
The payload bay doors of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia were opened for the first time today using the orbiter's onboard door operation system. The hinges of the payload bay doors are not designed to support the weight of the doors while open horizontally in the Earth's one 'g' environment and a counterweight zero 'g' device supports the weight of the doors while they are open for processing in the OPF.
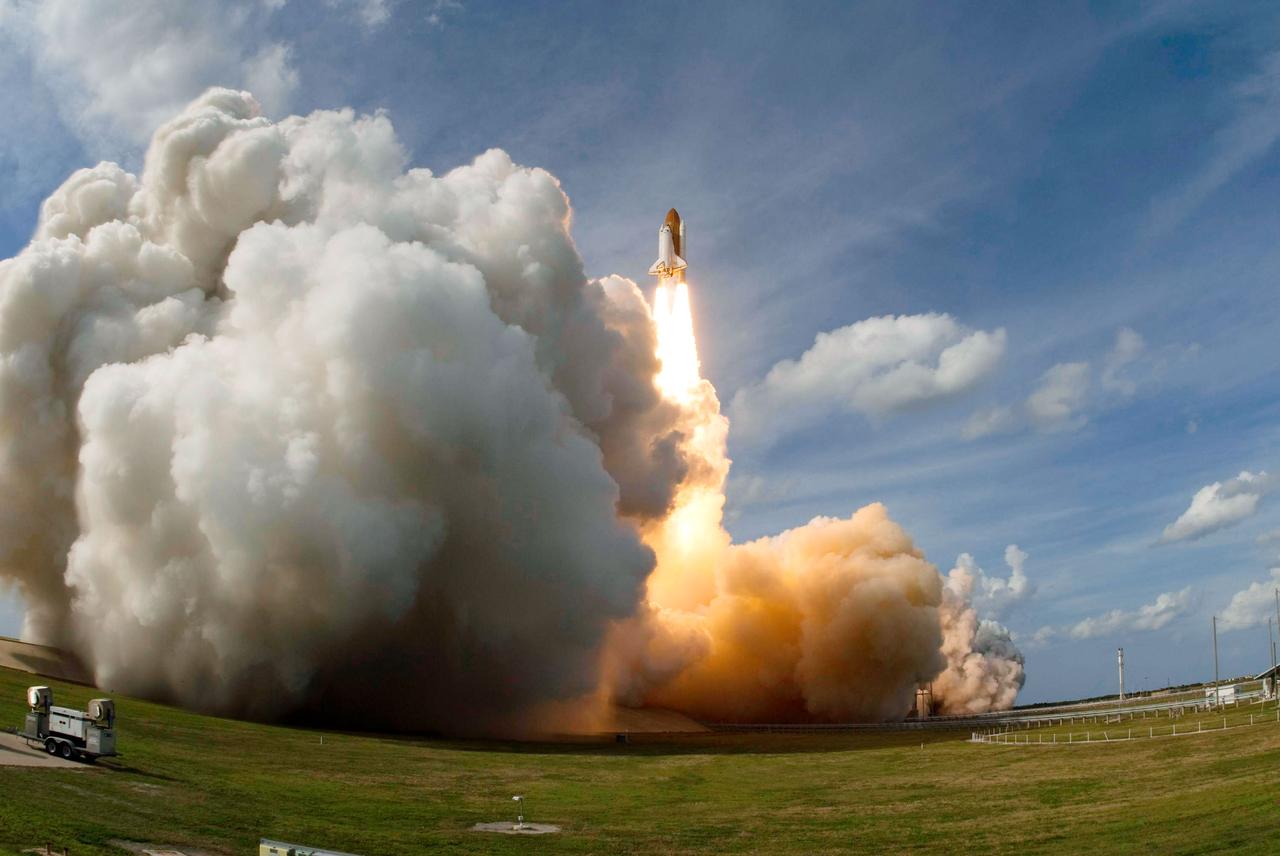

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
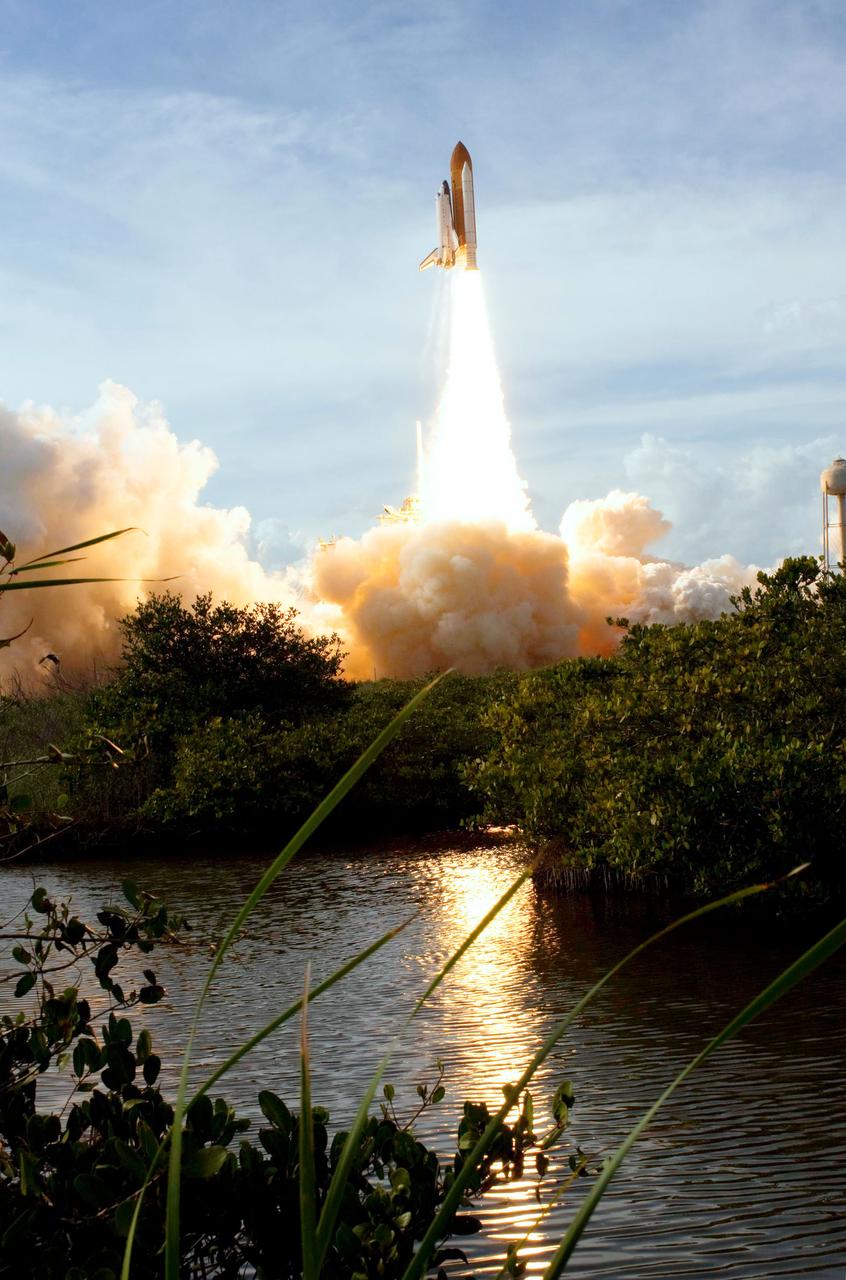

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
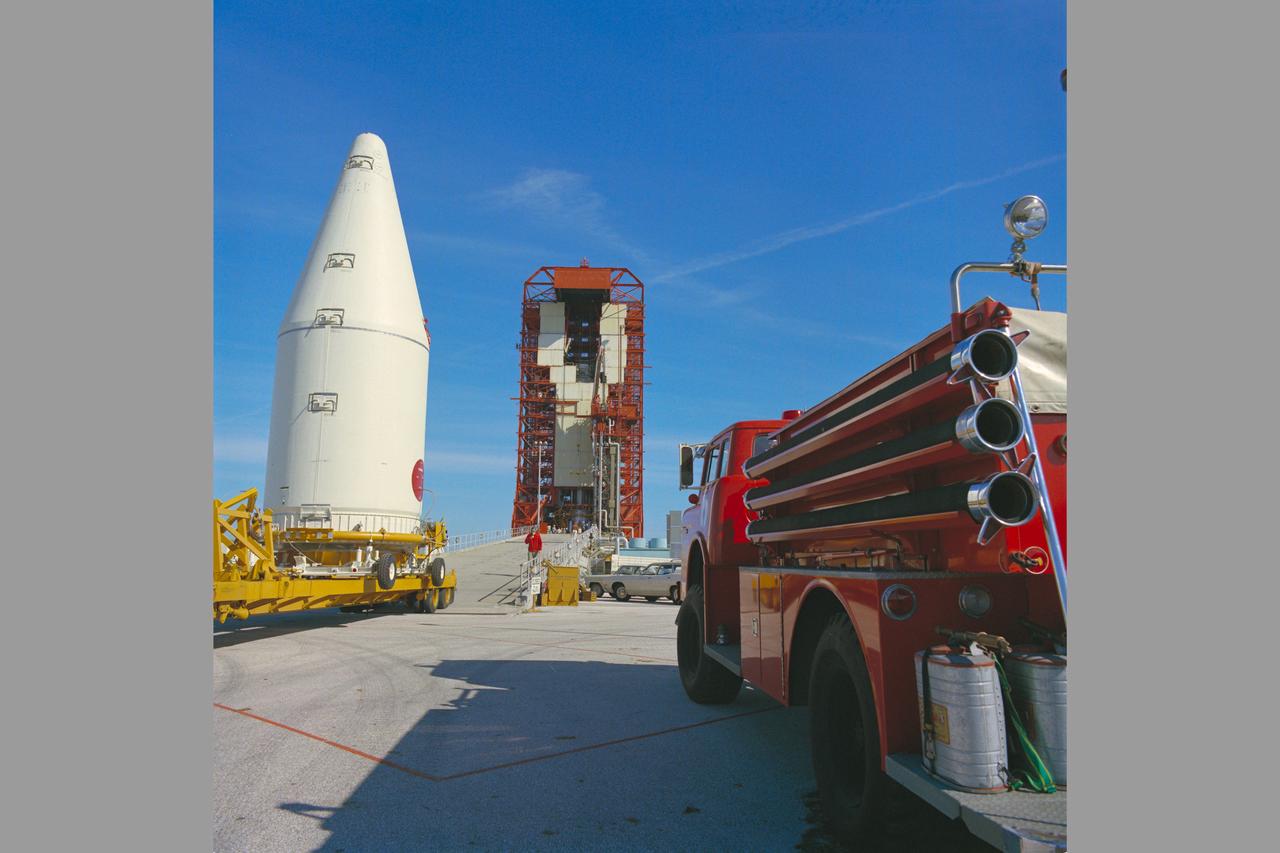

Pioneer-10 (or F) spacecraft encapsulated and moving to pad at Cape Kennedy for matting with a Atlas-Centaura launch vehicle in preparation for mission to Jupiter
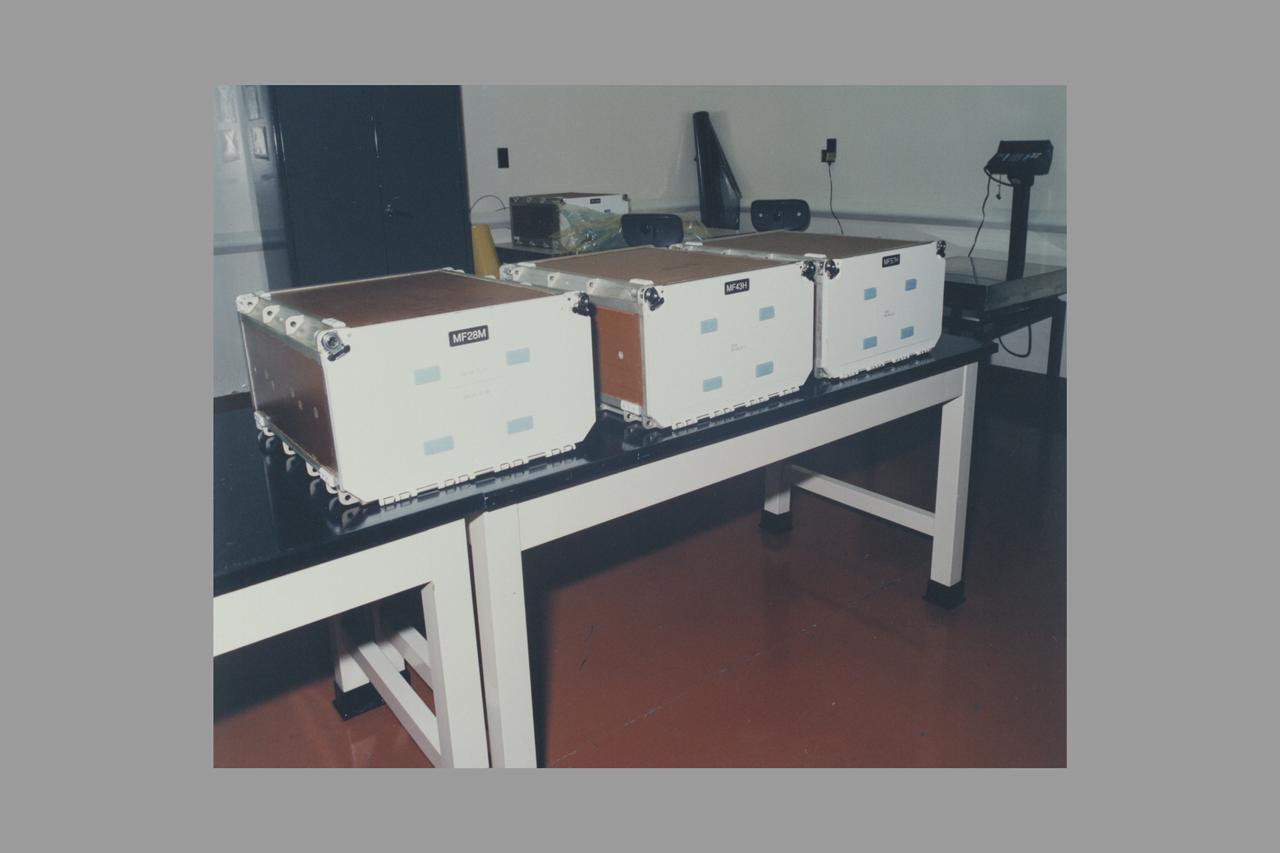

European Space Agency's Biorack middeck lockers
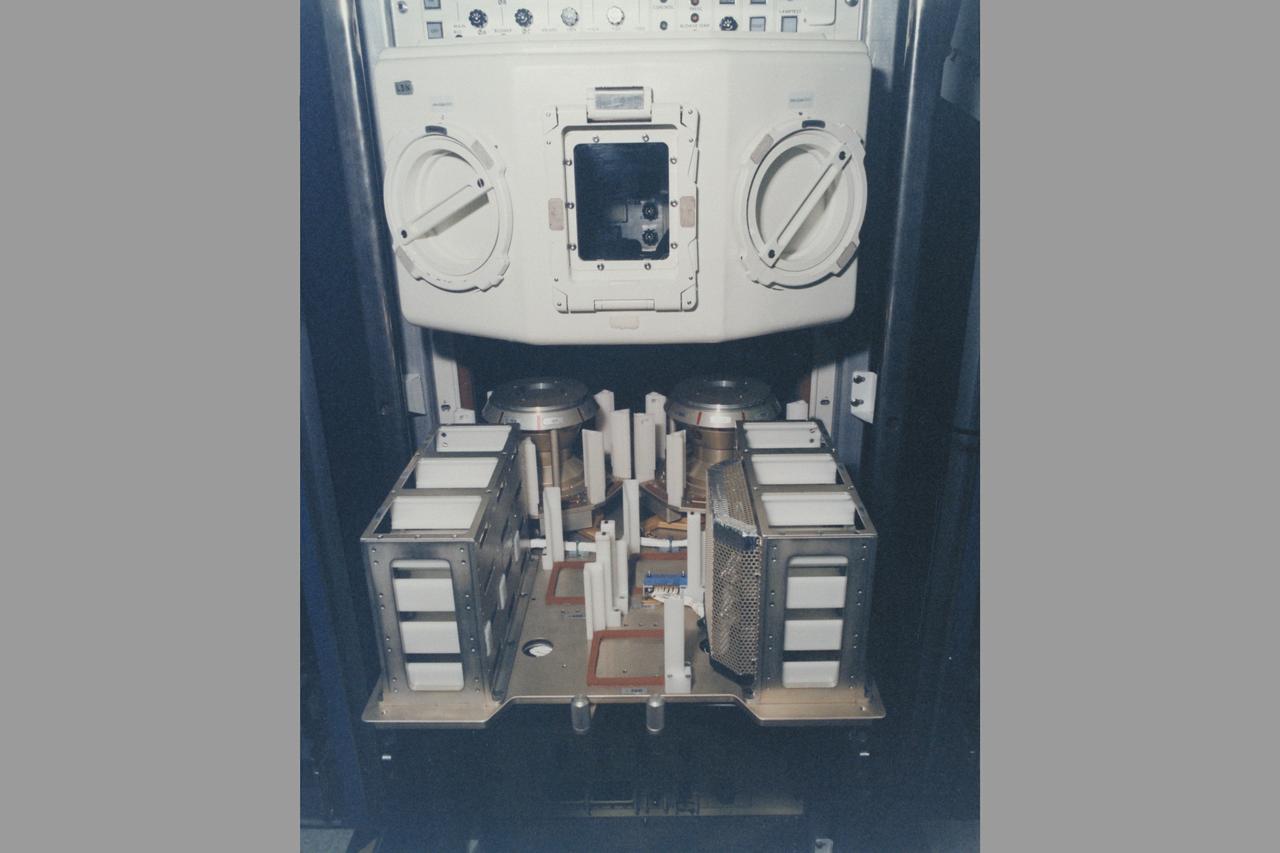

European Space Agency's Biorack incubator (37deg C)
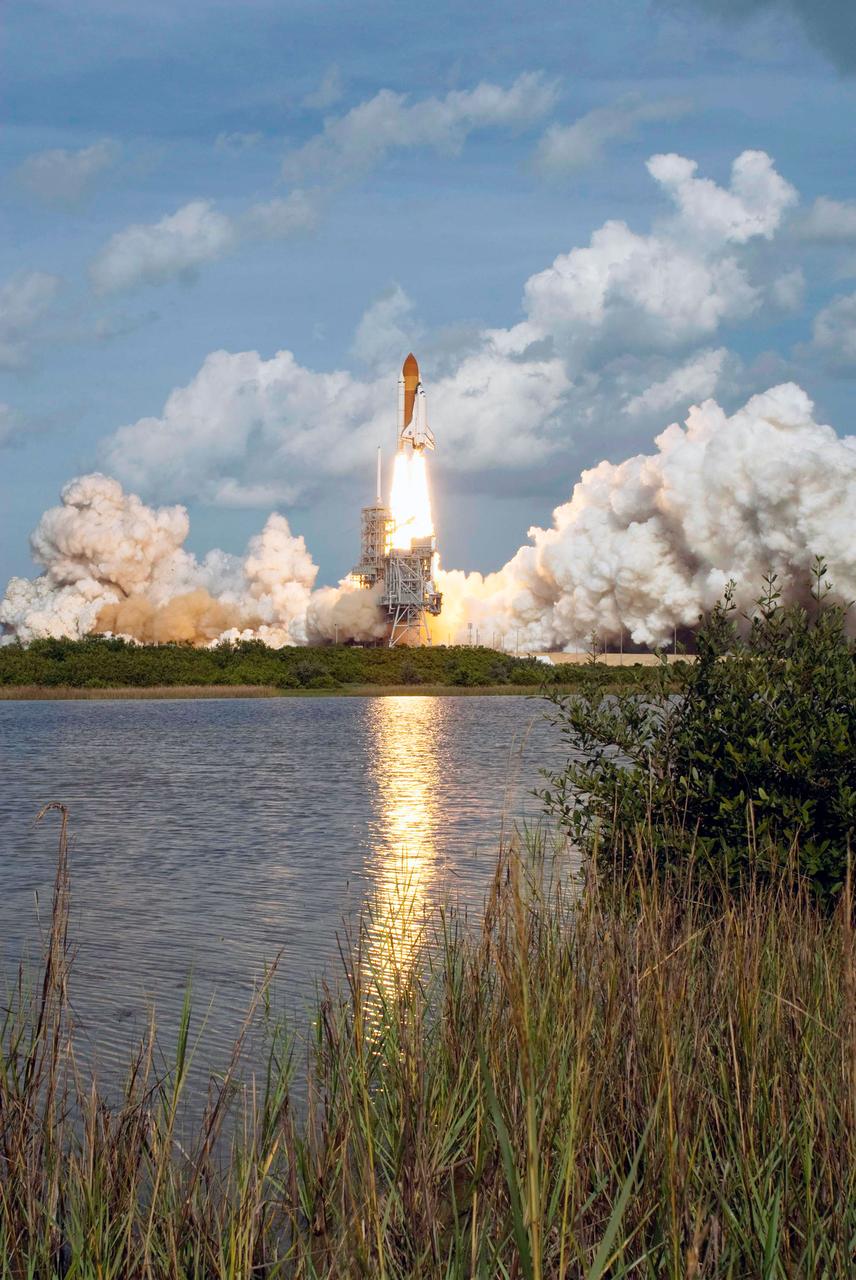

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
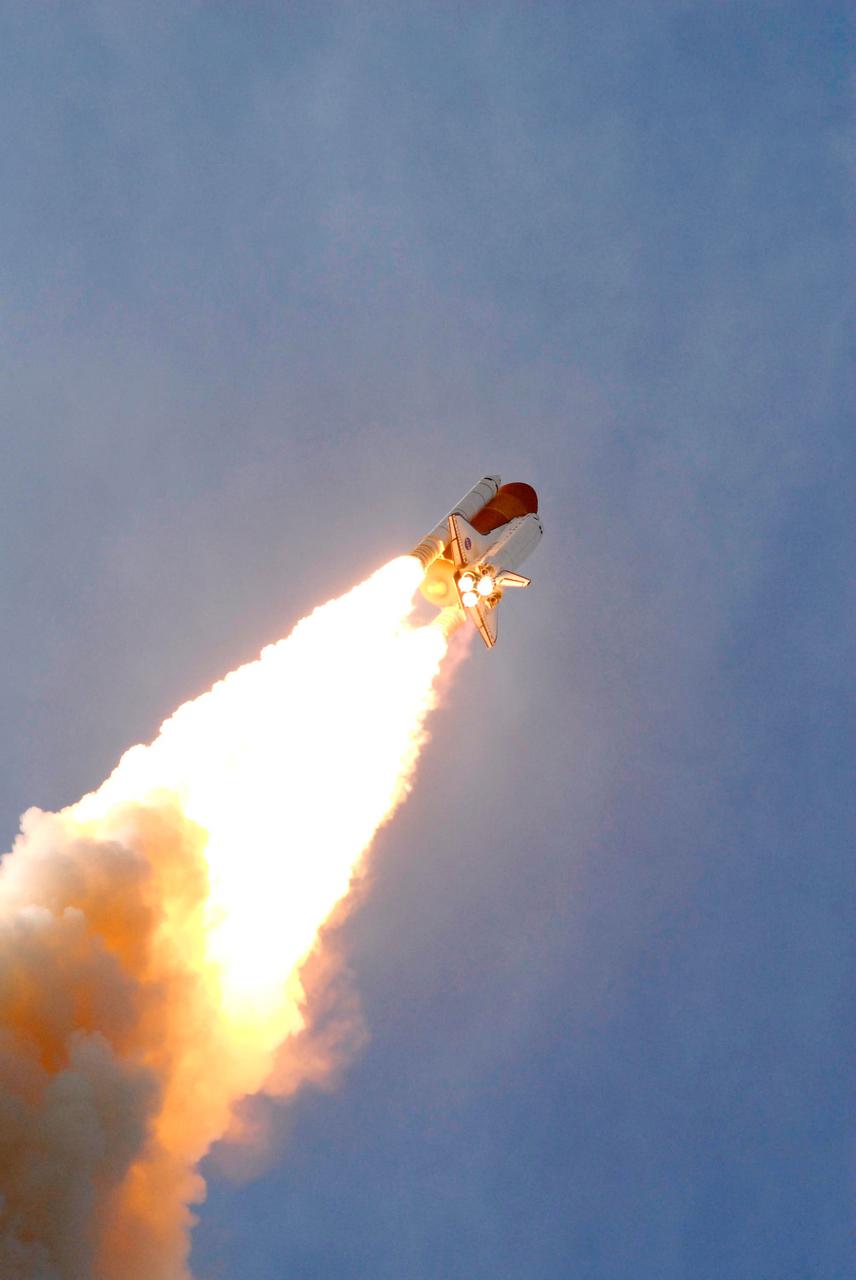

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
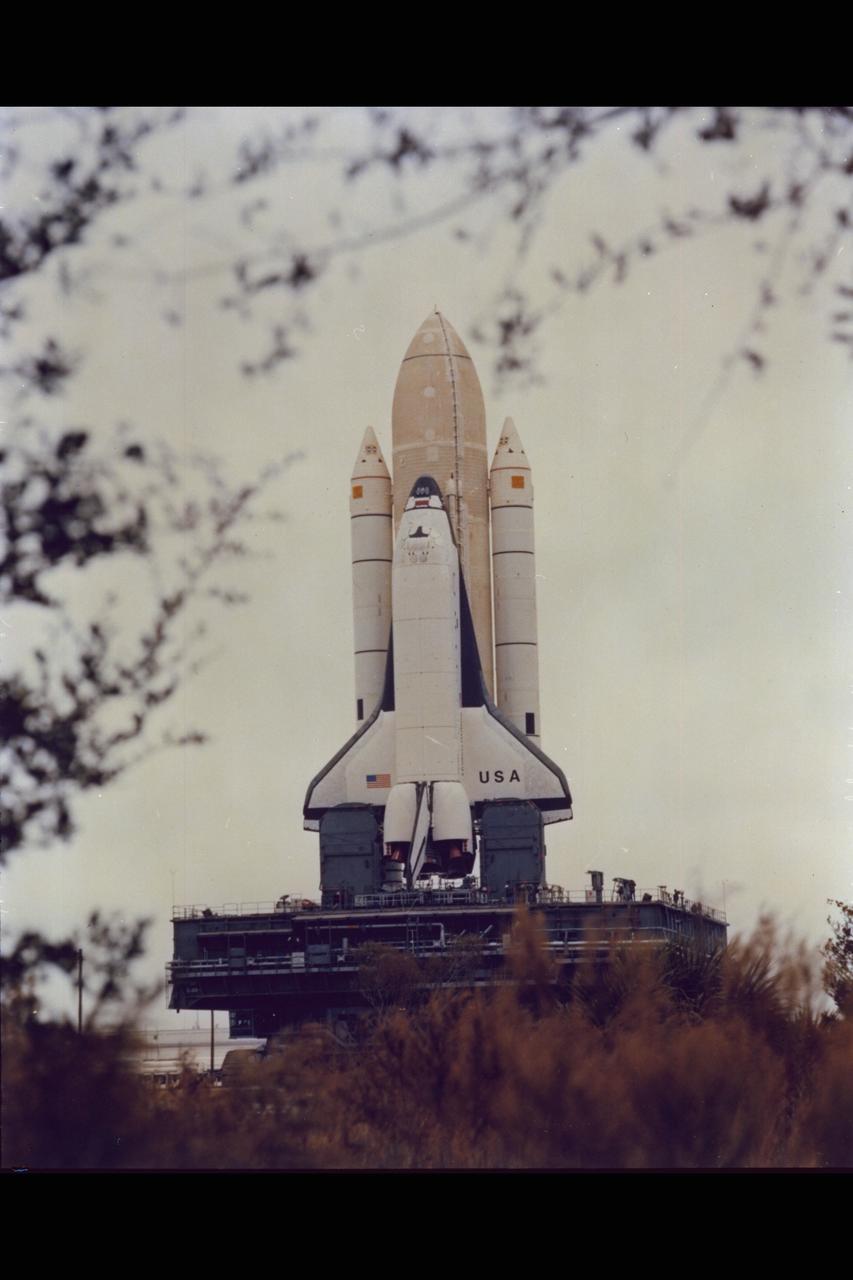
Space Shuttle Columbia at Launch Site. (ref: 81-HC-1)
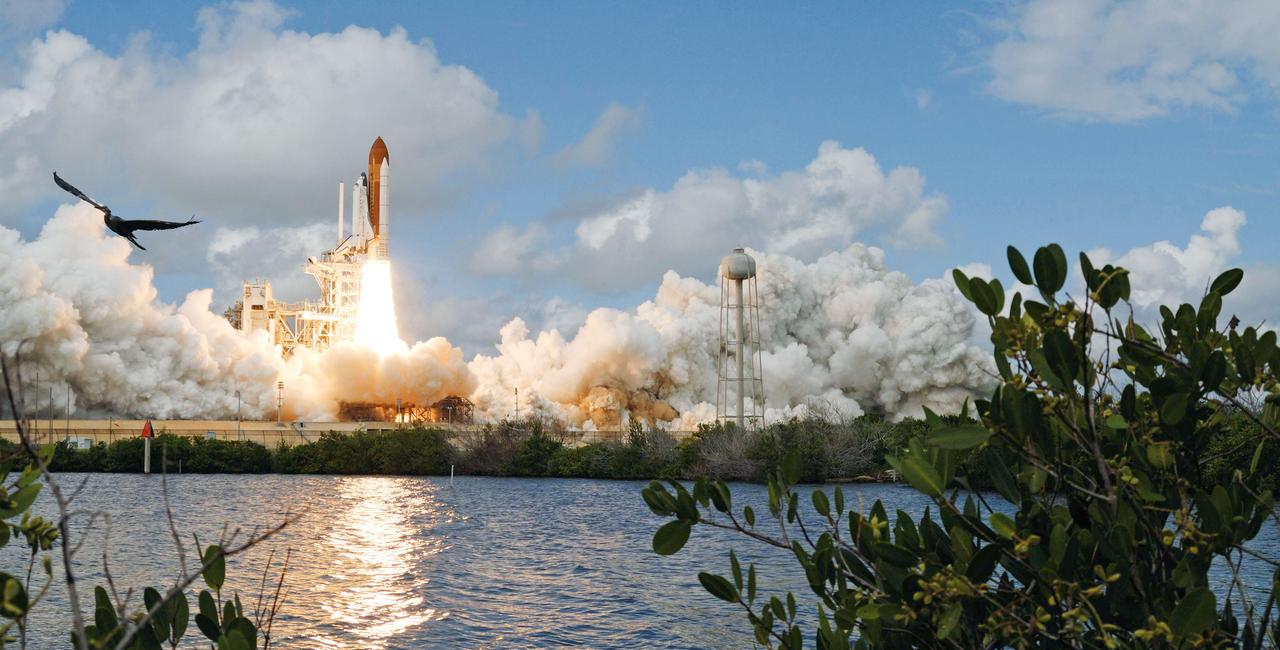

STS120-S-031 (23 Oct. 2007) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member STS-120 crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39A occurred at 11:38:19 a.m. (EDT). Onboard are astronauts Pam Melroy, commander; George Zamka, pilot; Scott Parazynski, Stephanie Wilson, Doug Wheelock, European Space Agency's (ESA) Paolo Nespoli and Daniel Tani, all mission specialists. Discovery will link up with the station on Thursday, Oct. 25, to begin a joint mission to continue construction by delivering the Italian-built U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. During the 14-day mission, the crew will install Harmony and move the P6 solar arrays to their permanent position and deploy them.
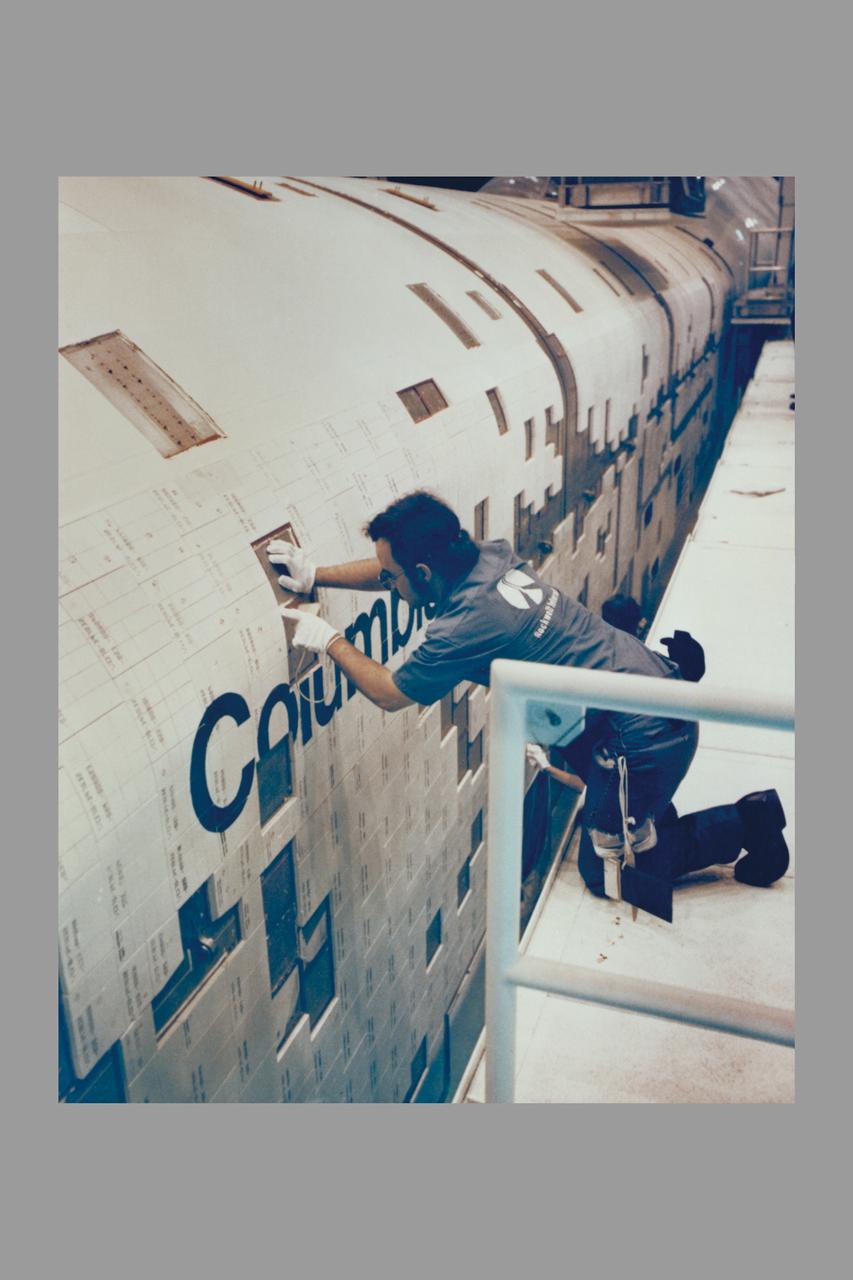

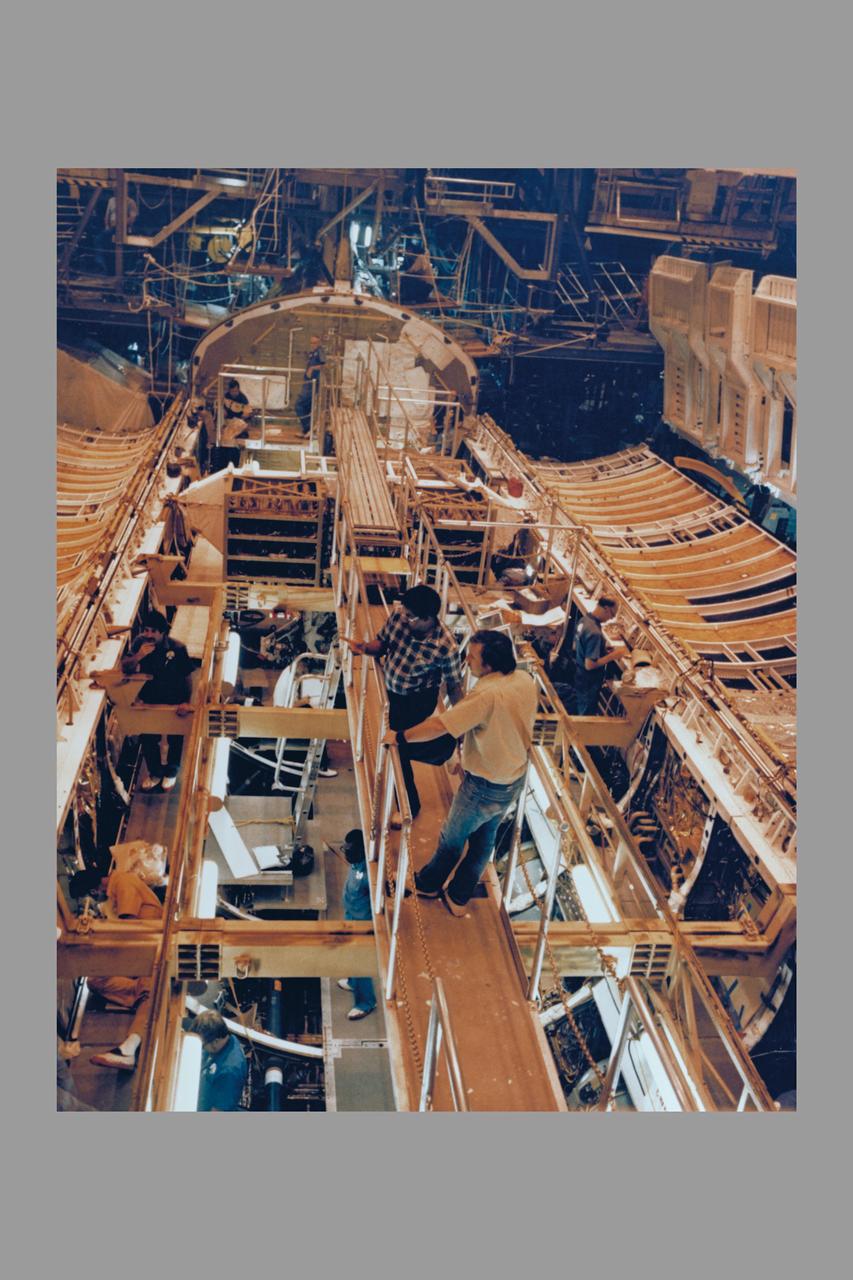
ROCKWELL INTERNATIONAL TECHNICIANS MOUNT SOME OF THE NEARLY 8,000 CERAMIC-COATED TILES THAT REMAIN TO BE INSTALLED ON THE EXTERNAL SURFACES OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE ORBITER COLUMBIA TO COMPLETE THE THERMAL PROTECTION SYSTEM THAT WILL ABSORB THE INTENSE HEAT OF REENTERING THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE AFTER A MISSION IN SPACE. TILE INSTALLATION IS DONE ON AN AROUND-THE-CLOCK BASIS IN THE ORBITER PROCESSING FACILITY WHERE COLUMBIA, THE FIRST IN A NEW BREED OF MANNED, REUSABLE SPACECRAFT, IS BEING READIED FOR THE FIRST LAUNCH OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE LATER THIS YEAR.

