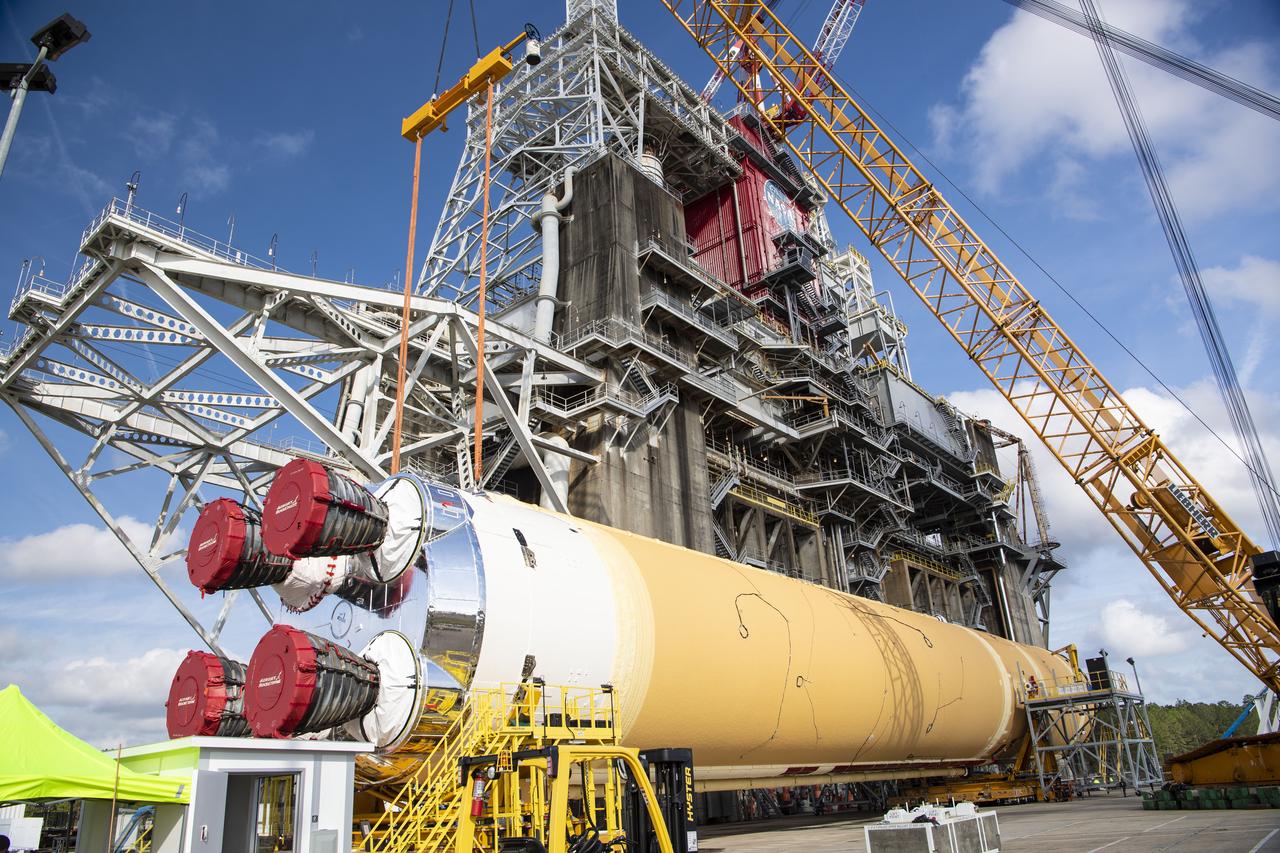

The first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System rocket arrived at Stennis Space Center on Jan. 12 for a series of tests prior to its maiden Artemis I flight. The core stage was transported from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the B-2 Test Stand dock at Stennis aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Soon after arrival, the stage was rolled off of Pegasus onto the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. After the stage is lifted and installed on the B-2 stand, it will undergo a series of “Green Run” systems test that represent the first integrated testing of its sophisticated systems.

Rick Gilbrech, director of NASA's Stennis Space Center, speaks to invited guests ahead of a second hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
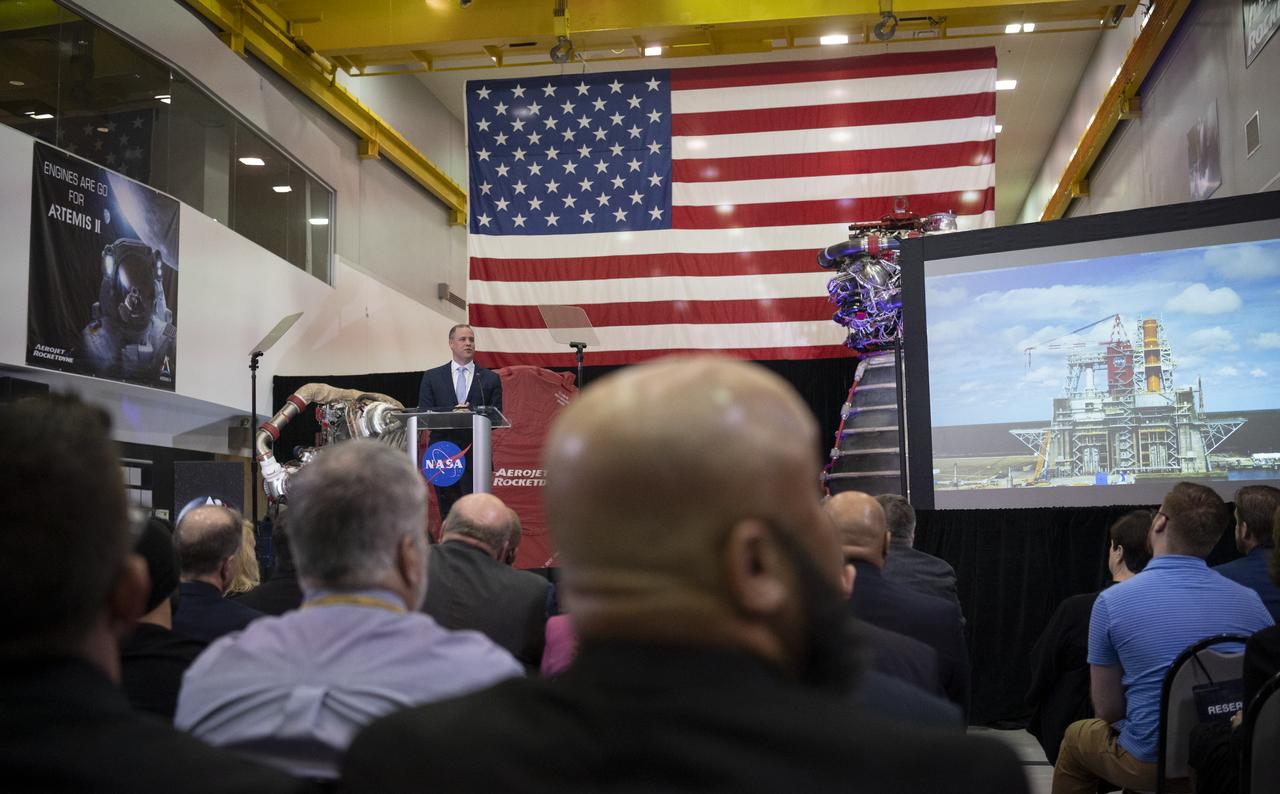

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine discusses the fiscal year 2021 budget proposal during a State of NASA address, Monday, Feb. 10, 2020, at Aerojet Rocketdyne’s facility at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
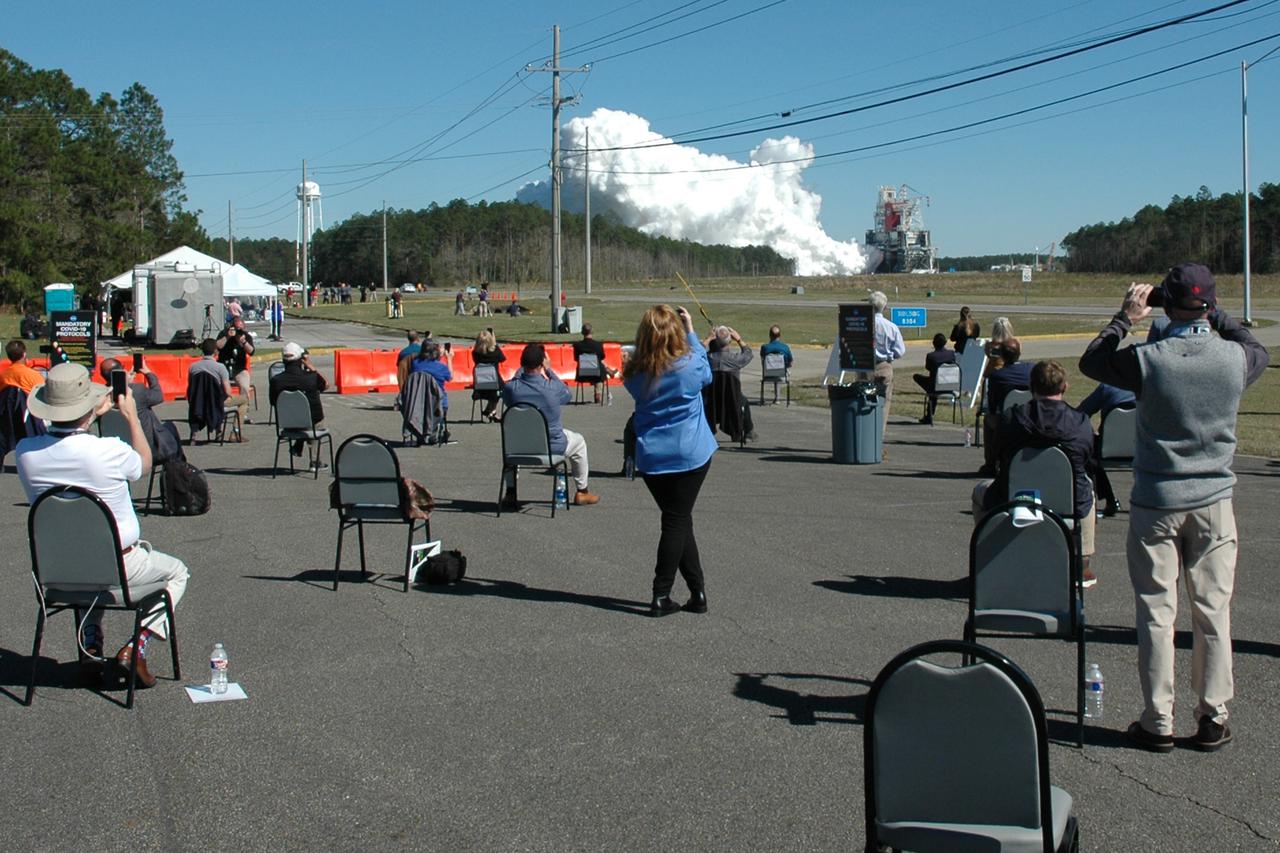

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
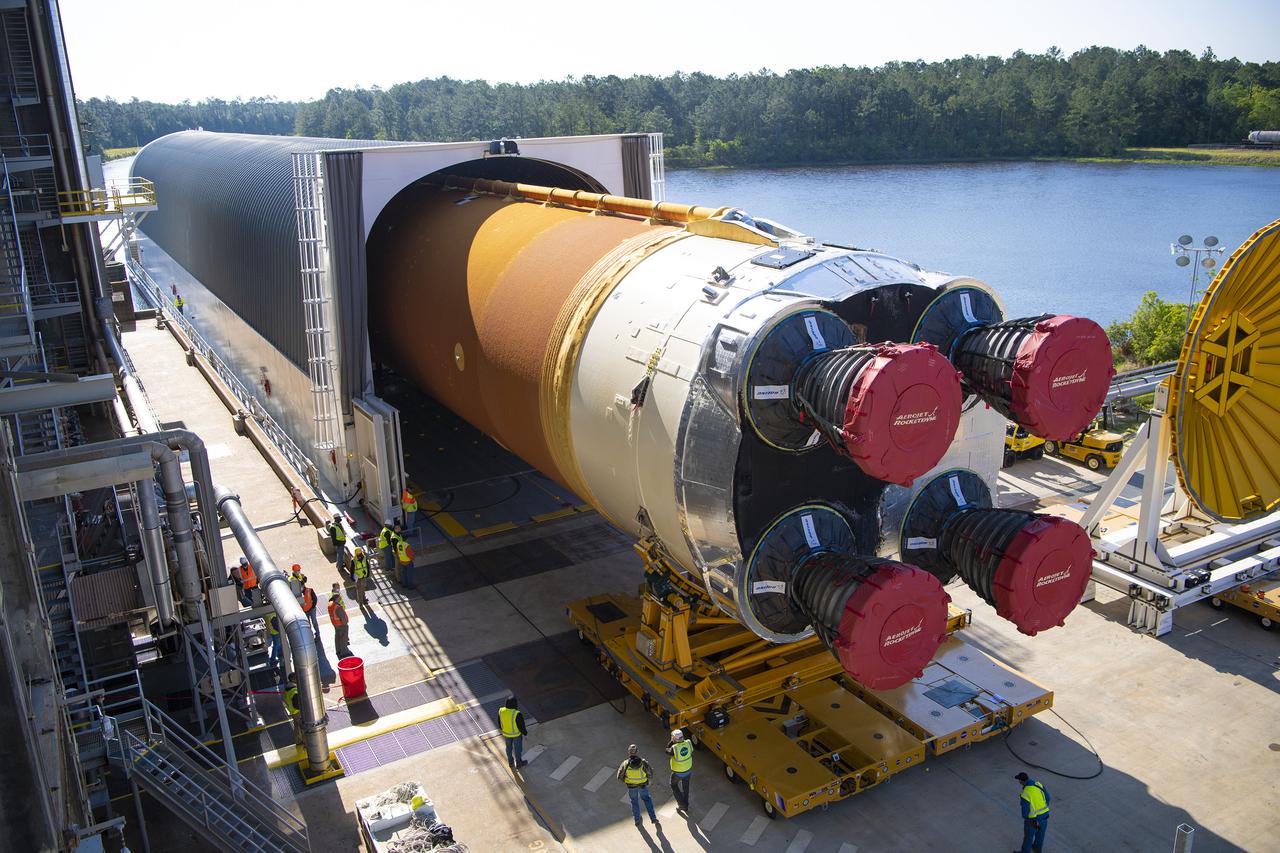

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
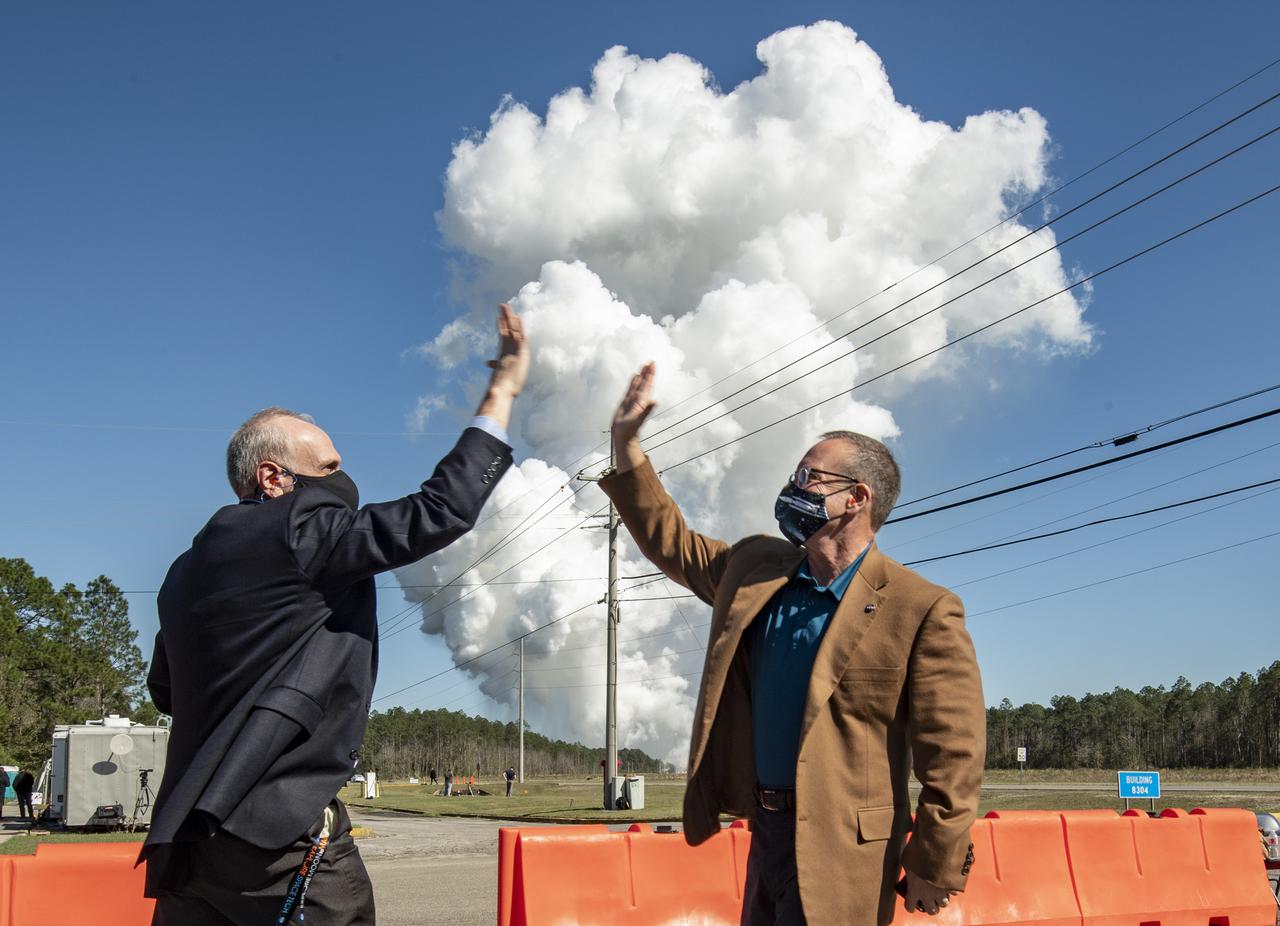

Acting NASA Administrator Steve Jurczyk, left, and Rick Gilbrech, director of NASA's Stennis Space Center, right, high five following a second hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
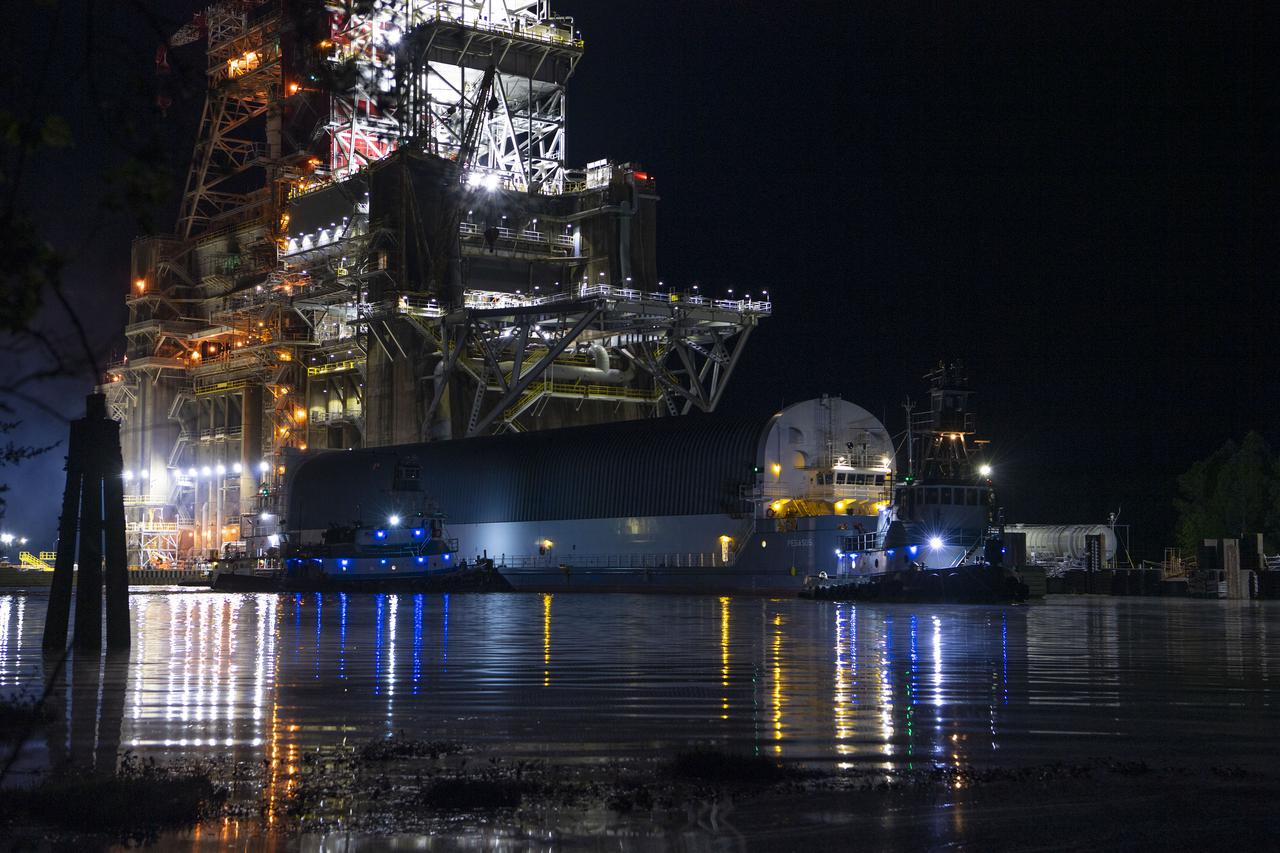

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
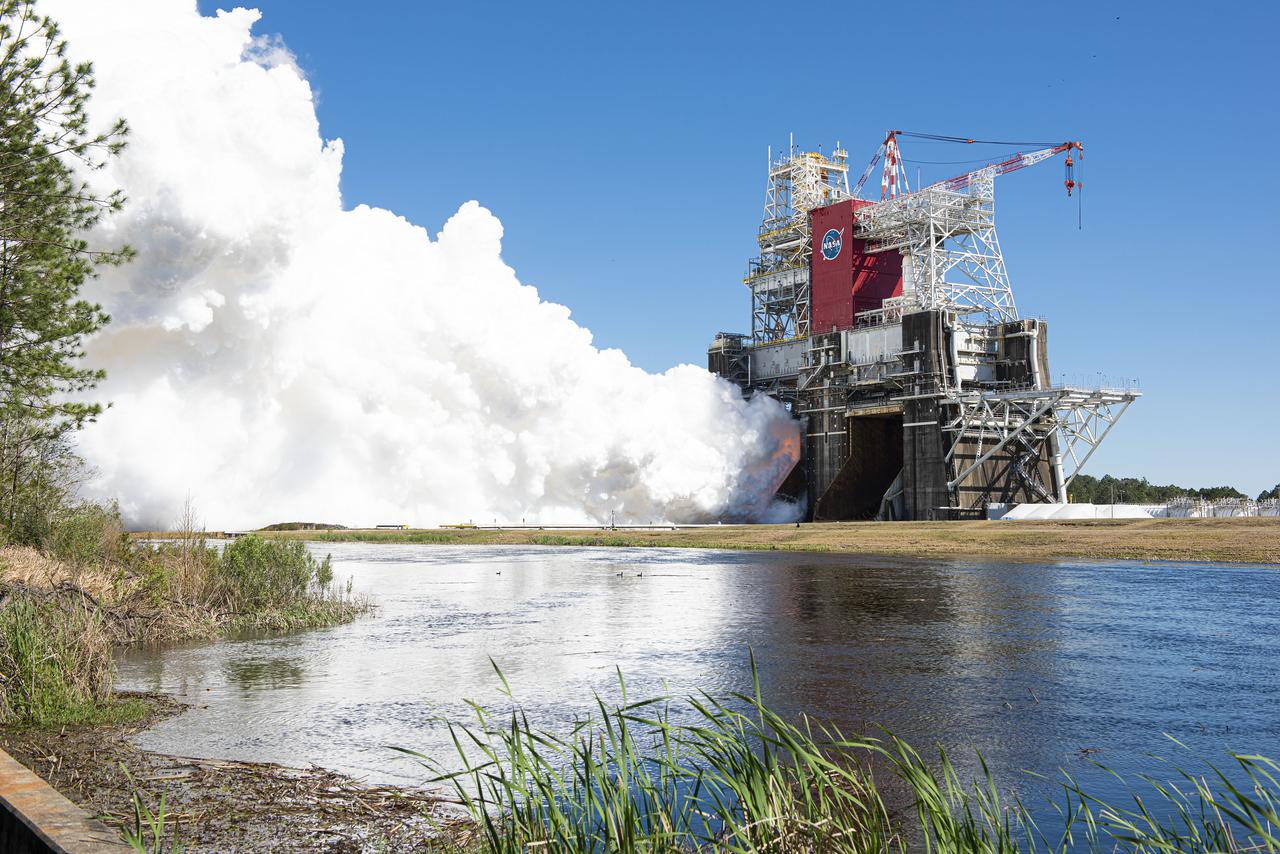

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
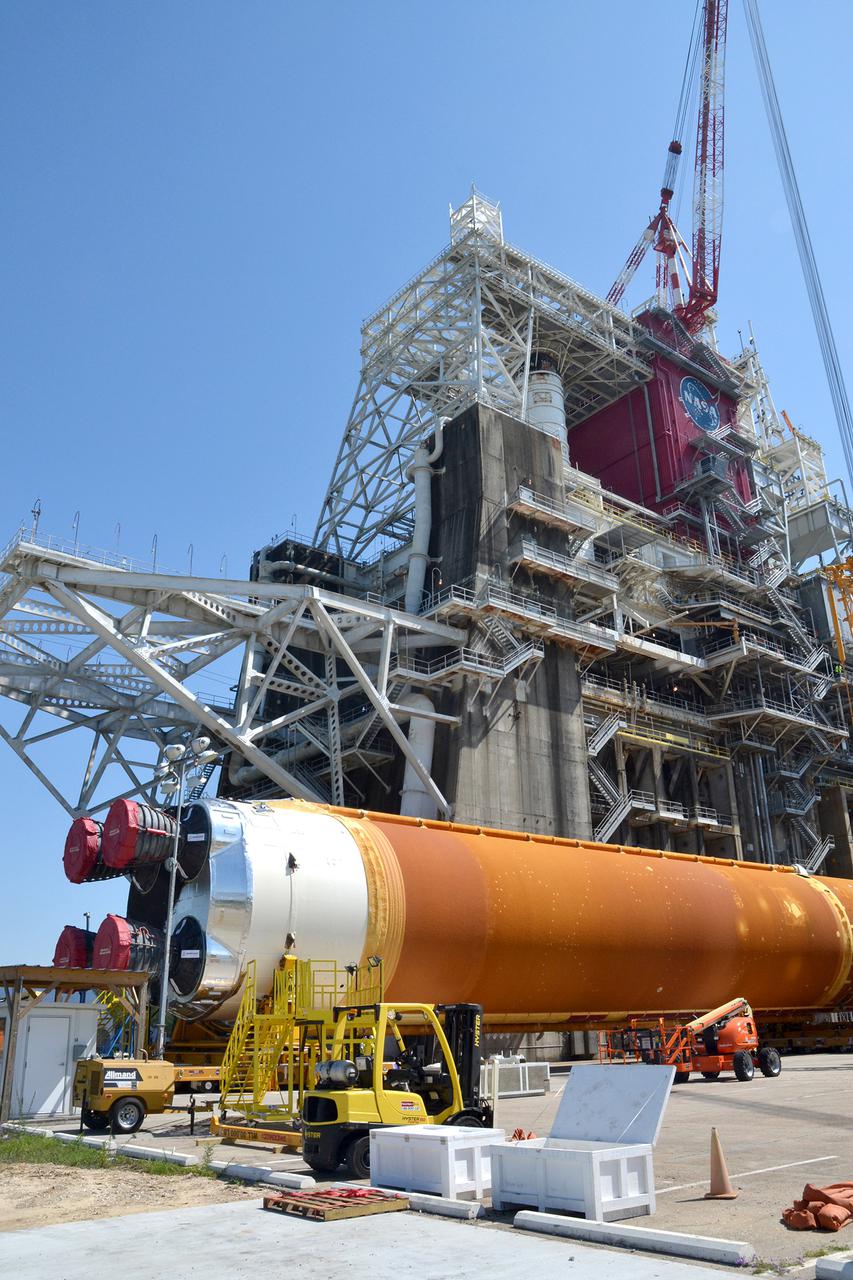

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks at an all-hands for employees following the State of NASA address, Monday, Feb. 10, 2020, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
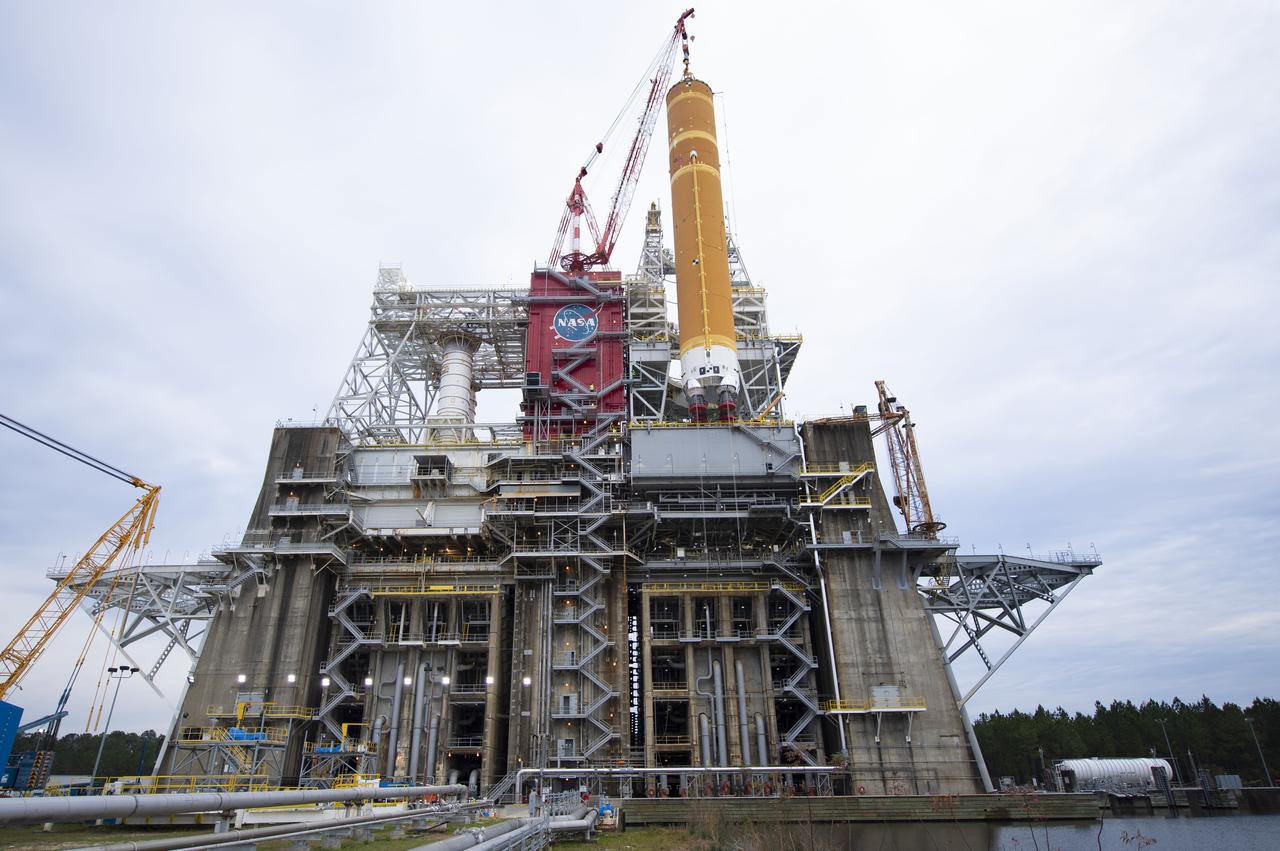

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
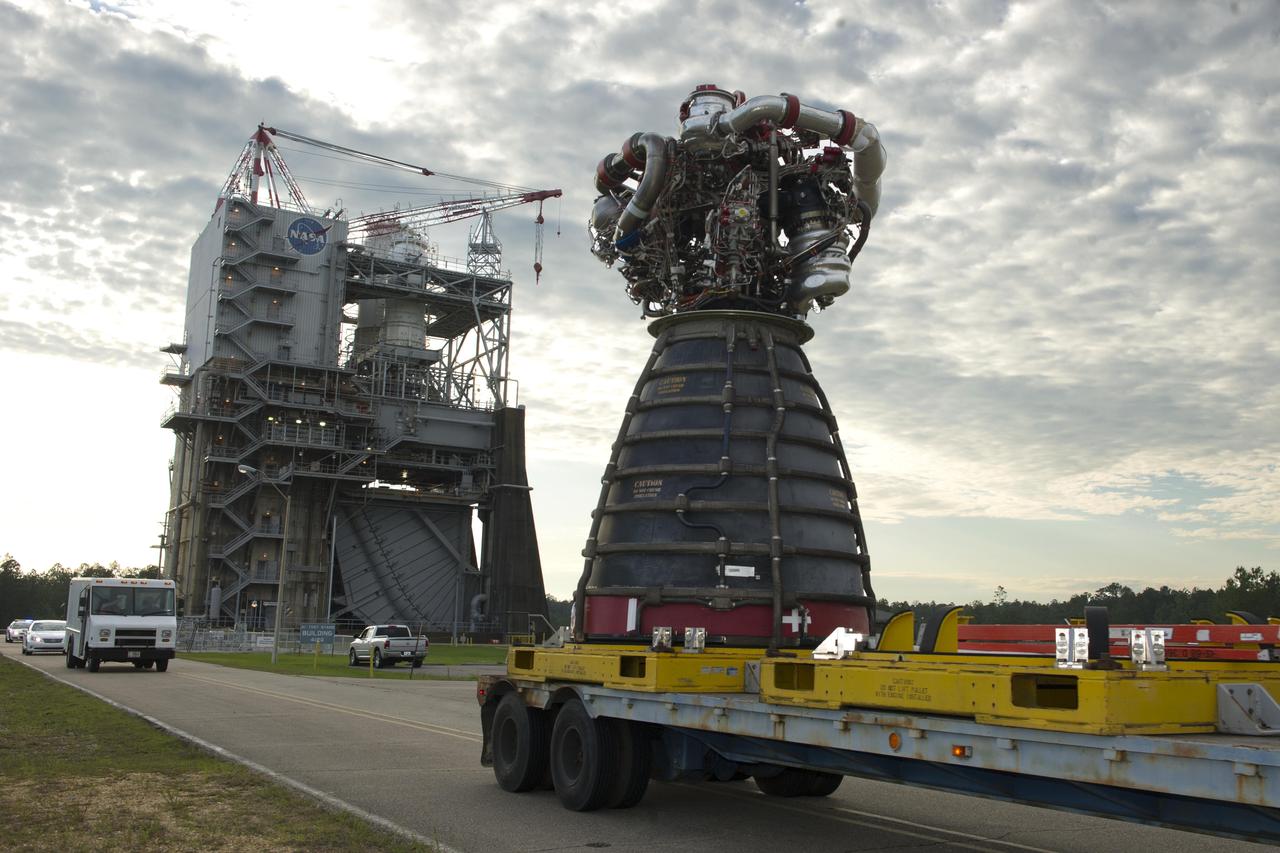

RS-25 rocket engine No. 2059 is removed from the A-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on May 19, 2016. The engine was tested March 10 on the stand and is ready for use on NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) vehicle. NASA is developing the SLS to carry humans deeper into space than ever before. The SLS core stage will be powered by four RS-25 engines. Engine No. 2059 is scheduled for use on the first crewed SLS mission, Exploration Mission-2, which will carry American astronauts beyond low-Earth orbit for the first time since 1972. The photo above shows the engine, as well as the yellow thrust frame adapter above it, which holds the engine in place for testing.
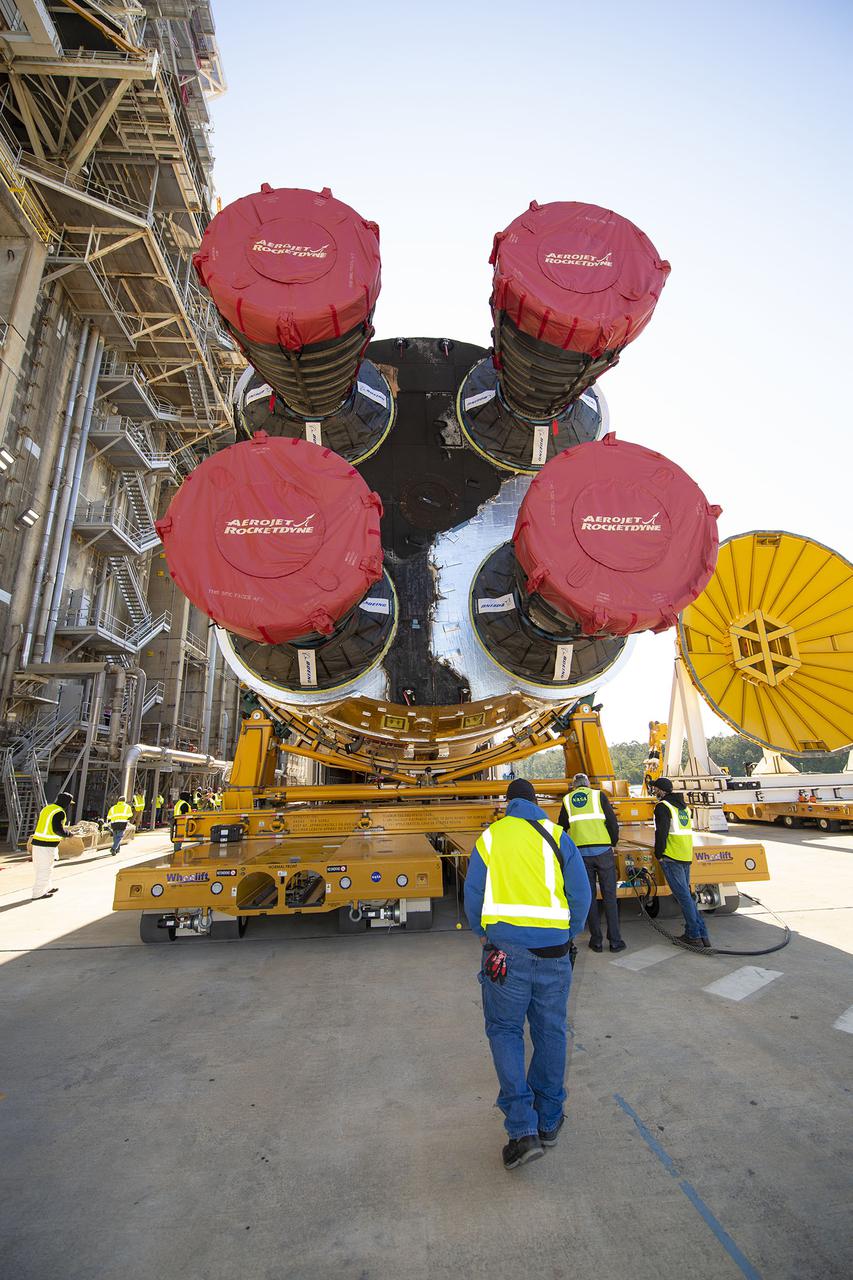

