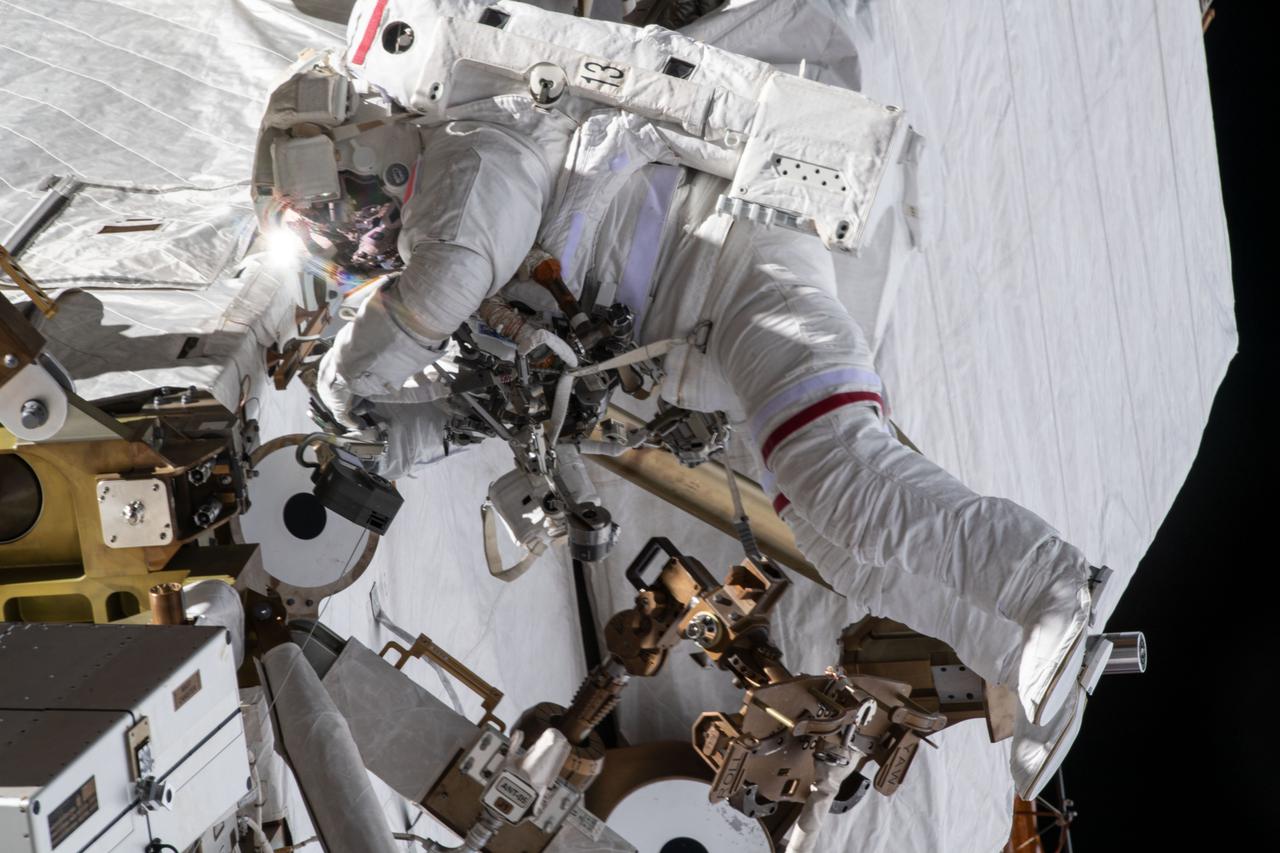

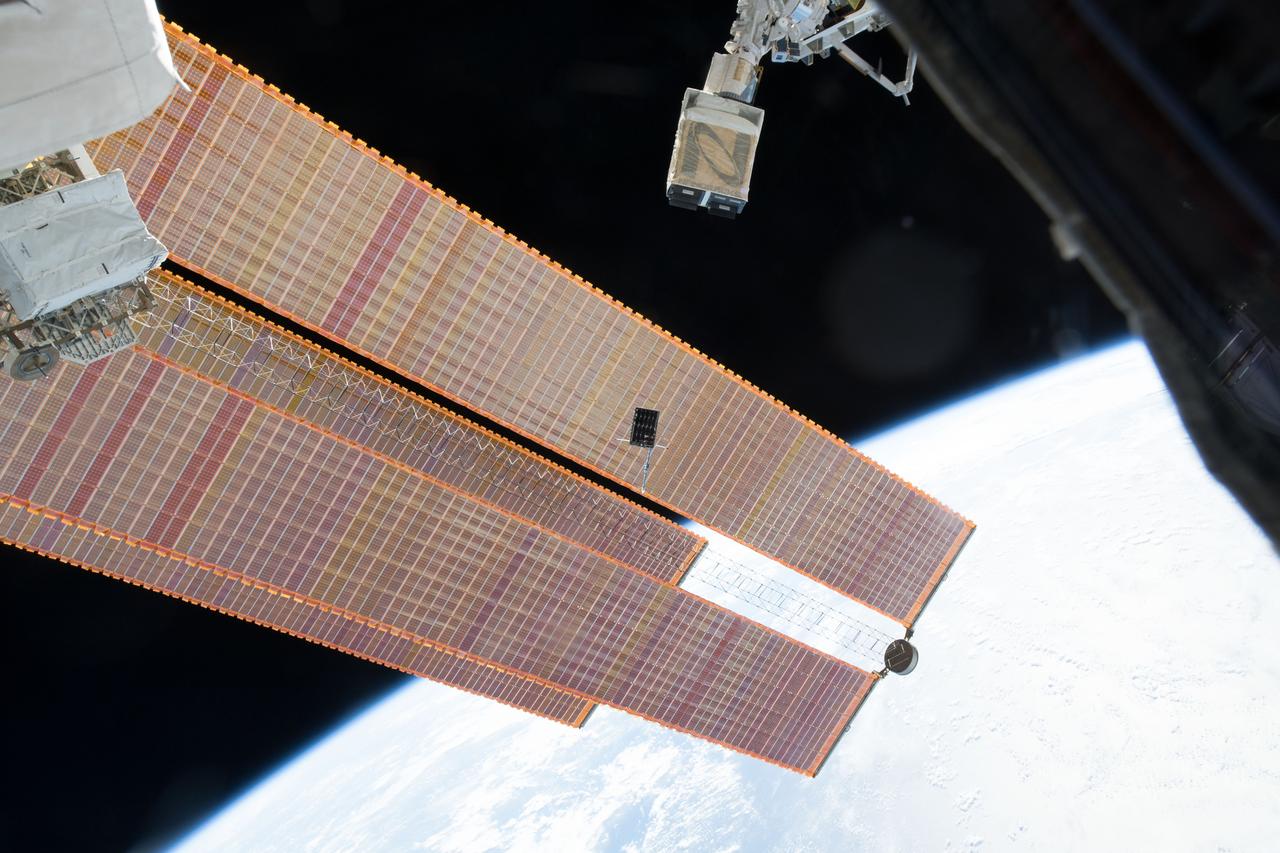
iss065e144990 (June 25, 2021) --- Spacewalker Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) works to complete the installation of the second roll out solar array on the International Space Station's Port-6 truss structure.
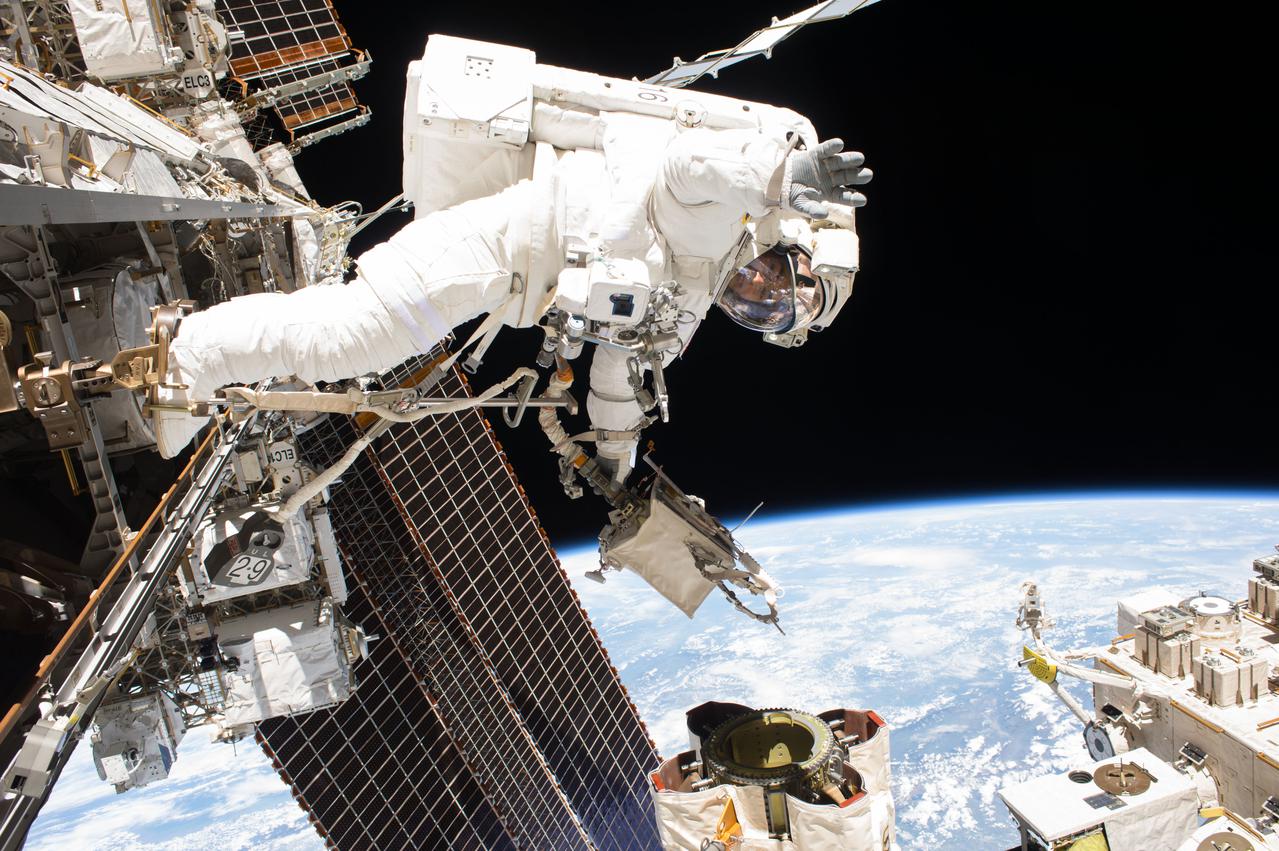

iss053e095794 (Oct. 10, 2017) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 53 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei is pictured during a spacewalk to service components on the Canadarm2 robotic arm during a spacewalk with NASA astronaut Randy Bresnik (out of frame).
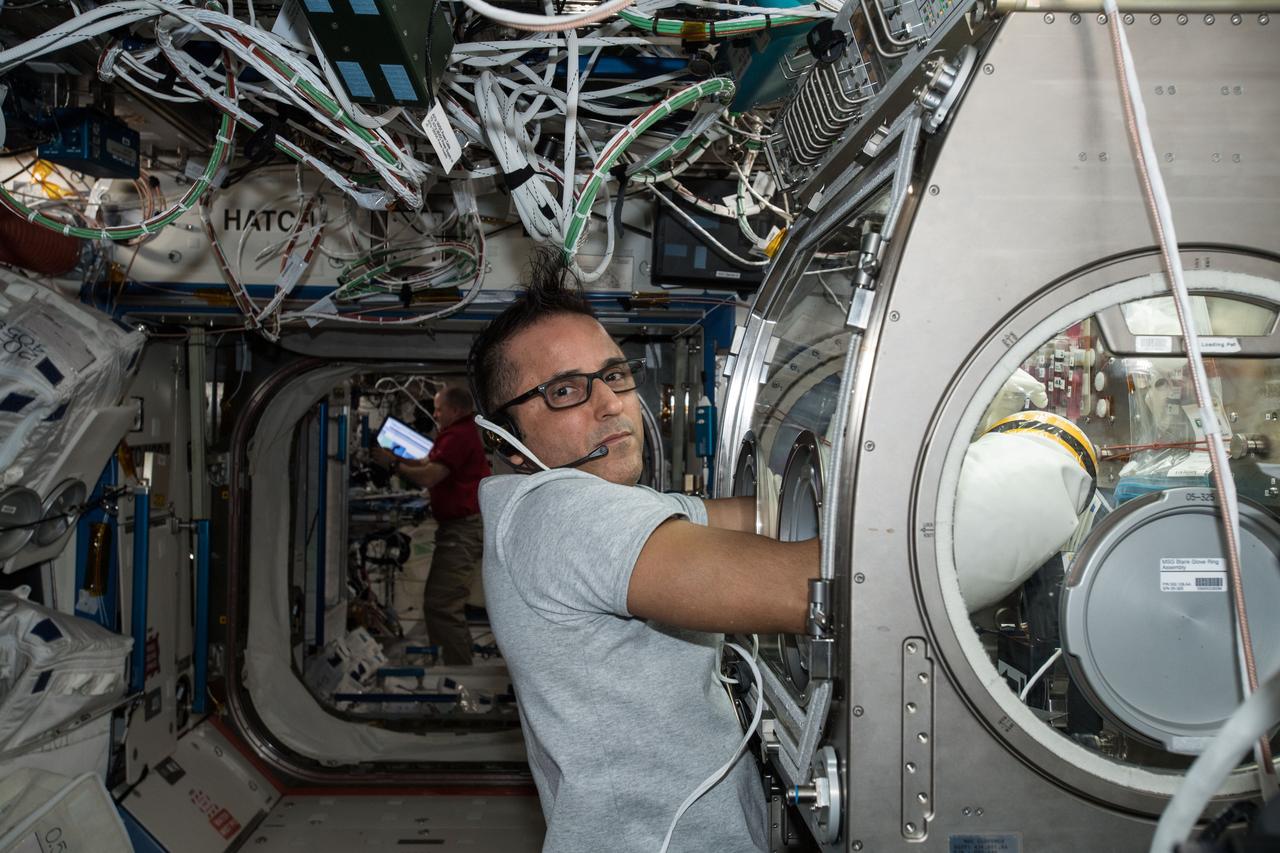

