Portrait of Dr. John C. Houbolt

Portrait of Dr. John C. Houbolt

Portrait of Dr. John C. Houbolt
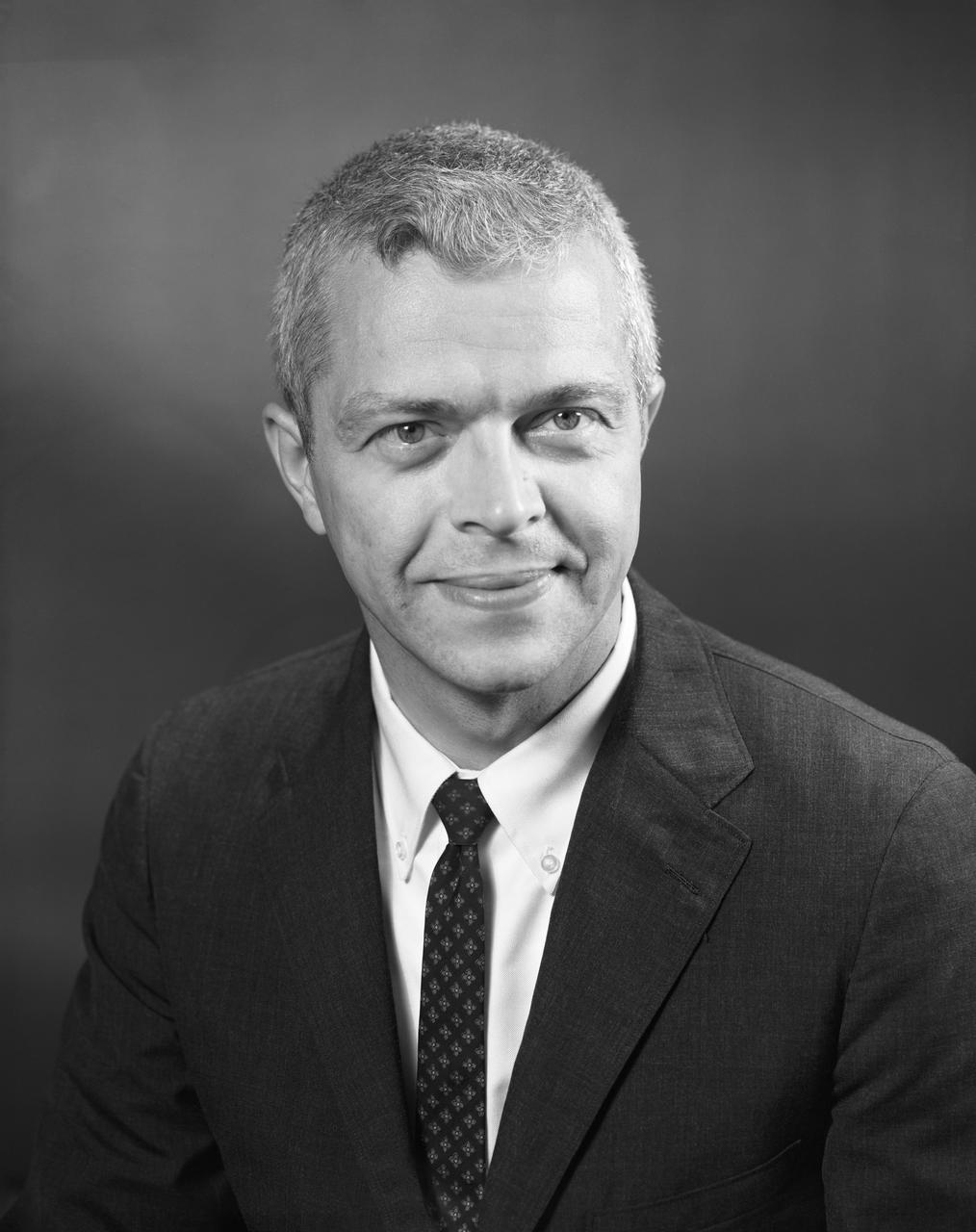

Portrait of Dr. John C. Houbolt
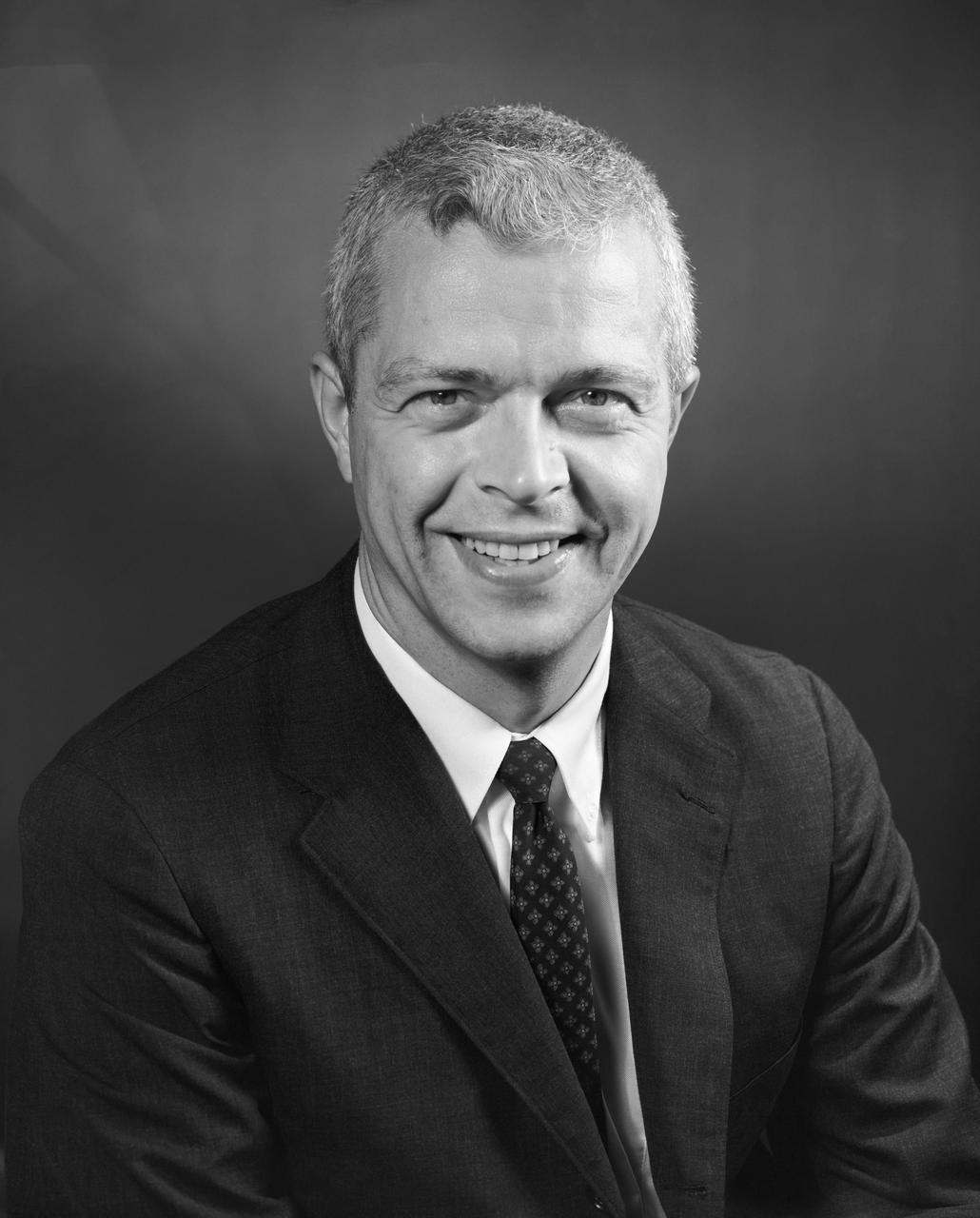

Portrait of Dr. John C. Houbolt
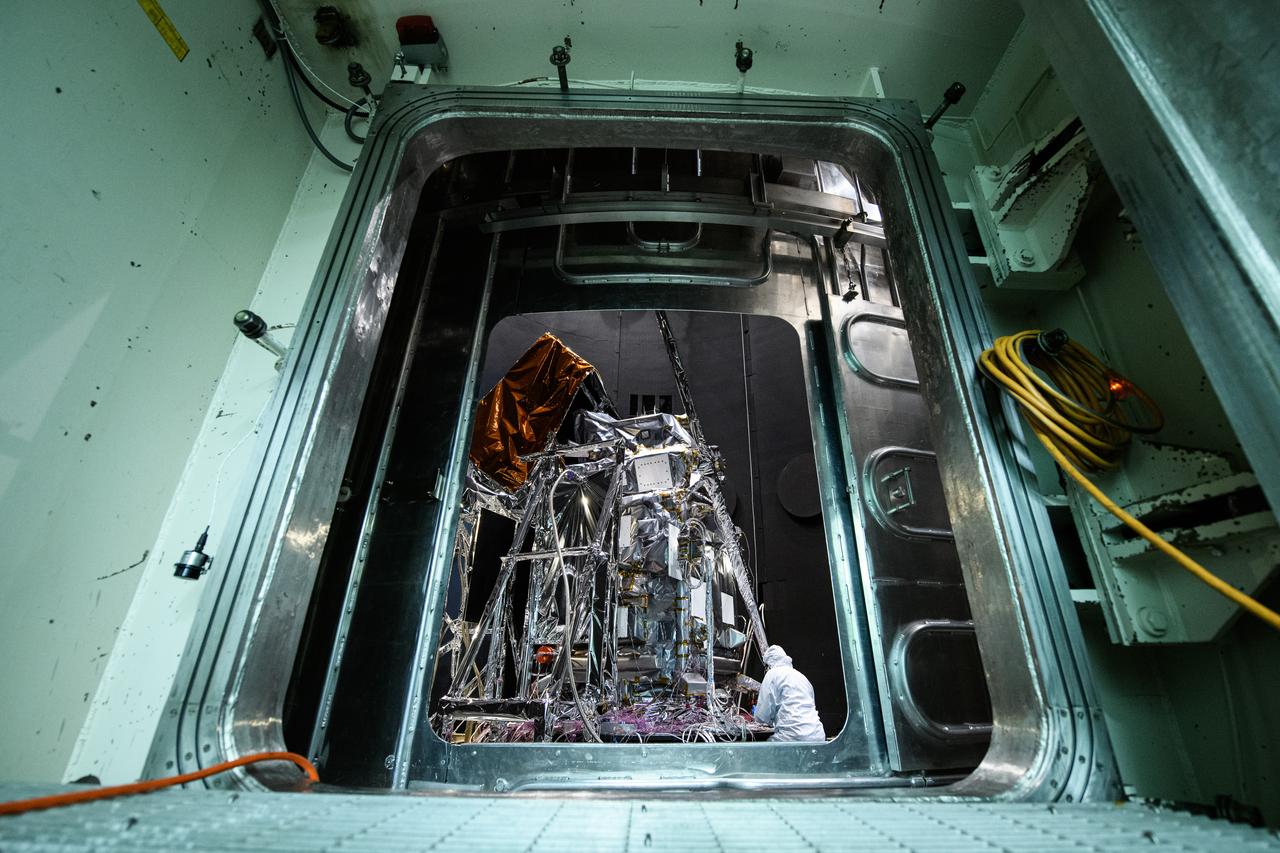
The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Observatory inside the Space Environment Simulator (SES) thermal vacuuum chamber before thermal environmental testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 16th, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
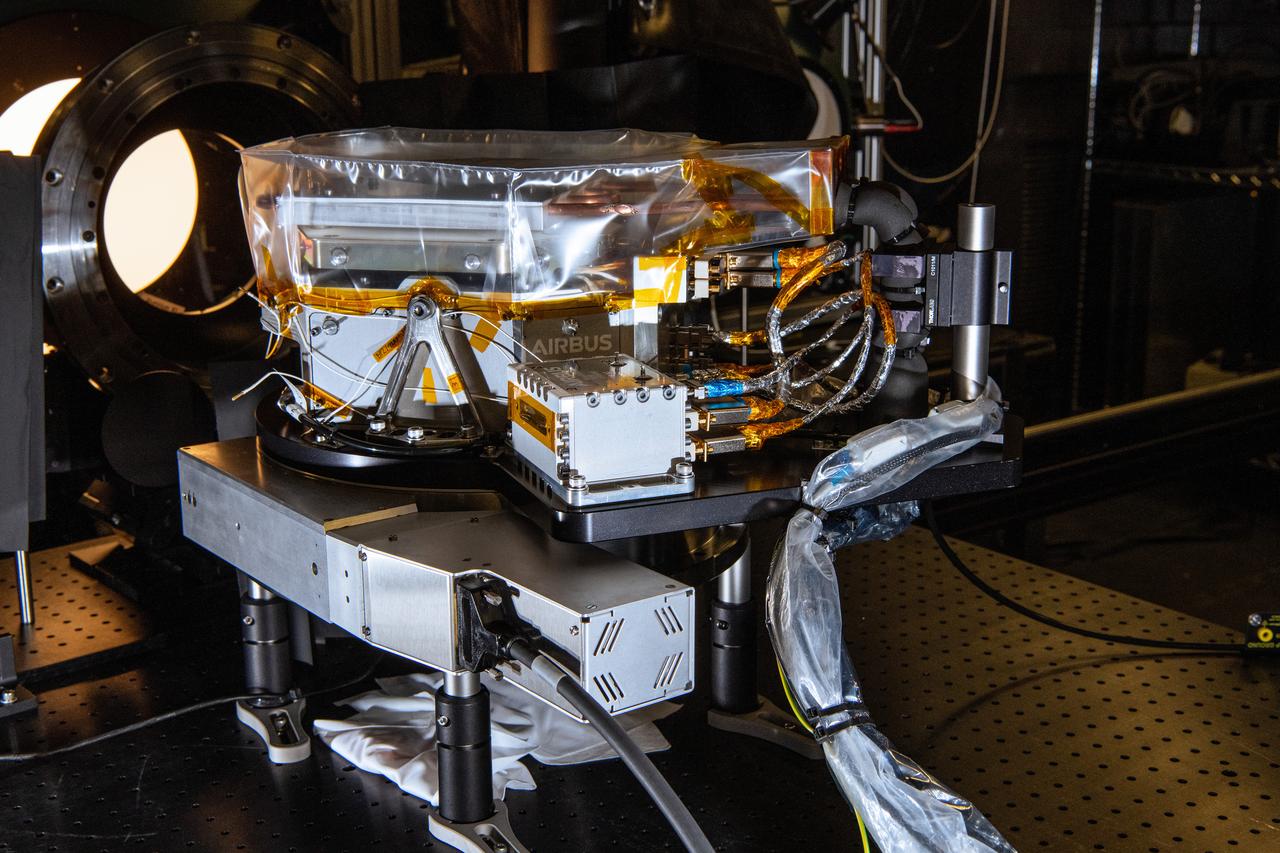
The SPEXone instrument undergoes Polarimetric Calibration at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt,Maryland on April 8th, 2021. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
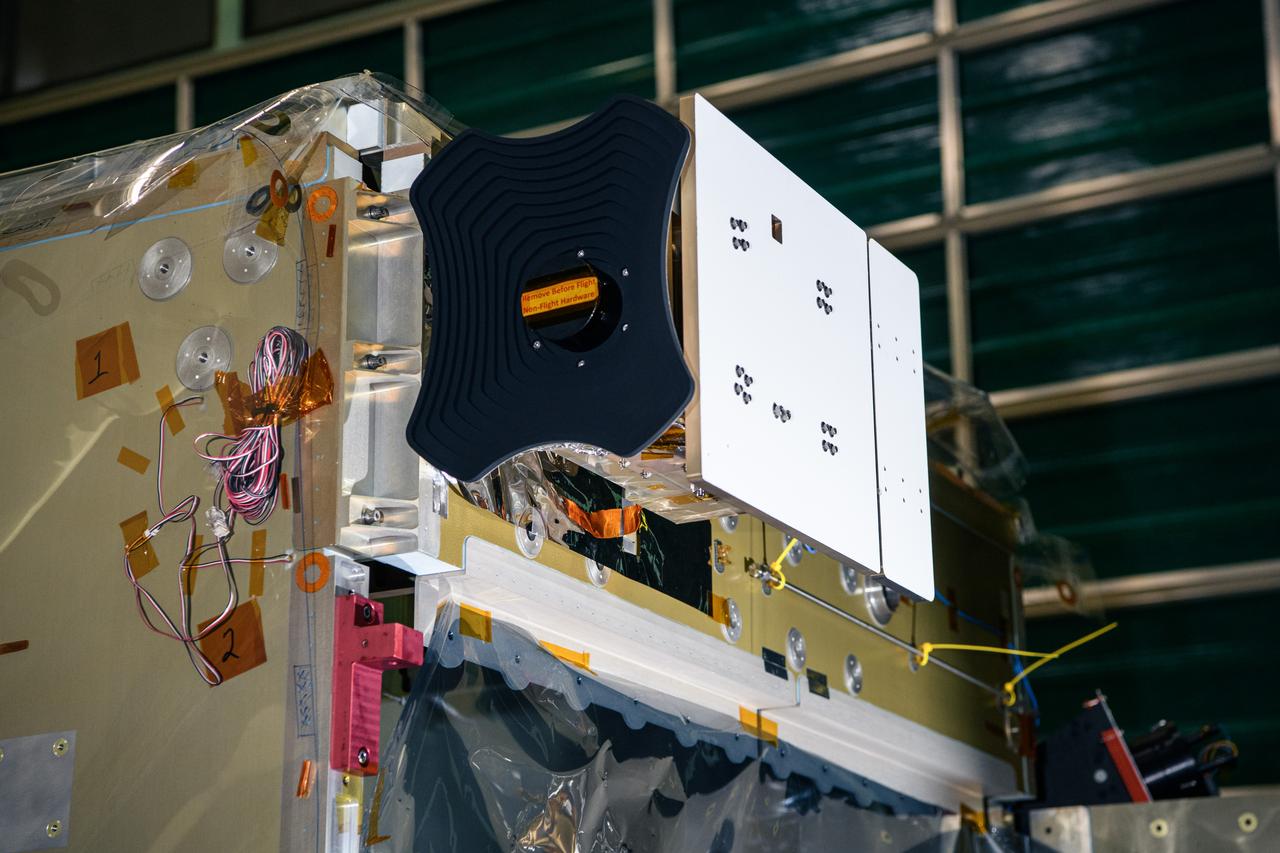

The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument after integration to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft bus at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 25th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's PACE observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
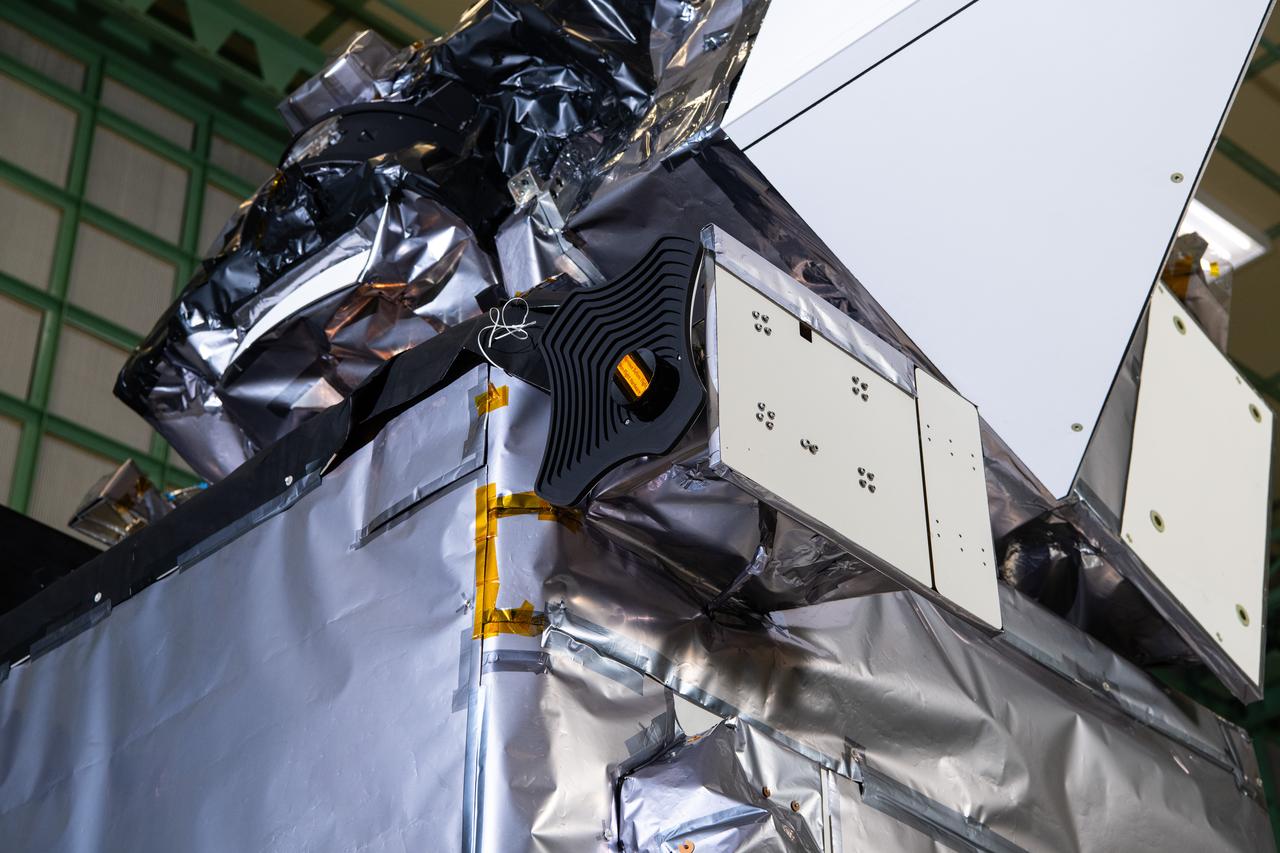

The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument on The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 31st, 2023. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's PACE observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
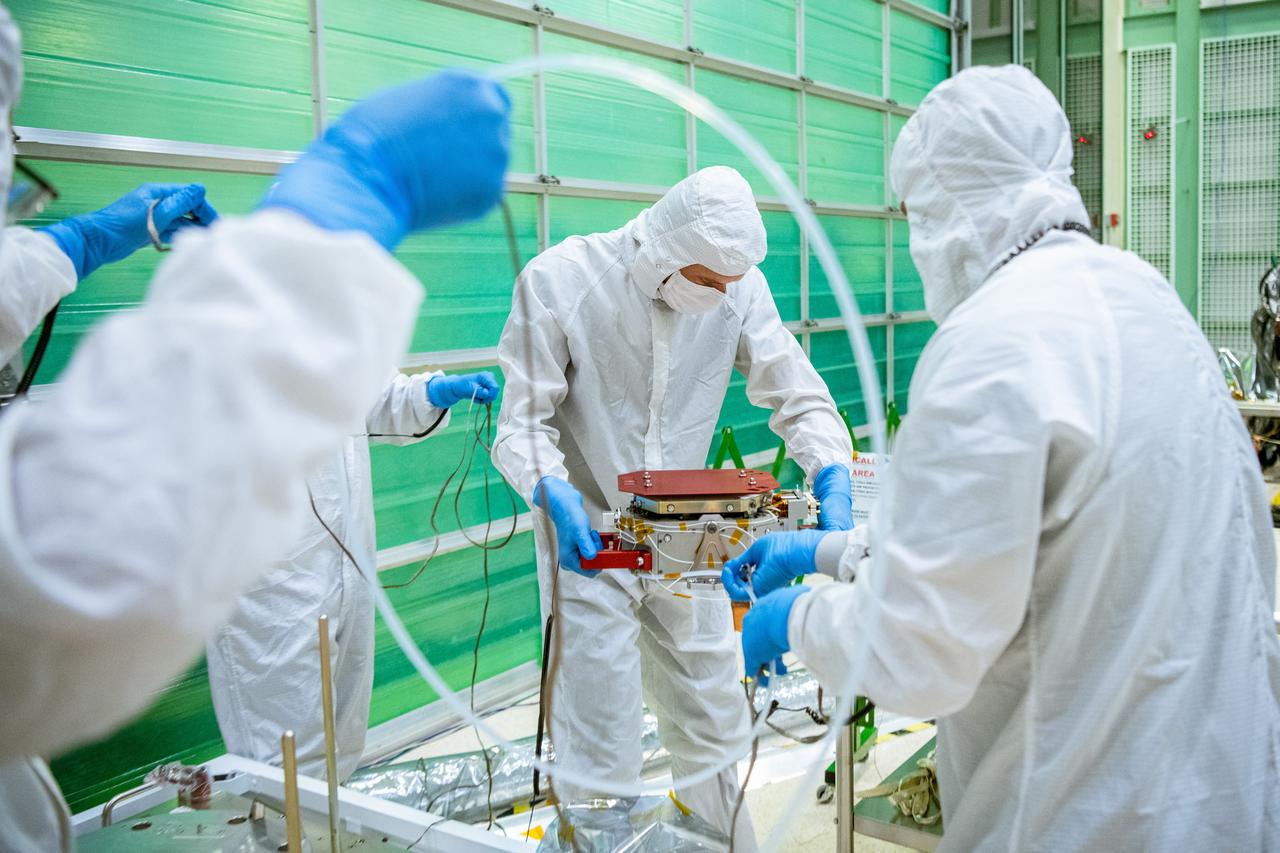

Senior Mechanical Design Engineer Alexander Eigenraam from SRON, the Netherlands Institute for Space Research, moves the SPEXone instrument before it is integrated onto the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Spacecraft at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 13th, 2022. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
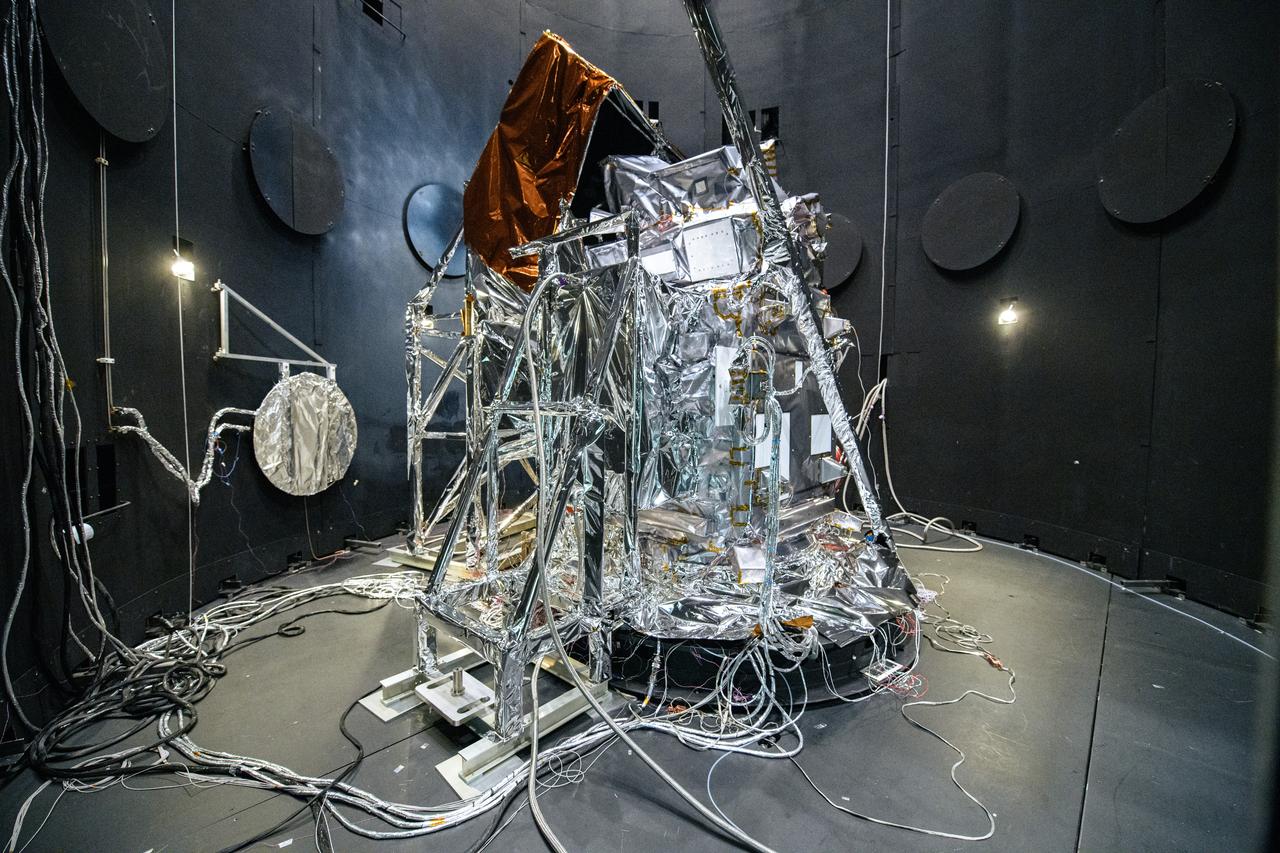

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Observatory inside the Space Environment Simulator (SES) thermal vacuuum chamber before thermal environmental testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 17th, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
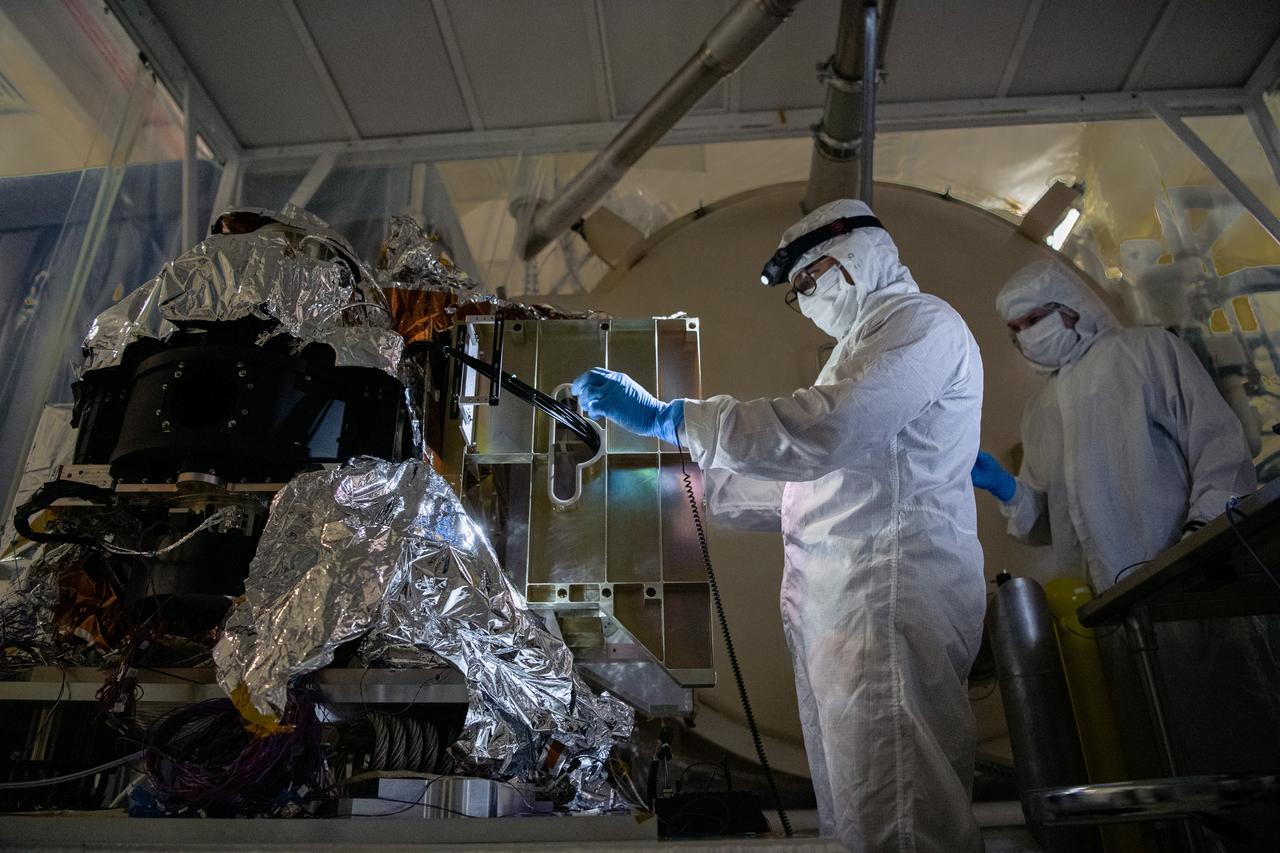

