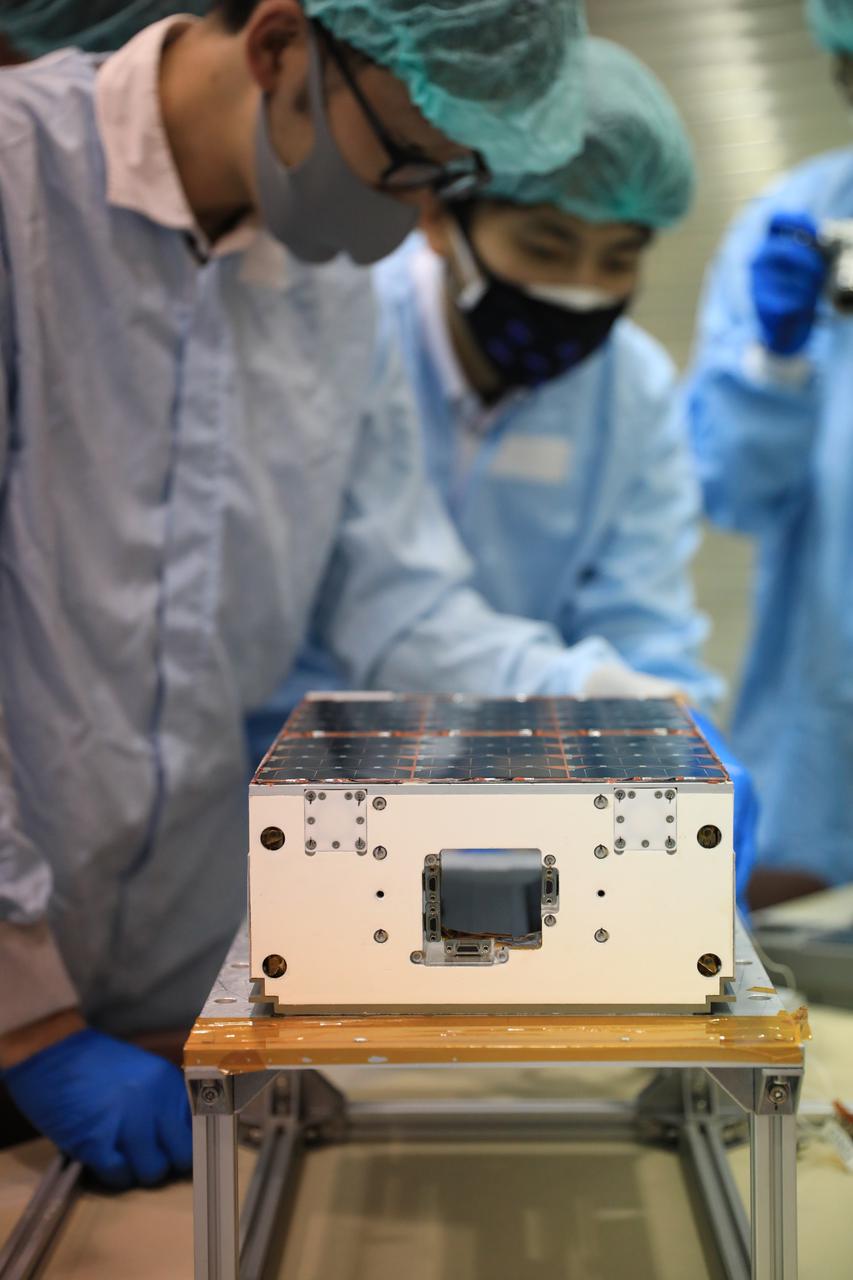
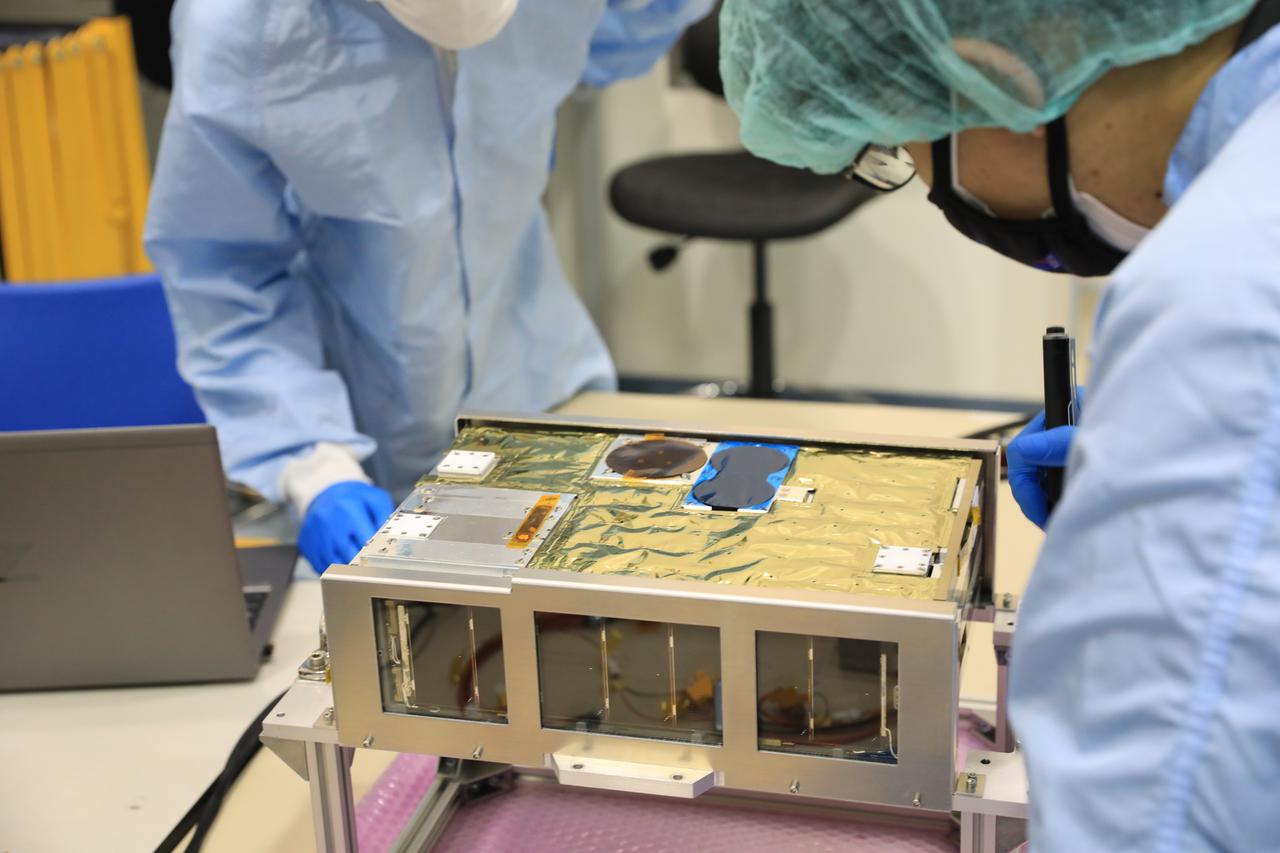
Teams worked on the final processing of their payloads that will fly aboard Artemis I. Housed within the Orion stage adapter, the satellites – called CubeSats – are roughly the size of a large shoe box and weigh no more than 30 pounds. Despite their small size, they enable science and technology experiments that may enhance our understanding of the deep space environment, expand our knowledge of the Moon, and demonstrate new technologies that could be used on future missions.
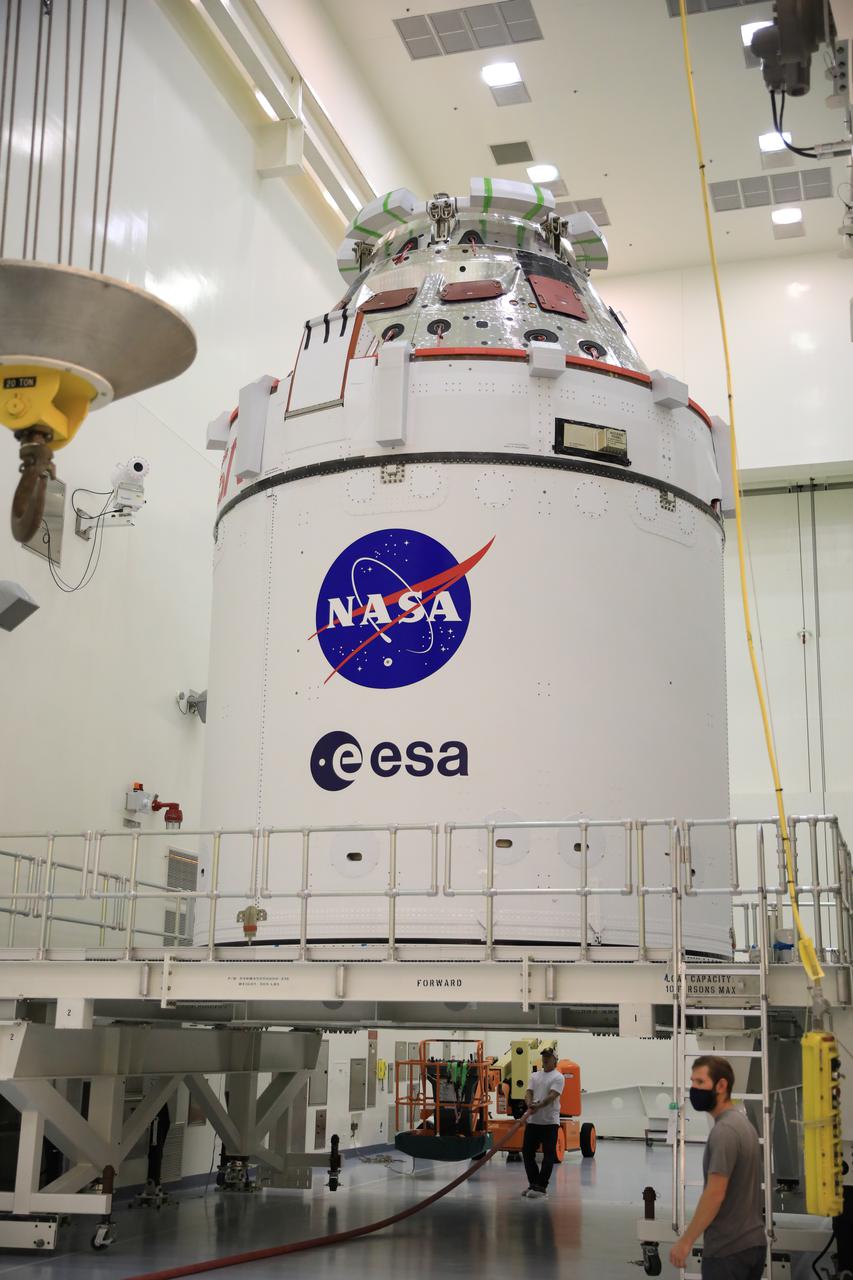