iss054e006421 912/21/2017) --- NASA astronaut Joe Acaba conducts fluid exchange and sampling for the Synthetic Bone experiment inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) in the Destiny U.S. Laboratory aboard the International Space Station (ISS).Synthetic Bone tests the functionality and effectiveness of a new material that can assist in recovery from bone injuries or dental work during long-term space travel.
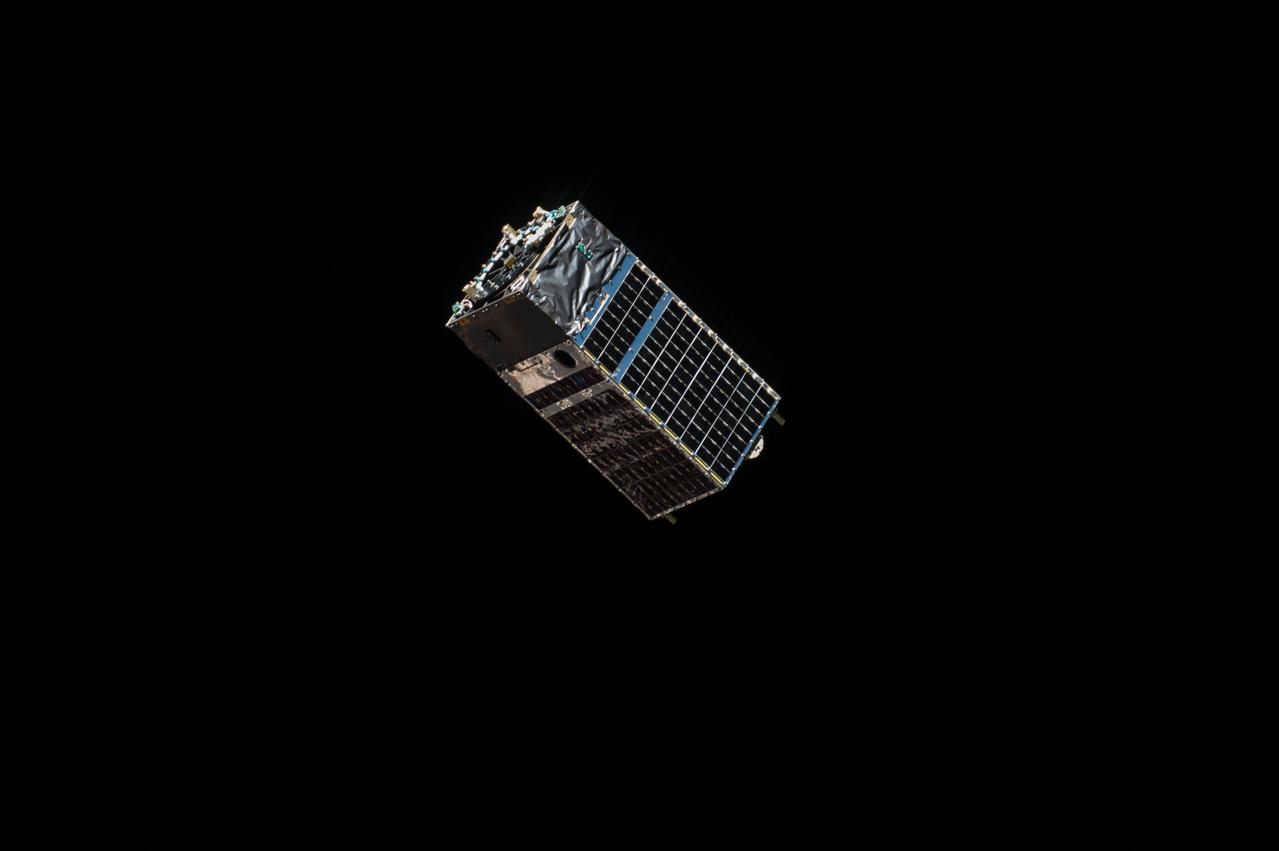

iss053e130267 (Oct. 24, 2017) --- The Kestrel Eye IIM (KE2M) CubeSat is pictured shortly after it was deployed from the tip of the Dextre attached to the Mobile Servicing System. The KE2M is carrying an optical imaging system payload that is being used to validate the concept of using microsatellites in low-Earth orbit to support critical operations.
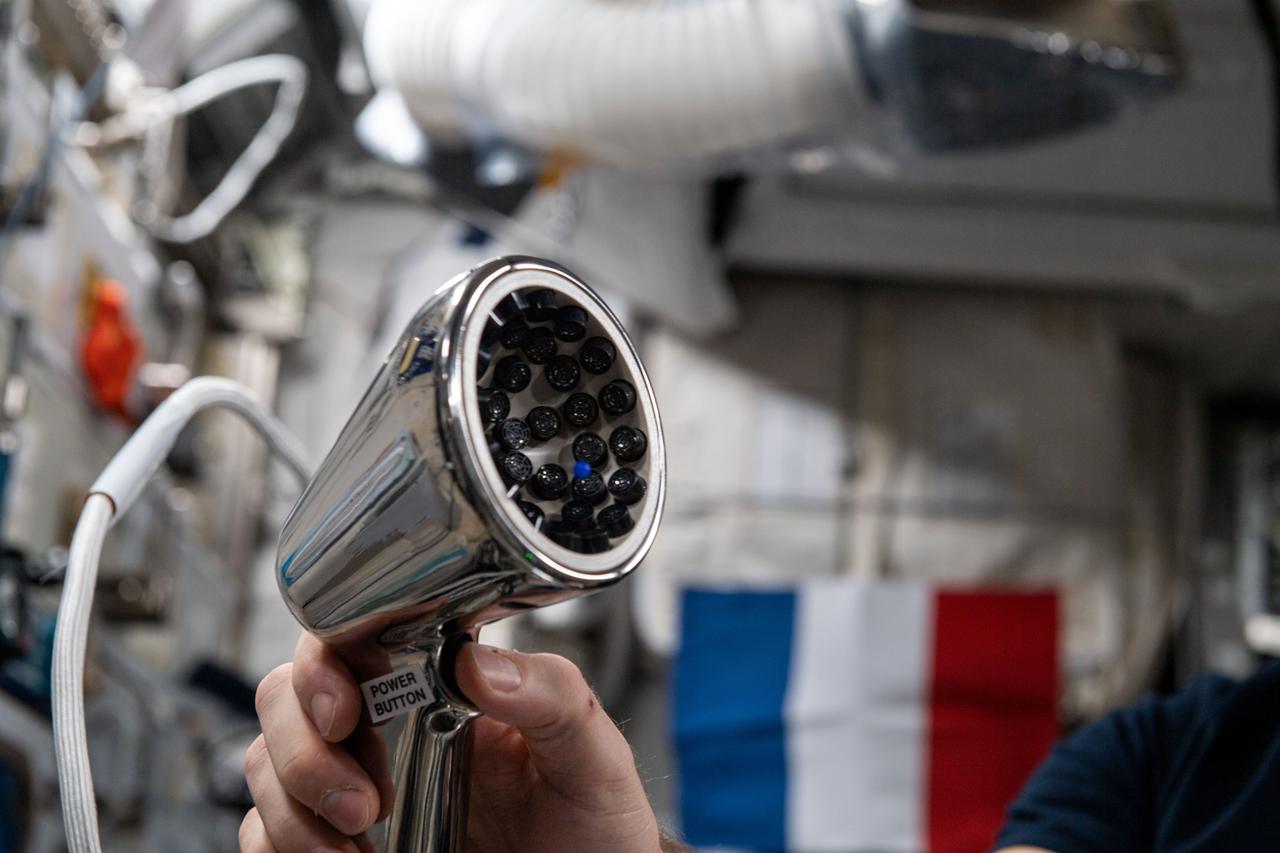

iss065e170080 (7/20/2021) --- Photo taken during the Ultrasonic Tweezers experiment setup and execution in the Columbus module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The objective of the Ultrasonic Tweezers project is to develop acoustic tweezers that use sound to allow for remote and contactless manipulation of materials in a microgravity context. An ultrasound beam is shaped so that it produces a trap from which an object cannot easily exit. By moving the beam, the object can be moved to a new position with a very good precision.

iss053e037294 (9/22/2017) --- A view of the Advanced Nano Step Cartridge Installation into the Solution Crystallization Observation Facility (SCOF) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Effects of Impurities on Perfection of Protein Crystals, Partition Functions, and Growth Mechanisms (Advanced Nano Step) experiment monitors and records how the incorporation of specific impurity molecules affect the development and quality of protein crystals, as they grow in a quartz cell aboard the ISS.
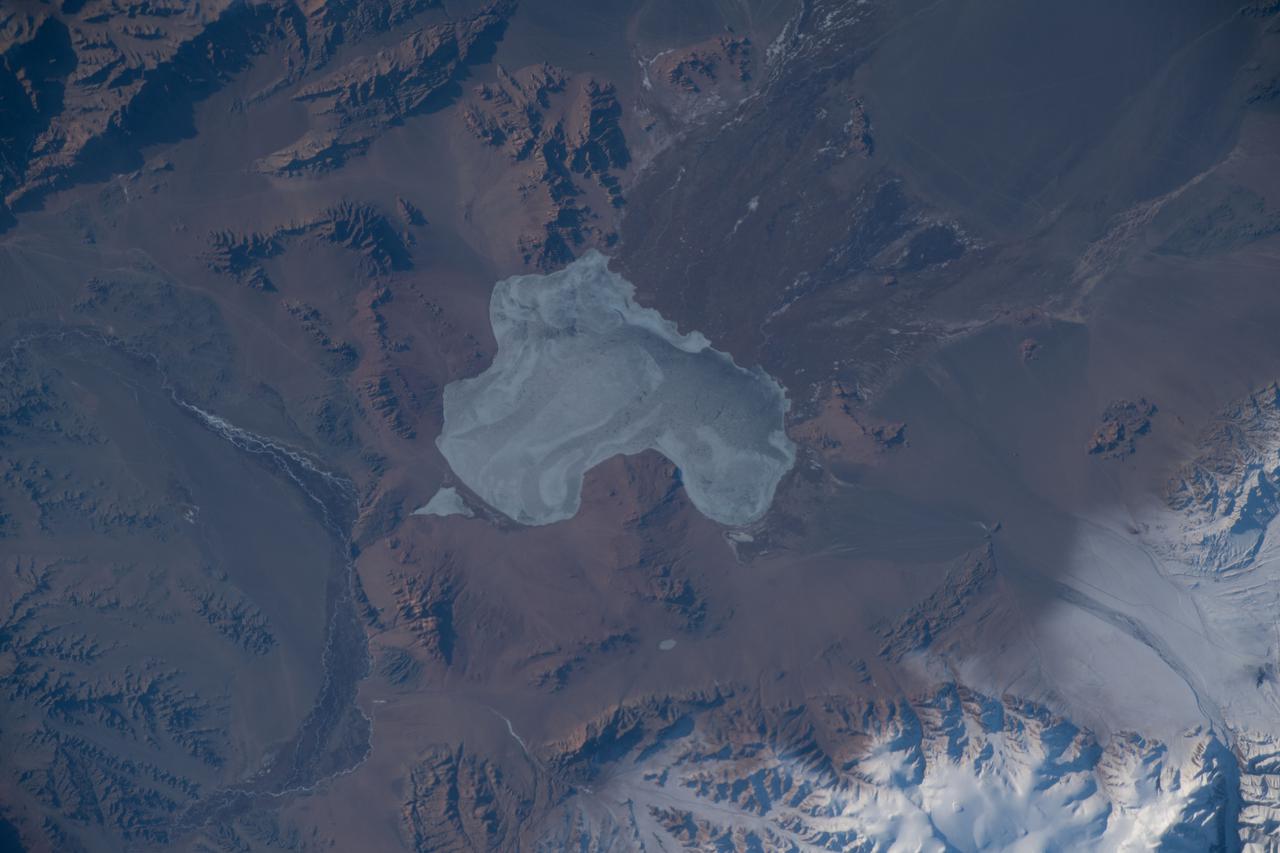

