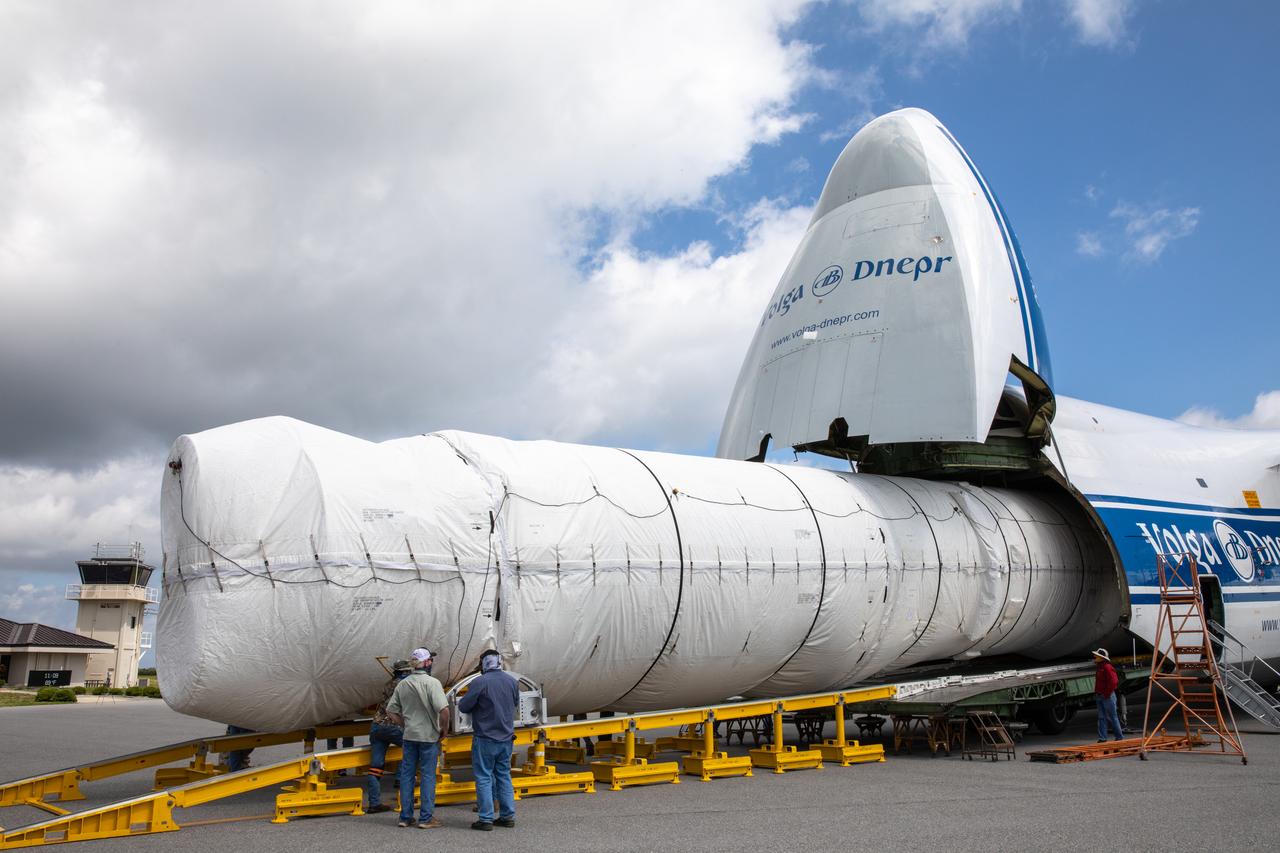

The United Launch Alliance booster for NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover is offloaded from the Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 19, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 at CCAFS. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

Students from various schools and organizations with a STEM (science, technology, engineering, math) focus are photographed with employees from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center at the Launch and Landing Facility following their arrival to Kennedy on Friday, Sept. 22, 2023, as part of Delta Air Lines’ Women Inspiring Our Next Generation (WING) flight. The all-female flight crew brought girls from Atlanta, Georgia, ranging in age from 12 to 18, to learn about the various careers available at the Florida spaceport. While at Kennedy, the group had the opportunity to view center facilities, hear from a panel of women with a combination of careers from Kennedy and Delta, and tour the visitor complex.
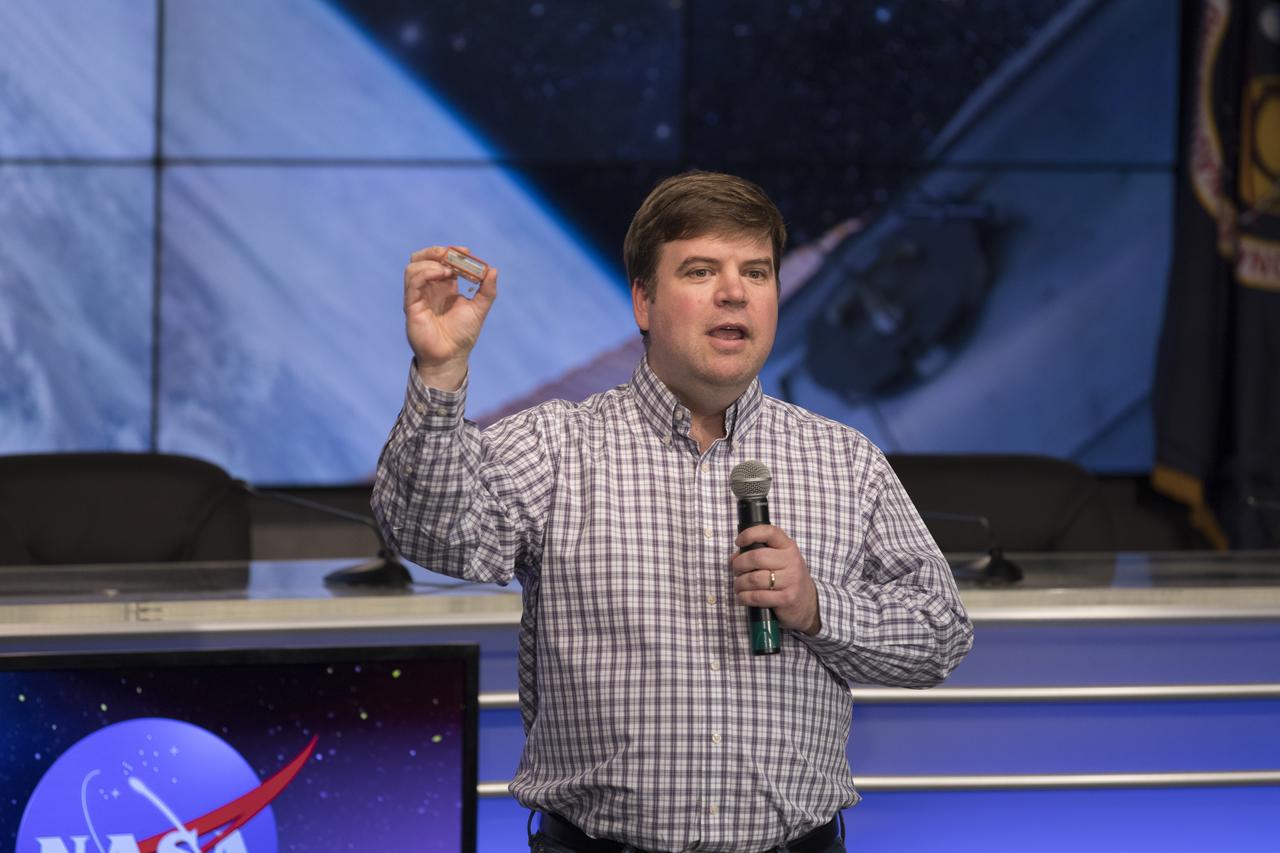

Chris Wolverton, Ph.D., professor of botany/microbiology at Ohio Wesleyan University, speaks on the Plant Gravity Perception experiment with members of social media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40 at 11:46 a.m. EST, on Dec. 12, 2017. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 13th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
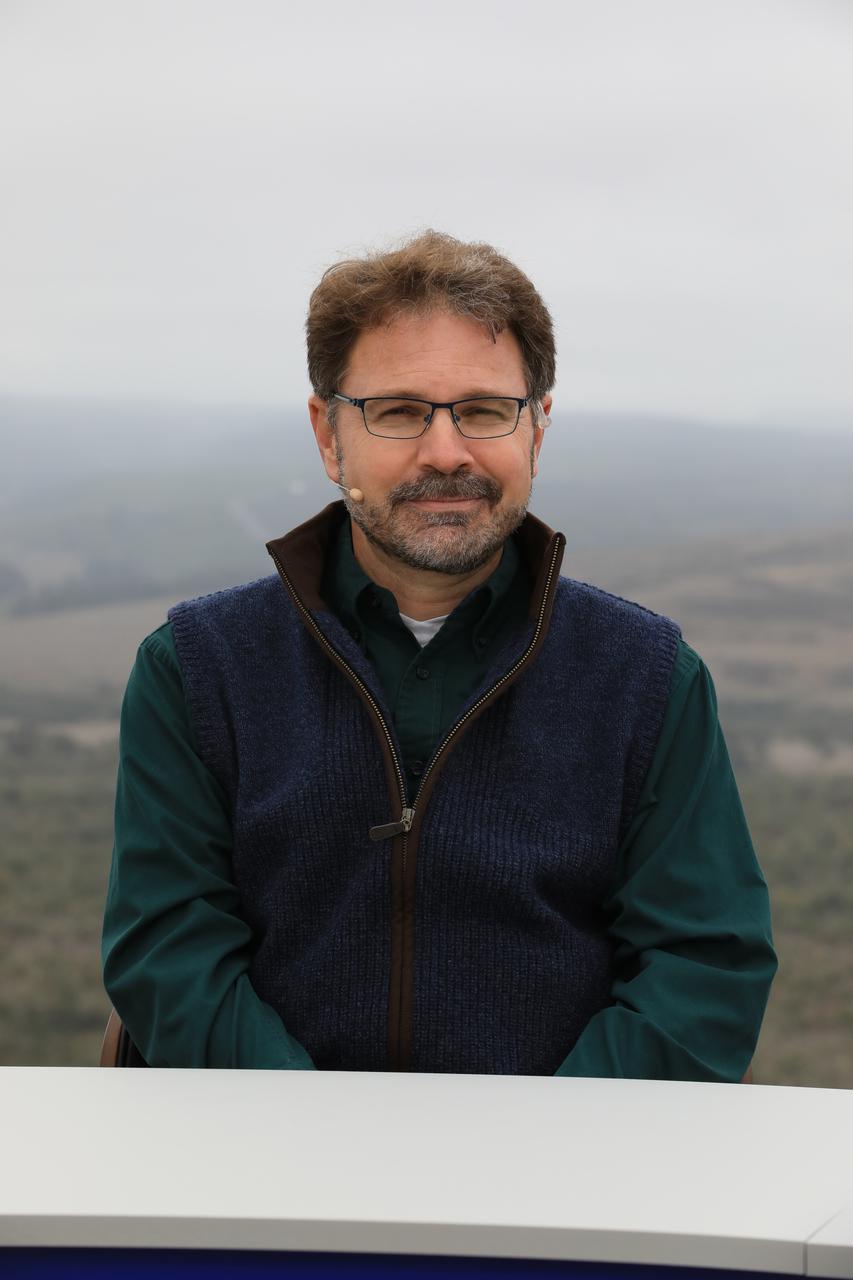

Dr. Pete Doucette, acting director, USGS Earth Resources, participates in the launch broadcast for the Landsat 9 mission on Sept. 27, 2021, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite launched on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 3 at 2:12 p.m. EDT (11:12 a.m. PDT). The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests. NASA Goddard manages the Landsat 9 mission. Goddard teams also built and tested one of the two instruments on Landsat 9, the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2) instrument. TIRS-2 will use thermal imaging to make measurements that can be used to estimate soil moisture and detect the health of plants.

The Apollo 1 tribute at the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center opened Jan. 27, 2017. Astronauts Gus Grissom, Ed White II and Chaffee perished in a fire at the launch pad on Jan. 27, 1967, during training for the mission. The tribute highlights the lives and careers of the astronauts. The tribute features numerous items recalling the lives of the three astronauts. The tribute also includes the three-part hatch to the spacecraft itself, the first time any part of the Apollo 1 spacecraft has been displayed publicly. A version of the hatch after it was redesigned is also showcased as an example of improvements NASA made throughout the agency and to the Apollo spacecraft that would later carry astronauts to the moon.
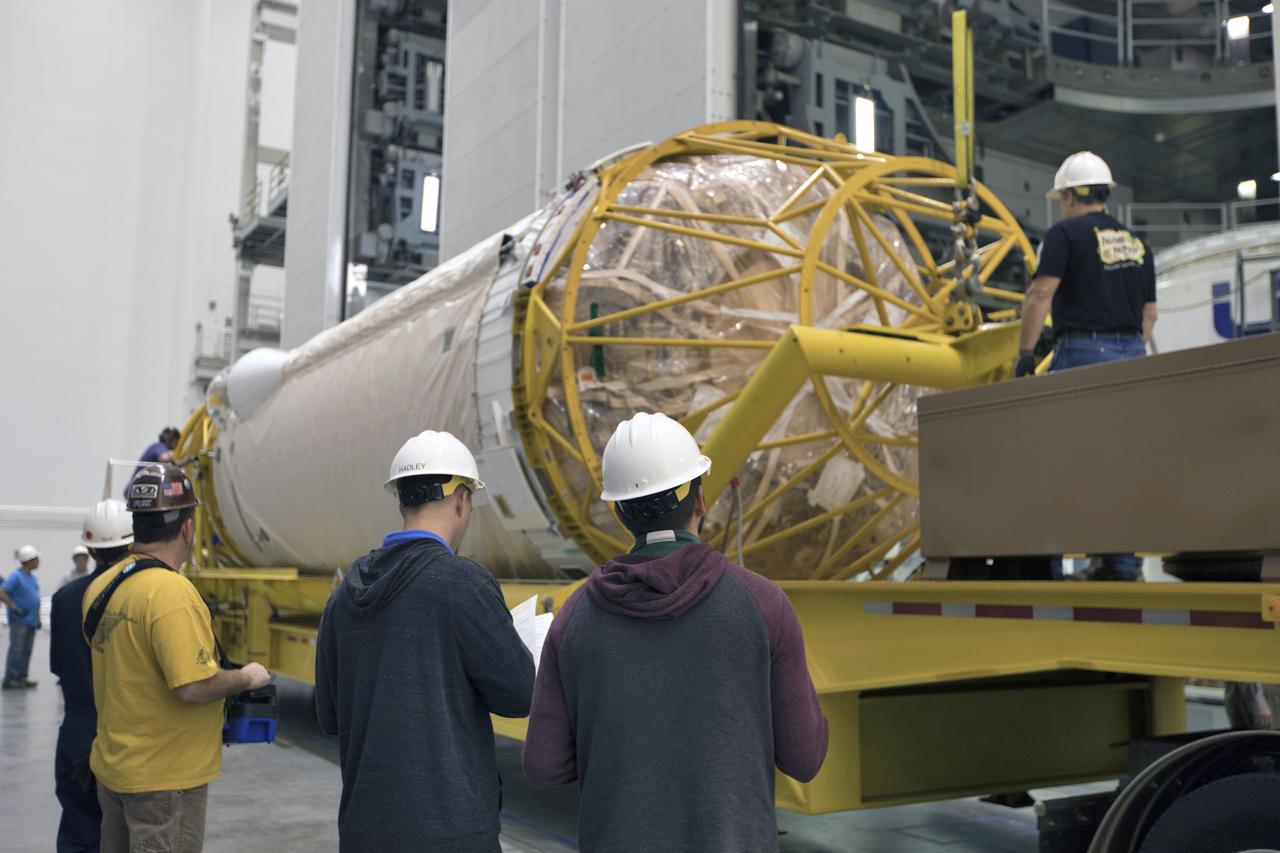

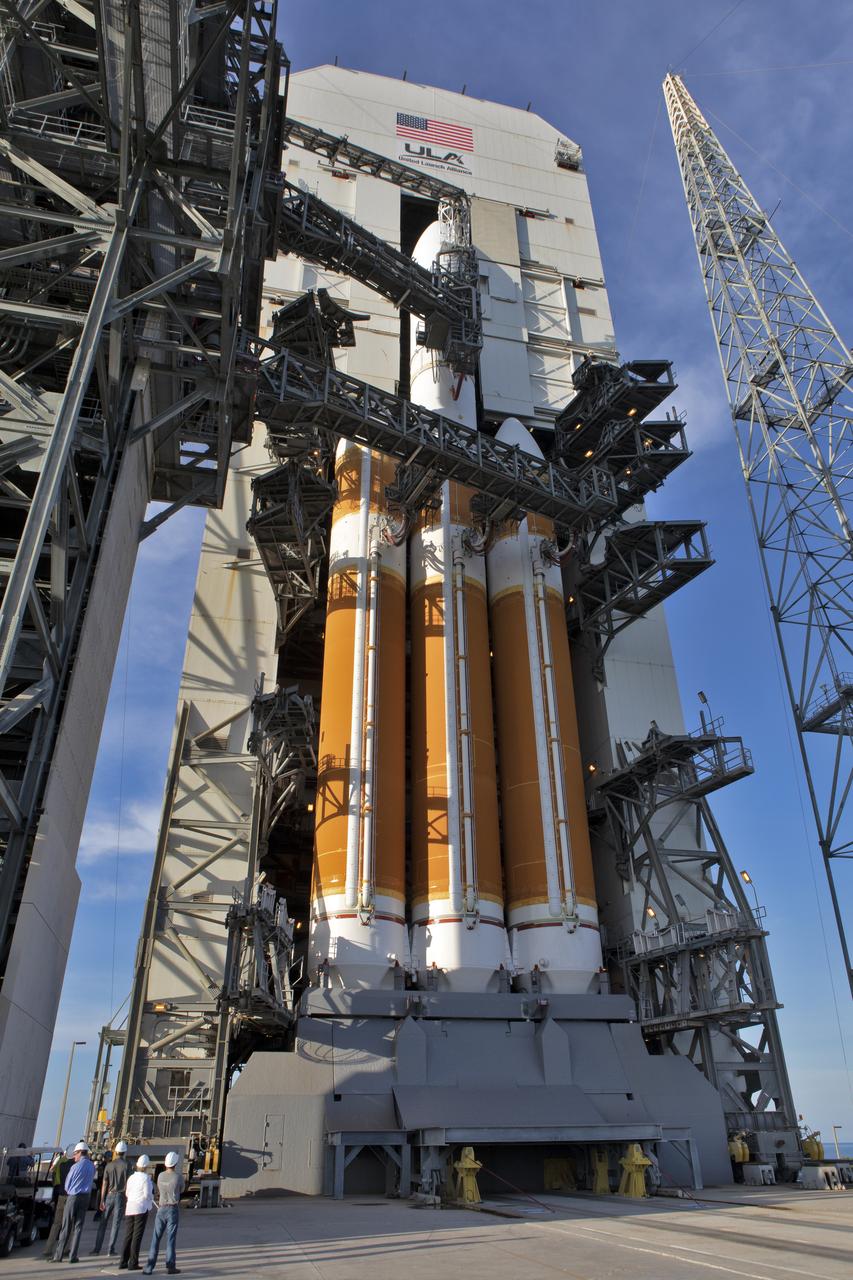
Under the watchful eyes of technicians and engineers, the Centaur upper stage that will help launch NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, arrives inside the Delta Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for further processing. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites. The GOES-R series - consisting of the GOES-R, GOES-S, GOES-T and GOES-U spacecraft - will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
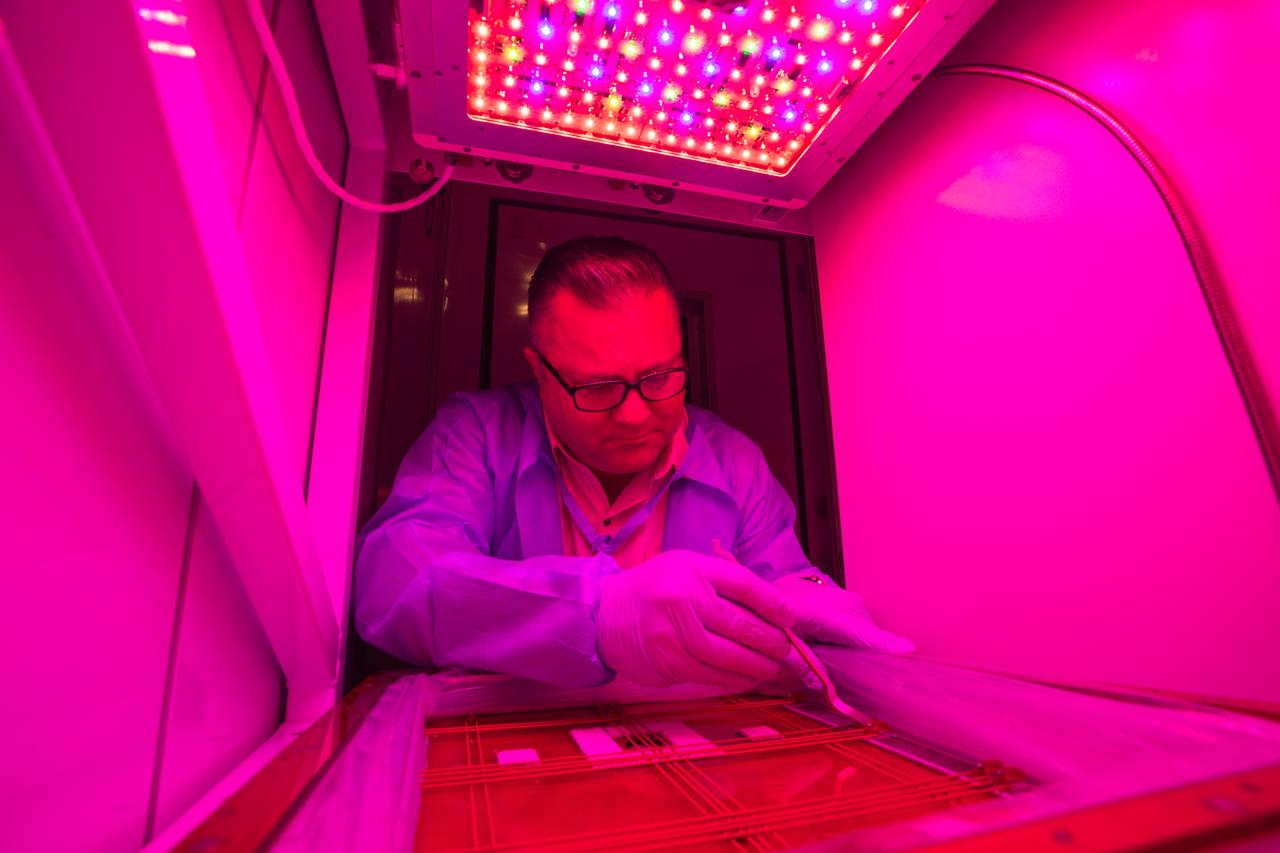

Matthew English is the Exploration Research and Technology facility manager for the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. English’s responsibilities include ensuring that the International Space Station teams inside the SSPF have the facilities, tools and capabilities they need to support their launch customers, thus providing the support necessary to enable further research and design discoveries within NASA.
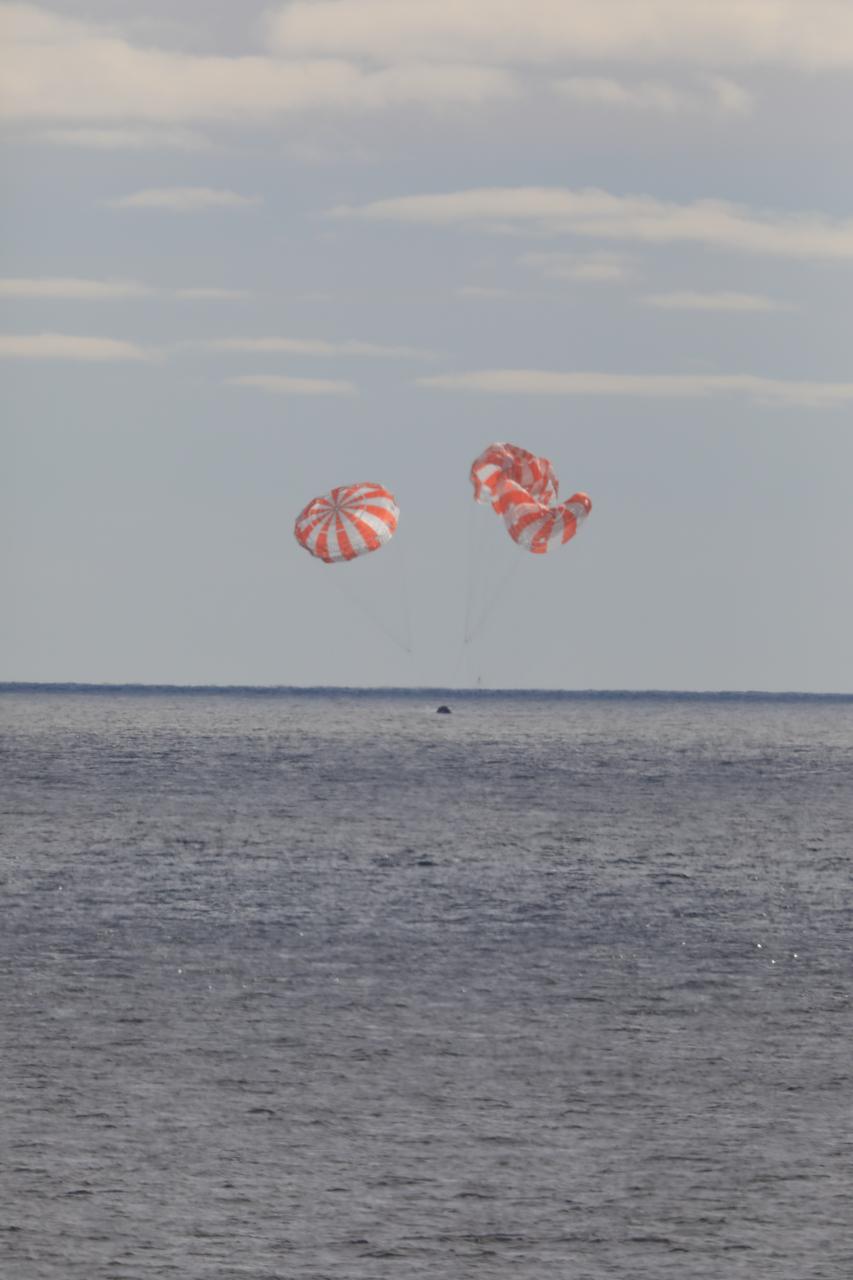

At 12:40 p.m. EST, Dec. 11, 2022, NASA’s Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission splashed down in the Pacific Ocean after a 25.5 day mission to the Moon. Orion will be recovered by NASA’s Landing and Recovery team, U.S. Navy and Department of Defense partners aboard the USS Portland.
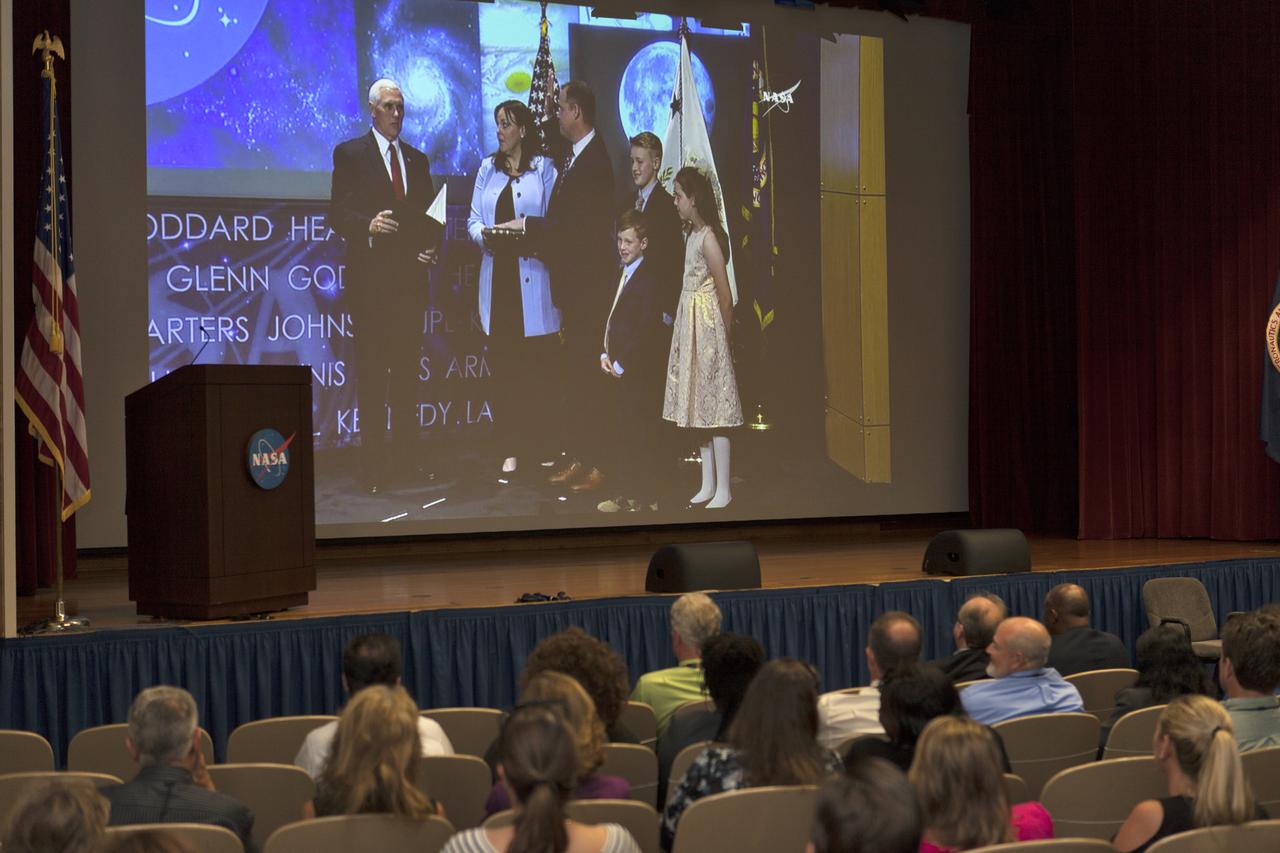

In the Training Auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, employees watch as Vice President Mike Pence, left, swears in Jim Bridenstine as the 13th NASA Administrator as Bridenstine's family watches on April 23, 2018, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Bridenstine was confirmed by the U.S. Senate on April 19.
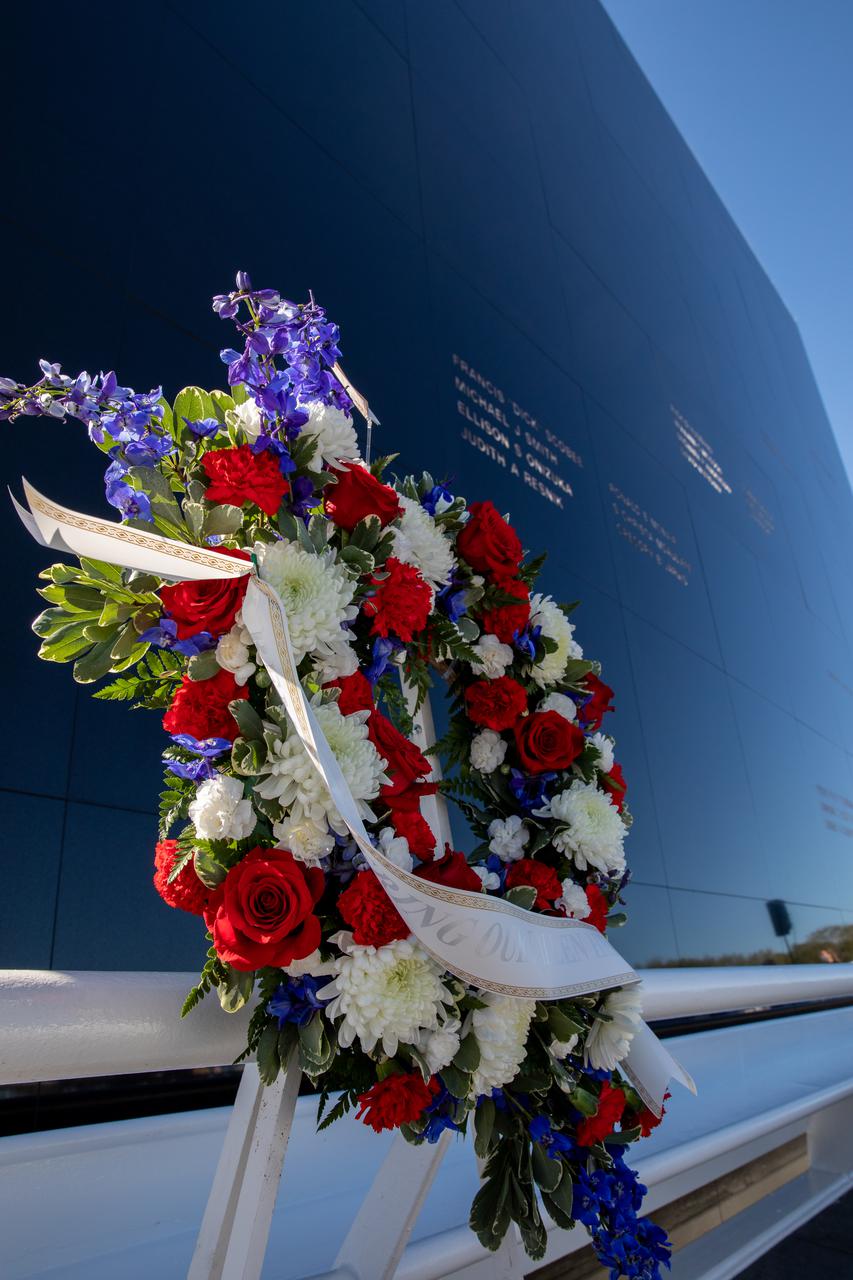

NASA’s Day of Remembrance is marked by a memorial wreath placed before the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, Jan. 28, 2021. The mirror was dedicated in 1991 to honor all astronauts who lost their lives on missions or during training. During the Day of Remembrance, NASA centers across the country honor those astronauts who have fallen in the pursuit of space exploration.
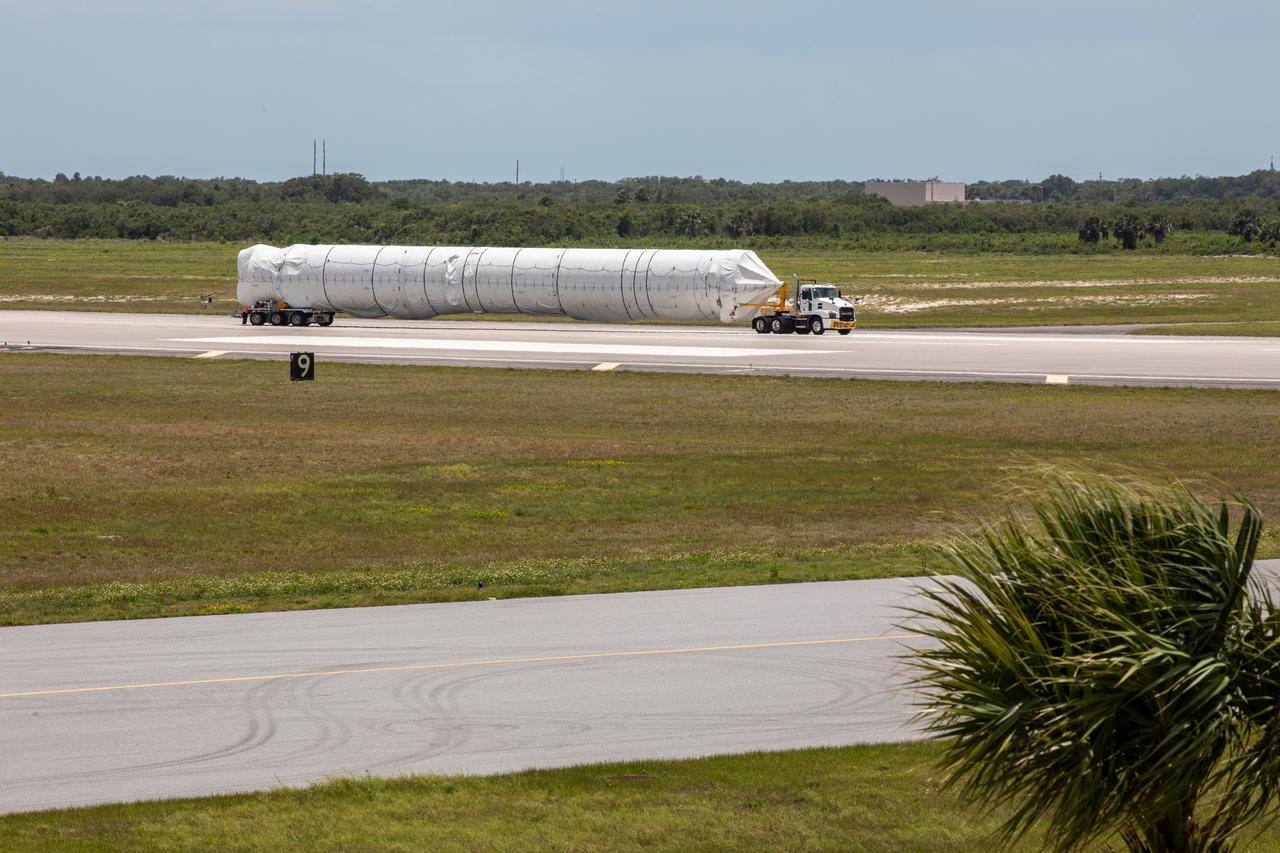

A flatbed truck carrying the United Launch Alliance booster for NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover departs the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 19, 2020. The booster arrived aboard the Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at the Skid Strip on May 18, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 at CCAFS. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

Tammy Long, NASA Communications, addresses the audience during a prelaunch news conference for the Lucy mission held inside the TV Auditorium at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 13, 2021. The mission is targeted to launch at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy, is managing the launch. Lucy is the first space mission to study the Trojan asteroids, which hold vital clues to the formation of our solar system.

