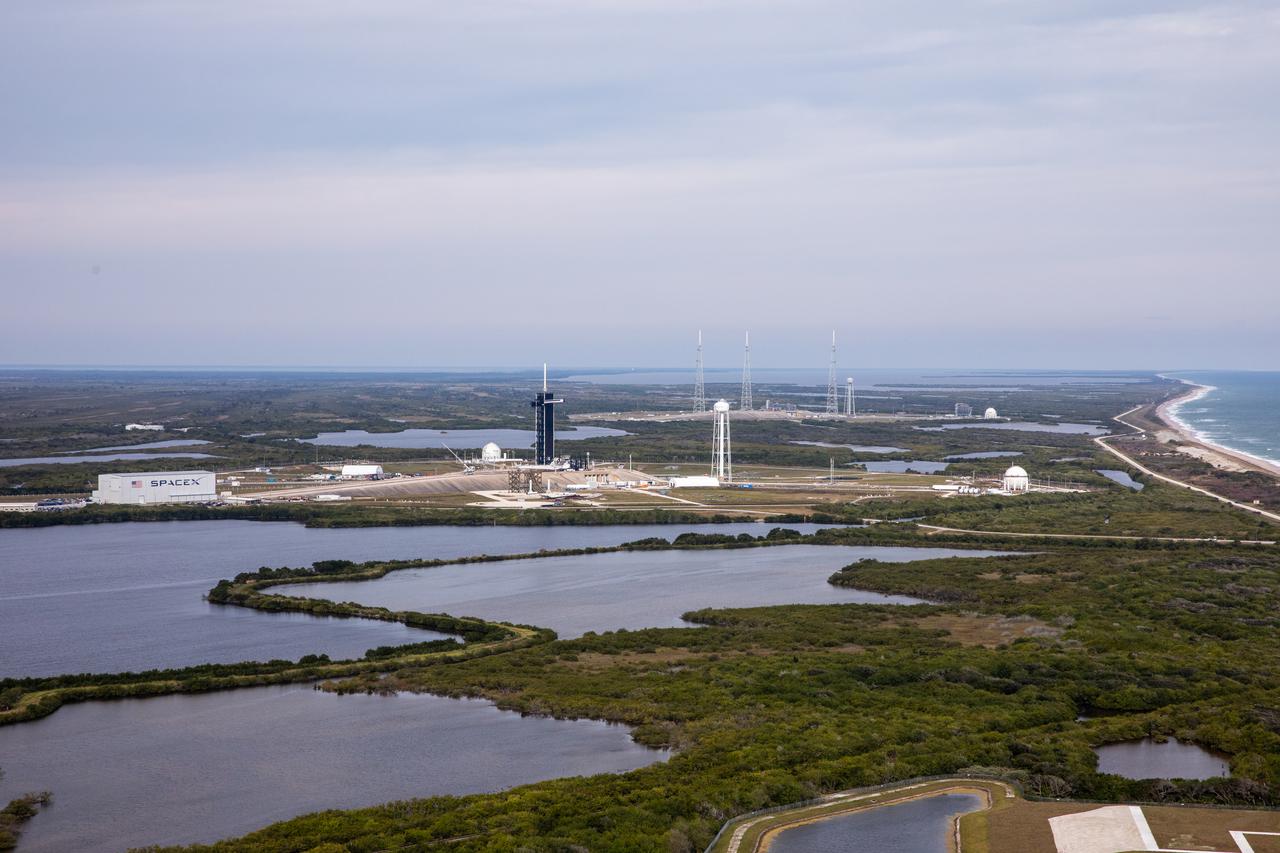

An aerial view looking north at SpaceX’s Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 13, 2021. Launch Complex 39B, from which NASA will launch Artemis missions, is just beyond. A proposed site for Launch Complex 49 is north of these historic launch pads on the Atlantic Ocean and still within Kennedy’s security perimeter.
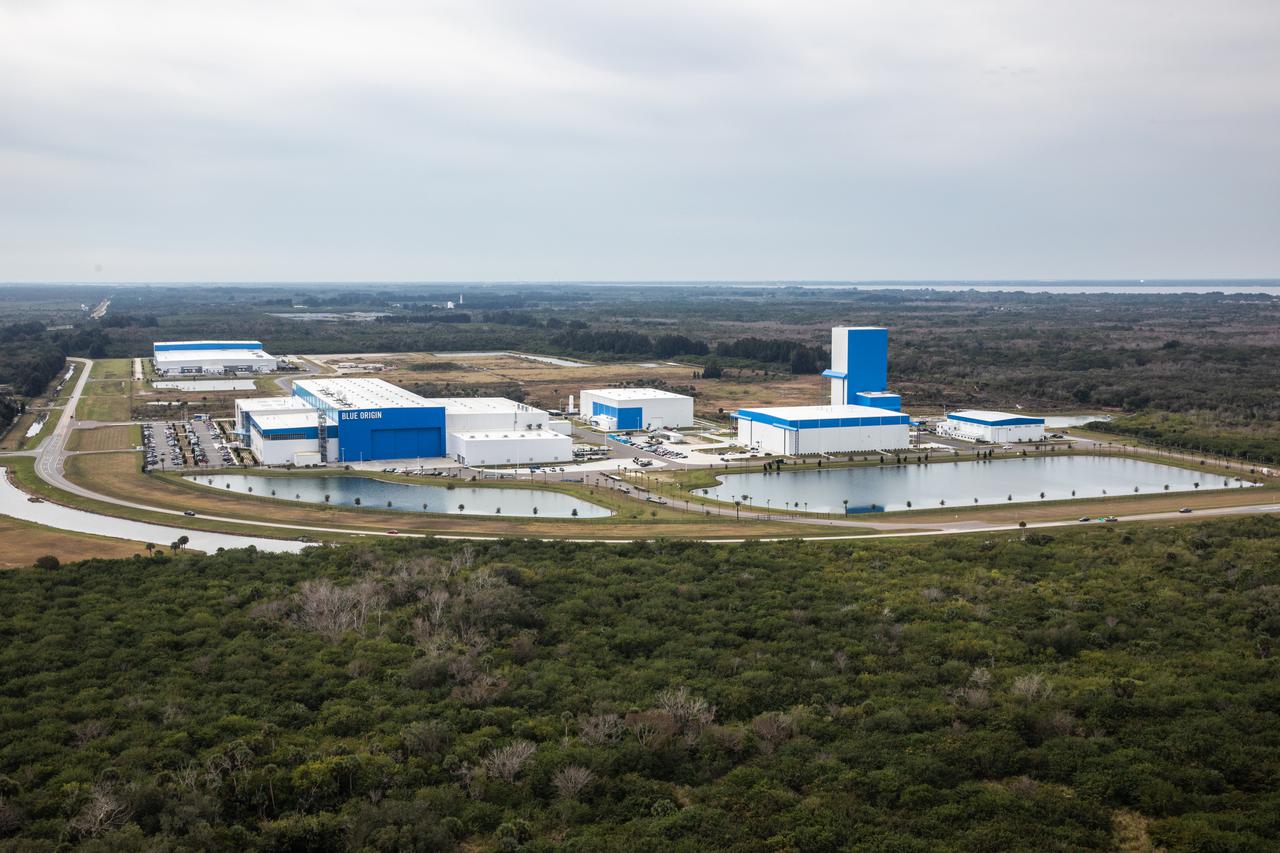

An aerial view of processing facilities at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 13, 2021.
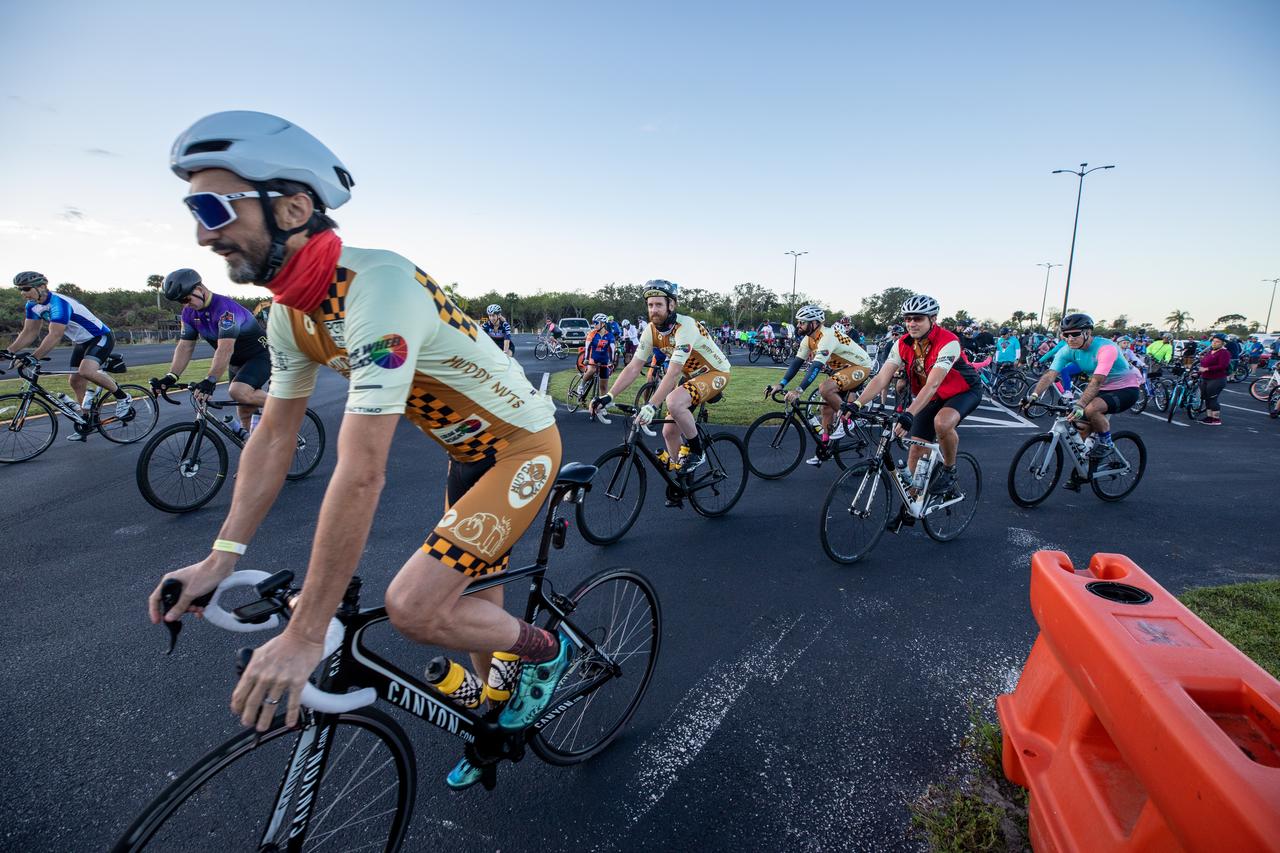

Kennedy Space Center employees and their guests participate in the Diamond Tour de KSC at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 22, 2022. This unique event, held for the first time since 2019, was part of the Safety organization’s Fall Into Safety and Health event, and named “diamond” to honor the center’s 60th anniversary. Cyclists covered three different routes and rode by historic landmarks, completing a total of about 37 miles.
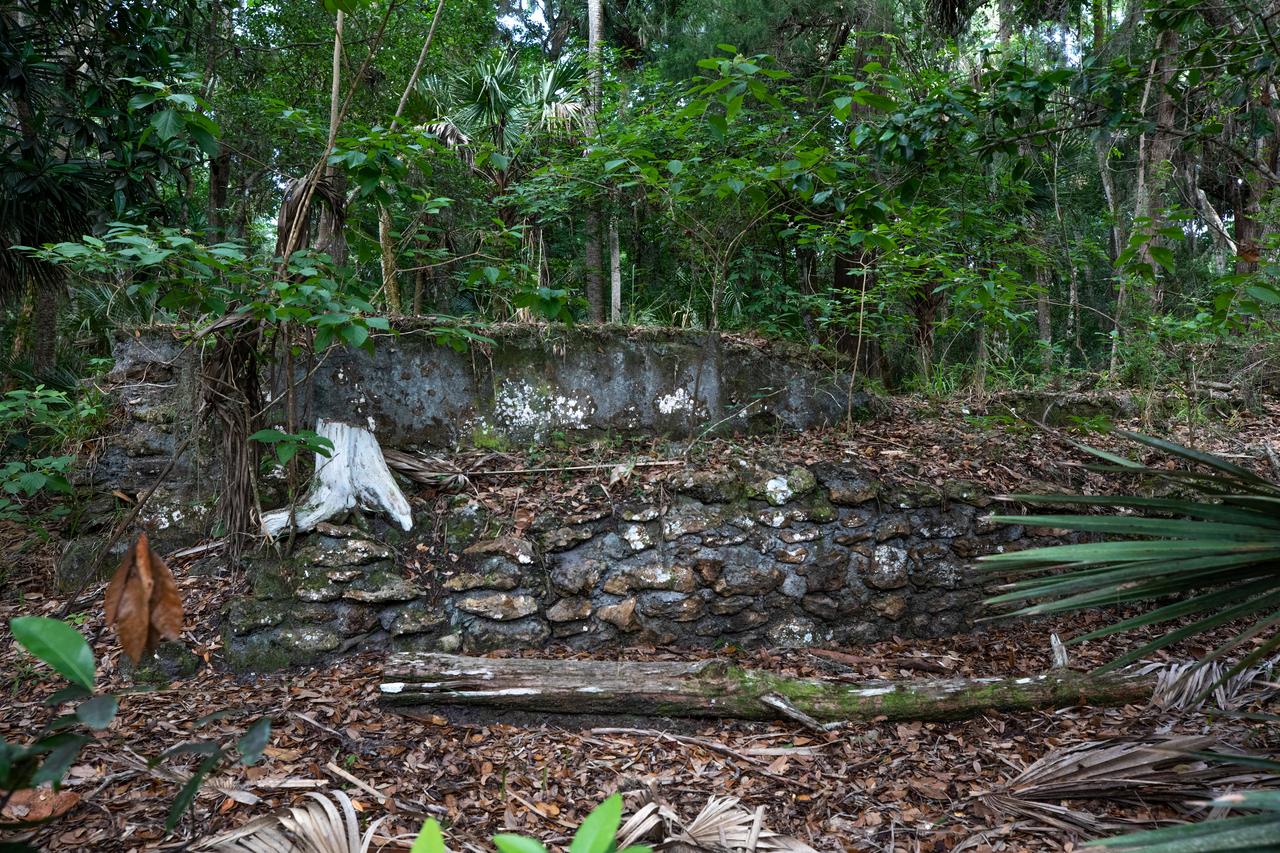

Archeological ruins of the Elliot Plantation sugar mill are revealed through the oak hammock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 26, 2022. The plantation’s enslaved community built the sugar mill structure, or sugar train, where sugar cane juice would be boiled during processing in graduated copper kettles until the liquid reduced into a thick syrup. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. The archeological site is managed through interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA.
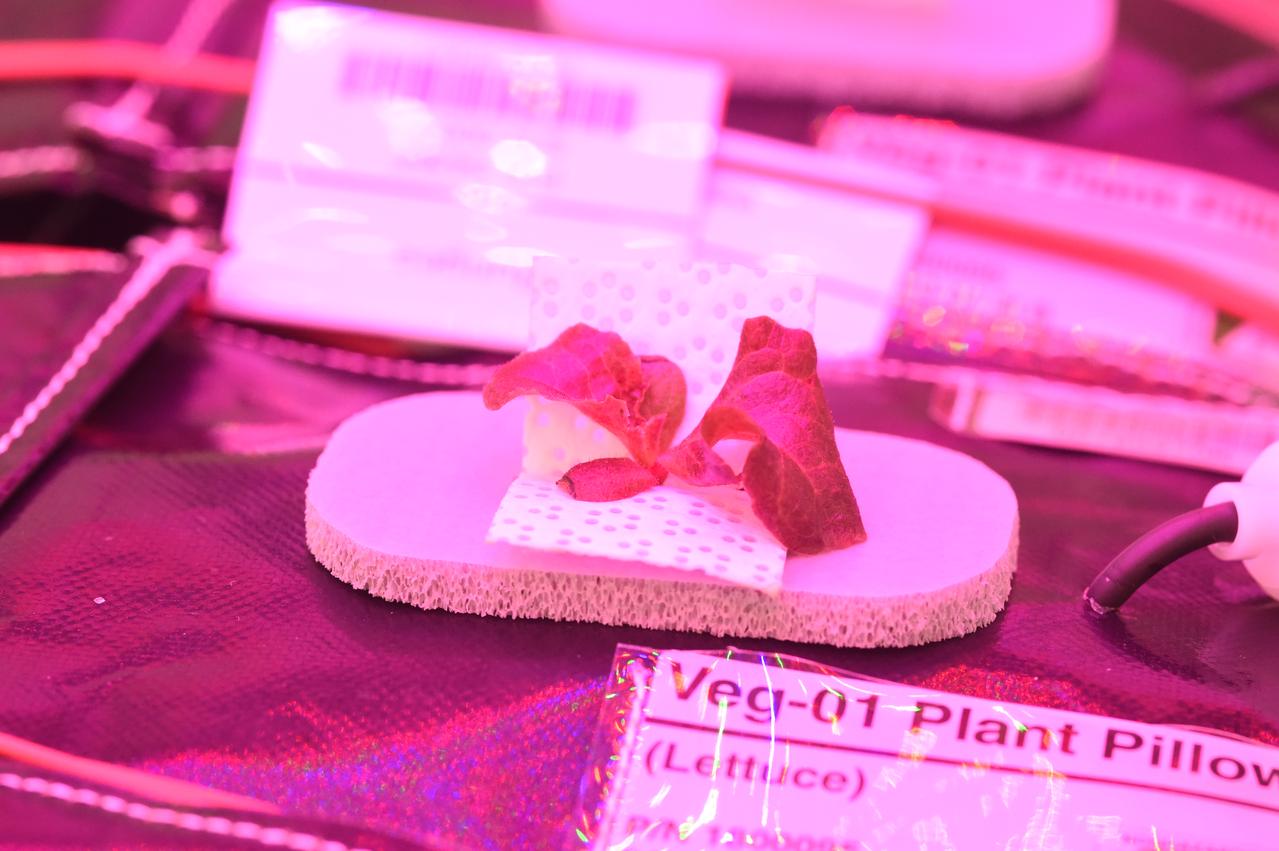

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
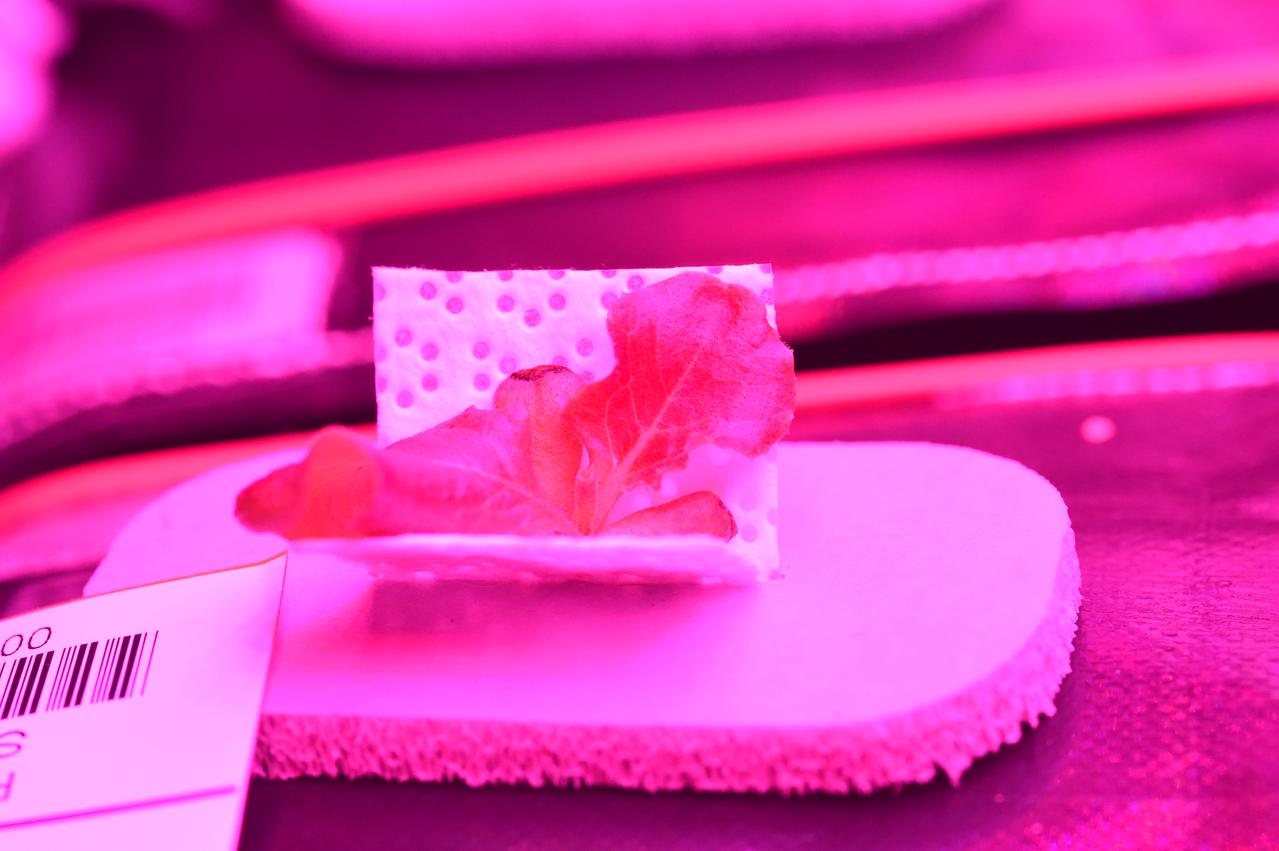

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
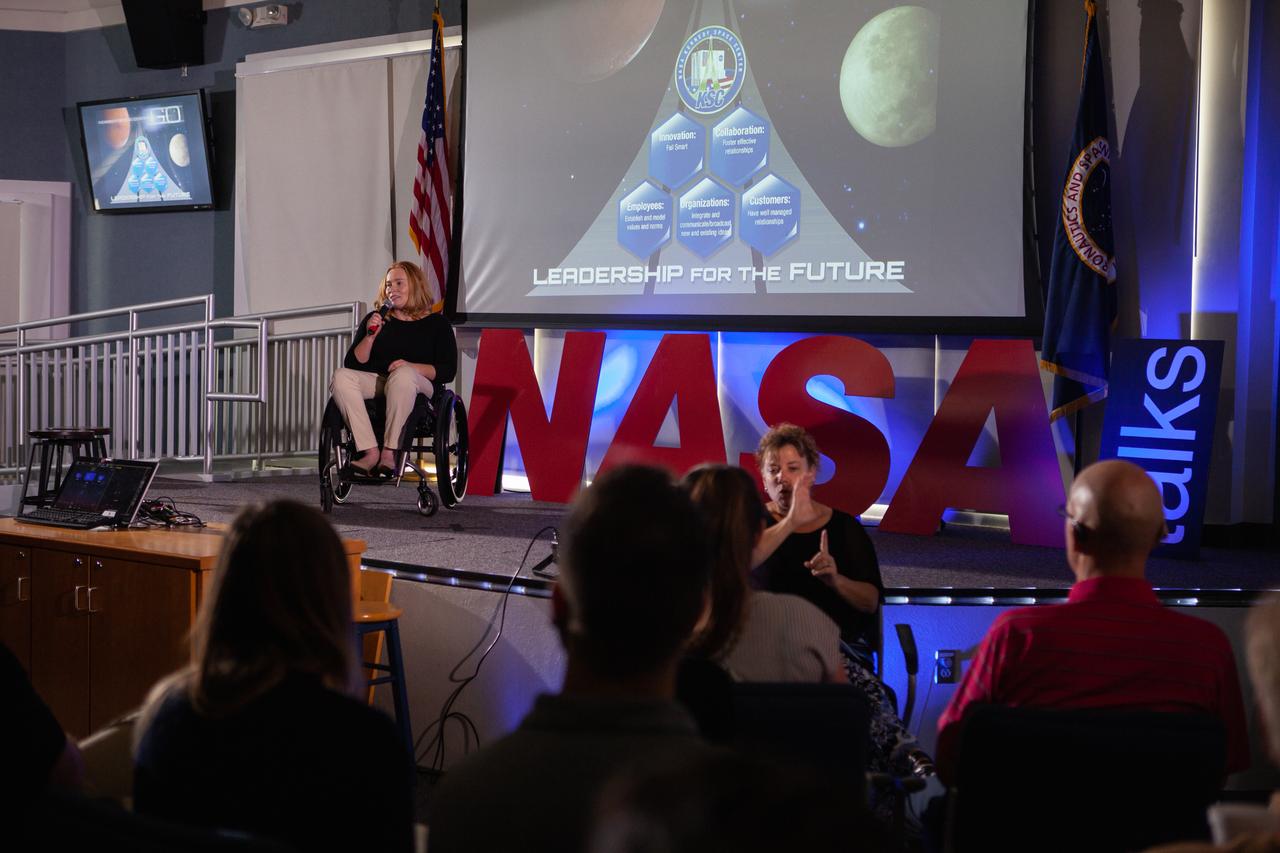