Fueling and servicing checks on the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission are completed inside Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility on July 8, 2021. The capsule will be transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will work to add parts of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

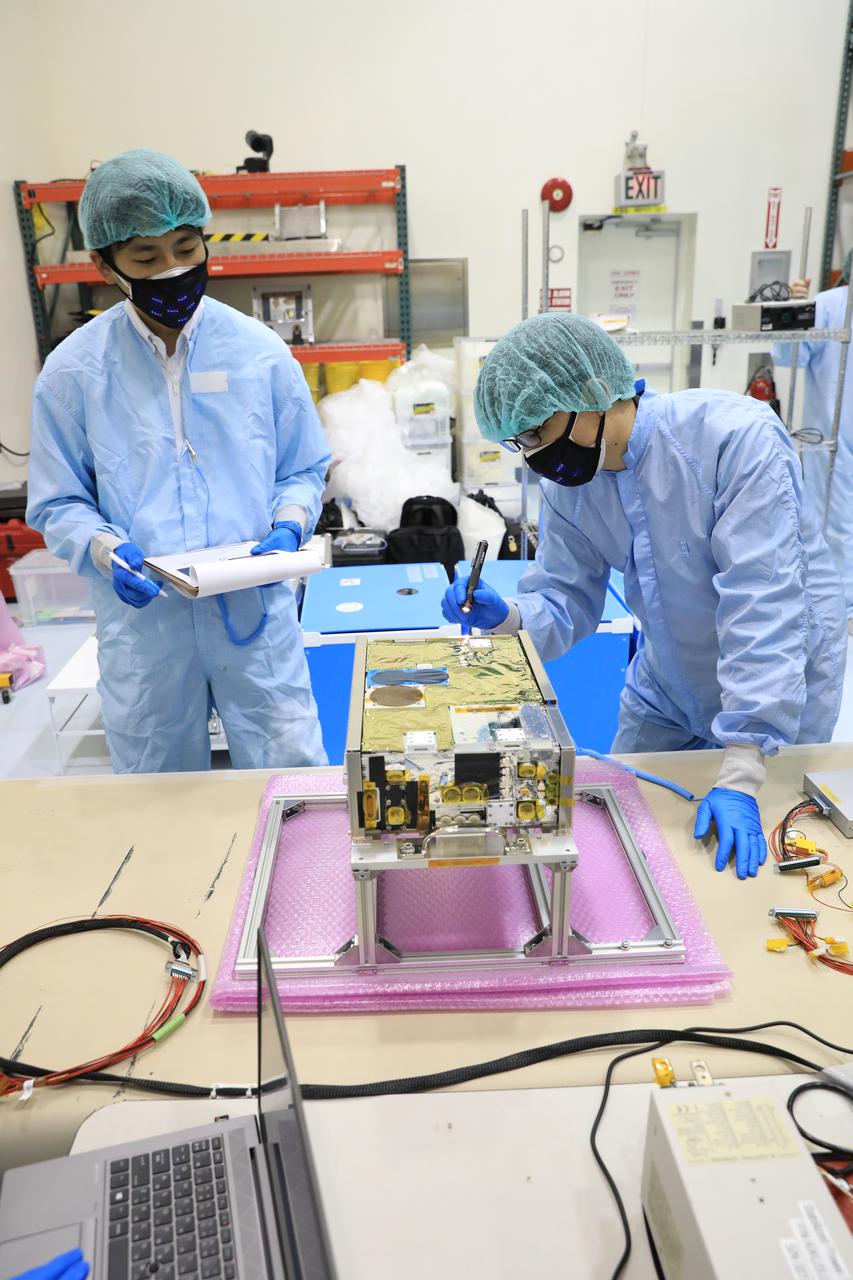
Small satellites, called CubeSats, are shown secured inside NASA’s Orion stage adapter at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 5, 2021. Technicians from Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs teams are working with developers of the shoebox-sized secondary payloads as they undergo final processing. The ring-shaped stage adapter will be connected to the Space Launch System’s Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, and the Orion spacecraft will be secured on top. The CubeSats will conduct a variety of science experiments and technology demonstrations that will expand our knowledge of the lunar surface during the Artemis I mission.
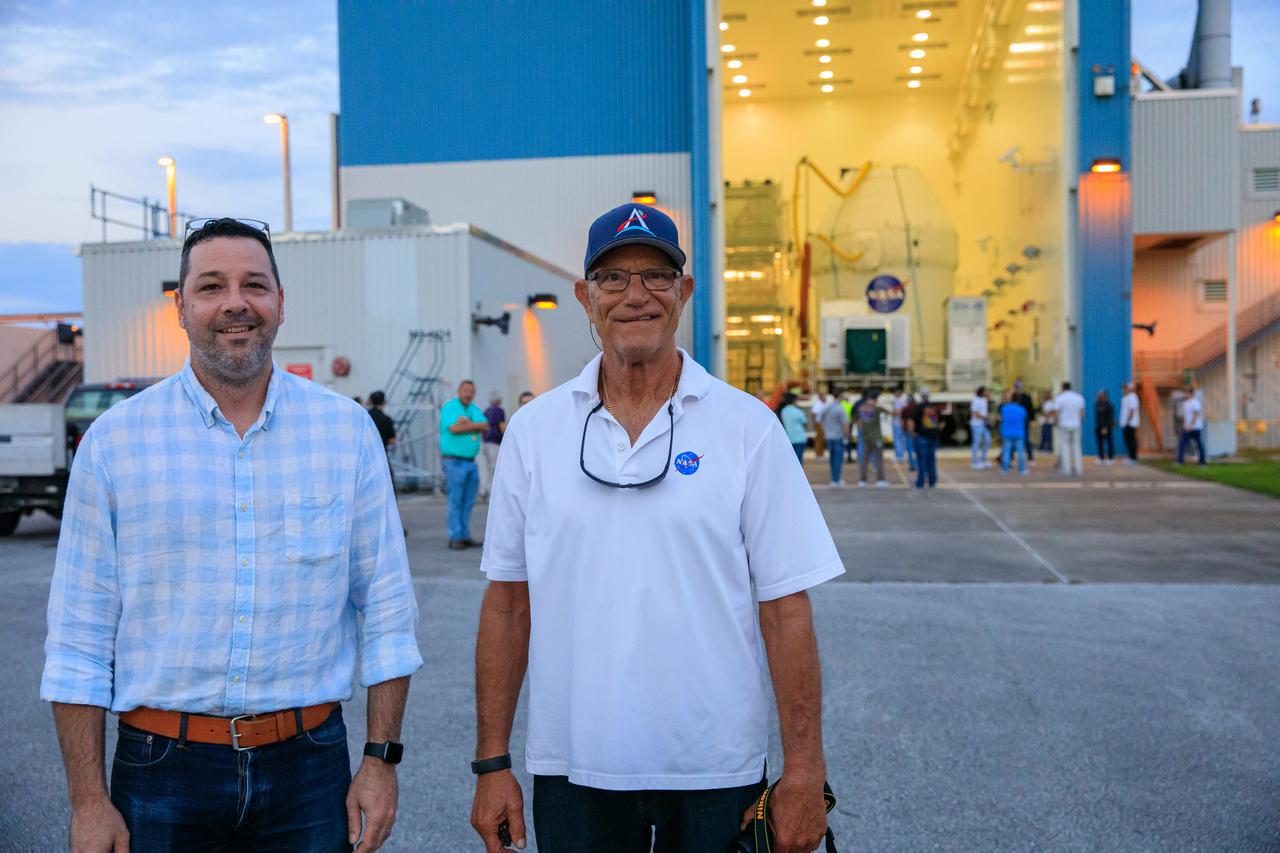
Mike Collins, NASA Operations manager for Spacecraft Offline Operations, left, and Skip Williams, operations manager for the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) spacecraft offline element integration team, stand in front of the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission, as the capsule moves out from Kennedy Space Center’s MFFP on July 10, 2021. Orion is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
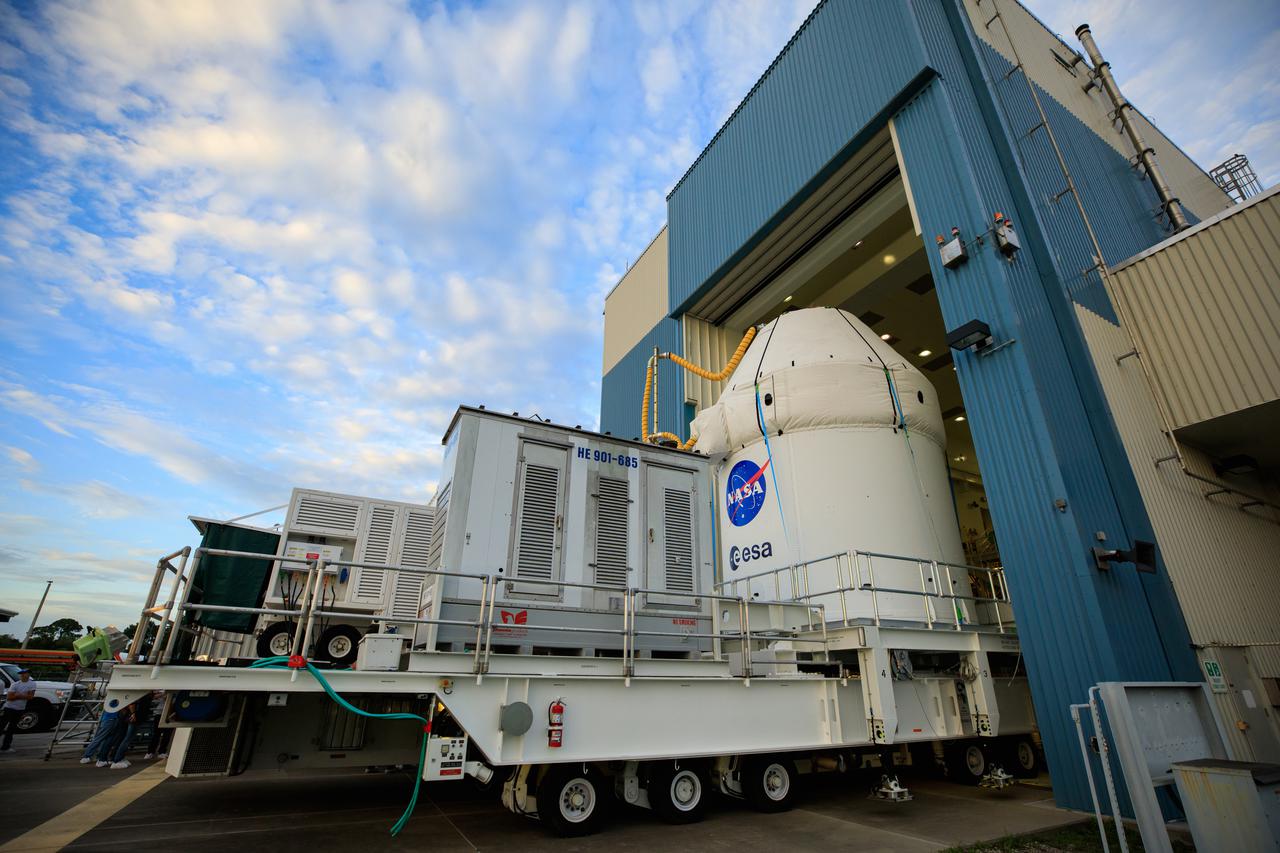

