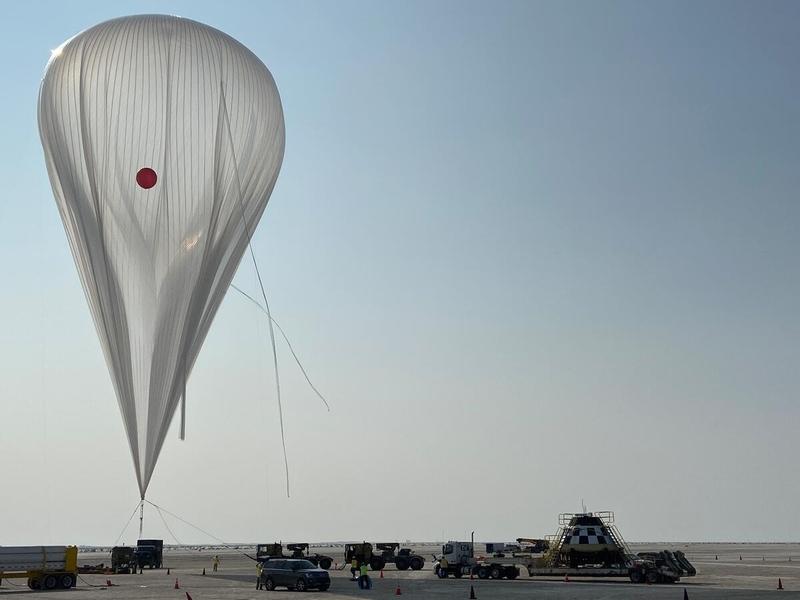

A Boeing CST-100 Starliner test article prepares to mate with a high altitude balloon ahead of its final parachute reliability drop test at White Sands, New Mexico, on Sept. 19, 2020. The test is part of a reliability campaign that will help strengthen the spacecraft’s landing system ahead of crewed flights to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
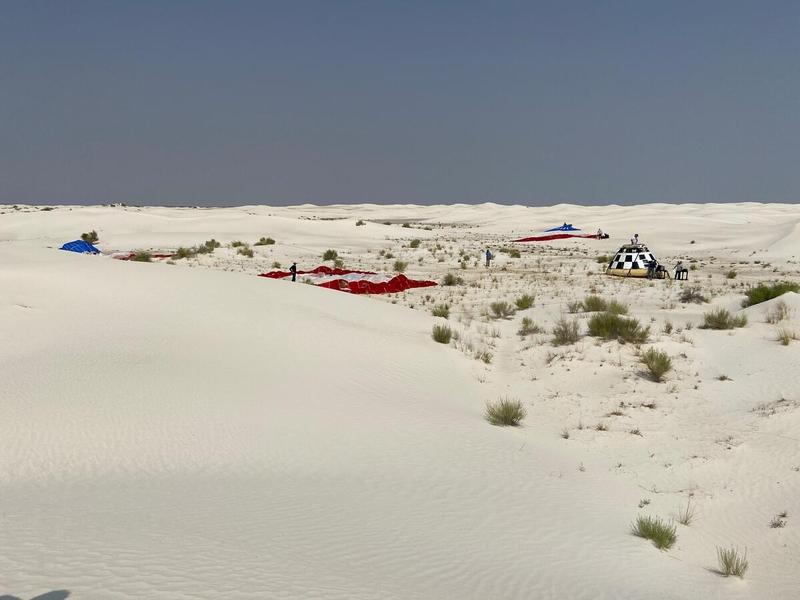

Recovery teams gather at the landing site of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner test article used in the spacecraft's final parachute reliability test at White Sands Space Harbor, New Mexico, on Sept. 19, 2020. The test is part of a reliability campaign that will help strengthen the spacecraft’s landing system ahead of crewed flights to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner's three main parachutes slow the test article to a safe and soft landing during the final balloon drop parachute test Sept. 19, 2020, at White Sands, New Mexico. The test is part of a reliability campaign that will help strengthen the spacecraft’s landing system ahead of crewed flights to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
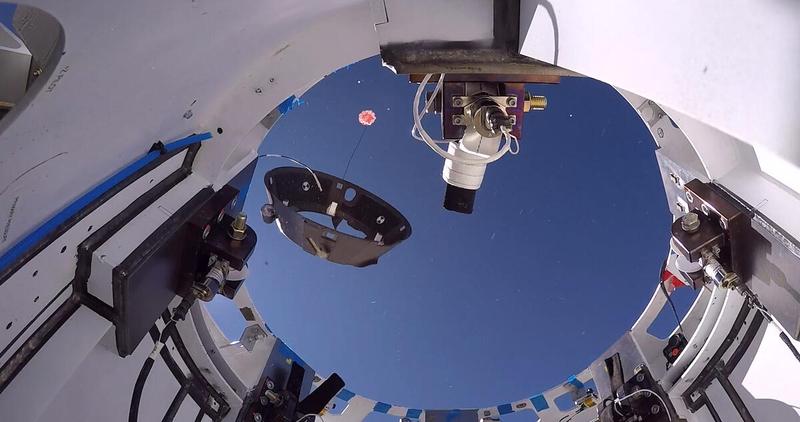

Boeing CST-100 Starliner’s forward heat shield jettisons from a test article during the vehicle’s final balloon drop parachute test at White Sands, New Mexico, on Sept 19, 2020. The test is part of a reliability campaign that will help strengthen the spacecraft’s landing system ahead of crewed flights to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
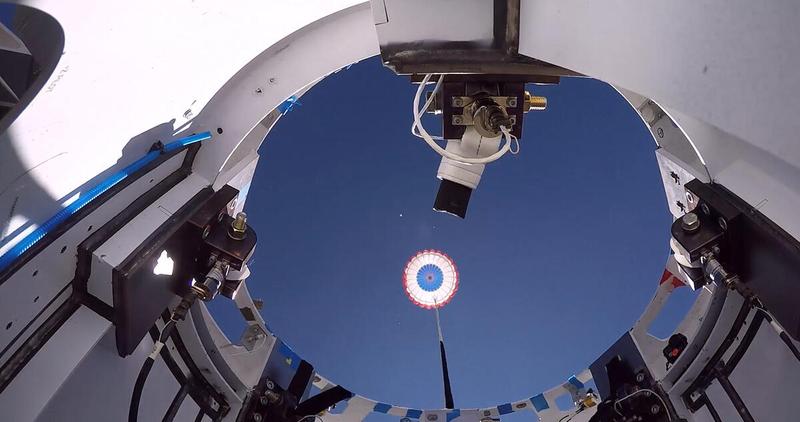
A reused drogue parachute deploys from Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner test article during the final balloon drop parachute test above White Sands, New Mexico, on Sept. 19, 2020. The test is part of a reliability campaign that will help strengthen the spacecraft’s landing system ahead of crewed flights to and from the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.