Kennedy Space Center’s Christine Shepperd addresses co-workers inside the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute on Oct. 17, 2019, during the third in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this third session was customers, and speakers included Kennedy employees Ryan Richards, Mike Williams and Dave Grau, with a skill-building section on active listening and negotiating by Tim Bass.
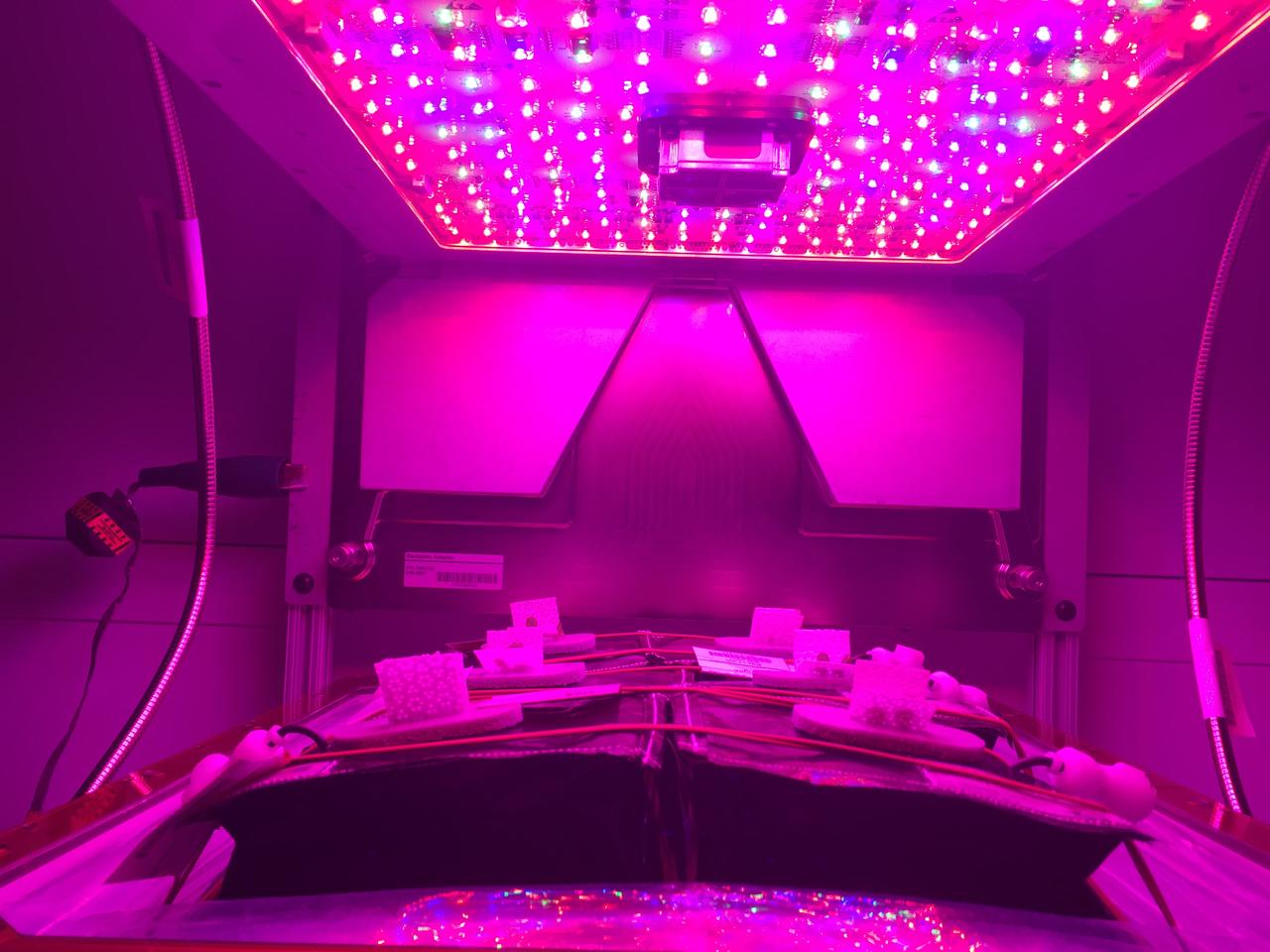

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
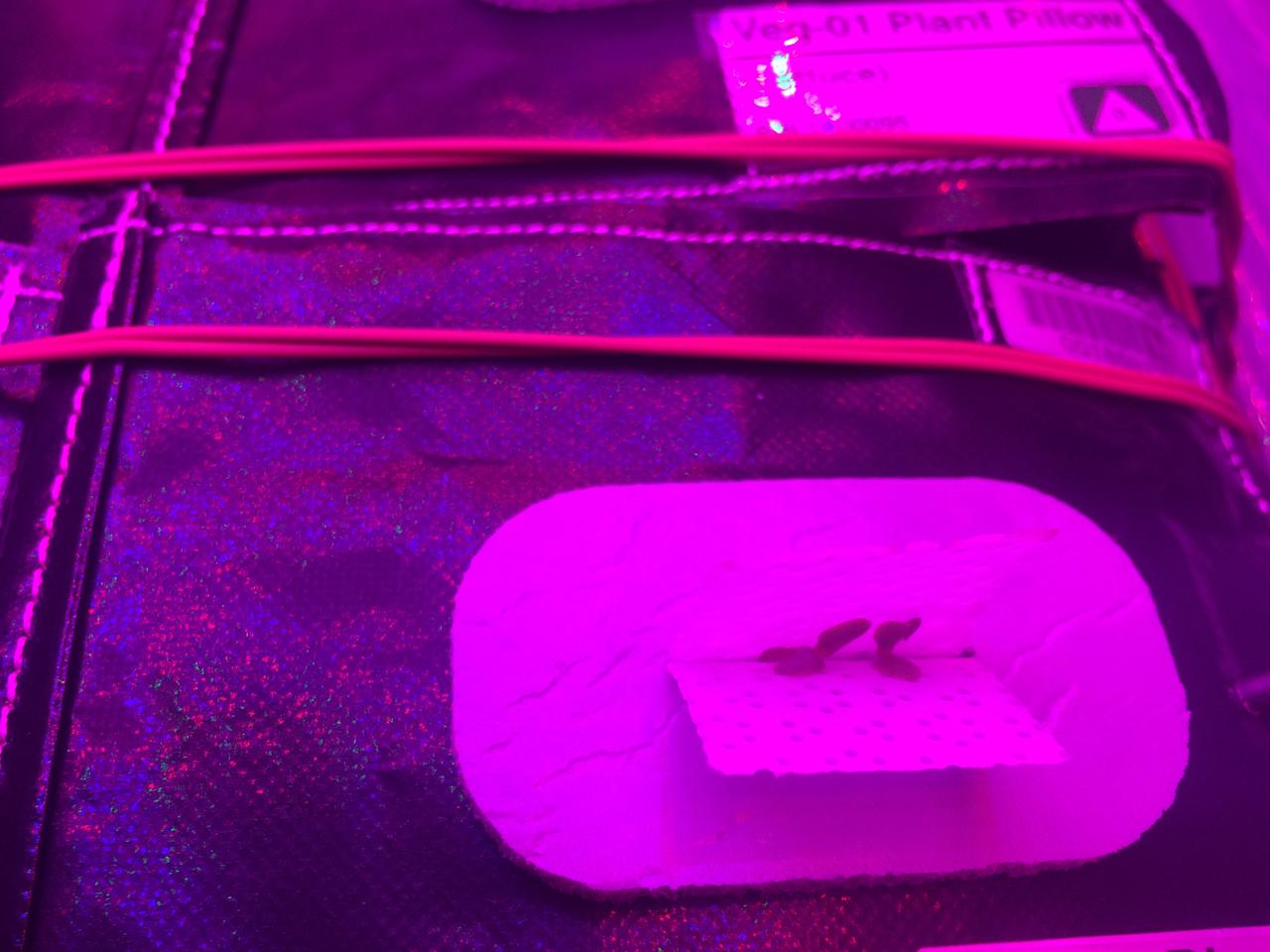

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
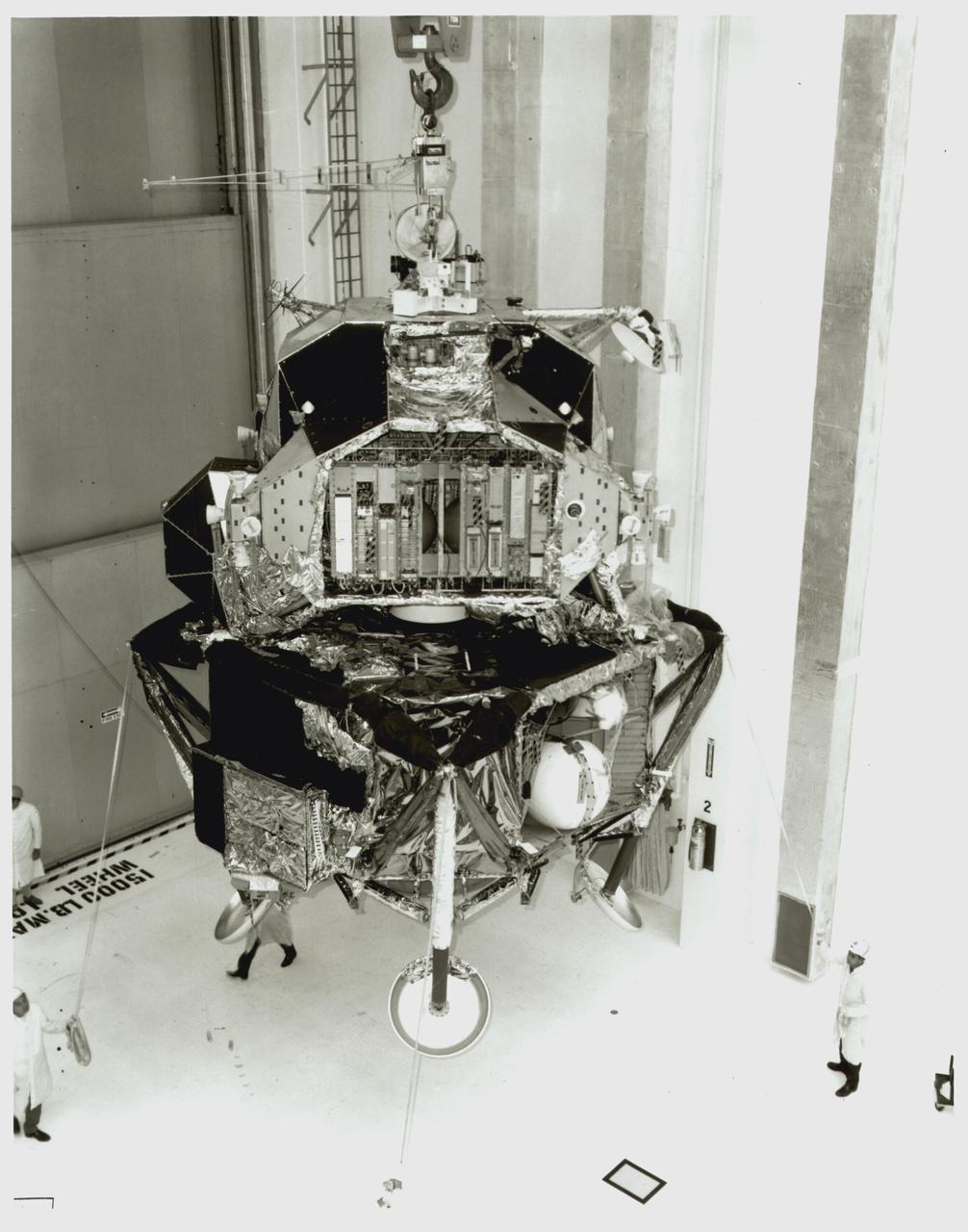
The Lunar Module for Apollo 11 moves from the landing gear fixture and mate to the spacecraft-lunar module adapter.
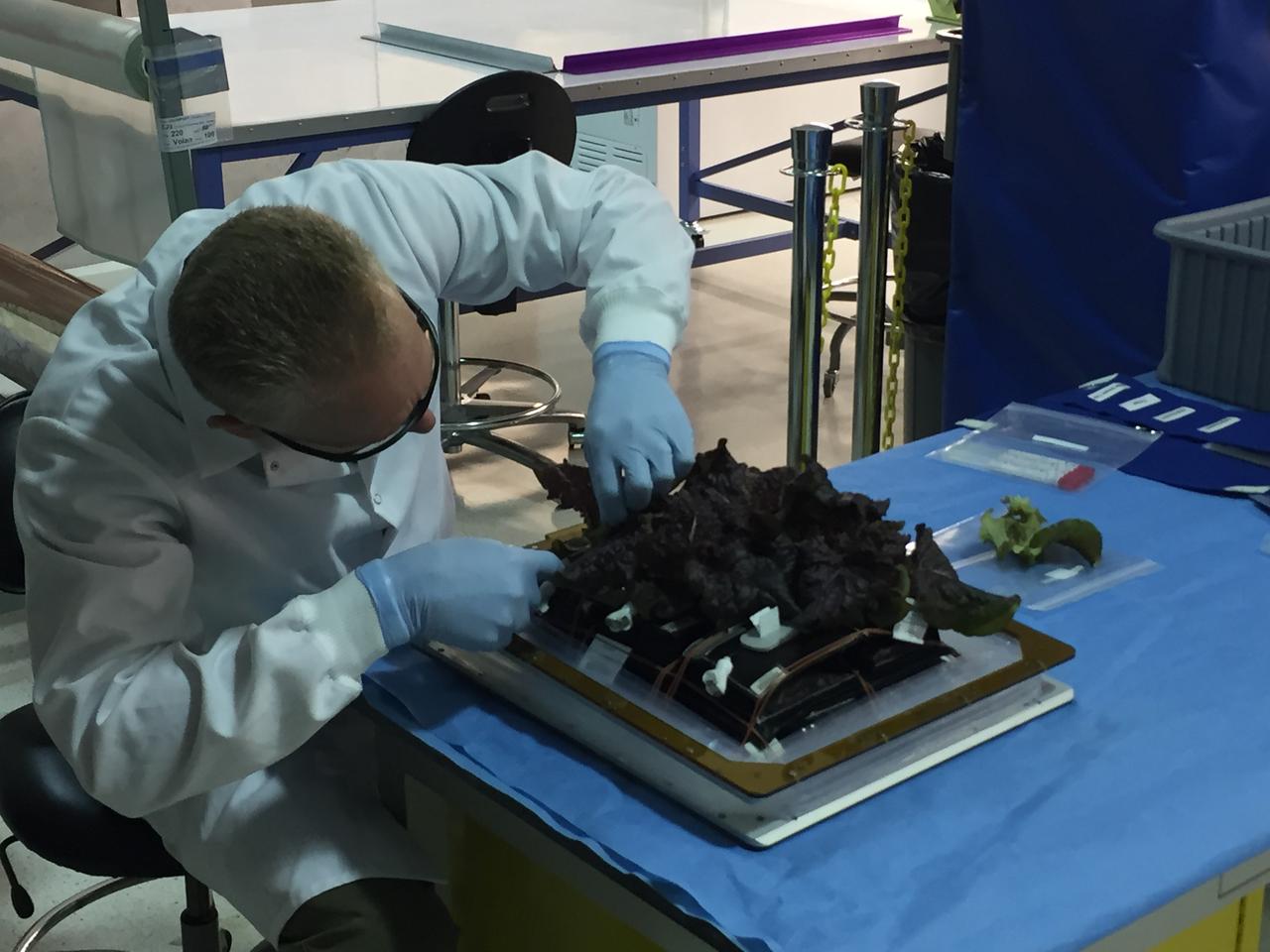

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
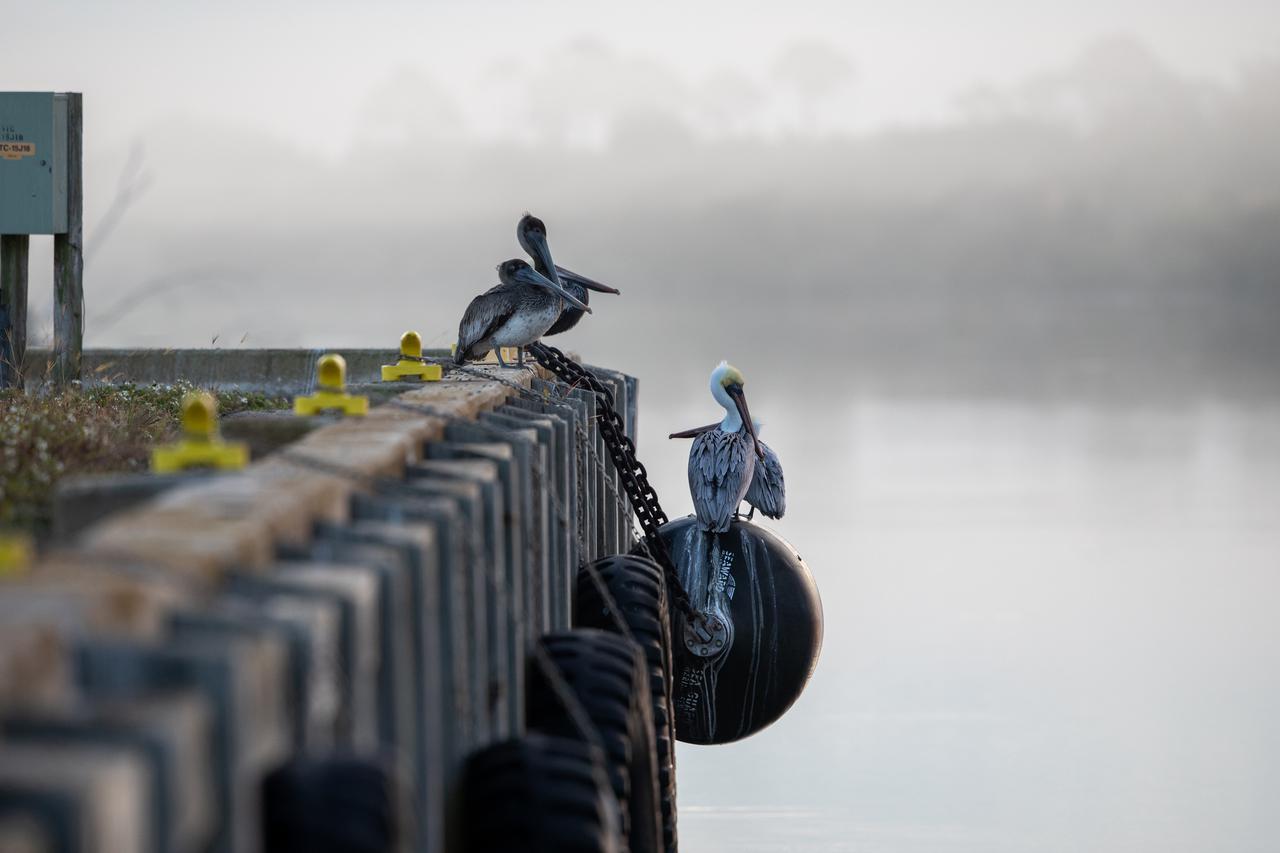

Pelicans perch on the support beams of an embankment on a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2021. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, along with 25 mammal, 117 fish, and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
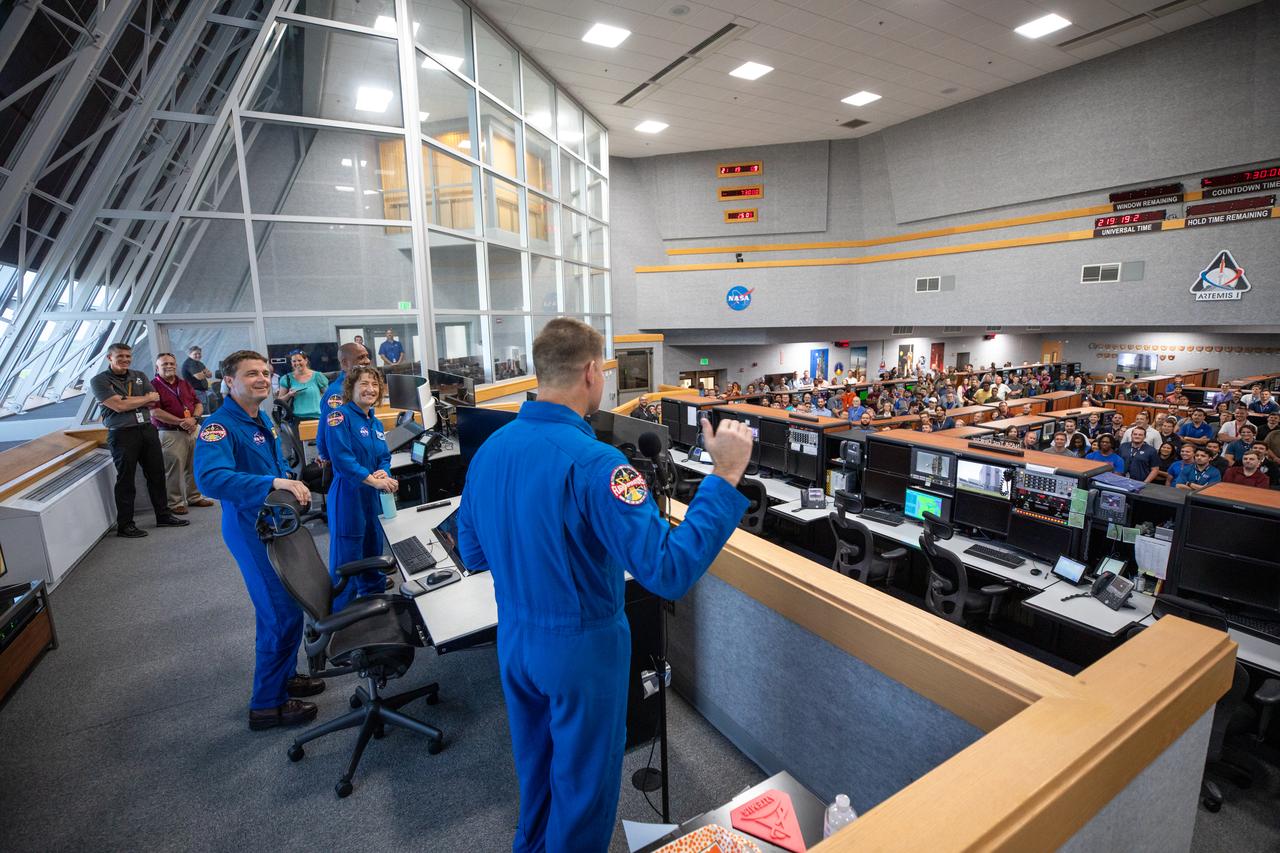

Artemis II astronauts visit the Artemis launch team inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 7, 2023. In front, from left are NASA astronauts Victor Glover (partially hidden), Christina Koch, and Reid Wiseman, and CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen. The approximately 10-day Artemis II flight will test NASA’s foundational human deep space exploration capabilities, the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, for the first time with astronauts and will pave the way for lunar surface missions, including landing the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon.

Artemis II crew members inspect their Orion crew module inside the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Aug. 7, 2023. Pictured from left are Christina Hammock Koch, mission specialist, and Victor Glover, pilot. The crew module is undergoing acoustic testing ahead of integration with the European Service Module. Artemis II is the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term lunar presence for science and exploration under Artemis.
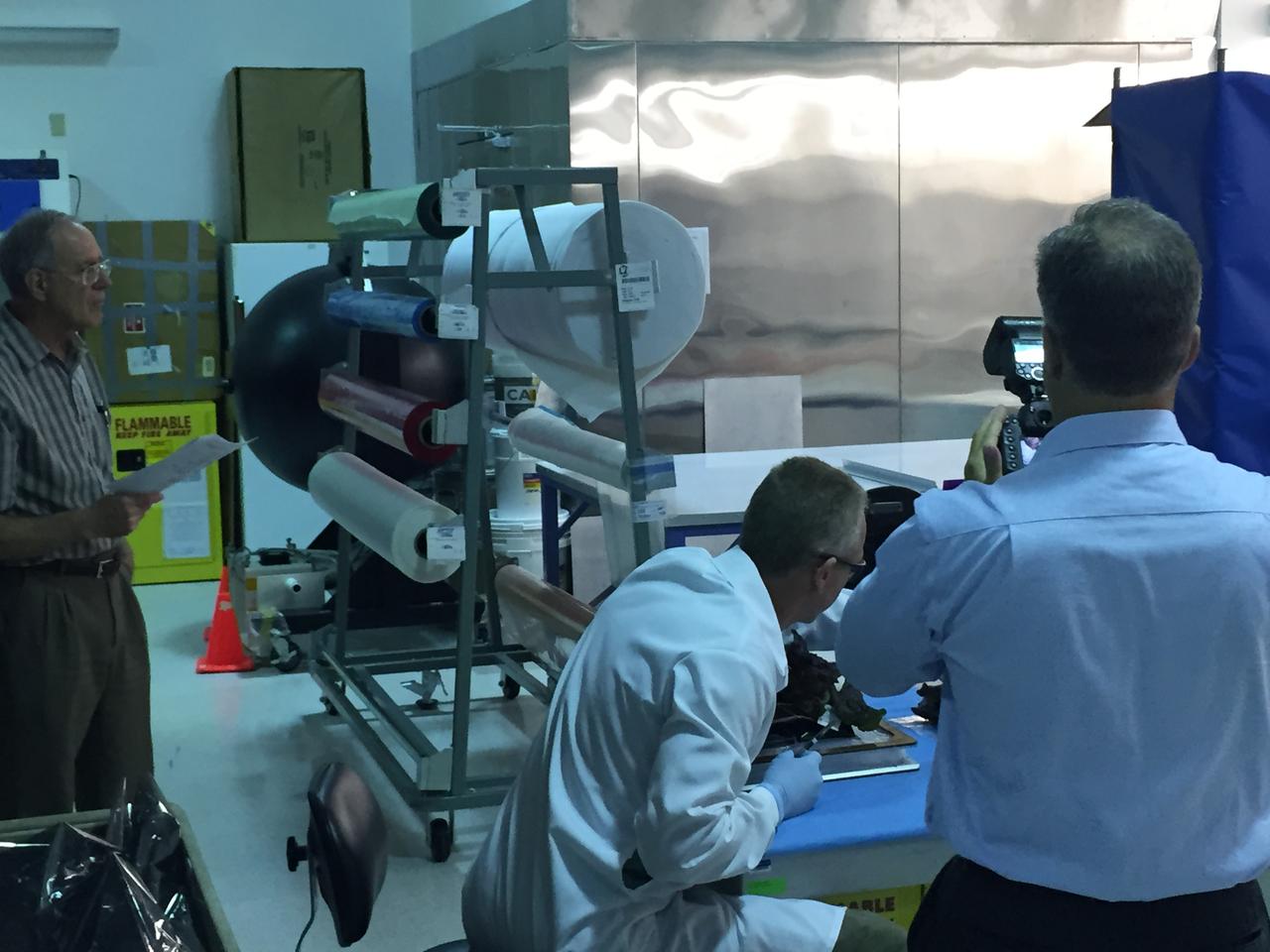

