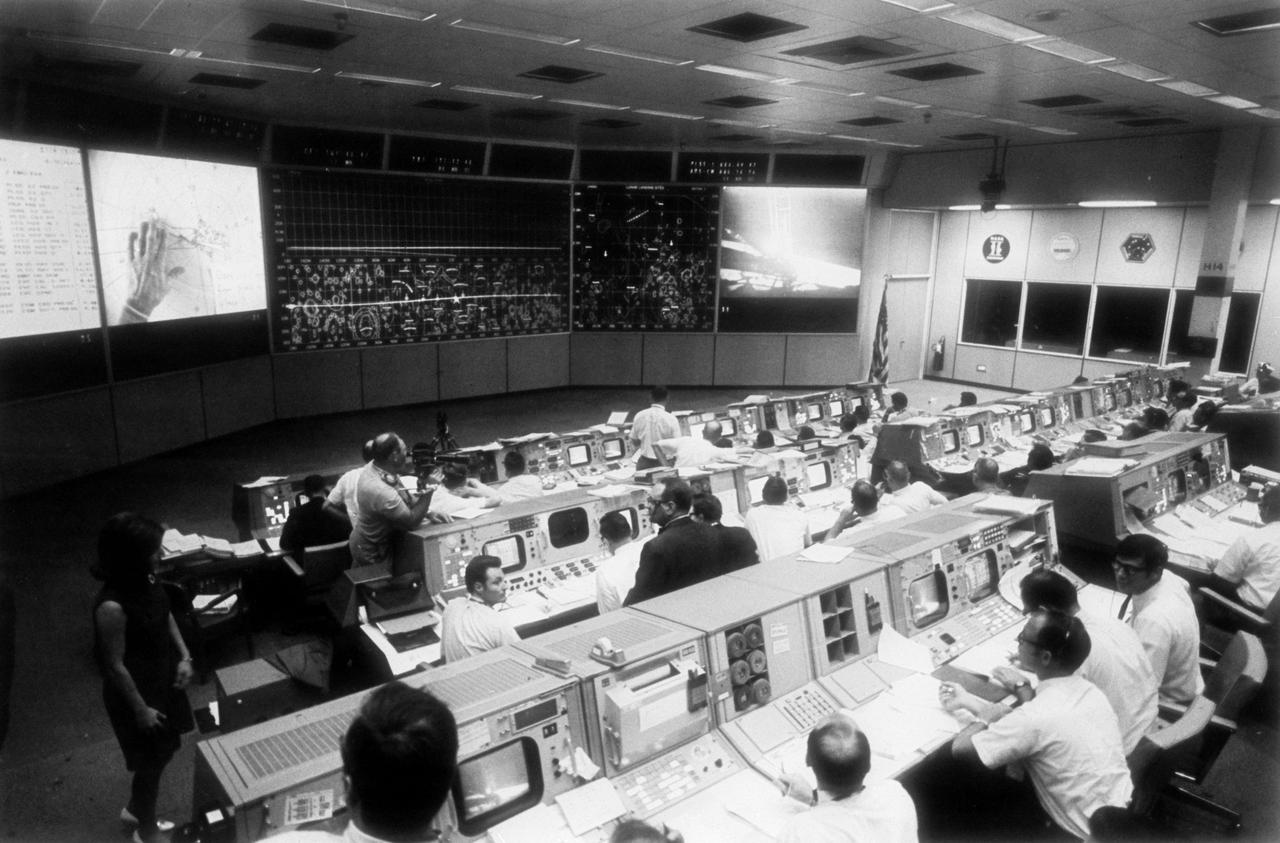

Overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center, bldg 30, during the lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) of Apollo 11 Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr.
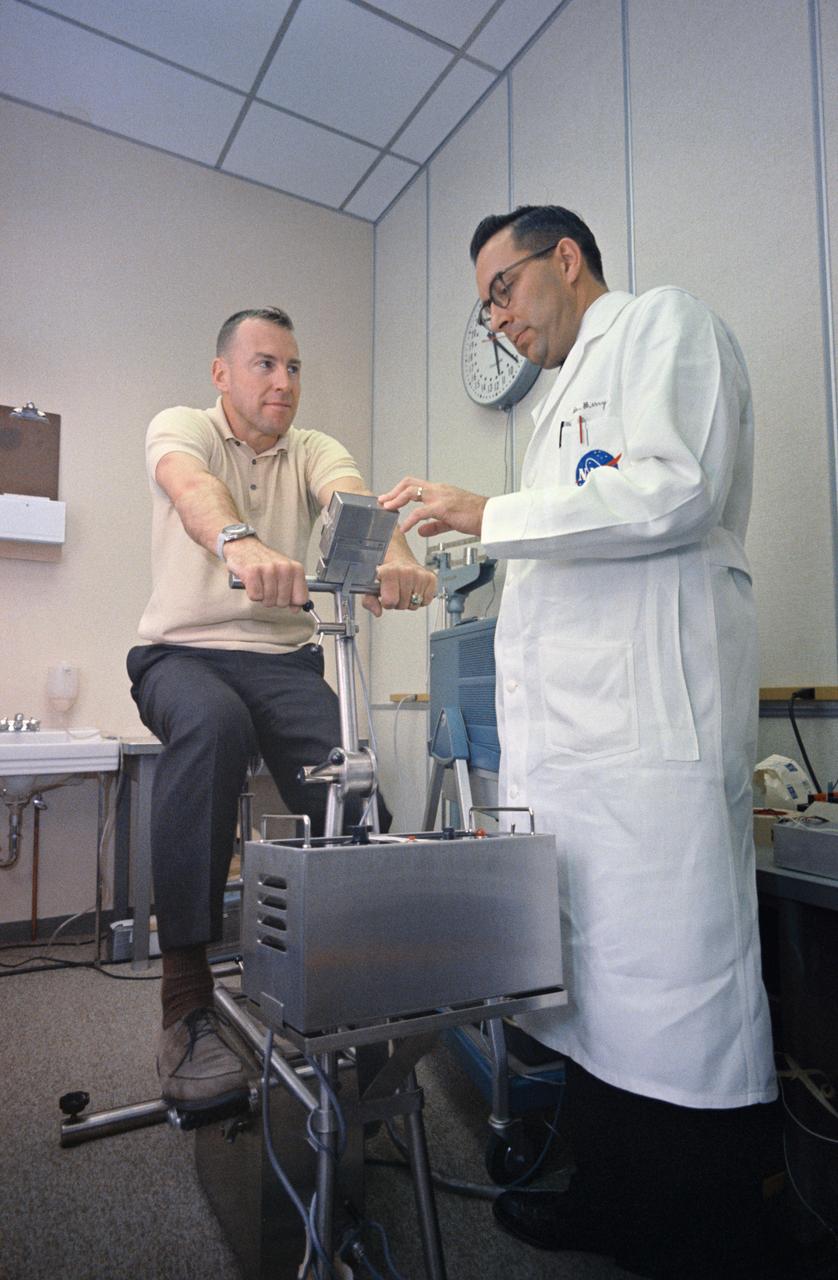
S65-60602 (2 Dec. 1965) --- Dr. Charles A. Berry checks astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Gemini-7 prime crew pilot, following a workout on an exercise machine. Results will be compared with those obtained during spaceflight for evaluation. Lovell and astronaut Frank Borman (not pictured), command pilot, will pilot the Gemini-7 spacecraft on a planned 14-day mission. Dr. Berry is chief, MSC Center Medical Programs. Photo credit: NASA