After recently completing fueling and servicing checks, the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission departs from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing on July 10, 2021. It is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

The Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission is transported from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility on July 10, 2021. Teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.

Teams worked on the final processing of their payloads that will fly aboard Artemis I. Housed within the Orion stage adapter, the satellites – called CubeSats – are roughly the size of a large shoe box and weigh no more than 30 pounds. Despite their small size, they enable science and technology experiments that may enhance our understanding of the deep space environment, expand our knowledge of the Moon, and demonstrate new technologies that could be used on future missions.
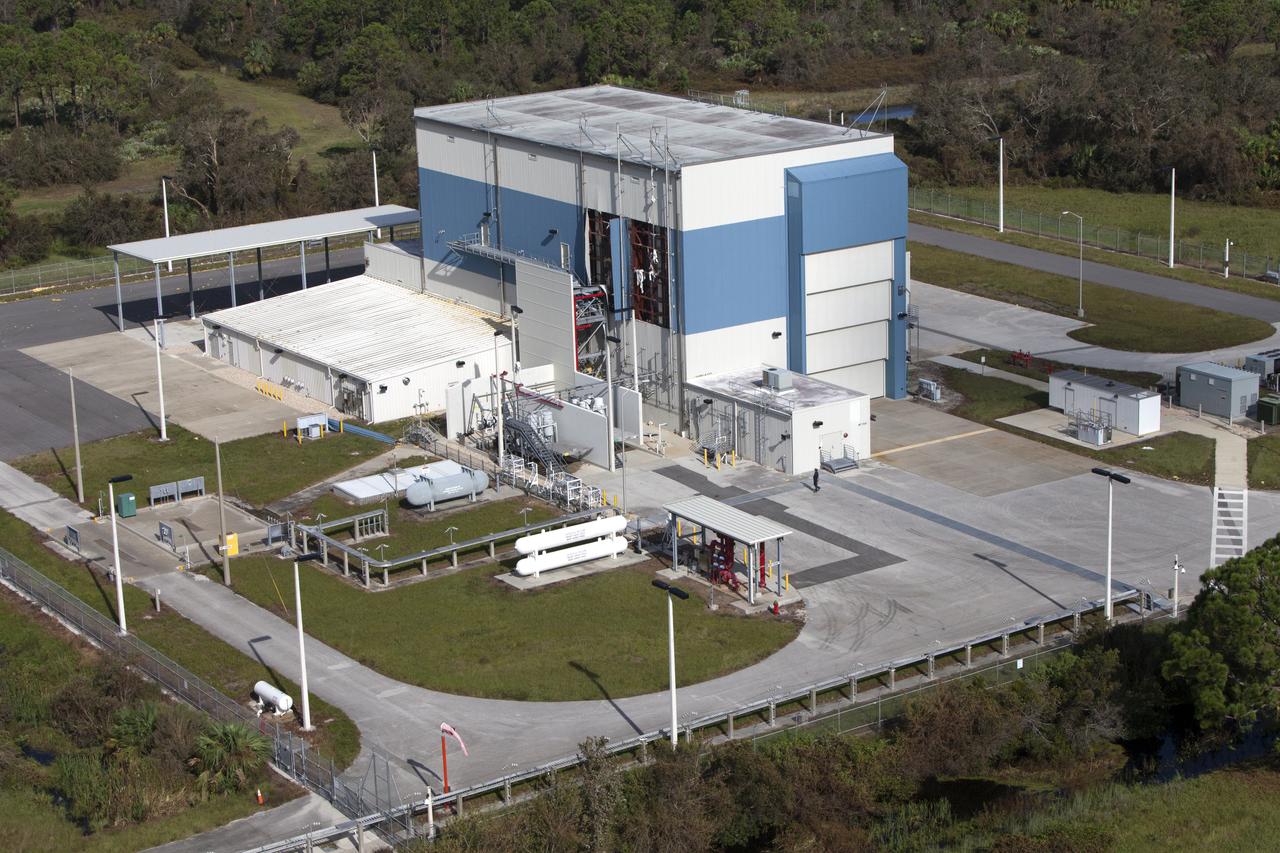

The Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) is seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on September 12, 2017. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Irma as the storm passed Kennedy on September 10, 2017. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm's onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.
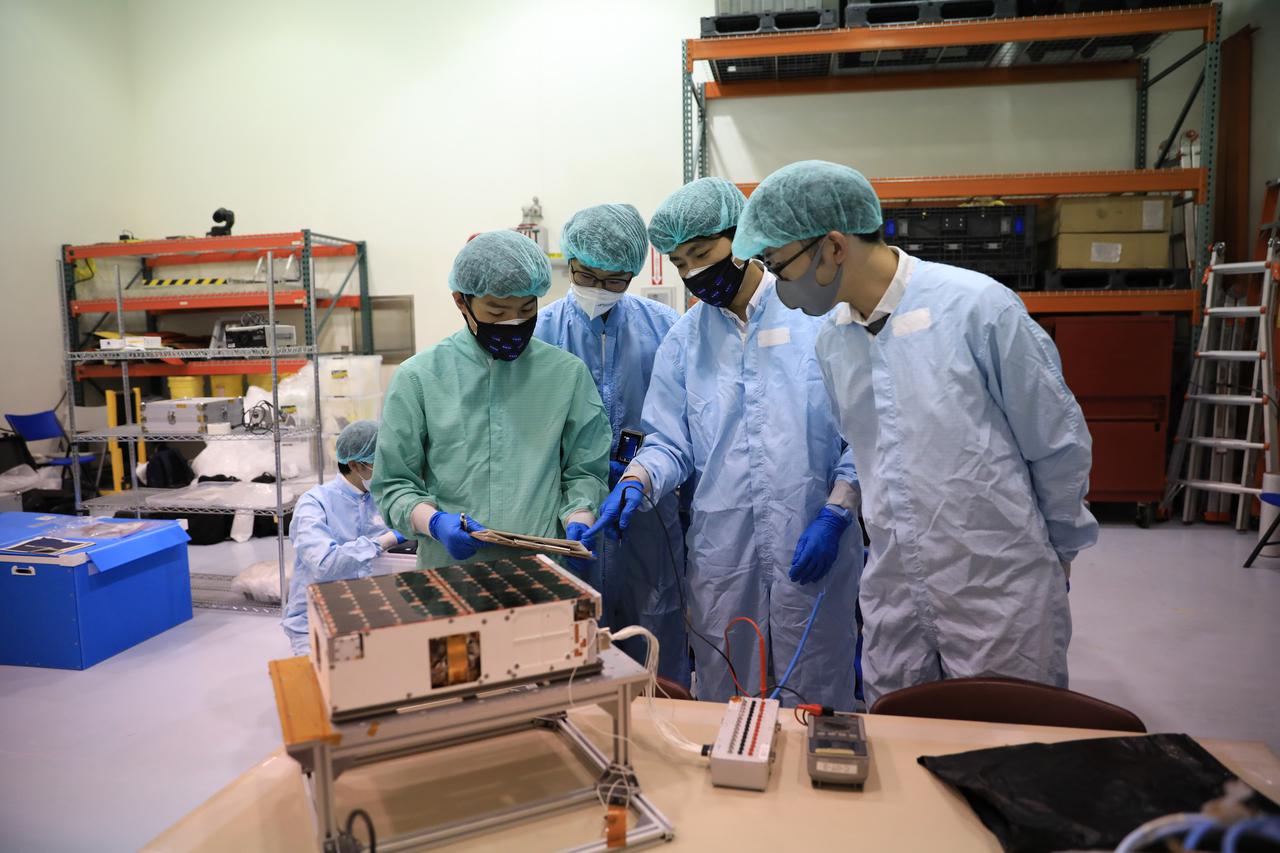

Teams worked on the final processing of their payloads that will fly aboard Artemis I. Housed within the Orion stage adapter, the satellites – called CubeSats – are roughly the size of a large shoe box and weigh no more than 30 pounds. Despite their small size, they enable science and technology experiments that may enhance our understanding of the deep space environment, expand our knowledge of the Moon, and demonstrate new technologies that could be used on future missions.
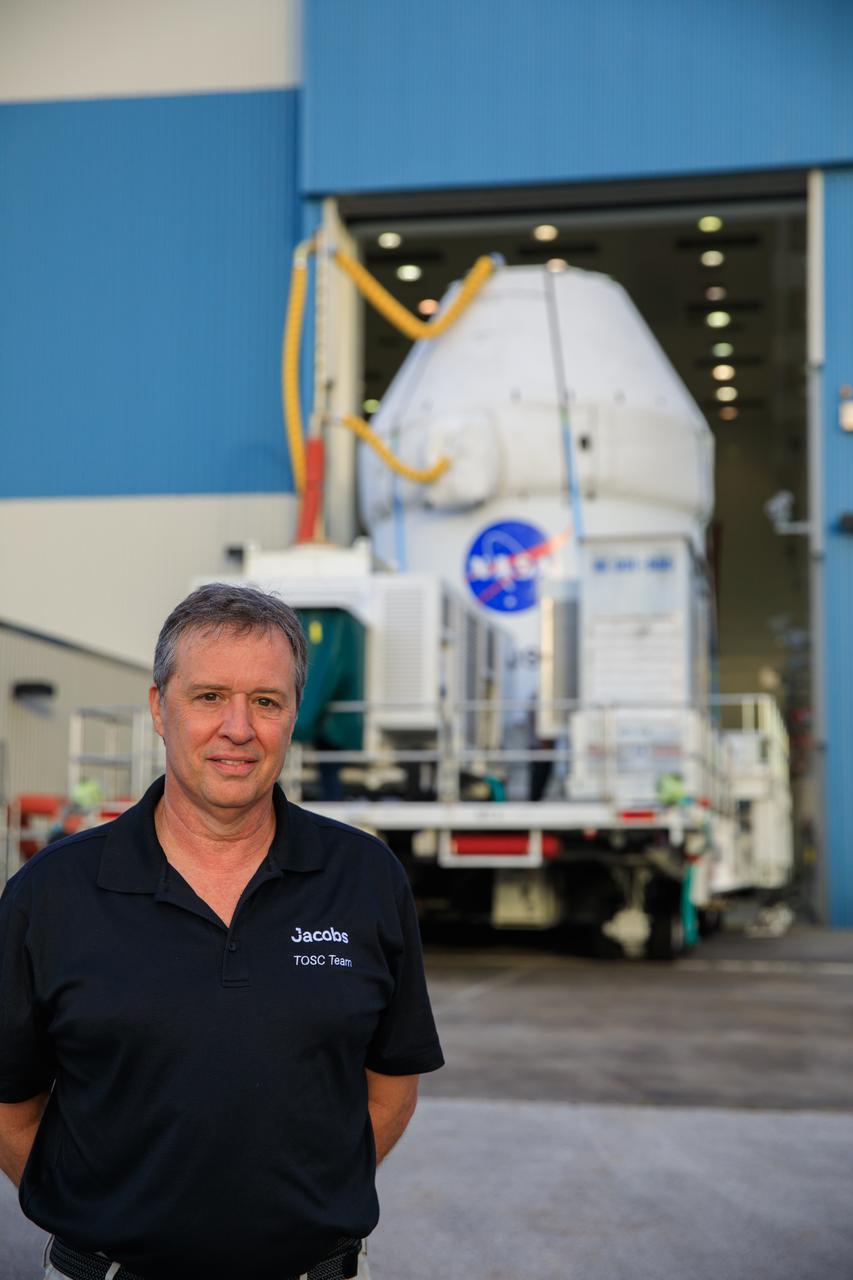