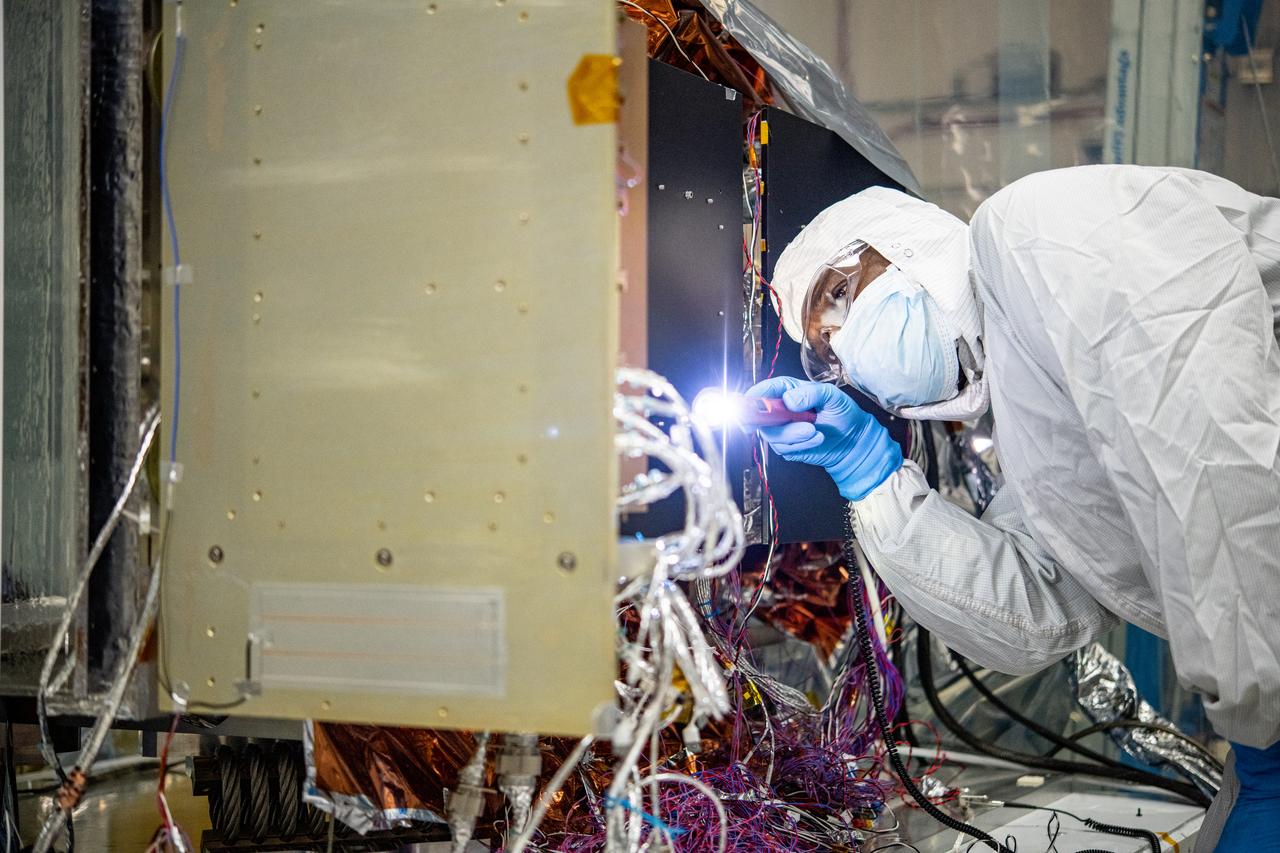
Alejandro Rodriguez Perez and Joe Thomes, members of the fiber optic & photonic team, configure the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) Engineering Test Unit (ETU) Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) Detector Asembly and Multi-lens Array (MLA) fibers for thermal testing. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
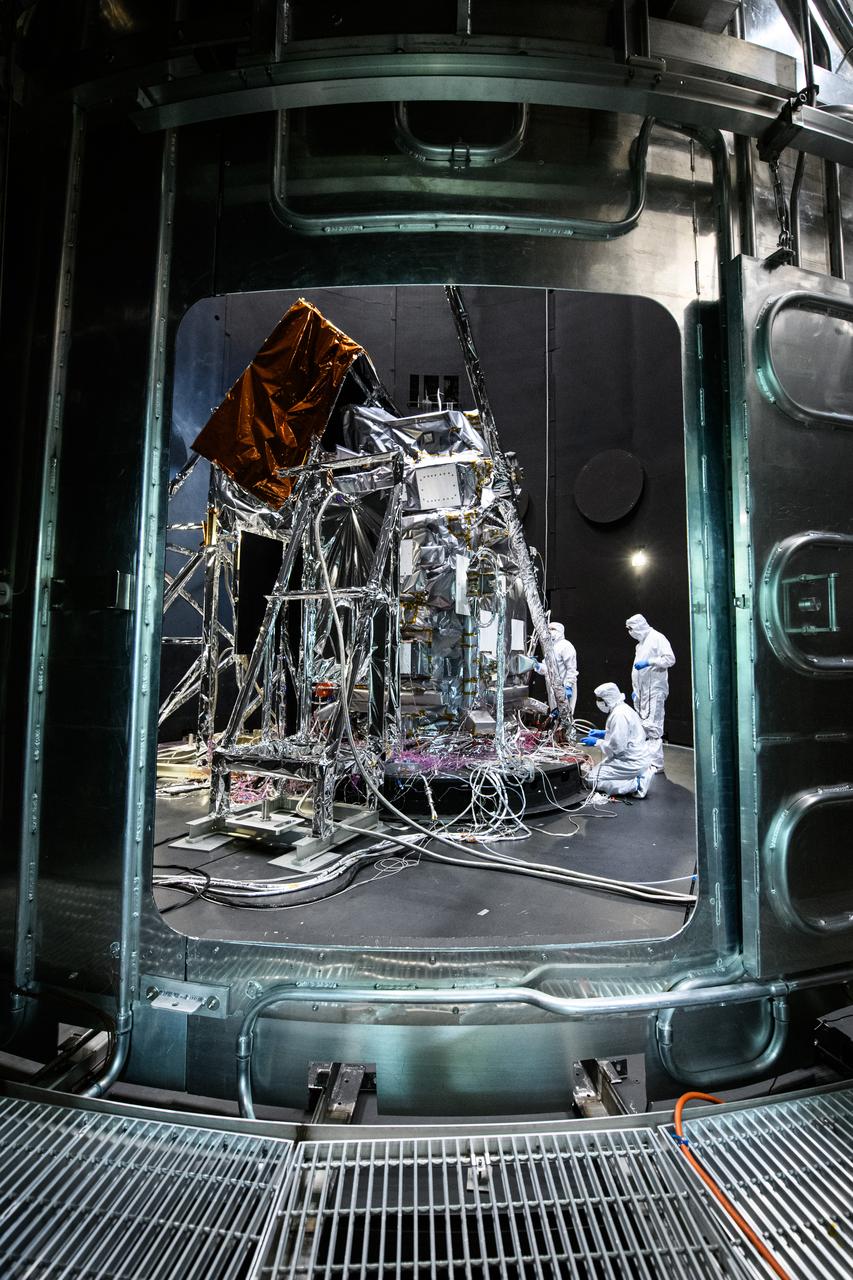

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Observatory inside the Space Environment Simulator (SES) thermal vacuuum chamber before thermal environmental testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 16th, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
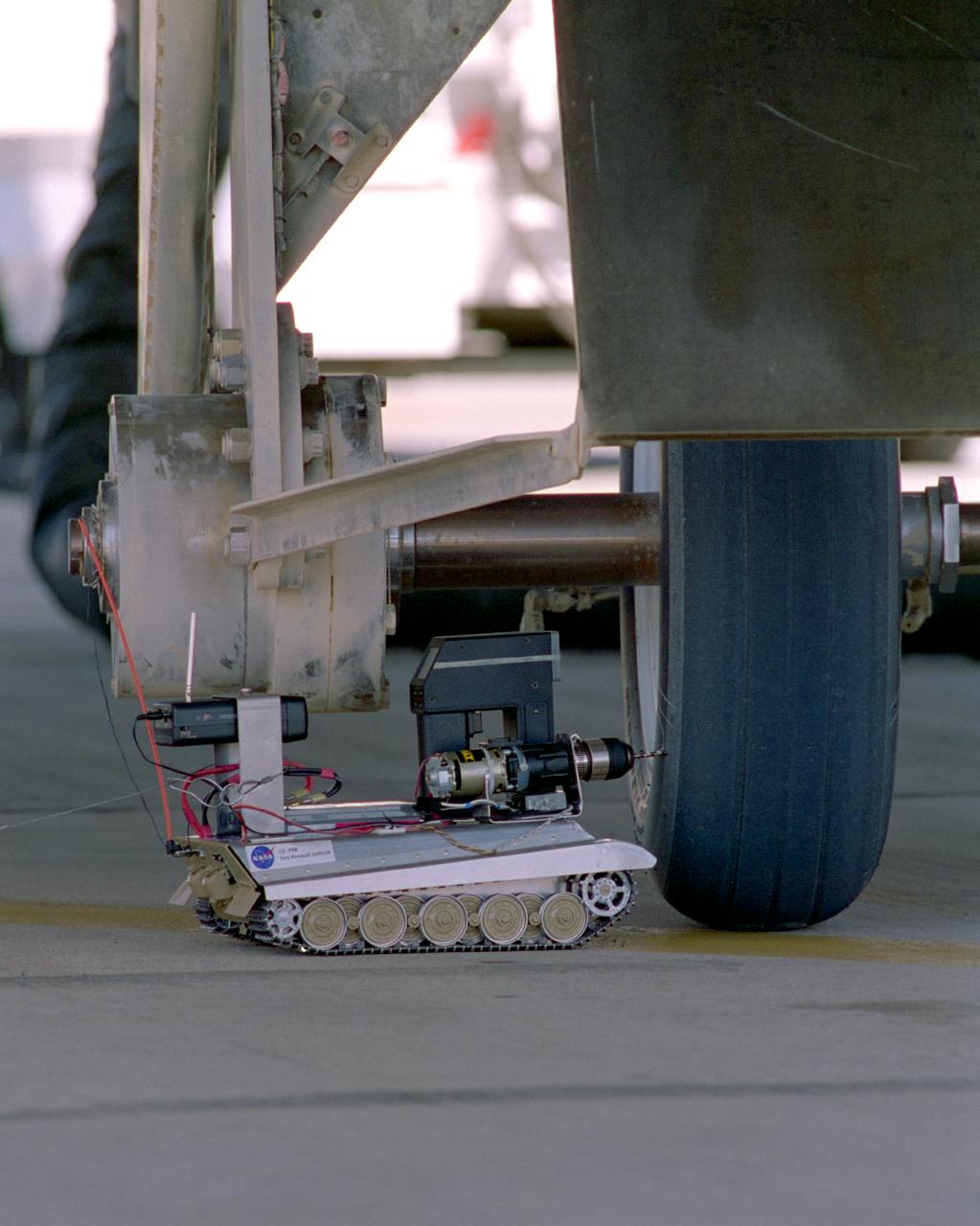
Created from a 1/16th model of a German World War II tank, the TAV (Tire Assault Vehicle) was an important safety feature for the Convair 990 Landing System Research Aircraft, which tested space shuttle tires. It was imperative to know the extreme conditions the shuttle tires could tolerate at landing without putting the shuttle and its crew at risk. In addition, the CV990 was able to land repeatedly to test the tires. The TAV was built from a kit and modified into a radio controlled, video-equipped machine to drill holes in aircraft test tires that were in imminent danger of exploding because of one or more conditions: high air pressure, high temperatures, and cord wear. An exploding test tire releases energy equivalent to two and one-half sticks of dynamite and can cause severe injuries to anyone within 50 ft. of the explosion, as well as ear injury - possibly permanent hearing loss - to anyone within 100 ft. The degree of danger is also determined by the temperature pressure and cord wear of a test tire. The TAV was developed by David Carrott, a PRC employee under contract to NASA.
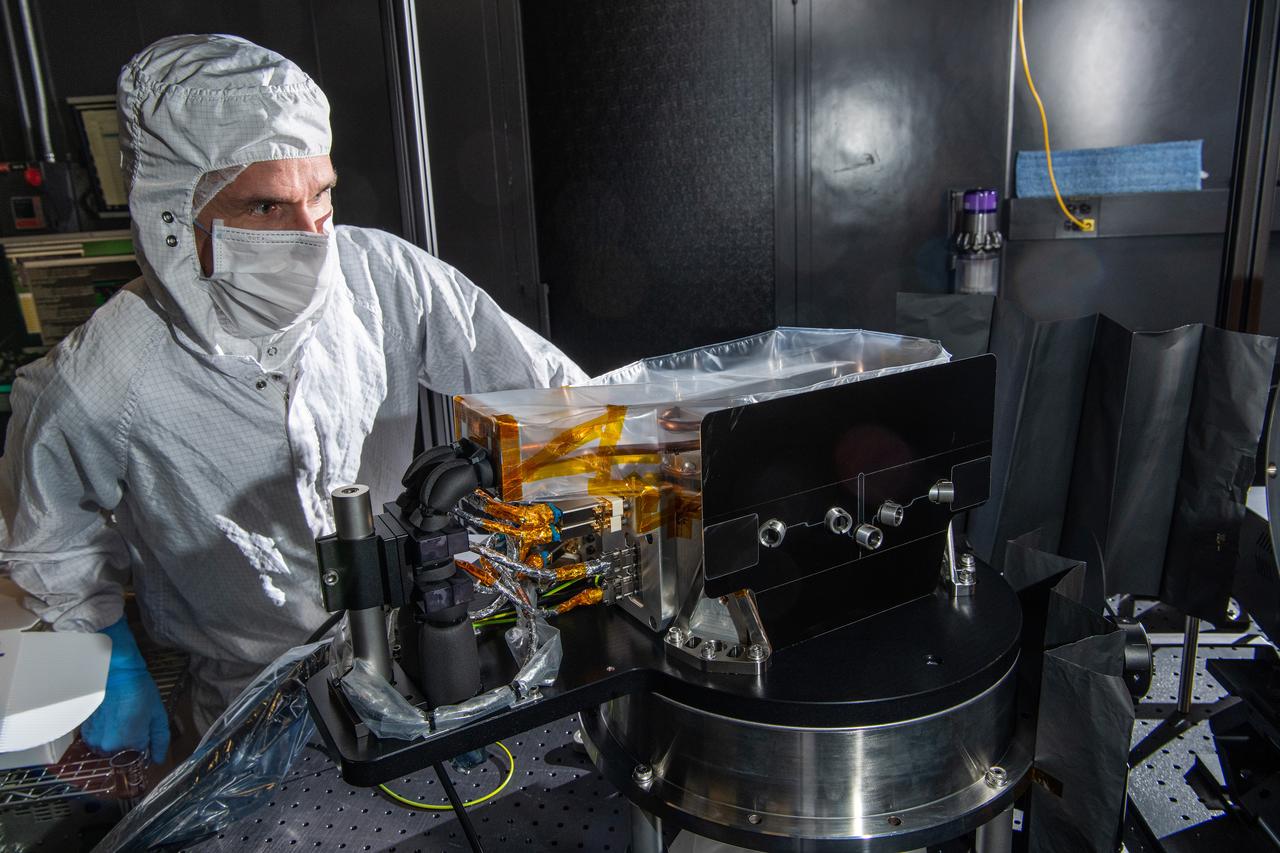

Jochen Campo from SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research with the The SPEXone Polarimetric Calibration at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt,Maryland on April 8th, 2021. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
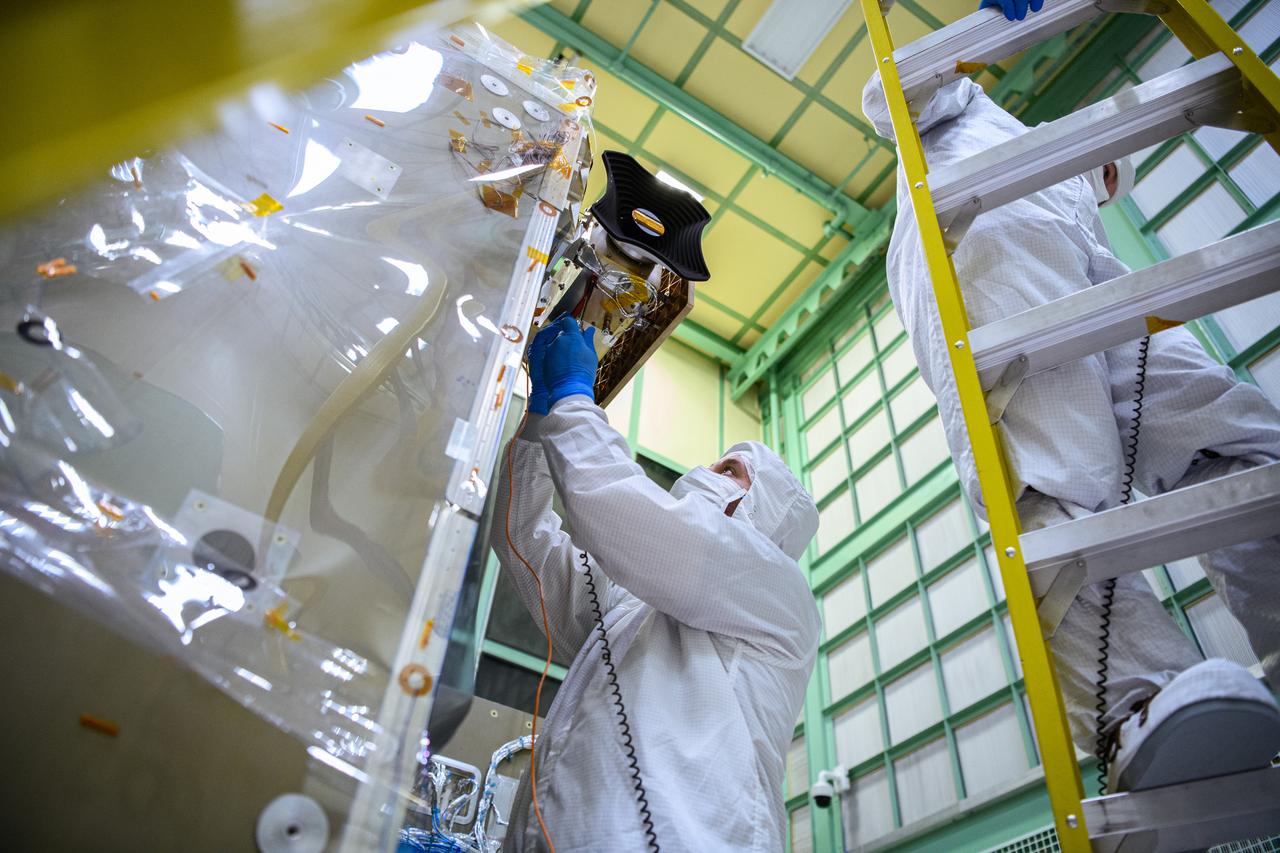

Technicians integrate the Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft bus at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 25th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's PACE observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
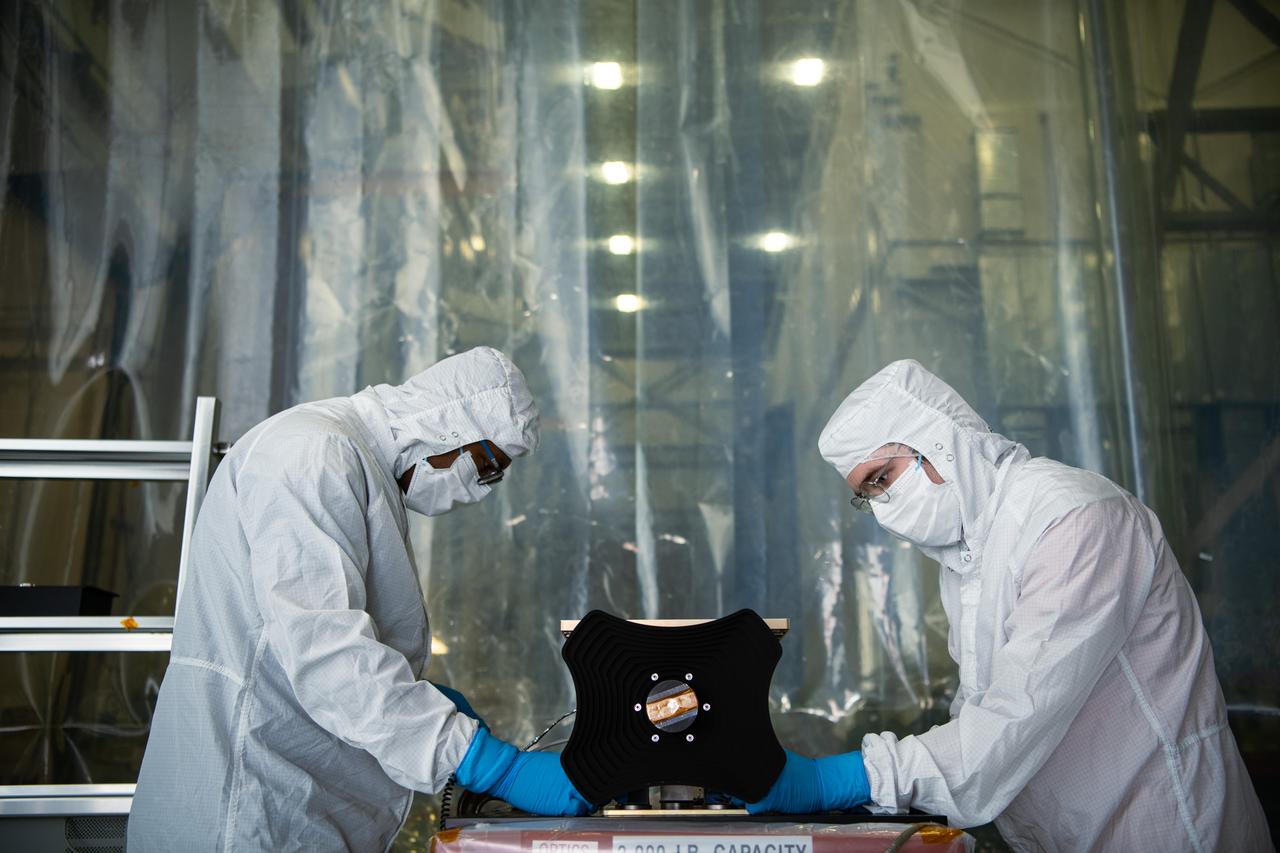

UMBC Earth and Space Institute engineers Yomiyu Fekadu (left) and Danny Nelson (right) prepare the Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument for thermal vacuum testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on August 8th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute.
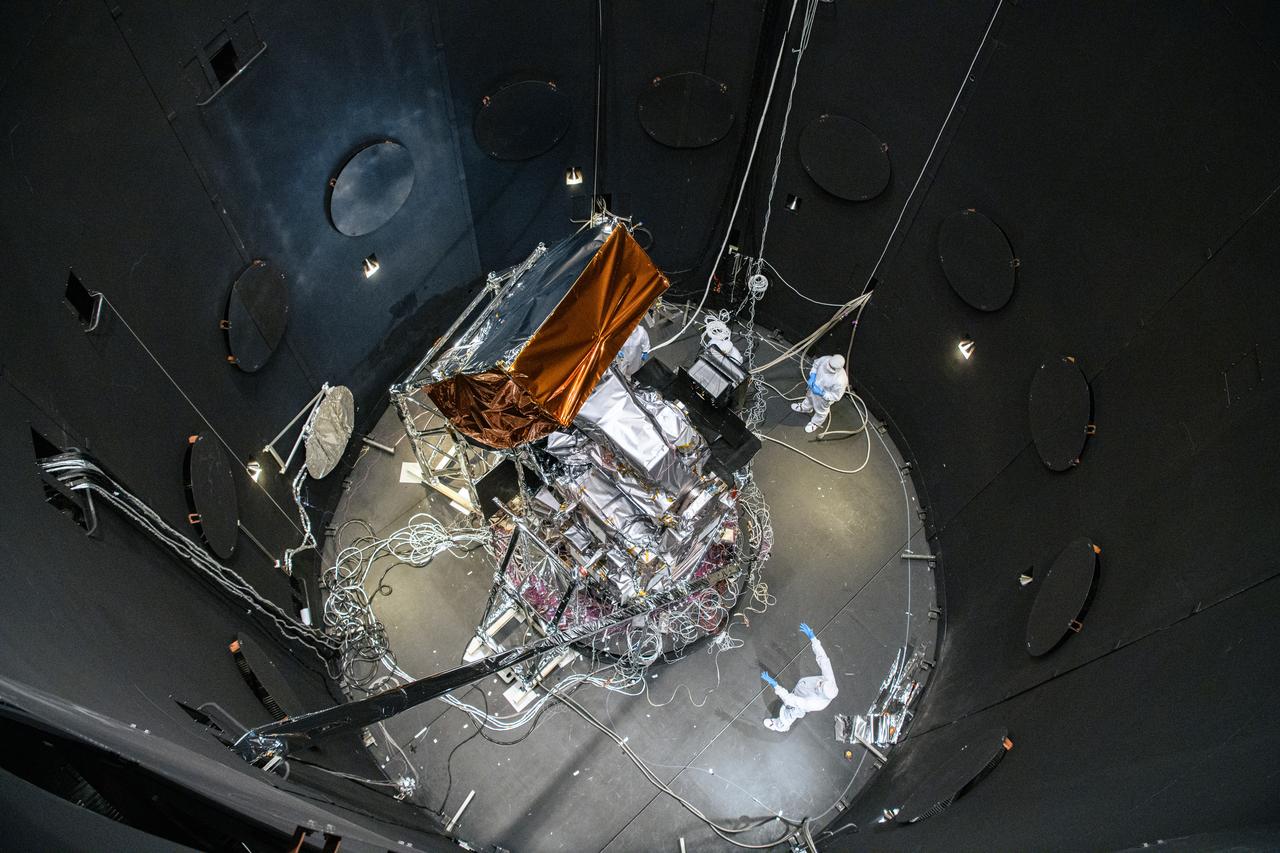

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Observatory inside the Space Environment Simulator (SES) thermal vacuuum chamber before thermal environmental testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 16th, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
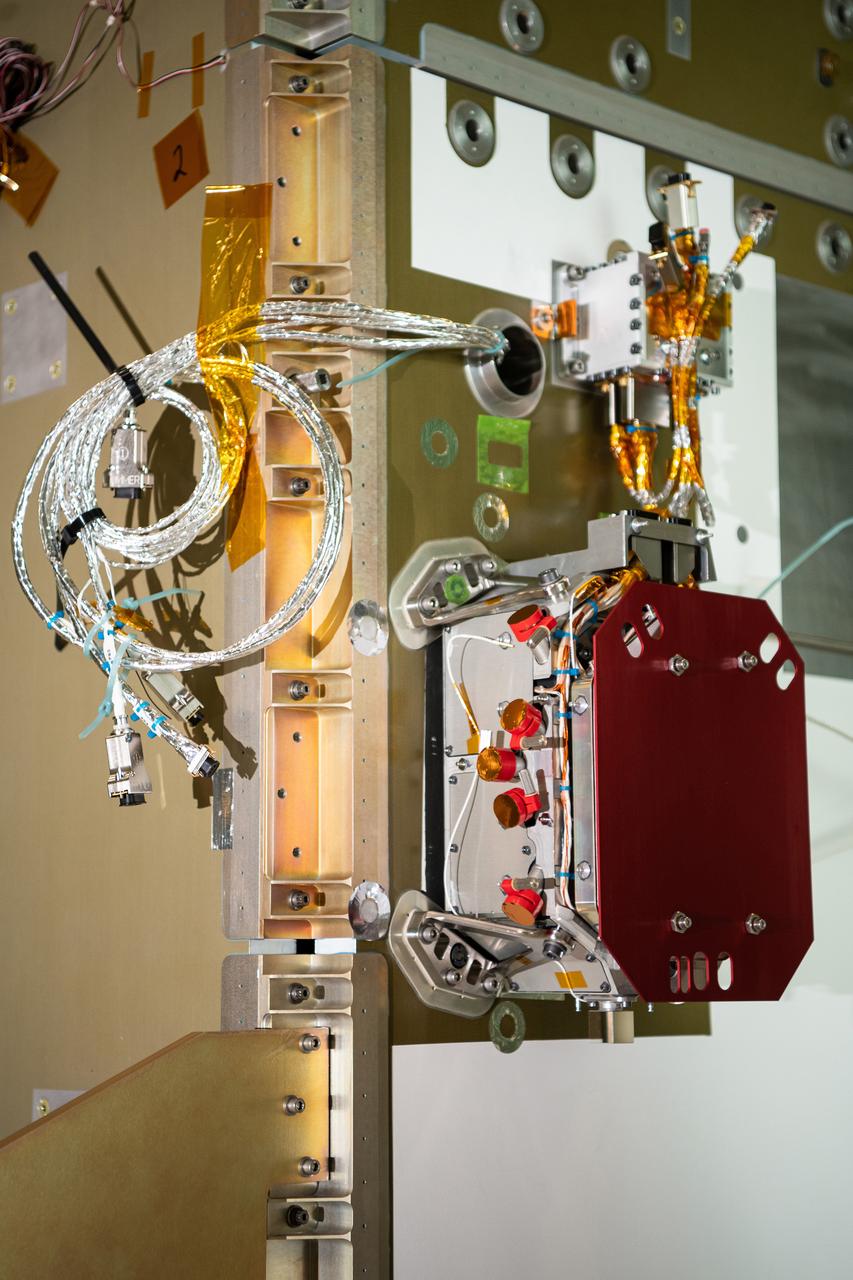
The SPEXone instrument after integration to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Observatory. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
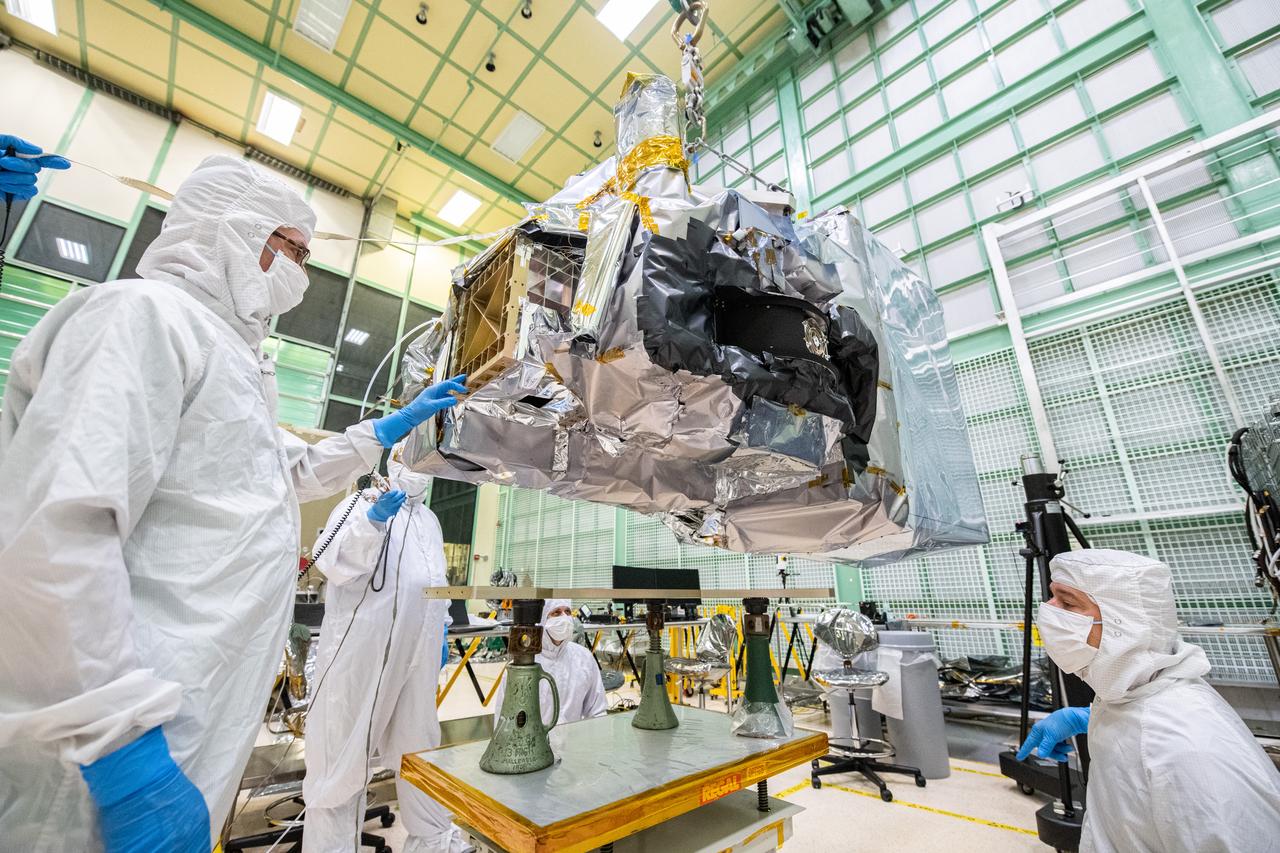

