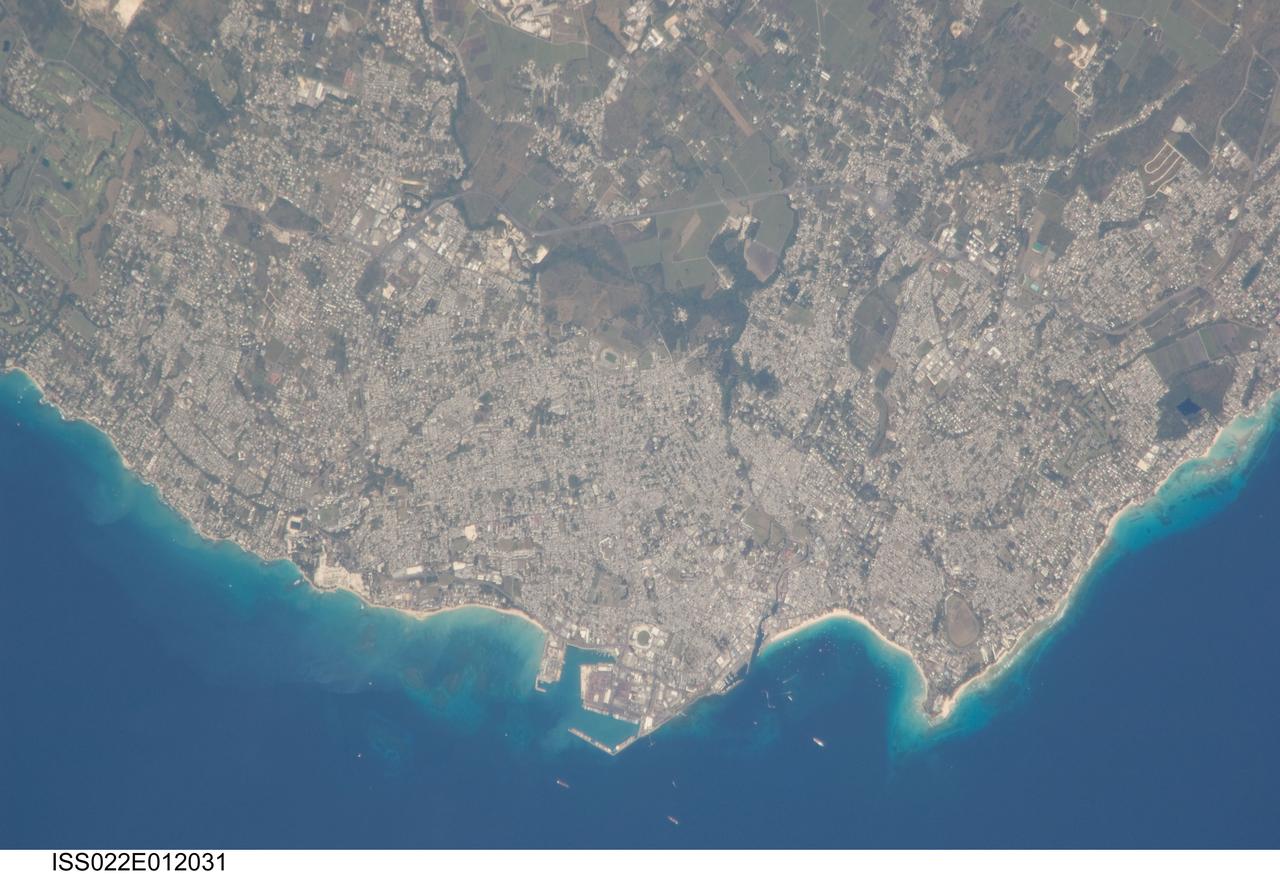

ISS022-E-012031 (16 Dec. 2009) --- Greater Bridgetown area, Barbados is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member on the International Space Station. Bridgetown is the capital city of the island nation of Barbados, located to the east of the Lesser Antilles Island chain. While Barbados is considered to be part of the Lesser Antilles, it is located within the western Atlantic Ocean rather than the Caribbean Sea region. Bridgetown is the largest city in Barbados in addition to being the seat of government. Barbados is a member of the British Commonwealth, and considers Queen Elizabeth II to be its constitutional monarch. Bridgetown, and the surrounding towns that make up the Greater Bridgetown area, is located along the southwestern coastline of the island. The metropolitan area is readily recognized in this image due to the gray and white rooftops and street grids (center) that contrast with green vegetated fields and riparian areas of the island?s interior to the northeast (top center). Bridgetown is a major port destination for both commercial and cruise ships serving the eastern Caribbean ? several ships are visible within Carlisle Bay. Water color in the image changes from light blue along the coastline ? indicating shallow water ? to the dark blue of deeper water away from the island.

ISS022-E-008282 (9 Dec. 2009) --- One of the world?s leading copper mines, Escondida, in the Atacama Desert of Chile, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member on the International Space Station. The copper mining industry is a major part of the Chilean economy. The mine is located 170 kilometers southeast of Chile?s port city of Antofagasta, in the hyper arid northern Atacama Desert at an elevation of 3,050 meters (approximately 10,000 feet) above sea level. Escondida produces mainly copper concentrates; assisted by gravity, the concentrates are piped as slurry down to the smaller port of Coloso just south of Antofagasta where they are dewatered for shipping. The photograph features a large light tan and gray waste or ?spoil? materials impoundment area (center) of the mine complex. The copper-bearing waste, which is a large proportion of the material excavated from open pits to the north (not in frame), is poured into the impoundment area as a liquid (green region at photo?s center), and dries to the lighter-toned spoil seen in the image. The spoil is held behind a retaining dam, just a little more than one kilometer in length, visible as a straight line at lower left. ?Escondida? means ?hidden? in Spanish, and refers to the fact that the copper ore body was buried beneath hundreds of meters of barren rock and had to be located by a laborious drilling program following a geologic trend established from other copper occurrences.
