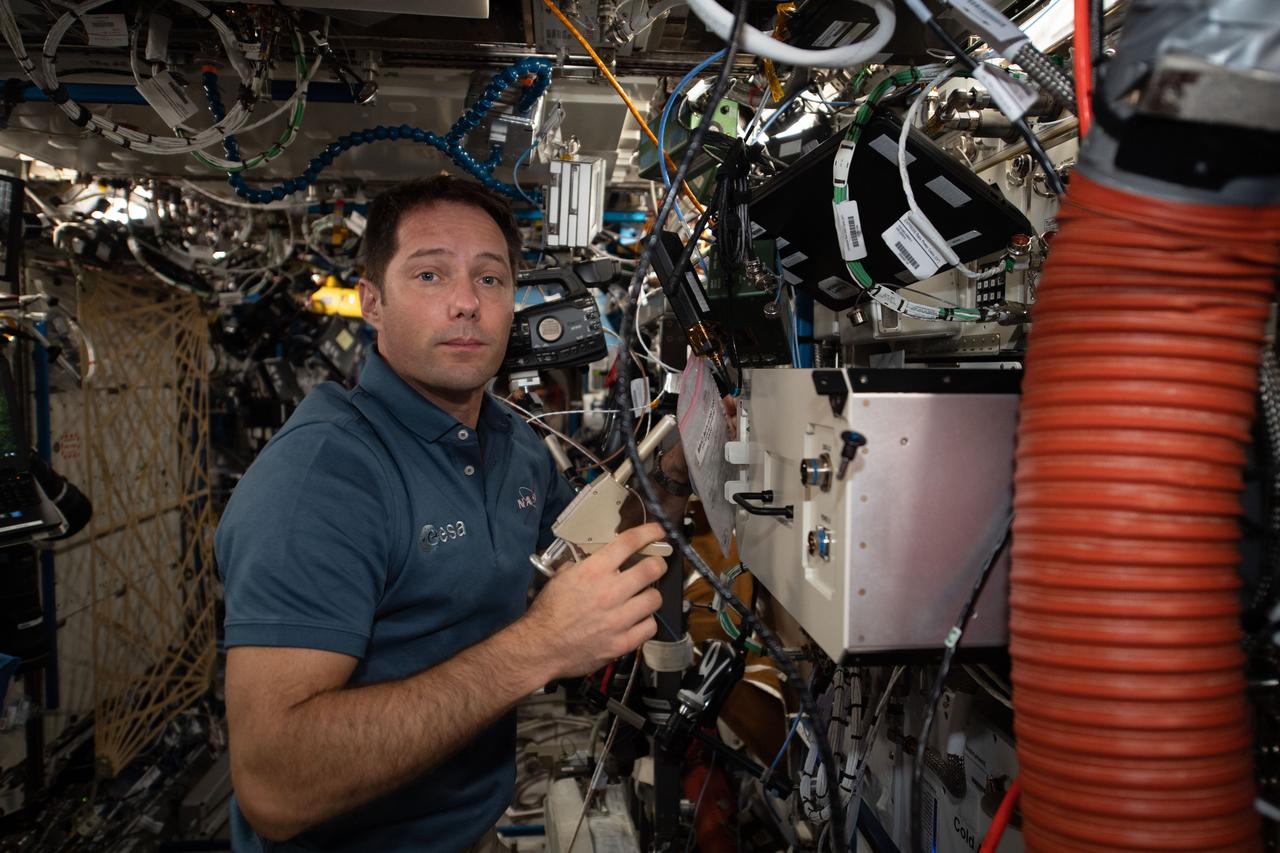

iss065e094087 (6/9/2021) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet is photographed aboard the International Space Station (ISS) during transfers of BRIC-24 Canisters to BRIC-LED Facility to stow.
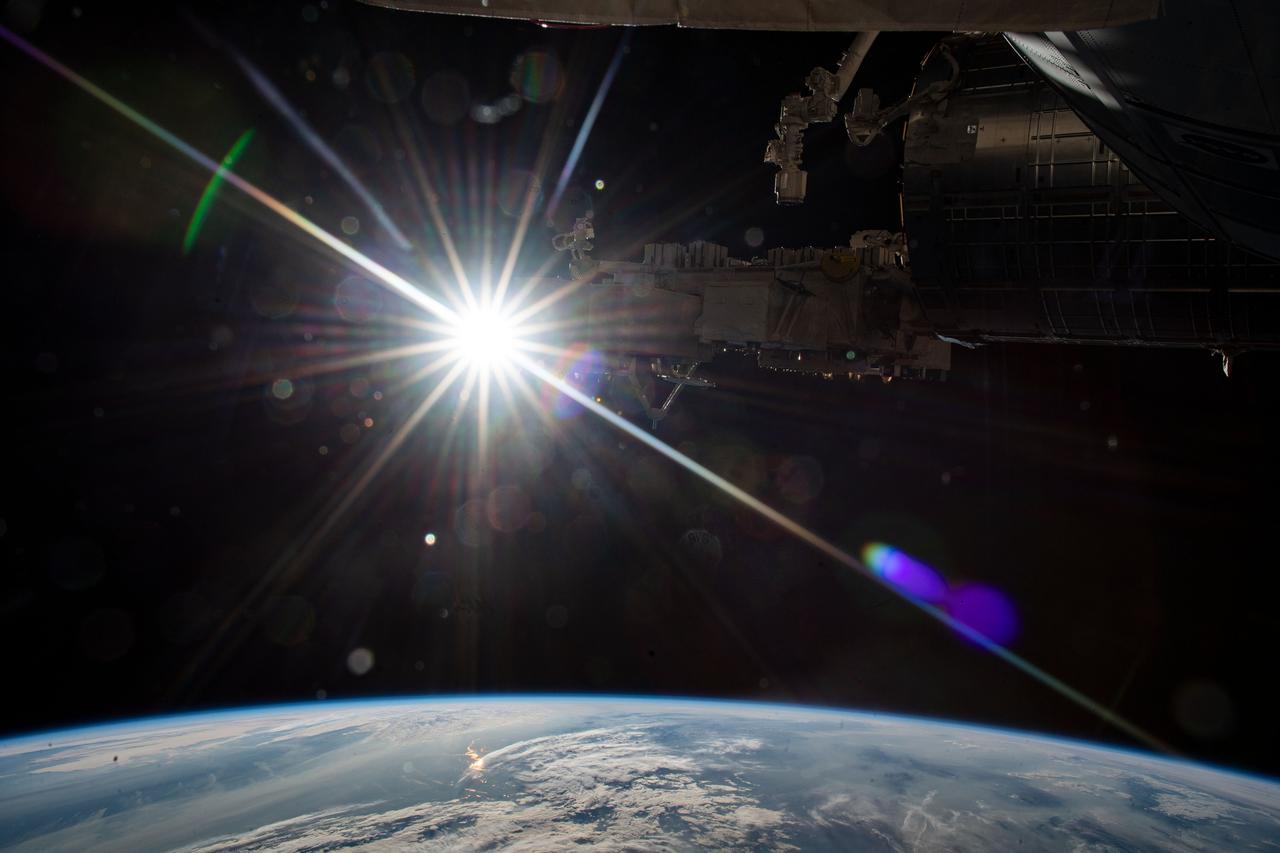

iss065e028811 (May 9, 2021) --- The sun's rays beam into the camera as the International Space Station orbited 265 miles above Kazakhstan. In the top foreground, is a portion of the Japanese Kibo laboratory module, Kibo's robotic arm and its Exposed Facility that hosts external space experiments.
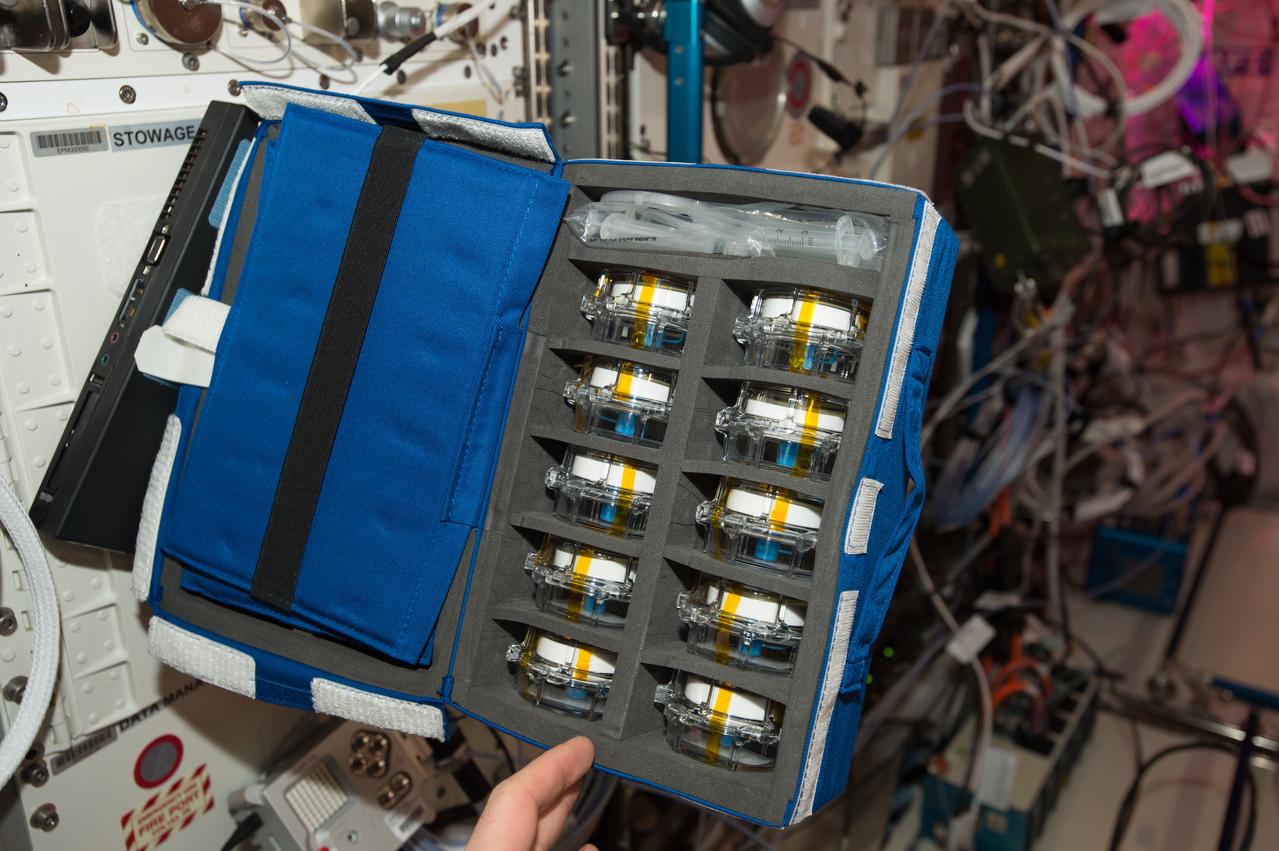

iss050e011332 (11/22/2016) --- A view of the Aquapad Sampling kit in a blue cargo transfer bag (CTB). Aquapad aims to improve the speed and efficiency of water potability tests onboard the ISS, by using a device that consists of a simple absorbent cotton, which is injected with 1 milliliter of water, and a tablet computer application,
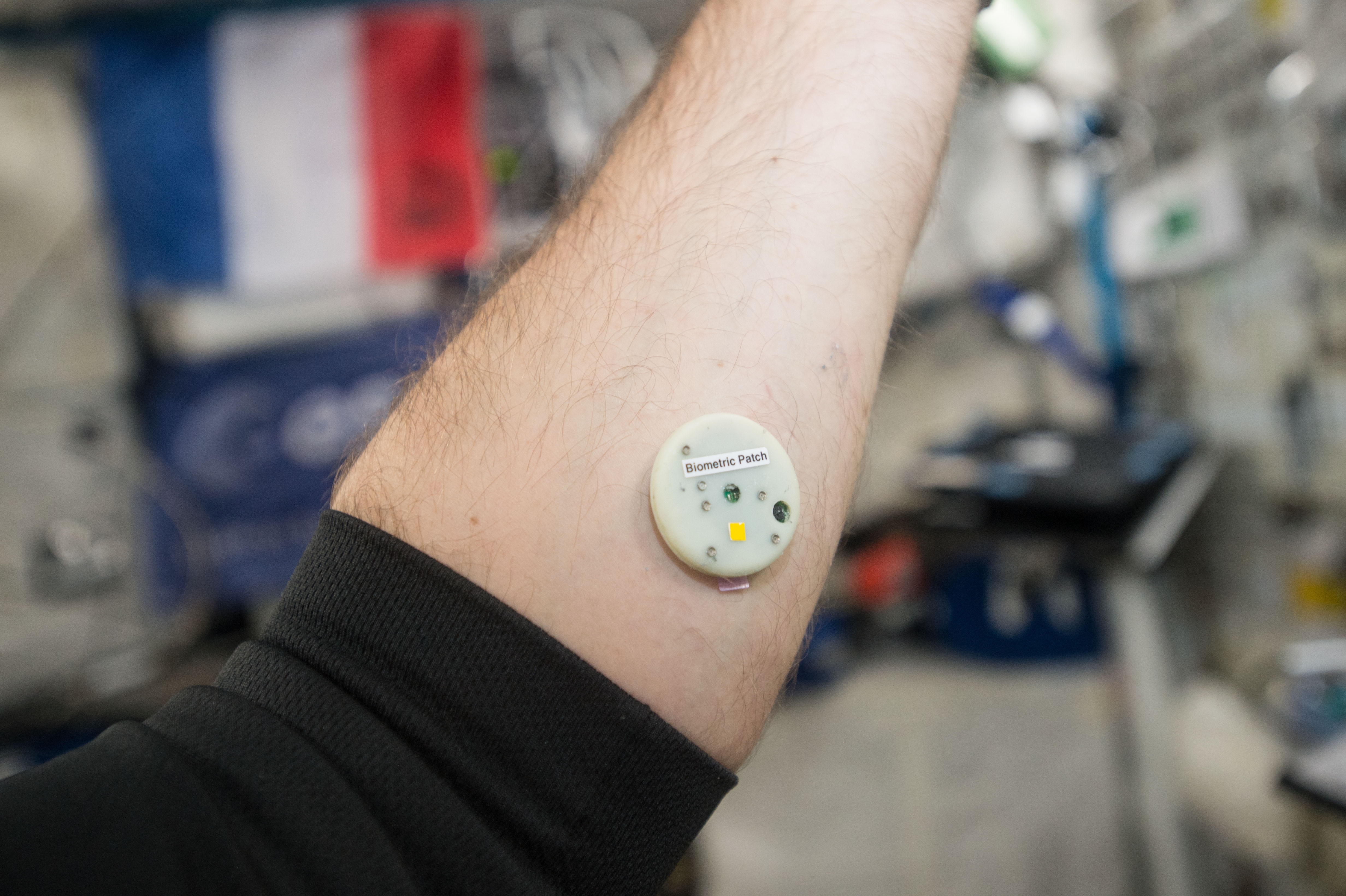

iss050e015078 (8/8/2016) --- View of Biometric patch (wearable sensor) connected to an International Space Station (ISS) iPad via bluetooth or via Lightbolt connector. The EVERYWEAR application allows a unified interface for physiology-related data collection and wireless communication.
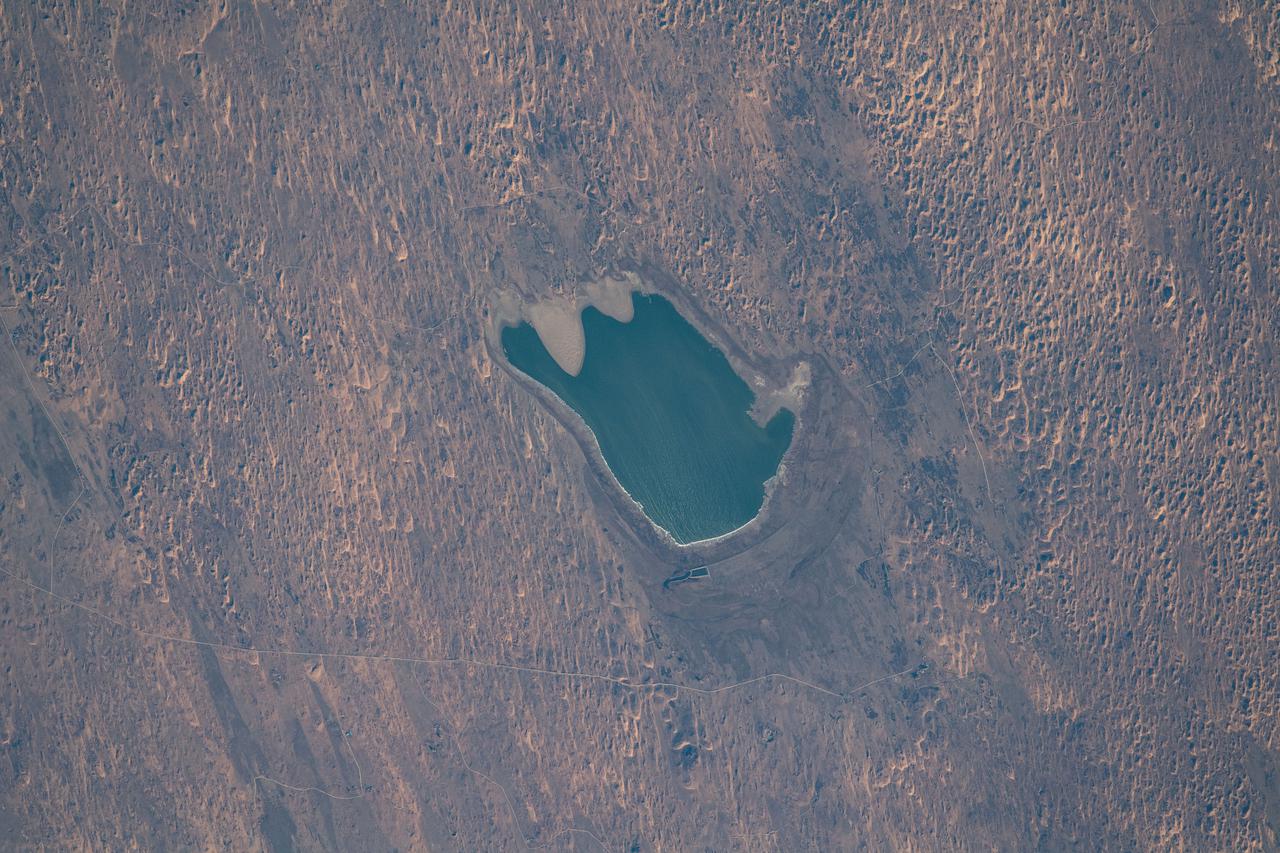

iss065e023073 (May 6, 2021) --- A small lake is pictured in Inner Mongolia, China, as the International Space Station orbited 264 miles above.
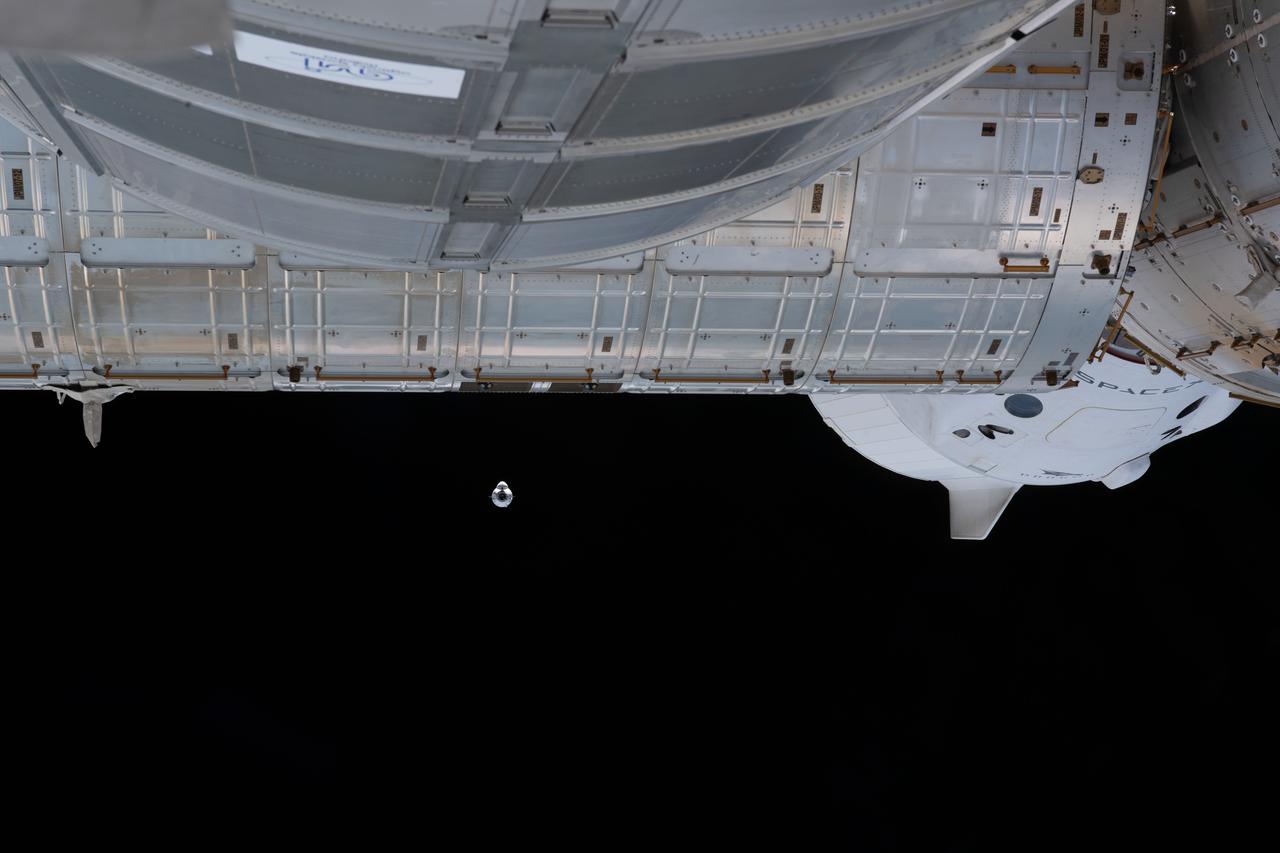

iss065e094372 (June 5, 2021) --- The SpaceX Cargo Dragon vehicle approaches the International Space Station on the SpaceX CRS-22 mission. At center right, is the SpaceX Crew Dragon spaceship docked to the Harmony module's forward-facing international docking adapter. The Cargo Dragon would dock adjacent to the Crew Dragon on Harmony's space-facing international docking adapter.
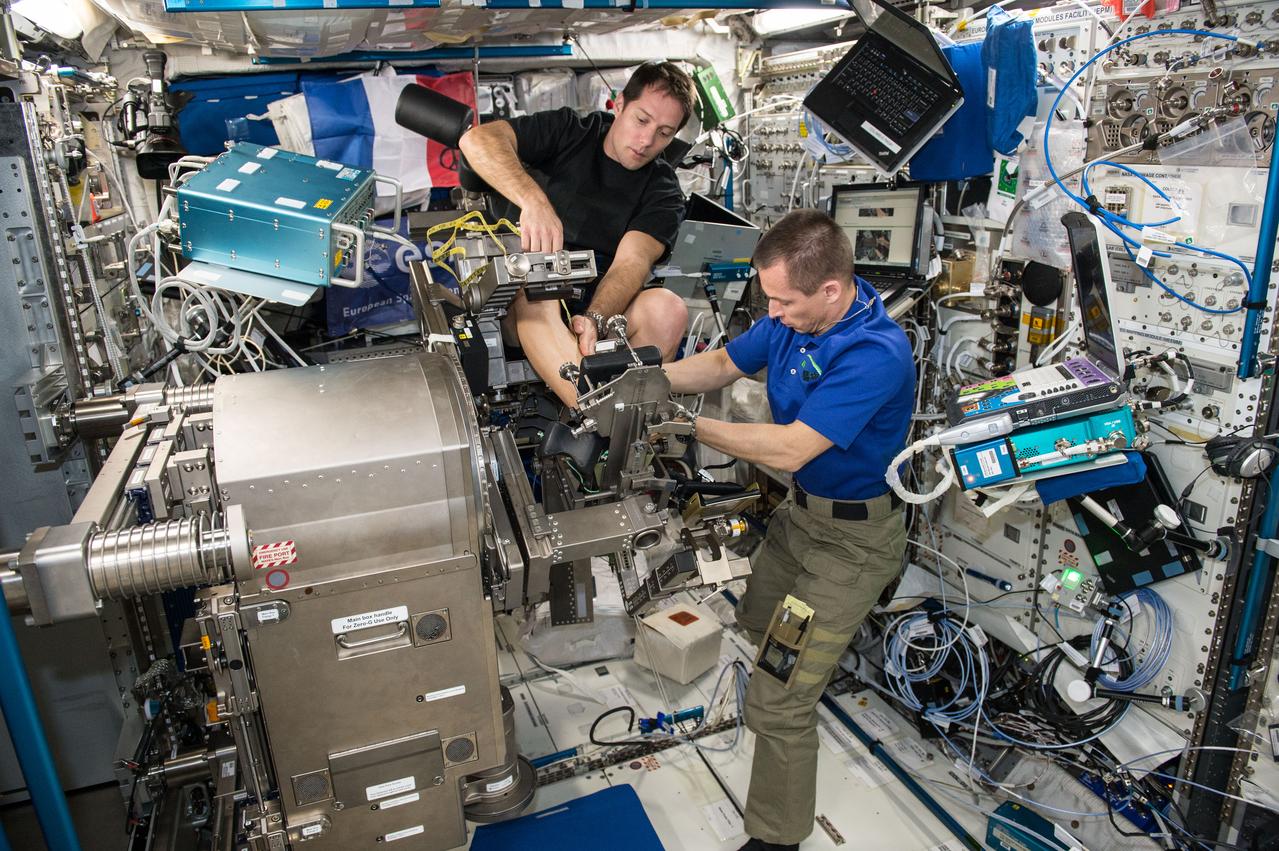

iss050e012379 (11/29/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) Thomas Pesquet and Cosmonaut Sergei Ryzhikov during the setup phase of the Sarcolab-3 Experiment, by configuring the Muscle Atrophy Resistive Exercise System (MARES), in the Columbus Module.
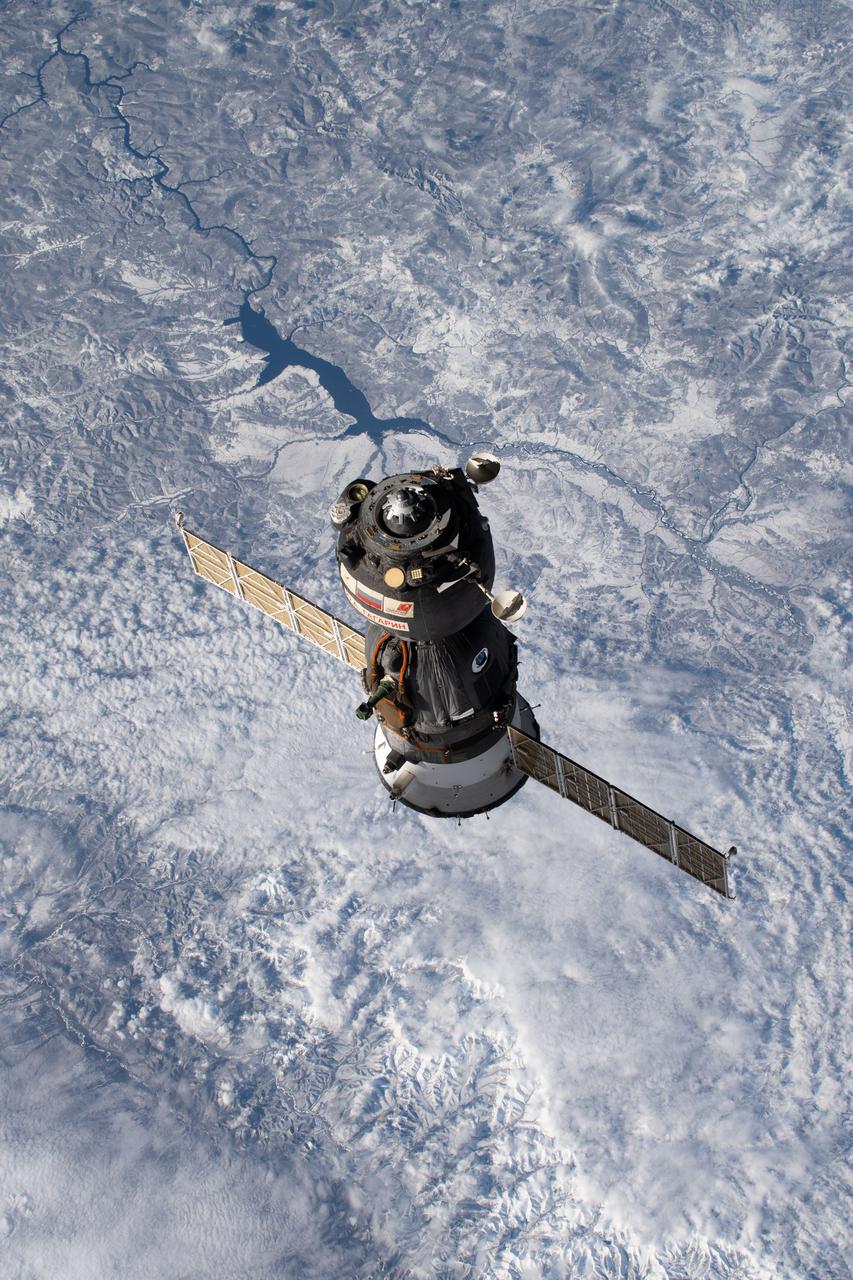

