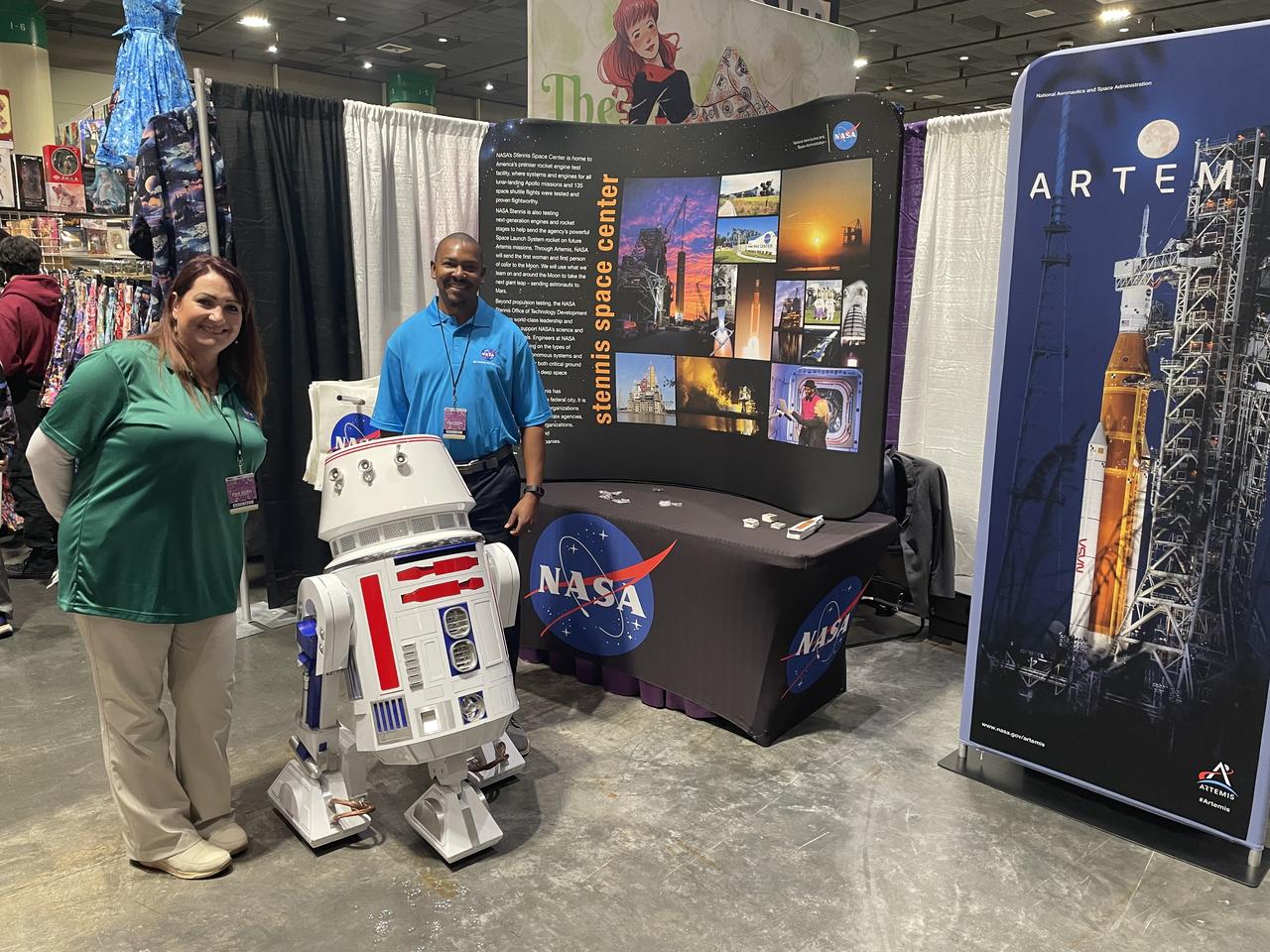
NASA reached out to inspire members of the Artemis Generation on Jan. 10-12, joining one of the largest comic con producers in the world to host an outreach booth at the 2025 FAN EXPO in New Orleans. Thousands of fans celebrating the best in pop culture such as movies, comics, and video gaming learned about NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, and its role to power space dreams.
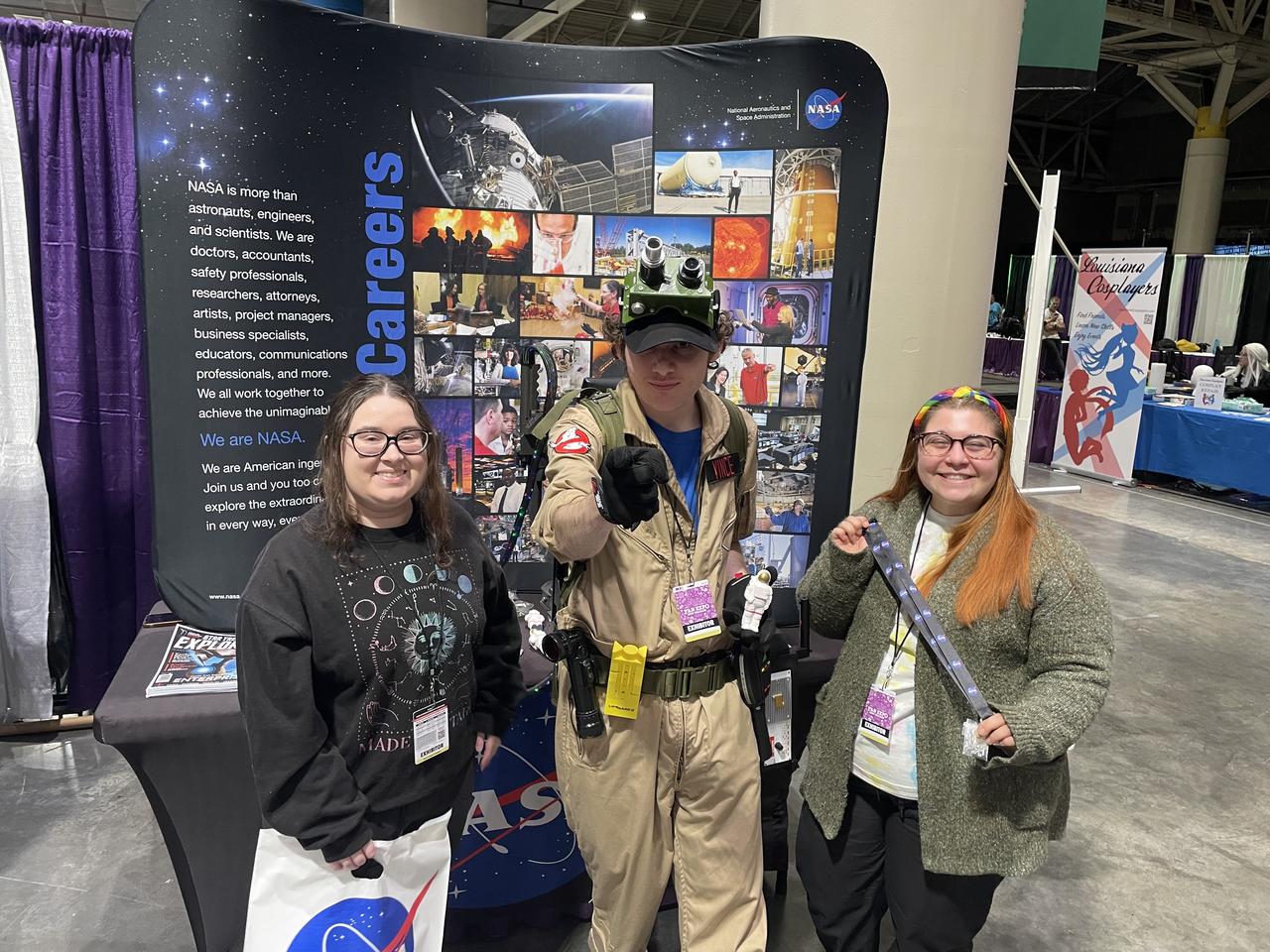

NASA reached out to inspire members of the Artemis Generation on Jan. 10-12, joining one of the largest comic con producers in the world to host an outreach booth at the 2025 FAN EXPO in New Orleans. Thousands of fans celebrating the best in pop culture such as movies, comics, and video gaming learned about NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, and its role to power space dreams.
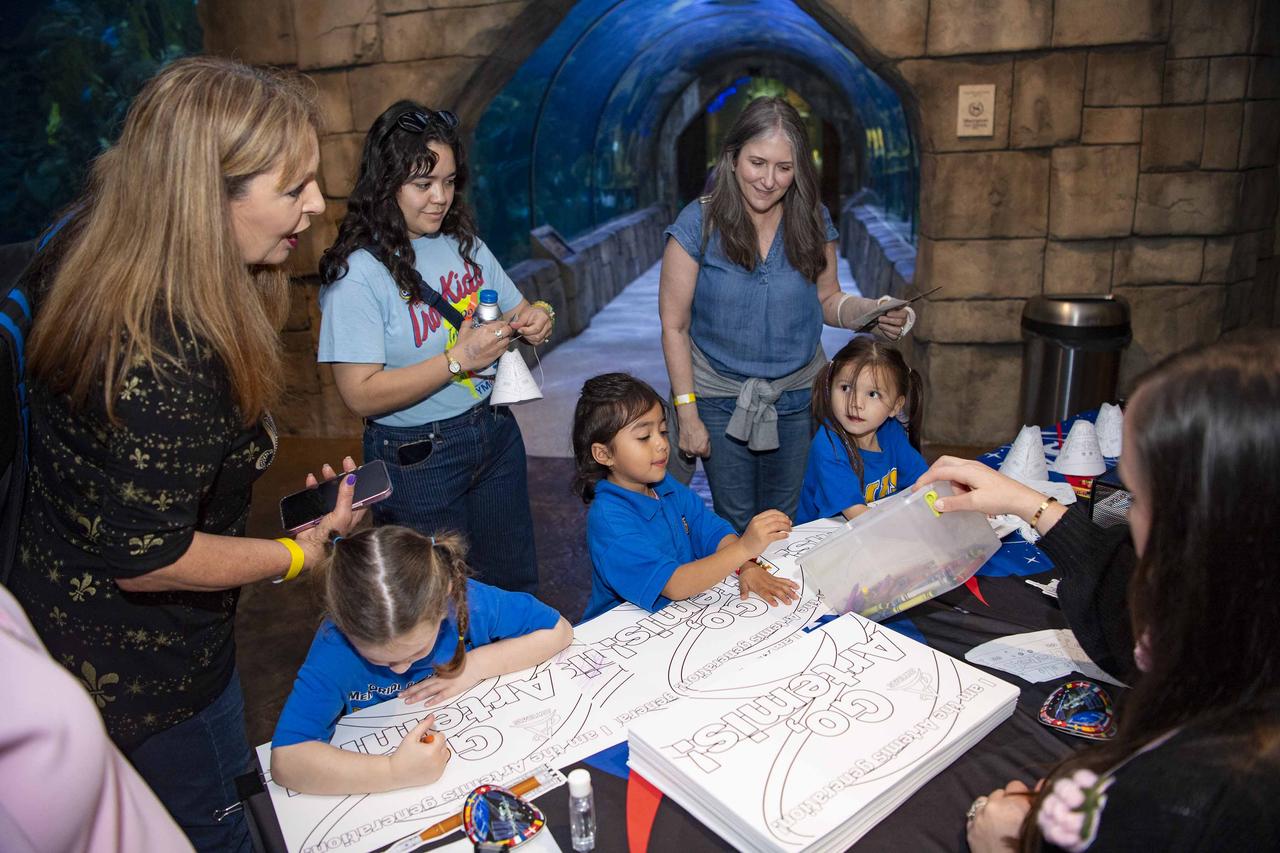

NASA Stennis representatives inspire the Artemis Generation at the Audubon Aquarium in New Orleans Feb. 7-8 with activities and displays highlighting space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

NASA reached out to inspire members of the Artemis Generation on Jan. 10-12, joining one of the largest comic con producers in the world to host an outreach booth at the 2025 FAN EXPO in New Orleans. Thousands of fans celebrating the best in pop culture such as movies, comics, and video gaming learned about NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, and its role to power space dreams.

NASA reached out to inspire members of the Artemis Generation on Jan. 10-12, joining one of the largest comic con producers in the world to host an outreach booth at the 2025 FAN EXPO in New Orleans. Thousands of fans celebrating the best in pop culture such as movies, comics, and video gaming learned about NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, and its role to power space dreams.

NASA Stennis representatives inspire the Artemis Generation at the Audubon Aquarium in New Orleans Feb. 7-8 with activities and displays highlighting space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.
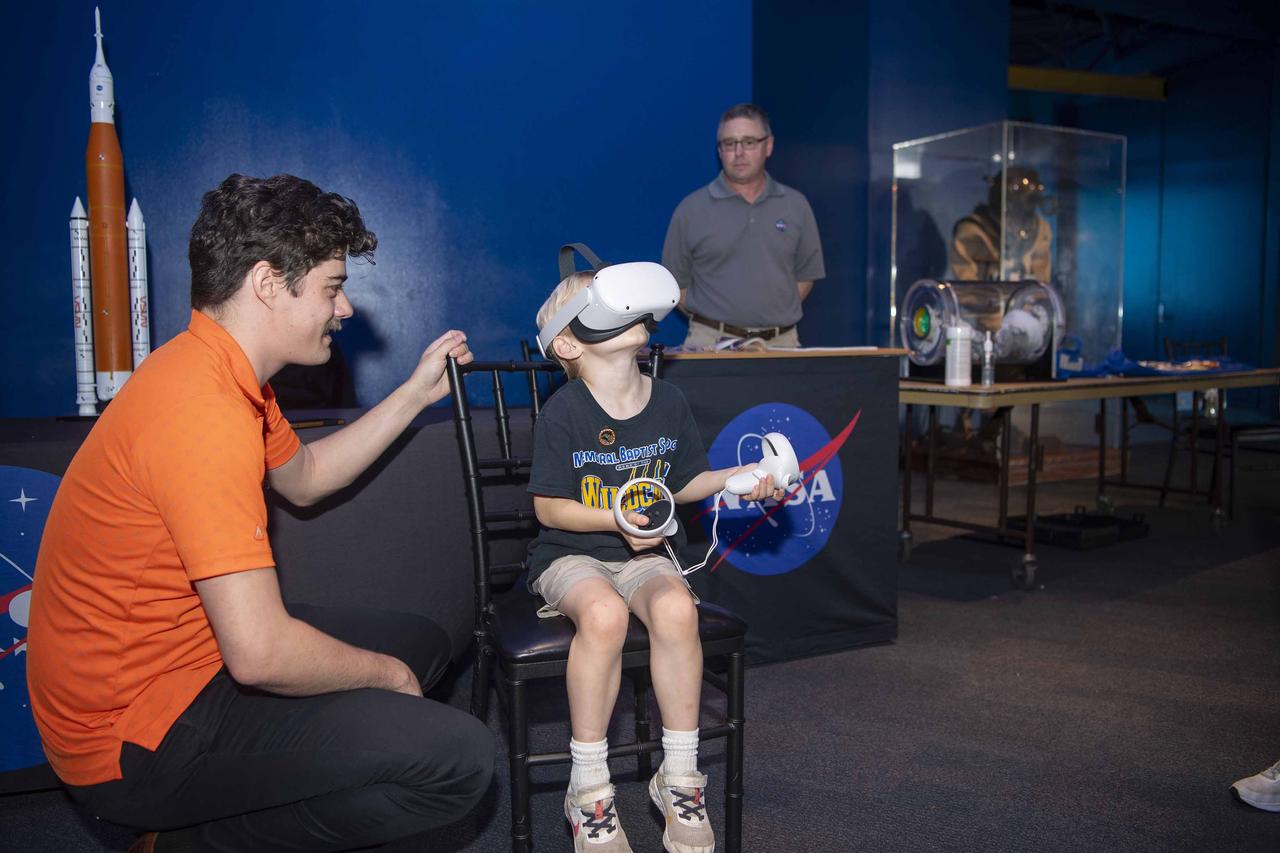

NASA Stennis representatives inspire the Artemis Generation at the Audubon Aquarium in New Orleans Feb. 7-8 with activities and displays highlighting space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

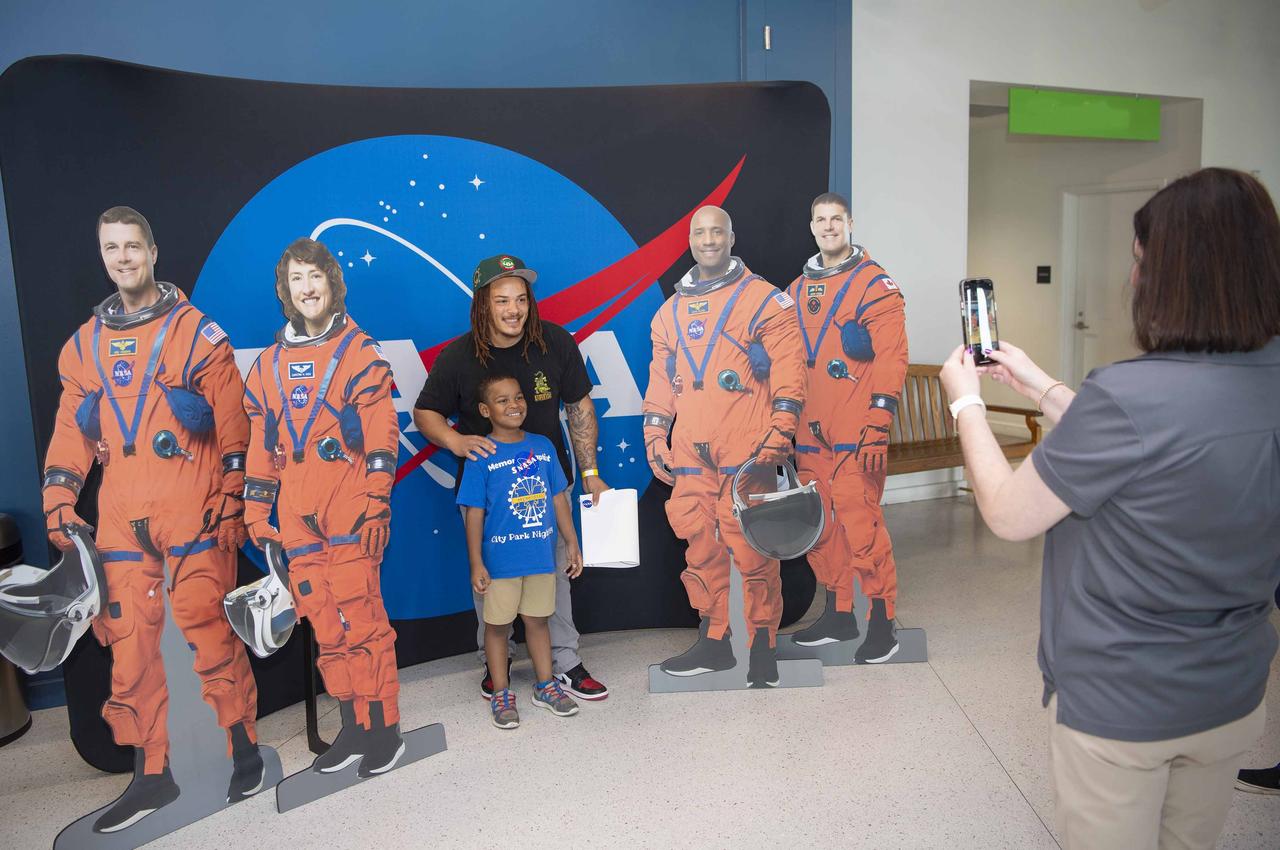
Fans at the 51st Annual Bayou Classic in New Orleans snap a photo with cardboard images of NASA’s Artemis II crew on Nov. 30.
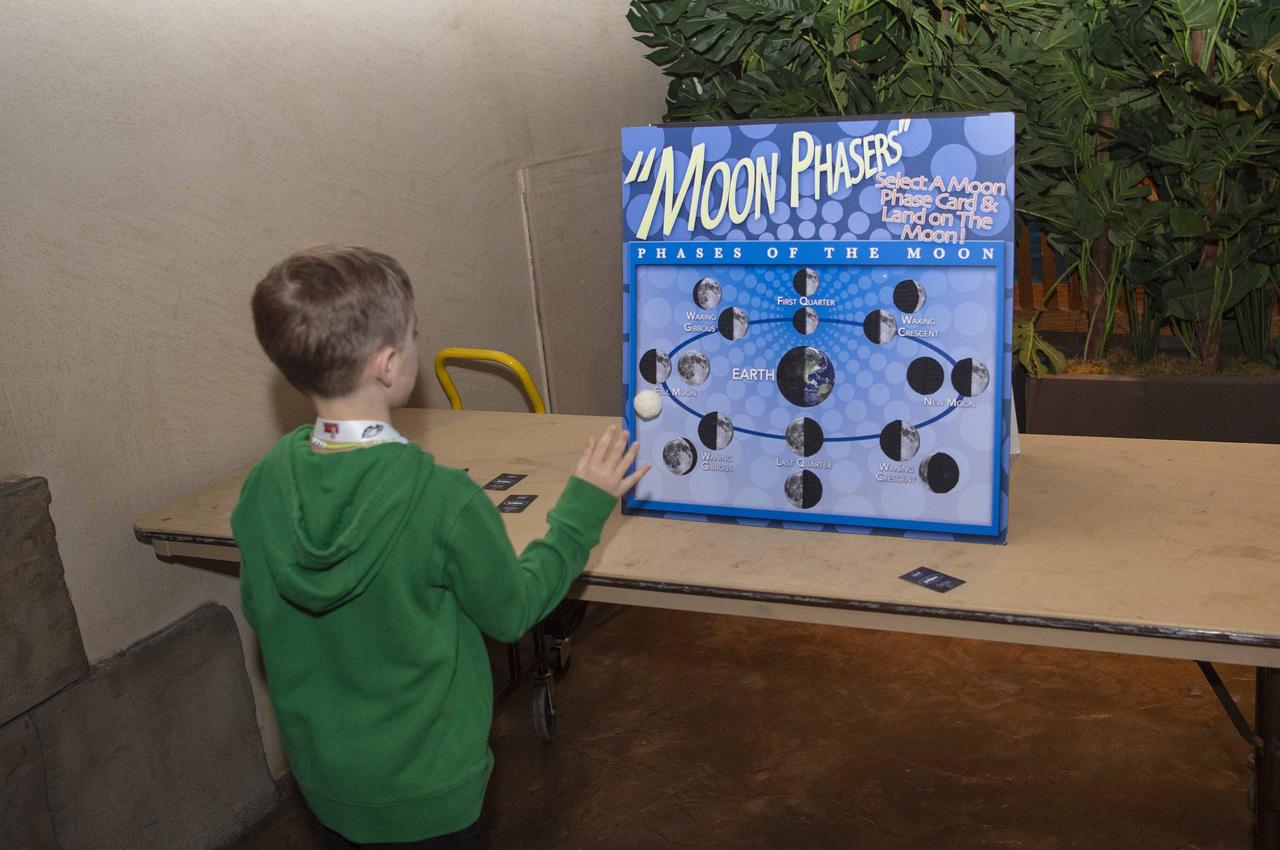

NASA Stennis representatives inspire the Artemis Generation at the Audubon Aquarium in New Orleans Feb. 7-8 with activities and displays highlighting space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

NASA Stennis representatives inspire the Artemis Generation at the Audubon Aquarium in New Orleans Feb. 7-8 with activities and displays highlighting space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

NASA reached out to inspire members of the Artemis Generation on Jan. 10-12, joining one of the largest comic con producers in the world to host an outreach booth at the 2025 FAN EXPO in New Orleans. Thousands of fans celebrating the best in pop culture such as movies, comics, and video gaming learned about NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, and its role to power space dreams.

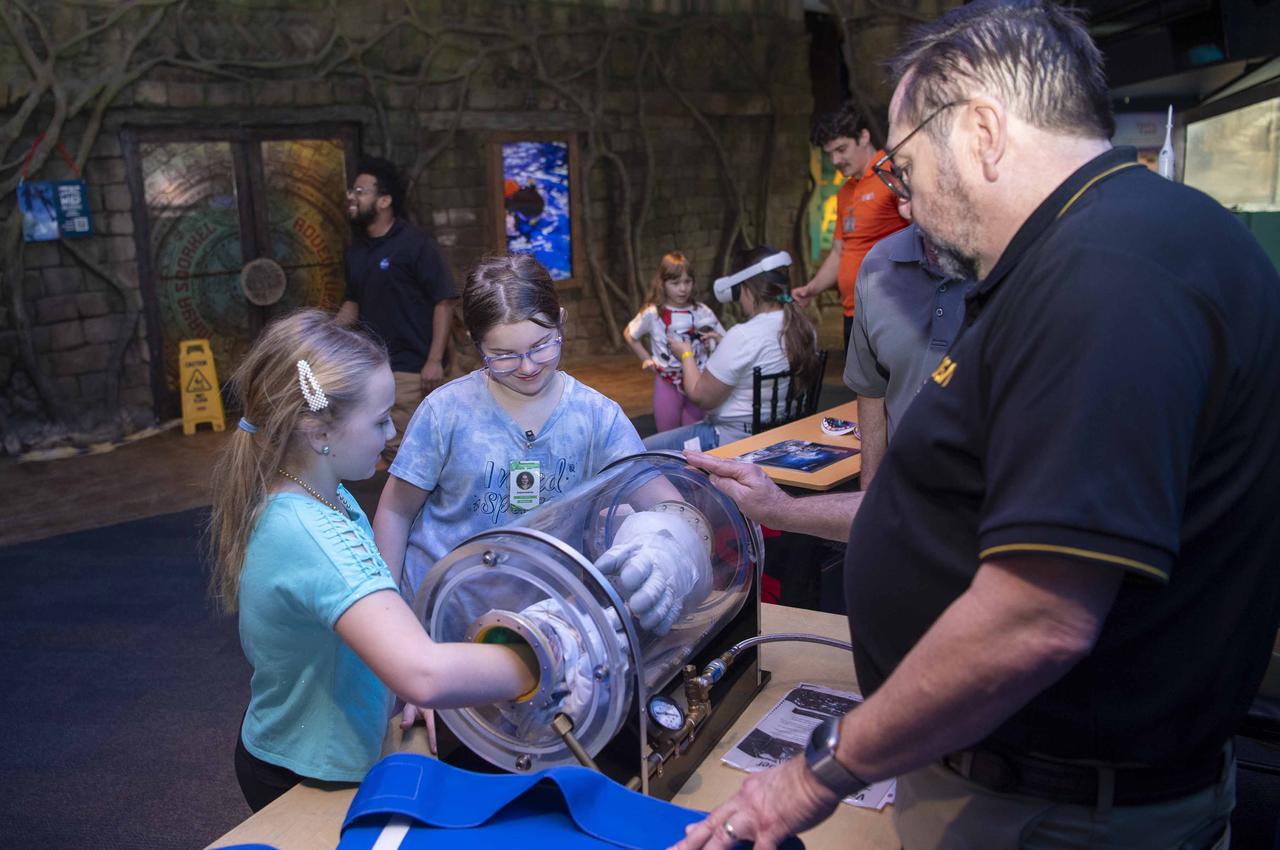
NASA Stennis representatives inspire the Artemis Generation at the Audubon Aquarium in New Orleans Feb. 7-8 with activities and displays highlighting space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.
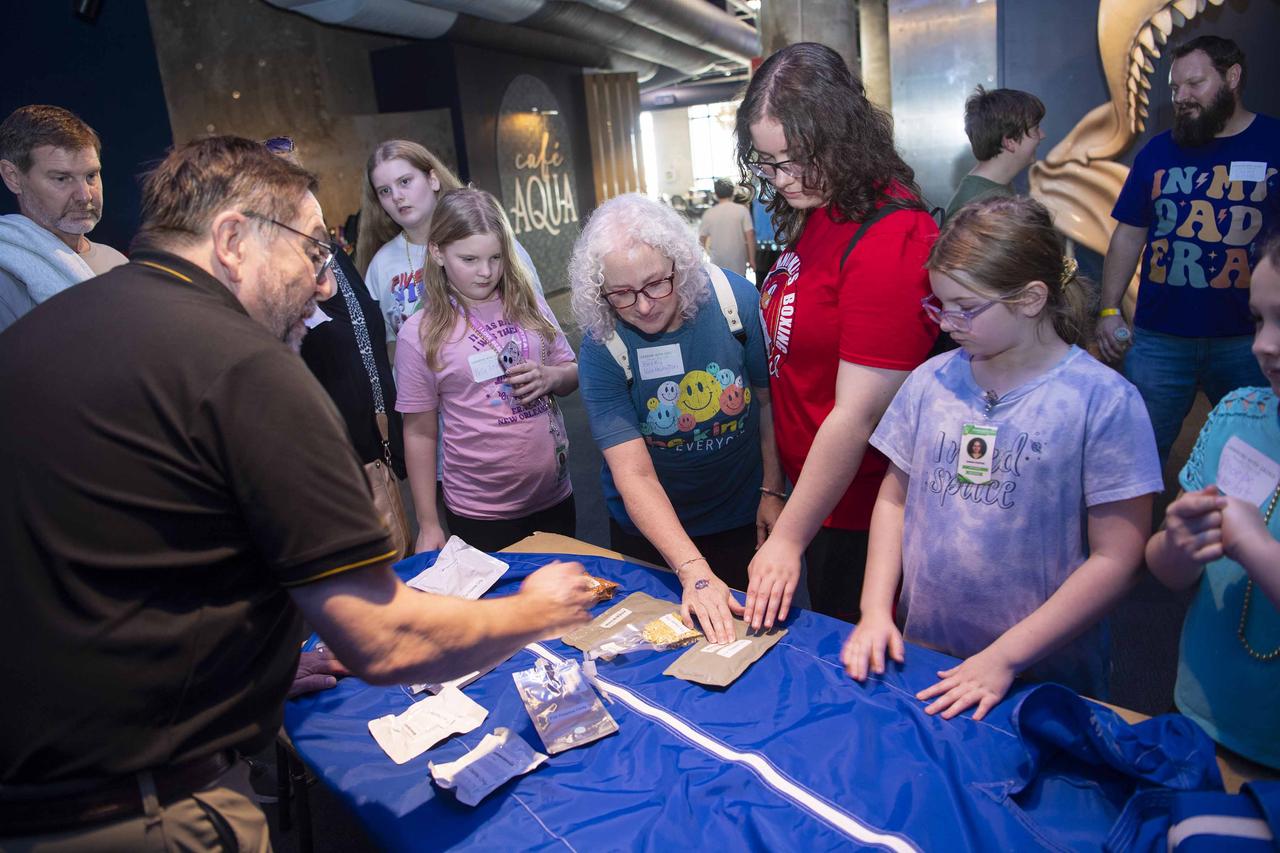

NASA Stennis representatives inspire the Artemis Generation at the Audubon Aquarium in New Orleans Feb. 7-8 with activities and displays highlighting space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.
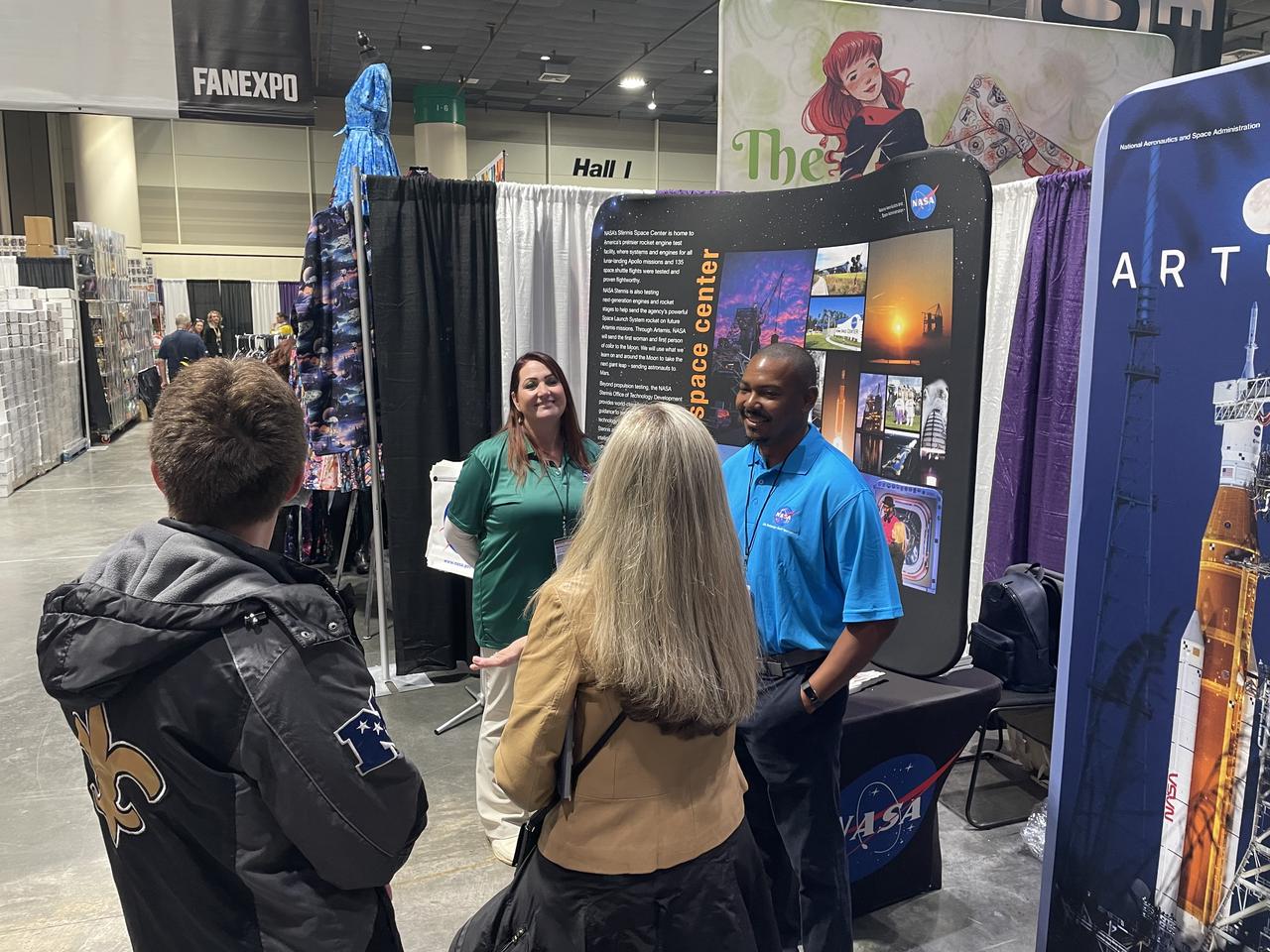