Mechanical technicians, Nicholas Kwiatkowski and Thomas Huber, guide the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) as it is suspended on a crane to install an adapter plate and for additional integration operations. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 31st, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
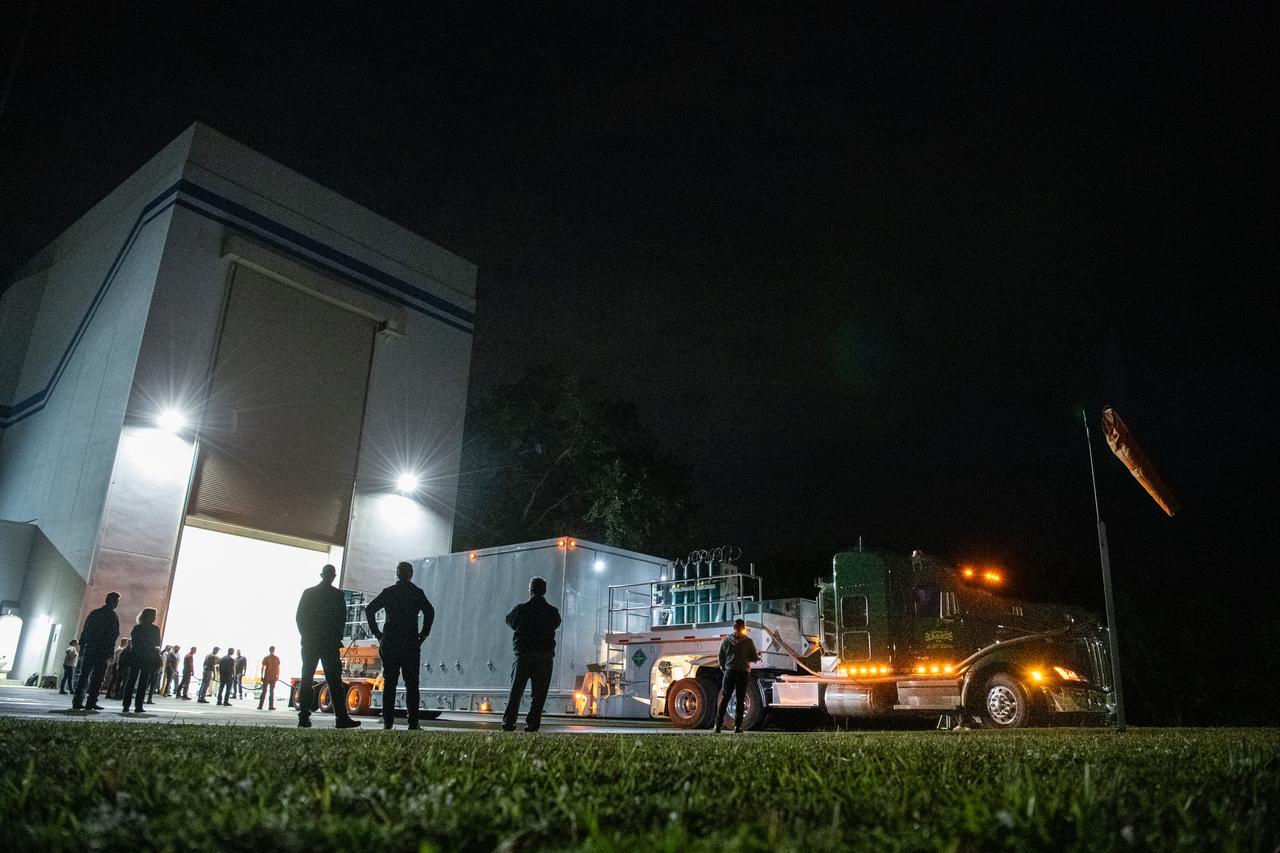

The transport carrier containing NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft arrives at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023. PACE was shipped from the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and is targeted to launch on January 30, 2024, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web.
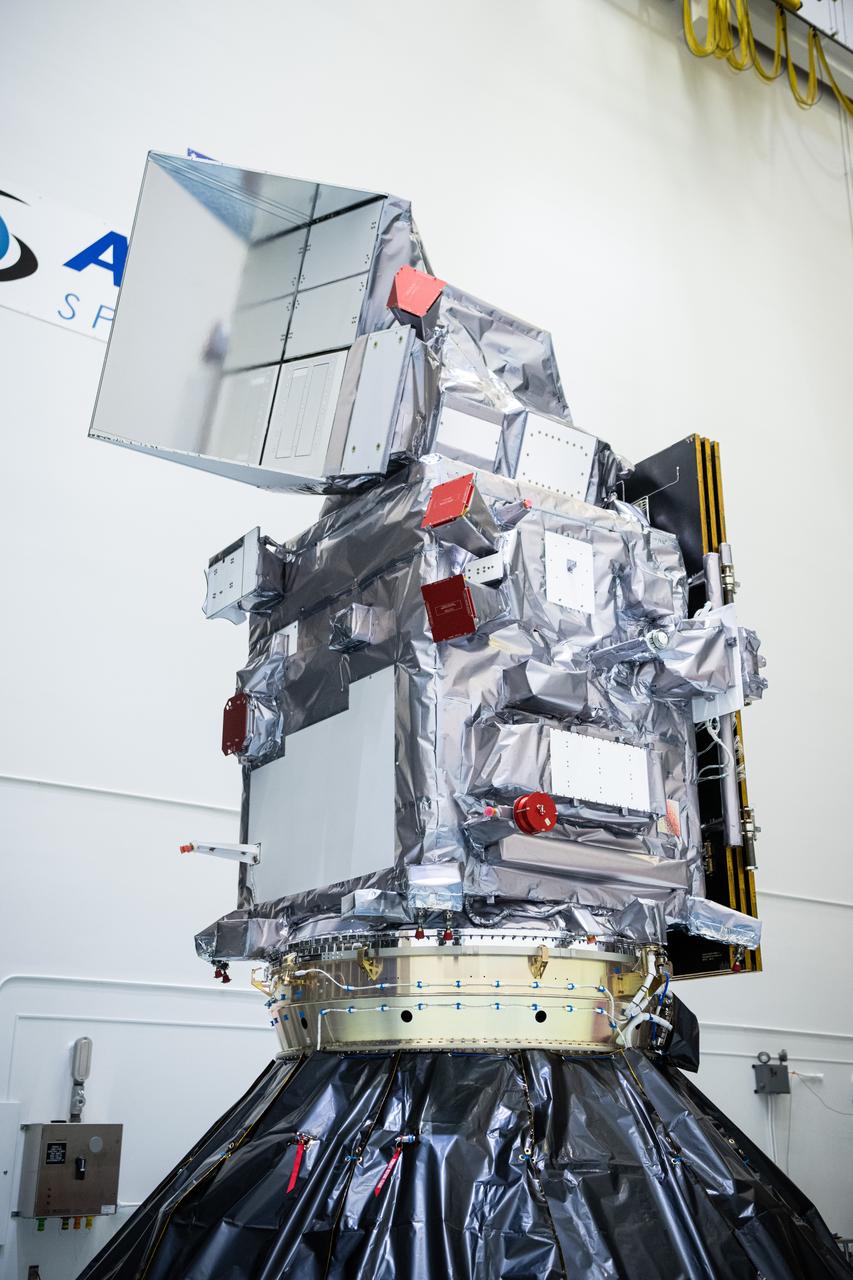

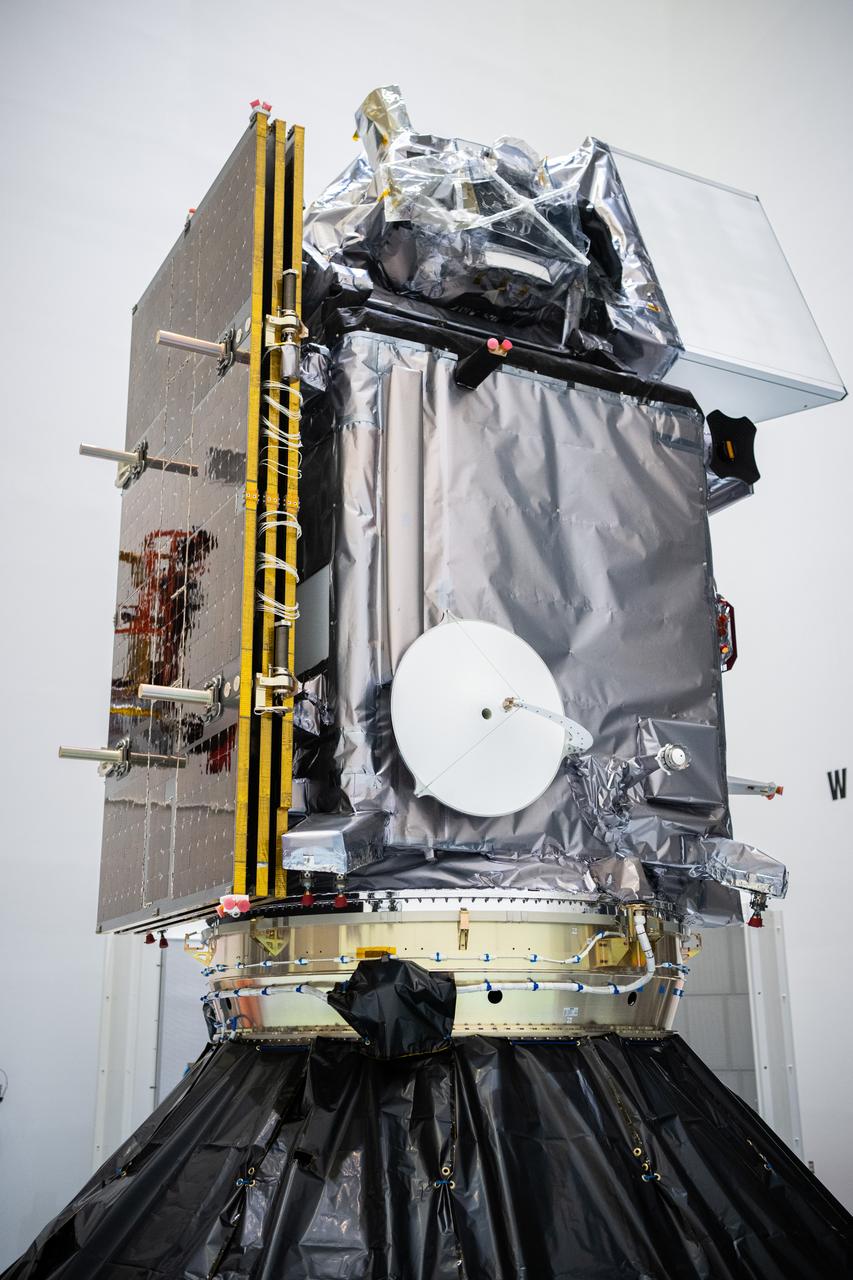
NASA and SpaceX technicians connect NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft to the payload adapter on Friday, Jan. 26, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6.
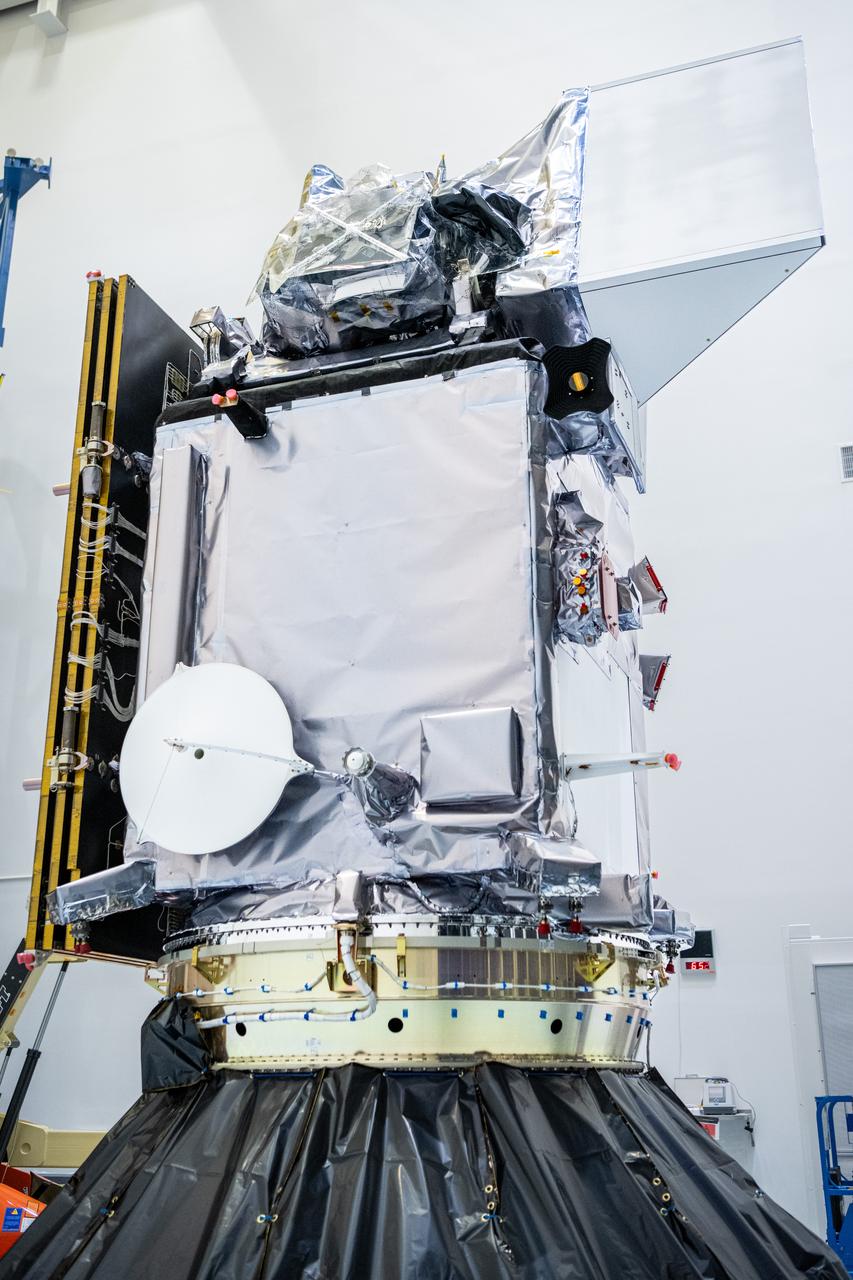

NASA and SpaceX technicians connect NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft to the payload adapter on Friday, Jan. 26, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6.
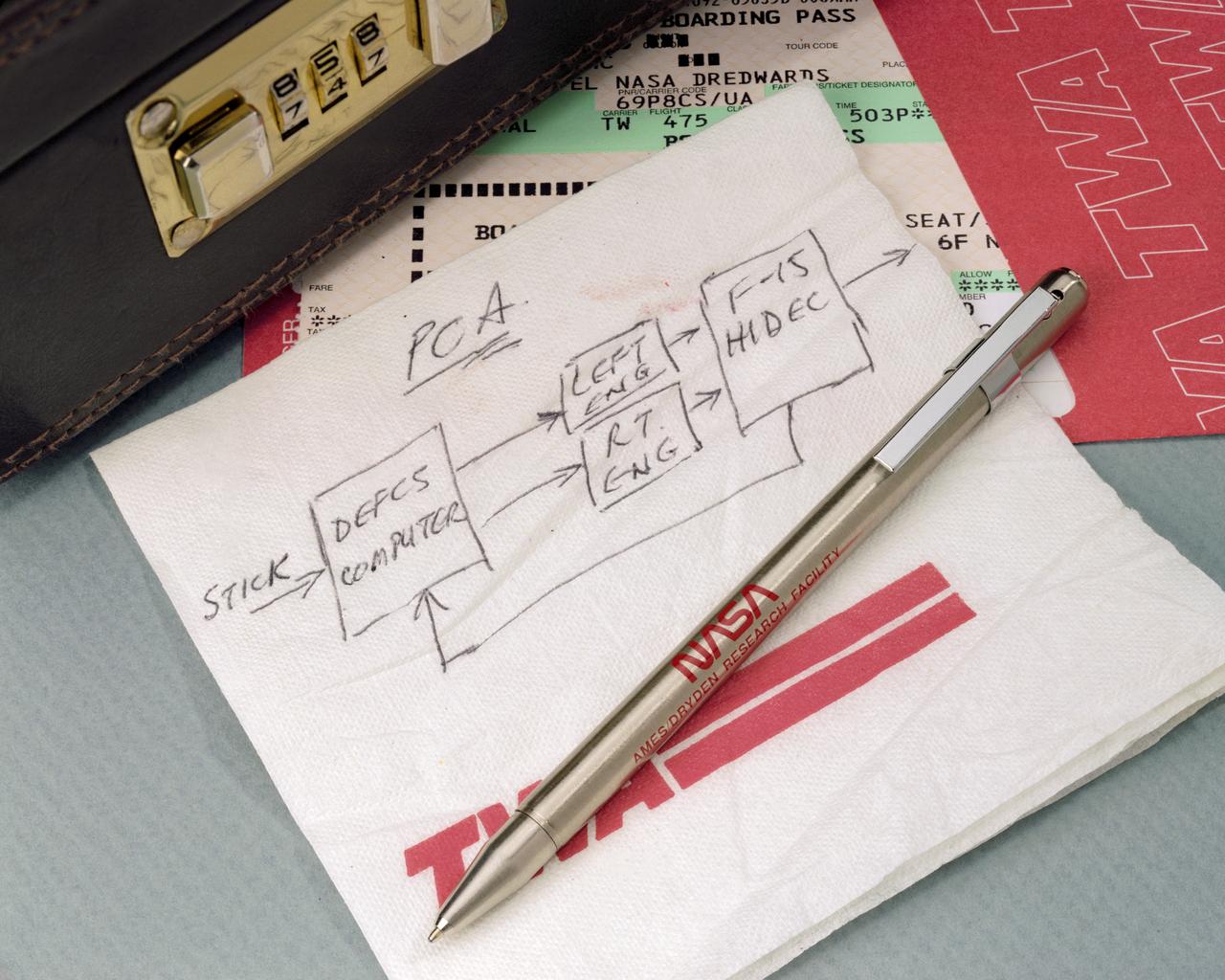
A simple sketch on a TWA napkin by NASA Dryden engineer Frank W. "Bill" Burcham led to development and validation of the Propulsion-Controlled Aircraft concept.

The Space Shuttle Discovery, mated to NASA's 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), takes to the air for its ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft, with a crew of six, was launched into a 57-degree high inclination orbit from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 3:23 p.m., 9 September 1994. The mission featured the study of clouds and the atmosphere with a laser beaming system called Lidar In-Space Technology Experiment (LITE), and the first untethered space walk in ten years. A Spartan satellite was also deployed and later retrieved in the study of the sun's corona and solar wind. The mission was scheduled to end Sunday, 18 September, but was extended one day to continue science work. Bad weather at the Kennedy Space Center on 19 September, forced a one-day delay to September 20, with a weather divert that day to Edwards. Mission commander was Richard Richards, the pilot Blaine Hammond, while mission specialists were Jerry Linenger, Susan Helms, Carl Meade, and Mark Lee.
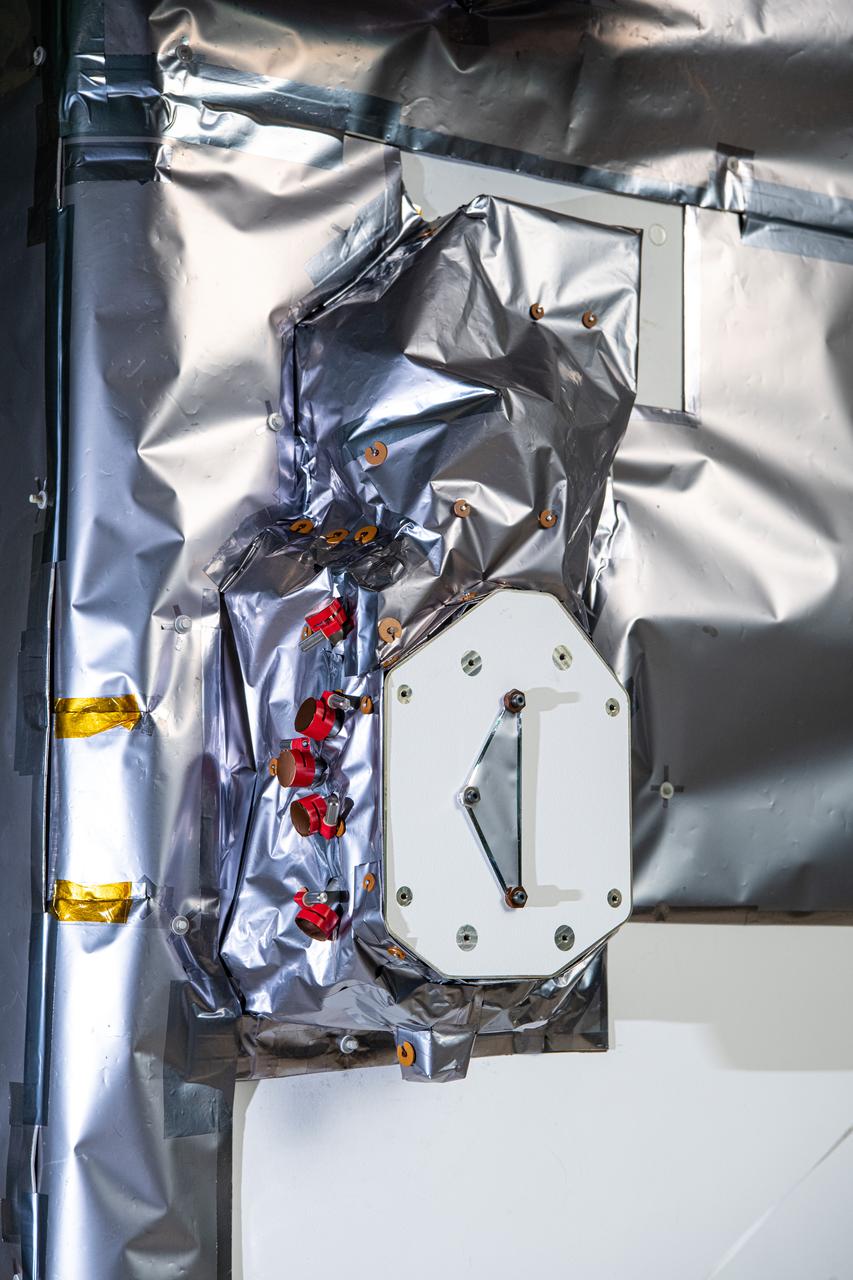

The SPEXone instrument on The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 31st, 2023. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.

jsc2023e064873 (8/8/2023) --- The NASA ILLUMA-T team in the Goddard Space Flight Center cleanroom in front of the payload. ILLUMA-T demonstrates two different data transfer speeds from low Earth orbit to the ground via a relay link. The links can be used to stream real-time data or for large bulk data transfers.
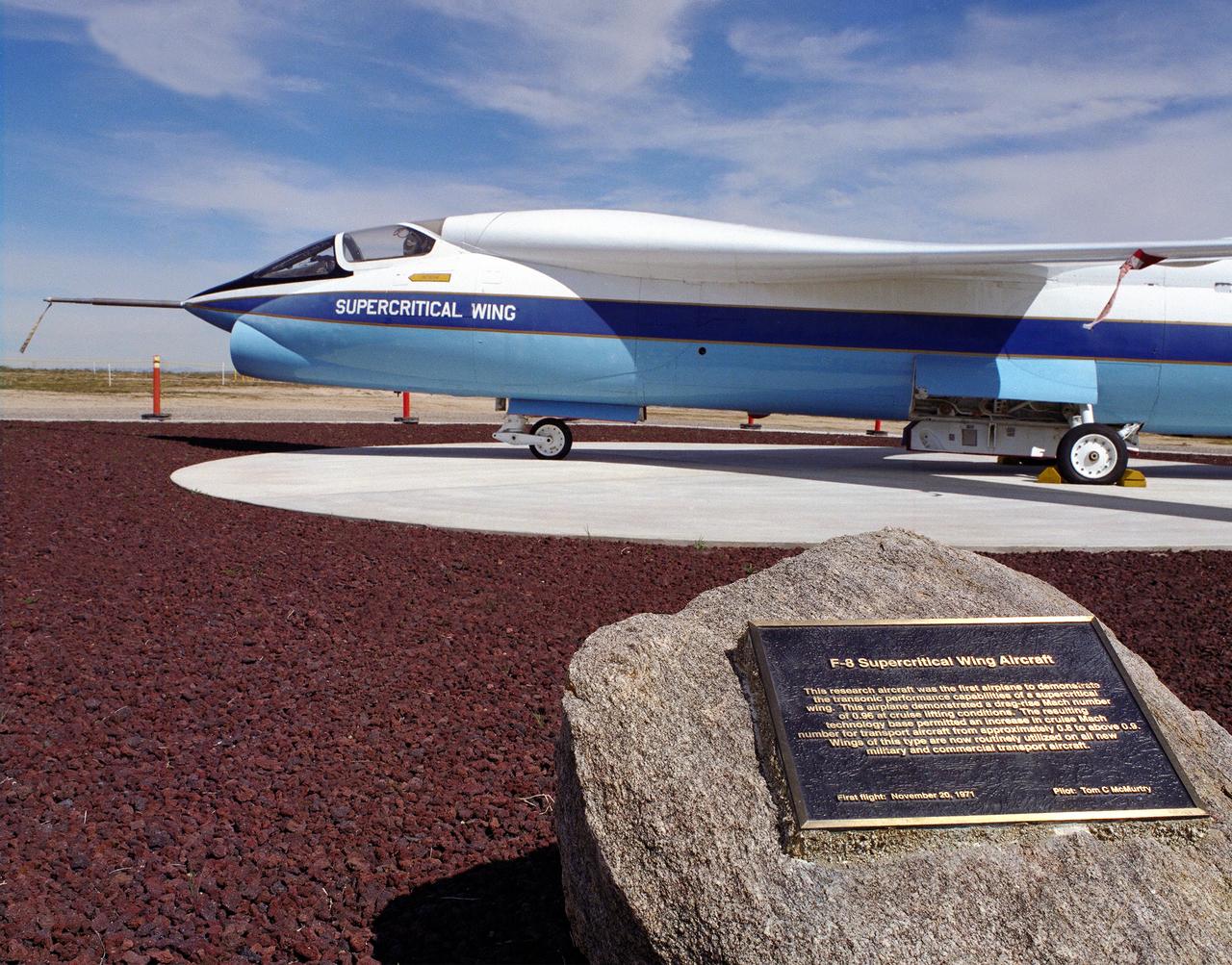

A Vought F-8A Crusader was selected by NASA as the testbed aircraft (designated TF-8A) to install an experimental Supercritical Wing (SCW) in place of the conventional wing. The unique design of the Supercritical Wing reduces the effect of shock waves on the upper surface near Mach 1, which in turn reduces drag. In the photograph the TF-8A Crusader with the Supercritical Wing is shown on static display in front of the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The F-8 SCW aircraft, along with the F-8 Digital Fly-By-Wire aircraft were placed on display on May 27, 1992, at a conference marking the 20th anniversary of the start of the two programs.
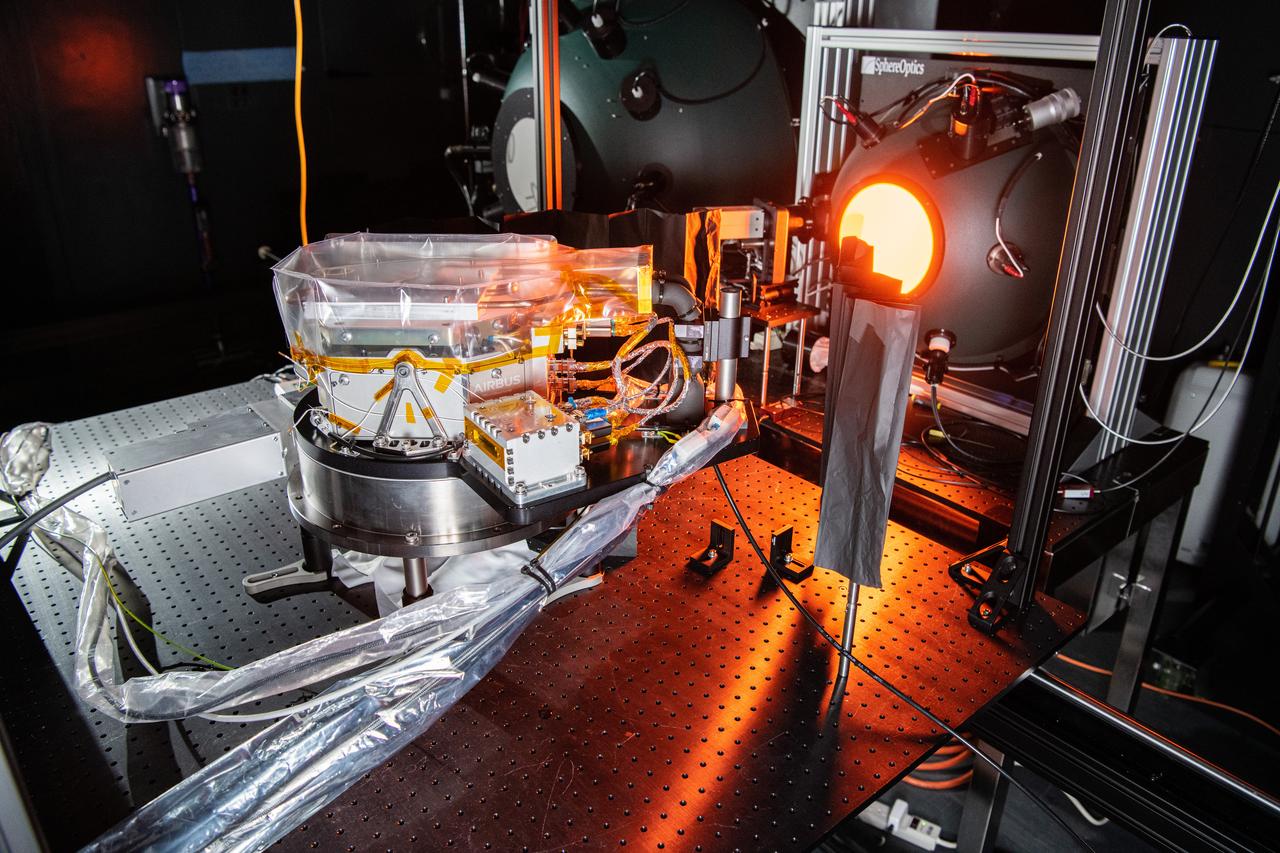
The SPEXone instrument undergoes cross calibration at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt,Maryland on April 20th, 2021. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.

