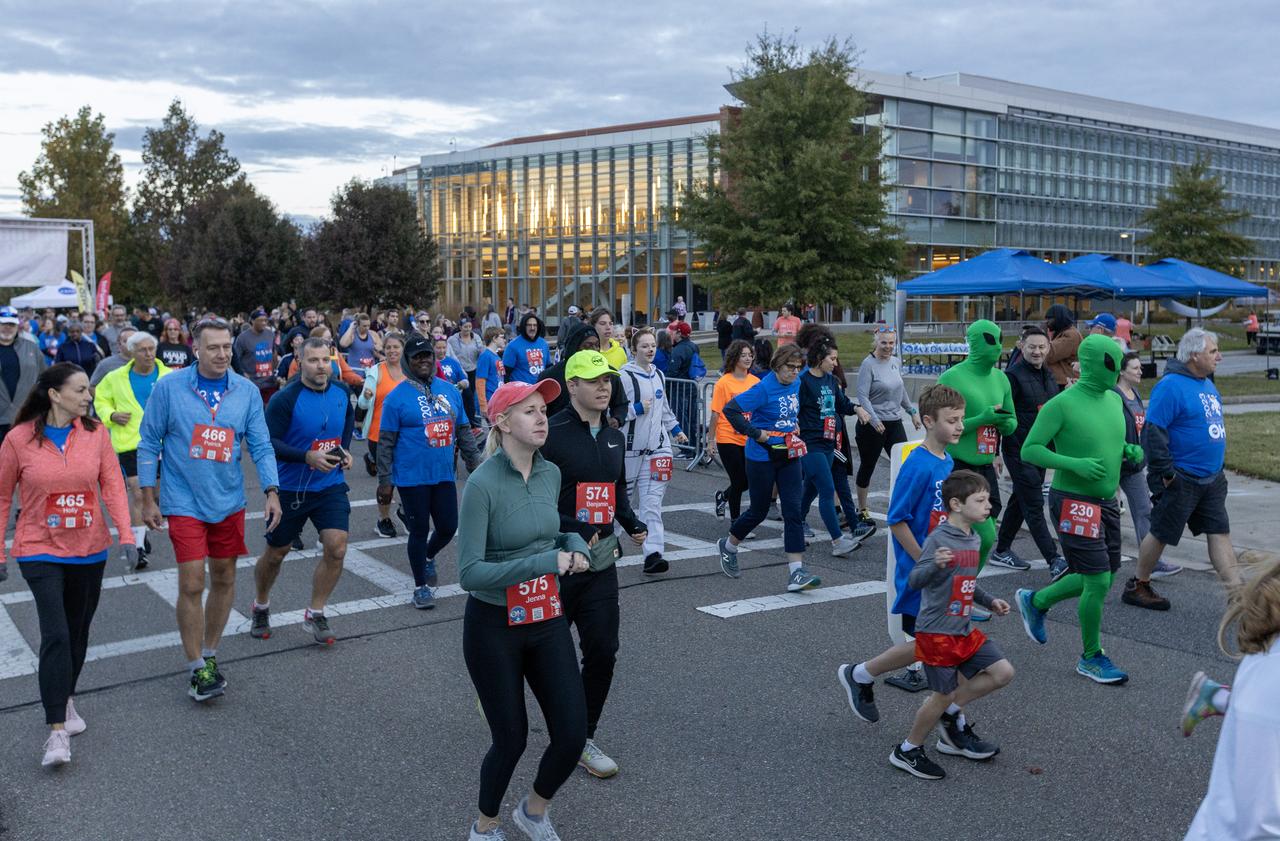

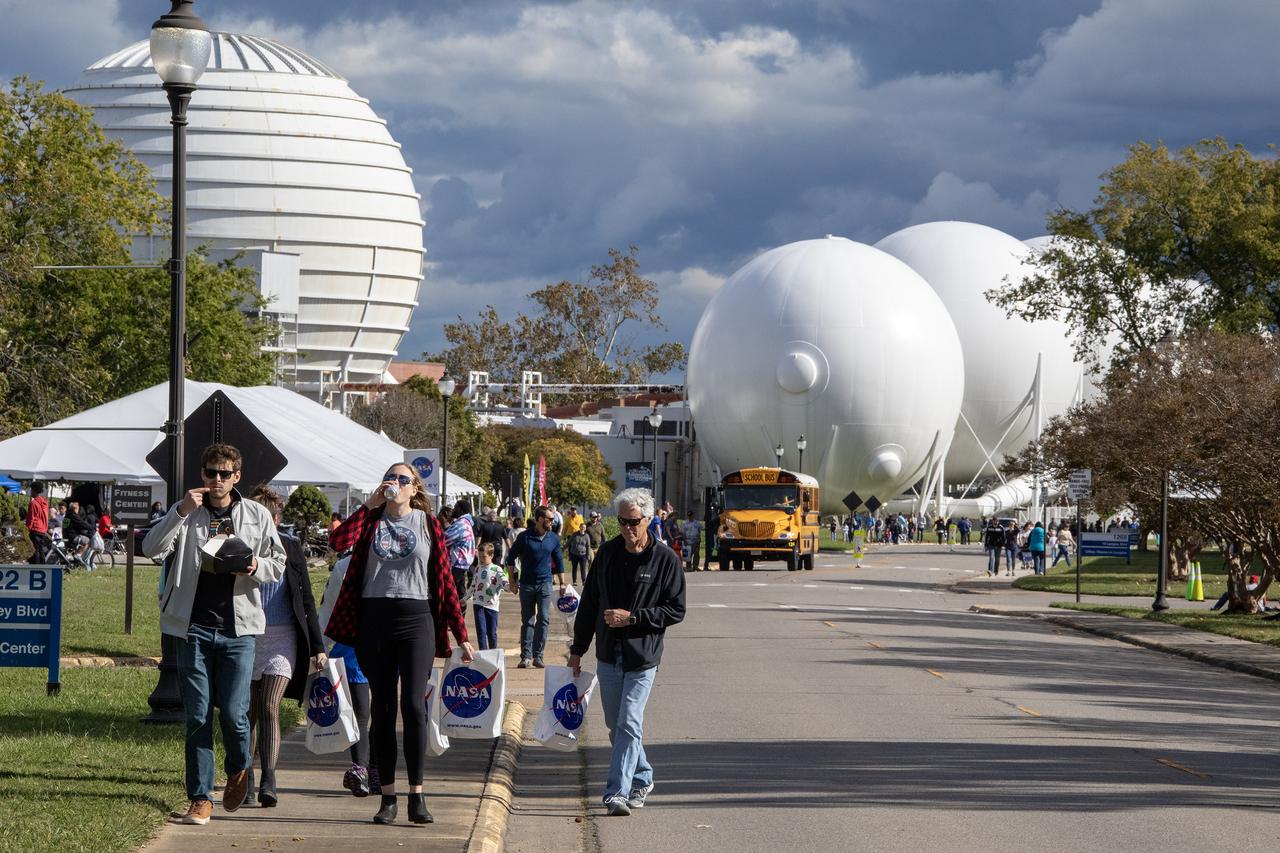
More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.

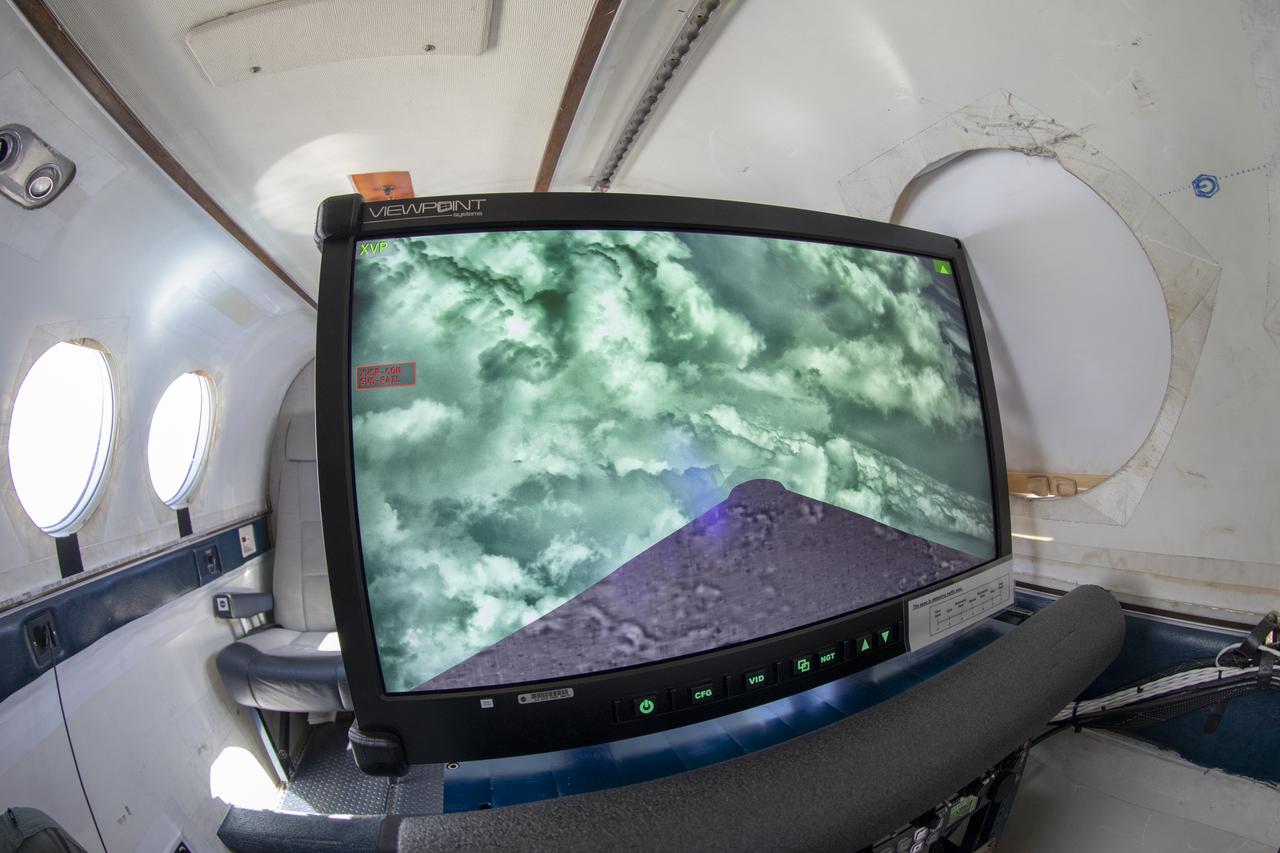
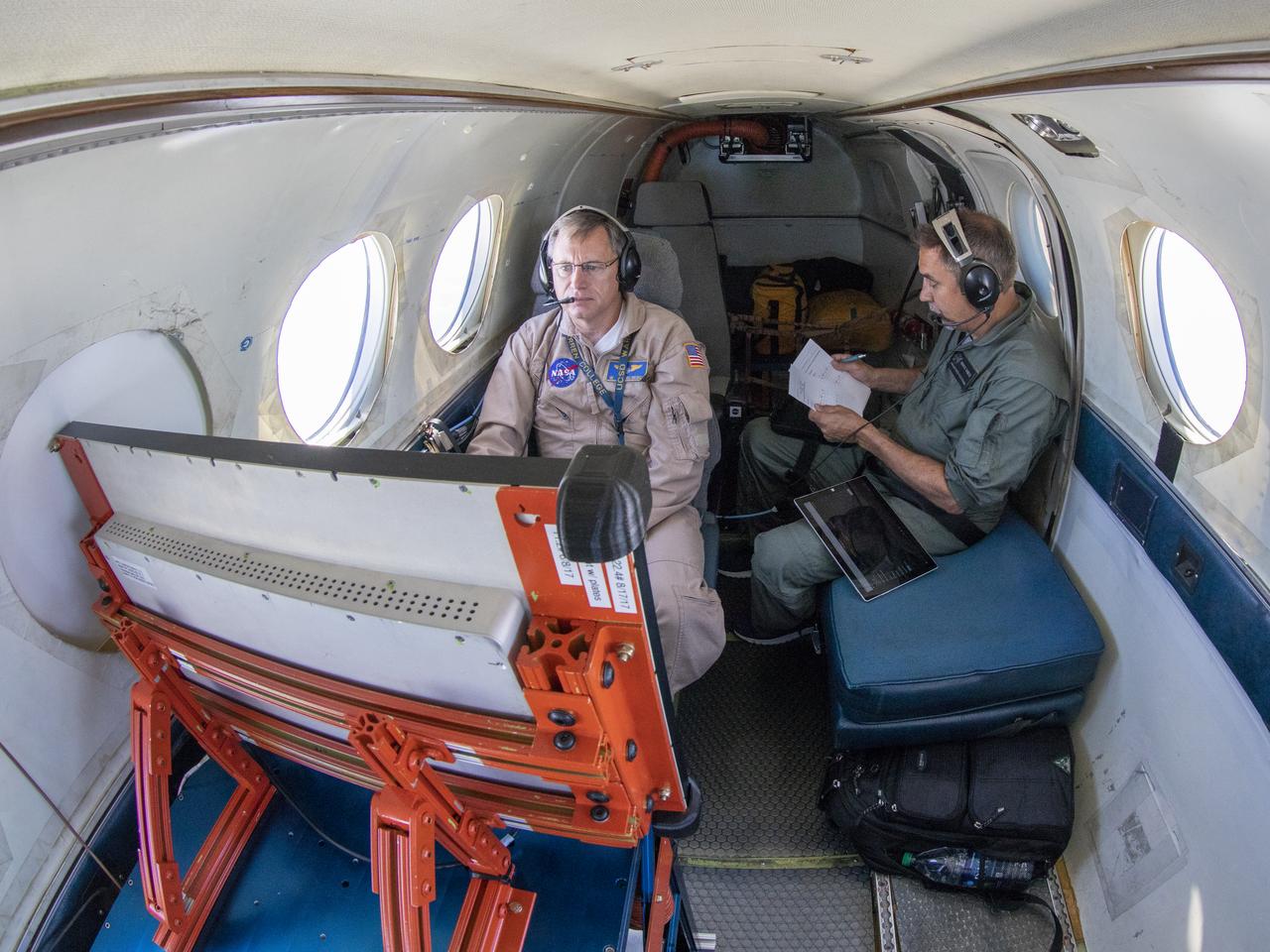
First test flight testing the visual display for the X59. The XVS display is aboard the B200 and the LC40 will be interacting as part of the test.
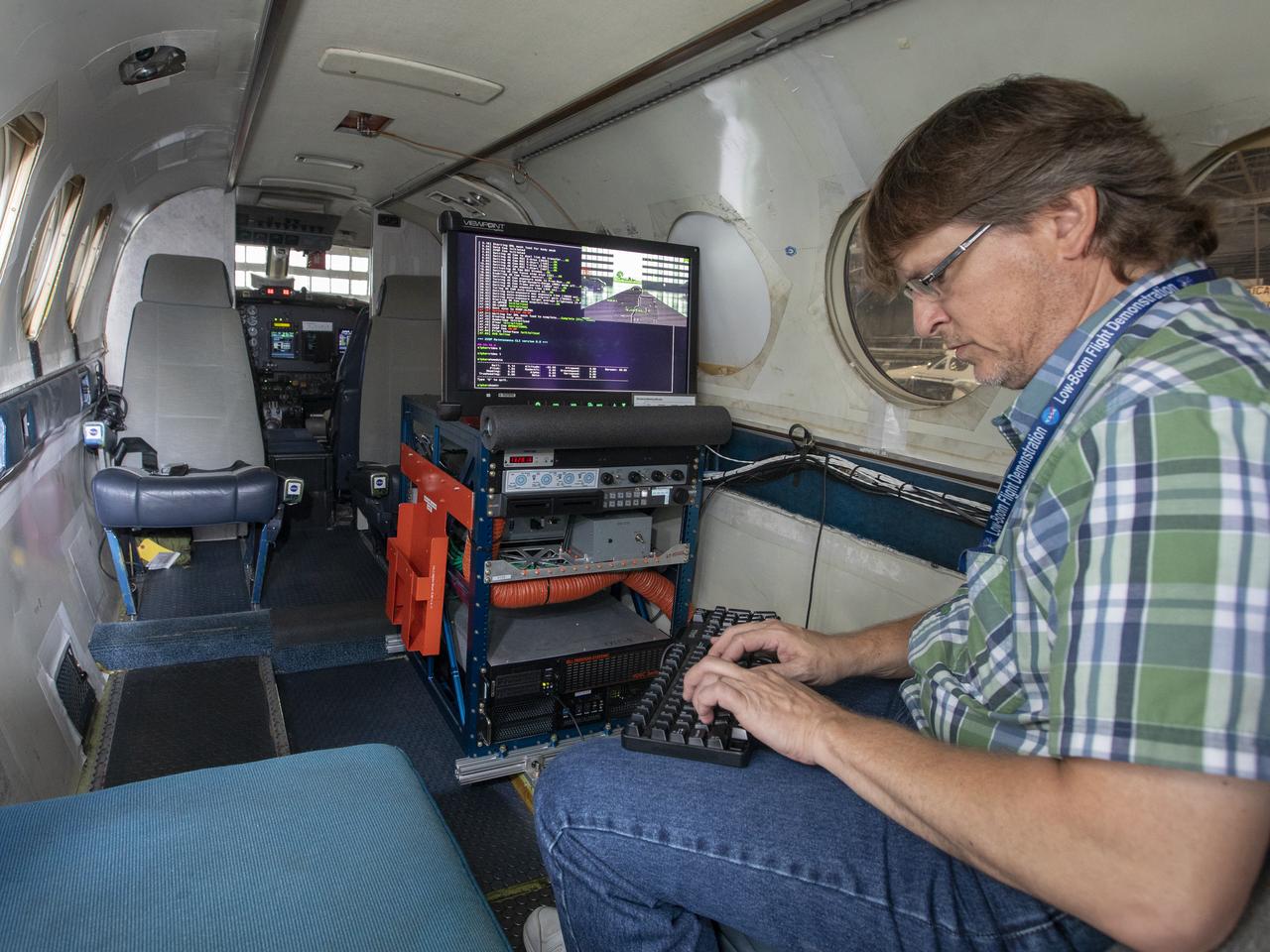

Steve Williams working on the software upgrade for the flight display for the X59.

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
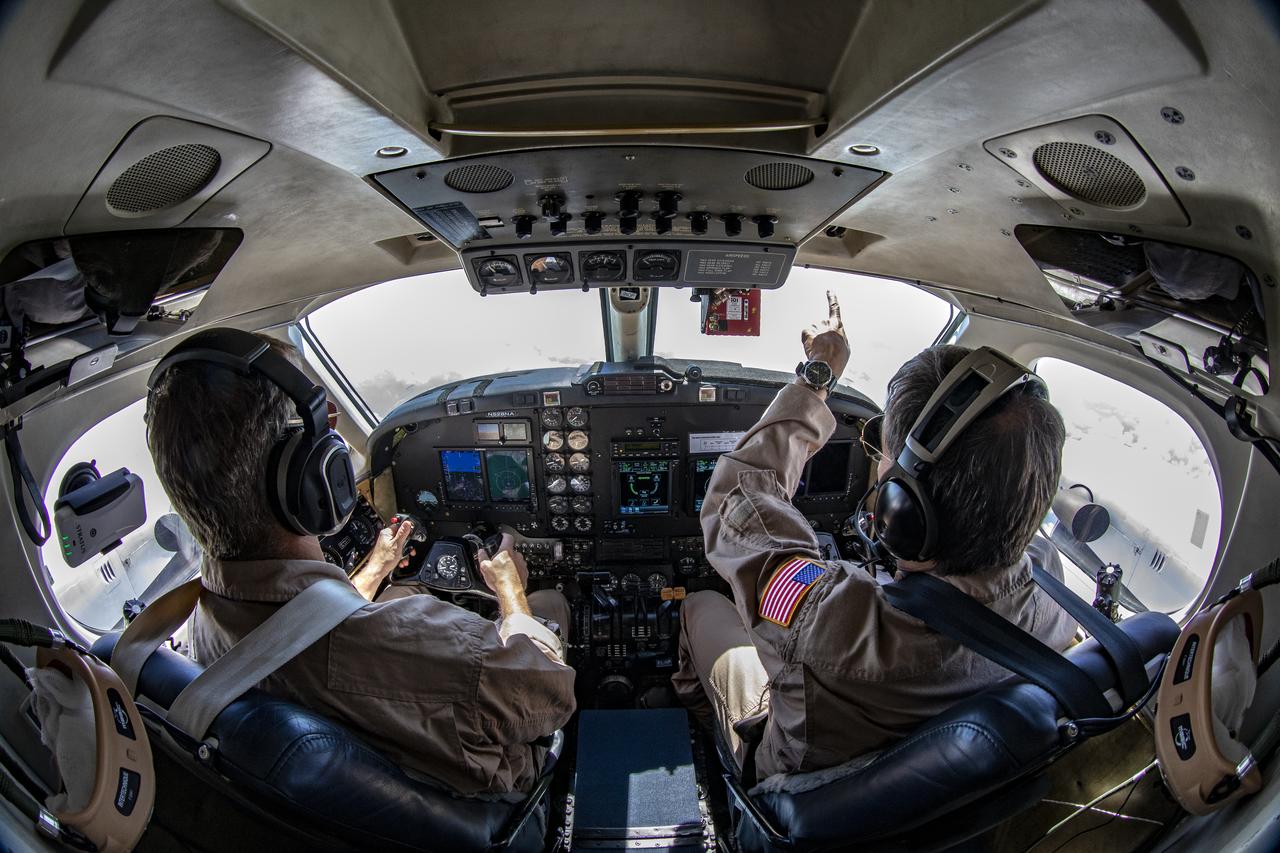

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
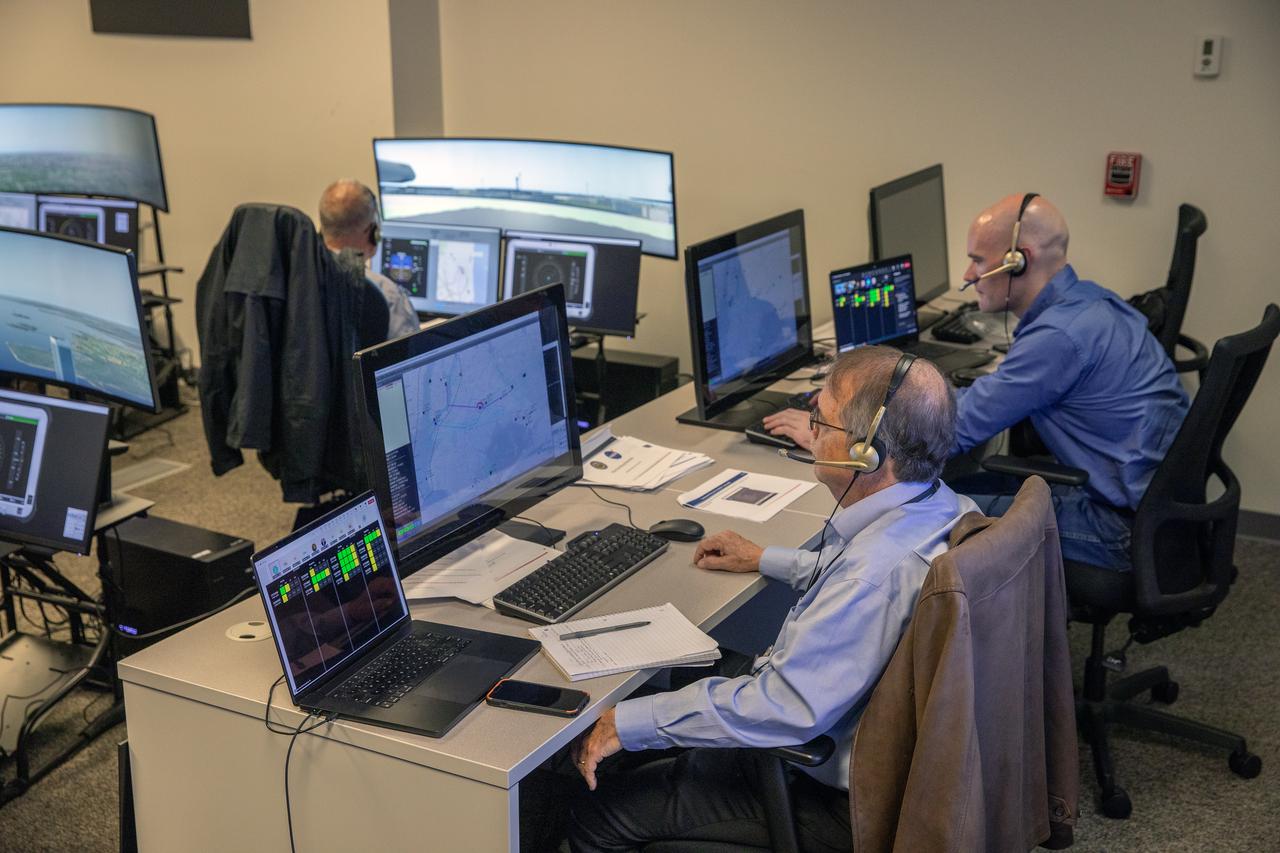

Focus on active photos –Class B Simulation Evaluation in the ATOL Lab at Langley (Also at FAA Tech Center) where team is working with one another in the lab, reviewing data on the monitors. Working the software, adjusting the software systems. Going over the shoulder to show the displays and screens as the software is running. John Foster (left) in the role of an air taxi pilot in the simulator chair with Jim Chamberlain and Terence McClain at the flight manager stations running virtual air taxi integration simulations focusing on urban air space at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia on Sept. 25, 2024.

Debriefing before the first test flight testing the visual display for the X59. The XVS display is aboard the B200.

Focus on active photos –Class B Simulation Evaluation in the ATOL Lab at Langley (Also at FAA Tech Center) where team is working with one another in the lab, reviewing data on the monitors. Working the software, adjusting the software systems. Going over the shoulder to show the displays and screens as the software is running. A pilot’s point of view from the controls of the air taxi simulator. An out-the-window simulation appears on the top screen, the primary flight display on the lower left, the virtual moving map in the middle, and the detect and avoid display on the lower right at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia on Sept. 25, 2024.
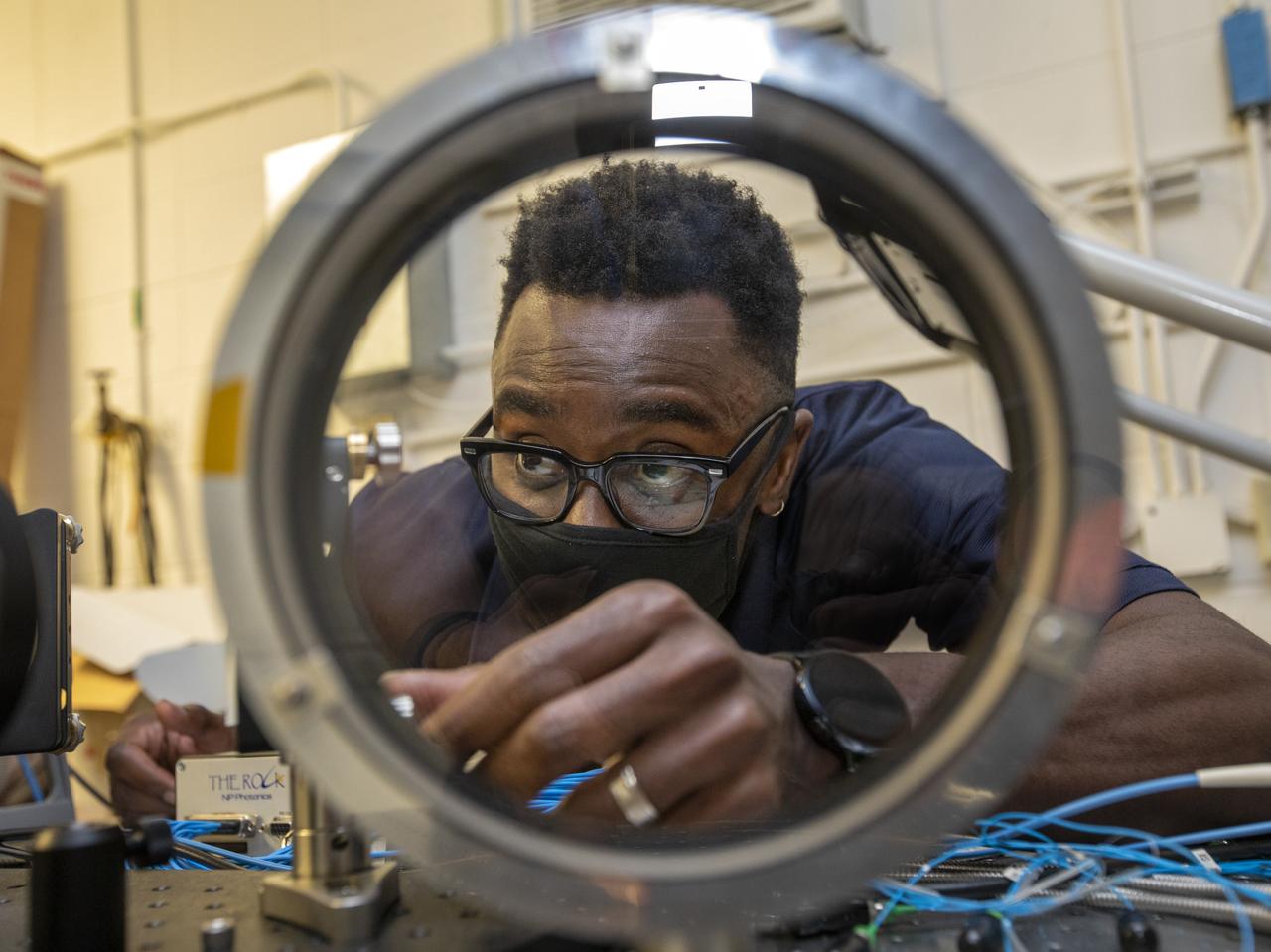

Framed through directional optics glass, Stanley Ikpe is latest of new engineers coming to work at NASA Langley.

Nose camera for the X59 is being prepared for testing on the B200 King Air.

More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.

Artemis II astronaut Victor J. Glover participates in NASA Langley’s Open House on Saturday, Oct. 21. More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.