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
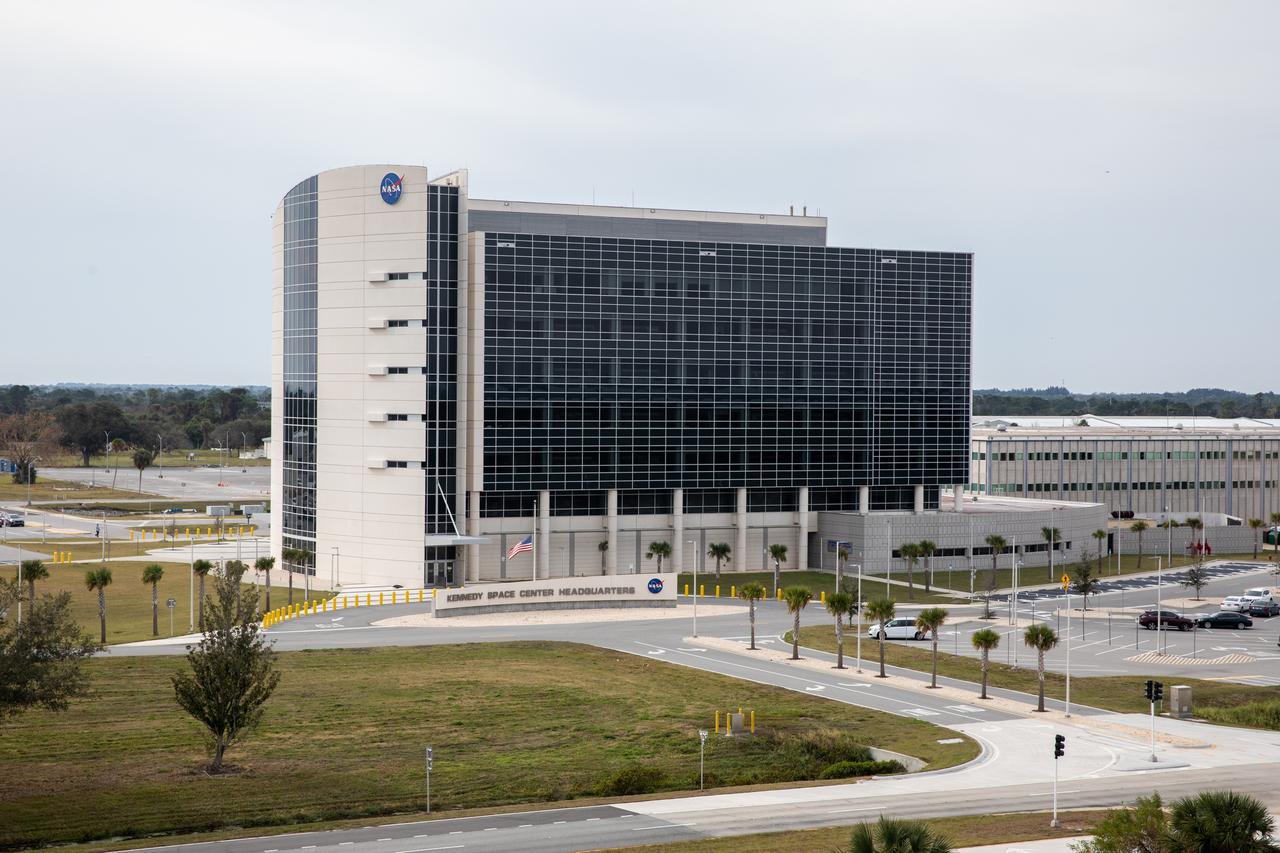

An aerial view of the Central Campus Headquarters Building in the industrial area at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 13, 2021.
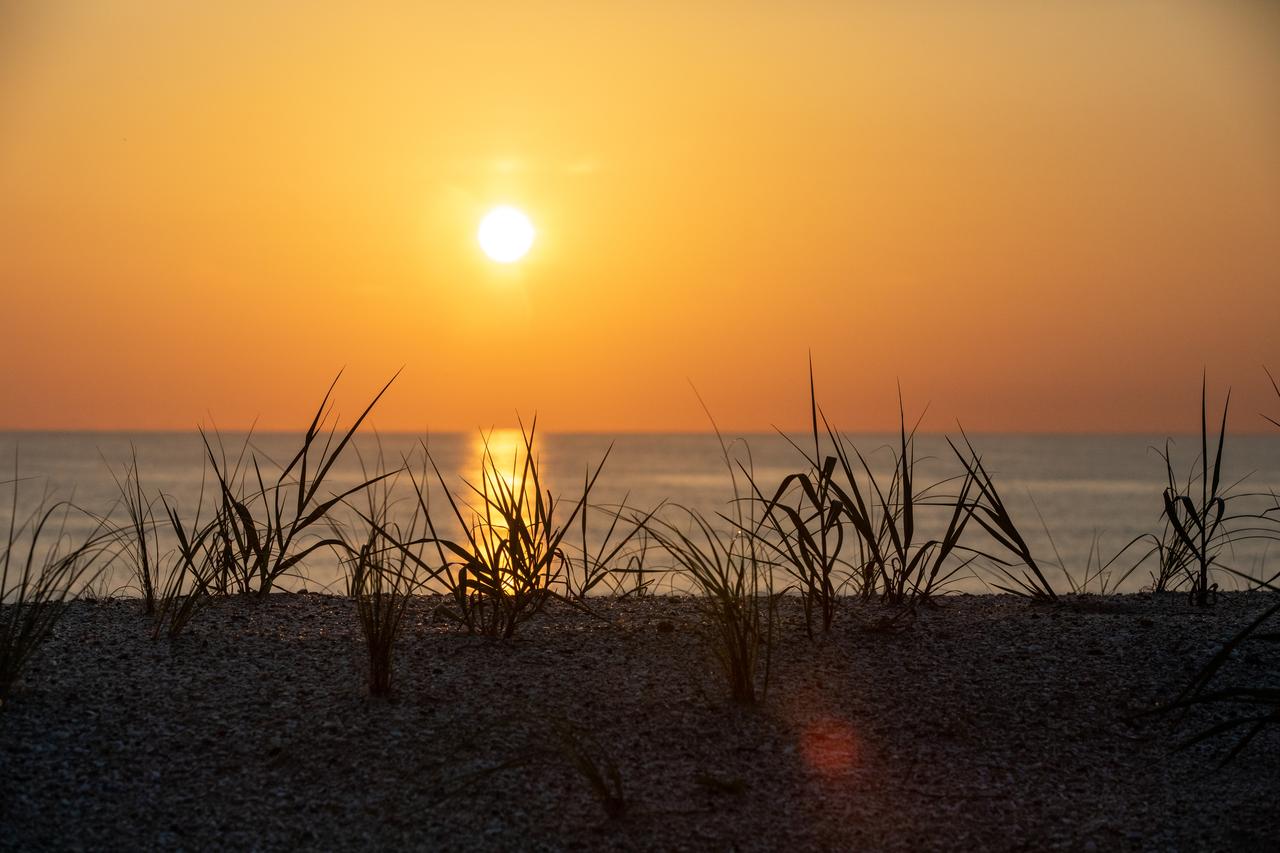

A beautiful sunrise is captured over sand dunes at the beach at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 15, 2020. Teams at Kennedy are working on dune restoration efforts, which has included bringing about 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand in to Kennedy’s beaches to build up dunes that have been affected by beach erosion and storm surges. Once the dunes were built up, native coastal vegetation was replanted to help stabilize the dunes and provide a habitat for wildlife at the Florida spaceport. The first phase of dune restoration efforts are now complete, and the second phase is scheduled to be completed by March 2021.
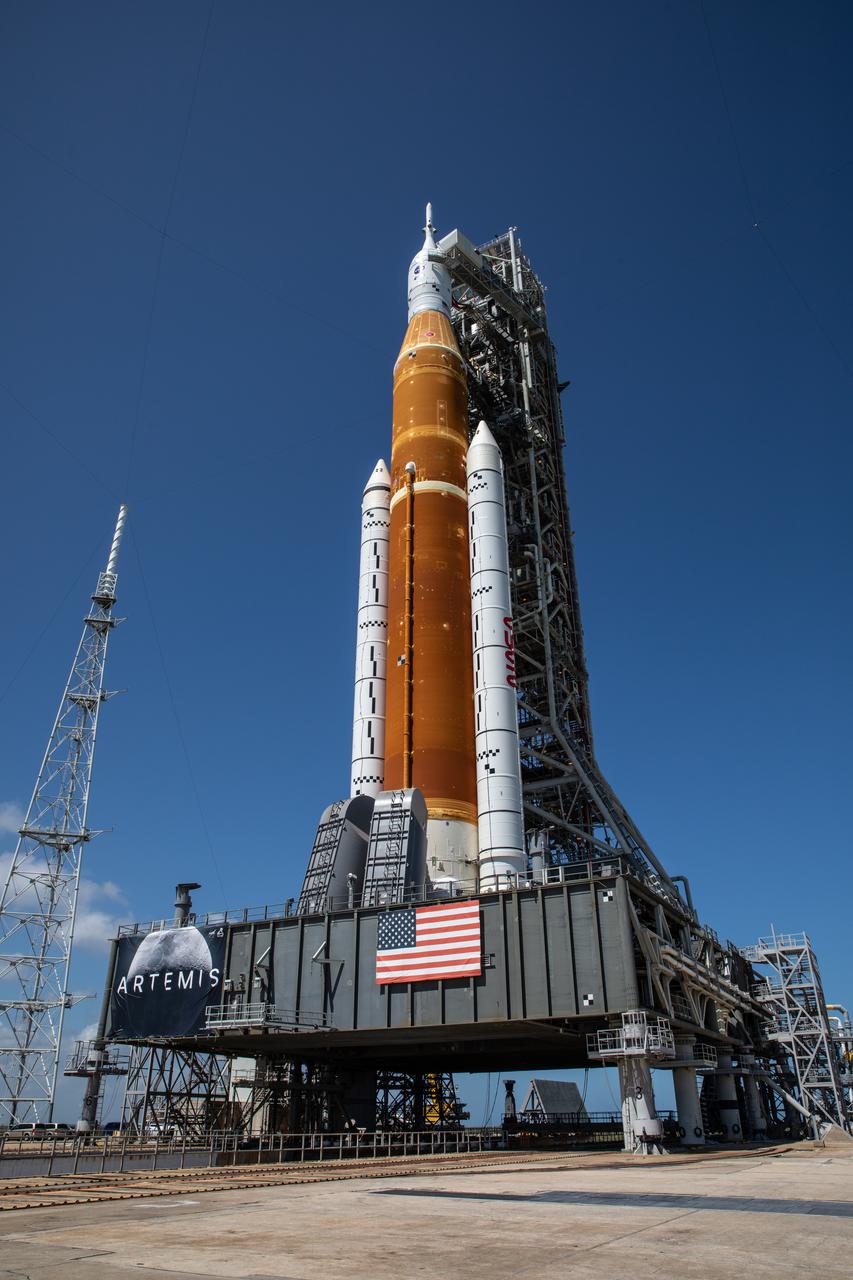

Standing atop the mobile launcher, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is photographed at Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 18, 2022. The rocket, with the Orion capsule atop, was carried from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the pad – a 4.2-mile journey that took nearly 11 hours to complete – by the agency’s crawler-transporter 2 for a wet dress rehearsal ahead of the uncrewed Artemis I launch. Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
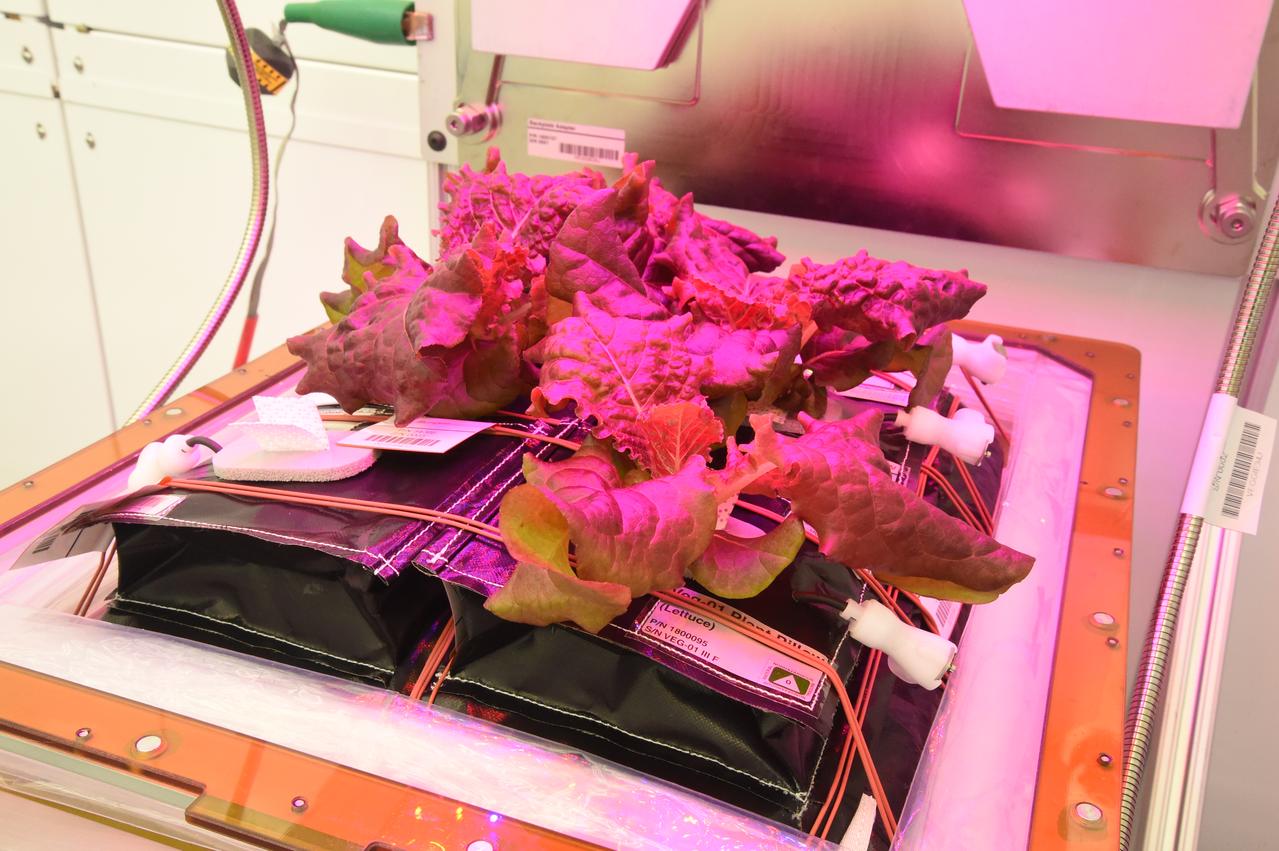

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
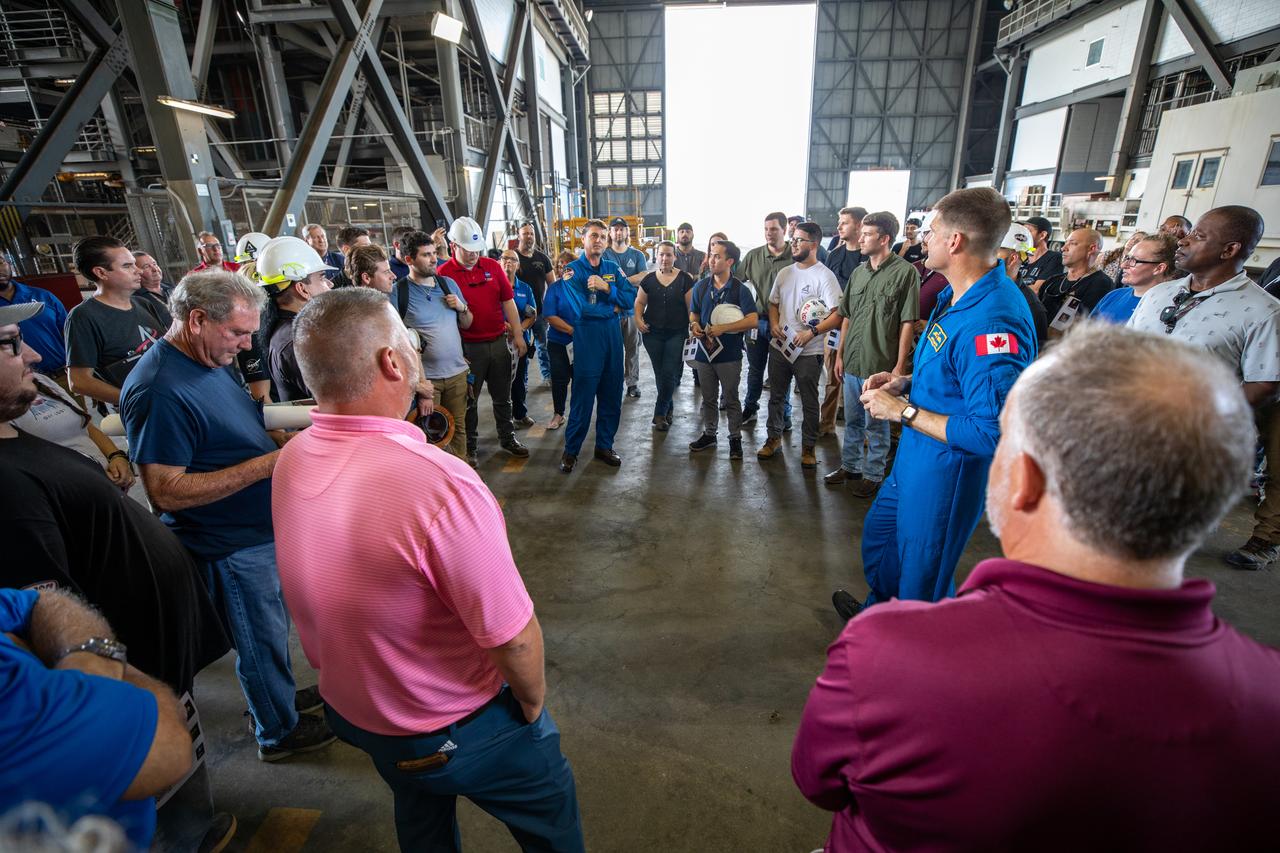

Artemis II NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman, in the center, and Jeremy Hansen, at right, CSA (Canadian Space Agency) Artemis II astronaut, talk with members of the Exploration Ground Systems team inside the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building during a visit to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 7, 2023. The approximately 10-day Artemis II flight will test NASA’s foundational human deep space exploration capabilities, the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, for the first time with astronauts and will pave the way for lunar surface missions, including landing the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon.
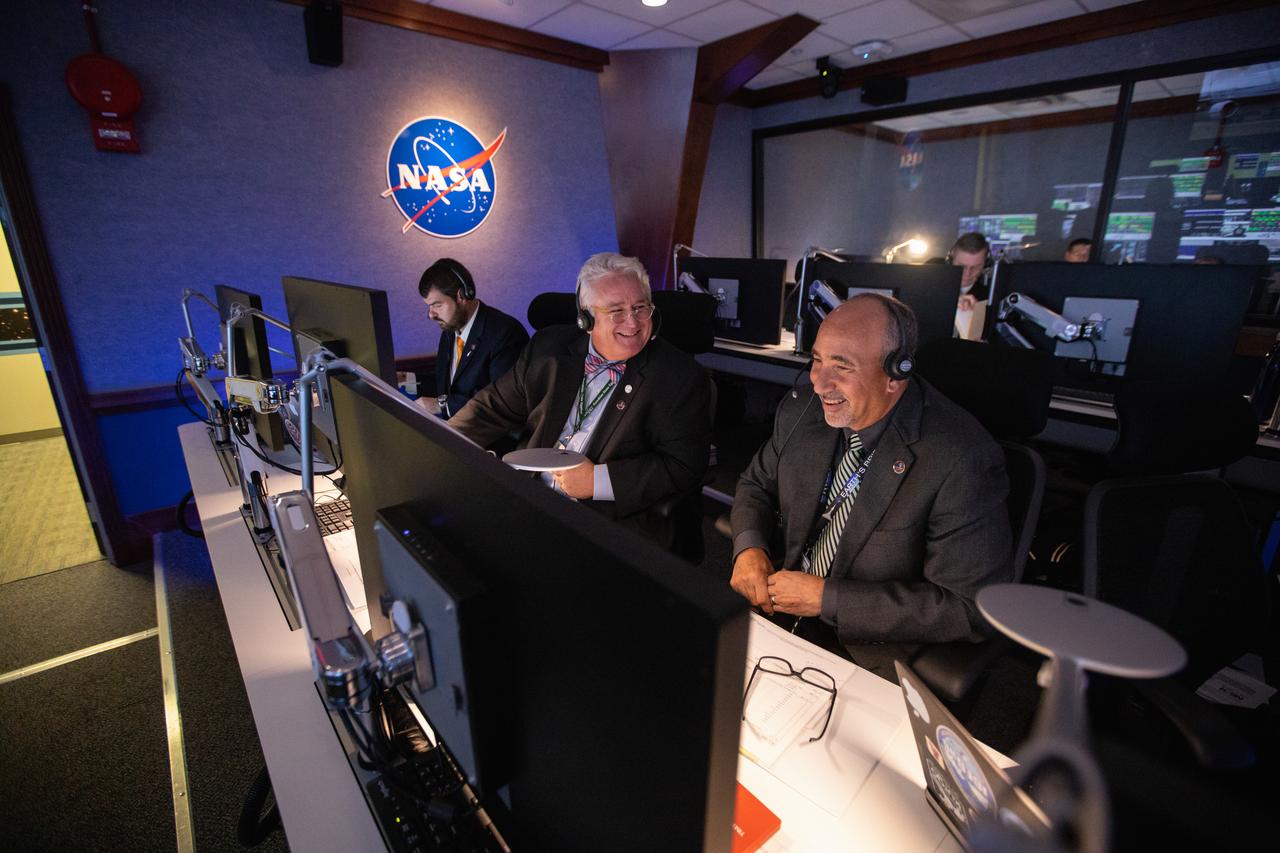

Albert Sierra (right), chief of NASA’s Launch Services Program’s (LSP) Flight Projects Office, and Garrett Lee Skrobot (second from right), senior mission manager, monitor the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The ICON launch was managed by LSP.
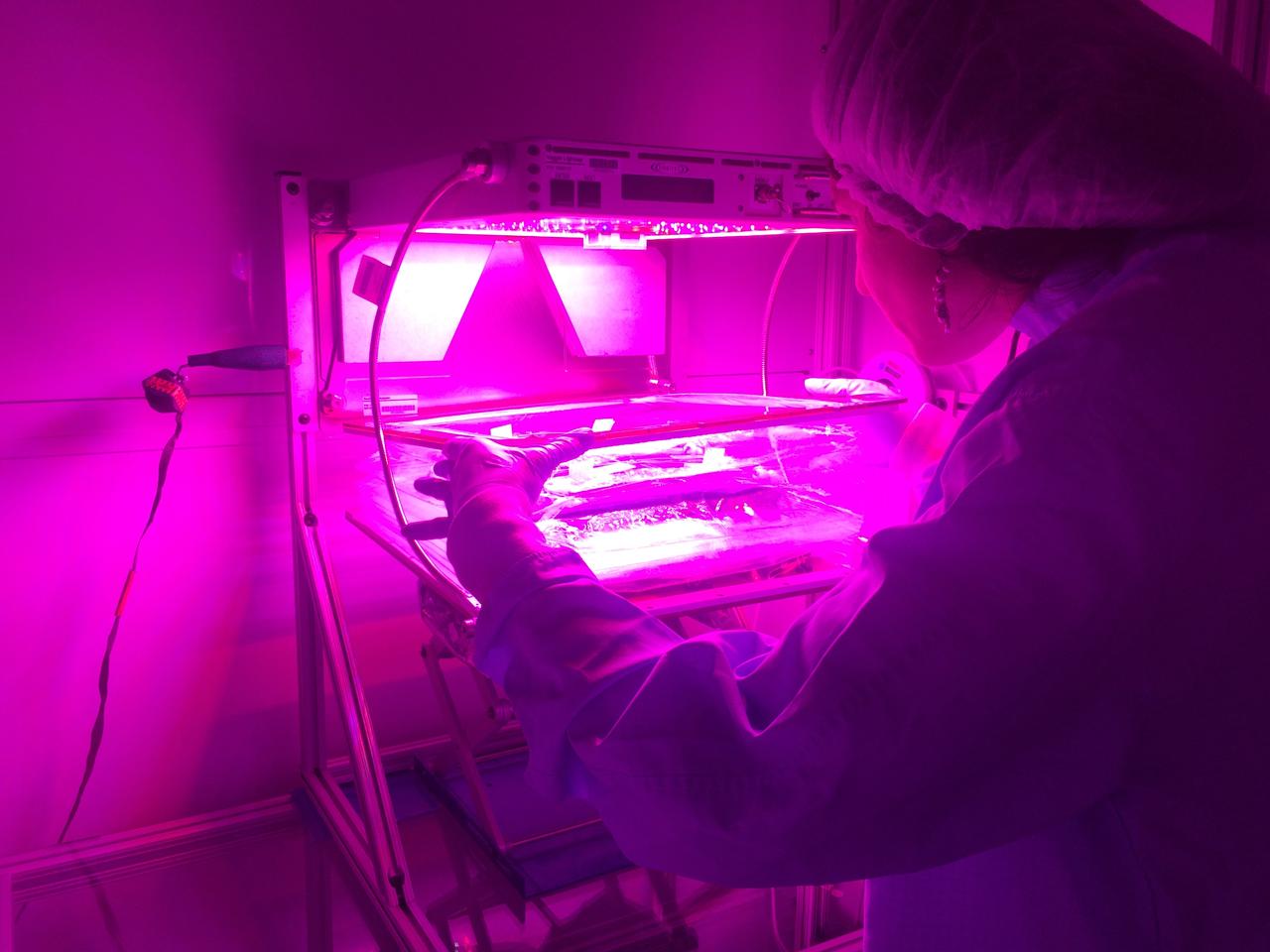