NASA reached out to inspire members of the Artemis Generation on Jan. 10-12, joining one of the largest comic con producers in the world to host an outreach booth at the 2025 FAN EXPO in New Orleans. Thousands of fans celebrating the best in pop culture such as movies, comics, and video gaming learned about NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, and its role to power space dreams.
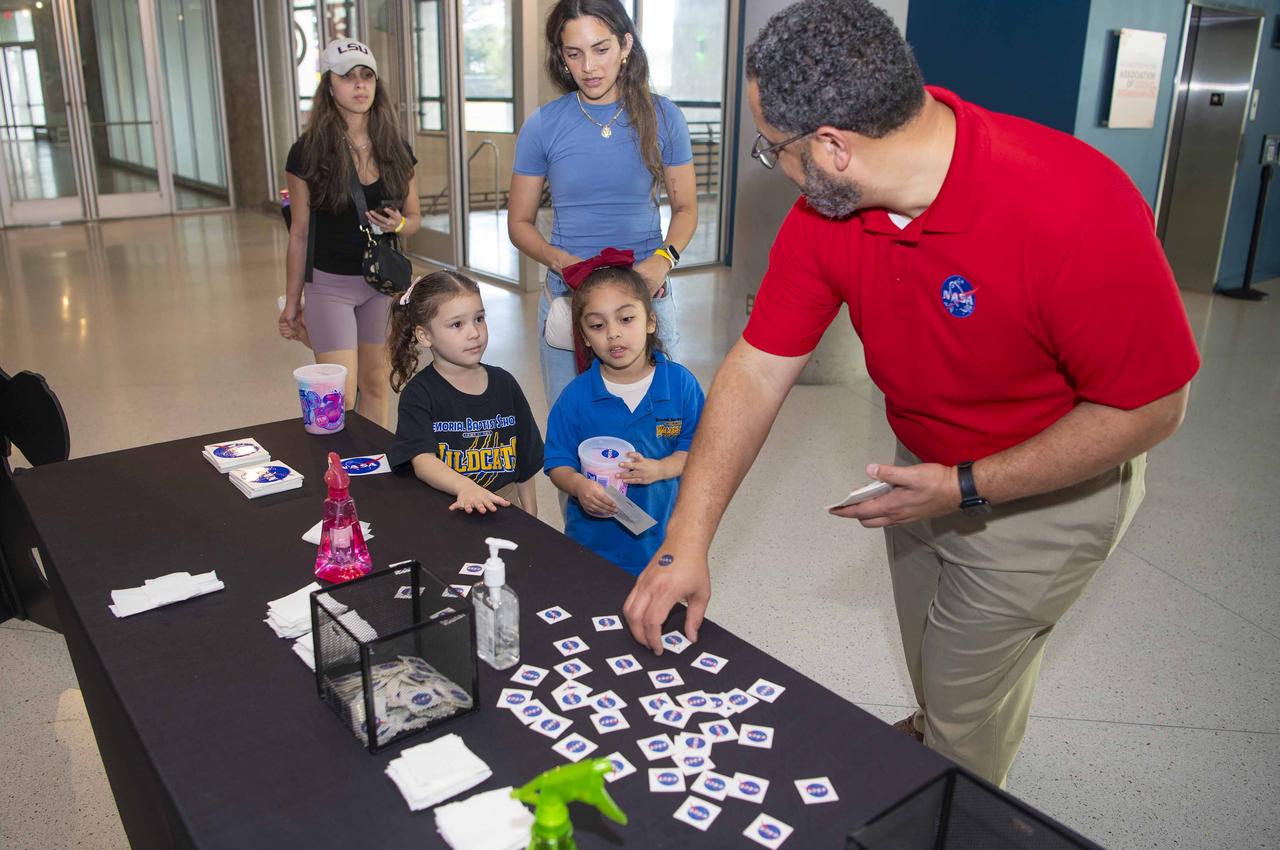

NASA Stennis representatives inspire the Artemis Generation at the Audubon Aquarium in New Orleans Feb. 7-8 with activities and displays highlighting space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.
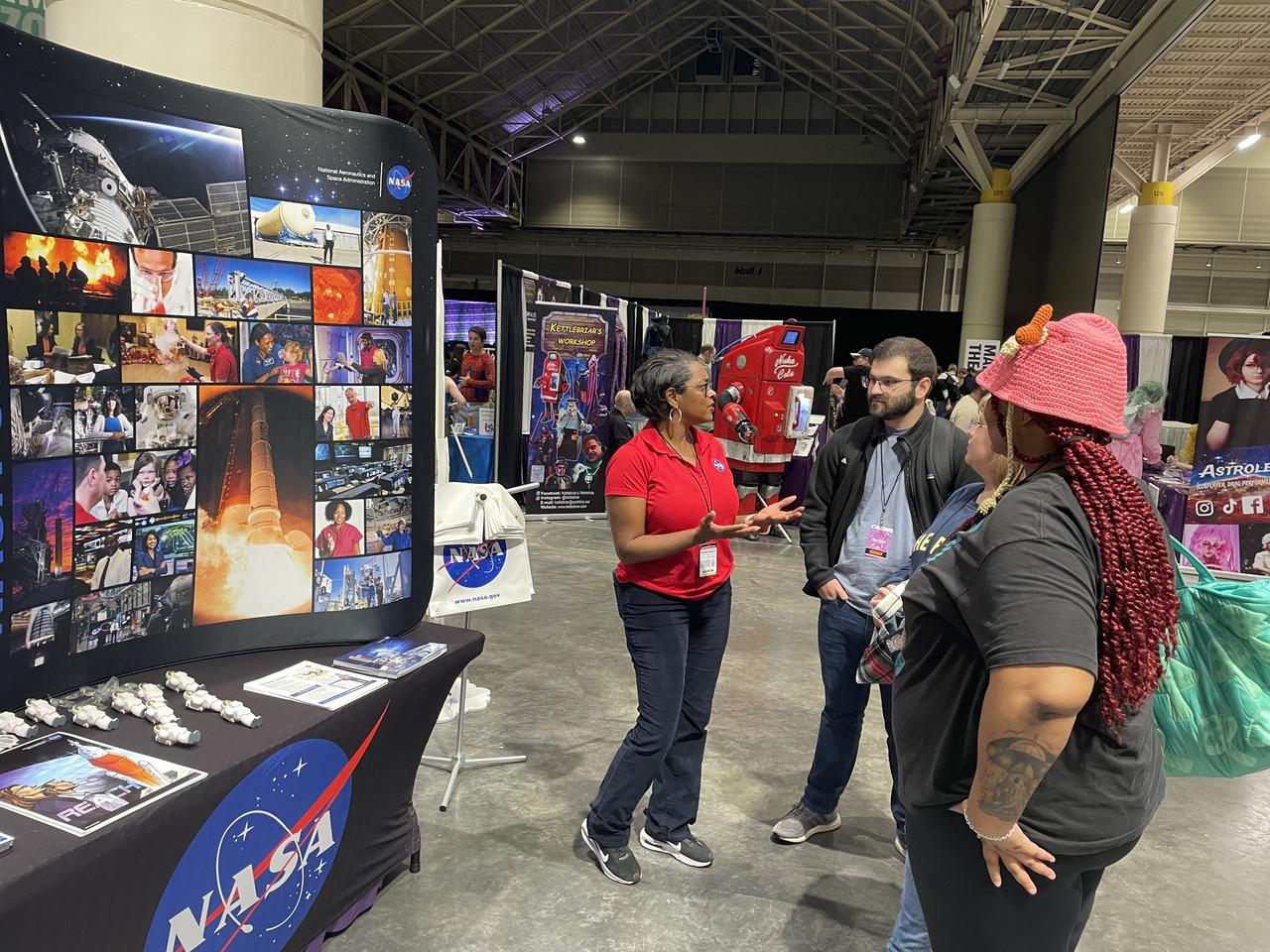

NASA reached out to inspire members of the Artemis Generation on Jan. 10-12, joining one of the largest comic con producers in the world to host an outreach booth at the 2025 FAN EXPO in New Orleans. Thousands of fans celebrating the best in pop culture such as movies, comics, and video gaming learned about NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, and its role to power space dreams.
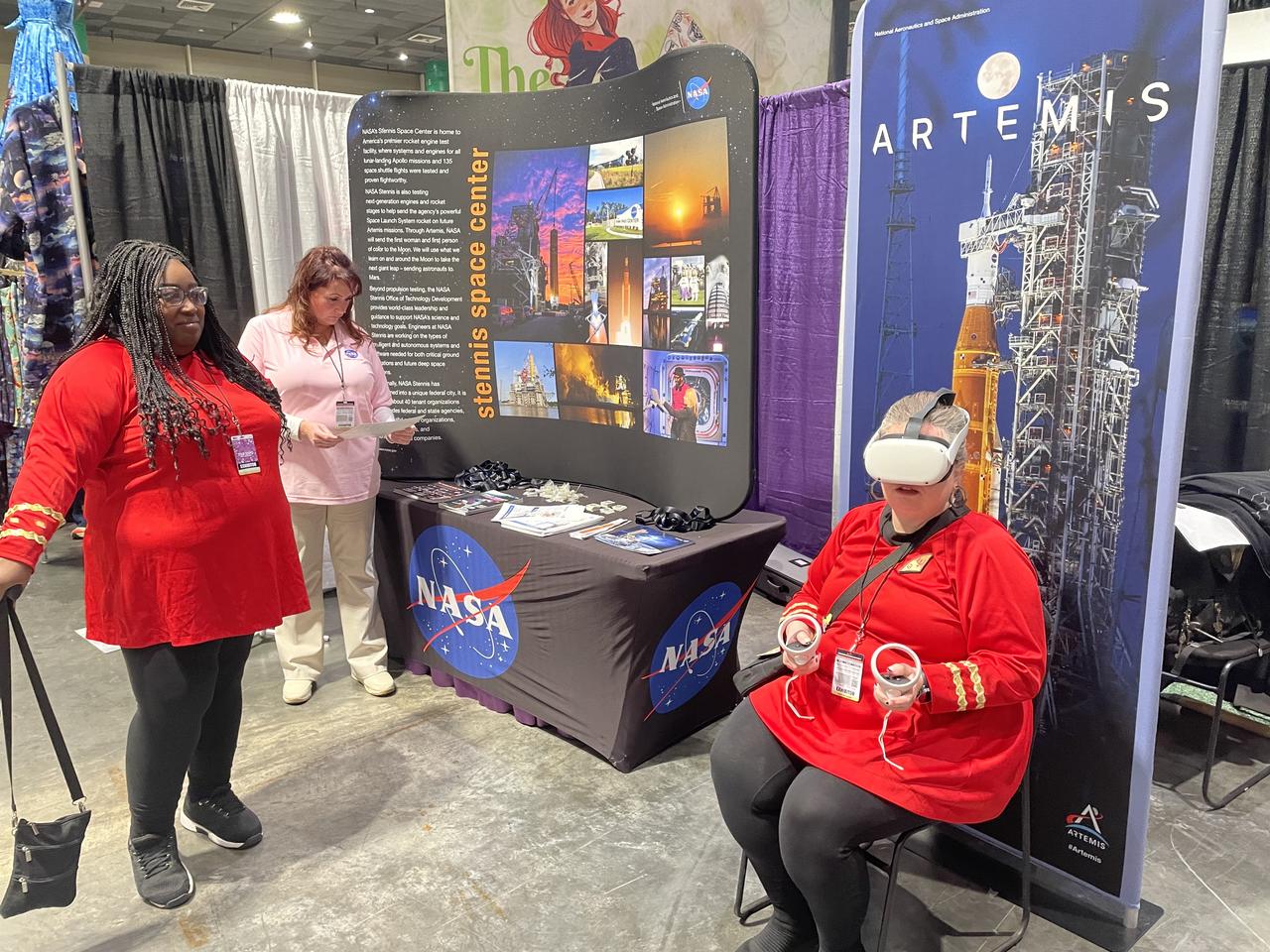

NASA reached out to inspire members of the Artemis Generation on Jan. 10-12, joining one of the largest comic con producers in the world to host an outreach booth at the 2025 FAN EXPO in New Orleans. Thousands of fans celebrating the best in pop culture such as movies, comics, and video gaming learned about NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, and its role to power space dreams.
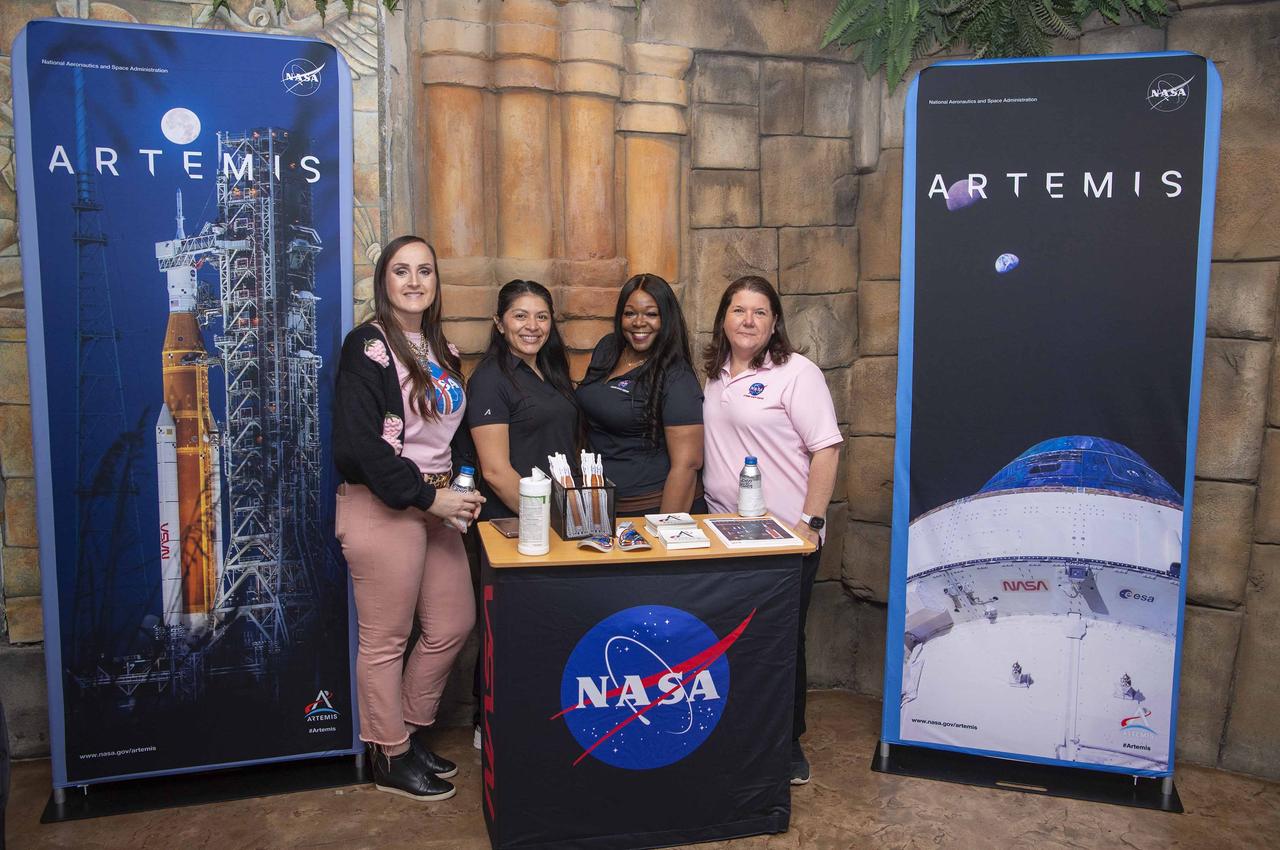

NASA Stennis representatives inspire the Artemis Generation at the Audubon Aquarium in New Orleans Feb. 7-8 with activities and displays highlighting space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon

NASA Stennis representatives inspire the Artemis Generation at the Audubon Aquarium in New Orleans Feb. 7-8 with activities and displays highlighting space exploration, including NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.
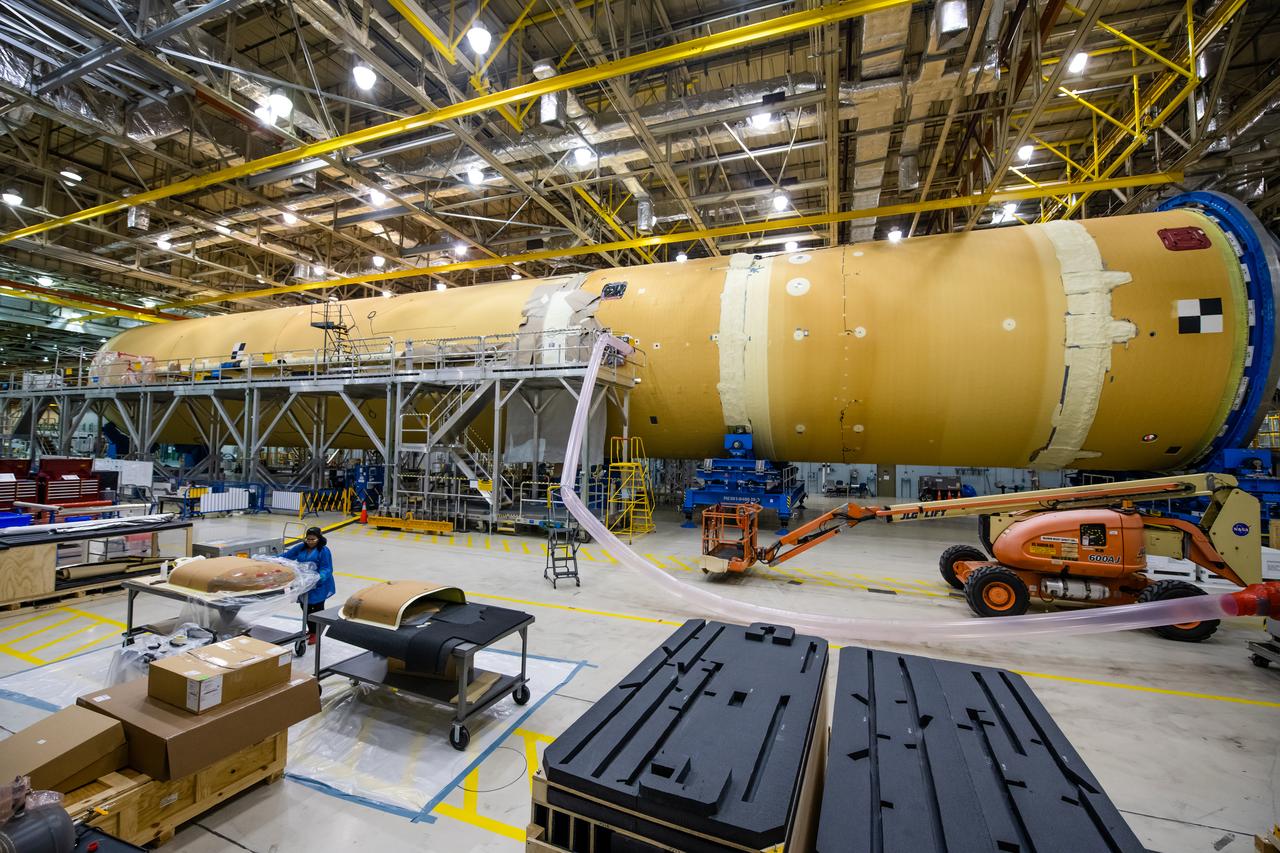

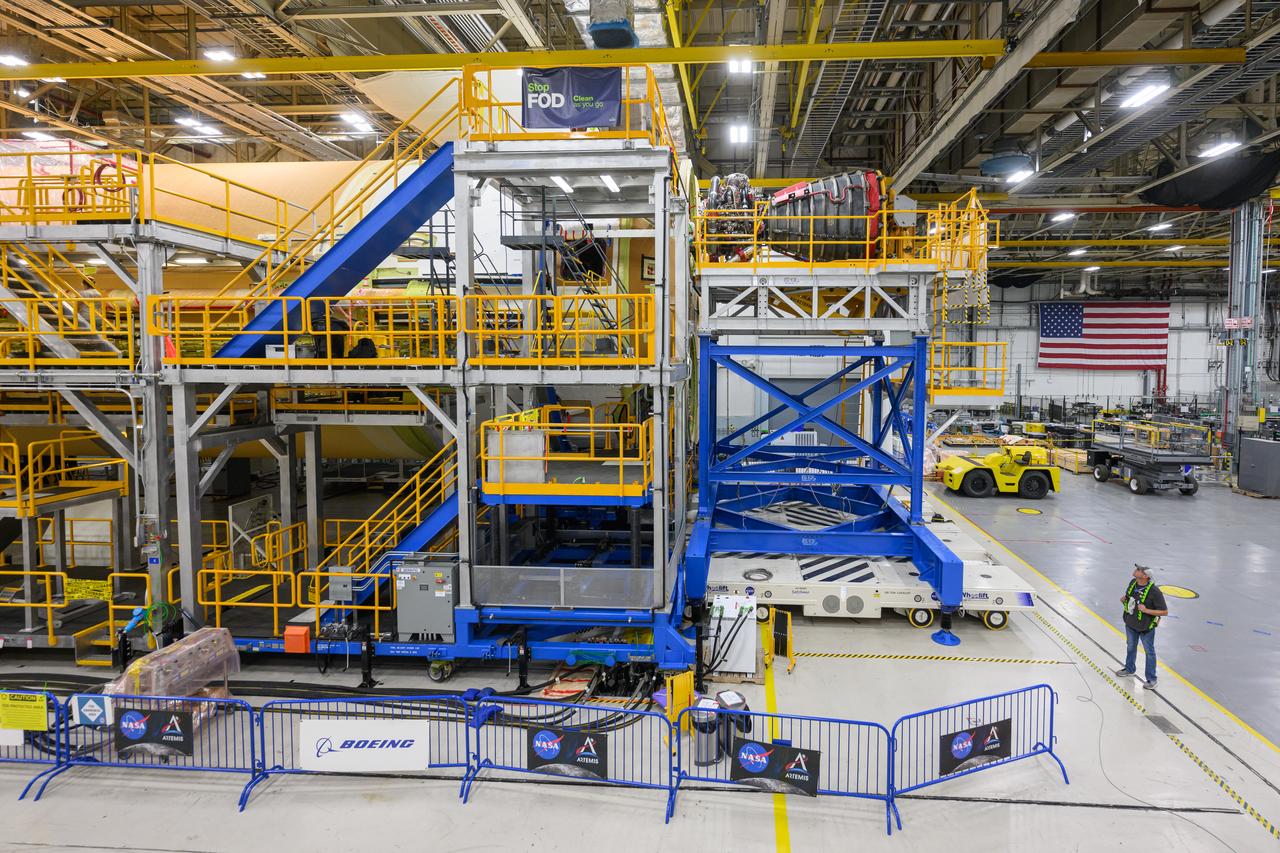
Space Launch System Corestage-1 (Artemis-1) in production at the Michoud Assembly Faclility in New Orleans.
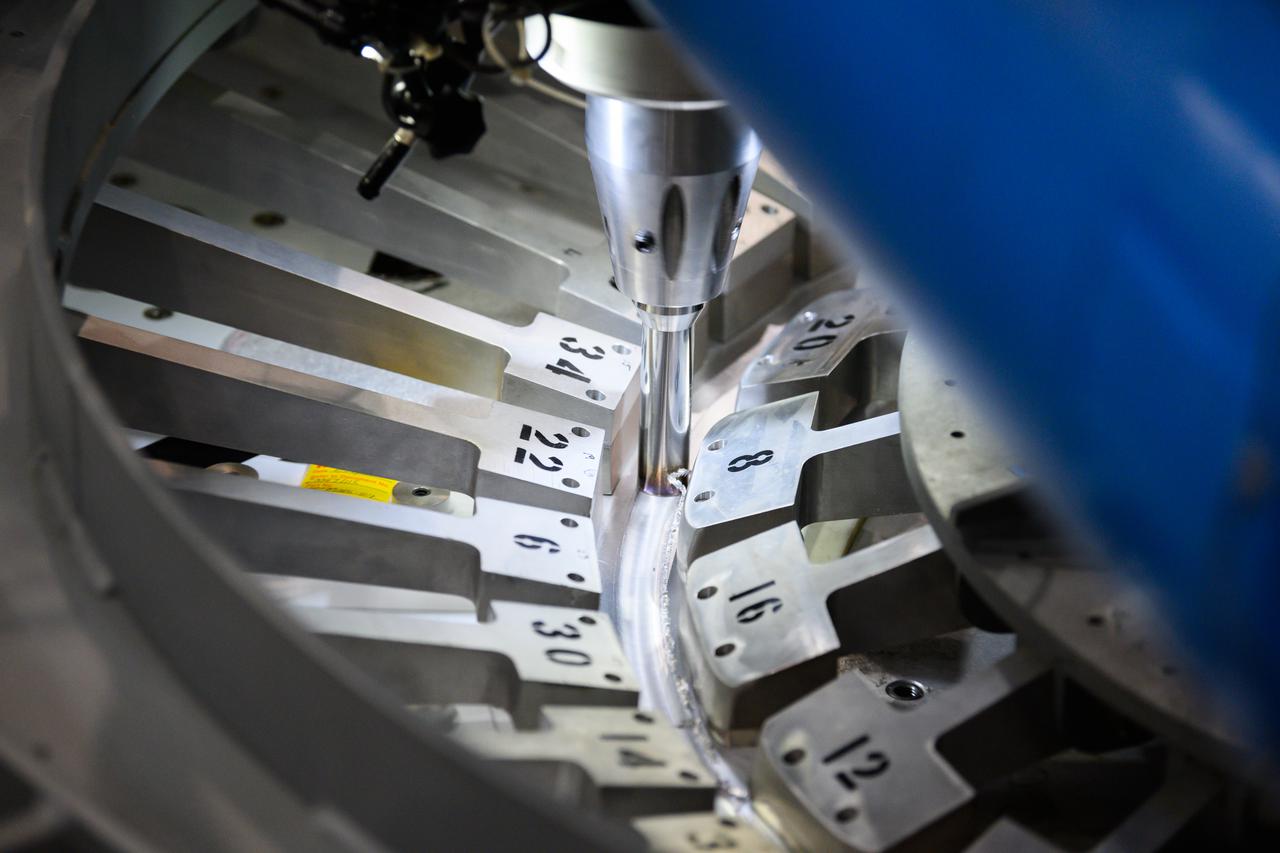

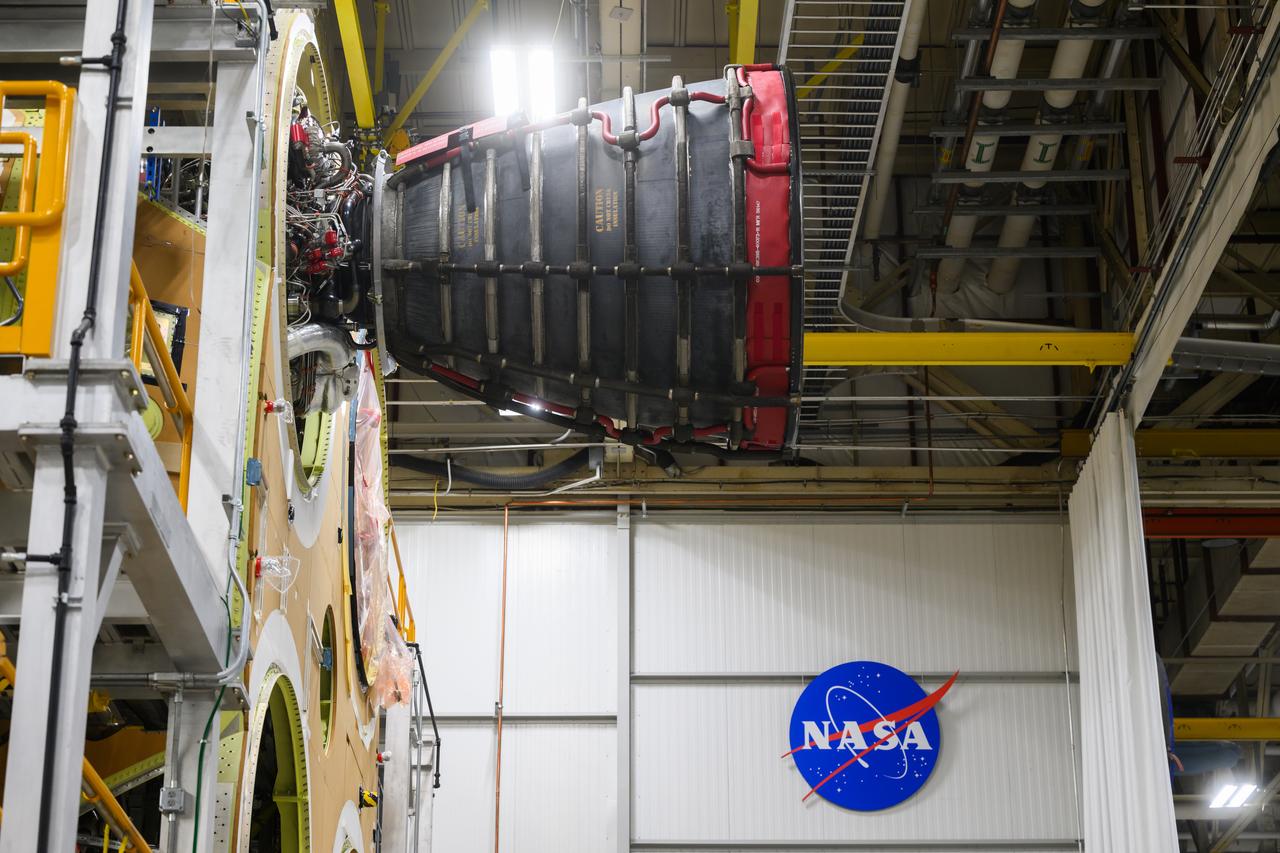
Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
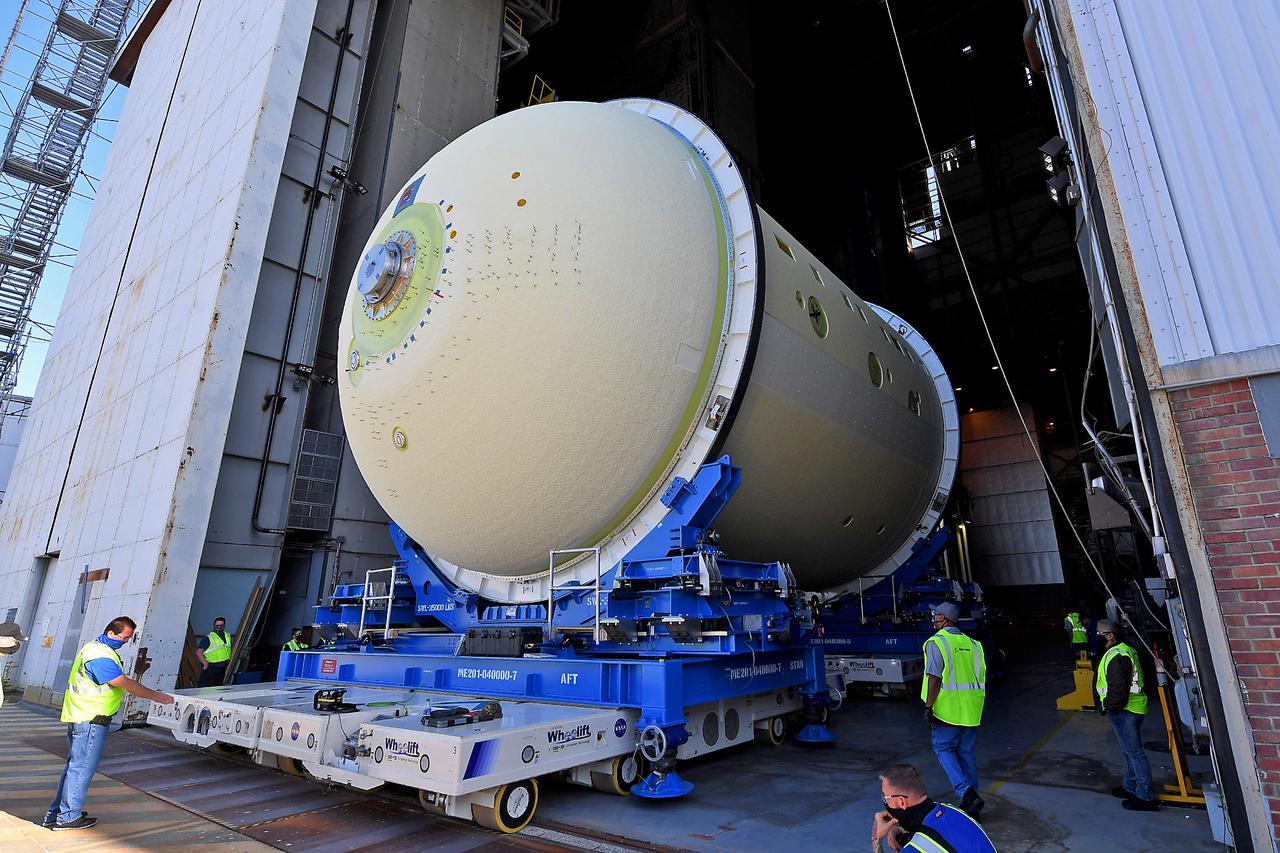

This image highlights the liquid oxygen tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’ Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of liquid oxygen cooled to minus 297 degrees Fahrenheit. The LOX hardware sits between the core stage’s forward skirt and the intertank. Along with the liquid hydrogen tank, it will provide fuel to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket can send astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This image highlights the liquid hydrogen tank that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program. The tank is being built at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the cores stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the human landing system, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket can send astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
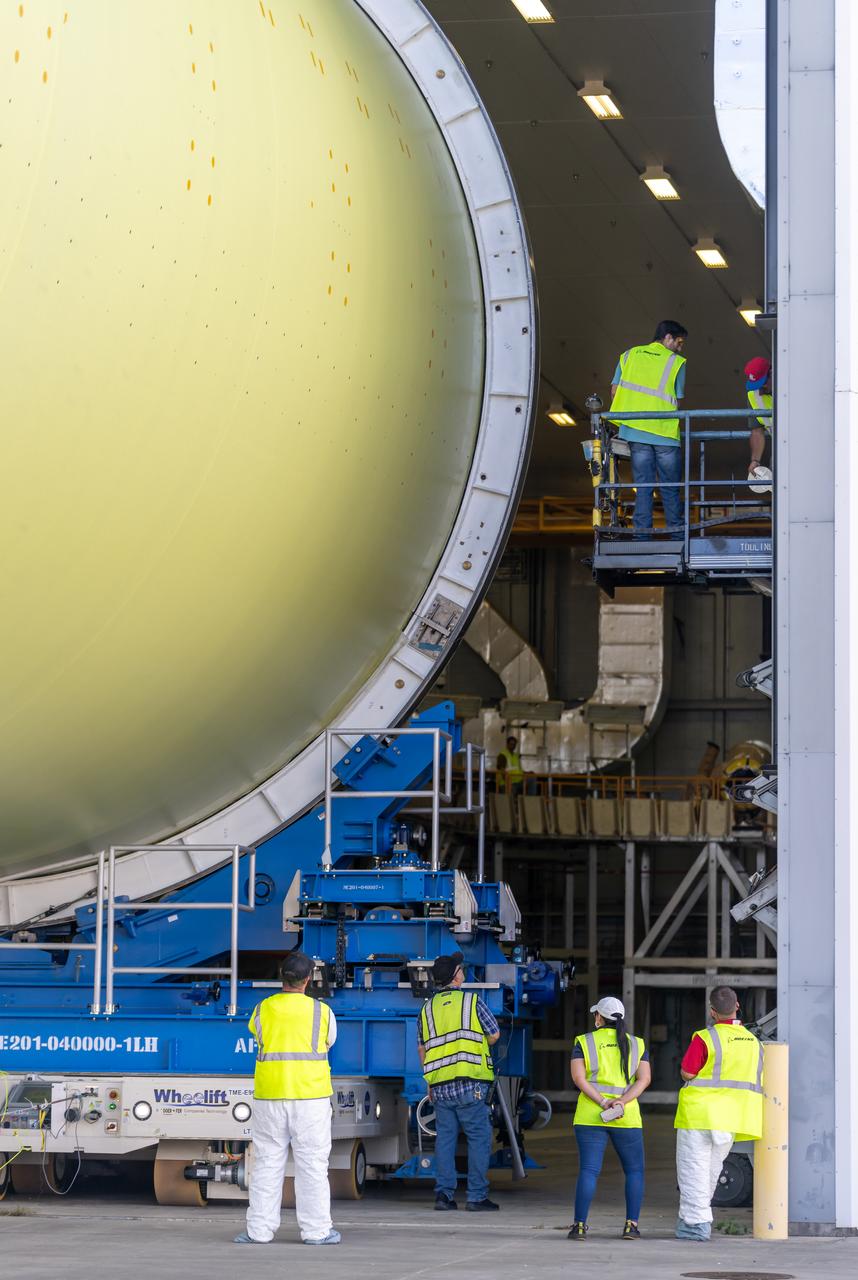