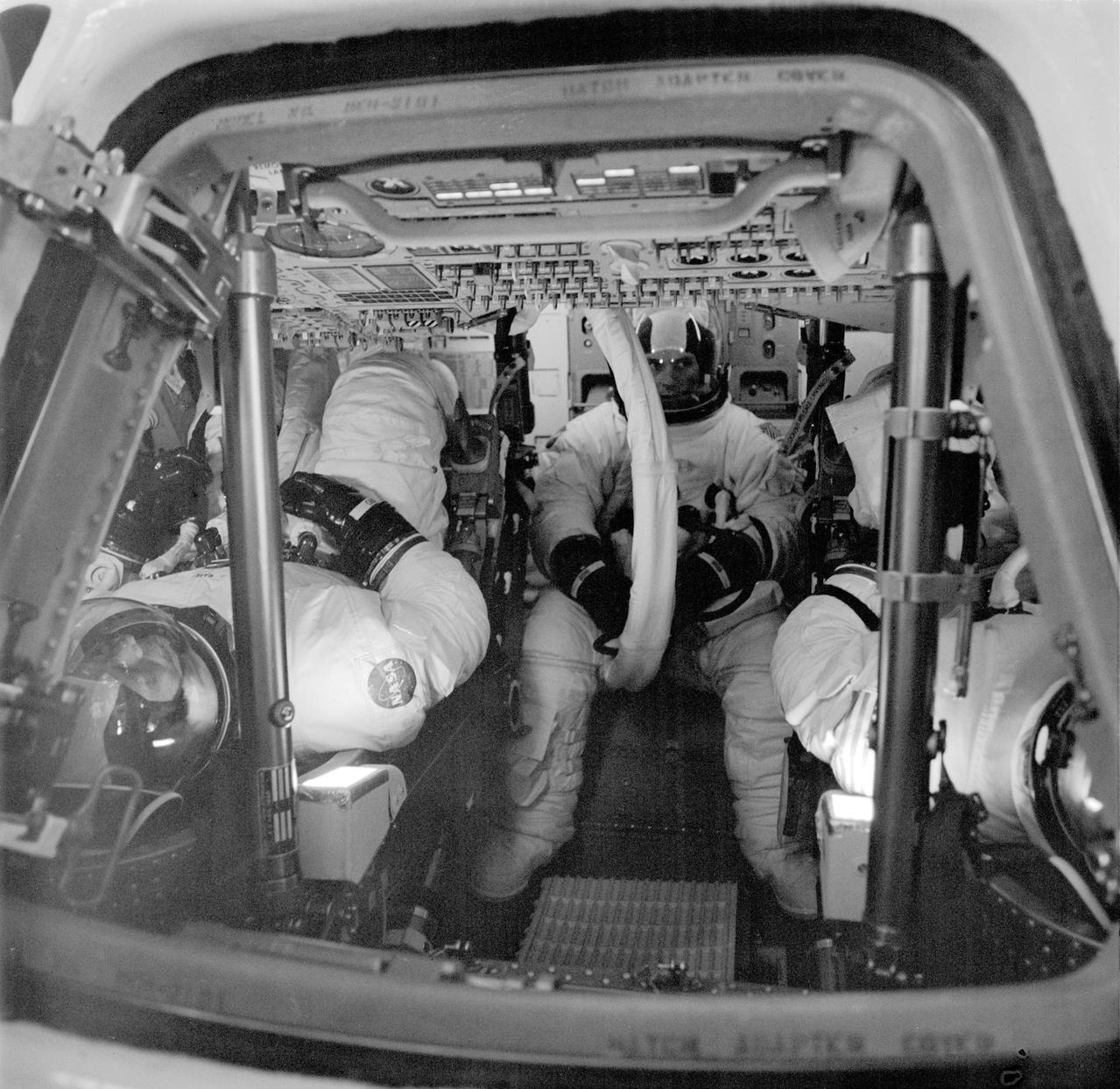

S73-34094 (6 Aug. 1973) --- The Skylab 4 crewmen, fully suited, are seated inside their Command Module, which has been undergoing high altitude chamber test runs at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) after being considered as a possible rescue vehicle, if needed, for the Skylab 3 crewmen. Facing the camera is scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot. Astronauts Gerald P. Carr, right, commander, and William R. Pogue, pilot, are also pictured. Photo credit: NASA
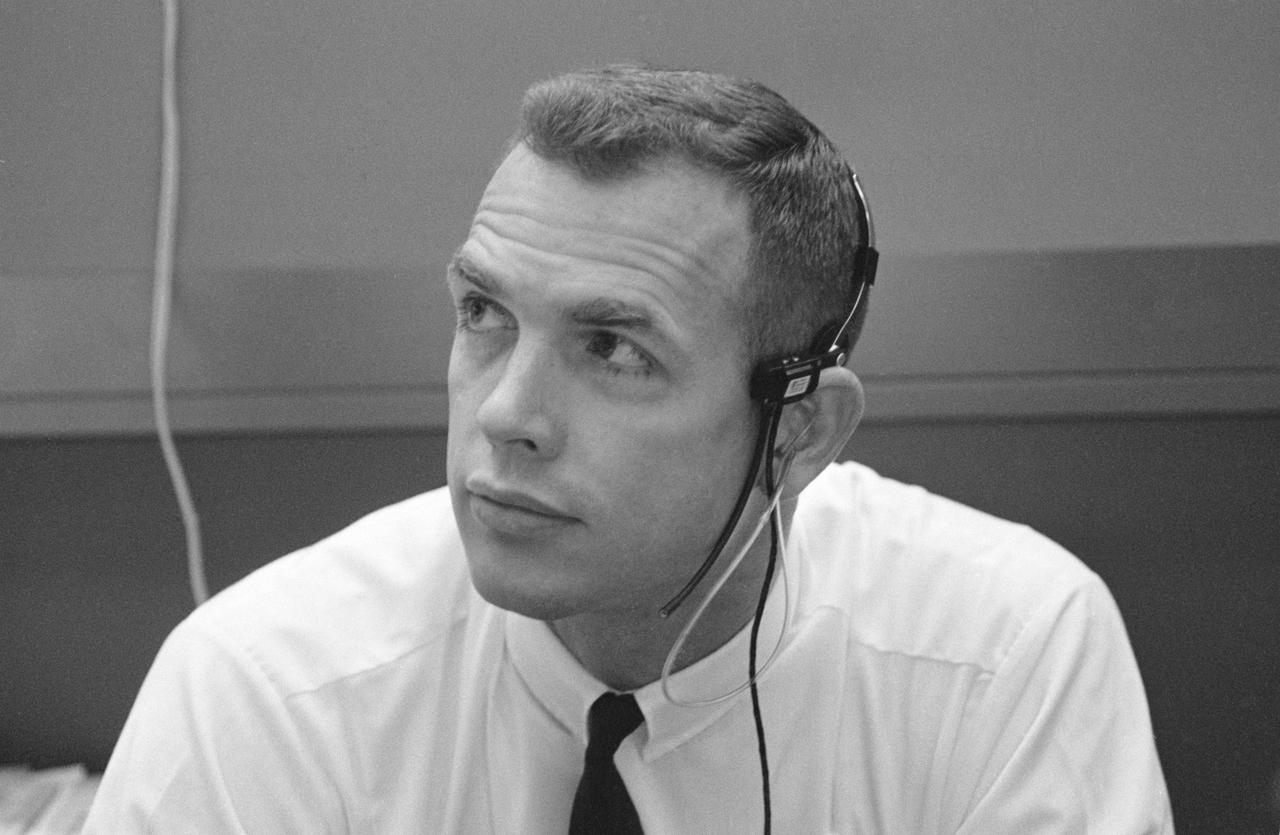

