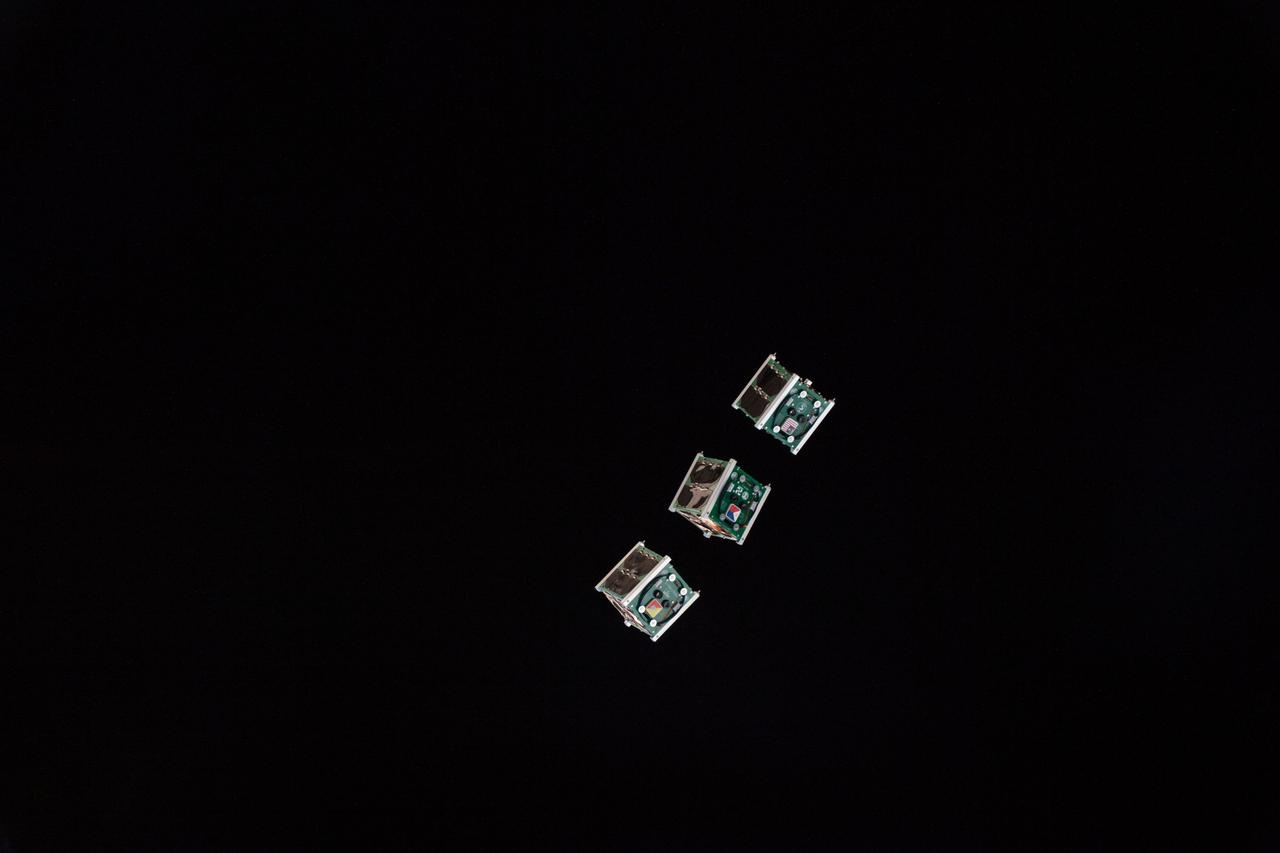
![iss057e006099 (10/6/2018) --- Documentation of two deployed Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) CubeSats, STARS-Me and RSP-00, during the JEM [Japanese Experiment Module]-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer 10 (J-SSOD 10) mission. Earth is in the background.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/iss057e006099/iss057e006099~medium.jpg)
iss057e006099 (10/6/2018) --- Documentation of two deployed Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) CubeSats, STARS-Me and RSP-00, during the JEM [Japanese Experiment Module]-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer 10 (J-SSOD 10) mission. Earth is in the background.
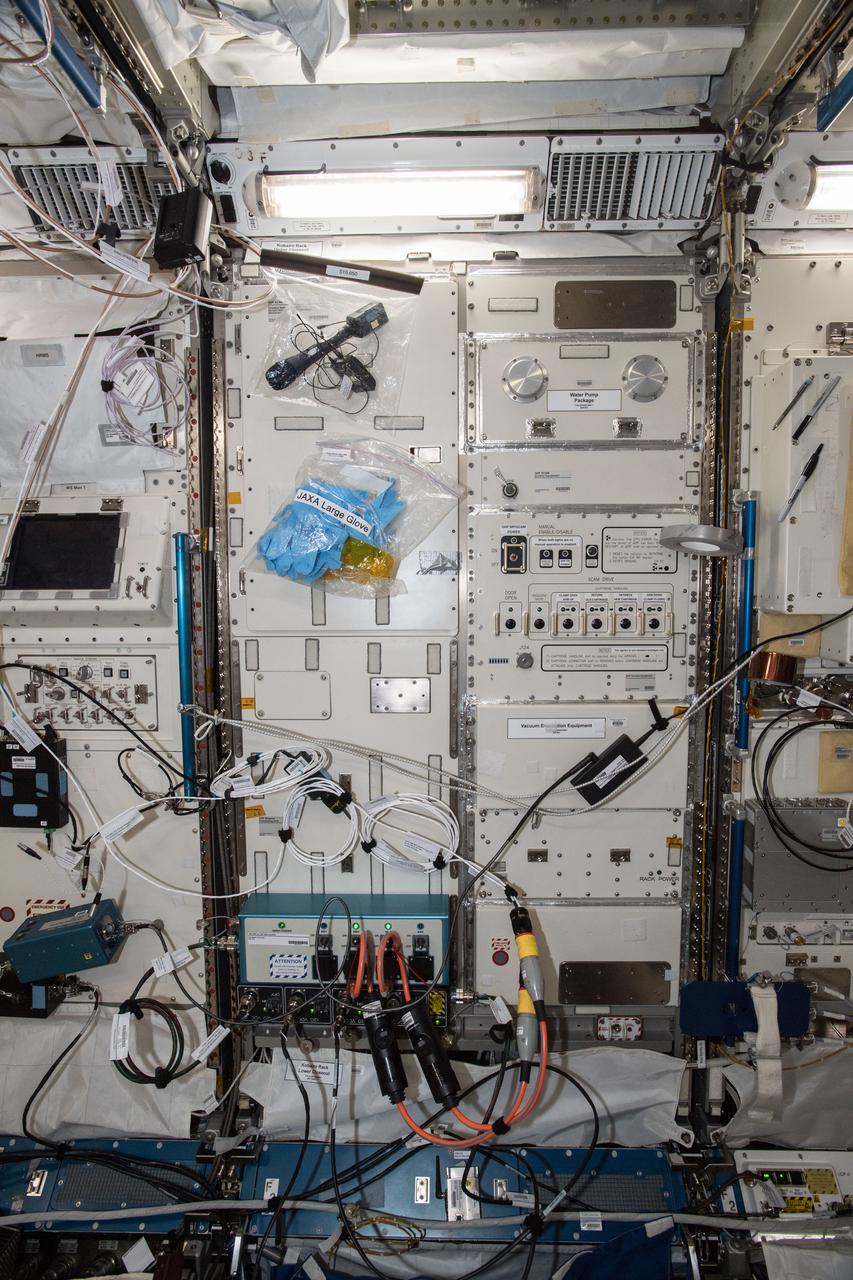