STS120-S-028 (23 Oct. 2007) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery and its seven-member STS-120 crew head toward Earth-orbit and a scheduled link-up with the International Space Station. Liftoff from Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39A occurred at 11:38:19 a.m. (EDT). Onboard are astronauts Pam Melroy, commander; George Zamka, pilot; Scott Parazynski, Stephanie Wilson, Doug Wheelock, European Space Agency's (ESA) Paolo Nespoli and Daniel Tani, all mission specialists. Discovery will link up with the station on Thursday, Oct. 25, to begin a joint mission to continue construction by delivering the Italian-built U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. During the 14-day mission, the crew will install Harmony and move the P6 solar arrays to their permanent position and deploy them.
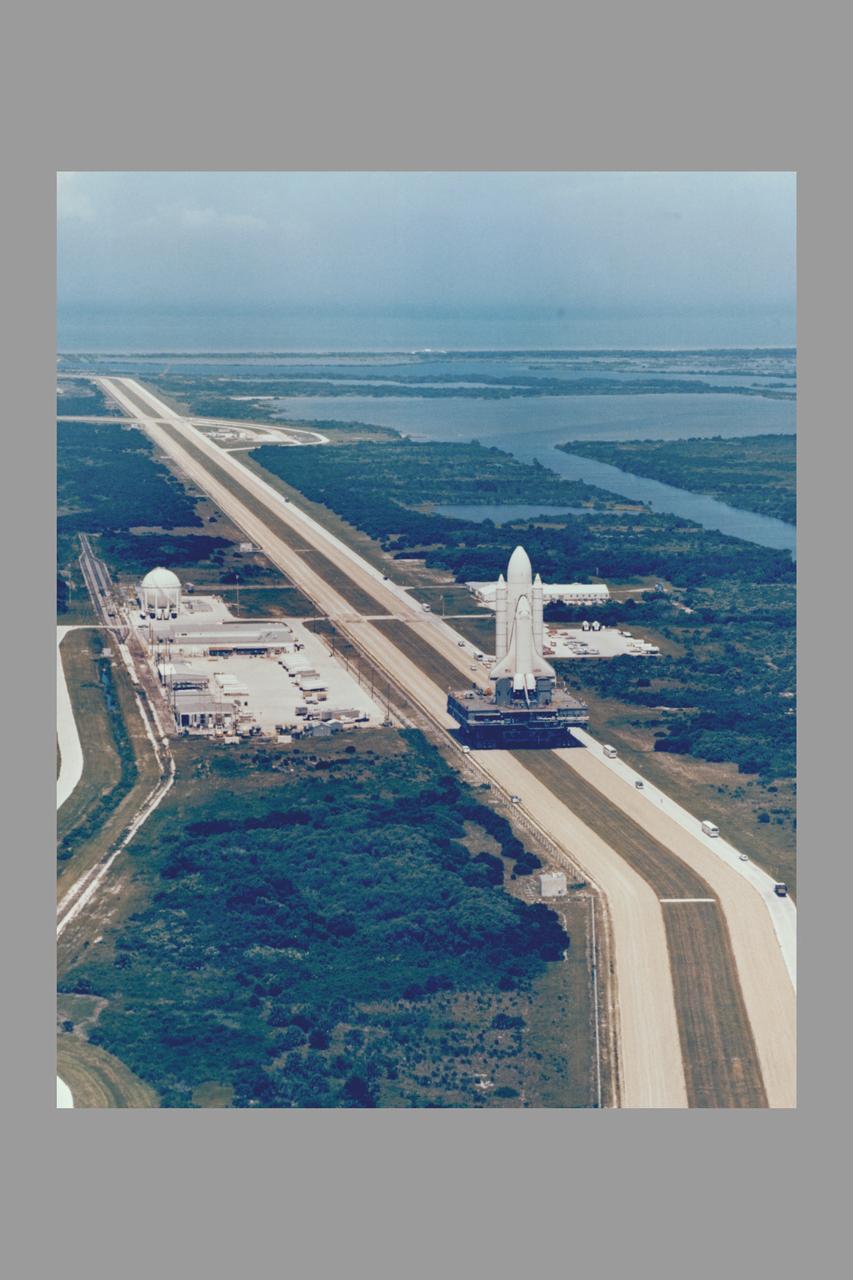

Space Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise, mated to a 15-story-tall external propellant tank and twin inert solid rocket boosters on top of a Mobile Launcher Platform, is rolled back to the Vehicle Assembly Building from Lauch Complex 39's Pad A July 23 at the completion of nearly three months of fit and function checks at the shuttle launch site as part of the exercise designed to help clear the way for the liftoff of its sister ship Columbia. The massive Crawler Transporter began moving its 11 million pound load the 3.5 miles from pad A to the VAB at 10:23 a.m. and reached the doorway to High Bay 1 at 3:48p.m. following serveral days of fit checks of modified extermiable platforms in the assembly bay, the nonlaunchable shuttle will be destacked. Enterprise will be returned to Rockwell International and stripped of parts for integration into orbiter destined for space, while the external tank and solid booster will be returned to their respective prime contractors and refurbished for use on a later shuttle mission.
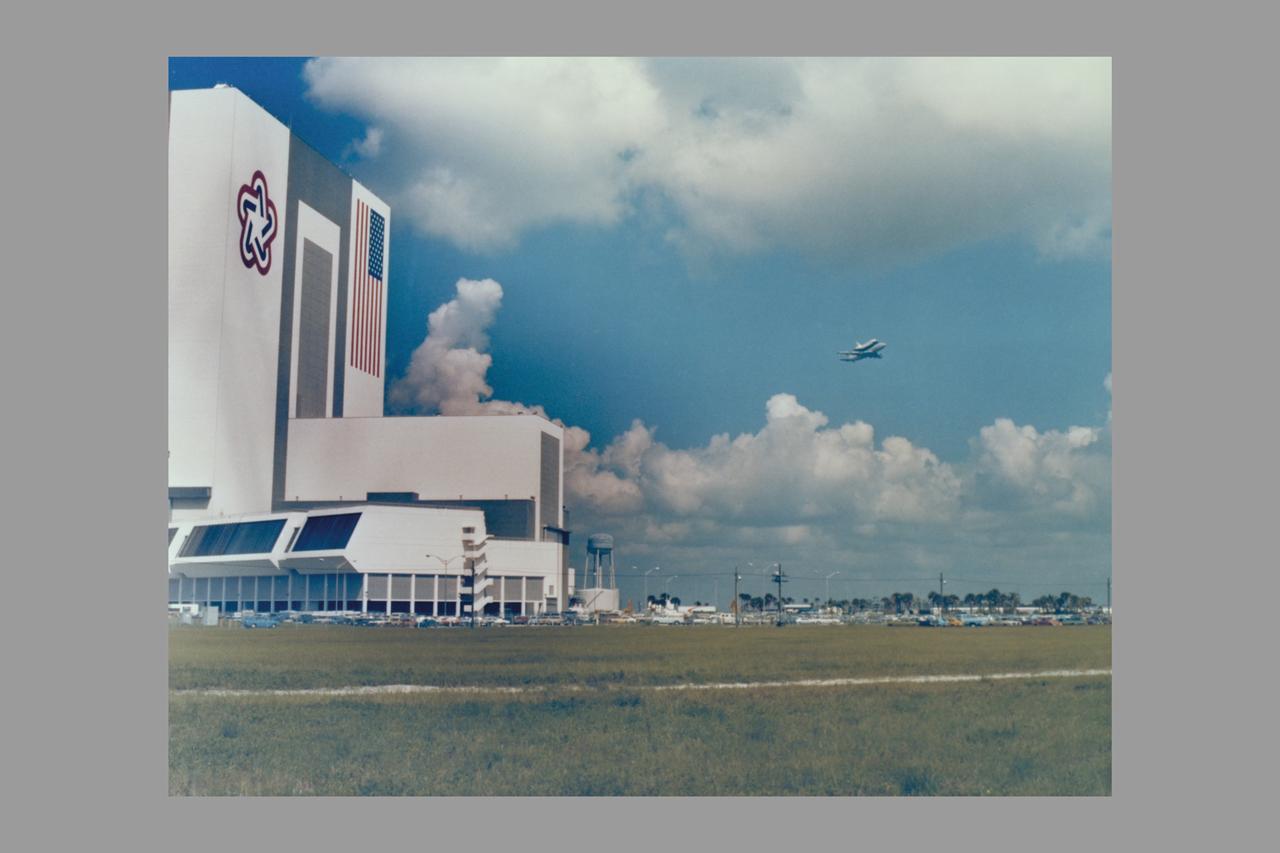

The 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, carrying the Space Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise piggyback, lifts off from the Shuttle Landing Facility's 15,000-foot-long runway at 11:03, August 10. Enterprise flown to KSC on April 10 for use in checking out assembly, test and launch facilities which will be used for the launch of its sister ship Columbia on the first Space Shuttle flight, will make a five-stop flight to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in California.

SPACE SHUTTLE ORBITER ENTERPRISE MATED TO AN EXTERNAL FUEL TANK AND TWO SOLID ROCKET BOOSTERS ON TOP OF A MOBIL LAUNCHER PLATFORM, UNDERGOES FIT AND FUNCTION CHECKS AT THE LAUNCH SITE FOR THE FIRST SPACE SHUTTLE AT LAUNCH COMPLEX 39'S PAD A. THE DUMMY SPACE SHUTTLE WAS ASSEMBLED IN THE VEHICLE ASSEMBLY BUILDING AND ROLLED OUT TO THE LAUNCH SITE ON MAY 1 AS PART OF AN EXERCISE TO MAKE CERTAIN SHUTTLE ELEMENTS ARE COMPATIBLE WITH THE SPACEPORT'S ASSEMBLY AND LAUNCH FACILITIES AND GROUND SUPPORT EQUIPMENT, AND HELP CLEAR THE WAY FOR THE LAUNCH OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE ORBITER COLUMBIA.
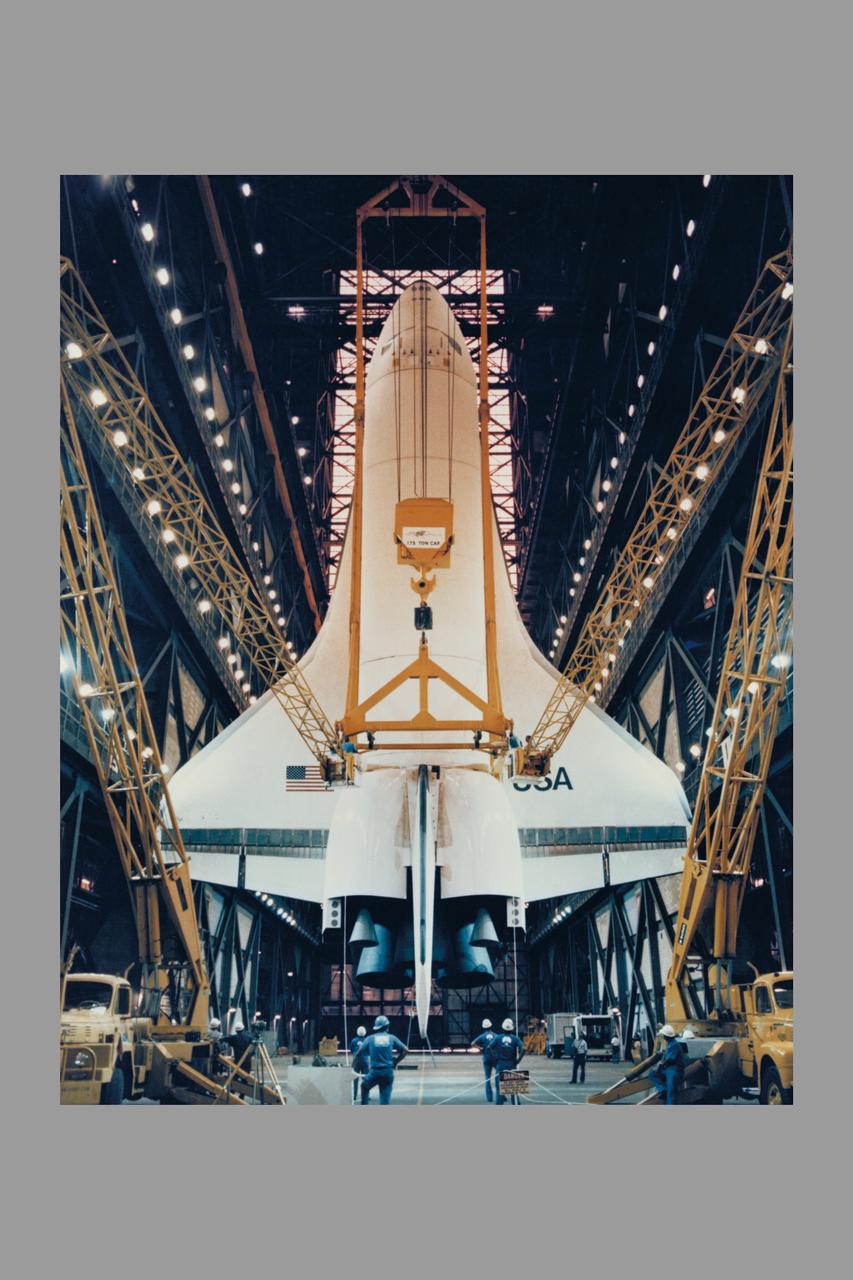

The Space Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise is lowered to the floor of the transfer aisle in the Vehicle Assembly Building during destacking operations. The Enterprise, mated to an external tank and twin inert solid rocket boosters, formed a nonlaunchable Space Shuttle which was used for fit and fuction checks of assembly, test and launch facilities at the nation's Spaceport. Enterprise will be transported to the Shuttle Landing Facility, mounted piggyback on its 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, and flown to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, CA.
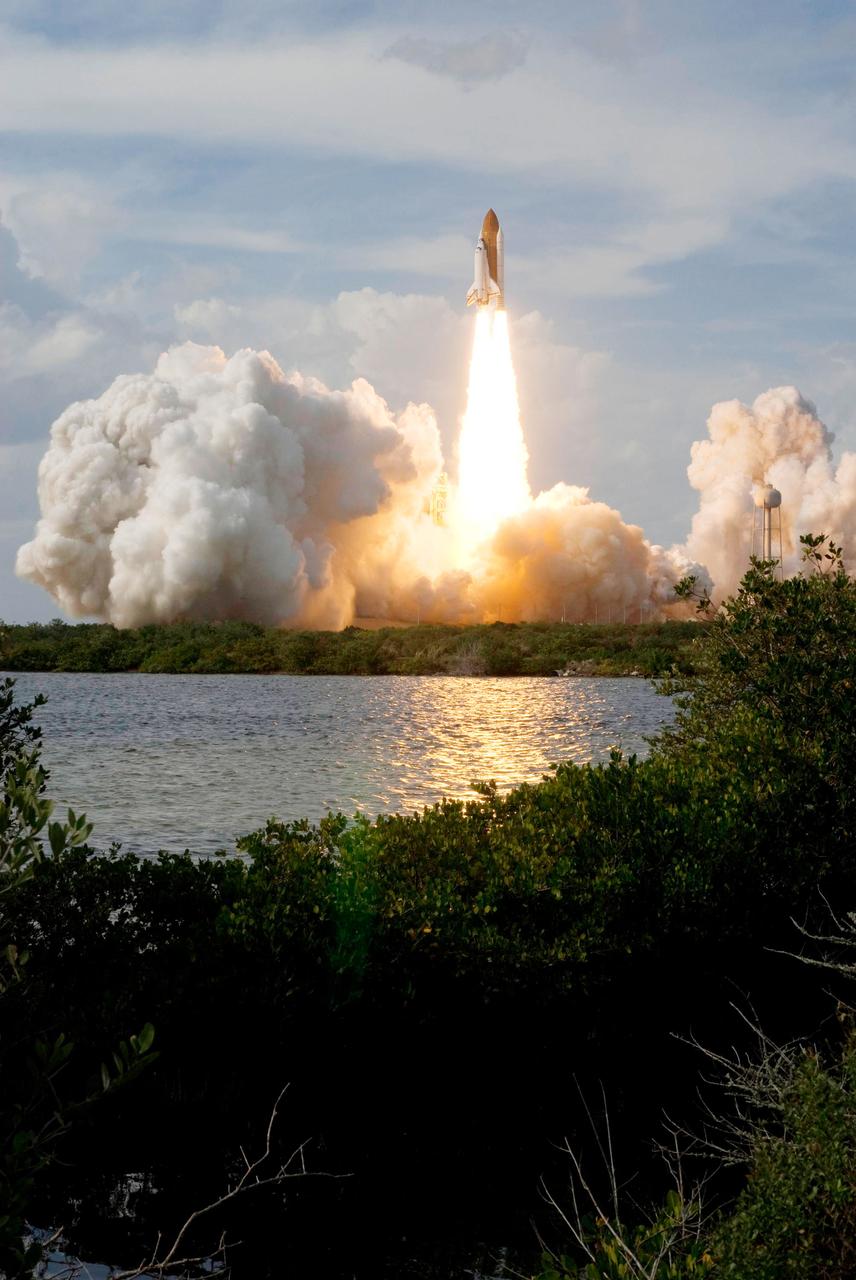

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
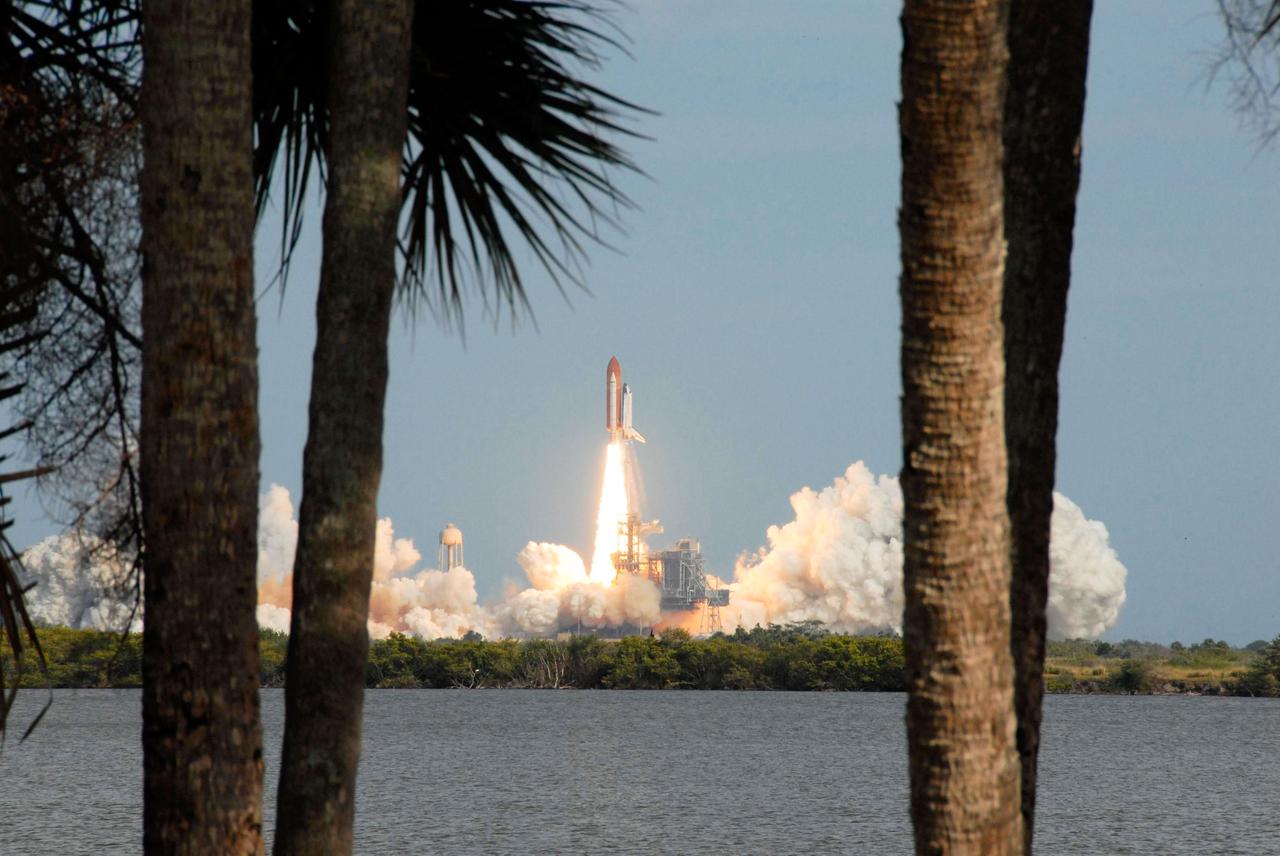

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
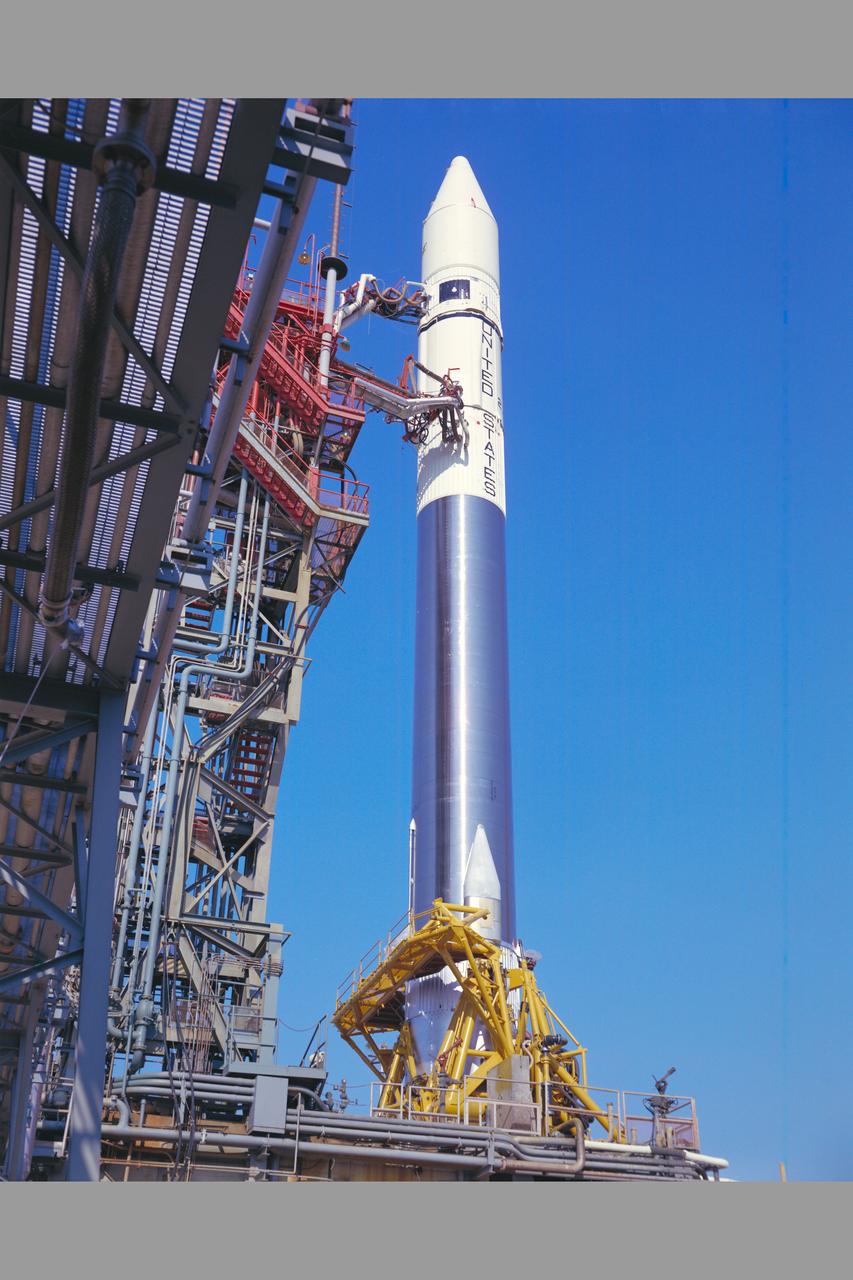

A pre launch view of Pioneer-10 (or F) spacecraft encapsulated and mated with a Atlas-Centaura launch vehicle in preparation for mission to Jupiter
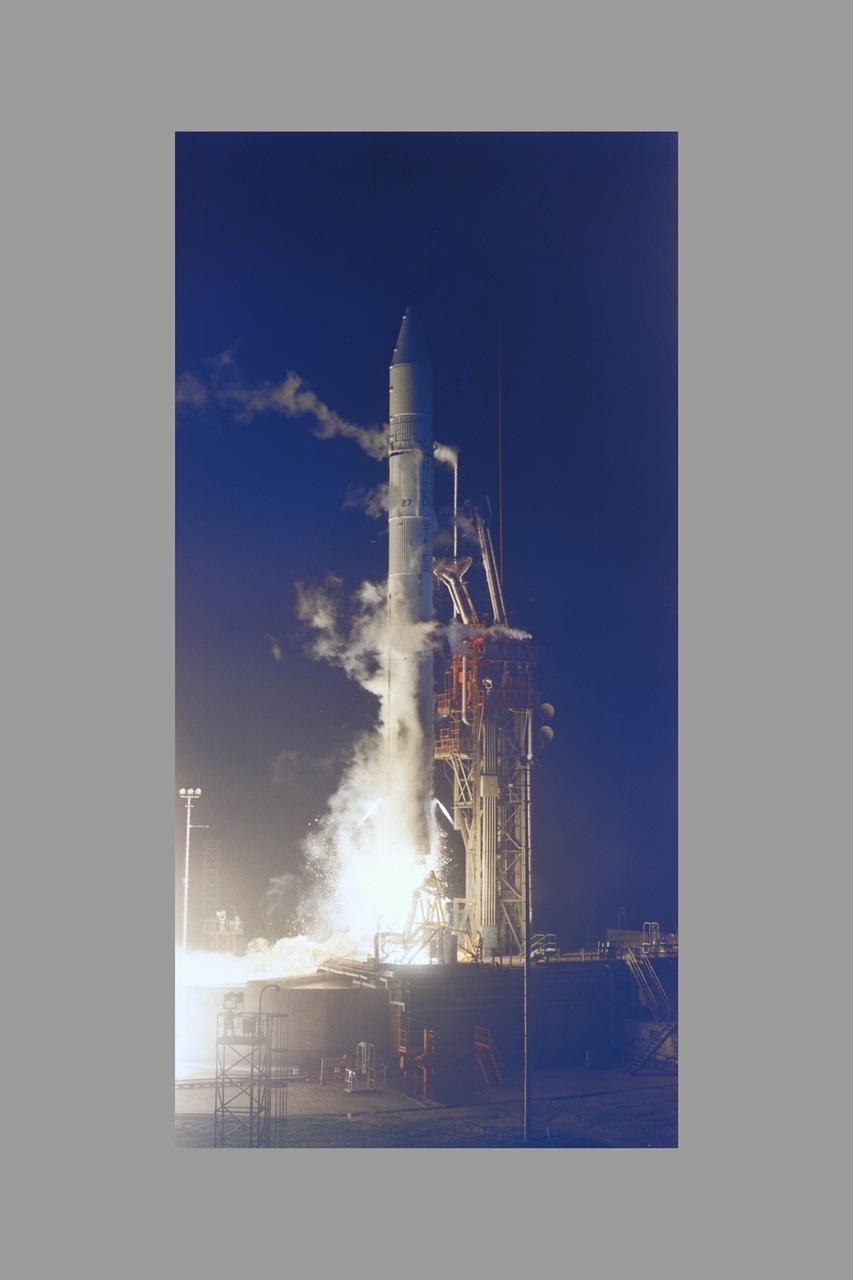

Launch of Pioneer 10 to Jupiter occured at 8:49 p.m. EST March 2, 1972
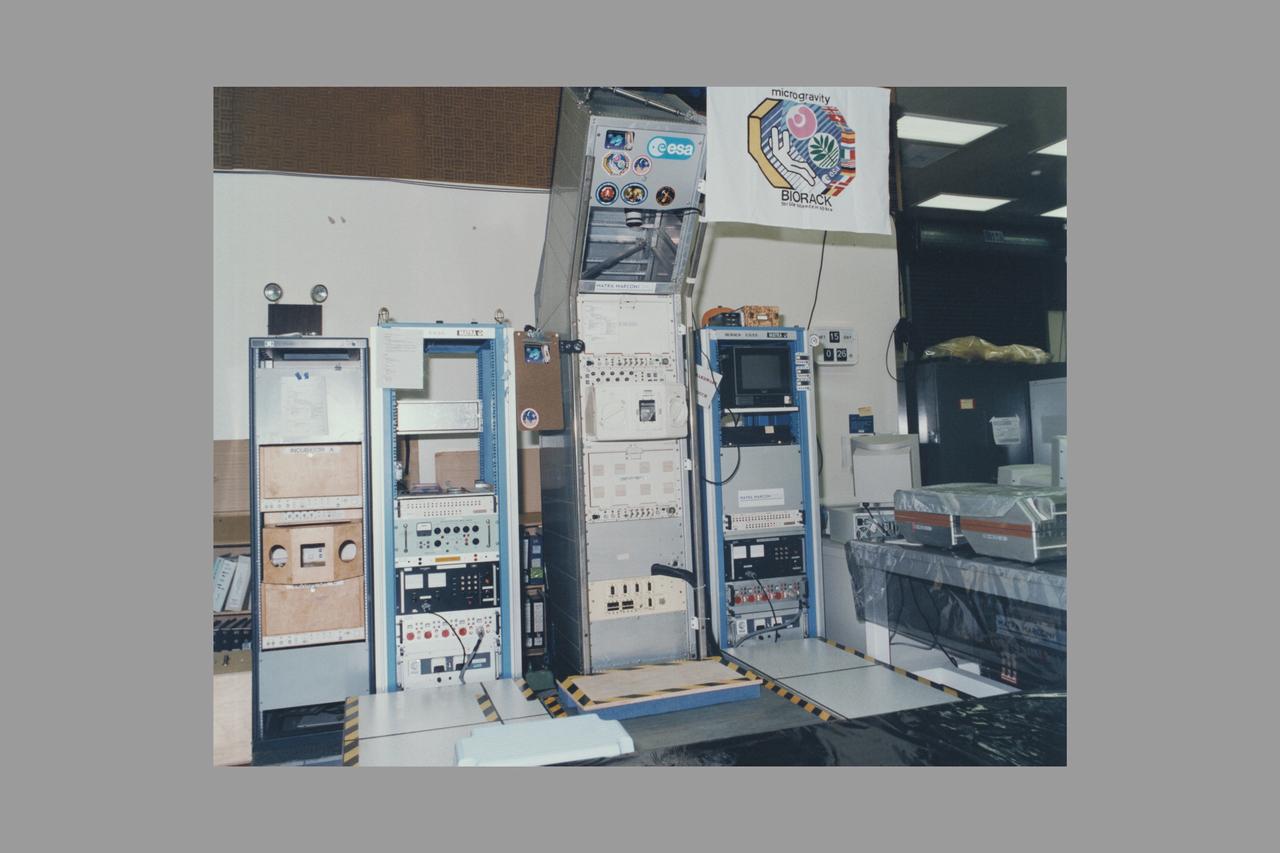

European Space Agency's Biorack facility

European Space Agency's Biorack incubator A (22deg C)
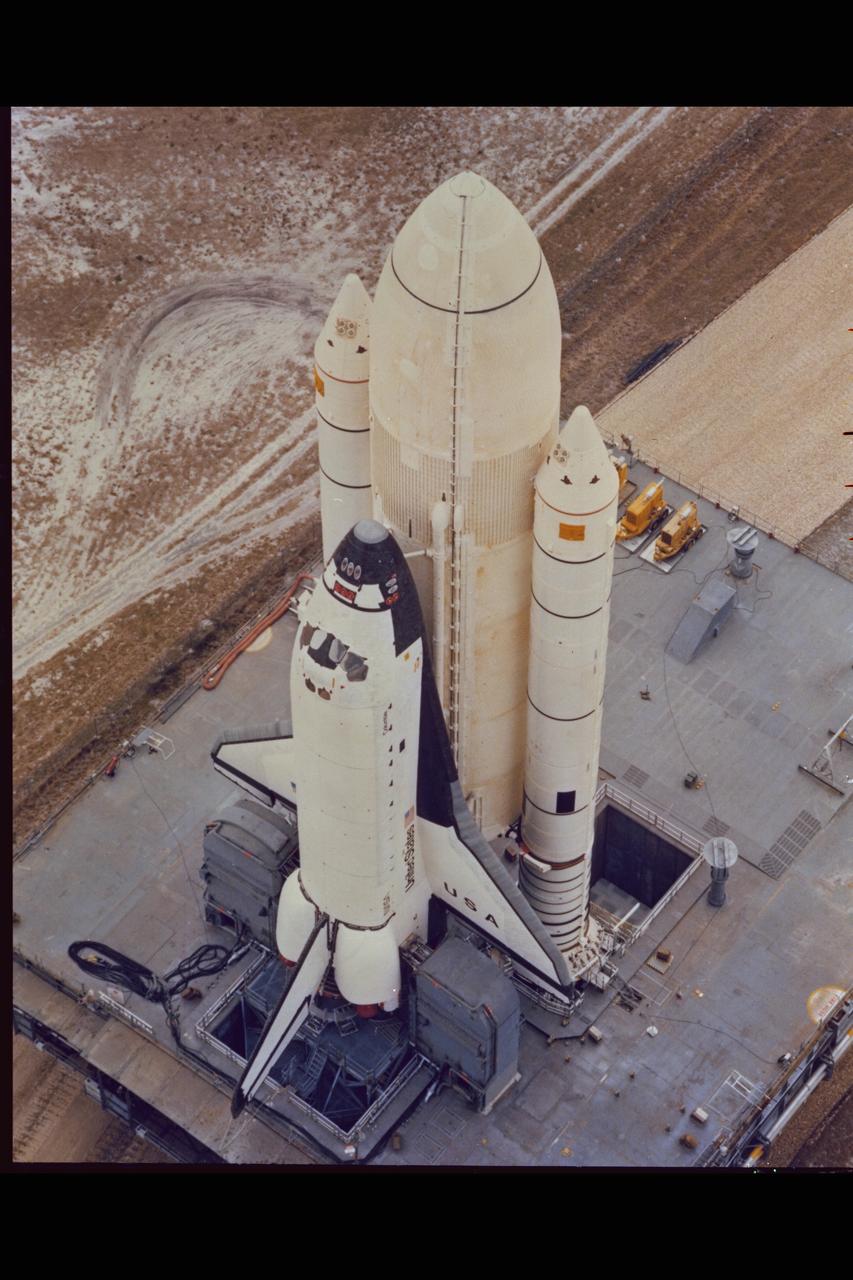

Space Shuttle Columbia at Launch Site. (ref: 81-HC-5)
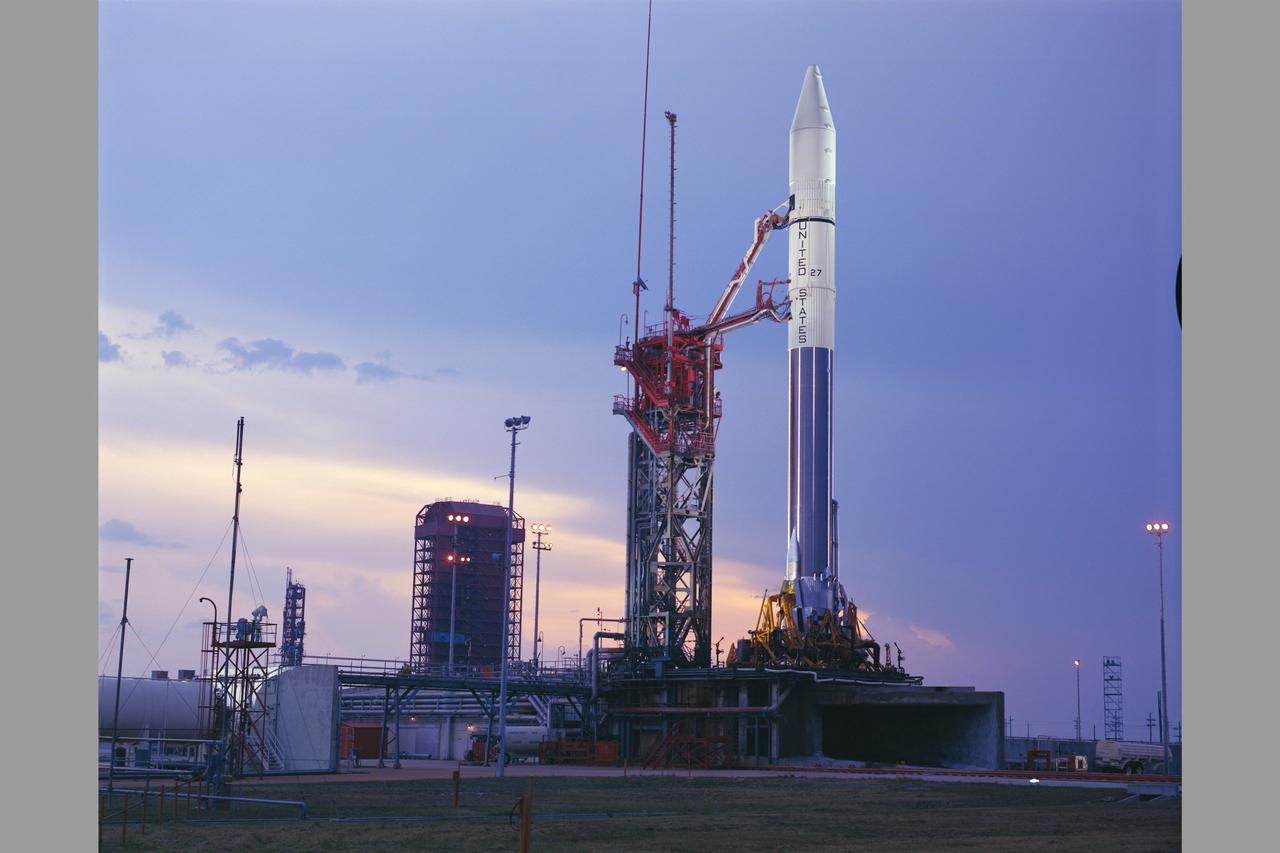

A pre launch view of Pioneer-10 (or F) spacecraft encapsulated and mated with a Atlas-Centaura launch vehicle in preparation for mission to Jupiter
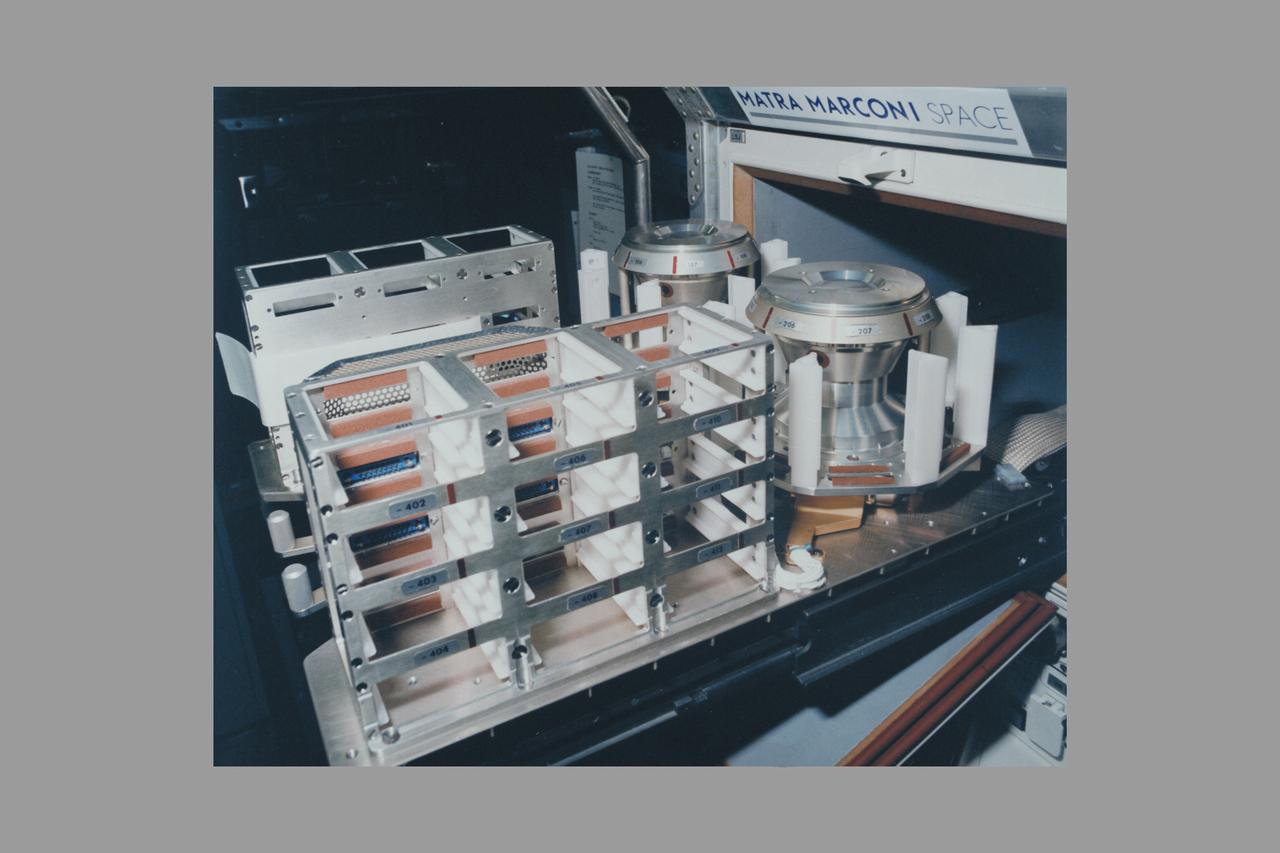
European Space Agency's Biorack incubator A (22deg C)
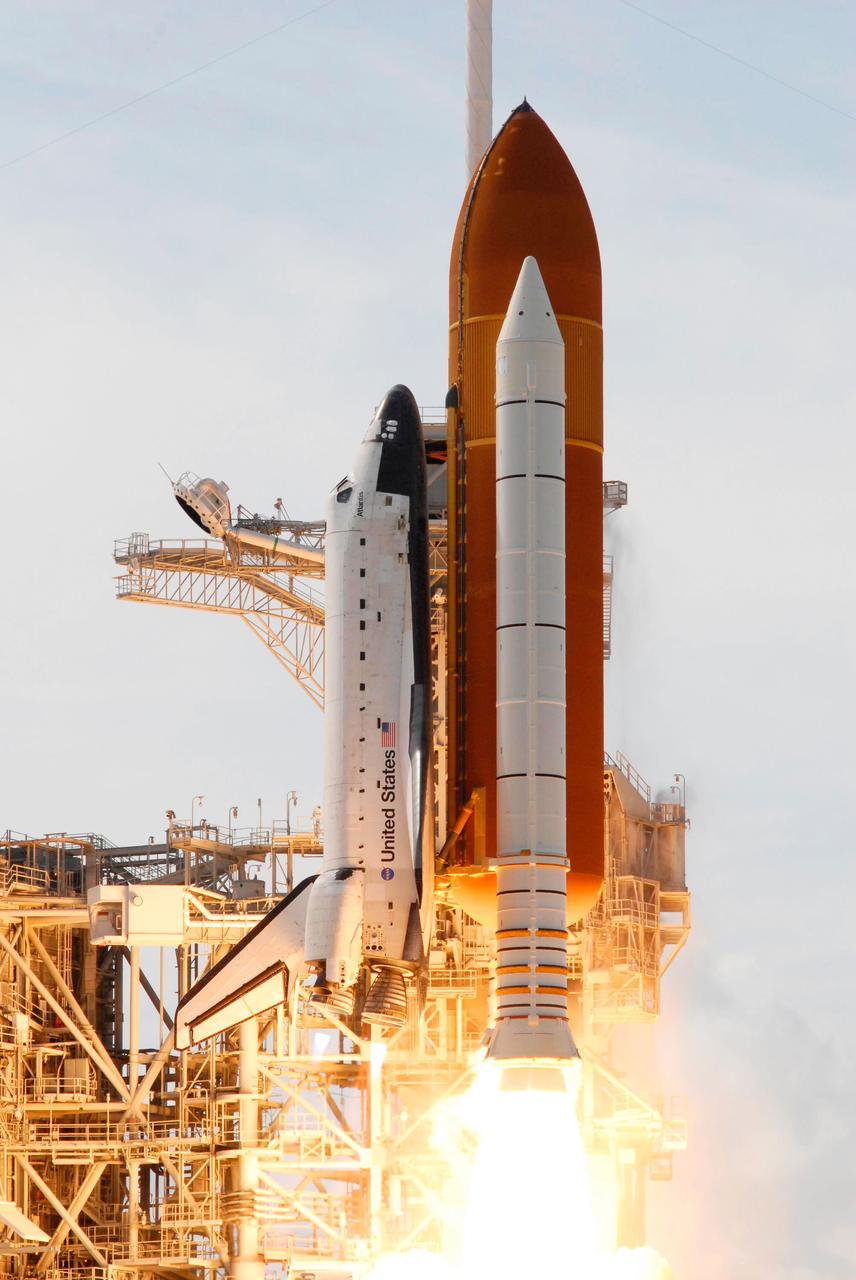

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
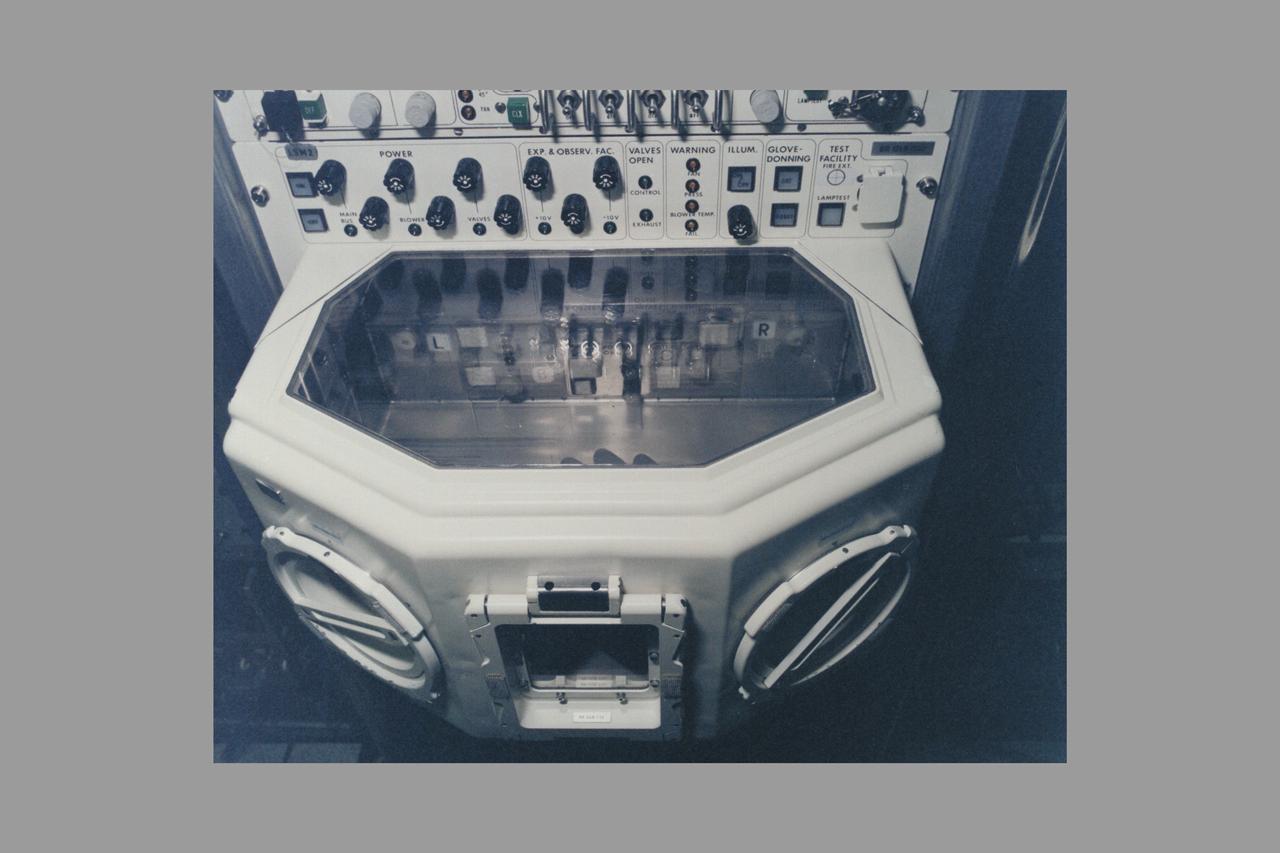