S69-39590 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut David R. Scott is seated at a console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC), Building 30, during the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. He is watching a television monitor during the lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) in which astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. participated. Scott is the backup crew commander for the scheduled Apollo 12 lunar landing mission.
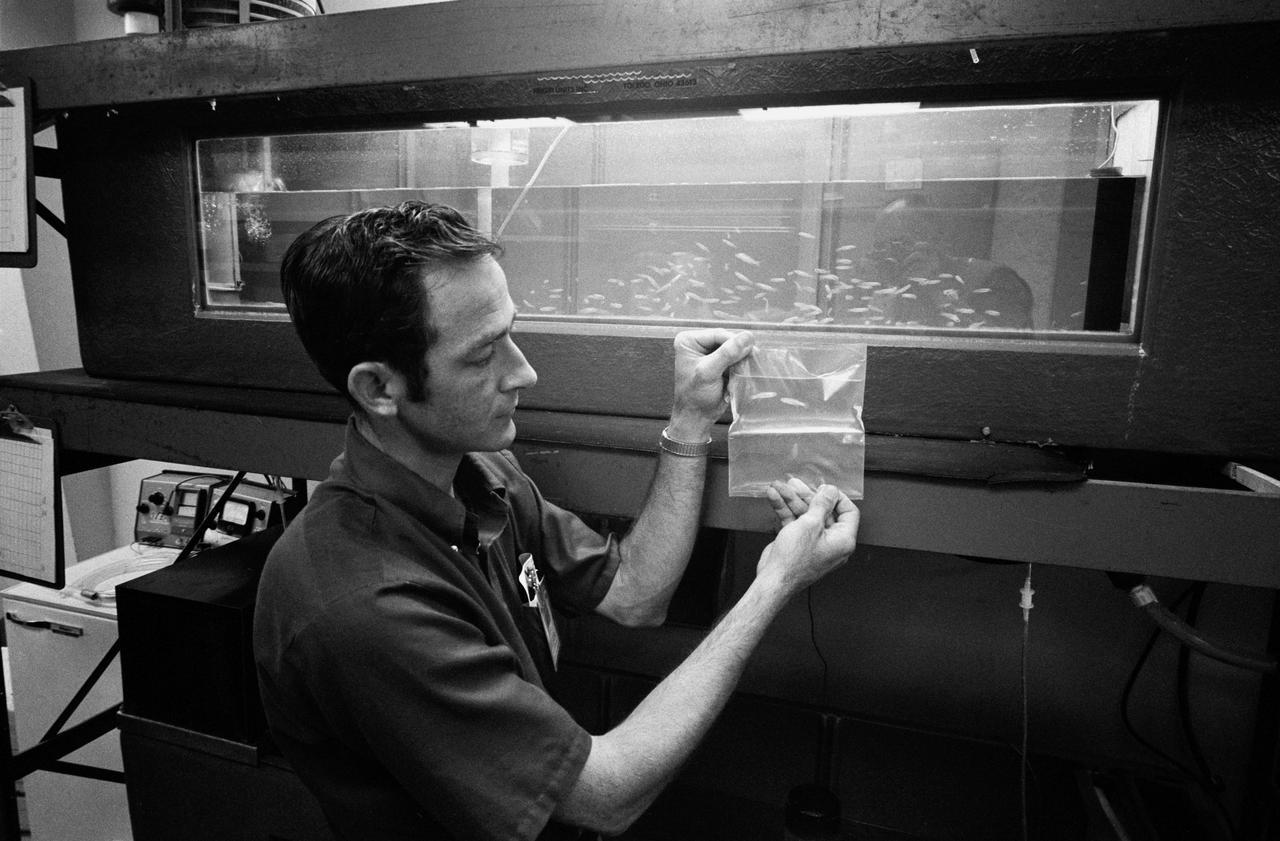

S73-30856 (29 June 1973) --- John Boyd observes a bag with two ?brackish water? minnows known as ?Mummichog Minnows? which will be onboard Skylab 3 with astronauts Alan L. Bean, Owen K. Garriott and Jack R. Lousma. The fish were added to the flight at the request of scientist-astronaut Dr. Owen K. Garriott, science pilot. Fifty eggs from the minnows will also be included in the bag. The objective of this experiment is to show what disorientation the fish will experience when exposed to weightlessness. Many fish have vestibular apparatus quite similar to man. Even though they live in an environment usually considered to resemble weightlessness, they do perceive a gravity vector. An aquarium of the minnows, caught off the coast of Beaufort, North Carolina, is in the background. Photo credit: NASA
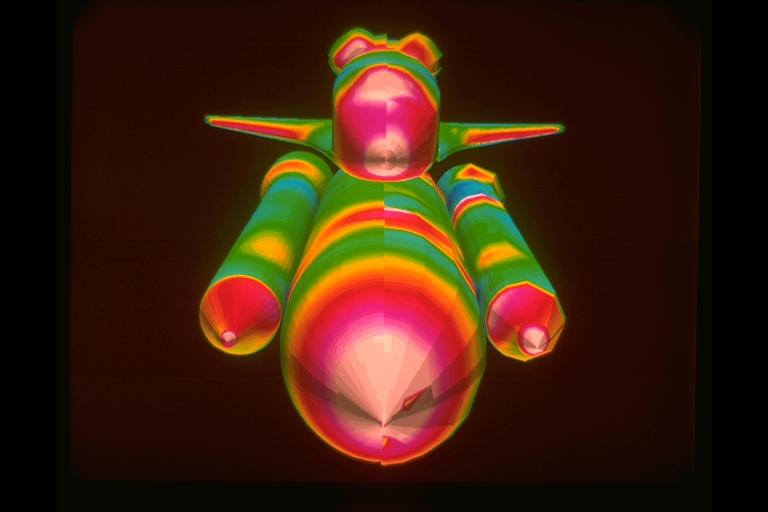