iss057e092614 (11/14/2018) --- Photo documentation of the Kobairo Rack front, JPM1F3 in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) aboard the International Space Staion (ISS). The KOBAIRO Rack houses the Gradient Heating Furnace (GHF), an experiment facility for investigating crystal growth of semiconductors. This furnace has the capability of directional solidification of samples.
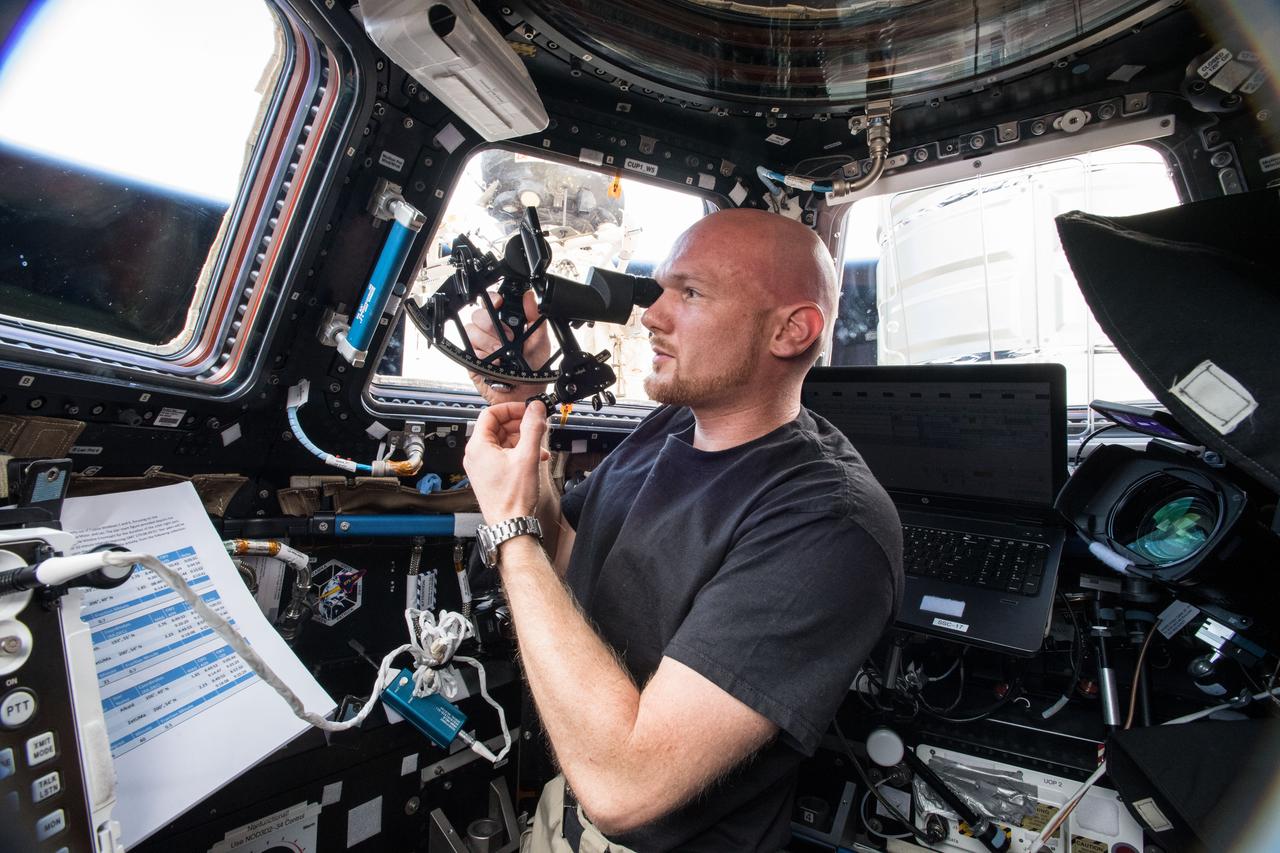

iss056e049856 (June 28, 2018) --- Astronaut Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency) calibrates and operates the Sextant Navigation device which is testing emergency navigation methods such as stability and star sighting in microgravity for future Orion exploration missions.
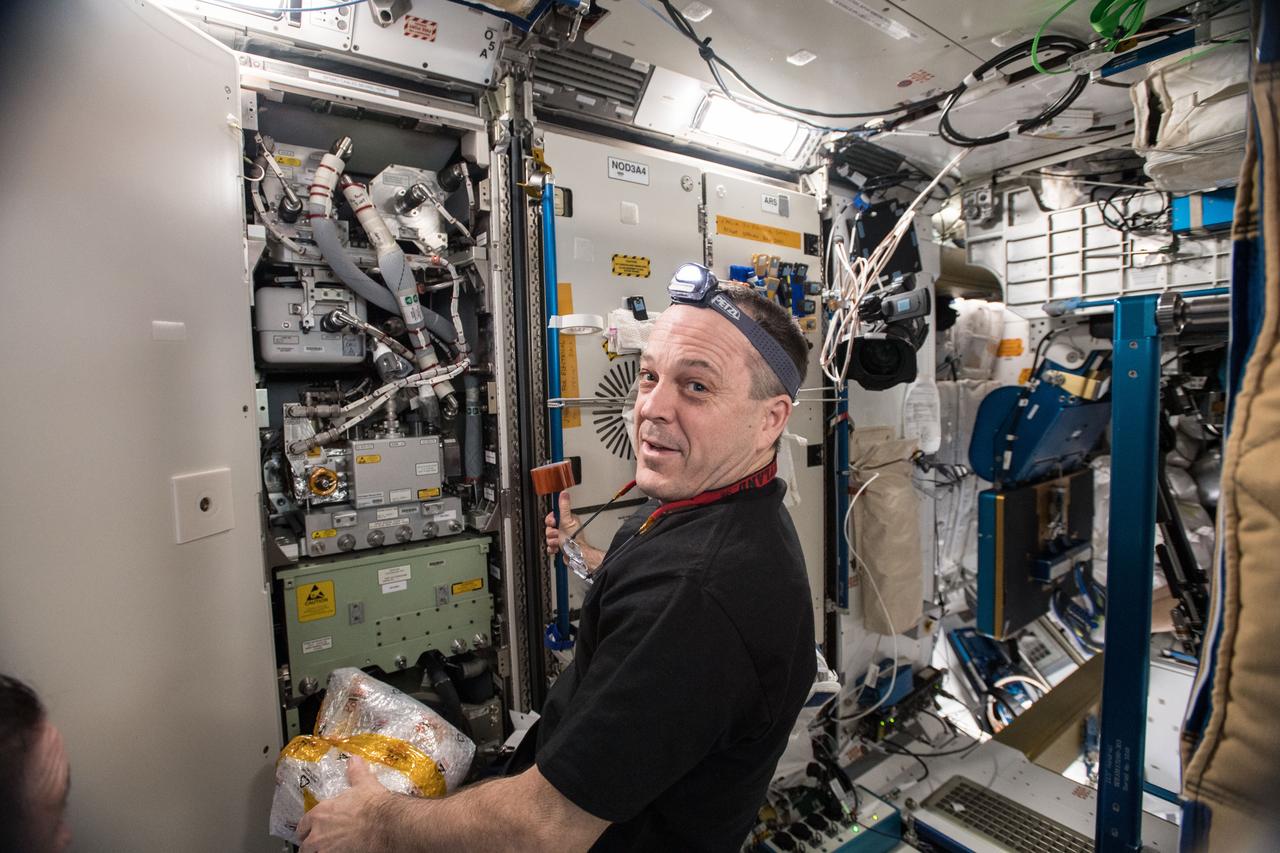

iss056e014487 (June 18, 2018) --- Expedition 56 Flight Engineer Ricky Arnold of NASA is pictured in the Unity module during life support maintenance work to remove and replace an Oxygen Generation System Hydrogen Sensor.
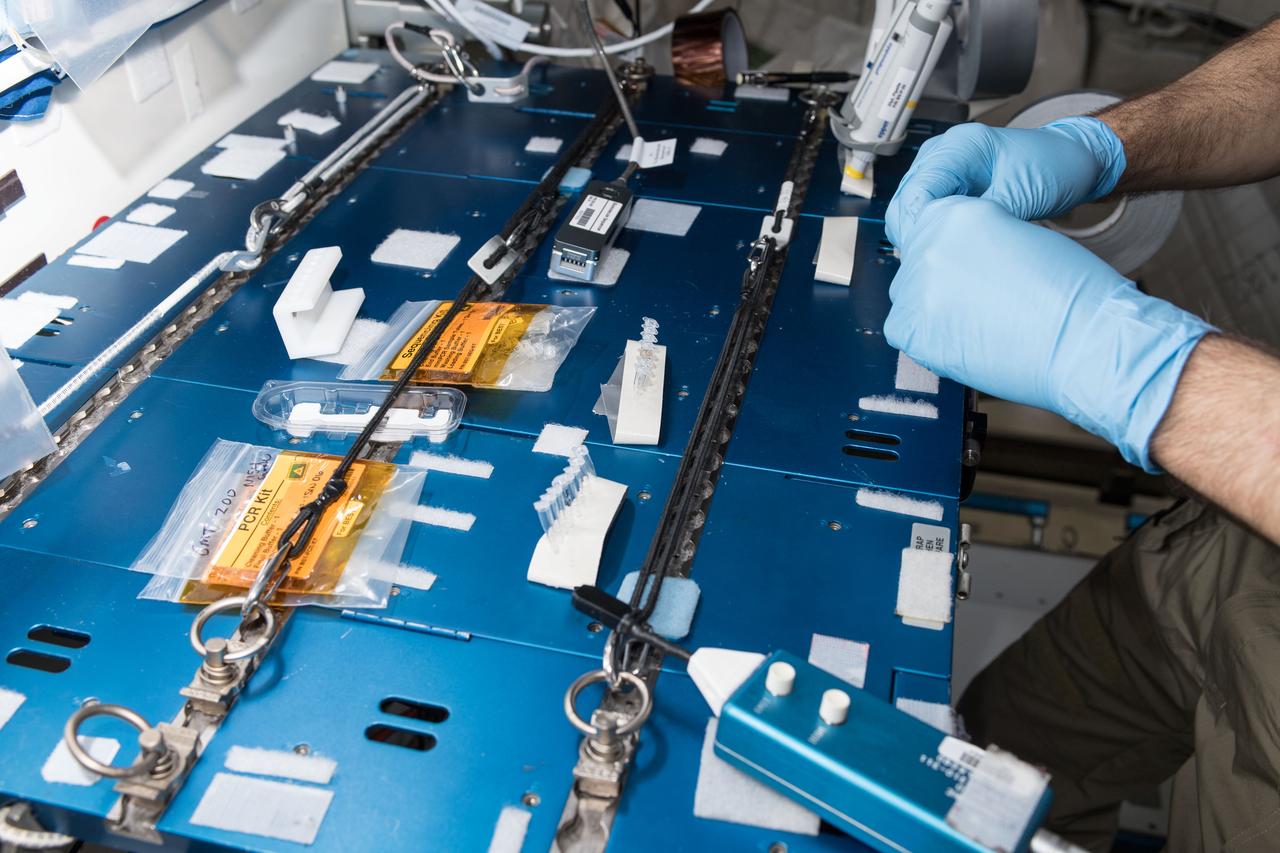