European Space Agency's Biorack glovebox
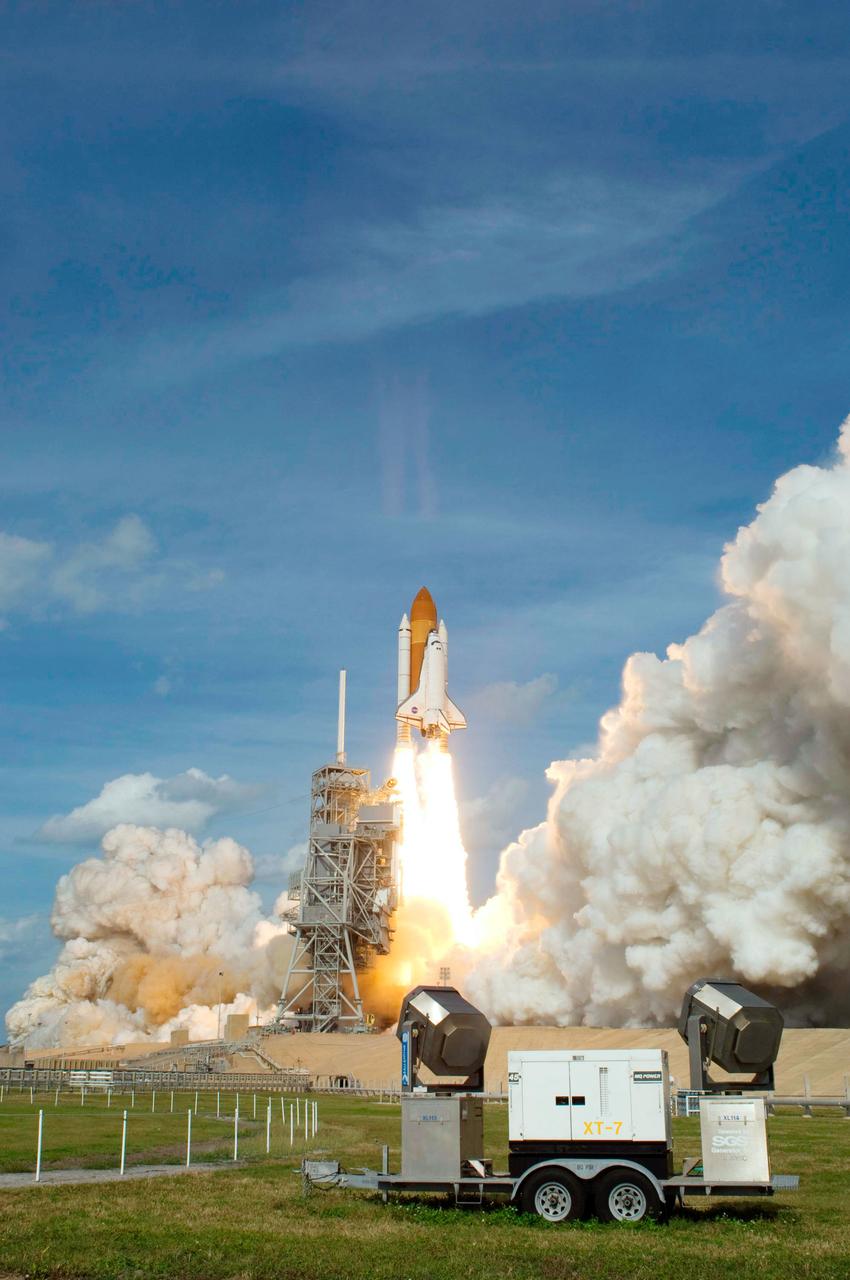

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
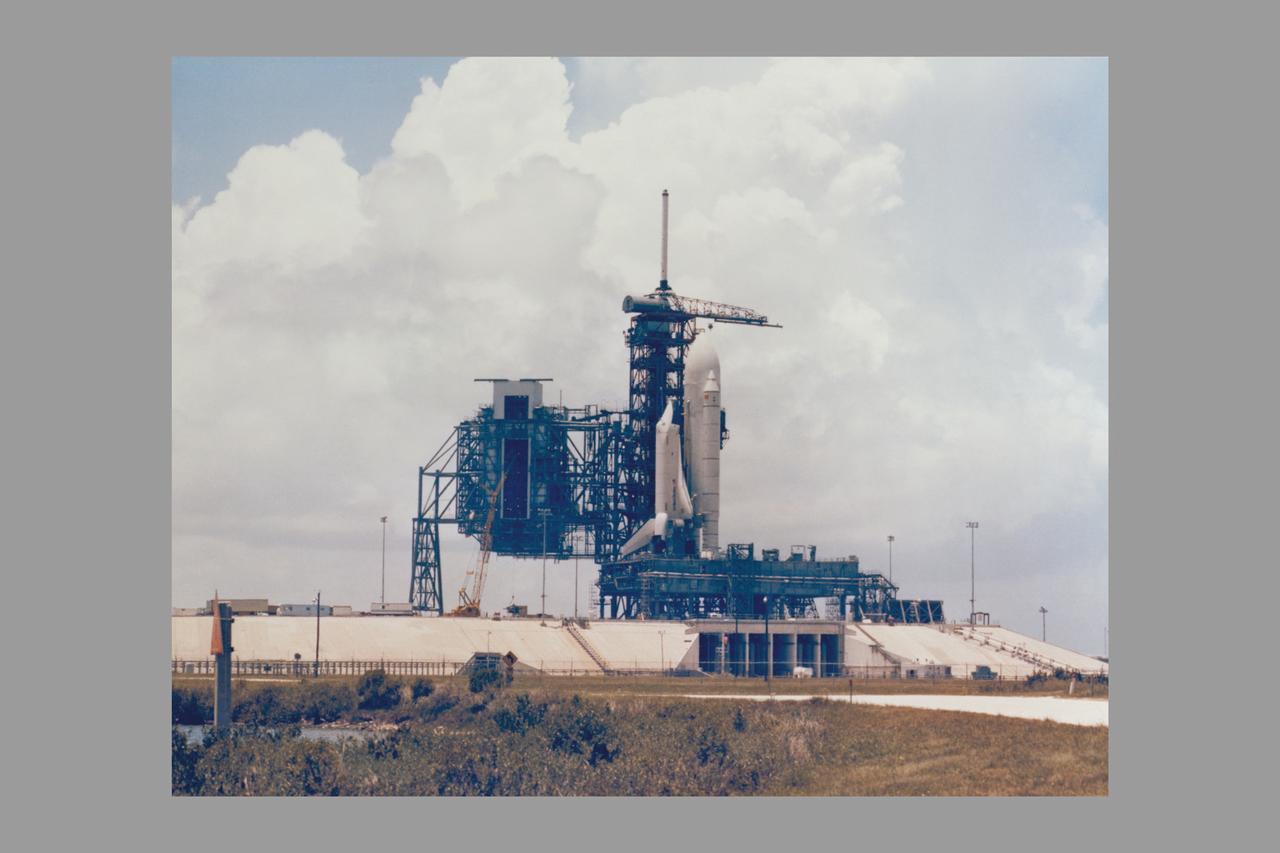

SPACE SHUTTLE ORBITER ENTERPRISE MATED TO AN EXTERNAL FUEL TANK AND TWO SOLID ROCKET BOOSTERS ON TOP OF A MOBIL LAUNCHER PLATFORM, UNDERGOES FIT AND FUNCTION CHECKS AT THE LAUNCH SITE FOR THE FIRST SPACE SHUTTLE AT LAUNCH COMPLEX 39'S PAD A. THE DUMMY SPACE SHUTTLE WAS ASSEMBLED IN THE VEHICLE ASSEMBLY BUILDING AND ROLLED OUT TO THE LAUNCH SITE ON MAY 1 AS PART OF AN EXERCISE TO MAKE CERTAIN SHUTTLE ELEMENTS ARE COMPATIBLE WITH THE SPACEPORT'S ASSEMBLY AND LAUNCH FACILITIES AND GROUND SUPPORT EQUIPMENT, AND HELP CLEAR THE WAY FOR THE LAUNCH OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE ORBITER COLUMBIA.
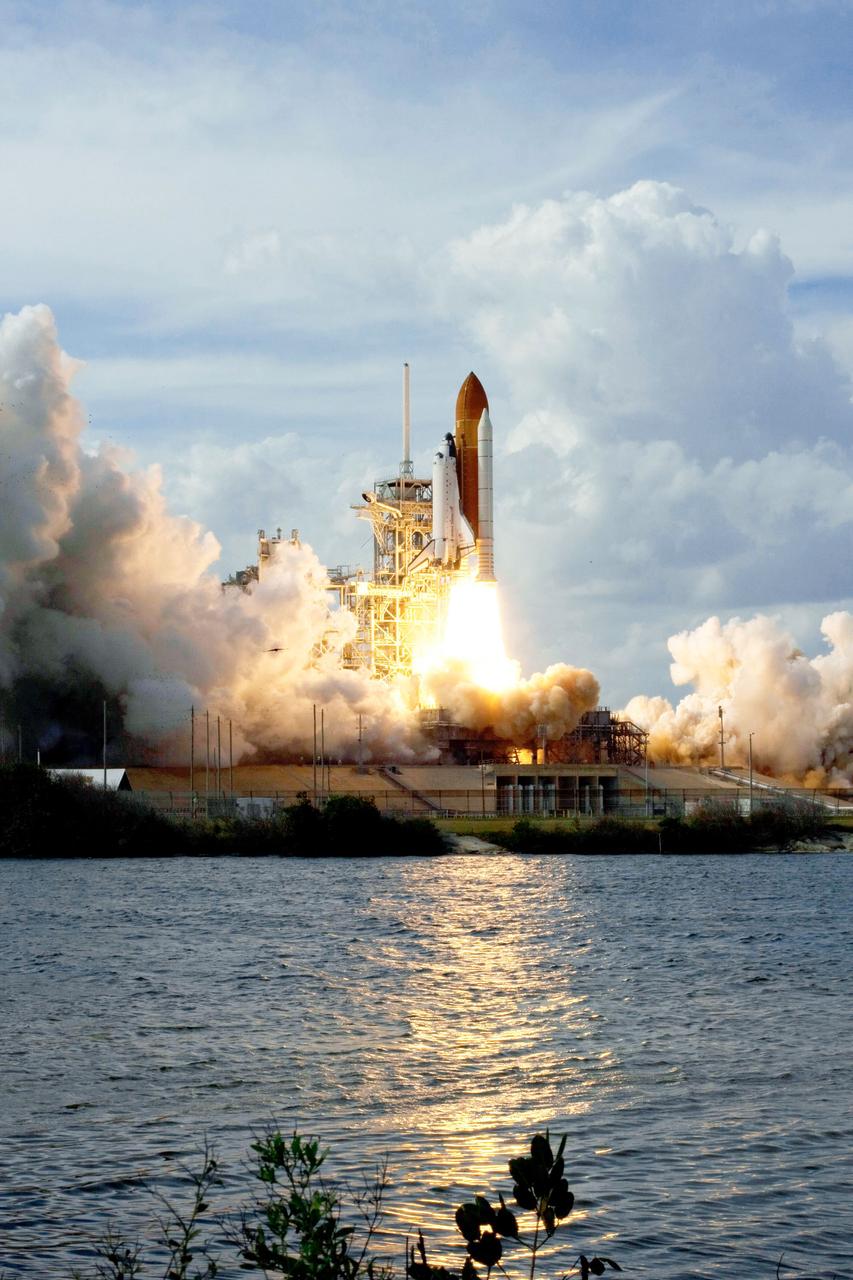

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
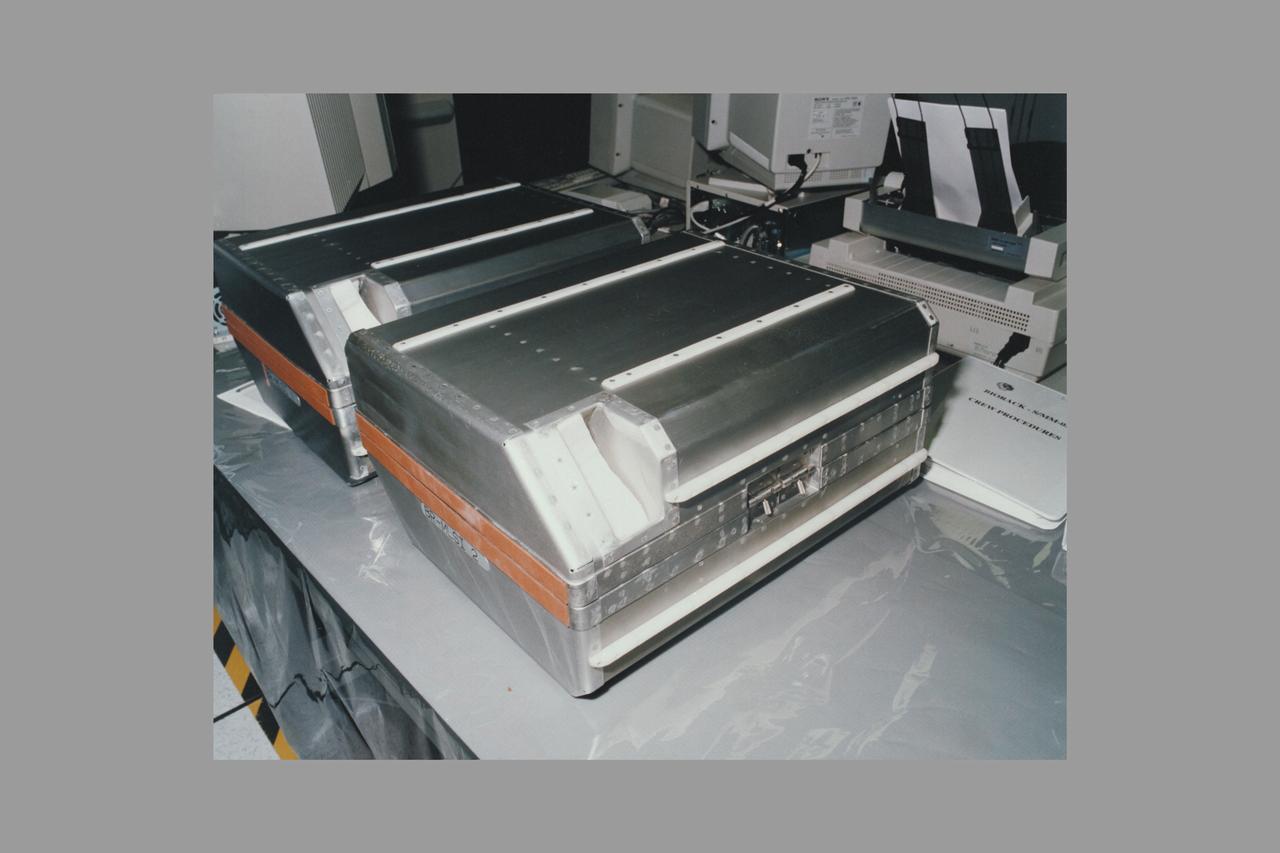

European Space Agency's Biorack MLSI (middeck locker stowage insert)
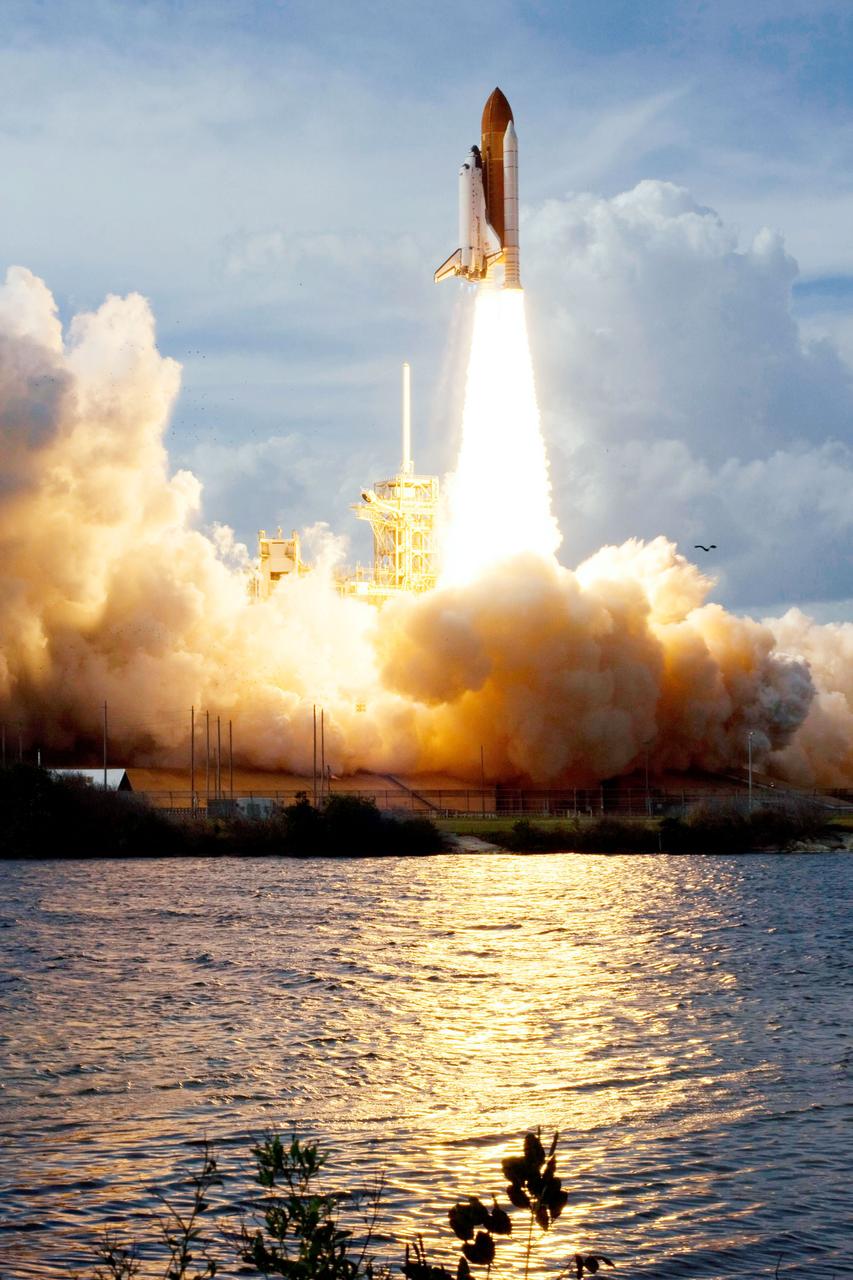

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
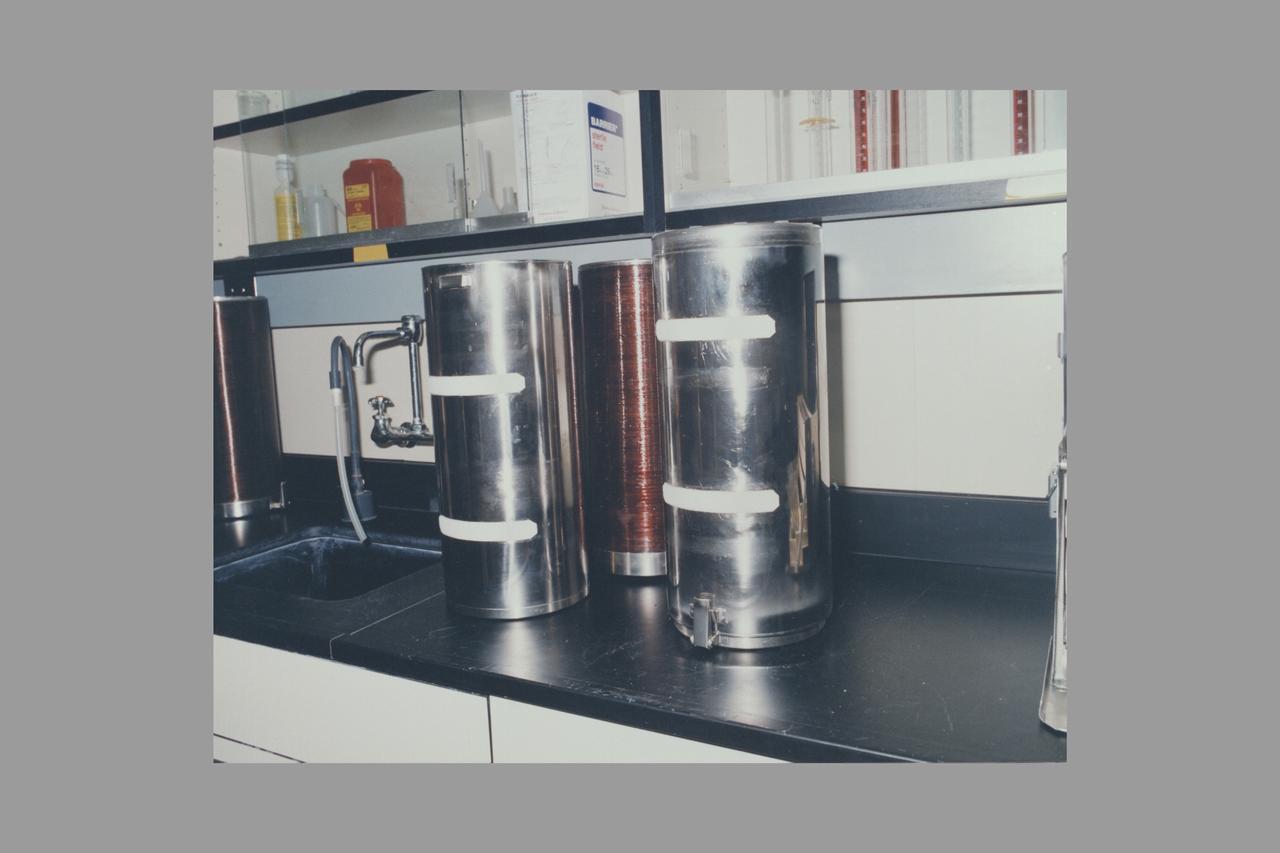

European Space Agency's Biorack passive thermal conditioning unit (PTCU)
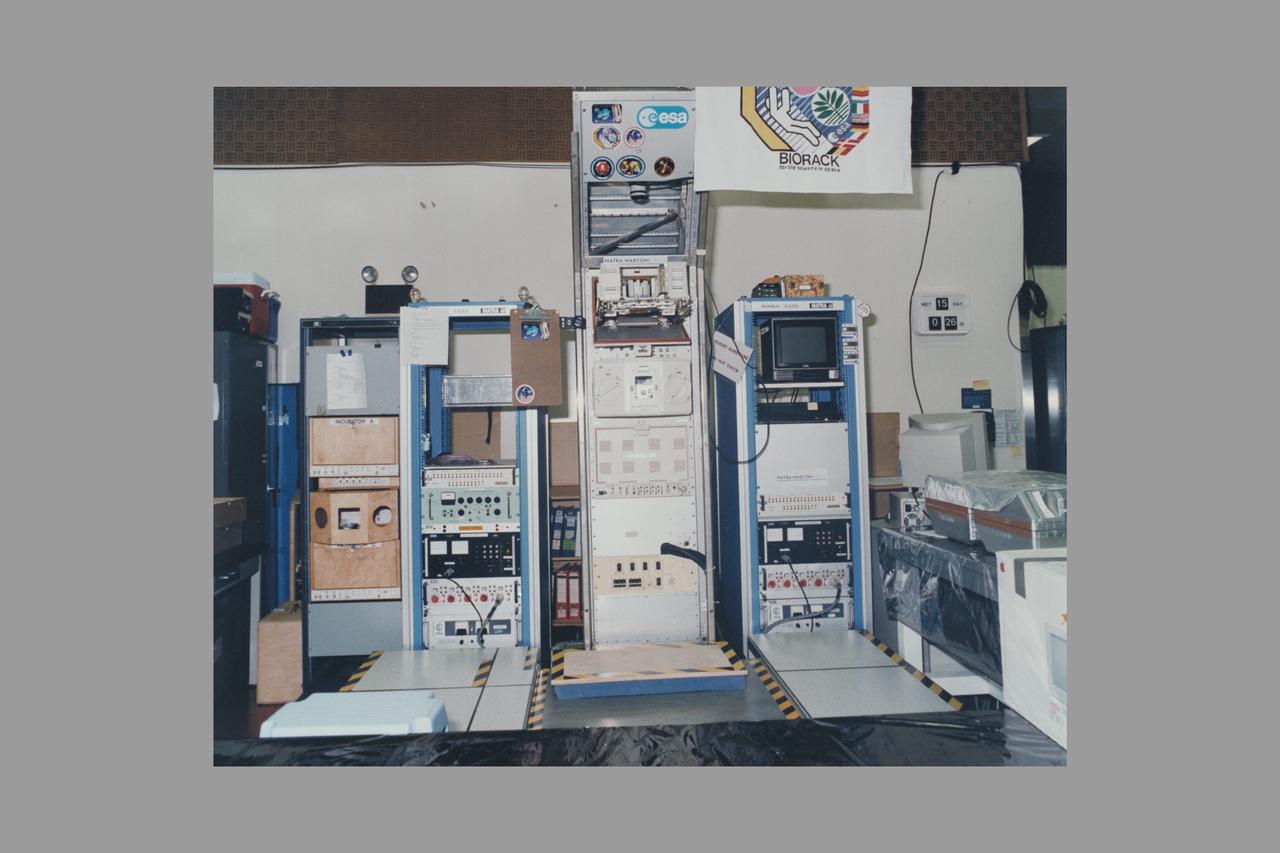

European Space Agency's Biorack facility
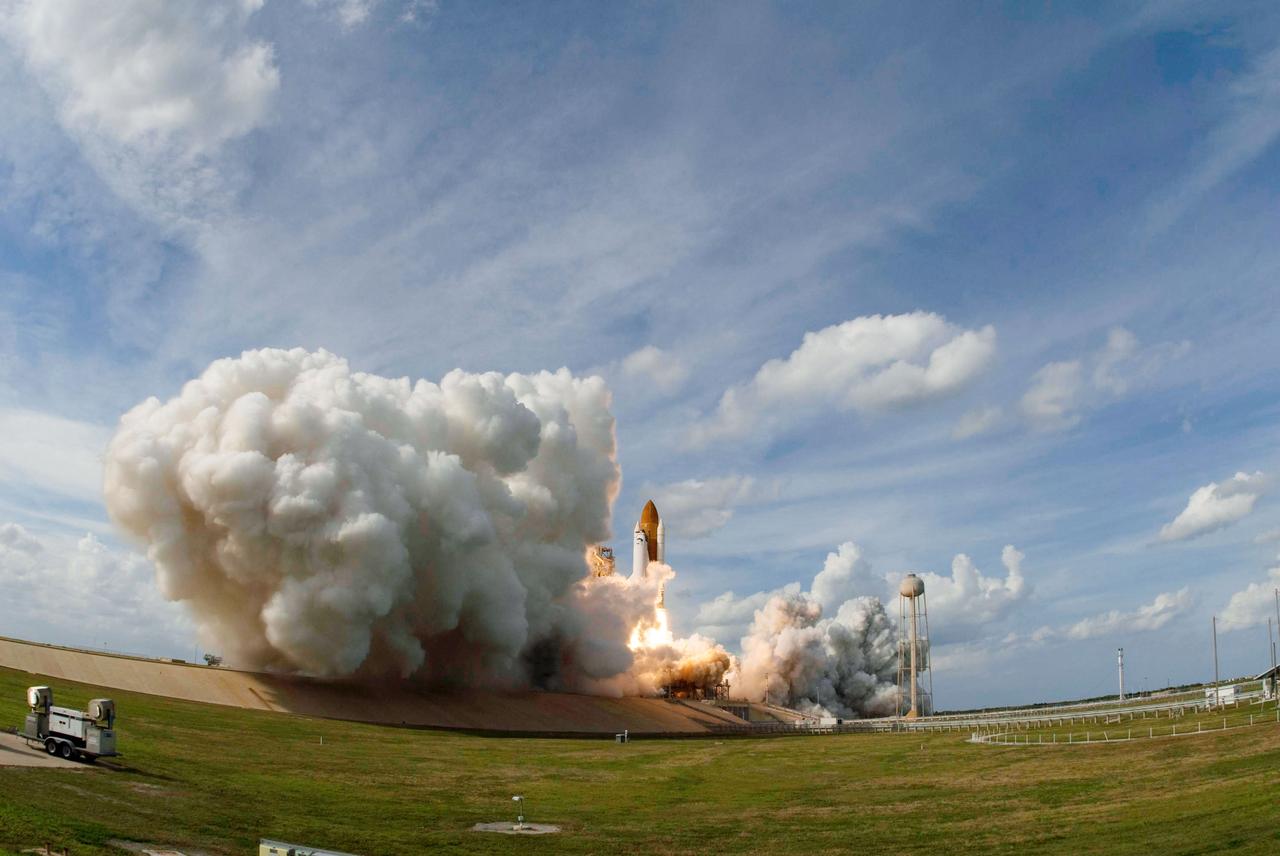

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
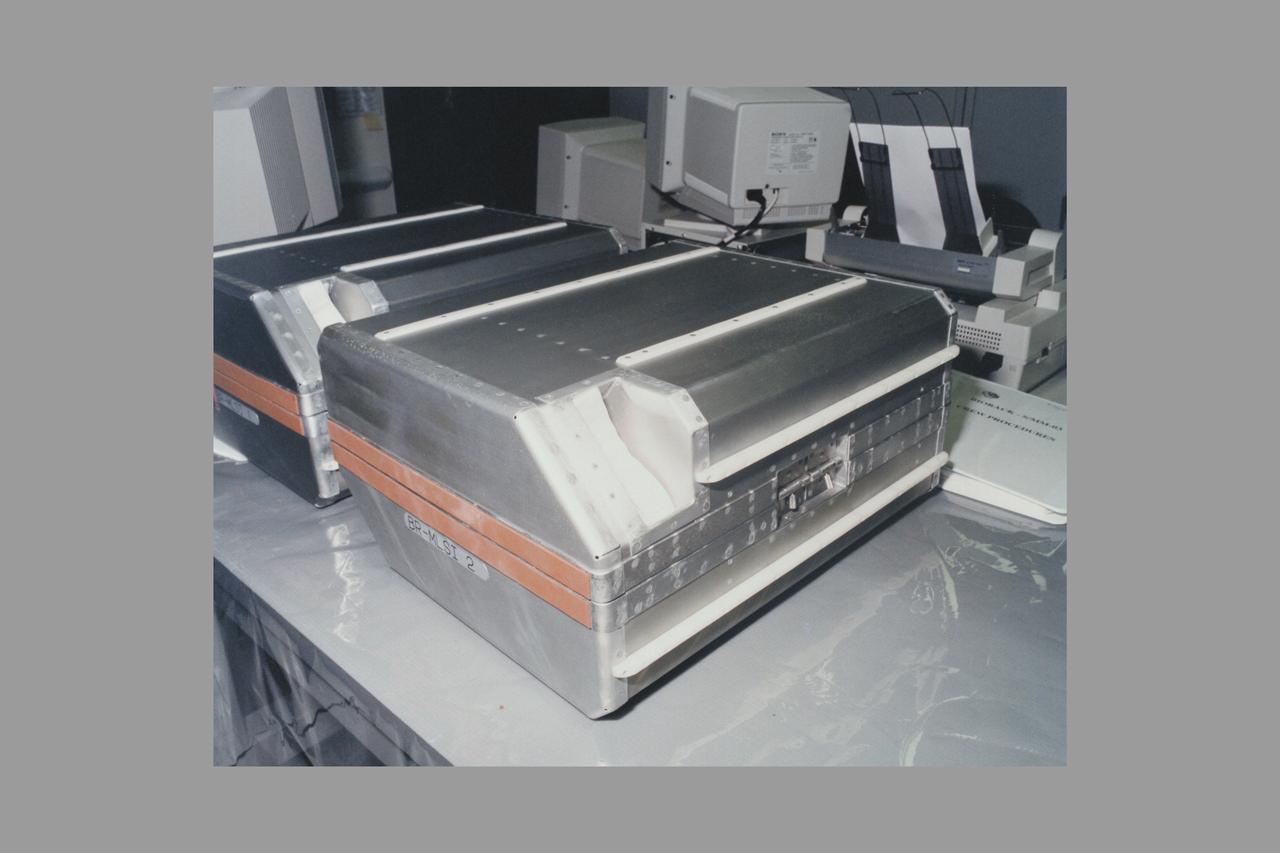

European Space Agency's Biorack MLSI (middeck locker stowage insert)
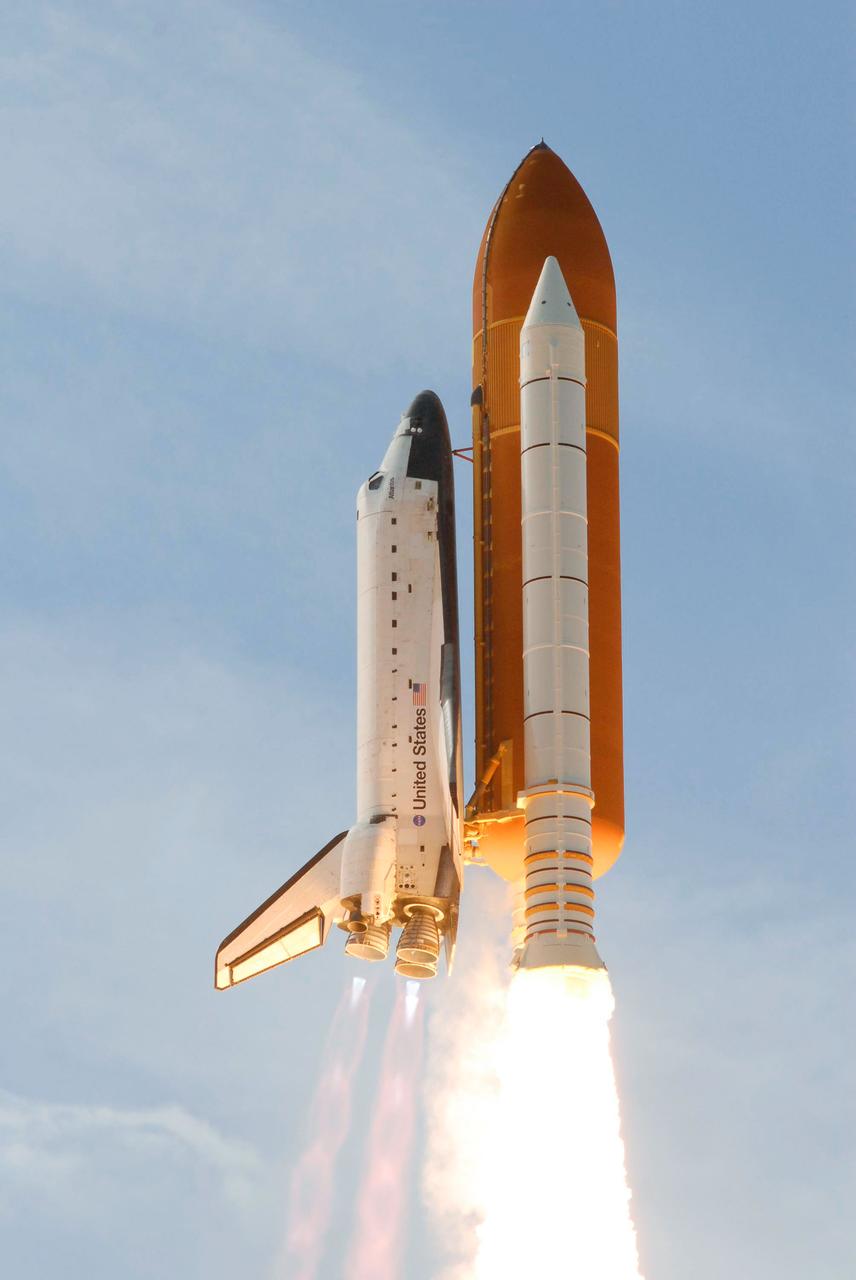

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
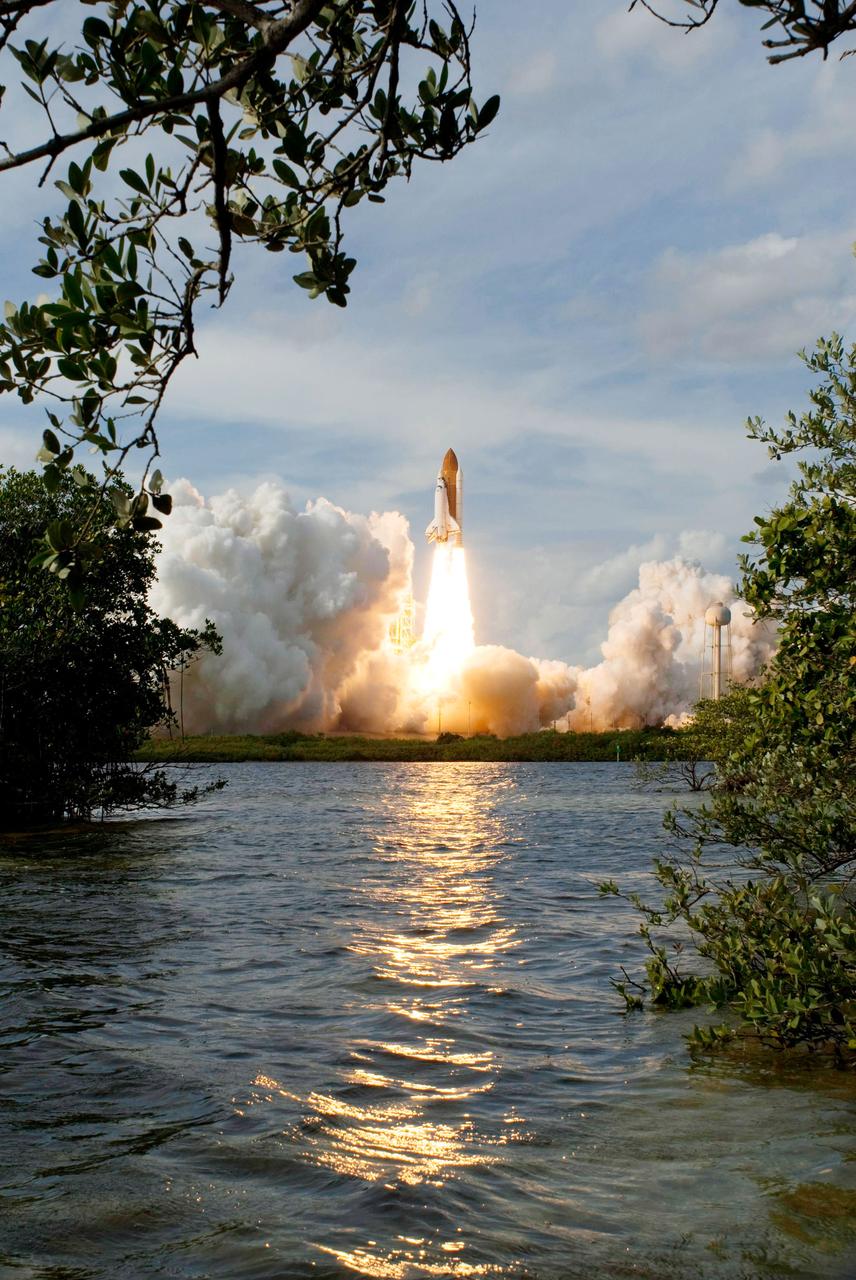

Launch of space shuttle Atlantis STS-122
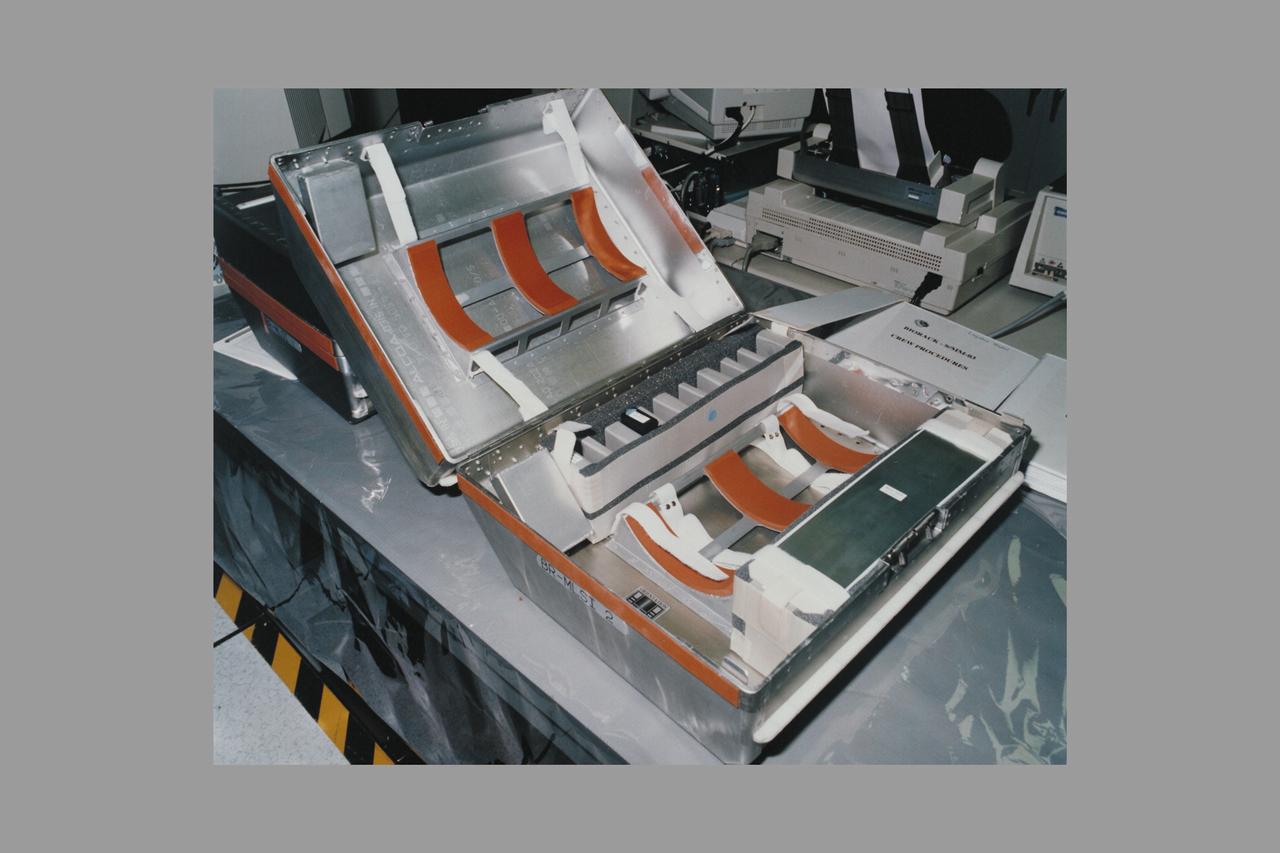

