
Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
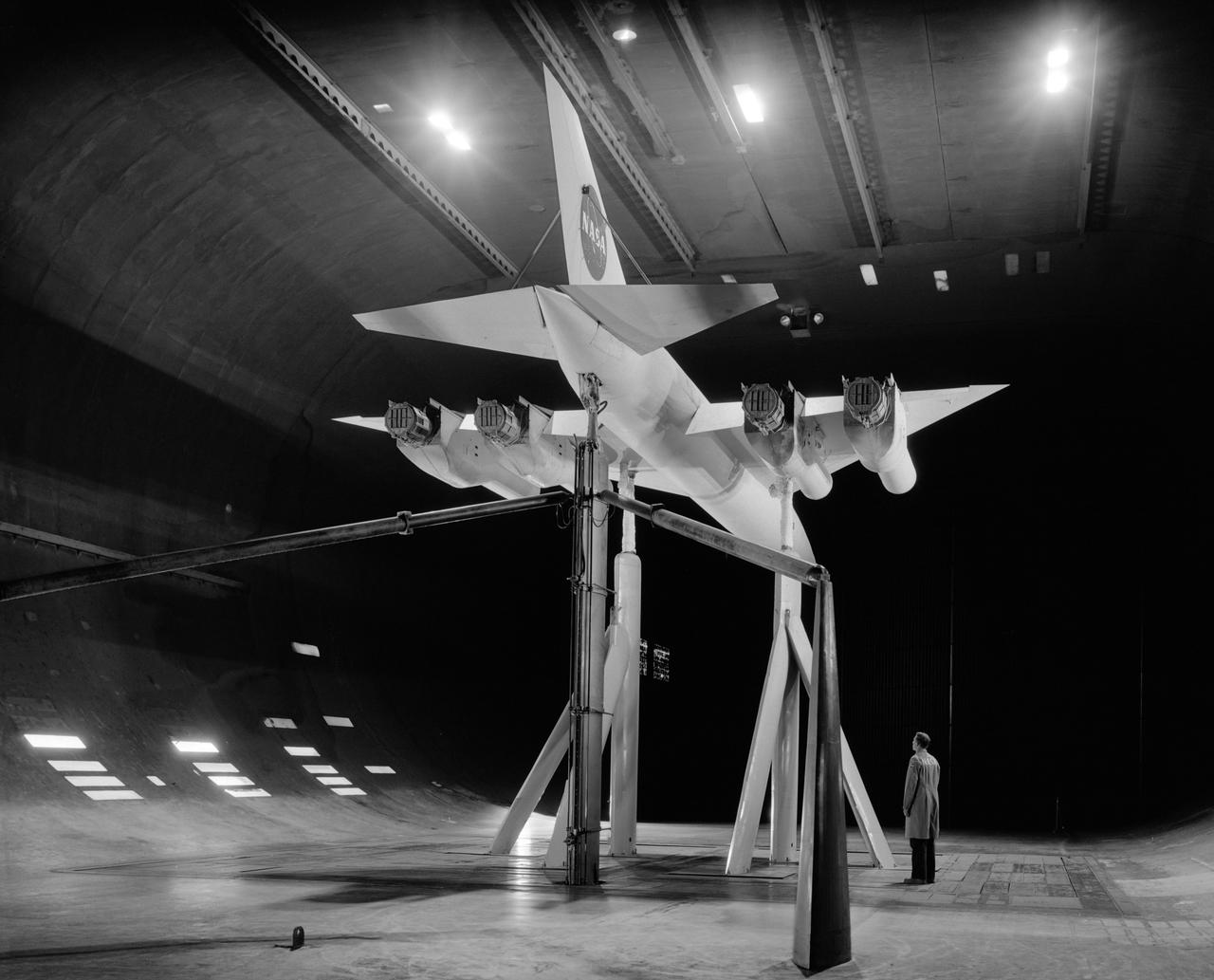

3/4 rear view of SCAT-17 supersonic transport with thrust reverser installed and trailing edge flaps deflected at 30 deg.
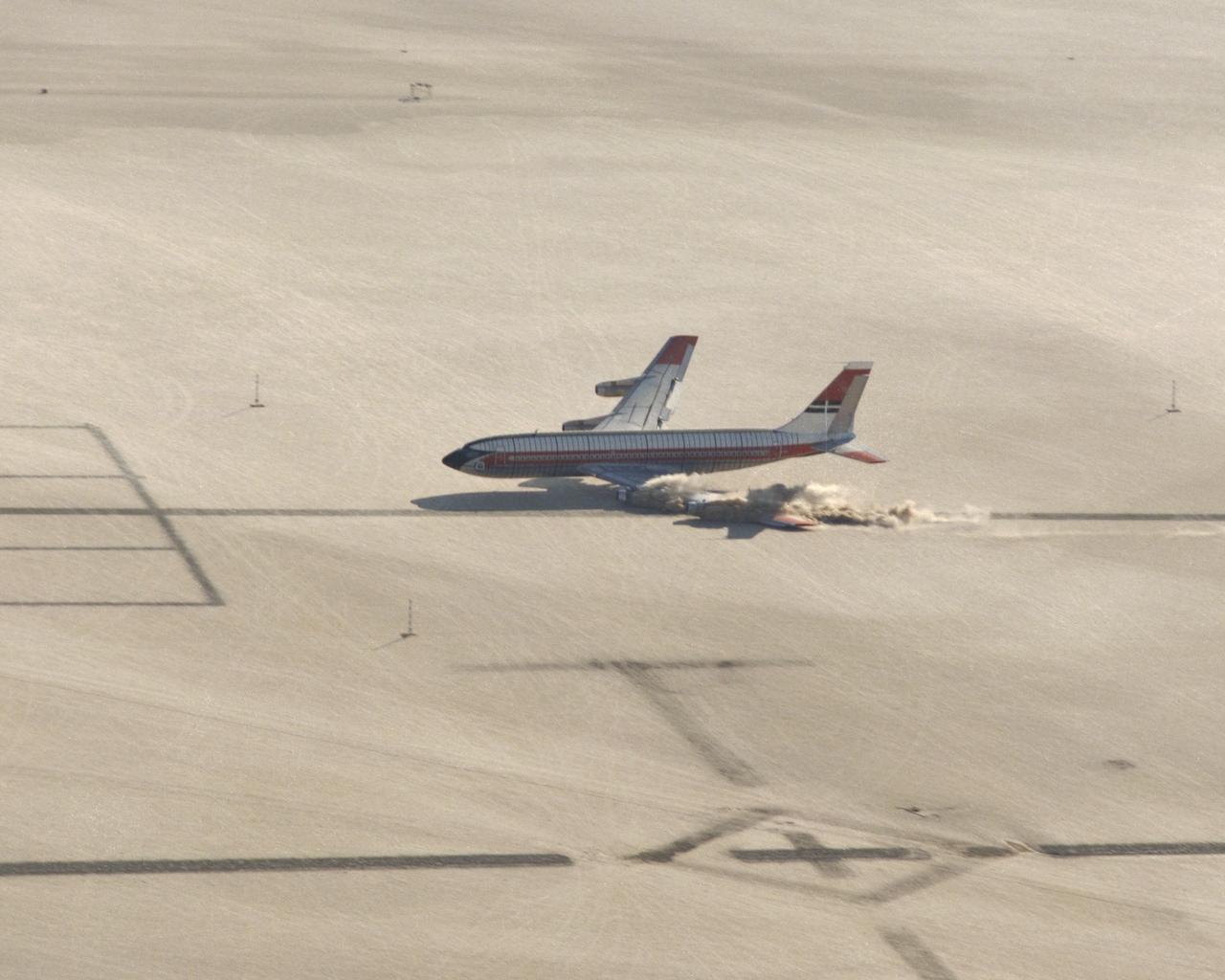

CID (Controlled Imact Demonstrator) Aircraft lakebed skid.
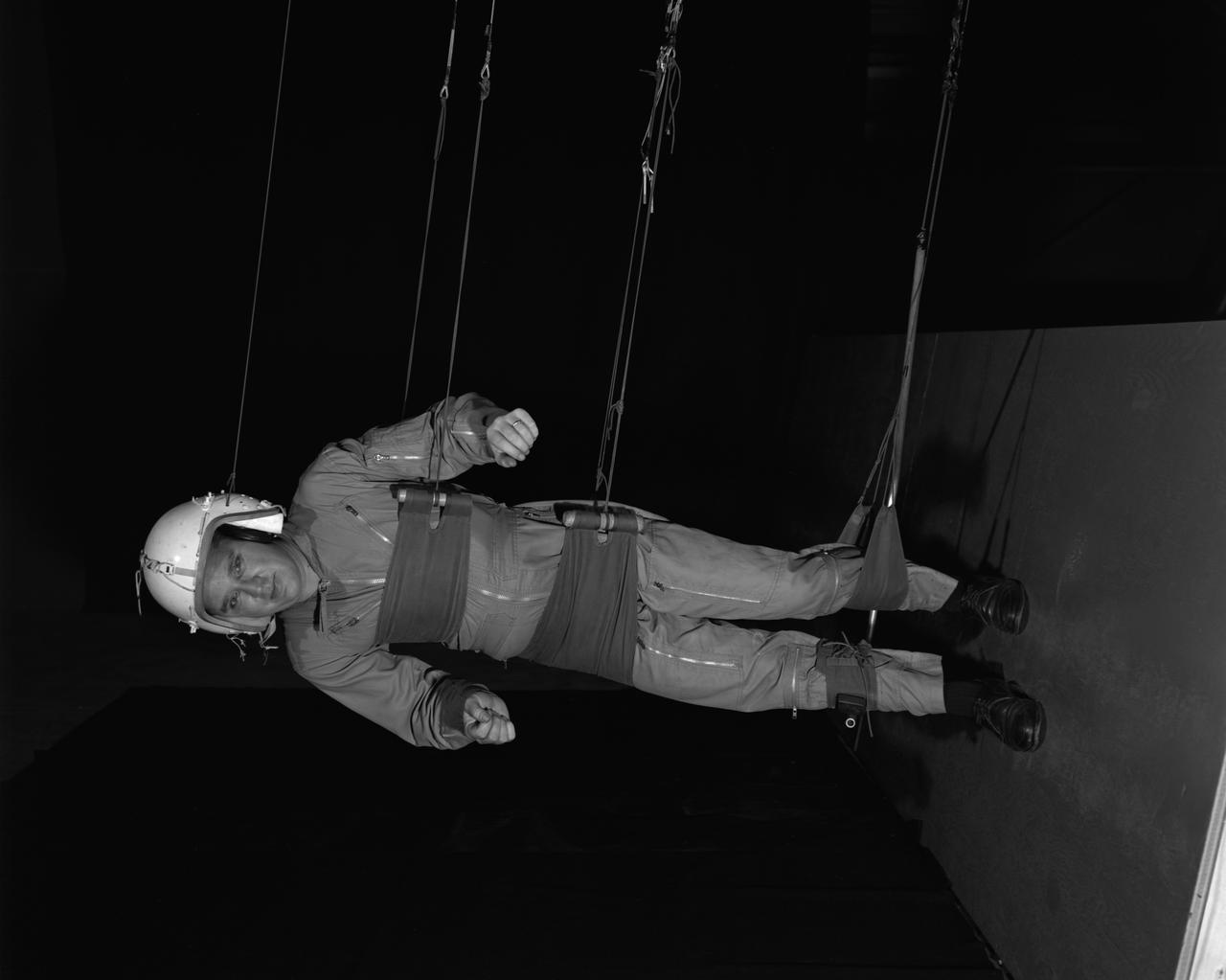

Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located in the hangar at Langley Research Center. The initial version of this simulator was located inside the hangar. Later a larger version would be located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil wrote in his paper Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research, When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject' s weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308, p. 377 A.W. Vigil, Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research, Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
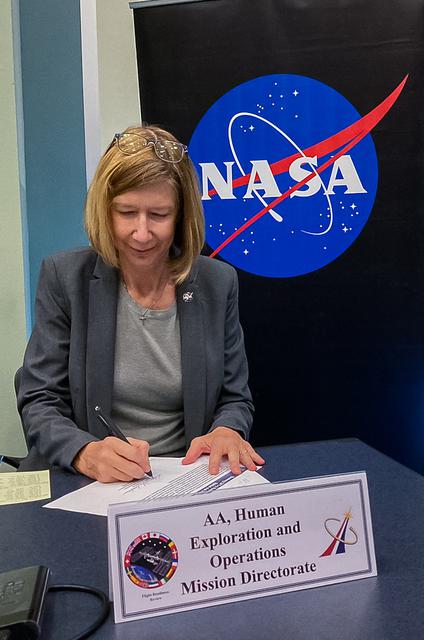

Associate Administrator of the Human Exploration and Operations (HEO) Mission Directorate Kathryn Lueders chaired the Flight Readiness Review for Boeing's upcoming Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) in Operations Support Building 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, July 22, 2021. At the conclusion of the meeting, all board members sign the Certificate of Flight Readiness certifying their readiness to proceed to the next milestones and launch of Boeing's CST-100 Starliner atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. Launch time remains 2:53 p.m. EDT Friday, July 30 for the uncrewed OFT-2 mission – Starliner's second flight to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
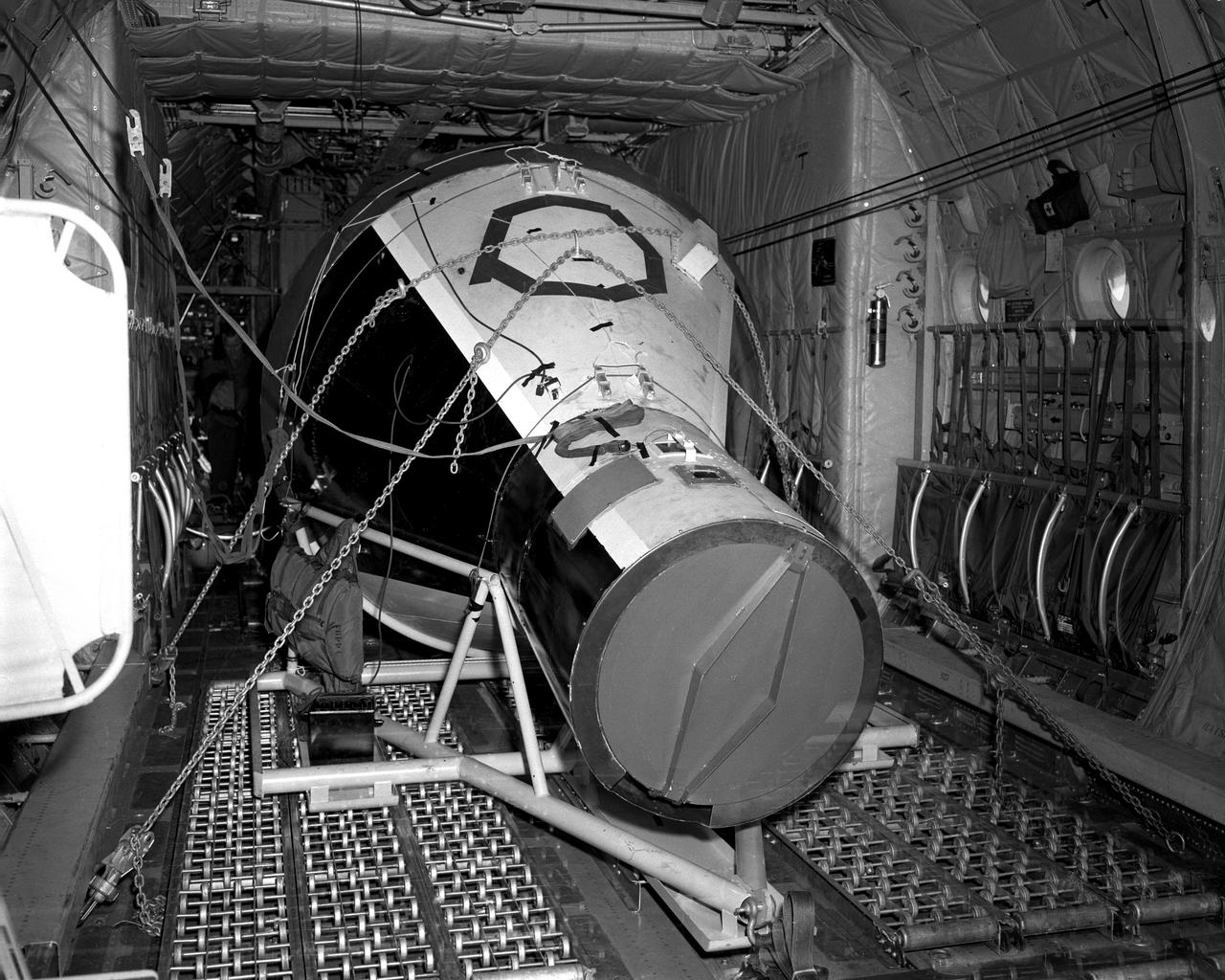

Vehicles and Missions Studies Charts, Space Capsule
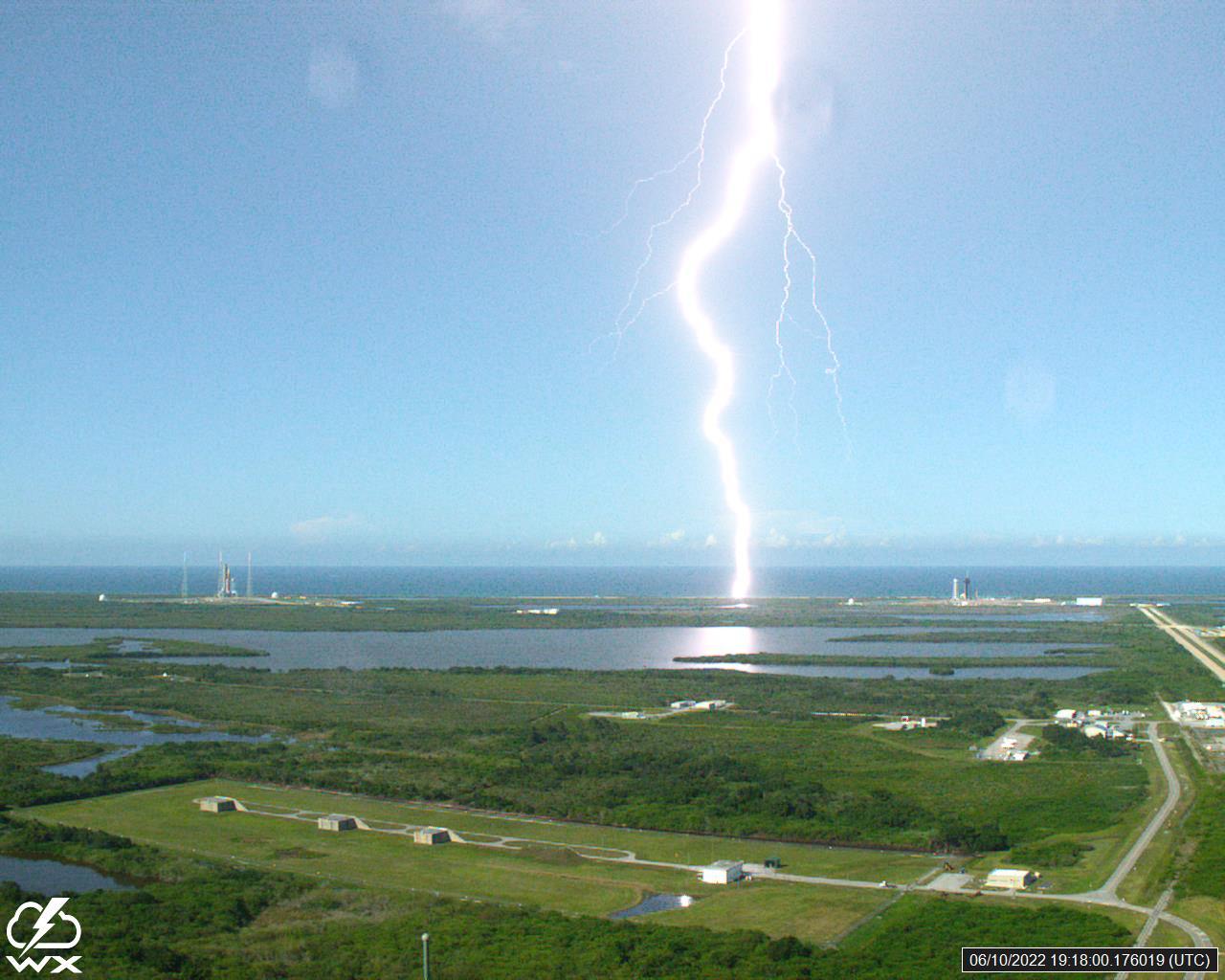

A lightning strike was recorded at Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 10, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher are on the launch pad in preparation for the Artemis I mission. The lightning strike was recorded by cameras stationed at the pad and mobile launcher using a special filter called a “clear day frame,” which provides an overlay of the raw frame on a reference image. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first woman of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.

ARCAS Rocket #E1-235 Image taken at Wallops Island
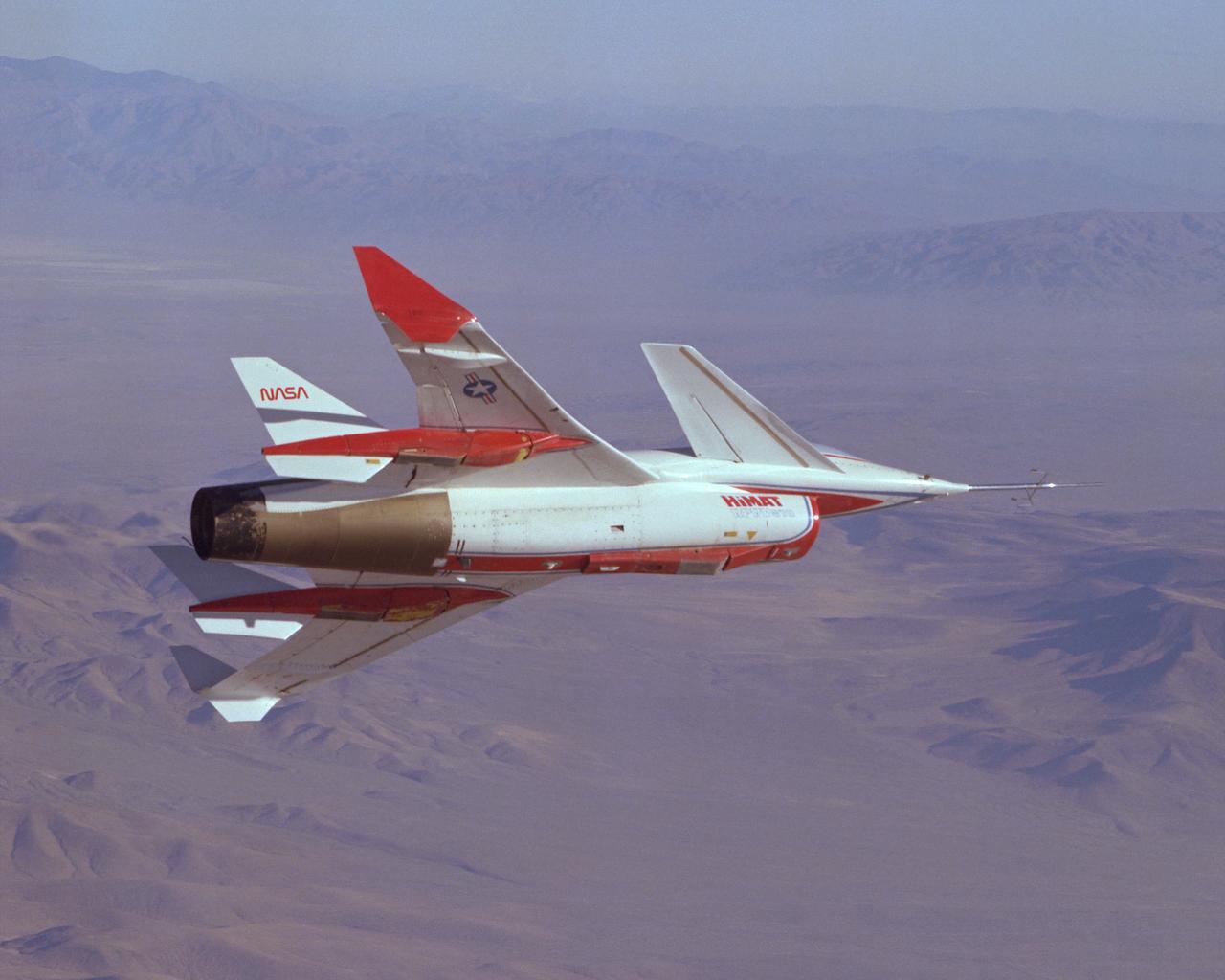

The HiMAT (Highly Maneuverable Aircraft Technology) subscale research vehicle, seen here during a research flight, was flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, from mid 1979 to January 1983. The aircraft demonstrated advanced fighter technologies that have been used in the development of many modern high performance military aircraft.
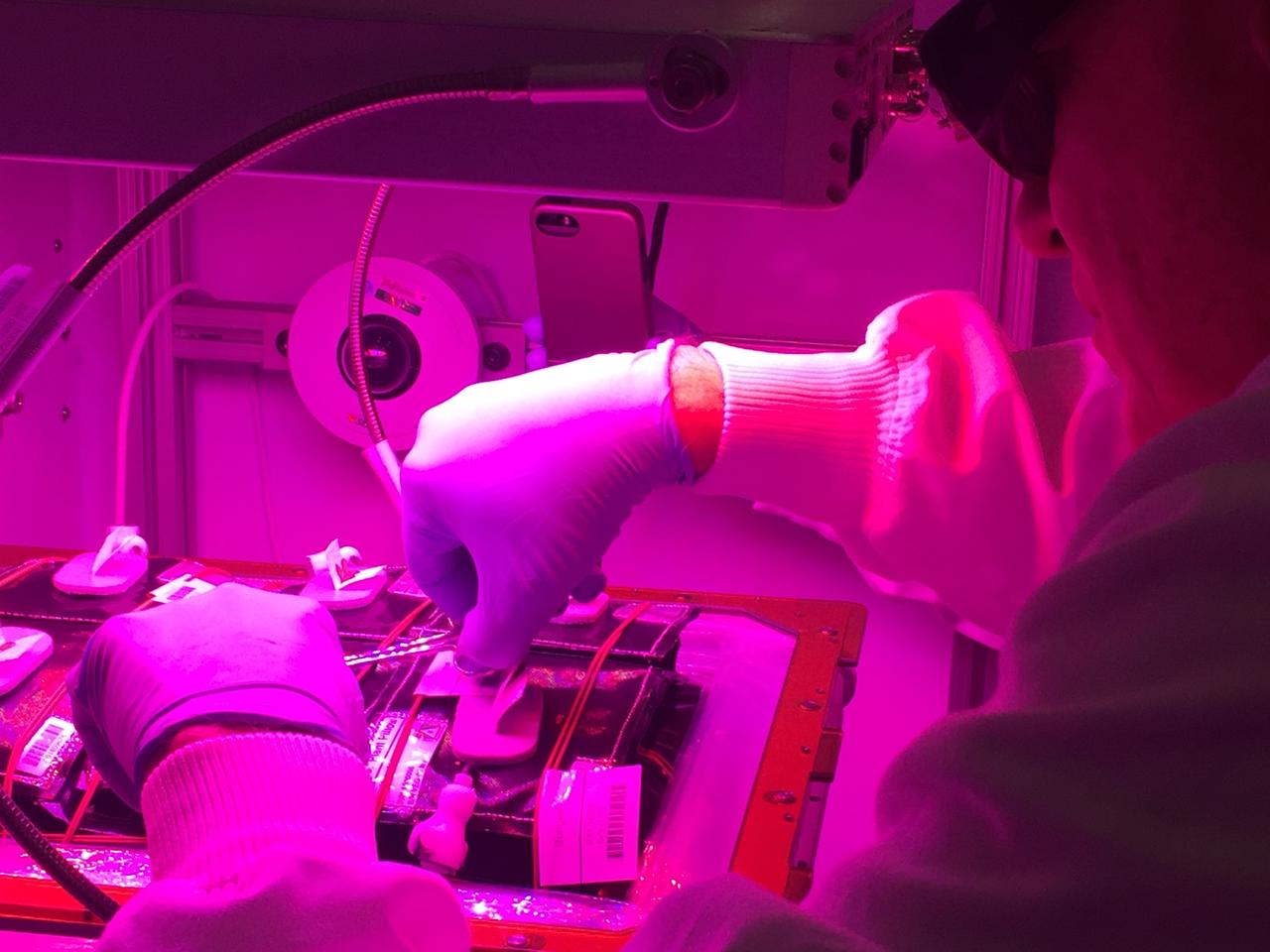

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
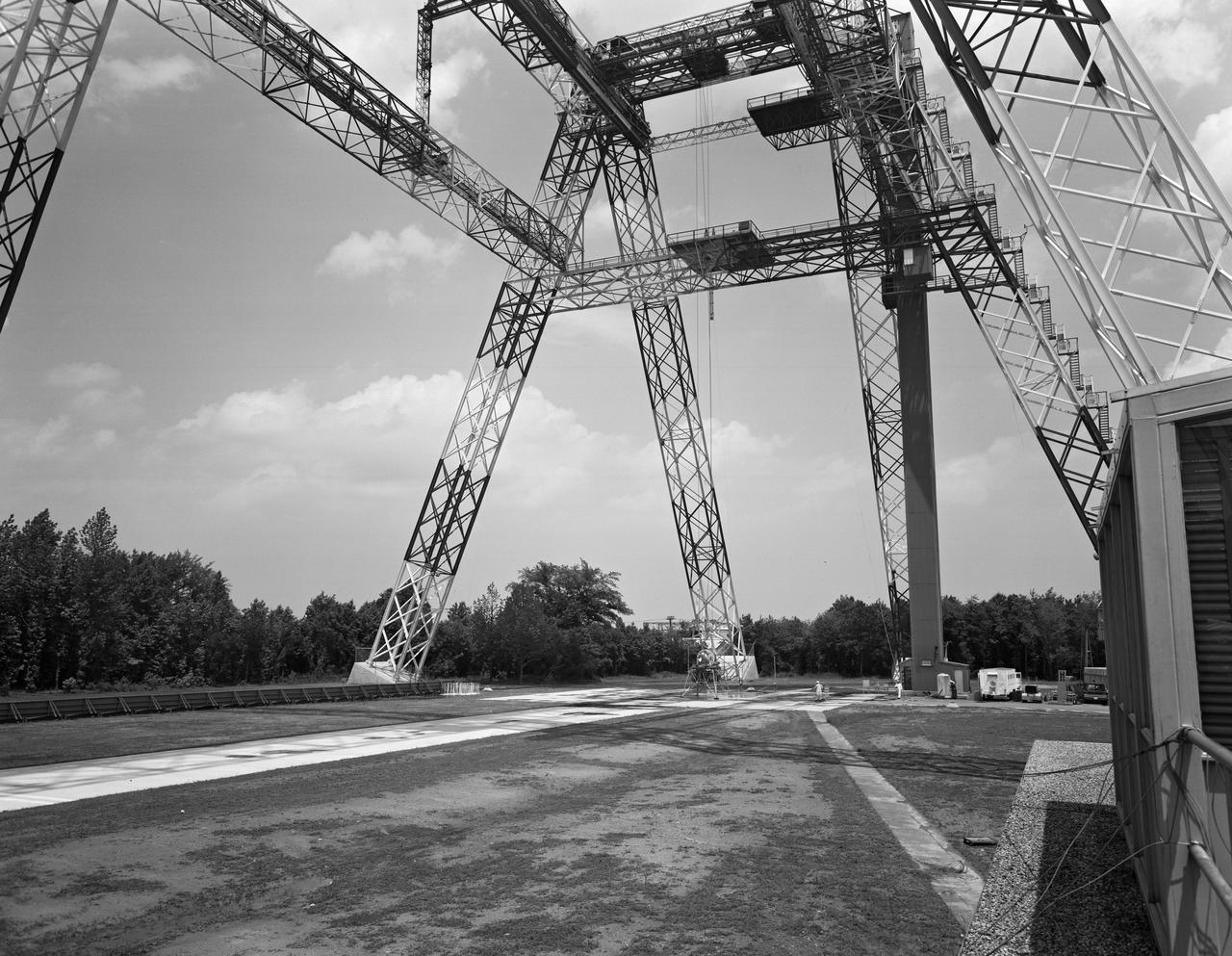

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
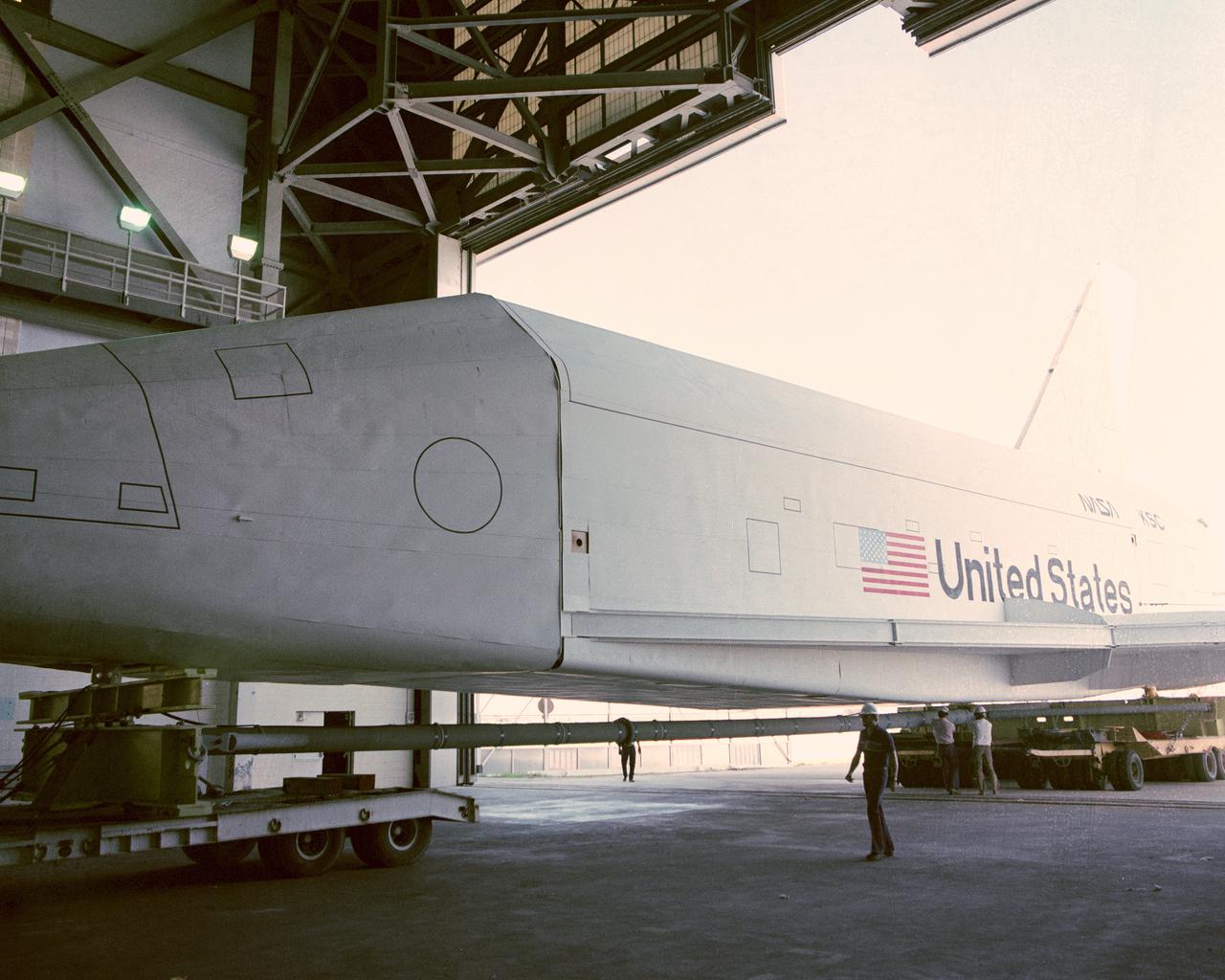