iss066e090079 (Dec. 11, 2021) --- The frozen Achit Lake, in the Altay Mountain range of the Central Asian nation of Mongolia, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 266 miles above. Just west of Achit Lake is the Harhiraa Uul mountain (at bottom right) with an elevation of 13,255 feet, or 4040 meters.
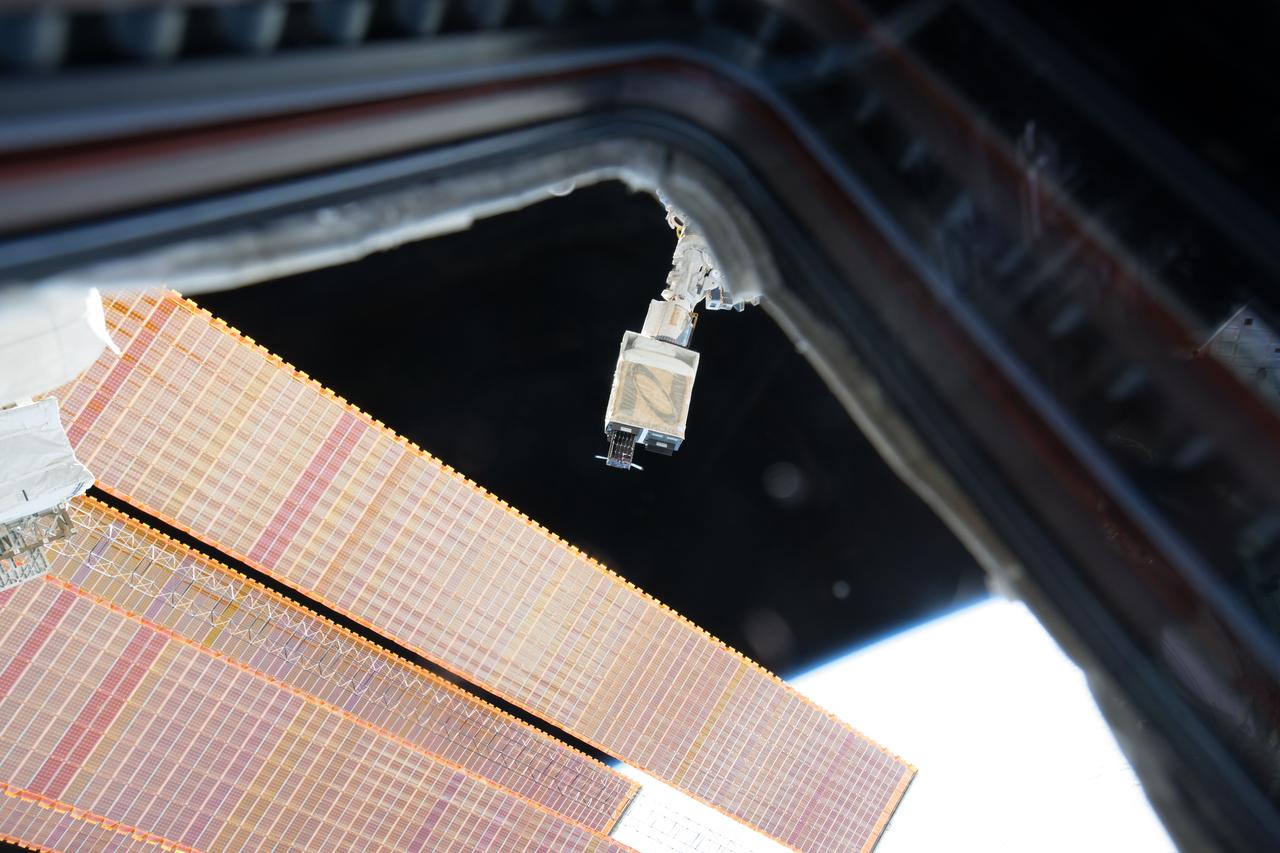
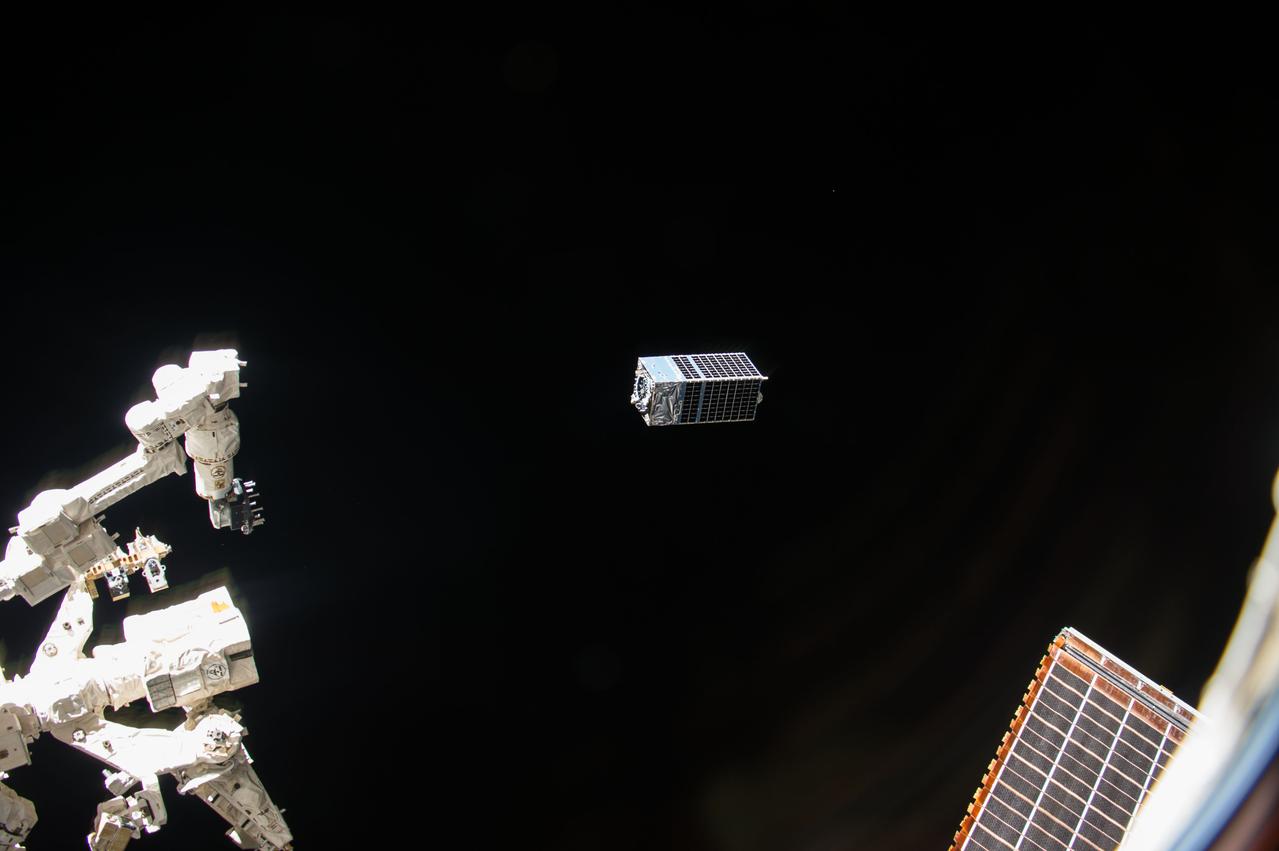
iss053e235231 (11/20/2017) --- A view of the Dellingr/RBLE Satellite deployment from the NanoRacks CubeSate Deployer Number 13 aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Dellingr/RBLE expands understanding of space weather risk by establishing baseline estimates of magnetic variation and particle fluxes in the exosphere. The instrument also observes cause and effect relationships between solar events and Earth’s atmosphere, which advances fundamental understanding of electromagnetic dynamics in the space environment.

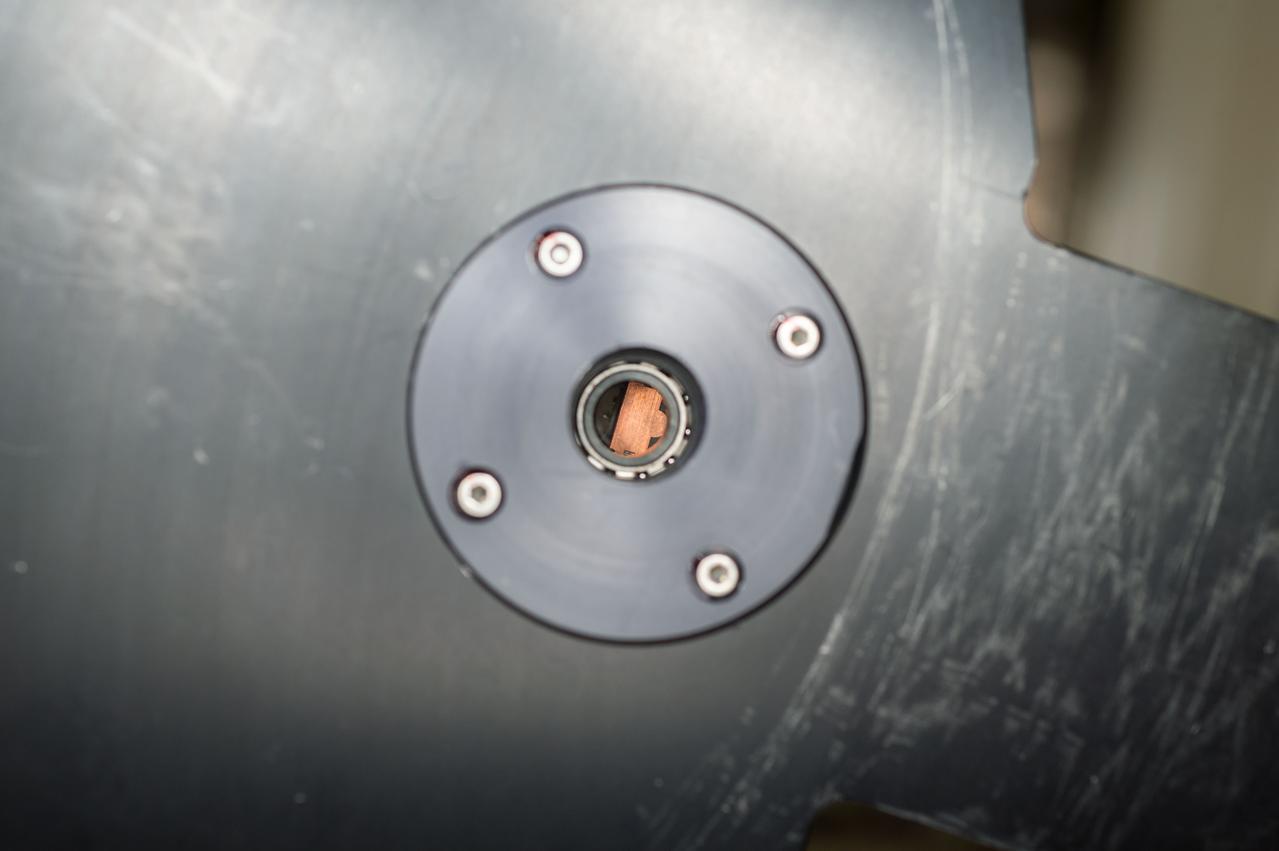
iss065e170116 (7/20/2021) --- Photo taken during the Ultrasonic Tweezers experiment setup and execution in the Columbus module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The objective of the Ultrasonic Tweezers project is to develop acoustic tweezers that use sound to allow for remote and contactless manipulation of materials in a microgravity context. An ultrasound beam is shaped so that it produces a trap from which an object cannot easily exit. By moving the beam, the object can be moved to a new position with a very good precision.
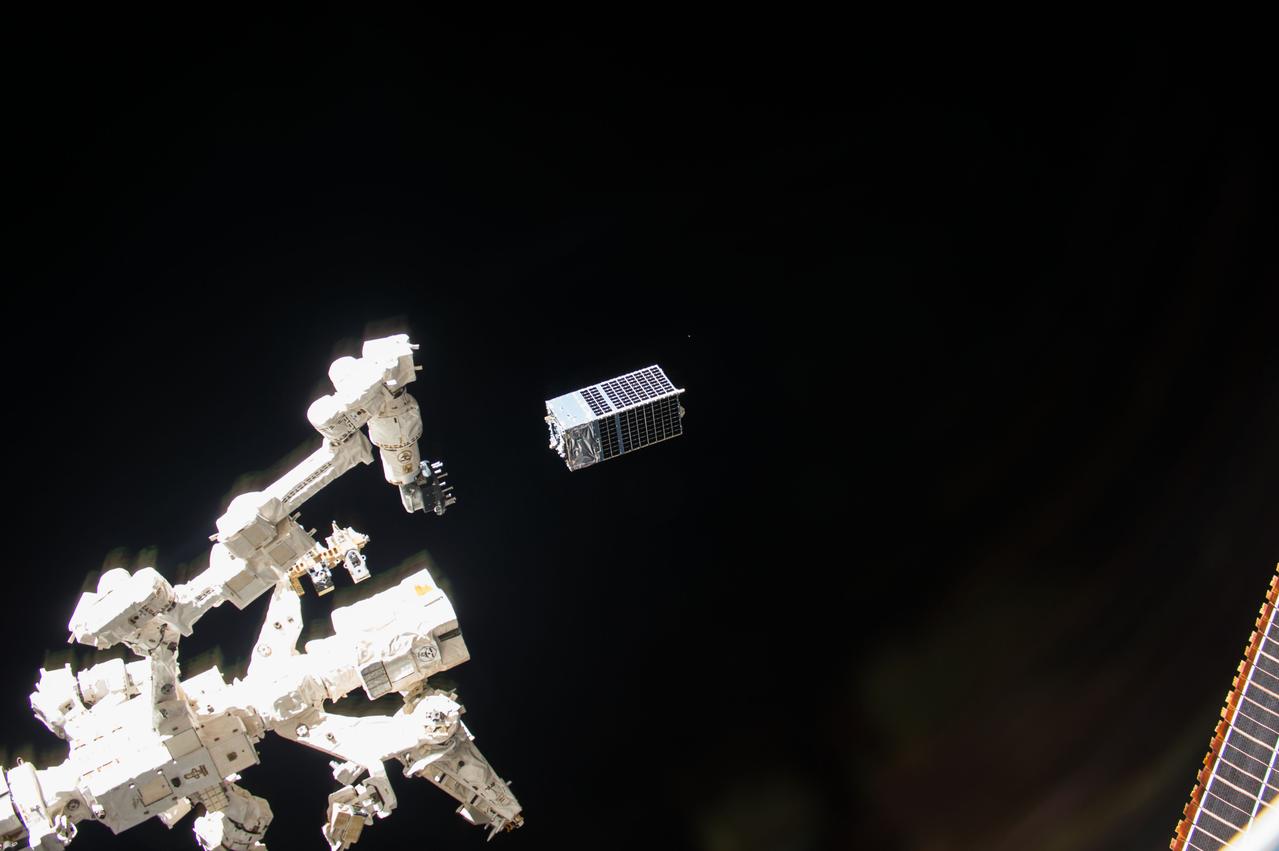

iss053e130267 (Oct. 24, 2017) --- The Kestrel Eye IIM (KE2M) CubeSat is deployed from the tip of the Dextre attached to the Mobile Servicing System. The KE2M is carrying an optical imaging system payload that is being used to validate the concept of using microsatellites in low-Earth orbit to support critical operations.
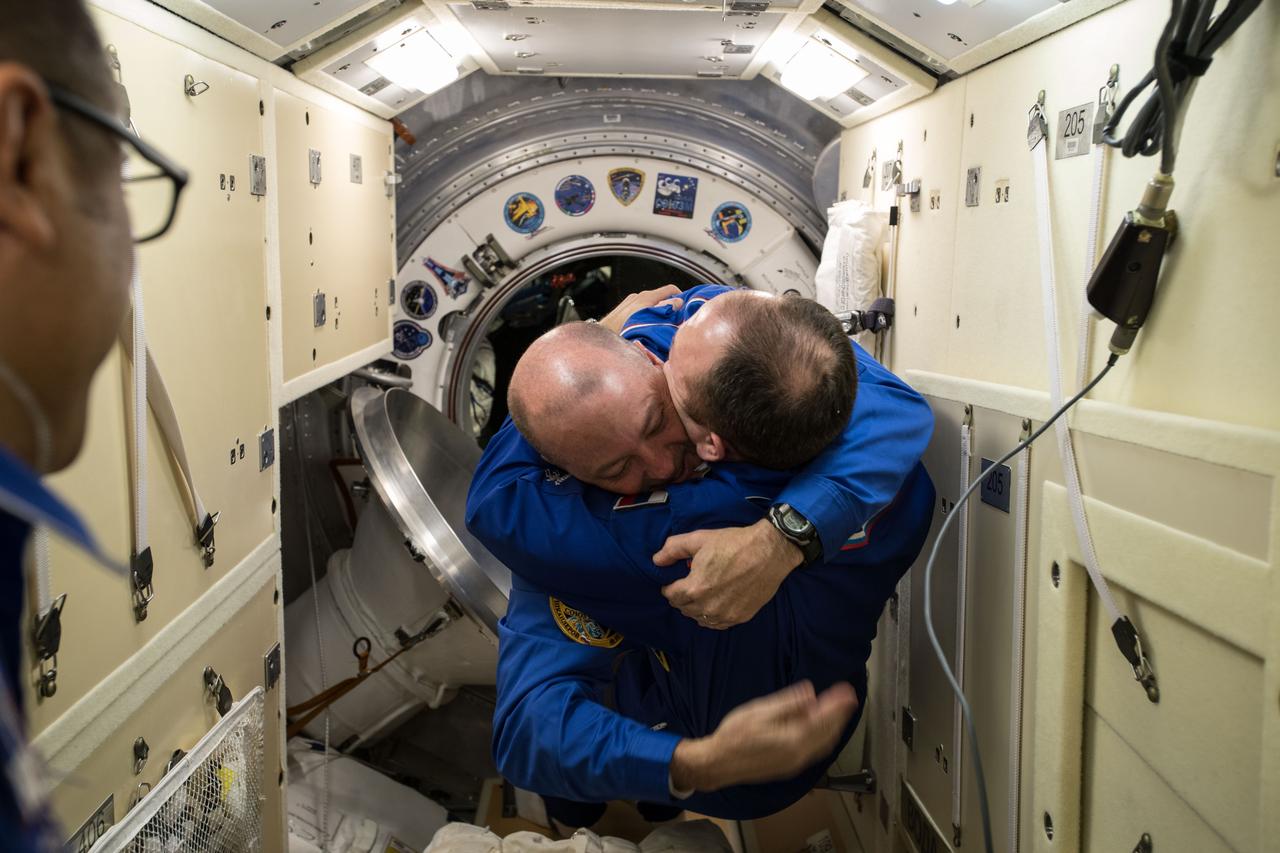