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
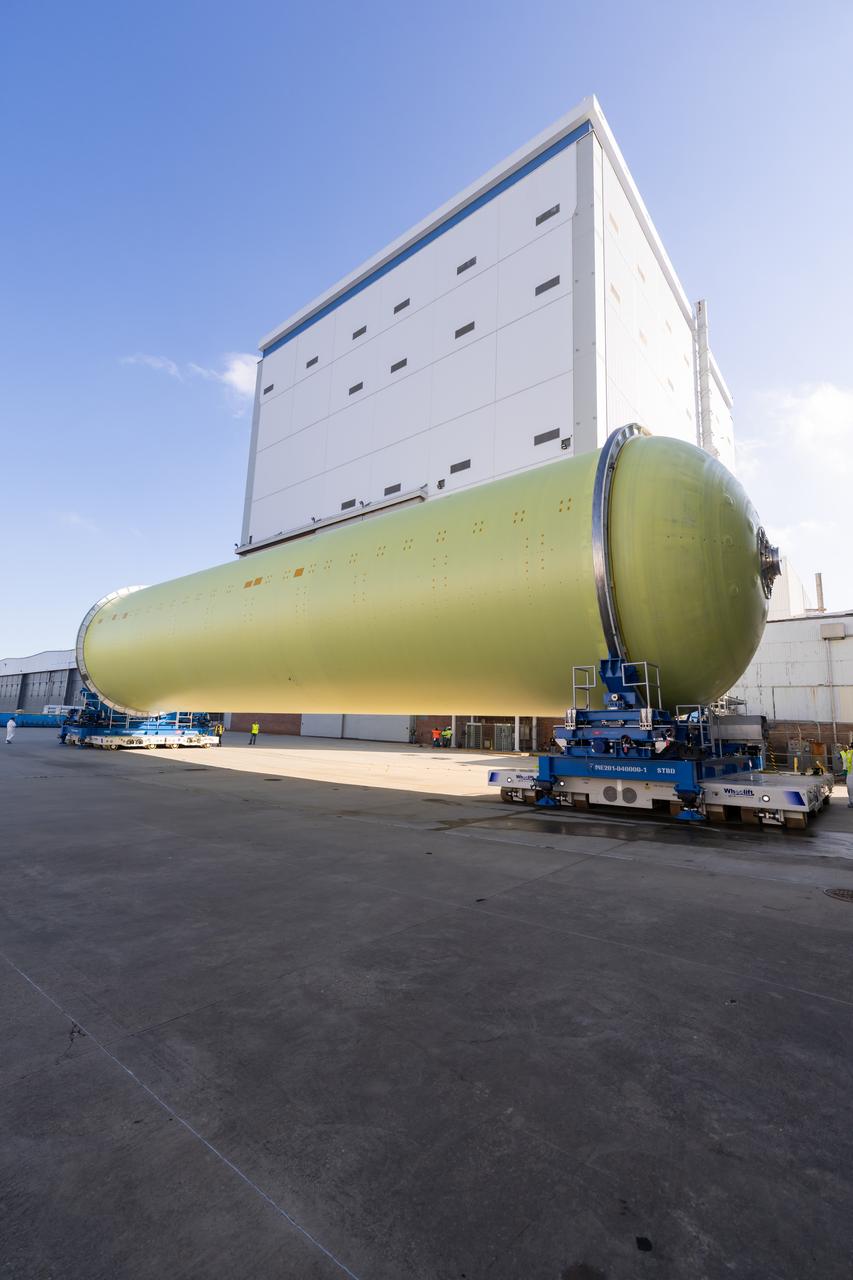

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
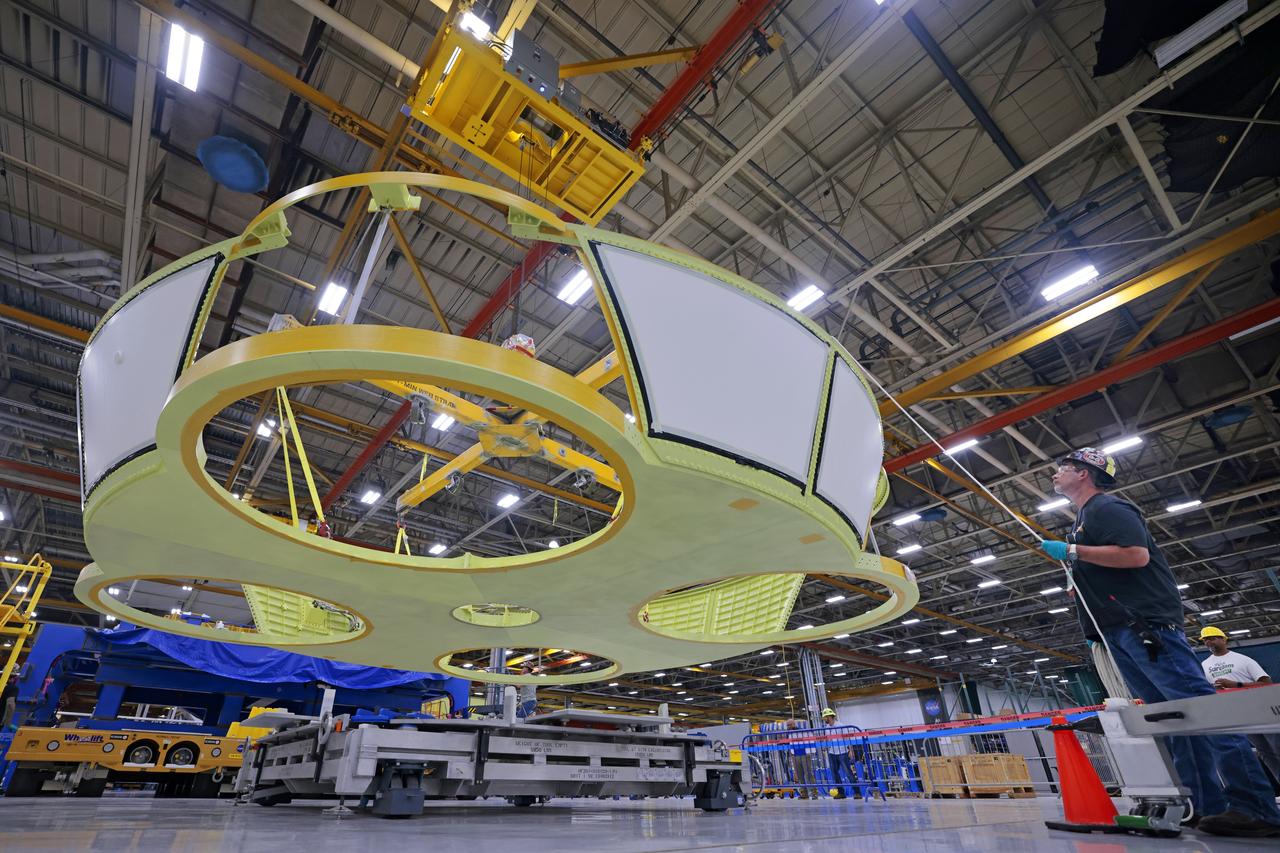

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

: These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the third and fourth RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Technicians added the first engine to the SLS core stage Sept. 11. The second engine was installed onto the stage Sept. 15 with the third and fourth engines following Sept. 19 and Sept. 20. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will now focus efforts on the complex tax of fully securing the engines to the stage and integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
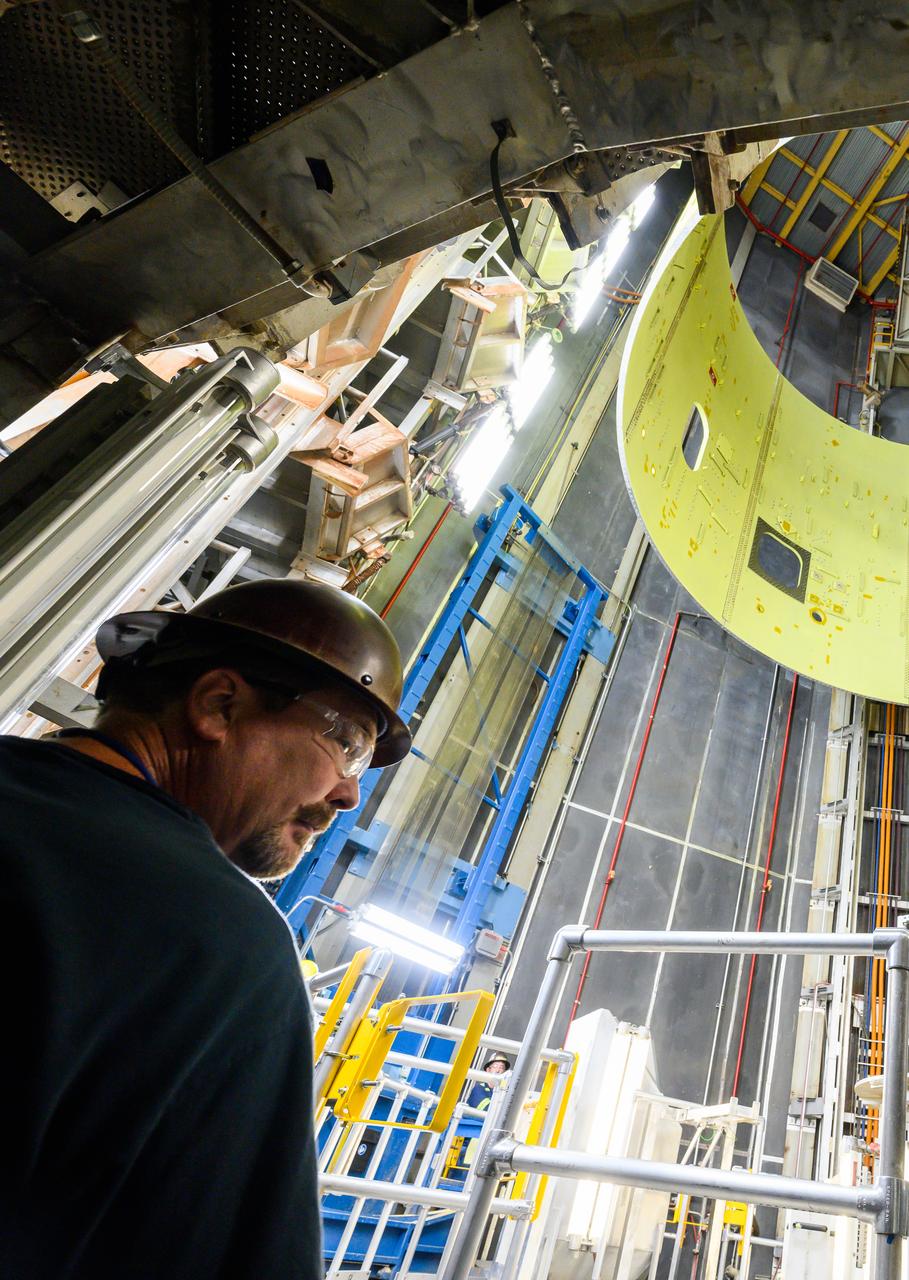

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
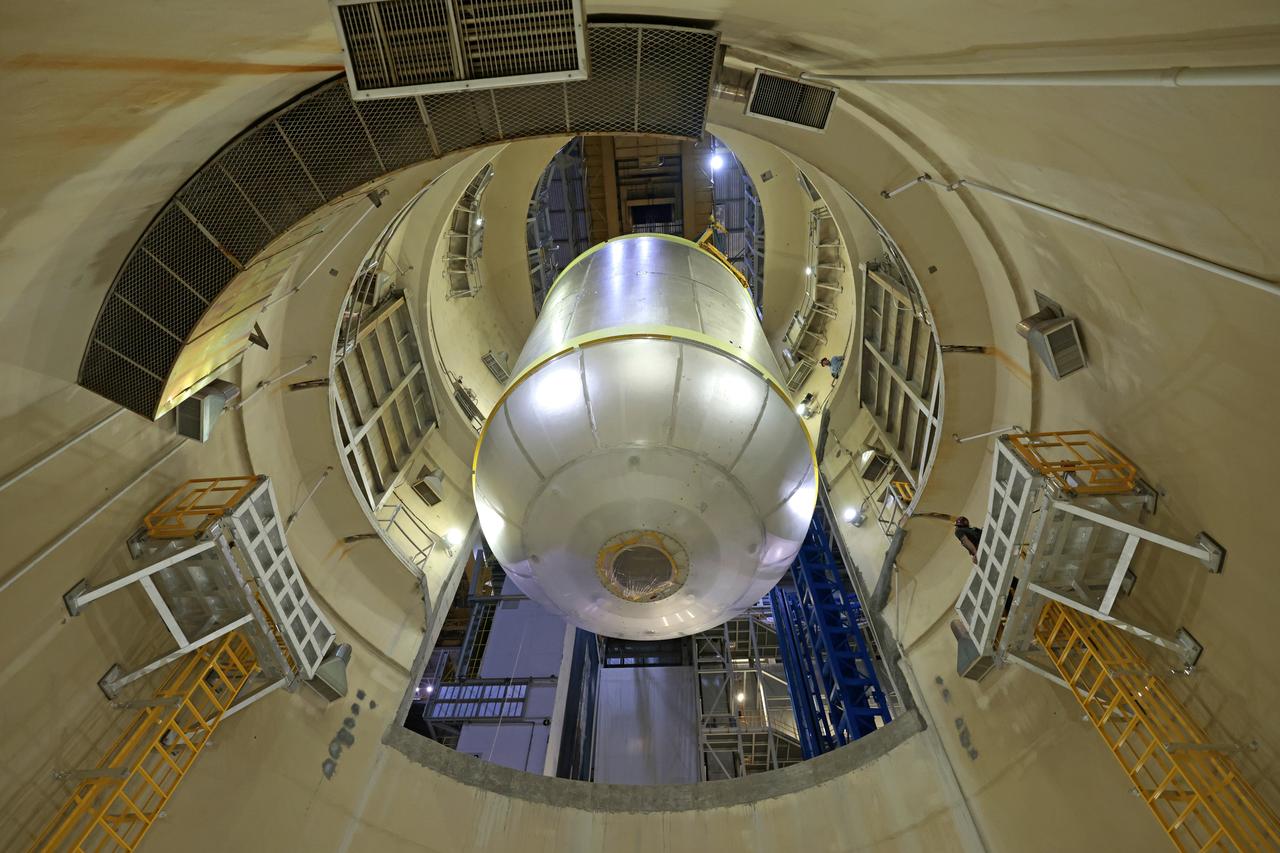

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid oxygen tank for its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to a cleaning cell inside the facility’s vertical assembly building on Oct. 11. The tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s Artemis III mission, will undergo an internal cleaning before moving on to its next phase of production. Inside the cleaning cell, a solution is sprayed into the tank to remove particulates which may collect during the manufacturing process. Once a tank is cleaned, teams use mobile clean rooms for internal access to the tank to prevent external contaminates from entering the hardware. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This image highlights the liquid oxygen tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’ Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of liquid oxygen cooled to minus 297 degrees Fahrenheit. The LOX hardware sits between the core stage’s forward skirt and the intertank. Along with the liquid hydrogen tank, it will provide fuel to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket can send astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
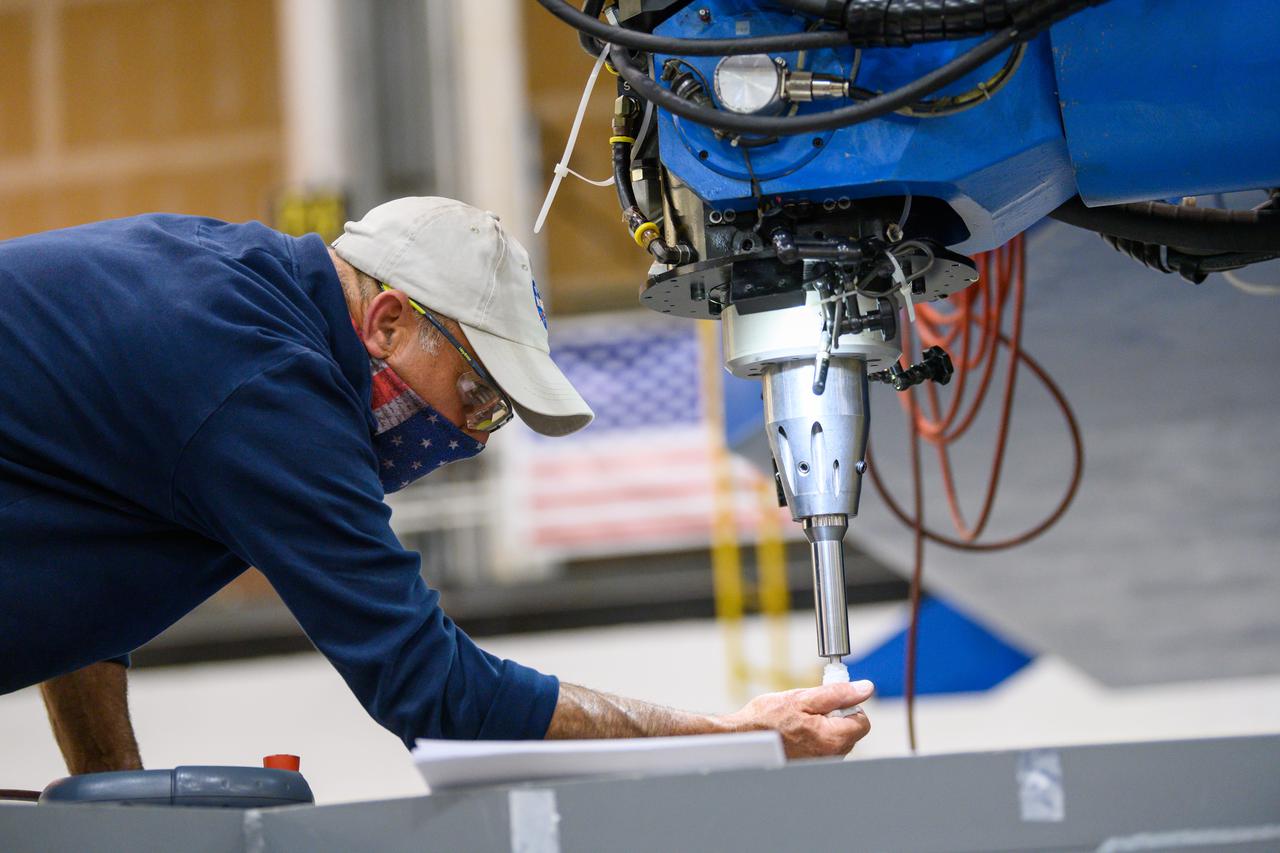
Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
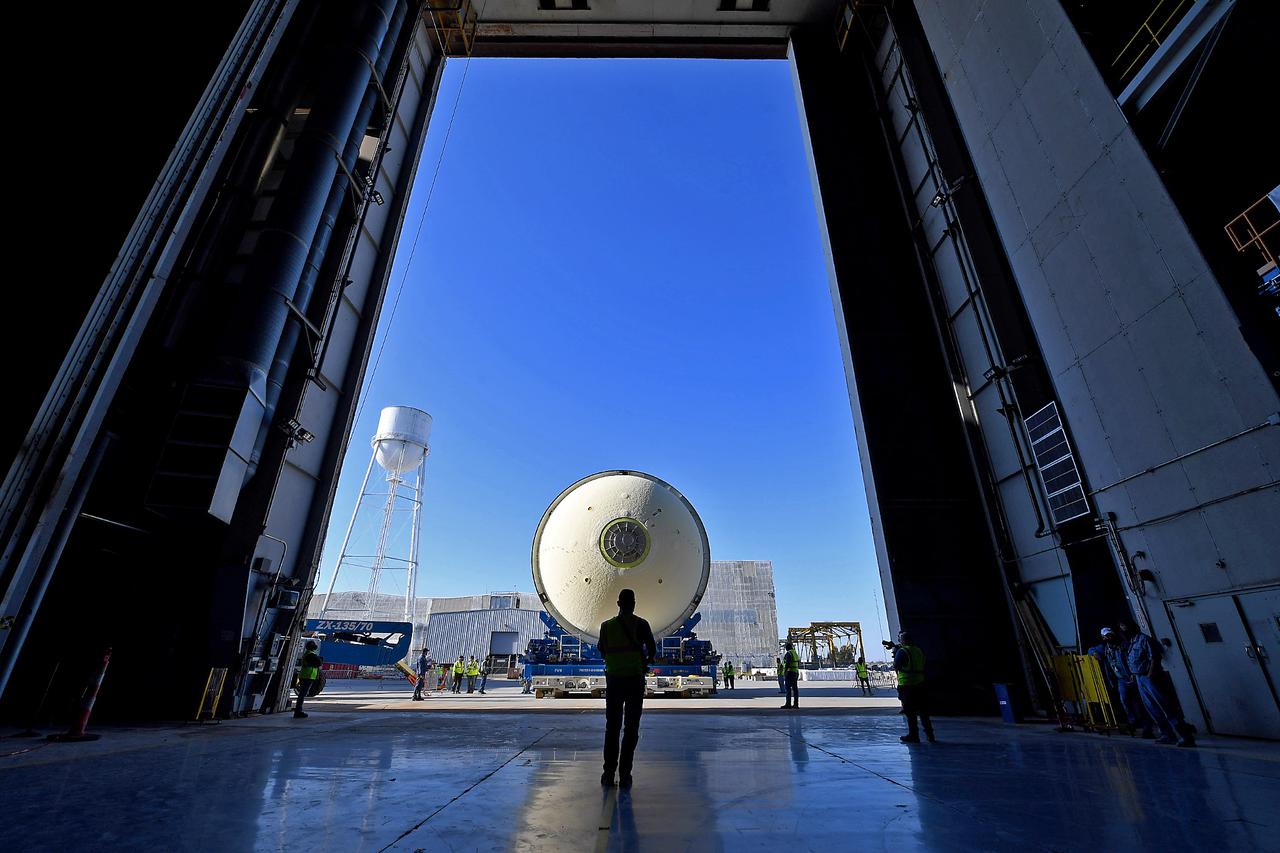

This image highlights the liquid oxygen tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’ Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of liquid oxygen cooled to minus 297 degrees Fahrenheit. The LOX hardware sits between the core stage’s forward skirt and the intertank. Along with the liquid hydrogen tank, it will provide fuel to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket can send astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
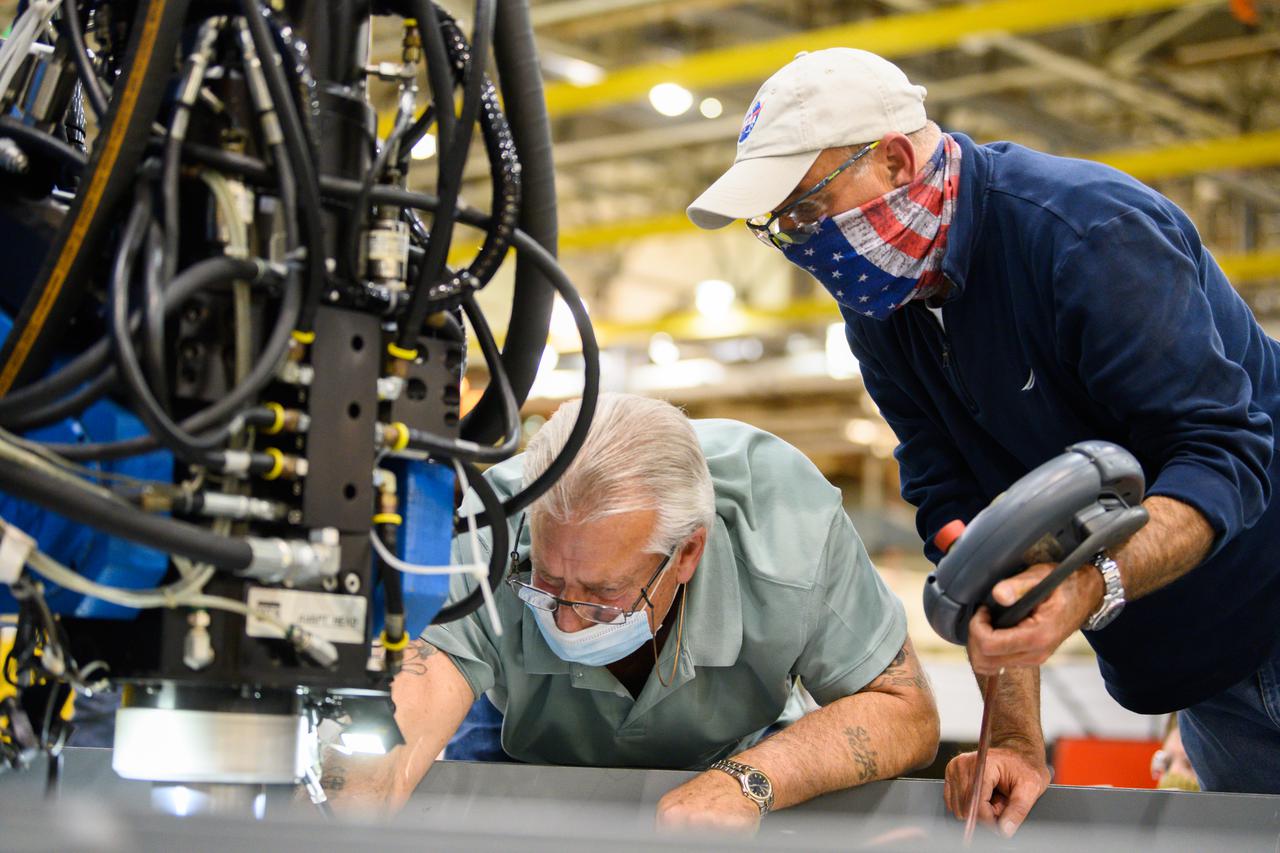

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
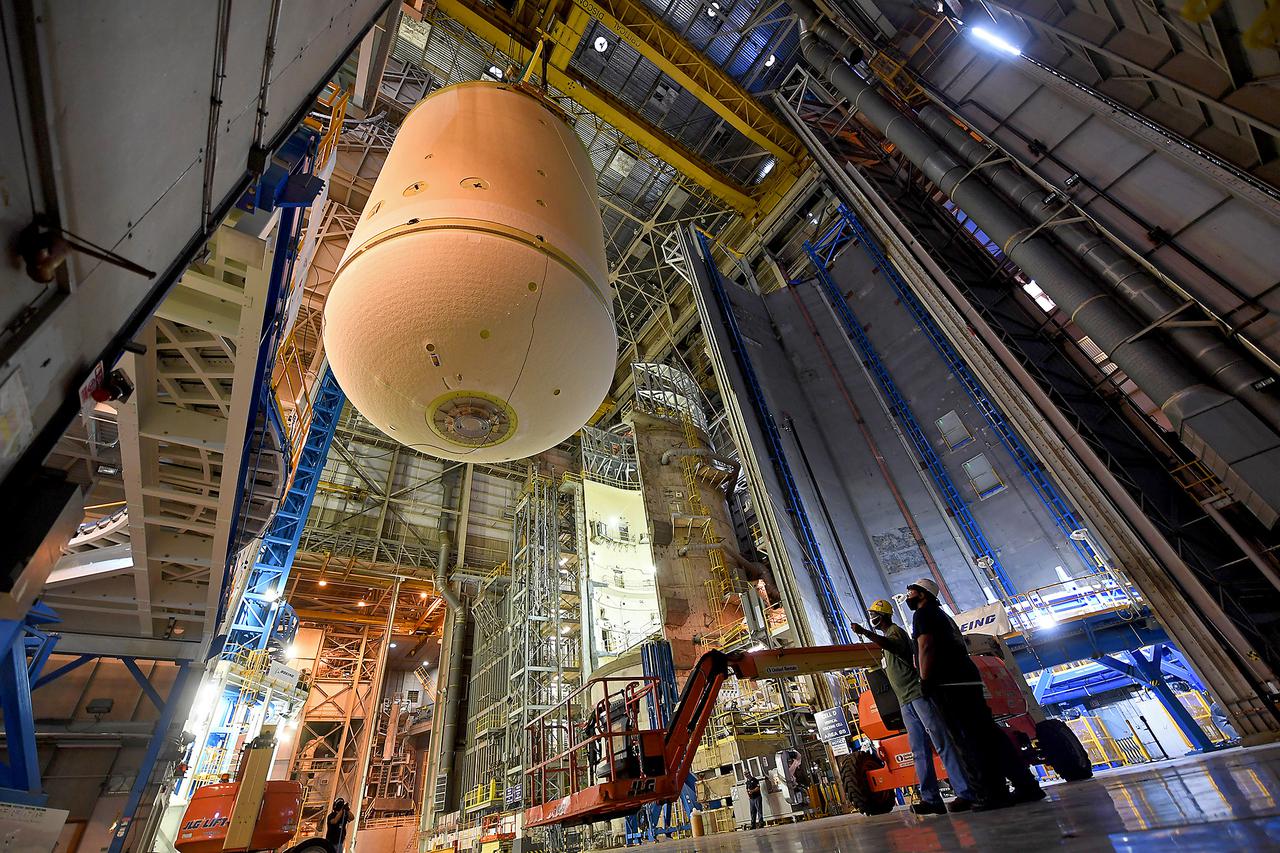

This image highlights the liquid oxygen tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’ Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of liquid oxygen cooled to minus 297 degrees Fahrenheit. The LOX hardware sits between the core stage’s forward skirt and the intertank. Along with the liquid hydrogen tank, it will provide fuel to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket can send astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
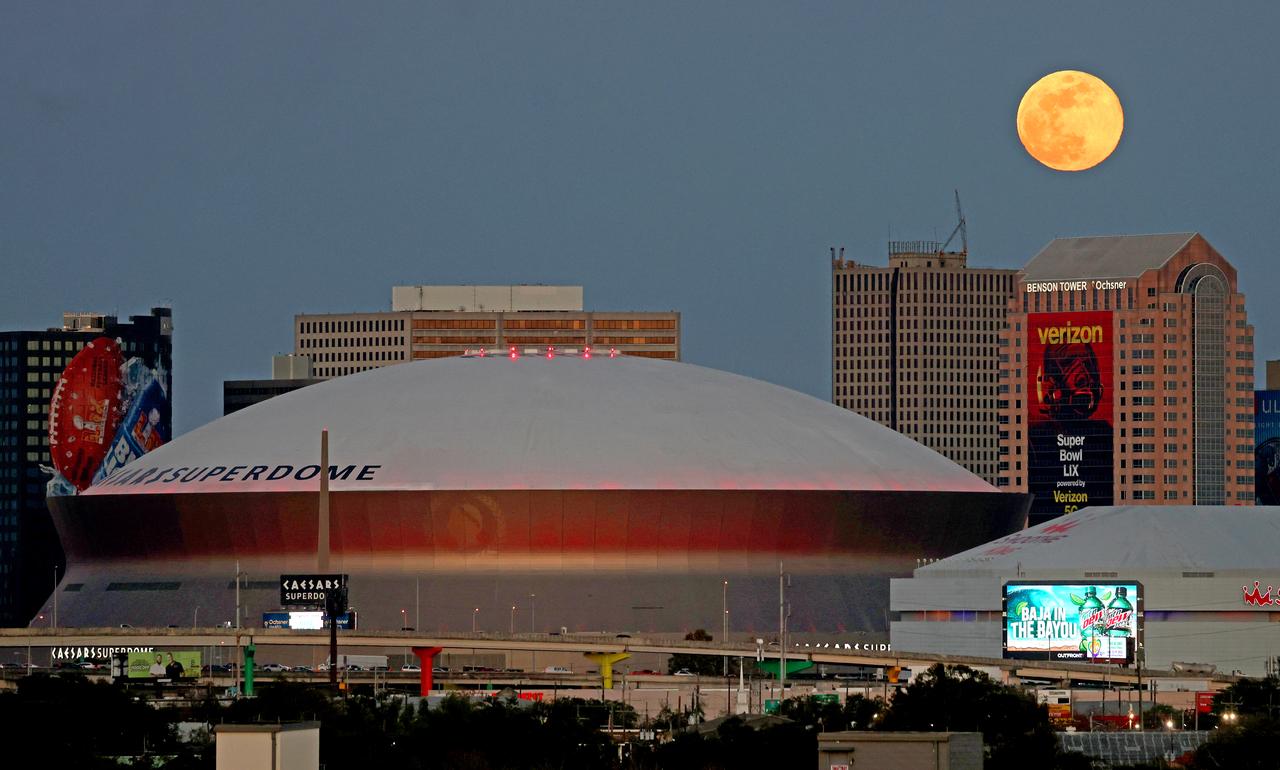

The full moon rises over the Superdome and the city of New Orleans, Louisiana on Monday evening, January 13, 2025. The Wolf Moon, also known as the Ice or Cold Moon, was full at 5:27 p.m. EST. New Orleans is home to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility where several pieces of hardware for the SLS (Space Launch system) are being built. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This image highlights the liquid hydrogen tank that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program. The tank is being built at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the cores stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the human landing system, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket can send astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
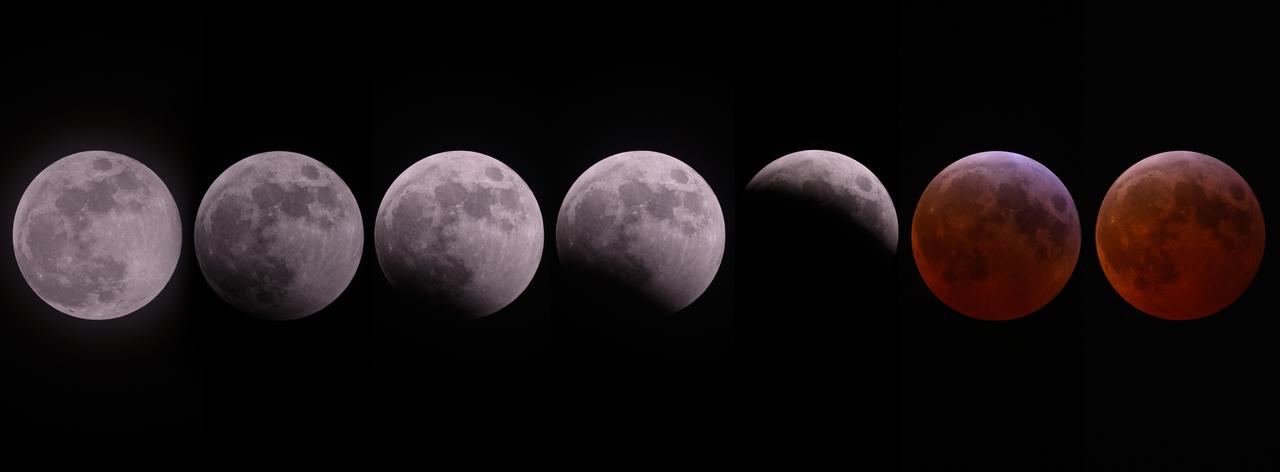

The blood Moon lunar eclipse over NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans is shown from the initial partial eclipse to totality in a composite of 7 images shot on Friday, March 14, 2025. Image credit: NASA/Eric Bordelon

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the third and fourth RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Technicians added the first engine to the SLS core stage Sept. 11. The second engine was installed onto the stage Sept. 15 with the third and fourth engines following Sept. 19 and Sept. 20. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will now focus efforts on the complex tax of fully securing the engines to the stage and integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

This image shows technicians and engineers move and connect the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) to the intertank as they continue the process of the forward join on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The forward join connects the forward skirt, the liquid oxygen tank (LOX) and the intertank structures to form the top part of the SLS rocket’s core stage. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

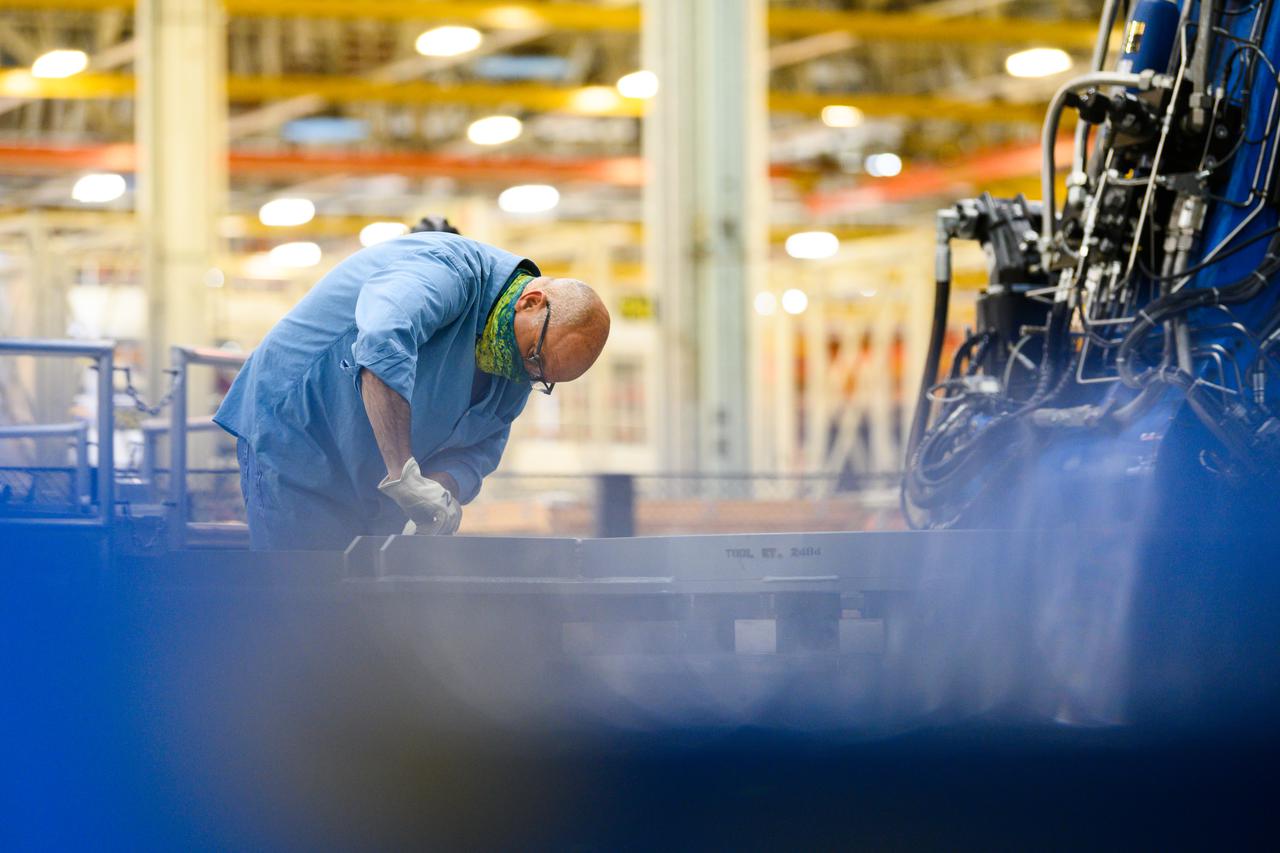
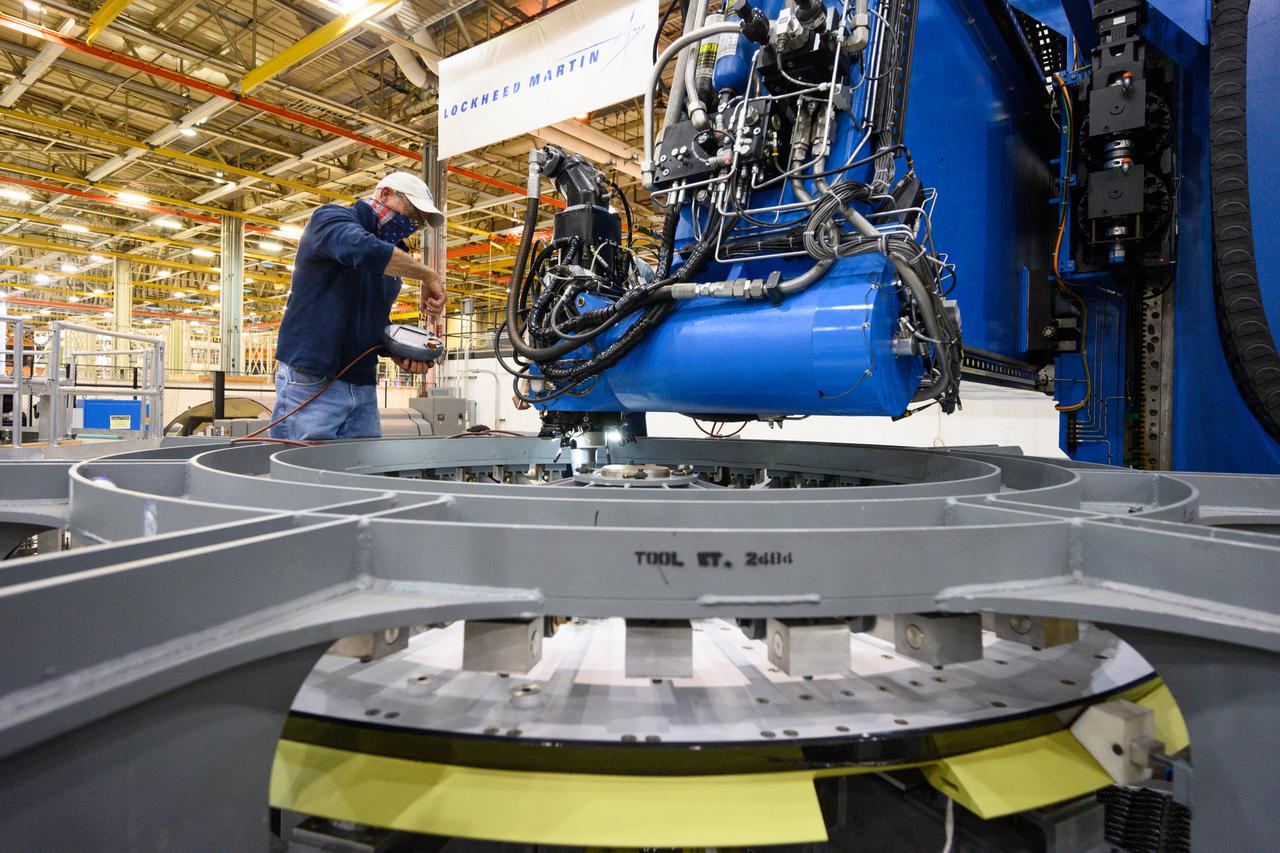
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.