More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
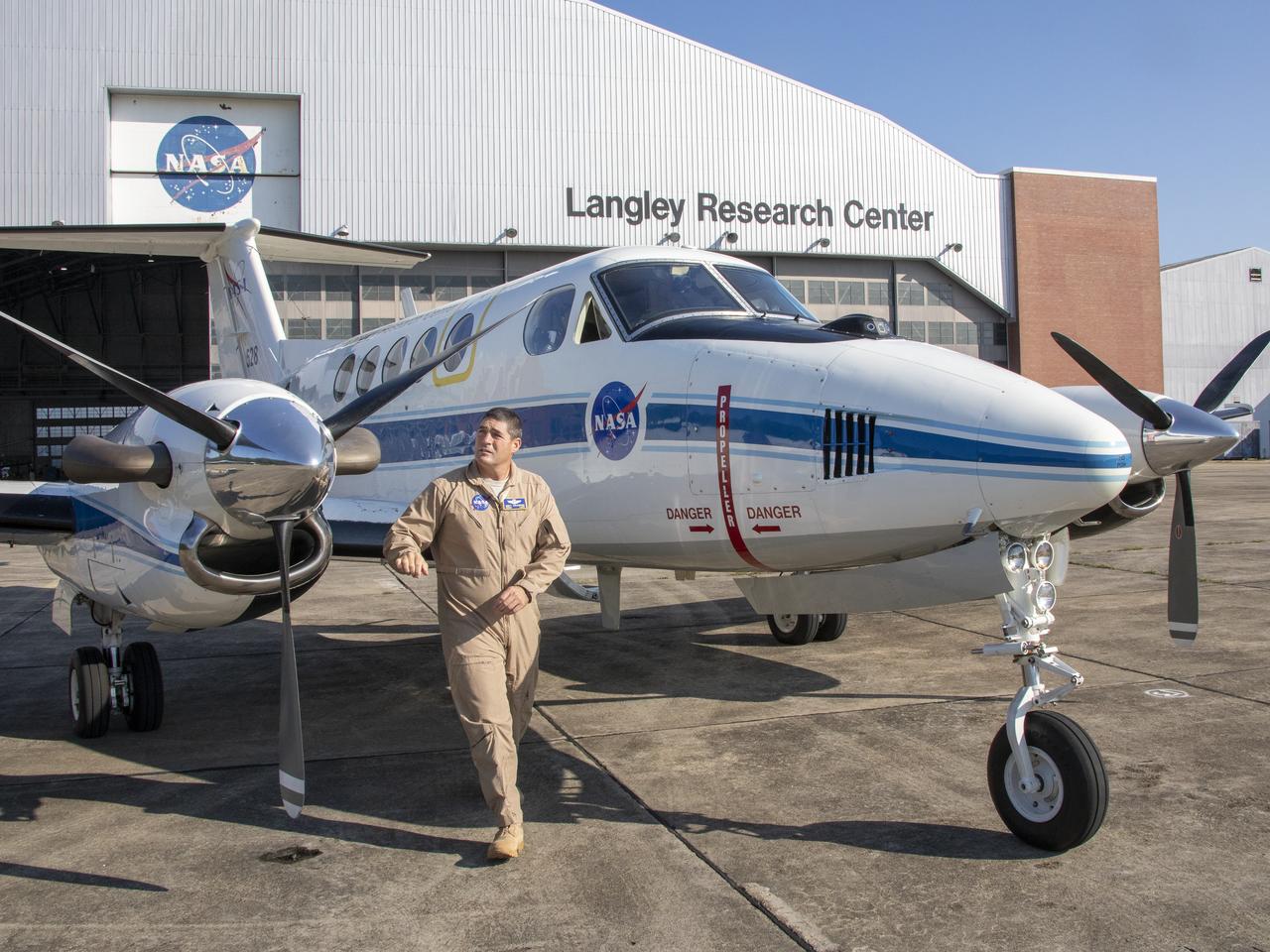

First test flight testing the visual display for the X59. Pilot Matt Coldsnow making a flight check before taking off.
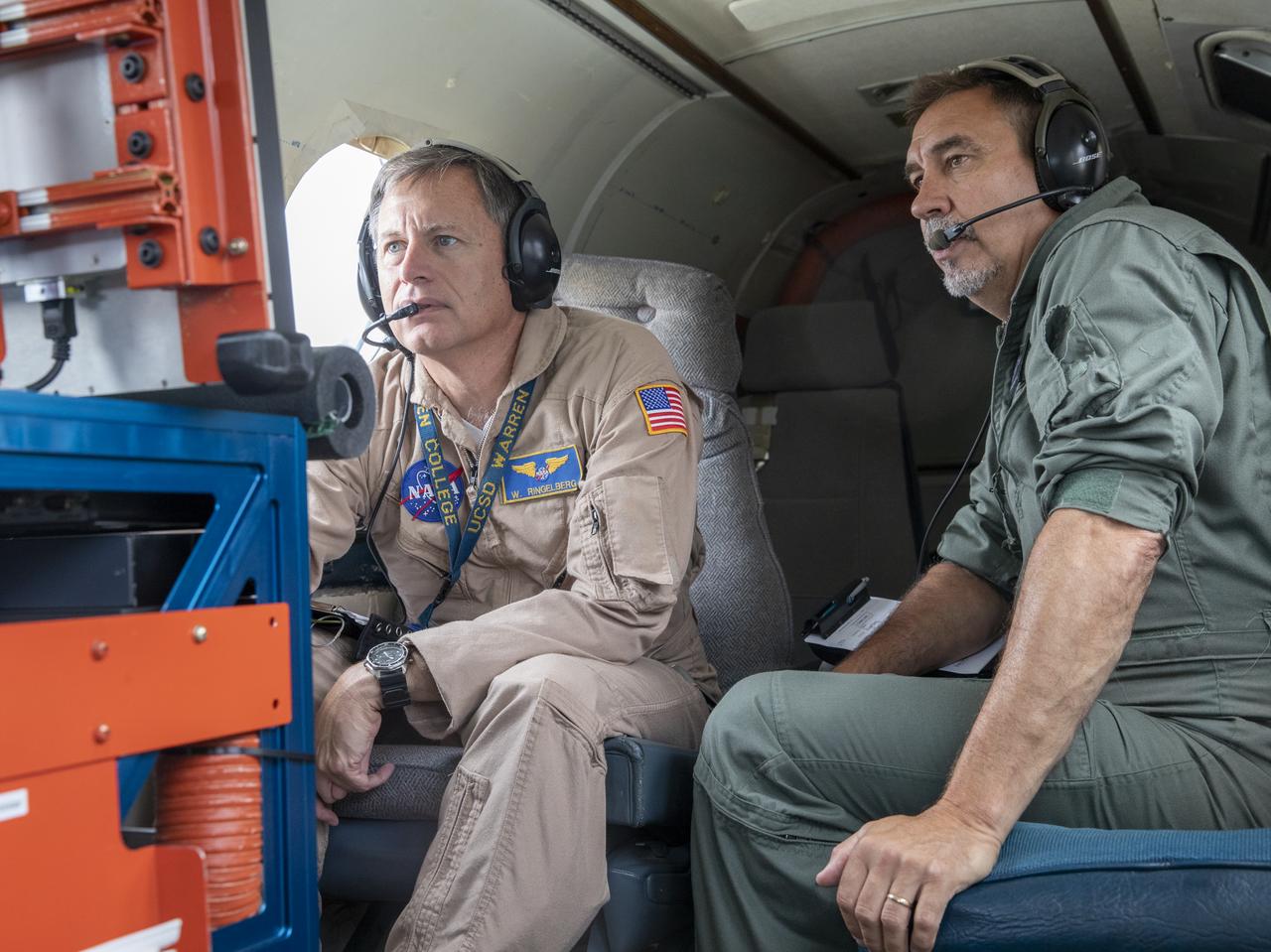

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
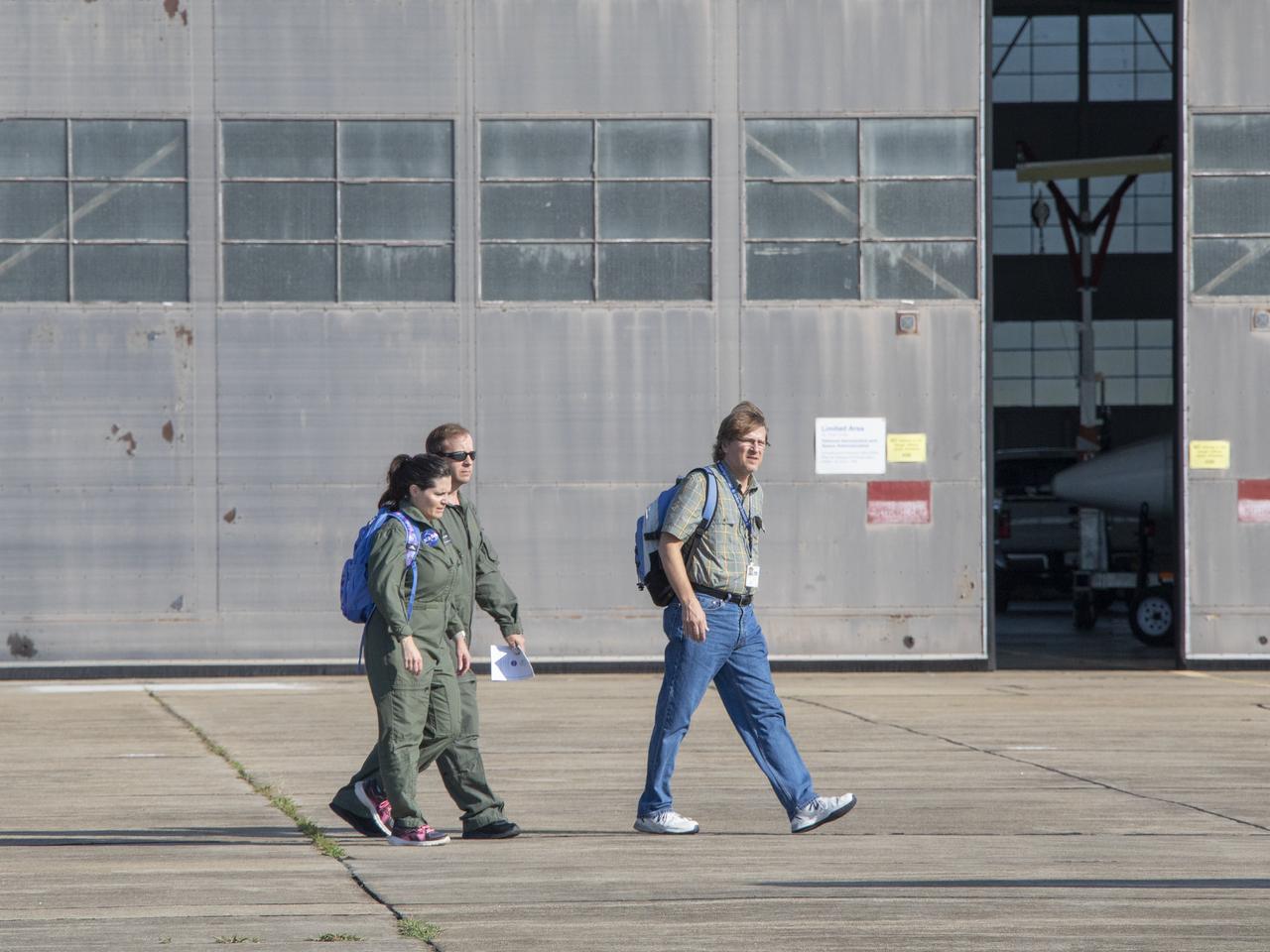

First test flight testing the visual display for the X59. The XVS display is aboard the B200 and the LC40 will be interacting as part of the test.
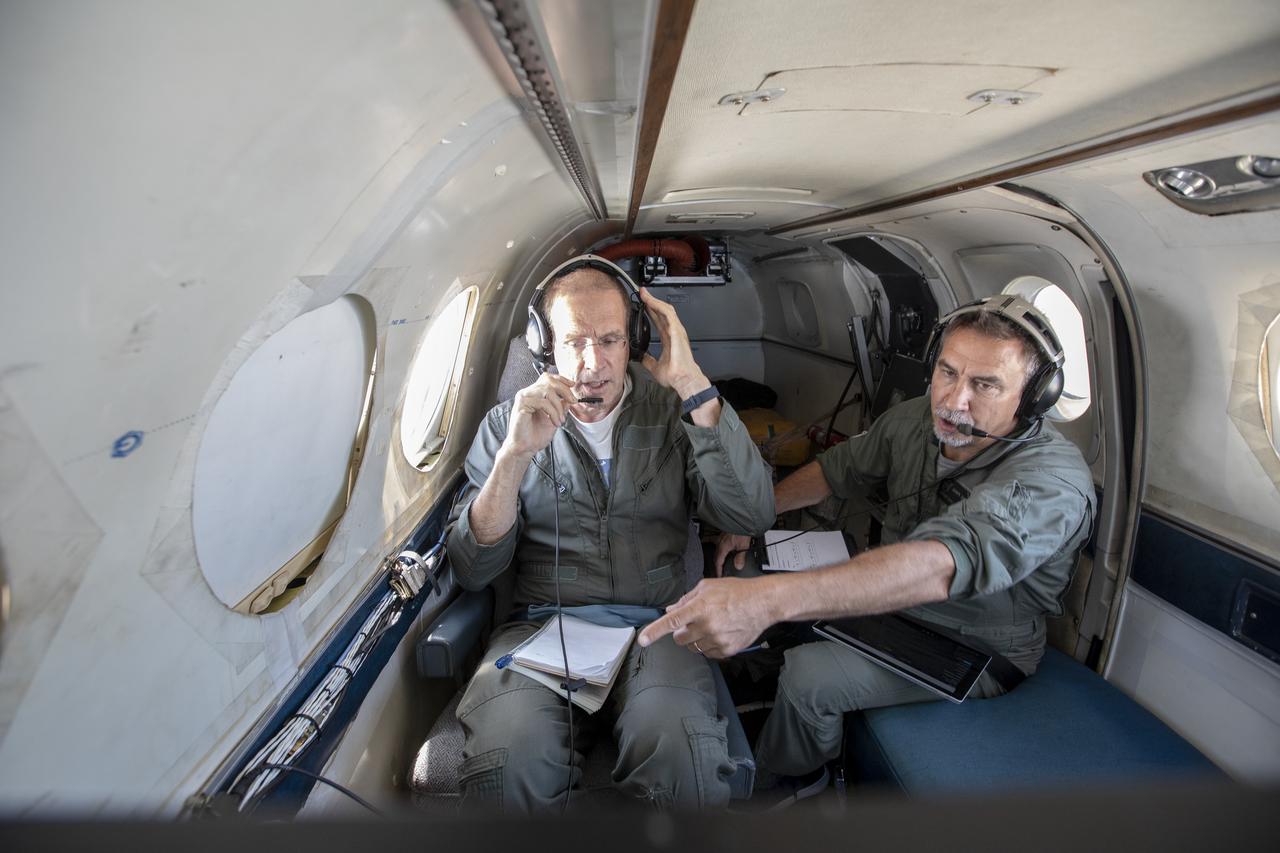

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
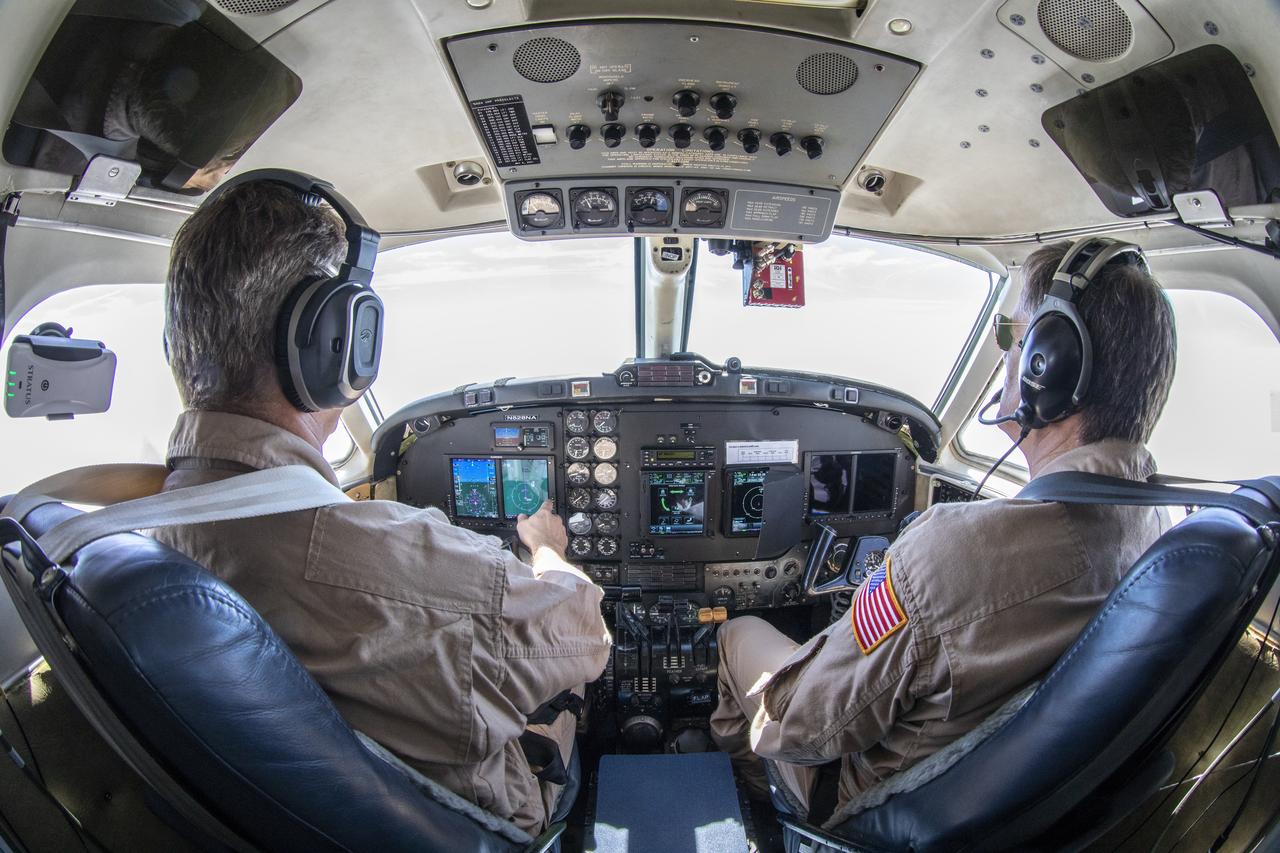

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
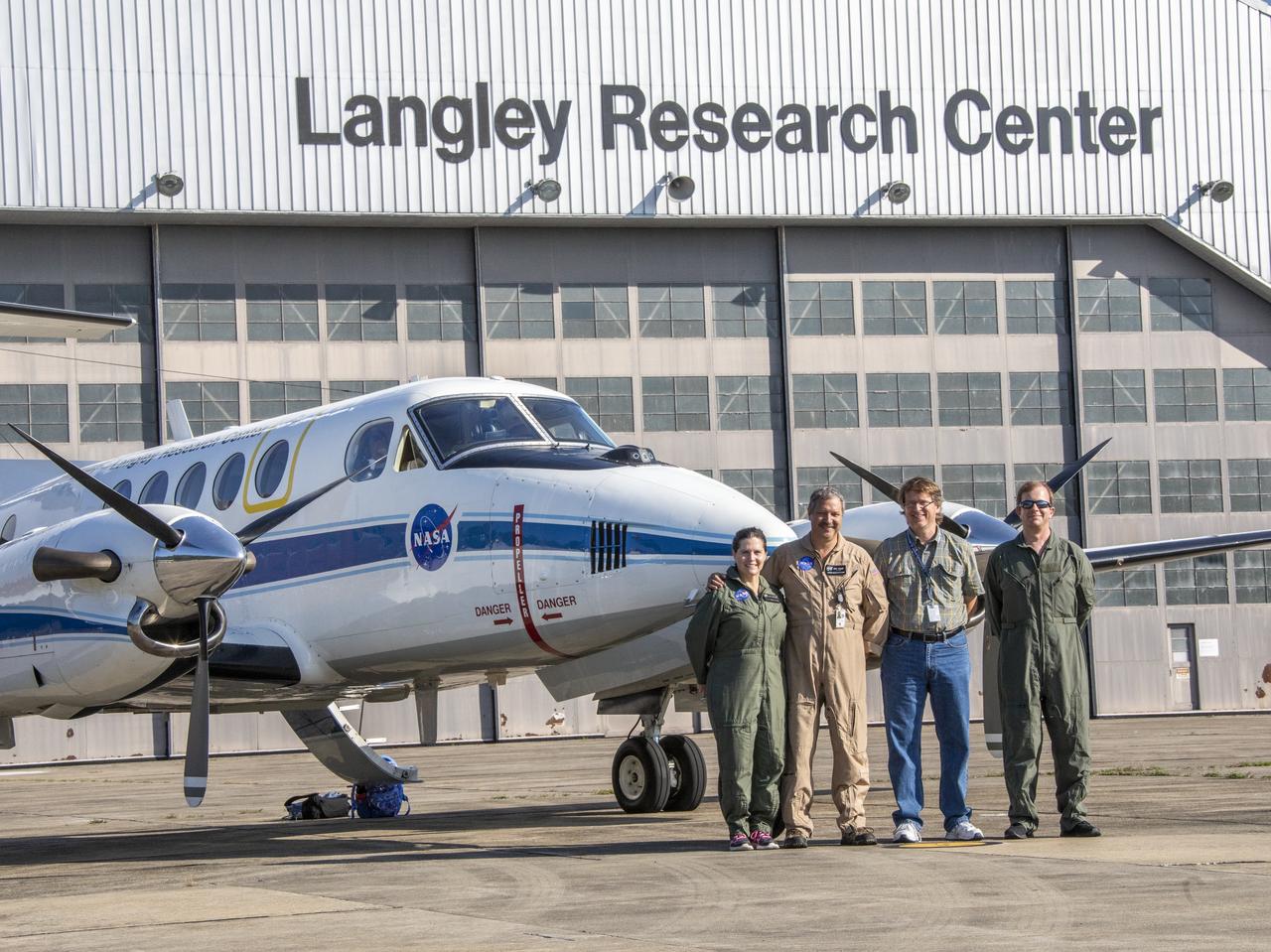

First test flight testing the visual display for the X59. Researchers Lynda Kramer, pilot Kevin Shelton, Steve Williams and ? pose for photo

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
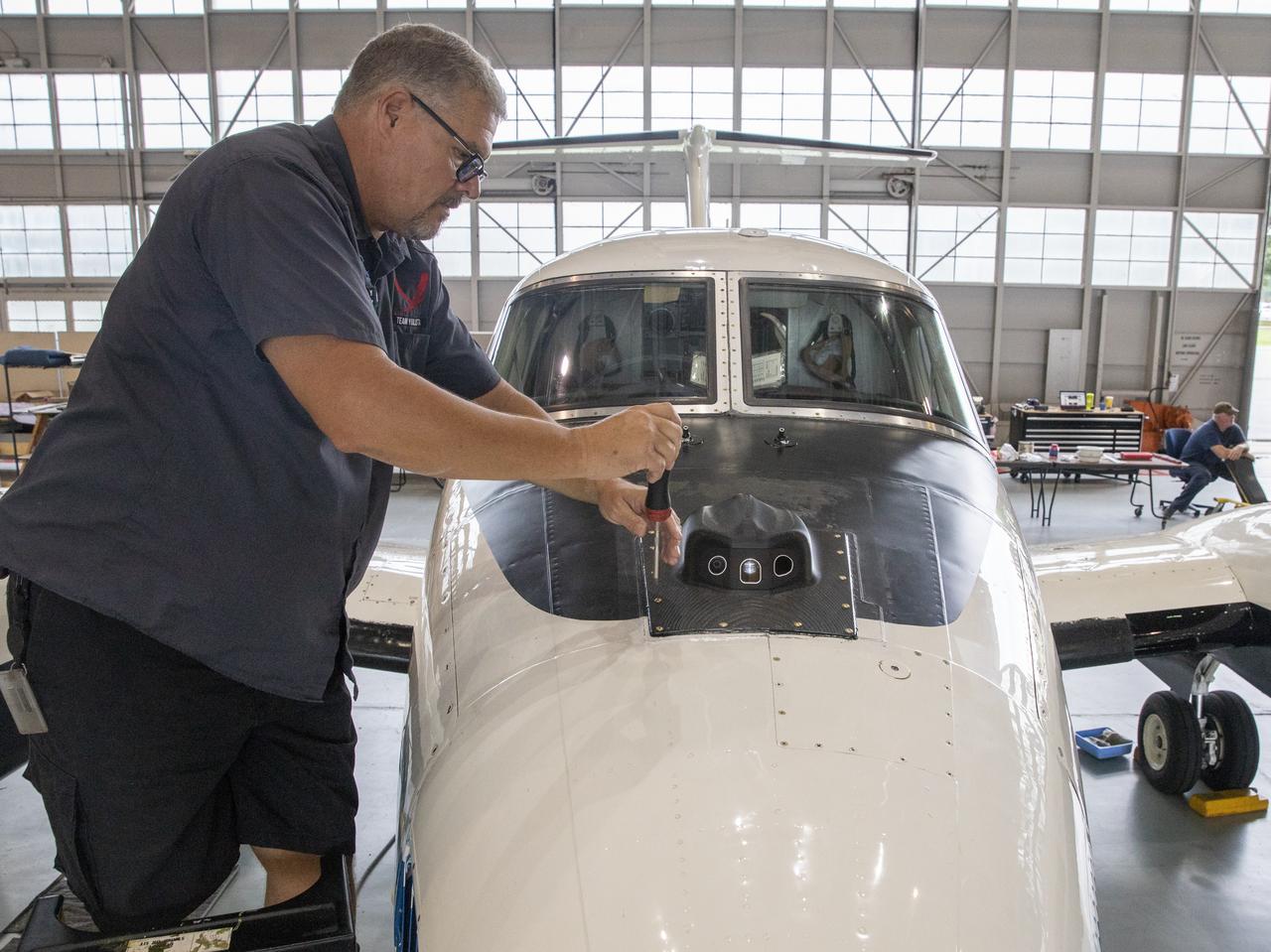

Aircraft mechanic C. Garber working on the camera housing to be tested for the flight display for the X59.

First test flight testing the visual display for the X59. The XVS display is aboard the B200 and the camera is mounted on the nose of the aircraft and inside the cockpit.
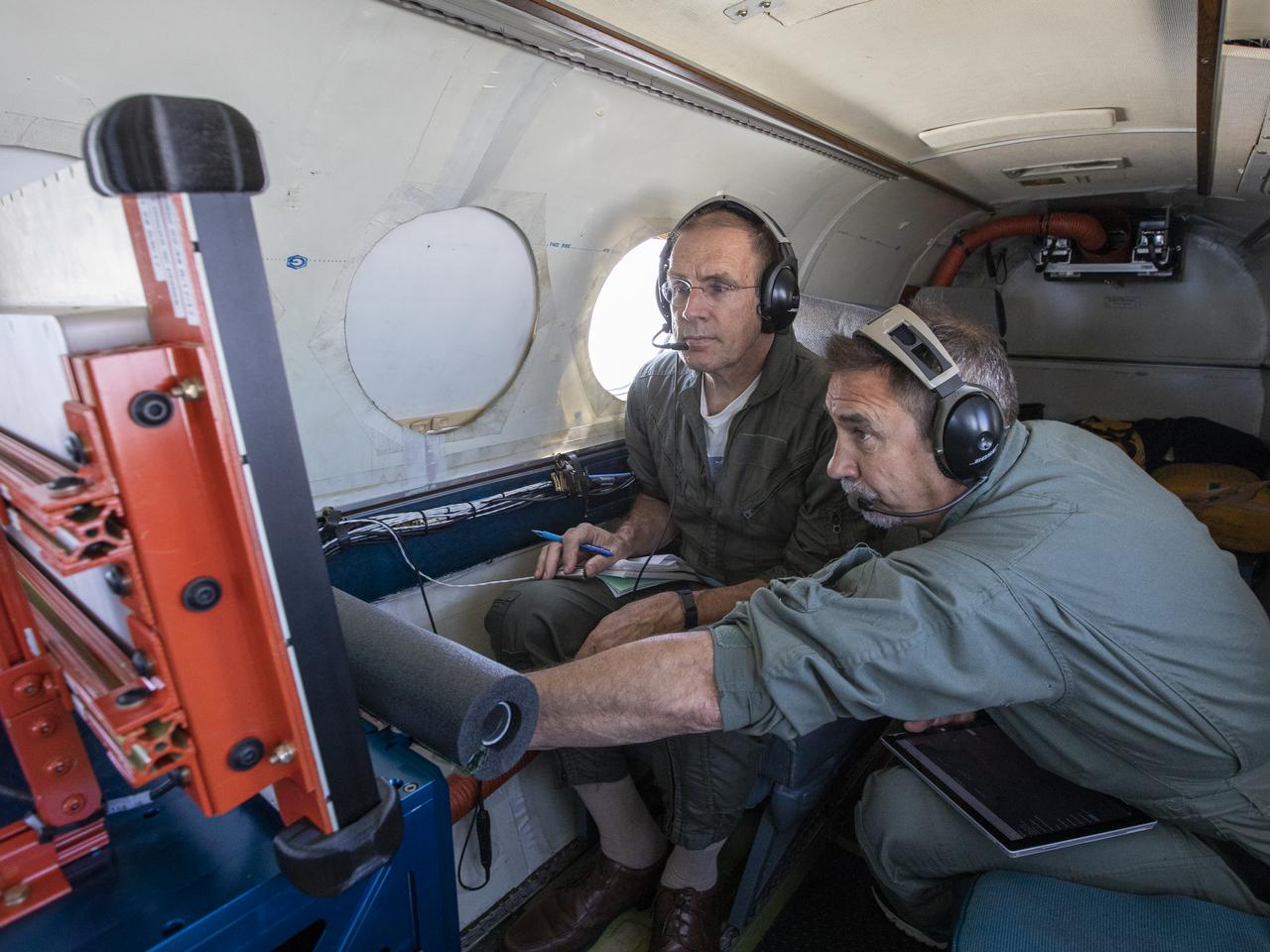

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
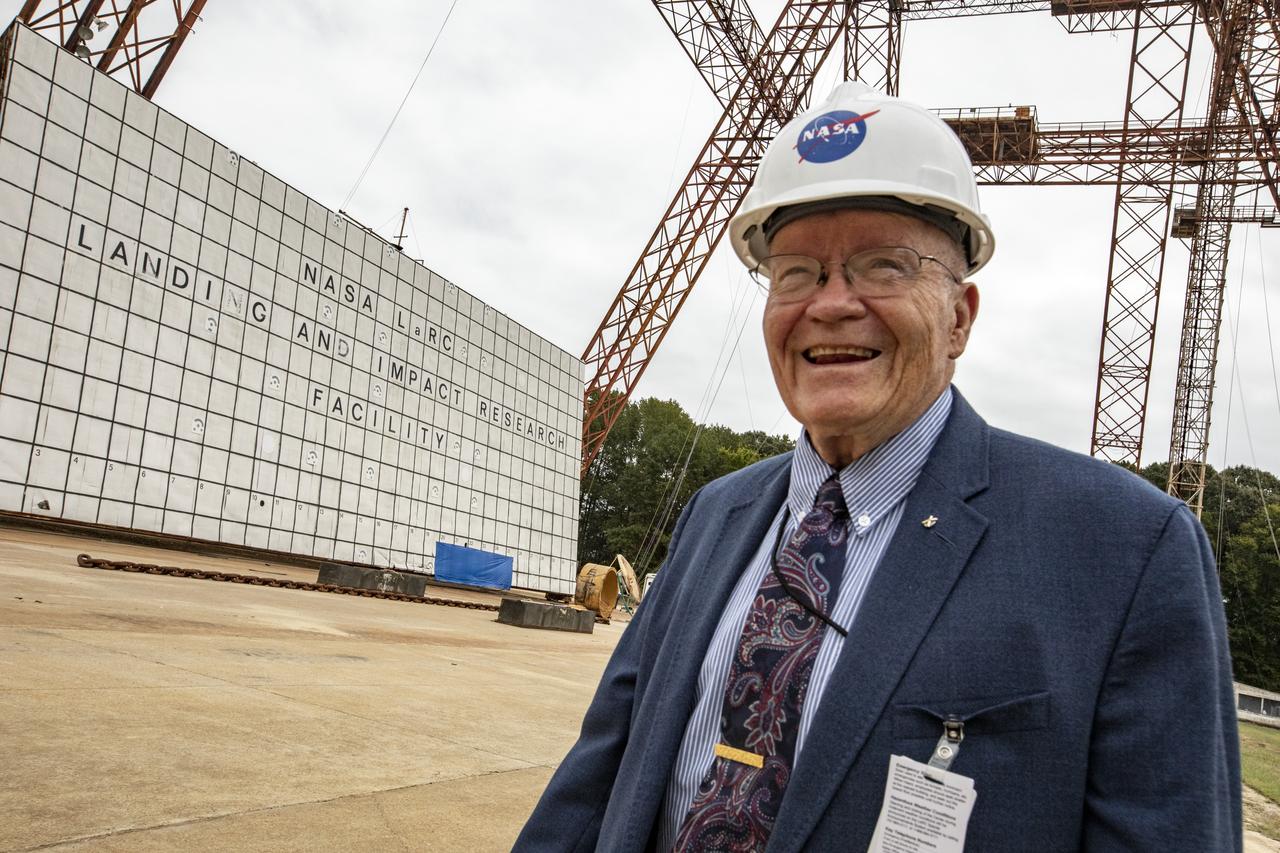

Apollo Astronaut Fred Haise visiting NASA Langley historic gantry where Fred once trained to fly the lunar lander.