iss054e001407 (Dec. 19, 2017) --- International Space Station Commander Alexander Misurkin welcomes newly arrived Flight Engineer Scott Tingle in the Rassvet Mini-Research Module 1 following the hatch opening of the Soyuz MS-07 spacecraft.
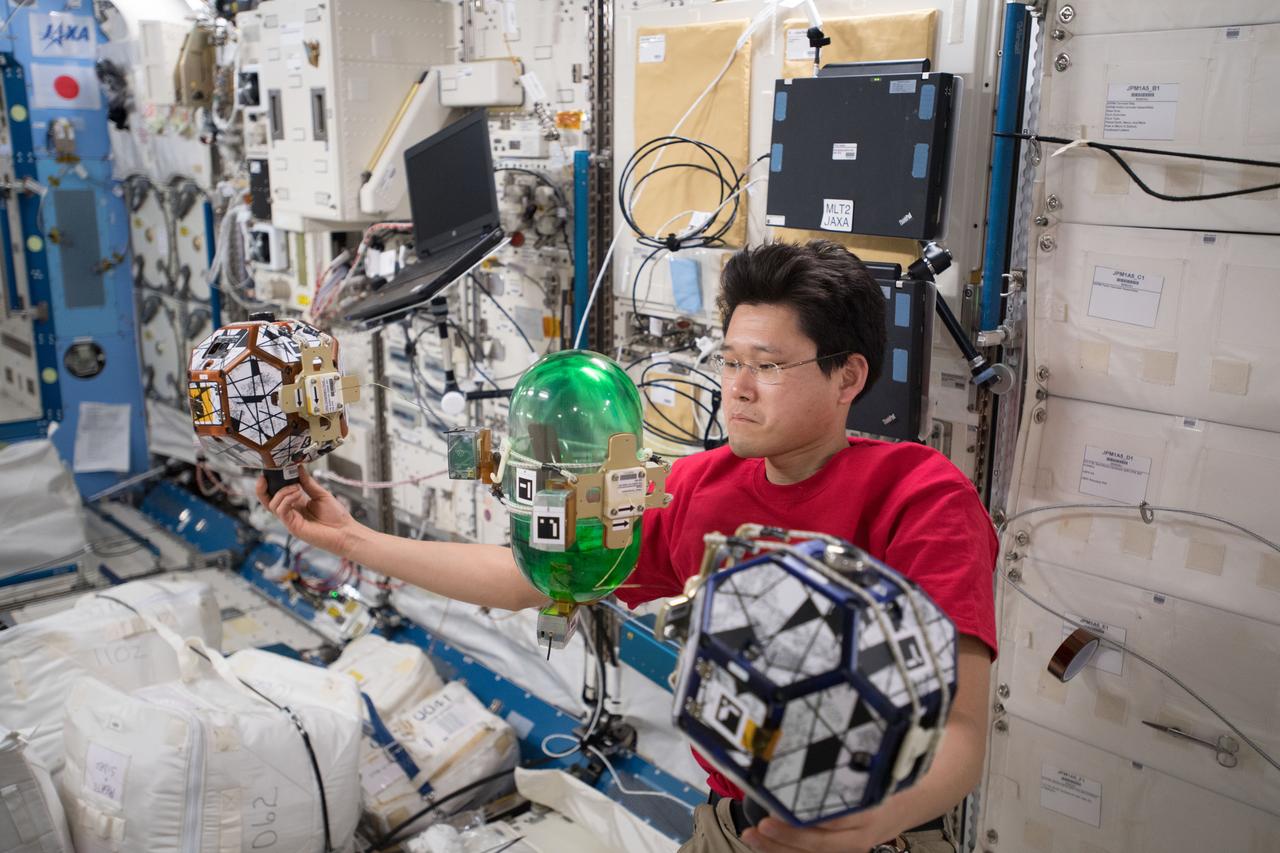

iss054e022175 (1/17/2018) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Norishige Kanai is photographed during a Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) Tether Slosh experiment test session run. Photo was taken in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). SPHERES Tether Slosh combines fluid dynamics equipment with robotic capabilities aboard the ISS to investigate automated strategies for steering passive cargo that contain fluids. In space, the fluid fuels used by spacecraft can slosh around in unpredictable ways making space maneuvers difficult. SPHERES Tether Slosh uses two Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) robots tethered to a fluid-filled container covered in sensors to test strategies for safely steering spacecraft such as dead satellites that might still have fuel in the tank.

iss065e170118 (7/20/2021) --- NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei working with the Ultrasonic Tweezers experiment setup and execution in the Columbus module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The objective of the Ultrasonic Tweezers project is to develop acoustic tweezers that use sound to allow for remote and contactless manipulation of materials in a microgravity context. An ultrasound beam is shaped so that it produces a trap from which an object cannot easily exit. By moving the beam, the object can be moved to a new position with a very good precision.
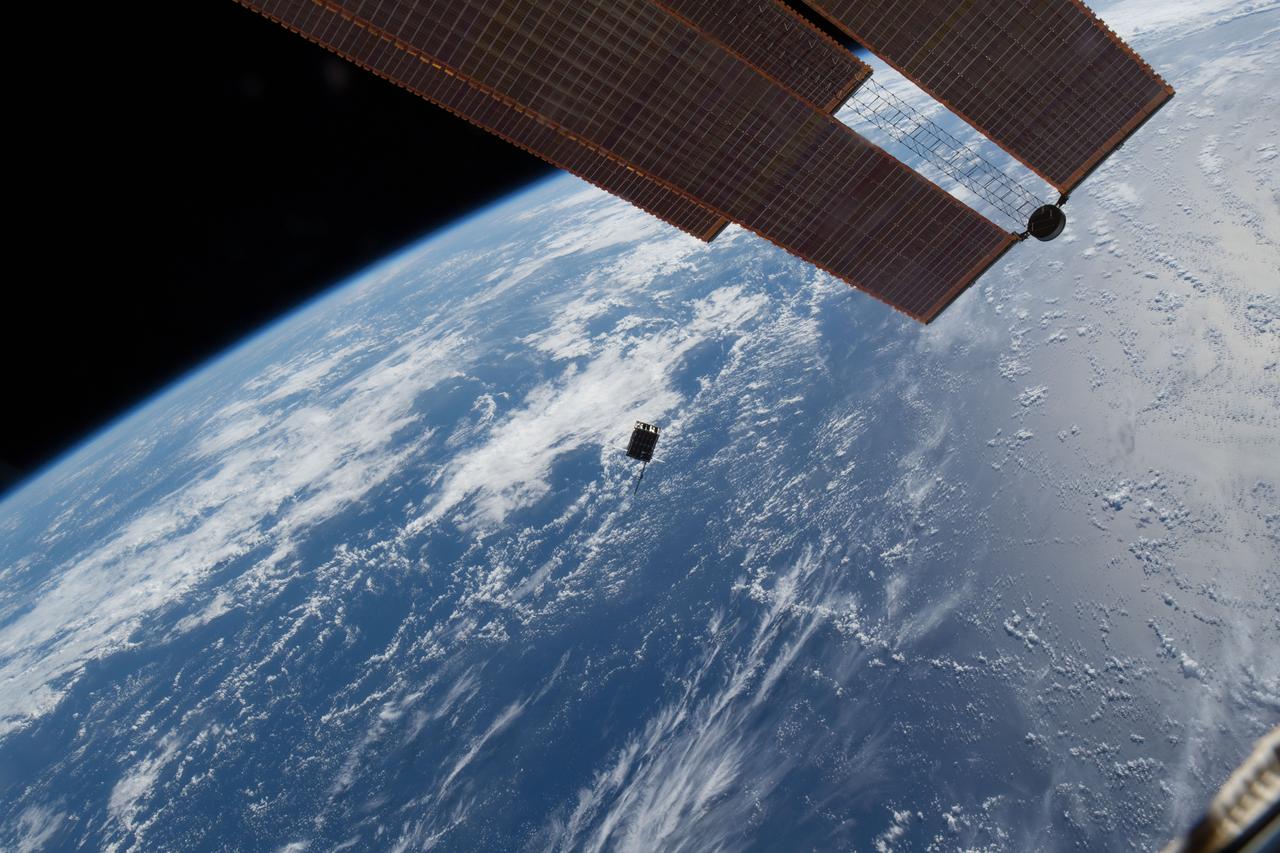

iss053e235256 (11/20/2017) --- A view of the Dellingr/RBLE Satellite deployment from the NanoRacks CubeSate Deployer Number 13 aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Dellingr/RBLE expands understanding of space weather risk by establishing baseline estimates of magnetic variation and particle fluxes in the exosphere. The instrument also observes cause and effect relationships between solar events and Earth’s atmosphere, which advances fundamental understanding of electromagnetic dynamics in the space environment.
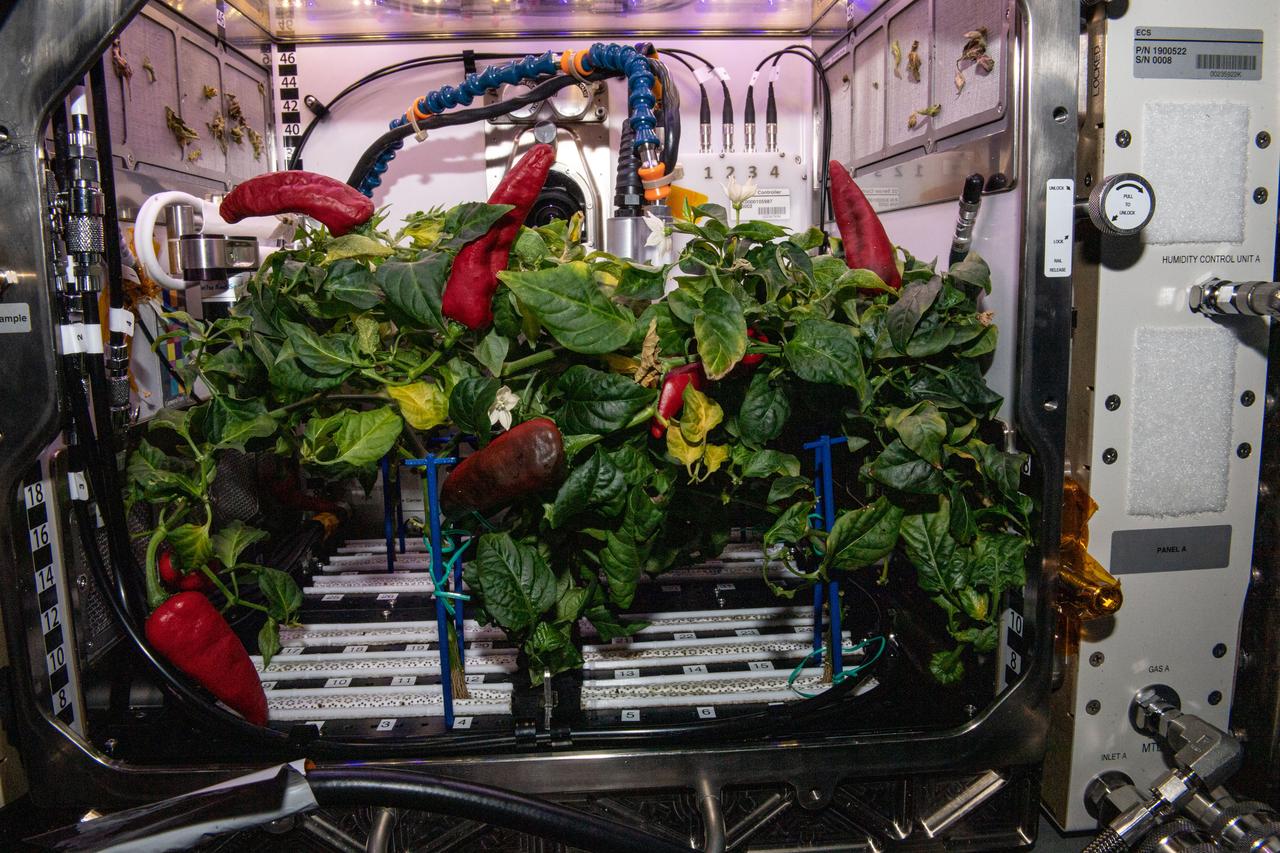