NAS CGI Space Shuttle Launch configuration showing surface pressure comparison (Computational/W.T.)
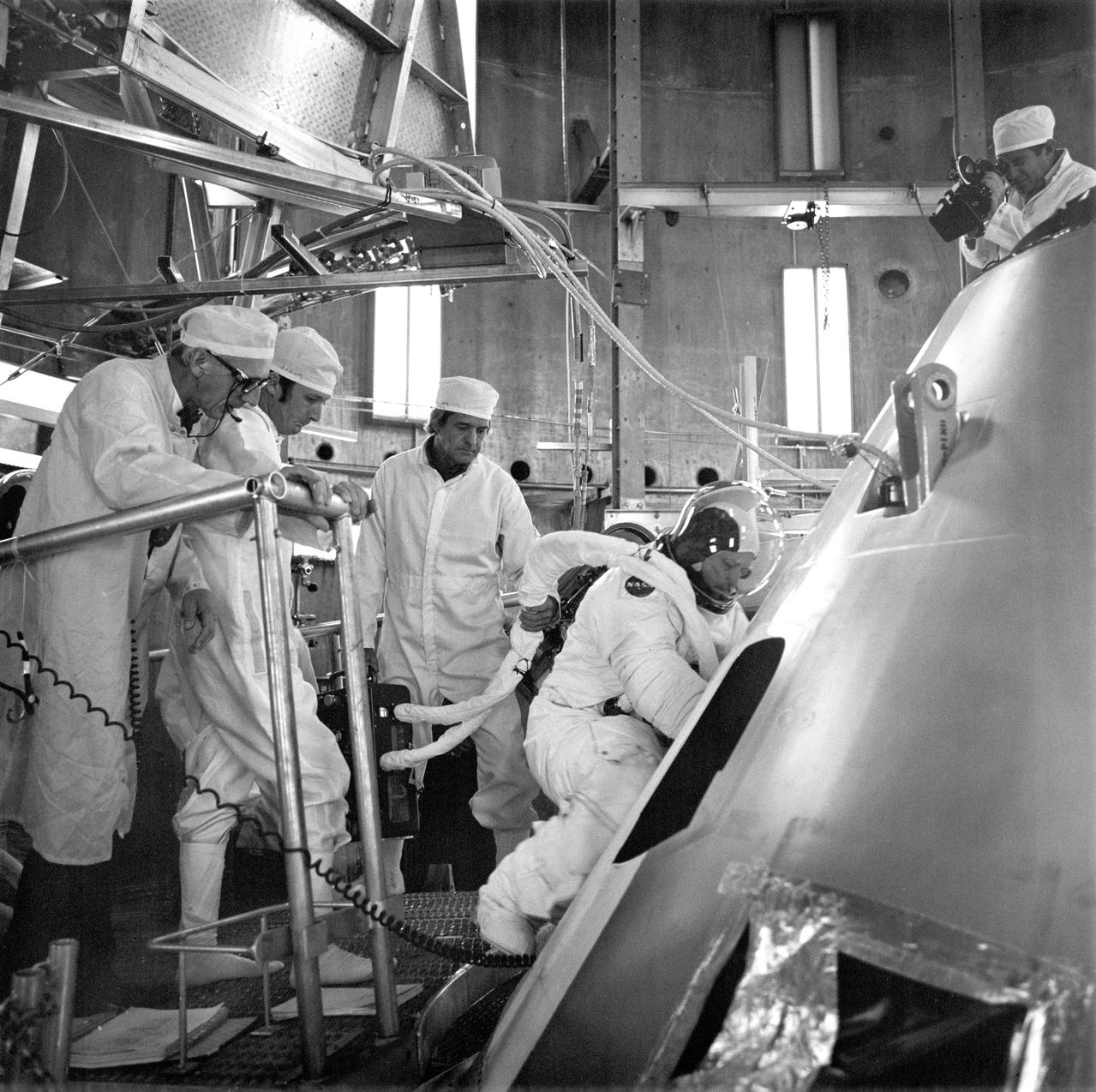

S73-34093 (6 Aug. 1973) --- Astronaut Gerald P. Carr, fully suited, Skylab 4 commander, prepares to enter spacecraft 118 (the Skylab 4 vehicle) at the start of a high altitude chamber test at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Also participating in the test were scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot, and astronaut William R. Pogue, pilot. The Skylab 4 spacecraft is to be moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Aug. 12, where it will be mated with the launch vehicle as a possible rescue craft for the Skylab 3 crewmen if needed. Photo credit: NASA
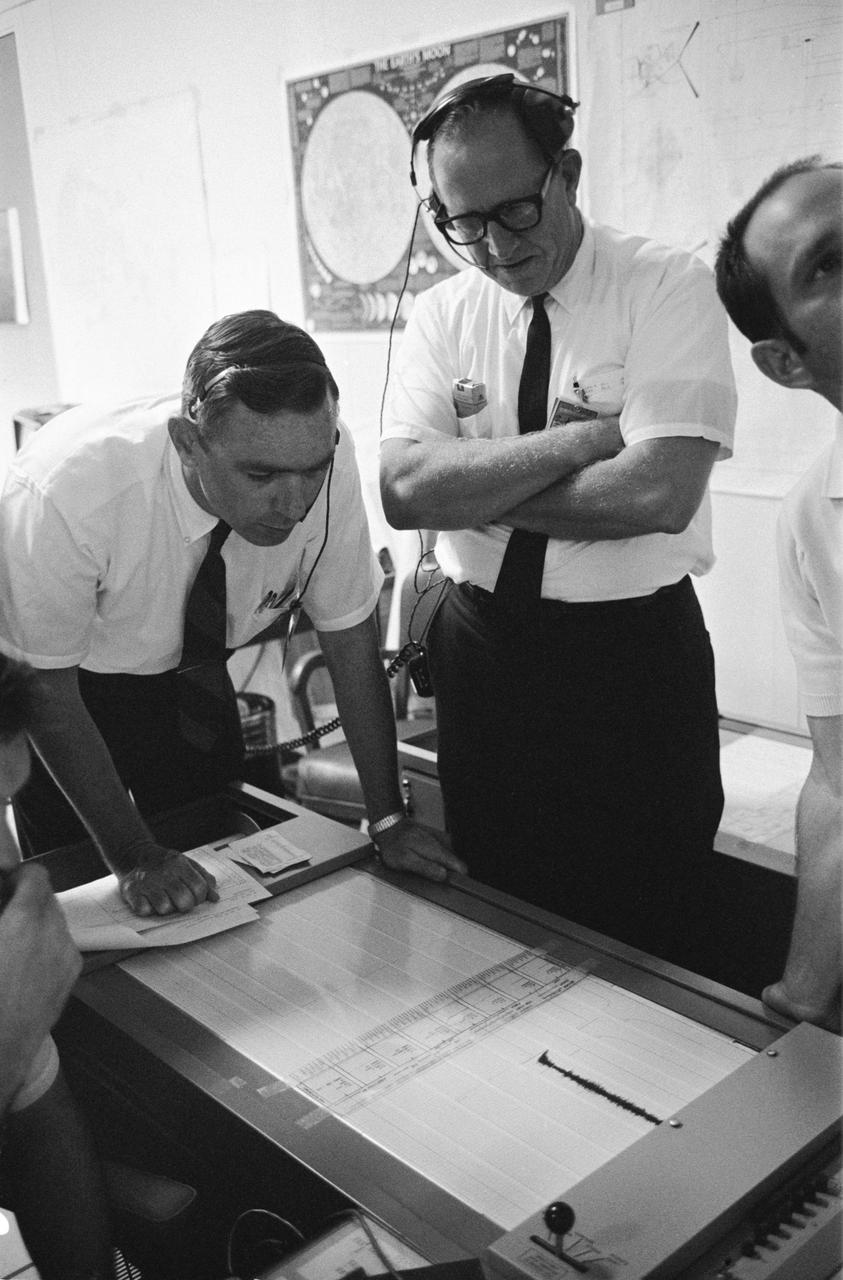

S69-39587 (20 July 1969) --- Dr. Garry Latham (left) with the Lamont Geological Observatory, studies seismometer tracings in the Mission Control Center's (MCC) ALSEP control room. The electronic data was coming from the Passive Seismic Experiments Package (PSEP) which the Apollo 11 astronauts had just deployed on the surface of the moon. Dr. Lamont is the principal investigator for the PSEP, a component of the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP). PSEP uses three long-period seismometers and one short-period vertical seismometer for measuring meteoroid impacts and moonquakes. Such data will be useful in determining the interior structure of the moon; for example, does the moon have a core and mantle like Earth? Here, the flapping of the PSEP's solar panels is picked up and registered as a tracing. The PSEP was sensitive enough to pick up the footsteps of astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., as they walked on the moon.