European Space Agency's Biorack MLSI (middeck locker stowage insert) for PTCU
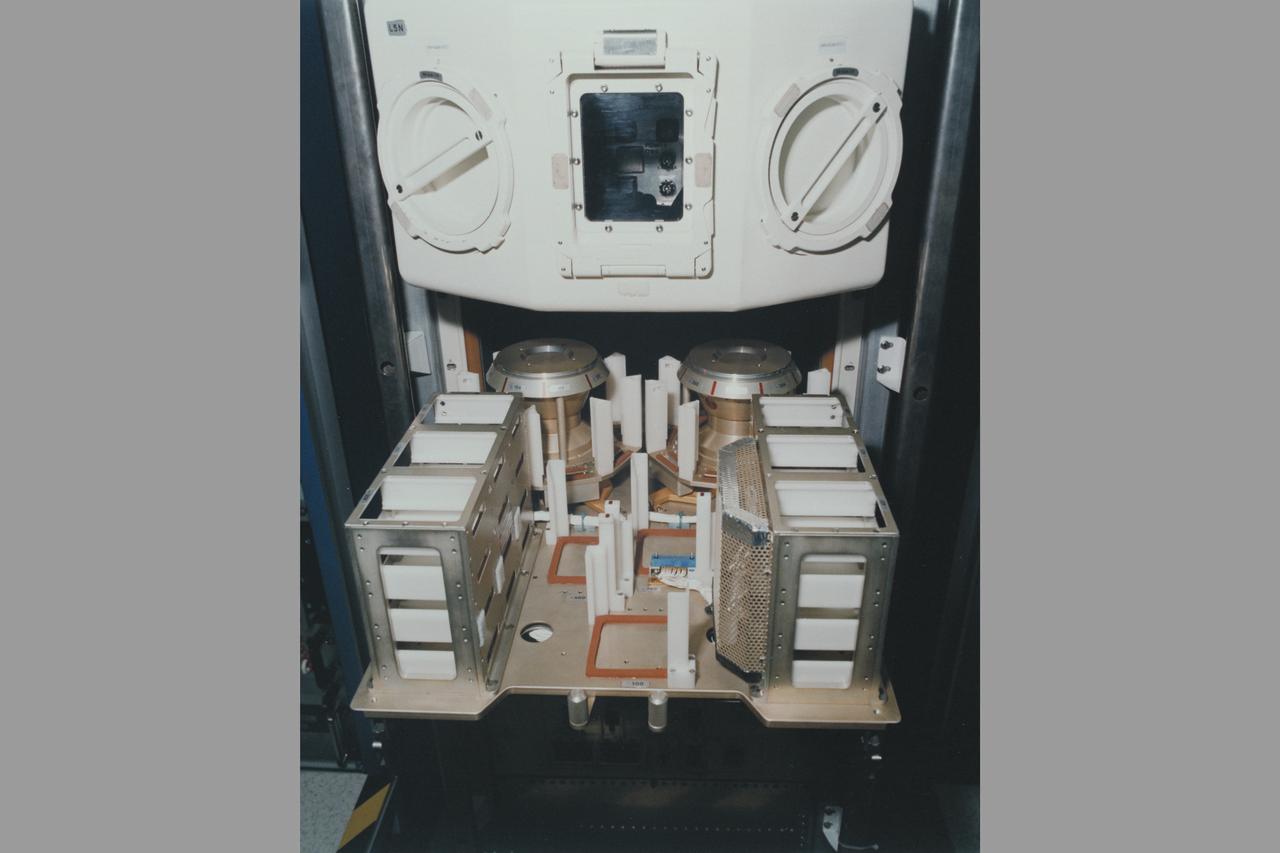

European Space Agency's Biorack incubator C (37deg C)
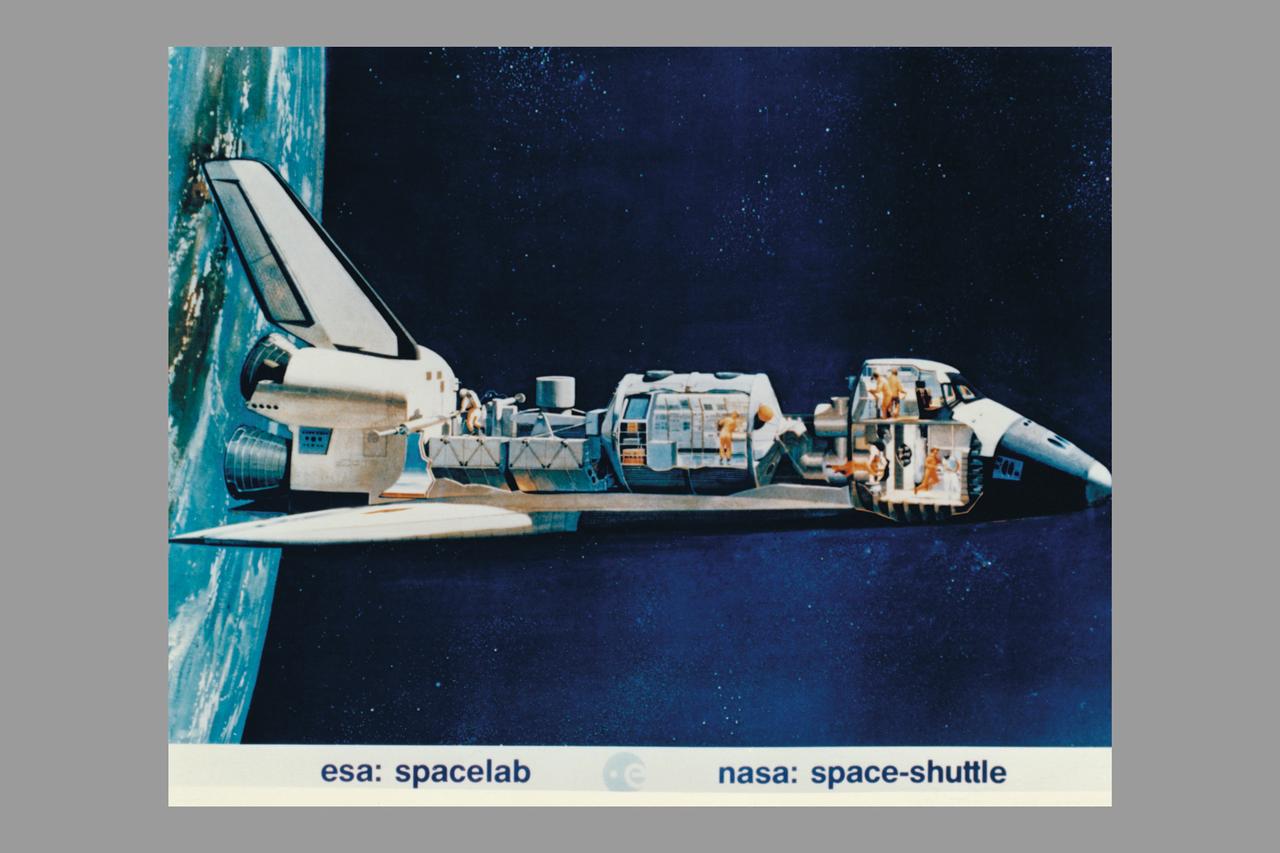
Space Shuttle cutaway showing astronauts working with ESA Spacelab
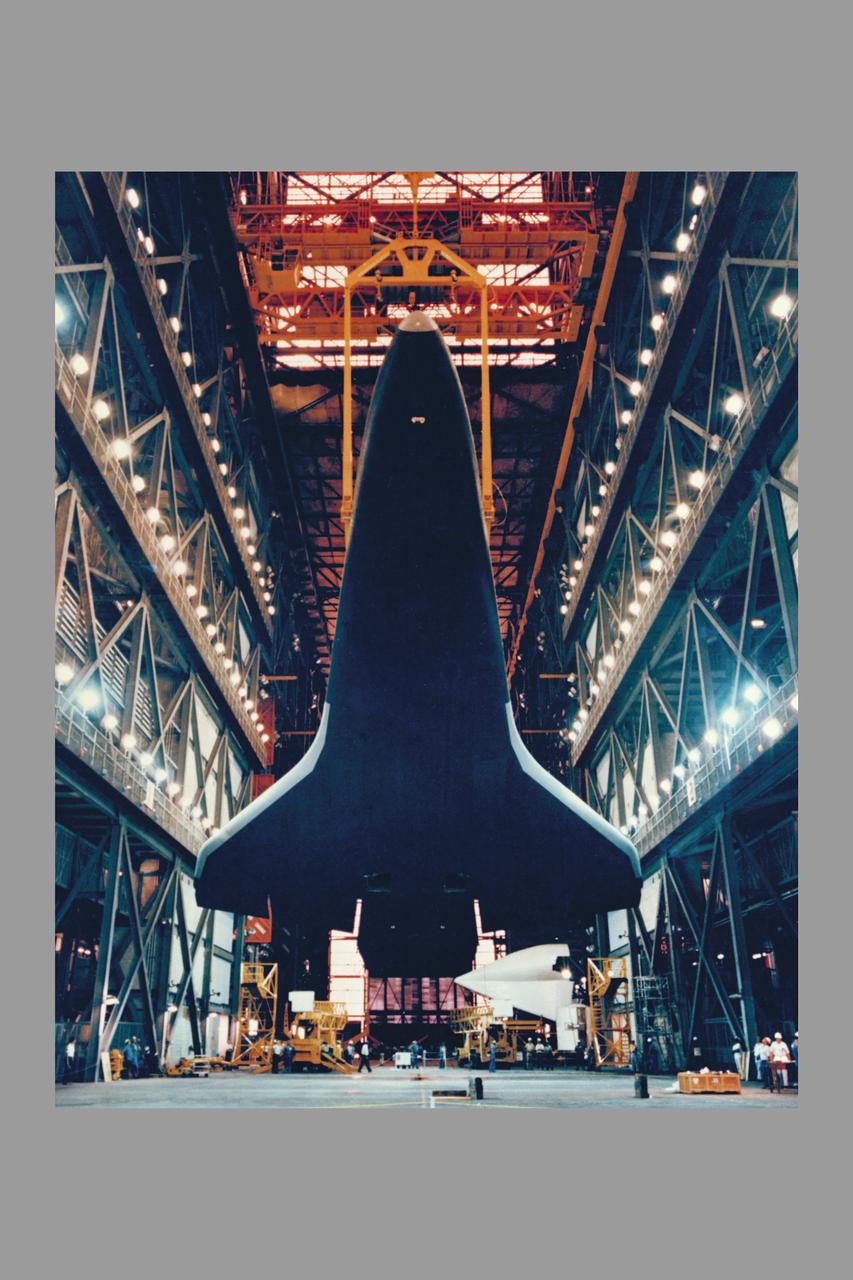

Space Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise is lowered to the floor of the transfer aisle in the Vehicle Assembly Building during destacking operations. The Enterprise, mated to an external tank and twin inert solid rocket boosters, formed a nonlaunchable Space Shuttle which was used for fit and function checks of assembly, test and launch facilities at the nation's Spaceport. Enterprise will be tansported to the Shuttle Landing Facility, mounted piggyback on its 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, and flown to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, California.
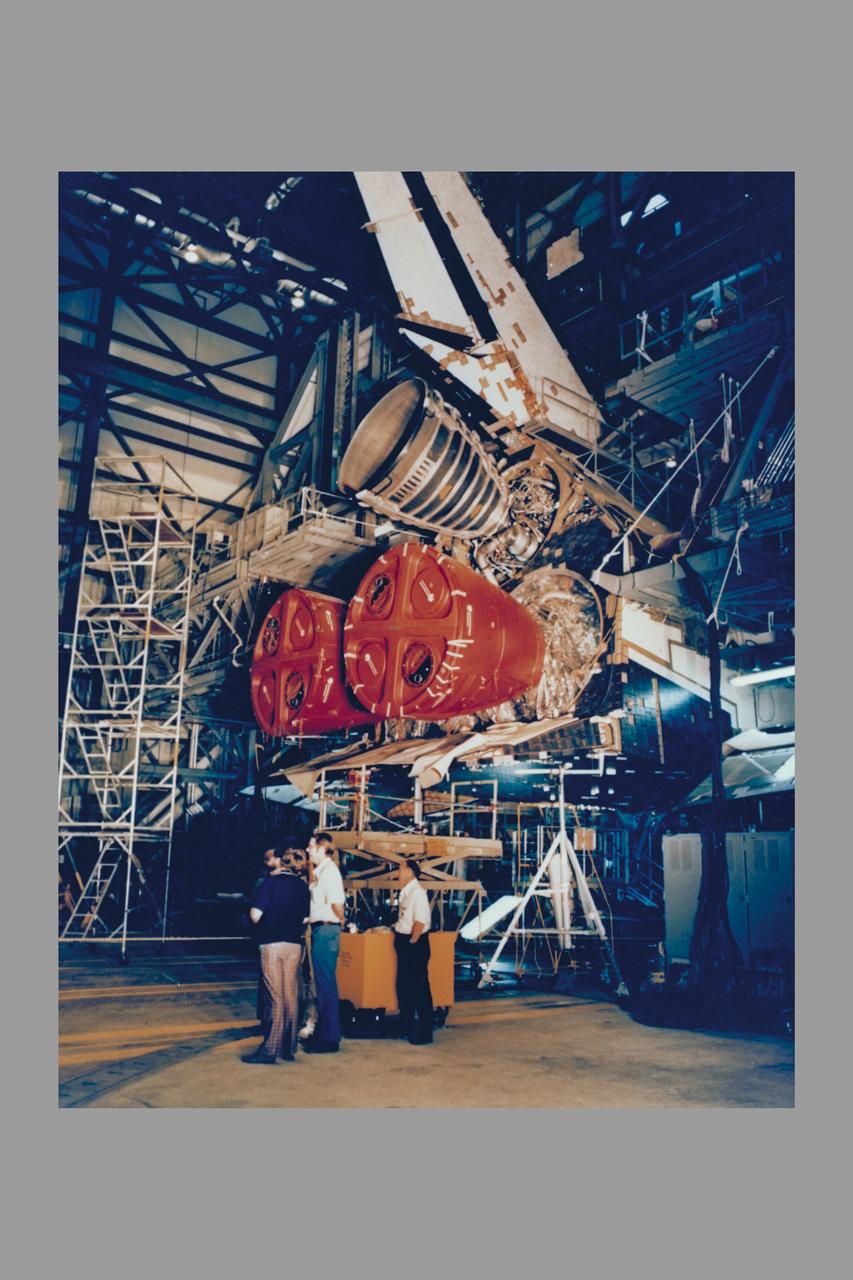

Outfitting the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia with the three main rocket engines that will boost the 75 ton spacecraft into orbit on its first flight is completed with the installation of Engine #2007 (top). At liftoff, each engine will be producing about 375,000 pounds of thrust, or about 12 million horsepower each, and gulping down its liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants at a rate of about 1,100 pounts per second. The Shuttle's main engines, the most efficient rocket engines ever built, are reusable and designed t operate over a life span of 55 missions.
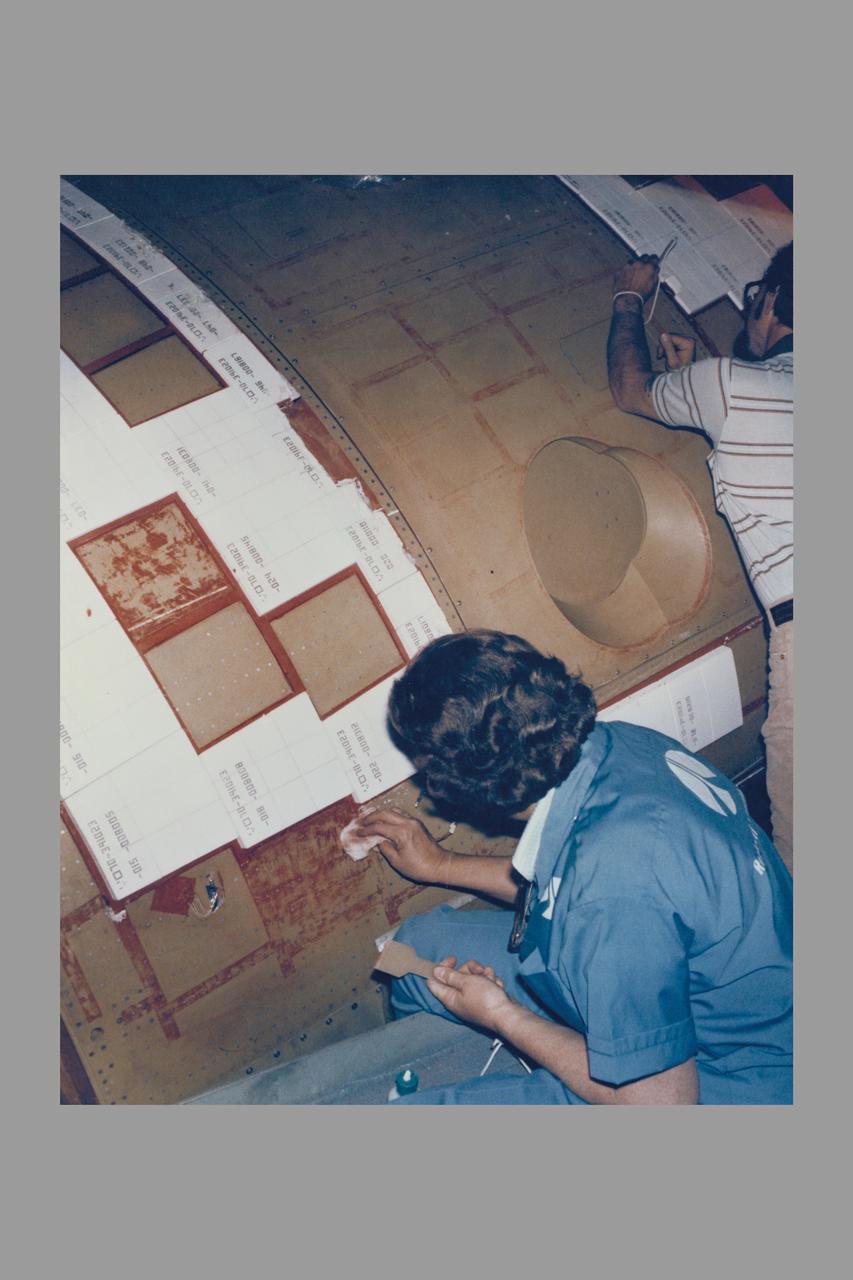

ROCKWELL INTERNATIONAL TECHNICIANS MOUNT SOME OF THE NEARLY 8,000 CERAMIC-COATED TILES THAT REMAIN TO BE INSTALLED ON THE EXTERNAL SURFACES OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE ORBITER COLUMBIA TO COMPLETE THE THERMAL PROTECTION SYSTEM THAT WILL ABSORB THE INTENSE HEAT OF REENTERING THE EARTH'S ATMOSPHERE AFTER A MISSION IN SPACE. TILE INSTALLATION IS DONE ON AN AROUND-THE-CLOCK BASIS IN THE ORBITER PROCESSING FACILITY WHERE COLUMBIA, THE FIRST IN A NEW BREED OF MANNED, REUSABLE SPACECRAFT, IS BEING READIED FOR THE FIRST LAUNCH OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE LATER THIS YEAR.
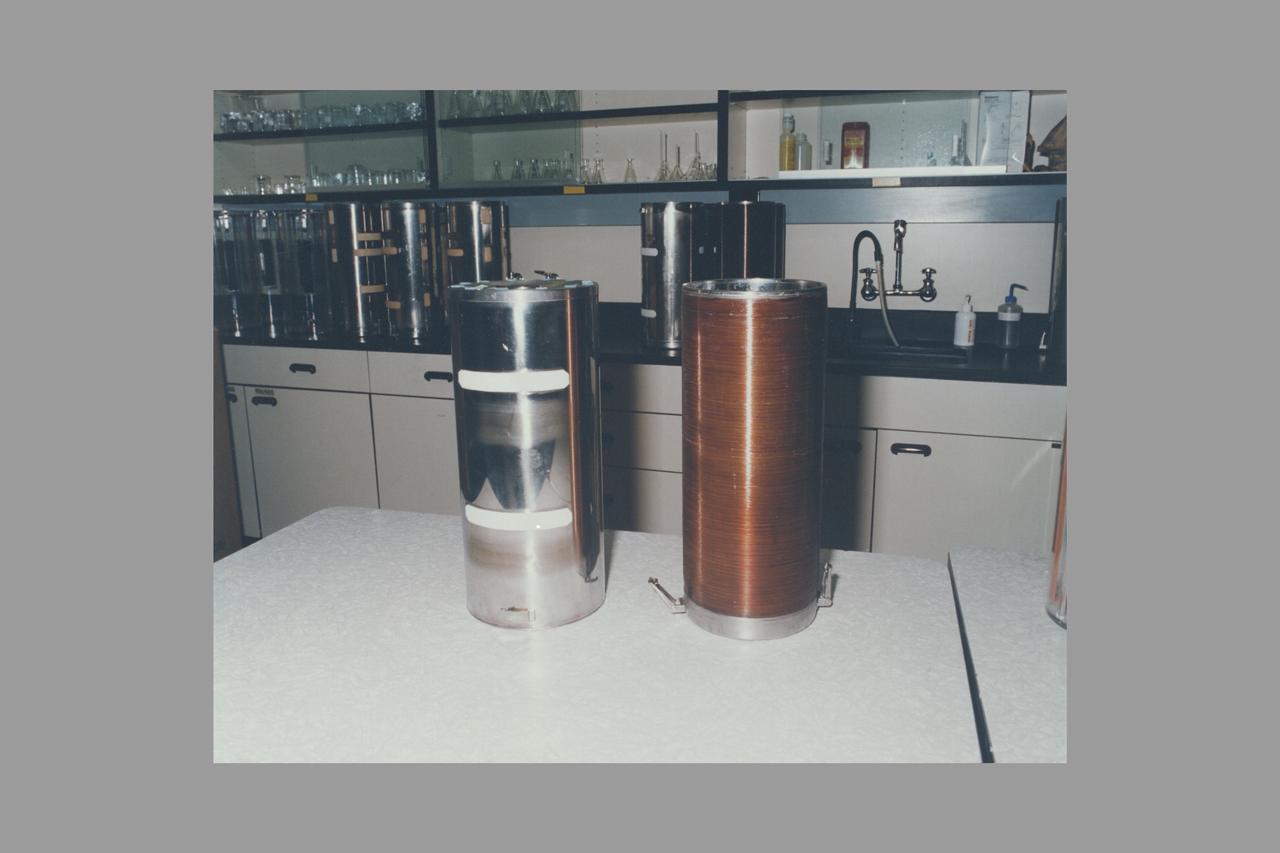

European Space Agency's Biorack passive thermal conditioning unit (PTCU)
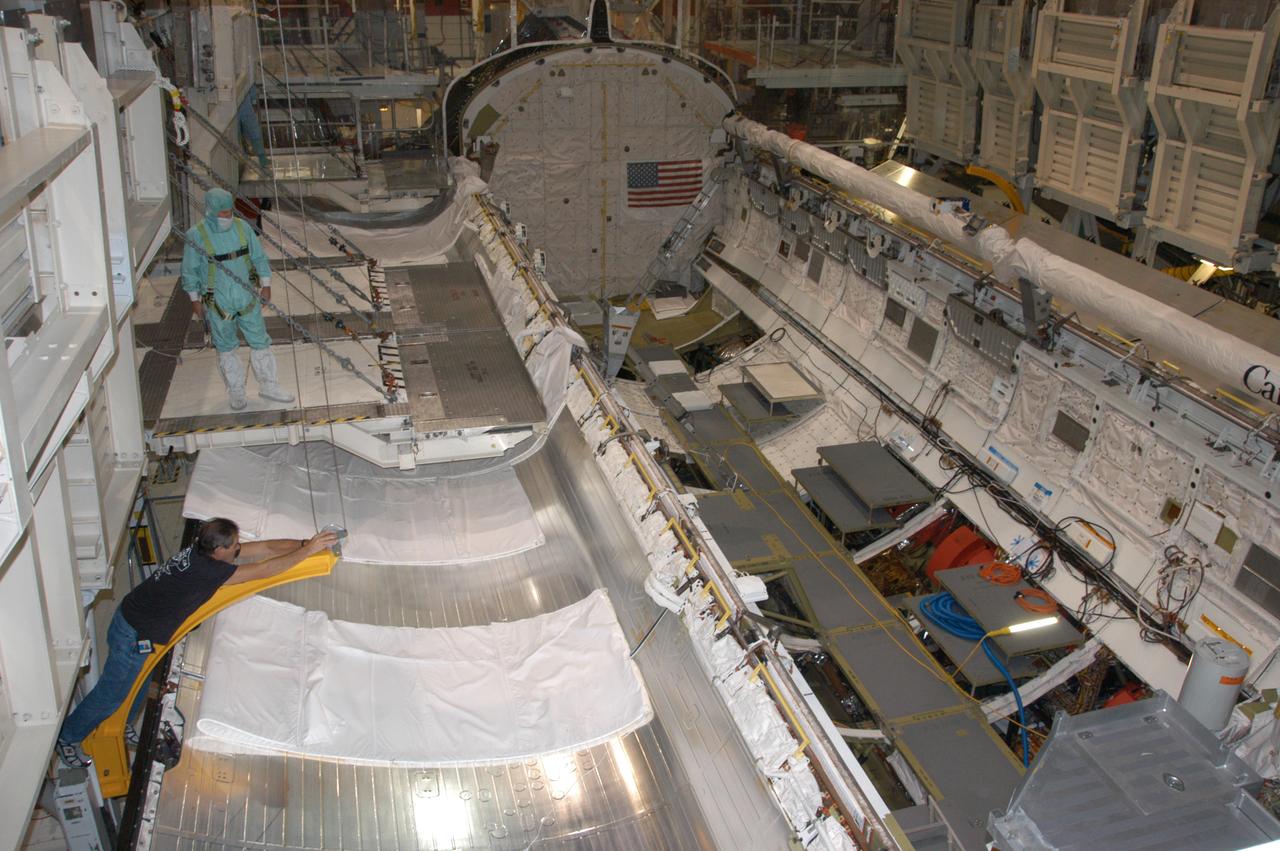

Endeavour's payload bay is open for payload configuration work in Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2. The orbiter is the vehicle designated for mission STS-118, scheduled to launch in late June. The mission will continue space station construction by delivering a third starboard truss segment, S5, as well as carrying the External Stowage Platform 3. The crew comprises six astronauts: Commander Scott Kelly, Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialists Dr. Dafydd (Dave) Williams, Barbara Morgan, Richard Mastracchio and Tracy Caldwell. Williams represents the Canadian Space Agency.
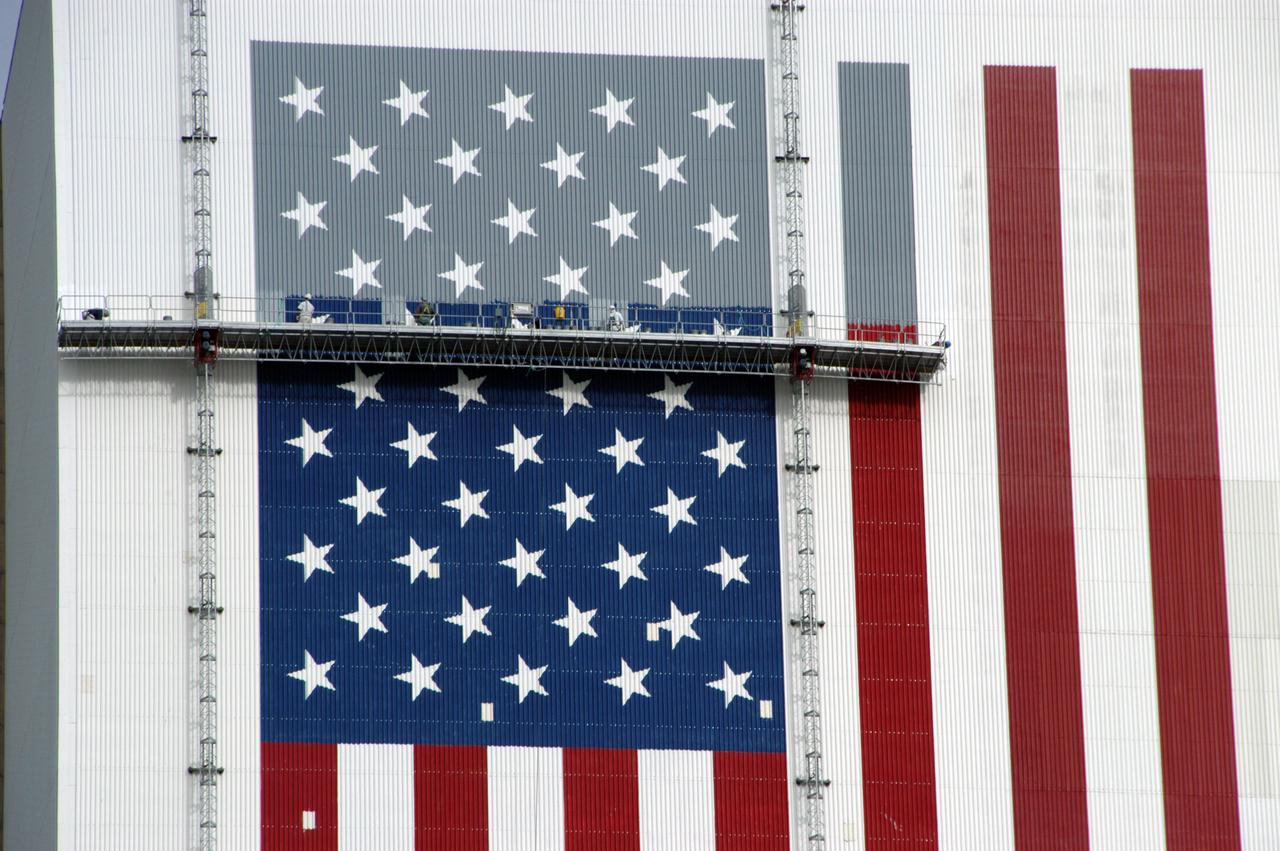

Workers painting the Flag and Meatball on the VAB.
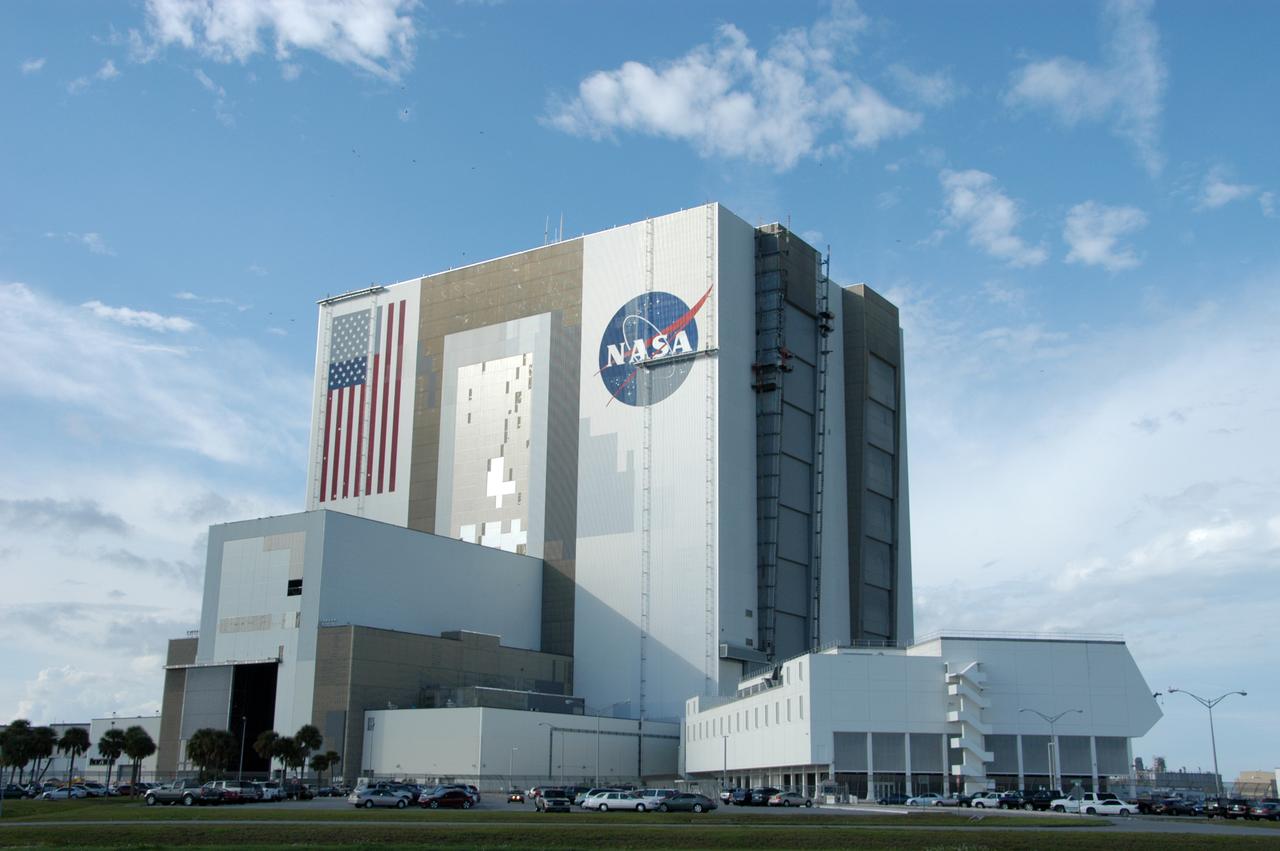

Elevated platforms are seen hanging in front of the NASA Logo on the side of Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building. Also in view on the east side of the building are platforms on the facility's large vertical doors. Workers, suspended on the platforms from the top of the 525-foot-high VAB, use rollers and brushes to do the painting. The flag and logo were last painted in 1998, honoring NASA's 40th anniversary. The flag spans an area 209 feet by 110 feet, or about 23, 437 square feet. Each stripe is 9 feet wide and each star is 6 feet in diameter. The logo, also known as the "meatball," measures 110 feet by 132 feet, or about 12,300 square feet.

Workers painting the Flag and Meatball on the VAB.
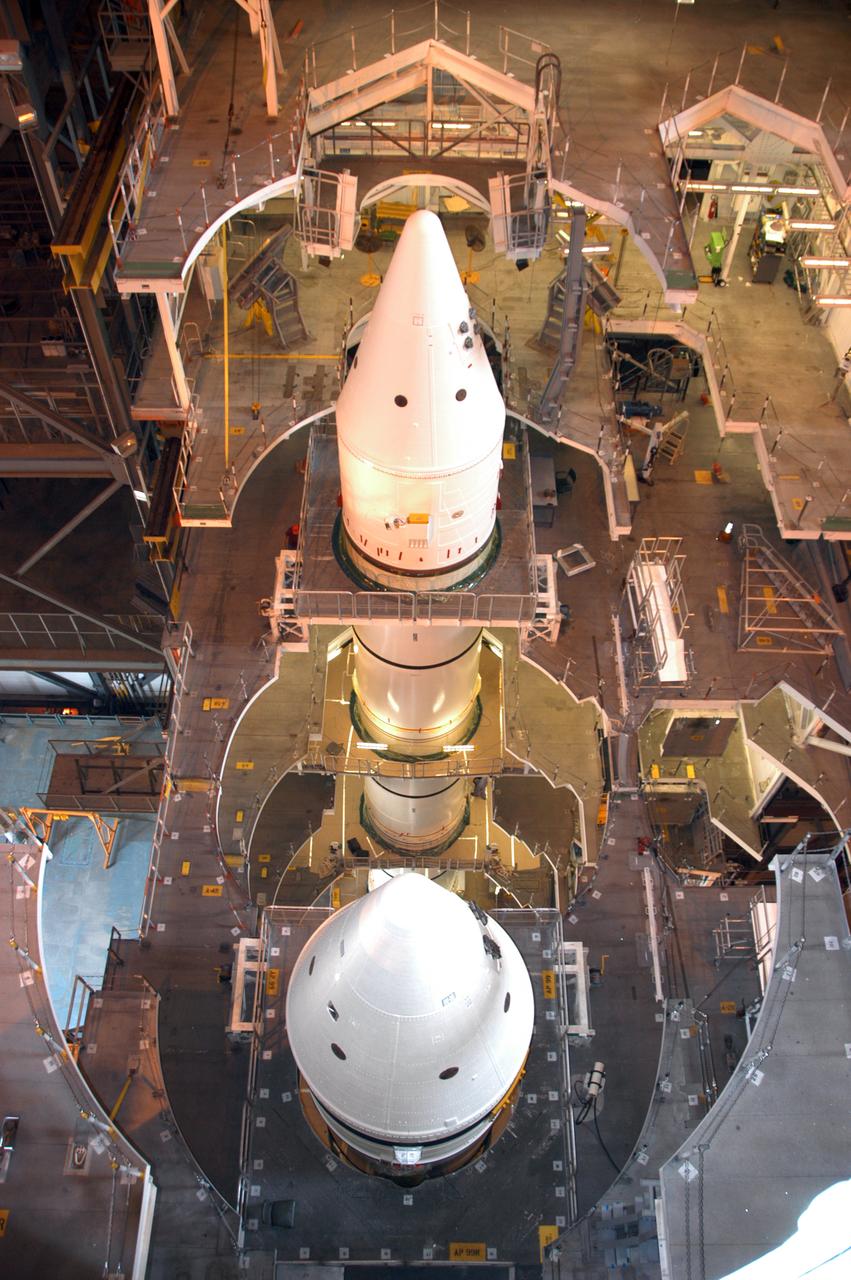

Lighting inside Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building seems to bathe the highbay 1 area in a golden hue as workers continue stacking the twin solid rocket boosters. The solid rocket boosters are being prepared for NASA's next Space Shuttle launch, mission STS-117. The mission is scheduled to launch aboard Atlantis no earlier than March 16, 2007.
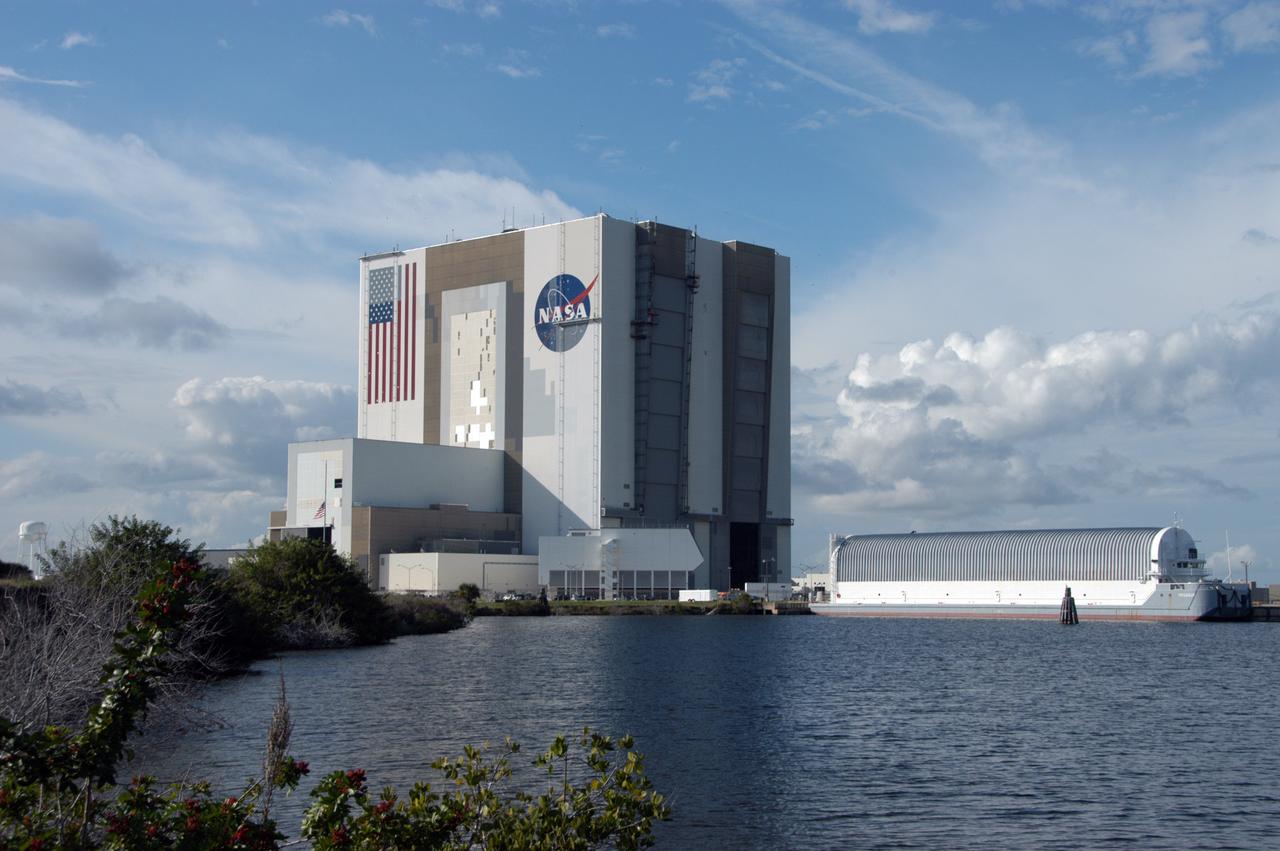

Elevated platforms are seen hanging on the side of Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building in a view looking across from the turn basin. To the right is the large external tank barge. Workers, suspended on the platforms from the top of the 525-foot-high VAB, use rollers and brushes to do the painting. The flag and logo were last painted in 1998, honoring NASA's 40th anniversary. The flag spans an area 209 feet by 110 feet, or about 23, 437 square feet. Each stripe is 9 feet wide and each star is 6 feet in diameter. The logo, also known as the "meatball," measures 110 feet by 132 feet, or about 12,300 square feet.