A memorial wreath has been placed in the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida following a ceremony honoring the memory of former astronaut Owen Garriott. The ceremony was held April 18, 2019. Garriott flew aboard the Skylab space station during the Skylab 3 mission and also on space shuttle Columbia for the STS-9/Spacelab-1 mission. He passed away April 15 at the age of 88.

On Friday, Aug. 10, 2018, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Mobile Service Tower gantry begins to roll back at Space Launch Complex 37, where the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket now stands ready to boost NASA's Parker Solar Probe on a mission to study the Sun. Parker Solar Probe will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
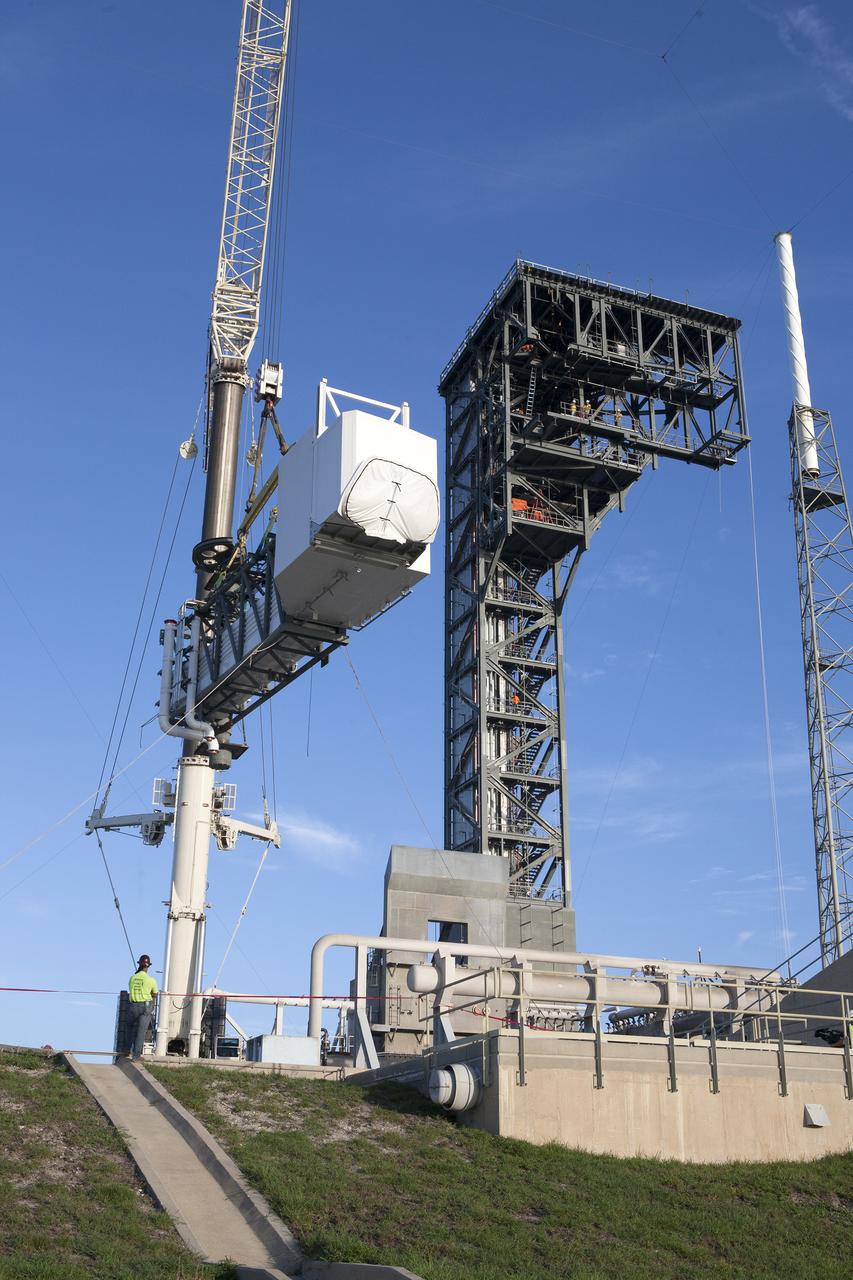

A crane lifts the Crew Access Arm and White Room for Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to be attached to the Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41. When attached to the 200-foot tall Crew Access Tower, the arm will serve as the connection that astronauts will walk through prior to boarding the Starliner spacecraft when stacked atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. This installation completes the major construction of the first new Crew Access Tower to be built at the Cape since the Apollo era. Under a Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) contract with NASA, Boeing’s Starliner system will be certified by NASA's Commercial Crew Program to fly crews to and from the International Space Station.
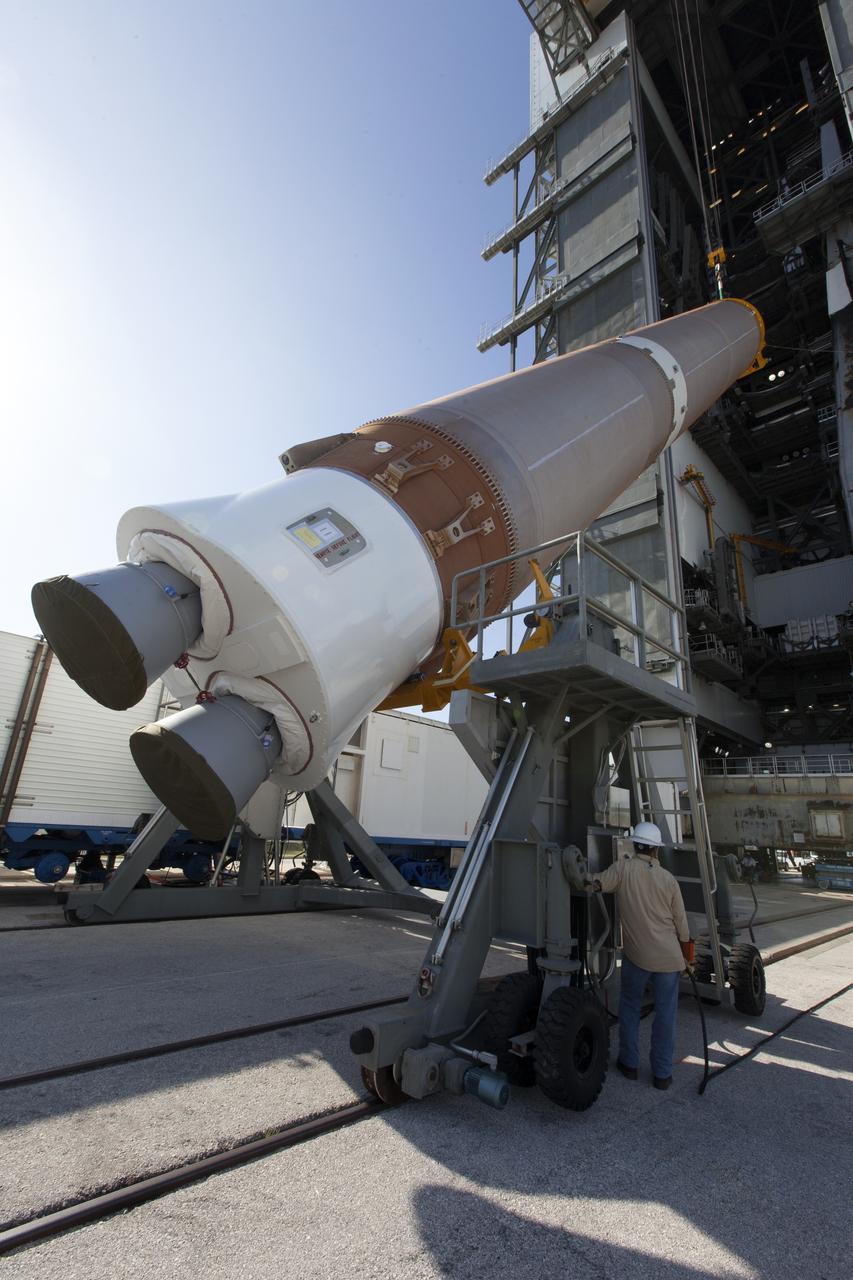

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.
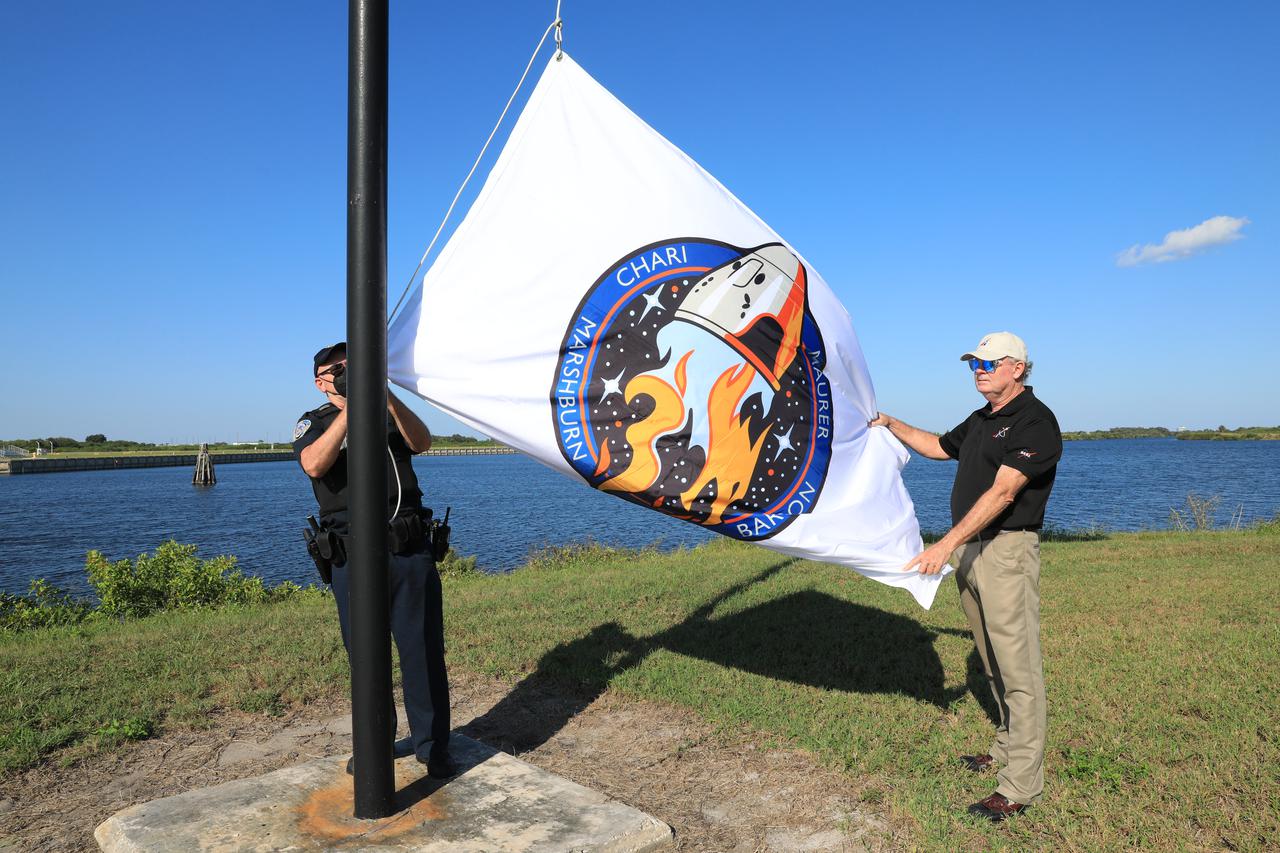

The SpaceX Crew-3 flag is raised near the News Center countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 26, 2021. The SpaceX Falcon 9 with Crew Dragon atop is scheduled to launch no earlier than Nov. 6, at 11:36 p.m. EDT from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Crew Dragon will carry four astronauts to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Crew-3 is the third crew rotation flight to the space station, and the first flight of a new Crew Dragon spacecraft.
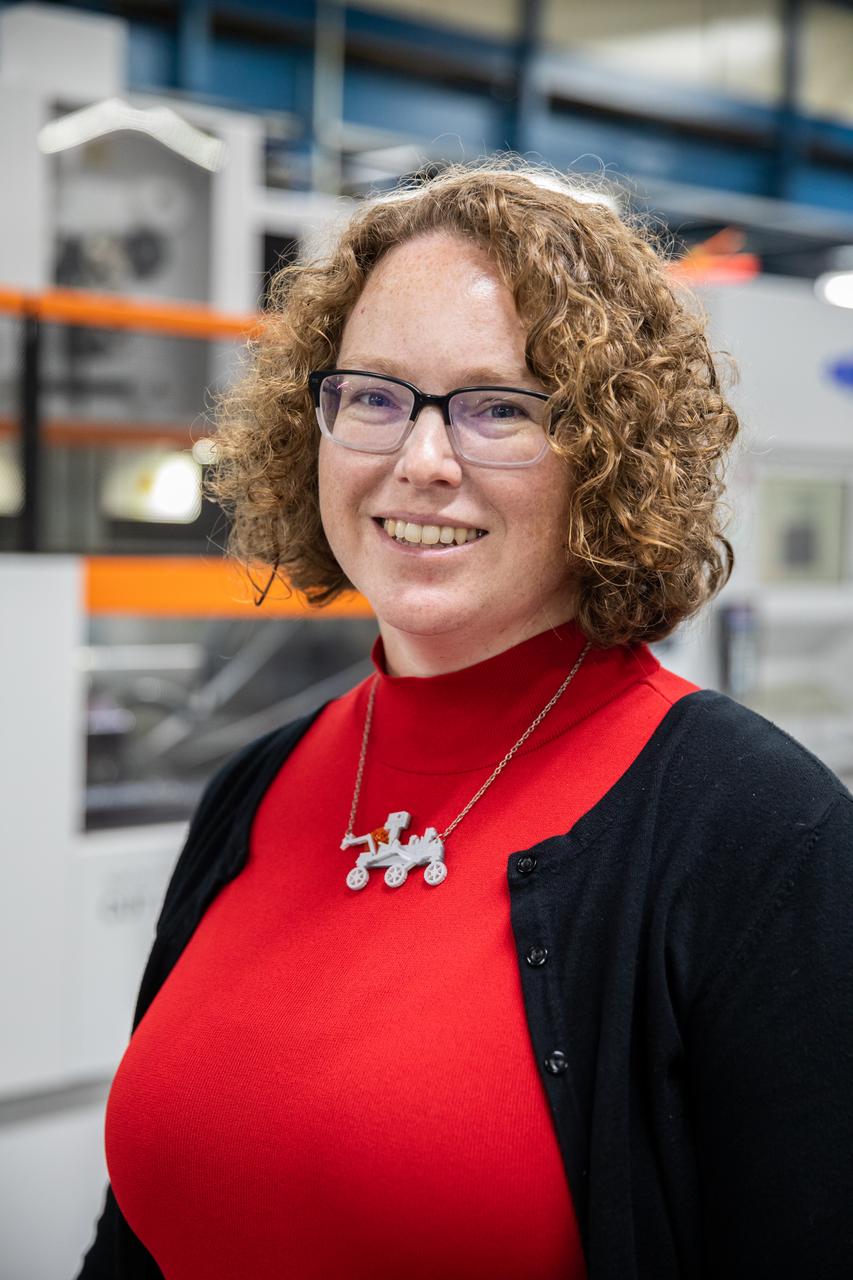

Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, is inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to begin testing on the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied to spacecraft and launch vehicles.
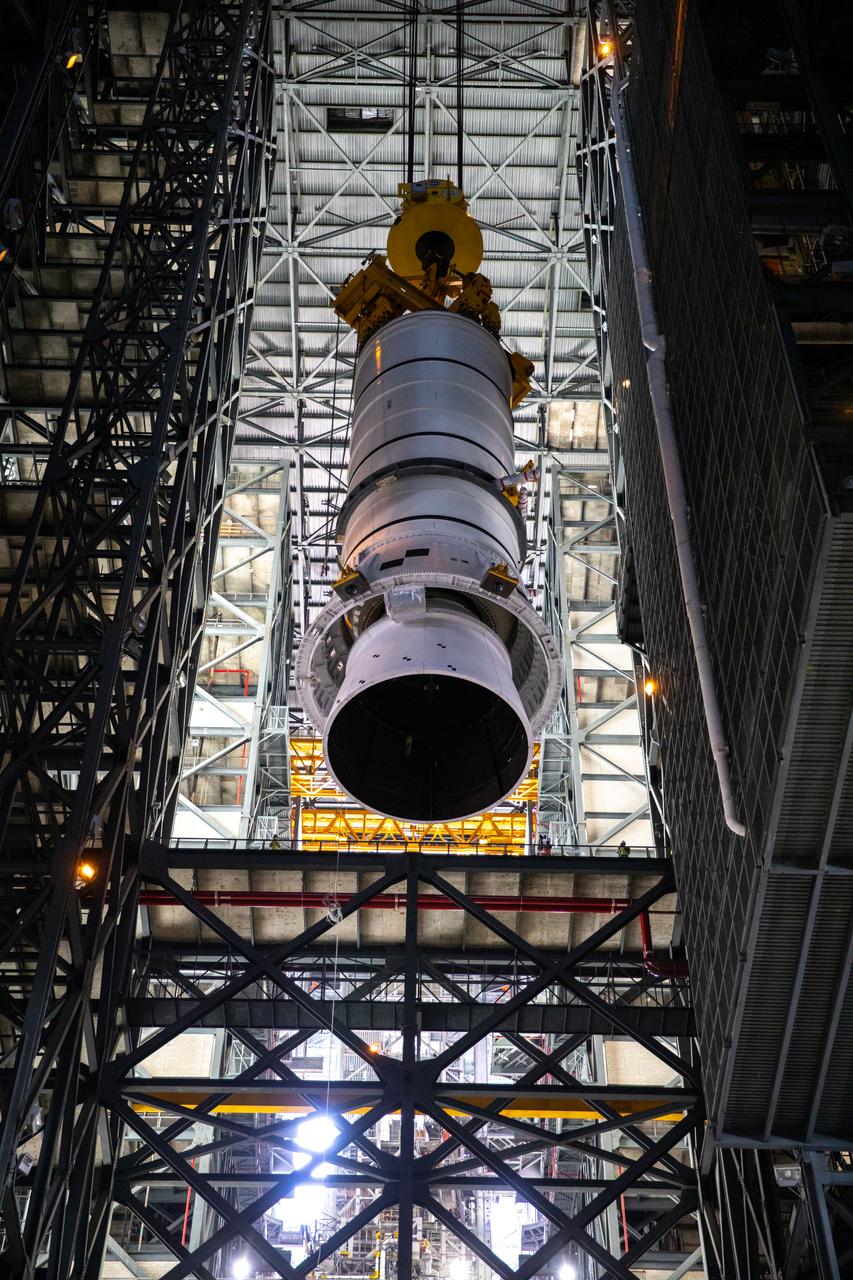

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems rehearse lifting operations using a mock-up of the Space Launch System (SLS) aft booster segment, referred to as a pathfinder, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 11, 2020, in preparation for Artemis I. The exercise involved preparing the aft pathfinder segment in High Bay 4 of the VAB and moving it over to High Bay 3, where it was placed on the mobile launcher. Stacking of the actual booster segments will occur later this year, before the SLS core stage arrives at Kennedy. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will test SLS and the Orion spacecraft as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
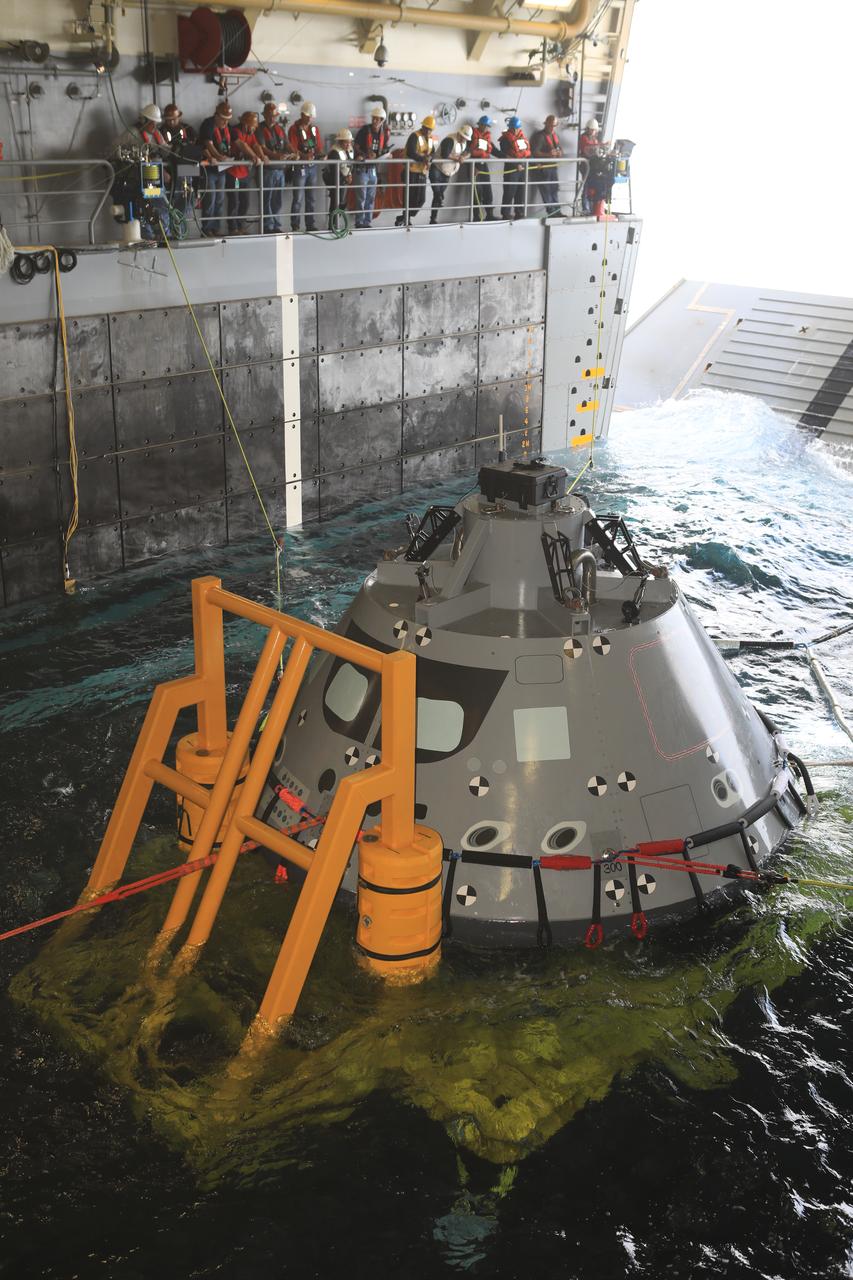
The Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) recovery team, along with the U.S. Navy, practice keeping an Orion test article under control in the well deck of a U.S. Navy ship as part of Underway Recovery Test-7 (URT-7) on Oct. 30, 2018, in the Pacific Ocean. EGS and the U.S. Navy will use a test version of the Orion crew module, several rigid hull inflatable boats and support equipment to verify and validate processes, procedures, hardware and personnel during recovery of Orion in open waters. The testing is one in a series of tests to verify and validate procedures and hardware that will be used to recover the Orion spacecraft after it splashes down in the Pacific Ocean following deep space exploration missions. Orion will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
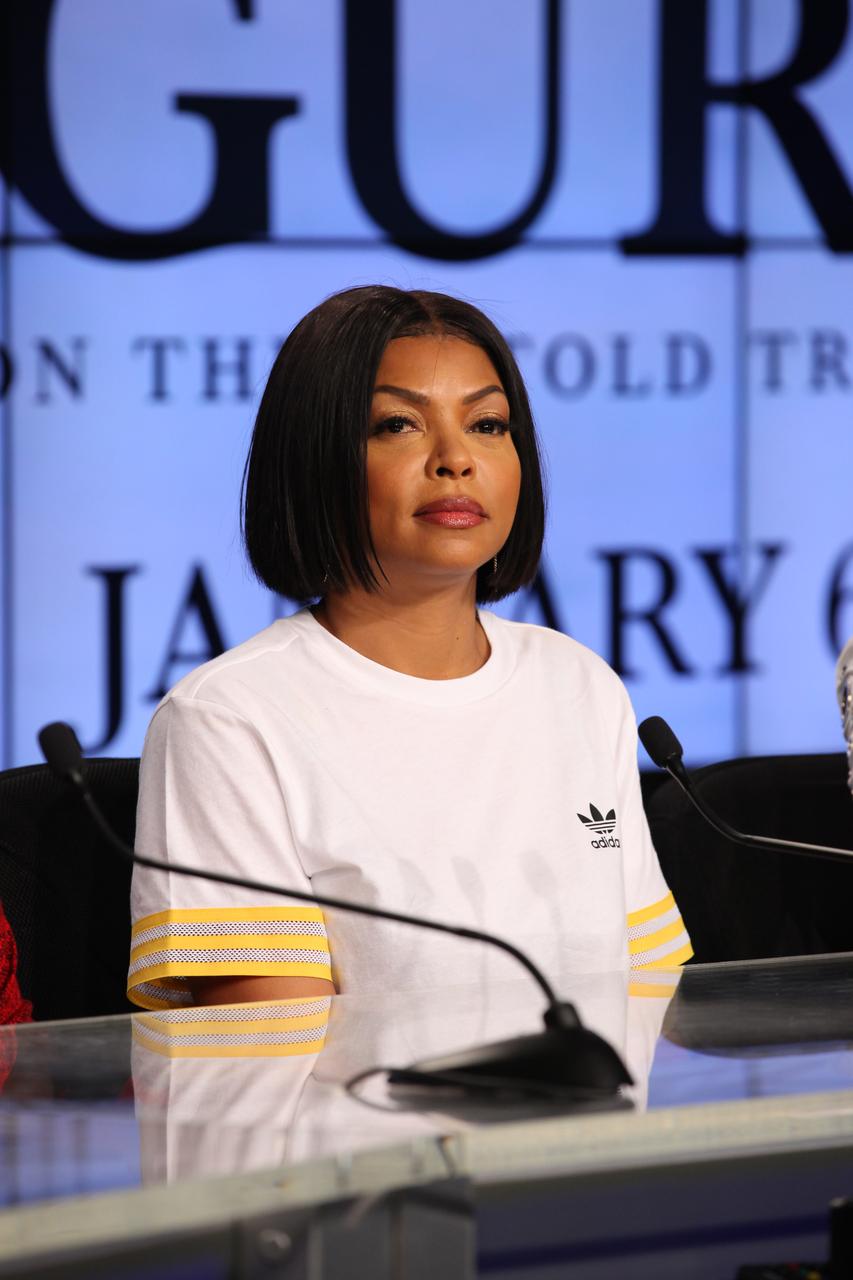

In the Press Site auditorium at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Taraji P. Henson speaks to members of the media during a news conference with other key individuals involved in the upcoming motion picture "Hidden Figures." The movie is based on the book of the same title, by Margot Lee Shetterly. It chronicles the lives of Katherine Johnson (played by Henson), Dorothy Vaughan and Mary Jackson, three African-American women who worked for NASA as human "computers.” Their mathematical calculations were crucial to the success of Project Mercury missions including John Glenn’s orbital flight aboard Friendship 7 in 1962. The film is due in theaters in January 2017.
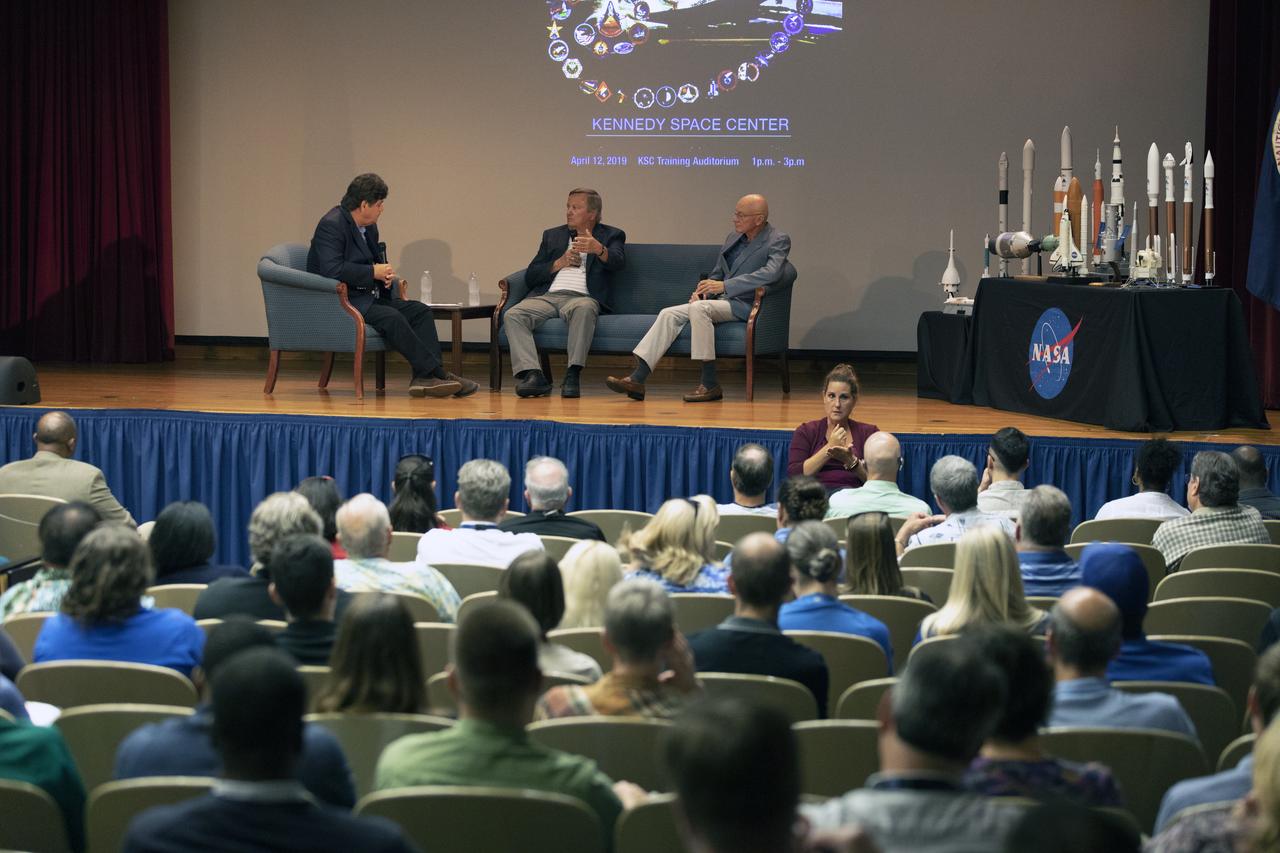

Veteran space reporter John Zarrella, left, moderates a “Lessons of Columbia” discussion with former space shuttle launch directors Mike Leinbach, center, and Bob Sieck in Kennedy Space Center’s Training Auditorium on April 12, 2019. The discussion took place during “Columbia: The Mission Continues,” an event organized by the Apollo Challenger Columbia Lessons Learned Program (ACCLLP). The event is part of the Space Shuttle Columbia national tour and took place on the 38th anniversary of STS-1, the first orbital spaceflight of NASA’s Space Shuttle Program. The tour launched at Kennedy and will make its way to each of the 10 NASA centers.
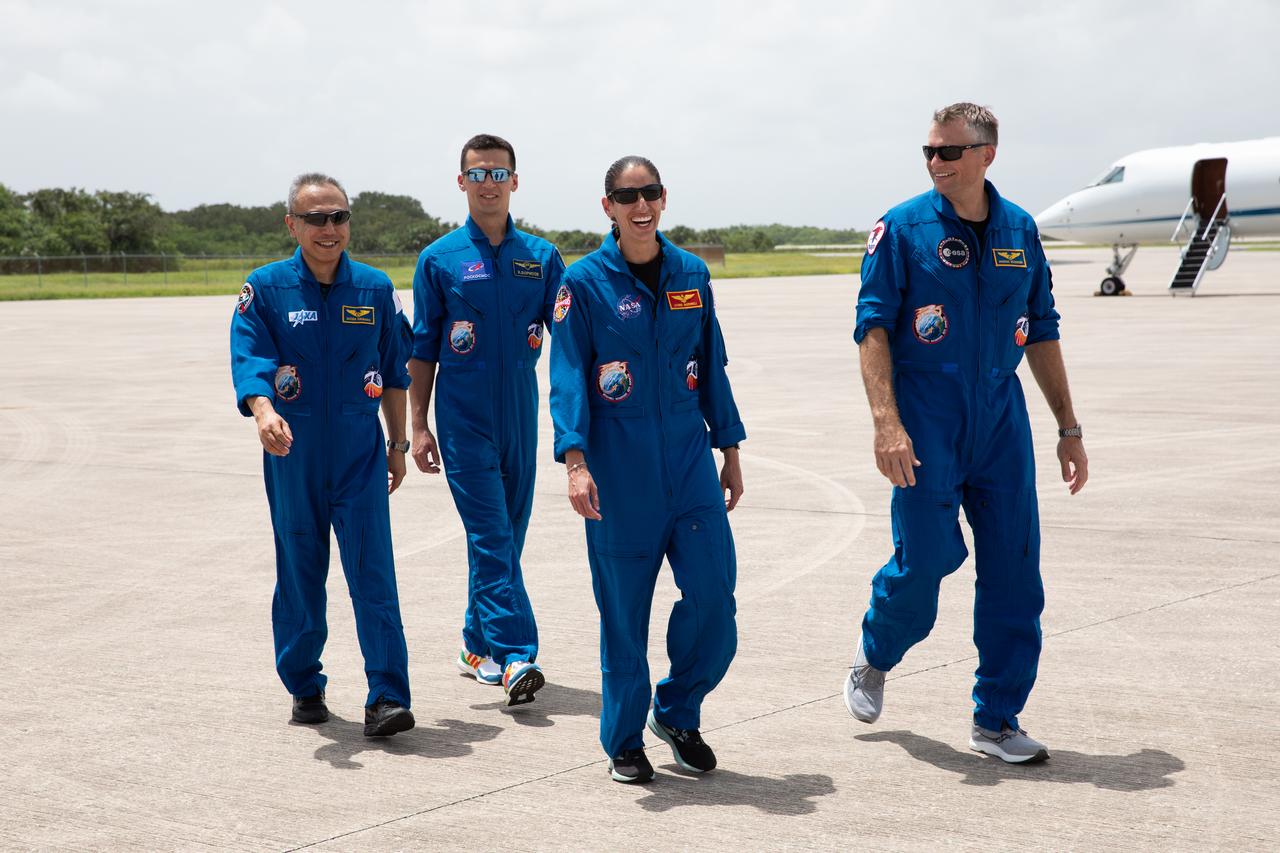