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the space shuttle mock-up, dubbed Pathfinder, enters the Vehicle Assembly Building for a fit-check May 15, 1978. The mock-up, constructed at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala., possessed the general dimensions, weight and balance of a real space shuttle. It was shipped to Kennedy by barge and then used to fit-check the work platforms of the Mate-Demate Device, orbiter processing facilities and Vehicle Assembly Building, as well as support ground crew training. It also was used to rehearse post-landing procedures at Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility. After being on display at the 'Great Space Shuttle Exposition' in Tokyo from June 1983 to August 1984, the mock-up returned to Marshall and now is on permanent display at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center near Huntsville. Photo credit: NASA
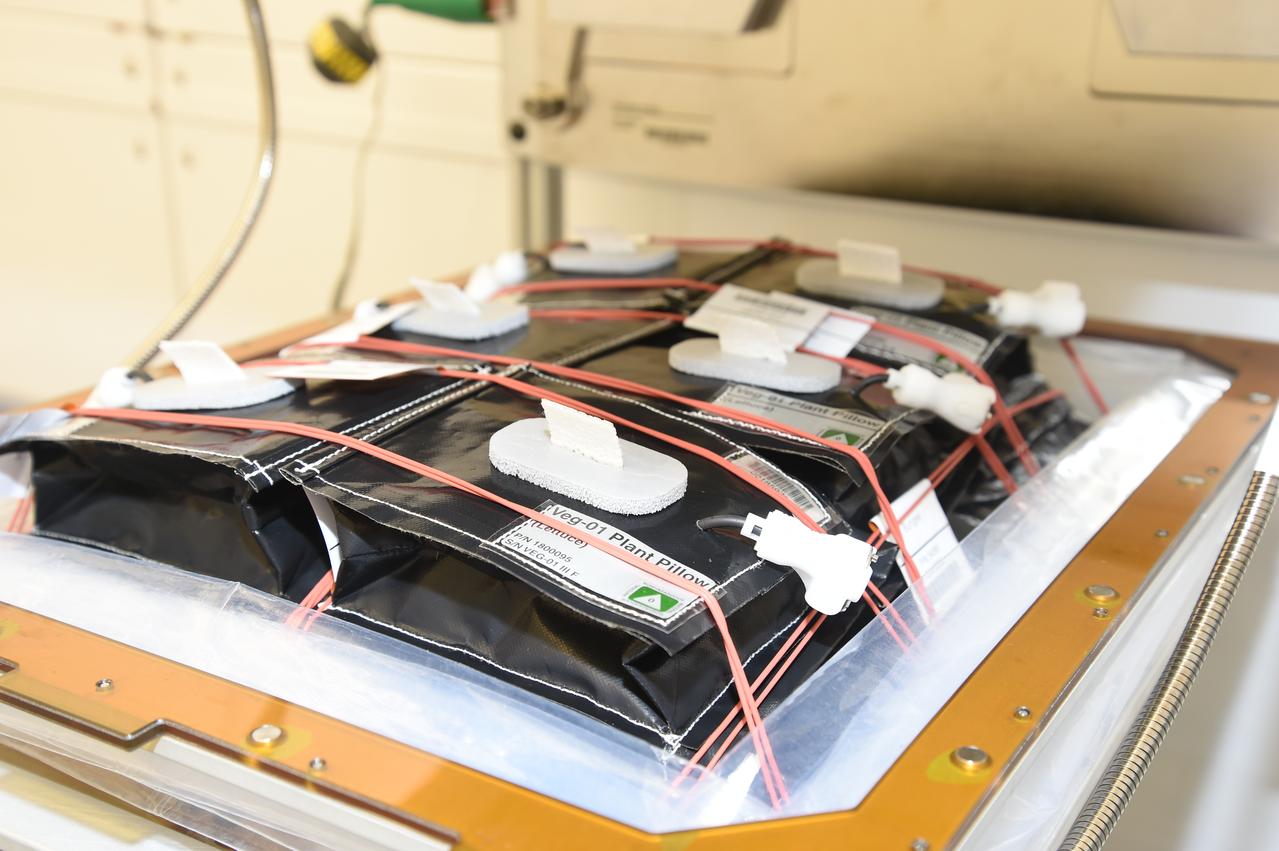

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

Tilt wing propeller model. 3/4 front view. 4 prop tilt wing nose down variable struts on ground board. Leo Holl, NASA Ames Engineer.
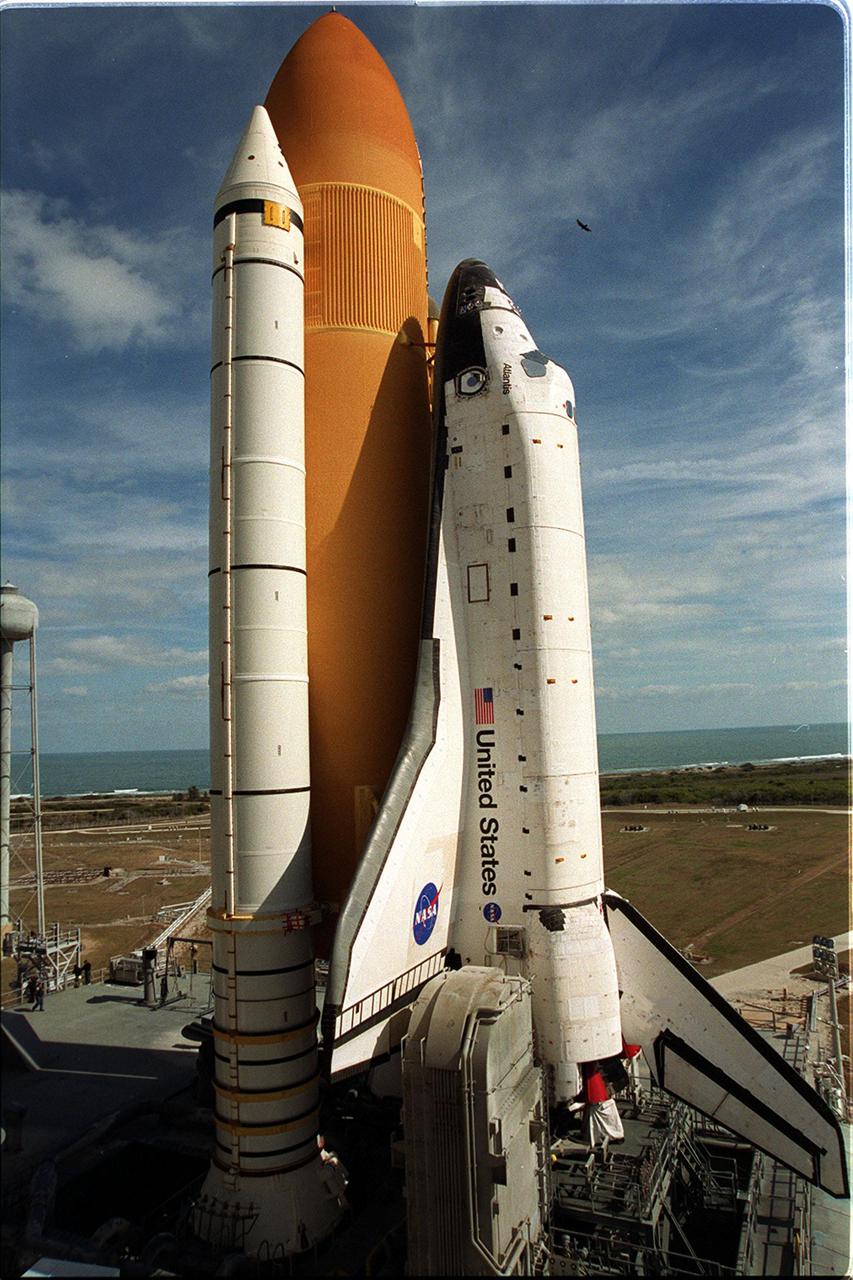

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The gate outside Launch Pad 39A heralds the STS-98 launch as Space Shuttle Atlantis makes its way to the pad. The Shuttle had returned to the Vehicle Assembly Building from the launch pad in order to undergo tests on the solid rocket booster cables. A prior extensive evaluation of NASA’s SRB cable inventory on the shelf revealed conductor damage in four (of about 200) cables. Shuttle managers decided to prove the integrity of the system tunnel cables already on Atlantis, causing return of the Shuttle to the VAB a week ago. The Shuttle will undergo preparations for a rescheduled launch Feb. 7 at 6:11 p.m. EST
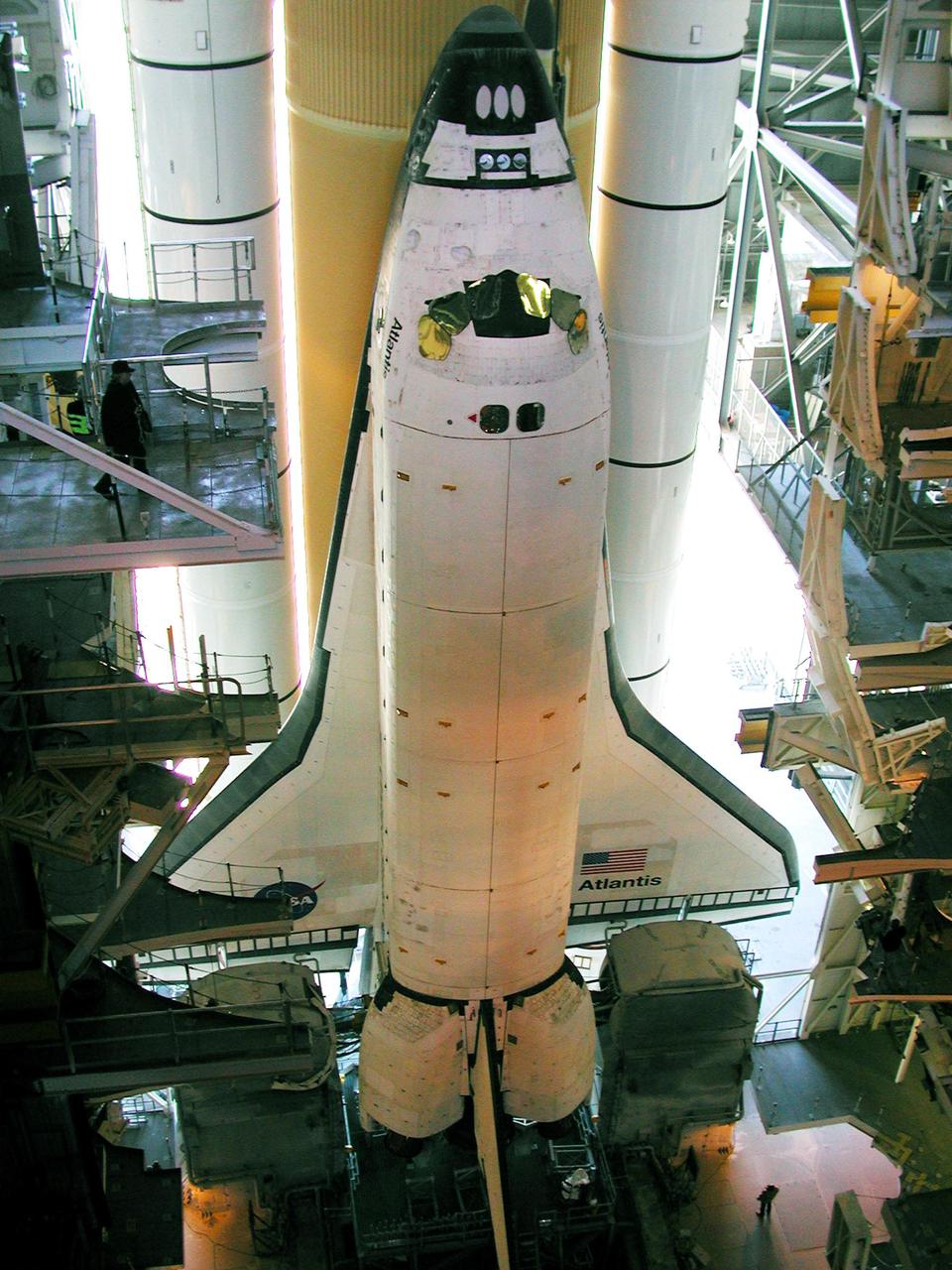
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Atlantis, on its Mobile Launcher Platform, begins to roll out to Launch Pad 39A, this time on another crawler transporter. An attempt to roll out on Jan. 2 incurred a failed computer processor on the first crawler transporter. The Shuttle was returned to the Vehicle Assembly Building Using a secondary computer processor on the vehicle. Atlantis will fly on mission STS-98, the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying the U.S. Laboratory, named Destiny. The lab module will have five system racks already installed inside. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. Atlantis is scheduled for launch no earlier than Jan. 19, 2001, with a crew of five
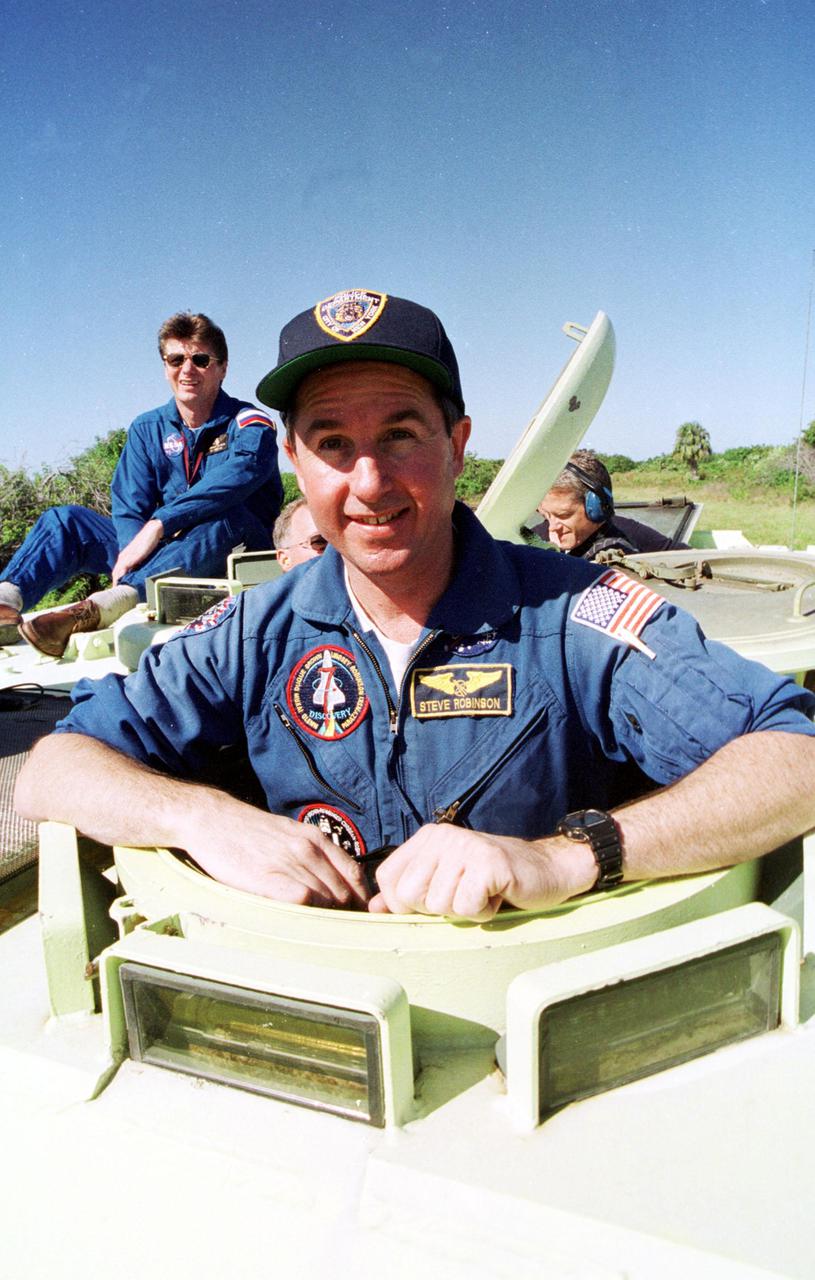

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Astronaut Stephen K. Robinson takes his turn at driving an M-113 armored personnel carrier. Robinson is a backup crew member for the International Space Station Expedition 4 crew, who are flying on Space Shuttle Endeavour as part of mission STS-108. Both the mission crew and Expedition 4 crews are at KSC for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities. The TCDT includes emergency exit from the launch pad and a simulated launch countdown. The 11-day mission will also carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello, filled with supplies and equipment. STS-108 is scheduled to launch Nov. 29
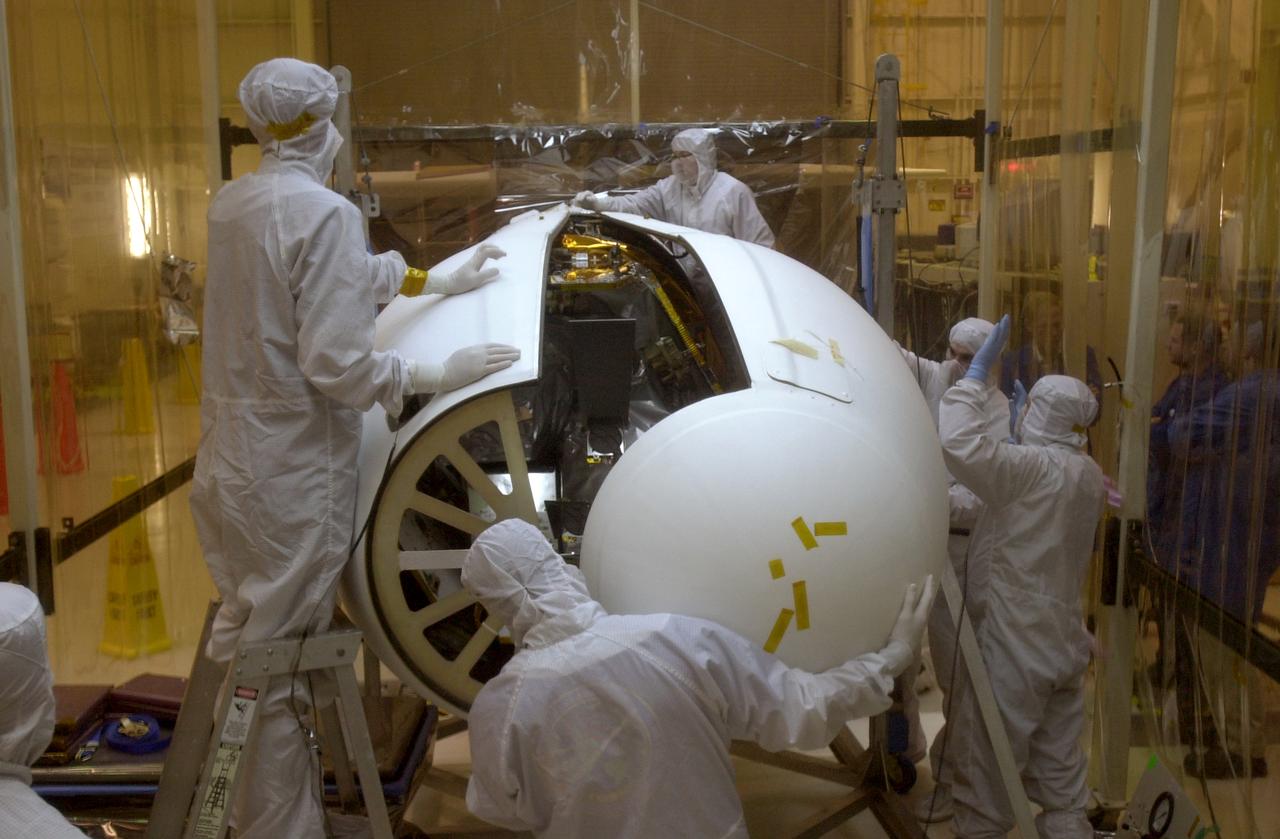

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, under the protective clean tent, technicians move the second half of the fairing into place around the AIM spacecraft. The fairing is a molded structure that fits around the spacecraft and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch. Launch will be from a Pegasus XL rocket, carried and released by Orbital Sciences L-1011 jet aircraft. AIM, which stands for Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, is being prepared for integrated testing and a flight simulation. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
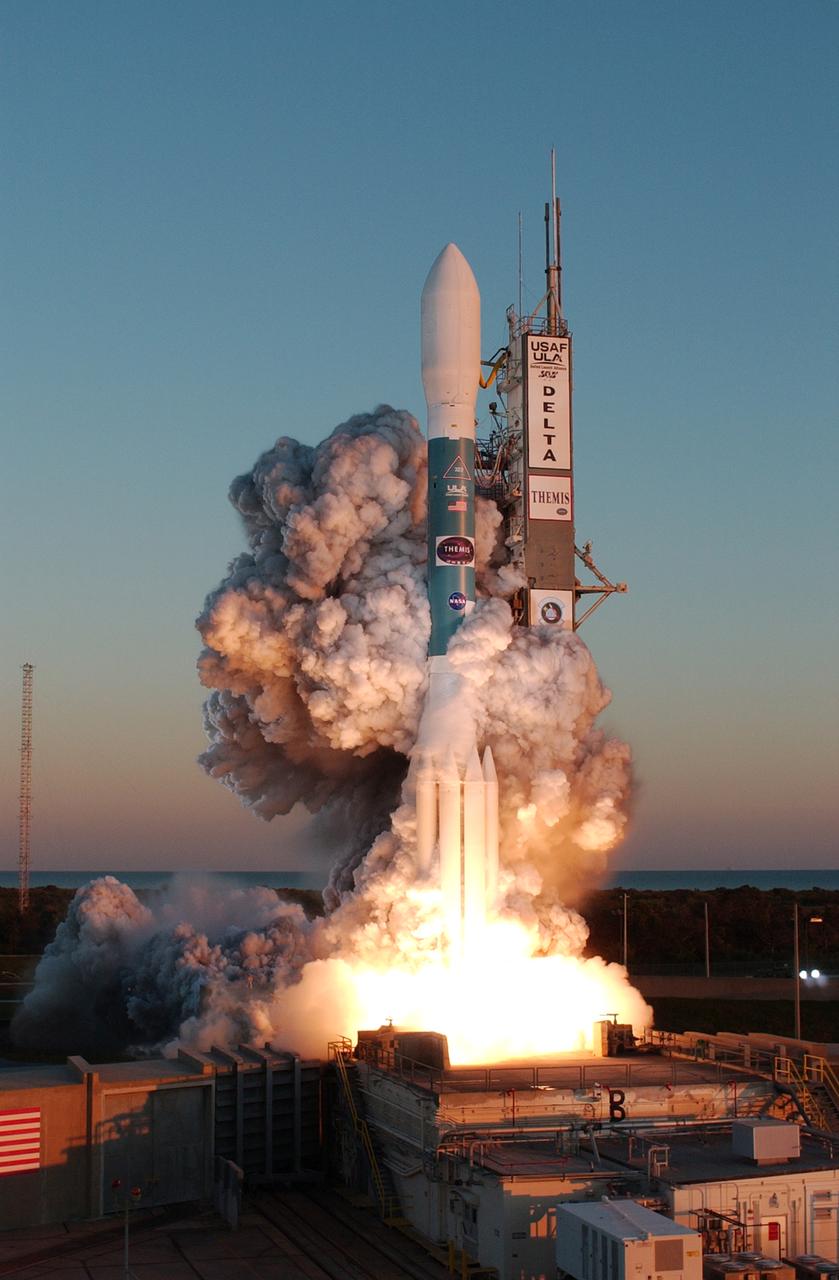

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, clouds of smoke form around the Delta II rocket with NASA's THEMIS spacecraft aboard as it blasts off Pad 17-B at 6:01 p.m. EST. THEMIS, an acronym for Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms, consists of five identical probes that will track violent, colorful eruptions near the North Pole. This will be the largest number of scientific satellites NASA has ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. The THEMIS mission aims to unravel the mystery behind auroral substorms, an avalanche of magnetic energy powered by the solar wind that intensifies the northern and southern lights. The mission will investigate what causes auroras in the Earth’s atmosphere to dramatically change from slowly shimmering waves of light to wildly shifting streaks of bright color.
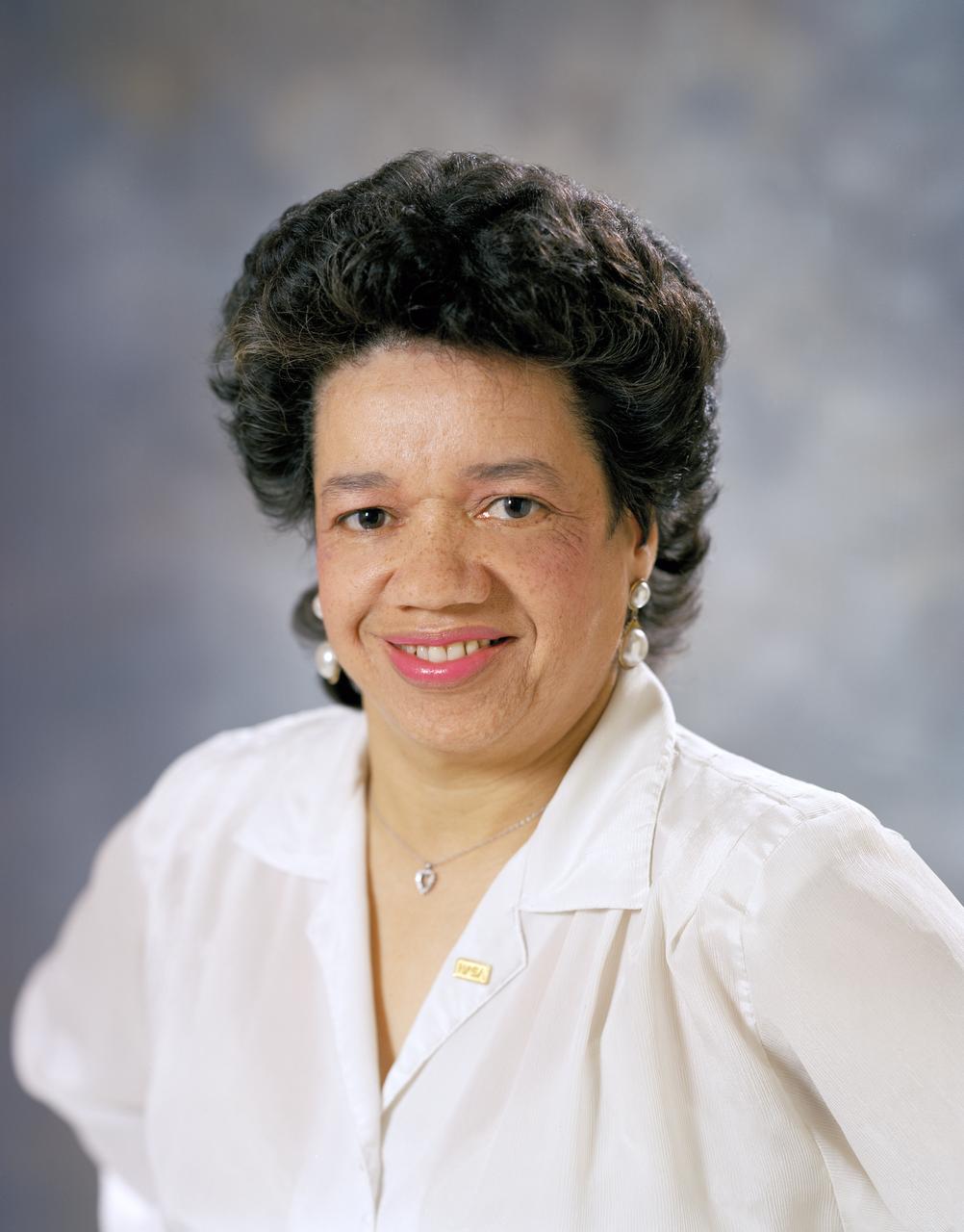

Portrait of Christine M. Darden
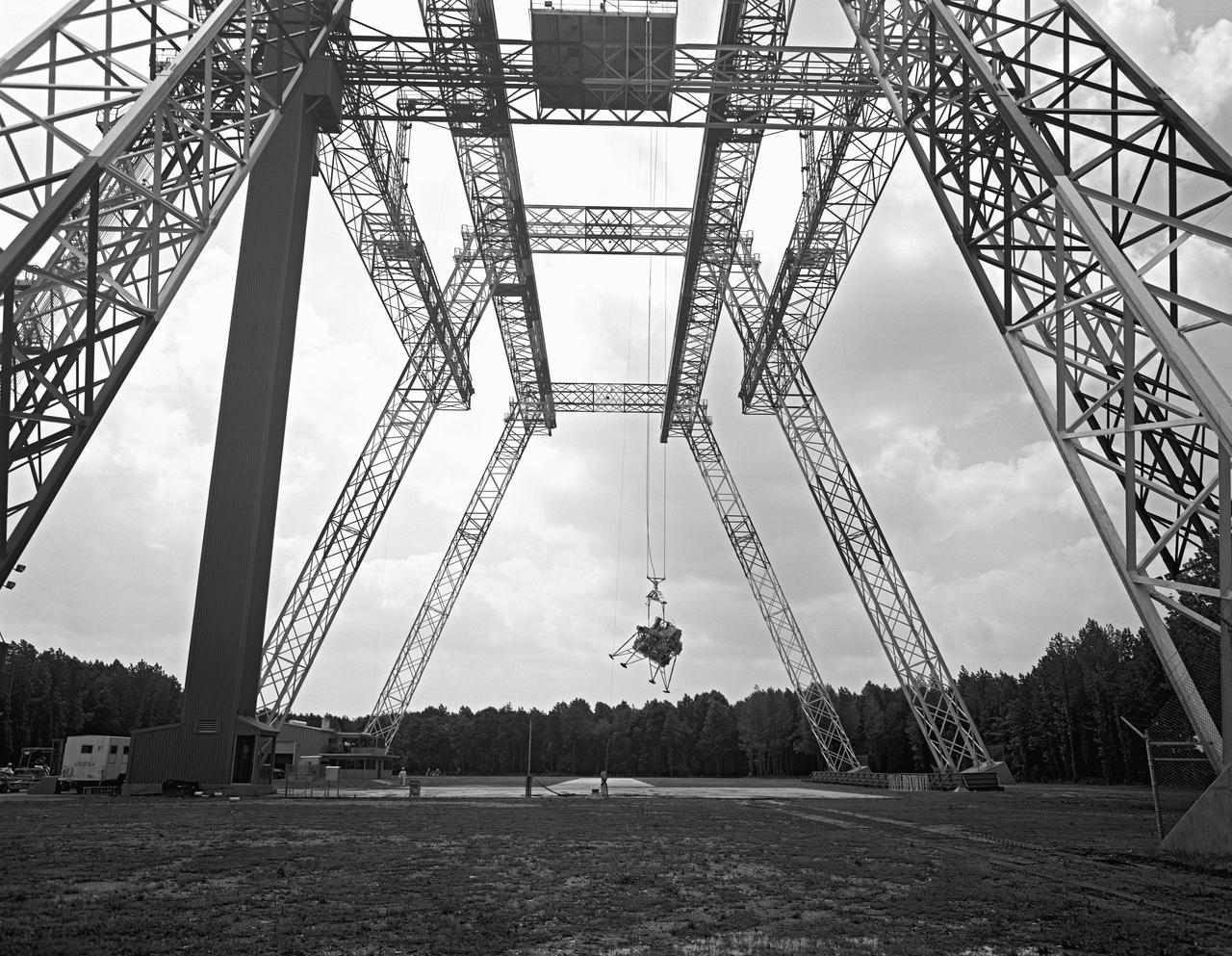

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Workers watch the rollback of the Rotating Service Structure (left) from around Space Shuttle Discovery on Launch Pad 39B. Poised above the orange external tank is the Gaseous Oxygen Vent Arm with the “beanie cap,” a vent hood. The RSS provides protected access to the orbiter for changeout and servicing of payloads. It is supported by a rotating bridge that pivots about a vertical axis on the west side of the pad’s flame trench. Space Shuttle Discovery is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:42 a.m. EST on the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. It carries the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, the primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. Leonardo will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny

L59-7932 First University of Michigan Strongarm sounding rocket on launcher at Wallops for test, November 10, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 701.E5-188 Shop and Launcher Pictures
![SCI2016_0001: SOFIA/GREAT [O I] spectrum at 4.7 THz (63 μm) superimposed on a picture of Mars. Absorption line depth is approximately 10% of the continuum. The abundance of atomic oxygen computed from the data is less than expected from the Forget et al. 1999 global circulation & photochemical model. Credit: SOFIA/GREAT spectrum: NASA/DLR/USRA/DSI/MPIfR/GREAT Consortium/MPIfS/Rezac et al. 2015; Mars image: NASA](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/ACD17-0168-003/ACD17-0168-003~medium.jpg)
SCI2016_0001: SOFIA/GREAT [O I] spectrum at 4.7 THz (63 μm) superimposed on a picture of Mars. Absorption line depth is approximately 10% of the continuum. The abundance of atomic oxygen computed from the data is less than expected from the Forget et al. 1999 global circulation & photochemical model. Credit: SOFIA/GREAT spectrum: NASA/DLR/USRA/DSI/MPIfR/GREAT Consortium/MPIfS/Rezac et al. 2015; Mars image: NASA
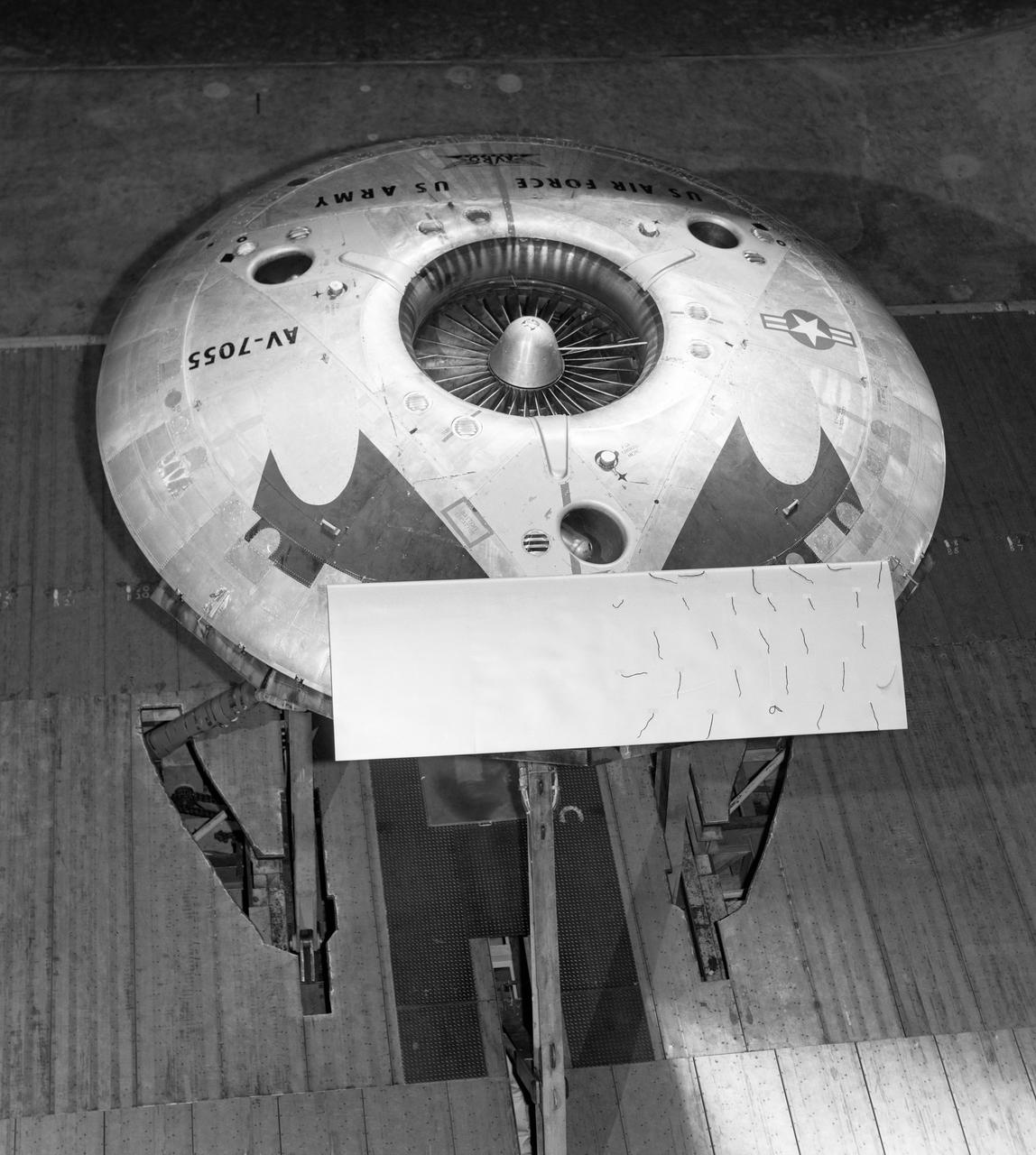
Top rear view of the avrocar with tail. Tufts (pieces of yarn) attached to top of horizontal tail. Avrocar mounted on variable height struts.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
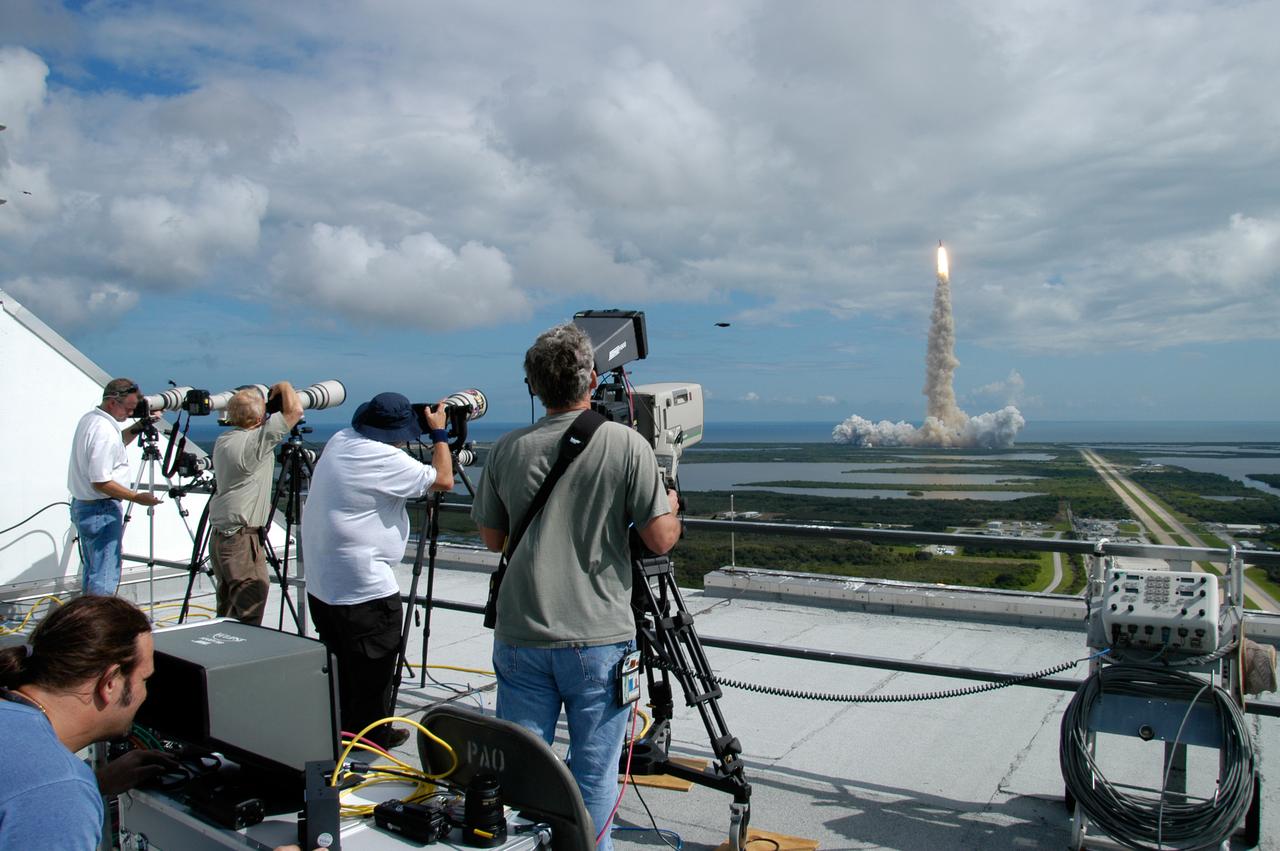