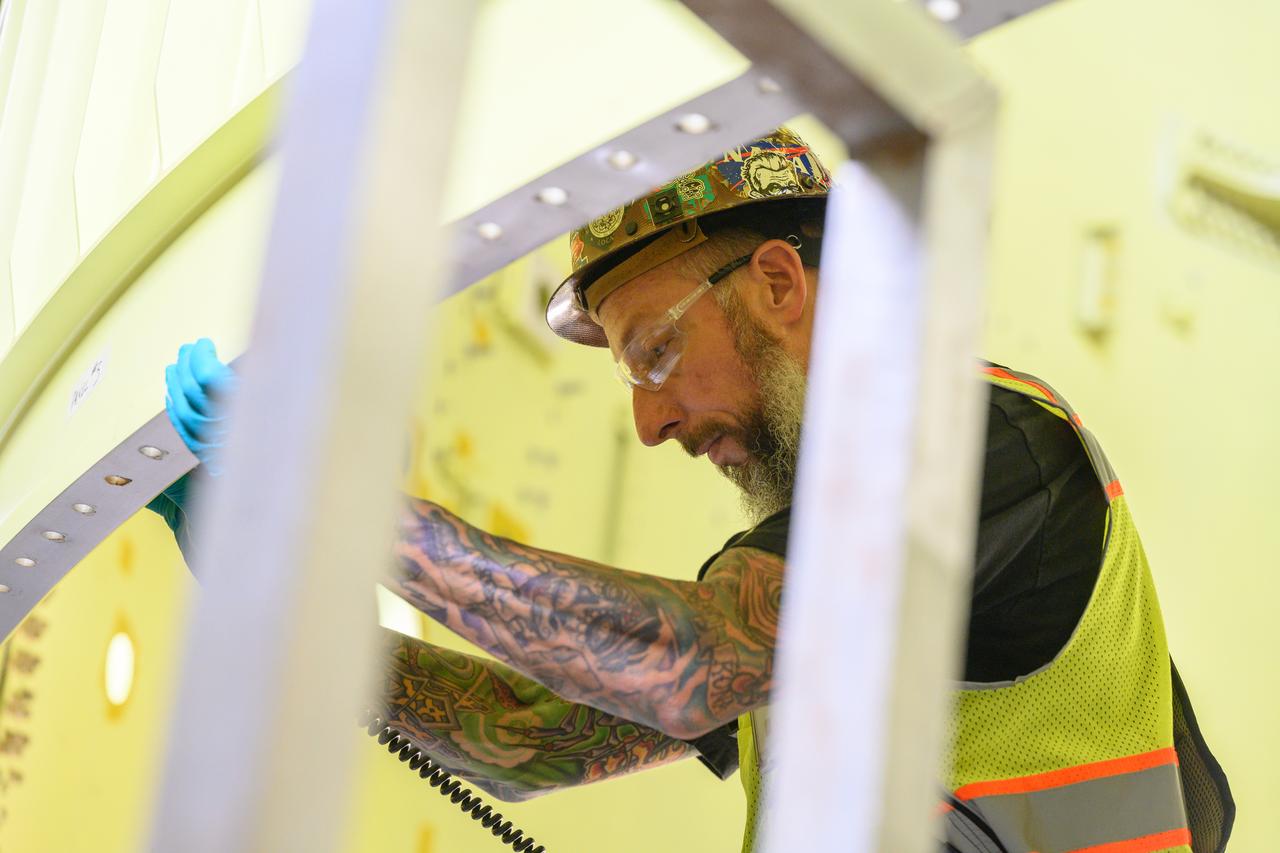
Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
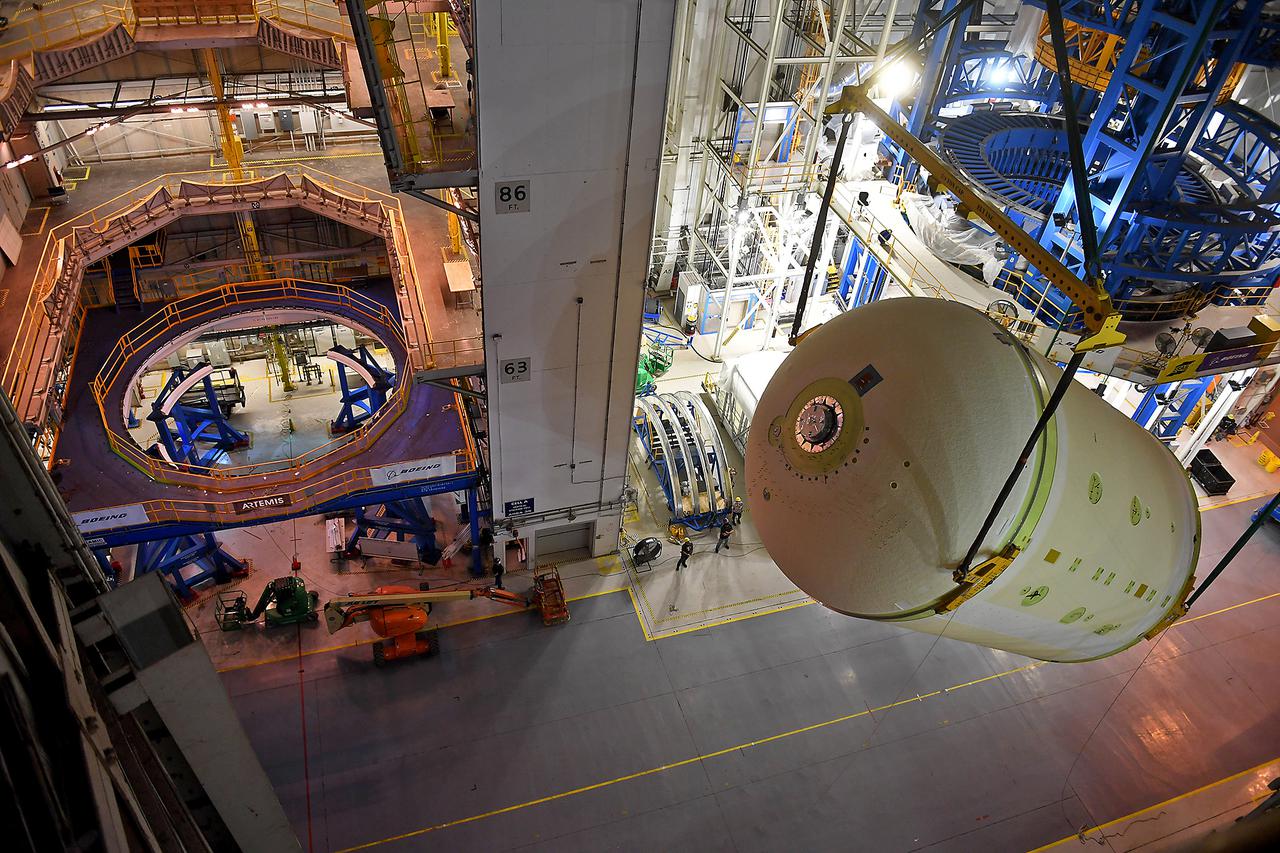

This image highlights the liquid oxygen tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’ Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of liquid oxygen cooled to minus 297 degrees Fahrenheit. The LOX hardware sits between the core stage’s forward skirt and the intertank. Along with the liquid hydrogen tank, it will provide fuel to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket can send astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
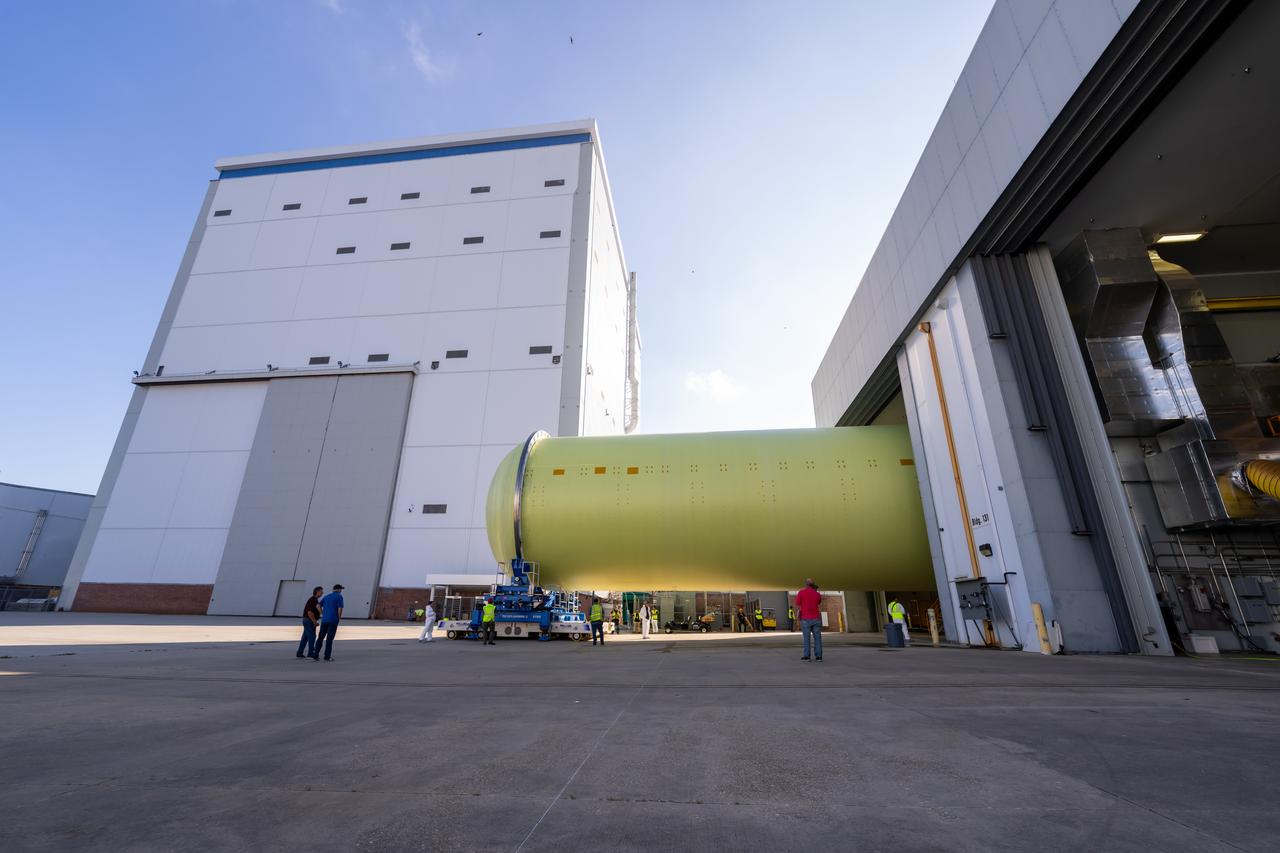

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.
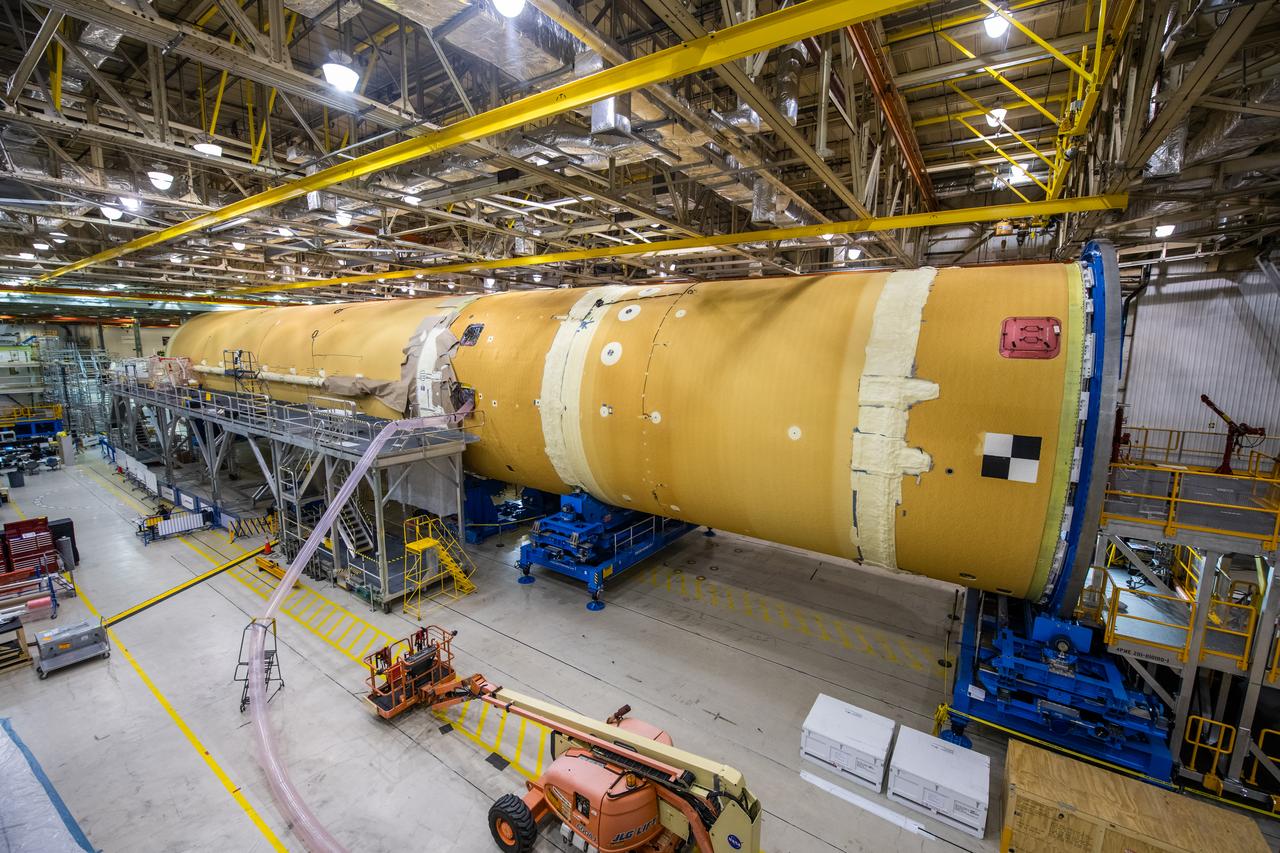

Space Launch System Corestage-1 (Artemis-1) in production at the Michoud Assembly Faclility in New Orleans.

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the third and fourth RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Technicians added the first engine to the SLS core stage Sept. 11. The second engine was installed onto the stage Sept. 15 with the third and fourth engines following Sept. 19 and Sept. 20. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will now focus efforts on the complex tax of fully securing the engines to the stage and integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
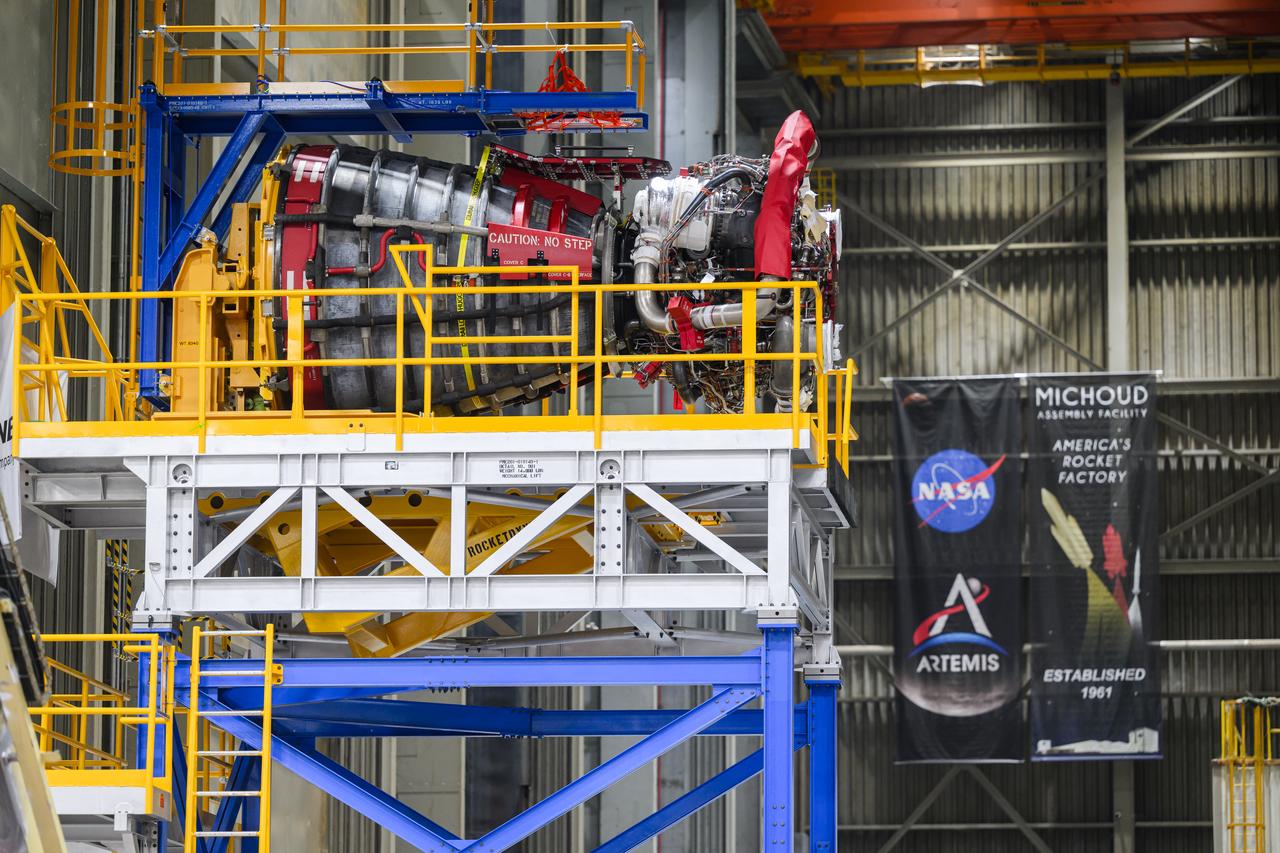

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
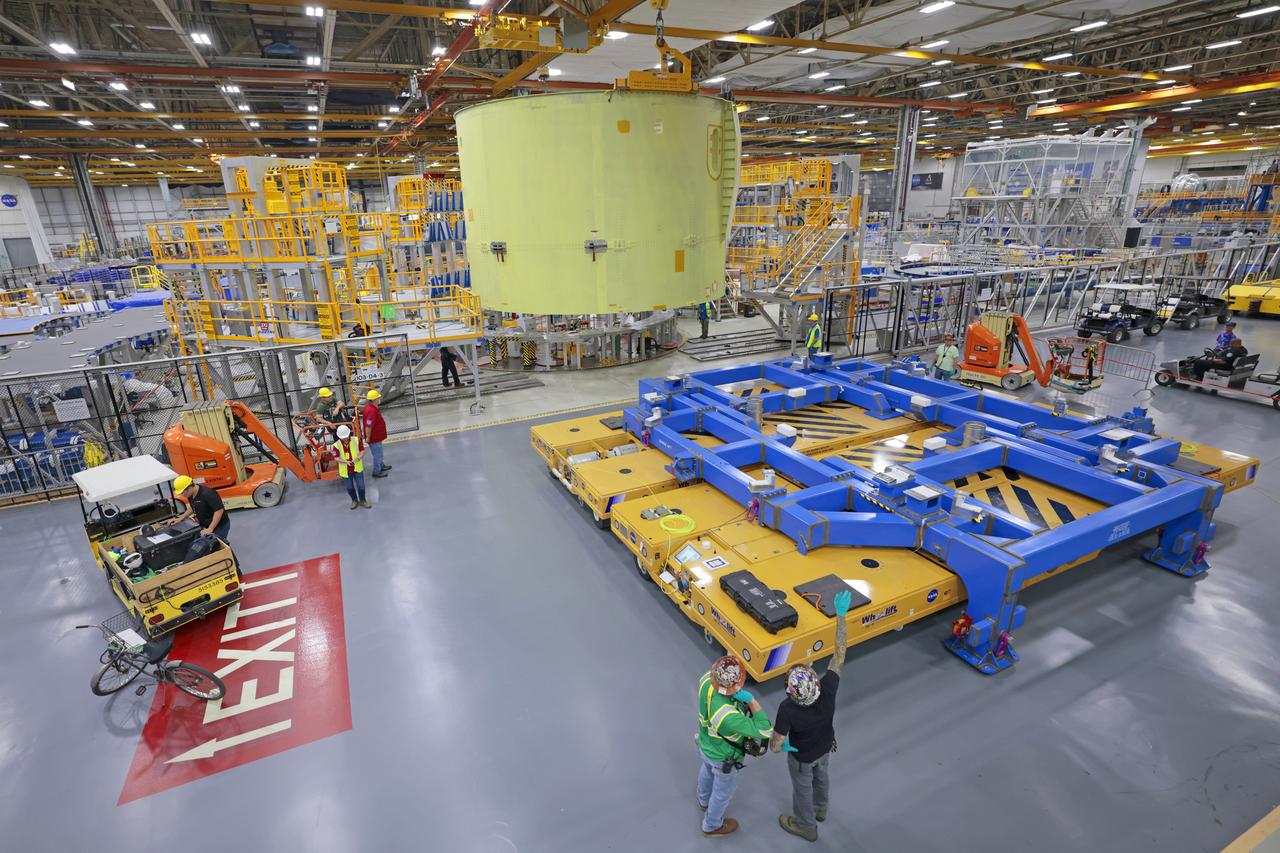

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
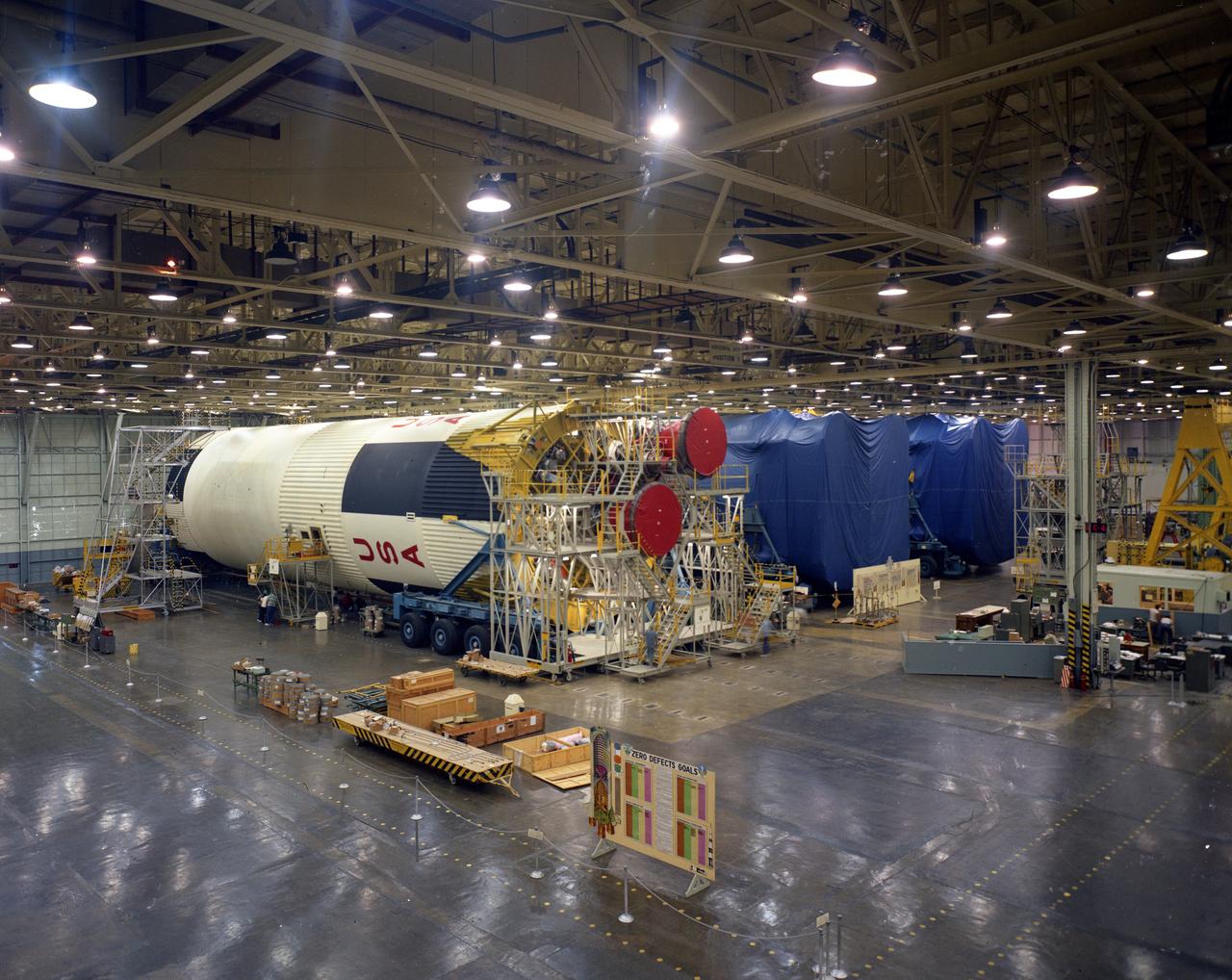

Saturn V S-1C boosters lined up in the Horizontal Assembly area of Michoud Assembly Facility. Image dated 10-5-1967.
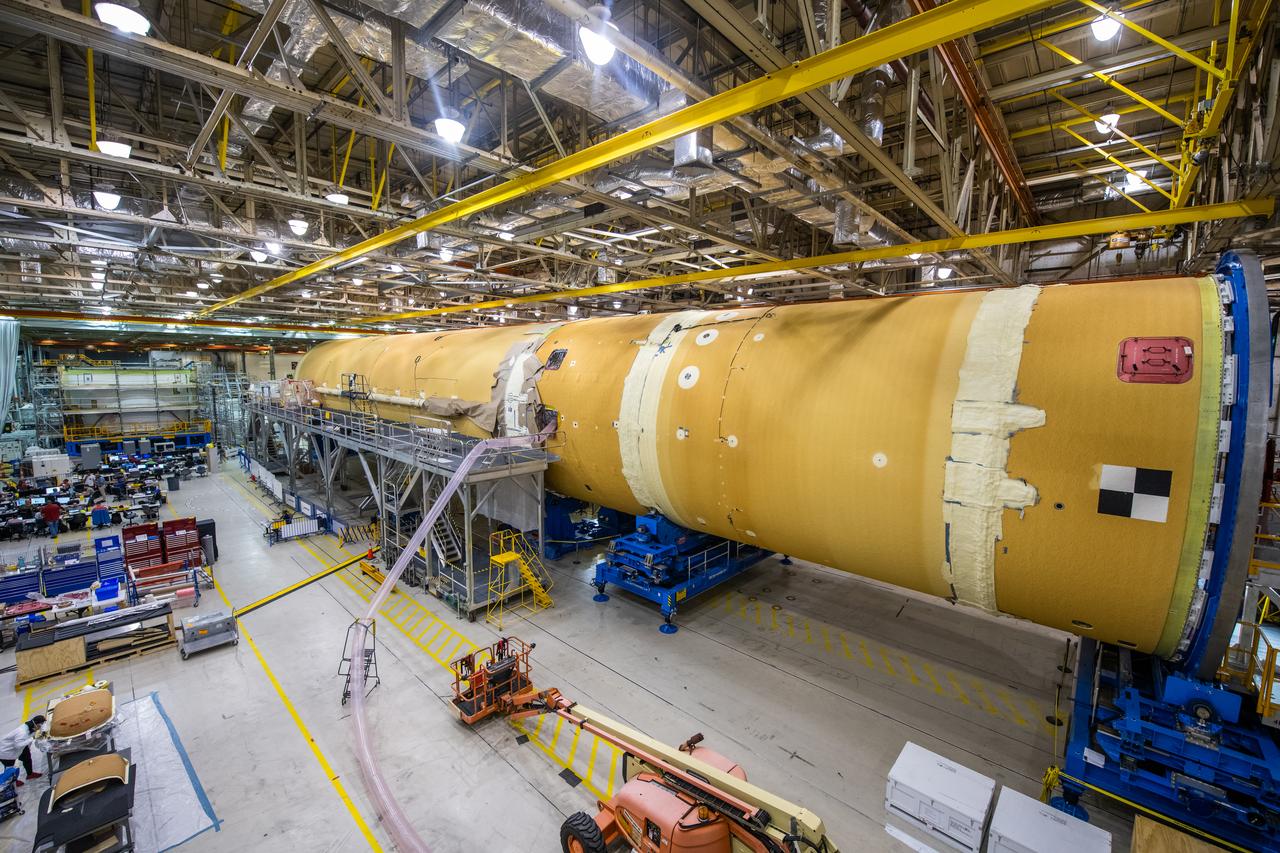

Space Launch System Corestage-1 (Artemis-1) in production at the Michoud Assembly Faclility in New Orleans.
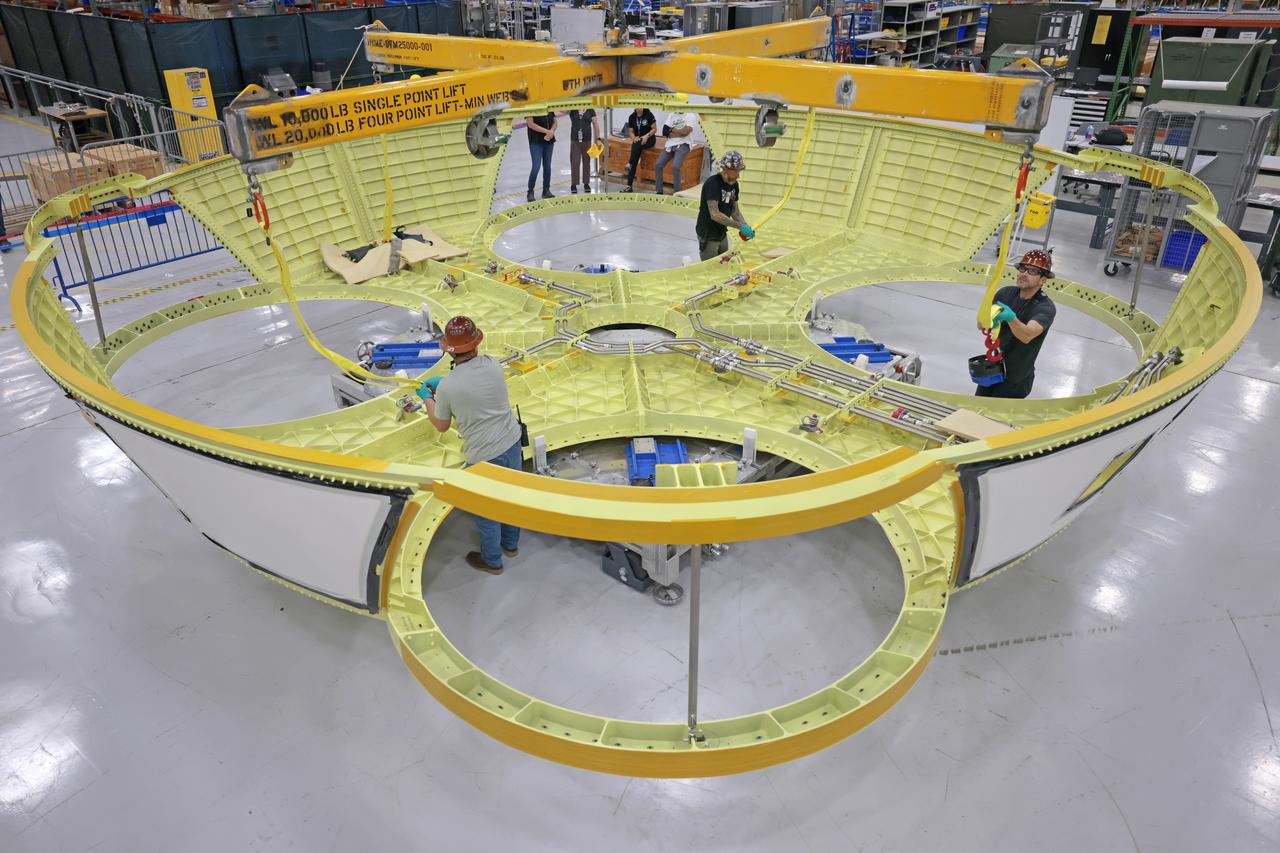