Crewmates for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-7 mission to the International Space Station walk along the runway at the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 20, 2023. From left, JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa, Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov, NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen will launch aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket at 3:49 a.m. EDT Friday, Aug. 25, 2023, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
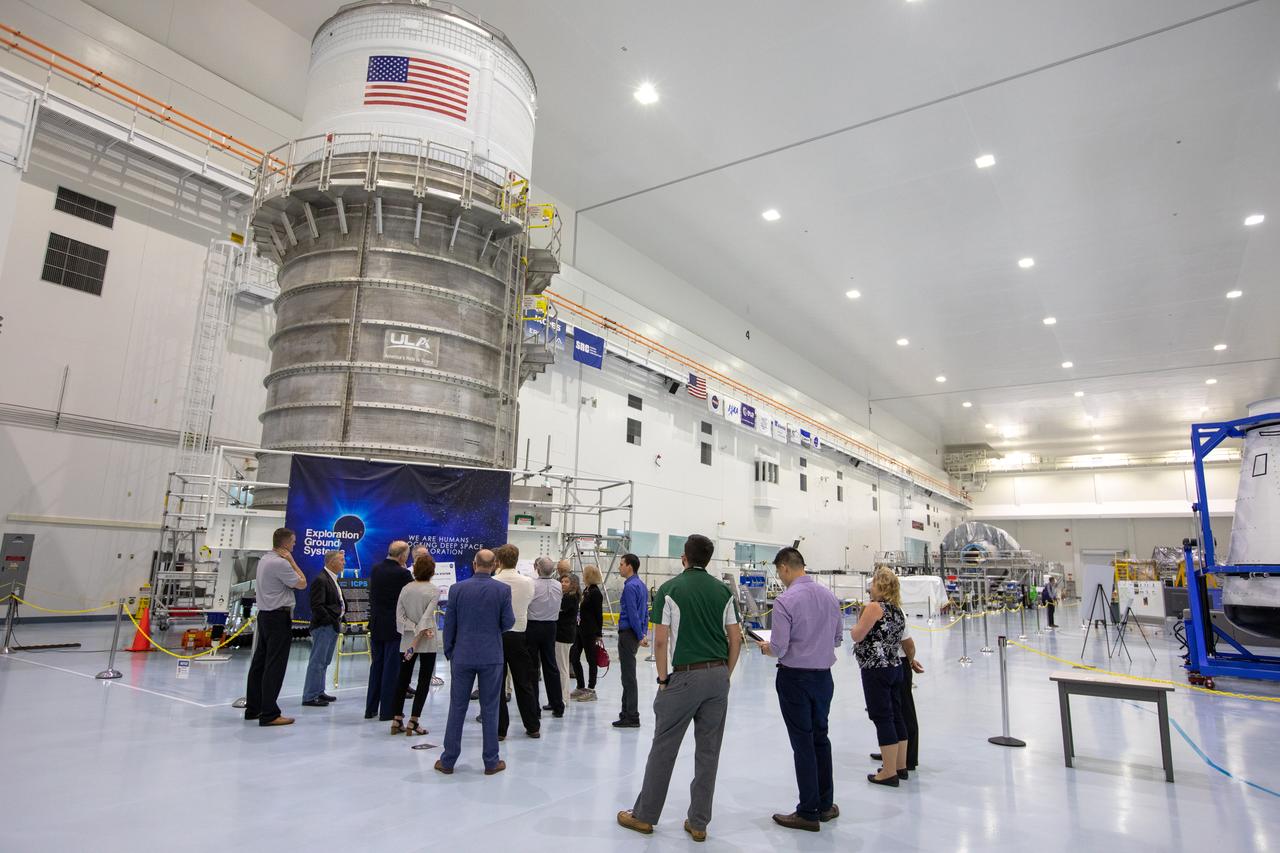

Members of the NASA Advisory Council toured the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 29, 2019. In view is the interim cryogenic propulsion stage for the Space Launch System rocket. The NASA Advisory Council provides the NASA administrator with counsel and advice on programs and issues of importance to the agency. Committee members conduct fact-finding sessions throughout the year in an effort to gain a broad understanding of current NASA issues and future mission implementation plans.
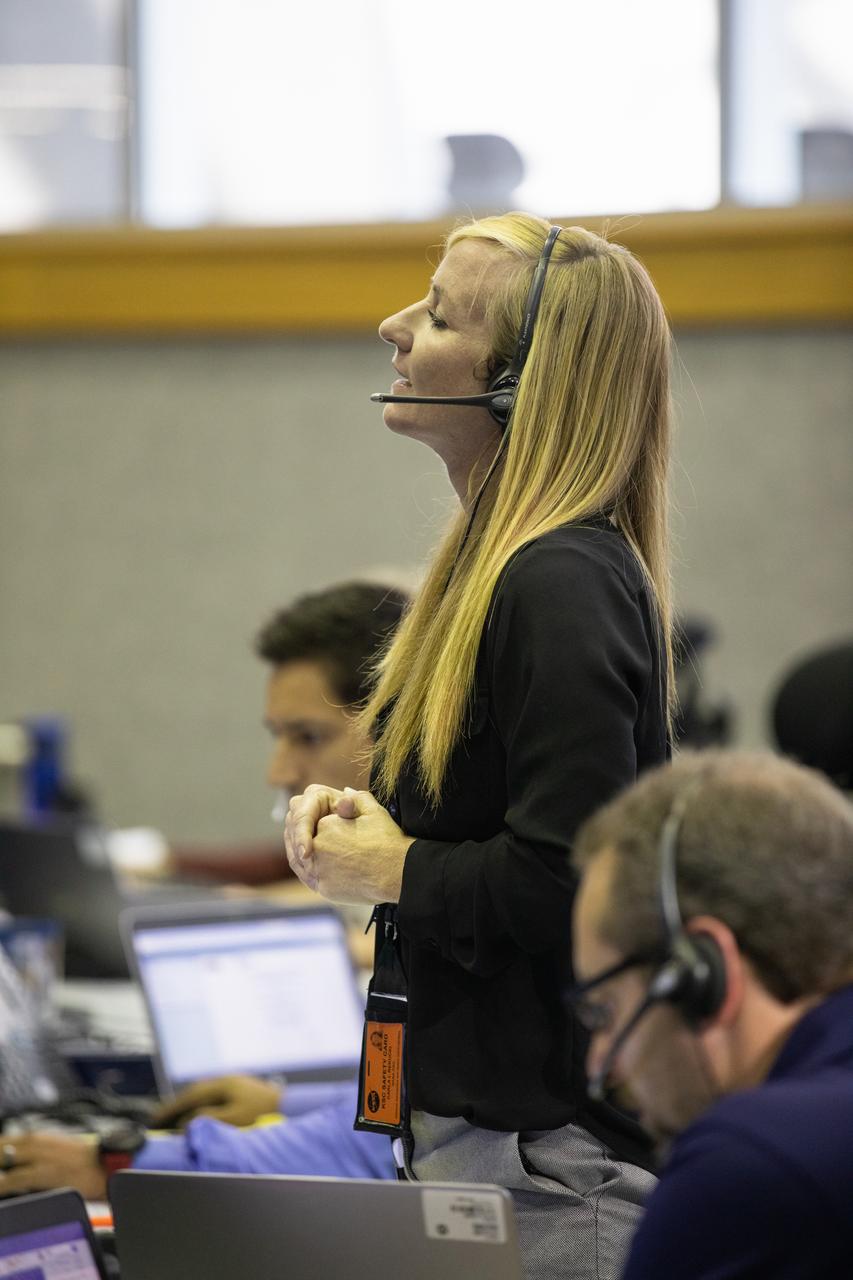

Carla Rekucki, lead NASA test director in NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS), center, and other launch team members participate in validation testing inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 11, 2019. The team includes personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and Jacobs Test and Operations Contract (TOSC). The simulation was designed to validate the firing room consoles and communications systems, as well as the new Spaceport Command and Control System (SCCS), which will operate, monitor and coordinate ground equipment in preparation for Artemis 1, the uncrewed first flight of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.
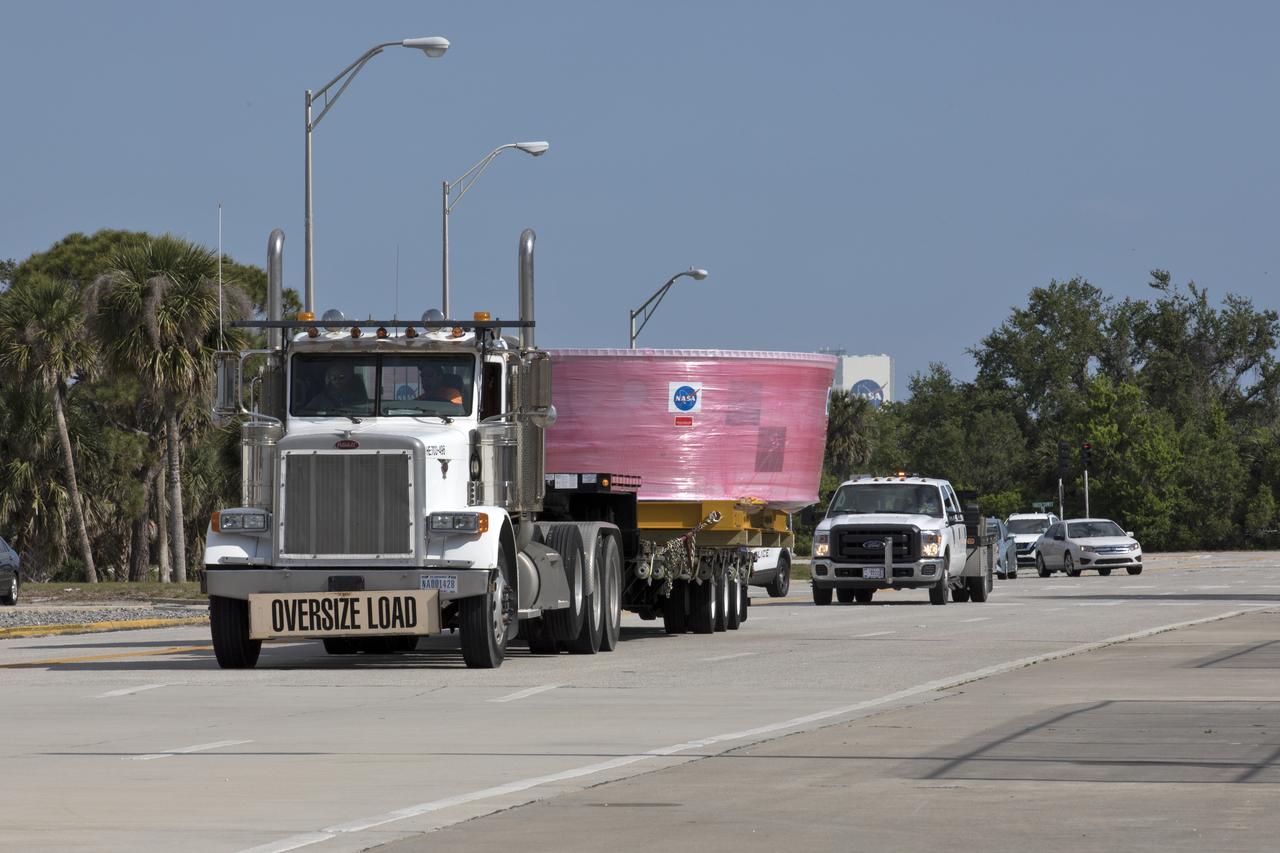

The Orion Stage Adapter (OSA), secured on flatbed transporter, is moved along State Road 3 to the Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSA is the second flight-hardware section of the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to arrive at Kennedy. The OSA will connect the Orion spacecraft to the upper part of the SLS, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Both the OSA and ICPS are being stored for processing in the SSPF in preparation for Exploration Mission-1, the first uncrewed, integrated launch of the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft.
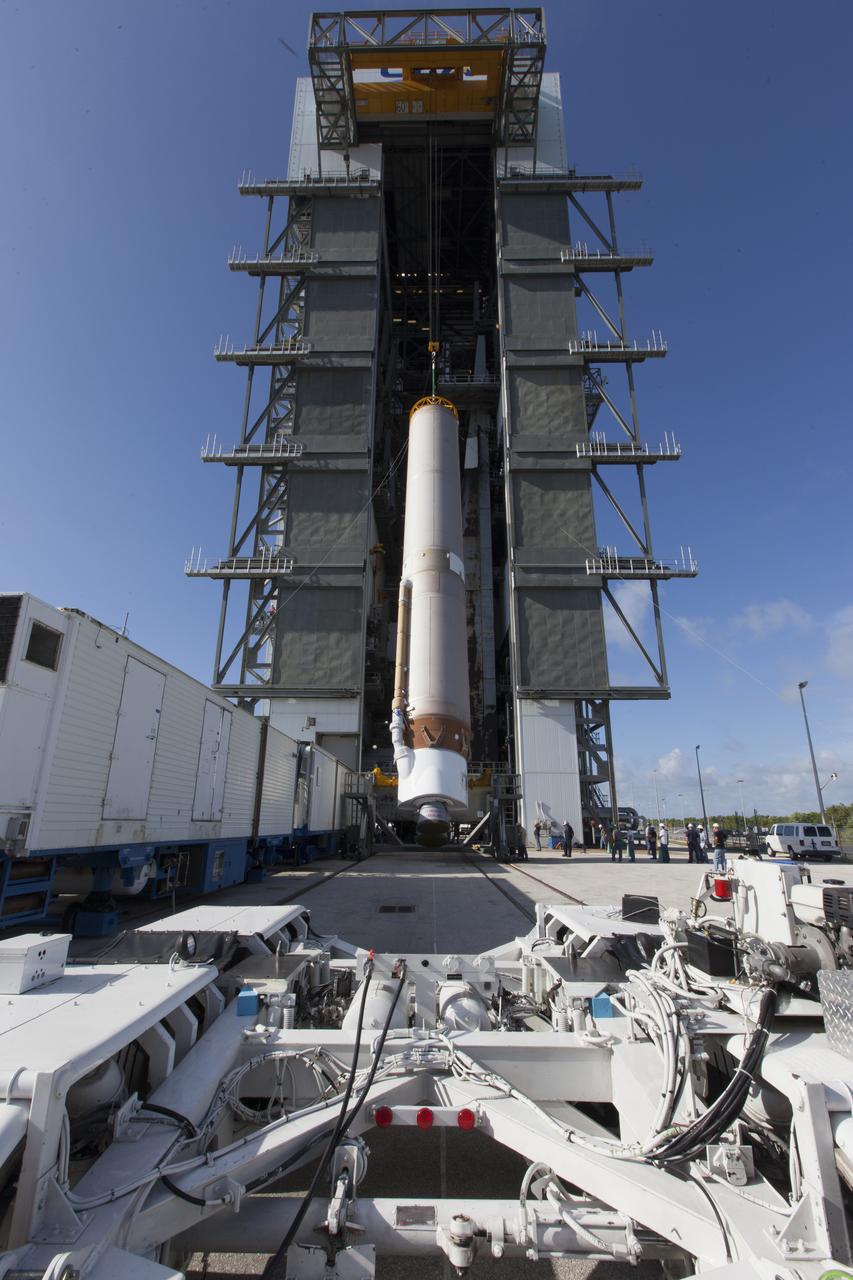

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The rocket is scheduled to launch the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-M. It will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Cape Canaveral's Space Launch Complex 41 on Aug. 3, 2017 at 9:02 a.m. EDT.
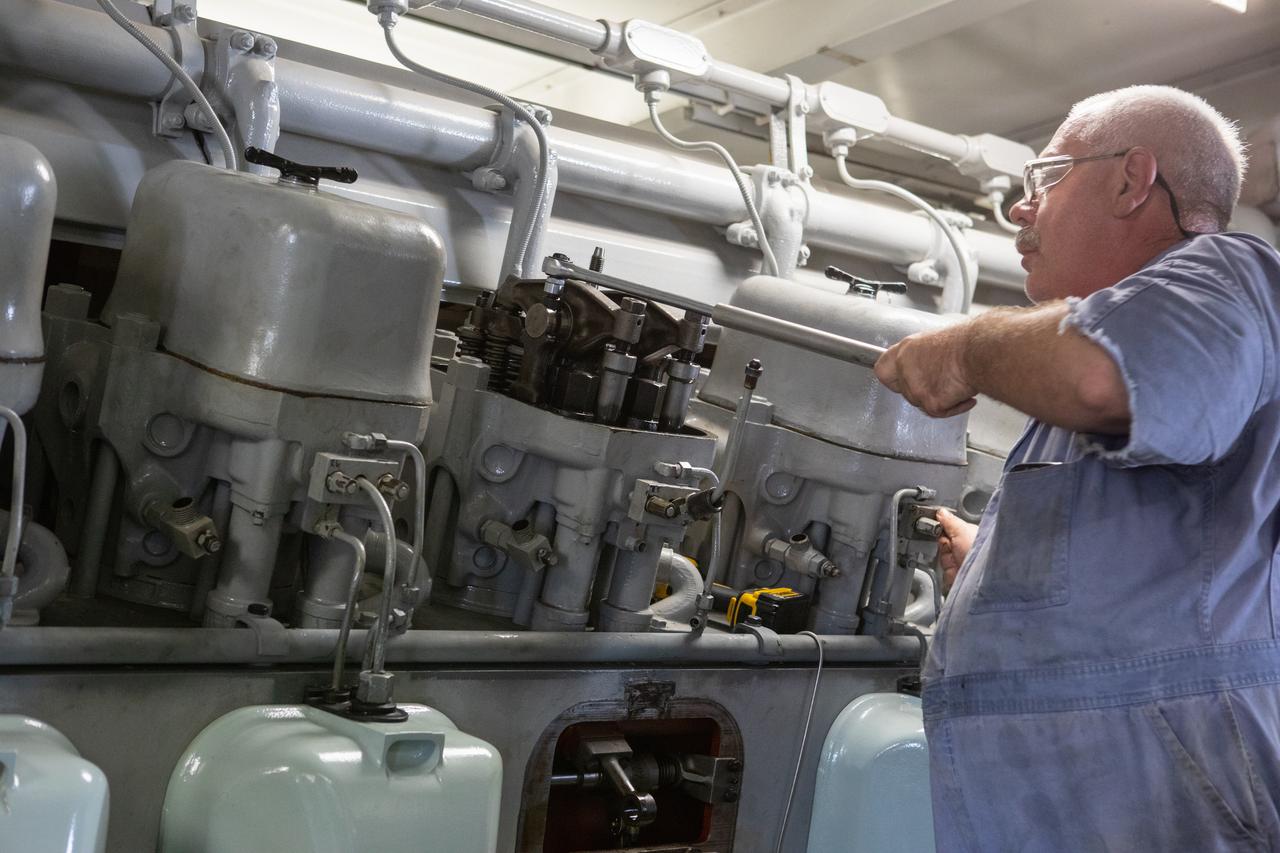

William Vardaman, mechanical technician with the Jacobs contracting team, performs engine maintenance on NASA's crawler-transporter 2 on March 26, 2019, in the crawler yard located in Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39 area. Recent engine work included rebuilding the vehicles’ fuel pump assemblies and installing new oil pumps that will help minimize future wear. This is one of two crawler-transporters that carried rockets and spacecraft, including the Apollo/Saturn V and space shuttle, from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems oversaw modifications and upgrades to crawler-transporter 2 so it can carry the mobile launcher and NASA's Space Launch System rocket, topped by the Orion spacecraft, to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission-1.
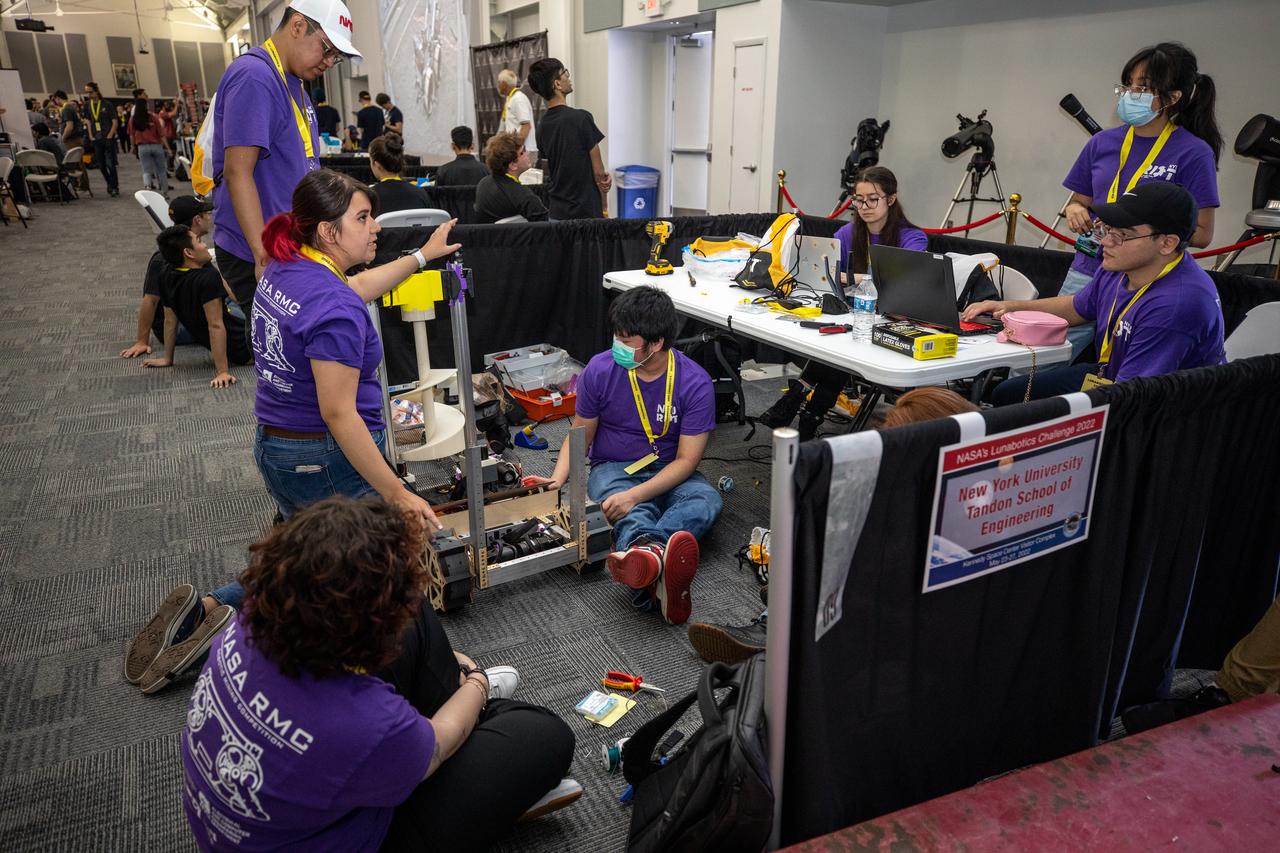

Students from the New York University Tandon School of Engineering prepare their robot for its turn to dig in the mining arena during NASA’s LUNABOTICS competition on May 24, 2022, at the Center for Space Education near the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. More than 35 teams from around the U.S. have designed and built remote-controlled robots for the mining competition. Teams use their autonomous or remote-controlled robots to maneuver and dig in a supersized sandbox filled with rocks and simulated lunar soil, or regolith. The objective of the challenge is to see which team’s robot can collect and deposit the most rocky regolith within a specified amount of time.
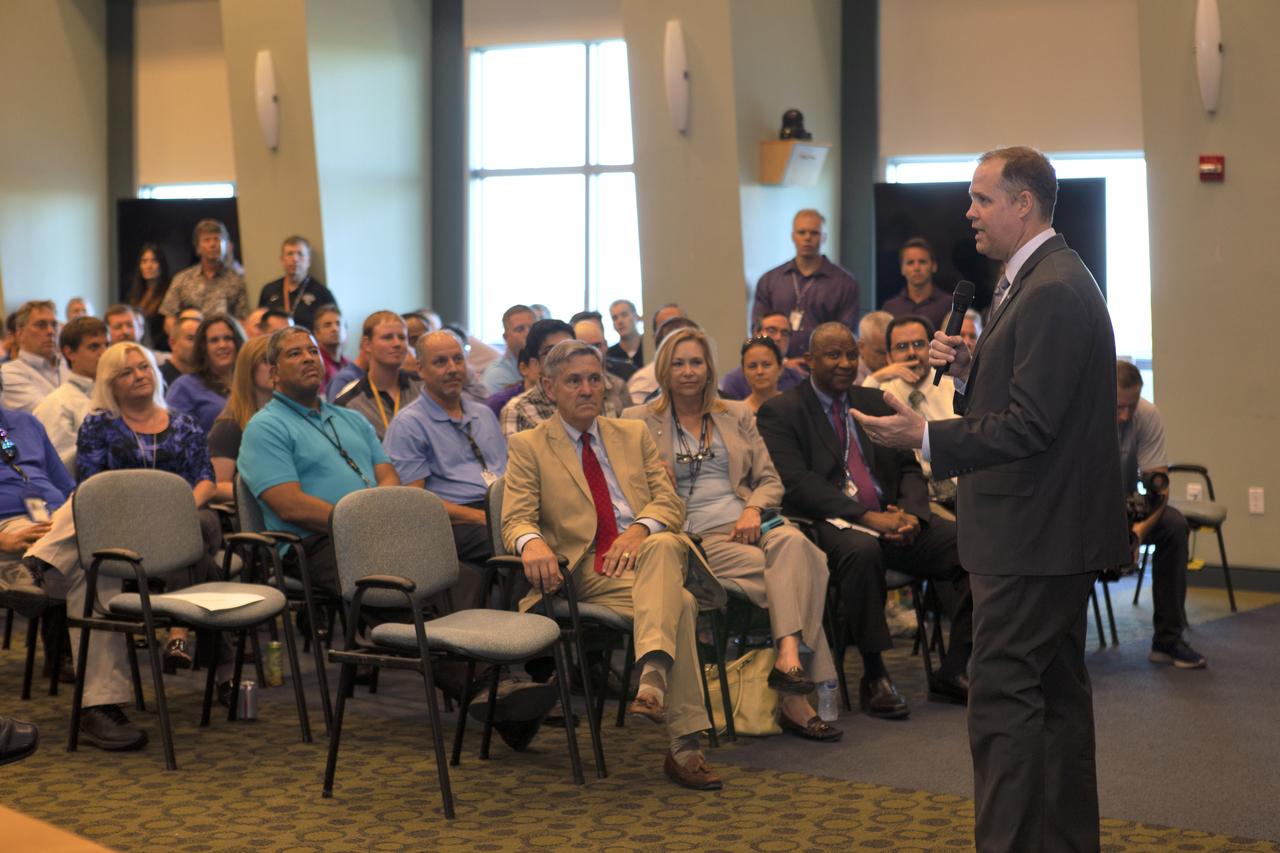

NASA Kennedy Space Center Engineering Directorate employees listen to a presentation by the agency's Administrator Jim Bridenstine. He made his first official visit to the Florida spaceport on Aug. 6 and 7, 2018.
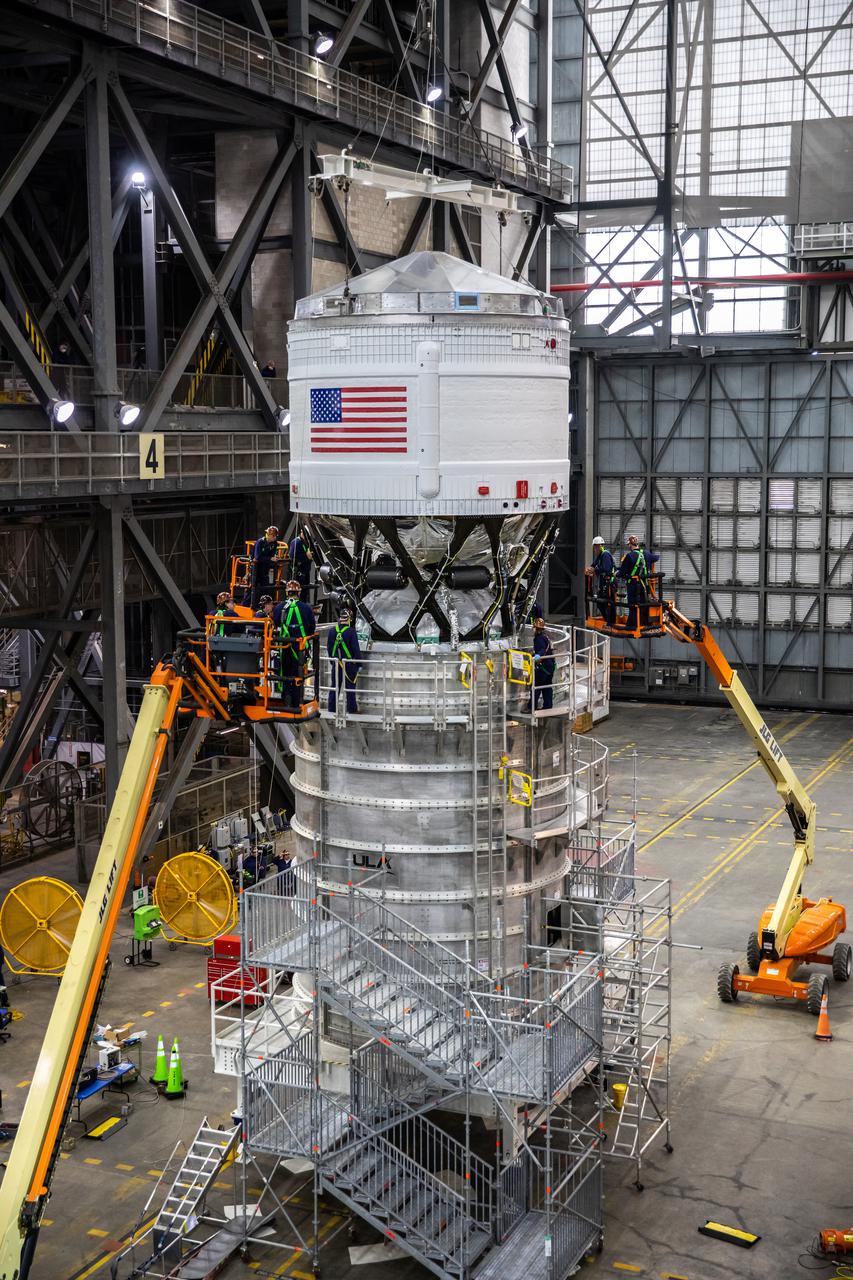

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Kennedy Space Center Deputy Director Janet Petro participates in a virtual town hall at the Florida spaceport’s Press Site auditorium on June 10, 2020, to share the plan for employees to safely return to on-site work during the time of COVID-19. Also participating were Center Director Bob Cabana and Dr. David Tipton, chief medical officer, not pictured.

Tylar Greene, NASA Communications, moderates a mission and science briefing for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2021. Virtual participants (not shown) are Jeff Masek, Landsat 9 project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center; Chris Crawford, Landsat 9 project scientist at USGS; Inbal Becker-Reshef, director of NASA’s Harvest food security and agriculture program; Del Jenstrom, Landsat 9 project manager at Goddard; Brian Sauer, Landsat 9 project manager at USGS; Sabrina Chapman, manager, system engineering, Northrop Grumman Space Systems; and Sarah Lipscy, OLI-2 senior engineer, Ball Aerospace & Technologies. Landsat 9 is scheduled to launch at 2:11 p.m. EDT (11:11 a.m. PDT) on Monday, Sept. 27, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Landsat 9 will join its sister satellite, Landsat 8, in orbit in collecting images from across the planet every eight days. This calibrated data will continue the Landsat program’s critical role in monitoring the health of Earth and helping people manage essential resources, including crops, irrigation water, and forests.
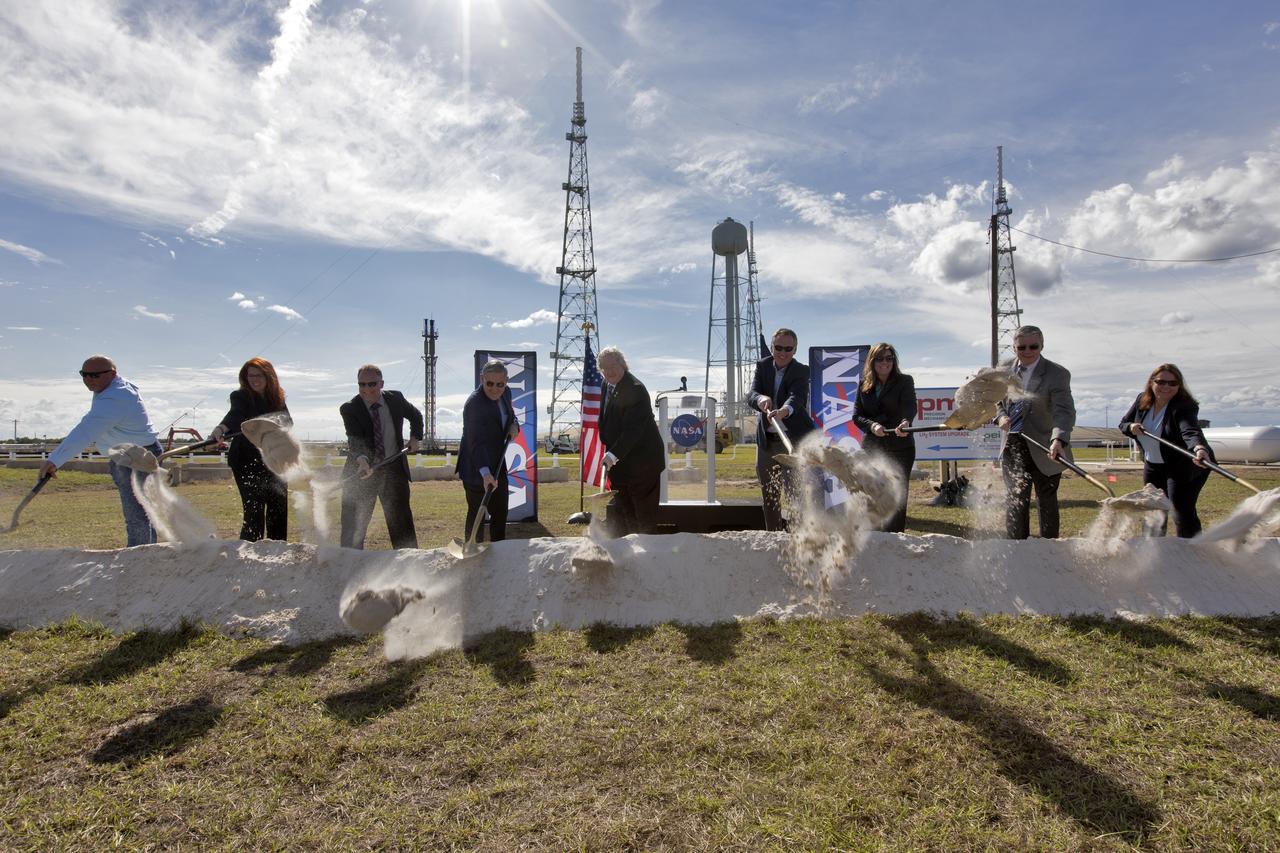

On Dec. 19, 2018, at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39B, agency and contractor managers break ground for a new liquid hydrogen tank. Participating, from the left, are Todd Gray, president of Precision Mechanical, prime contractor for the project; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, launch director; Shawn Quinn, director of Engineering; Bob Cabana, center director; Bill Hill, deputy associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development at NASA Headquarters in Washington; Mike Bolger, program manager for Exploration Ground Systems (EGS); Jennifer Kunz, deputy program manager for EGS, Andy Allen, general manager for Jacobs, NASA's Test and Operations Support Contractor; and Regina Spellman, launch pad senior project manager in EGS. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.
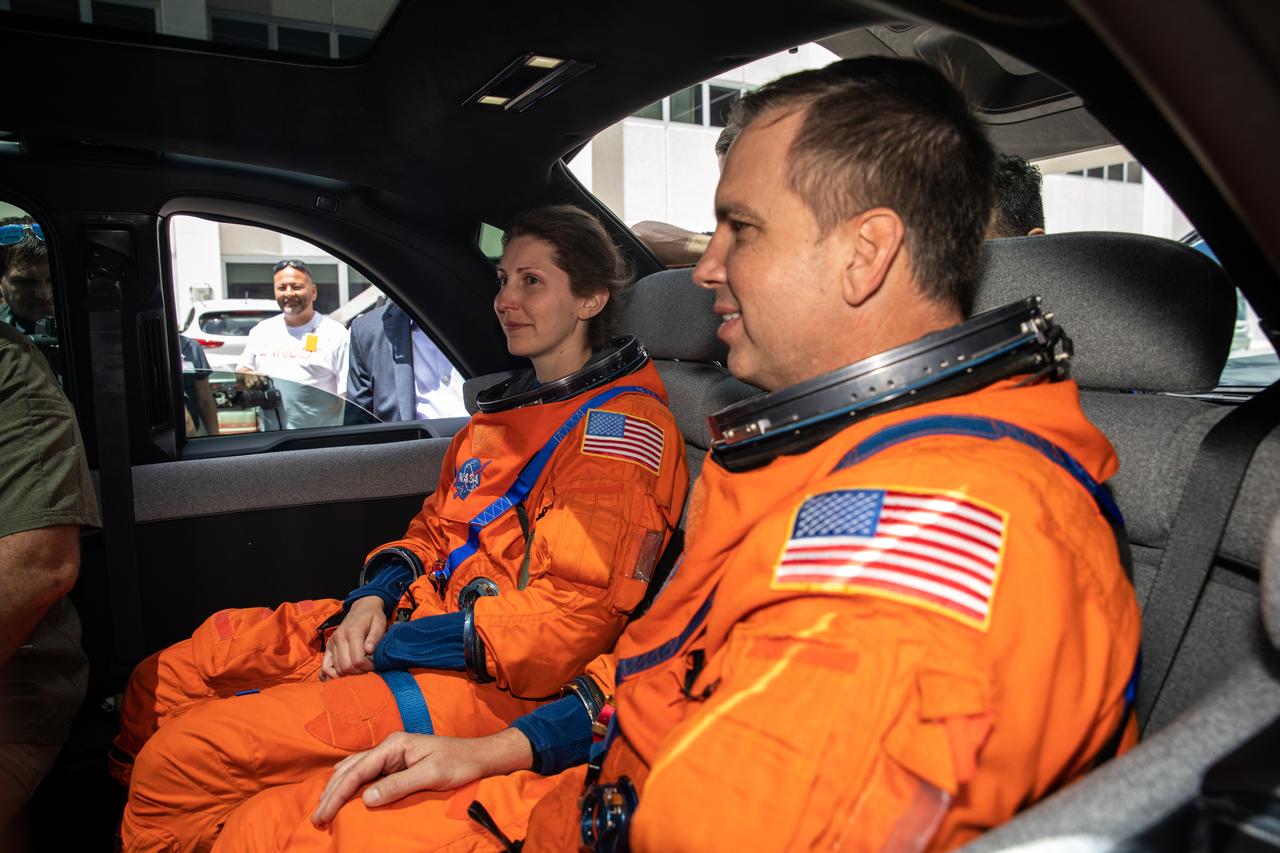