From the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, media photographers capture the launch of space shuttle Discovery as it soars from its seaside launch pad. Liftoff was on time at 11:38:19 a.m. EDT. Discovery carries the Italian-built U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. During the 14-day STS-120 mission, the crew will install Harmony and move the P6 solar arrays to their permanent position and deploy them. Discovery is expected to complete its mission and return home at 4:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 6.
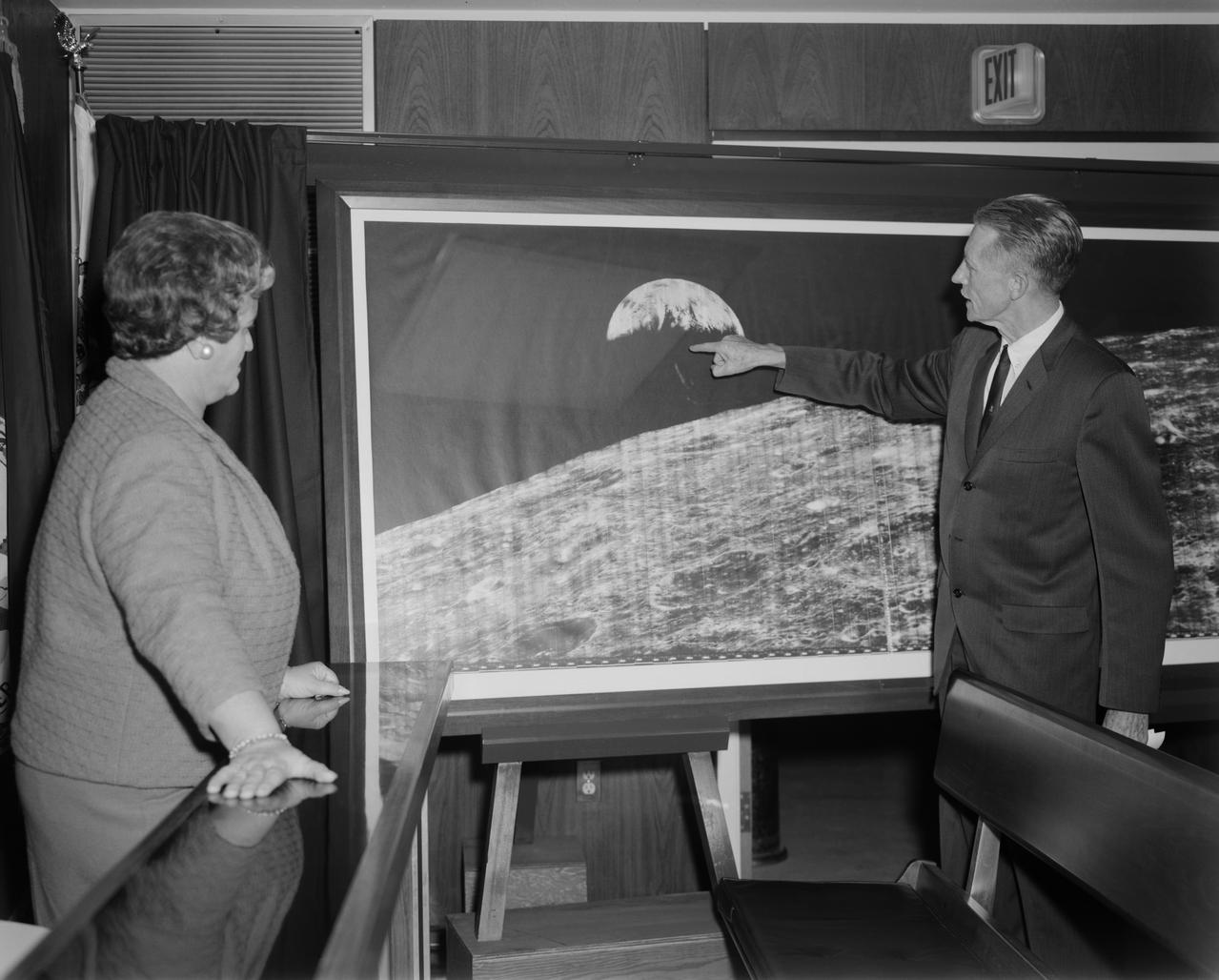

Langley Center Director Floyd Thompson shows Ann Kilgore the "picture of the century." This was the first picture of the earth taken from space. From Spaceflight Revolution: "On 23 August 1966 just as Lunar Orbiter I was about to pass behind the moon, mission controllers executed the necessary maneuvers to point the camera away from the lunar surface and toward the earth. The result was the world's first view of the earth from space. It was called "the picture of the century' and "the greatest shot taken since the invention of photography." Not even the color photos of the earth taken during the Apollo missions superseded the impact of this first image of our planet as a little island of life floating in the black and infinite sea of space." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), pp. 345-346. Mayor Ann Kilgore was married to NASA researcher Edwin Carroll Kilgore. Mrs. Kilgore was Mayor from 1963-1971 and again from 1974-1978.
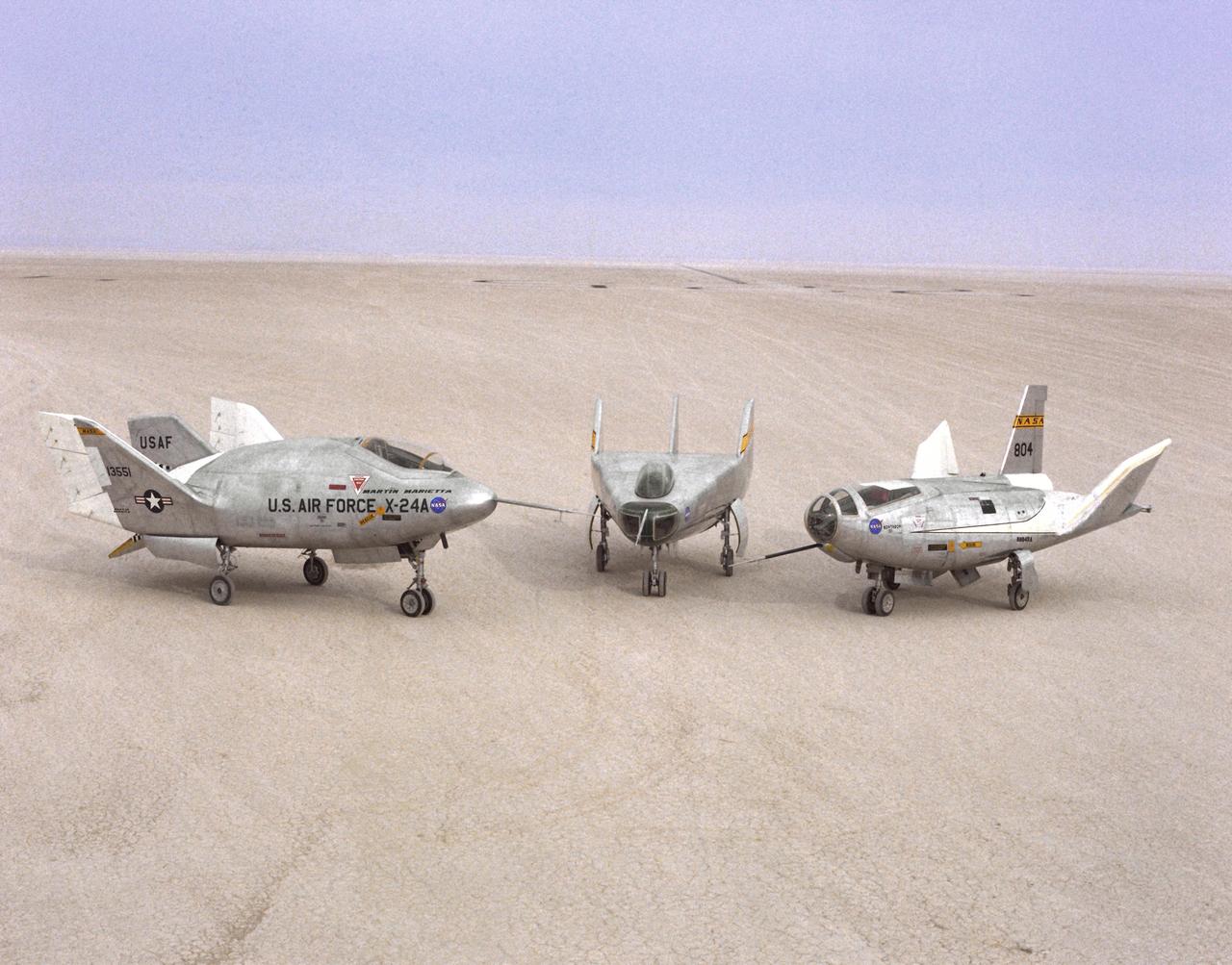

The wingless, lifting body aircraft sitting on Rogers Dry Lake at what is now NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, from left to right are the X-24A, M2-F3 and the HL-10. The lifting body aircraft studied the feasibility of maneuvering and landing an aerodynamic craft designed for reentry from space. These lifting bodies were air launched by a B-52 mother ship, then flew powered by their own rocket engines before making an unpowered approach and landing. They helped validate the concept that a space shuttle could make accurate landings without power. The X-24A flew from April 17, 1969 to June 4, 1971. The M2-F3 flew from June 2, 1970 until December 22, 1972. The HL-10 flew from December 22, 1966 until July 17, 1970, and logged the highest and fastest records in the lifting body program.
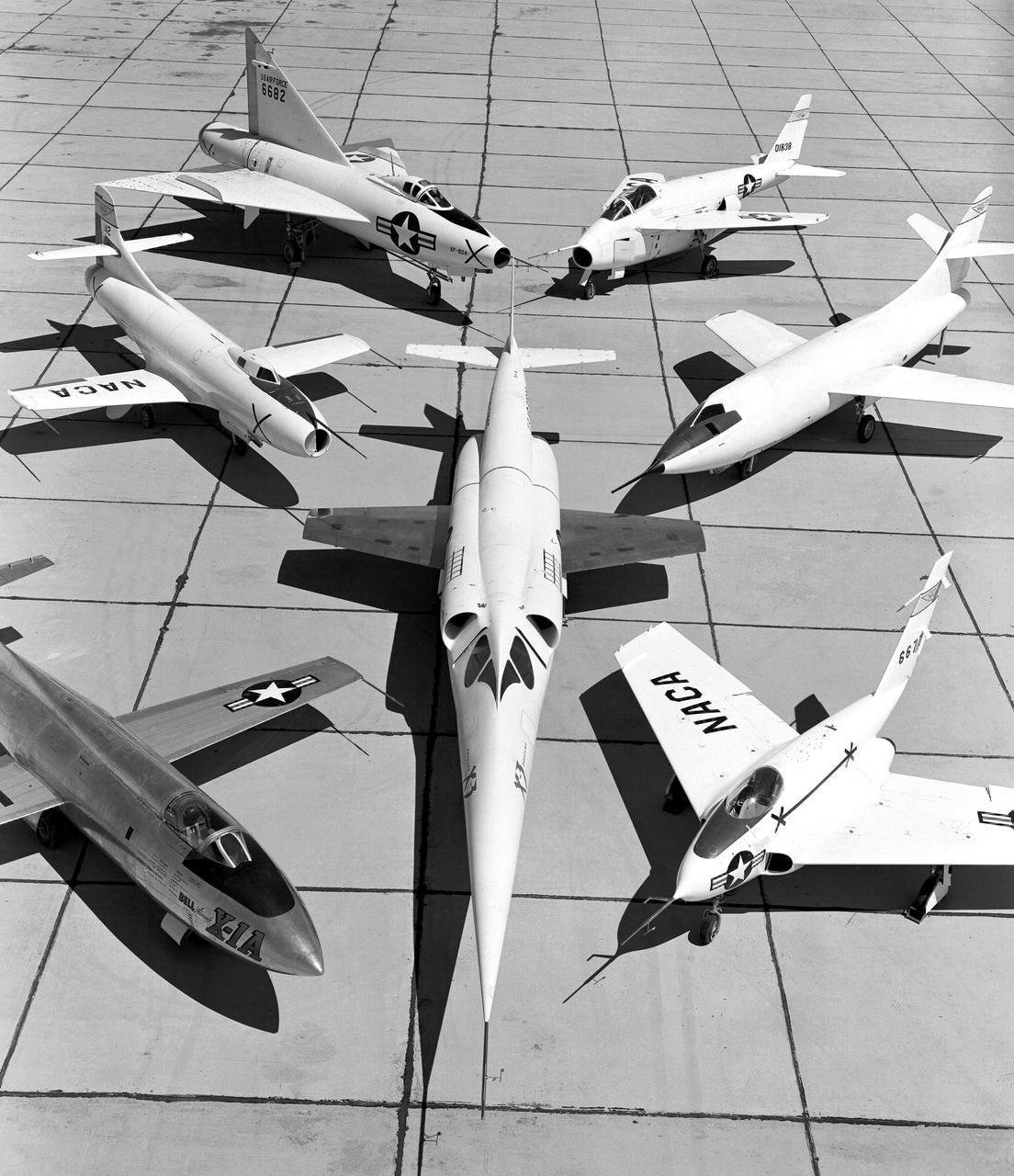

X-3 (center), and clockwise from left: X-1A, D-558-I, XF-92A, X-5, D-558-II, and X-4.
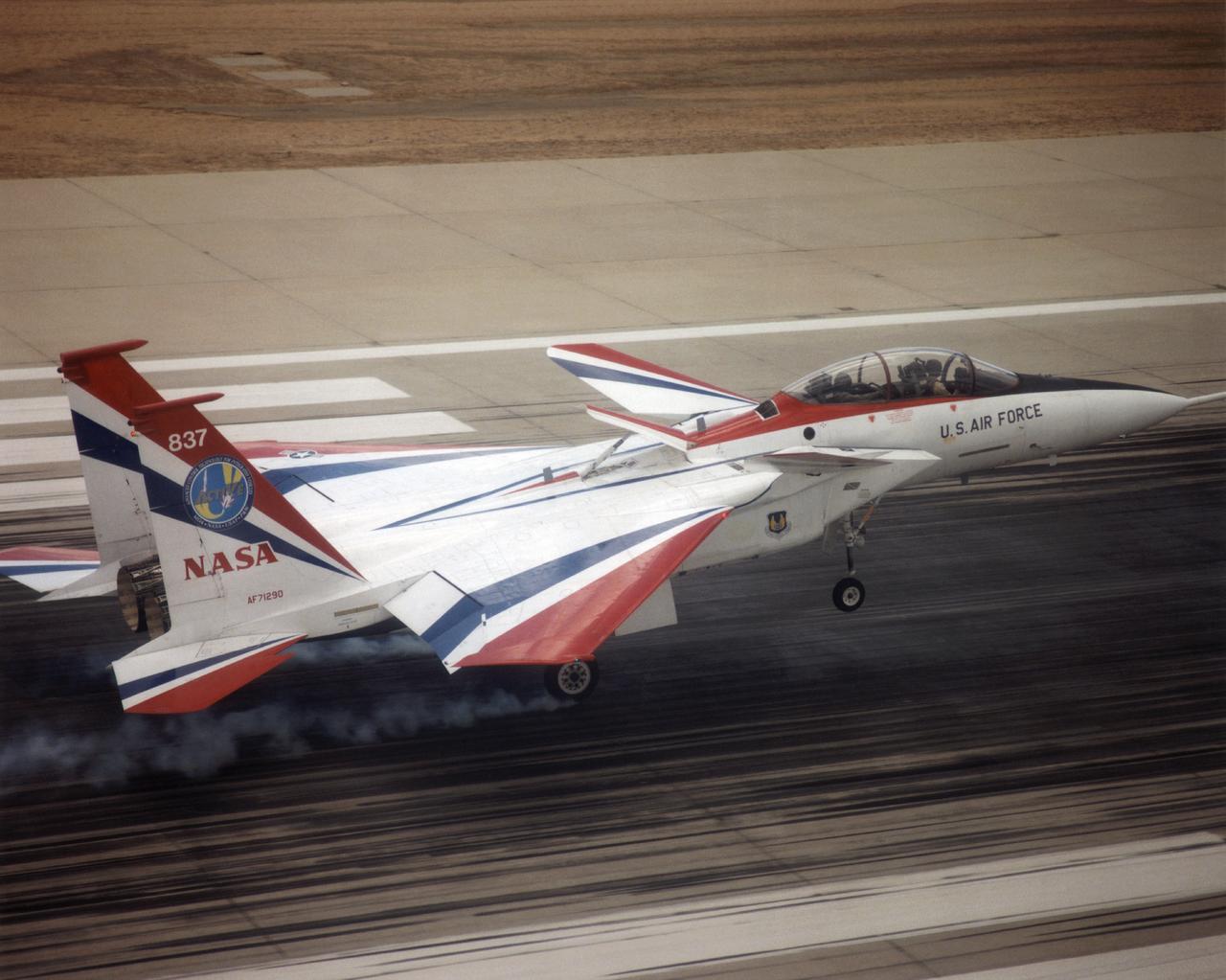

The F-15 ACTIVE touches down on the Edwards runway following its April 14, 1998 flight. The nose is high while the canards have their rear edge raised. the aircraft's speed brake, located on the top of the aircraft behind the canopy, is also raised.
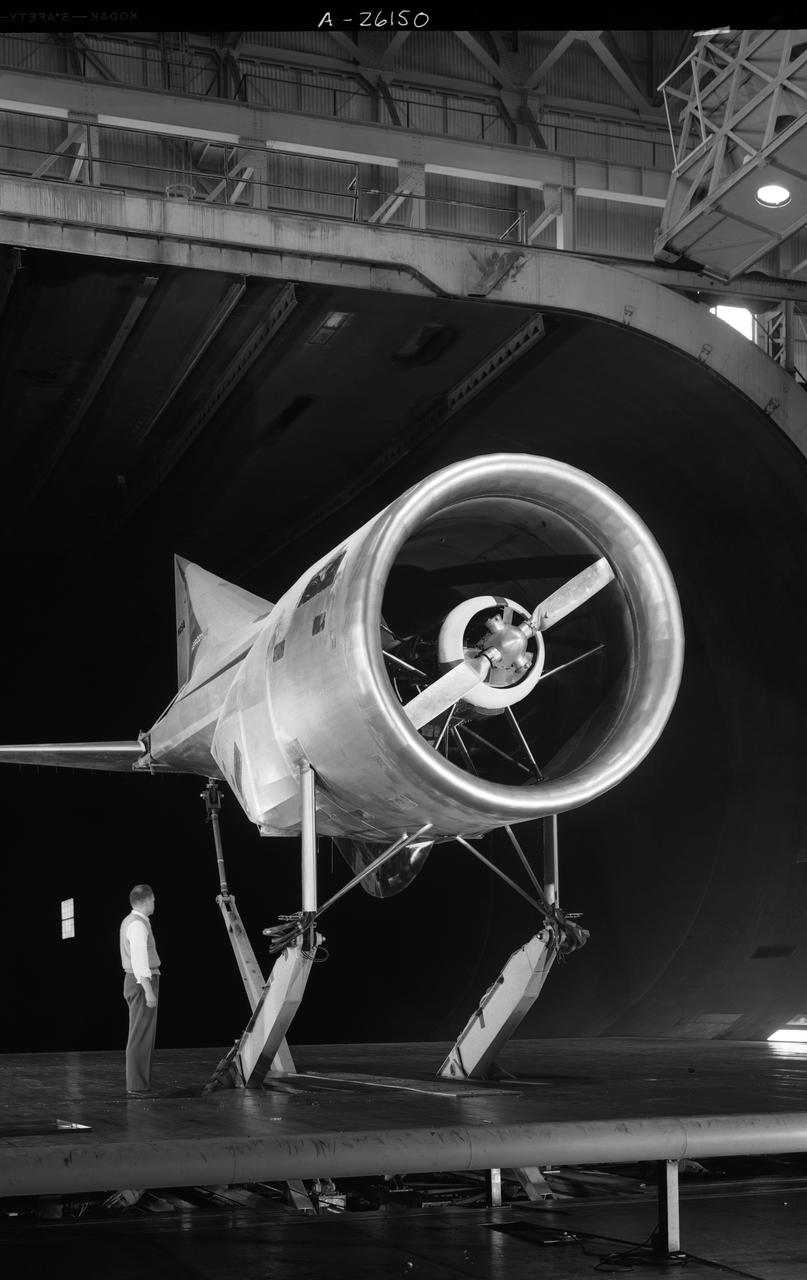

Collins Aerodyne vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft investigations. Ground plane support system. 3/4 front view. Dave Koening (from Collins Aerodyne) in photo. Mounted on variable height struts, ground board system, zero degree angle of attack. 01/11/1960
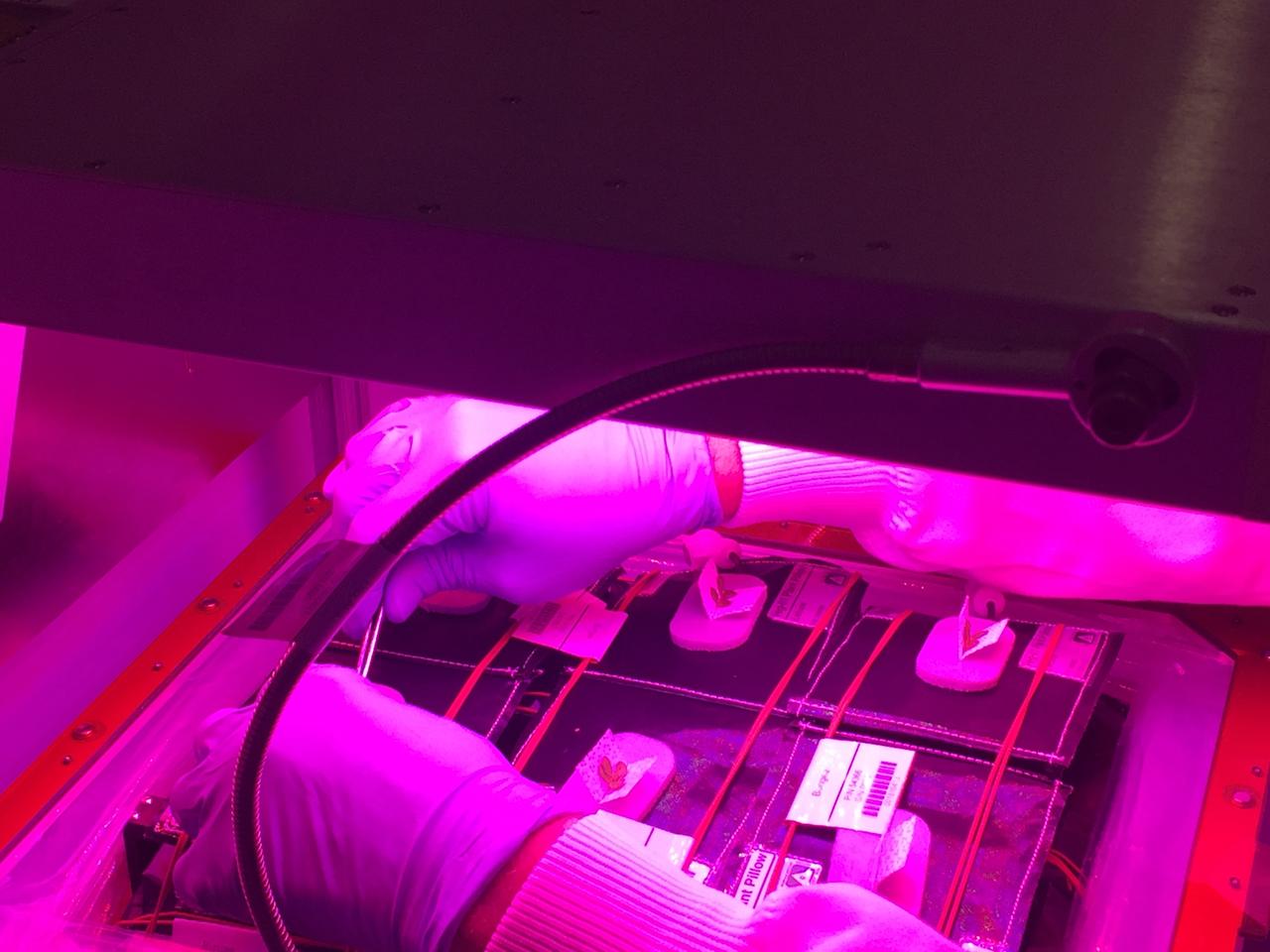

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
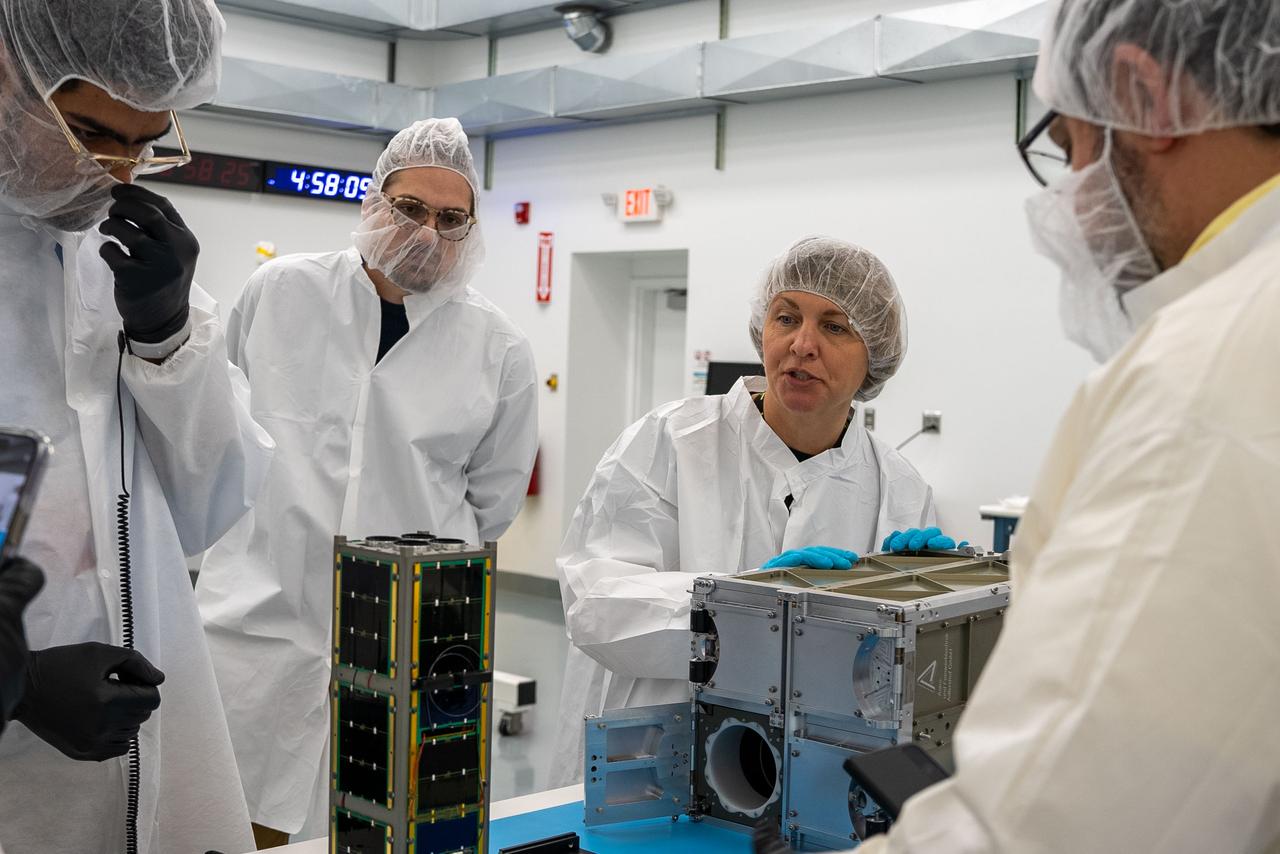

Technicians from the University of Maine prepare CubeSat MESAT-1 for integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Monday, April 22, 2024. MESAT-1, along with seven other payloads, will be integrated into a Firefly Aerospace Alpha rocket for NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.

3/4 front view with cascade exit vane in Ames 40x80 foot wind tunnel, with Tom Seymore, mechanic for Ames.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
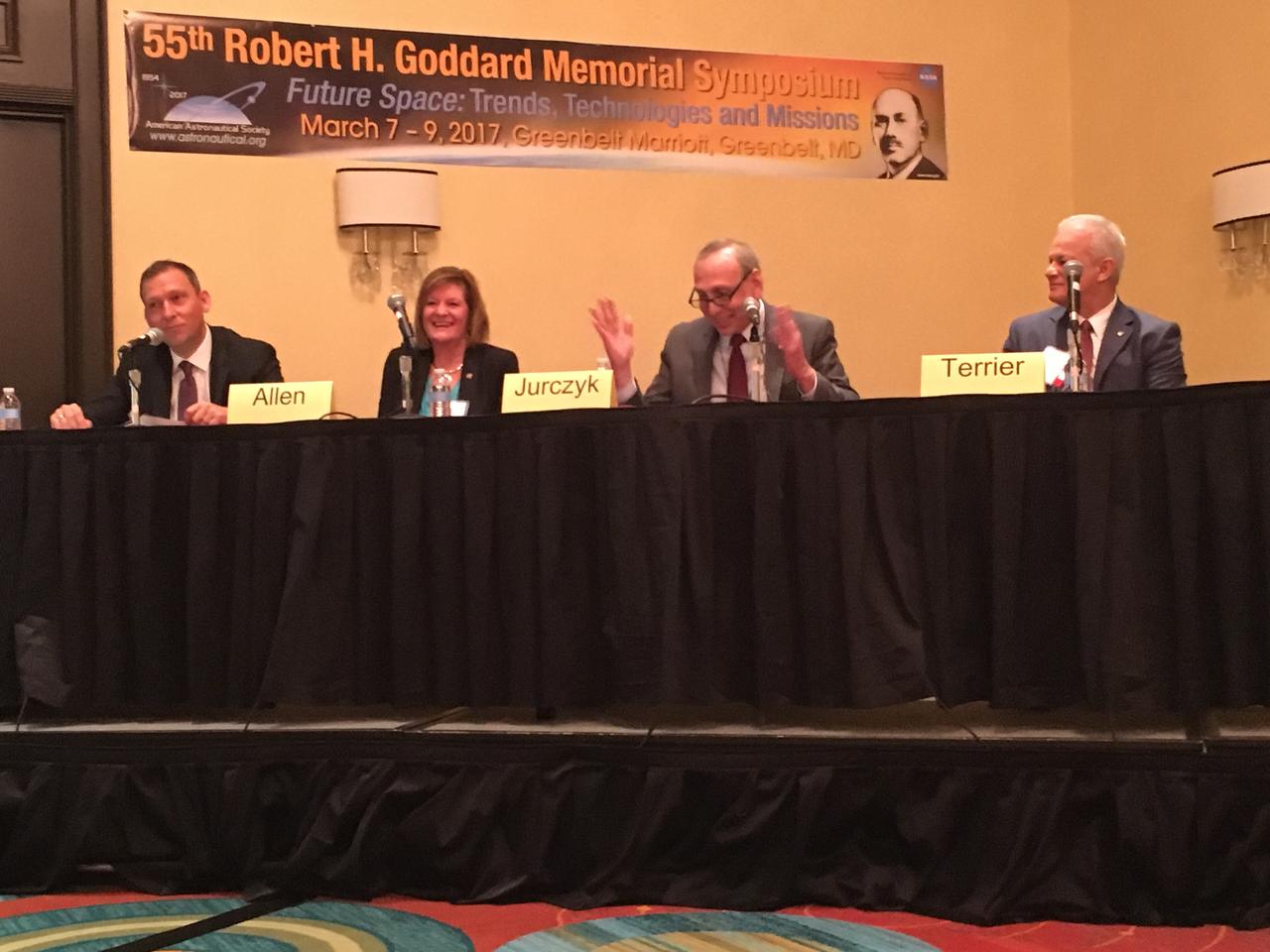

NASA Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier moderated the discussion “NASA Leadership in the Future of Science and Technology" during the AAS 55th Robert H. Goddard Memorial Symposium on March 8, 2017. Terrier was joined by Associate Administrator for Space Technology Steve Jurczyk, Chief Scientist Gale Allen and Associate Administrator for Science Thomas Zurbuchen.
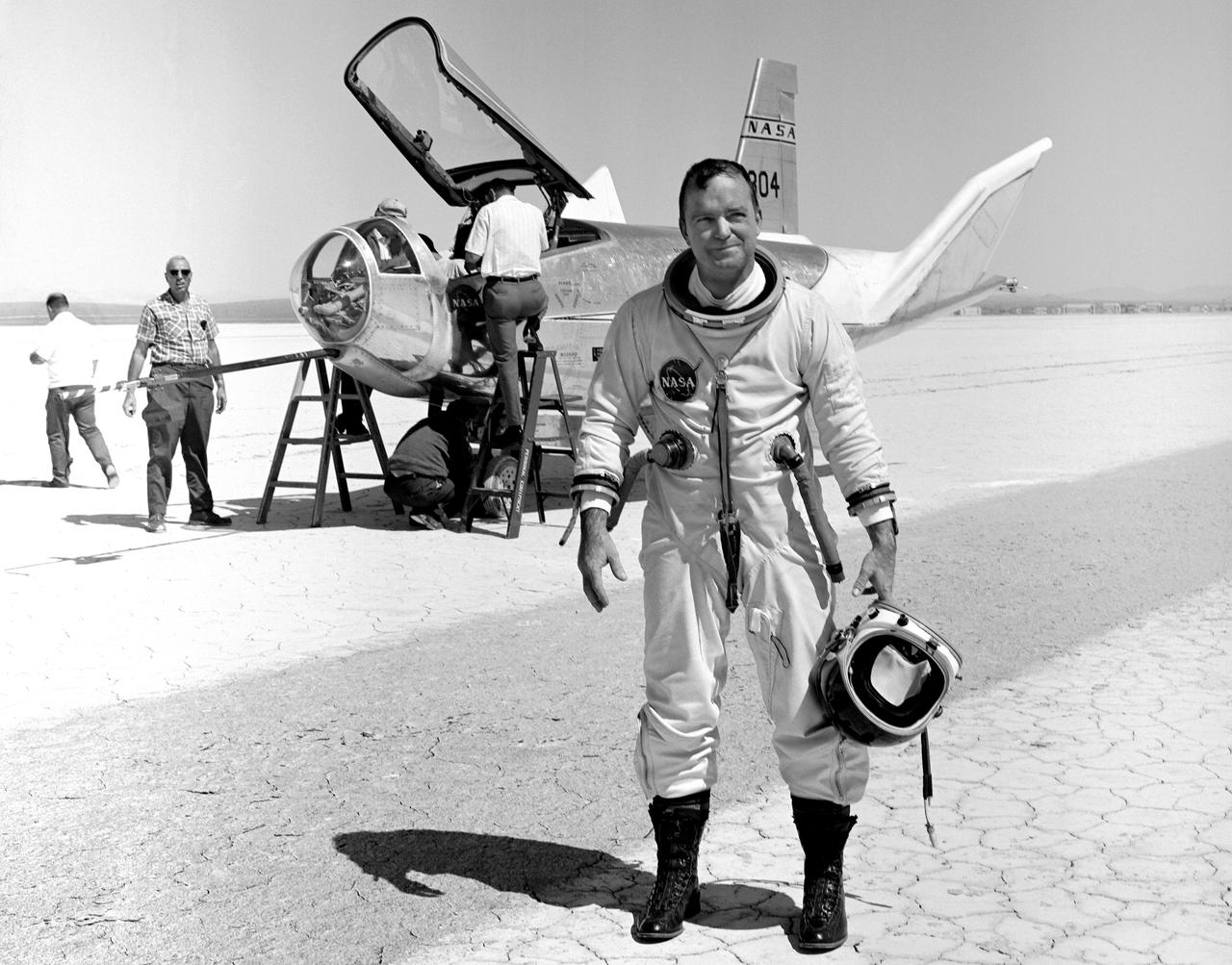

NASA research pilot Bill Dana stands in front of the HL-10 Lifting Body following his first glide flight on April 25, 1969. Dana later retired as Chief Engineer at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, (called the NASA Flight Research Center in 1969). Prior to his lifting body assignment, Dana flew the X-15 research airplane. He flew the rocket-powered aircraft 16 times, reaching a top speed of 3,897 miles per hour and a peak altitude of 310,000 feet (almost 59 miles high).

