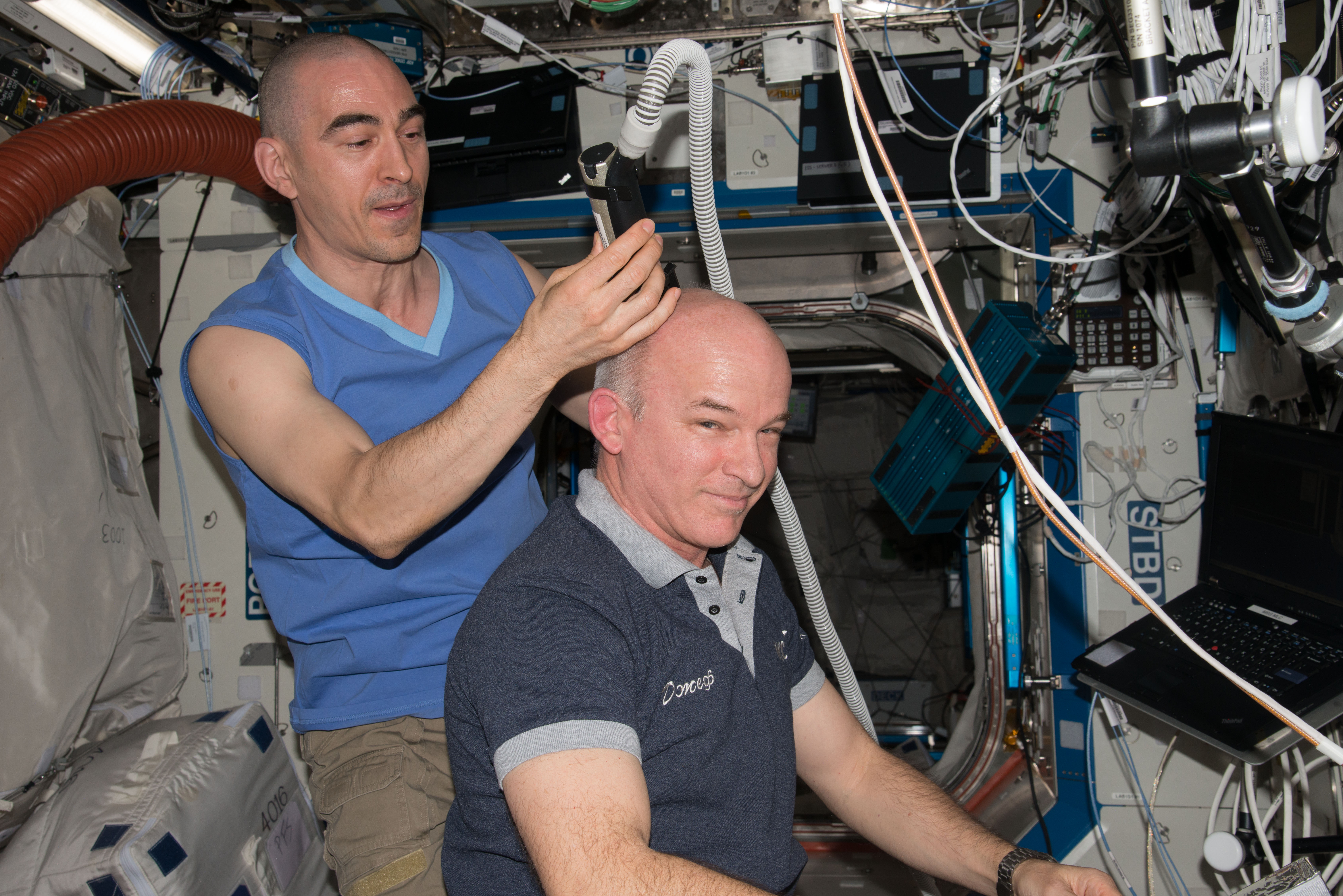

ISS048e026760 (07/16/2016) --- NASA astronaut Jeff Williams (right) gets a haircut aboard the International Space Station from Russian cosmonaut Anatoly Ivanishin (left.) The electric razor includes a vacuum hose to keep the tiny hair follicles from floating away

iss048e049904 (8/8/2016) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut Anatoly Ivanishin is photographed during Splanh (Splankh) experiment operations (OPS) in the Zvezda Service Module (SM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
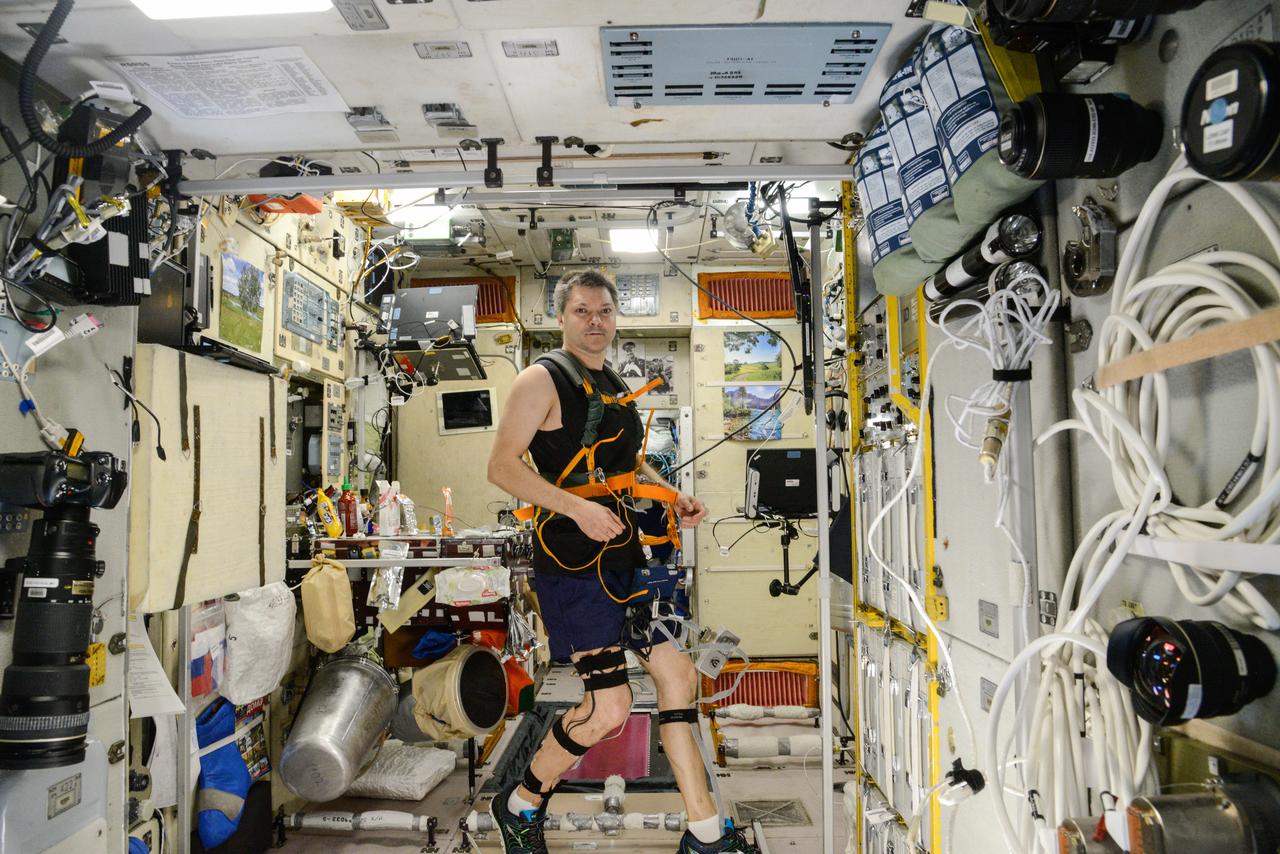

iss045e082558 (10/28/2015) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko, wearing a harness and electrodes, is photographed during Motocard experiment operations in the Zvezda Service Module (SM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Mechanisms of Sensory-Motor Coordination in Weightlessness (Motocard) investigation is carried out on the treadmill and involves locomotion in various modes of running and walking during various modes of operation of the treadmill. During the test, electromyography of the thigh and calf muscles, support structure response, heart rate, and treadmill load parameters (actual speed, time elapsed, distance, integrated indicators for support structure response) are recorded.
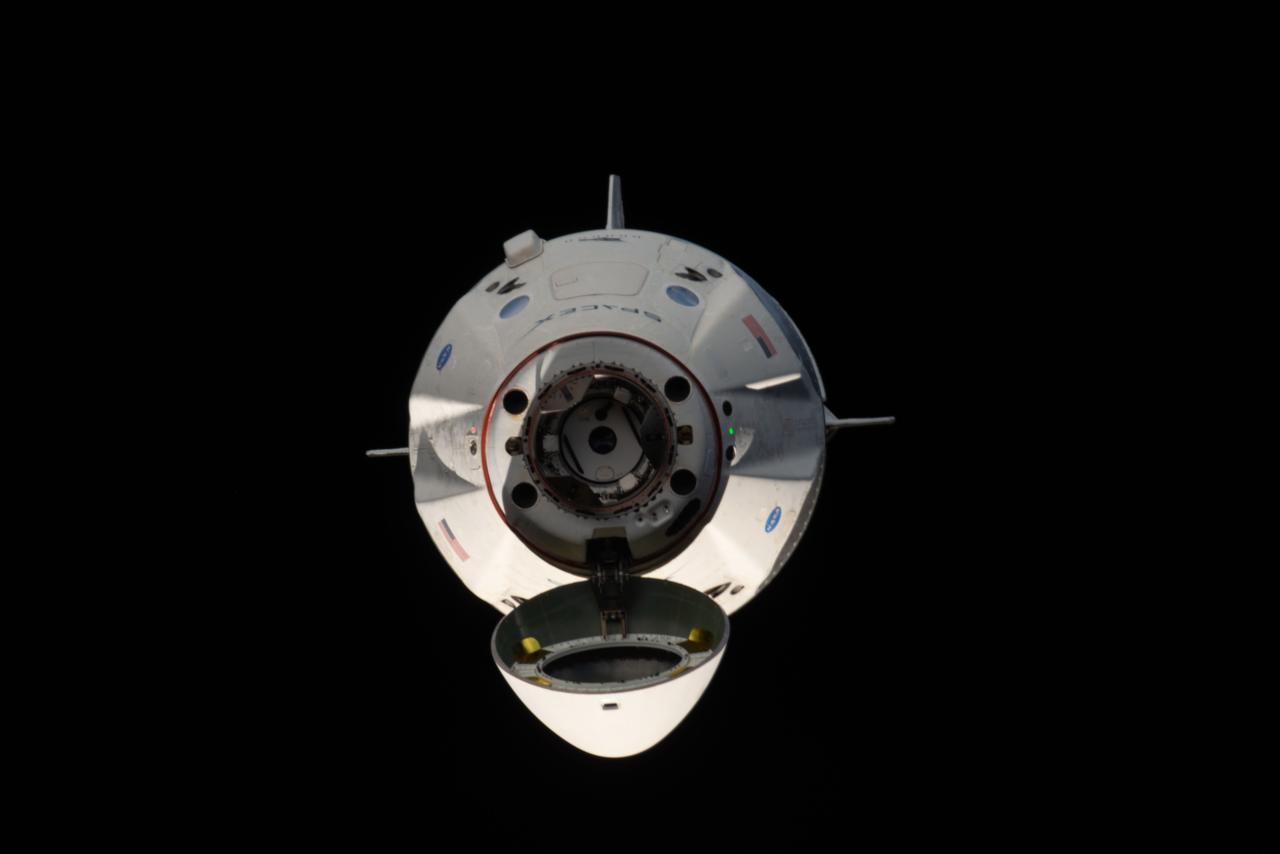

iss058e027548 (March 4, 2019) --- The uncrewed SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft is the first Commercial Crew vehicle to visit the International Space Station. Here it is pictured with its nose cone open revealing its docking mechanism while approaching the station's Harmony module. The Crew Dragon would automatically dock moments later to the international docking adapter attached to the forward end of Harmony.
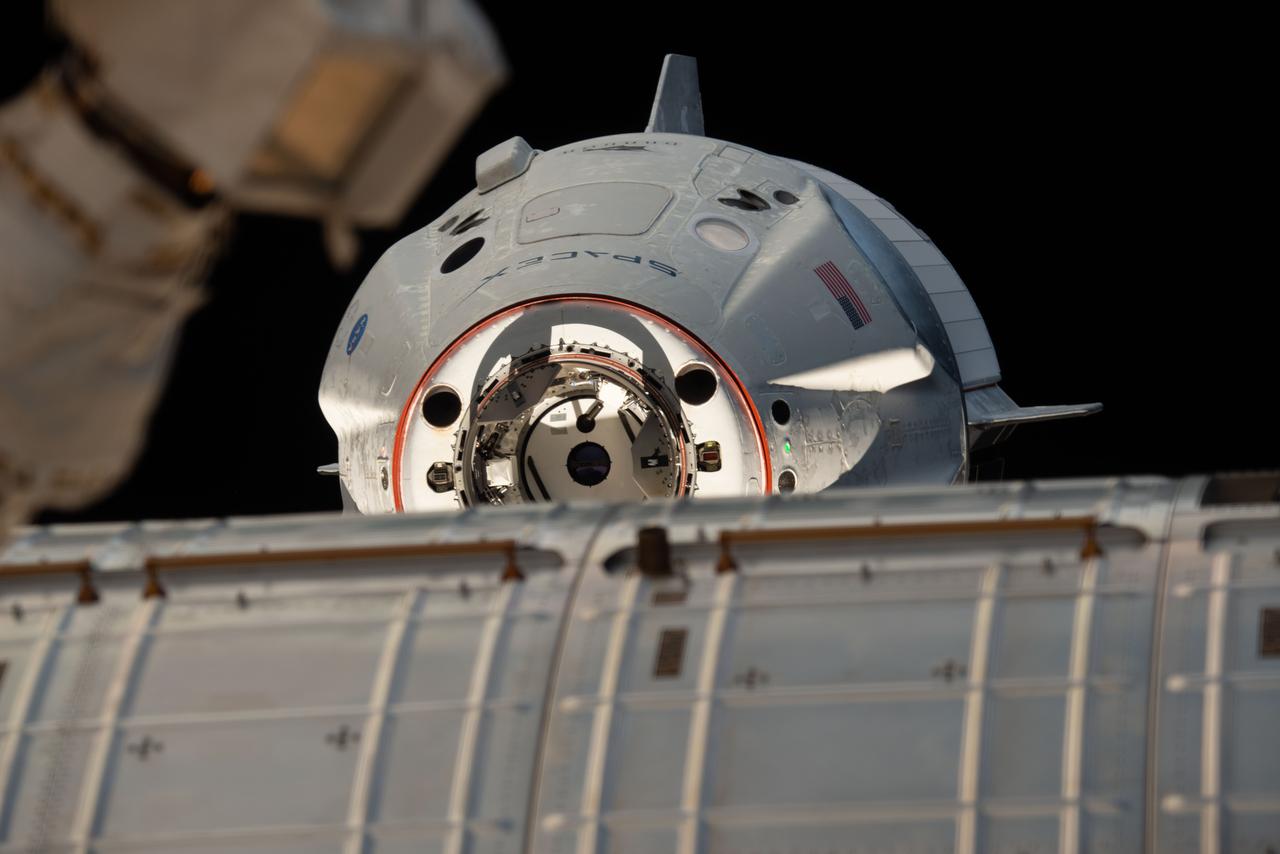

iss058e027550 (March 4, 2019) --- The uncrewed SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft is the first Commercial Crew vehicle to visit the International Space Station. Here it is pictured with its nose cone open revealing its docking mechanism while approaching the station's Harmony module. The Crew Dragon would automatically dock moments later to the international docking adapter attached to the forward end of Harmony.
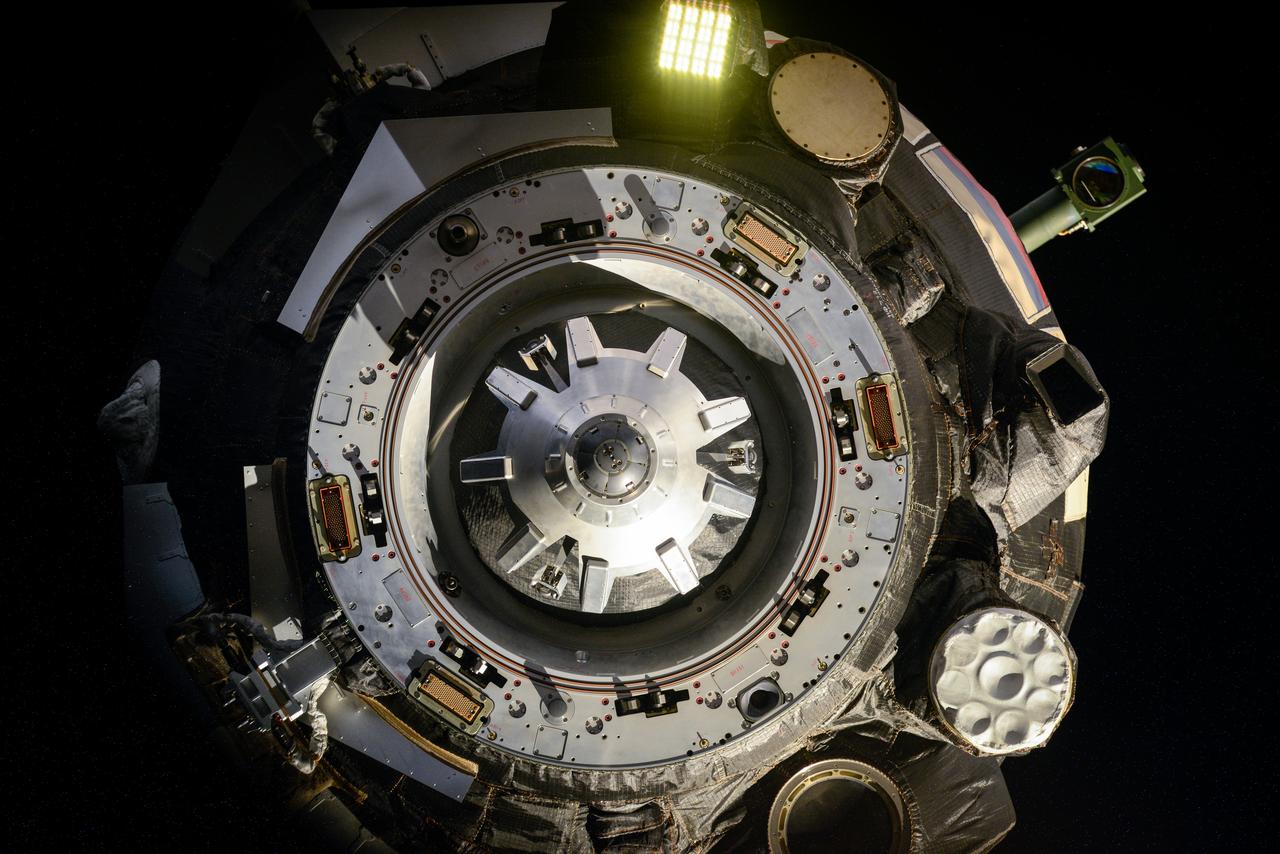

iss063e000001 (April 17, 2020) --- The docking module of the Soyuz MS-15 crew ship is pictured moments after undocking from the Zvezda service module with the Expedition 62 crewmembers, Oleg Skripochka, Jessica Meir and Andrew Morgan, onboard. They would parachute to a landing on Earth less than three-and-a-half hours later inside the Soyuz descent module.
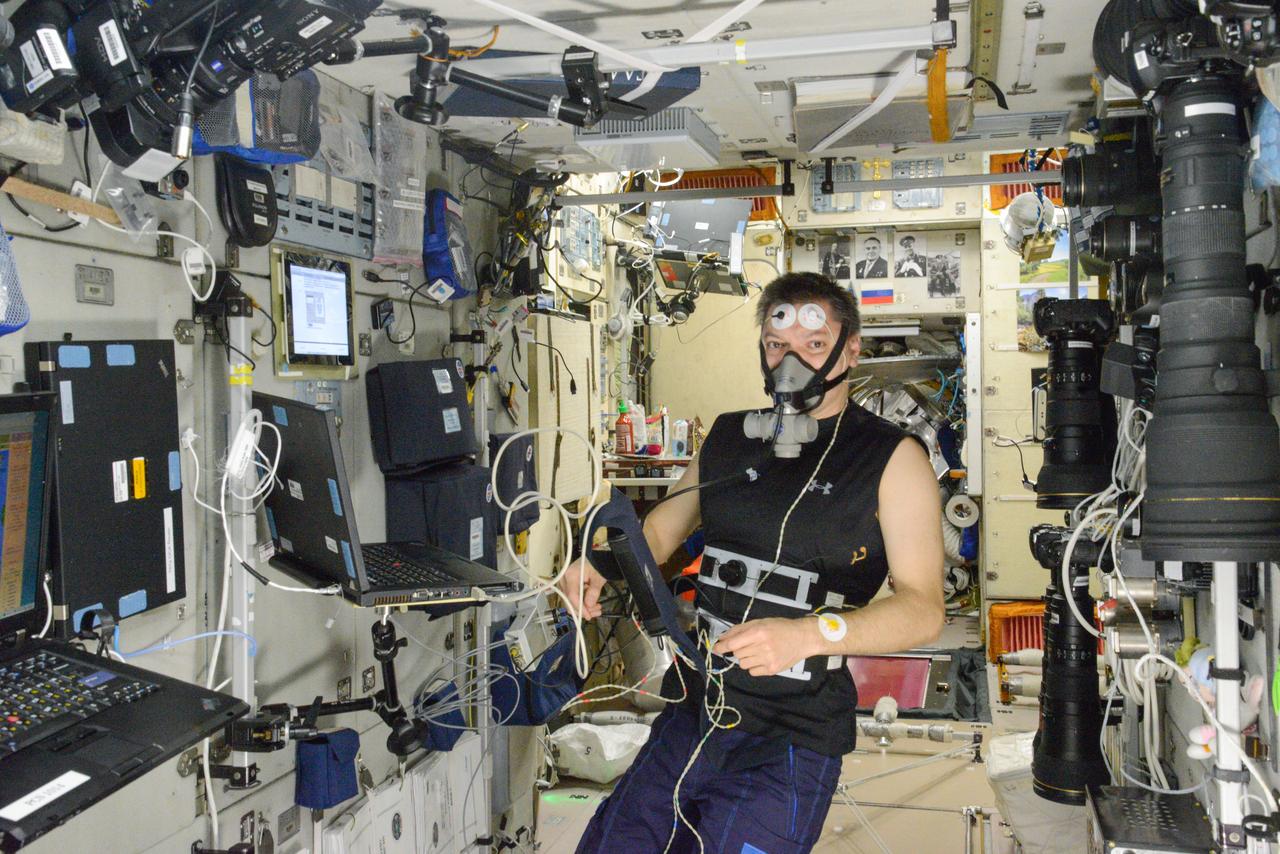

iss045e075926 (10/22/2015) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko is photographed during UDOD experiment operations in the Zvezda Service Module (SM). He is using hardware from the Dykhanie-1 and Sprut-2 Kits.
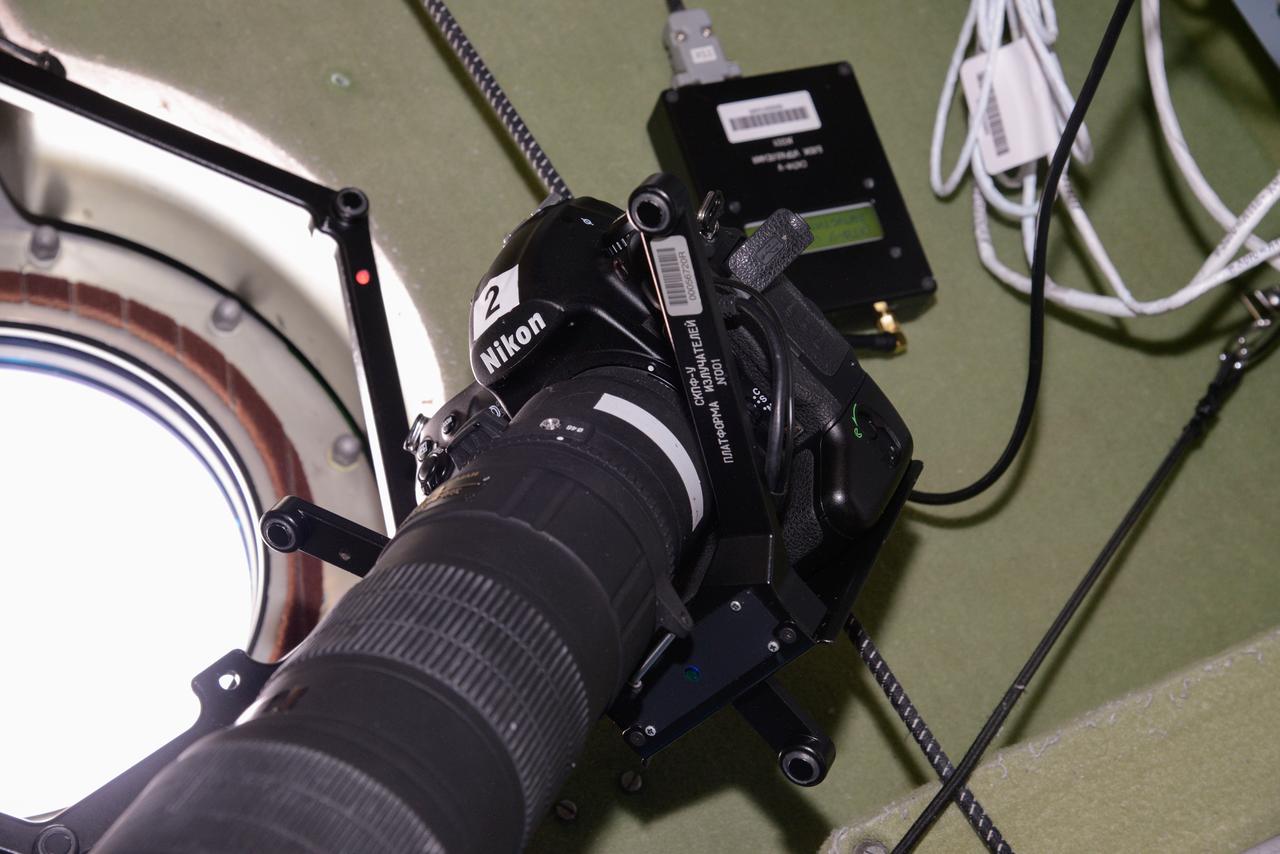

iss048e014045 (6/27/2016) --- Photo documentation of a still camera and Photo Image Coordinate Reference System (СКПФ-У) hardware in use during a Vizir experiment session in the Zvezda Service Module (SM). The Experimental Testing of a System of Photo Imagery Coordinate Referencing Using Ultrasound Sensors (Vizir) tests the technology of automated coordinate referencing of images of the Earth’s surface, and space, taken by crewmembers using “free-floating” photography equipment in weightlessness.
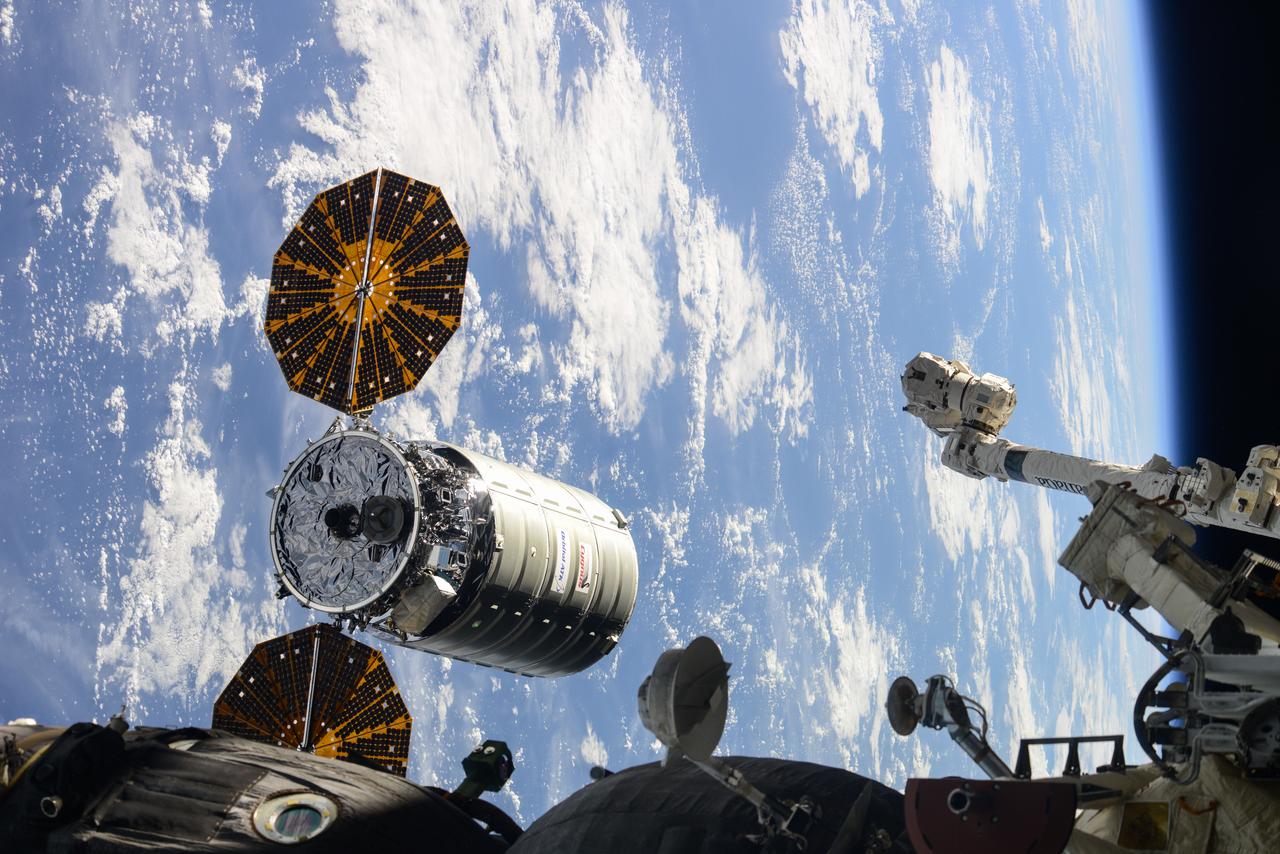

iss047e155876 (March 26, 2016) --- Orbital ATK's Cygnus resupply ship slowly maneuvers its way toward the International Space Station before its robotic capture and installation during Expedition 47 in March of 2016.
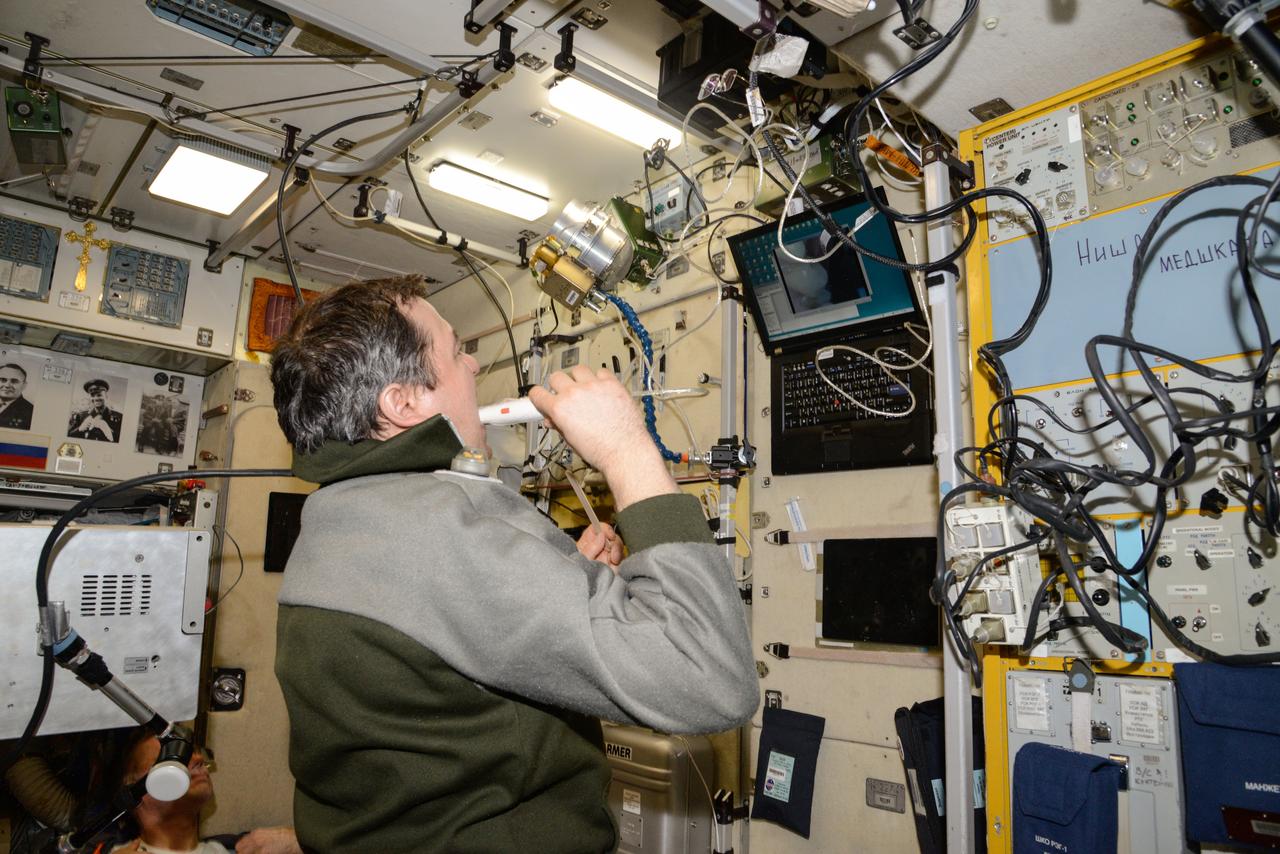