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
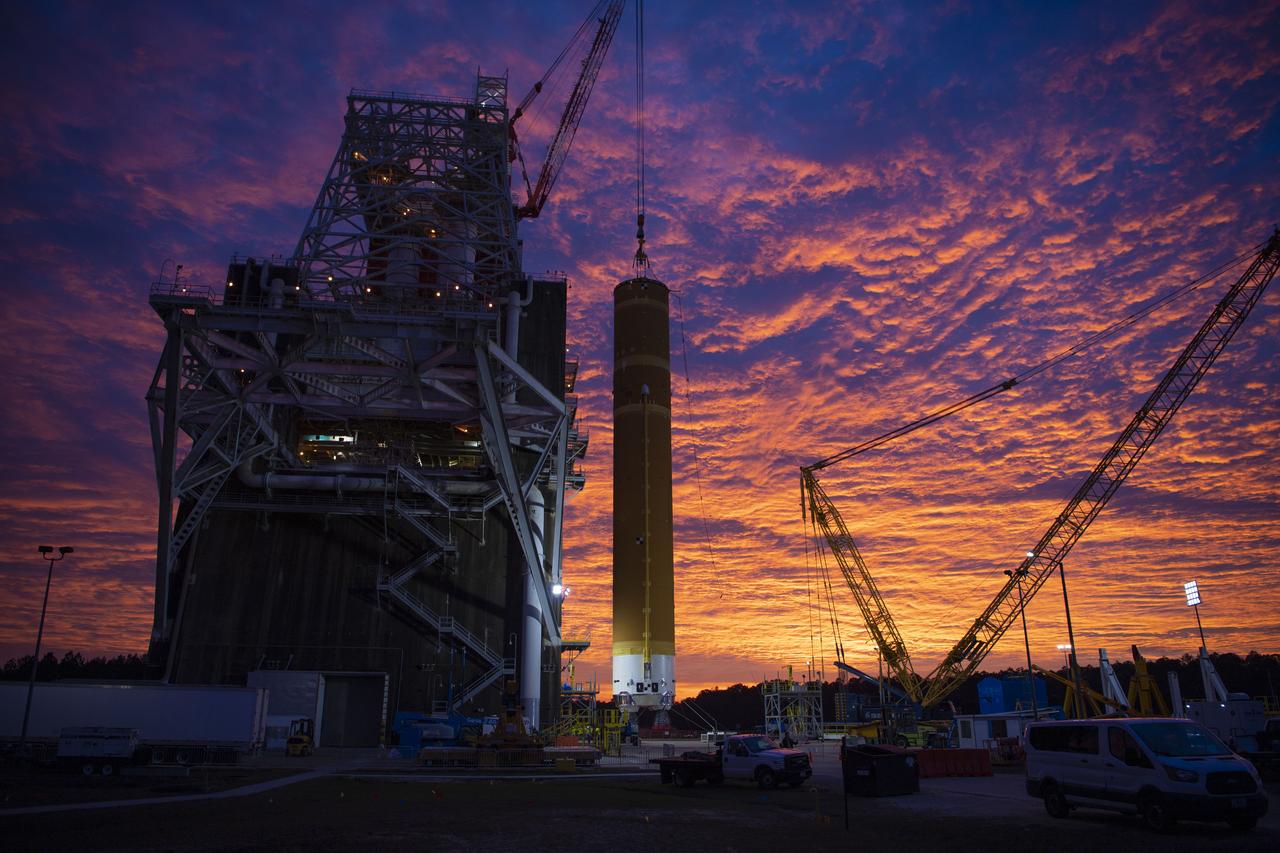

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
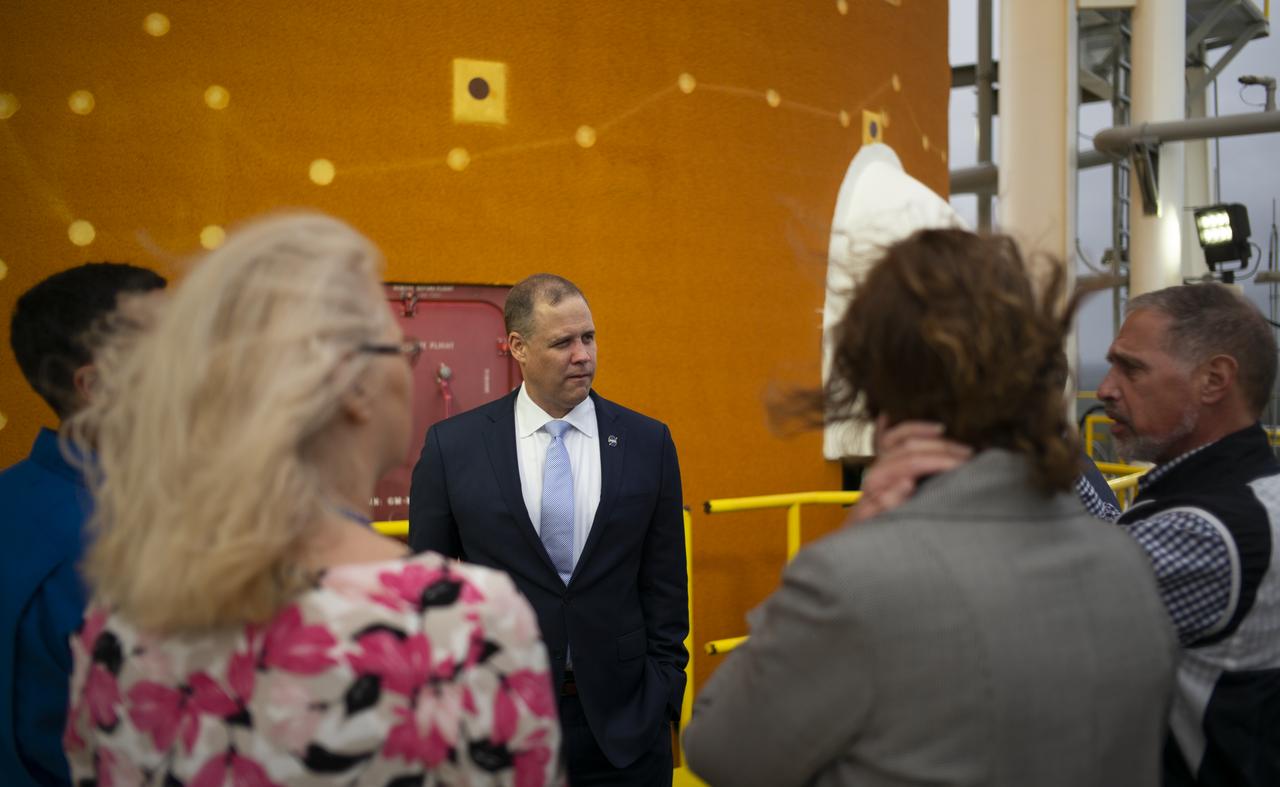

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, center, is seen next to the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket along with Lisa Bates, SLS Deputy Stages Manager at NASA, Mark Nappi, Boeing Green Run Test Manager, Richard Gilbrech, Director of NASA's Stennis Space Center, Julie Bassler, SLS Stages Manager at NASA, and NASA astronaut Raja Chari, during a tour of the B-2 Test Stand, Monday, Feb. 10, 2020, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Over the coming months, the first core stage of NASA’s SLS rocket will be undergoing a series of integrated Green Run tests prior to its maiden flight. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
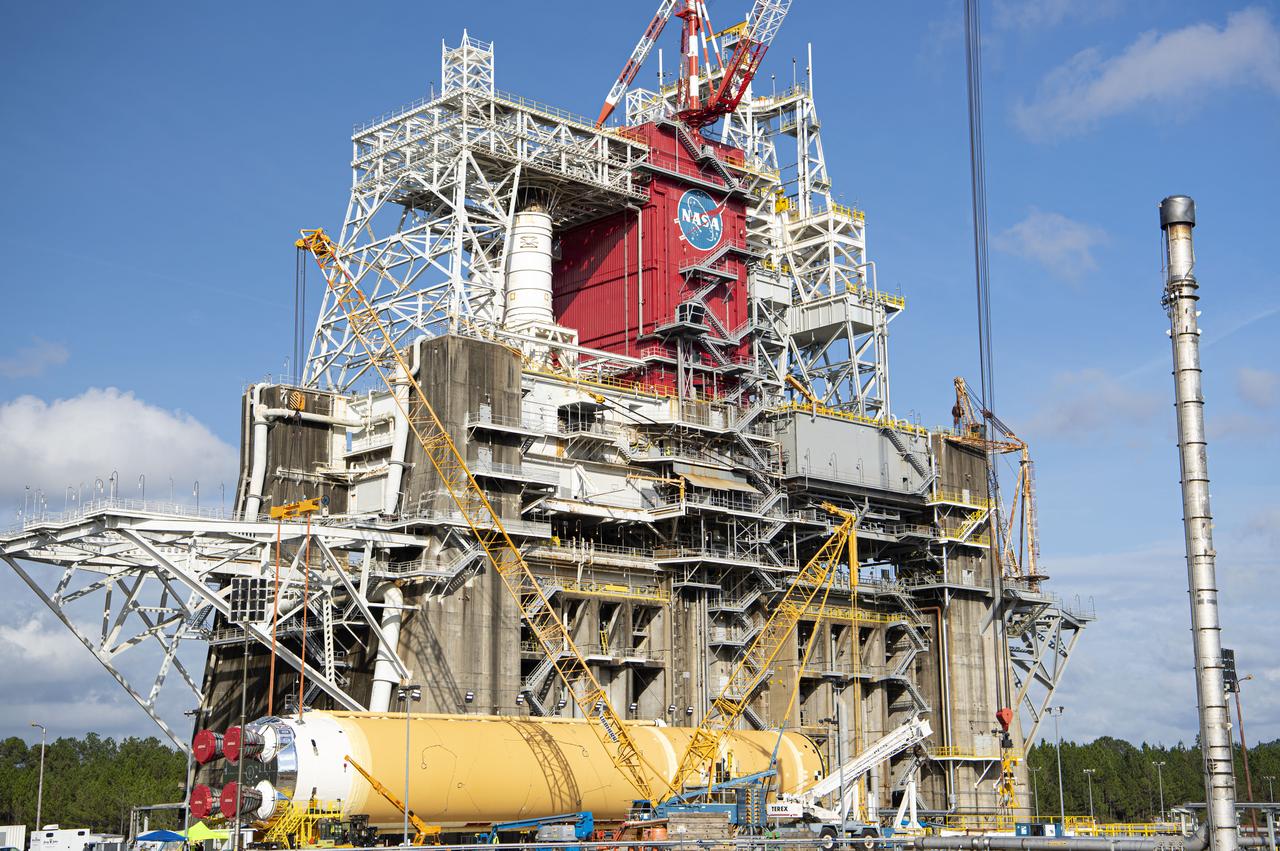

The first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System rocket arrived at Stennis Space Center on Jan. 12 for a series of tests prior to its maiden Artemis I flight. The core stage was transported from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the B-2 Test Stand dock at Stennis aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Soon after arrival, the stage was rolled off of Pegasus onto the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. After the stage is lifted and installed on the B-2 stand, it will undergo a series of “Green Run” systems test that represent the first integrated testing of its sophisticated systems.
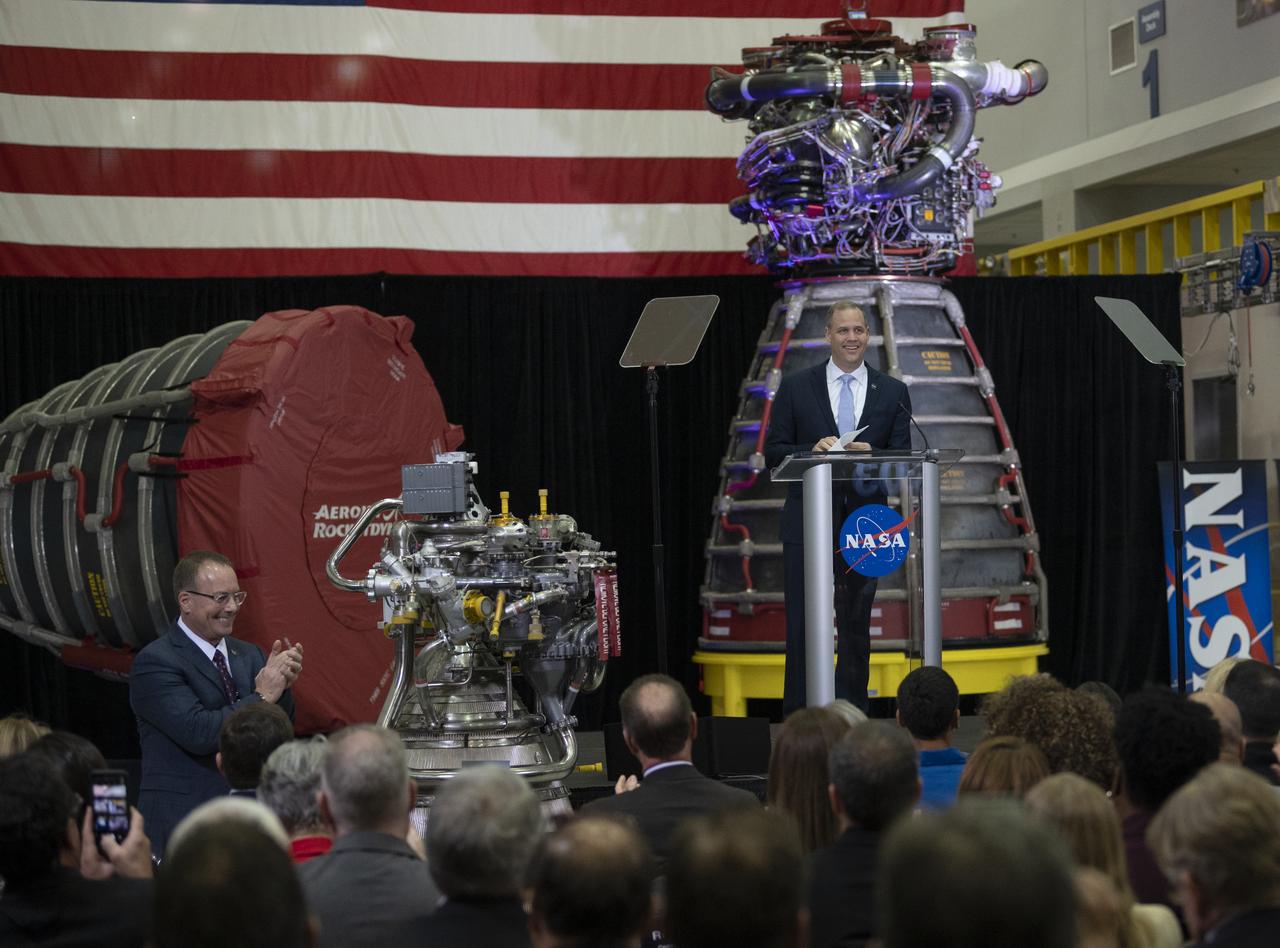

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine discusses the fiscal year 2021 budget proposal during a State of NASA address, Monday, Feb. 10, 2020, at Aerojet Rocketdyne’s facility at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

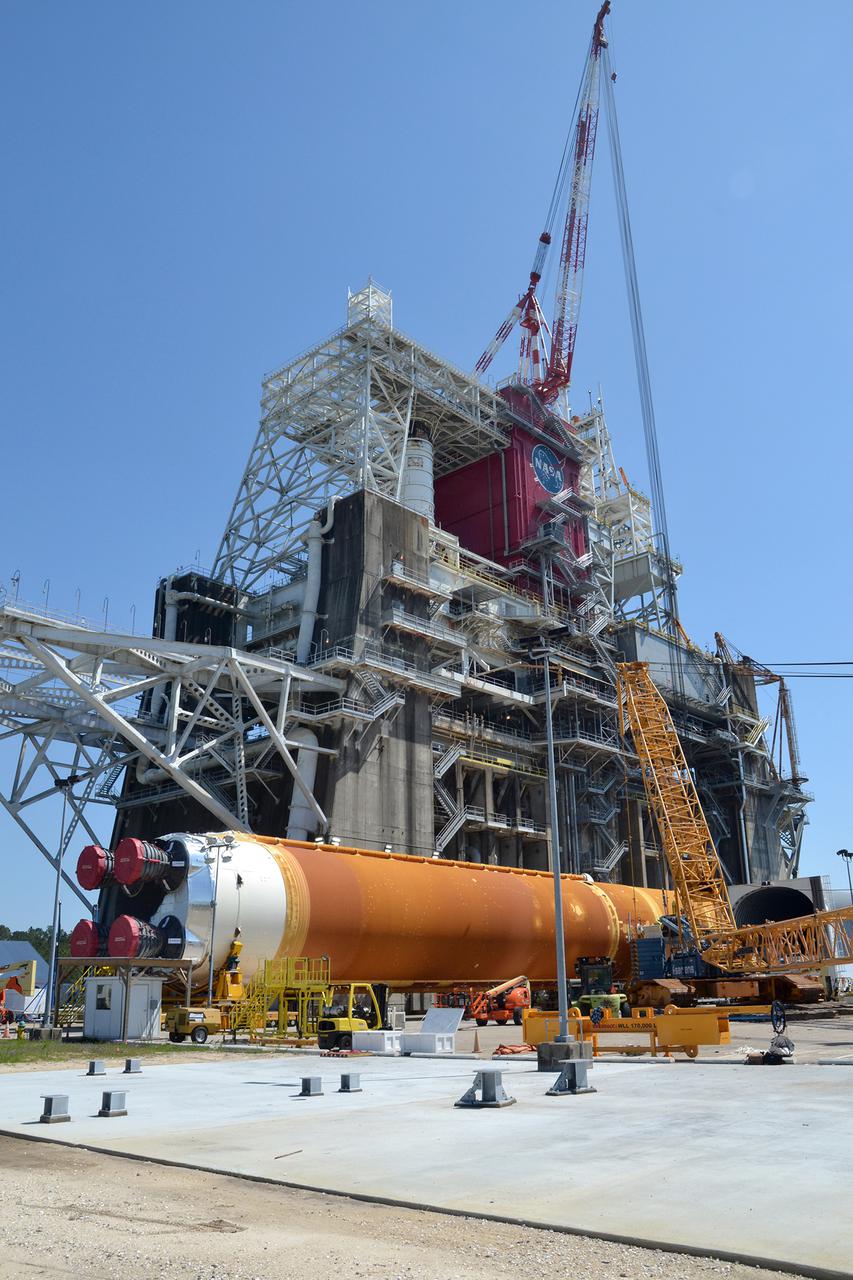
On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
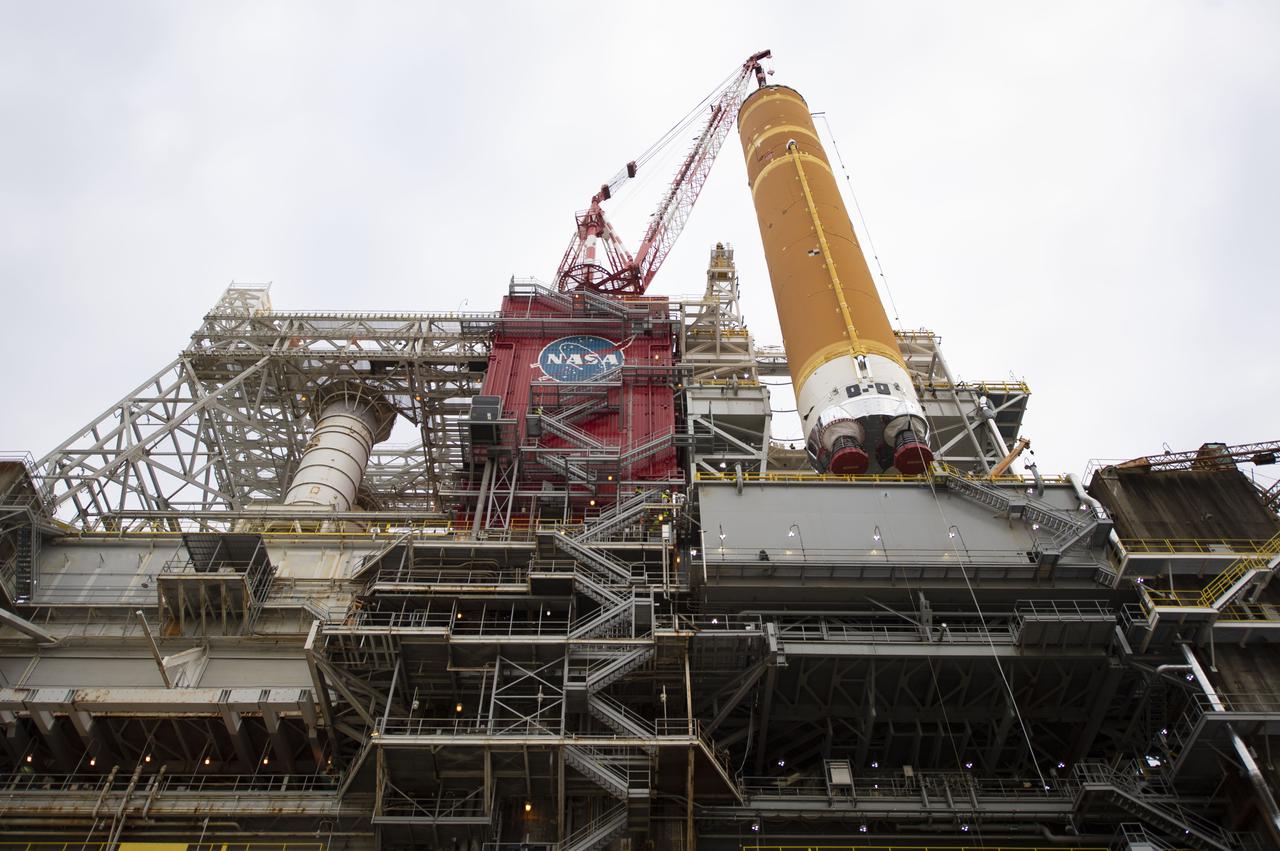

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.

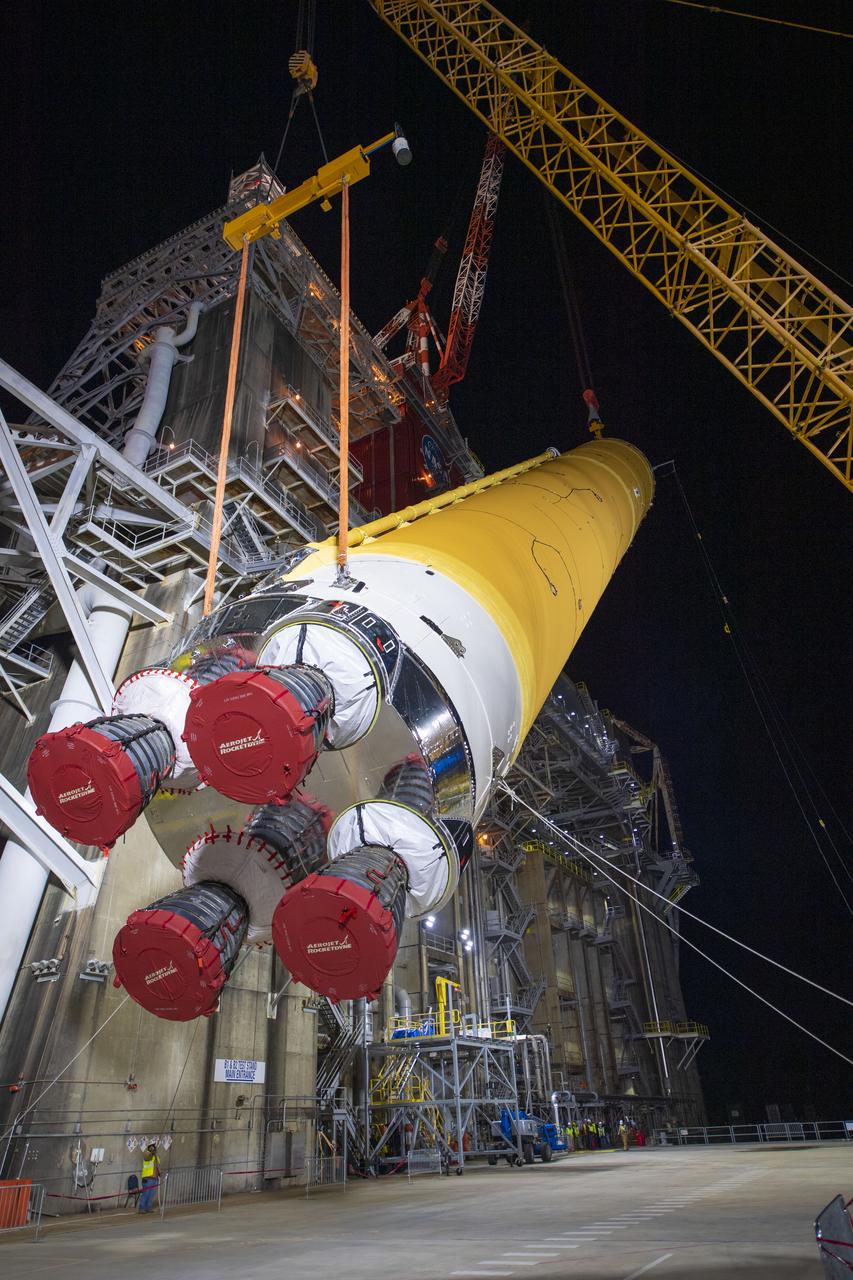
Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
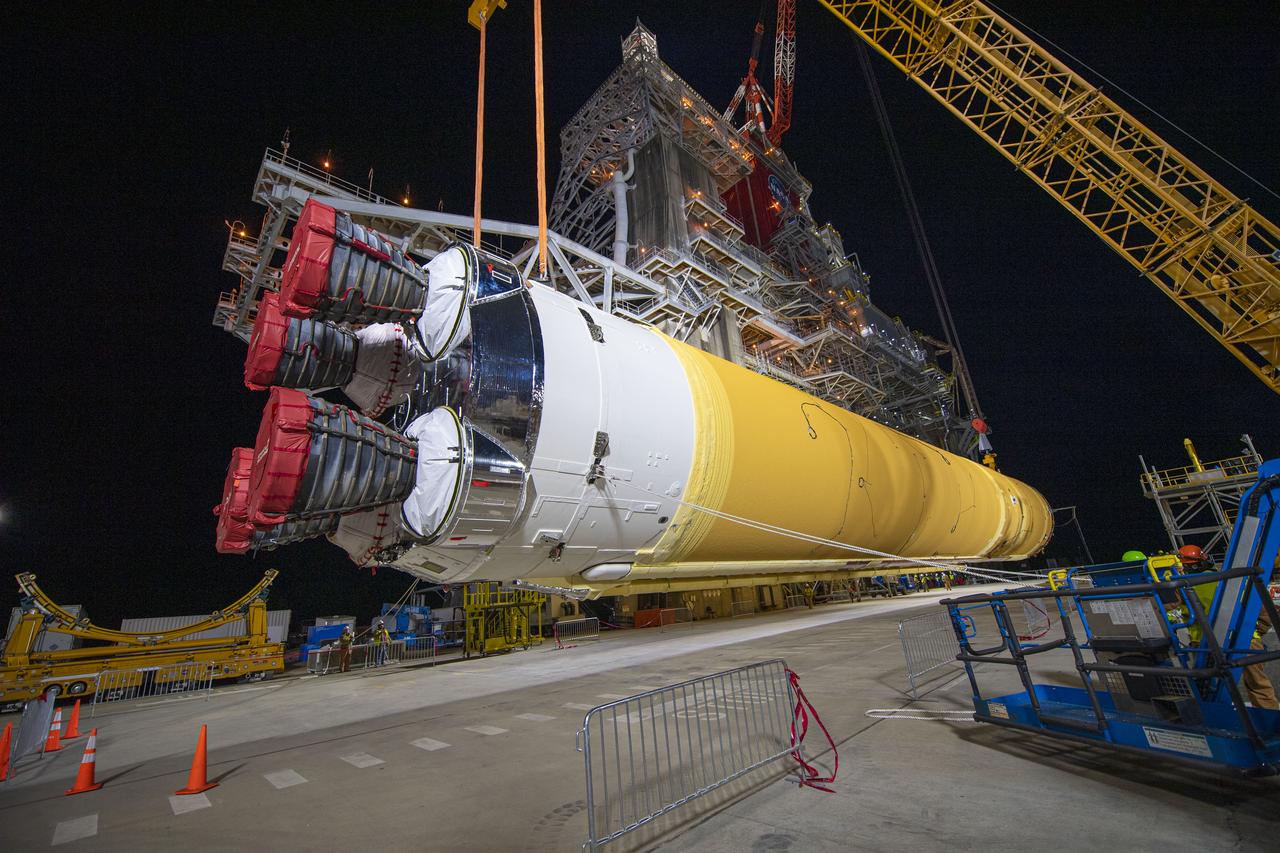

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
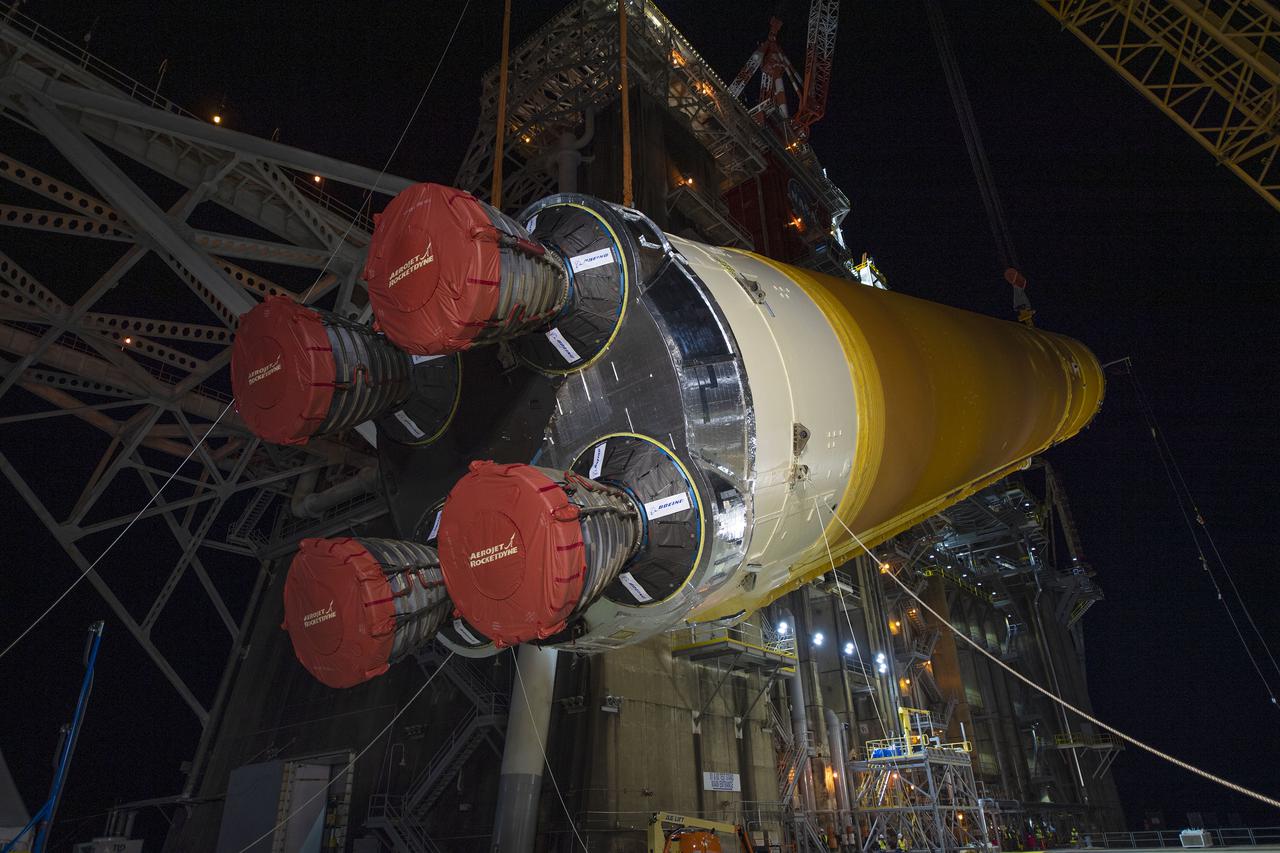
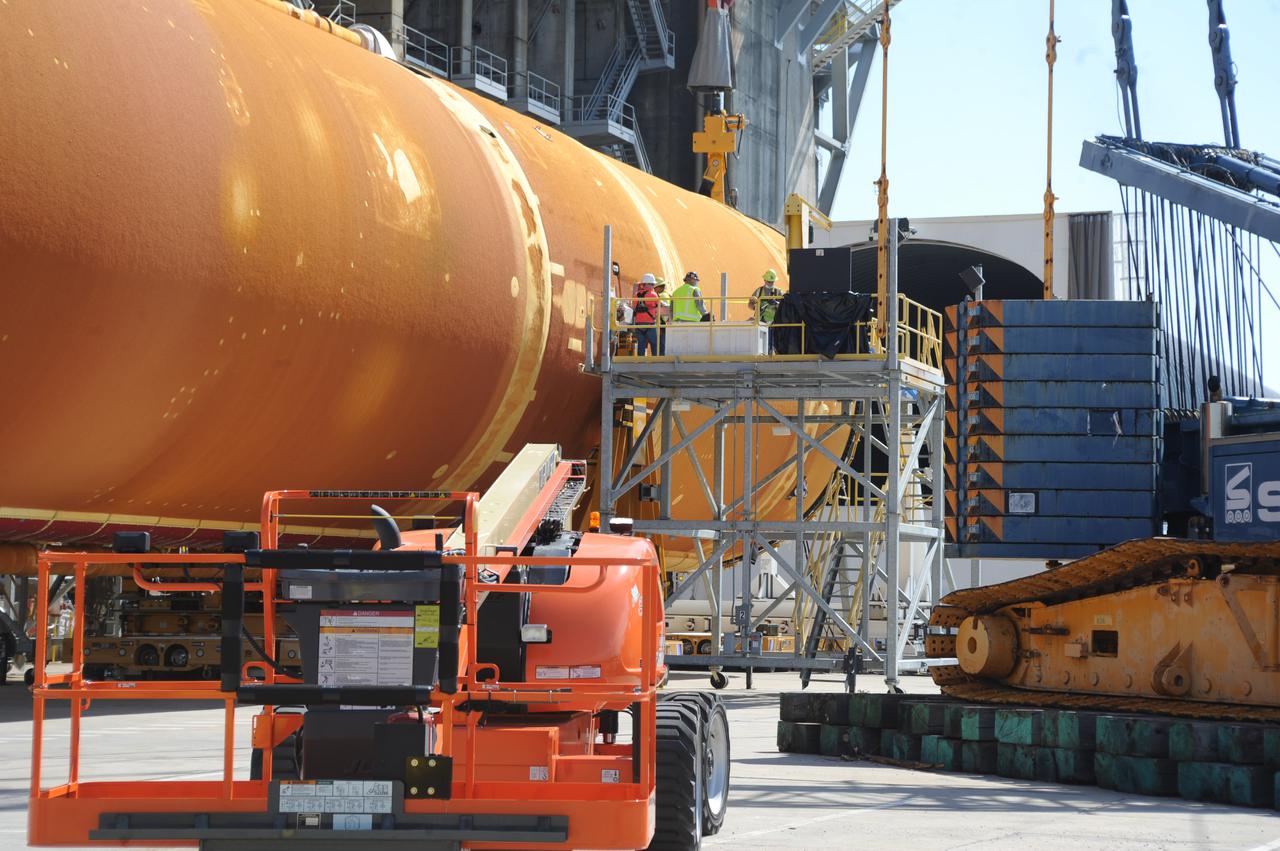
Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
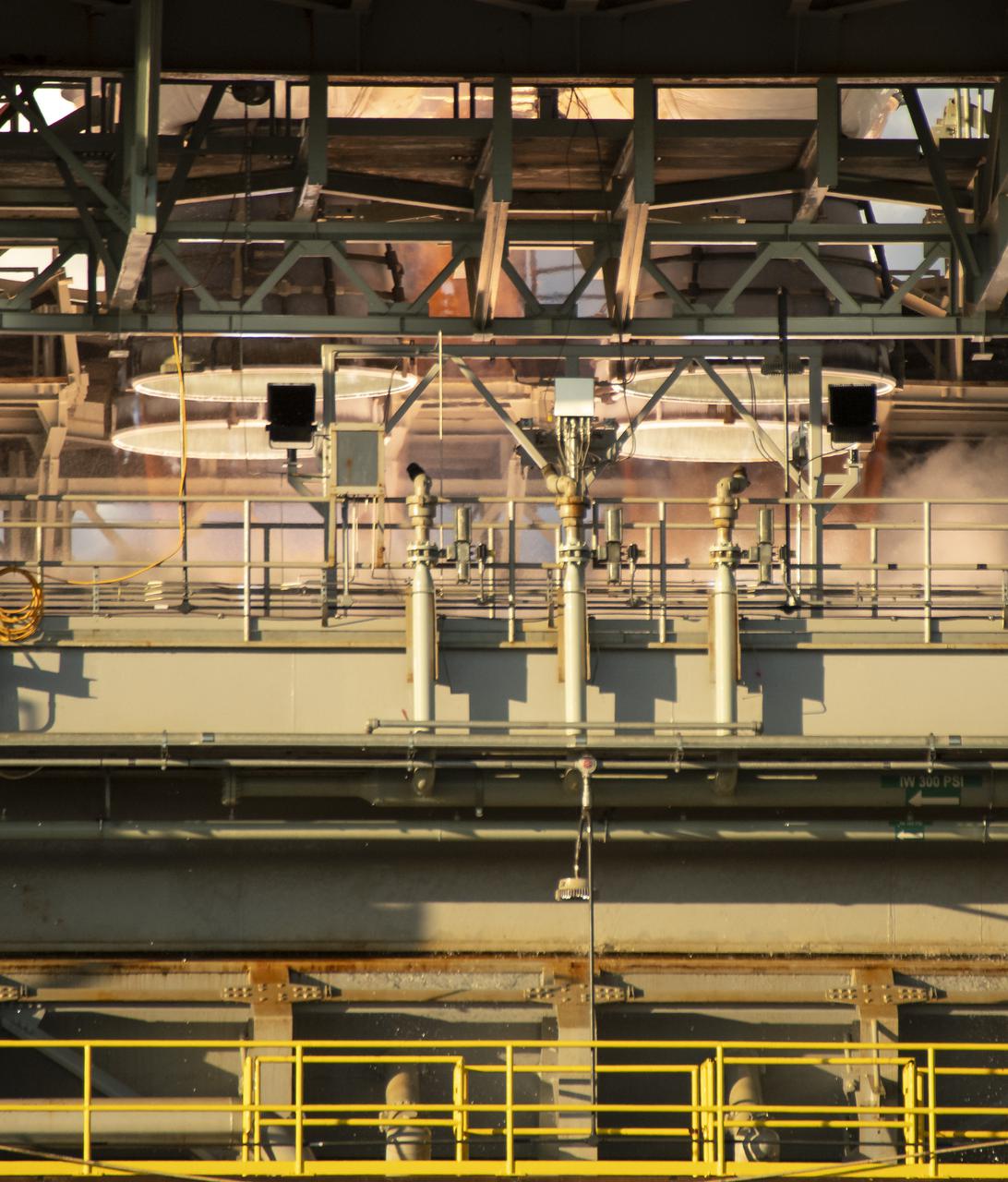

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
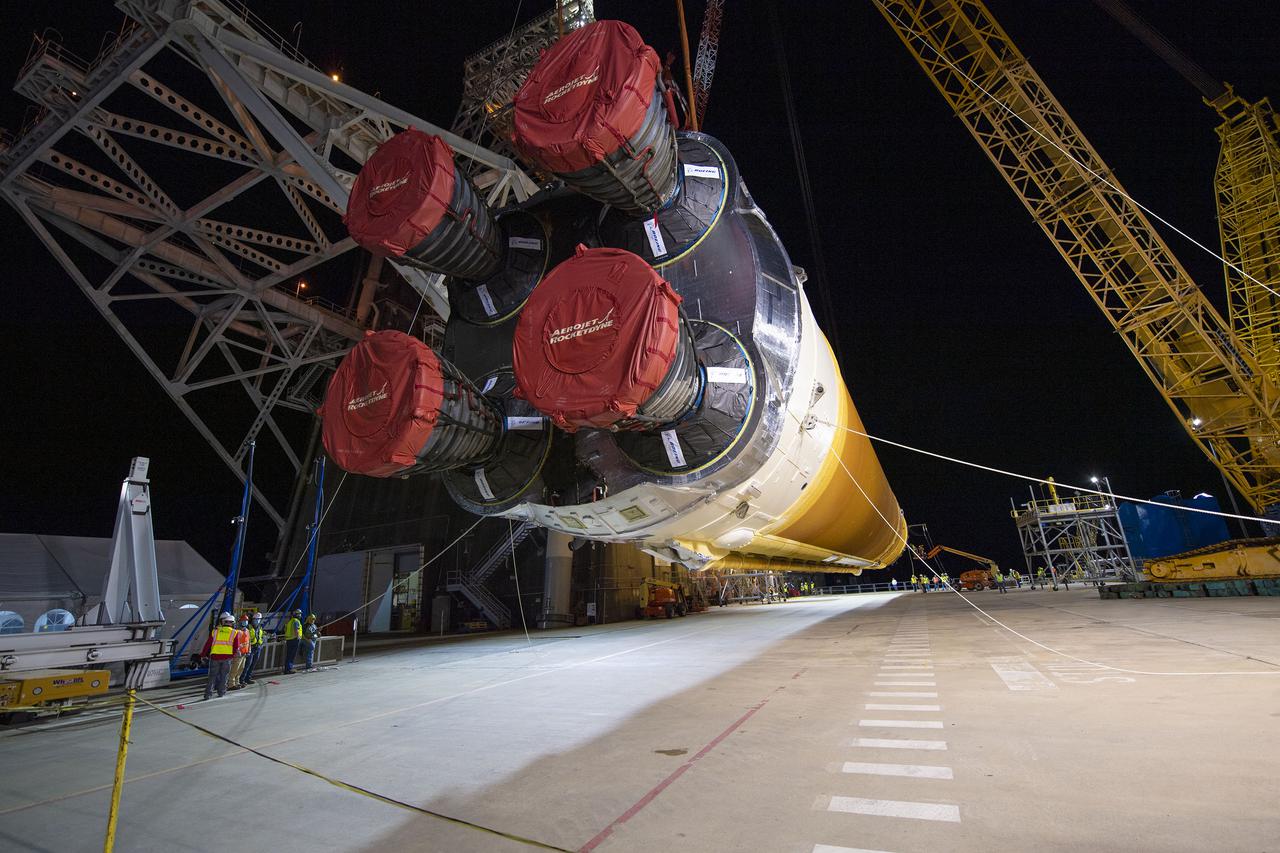