Miscellaneous Charts, Space Capsule
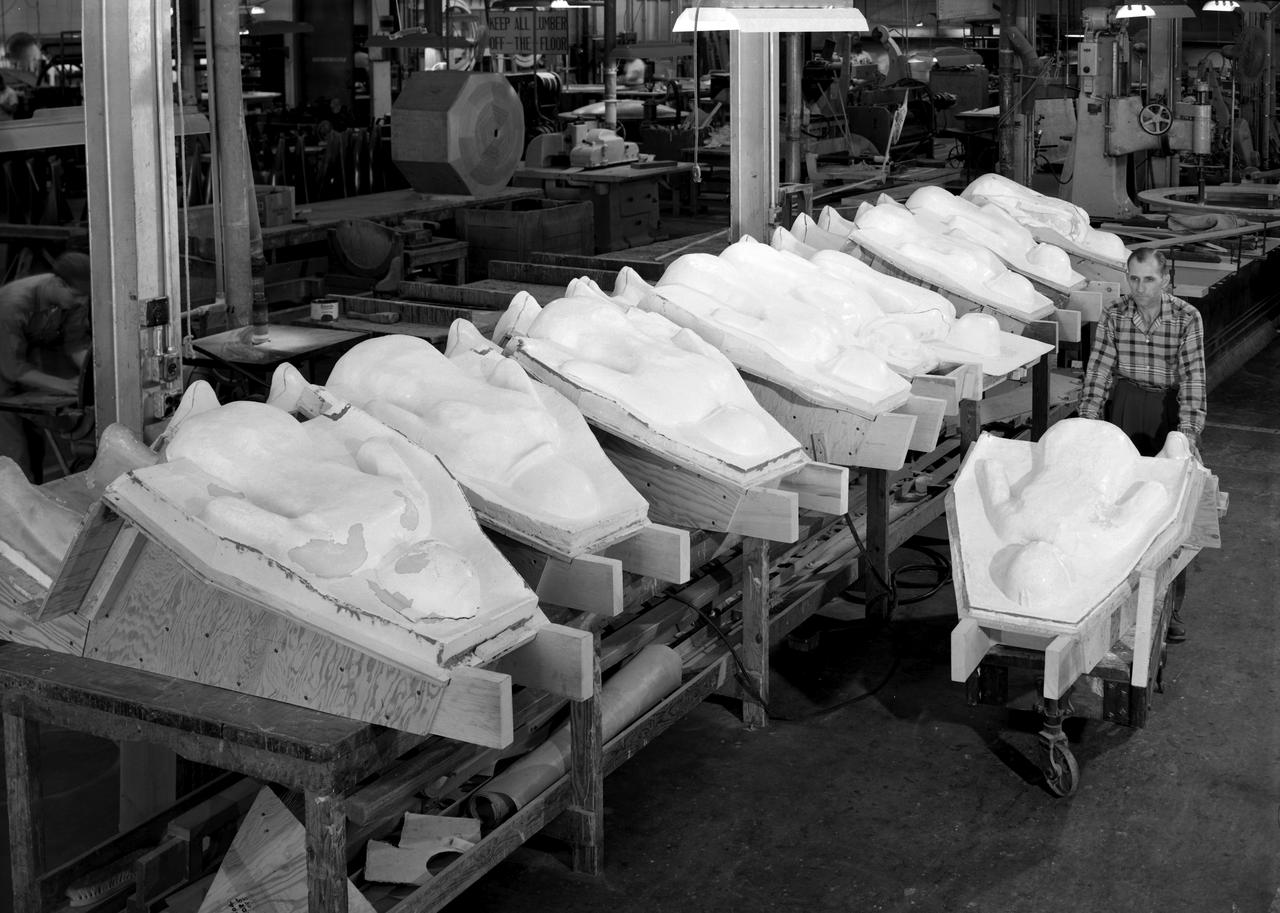

Plaster Molds for Space Couch
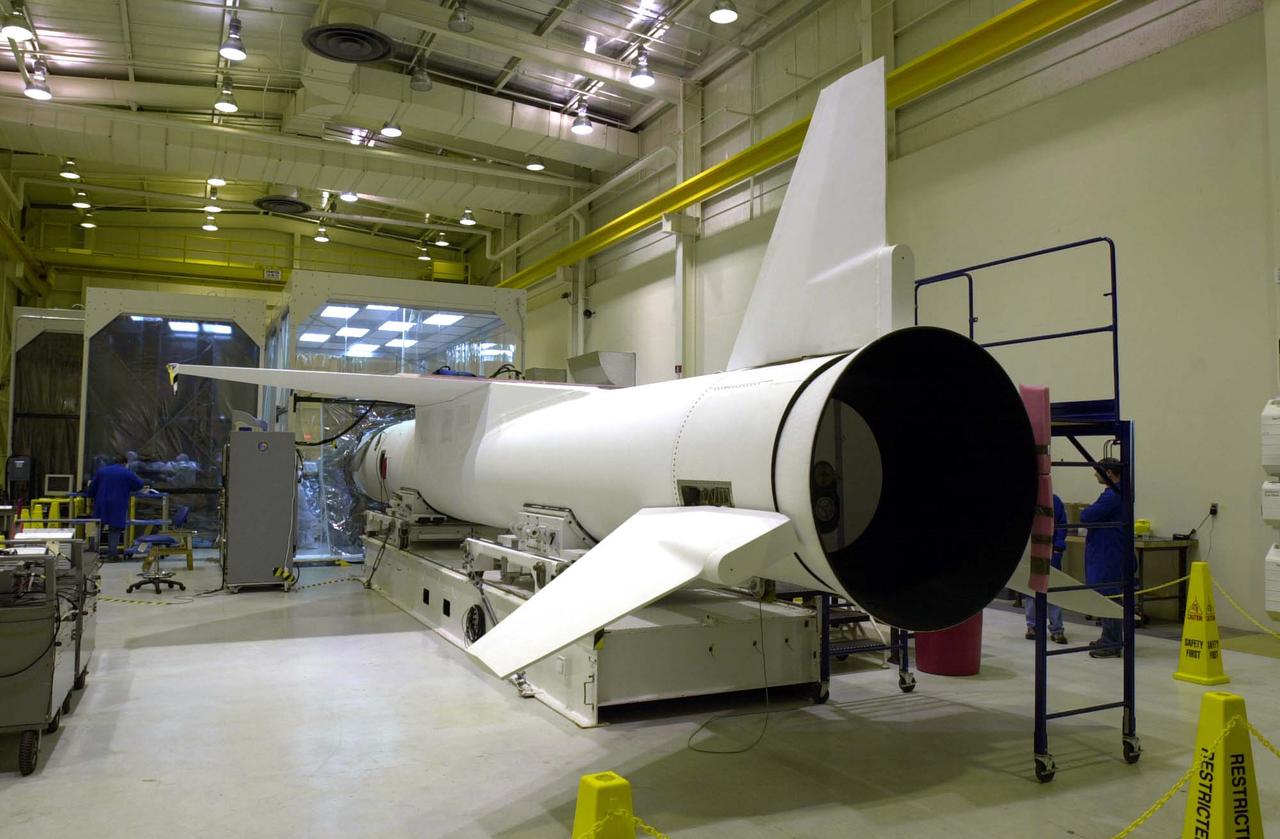

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket is ready for mating to the AIM spacecraft. AIM, which stands for Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, is being prepared for integrated testing and a flight simulation. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. Launch from the Pegasus XL rocket is scheduled for April 25.
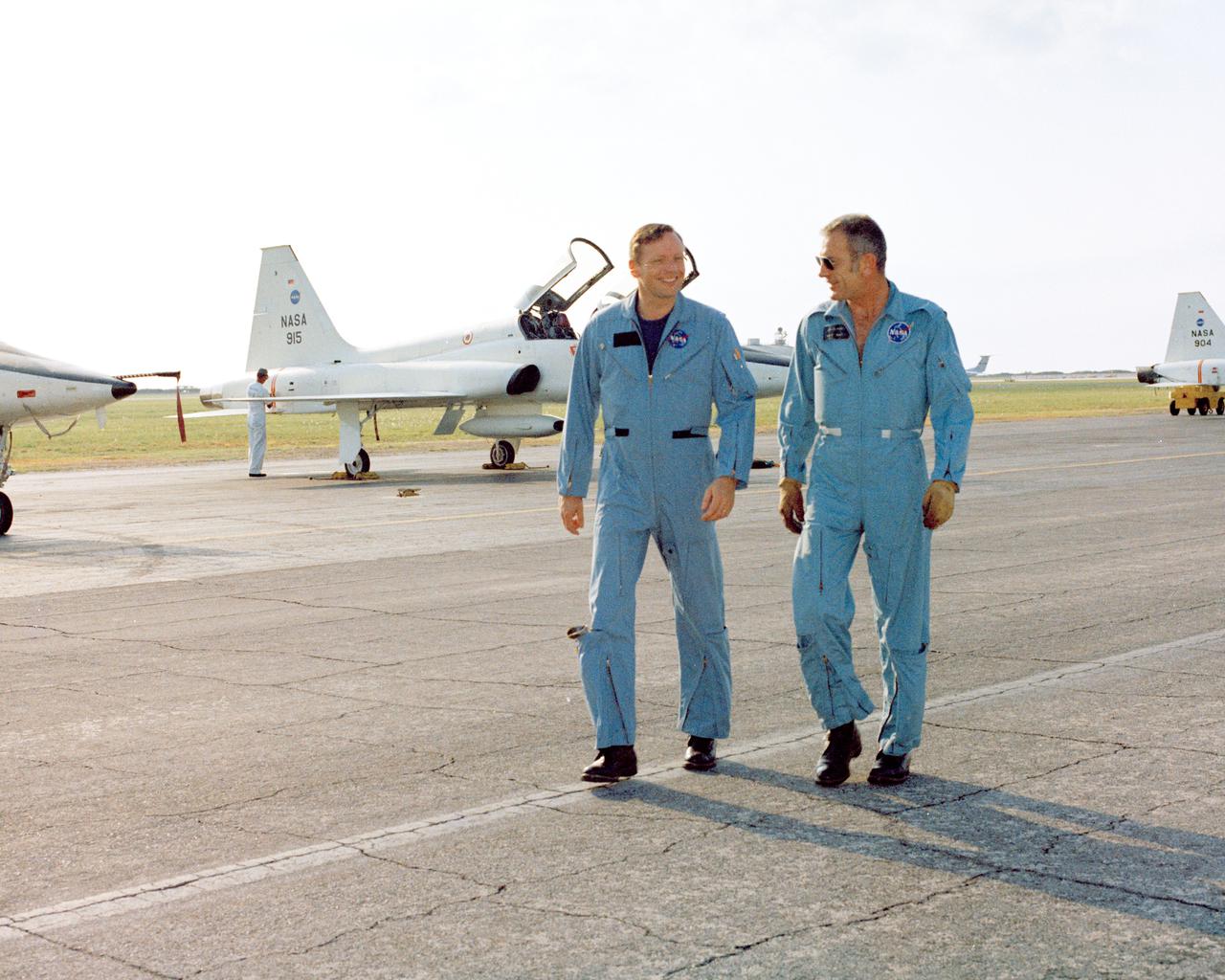

PATRICK AFB, Fla. – Apollo 11 commander Neil A. Armstrong, left, and Donald K. Slayton, chief astronaut and director of flight crew operations, just arrived at Patrick Air Force Base in a T-38 jet in preparation of the nation’s first lunar landing mission. Lift off atop a Saturn V launch vehicle is scheduled for July 16, 1969. During Apollo 11 the command module, Columbia, will remain in orbit around the moon while the lunar module, Eagle, carrying Armstrong and Aldrin, lands on the lunar surface. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew plans to collect lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. For more: http:__www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov_history_apollo_apollo-11_apollo-11.htm Photo credit: NASA

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
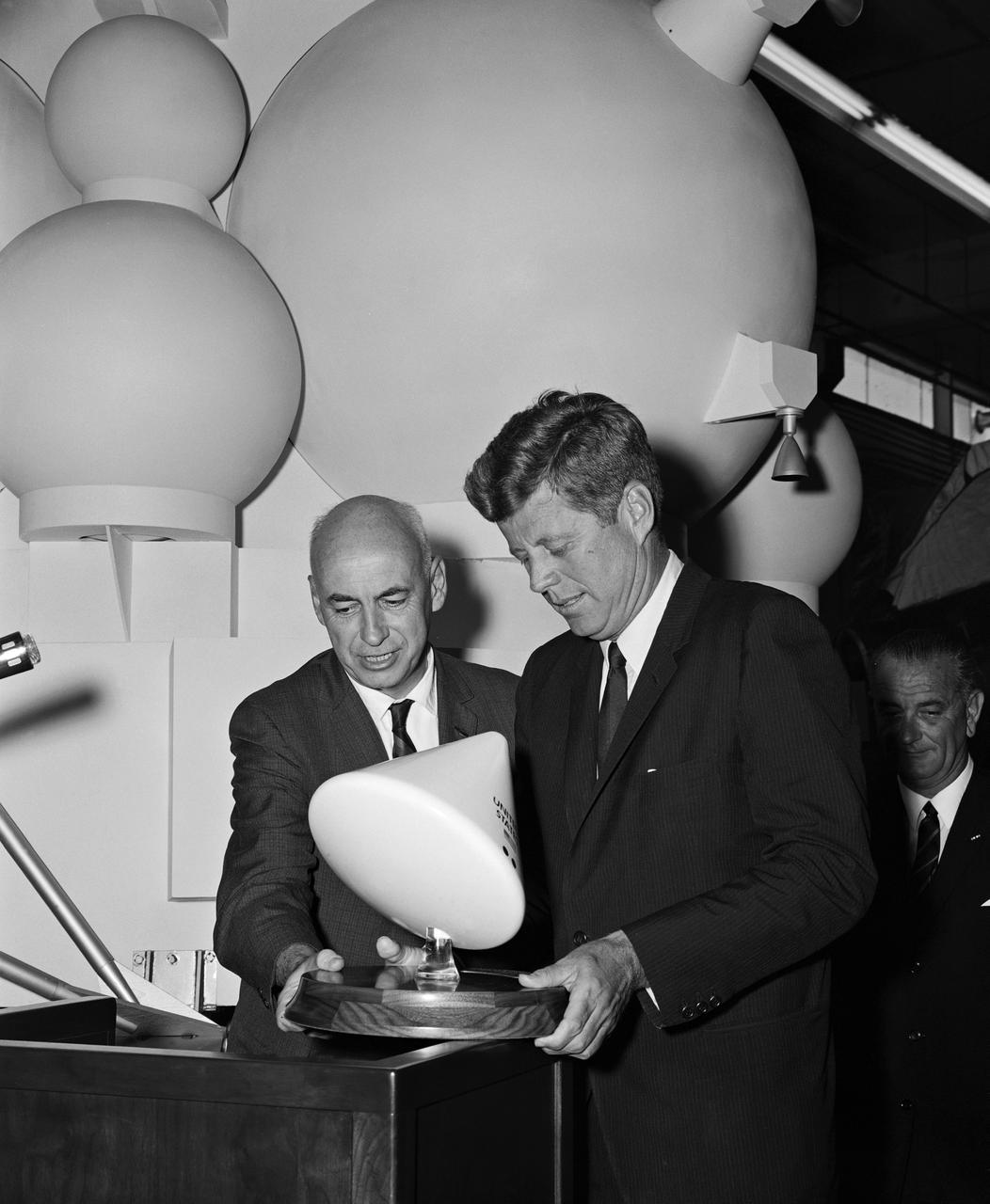

Dr. Robert R. Gilruth (left), director of what is now NASA’s Johnson Space Center, and President John F. Kennedy look at a small model of the Apollo Command Module on September 1, 1962.

Air Force Javelin Rocket on Launcher (USAF JV-1) Wallops Model D4-78 L59-5144 First AFSWC Javelin sounding rocket ready for flight test, July 7, 1959. Photograph published in A New Dimension Wallops Island Flight Test Range: The First Fifteen Years by Joseph Shortal. A NASA publication. Page 704.
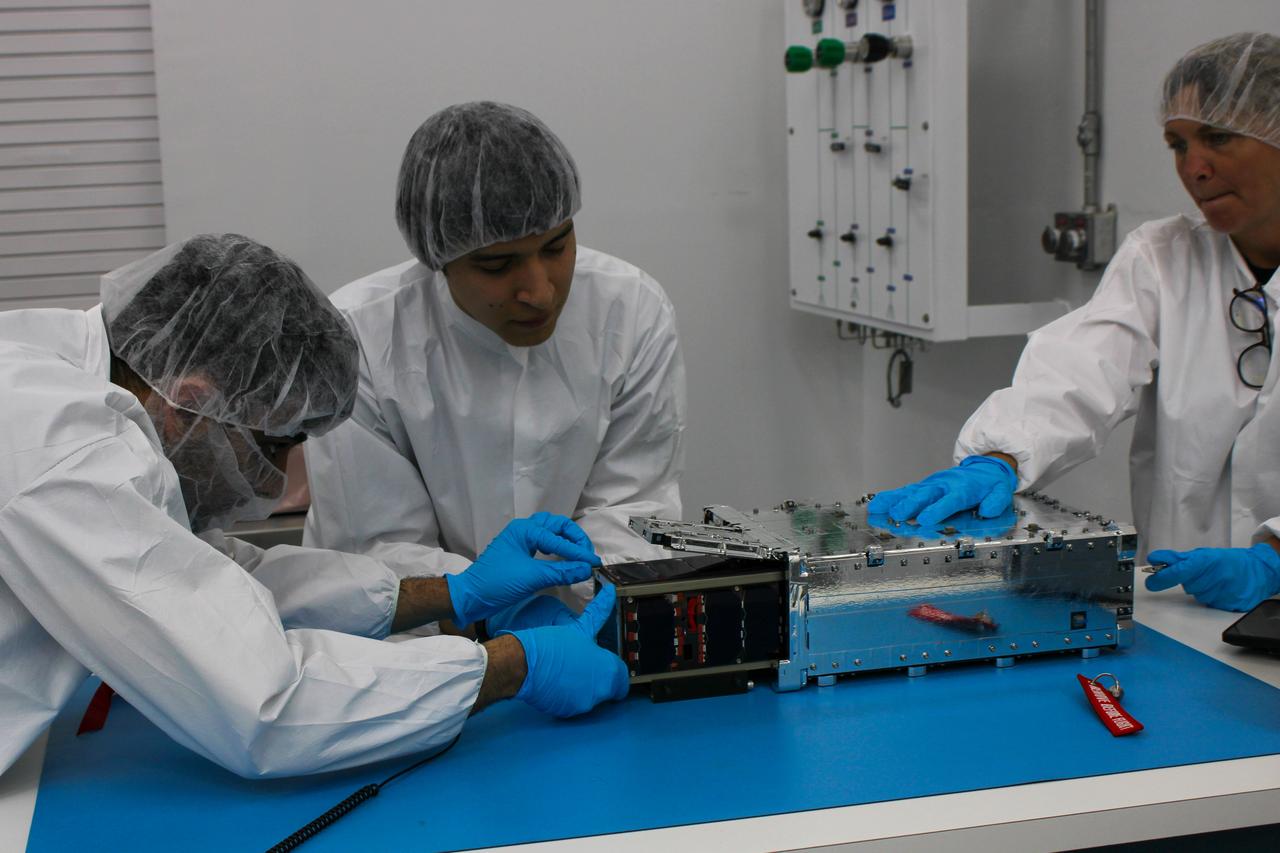

A Satellite for Optimal Control and Imaging (SOC-i) CubeSat awaits integration at Firefly’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California on Thursday, June 6, 2024. SOC-i, along with several other CubeSats, will launch to space on an Alpha rocket during NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa) 43 mission as part of the agency’s CubeSat Launch Initiative and Firefly’s Venture-Class Launch Services Demonstration 2 contract.
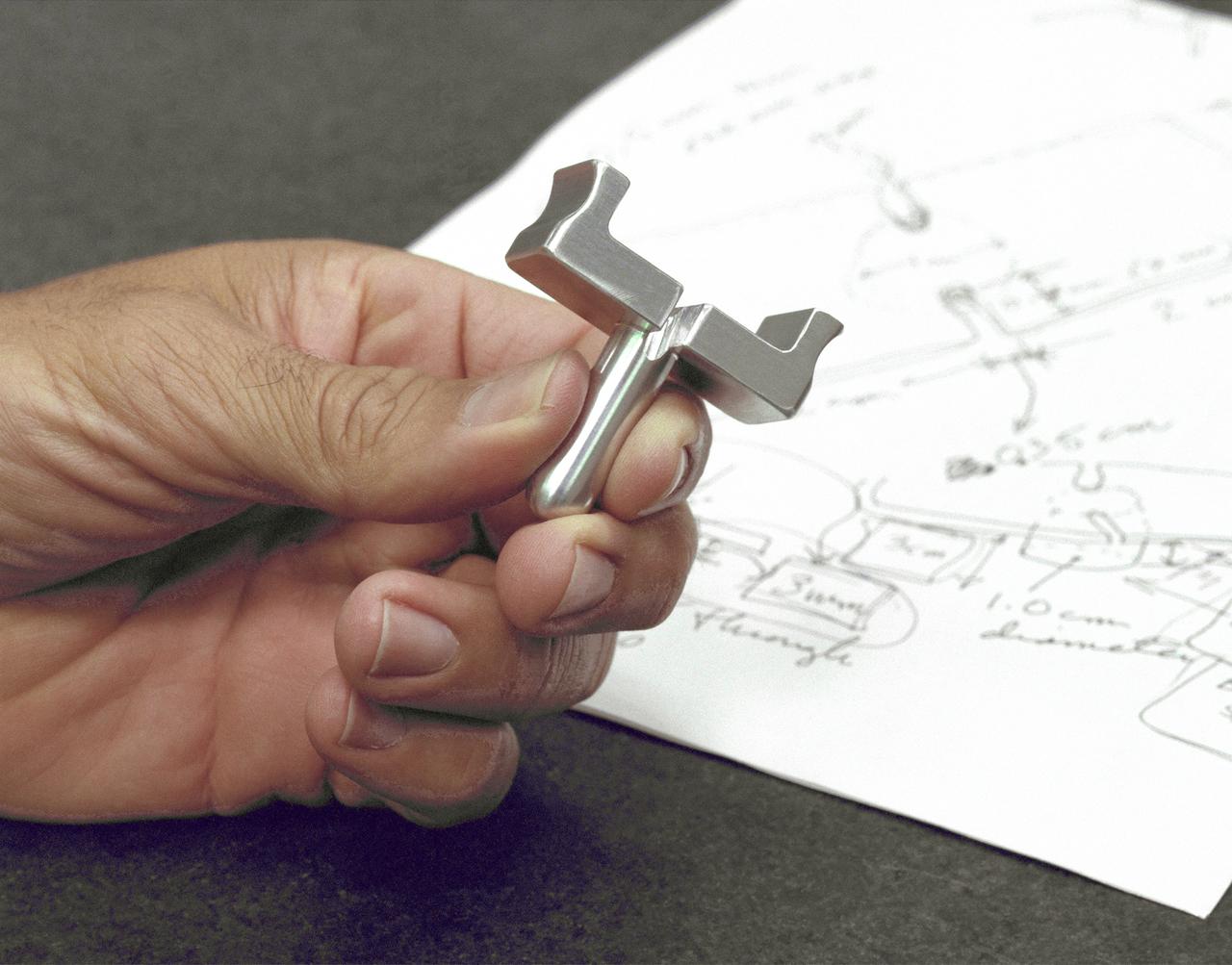
Dryden-built surgical suture instrument
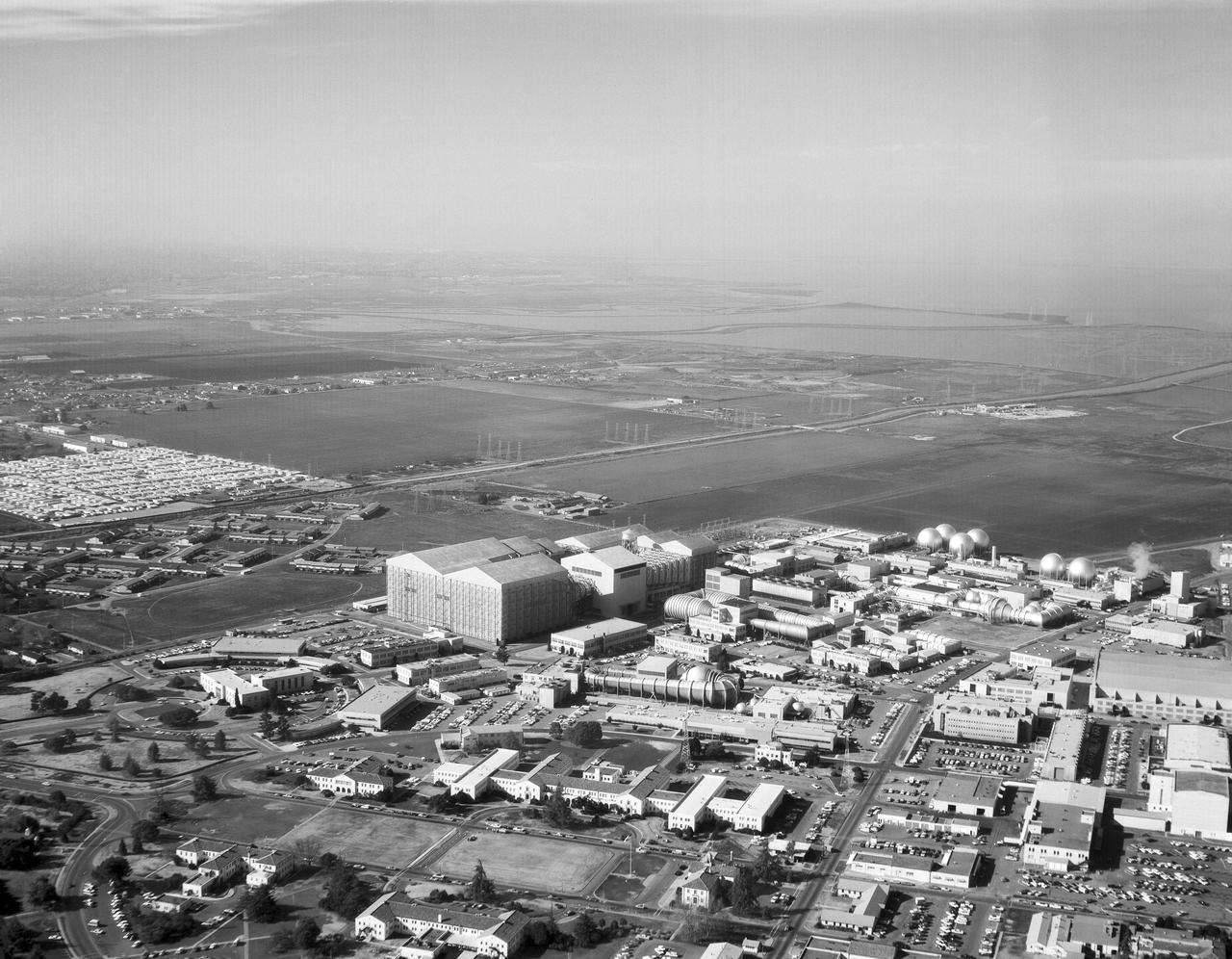

Helicopter view showing west area, south San Francisco Bay in background
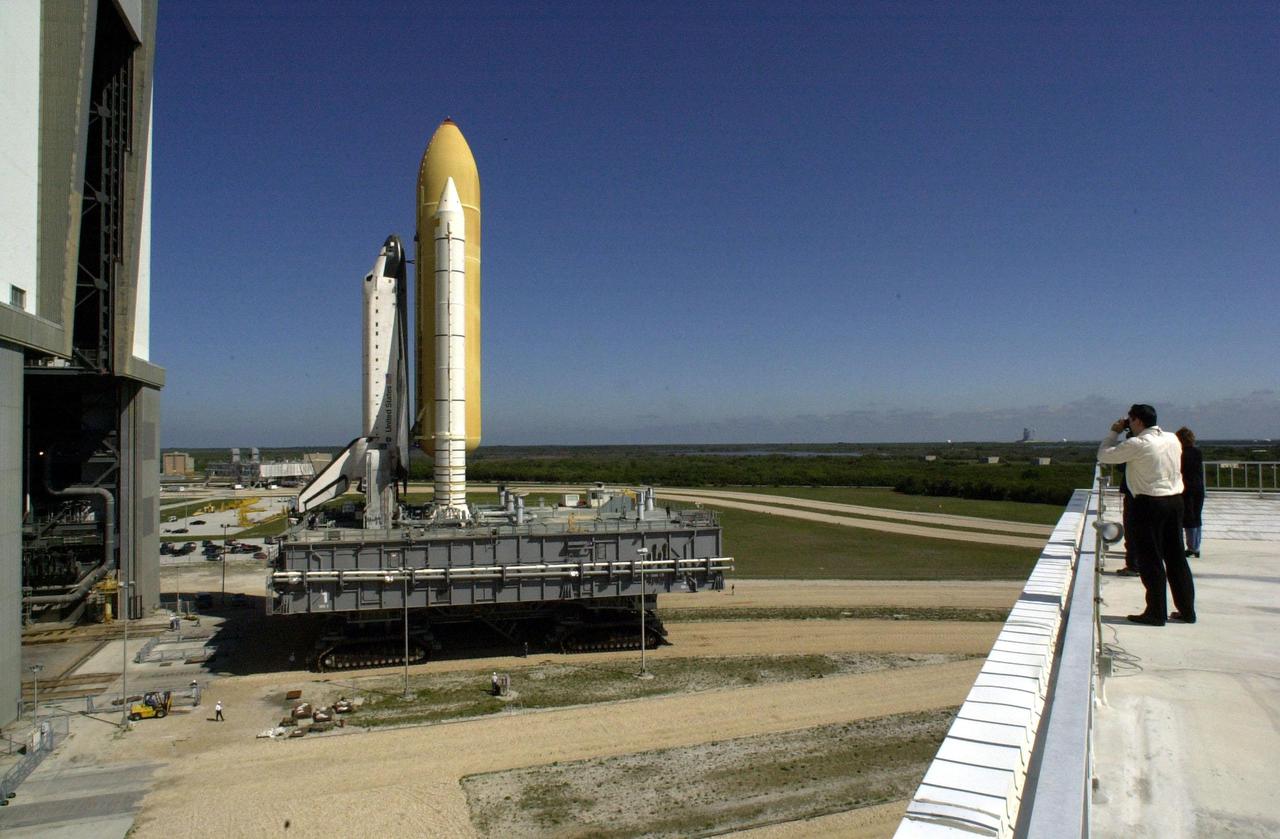

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Endeavour leaves the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 3 (open door) atop a Mobile Launcher Platform and begins rolling to Launch Pad 39A via a crawler-transporter. The combined height of the Shuttle, MLP and transporter is 235.2 ft. (71.6 m). Once at the pad, routine launch pad validations will commence, verifying all vehicle and facility interfaces. Endeavour is expected to lift off on mission STS-100 on April 19, carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, to the International Space Station
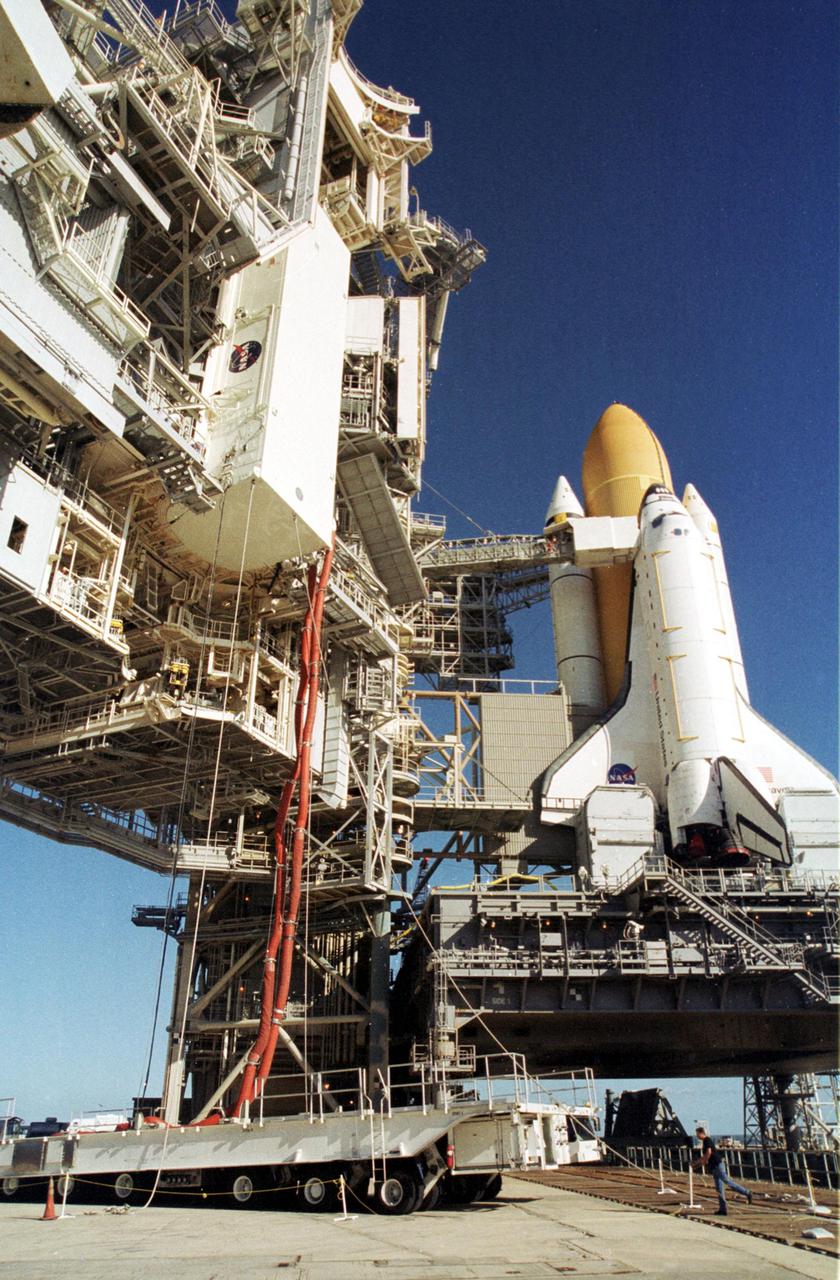

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At the launch pad, a payload canister carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello is lifted up the Rotating Service Structure (left) to the Payload Changeout Room. From there the MPLM will be moved into Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The Shuttle with its external tank and one solid rocket booster is seen at right. Endeavour is scheduled to launch Nov. 29 on the first Utilization Flight to the International Space Station. Raffaello is filled with supplies and equipment for the Station. Endeavour will also carry the replacement Expedition 4 crew to the Station and return to Earth with the Expedition 3 crew