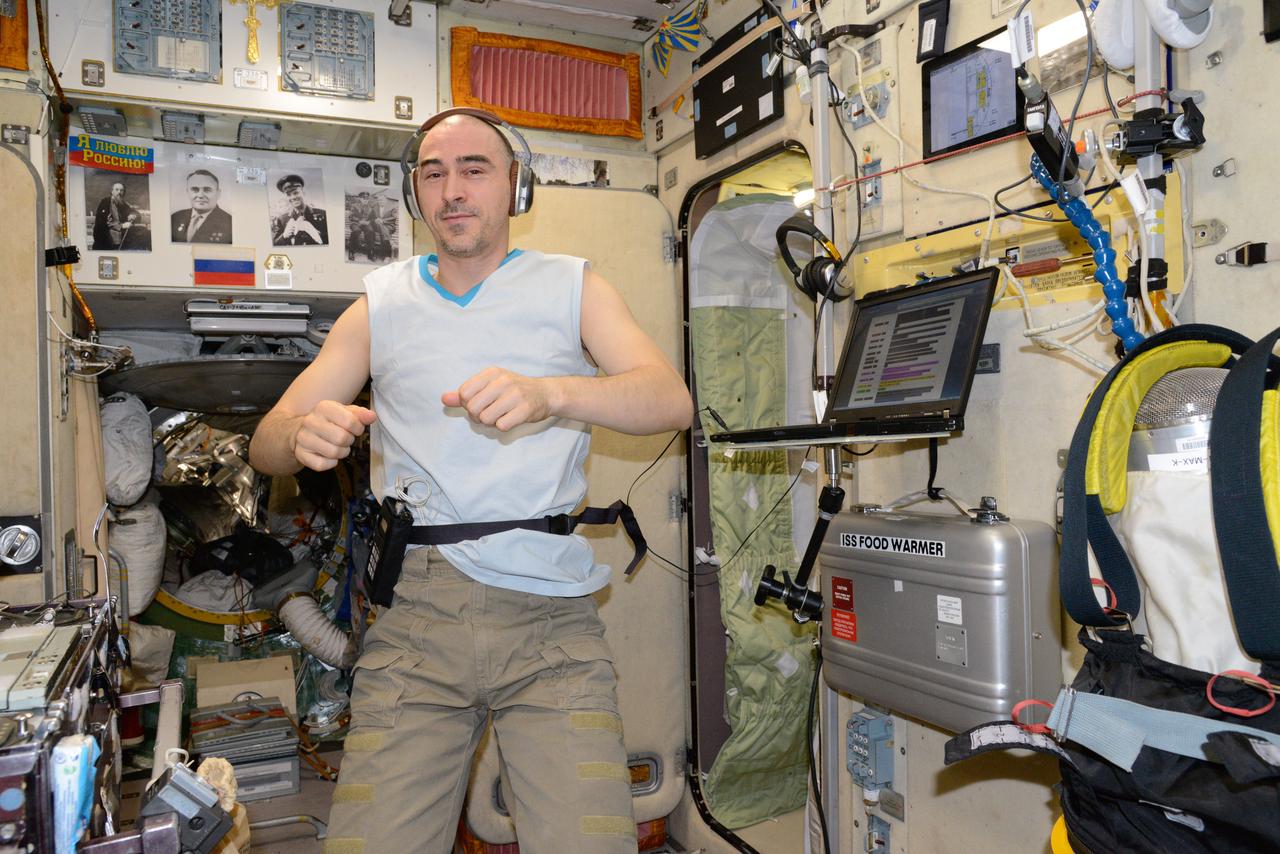
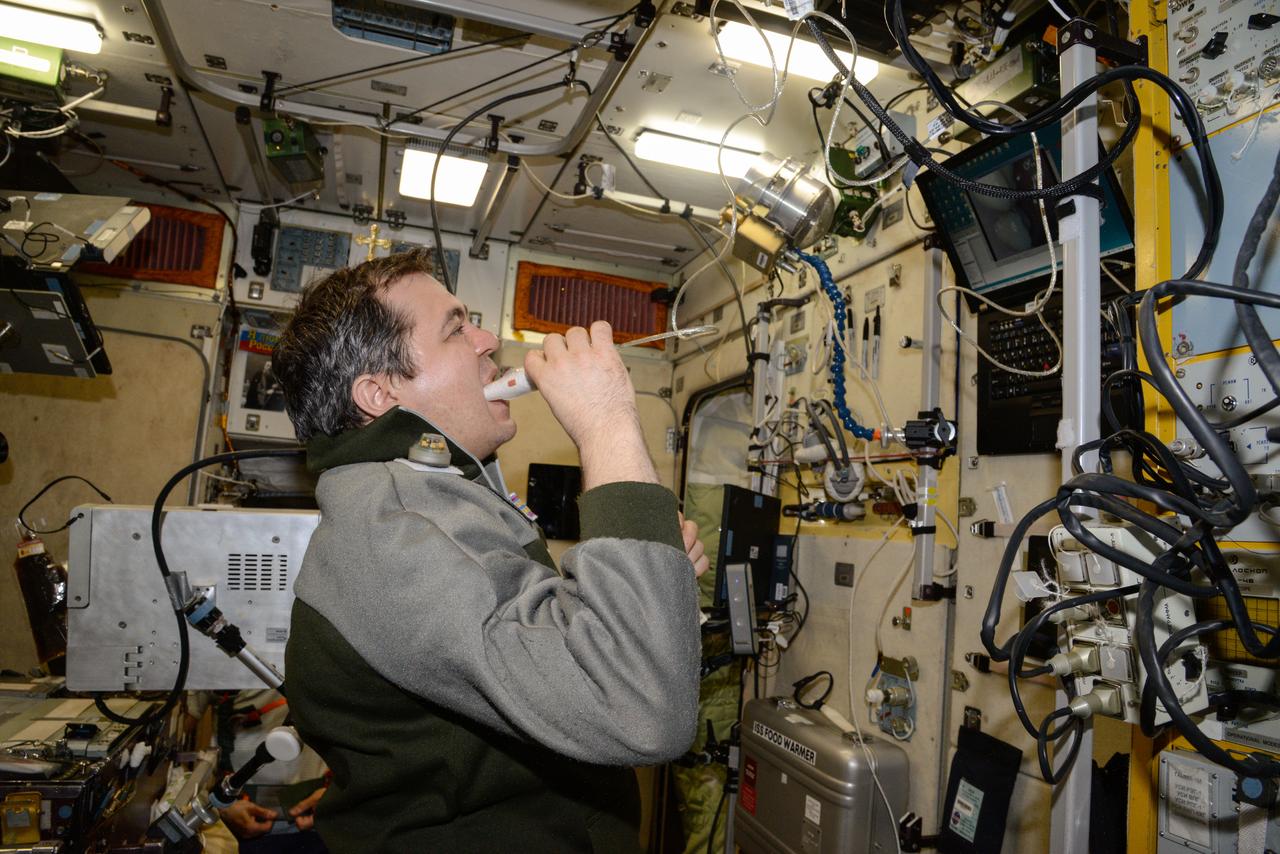
iss047e136529 (6/2/2016) --- A view of Cosmonaut Oleg Skripochka, during a BIMS Experiment session in the Service module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Study of Processes for Informational Support of In-Flight Medical Support using an Onboard Medical Information System Integrated into the Information Control System of the ISS Russian Segment (BIMS) uses telemedicine technologies to collect information by non-contact means from the ear, nose, and throat (ENT), gums, teeth, and small areas of skin from International Space Station (ISS) crews for medical support of manned spaceflights and in-flight biomedical research.
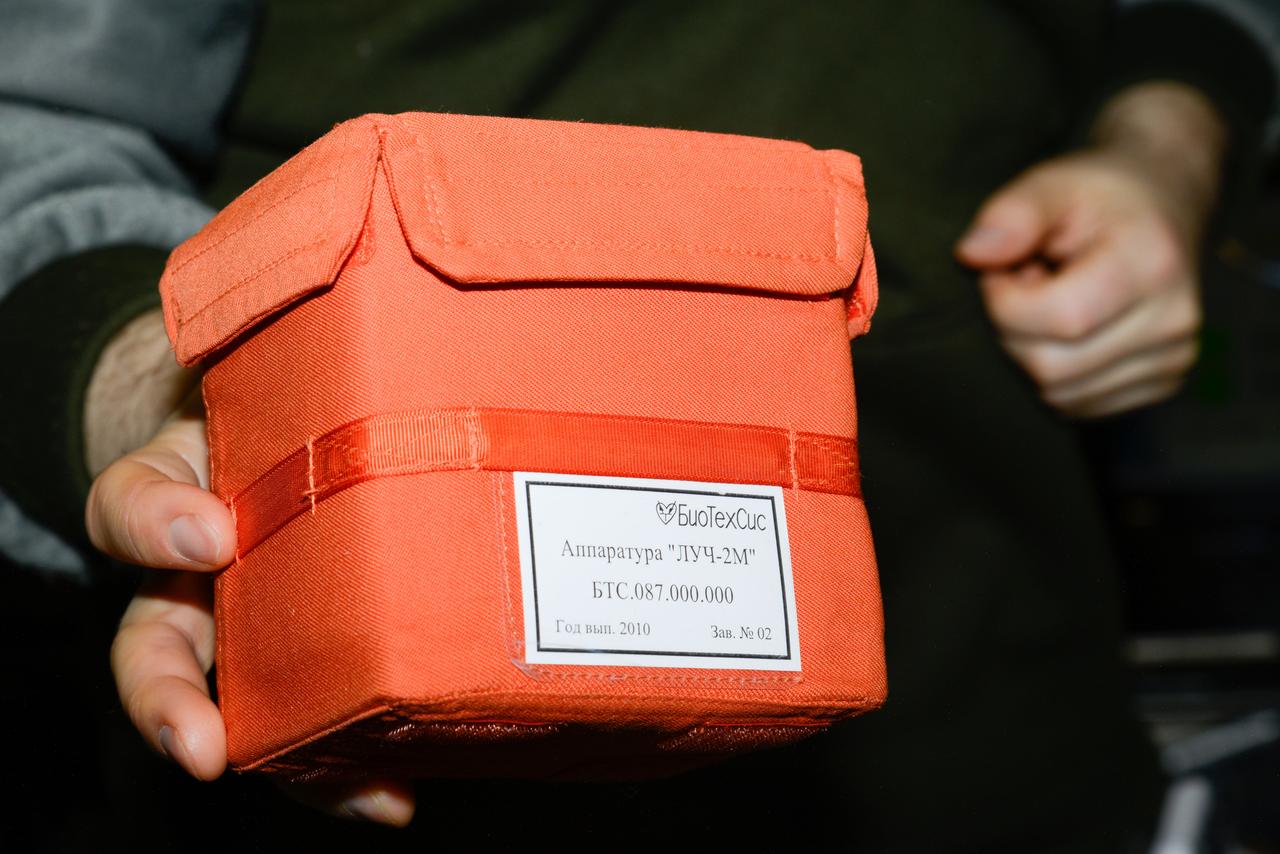

iss047e154711 (6/17/2016) --- Photographic documentation of Luch-2M Multipurpose Crystallization Cassette (УБК) within orange case. Struktura is a study of protein crystallization processes and growth of single crystals which are suitable for X-ray structural analysis and structural decoding.
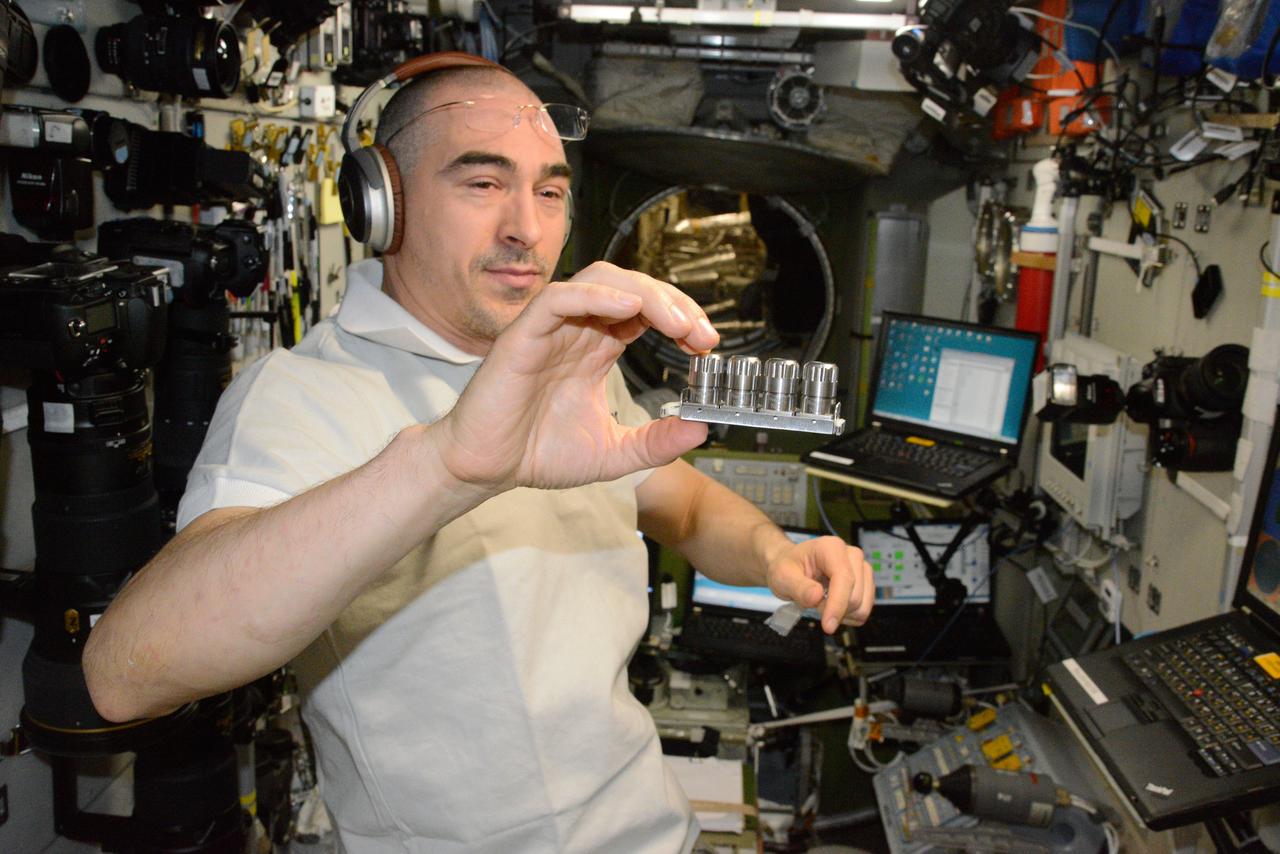

iss048e038163 (7/17/2016) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut Anatoly Ivanishin displays Luch-2M Multipurpose Crystallization Cassette (УБК) No. 3 during Struktura-Luch-2M (Structure-Beam-2M) experiment hardware activation and deployment. Image was taken in the Zvezda Service Module (SM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Struktura is a study of protein crystallization processes and growth of single crystals which are suitable for X-ray structural analysis and structural decoding.
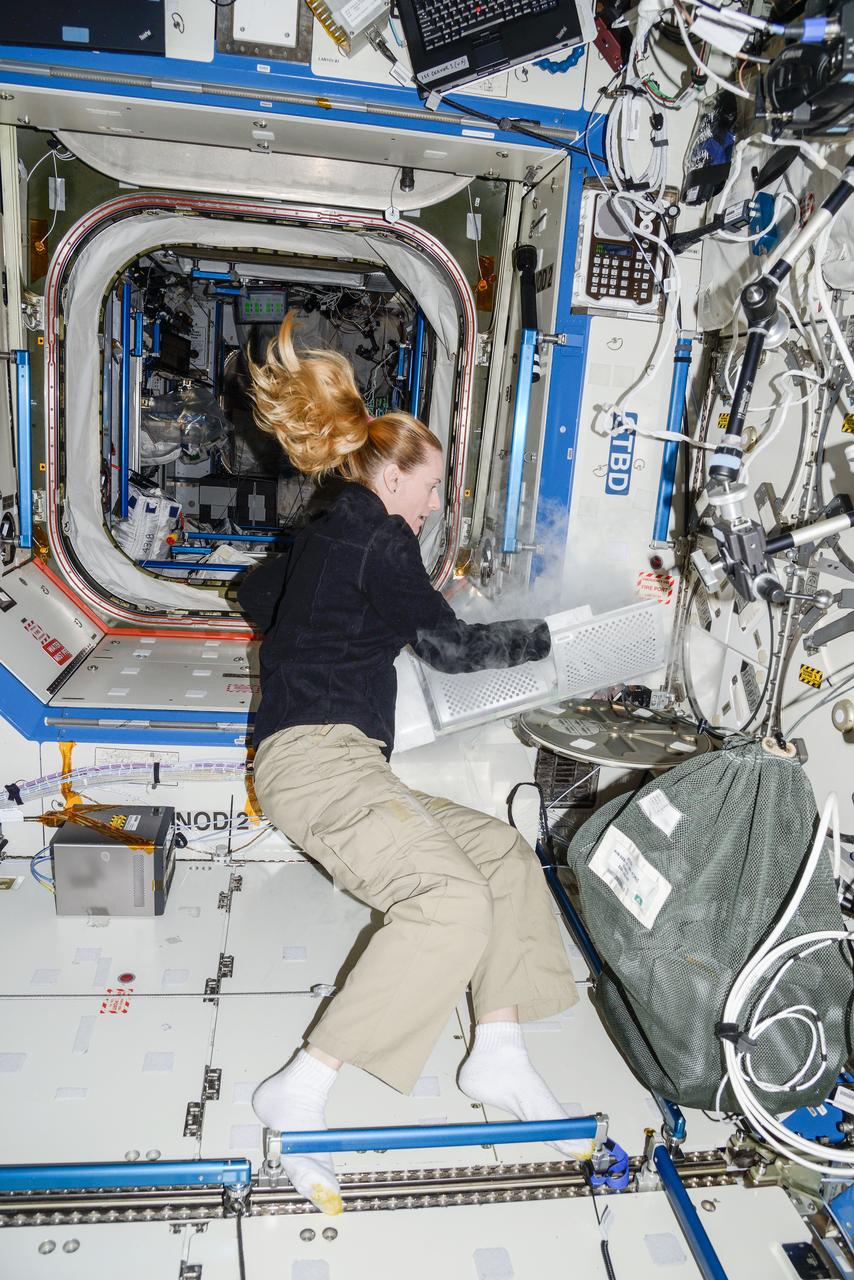

iss049e053079 (9/23/2016) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins is photographed in U.S. lab aboard the International Space Station (ISS) performing the second harvest of the Plant RNA Regulation experiment by stowing the European Modular Cultivation System (EMCS) Seed Cassettes from EMCS Rotors A and B in an EMCS Cold Stowage Pouch and placing them in Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI). The Plant RNA Regulation investigation studies the first steps of gene expression involved in development of roots and shoots. Scientists expect to find new molecules that play a role in how plants adapt and respond to the microgravity environment of space, which provides new insight into growing plants for food and oxygen supplies on long-duration missions. Sent as part of Russian Return imagery on 47S.
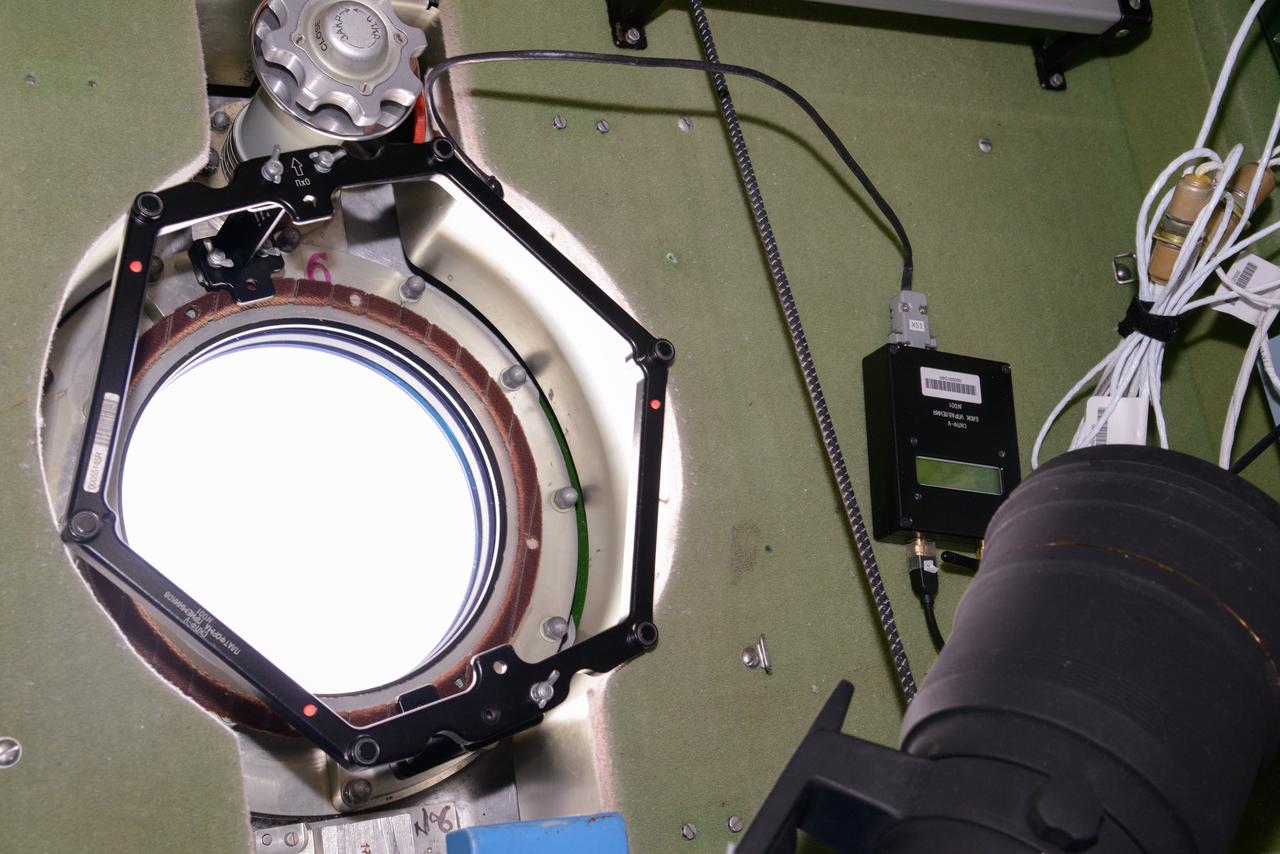
iss048e014043 (6/27/2016) --- Photo documentation of Photo Image Coordinate Reference System (СКПФ-У) hardware in use during a Vizir experiment session in the Zvezda Service Module (SM). The Experimental Testing of a System of Photo Imagery Coordinate Referencing Using Ultrasound Sensors (Vizir) tests the technology of automated coordinate referencing of images of the Earth’s surface, and space, taken by crewmembers using “free-floating” photography equipment in weightlessness.

ISS047e004413 (03/09/2016) --- Expedition 47 Commander NASA astronaut Tim Kopra is seen here working on a Laptop in the Service Module of the International Space Station.
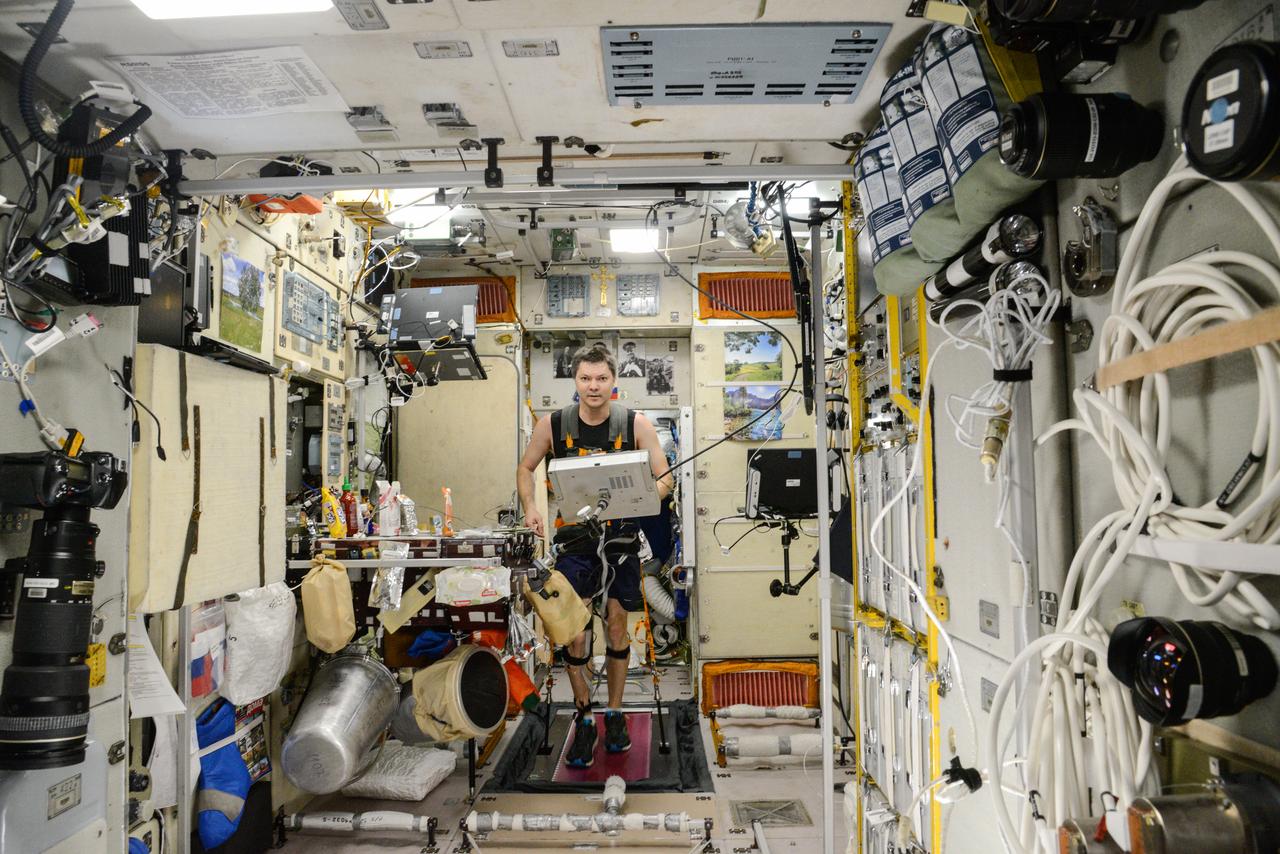

iss045e082560 (10/28/2015) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko, wearing a harness and electrodes, is photographed during Motocard experiment operations in the Zvezda Service Module (SM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Mechanisms of Sensory-Motor Coordination in Weightlessness (Motocard) investigation is carried out on the treadmill and involves locomotion in various modes of running and walking during various modes of operation of the treadmill. During the test, electromyography of the thigh and calf muscles, support structure response, heart rate, and treadmill load parameters (actual speed, time elapsed, distance, integrated indicators for support structure response) are recorded.
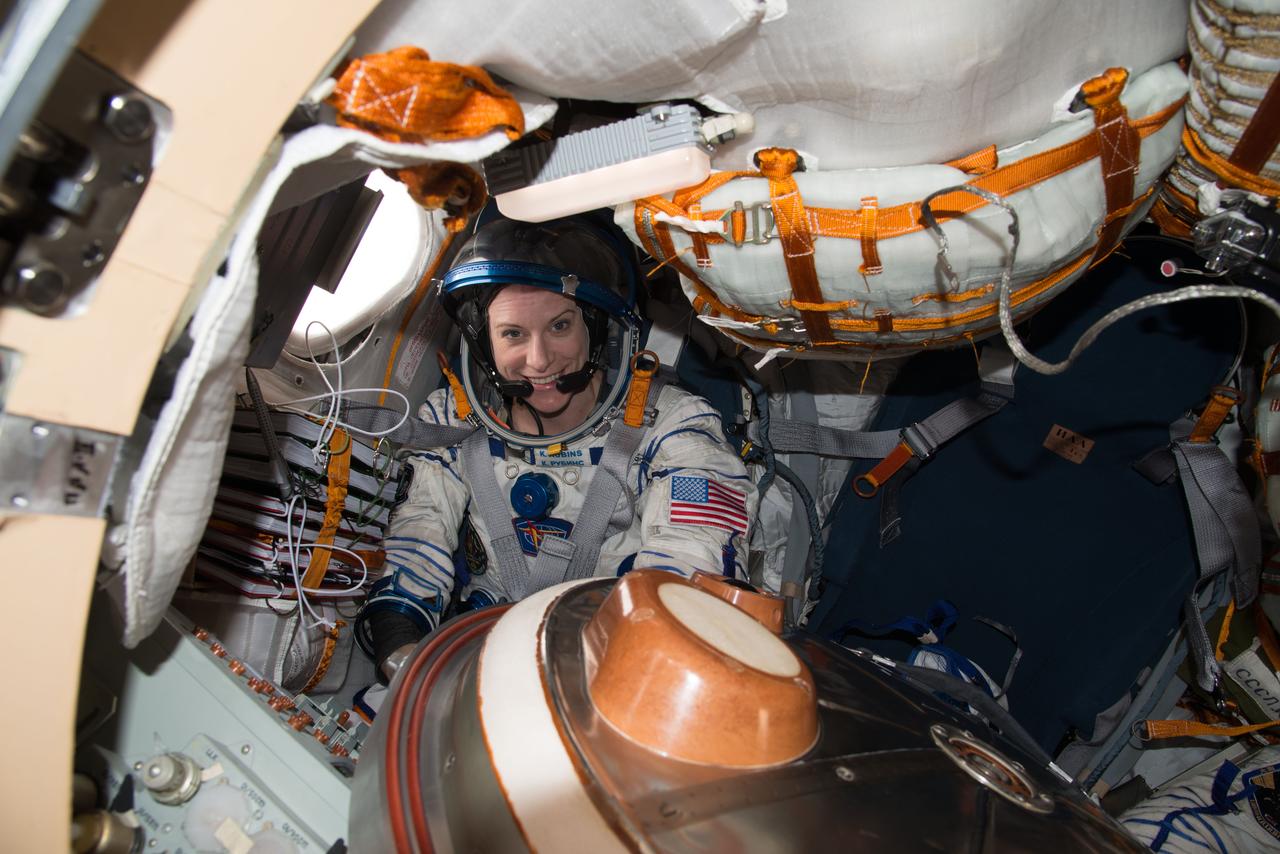

ISS049e040733 (10/19/2016) --- NASA astronaut Kate Rubins is pictured inside of the Soyuz MS-01 spacecraft while conducting routine spacesuit checks. Rubins, suited up in a Russian Sokol Launch and Entry suit, was conducting leak checks in advance of her upcoming landing along with Japanese astronaut Takuya Onishi and Russian cosmonaut Anatoly Ivanishin. The trio are scheduled to land Oct. 29, U.S. time.

iss048e038166 (7/19/2016) --- Photographic documentation of the Luch-2M Unit for the Struktura-Luch-2M (Structure-Beam-2M) experiment deployed on Panel 406 in the Zvezda Service Module. (SM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Struktura is a study of protein crystallization processes and growth of single crystals which are suitable for X-ray structural analysis and structural decoding.

iss047e136530 (6/2/2016) --- A view of Cosmonaut Oleg Skripochka, during a BIMS Experiment session in the Service module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Study of Processes for Informational Support of In-Flight Medical Support using an Onboard Medical Information System Integrated into the Information Control System of the ISS Russian Segment (BIMS) uses telemedicine technologies to collect information by non-contact means from the ear, nose, and throat (ENT), gums, teeth, and small areas of skin from International Space Station (ISS) crews for medical support of manned spaceflights and in-flight biomedical research.
iss048e038162 (7/19/2016) --- The hand of a crewmember displays Luch-2M Multipurpose Crystallization Cassette (УБК) No. 2 during Struktura-Luch-2M (Structure-Beam-2M) experiment hardware activation and deployment. Image was taken in the Zvezda Service Module (SM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Struktura is a study of protein crystallization processes and growth of single crystals which are suitable for X-ray structural analysis and structural decoding.
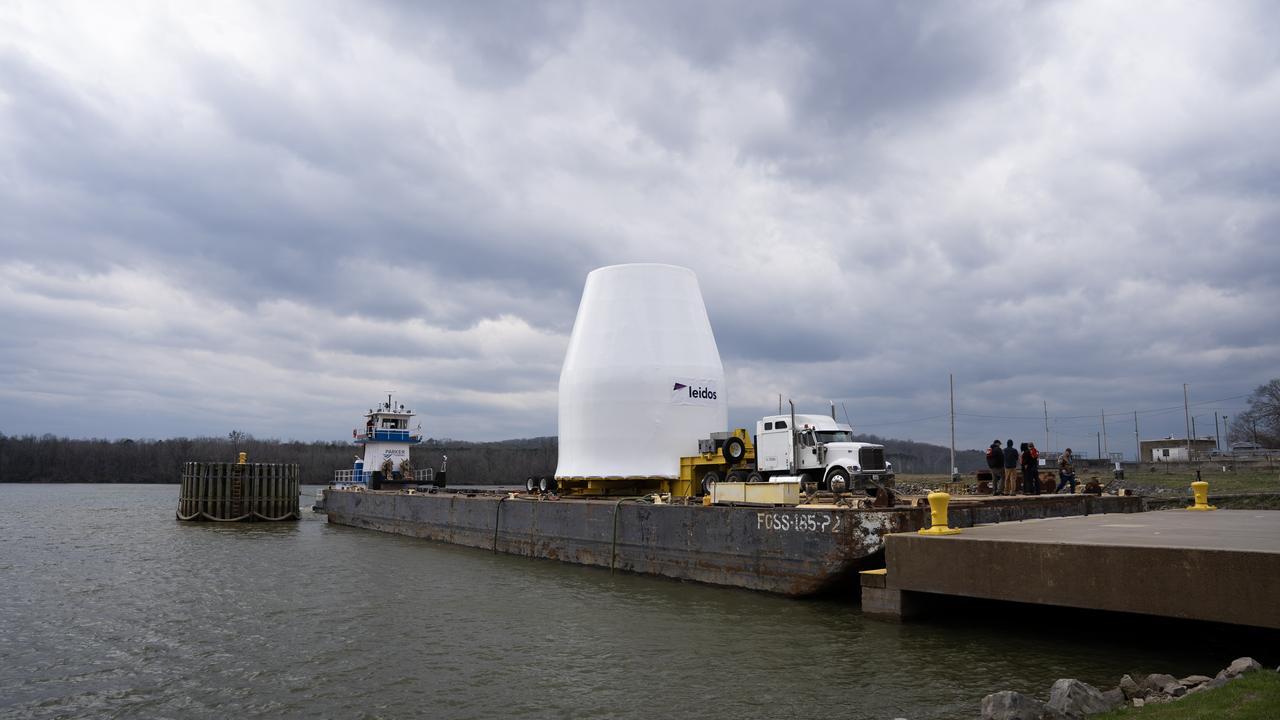

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
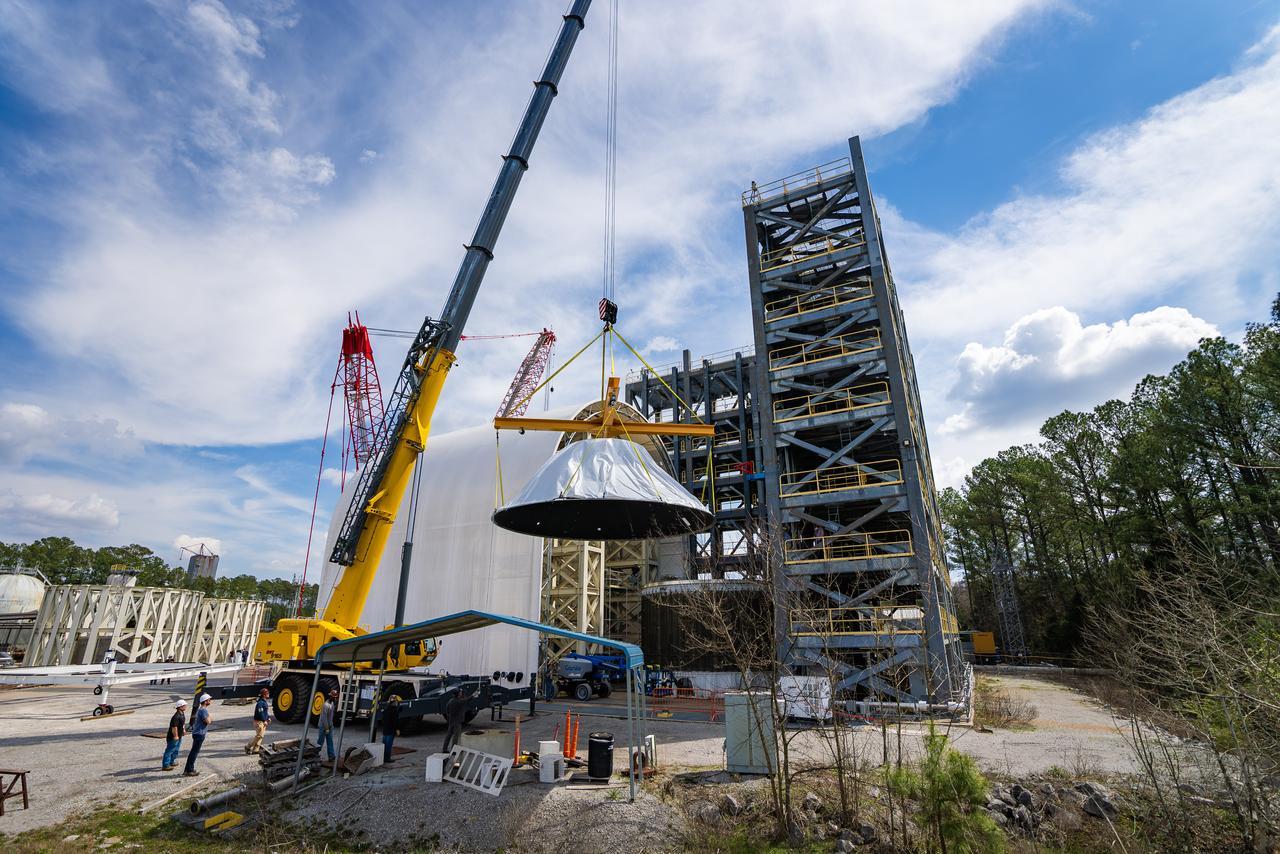

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
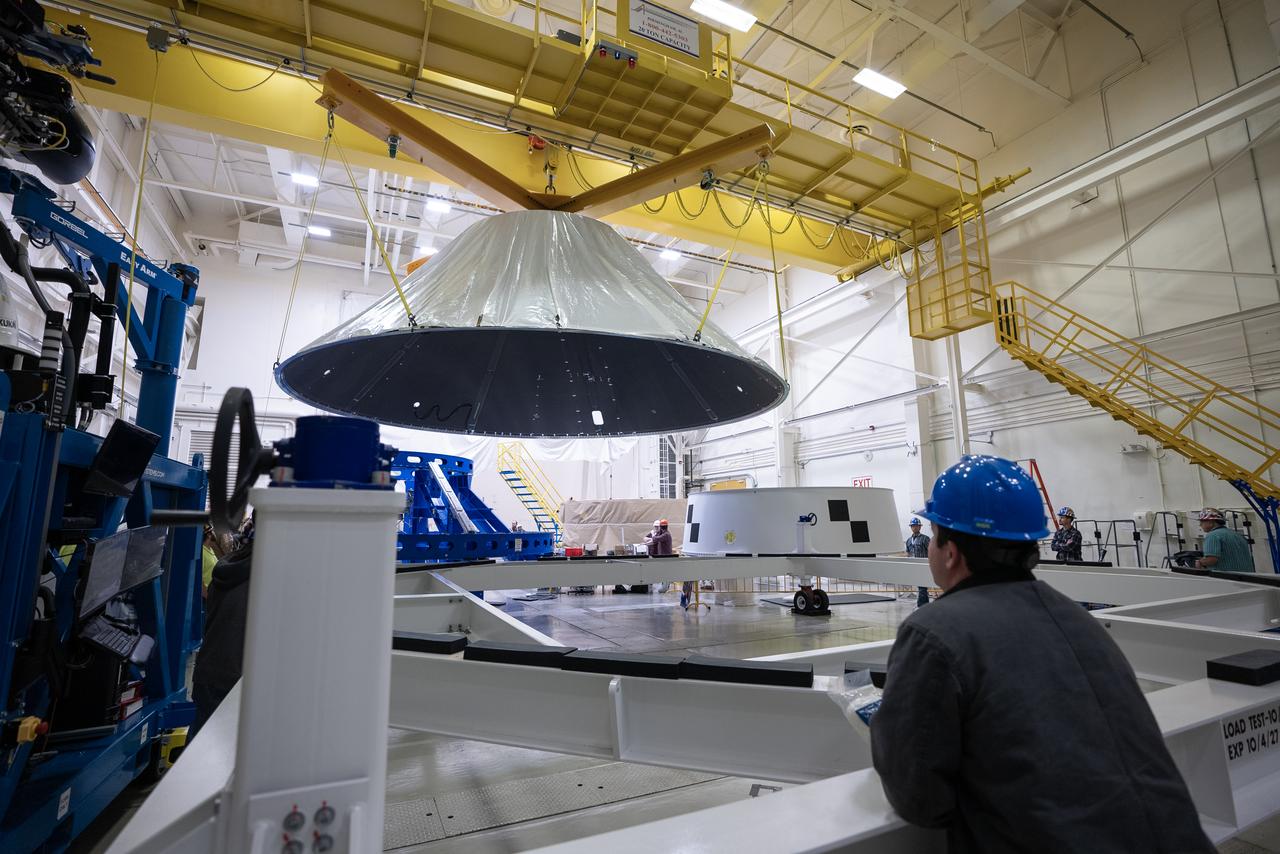