iss056e097517 (July 20, 2018) --- NASA astronaut Ricky Arnold swabbed surfaces in the International Space Station to collect microbe samples. He then processed the microbial DNA using the Biomolecule Sequencer, a device that enables DNA sequencing in microgravity, to identify microbes able to survive in microgravity.
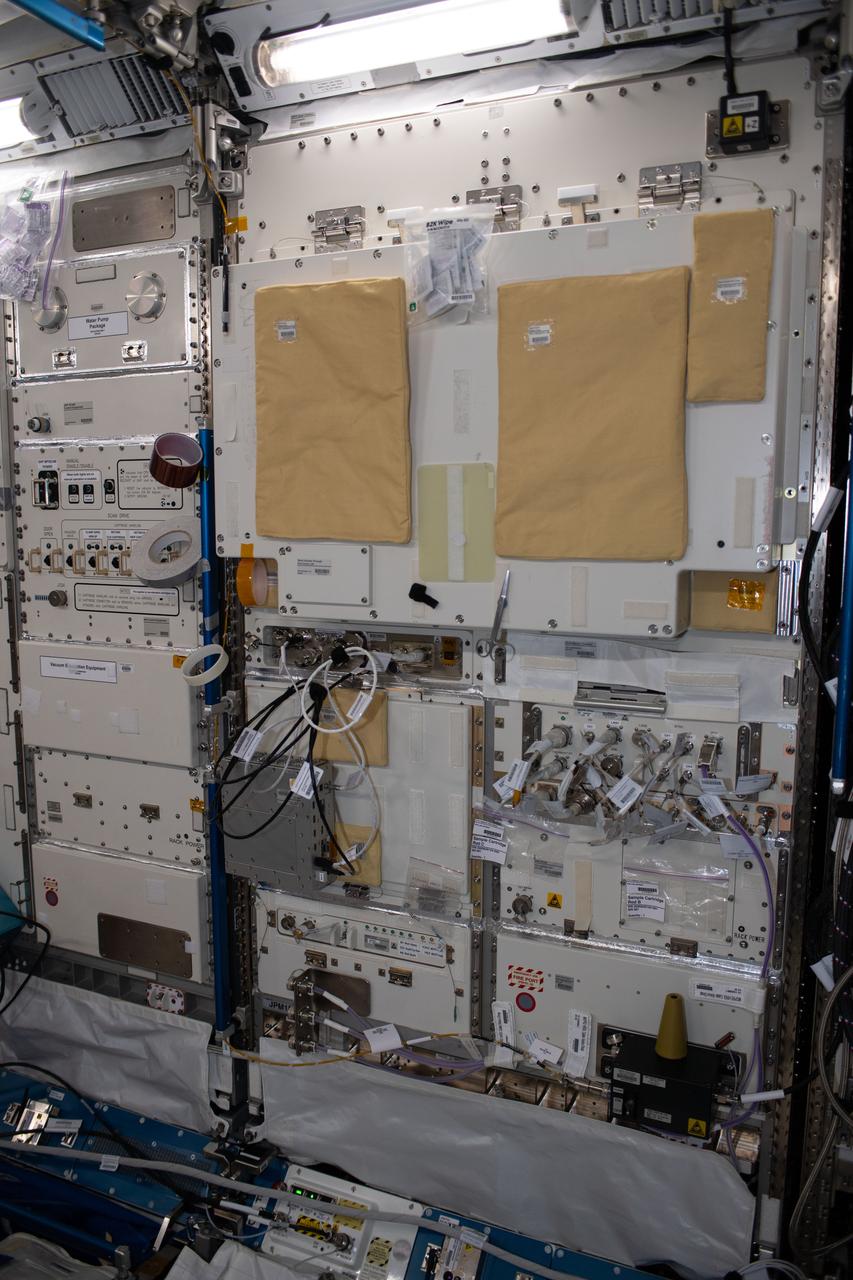

iss056e150256 (8/21/2018) --- A view of the Multi purpose Small Payload Rack (MSPR) 2 in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Multi Purpose Small Payload Rack-2 (MSPR-2) is a second multipurpose payload rack system used in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). Similar to the original MSPR (still in use), MSPR-2 has two workspaces and a work table that can be used for wide fields of space environment utilization including science and educational missions.
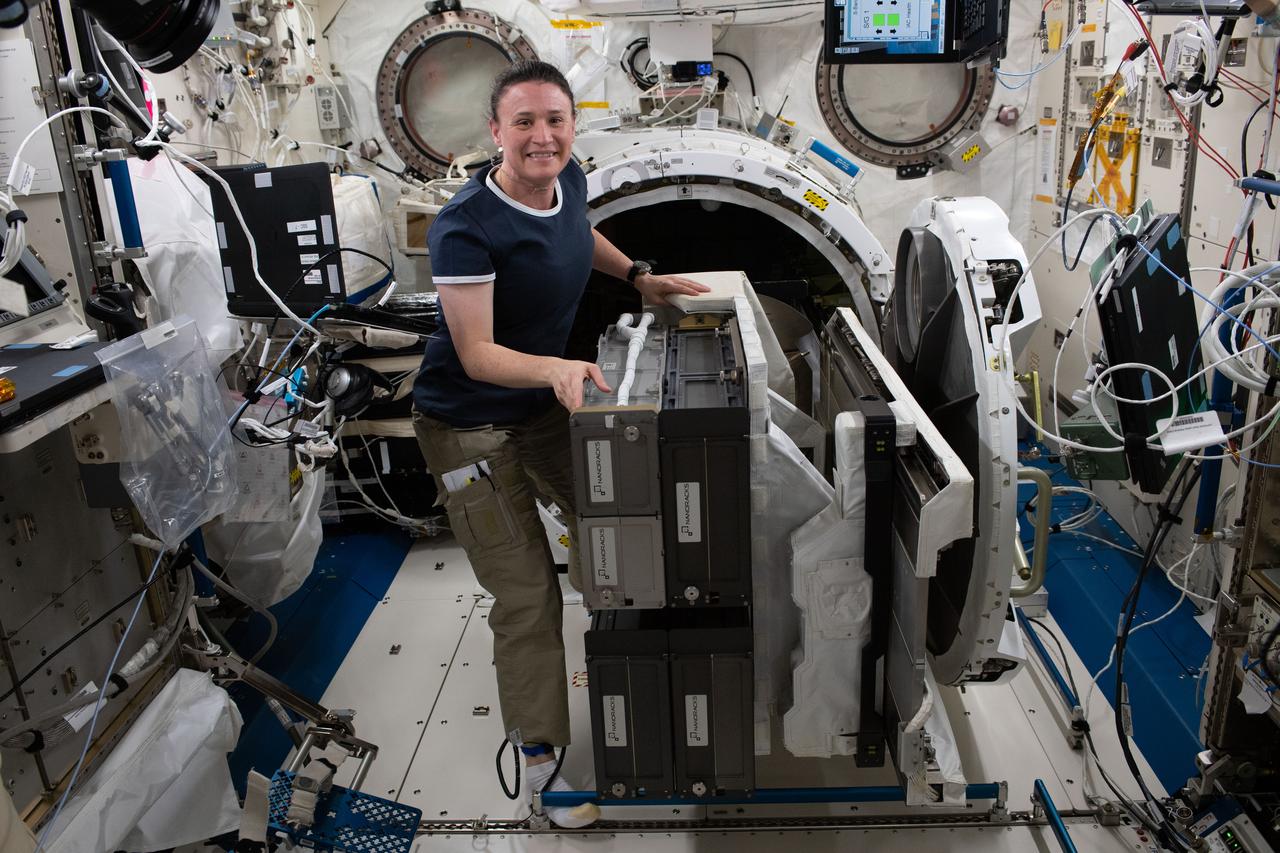

iss056e033124 (June 25, 2018) --- Expedition 56 Flight Engineer Serena Auñón-Chancellor installs the NanoRacks Cubesat Deployer-14 (NRCSD-14) on the Multipurpose Experiment Platform inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module. The NRCSD-14 was then placed in the Kibo airlock and moved outside of the space station to deploy a variety of cubesats into Earth orbit.