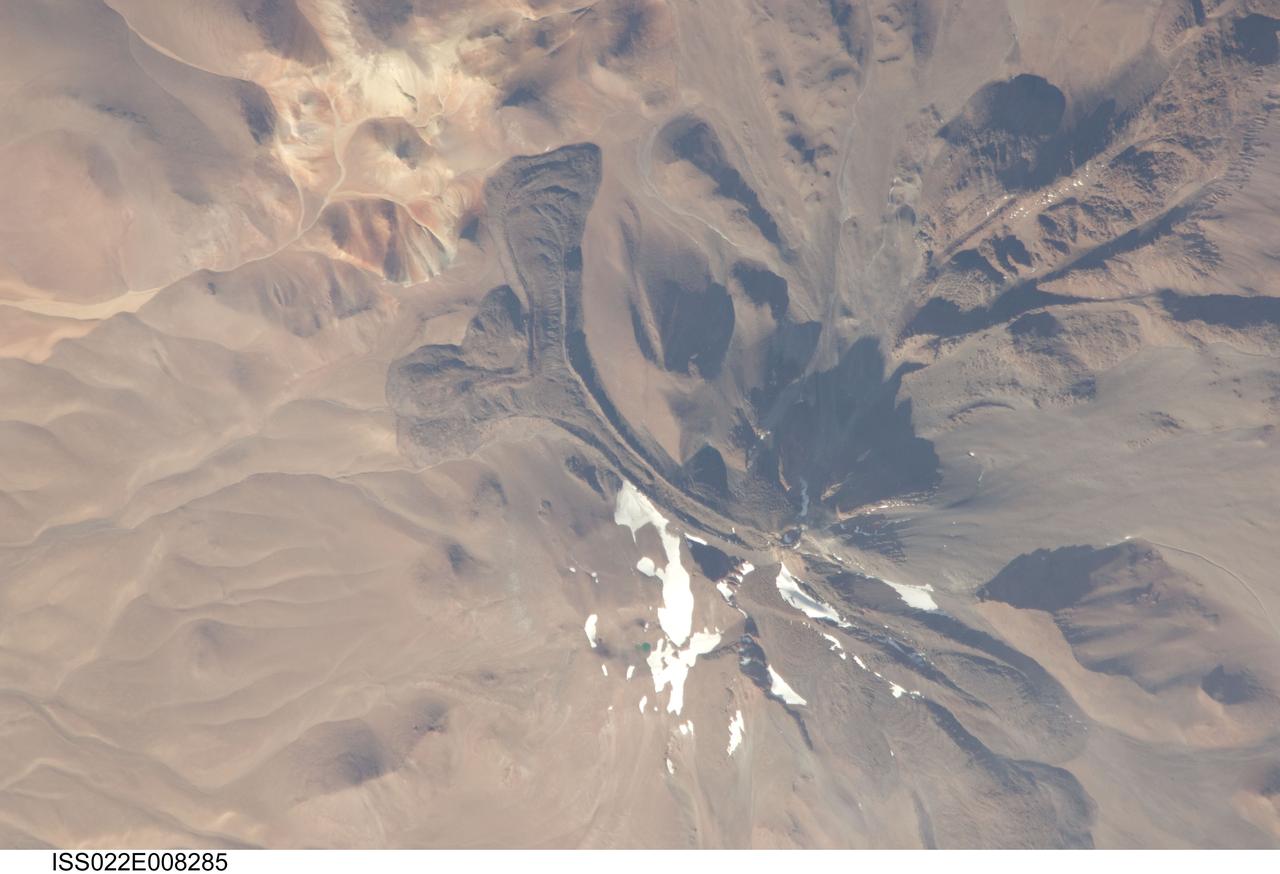
ISS022-E-008285 (9 Dec. 2009) --- Llullaillaco volcano on the Argentina-Chile border is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member on the International Space Station. The summit of Llullaillaco volcano has an elevation of 6,739 meters above sea level, making it the highest historically active volcano in the world. The current Llullaillaco stratovolcano ? a typically high, cone-shaped volcano built from successive layers of thick lava flows and eruption products like ash and rock fragments ? is built on top of an older stratovolcano. The last explosive eruption of the volcano occurred in 1877 based on historical records. This detailed photograph of Llullaillaco illustrates an interesting volcanic feature known as a coulee (top left). Coulees are formed from highly viscous, thick lavas that flow onto a steep surface; as they flow slowly downwards, the top of the flow cools and forms a series of parallel ridges oriented at 90 degrees to the direction of flow (somewhat similar in appearance to the pleats of an accordion). The sides of the flow can also cool faster than the center, leading to the formation of wall-like structures known as flow levees (center).