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
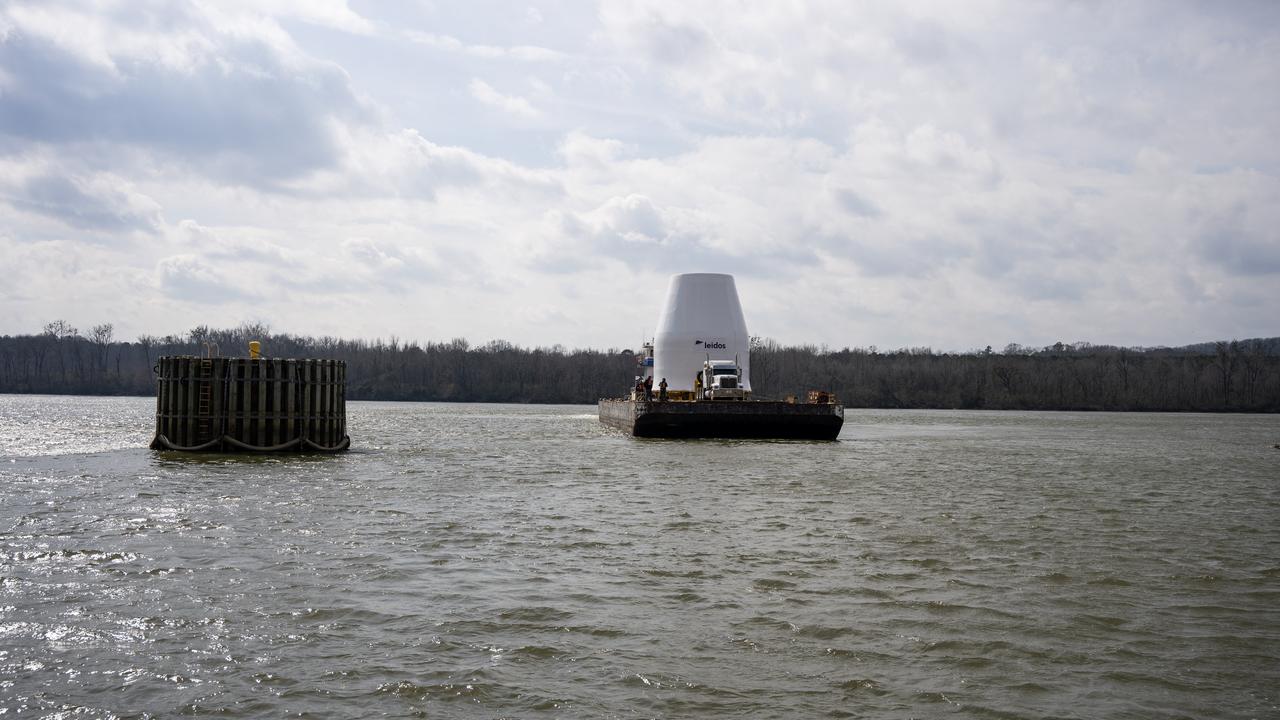

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
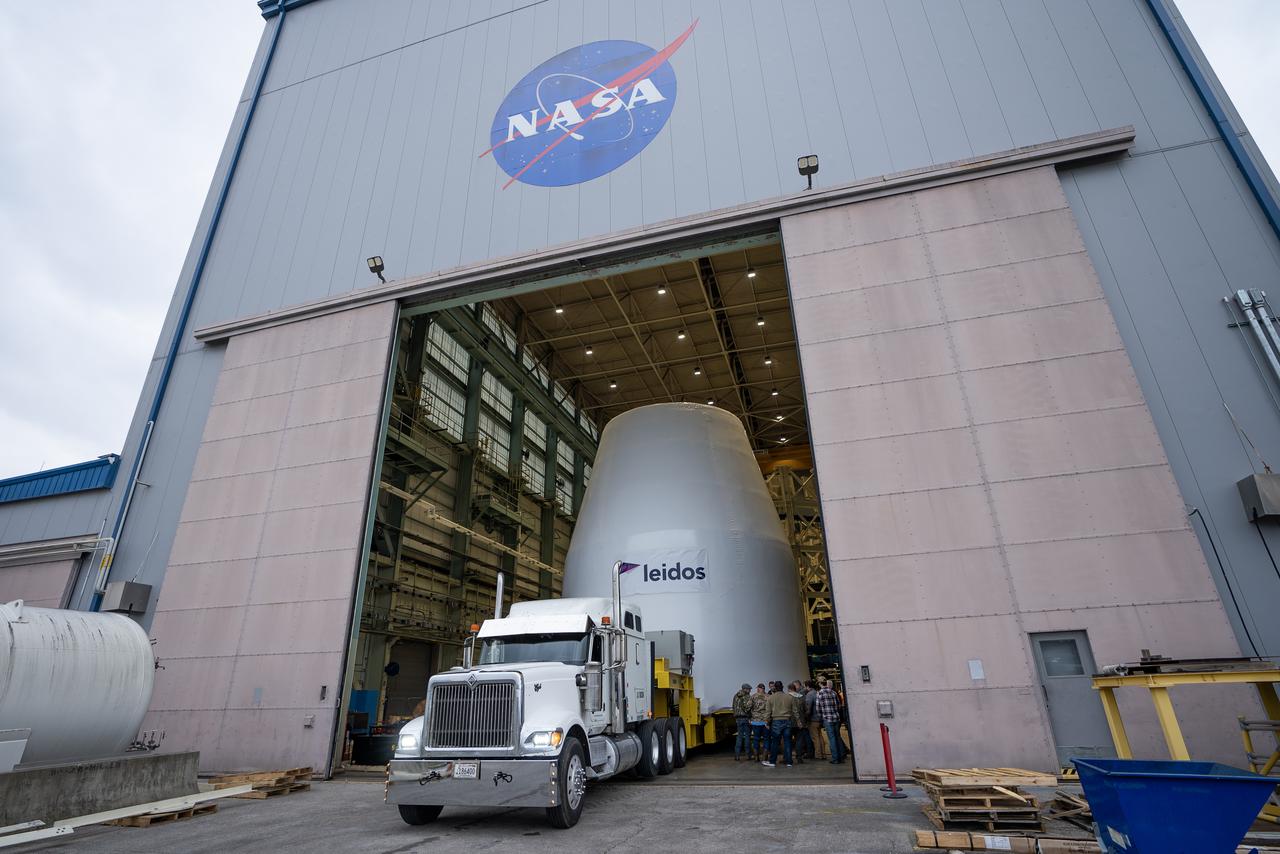

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
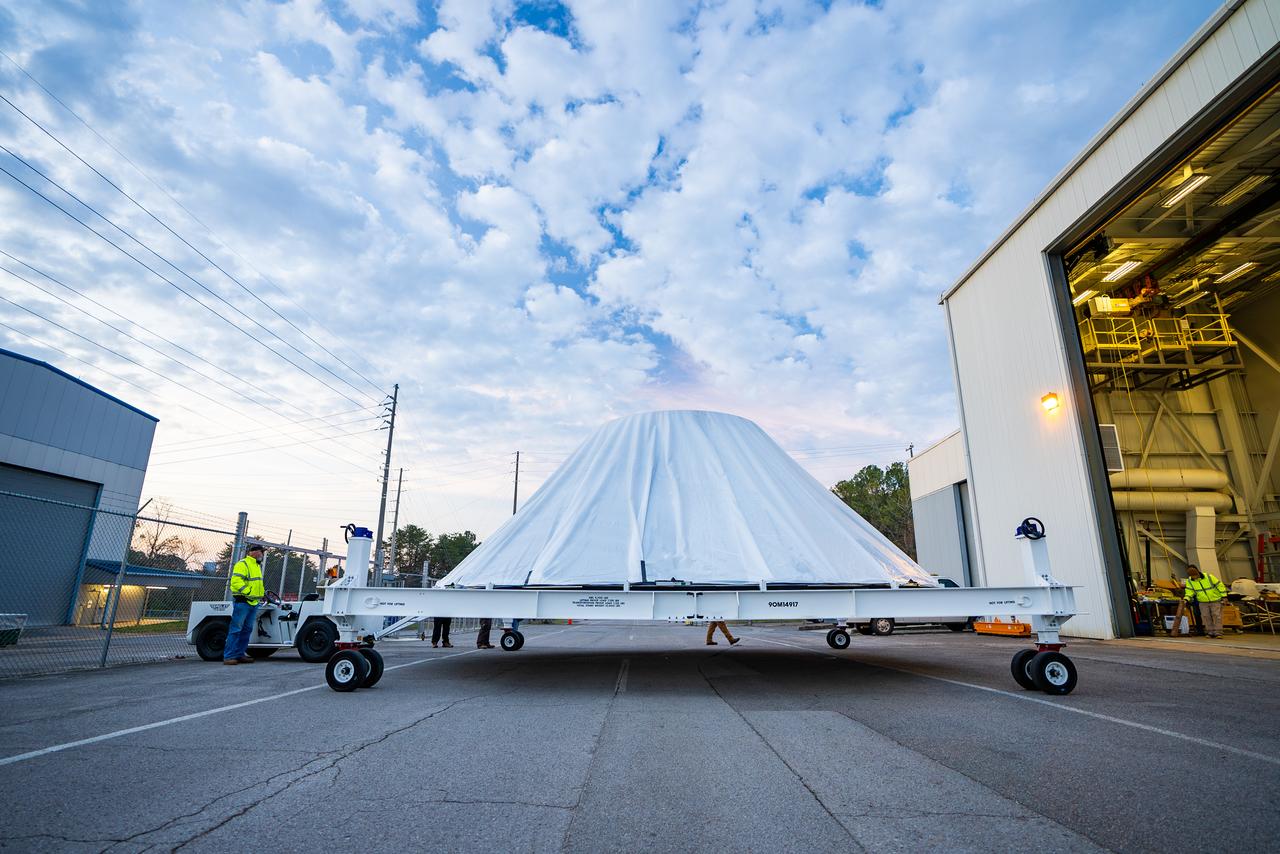

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
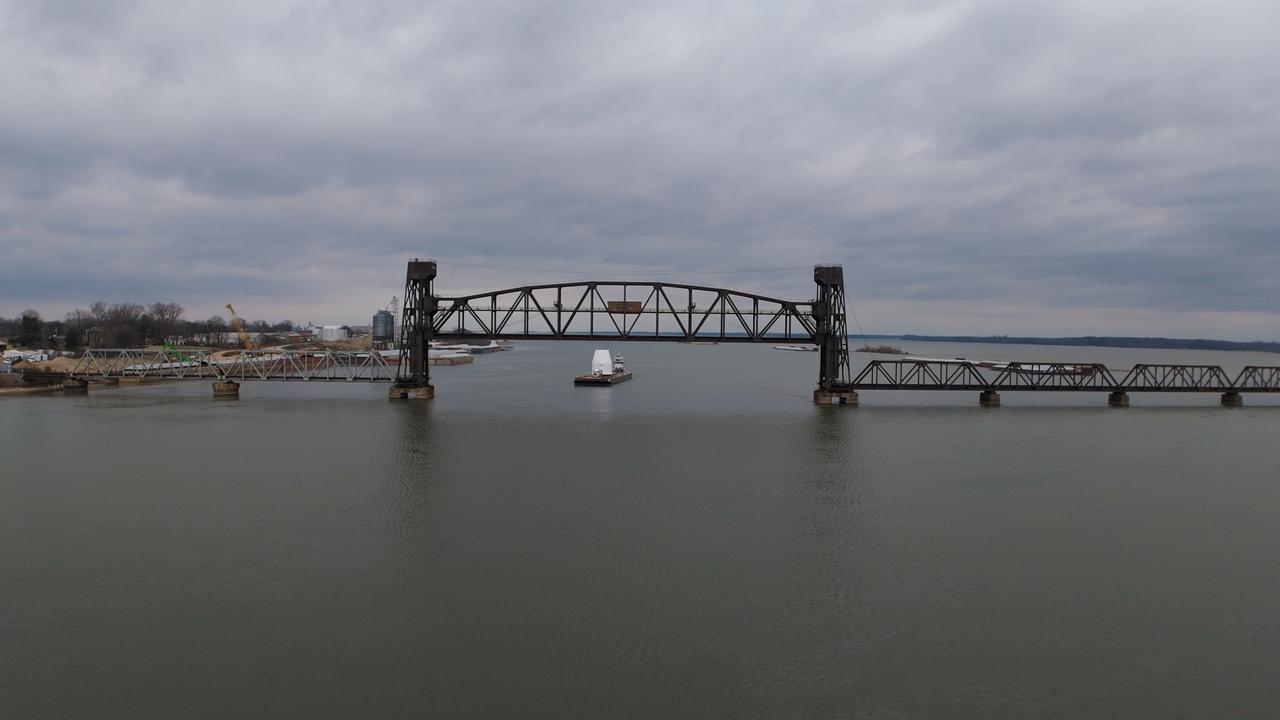

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
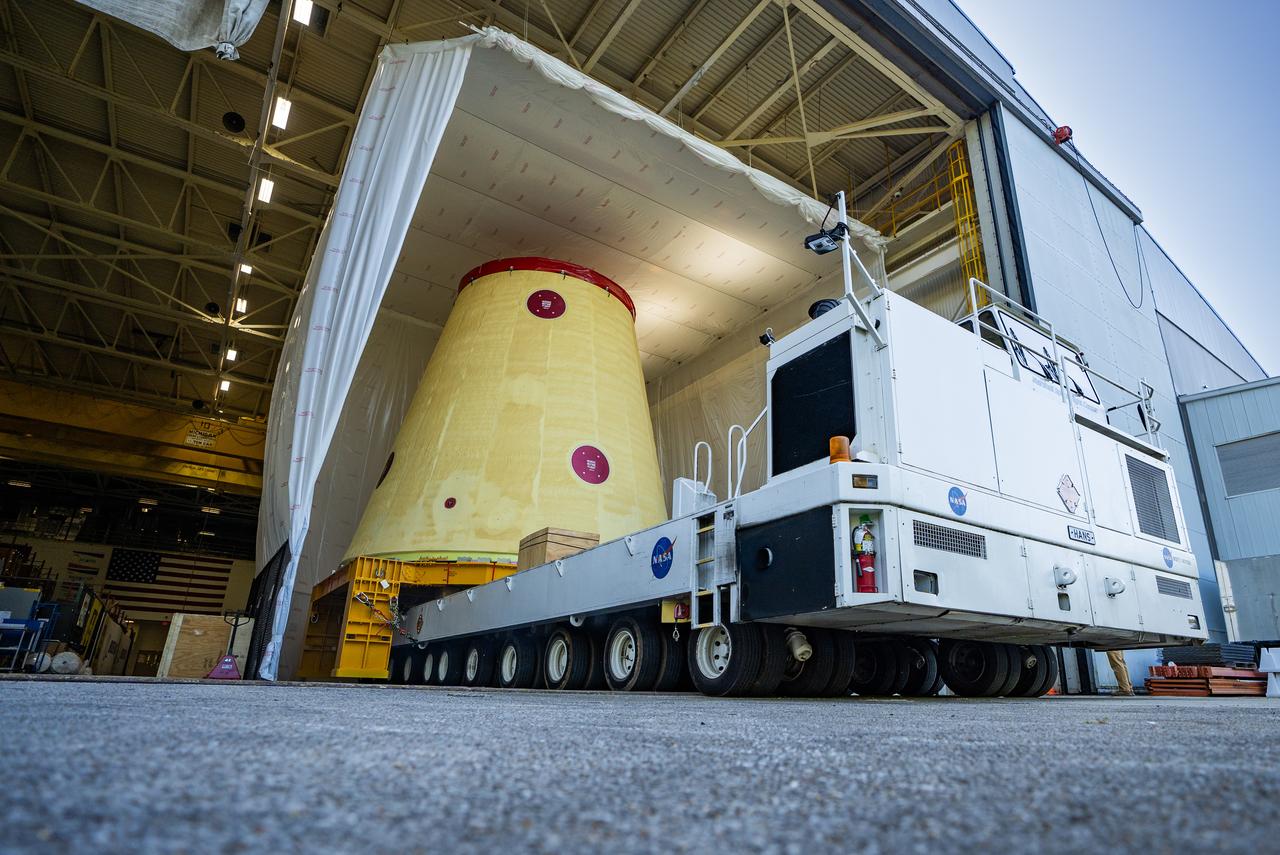

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
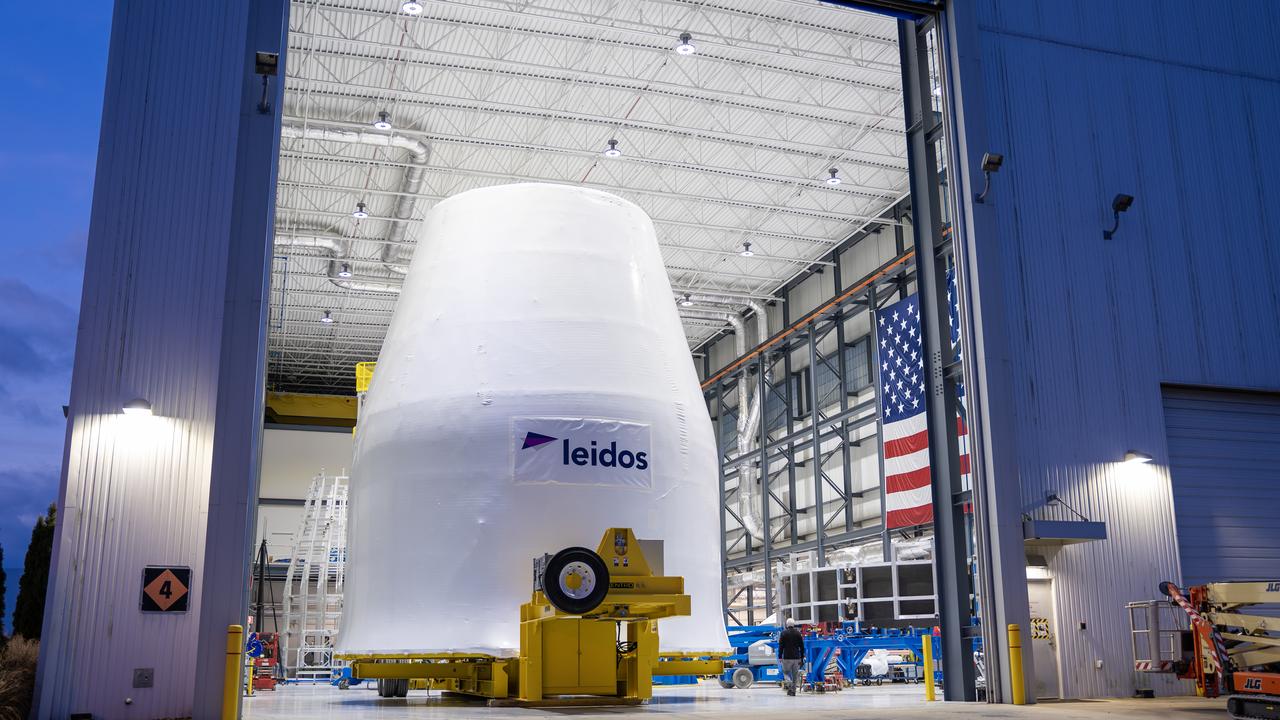

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These images show NASA employees attending an event April 10, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
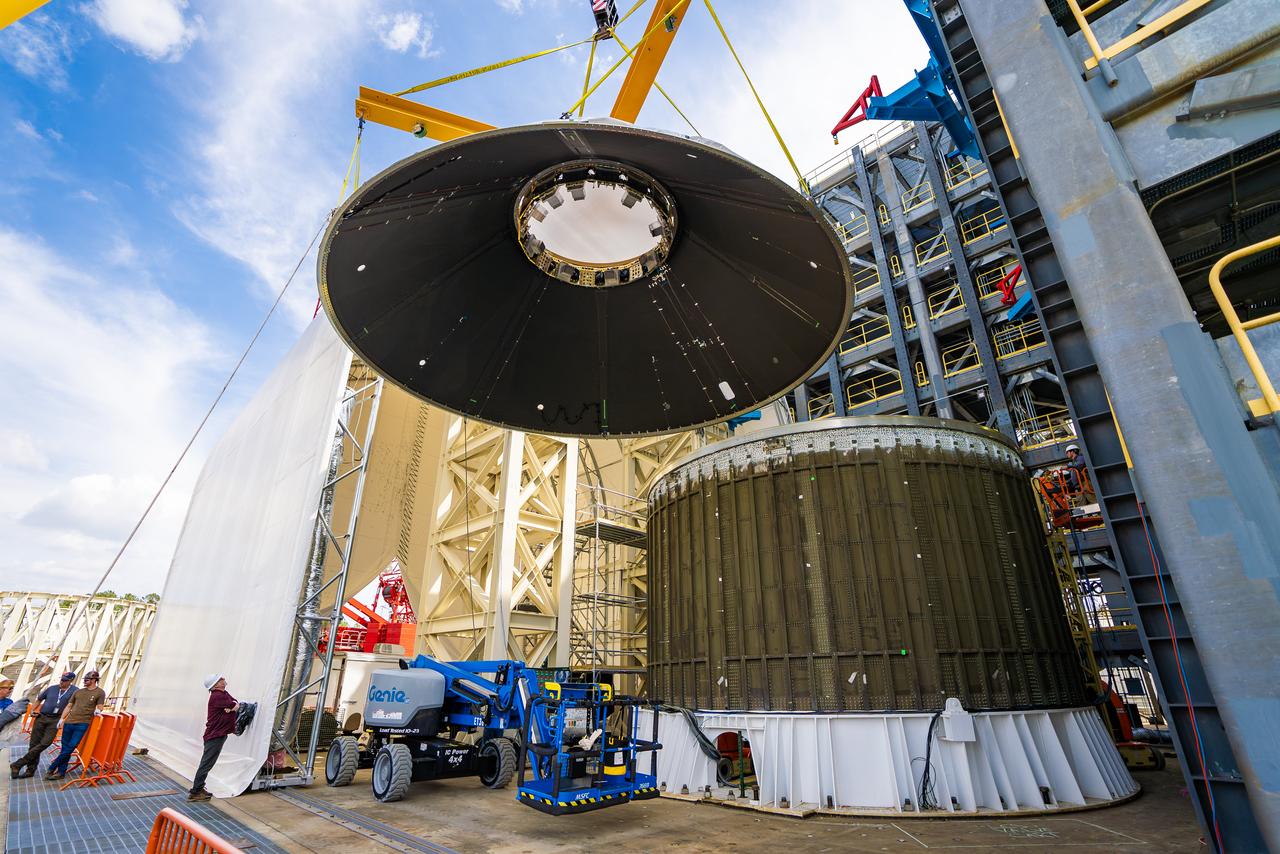

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
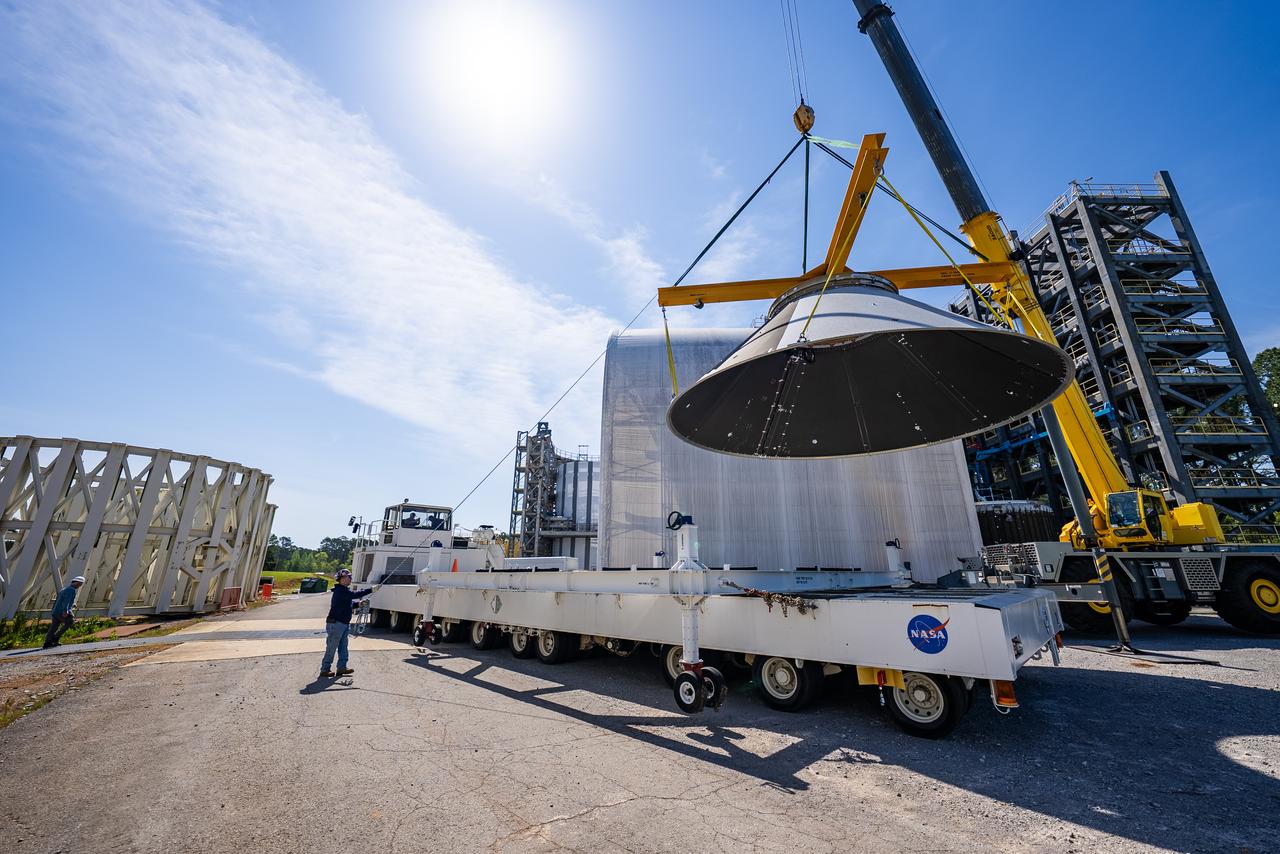

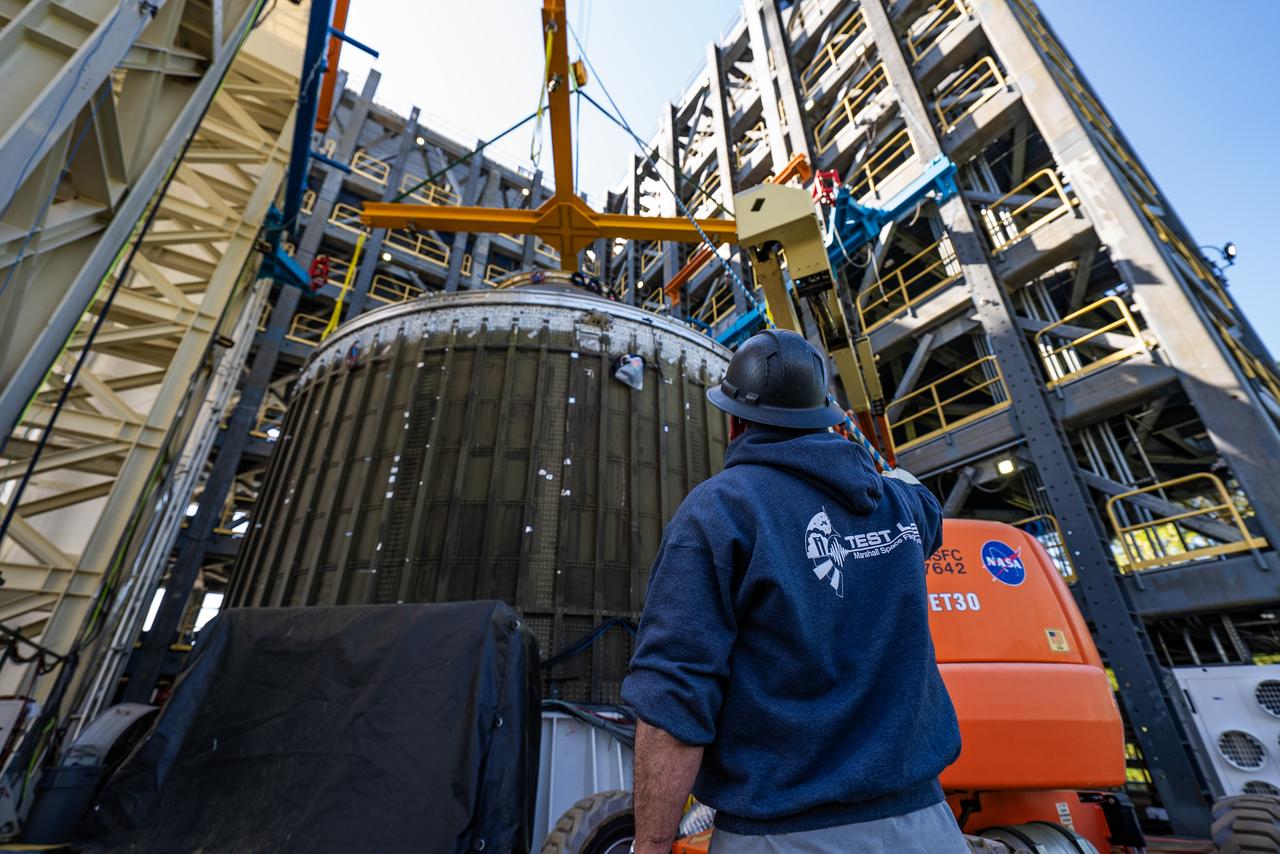
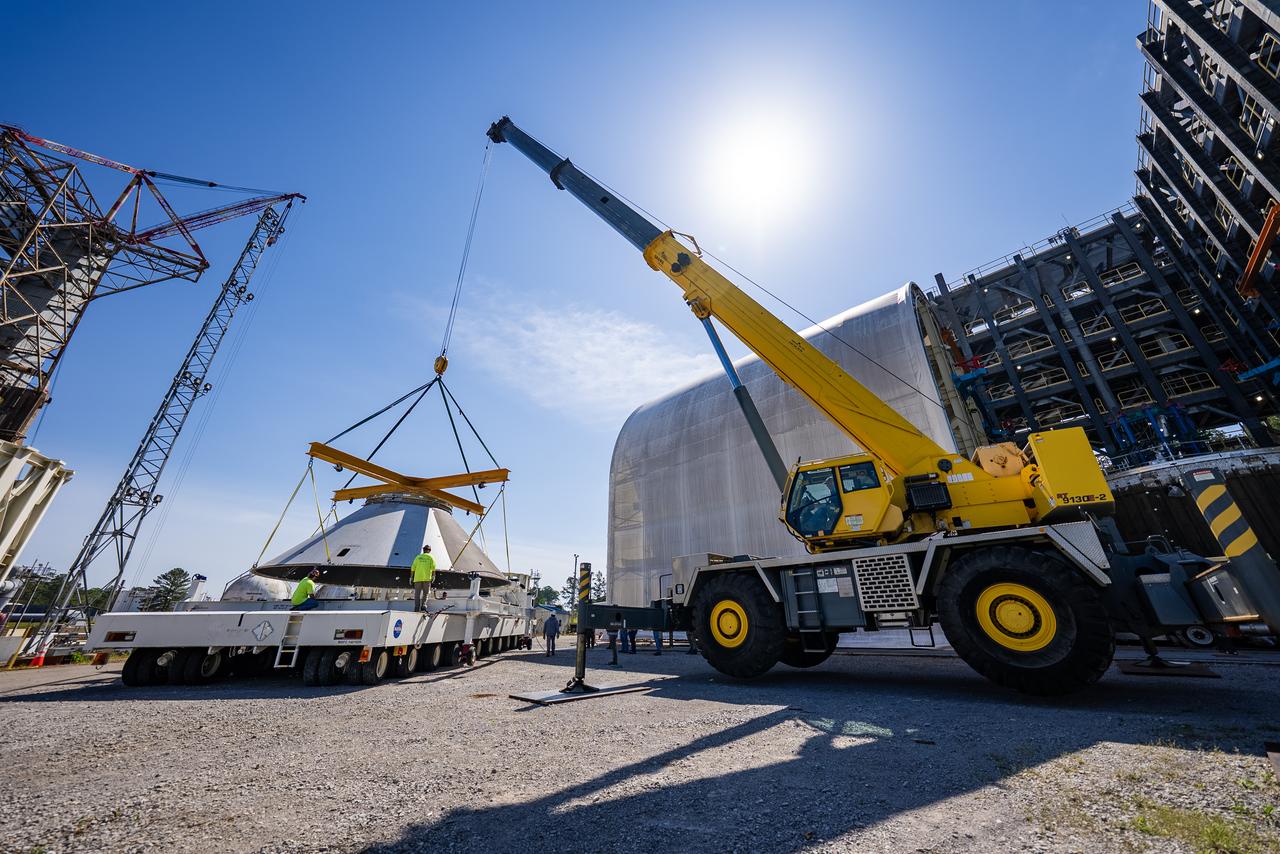
Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
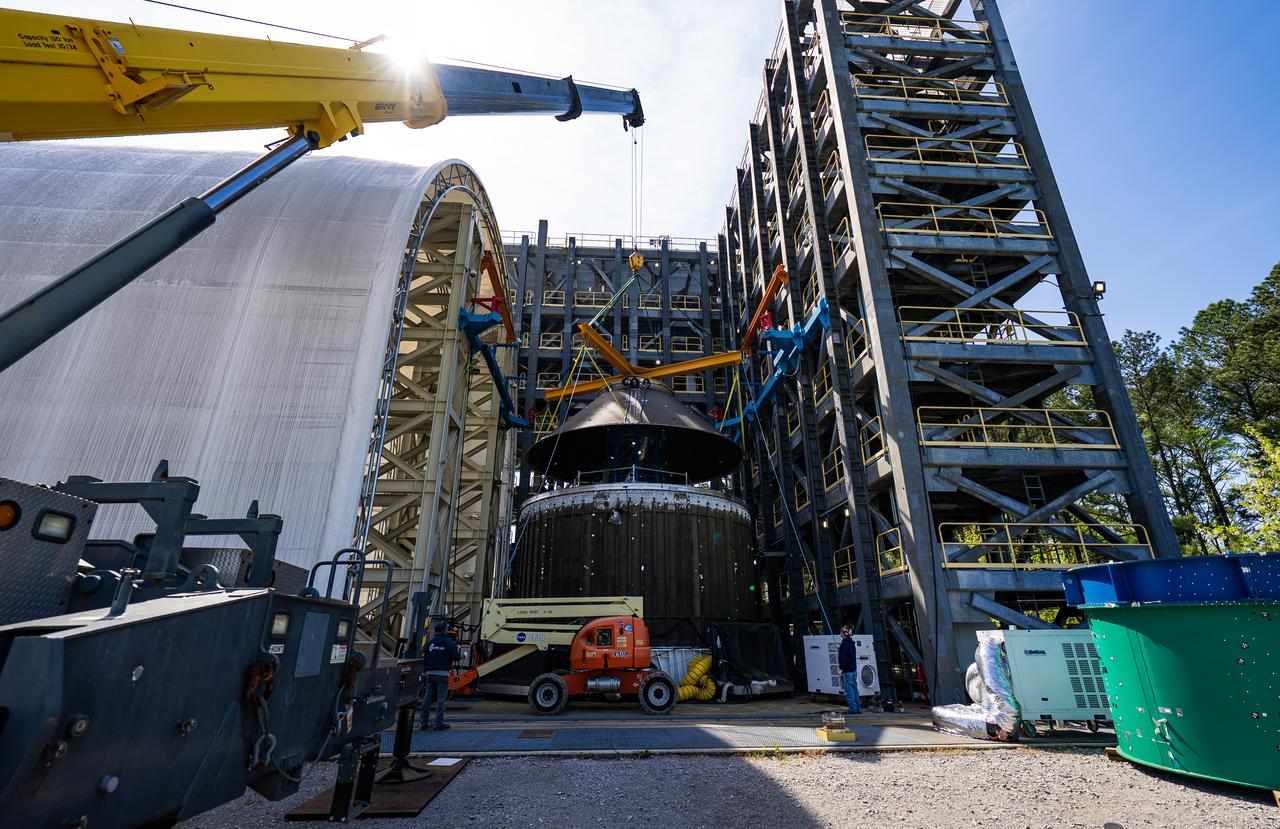

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
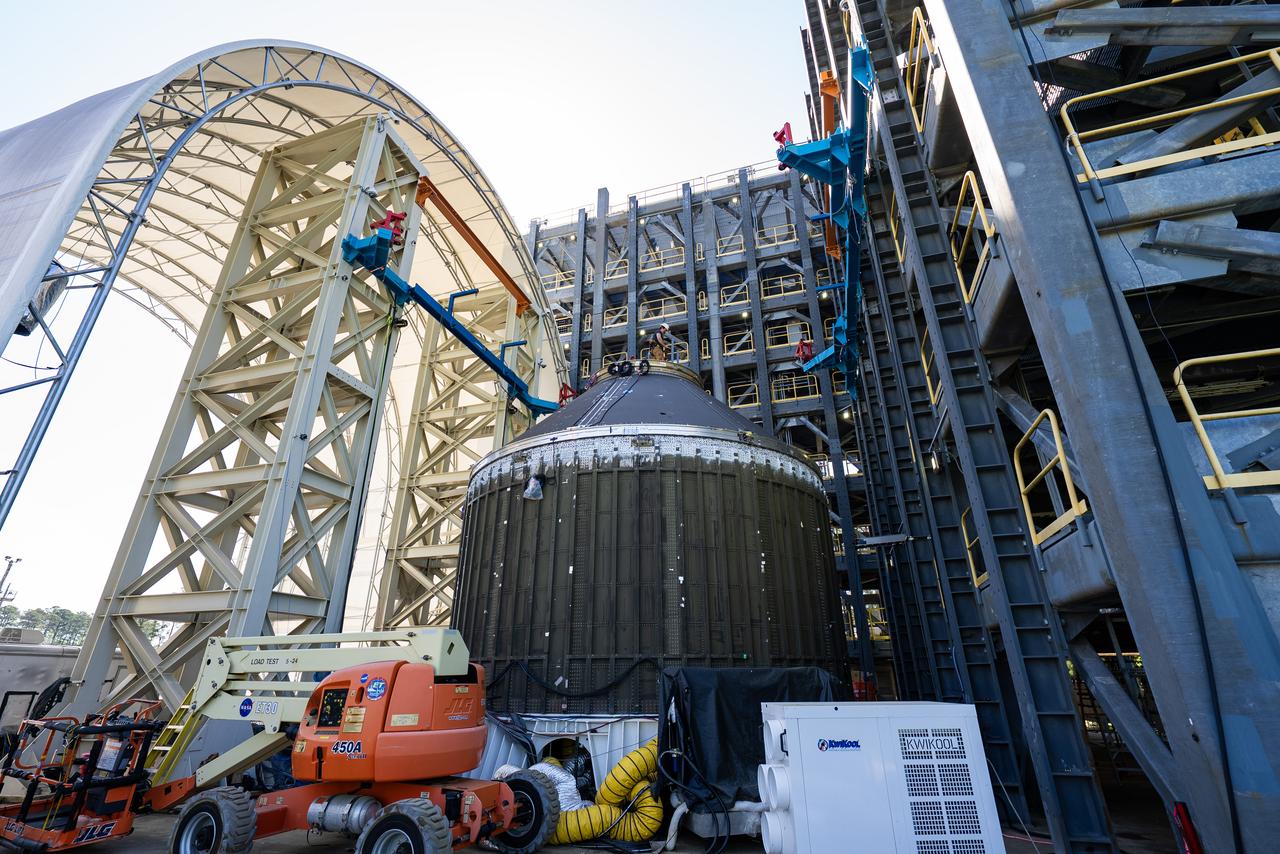