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
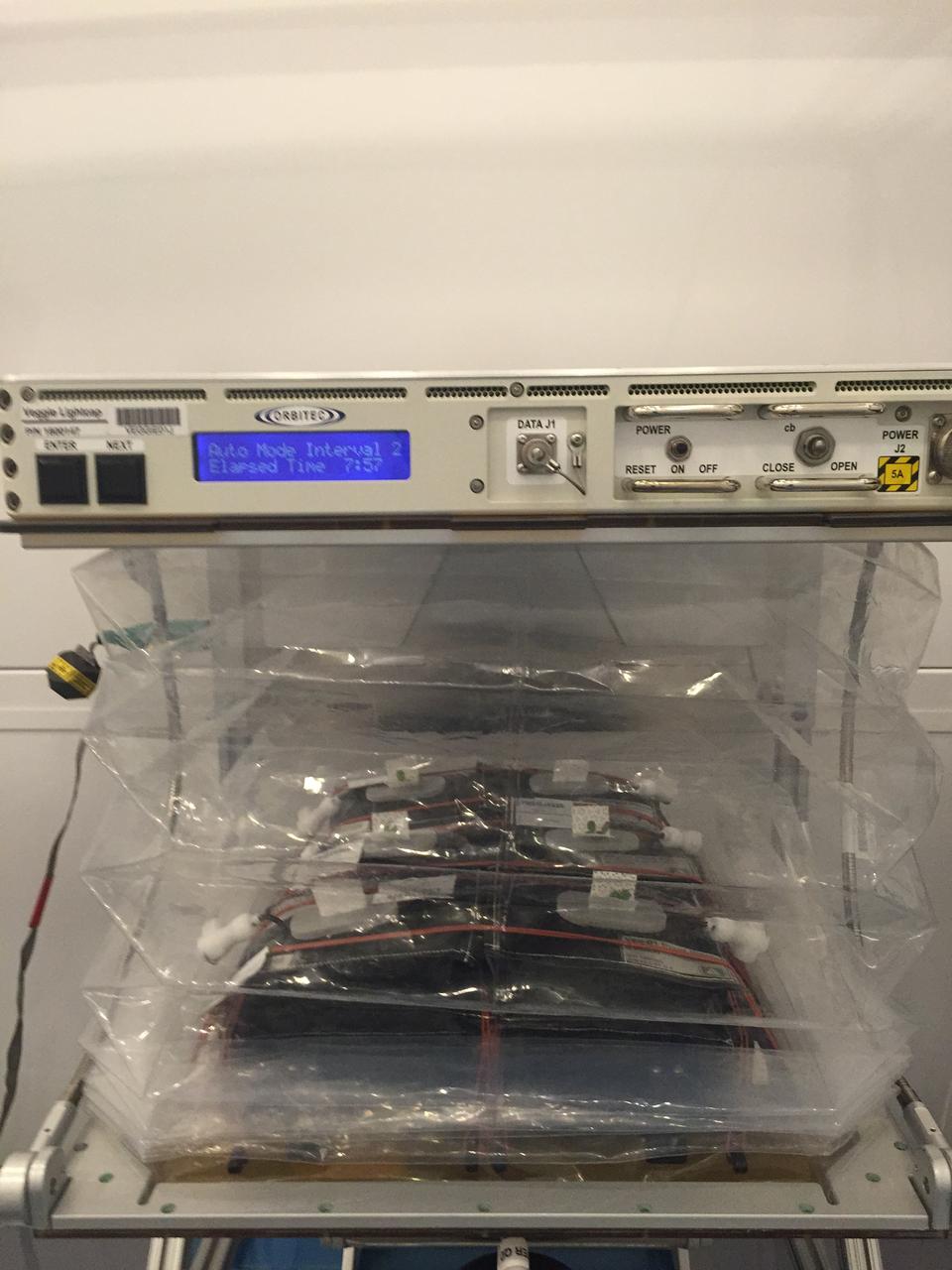

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

Kennedy Space Center’s Tim Bass addresses co-workers inside the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute on Oct. 17, 2019, during the third in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this third session was customers, and additional speakers included Kennedy employees Ryan Richards, Mike Williams and Dave Grau.
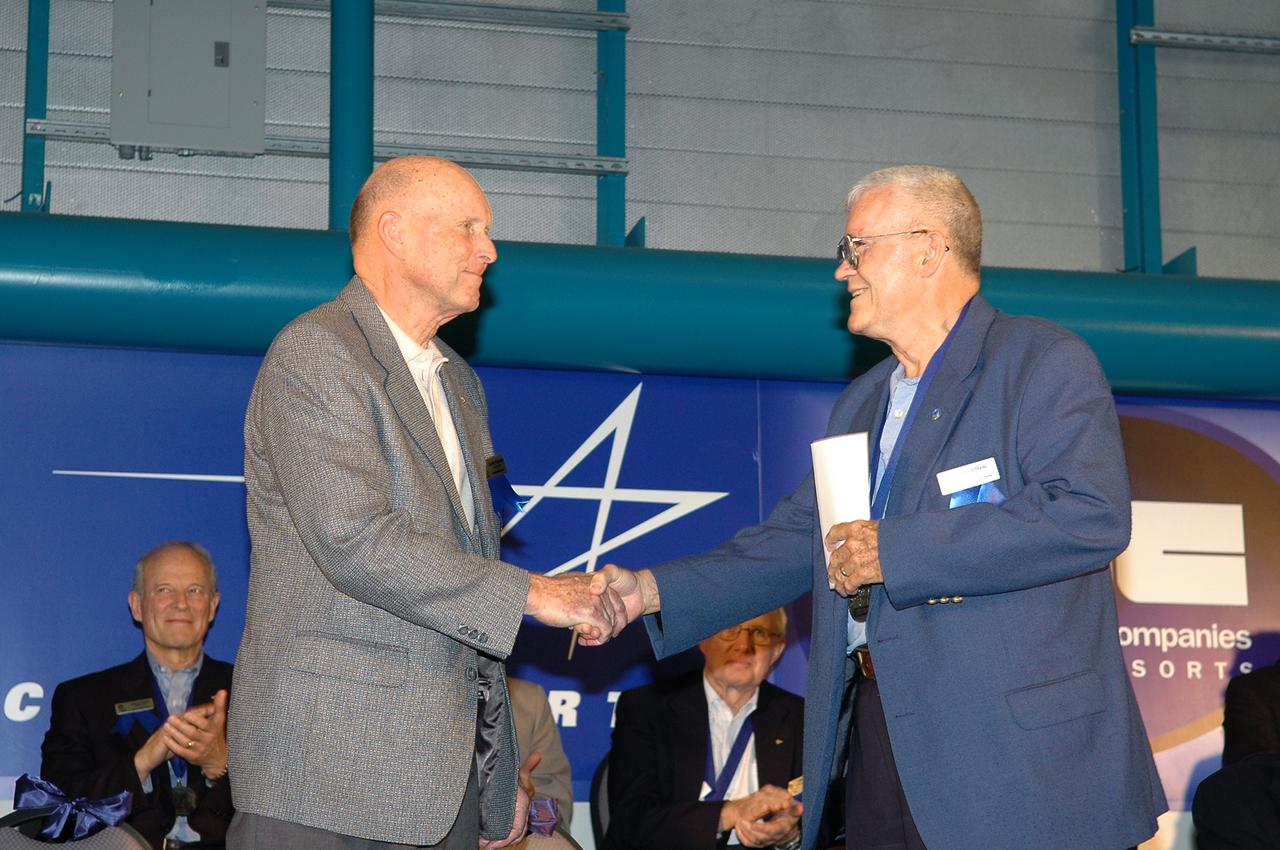

Former astronaut Gordon Fullerton (left), currently chief research pilot at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base, is congratulated by former astronaut Fred Haise (right) upon Fullerton's induction into the Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida on April 30, 2005. Fullerton and Haise were one of two flight crews who flew the Approach and Landing Tests of the prototype Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise at Dryden in 1977. Fullerton, who had served on the support crews for four Apollo moon landing missions in the early 1970s, went on to fly two Shuttle missions, STS-3 in 1982 and STS-51F in 1985. STS-3 became the only Shuttle mission to date to land at White Sands, N.M., and STS-51F was completed successfully despite the failure of one of the Shuttle's main engines during ascent to orbit. Haise, a member of the crew on the ill-fated Apollo 13 mission, was also a research pilot at NASA Dryden during his pre-astronaut career. Former astronauts Joseph Allen and Bruce McCandless were also inducted during the 2005 ceremonies at the KSC Visitor Center. In addition to honoring former members of NASA's astronaut corps who have made significant contributions to the advancement of space flight, the annual induction ceremonies serve as a fund-raiser for the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation. The foundation funded 17 $10,000 scholarships to college students studying science and engineering in 2004.
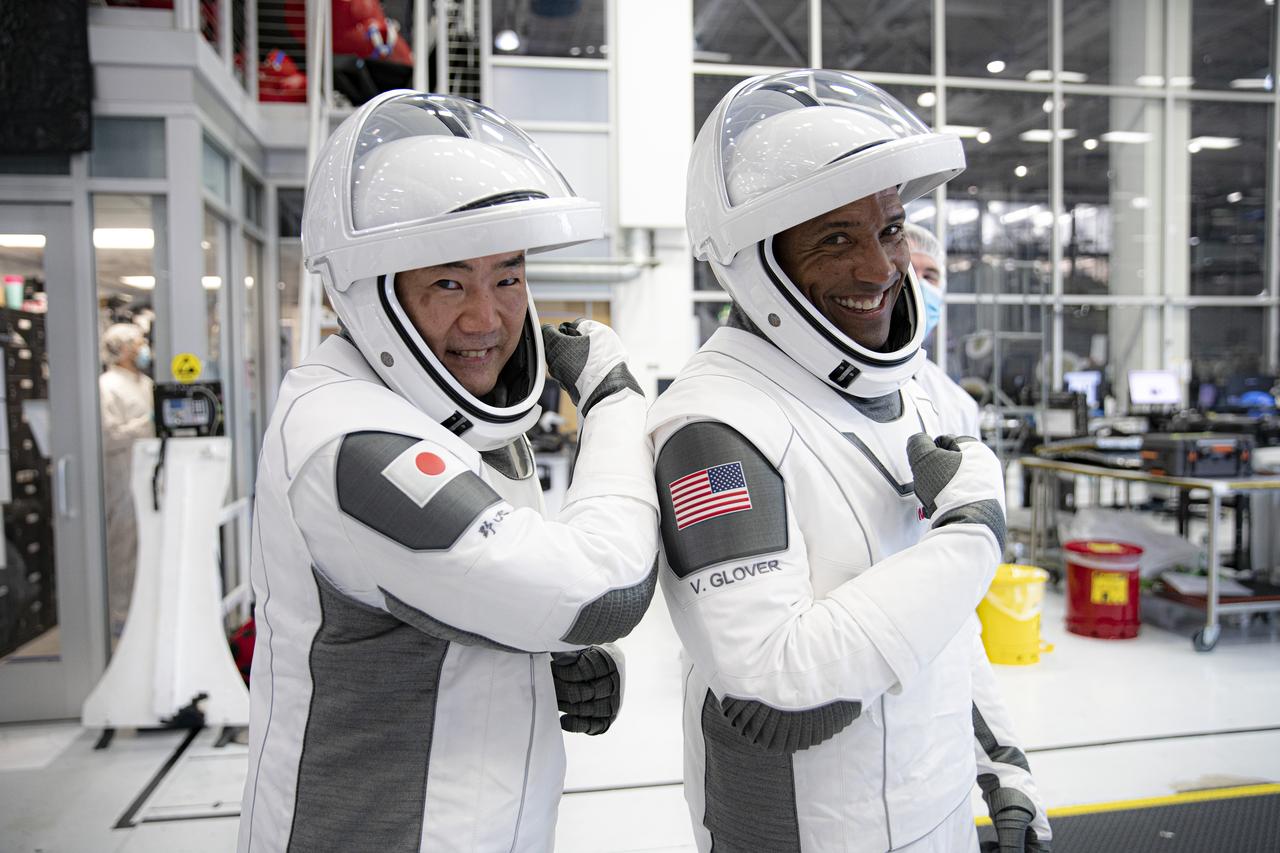

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 astronauts participate in crew equipment interface testing at SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, on Sept. 24, 2020. From left are mission specialist Soichi Noguchi, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut, and pilot Victor Glover, NASA astronaut. The other crew members training, but not pictured, are mission specialist Shannon Walker, and Crew Dragon commander Michael Hopkins, both NASA astronauts. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission is the first crew rotational flight of a U.S. commercial spacecraft with astronauts to the International Space Station. The Crew-1 mission will launch from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Crew-1 is part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program, which has returned human spaceflight capabilities to the U.S.
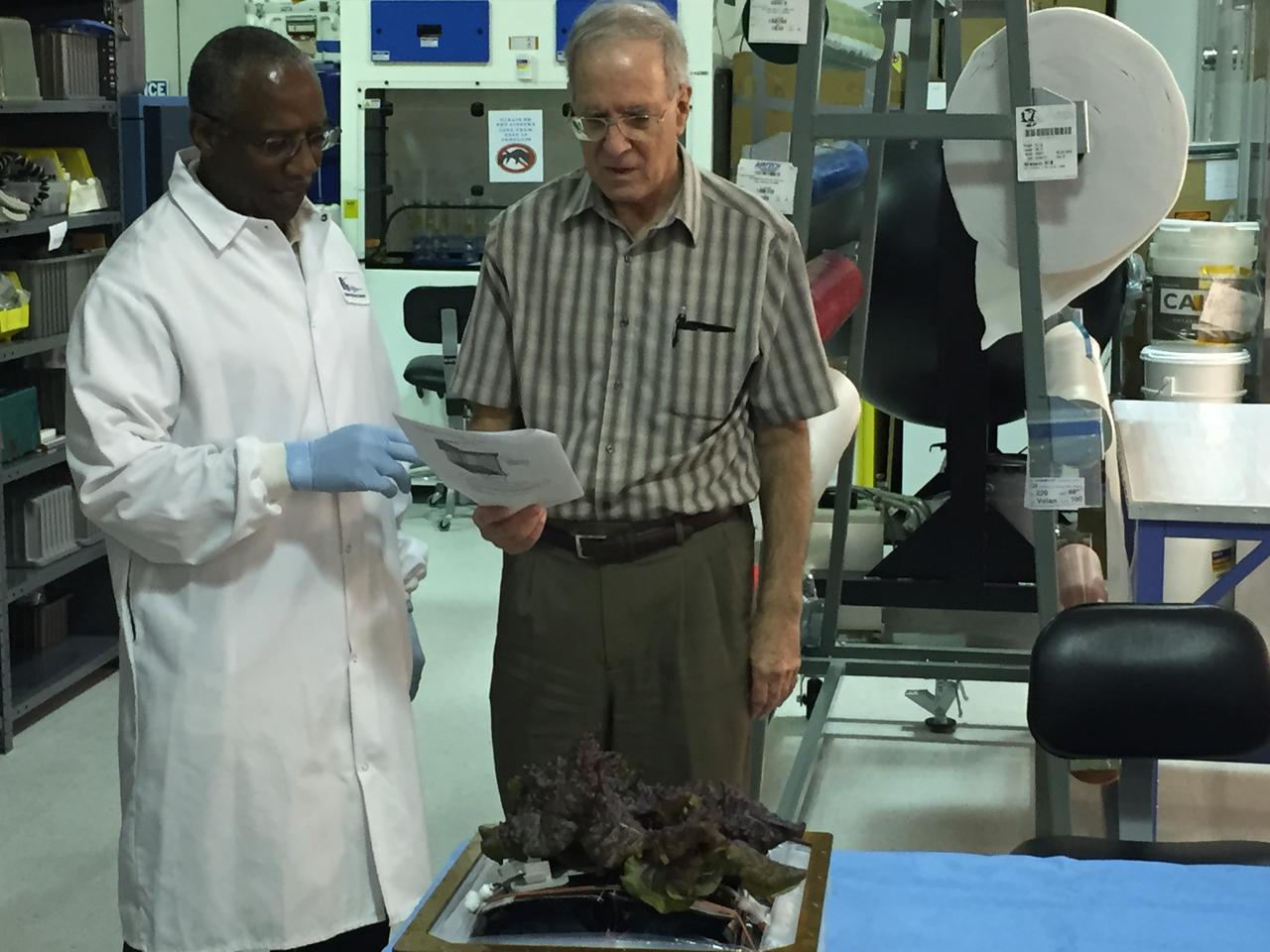

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

AERIALS - SR3 SOLAR FACILITY & NEW EXPANSION SITE, EXLORATION PARK
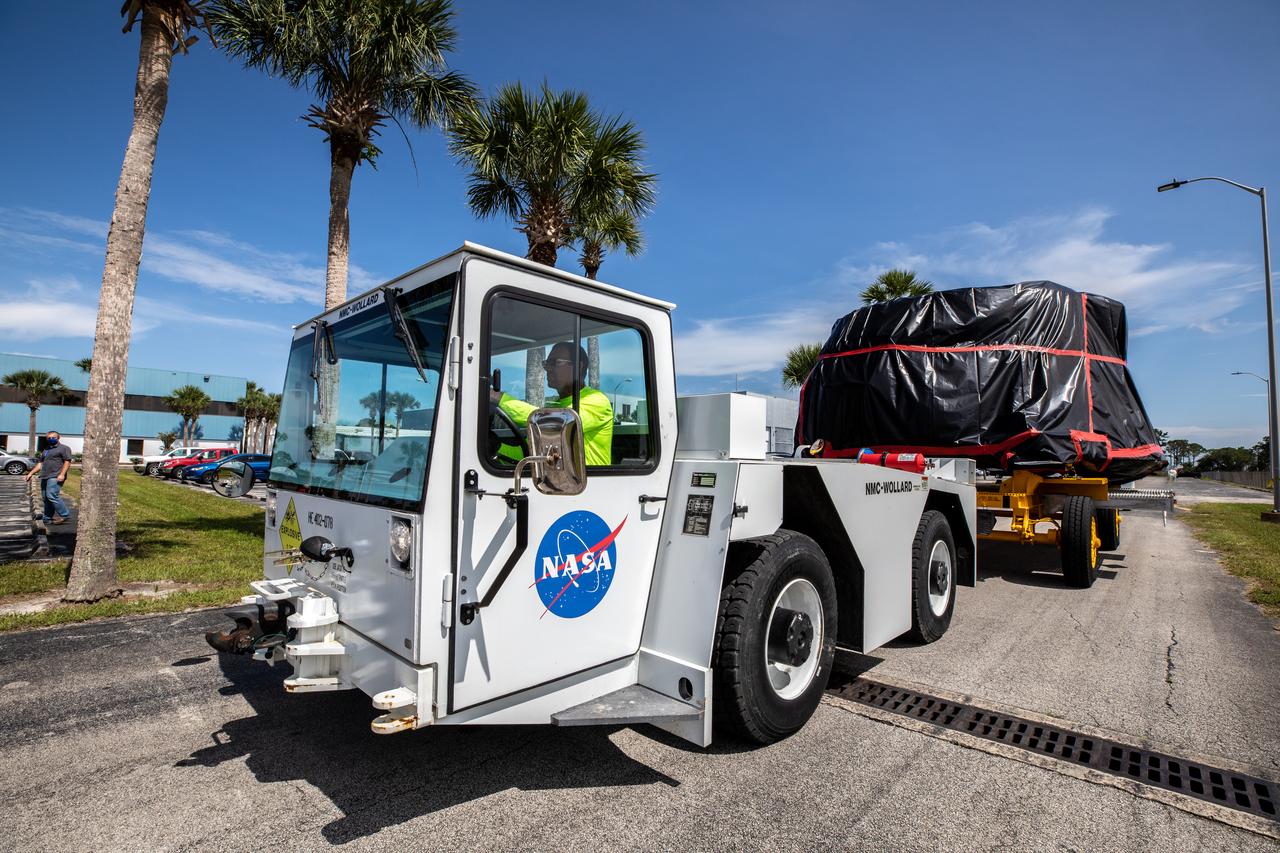

The Artemis I aft skirts for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s twin solid rocket boosters are transported to the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2020. The aft skirts were refurbished by Northrop Grumman. They house the thrust vector control system, which controls 70 percent of the steering during initial ascent of the SLS rocket. The segments will remain in the RPSF until ready for stacking with the forward and aft parts of the boosters on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Through the Artemis Program, NASA is working to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
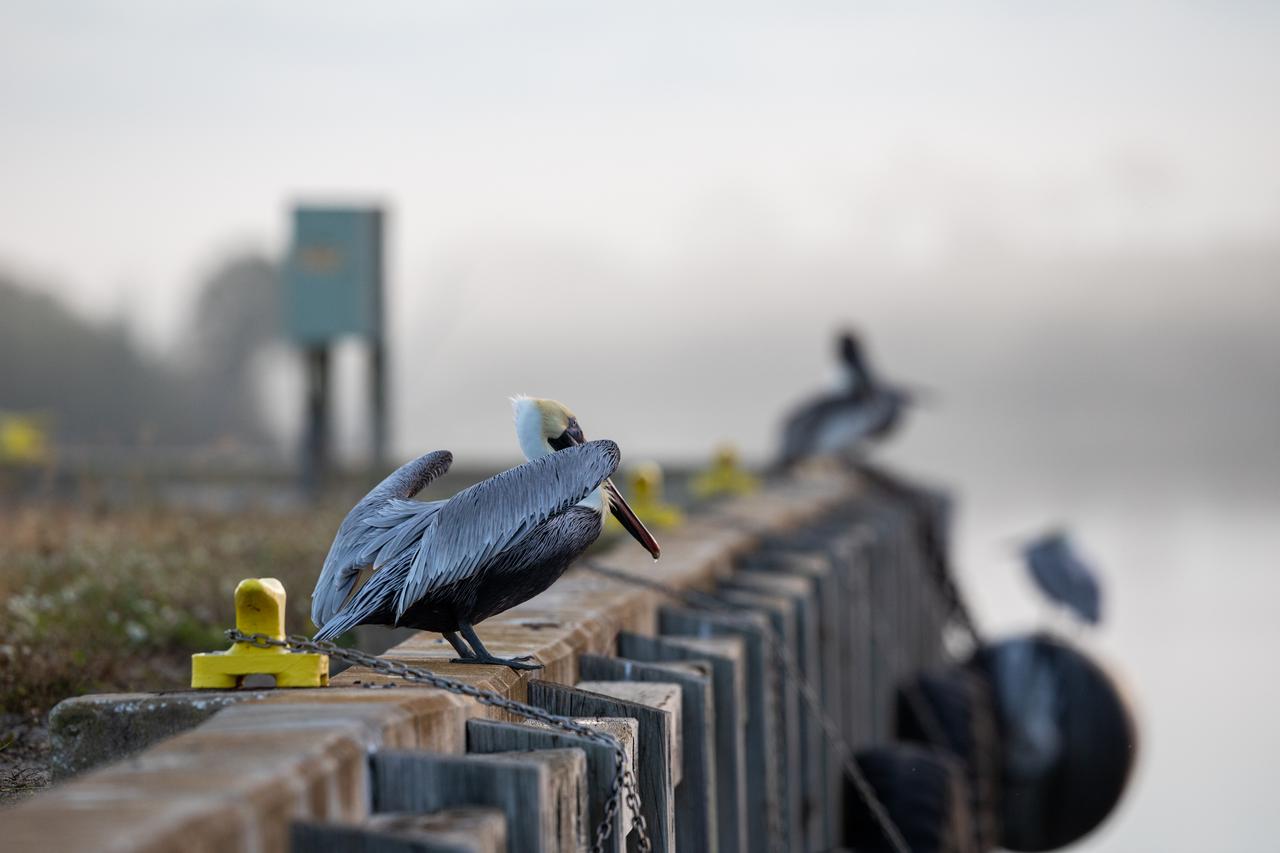

Pelicans perch on the support beams of an embankment on a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2021. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, along with 25 mammal, 117 fish, and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
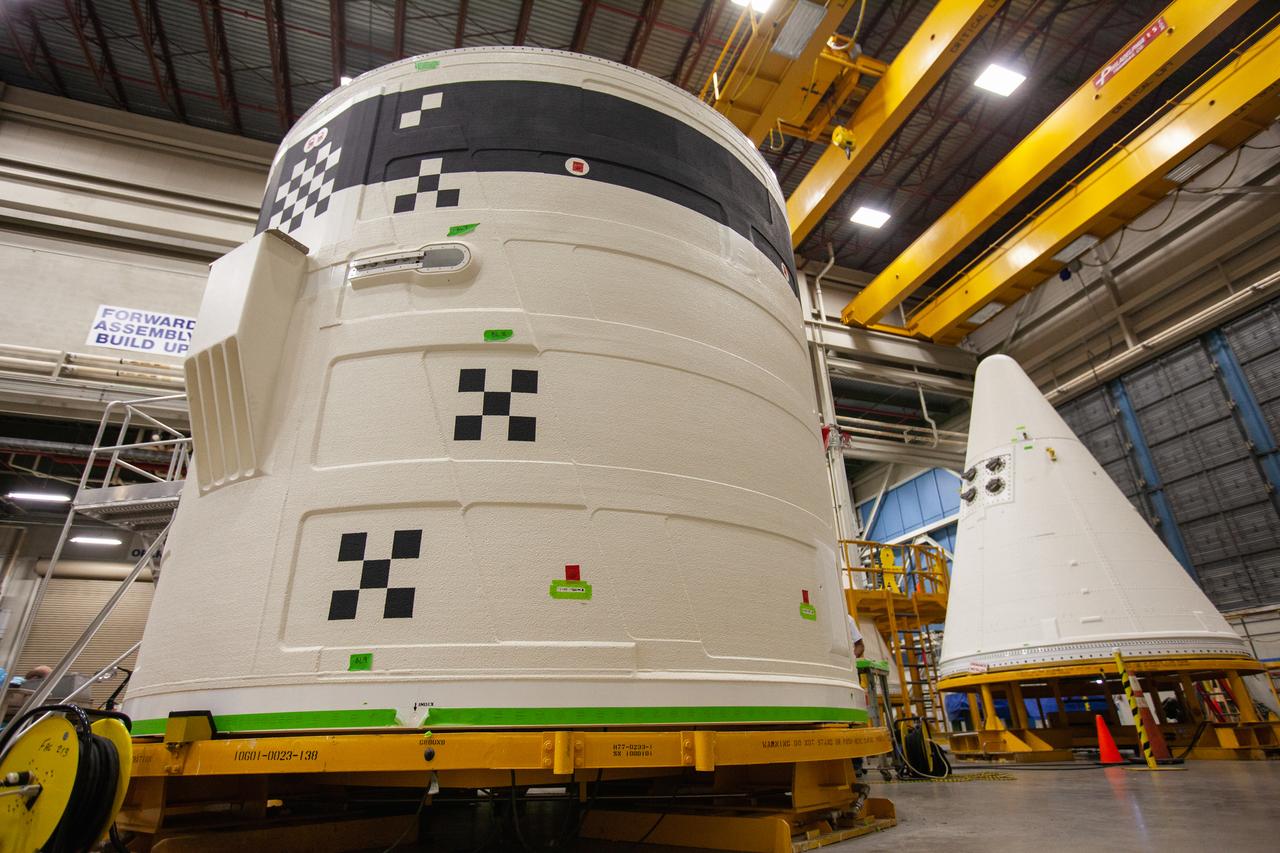