Workers painting the Flag and Meatball on the VAB.
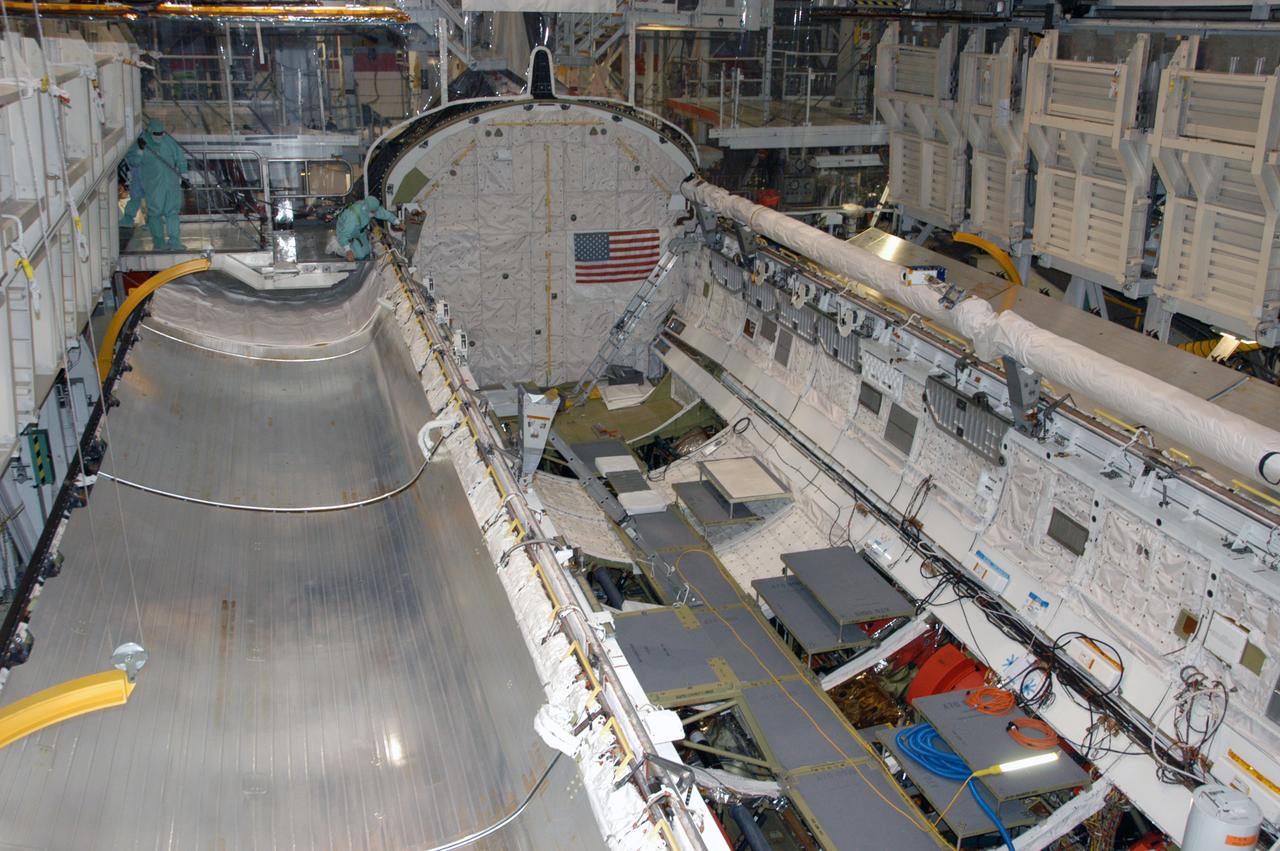

Endeavour's payload bay is open for payload configuration work in Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2. The orbiter is the vehicle designated for mission STS-118, scheduled to launch in late June. The mission will continue space station construction by delivering a third starboard truss segment, S5, as well as carrying the External Stowage Platform 3. The crew comprises six astronauts: Commander Scott Kelly, Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialists Dr. Dafydd (Dave) Williams, Barbara Morgan, Richard Mastracchio and Tracy Caldwell. Williams represents the Canadian Space Agency.

Workers painting the Flag and Meatball on the VAB.
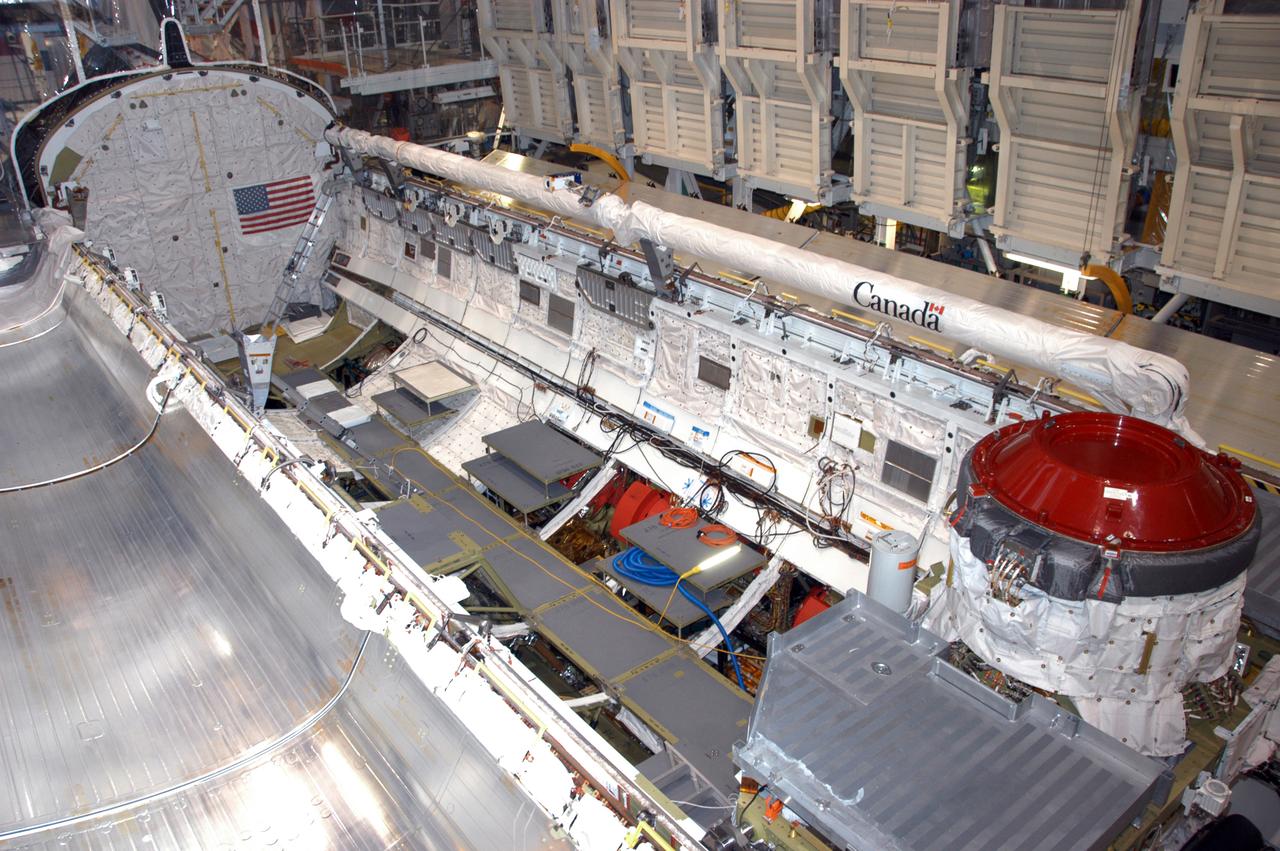
Endeavour's payload bay is open for payload configuration work in Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2. The orbiter is the vehicle designated for mission STS-118, scheduled to launch in late June. The mission will continue space station construction by delivering a third starboard truss segment, S5, as well as carrying the External Stowage Platform 3. The crew comprises six astronauts: Commander Scott Kelly, Pilot Charles Hobaugh and Mission Specialists Dr. Dafydd (Dave) Williams, Barbara Morgan, Richard Mastracchio and Tracy Caldwell. Williams represents the Canadian Space Agency.
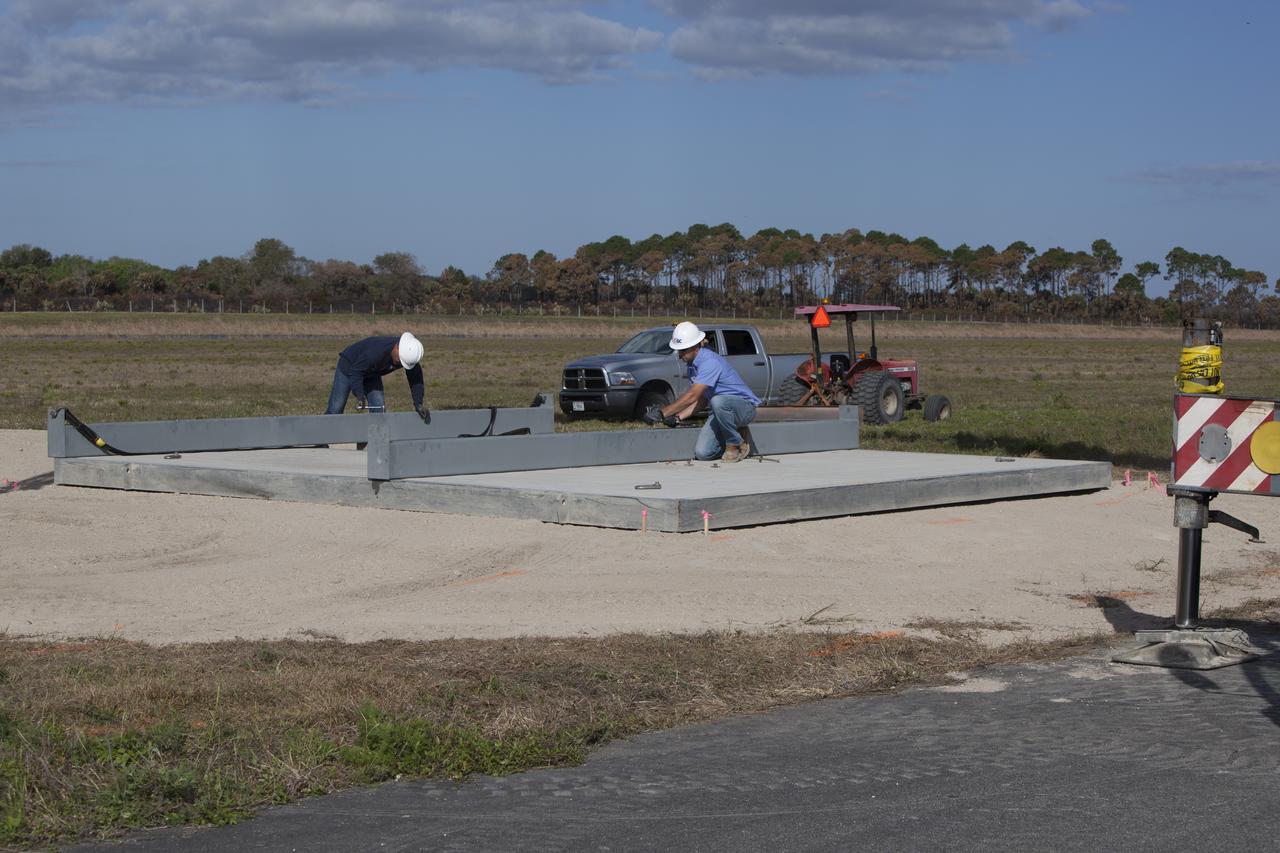

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction workers begin to reassemble the launch pad for the Project Morpheus prototype lander at a new location at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The launch pad was moved to a different location to support the next phase of flight testing. Morpheus completed its seventh free flight test on March 11. The 83-second test began at 3:41 p.m. EDT with the Morpheus lander launching from the ground over a flame trench and ascending to 580 feet. Morpheus then flew its fastest downrange trek at 30 mph, travelling farther than before, 837 feet. The lander performed a 42-foot divert to emulate a hazard avoidance maneuver before descending and touching down on Landing Site 2, at the northern landing pad inside the automated landing and hazard avoidance technology ALHAT hazard field. Morpheus landed within one foot of its intended target. Project Morpheus tests NASA’s ALHAT and an engine that runs on liquid oxygen and methane, or green propellants, into a fully-operational lander that could deliver cargo to other planetary surfaces. The landing facility provides the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus’ ALHAT payload allows it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is being managed under the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, Division in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. The efforts in AES pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
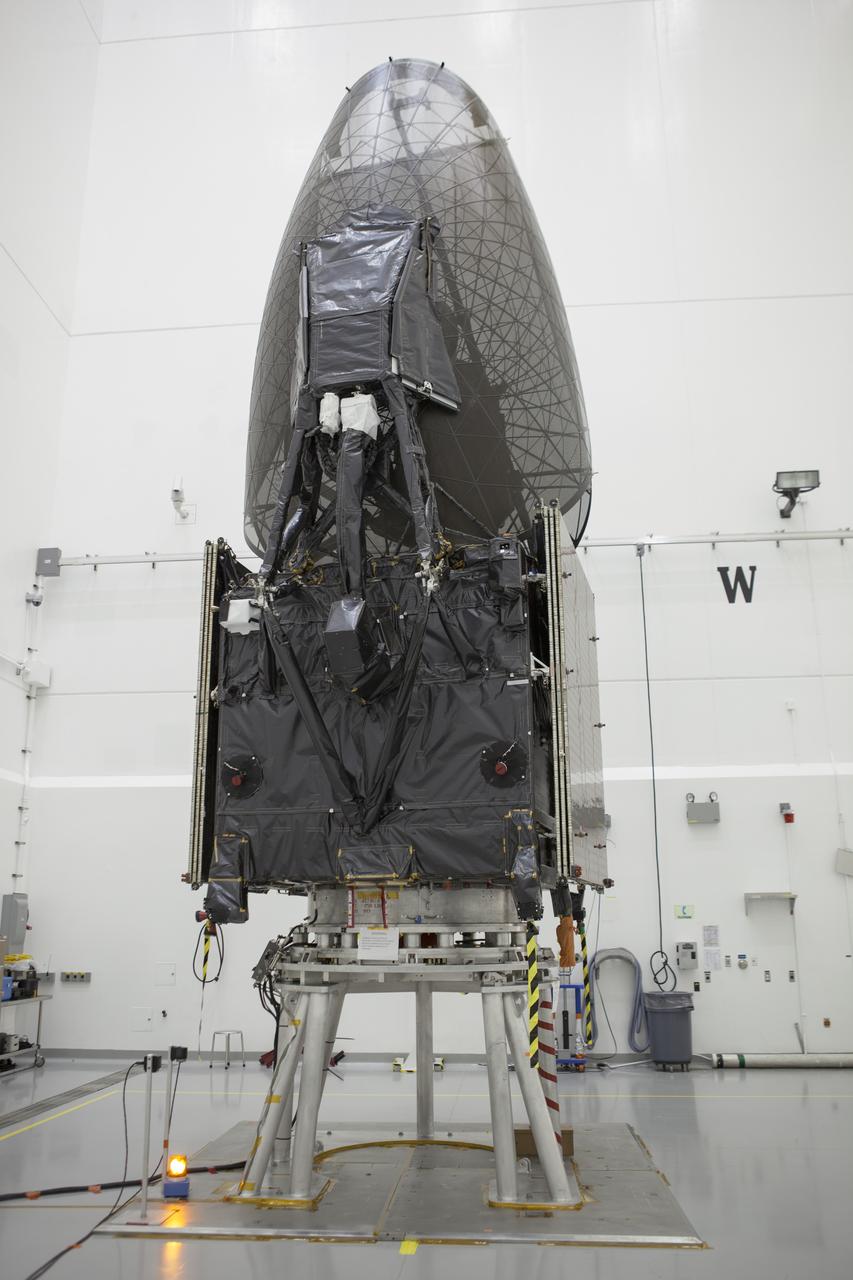

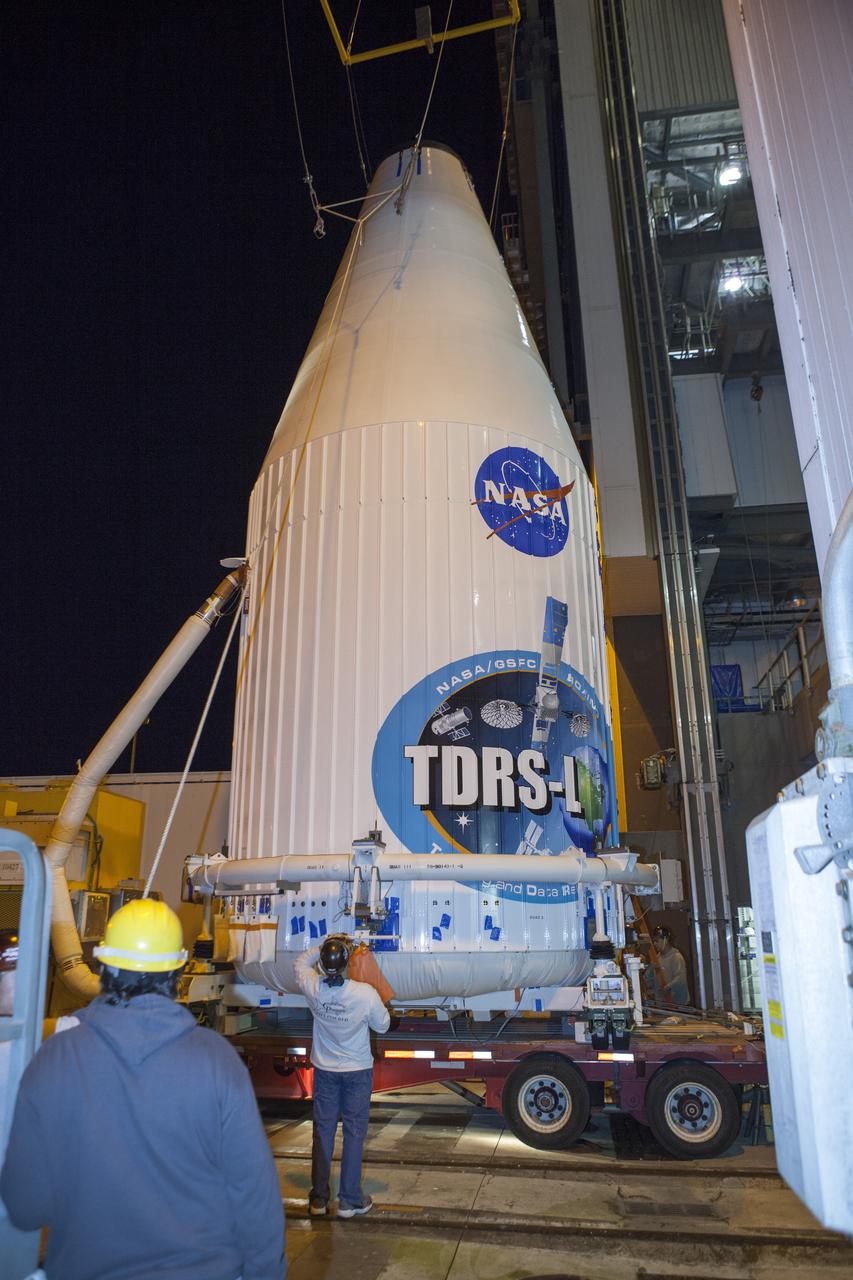
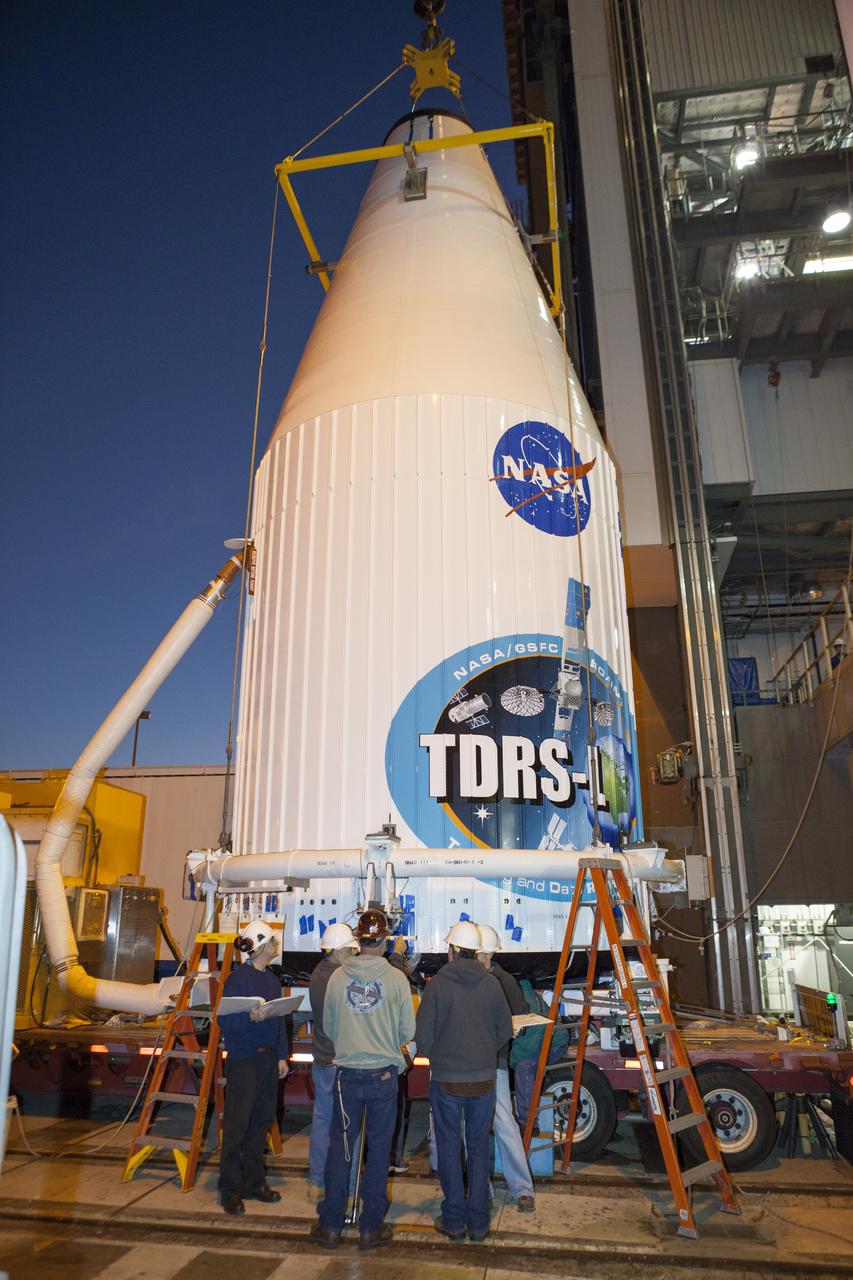
Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft is undergoing preflight processing.
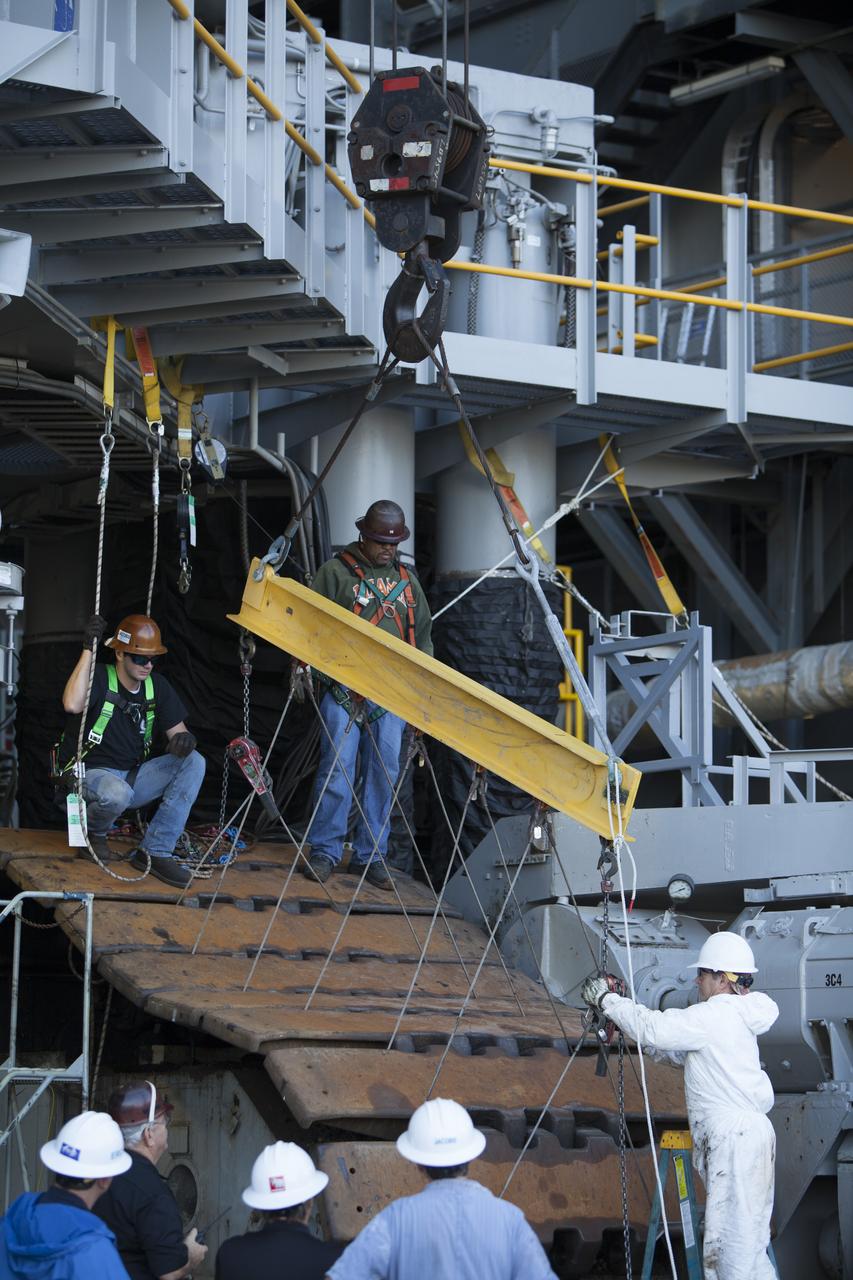

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, ground support technicians attach crane lines to the treads on the C truck of crawler-transporter 2, or CT-2, so they can be lifted up and away. The treads are being removed in order to gain access to remove the gear boxes. Work continues in high bay 2 to upgrade CT-2. The modifications are designed to ensure CT-2’s ability to transport launch vehicles currently in development, such as the agency’s Space Launch System, to the launch pad. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy is overseeing the upgrades. For more than 45 years the crawler-transporters were used to transport the mobile launcher platform and the Apollo-Saturn V rockets and, later, space shuttles to Launch Pads 39A and B. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/crawler-transporter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
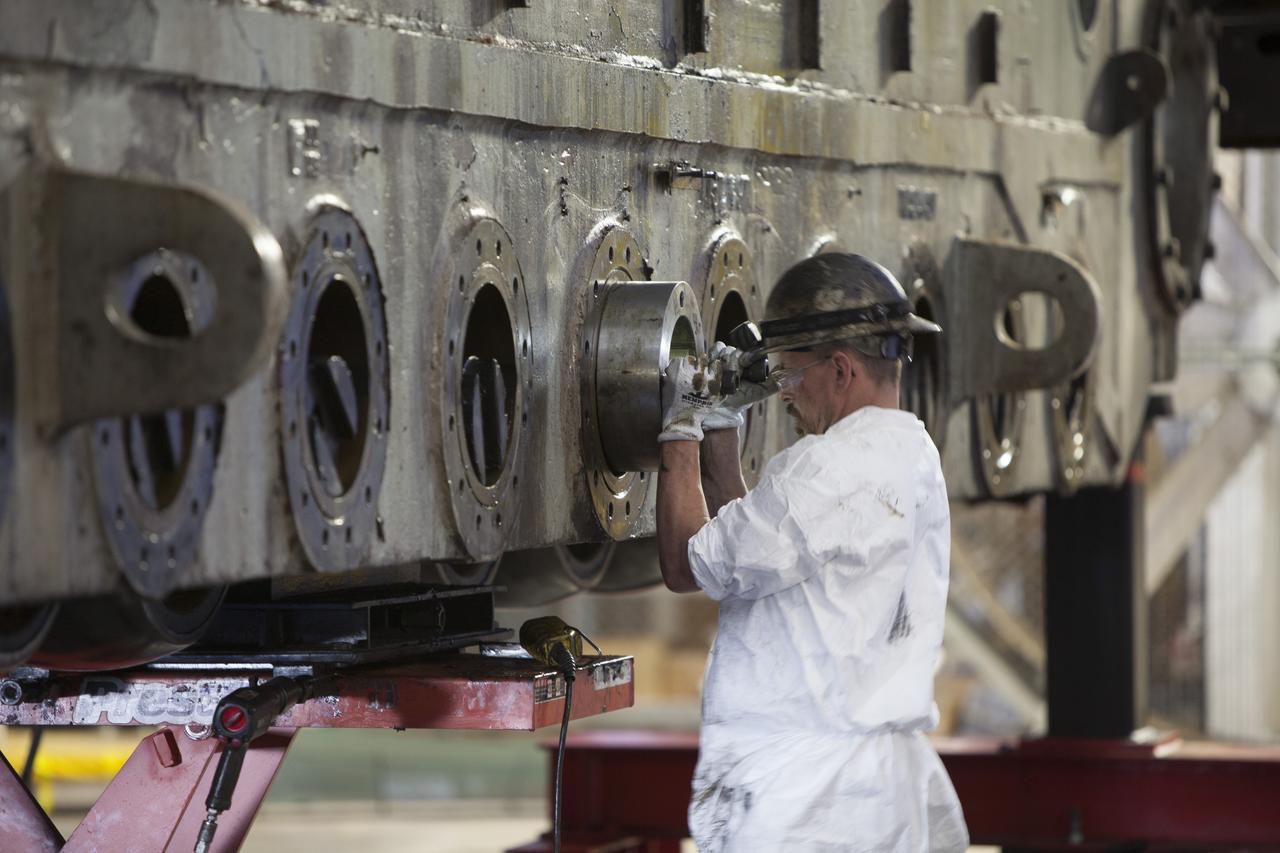

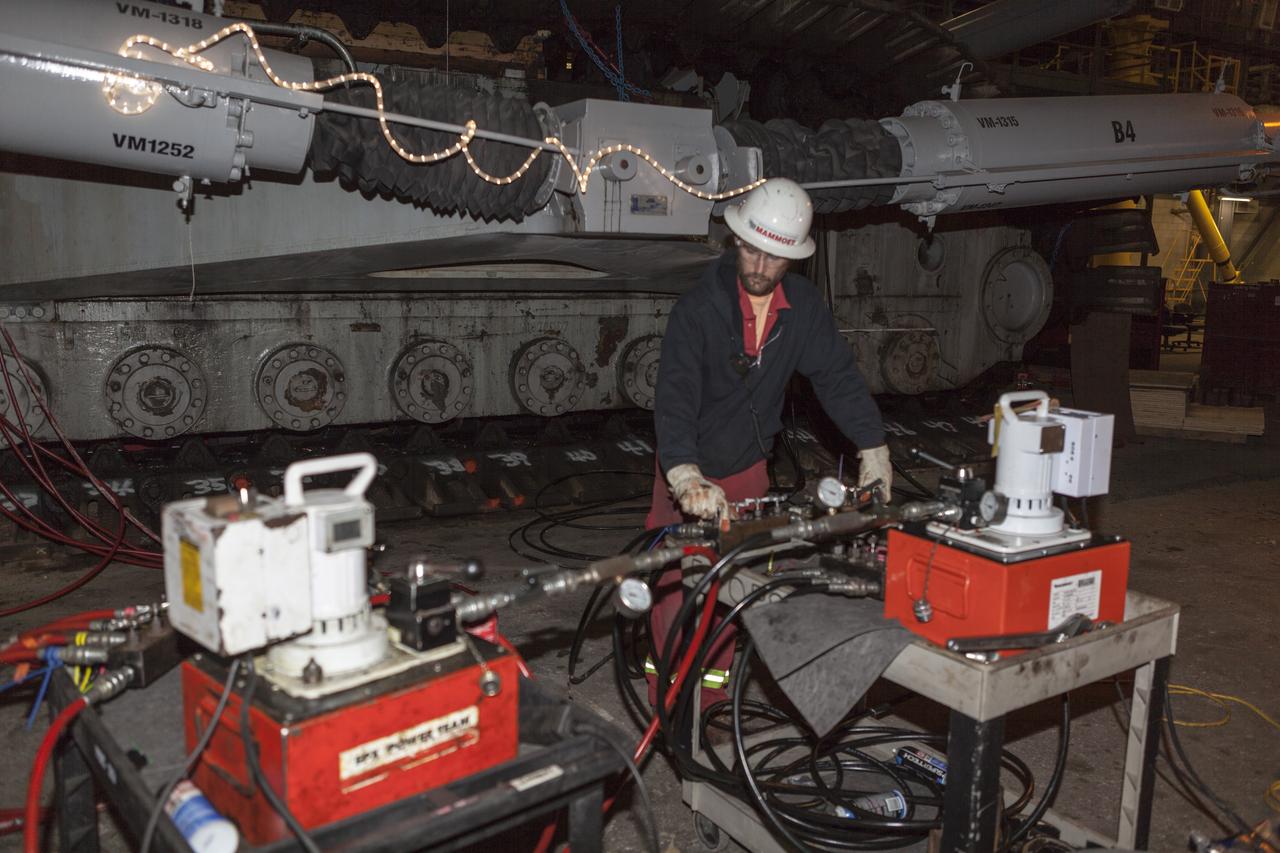
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a ground support technician assists with removal of a bearing from the B truck tread of crawler-transporter 2, or CT-2. New roller bearing assemblies will be installed. Work continues in high bay 2 to upgrade CT-2. The modifications are designed to ensure CT-2’s ability to transport launch vehicles currently in development, such as the agency’s Space Launch System, to the launch pad. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy is overseeing the upgrades. For more than 45 years the crawler-transporters were used to transport the mobile launcher platform and the Apollo-Saturn V rockets and, later, space shuttles to Launch Pads 39A and B. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/crawler-transporter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
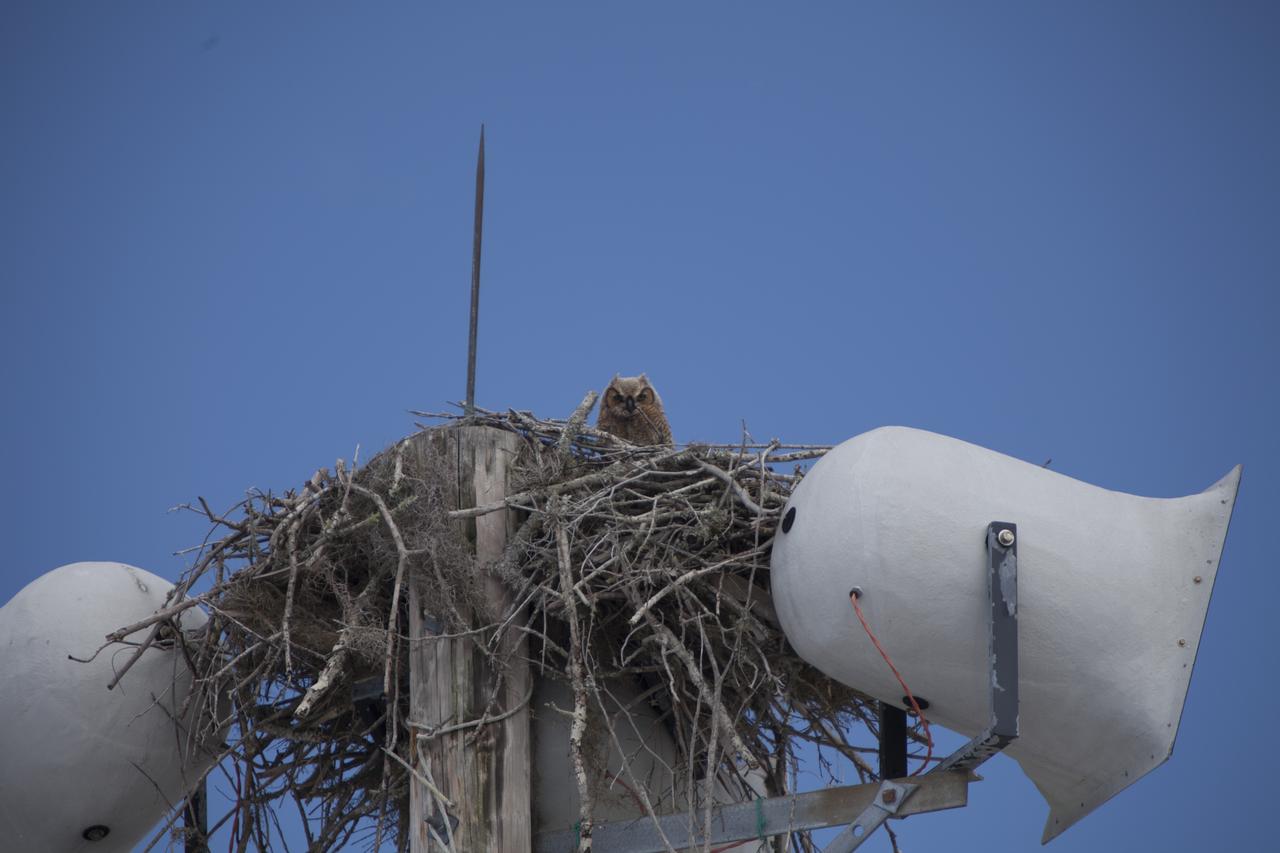

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an Owl occupies a nest originally build by an Osprey atop a loudspeaker utility pole. Kennedy Space Center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. The Refuge encompasses 140,000 acres that are a habitat for more than 331 species of birds, 31 mammals, 117 fishes, and 65 amphibians and reptiles. The marshes and open water of the refuge provide wintering areas for 23 species of migratory waterfowl, as well as a year-round home for great blue herons, great egrets, wood storks, cormorants, brown pelicans and other species of marsh and shore birds, as well as a variety of insects. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/shuttleoperations/alligators/kscovr.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Members of the news media are given an up-close look at the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft undergoing preflight processing inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville. TDRS-L is being prepared for encapsulation inside its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
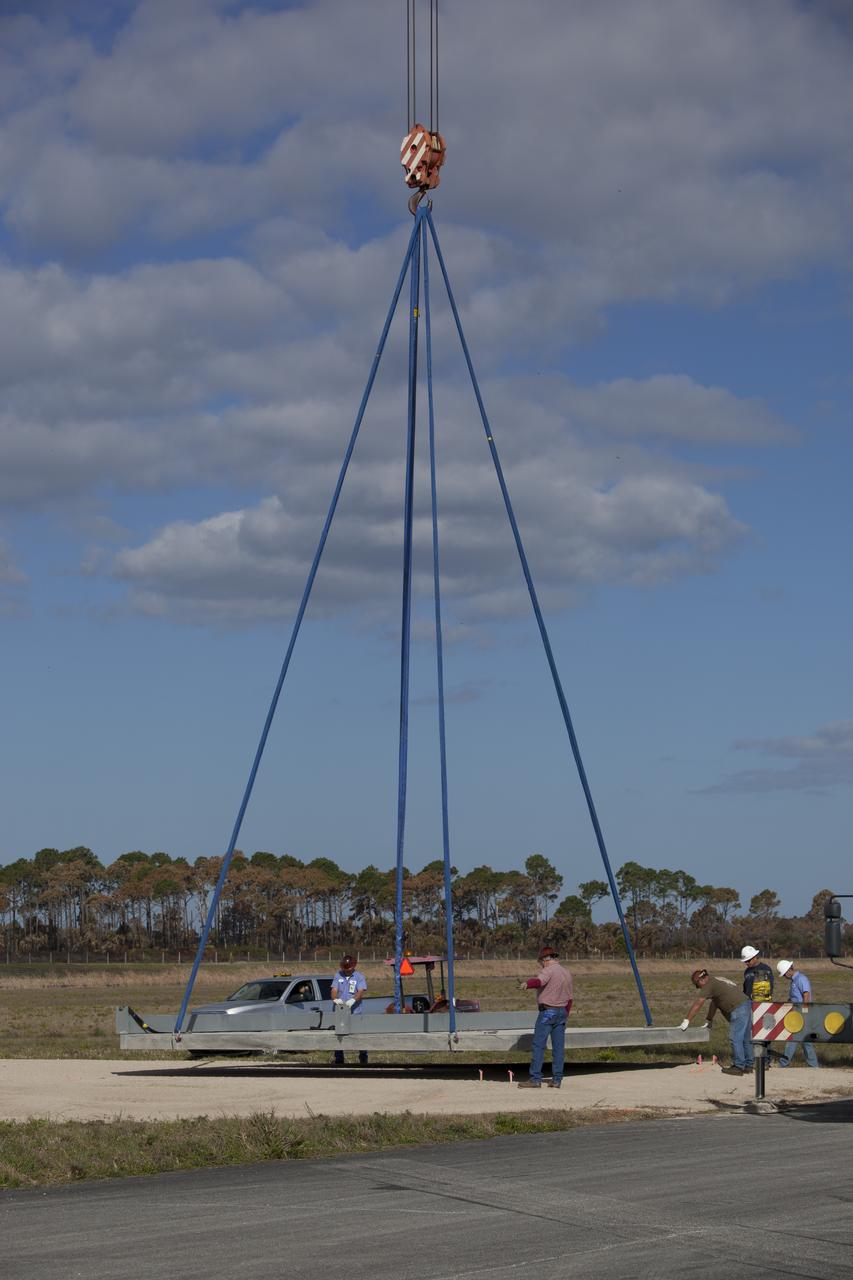

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A crane is used to lower the launch pad for the Project Morpheus prototype lander onto a new location at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The launch pad was moved to a different location to support the next phase of flight testing. Morpheus completed its seventh free flight test on March 11. The 83-second test began at 3:41 p.m. EDT with the Morpheus lander launching from the ground over a flame trench and ascending to 580 feet. Morpheus then flew its fastest downrange trek at 30 mph, travelling farther than before, 837 feet. The lander performed a 42-foot divert to emulate a hazard avoidance maneuver before descending and touching down on Landing Site 2, at the northern landing pad inside the automated landing and hazard avoidance technology ALHAT hazard field. Morpheus landed within one foot of its intended target. Project Morpheus tests NASA’s ALHAT and an engine that runs on liquid oxygen and methane, or green propellants, into a fully-operational lander that could deliver cargo to other planetary surfaces. The landing facility provides the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus’ ALHAT payload allows it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is being managed under the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, Division in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. The efforts in AES pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
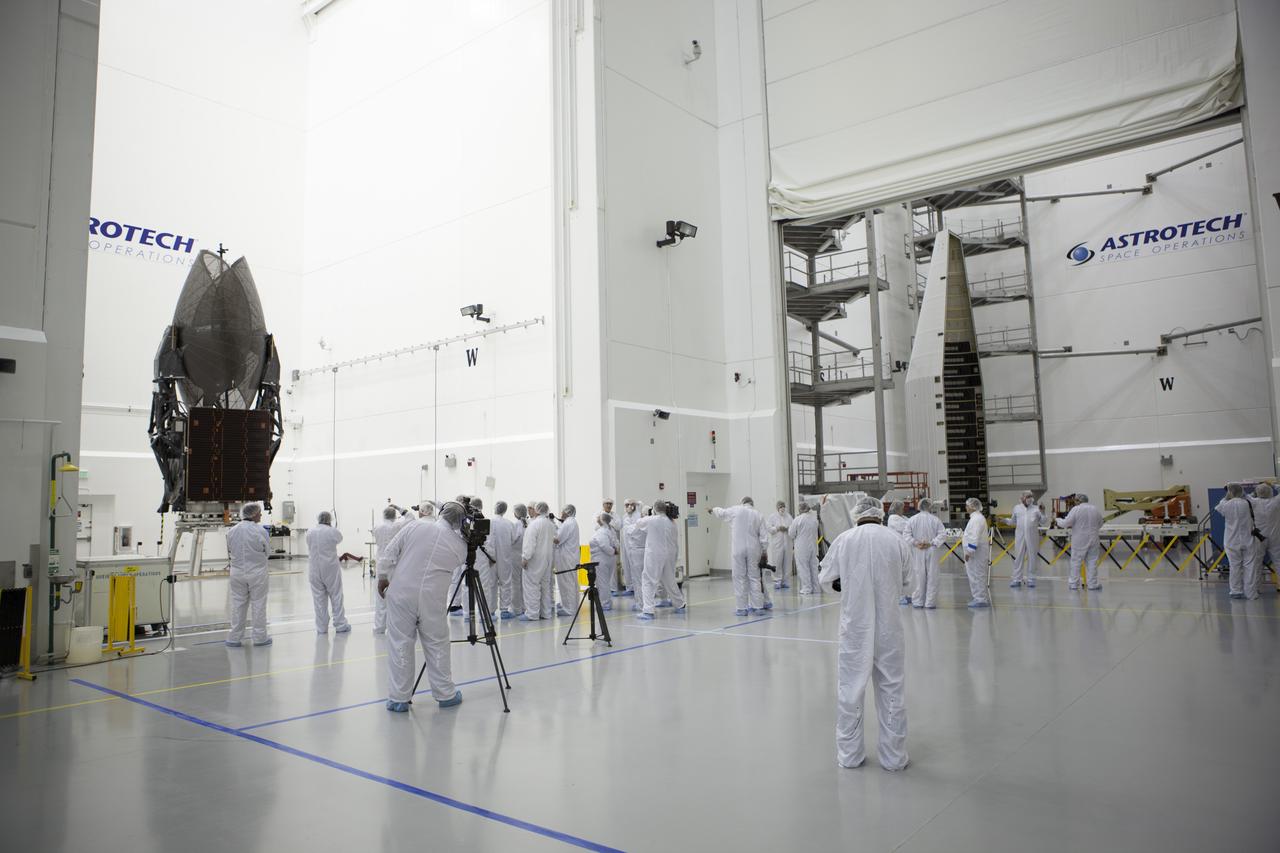