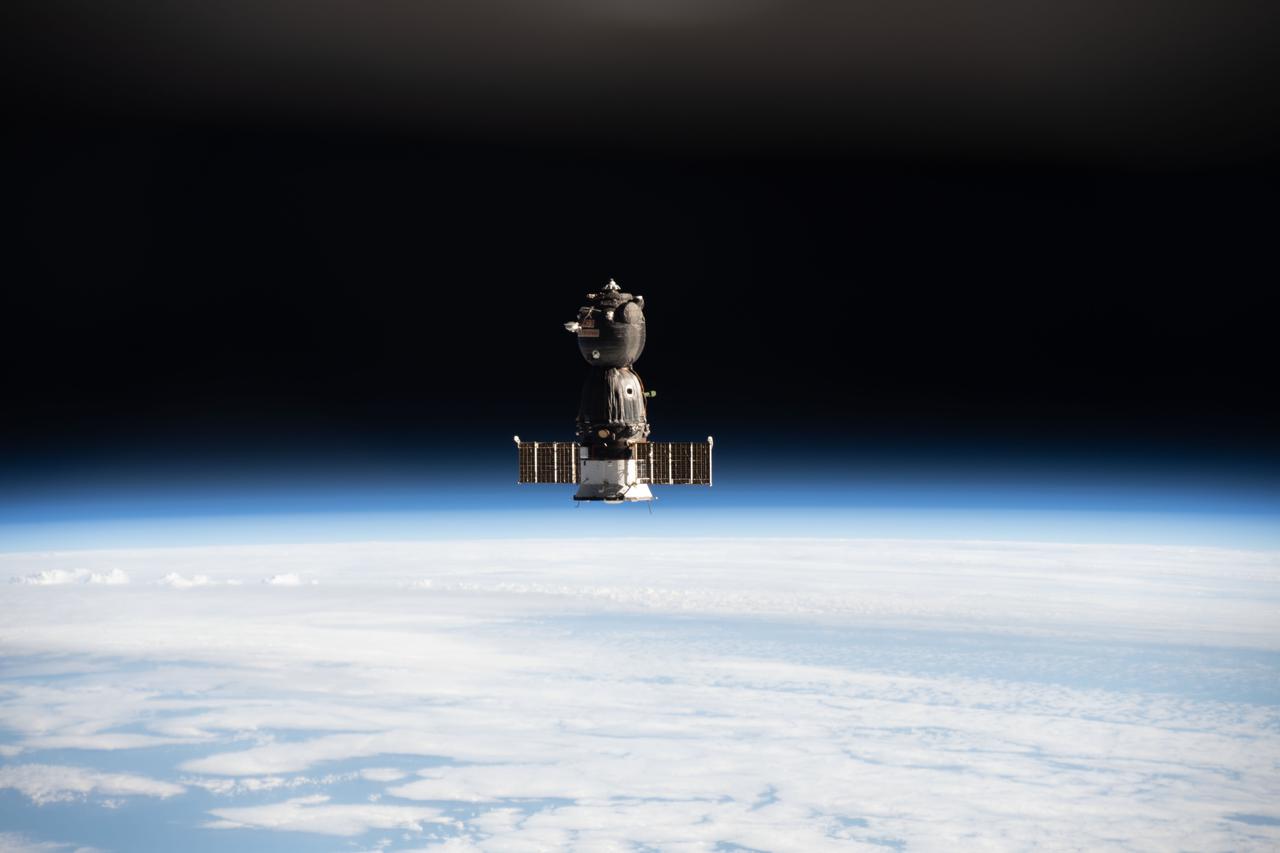
iss066e001106 (Oct. 17, 2021) --- The Soyuz MS-18 crew ship, carrying Soyuz Commander Oleg Novitskiy and spaceflight participants Yulia Peresild and Klim Shipenko, is pictured moments after undocking from the International Space Station's Nauka multipurpose laboratory module as both spacecraft were orbiting 263 miles above far eastern Russia.
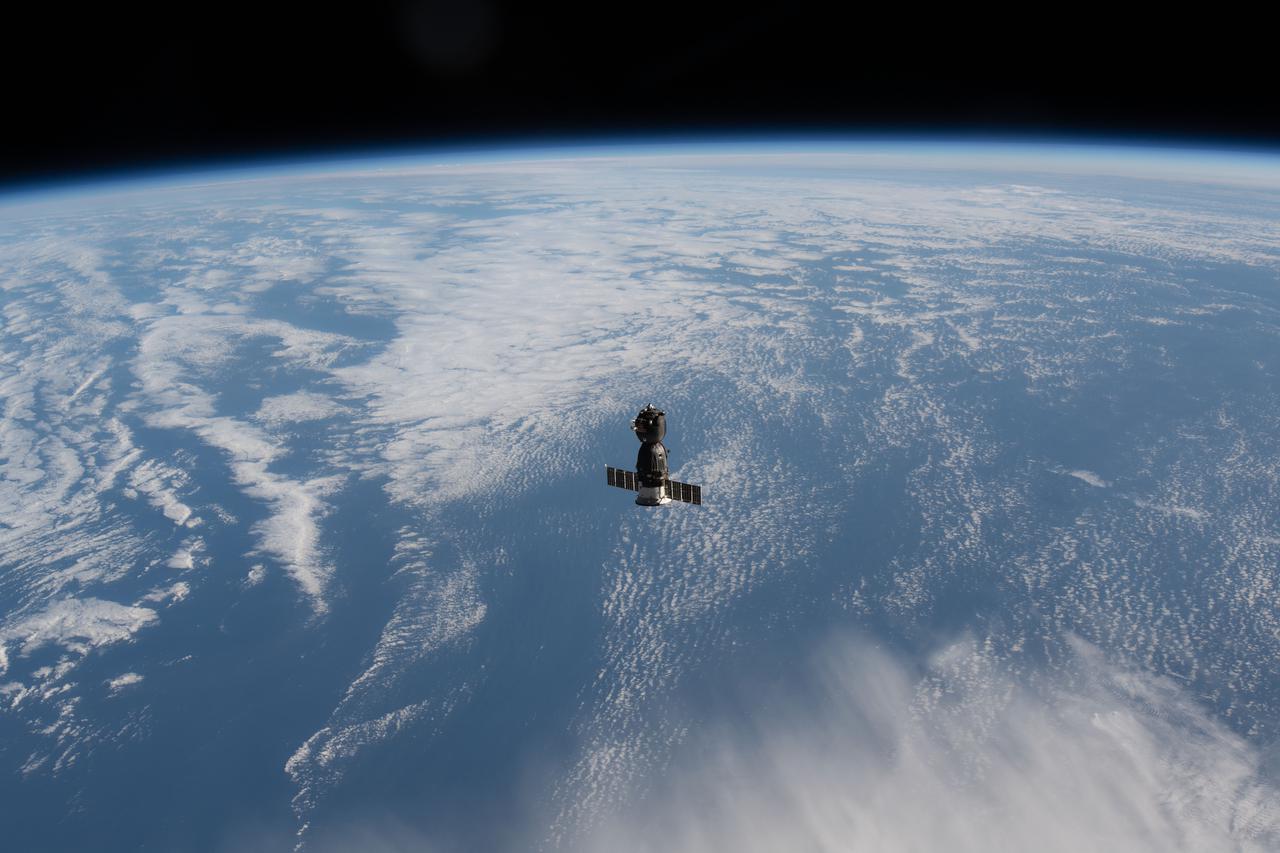

iss066e001149 (Oct. 17, 2021) --- The Soyuz MS-18 crew ship, carrying Soyuz Commander Oleg Novitskiy and spaceflight participants Yulia Peresild and Klim Shipenko, is pictured departing the vicinity of the International Space Station as both spacecraft were orbiting 263 miles above far eastern Russia.
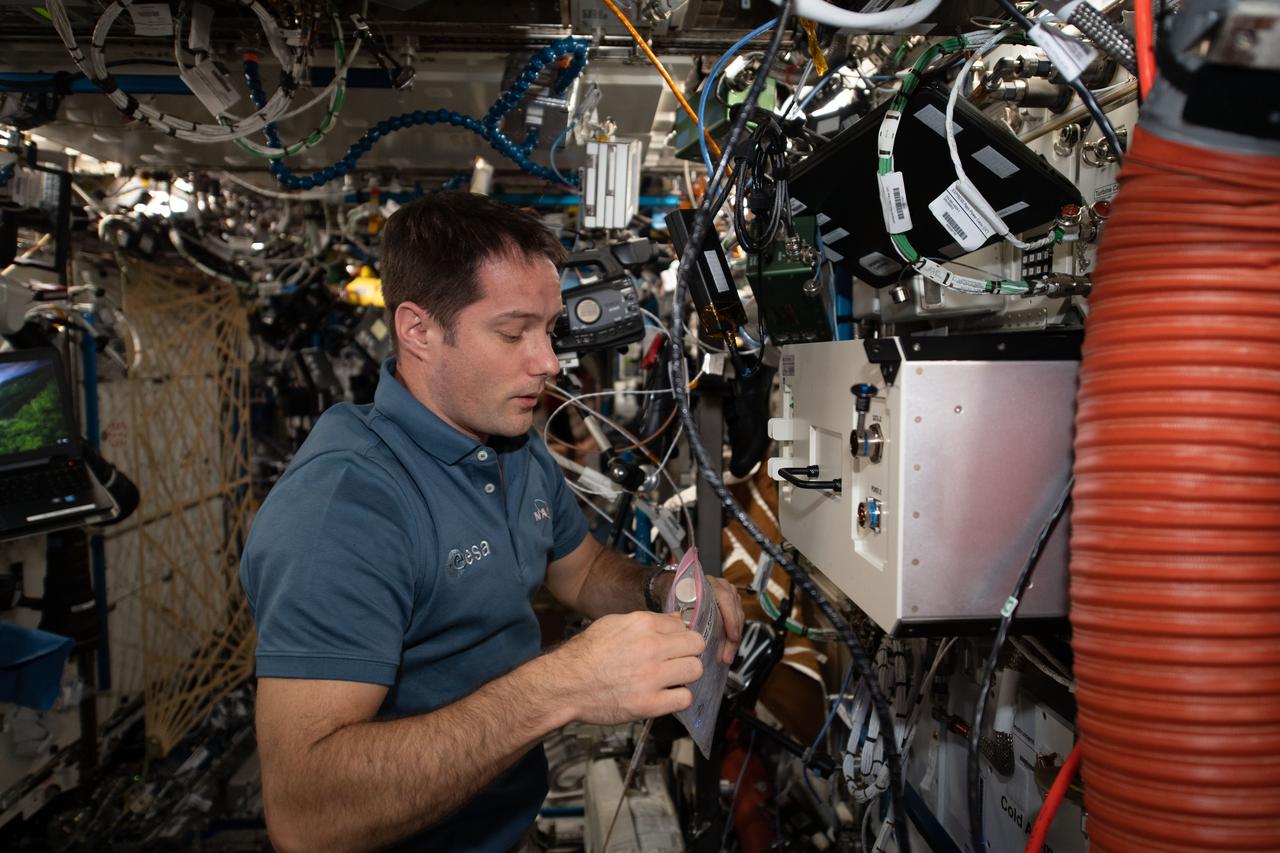

iss065e094086 (6/9/2021) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet is photographed aboard the International Space Station (ISS) during transfers of BRIC-24 Canisters to BRIC-LED Facility to stow.
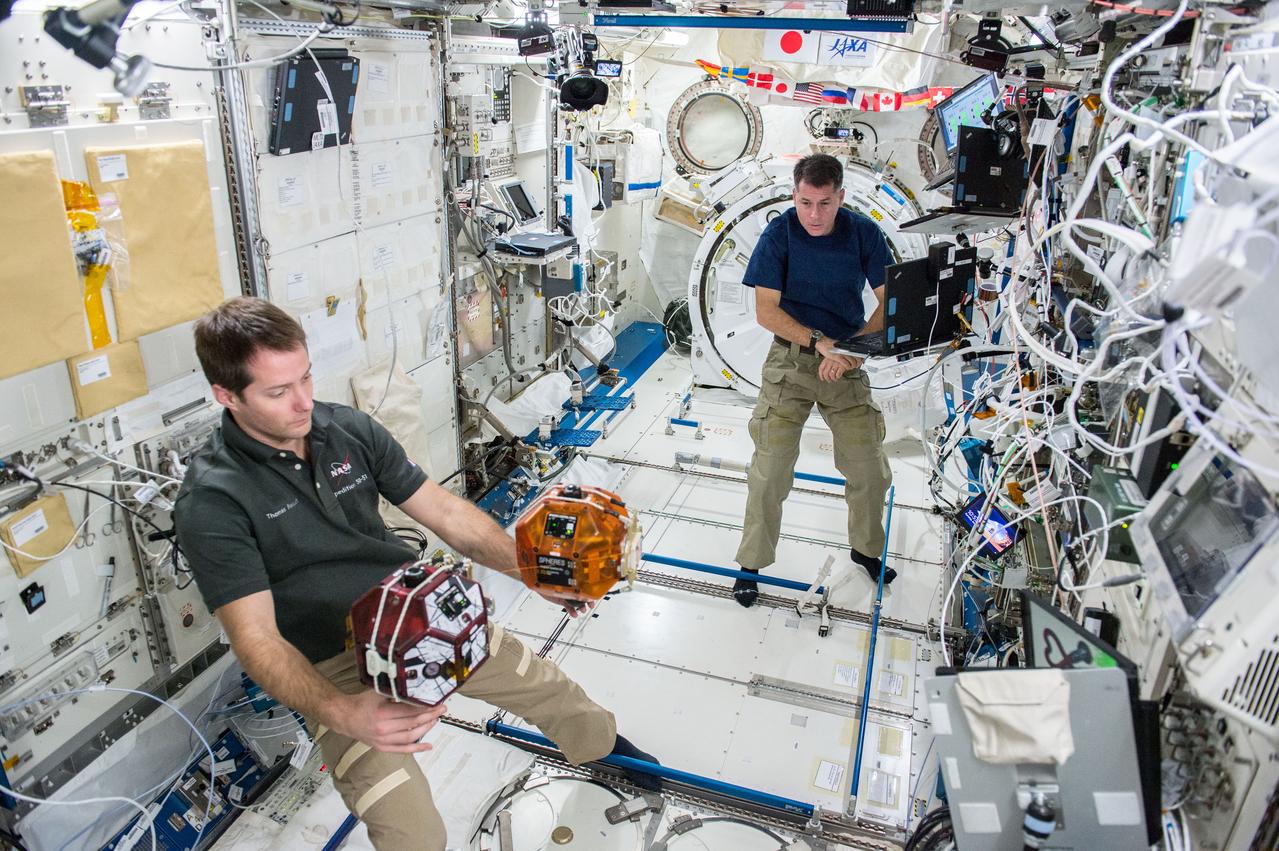

iss050e013146 (12/1/2016) --- NASA astronaut Shane Kimbrough and European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet during the Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites Tether Demo, in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Pressurized Module (JPM). The SPHERES Tether Demo studies the dynamics of a tethered capture object and a “space tug” chase vehicle, improving computer programs needed for removing space debris as well as capturing scientific samples from other planets.
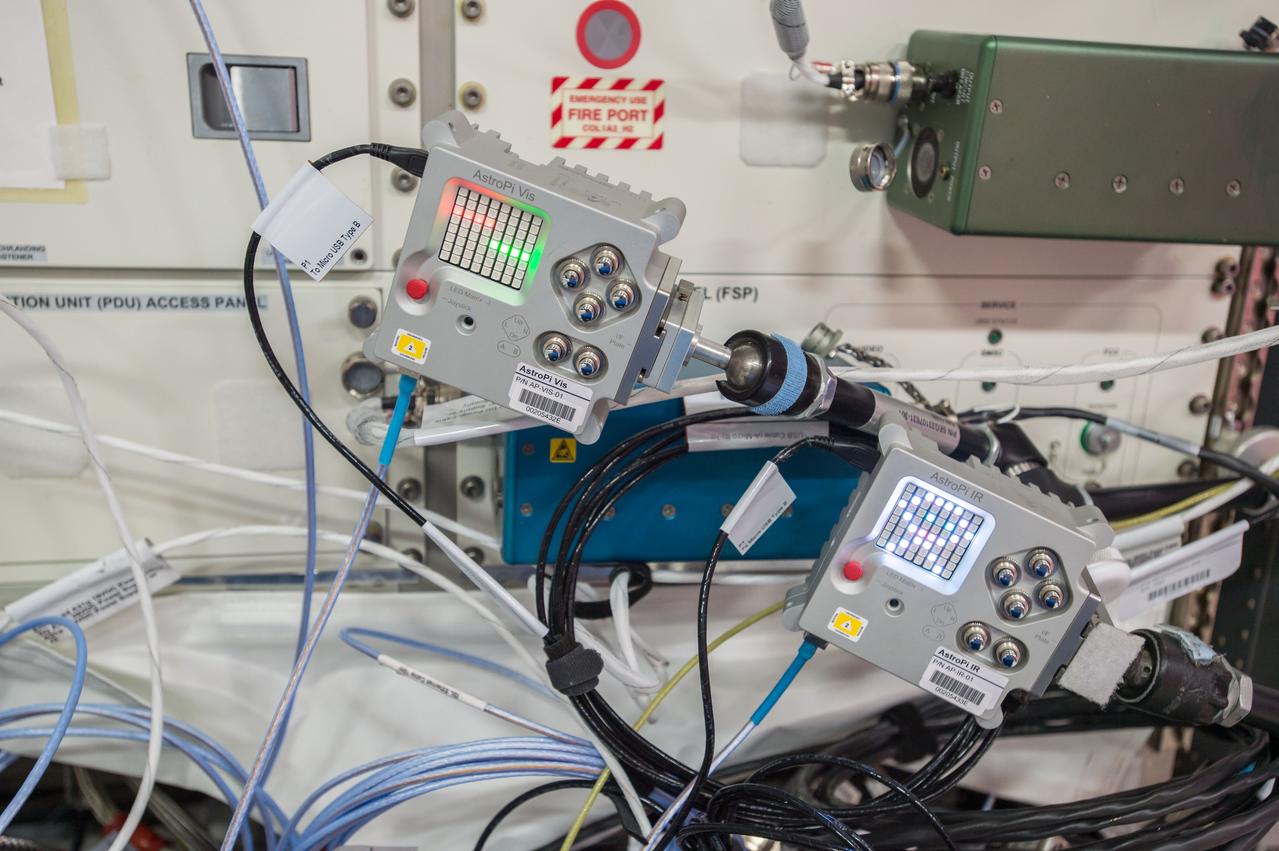
iss051e037699 (5/4/2017) --- A view of two AstroPi Raspberry Pi computers equipped with Visual and Infrared Cameras. The image was taken during ongoing European Space Agency Education Payload Operation-Pesquet (ESA-EPO-Pesquet) activities in the Columbus European Laboratory. The activities related to this project are intended to encourage and strengthen the teaching of computing and coding curriculums, and through this stimulate the curiosity of students and motivate them towards further study of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) subjects.

iss066e001176 (Oct. 17, 2021) --- The Soyuz MS-18 crew ship, carrying Soyuz Commander Oleg Novitskiy and spaceflight participants Yulia Peresild and Klim Shipenko, is pictured departing the vicinity of the International Space Station as both spacecraft were orbiting 263 miles above the Pacific Ocean off the coast of far eastern Russia.
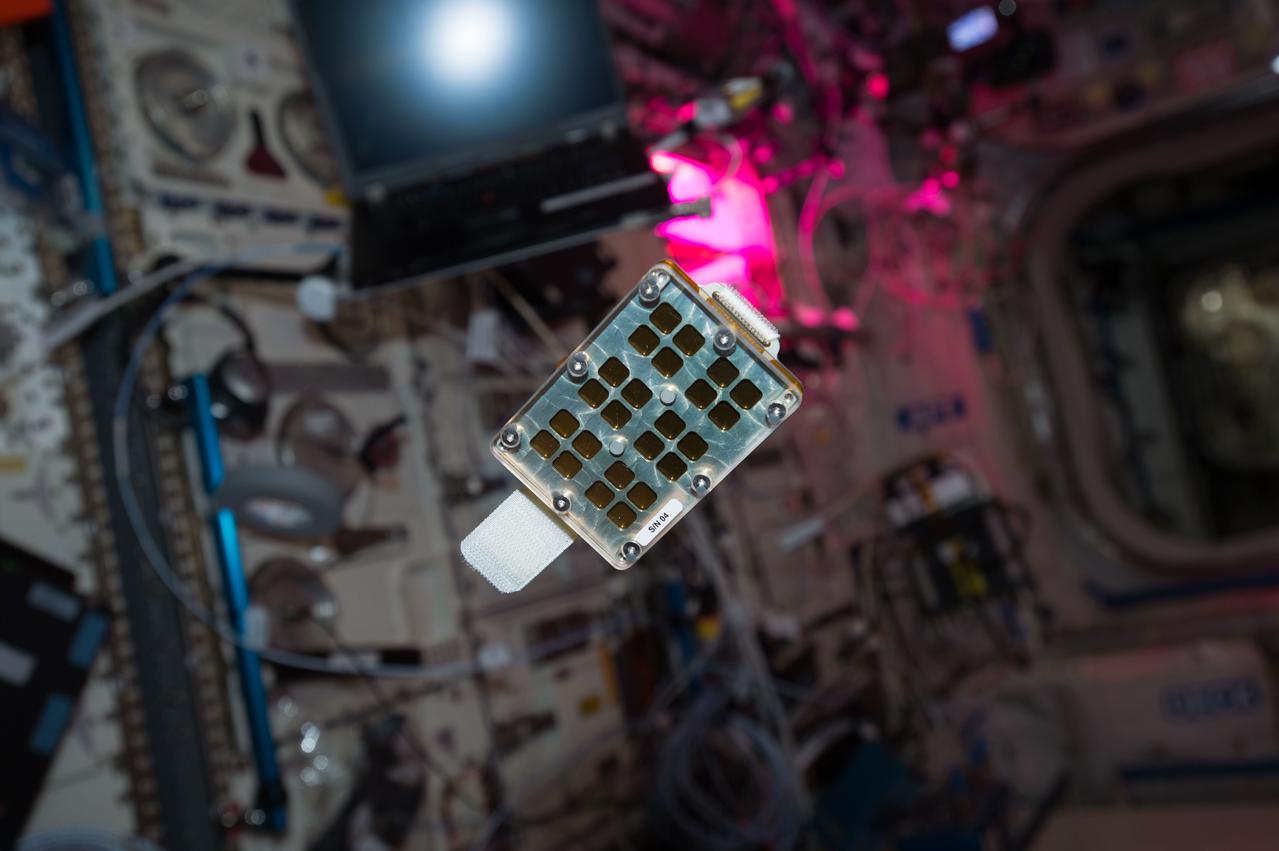
iss050e010908 911/21/2016) --- A view of Matiss floating in the Columbus Module. The Microbial Aerosol Tethering on Innovative Surfaces in the International Space Station (MATISS) experiment investigates the antibacterial properties of materials in space to see if future spacecraft could be made easier to clean. The experiment aims to understand the mechanisms of attachment of biofilms in microgravity conditions.
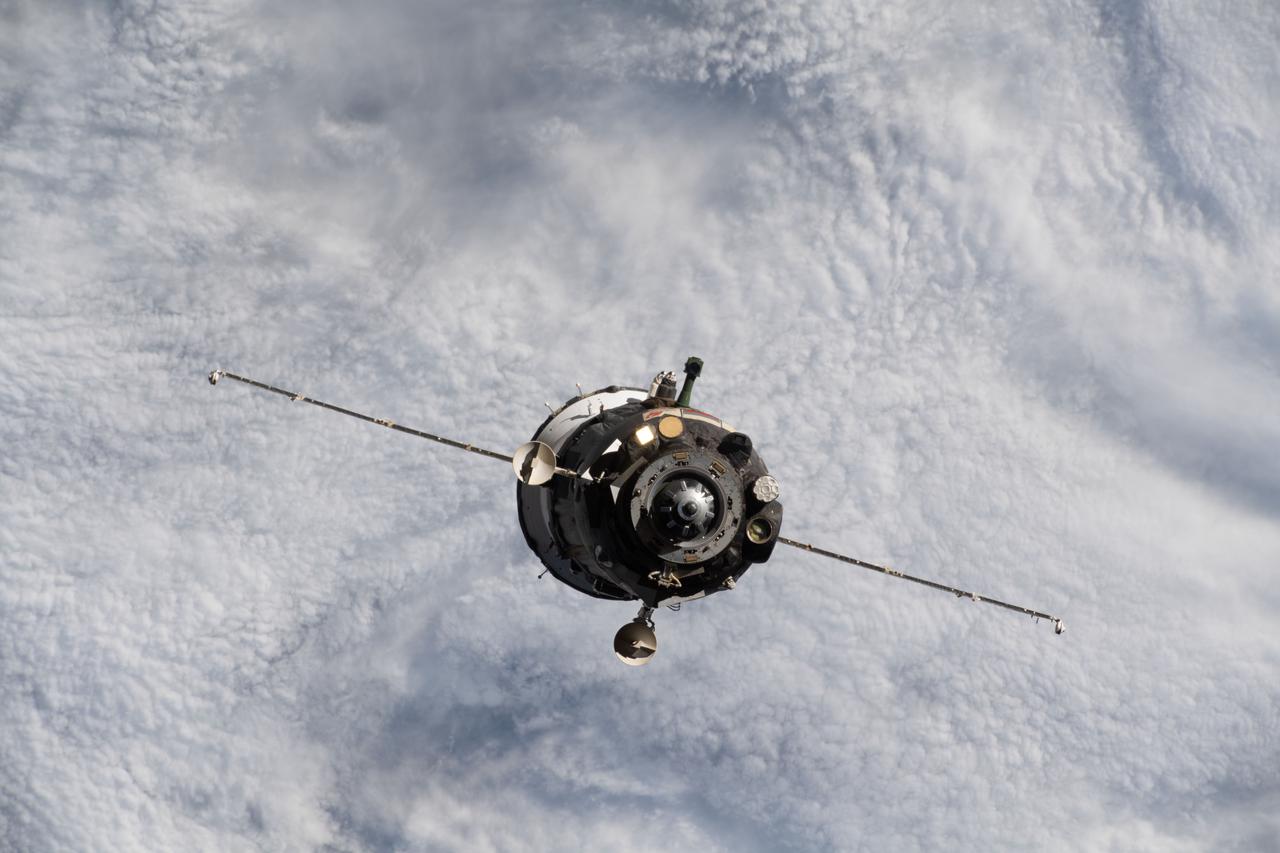