iss056e130414 (July 28, 2018) --- Astronaut Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency) cleans the Crew Medical Restraint System (CMRS) inside the International Space Station's U.S. Destiny Laboratory. In the event of a medical emergency aboard the station a crew member would be secured in the CMRS.
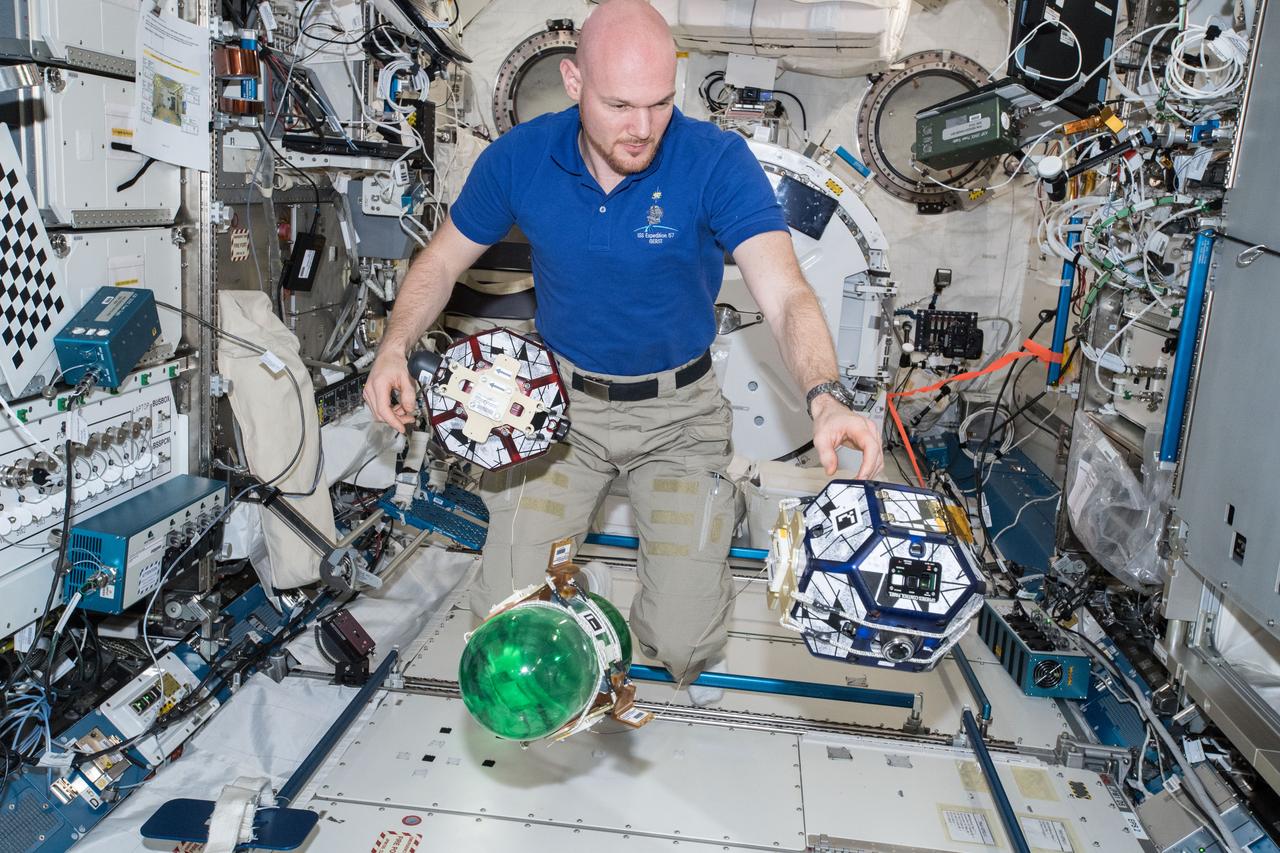

iss057e055052 (10/18/2018) --- European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst is photographed during a Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) Tether Slosh experiment test session run. Photo was taken in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). SPHERES Tether Slosh combines fluid dynamics equipment with robotic capabilities aboard the ISS to investigate automated strategies for steering passive cargo that contain fluids.
![iss057e006046 (10/6/2018) --- Documentation of two Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) CubeSats, STARS-Me and RSP-00, deployed from JEM [Japanese Experiment Module]-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer 10 (J-SSOD 10) equipment on the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP).](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/iss057e006046/iss057e006046~medium.jpg)
iss057e006046 (10/6/2018) --- Documentation of two Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) CubeSats, STARS-Me and RSP-00, deployed from JEM [Japanese Experiment Module]-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer 10 (J-SSOD 10) equipment on the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP).
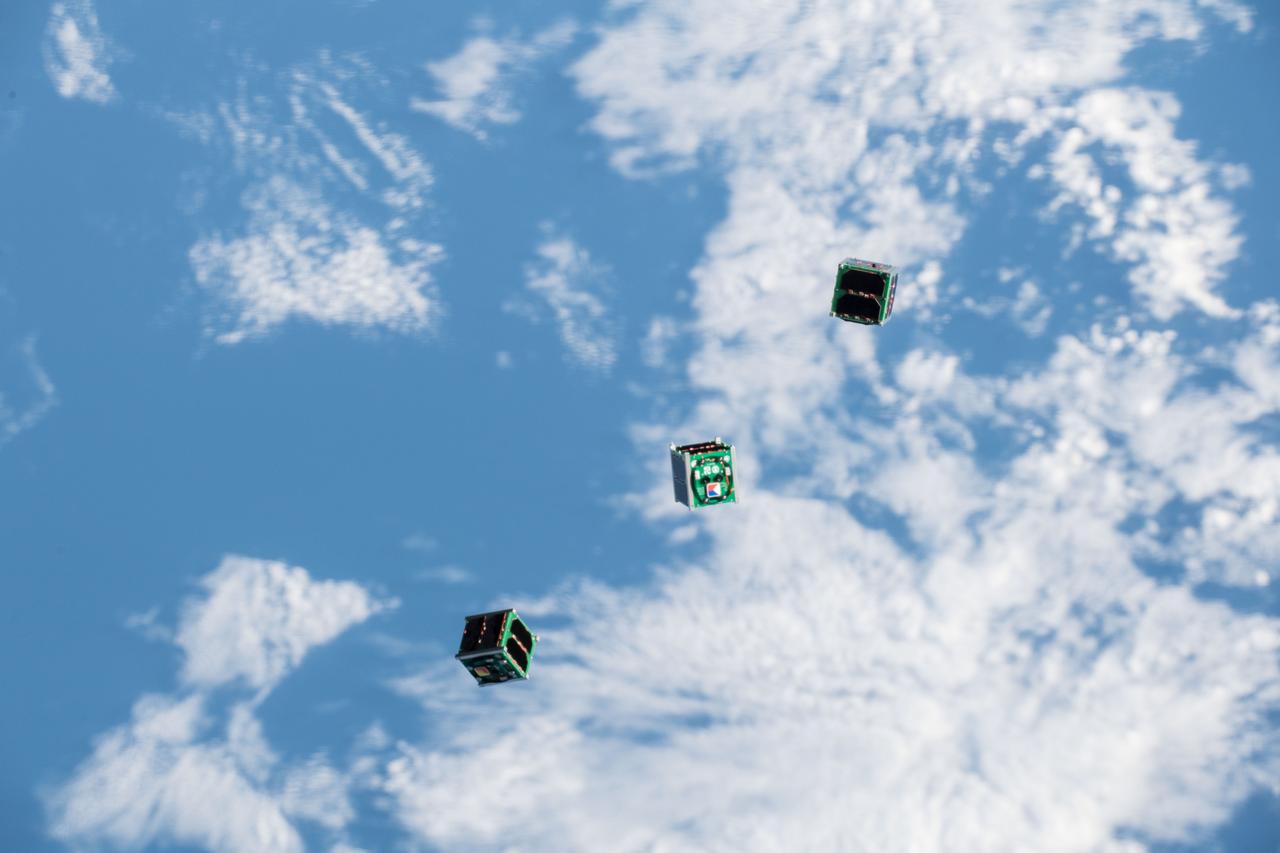