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Members of the news media are given an up-close look at the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft undergoing preflight processing inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville. TDRS-L is being prepared for encapsulation inside its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
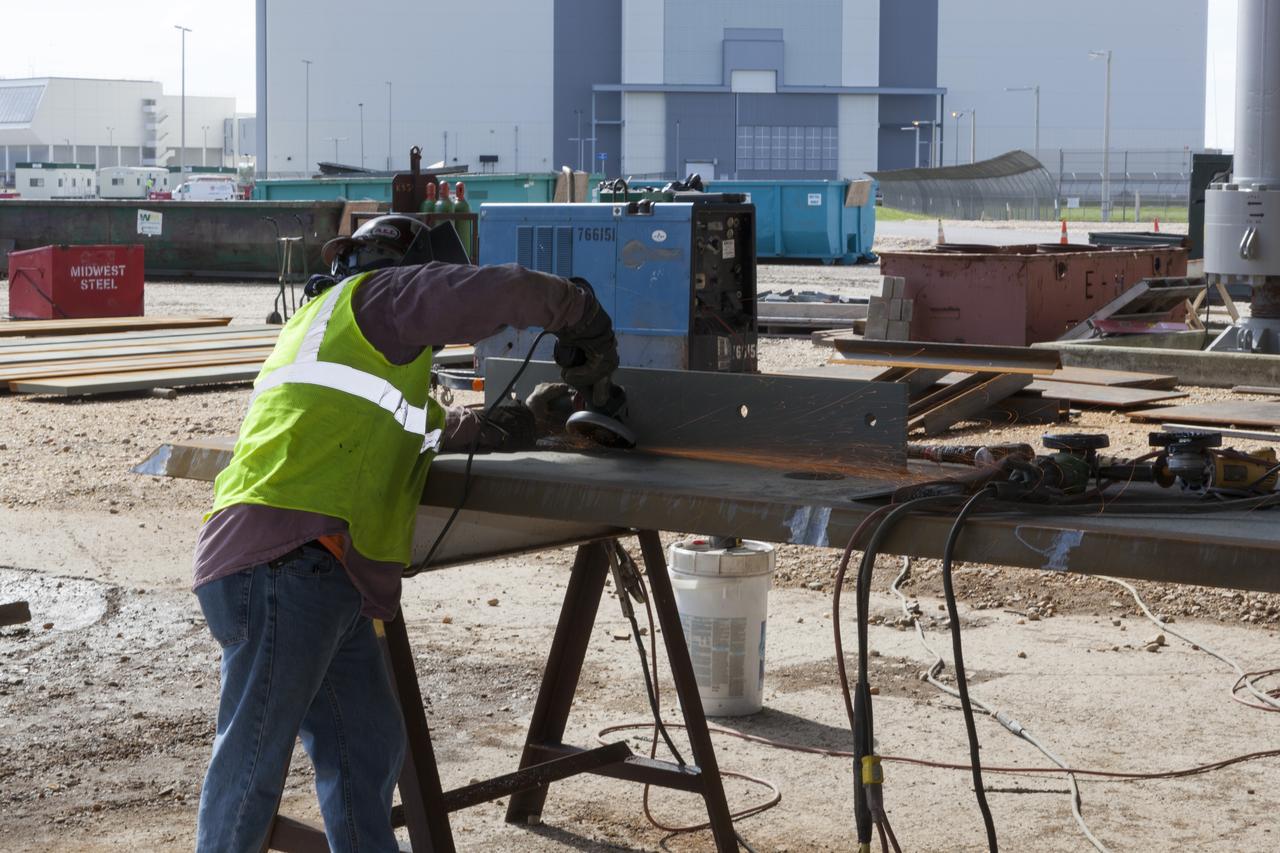

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Modifications continue on the Mobile Launcher, or ML, at the Mobile Launcher Park Site at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A construction worker prepares a metal beam that will be attached to the ML. In 2013, the agency awarded a contract to J.P. Donovan Construction Inc. of Rockledge, Fla., to modify the ML, which is one of the key elements of ground support equipment that is being upgraded by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy. The ML will carry the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft to Launch Pad 39B for its first mission, Exploration Mission 1, in 2017. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
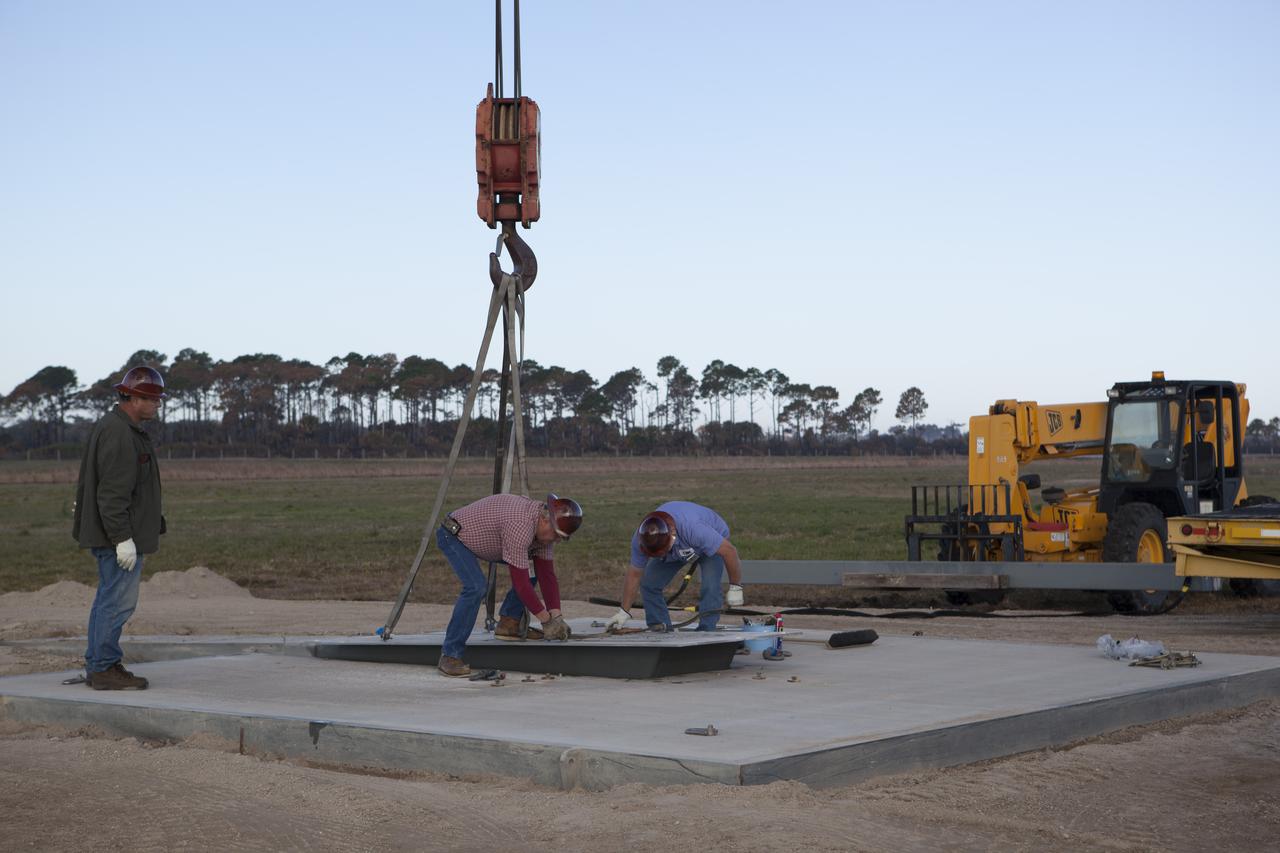

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction workers attach a crane to part of the launch pad for the Project Morpheus prototype lander at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The launch pad will be moved to a different location at the landing facility to support the next phase of flight testing. The seventh free flight test of Morpheus occurred on March 11. The 83-second test began at 3:41 p.m. EDT with the Morpheus lander launching from the ground over a flame trench and ascending to 580 feet. Morpheus then flew its fastest downrange trek at 30 mph, travelling farther than before, 837 feet. The lander performed a 42-foot divert to emulate a hazard avoidance maneuver before descending and touching down on Landing Site 2, at the northern landing pad inside the automated landing and hazard avoidance technology ALHAT hazard field. Morpheus landed within one foot of its intended target. Project Morpheus tests NASA’s ALHAT and an engine that runs on liquid oxygen and methane, or green propellants, into a fully-operational lander that could deliver cargo to other planetary surfaces. The landing facility provides the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus’ ALHAT payload allows it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is being managed under the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, Division in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. The efforts in AES pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41, engineers and technicians prepare to lift NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft for mounting atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Jan. 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

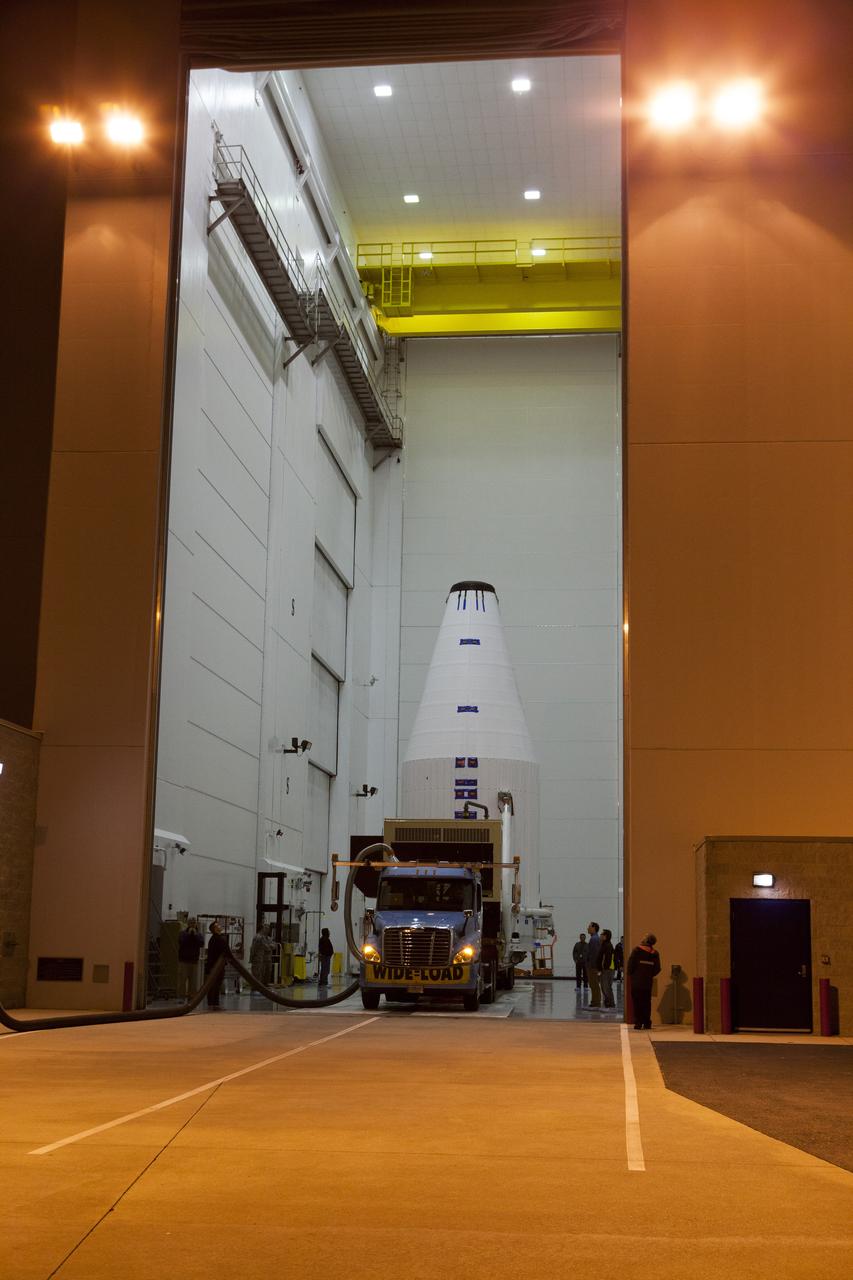
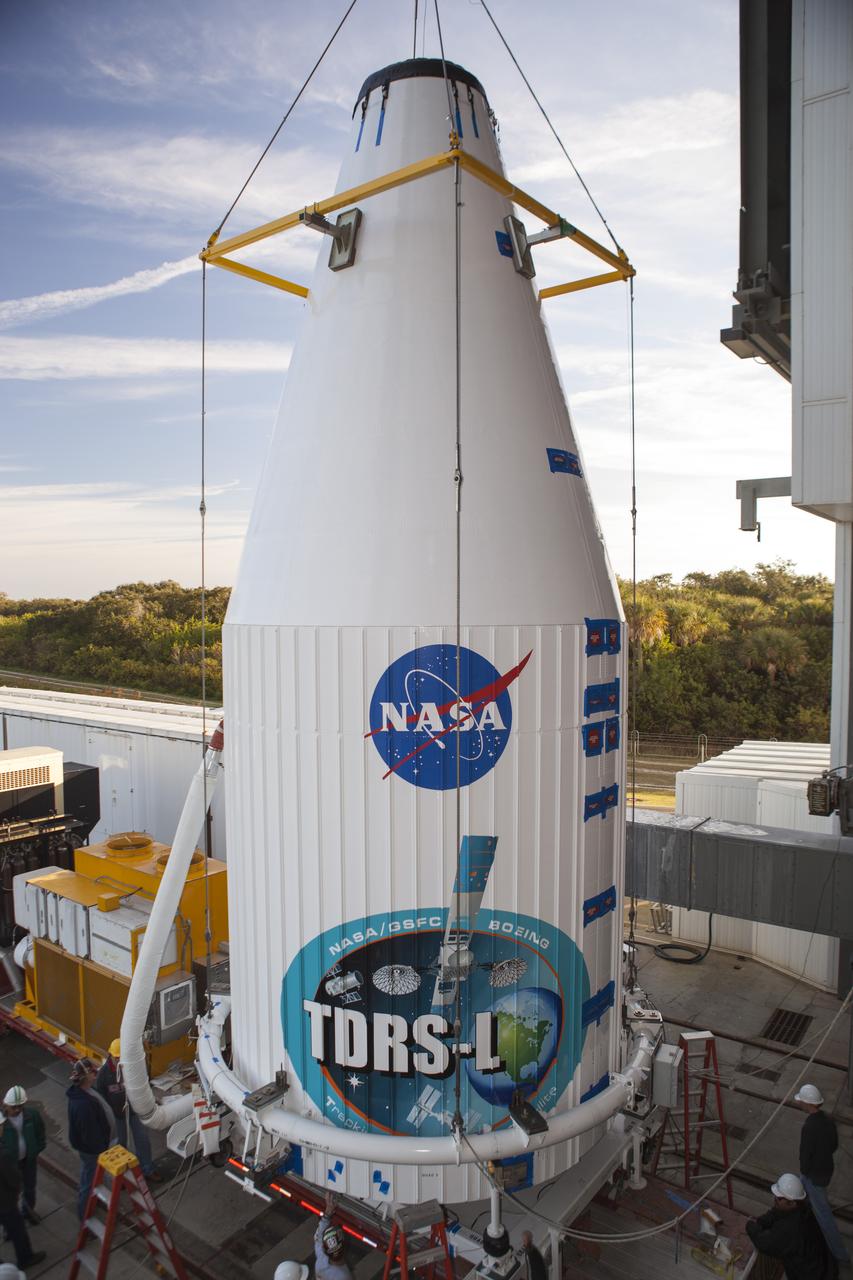
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft has been mounted on a transporter for its trip from the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
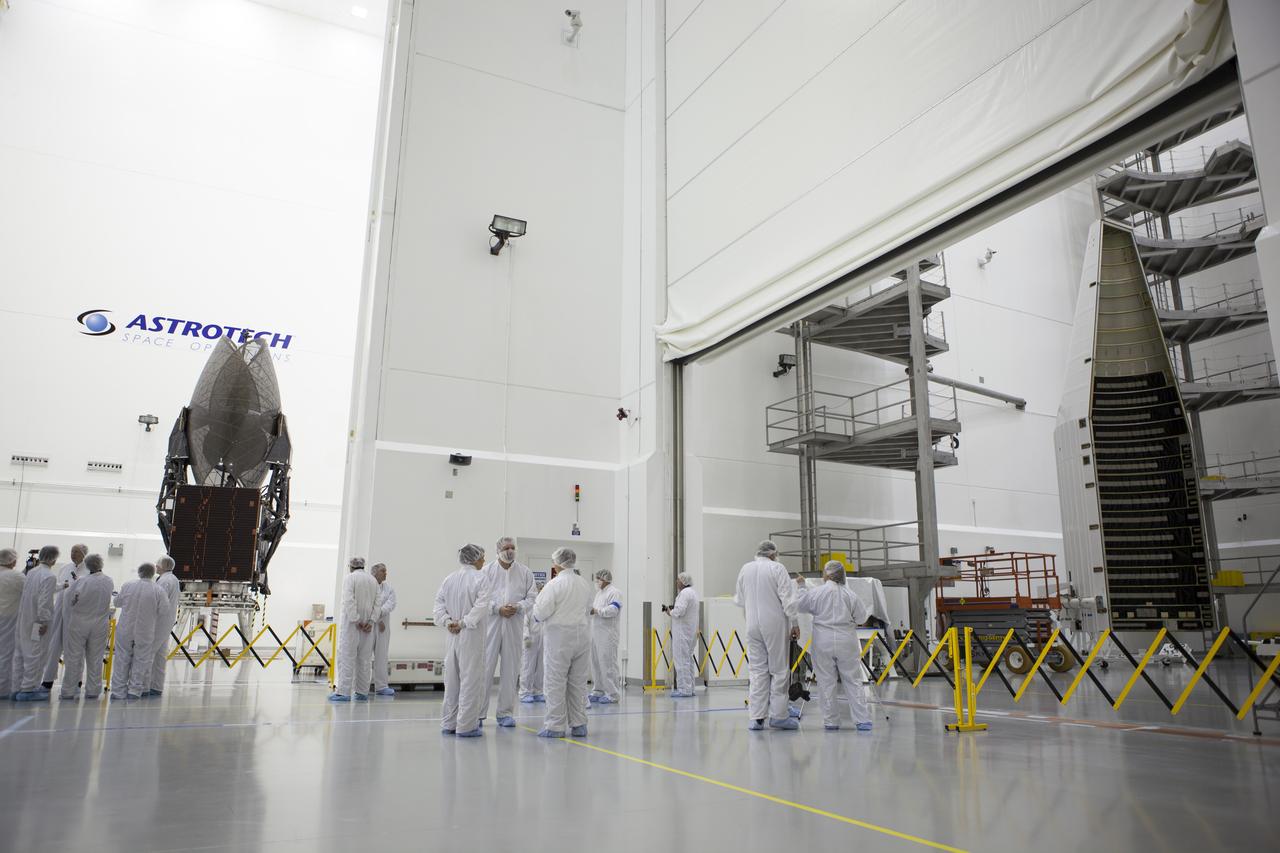

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Members of the news media are given an up-close look at the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft undergoing preflight processing inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville. TDRS-L is being prepared for encapsulation inside its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
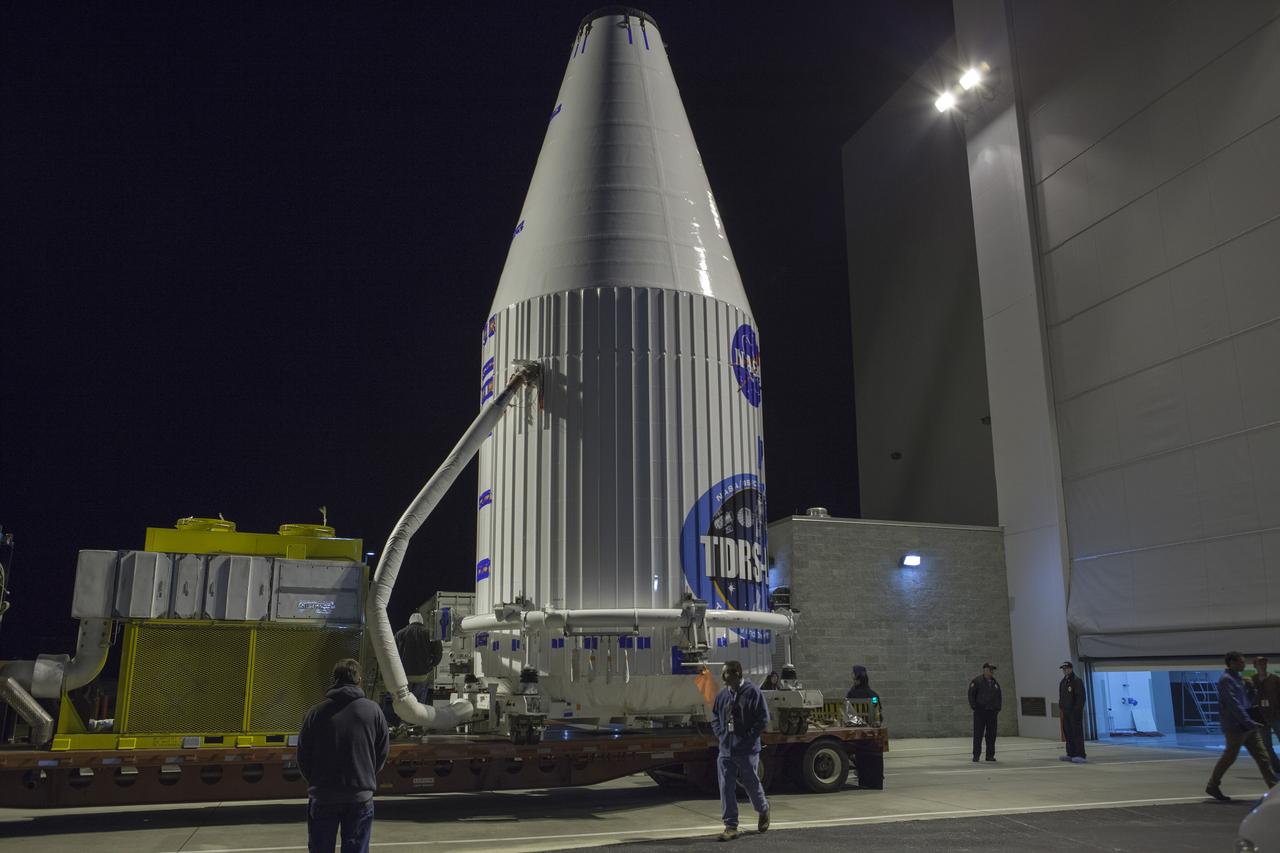

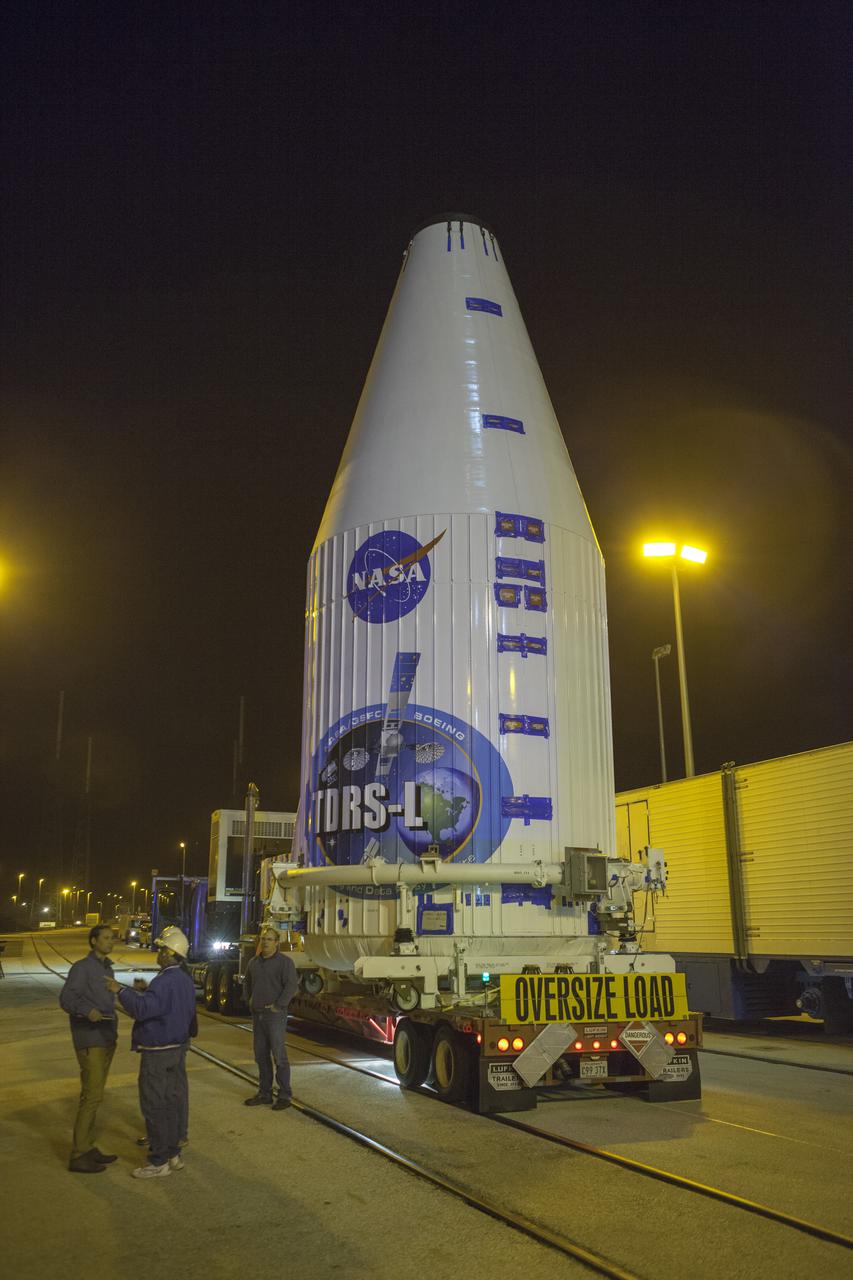
TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft begins it trip from the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
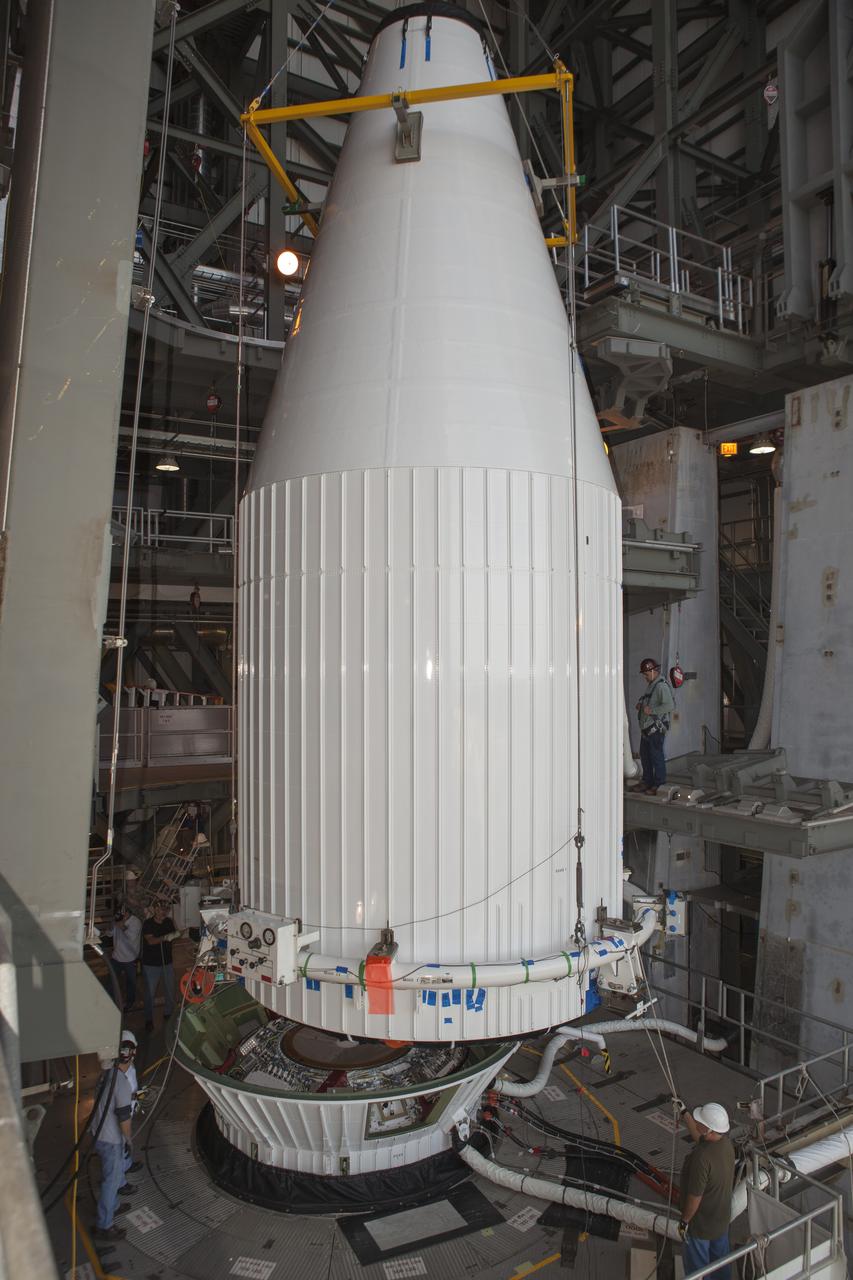

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft is moved into position for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Jan. 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
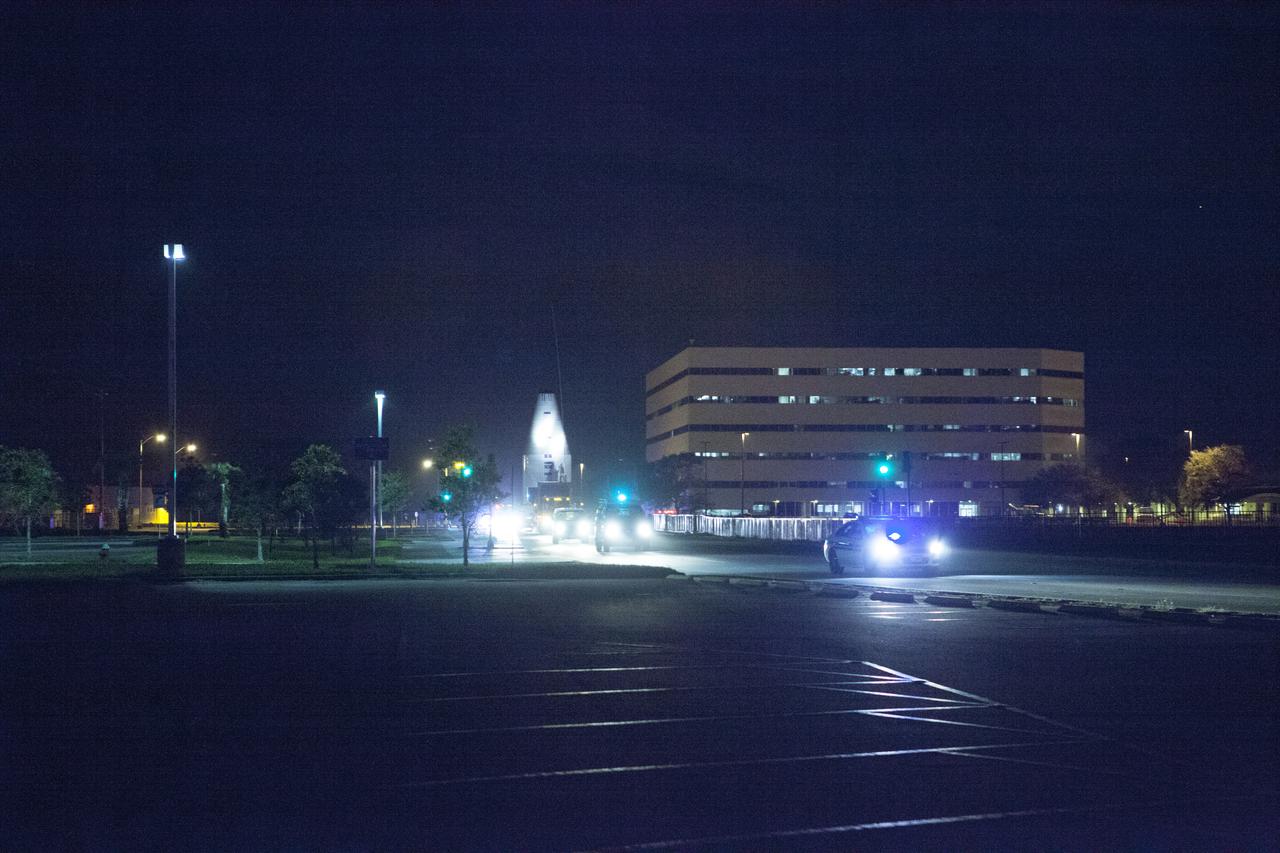

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft is transported along the Saturn Causeway at the Kennedy Space Center on its way to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
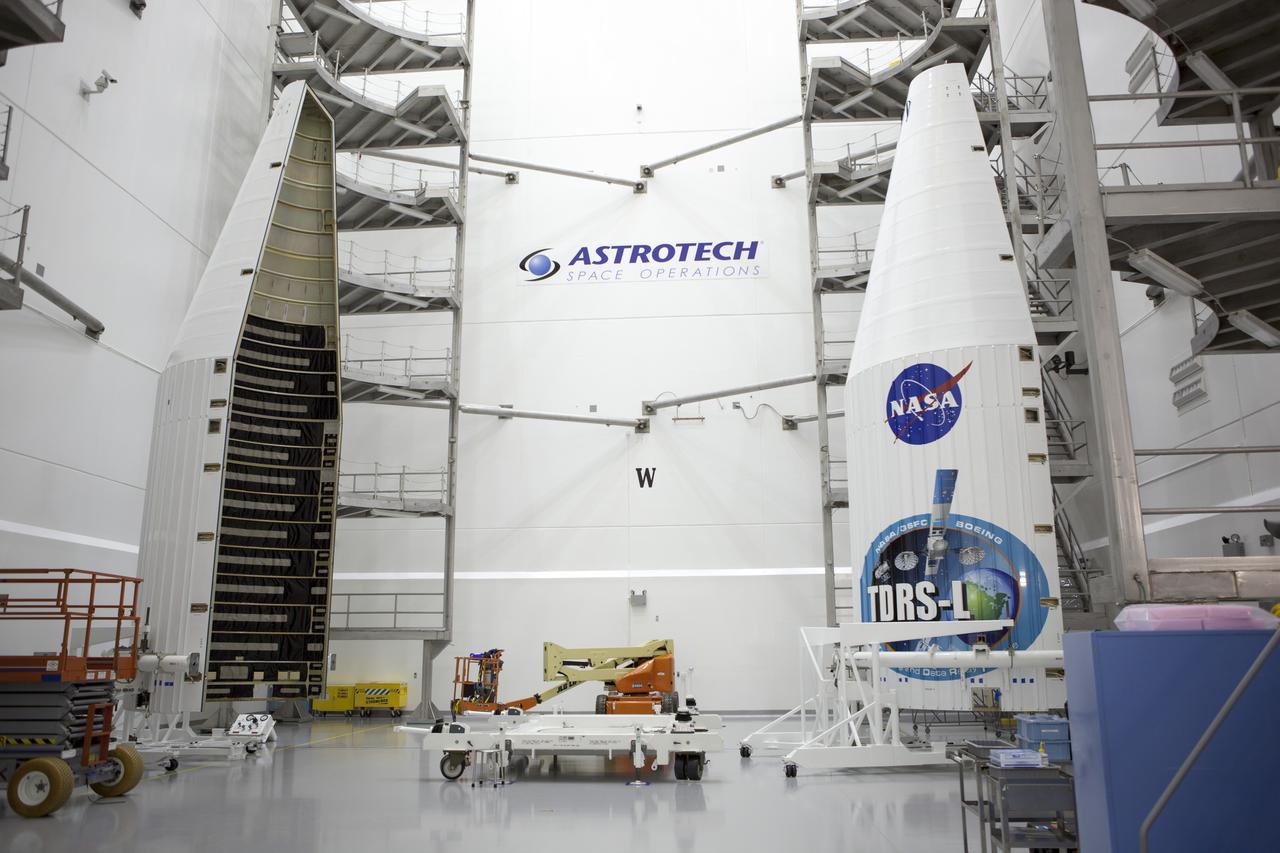

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, members of the news media are given an opportunity for an up-close look at the payload fairing that will encapsulate the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
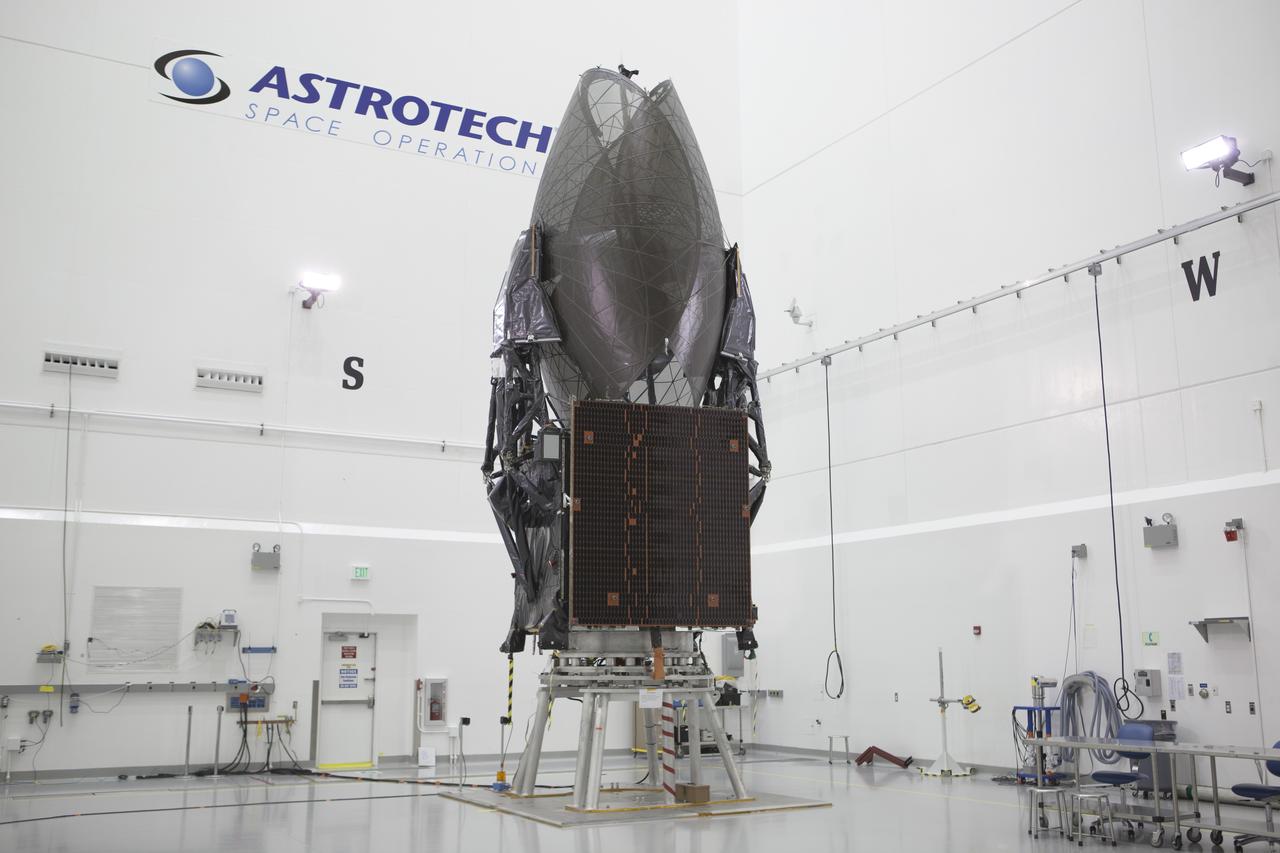

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Members of the news media are given an opportunity for an up-close look at the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft undergoing preflight processing inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville. TDRS-L is being prepared for encapsulation inside its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
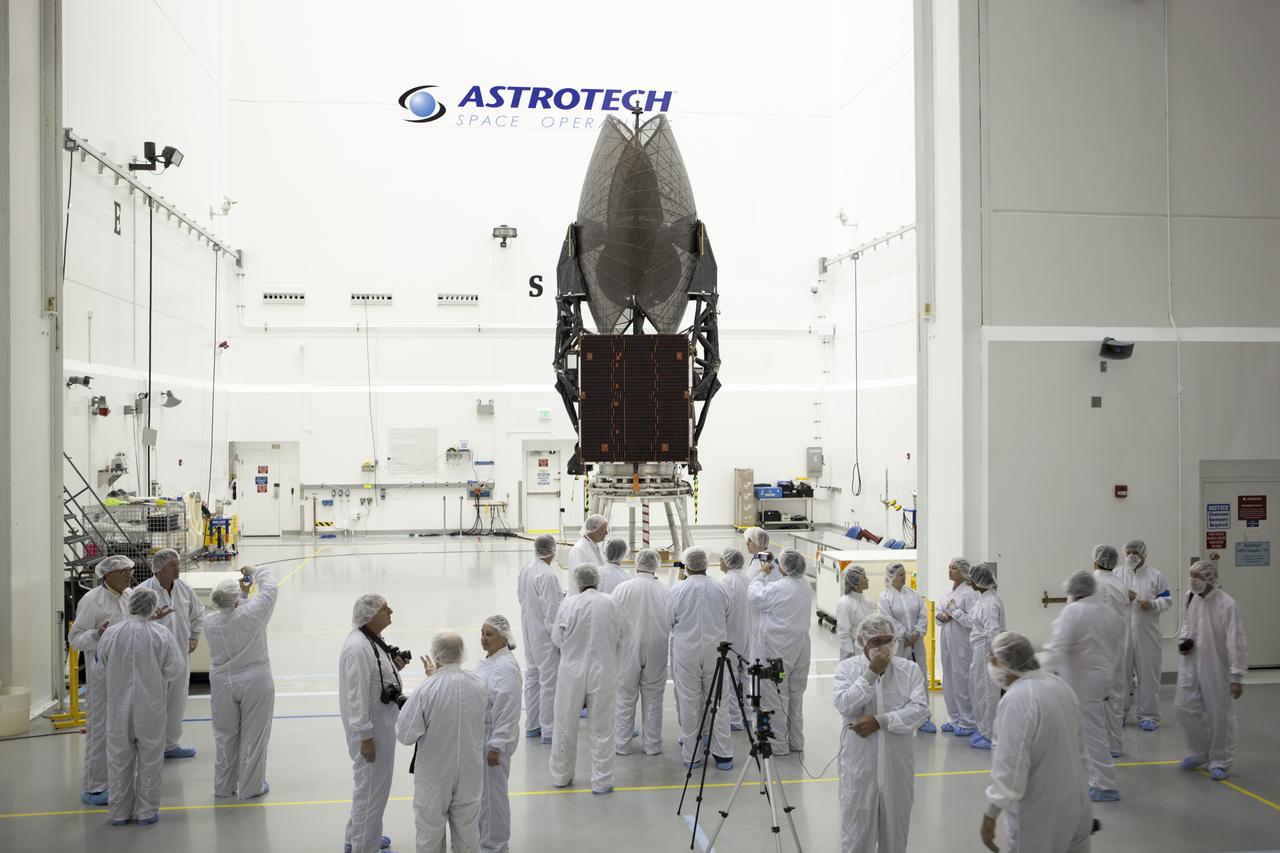