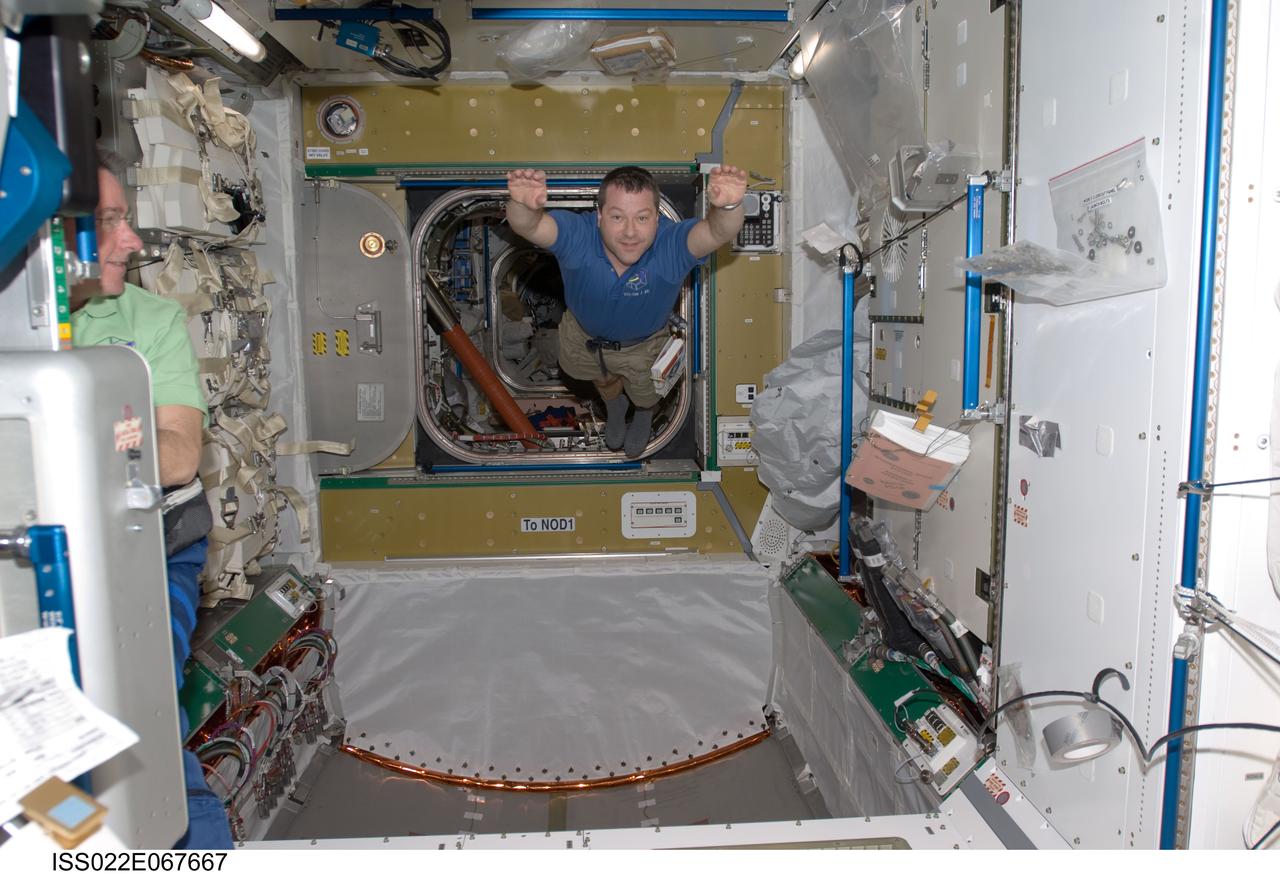

ISS022-E-067667 (14 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Nicholas Patrick, STS-130 mission specialist, floats freely in newly-installed Tranquility node of the International Space Station while space shuttle Endeavour remains docked with the station.
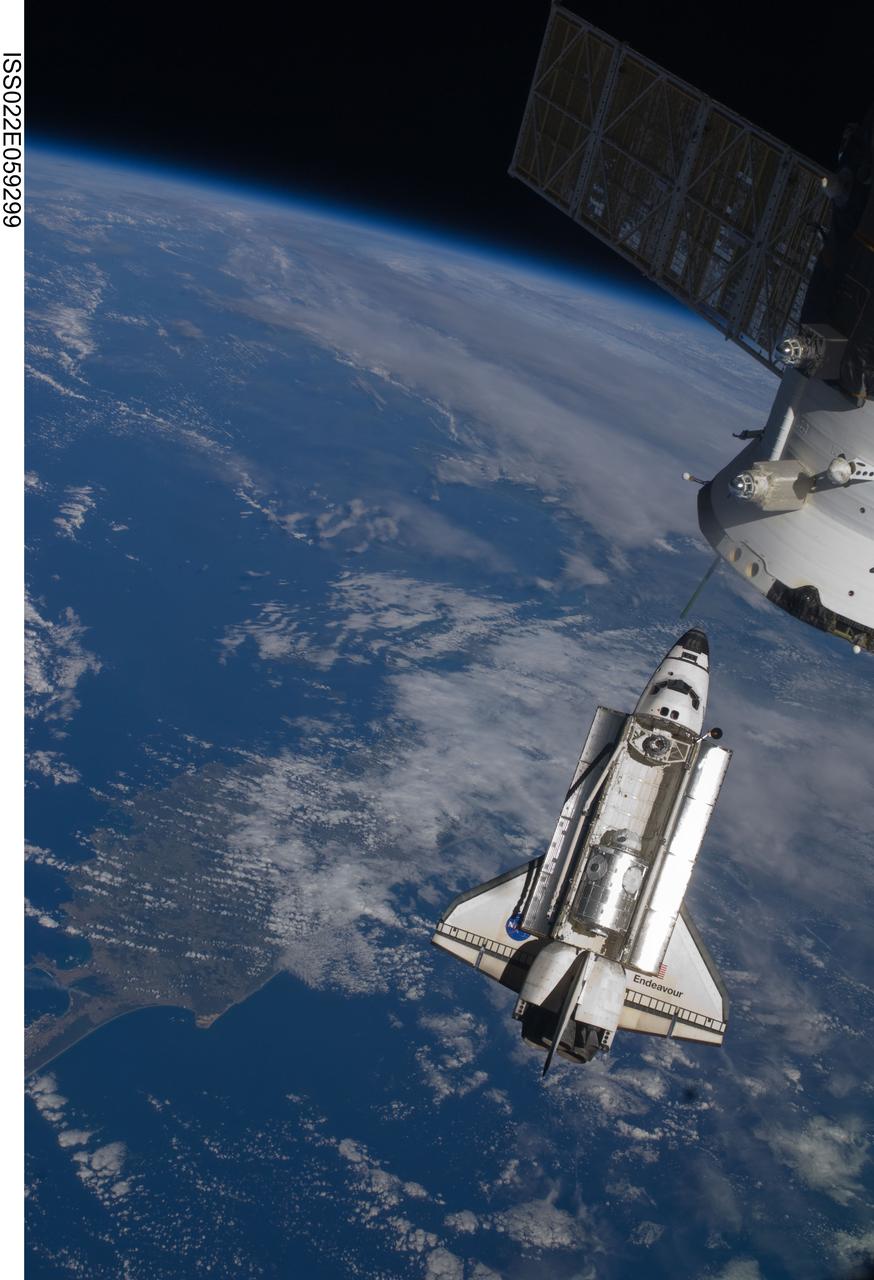

ISS022-E-059299 (9 Feb. 2010) --- Seen flying above part of North Island, New Zealand, the space shuttle Endeavour is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member during STS-130 rendezvous and docking operations with the International Space Station. Docking occurred at 11:06 p.m. (CST) on Feb. 9, 2010.