View of Chile Peppers growing inside the Advanced Plant Habitat in the Columbus Module during Expedition 66.
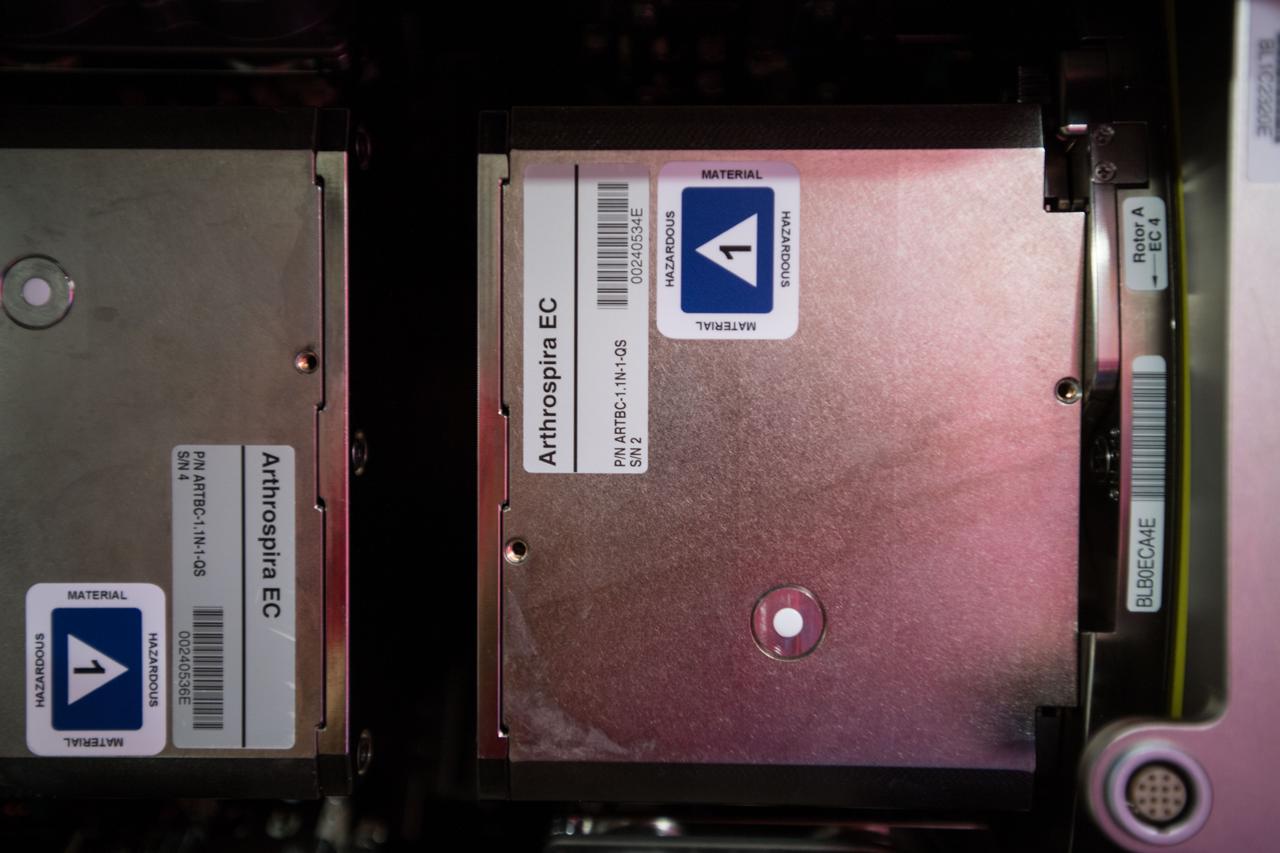

iss054e005660 (Dec. 27, 2017) --- Experiment Containers (EC) for the Arthrospira B experiment inside BioLab to test the oxygen production of plants in space for a closed regenerative life support system.
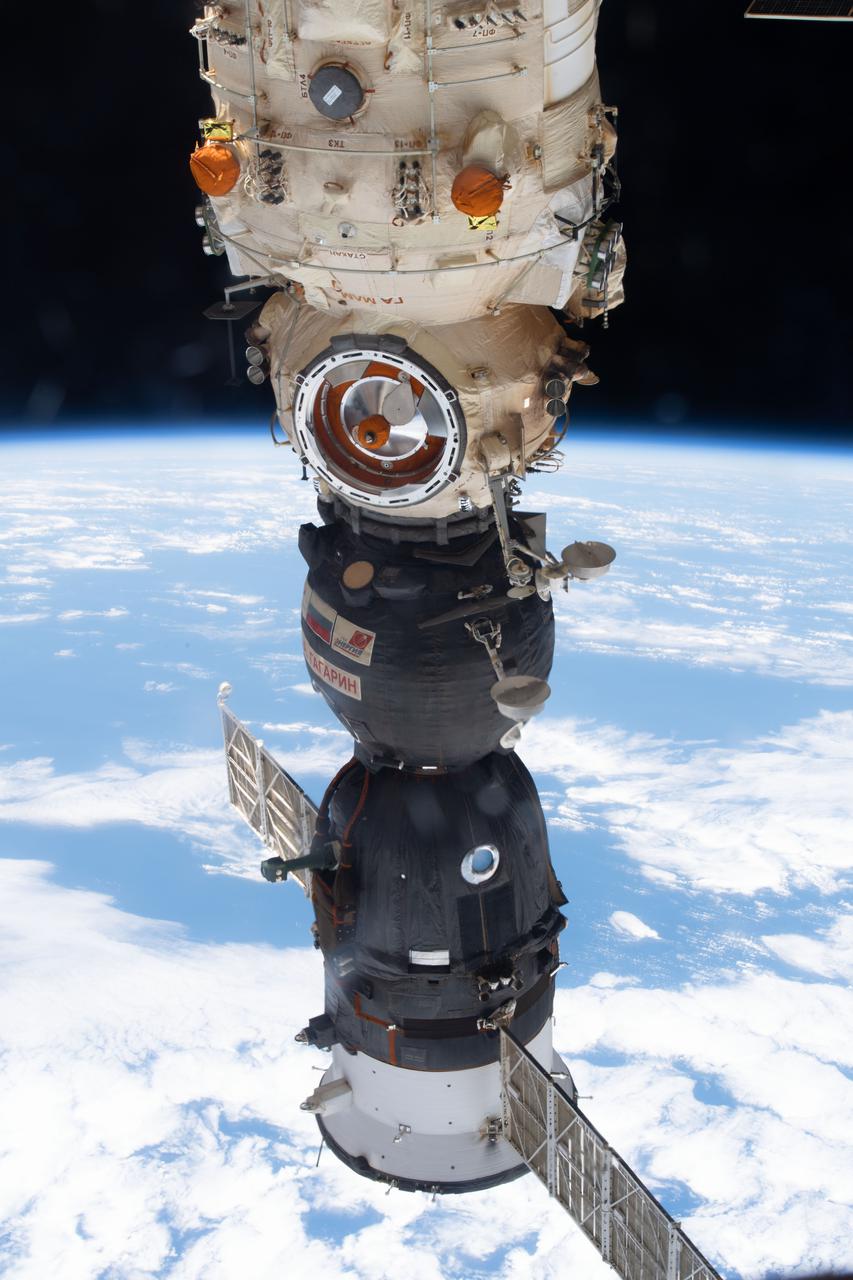

iss065e439837 (Oct. 2, 2021) --- The Soyuz MS-18 crew ship is docked to the Nauka multipurpose laboratory module in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above the Pacific Ocean off the coast of Mexico.
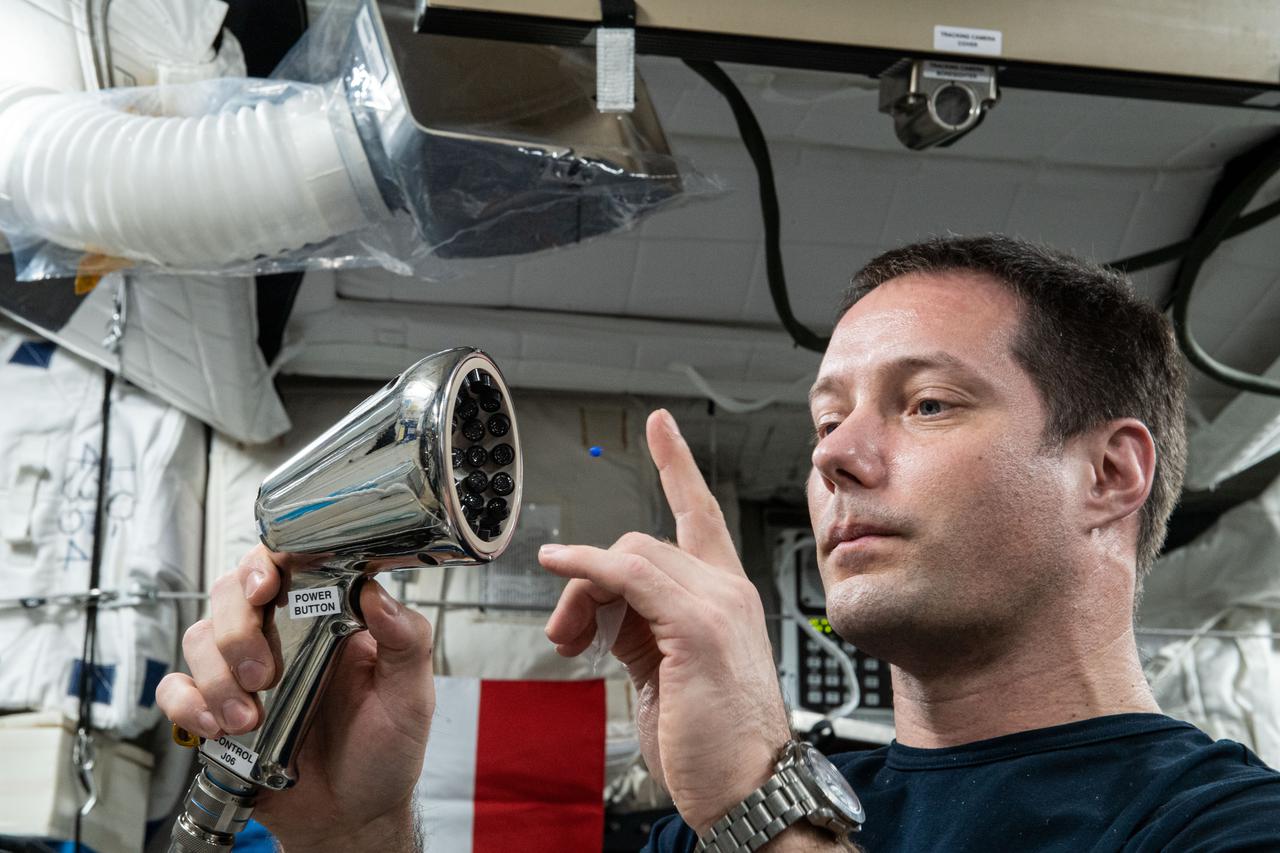

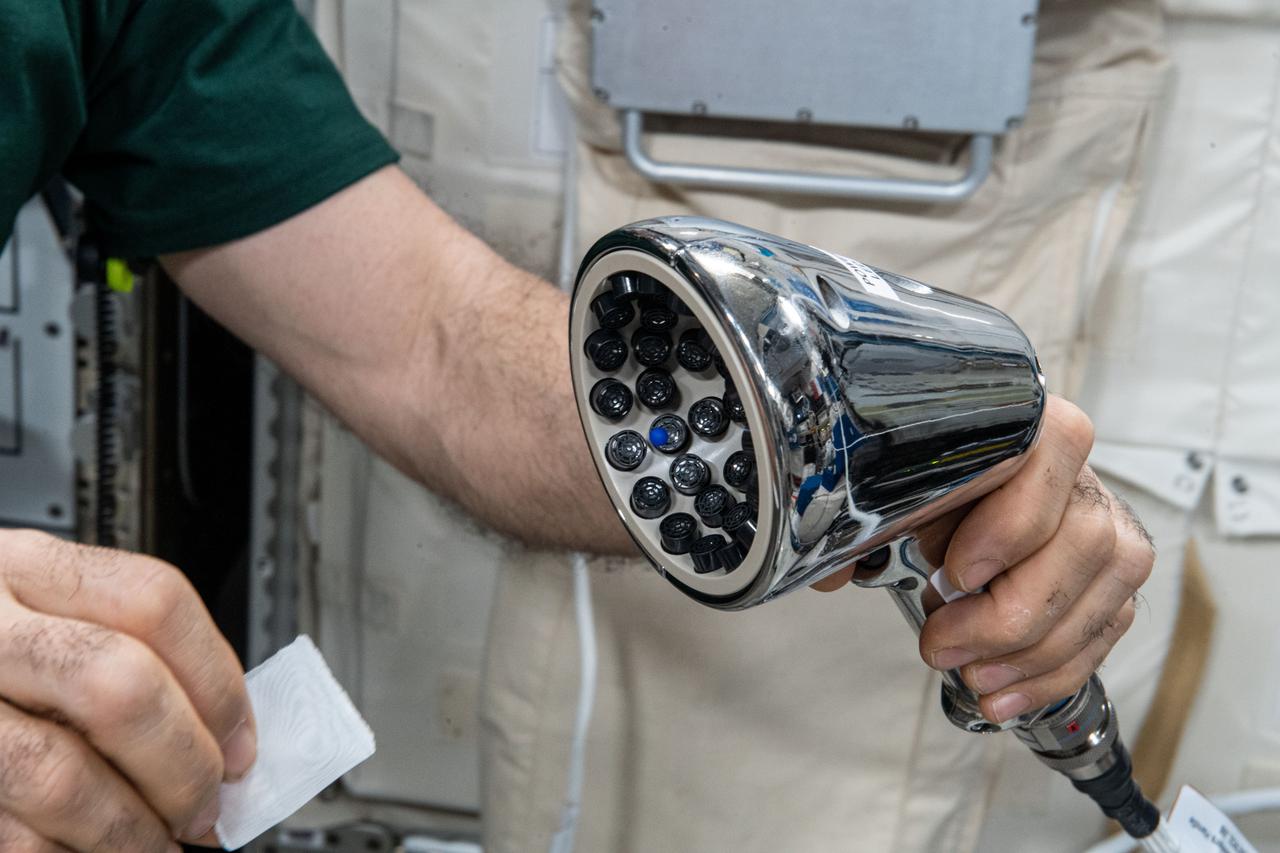
iss065e170099 (7/20/2021) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet working with the Ultrasonic Tweezers experiment setup and execution in the Columbus module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The objective of the Ultrasonic Tweezers project is to develop acoustic tweezers that use sound to allow for remote and contactless manipulation of materials in a microgravity context. An ultrasound beam is shaped so that it produces a trap from which an object cannot easily exit. By moving the beam, the object can be moved to a new position with a very good precision.
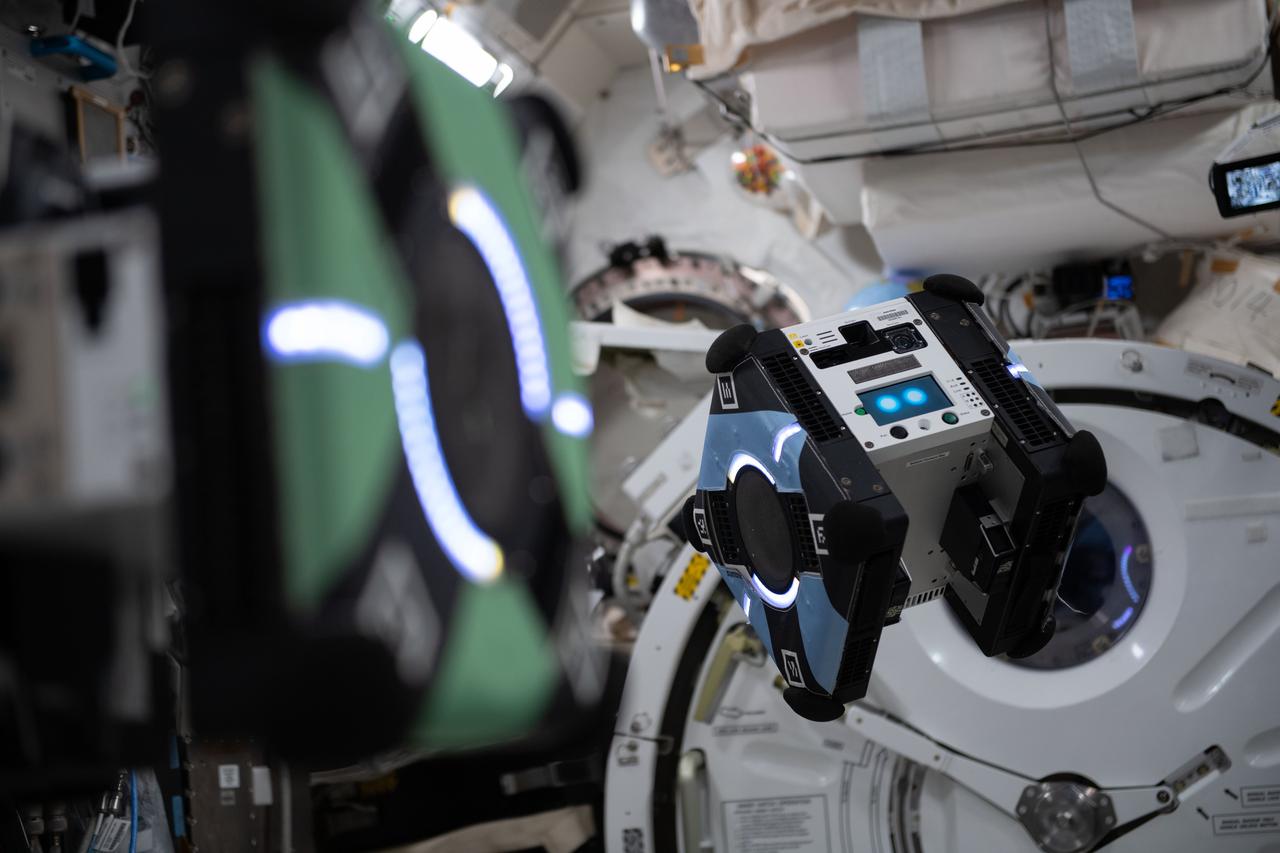