CFD: Space Shuttle Launch Configuration surface pressure comparison (right) computation and wind tunnel
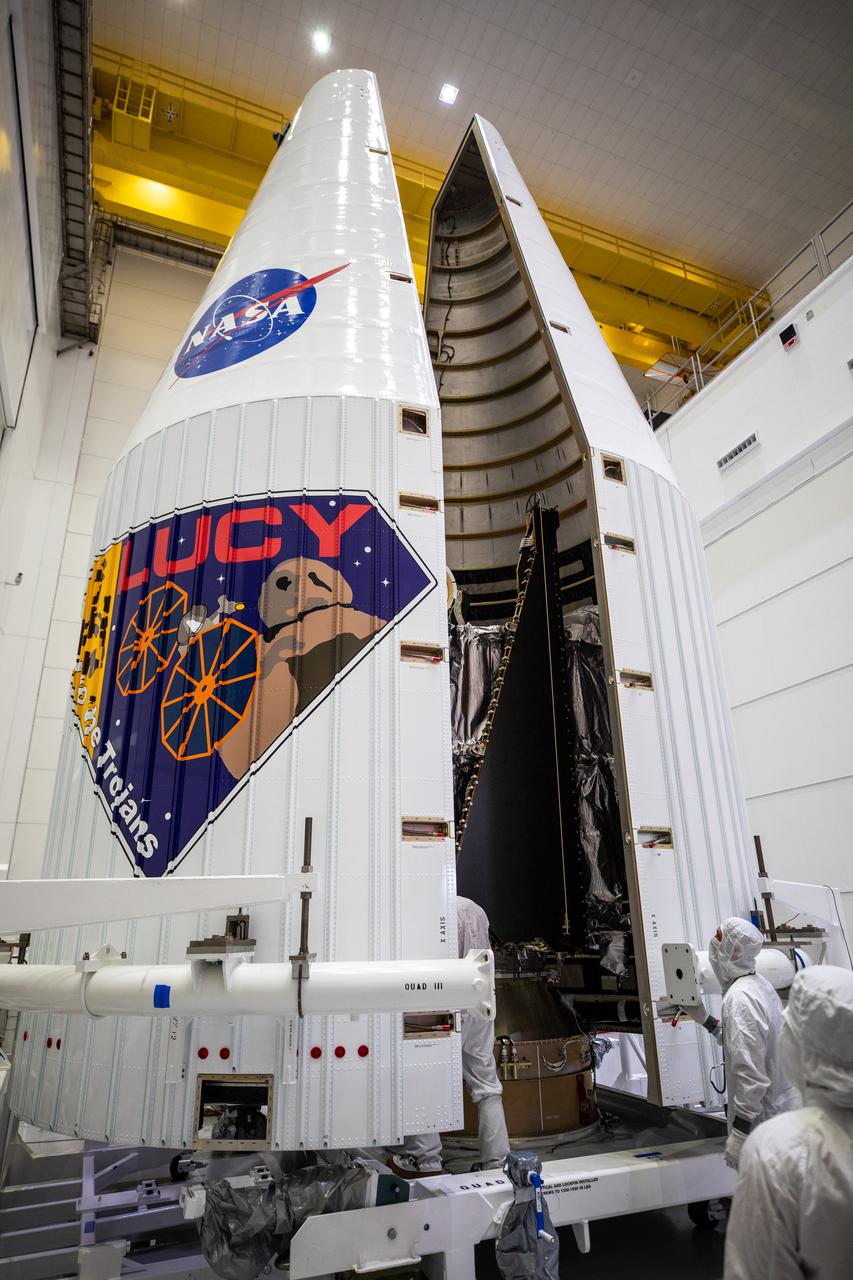

Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move both halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing around NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
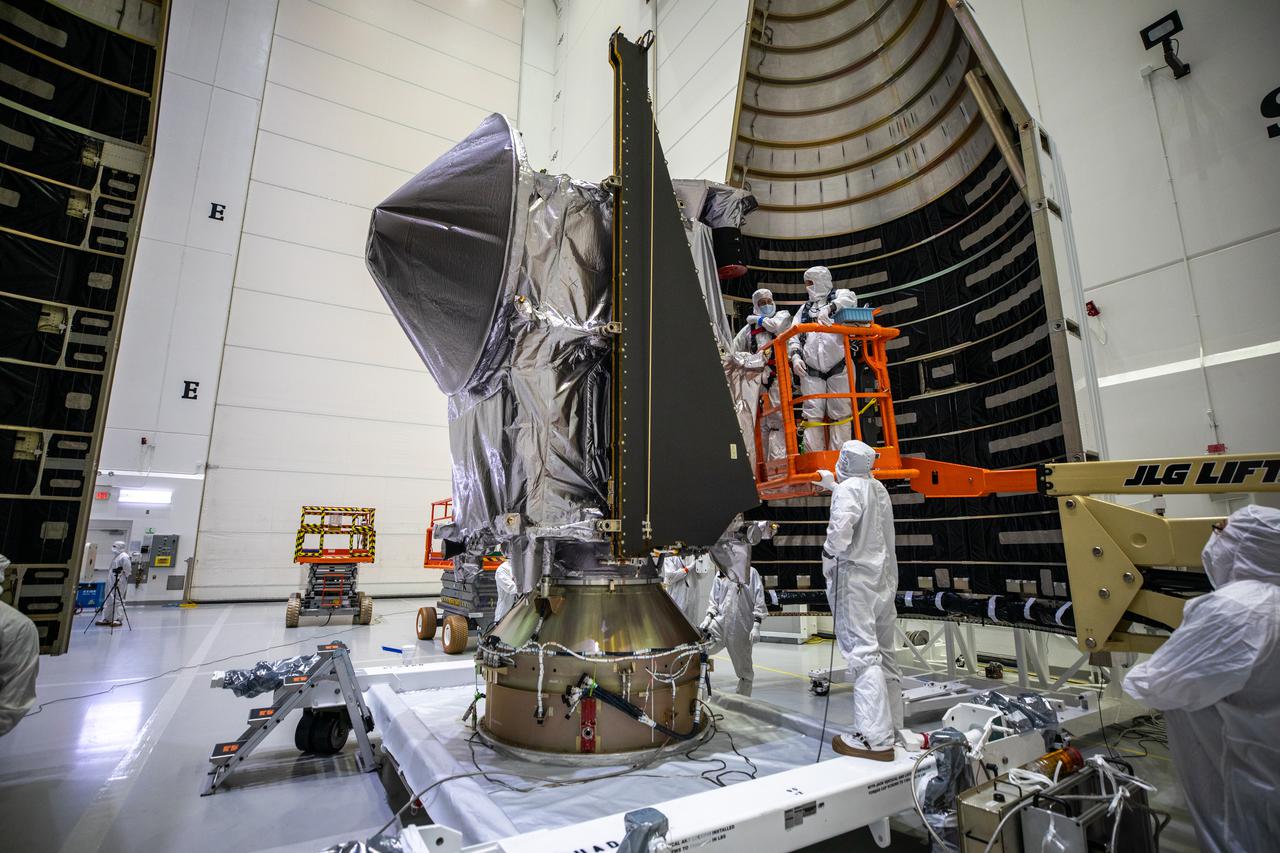
Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
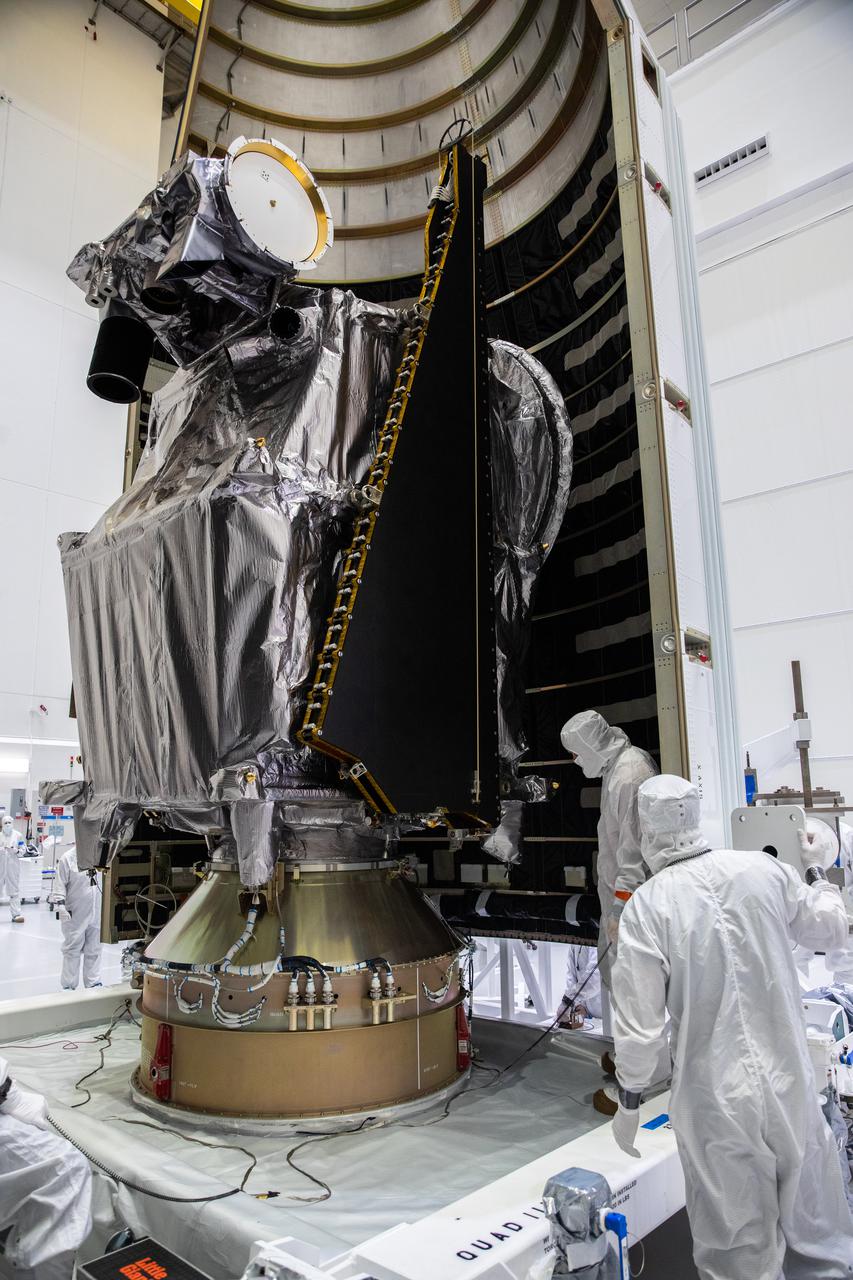

Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
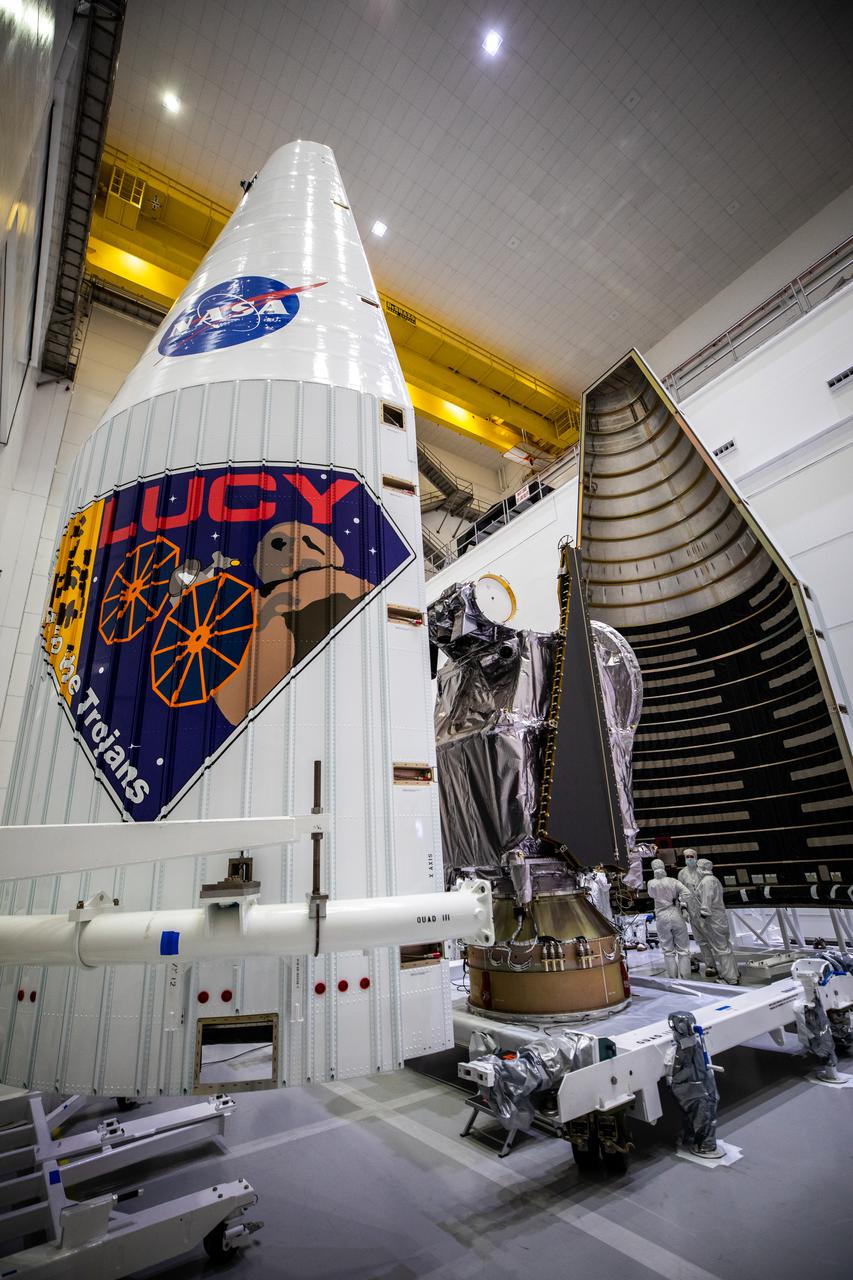

Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The other half is in view in the foreground. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
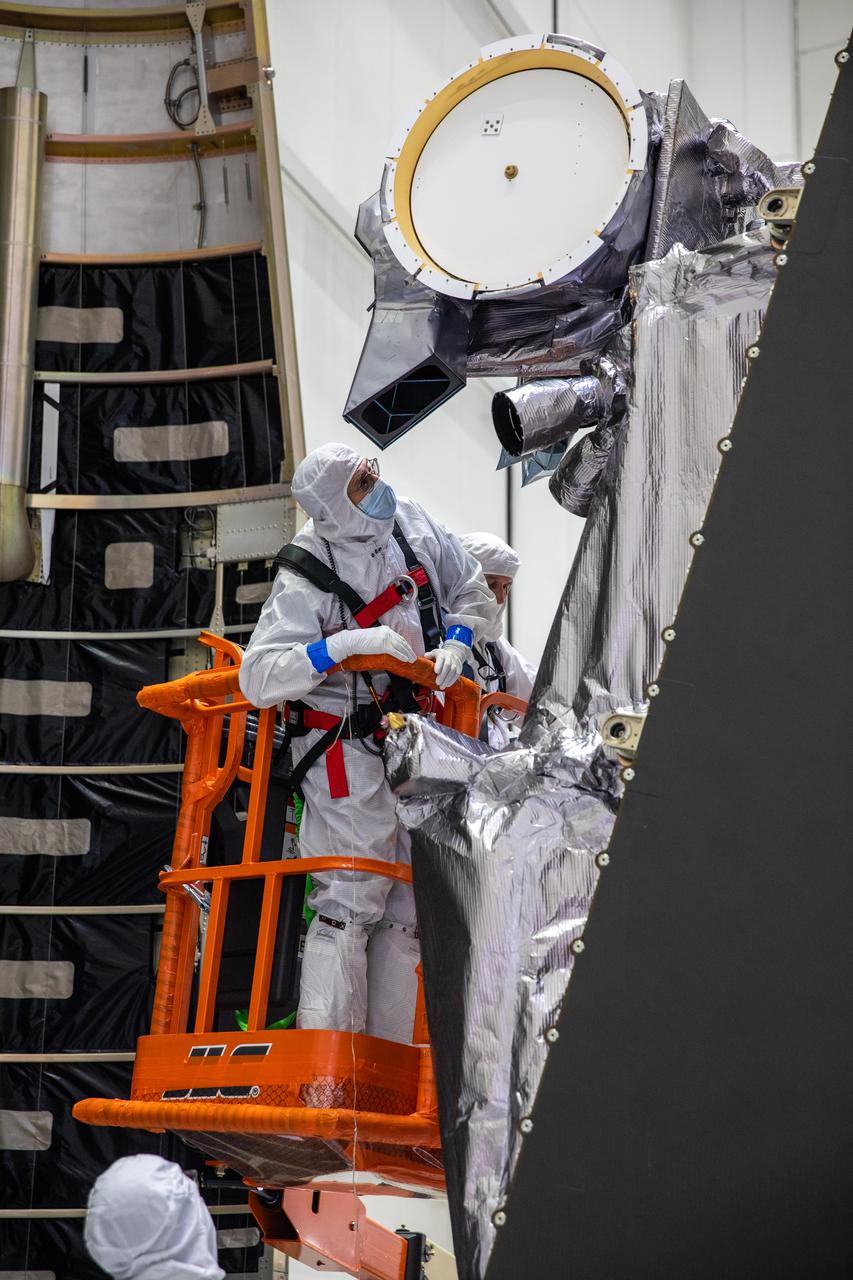

Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.

Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
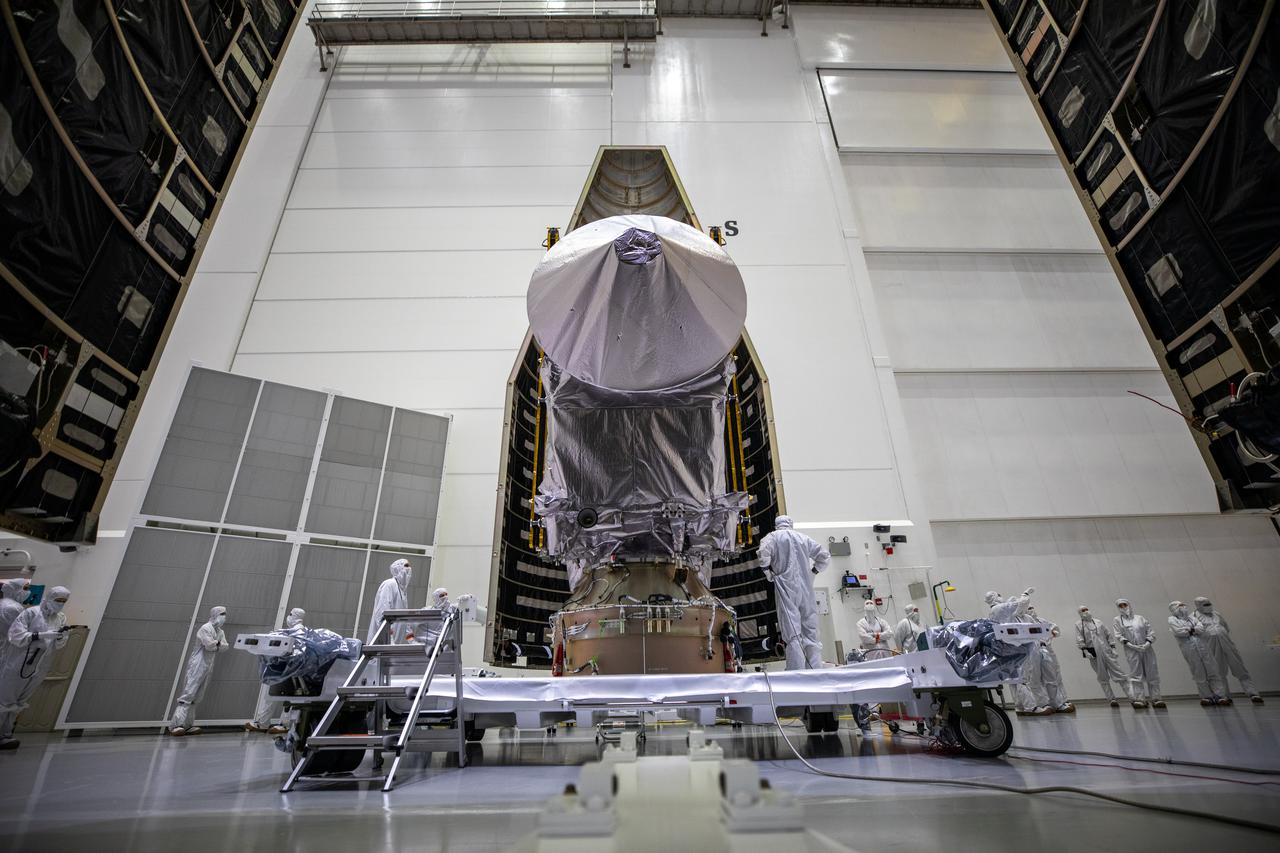

Inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing is moved toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
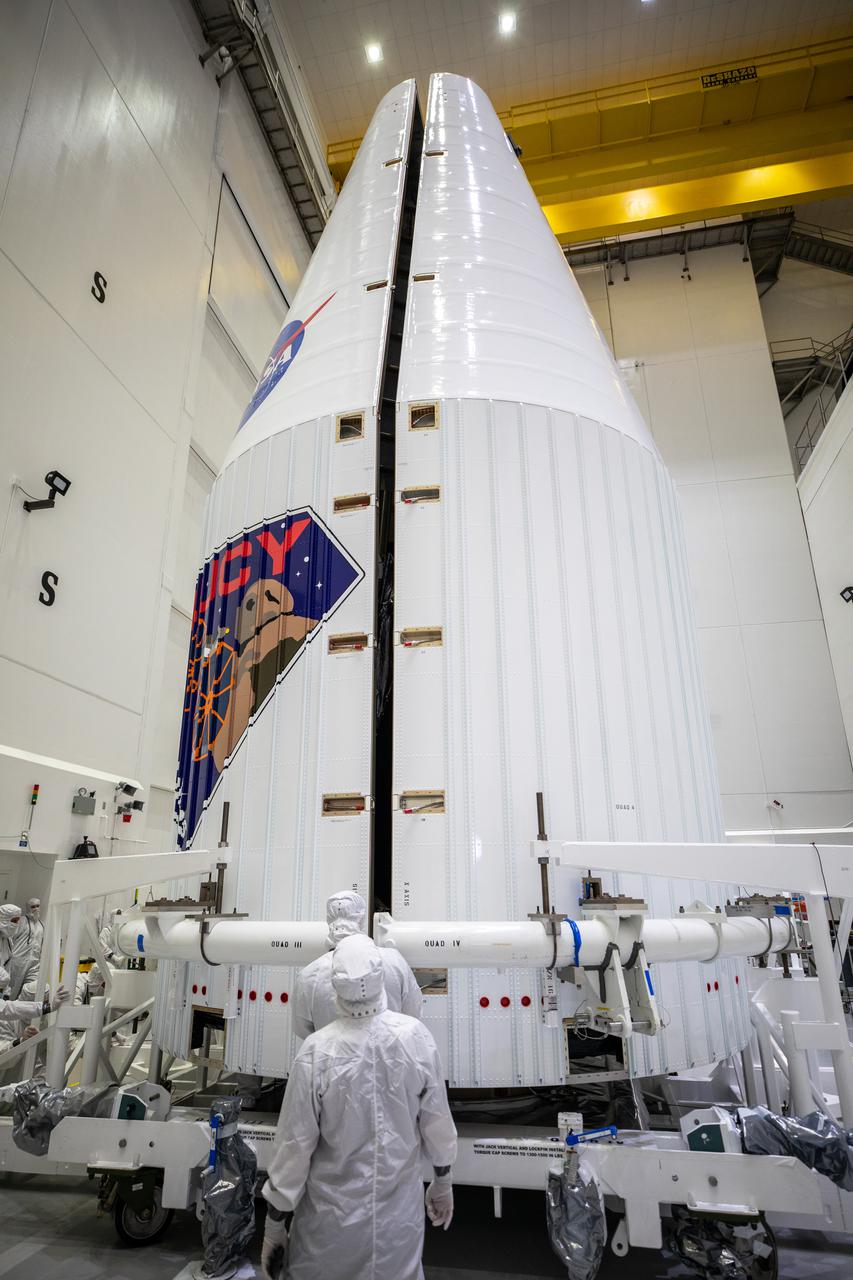

Inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, workers help secure both halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing around NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
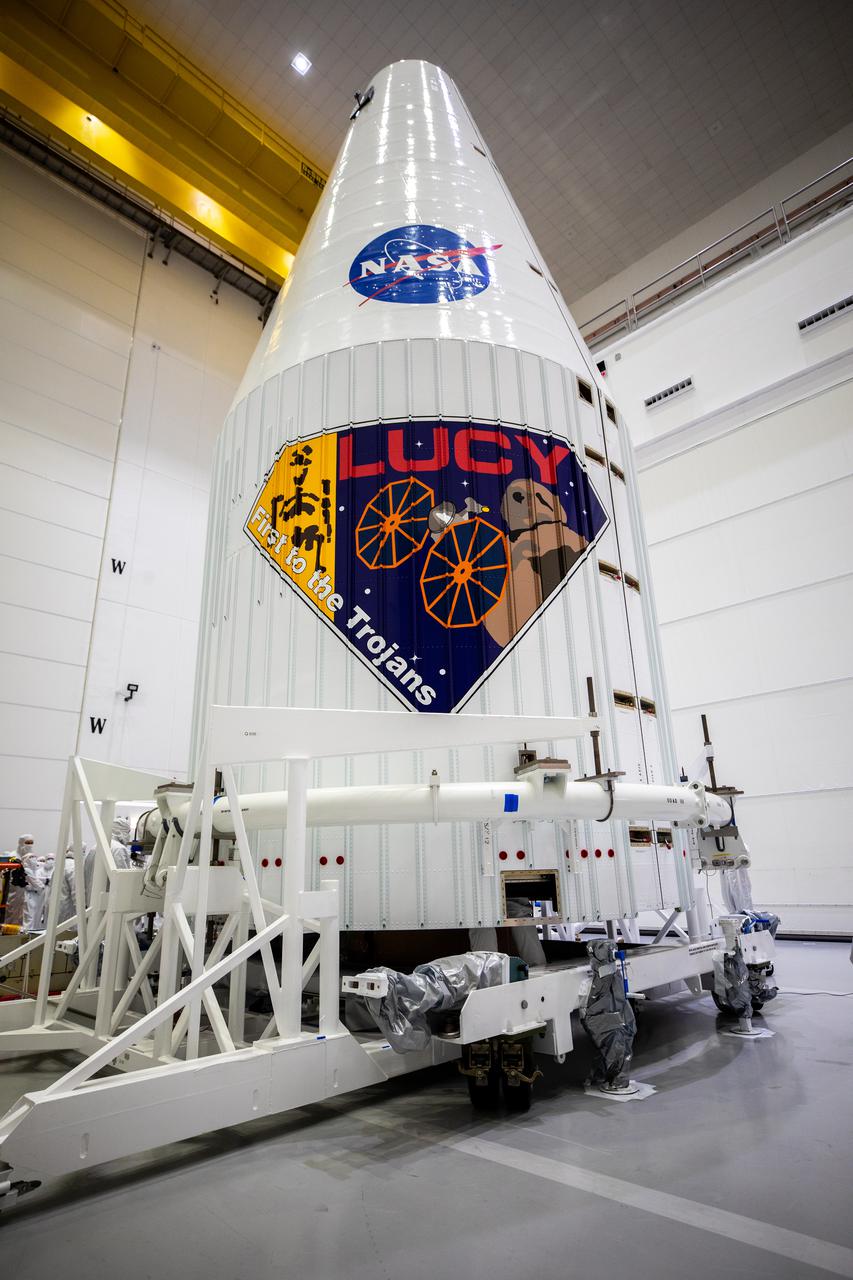

Inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing has been secured around NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.