iss066e001123 (Oct. 17, 2021) --- The Soyuz MS-18 crew ship, carrying Soyuz Commander Oleg Novitskiy and spaceflight participants Yulia Peresild and Klim Shipenko, is pictured departing the vicinity of the International Space Station as both spacecraft were orbiting 263 miles above the Sea of Okhotsk.
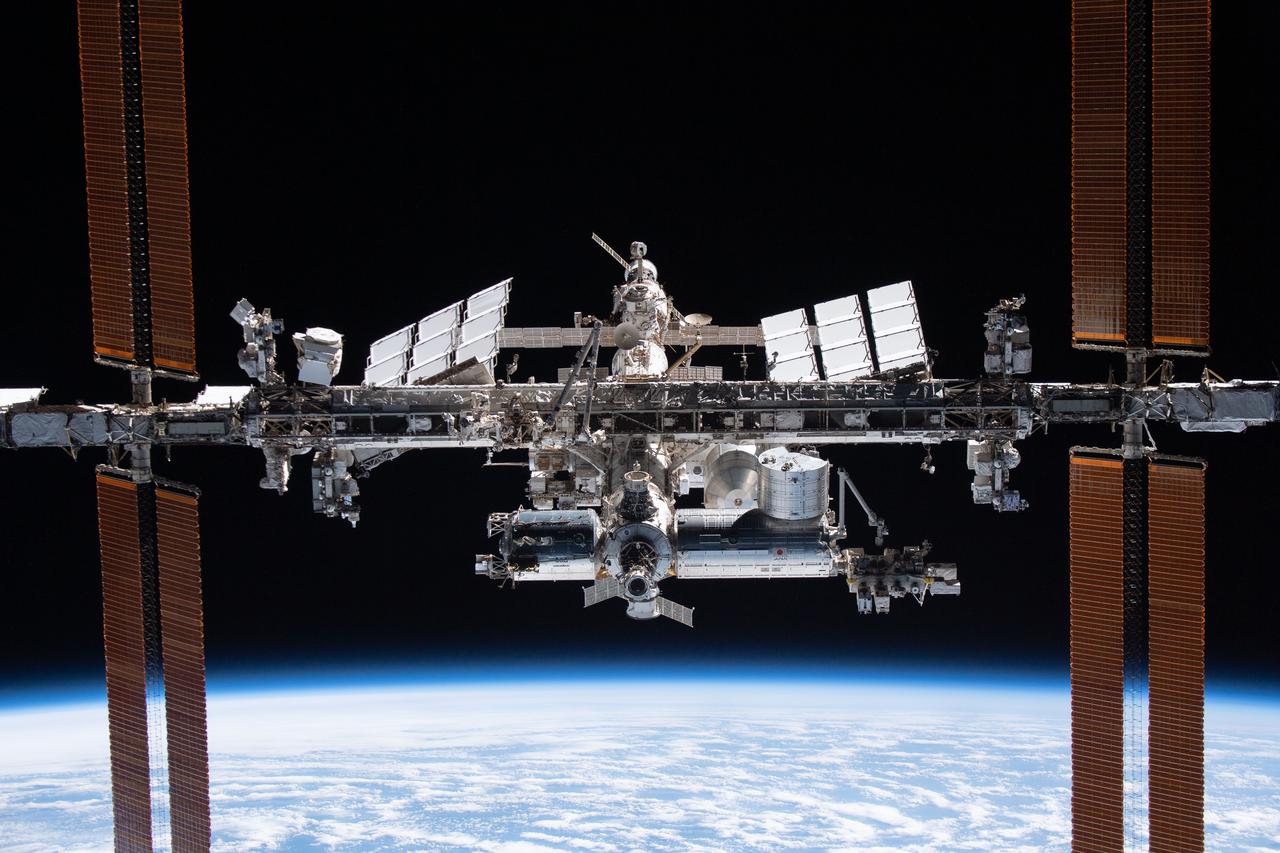

iss066e081130 (Nov. 8, 2021) -- The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021. The orbital complex was flying 263 miles above the Marshall Islands in the Pacific Ocean when this photograph was taken.
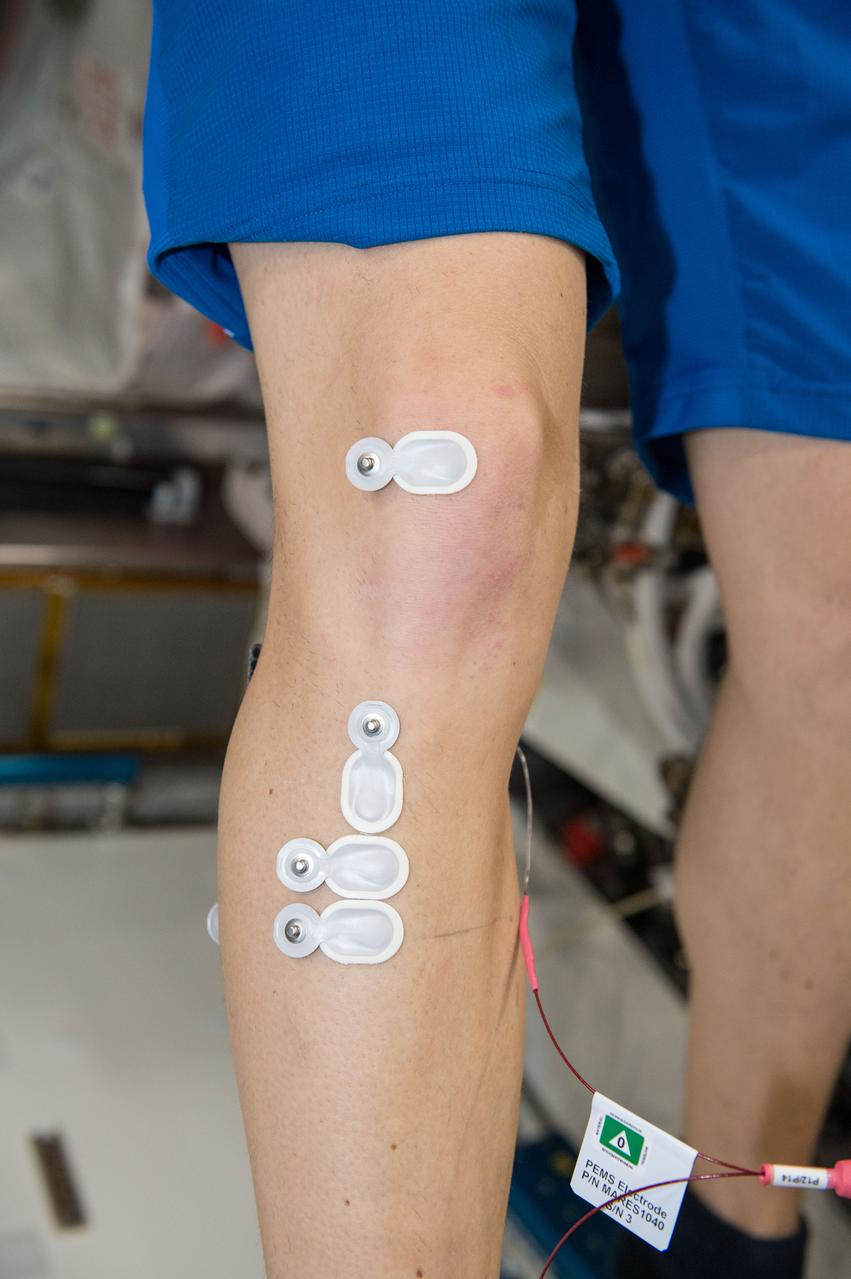
iss050e012907 (11/29/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) Thomas Pesquet (only leg - wearing electrodes) during the setup phase of the Sarcolab-3 Experiment in the Columbus Module. Myotendinous and Neuromuscular Adaptation to Long-term Spaceflight (Sarcolab) investigates the adaptation and deterioration of the soleus, or calf muscle, where it joins the Achilles tendon, which links it to the heel and carries loads from the entire body. Muscle fiber samples are taken from crew members before and after flight, and analyzed for changes in structural and chemical properties.
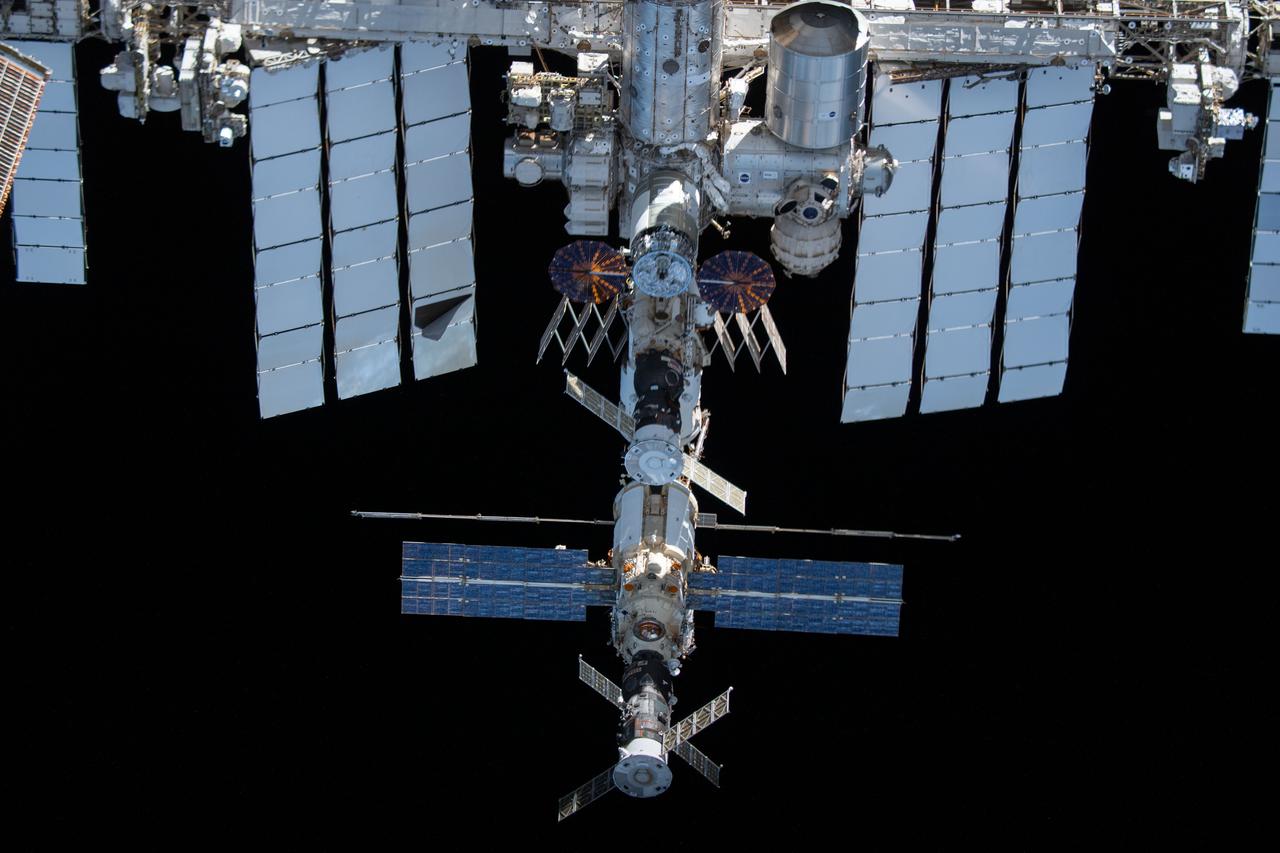

iss066e080481 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station's Russian segment and portions of the U.S. segment are pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021. Prominent in this view are the Progress 78 cargo craft, the Soyuz MS-19 crew ship and the Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply ship.
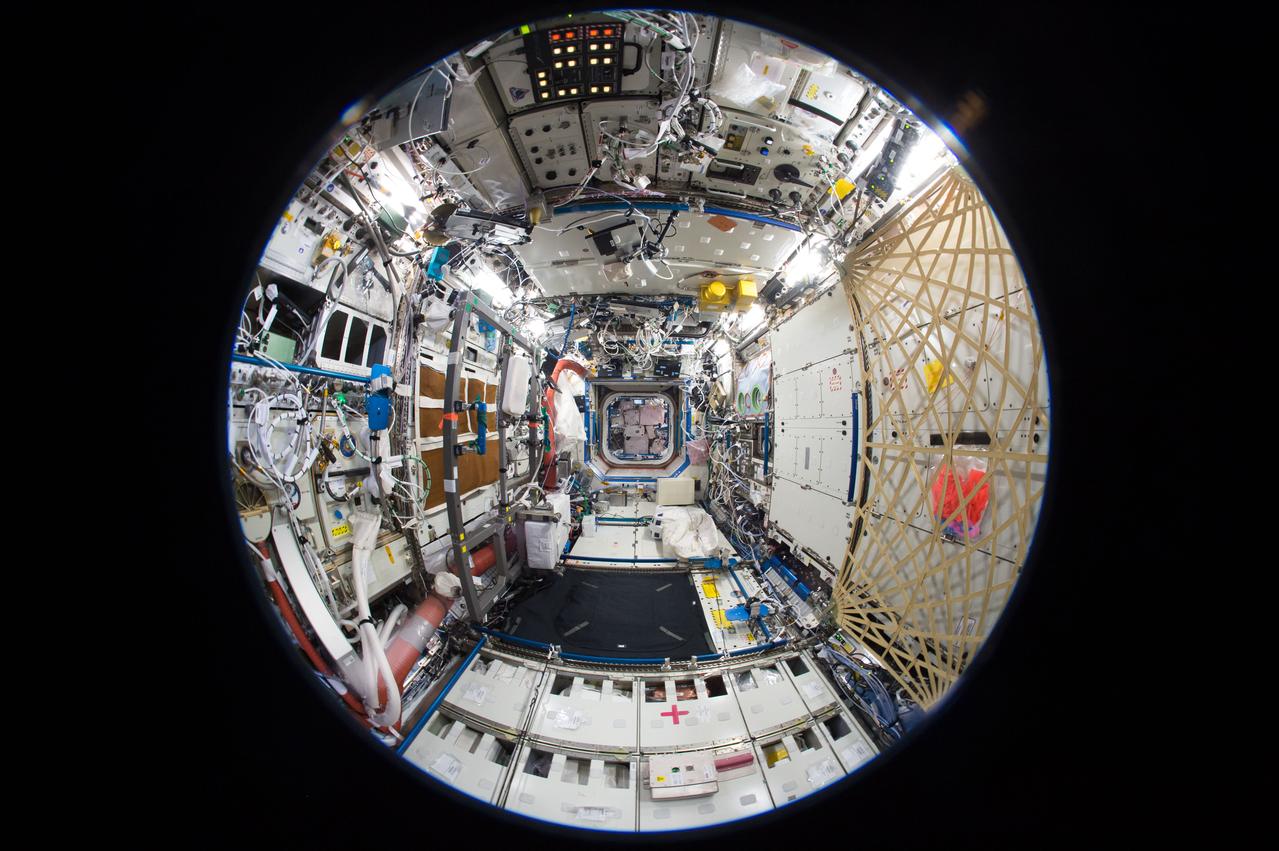

iss050e050873 (2/19/2017) --- A fish-eye view of the U.S. Laboratory taken for a Google Street View of the ISS.
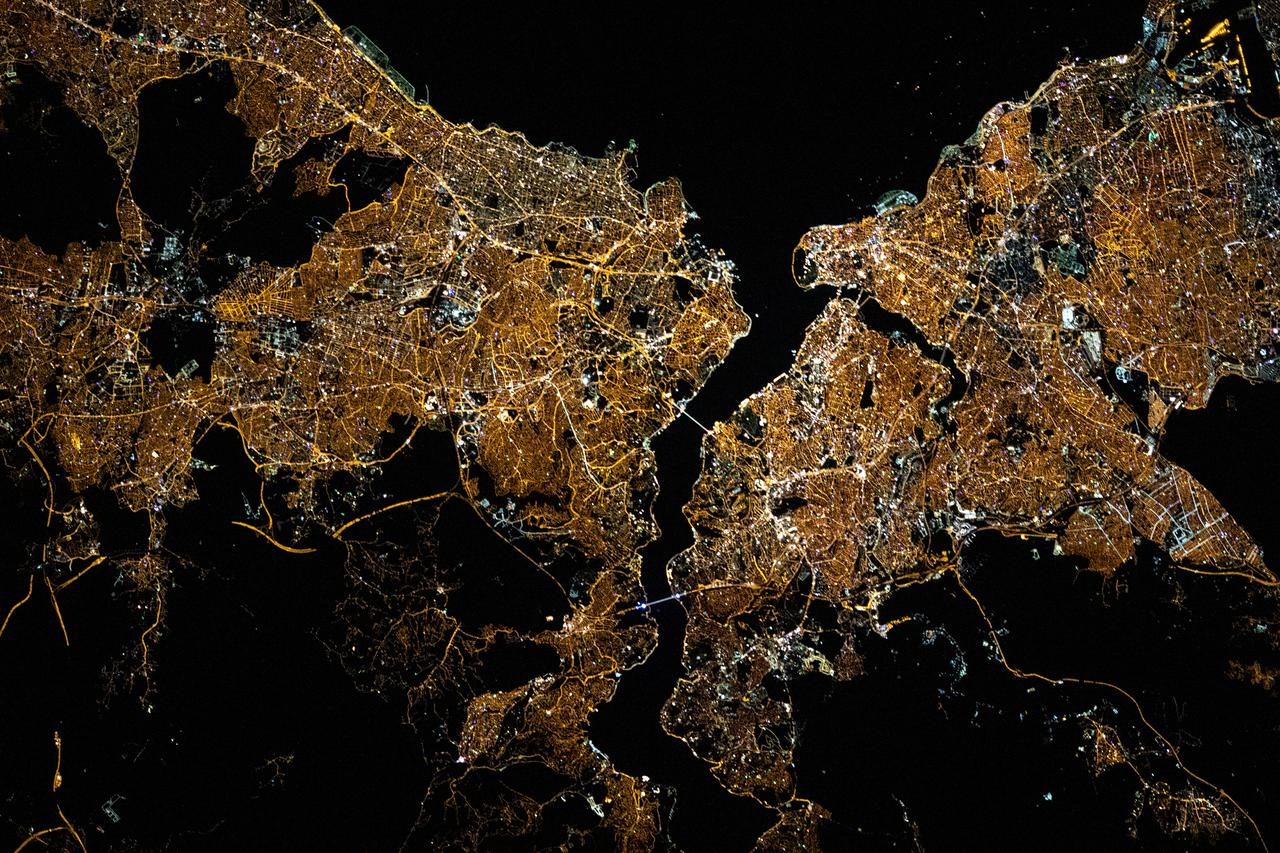

iss065e030820 (May 10, 2021) --- The night lights of Istanbul, Turkey, split by the Bosphorus Strait and the Golden Horn, are pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the Black Sea.

iss050e015683 (Dec. 13, 2016) --- JAXA's (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) H-II Transfer Vehicle-6, also known as the "Kounotori," is pictured moments away from being captured by the International Space Station's Canadarm2 robotic arm. Expedition 50 Commander Shane Kimbrough of NASA and Flight Engineer Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) successfully captured Kounotori on Dec. 13, 2016.
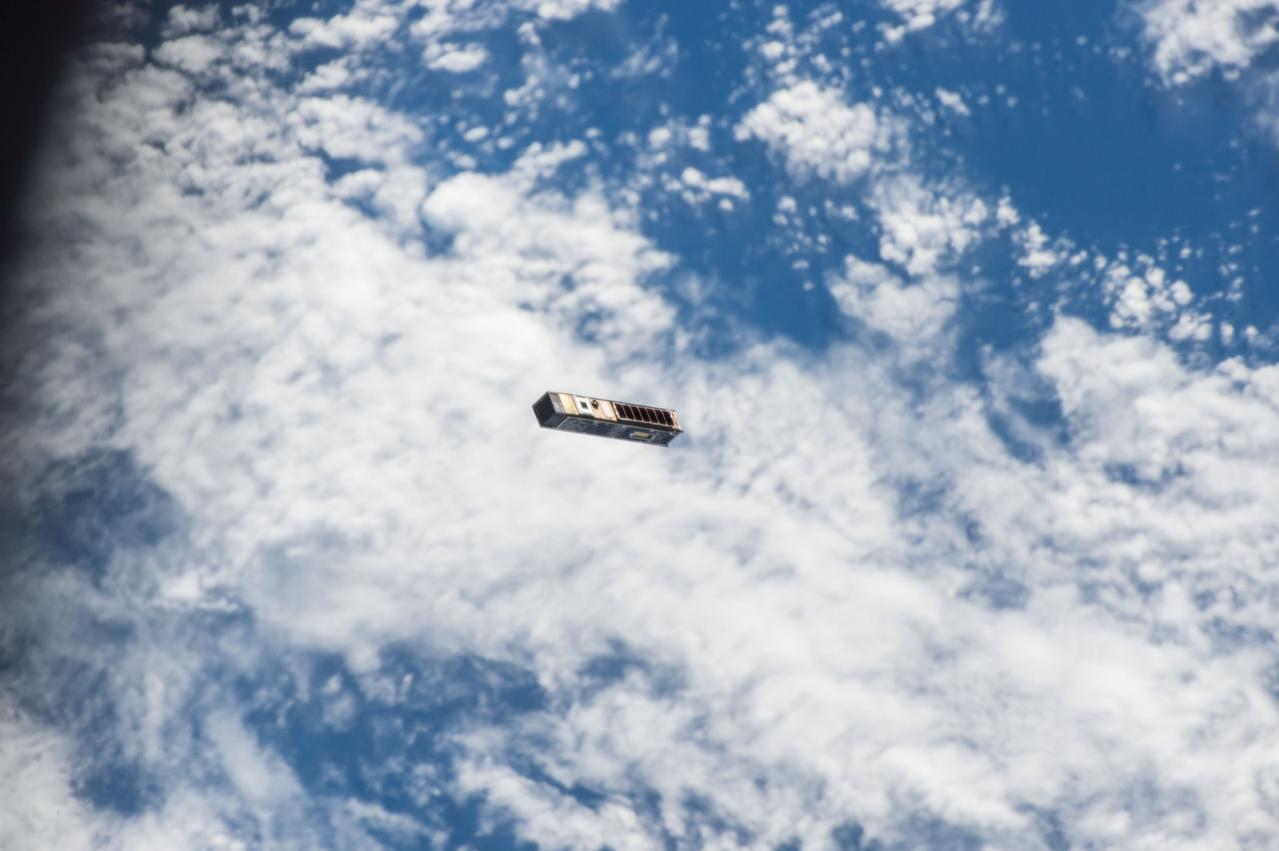

iss051e044839 (5/17/2017) -- The NanoRacks CubeSat Deployer "ejects" the Spacecraft for High Accuracy Radar Calibrationa (SHARC) microsatellite into orbit from the International Space Station.
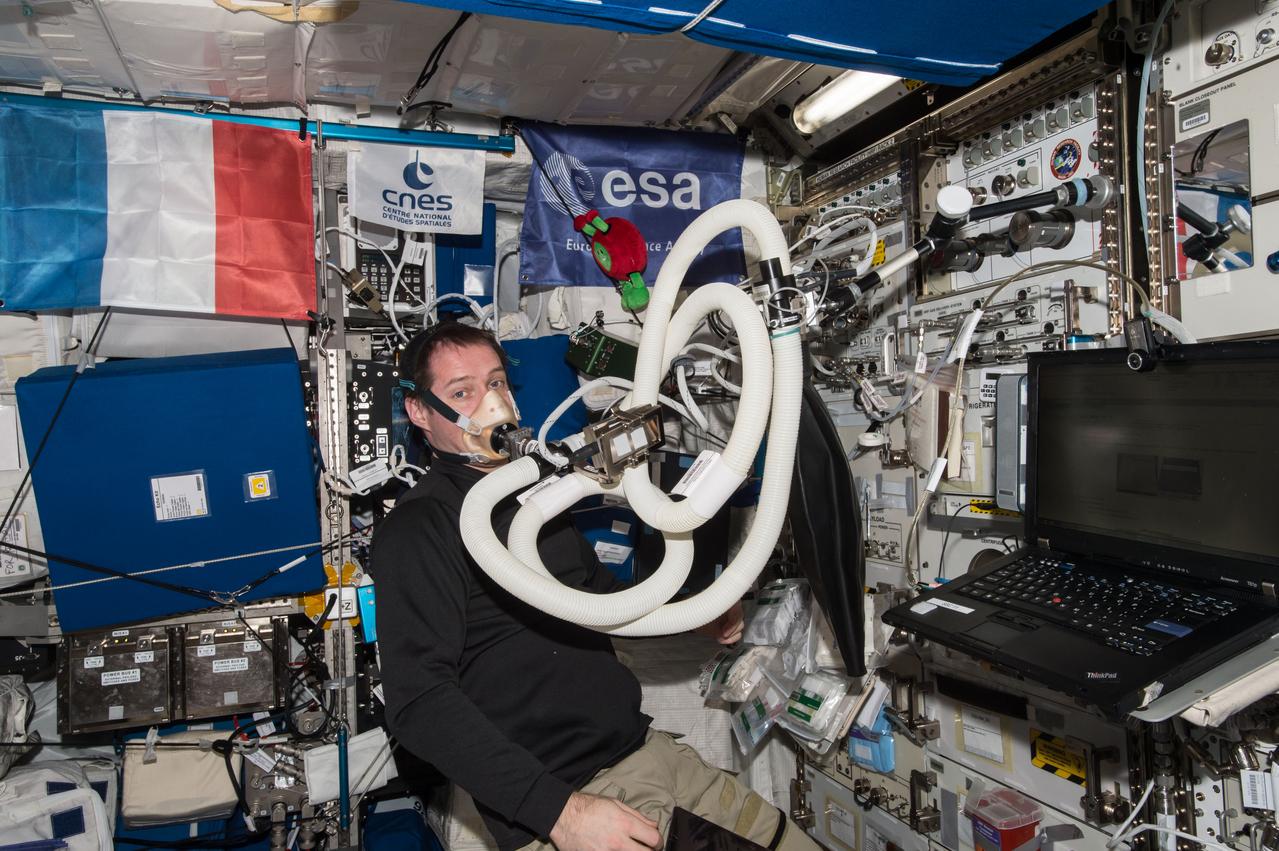

iss050e055526 (3/8/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet utilizing the Pulmonary Function System (PFS) to perform a series of Oxygen Uptake Measurements (OUMs) after prescribed meals and scheduled fluid collections, in the Columbus Module. The Energy investigation measures an Astronaut's Energy Requirements for Long-Term Space Flight, a crucial factor needed for sending the correct amount of the right types of food with space crews.
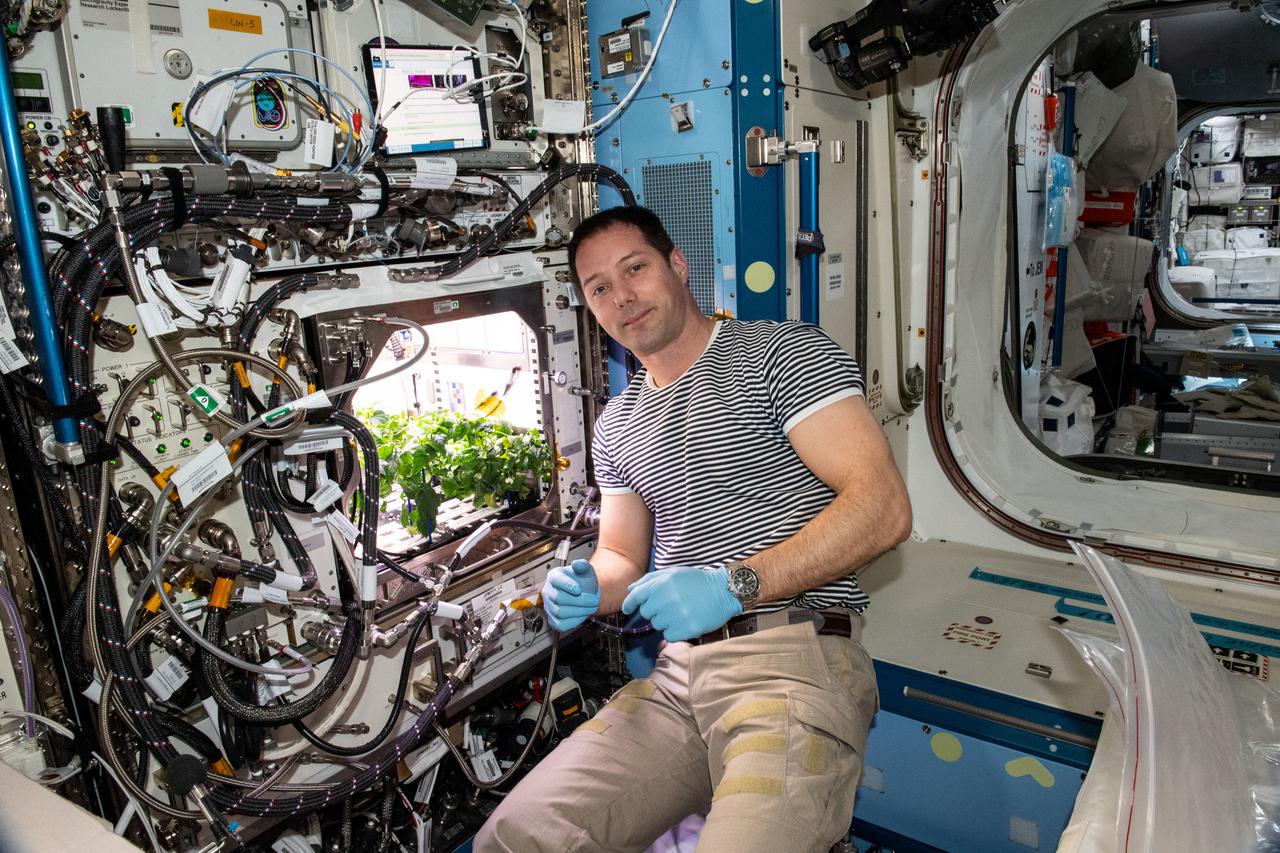