Technicians from Johnson Space Center, dressed in flight suits, secure themselves inside a prototype of a crew transportation vehicle (CTV) for Artemis crewed missions outside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 11, 2022. Canoo Technologies Inc., was awarded a contract to design and provide the next generation of CTVs for the Artemis crewed missions. Representatives with Canoo were at the spaceport demonstrating the environmentally friendly fleet of vehicles. Artemis II will be the first Artemis mission flying crew aboard Orion. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
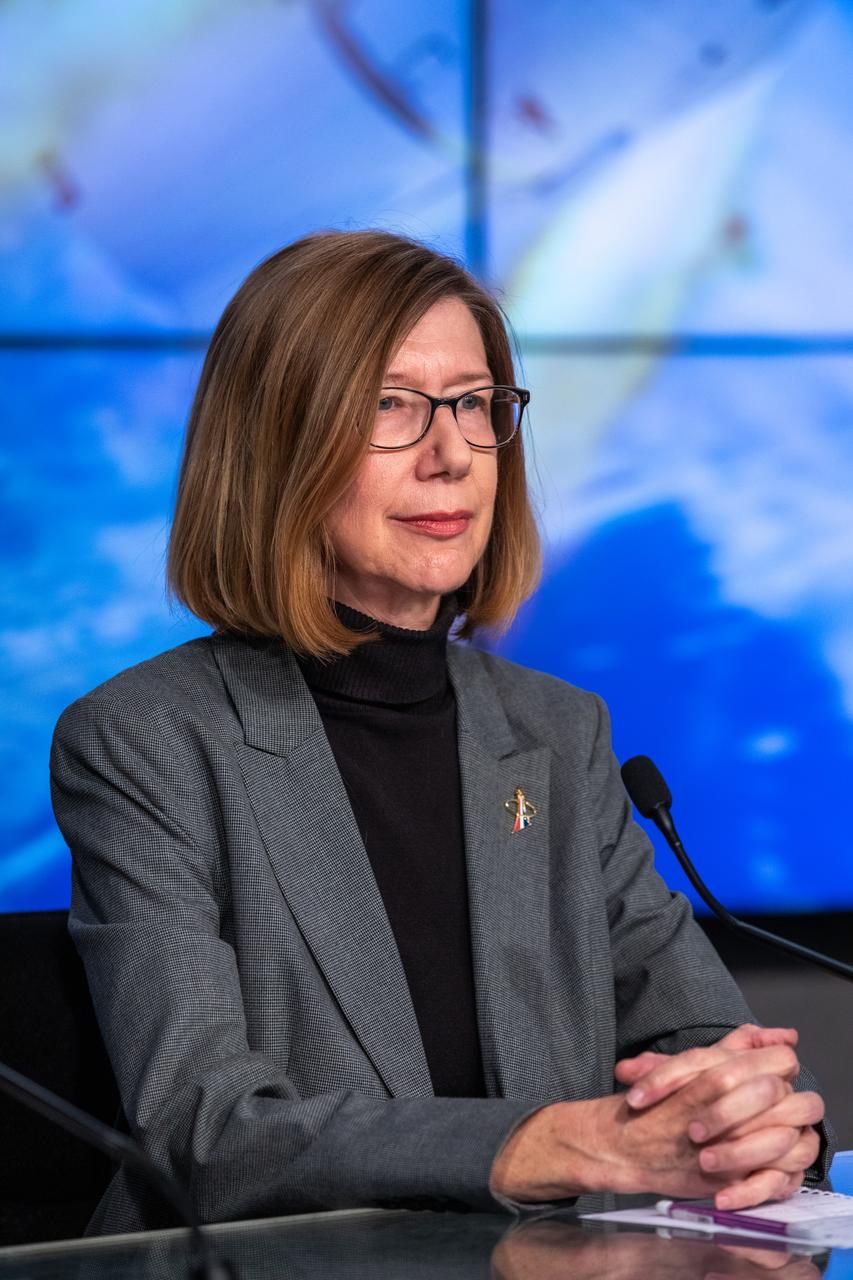

Kathy Lueders, manager of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, participates in a briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the company’s uncrewed In-Flight Abort Test on Jan. 19, 2020. During the flight test, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifted off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A and began a planned launch-abort sequence demonstrating the spacecraft’s escape capabilities. The Crew Dragon splashed down in the Atlantic Ocean as expected. The In-Flight Abort Test is a critical milestone in preparation for crewed flights to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
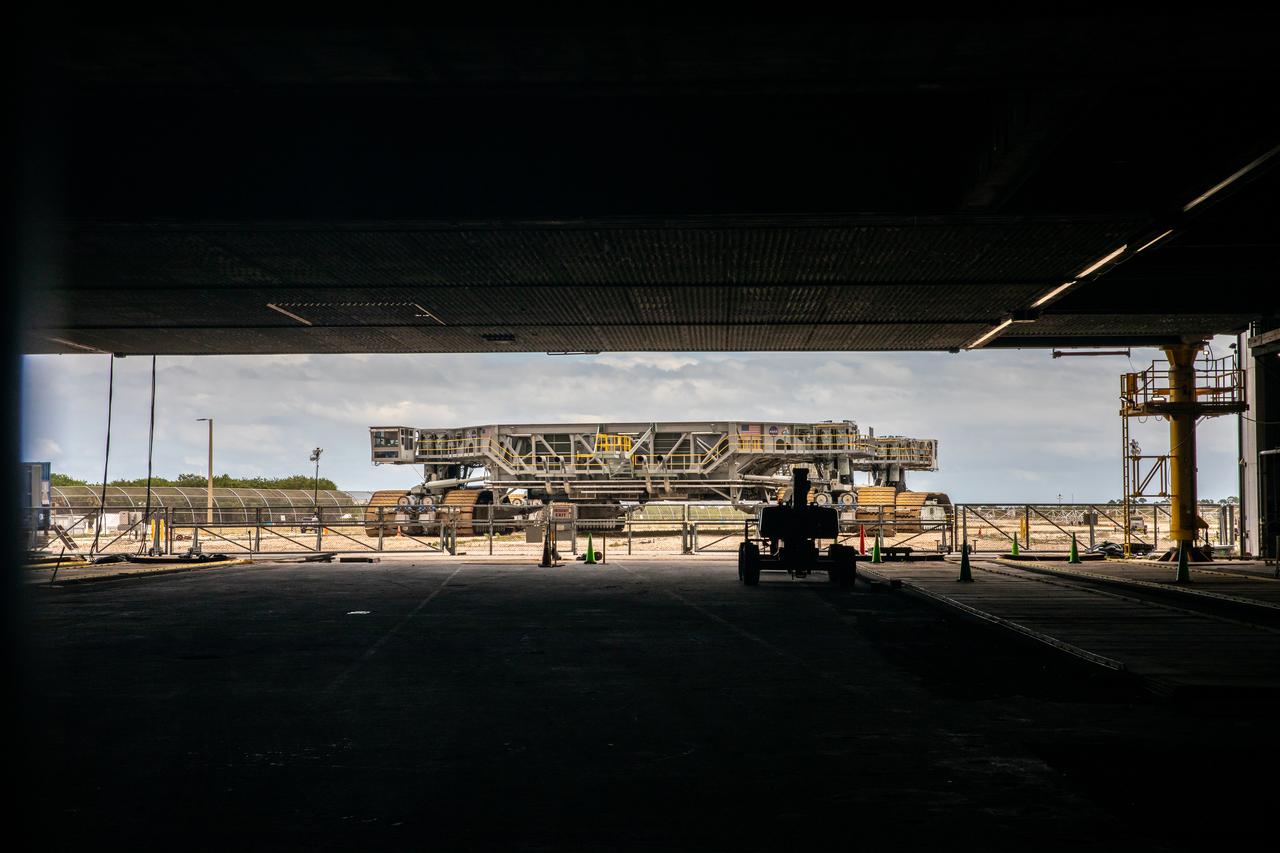

Crawler-transporter 2 is in view just outside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 14, 2022. Soon the crawler will be driven inside to transport the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft stack atop the mobile launcher for a trip along the crawlerway to Launch Complex 39B for a wet dress rehearsal. The Kennedy ground systems team is working to remove equipment and scaffolding away from the rocket and will continue retracting the platforms until the entire rocket is revealed ahead of the wet dress rehearsal test, which is scheduled to occur approximately two weeks after it arrives to 39B. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration to the Moon and Mars.

Artemis II NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman, commander, tours Artemis II operations with Artemis team members inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA Kennedy on Thursday, Feb. 27, 2025. For Artemis II, four astronauts will venture around the Moon, the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term presence for science and exploration through Artemis.

From left, NASA’s Artemis Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson and Space Launch System Resident Management Office Manager Elkin Norena participate in an Artemis I student media briefing inside the John Holliman Auditorium of the News Center at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 19, 2023. As part of NASA’s NextGen STEM project, students from Florida’s St. Cloud High School and Storm Grove Middle School in Vero Beach participated in person during the briefing, while middle and high school students across the country had the opportunity to ask questions of the panel via phone to discuss the Artemis I mission and the agency’s future of human space exploration.
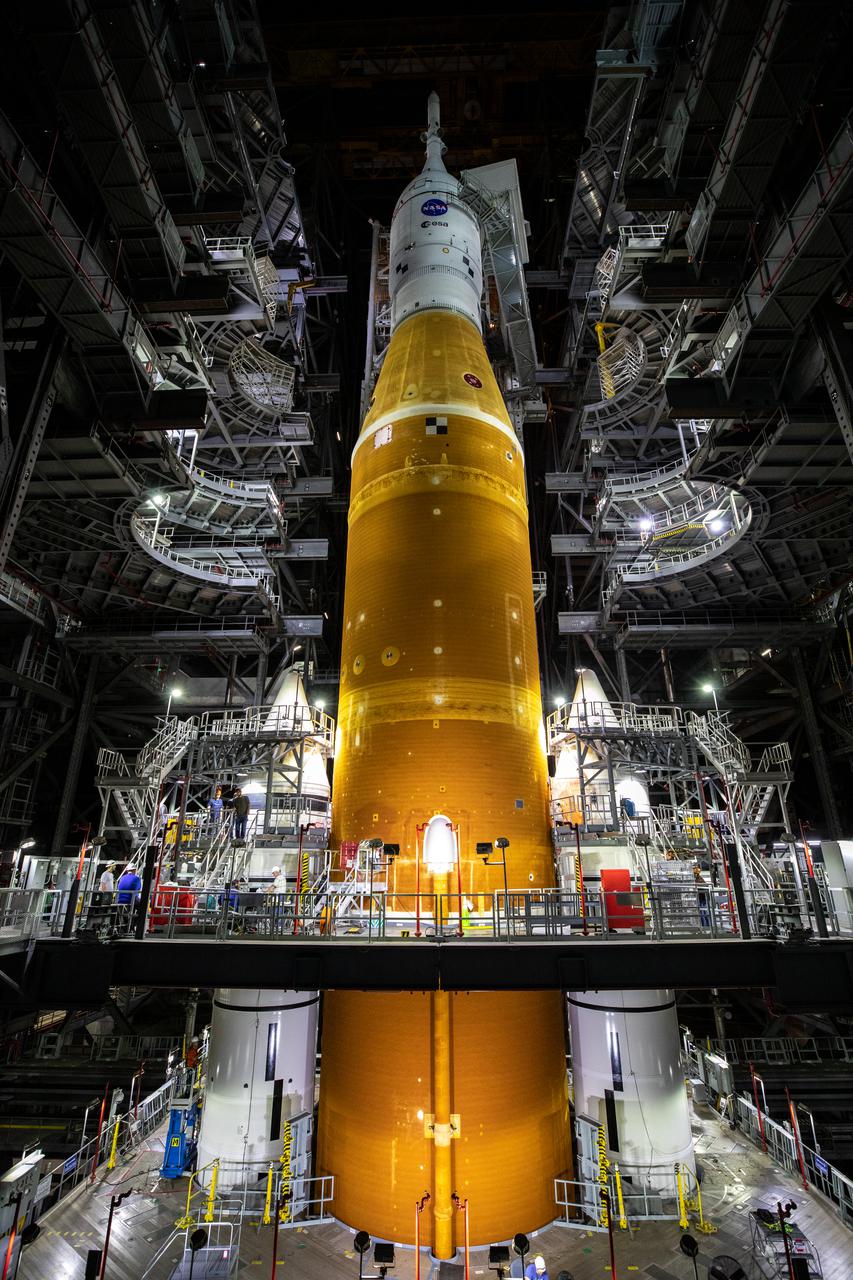

In this view looking up inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 10, 2022, the work platforms are being retracted from around the Artemis I Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation to roll out to launch pad 39B. The Kennedy ground systems team is working to remove equipment and scaffolding away from the rocket and will continue retracting the platforms until the entire rocket is revealed ahead of the wet dress rehearsal test, which is scheduled to occur approximately two weeks after it arrives at the pad.
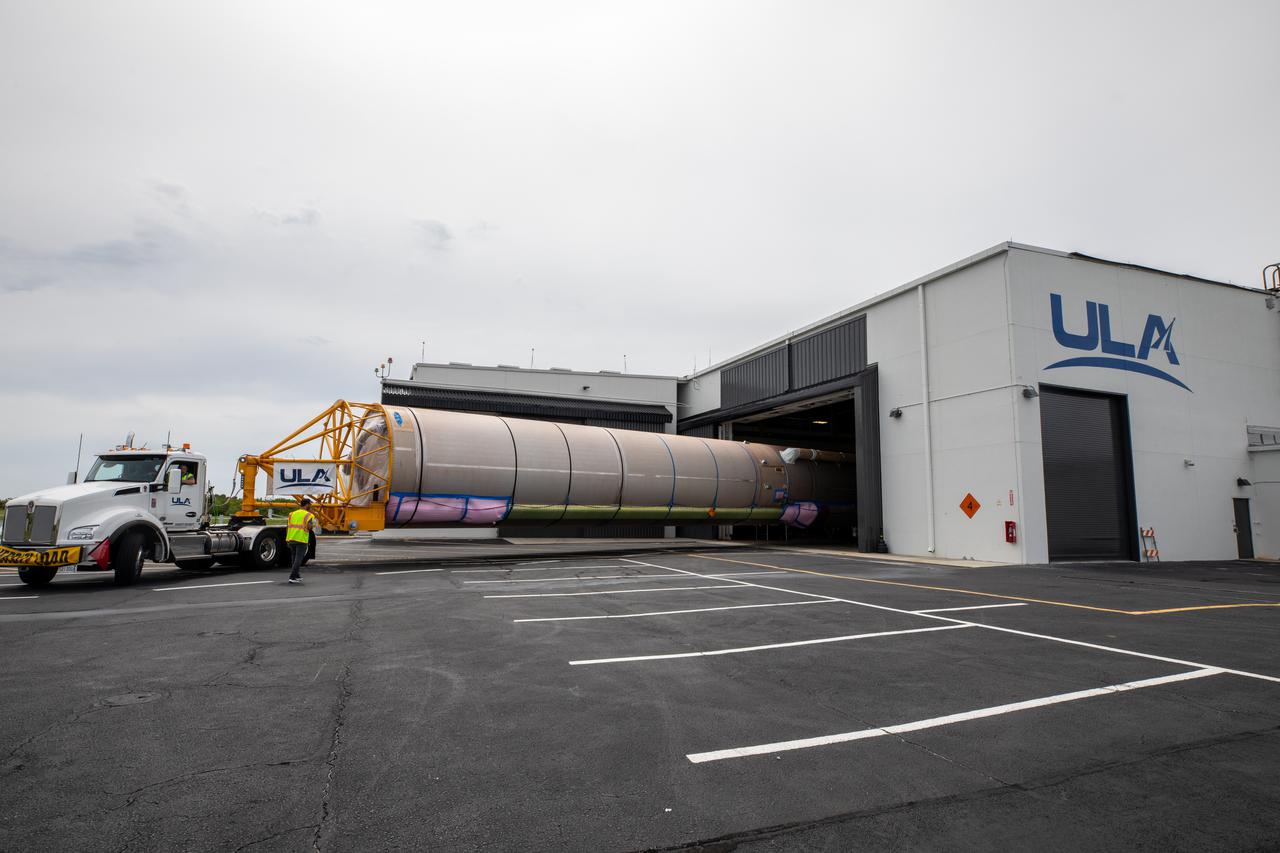

A flatbed truck delivers the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster and Centaur upper stage for Boeing's CST-100 Starliner Crew Flight Test (CFT) to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on June 21, 2021. Starliner's first flight with astronauts aboard, CFT will launch from SLC-41. The flight test will demonstrate the ability of the Atlas V and Starliner to safely carry astronauts to and from the International Space Station for the agency's Commercial Crew Program.
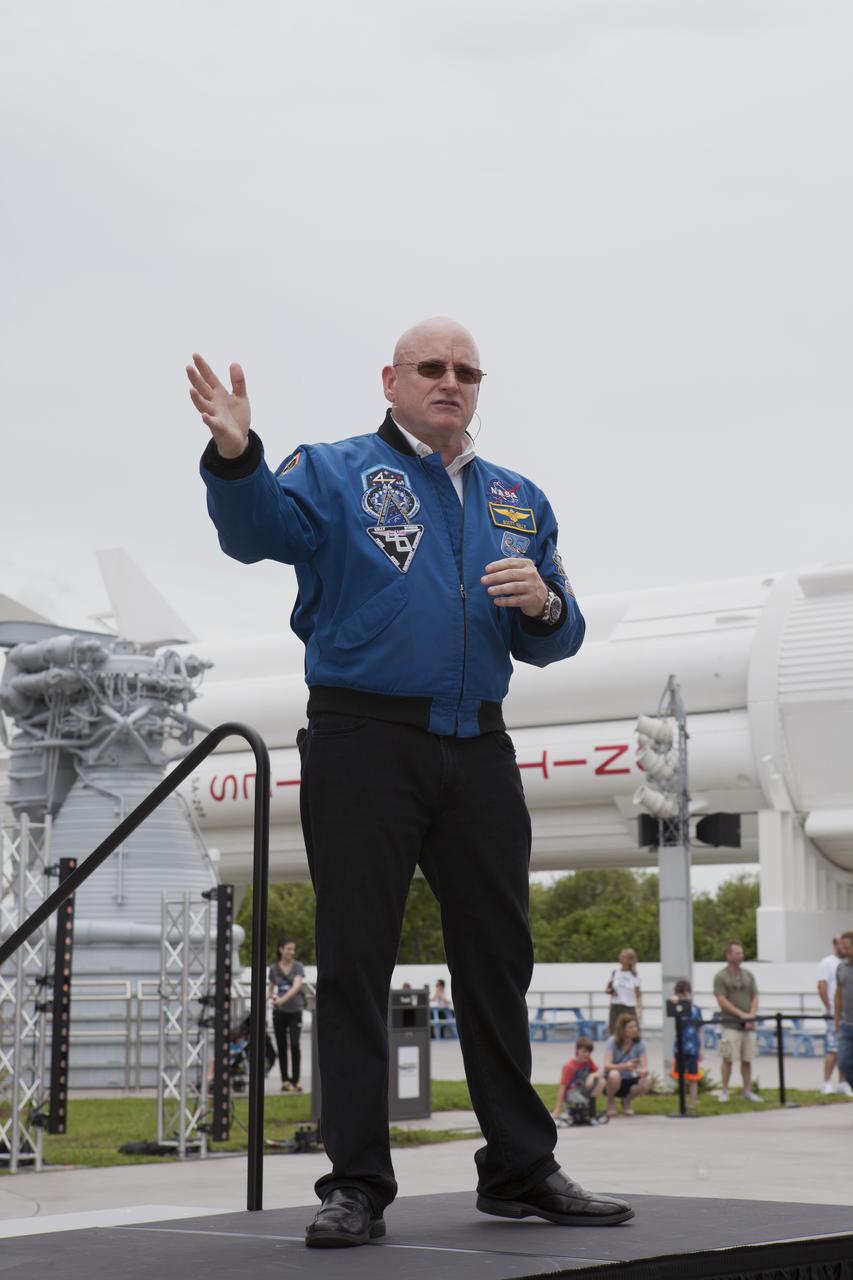

The Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex kicked off its "Summer of Mars" promotion with a ceremony which included former NASA astronaut Scott Kelly. During his appearance, Kelly shared some of his experiences during a one-year stay aboard the International Space Station. The "Summer of Mars" program is designed to provide guests with a better understanding of NASA's studies of the Red Planet.
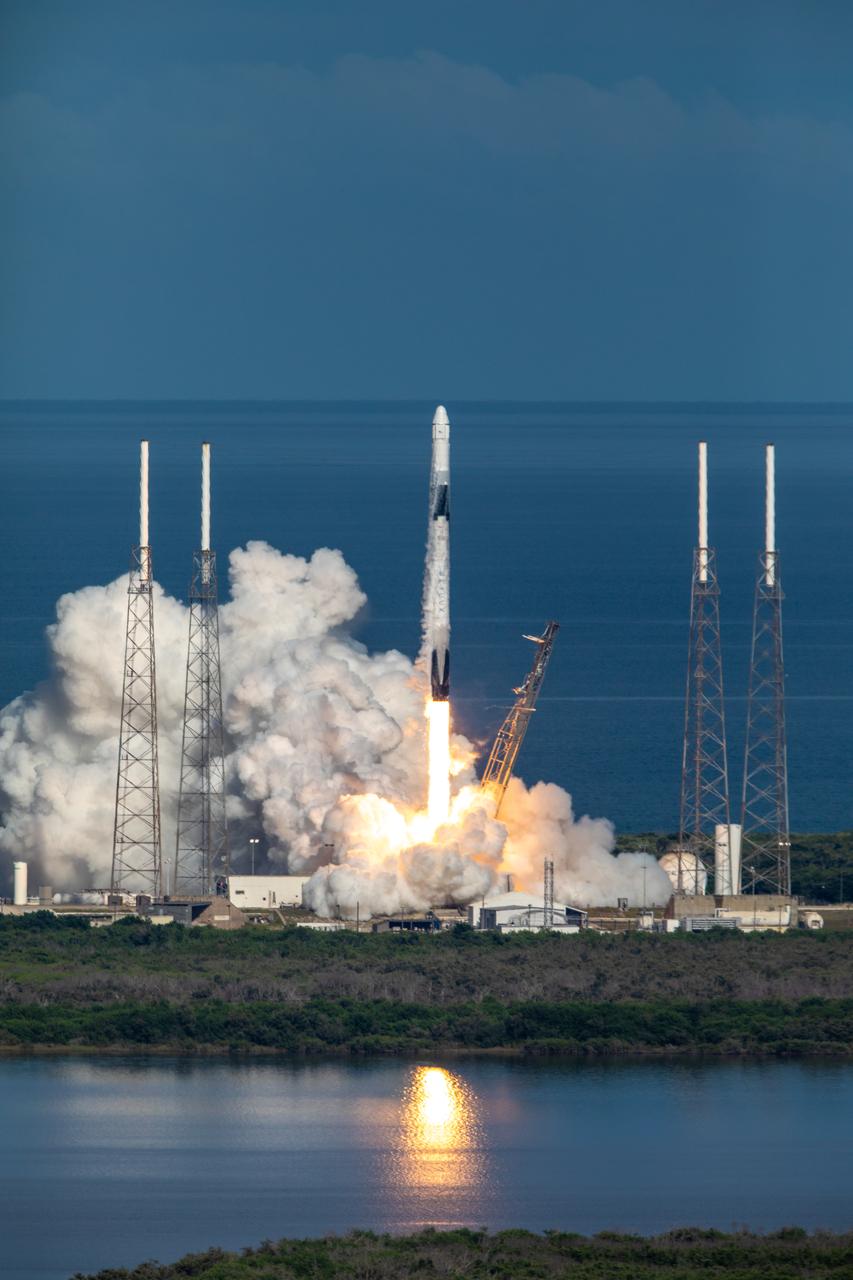

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida at 6:01 p.m. EDT on July 25, 2019, carrying the Dragon spacecraft on the company’s 18th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-18) mission to the International Space Station. The uncrewed Dragon spacecraft will deliver about 5,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbiting laboratory.
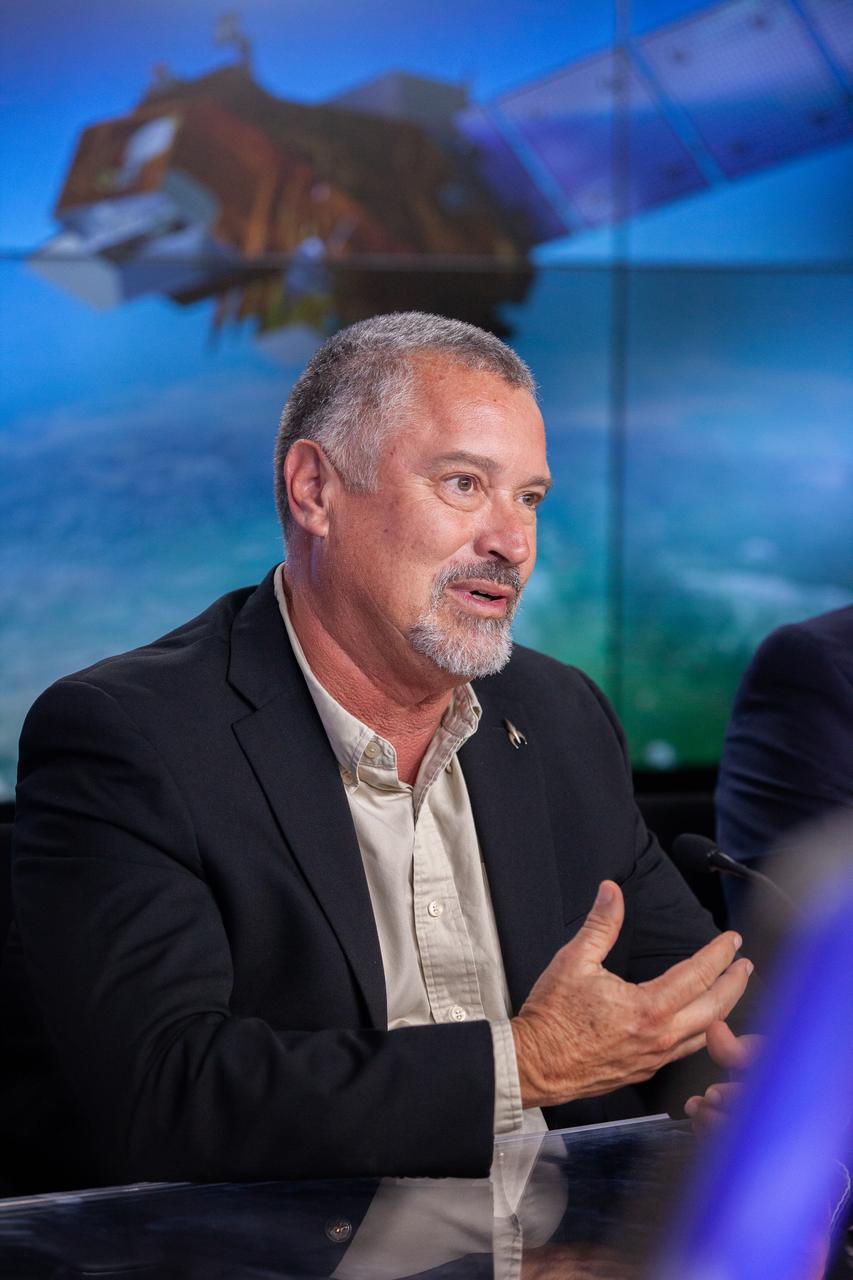

Omar Baez, launch director, NASA’s Launch Services Program, participates in a prelaunch news conference for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) and NASA Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) technology demonstration at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 28, 2022. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the polar satellite series and is expected to capture data to improve weather forecasts, helping scientists predict and prepare for extreme weather events and climate change. JPSS-2 is scheduled to launch at 2:25 a.m. PDT Tuesday, Nov. 1, on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Launching with JPSS-2 is NASA’s LOFTID technology demonstration. After JPSS-2 safely reaches orbit, LOFTID will follow a re-entry trajectory from low-Earth orbit to demonstrate the inflatable heat shield’s ability to slow down and survive re-entry. LOFTID is a partnership with ULA and is dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter, one of the company’s engineers who played a key role in developing the technology. LOFTID will demonstrate how the inflatable aeroshell, or heat shield, can slow down and survive re-entry in conditions relevant to many potential applications, whether landing humans on Mars, new missions to Venus and Titan, or returning heavier payloads and samples from low-Earth orbit.
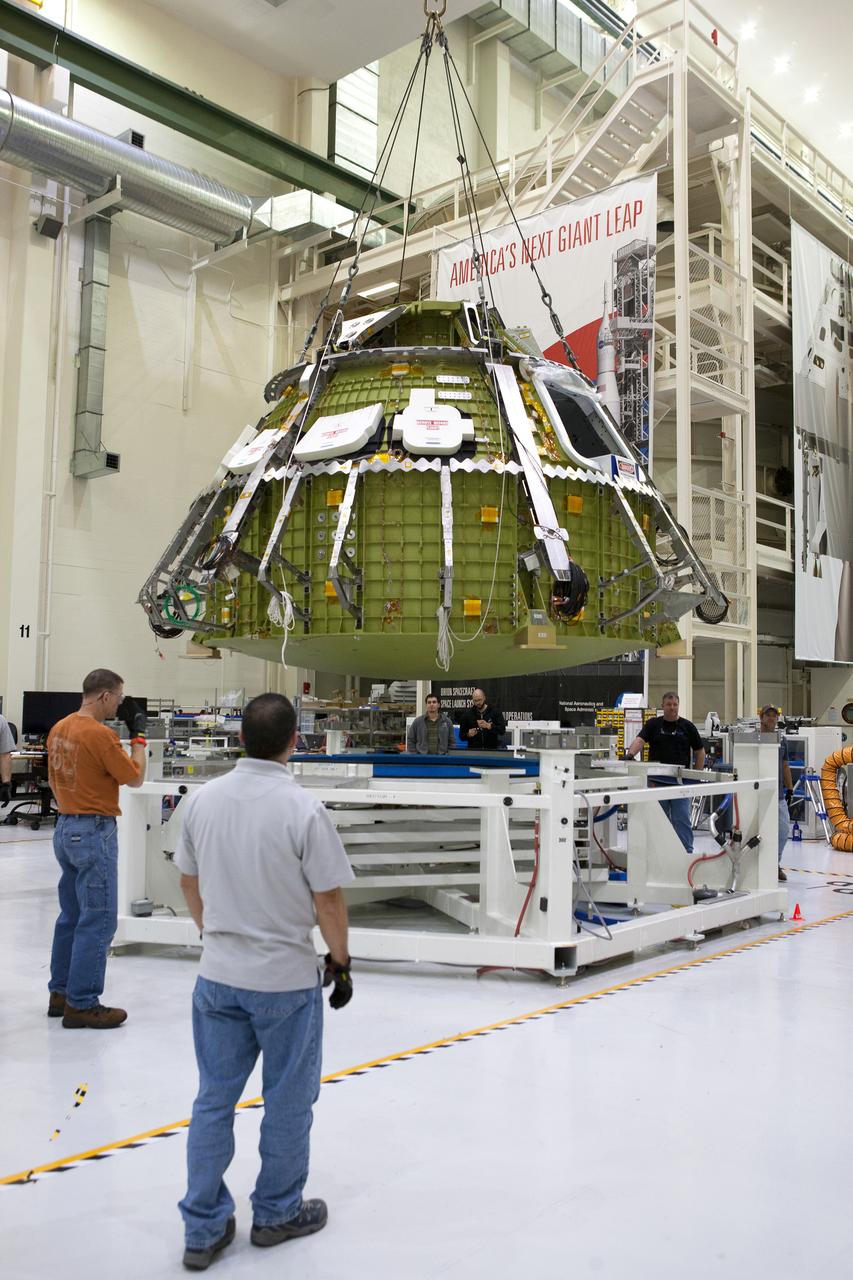

The Orion crew module for Artemis I is lifted into a test stand for pressure testing in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 21, 2016.

Andres Bratt-Leal, Ph.D., of Aspen Neuroscience, talks to NASA Social participants during a What’s On Board science briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 23, 2019. Bratt-Leal is a principal investigator for the Effects of Microgravity on Microglia 3-Dimensional Models of Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple Sclerosis (Space Tango-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells) payload. The briefing was held for SpaceX’s 18th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-18) mission to the International Space Station. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and uncrewed Dragon spacecraft are scheduled to launch July 24, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 at Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

Elected officials and guests visit after a ribbon cutting ceremony on Aug. 16, 2019, in High Bay 2 of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At far right is Florida State Senator Thad Altman. The VAB is getting its first commercial tenant. Northrop Grumman signed a Reimbursable Space Act Agreement with NASA for use of the facilities. The company will assemble and test its new OmegA rocket inside the massive facility’s High Bay 2. The company also will modify mobile launcher platform-3 to serve as the launch vehicle’s assembly and launch platform. Northrop Grumman is developing the OmegA rocket, an intermediate/heavy-class launch vehicle, as part of a launch services agreement with the U.S. Air Force.
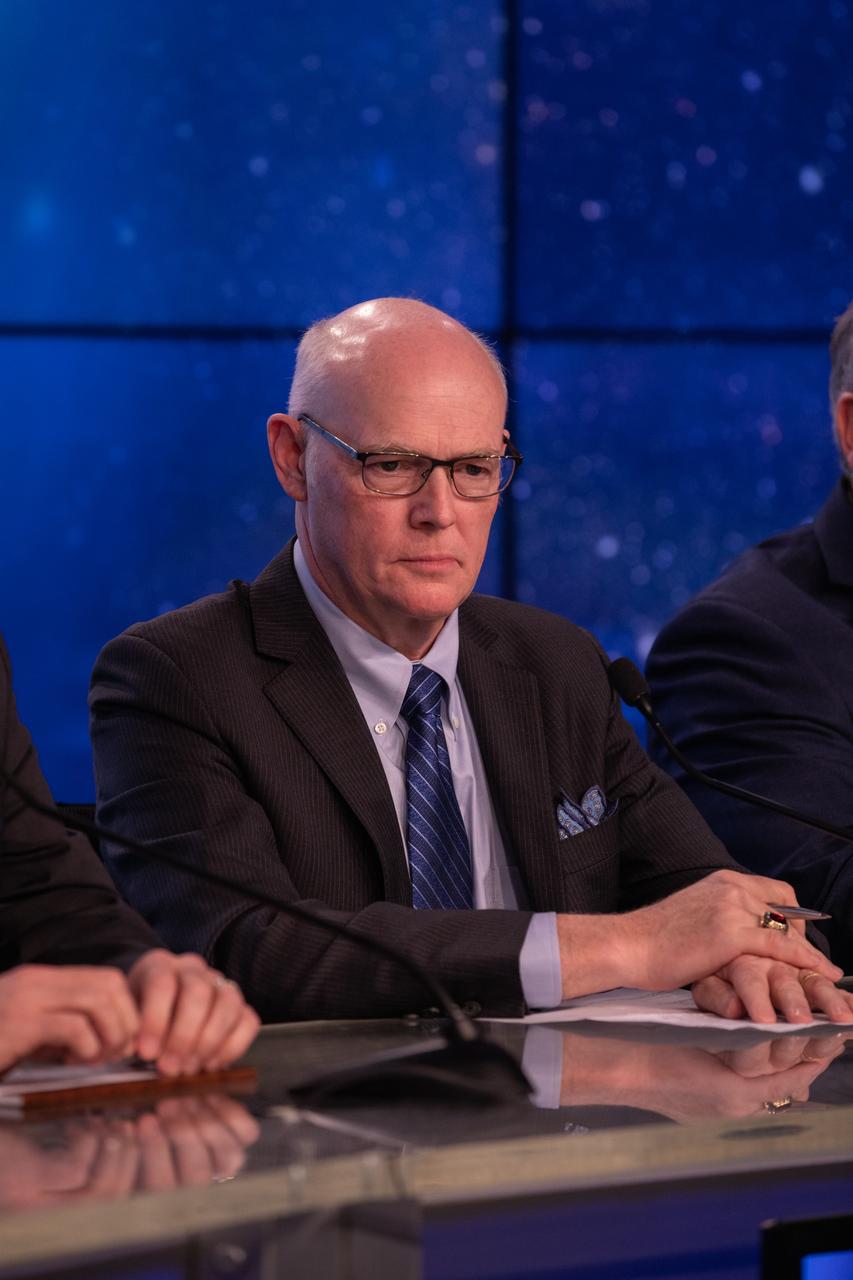

Tory Bruno, president and CEO of United Launch Alliance, listens during a briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following launch of Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test, Dec. 20, 2019. Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft launched atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 6:36 a.m. EST. The uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is the Starliner’s first flight for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.

Painting of the NASA logo, also called the meatball, is underway on the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 8, 2020. HM2 and H.I.S. Painting of Titusville, Florida, are repainting the meatball and the American Flag on the iconic building. High Bay 3 inside the VAB has been upgraded with 10 new levels of work platforms that will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing upgrades to the VAB to support the launch of the SLS and Orion for Artemis missions. Under the Artemis program, NASA will send the first woman and next man to the Moon.