In the Vehicle Assembly Building, markers show the hail damage being repaired on the external tank of Space Shuttle Atlantis. The white hole with a red circle around it is a hole prepared for molding and material application. The red material is sealant tape so the mold doesn't leak when the foam rises against the mold. The white/ translucent square mold is an area where the foam has been applied and the foam has risen and cured against the mold surface. The area will be de-molded and sanded flush with the adjacent area. In late February, Atlantis' external tank received hail damage during a severe thunderstorm that passed through the Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 area. The hail caused visible divots in the giant tank's foam insulation as well as minor surface damage to about 26 heat shield tiles on the shuttle's left wing. The launch now is targeted for June 8.
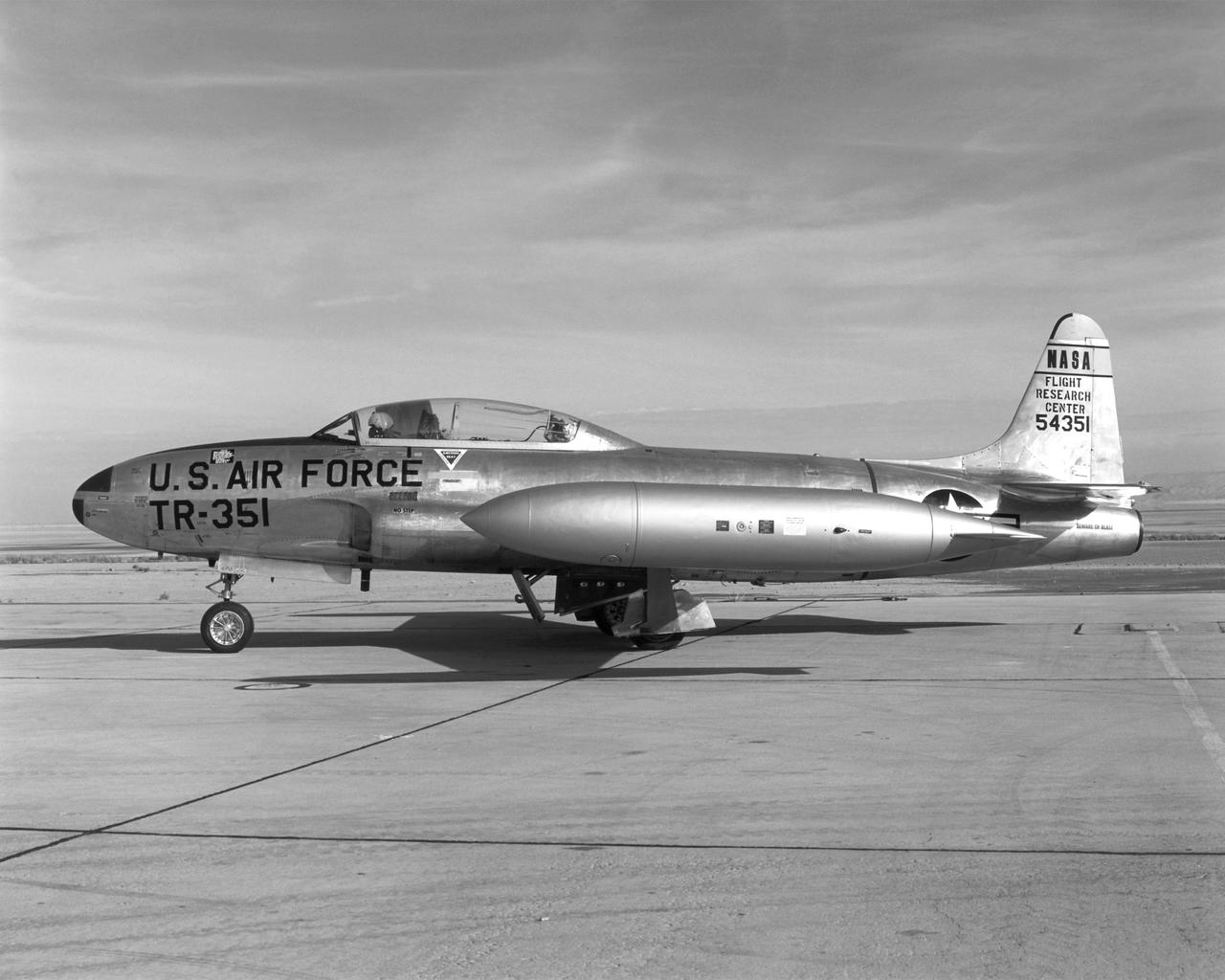

Arrived at NASA FRC January 9, 1963 Departed September 10, 1973 to Redding, California This aircraft, one of four T-33A jet trainers which NASA Dryden used from 1958 to 1973, was used in a monocular vision landing study. The T-33 was the first U.S. Air Force jet trainer, and was originally developed as a two-seat version of the F-80. The T-33 was used by not only the U.S. military, but also by foreign air forces as a trainer, fighter, and reconnaissance aircraft.
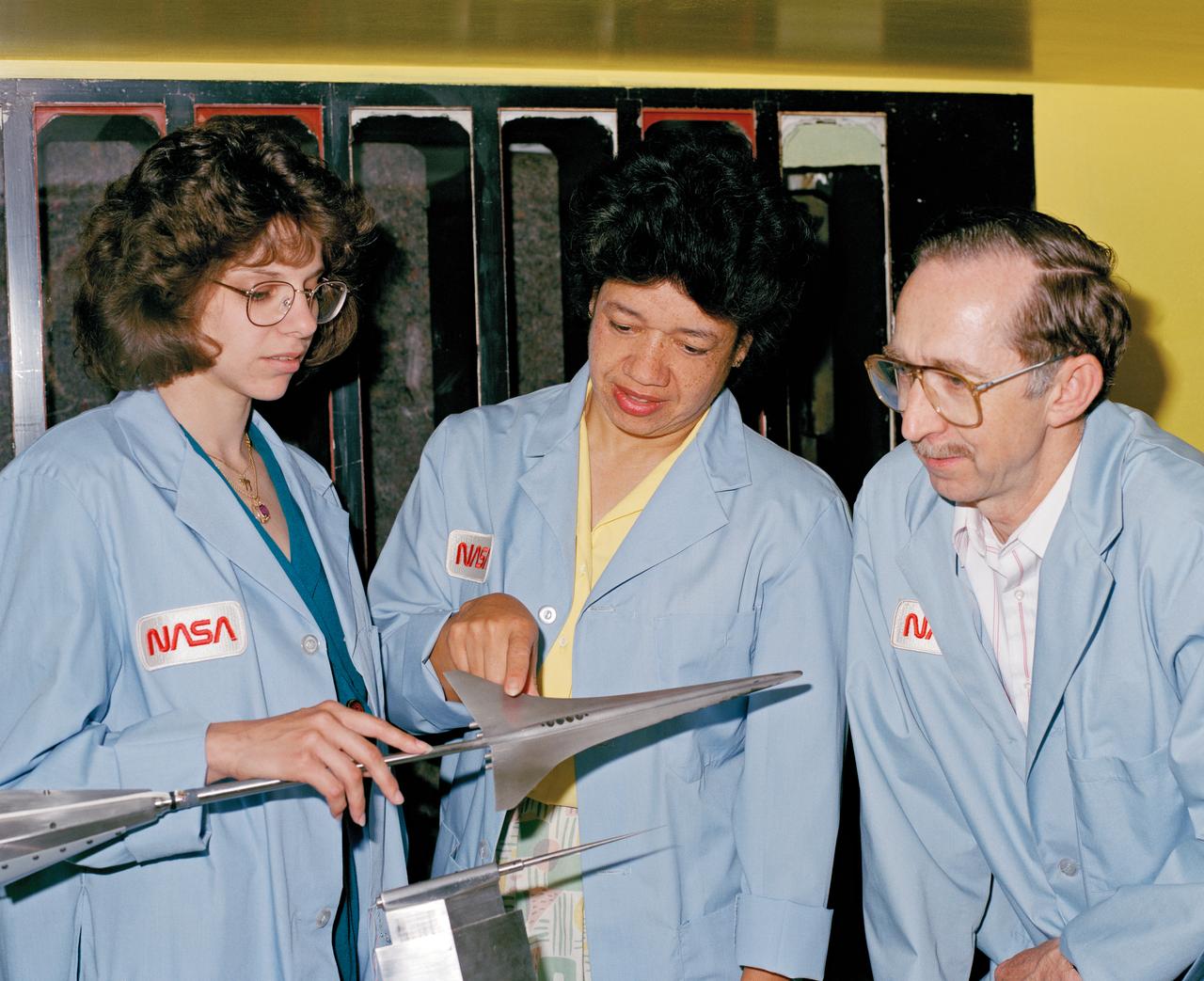

NASA Staff Dr.Darden, Matthew Overhold, Kathy Needleman,Robert Mack.
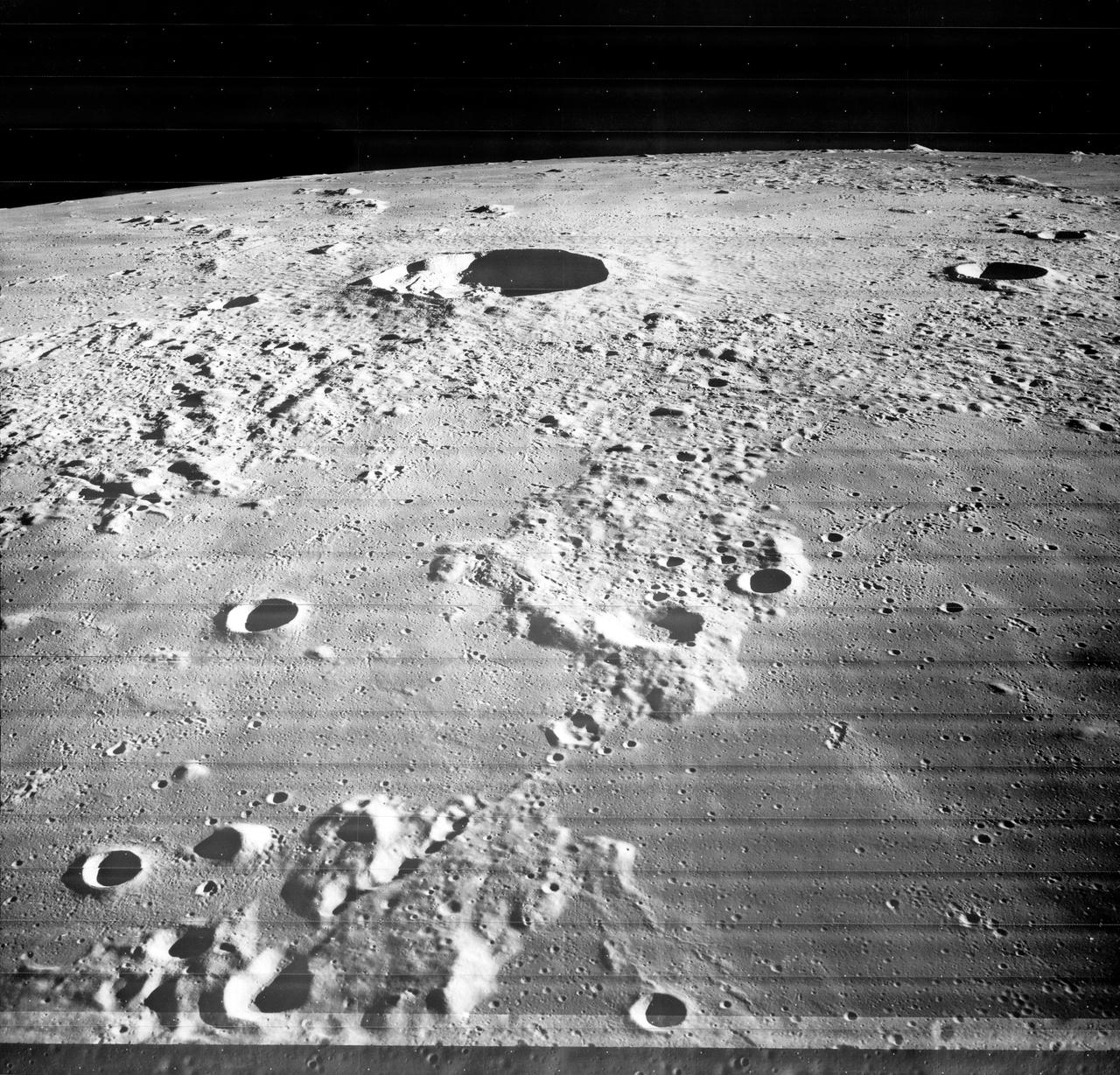

Small light colored area within the crater is Surveyor 1 on lunar surface photographed by Lunar Orbiter III. Published in the book "A Century at Langley" by Joseph Chambers. pg. 93 Moon Lunar Orbiter-Lunar Orbiter III: The hidden or dark side of the Moon was taken by Lunar Orbiter III During its mission to photograph potential lunar-landing sites for Apollo missions. -- Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication (page 94), by James Schultz. Photo Number:67-H-328 is 1967-L-04026

jsc2024e043916 (3/29/2024) ---The Packed Bed Reactor Experiment – Water Recovery (PBRE-WR) completed a series of tests in the Microgravity Science Glovebox on the International Space Station. Image of PBRE-WR during low flow conditions. Bubbles and voids (darker spots) are captured using a high-speed video camera at 10 fps. They are measured to determine gas holdup during various test conditions. In this image, the liquid flow was 20 kg/hr and the gas flow was 100 gr/hr. Scientists aim to learn more about how reduced gravity affects the performance and reliability of various filtration systems.
Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
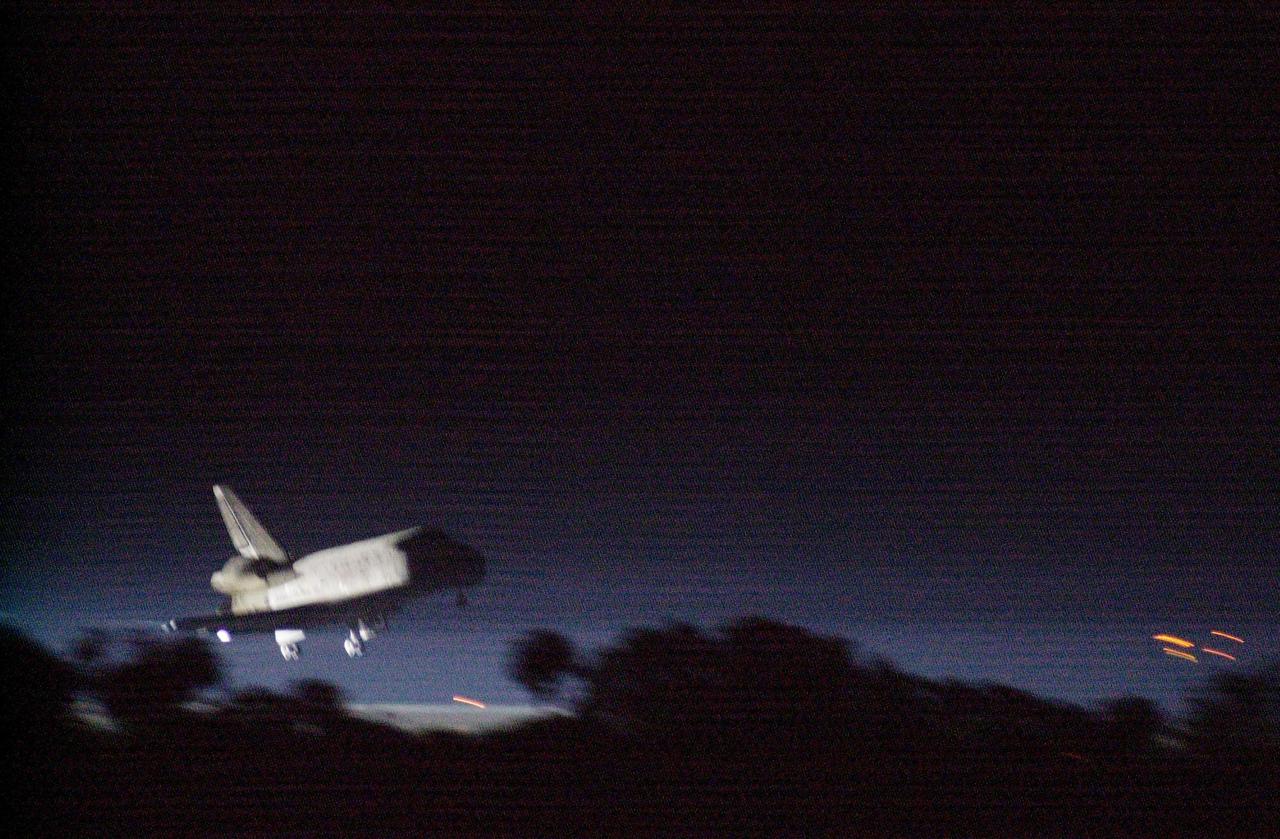

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Getting a break in the weather, Space Shuttle Discovery prepares to land at the KSC Shuttle Landing Facility March 21, on runway 15. Main gear touchdown occurred at 2:31:42 a.m. EST, nose wheel touchdown at 2:31:54 a.m., and wheel stop at 2:33:06 a.m. The landing on orbit 201 concluded mission STS-102, the eighth flight to the International Space Station, carrying the first Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo, to the ISS and Expedition Two, a replacement crew for the Station. The 12-day, 19-hour, 51-minute mission returned both the Leonardo and the first resident crew of the ISS, Expedition One, to KSC. Discovery logged 5.3 million miles on this mission. The landing marked the 54th at KSC in the history of the program, and the 12th night landing at KSC
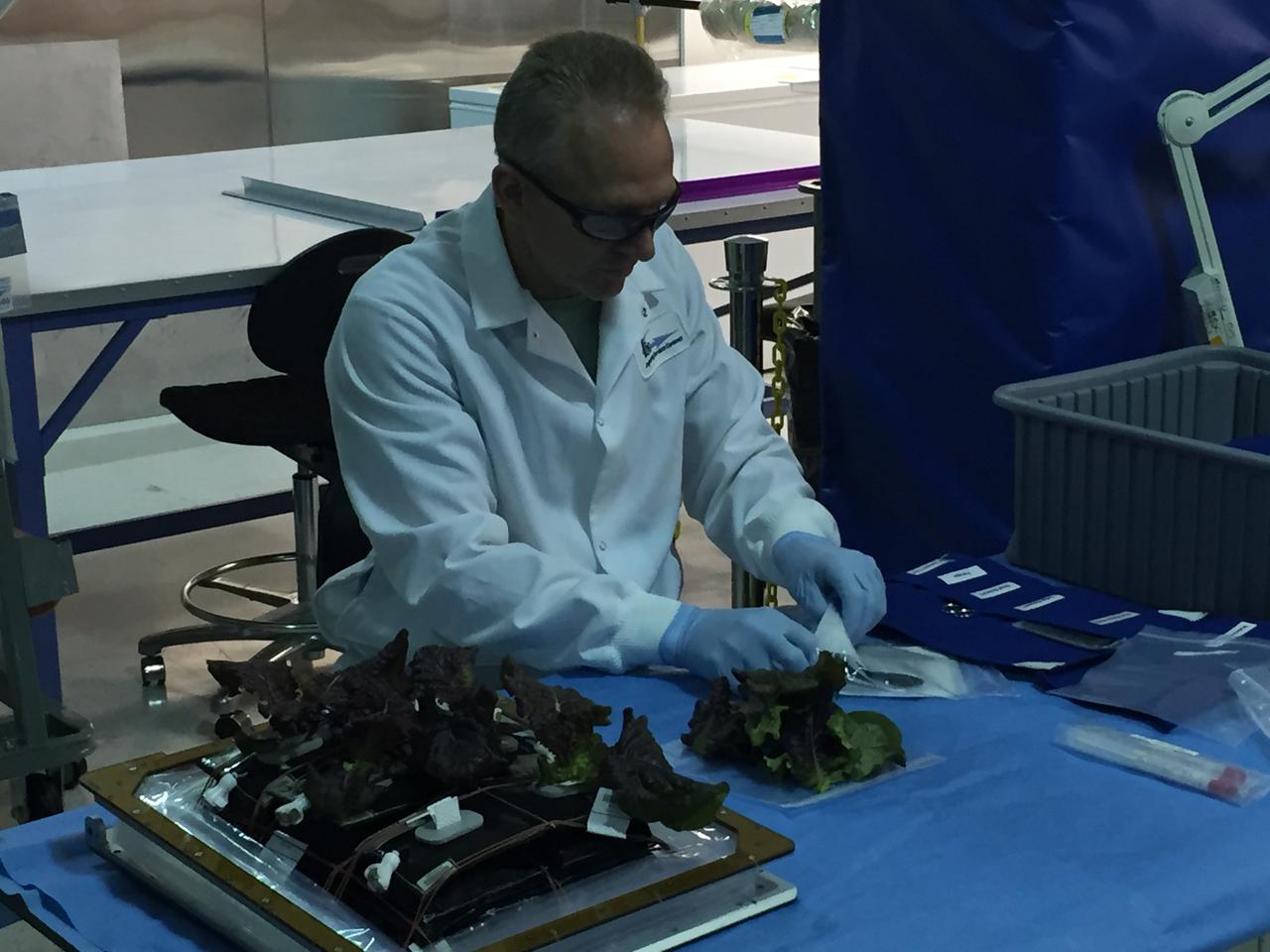

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

The mated Pegasus XL rocket - AIM spacecraft is moved onto a transporter in Building 1655 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The launch vehicle will be transferred to a waiting Orbital Sciences Stargazer L-1011 aircraft for launch. AIM, which stands for Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, is being prepared for integrated testing and a flight simulation. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
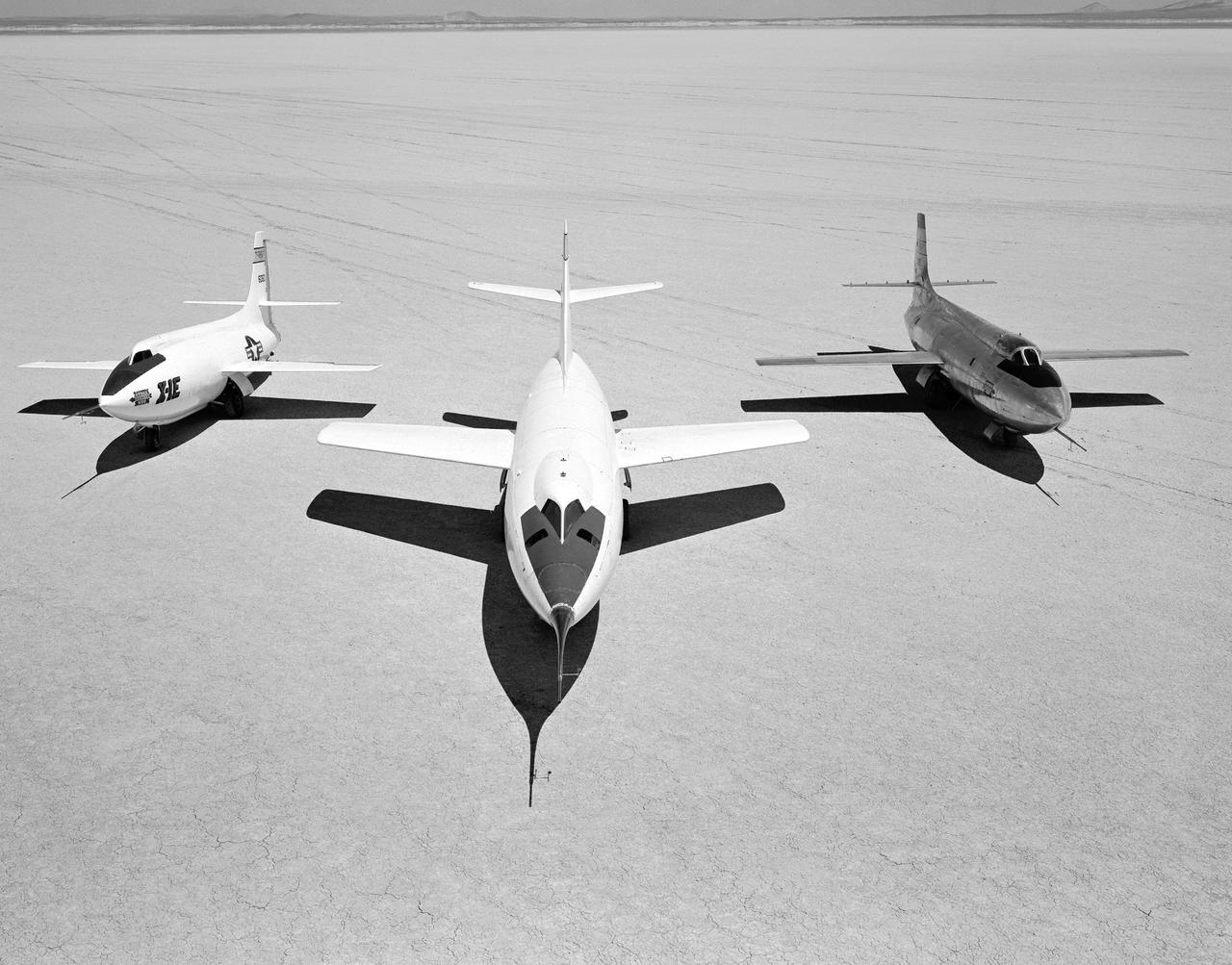

Early NACA research aircraft on the lakebed at the High Speed Research Station in 1955: Left to right: X-1E, D-558-II, X-1B
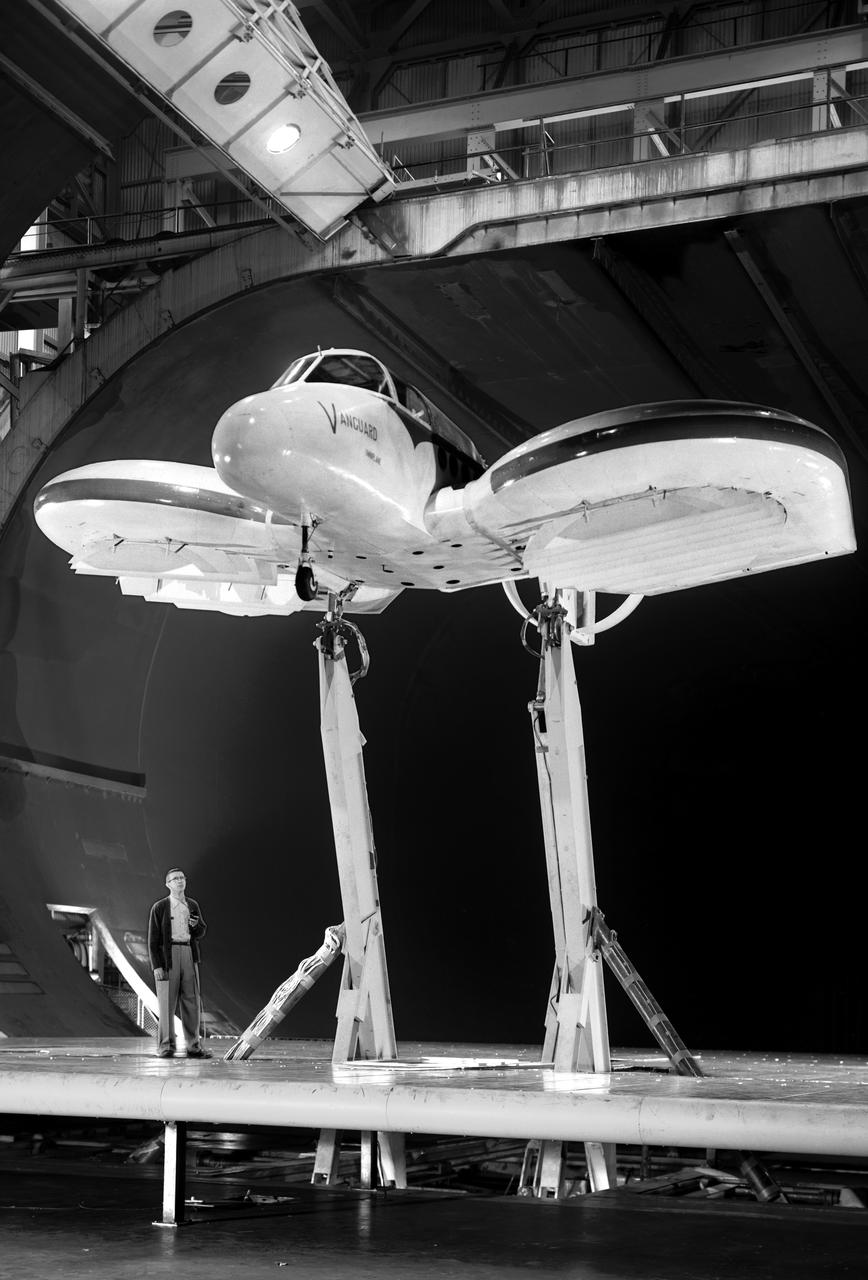

Vanguard 2C vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) airplane, wind tunnel test. Front view from below, model 14 1/2 feet high disk off. Nasa Ames engineer Ralph Maki in photo. Variable height struts and ground plane, low pressure ratio, fan in wing. 02/01/1960.
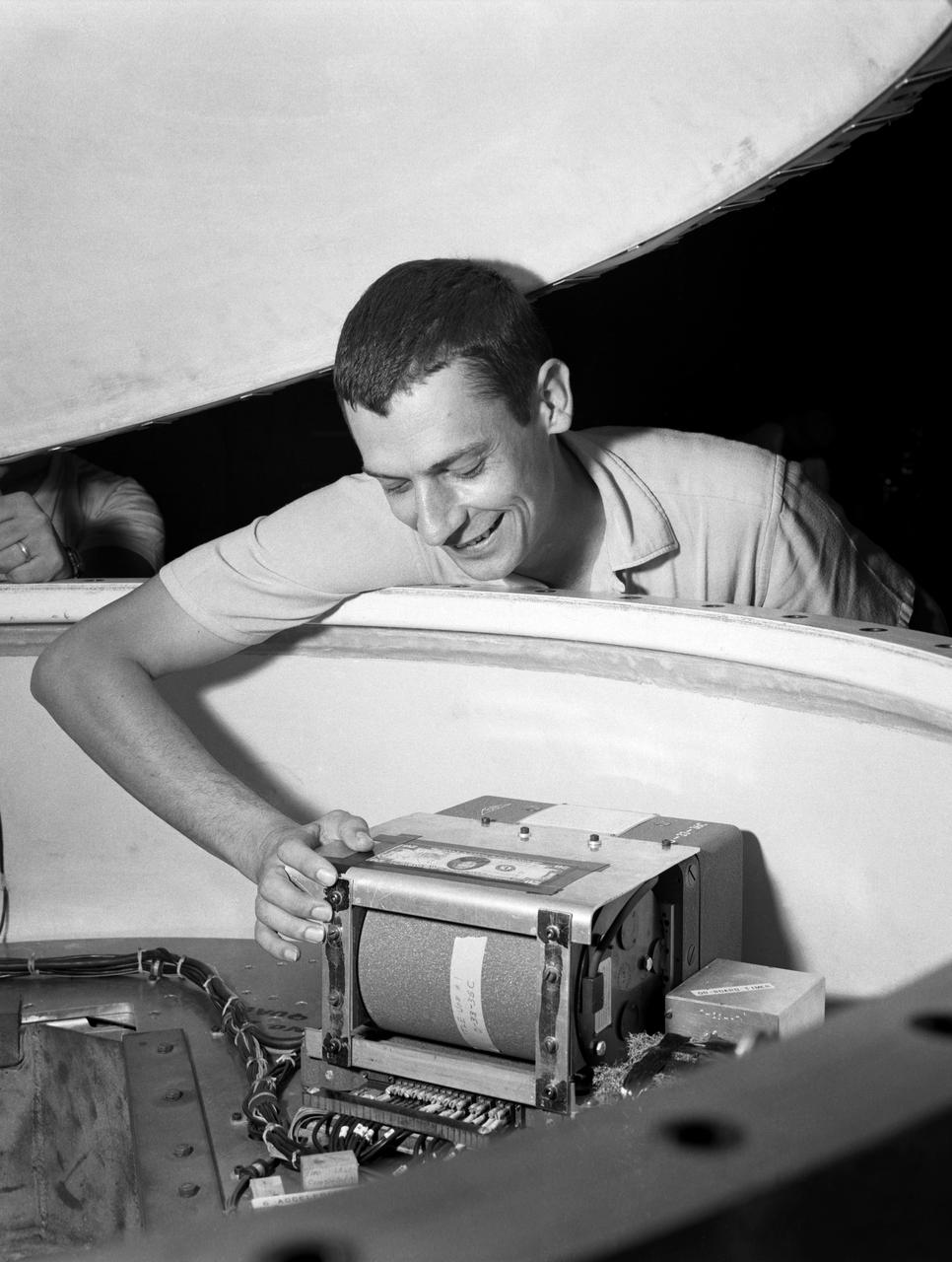

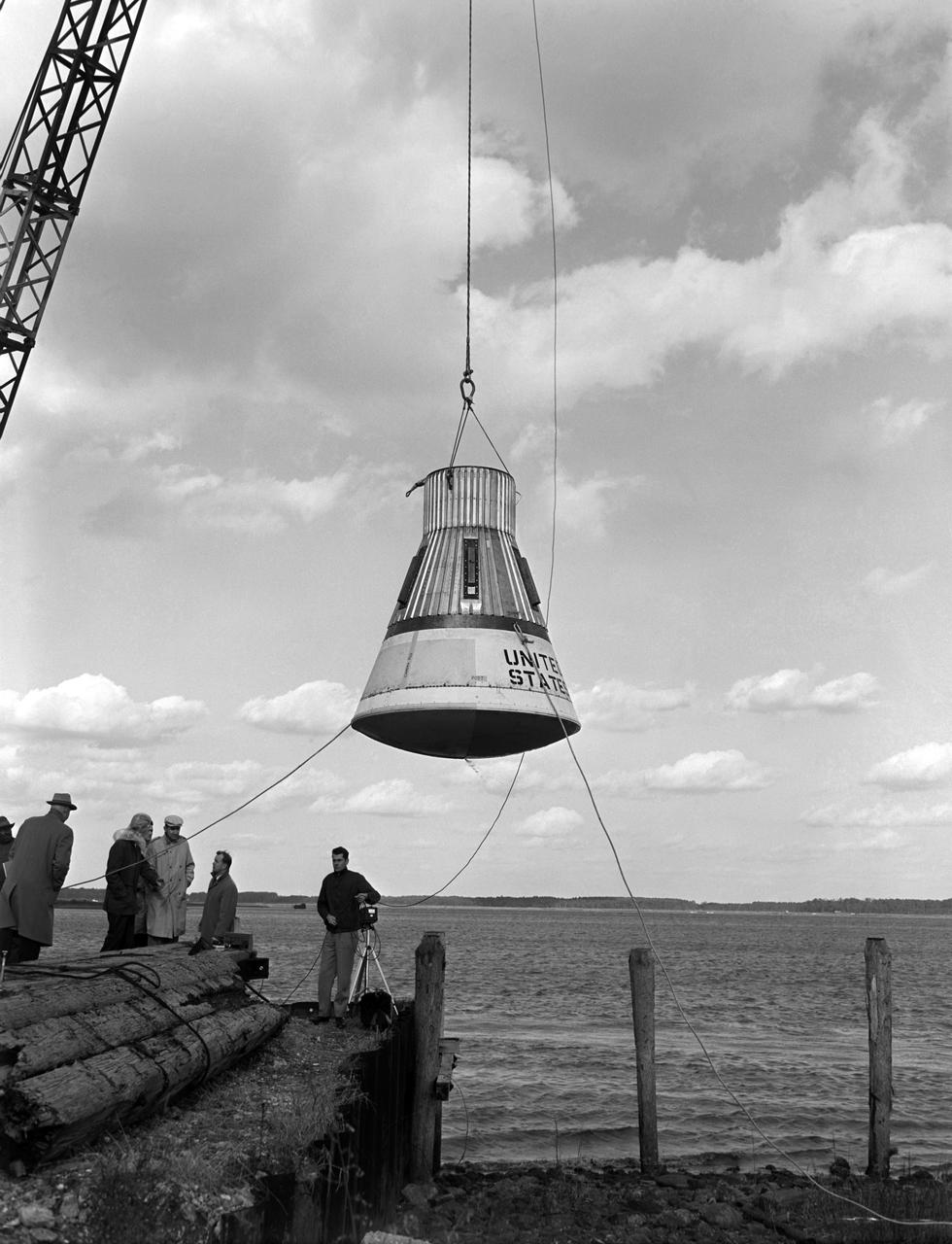
Technicians adjust the rocket motor during the attachment of the escape tower to the Mercury capsule prior to assembly with Little Joe launcher, August 20, 1959. Joseph Shortal wrote (vol. 3., p. 33): The escape tower and rocket motors were taken from the Mercury capsule production. The tower is shown being attached to the capsule.... The escape rocket was a Grand Central 1-KS-52000 motor with three canted nozzles. The tower-jettison motor was an Atlantic Research Corp. 1.4-KS-785 motor. This was the same design tested in a beach abort test...and had the offset thrust line as used in the beach abort test to insure that the capsule would get away from the booster in an emergency. The escape system weighed 1,015 pounds, including 236 pounds of ballast for stability. The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
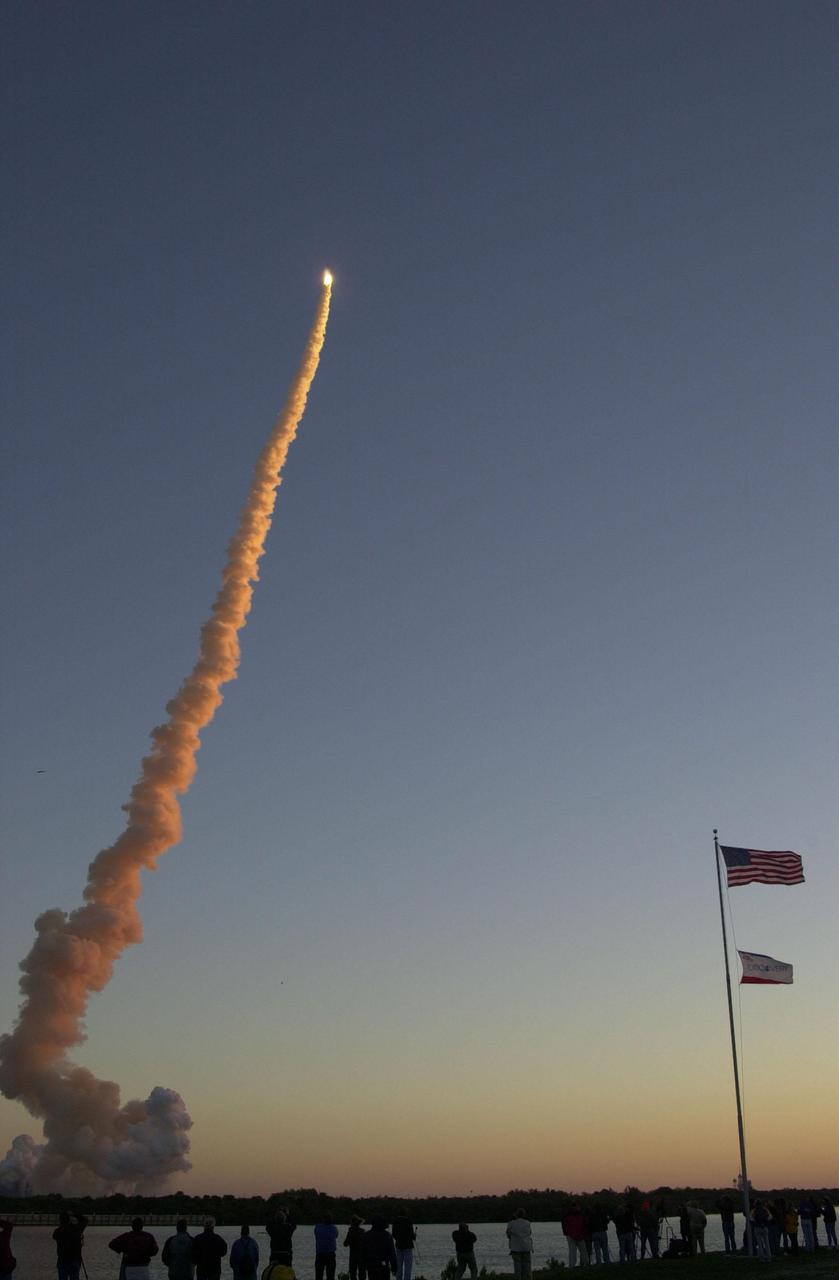