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
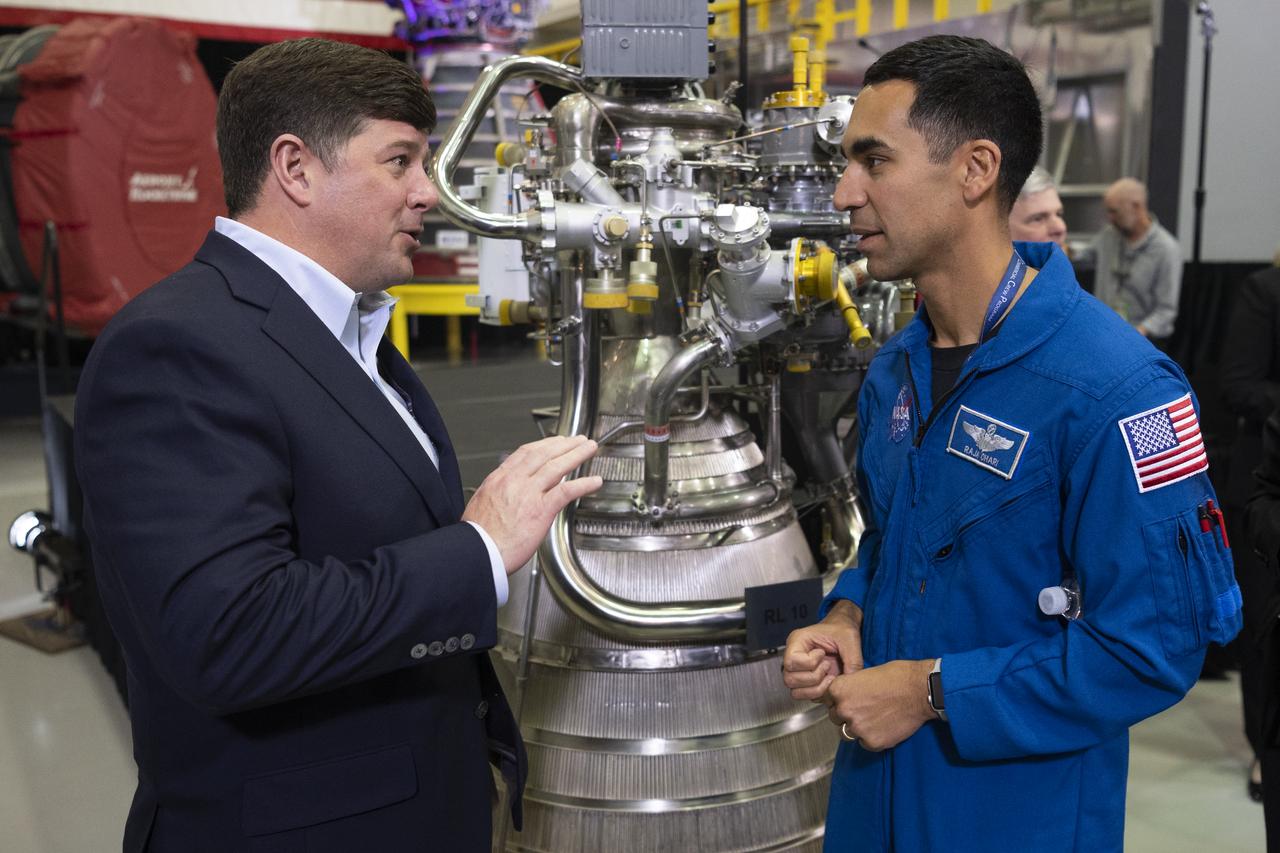

U.S. Representative Steven Palazzo (R-Miss.), left, speaks with NASA astronaut Raja Chari following the State of NASA address, Monday, Feb. 10, 2020, at Aerojet Rocketdyne’s facility at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
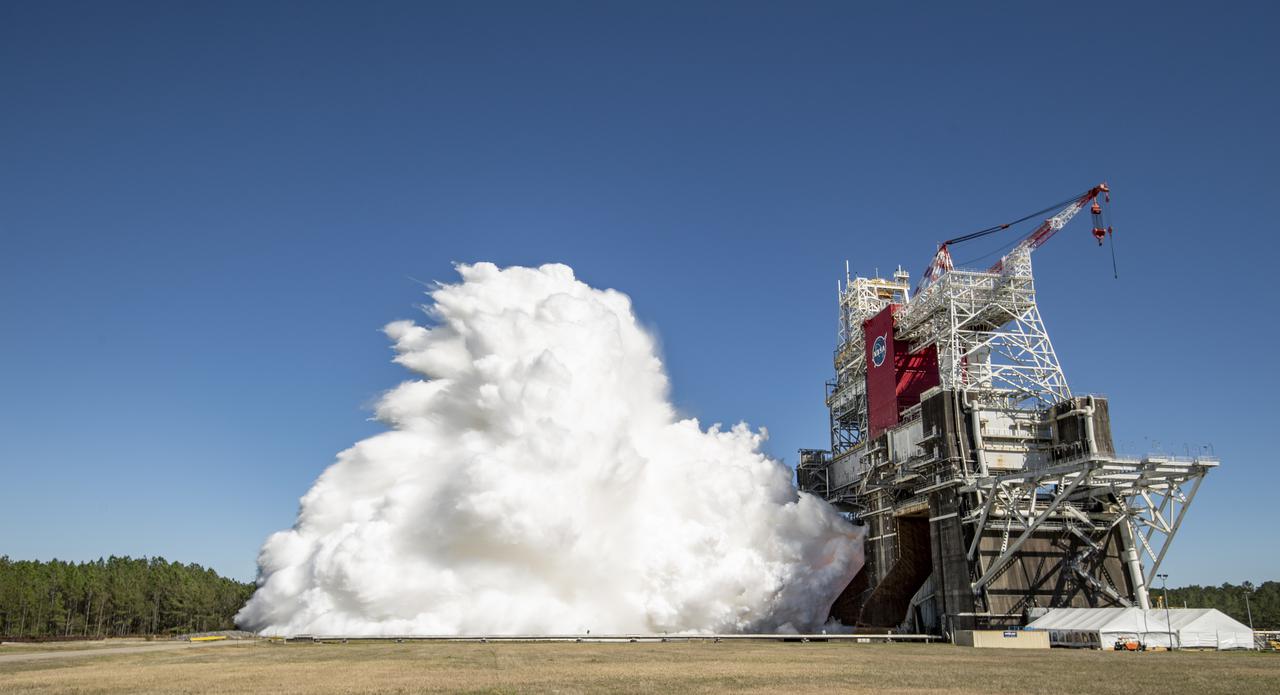

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a second hot fire test, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
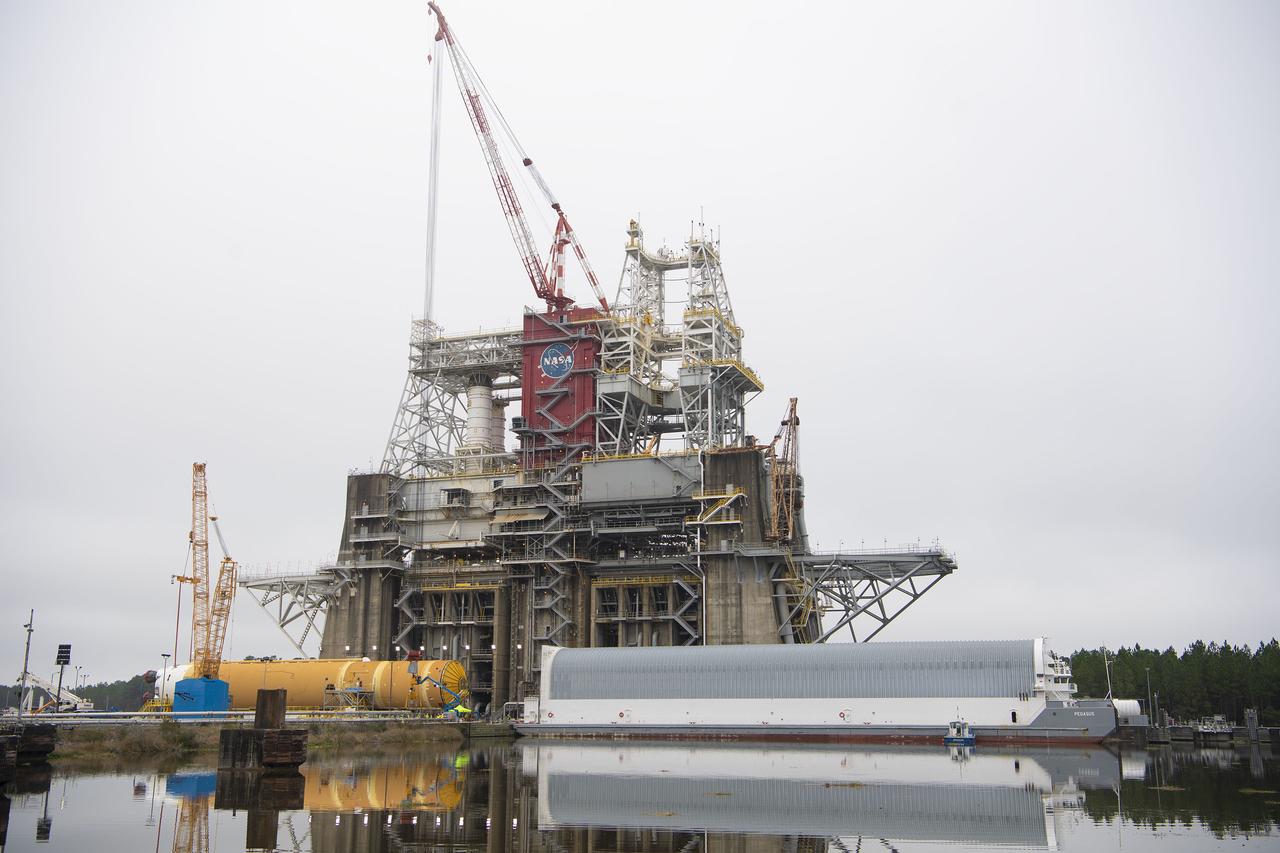

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
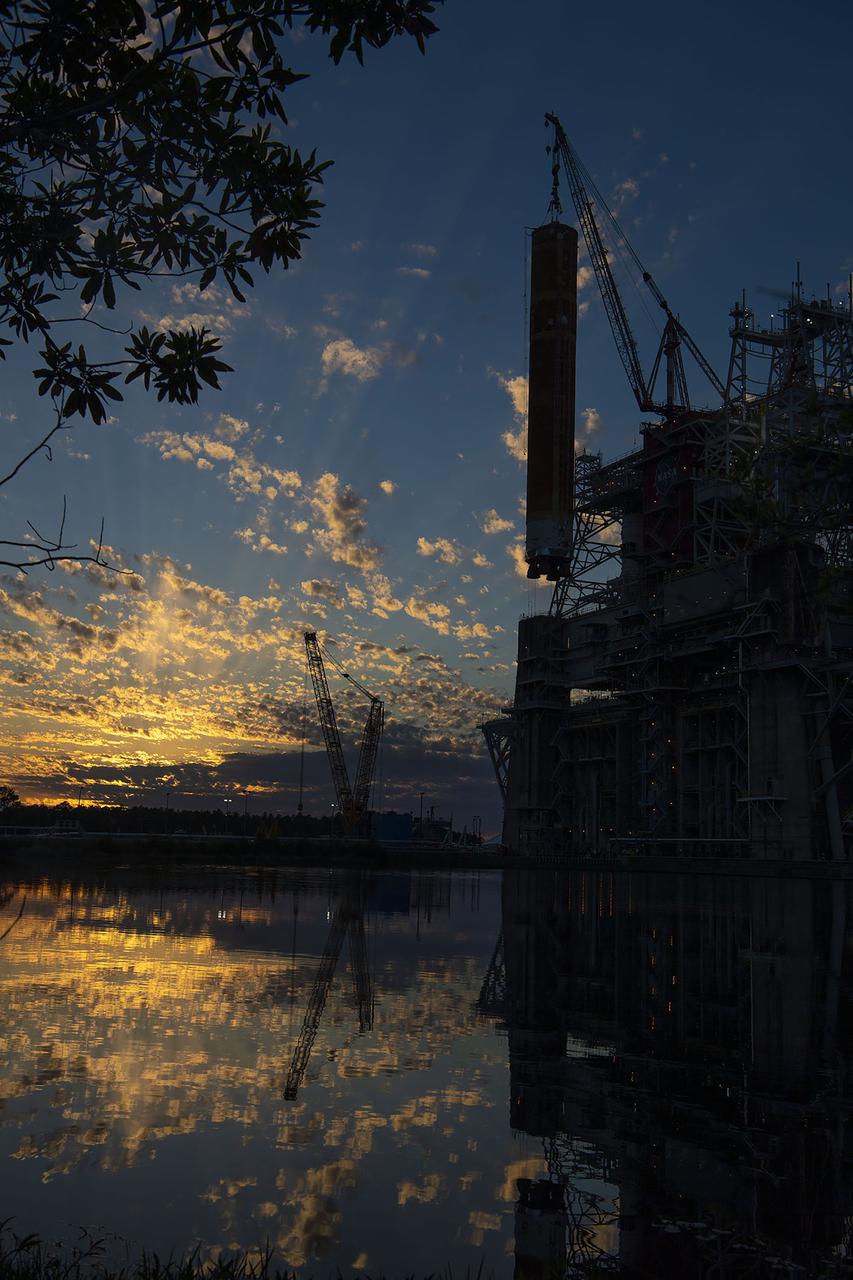

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
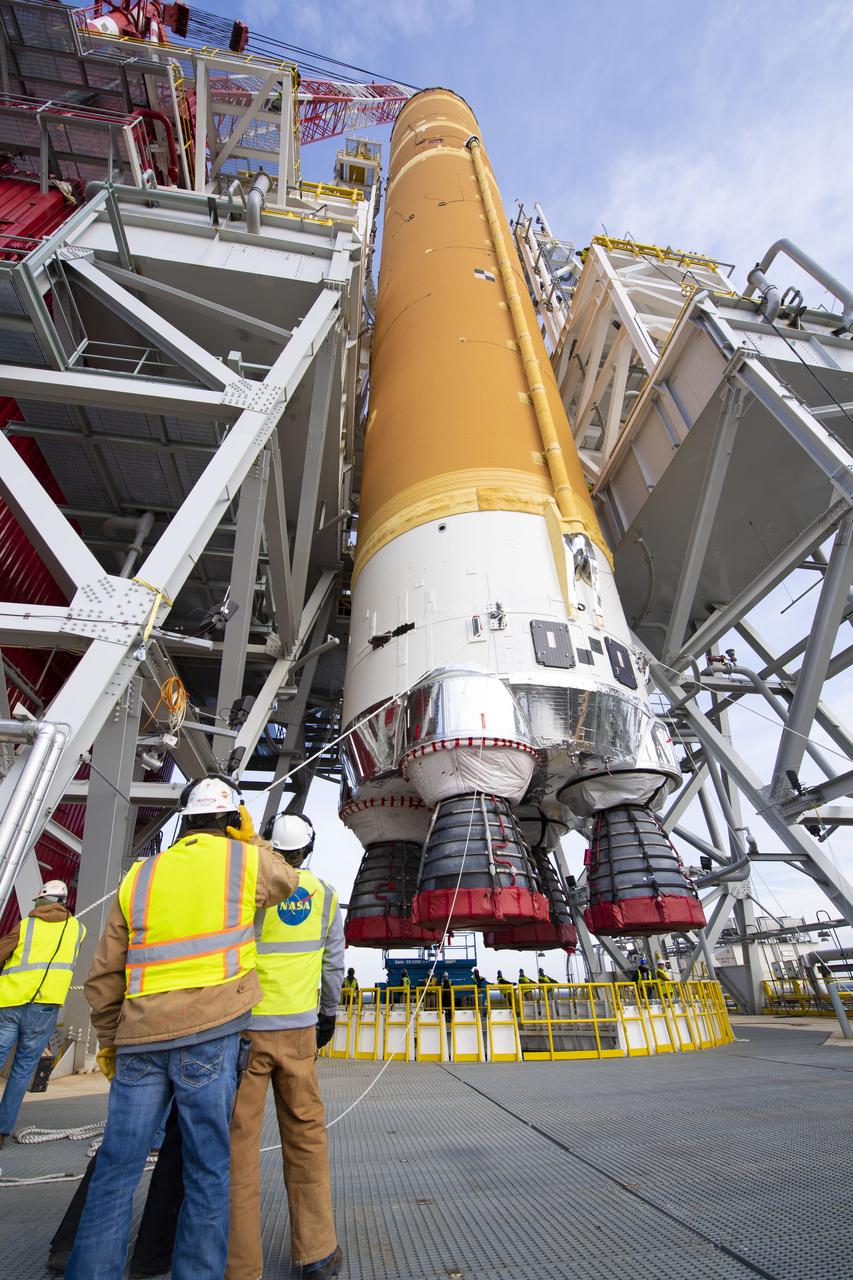

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
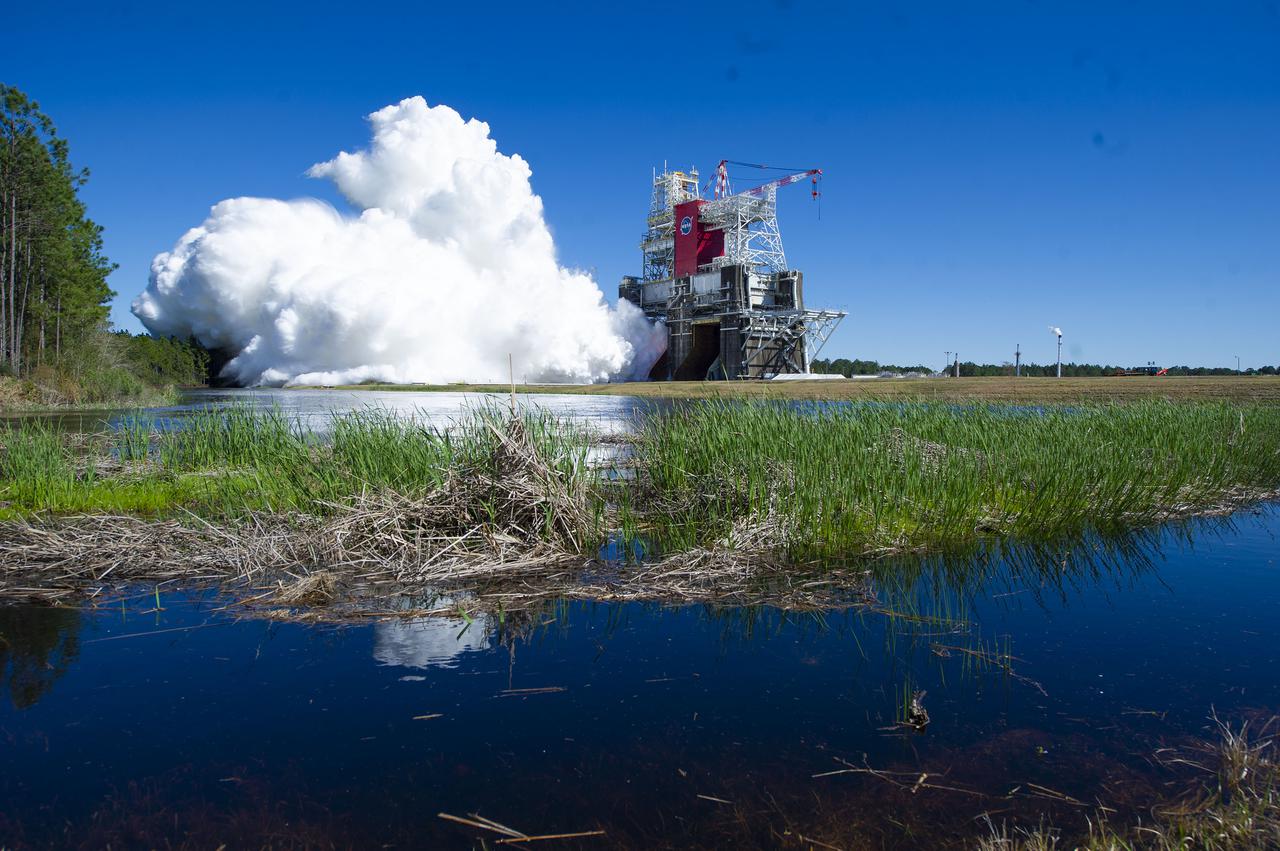

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
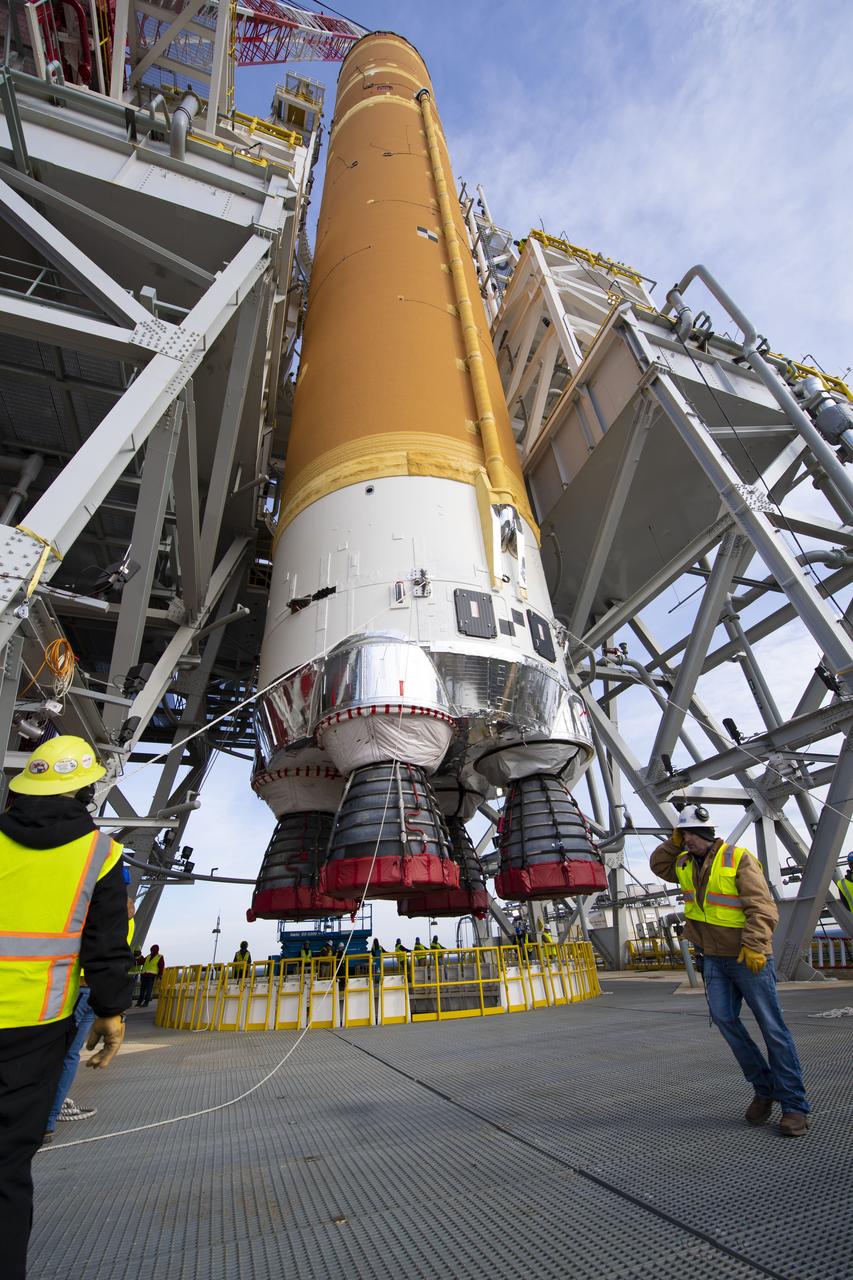

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
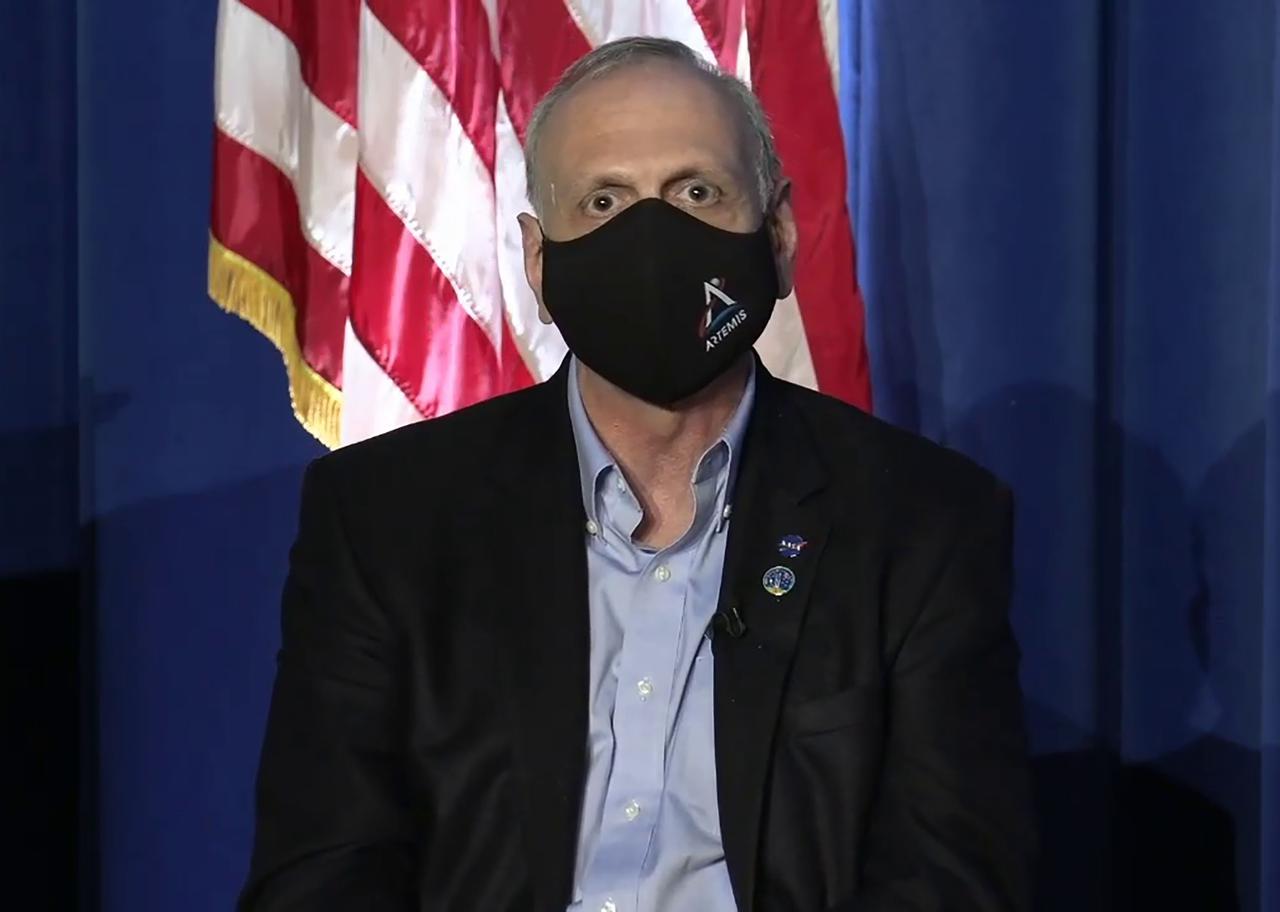

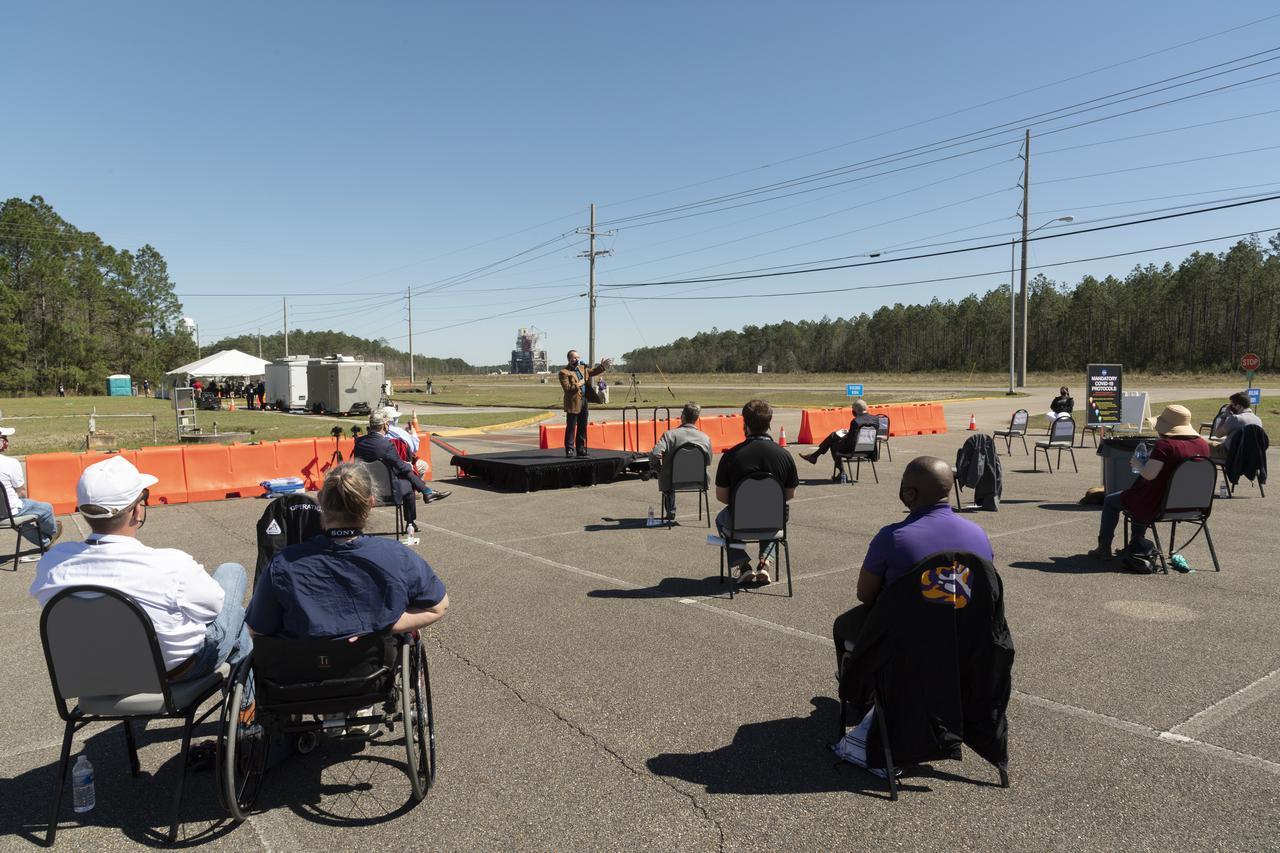
NASA leaders participated in a virtual press briefing following the Space Launch System core stage hot fire test at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18. The leaders fielded questions submitted by offsite media during the post-test session. Agency participants present at Stennis included NASA acting Administrator Steve Jurczyk.

Stennis Space Center; Lunar Eclipse over A-1 test stand
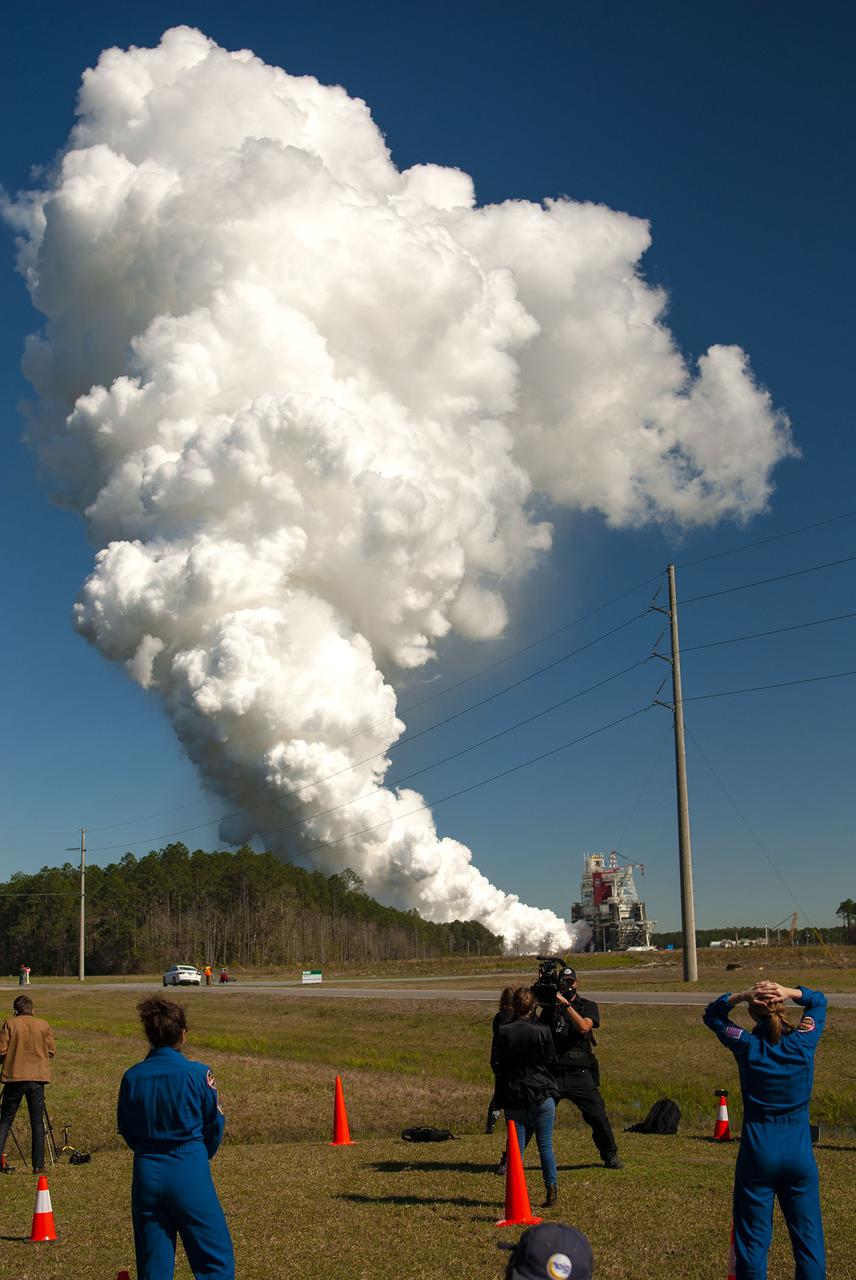

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
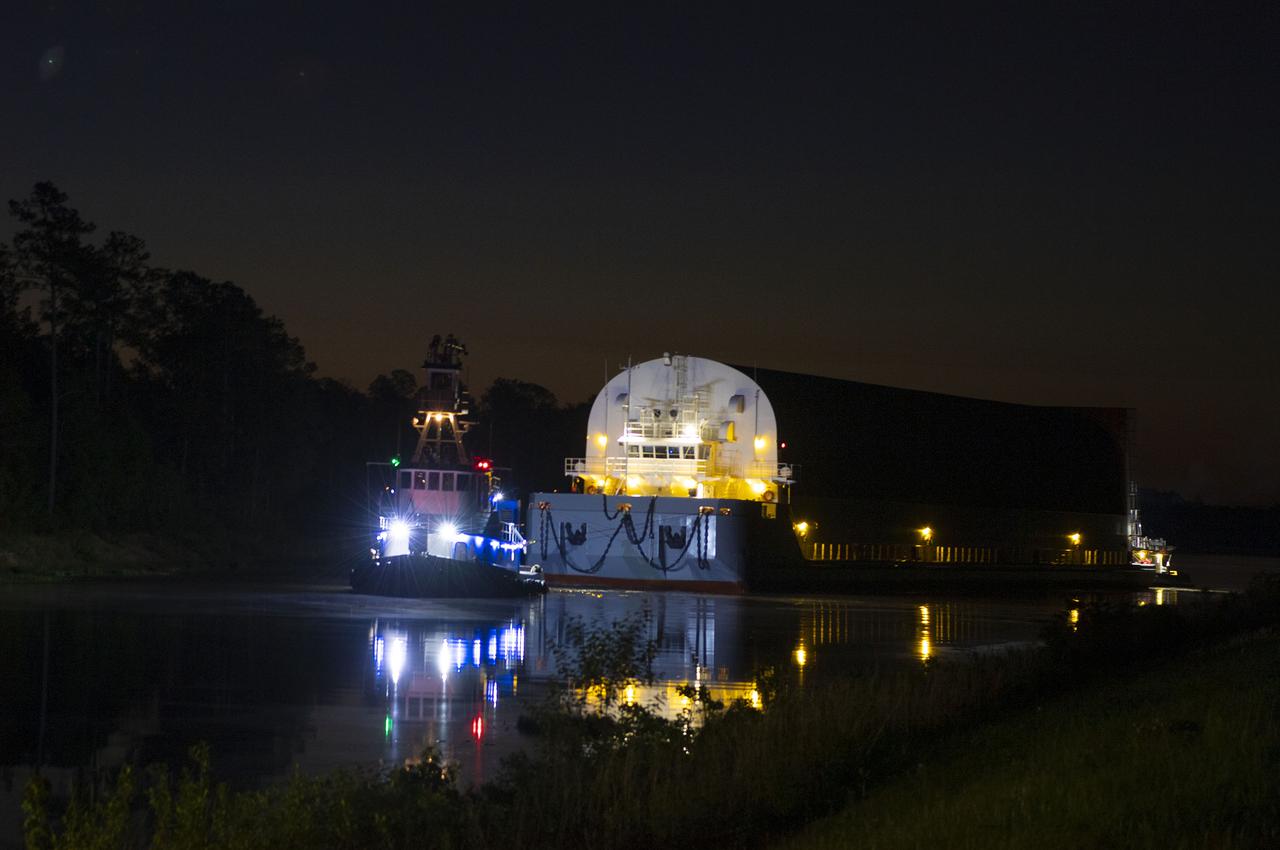