iss065e398621 (Sept. 20, 2021) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Thomas Pesquet cleans up debris in the International Space Station’s Plant Habitat which is growing Hatch Green chiles for the Plant Habitat-04 space crop experiment.
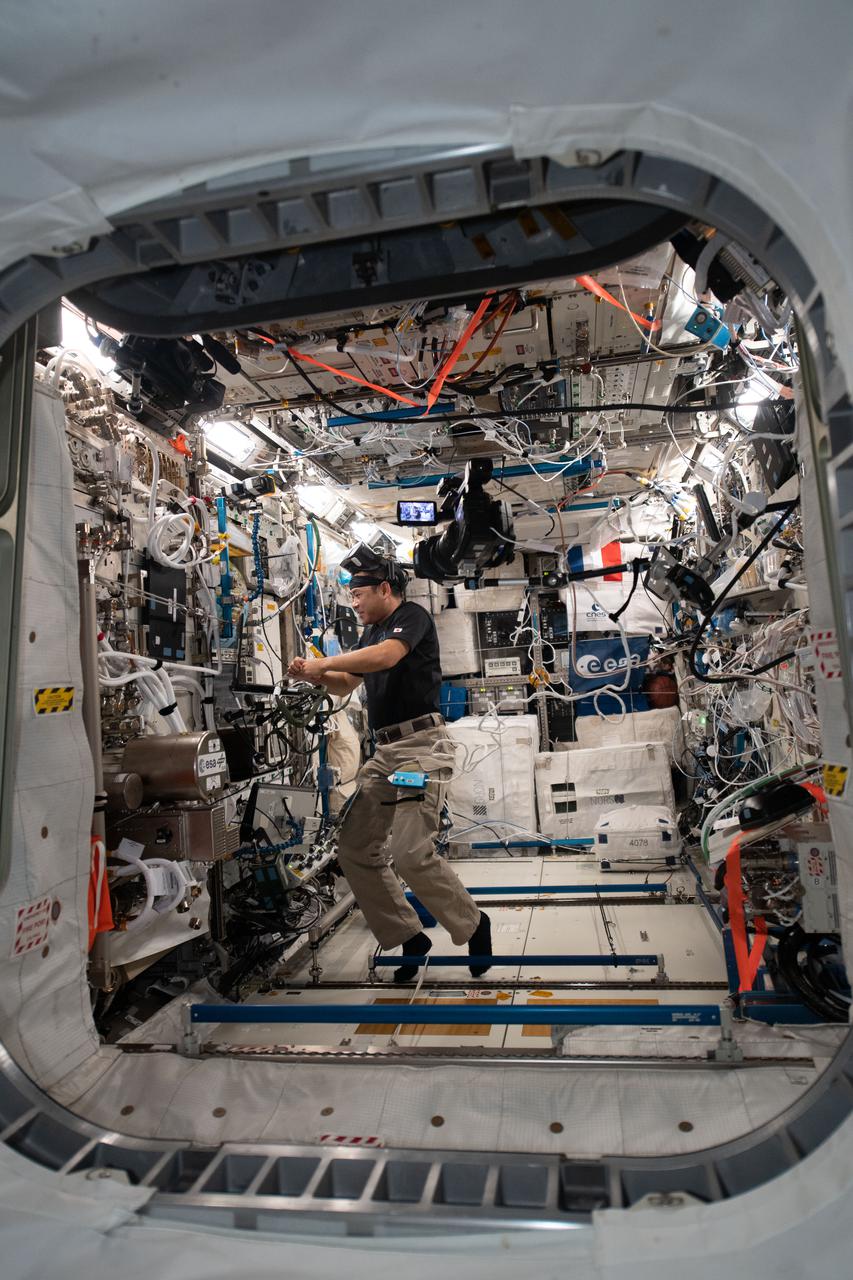

iss065e048413 (May 19, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Commander Akihiko Hoshide of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency is pictured inside the Columbus laboratory module wrapping up activities for the Time Perception experiment. During the investigation a crew member wears a virtual reality headset and clicks on a trackball to explore how astronauts perceive time and space which may impact navigation and fine motor coordination in microgravity.
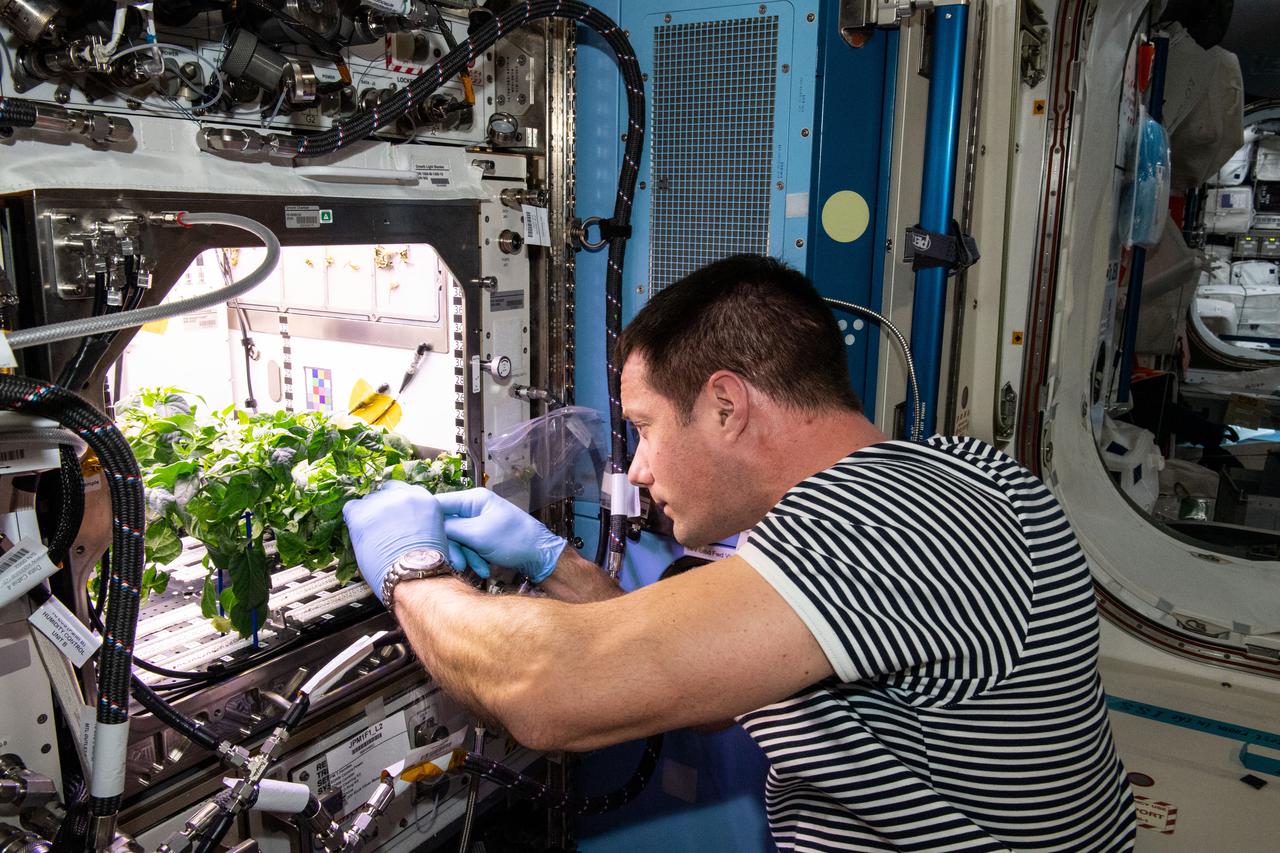

iss065e398600 (Sept. 20, 2021) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Thomas Pesquet cleans up debris in the International Space Station’s Plant Habitat which is growing Hatch Green chiles for the Plant Habitat-04 space crop experiment.
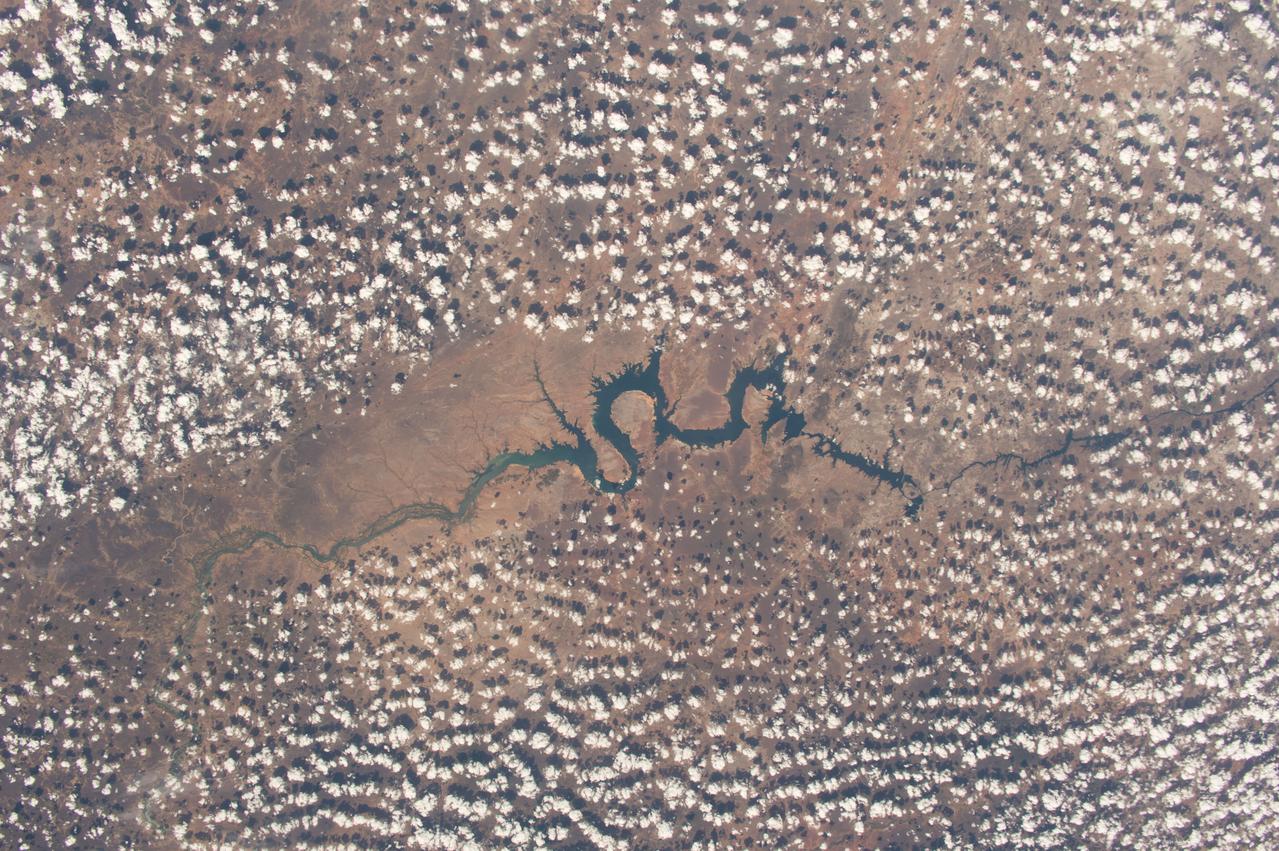

iss050e013545 (12/2/2016) --- A view of the São Francisco River in Brazil. Crew Earth Observations (CEO) imagery provides researchers on Earth with key data to understand the planet from the perspective of the ISS. Crew members have been photographing Earth from space since the early Mercury missions beginning in 1961. The images taken from the ISS ensure this record remains unbroken.
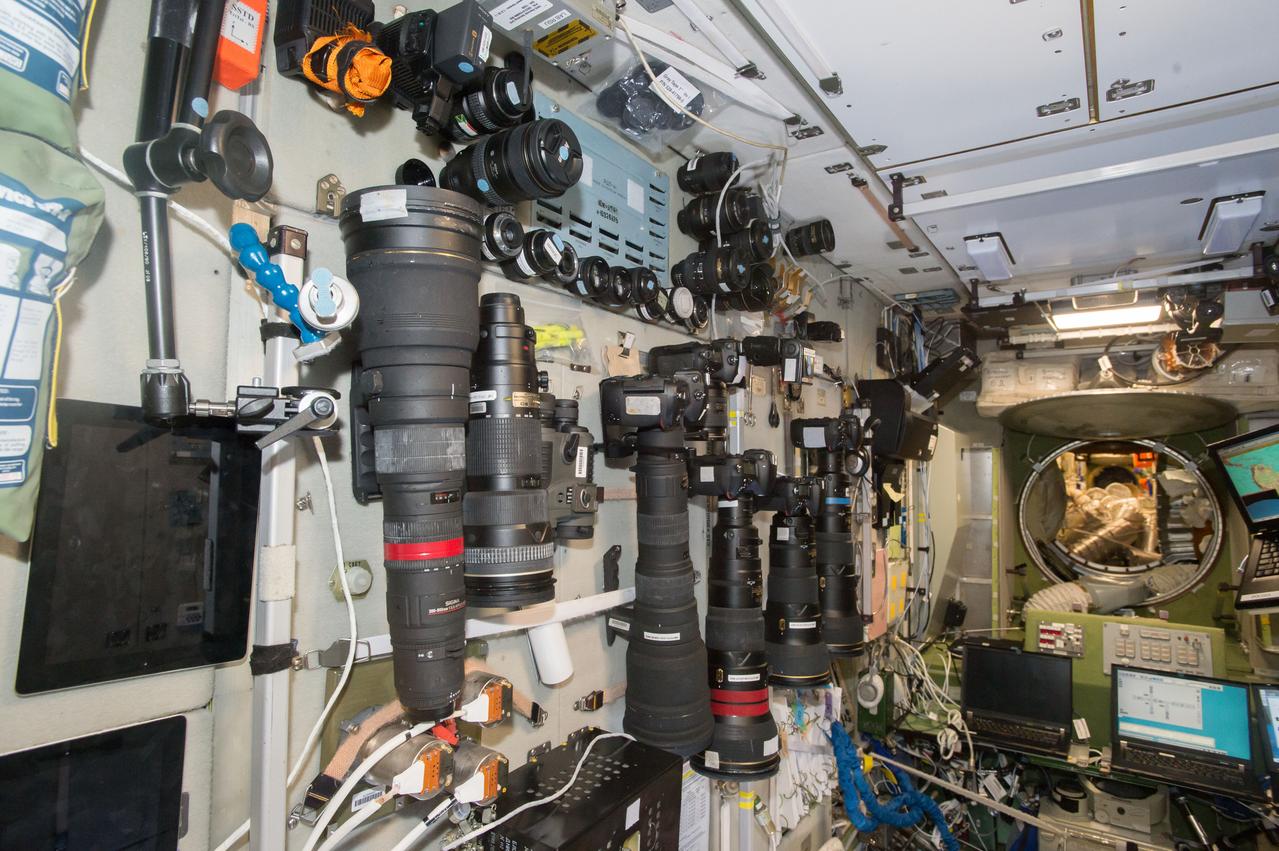

iss050e029074 (1/7/2017) --- A large selection of cameras and lenses are available to take Crew Earth Observations (CEO) photos. These cameras are in the Services Module part of the Russian Segment and near one of the windows used for Earth photography. CEO imagery provides researchers on Earth with key data to understand the planet from the perspective of the ISS. Crew members have been photographing Earth from space since the early Mercury missions beginning in 1961. The images taken from the ISS ensure this record remains unbroken.
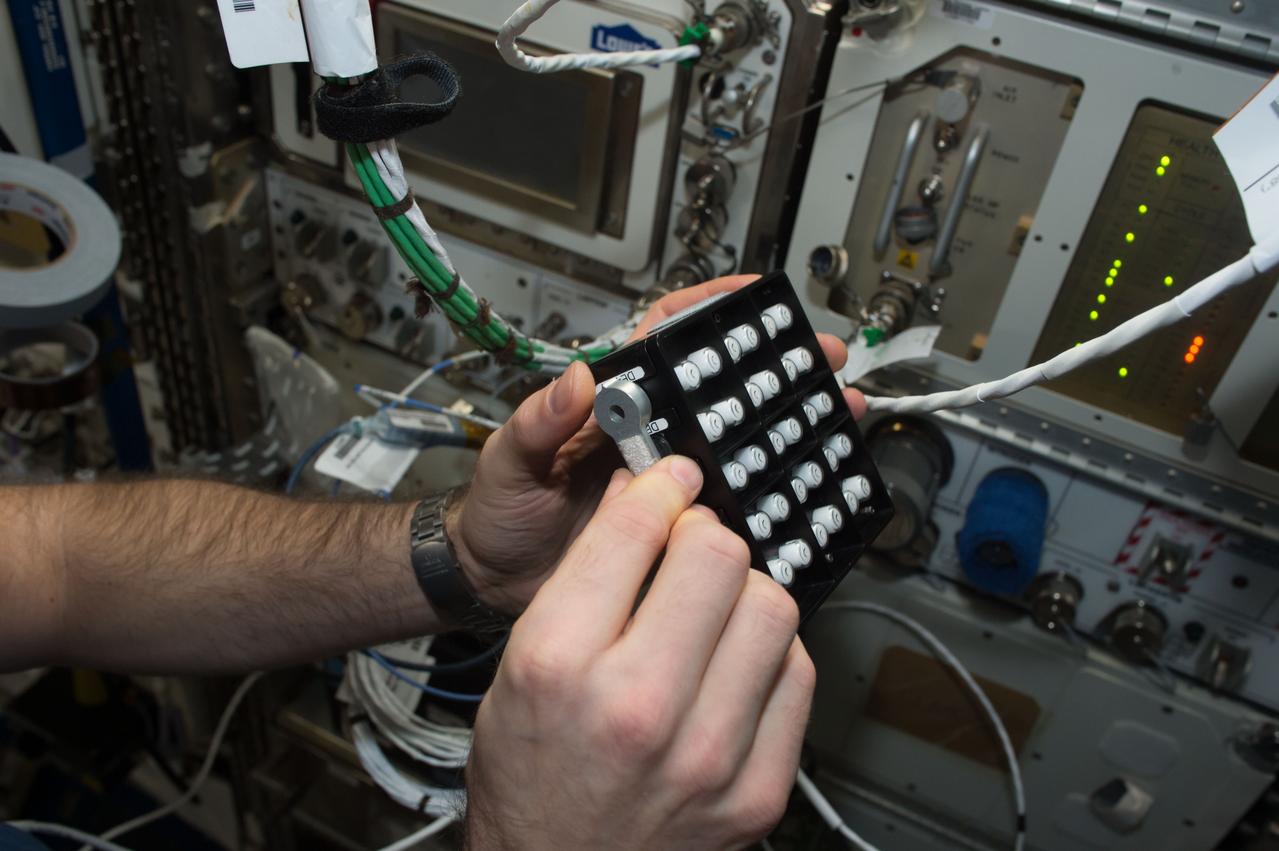

iss050e058807 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
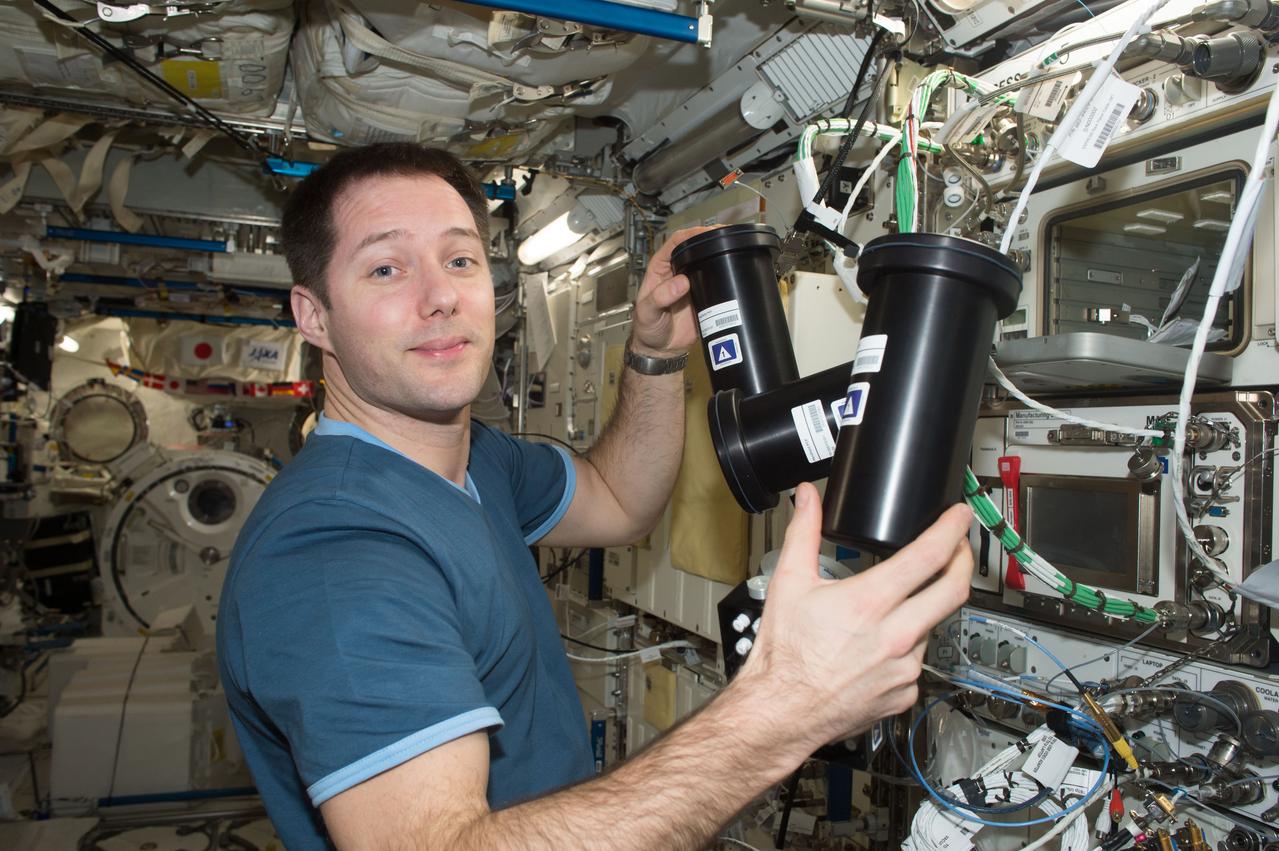

iss050e058812 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.

iss050e052741 (2/24/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) Thomas Pesquet (upside down) posing with Tomatospheres-5 within ziplock bags, in the U.S. Laboratory. The Tomatosphere 5 investigation consists of a shipment of 1.2 million tomato seeds to the International Space Station (ISS), where they visit for a short while aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft before returning to Earth. Approximately 15 000 students in schools across Canada and the United States receive the space-flown seeds, as well as seeds that remained on Earth, and grow both types in a blind study that measures their germination, growth rate, and general vigor.
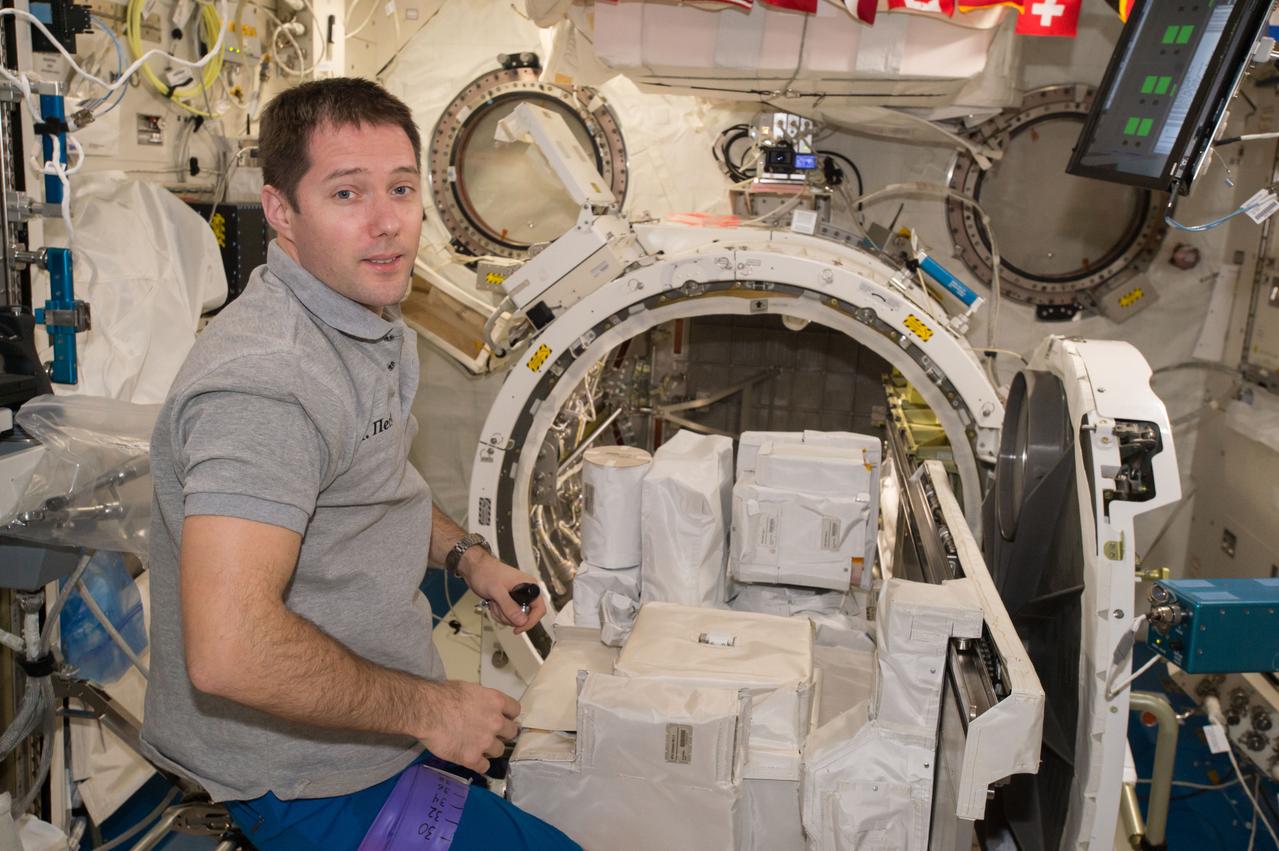

iss050e039213 (2/7/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet during the installation of the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) High Definition Television (HDTV) to Exposed Facility Unit (EFU) Adapter on JEM Airlock (JEMAL) Slide Table. The High Definition Television Camera-Exposed Facility 2 (HDTV-EF2) is a high-definition television camera system that is used for Earth observation from the International Space Station (ISS). HDTV-EF2 is exposed to the space environment on the Japanese Experiment Module -Exposed Facility (JEM-EF).
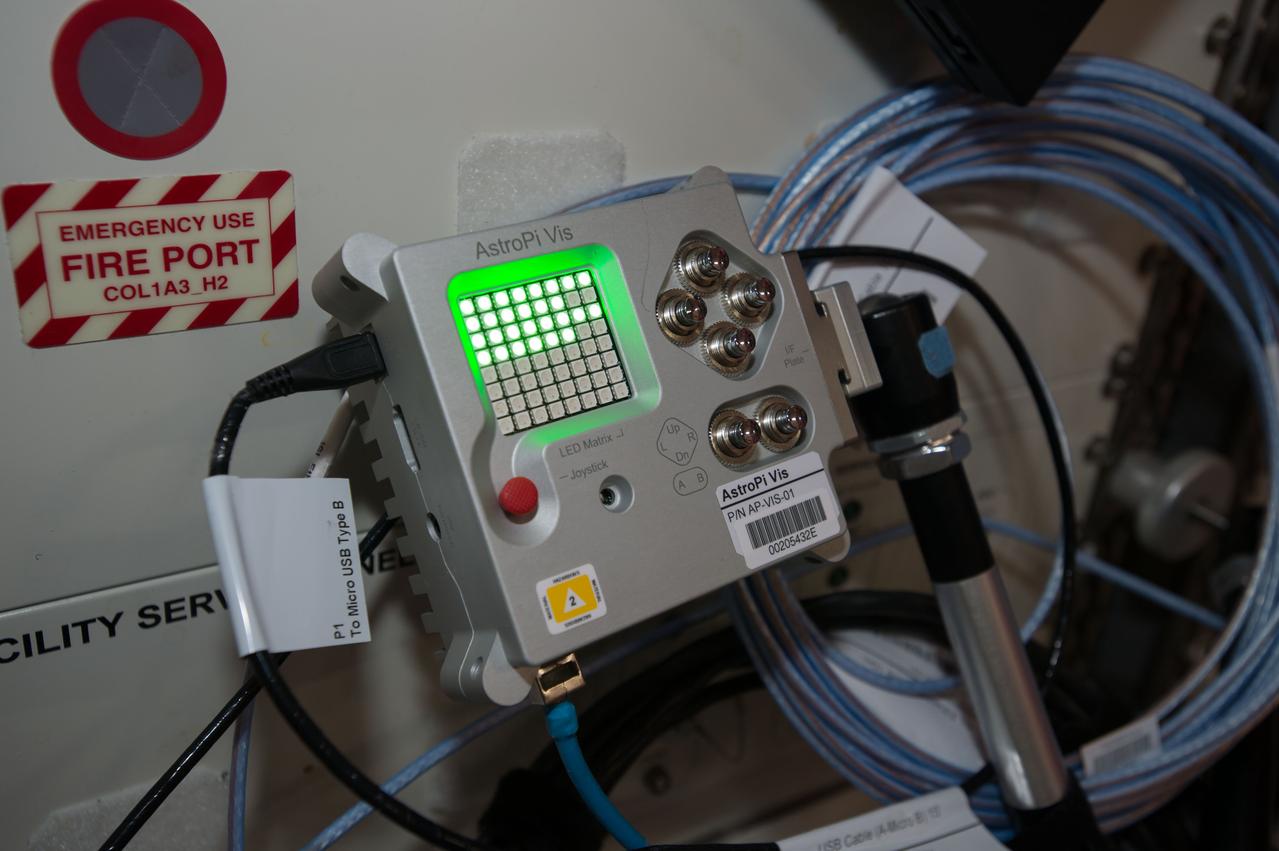