jsc2023e064874 (8/8/2023) --- NASA’s ILLUMA-T payload at Goddard Space Flight Center fully tested and integrated prior to its delivery to Kennedy Space Center. ILLUMA-T demonstrates two different data transfer speeds from low Earth orbit to the ground via a relay link. The links can be used to stream real-time data or for large bulk data transfers.
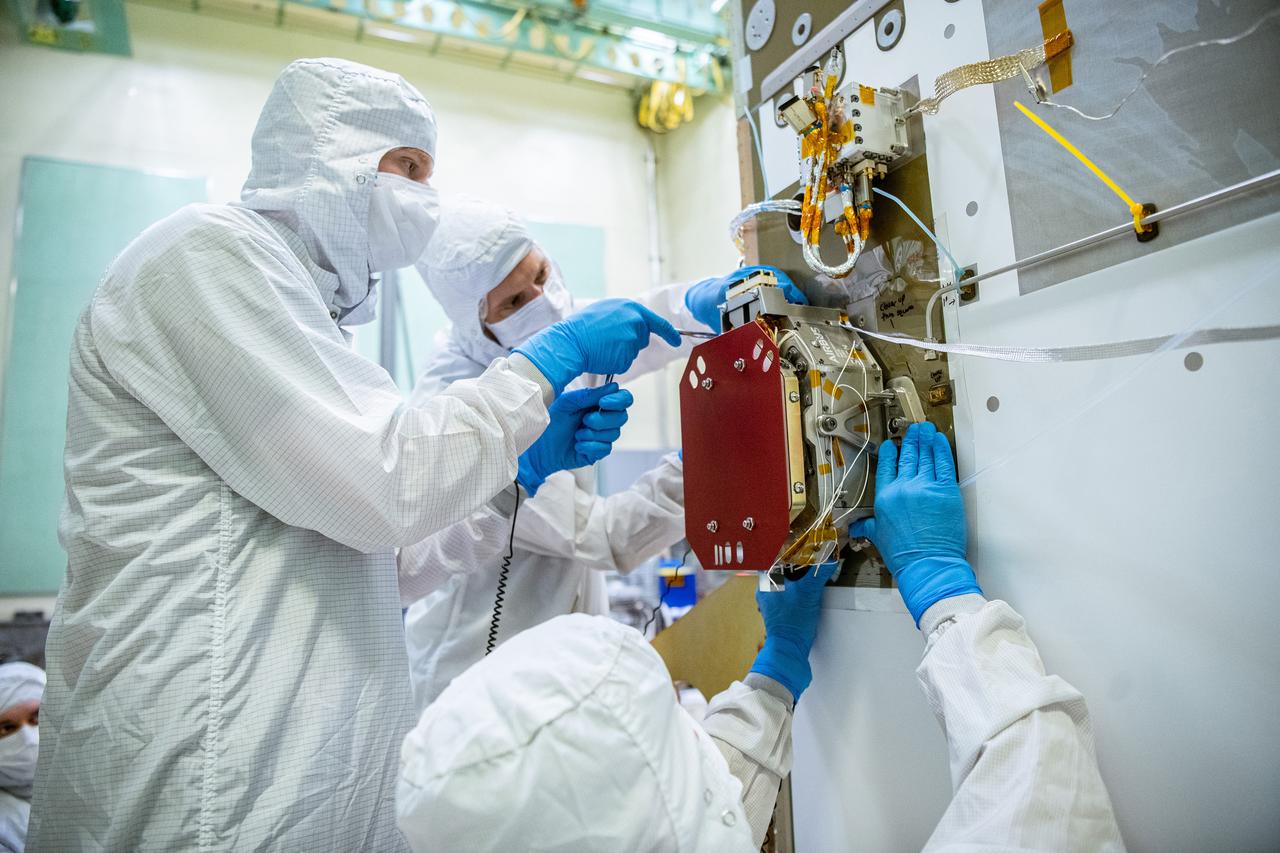

NASA technicians and Engineers from SRON, the Netherlands Institute for Space Research, integrate the SPEXone instrument to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Spacecraft at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 13th, 2022. SPEXone is a compact, optical satellite instrument that will characterize aerosols from low Earth orbit as part of the NASA PACE mission. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
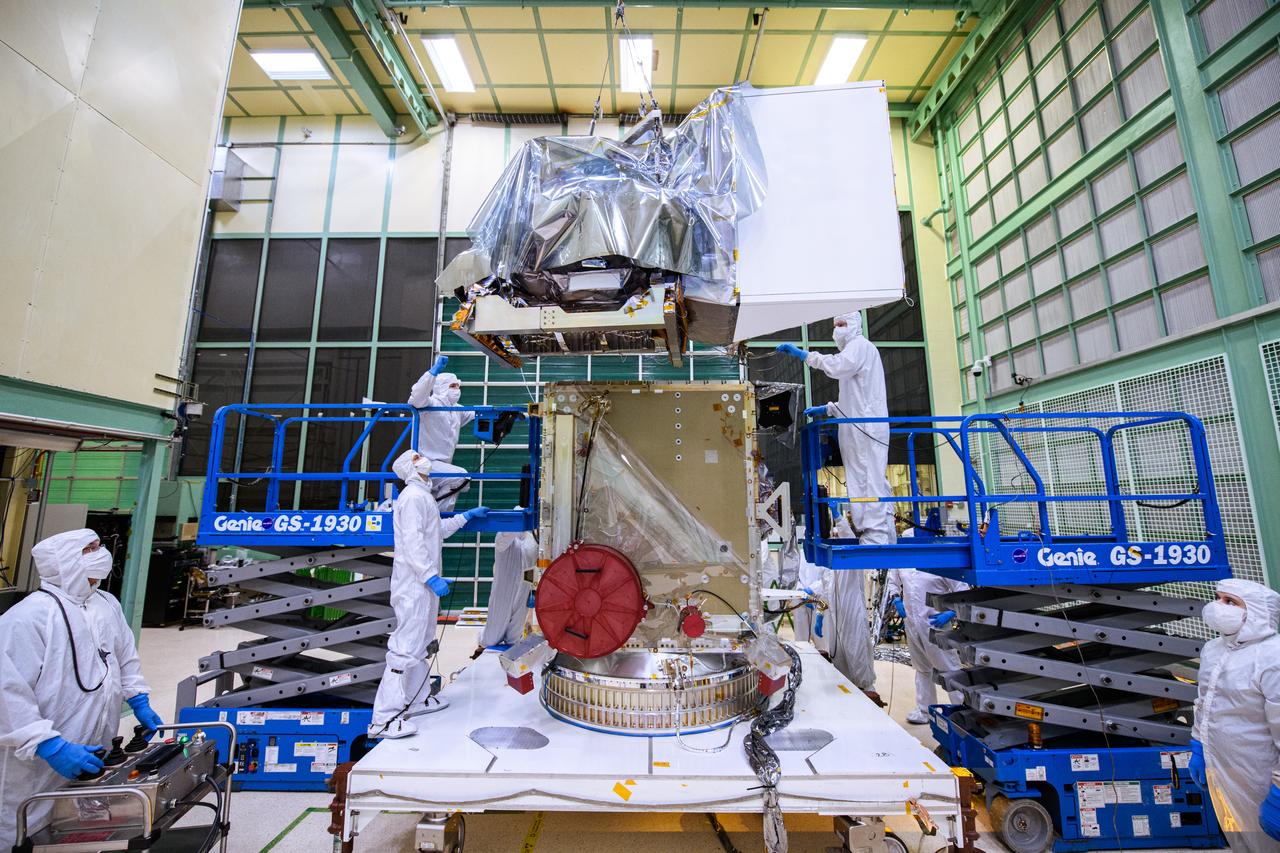

Mechanical technicians install the Flight Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) and Tilt Platform Assembly to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft. By installing the instrument, the spacecraft is now considered an observatory. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
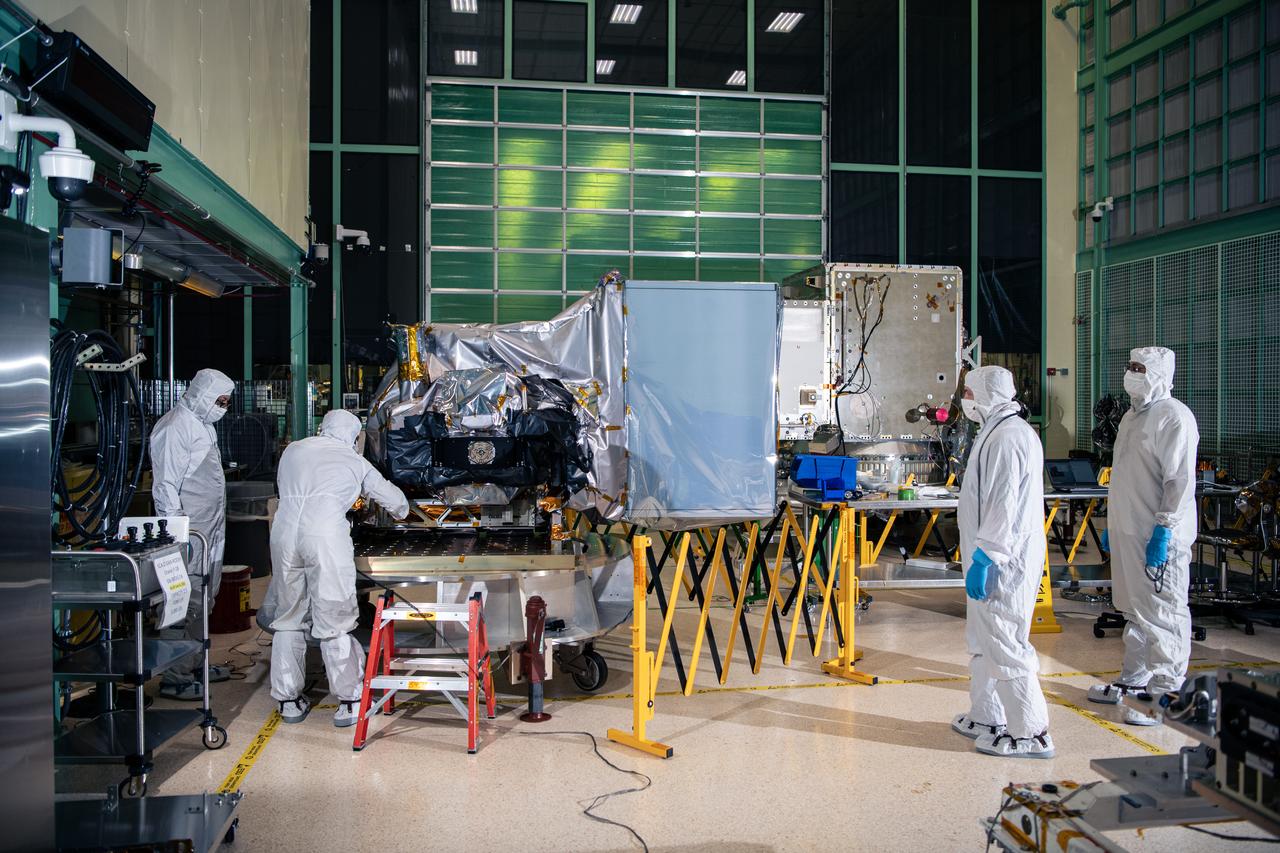

Engineers and technicians prepare for a crane lift to deintegrate the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) from the Tilt Mechanism after successful environmental testing. The PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft is seen in the background in the Spacecraft Checkout Area (SCA) cleanroom. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
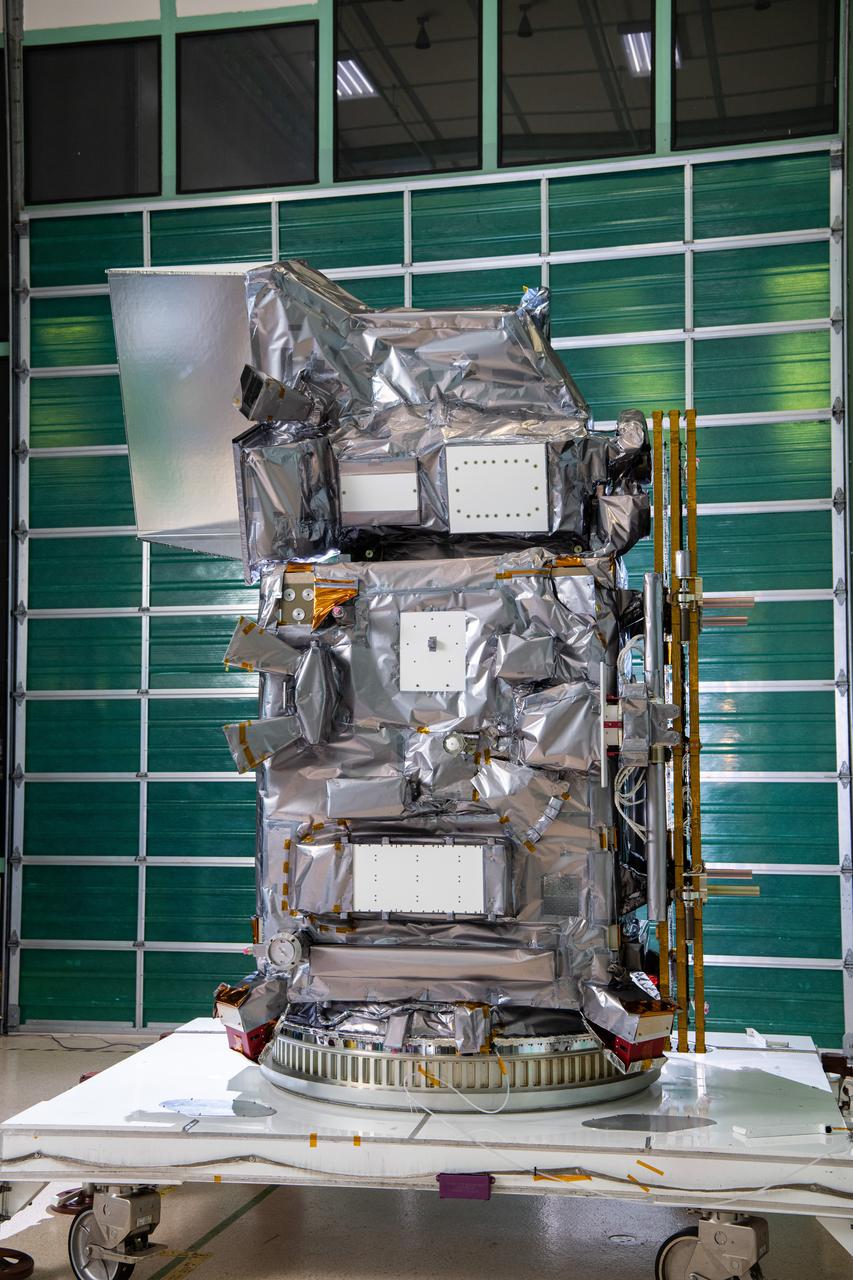

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 31st, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
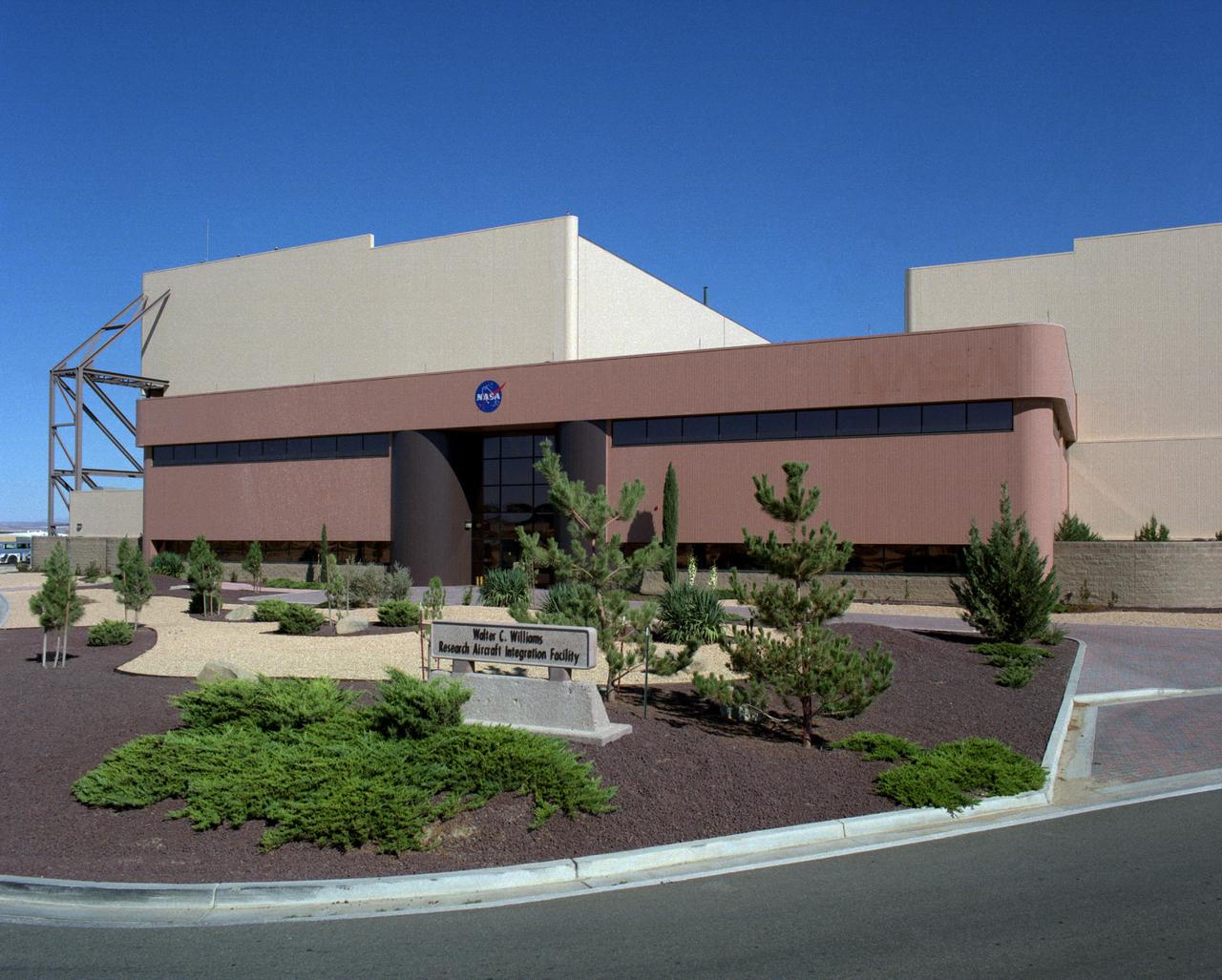

Walter C. Williams Research Aircraft Integration Facility (RAIF)
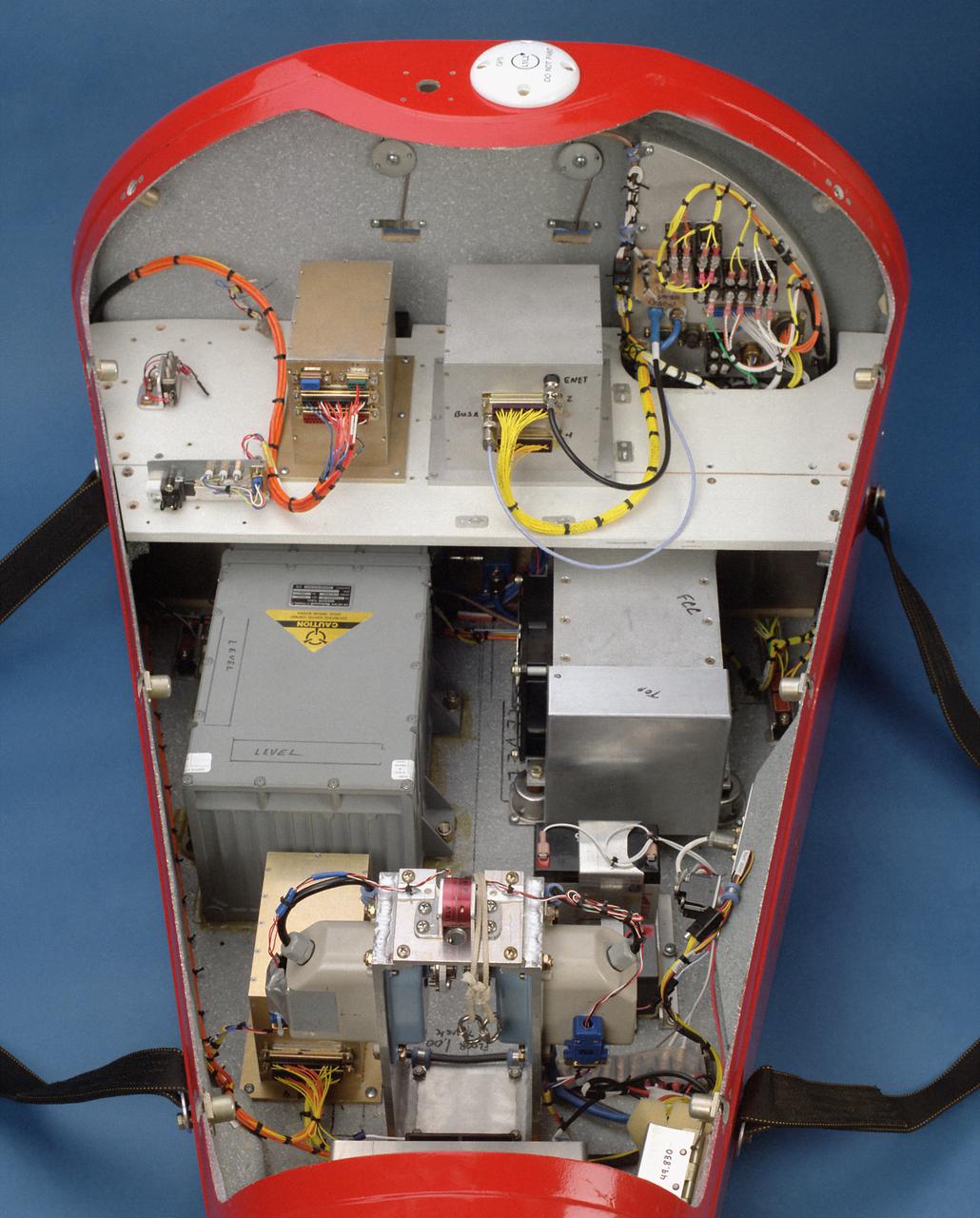
This photo shows the instrumentation and equipment inside the Spacewedge #3, a remotely-piloted research vehicle flown at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, to help develop technology for autonomous return systems for spacecraft as well as methods to deliver large Army cargo payloads to precise landings.
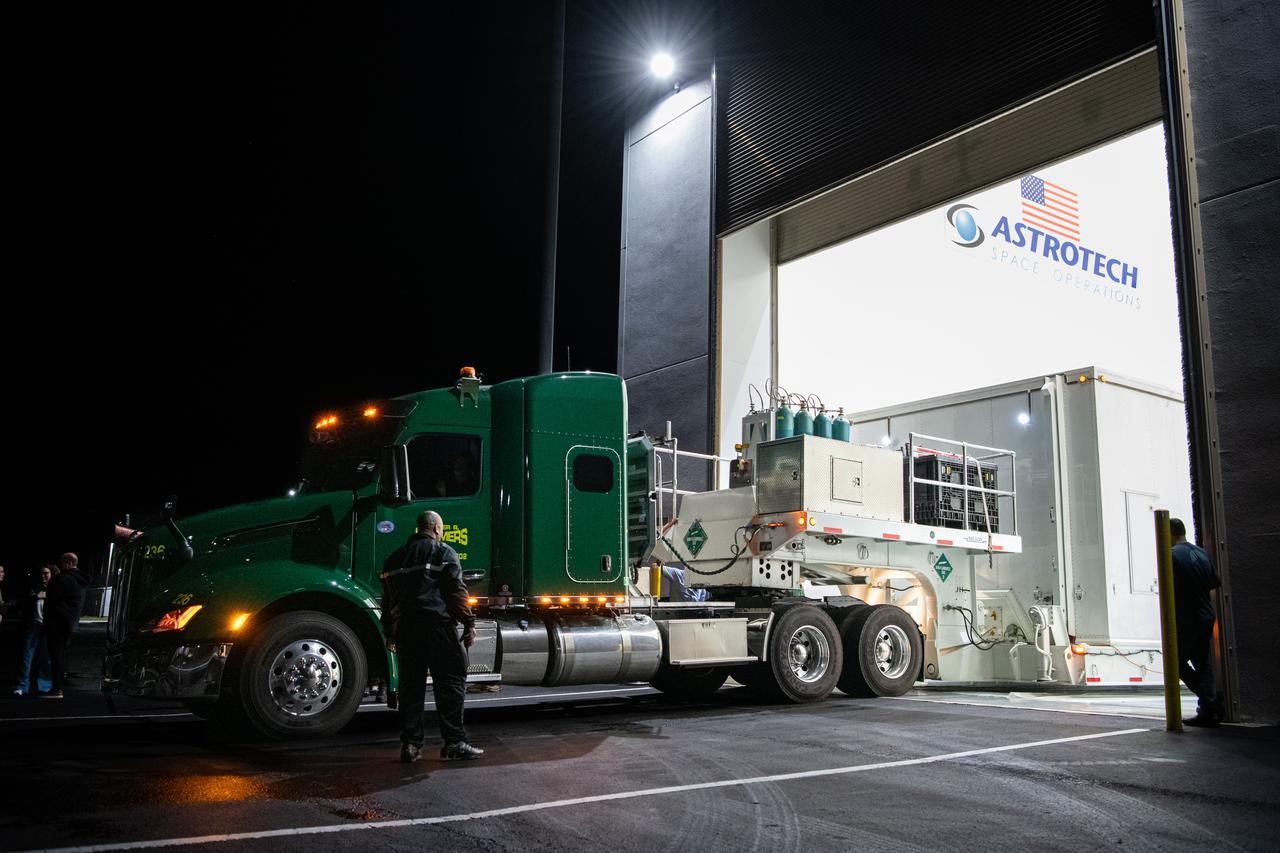

The transport carrier containing NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft arrives at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023. PACE was shipped from the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and is targeted to launch on January 30, 2024, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web.
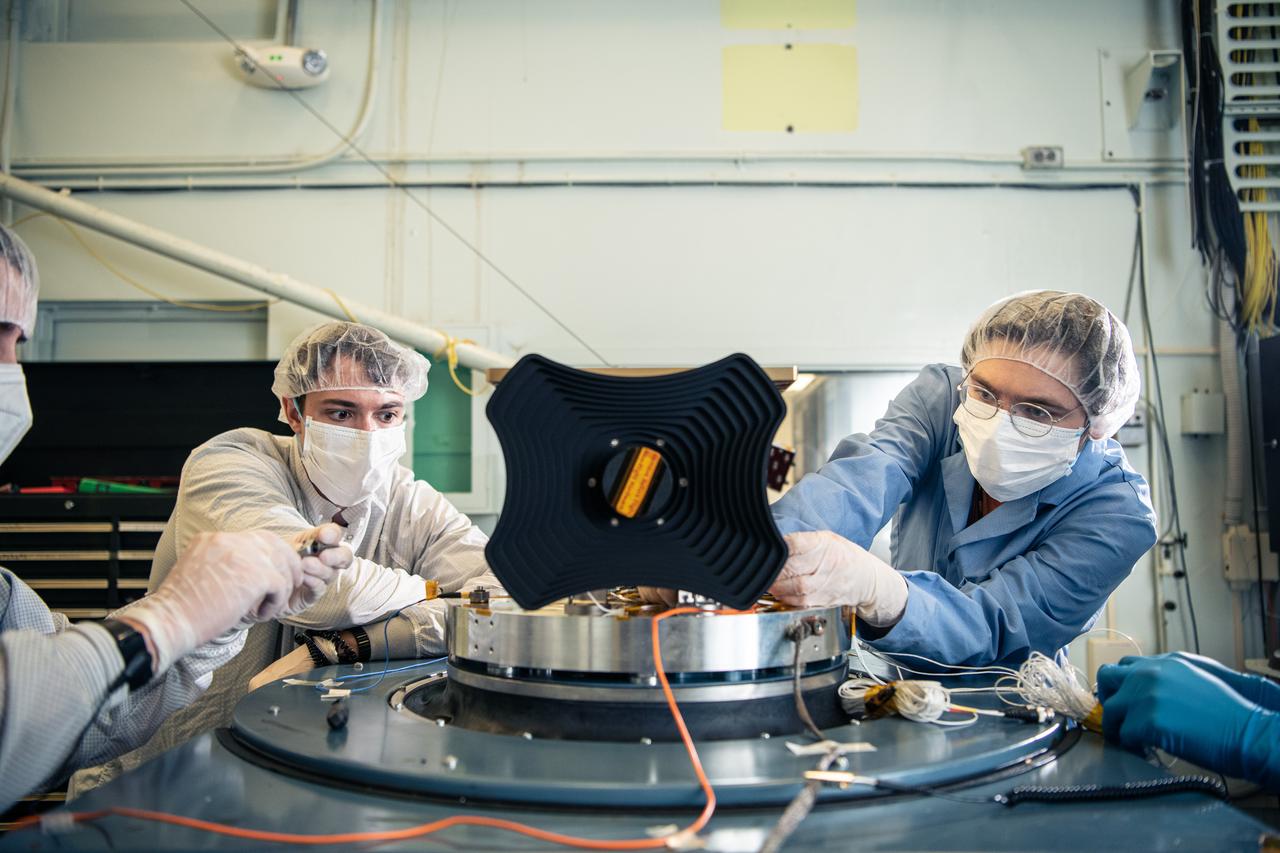
UMBC Earth and Space Institute engineers Ian Decker (left) and Danny Nelson (right) attach the Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument to the shaker table for vibration testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on August 8th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute.
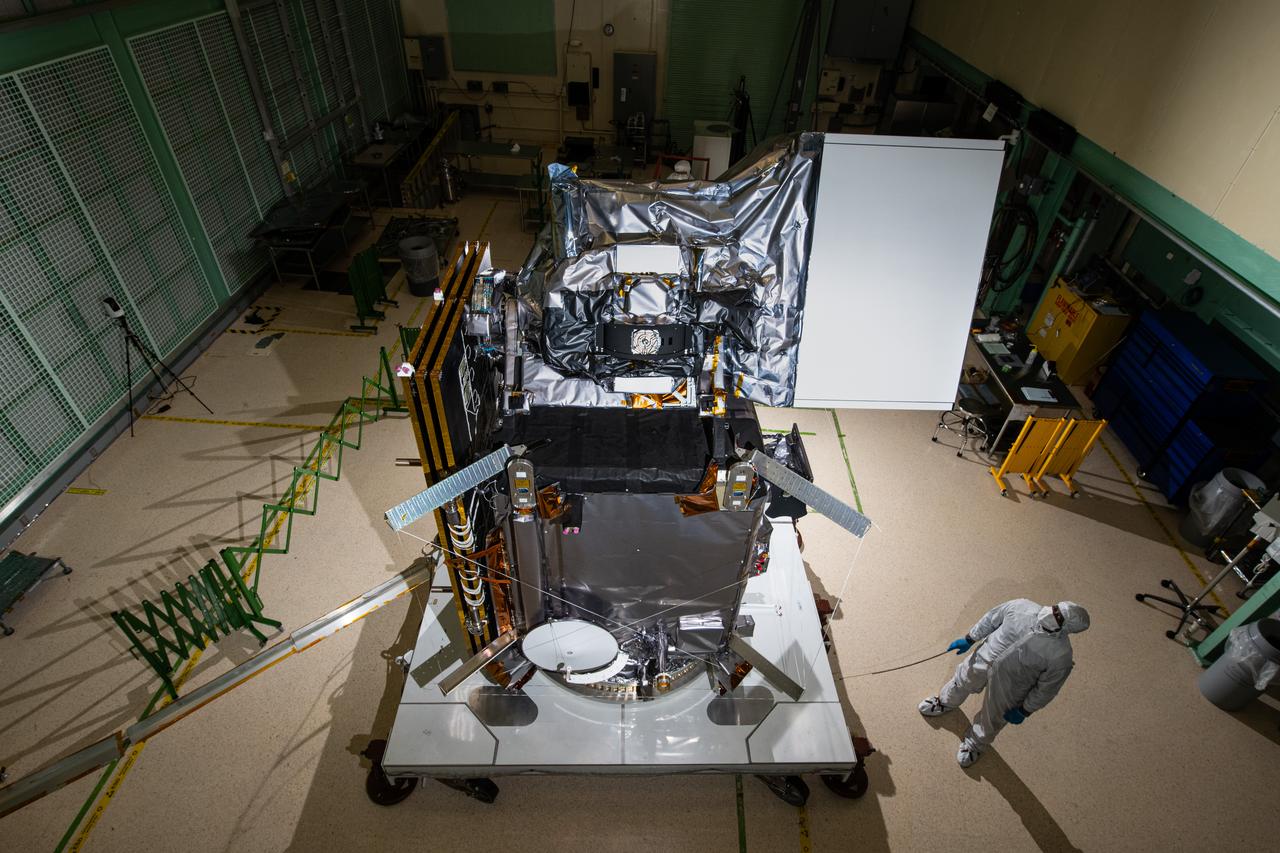
Quality Engineer Larry Morgan looks at the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory in the cleanroom at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on November 2nd, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
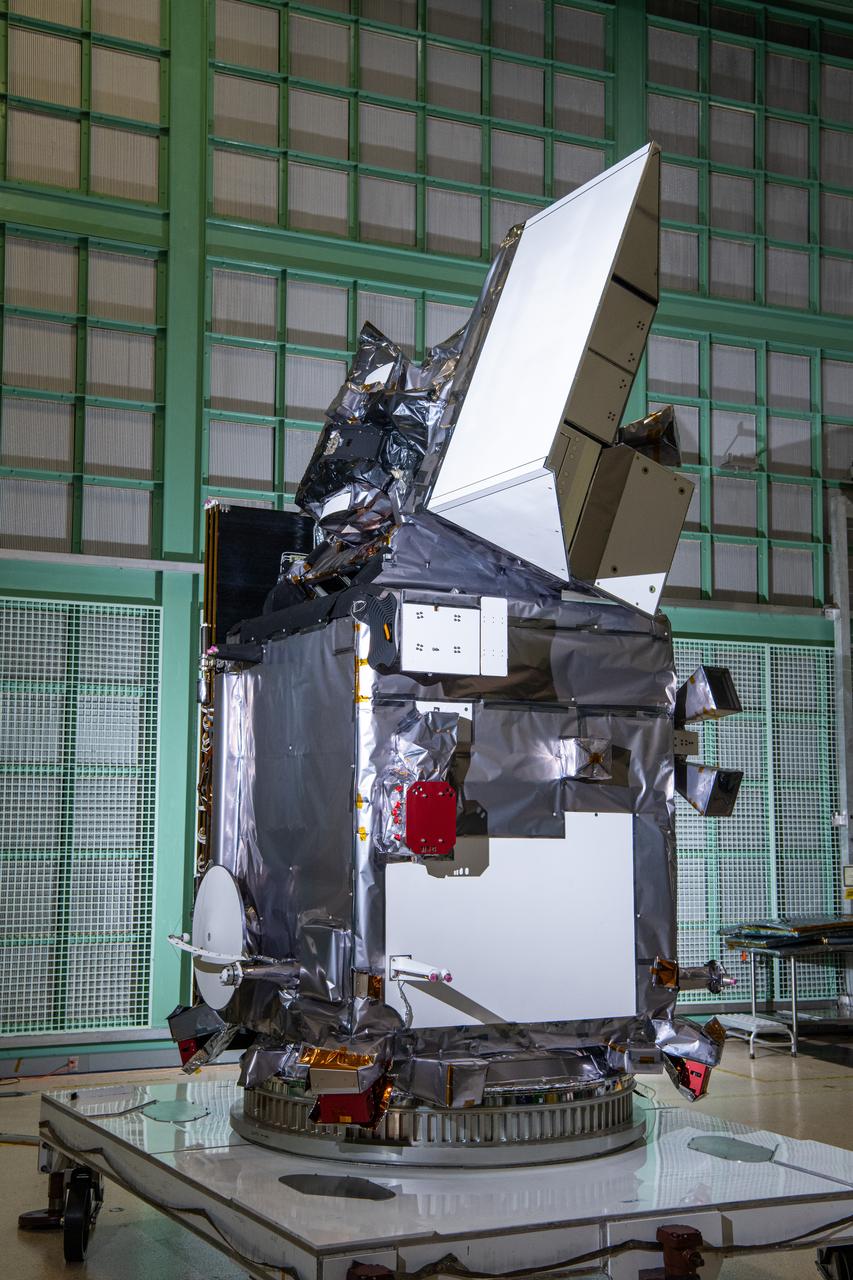