iss056e130515 (8/10/2018) --- A view of the BIRDS-2 Satellite Deployment during JSSOD-9 operations. The JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) provides a novel, safe, small satellite launching capability to the International Space Station (ISS).
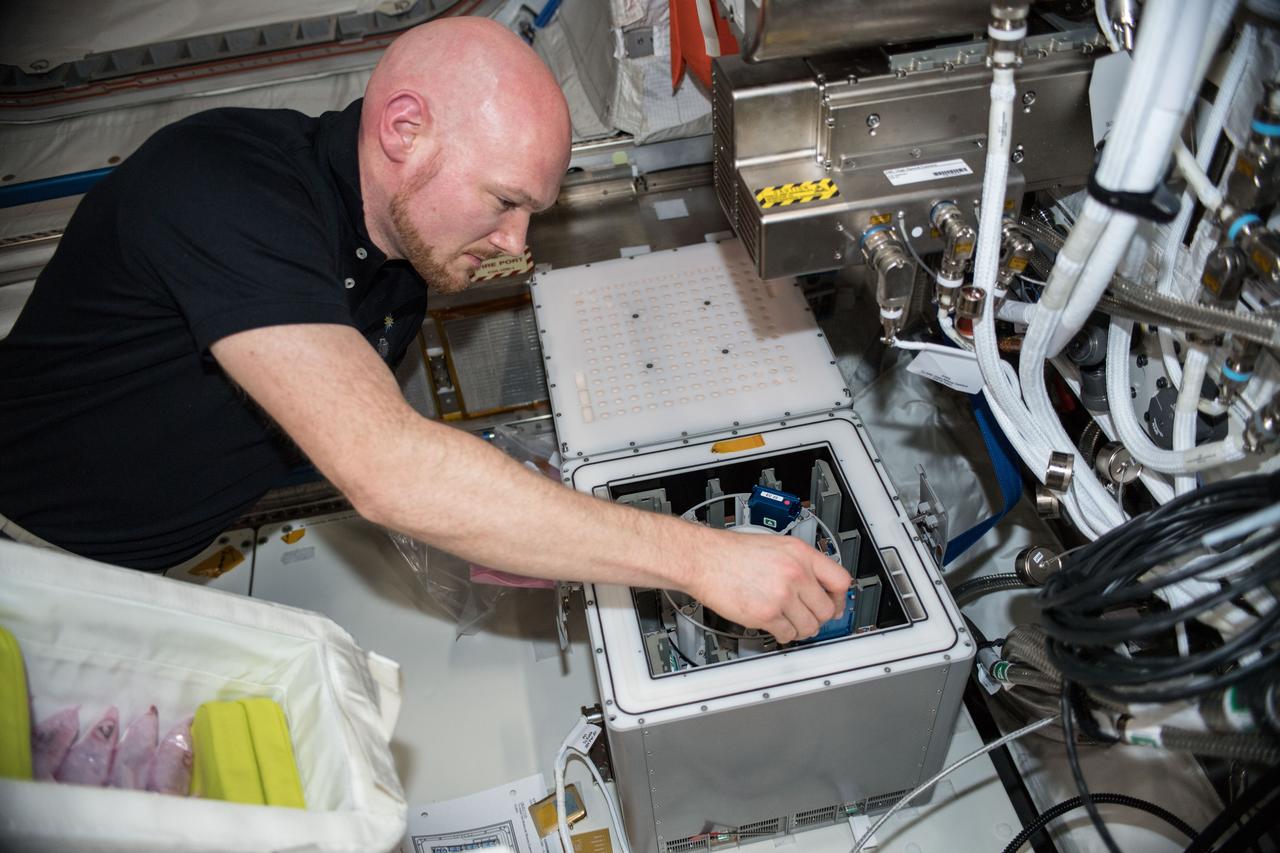

iss057e114873 (12/9/2018) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Alexander Gerst placing the experiment canisters for the Molecular Muscle investigation into the Kubik incubator located on the Columbus module. The Molecular Muscle investigation examines the molecular causes of muscle abnormalities during spaceflight in order to establish effective countermeasures. Using the validated model organism C. elegans, combined with flight-validated methodologies, this experiment targets the molecular alterations that are most consistently correlated with muscular and metabolic abnormalities across species in spaceflight (i.e. insulin- and attachment-mediated signaling). The success of the interventions in recovering muscle health is assessed by successfully preventing the gene and protein expression changes that are repeatedly observed in spaceflight.

iss056e014488 (June 18, 2018) --- Expedition 56 Flight Engineers Serena Auñón-Chancellor (right) and Ricky Arnold of NASA are pictured in the Unity module during life support maintenance work to remove and replace an Oxygen Generation System Hydrogen Sensor.

iss056e130490(8/10/2018) --- A view of the BIRDS-2 Satellite Deployment during JSSOD-9 operations. The JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) provides a novel, safe, small satellite launching capability to the International Space Station (ISS).
![iss056e200730 (10/3/2018) --- Photo documentation of the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (SSOD) on the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP) installation in preparation of the [Japanese Experiment Module]-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer 10 (J-SSOD 10) mission. J-SSOD-10 deploys the cubesats SPATIUM-I from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, and the Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan, RSP-00 from Ryman Sat Spaces General Incorporated Association, Japan, and STARS-Me from Shizuoka University, Japan.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/iss056e200730/iss056e200730~medium.jpg)
iss056e200730 (10/3/2018) --- Photo documentation of the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (SSOD) on the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP) installation in preparation of the [Japanese Experiment Module]-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer 10 (J-SSOD 10) mission. J-SSOD-10 deploys the cubesats SPATIUM-I from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, and the Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan, RSP-00 from Ryman Sat Spaces General Incorporated Association, Japan, and STARS-Me from Shizuoka University, Japan.
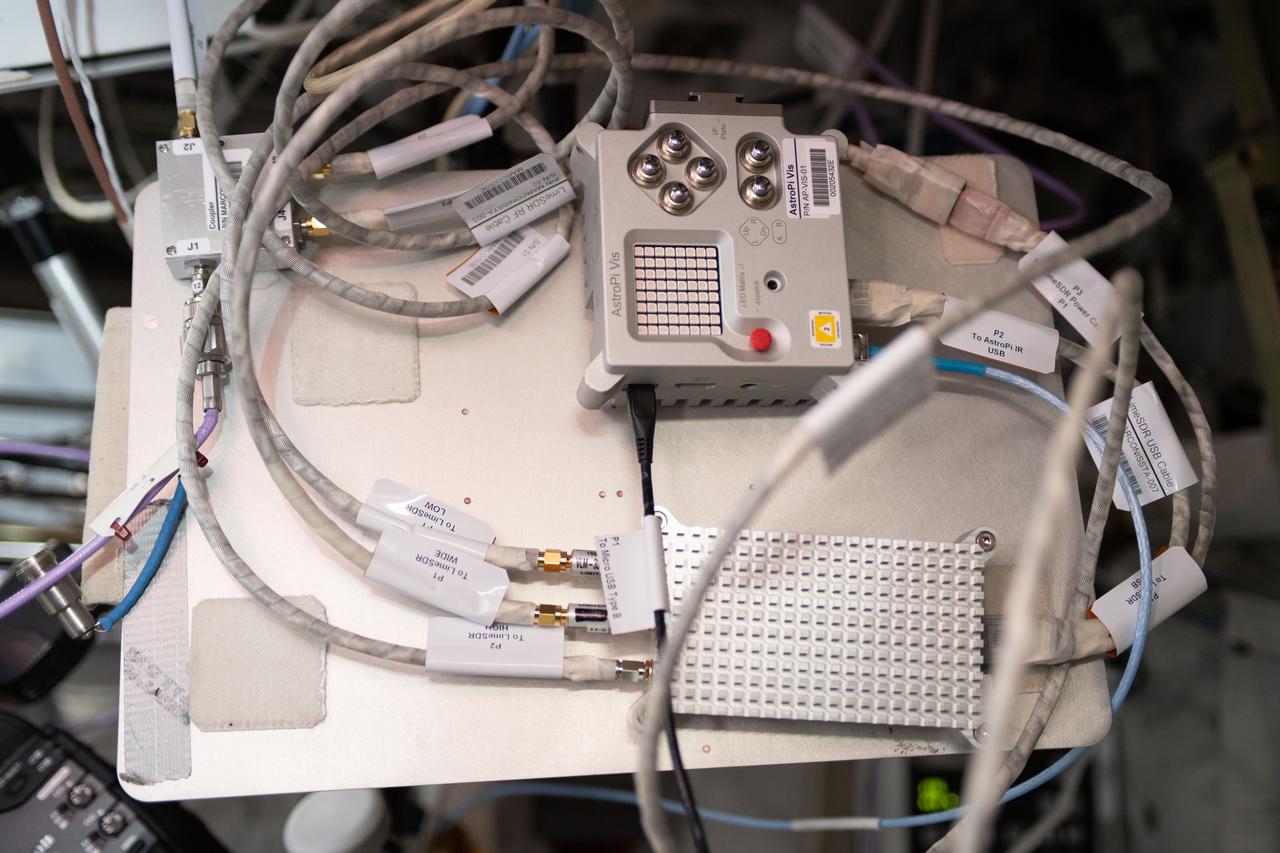