First test flight testing the visual display for the X59. The XVS display is aboard the B200 and the LC40 will be interacting as part of the test.
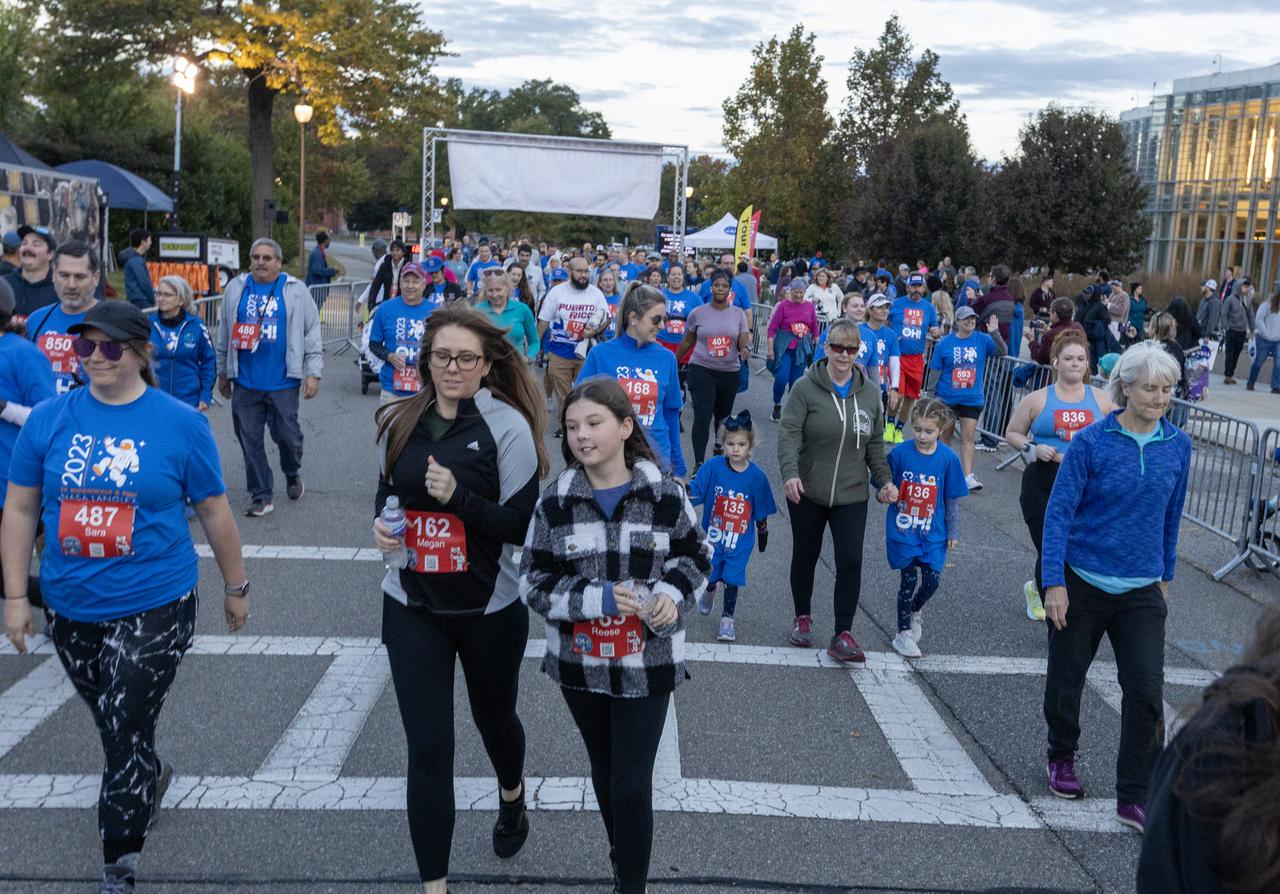

More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.

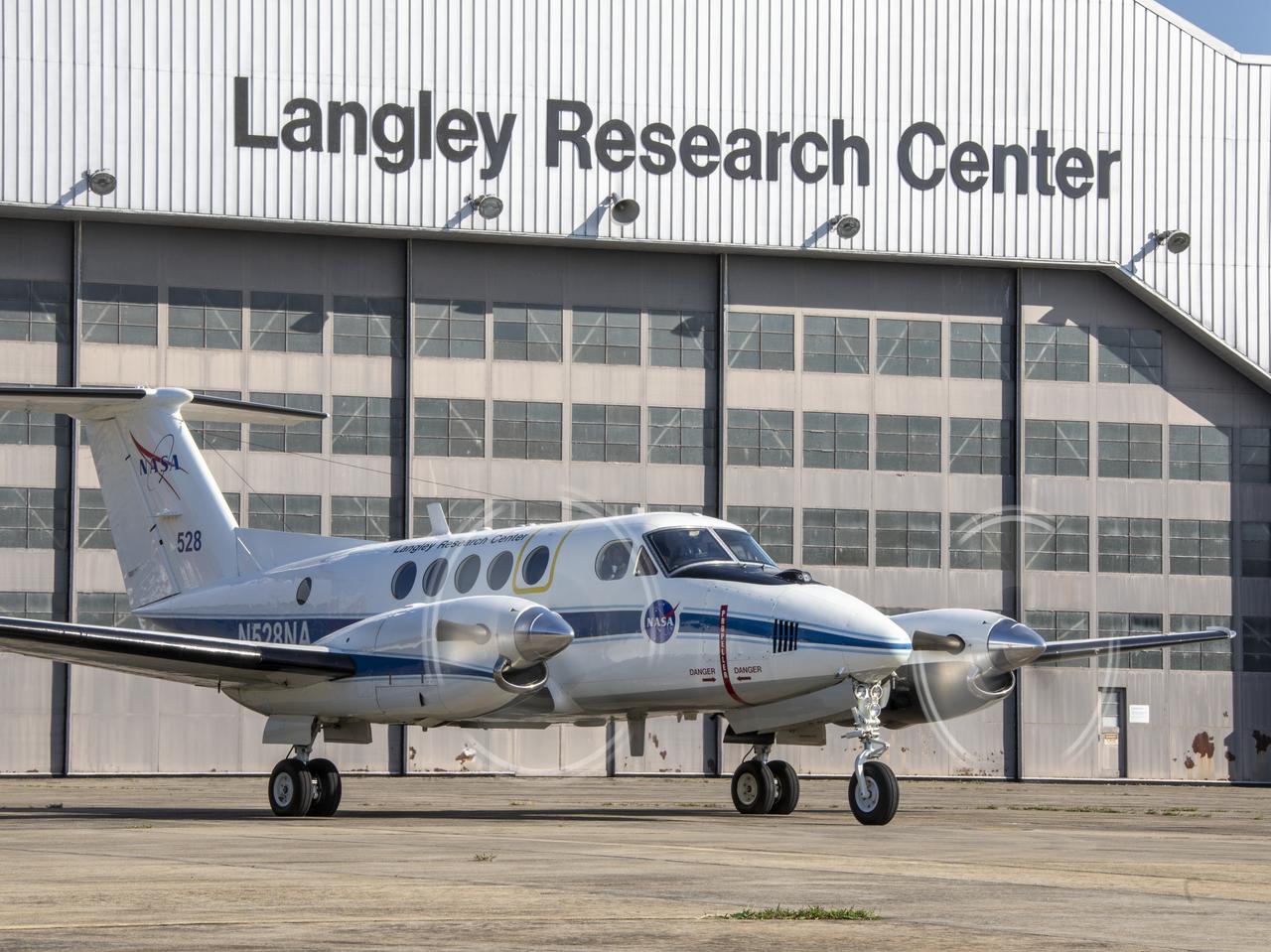
Testing of the External Vision System (EVS) Software on the B200 King Air
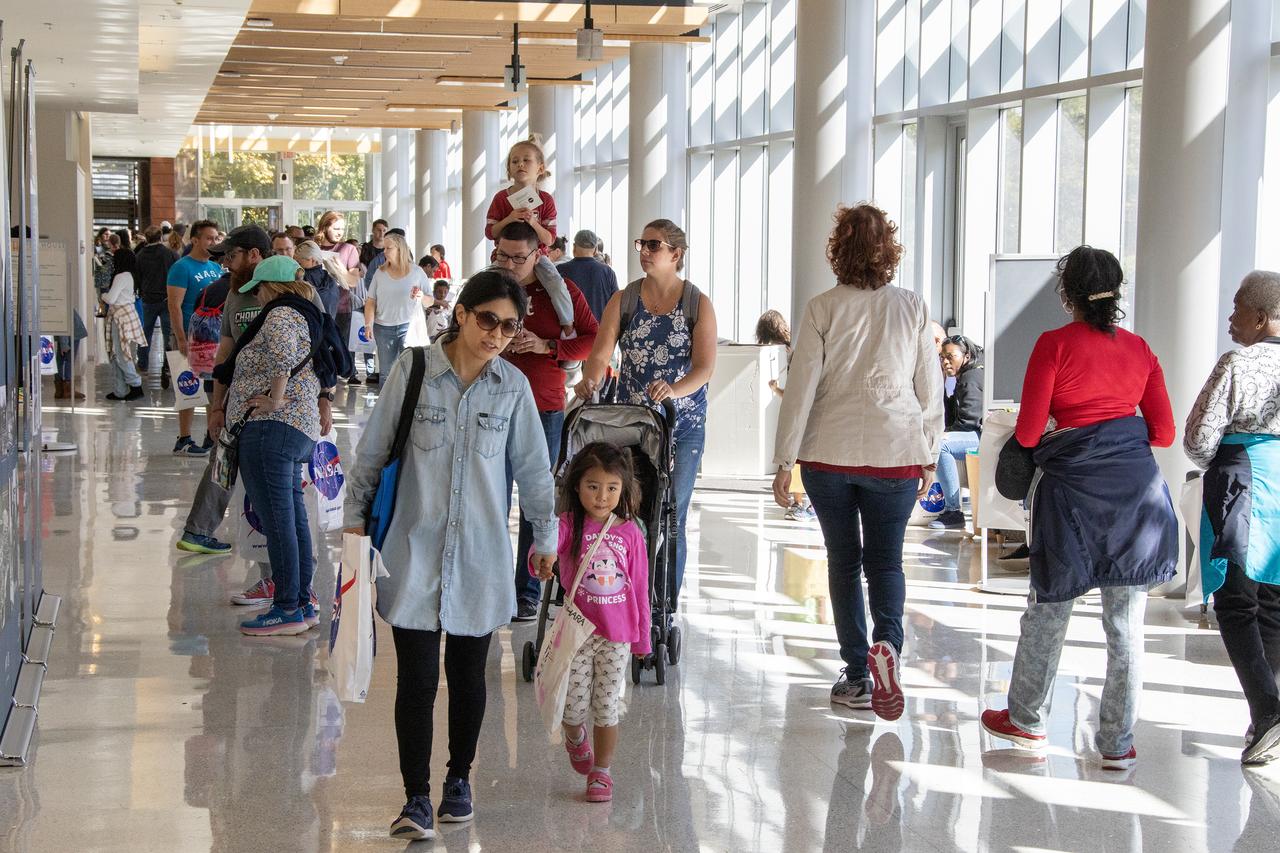

More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.
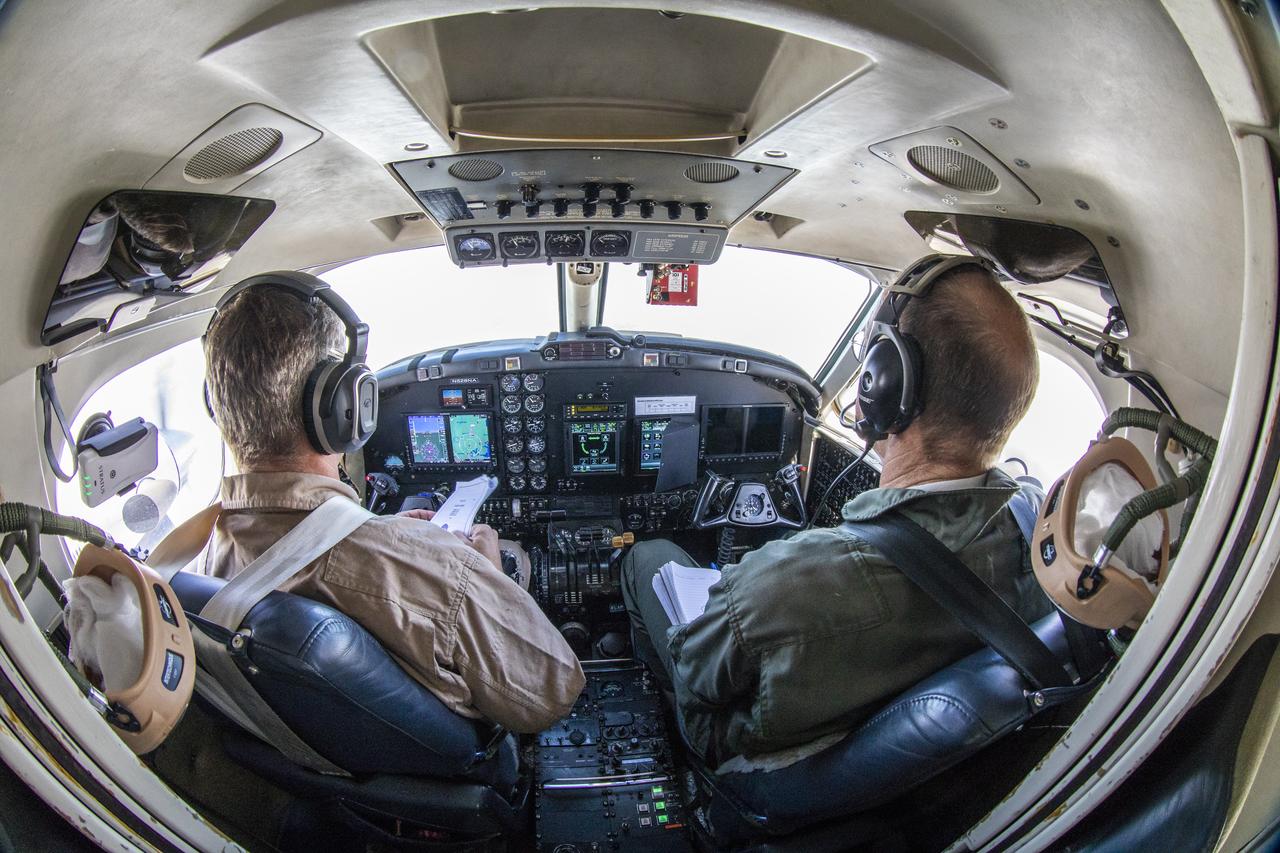

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
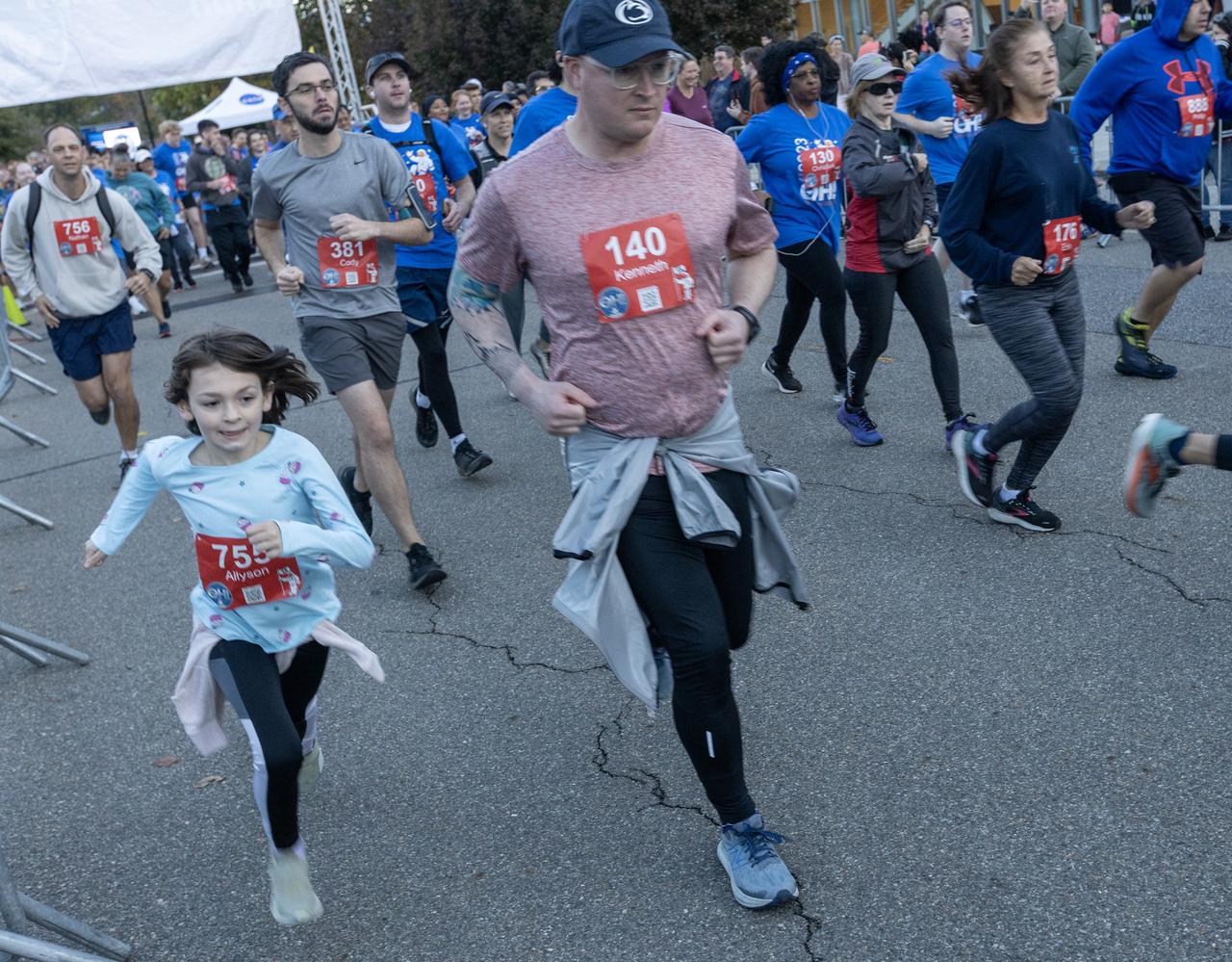

More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.
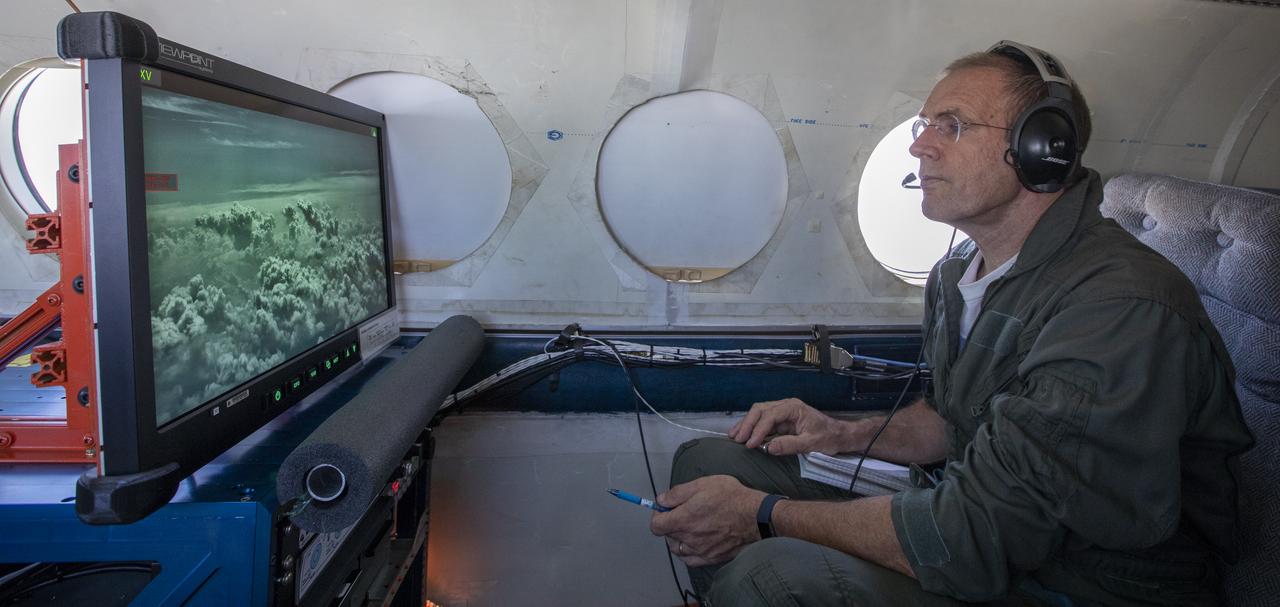

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.

NASA employees Broderic J. Gonzalez, left, and David W. Shank, right, install pieces of a 7-foot wing model in preparation for testing in the 14-by-22-Foot Subsonic Wind Tunnel at NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, in May 2025. The lessons learned from this testing will be shared with the public to support advanced air mobility aircraft development.

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
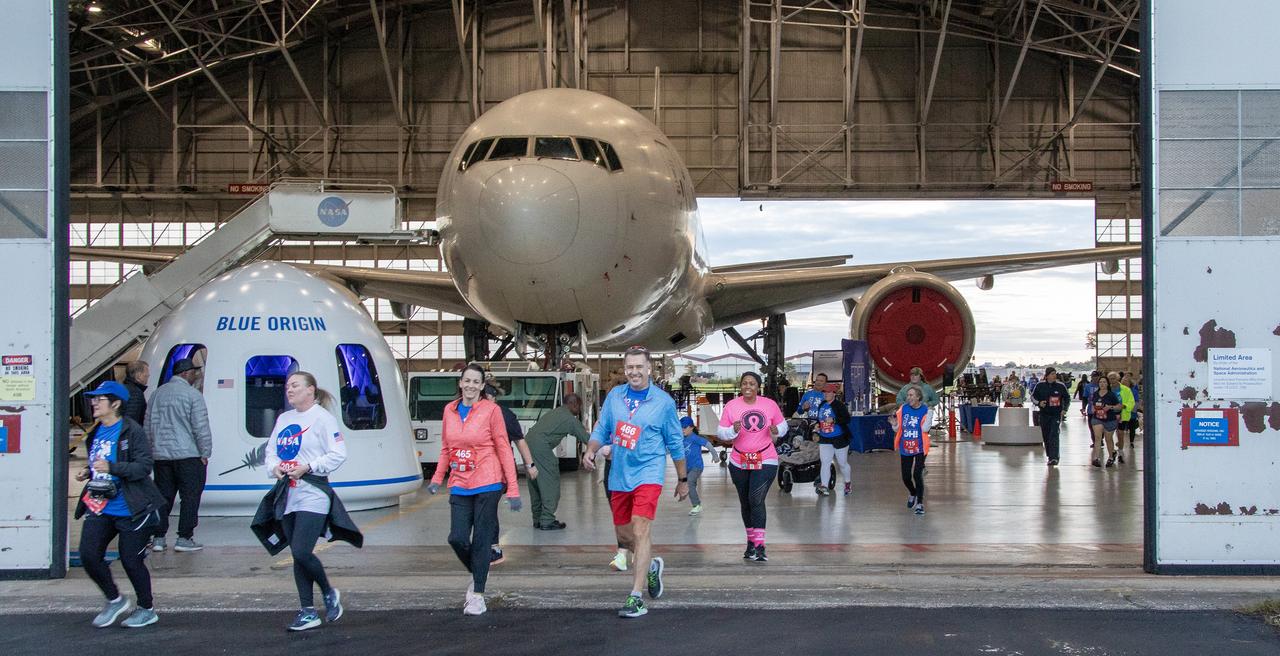

More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.

Artemis II astronaut Victor J. Glover participates in NASA Langley’s Open House on Saturday, Oct. 21. More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.
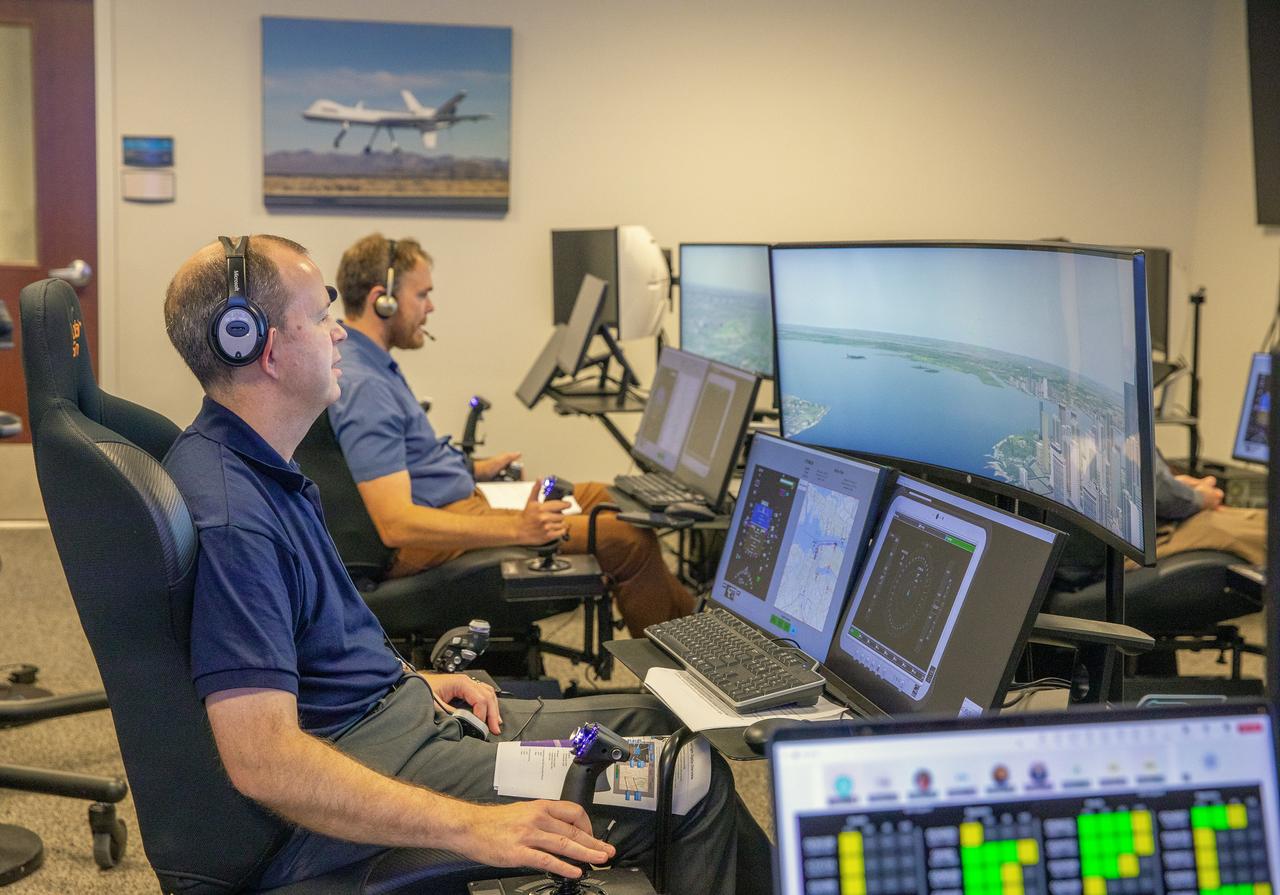

Focus on active photos –Class B Simulation Evaluation in the ATOL Lab at Langley (Also at FAA Tech Center) where team is working with one another in the lab, reviewing data on the monitors. Working the software, adjusting the software systems. Going over the shoulder to show the displays and screens as the software is running. Andy Burroughs (left) and Paul Friz in the roles of air taxi pilots running through air taxi integration simulations focusing on urban air space at NASA’s Langley Research in Hampton, Virginia on Sept. 25, 2024.
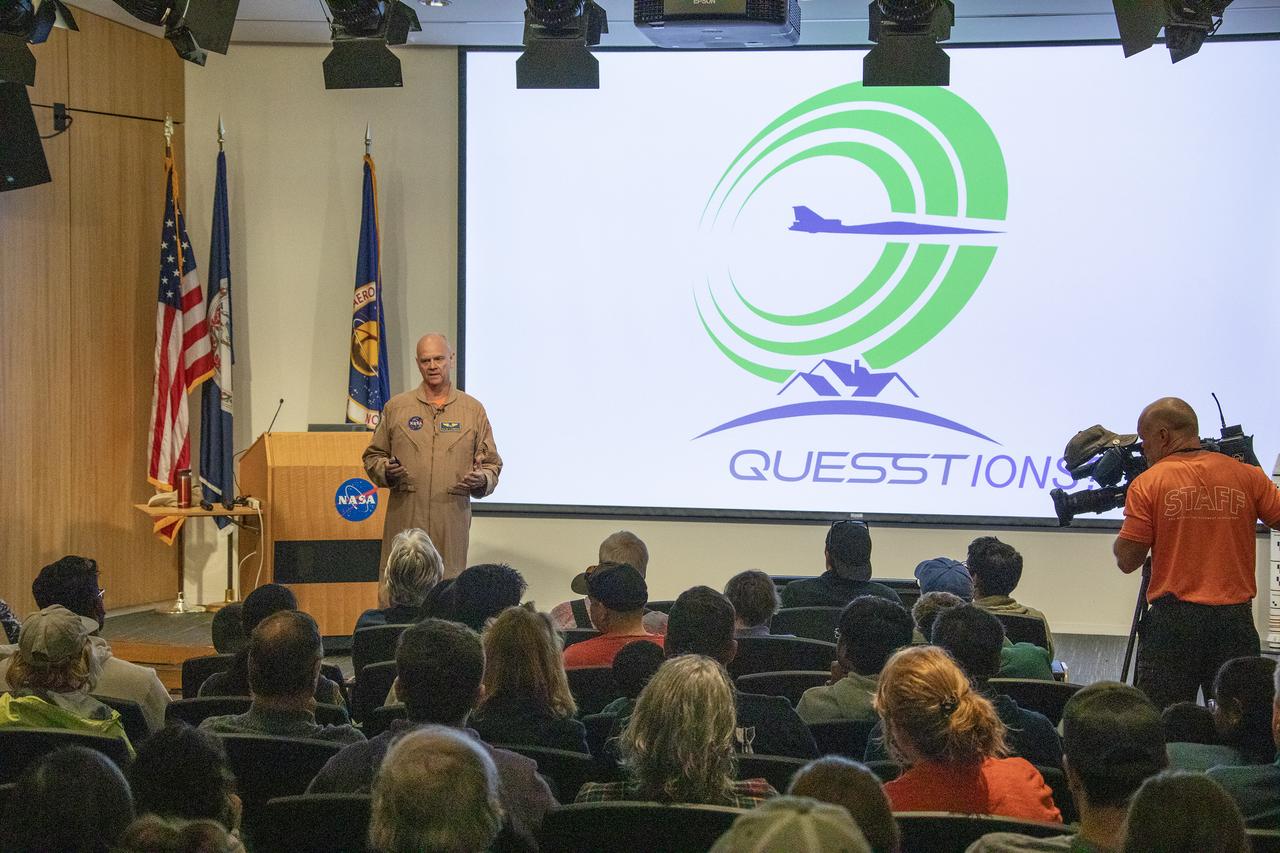