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
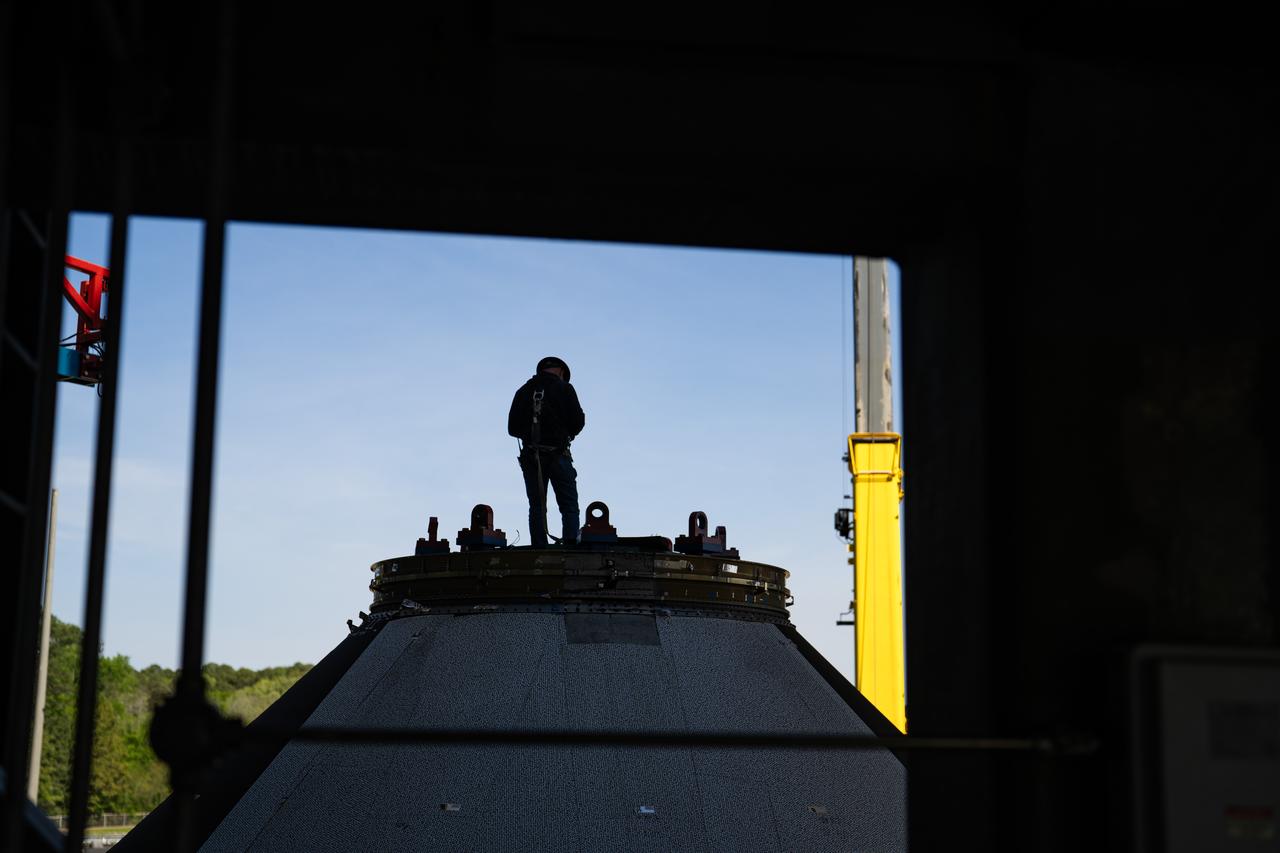

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

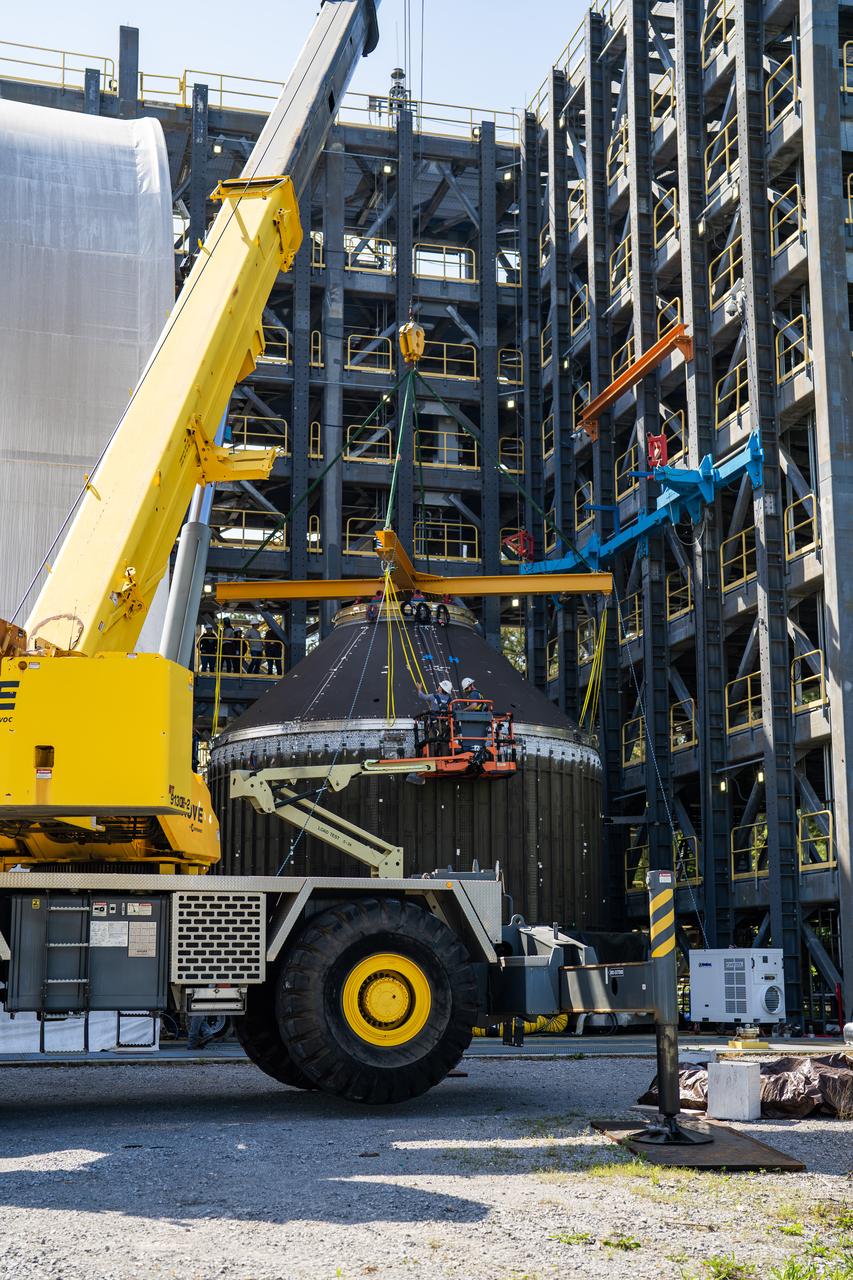
These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
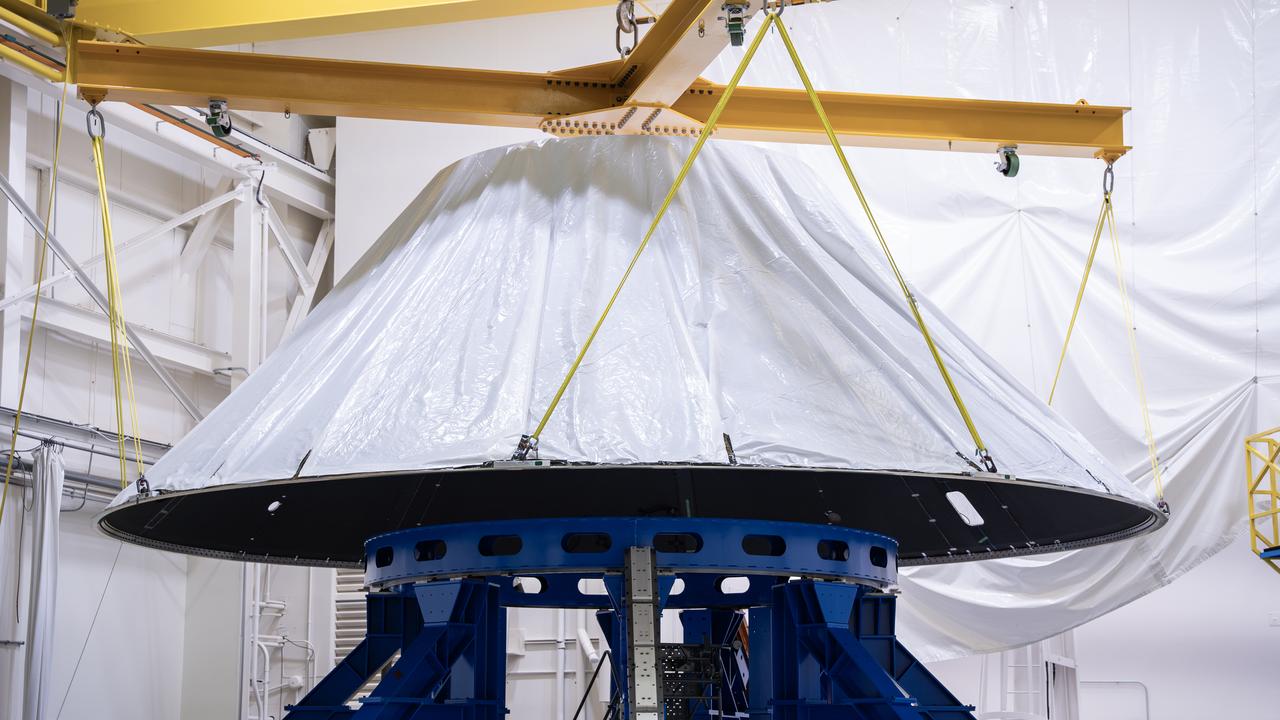

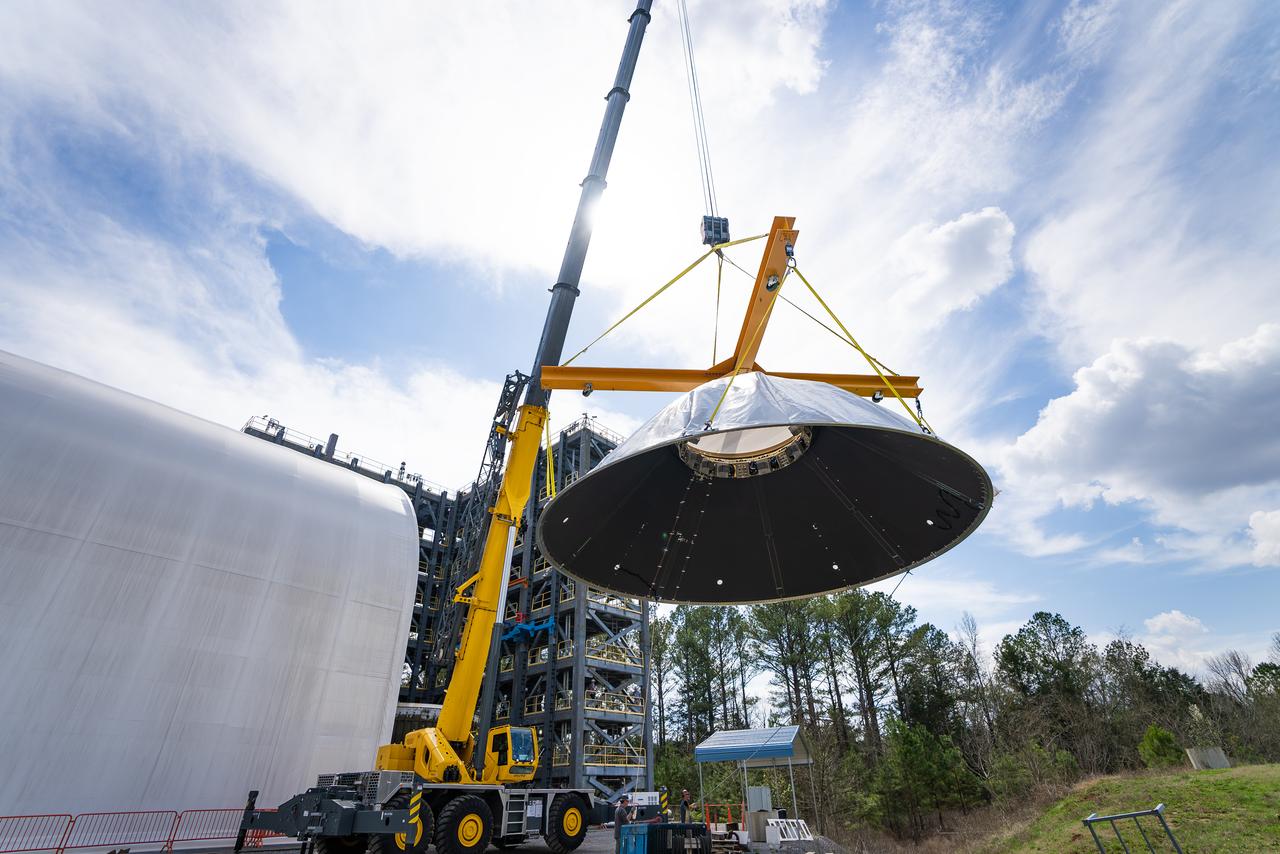
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
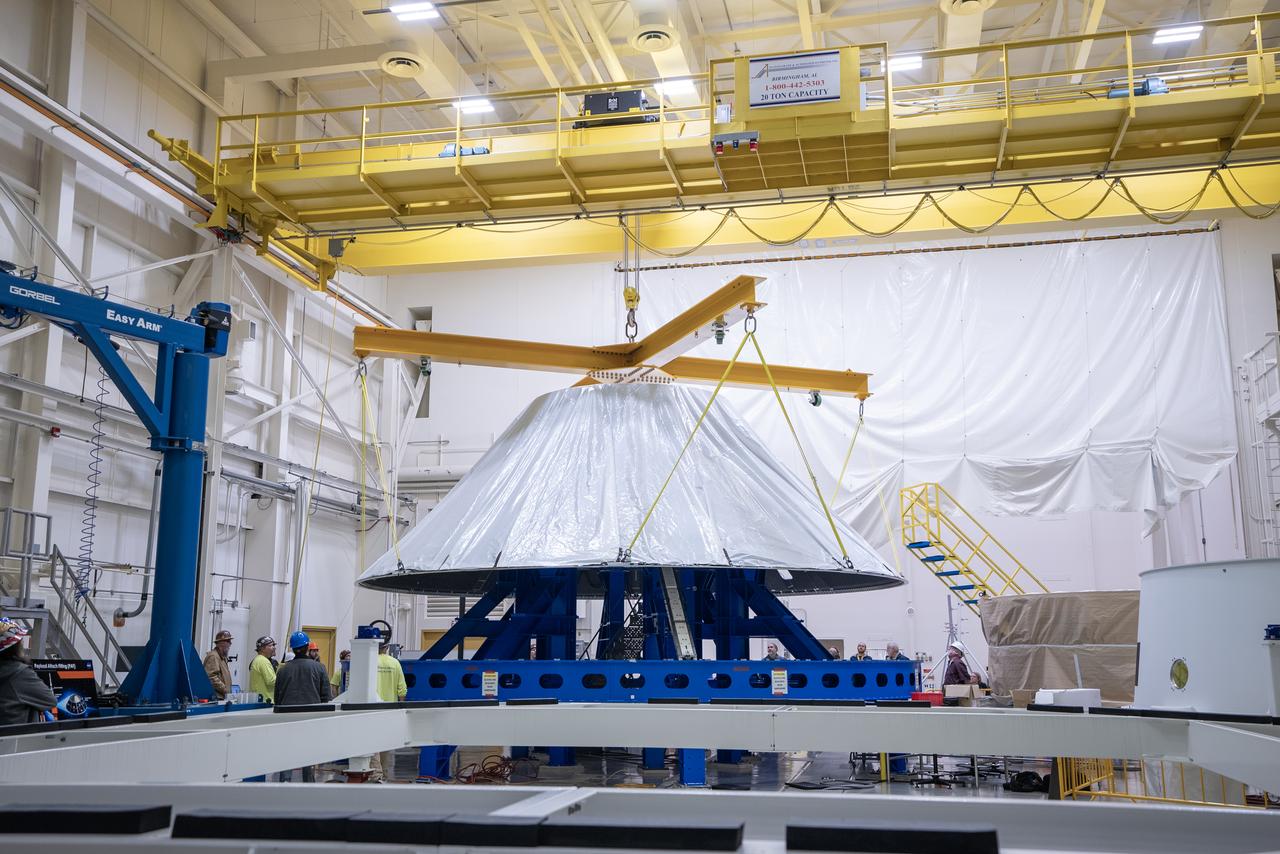

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
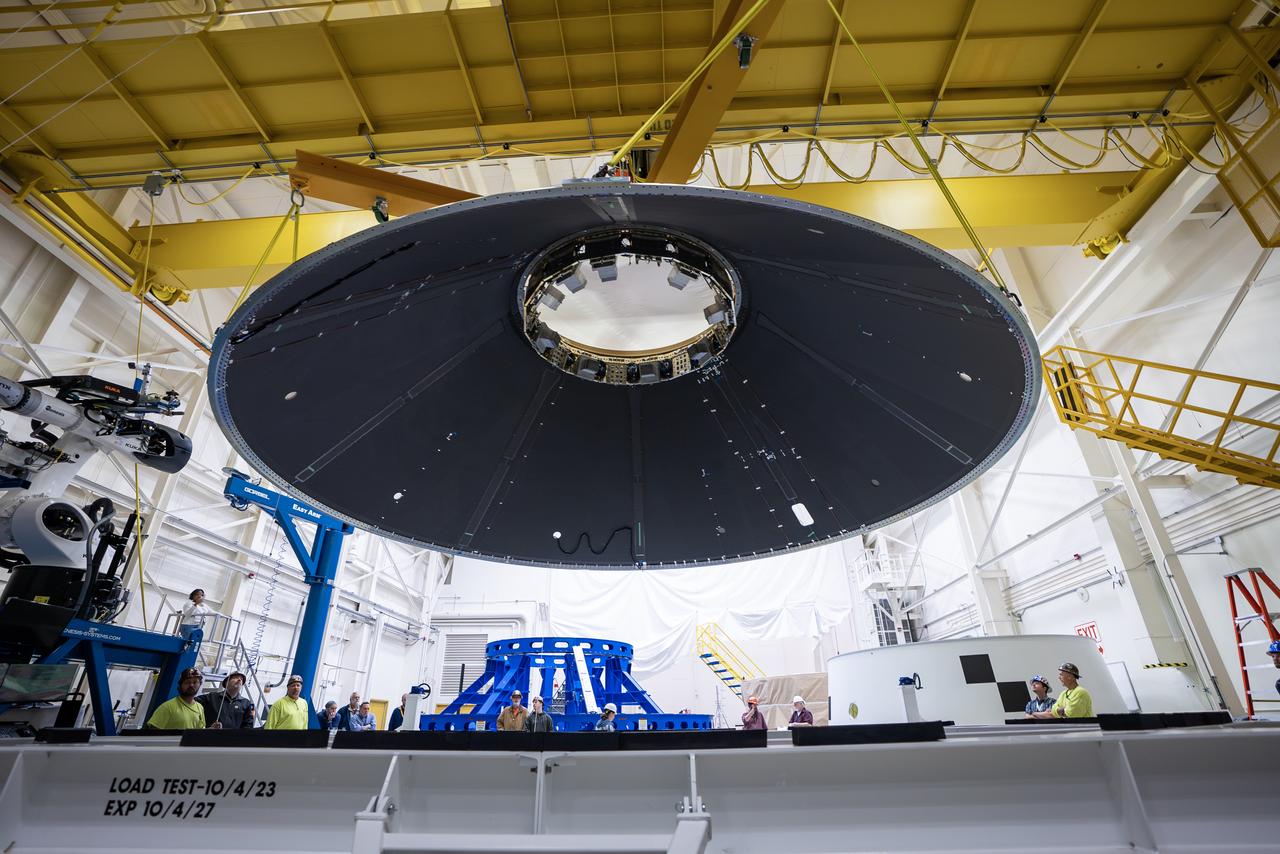

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
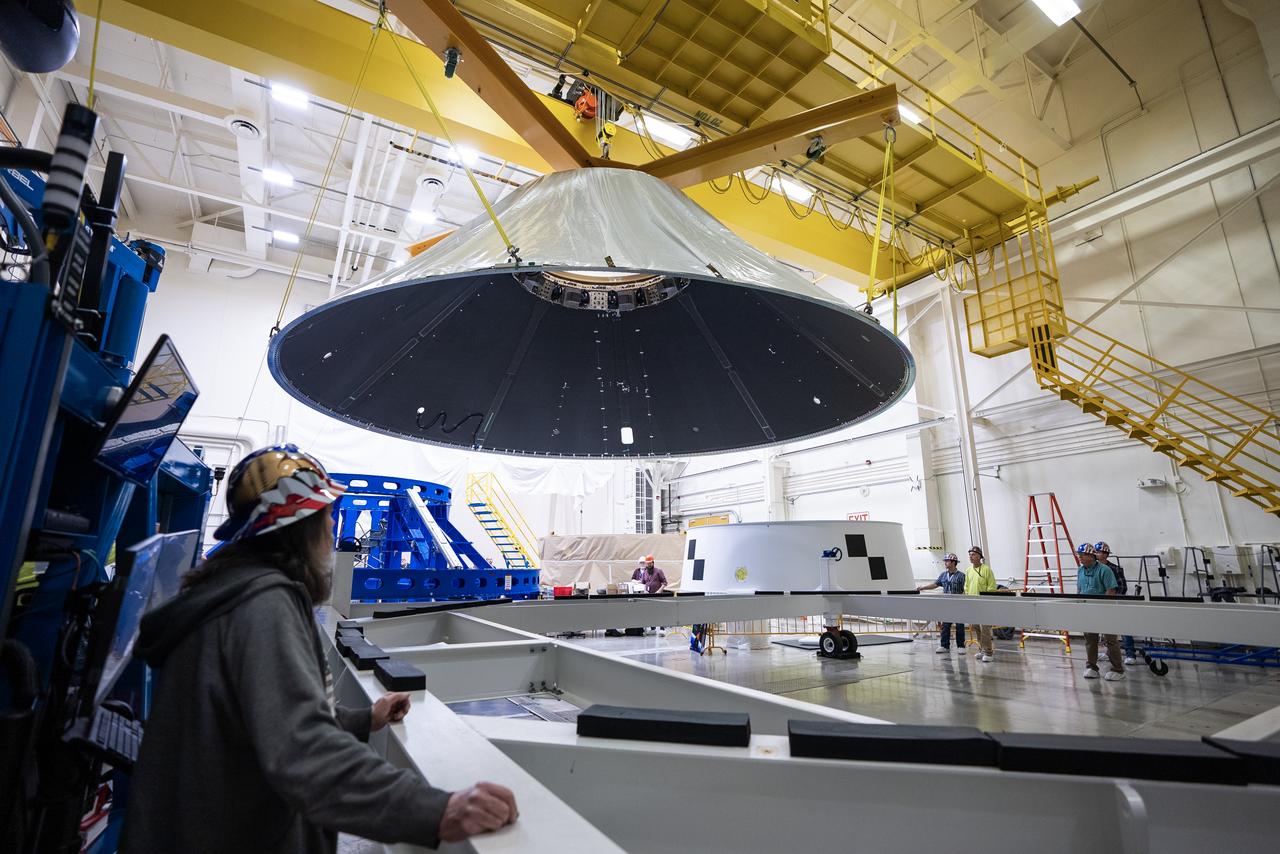

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
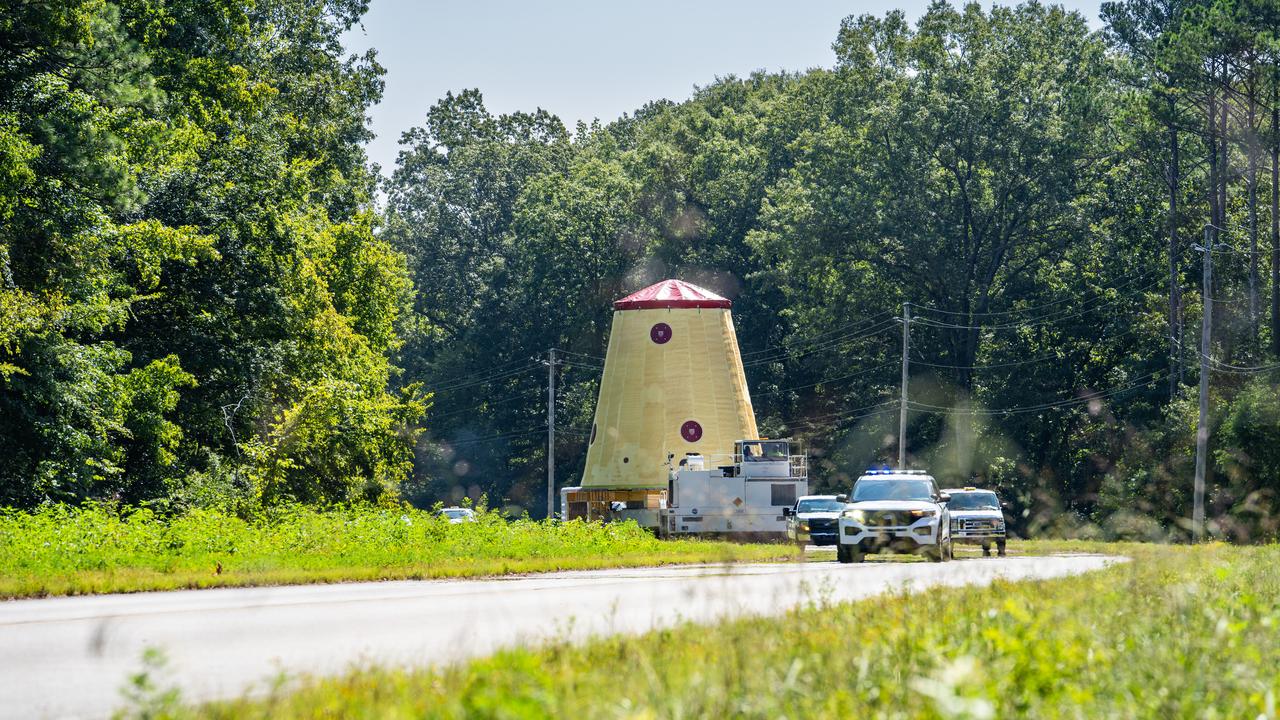

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch
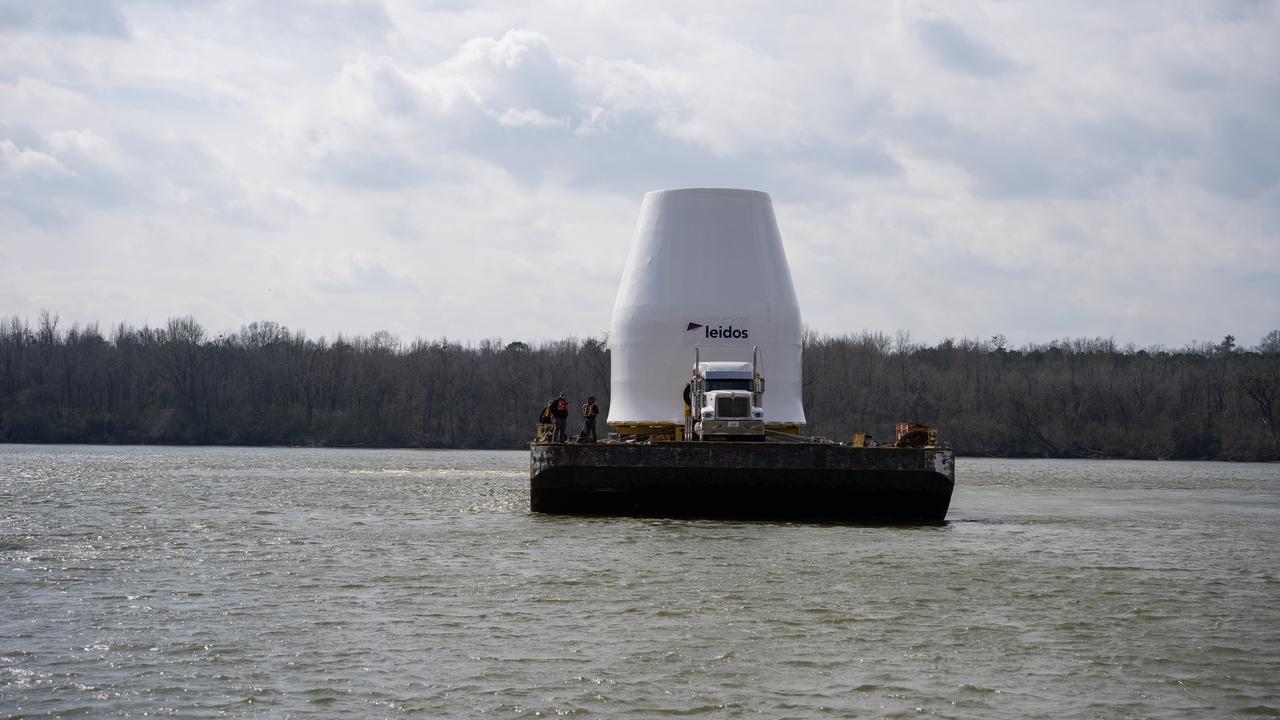

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
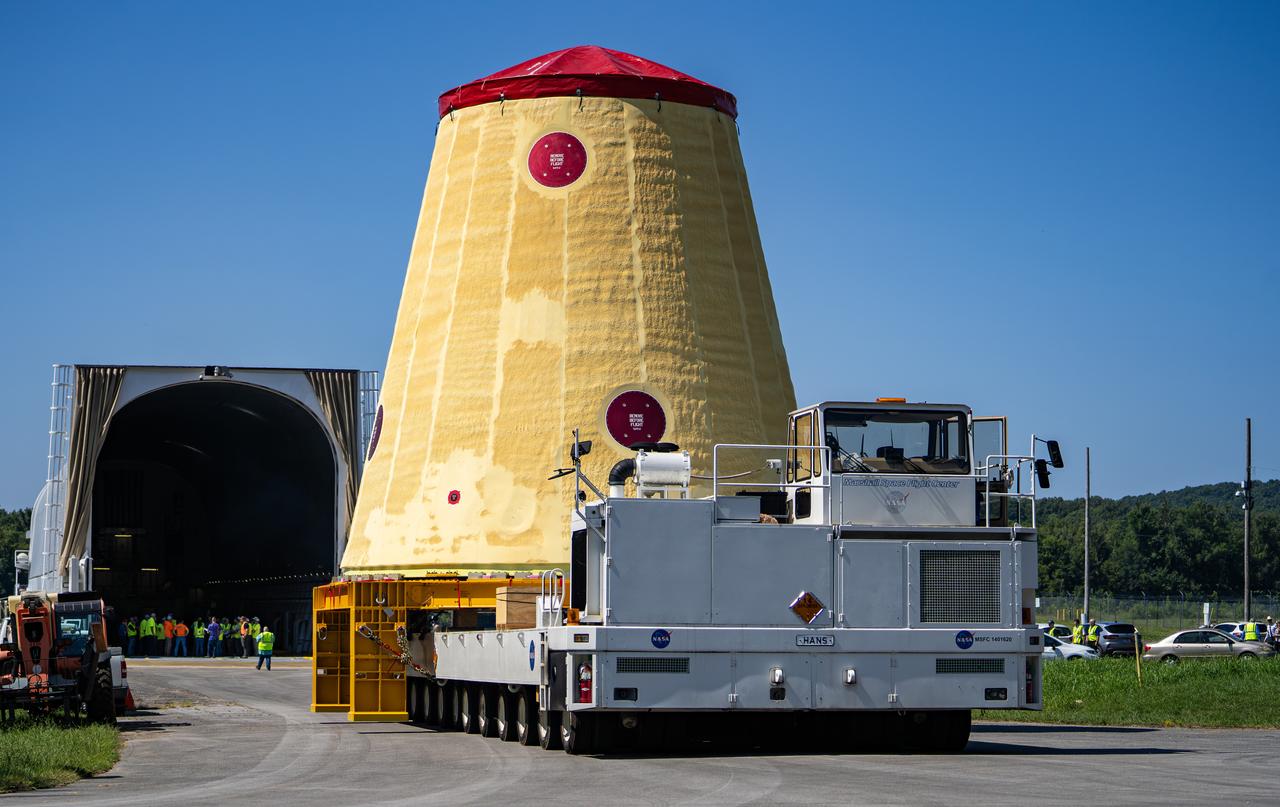

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
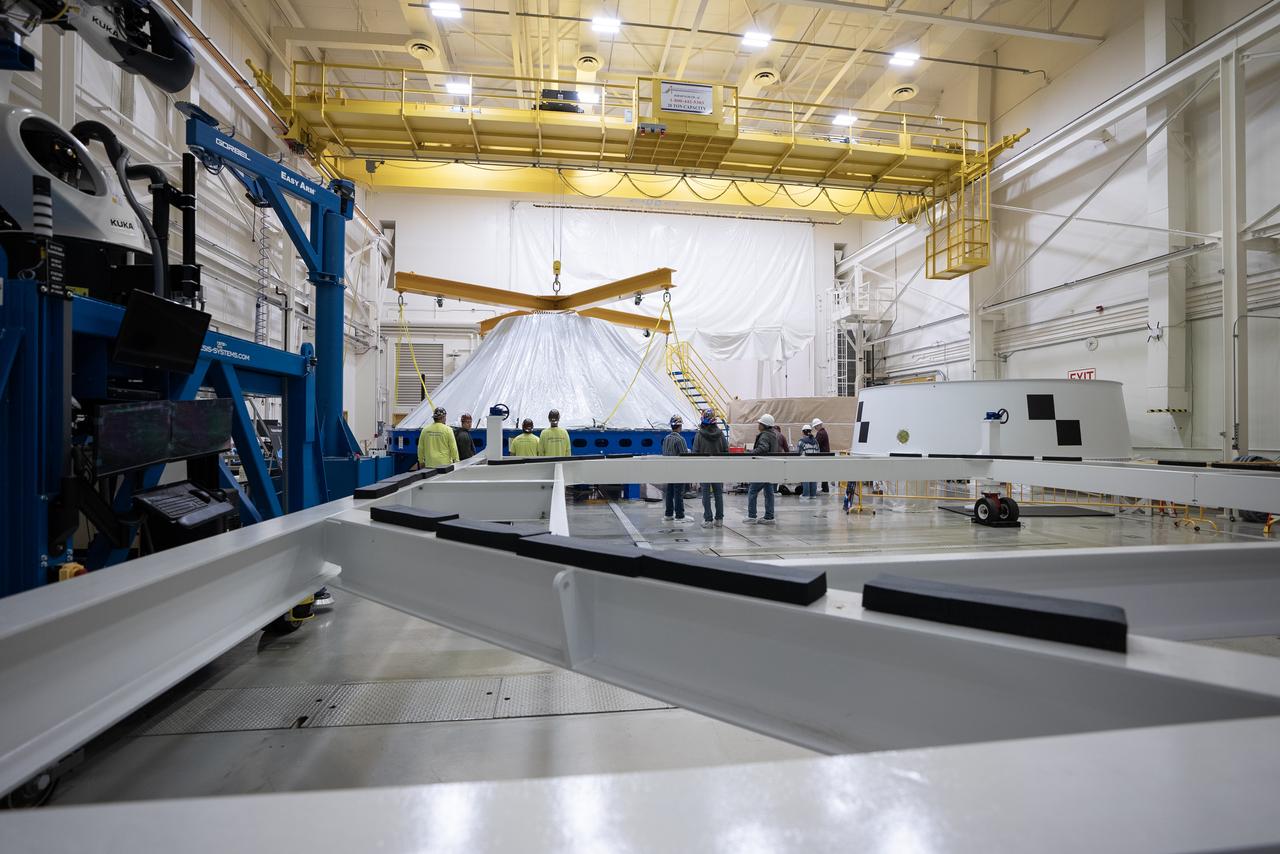