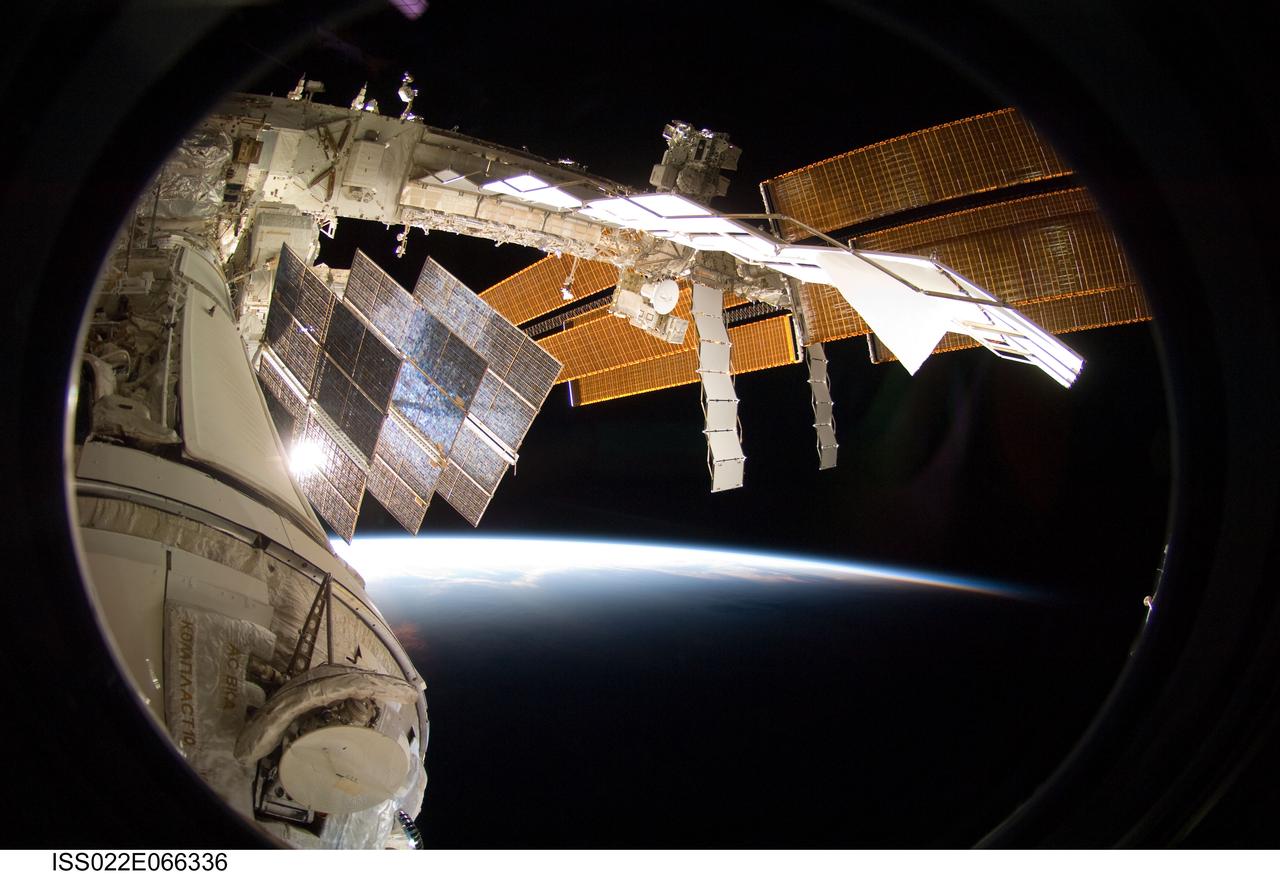

ISS022-E-066336 (15 Feb. 2010) --- Backdropped by Earth?s horizon and the blackness of space, a portion of the International Space Station is featured in this image photographed by a crew member on the ISS while space shuttle Endeavour (STS-130) remains docked with the station.