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
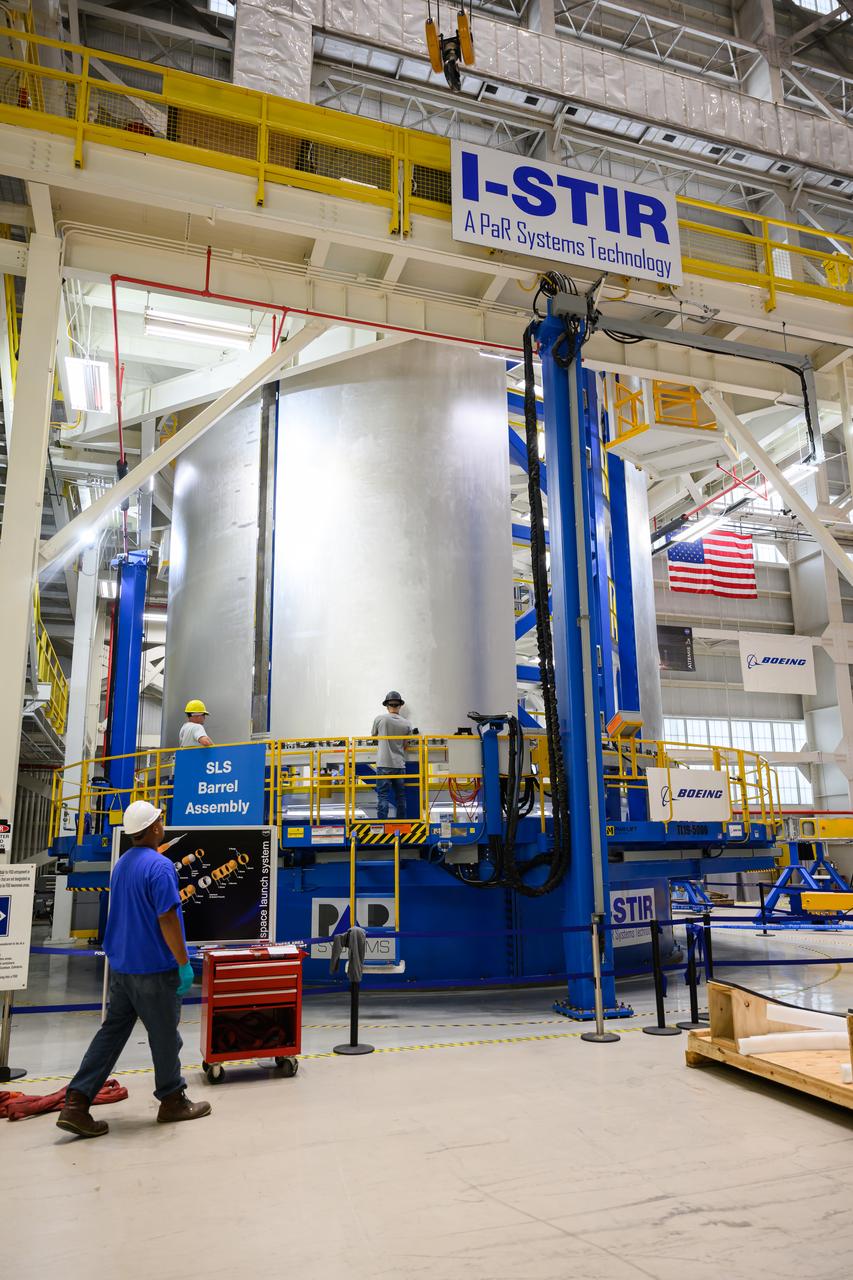

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans load alluminum alloy panels into the Vertical Weld Center June 1. The Vertical Weld Center is a friction-stir weld tool for the large structures of the core stage for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. Teams load the panels into the VWC using an overhead crane system, then multiple panels are welded together to create entire barrels. The panels in these images are some of the five barrels that will form the SLS liquid hydrogen propellant tank for the SLS rocket that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which is also the first flight of SLS in its more powerful Block 1B configuration. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid hydrogen propellant tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, provides propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis IV mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

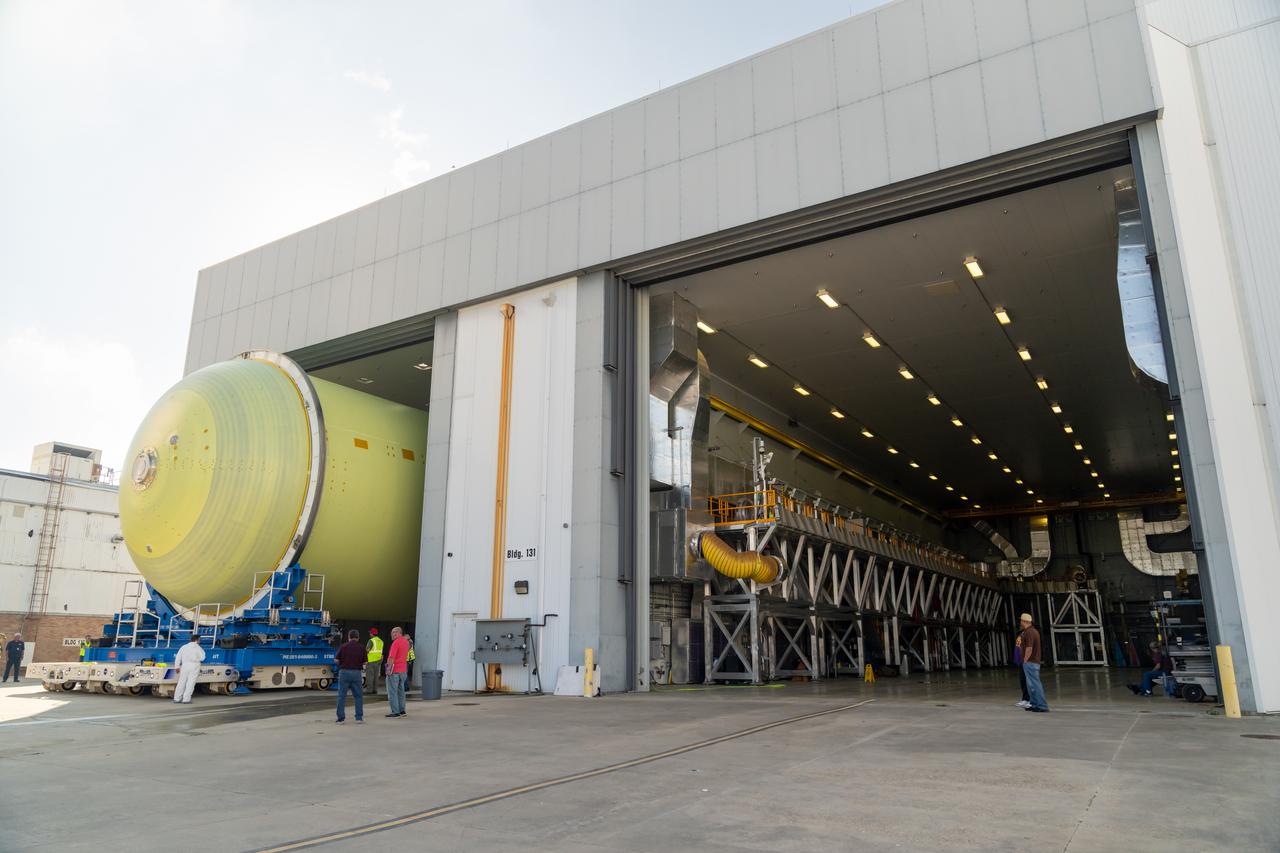
These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
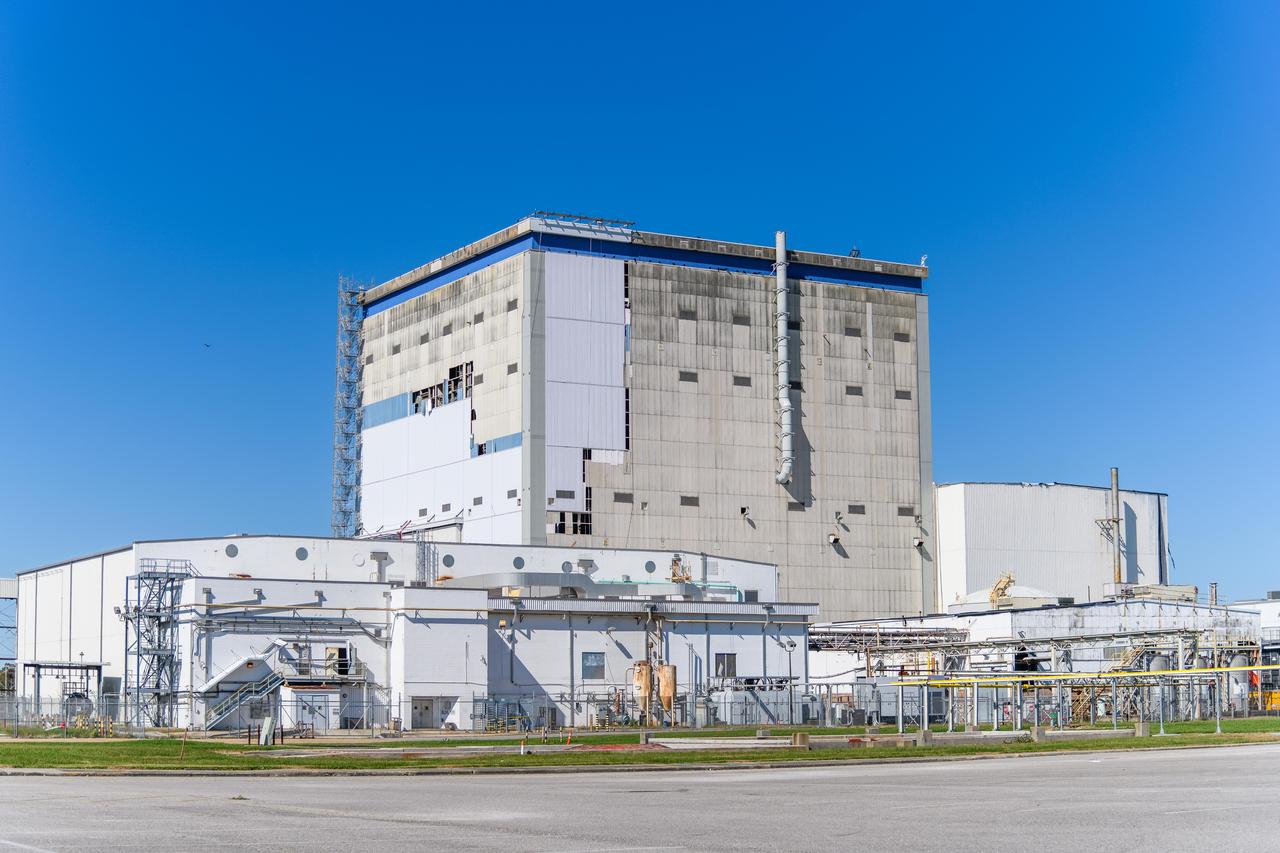

Hurricane Zeta damage to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility – South side of Bldg. 110 the Vertical Assembly Building (VAB).

Teams move a liquid hydrogen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a priming cell and into an adjacent cell on May 20 at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Inside the cell, the tank, which will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Artemis III mission, will receive its thermal protection system. The thermal protection system, or spray-on foam insulation, provides protection to the core stage during launch. It is flexible enough to move with the rocket yet can withstand the aerodynamic pressures as the SLS accelerates from 0 to 17,500 mph and soars to more than 100 miles above the Earth. This third-generation insulation is more environmentally friendly and keeps the cryogenic propellant, which powers the rocket’s four RS-25 engines, extremely cold (the liquid hydrogen must remain at minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit/253 degrees Celsius) to remain in its liquid state. When applied the thermal protection system is a light-yellow color, which “tans” once exposed to the Sun’s ultraviolet rays, giving the SLS core stage its signature orange color.

This image highlights the liquid hydrogen tank that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program. The tank is being built at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the cores stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the human landing system, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket can send astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
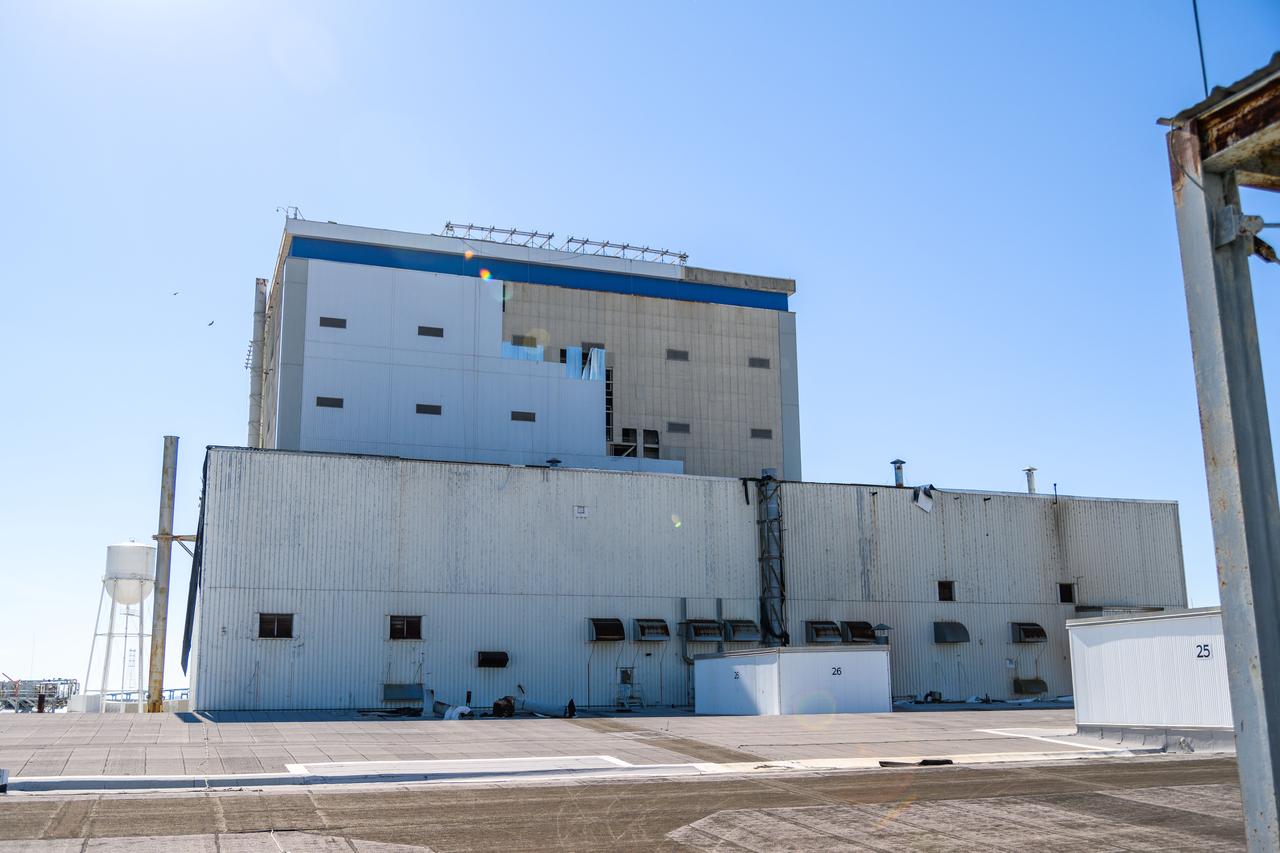

Hurricane Zeta damage to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility – East side of Bldg. 110 the Vertical Assembly Building (VAB).
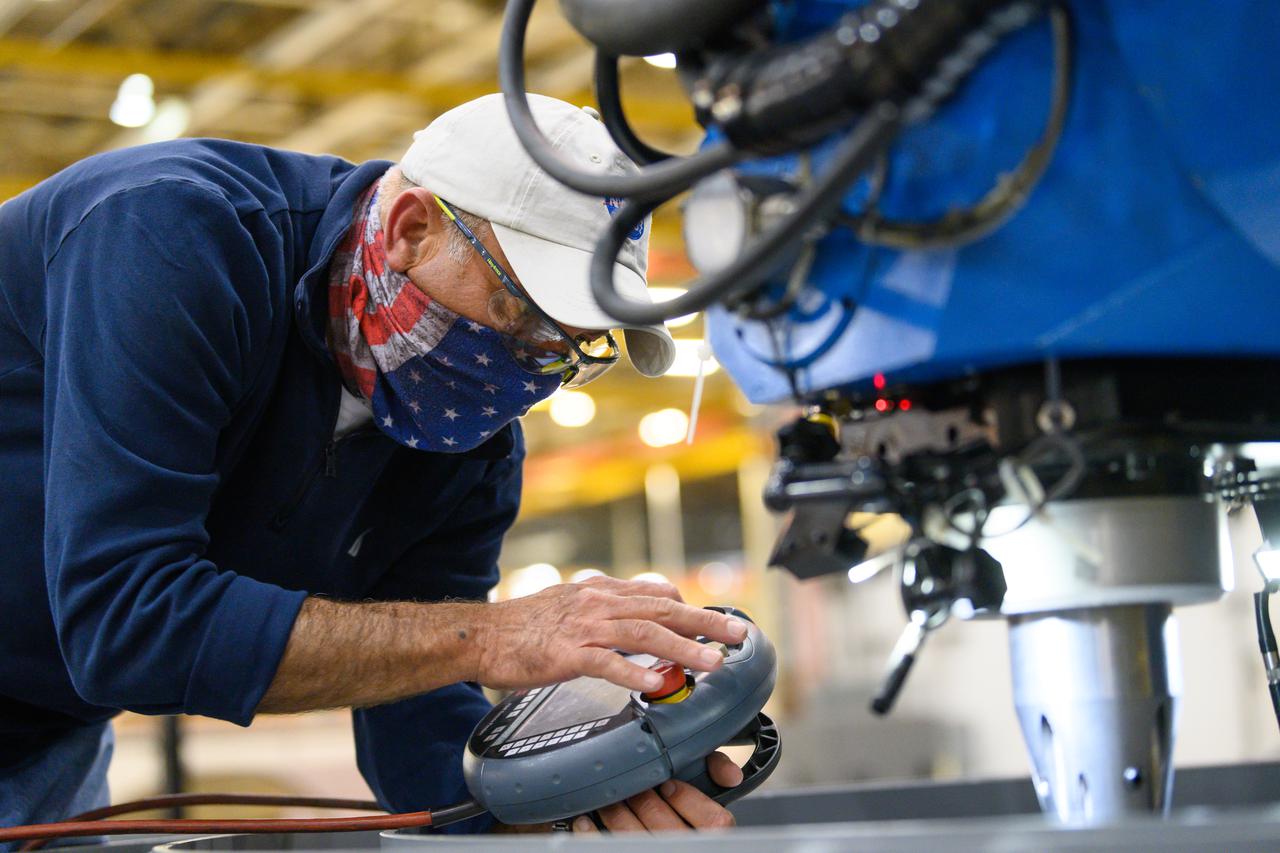

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
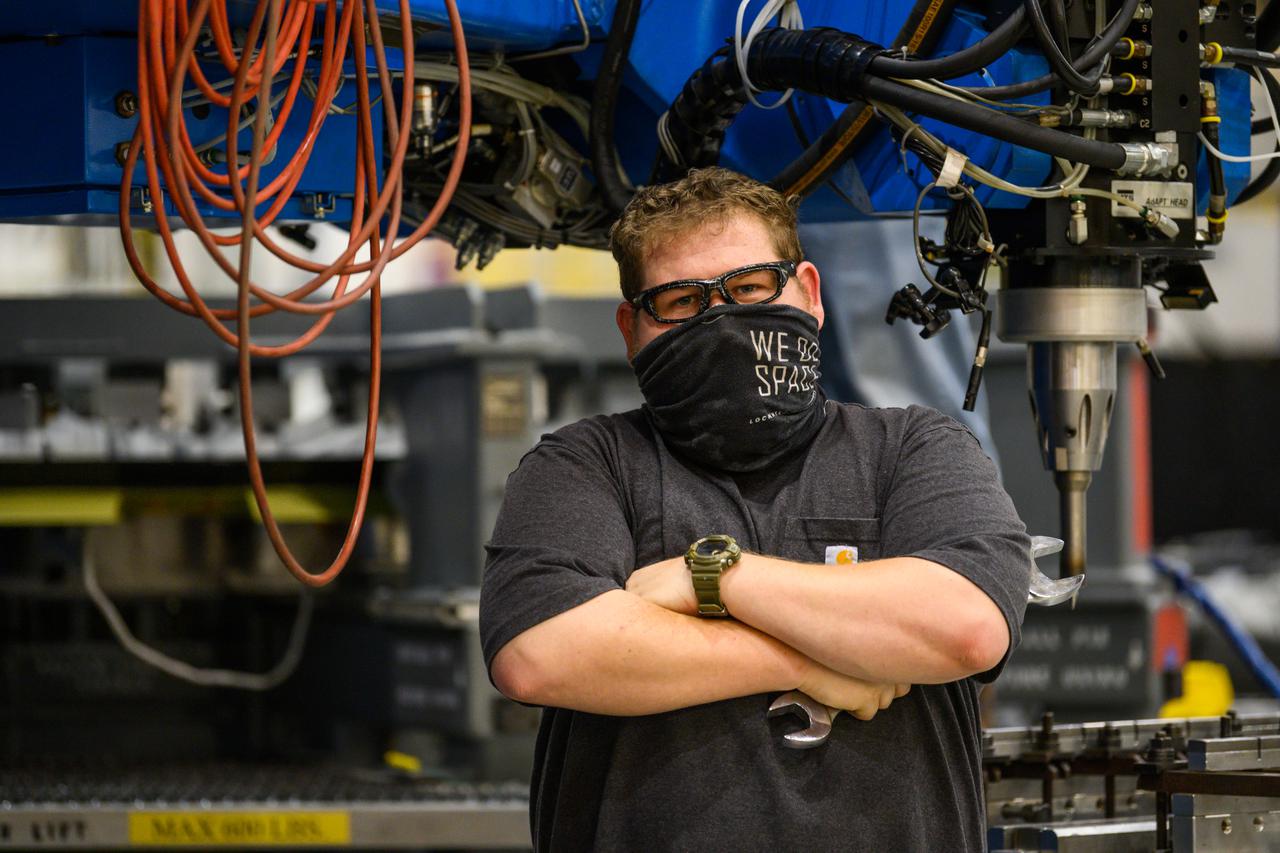

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
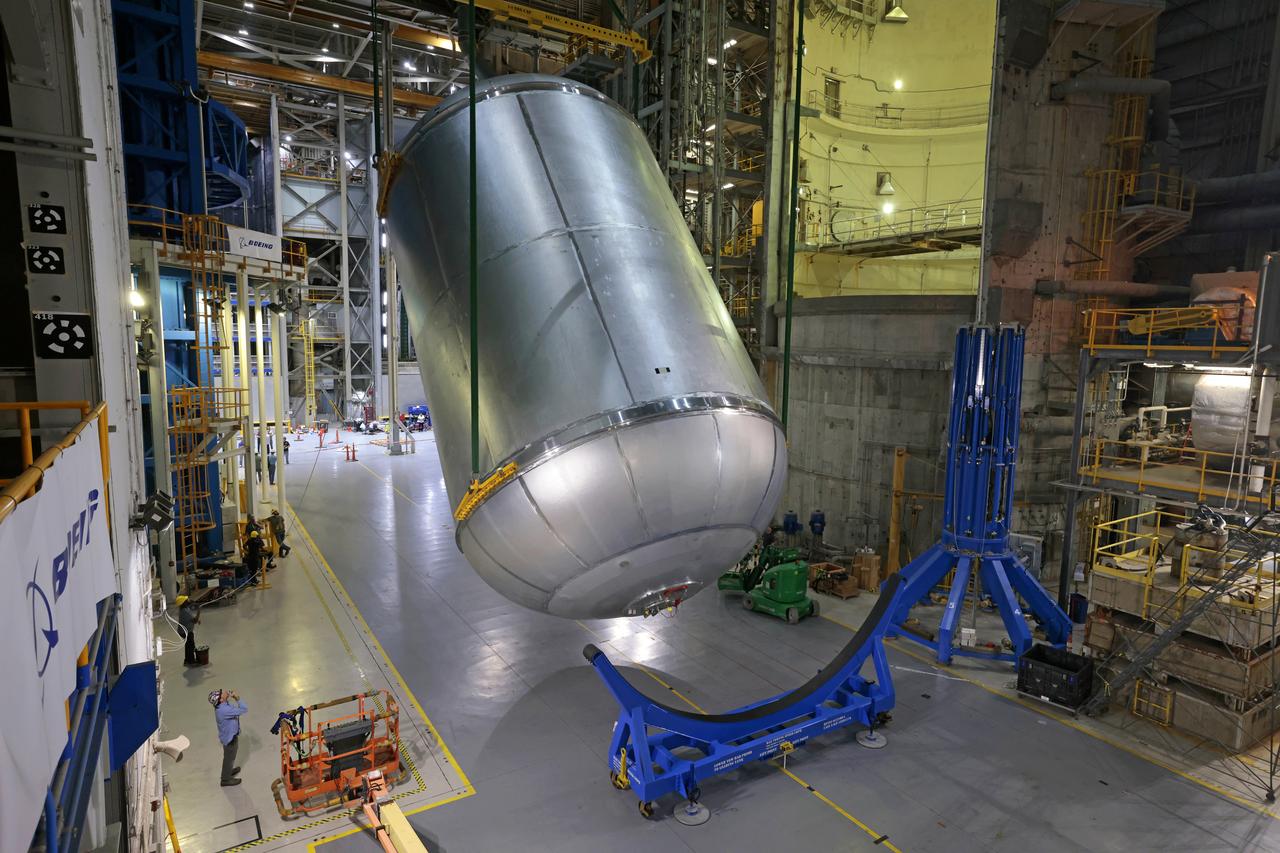

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans successfully completed hydrostatic proof testing of the core stage liquid oxygen tank for the agency’s Artemis III mission. The non-destructive evaluation method tests the structural integrity of the tank’s welds by filling the tank with water, simulating the propellant used during launch. The hardware was then moved to an adjacent cell for internal cleaning. Next, the tank will be readied for primer and application of its thermal protection system. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the third and fourth RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Technicians added the first engine to the SLS core stage Sept. 11. The second engine was installed onto the stage Sept. 15 with the third and fourth engines following Sept. 19 and Sept. 20. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will now focus efforts on the complex tax of fully securing the engines to the stage and integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
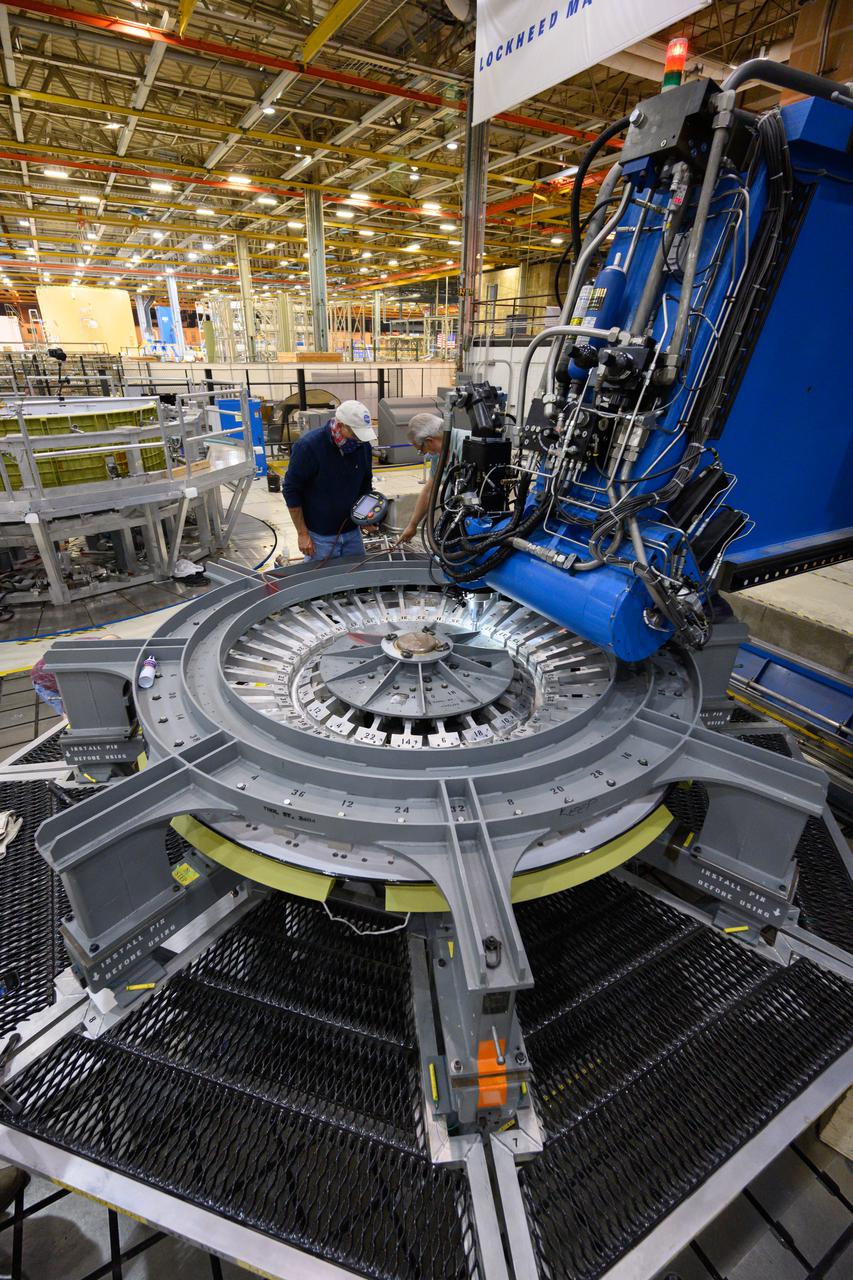

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
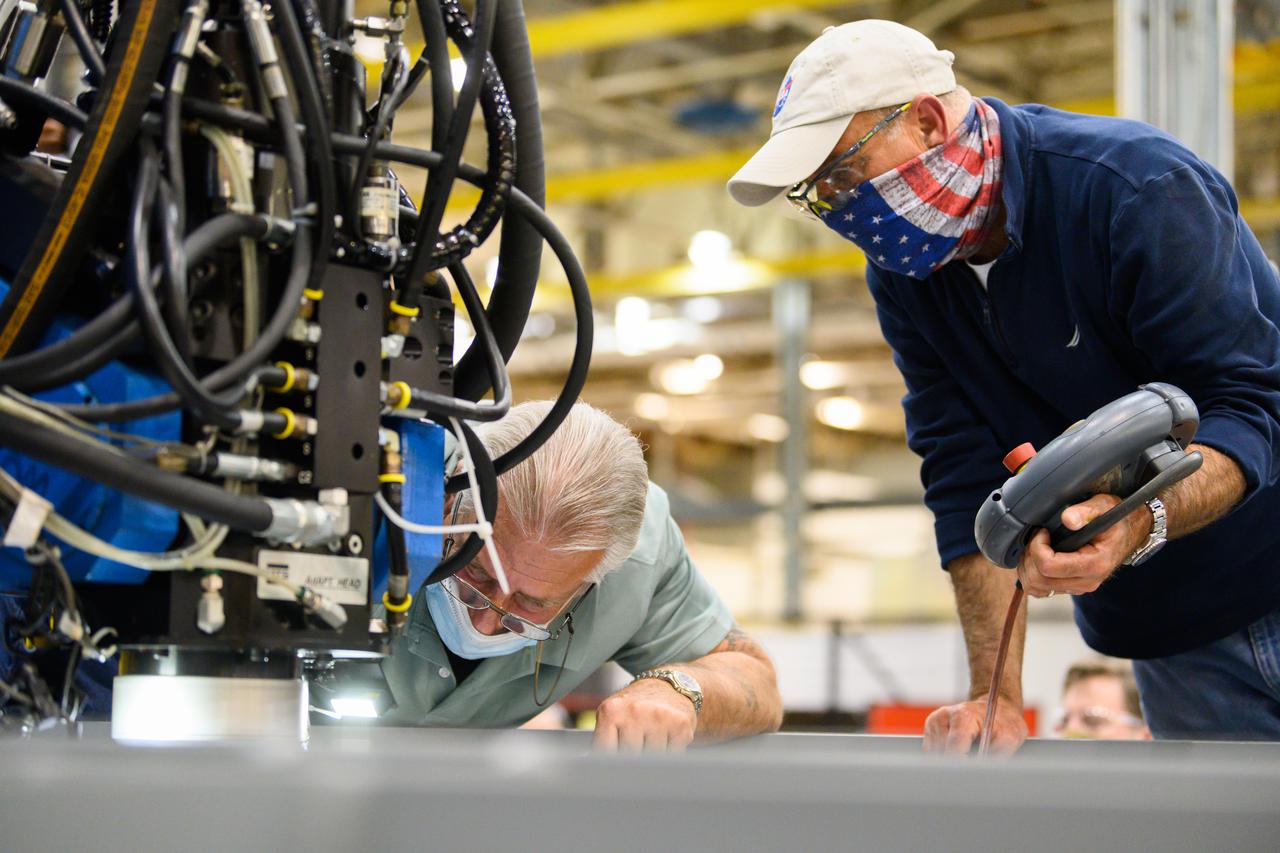

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
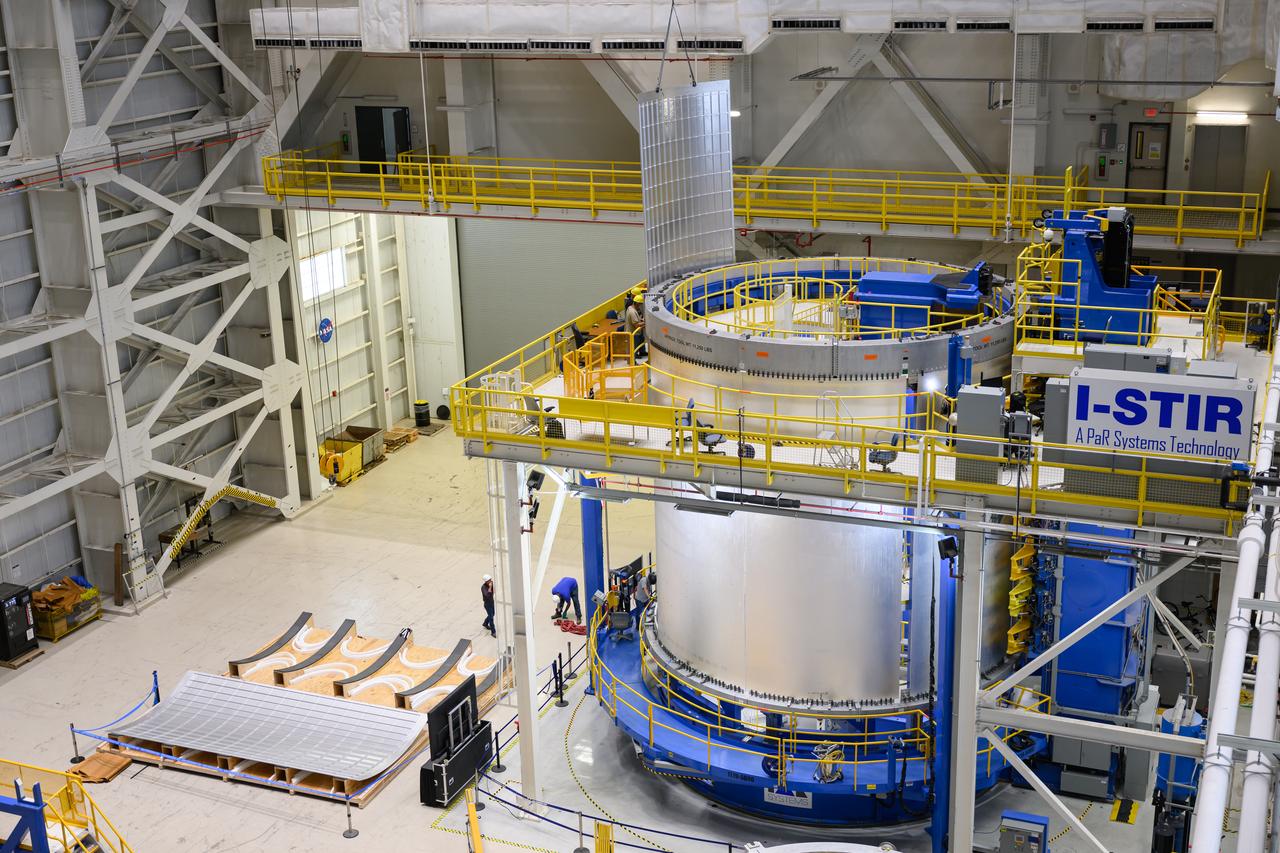