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
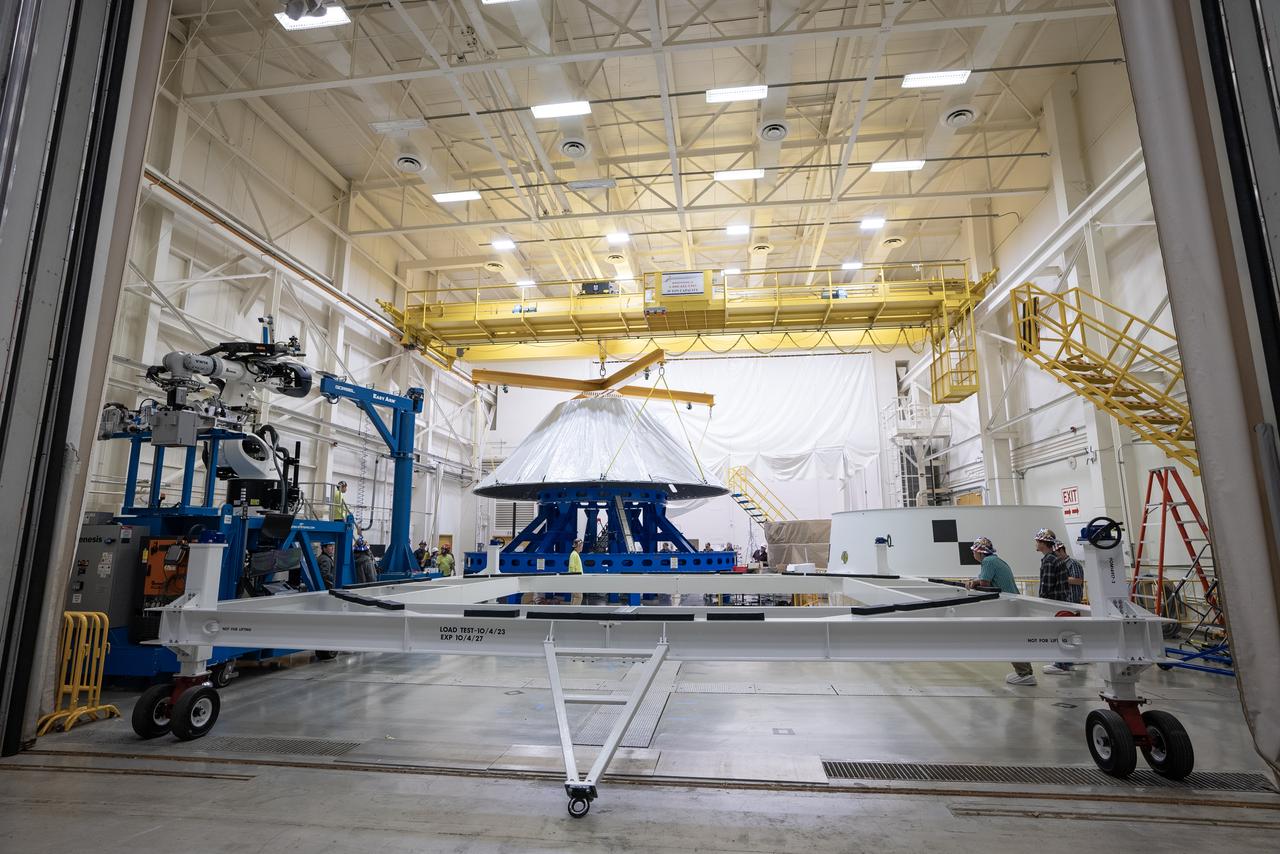

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
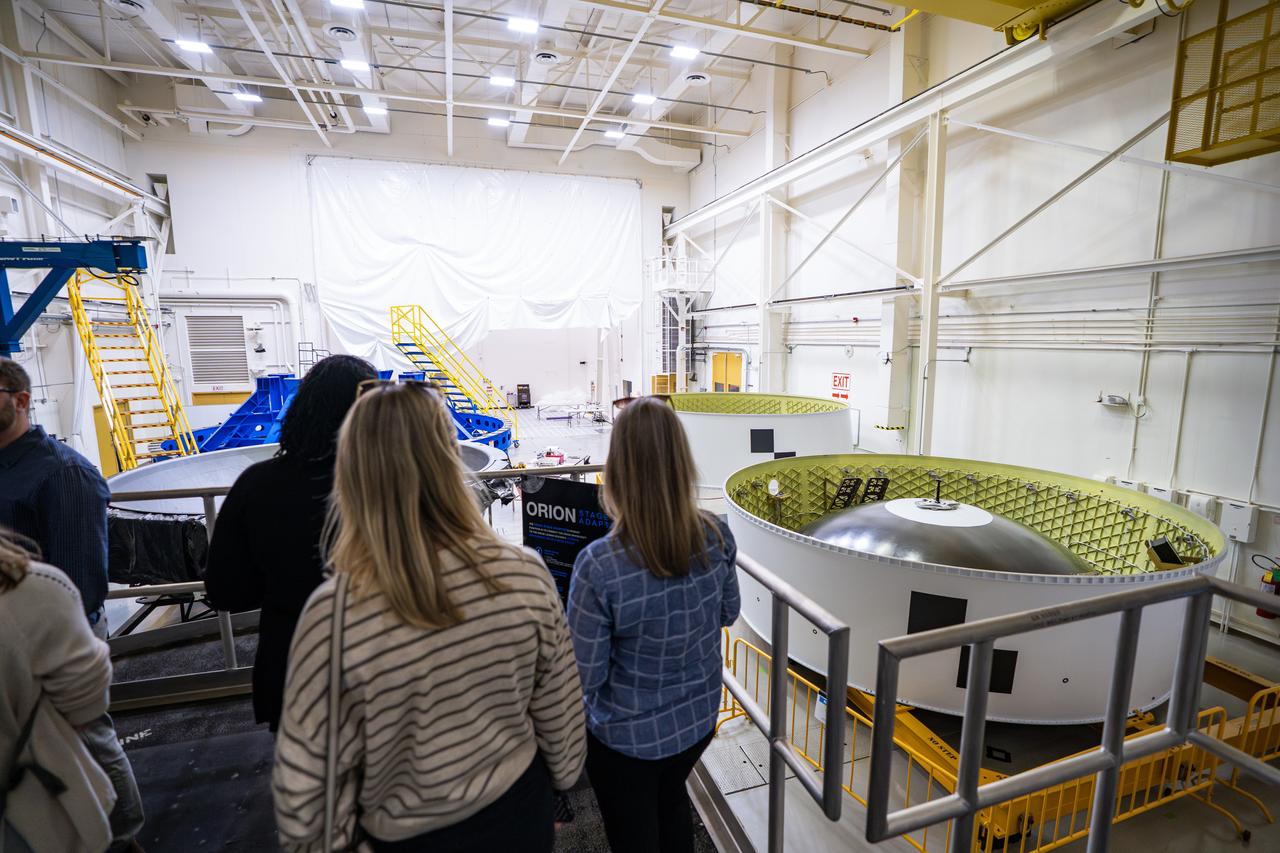

These images show NASA employees attending an event April 10, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
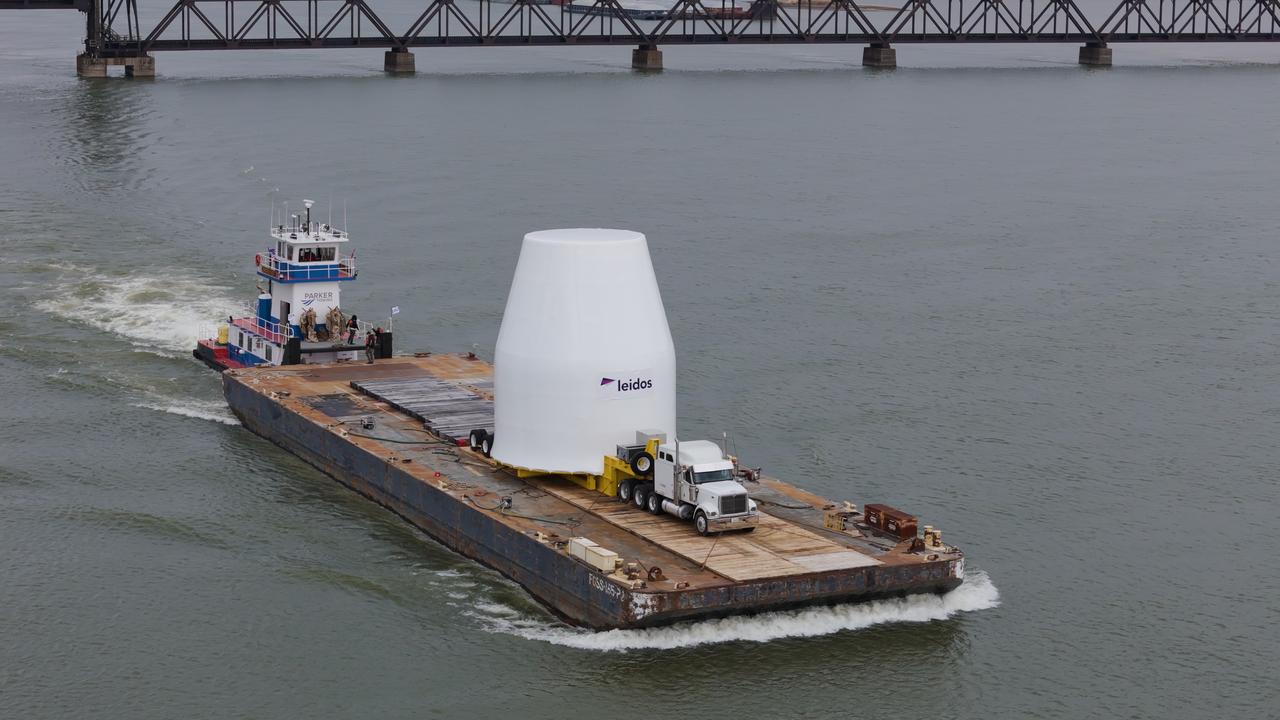

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
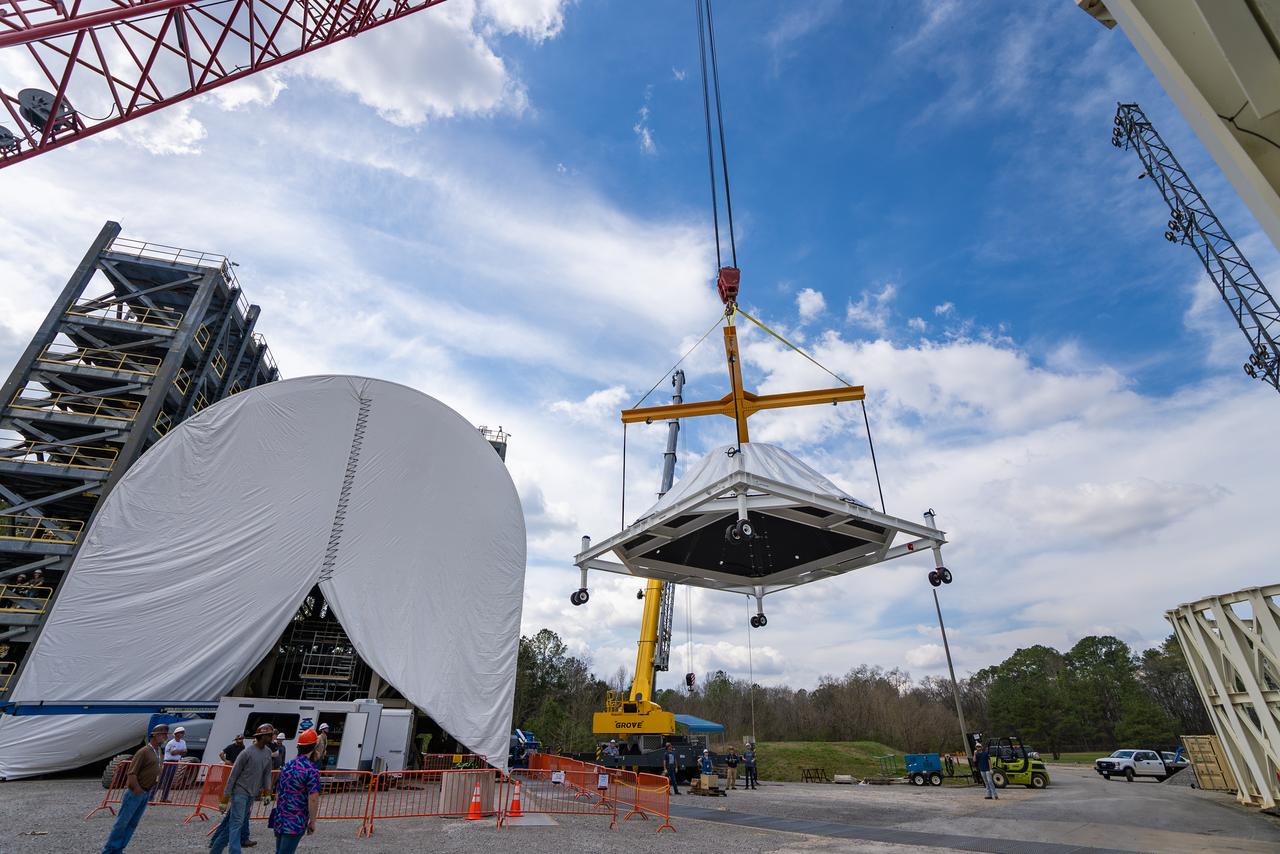

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
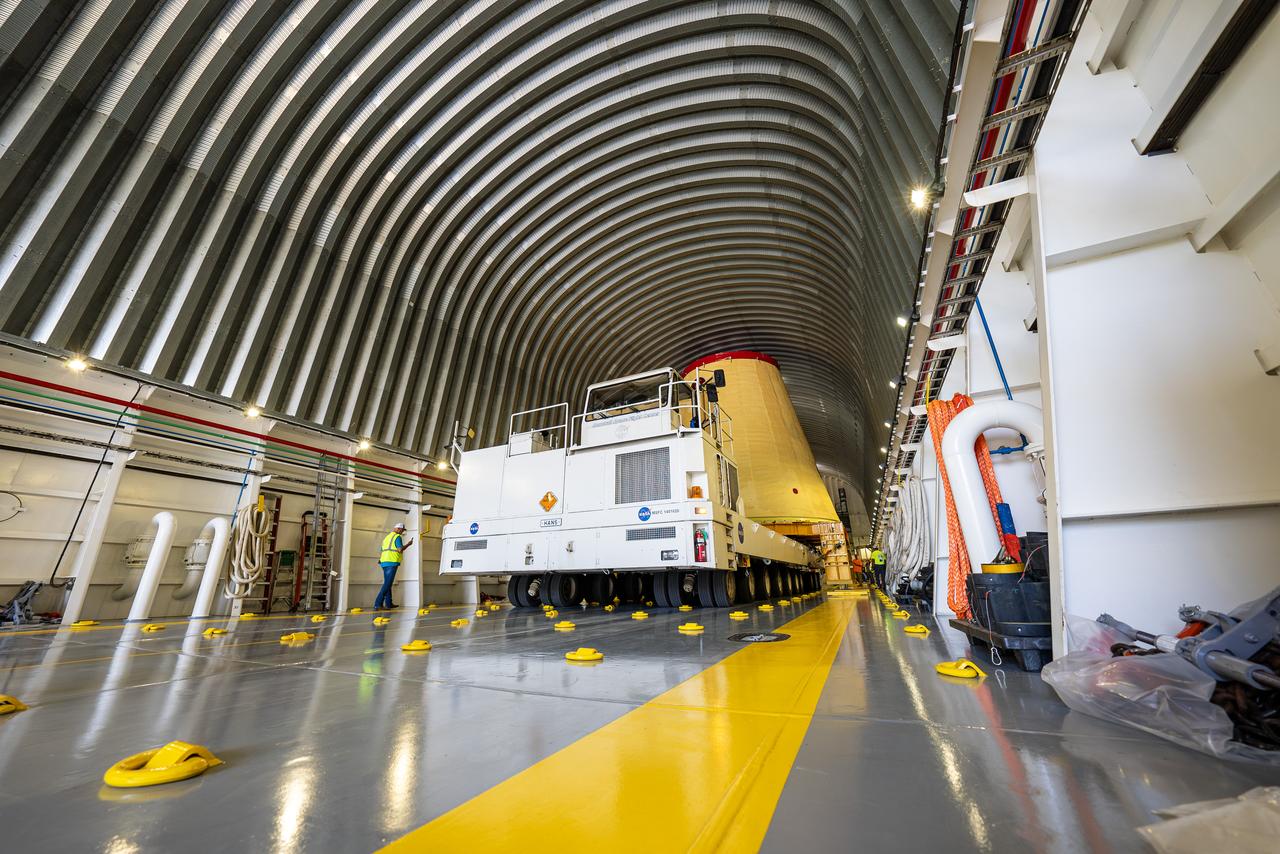

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
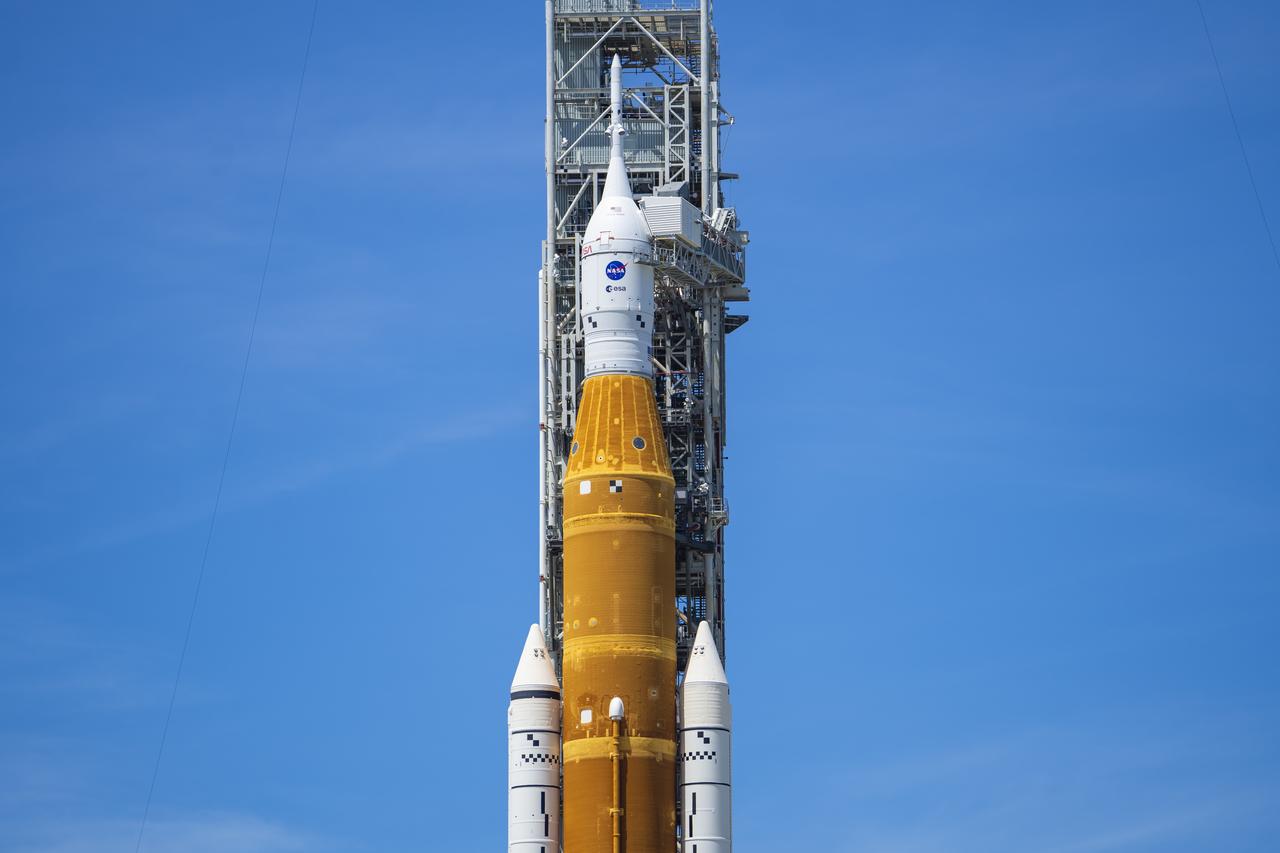

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson (second from right) meets with members of the “red crew” after the launch of Artemis I at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 16, 2022. Members of the red crew include Jacobs/TOSC ERC employees Billy Cairns, cryogenic engineering technician (left); Chad Garrett (second from left), safety engineer; and Trent Annis (right), cryogenic engineering technician. The team of technicians are part of the personnel specially trained to conduct operations at the launch pad during cryogenic loading operations at the launch pad. Prior to the launch of Artemis I, the red crew entered the zero deck, or base, of the mobile launcher and tightened several bolts to troubleshoot a valve used to replenish the core stage with liquid hydrogen which showed a leak with readings above limits. NASA has historically sent teams to the pad to conduct inspections during active launch operations as needed. Artemis I launch successfully at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.
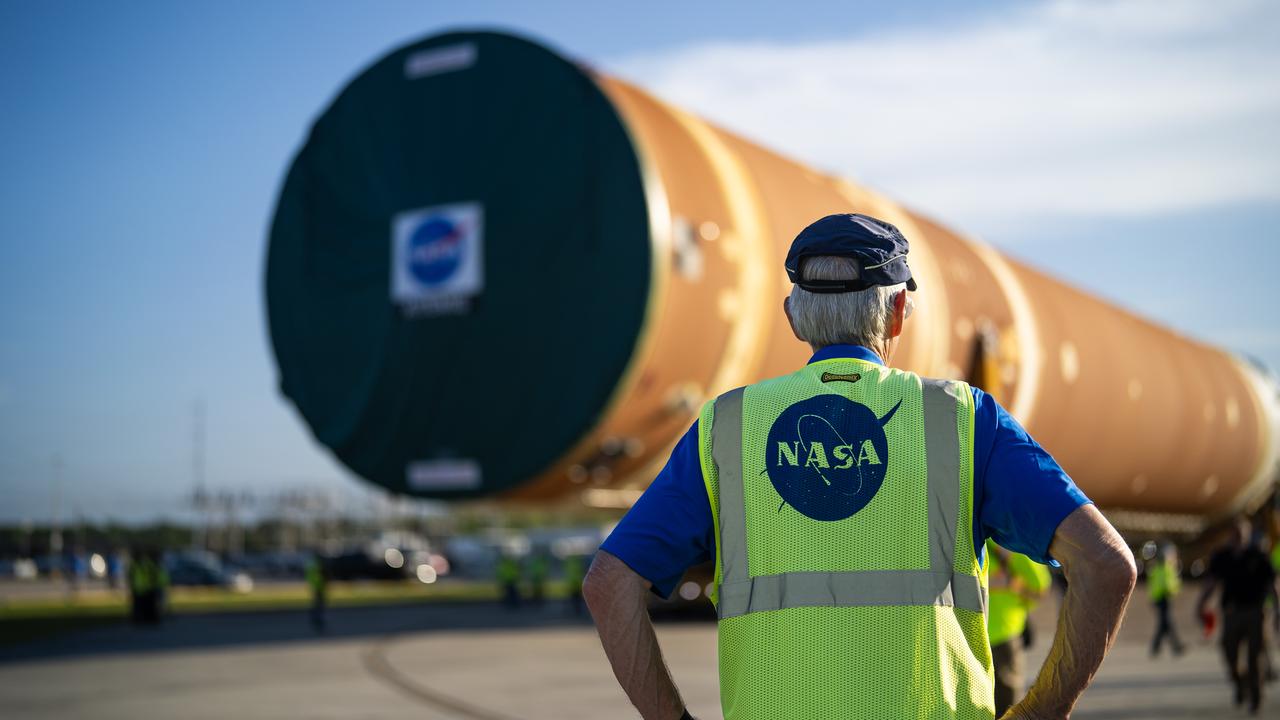

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
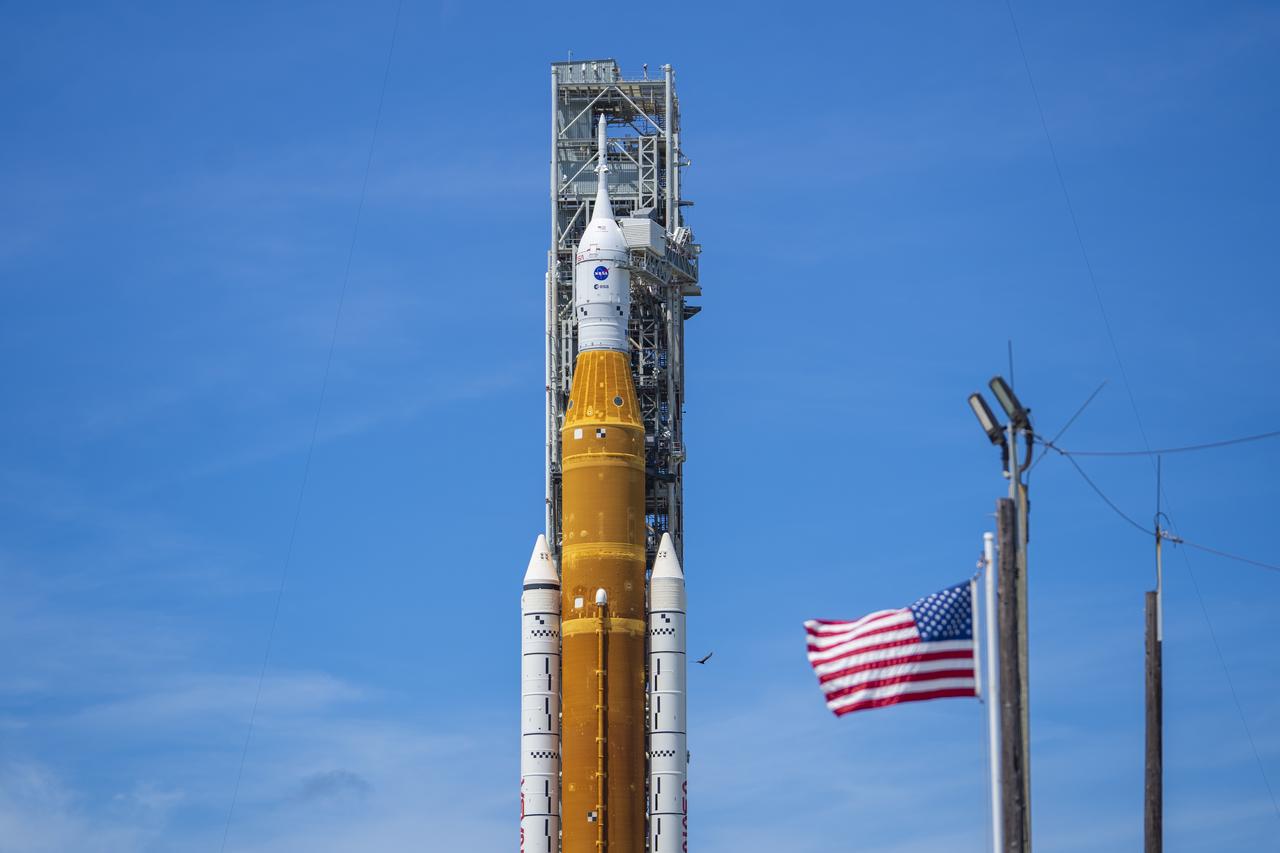

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
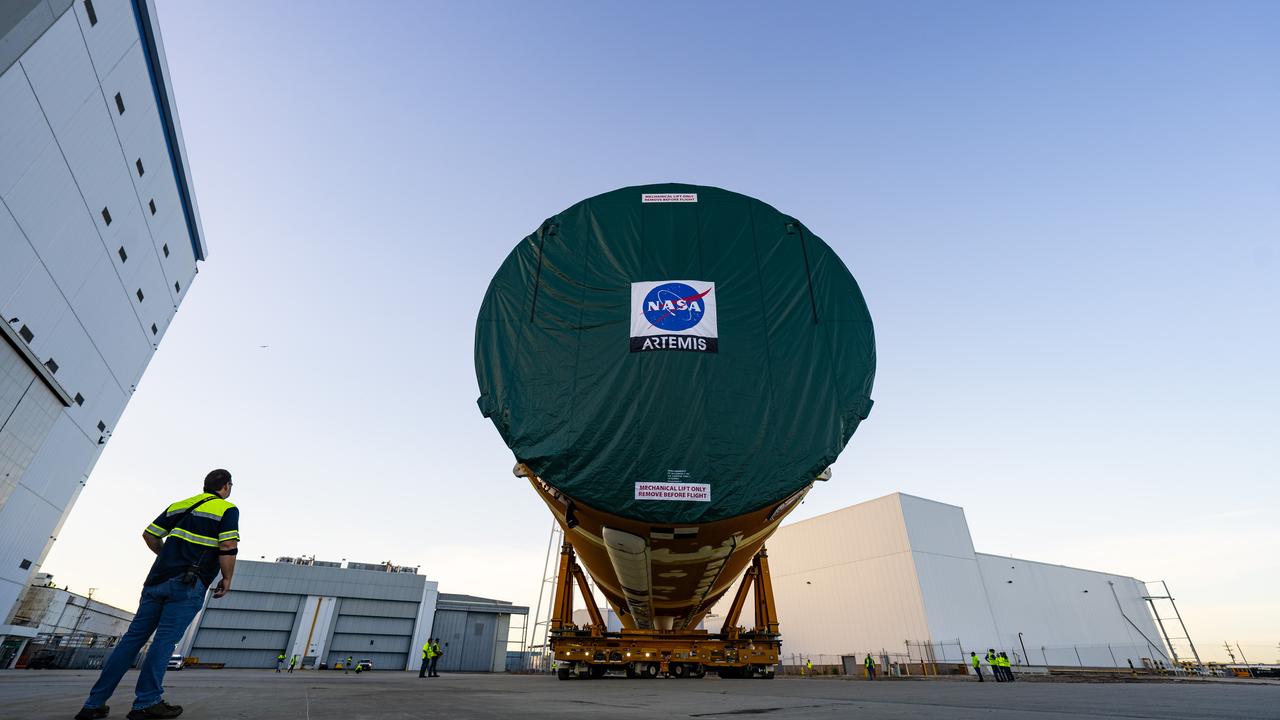

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
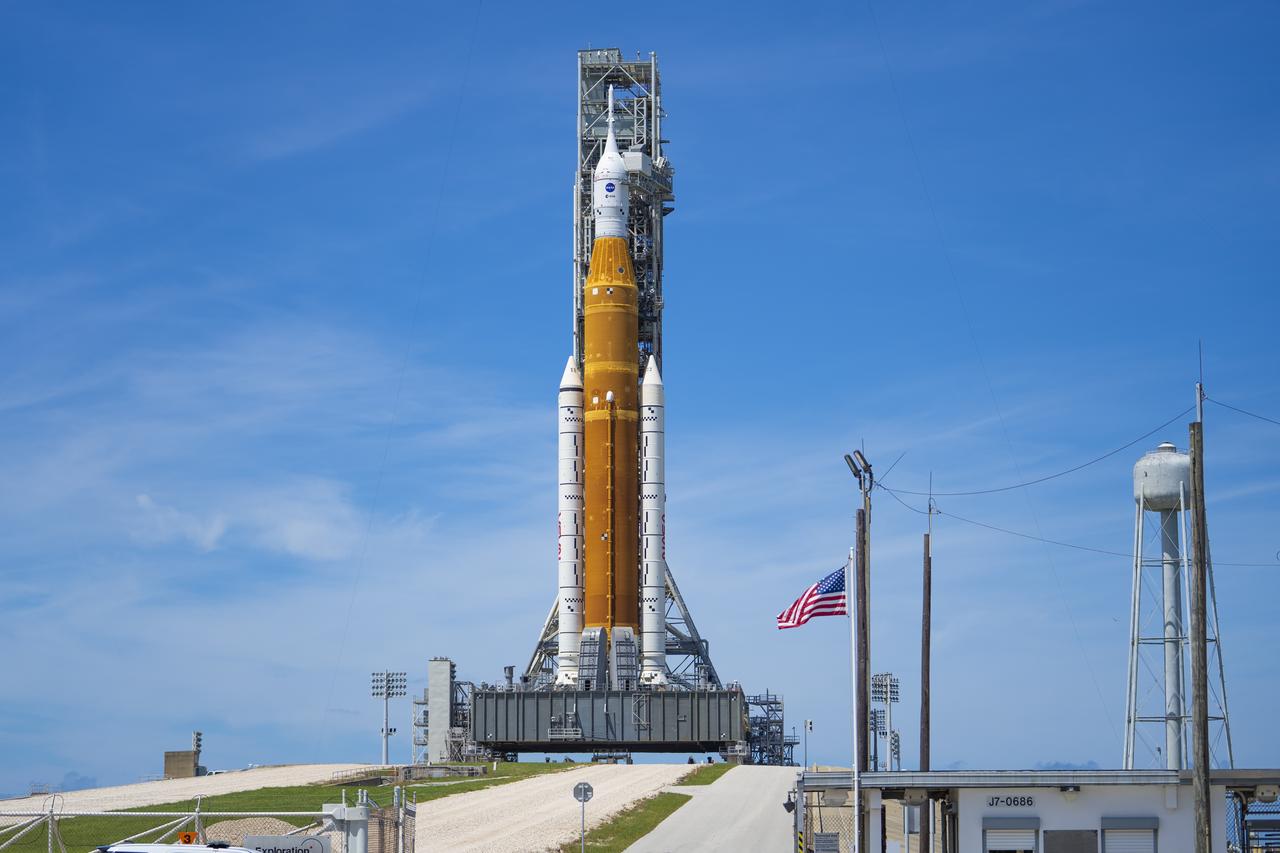

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
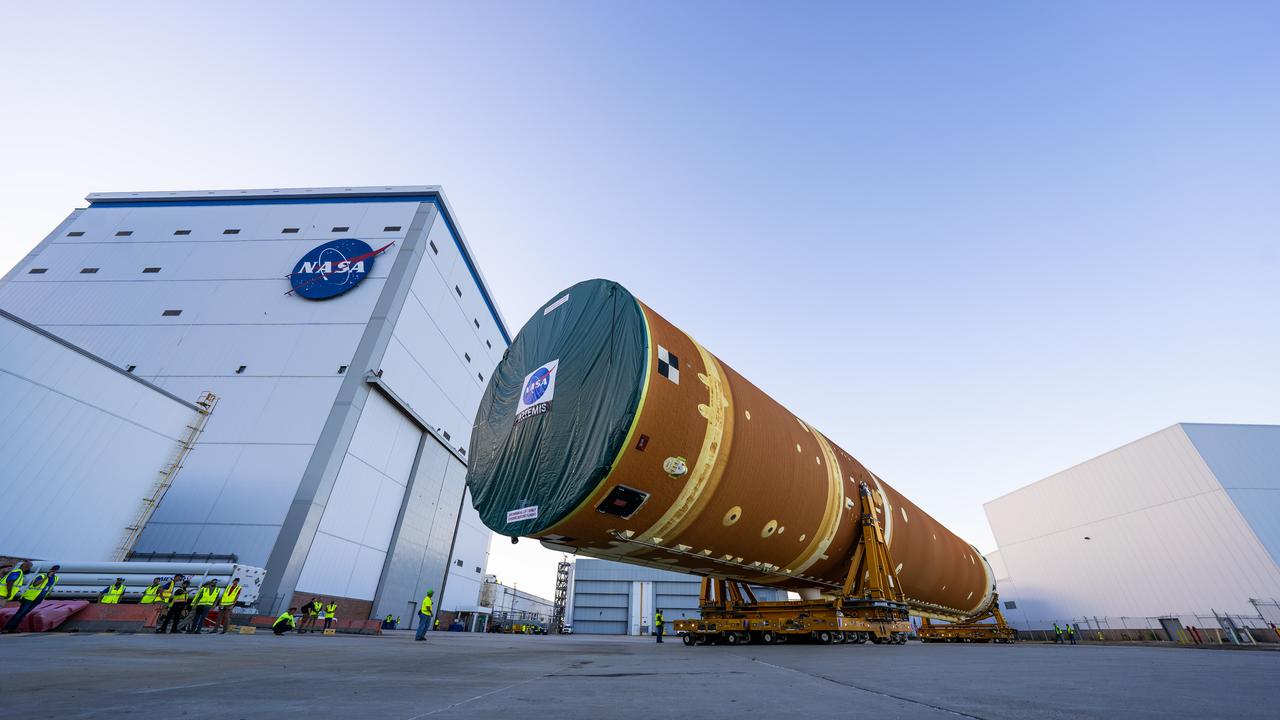

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
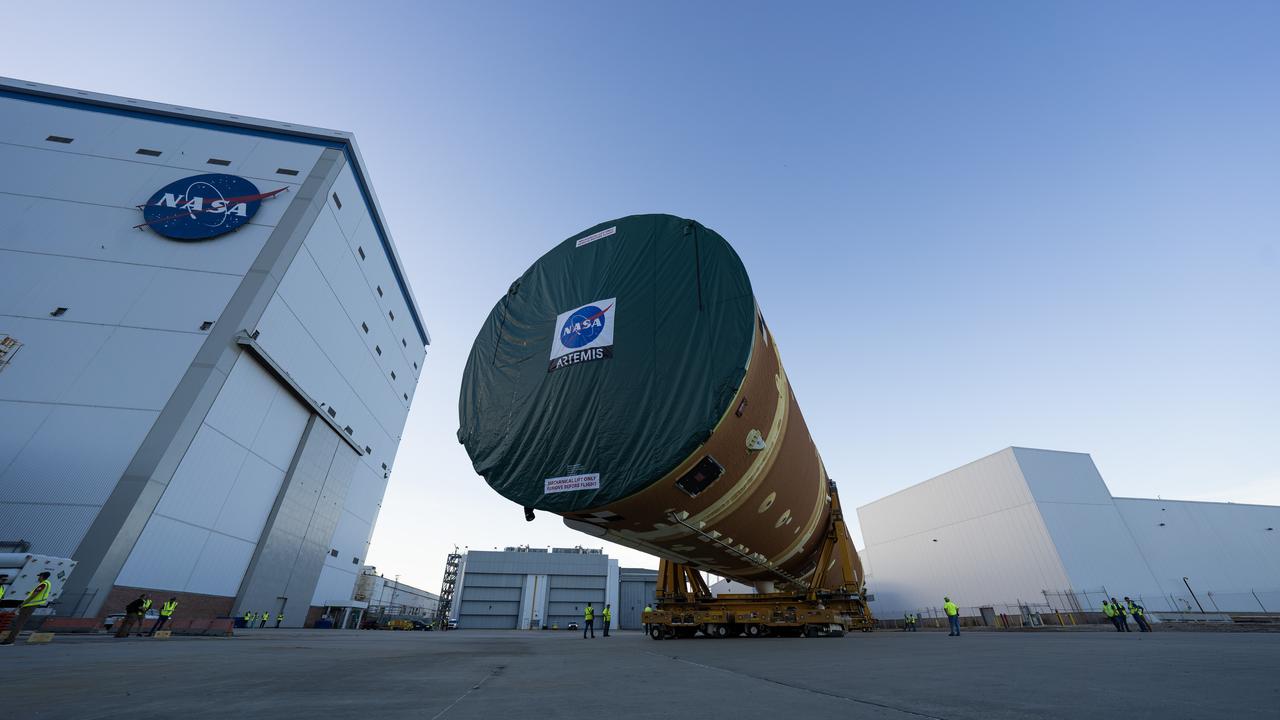