ISS022-E-005403 (2 Dec. 2009) --- Giens Peninsula, France is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member on the International Space Station. This detailed image depicts the Giens Peninsula located along the Mediterranean coastline of France. The peninsula is part of the Cote d?Azur, also known as the French Riviera, the coastal region bounded by the Rhone River to the west, to the north by the Rhone Alps, and the east by the Italian border. The peninsula itself, extended out southwards from the city of Hyeres to the resort community of Giens, is formed from two tombolos. A tombolo is a ridge of beach material (typically sand) built by wave action that connects an island to the mainland. Tombolos, like many coastal features, typically change dramatically over geologic time due to fluctuating sediment supply, coastal currents, sea levels and storm events. The tombolos of the Giens Peninsula have been modified by human activities including sand dune removal, construction of roadways, and replacement of the original sand by other materials. The long-term survival of these tombolos will be determined by the effects of these changes on the natural coastal processes, with potential sea level rise presenting an additional threat. In addition to Giens, three other urban areas are visible in this image; Carqueiranne, Hyeres, and La Londe-les-Maures. The urban areas are recognizable by both light pink rooftops and grey street grids. These contrast with green to brown vegetated areas including agricultural fields (between Hyeres and La Londe-les-Maures, top center) and dark green vegetated hillslopes (between Hyeres and Carqueiranne, top left). Small white dots and streaks in the Mediterranean Sea are actually yachts and other pleasure craft.
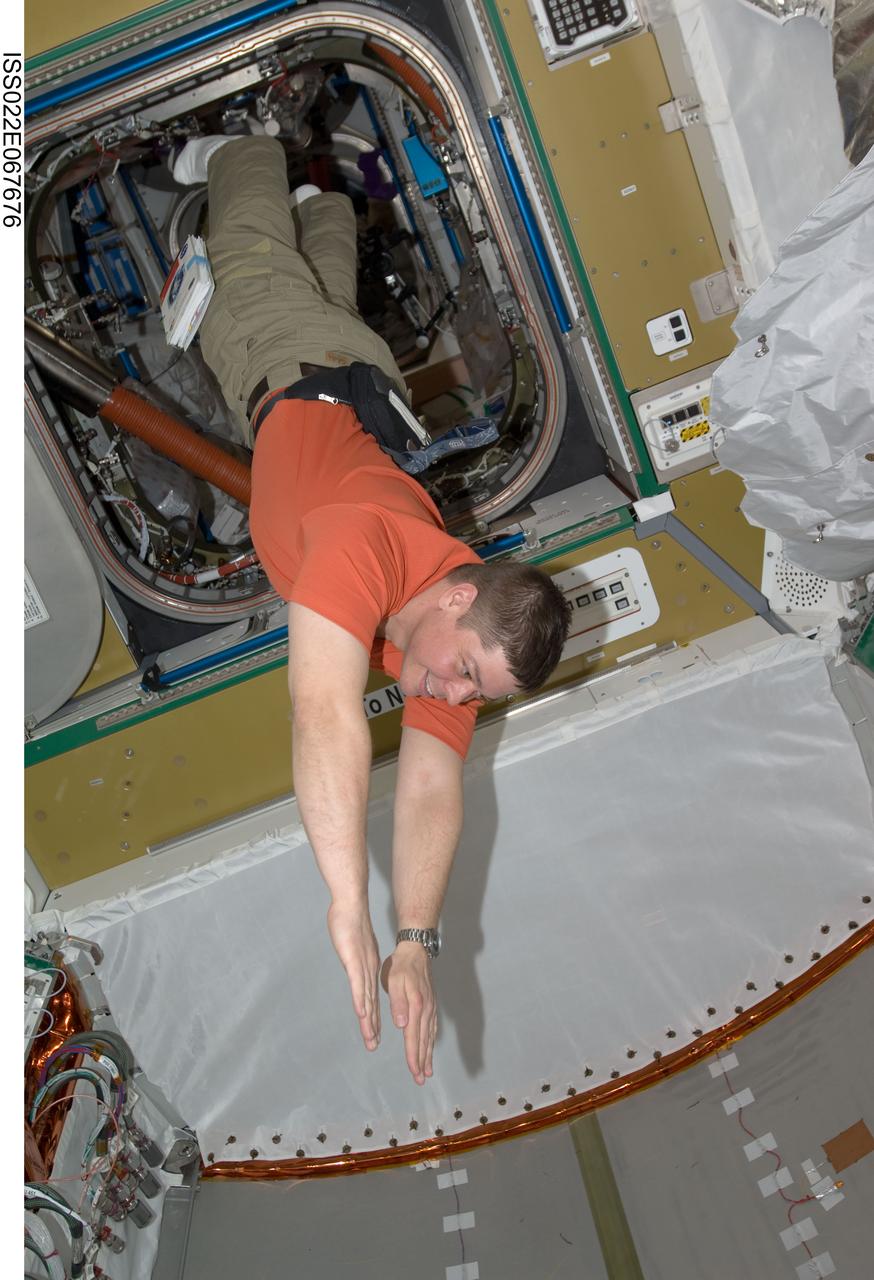

ISS022-E-067676 (14 Feb. 2010) --- NASA astronaut Robert Behnken, STS-130 mission specialist, floats freely in newly-installed Tranquility node of the International Space Station while space shuttle Endeavour remains docked with the station.