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Space Shuttle Discovery outshines a rising sun as it blasts off on mission STS-102, the eighth construction flight to the International Space Station. The lower smoke plumes appear red from the dawn’s rays. Liftoff occurred on time at 6:42:09 EST

An employee with contractor Jacobs from contractor Jacobs transports research cargo from the International Space Station for processing inside the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 10, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 22nd commercial resupply services mission. After its successful parachute-assisted splashdown off the coast of Tallahassee, Florida at 11:29 p.m. EST on Friday, July 9, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 5,300 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. Splashing down off the coast of Florida enables quick transportation of the science aboard the capsule to the SSPF, delivering some science back into the hands of the researchers as soon as four to nine hours after splashdown. This shorter transportation timeframe allows researchers to collect data with minimal loss of microgravity effects.
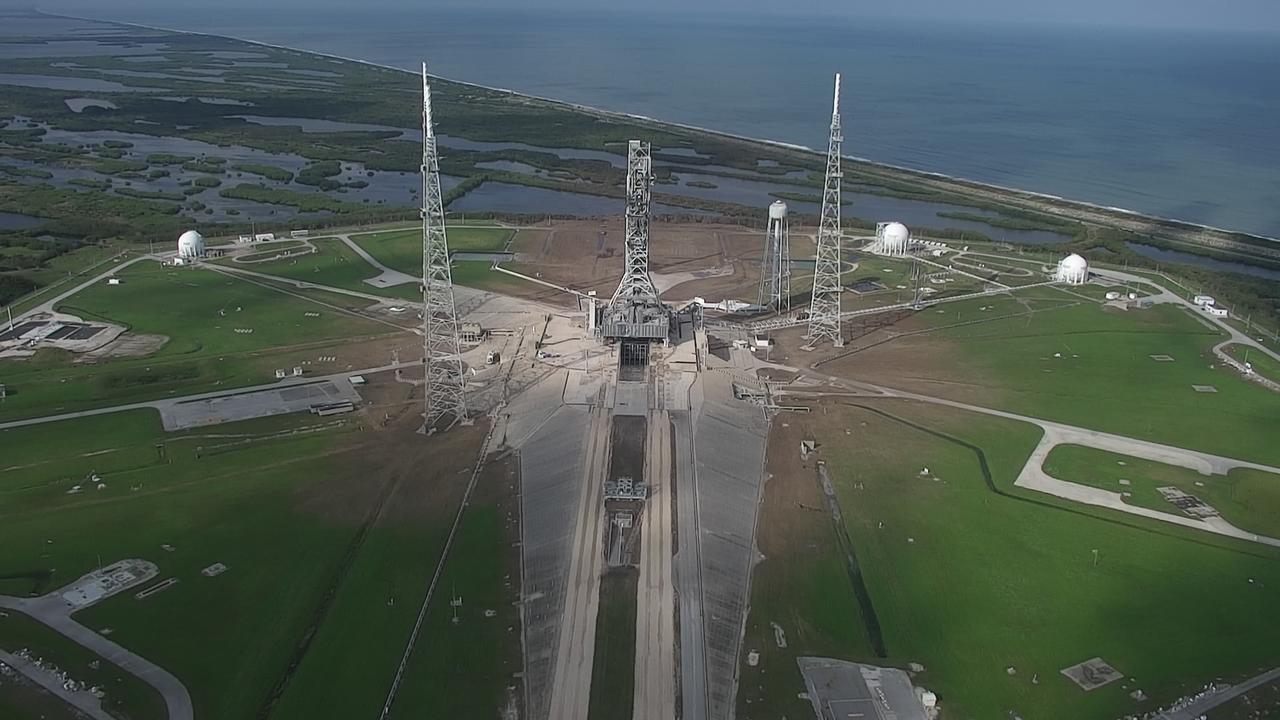

Following NASA’s successful Artemis I launch from Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 16, 2022, teams with the Exploration Ground Systems conducted a post-launch assessment for the ground systems, which began the day of launch and concluded Friday, Nov. 18. This enabled teams to inspect areas on the mobile launcher and identify specific damage and debris around the pad. Engineers have determined the overall mobile launcher and pad systems performed as designed during launch and are structurally sound.
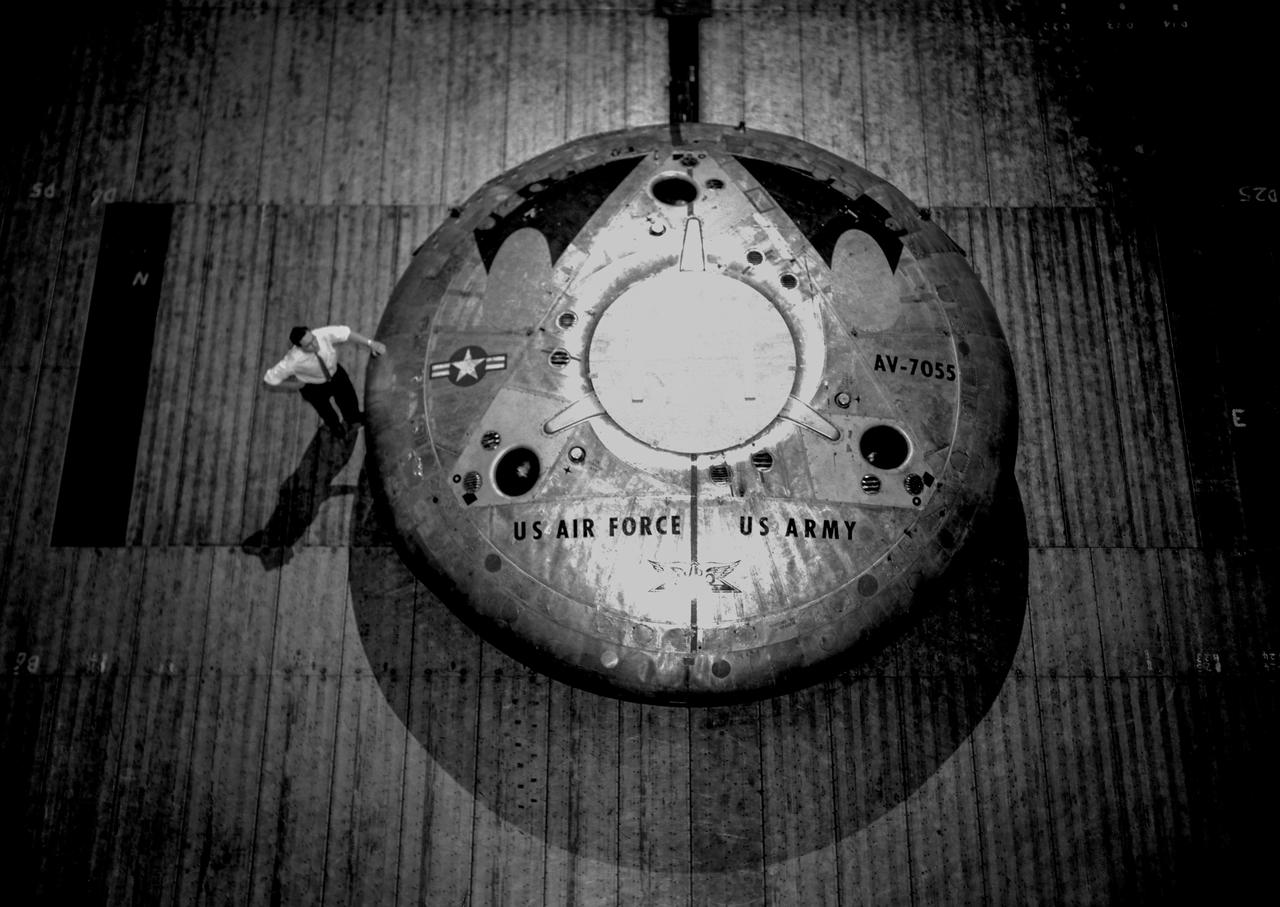

Avrocar Annular Jet VTOL Airplane in Ames 40x80 foot Wind Tunnel.
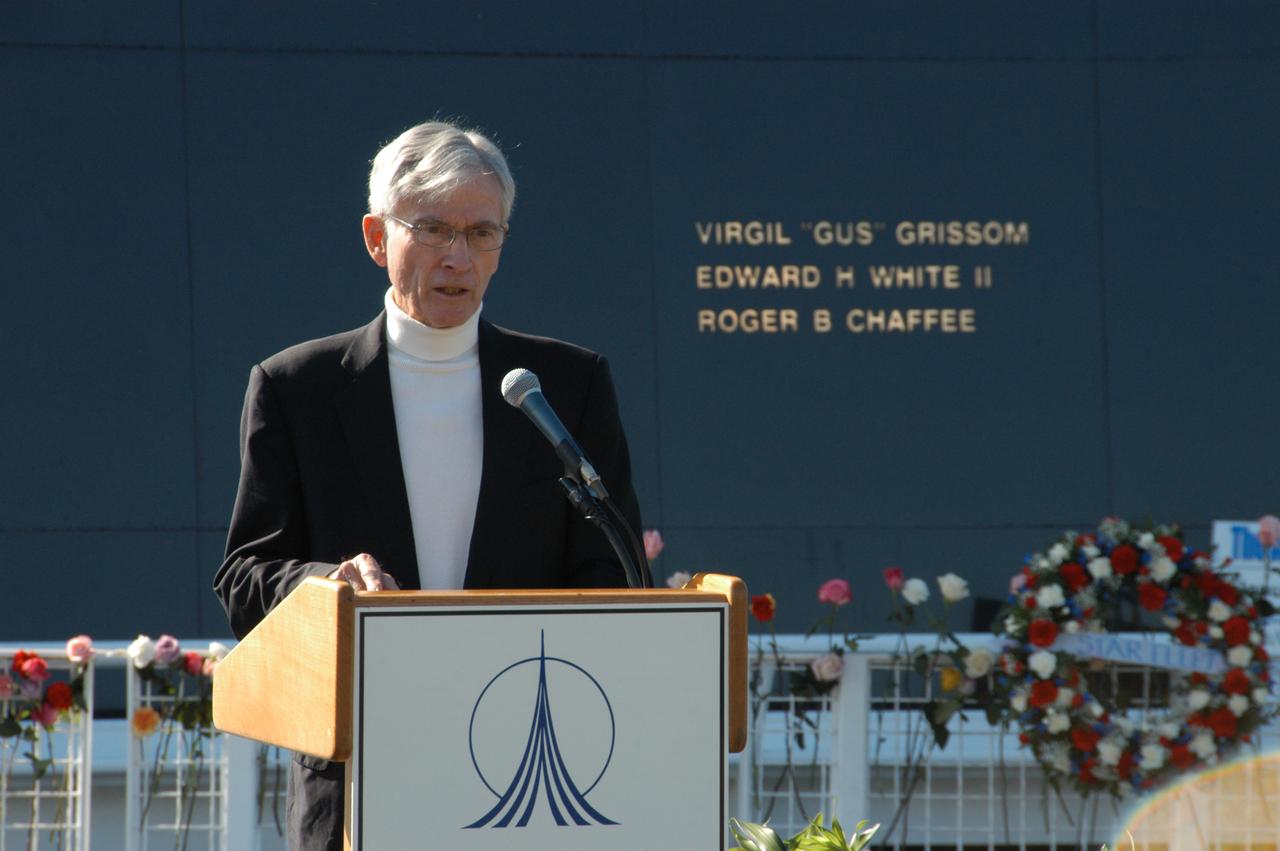

Former astronaut John Young addresses guests and attendees at a ceremony at the KSC Visitor Complex held in remembrance of the astronauts lost in the Apollo 1 fire: Virgil "Gus" Grissom, Edward H. White II and Roger B. Chaffee. Members of their families, along with Associate Administrator for Space Operations William Gerstenmaier, President of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation Stephen Feldman, Chairman of the Board of Directors of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation William Potter and former astronaut John Young, attended the ceremony. Behind the stage is the Space Mirror Memorial, designated as a national memorial by Congress and President George Bush in 1991 to honor fallen astronauts. Their names are emblazoned on the monument’s 42-1/2-foot-high by 50-foot-wide black granite surface as if to be projected into the heavens.
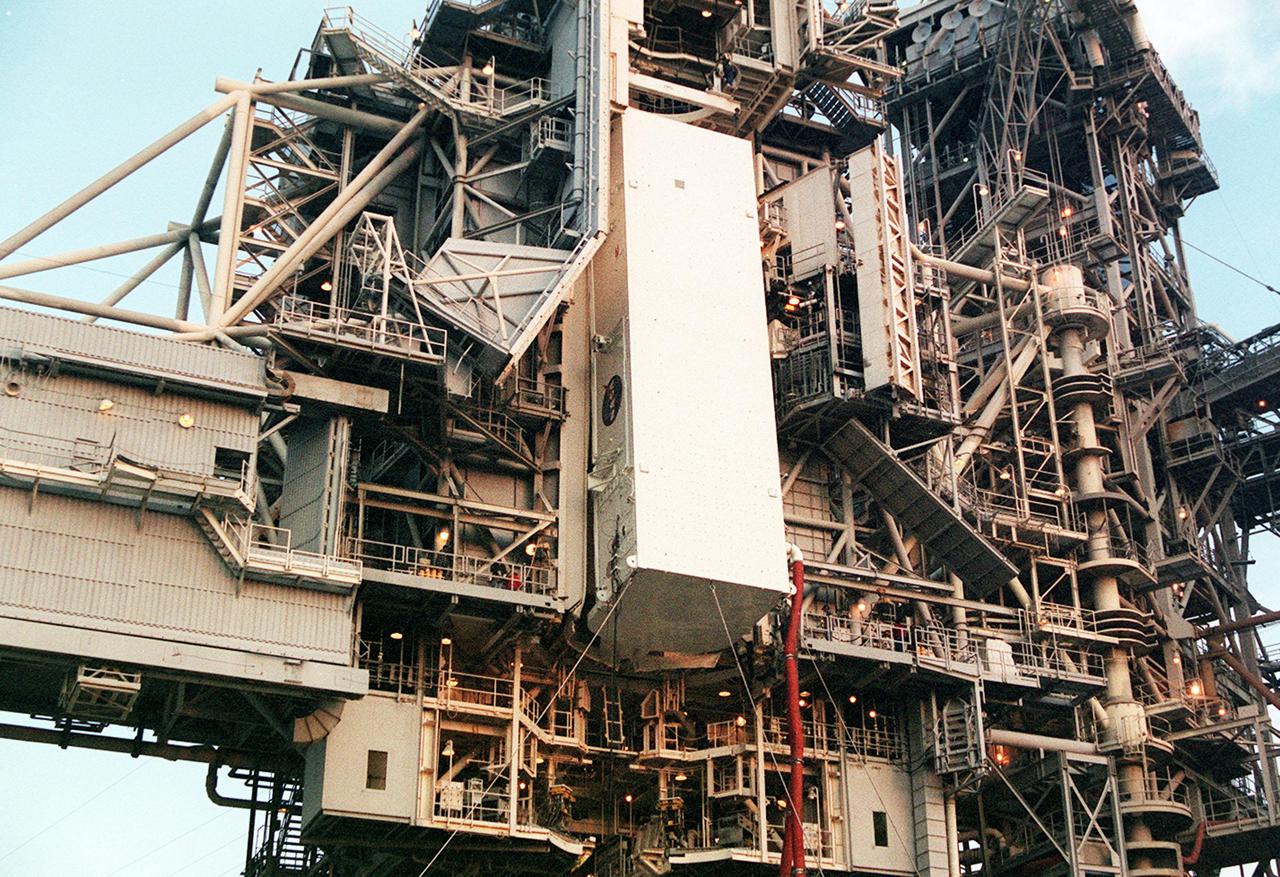
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39B the payload canister, with the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo inside, nears the payload changeout room on the Rotating Service Structure. Umbilical hoses, maintaining a controlled environment for the cargo, are still attached to the lower end of the canister. At the PCR, the payload ground-handling mechanism (PGHM) will be used to transfer Leonardo out of the canister and then into Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. One of Italy’s major contributions to the International Space Station program, Leonardo is a reusable logistics carrier. It is the primary delivery system used to resupply and return Station cargo requiring a pressurized environment. Leonardo is the primary payload on mission STS-102 and will deliver up to 10 tons of laboratory racks filled with equipment, experiments and supplies for outfitting the newly installed U.S. Laboratory Destiny. STS-102 is scheduled to launch March 8 at 6:45 a.m. EST
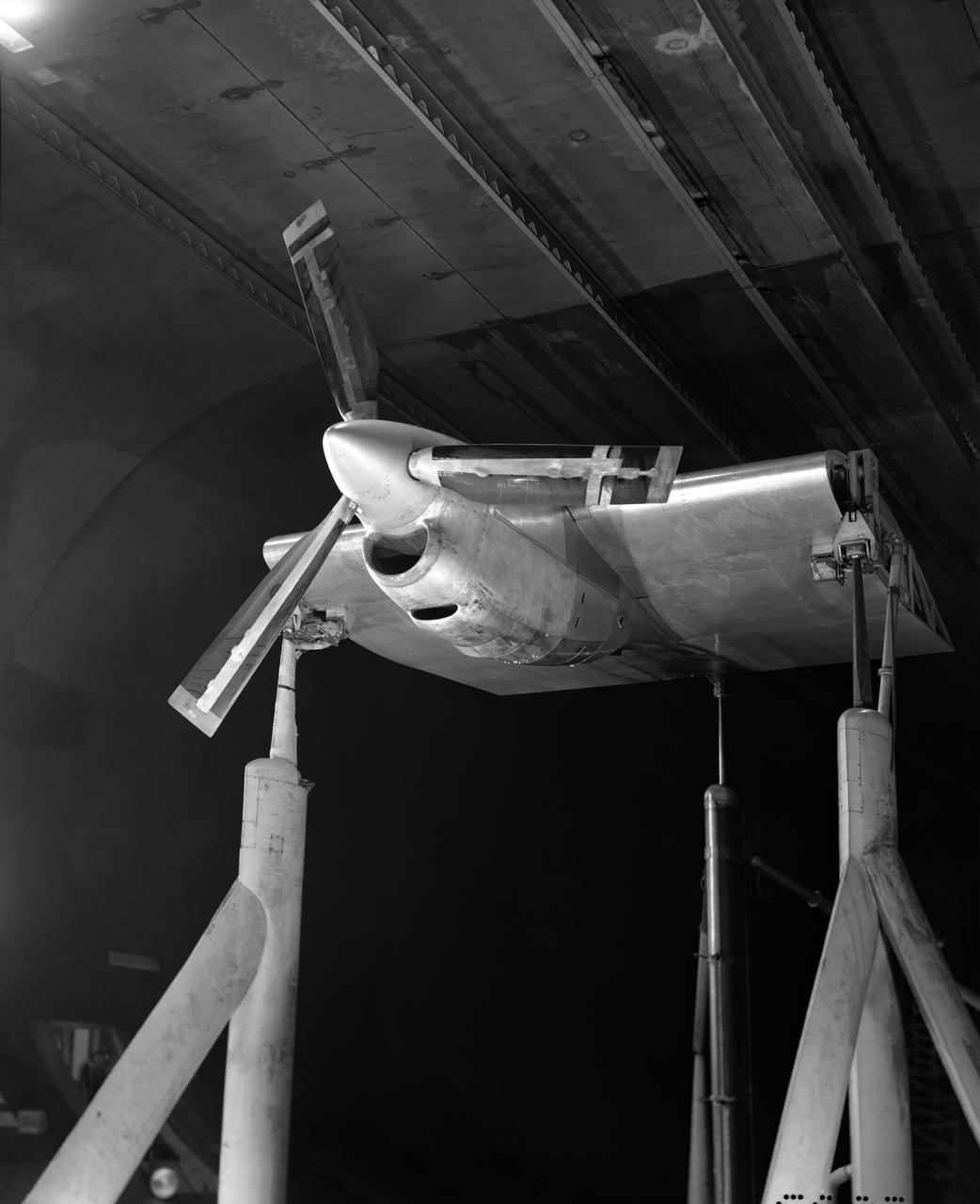

Test of Lockheed YC-130 Turbo-Propeller Installation in Ames 40x80 Foot Wind Tunnel. 3/4 front view from below.
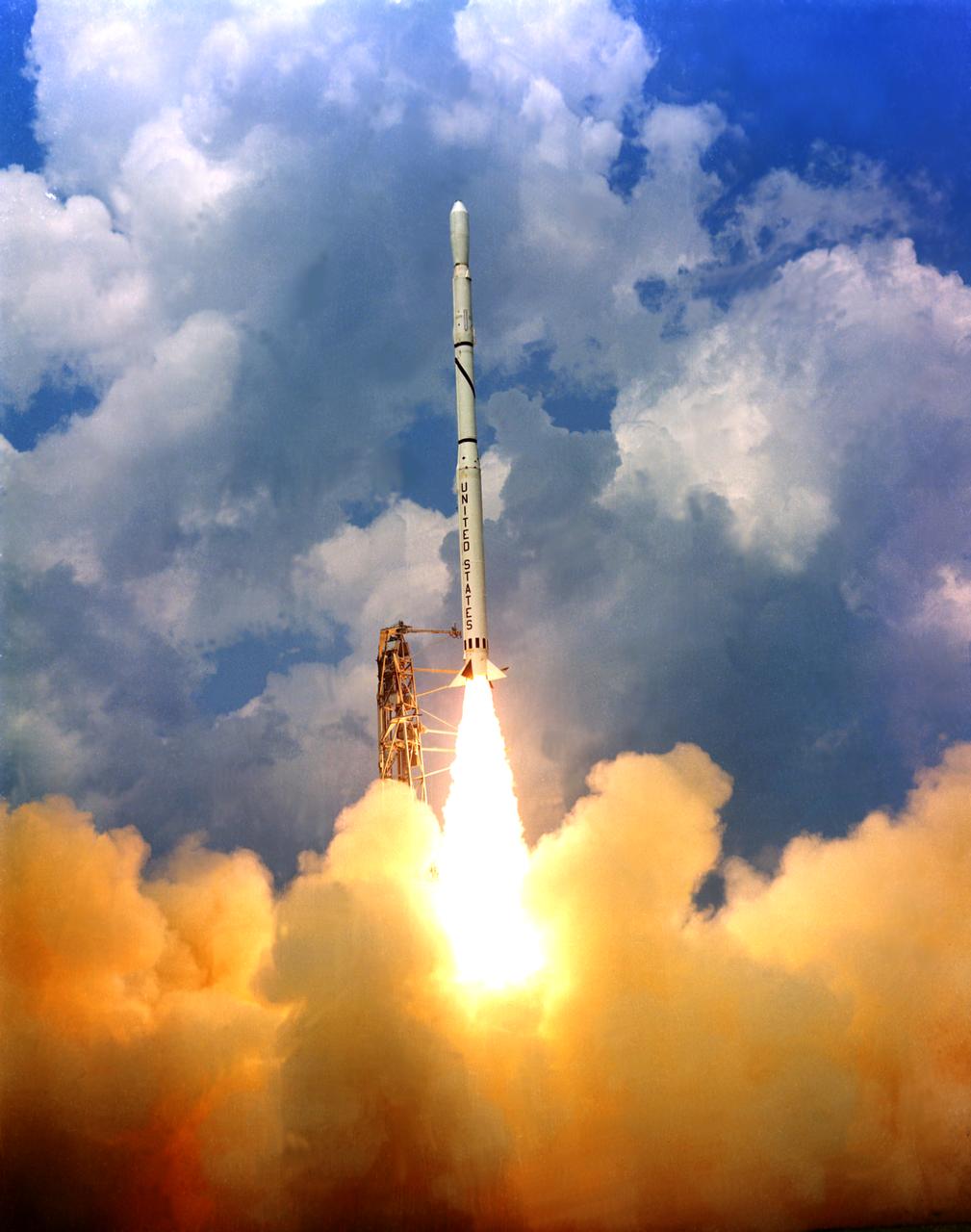

Scout launch vehicle lift off on Wallops Island in 1965. The Scout launch vehicle was used for unmanned small satellite missions, high altitude probes, and reentry experiments. Scout, the smallest of the basic launch vehicles, is the only United States launch vehicle fueled exclusively with solid propellants. Published in the book " A Century at Langley" by Joseph Chambers pg. 92
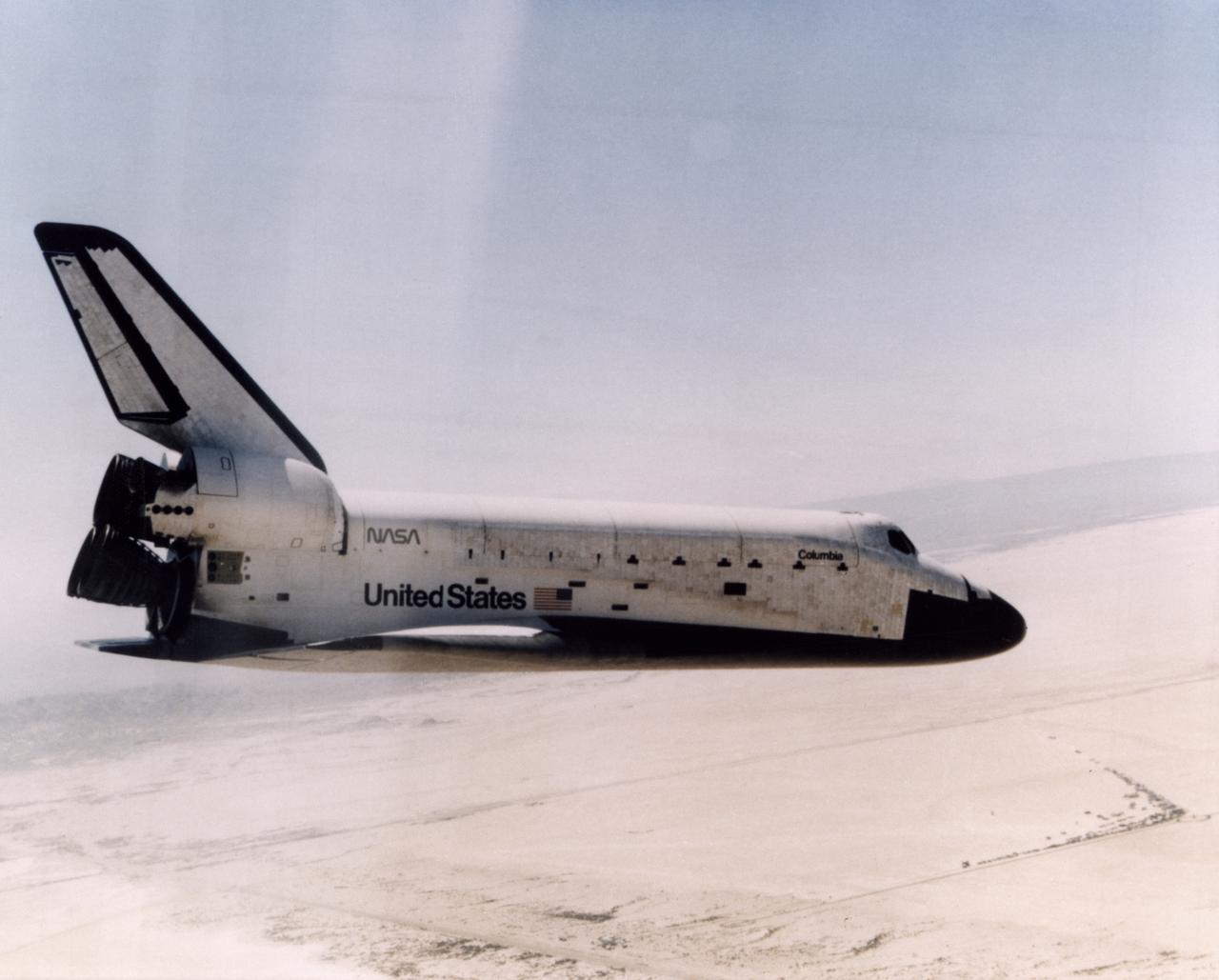

FIRST SHUTTLE LANDING -- The Space Shuttle Columbia glides down over Rogers Dry Lake as it heads for a landing at Edwards Air Force Base at the conclusion of its first orbital mission on April 14, 1981.
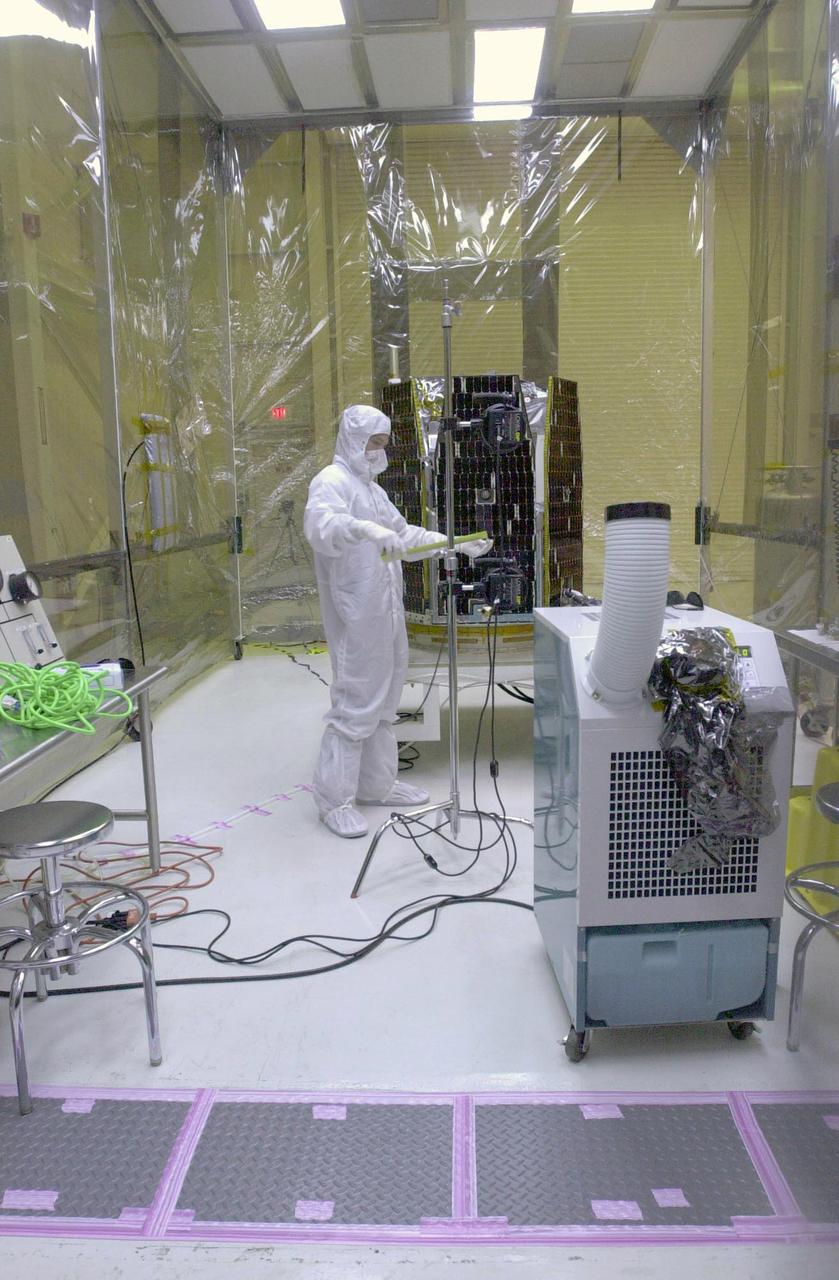

In a clean-room environment containing the AIM spacecraft (background) at North Vandenberg Air Force Base, a technician studies results of illumination testing on the spacecraft's solar array panels. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study those clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. AIM is scheduled to be mated to the Pegasus XL during the second week of April, after which final inspections will be conducted. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
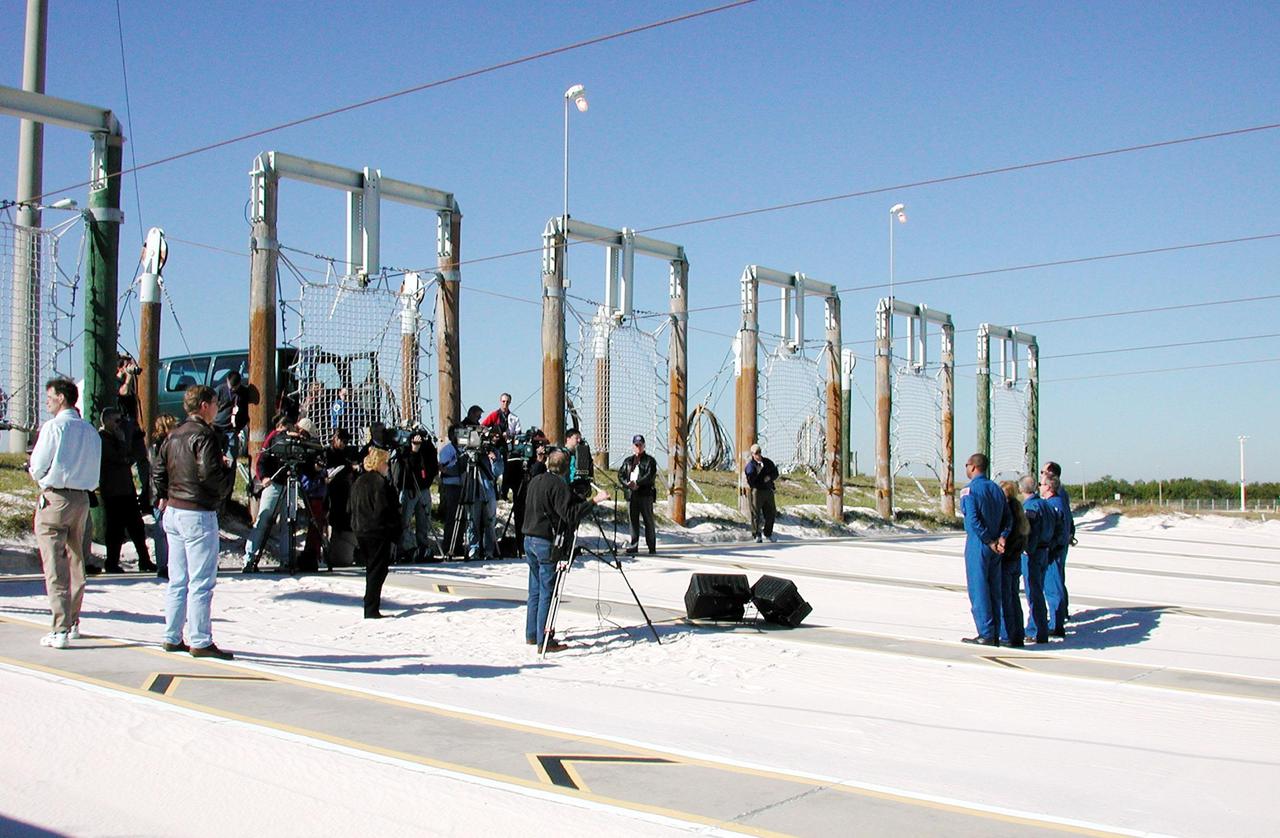