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 31st, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
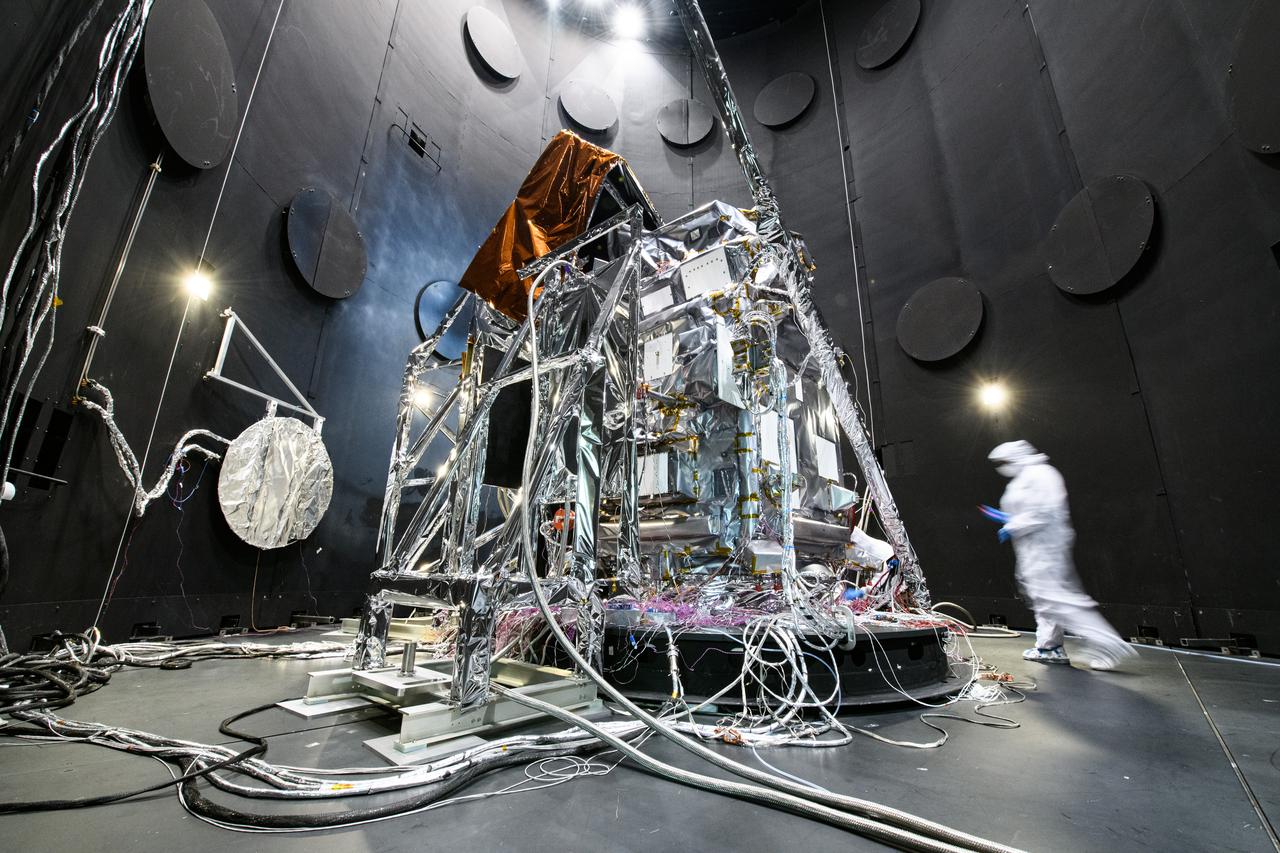

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Observatory inside the Space Environment Simulator (SES) thermal vacuuum chamber before thermal environmental testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 16th, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
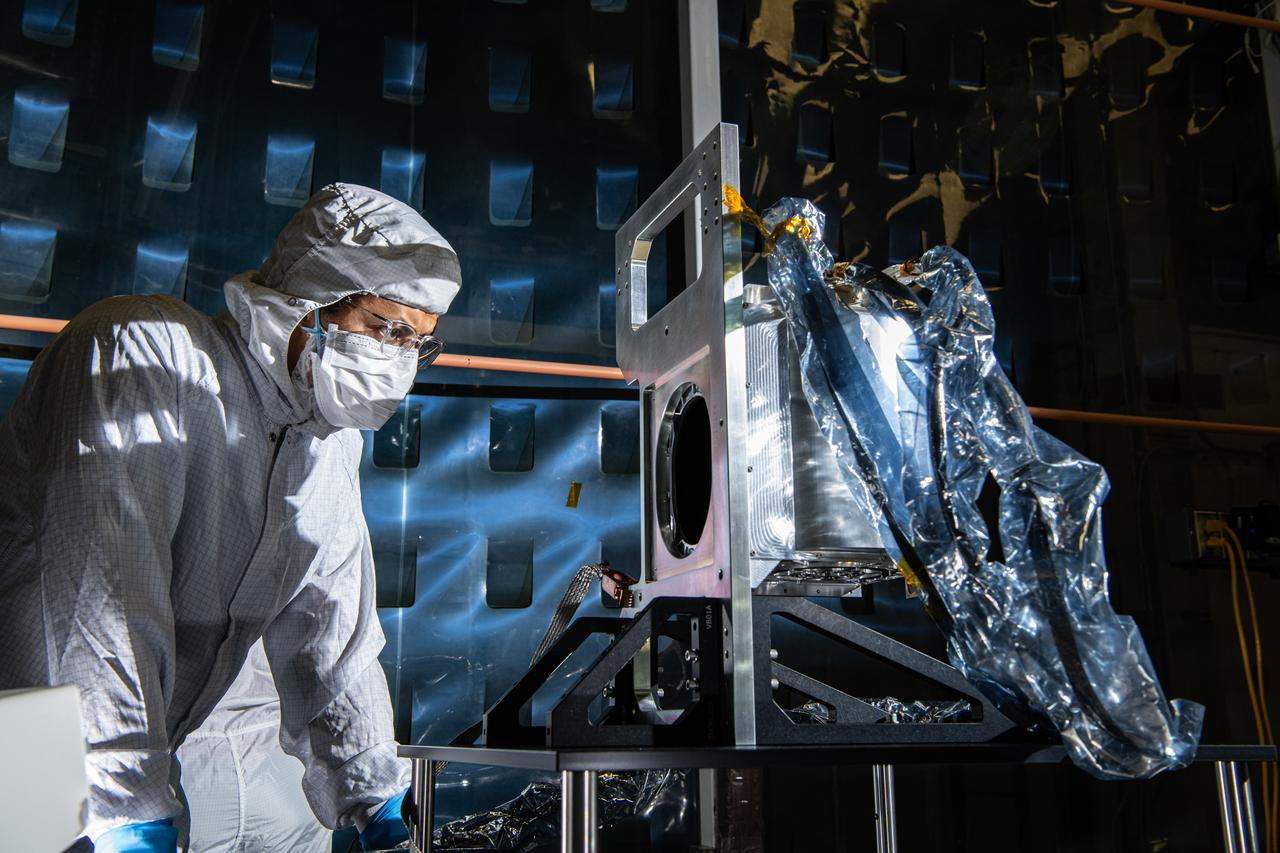

Aerospace Engineer, Daniel Senai, inspects the Solar Calibration Assembly (SCA) Life Test Unit mechanism for the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) to ensure it is ready for the next level of assembly. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
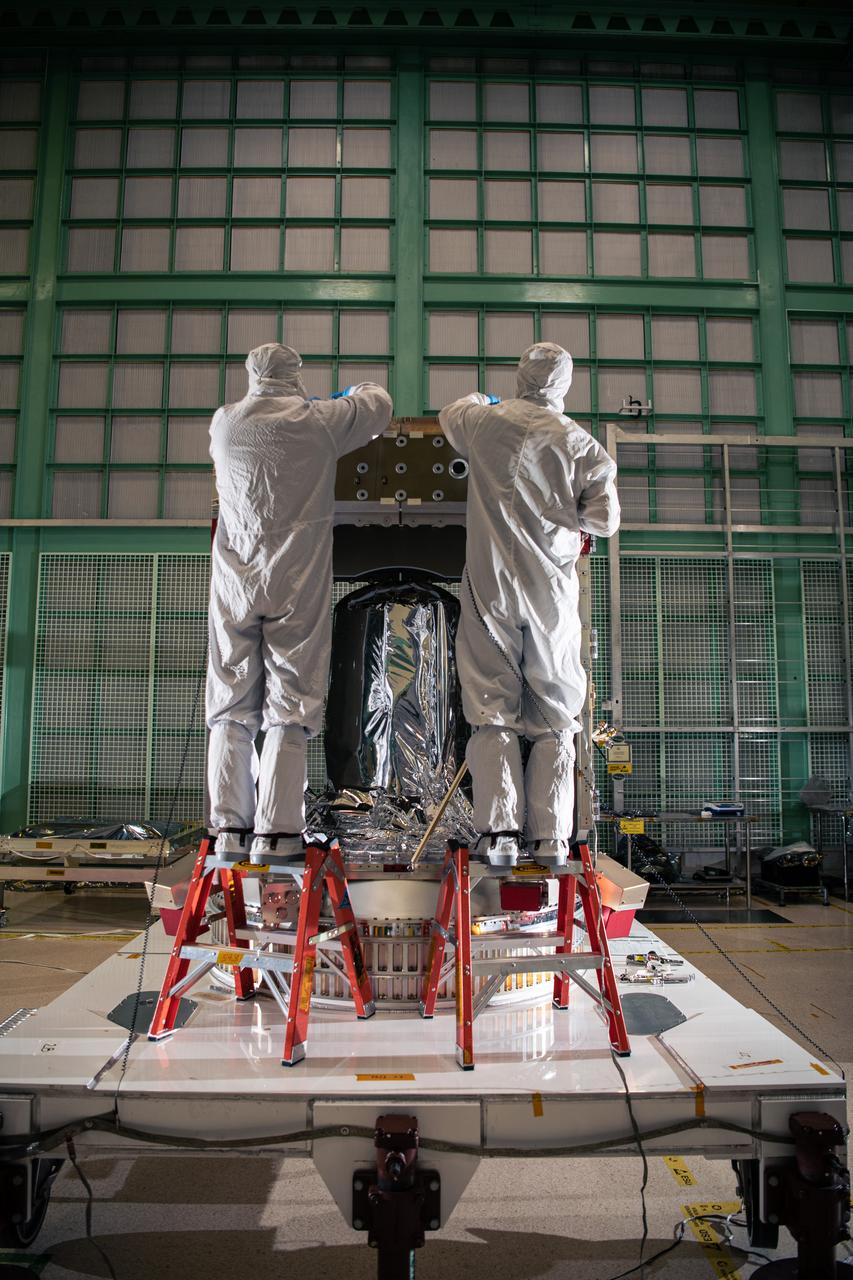

Engineering Technicians Alex Schaeffer and Eric Norris assemble the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Spacecraft structure in the cleanroom at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on February 24th, 2022. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
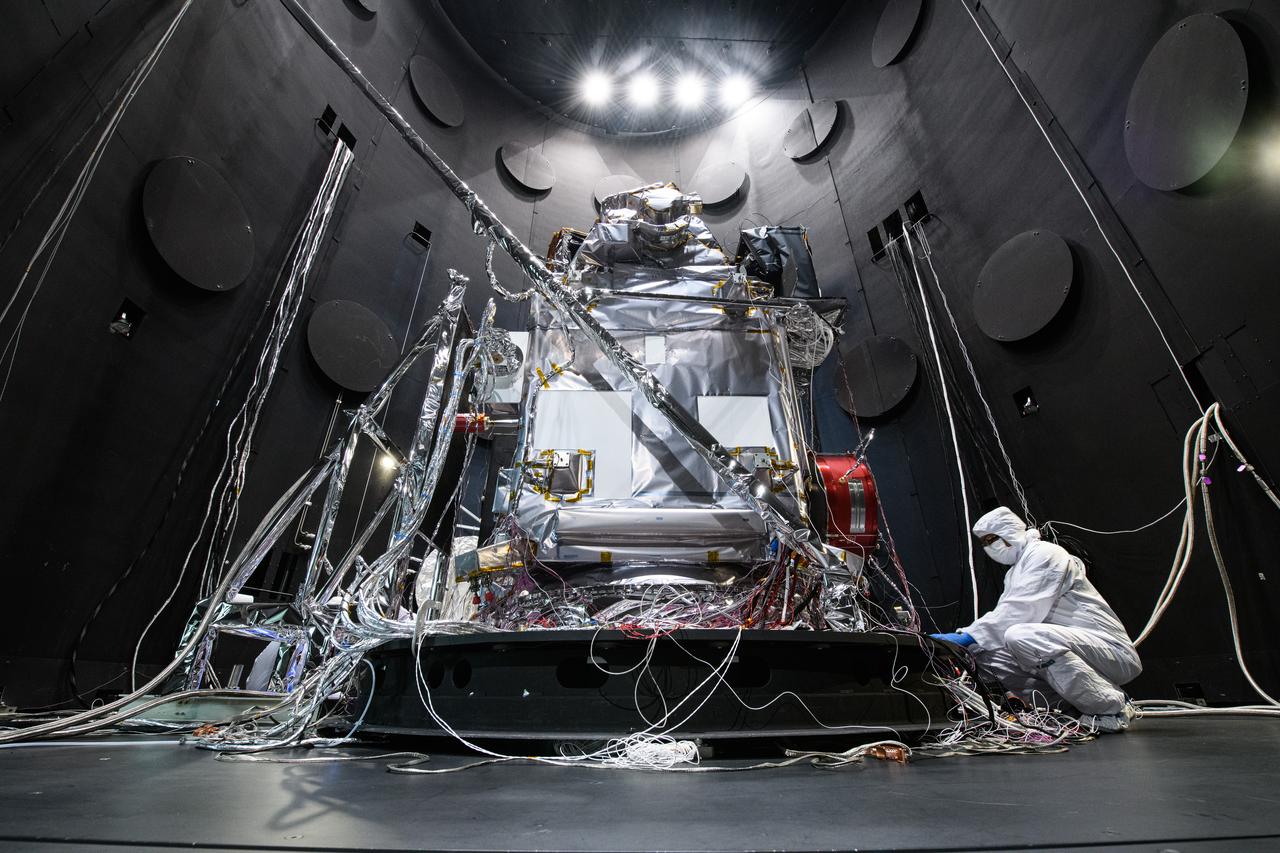

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Observatory inside the Space Environment Simulator (SES) thermal vacuuum chamber before thermal environmental testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 16th, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
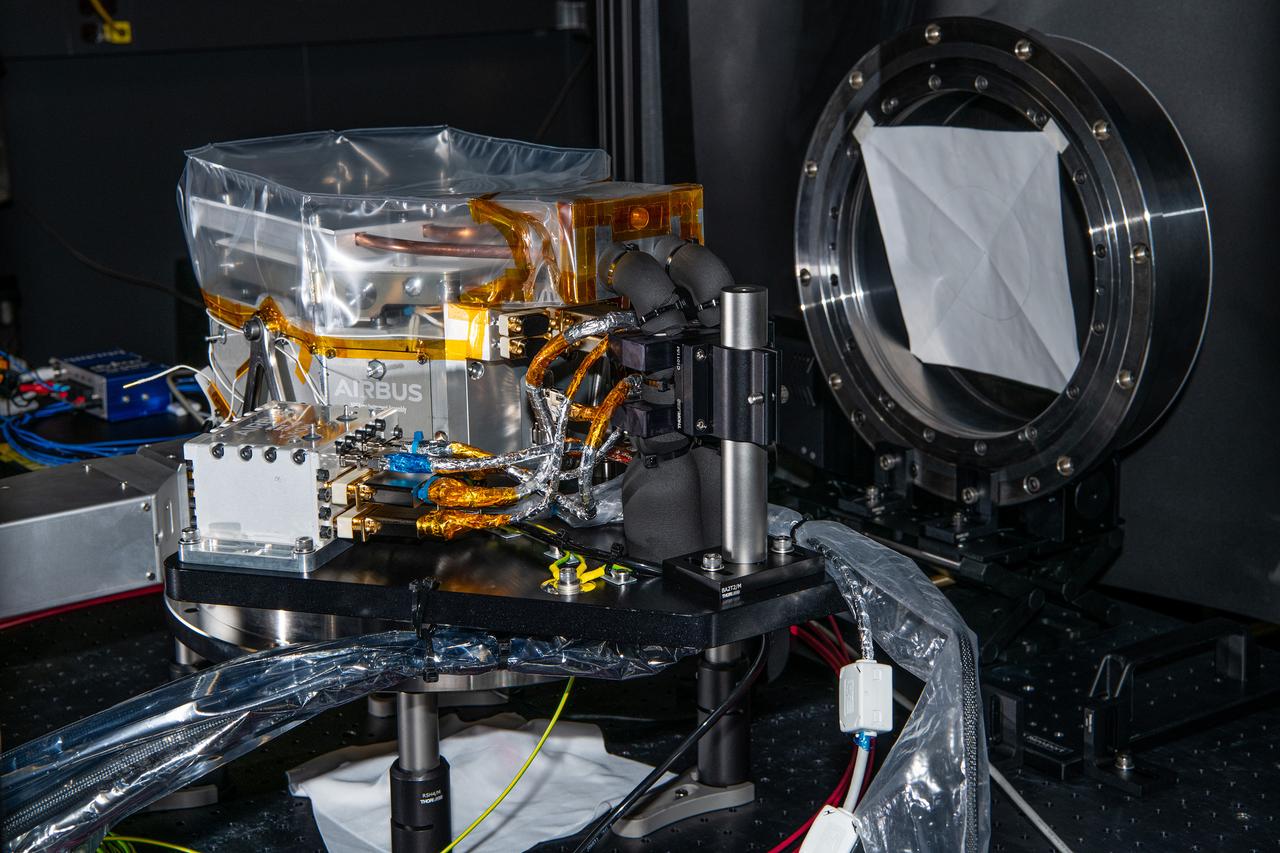
The SPEXone instrument undergoes comprehensive performace and calibration testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt,Maryland on April 8th, 2021. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
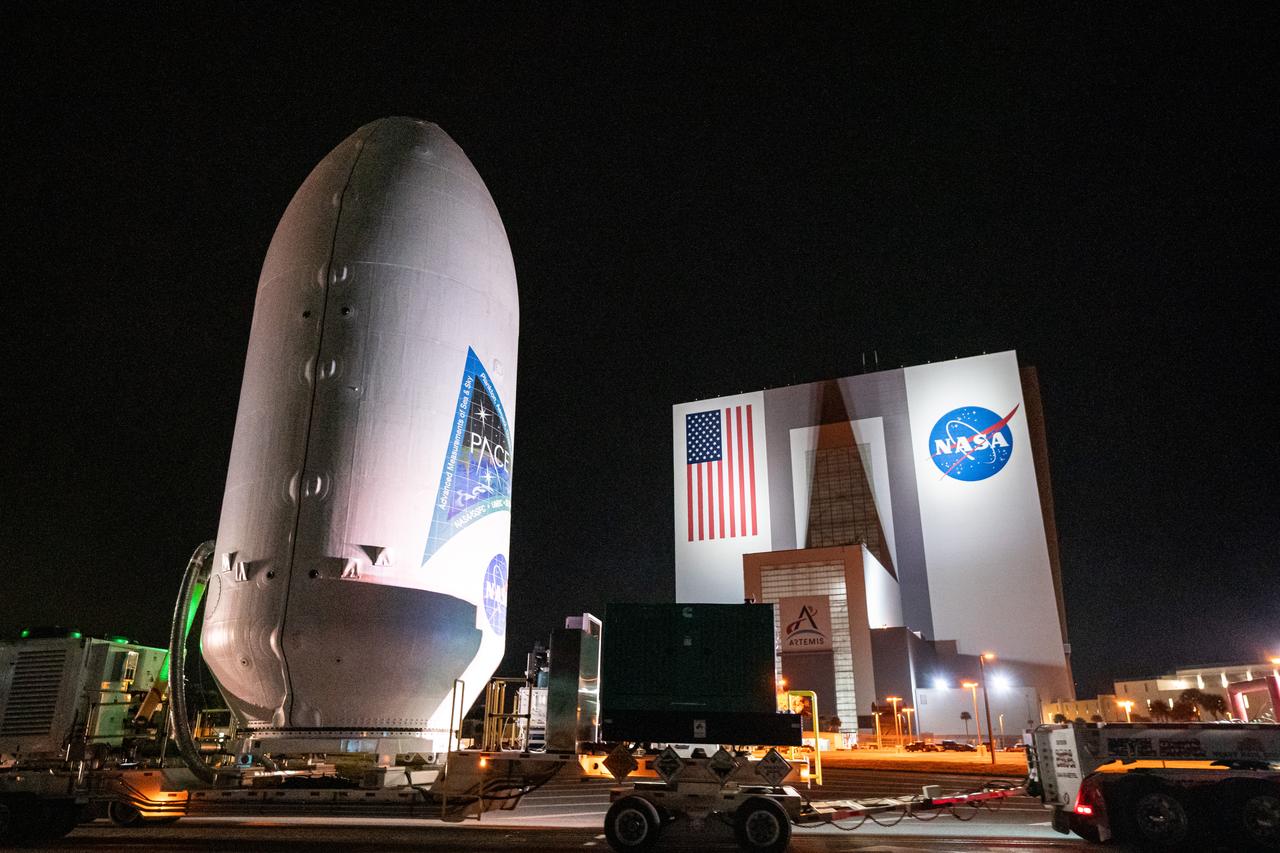

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft encapsulated inside SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings is transported from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, to be mated with a SpaceX Falcon 9 in preparation for liftoff set for no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6, 2024. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
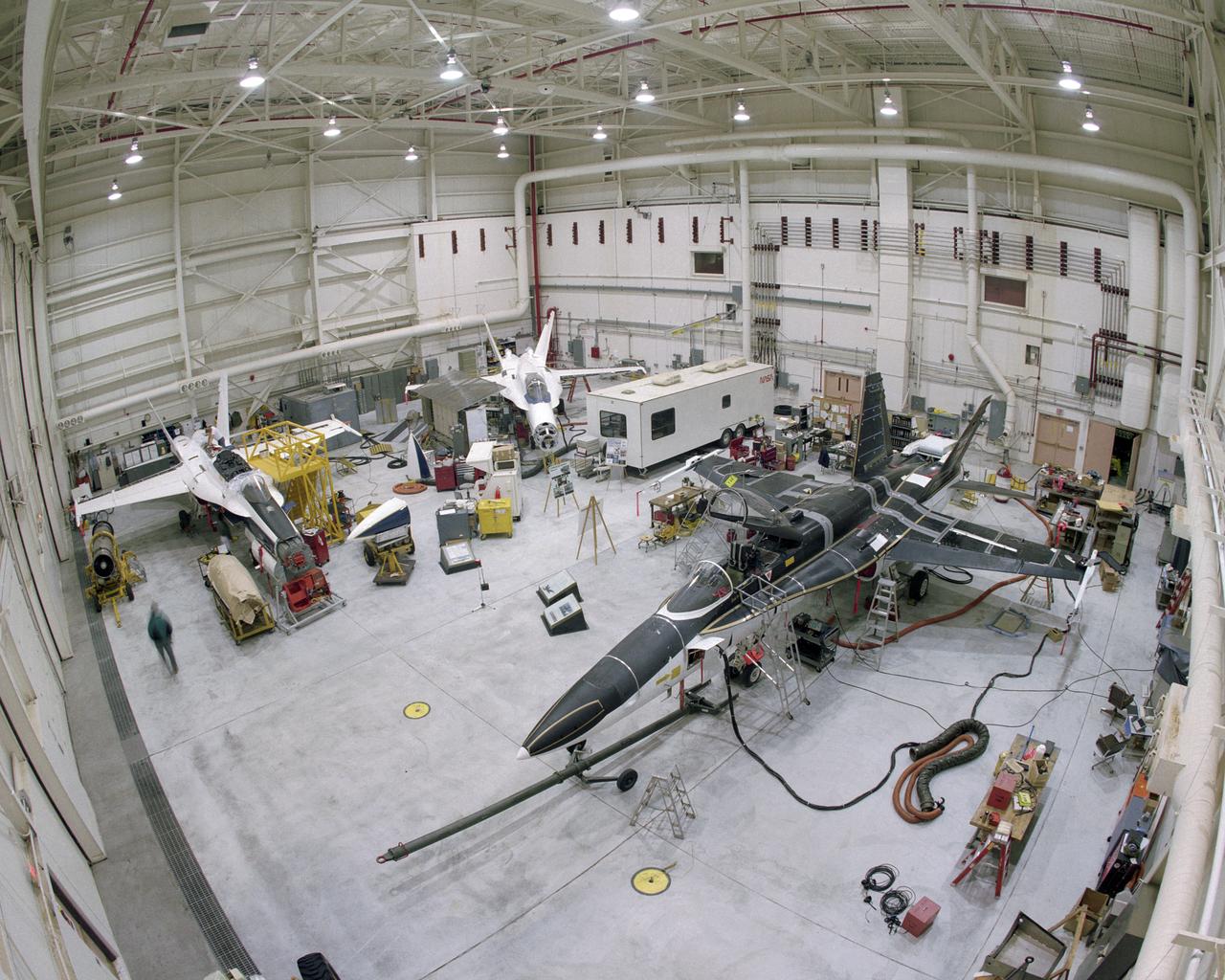

RAIF Hangar Bays 1 and 2. Three of NASA's F-18 aircraft can be seen in this photo. The SRA, or Systems Research Aircraft, is at the far left. In the middle is the F-18 Iron Bird, used for full-scale, hardware-in-the-loop simulations. On the right is the F-18 High Alpha Research Vehicle, or HARV.
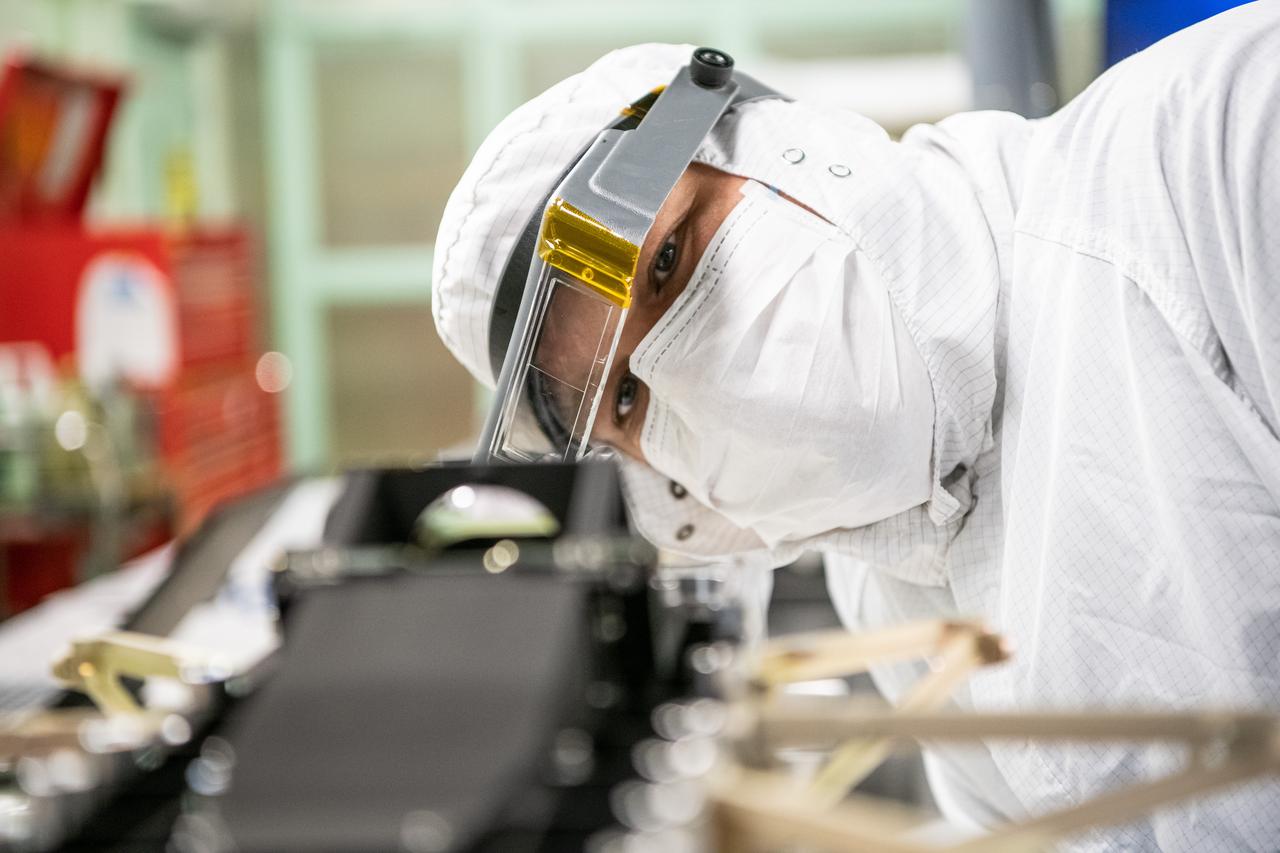