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Members of the news media are given an up-close look at the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft undergoing preflight processing inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville. TDRS-L is being prepared for encapsulation inside its payload fairing prior to being transported to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Journalists visited Astrotech as part of TDRS-L Media Day to conduct interviews and photograph the satellite that will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop an Atlas V rocket in January 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html
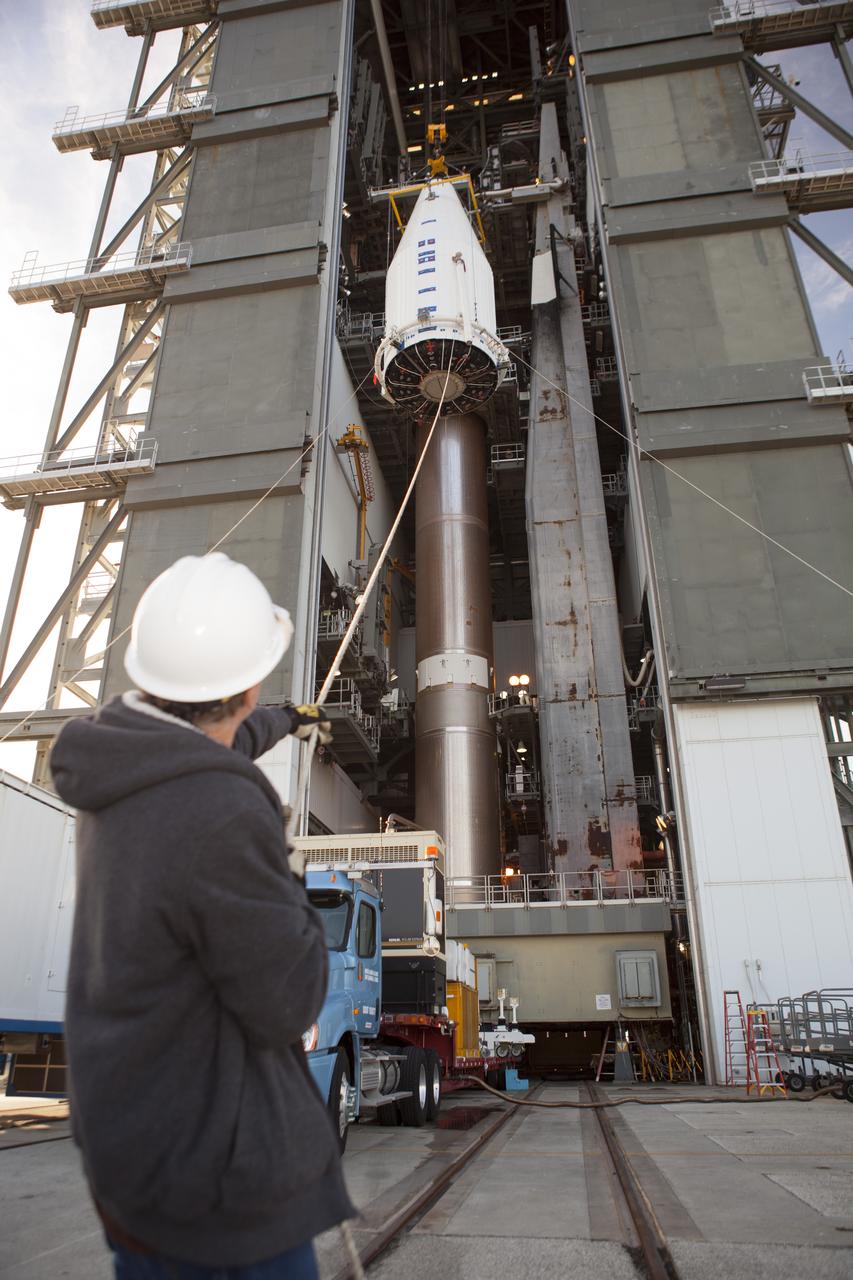

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41, a technician uses a support line to steady NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft as it is lifted for mounting atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Jan. 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
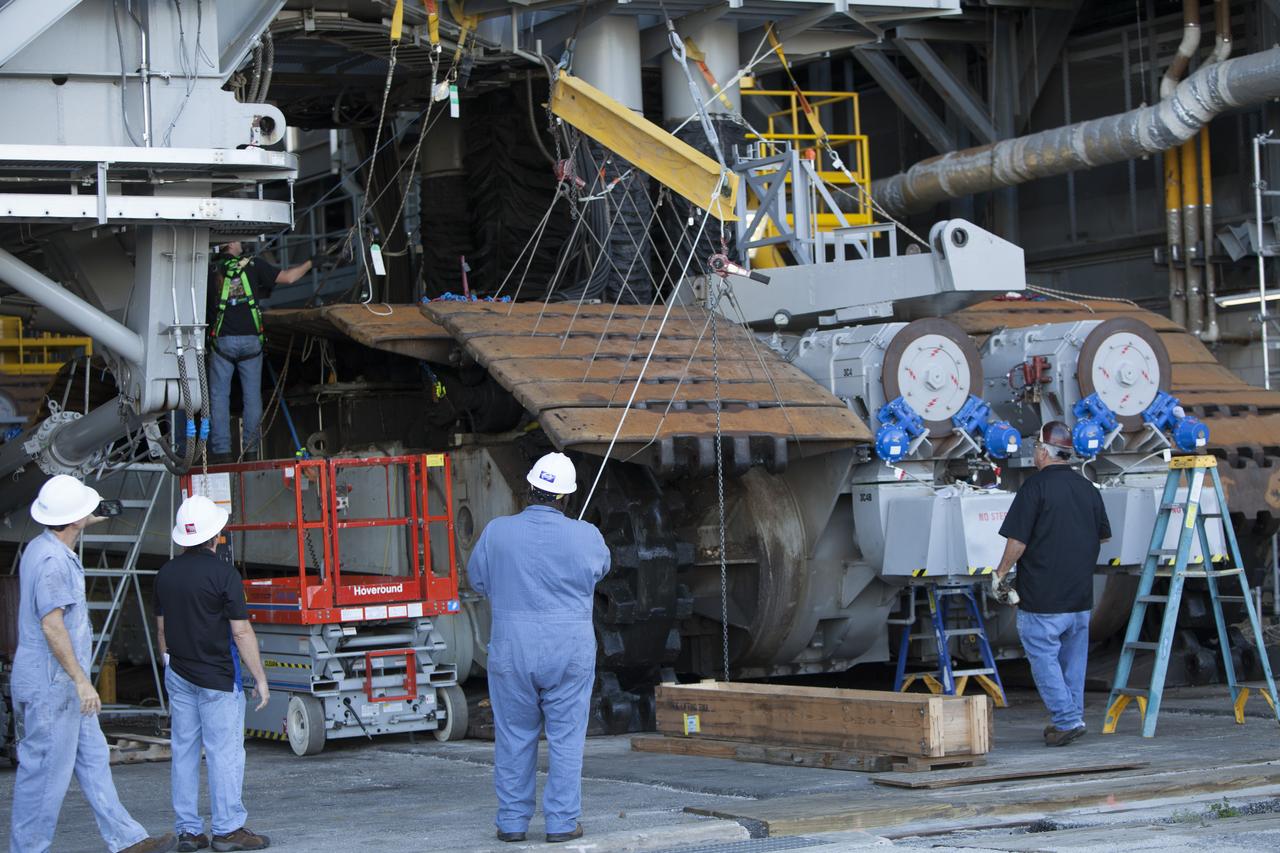

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, ground support technicians have attached crane lines to a portion of the treads on the C truck of crawler-transporter 2, or CT-2, so they can be lifted up and away. The treads are being removed in order to gain access to remove the gear boxes. Work continues in high bay 2 to upgrade CT-2. The modifications are designed to ensure CT-2’s ability to transport launch vehicles currently in development, such as the agency’s Space Launch System, to the launch pad. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy is overseeing the upgrades. For more than 45 years the crawler-transporters were used to transport the mobile launcher platform and the Apollo-Saturn V rockets and, later, space shuttles to Launch Pads 39A and B. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/crawler-transporter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
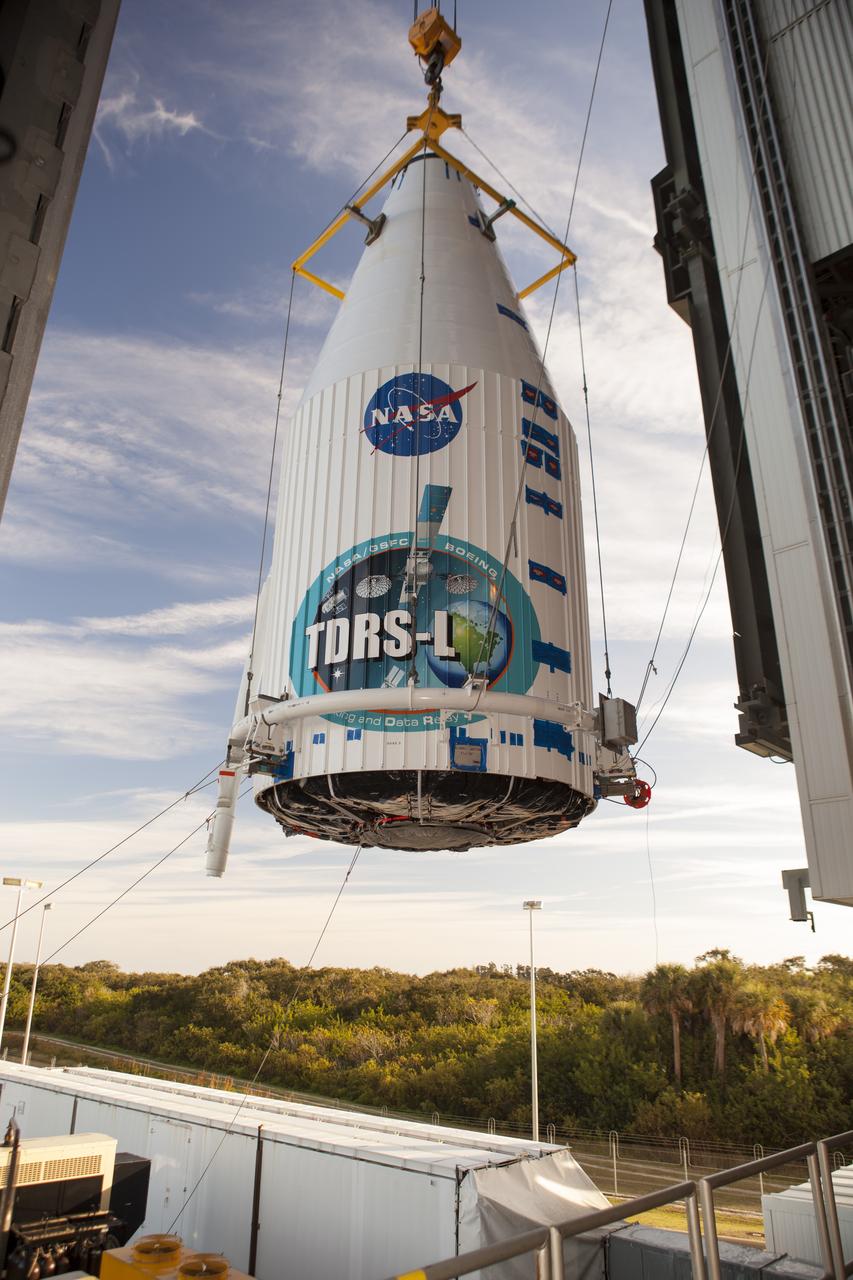

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41, engineers and technicians begin lifting NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft for mounting atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Jan. 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41, engineers and technicians begin lifting NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft for mounting atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Jan. 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the B and D truck sections of crawler-transporter 2, or CT-2, are being raised up to prepare for installation of new roller bearing assemblies. Work continues in high bay 2 to upgrade CT-2. The modifications are designed to ensure CT-2’s ability to transport launch vehicles currently in development, such as the agency’s Space Launch System, to the launch pad. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy is overseeing the upgrades. For more than 45 years the crawler-transporters were used to transport the mobile launcher platform and the Apollo-Saturn V rockets and, later, space shuttles to Launch Pads 39A and B. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/crawler-transporter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
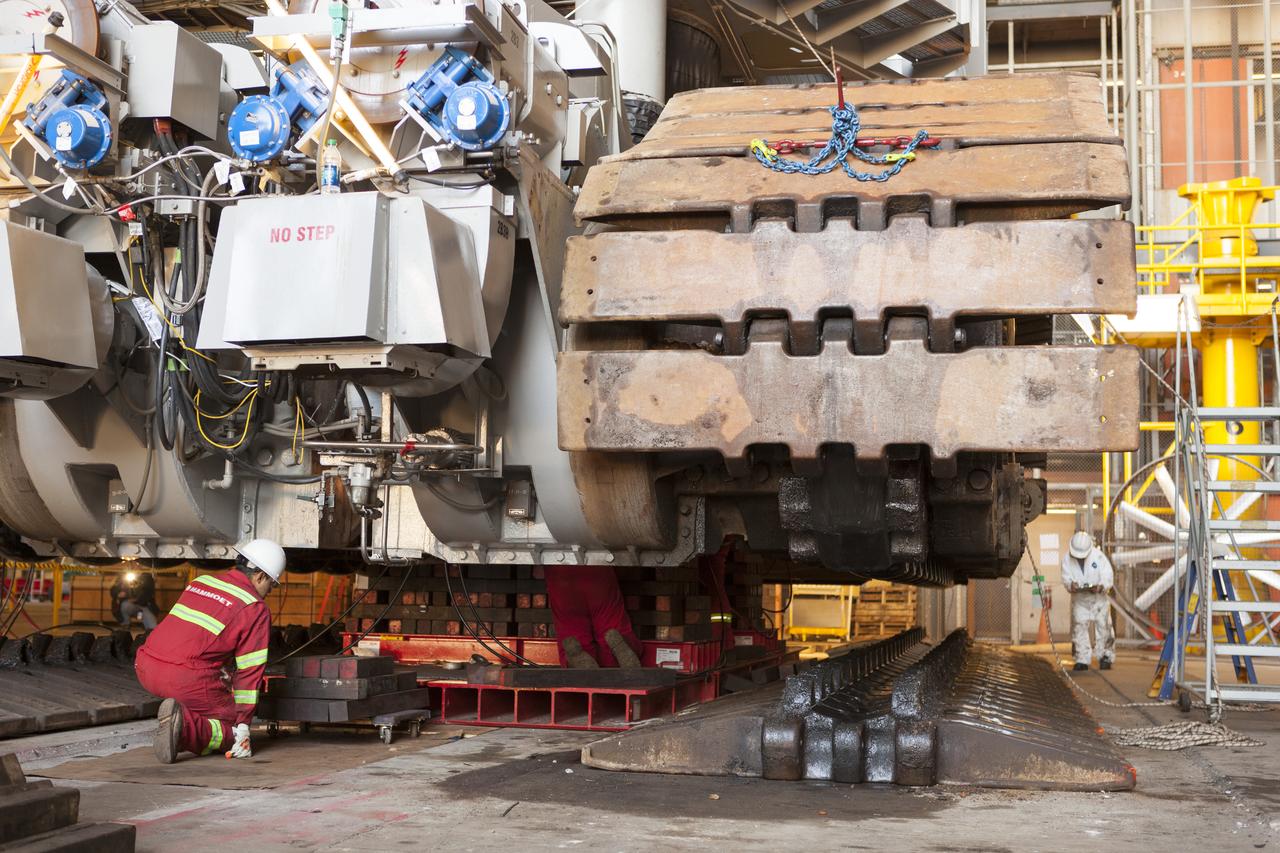

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, ground support technicians monitor the progress as the B and D truck sections of crawler-transporter 2, or CT-2, are being raised up to prepare for installation of new roller bearing assemblies. Sections of the crawler’s large metal tracks have been removed. Work continues in high bay 2 to upgrade CT-2. The modifications are designed to ensure CT-2’s ability to transport launch vehicles currently in development, such as the agency’s Space Launch System, to the launch pad. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy is overseeing the upgrades. For more than 45 years the crawler-transporters were used to transport the mobile launcher platform and the Apollo-Saturn V rockets and, later, space shuttles to Launch Pads 39A and B. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/crawler-transporter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
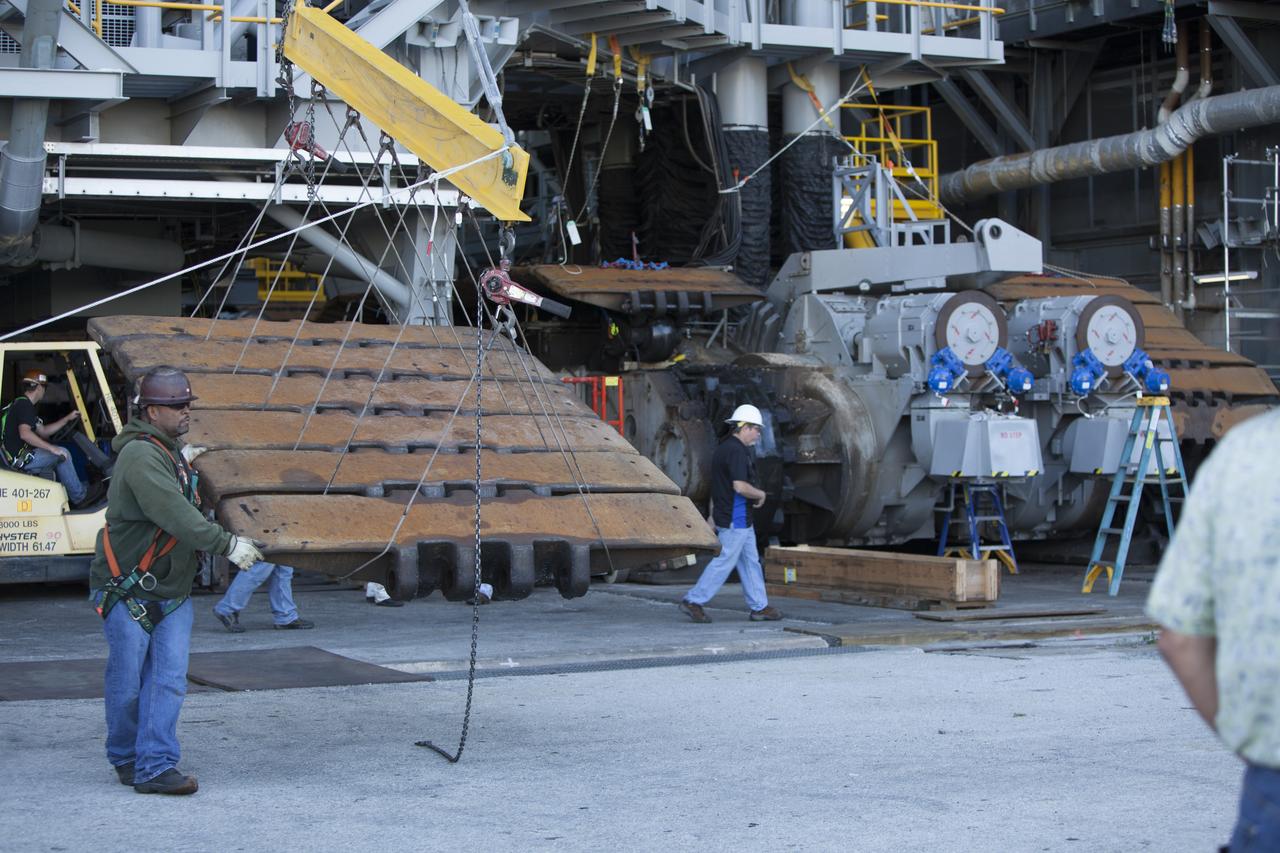

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, ground support technicians assist as a crane lifts a portion of the treads on the C truck of crawler-transporter 2, or CT-2, away from the vehicle. The treads are being removed in order to gain access to remove the gear boxes. Work continues in high bay 2 to upgrade CT-2. The modifications are designed to ensure CT-2’s ability to transport launch vehicles currently in development, such as the agency’s Space Launch System, to the launch pad. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy is overseeing the upgrades. For more than 45 years the crawler-transporters were used to transport the mobile launcher platform and the Apollo-Saturn V rockets and, later, space shuttles to Launch Pads 39A and B. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/crawler-transporter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
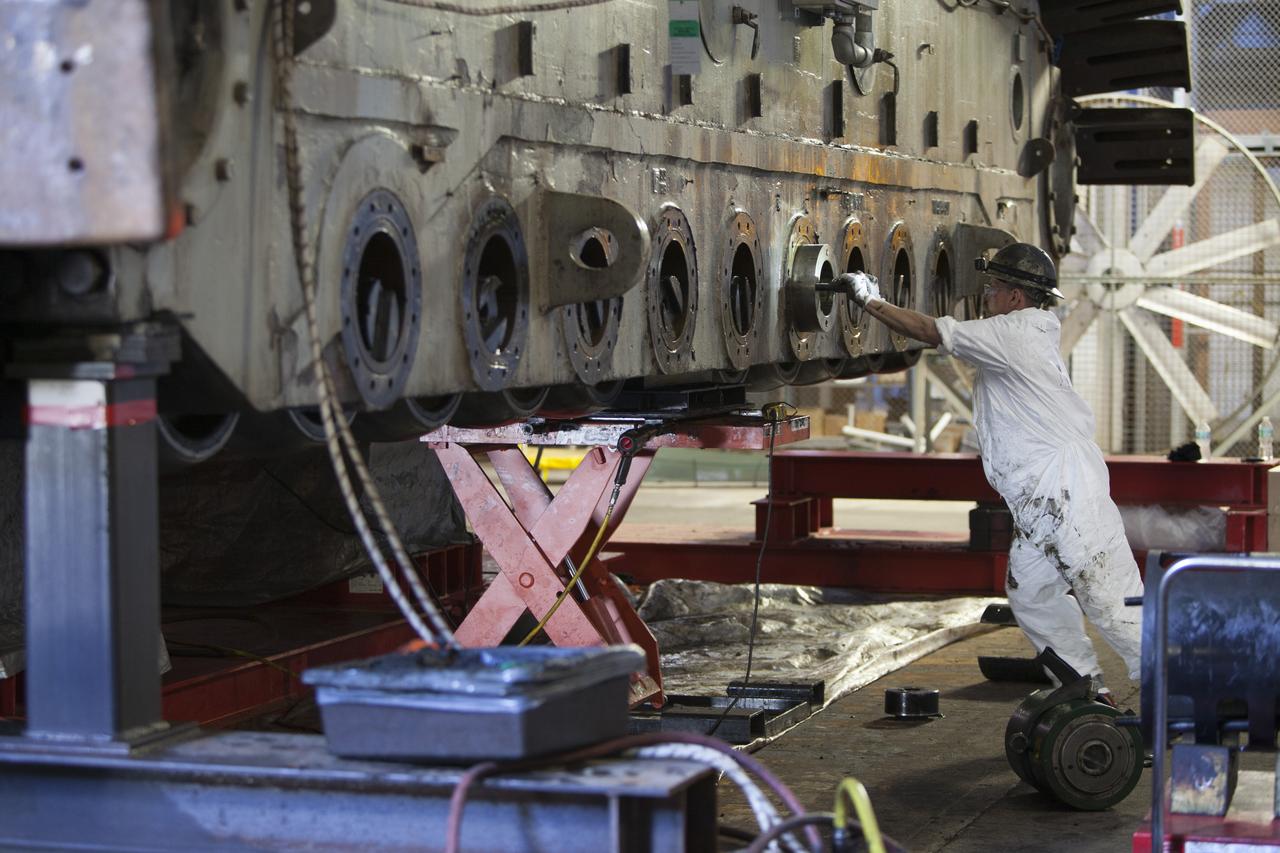

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a ground support technician assists with removal of bearings from the B truck tread of crawler-transporter 2, or CT-2. New roller bearing assemblies will be installed. Work continues in high bay 2 to upgrade CT-2. The modifications are designed to ensure CT-2’s ability to transport launch vehicles currently in development, such as the agency’s Space Launch System, to the launch pad. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy is overseeing the upgrades. For more than 45 years the crawler-transporters were used to transport the mobile launcher platform and the Apollo-Saturn V rockets and, later, space shuttles to Launch Pads 39A and B. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/crawler-transporter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
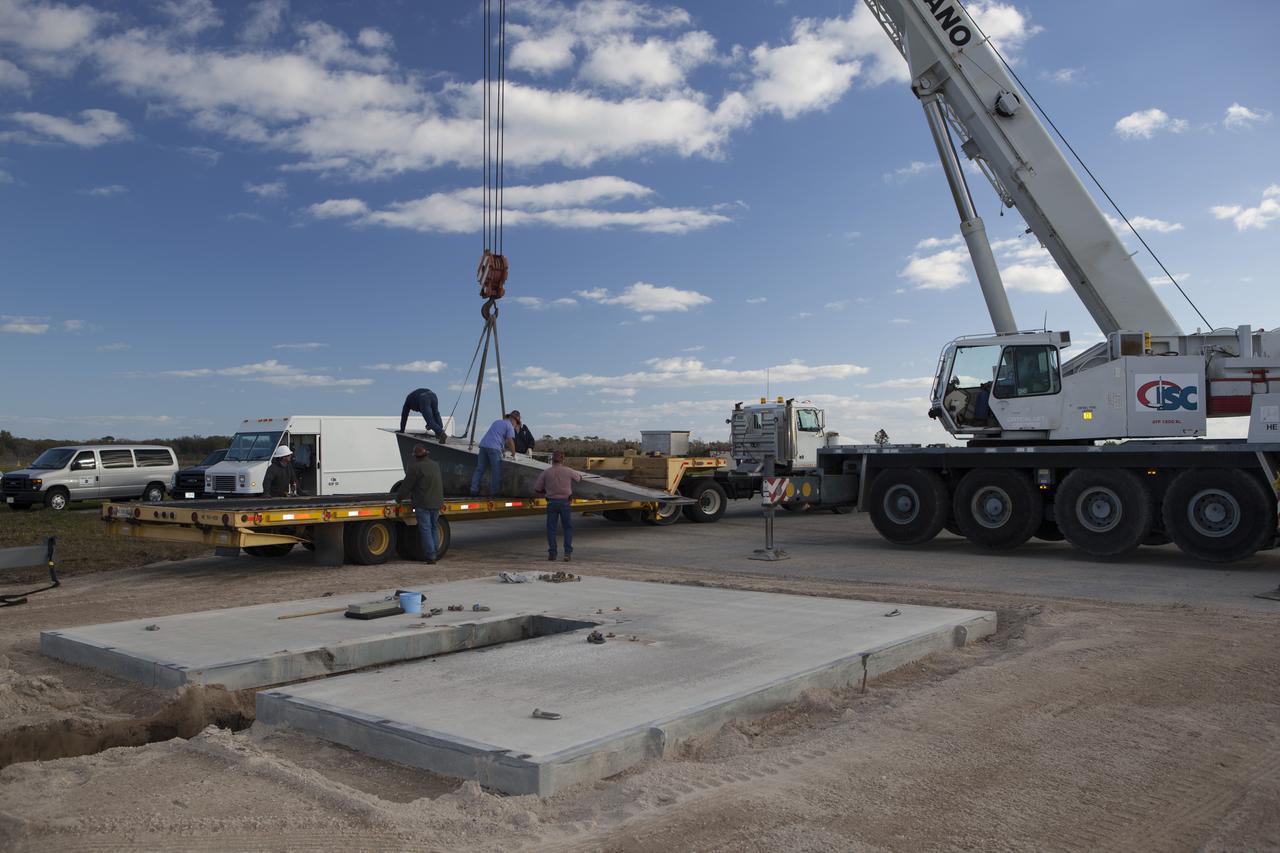

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction workers assist as a crane lowers a portion of the launch pad for the Project Morpheus prototype lander onto a transporter at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The launch pad is being moved to a different location at the landing facility to support the next phase of flight testing. Morpheus completed its seventh free flight test on March 11. The 83-second test began at 3:41 p.m. EDT with the Morpheus lander launching from the ground over a flame trench and ascending to 580 feet. Morpheus then flew its fastest downrange trek at 30 mph, travelling farther than before, 837 feet. The lander performed a 42-foot divert to emulate a hazard avoidance maneuver before descending and touching down on Landing Site 2, at the northern landing pad inside the automated landing and hazard avoidance technology ALHAT hazard field. Morpheus landed within one foot of its intended target. Project Morpheus tests NASA’s ALHAT and an engine that runs on liquid oxygen and methane, or green propellants, into a fully-operational lander that could deliver cargo to other planetary surfaces. The landing facility provides the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus’ ALHAT payload allows it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is being managed under the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, Division in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. The efforts in AES pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
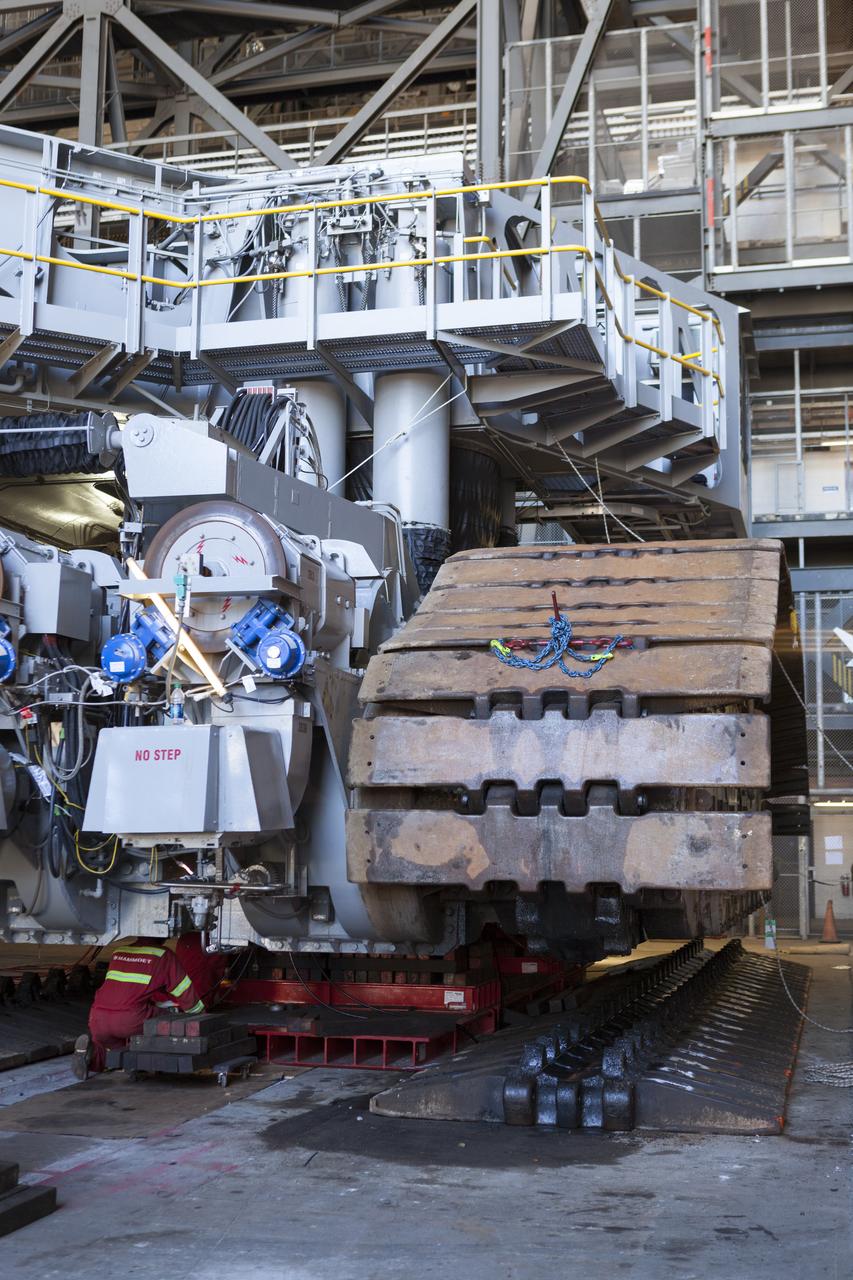

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the B and D truck sections of crawler-transporter 2, or CT-2, are being raised up to prepare for installation of new roller bearing assemblies. Sections of the crawler’s large metal tracks have been removed. Work continues in high bay 2 to upgrade CT-2. The modifications are designed to ensure CT-2’s ability to transport launch vehicles currently in development, such as the agency’s Space Launch System, to the launch pad. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy is overseeing the upgrades. For more than 45 years the crawler-transporters were used to transport the mobile launcher platform and the Apollo-Saturn V rockets and, later, space shuttles to Launch Pads 39A and B. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/crawler-transporter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
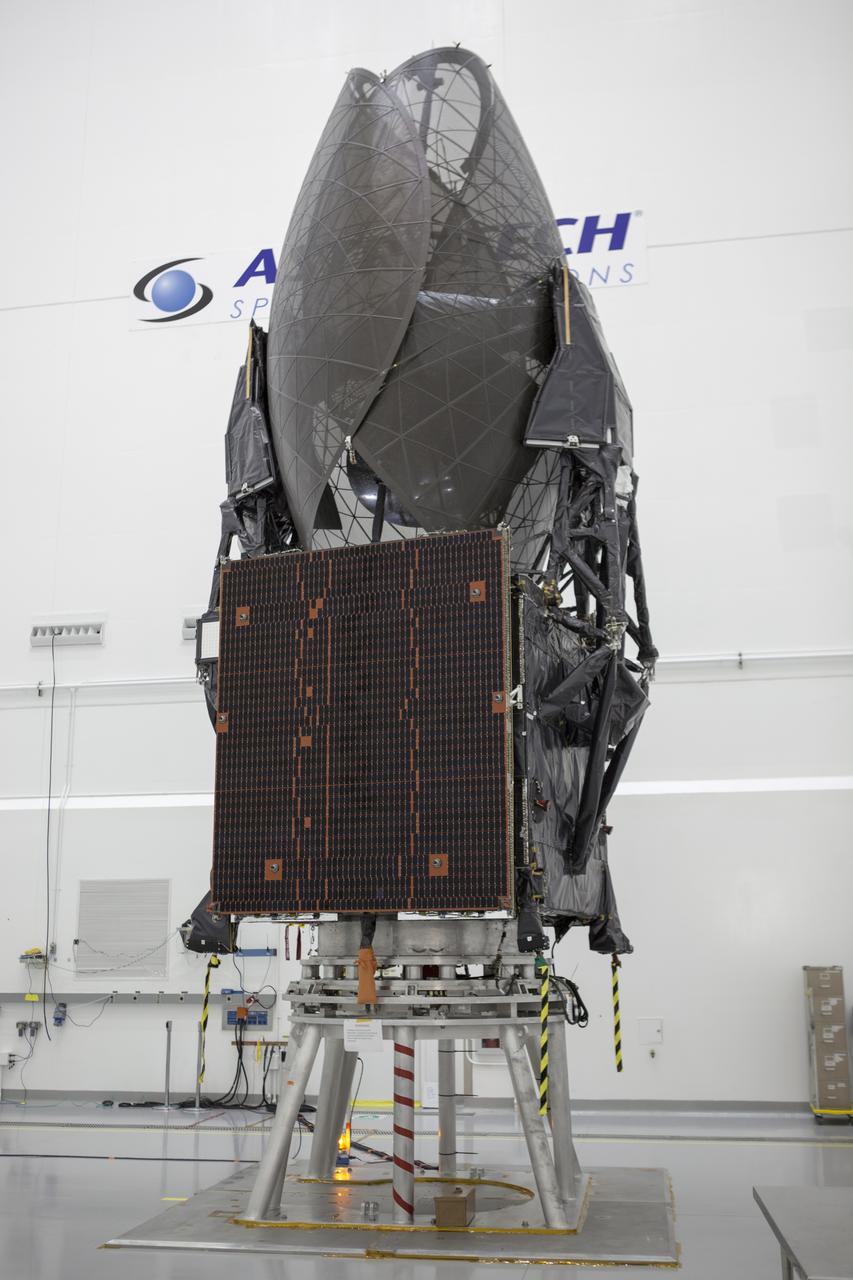

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft is undergoing preflight processing.
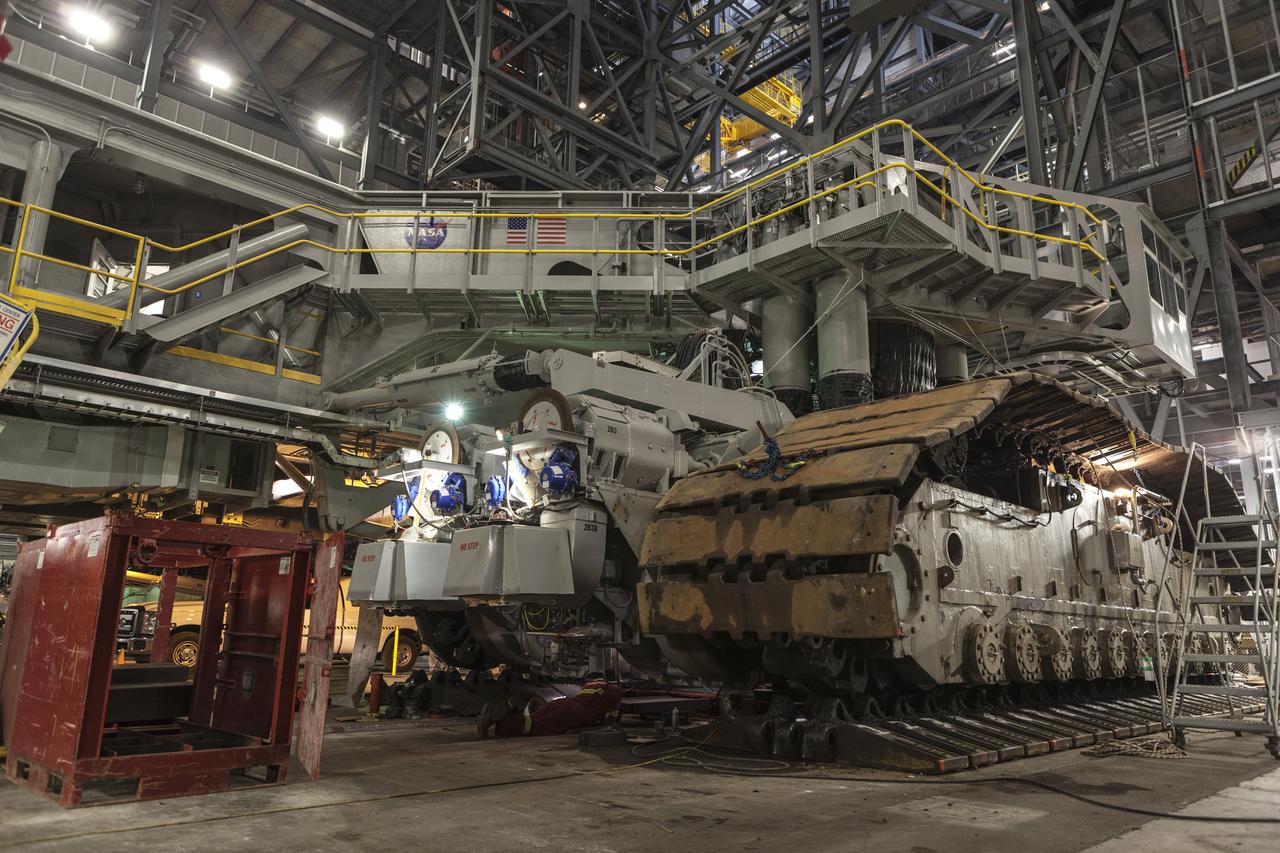

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the B and D truck sections of crawler-transporter 2, or CT-2, are being raised up to prepare for installation of new roller bearing assemblies. Work continues in high bay 2 to upgrade CT-2. The modifications are designed to ensure CT-2’s ability to transport launch vehicles currently in development, such as the agency’s Space Launch System, to the launch pad. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy is overseeing the upgrades. For more than 45 years the crawler-transporters were used to transport the mobile launcher platform and the Apollo-Saturn V rockets and, later, space shuttles to Launch Pads 39A and B. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/crawler-transporter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
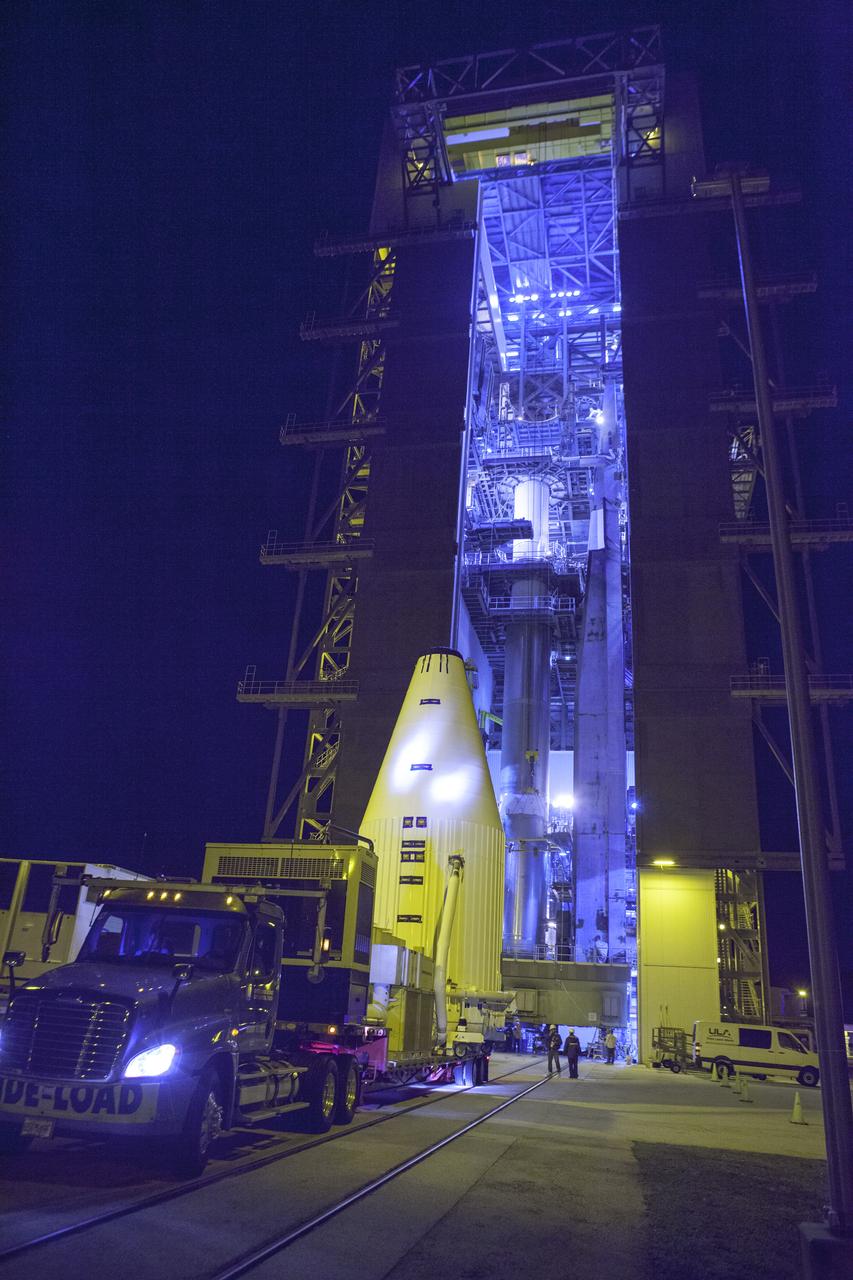