Speaker David Nils Larson on the X59. More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.
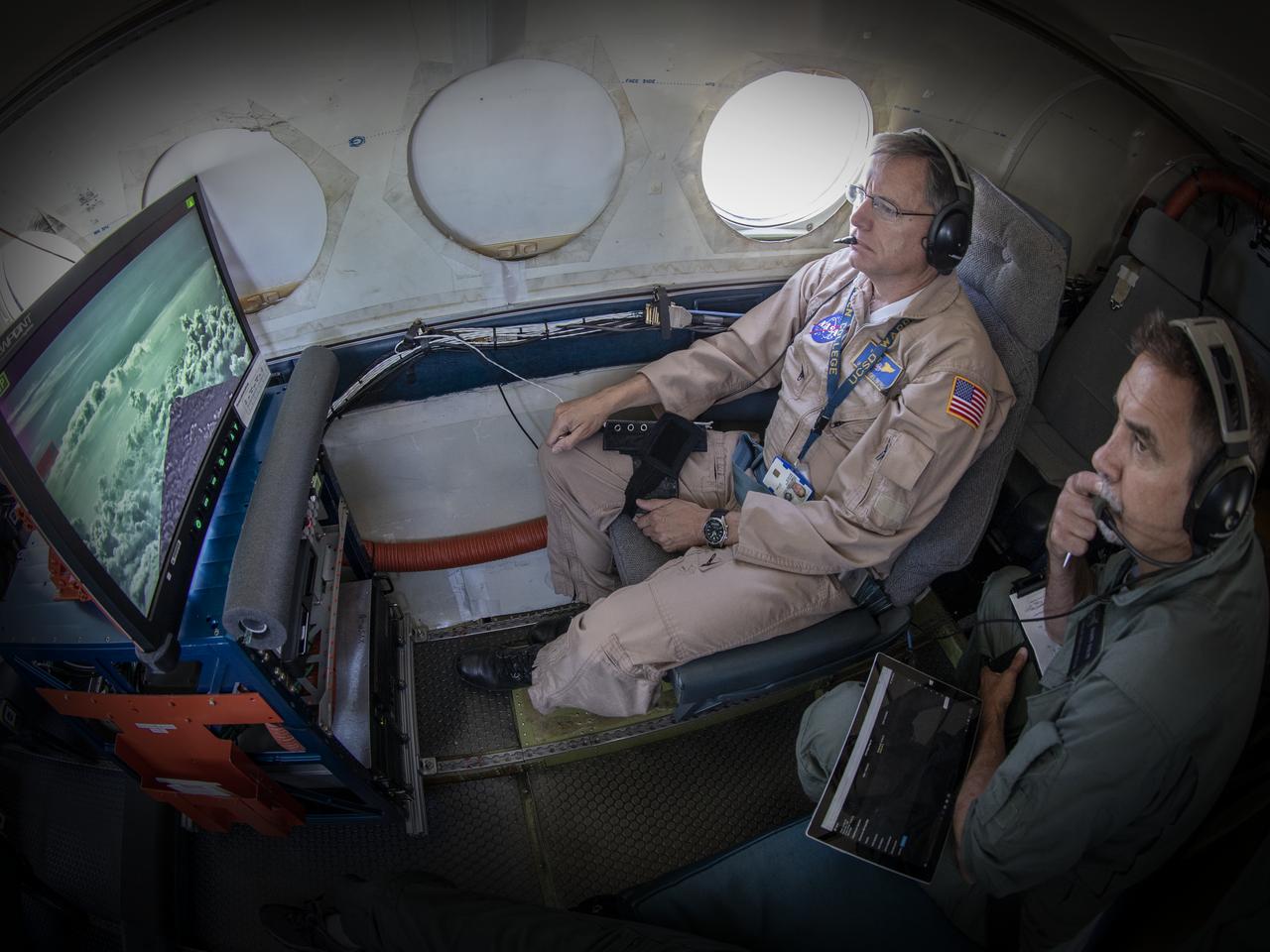

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
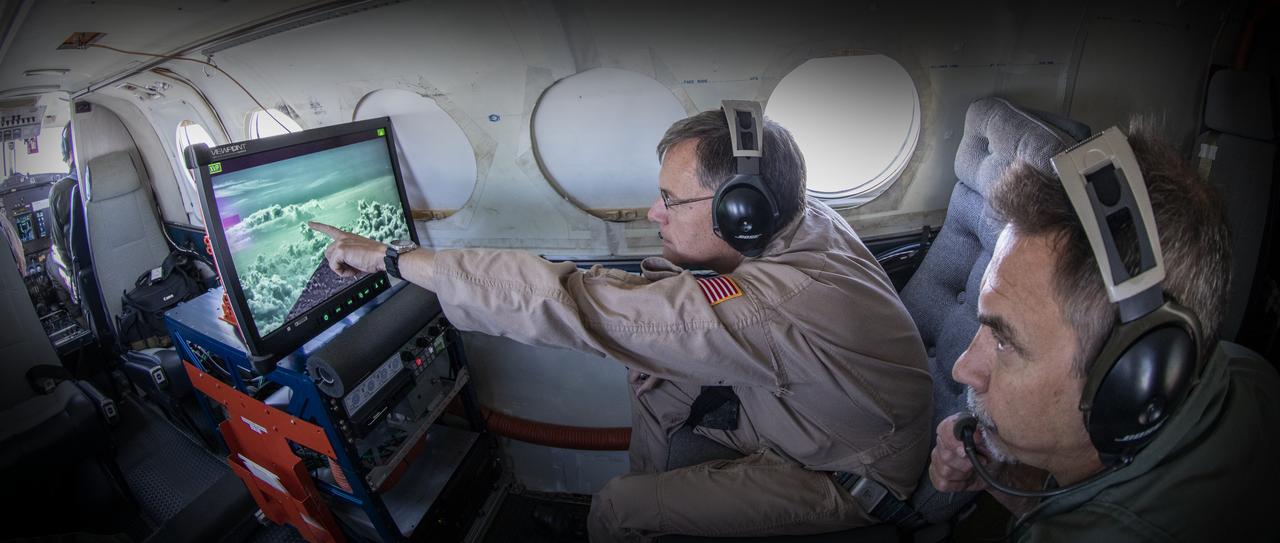

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
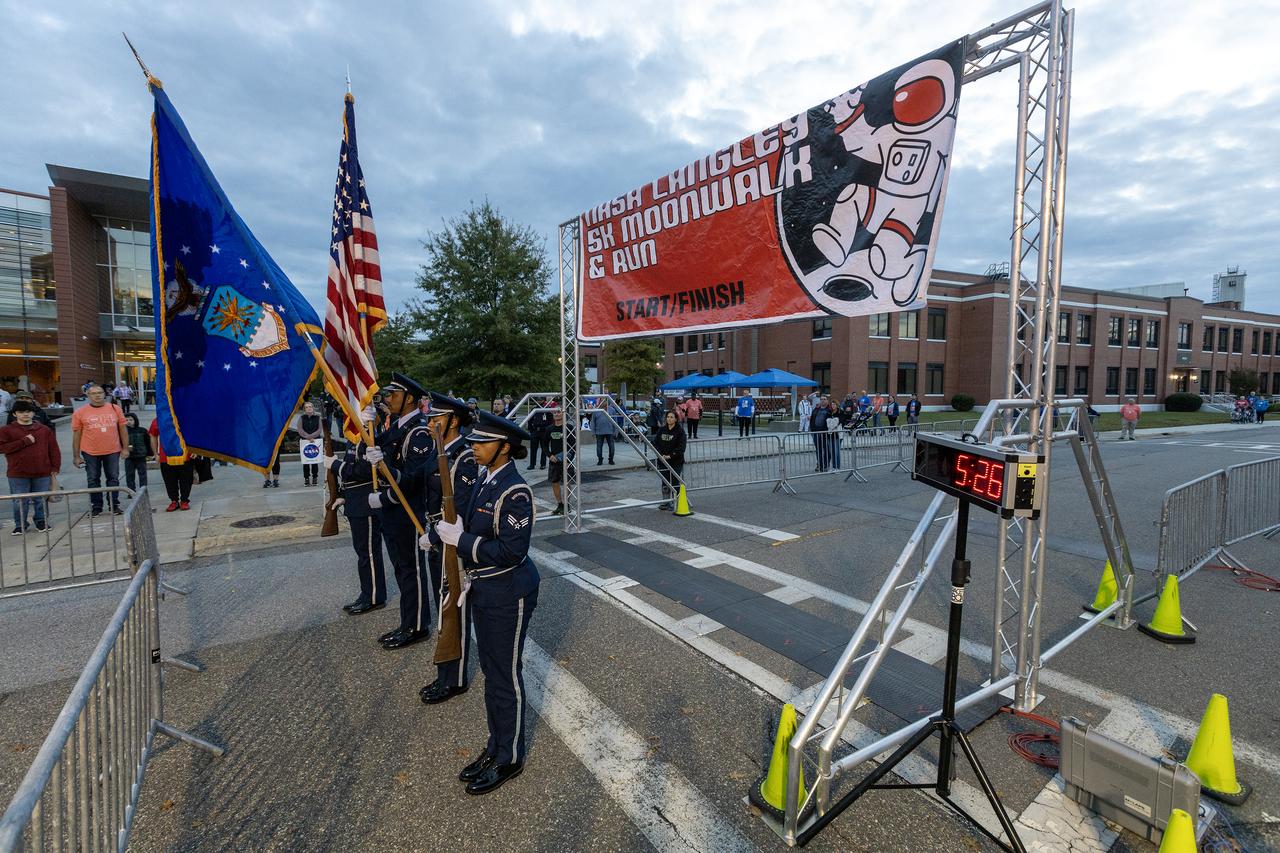

More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.
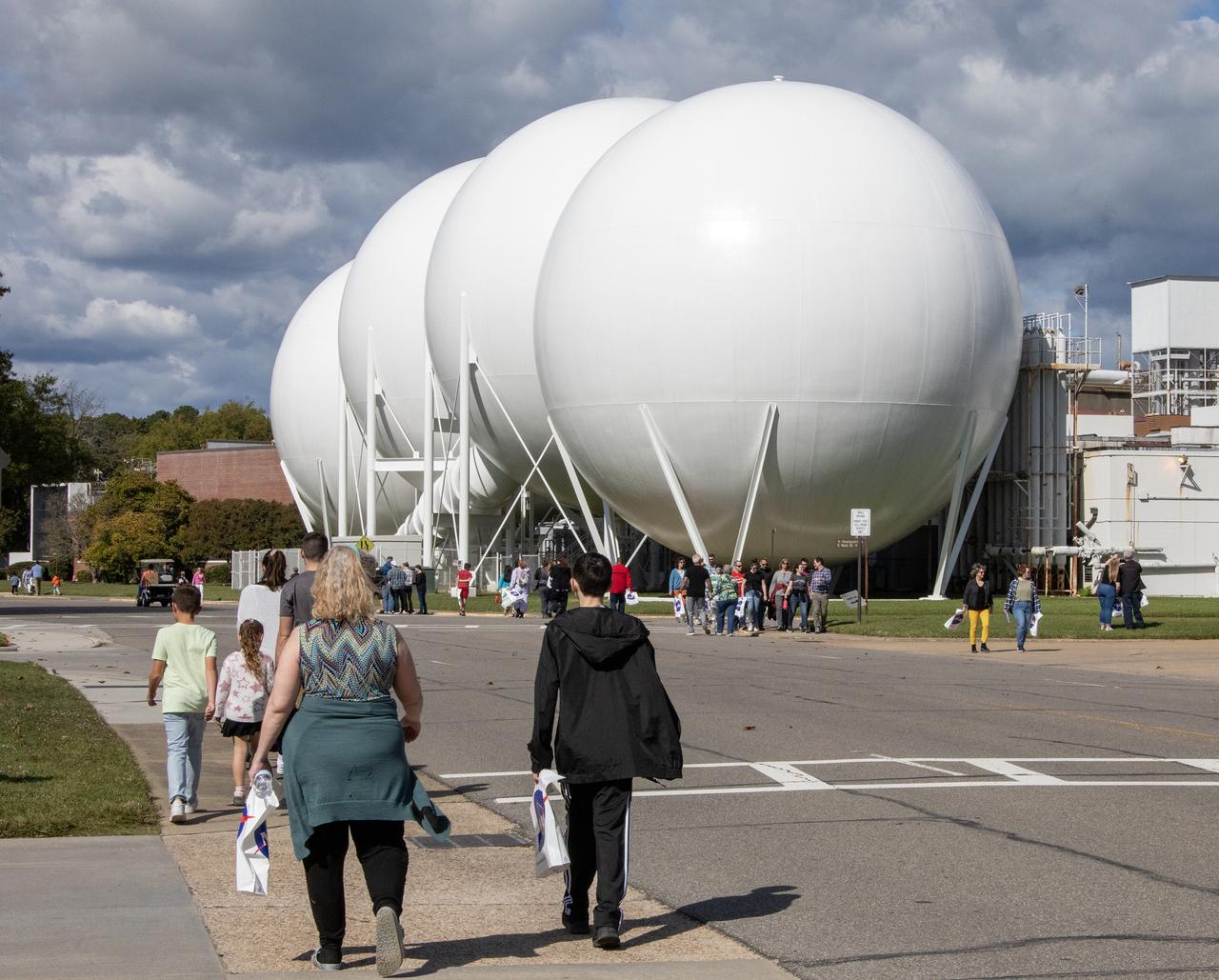

More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.
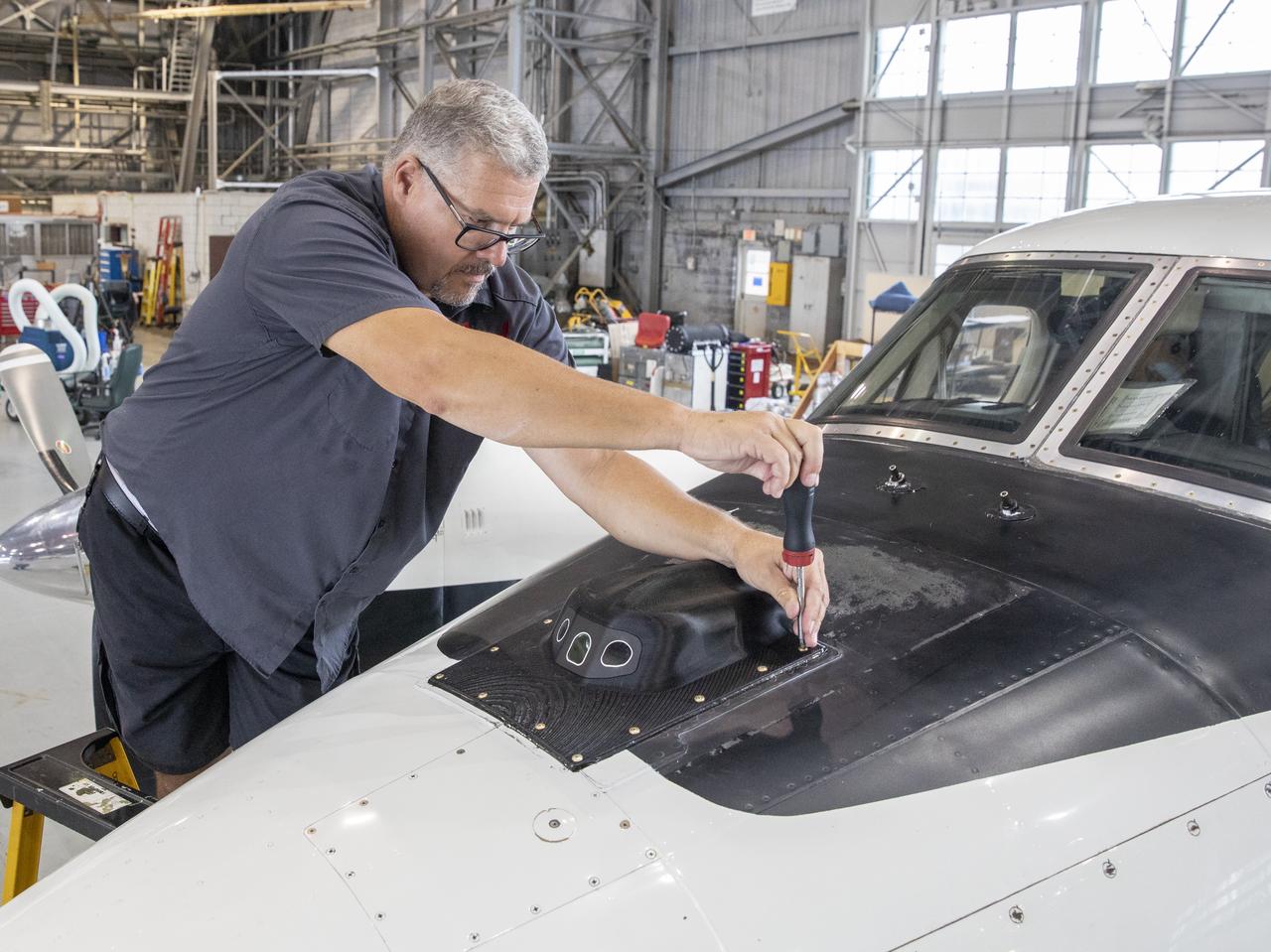

Aircraft mechanic C. Garber working on the camera housing for the flight display for the X59 to tested on the B200 King Air.
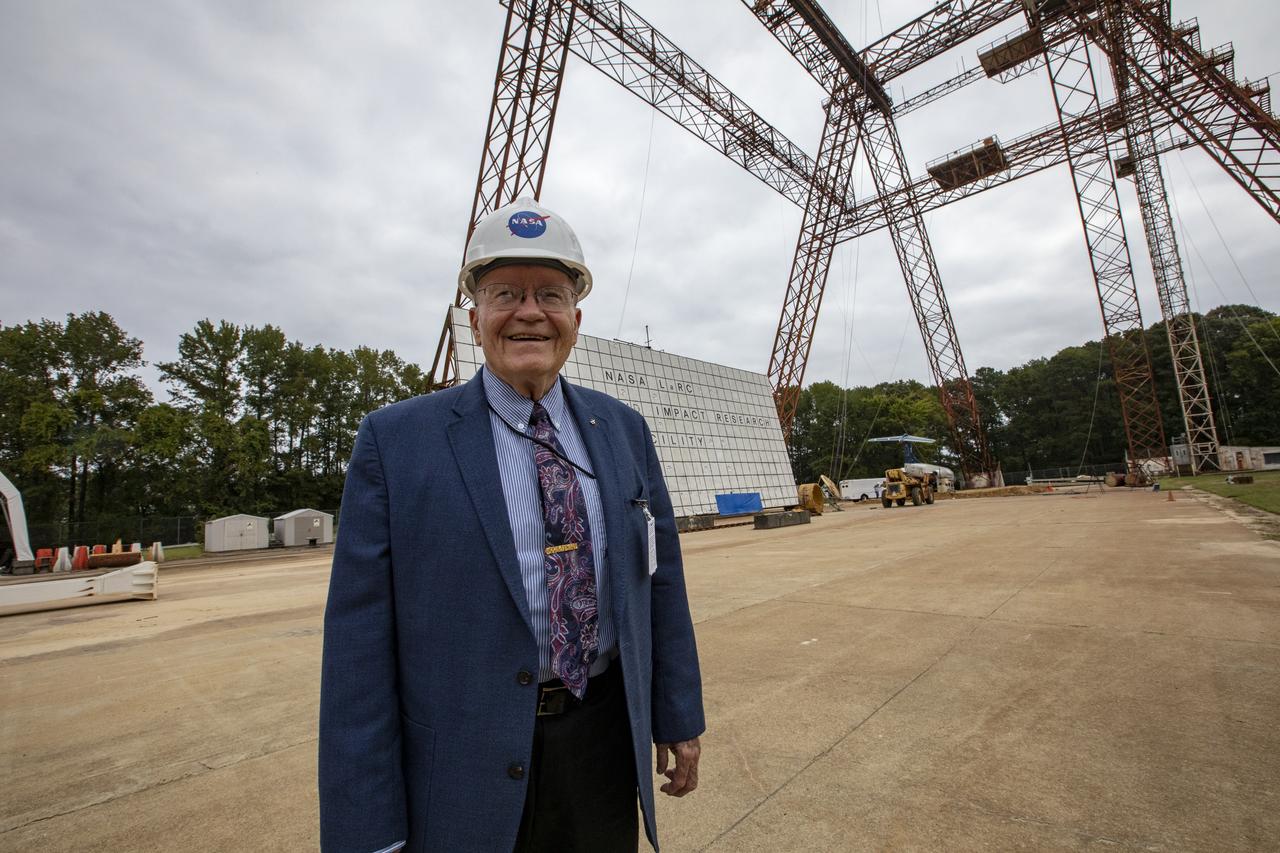

Astronaut Fred Haise visiting the gantry at Langley Research Center; a place where he once trained for the Apollo Mission.

Testing the External Vision System (XVS) software on the B200 King Air. Pilots, Peter Coen and Wayne Ringelberg attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the XVS monitor.
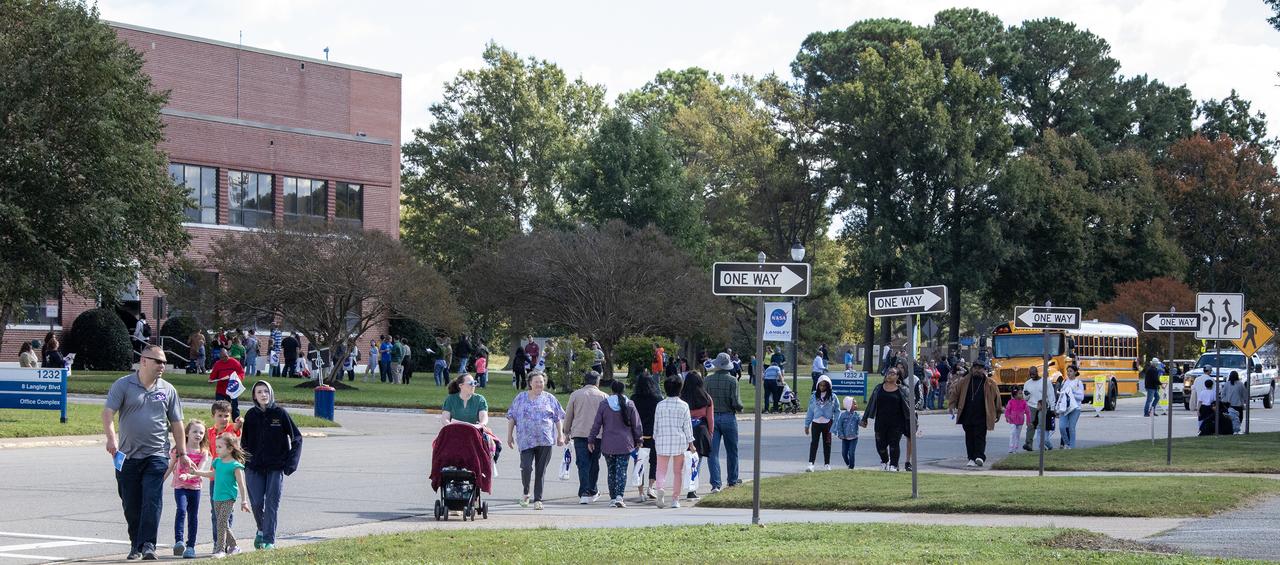

More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.
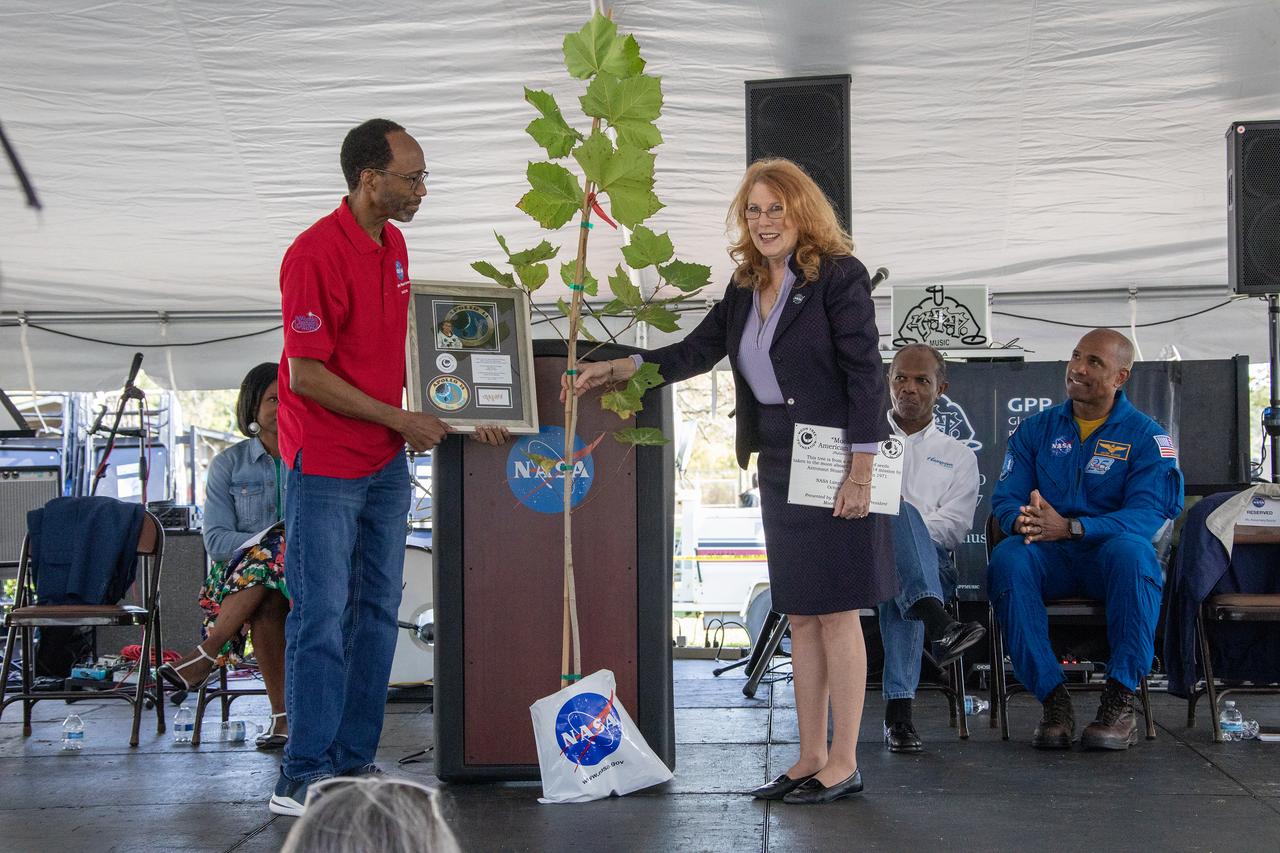

"Moon Tree" American Sycamore tree presented to Langley Center Director Clayton Moore by Rosemary Roosa, President of Moon Tree Foundation. More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.
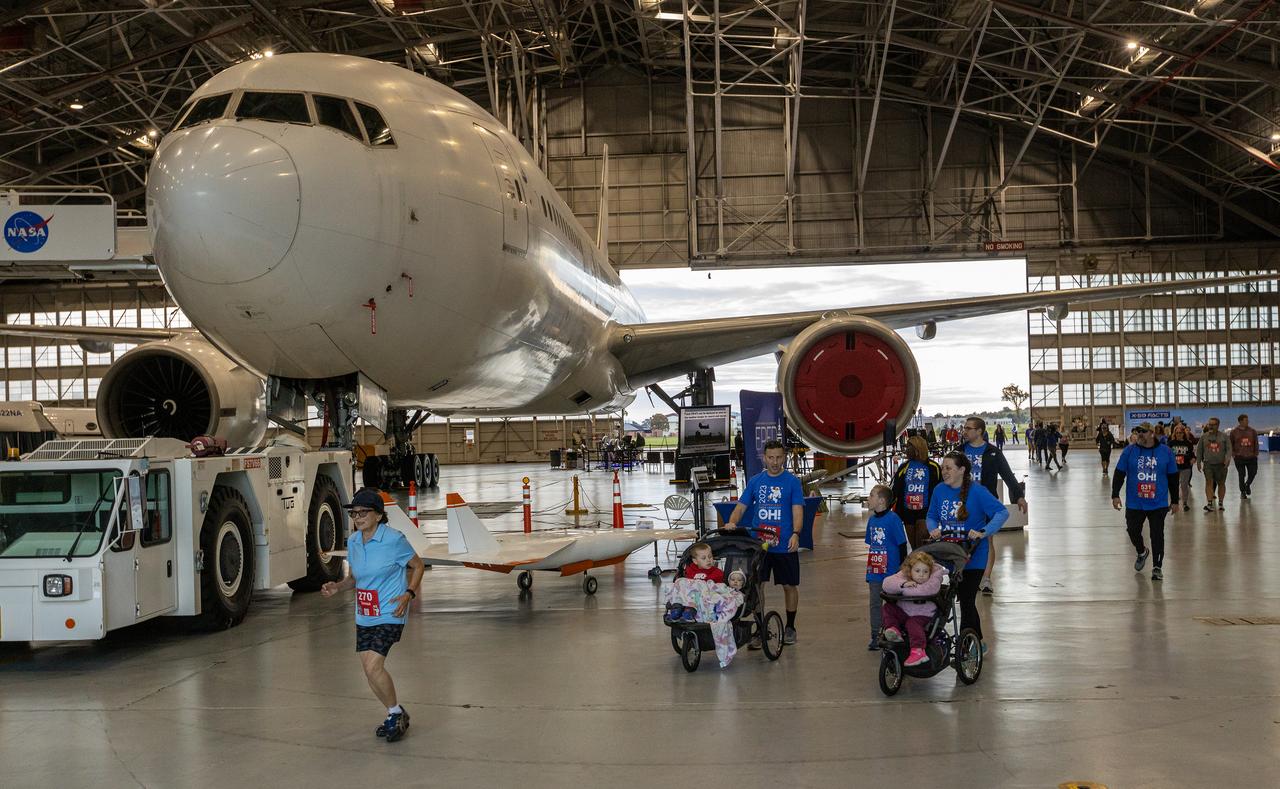

More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.

First test flight testing the visual display for the X59. The XVS display is aboard the B200 and the camera is mounted on the nose of the aircraft and inside the cockpit.