Mechanical technician, Andrew Scharmann, installs a shim and inspects an optic on the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) rotating telescope prior to integrating other hardware and optical components. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
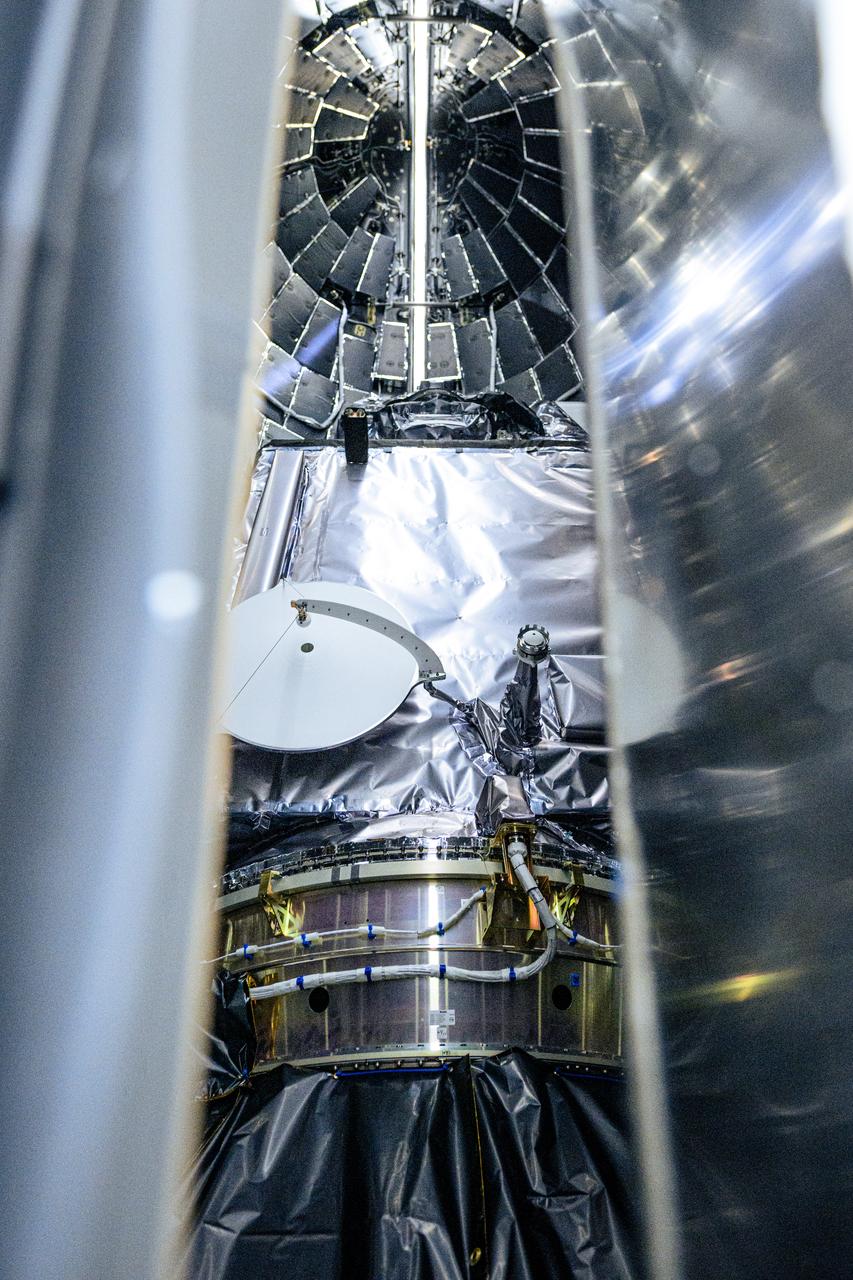

NASA and SpaceX technicians safely encapsulate NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft in SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings on Monday, Jan. 29, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fairing halves protect the spacecraft from aerodynamic pressure and heating during the ascent phase of launch. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6, 2024.
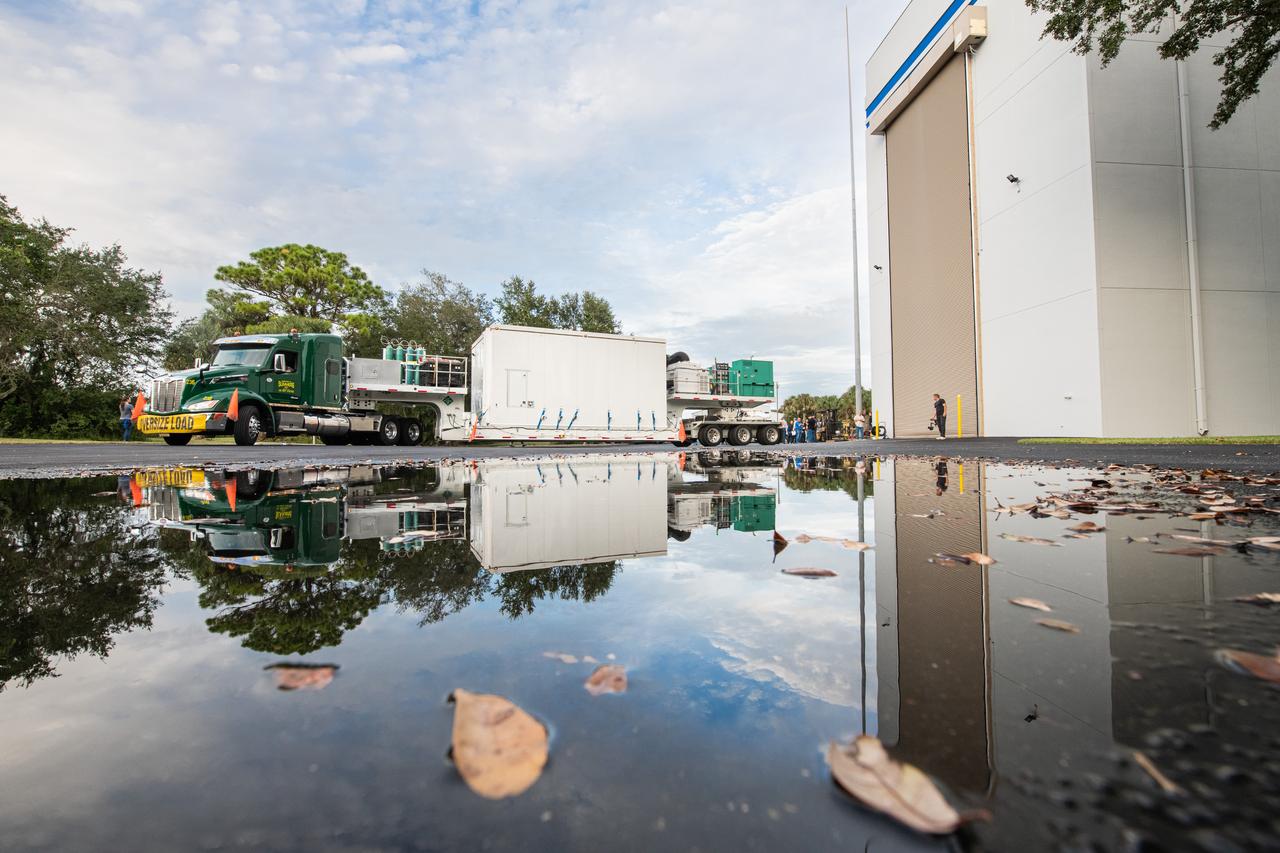

The transport carrier containing NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft arrives at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Nov. 14, 2023. PACE was shipped from the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and is targeted to launch on January 30, 2024, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifting off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. The PACE observatory will help us better understand how the ocean and atmosphere exchange carbon dioxide, measure key atmospheric variables associated with air quality and Earth's climate, and monitor ocean health, in part by studying phytoplankton, tiny plants and algae that sustain the marine food web.

NASA and SpaceX technicians connect NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft to the payload adapter on Friday, Jan. 26, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6.

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft bus with mass mockups installed is lifted before structural proof testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on May 26th, 2021. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
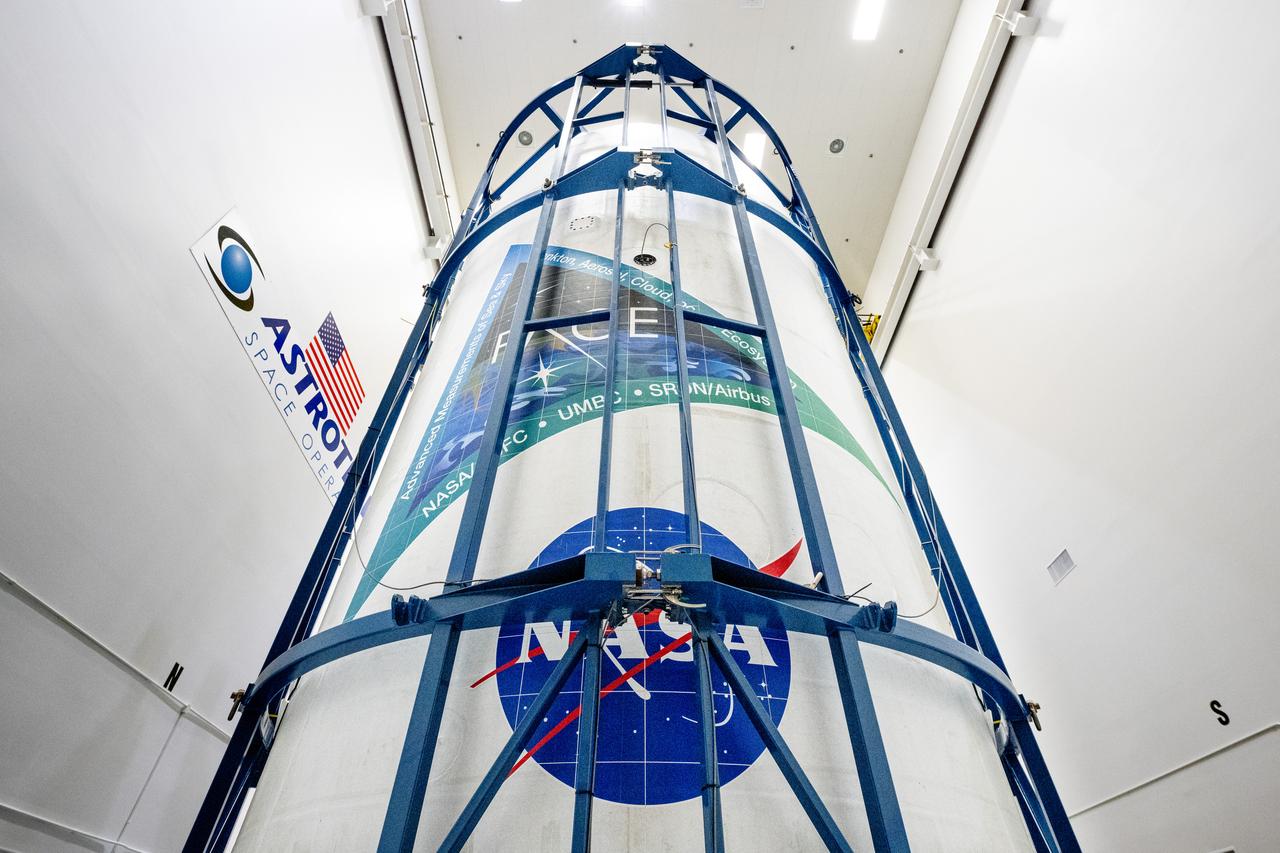

NASA and SpaceX technicians safely encapsulate NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft in SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings on Monday, Jan. 29, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fairing halves protect the spacecraft from aerodynamic pressure and heating during the ascent phase of launch. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6, 2024.
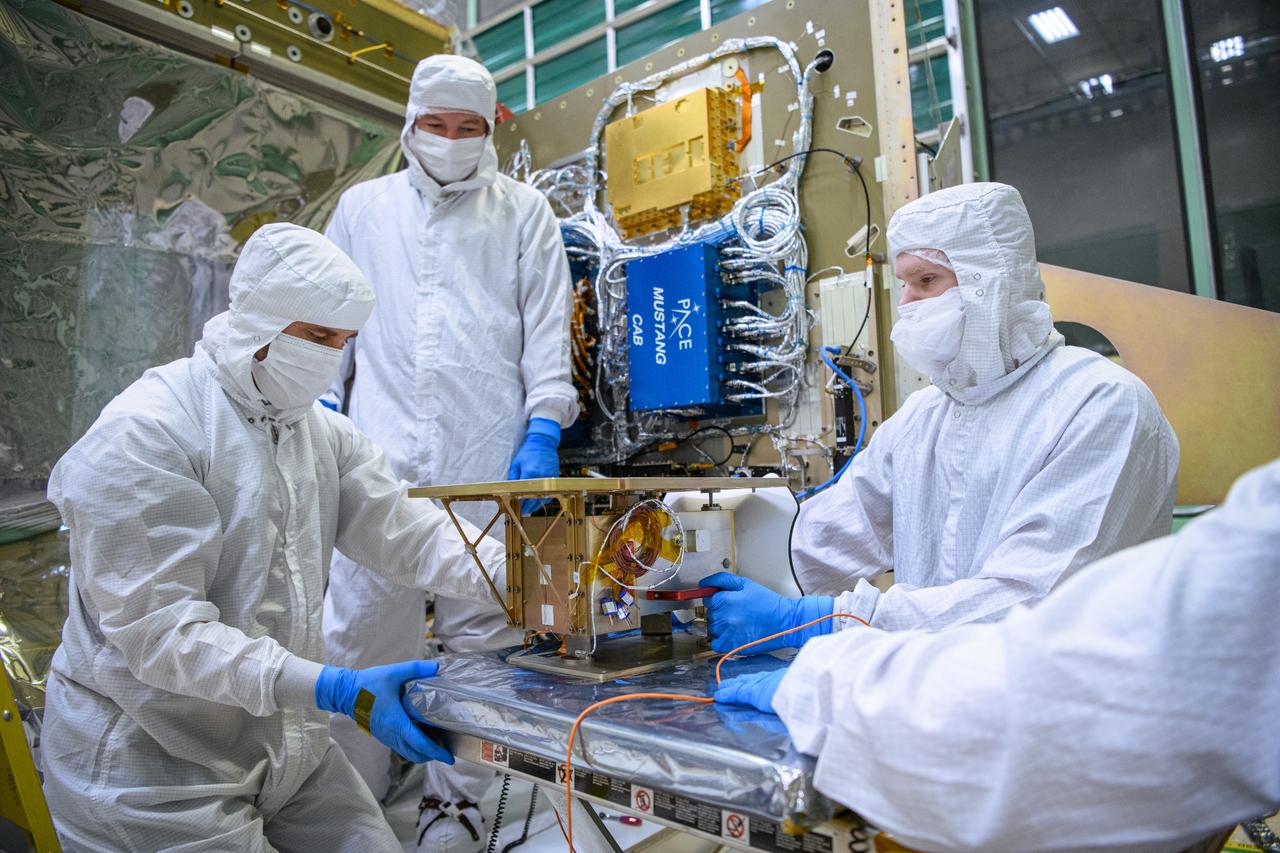

Technicians prepare to integrate the Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft bus at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 25th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's PACE observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
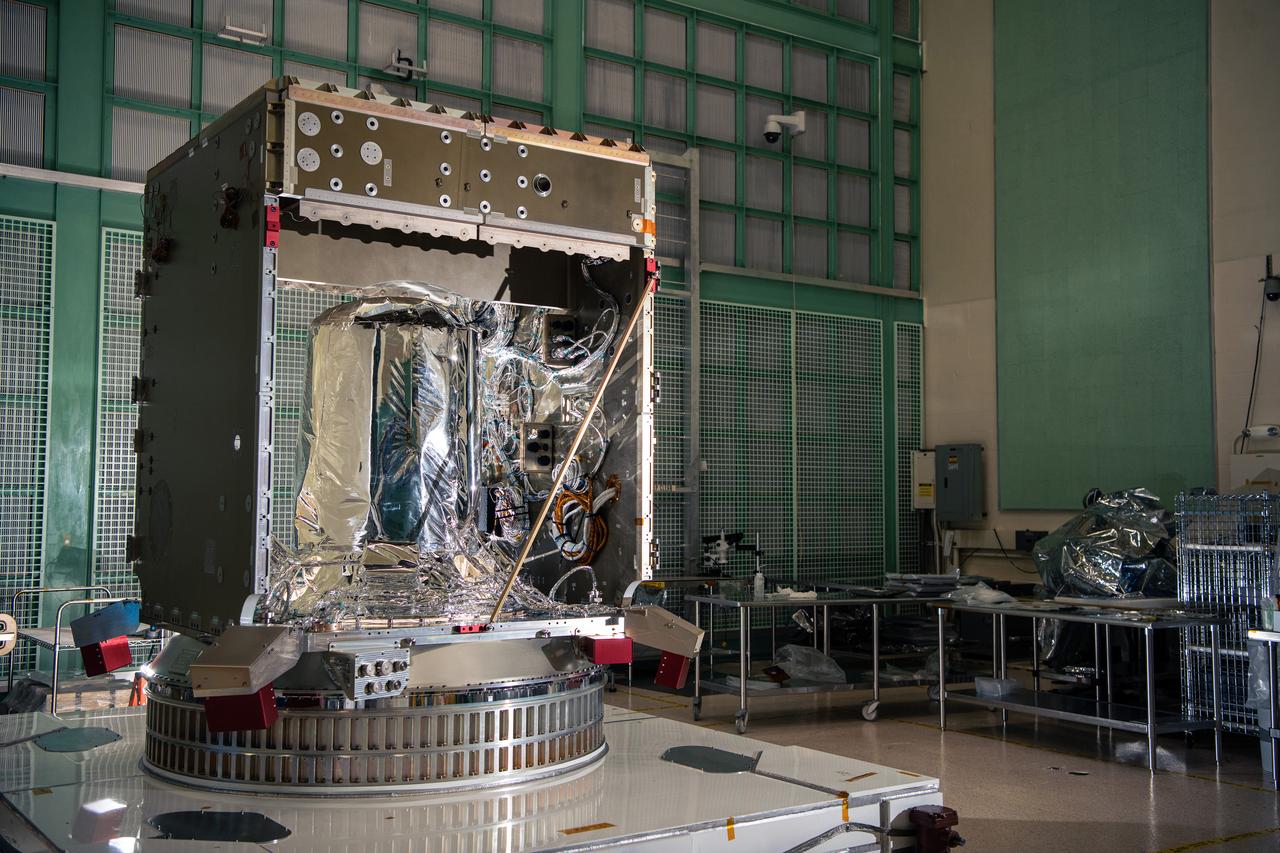

The flight propellant tank is visible inside the partially assembled Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Spacecraft structure in the cleanroom at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on February 24th, 2022. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
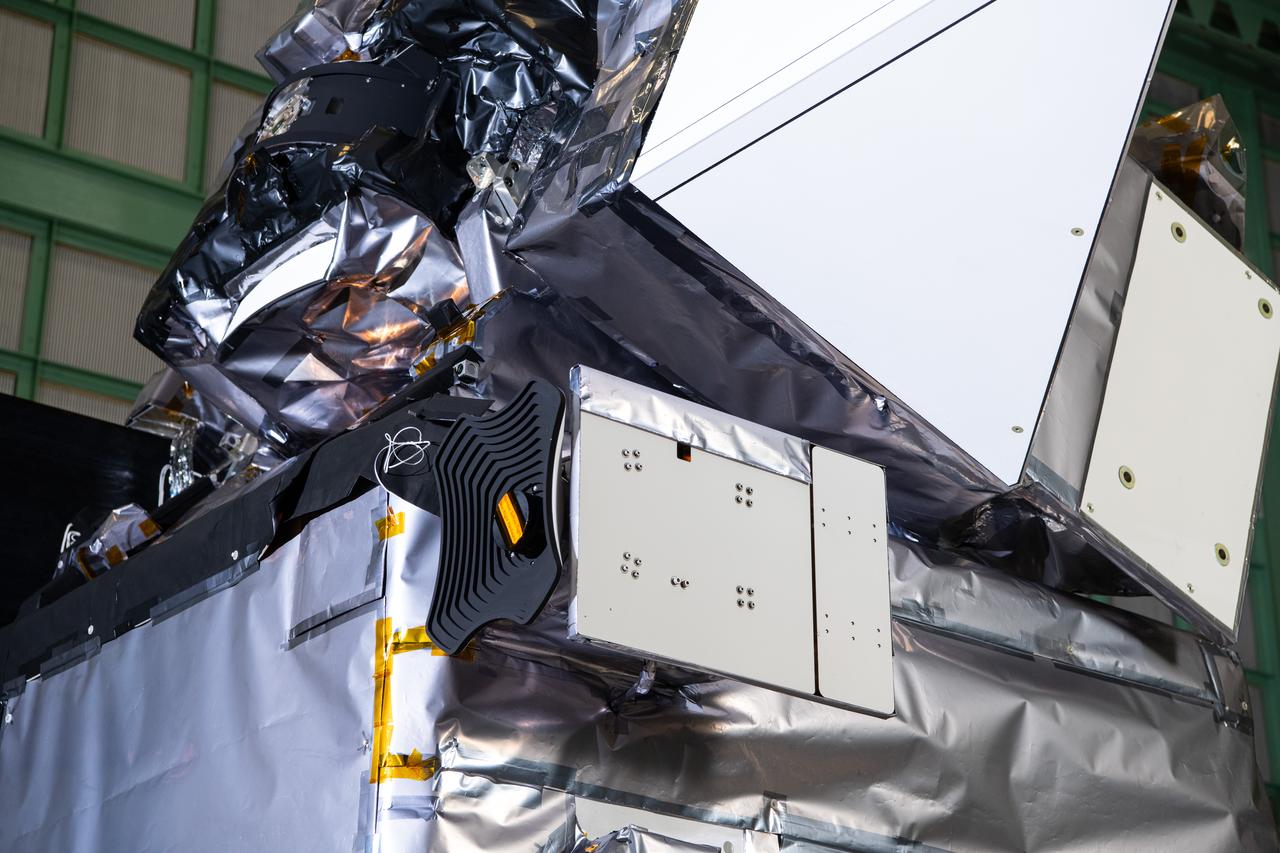

The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument on The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 31st, 2023. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's PACE observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
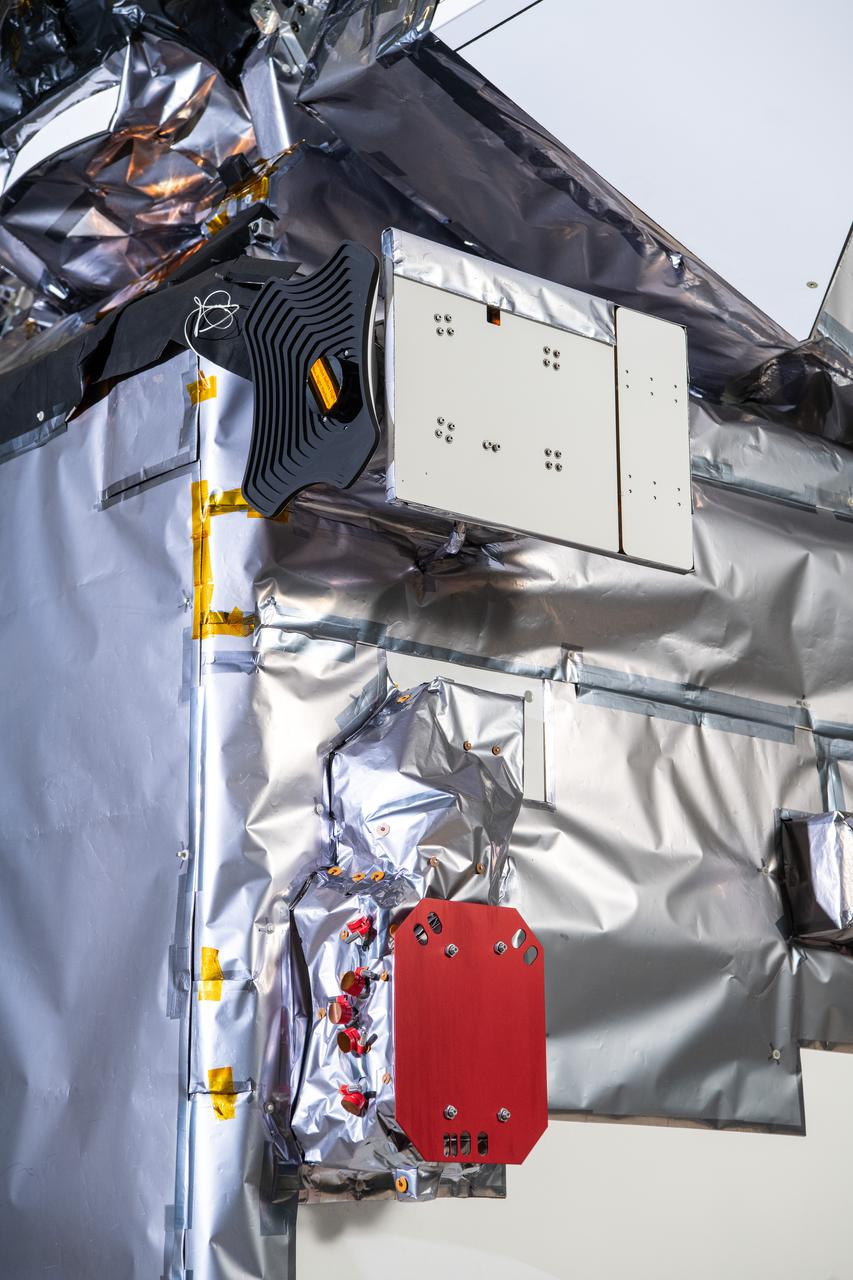

The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument (top) and the SPEXone instrument on The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 31st, 2023. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's PACE observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute. SPEXone has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
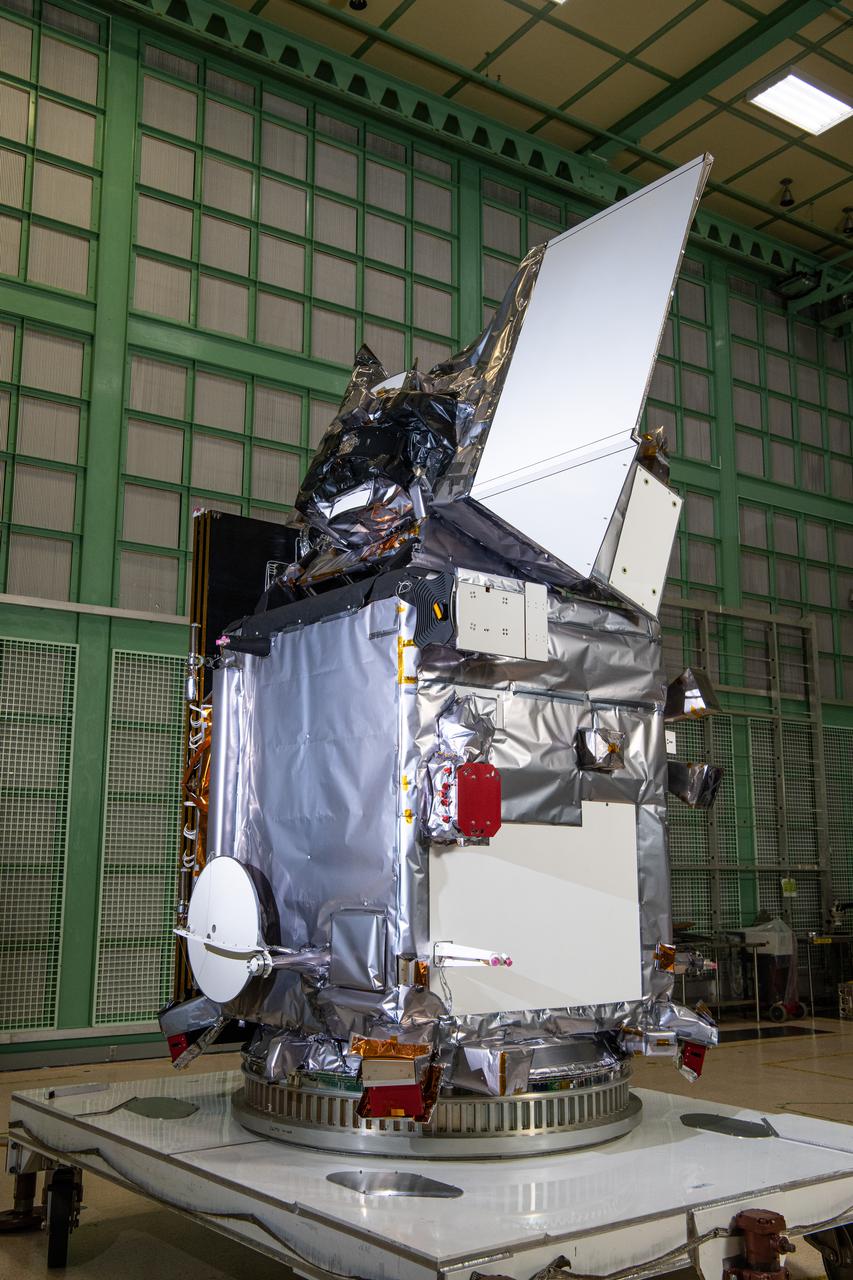