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
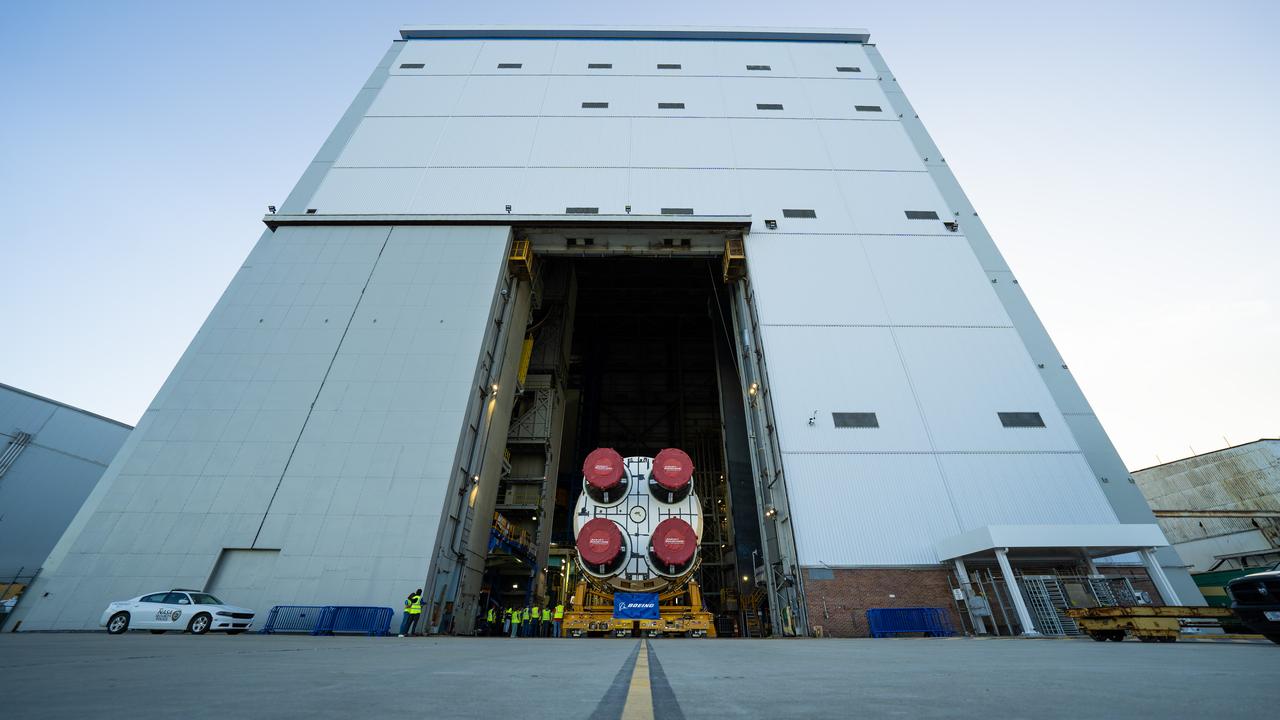

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
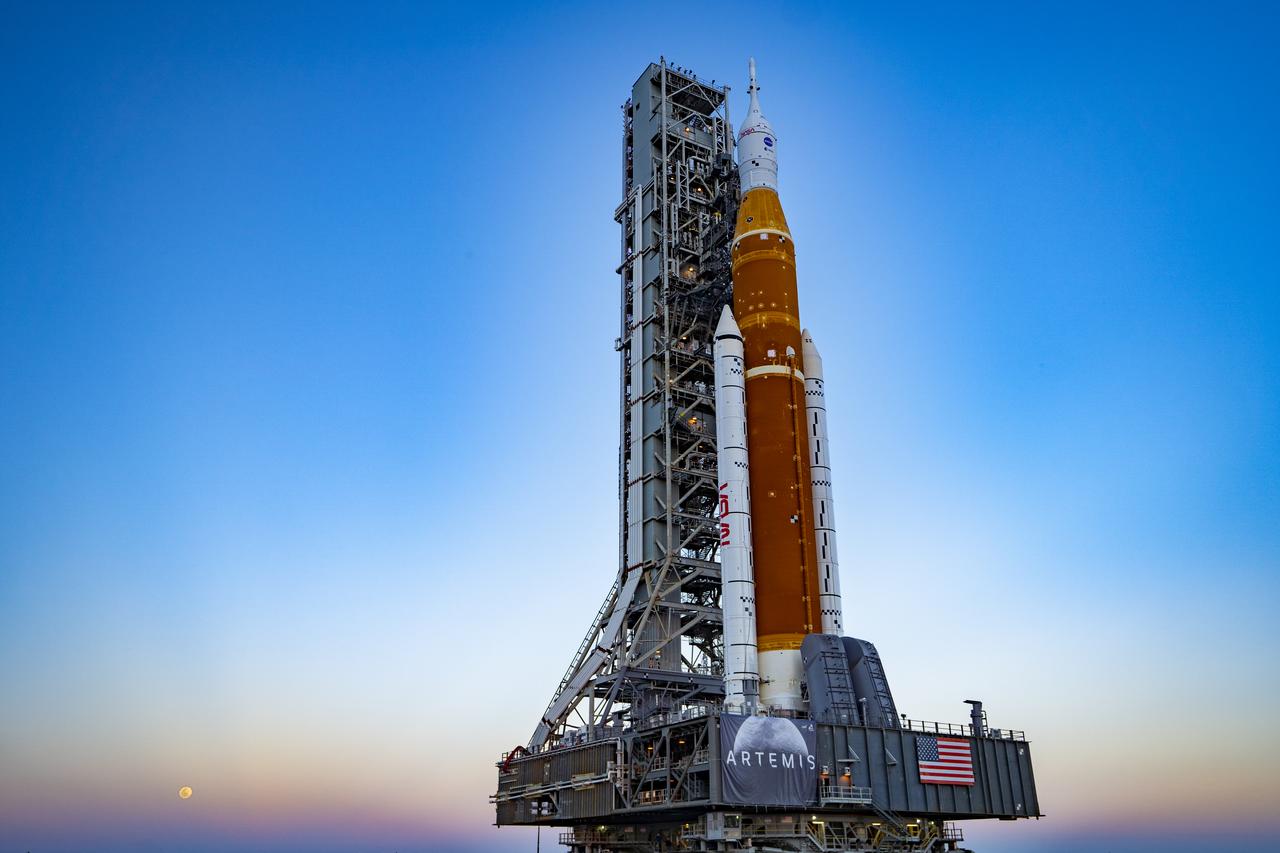

Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft rollout at Kennedy Space Center
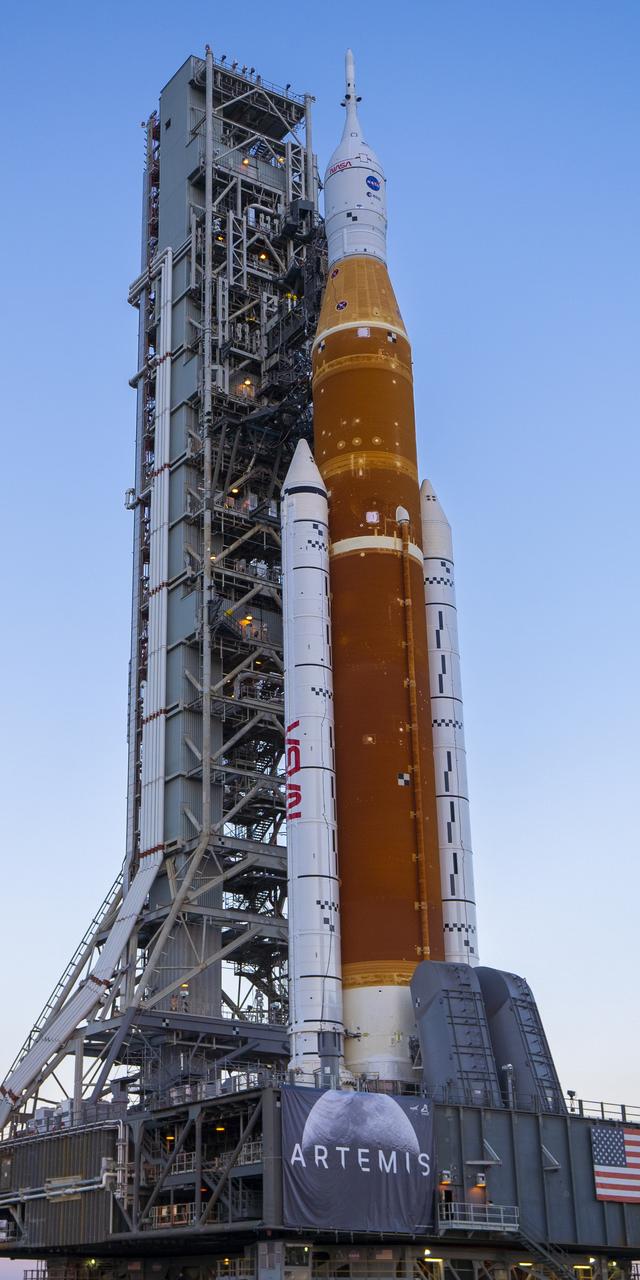

Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft rollout at Kennedy Space Center
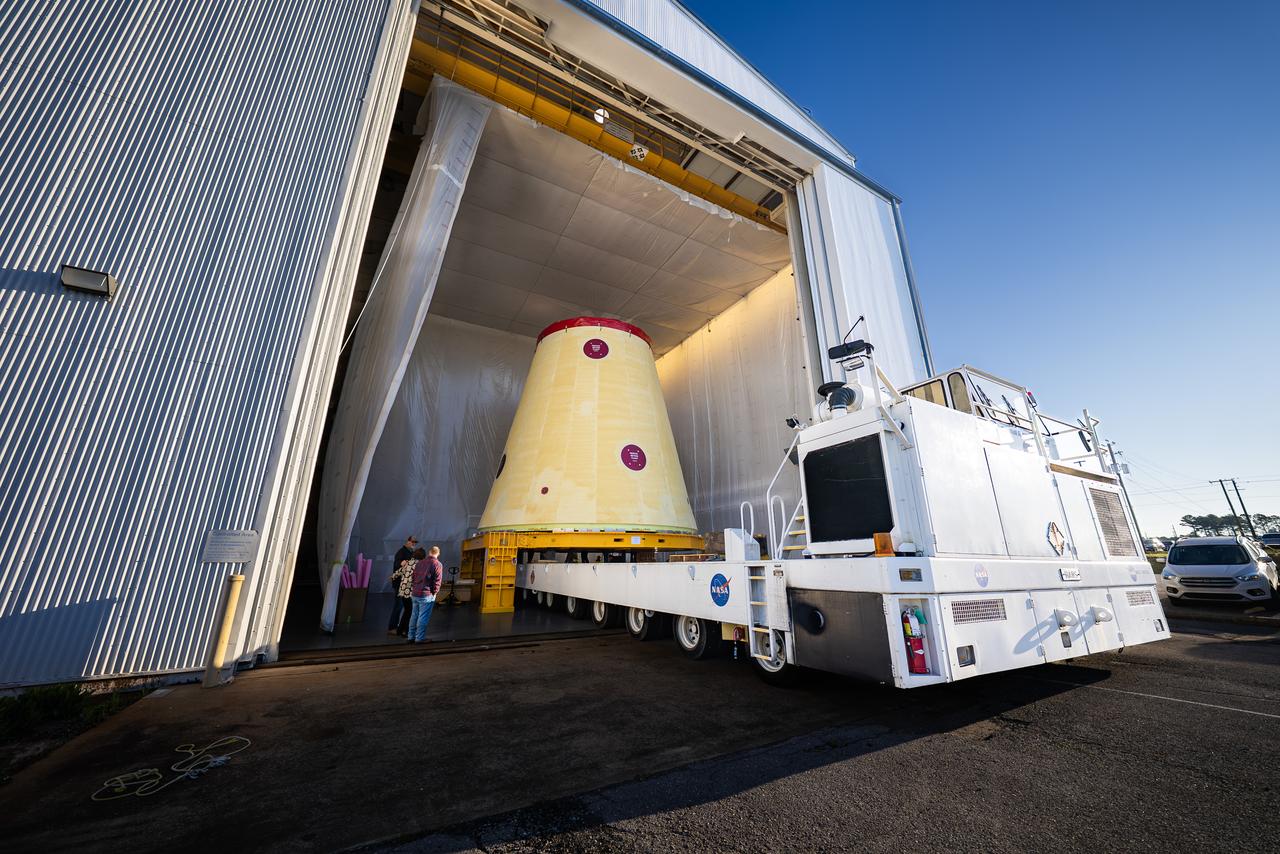

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
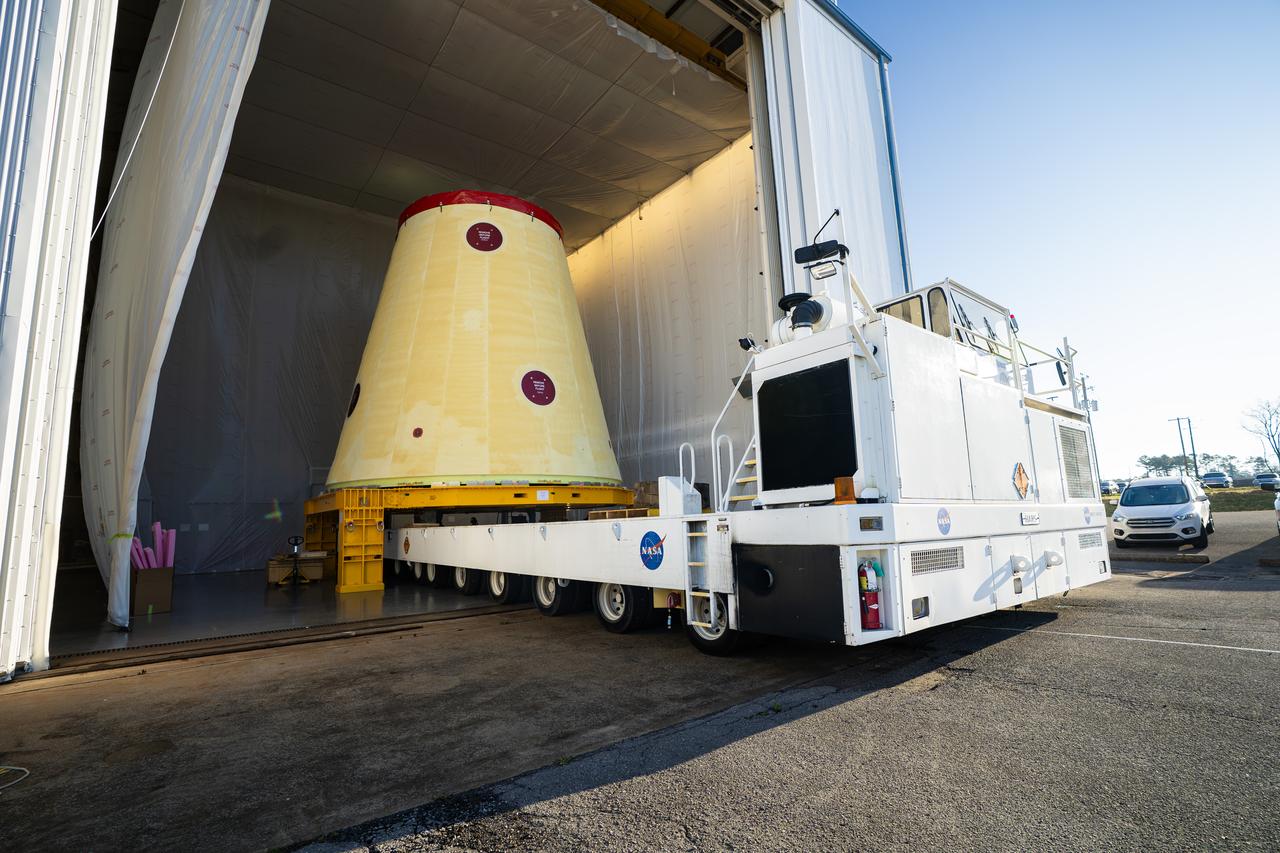

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
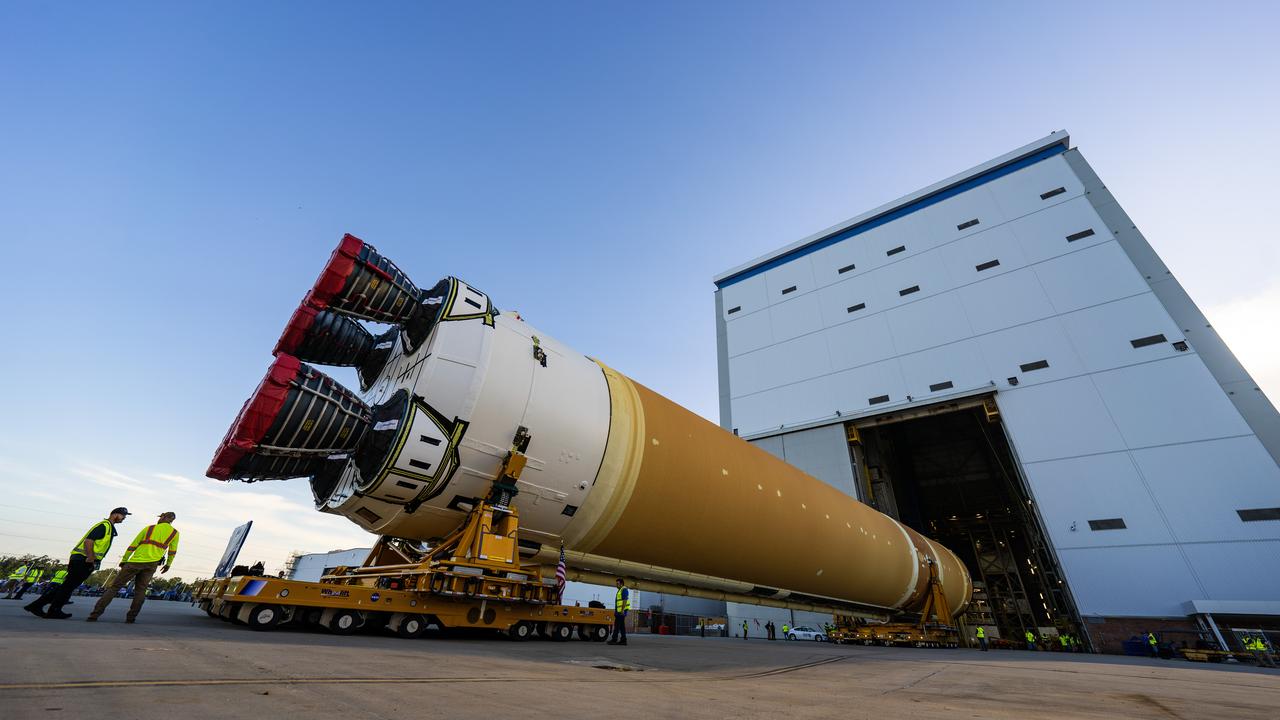

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
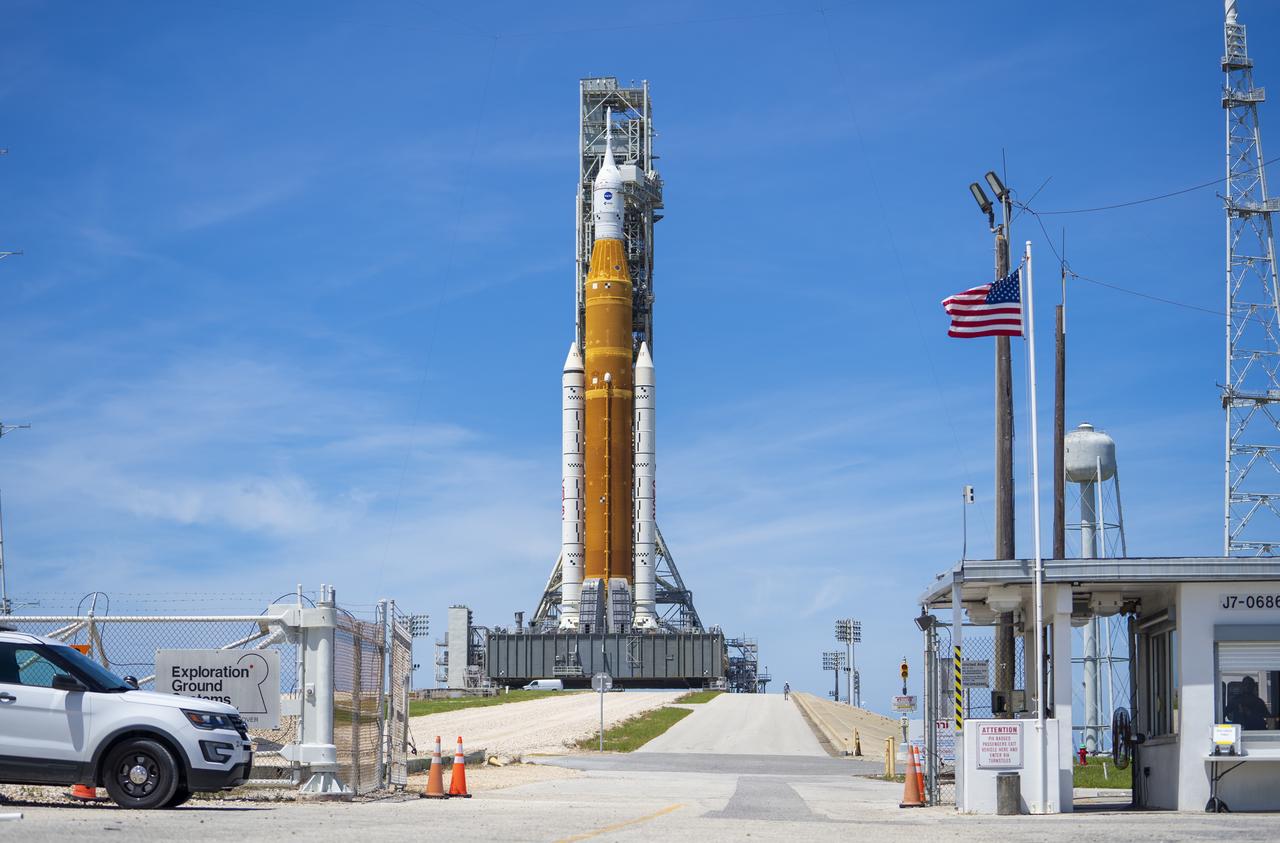

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
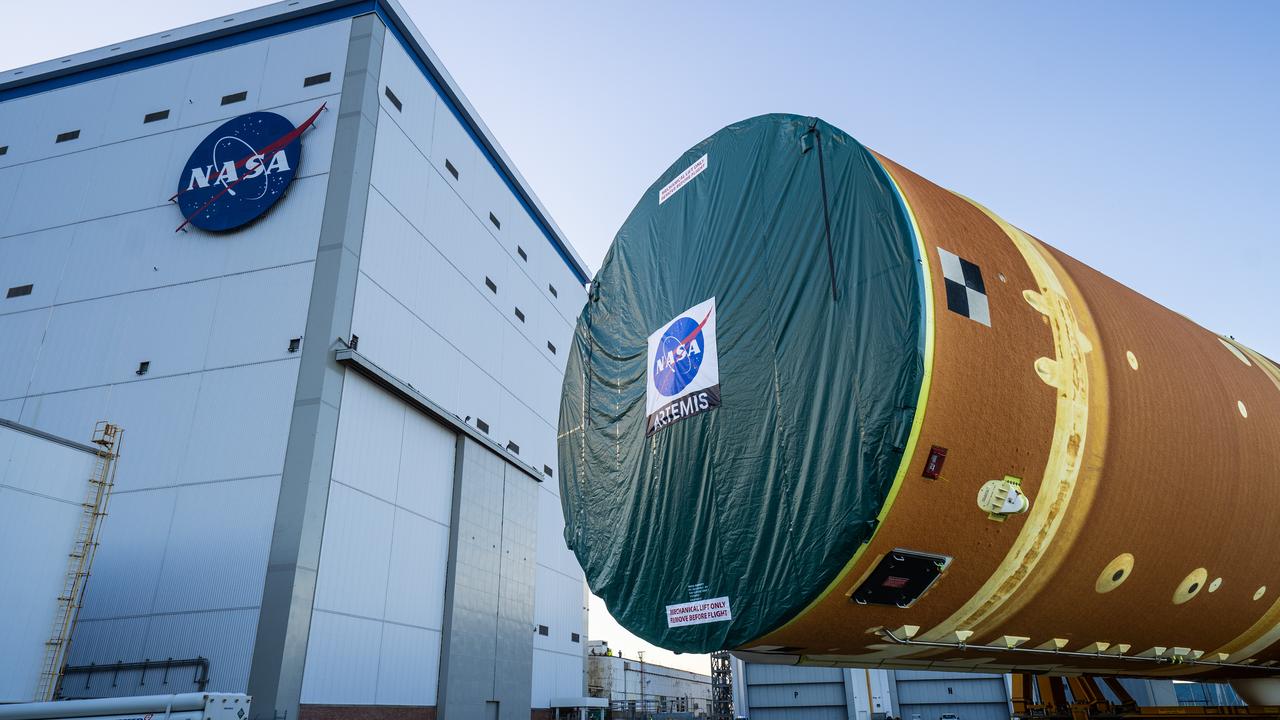

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These images and videos show Reid Wiseman and Jeremy Hansen, members of the Artemis II crew, viewing the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility on Tuesday, July 16, 2024. The Artemis II astronauts met with team members at Michoud and the crew of NASA’s Pegasus barge prior to their departure to deliver the core stage to the Space Coast. NASA astronaut and pilot of the Artemis II mission Victor Glover met the crew July 15. Wiseman and Hansen visited the barge July 16, shortly before the flight hardware was loaded onto it. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. Pegasus – previously used to ferry space shuttle tanks – was modified and refurbished to ferry the SLS rocket’s massive core stage. At 212 feet in length and 27.6 feet in diameter, the Moon rocket stage is more than 50 feet longer than the space shuttle external tank. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
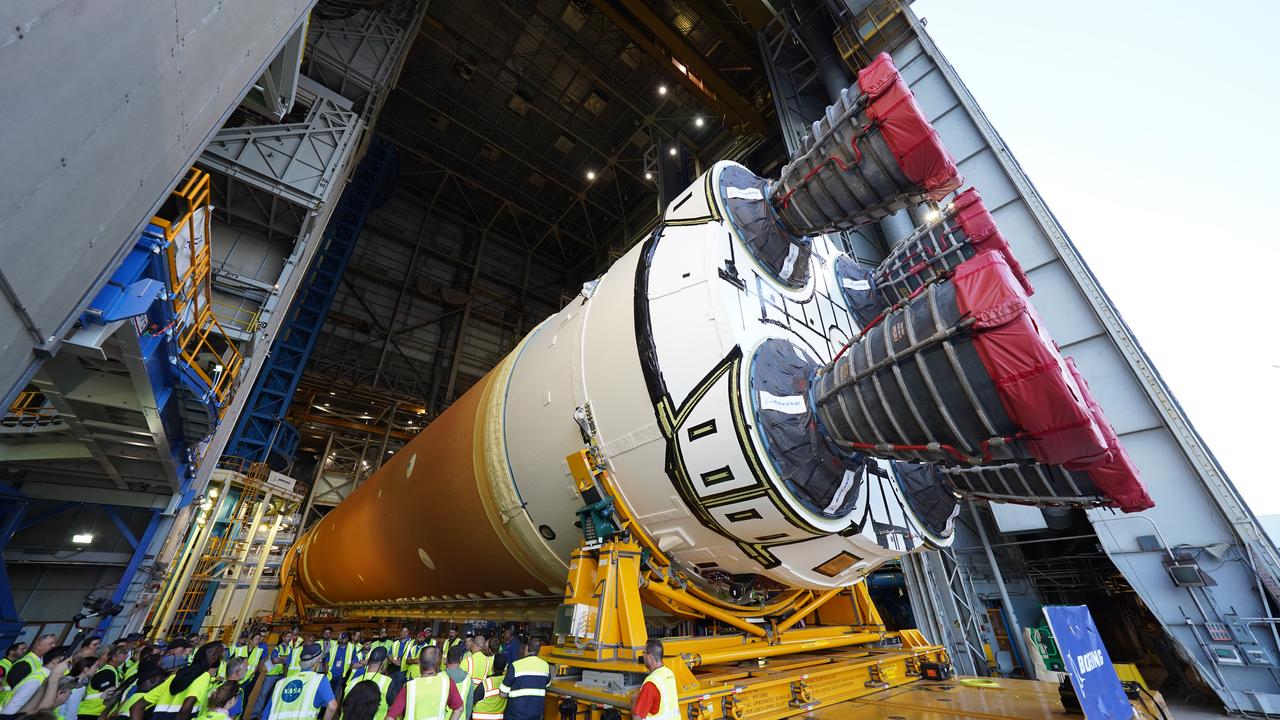

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
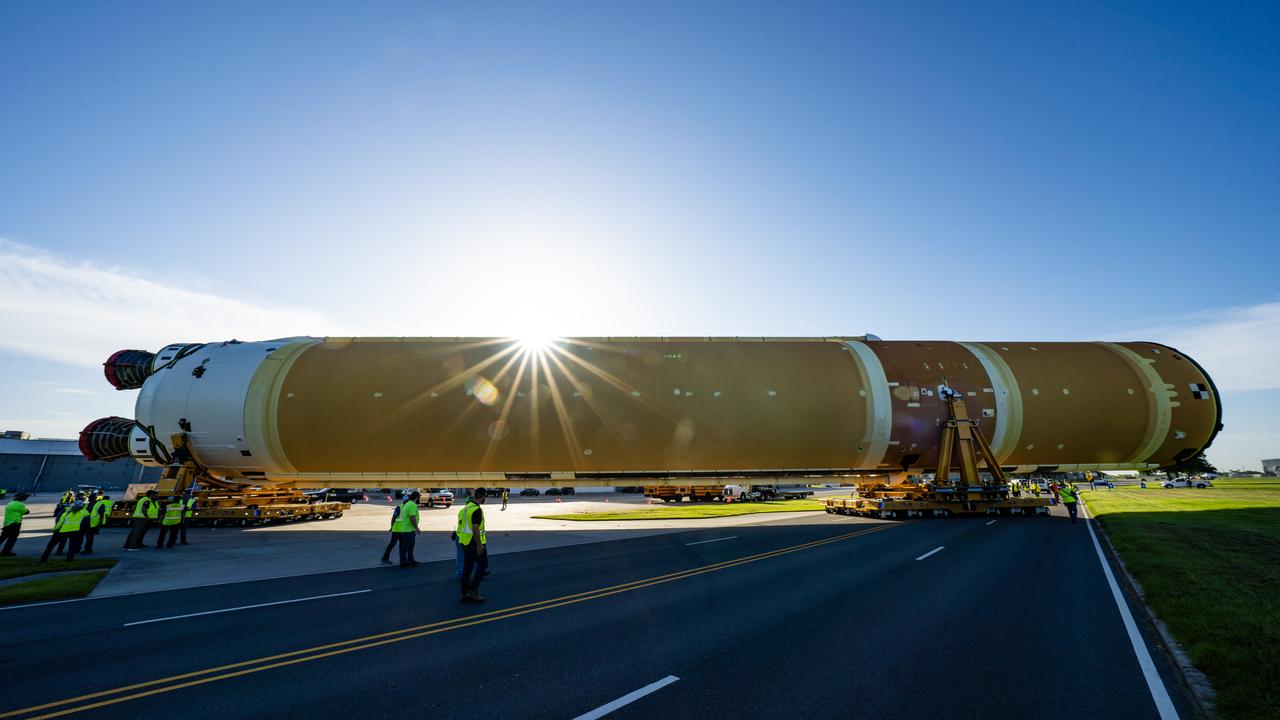

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
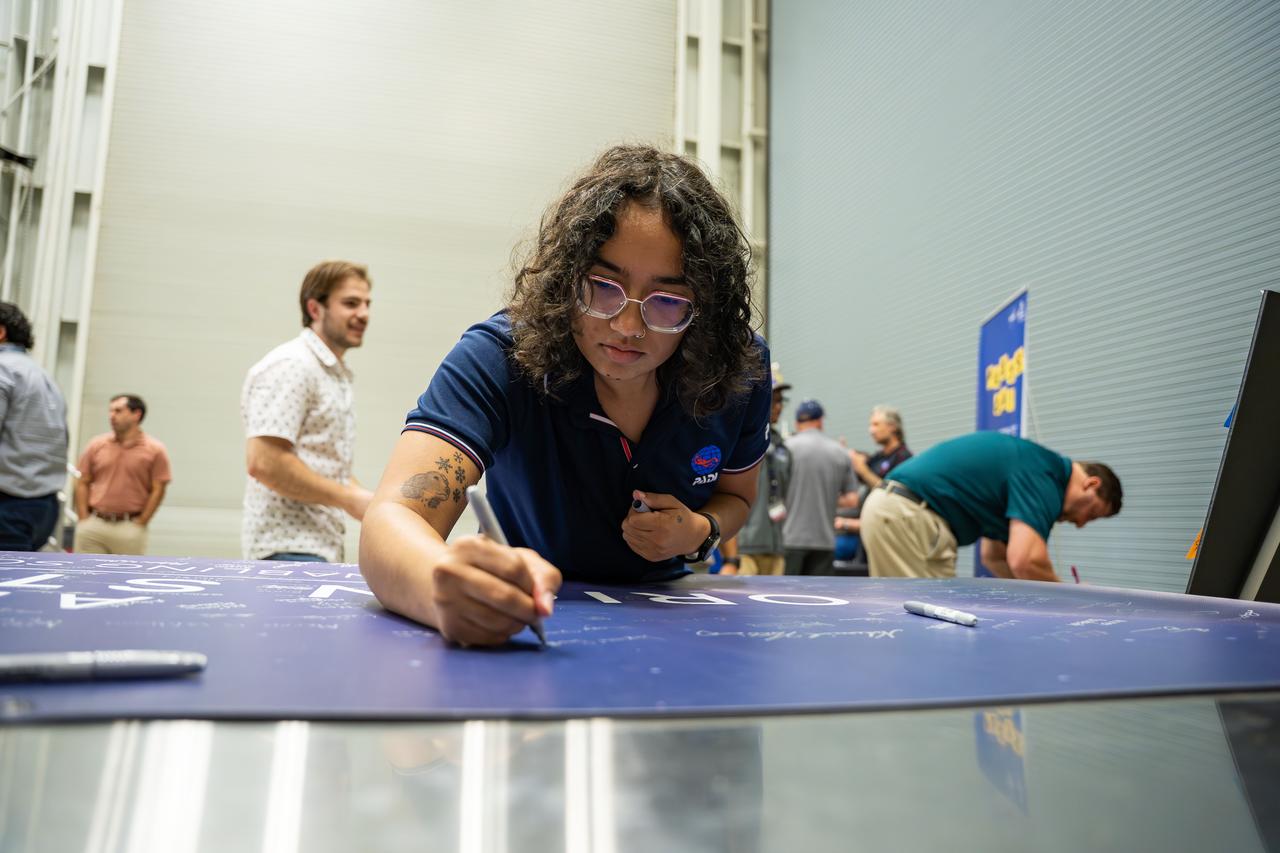

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
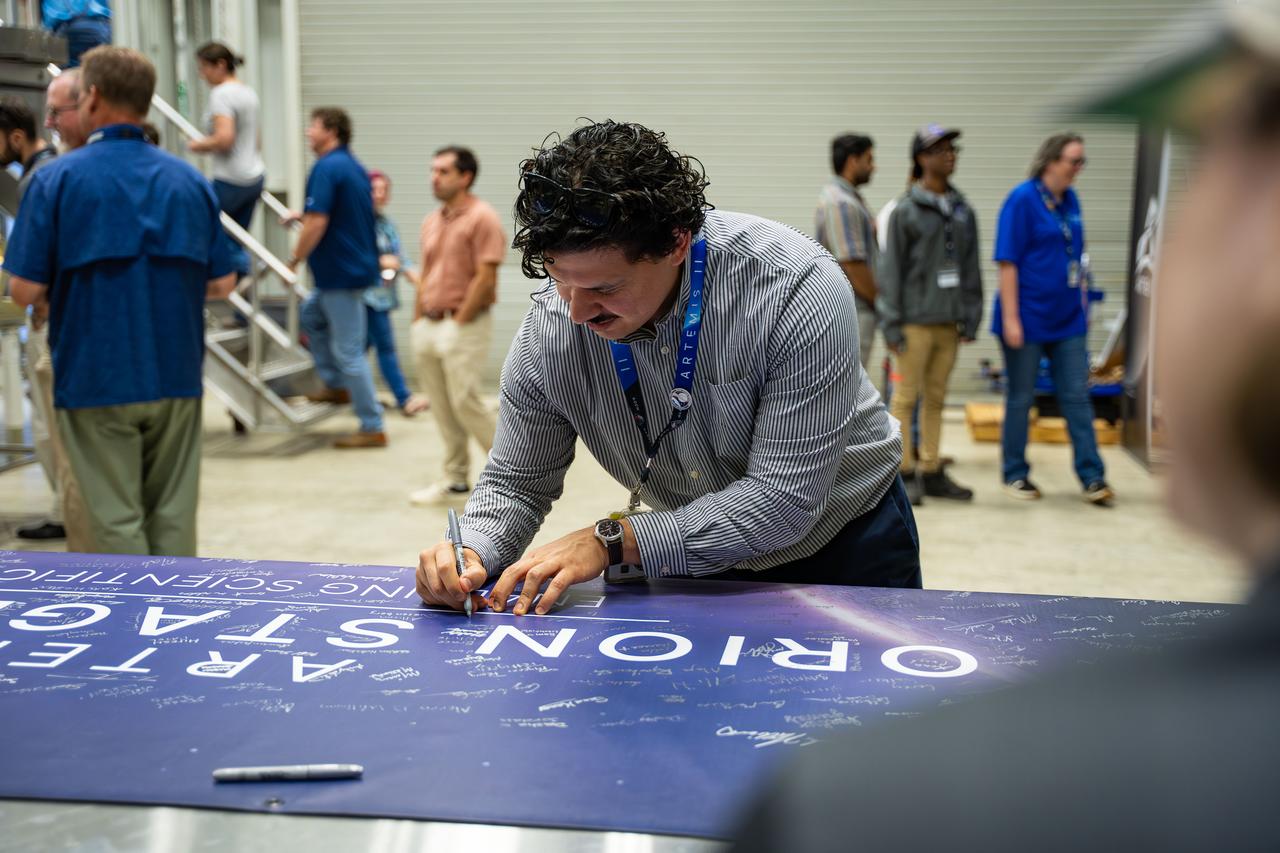