iss050e011416 (11/23/2016) --- A view of Astro PI Camera VIS being powered up. One of the goals of the Astro Pi mission was to enable school-age students to gain inexpensive access to the same computer used by the crew of the ISS. This is made possible by the low-cost Raspberry Pi. Photo was taken during Expedition 50 onboard the International Space Station (ISS).
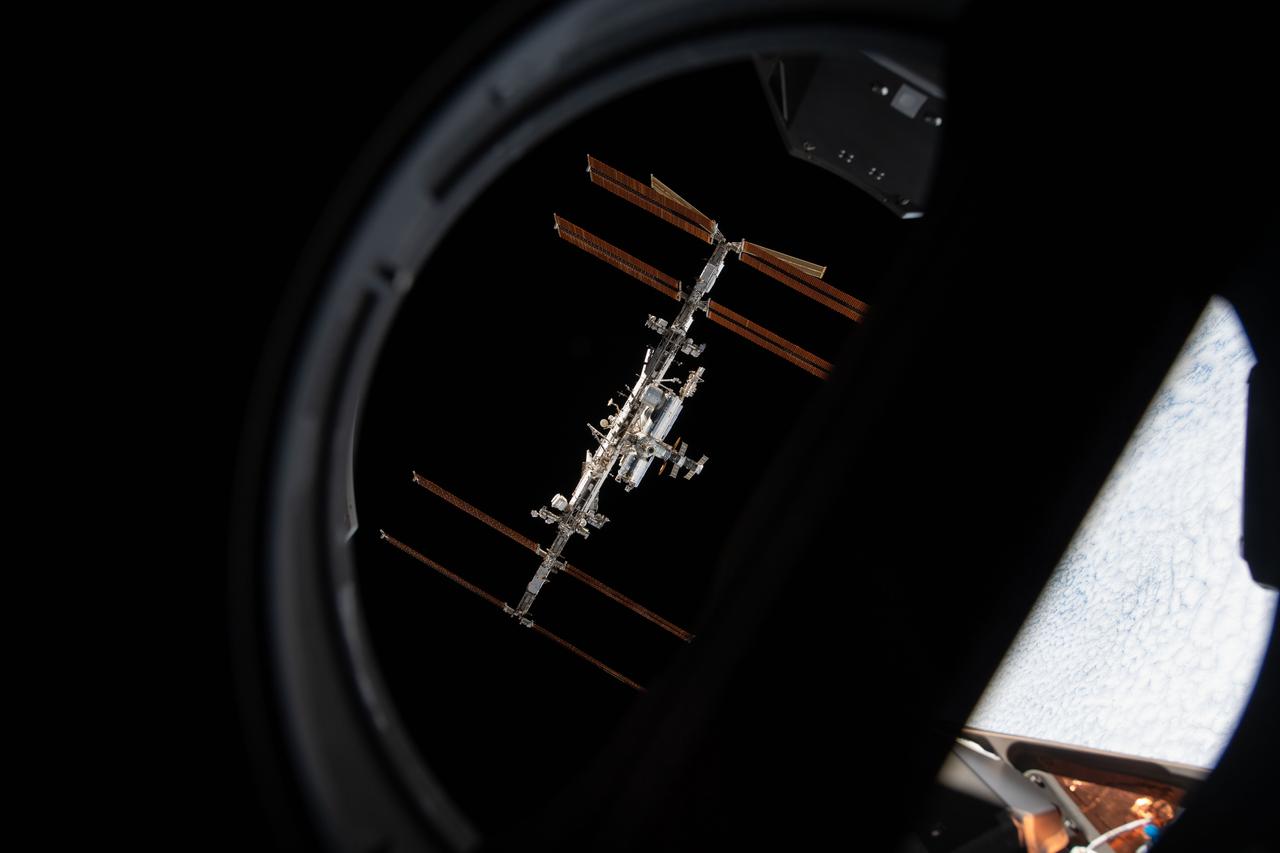
iss066e080912 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station is pictured from inside a window aboard the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021.
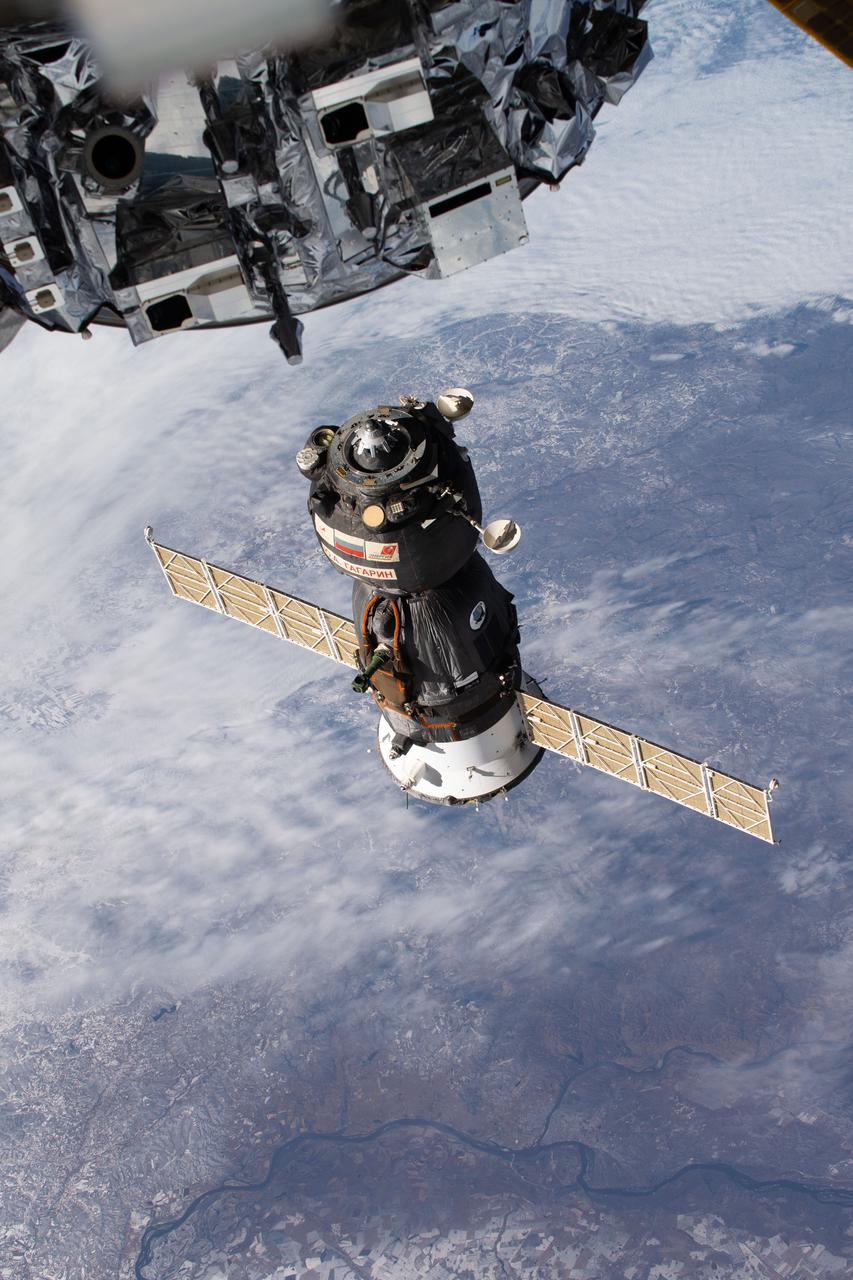

iss066e001096 (Oct. 17, 2021) --- The Soyuz MS-18 crew ship, carrying Soyuz Commander Oleg Novitskiy and spaceflight participants Yulia Peresild and Klim Shipenko, is pictured moments after undocking from the International Space Station's Nauka multipurpose laboratory module as both spacecraft were orbiting 263 miles above far eastern Russia.
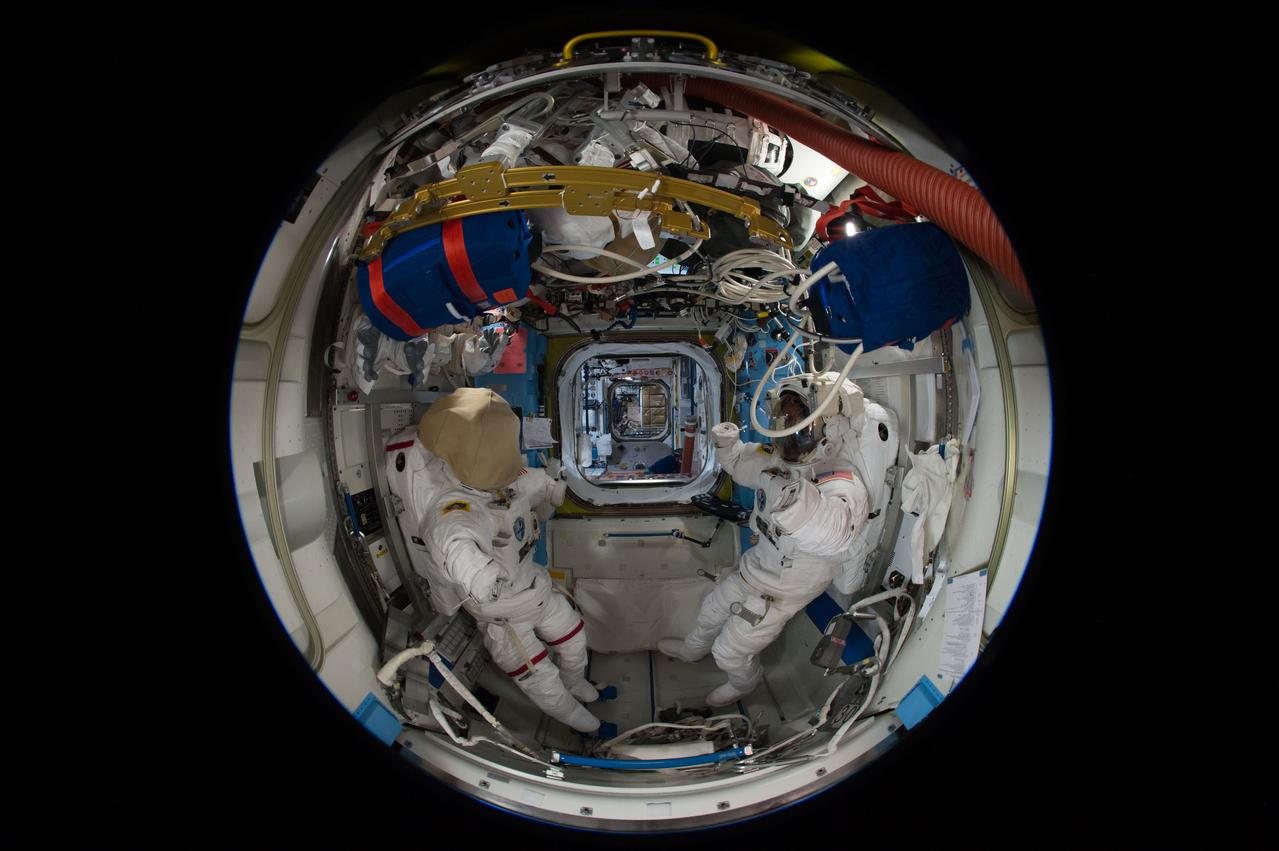
iss051e041018 (5/11/2017) --- A fish-eye view looking port in the Quest Airlock (A/L), taken for a Google Street View of the ISS. The port hatch into the Unity Node 1 is in view.
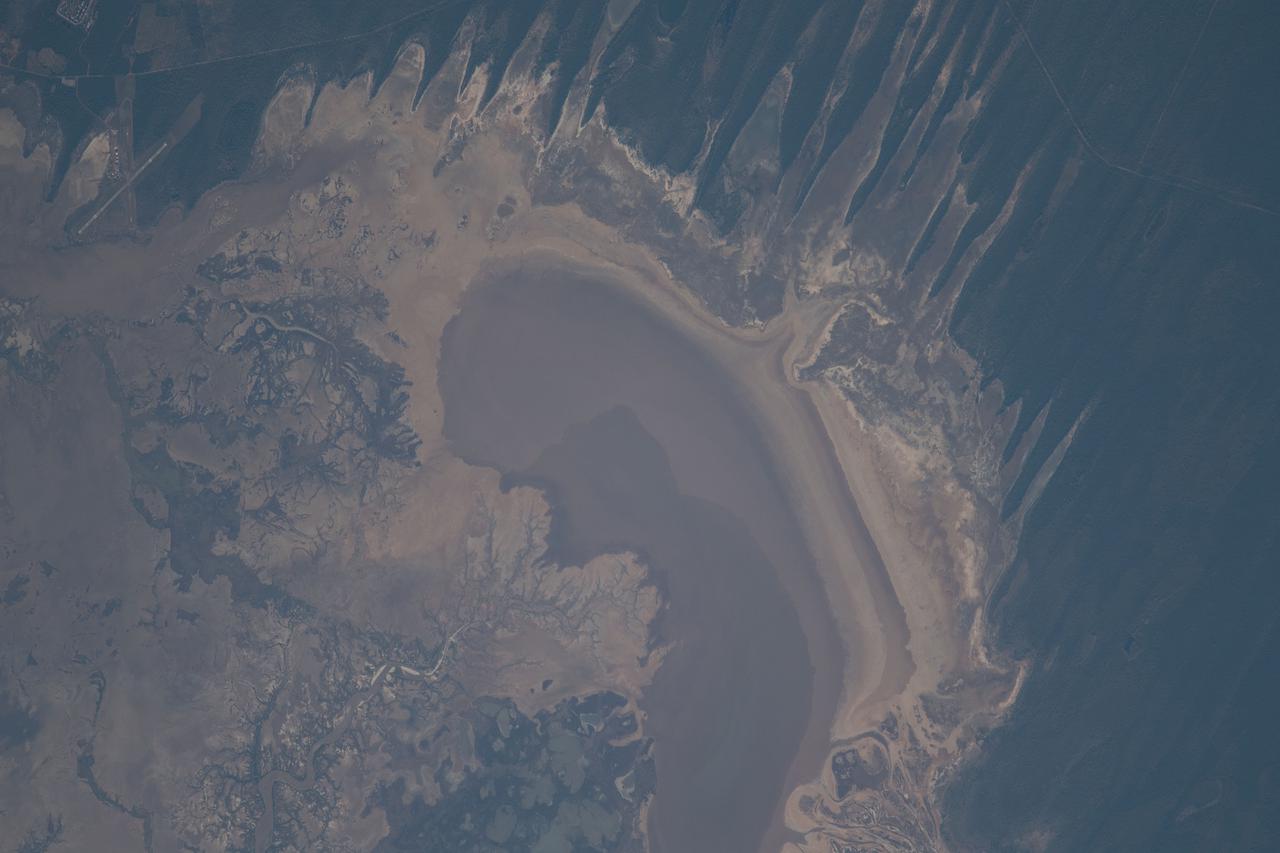

iss065e046534 (May 14, 2021) --- A portion of Western Australia off the coast of the Indian Ocean is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 265 miles above.
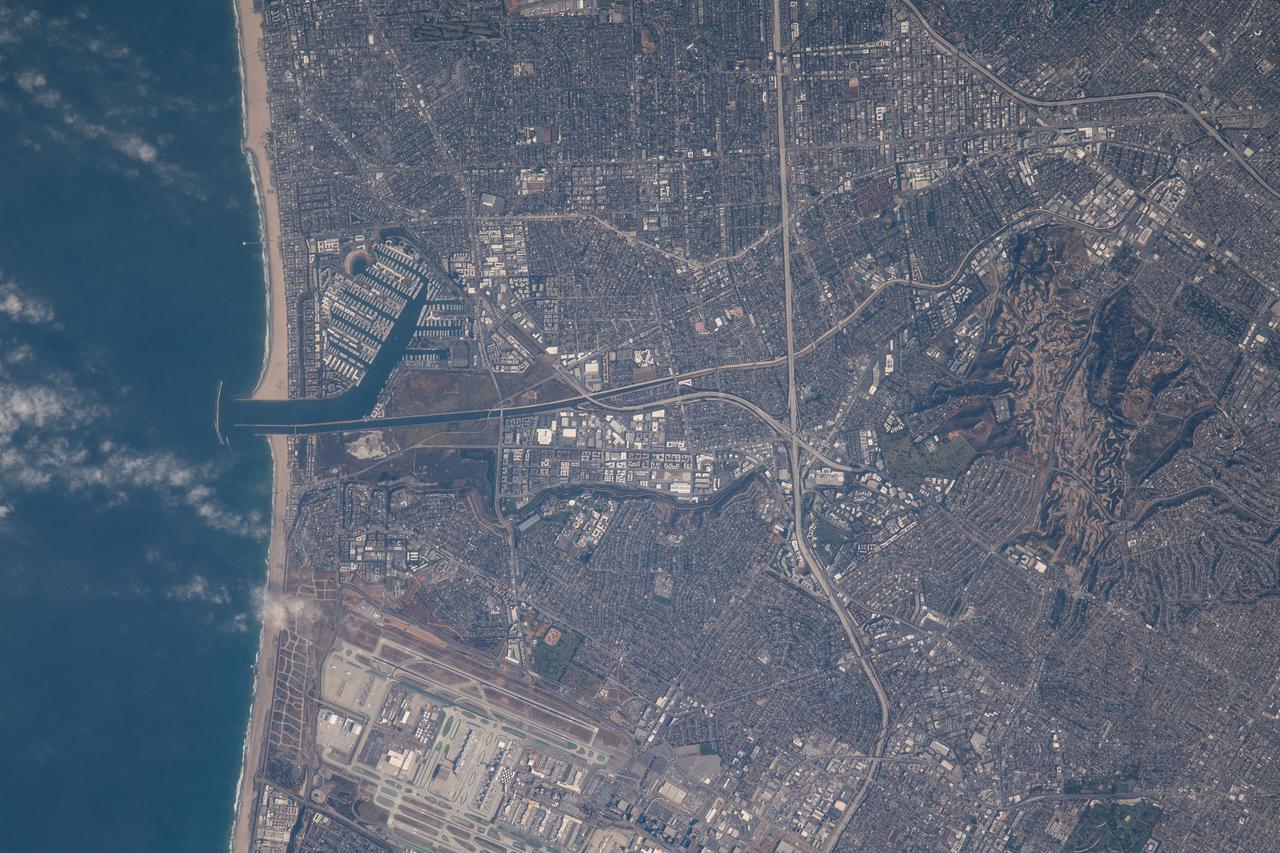

iss065e020971 (May 5, 2021) --- The unincorporated community of Marina Del Rey west of Los Angeles is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the Pacific Ocean.
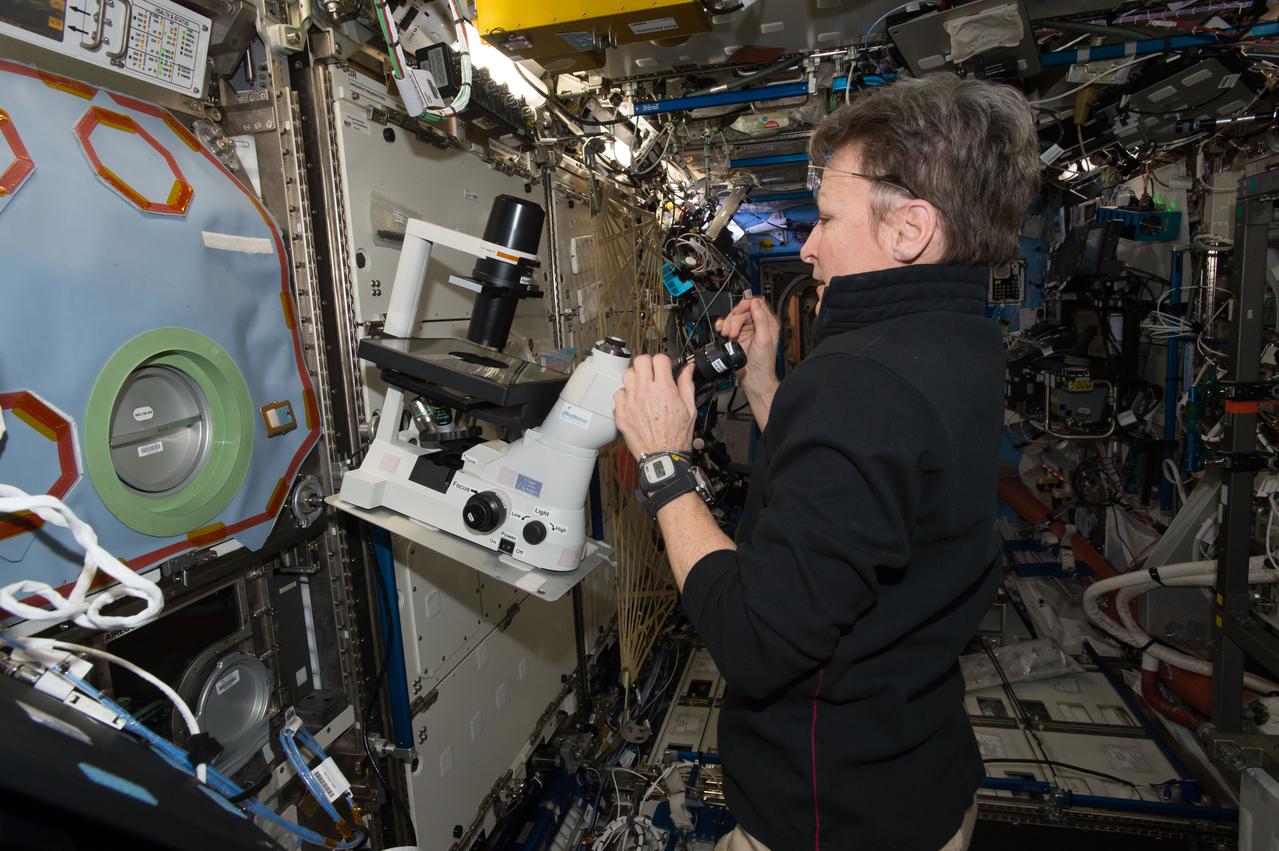

iss050e052142 (Feb. 21, 2017) --- Expedition 50 Flight Engineer Peggy Whitson sets up a microscope in support of the Microgravity Expanded Stem Cells payload outside the Microgravity Science Glovebox housed inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module.

iss051e018869 (4/18/2017) --- A fish-eye view looking port in the Zvezda Service Module (SM), taken for a Google Street View of the ISS.
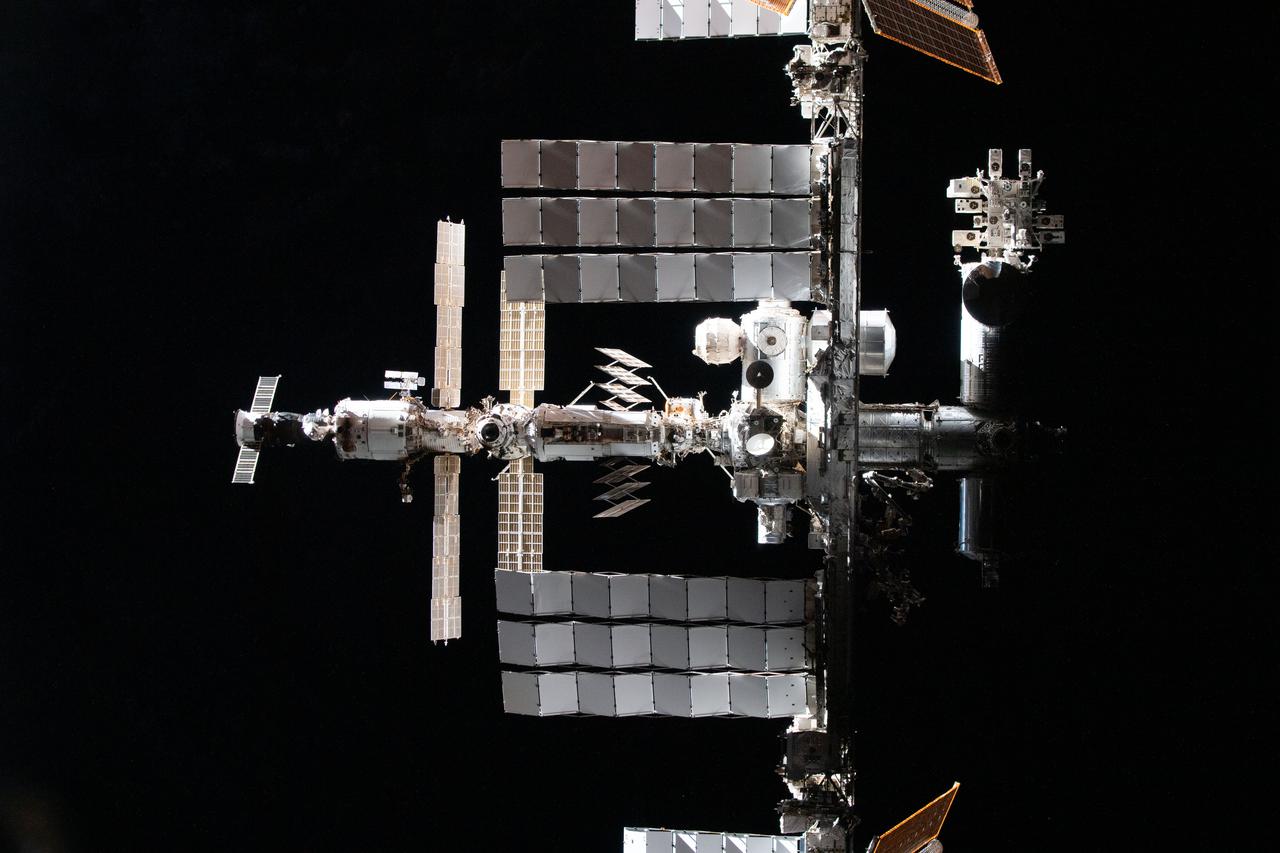