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
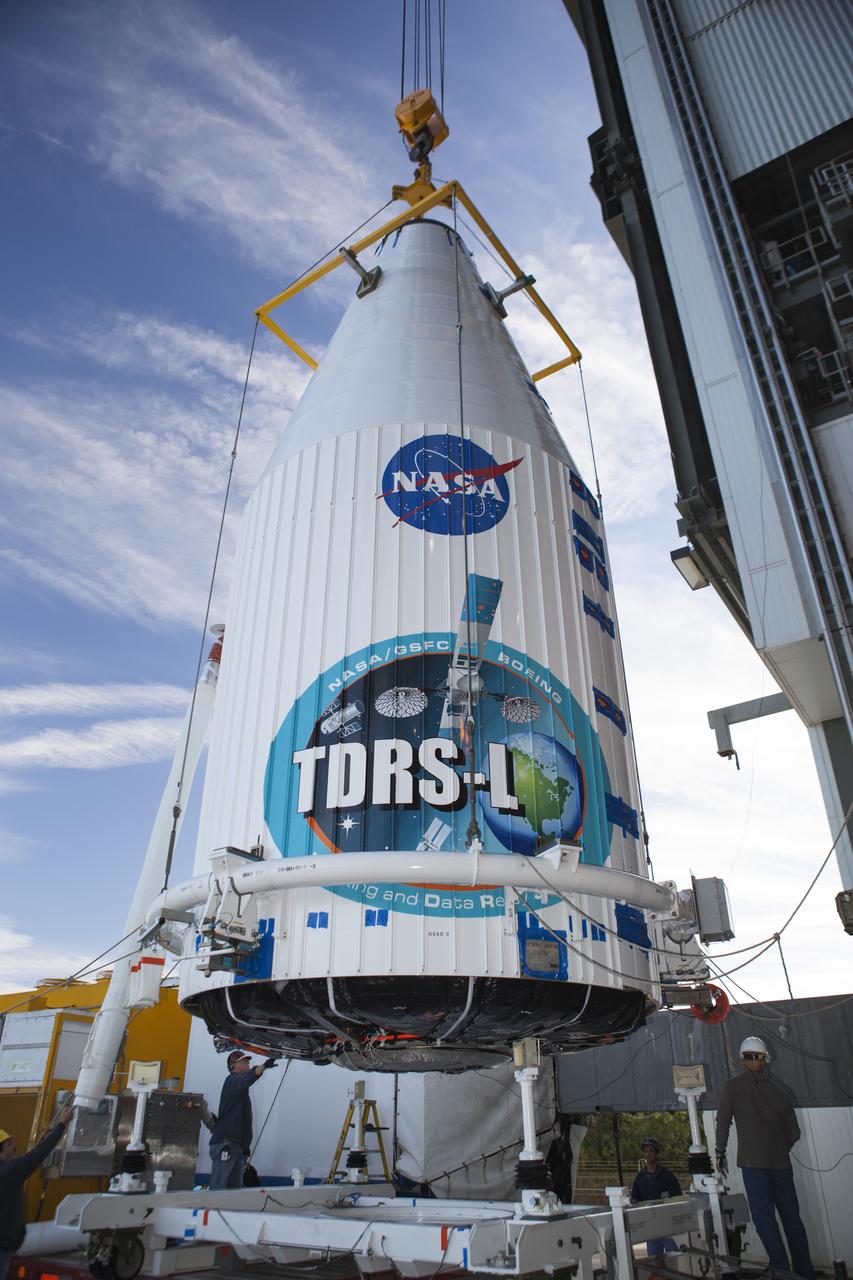

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41, engineers and technicians begin lifting NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft for mounting atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Jan. 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
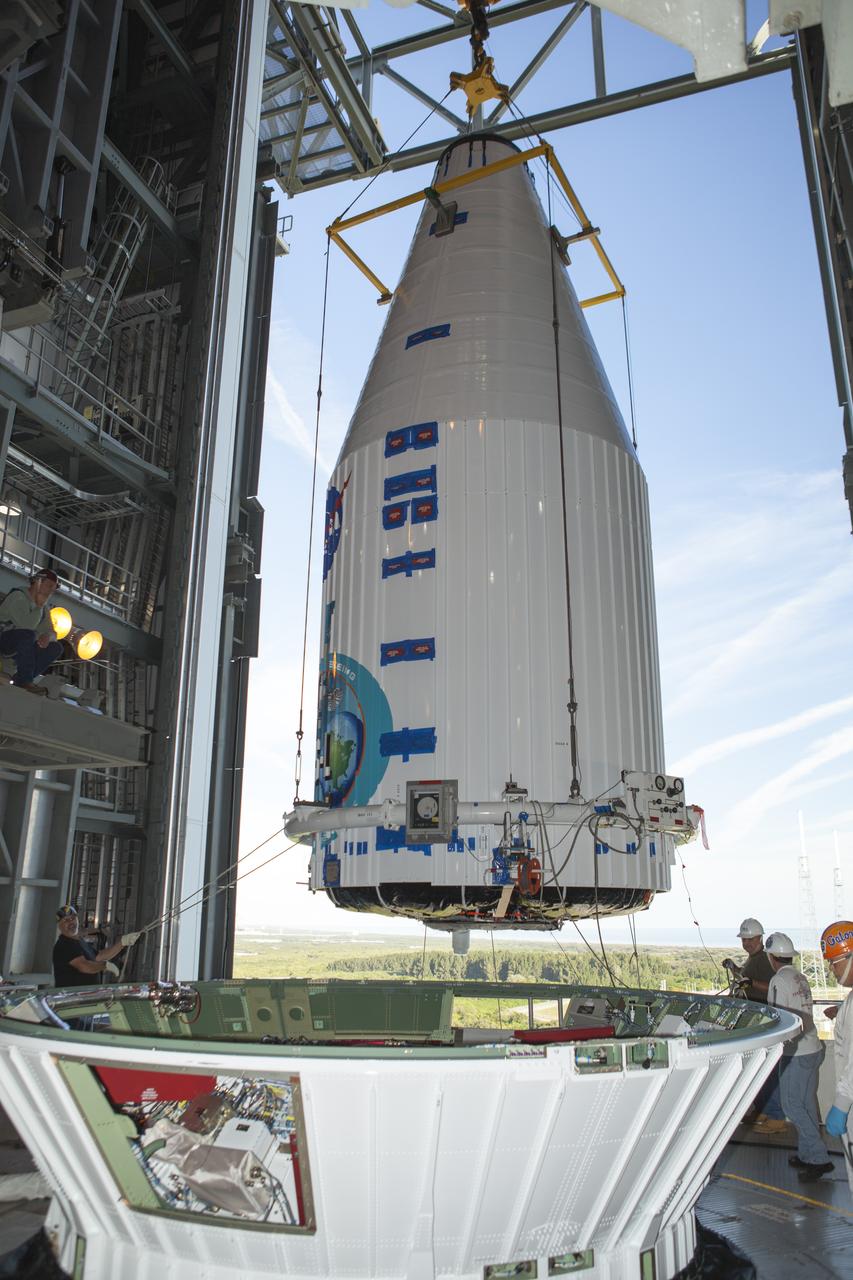

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft is lifted for mounting atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Jan. 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
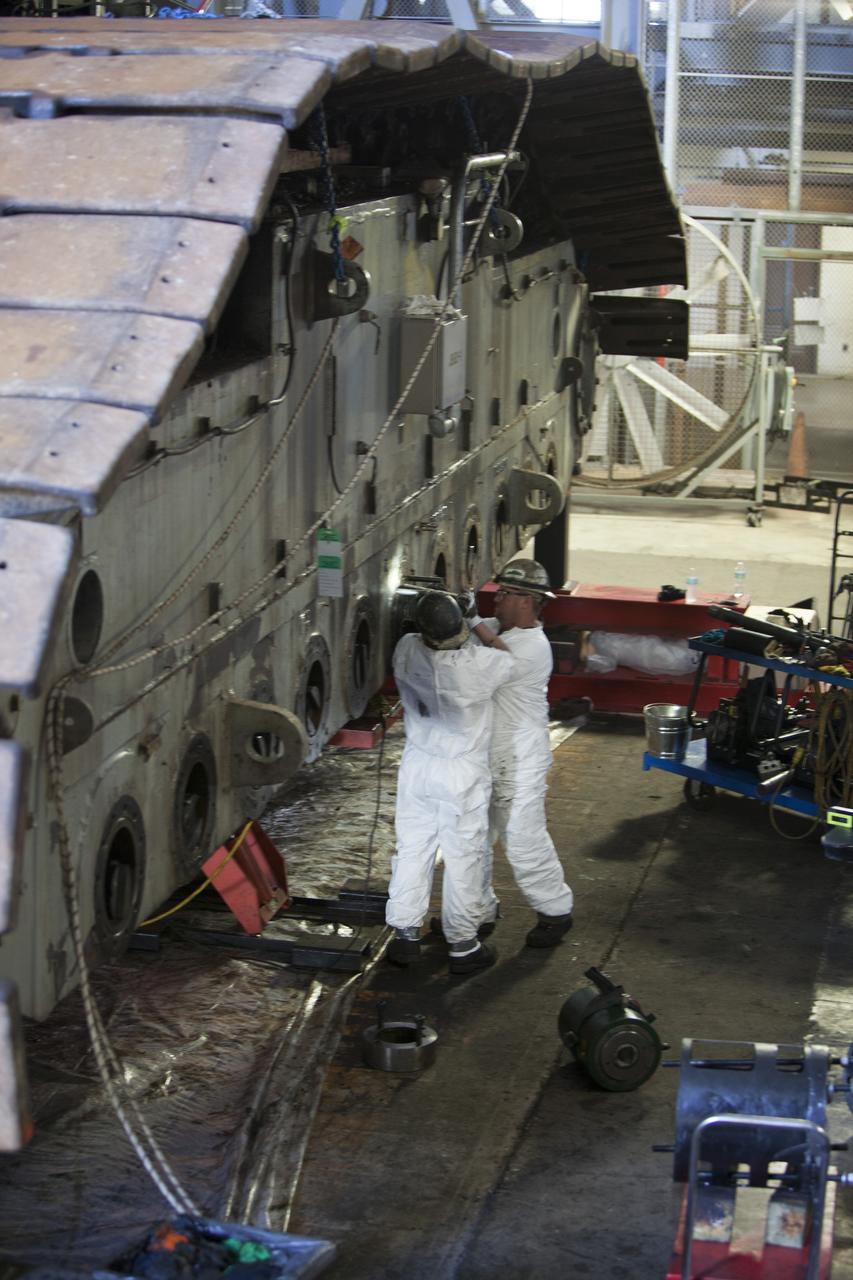

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, ground support technicians assist with removal of bearings from the B truck tread of crawler-transporter 2, or CT-2. New roller bearing assemblies will be installed. Work continues in high bay 2 to upgrade CT-2. The modifications are designed to ensure CT-2’s ability to transport launch vehicles currently in development, such as the agency’s Space Launch System, to the launch pad. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy is overseeing the upgrades. For more than 45 years the crawler-transporters were used to transport the mobile launcher platform and the Apollo-Saturn V rockets and, later, space shuttles to Launch Pads 39A and B. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/crawler-transporter. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
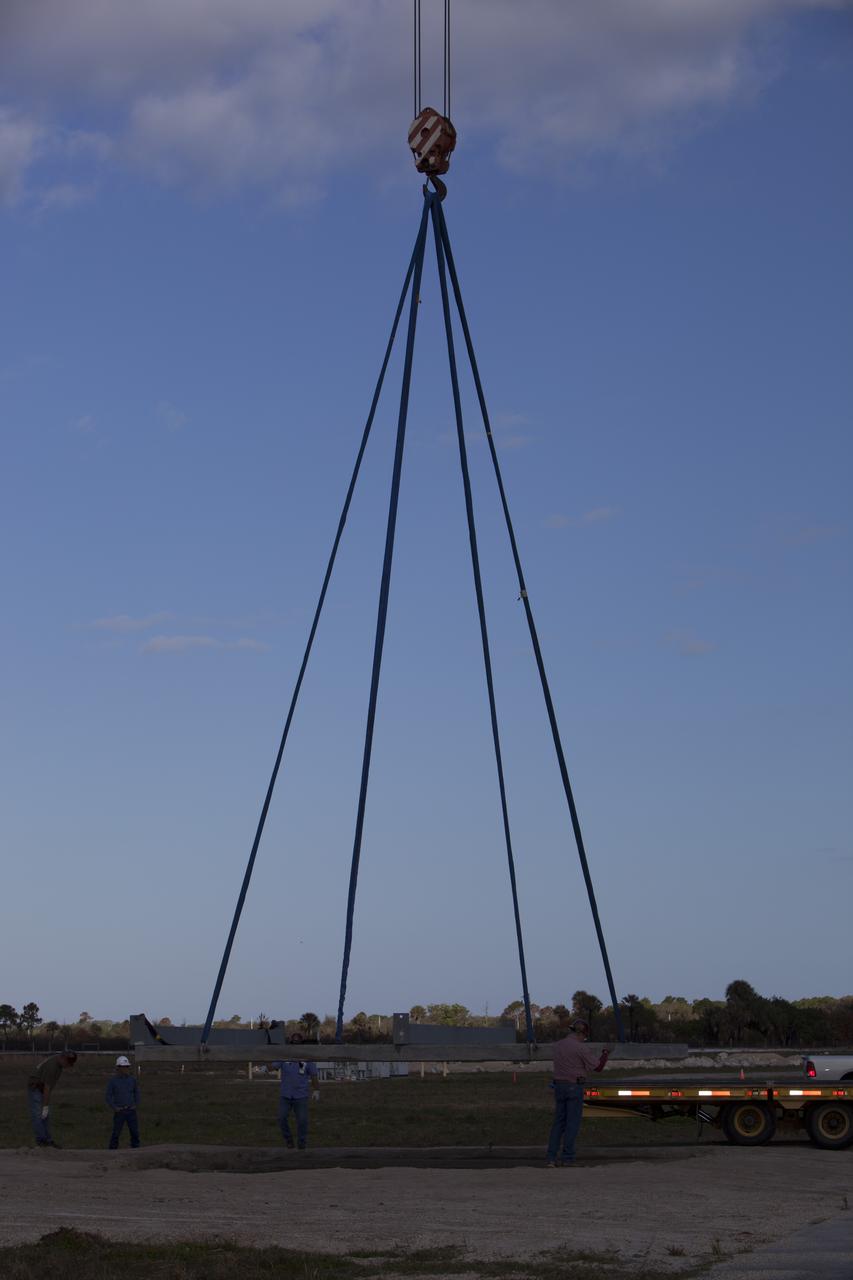

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction workers assist as a crane is used to lift a large portion of the launch pad for the Project Morpheus prototype lander onto a transporter at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The launch pad is being moved to a different location at the landing facility to support the next phase of flight testing. Morpheus completed its seventh free flight test on March 11. The 83-second test began at 3:41 p.m. EDT with the Morpheus lander launching from the ground over a flame trench and ascending to 580 feet. Morpheus then flew its fastest downrange trek at 30 mph, travelling farther than before, 837 feet. The lander performed a 42-foot divert to emulate a hazard avoidance maneuver before descending and touching down on Landing Site 2, at the northern landing pad inside the automated landing and hazard avoidance technology ALHAT hazard field. Morpheus landed within one foot of its intended target. Project Morpheus tests NASA’s ALHAT and an engine that runs on liquid oxygen and methane, or green propellants, into a fully-operational lander that could deliver cargo to other planetary surfaces. The landing facility provides the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus’ ALHAT payload allows it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is being managed under the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, Division in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. The efforts in AES pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
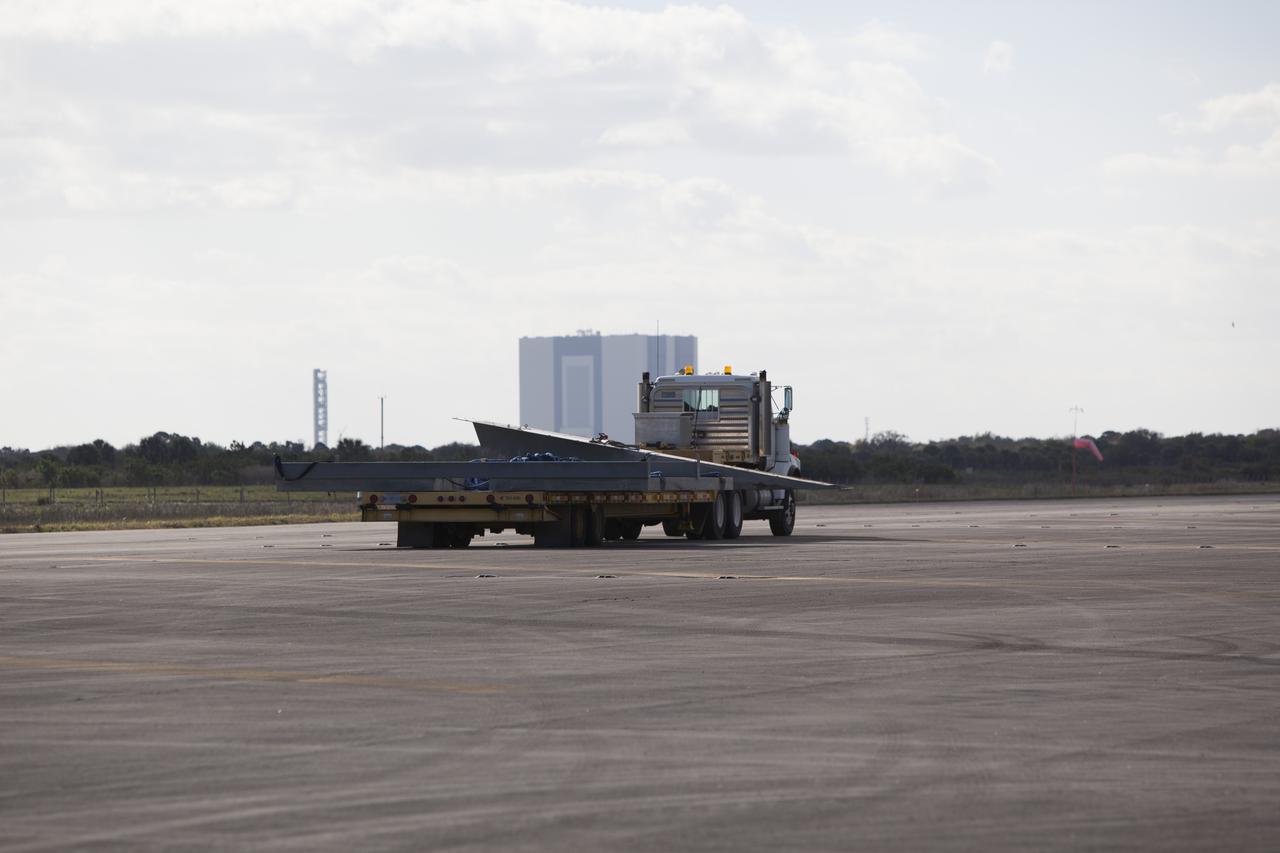

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A flatbed truck carries the launch pad for the Project Morpheus prototype lander to a new location at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The launch pad is being moved to a different location to support the next phase of flight testing. Morpheus completed its seventh free flight test on March 11. The 83-second test began at 3:41 p.m. EDT with the Morpheus lander launching from the ground over a flame trench and ascending to 580 feet. Morpheus then flew its fastest downrange trek at 30 mph, travelling farther than before, 837 feet. The lander performed a 42-foot divert to emulate a hazard avoidance maneuver before descending and touching down on Landing Site 2, at the northern landing pad inside the automated landing and hazard avoidance technology ALHAT hazard field. Morpheus landed within one foot of its intended target. Project Morpheus tests NASA’s ALHAT and an engine that runs on liquid oxygen and methane, or green propellants, into a fully-operational lander that could deliver cargo to other planetary surfaces. The landing facility provides the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus’ ALHAT payload allows it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is being managed under the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, Division in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. The efforts in AES pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
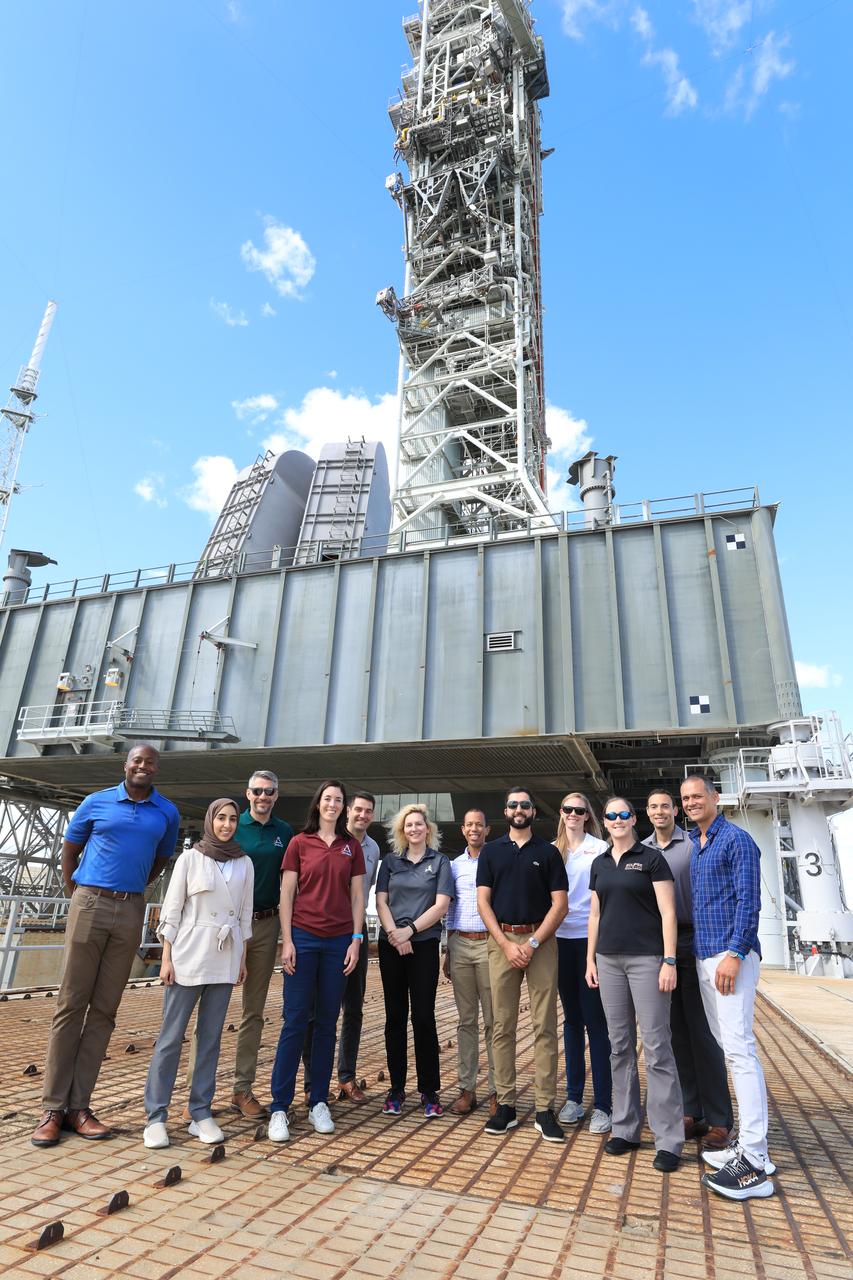

NASA’s 2021 class of astronaut candidates visit the mobile launcher at Launch Complex 39B during a familiarization tour of facilities on Monday, Oct. 16, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41, engineers and technicians prepare to lift NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft for mounting atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Jan. 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
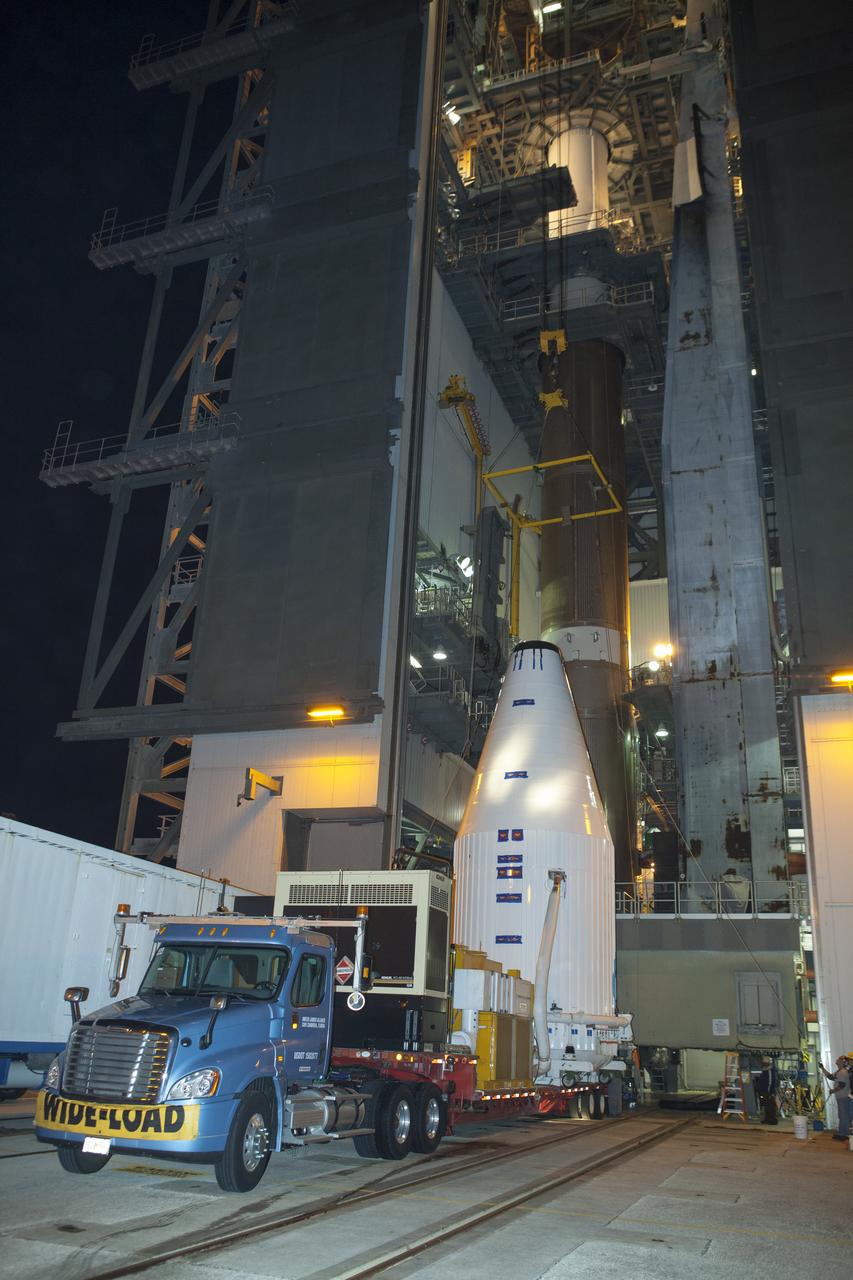

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Vertical Integration Facility at Launch Complex 41. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Jan. 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
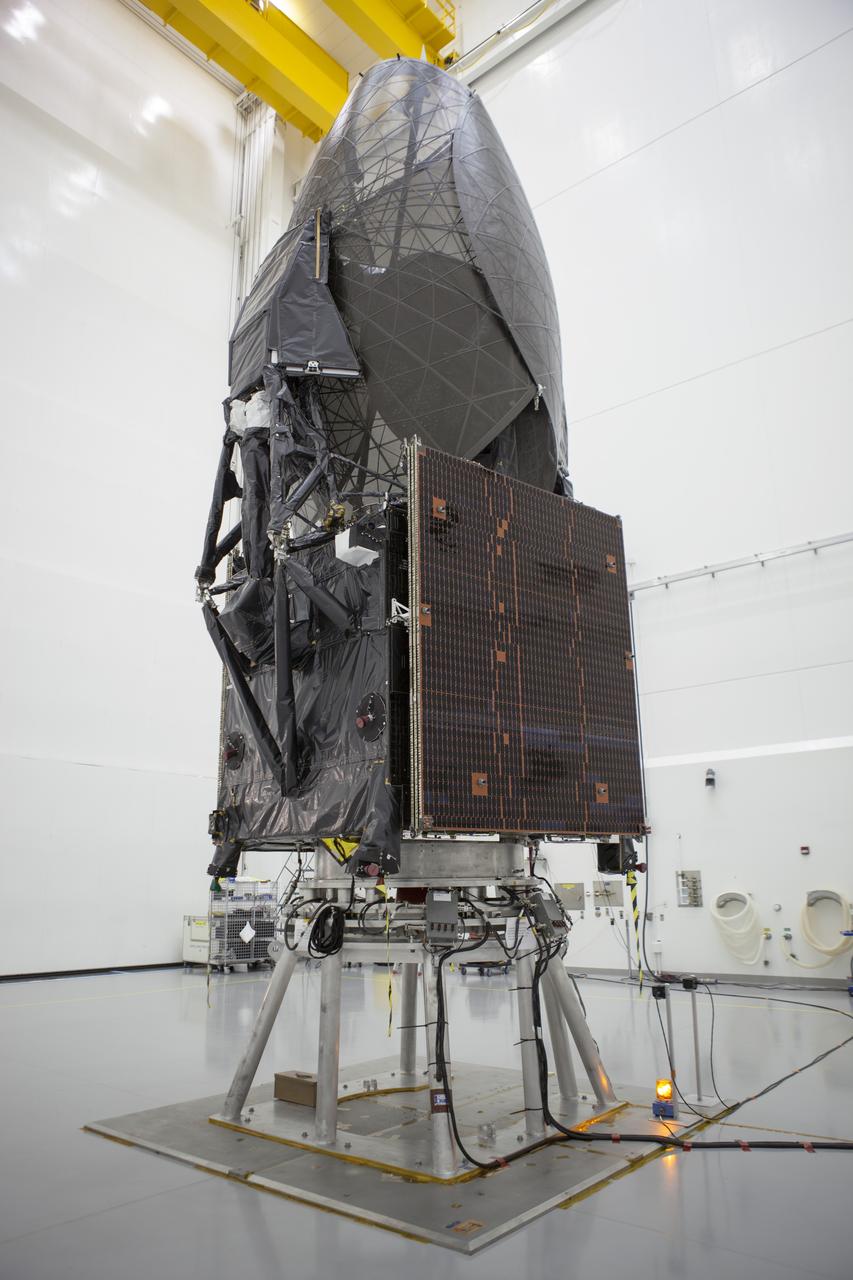

Inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft is undergoing preflight processing.
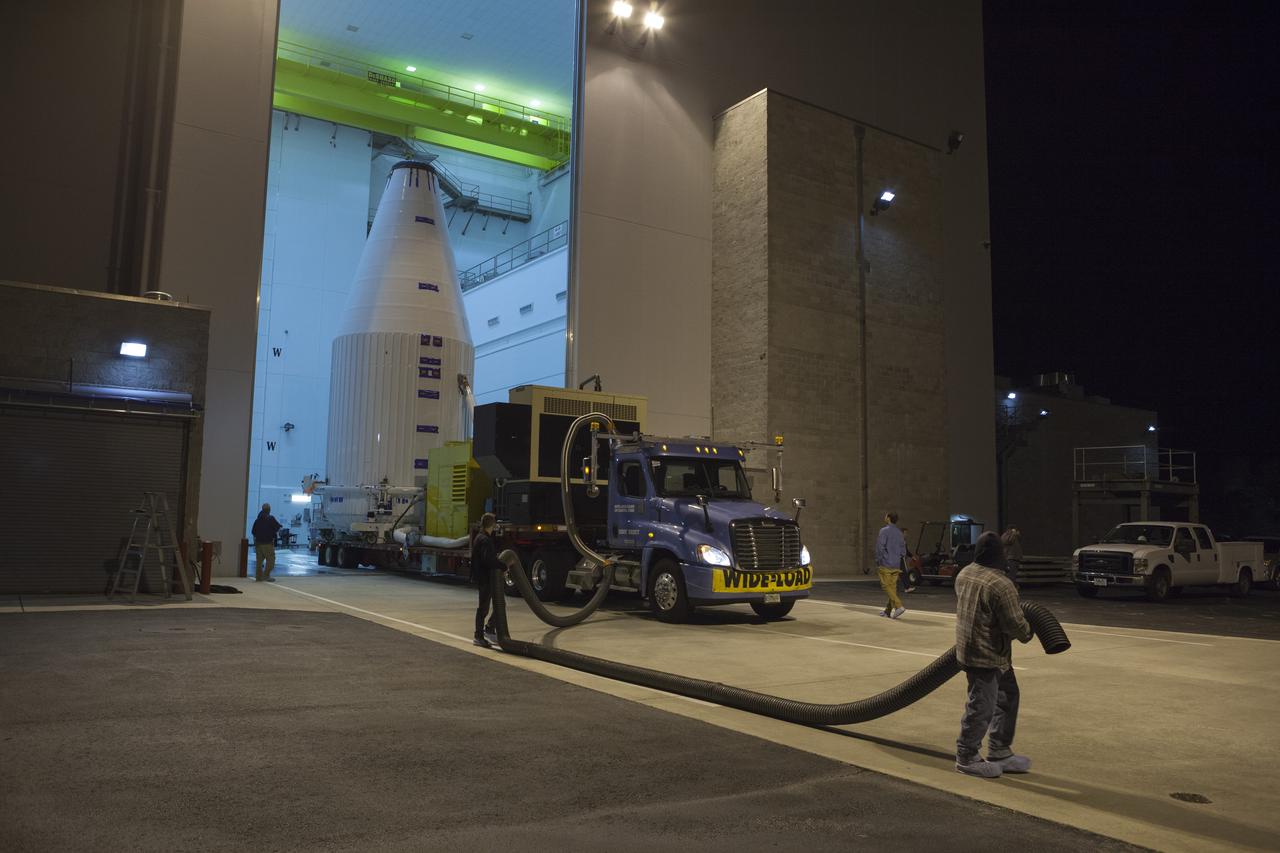

TITUSVILLE, Fla. – Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft begins it trip from the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville to Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The TDRS-L satellite will be a part of the second of three next-generation spacecraft designed to ensure vital operational continuity for the NASA Space Network. It is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on January 23, 2014. The current Tracking and Data Relay Satellite system consists of eight in-orbit satellites distributed to provide near continuous information relay contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/tdrs/home/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
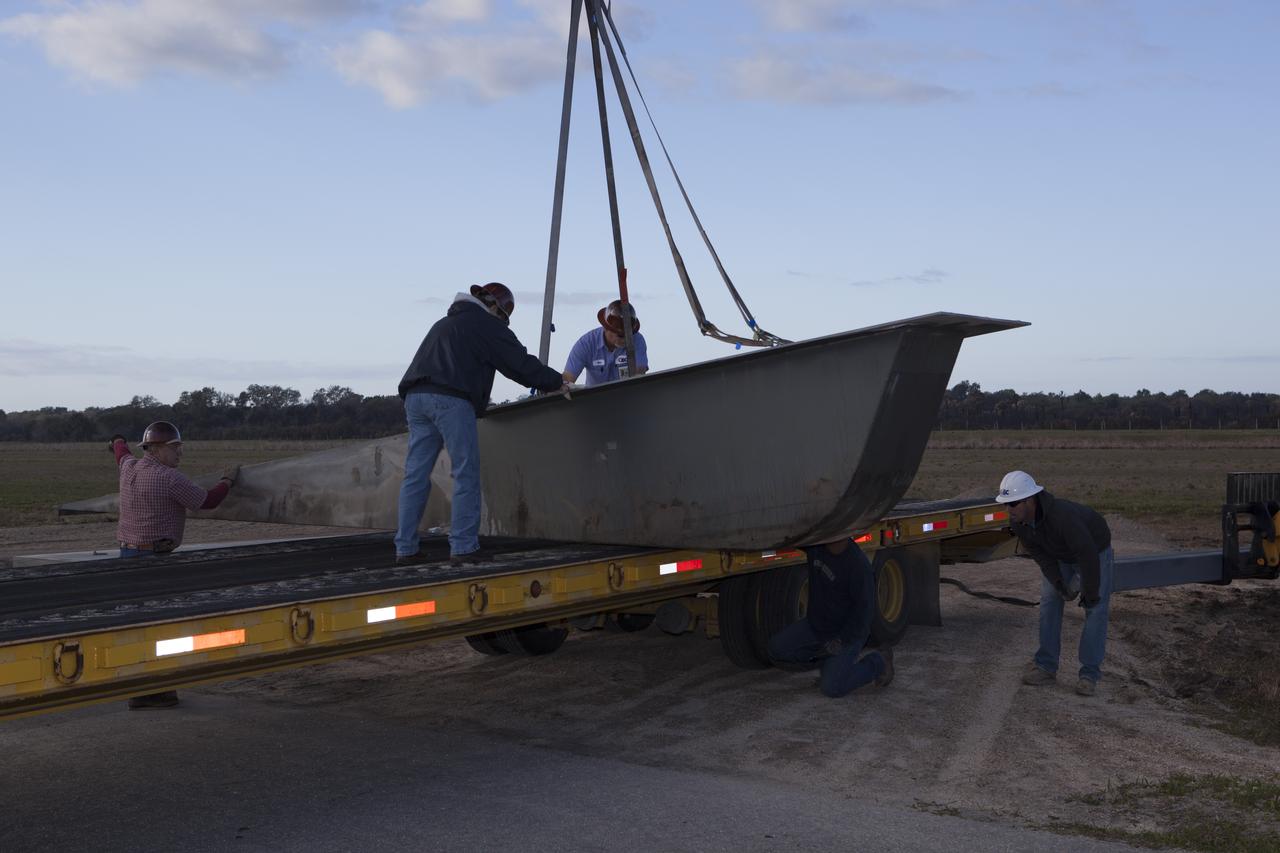

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction workers assist as a crane lowers a portion of the launch pad for the Project Morpheus prototype lander onto a transporter at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The launch pad is being moved to a different location at the landing facility to support the next phase of flight testing. Morpheus completed its seventh free flight test on March 11. The 83-second test began at 3:41 p.m. EDT with the Morpheus lander launching from the ground over a flame trench and ascending to 580 feet. Morpheus then flew its fastest downrange trek at 30 mph, travelling farther than before, 837 feet. The lander performed a 42-foot divert to emulate a hazard avoidance maneuver before descending and touching down on Landing Site 2, at the northern landing pad inside the automated landing and hazard avoidance technology ALHAT hazard field. Morpheus landed within one foot of its intended target. Project Morpheus tests NASA’s ALHAT and an engine that runs on liquid oxygen and methane, or green propellants, into a fully-operational lander that could deliver cargo to other planetary surfaces. The landing facility provides the lander with the kind of field necessary for realistic testing, complete with rocks, craters and hazards to avoid. Morpheus’ ALHAT payload allows it to navigate to clear landing sites amidst rocks, craters and other hazards during its descent. Project Morpheus is being managed under the Advanced Exploration Systems, or AES, Division in NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. The efforts in AES pioneer new approaches for rapidly developing prototype systems, demonstrating key capabilities and validating operational concepts for future human missions beyond Earth orbit. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
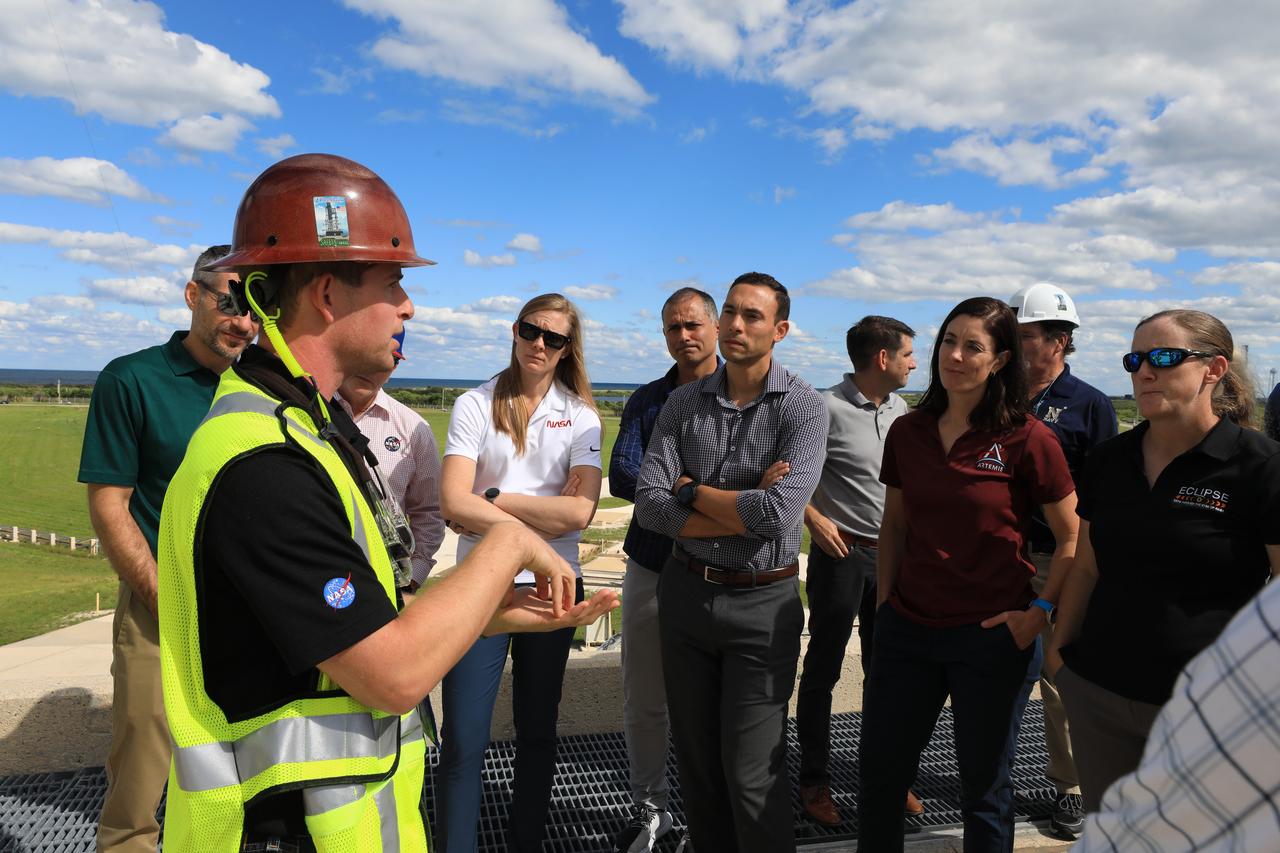

NASA’s 2021 class of astronaut candidates talk with Exploration Ground Systems engineers atop the mobile launcher at Launch Complex 39B during a familiarization tour of facilities on Monday, Oct. 16, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.