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
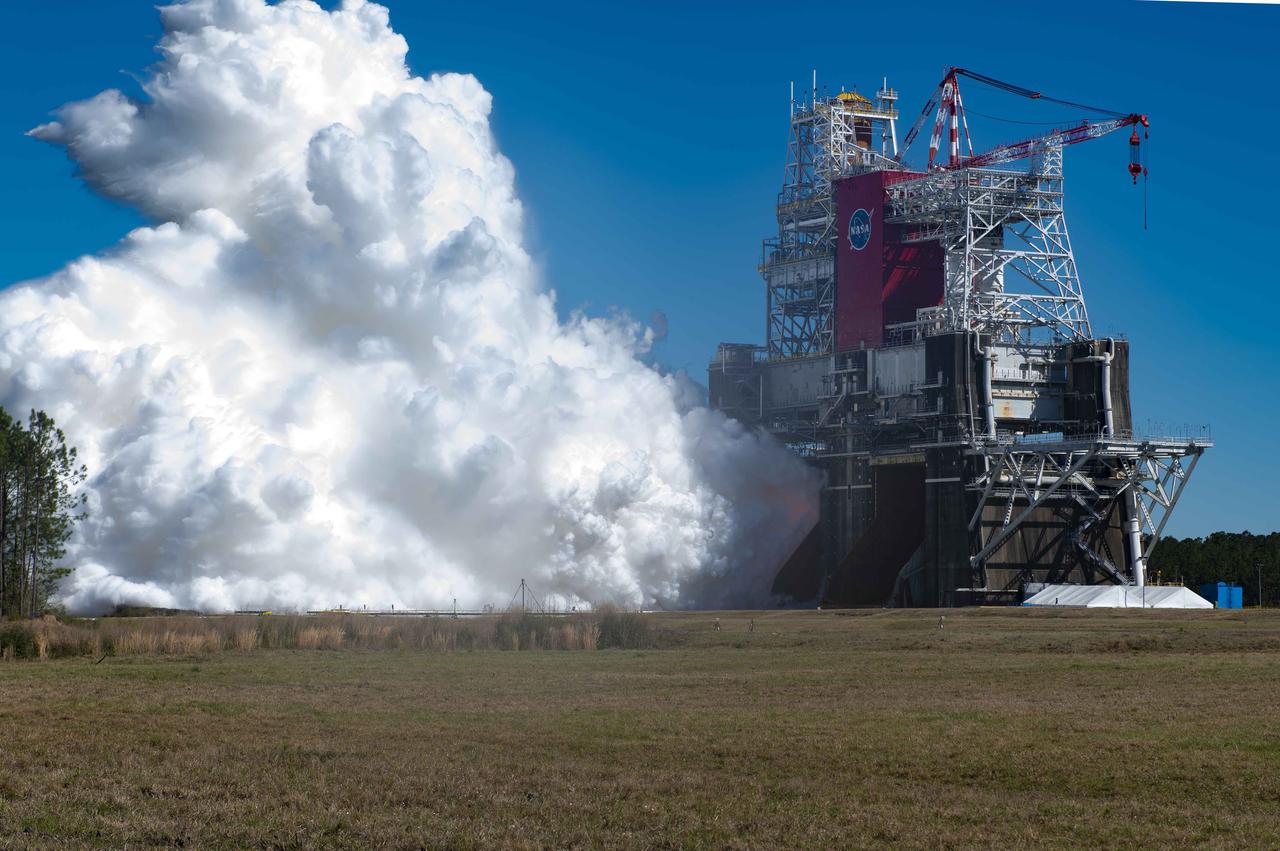

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
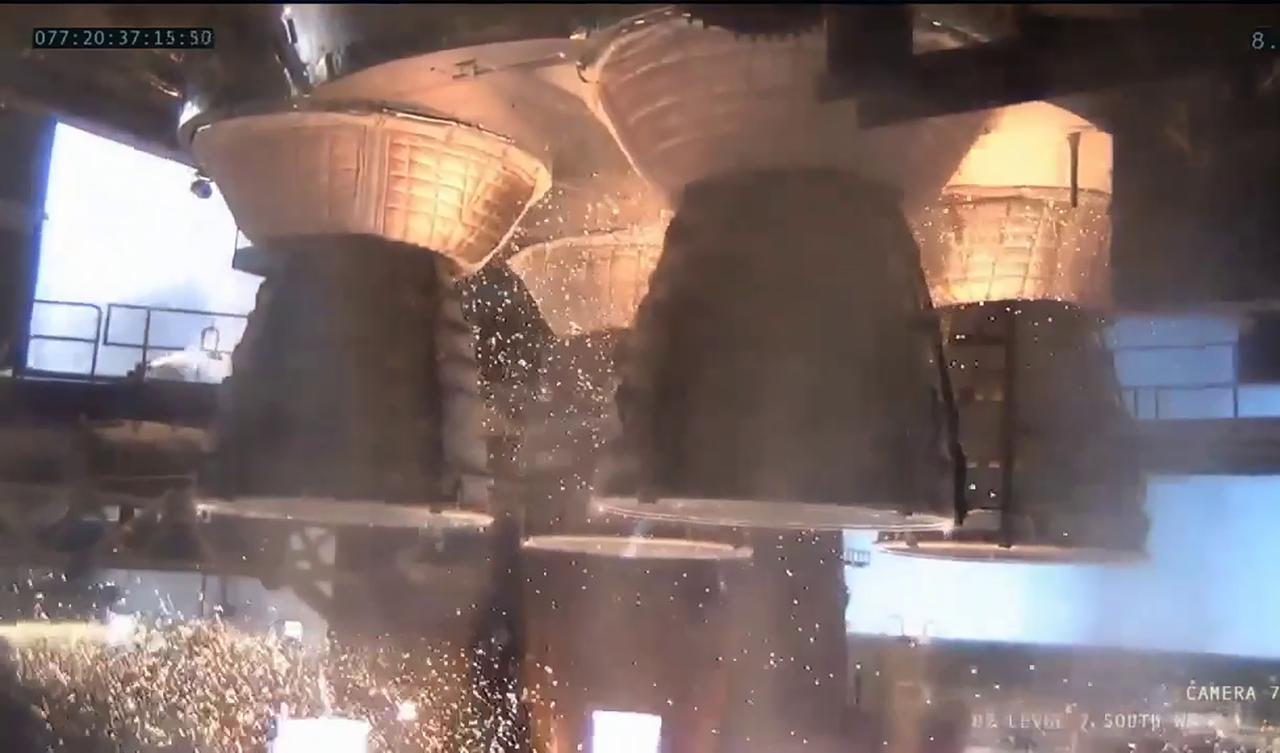

A on-stand camera offers a close-up view as NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines shown in the photo generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
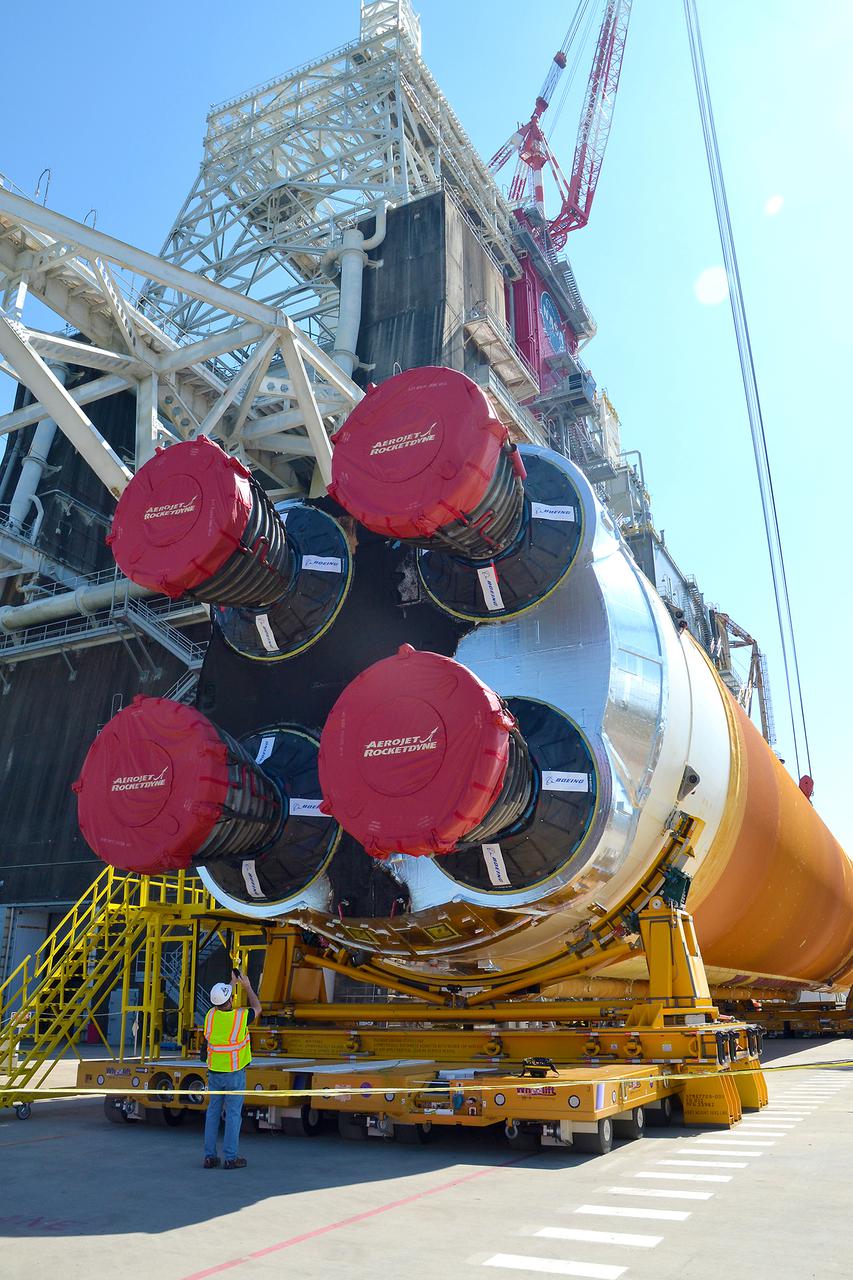

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
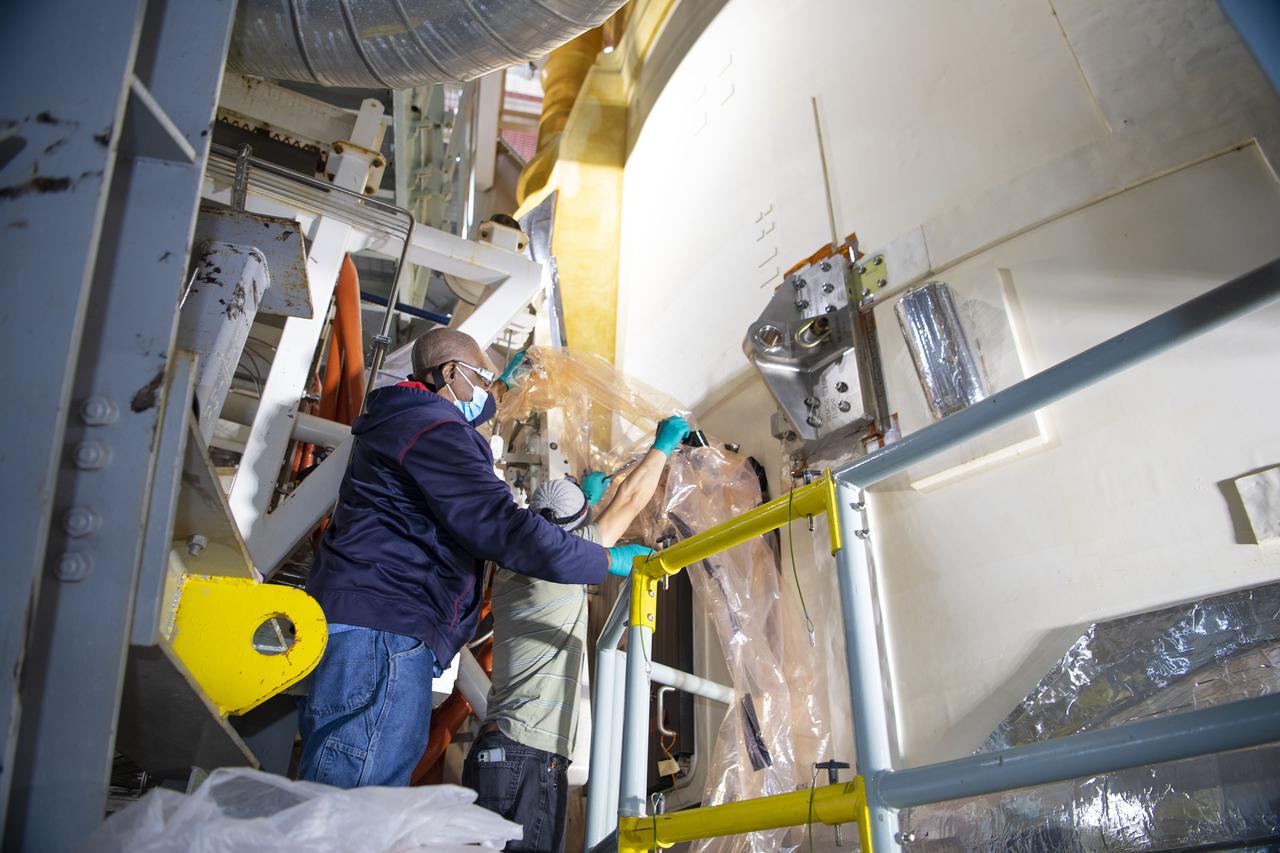

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, complete refurbishment work on the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The work followed a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines March 18. The hot fire marked the culmination of a yearlong Green Run series of tests of the stage and its integrated systems. Following refurbishment work, the core stage will be removed from the test stand and transported to Kennedy Space Center in Florida, aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge, shown delivering equipment to the B-2 Test Stand. At Kennedy, the core stage will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
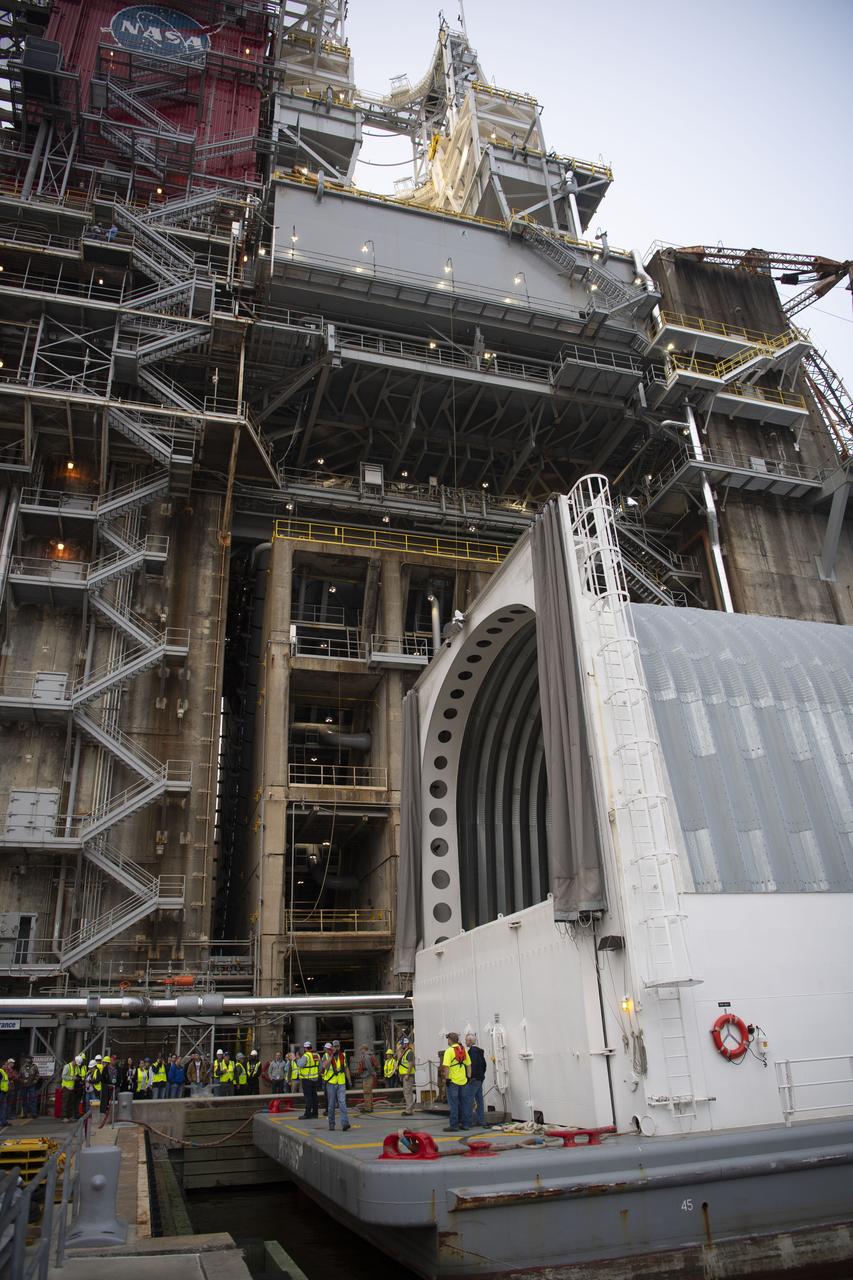

The first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System rocket arrived at Stennis Space Center on Jan. 12 for a series of tests prior to its maiden Artemis I flight. The core stage was transported from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the B-2 Test Stand dock at Stennis aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Soon after arrival, the stage was rolled off of Pegasus onto the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. After the stage is lifted and installed on the B-2 stand, it will undergo a series of “Green Run” systems test that represent the first integrated testing of its sophisticated systems.
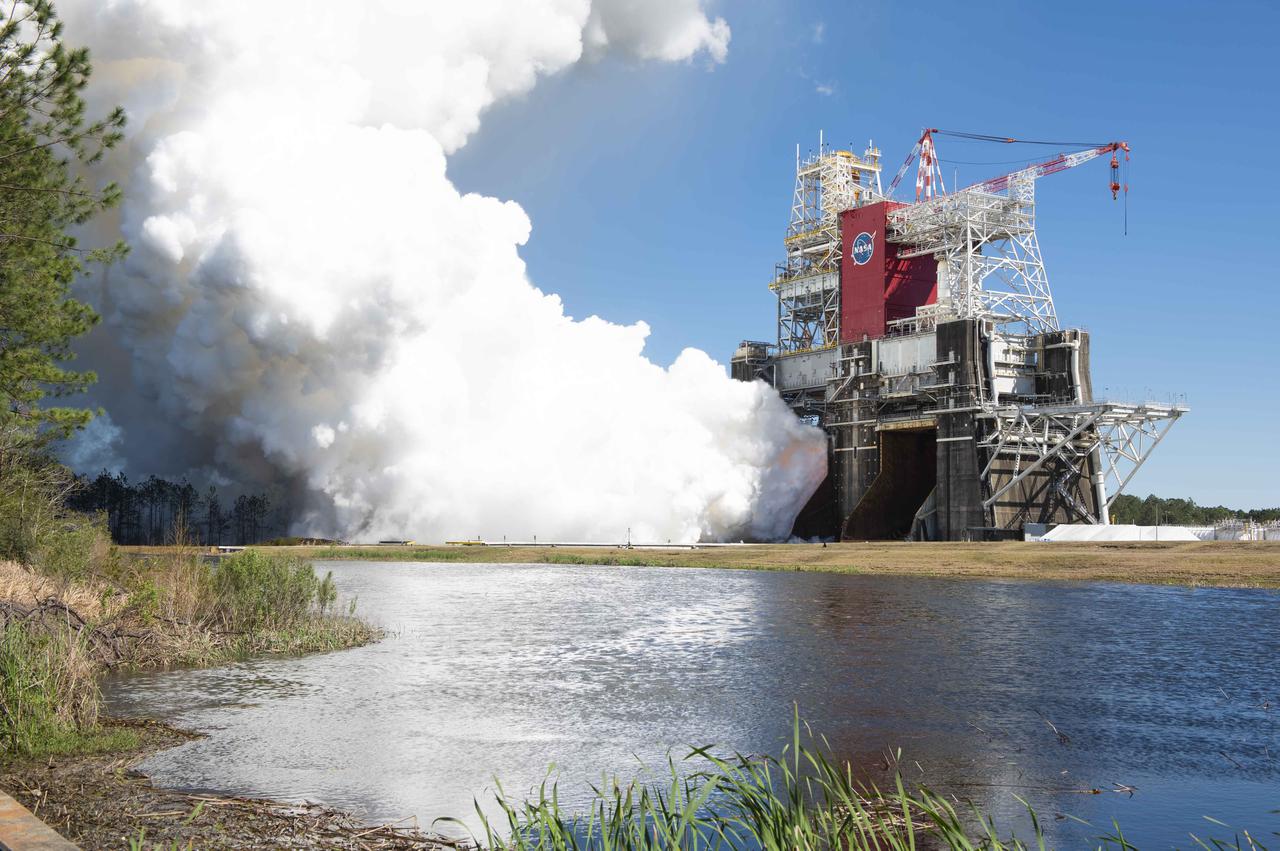

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
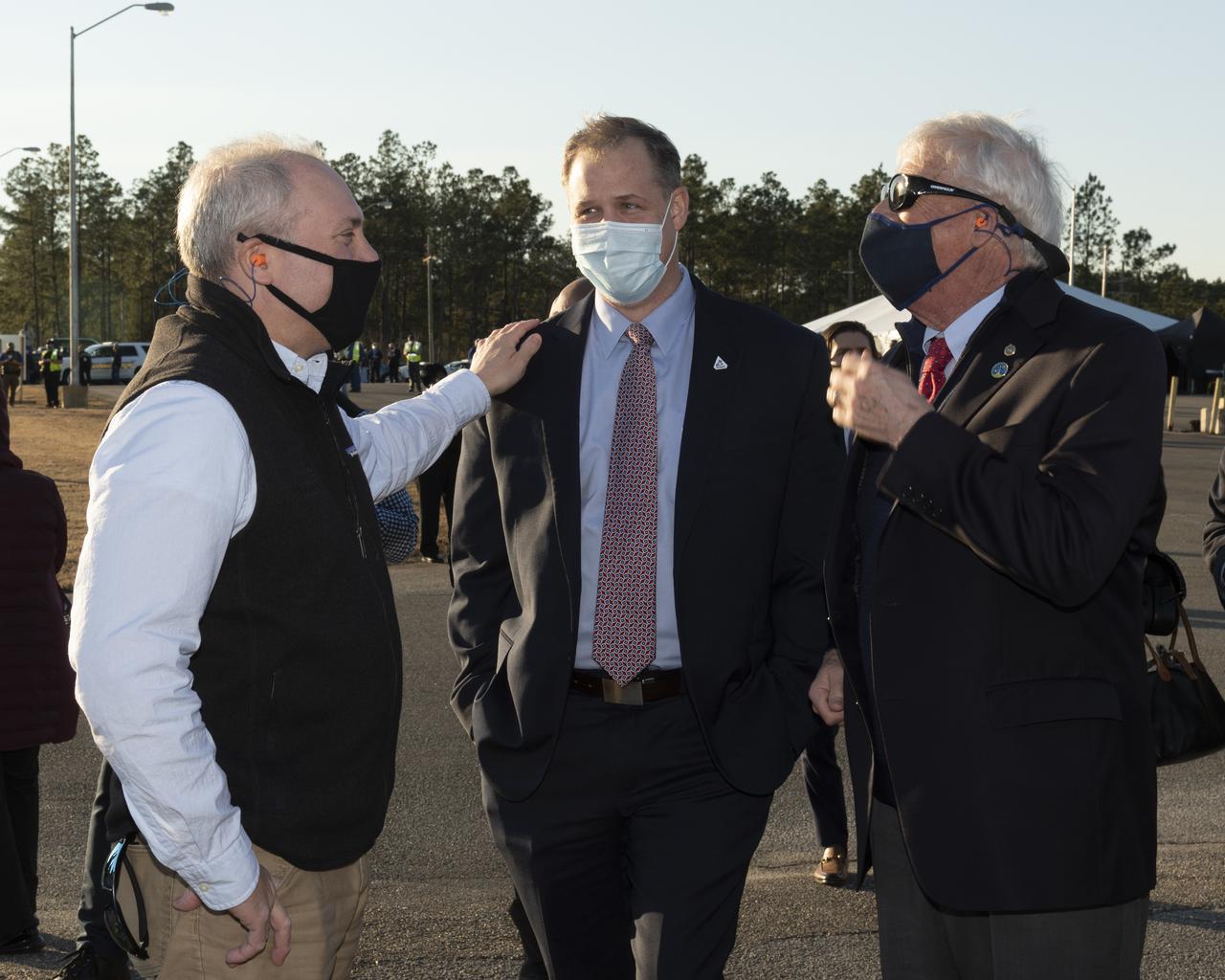

U.S. Representative Steve Scalise, left, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine and U.S. Senator Roger Wicker, right gather to watch as the core stage for the first flight of NASA's Space Launch System rocket undergoes a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
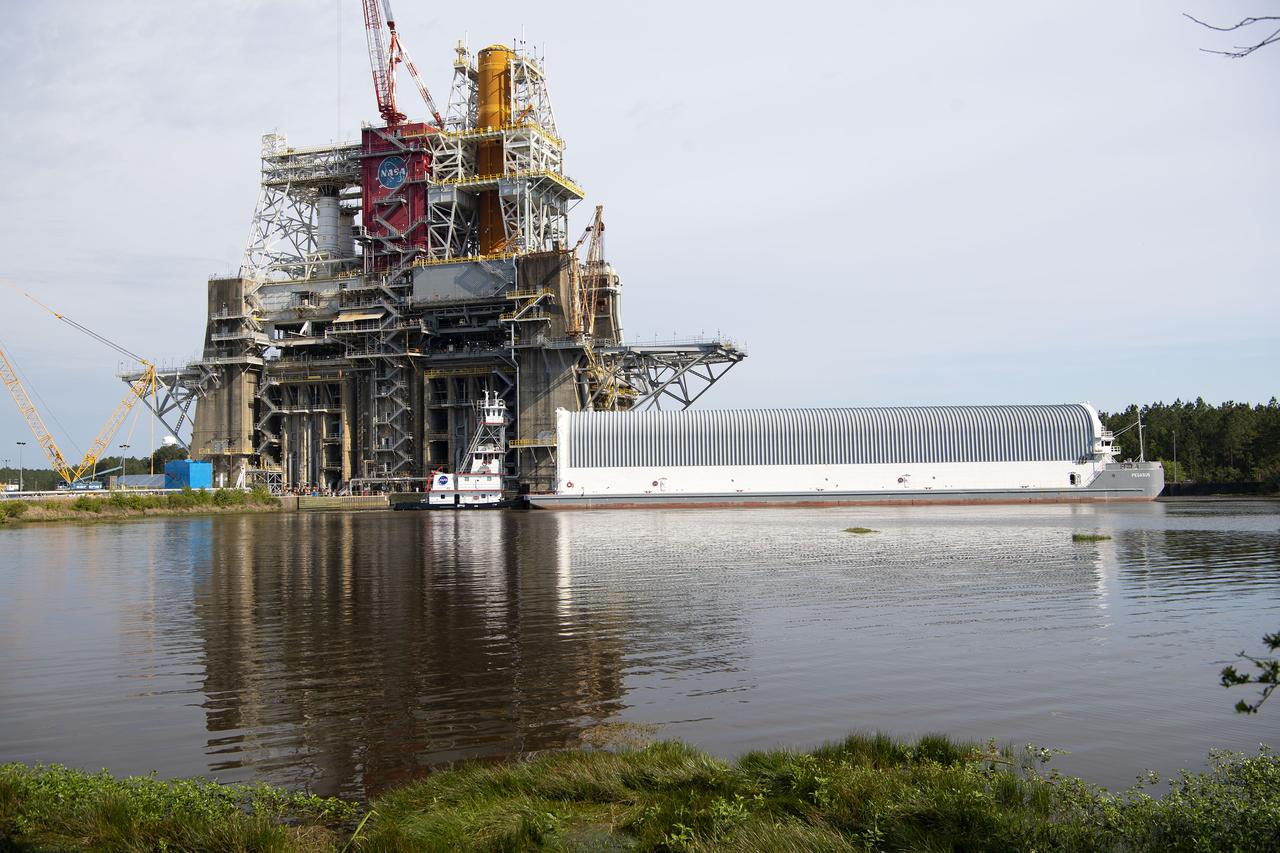

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, complete refurbishment work on the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The work followed a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines March 18. The hot fire marked the culmination of a yearlong Green Run series of tests of the stage and its integrated systems. Following refurbishment work, the core stage will be removed from the test stand and transported to Kennedy Space Center in Florida, aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge, shown delivering equipment to the B-2 Test Stand. At Kennedy, the core stage will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
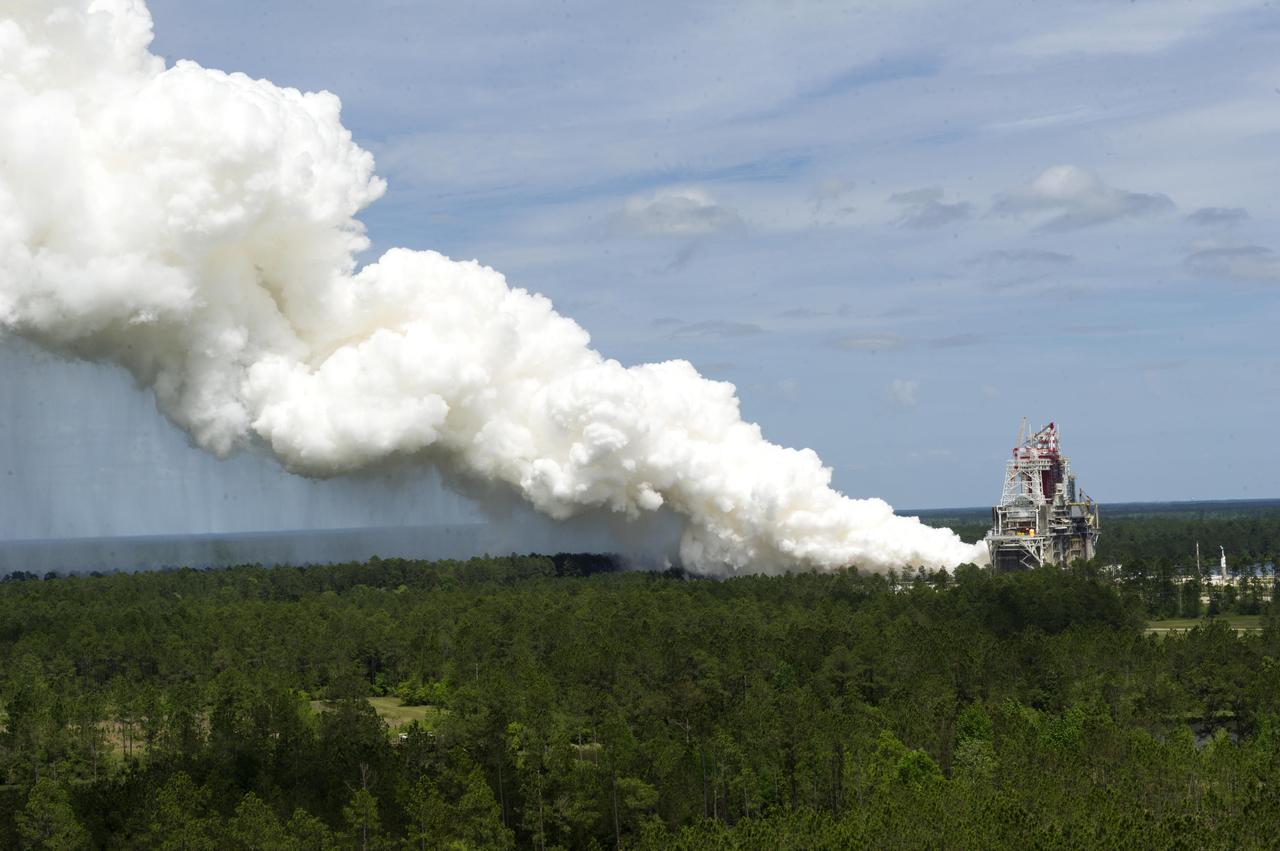

What better way to mark 50 years of rocket engine testing than with a rocket engine test? Stennis Space Center employees enjoyed a chance to view an RS-68 engine test at the B-1 Test Stand on April 19, almost 50 years to the day that the first test was conducted at the south Mississippi site in 1966. The test viewing was part of a weeklong celebration of the 50th year of rocket engine testing at Stennis. The first test at the site occurred April 23, 1966, with a 15-second firing of a Saturn V second stage prototype (S-II-C) on the A-2 Test Stand. The center subsequently tested Apollo rocket stages that carried humans to the moon and every main engine used to power 135 space shuttle missions. It currently tests engines for NASA’s new Space Launch System vehicle.
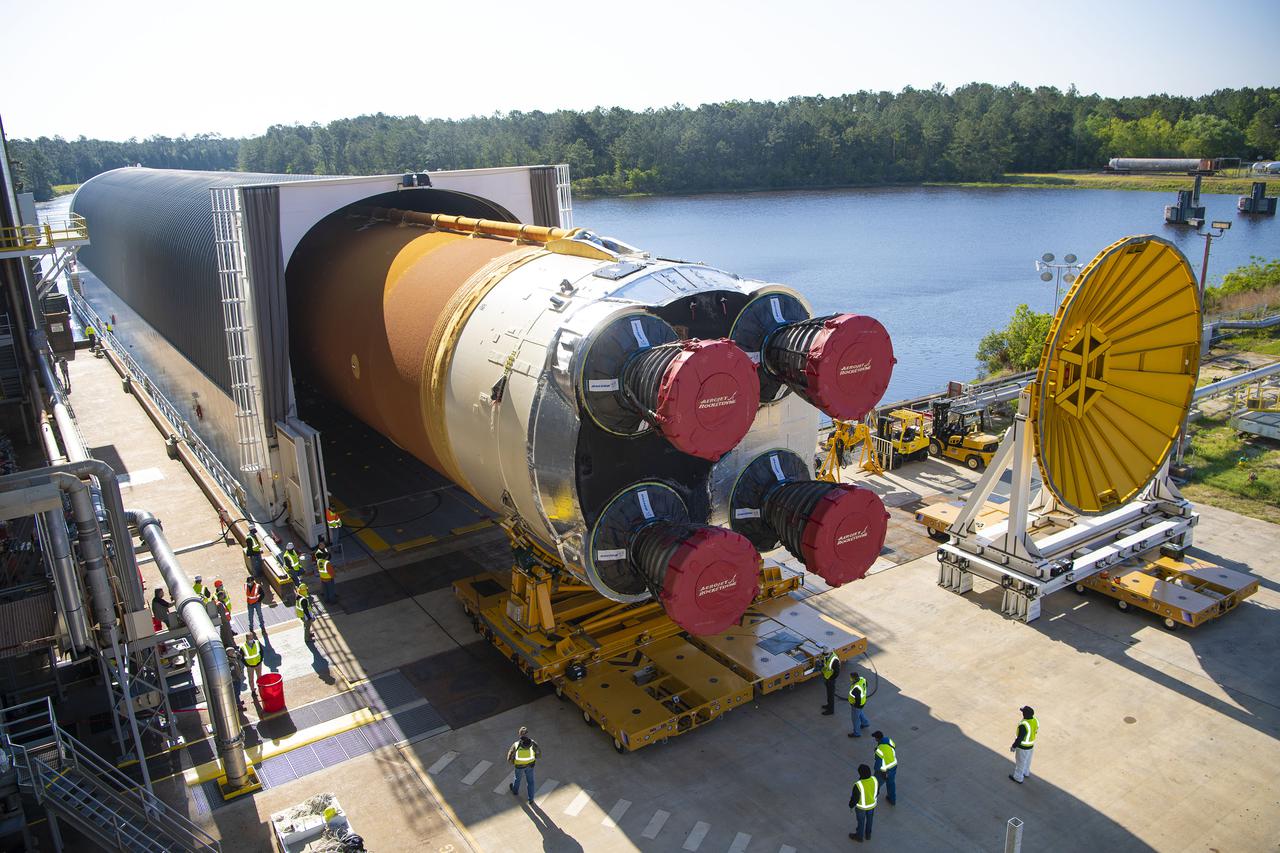

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
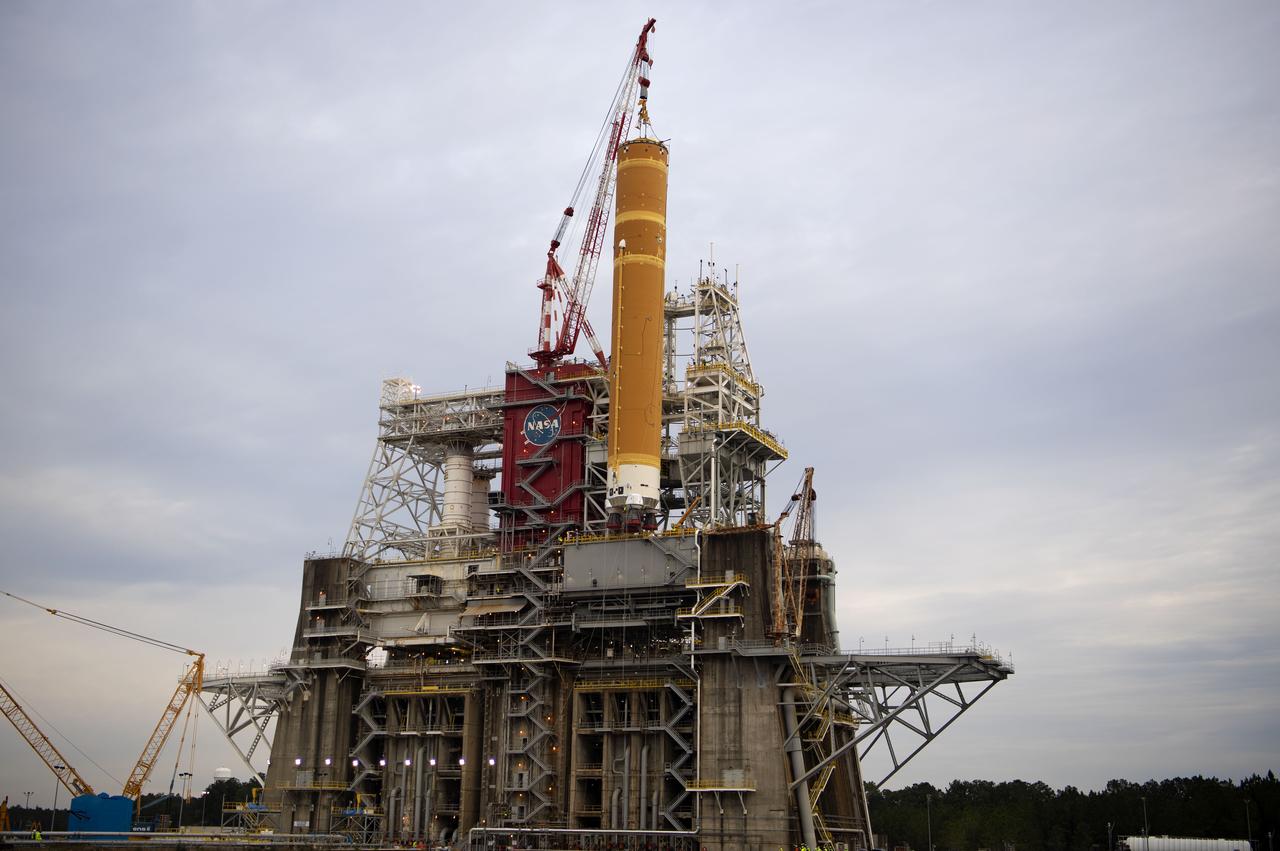

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
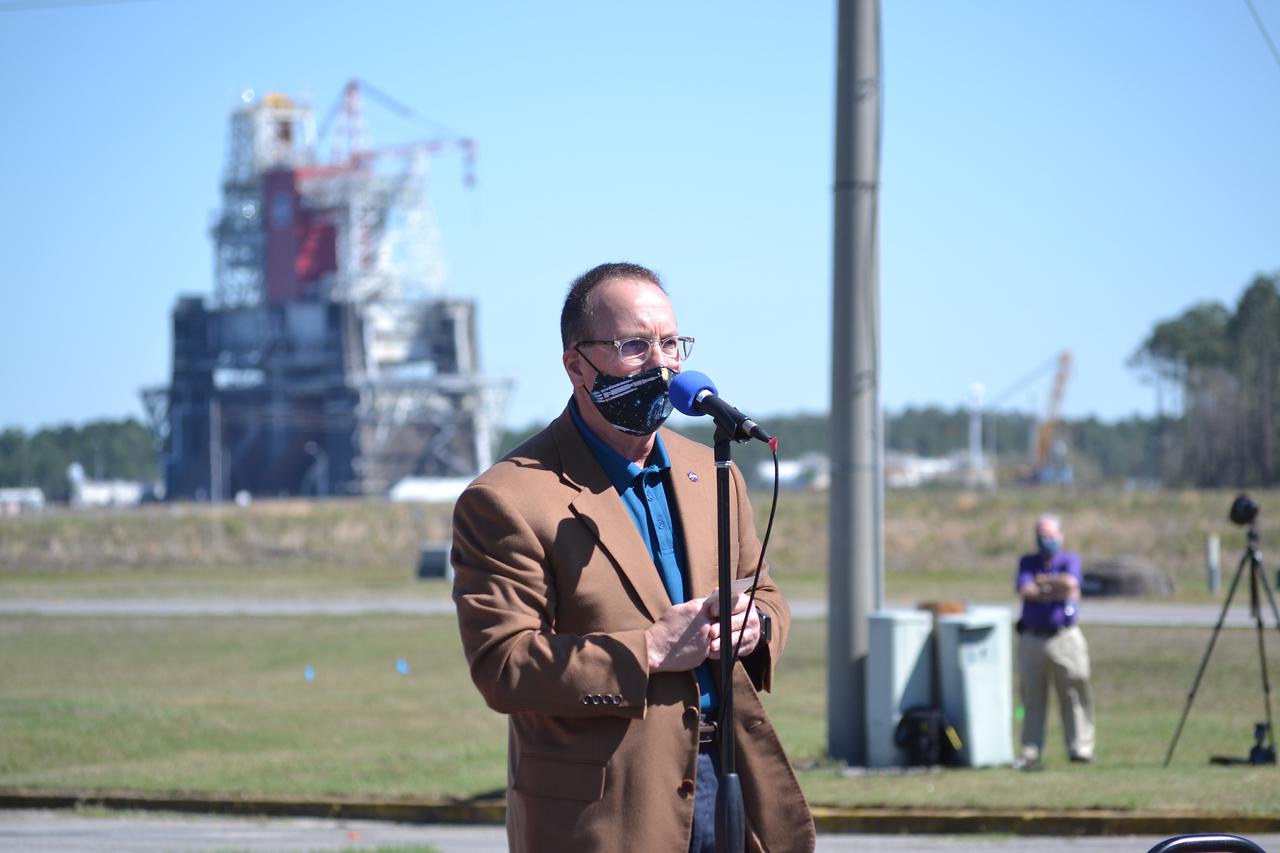