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans load alluminum alloy panels into the Vertical Weld Center June 1. The Vertical Weld Center is a friction-stir weld tool for the large structures of the core stage for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. Teams load the panels into the VWC using an overhead crane system, then multiple panels are welded together to create entire barrels. The panels in these images are some of the five barrels that will form the SLS liquid hydrogen propellant tank for the SLS rocket that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which is also the first flight of SLS in its more powerful Block 1B configuration. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid hydrogen propellant tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 432 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, provides propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the core stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch the Artemis IV mission to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
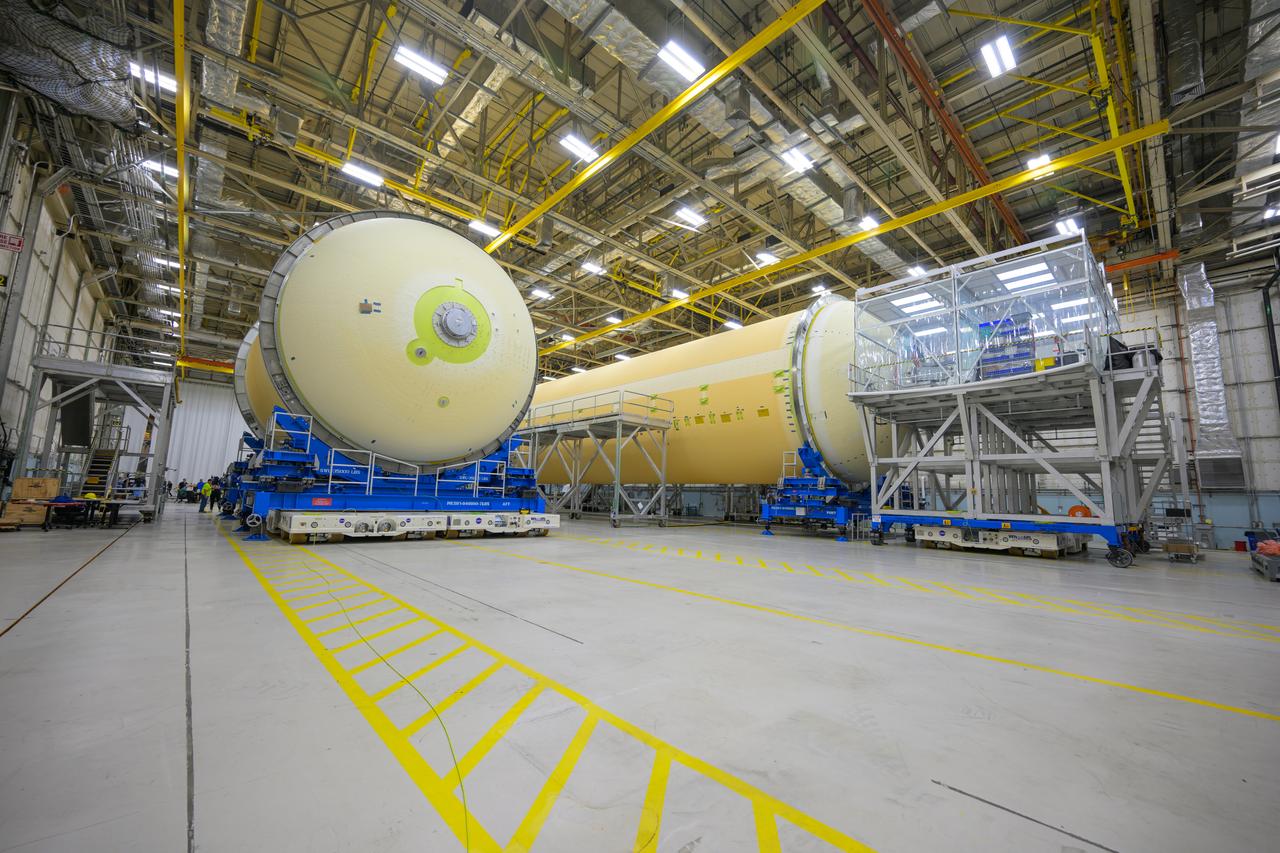

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid oxygen tank into final assembly production area on Aug. 27, 2025. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor,Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
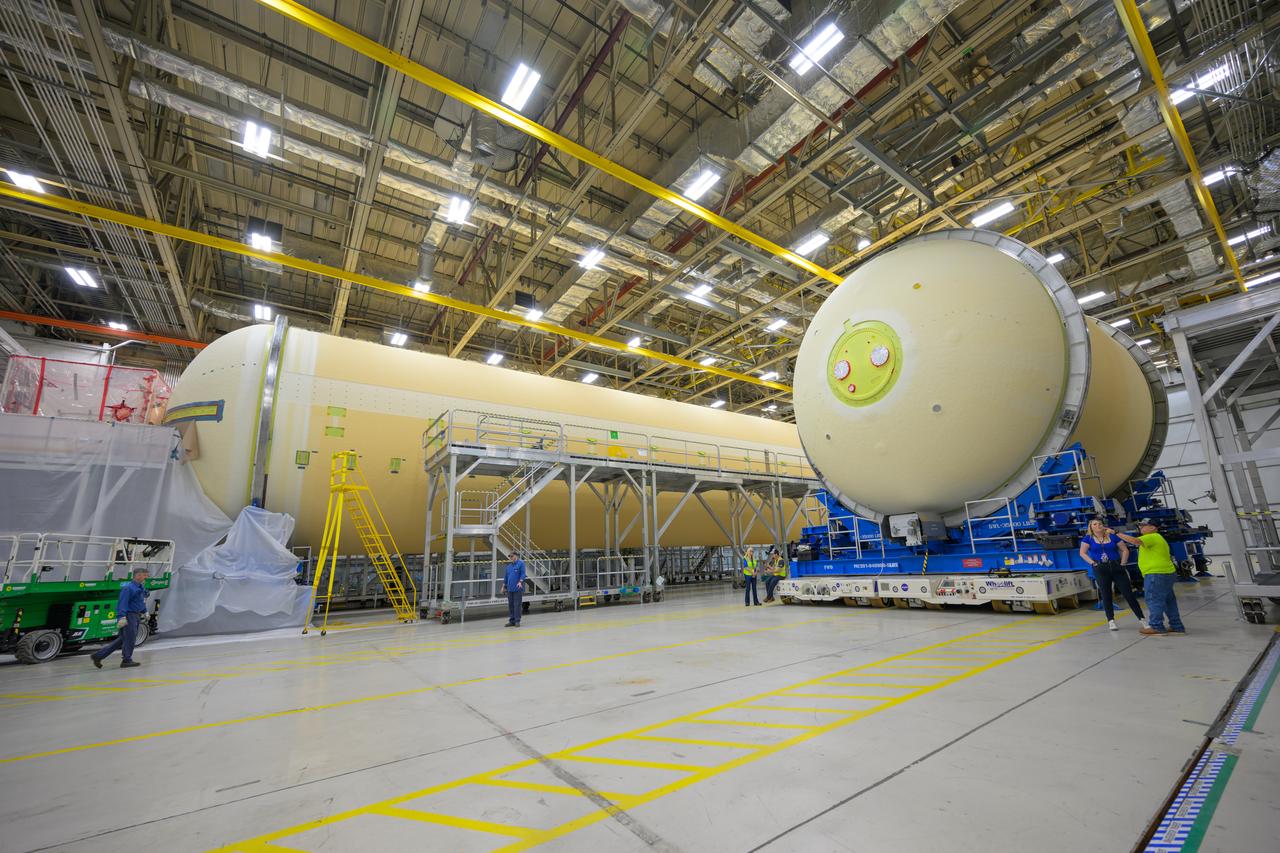

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid oxygen tank into final assembly production area on Aug. 27, 2025. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
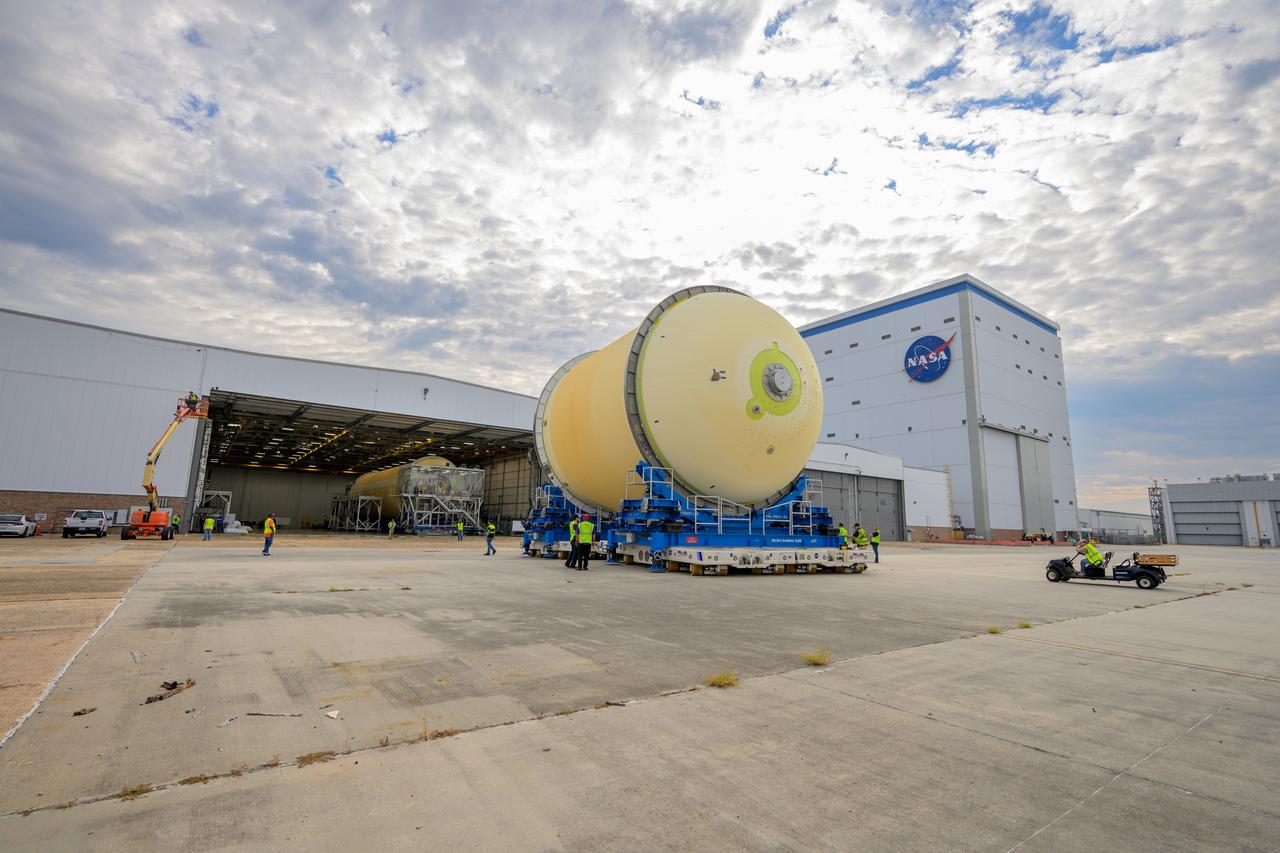

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid oxygen tank into final assembly production area on Aug. 27, 2025. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
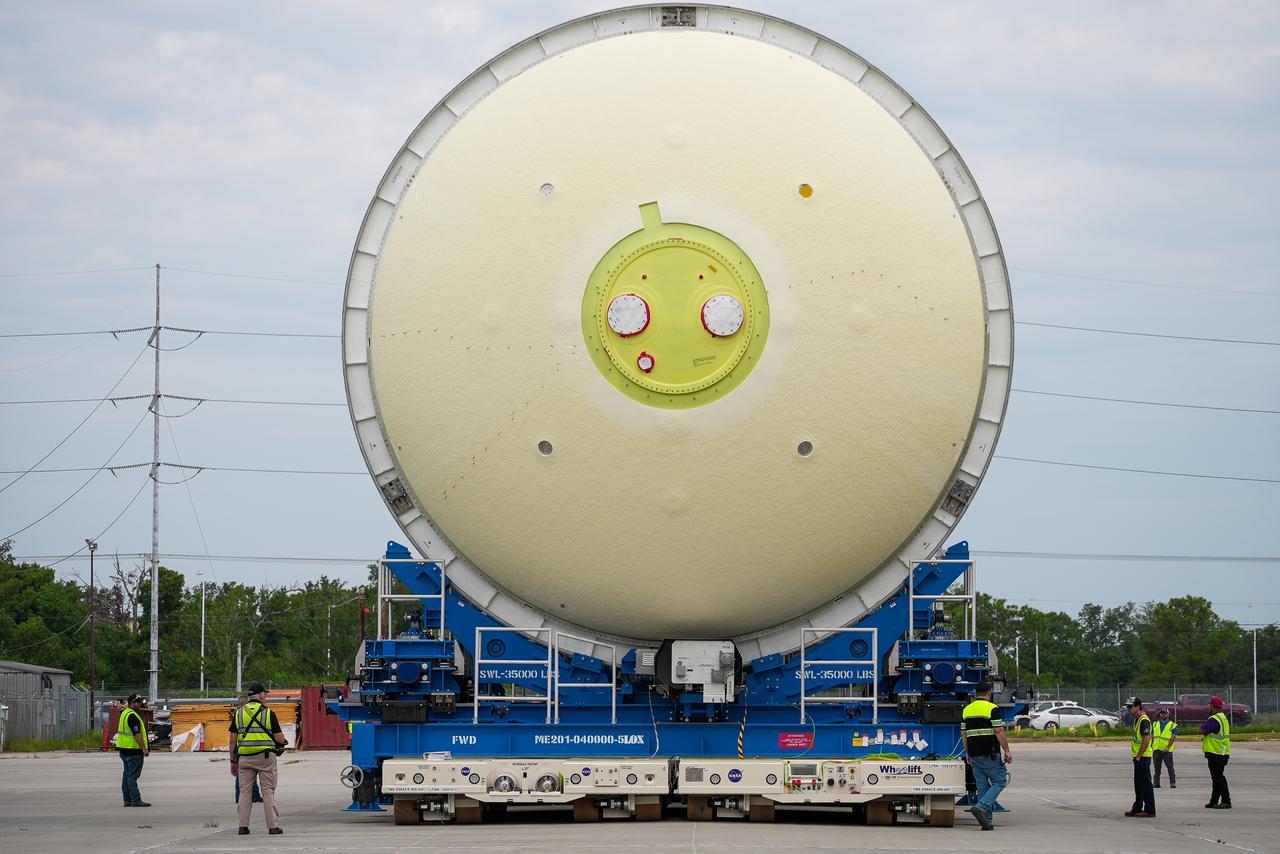

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid oxygen tank into final assembly production area on Aug. 27, 2025. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
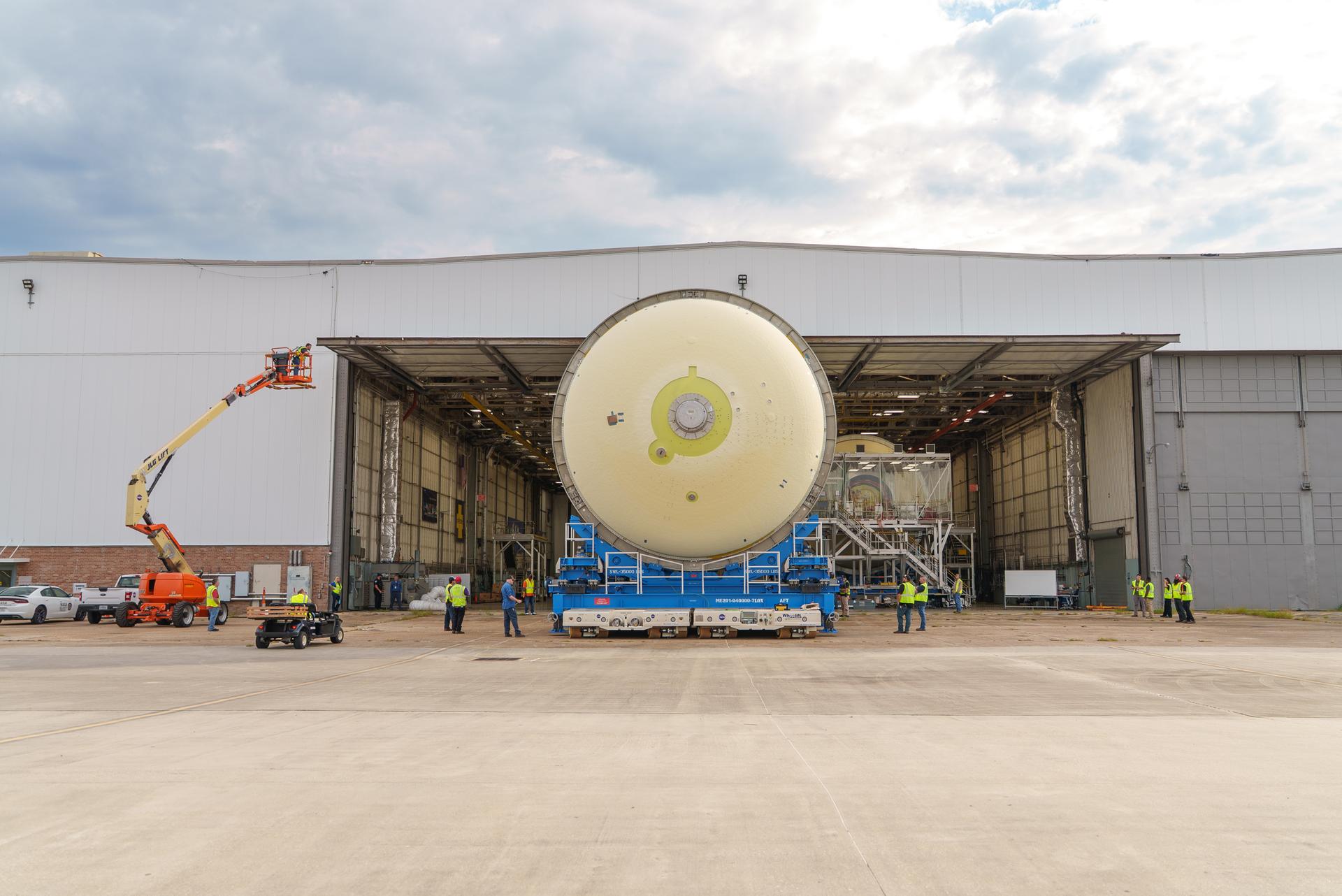

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the liquid oxygen tank into final assembly production area on Aug. 27, 2025. There, it will undergo integration of the forward dome by SLS (Space Launch System) prime contractor, Boeing. Eventually, the liquid oxygen tank will be moved back to the high bay where it will be mated with the intertank and forward skirt to complete the forward join of the Artemis III core stage. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
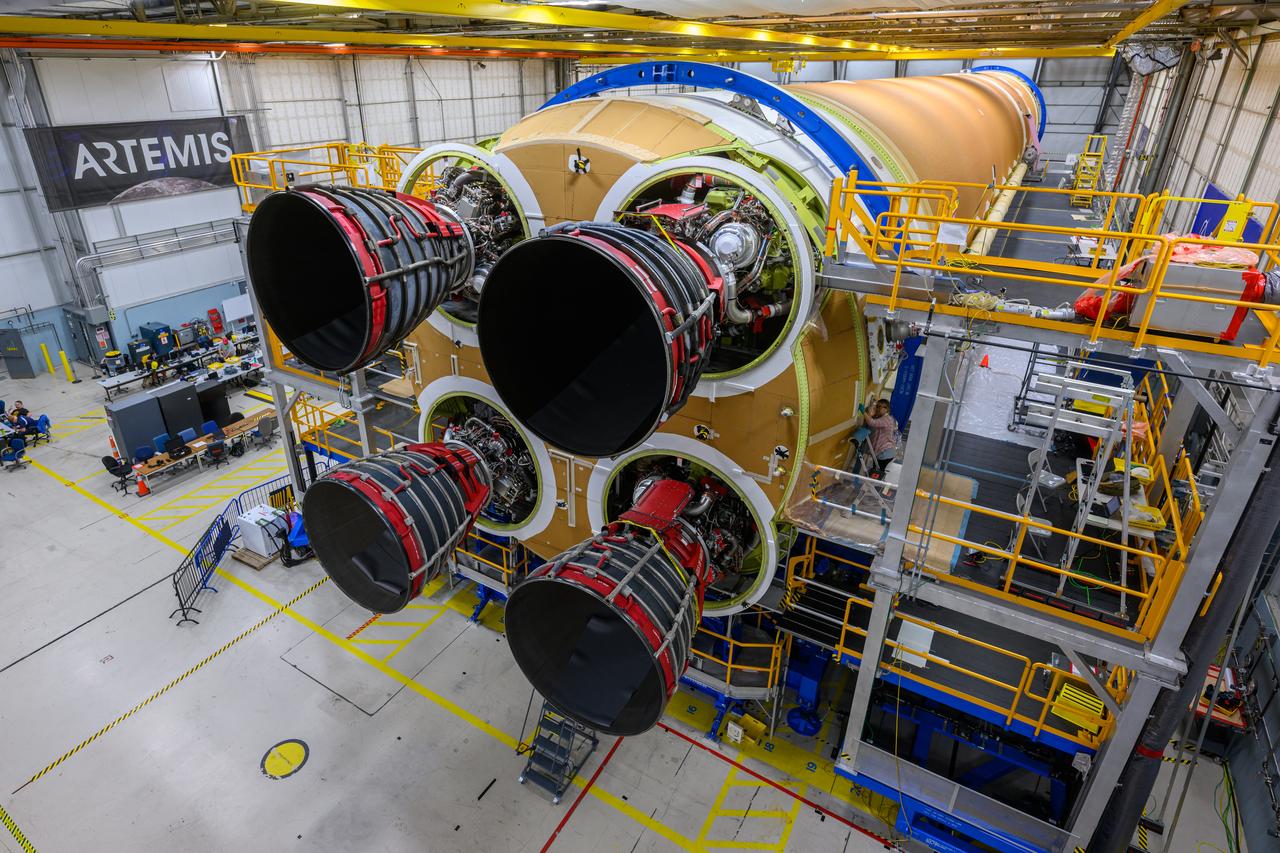
These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the third and fourth RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Technicians added the first engine to the SLS core stage Sept. 11. The second engine was installed onto the stage Sept. 15 with the third and fourth engines following Sept. 19 and Sept. 20. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will now focus efforts on the complex tax of fully securing the engines to the stage and integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
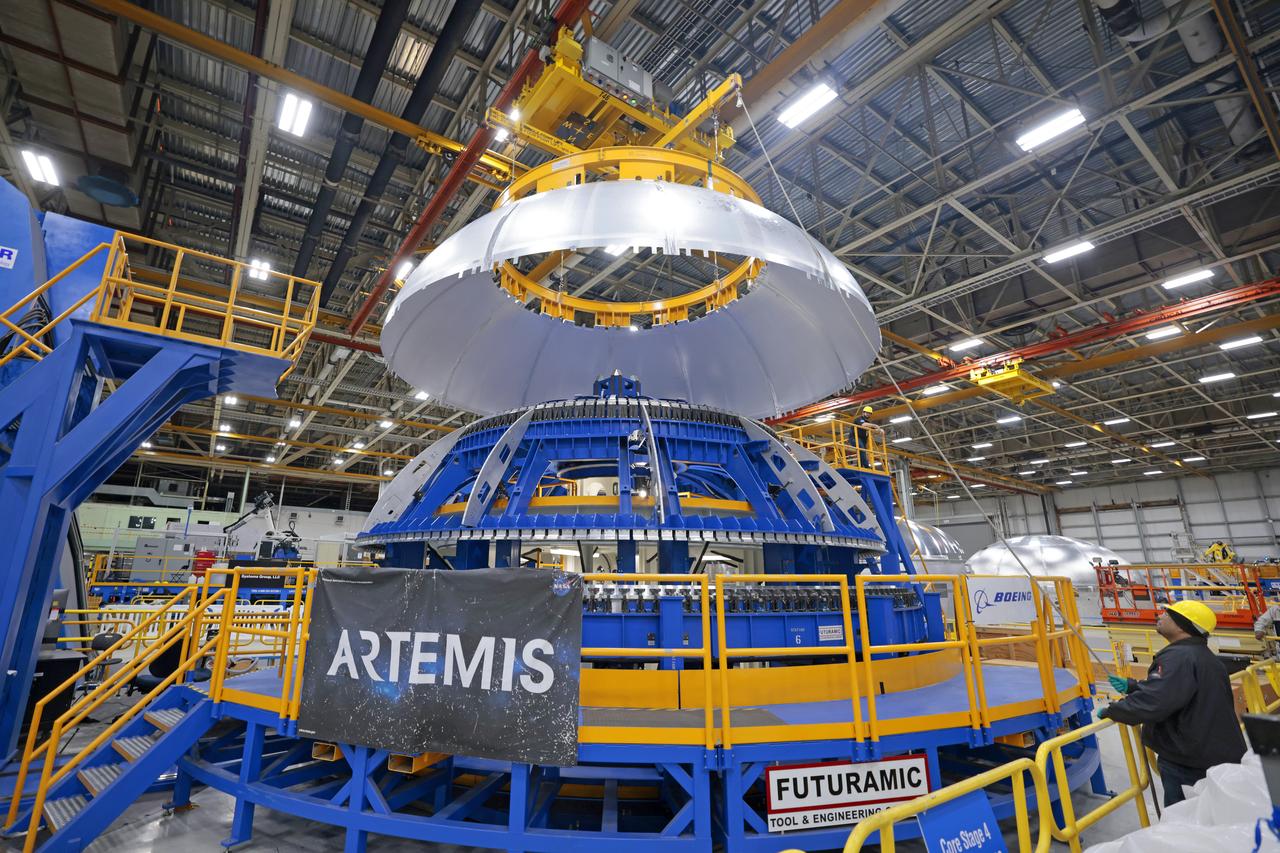

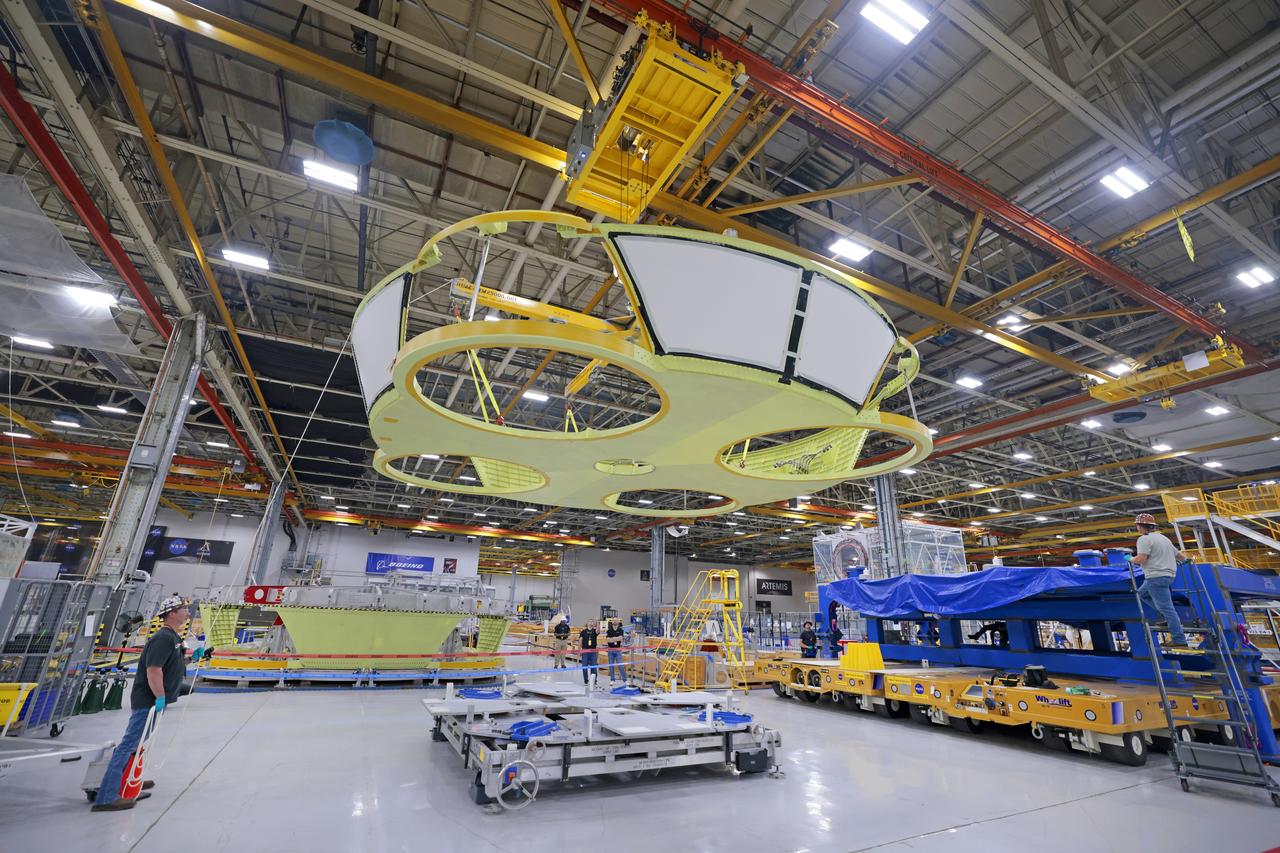
This image shows teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lifting a completed dome off of a robotic weld tool on Nov. 21. The dome, which will cap off the aft end of the liquid hydrogen tank, will be used on the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis IV mission. Later, technicians from Boeing – NASA’s prime contractor for SLS – will join the aft dome with five barrels and a forward dome to complete the liquid hydrogen tank. Artemis IV is the first flight of SLS in its Block 1B configuration. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the third and fourth RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Technicians added the first engine to the SLS core stage Sept. 11. The second engine was installed onto the stage Sept. 15 with the third and fourth engines following Sept. 19 and Sept. 20. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will now focus efforts on the complex tax of fully securing the engines to the stage and integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
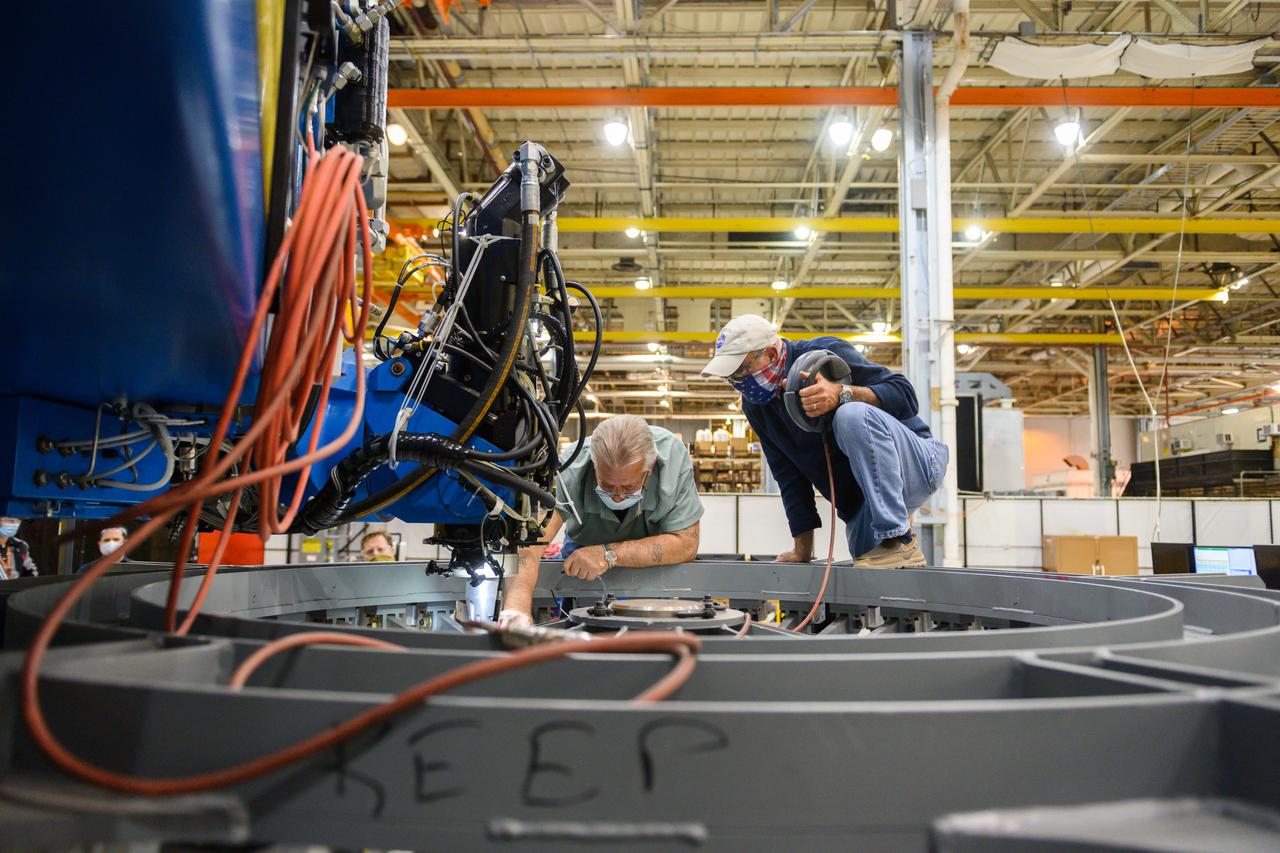

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
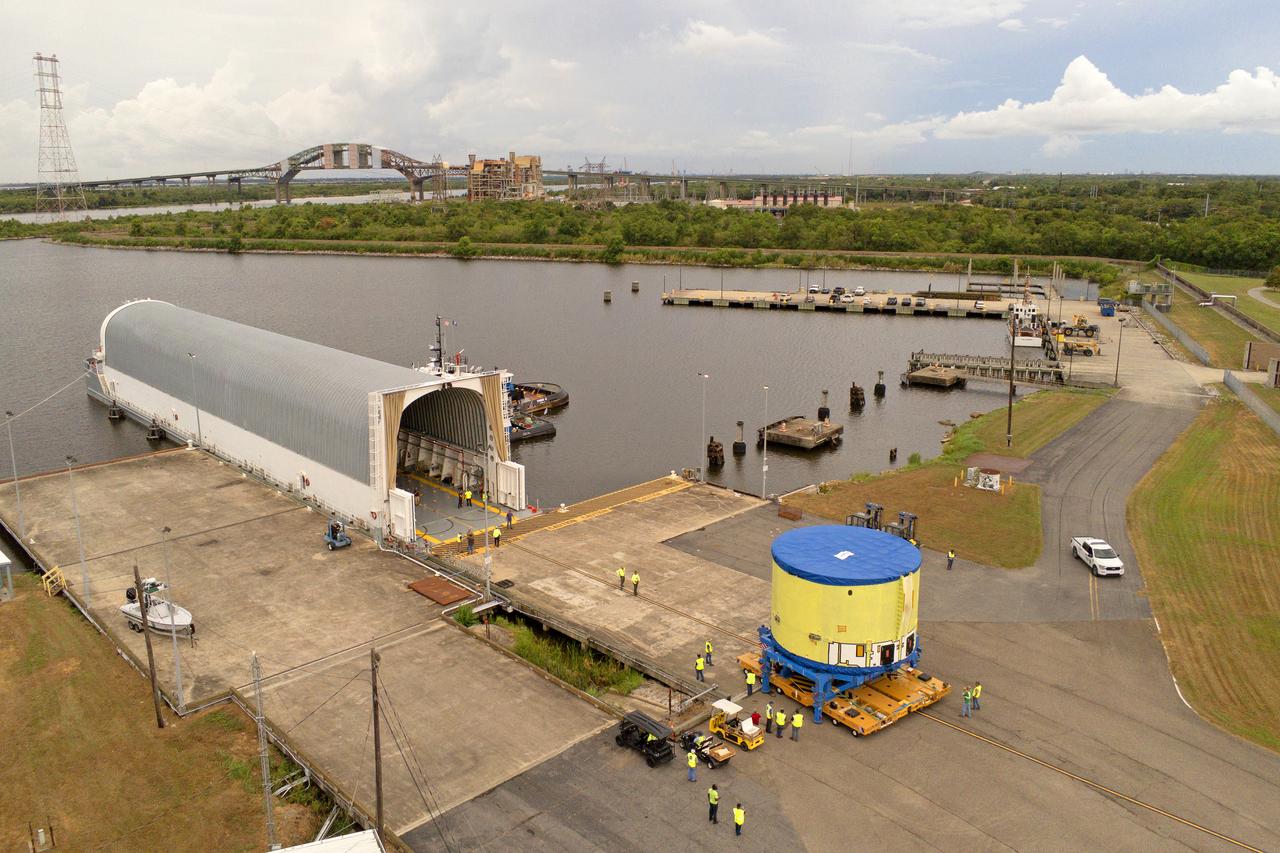