iss066e079887 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021.
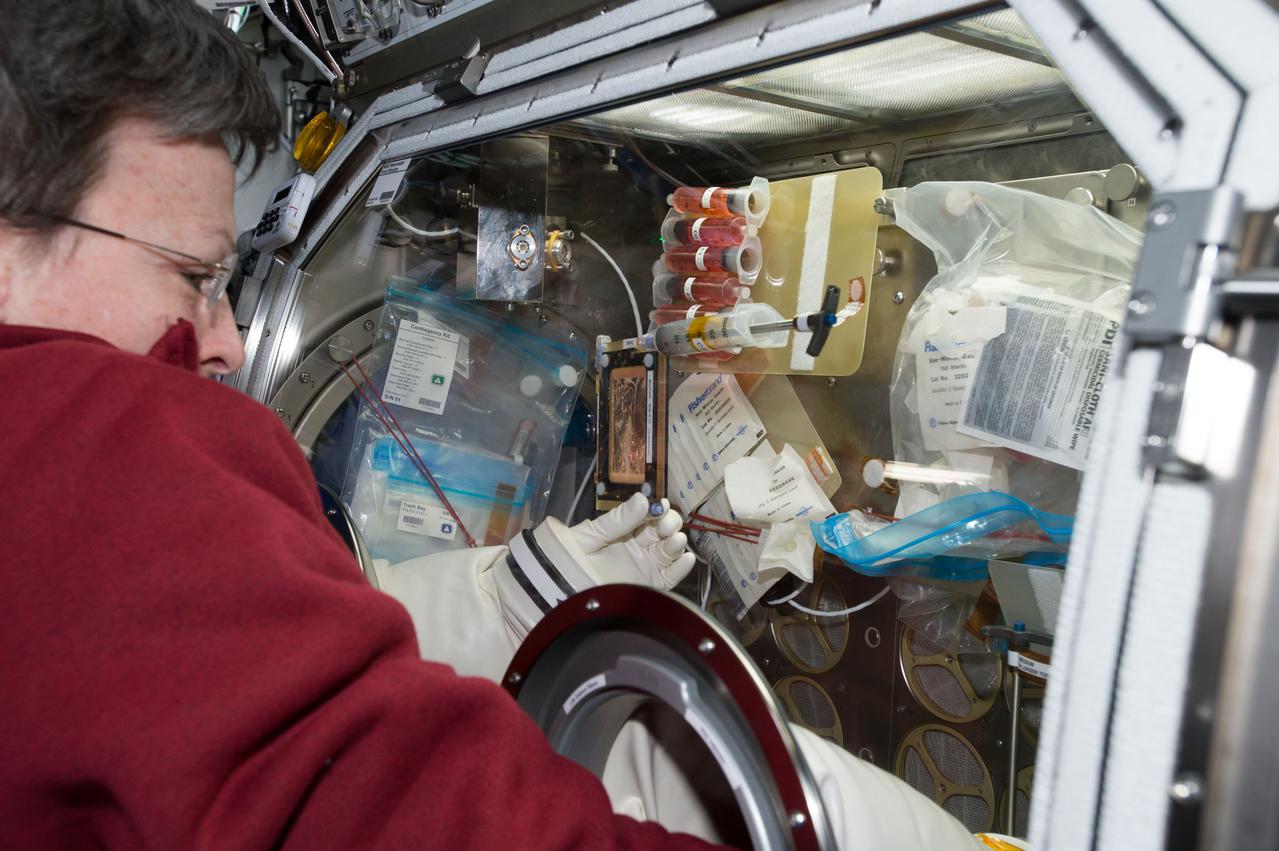

iss051e036121 (5/3/2017) --- An over-the-shoulder look at Commander Peggy Whitson working inside the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox (MSG) to change the media in the BioCell for the OsteoOmics experiment. Image was taken in the Destiny U.S. Laboratory. Gravitational Regulation of Osteoblast Genomics and Metabolism (OsteoOmics) aims to validate if magnetic levitation is a reasonable simulation of orbital free fall by measuring biological endpoints, such as signaling pathways and gene expression in osteoblast and osteoclast cells. Cells are exposed to a microgravity environment and ground based cells are exposed to magnetic levitation. If the validation is successful, then ground-based magnetic levitation will be an important ground-based tool to investigate the effect of gravitational force on biological systems.
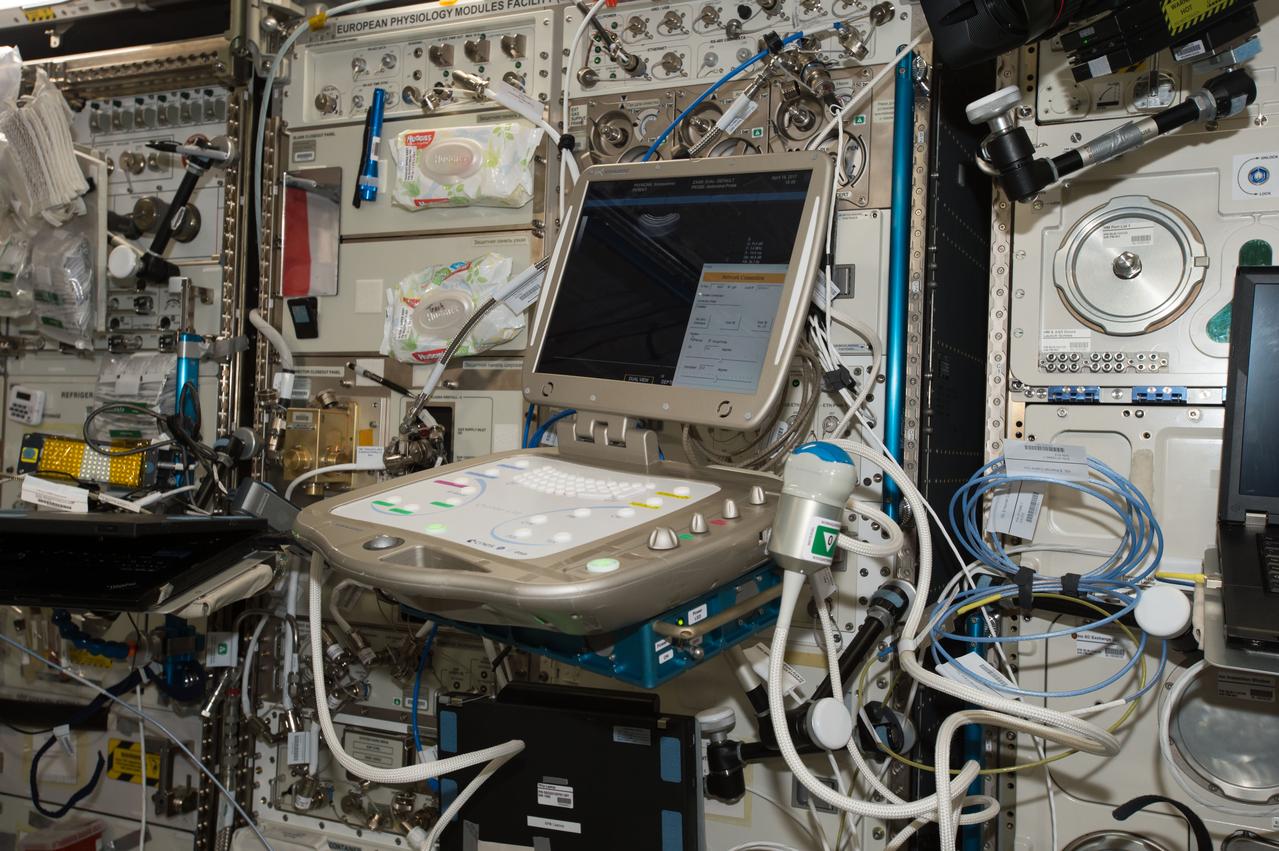

iss051e018997 (4/18/2017) --- Photo documentation of the Echo Unit during setup for Echo experiment commissioning operations (OPS) in the Columbus module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The purpose of the ECHO investigation is to evaluate a tele-operated ultrasound system, equipped with motorized probes that are controlled by flight controllers on the ground. Additionally, this investigation serves to perform the commissioning of the Echo instrument, which is planned to be used for the Vascular Echo experiment in the future.
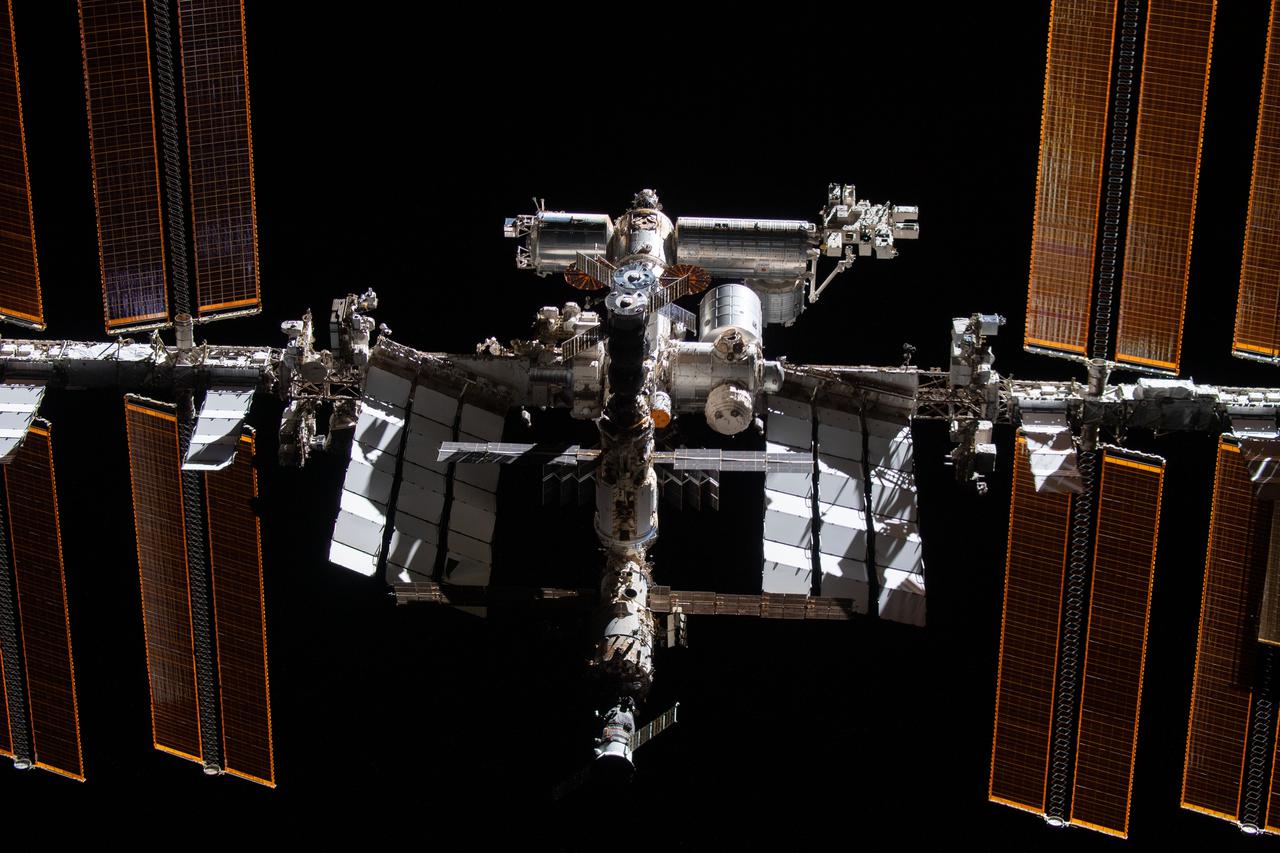
iss066e080193 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021.
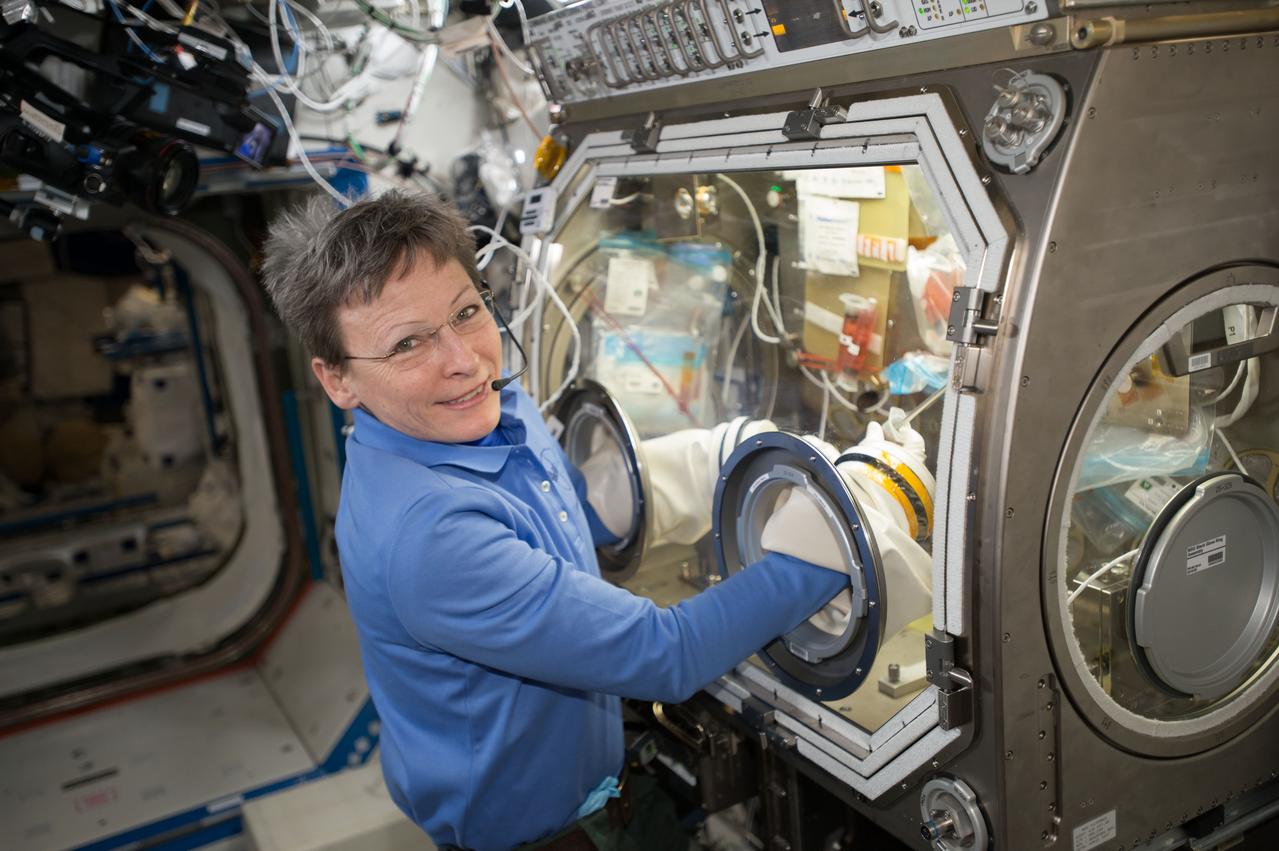

iss051e034104 (5/02/2017) --- NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson pauses for a photo while working inside the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox (MSG) to conduct the first BioCell media change for the OsteoOmics experiment. Image was taken in the Destiny U.S. Laboratory.
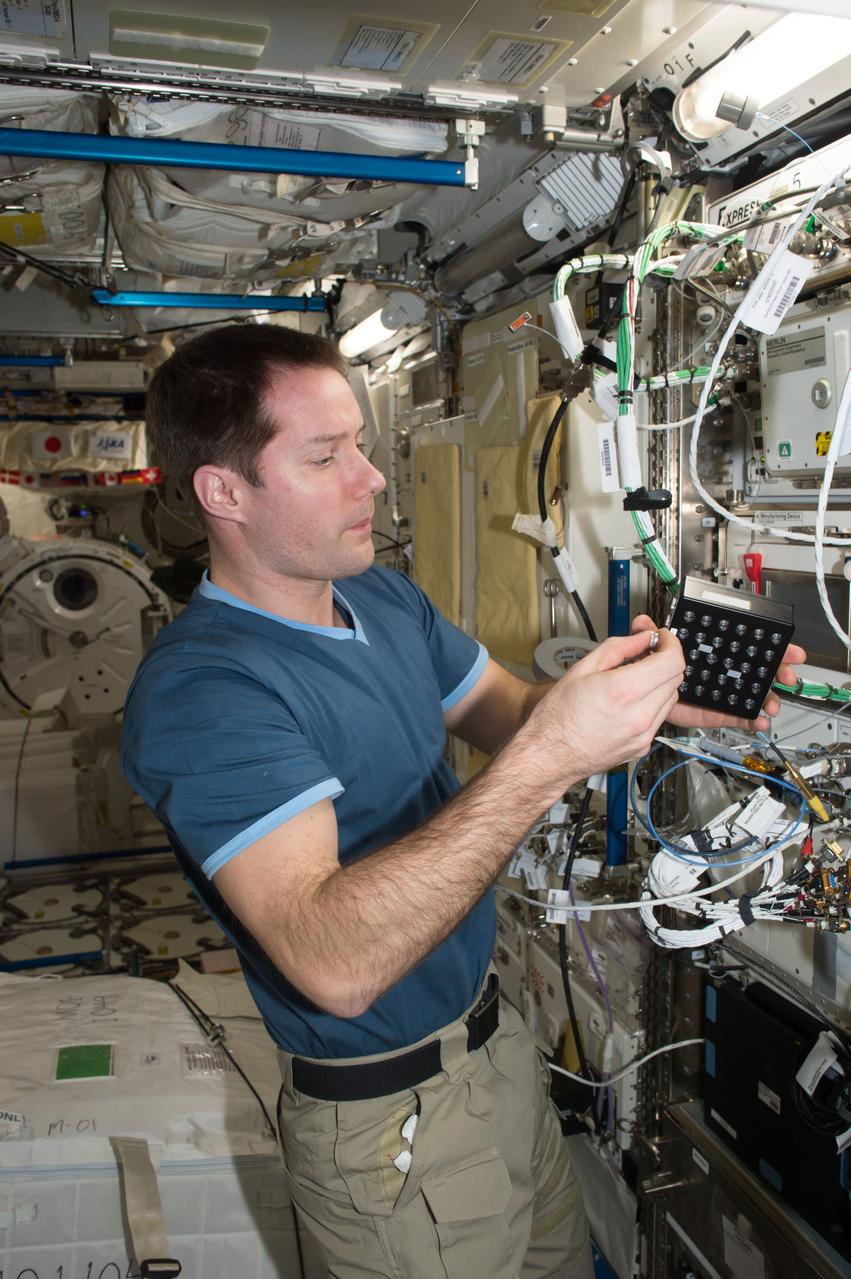

iss050e058802 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
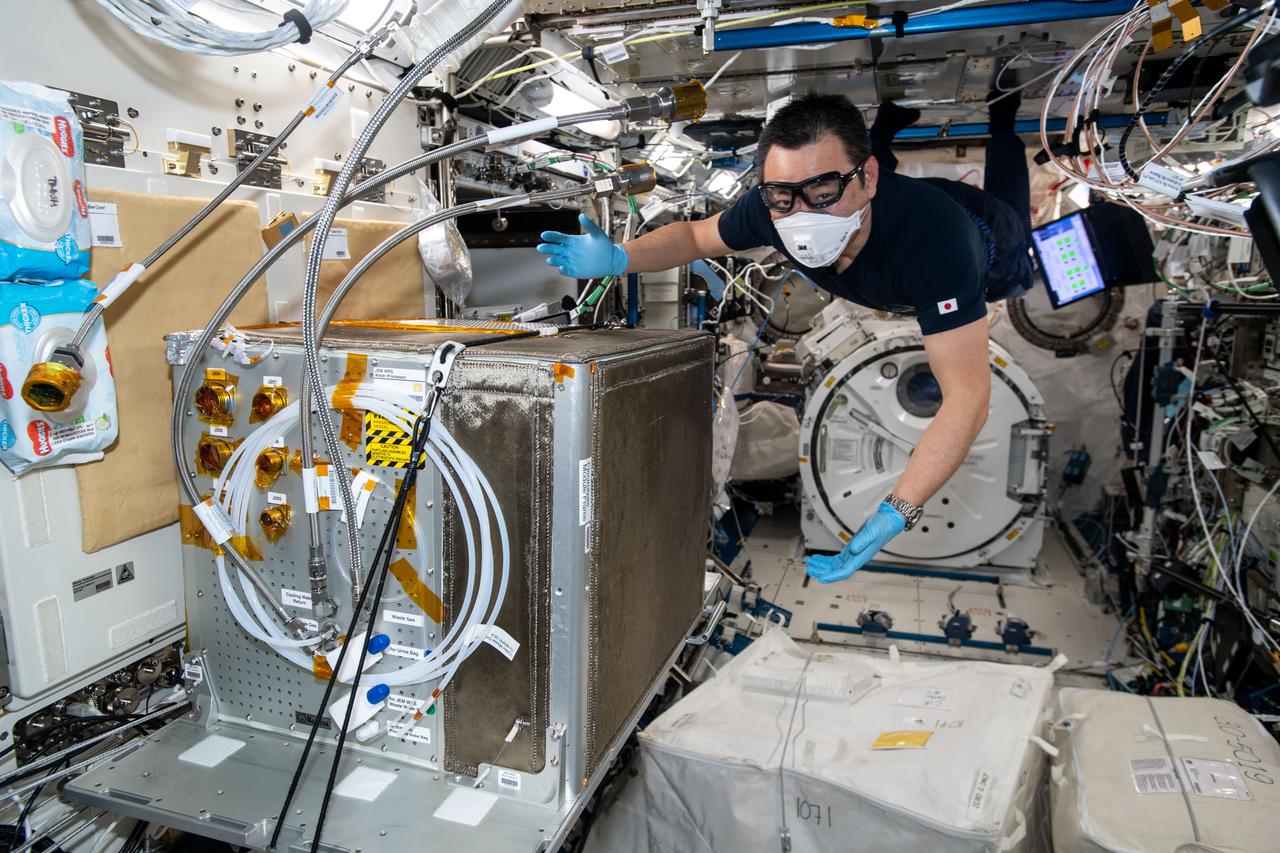

iss065e333421 (8/30/2021) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Akihiko Hoshide is photographed during the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Water Recovery System (JWRS) Gas Trap and Bypass Line Installation. Future water recovery systems will require high recovery rates, a more compact size, and less power consumption than conventional systems. The JWRS demonstrates new technologies on orbit, aboard the International Space Station (ISS), to meet these requirements.

iss050e052652 (2/26/2017) --- A view of the Space Test Program - Houston5 (STP-H5). The Space Test Program-H5-Lightning Imaging Sensor (STP-H5 LIS) on the International Space Station (ISS) measures the amount, rate, and energy of lightning around the world. Improved understanding of lightning and its connections to weather provides crucial insight for weather forecasting, climate change, atmospheric chemistry and physics, and aircraft and spacecraft safety.
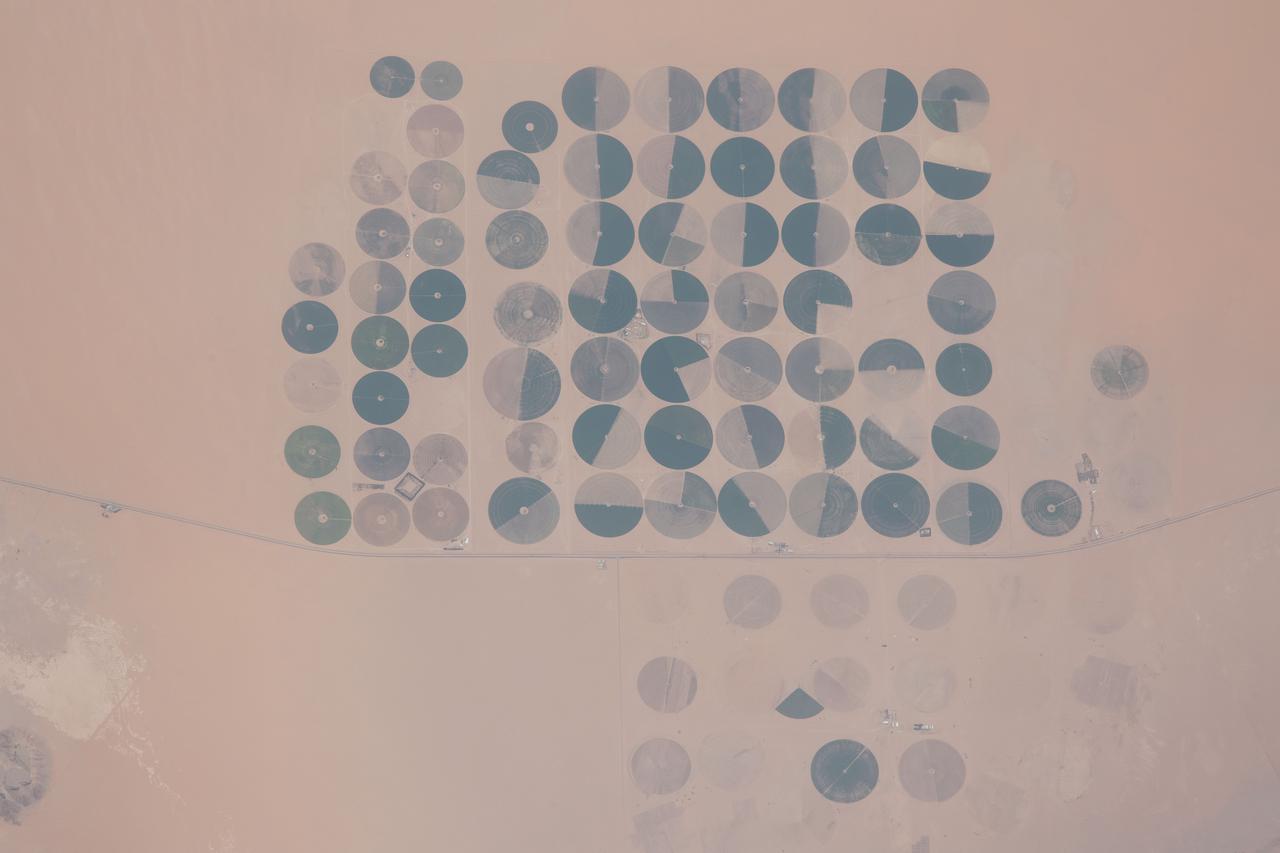

iss065e143195 (June 23, 2021) --- An agricultural development is pictured in the Saudi Arabian town of Wadi Al-Dawasir as the International Space Station orbited 260 miles above.
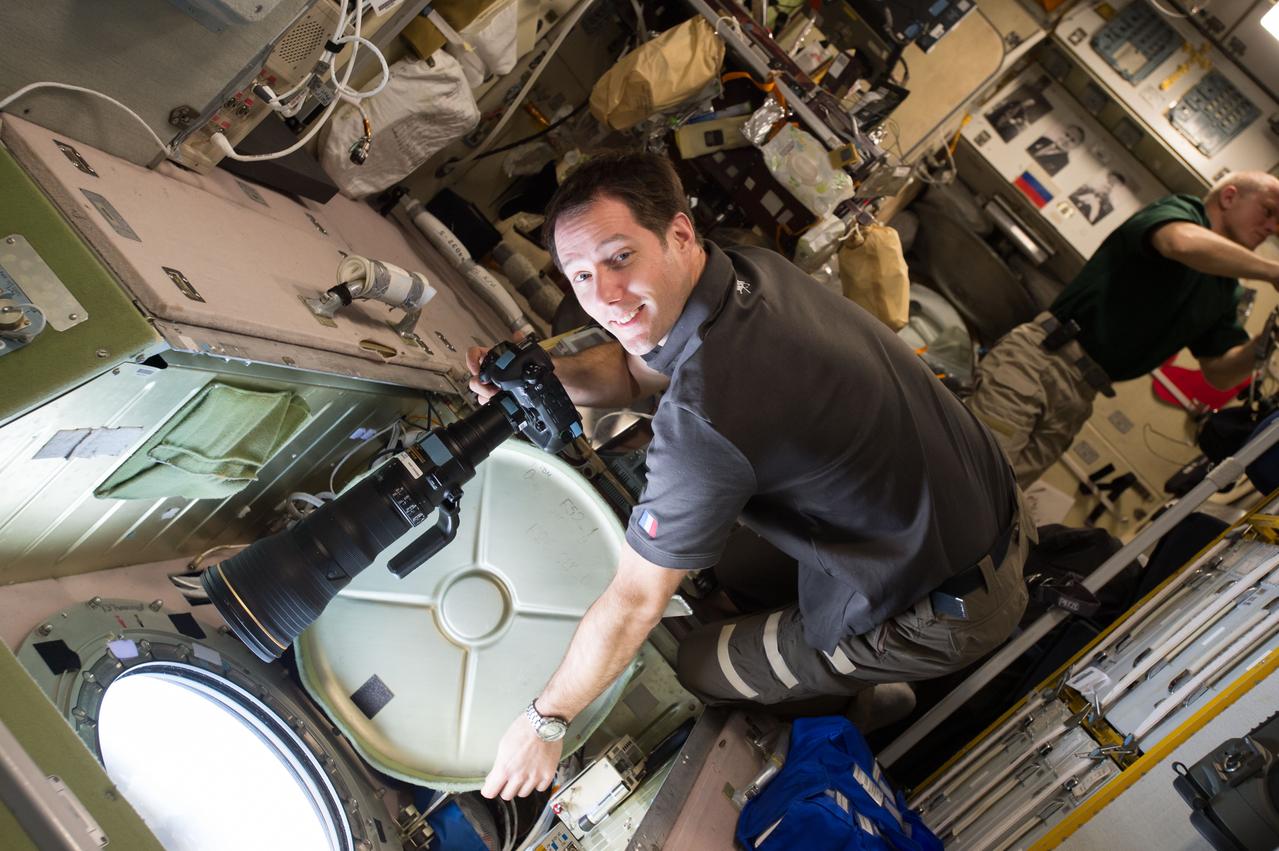