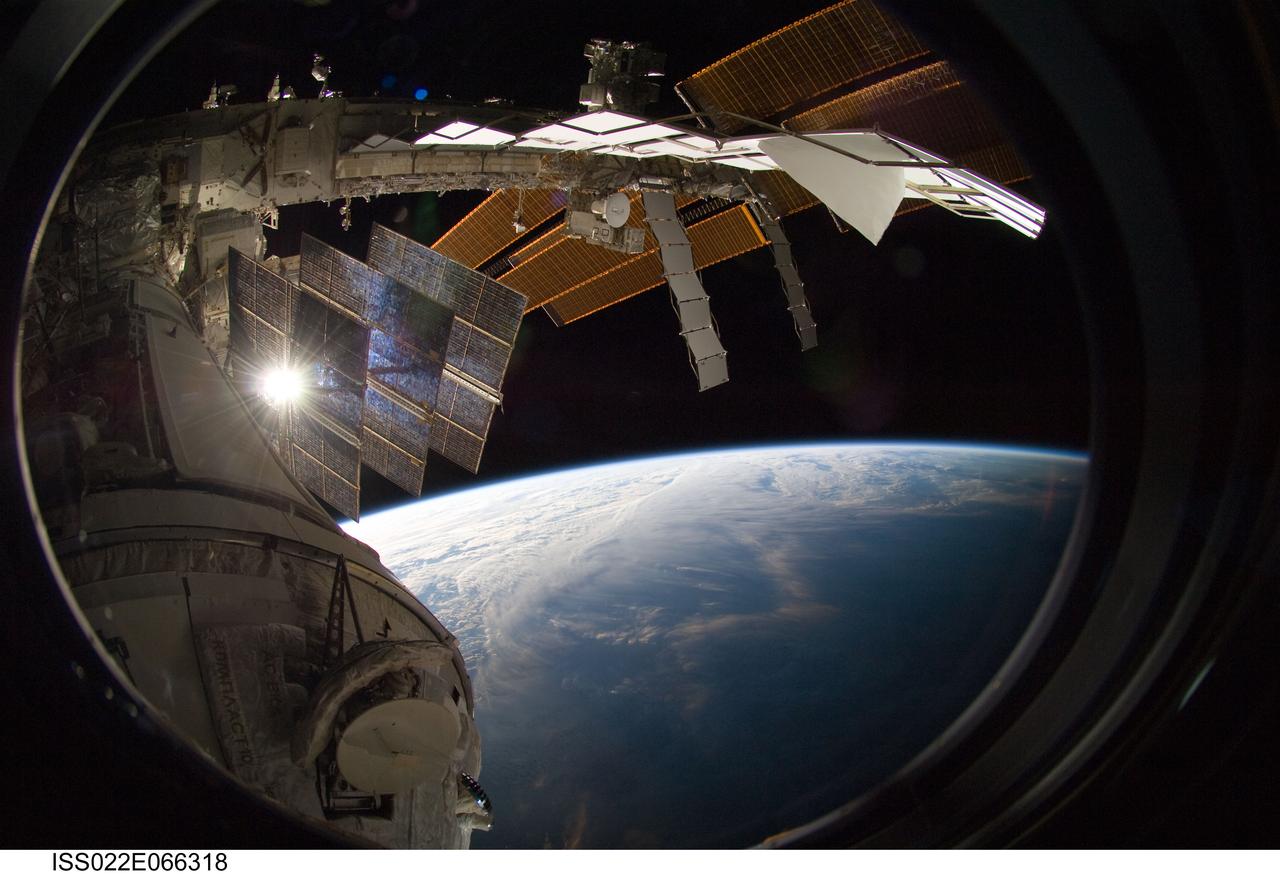

ISS022-E-066318 (15 Feb. 2010) --- Backdropped by Earth?s horizon and the blackness of space, a portion of the International Space Station is featured in this image photographed by a crew member on the ISS while space shuttle Endeavour (STS-130) remains docked with the station.
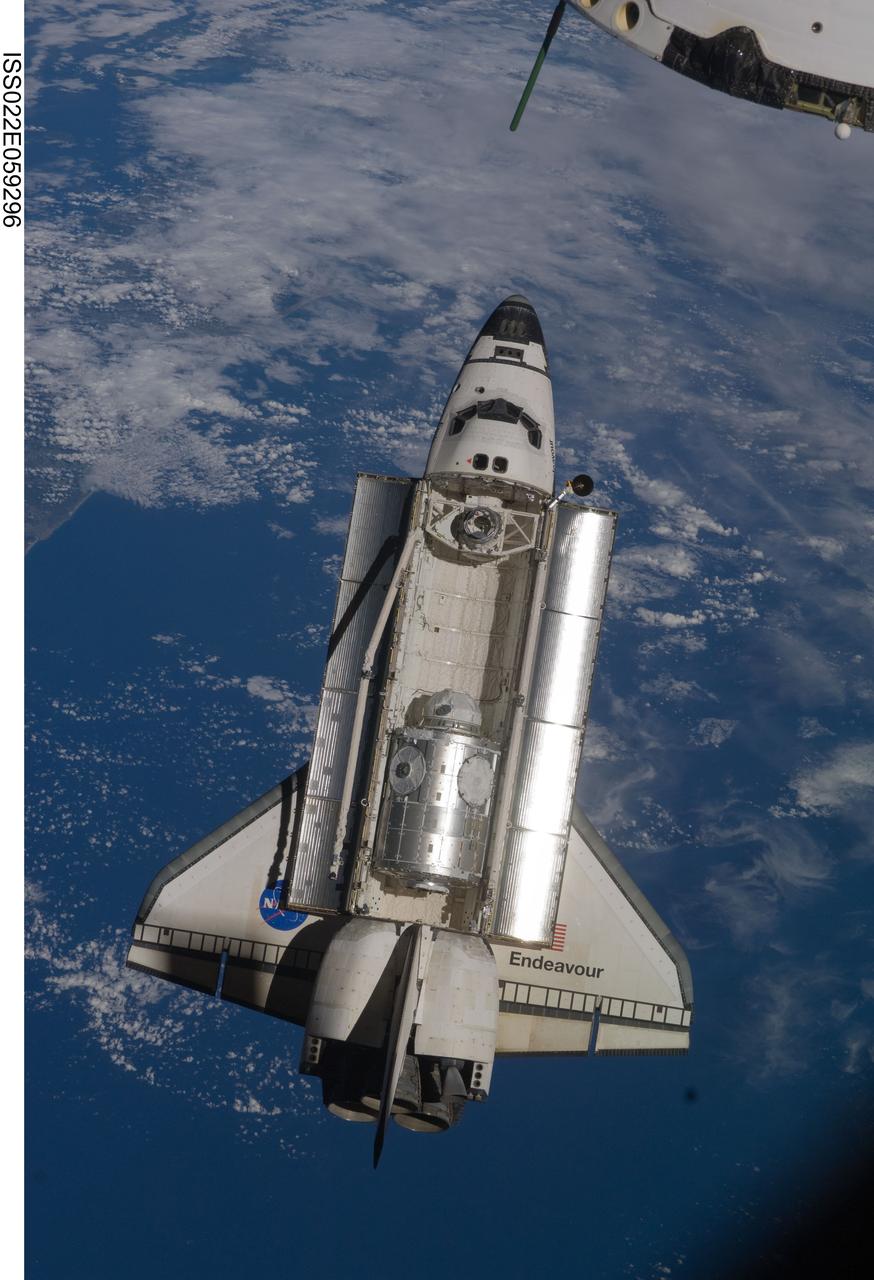

ISS022-E-059296 (9 Feb. 2010) --- Backdropped by a blue and white part of Earth, space shuttle Endeavour is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member as the shuttle approaches the International Space Station during STS-130 rendezvous and docking operations. Docking occurred at 11:06 p.m. (CST) on Feb. 9, 2010.
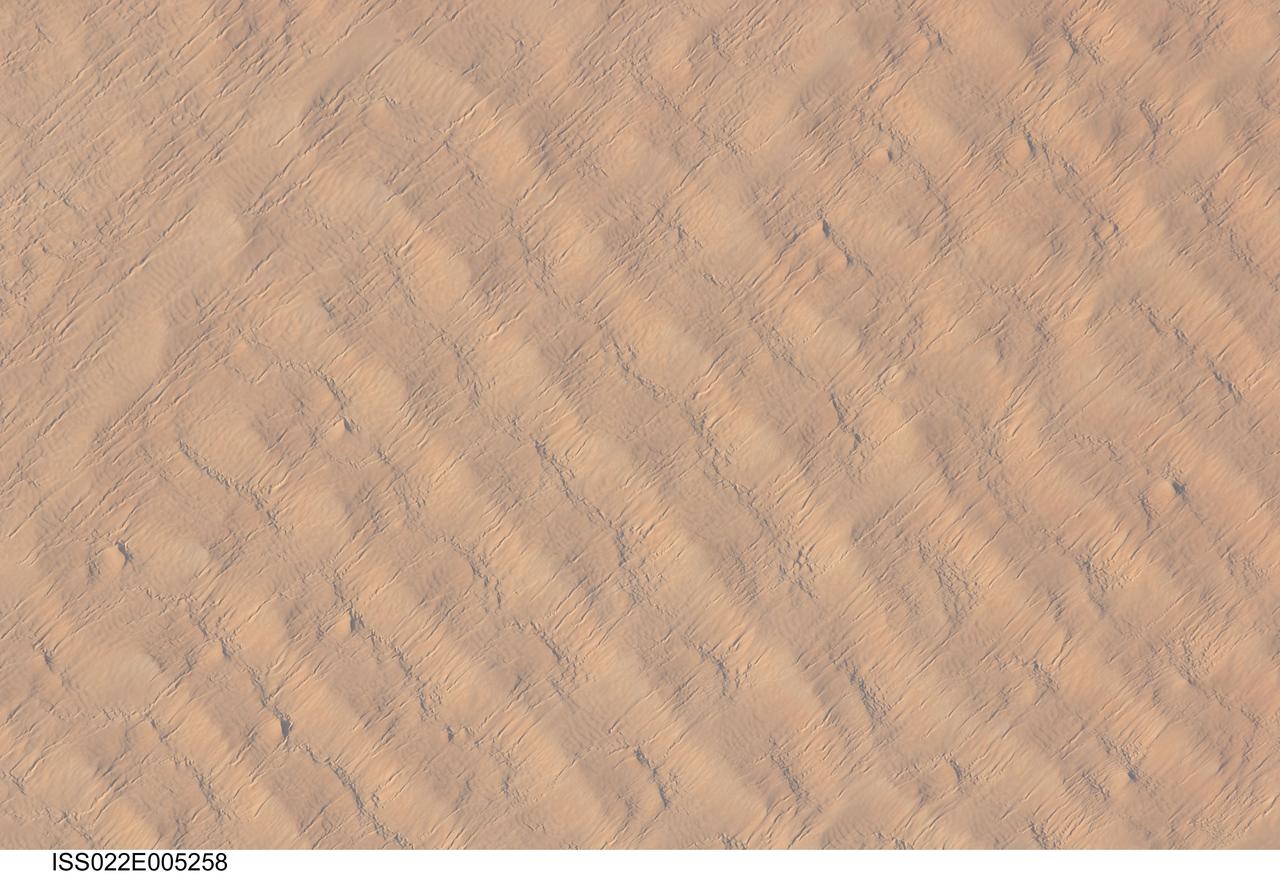

ISS022-E-005258 (1 Dec. 2009) --- This detailed hand-held digital camera?s image recorded from the International Space Station highlights sand dunes in the Fachi-Bilma erg, or sand sea, which is part of the central eastern Tenere Desert. The Tenere occupies much of southeastern Niger and is considered to be part of the larger Sahara Desert that stretches across northern Africa. Much of the Sahara is comprised of ergs ? with an area of approximately 150,000 square kilometers, the Fachi-Bilma is one of the larger sand seas. Two major types of dunes are visible in the image. Large, roughly north-south oriented transverse dunes fill the image frame. This type of dune tends to form at roughly right angles to the dominant northeasterly winds. The dune crests are marked in this image by darker, steeper sand accumulations that cast shadows. The lighter-toned zones between are lower interdune ?flats?. The large dunes appear to be highly symmetrical with regard to their crests. This suggests that the crest sediments are coarser, preventing the formation of a steeper slip face on the downwind side of the dune by wind-driven motion of similarly-sized sand grains. According to NASA scientists, this particular form of transverse dune is known as a zibar, and is thought to form by winnowing of smaller sand grains by the wind, leaving the coarser grains to form dune crests. A second set of thin linear dunes oriented at roughly right angles to the zibar dunes appears to be formed on the larger landforms and is therefore a younger landscape feature. These dunes appear to be forming from finer grains in the same wind field as the larger zibars. The image was taken with digital still camera fitted with a 400 mm lens, and is provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations experiment and Image Science & Analysis Laboratory, Johnson Space Center.