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 31st, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
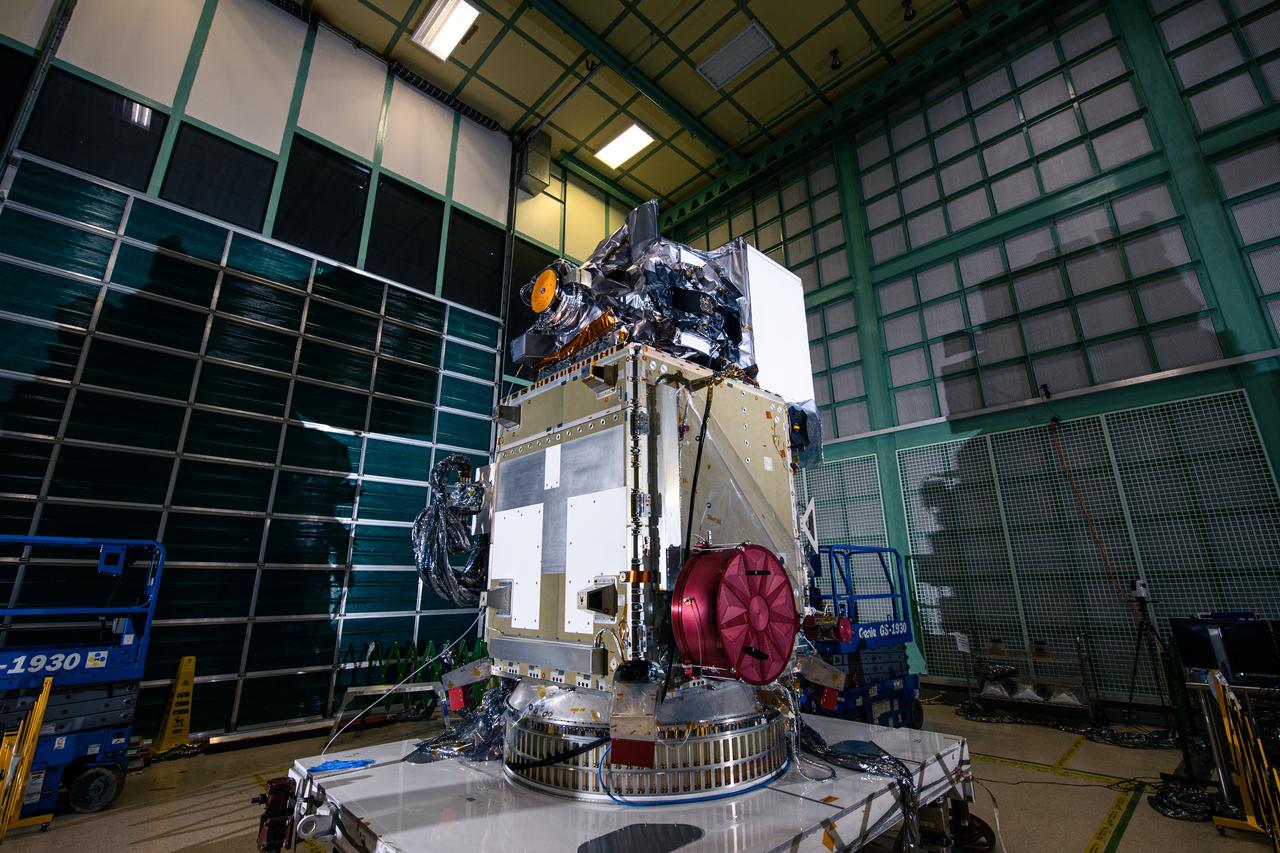
The Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) is installed on the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory spacecraft. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
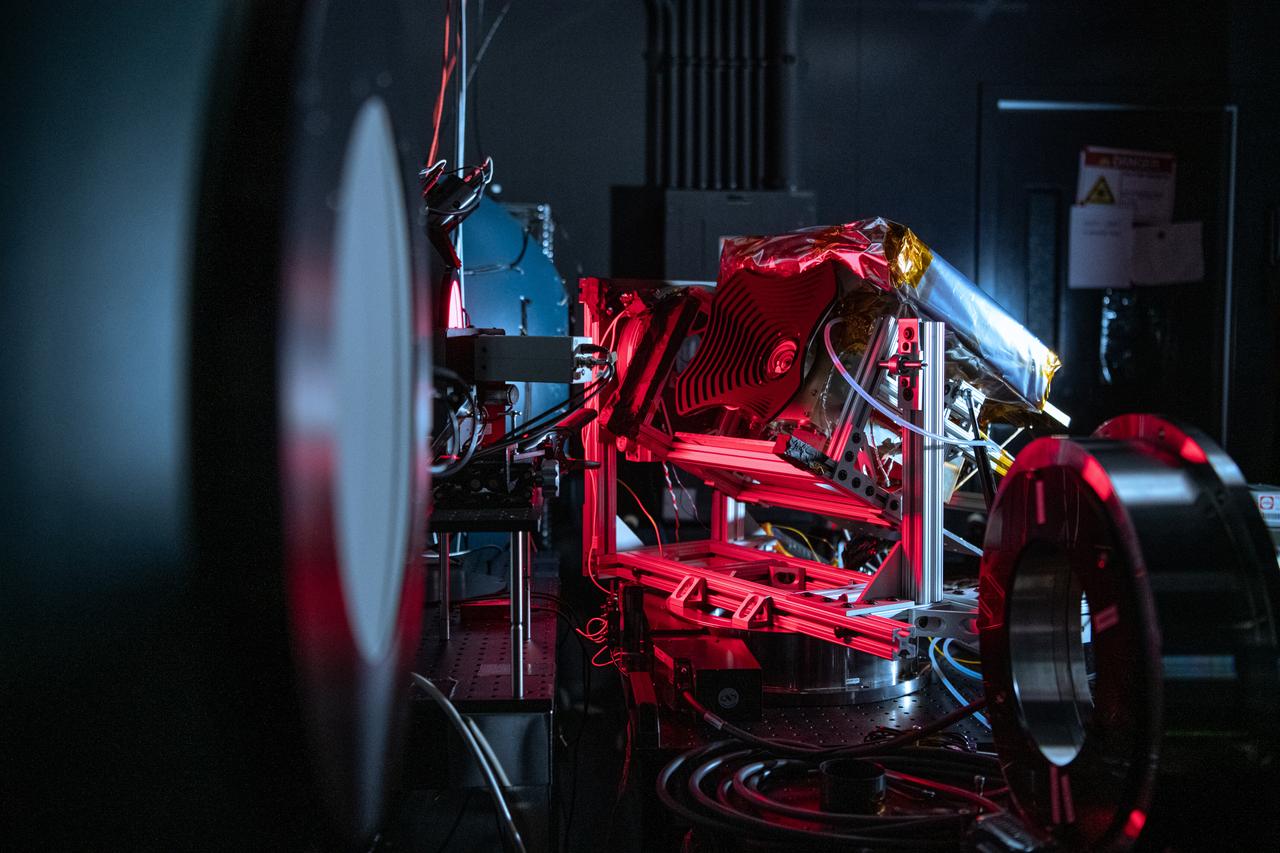

The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument undergoes calibration testing after at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on October 4th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute.
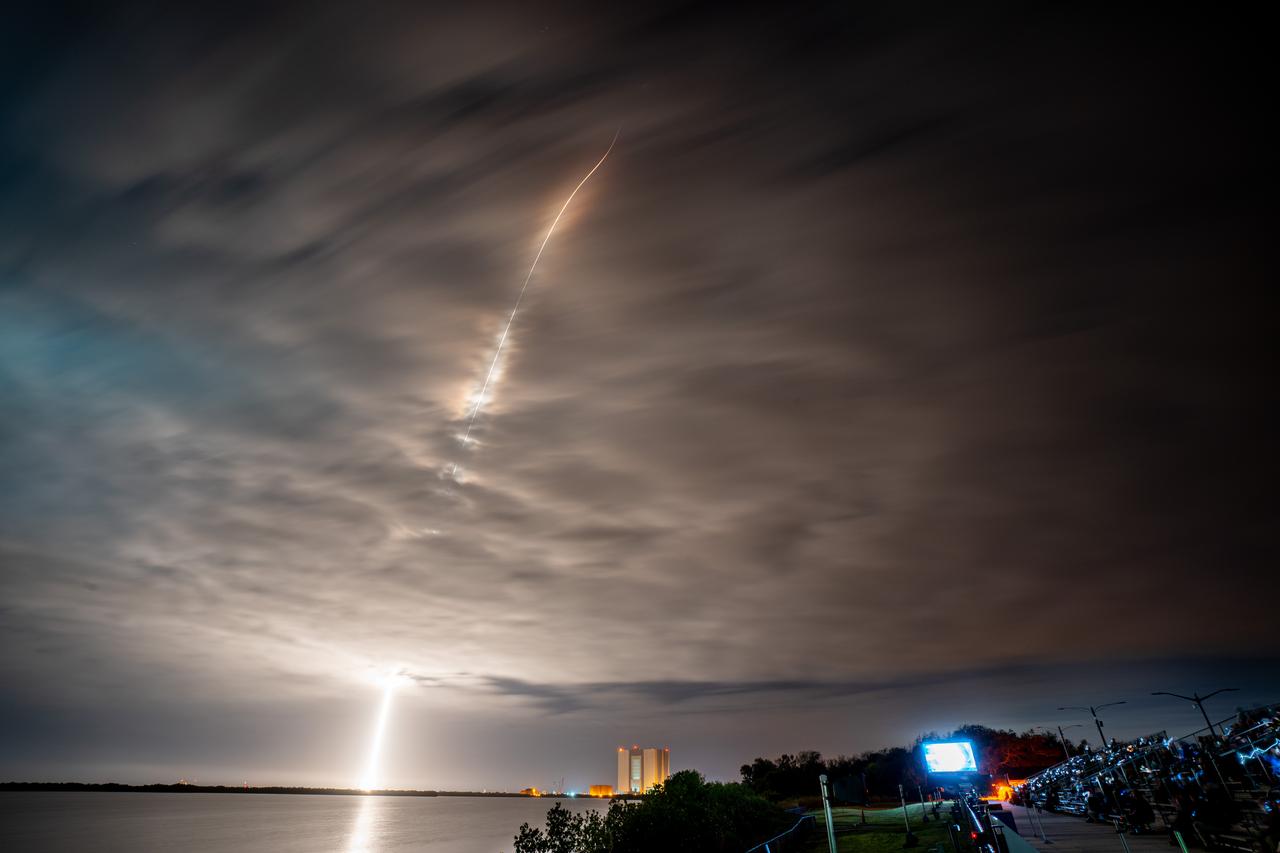

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft is seen in this long exposure photograph as it launched atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST Thursday, Feb. 8. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
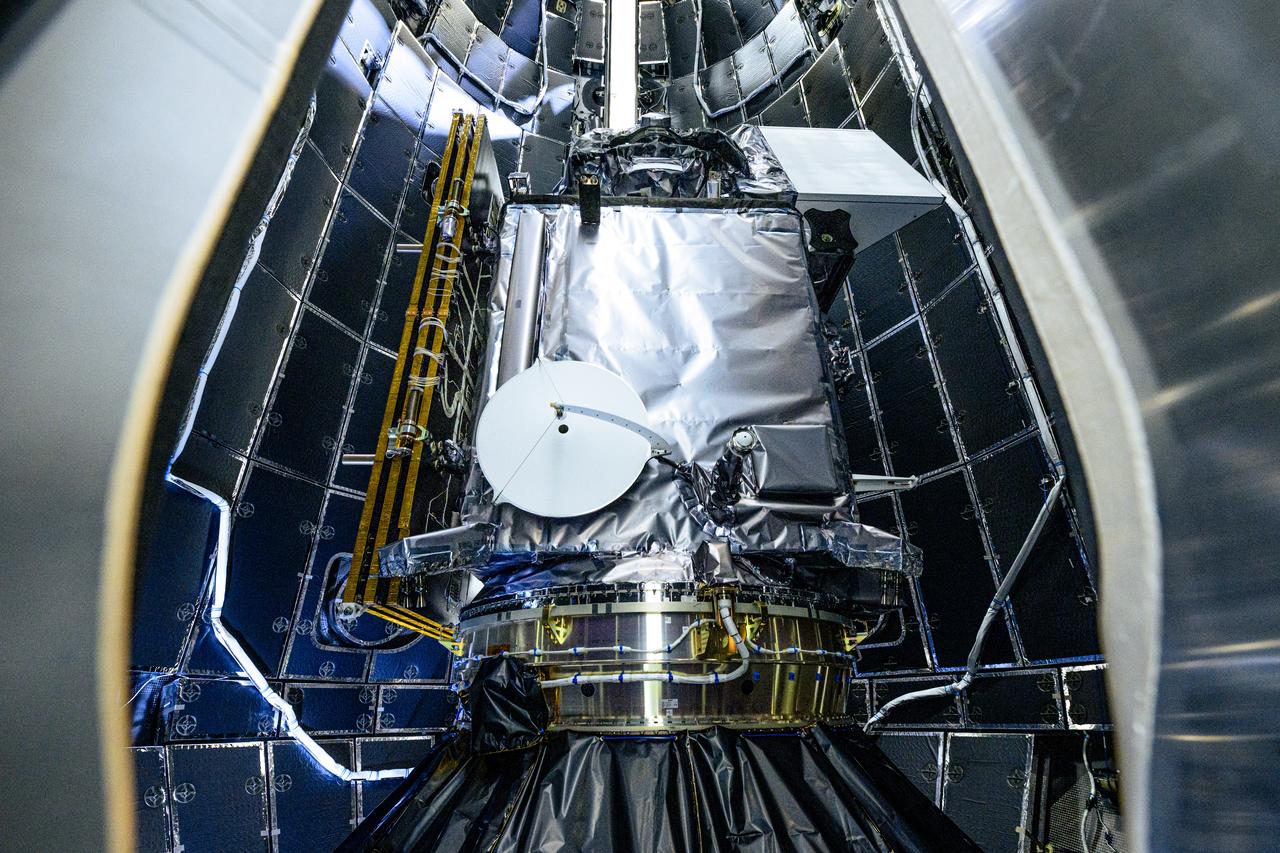

NASA and SpaceX technicians safely encapsulate NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft in SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The fairing halves protect the spacecraft from aerodynamic pressure and heating during the ascent phase of launch. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6, 2024.
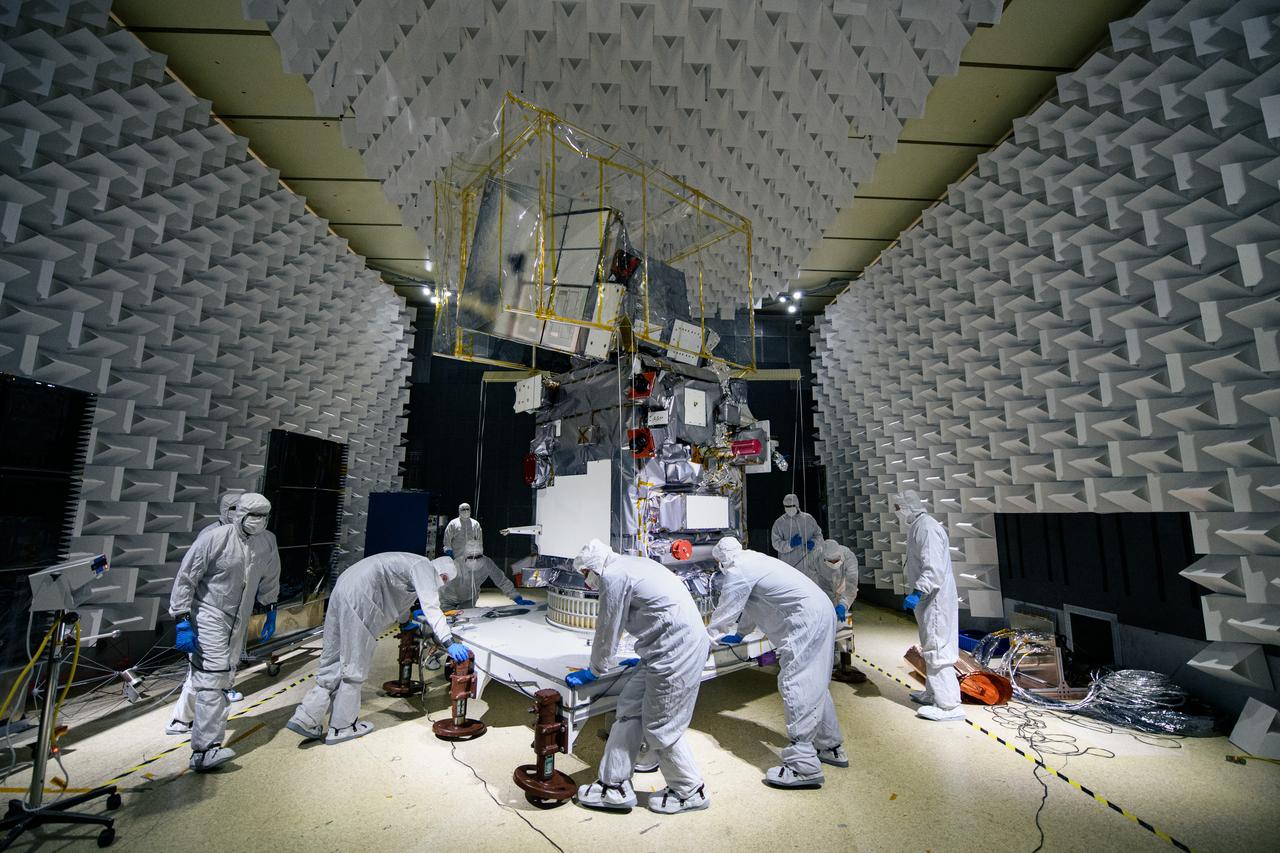

Technicians move the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory inside the Electromagnetic Interference testing facility at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on January 30th, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
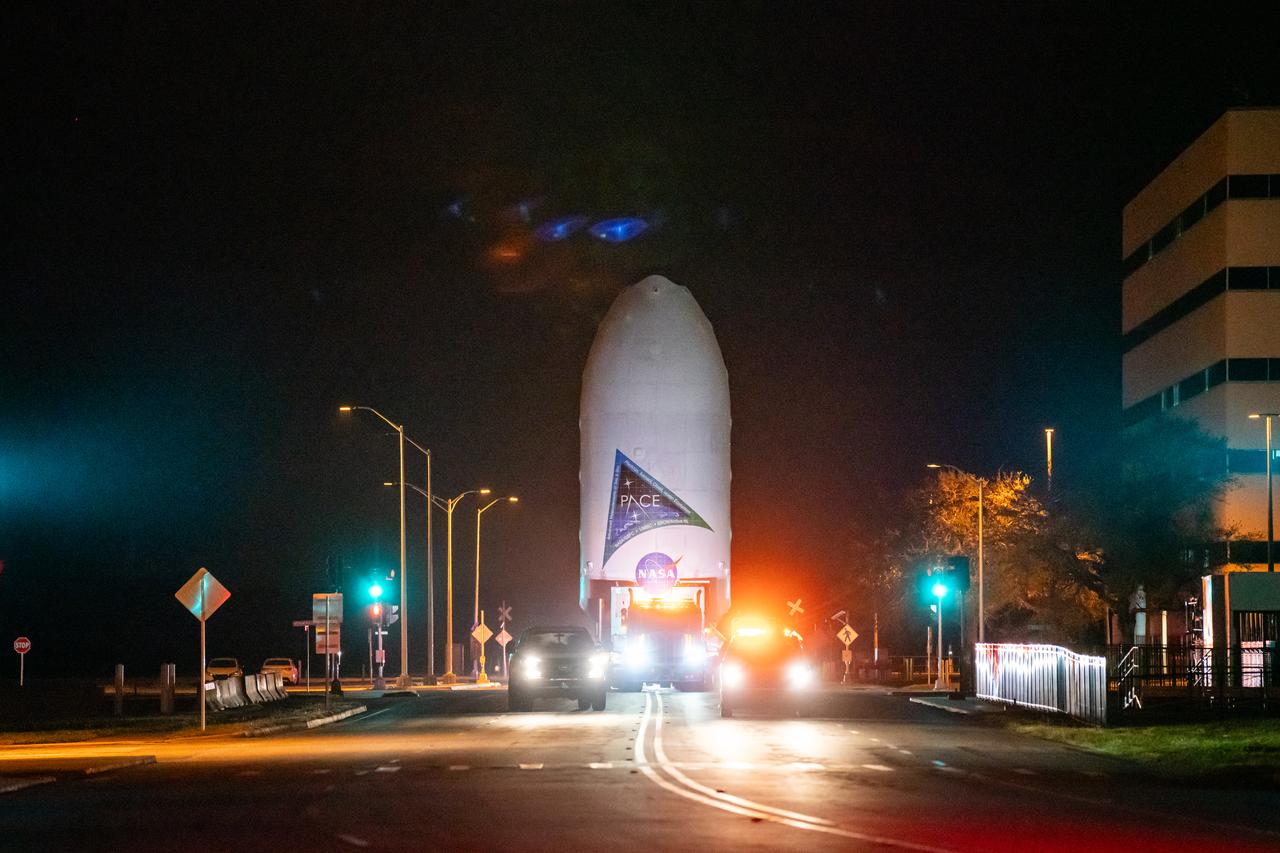

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft encapsulated inside SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings is transported from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, to be mated with a SpaceX Falcon 9 in preparation for liftoff set for no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6, 2024. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols.

The space shuttle Atlantis atop NASA's 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) during takeoff for a return ferry flight to the Kennedy Space Center from Edwards, California. The STS-66 mission was dedicated to the third flight of the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science-3 (ATLAS-3), part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth program. The astronauts also deployed and retrieved a free-flying satellite designed to study the middle and lower thermospheres and perform a series of experiments covering life sciences research and microgravity processing. The landing was at 7:34 a.m. (PST) 14 November 1994, after being waved off from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida, due to adverse weather.

Technicians integrate the Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument to the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft bus at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 25th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's PACE observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
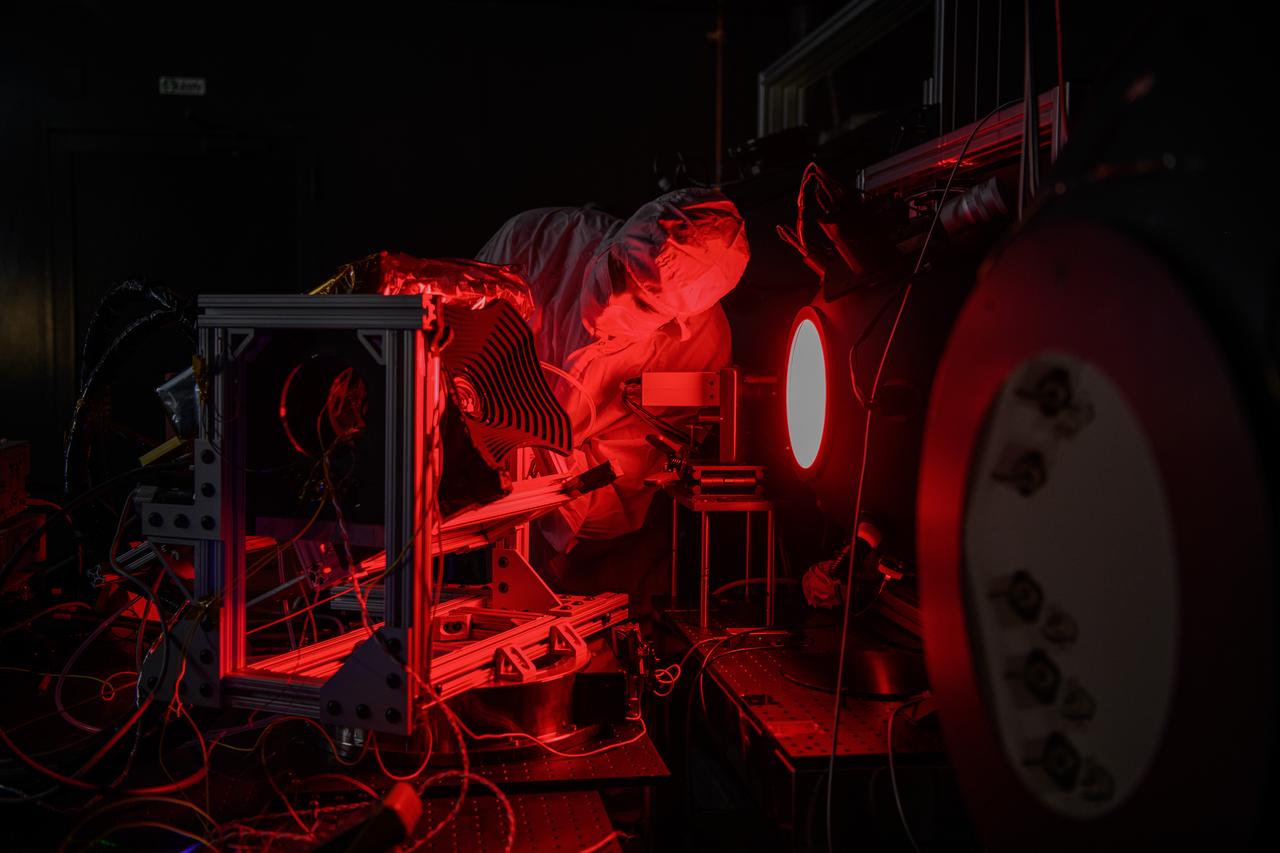

An engineer inspects the The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument during calibration testing after at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on October 4th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute.
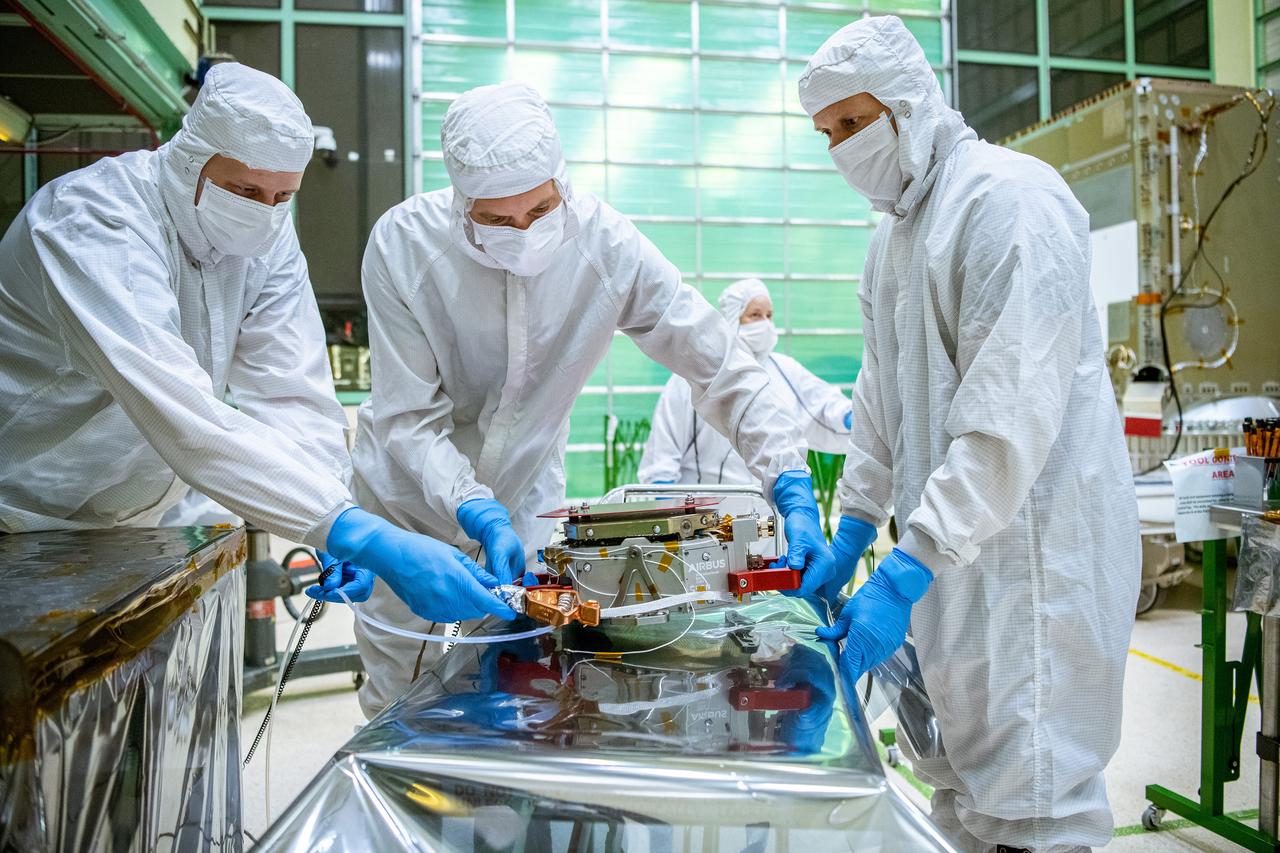

Engineers from SRON, the Netherlands Institute for Space Research, move the SPEXone instrument before it is integrated onto the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Spacecraft at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 13th, 2022. SPEXone is a compact, optical satellite instrument that will characterize aerosols from low Earth orbit as part of the NASA PACE mission. SPEXone is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory and has been developed by a Dutch consortium consisting of SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, supported by opto-mechanical expertise from TNO. SRON and Airbus DS NL are responsible for the design, manufacturing and testing of the instrument. The scientific lead is in the hands of SRON. SPEXone is a public-private initiative, funded by the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research (NWO), SRON and Airbus DS NL.
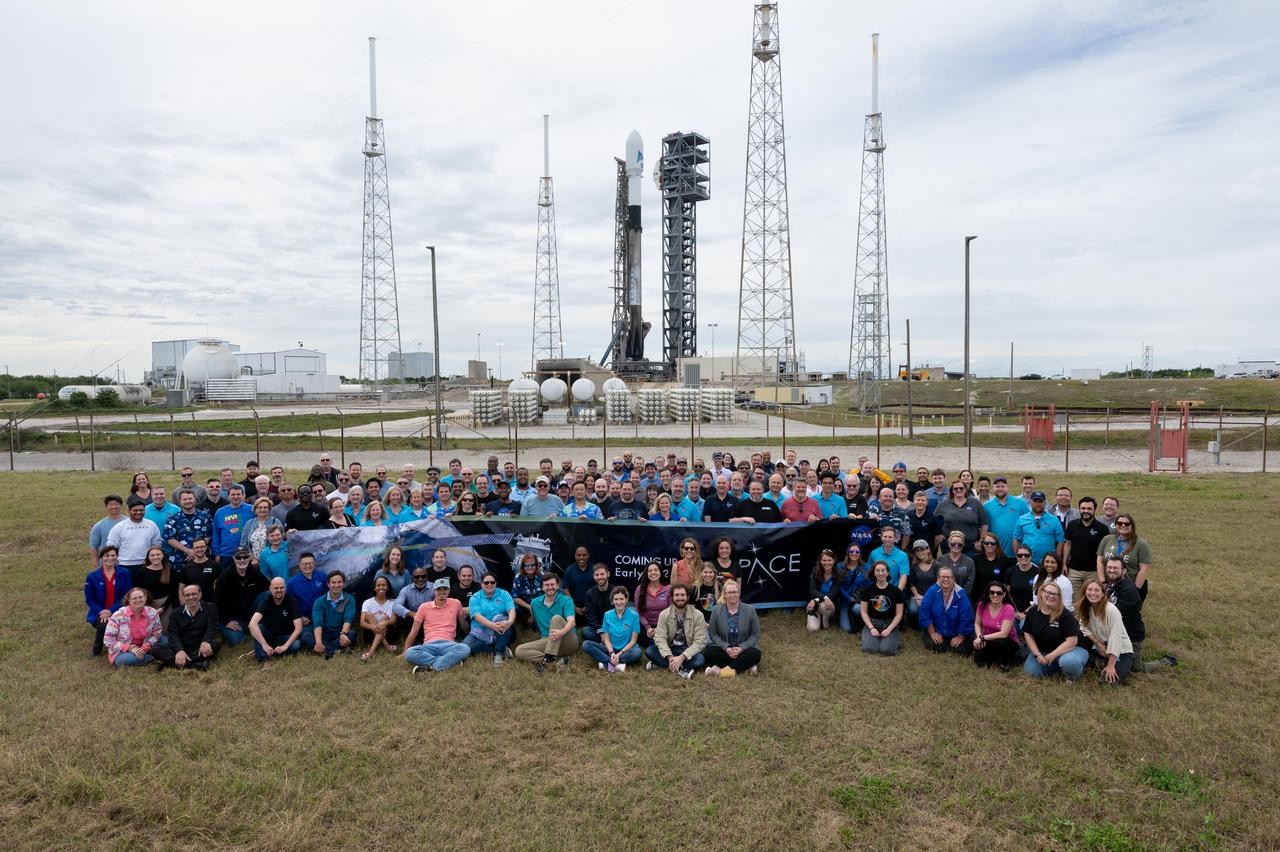