Artemis II astronaut Victor J. Glover participates in NASA Langley’s Open House on Saturday, Oct. 21. More than 37,000 people registered to attend the NASA Langley open house. Starting with the Annual 5K Moon Walk Run and the talented Nils Larson, X59 pilot and Astronaut Victor Glover reunited at Langley’s hangar and hosted by Center Director Clayton Turner.
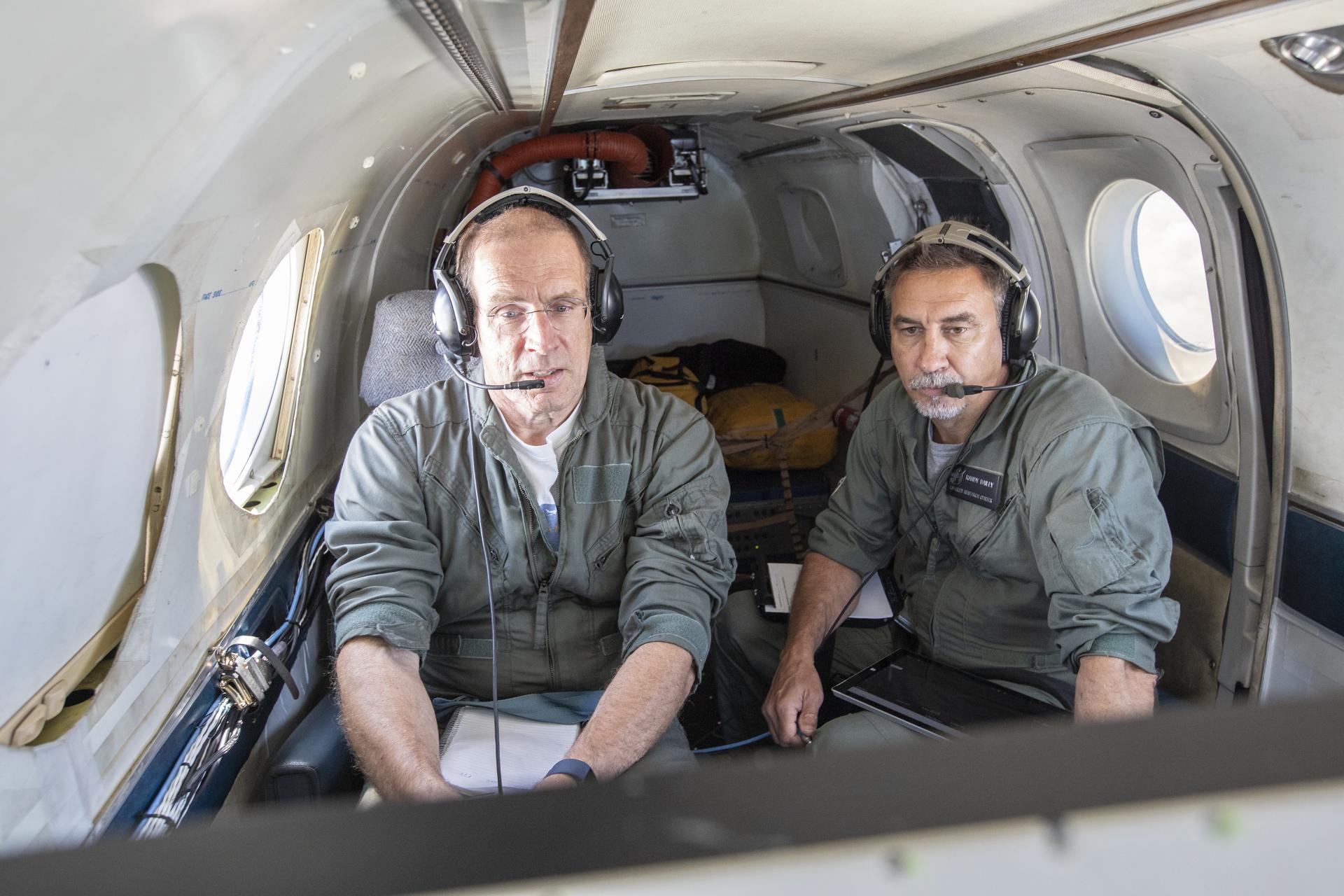

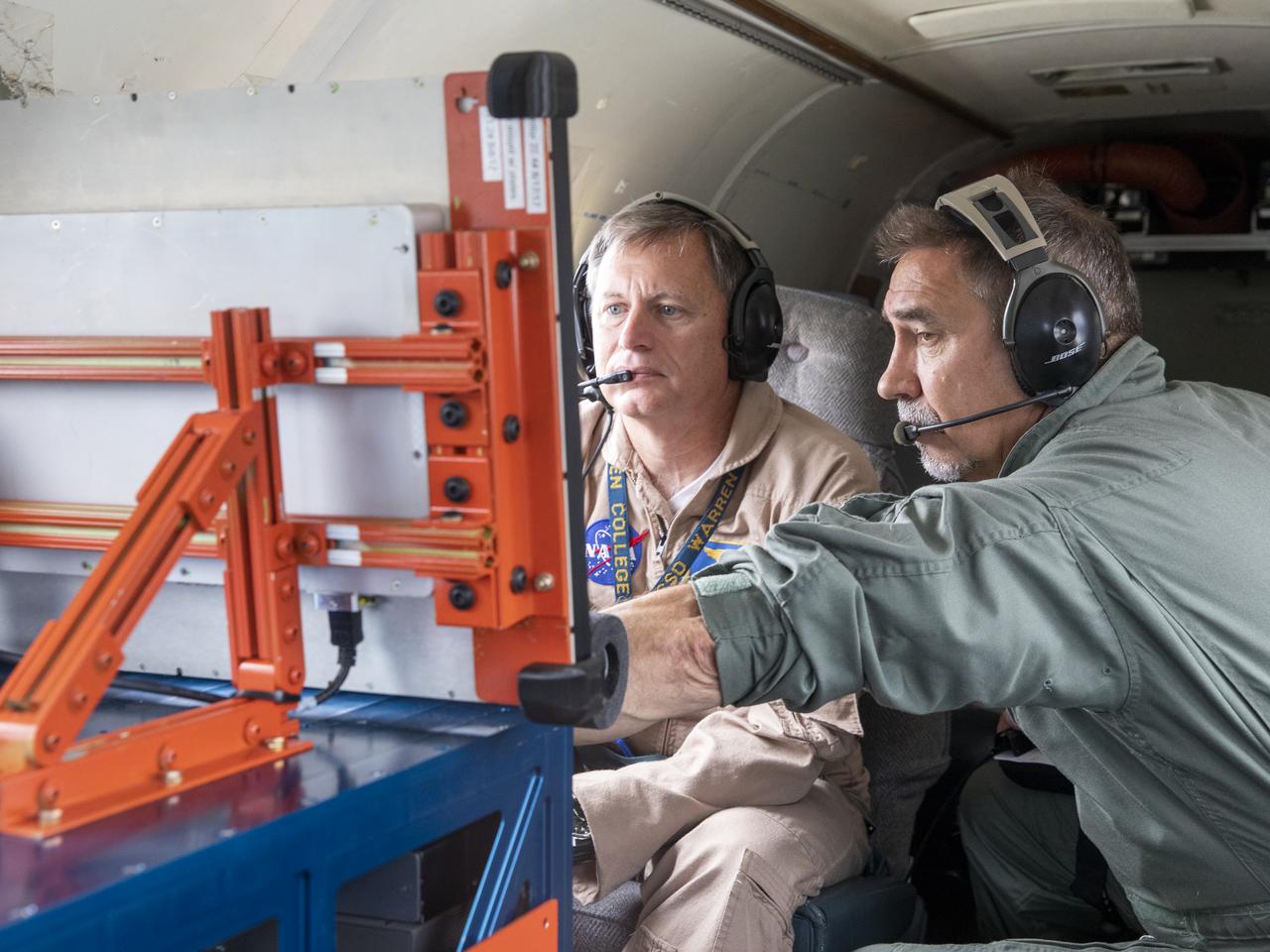
Aerospace Engineers, “from left to right” Peter Coen and Randy Bailey attempt to spot an incoming aircraft on the monitor while performing tests on the External Vision System (XVS) Software. The software testing is being conducted on the B200 King Air Beechcraft airplane.
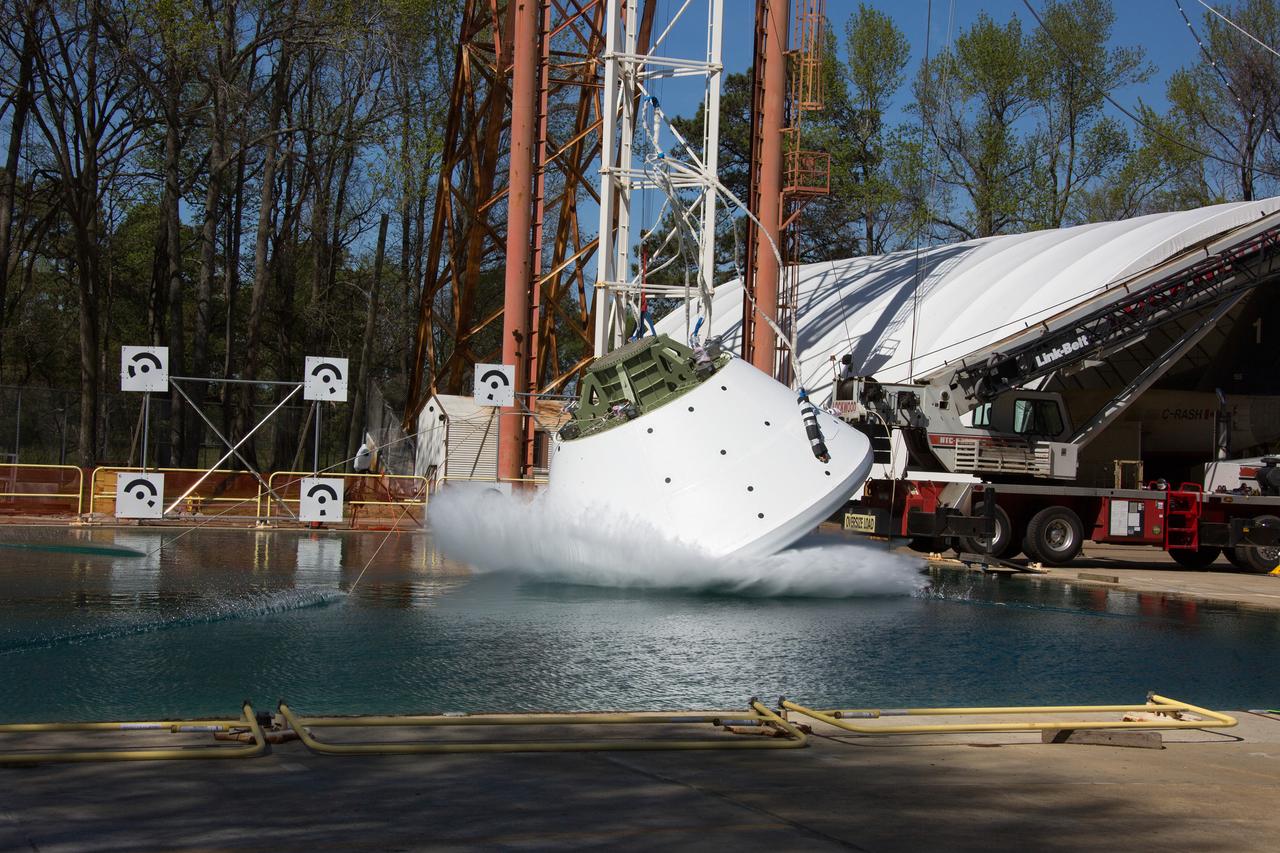

On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.
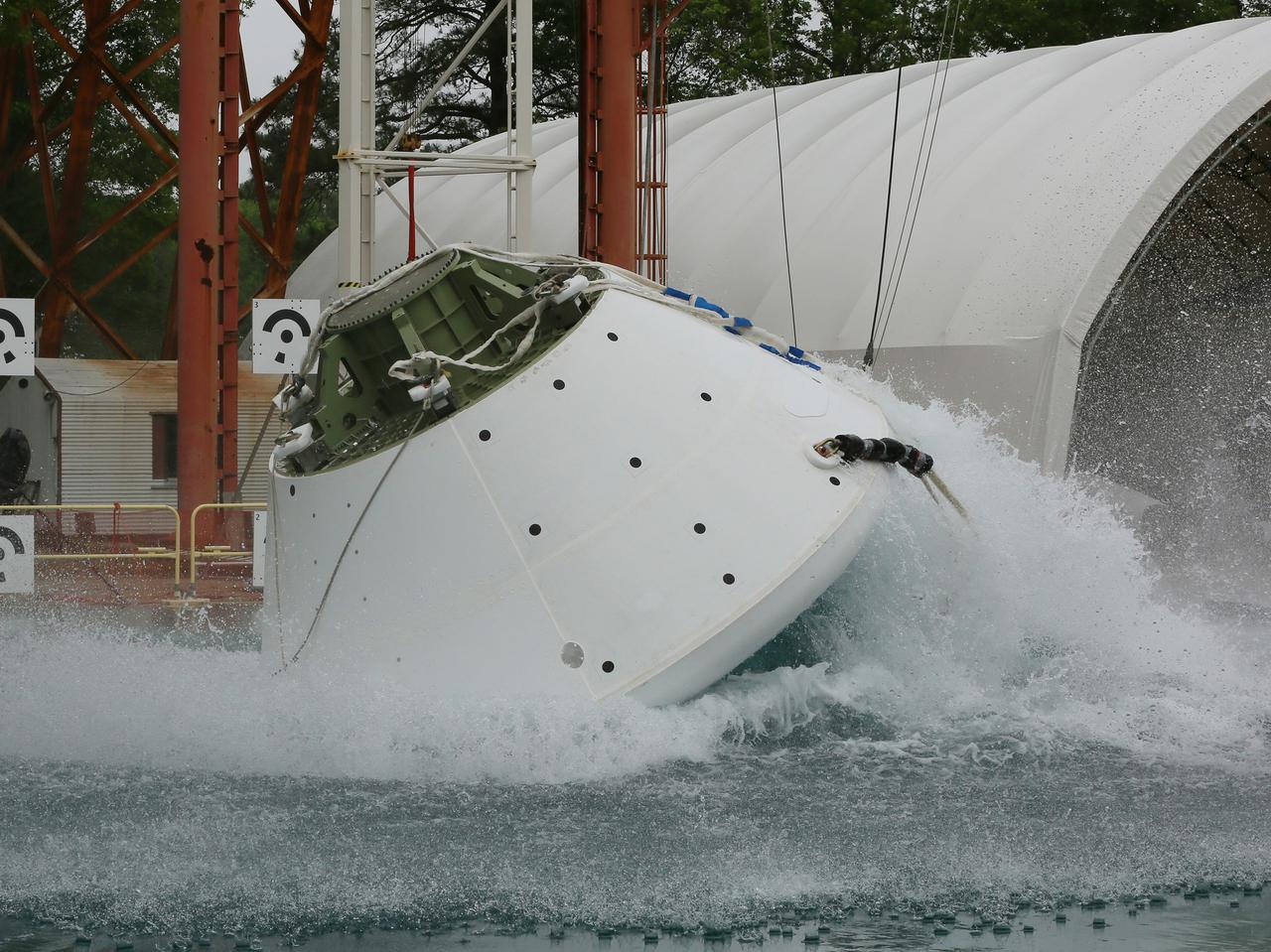

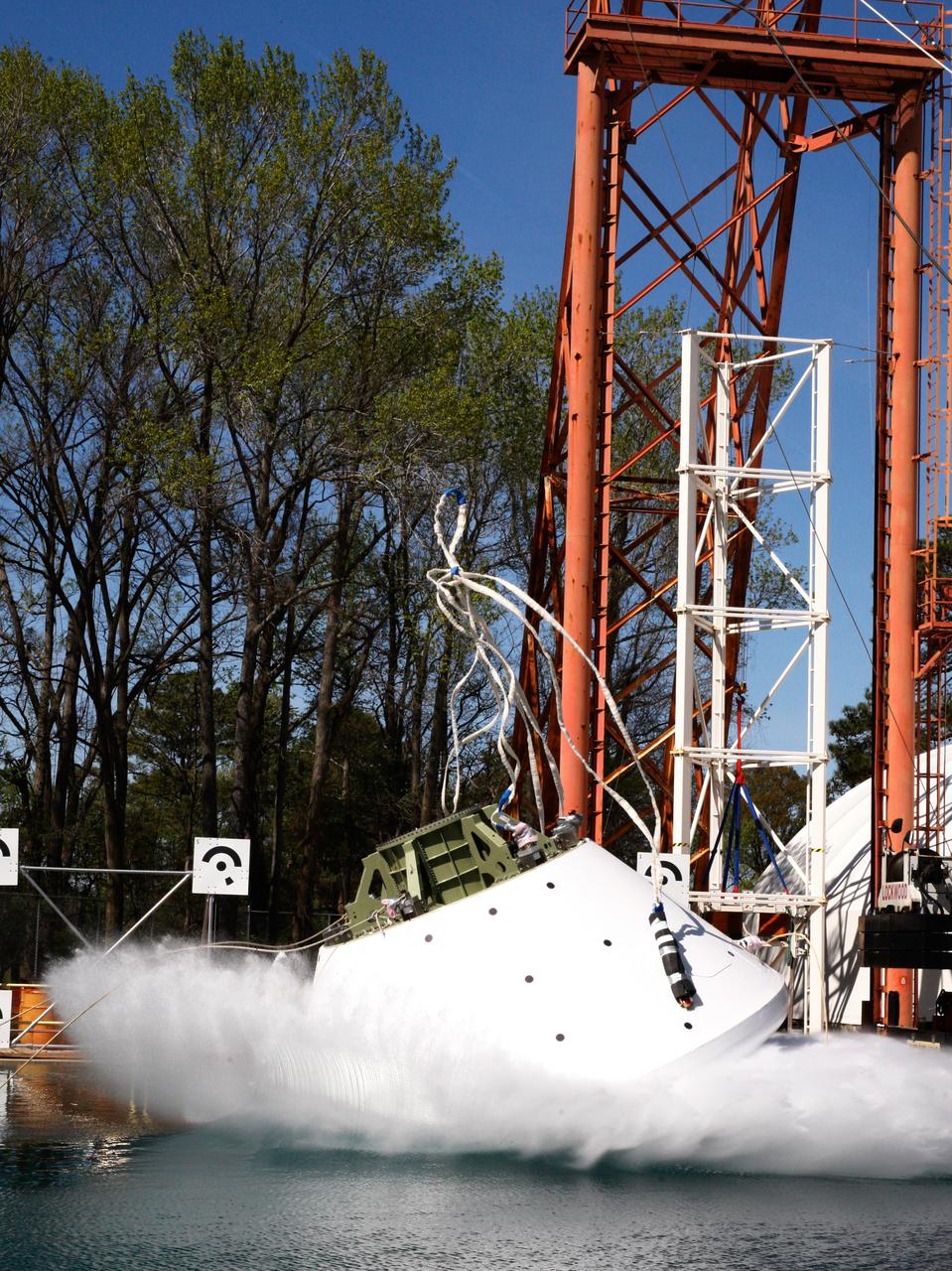
An Orion water drop test, with instrumented test dummies, takes place on May 11, 2016 at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia.
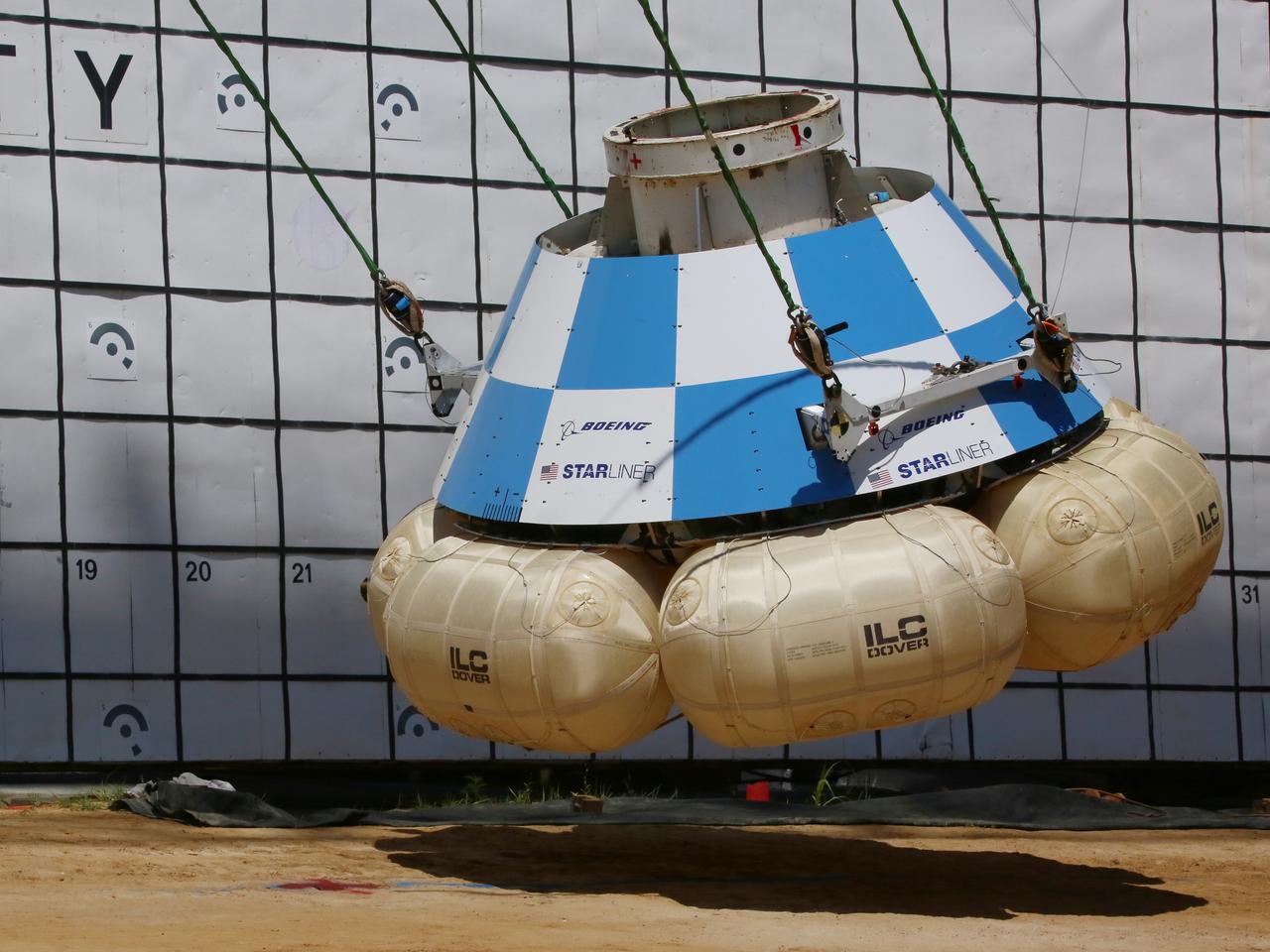

At NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, a mock-up of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft goes through a series of land landing qualification tests to simulate what the actual spacecraft and crew members may experience while returning to Earth from space. The Starliner is being developed in collaboration with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Along with SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, the spacecraft is part of the agency’s effort to return America’s capability to launch astronauts from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the International Space Station.

An Orion water drop test, with instrumented test dummies, takes place on May 11, 2016 at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia.

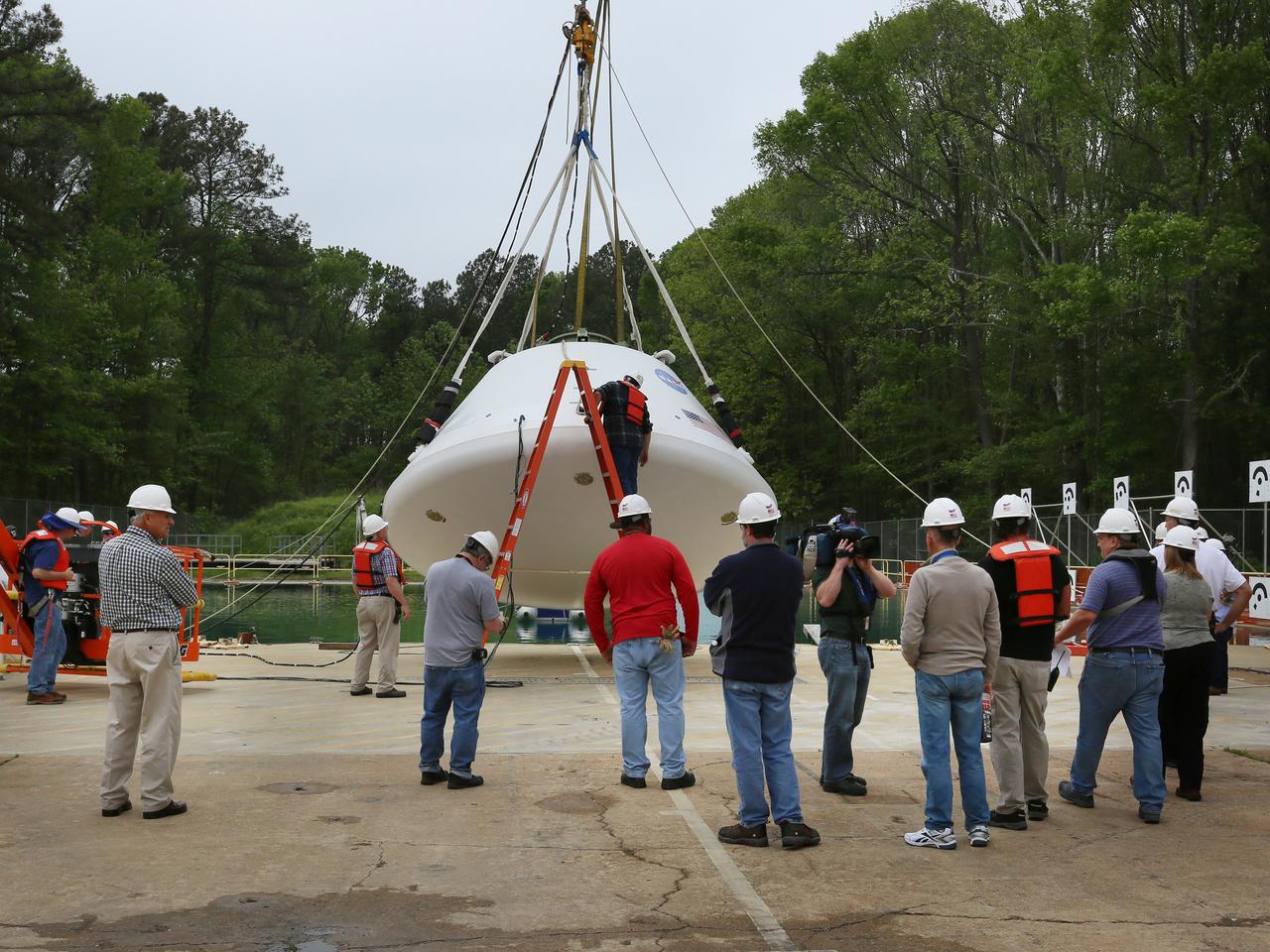
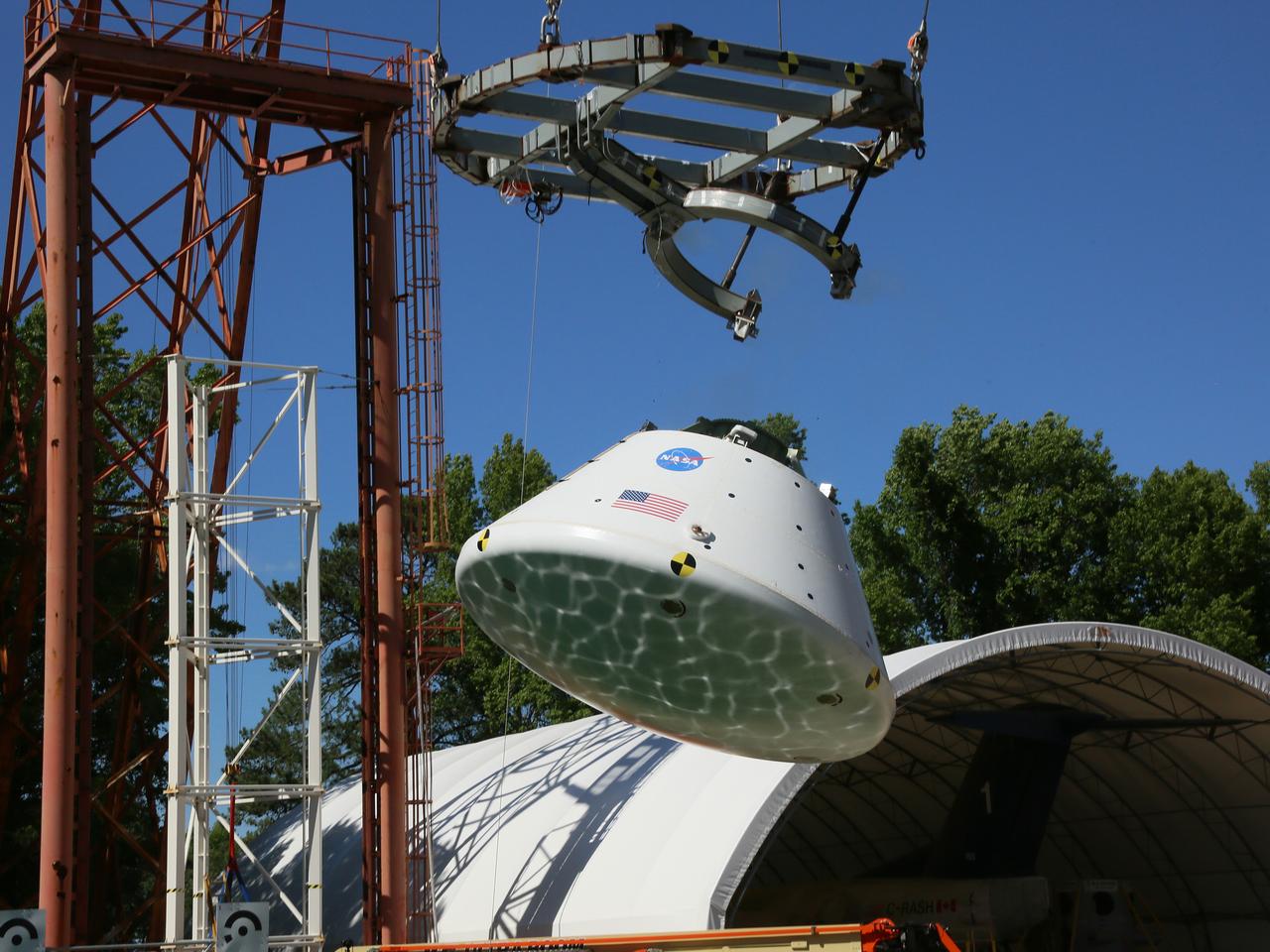
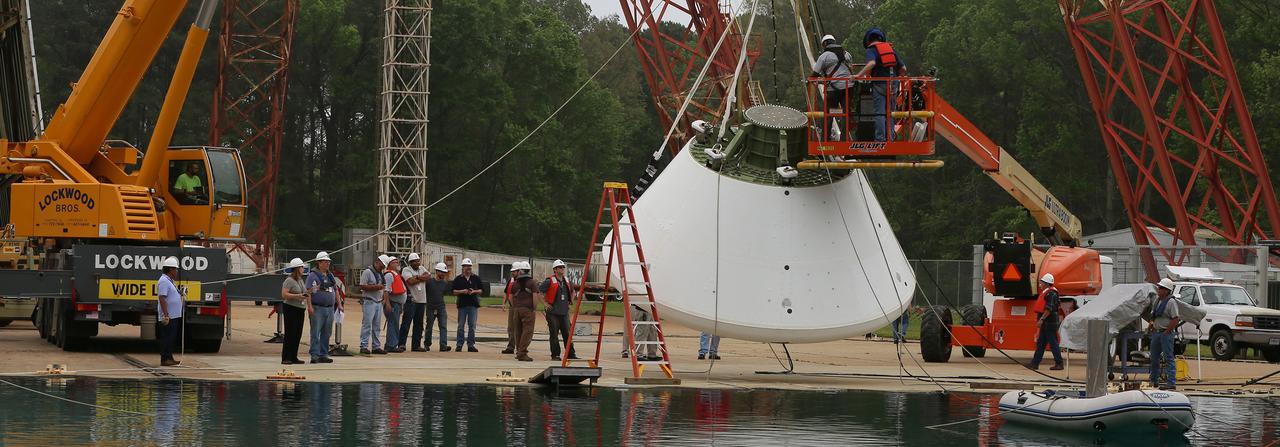
Engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, install test dummies into the seats of an Orion test article on Feb. 26, 2016. The capsule, coupled with the heat shield from the spacecraft’s first flight, will be used for water-impact testing to simulate what astronauts will experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean during a real mission.
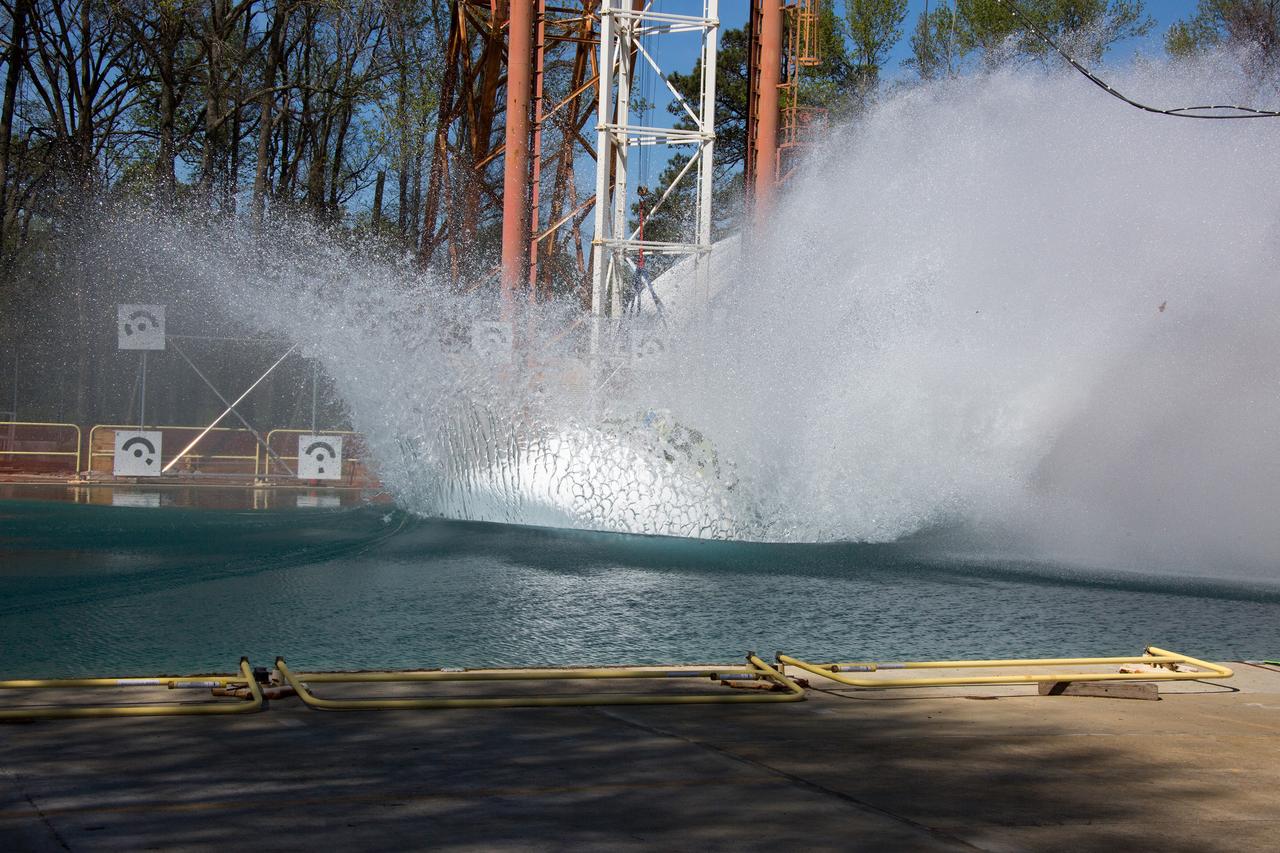

On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.