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

The first RS-25 flight engine, engine No. 2059, is lifted onto the A-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Nov. 4, 2015. The engine was tested in early 2016 to certify it for use on NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS). The SLS core stage will be powered by four RS-25 engines, all tested at Stennis Space Center. NASA is developing the SLS to carry humans deeper into space than ever before, including on a journey to Mars.
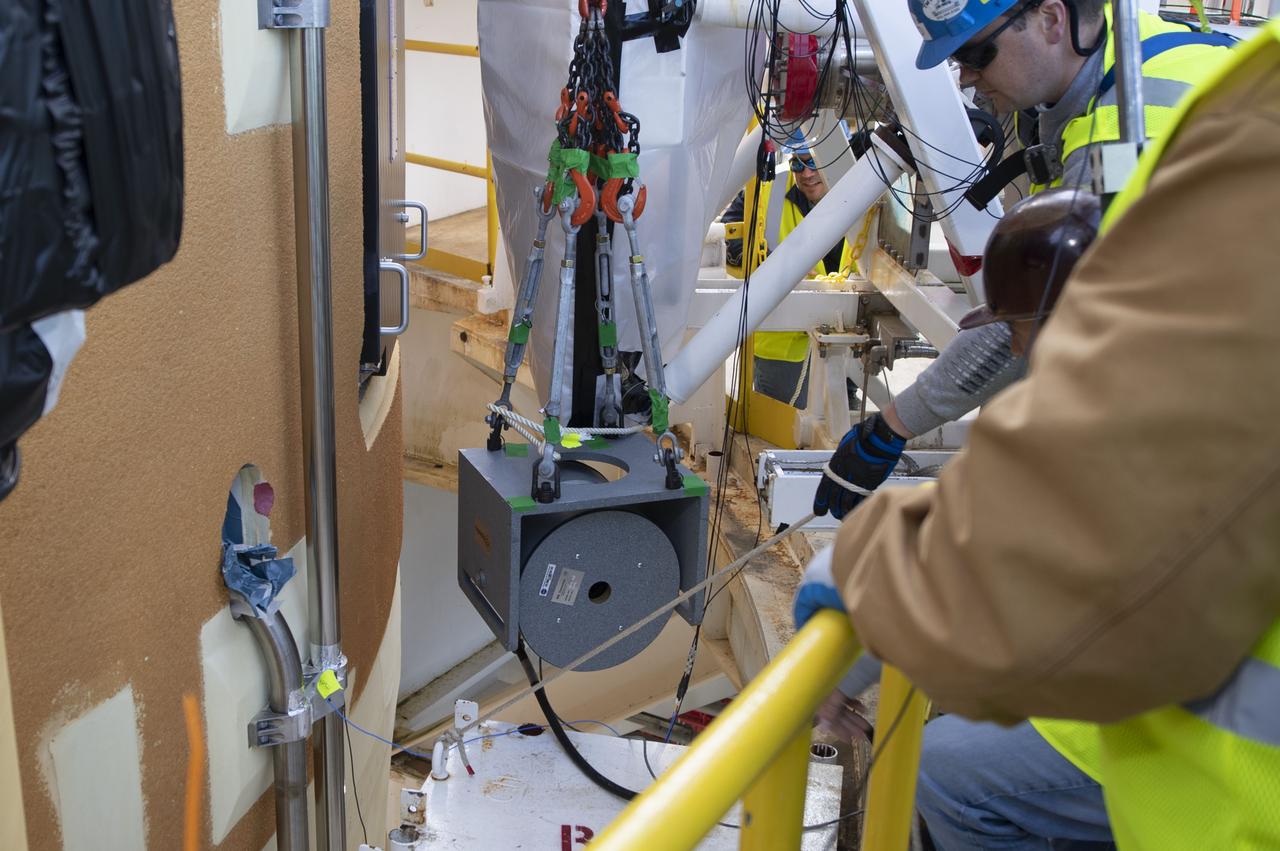

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
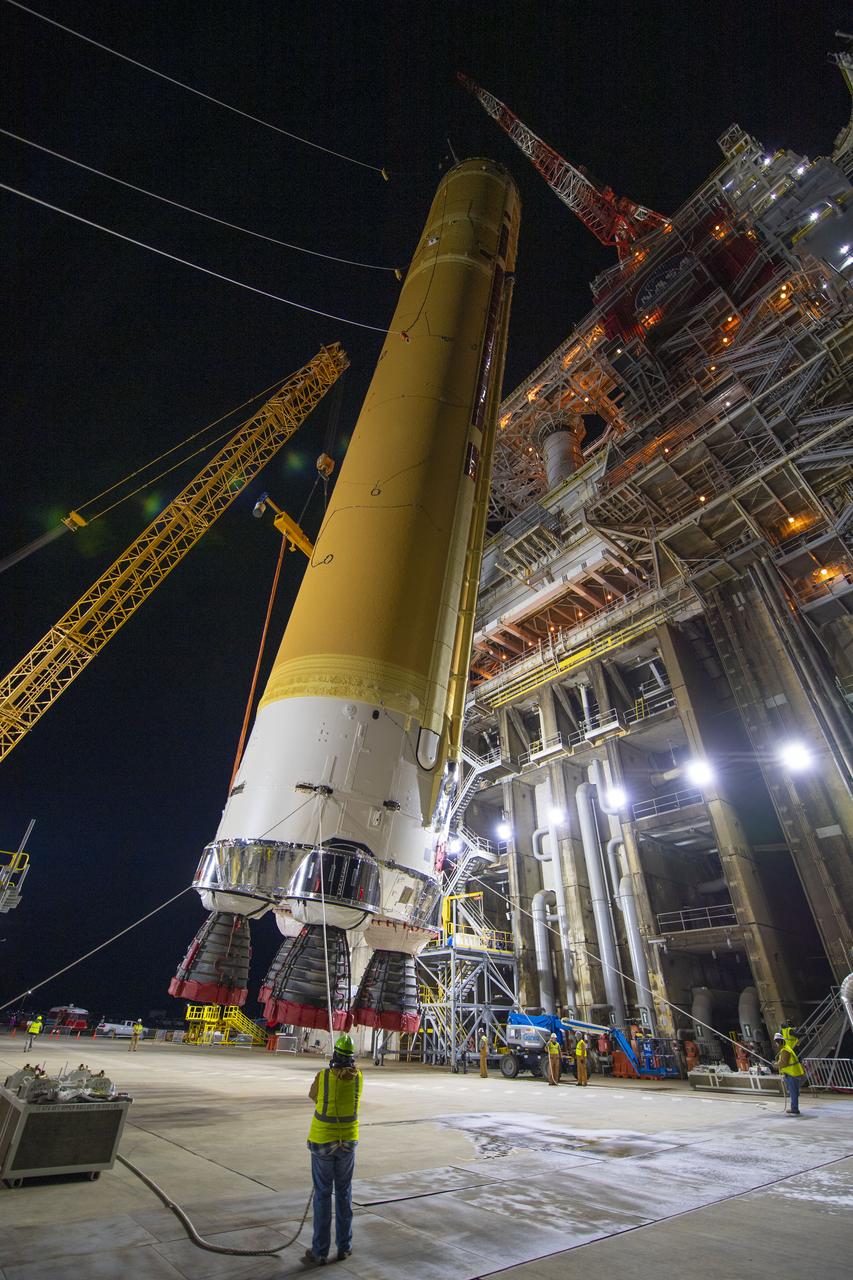

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
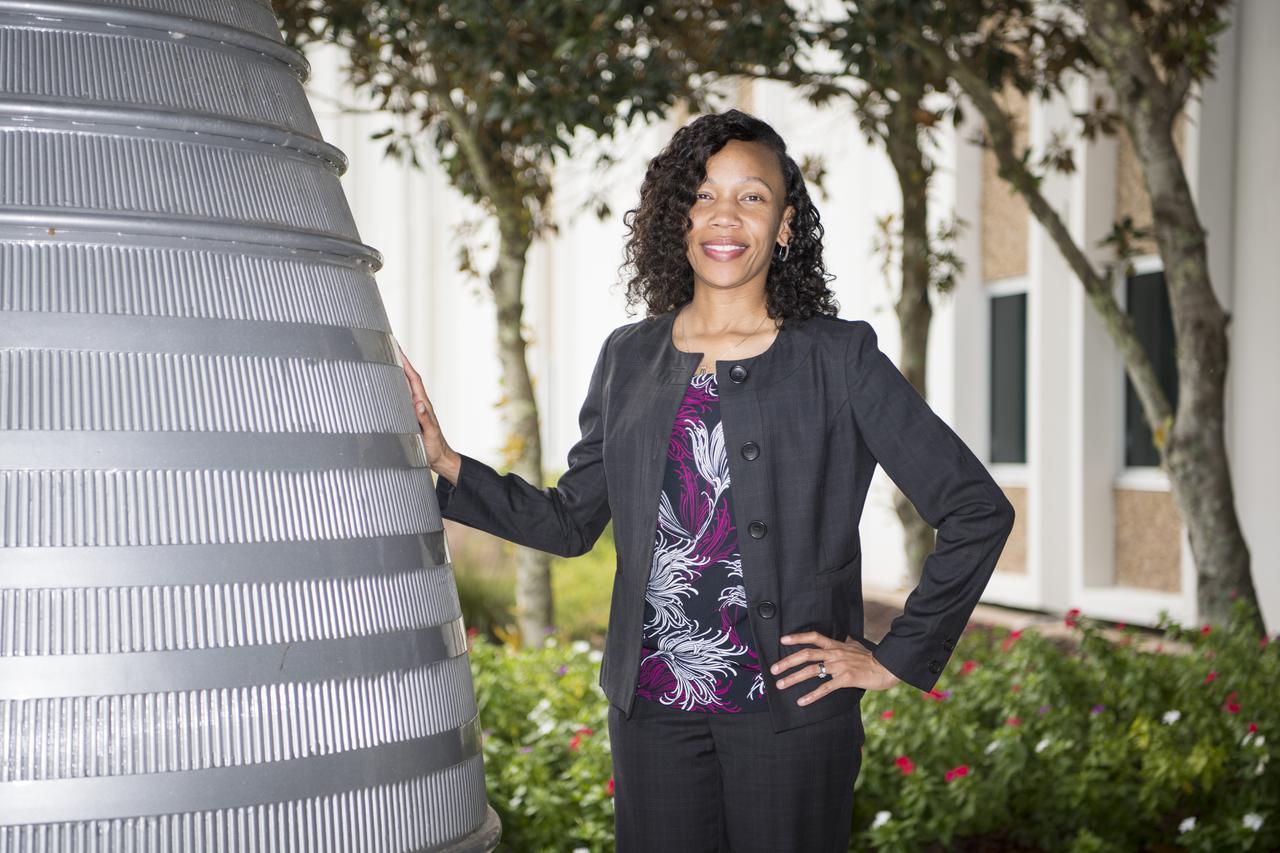
Portrait; Mary Horne, a NASA reimbursable accountant at Stennis Space Center, performs analysis and budgeting funds for SSC tenants and commercial customers. This photo was taken as part of a monthy feature called “Faces of Stennis.”

Year 2015 got off to a blazing start as NASA conducted its first test of an RS-25 rocket engine on the A-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center on Jan. 9, 2015. The 500-second test provided critical data on engine performance. RS-25 engines will help power the core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System vehicle, being developed to carry humans deeper into space than ever before.

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
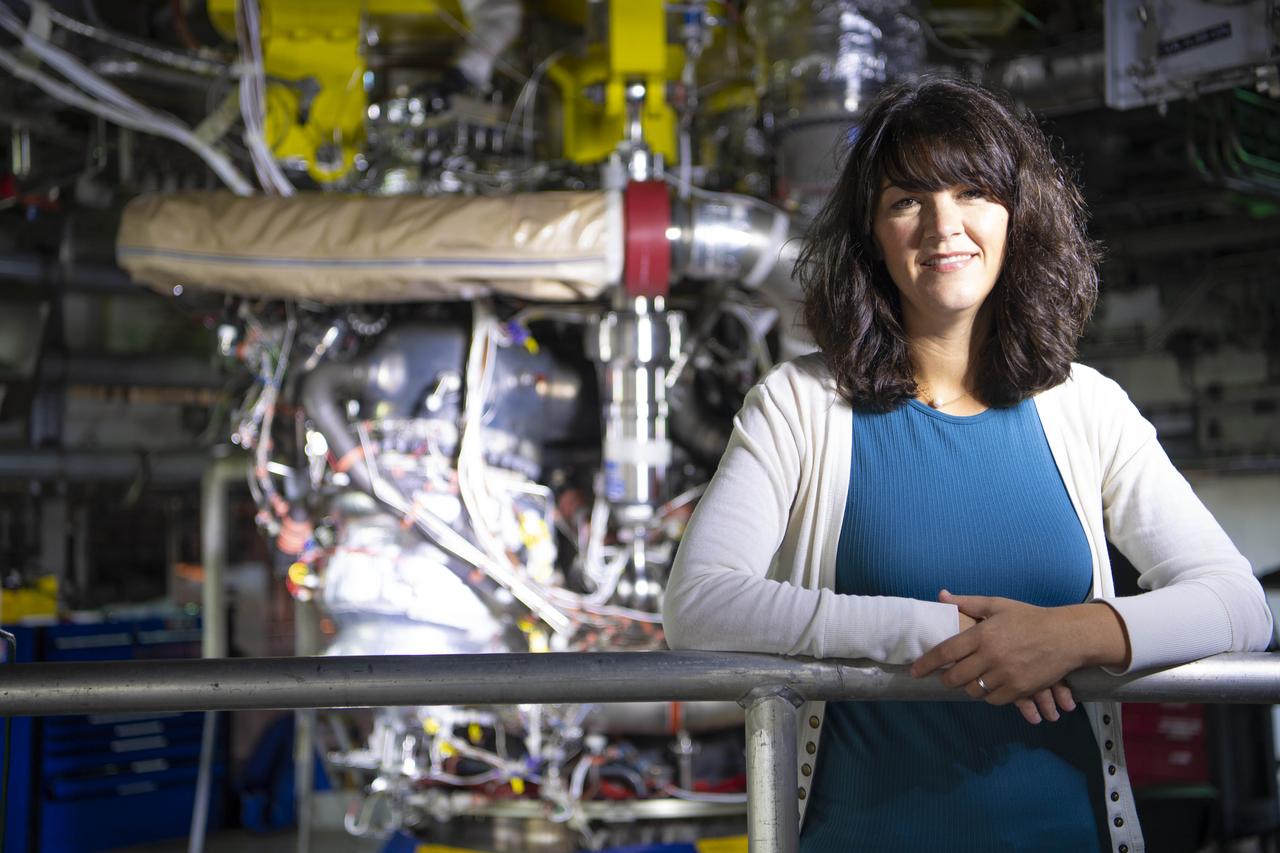
Nyla Trumbach, a NASA lead mechanical engineer, broke barriers as the first female to conduct a J-2X powerpack engine test at Stennis Space Center. She currently works on testing of the RS-25 rocket engine, shown installed on the A-1 Test Stand at SSC.
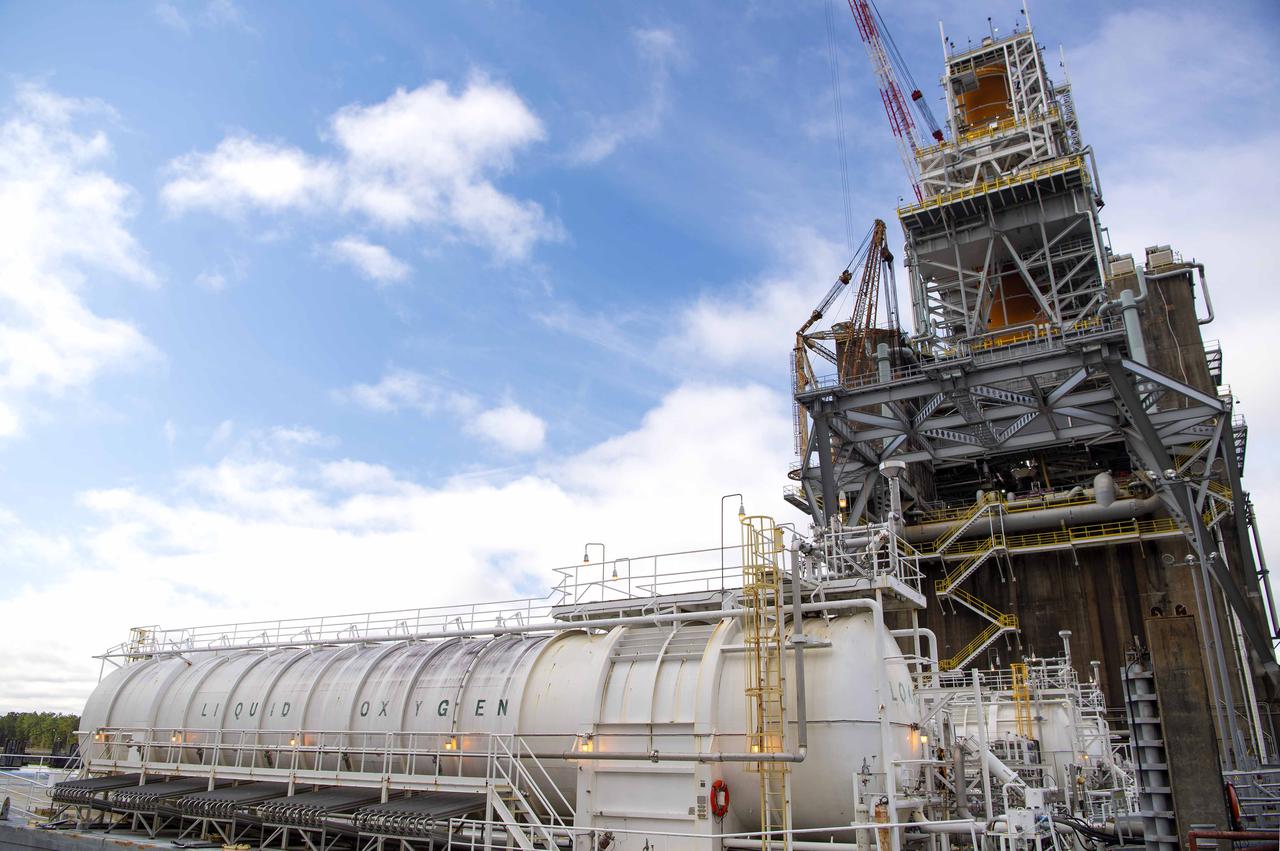

Barges are docked at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, during preparations for a wet dress rehearsal exercise with the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. During the wet dress rehearsal, operators will fully load the core stage’s propellant tanks for the first time and countdown just shy of engine ignition. The wet dress rehearsal is the seventh in a series of eight Green Run tests of the core stage’s integrated systems prior to its transport to Kennedy Space Center and launch on the Artemis I mission.
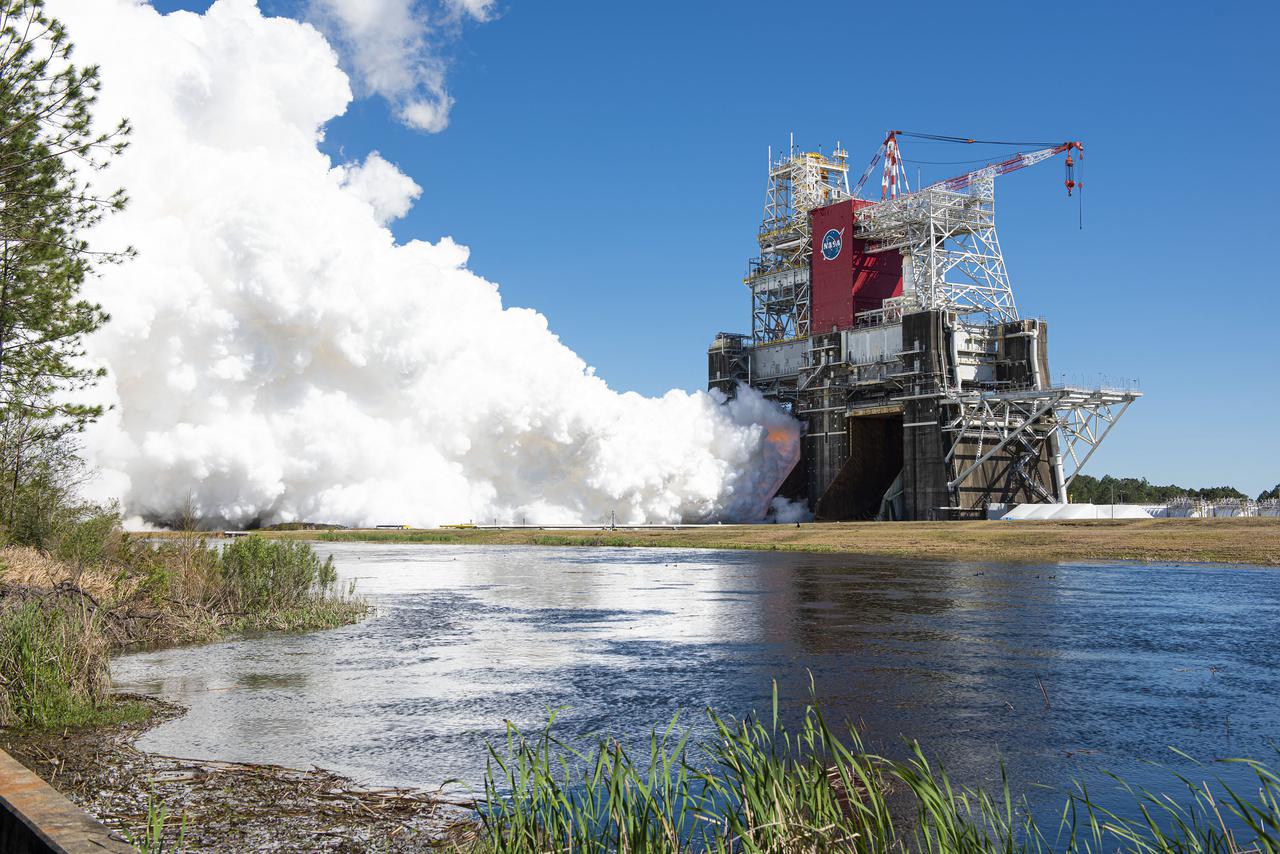

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
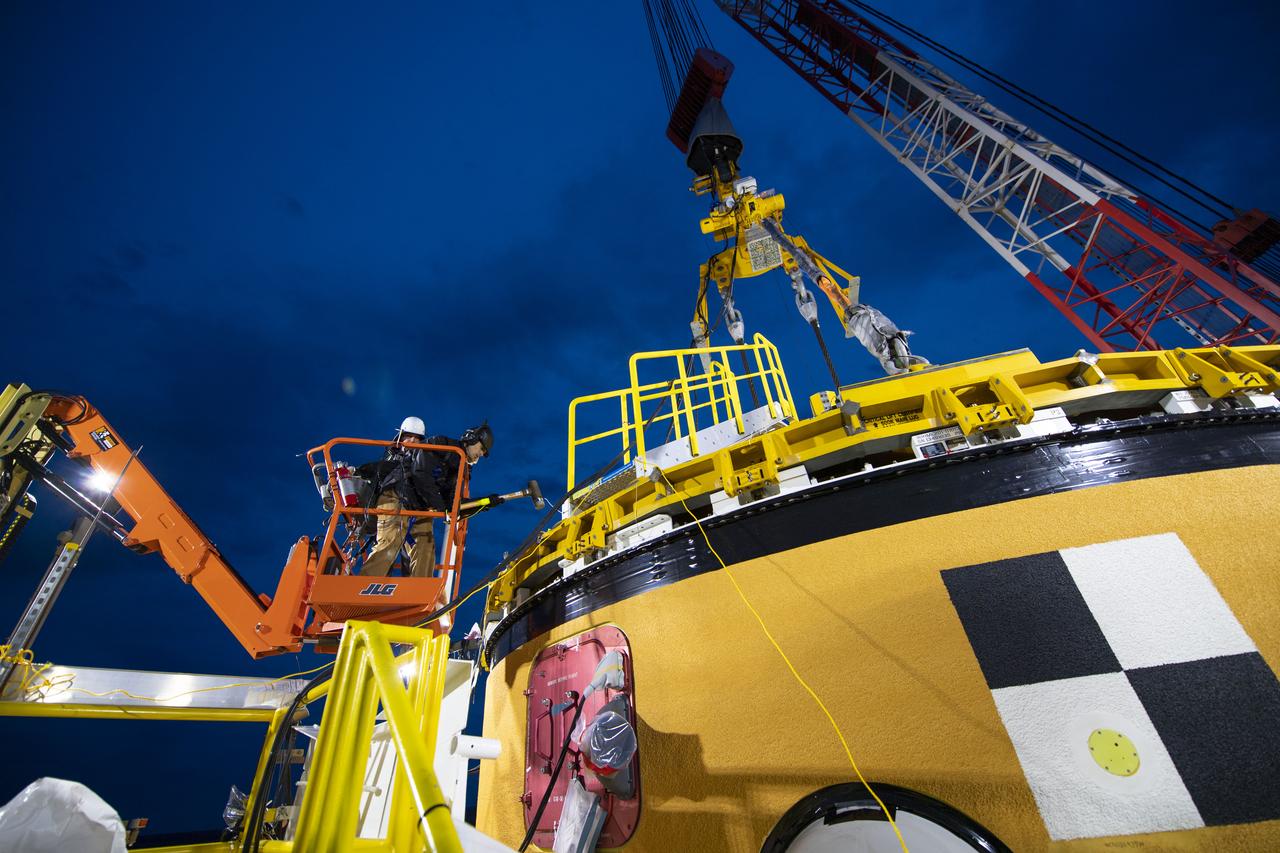

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
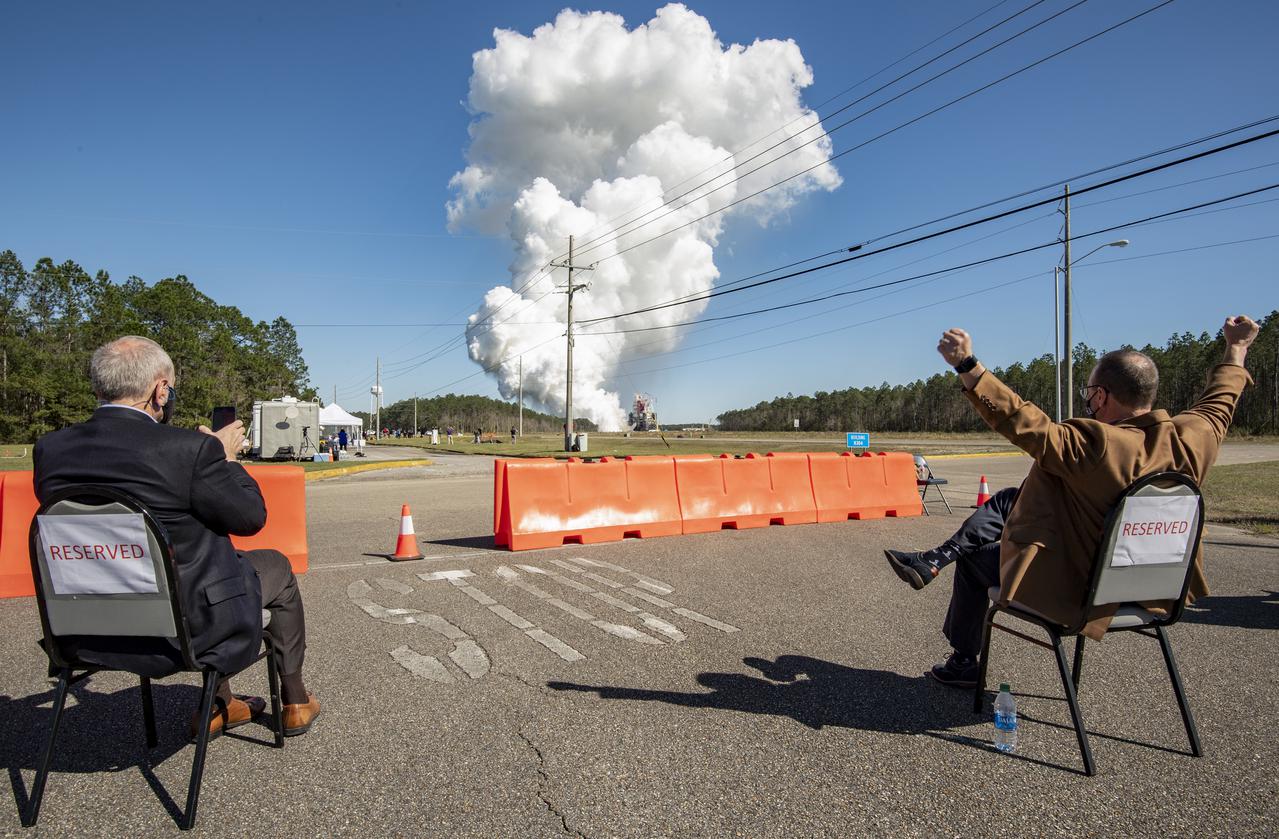

Acting NASA Administrator Steve Jurczyk, left, and Rick Gilbrech, director of NASA's Stennis Space Center, right, watch as the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket undergoes a second hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
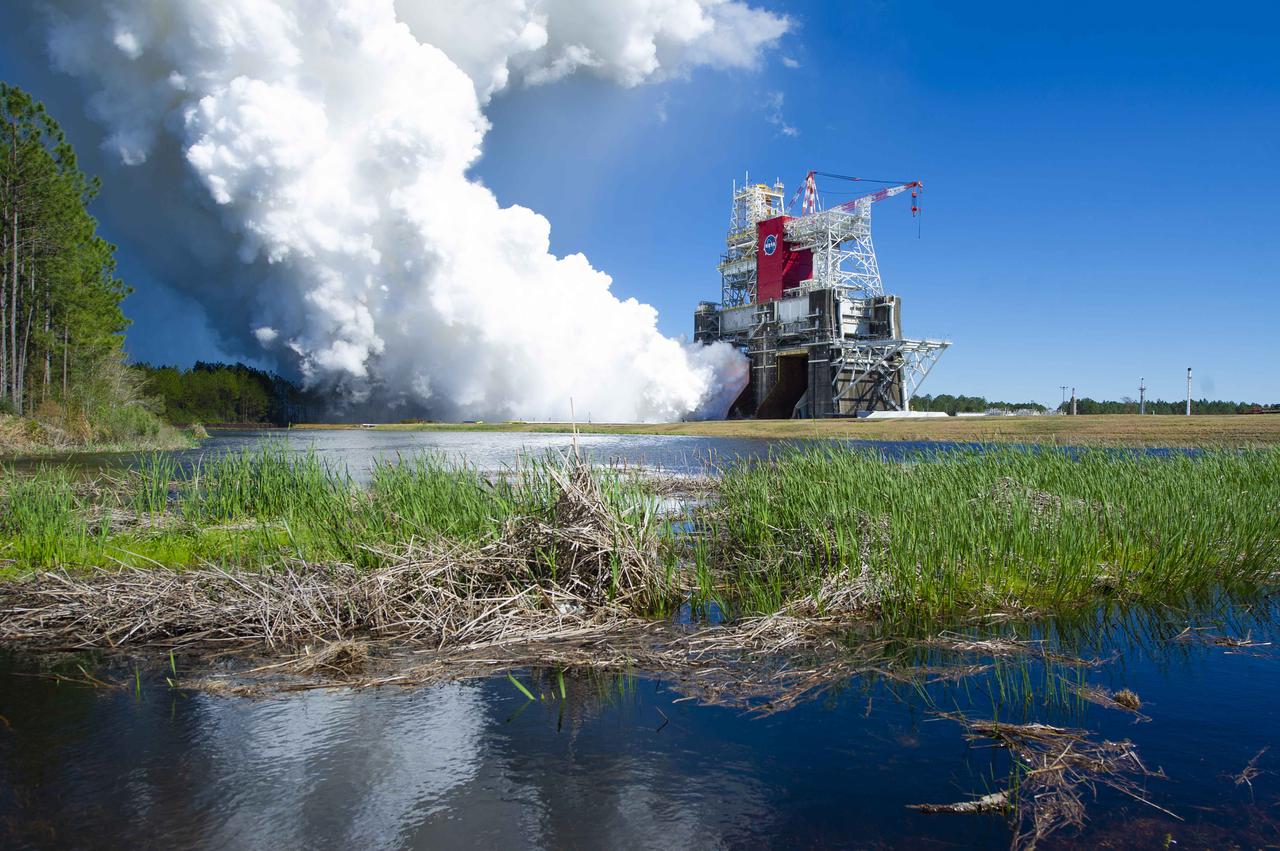

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
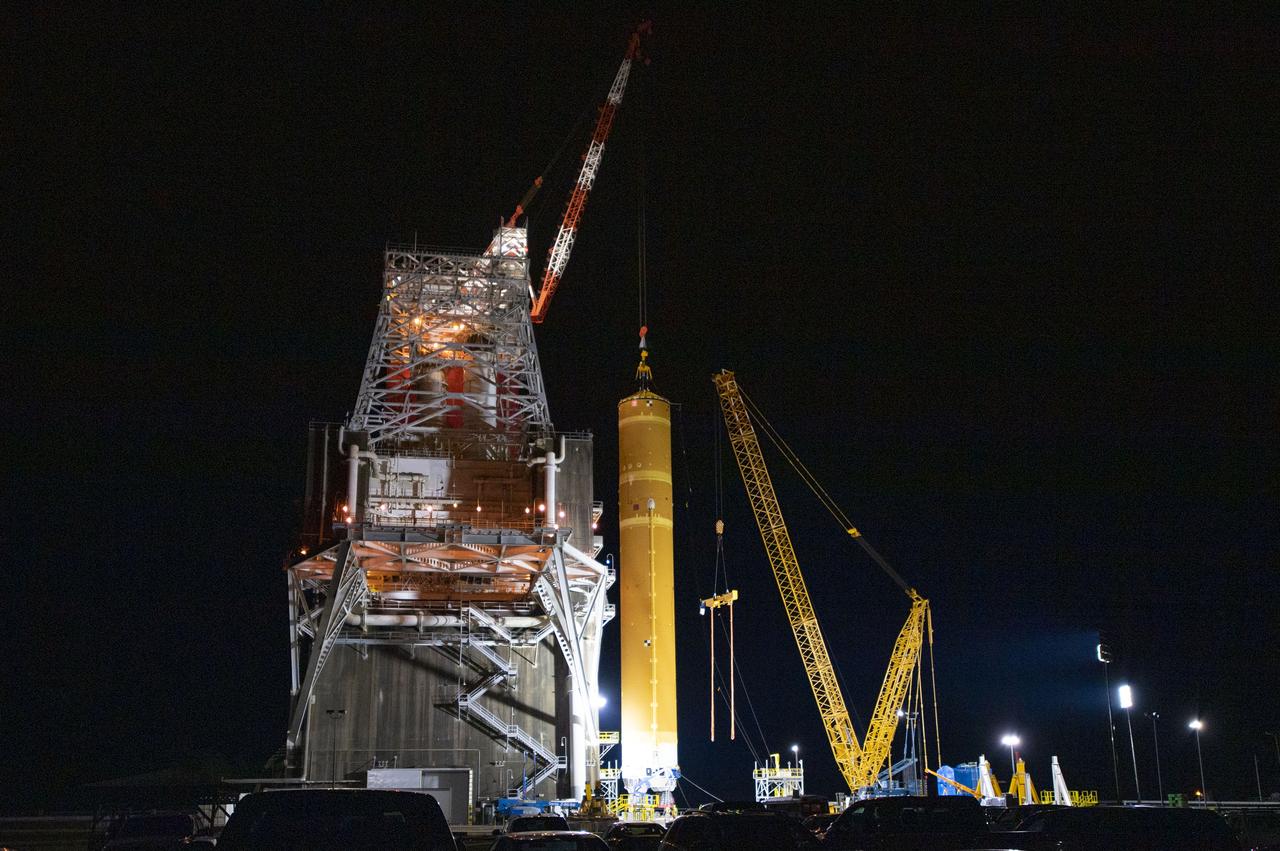

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
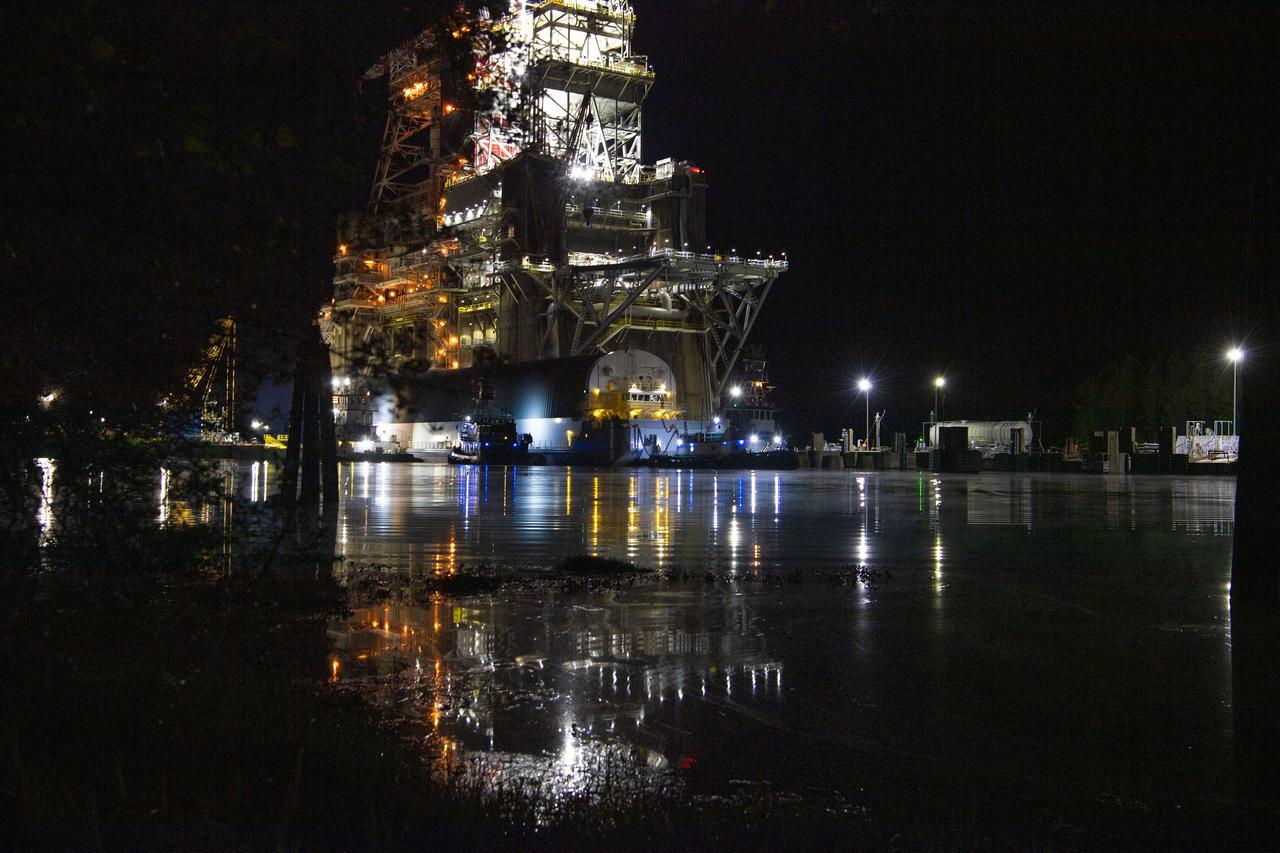