ISS022-E-066322 (15 Feb. 2010) --- Backdropped by Earth?s horizon and the blackness of space, a portion of the International Space Station is featured in this image photographed by a crew member on the ISS while space shuttle Endeavour (STS-130) remains docked with the station.
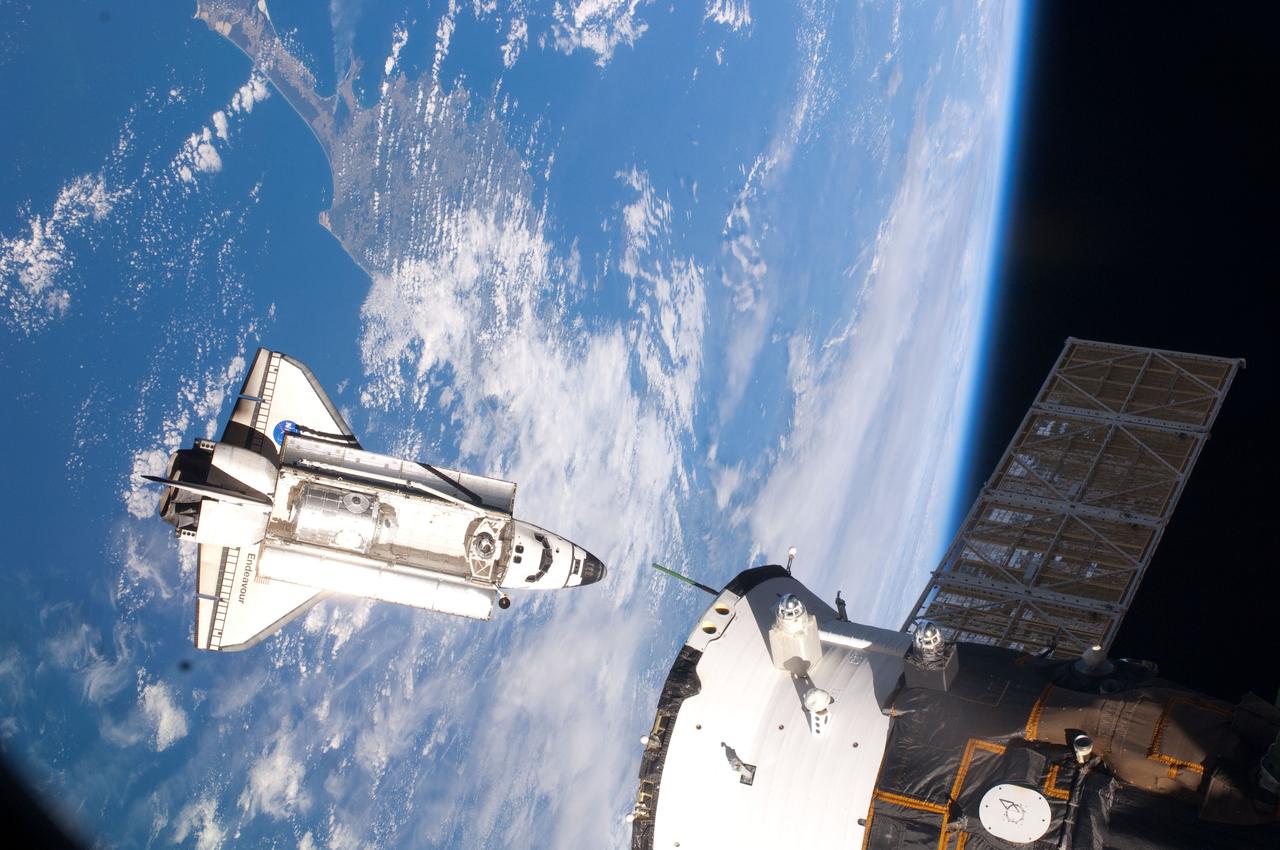

ISS022-E-059298 (9 Feb. 2010) --- Seen flying above part of North Island, New Zealand, the space shuttle Endeavour is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member during STS-130 rendezvous and docking operations with the International Space Station. Docking occurred at 11:06 p.m. (CST) on Feb. 9, 2010.