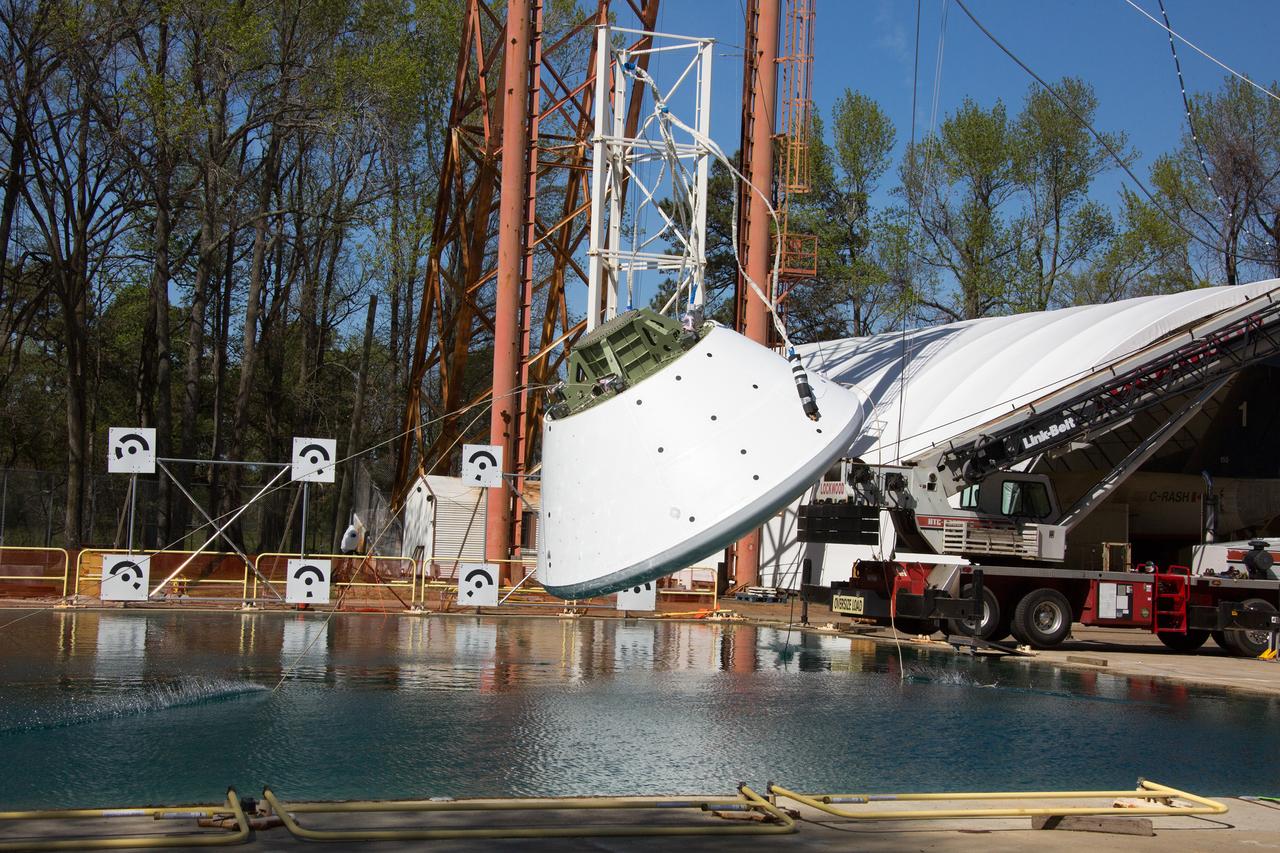
The Orion Ground Test Article completes its first swing water impact test at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia on June 8, 2016.

The Orion aerosciences team has performed more than 30 tests across the United States in support of the program, investigating the heating of the spacecraft during re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere. Testing recently concluded at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia with a 6-inch Orion heat shield model in the 20-inch Mach 6 wind tunnel, shown here on Feb. 4, 2019. The team includes engineers at Langley, NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, and NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley.

An Orion water drop test, with instrumented test dummies, takes place on May 11, 2016 at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia.
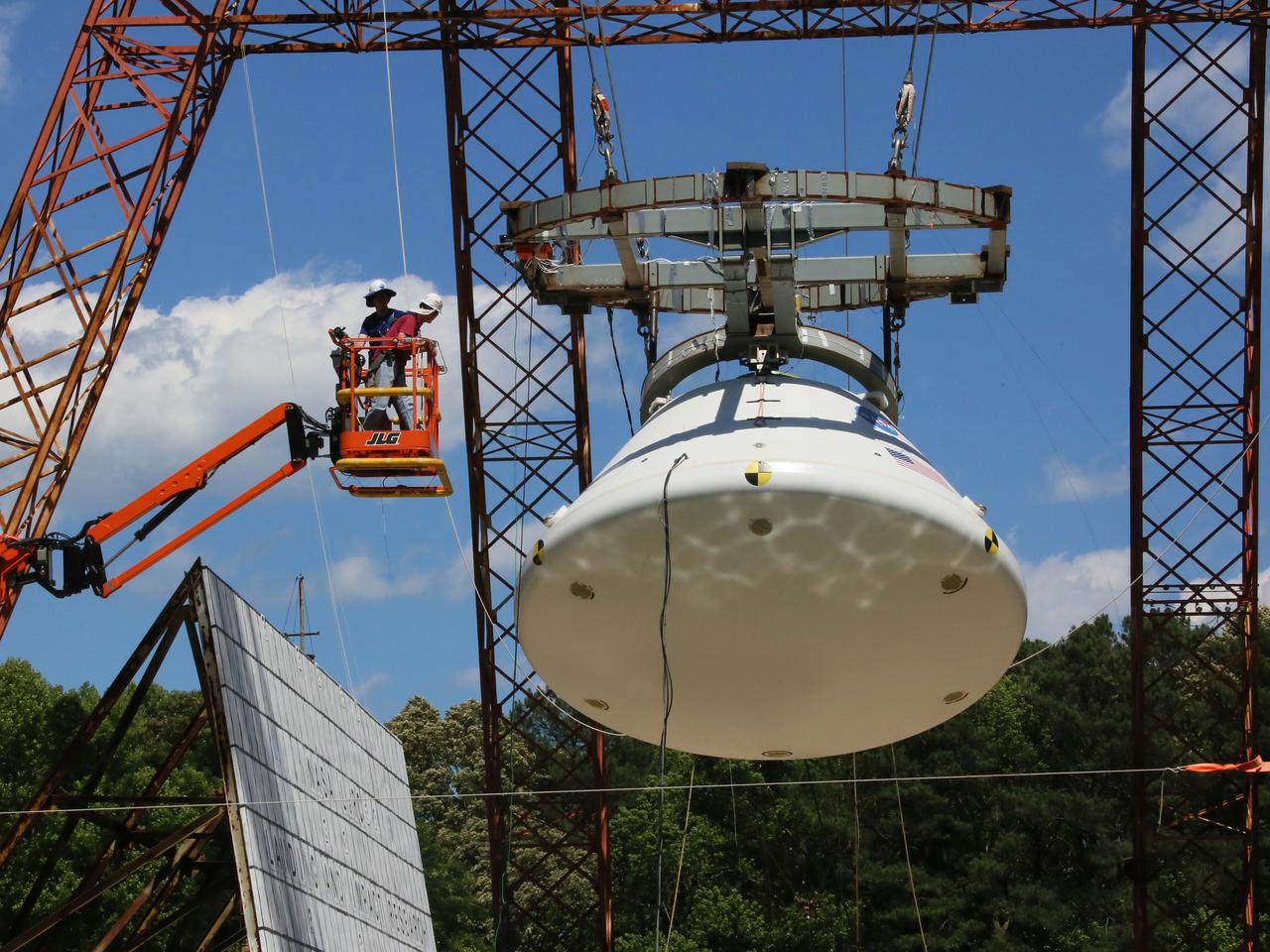

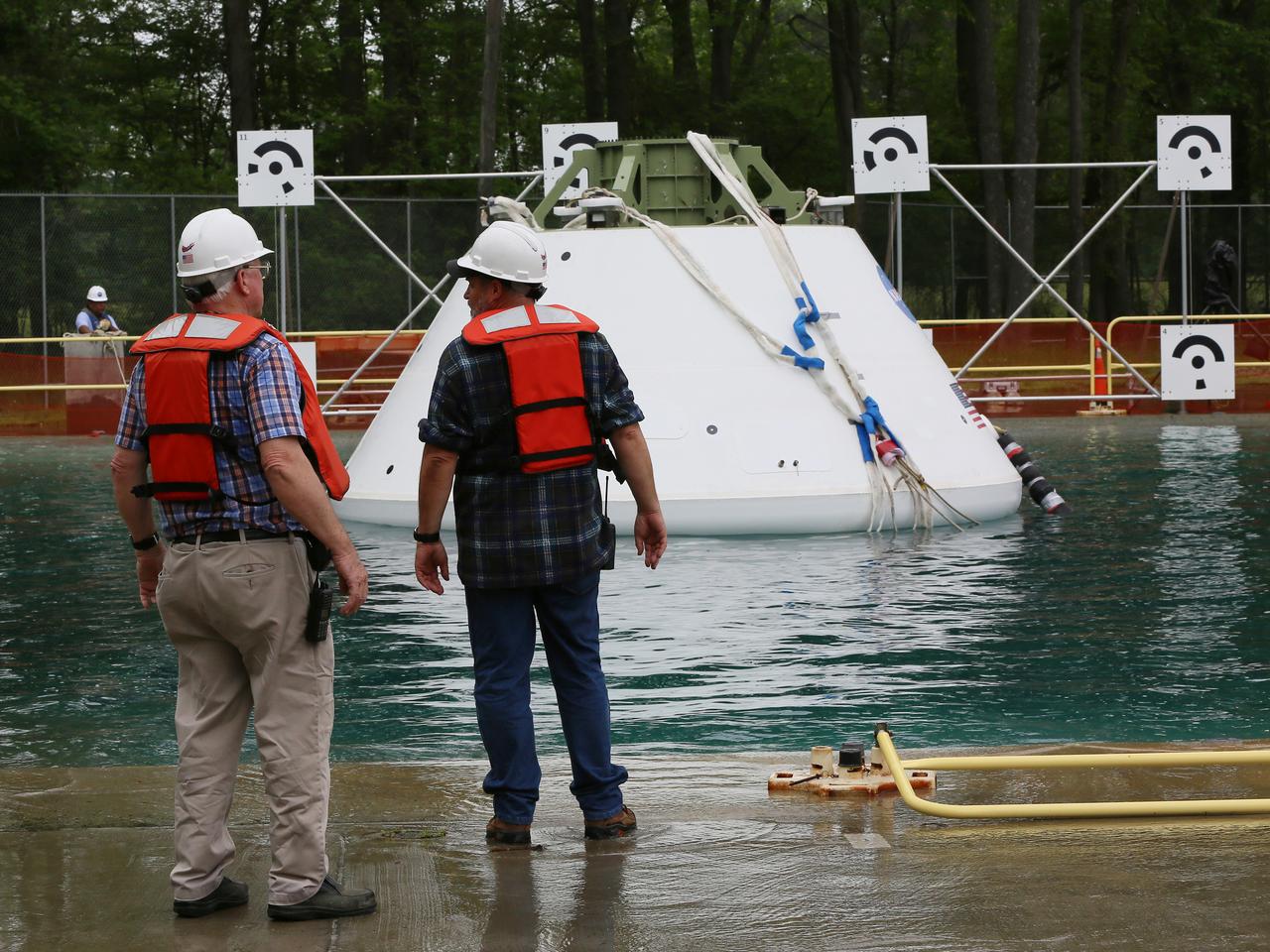
The Orion Ground Test Article completes its first swing water impact test at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia on June 8, 2016.

On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.

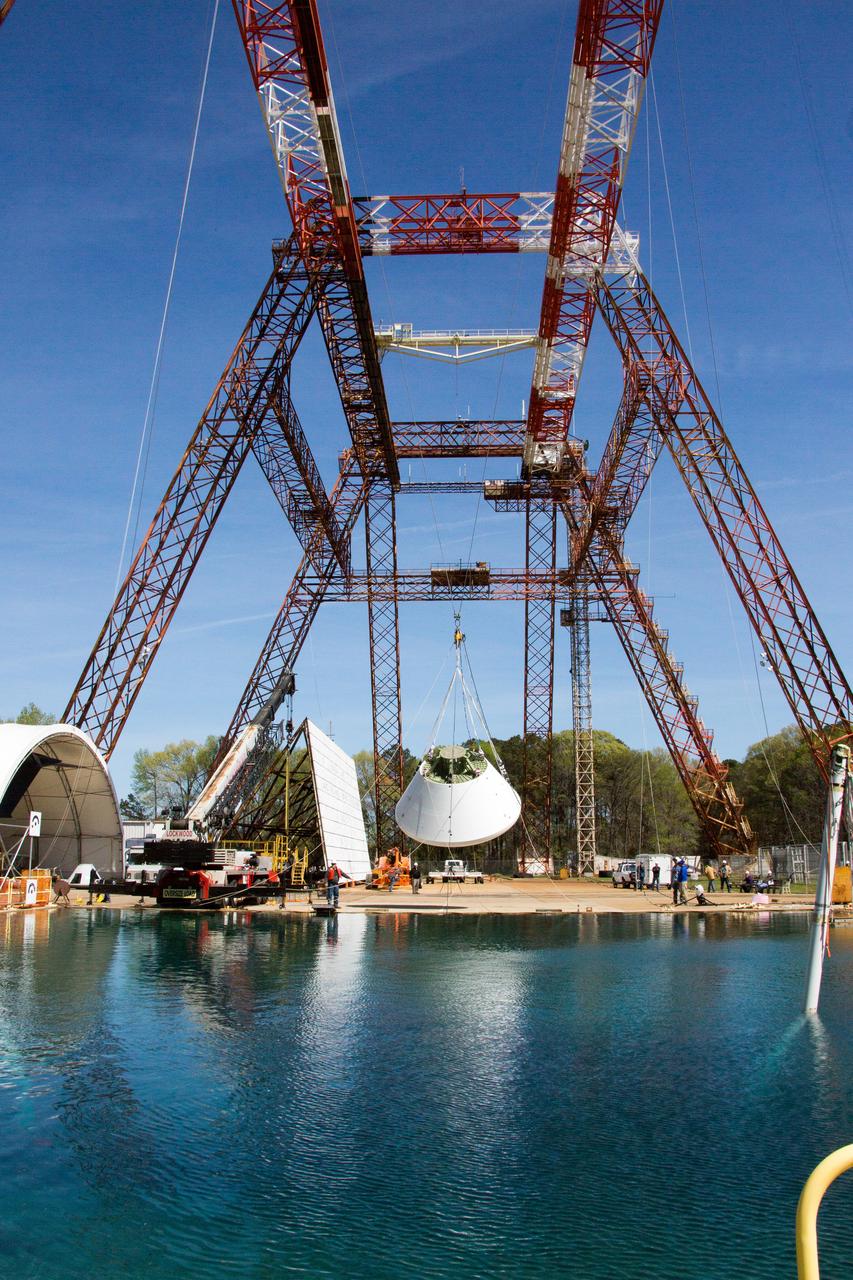
At NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, a mock-up of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft goes through a series of land landing qualification tests to simulate what the actual spacecraft and crew members may experience while returning to Earth from space. The Starliner is being developed in collaboration with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Along with SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, the spacecraft is part of the agency’s effort to return America’s capability to launch astronauts from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the International Space Station.

On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.

The Orion Ground Test Article completes its first swing water impact test at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia on June 8, 2016.
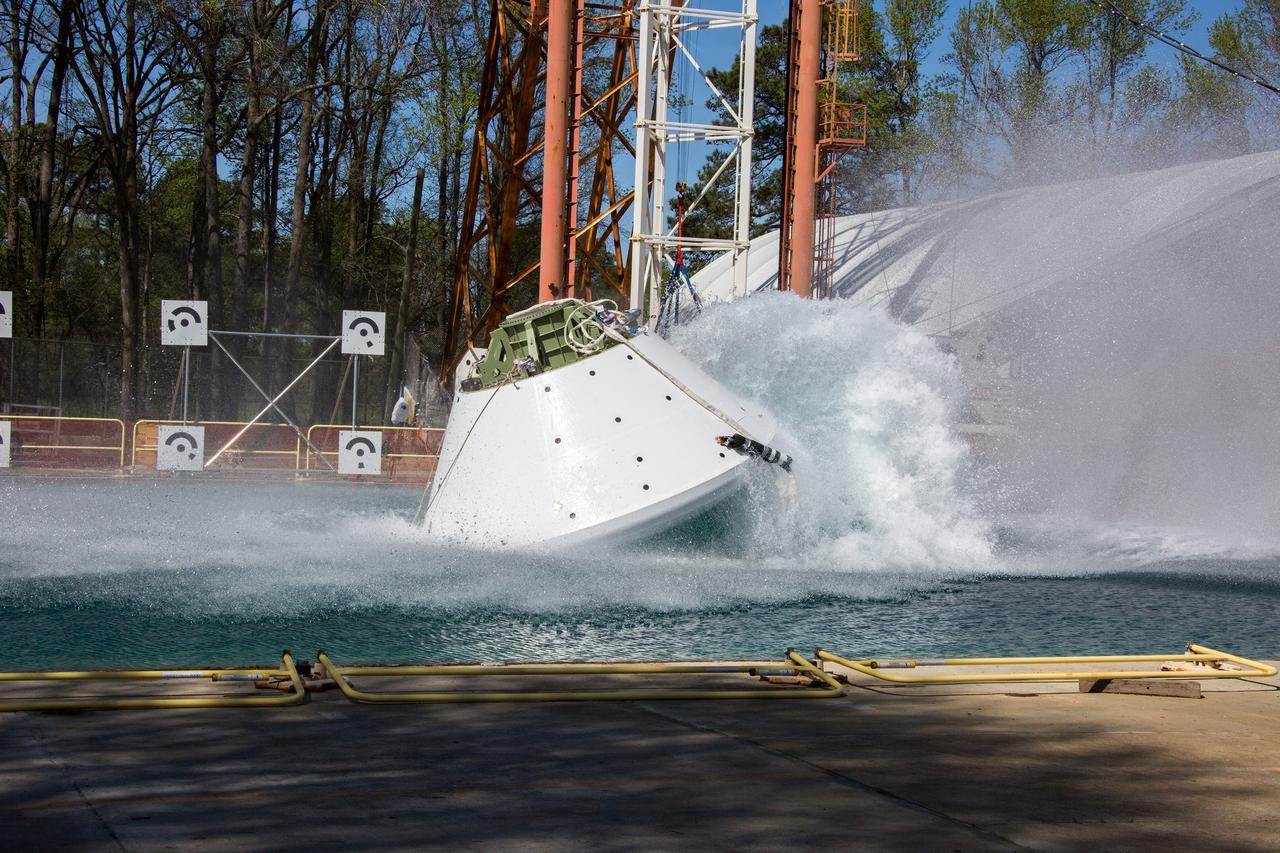

On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.
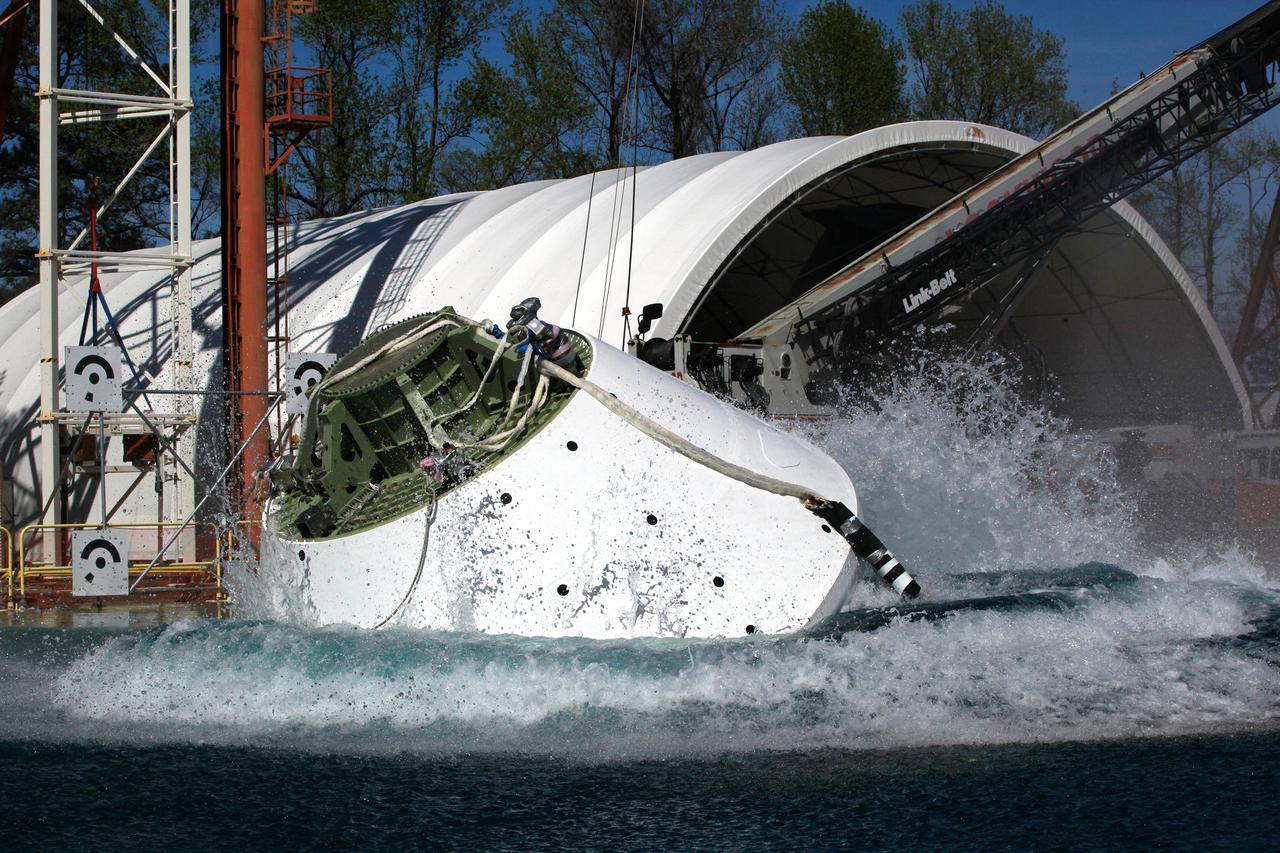

On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.
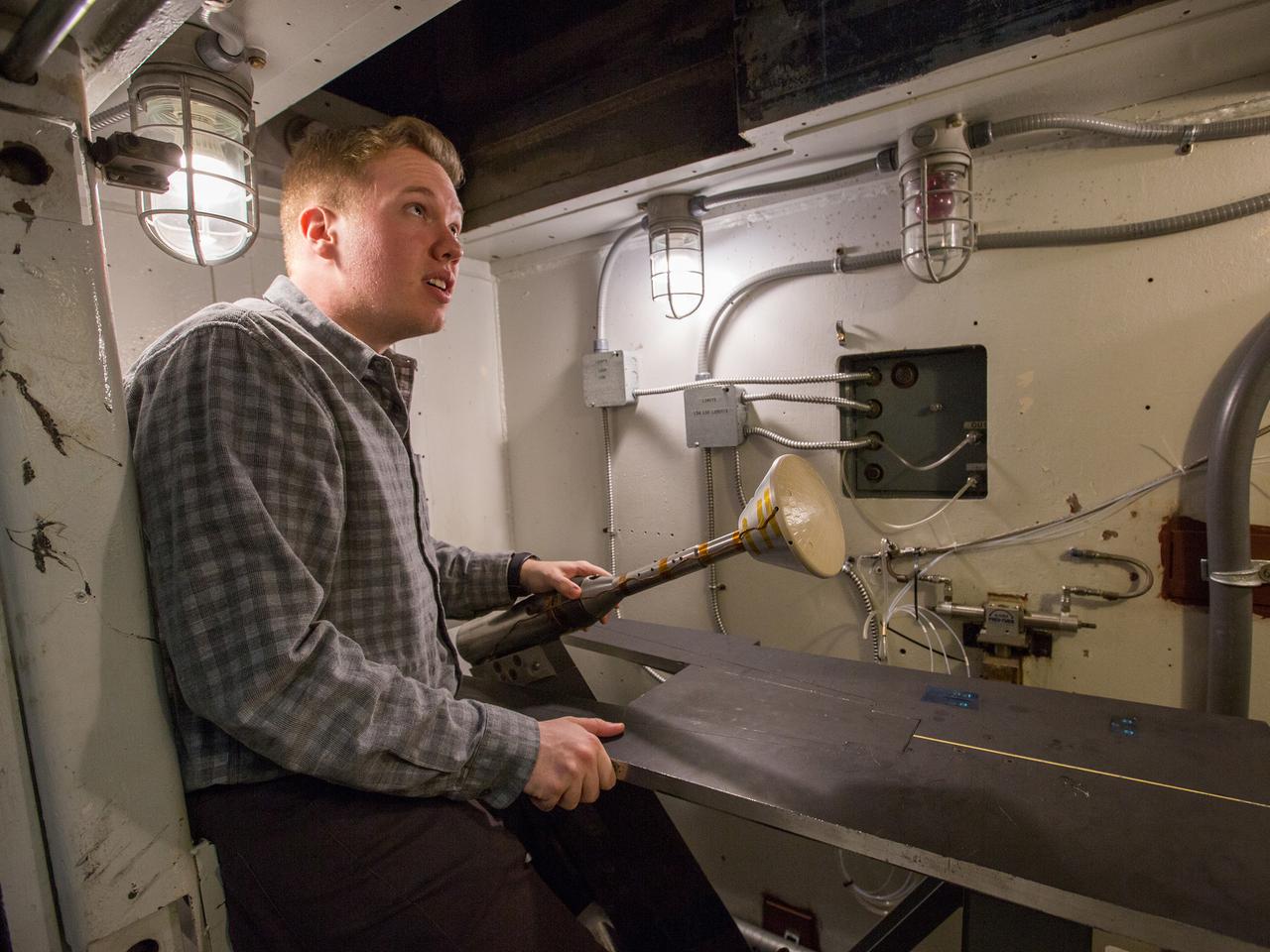

The Orion aerosciences team has performed more than 30 tests across the United States in support of the program, investigating the heating of the spacecraft during re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere. Testing recently concluded at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia with a 6-inch Orion heat shield model in the 20-inch Mach 6 wind tunnel, shown here on Feb. 4, 2019. The team includes engineers at Langley, NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, and NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley.
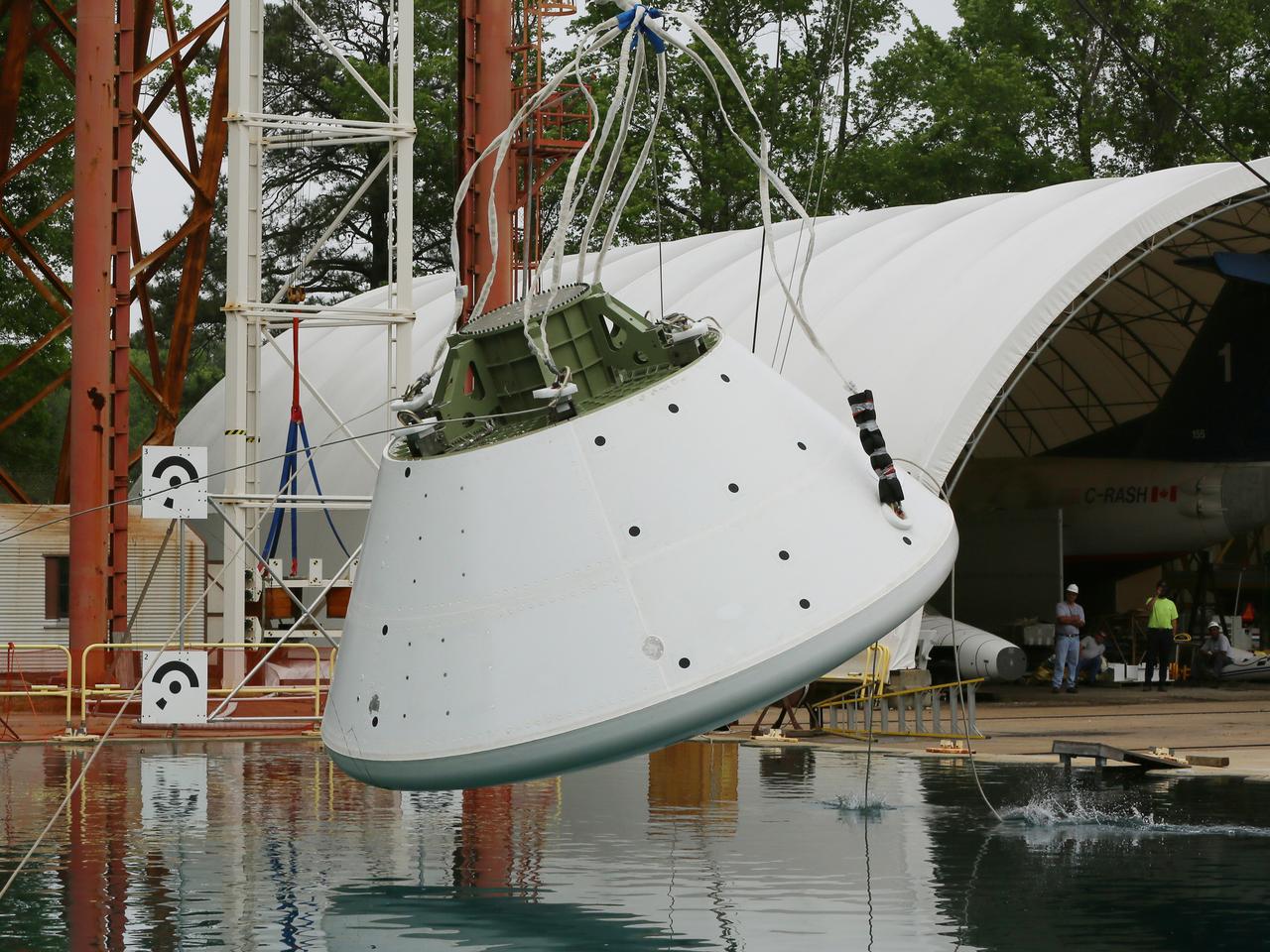