Nick Kindred, Jacobs flow manager, stands in front of the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission, as the capsule moves out from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility on July 10, 2021. Orion is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
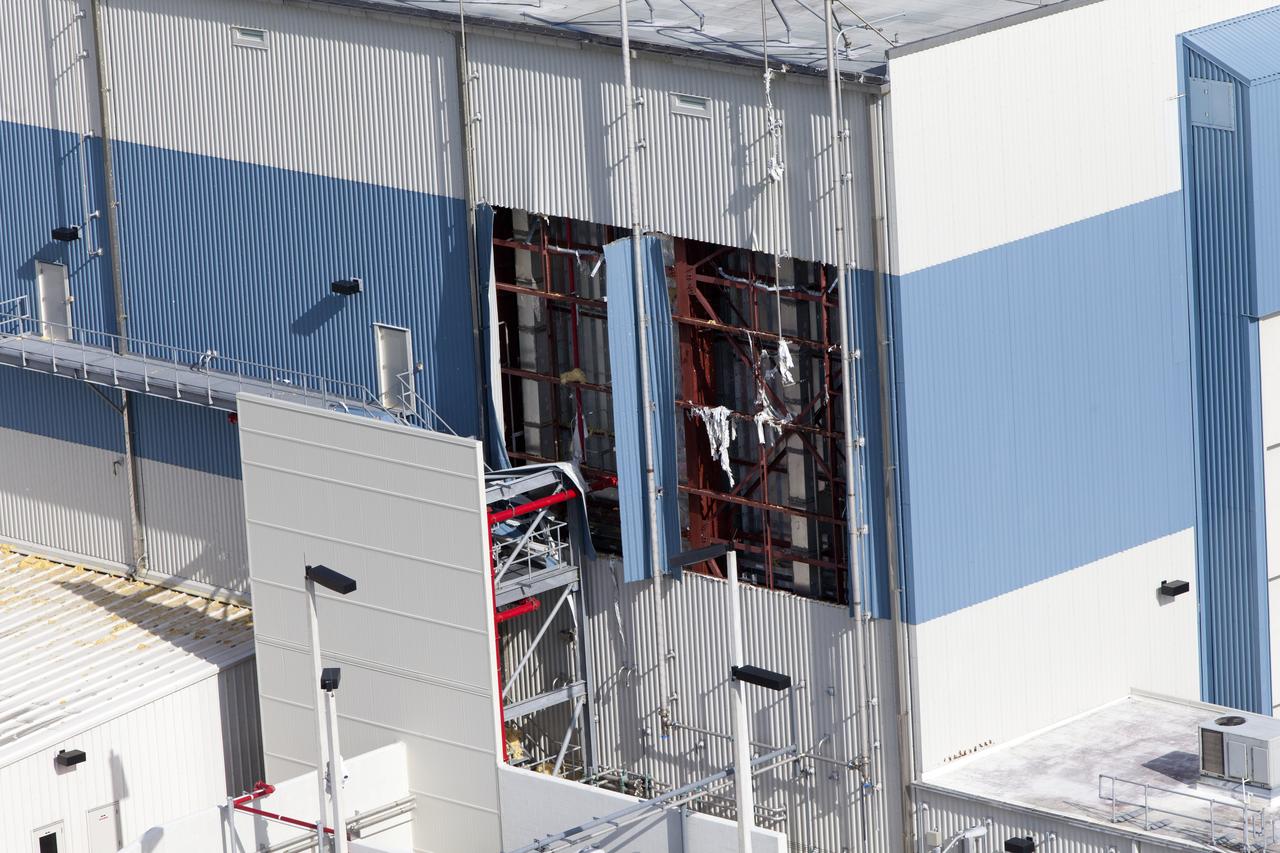

The Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) is seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on September 12, 2017. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Irma as the storm passed Kennedy on September 10, 2017. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm's onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.

The Artemis I Orion crew module, now known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), arrives to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024, following an 11-month test campaign at NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio. The ETA will undergo propulsion functional testing at Kennedy’s Multi Payload Processing Facility. The ETA splashed down in the Pacific Ocean on Sunday, Dec. 11, 2022, following its journey around the Moon during the Artemis I mission.
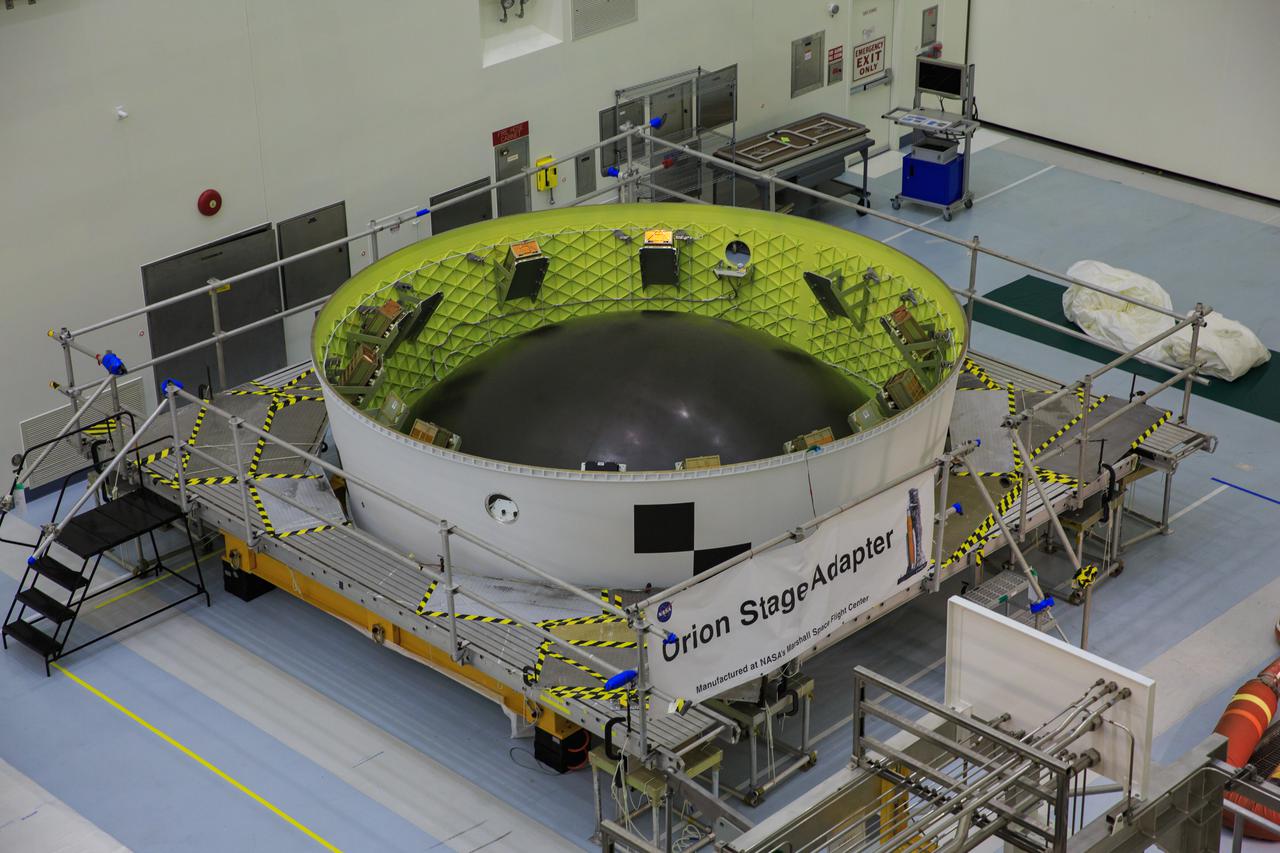

Small satellites, called CubeSats, are shown secured inside NASA’s Orion stage adapter at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 5, 2021. Technicians from Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs teams are working with developers of the shoebox-sized secondary payloads as they undergo final processing. The ring-shaped stage adapter will be connected to the Space Launch System’s Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, and the Orion spacecraft will be secured on top. The CubeSats will conduct a variety of science experiments and technology demonstrations that will expand our knowledge of the lunar surface during the Artemis I mission.