iss066e134729 (Feb. 2, 2022) --- A view of an Astrobee ROAM Operations Session 2 in the JEM during Expedition 66. ROAM demonstrates processes for a robotic craft to rendezvous with debris in space. Space debris includes satellites that could be repaired or taken out of orbit, but many of these objects are tumbling, making rendezvous and docking challenging. ROAM uses the space station’s Astrobee robots to observe and understand how targets tumble and uses this information to plan ways to safely reach them.
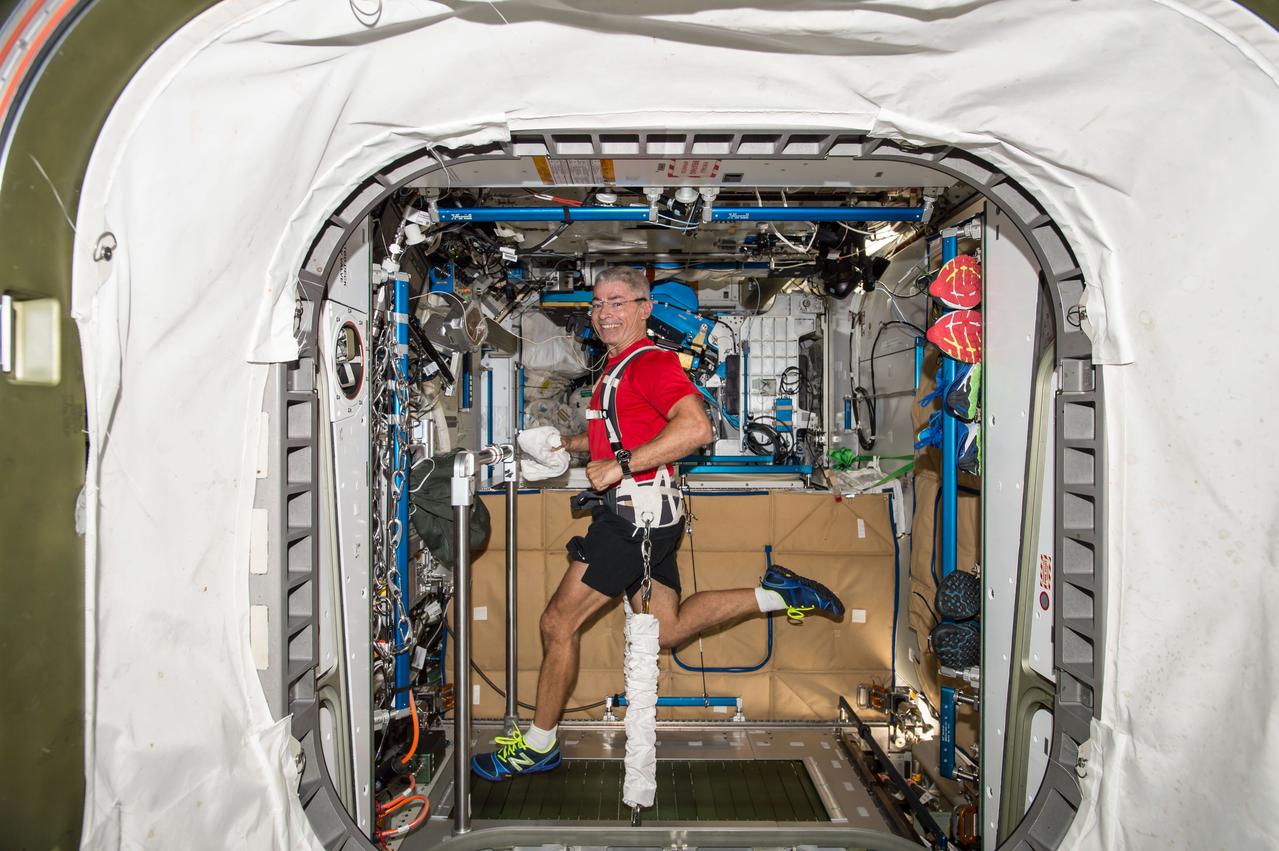

iss053e040103 (ept. 23, 2017) --- Astronaut Mark Vande Hei, Expedition 53 Flight Engineer, exercises on the COLBERT (Combined Operational Load Bearing External Resistance Treadmill) in the Tranquility module.
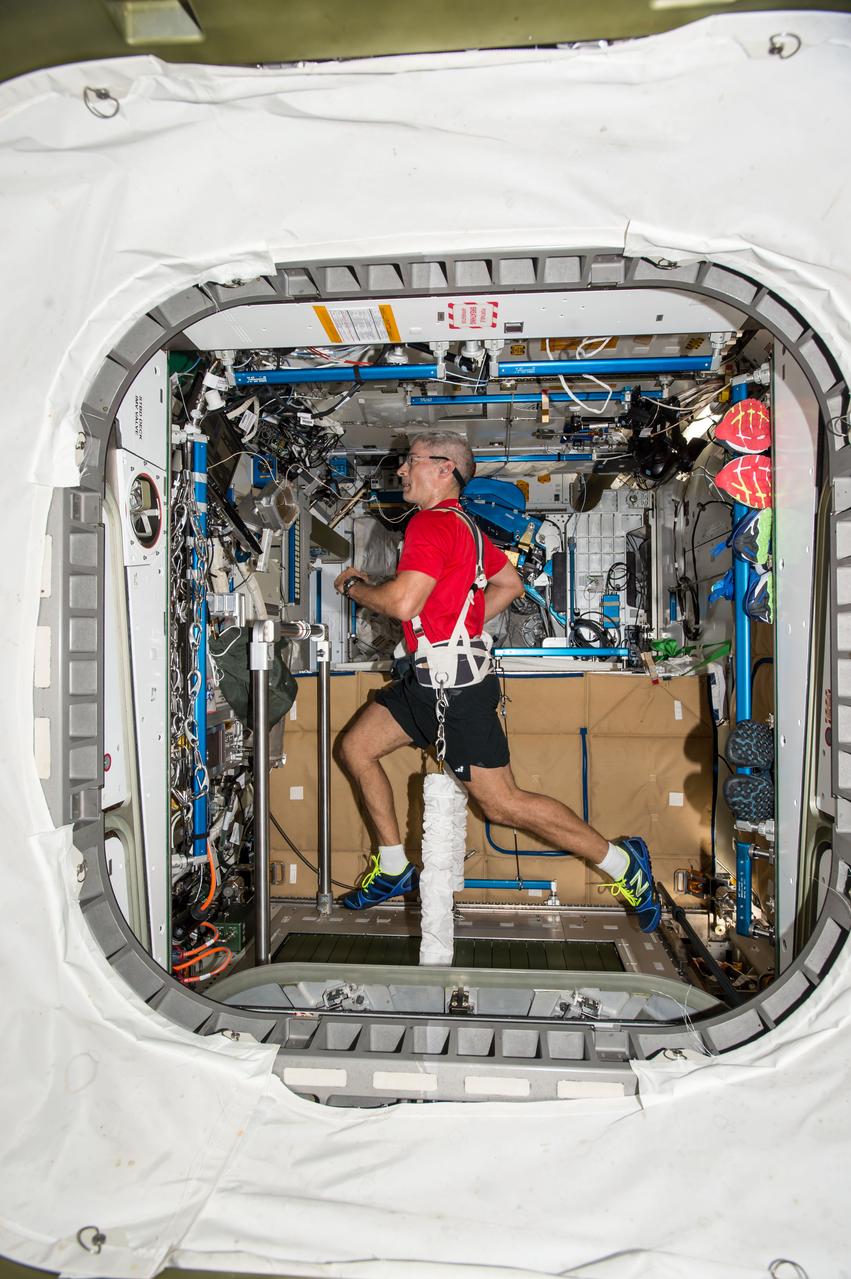

iss053e040100 (Sept. 23, 2017) --- NASA astronaut Mark Vande Hei jogs on a treadmill inside the space station.
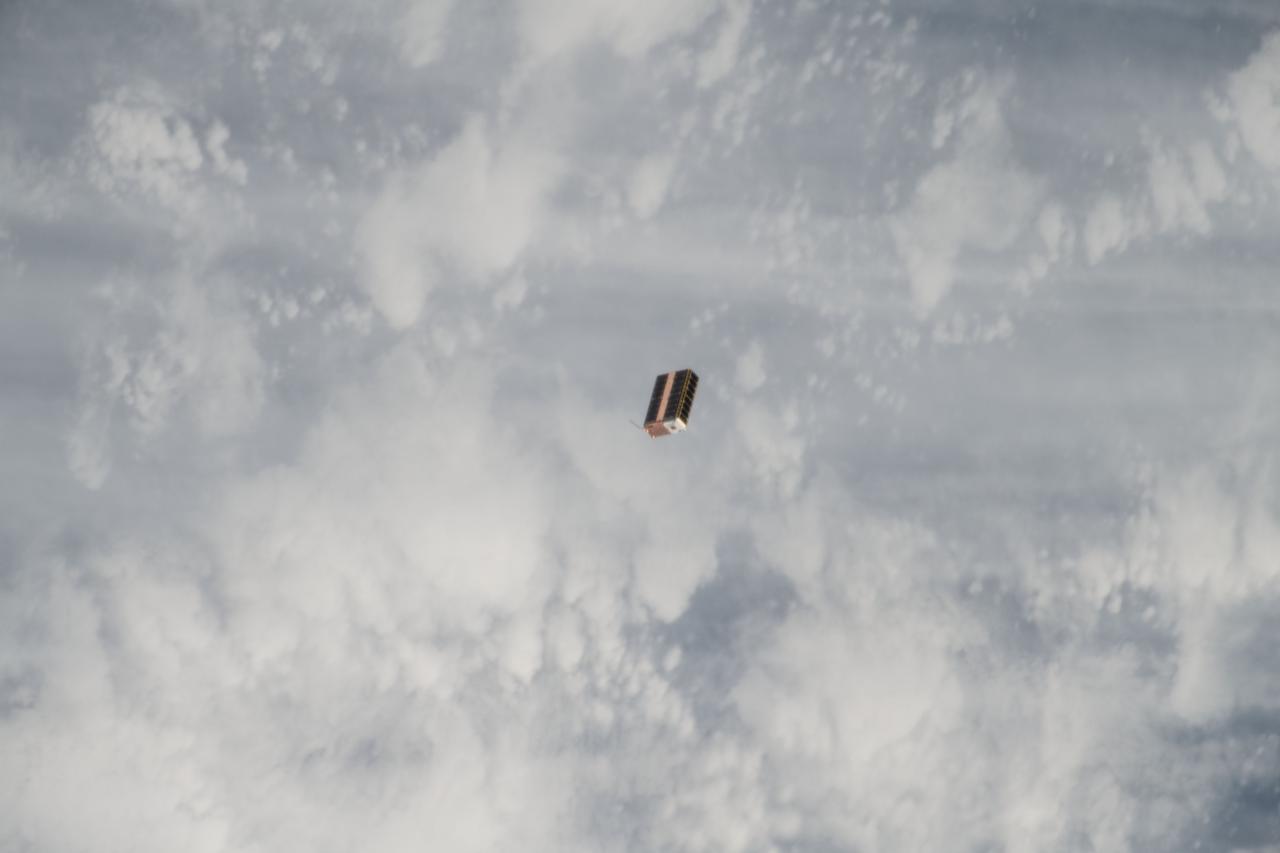