iss050e020100 (12/28/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astonaut Thomas Pesquet preparing to take Crew Earth Observations (CEO) photos from the Service Module (SM) window. Cosmonaut Oleg Novitskiy is visible in the background. CEO imagery provides researchers on Earth with key data to understand the planet from the perspective of the ISS. Crew members have been photographing Earth from space since the early Mercury missions beginning in 1961. The images taken from the ISS ensure this record remains unbroken.
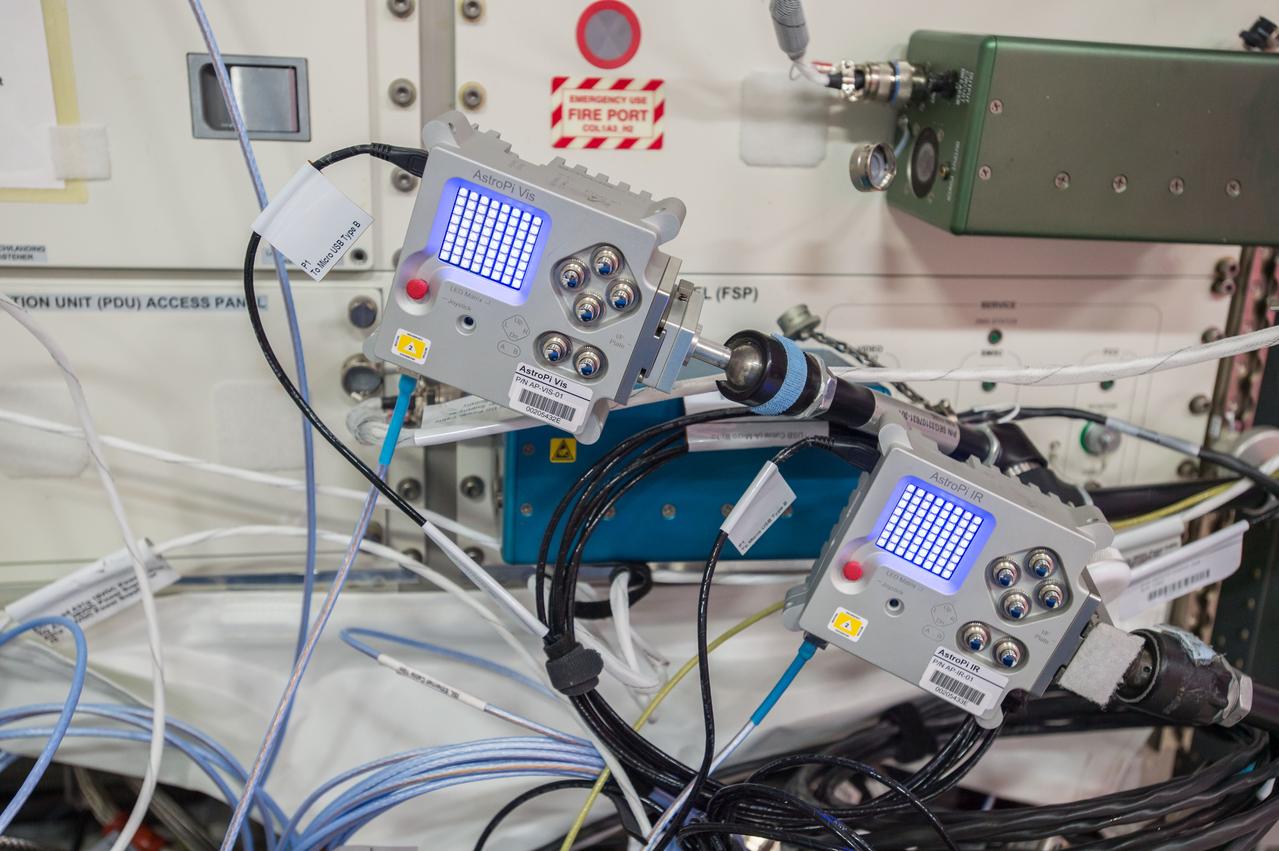
iss051e037888 (5/4/2017) --- A view of two AstroPi Raspberry Pi computers, one equipped with a Visual camera and the other with an Infrared Camera in the Columbus module aboard the International space Station (ISS).
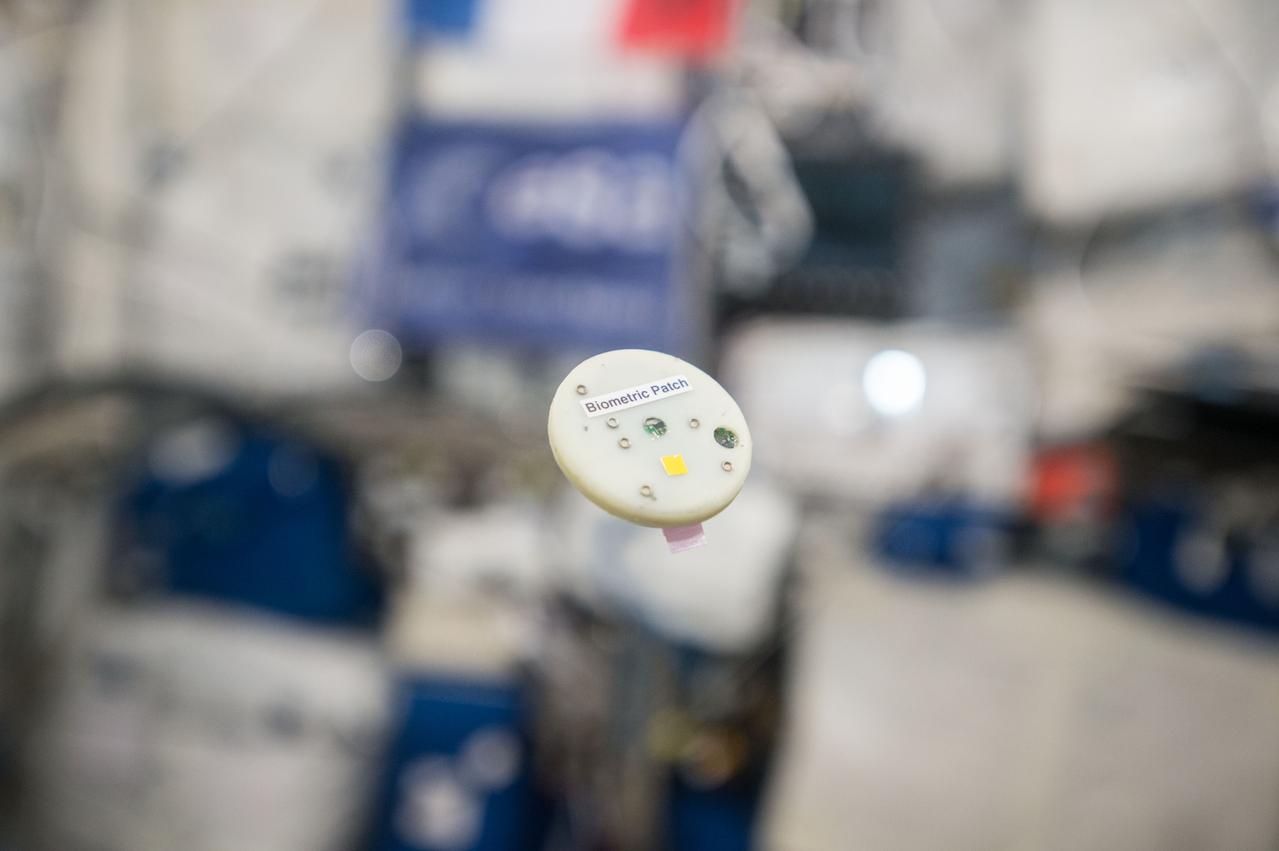

iss050e015097 (8/8/2016) --- View of floating Biometric patch (wearable sensor) connected to an International Space Station (ISS) iPad via bluetooth or via Lightbolt connector. The EVERYWEAR application allows a unified interface for physiology-related data collection and wireless communication.
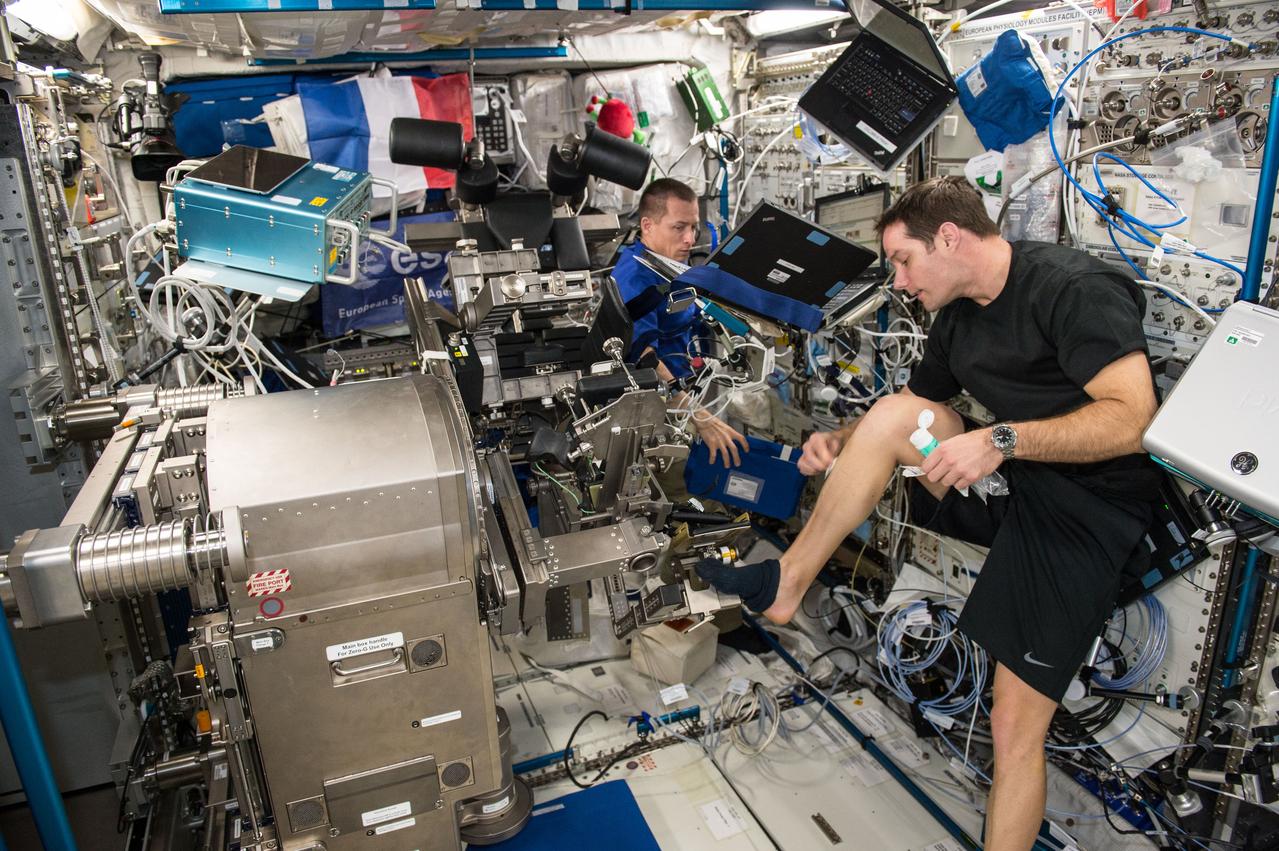
iss050e012767 (11/29/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) Thomas Pesquet and Cosmonaut Sergei Ryzhikov during the setup phase of the Sarcolab-3 Experiment, by deploying and configuring the Muscle Atrophy Resistive Exercise System (MARES), in the Columbus Module. Myotendinous and Neuromuscular Adaptation to Long-term Spaceflight (Sarcolab) investigates the adaptation and deterioration of the soleus, or calf muscle, where it joins the Achilles tendon, which links it to the heel and carries loads from the entire body. Muscle fiber samples are taken from crew members before and after flight, and analyzed for changes in structural and chemical properties.
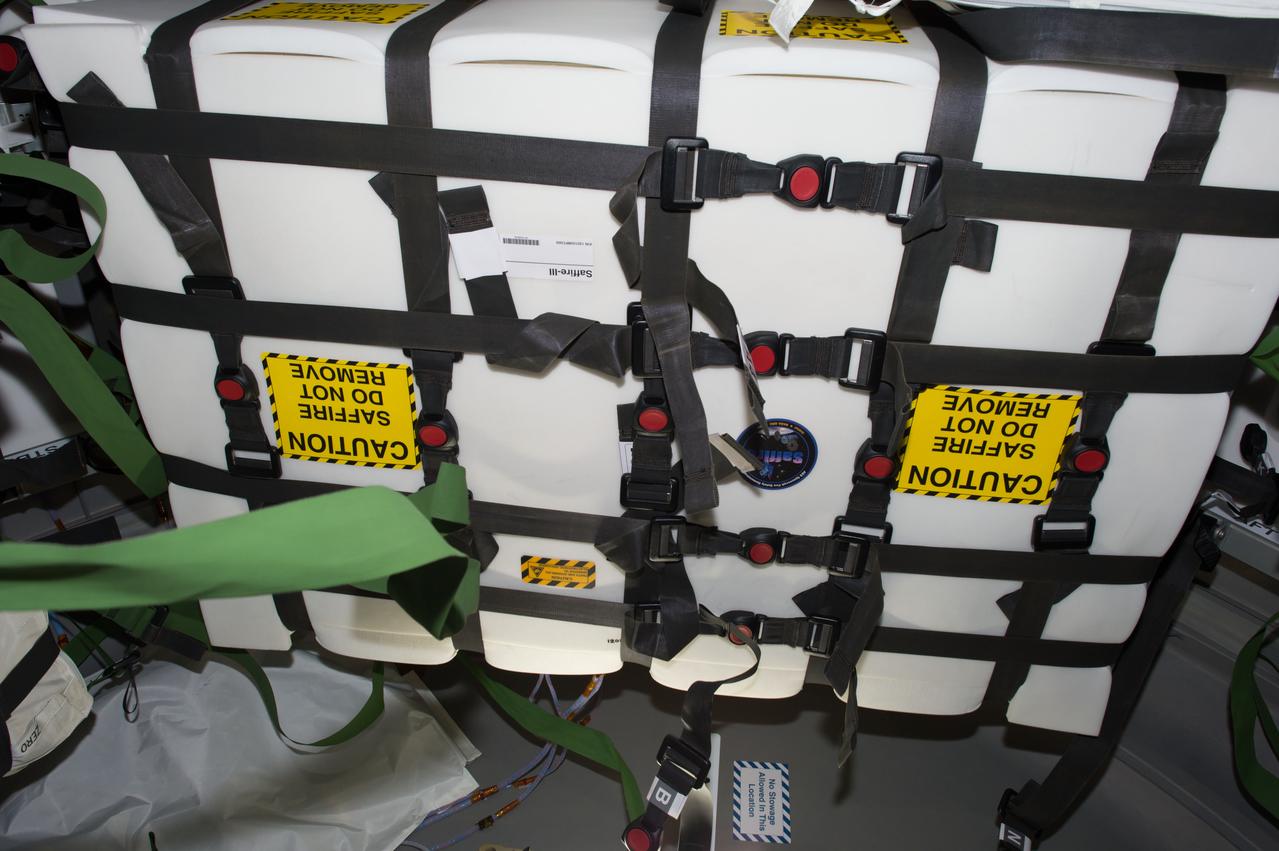

iss051e039882 (5/8/2017) --- A view of Spacecraft Fire Experiment-III (Saffire-III) award the John Glenn Orbital ATK 7 (OA-7) Cygnus spacecraft, taken during cargo transfer operations (OPS). The NASA Advanced Exploration Systems program began a project to develop and demonstrate spacecraft fire safety technologies in relevant environments. The keystone of these demonstrations is a large-scale fire safety experiment conducted on an International Space Station (ISS) re-supply vehicle after it has undocked from the ISS and before it enters the atmosphere.
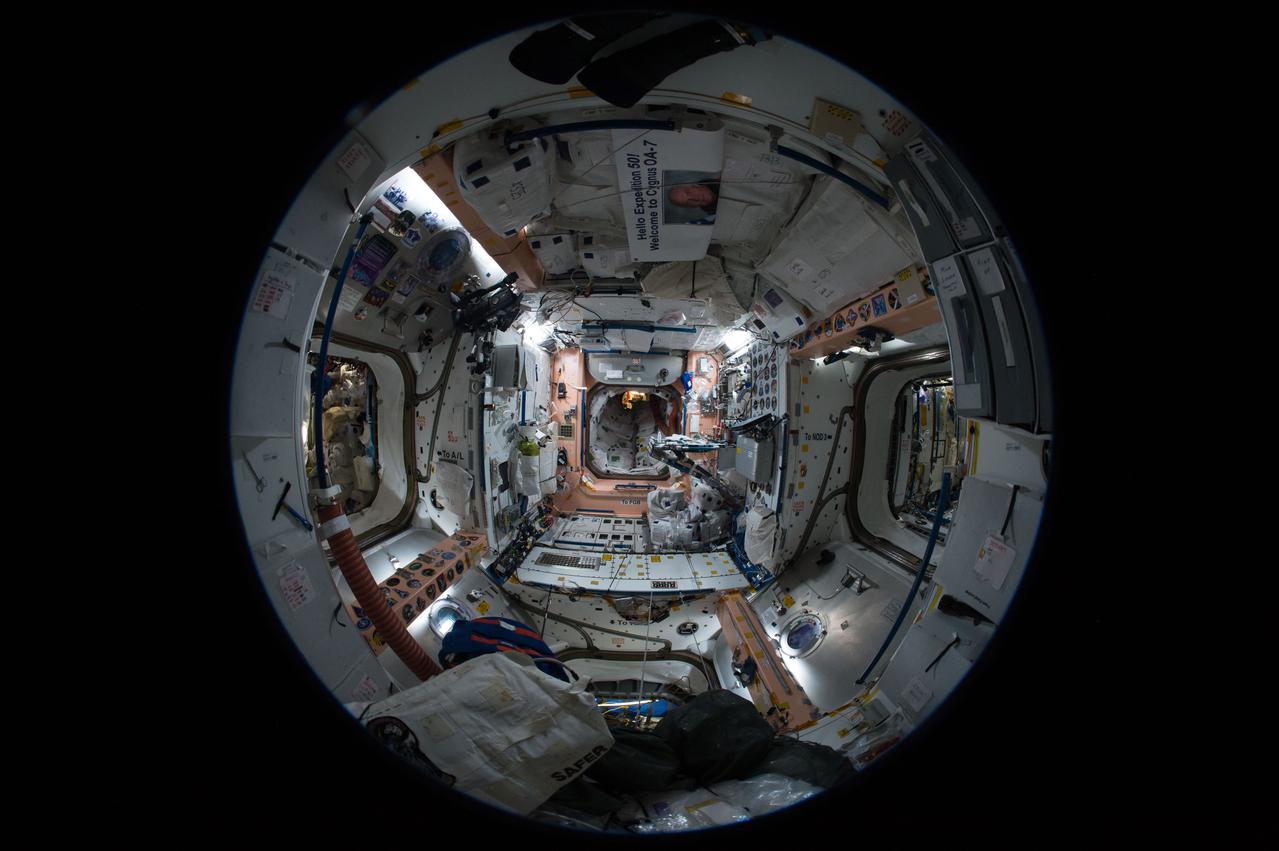

iss051e040946 (5/11/2017) --- A fish-eye view looking aft in the Unity Node 1, taken for a Google Street View of the ISS.
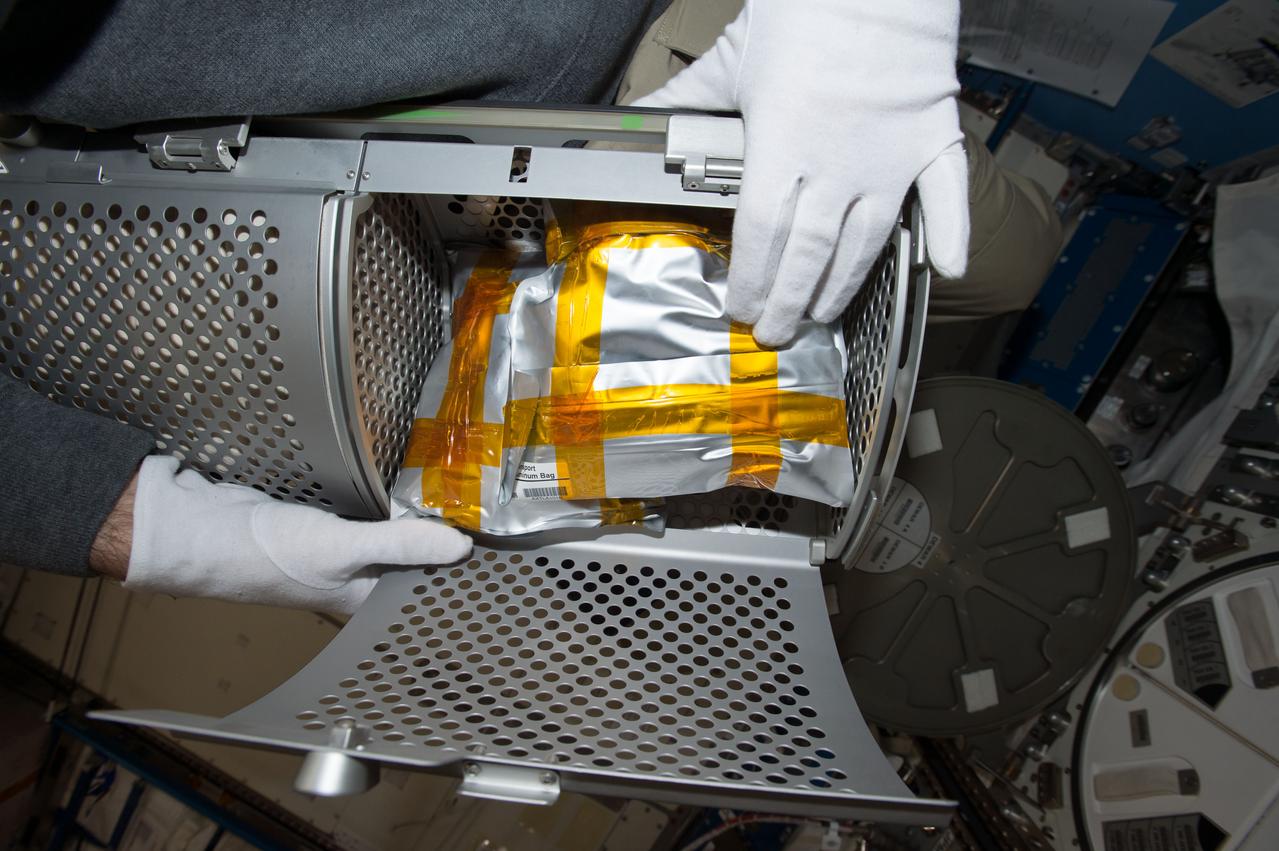

iss050e057655 (3/15/2020) --- Photographic documentation during Auxin Transport sample transfer to Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) insertion. Studies on Gravity-Controlled Growth and Development in Plants Using True Microgravity Conditions (Auxin Transport) clarifies the role of auxins in pea and maize (corn) seedlings grown in microgravity, leading to new insight into how gravity, or the lack of gravity, affects plant development.
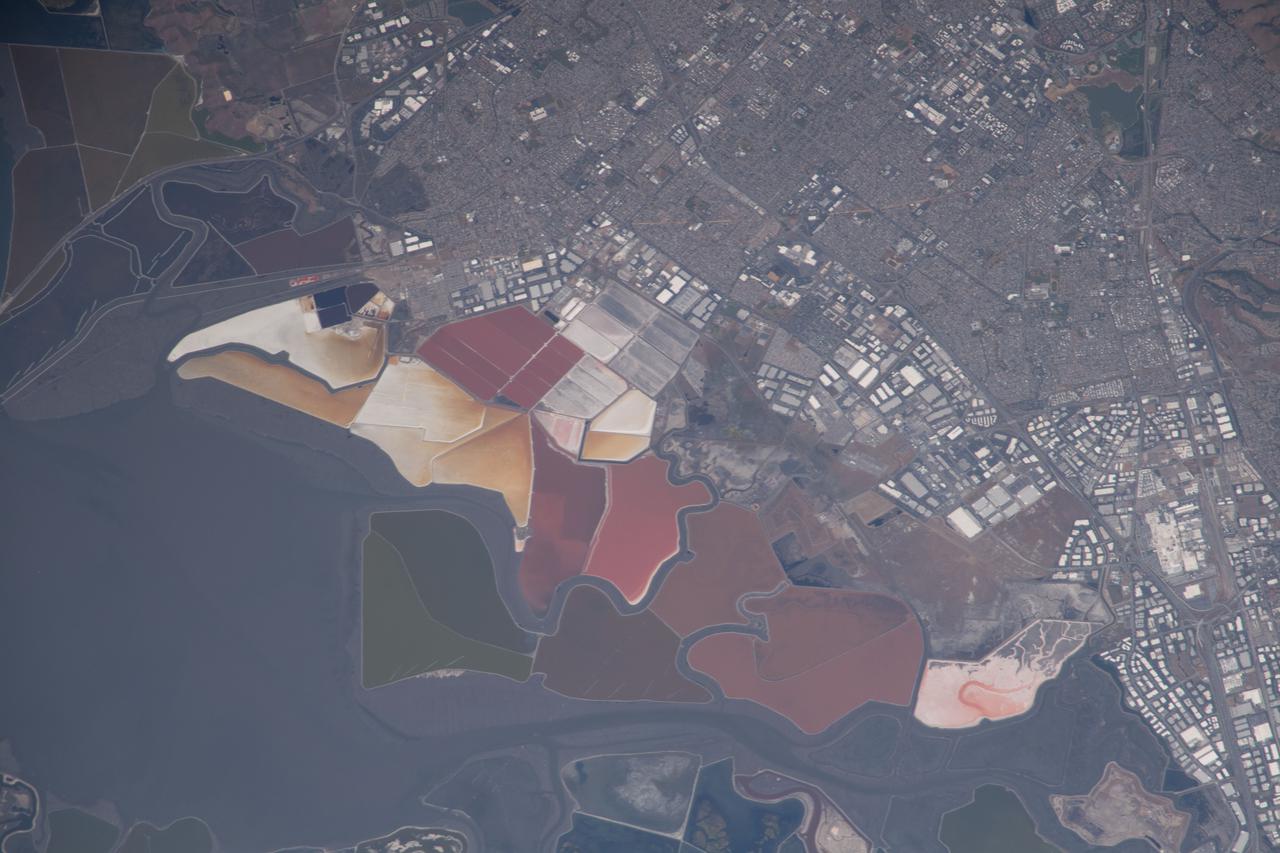

iss065e007130 (April 27, 2021) --- The southern end of San Francisco Bay hosts Don Edwards San Francisco Bay National Wildlife Refuge and is surrounded by the California cities of Newark and Baylands. This photograph was taken from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the Pacific Ocean near the coast.
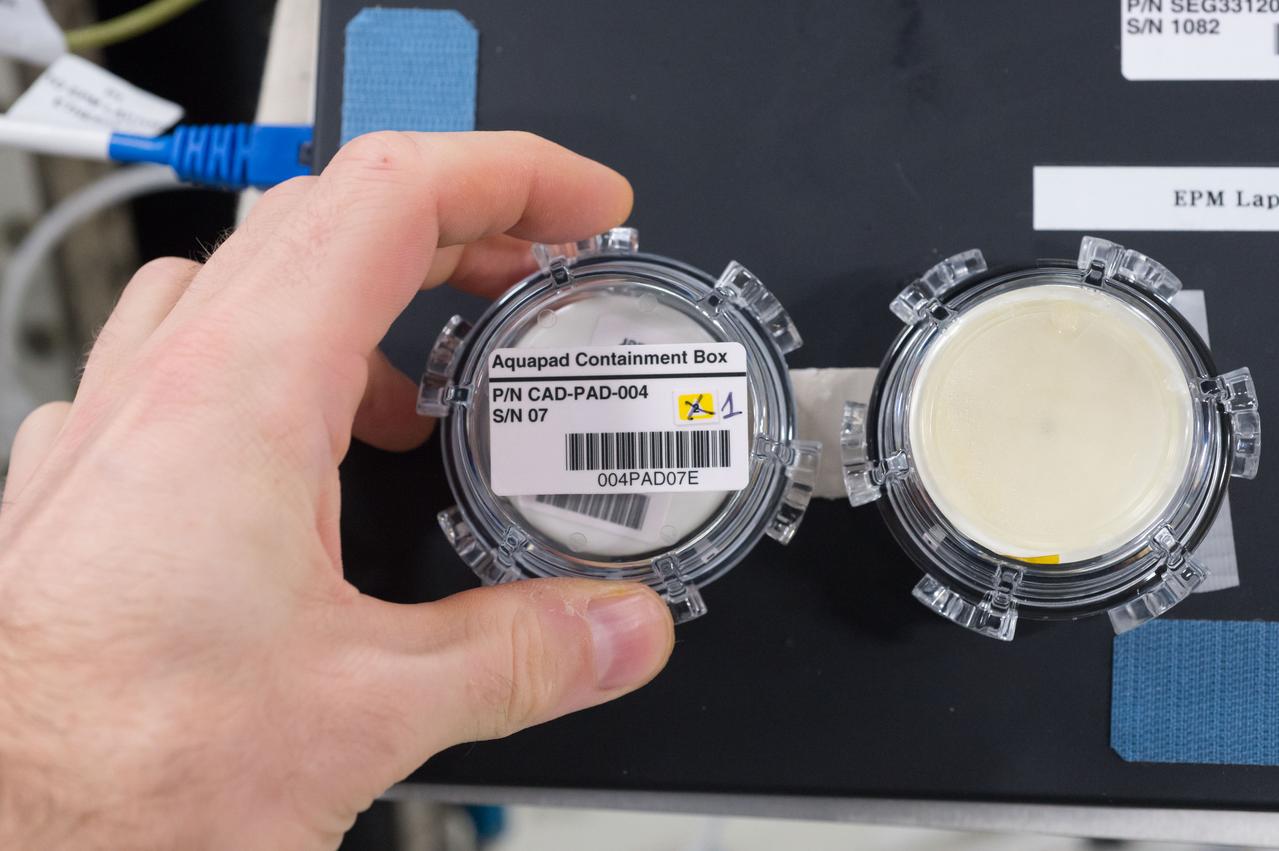