Teams worked on the final processing of their payloads that will fly aboard Artemis I. Housed within the Orion stage adapter, the satellites – called CubeSats – are roughly the size of a large shoe box and weigh no more than 30 pounds. Despite their small size, they enable science and technology experiments that may enhance our understanding of the deep space environment, expand our knowledge of the Moon, and demonstrate new technologies that could be used on future missions.
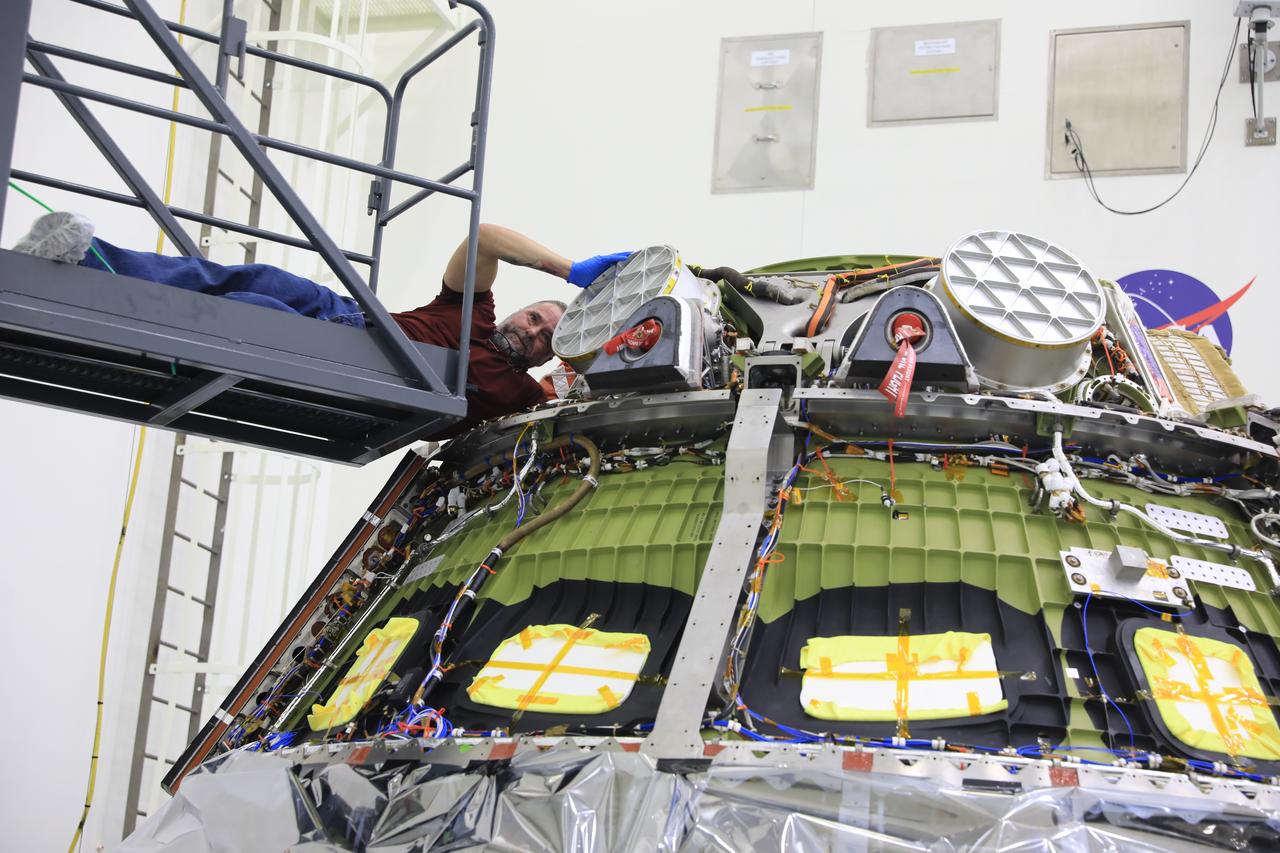

The Artemis I Orion crew module, now known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), arrives to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024, following an 11-month test campaign at NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio. The ETA will undergo propulsion functional testing at Kennedy’s Multi Payload Processing Facility. The ETA splashed down in the Pacific Ocean on Sunday, Dec. 11, 2022, following its journey around the Moon during the Artemis I mission.
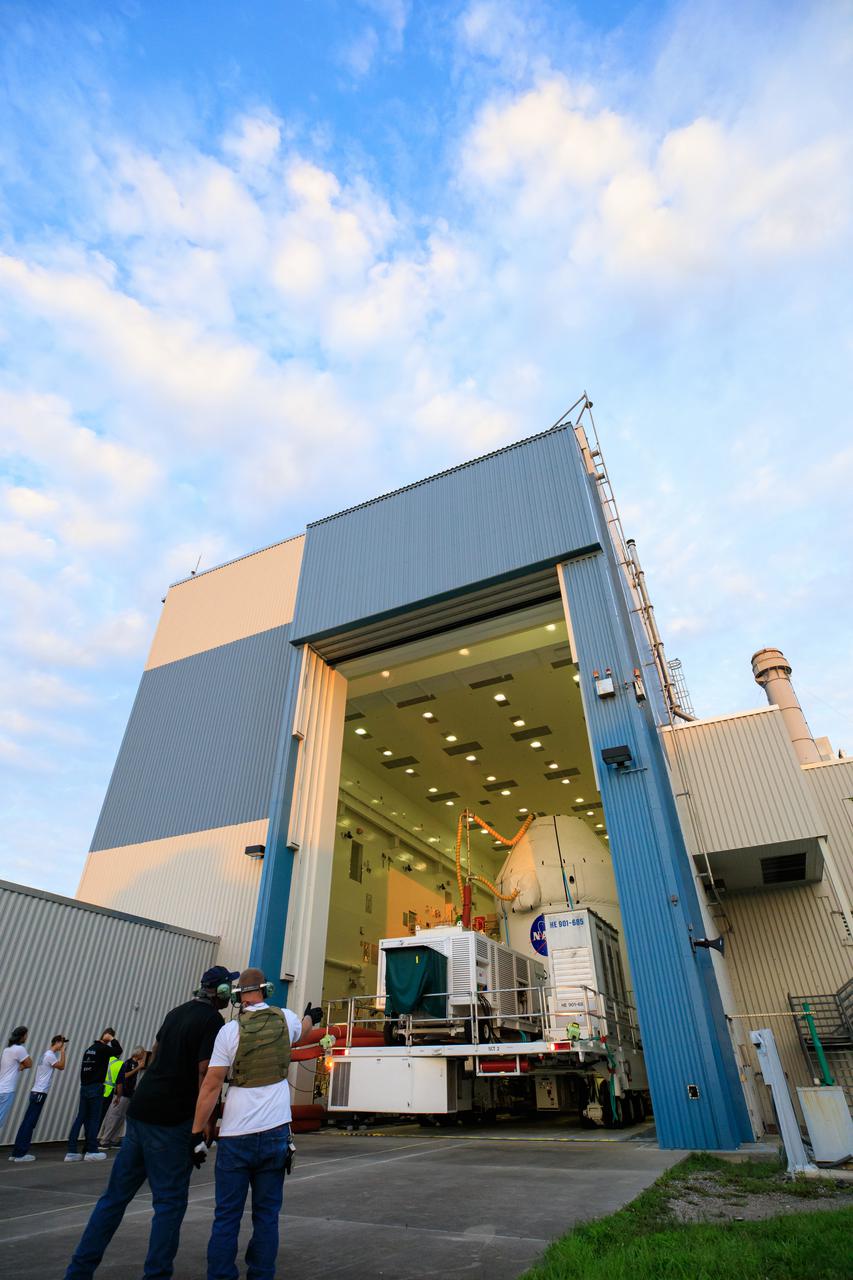