iss053e216632 (Nov. 20, 2017) --- The EcAMSat, short for E. coli AntiMicrobial Satellite, is seen moments after being ejected from the NanoRacks CubeSat Deployer attached to the outside of Kibo laboratory module from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. The E. coli AntiMicrobial Satellite (EcAMSat) mission will investigate space microgravity effects on the antibiotic resistance of E. coli, a bacterial pathogen responsible for urinary tract infection in humans and animals.
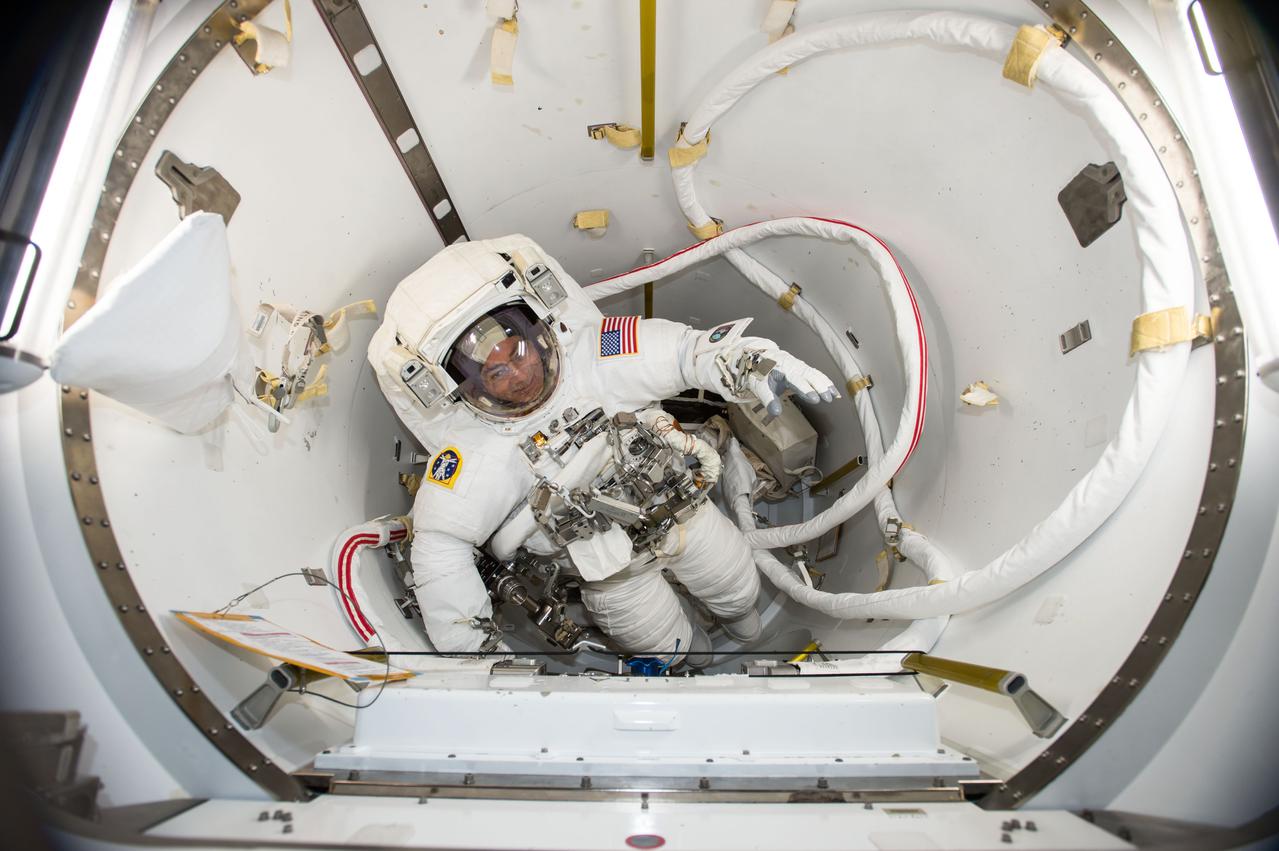

iss053e064252 (Sept. 29, 2017) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 53 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei verifies his U.S. spacesuit fits while inside the International Space Station's U.S. Quest airlock.
iss053e130305 (Oct. 24, 2017) --- The Kestrel Eye IIM (KE2M) CubeSat is deployed from the tip of the Dextre attached to the Mobile Servicing System. The KE2M is carrying an optical imaging system payload that is being used to validate the concept of using microsatellites in low-Earth orbit to support critical operations.

iss053e235238(11/20/2017) --- A view of the Dellingr/RBLE Satellite deployment from the NanoRacks CubeSate Deployer Number 13 aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Dellingr/RBLE expands understanding of space weather risk by establishing baseline estimates of magnetic variation and particle fluxes in the exosphere. The instrument also observes cause and effect relationships between solar events and Earth’s atmosphere, which advances fundamental understanding of electromagnetic dynamics in the space environment.
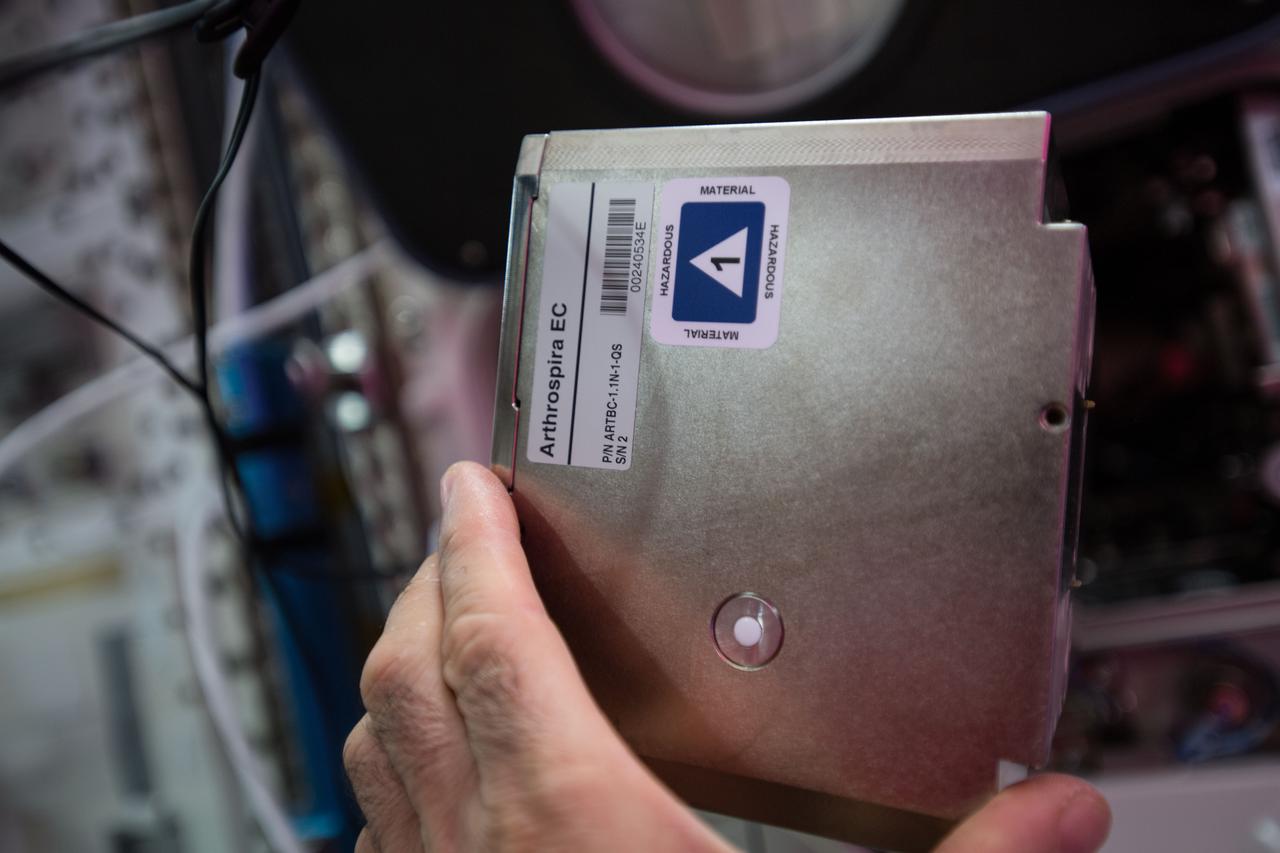

iss054e005663 (Dec. 27, 2017) --- Experiment Container (EC) for the Arthrospira B experiment to test the oxygen production of plants in space for a closed regenerative life support system.
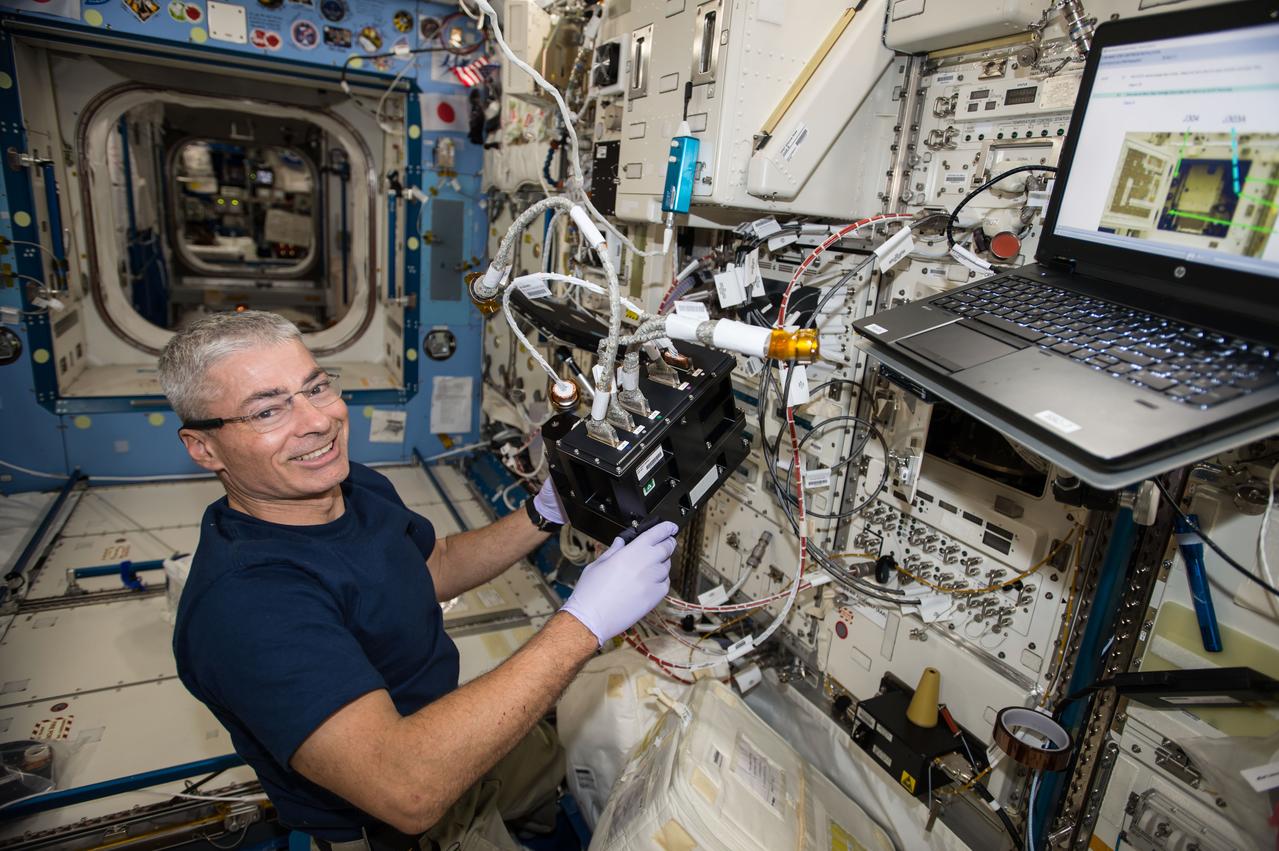

iss053e039947 (9/22/2017) --- NASA astronaut Mark T. Vande Hei is shown with the Advanced Nano Step Cartridge in the Solution Crystallization Observation Facility (SCOF) during installation. The Effects of Impurities on Perfection of Protein Crystals, Partition Functions, and Growth Mechanisms (Advanced Nano Step) experiment monitors and records how the incorporation of specific impurity molecules affect the development and quality of protein crystals, as they grow in a quartz cell aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
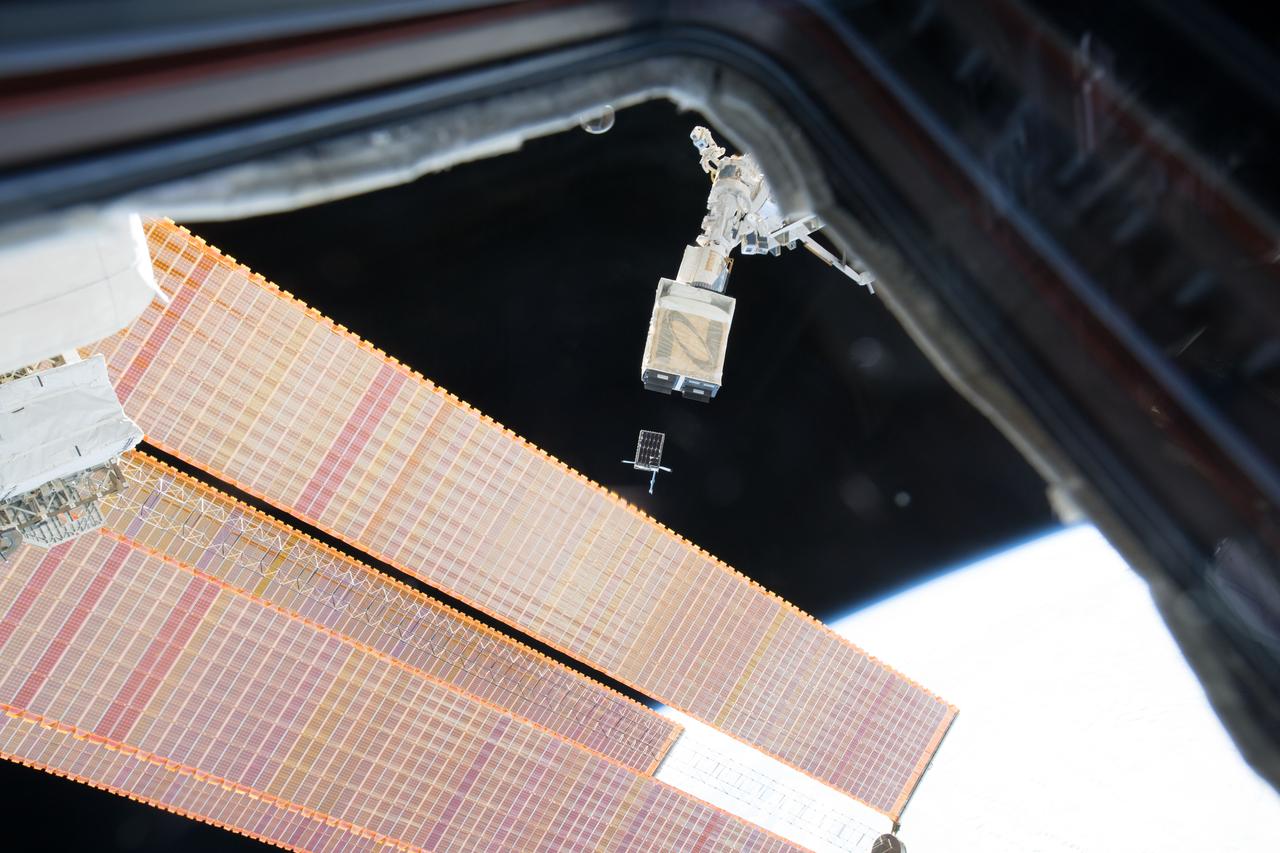
iss053e235232 (11/20/2017) --- A view of the Dellingr/RBLE Satellite deployment from the NanoRacks CubeSate Deployer Number 13 aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Dellingr/RBLE expands understanding of space weather risk by establishing baseline estimates of magnetic variation and particle fluxes in the exosphere. The instrument also observes cause and effect relationships between solar events and Earth’s atmosphere, which advances fundamental understanding of electromagnetic dynamics in the space environment.