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
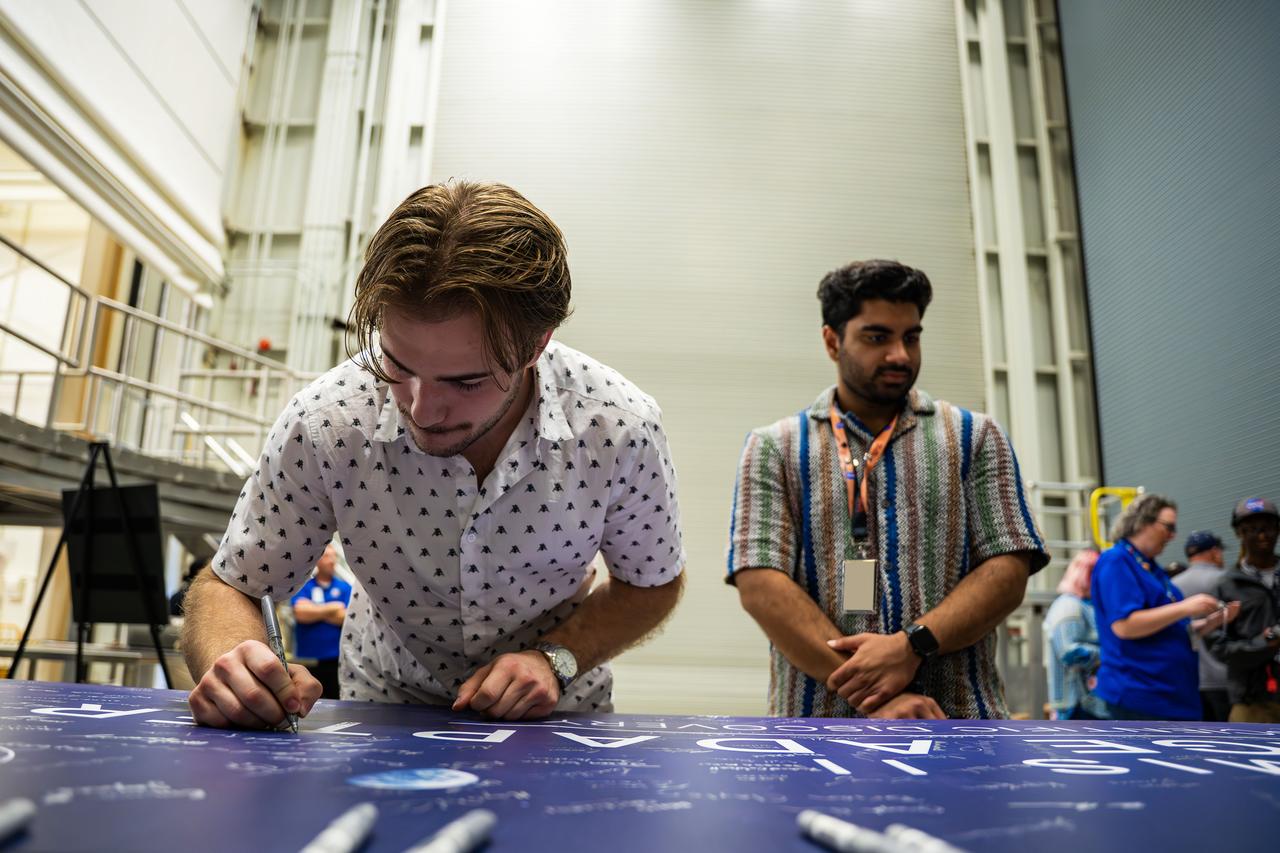

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
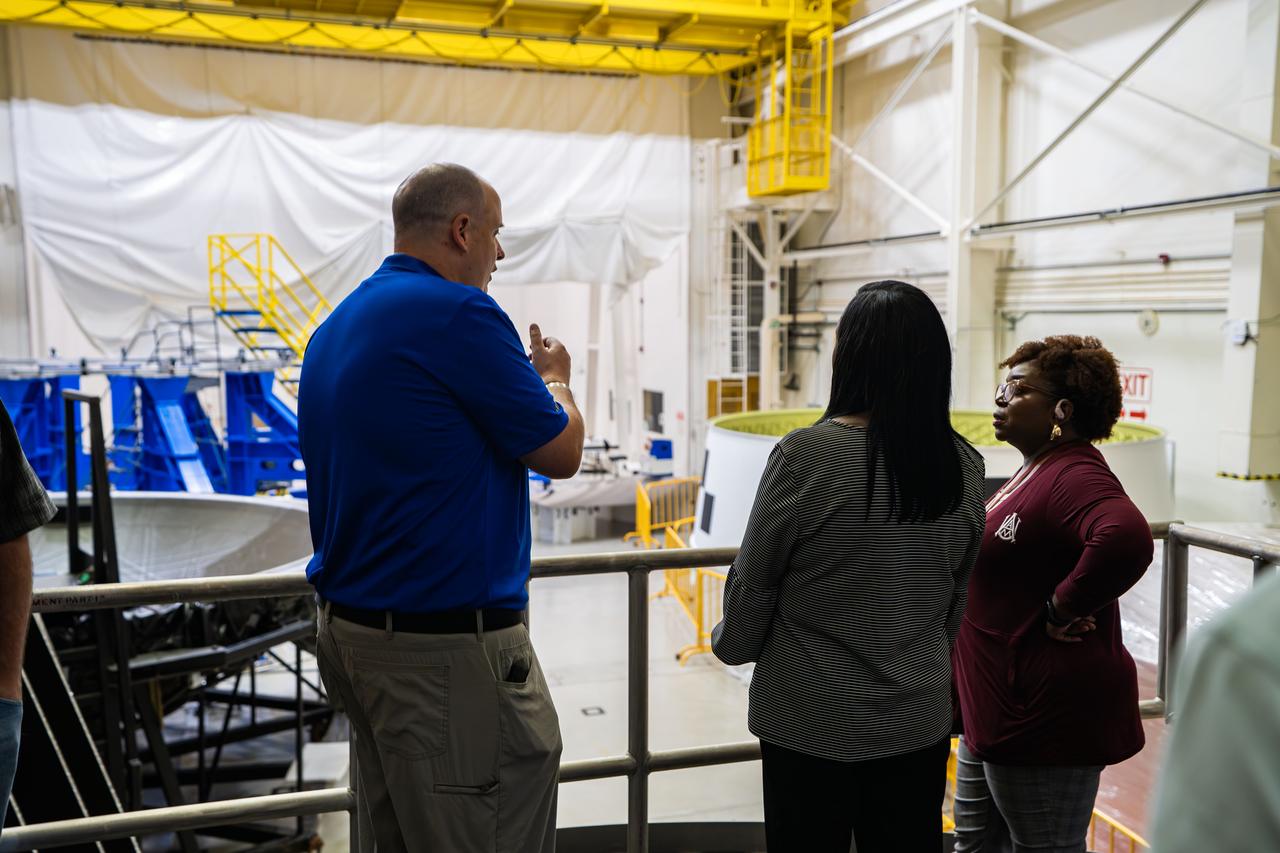

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
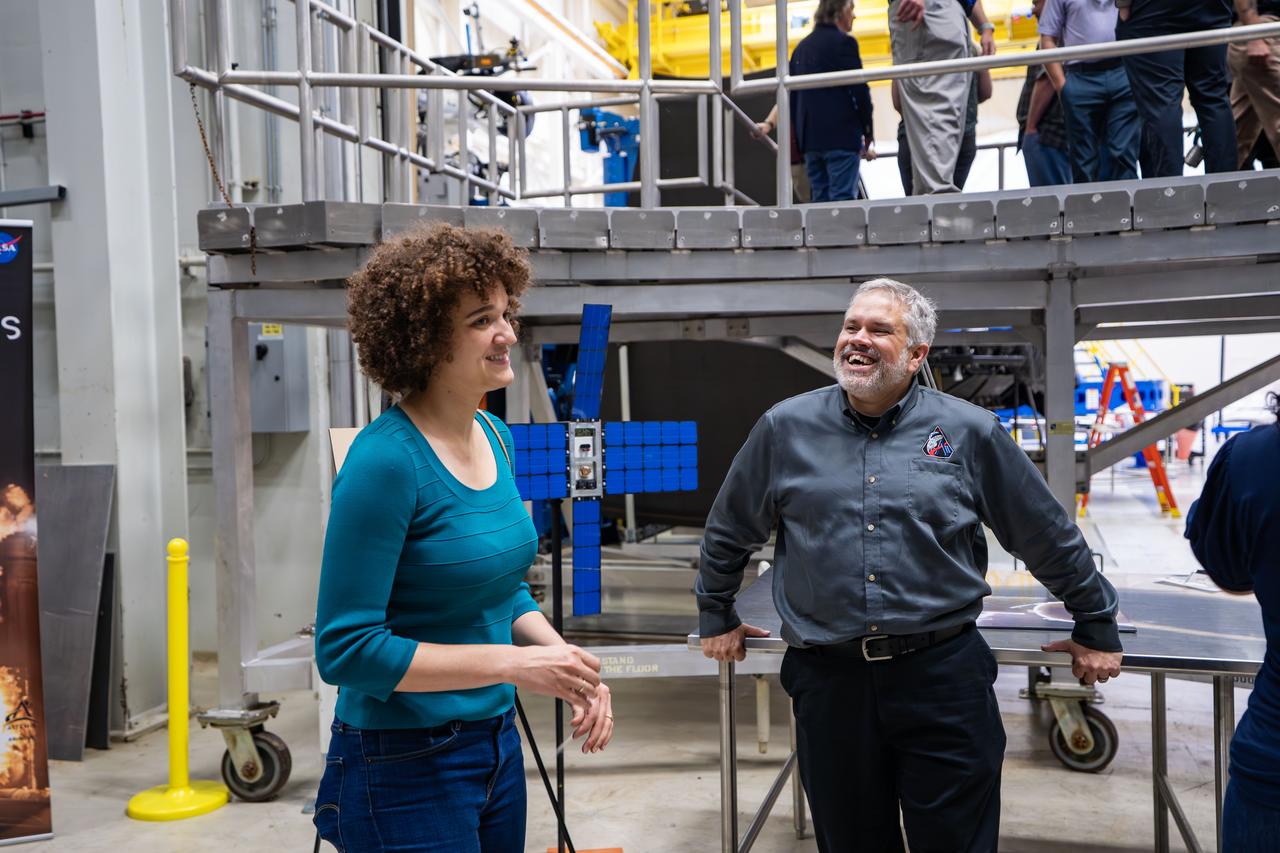

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
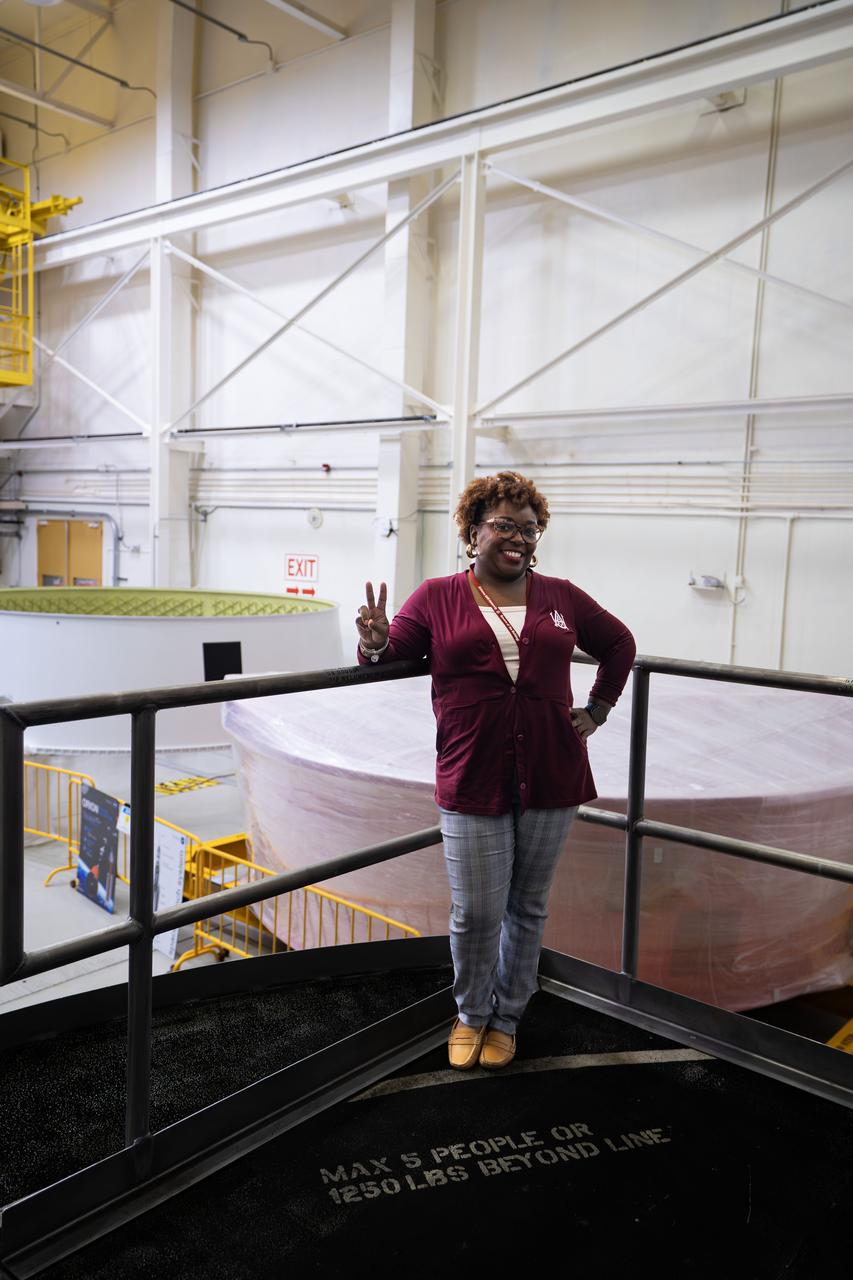

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
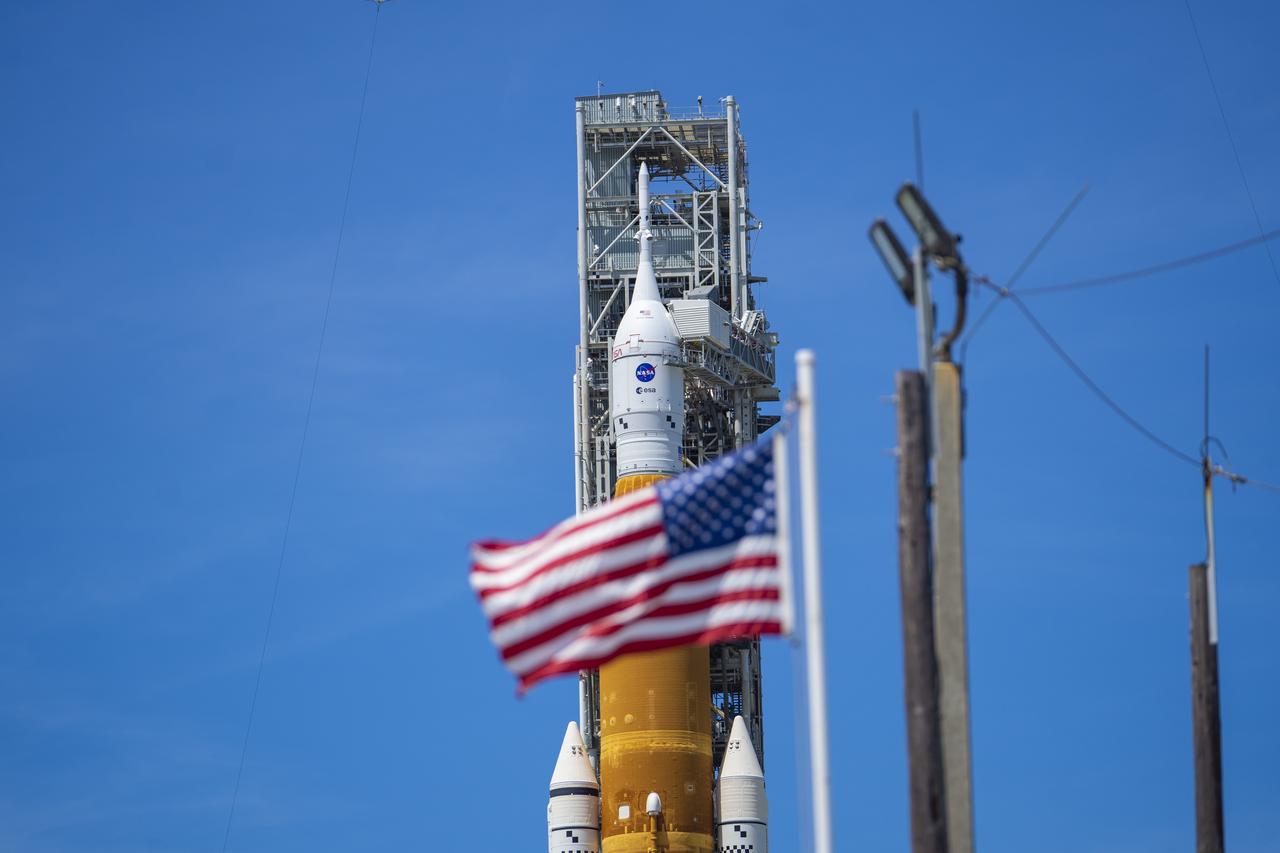

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
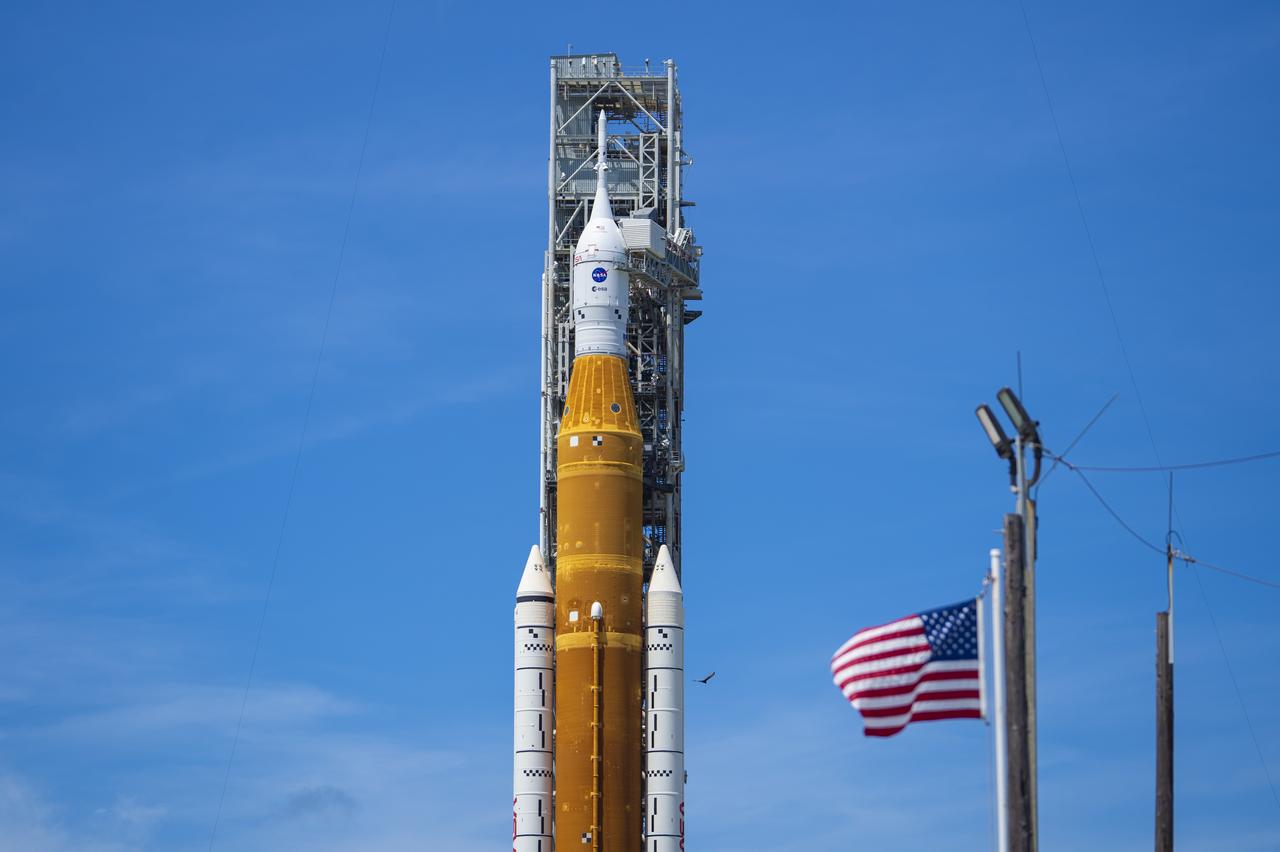

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
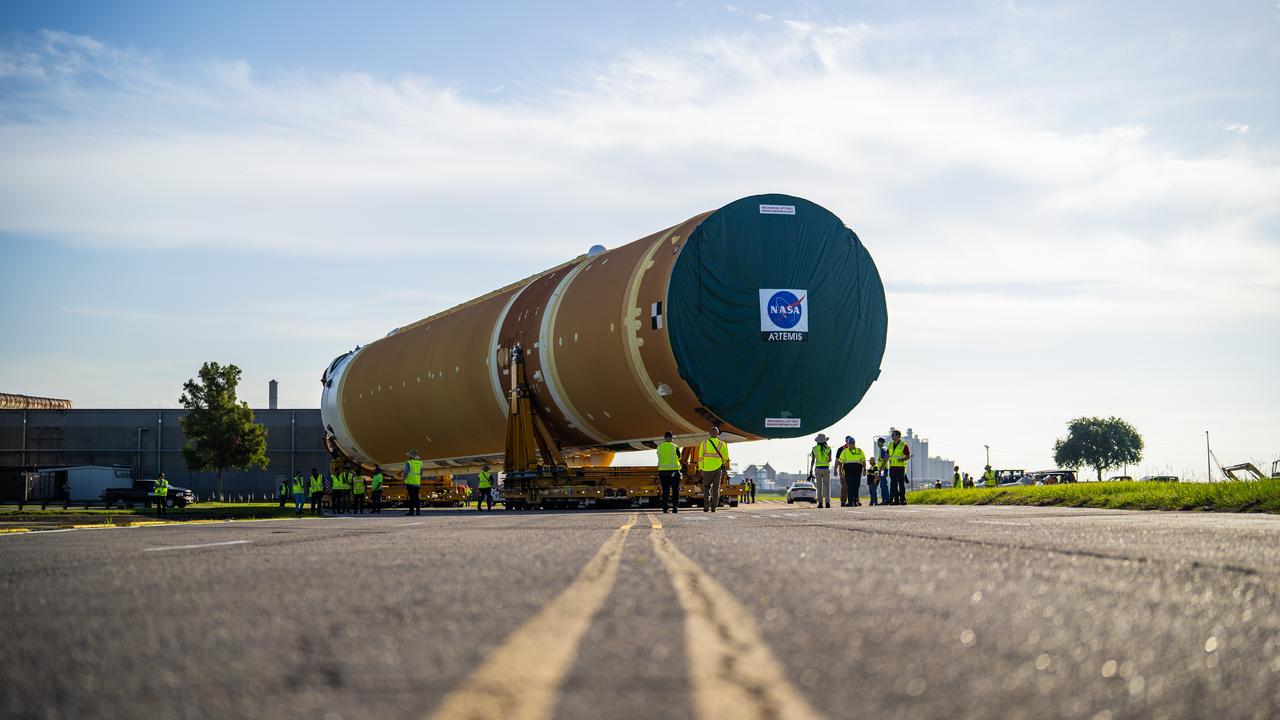

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
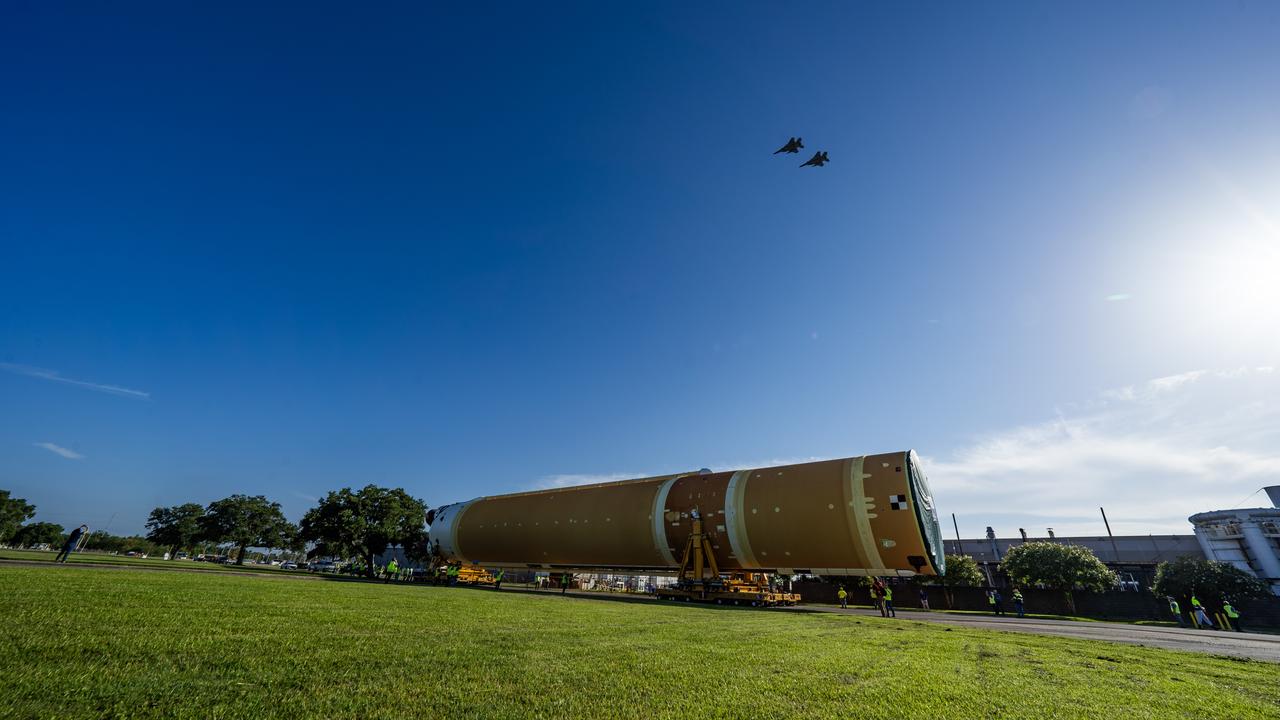

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
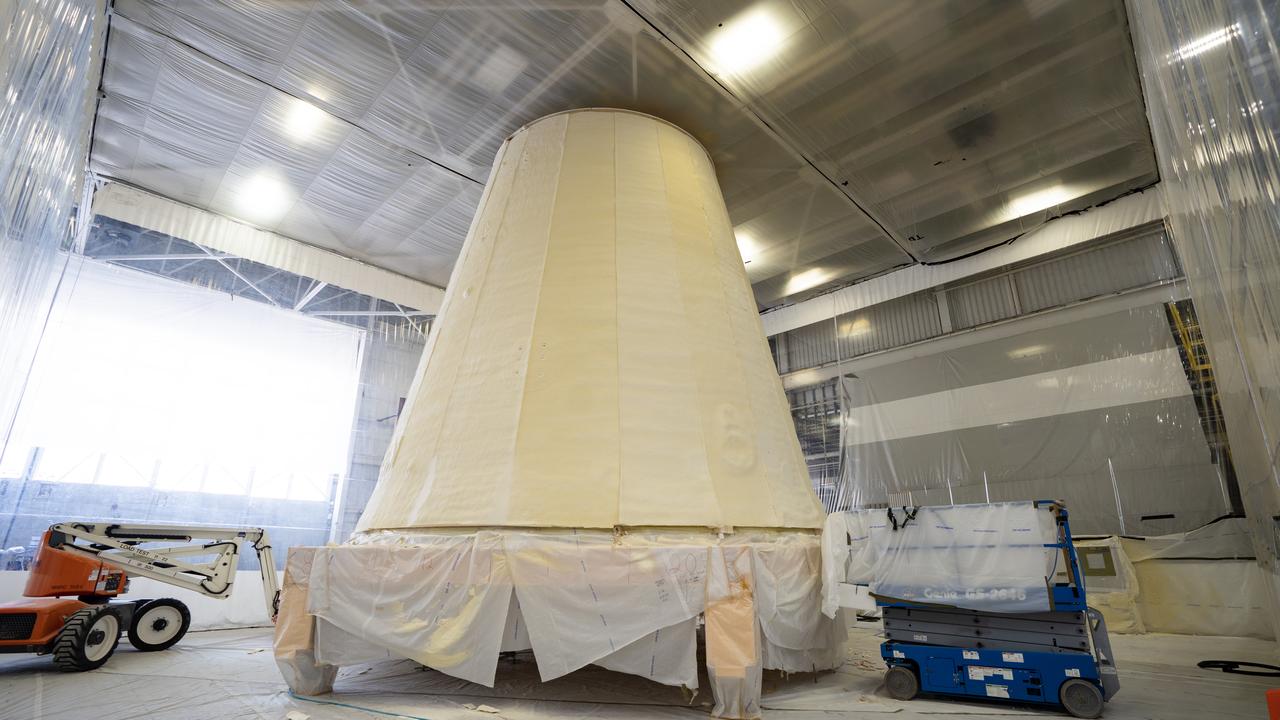

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

The Space Launch System (SLS) program heralds the arrival of the SLS core stage with a symbolic “passing of the baton” to NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) on April 28, 2021, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, marking the transition into final preparations for flight. Journeying from NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi aboard the Pegasus barge, the core stage arrived at the Florida spaceport on April 27. It is the final piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at Kennedy and will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher with the completed stack of solid rocket boosters ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
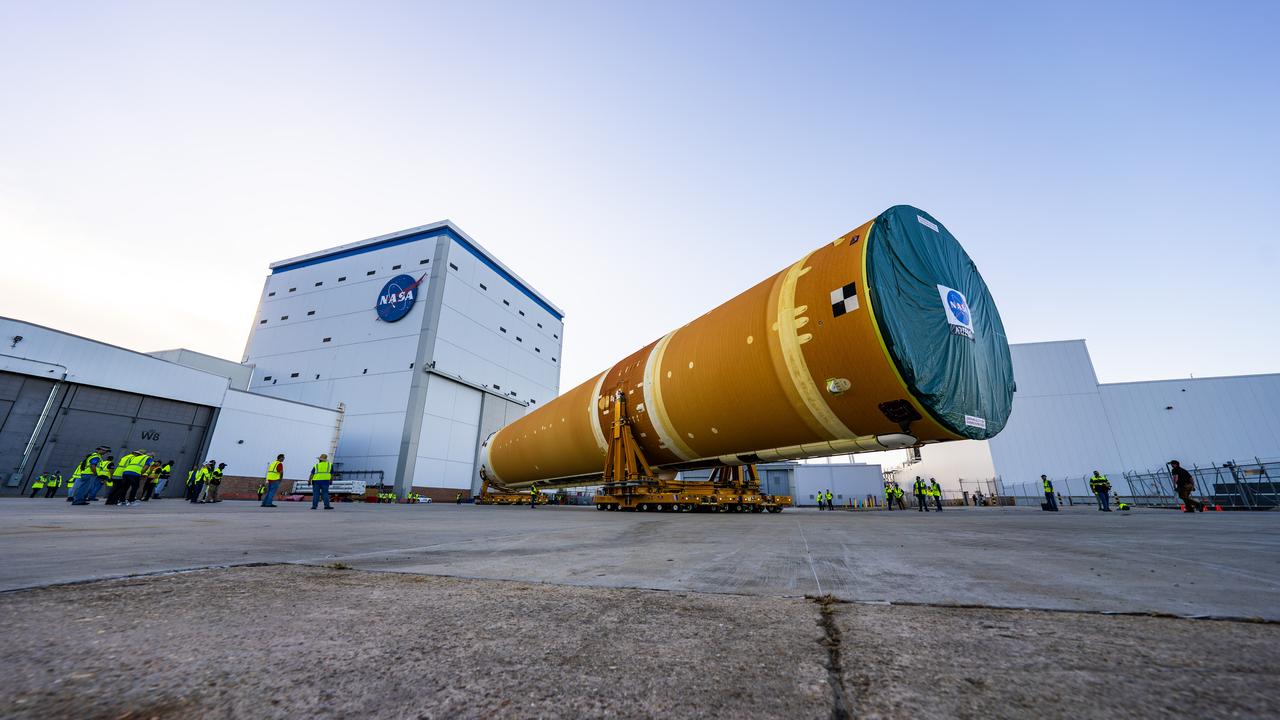

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
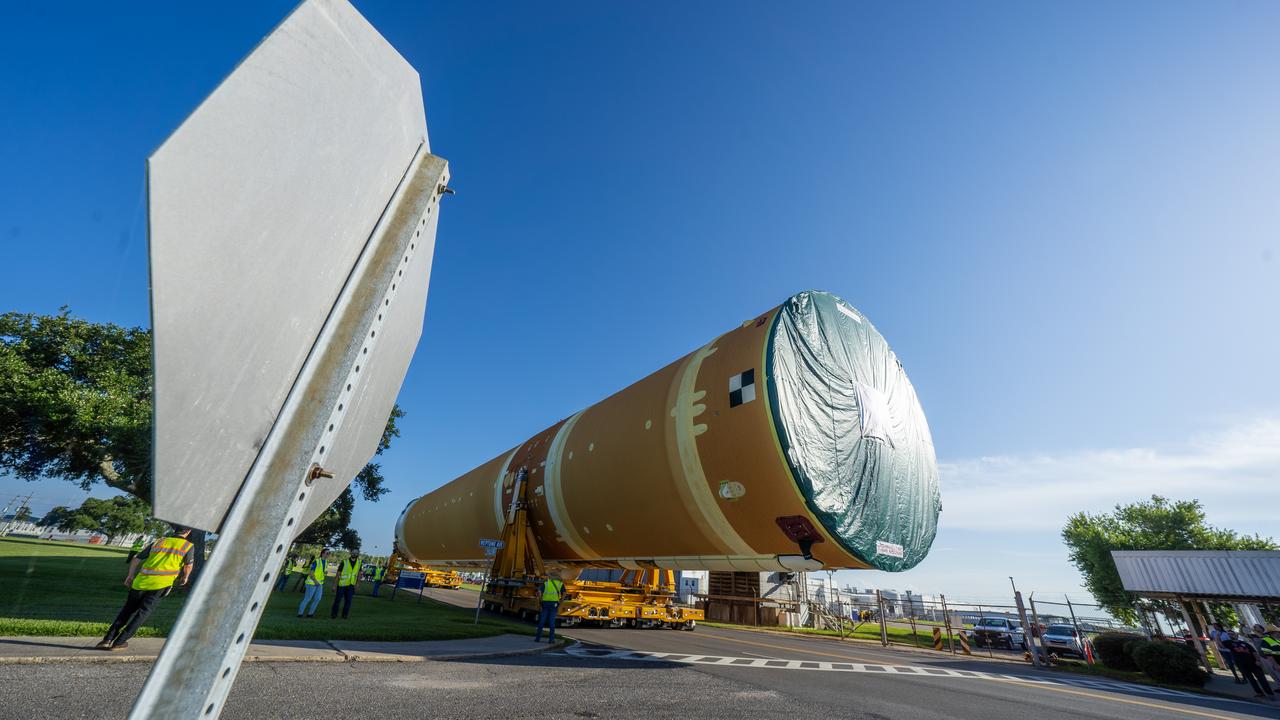