Standing atop the mobile launcher, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft can be seen at Launch Pad 39B at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 18, 2022. The Artemis I stack was carried from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the pad – a 4.2-mile journey that took nearly 11 hours to complete – by the agency’s crawler-transporter 2 for a wet dress rehearsal ahead of the uncrewed launch. Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
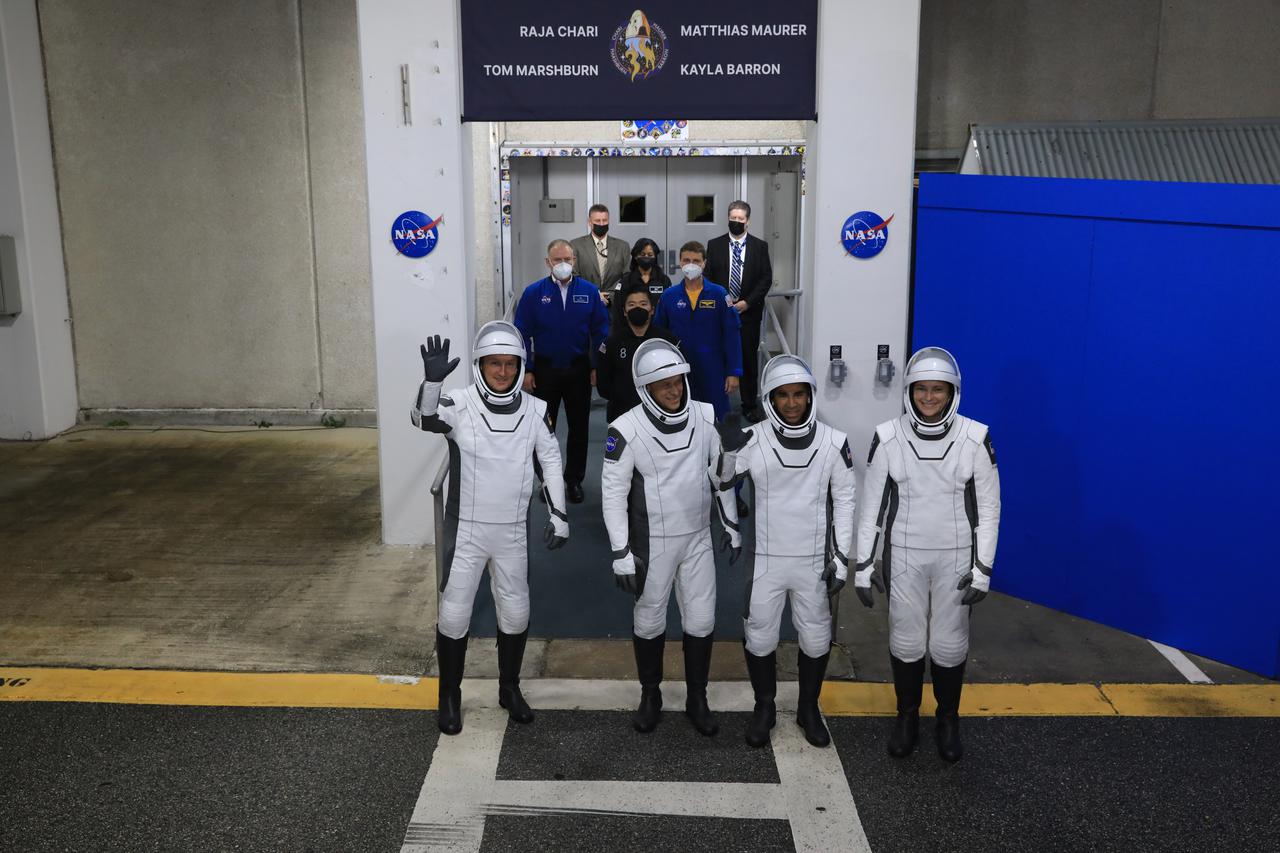

The SpaceX Crew-3 astronauts wave to family and friends after walking out through the double doors below the Neil A. Armstrong Building’s Astronaut Crew Quarters at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on launch day, Nov. 10, 2021. They will make their way to the customized Tesla Model X cars that will take them to their spacecraft at Launch Complex 39A. From left are Matthias Maurer, ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and mission specialist, and NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn; pilot; Raja Chari, commander; and Kayla Barron, mission specialist. The Falcon 9 rocket with Crew Dragon Endurance will launch the four-person crew to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Crew-3 is scheduled to launch at 9:03 p.m. EST from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy.
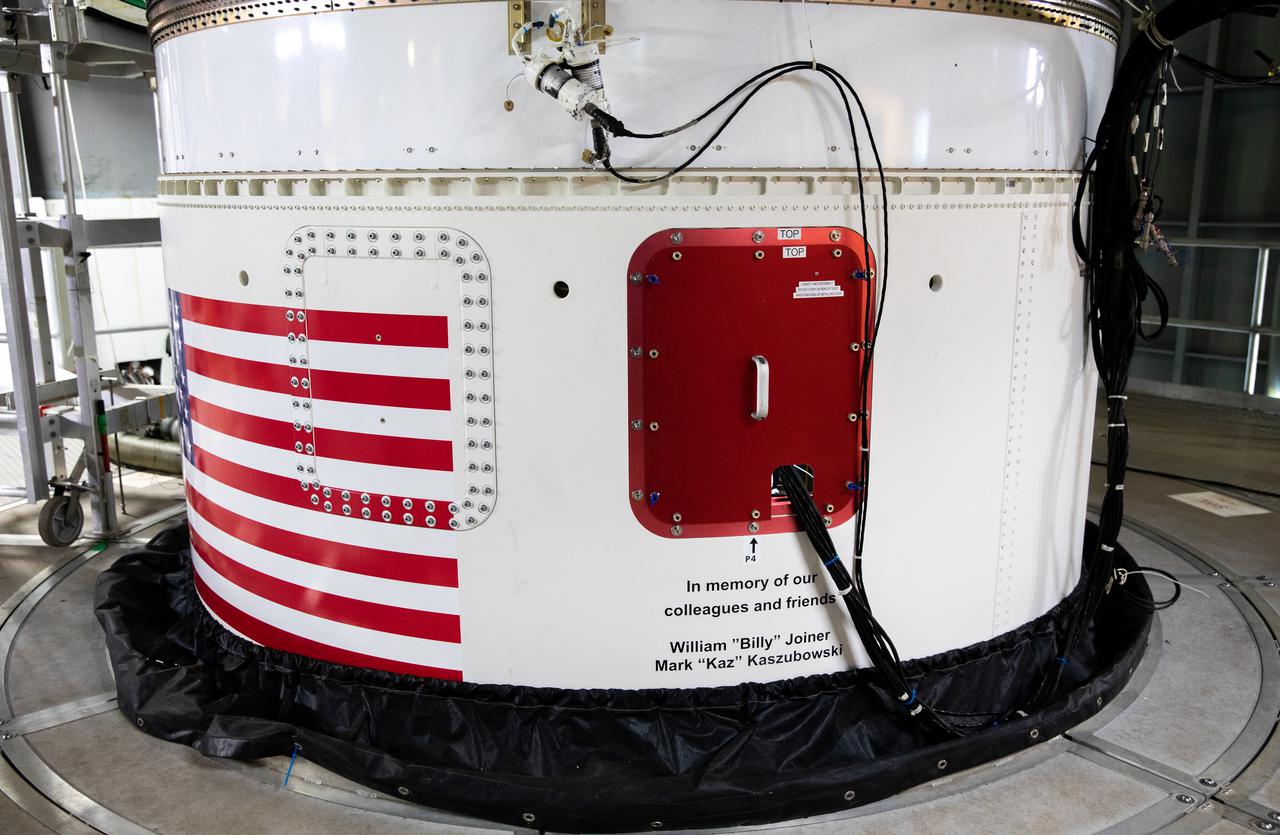
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket that will launch NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on its 12-year mission to study the Trojan asteroids is shown inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 (SLC-41) at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Oct. 8, 2021. Three dedication laminates were added to the rocket. The first is in memory of Craig M. Whittaker, a colleague and friend of NASA’s Launch Services Program (LSP) and ULA teams. The second is in memory of two colleagues: William “Billy” Joiner II – a former Lockheed Martin and ULA technician – and Mark “Kaz” Kaszubowski – an accomplished engineer and mentor. The third plaque is dedicated to NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Lucy Mission Team for its dedication shown throughout the pandemic. Lucy is targeted to lift off from SLC-41 at 5:34 a.m. EDT Saturday, Oct. 16. LSP, based at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, is managing the launch.
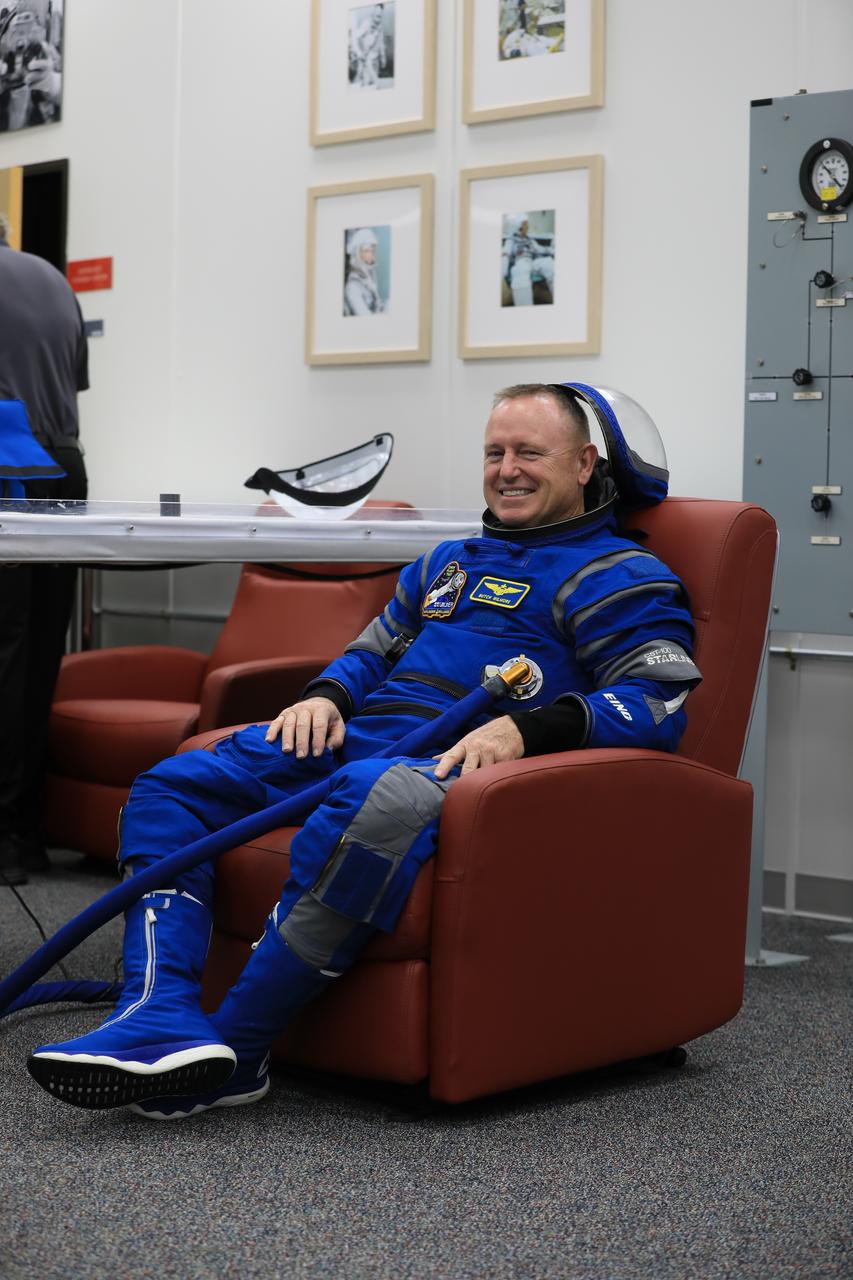

NASA astronaut Barry “Butch” Wilmore, Boeing Crew Flight Test (CFT) commander, checks his spacesuit during a crew validation test inside the Astronaut Crew Quarters at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 18, 2022. Wilmore, along with NASA astronauts Suni Williams, CFT pilot, and Mike Fincke, CFT backup spacecraft test pilot, with assistance from the Boeing team, successfully completed the validation test during which they suited up and tested out the pressurized crew module to ensure seat fit, suit functionality, cabin temperature, audio system, and day of launch operations. Boeing’s CFT is scheduled to launch in April 2023.
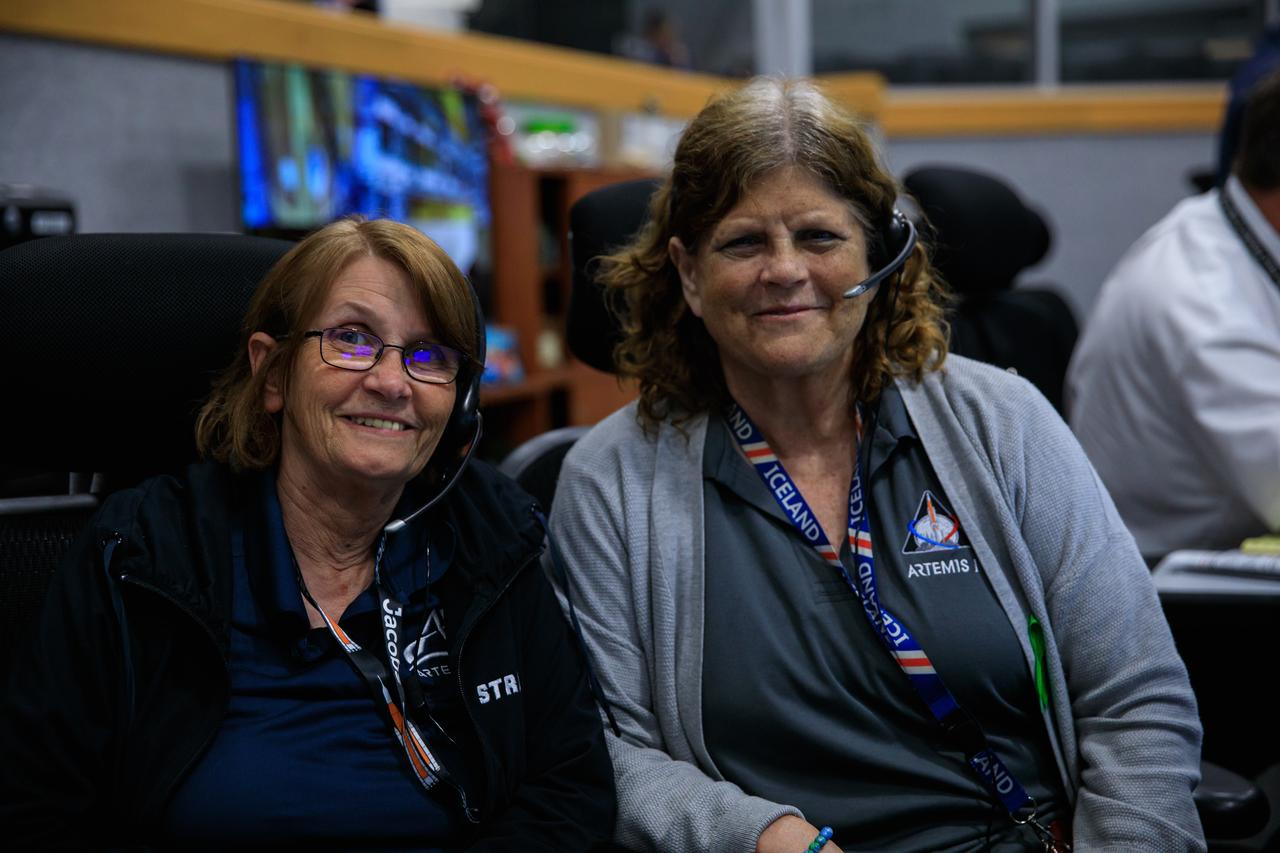

NASA Test Conductors Teresa Annulis, at left, and Roberta Wyrick, monitor launch countdown activities inside Firing Room 1 of the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 16, 2022. Liftoff of the agency’s Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft from Launch Complex 39B was at 1:47 a.m. EST. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate our commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
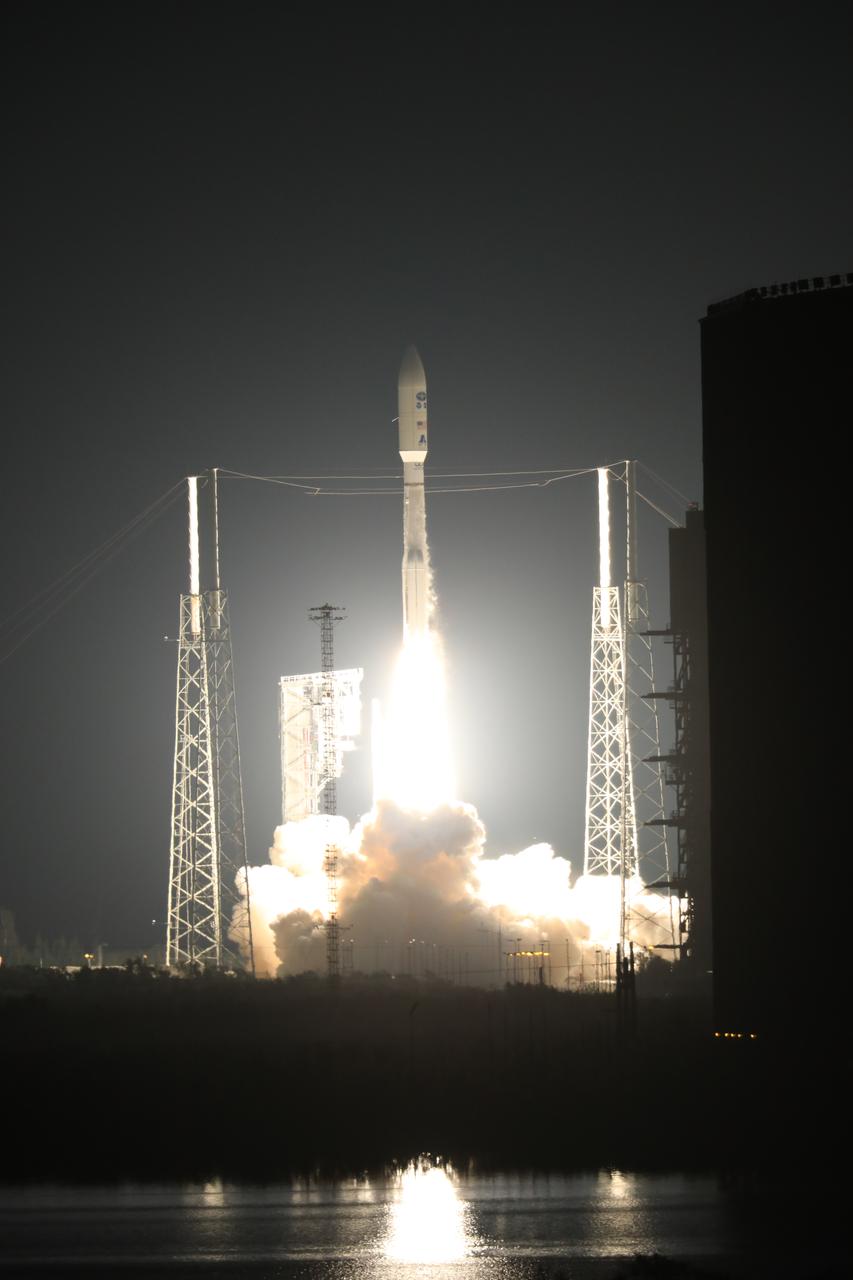

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 41, an Atlas V rocket with NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-R, lifts off at 6:42 p.m. EST. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation GOES satellites for NOAA, the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration. It will launch to a geostationary orbit over the western hemisphere to provide images of storms and help meteorologists predict severe weather conditionals and develop long-range forecasts.
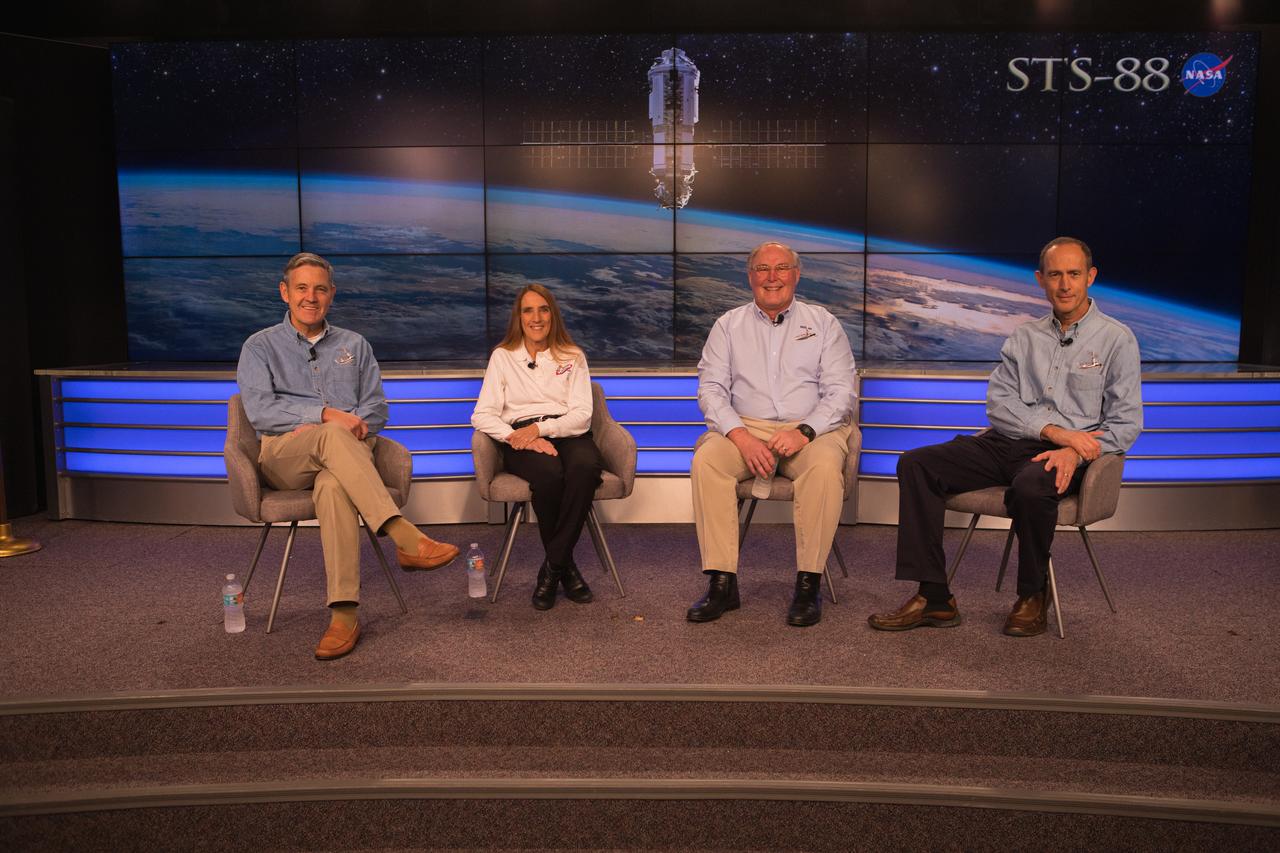

From left, Kennedy Space Center Director and STS-88 commander Bob Cabana, along with STS-88 mission specialists Nancy Currie-Gregg, Jerry Ross and Jim Newman, are recognized Dec. 10, 2018, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a 20th anniversary celebration of the first International Space Station assembly mission. The STS-88 mission paved the way for humans to live and work on the space station.
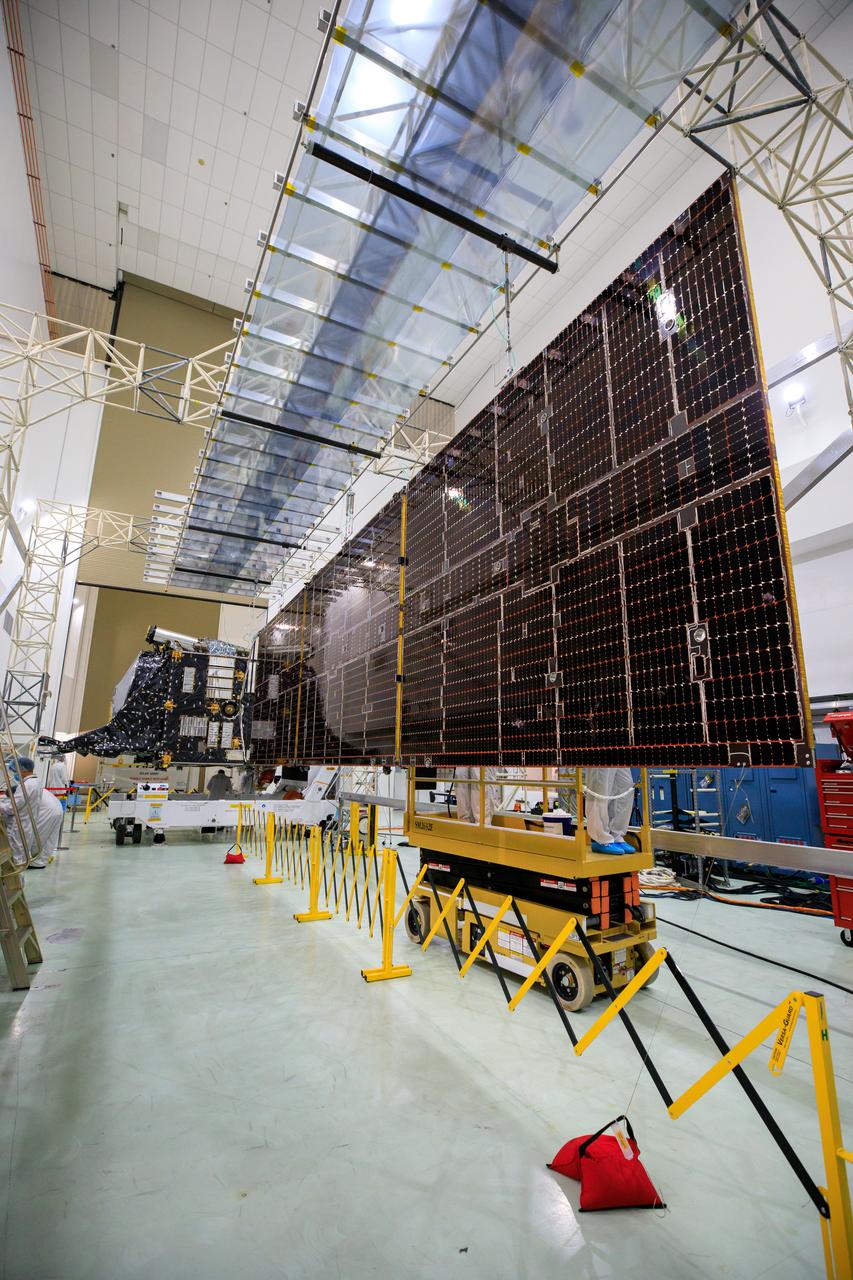

Technicians are preparing to integrate one of two solar arrays to NASA’s Psyche spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 24, 2023. The solar arrays were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San Jose, California. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
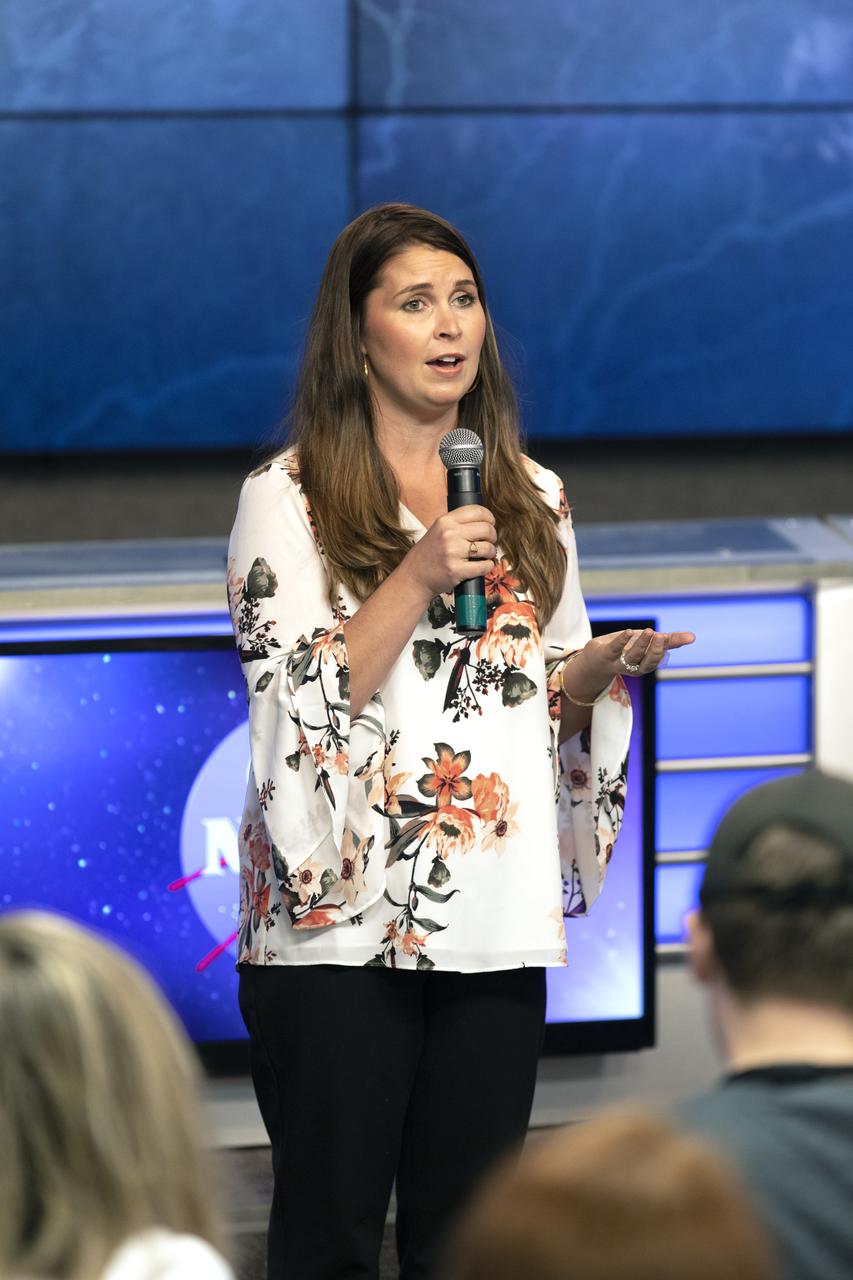

Dr. Nicole Wagner president and CEO for LambdaVision Inc. in Farmington, Connecticut, speaks to members of the media in the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium. The briefing focused on research planned for launch to the International Space Station. The scientific materials and supplies will be aboard a Dragon spacecraft scheduled for liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 40. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will launch the company's 16th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
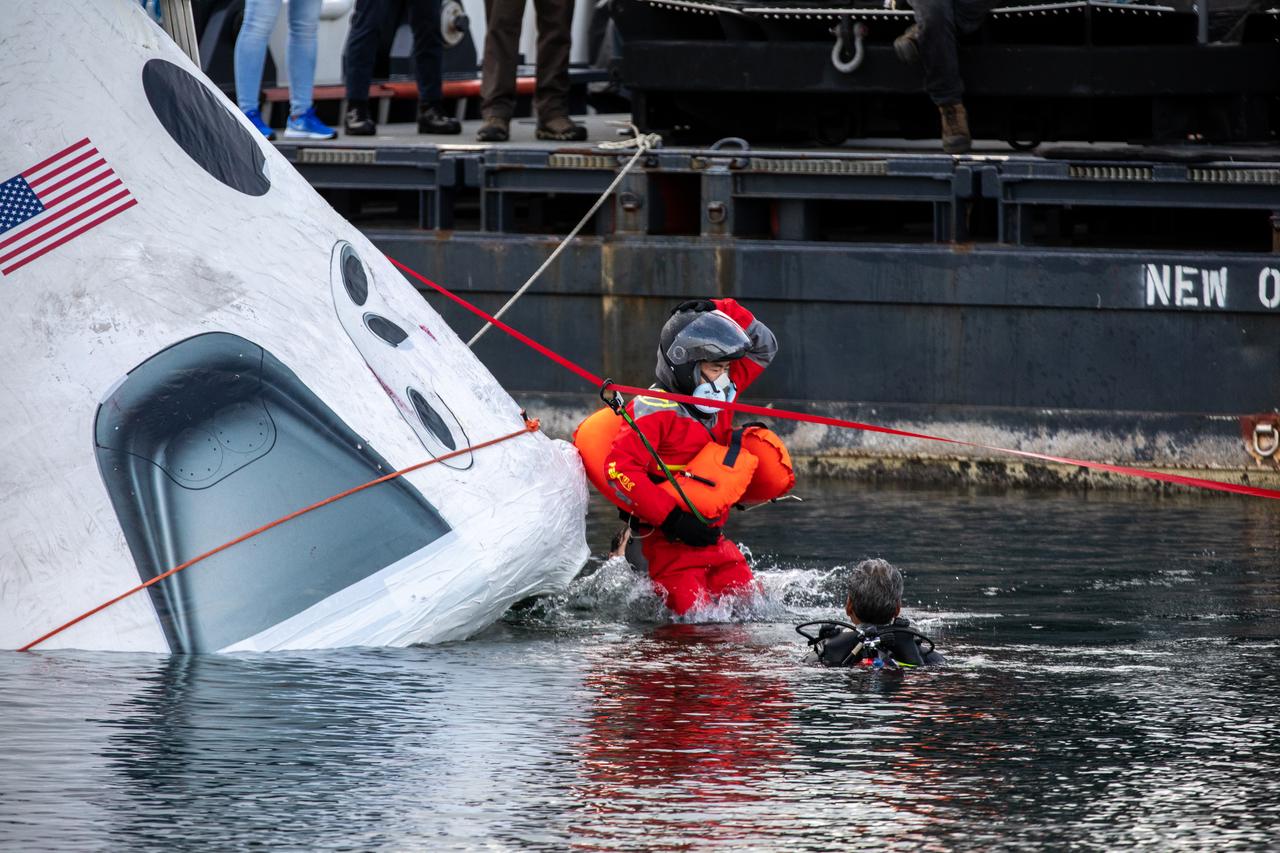

NASA astronauts Shane Kimbrough and Megan McArthur, Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Akihiko Hoshide, and European Space Agency astronaut Thomas Pesquet participate in an egress training exercise in Port Canaveral, Florida, on Oct. 1, 2020, in preparation for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-2 mission as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. The exercise involved simulating an emergency situation after splashdown of the Crew Dragon spacecraft. Using a mock-up of the Crew Dragon, the crew practiced exiting the capsule and jumping into the water. Crew-2 is targeted to launch from Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A in spring 2021.
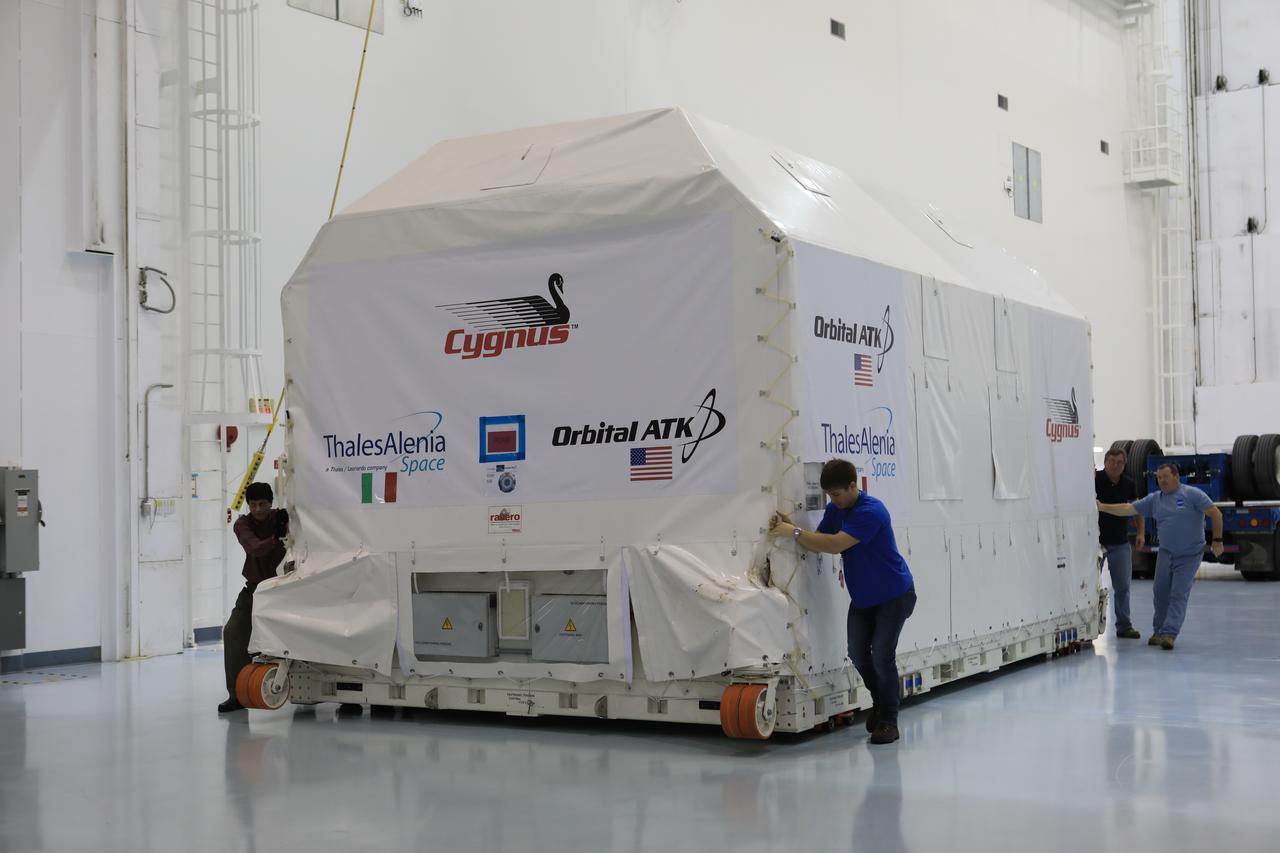