An Orion water drop test, with instrumented test dummies, takes place on May 11, 2016 at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia.
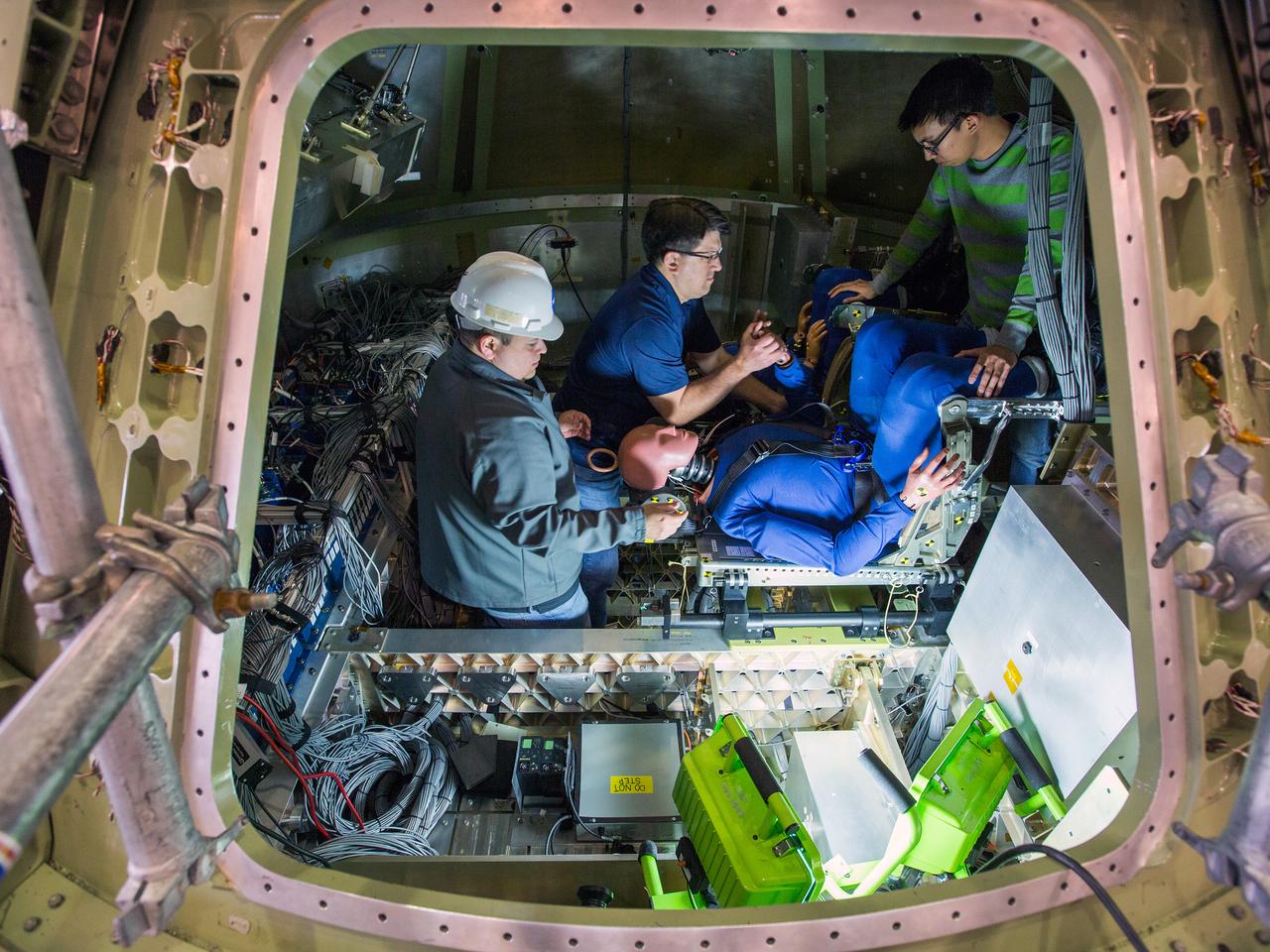

Engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, install test dummies into the seats of an Orion test article on Feb. 26, 2016. The capsule, coupled with the heat shield from the spacecraft’s first flight, will be used for water-impact testing to simulate what astronauts will experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean during a real mission.
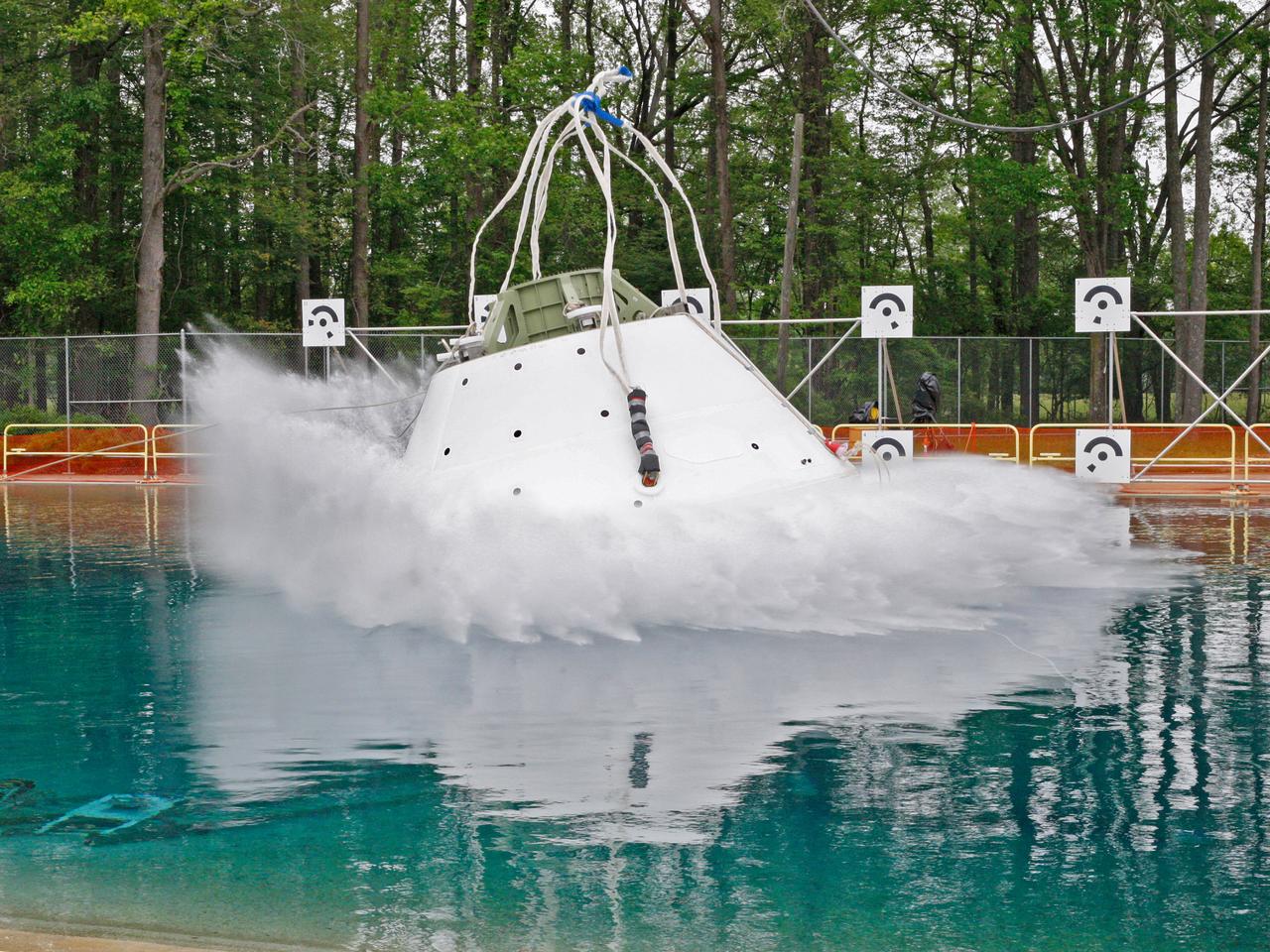
An Orion water drop test, with instrumented test dummies, takes place on May 11, 2016 at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia.
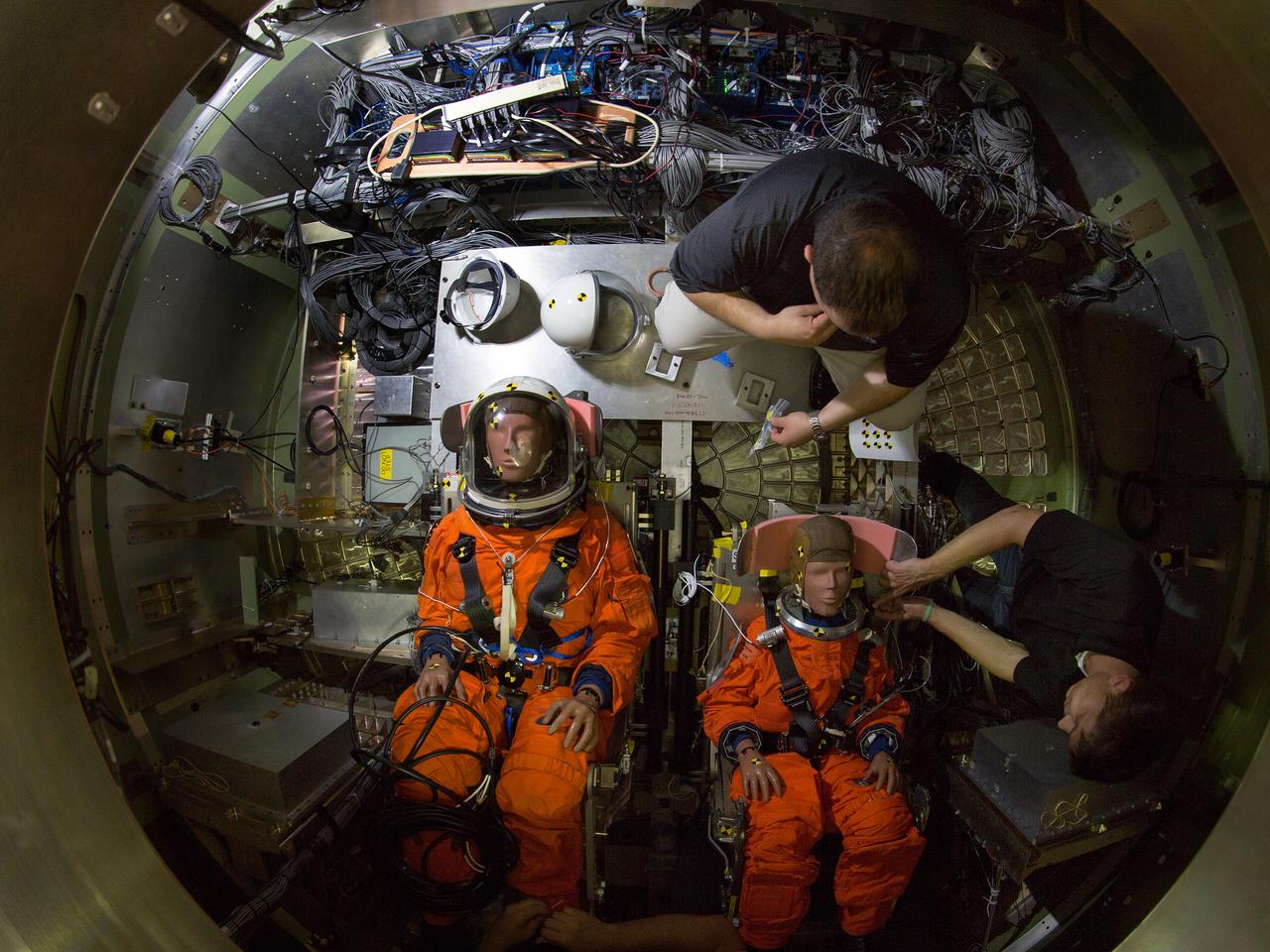

Orion's 2016 water drop test series included heavily instrumented test dummies, shown here on May 6, 2016, to assess the impact future crews will experience in Orion splashdown scenarios.
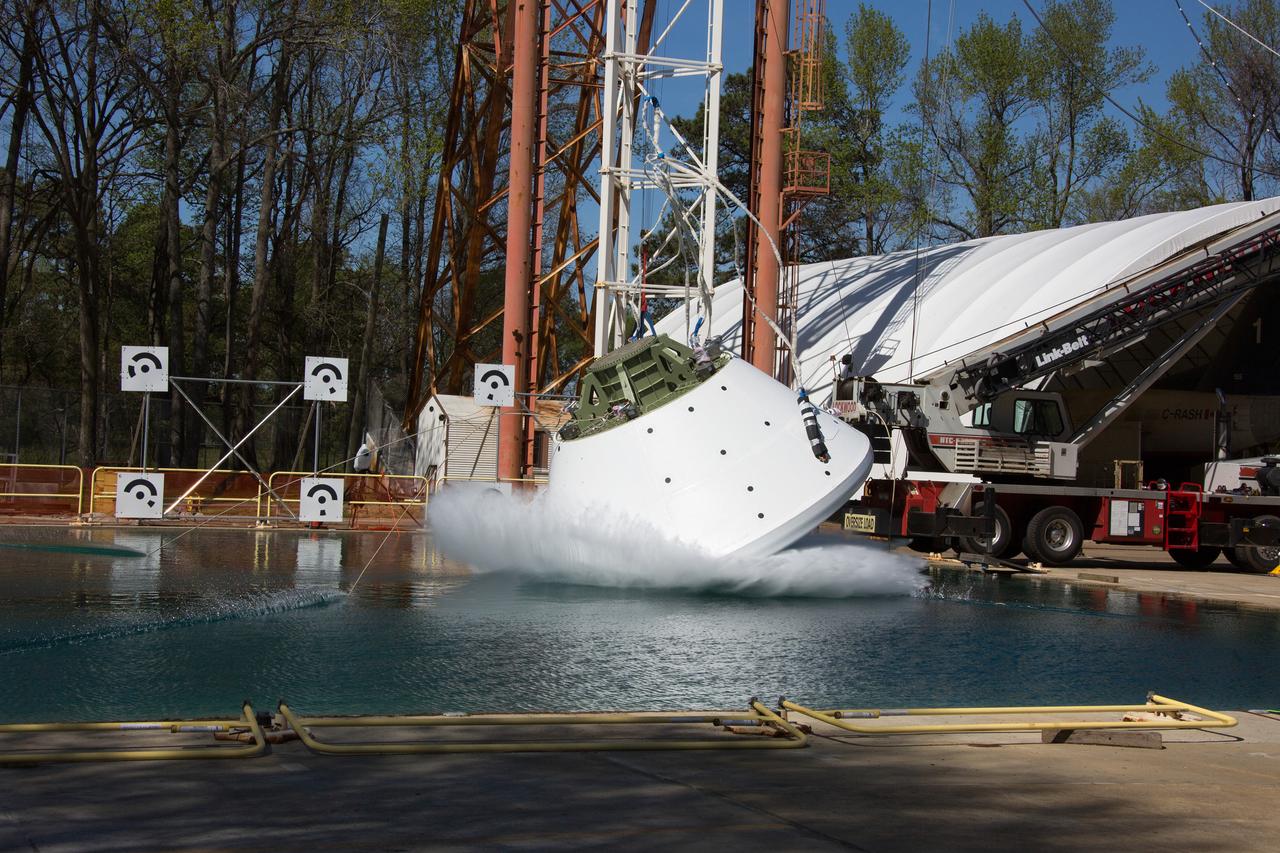

On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.
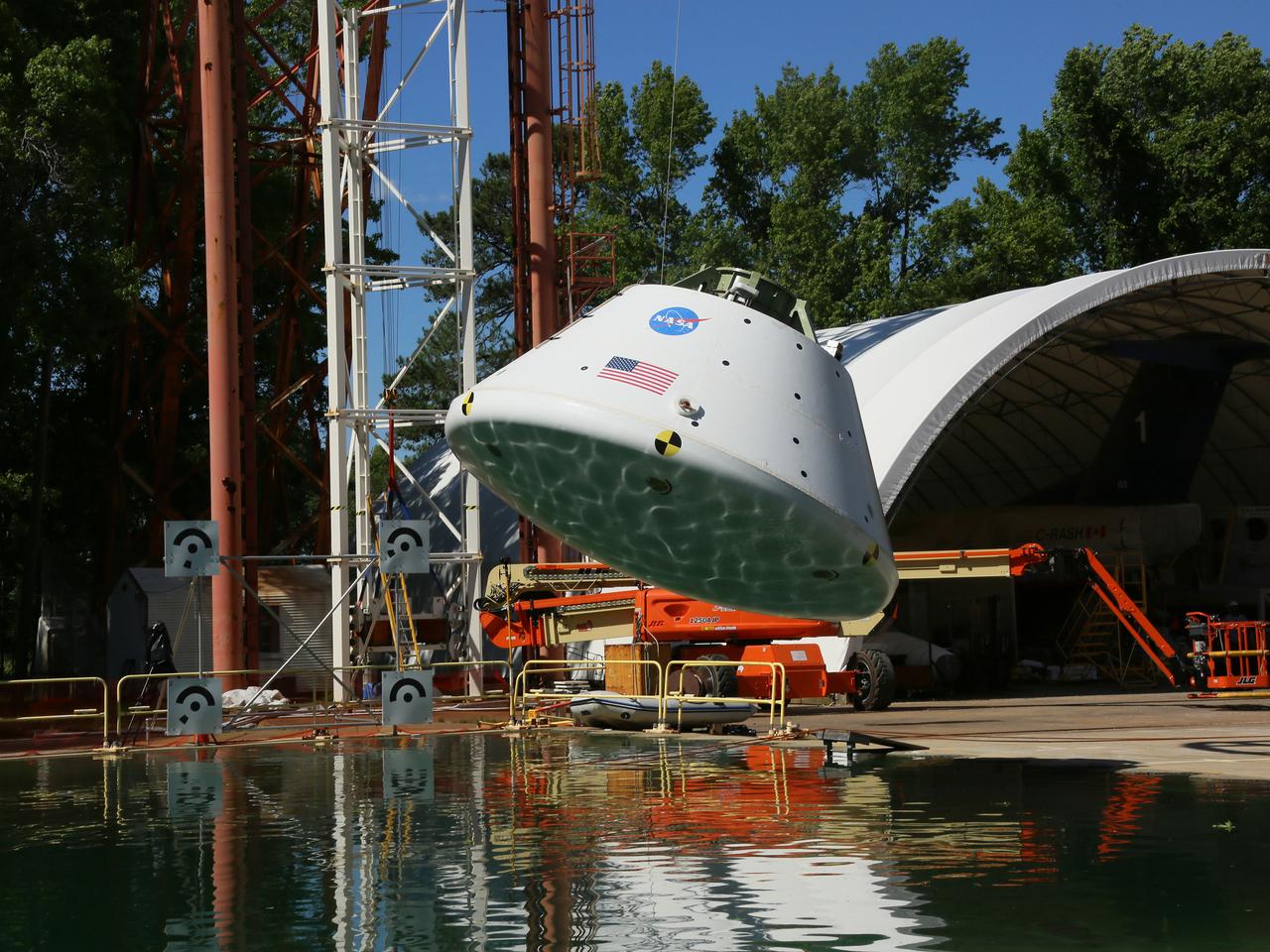

The Orion Ground Test Article completes its first swing water impact test at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia on June 8, 2016.

The Orion Ground Test Article completes its first swing water impact test at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia on June 8, 2016.

Data from the American Airlines ramp tower at Charlotte airport is among the information to be coordinated as part of ATD-2.
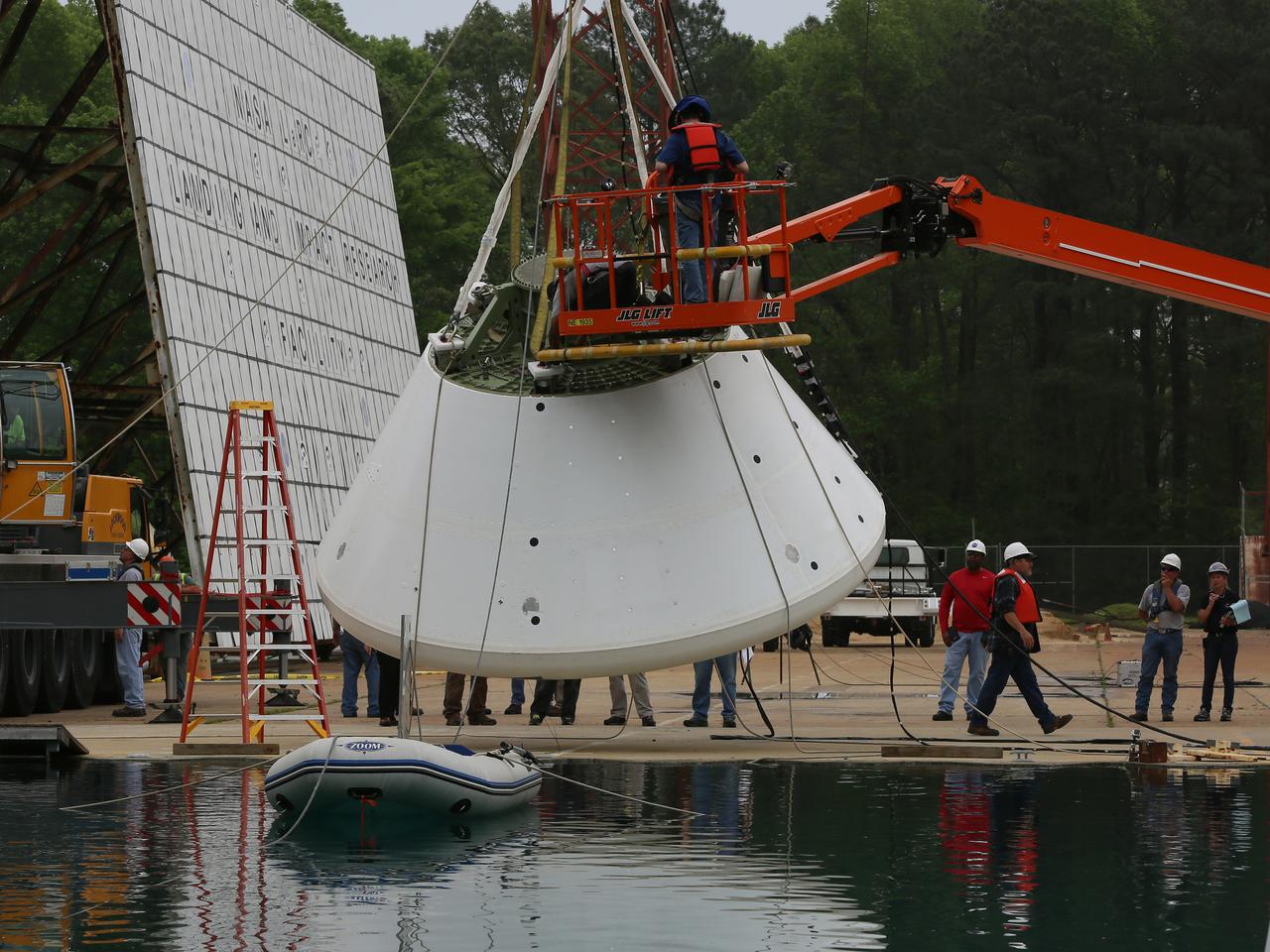

An Orion water drop test, with instrumented test dummies, takes place on May 11, 2016 at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia.
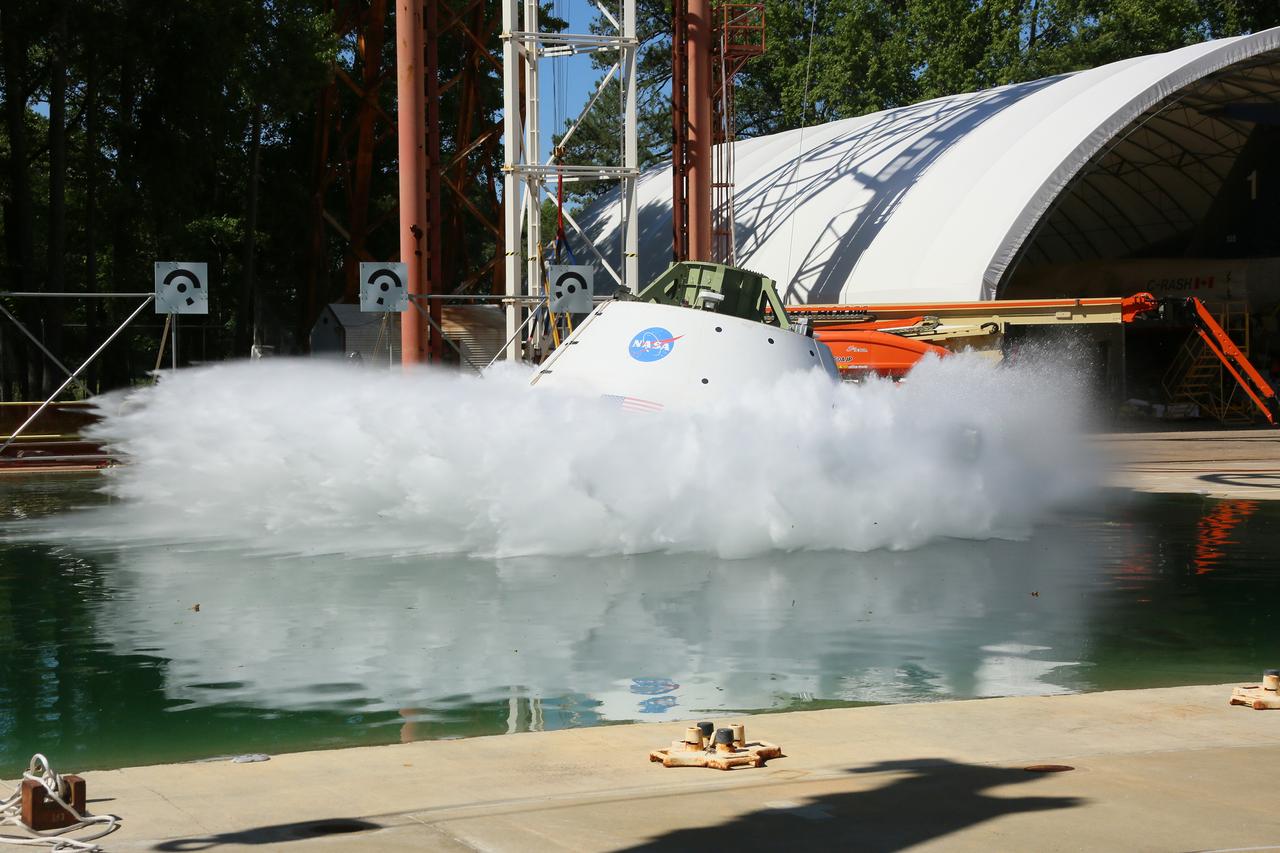

The Orion Ground Test Article completes its first swing water impact test at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia on June 8, 2016.

Engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, install test dummies into the seats of an Orion test article on Feb. 26, 2016. The capsule, coupled with the heat shield from the spacecraft’s first flight, will be used for water-impact testing to simulate what astronauts will experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean during a real mission.
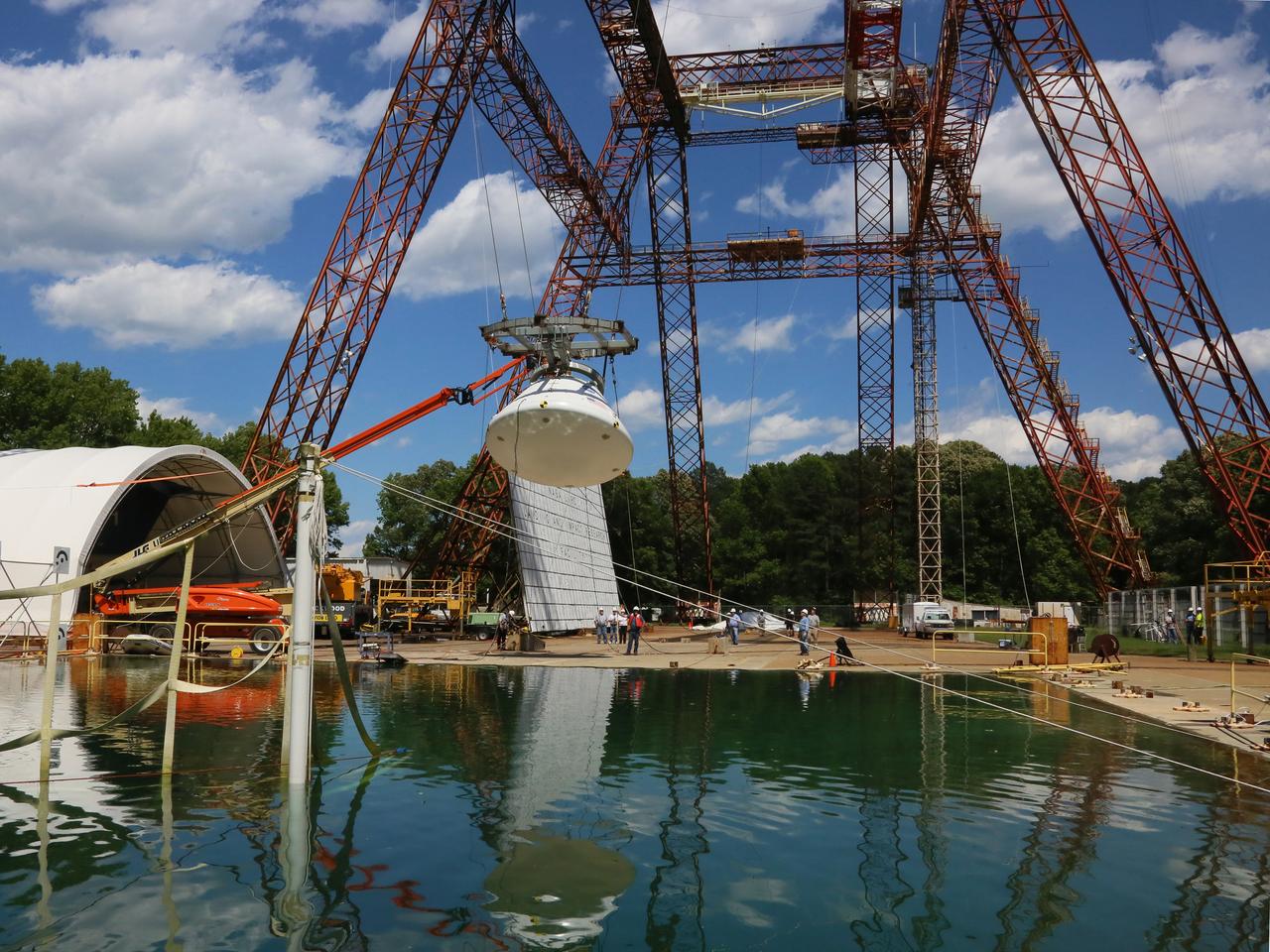

The Orion Ground Test Article completes its first swing water impact test at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia on June 8, 2016.
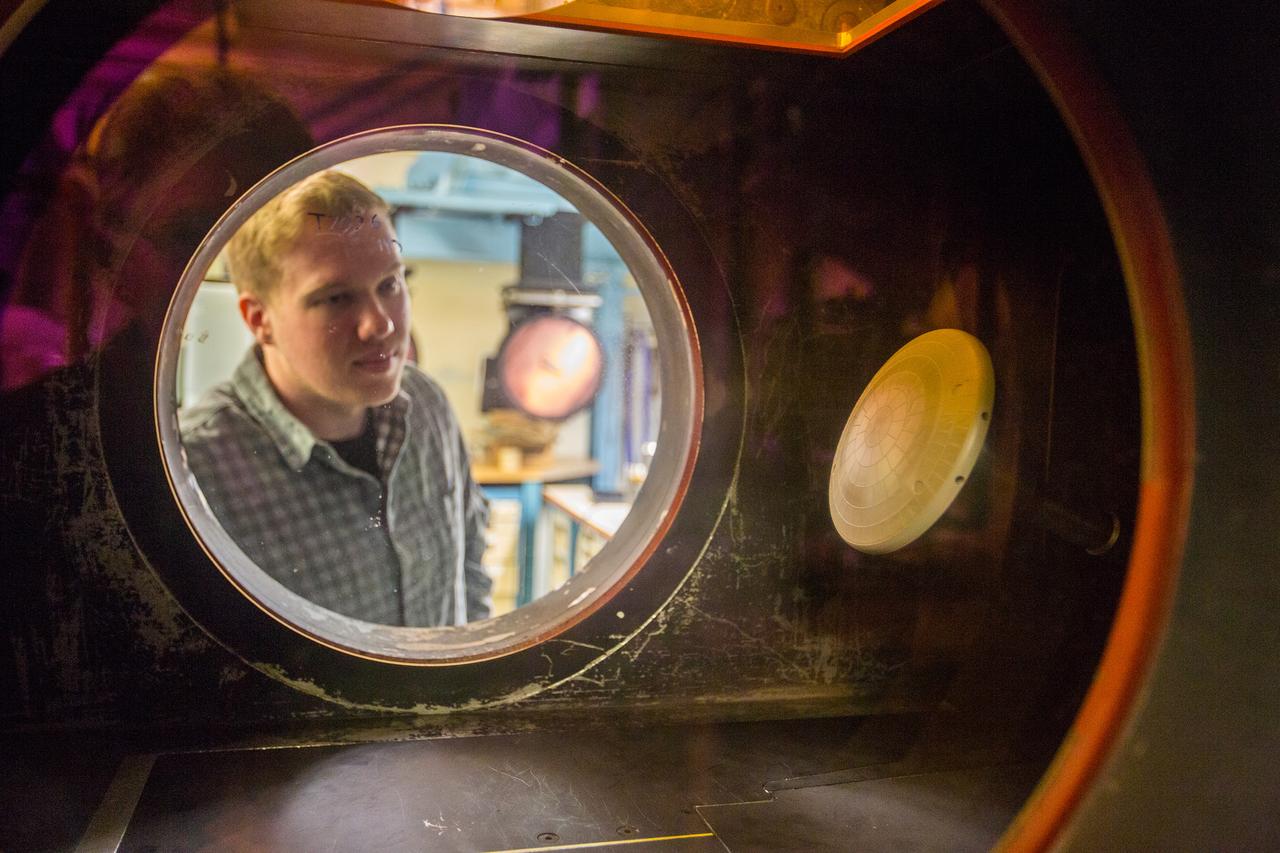