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.
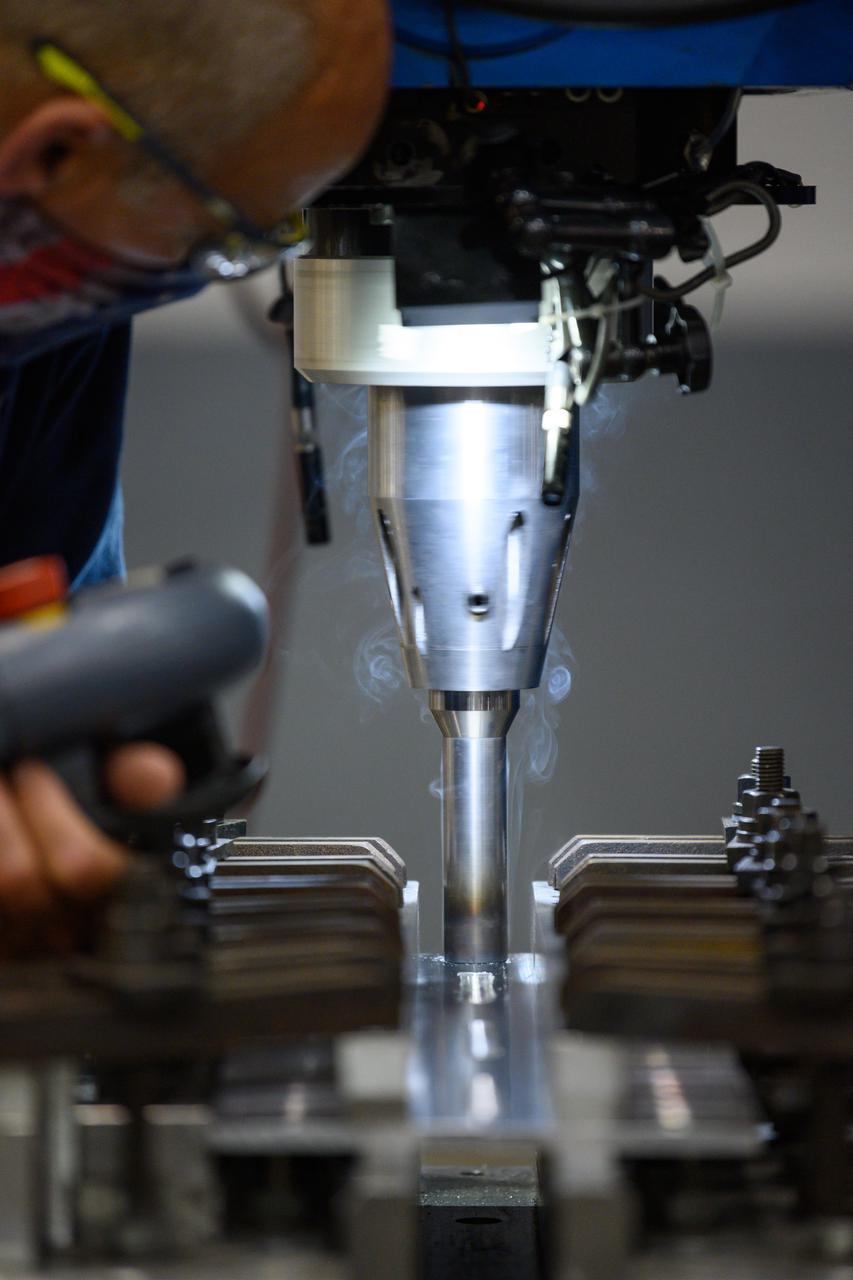

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
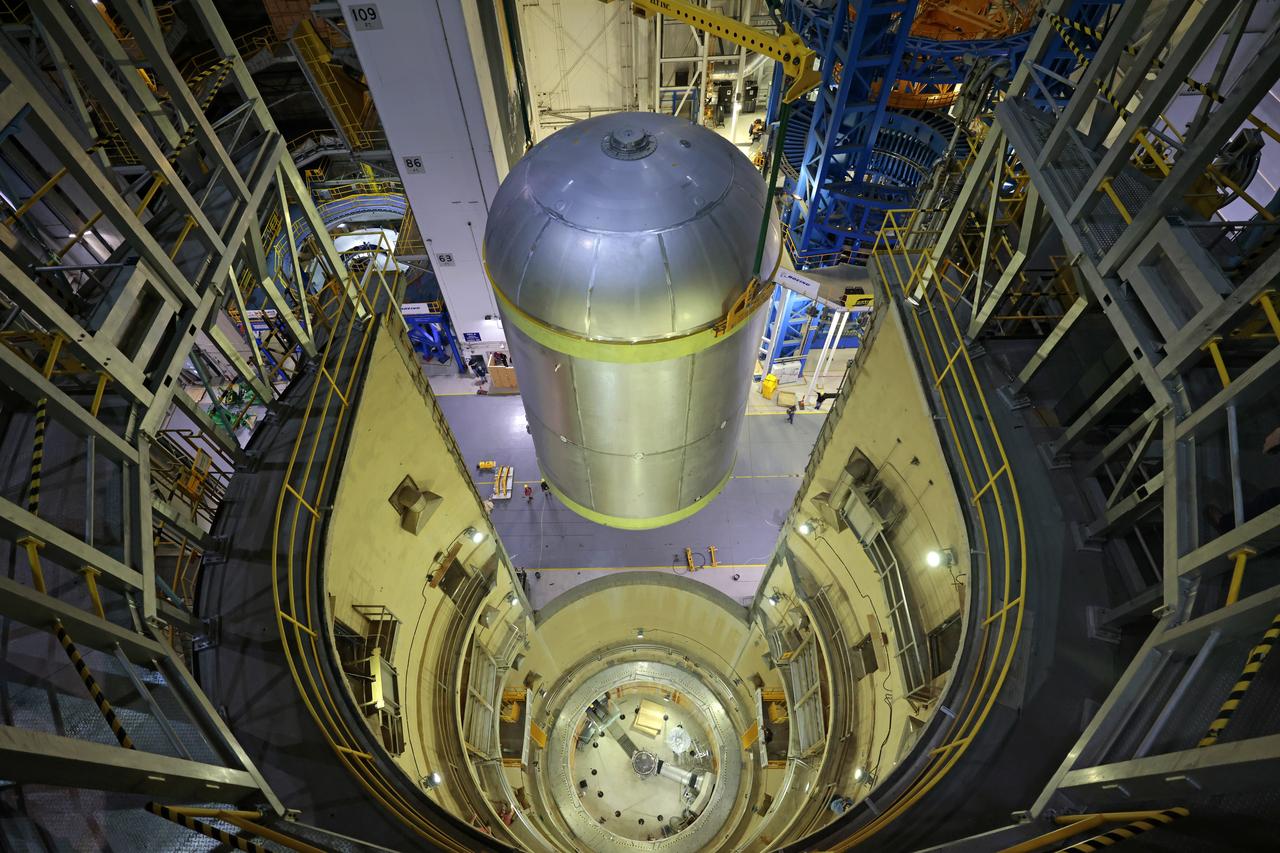

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid oxygen tank for its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to a cleaning cell inside the facility’s vertical assembly building on Oct. 11. The tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s Artemis III mission, will undergo an internal cleaning before moving on to its next phase of production. Inside the cleaning cell, a solution is sprayed into the tank to remove particulates which may collect during the manufacturing process. Once a tank is cleaned, teams use mobile clean rooms for internal access to the tank to prevent external contaminates from entering the hardware. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
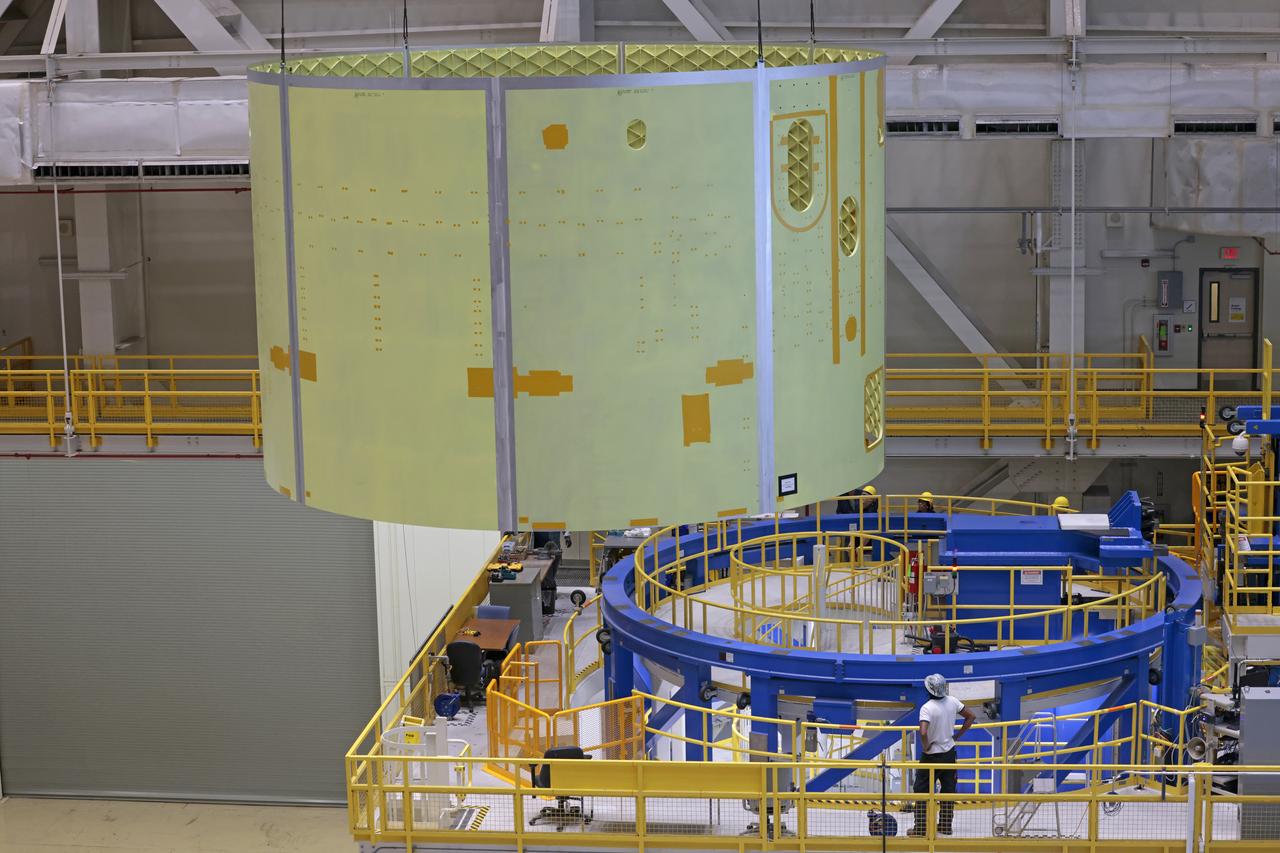

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis V on December 18, 2024, at NASA Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, LA. Throughout 2024, new tooling was erected in bldg. 115 for the upcoming iterations of the Space Launch System (SLS), Exploration Upper Stage (EUS), and the test articles required to develop and assemble each efficiently and effectively. This barrel is the sixty-fourth produced for the Space Launch System program since its inception and is the first barrel weld completed for the core stage of the Artemis V mission. This engine section will be used on the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. It is one of the first components that will make up a portion of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis V mission. According to a Boeing engineer, as of this barrel, the VWC has now completed 515 production welds, with friction-stir welding a cumulative distance of 111,568 inches. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
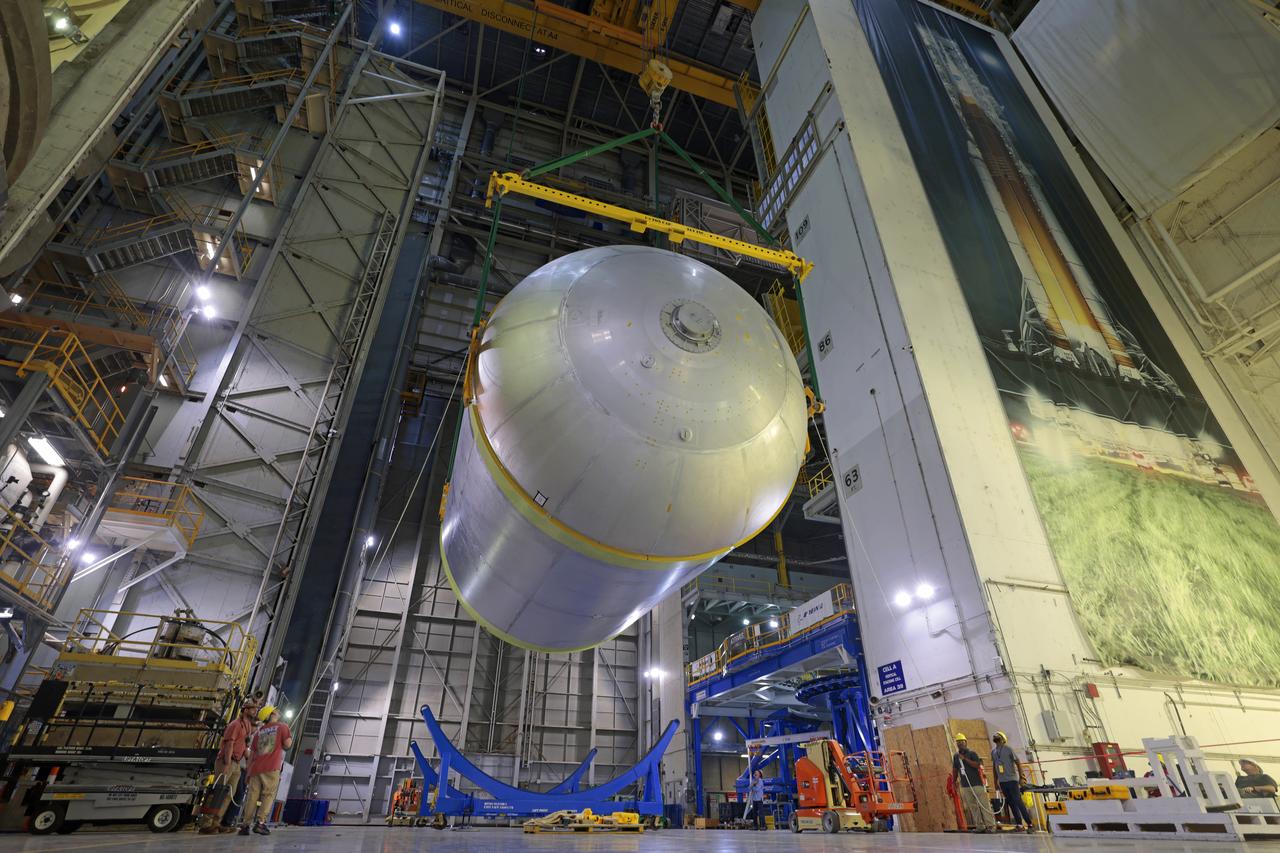

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid oxygen tank for its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to a cleaning cell inside the facility’s vertical assembly building on Oct. 11. The tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s Artemis III mission, will undergo an internal cleaning before moving on to its next phase of production. Inside the cleaning cell, a solution is sprayed into the tank to remove particulates which may collect during the manufacturing process. Once a tank is cleaned, teams use mobile clean rooms for internal access to the tank to prevent external contaminates from entering the hardware. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
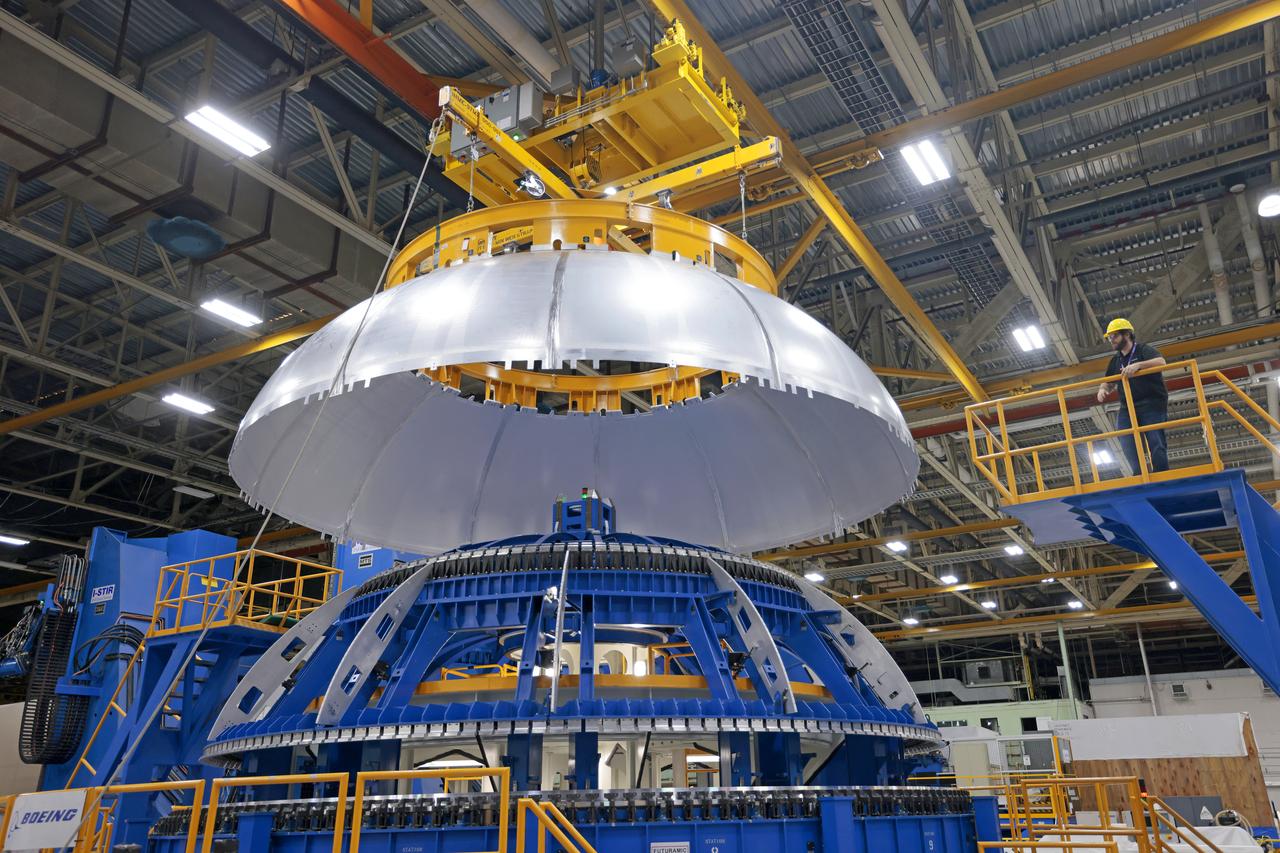

This image shows teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility lifting a completed dome off of a robotic weld tool on Nov. 21. The dome, which will cap off the aft end of the liquid hydrogen tank, will be used on the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis IV mission. Later, technicians from Boeing – NASA’s prime contractor for SLS – will join the aft dome with five barrels and a forward dome to complete the liquid hydrogen tank. Artemis IV is the first flight of SLS in its Block 1B configuration. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
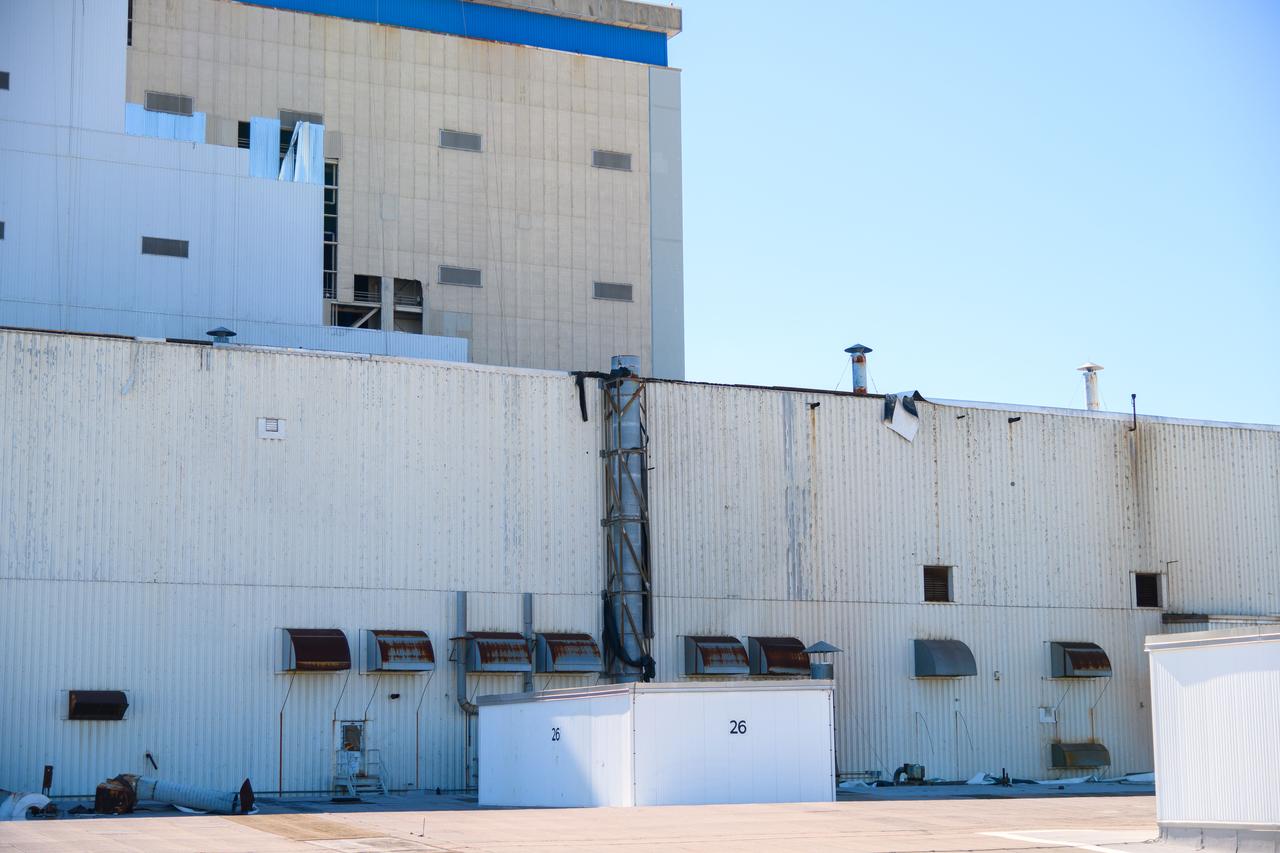

Hurricane Zeta damage to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility – East side of Bldg. 110 the Vertical Assembly Building (VAB).
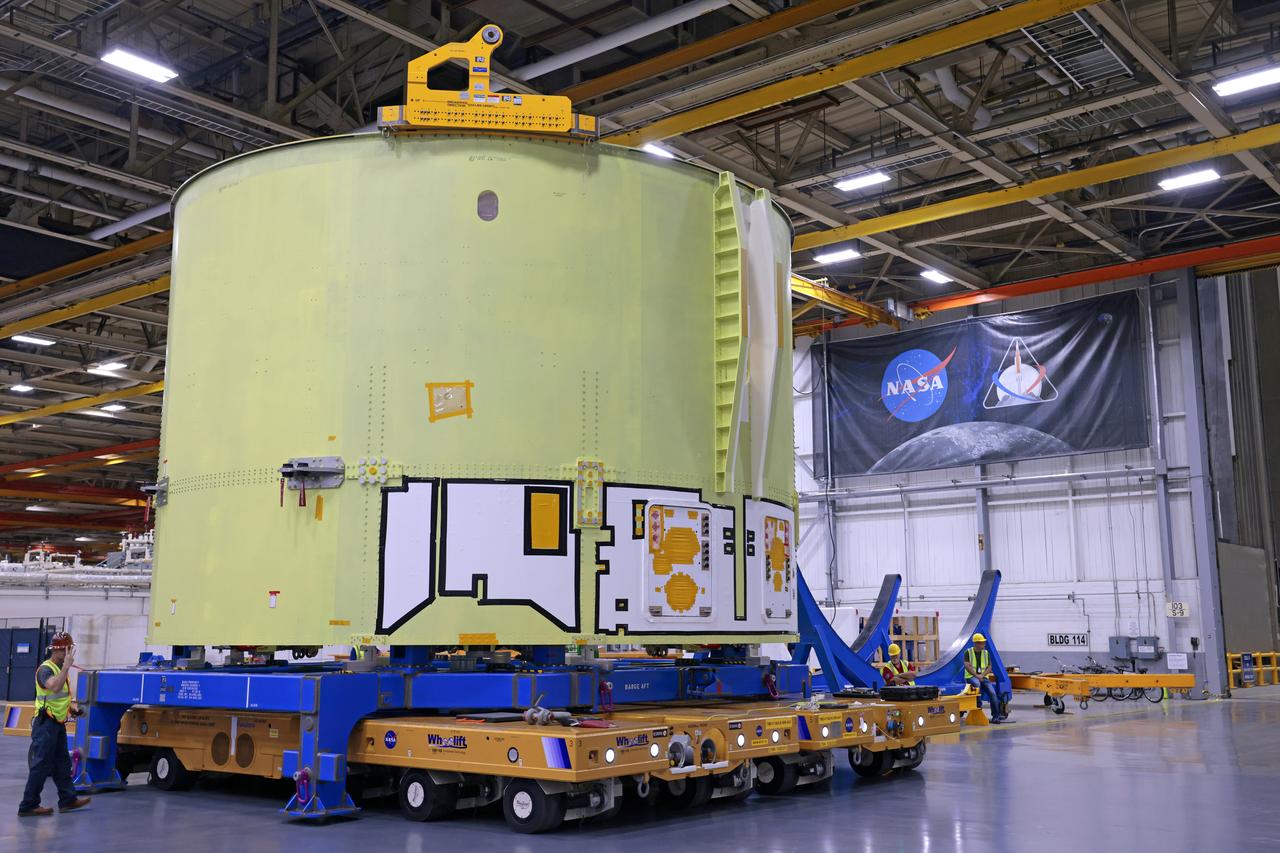

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
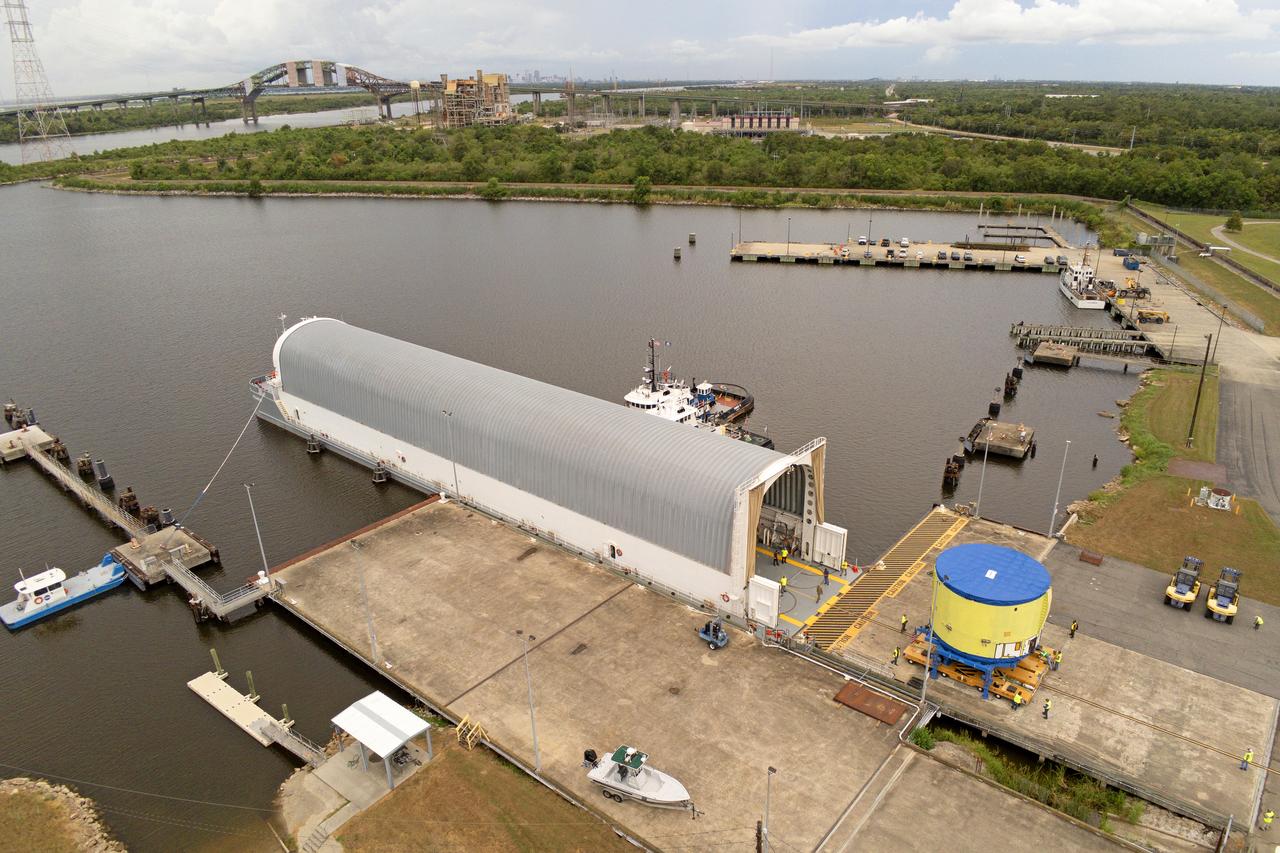

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the third and fourth RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Technicians added the first engine to the SLS core stage Sept. 11. The second engine was installed onto the stage Sept. 15 with the third and fourth engines following Sept. 19 and Sept. 20. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will now focus efforts on the complex tax of fully securing the engines to the stage and integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
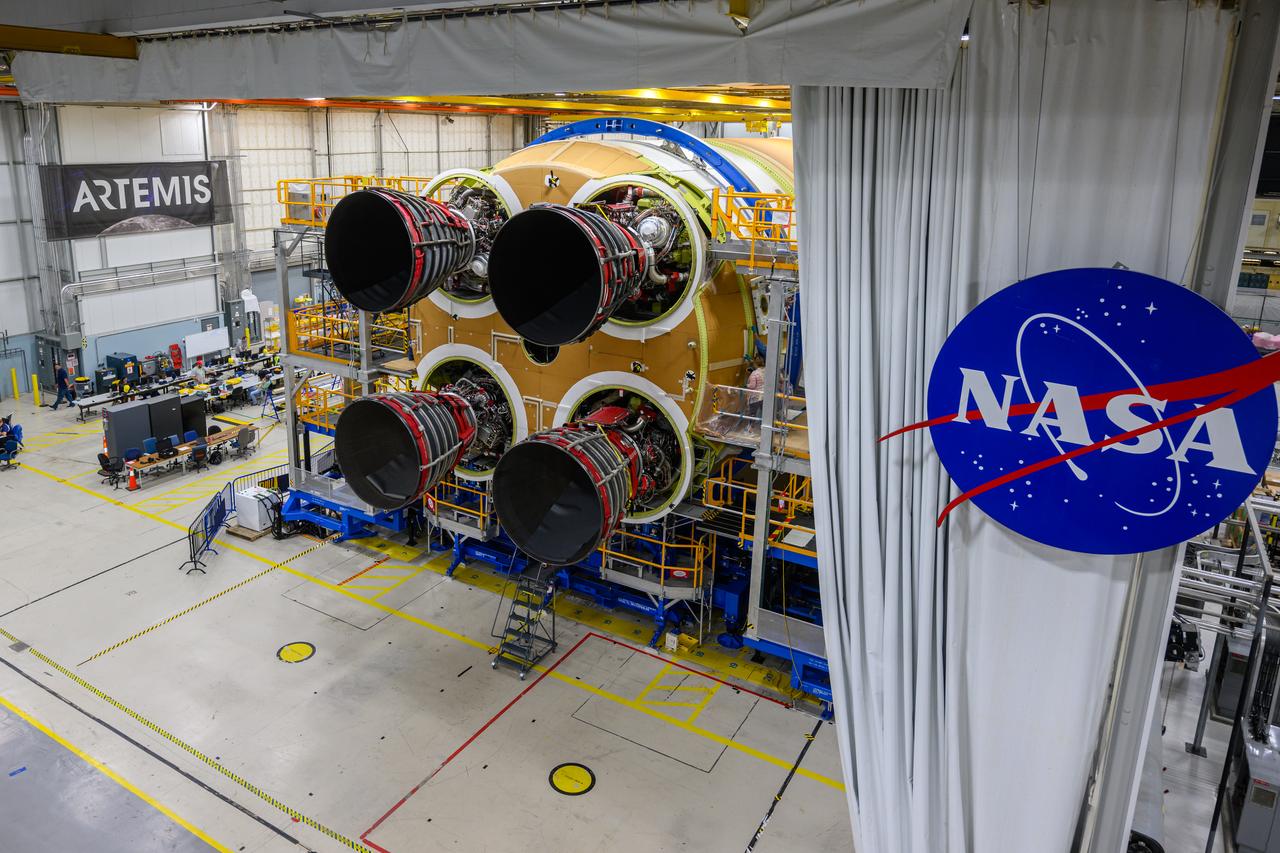

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the third and fourth RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Technicians added the first engine to the SLS core stage Sept. 11. The second engine was installed onto the stage Sept. 15 with the third and fourth engines following Sept. 19 and Sept. 20. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will now focus efforts on the complex tax of fully securing the engines to the stage and integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
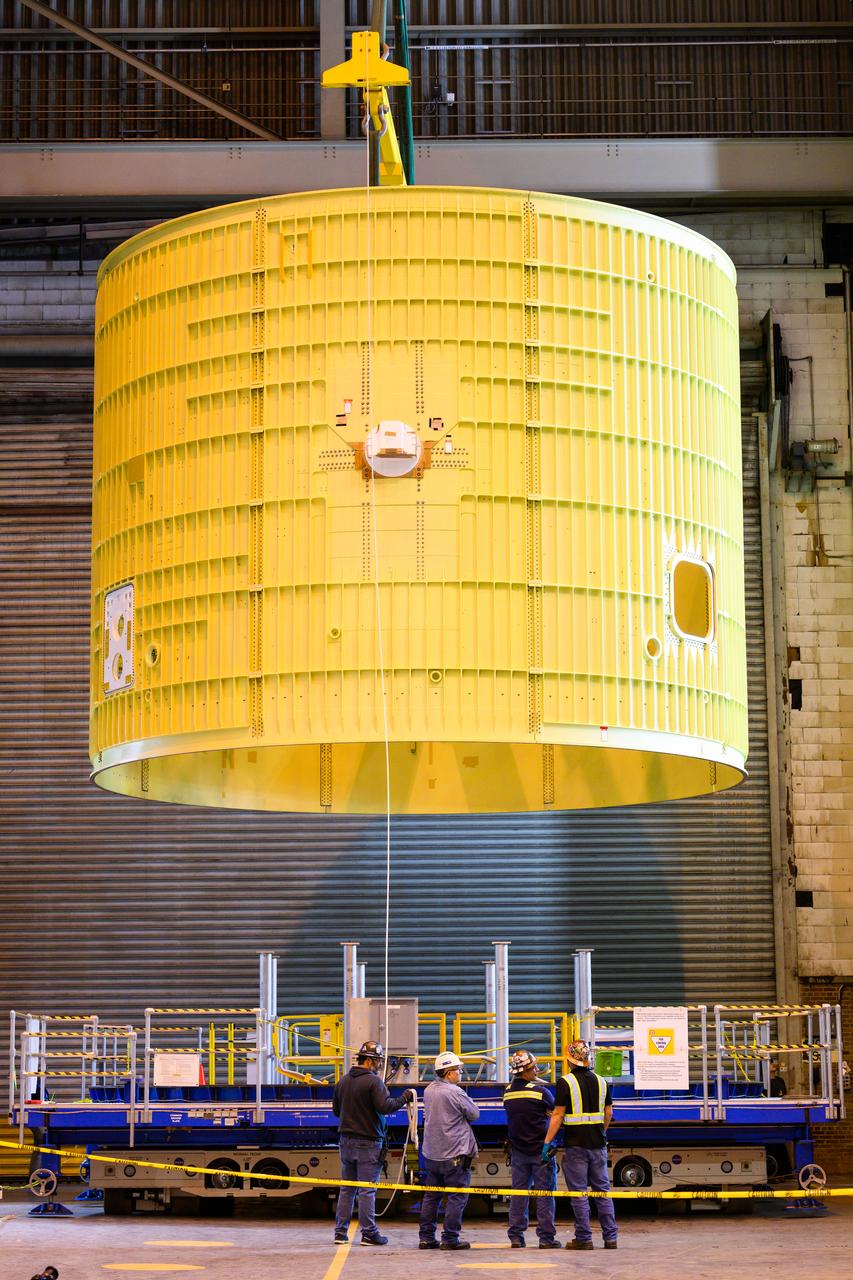

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
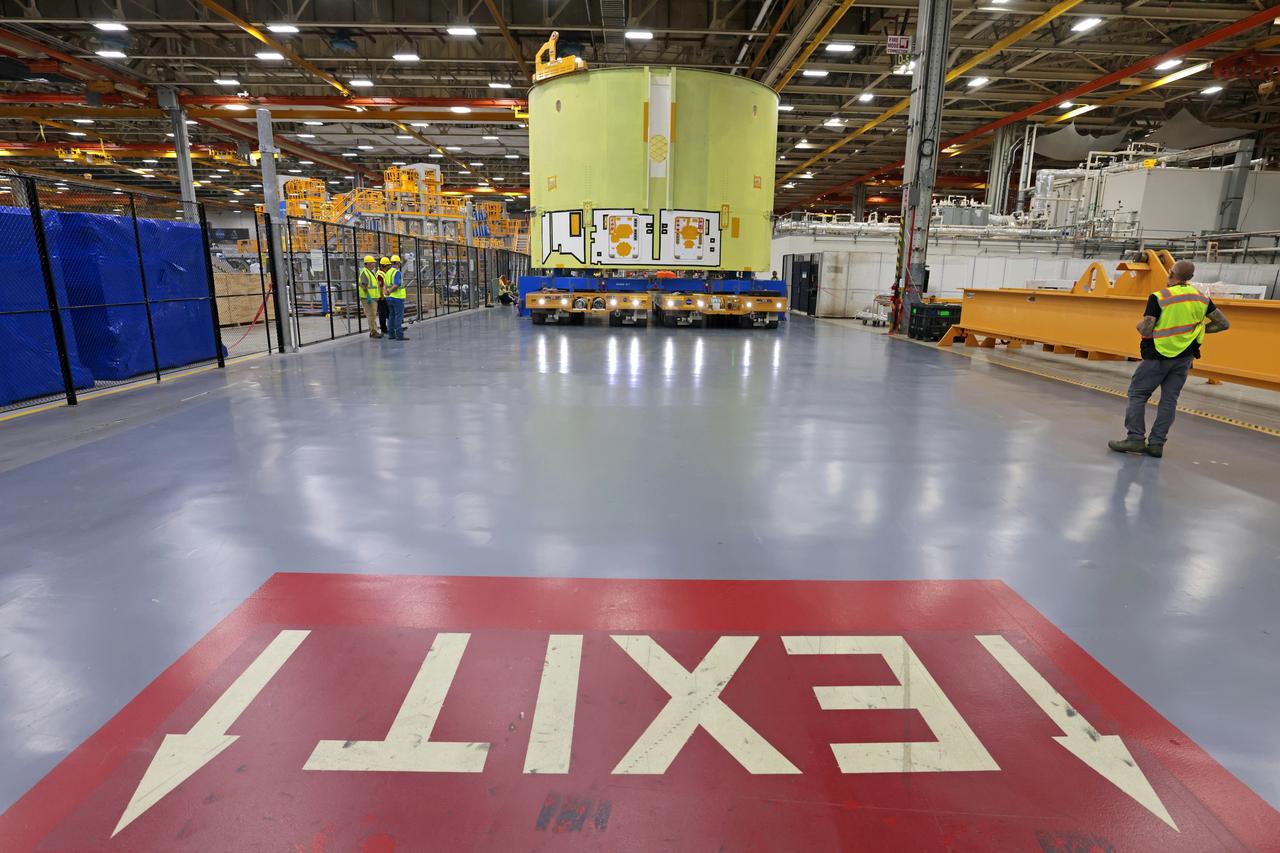

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.
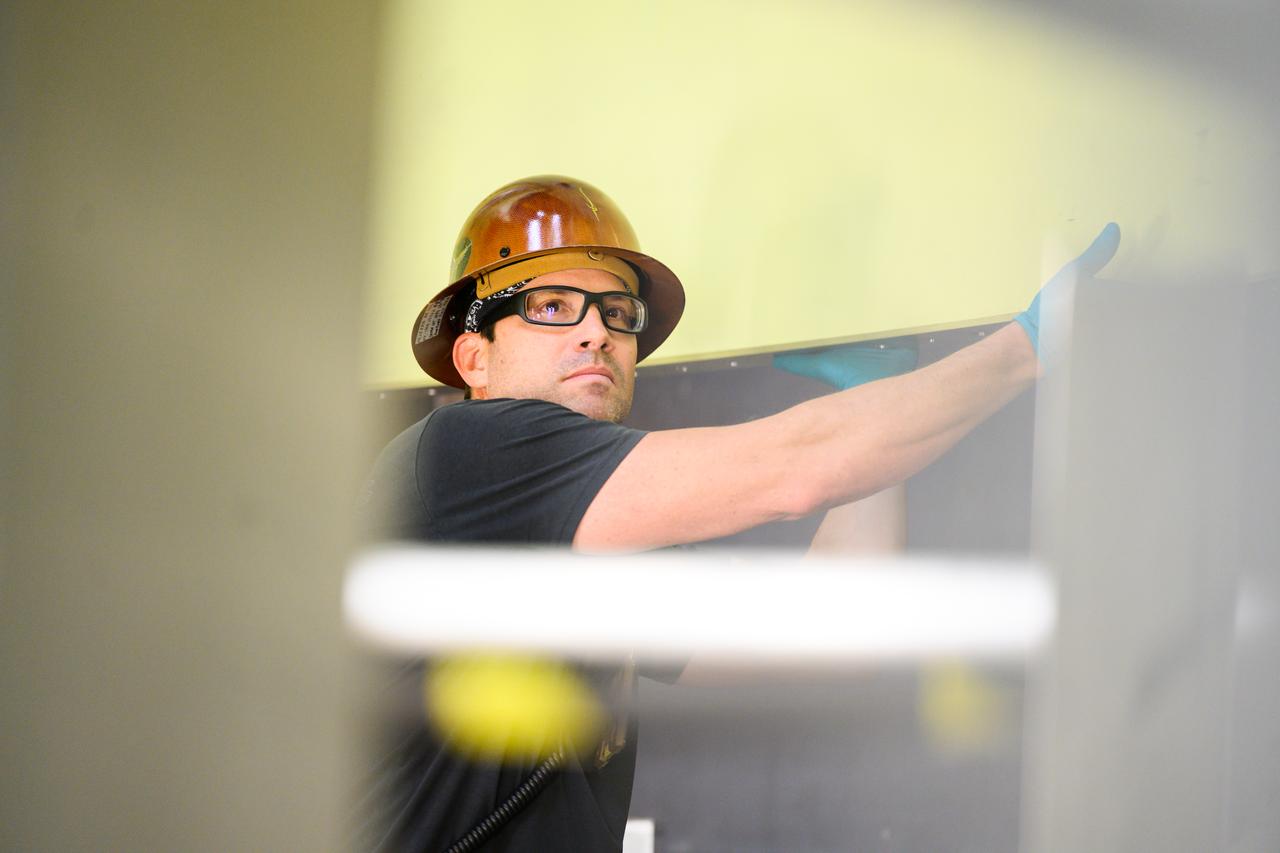

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
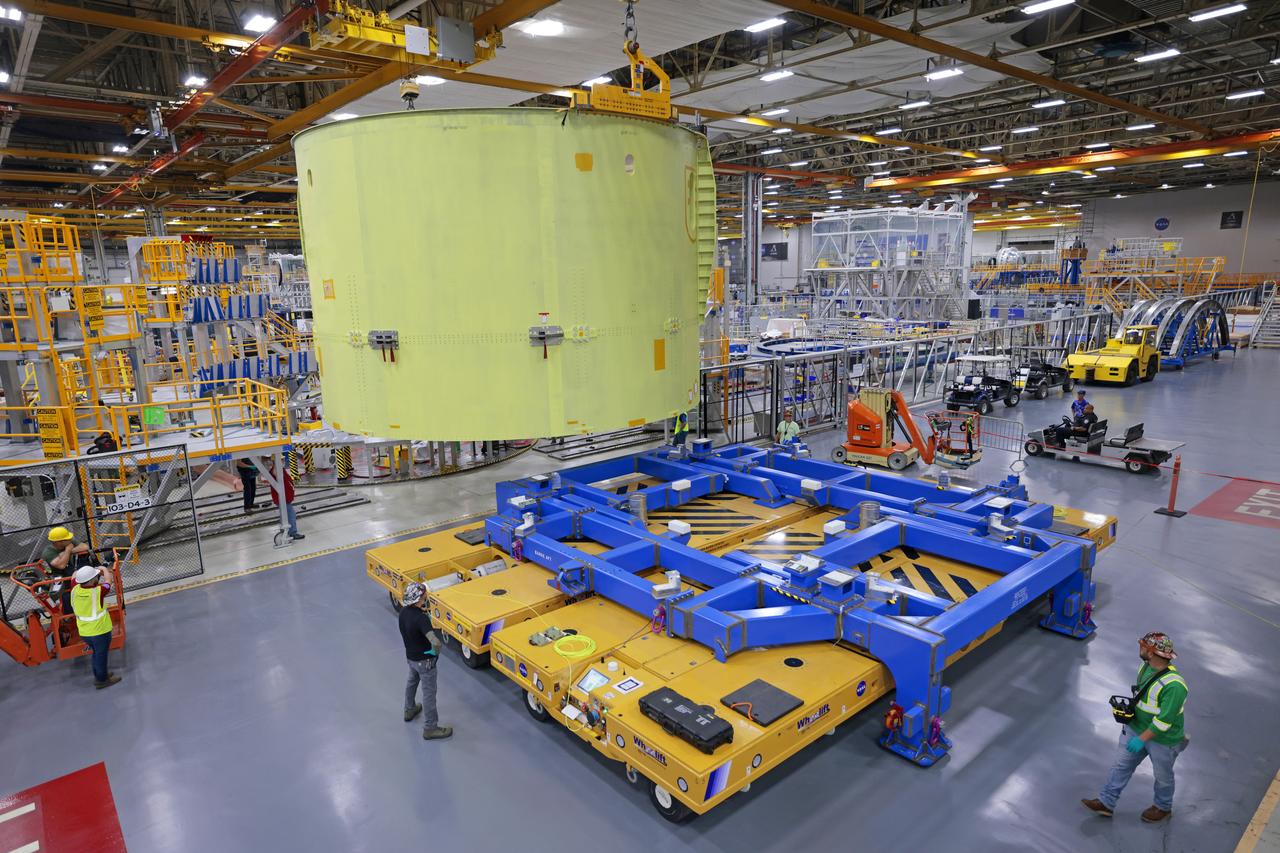

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This image highlights the liquid hydrogen tank that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program. The tank is being built at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen cooled to minus 423 degrees Fahrenheit and sits between the core stage’s intertank and engine section. The liquid hydrogen hardware, along with the liquid oxygen tank, will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines at the bottom of the cores stage to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to launch NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the human landing system, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket can send astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
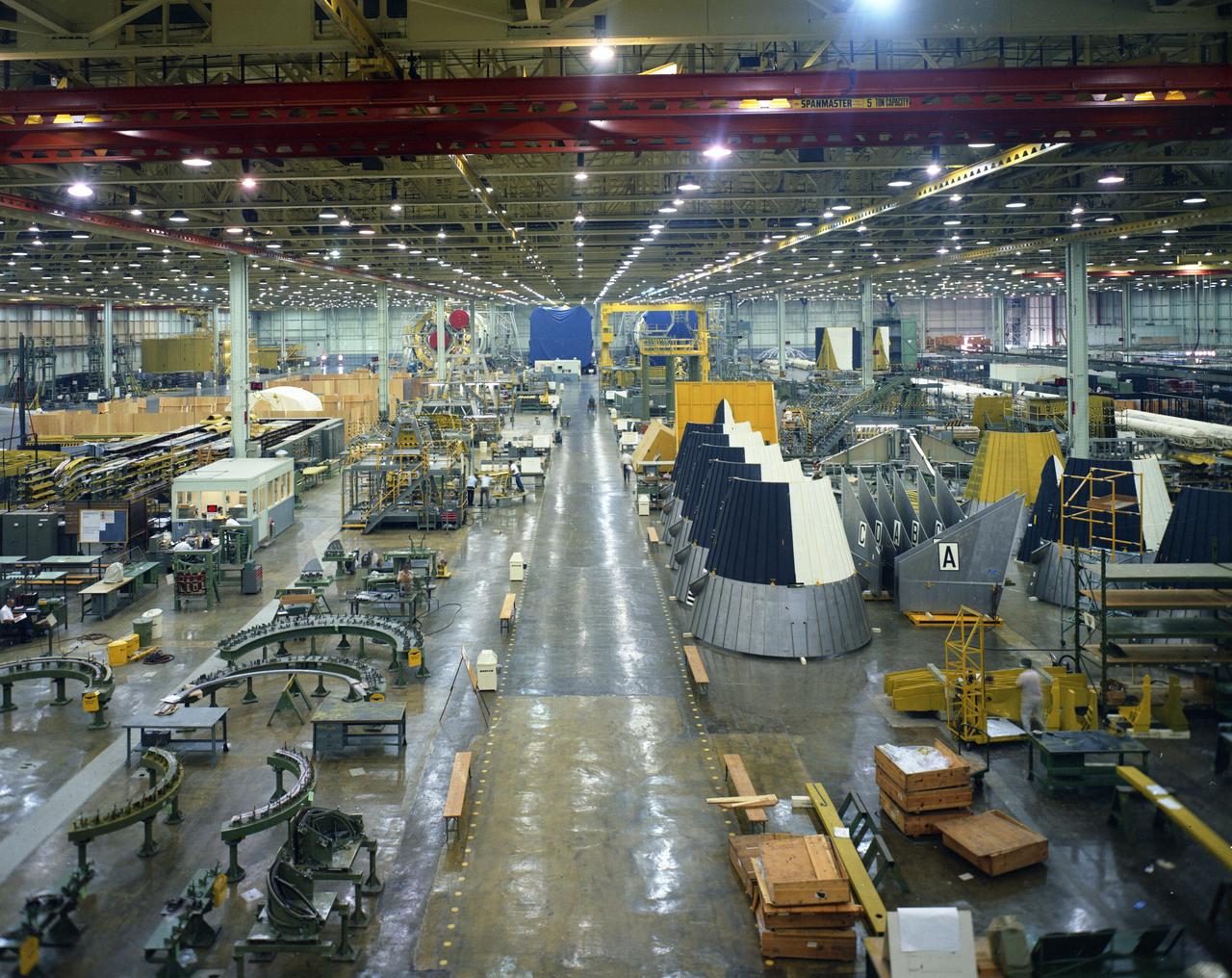

New Orleans, LA - Parts of the Saturn V first stage await assembly at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in October of 1967. In the far end of the image, S-1C stages are nearing completion. Image dated 10-5-1967.
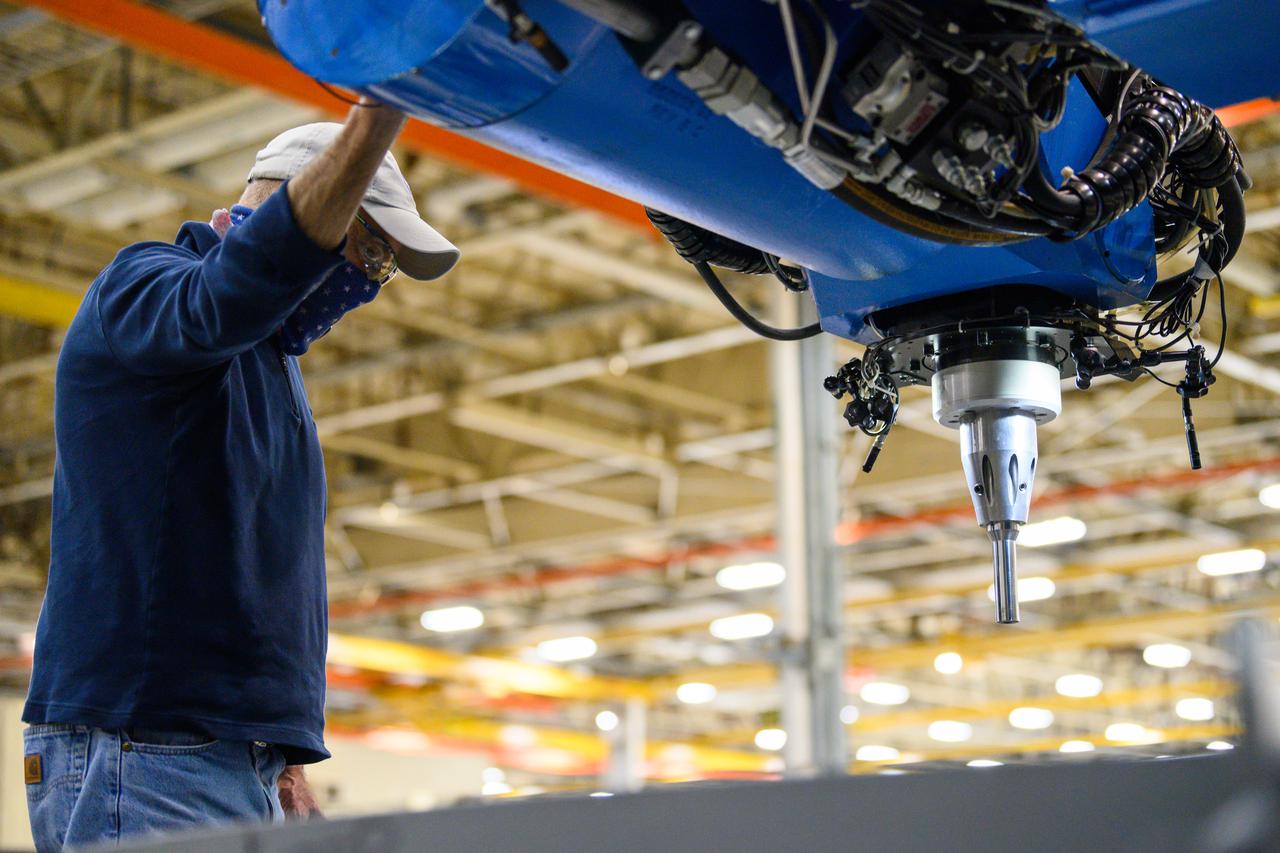

Technicians from Orion Prime Contractor Lockheed Martin weld the forward bulkhead of the pressure vessel to the tunnel hardware on the Orion Spacecraft for the Artemis III mission at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The crew module’s primary structure, the pressure vessel, is comprised of seven machined aluminum alloy pieces that are welded together through a weld process that produces a strong, air-tight habitable space for astronauts during the mission. The pressure vessel is designed to withstand the harsh and demanding environment of deep space and is the core structure upon which all the other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. This pressure vessel weld is the next step following the completion of the crew module cone panel welds and creates the top of the spacecraft. Work will then begin to join the barrel with the aft bulkhead to form the bottom of Orion. Last, the forward bulkhead will be welded to the top of the panels and, for the seventh and closeout weld, the bottom of the cone panels will be joined to the barrel to complete the pressure vessel. Once welding of the Artemis III crew module primary structure is complete, it will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida where it will undergo further assembly beginning this fall. Orion, the Space Launch System, and Exploration Ground Systems programs are foundational elements of the Artemis program. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of Orion and SLS and is targeted to launch later this year. Artemis II will follow and is the first crewed mission, taking humans farther into space than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
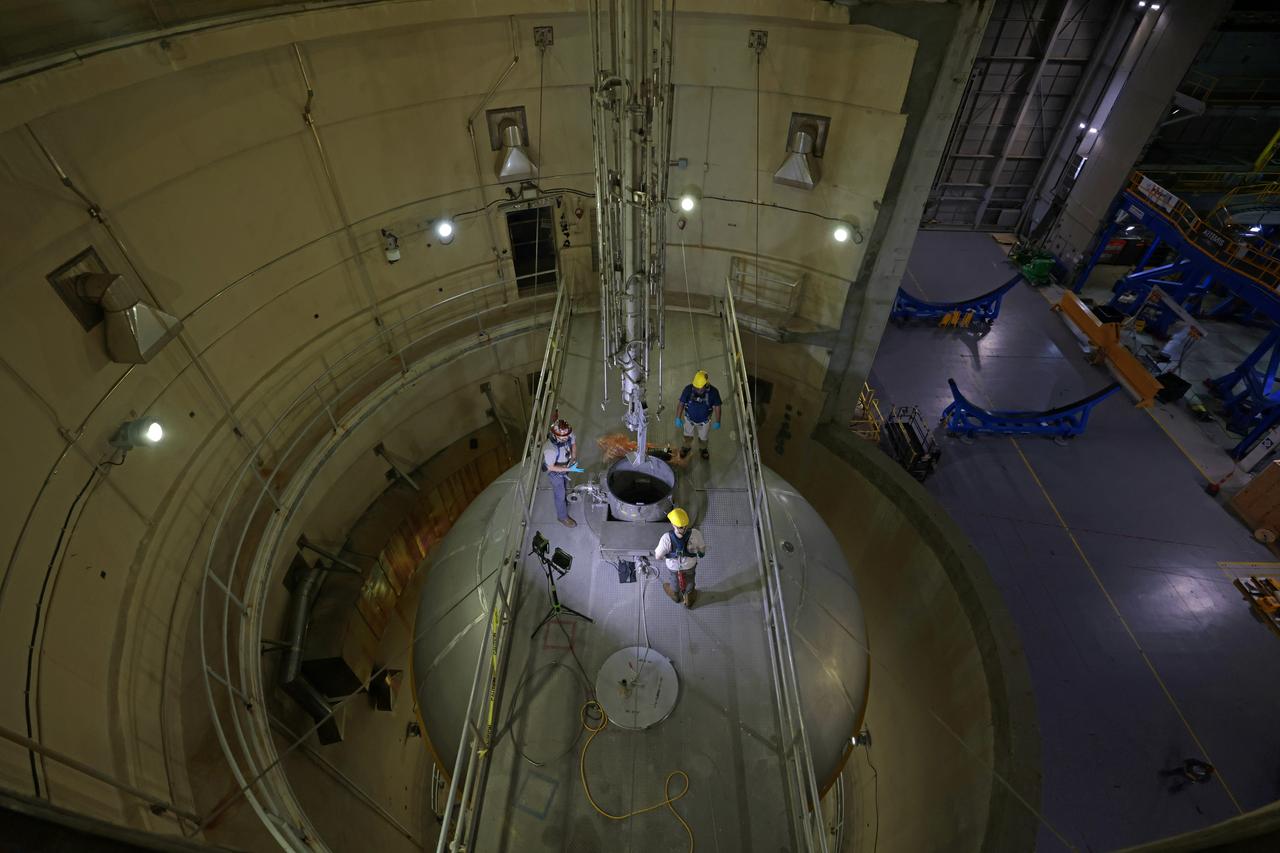

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans install wash probes into a liquid oxygen tank inside the factory’s cleaning cell on Oct. 25. The tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission, will undergo an internal cleaning before moving on to its next phase of production. Inside the cleaning cell, a solution is sprayed into the tank to remove particulates which may collect during the manufacturing process. Once a tank is cleaned, teams use mobile clean rooms for internal access to the tank to prevent external contaminates from entering the hardware. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
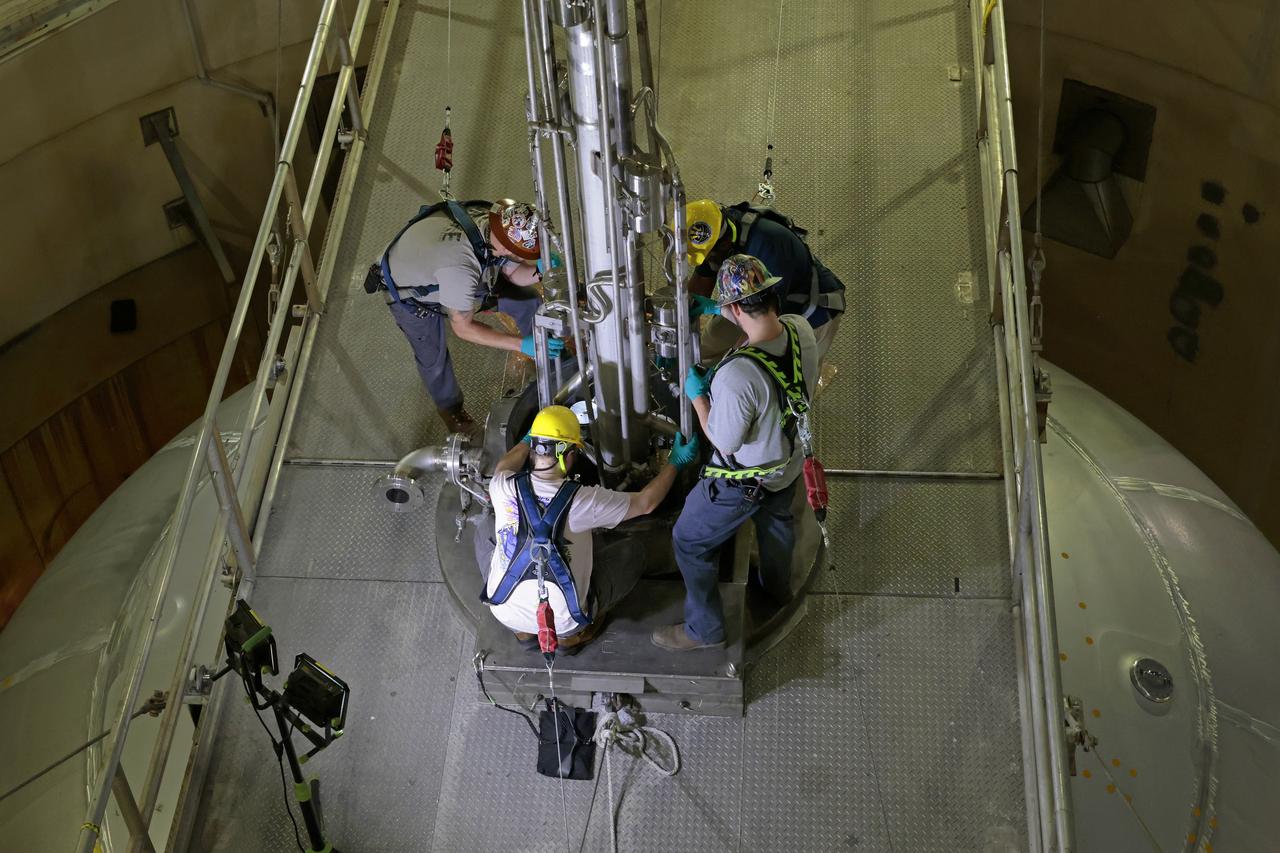

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans install wash probes into a liquid oxygen tank inside the factory’s cleaning cell on Oct. 25. The tank, which will be used on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission, will undergo an internal cleaning before moving on to its next phase of production. Inside the cleaning cell, a solution is sprayed into the tank to remove particulates which may collect during the manufacturing process. Once a tank is cleaned, teams use mobile clean rooms for internal access to the tank to prevent external contaminates from entering the hardware. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
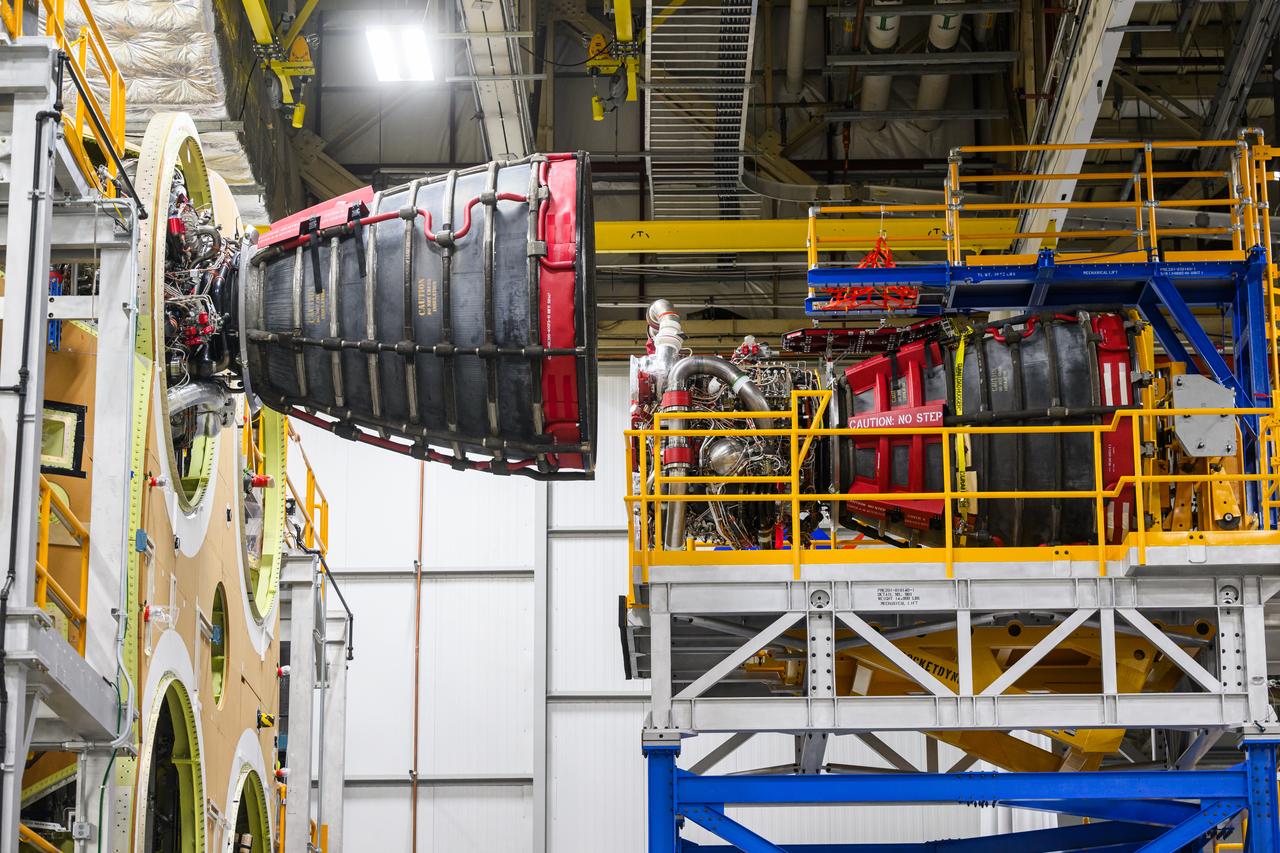

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars.
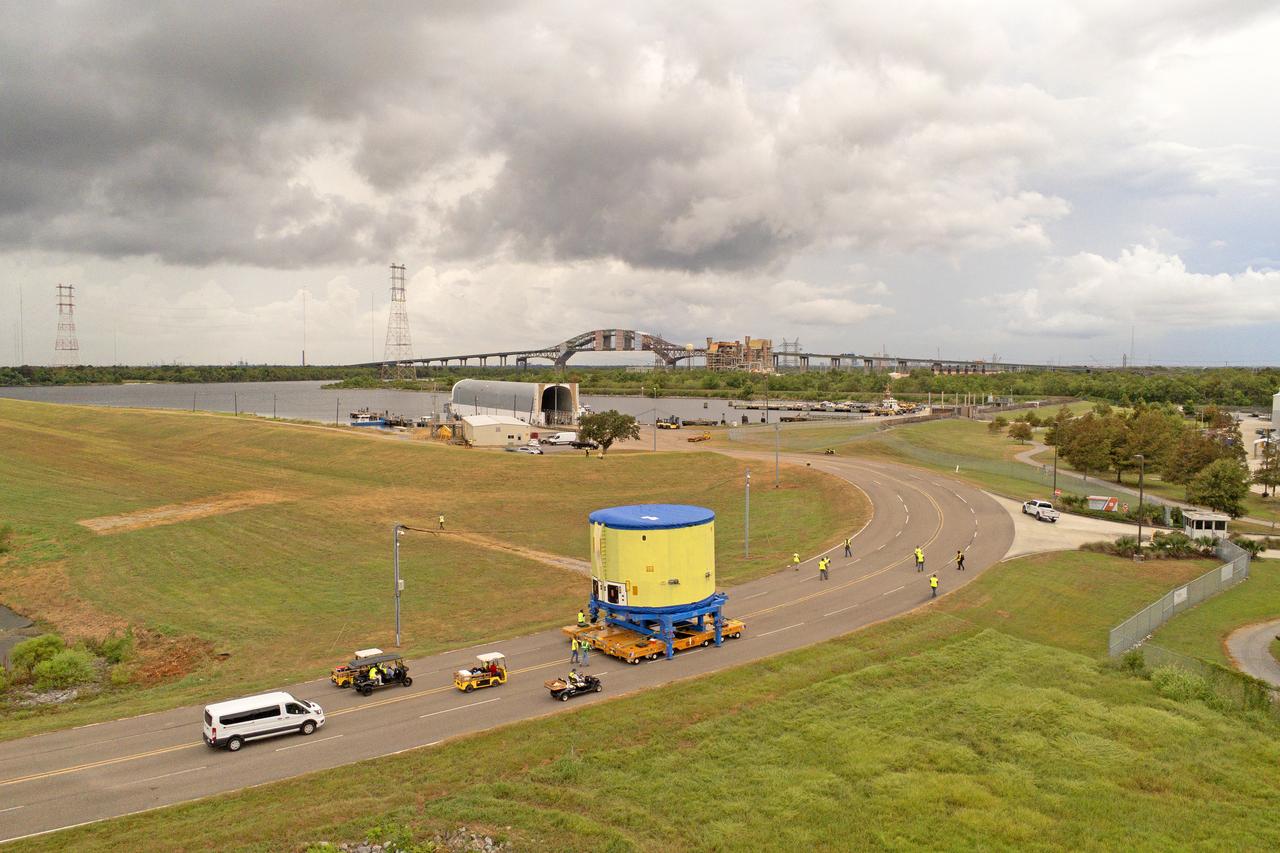

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section of a future SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to NASA’s Pegasus barge Aug. 28. The hardware will form the bottom-most section of the SLS core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis IV mission, which will be the first mission to the Gateway space station in lunar orbit under the Artemis campaign. The barge will transport the spaceflight hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Once in Florida, the engine section will undergo final outfitting inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility.