iss056e136189 (8/13/2020) --- A view of the Marconissta setup connected to the Amateur Radio on International Space Station (ARISS) antennas in the Columbus Module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). MarconISSta is a radio spectrum analyzer payload launched to ISS. MarconISSta monitors parts of the radio frequency spectrum in VHF, UHF, L, and S band in order to analyze current use and availability of bands for satellite communication.
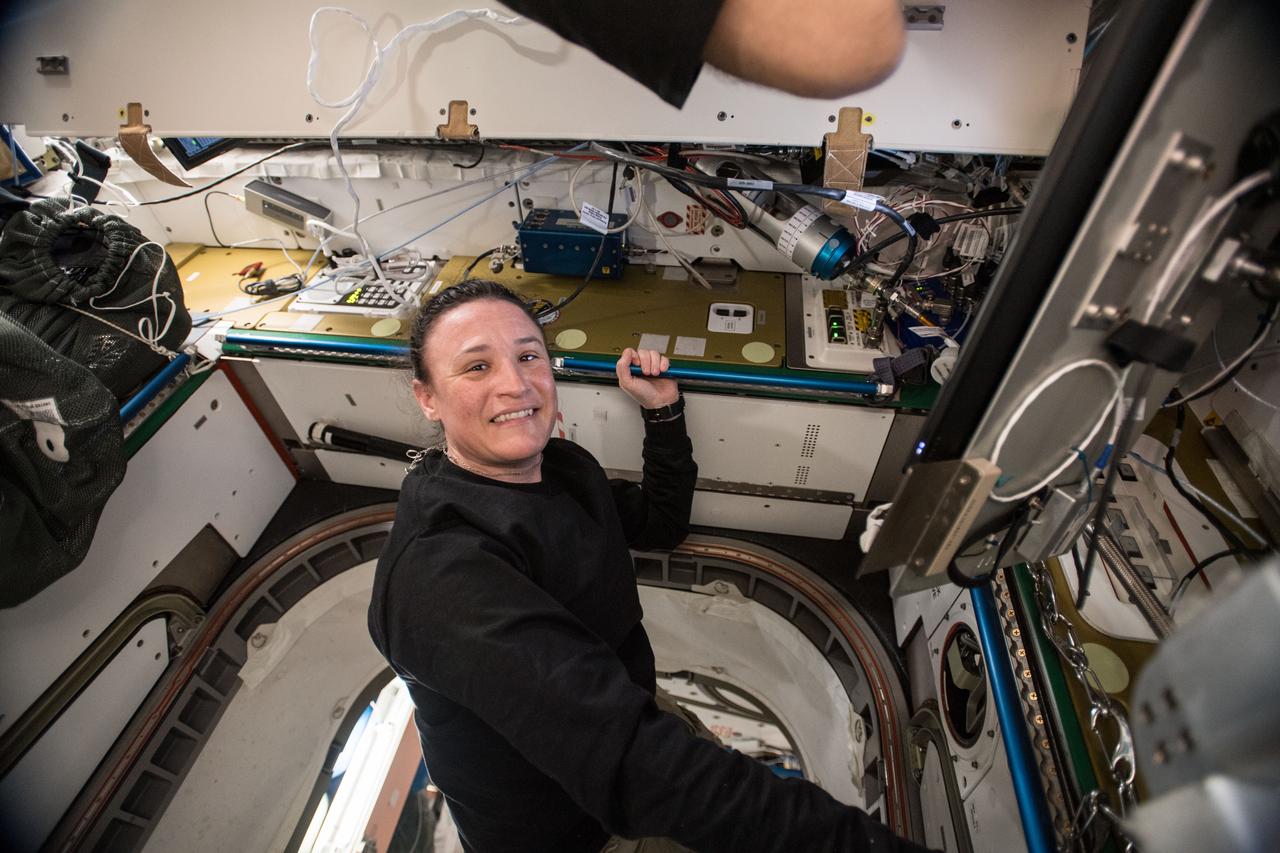

iss056e014502 (June 18, 2018) --- Expedition 56 Flight Engineer Serena Auñón-Chancellor of NASA is pictured in the Unity module during life support maintenance work to remove and replace an Oxygen Generation System Hydrogen Sensor.
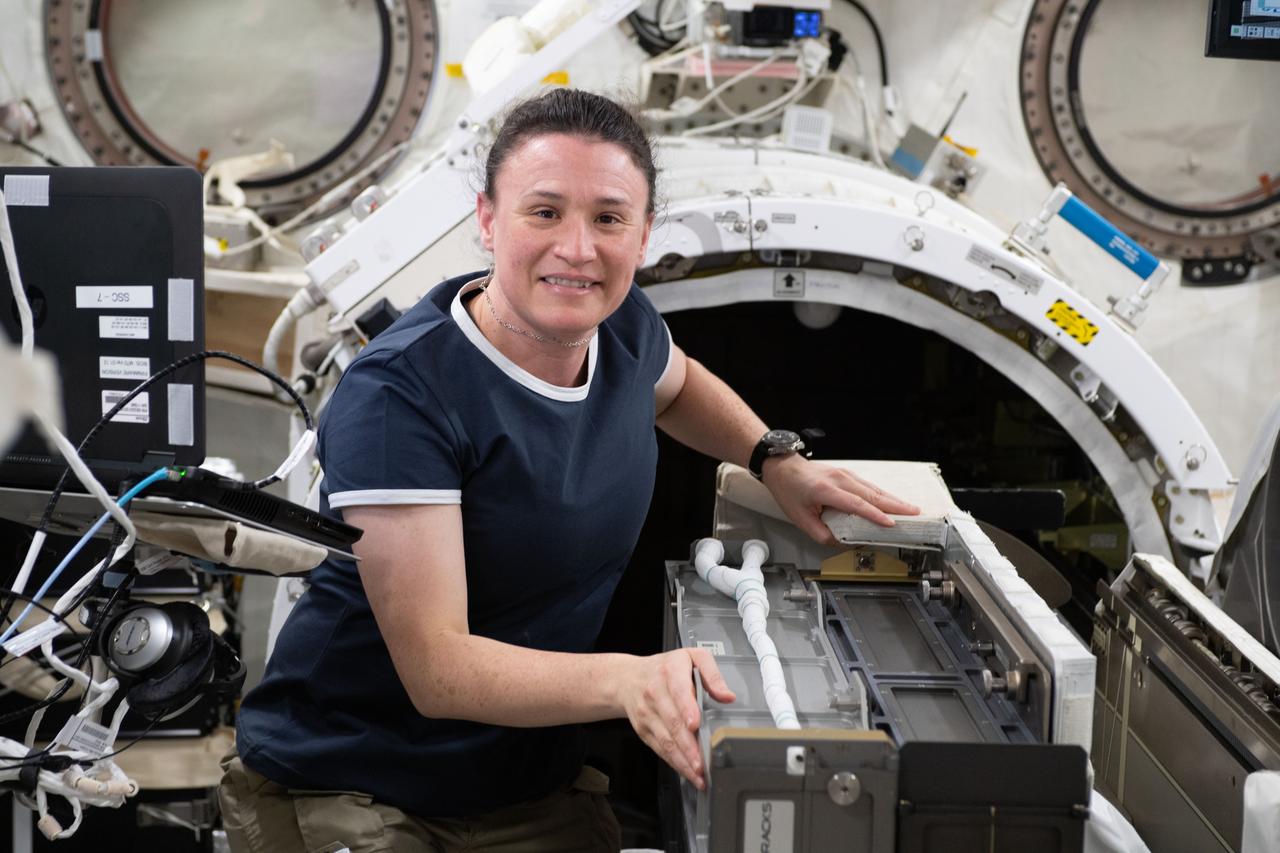

iss056e033126 (June 25, 2018) --- Expedition 56 Flight Engineer Serena Auñón-Chancellor installs the NanoRacks Cubesat Deployer-14 (NRCSD-14) on the Multipurpose Experiment Platform inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module. The NRCSD-14 was then placed in the Kibo airlock and moved outside of the space station to deploy a variety of cubesats into Earth orbit.
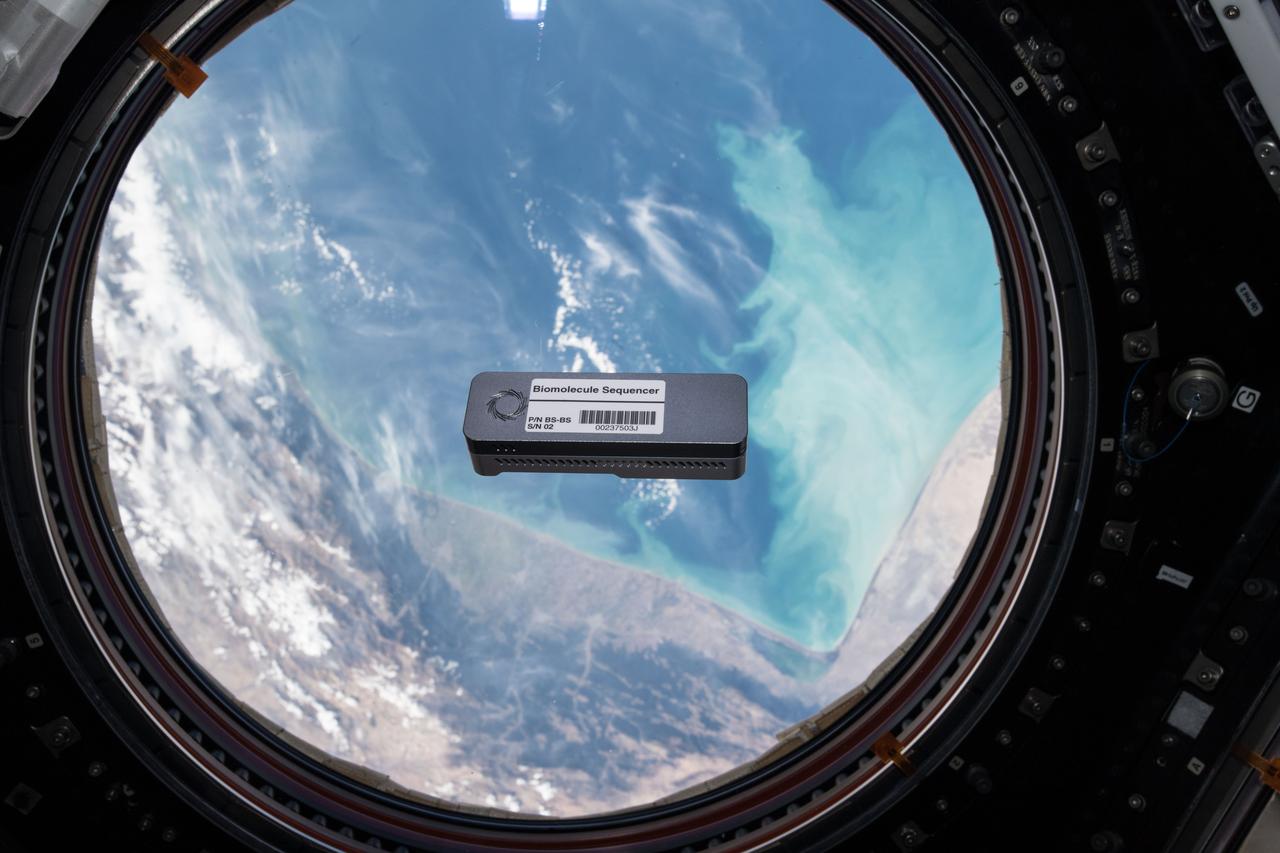