iss054e005642 (Dec. 27, 2017) --- Experiment Container (EC) for the Arthrospira B experiment to test the oxygen production of plants in space for a closed regenerative life support system.
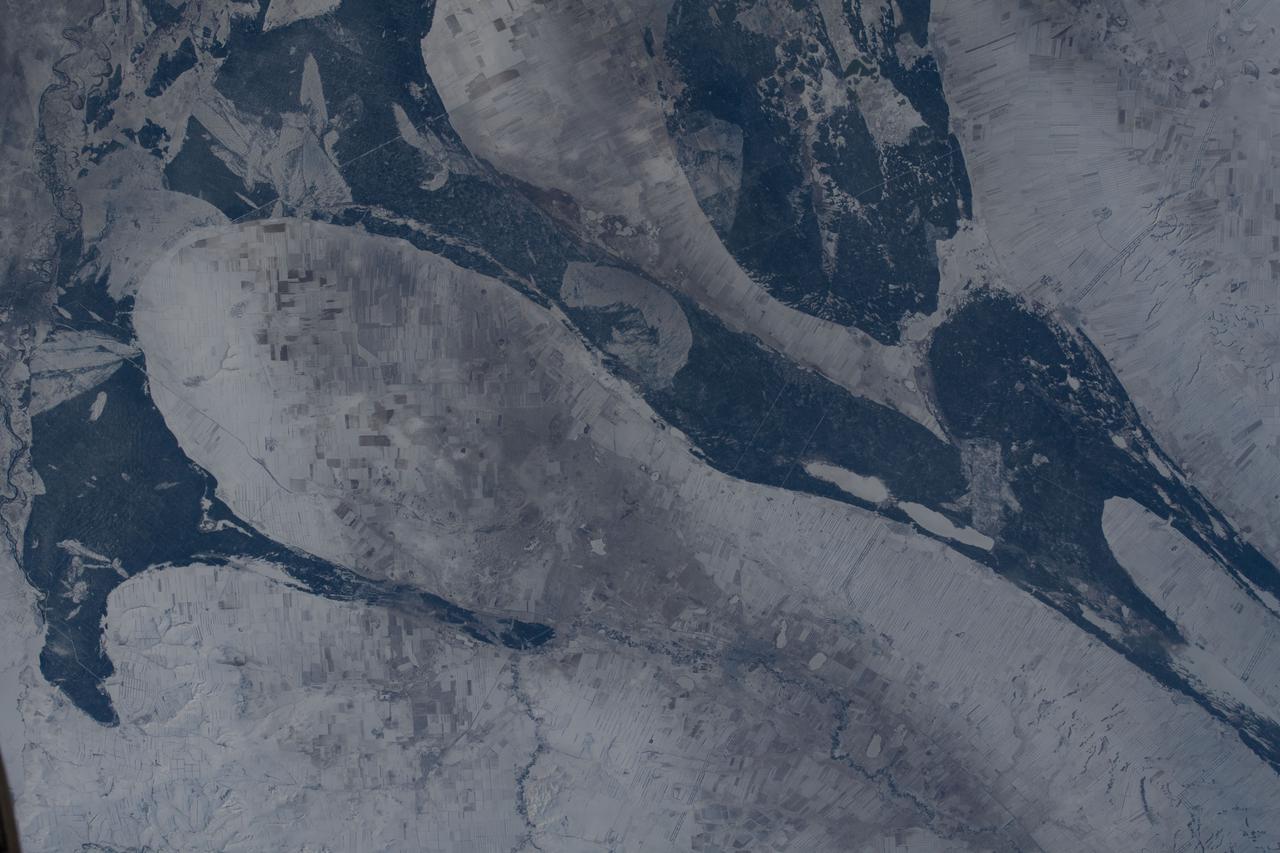

iss066e089960 (Dec. 11, 2021) --- Kazakhstan's snowy, northeast border with Russia is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 266 miles above central Asia.
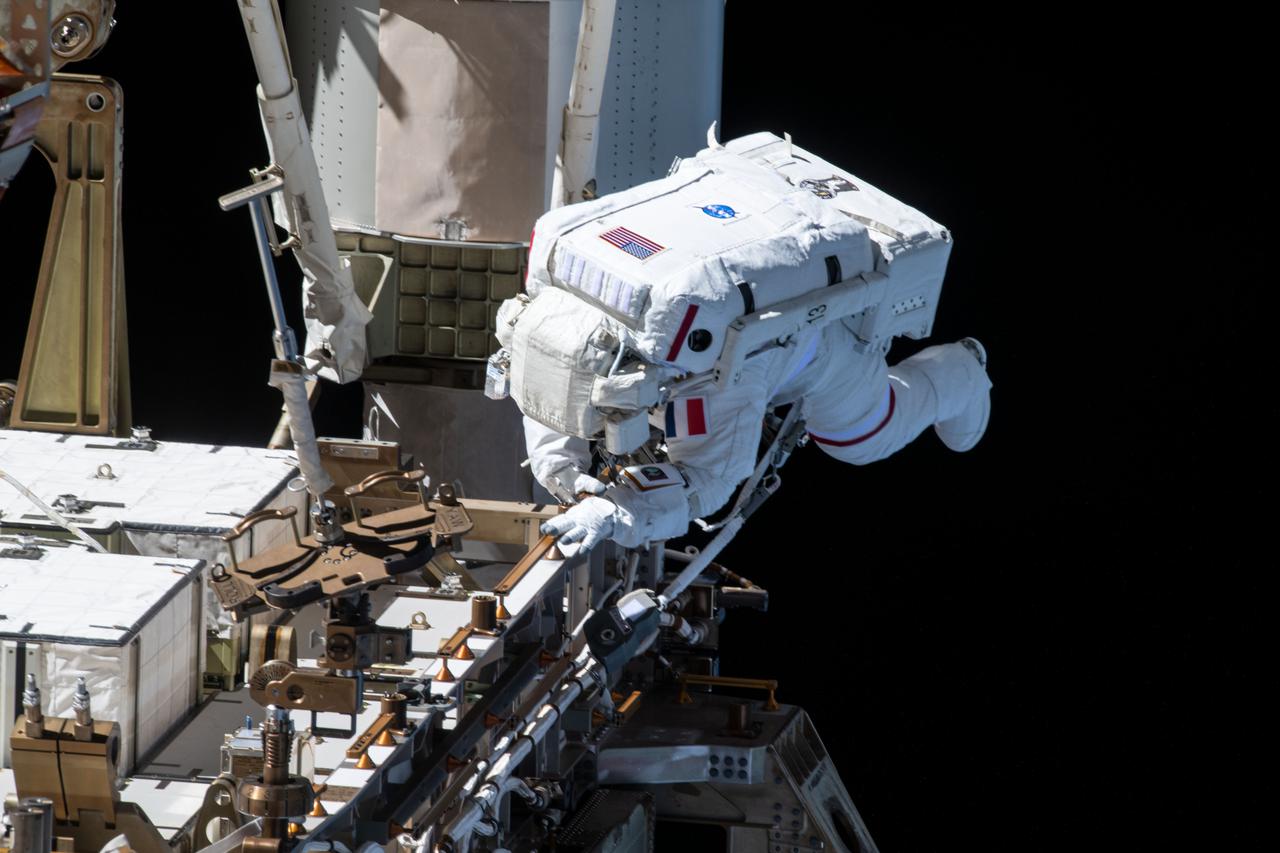

iss065e144936 (June 25, 2021) --- Spacewalker Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) works to complete the installation of the second roll out solar array on the International Space Station's Port-6 truss structure.
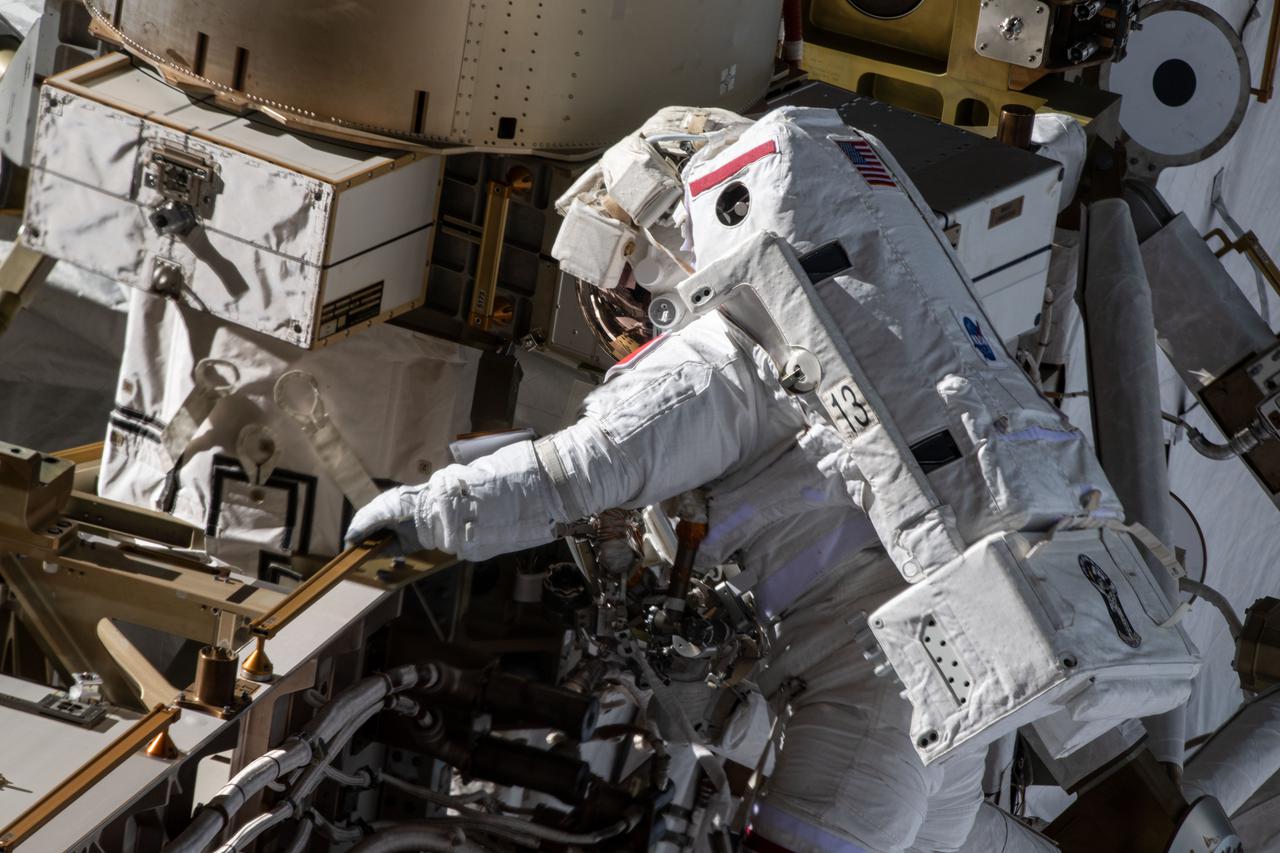

iss065e145037 (June 25, 2021) --- Spacewalker Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) works to complete the installation of the second roll out solar array on the International Space Station's Port-6 truss structure.
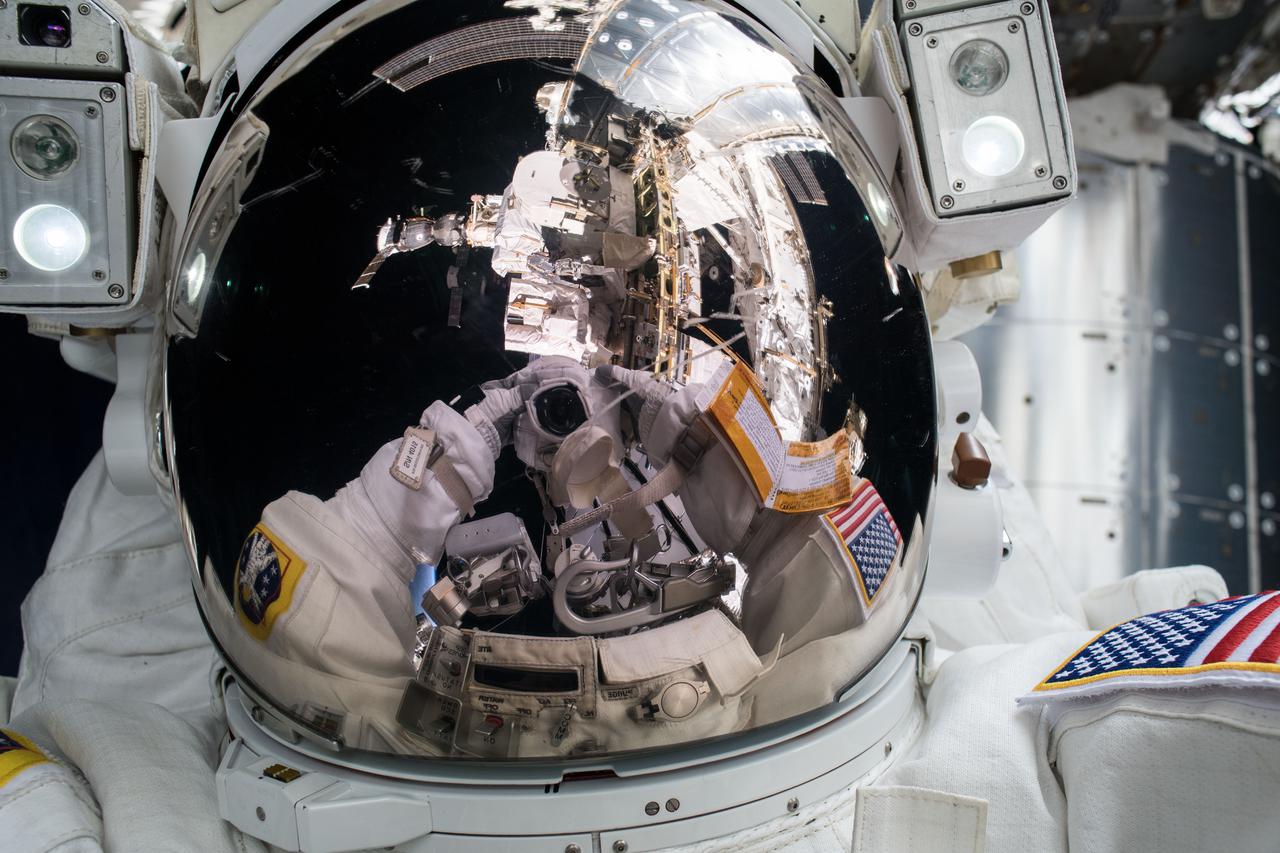

iss054e047709 (Feb. 16, 2018) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 54 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei takes a "space-selfie" during a spacewalk with astronaut Norishige Kanai (out of frame) of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The duo spent nearly six hours servicing components on the Canadarm2 robotic arm.