The forward skirt for one of the Space Launch System’s (SLS) two solid boosters is inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 16, 2019. Segments of the boosters are being inspected and prepared for Artemis I, the agency’s first uncrewed flight of Orion atop the SLS. The forward skirt houses booster avionics that communicate with the SLS avionics to monitor booster conditions and steer the booster exhaust nozzle.
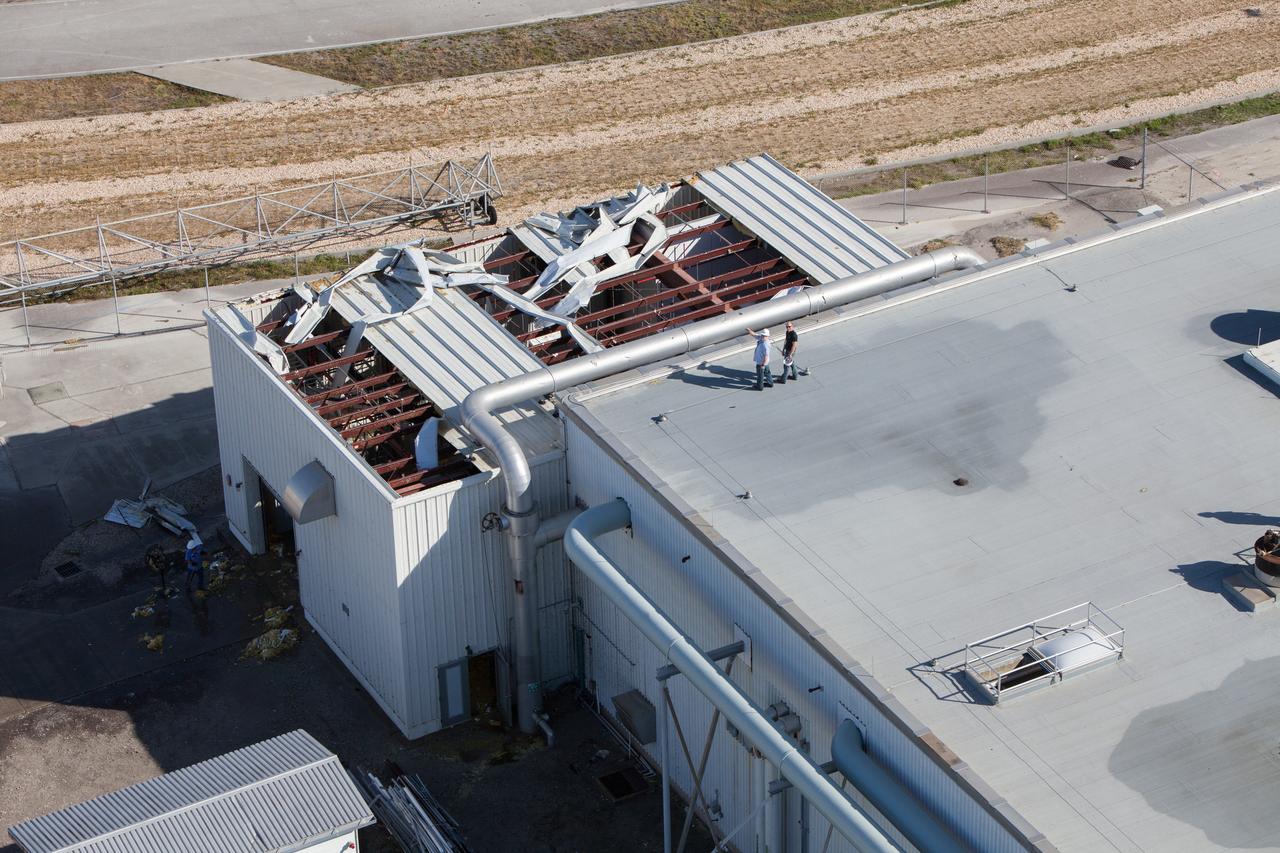

A support building is seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Matthew as the storm passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. Officials determined that the center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm’s onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.
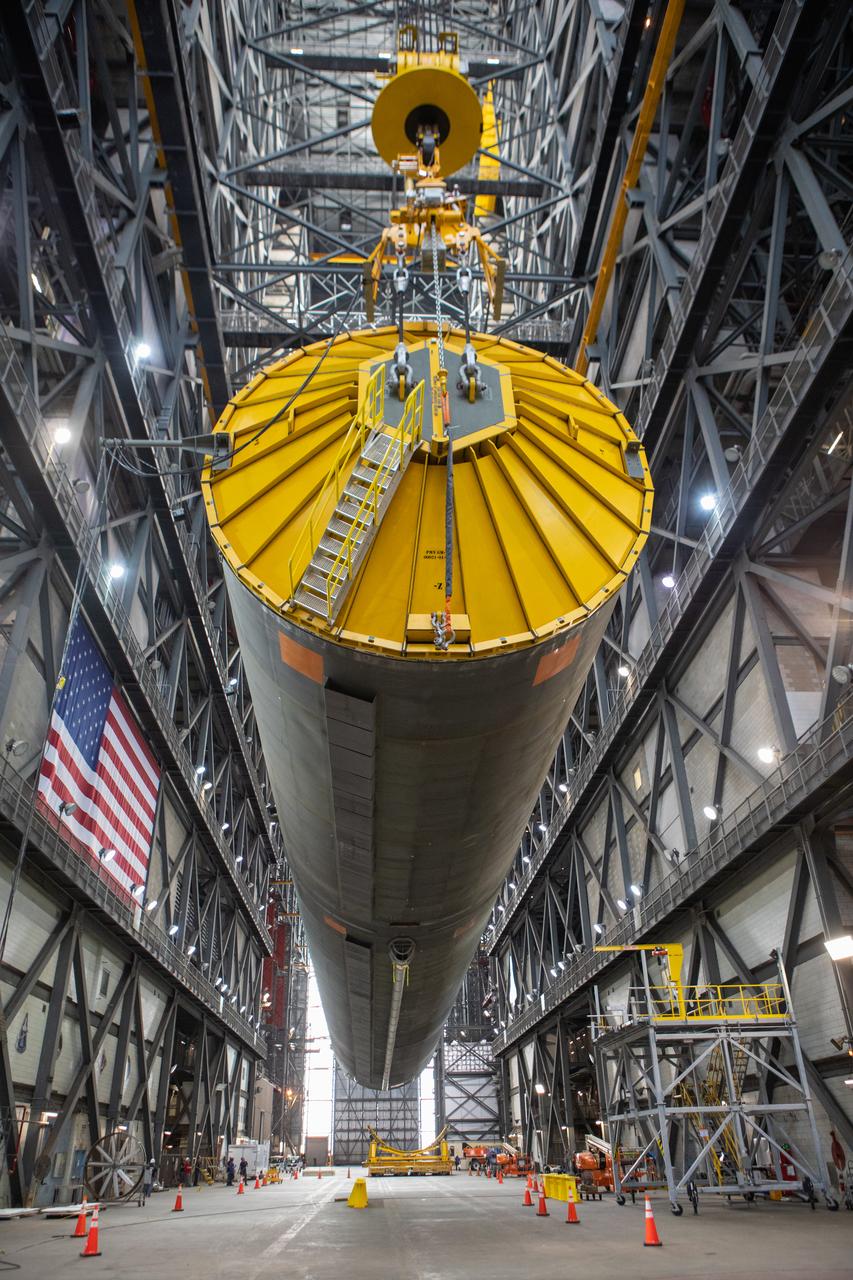

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage pathfinder is suspended by two cranes in the horizontal position above the transfer aisle on Oct. 15, 2019. The 212-foot-long core stage pathfinder arrived on NASA's Pegasus Barge at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Sept. 27, 2019. The Pegasus Barge made its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The pathfinder is being used by Exploration Ground Systems and its contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy through at least the month of October before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
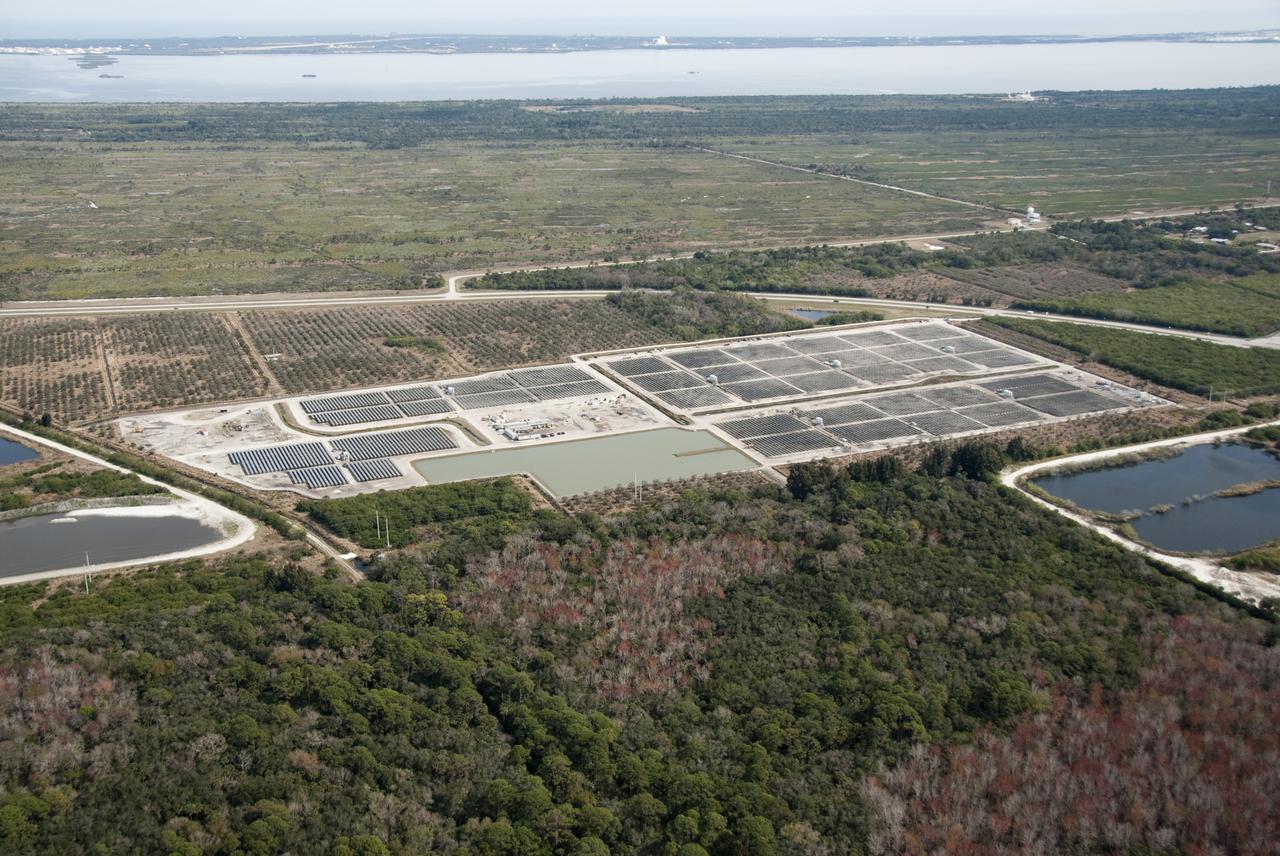

AERIALS - SR3 SOLAR FACILITY & NEW EXPANSION SITE, EXLORATION PARK
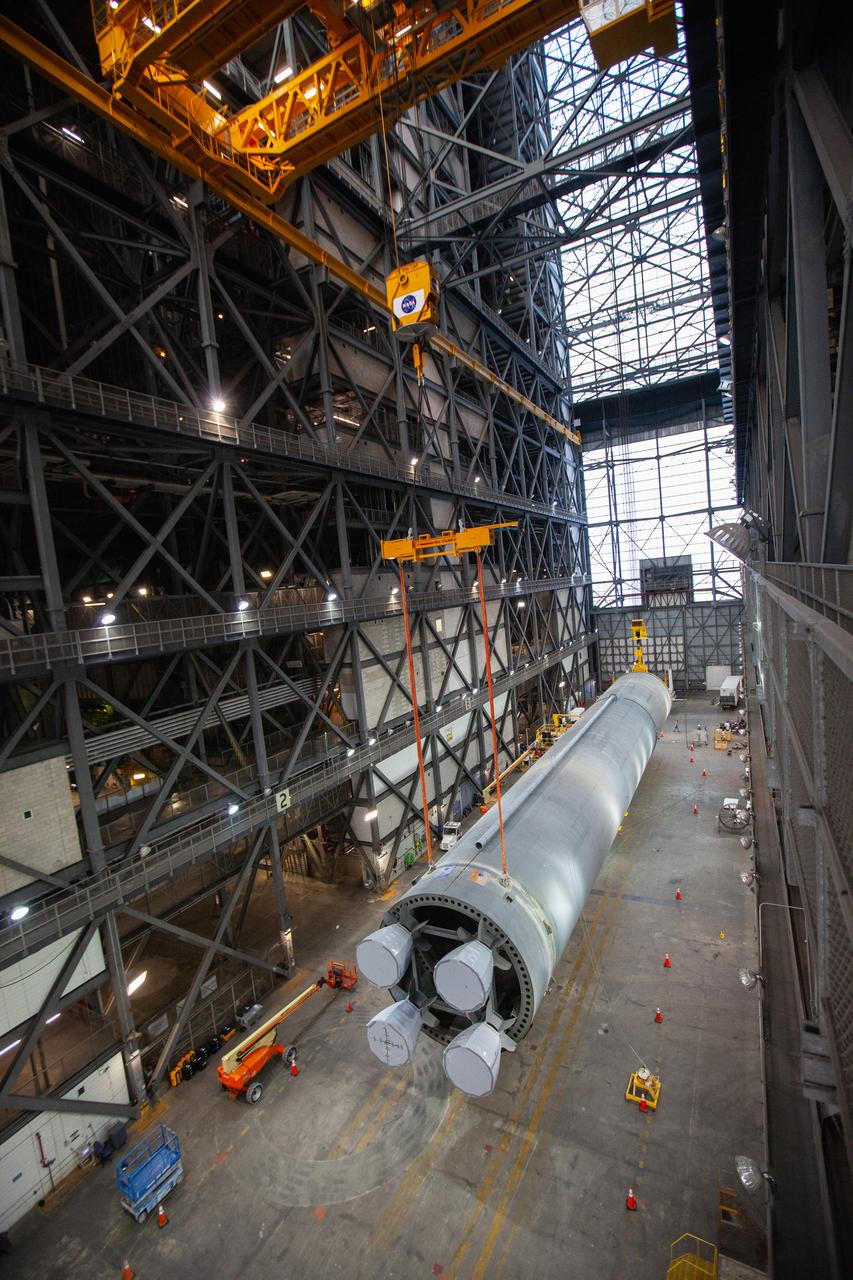

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage pathfinder is lifted horizontally in the transfer aisle on Oct. 15, 2019. The 212-foot-long core stage pathfinder arrived on NASA's Pegasus Barge at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Sept. 27, 2019. The Pegasus Barge made its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The pathfinder is being used by Exploration Ground Systems and its contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy through at least the month of October before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.

The rock band X Ambassadors is photographed in front of NASA’s Artemis II Orion crew module inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. X Ambassadors visited Kennedy on Oct. 21, 2019, and had the opportunity to tour areas around the multi-user spaceport such as the O&C, Launch Complex 39B and Swamp Works. The title of the band’s latest album, Orion, led them to an up-close look at the spacecraft that will take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before.
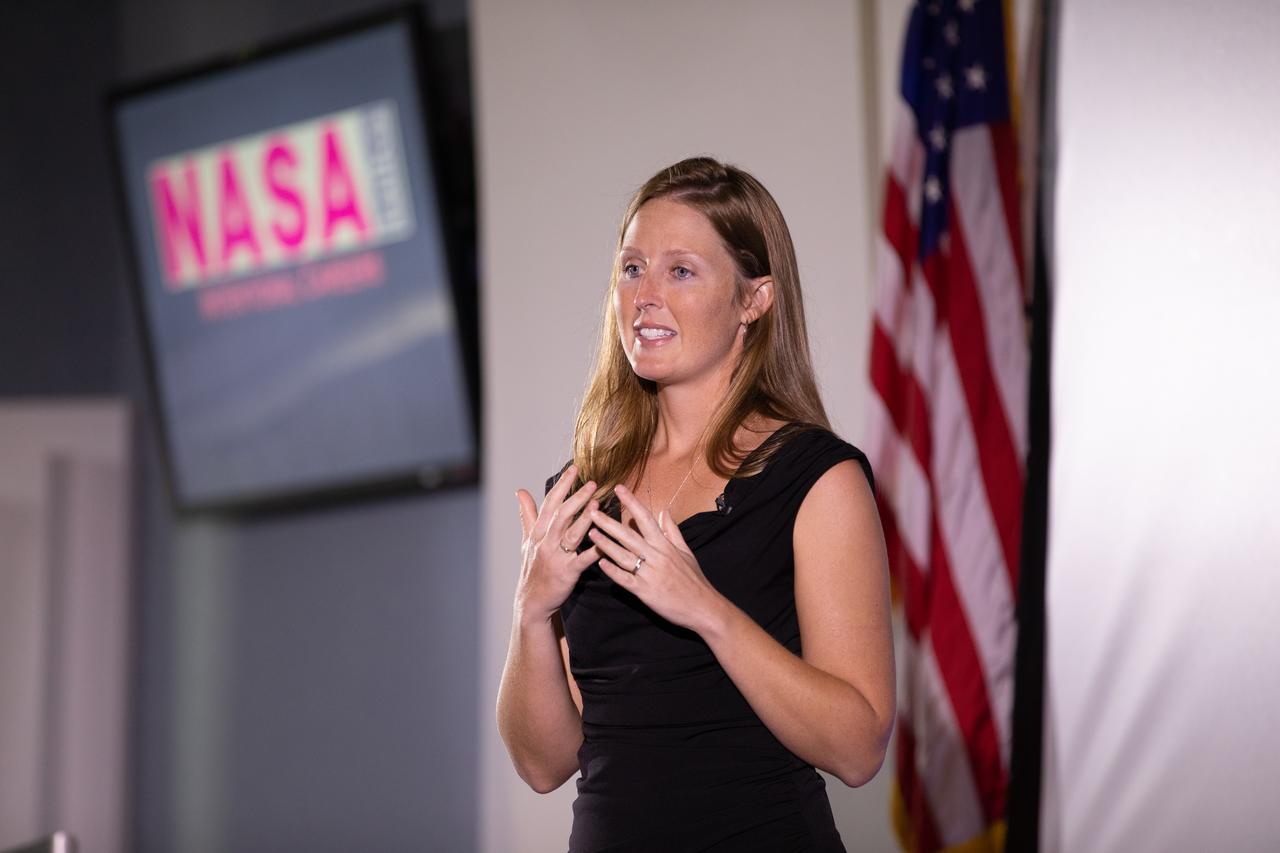

Kennedy Space Center’s Stephanie Martin speaks at the second in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this second session was collaboration, and additional speakers included Kennedy employees Jennifer Lane and Skyler Kleinschmidt, with a skill-building section on networking in the digital age by Madison Tuttle.
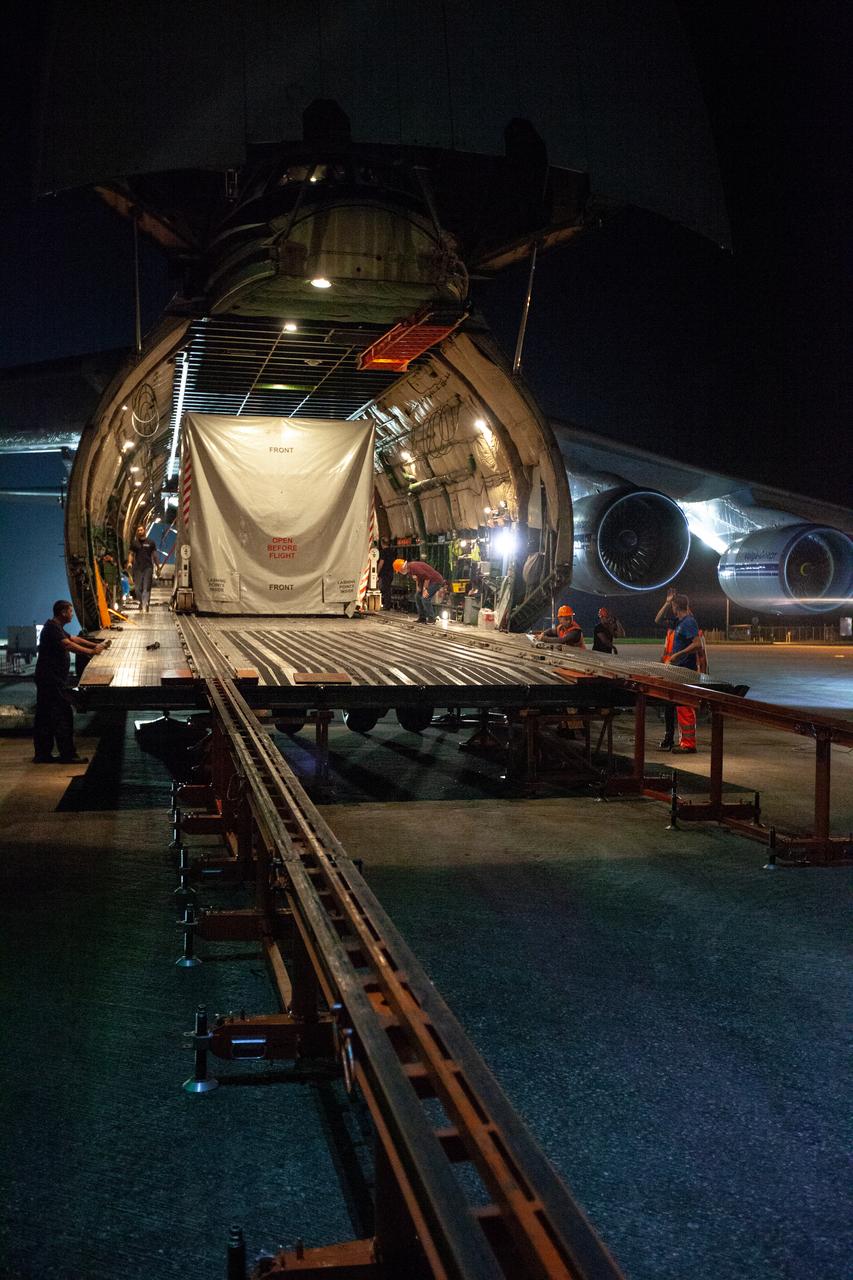

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is moved out of an Antonov An-124 cargo plane at NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility on Nov. 1, 2019. The spacecraft was delivered to the Florida spaceport from Munich, Germany, then transported to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in nearby Titusville. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.

An alligator moves through a brackish waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.