iss057e000180 (10/8/2018) - Biomolecule Sequencer for the BEST experiment floating in front of Window 7 in the Cupola module. Earth is in the background. The Biomolecule Sequencer seeks to demonstrate, for the first time, that DNA sequencing is feasible in an orbiting spacecraft. A space-based DNA sequencer could identify microbes, diagnose diseases and understand crew member health, and potentially help detect DNA-based life elsewhere in the solar system.
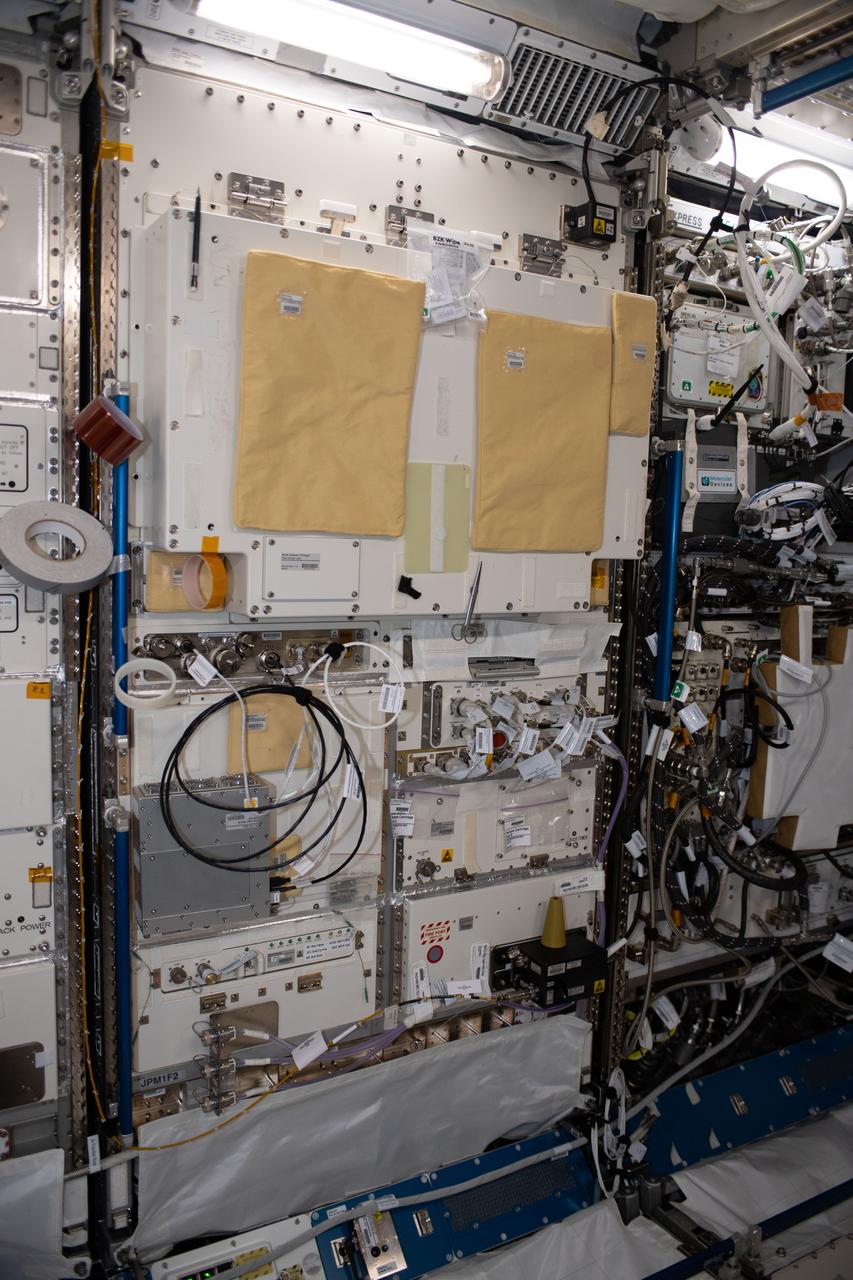

iss056e150255 (8/21/2018) --- A view of the Multi purpose Small Payload Rack (MSPR) 2 in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Multi Purpose Small Payload Rack-2 (MSPR-2) is a second multipurpose payload rack system used in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). Similar to the original MSPR (still in use), MSPR-2 has two workspaces and a work table that can be used for wide fields of space environment utilization including science and educational missions.
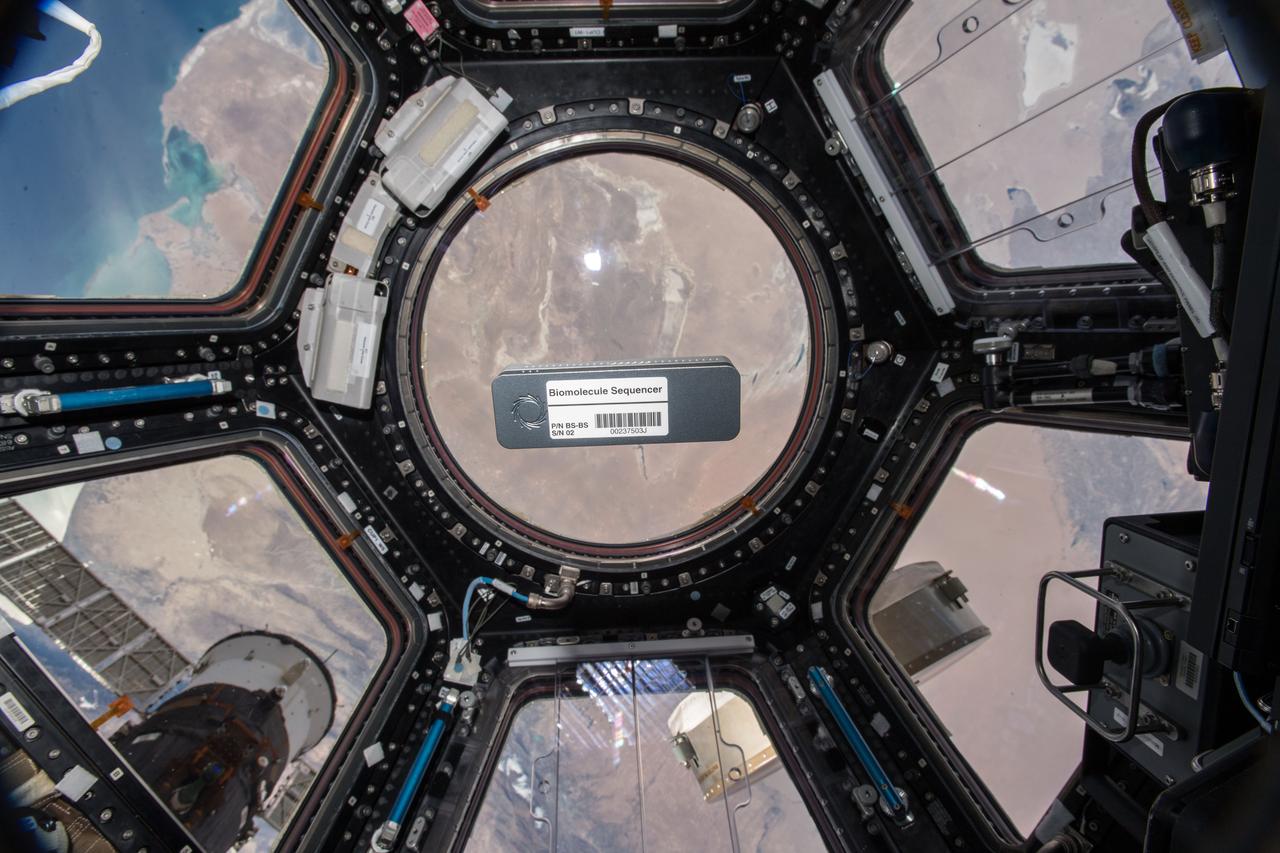