After recently completing fueling and servicing checks, the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission departs from Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing on July 10, 2021. It is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
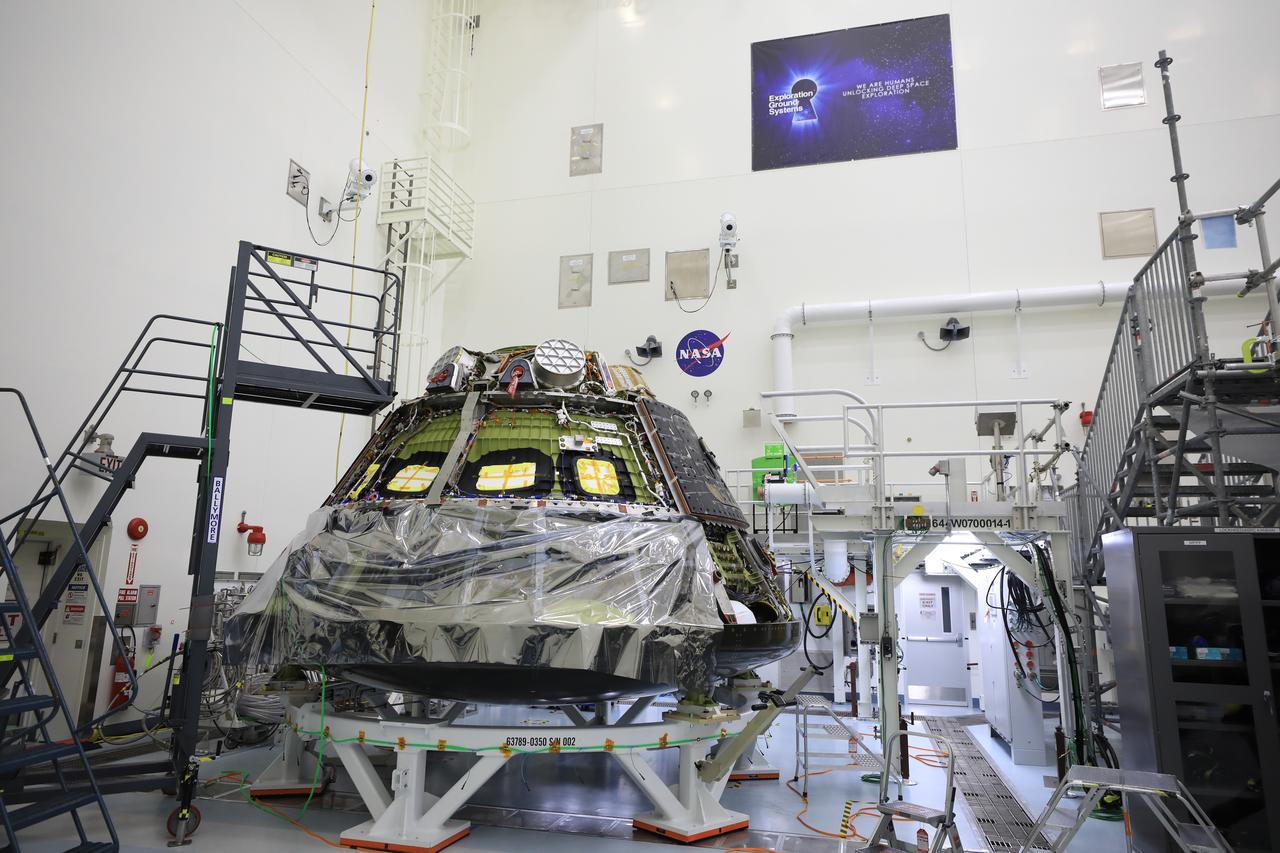

The Artemis I Orion crew module, now known as the Orion Environmental Test Article (ETA), arrives to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Dec. 21, 2024, following an 11-month test campaign at NASA’s Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky, Ohio. The ETA will undergo propulsion functional testing at Kennedy’s Multi Payload Processing Facility. The ETA splashed down in the Pacific Ocean on Sunday, Dec. 11, 2022, following its journey around the Moon during the Artemis I mission.
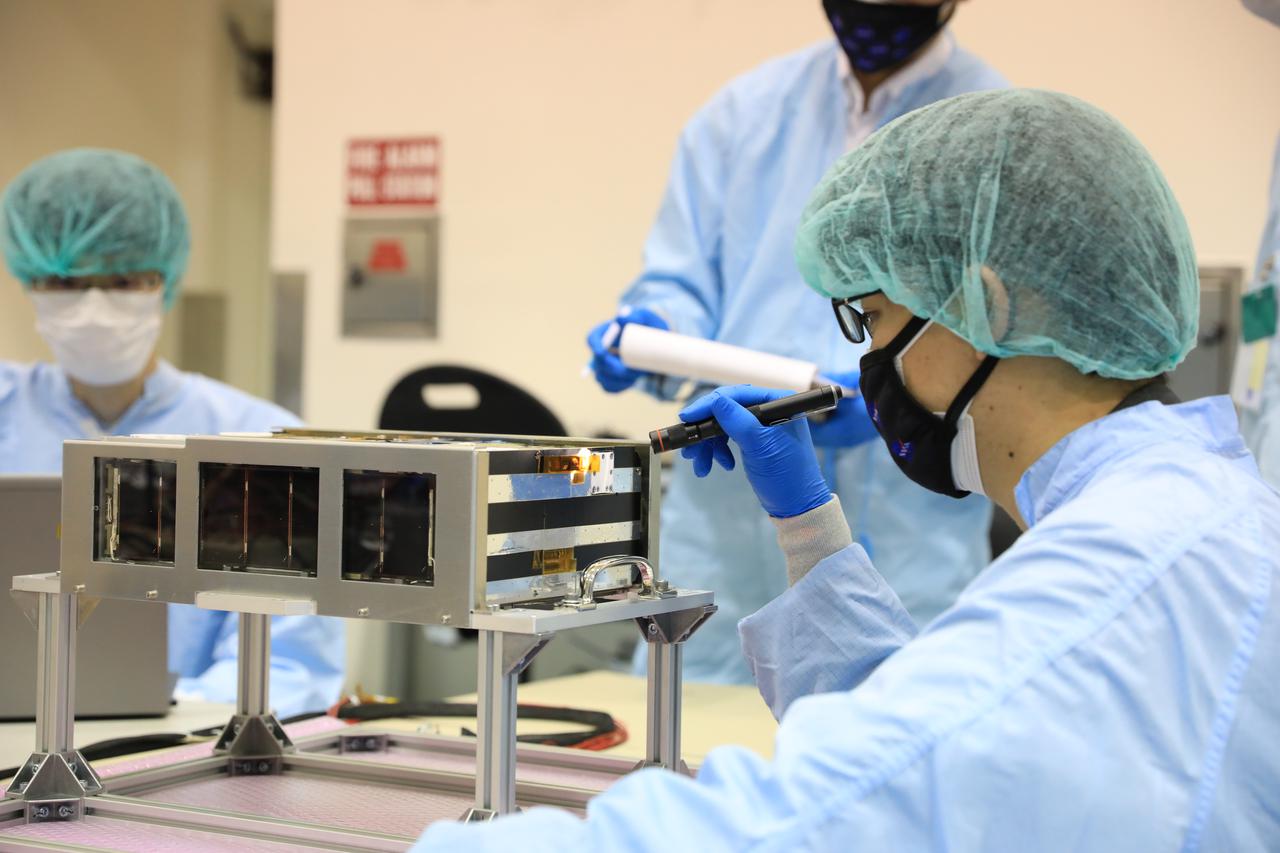

Teams worked on the final processing of their payloads that will fly aboard Artemis I. Housed within the Orion stage adapter, the satellites – called CubeSats – are roughly the size of a large shoe box and weigh no more than 30 pounds. Despite their small size, they enable science and technology experiments that may enhance our understanding of the deep space environment, expand our knowledge of the Moon, and demonstrate new technologies that could be used on future missions.
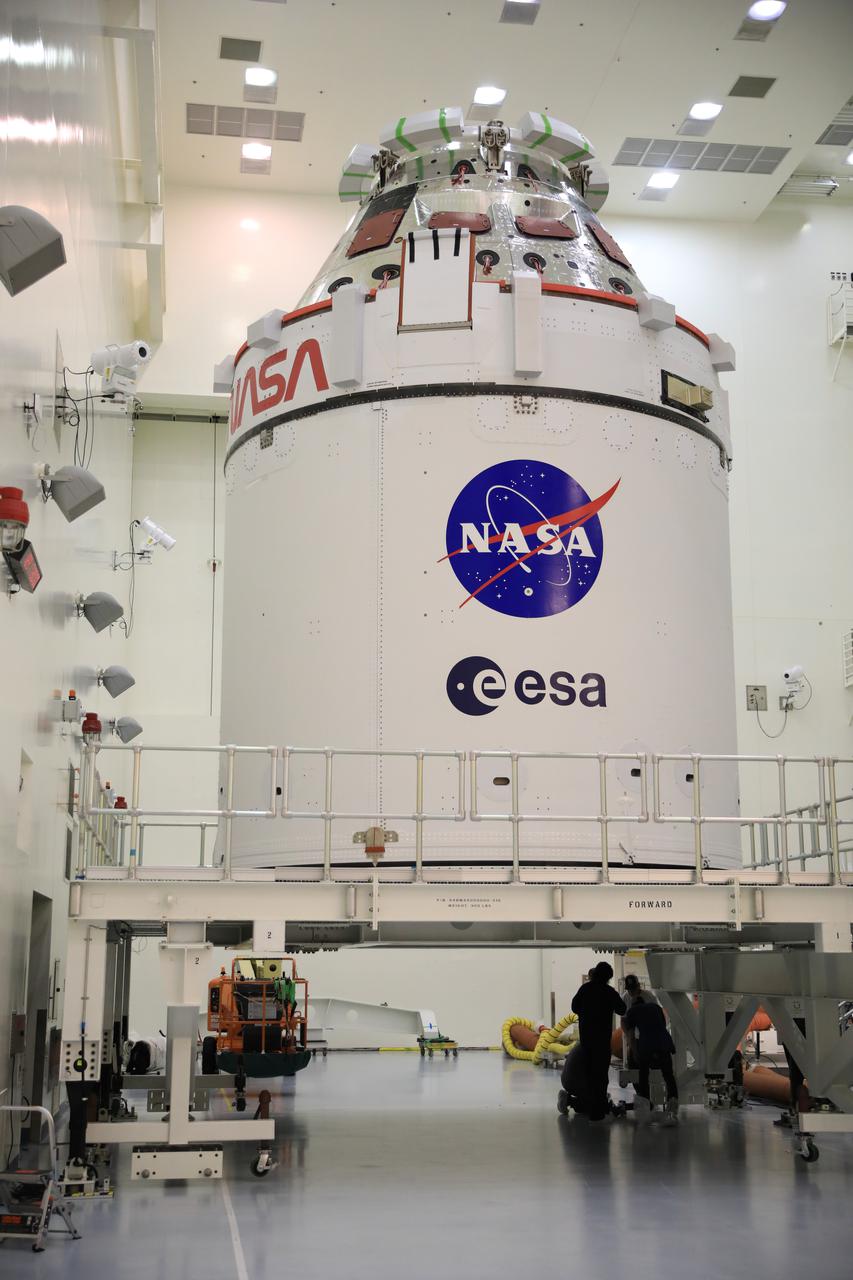