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
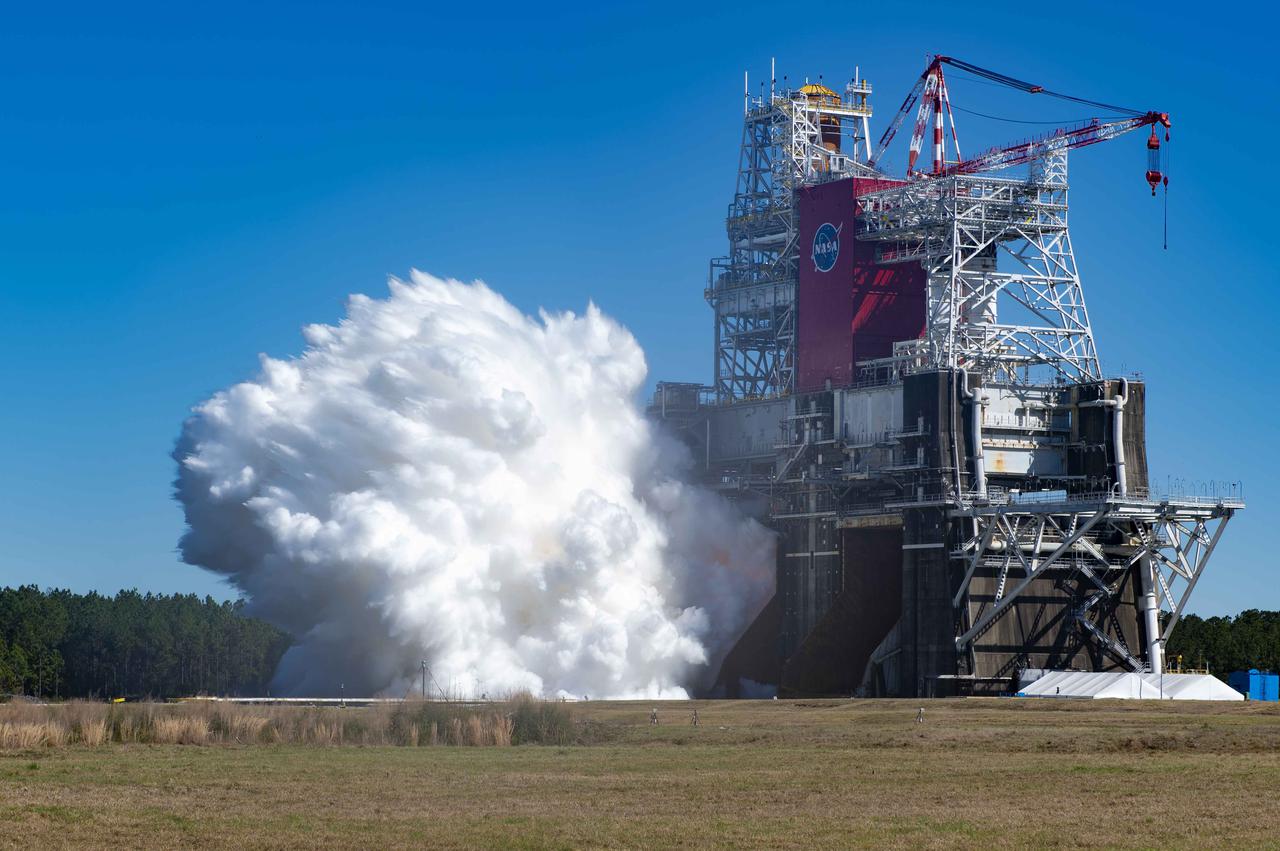

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
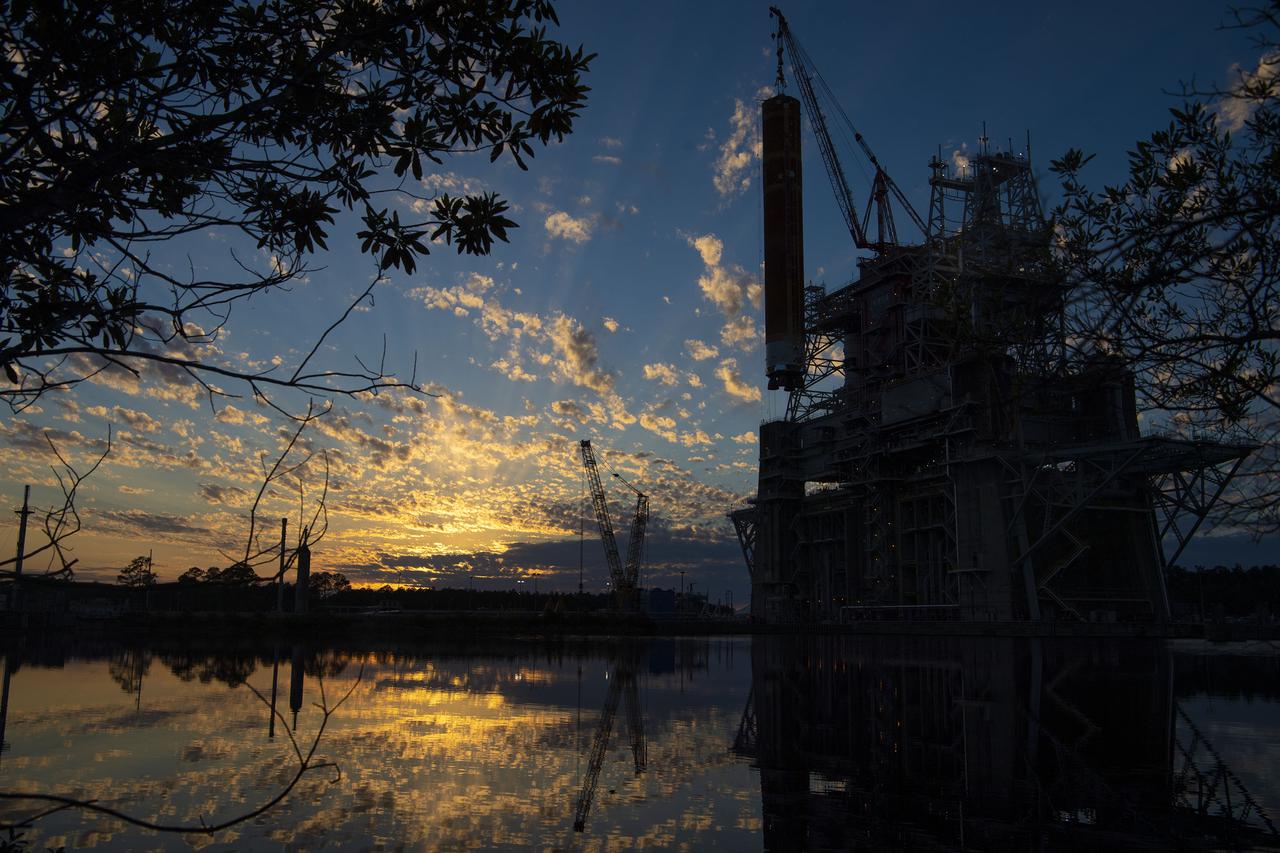

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
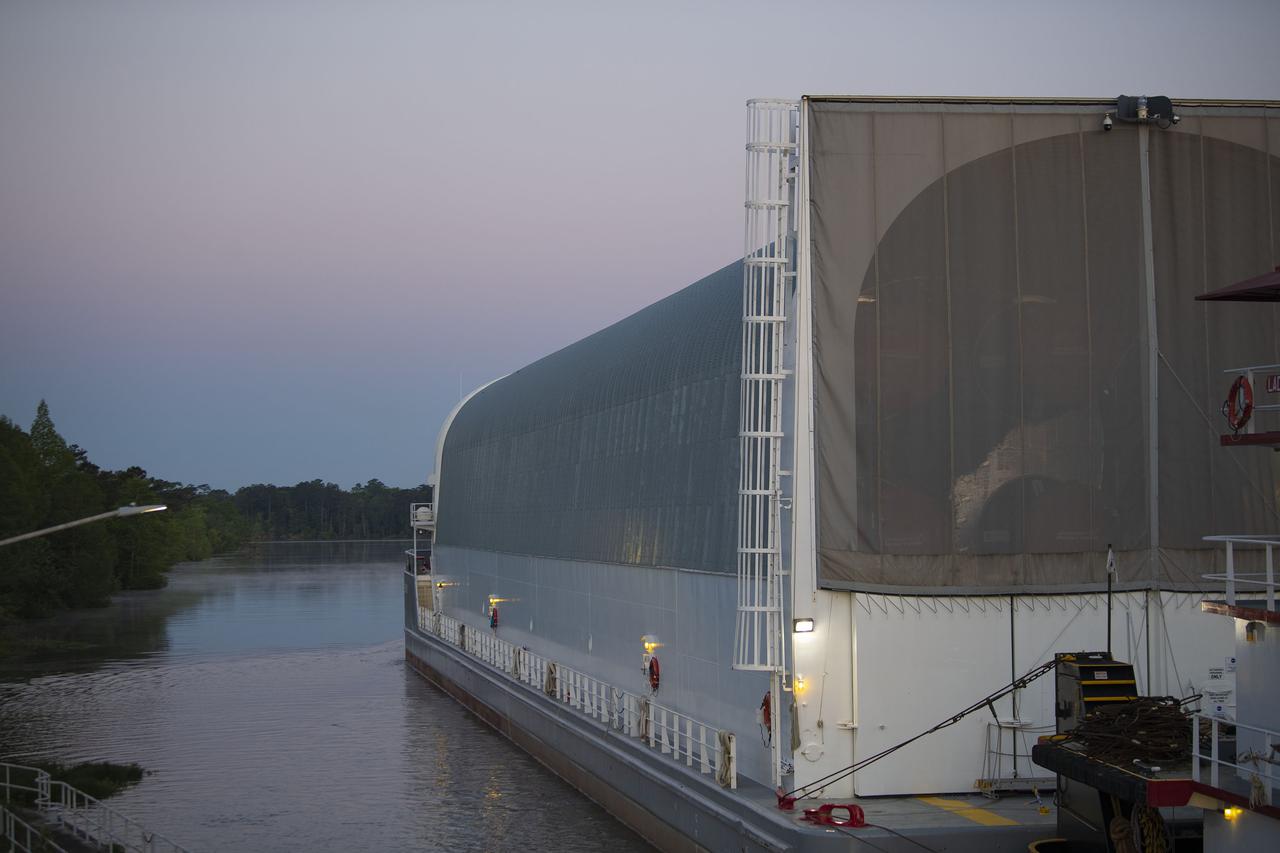

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
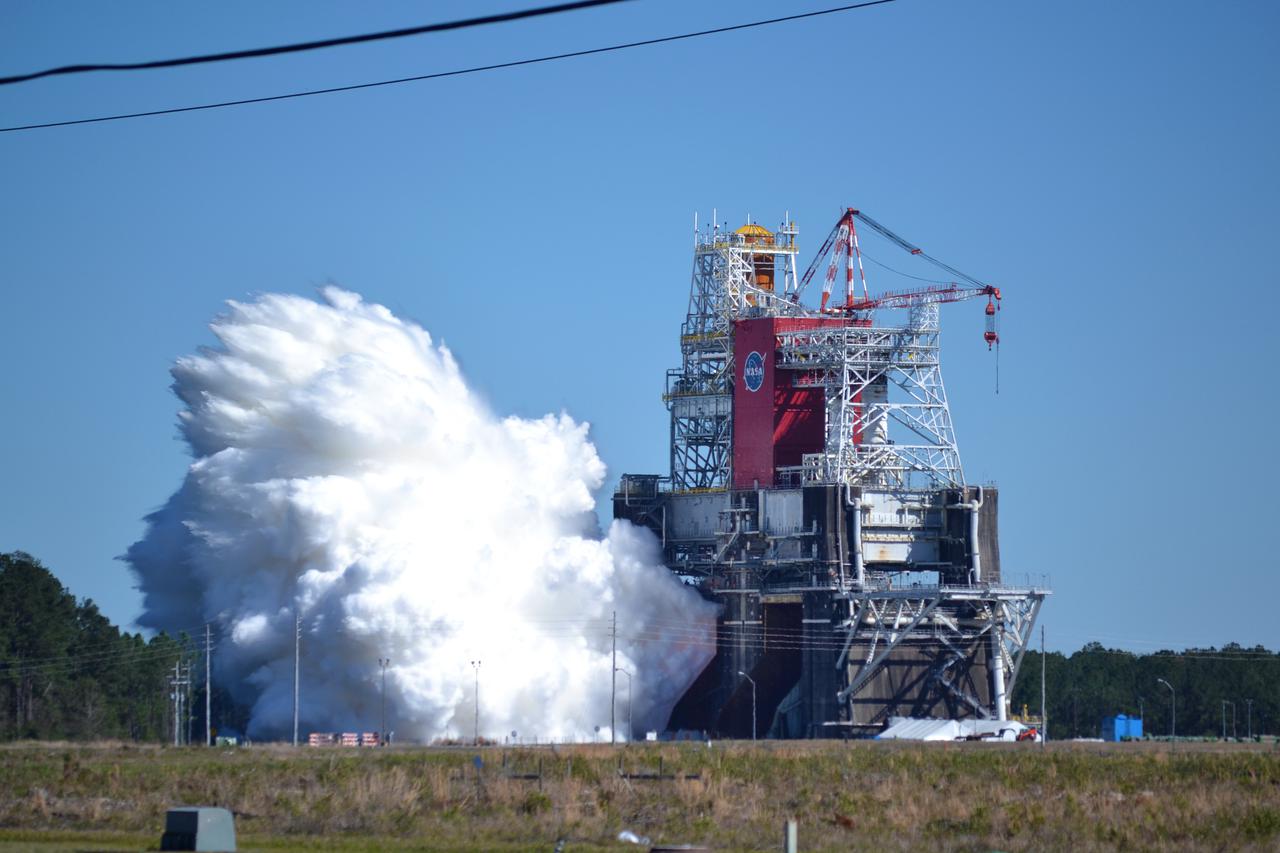

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
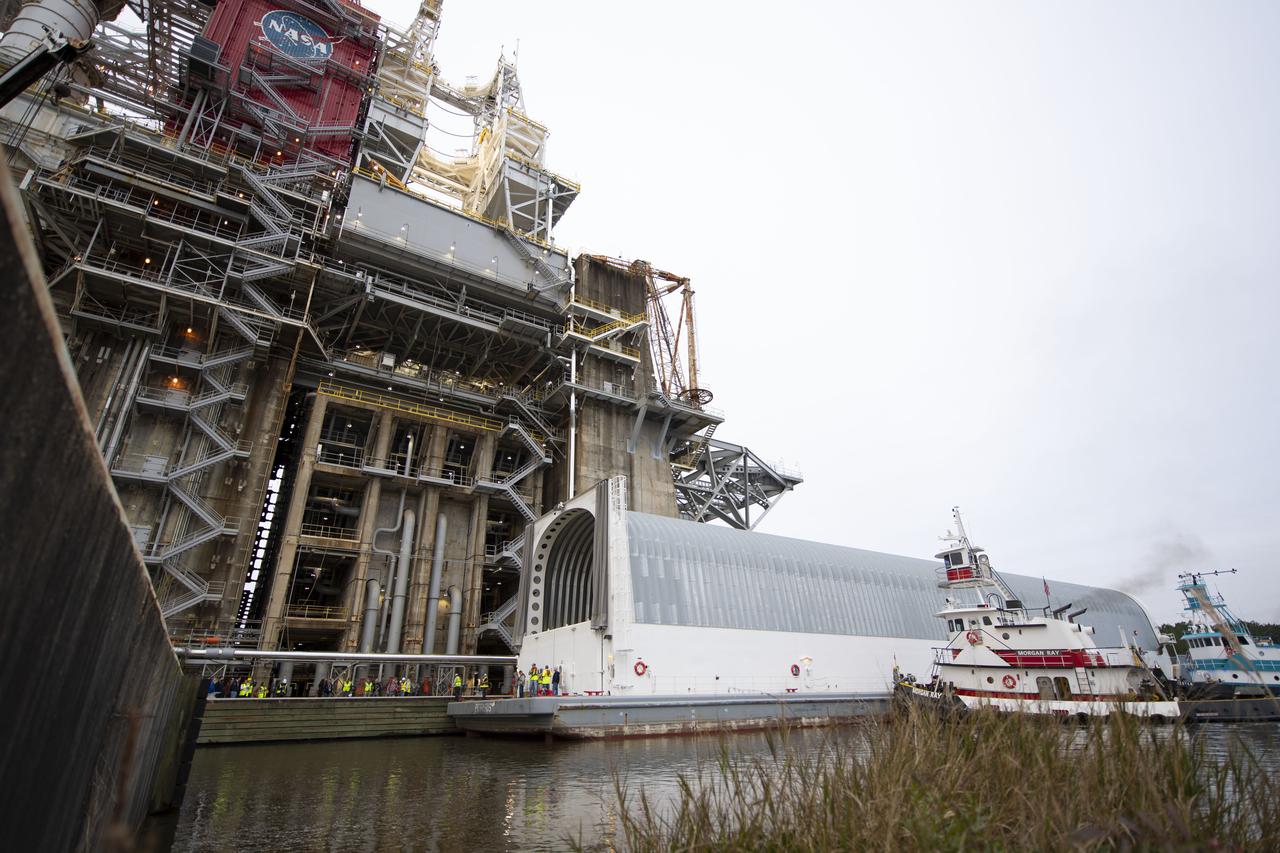

The first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System rocket arrived at Stennis Space Center on Jan. 12 for a series of tests prior to its maiden Artemis I flight. The core stage was transported from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the B-2 Test Stand dock at Stennis aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Soon after arrival, the stage was rolled off of Pegasus onto the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. After the stage is lifted and installed on the B-2 stand, it will undergo a series of “Green Run” systems test that represent the first integrated testing of its sophisticated systems.
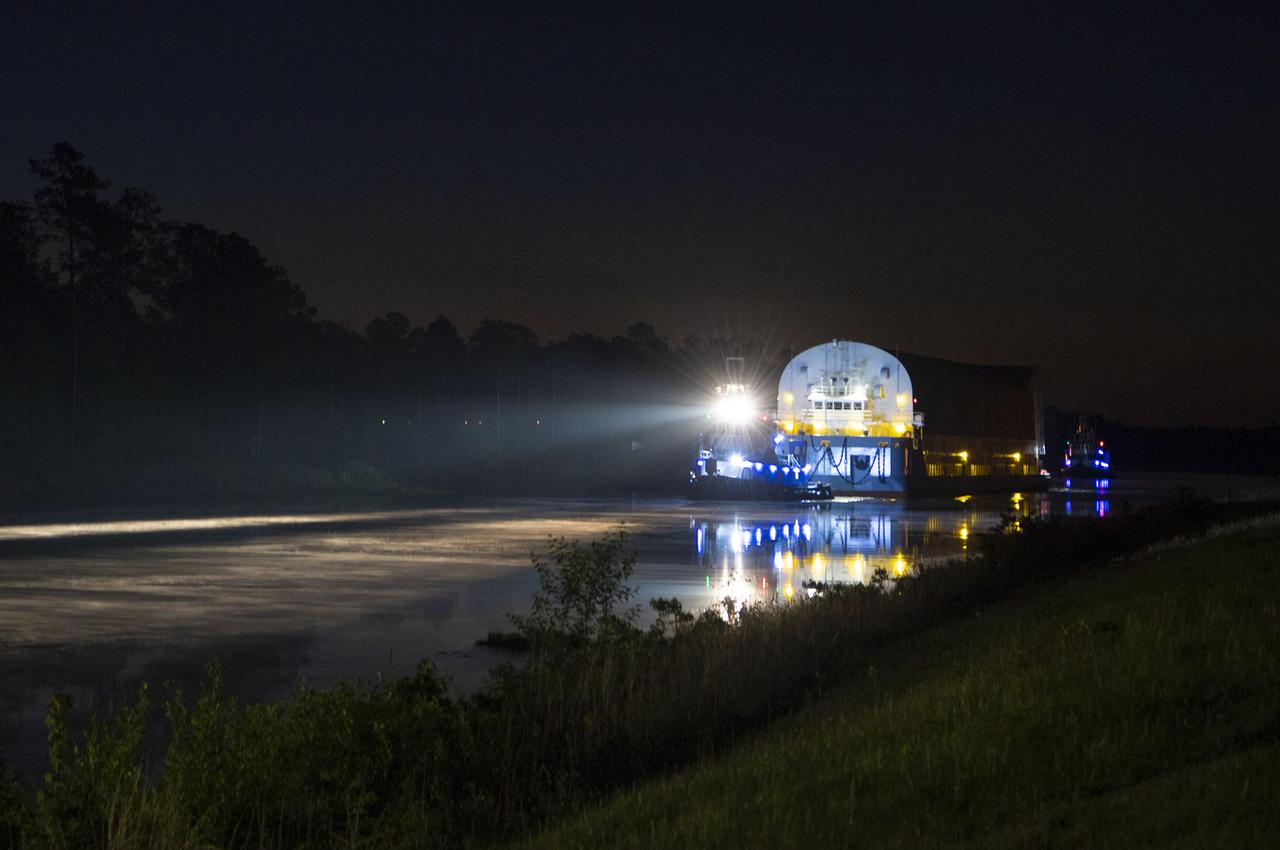

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
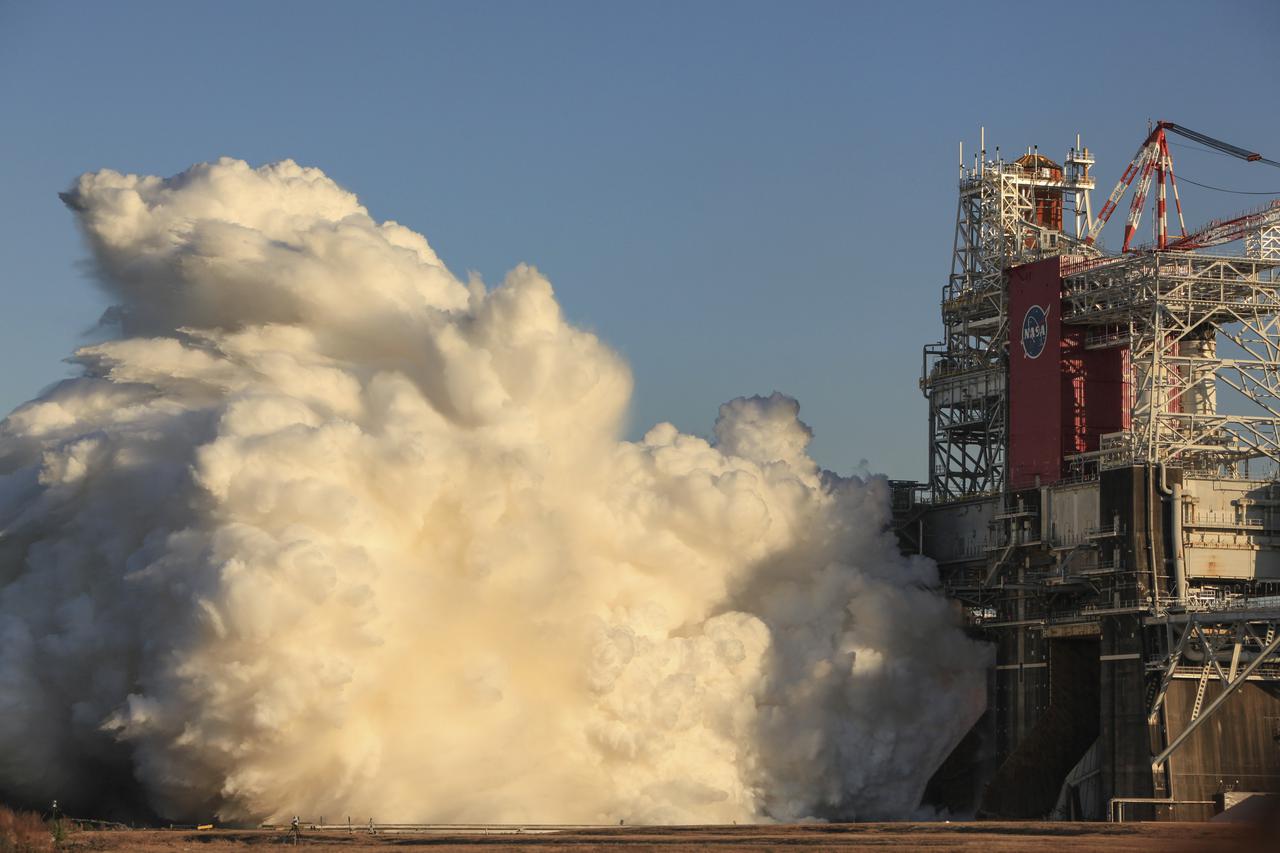

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
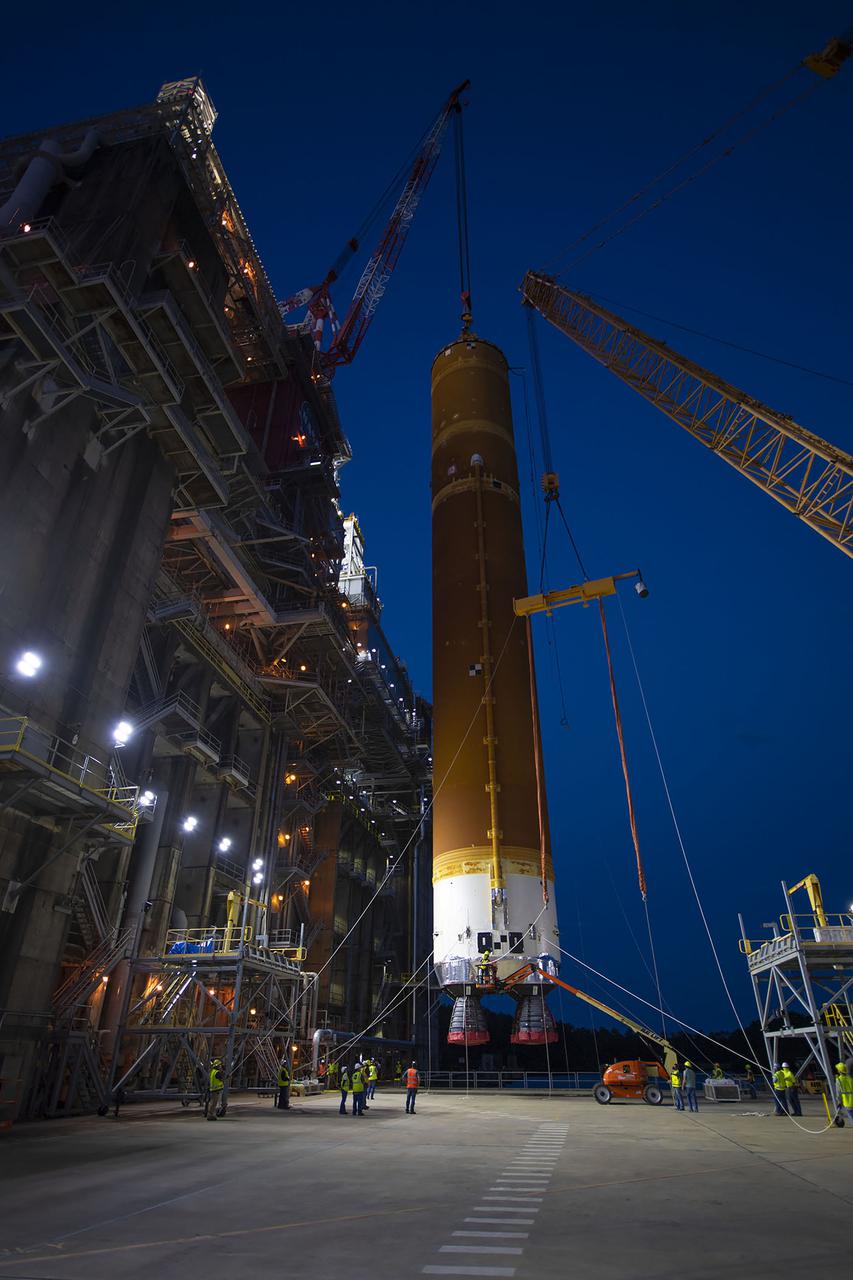

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
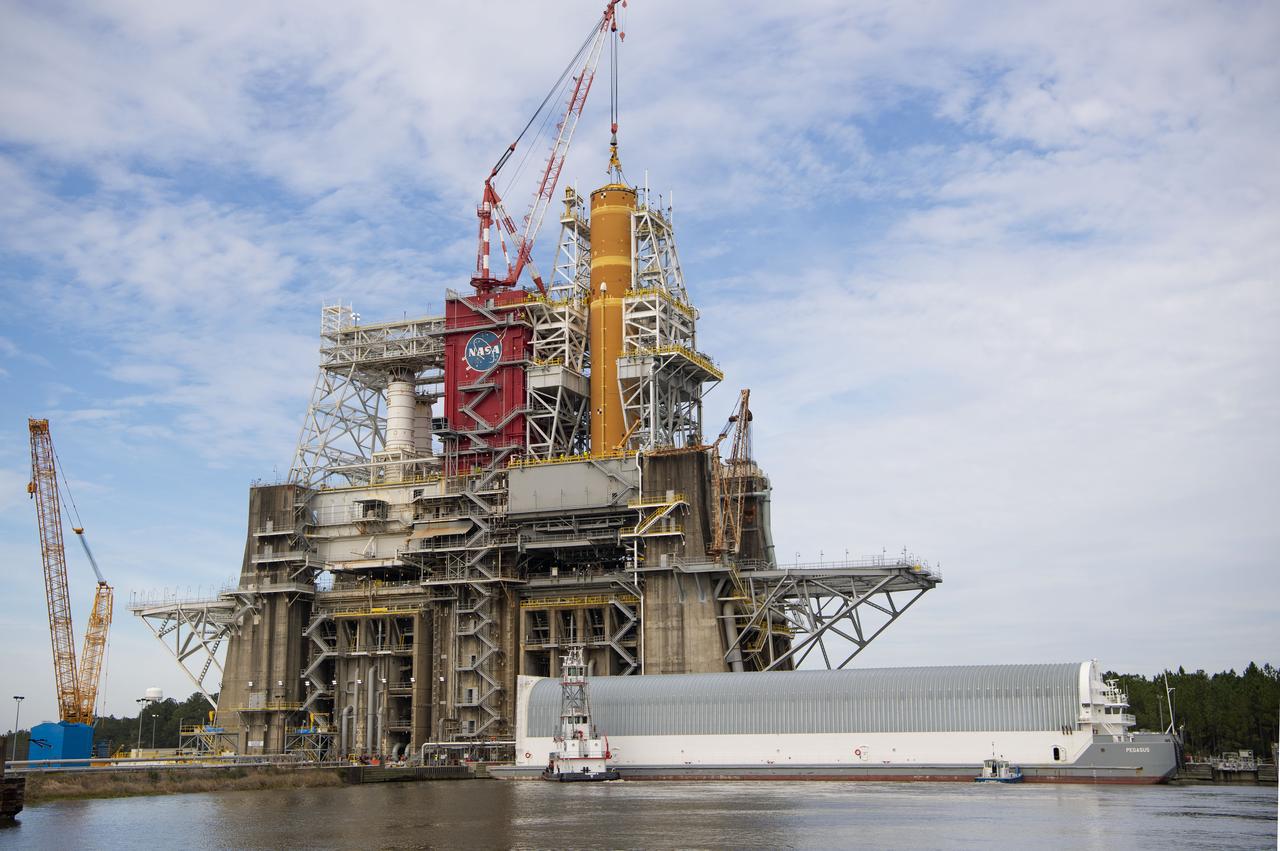

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine and NASA astronaut Raja Chari speak with workers involved modal testing of the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket at the B-2 Test Stand,x3 Monday, Feb. 10, 2020, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Over the coming months, the first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket will be undergoing a series of integrated Green Run tests prior to its maiden flight. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
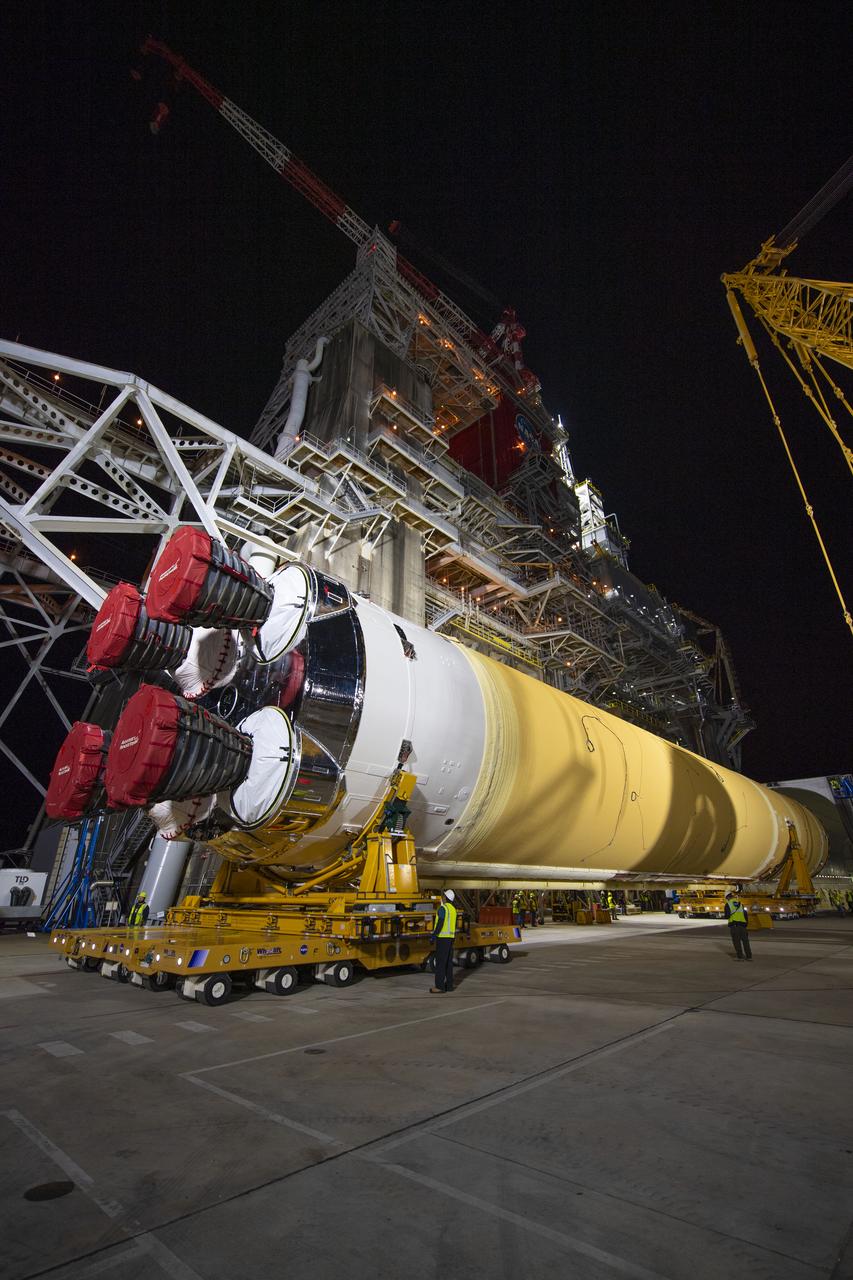

The first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System rocket arrived at Stennis Space Center on Jan. 12 for a series of tests prior to its maiden Artemis I flight. The core stage was transported from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the B-2 Test Stand dock at Stennis aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Soon after arrival, the stage was rolled off of Pegasus onto the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. After the stage is lifted and installed on the B-2 stand, it will undergo a series of “Green Run” systems test that represent the first integrated testing of its sophisticated systems.
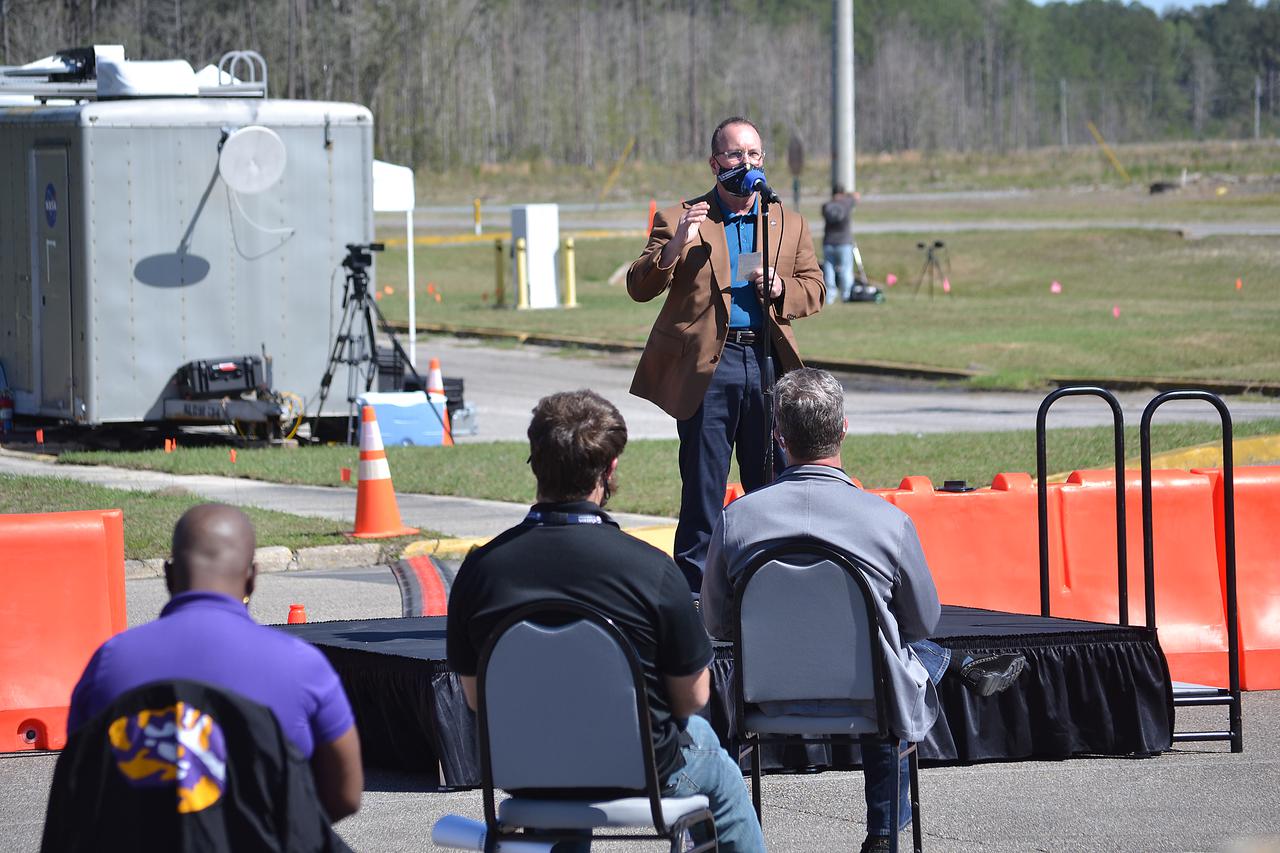