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
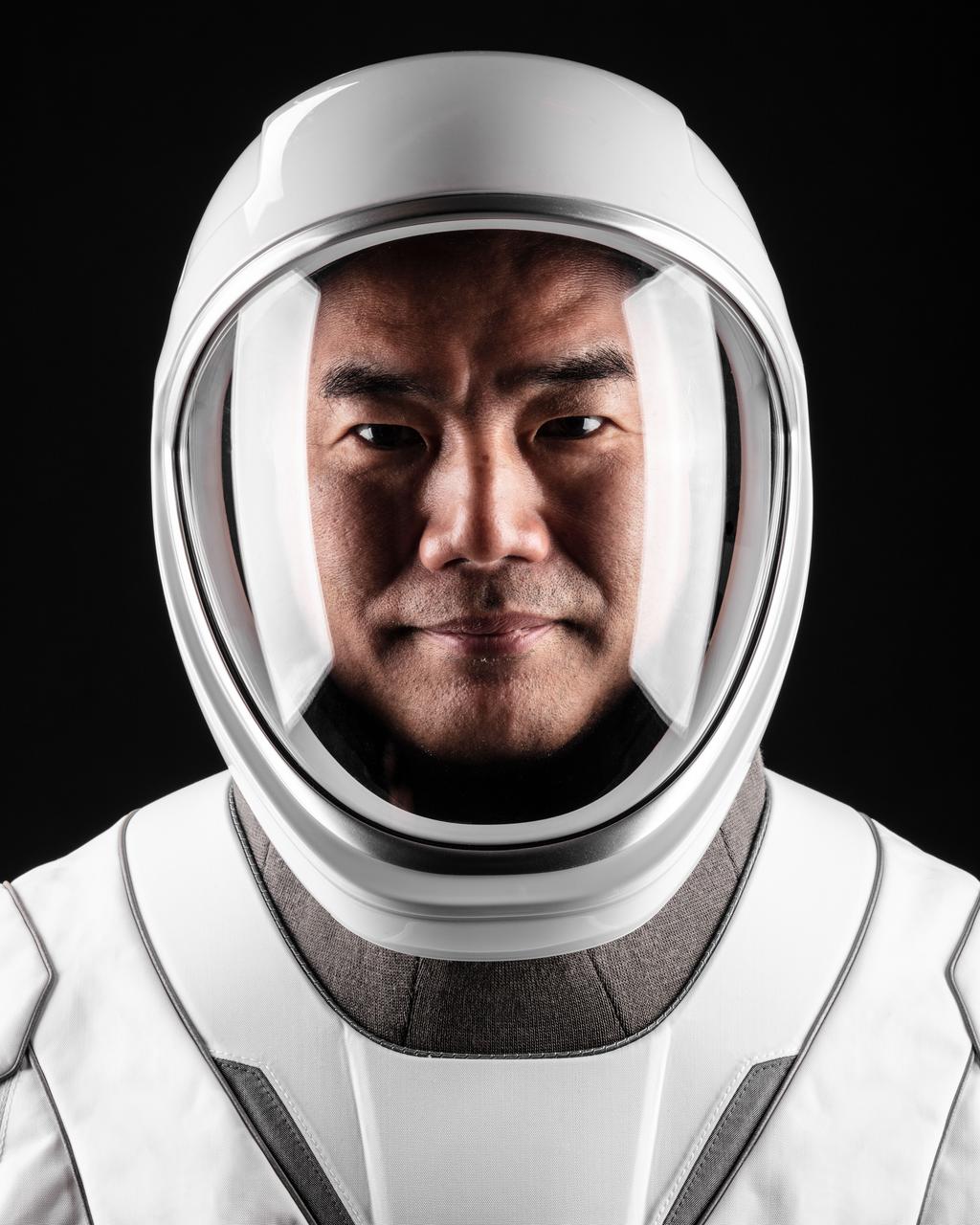

jsc2020e040988 (June 25, 2020) --- Astronaut Soichi Noguchi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) is a mission specialist for the first operational SpaceX Crew Dragon mission designated as Crew-1. Credit: SpaceX/Sam Friedman
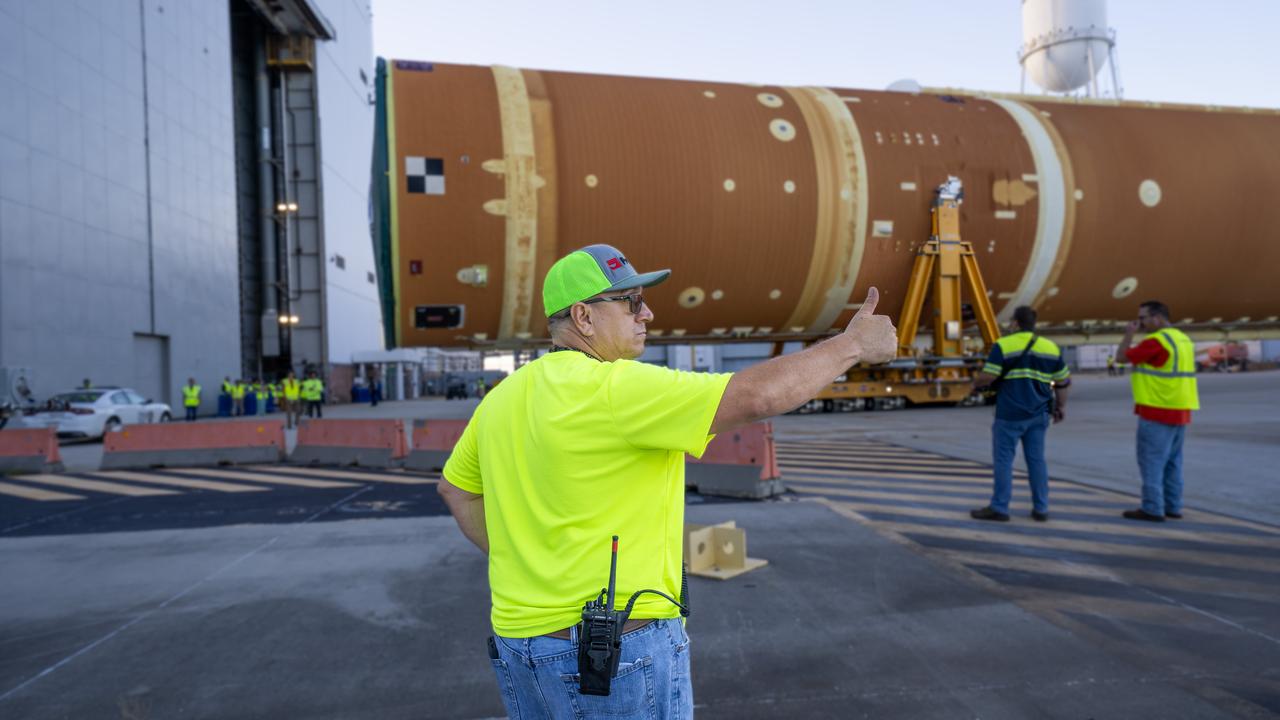

These images and videos show team members moving the first core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. The move marked the first time a fully assembled Moon rocket stage for a crewed mission has rolled out from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans since the Apollo Program, The core stage was moved onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
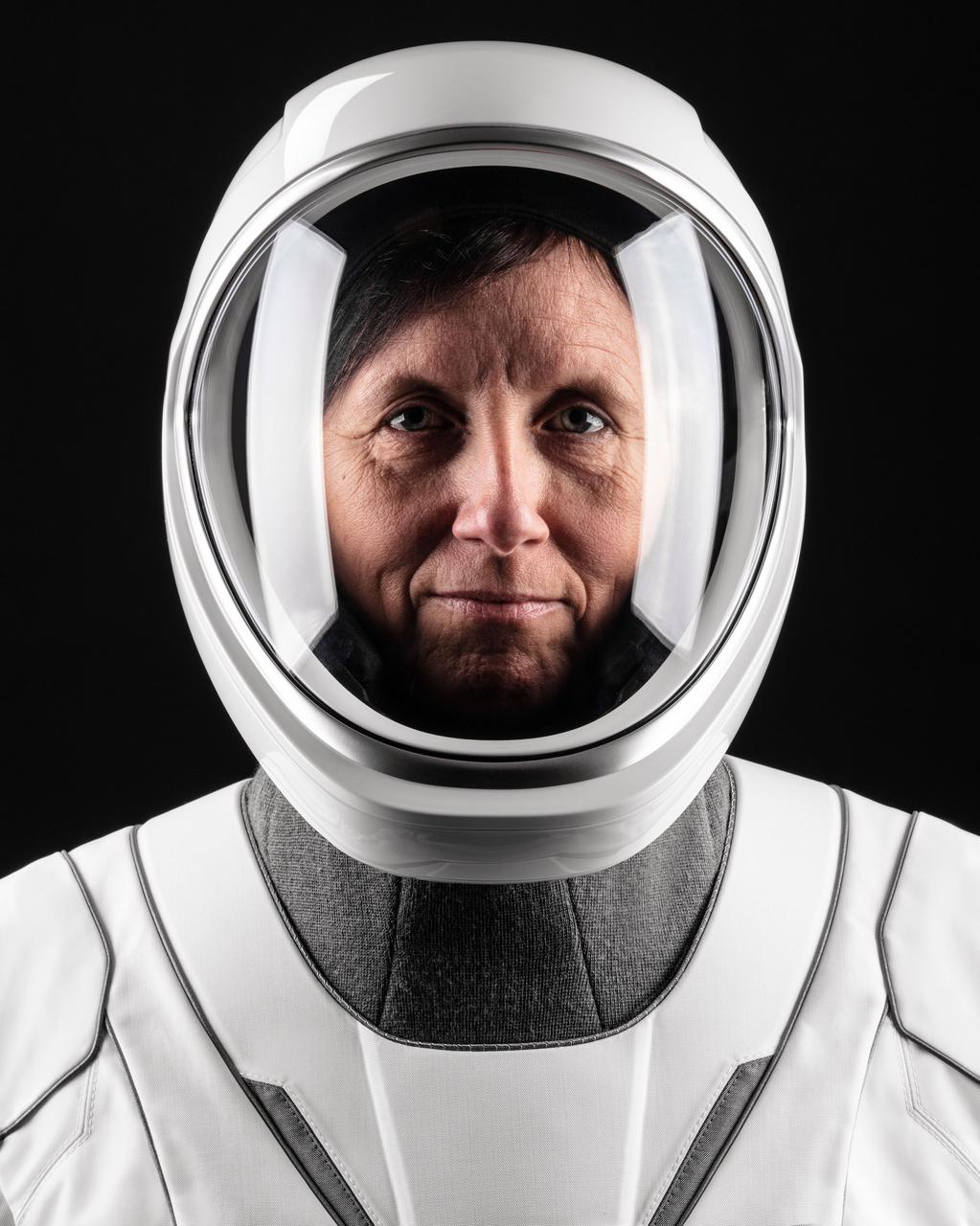

jsc2020e040987 (June 25, 2020) --- Astronaut Shannon Walker of NASA's Commercial Crew Program is a mission specialist for the first operational SpaceX Crew Dragon mission designated as Crew-1. Credit: SpaceX/Sam Friedman
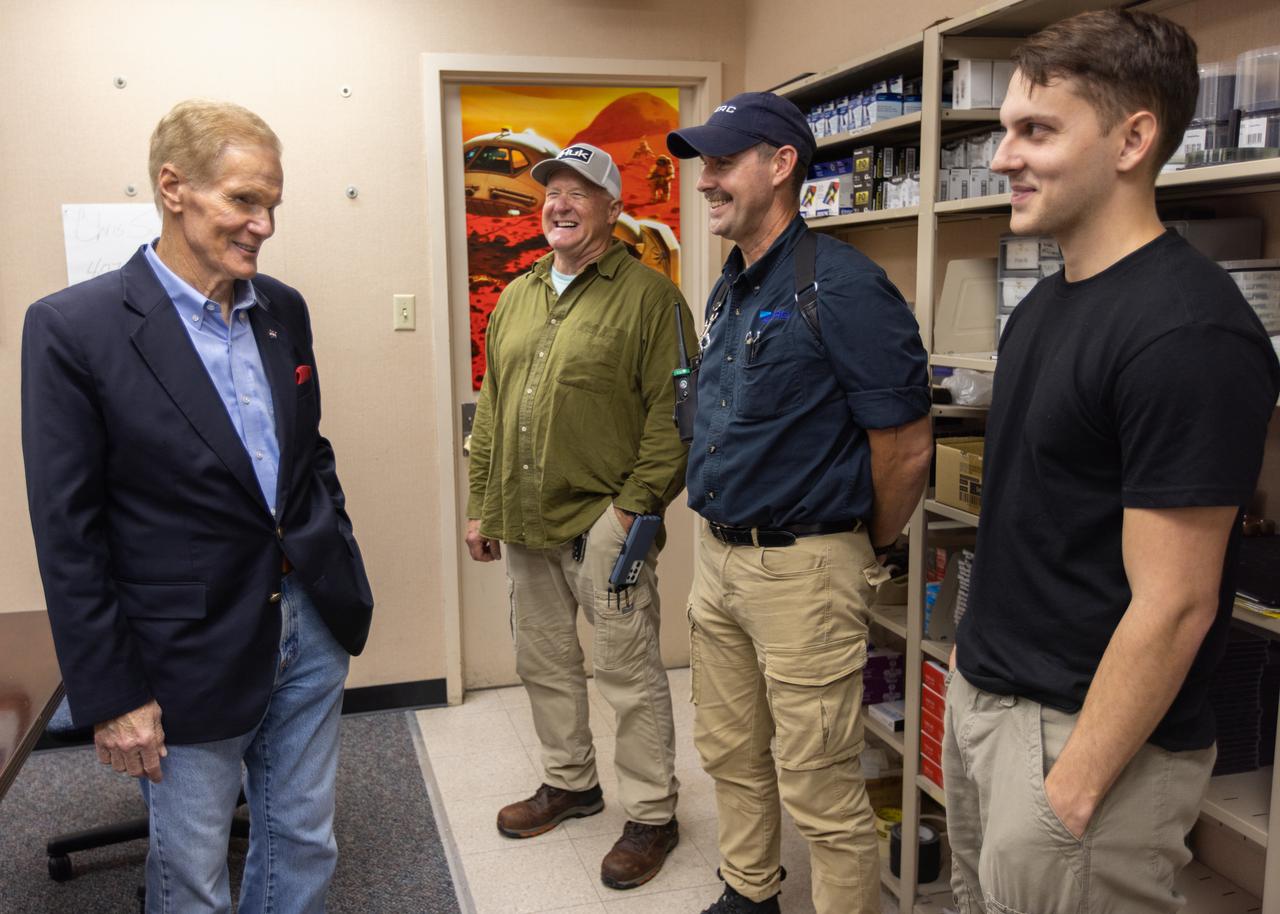

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson (left) meets with members of the “red crew,” Jacobs/TOSC ERC employees Billy Cairns (second from left), cryogenic engineering technician; Chad Garrett (second from right), safety engineer; and Trent Annis (right), cryogenic engineering technician, after the launch of Artemis I at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 16, 2022. The team of technicians are part of the personnel specially trained to conduct operations at the launch pad during cryogenic loading operations at the launch pad. Prior to the launch of Artemis I, the red crew entered the zero deck, or base, of the mobile launcher and tightened several bolts to troubleshoot a valve used to replenish the core stage with liquid hydrogen which showed a leak with readings above limits. NASA has historically sent teams to the pad to conduct inspections during active launch operations as needed. Artemis I launch successfully at 1:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 16, from Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.
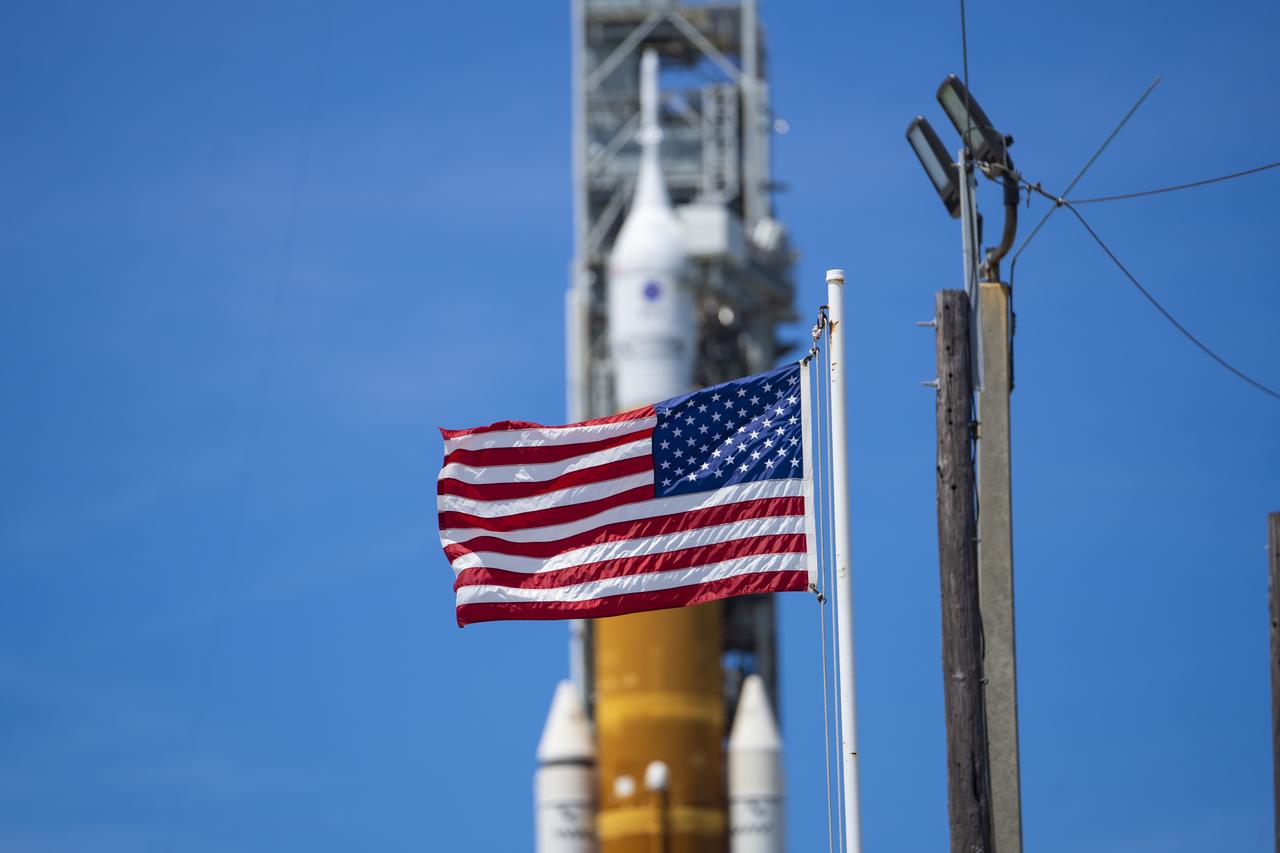

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
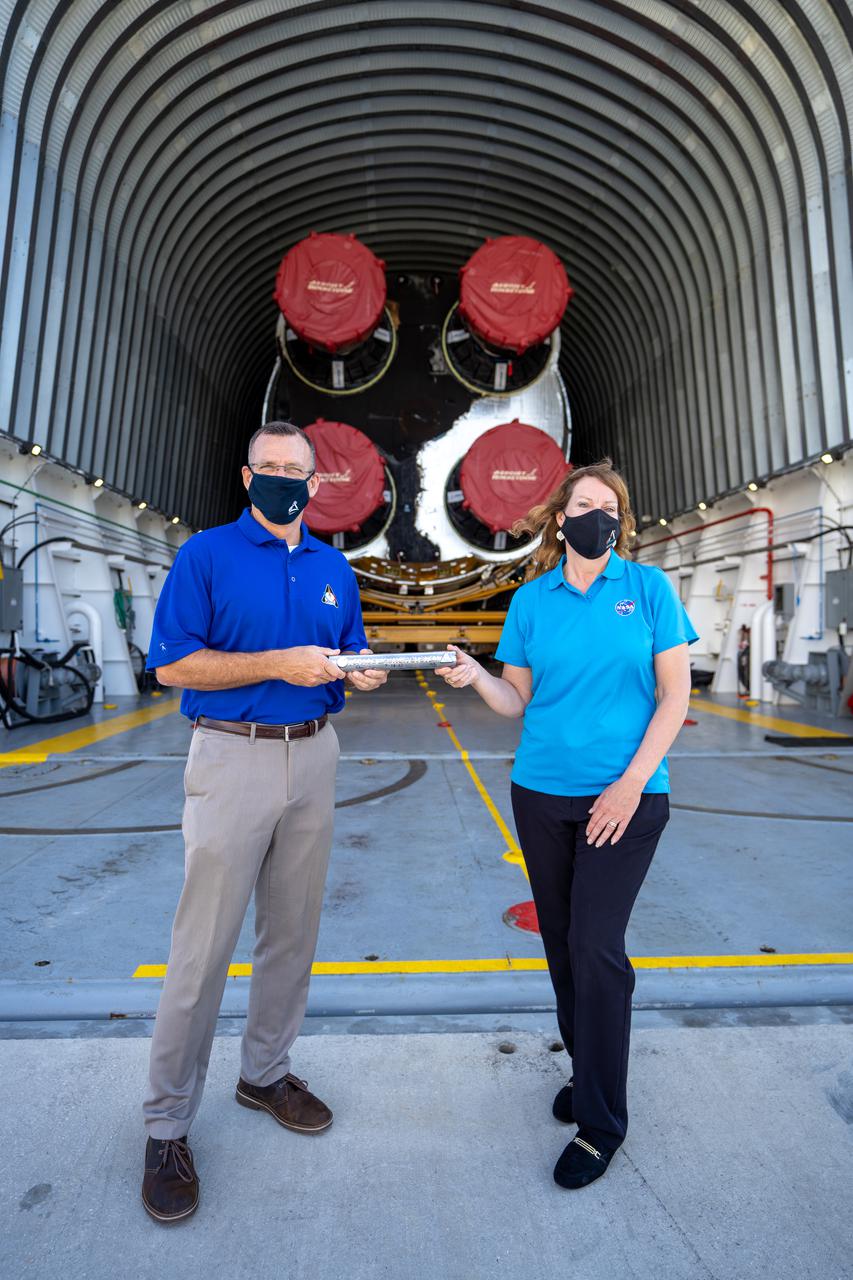

Space Launch System (SLS) Stages Manager Julie Bassler, right, celebrates the arrival of the SLS core stage by symbolically “passing the baton” to Exploration Ground Systems’ (EGS) Senior Vehicle Operations Manager Cliff Lanham on April 28, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Journeying from the agency’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi aboard the Pegasus barge, the core stage arrived at the Florida spaceport on April 27 to be processed for flight by EGS. It is the final piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at Kennedy and will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher with the completed stack of solid rocket boosters ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Space Launch System (SLS) Stages Manager Julie Bassler, right, celebrates the arrival of the SLS core stage by symbolically “passing the baton” to Exploration Ground Systems’ (EGS) Senior Vehicle Operations Manager Cliff Lanham on April 28, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Journeying from the agency’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi aboard the Pegasus barge, the core stage arrived at the Florida spaceport on April 27 to be processed for flight by EGS. It is the final piece of Artemis hardware to arrive at Kennedy and will be offloaded and moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building, where it will be prepared for integration atop the mobile launcher with the completed stack of solid rocket boosters ahead of the Artemis I launch. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
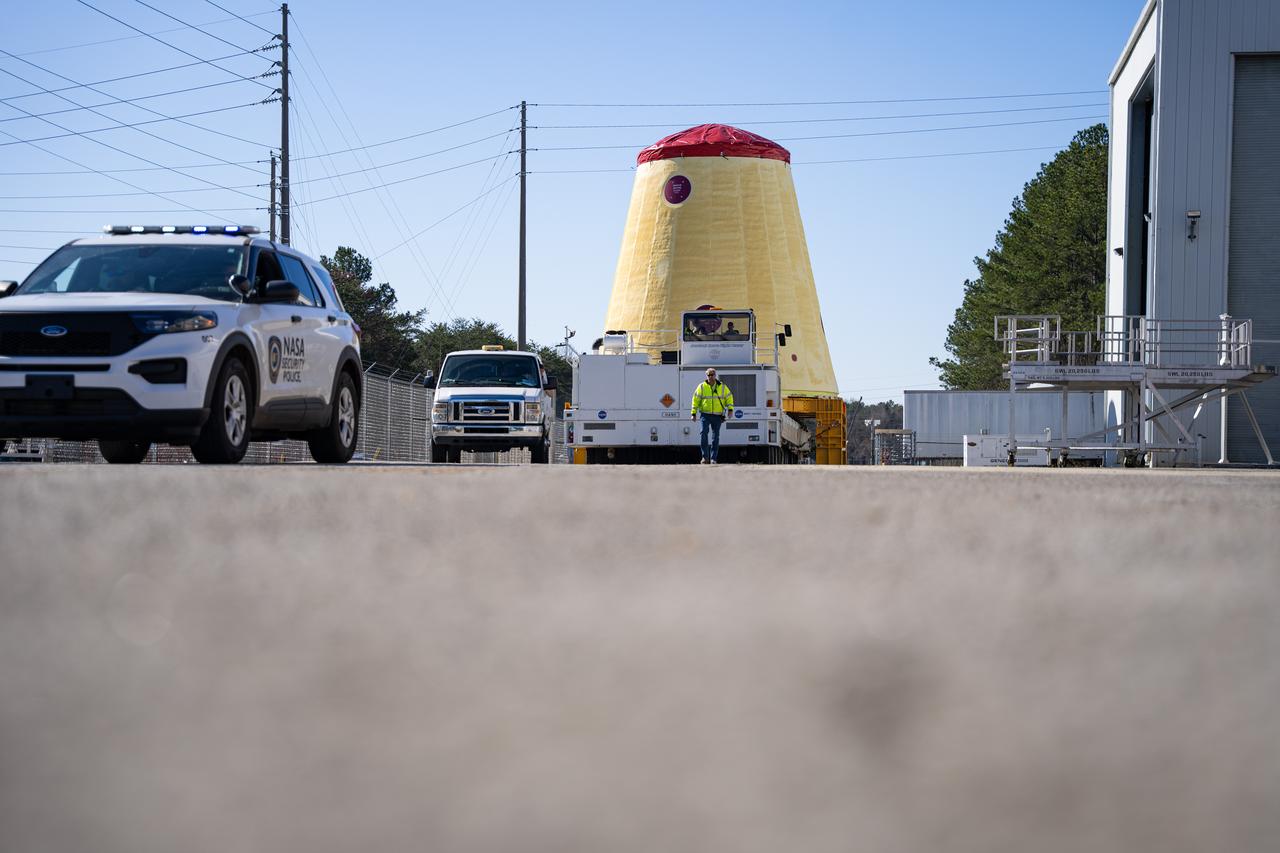

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708, where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
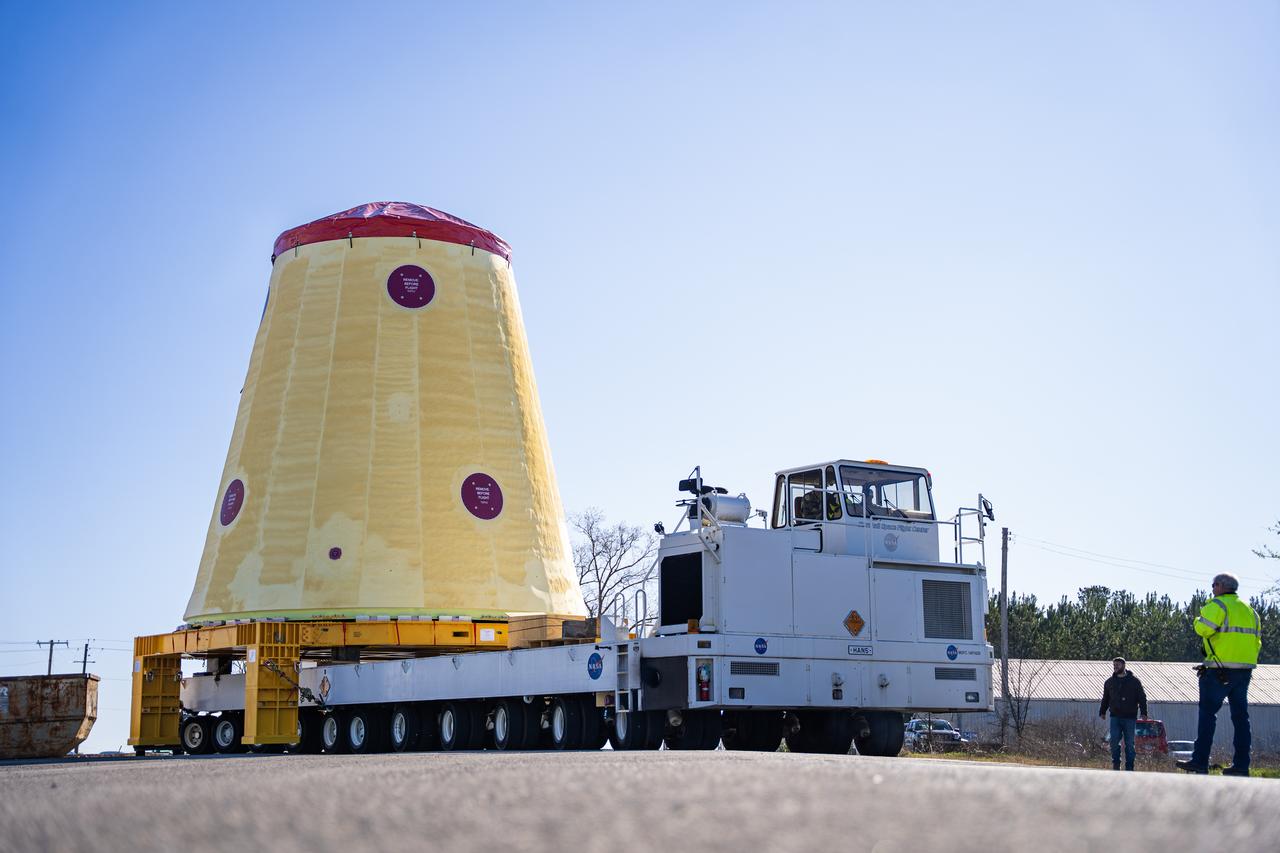

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
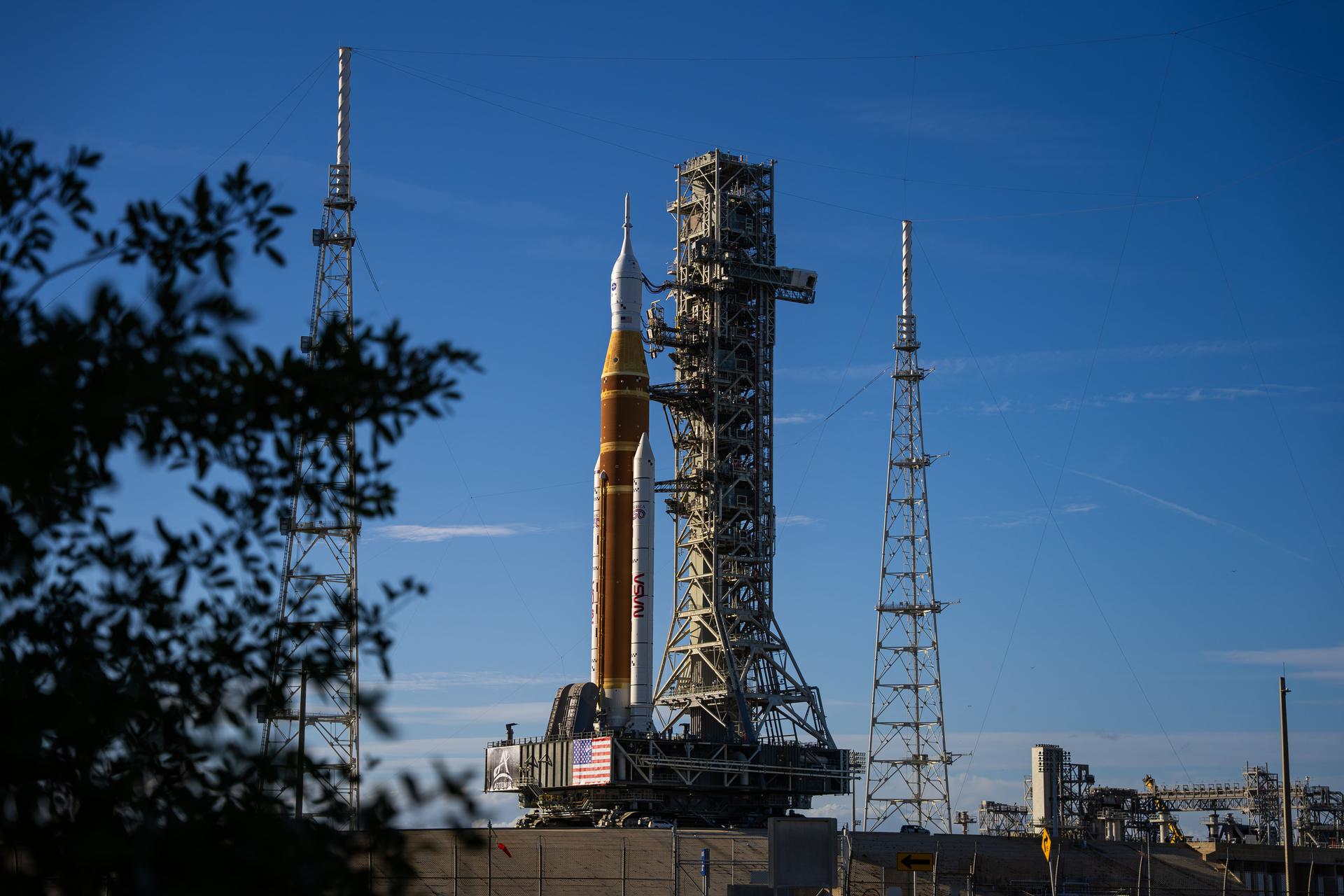

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
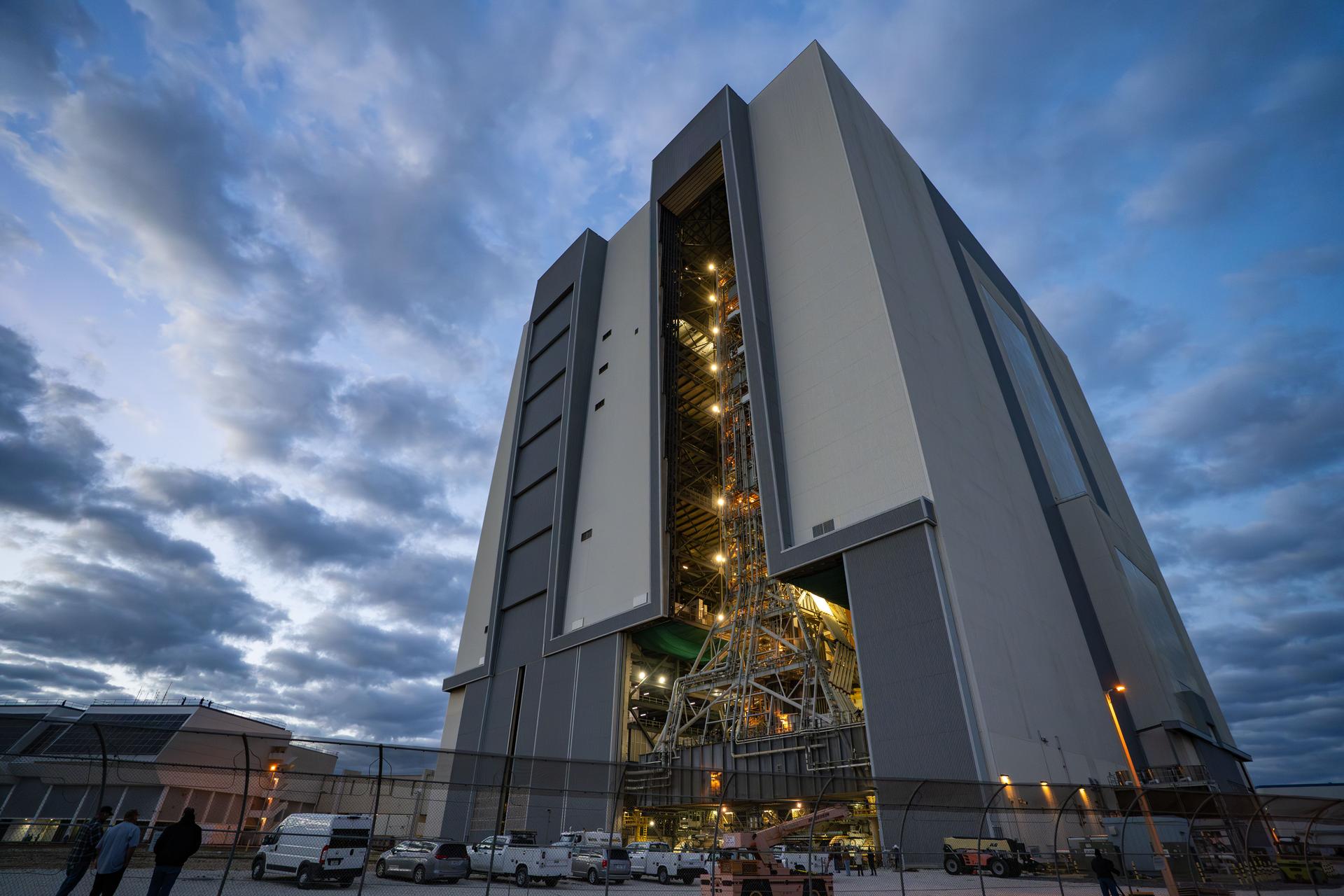

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
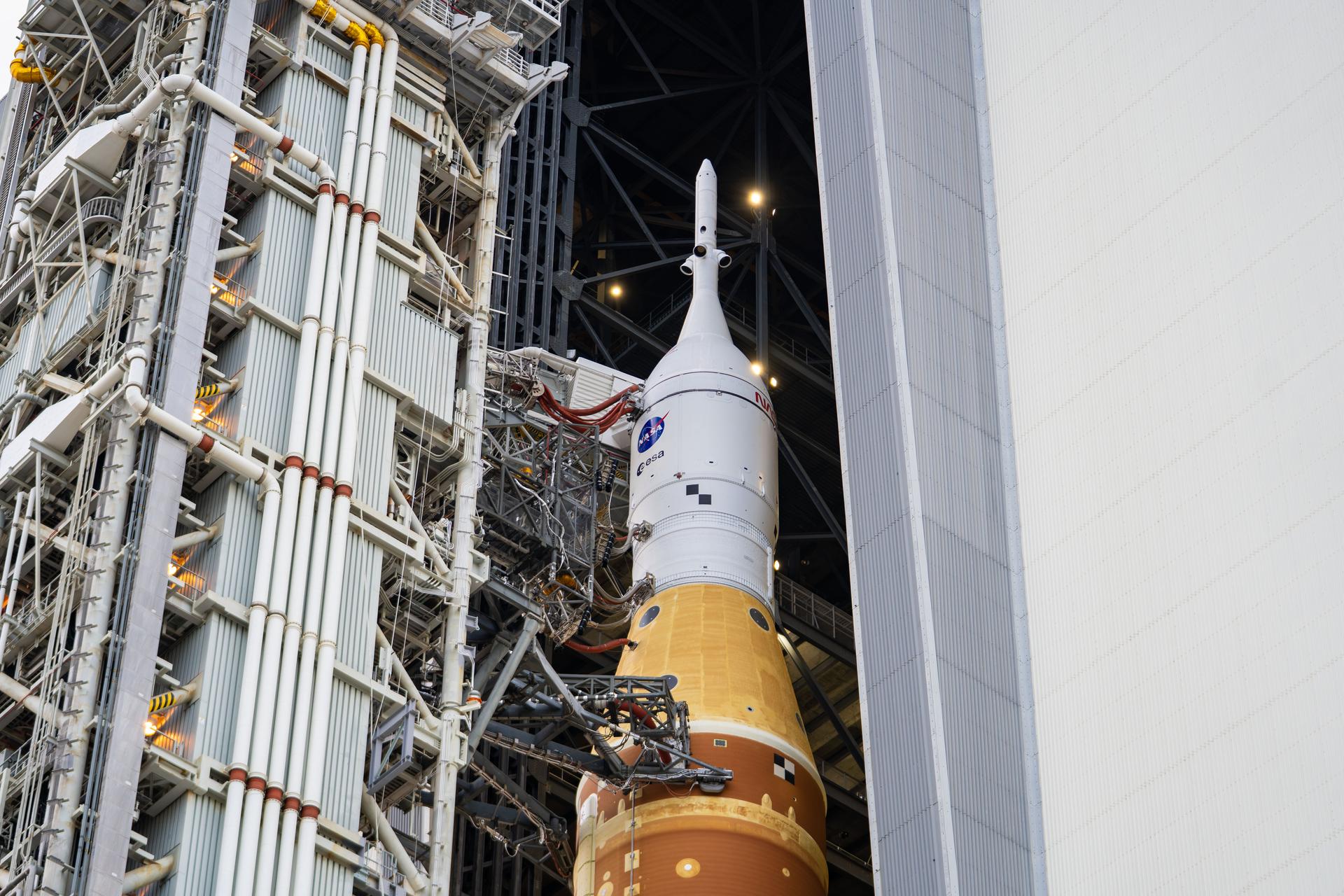

This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.