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The STS-98 crew (right) gathers at Launch Pad 39A for a media briefing before continuing their emergency egress training. Facing an audience (left) of photographers, videographers and writers, along with KSC media escorts, are (left to right) Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam and Marsha Ivins, Commander Ken Cockrell, Mission Specialist Thomas Jones and Pilot Mark Polansky. They are standing in the landing zone for the slidewire baskets that provide an escape route for personnel aboard the Space Shuttle and orbiter access arm until 30 seconds before launch. The crew is at KSC to take part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities, which also include a simulated launch countdown. STS-98 is the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station, carrying as payload the U.S. Lab Destiny, a key element in the construction of the ISS. Launch of STS-98 is scheduled for Jan. 19 at 2:11 a.m. EST
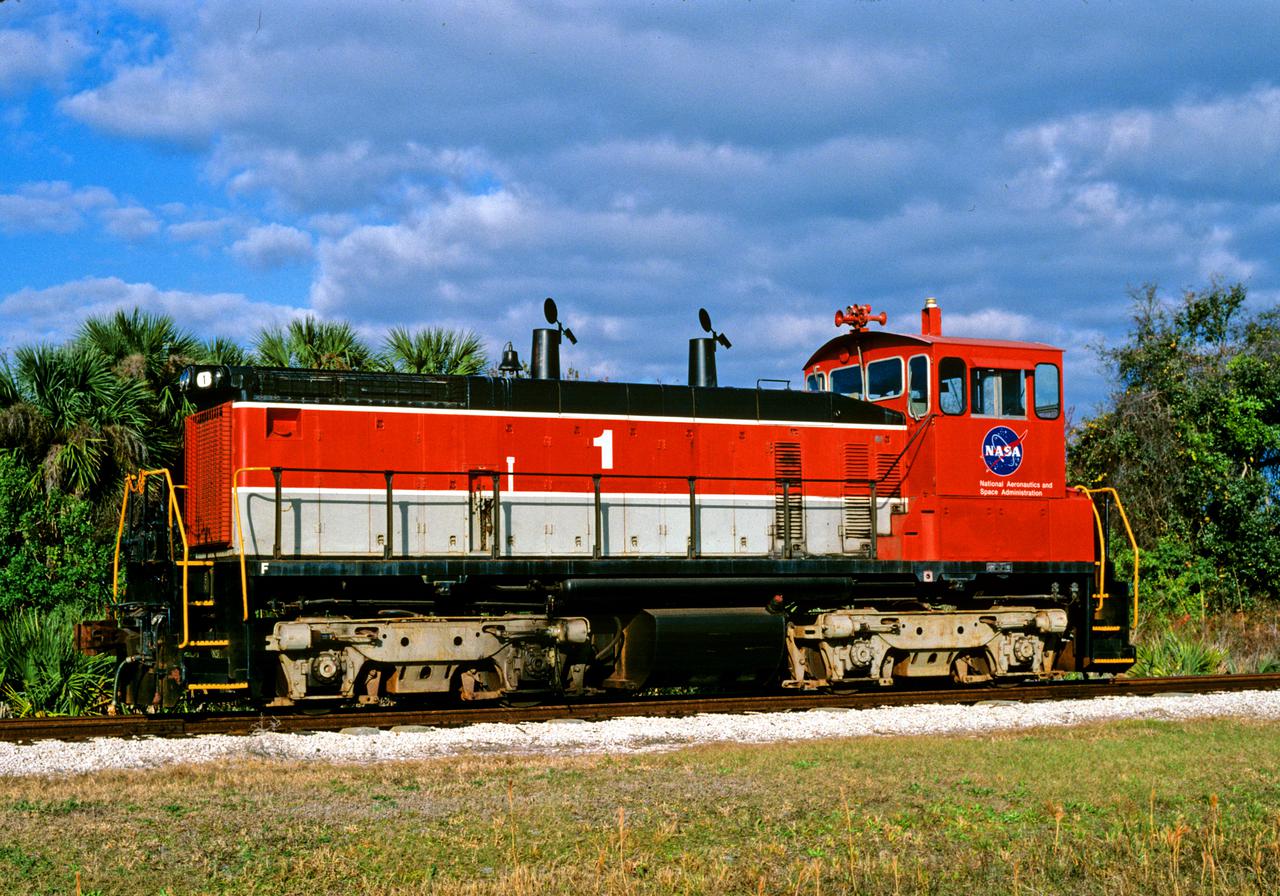

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A NASA railroad locomotive at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida is part of the space agency's railroad operation to not only move equipment at Kennedy, but to transport hardware to and from contractor facilities across the nation. Photo credit: NASA
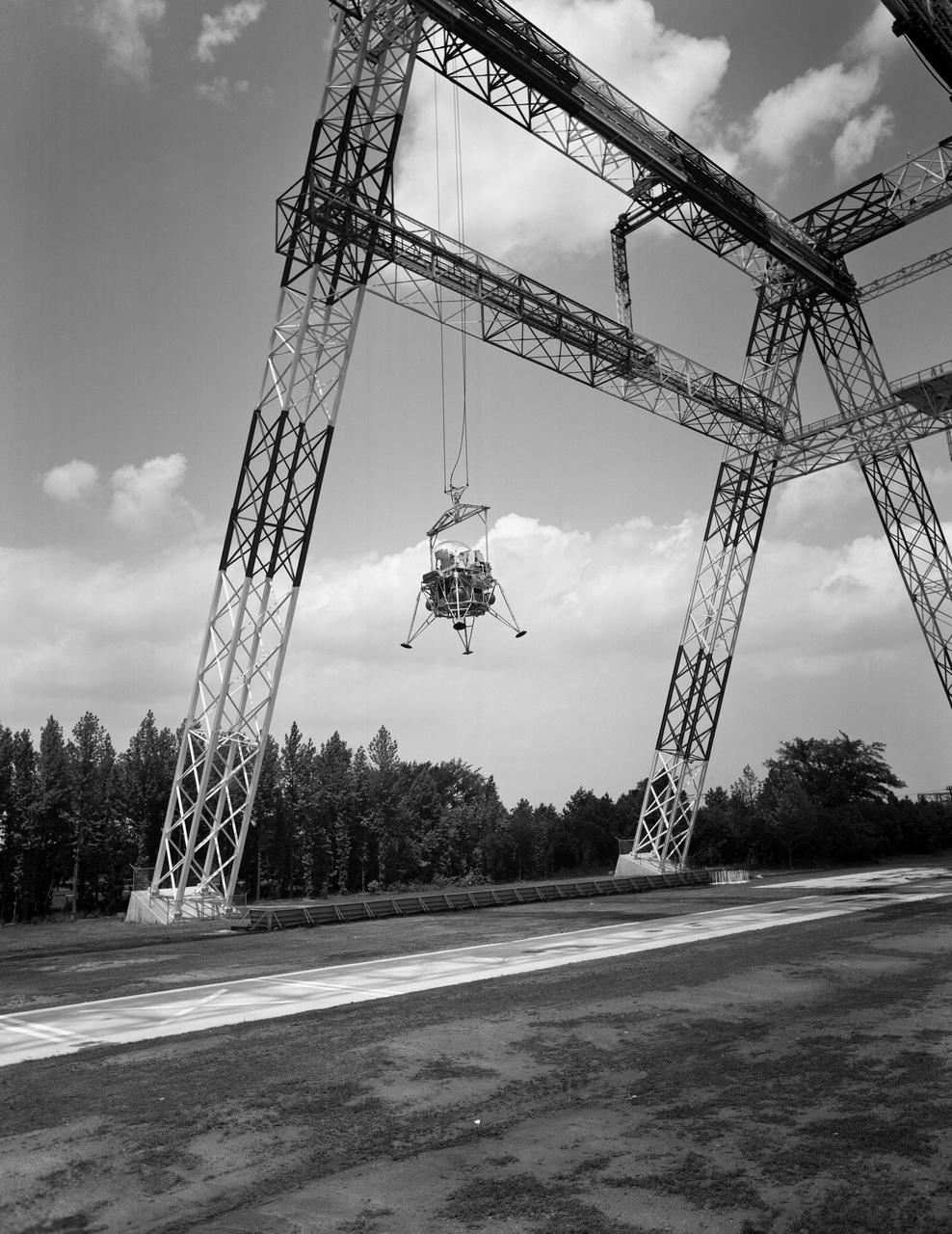

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
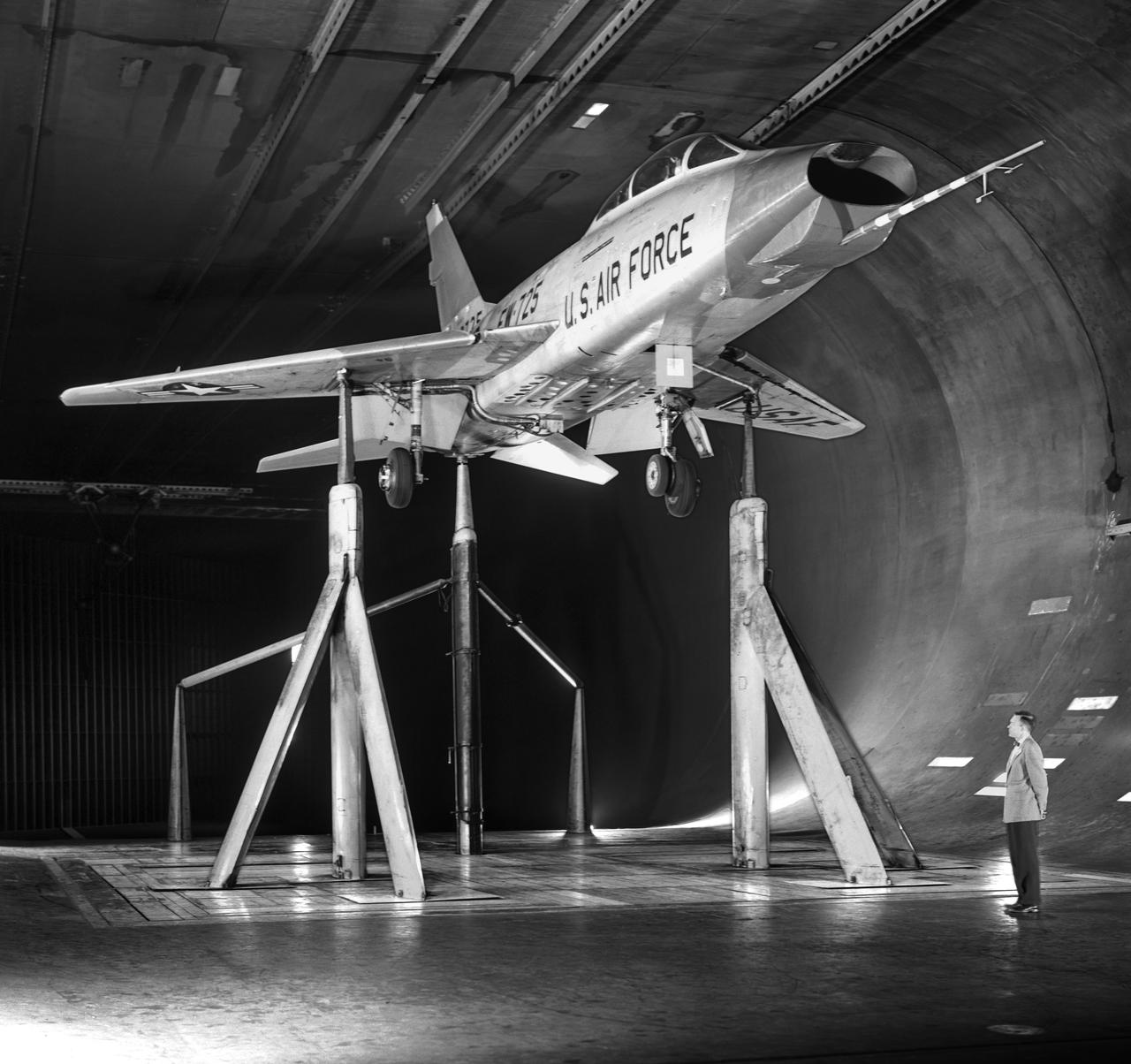

North American F-100-F airplane, equipped with thrust reversers, full scale wind tunnel test. 3/4 front view of F-100-F airplane with North American Aviation thrust reverser. On standard 40x80 struts landing gear down. Mark Kelly, branch chief in photo.
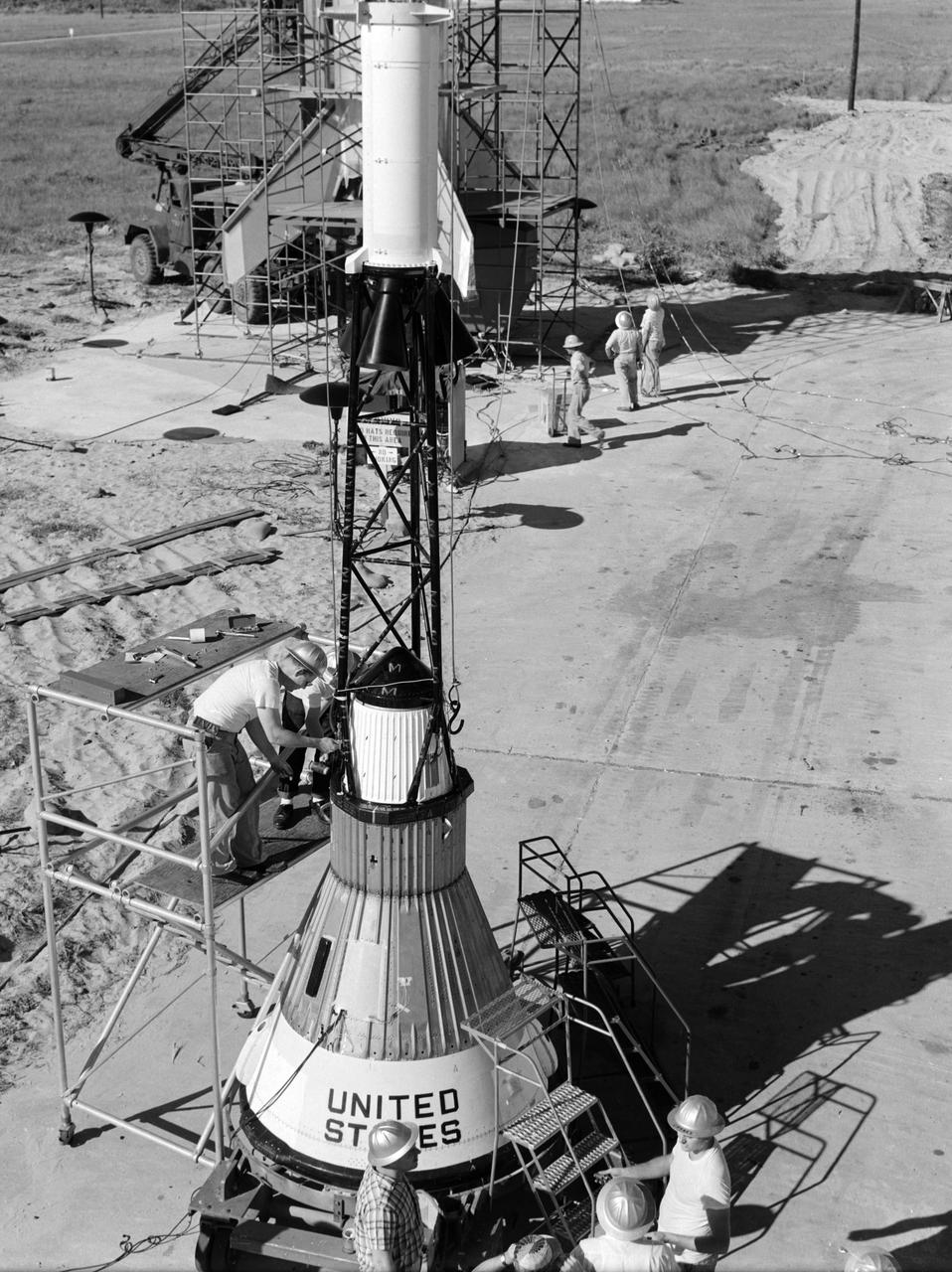

Technicians attach the escape tower to the Mercury capsule prior to assembly with Little Joe launcher, August 20, 1959. Joseph Shortal describe this as follows (vol. 3., p. 33): The escape tower and rocket motors were taken from the Mercury capsule production. The tower is shown being attached to the capsule.... The escape rocket was a Grand Central 1-KS-52000 motor with three canted nozzles. The tower-jettison motor was an Atlantic Research Corp. 1.4-KS-785 motor. This was the same design tested in a beach abort test...and had the offset thrust line as used in the beach abort test to insure that the capsule would get away from the booster in an emergency. The escape system weighed 1,015 pounds, including 236 pounds of ballast for stability. The Little Joe booster was assembled at Wallops on its special launcher in a vertical attitude. It is shown in the on the left with the work platform in place. The launcher was located on a special concrete slab in Launching Area 1. The capsule was lowered onto the booster by crane.... After the assembly was completed, the scaffolding was disassembled and the launcher pitched over to its normal launch angle of 80 degrees.... Little Joe had a diameter of 80 inches and an overall length, including the capsule and escape tower of 48 feet. The total weight at launch was about 43,000 pounds. The overall span of the stabilizing fins was 21.3 feet. Although in comparison with the overall Mercury Project, Little Joe was a simple undertaking, the fact that an attempt was made to condense a normal two-year project into a 6-month one with in house labor turned it into a major undertaking for Langley. -- Published in Joseph A. Shortal, History of Wallops Station: Origins and Activities Through 1949, (Wallops Island, VA: National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Wallops Station, nd), Comment Edition.
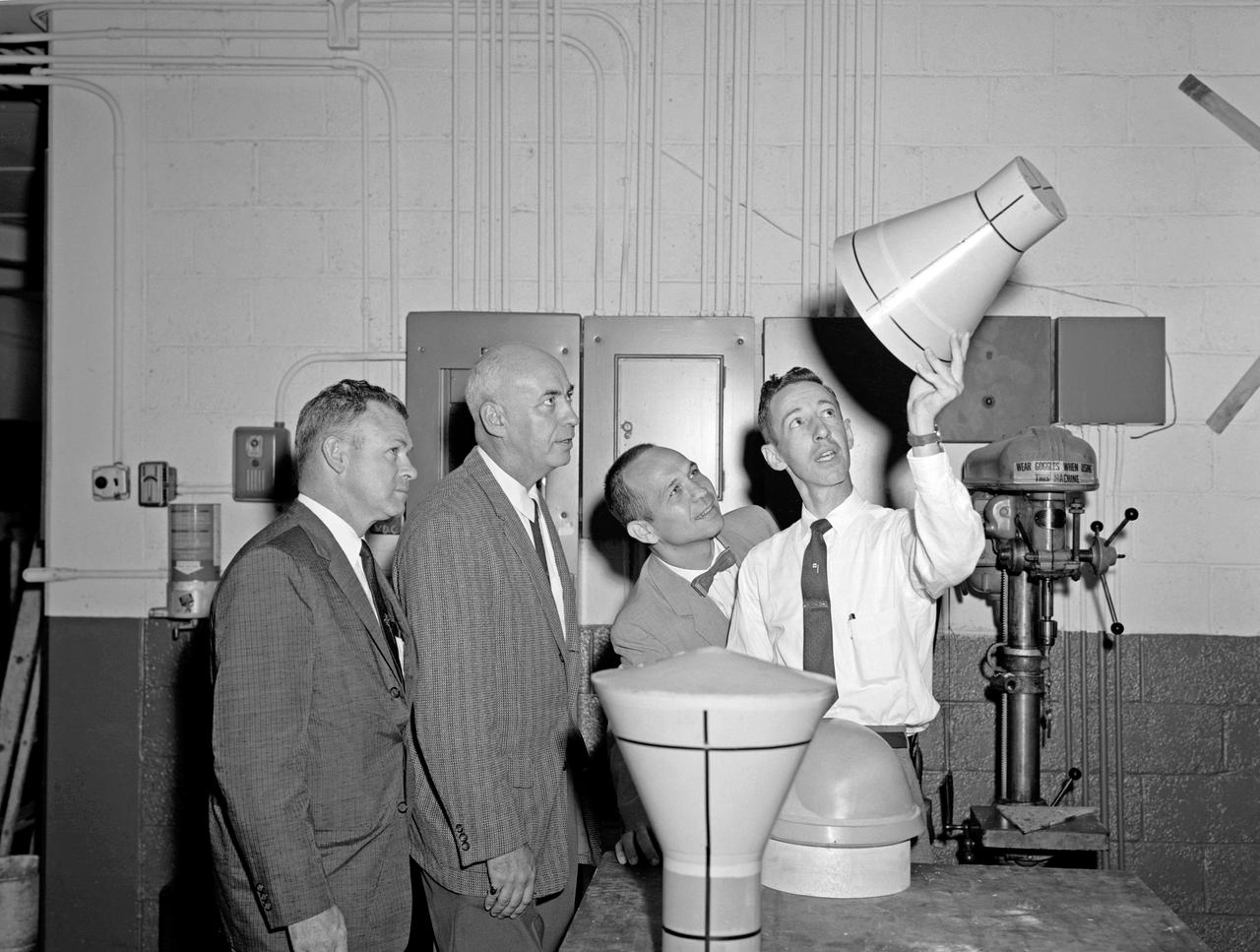

From left to right: Charles Donlan, deputy head, and Robert Gilruth, head of STG, look at a scale model of a Mercury space capsule.
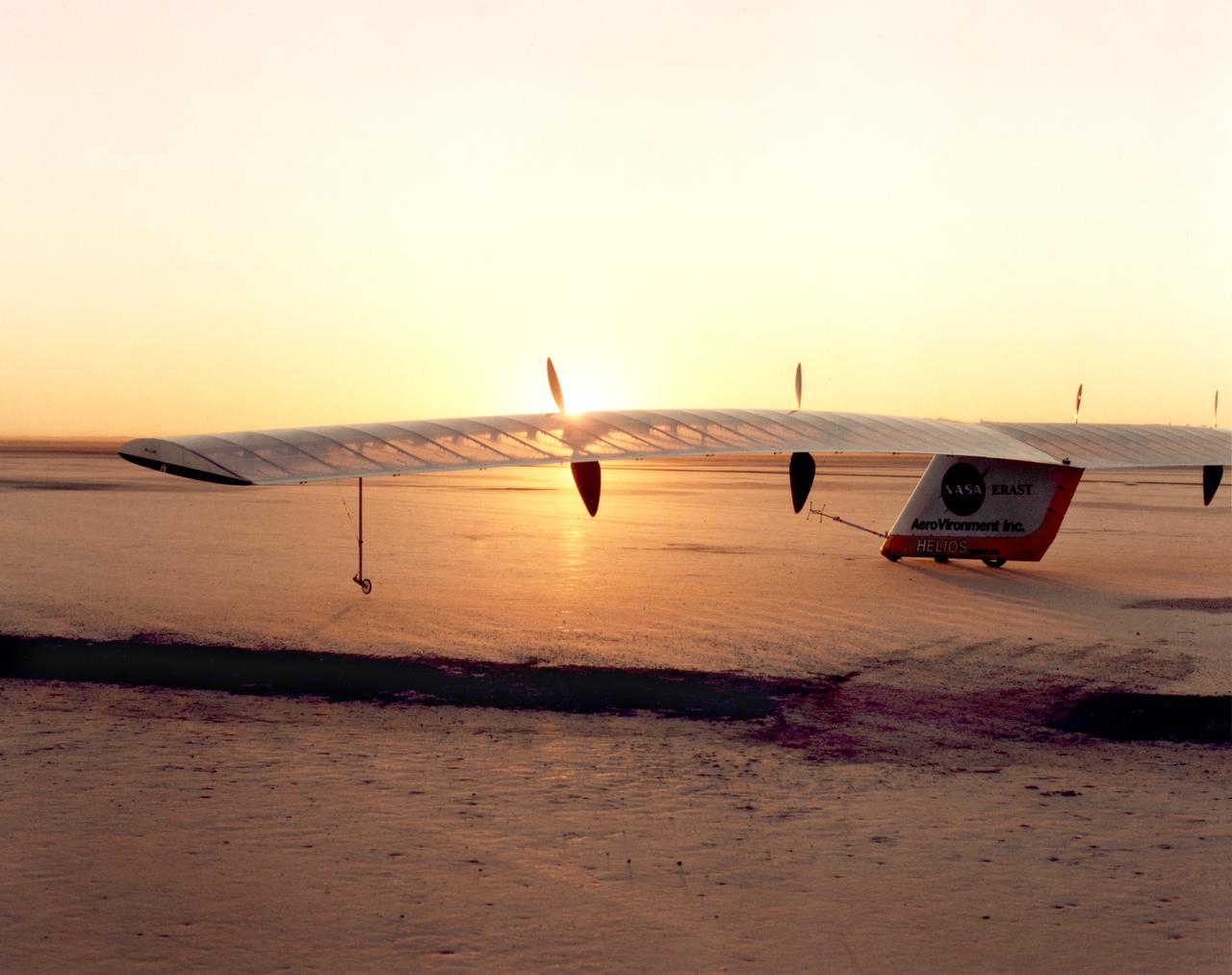

Helios Prototype on lakebed prior to first battery-powered flight

ER-2 tail number 706, was one of two Airborne Science ER-2s used as science platforms by Dryden. The aircraft were platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They were also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation.
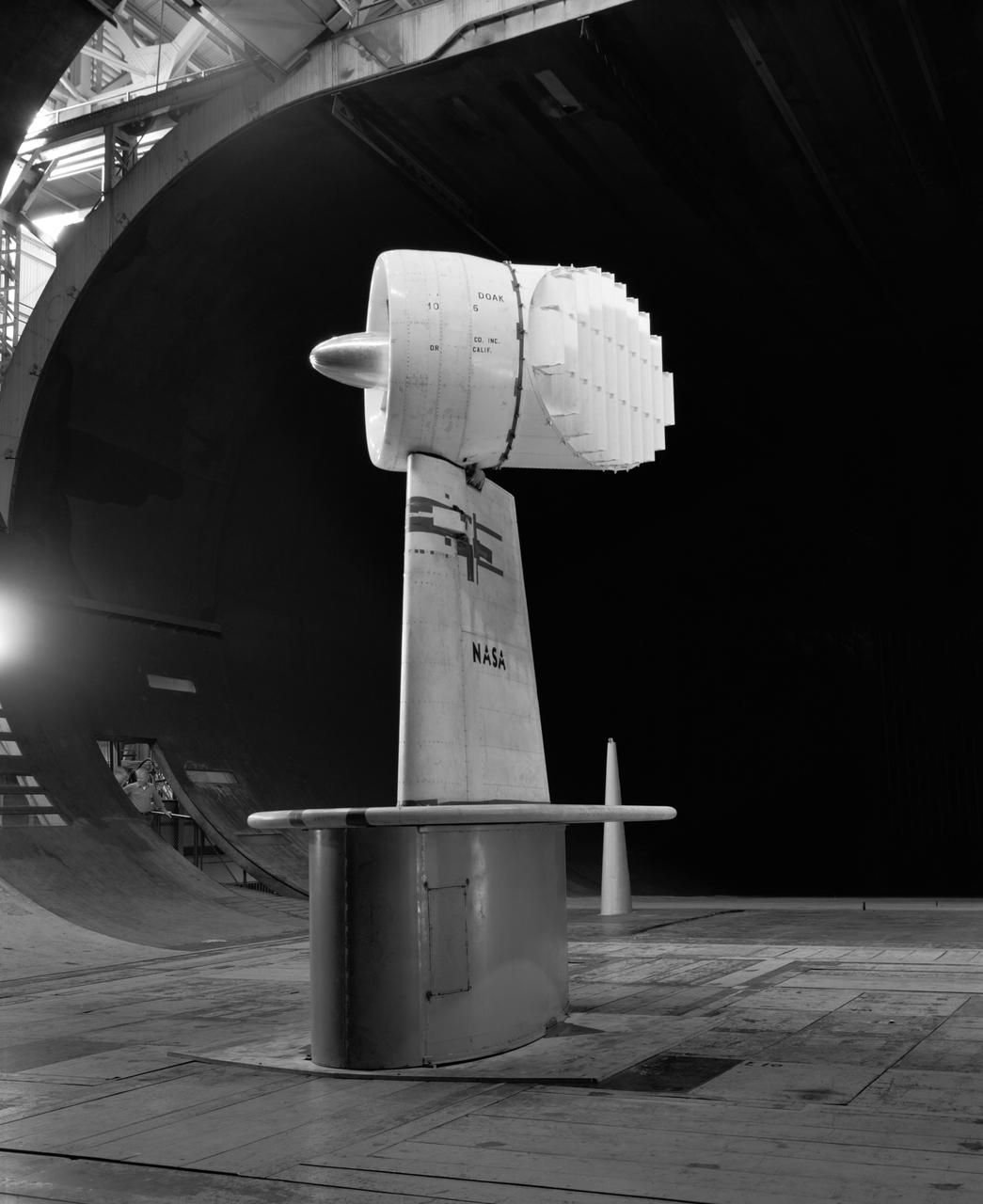

3/4 front view of Ducted fan model with 40 deg. exit vane cascade, semi span model.
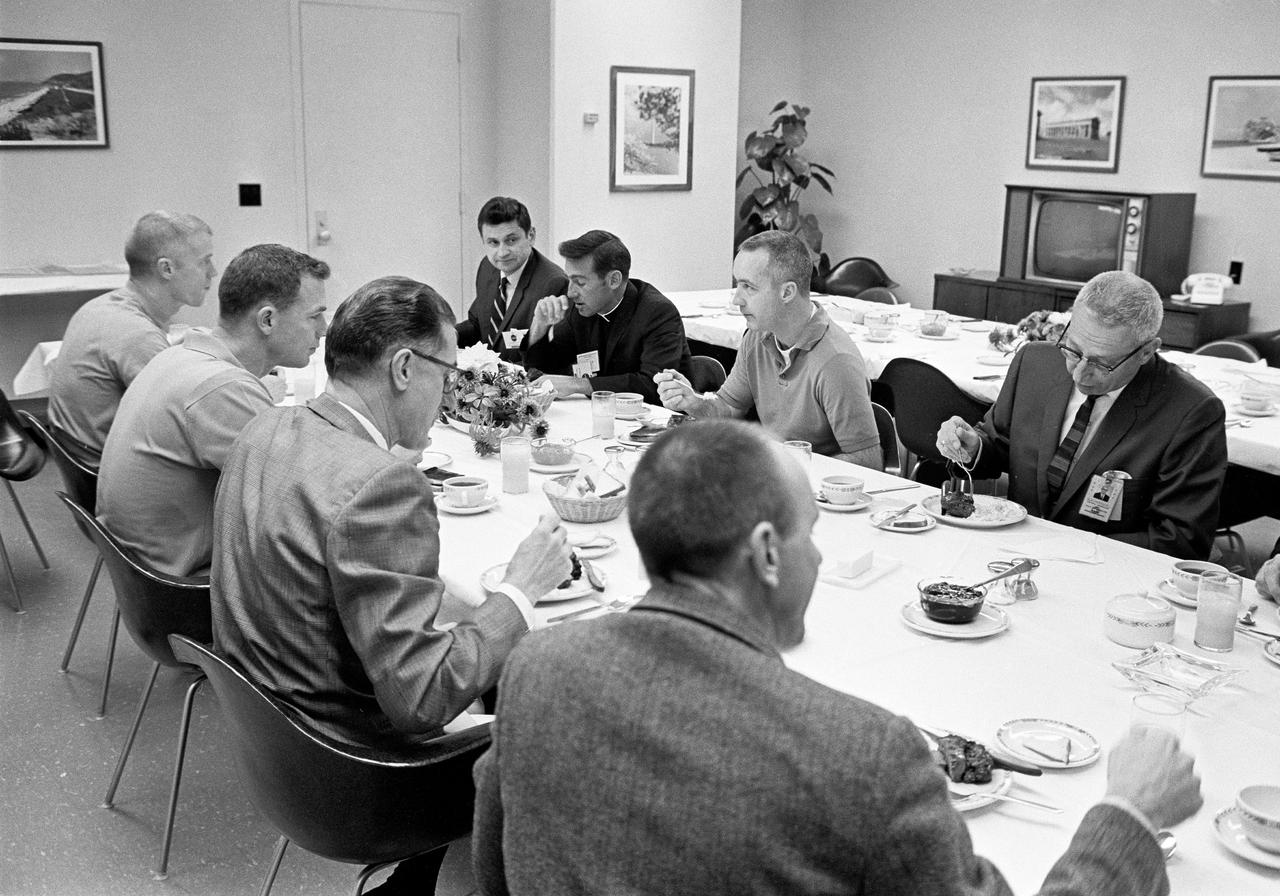

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Apollo 9 astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart breakfast today with mission officials in their crew quarters at the Kennedy Space Center a few hours prior to their scheduled launch into Earth orbit. Seated in the foreground, left to right, are astronauts Schweickart and Scott Brig. Gen. C. H. Bolendar, manager, Lunar Module and backup Lunar Module Pilot Alan L. Bean. Across the table, left to right, George Skurla, Grumman Aircraft Base Manager at the Spaceport McDivitt's clergyman from his home church at Nassau Bay, Texas, The Rev. Laurence Connelly McDivitt and Kenneth Kleinknecht, manager, Command and Service Modules at the Manned Spacecraft Center. Grumman builds the two-man lunar module spacecraft that will be tested during the planned 10-day space mission. Photo credit: NASA
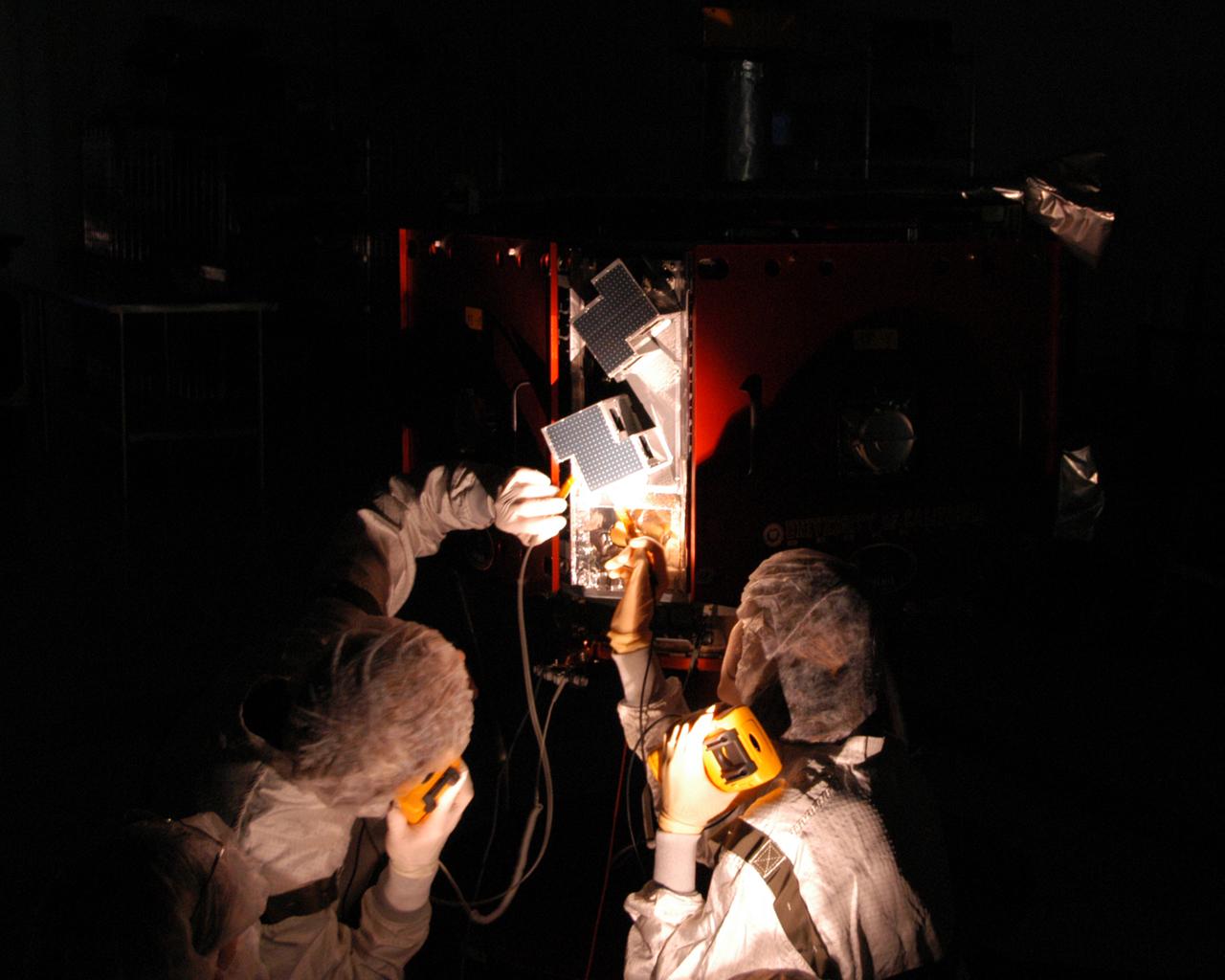

At Astrotech Space Operations, technicians conduct white light inspection of the THEMIS probes. They will also undergo black light inspection. White light inspection assures the telemetry is operating. Black light inspection uses UVA fluorescence to detect possible particulate microcontamination, minute cracks or fluid leaks. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
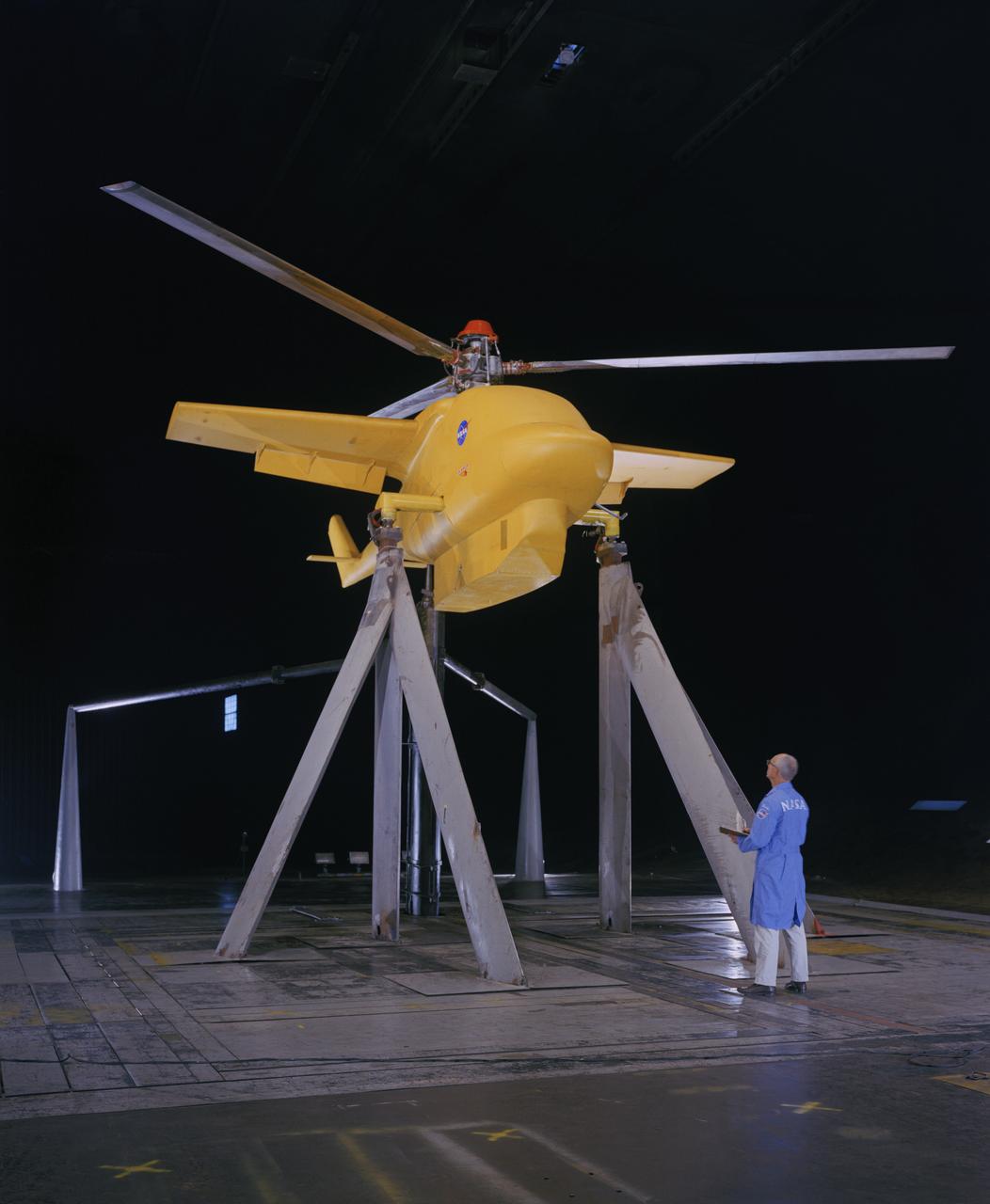

3/4 front view of Lockheed Stopped Rotor.