Fueling and servicing checks on the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission are completed inside Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing Facility on July 8, 2021. The capsule will be transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will work to add parts of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.
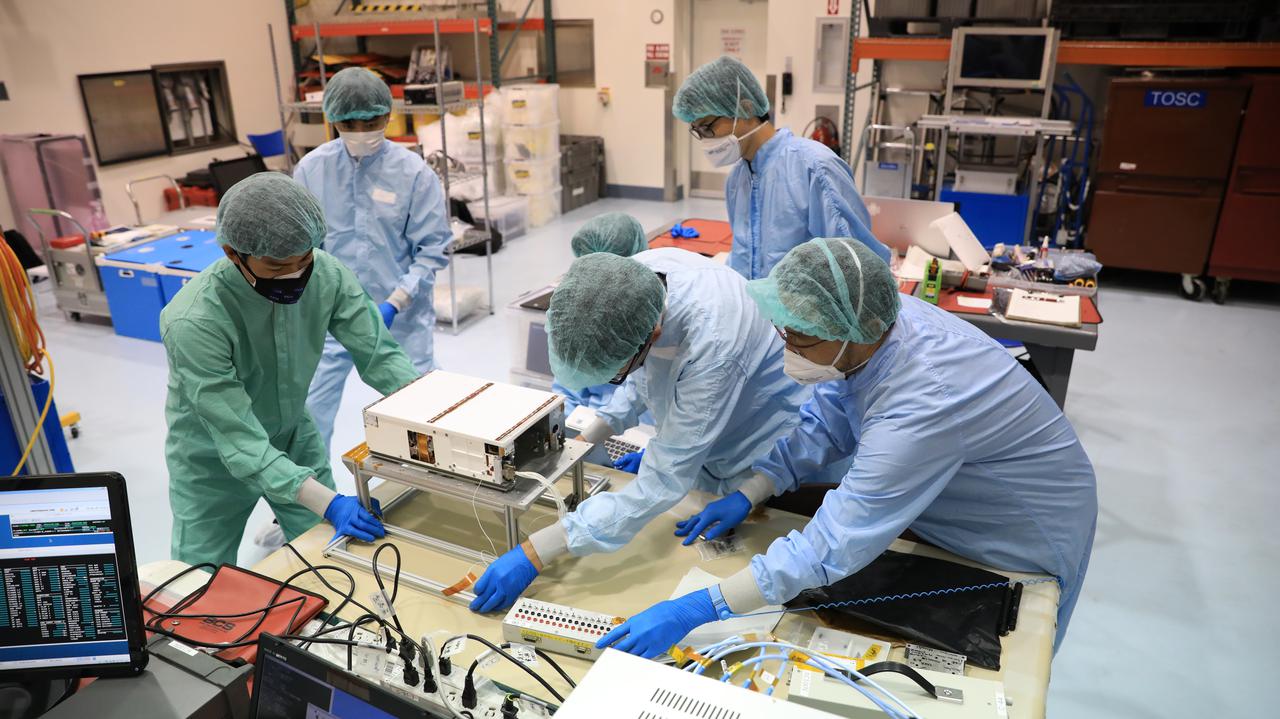

Teams worked on the final processing of their payloads that will fly aboard Artemis I. Housed within the Orion stage adapter, the satellites – called CubeSats – are roughly the size of a large shoe box and weigh no more than 30 pounds. Despite their small size, they enable science and technology experiments that may enhance our understanding of the deep space environment, expand our knowledge of the Moon, and demonstrate new technologies that could be used on future missions.
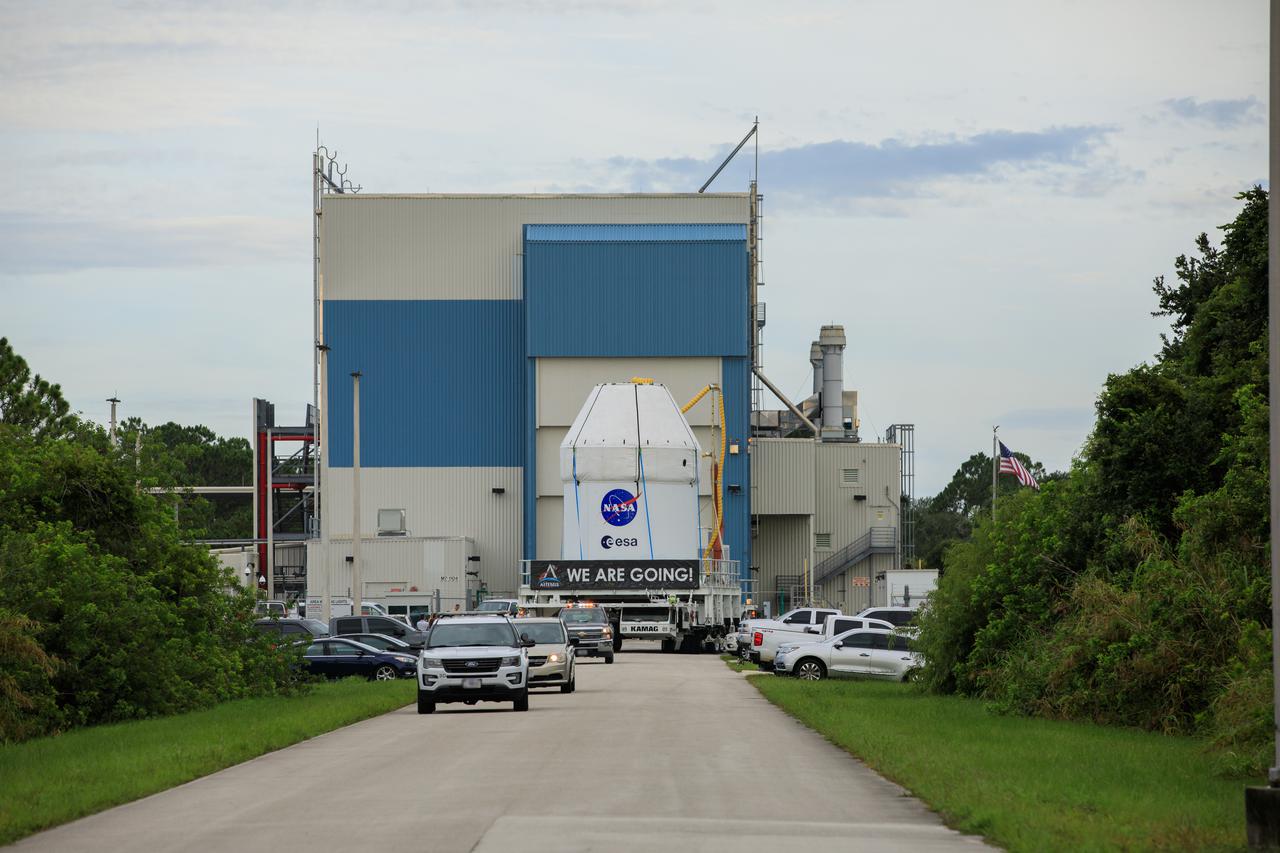

After recently completing fueling and servicing checks, the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission departs Kennedy Space Center’s Multi-Payload Processing on July 10, 2021. The capsule is being transported to the Florida spaceport’s Launch Abort System Facility, where teams with Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs will integrate components of the launch abort system onto the spacecraft. Launching later this year, Artemis I will be a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon.