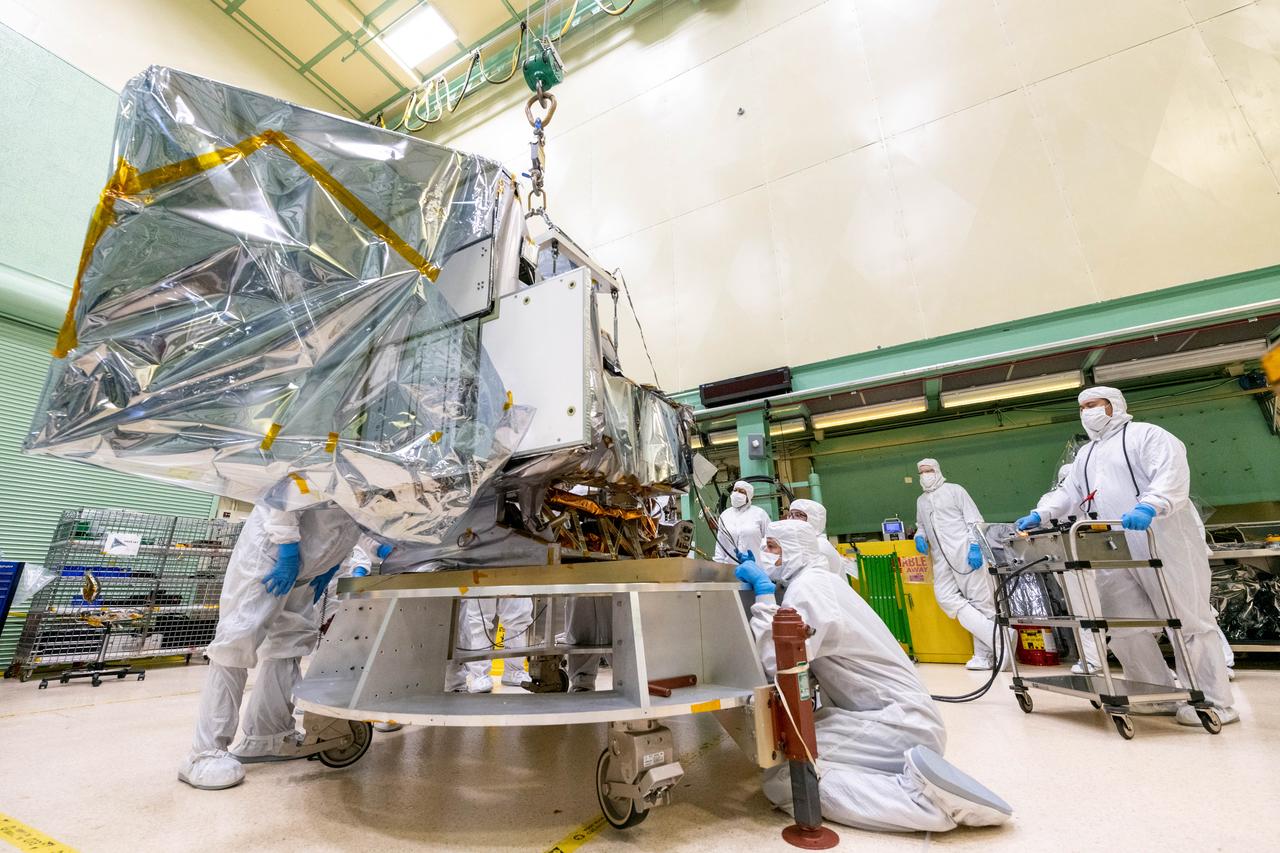

Mechanical technicians crane lift the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) onto the Tilt Mechanism. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
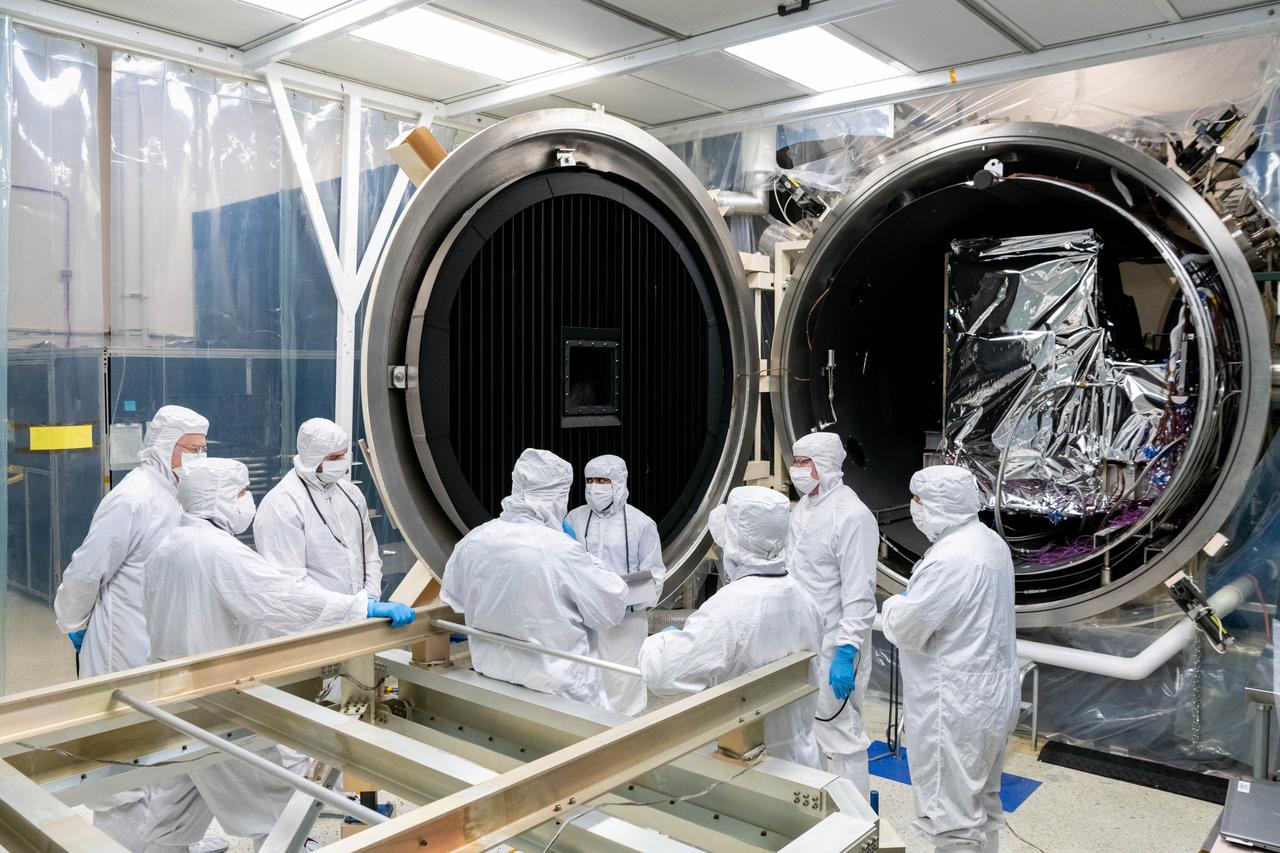

The Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) team reviews test plans and inspects the instrument in the thermal vacuum chamber prior to closing the large door for a sixty day thermal test which ensures the instrument will perform effectively once it launches into the airless environment of space. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.

The Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI) & Electrical Ground Support Equipment (EGSE) Team pose in the control room. From this room, they are able to analyze the data from the test remotely and send commands through electrical cables that run through the walls into the EMI lab. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.

Mechanical technician, Thomas Huber and mechanical engineer Peter Steigner, install an electronic box onto the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) deck. Once the remaining boxes are installed, electrical connections will be made and testing will be performed. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
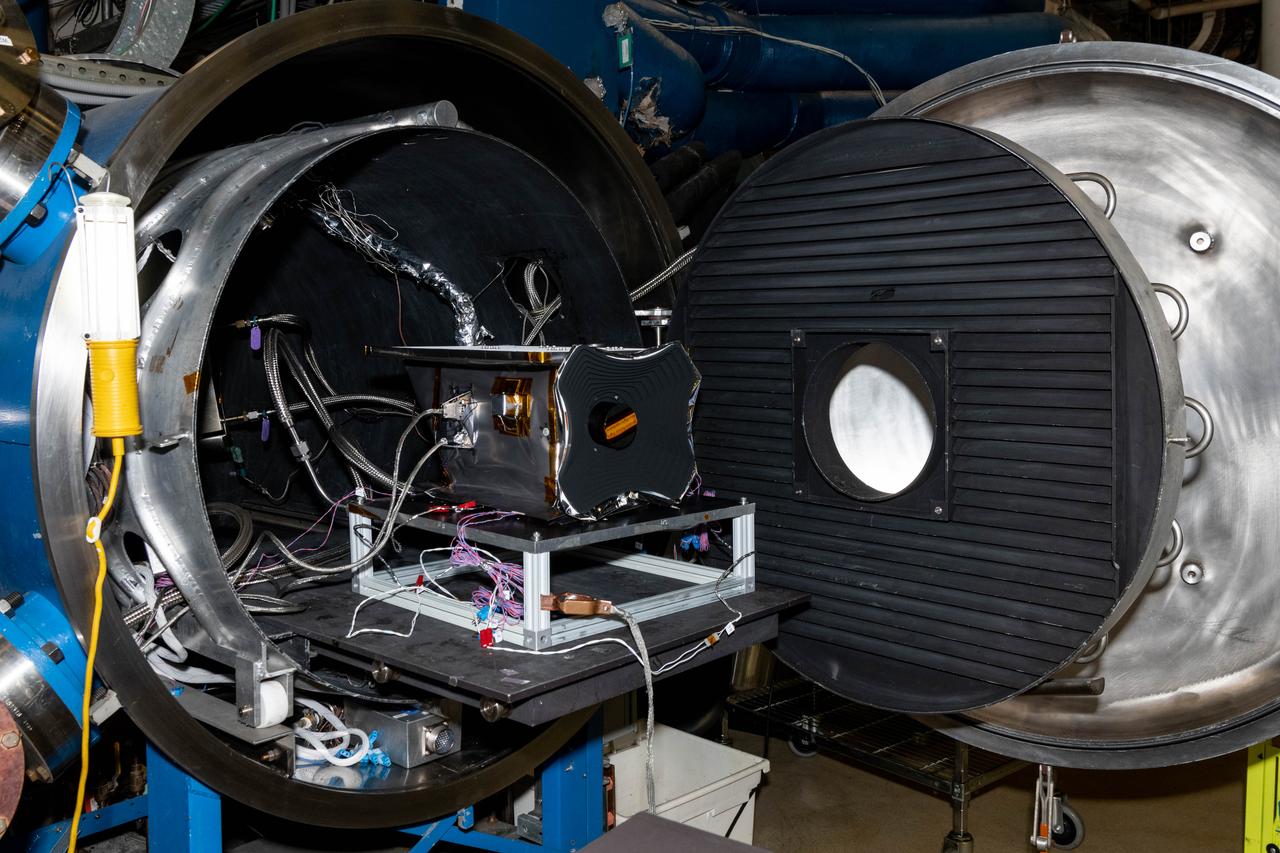

The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument prior to thermal vacuum testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on August 8th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute.
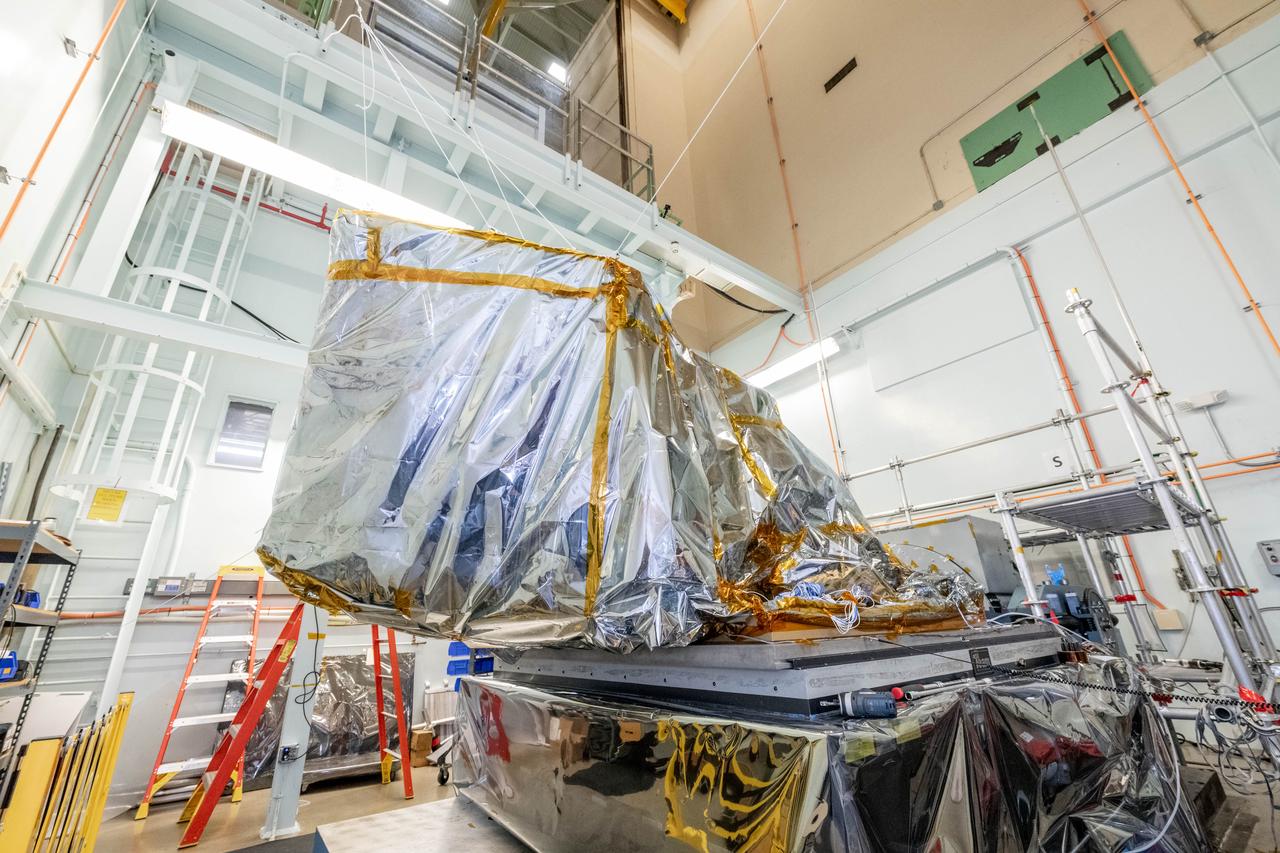

The Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) is configured for vibration testing. OCI is bagged with Dun-Shield to protect the instrument from contamination outside of a cleanroom environment, and also provides protection from static electricity. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
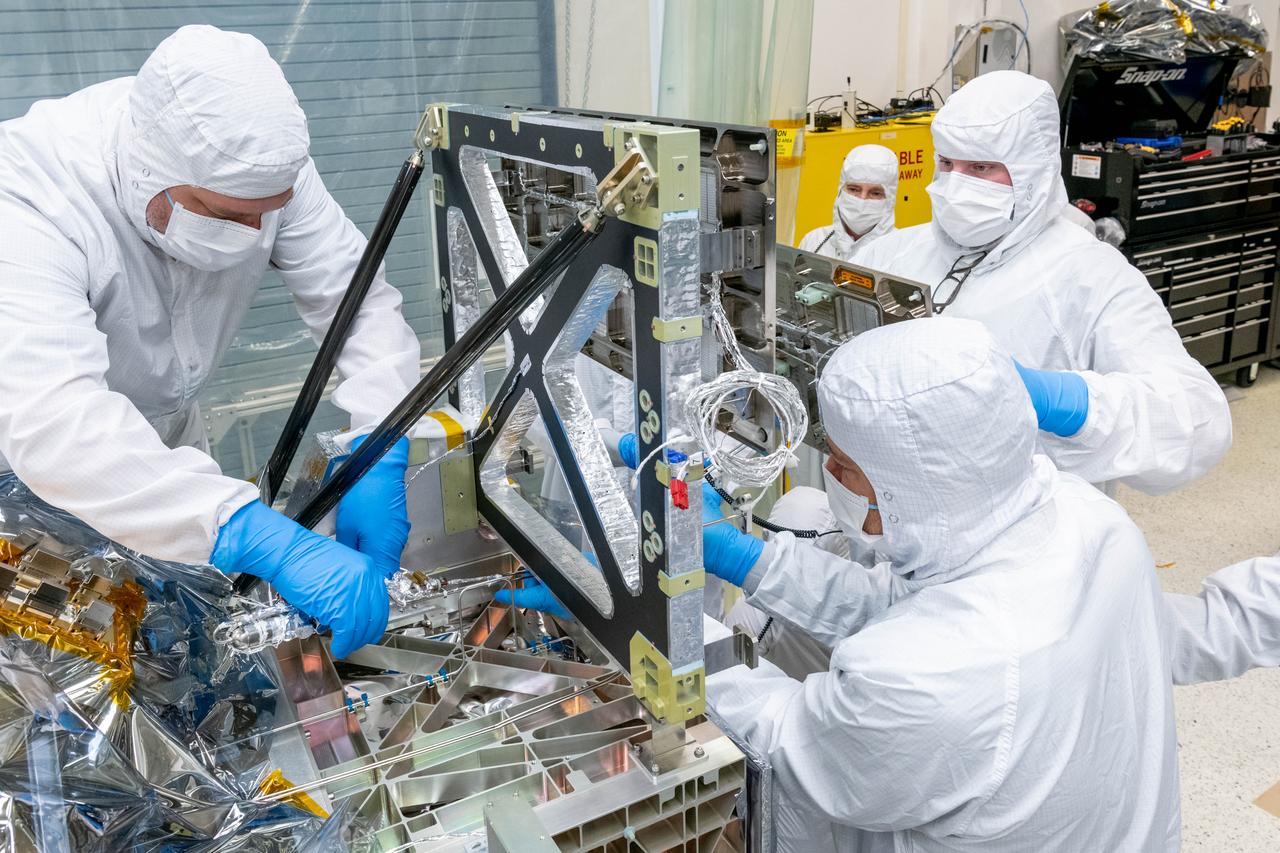

Mechanical technicians and thermal engineers work together to carefully feed the lines of a Loop Heat Pipe onto the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI). This integration operation will allow proper heat transfer throughout the instrument. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
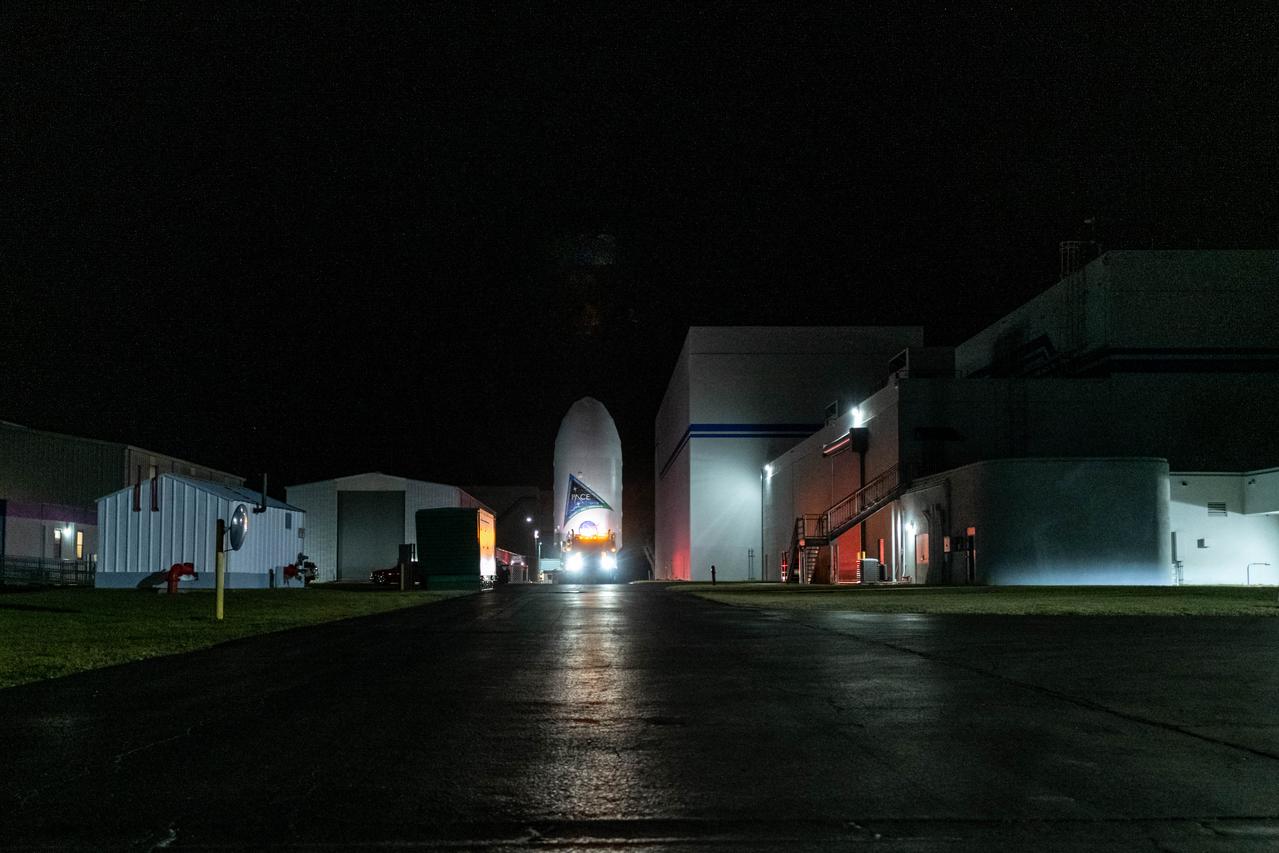

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft encapsulated inside SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings is transported from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, to be mated with a SpaceX Falcon 9 in preparation for liftoff set for no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6, 2024. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
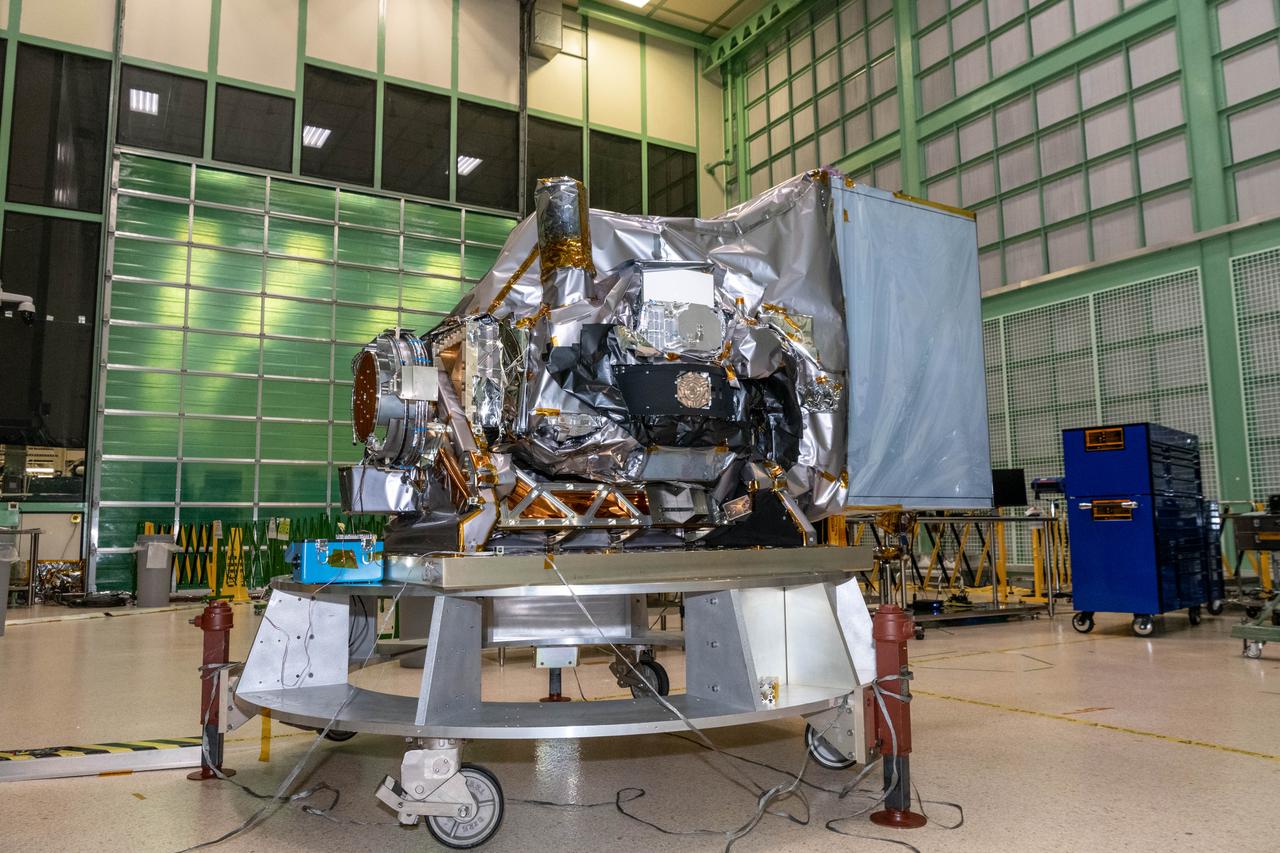

The Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) is integrated on the Tilt Mechanism prior to environmental testing in the Spacecraft Checkout Area (SCA) cleanroom. The OCI Tilt will help the instrument avoid sun glint in a space environment. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
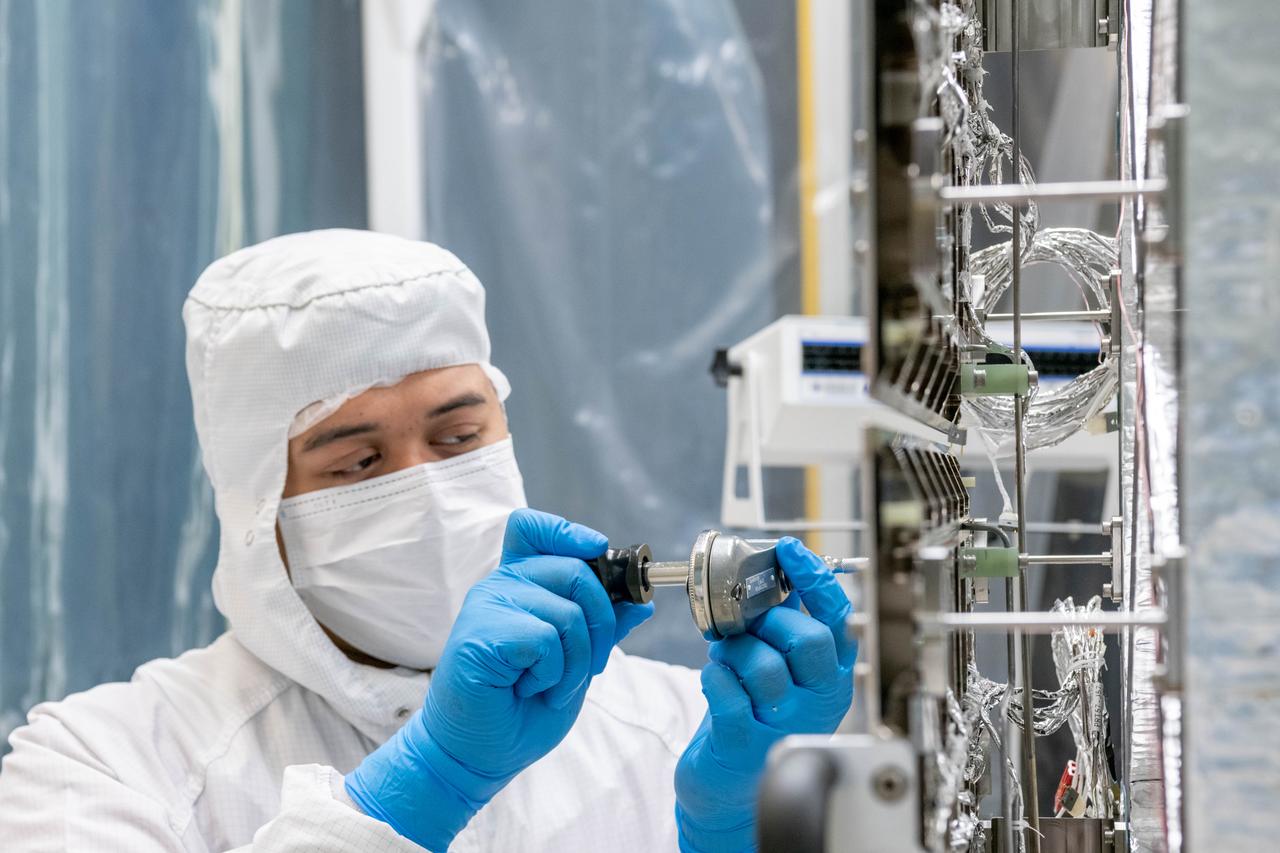

Mechanical technician, Dan Dizon, tightens bolts on the loop heat pipe radiator on the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) in a clean tent where the final hardware of the OCI are installed and tested. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
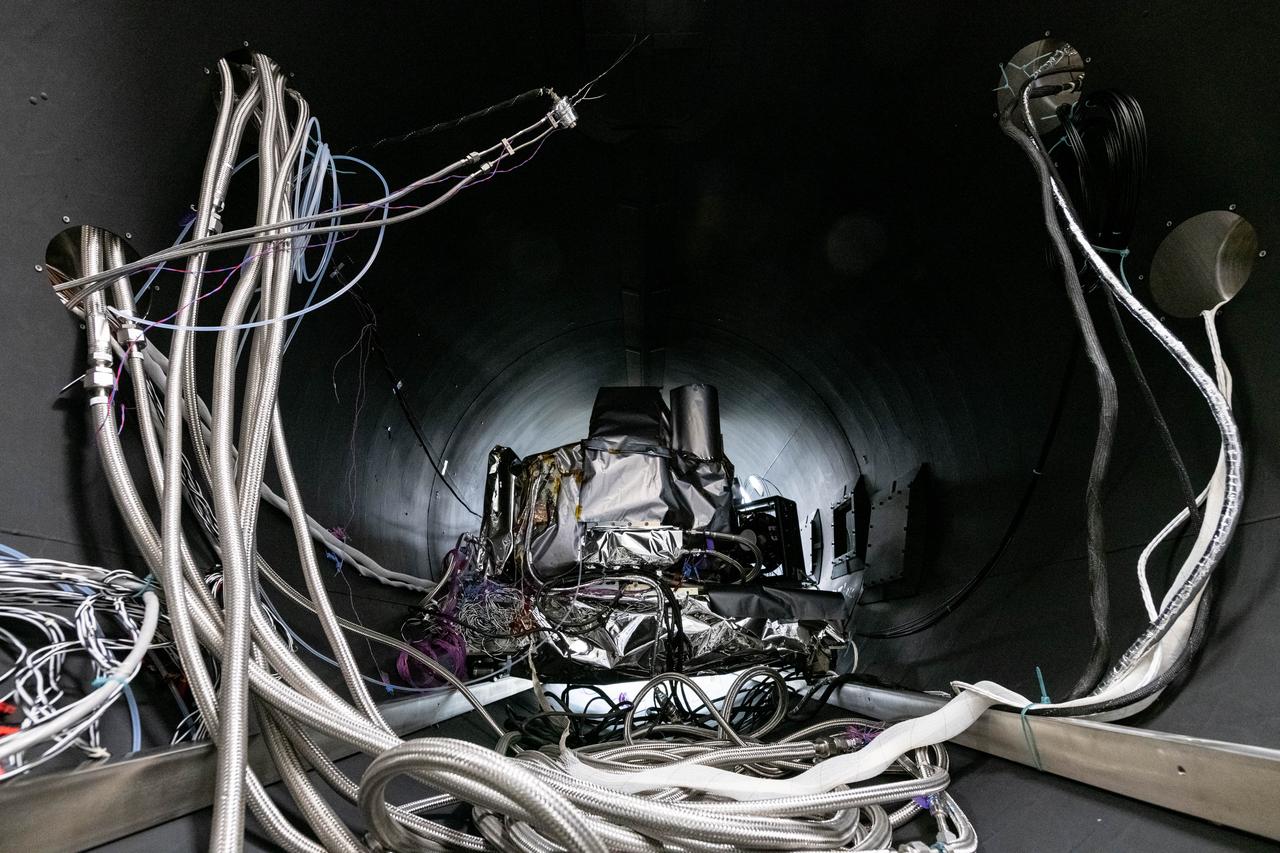

The flight Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) is connected to flex lines and other alignment calibration hardware in a thermal vacuum chamber as it is prepared for thermal testing in a clean tent at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.

NASA and SpaceX technicians safely encapsulate NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft in SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings on Wednesday, Jan. 30, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fairing halves protect the spacecraft from aerodynamic pressure and heating during the ascent phase of launch. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6, 2024.
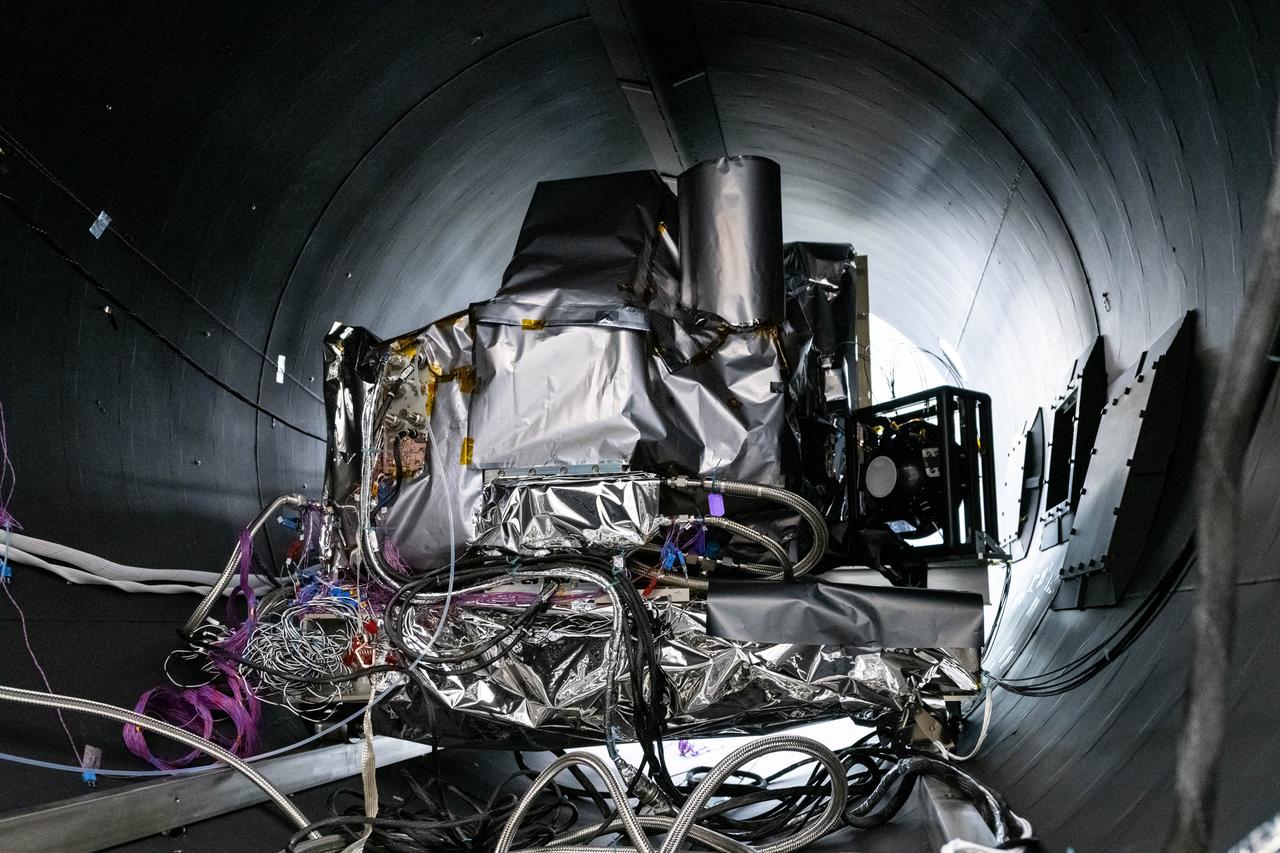

The flight Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) is connected to flex lines and other alignment calibration hardware in a thermal vacuum chamber as it is prepared for thermal testing in a clean tent at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
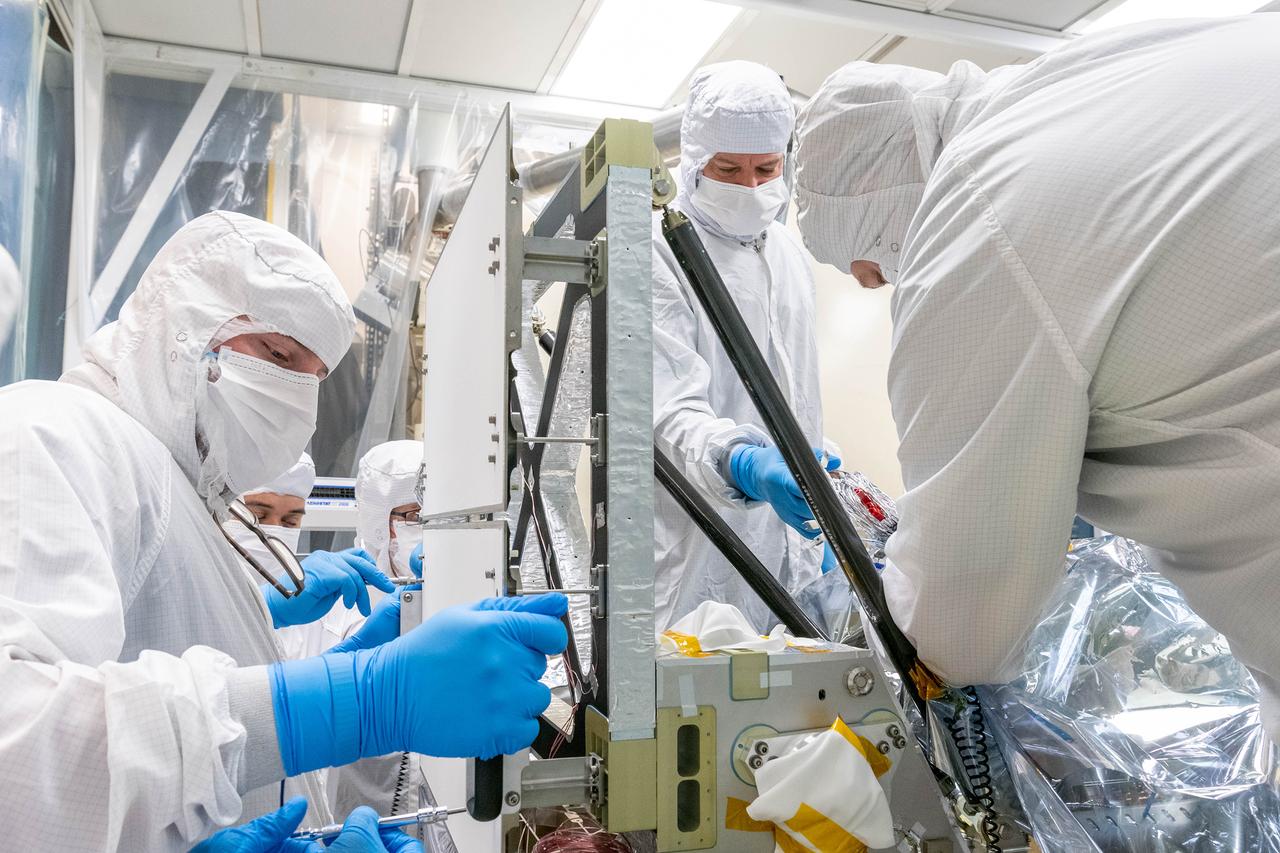

Mechanical technicians and thermal engineers work together to carefully feed the lines of a Loop Heat Pipe onto the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI). This integration operation will allow proper heat transfer throughout the instrument. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
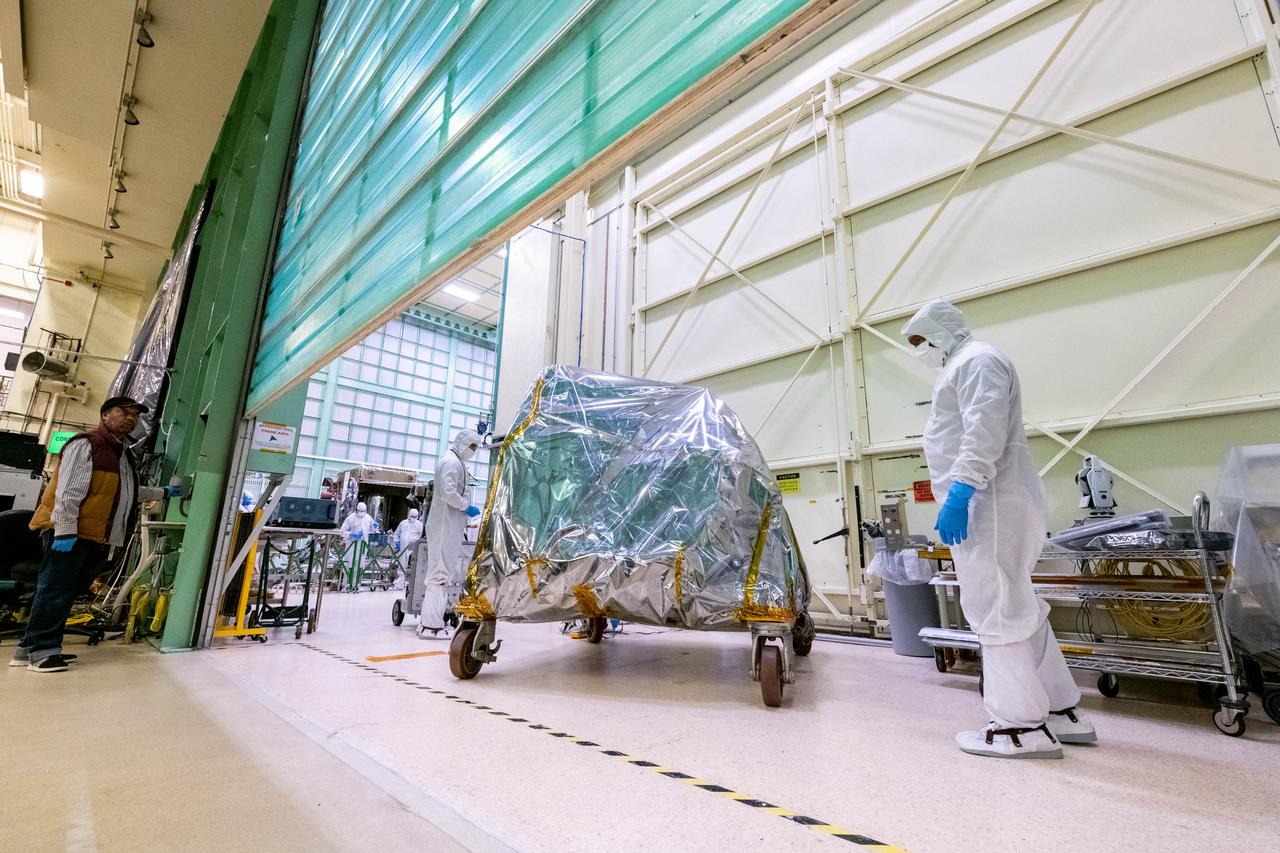

The Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) team transports the instrument on its dolly to a cleanroom at Goddard Space Flight Center for final operations prior to integration to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.

Mechanical technicians, Thomas Huber and John Poulsen, don safety harnesses and carefully guide the crane lifted Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) from the vibration table after successful testing. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
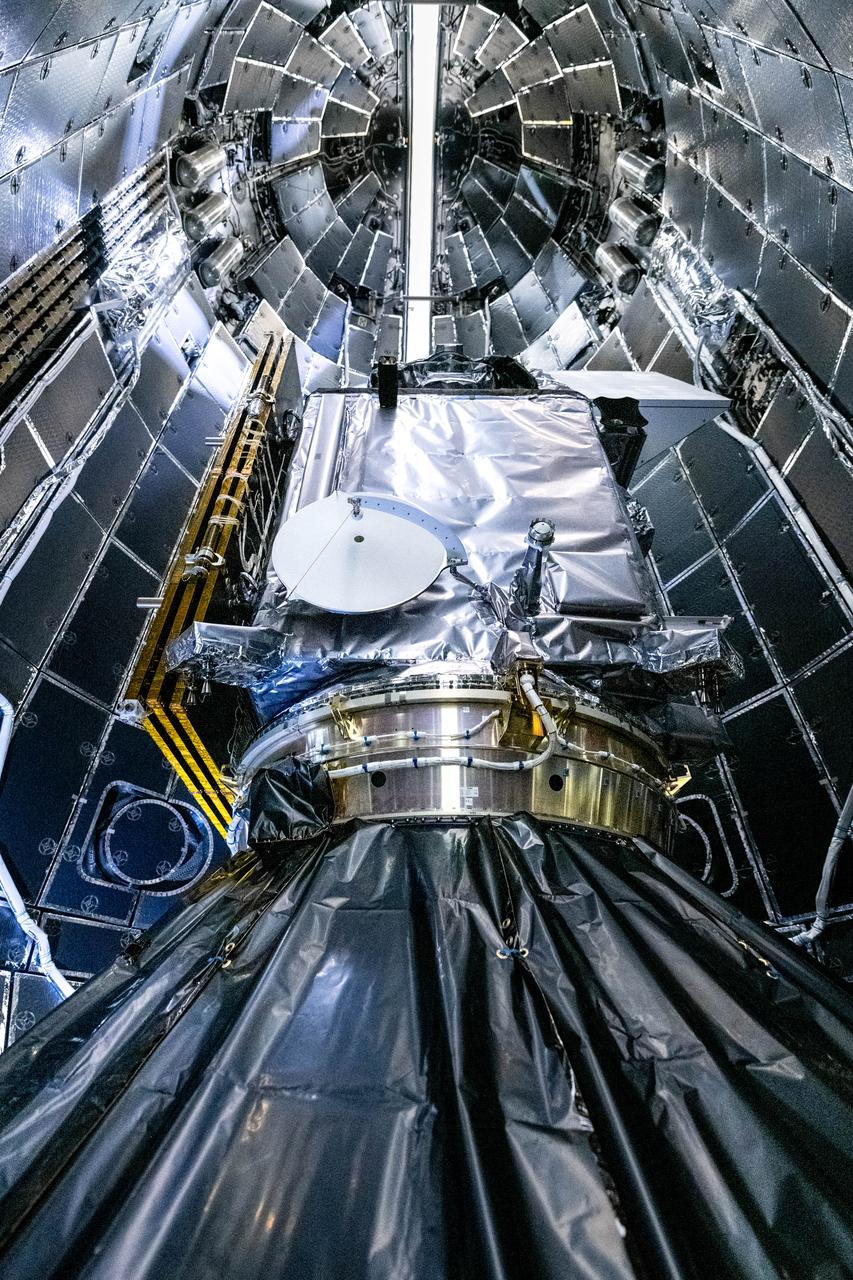

NASA and SpaceX technicians safely encapsulate NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft in SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fairing halves protect the spacecraft from aerodynamic pressure and heating during the ascent phase of launch. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6, 2024.
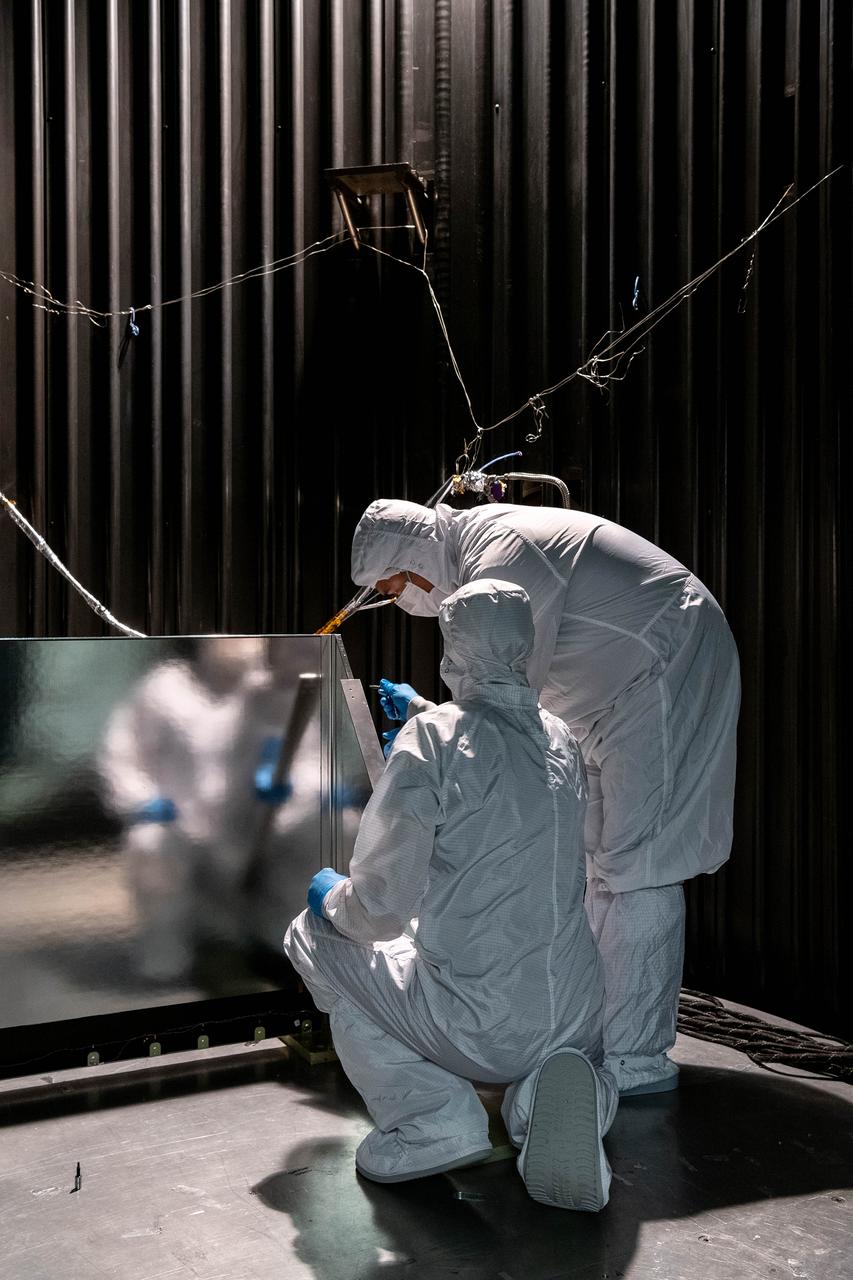

Mechanical Technicians, Daniel Dizon and Joseph Eddy, install the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) Earth Shade into a thermal vacuum chamber so that team members can test the thermal capabilities of the hardware under a simulated space environment. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
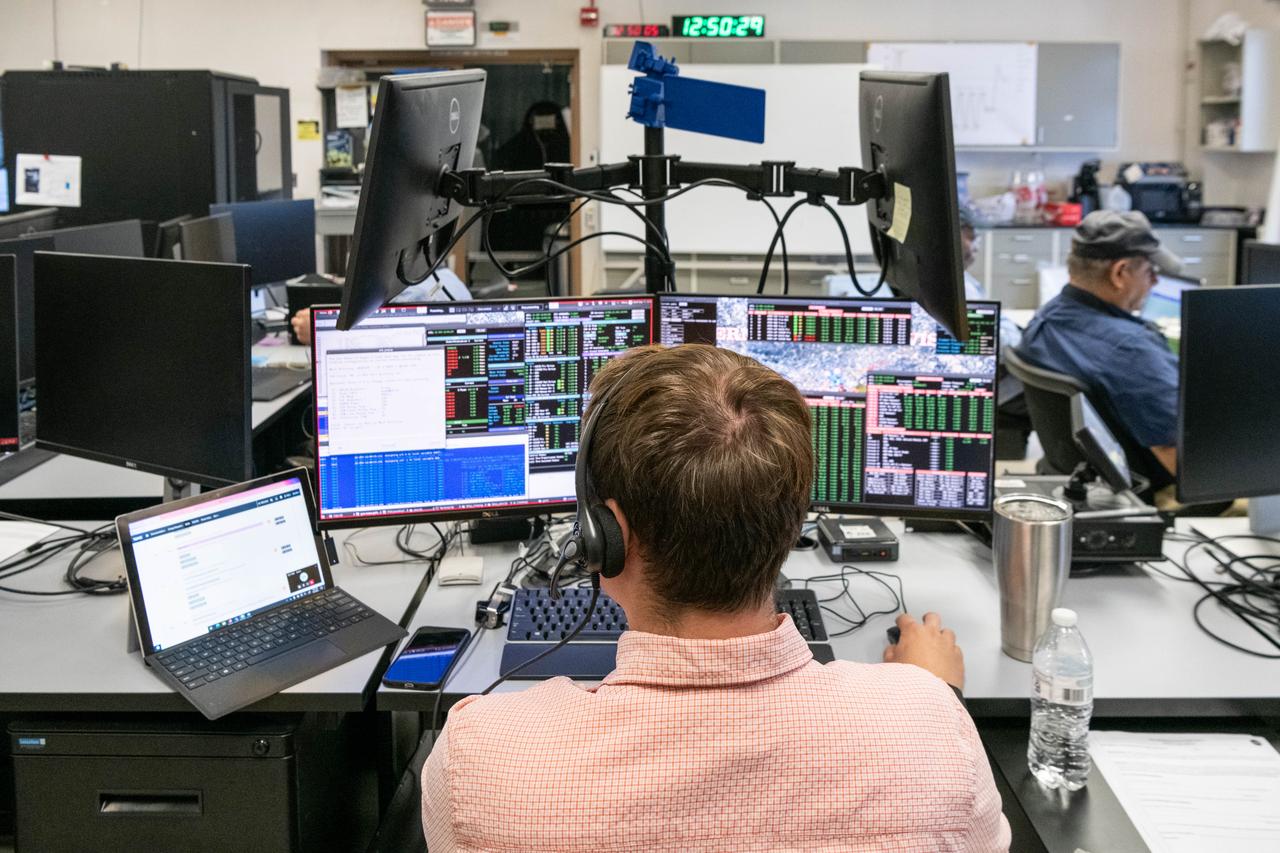

Test conductor, Lucas Tucker, monitors thermal vacuum testing operations in the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) control room during the environmental test campaign. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
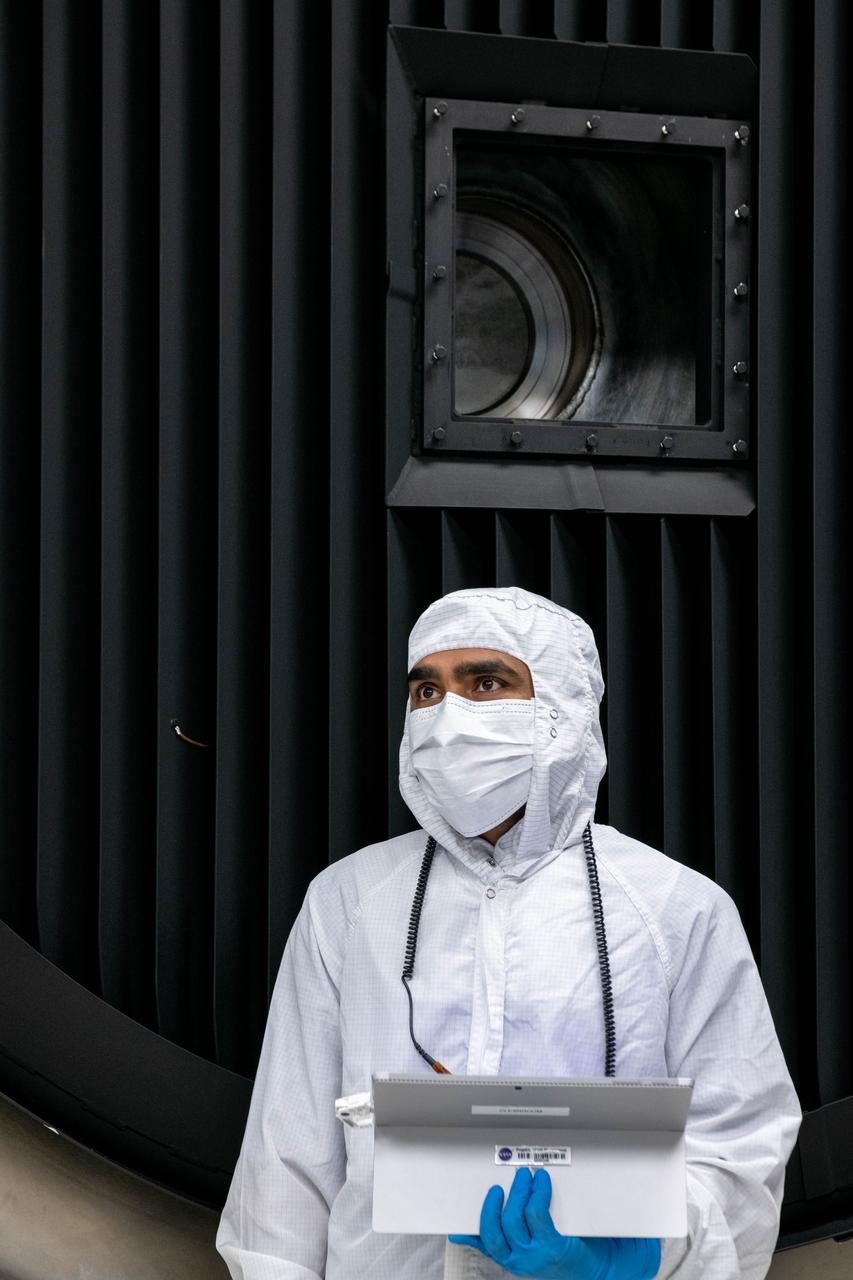

Thermal Engineer, Deepak Patel, reviews test plans and inspects the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) in the thermal vacuum chamber prior to the door for the instruments sixty day thermal test to ensure it will perform effectively once it launches into the airless environment of space. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
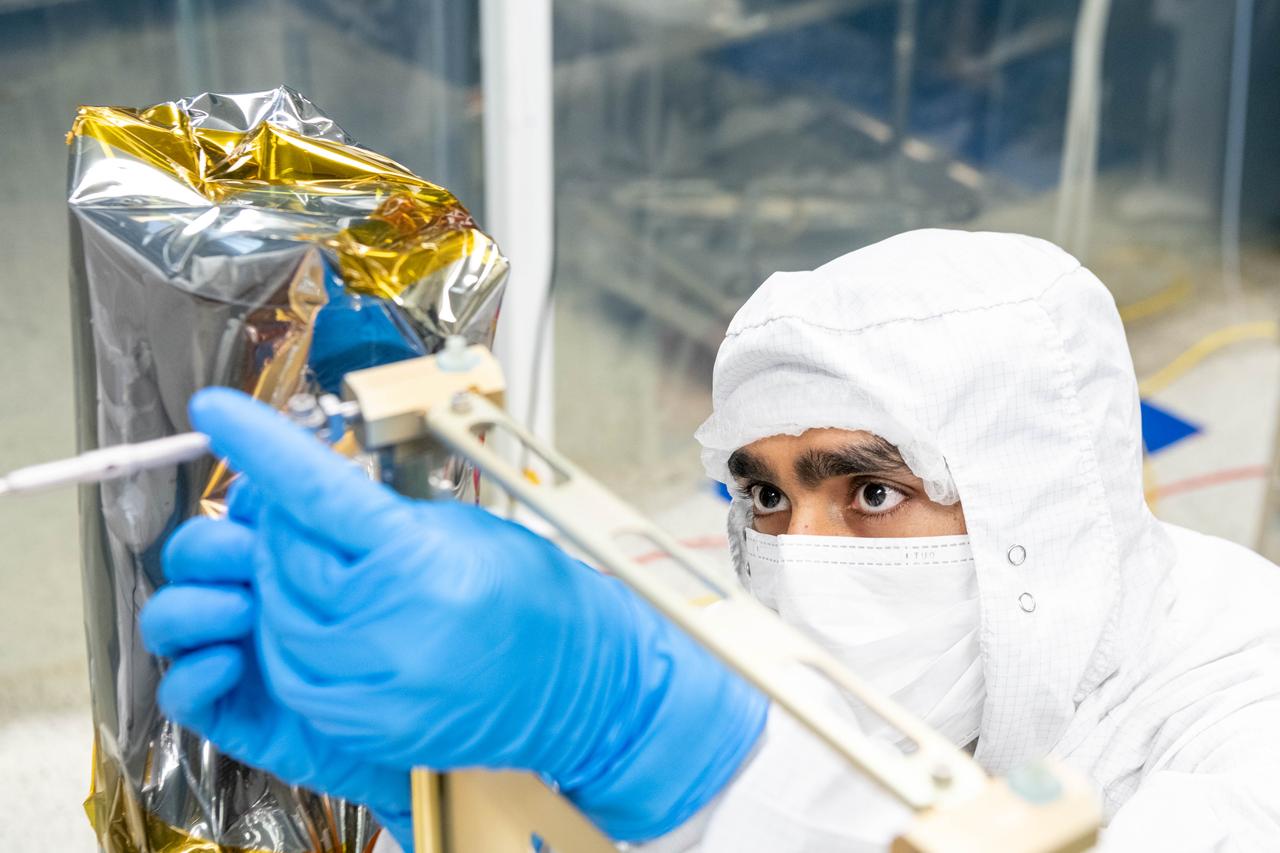

Thermal engineer, Deepak Patel, inspects the tightness on a tensioning cable on the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI). After his inspection, technicians will install thermal blanketing to insulate the flight hardware for further testing. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
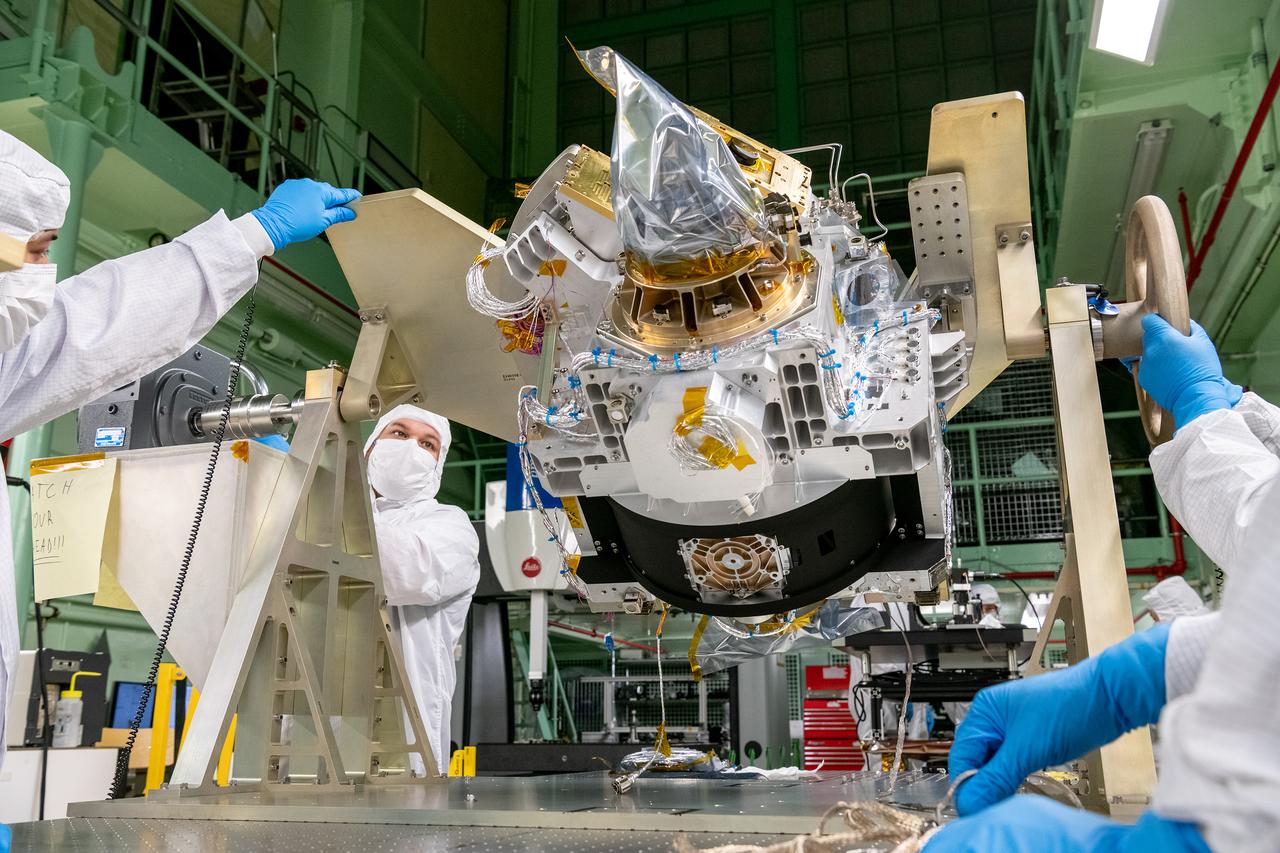

Mechanical technicians reorient the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) Optical Module on a rotation fixture to allow for additional hardware integration. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
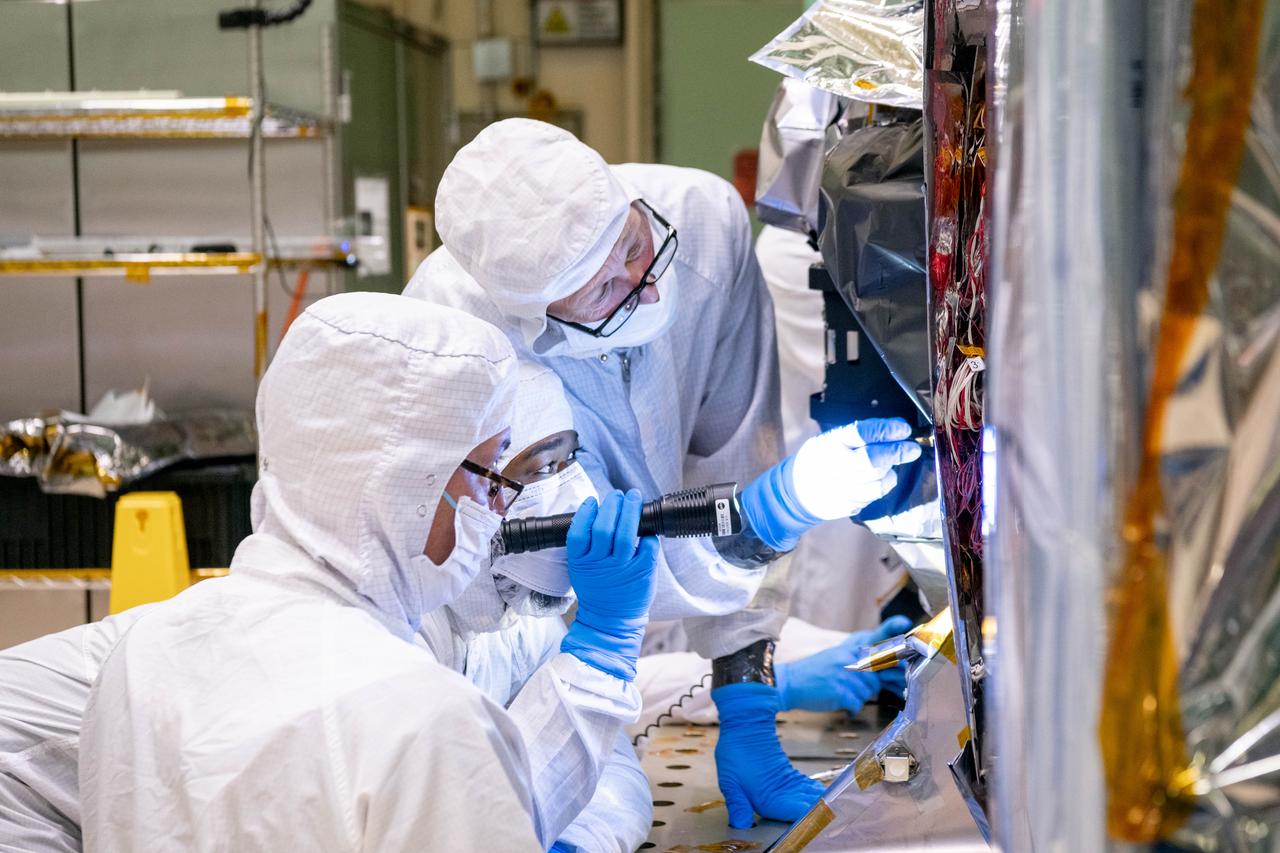

Mechanical technicians, Nicholas Kwaitkowski, Tyere Garner, and Gary Sheridon, use a flashlight to check for clearances between the Tilt Mechanism and the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI). OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
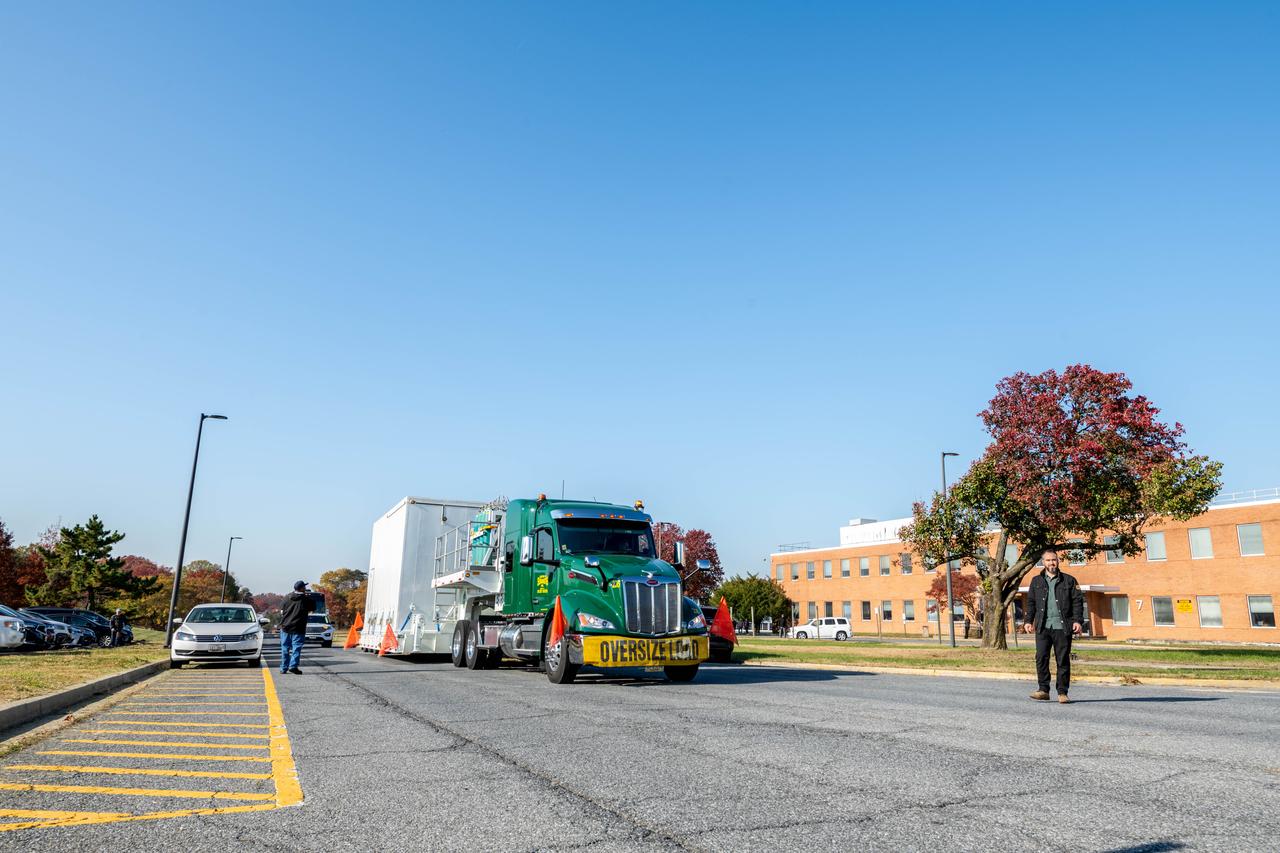

The transport carrier containing NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft departs NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on Monday, Nov. 13, 2023. PACE is traveling to Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. PACE is targeted to launch on January 30, 2024, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web.
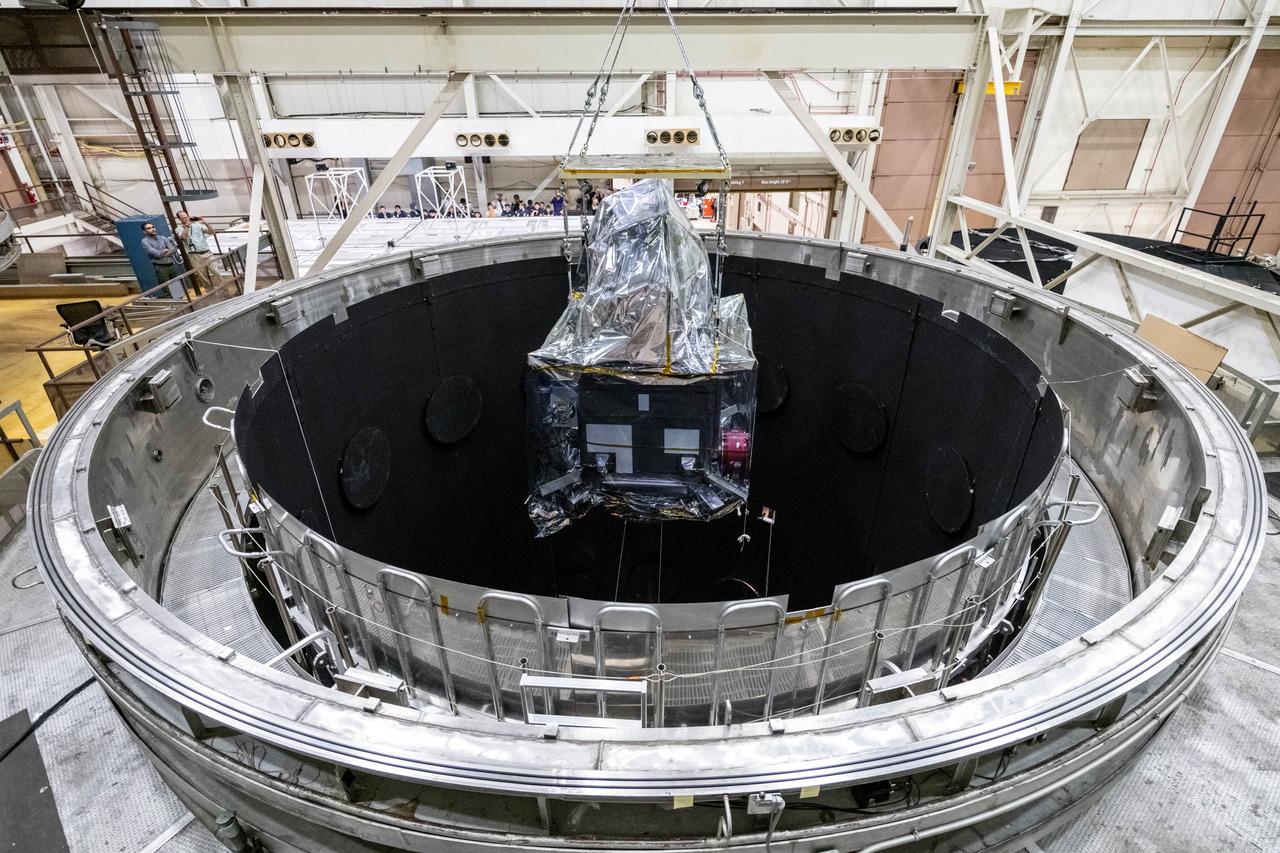
The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Observatory is lowered into the Space Environment Simulator (SES) thermal vacuuum chamber at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 1st, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.

The transport carrier containing NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft departs NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on Monday, Nov. 13, 2023. PACE is traveling to Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. PACE is targeted to launch on January 30, 2024, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web.
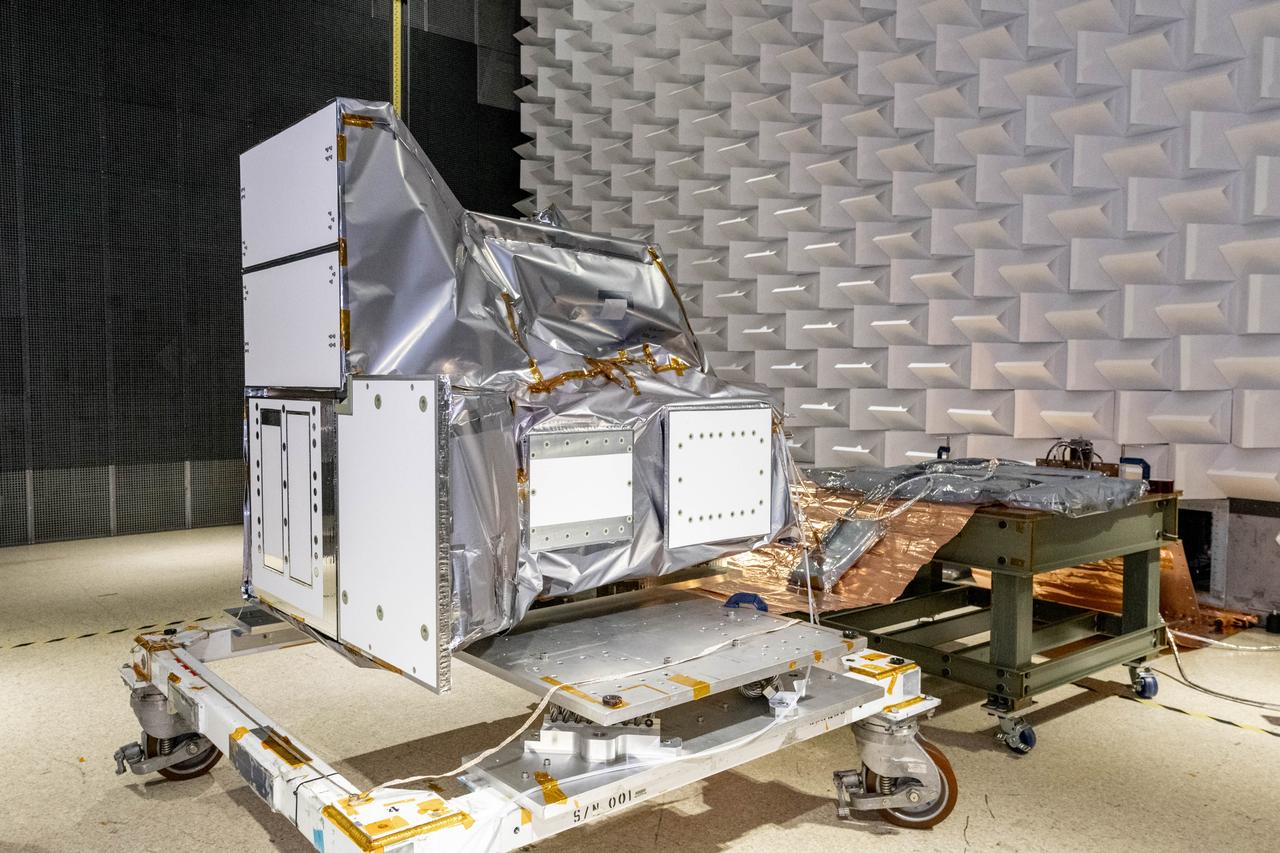

The Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) is prepared for testing in the Electro Magnetic Interference (EMI) chamber showing the radiator side of the instrument. This test will help engineers and scientists learn if OCI will be compatible with the electromagnetic environment on the spacecraft. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
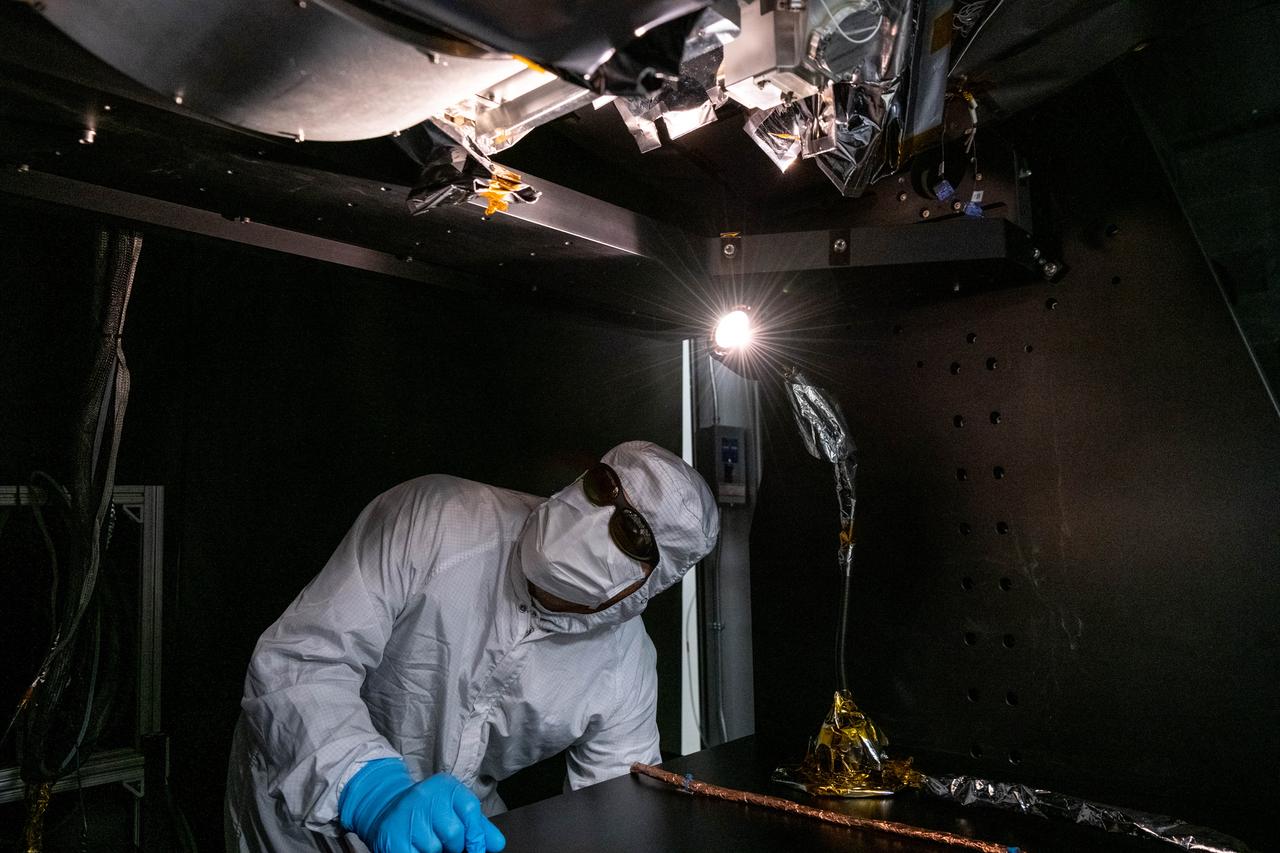

Manufacturing engineer, Roman Nilov, inspects flight hardware after technicians install the Short Wave Infrared (SWIR) Pulse Calibration Assembly (SPCA) fold mirror assembly to the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI). OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
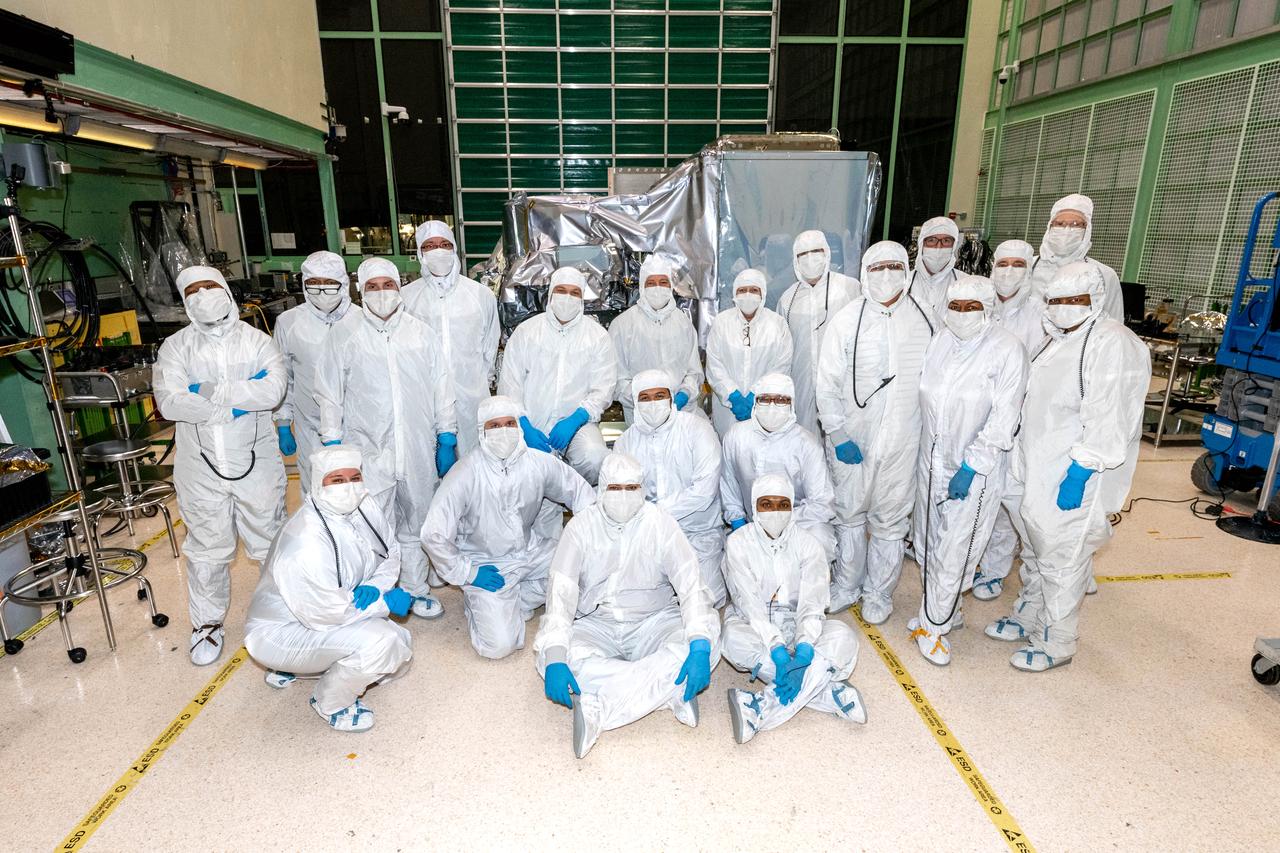

Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) team members pose with the flight hardware after successful instrument integration to the Tilt mechanism. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
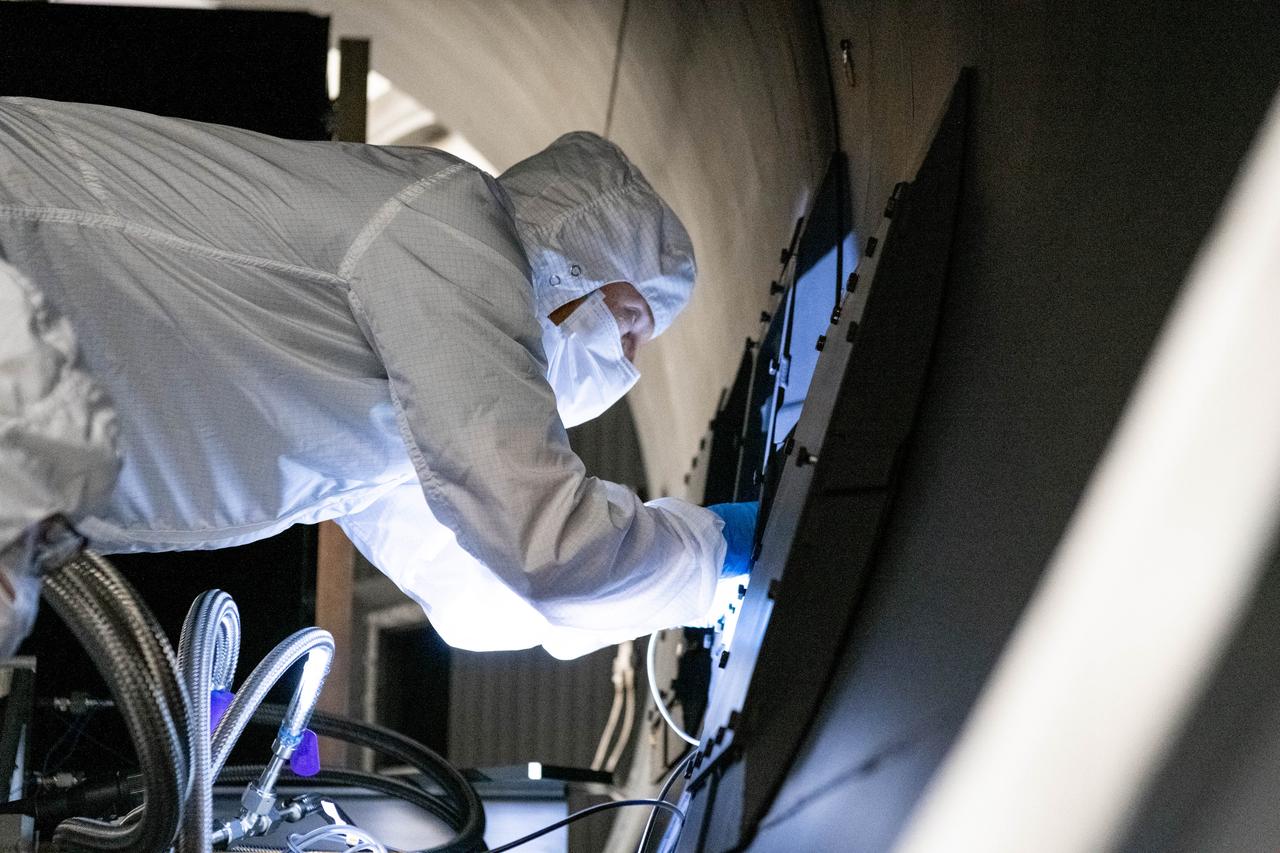

Optical engineer, Brendan McAndrew, installs radiometers inside the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) thermal vacuum chamber in preparation for window calibration testing. The testing will help scientists and engineers know if the optical components of OCI are aligned correctly before it gets integrated to the PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
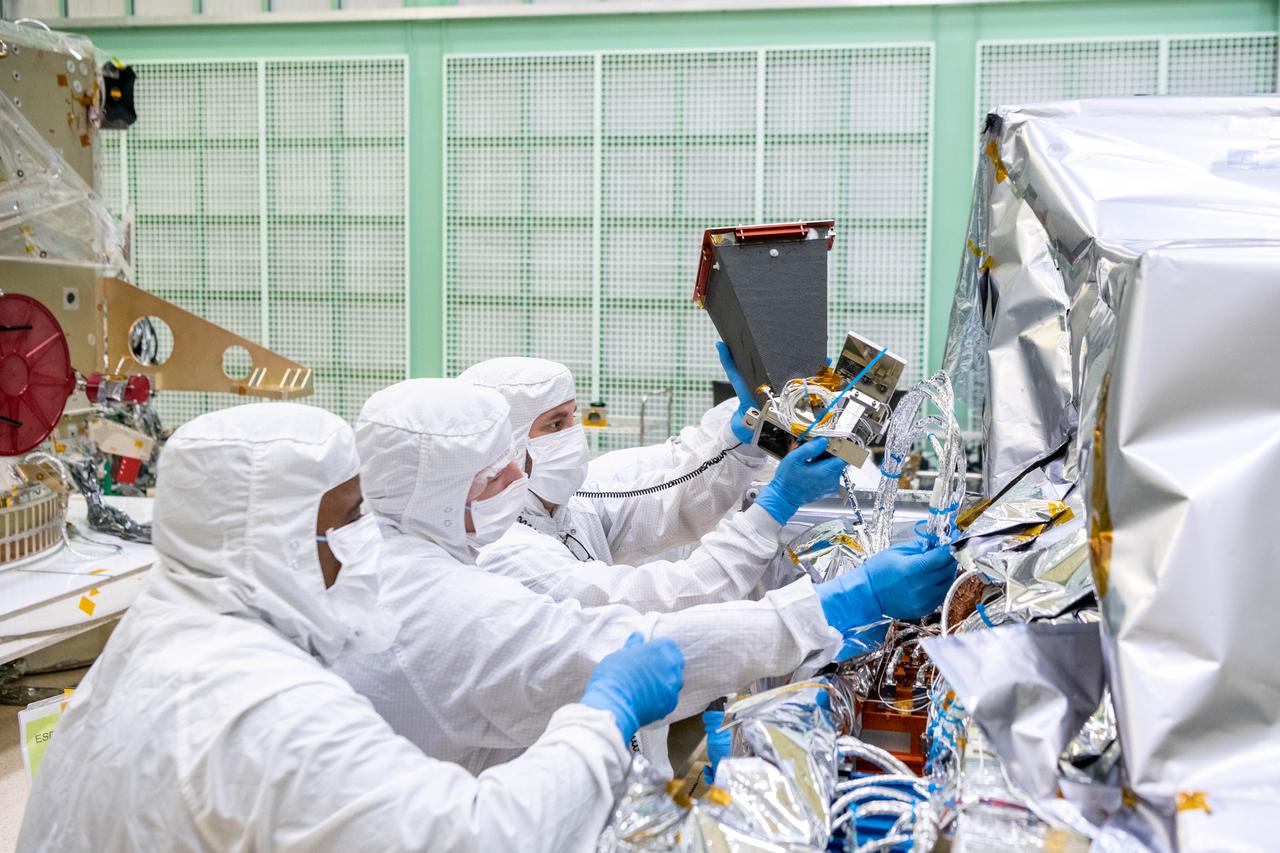

Engineer, Marton Sharpe, and mechanical technicians, Alexander Schaeffer and Eric Norris, install the Star Tracker to the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) prior to integration to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft. The Star Tracker is a specially designed sextant to measure the angle between different celestial bodies in relation to each other or the horizon. This is important not just for navigation but for providing better images and science data. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
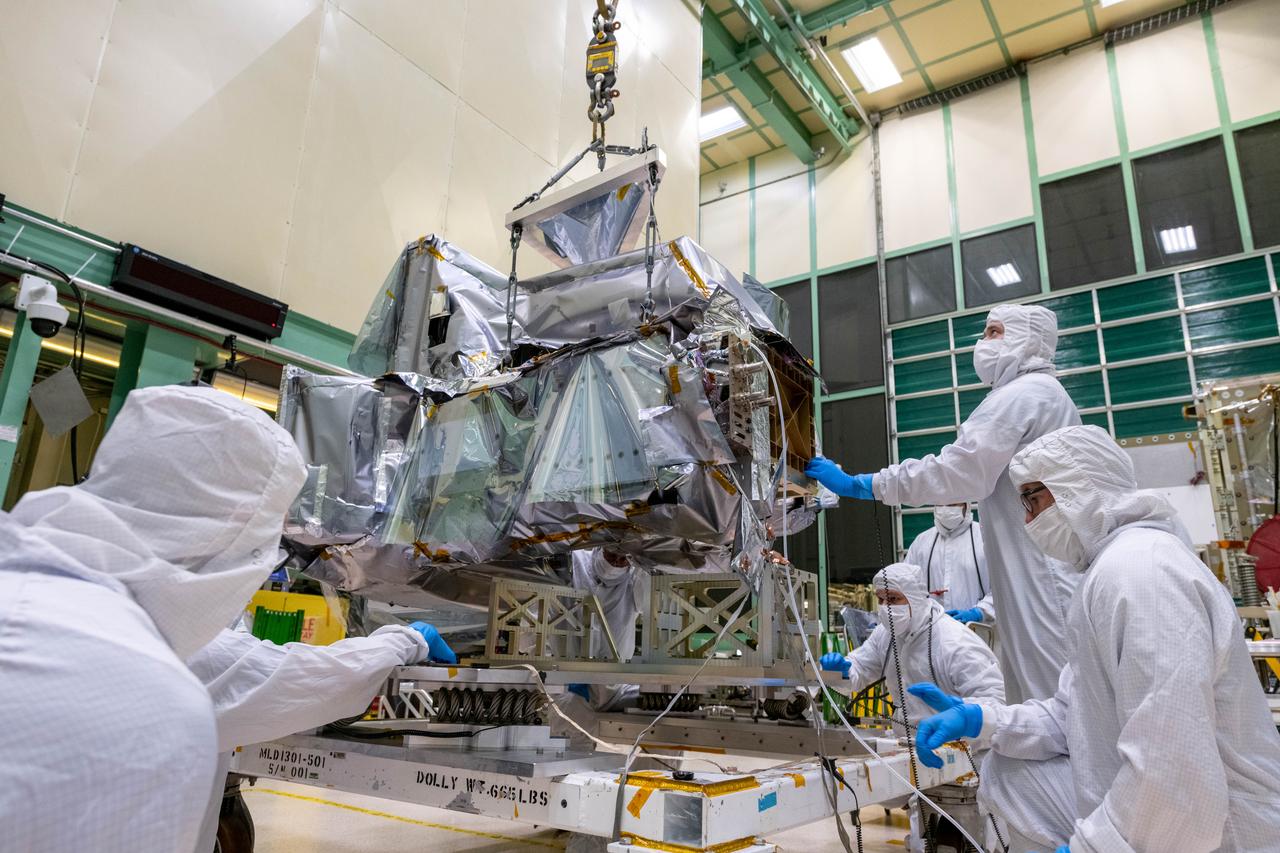

Mechanical technicians crane lift the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) off of the transportation dolly. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
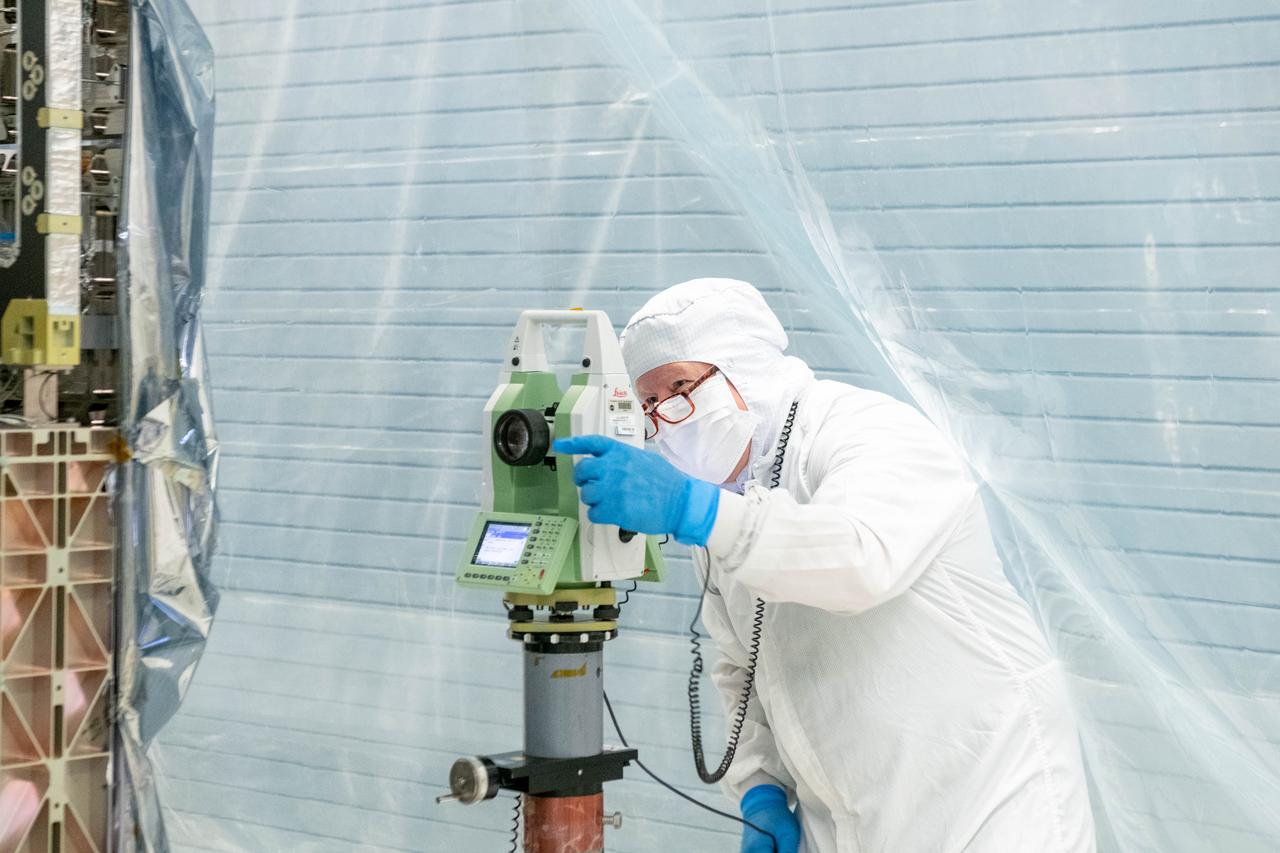

Optical technician, Timothy Madison, uses a theodolite to perform optical measurements on the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI). As he collects data and measures angles on OCI, he is able to determine if the newly integrated flight hardware is in the correct position. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, successfully lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST Thursday, Feb. 8. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
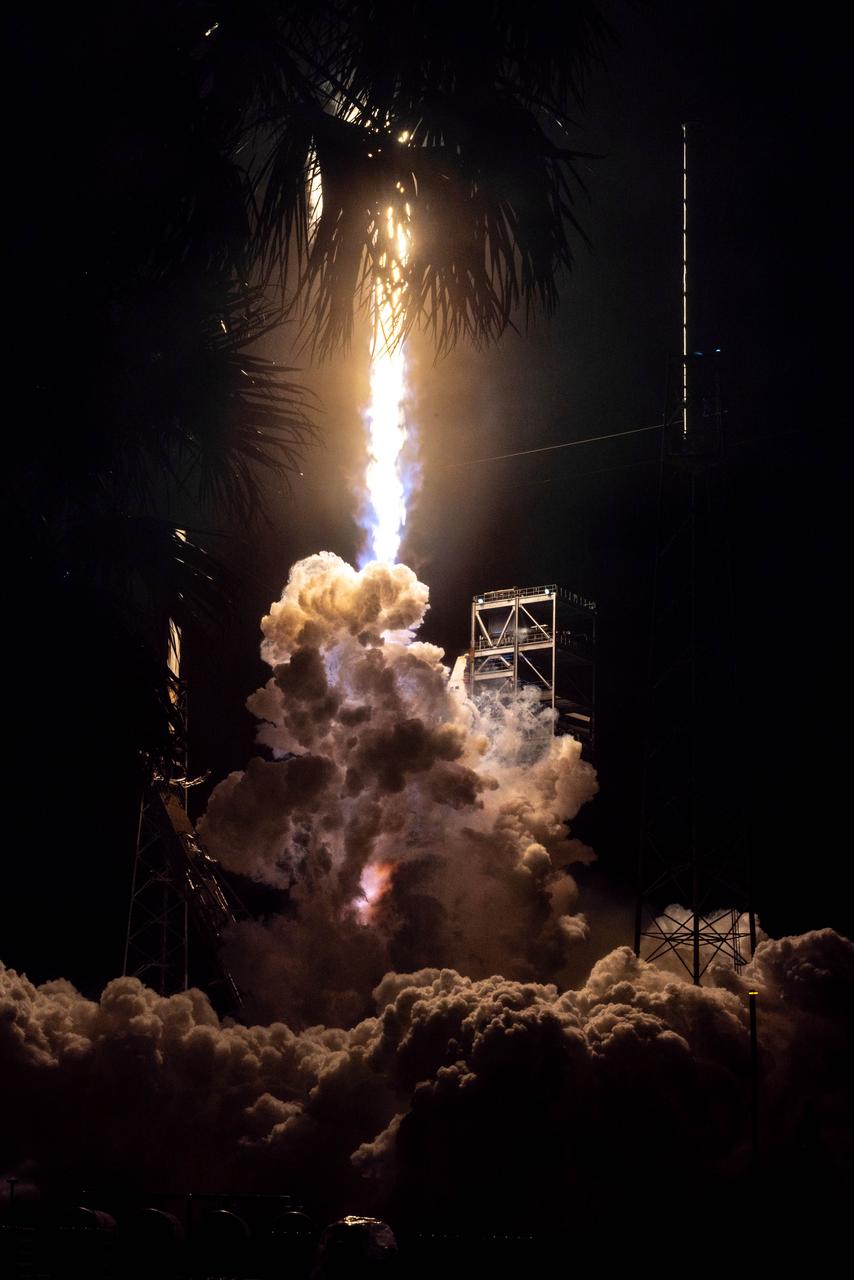

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, successfully lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST Thursday, Feb. 8. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
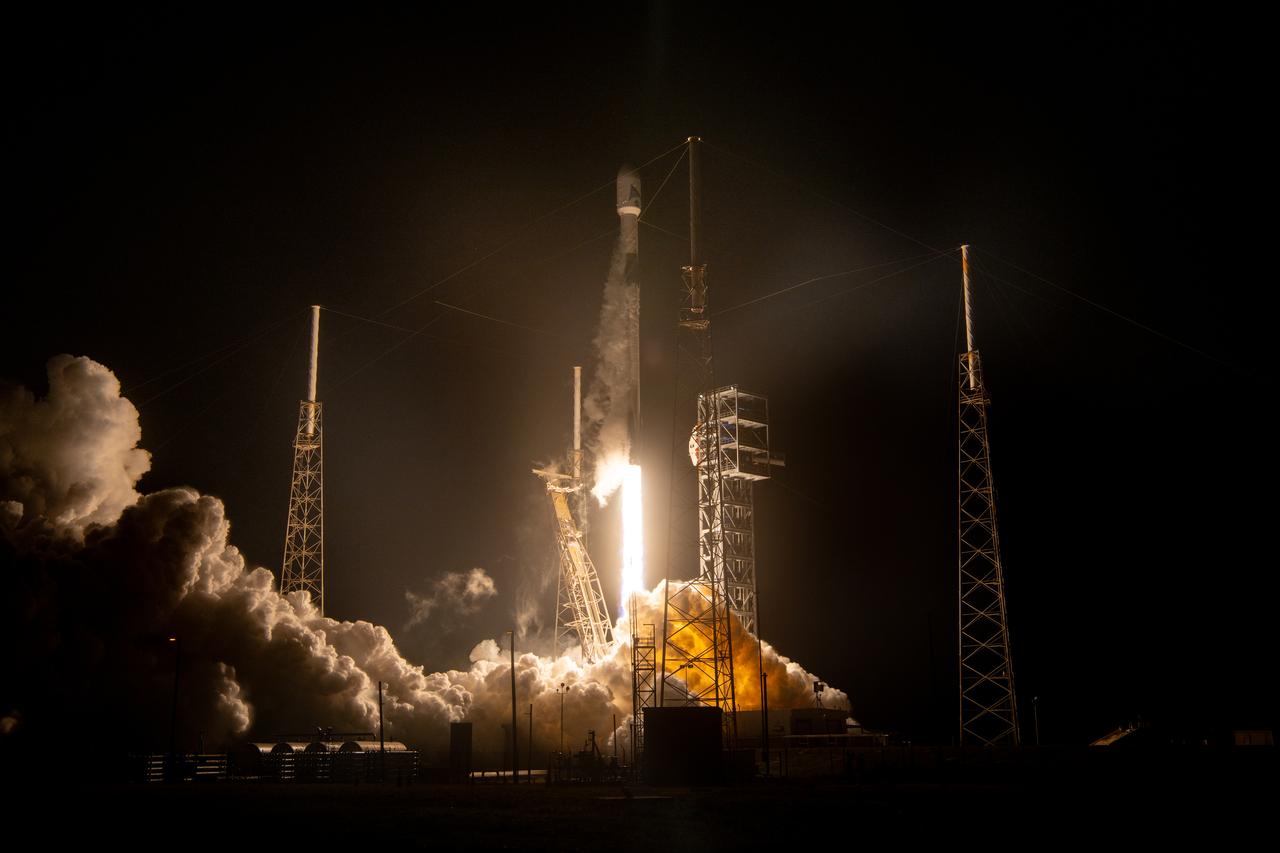

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, successfully lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST Thursday, Feb. 8. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
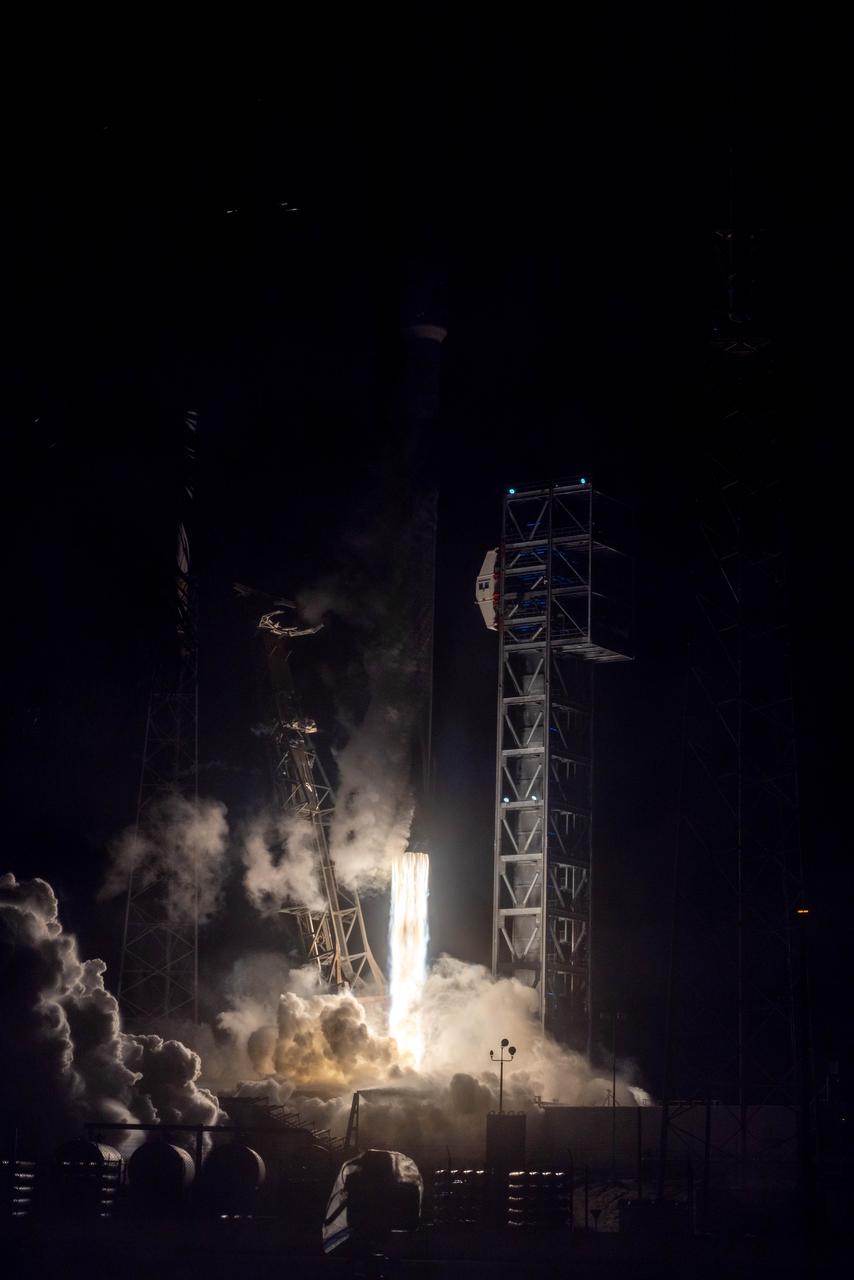

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, successfully lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST Thursday, Feb. 8. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
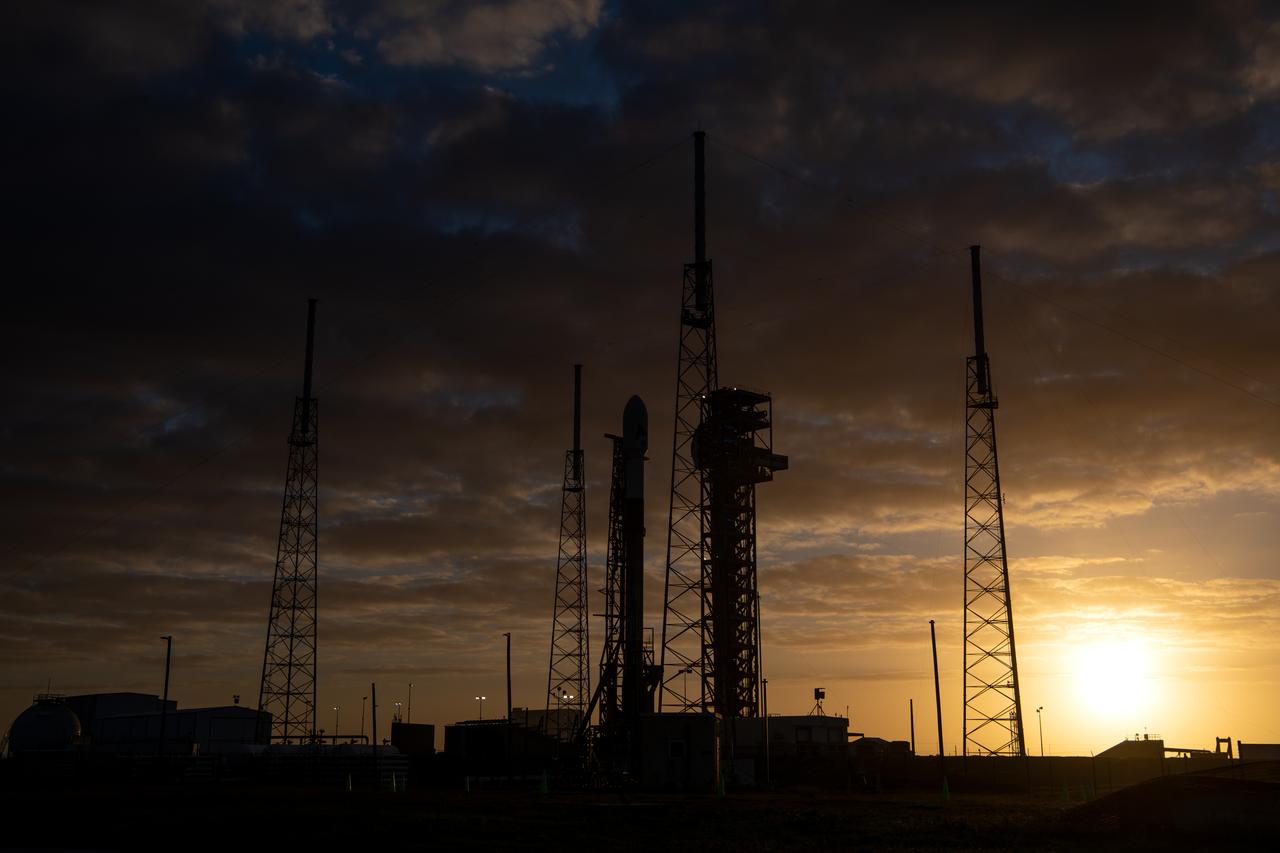

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft stands vertical at Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Feb. 5, 2024. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols. Liftoff of the PACE mission is set for no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Wednesday, Feb. 7, 2024.