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
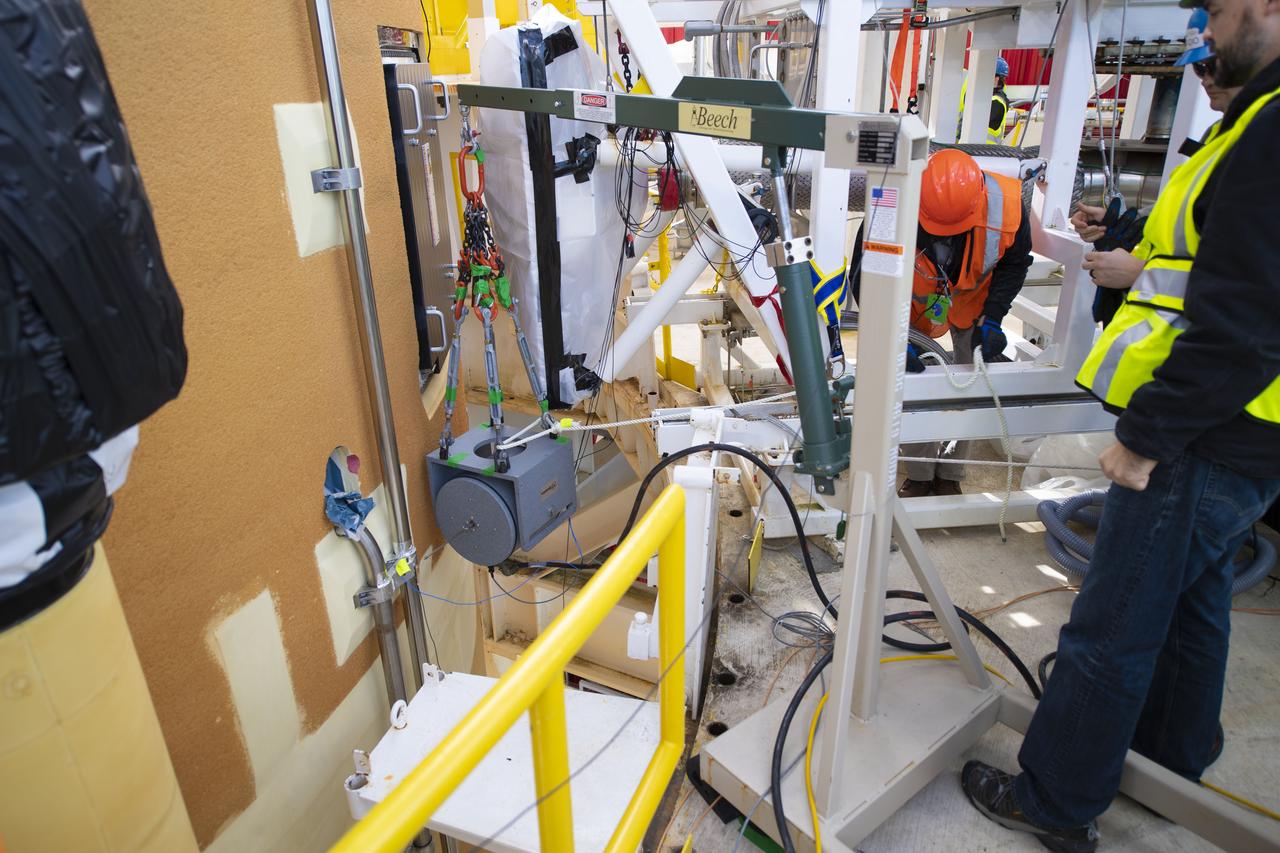

On Jan. 30, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center successfully conducted modal testing of the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Data from the modal test will be used to verify structural vibration modes and verify flight control parameters. The test is part of a Green Run series of testing that represents the first top-to-bottom integrated testing of the stage’s systems prior to its maiden Artemis I test mission.
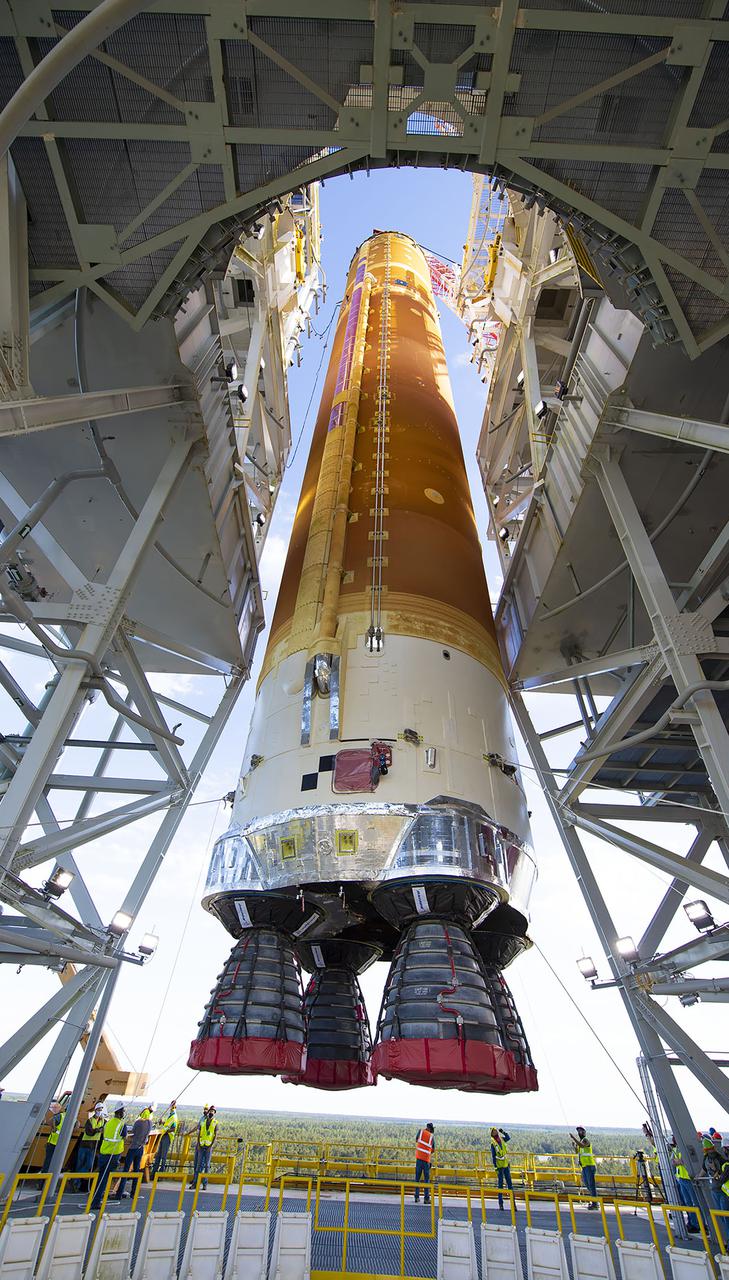

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
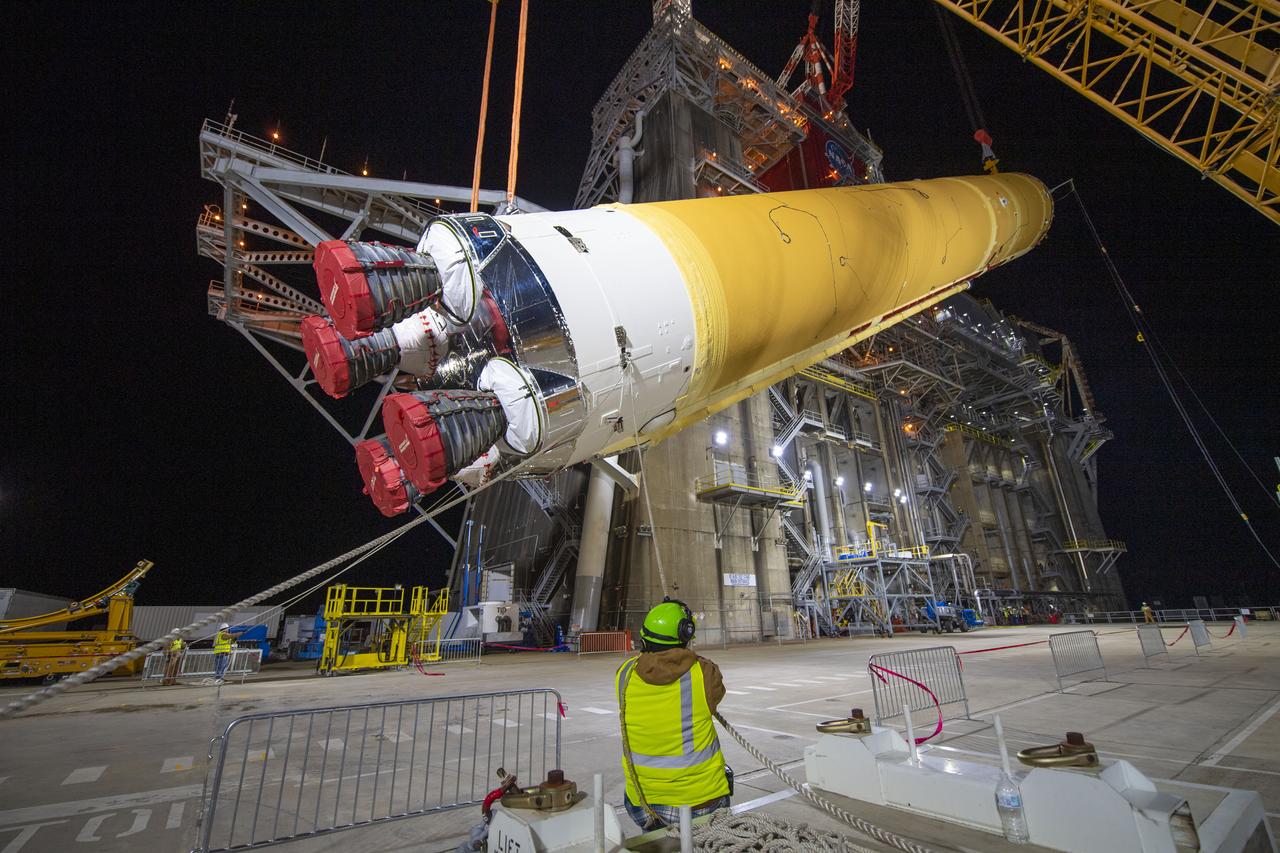

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
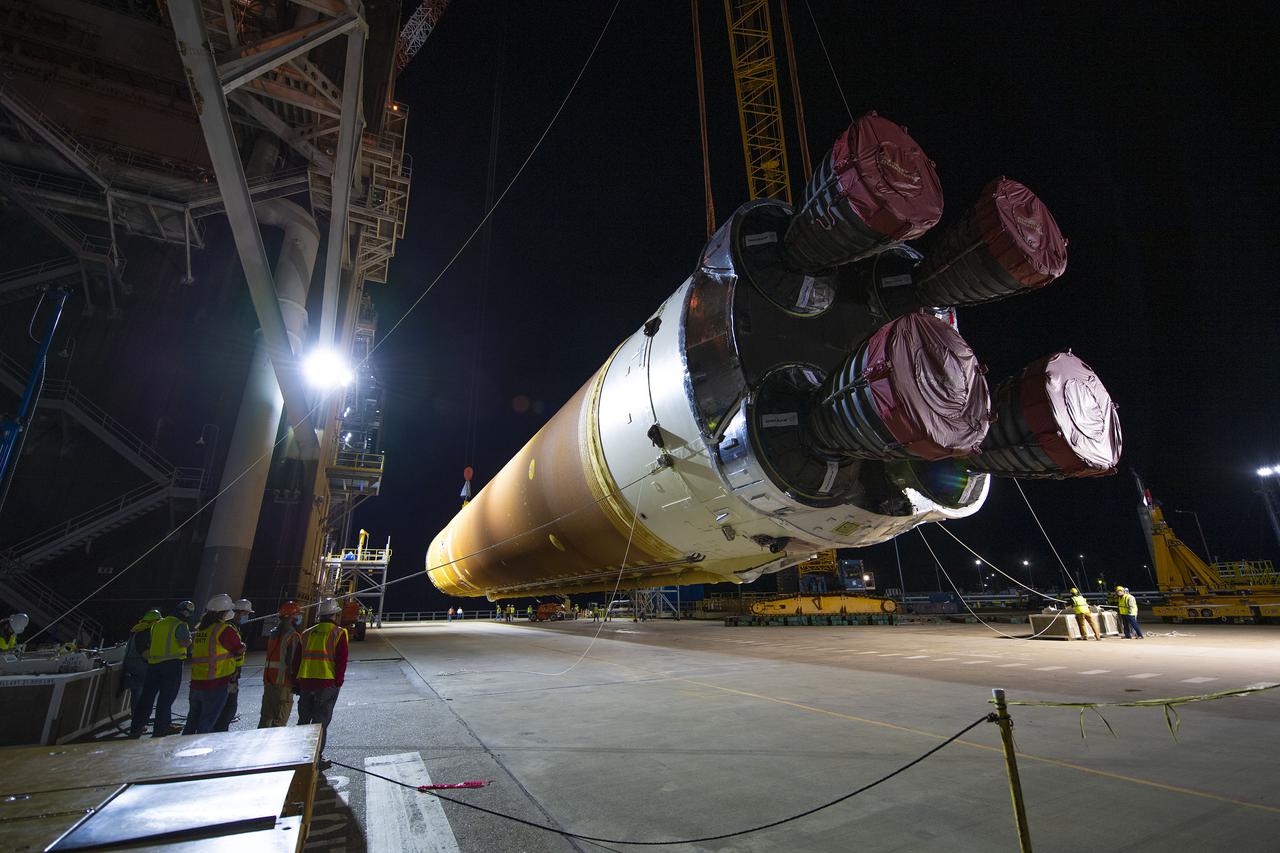

Following a successful Green Run hot fire at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, on March 18, members of a blended team work April 19-20 to remove the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from the B-2 Test Stand. The work required crews to lift the core stage from its vertical placement in the stand and lower it to a horizontal position on the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. The stage now will be loaded on NASA’s Pegasus barge for transport to Kennedy, where it will be prepared for launch of the Artemis I mission. Removal of the largest rocket stage ever built by NASA followed completion of a series of eight Green Run tests over the past year. During the Green Run series, teams performed a comprehensive test of the stand’s sophisticated and integrated systems. Photo Credit: NASA
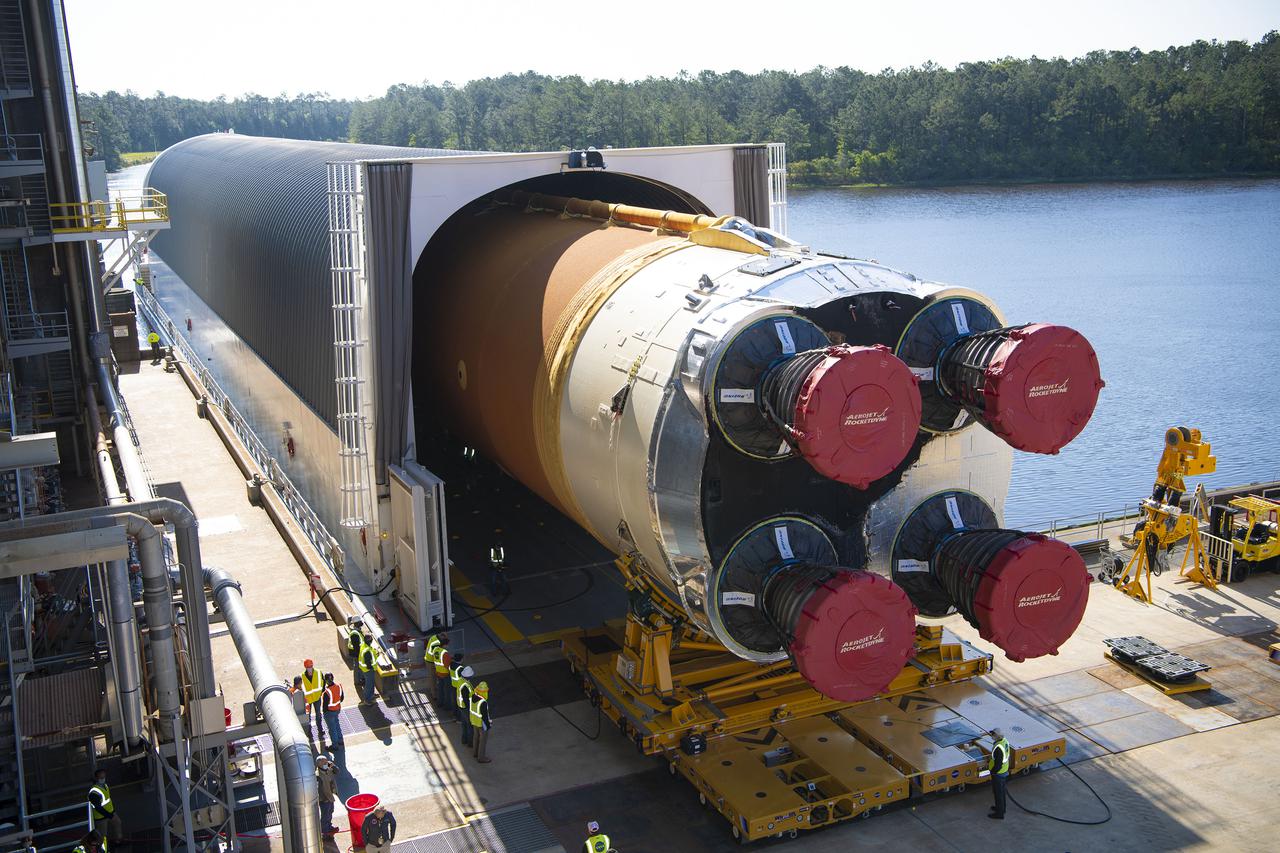

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
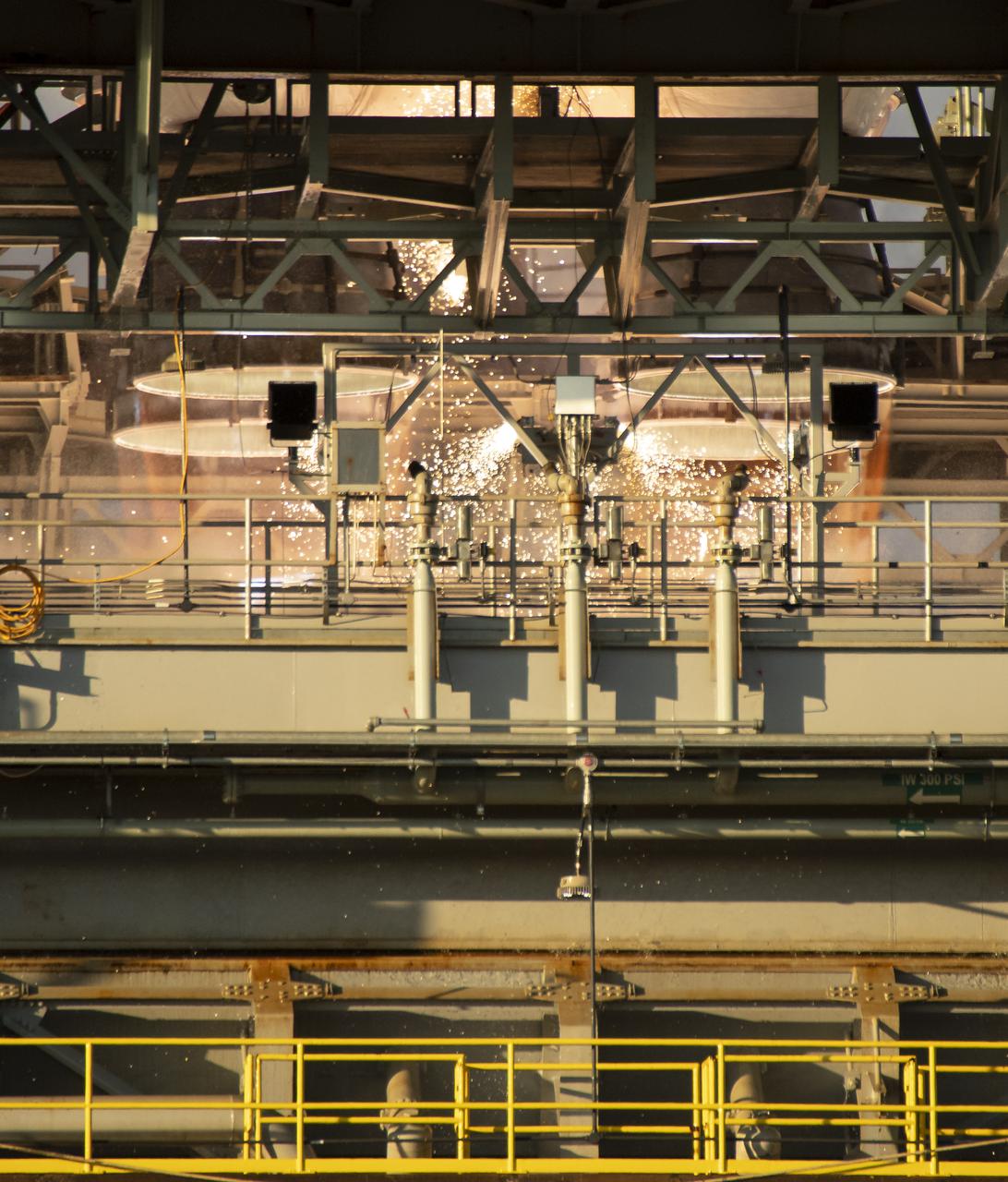

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
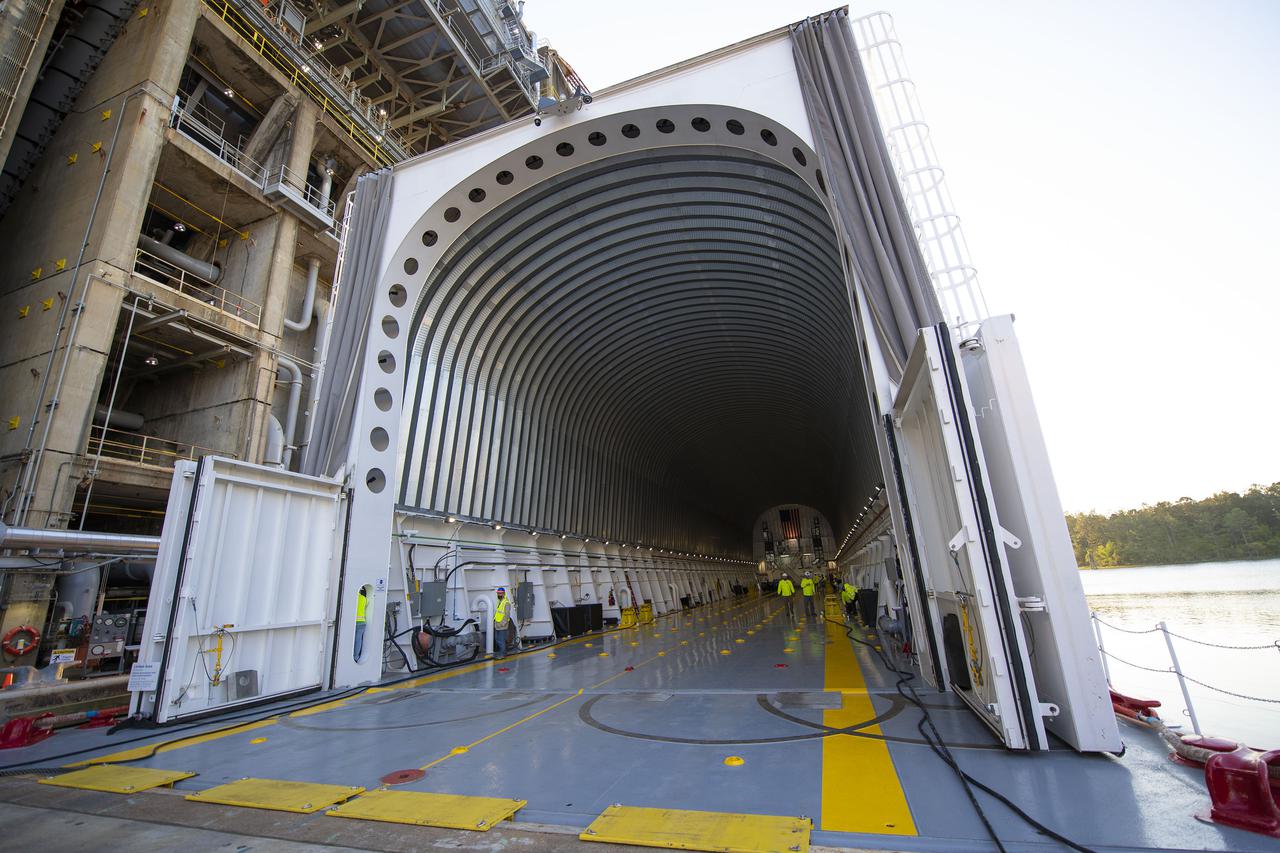

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
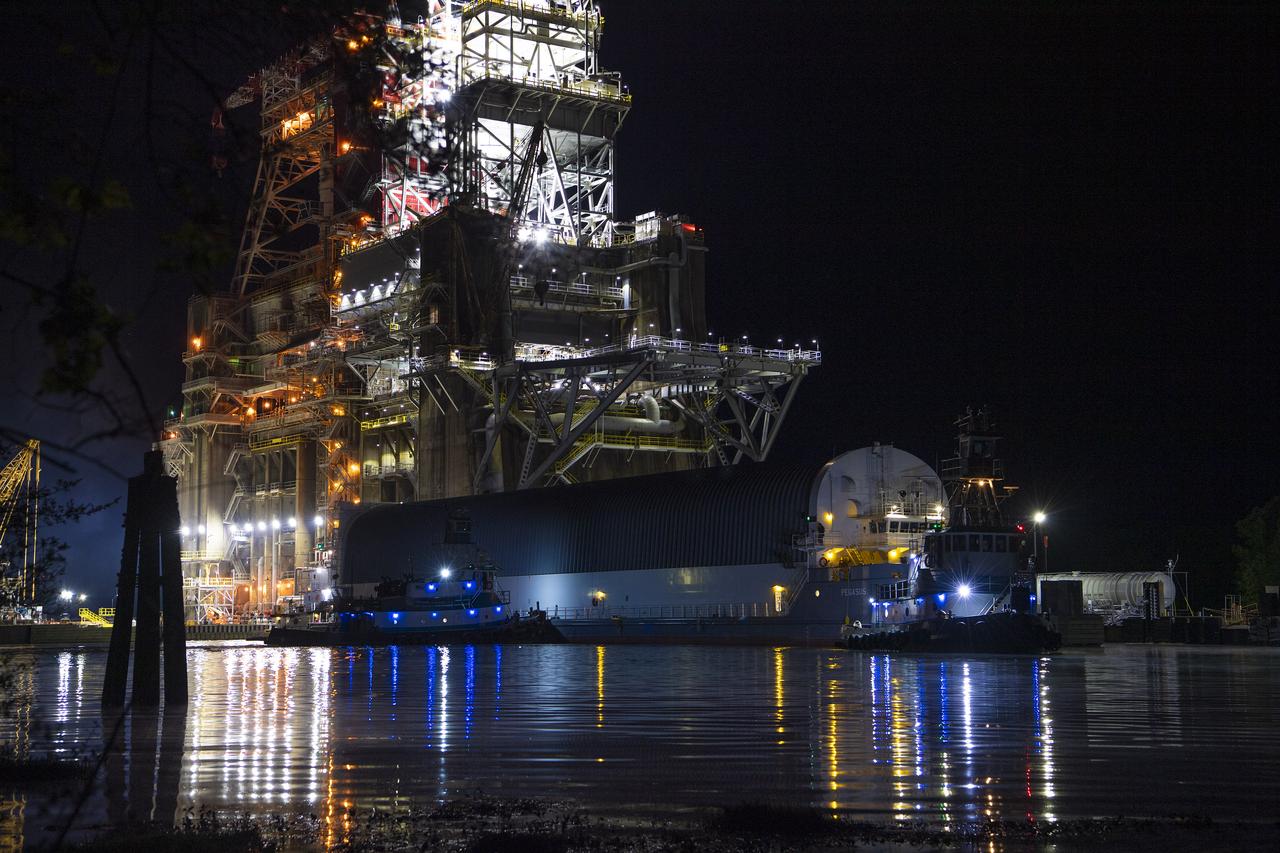

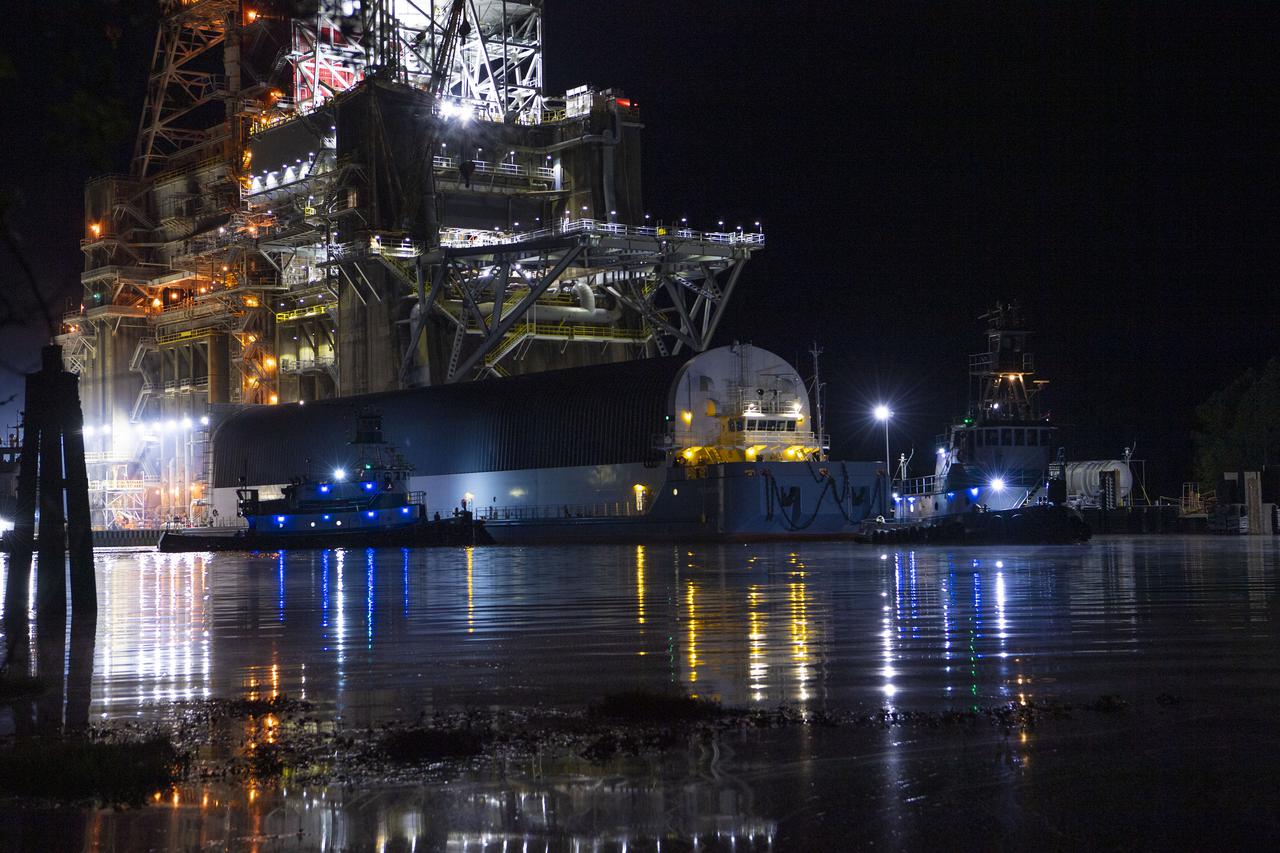
After a series of successful tests conducted the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) core stage was loaded on the Pegasus barge and departed the test stand in the early morning hours of April 22, 2021, beginning its journey to Kennedy Space Center.
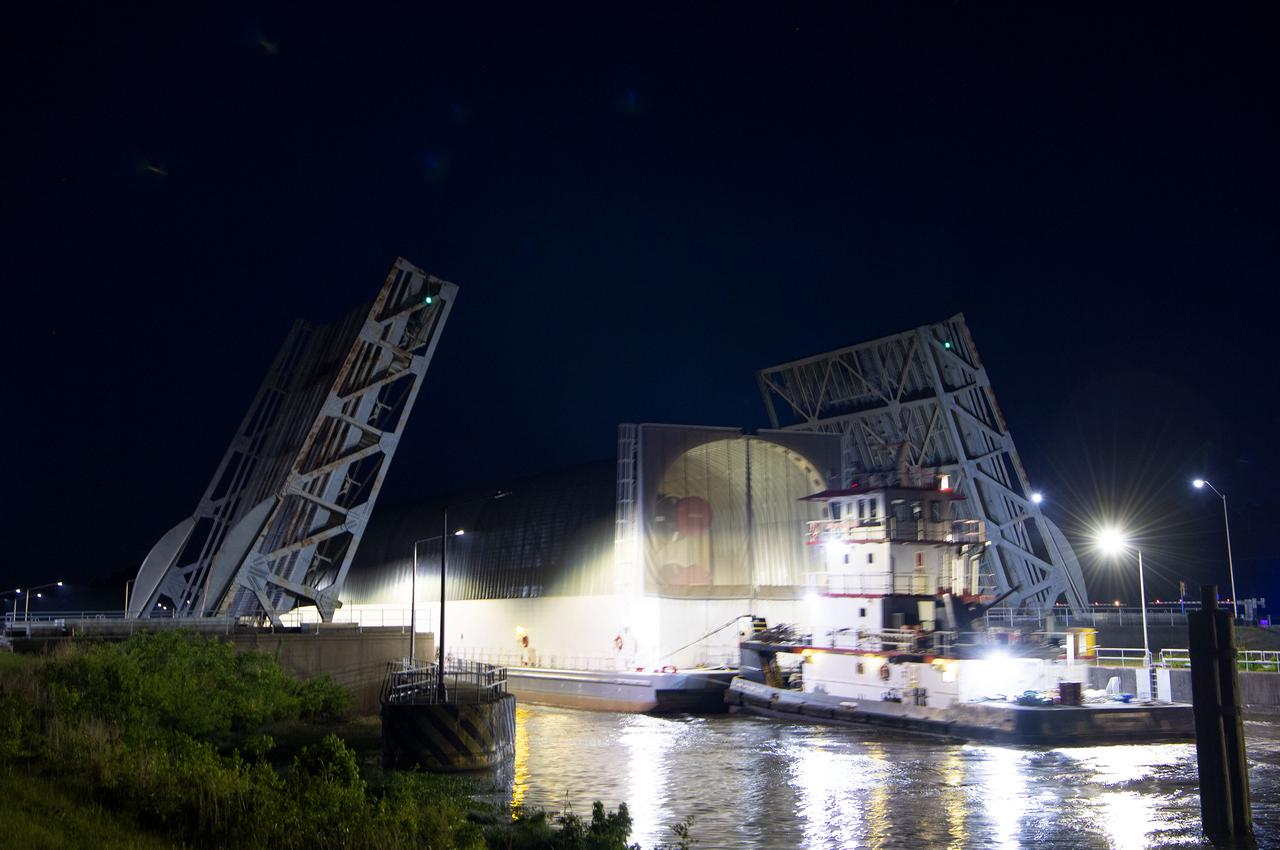

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
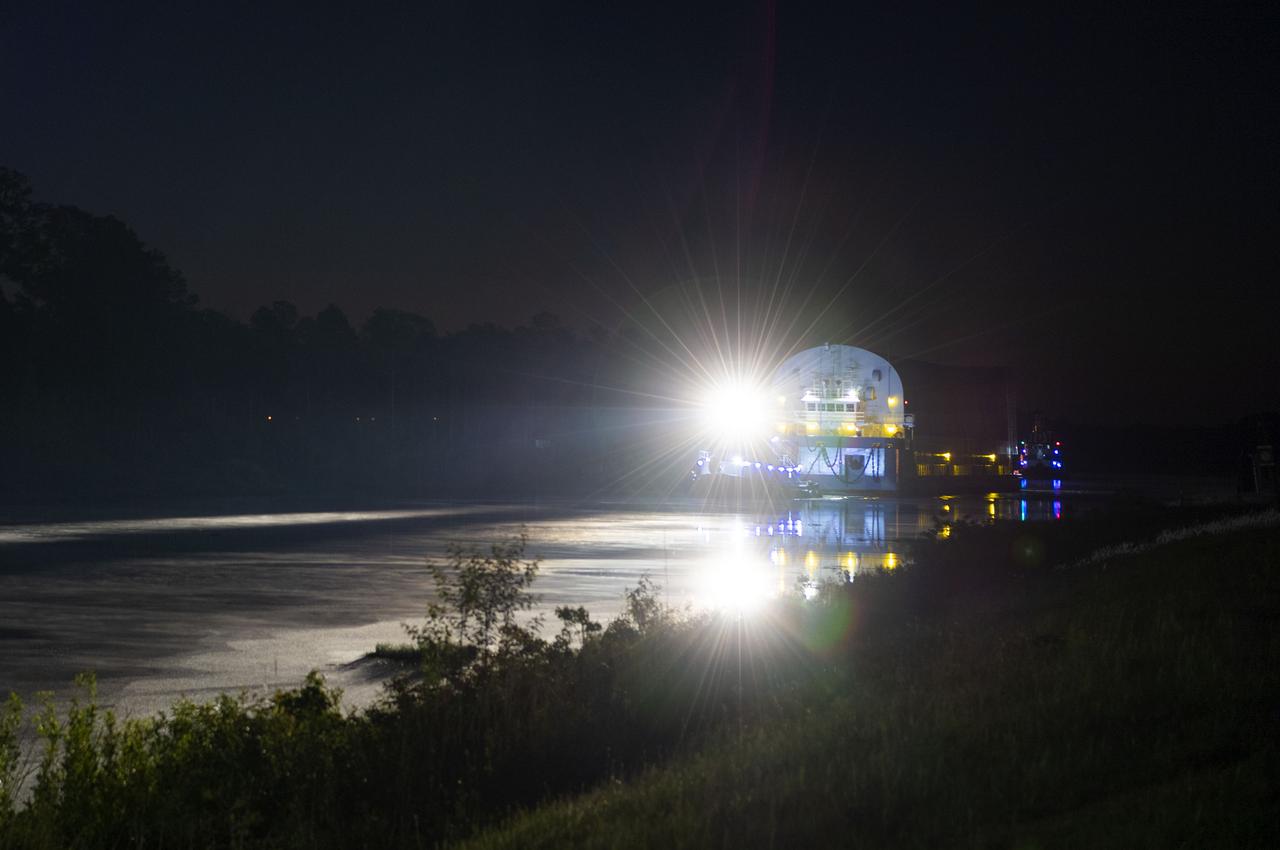

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
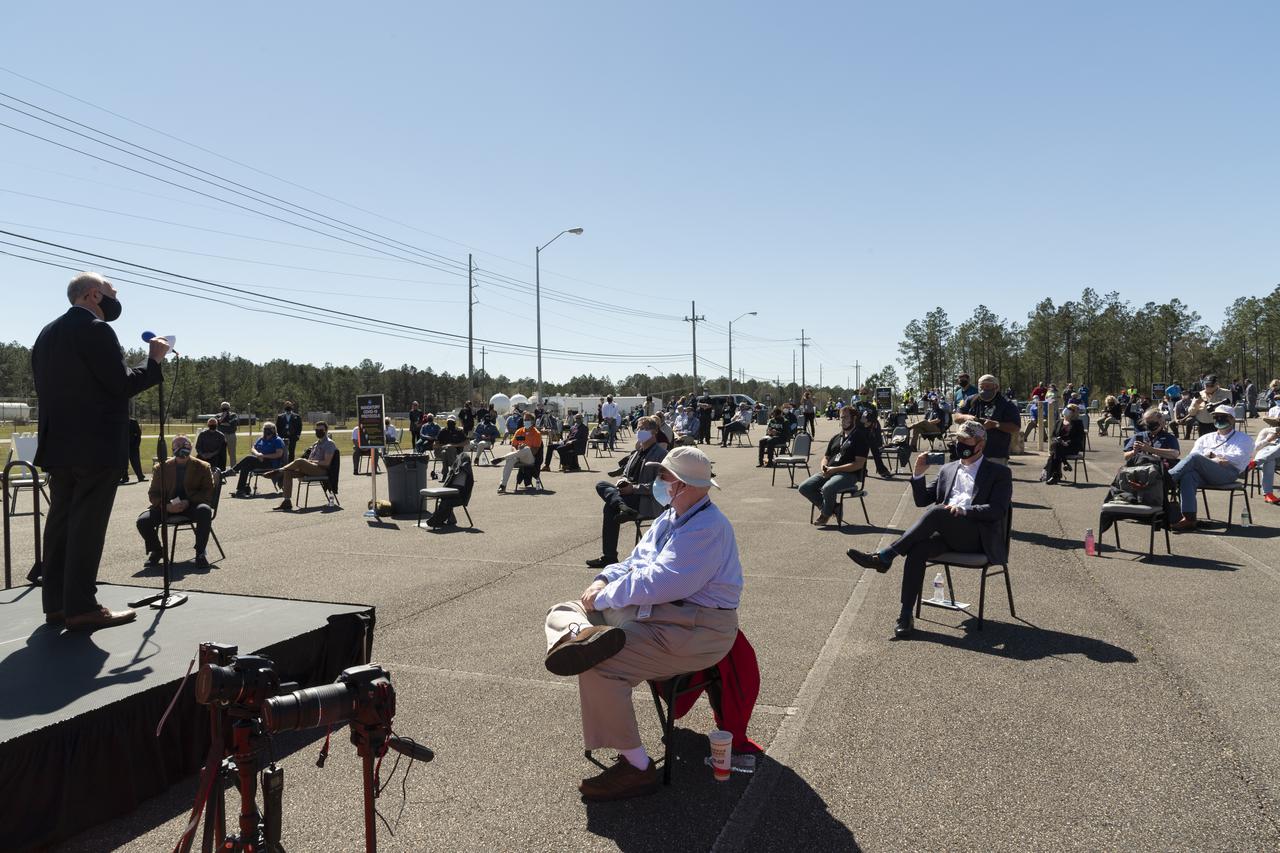

Acting NASA Administrator Steve Jurczyk speaks to invited guests ahead of a second hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
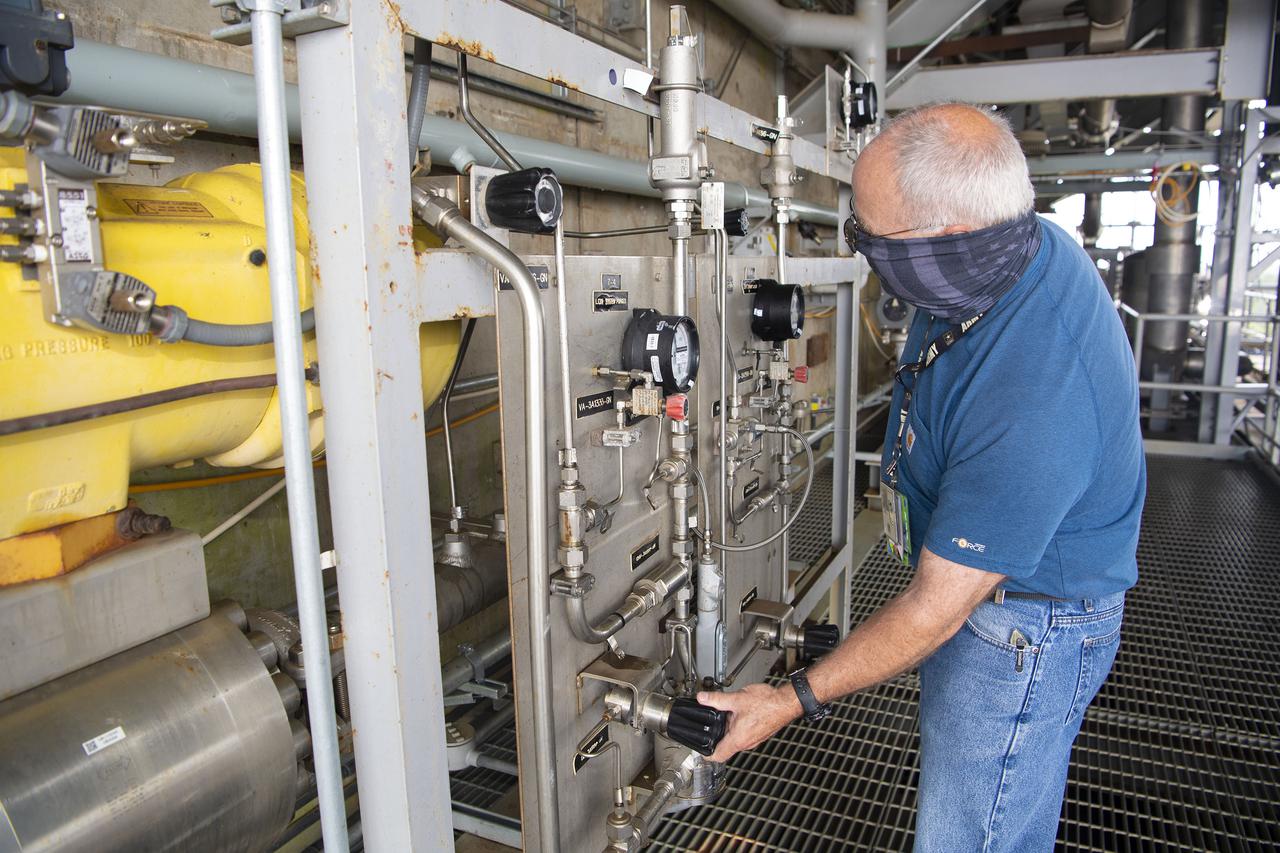

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, complete refurbishment work on the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The work followed a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines March 18. The hot fire marked the culmination of a yearlong Green Run series of tests of the stage and its integrated systems. Following refurbishment work, the core stage will be removed from the test stand and transported to Kennedy Space Center in Florida, aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge, shown delivering equipment to the B-2 Test Stand. At Kennedy, the core stage will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
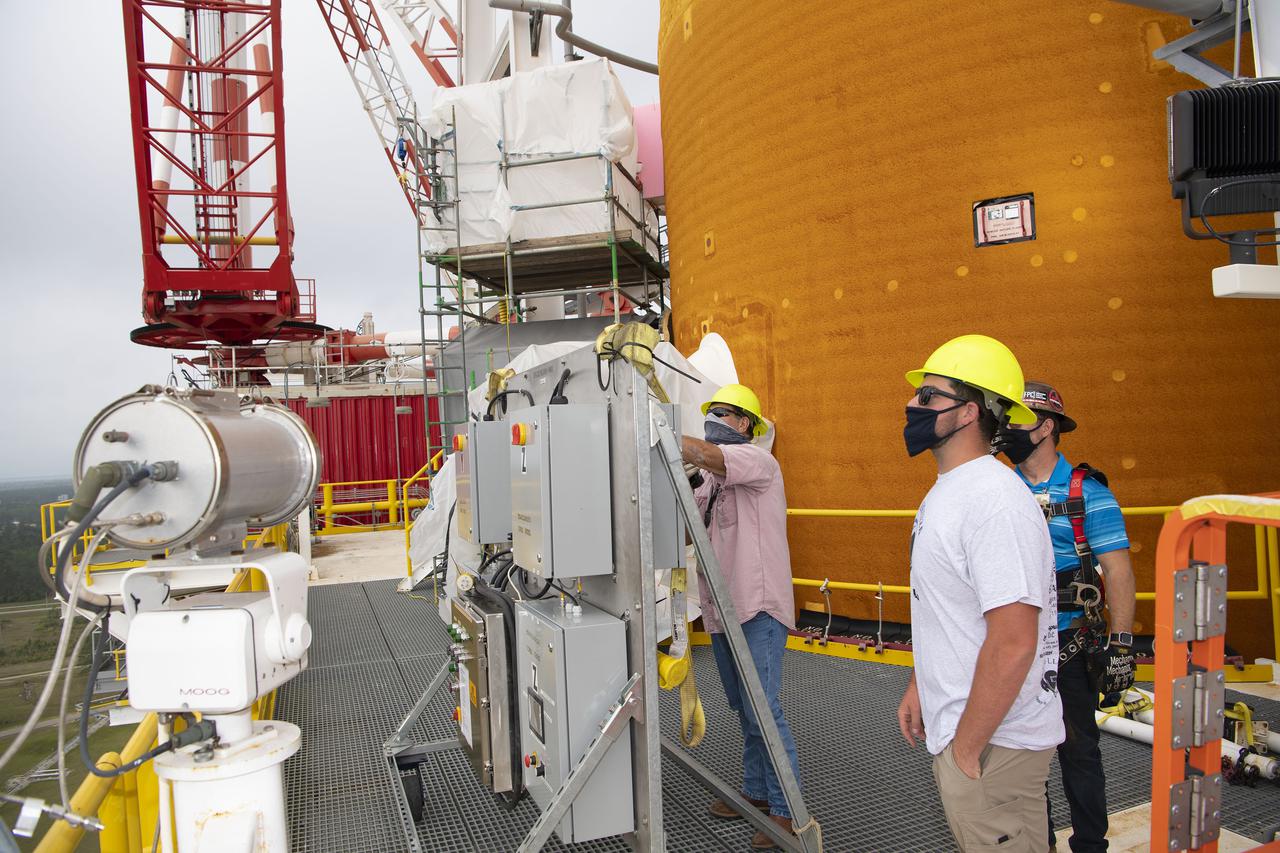

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, complete refurbishment work on the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. The work followed a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines March 18. The hot fire marked the culmination of a yearlong Green Run series of tests of the stage and its integrated systems. Following refurbishment work, the core stage will be removed from the test stand and transported to Kennedy Space Center in Florida, aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge, shown delivering equipment to the B-2 Test Stand. At Kennedy, the core stage will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
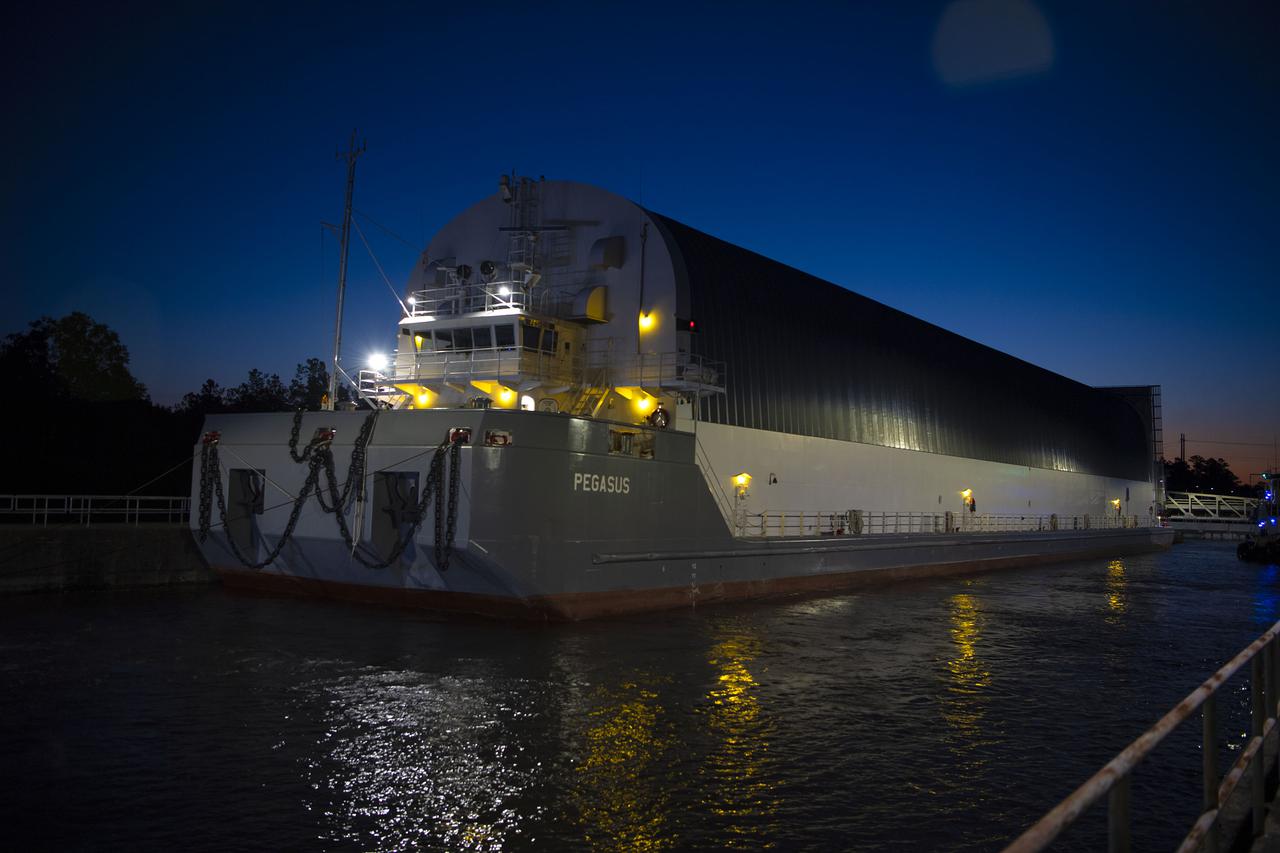

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
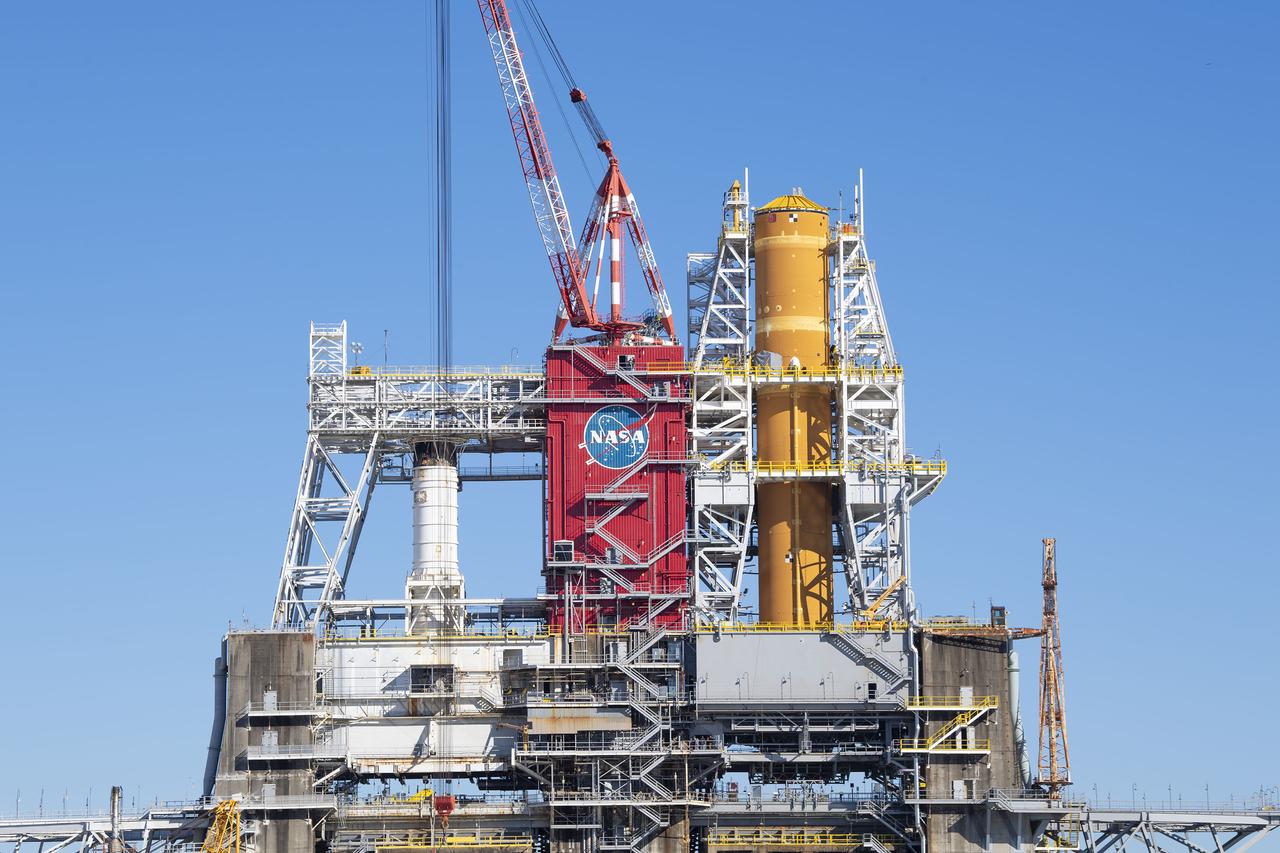

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
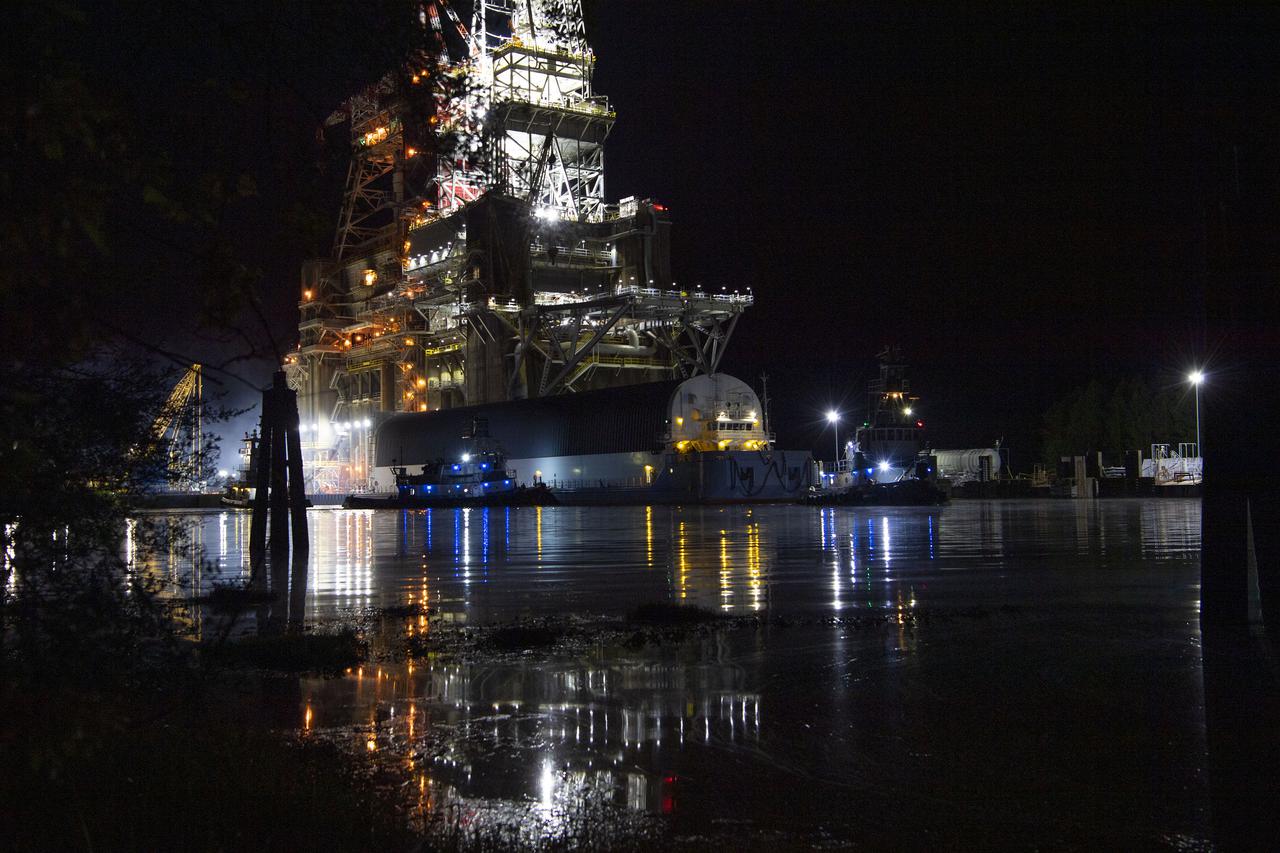

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
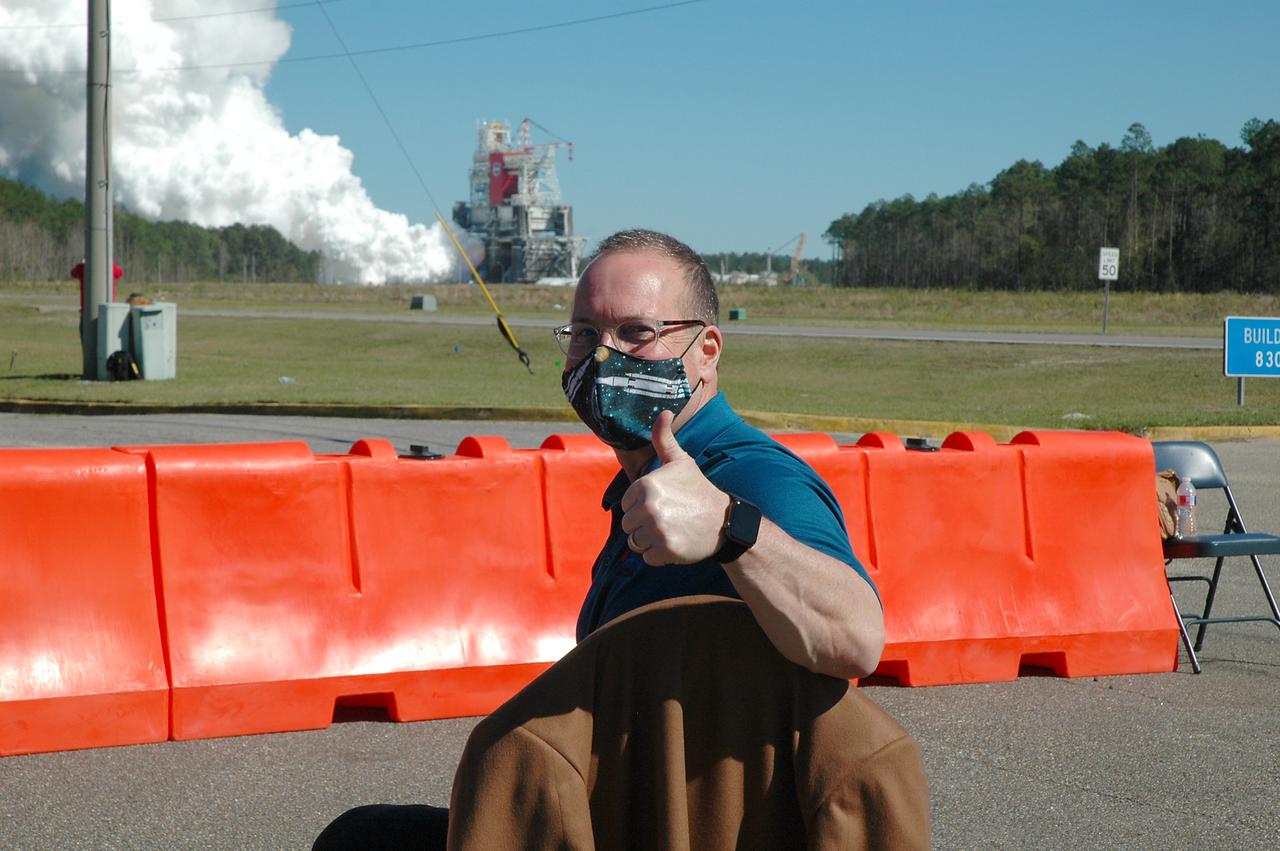

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
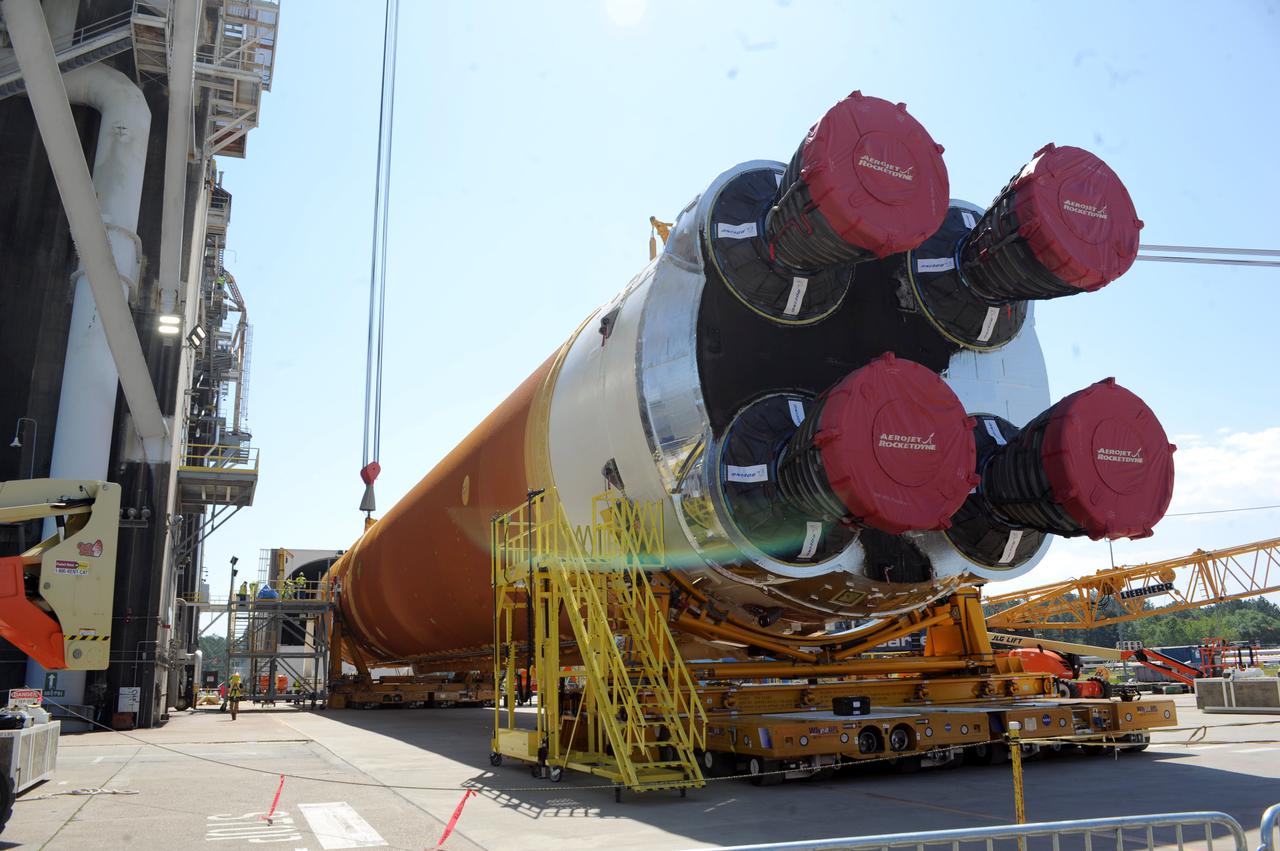

Team members at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, load the first core stage of the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on to the agency’s Pegasus barge in preparation for its transport to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The loading activity followed removal of the stage from the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis on April 19-20, 2021. It comes about a month after NASA conducted a successful hot fire of the stage and its four RS-25 engines on March 18 and after teams completed various refurbishment activities. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
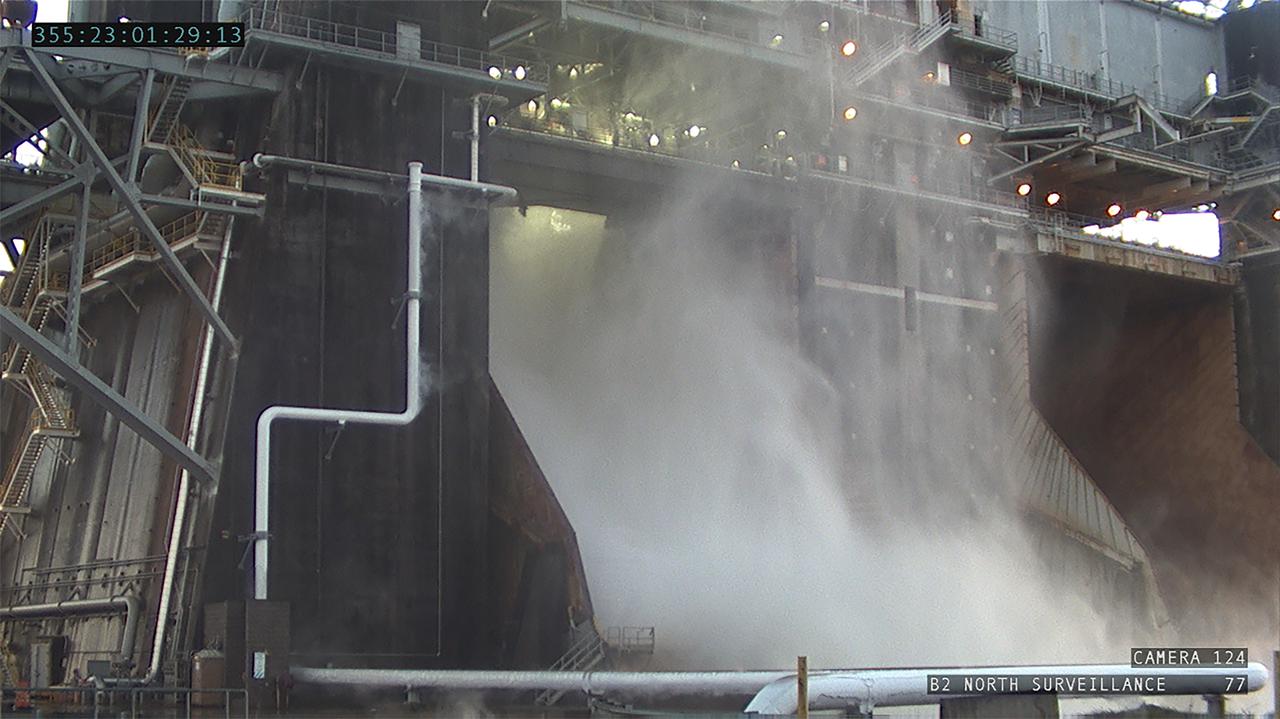

Operators at the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, conducted a wet dress rehearsal for the hot fire test of the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System on Dec. 21, 2020. In this image, water flows from the B-2 Test Stand flame deflector, just as it will during an actual hot fire test. The hot fire will conclude a series of eight Green Run tests of all core stage systems before it is transported to Kennedy Space Center for launch on the Artemis I mission.
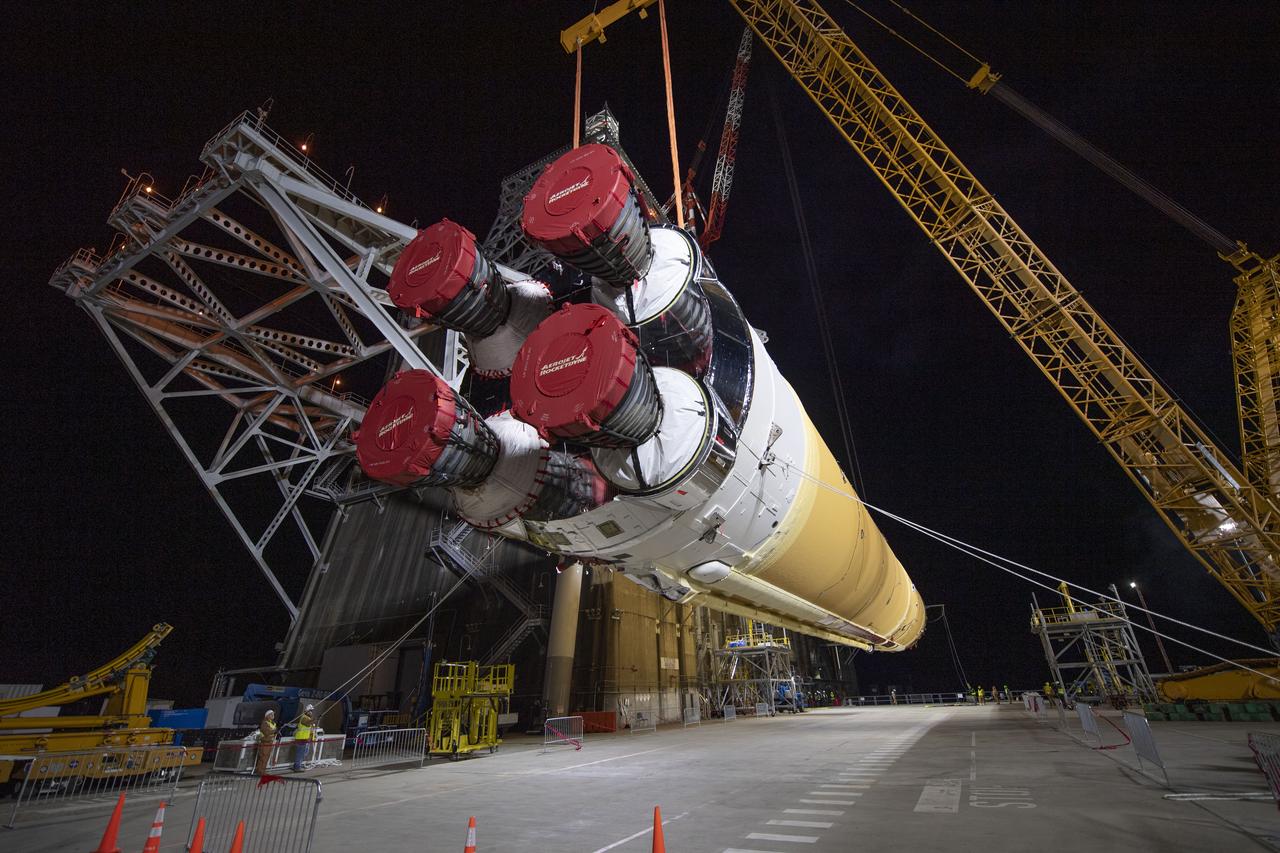

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.

On Jan. 21-22, 2020, crews at Stennis Space Center lifted and installed the first core stage of NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket onto the B-2 Test Stand. In upcoming months, a top-to-bottom, integrated series of Green Run tests will be conducted on the stage and its sophisticated systems. Following testing, the stage will be used to help launch the maiden Artemis I test mission of SLS and the Orion spacecraft. Through the Artemis program, NASA will send humans, including the first woman and next man, to the Moon to establish a sustainable presence.
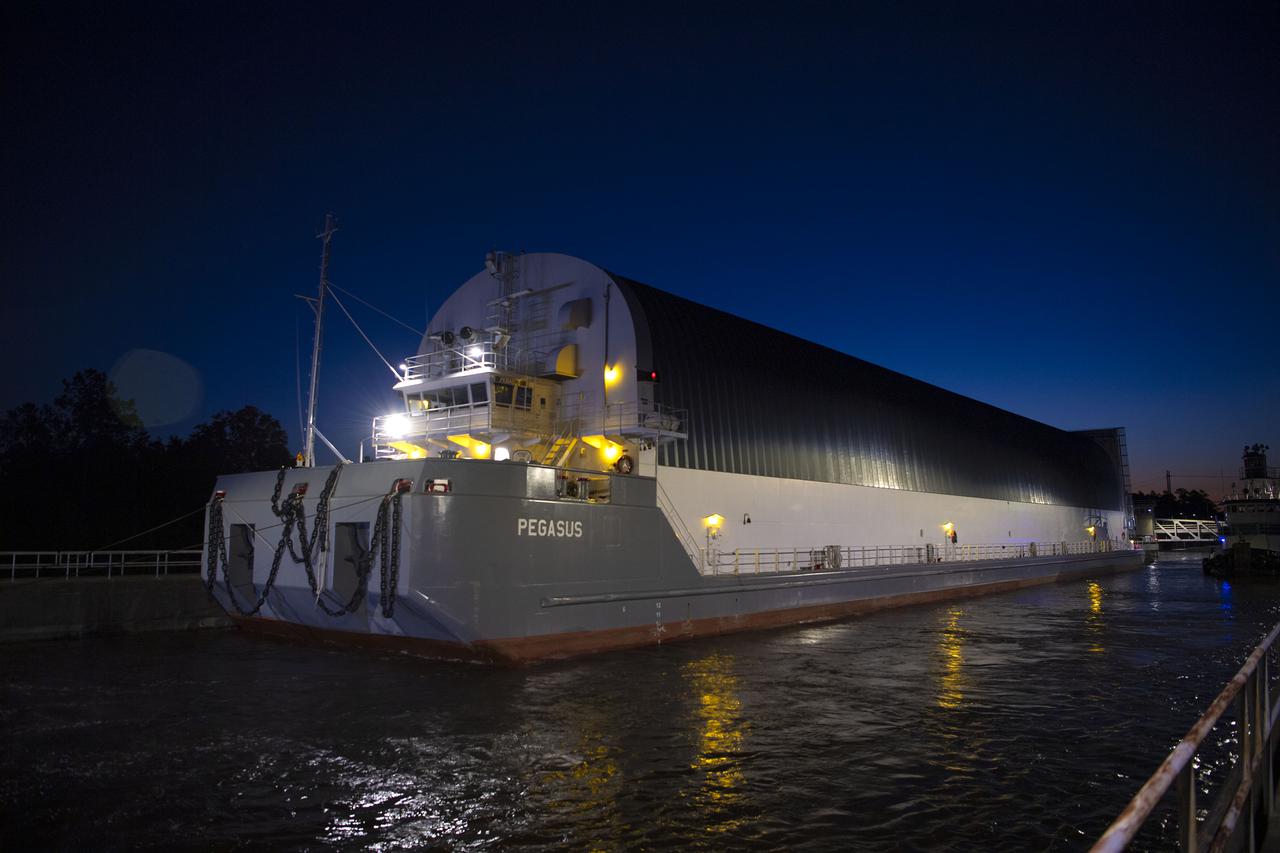

The first core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, loaded onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, departs Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, headed to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The departure of the core stage in mid-April 2021 followed completion of a Green Run test series of the stage systems in preparation for its launch on the Artemis I mission. The Green Run series concluded with a March 18 hot fire of the stage’s four RS-25 engines on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis, just as during an actual launch. Following refurbishment work, the stage was removed from the B-2 stand and loaded onto the Pegasus barge for transport. Once at Kennedy, the will be integrated with the rest of SLS rocket and prepared for the launch of the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: NASA
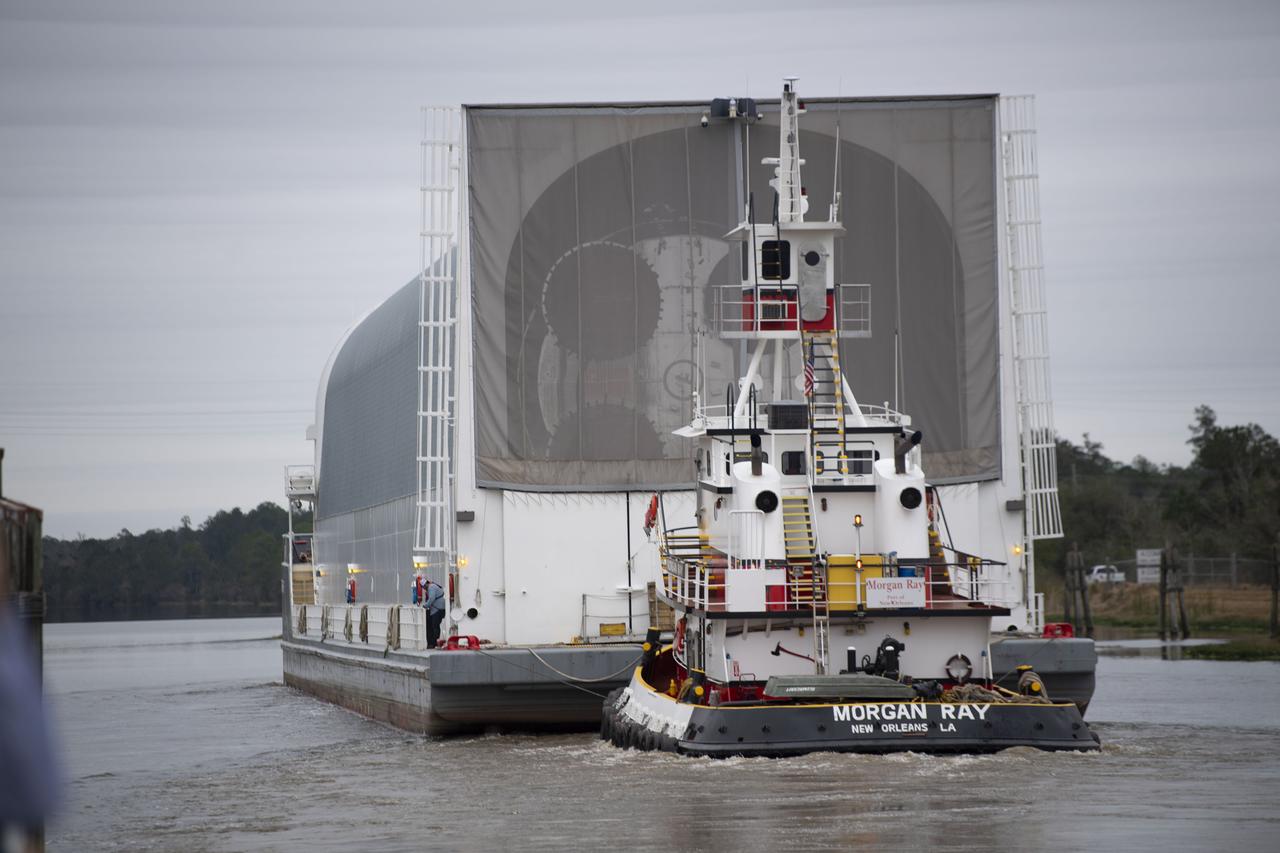

The first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System rocket arrived at Stennis Space Center on Jan. 12 for a series of tests prior to its maiden Artemis I flight. The core stage was transported from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the B-2 Test Stand dock at Stennis aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Soon after arrival, the stage was rolled off of Pegasus onto the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. After the stage is lifted and installed on the B-2 stand, it will undergo a series of “Green Run” systems test that represent the first integrated testing of its sophisticated systems.