Artifacts retrieved from the ruins of Elliot Plantation on NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida show high-status fine dining wares imported from 18th century England. The white salt-glazed stoneware and creamware dining wares were found scattered near a large structure, determined by archeologists to be the dwelling of the plantation overseer. The dining wares have known dates of time for manufacturing and use during the 1760s through the 1770s and helped archeologists confirm the site was from the same period. The ruins of Elliot Plantation date from the 1760s and represent the largest, earliest, and southernmost British period sugar plantation in the U.S., as well as one of the most intact and best examples of a completely preserved enslaved landscape. In interagency cooperation between the National Park Service, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and NASA, and with the assistance of volunteers from the Indian River Anthropological Society, and historic preservation offices of Brevard and Volusia counties, approximately 200 shovel tests and 20 excavation units were completed in three areas of the plantation complex from 2008 to 2009.
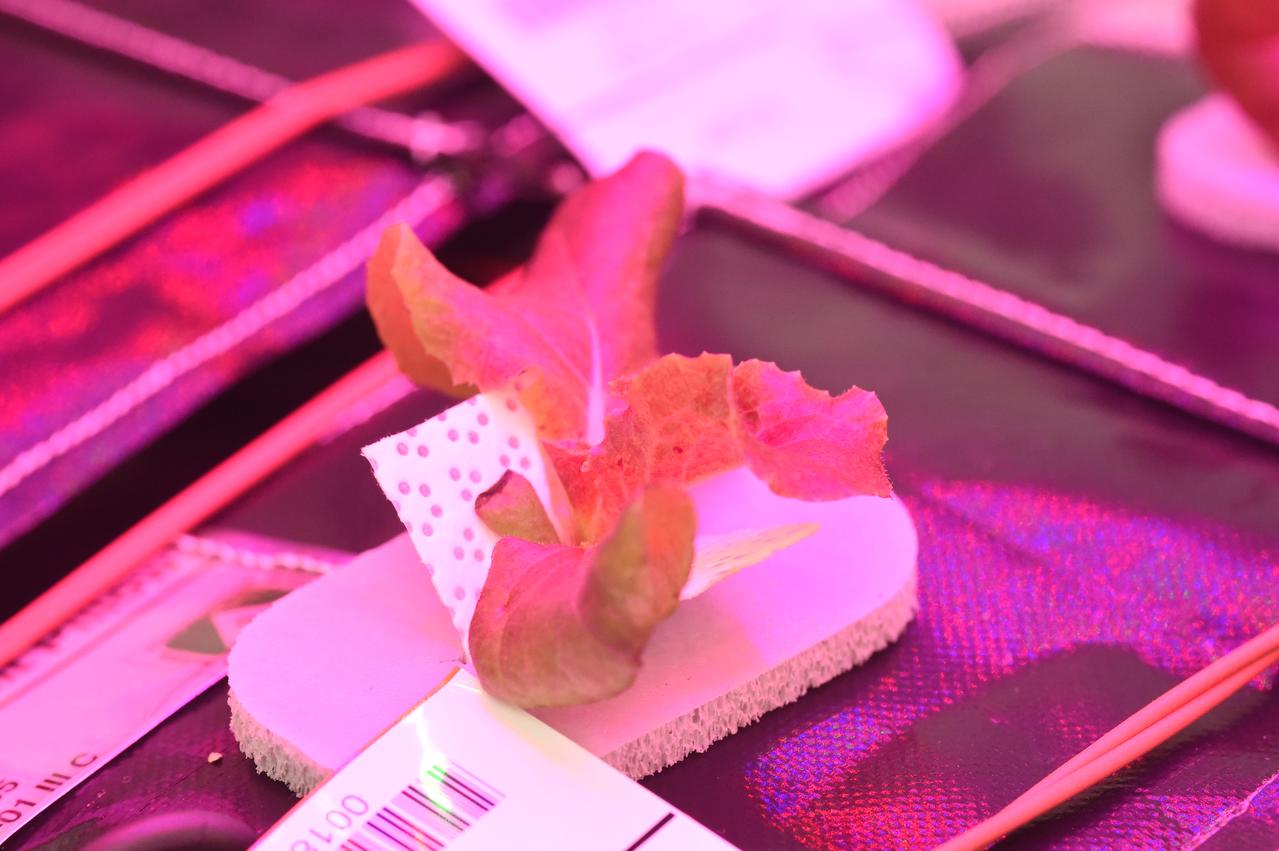

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

Kennedy Space Center’s Stephanie Martin addresses co-workers inside the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute on Oct. 10, 2019, during the second in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this second session was collaboration, and additional speakers included Kennedy employees Jennifer Lane and Skyler Kleinschmidt, with a skill-building section on networking in the digital age by Madison Tuttle.
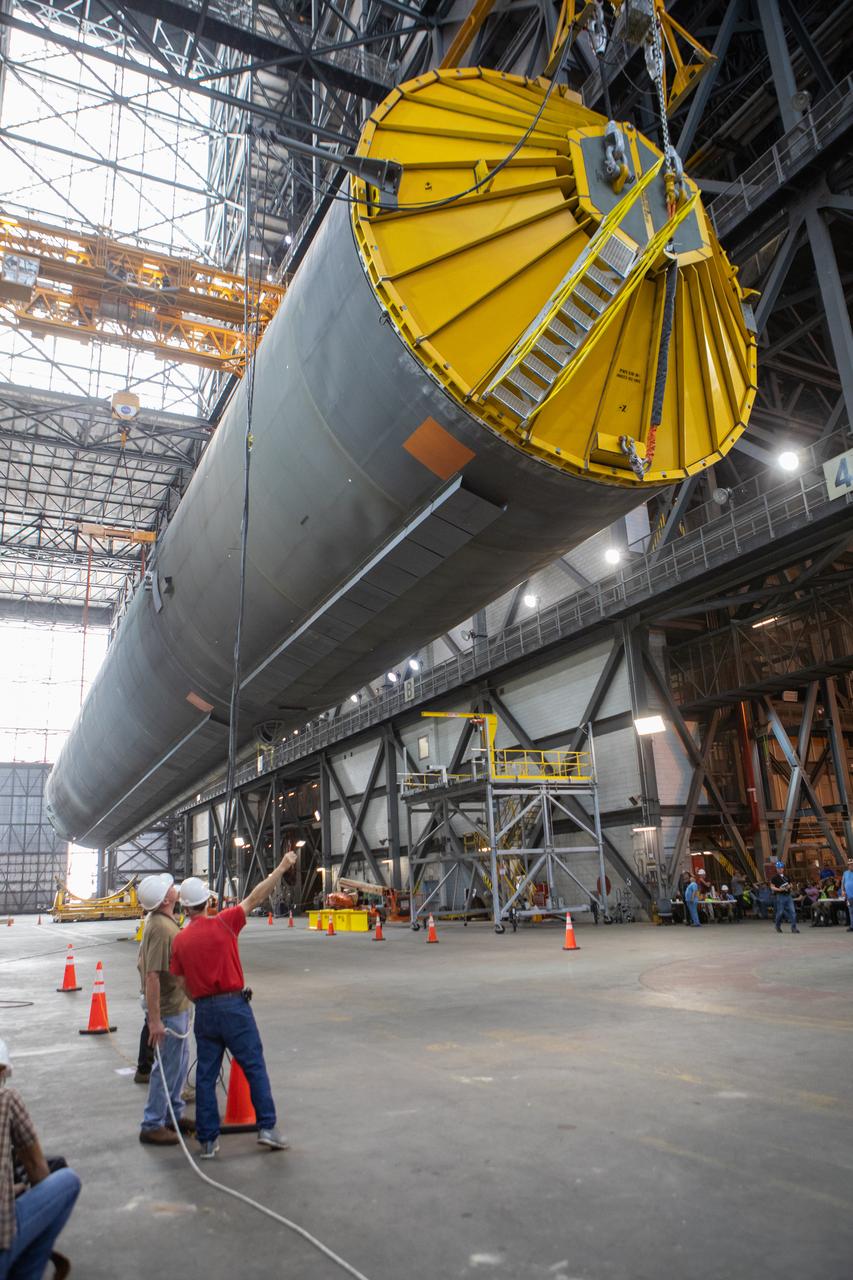

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers assist as the Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage pathfinder is suspended by two cranes in the horizontal position above the transfer aisle on Oct. 15, 2019. The 212-foot-long core stage pathfinder arrived on NASA's Pegasus Barge at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Sept. 27, 2019. The Pegasus Barge made its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The pathfinder is being used by Exploration Ground Systems and its contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy through at least the month of October before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
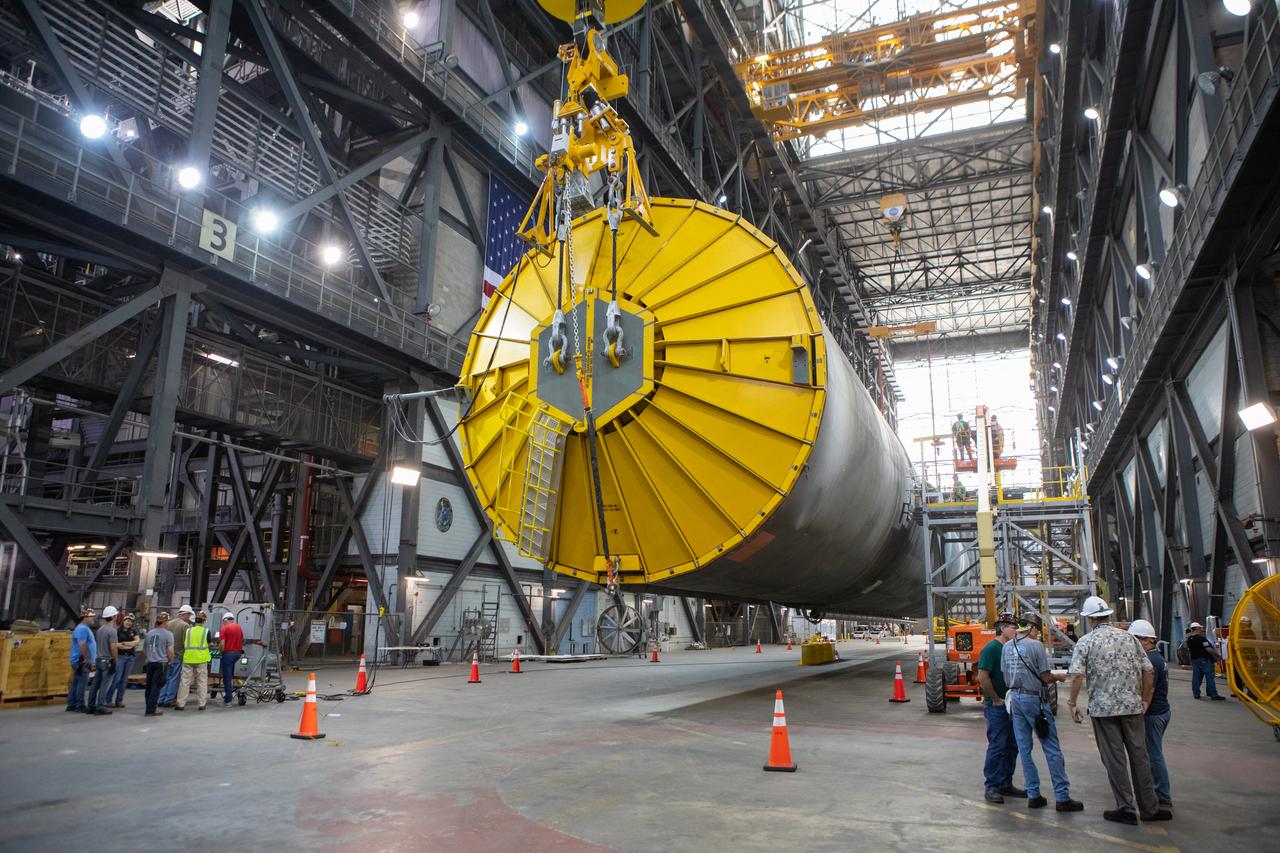

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers watch the progress as two cranes are used to lift the Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage pathfinder horizontally in the transfer aisle on Oct. 15, 2019. The 212-foot-long core stage pathfinder arrived on NASA's Pegasus Barge at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Sept. 27, 2019. The Pegasus Barge made its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The pathfinder is being used by Exploration Ground Systems and its contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy through at least the month of October before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
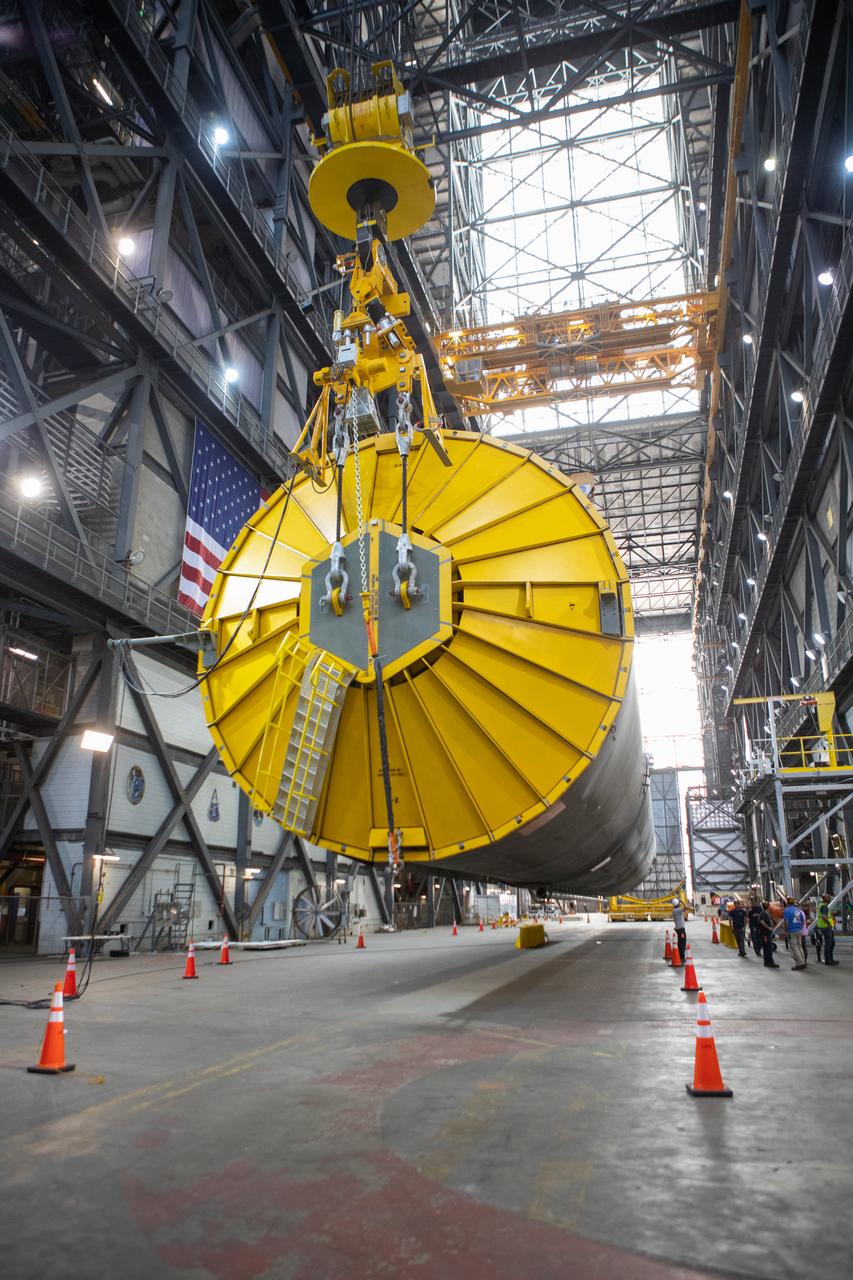

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, two cranes are used to lift the Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage pathfinder horizontally in the transfer aisle on Oct. 15, 2019. A cover, called the spider, is in view on the top of the pathfinder. A crane is attached to the spider to help lift the pathfinder. The 212-foot-long core stage pathfinder arrived on NASA's Pegasus Barge at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Sept. 27, 2019. The Pegasus Barge made its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The pathfinder is being used by Exploration Ground Systems and its contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy through at least the month of October before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
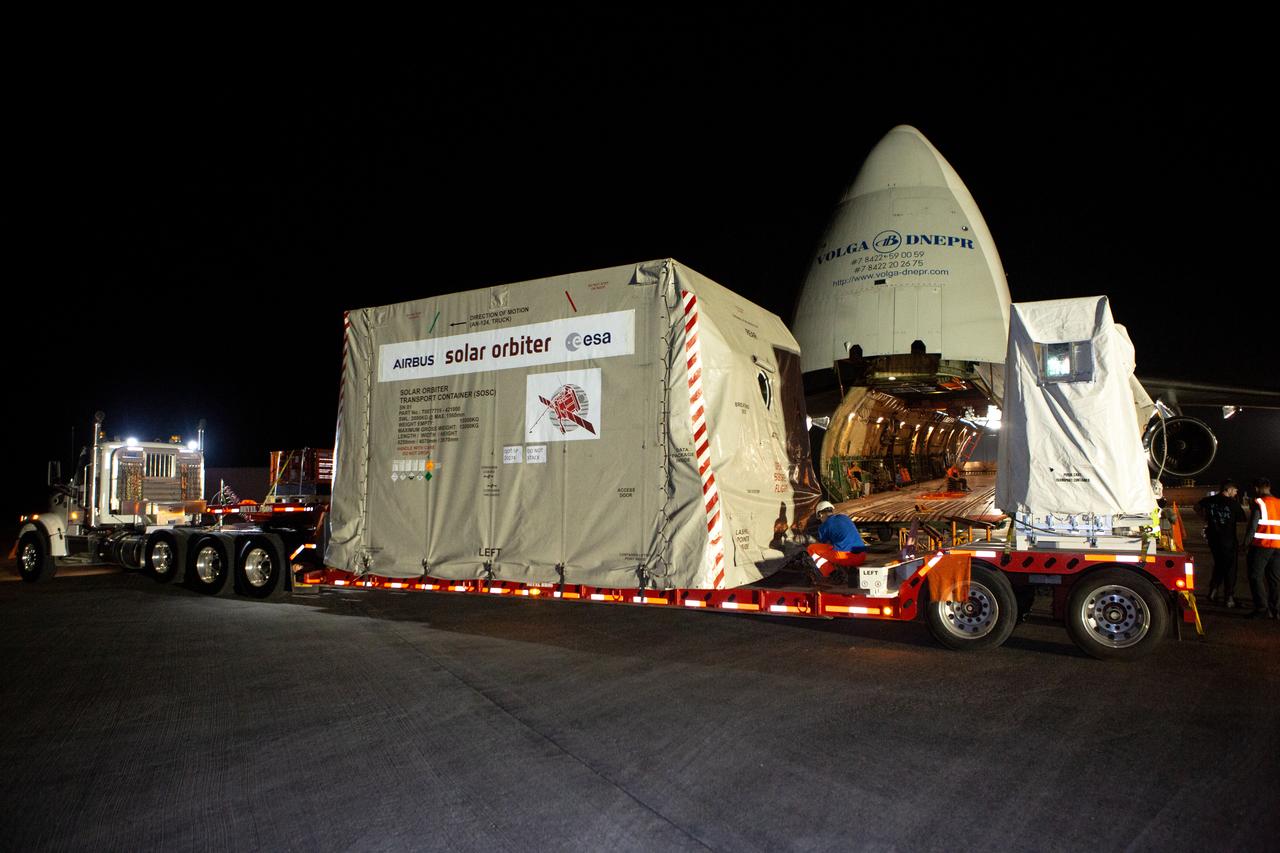

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is placed on a truck for transportation from the Launch and Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the Astrotech Space Operations facility in nearby Titusville on Nov. 1, 2019. The spacecraft was delivered to the Florida spaceport aboard an Antonov An-124 cargo plane from Munich, Germany. Solar Orbiter is a European Space Agency mission with strong NASA participation. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar winds. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. Liftoff is scheduled for Feb. 5, 2020, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
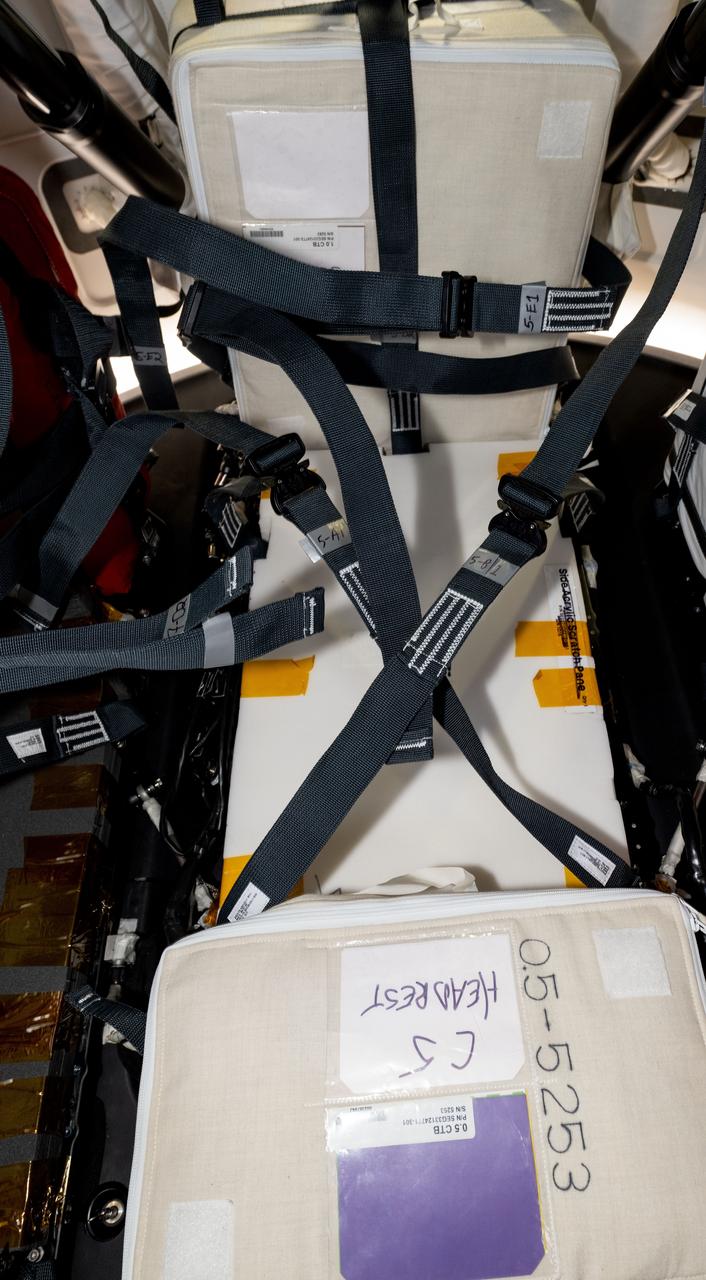

This image shows one of the temporary seat structures built and installed on the Crew-8 Dragon in cargo pallet locations C7 and C5 using foam, straps, and other station soft goods such as cushions.
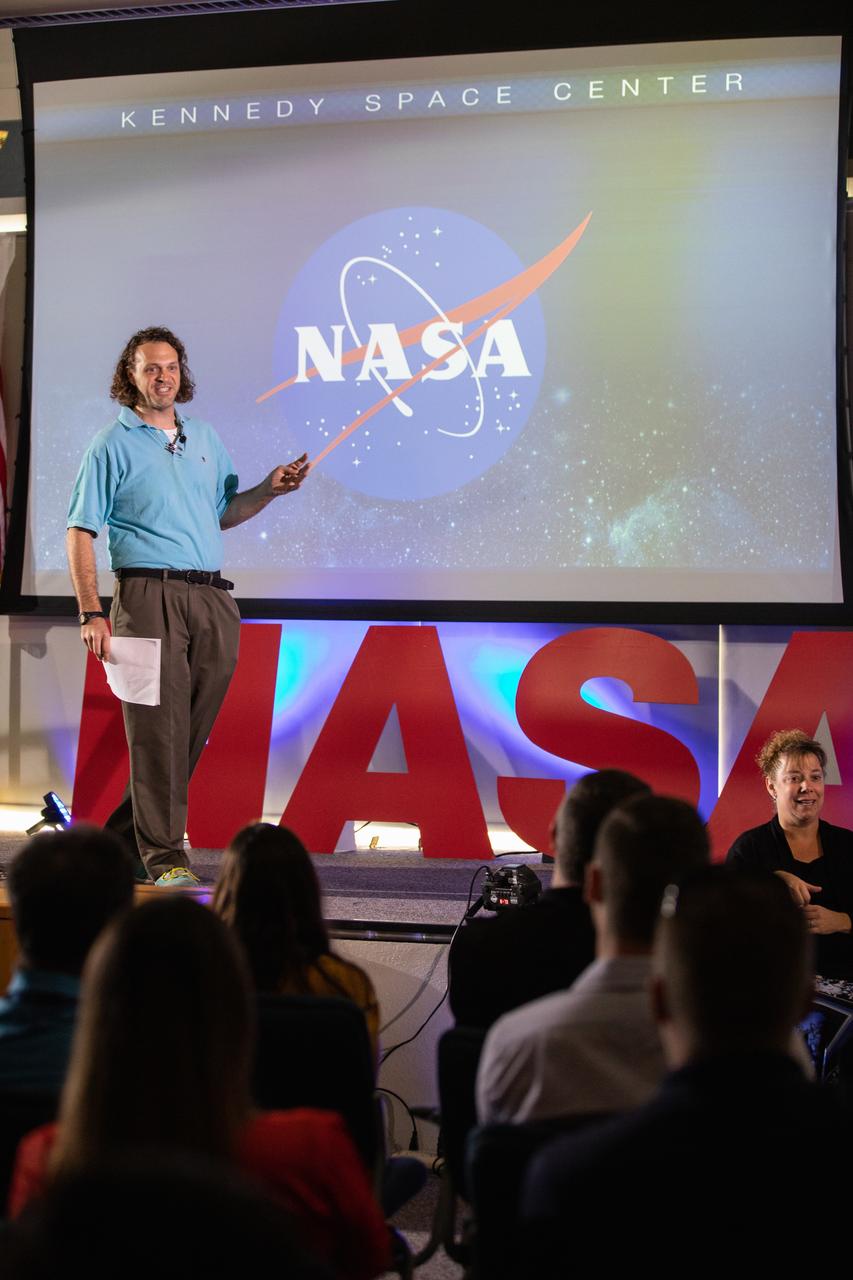

Kennedy Space Center’s Tim Bass addresses co-workers inside the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute on Oct. 17, 2019, during the third in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this third session was customers, and additional speakers included Kennedy employees Ryan Richards, Mike Williams and Dave Grau.
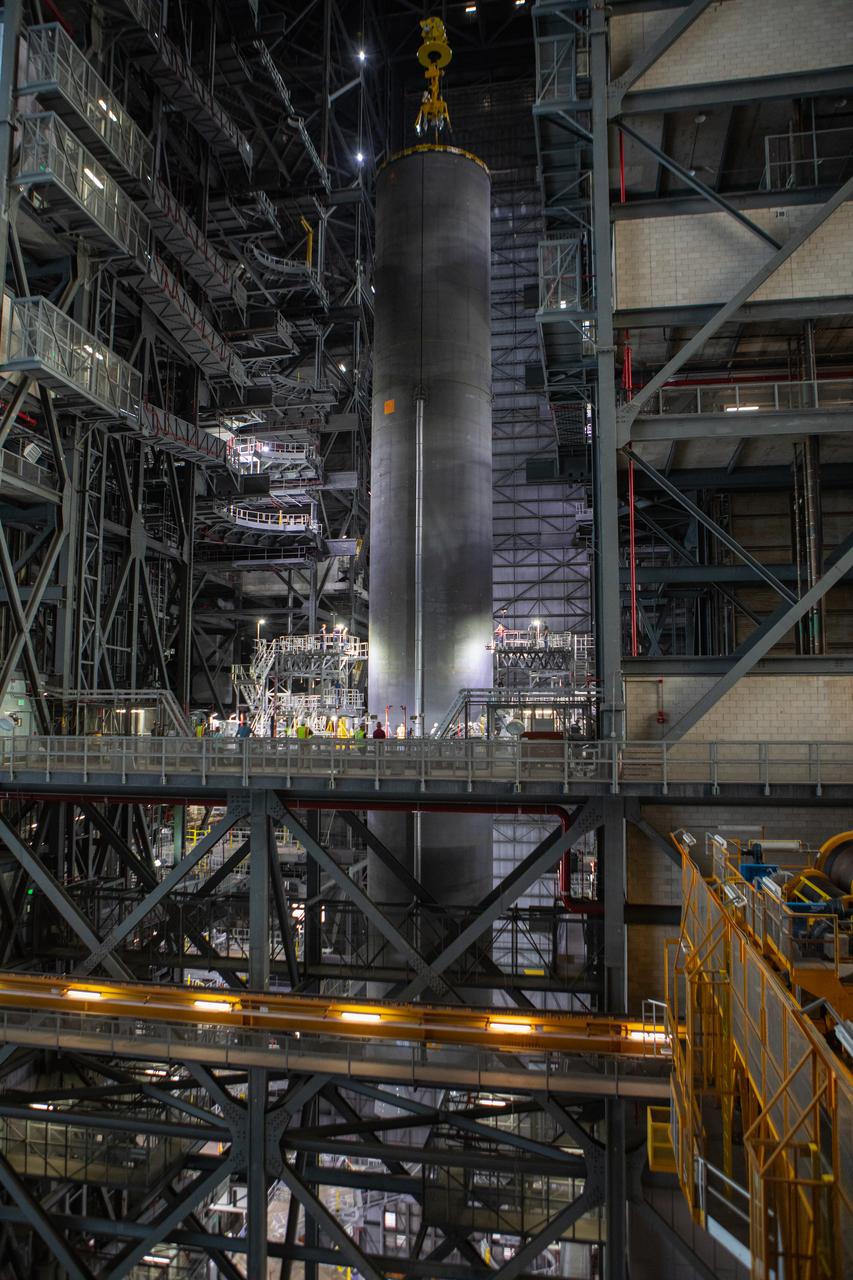