Members of the PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem), OCI (The Ocean Color Instrument), HARP2, and SpexONE teams pose with the PACE Spacecraft atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST Thursday, Feb. 8. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
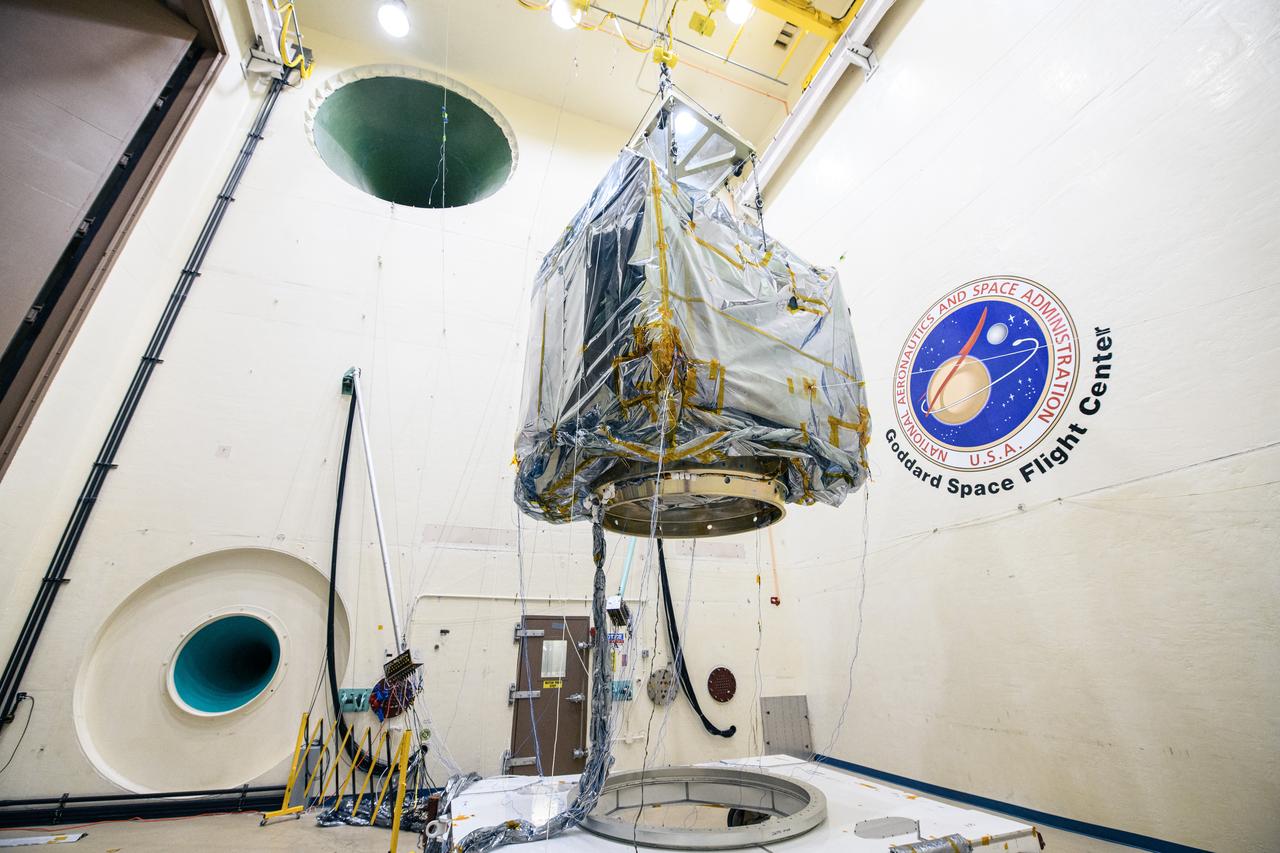

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory suspended for acoustic testing in the acoustic test facility at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on April 17th, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
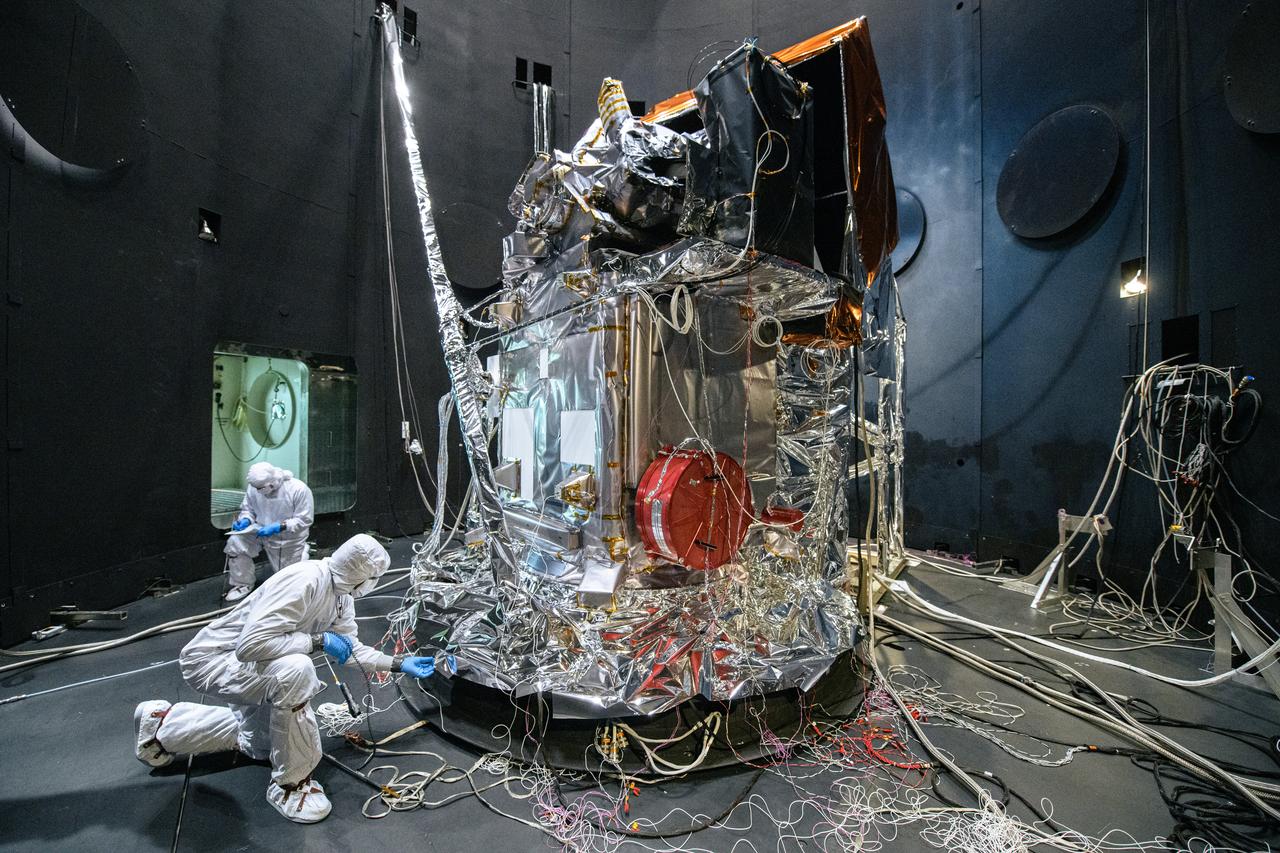

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) Observatory inside the Space Environment Simulator (SES) thermal vacuuum chamber before thermal environmental testing at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on June 17th, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
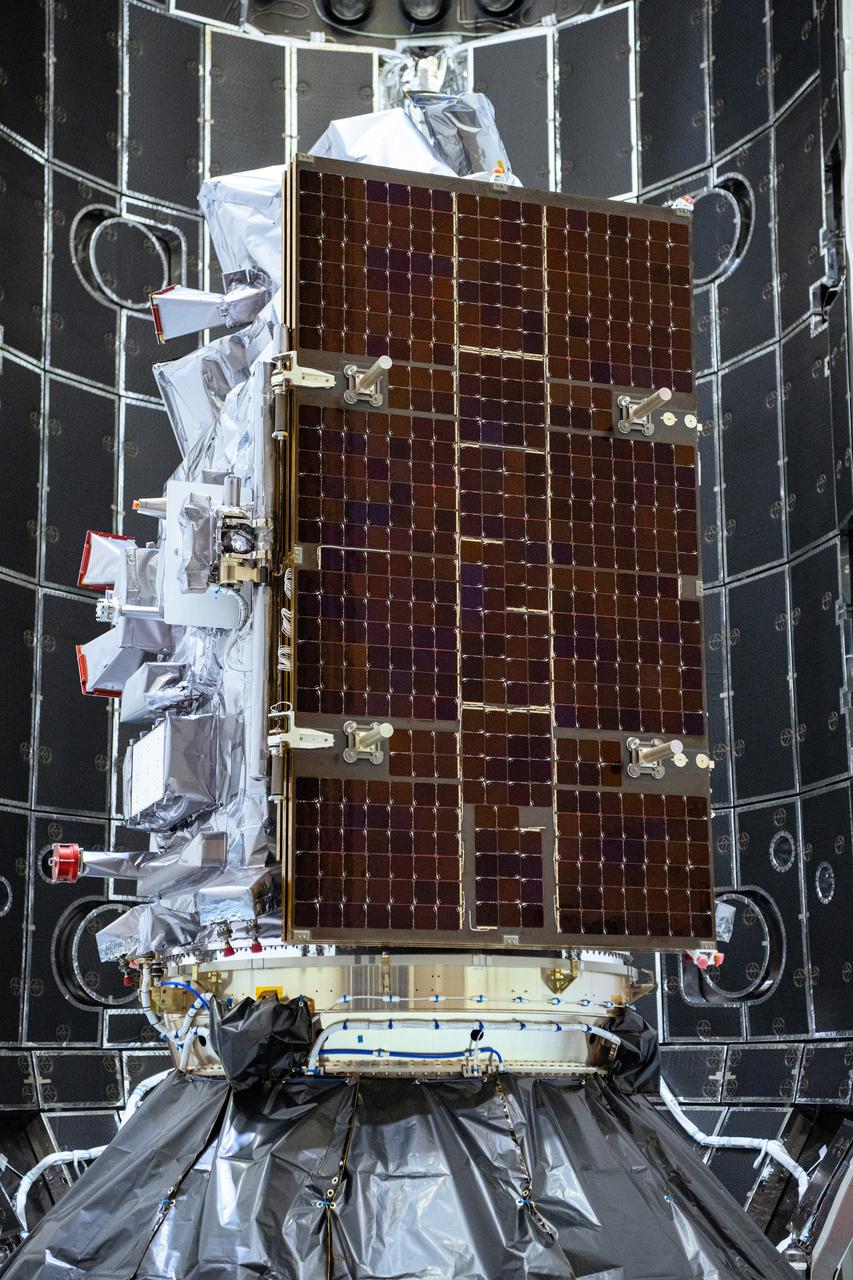

NASA and SpaceX technicians connect NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft to the payload adapter on Friday, Jan. 26, 2024, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols. PACE is set to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST on Tuesday, Feb. 6.
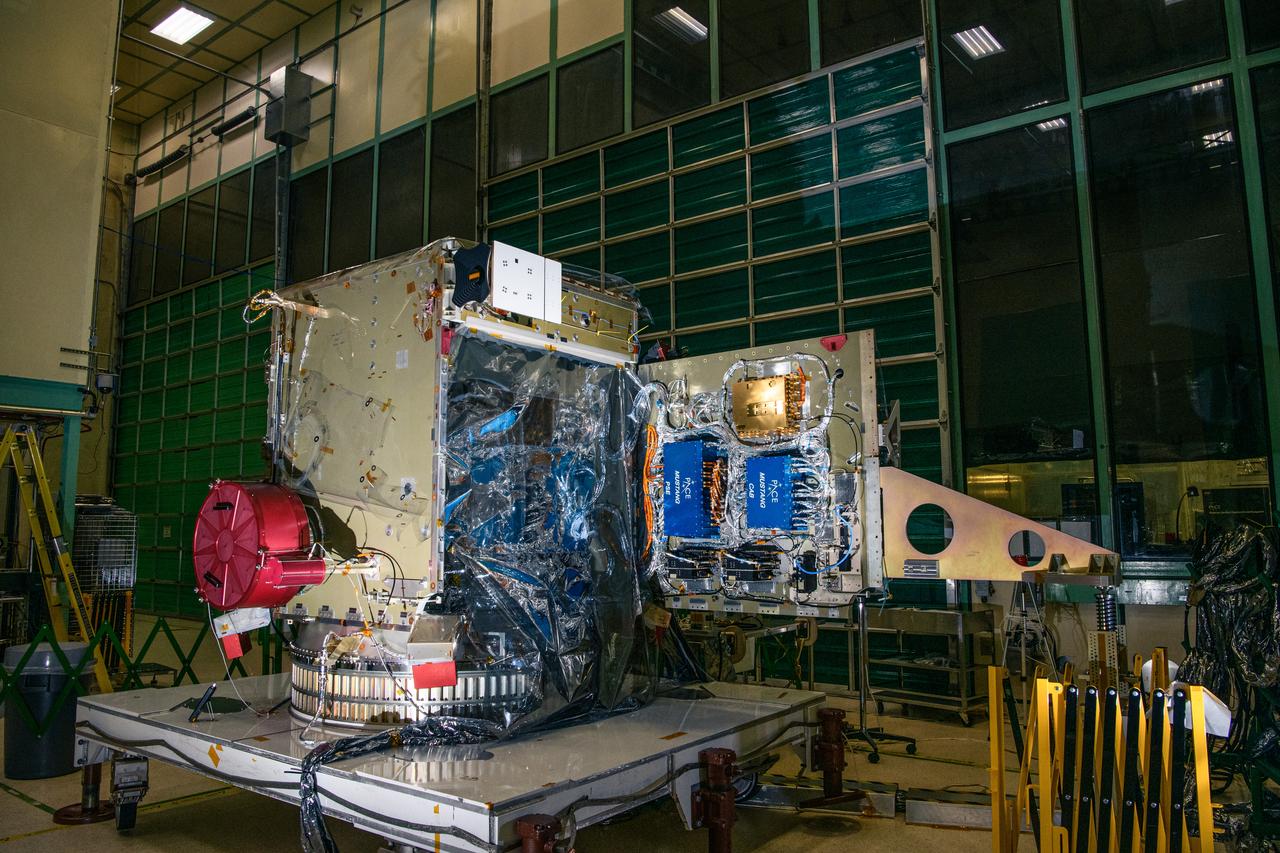

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft bus after integration of The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on October 25th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's PACE observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.
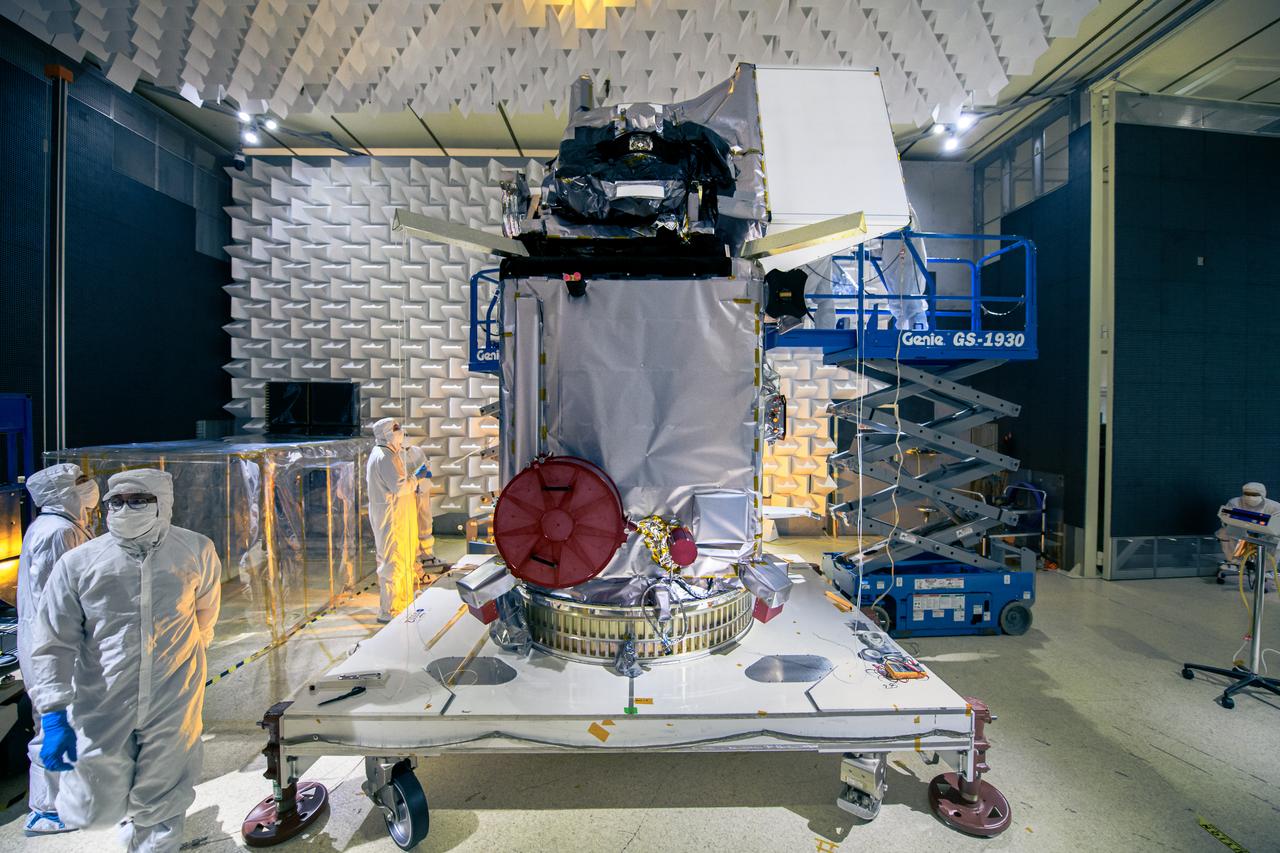

The Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory inside the Electromagnetic Interference testing facility at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland on January 30th, 2023. PACE's unprecedented spectral coverage will provide the first-ever global measurements designed to identify phytoplankton community composition. The mission will make global ocean color measurements, using the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI), to provide extended data records on ocean ecology and global biogeochemistry along with polarimetry measurements, using the Spectro-polarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone) and the Hyper Angular Research Polarimeter (HARP2) to provide extended data records on clouds and aerosols. The Earth-observing satellite mission, built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, will continue and advance observations of global ocean color, biogeochemistry, and ecology, as well as the carbon cycle, aerosols and clouds.

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, successfully lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST Thursday, Feb. 8. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
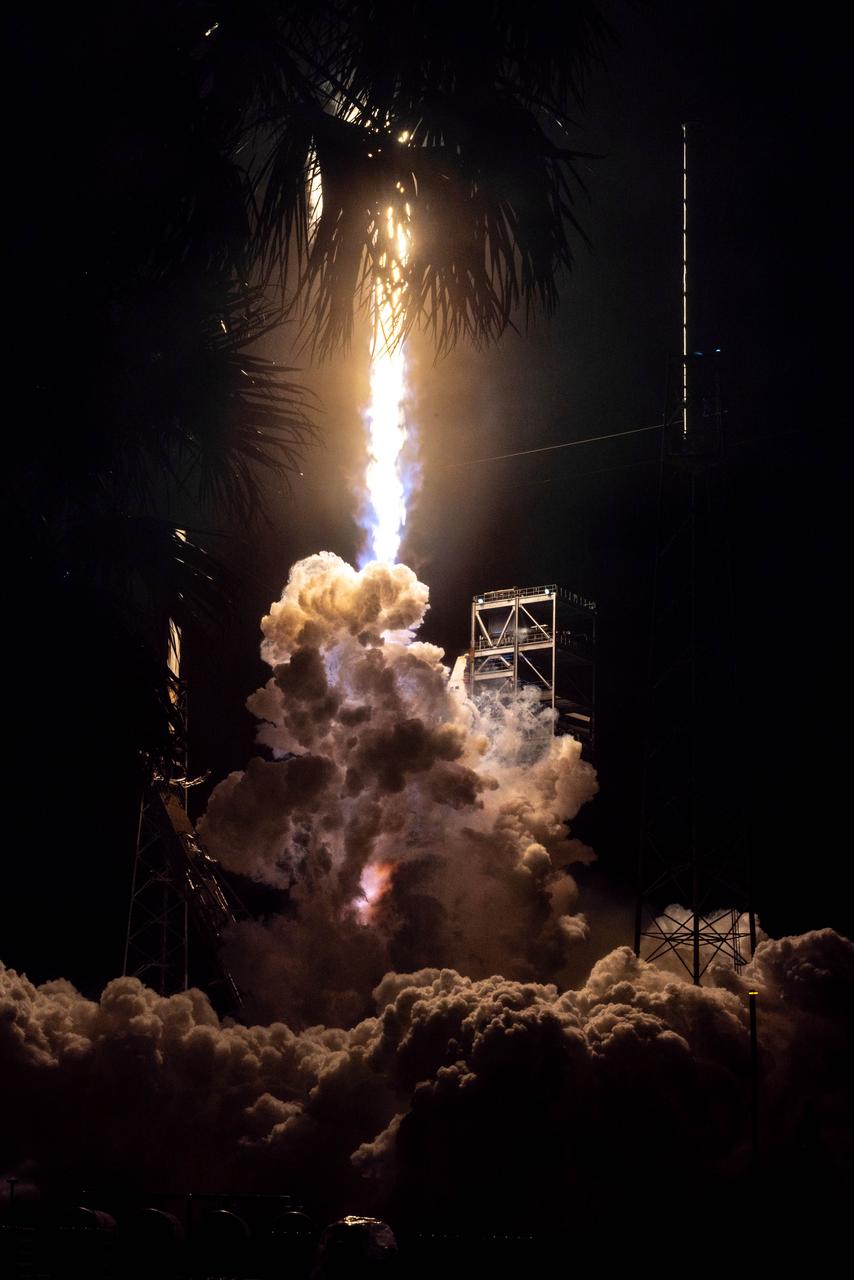

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, successfully lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST Thursday, Feb. 8. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
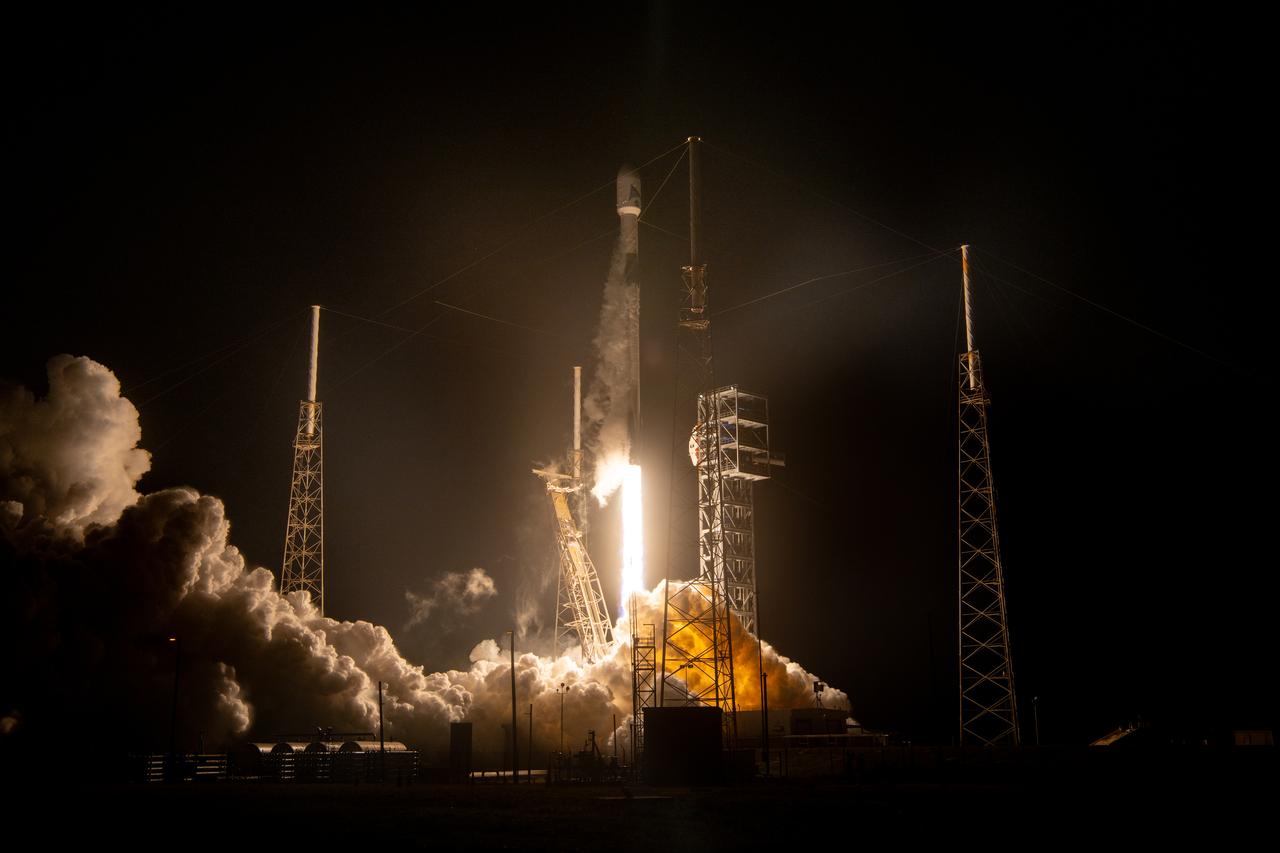

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, successfully lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST Thursday, Feb. 8. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
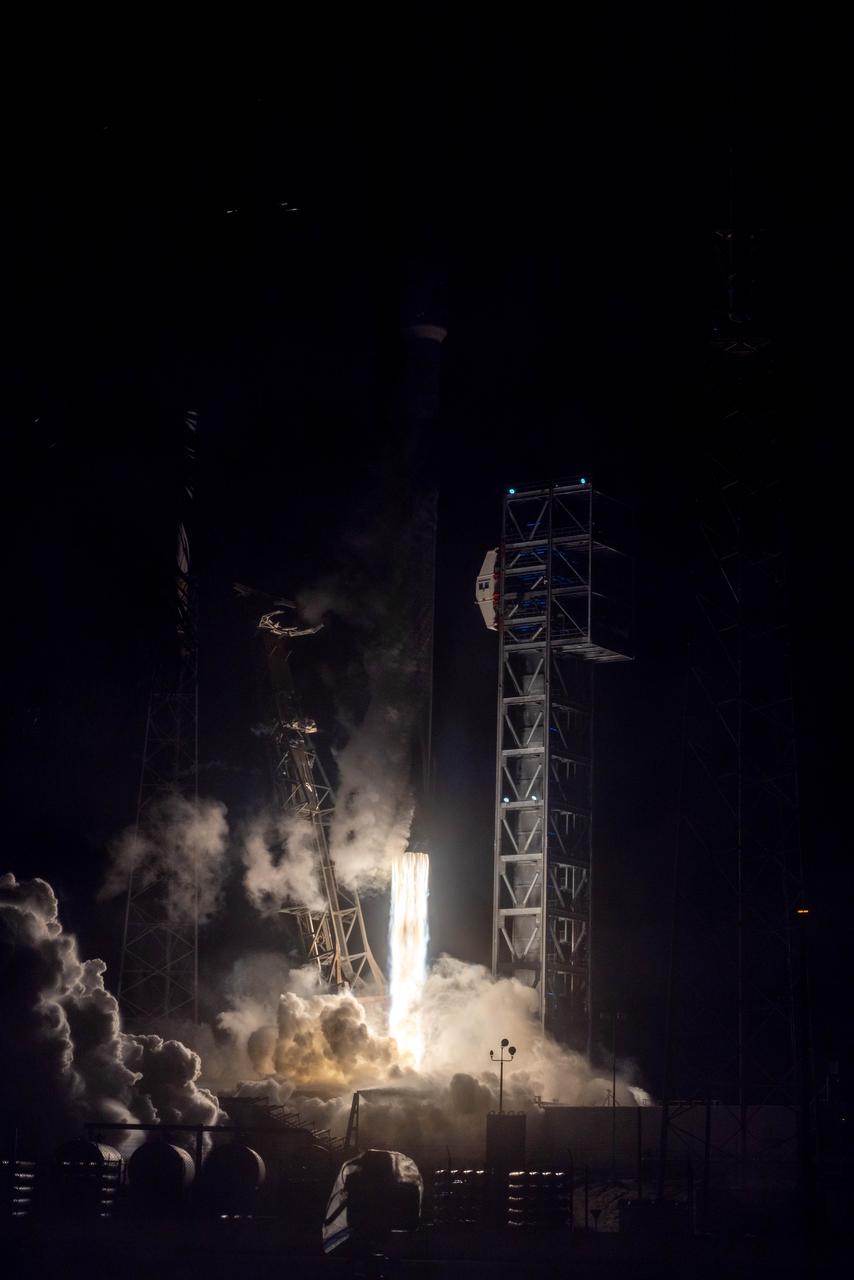

NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, successfully lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 1:33 a.m. EST Thursday, Feb. 8. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton, as well new data on clouds and aerosols.
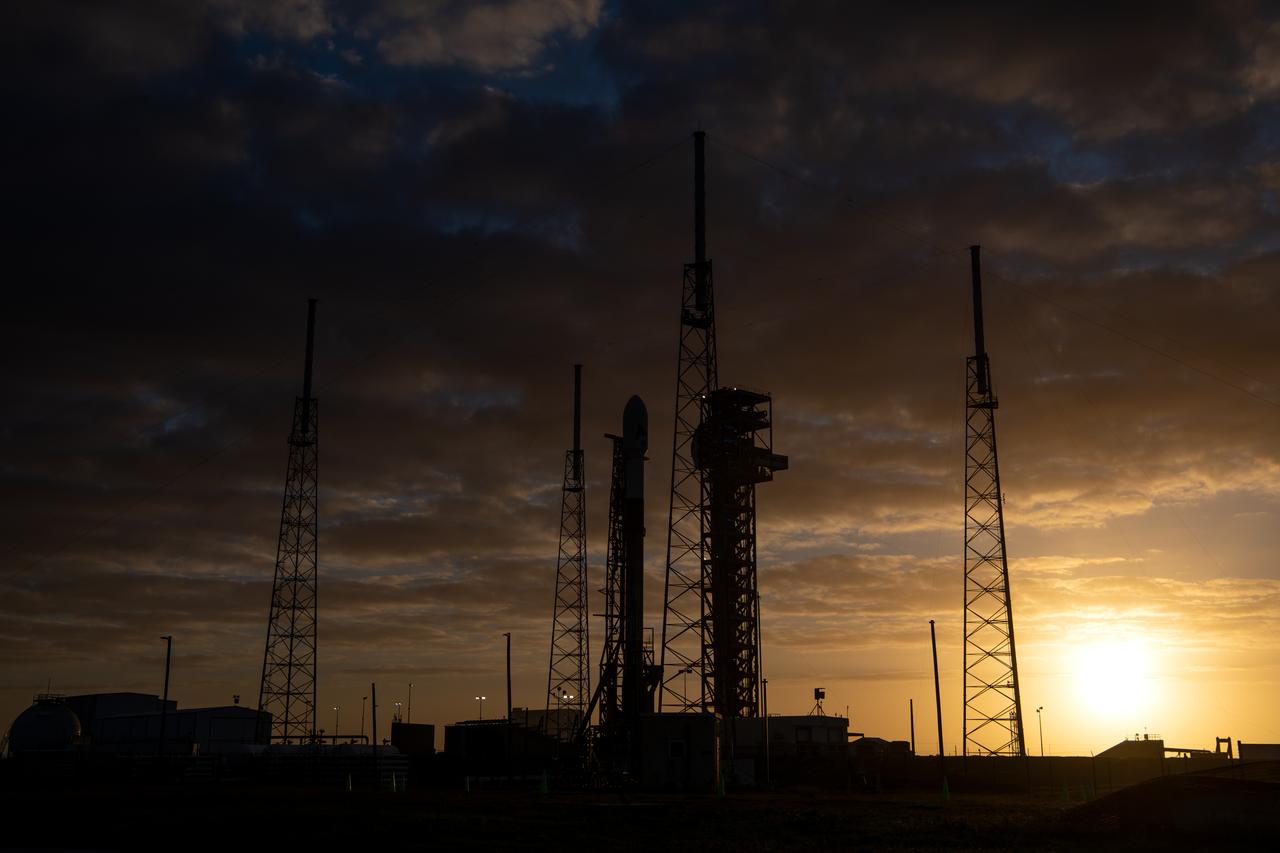

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) spacecraft stands vertical at Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Monday, Feb. 5, 2024. PACE is NASA’s newest earth-observing satellite that will help increase our understanding of Earth’s oceans, atmosphere, and climate by delivering hyperspectral observations of microscopic marine organisms called phytoplankton as well new data on clouds and aerosols. Liftoff of the PACE mission is set for no earlier than 1:33 a.m. EST on Wednesday, Feb. 7, 2024.