Inside an environmentally controlled shipping container the Orbital ATK OA-7 Cygnus spacecraft's pressurized cargo module (PCM) moves from an airlock to the high bay of the Space Station Processing Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Scheduled to launch on March 19, 2017, the Orbital ATK OA-7 mission will lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station will deliver thousands of pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
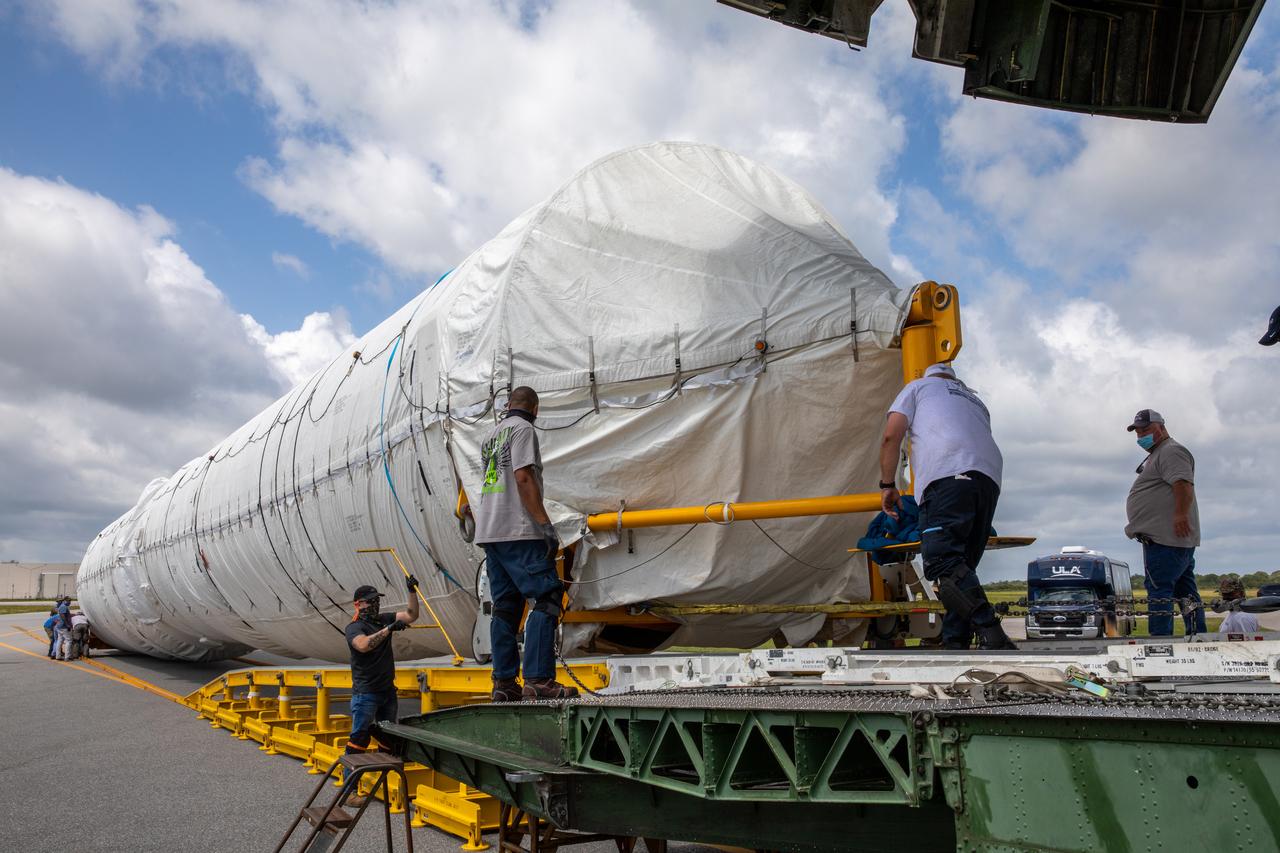

Workers secure the United Launch Alliance booster for NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover as it is offloaded from the Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 19, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 at CCAFS. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
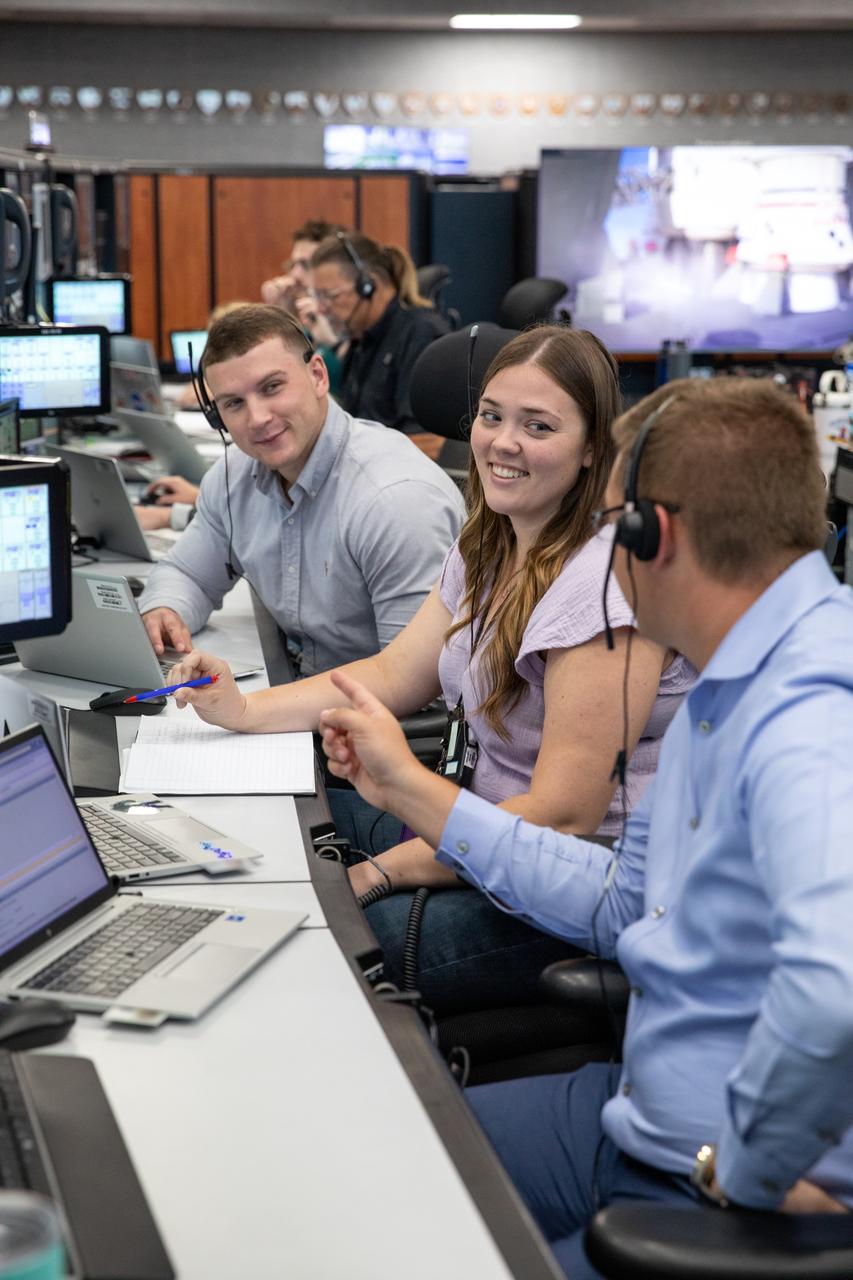

Members of the Artemis II launch team, including personnel with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs, monitor activities during the Artemis II terminal countdown simulation inside Firing Room 1 in the Launch Control Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 11, 2023. This is part of a series of simulations to help the team prepare for the launch of Artemis II, the first mission with astronauts under Artemis that will test and check out all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems needed for future crewed missions.
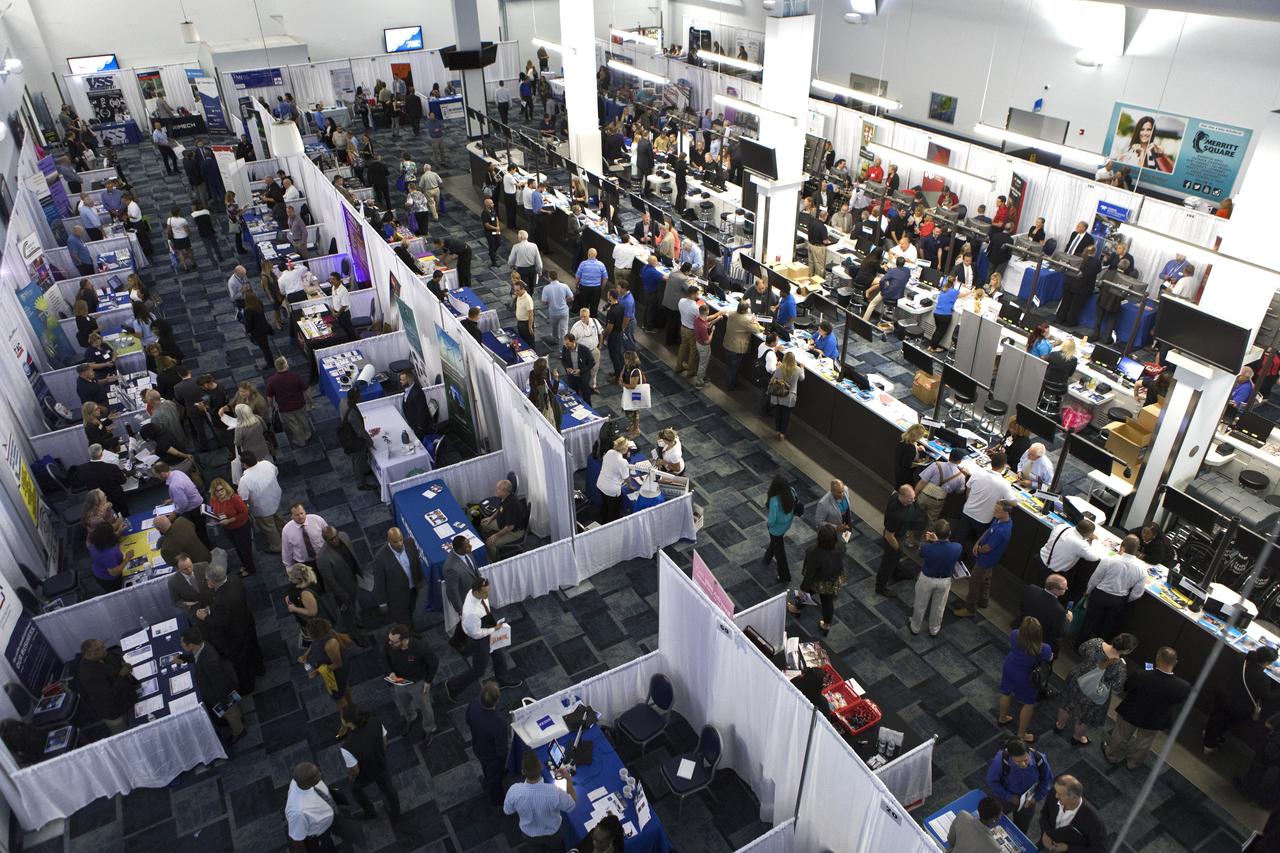

Attendees talk with representatives from a variety of business and government agencies during NASA's Business Opportunities Expo 2018, on Oct. 23, inside Cruise Terminal 6 at Port Canaveral in Florida. The 28th Business Opportunities Expo featured more than 200 businesses, large and small, and government exhibitors from throughout the Space Coast and the nation. The Business Opportunities Expo is facilitated by Kennedy's Small Business Programs Office and Prime Contractor Board, along with the U.S. Air Force 45th Space Wing and Canaveral Port Authority. Vendors from a variety of product and service areas, such as computer technology, engineering services, communication equipment and services, and construction and safety products, to name a few, were at the expo. Representatives from the 45th Space Wing, Kennedy prime contractors, NASA and many more agencies and organizations were on hand to provide information and answer questions.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
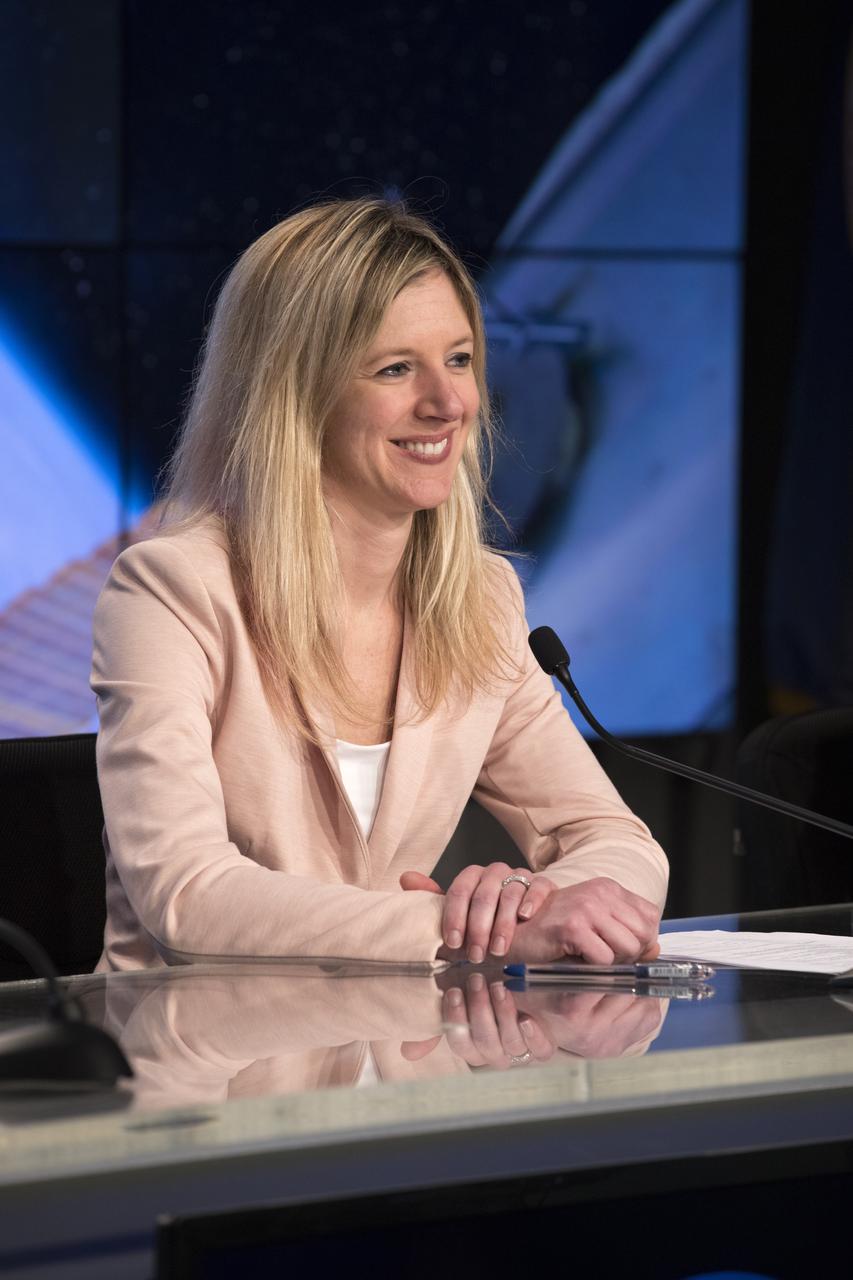

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, agency and industry leaders speak to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for the SpaceX CRS-10 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. Jessica Jensen, director of Dragon mission management for SpaceX, answers questions.
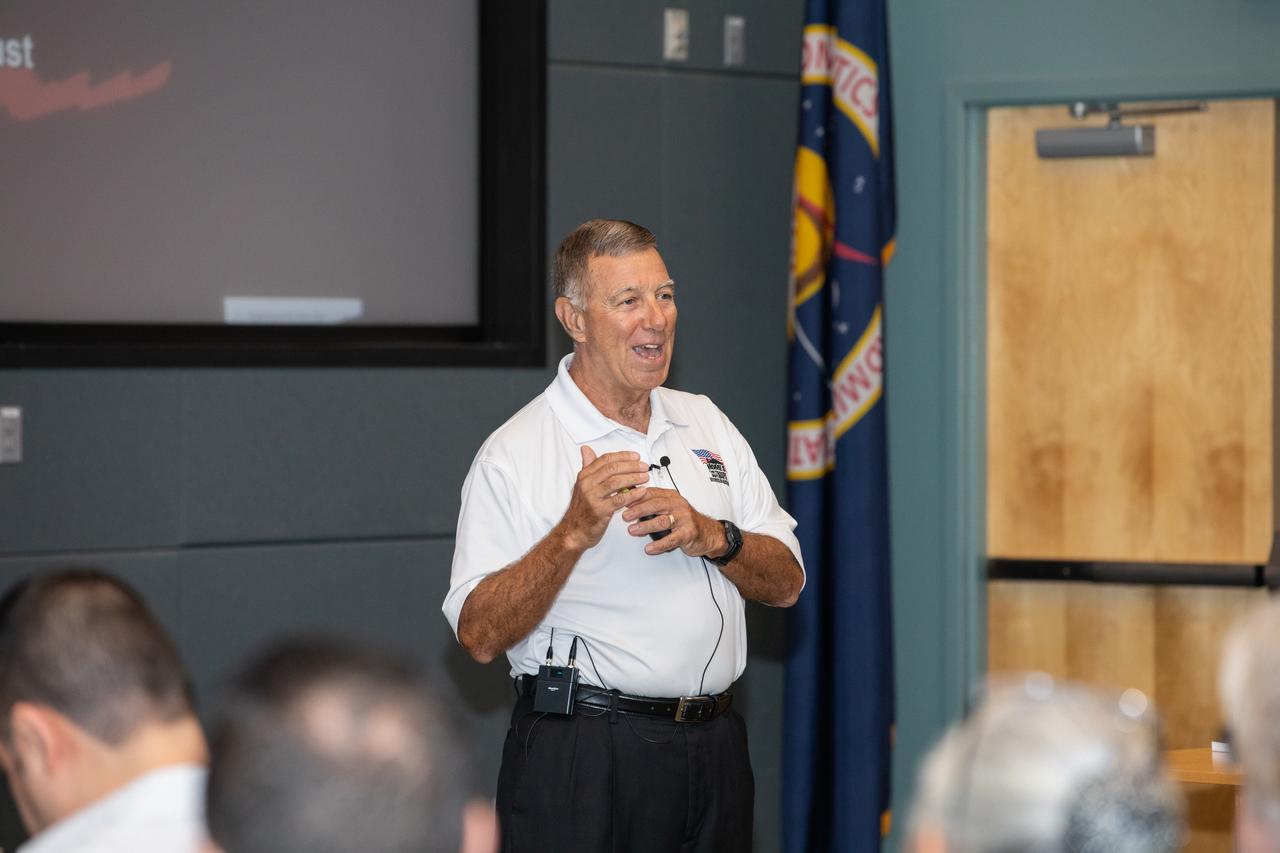

Danny McKnight, a U.S. Army retired colonel, speaks to Kennedy Space Center employees inside the Florida spaceport’s Operations Support Building II on March 3, 2020, during the center’s annual Safety and Health Days. Taking place March 2 through March 6, Safety and Health Days provides Kennedy employees with a variety of presentations to attend – all of which focus on how to maintain a safe and healthy workforce. McKnight’s presentation included information on the commitment and leadership required to be successful when operating in difficult conditions.

A close-up view of the single-engine Centaur upper stage for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover as it is being lifted up into the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on June 10, 2020. The Centaur will be lifted up and attached to the rocket’s first stage. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch atop the Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 on July 20, 2020. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover’s seven instruments will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
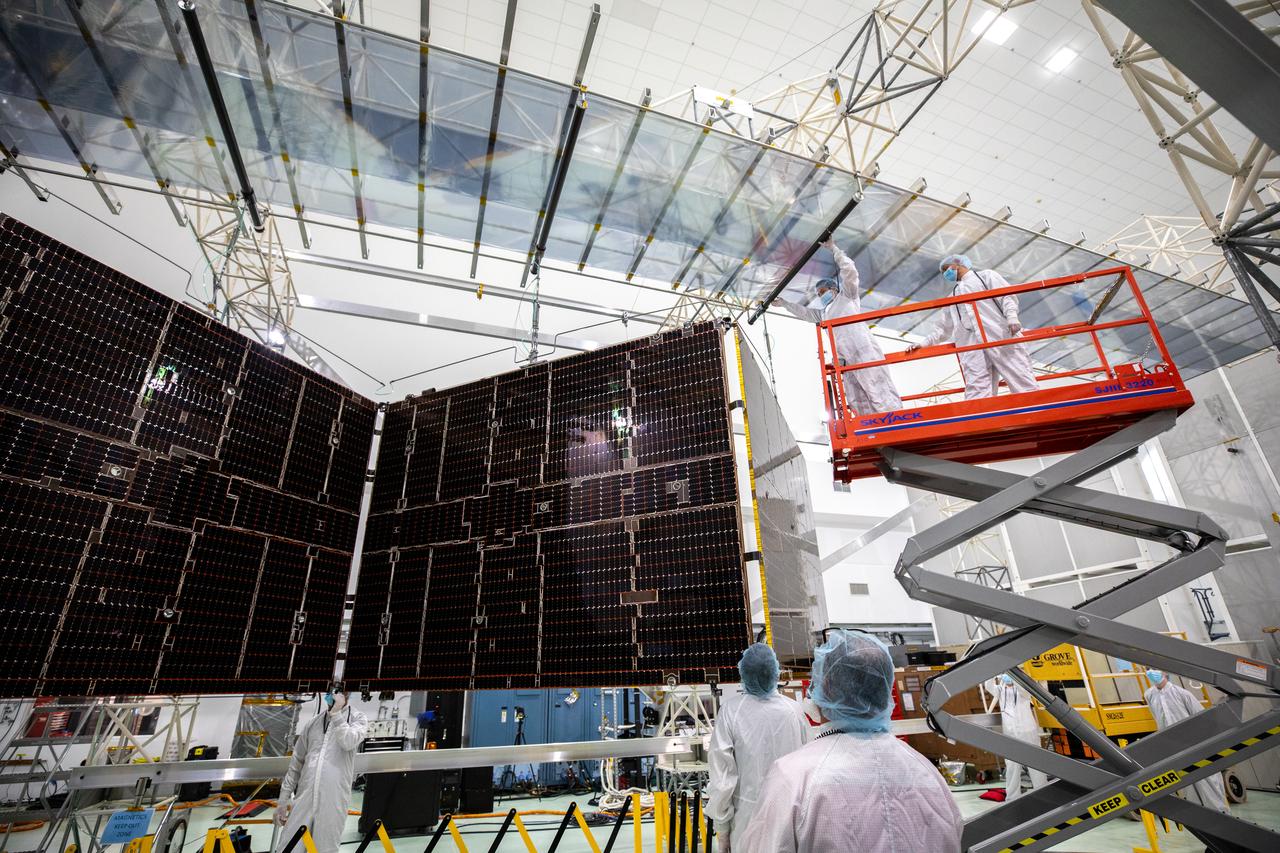

Technicians begin to retract one of the two solar arrays attached to NASA’s Psyche spacecraft inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 25, 2023. The solar arrays, which were shipped from Maxar Technologies, in San Jose, California, are being stowed for launch. They are part of the solar electric propulsion system, provided by Maxar, that will power the spacecraft on its journey to explore a metal-rich asteroid. Psyche will launch atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Launch is targeted for Oct. 5, 2023. Riding with Psyche is a pioneering technology demonstration, NASA’s Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment.
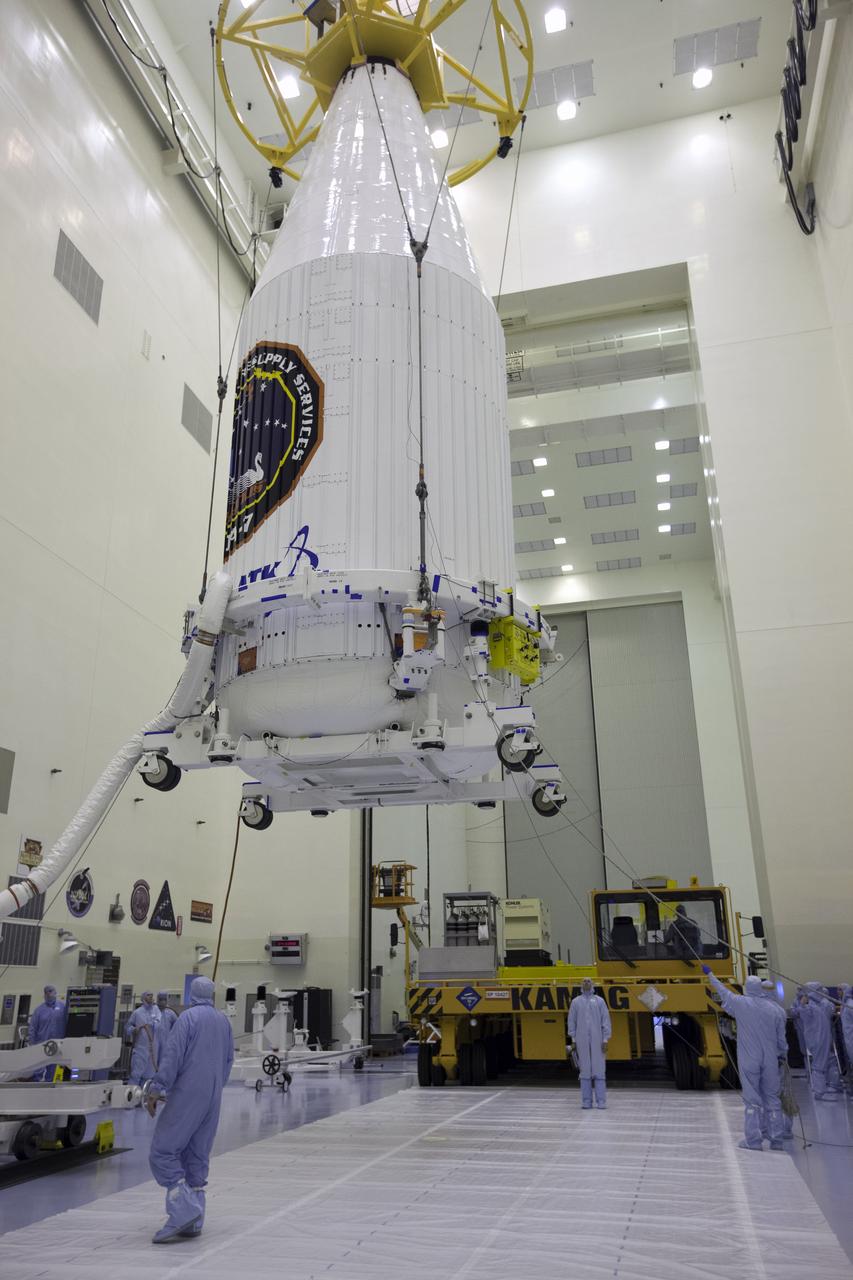

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a crane is used to lift the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized cargo module, enclosed in its payload fairing, for transfer to a KAMAG transporter. The Orbital ATK CRS-7 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Cygnus will deliver 7,600 pounds of supplies, equipment and scientific research materials to the space station.
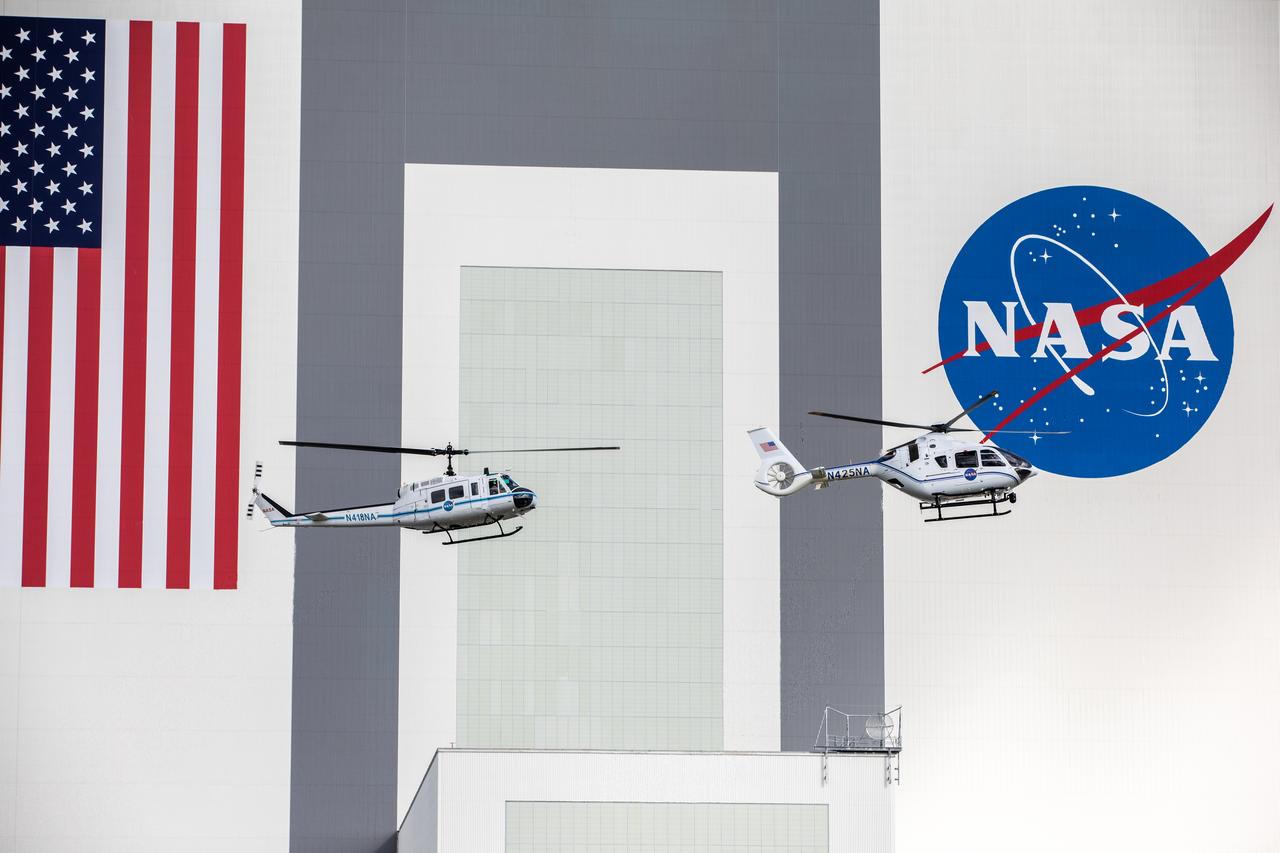

On Oct. 27, 2020, in front of the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, the Bell Huey 2 (left) and Airbus H135 helicopters used for security operations at the Florida spaceport perform one flight together before the Hueys are retired from their service. The Airbus H135s are replacing the three Bell Huey 2 aircraft maintained by Kennedy’s Flight Operations team. Kennedy received two of the H135 aircraft on Sept. 30, and the third is expected to arrive in spring 2021. These new helicopters provide a number of technological and safety advantages over the Hueys, such as more lifting power, greater stability in the air, and expanded medical capabilities.