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage pathfinder into High Bay 3 on Oct. 65, 2019. The 212-foot-long core stage pathfinder arrived on NASA's Pegasus Barge at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Sept. 27, 2019. The Pegasus Barge made its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The pathfinder is being used by Exploration Ground Systems and its contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy through at least the month of October before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
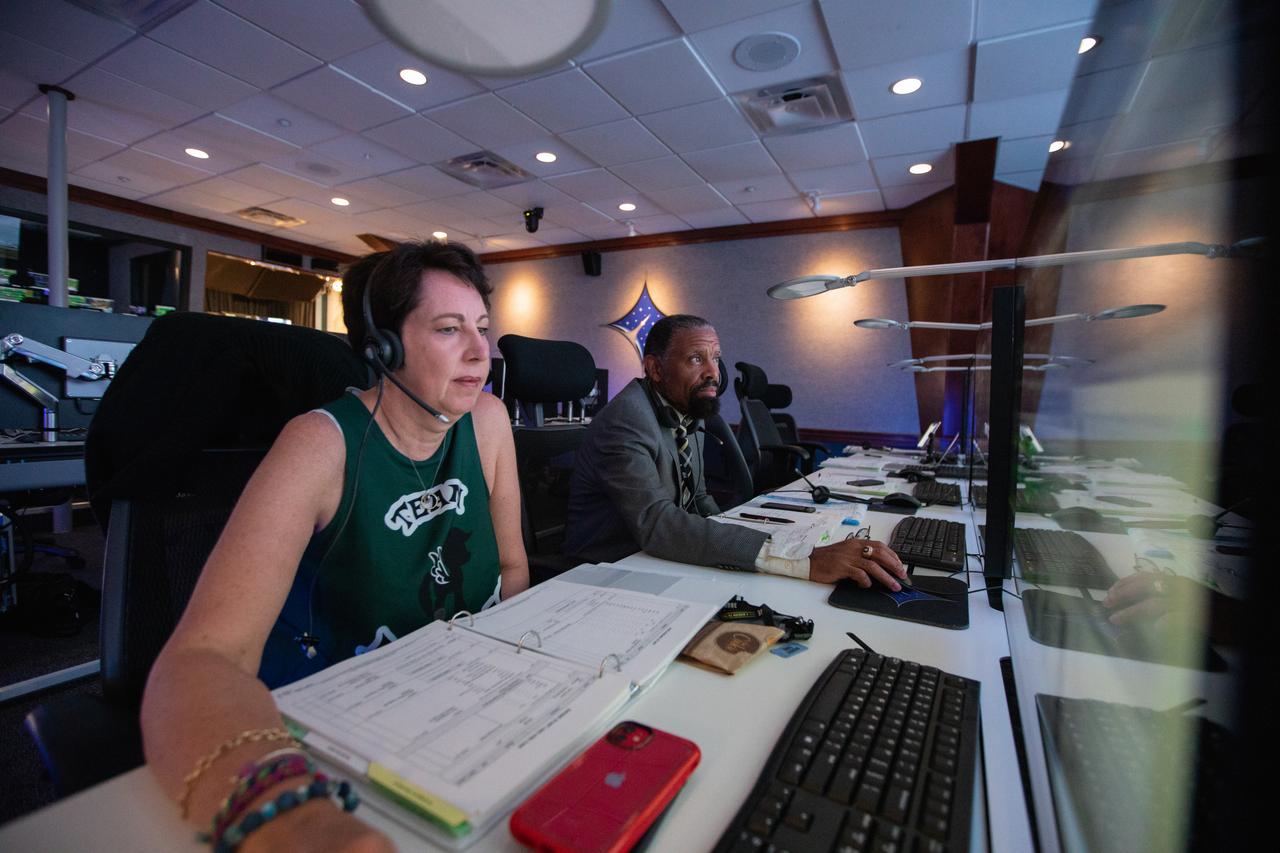

Inside Hangar AE’s Mission Director’s Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Nicola Fox, left, Heliophysics division director in NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, monitors the launch of the agency’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) satellite. The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket carrying ICON was released from the company’s L-1011 Stargazer aircraft at 9:59 p.m. EDT on Oct. 10, 2019, over the Atlantic Ocean about 50 miles from Daytona Beach, Florida, following takeoff from CCAFS. ICON will spend two years studying the Earth’s ionosphere – the dynamic zone in our atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather from above. The launch was managed by the agency’s Launch Services Program.
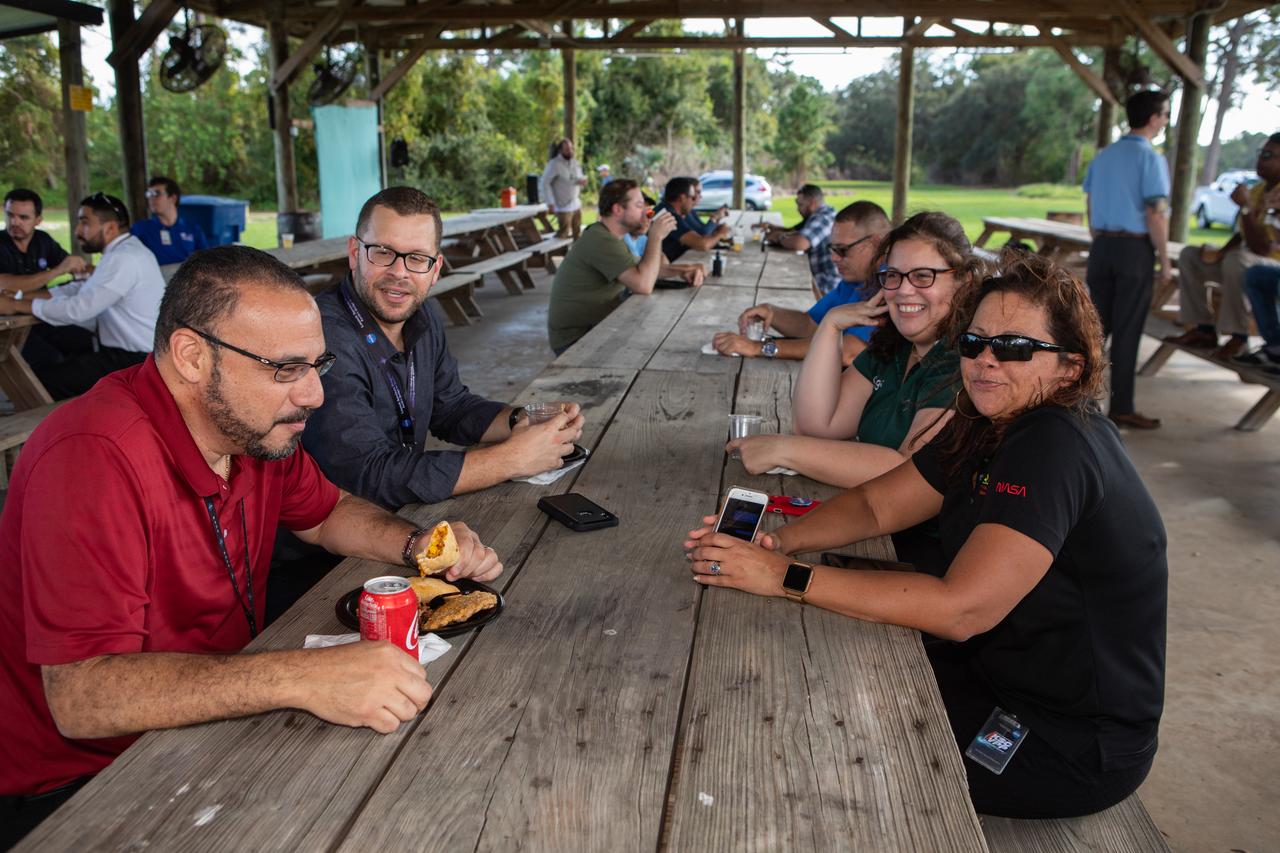

NASA Kennedy Space Center workers gather at KARS Park II to celebrate Hispanic Heritage Month on Oct. 17, 2019. The event was hosted by the center’s Hispanic Outreach and Leadership Alliance (HOLA) employee resource group for Hispanic Heritage Month. This year’s theme is “Hispanic Americans: A History of Serving our Nation.” HOLA’s initiatives include education and recruitment, professional networking and development, and community outreach and media support.
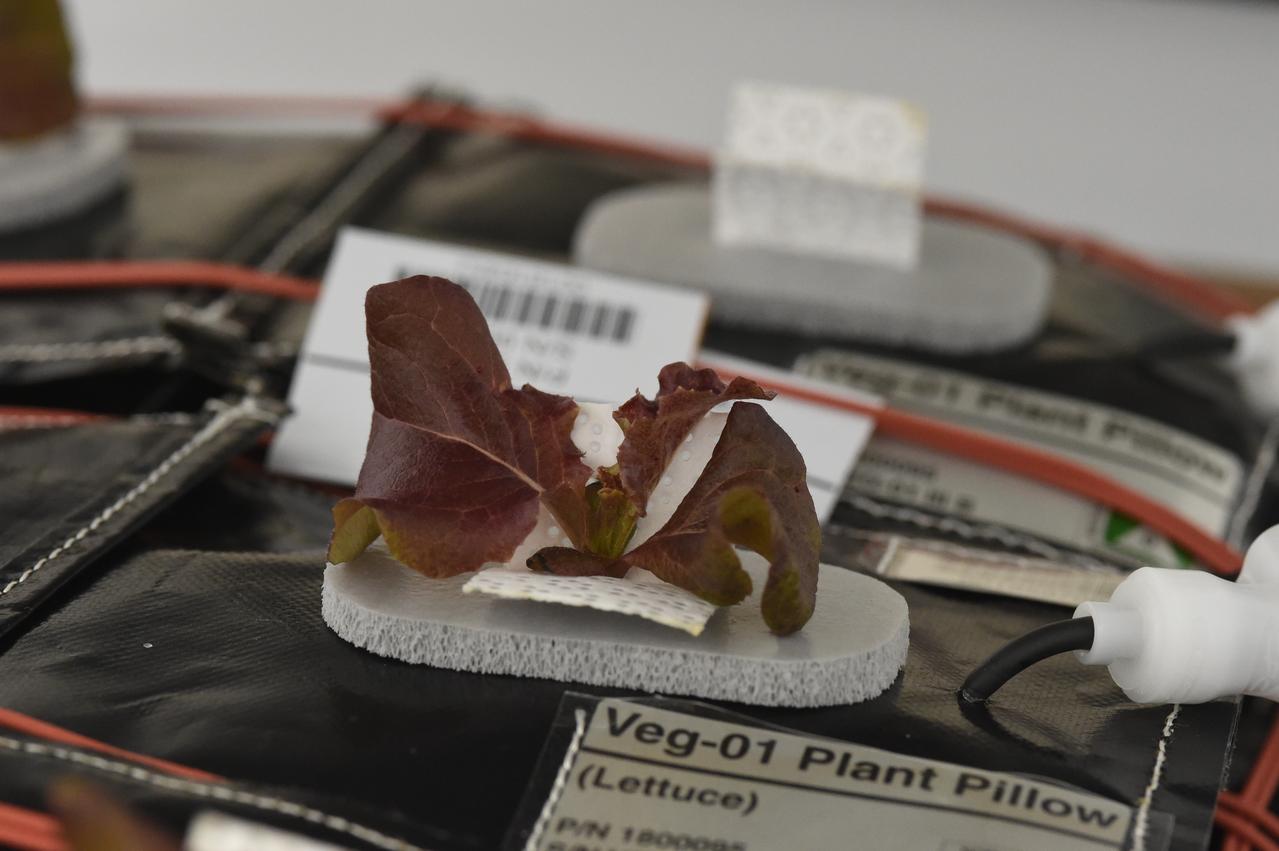

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
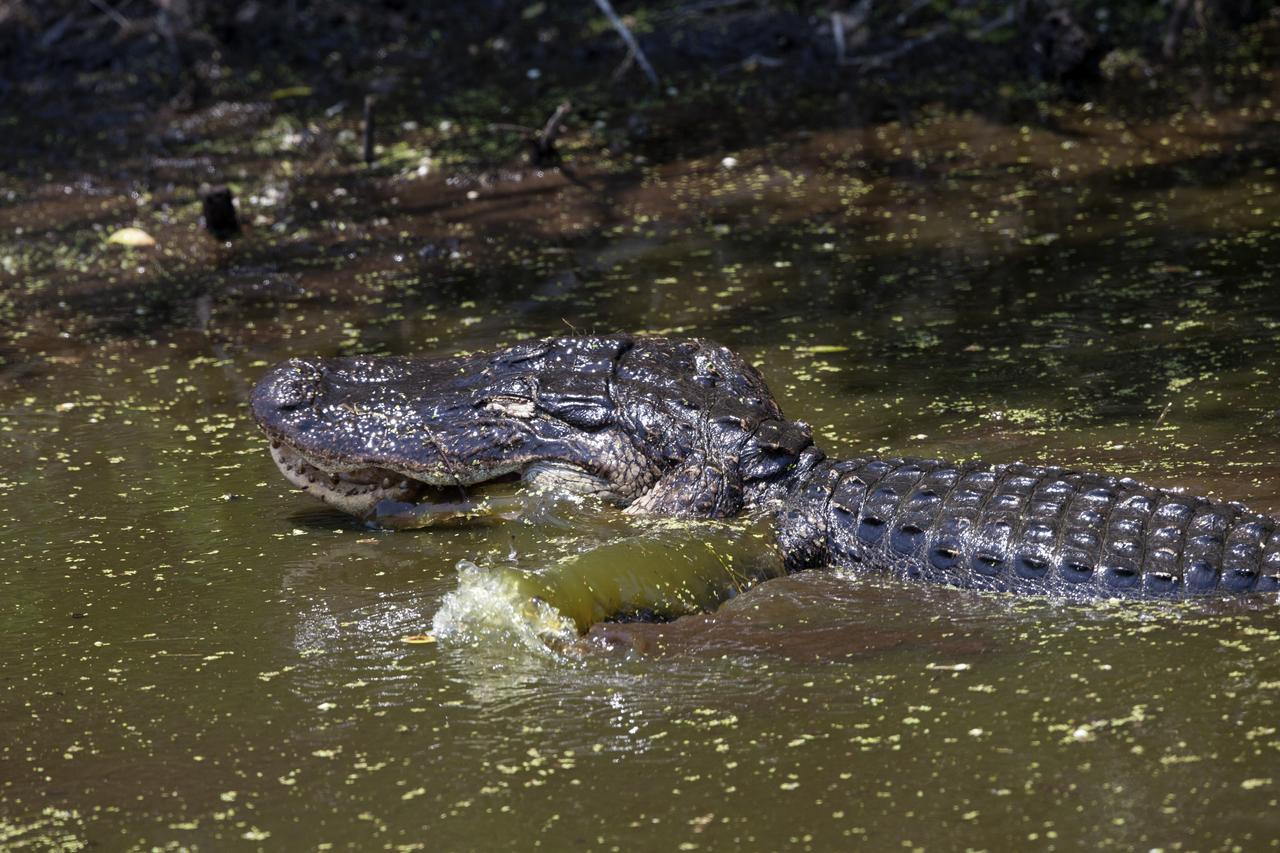

An alligator moves through a brackish waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.

The mobile launcher for NASA’s Artemis missions rolls out of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 10, 2019, after spending a week and a half inside due to the approach of Hurricane Dorian. The nearly 400-foot-tall structure was moved from Launch Pad 39B to the VAB for safekeeping on Aug. 30. The storm passed about 70 miles east of the spaceport during the overnight hours Tuesday, Sept. 3, and Wednesday, Sept. 4. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems is moving the mobile launcher back to the launch pad, where teams will complete testing and checkout on the launcher in the coming weeks for the Artemis I mission.
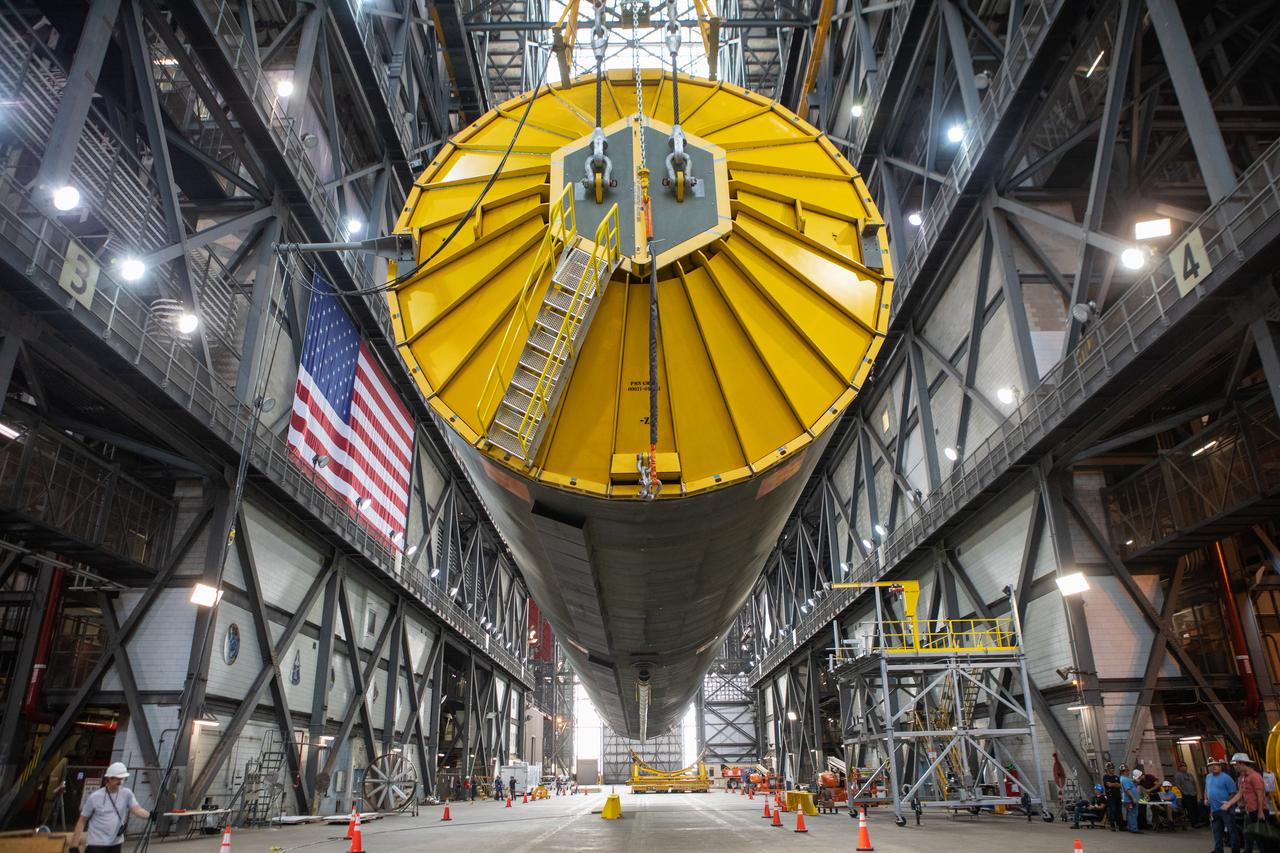

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage pathfinder is suspended by two cranes in the horizontal position above the transfer aisle on Oct. 15, 2019. The 212-foot-long core stage pathfinder arrived on NASA's Pegasus Barge at Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf on Sept. 27, 2019. The Pegasus Barge made its first delivery to Kennedy in support of the agency's Artemis missions. The pathfinder is being used by Exploration Ground Systems and its contractor, Jacobs, to practice offloading, moving and stacking maneuvers, using important ground support equipment to train employees and certify all the equipment works properly. The pathfinder will stay at Kennedy through at least the month of October before trekking back to NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
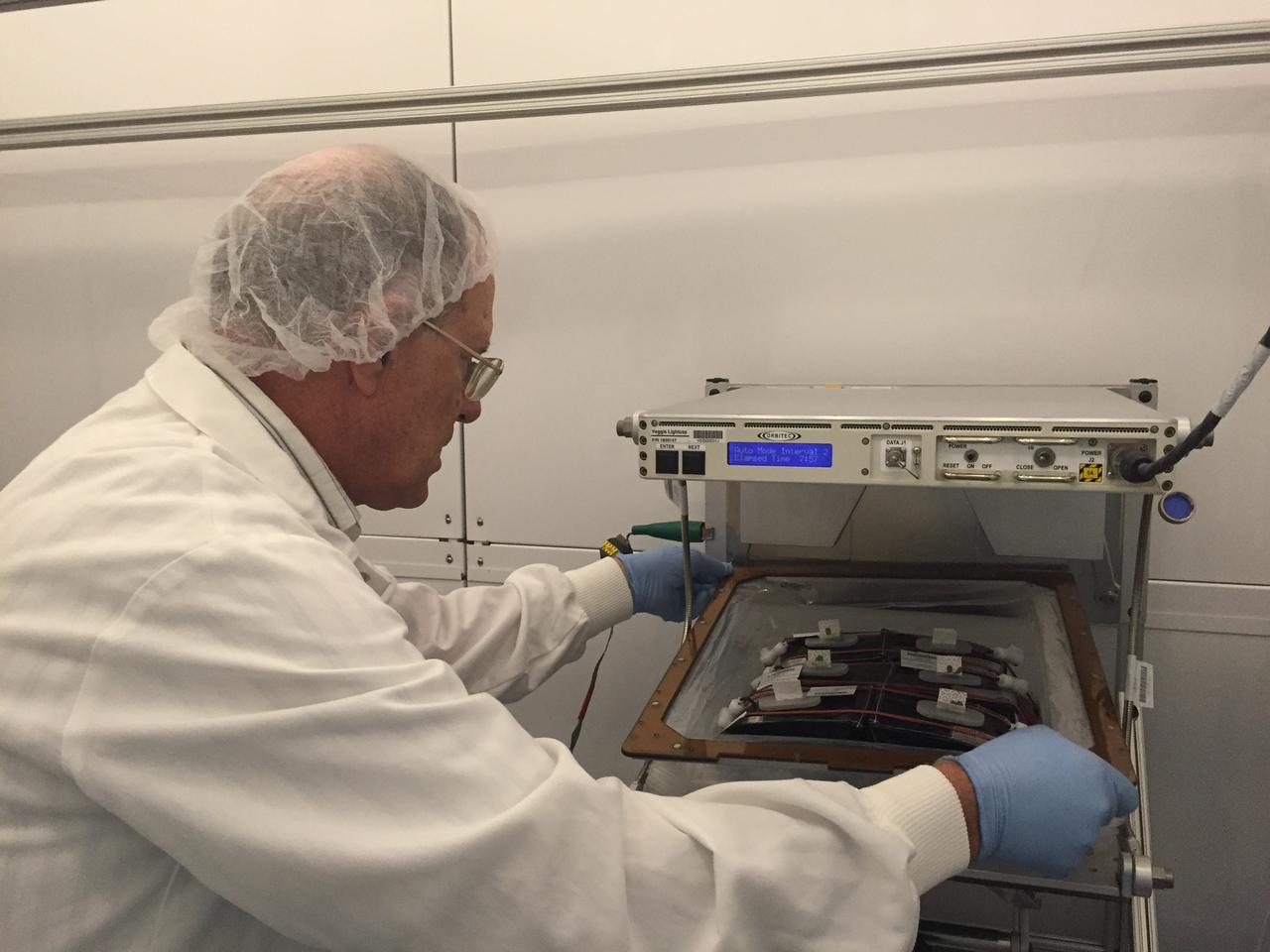

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
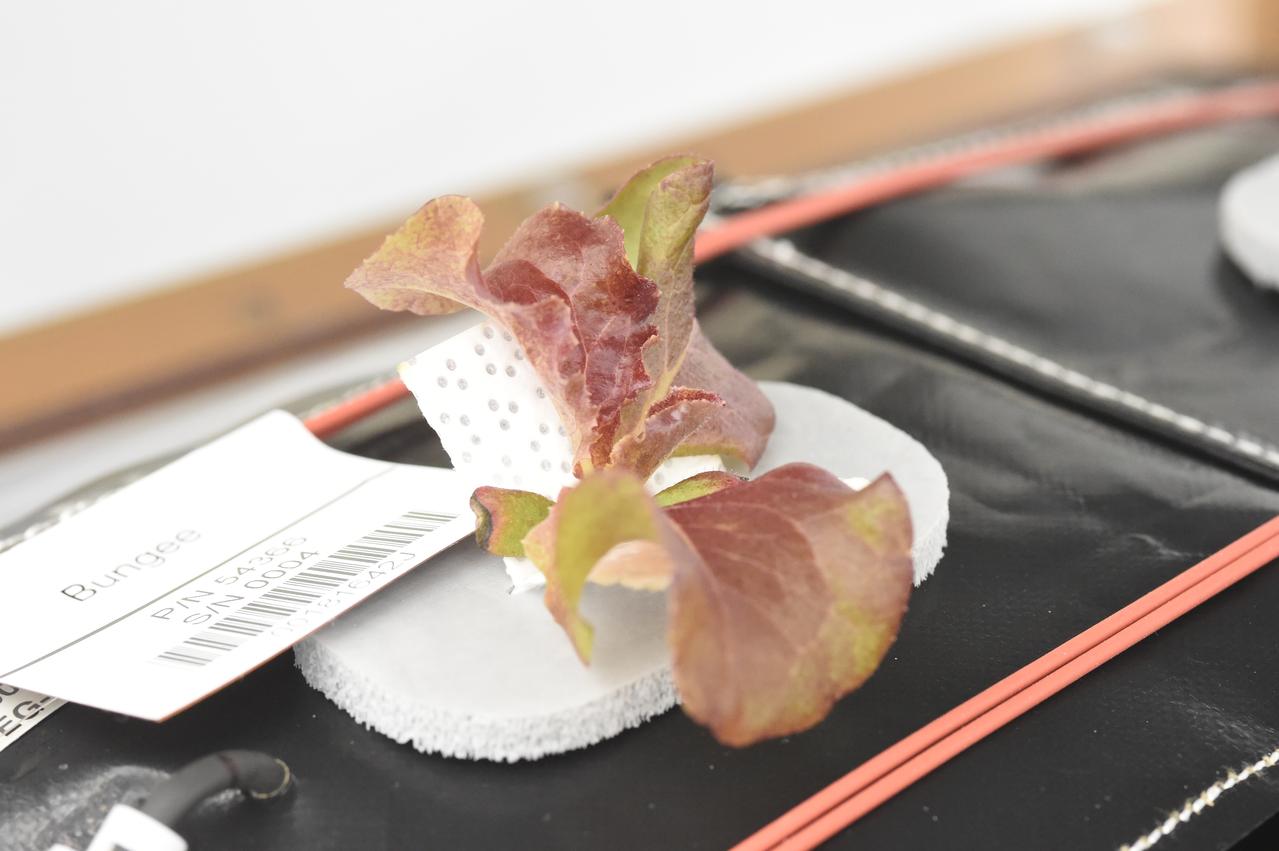