iss057e000185 (10/8/2018) - Biomolecule Sequencer for the BEST experiment floating in front of Window 7 in the Cupola module. Earth is in the background. The Biomolecule Sequencer seeks to demonstrate, for the first time, that DNA sequencing is feasible in an orbiting spacecraft. A space-based DNA sequencer could identify microbes, diagnose diseases and understand crew member health, and potentially help detect DNA-based life elsewhere in the solar system.
![iss057e006069 (10/6/2018) --- Documentation of two deployed Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) CubeSats, STARS-Me and RSP-00, during the JEM [Japanese Experiment Module]-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer 10 (J-SSOD 10) mission. Earth is in the background.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/iss057e006069/iss057e006069~medium.jpg)
iss057e006069 (10/6/2018) --- Documentation of two deployed Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) CubeSats, STARS-Me and RSP-00, during the JEM [Japanese Experiment Module]-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer 10 (J-SSOD 10) mission. Earth is in the background.
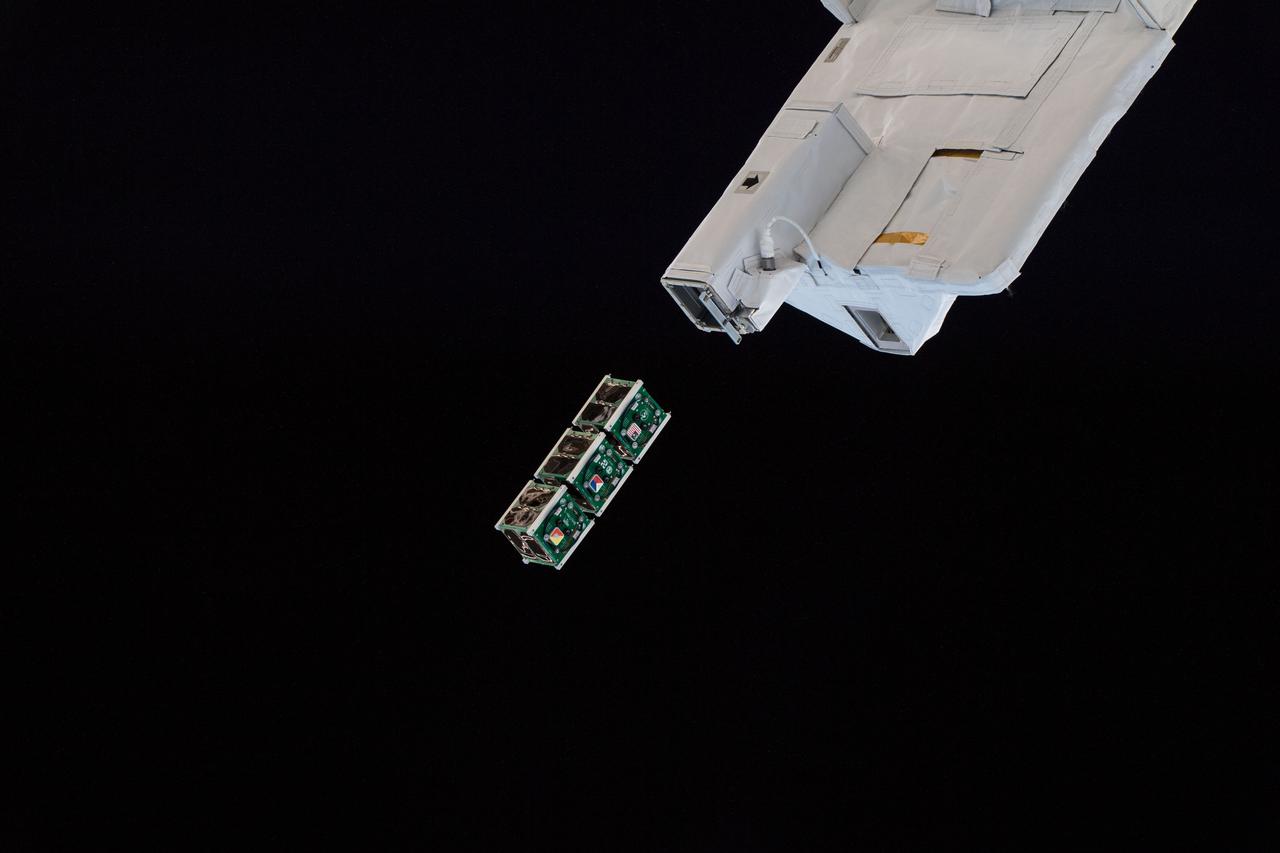
iss056e130478 (8/10/2018) --- A view of the BIRDS-2 Satellite Deployment during JSSOD-9 operations. The JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) provides a novel, safe, small satellite launching capability to the International Space Station (ISS). Once the J-SSOD including satellite install cases with small satellites are installed on the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP) by crewmembers, it is passed through the JEM airlock for retrieval, positioning and deployment by the JEMRMS.
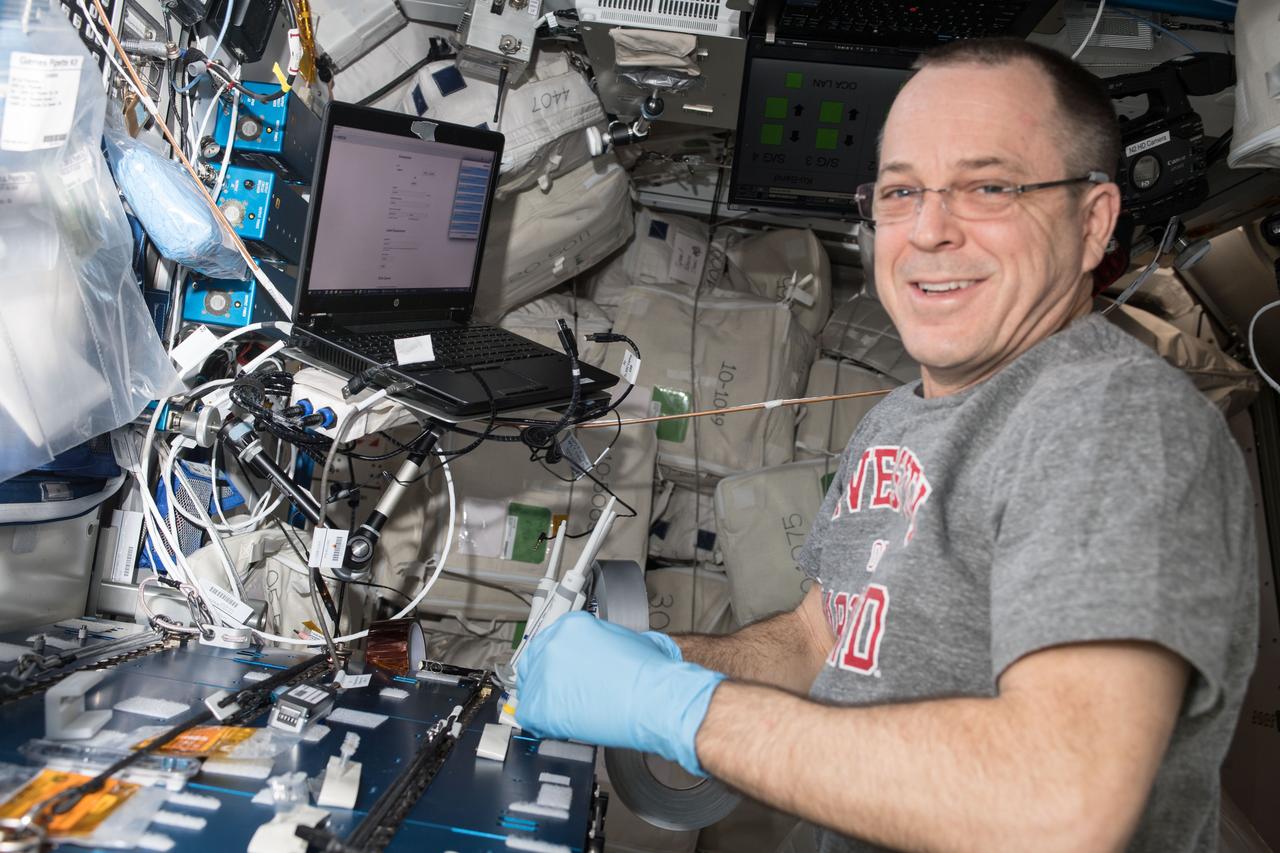

iss056e097518 (July 20, 2018) --- Expedition 56 Flight Engineer Ricky Arnold prepares amplified DNA collected from microbes living aboard the International Space Station for sequencing using the Biomolecule Sequencer. The Biomolecule Extraction and Sequencing Technology (BEST) investigation studies the use of DNA sequencing for the identification of unknown microbial organisms living on the station and to understand how humans, plants and microbes adapt to living in space.

iss056e033143 (June 25, 2018) --- A view during installation the NanoRacks Cubesat Deployer-14 (NRCSD-14) on the Multipurpose Experiment Platform inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module. The NRCSD-14 was then placed in the Kibo airlock and moved outside of the space station to deploy a variety of cubesats into Earth orbit.