The shipping container holding NASA's Lucy spacecraft is unloaded from a United States Air Force C-17 cargo plane, stationed out of Charleston Air Force Base in South Carolina, on the runway of the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 30, 2021. From there, the Lucy spacecraft will move to the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility in nearby Titusville, Florida, before its scheduled launch on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on October 16, 2021. The Lucy mission will be the first space mission to explore a diverse population of small bodies known as the Jupiter Trojan asteroids. The launch is being managed by NASA's Launch Services Program based at Kennedy, America's multi-user spaceport.
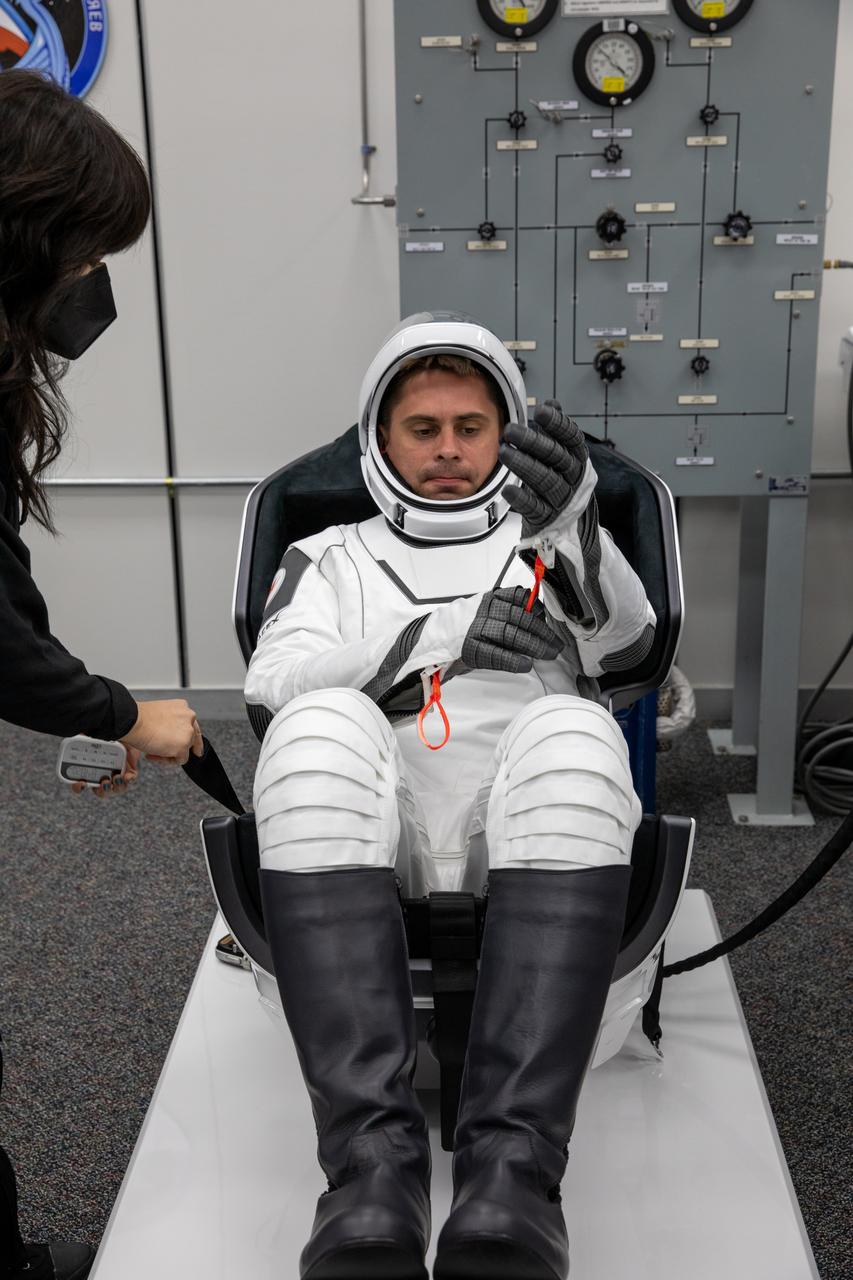

Andrey Fedyaev, Roscosmos cosmonaut and mission specialist for Crew-6, checks his SpaceX spacesuit inside the crew suit-up room in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a countdown dress rehearsal on Feb. 23, 2023, to prepare for the upcoming Crew-6 launch. Fedyaev, along with NASA astronaut Stephen Bowen, spacecraft commander; NASA astronaut Warren “Woody” Hoburg, pilot; and Sultan Alneyadi, UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and mission specialist will launch to the International Space Station aboard the Crew Dragon Endeavour on a SpaceX Falcon 9. Launch is targeted for 1:45 a.m. EST on Feb. 27 from Launch Complex 39A. Crew-6 is the sixth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the station, and the seventh flight of Dragon with people as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
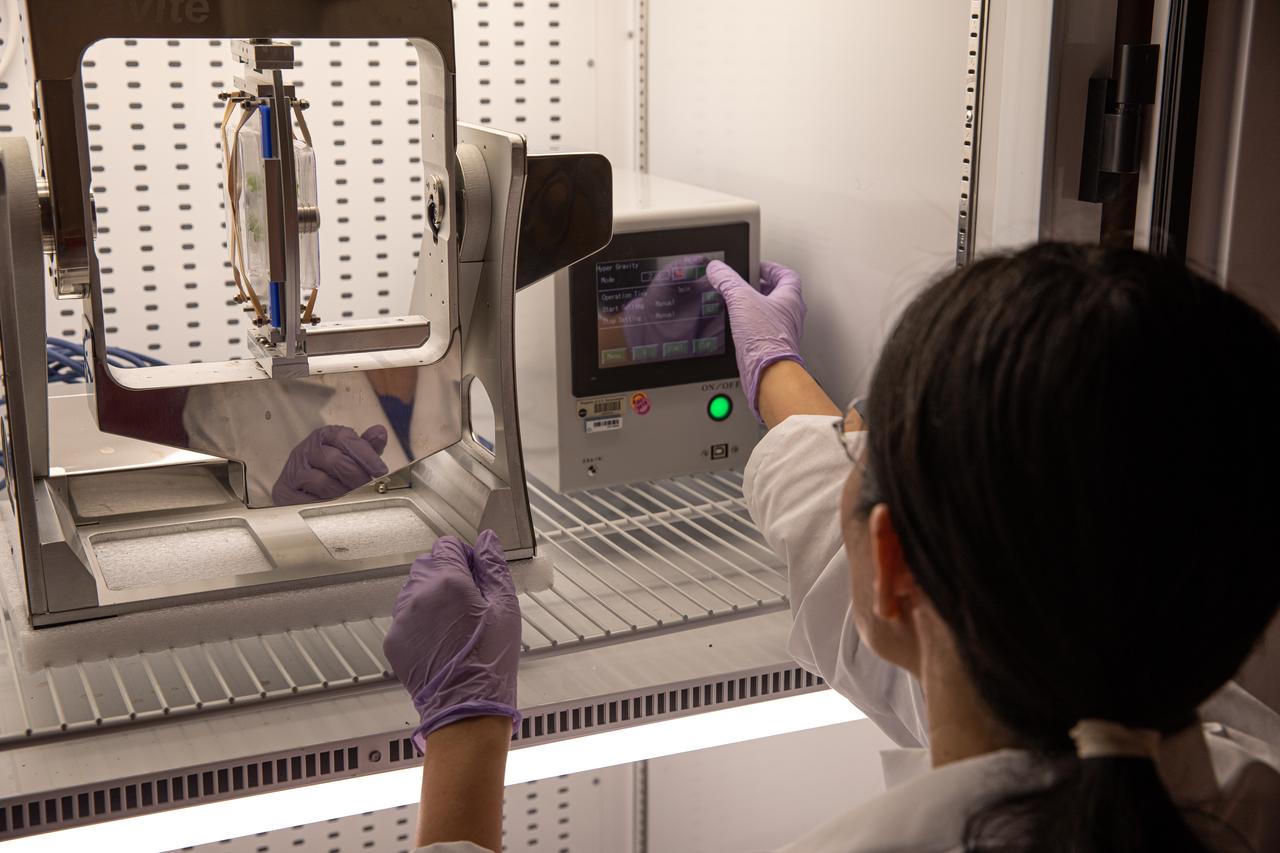

Ye Zhang, a project scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida runs a test on a Gravite 3d clinostat device in the Microgravity Simulation Support Facility (MSSF) inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout building on Feb. 11, 2020. The facility was developed to provide ground simulation capability to the U.S. research community in order to supplement the limited opportunities to access the International Space Station and other platforms for microgravity research. The MSSF is designed to support biological research on microorganisms, cells, tissues, small plants and small animals. The simulator provides NASA with an alternative platform for microgravity research and creates the opportunity to conduct experiments on the space station in parallel with conditions of simulated microgravity on the ground.
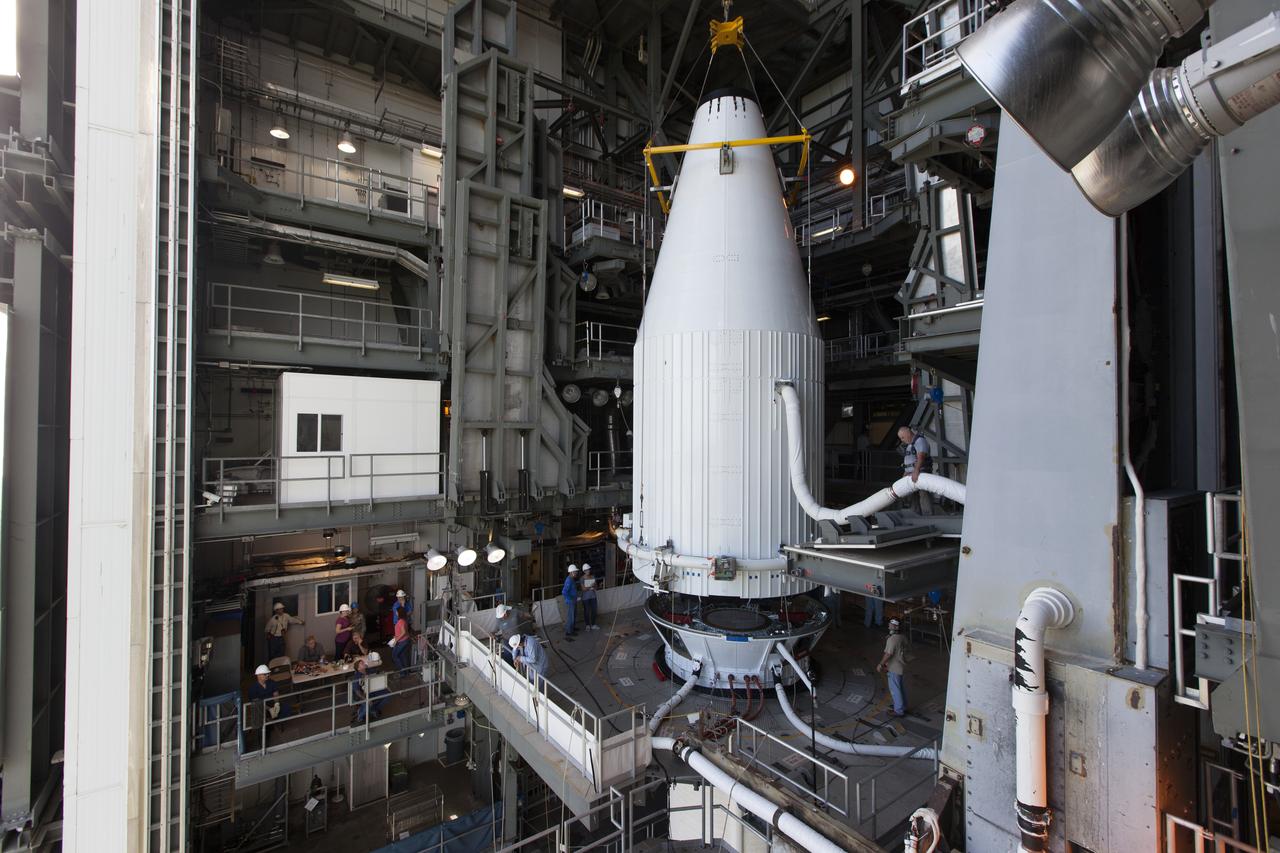

Encapsulated in its payload fairing, Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-M) is mated to the United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur upper stage in the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. TDRS-M will be the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop the ULA Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Aug. 18, 2017.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program prepare to transfer one of the aft assemblies of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission with an overhead crane inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Nov. 13, 2024. The booster segments are being transferred to the NASA Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building via a transporter for stacking operations in preparation for launch of the Artemis II mission.

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, Mike McAleenan, launch weather officer for the U.S. Air Force 45th Weather Squadron, speaks to members of the media during a prelaunch news conference for the SpaceX CRS-11 commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. A Dragon spacecraft is scheduled to be launched from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A on June 1 atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on the company's 11th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the space station.
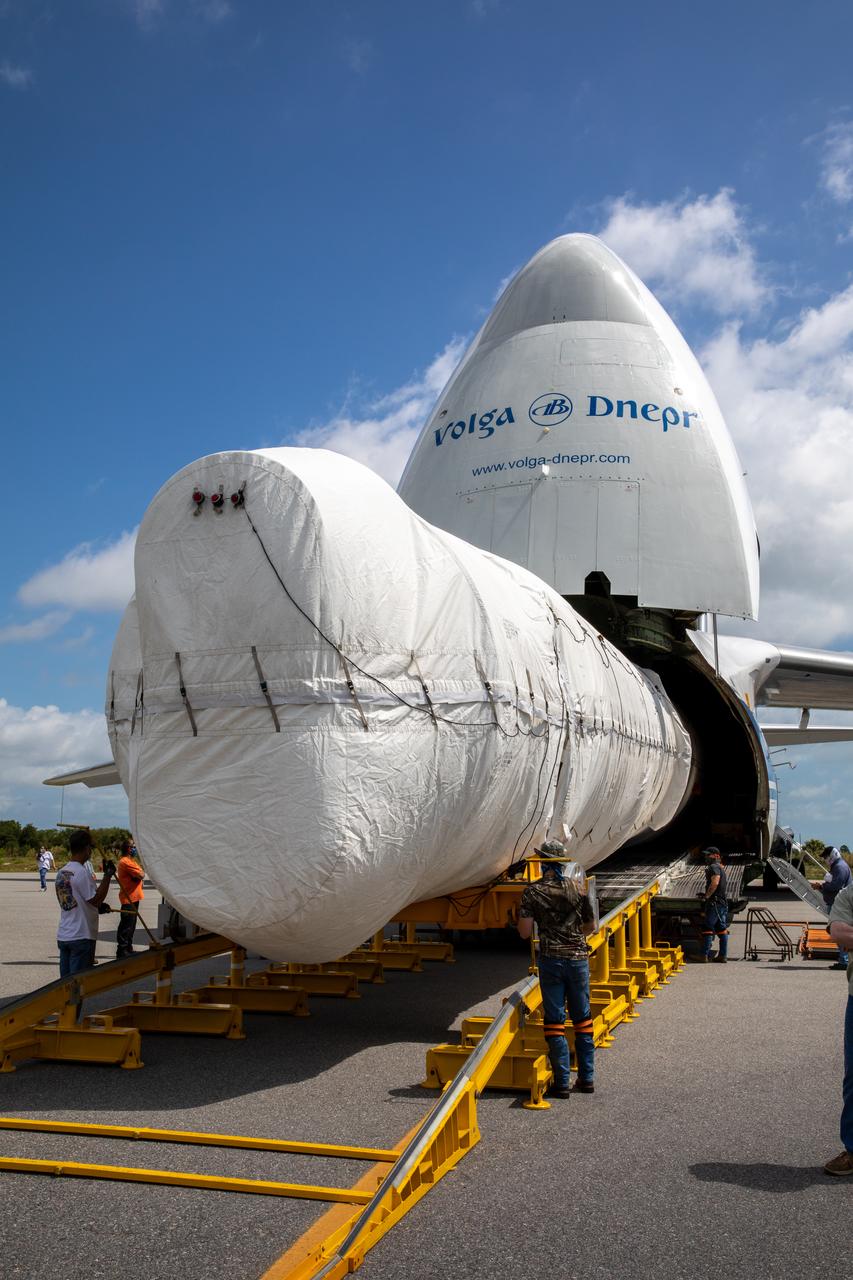

The United Launch Alliance booster for NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover is offloaded from the Antonov 124 cargo aircraft at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida on May 19, 2020. The Mars Perseverance rover is scheduled to launch in mid-July atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 541 rocket from Pad 41 at CCAFS. The rover is part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program, a long-term effort of robotic exploration of the Red Planet. The rover will search for habitable conditions in the ancient past and signs of past microbial life on Mars. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

Mike McAleenan, launch weather officer, U.S. Air Force 45th Space Wing, gives a weather update to members of the news media during a prelaunch news conference on Dec. 3, 2019, for SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-19) mission for NASA to the International Space Station, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the news media during the news conference. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon cargo module are scheduled to launch on Dec. 4, 2019, from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
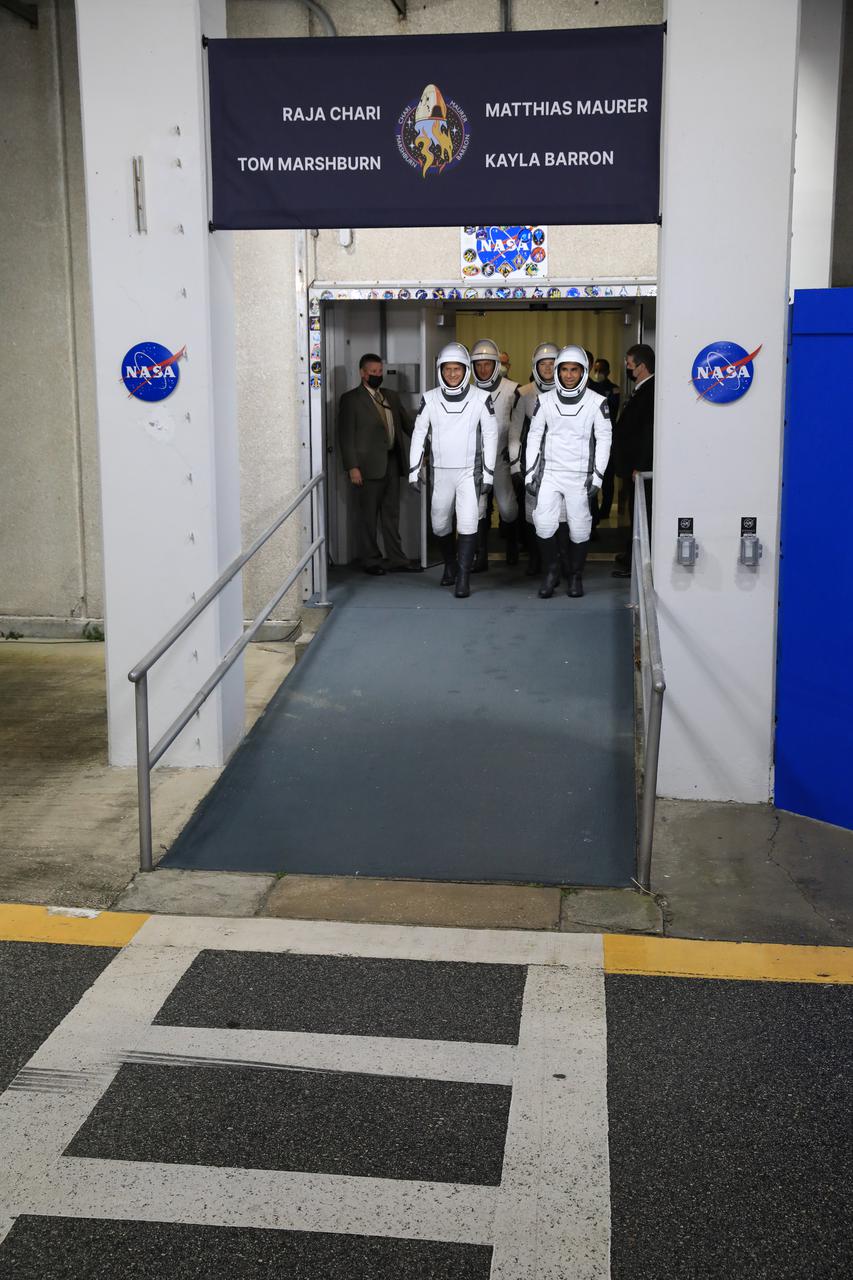

The SpaceX Crew-3 astronauts walk out through the double doors below the Neil A. Armstrong Building’s Astronaut Crew Quarters at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 10, 2021. They will make their way to the customized Tesla Model X cars that will take them to their spacecraft at Launch Complex 39A. In front, from left, are NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn, pilot, and Raja Chari, commander. Behind them, from left, are Matthias Maurer, ESA (European Space Agency astronaut) and mission specialist; and NASA astronaut Kayla Barron, mission specialist. The Falcon 9 rocket with Crew Dragon Endurance will launch the four-person crew to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Crew-3 is scheduled to launch at 9:03 p.m. EST from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy.

Just before a ribbon cutting ceremony on Aug. 16, 2019, in High Bay 2 of the Vehicle Assembly (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Center Director Bob Cabana, at right, shakes hands with Kent Rominger, Northrop Grumman’s vice president and capture lead for the OmegA launch system. In the center is Tom Engler, director of the Center Planning and Development Office at Kennedy. The VAB is getting its first commercial tenant. Northrop Grumman signed a Reimbursable Space Act Agreement with NASA for use of the facilities. The company will assemble and test its new OmegA rocket inside the massive facility’s High Bay 2. The company also will modify the space shuttle-era mobile launcher platform-3 to serve as the launch vehicle’s assembly and launch platform. Northrop Grumman is developing the OmegA rocket, an intermediate/heavy-class launch vehicle, as part of a launch services agreement with the U.S. Air Force.

NASA Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, at right, greets engineers and technicians at Launch Pad 39B at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Blackwell-Thompson will observe the first major tanking operation of liquid oxygen, or LO2, into the giant storage sphere at the northwest corner of the pad to prepare for the launch of the agency's Orion spacecraft atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. During the operation, several Praxair trucks will slowly offload LO2 to gradually chill down the sphere from normal temperature to about negative 298 degrees Fahrenheit. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to pad B to support the launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1, deep space missions and NASA’s journey to Mars.
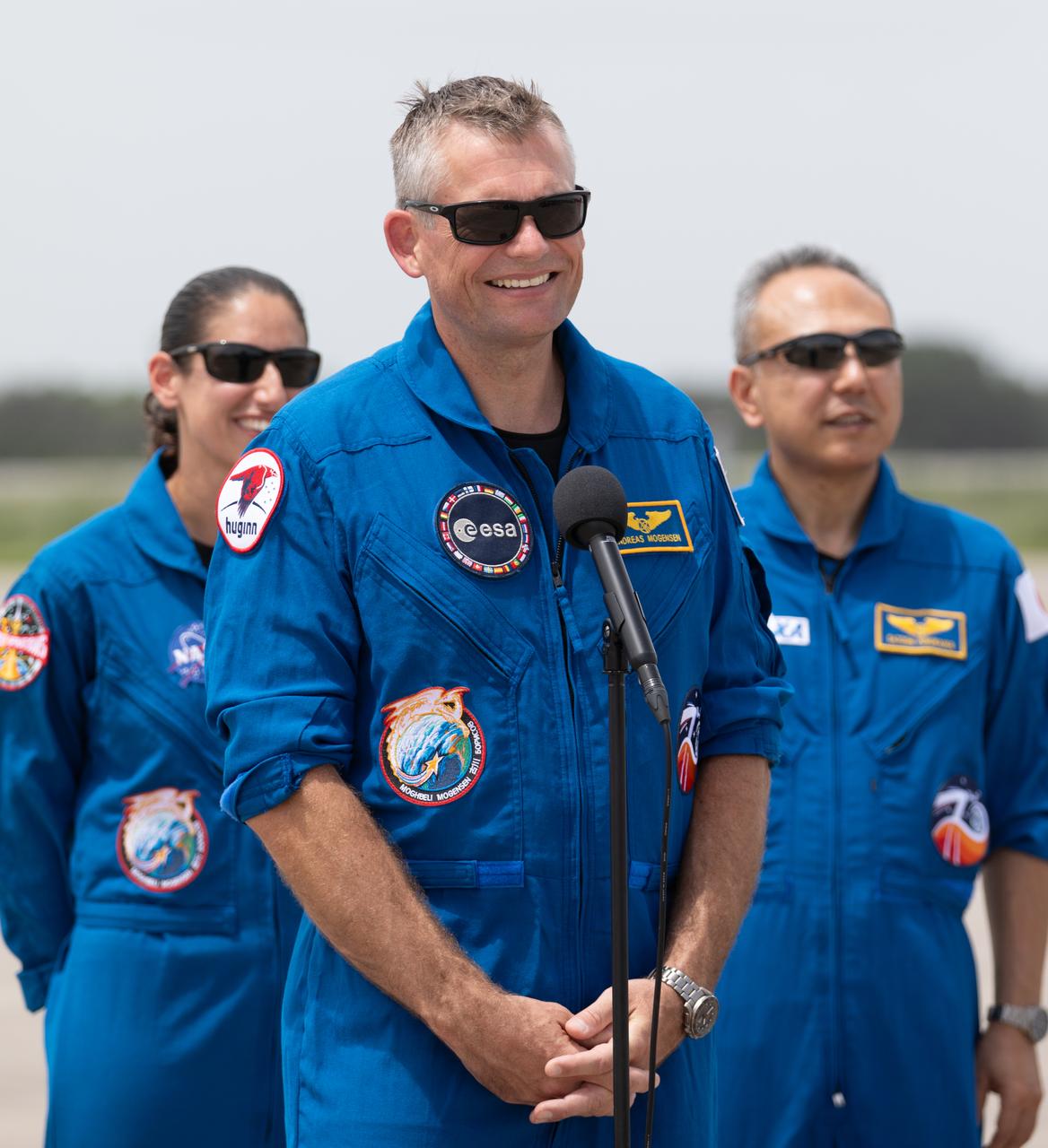

ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen addresses members of the news media during NASA’s SpaceX Crew-7 crew arrival event at the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 20, 2023. In the background, from left, is NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa. Liftoff for the Crew-7 mission is targeted for 3:49 a.m. EDT Friday, Aug. 25, 2023, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Director Bob Cabana, at the podium, speaks to members of the news media at the NASA News Center on May 23, 2019. At left is NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine. News media were at the center for an Apollo 11 Media Day. They toured several facilities, including the Vehicle Assembly and Launch Complex 39B for a look back at the Apollo missions and a look ahead to NASA’s new Moon 2024 initiative, the Artemis 1 mission and the Gateway lunar outpost.

Kennedy Space Center Janet Petro recognizes the Red Crew/High Crew for their support of the Artemis I test flight.
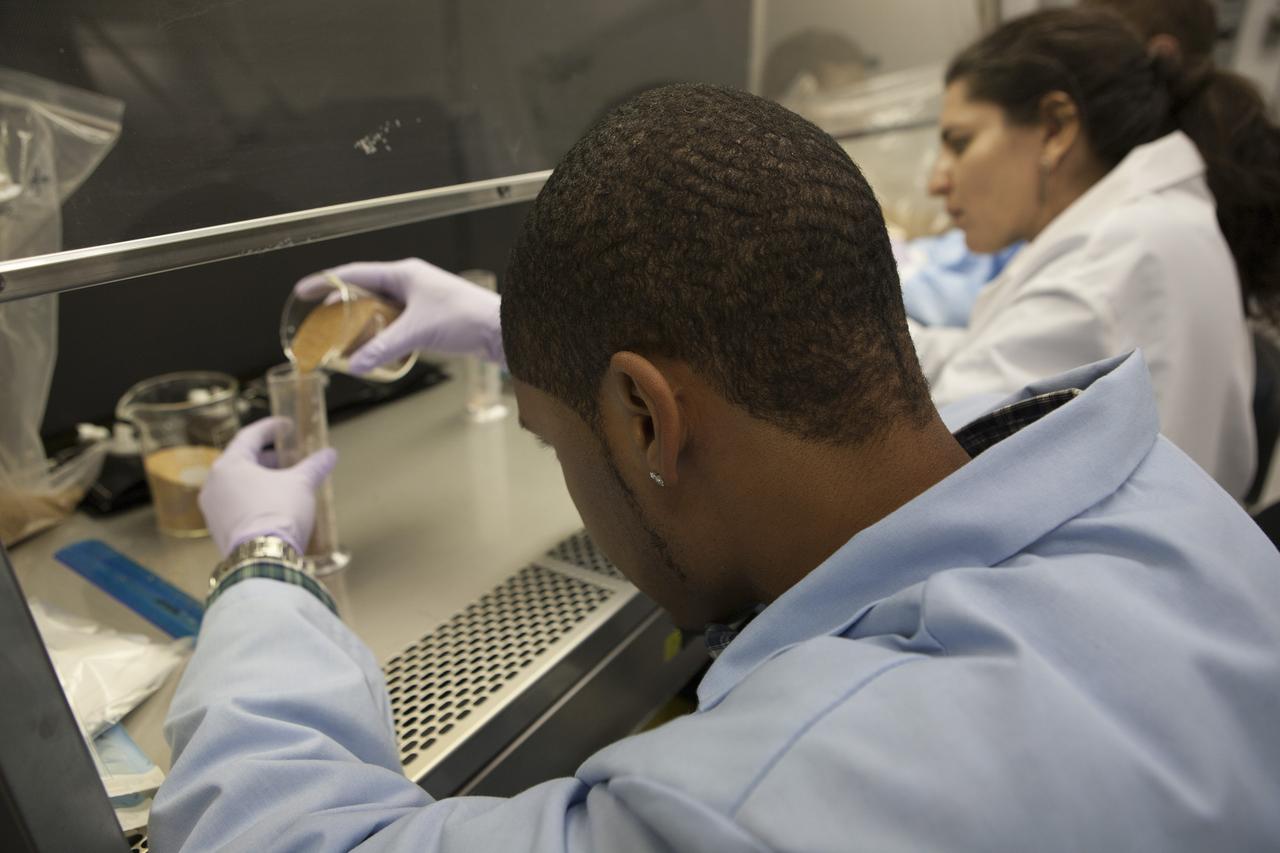

Inside a laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, research scientists prepare the plant pillows for the Veg-03 experiment that will be delivered to the International Space Station aboard the eighth SpaceX Dragon commercial resupply mission. Matt Romeyn, a NASA pathways intern, measures out the calcined clay, or space dirt, for one of the plant pillows. To his right is Dr. Gioia Massa, NASA payload scientist for Veggie. The Veg-03 plant pillows will contain ‘Tokyo Bekana’ cabbage seeds and lettuce seeds for NASA’s third Veggie plant growth system experiment. The experiment will continue NASA’s deep space plant growth research to benefit the Earth and the agency’s journey to Mars.
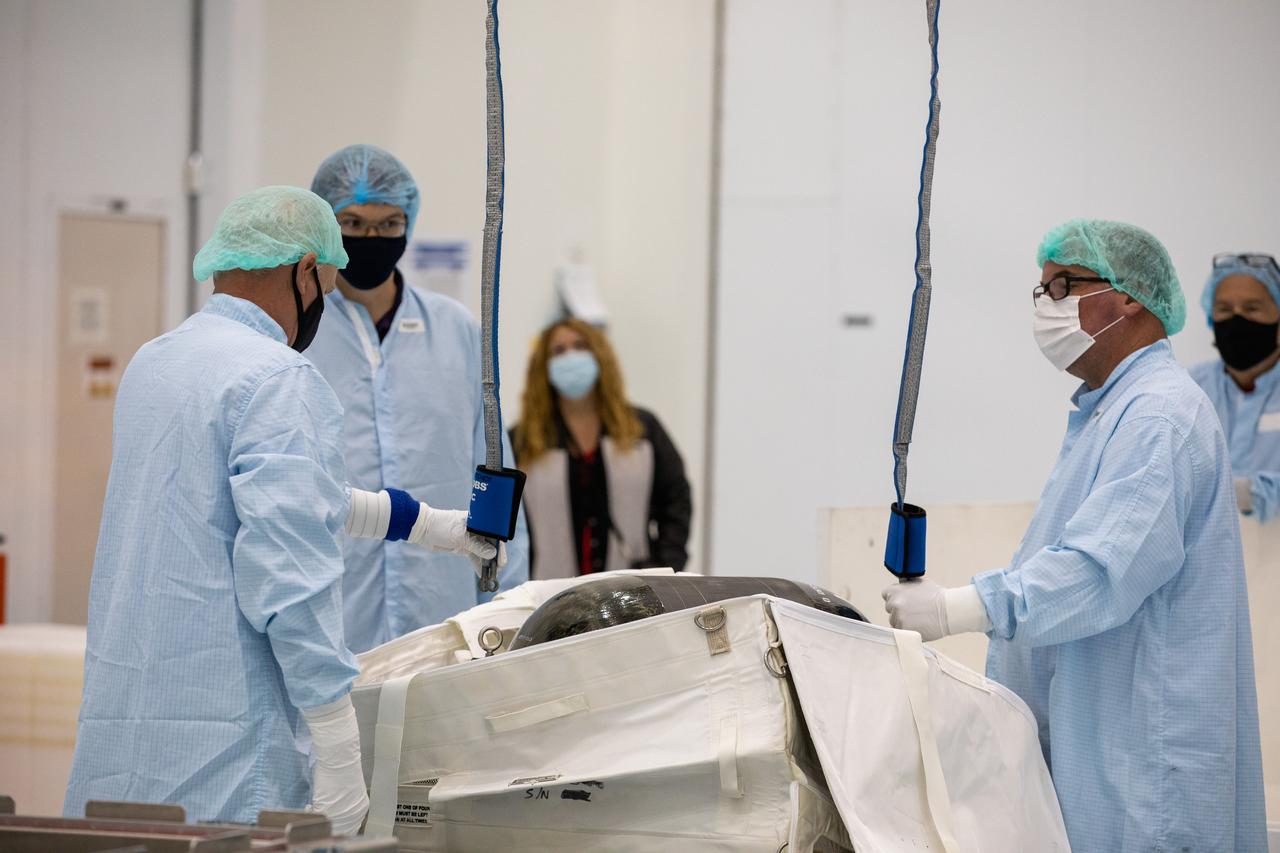

Technicians prepare to unpack and inspect a Nitrogen/Oxygen Recharge System (NORS) tank inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 2020. The NORS tanks and their support fixtures are designed to connect to the International Space Station’s existing air supply network to refill the previous generation of tanks installed during construction of the space station. These reusable tanks measure 3 feet long and 21 inches in diameter, and weigh about 200 pounds when filled. Once onboard, the tanks will be used to fill the oxygen and nitrogen tanks that supply the needed gases to the space station’s airlock for spacewalks. They could also be used to replenish the atmosphere inside the station. The NORS tanks will launch to the station later in the year on a commercial resupply mission.
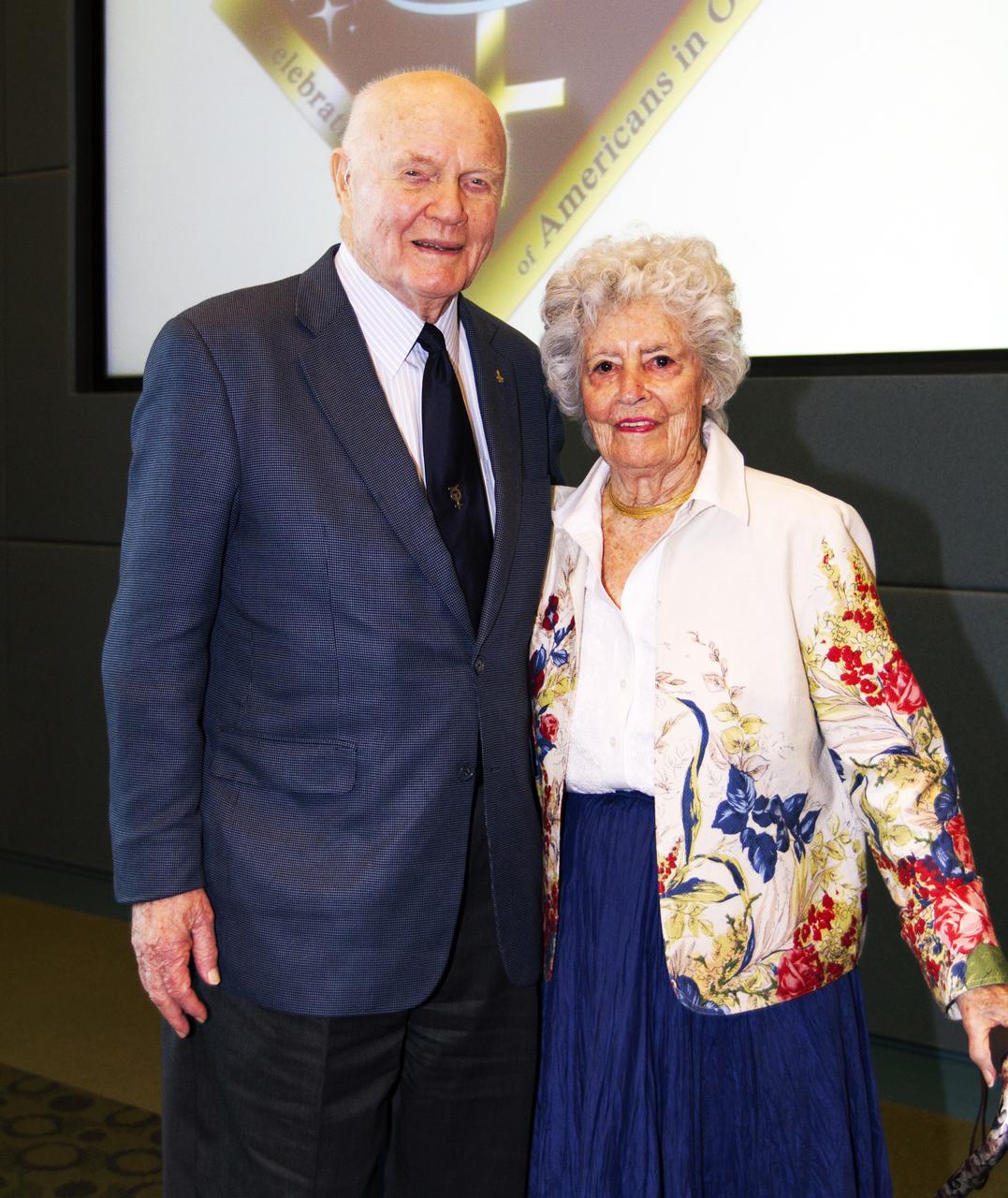

Mercury astronaut John Glenn and his wife, Annie, pose during a luncheon Feb. 17, 2012, celebrating 50 years of Americans in orbit, an era which began with Glenn's Mercury mission MA-6, on Feb. 20, 1962. Glenn's launch aboard an Atlas rocket took with it the hopes of an entire nation and ushered in a new era of space travel that eventually led to Americans walking on the moon by the end of the 1960s. Glenn soon was followed into orbit by Scott Carpenter, Walter Schirra and Gordon Cooper. Their fellow Mercury astronauts Alan Shepard and Virgil "Gus" Grissom flew earlier suborbital flights. Deke Slayton, a member of NASA's original Mercury 7 astronauts, was grounded by a medical condition until the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975.
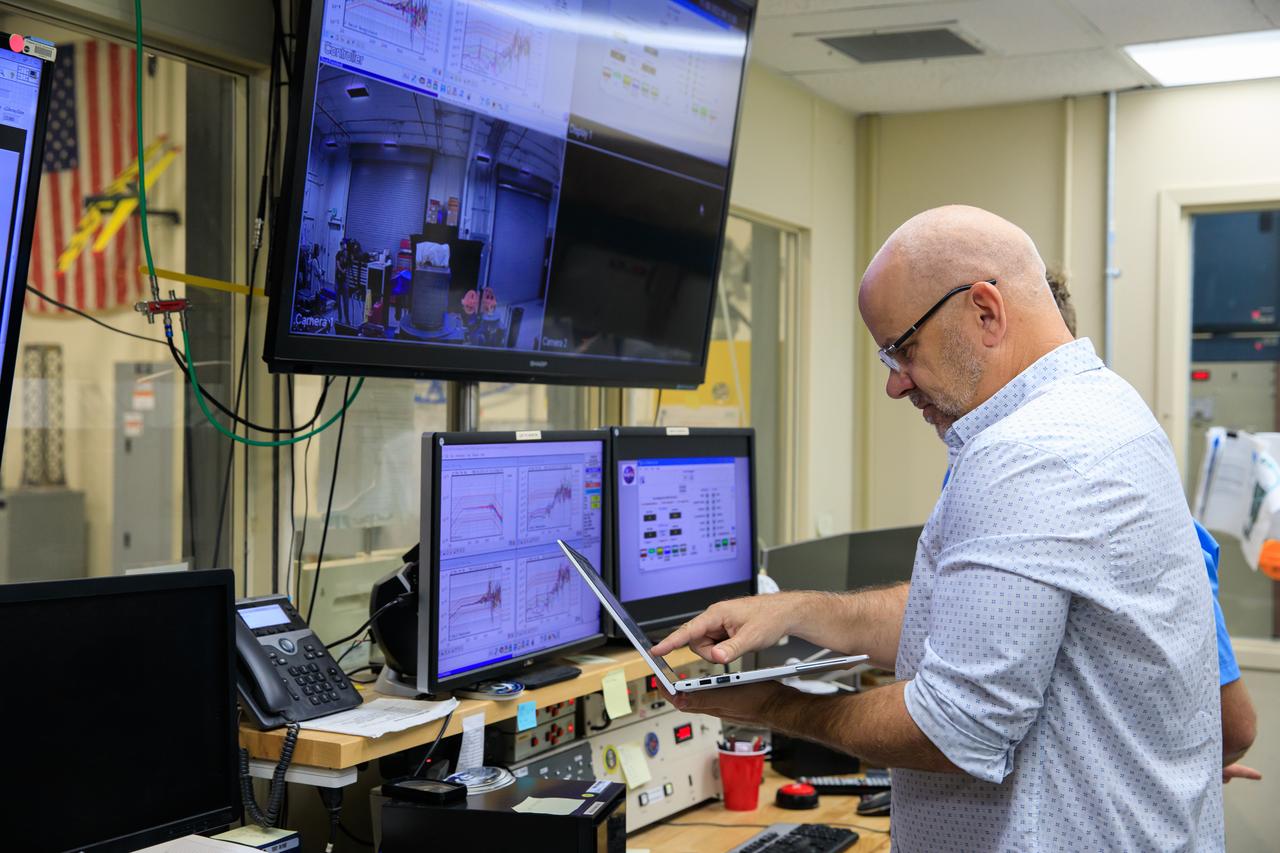