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
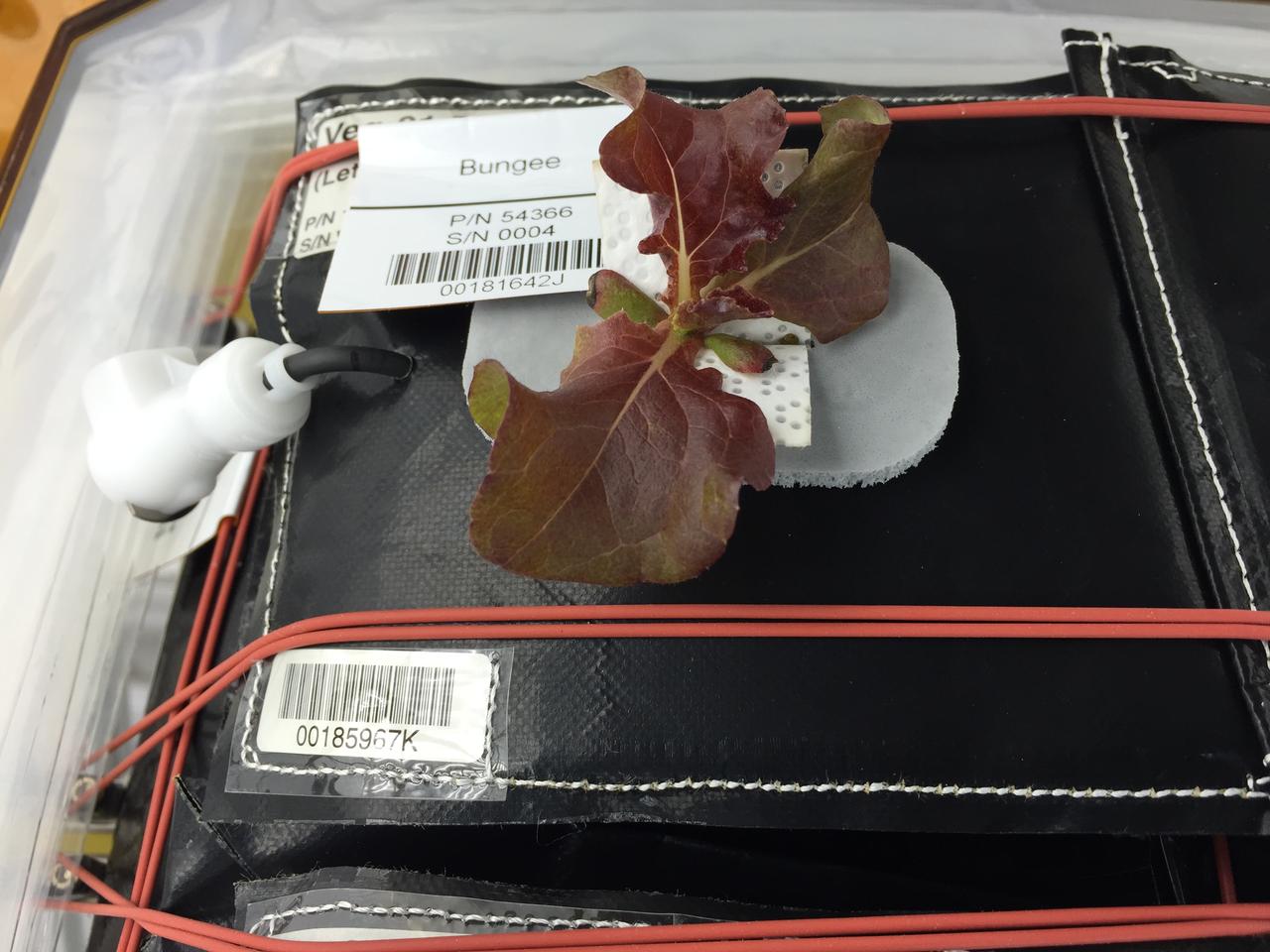

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
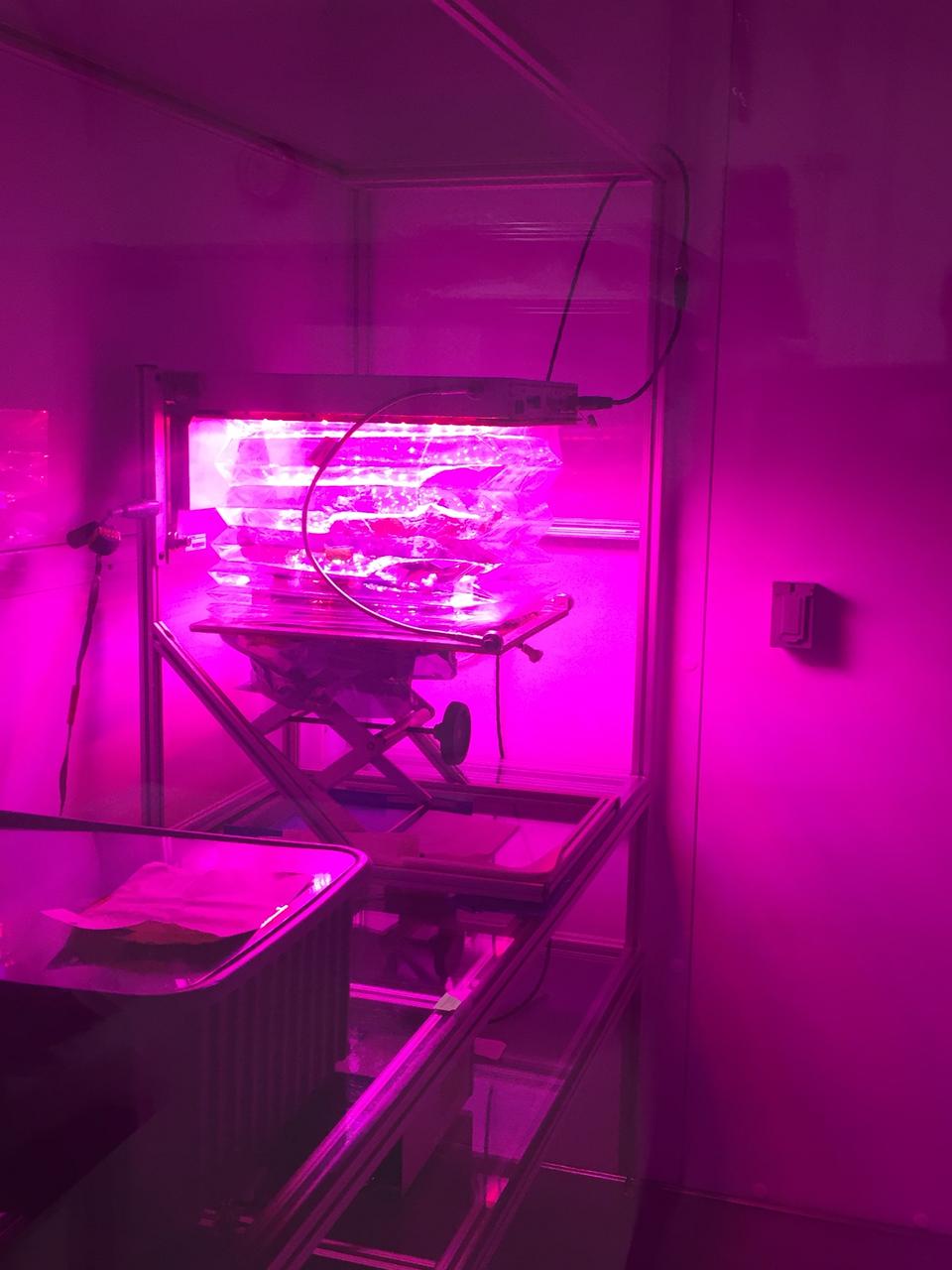

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
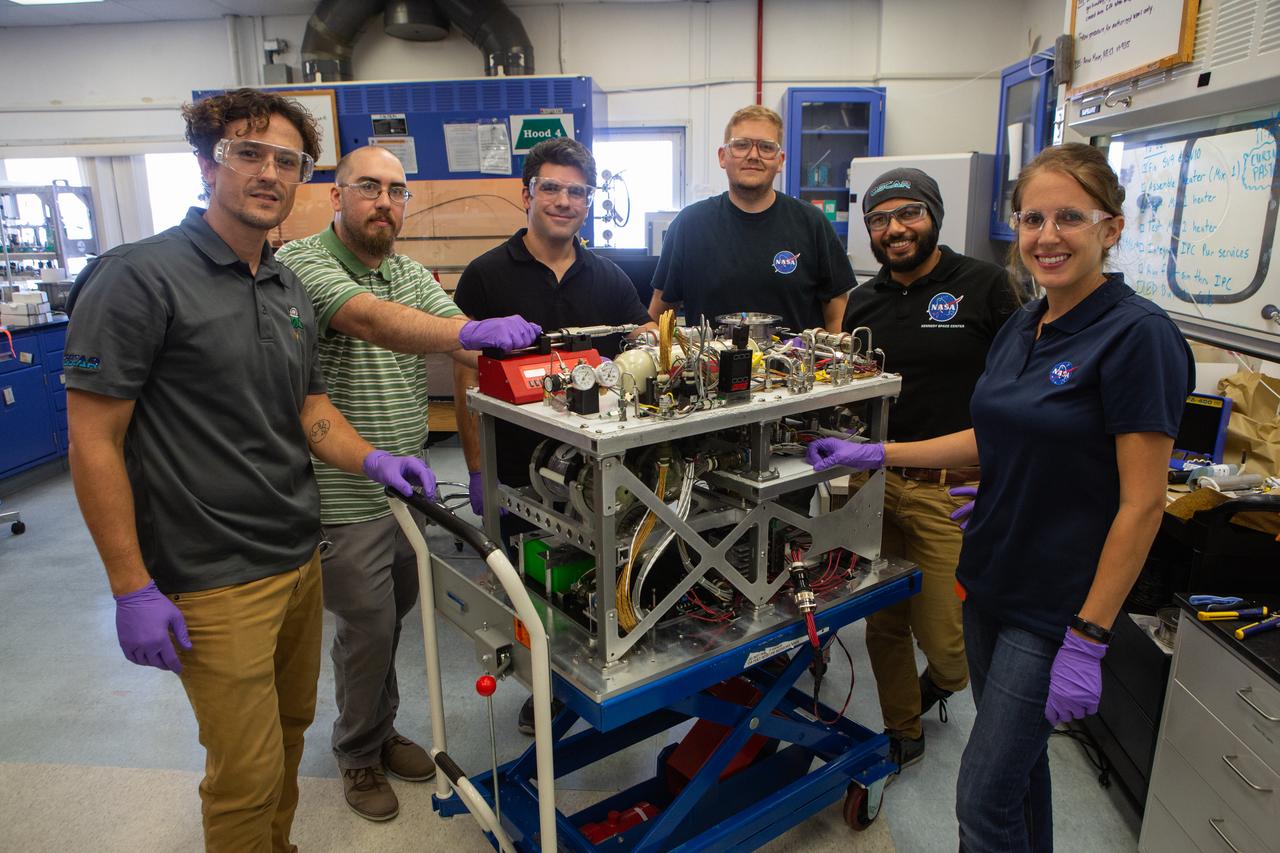
Members of NASA’s Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor, or OSCAR, team pause for a photo with the flight hardware on Oct. 10, 2019, in the Space Station Processing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Gino Carro, Tom Cauvel, Jaime Toro, Evan Bell, Malay Shah and Annie Meier. OSCAR is an Early Career Initiative project at the spaceport that studies technology to convert trash and human waste into useful gasses such as methane, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. By processing small pieces of trash in a high-temperature reactor, OSCAR is advancing new and innovative technology for managing waste in space. A prototype has been developed, and the team is in the process of constructing a new rig for a suborbital flight test.
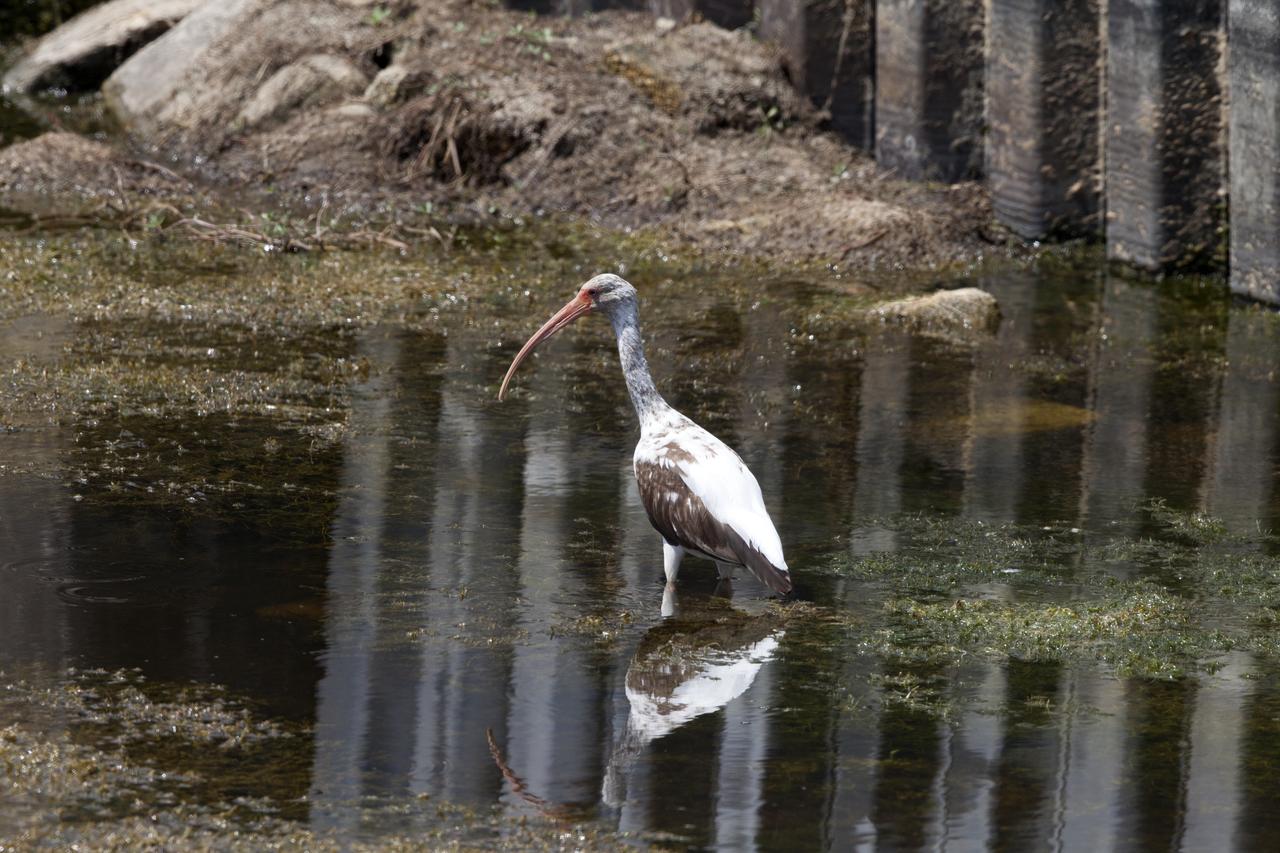

A juvenile white ibis stands in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
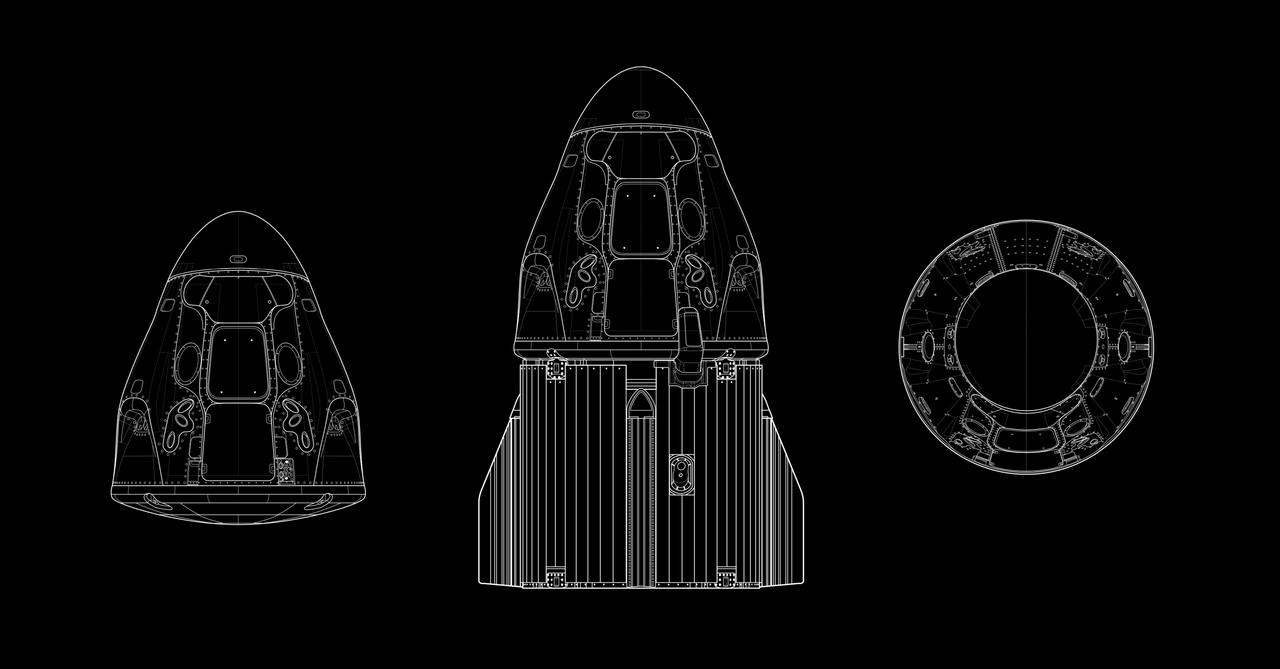
This graphic details the makeup of SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. Crew Dragon is used for all crewed SpaceX missions to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
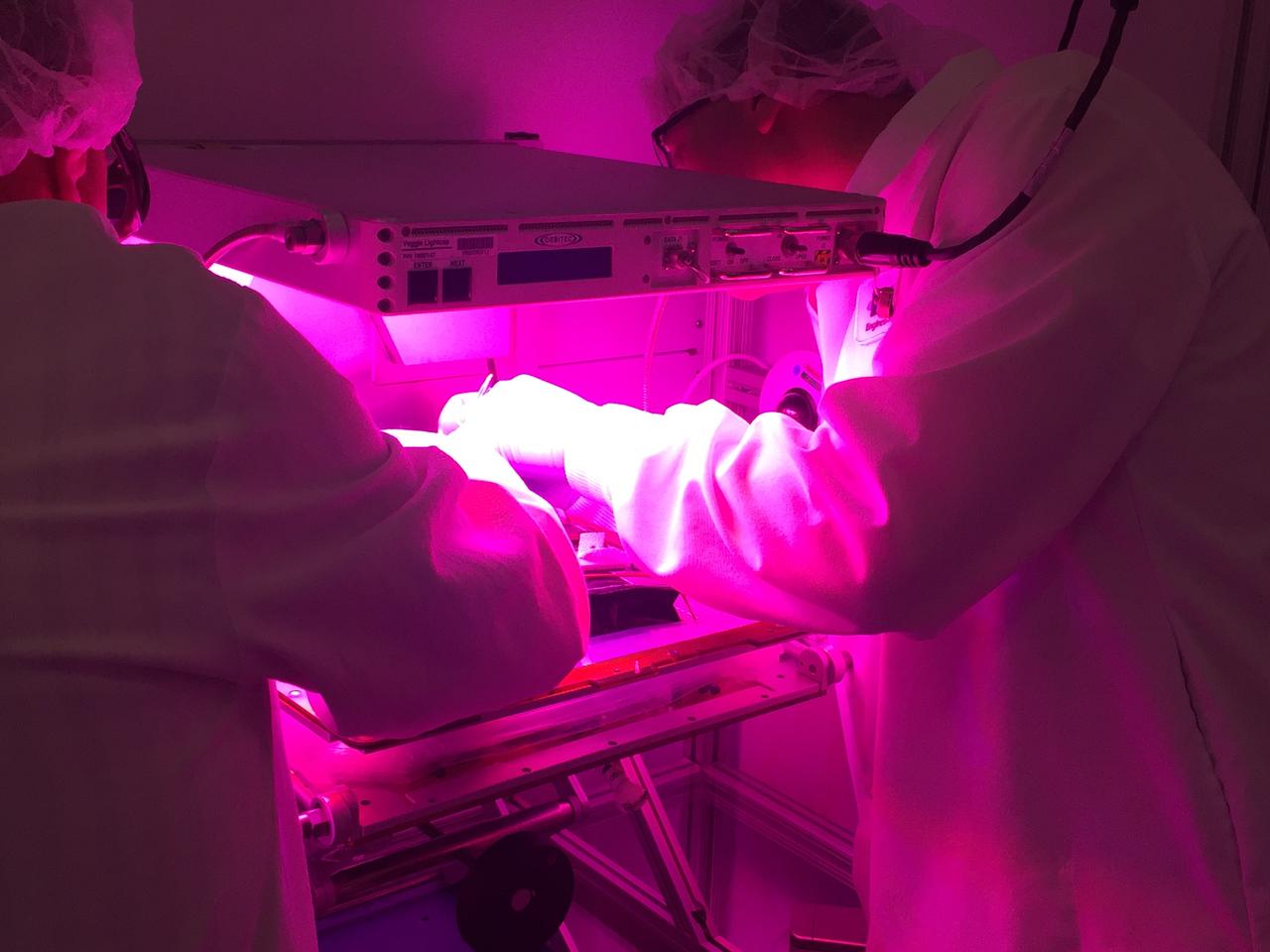

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

AERIALS - SR3 SOLAR FACILITY & NEW EXPANSION SITE, EXLORATION PARK
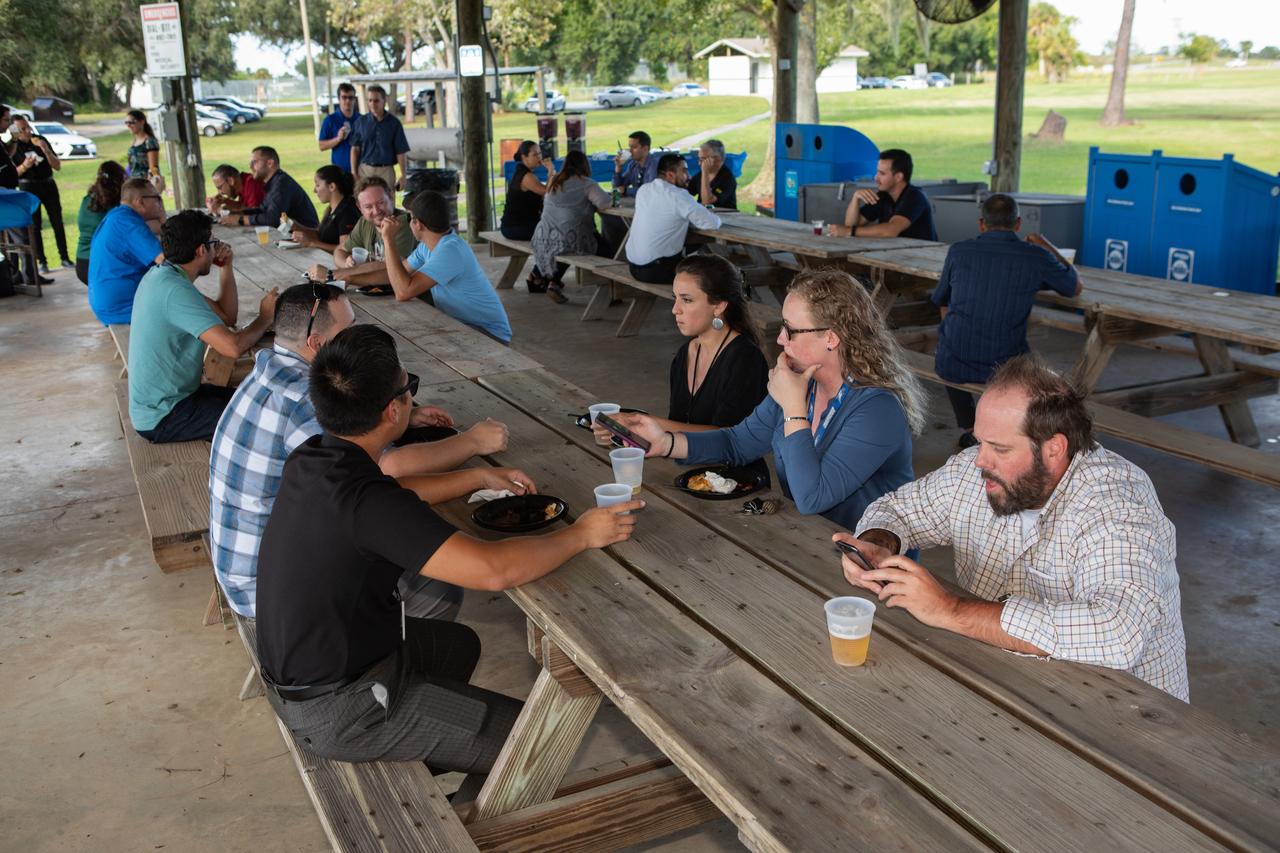

NASA Kennedy Space Center workers gather at KARS Park II to celebrate Hispanic Heritage Month on Oct. 17, 2019. The event was hosted by the center’s Hispanic Outreach and Leadership Alliance (HOLA) employee resource group for Hispanic Heritage Month. This year’s theme is “Hispanic Americans: A History of Serving our Nation.” HOLA’s initiatives include education and recruitment, professional networking and development, and community outreach and media support.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.