At Astrotech Space Operations, workers look over the integrated THEMIS spacecraft before spin-balance testing. THEMIS consists of five identical probes, the largest number of scientific satellites ever launched into orbit aboard a single rocket. This unique constellation of satellites will resolve the tantalizing mystery of what causes the spectacular sudden brightening of the aurora borealis and aurora australis - the fiery skies over the Earth's northern and southern polar regions. THEMIS is scheduled to launch Feb. 15 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
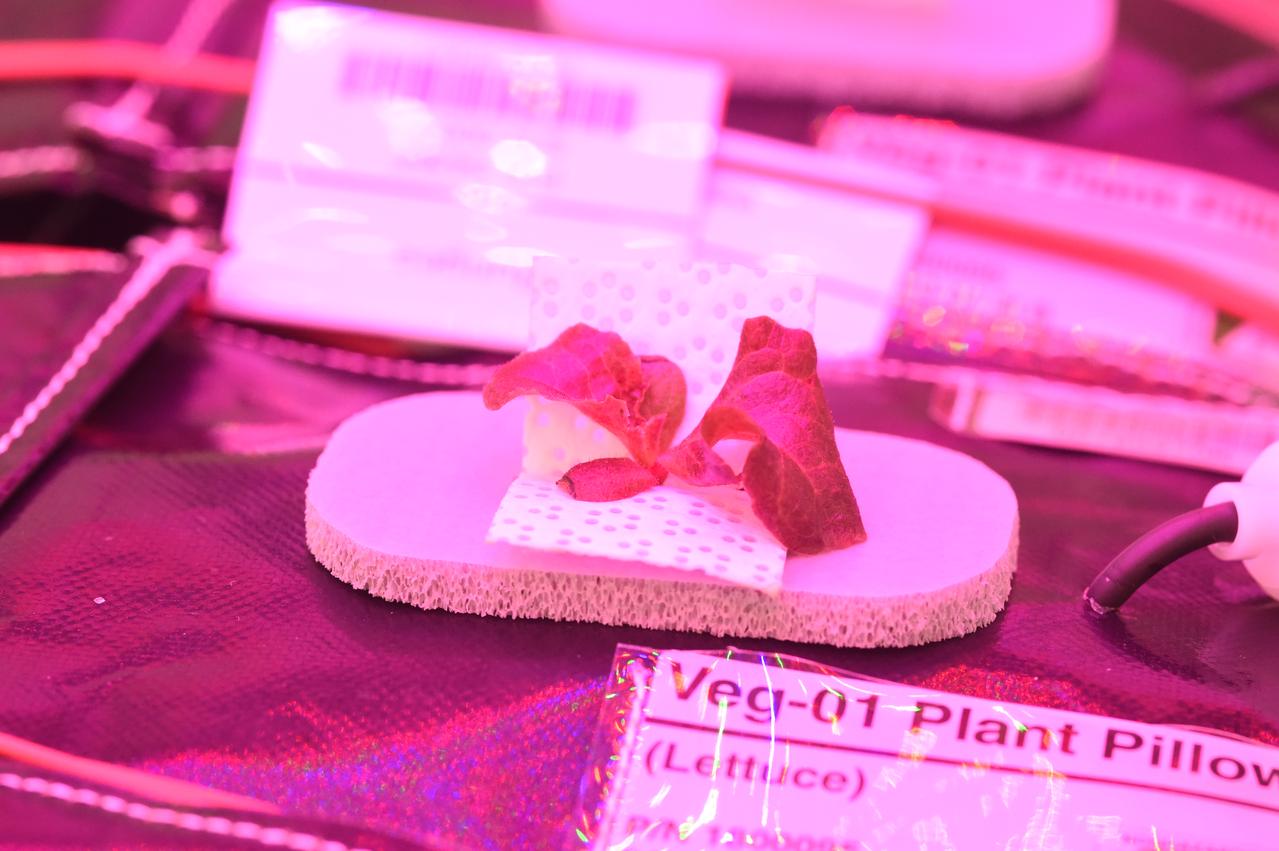

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
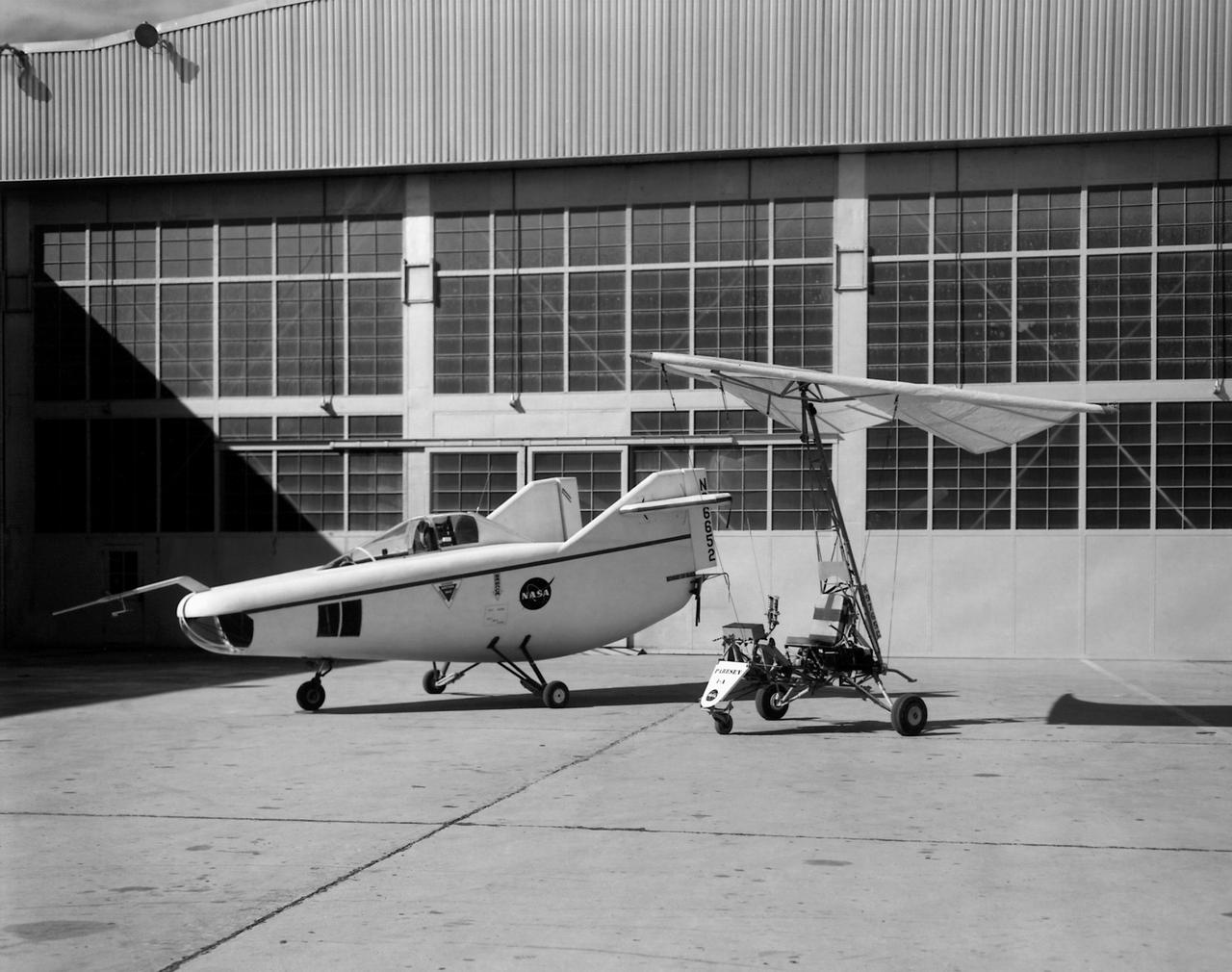

In this photo of the M2-F1 lifting body and the Paresev 1B on the ramp, the viewer sees two vehicles representing different approaches to building a research craft to simulate a spacecraft able to land on the ground instead of splashing down in the ocean as the Mercury capsules did. The M2-F1 was a lifting body, a shape able to re-enter from orbit and land. The Paresev (Paraglider Research Vehicle) used a Rogallo wing that could be (but never was) used to replace a conventional parachute for landing a capsule-type spacecraft, allowing it to make a controlled landing on the ground.
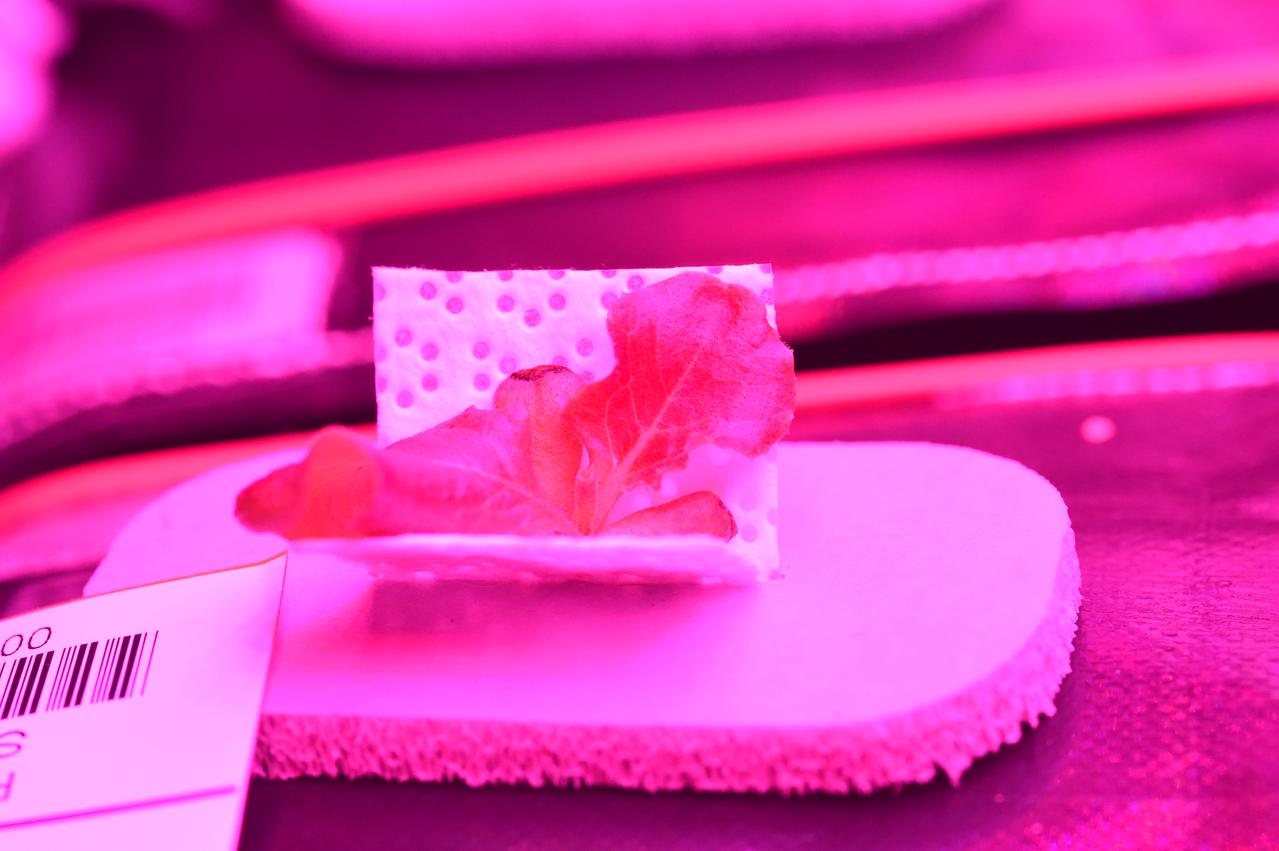

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
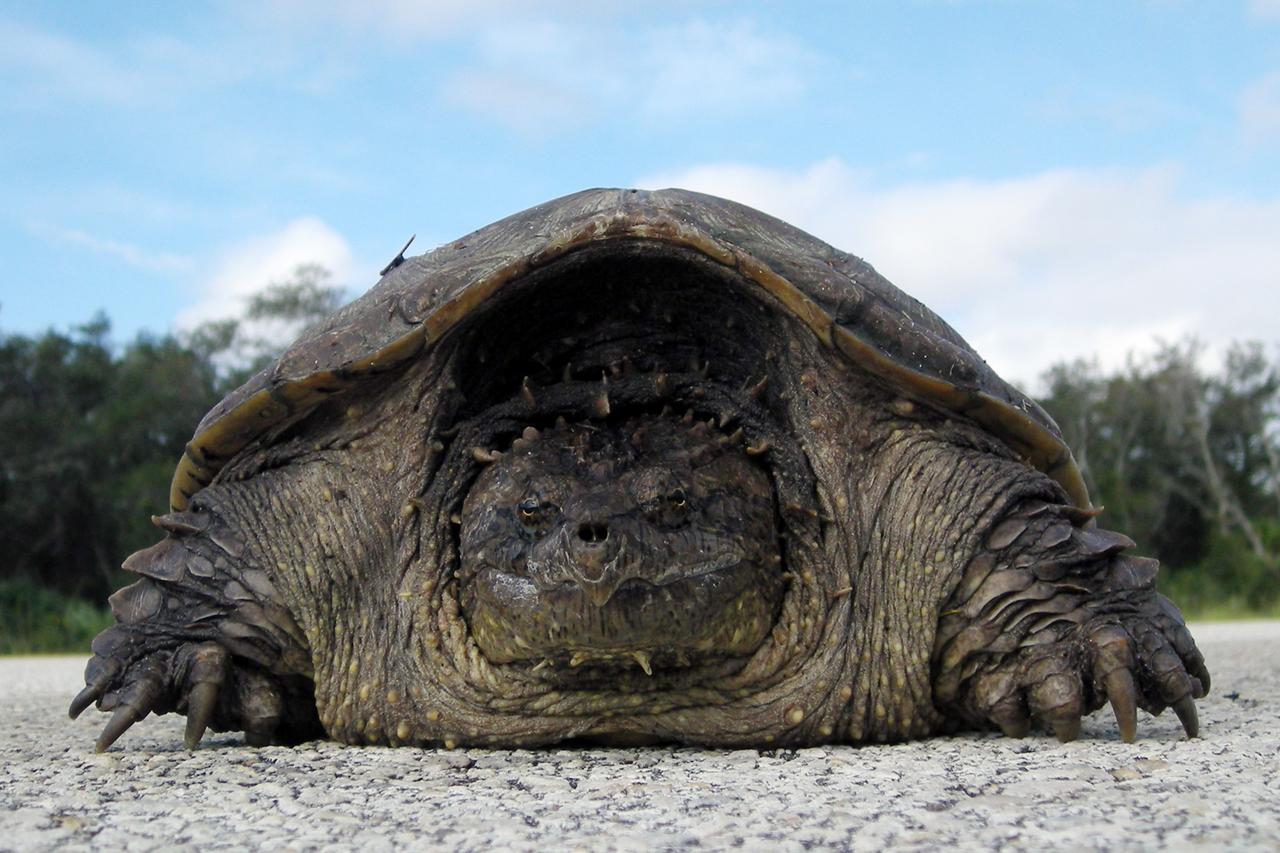

A rare photo of a Florida snapping turtle out in the open on Beach Road, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Found only in Florida and Georgia, this species is related to the common snapping turtle. It is considered a dangerous turtle because it can snap very quickly with its extremely strong jaws. Its tail, which is almost as long as its shell, has saw-edges along the top. The shell also has rough points down the middle. The shell is tan to dark brown and may have green algae growing on it. It can grow to 17 inches long and weigh 45 pounds. Snapping turtles usually live in ponds under the shadows and don’t like to rest in the sun like most turtles. They eat almost anything: water bugs, fish, lizards, small birds, mice, plants and even dead animals

Infographic illustrating the Passive Orbital Nutrient Delivery System (PONDS) plant growth unit. The PONDS units are an entirely passive system – meaning no electricity, no pumps and no moving parts – and the basic concept involves using a free-standing reservoir of water that plants can draw from when needed, cutting down on time astronauts would spend watering plants during the growth interval.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
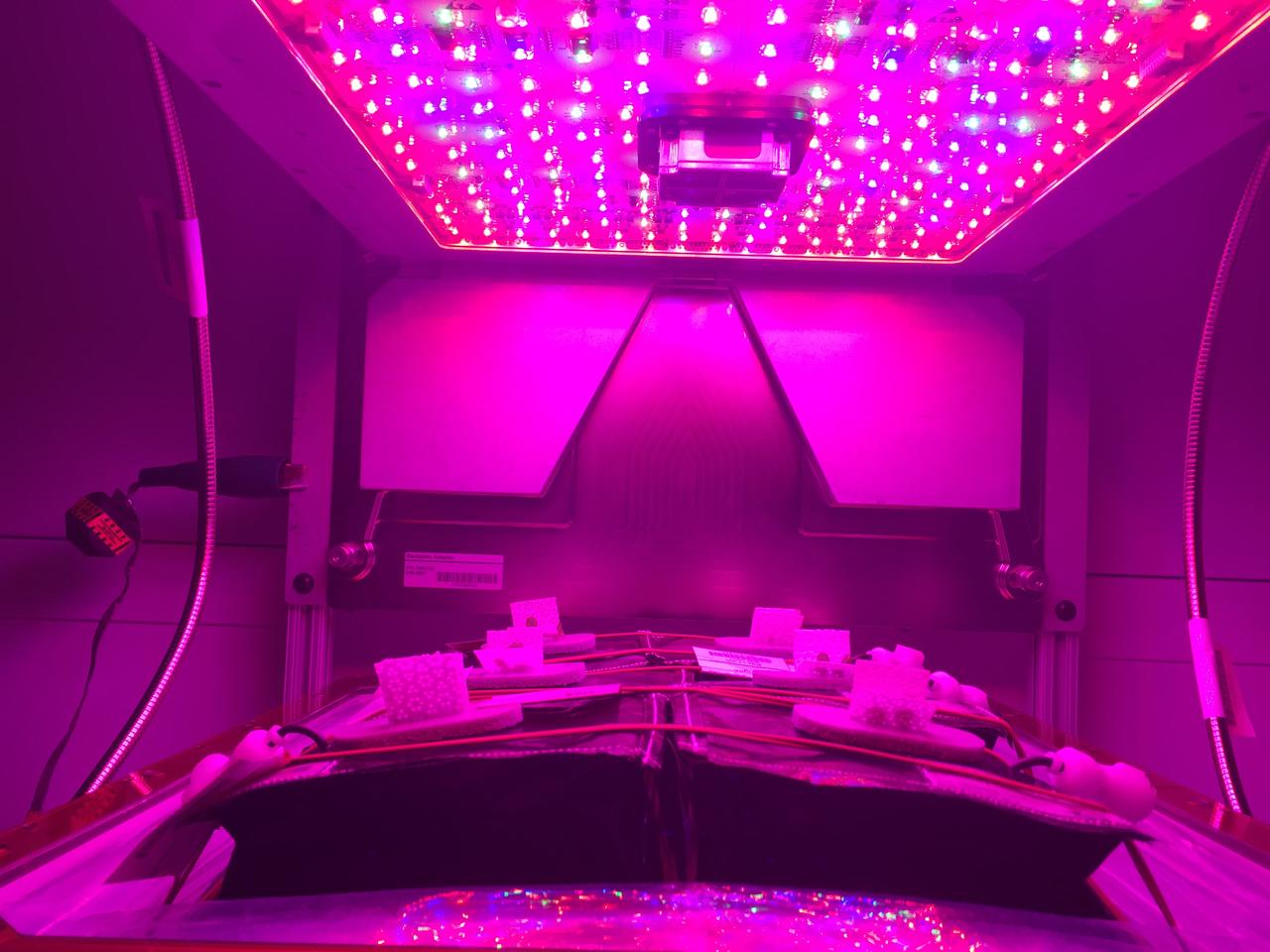

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

Water drop and recovery from shore-based crane at Langley's back river.
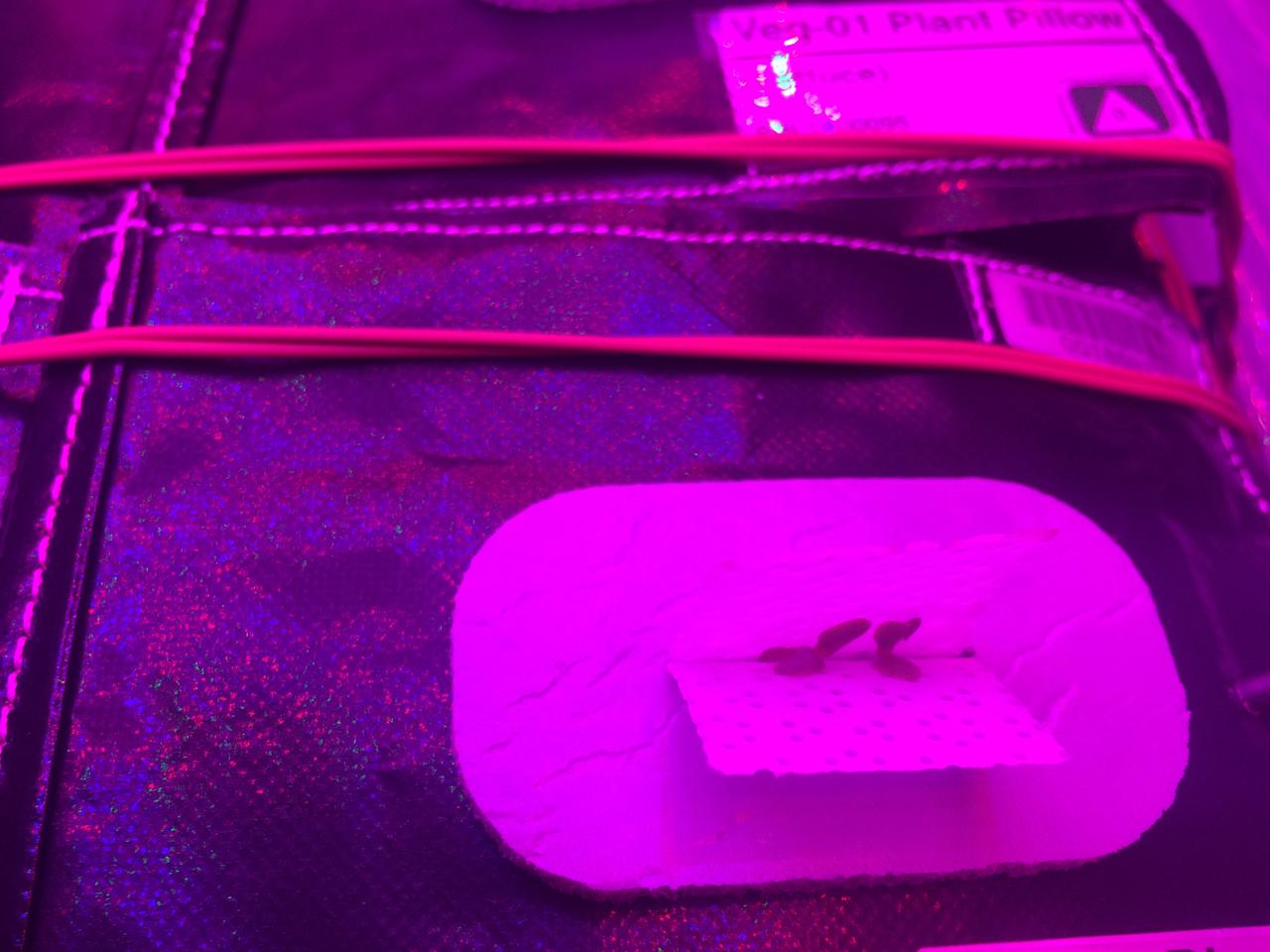

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
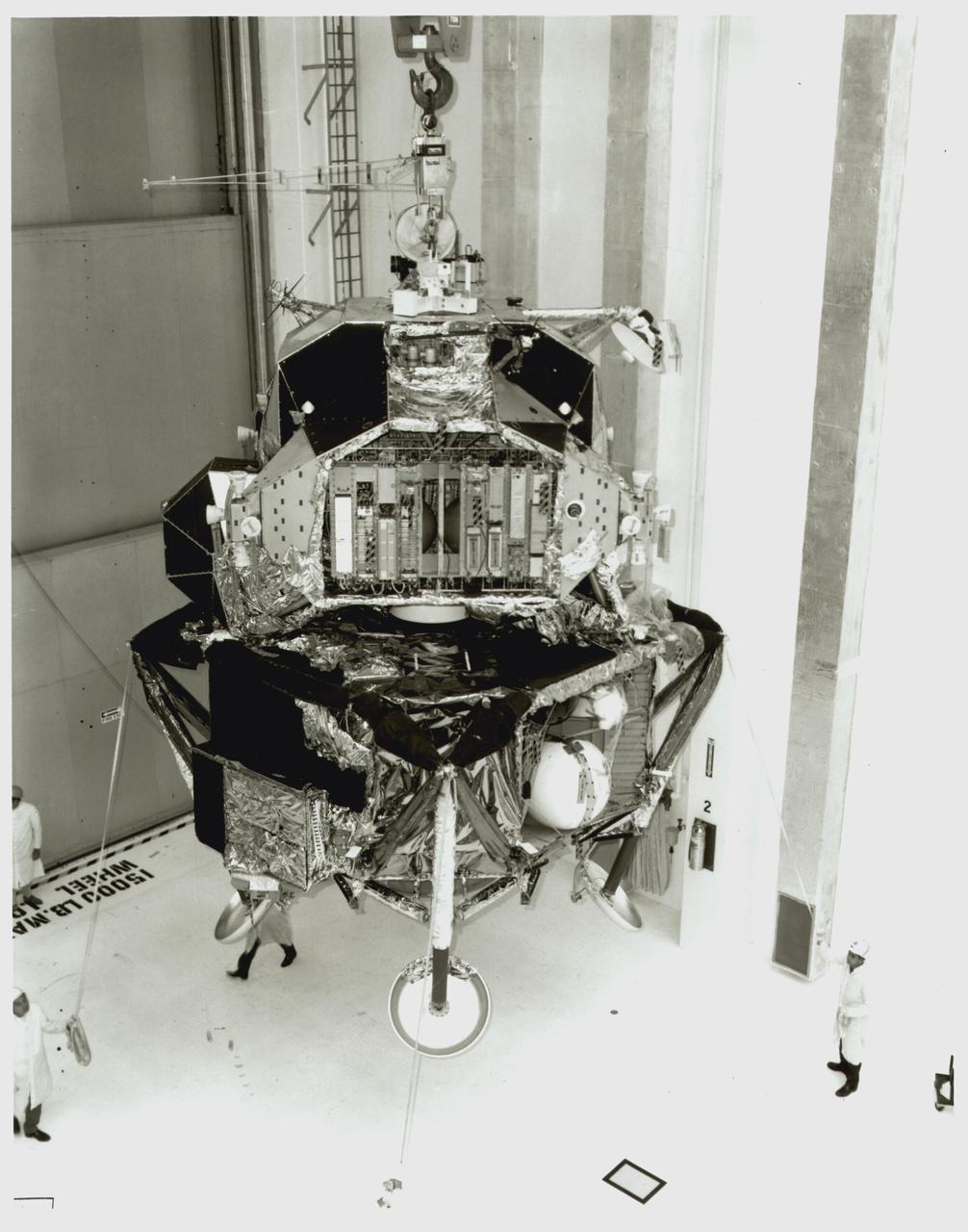
The Lunar Module for Apollo 11 moves from the landing gear fixture and mate to the spacecraft-lunar module adapter.
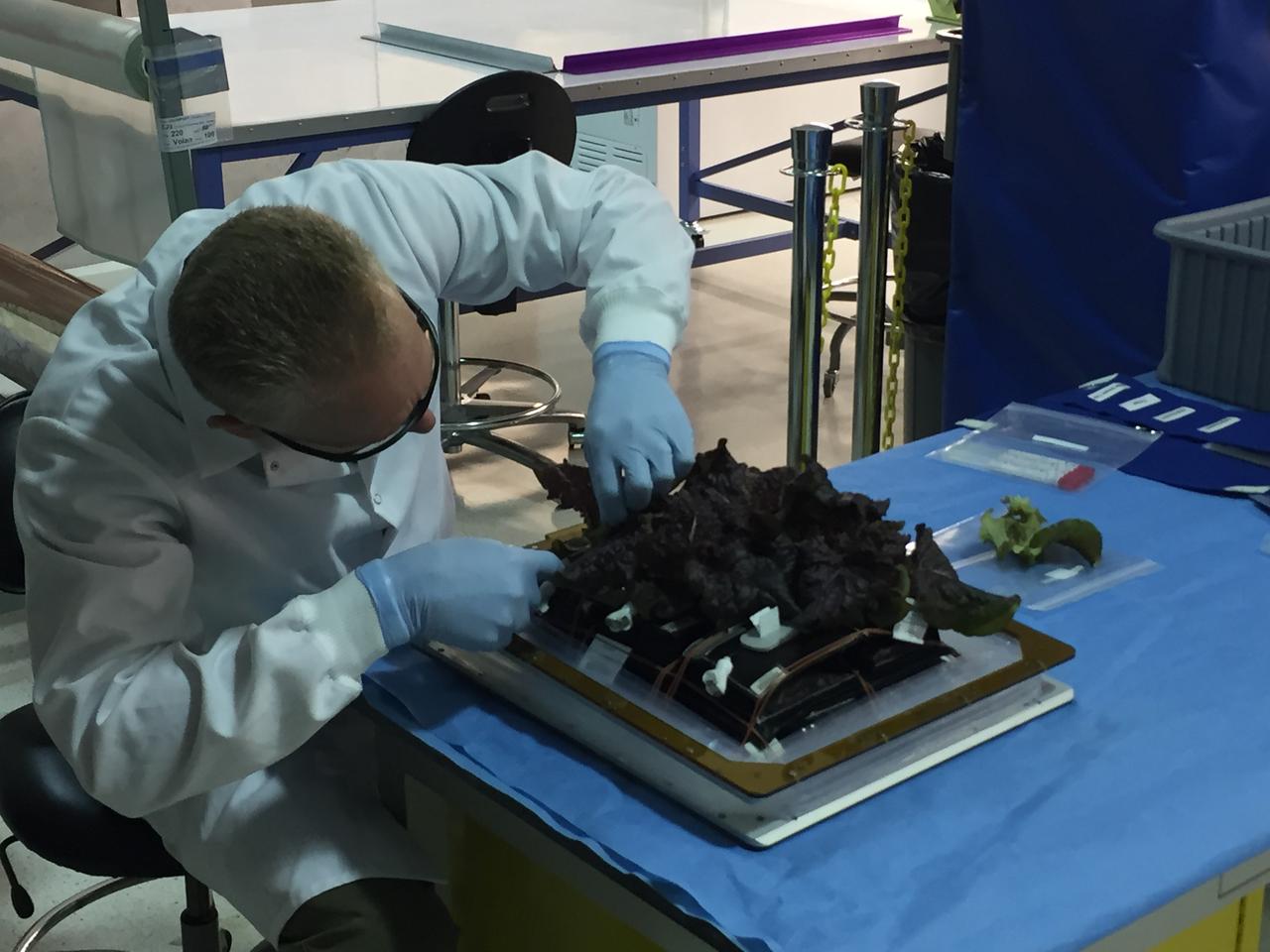

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.

The HiMAT (Highly Maneuverable Aircraft Technology) subscale research vehicle, seen here during a research flight, was flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, from mid 1979 to January 1983. The aircraft demonstrated advanced fighter technologies that have been used in the development of many modern high performance military aircraft.