Preparations are underway to conduct a vibration test on the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) for NASA’s VIPER mission inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 8, 2022. Exposing the instrument to vibration environments that it might see during launch helps engineers to find issues prior to liftoff. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo will be part of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) mission where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will be used to perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
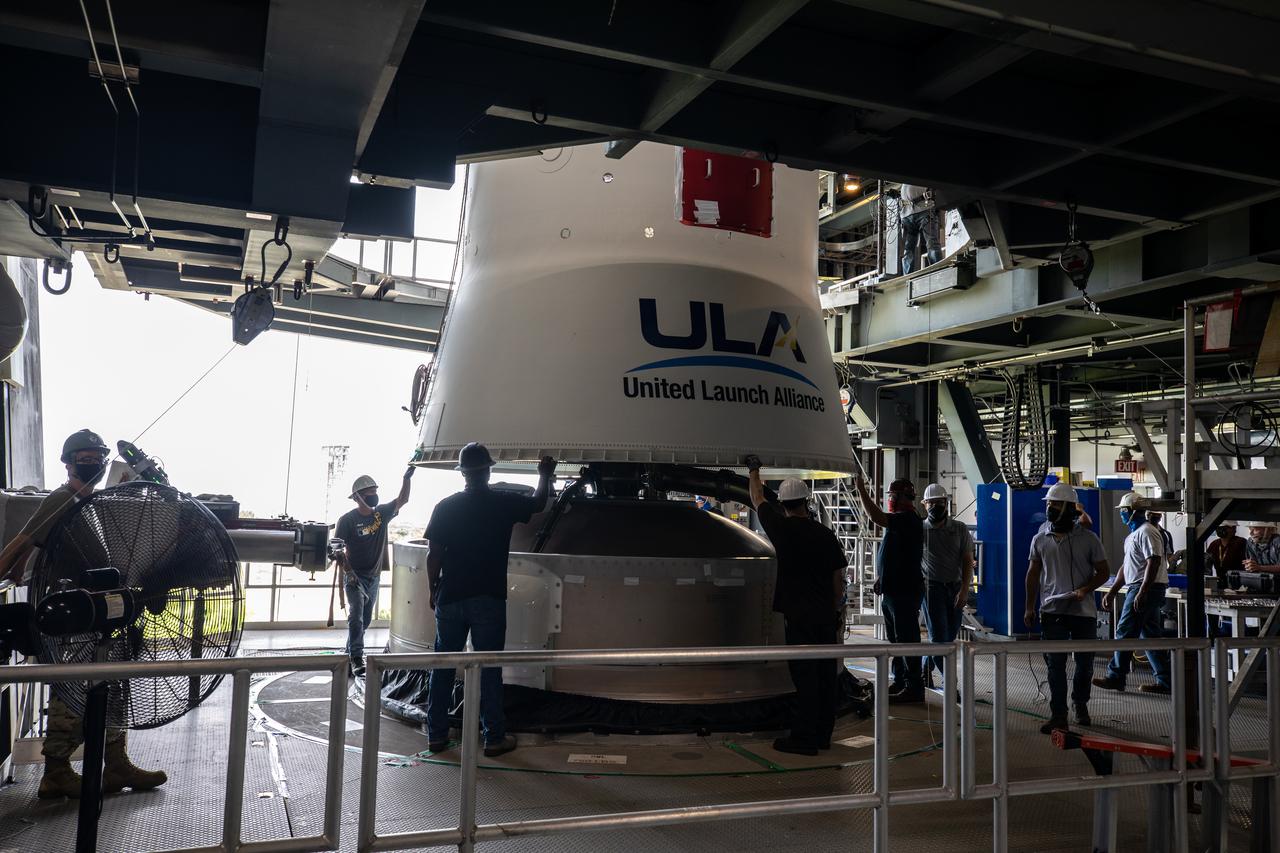

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Centaur stage for NASA’s Lucy mission is lowered onto the Atlas V first stage on Sept. 16, 2021. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Pad 41. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
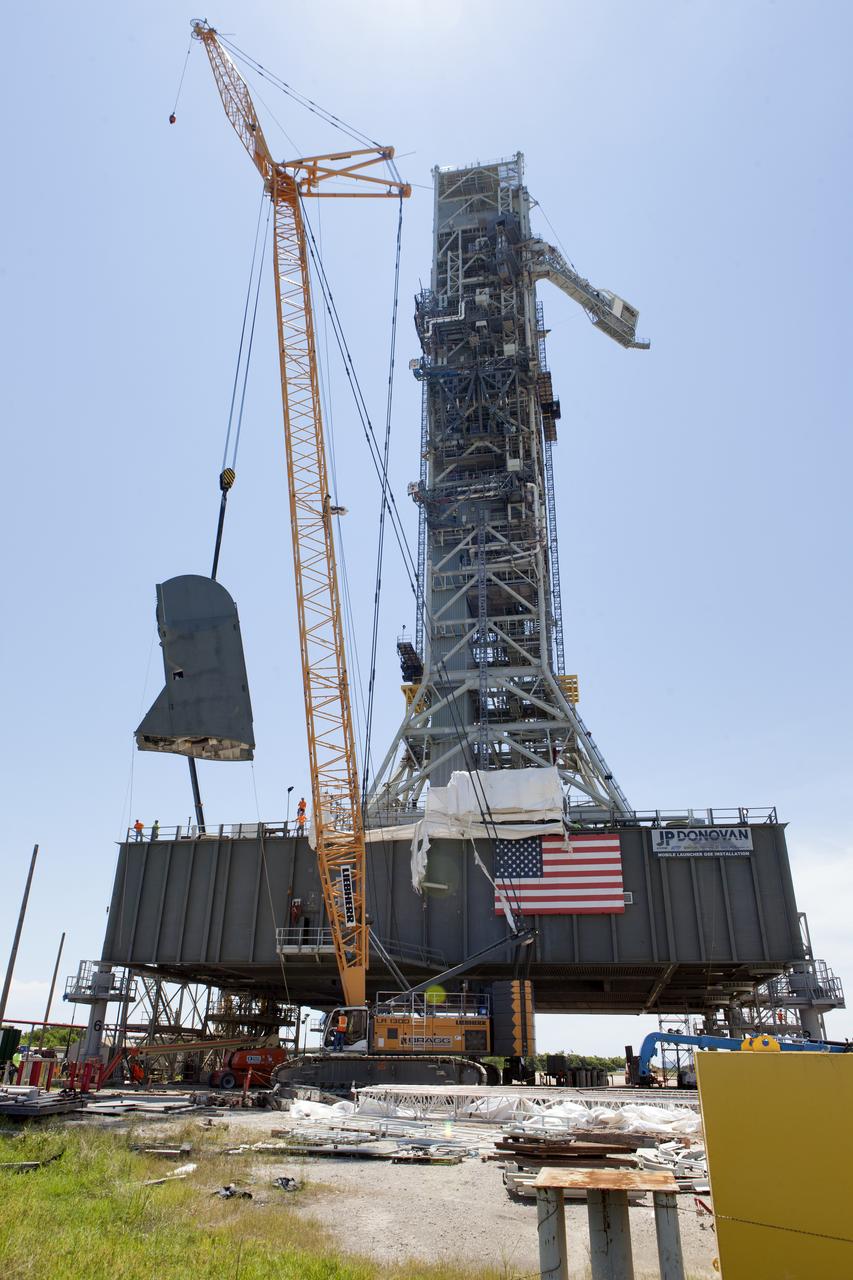

A crane is used to lift up the first of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 12, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
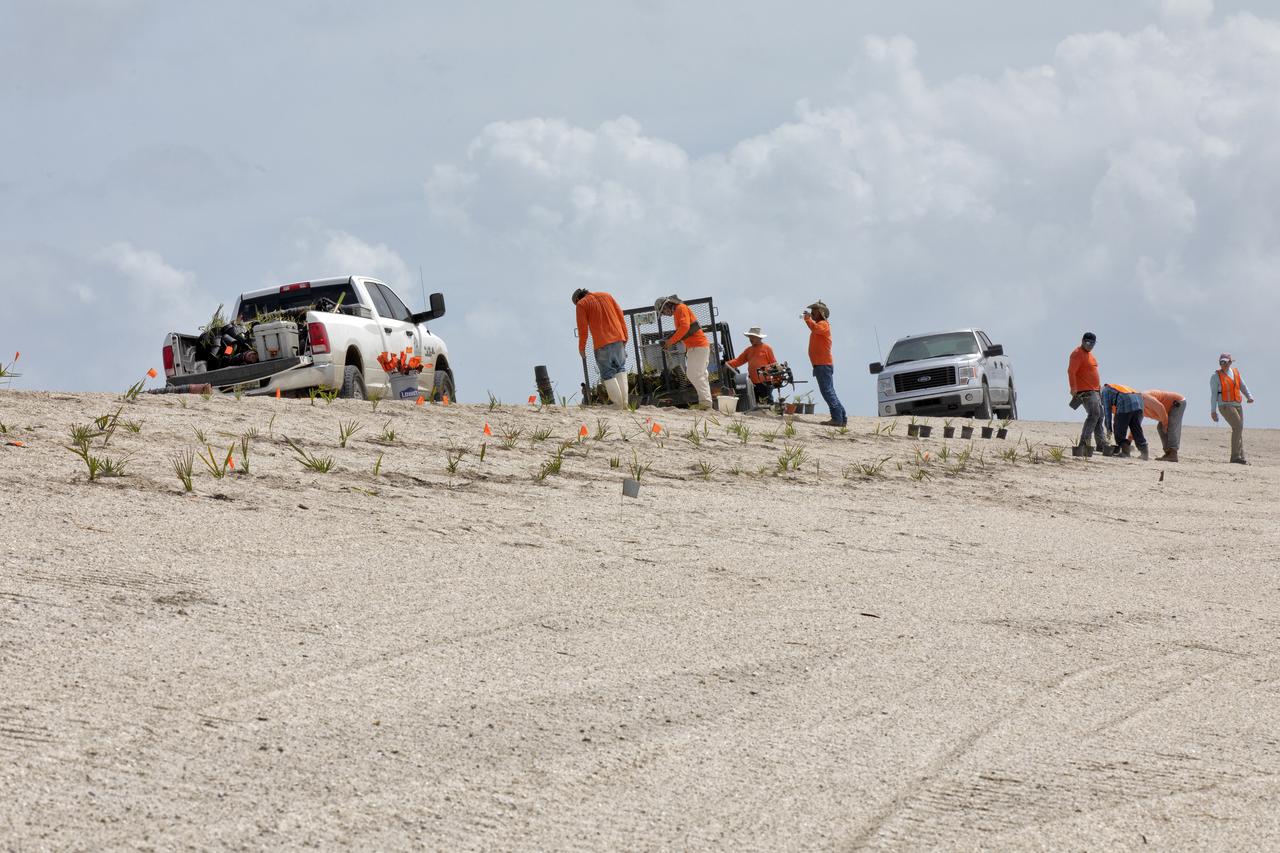

Native vegetation is being planted in a portion of the restored dunes at the north beaches at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 8, 2018. About 450,000 cubic yards of beach-quality sand, tested for compatibility, is being transported to the space center’s beaches. One the dune is built up, native coastal vegetation will be replanted, helping to stabilize the dune and offer a habitat for Kennedy’s coast wildlife. Dunes are affected by beach erosion and storm surge from tropical events, such as hurricanes. Restoration began in spring 2018 and is targeted to be completed by April 2019.

Orion is buttoned up and ready to march towards the Multi-Payload Processing Facility to begin ground processing by the Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs teams ahead of the Artemis I launch. Shielded by a protective covering for transport, the spacecraft departs its home at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 16, 2021.
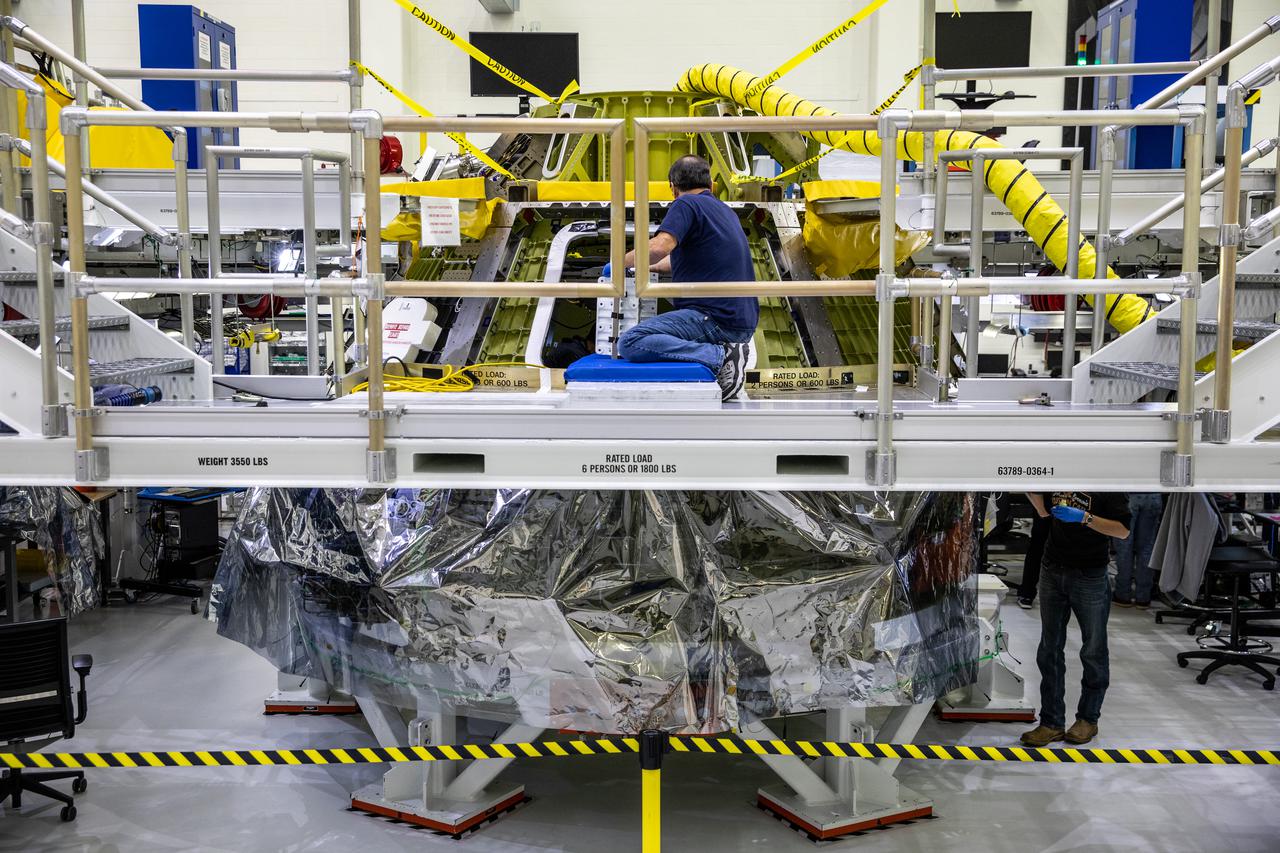

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, assembly continues on Orion’s Artemis II crew module on Feb. 5, 2021. The capsule will house astronauts during its mission around the Moon. Recently, teams removed the spacecraft from its clean room environment, where they have been performing the buildup of the Environmental Control and Propulsion System (ECPS) prior to their installation into the crew module. It will return to the clean room to complete ECPS final welds and assemblies. Artemis II will confirm all of the Orion spacecraft’s systems operate as designed in the actual environment of deep space with astronauts aboard. As part of the Artemis Program, NASA will send the first woman and next man to the Moon.
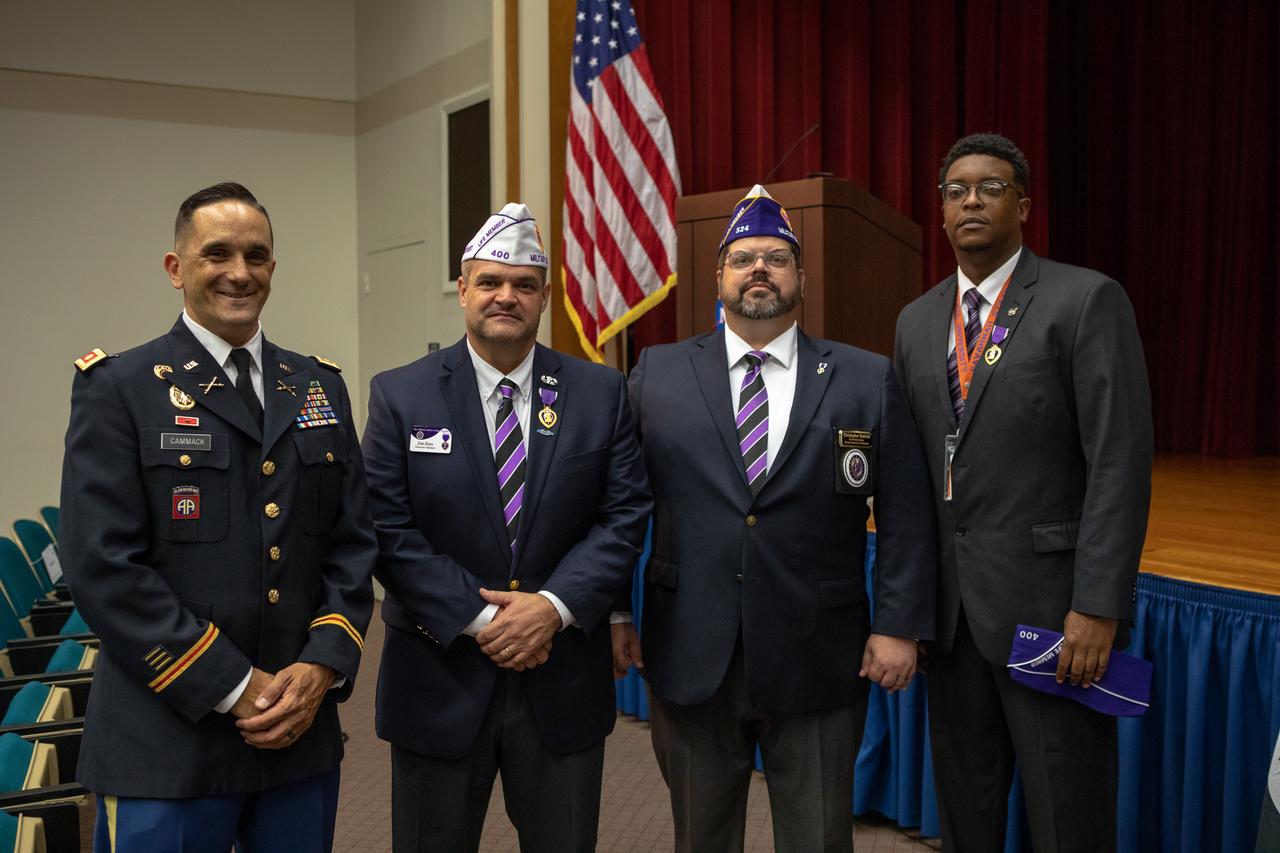

From left, NASA Public Affairs Officer Dustin Cammack, Military Order of the Purple Heart National Adjutant Ernie Rivera, Military Order of the Purple Heart Department of Florida Commander Christopher Vedvick and NASA Public Affairs Officer Derrick Matthews are photographed inside Kennedy Space Center’s Training Auditorium during a Veterans Day observance ceremony on Nov. 7, 2019. During the event, Kennedy was named a Purple Heart Entity by the Military Order of the Purple Heart, becoming the first NASA center to receive this designation for support and services provided to veterans through the Florida spaceport’s Veterans employee resource group. Attendees included Kennedy employees and more than 20 Purple Heart recipients. Following the award presentation, Vedvick, a combat wounded veteran, spoke about his experience serving in the United States Army before retiring, his involvement in the Military Order of the Purple Heart and the purpose of the organization.
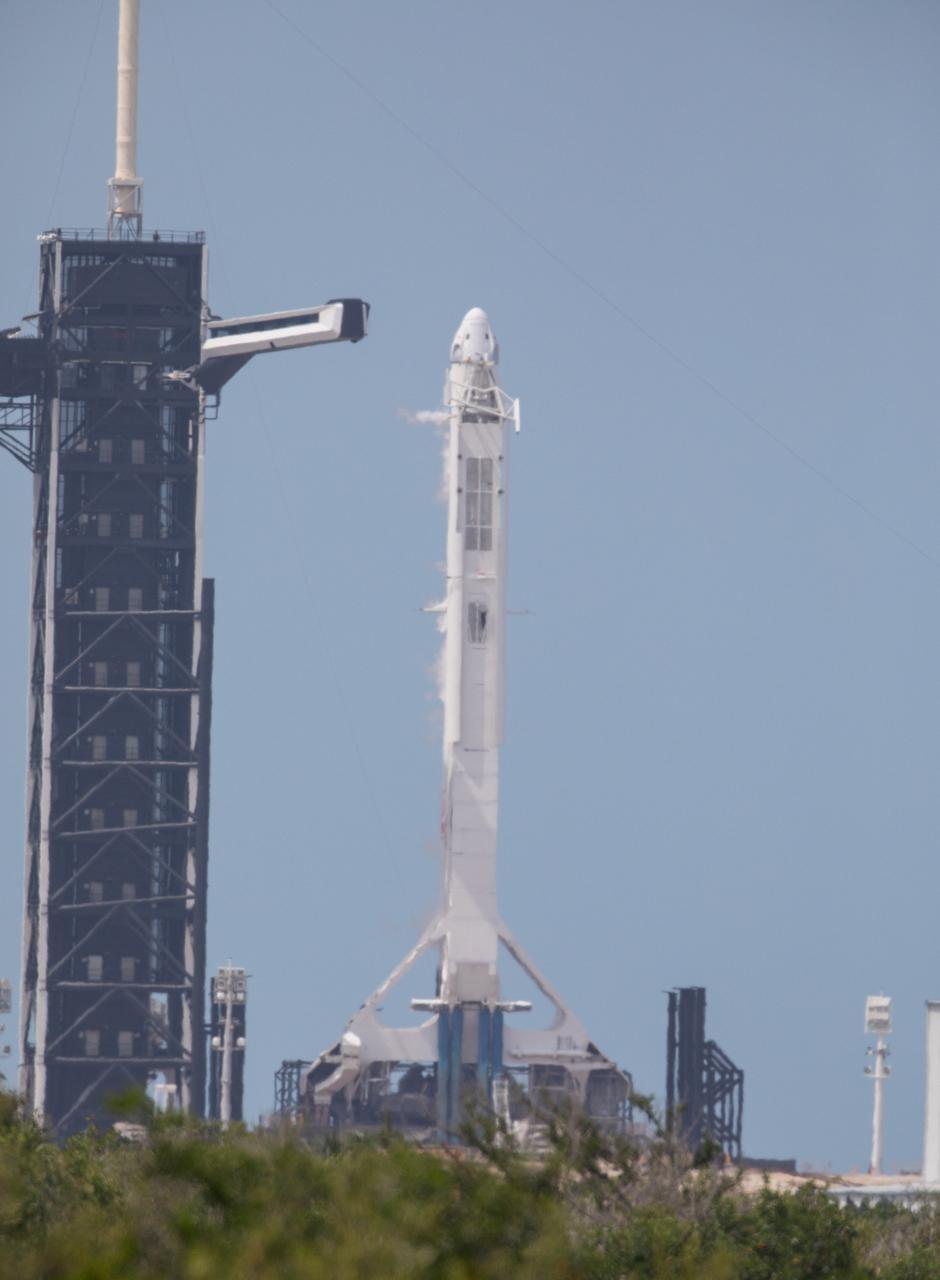

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft stand poised for launch at historic Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
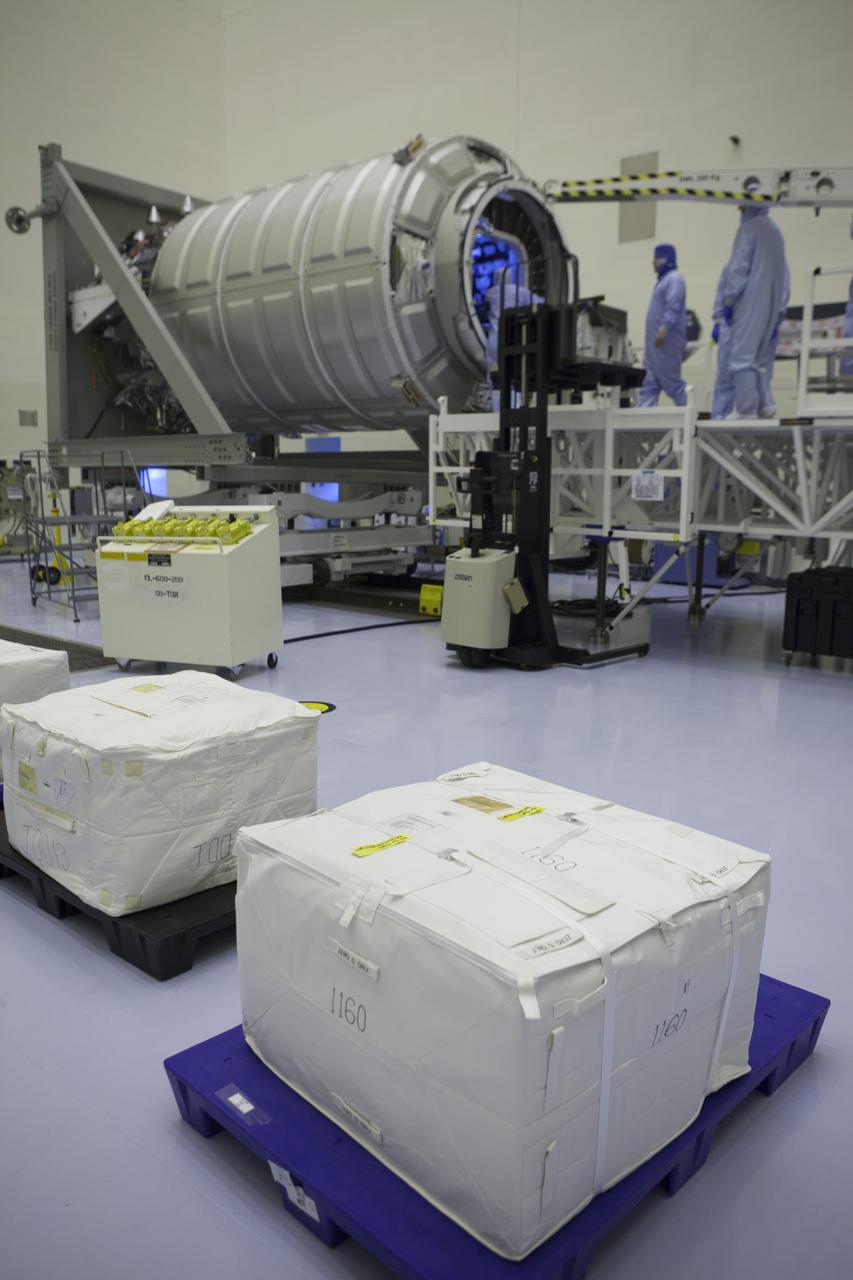

Carefully packaged cargo waits on pallets inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the background, technicians prepare to begin loading the cargo into the Orbital ATK Cygnus pressurized module during late stowage operations. The spacecraft is scheduled for the upcoming Orbital ATK Commercial Resupply Services-6 mission to deliver hardware and supplies to the International Space Station. The Cygnus is scheduled to lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on March 22.

In the Press Site auditorium at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media participate in a news conference with key individuals from the upcoming motion picture "Hidden Figures." From the left are: Ted Melfi (partially visible), writer and director of “Hidden Figures”; Octavia Spencer, who portrays Dorothy Vaughan; Taraji P. Henson, who portrays Katherine Johnson in the film; Janelle Monáe, who portrays Mary Jackson; Pharrell Williams, musician and producer of “Hidden Figures"; and Bill Barry, NASA's chief historian. The movie is based on the book of the same title, by Margot Lee Shetterly. It chronicles the lives of Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan and Mary Jackson, three African-American women who worked for NASA as human "computers.” Their mathematical calculations were crucial to the success of Project Mercury missions including John Glenn’s orbital flight aboard Friendship 7 in 1962. The film is due in theaters in January 2017.

In the Press Site auditorium at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media participate in a news conference with key individuals involved in the upcoming motion picture "Hidden Figures." From the left are: Janelle Monáe, who portrays Mary Jackson; Pharrell Williams, musician and producer of “Hidden Figures;" and Bill Barry, NASA's chief historian. The movie is based on the book of the same title, by Margot Lee Shetterly. It chronicles the lives of Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan and Mary Jackson, three African-American women who worked for NASA as human "computers.” Their mathematical calculations were crucial to the success of Project Mercury missions including John Glenn’s orbital flight aboard Friendship 7 in 1962. The film is due in theaters in January 2017.
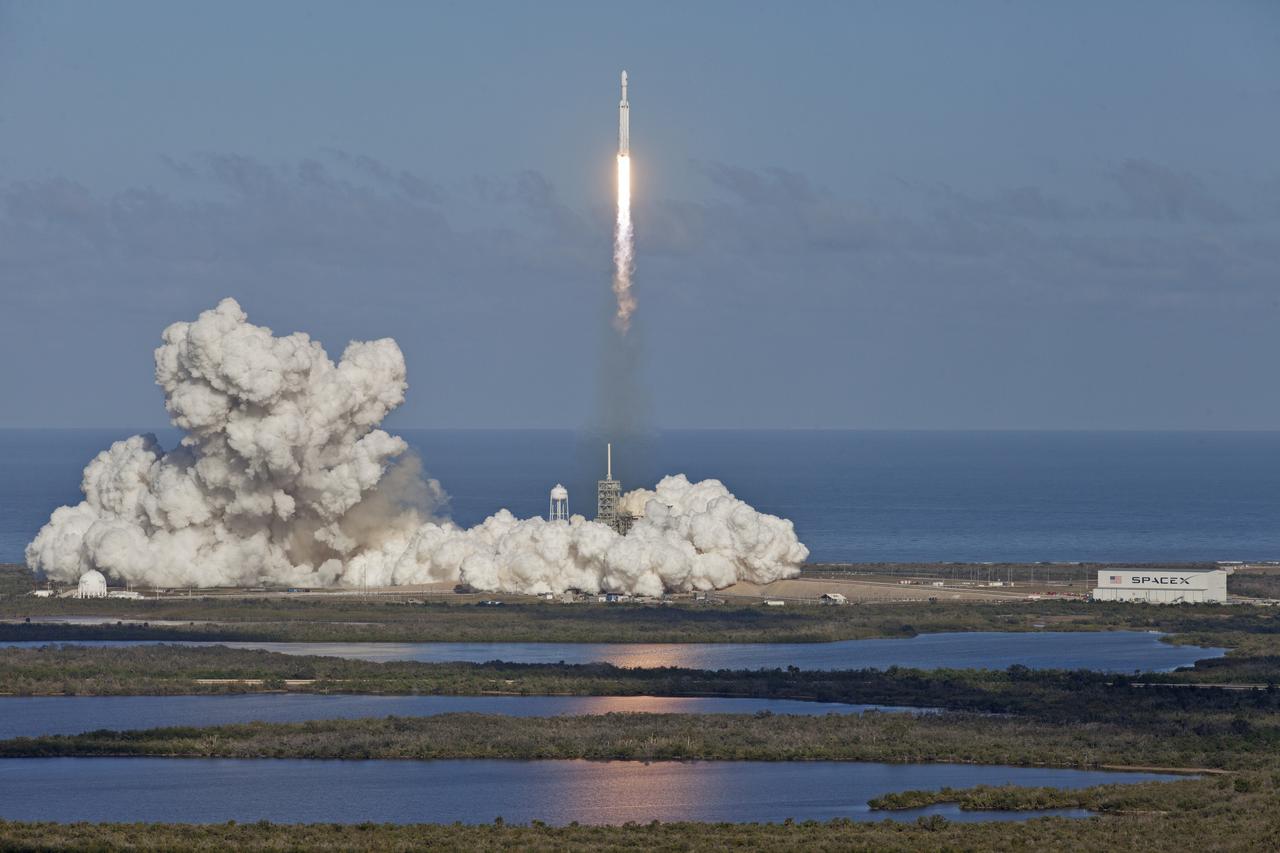

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket begins its demonstration flight with liftoff at 3:45 p.m. EST from from Launch Complex 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This is a significant milestone for the world's premier multi-user spaceport. In 2014, NASA signed a property agreement with SpaceX for the use and operation of the center's pad 39A, where the company has launched Falcon 9 rockets and prepared for the first Falcon Heavy. NASA also has Space Act Agreements in place with partners, such as SpaceX, to provide services needed to process and launch rockets and spacecraft.
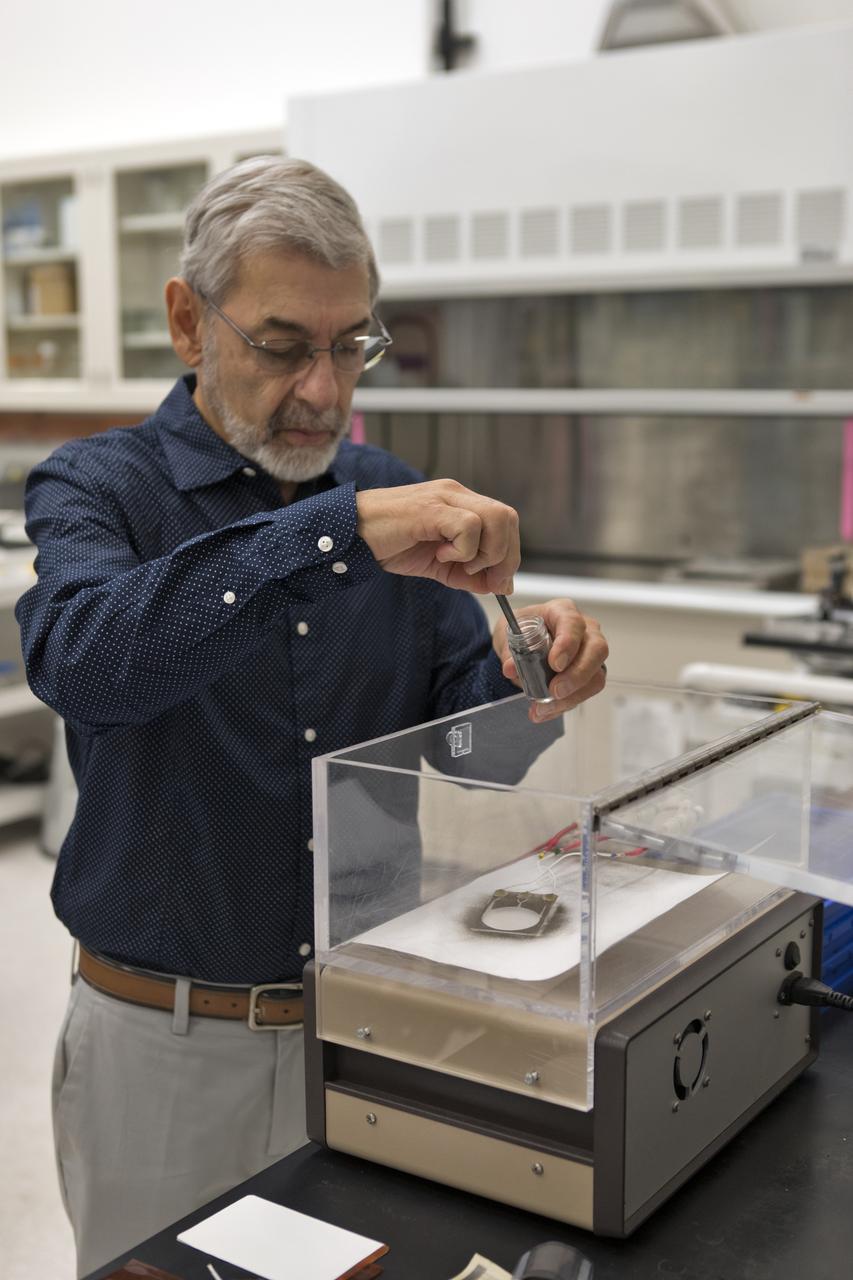

Dr. Carlos Calle, lead scientist in the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares an Electrostatic Dust Shield for testing on Thursday, July 19, 2018. Scientists are developing the Electrostatic Dust Shield to help mitigate the problem of dust on equipment, astronauts' space suits and helmet visors of astronauts exploring the Moon or Mars. The device is slated for analysis aboard International Space Station in the spring of 2019 to verify the effects of the space environment.