The Orion aerosciences team has performed more than 30 tests across the United States in support of the program, investigating the heating of the spacecraft during re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere. Testing recently concluded at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia with a 6-inch Orion heat shield model in the 20-inch Mach 6 wind tunnel, shown here on Feb. 4, 2019. The team includes engineers at Langley, NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, and NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley.
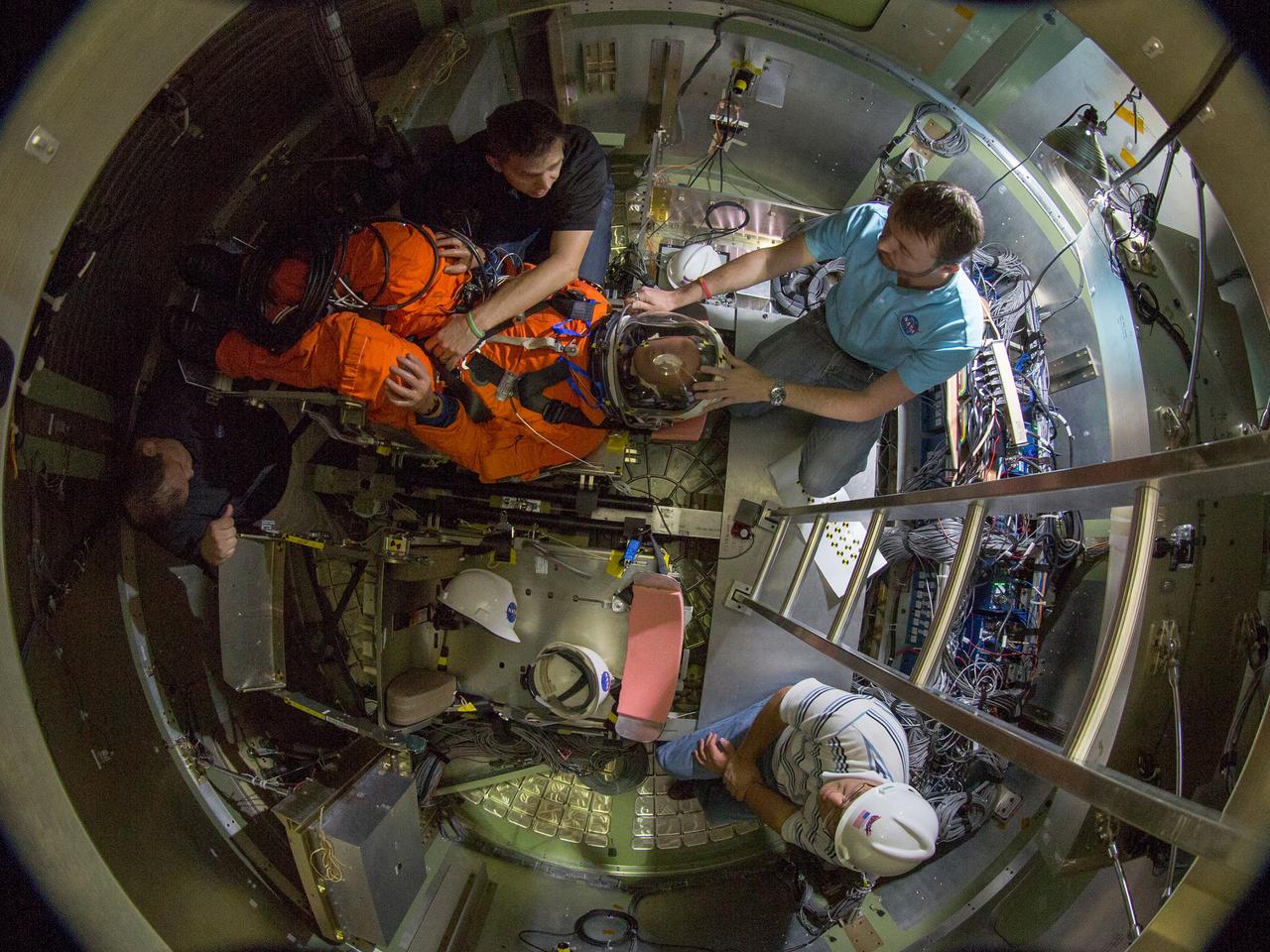

Orion's 2016 water drop test series included heavily instrumented test dummies, shown here on May 6, 2016, to assess the impact future crews will experience in Orion splashdown scenarios.
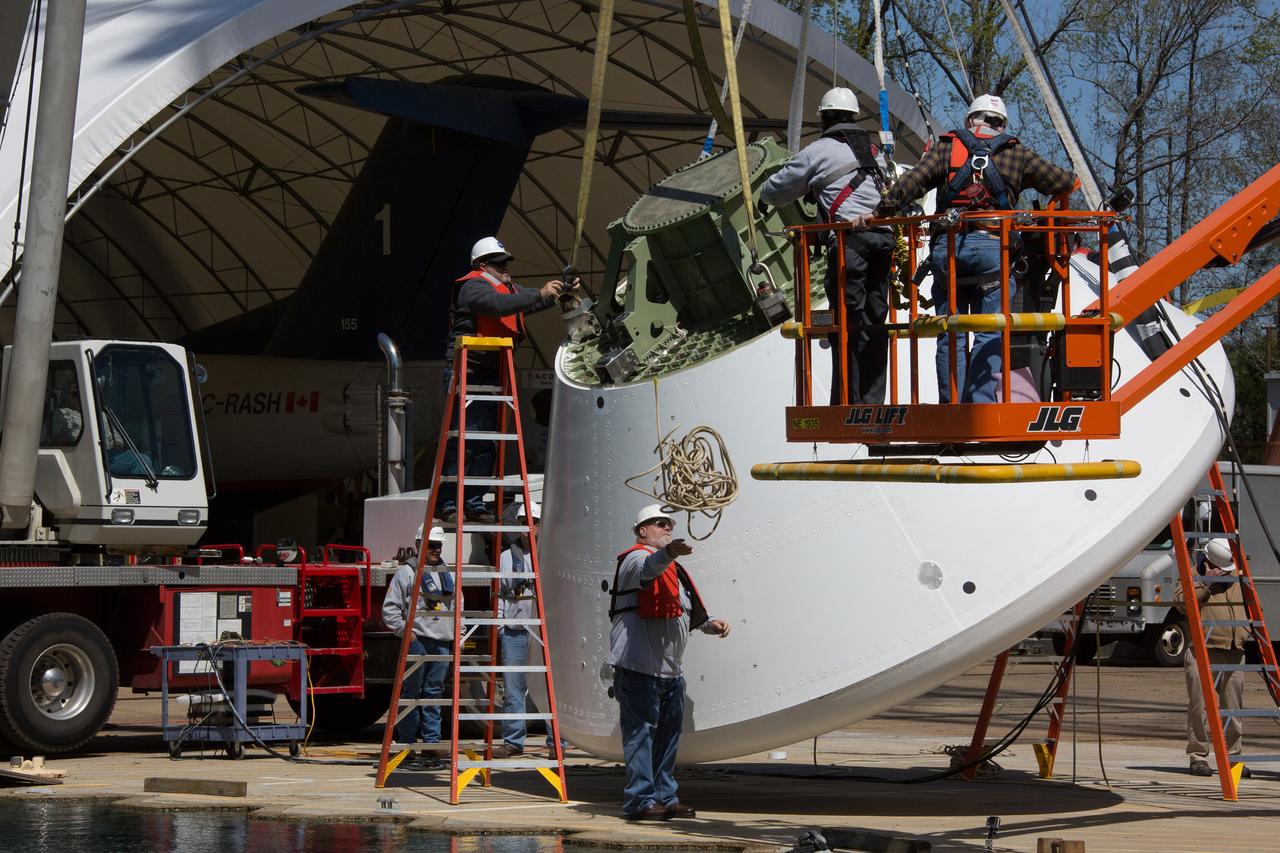

On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.
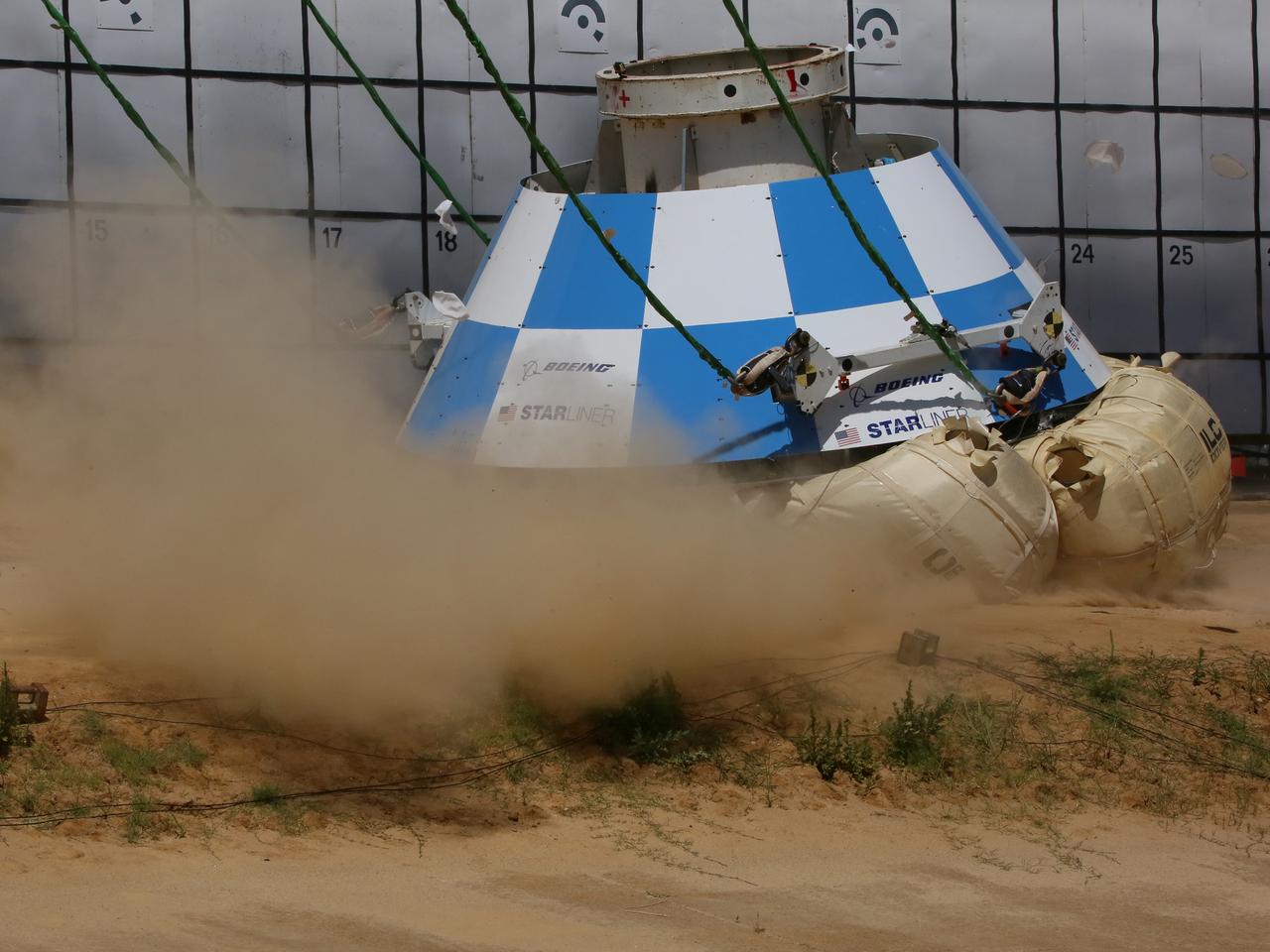

At NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, a mock-up of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft goes through a series of land landing qualification tests to simulate what the actual spacecraft and crew members may experience while returning to Earth from space. The Starliner is being developed in collaboration with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Along with SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, the spacecraft is part of the agency’s effort to return America’s capability to launch astronauts from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the International Space Station.
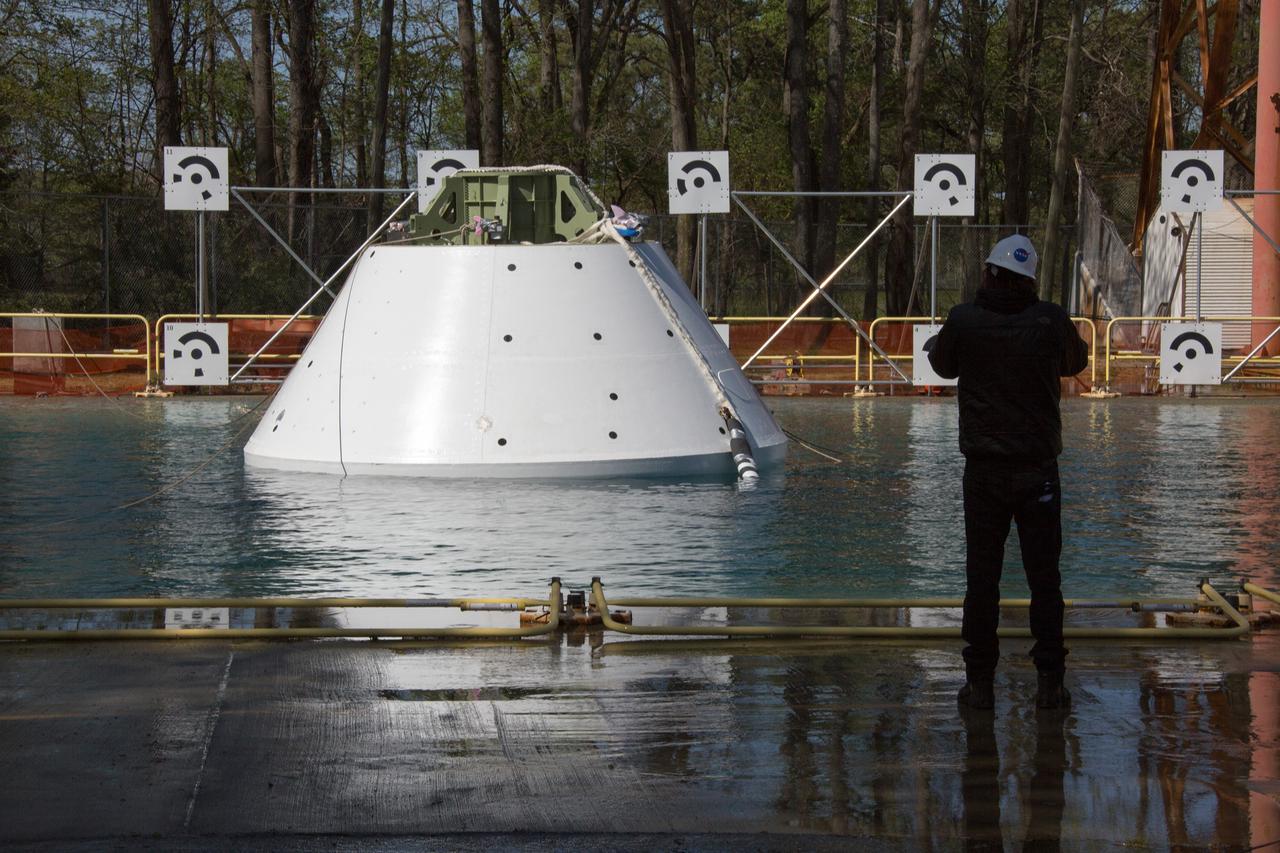

On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.
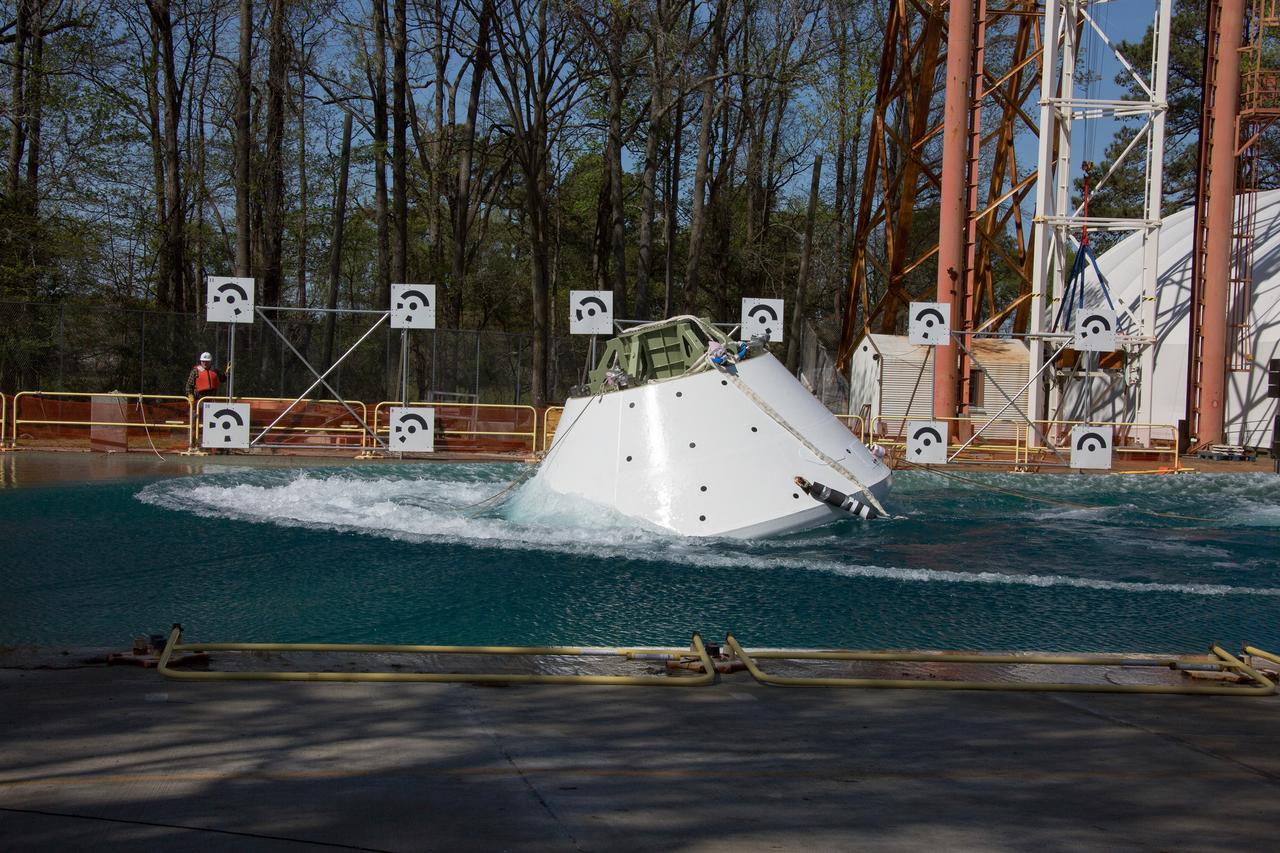
On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.
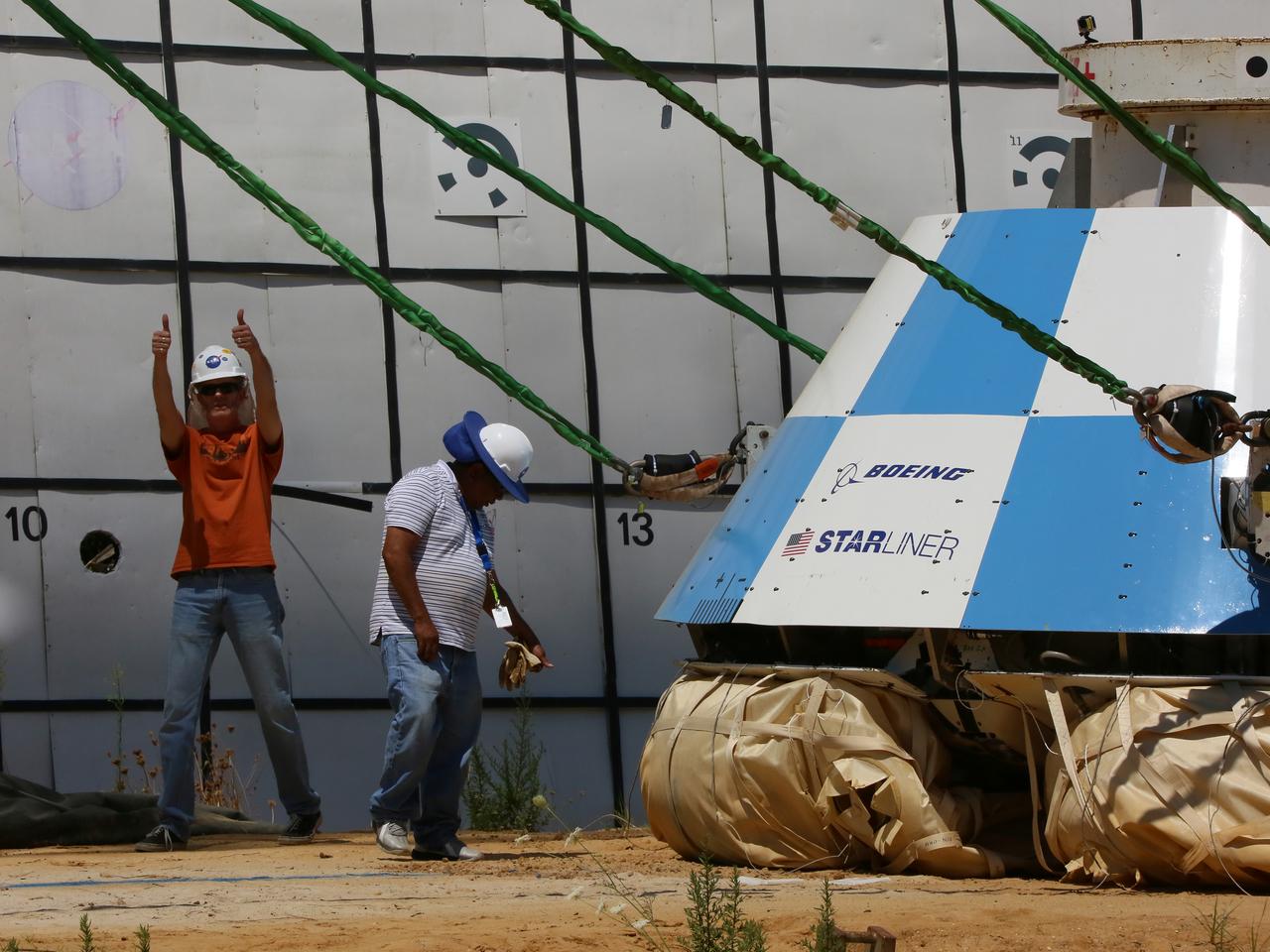

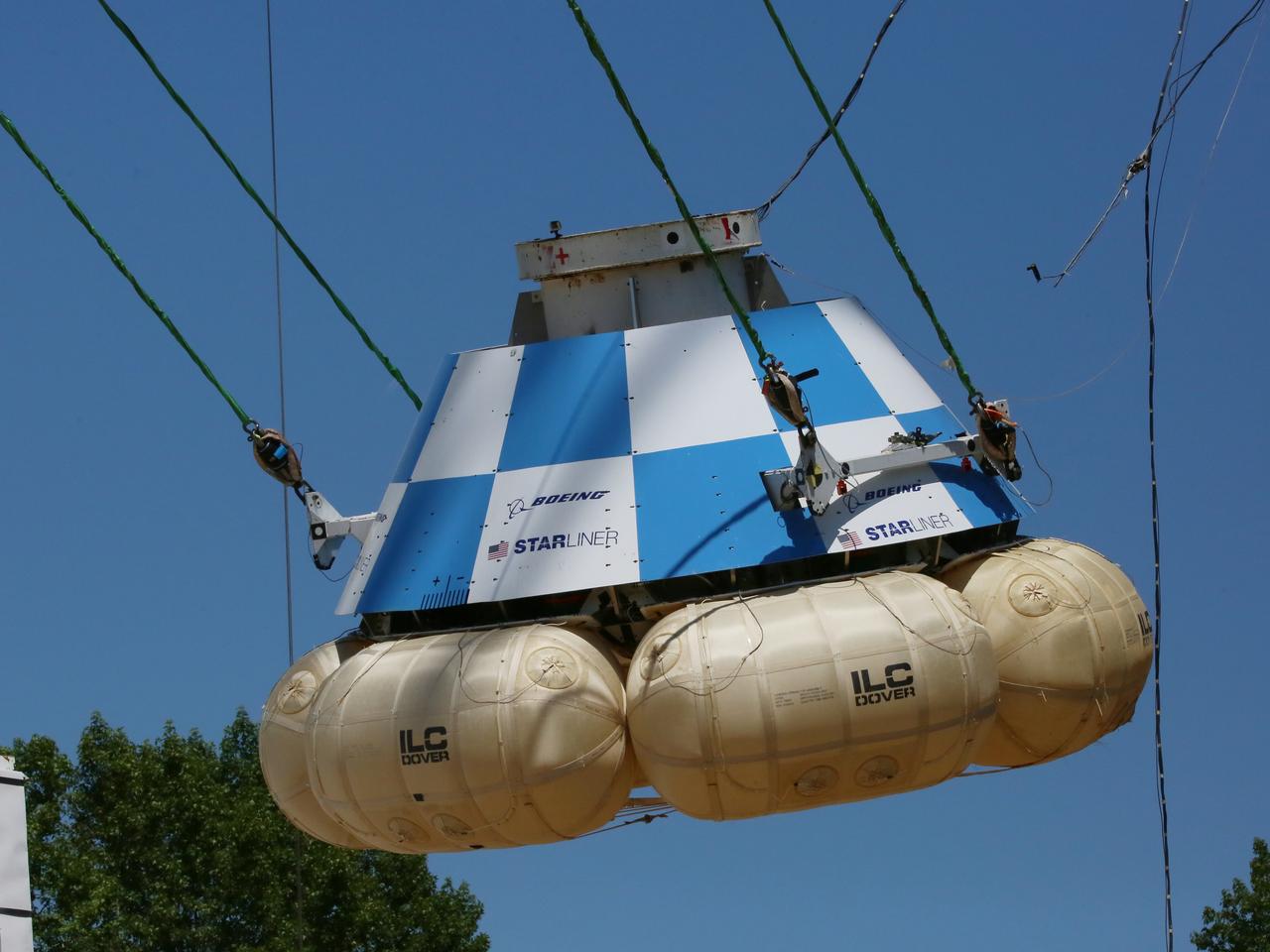
"Thumbs up" is signaled by ground personnel at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, after a mock-up of the Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft completed a land landing qualification test. The operation was to simulate what the actual spacecraft and crew members may experience while returning to Earth from space. The Starliner is being developed in collaboration with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Along with SpaceX’s Crew Dragon, the spacecraft is part of the agency’s effort to return America’s capability to launch astronauts from the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the International Space Station.
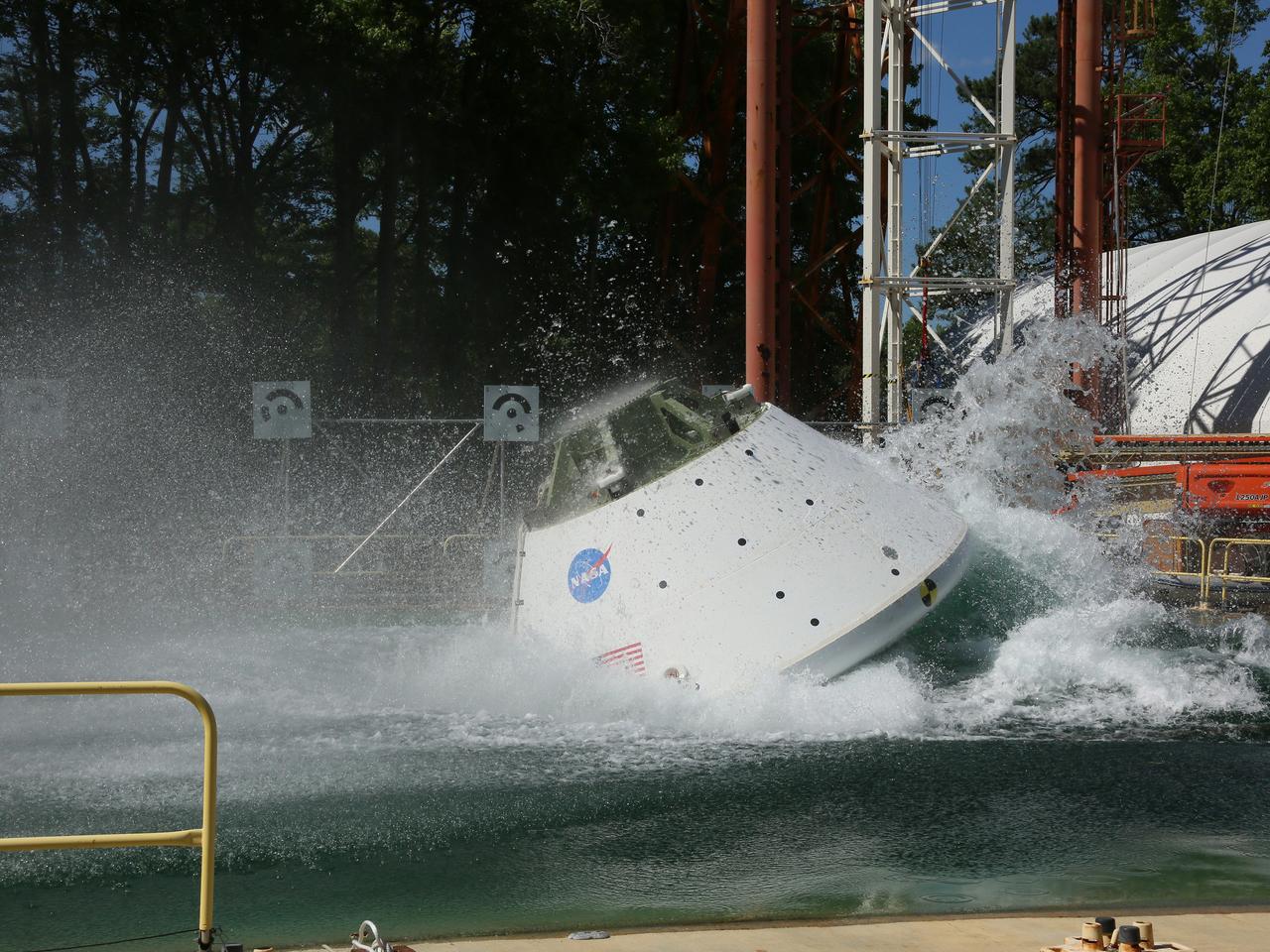

The Orion Ground Test Article completes its first swing water impact test at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia on June 8, 2016.

An Orion water drop test, with instrumented test dummies, takes place on May 11, 2016 at NASA's Langley Research Center in Virginia.

On April 6, 2016, engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, kicked off a series of nine drop tests of a representative Orion crew capsule with crash test dummies inside to understand what the spacecraft and astronauts may experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean after deep-space missions. The high-fidelity capsule, coupled with the heat shield from Orion's first flight in space, was hoisted approximately 16 feet above the water and vertically dropped into Langley’s 20-foot-deep Hydro Impact Basin. The crash test dummies were instrumented to provide data and secured inside the capsule to help provide information engineers need to ensure astronauts will be protected from injury during splashdown. Each test in the series simulates different scenarios for Orion’s parachute-assisted landings, wind conditions, velocities and wave heights the spacecraft may experience when touching down in the ocean.

Engineers at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, install test dummies into the seats of an Orion test article on Feb. 26, 2016. The capsule, coupled with the heat shield from the spacecraft’s first flight, will be used for water-impact testing to simulate what astronauts will experience when landing in the Pacific Ocean during a real mission.