iss050e057692 (3/16/2017) --- View of Aquapad Microbial Contamination within container during analysis of water samples. Photo was taken during Expedition 50.
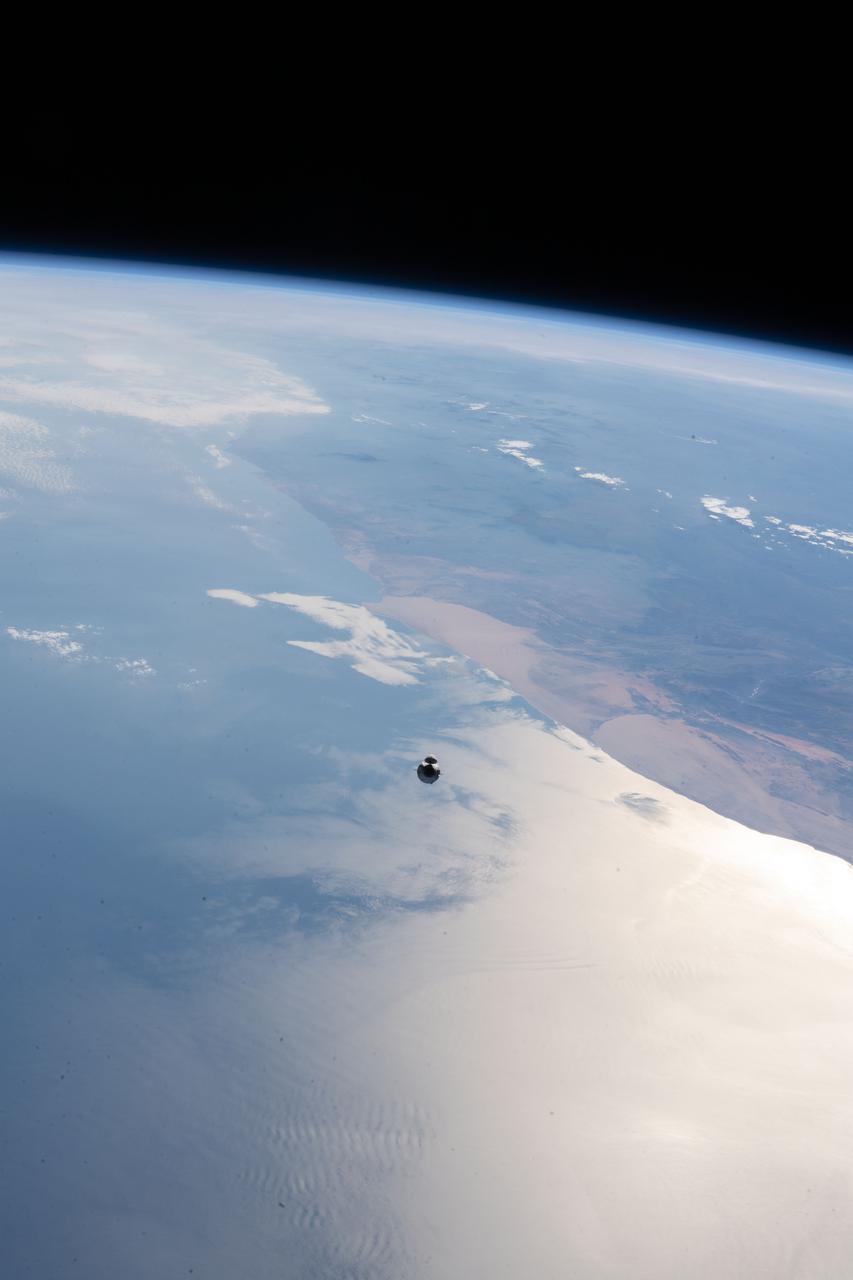

iss065e094357 (June 5, 2021) --- The SpaceX Cargo Dragon vehicle, on the SpaceX CRS-22 mission, approaches the International Space Station 265 miles above the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Namibia on the African continent.

iss050e020199 (12/29/2016) --- NASA astronaut Shane Kimbrough reconfiguring the Combustion Integrated Rack (CIR) High Bit Depth/Multispectral (HiBMS) imaging packages at Universal Mounting Location (UML) 7 and UML 8. The CIR is used to perform combustion experiments in microgravity and can be reconfigured easily on orbit to accommodate a variety of combustion experiments.
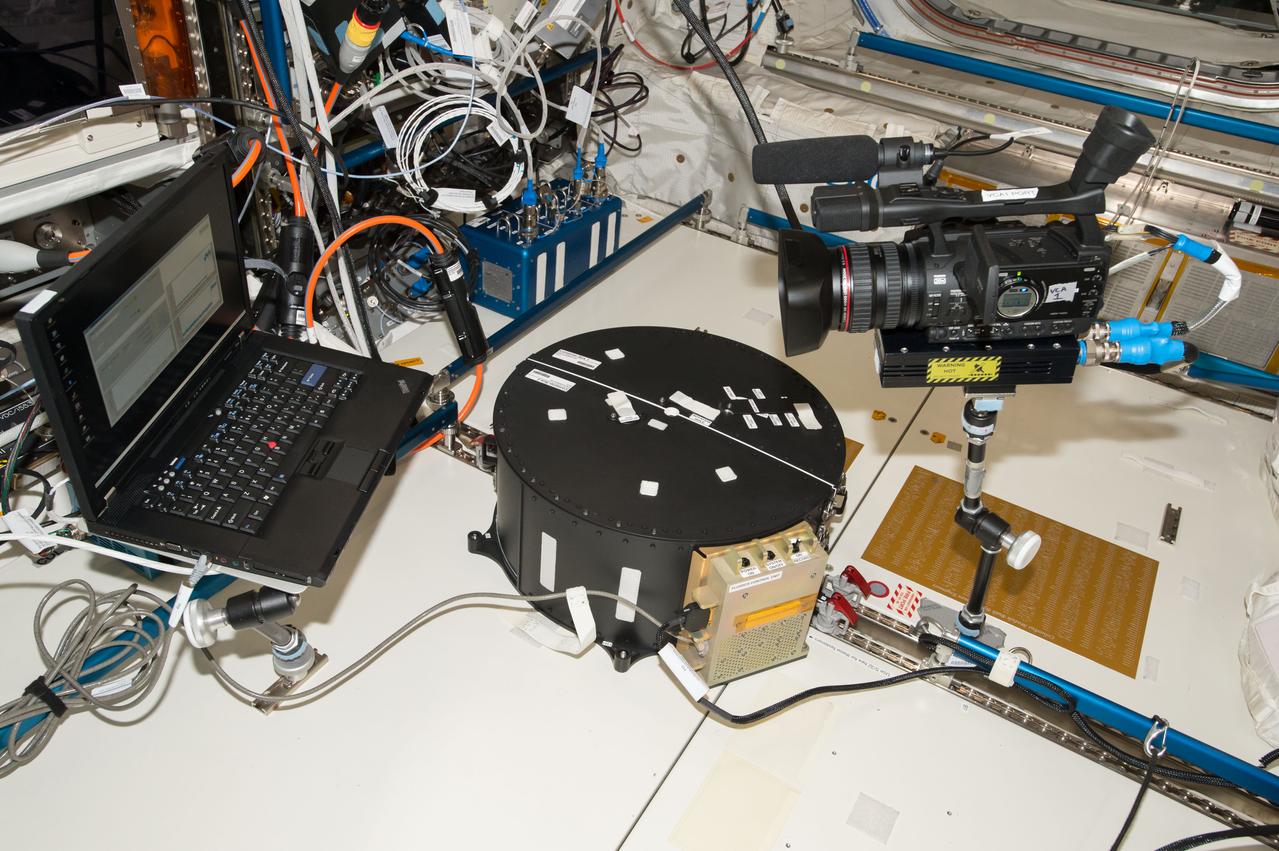
iss051e034000 (5/2/2017) --- A view taken to document hardware setup during the first run of the Fluid Dynamics in Space (FLUIDICS) experiment. The Container Box is attached to the Seat Track at COL1D1-D2, and a video camera records experiment data on the screen of a laptop computer. Image was taken in the Columbus European Laboratory. The FLUIDICS investigation evaluates the Center of Mass (CoM) position regarding a temperature gradient on a representation of a fuel tank. The observation of capillary wave turbulence on the surface of a fluid layer in a low-gravity environment can provide insights into measuring the existing volume in a sphere.
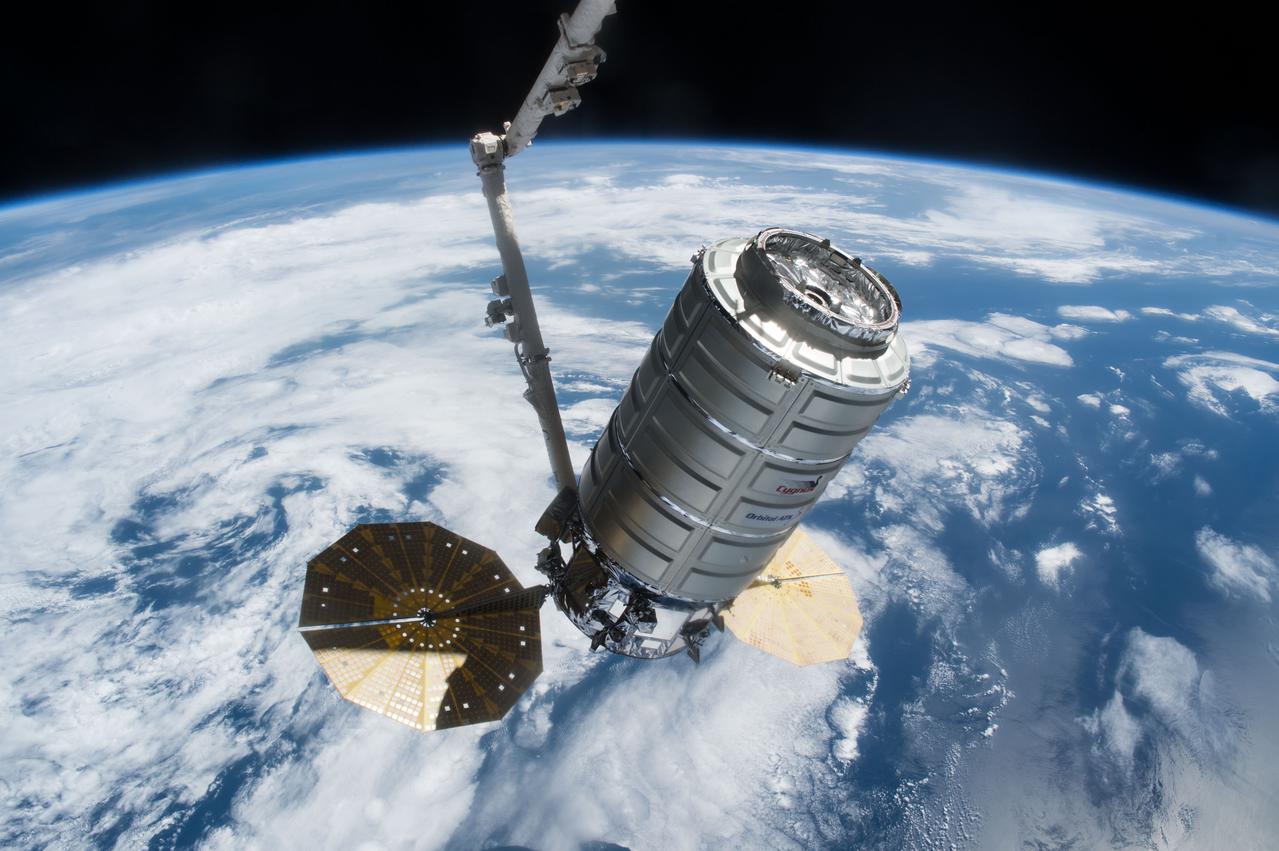

iss051e020824 (April 22, 2018) --- The Orbital ATK Cygnus resupply ship is pictured in the grips of the Canadarm2 robotic arm shortly after its capture in April of 2017 during Expedition 51.
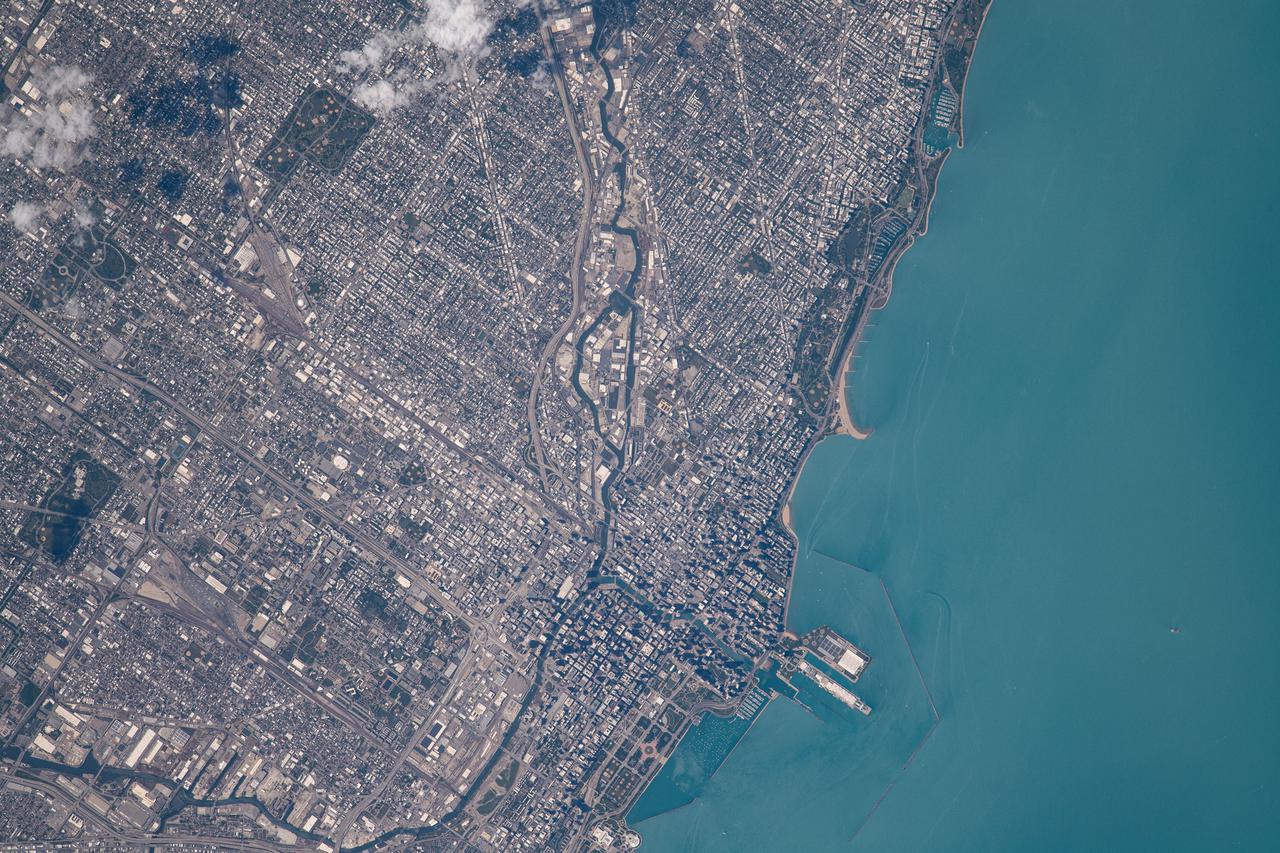

iss065e086284 (June 3, 2021) --- Chicago, Illinois, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 262 miles above Lake Michigan.
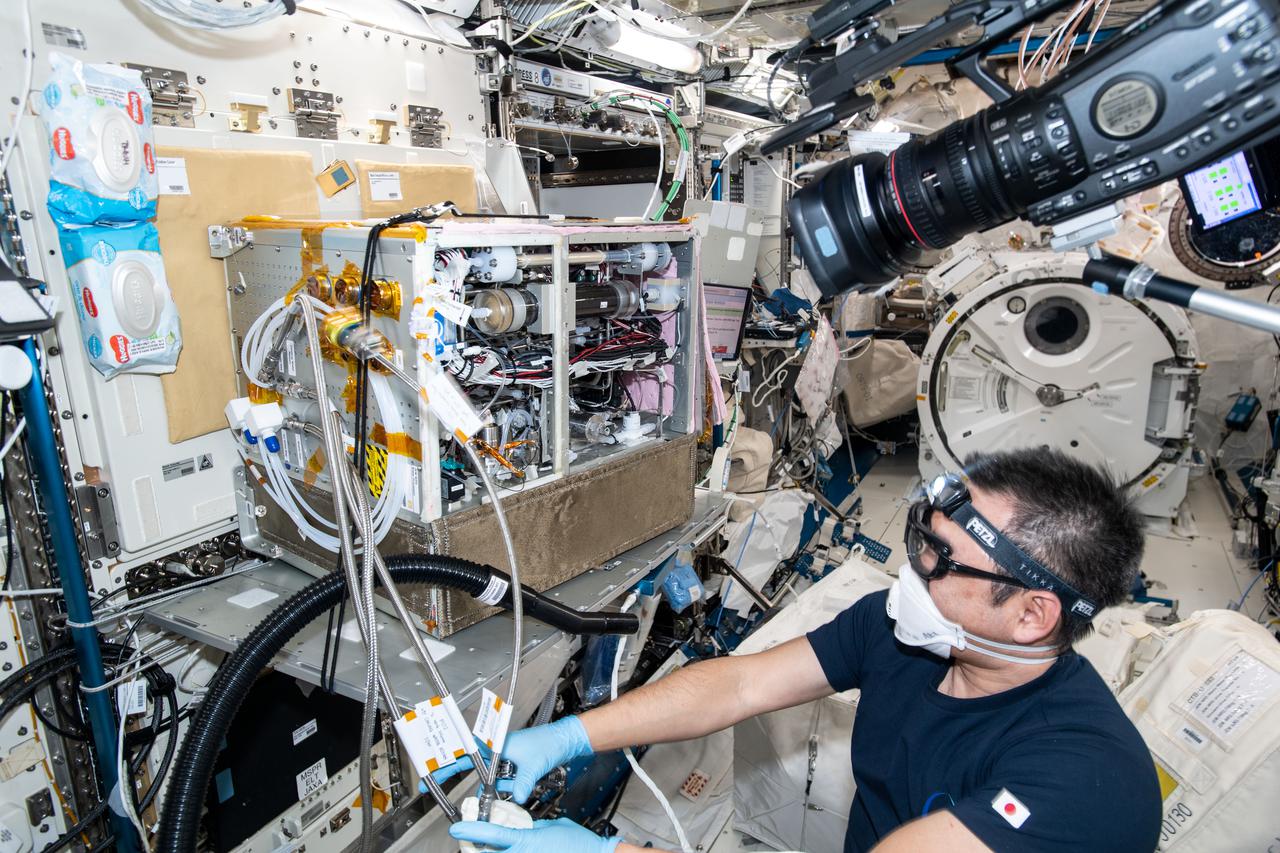

iss065e333427 (8/30/2021) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Akihiko Hoshide is photographed during the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Water Recovery System (JWRS) Gas Trap and Bypass Line Installation. Future water recovery systems will require high recovery rates, a more compact size, and less power consumption than conventional systems. The JWRS demonstrates new technologies on orbit, aboard the International Space Station (ISS), to meet these requirements.
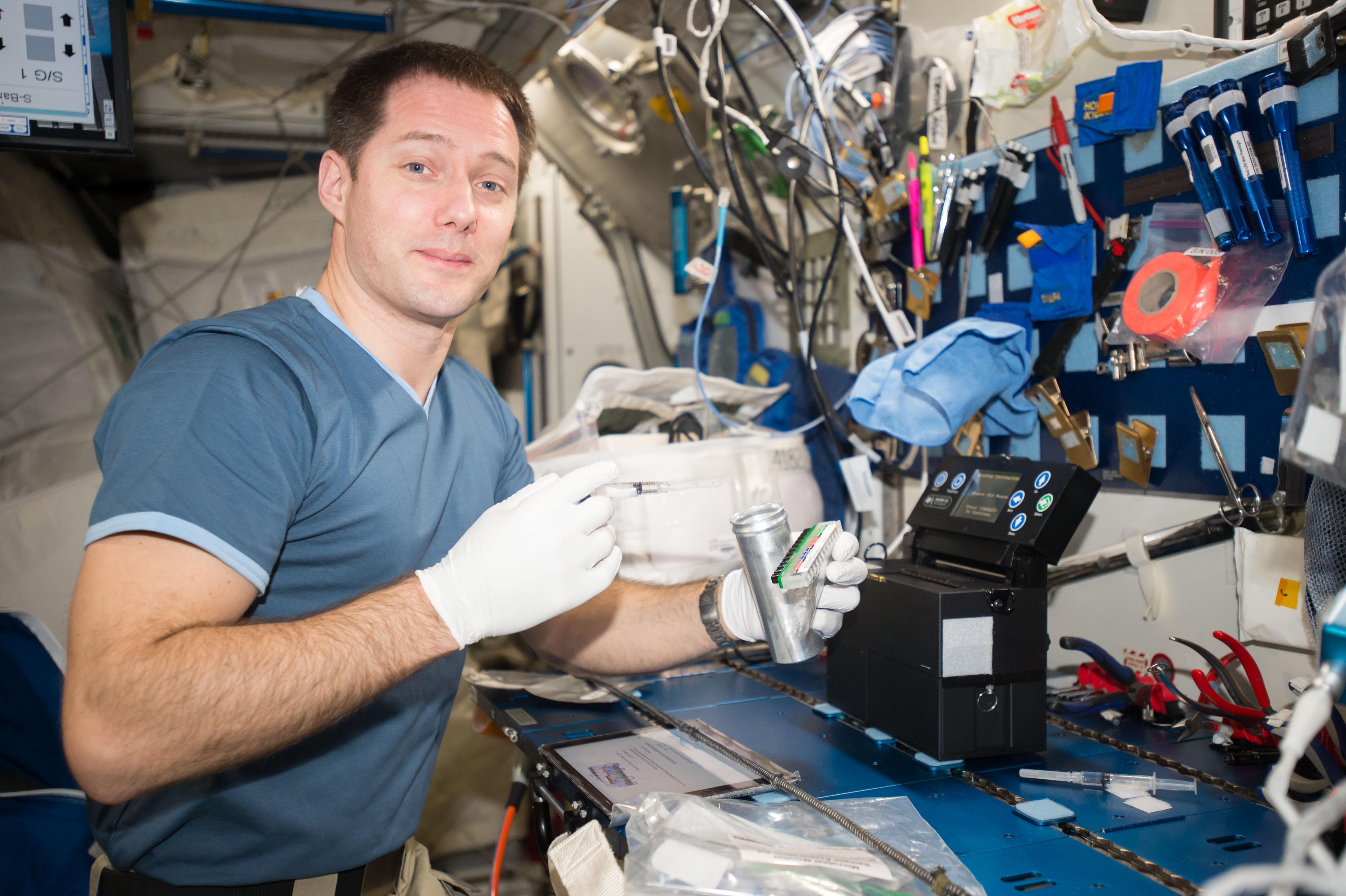

iss050e057206 (3/14/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) Thomas Pesquet used the Microbial Monitoring System (MMS) portion of the Water Monitoring Suite (WMS) experiment to perform the Aquapad demonstration and sampling. The Water Monitoring Suite is a set of hardware that monitors microbes, silica and organic material in the water supply on the International Space Station. The hardware ensures crew members can test and monitor the safety of their water supplies on future space missions, especially on long-duration missions to Mars, asteroids or other destinations where Earth-based testing would be difficult or impossible.

iss065e023015 (May 6, 2021) --- Guantanamo Bay in Cuba is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above the Caribbean Sea.
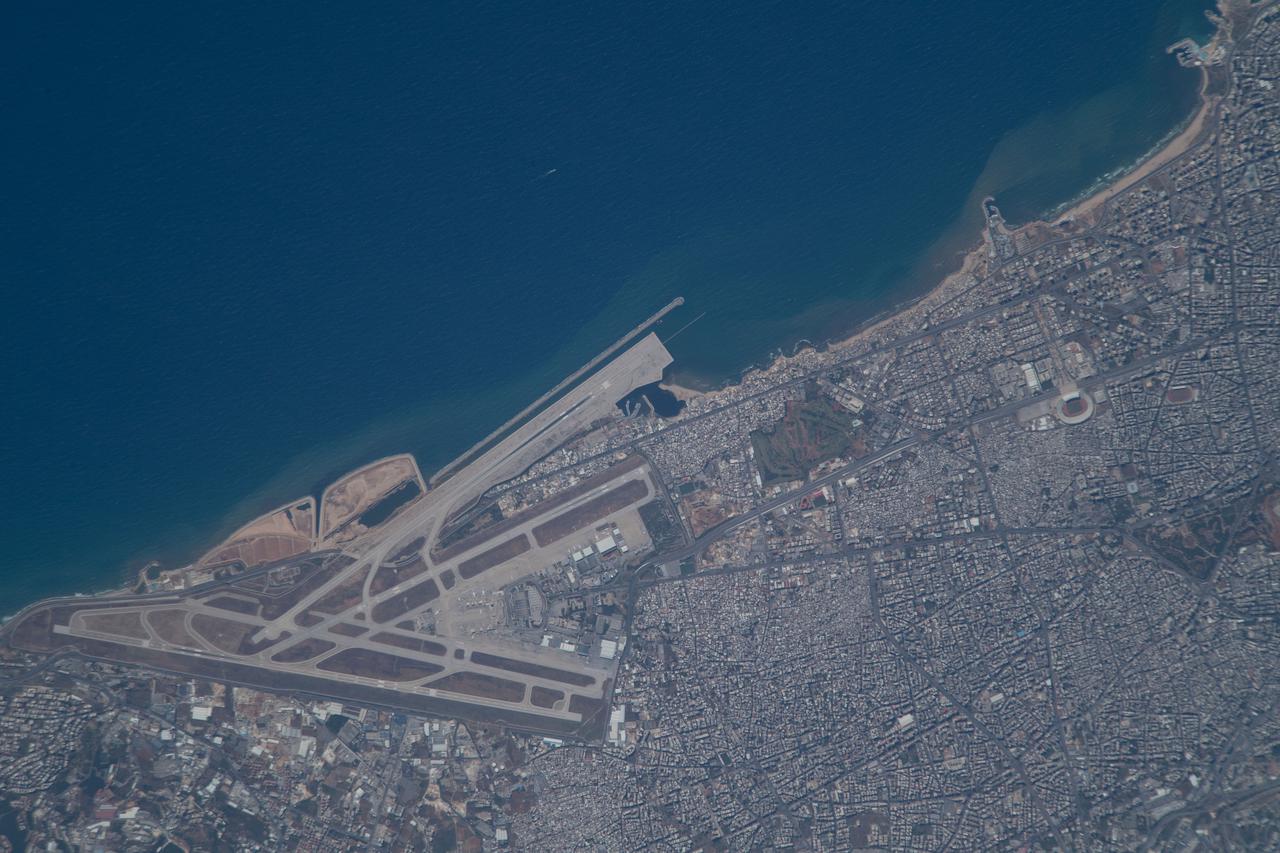

iss065e078580 (May 29, 2021) --- Lebanon's Beirut-Rafic Hariri International Airport on the Mediterranean coast is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above the Middle Eastern nation.
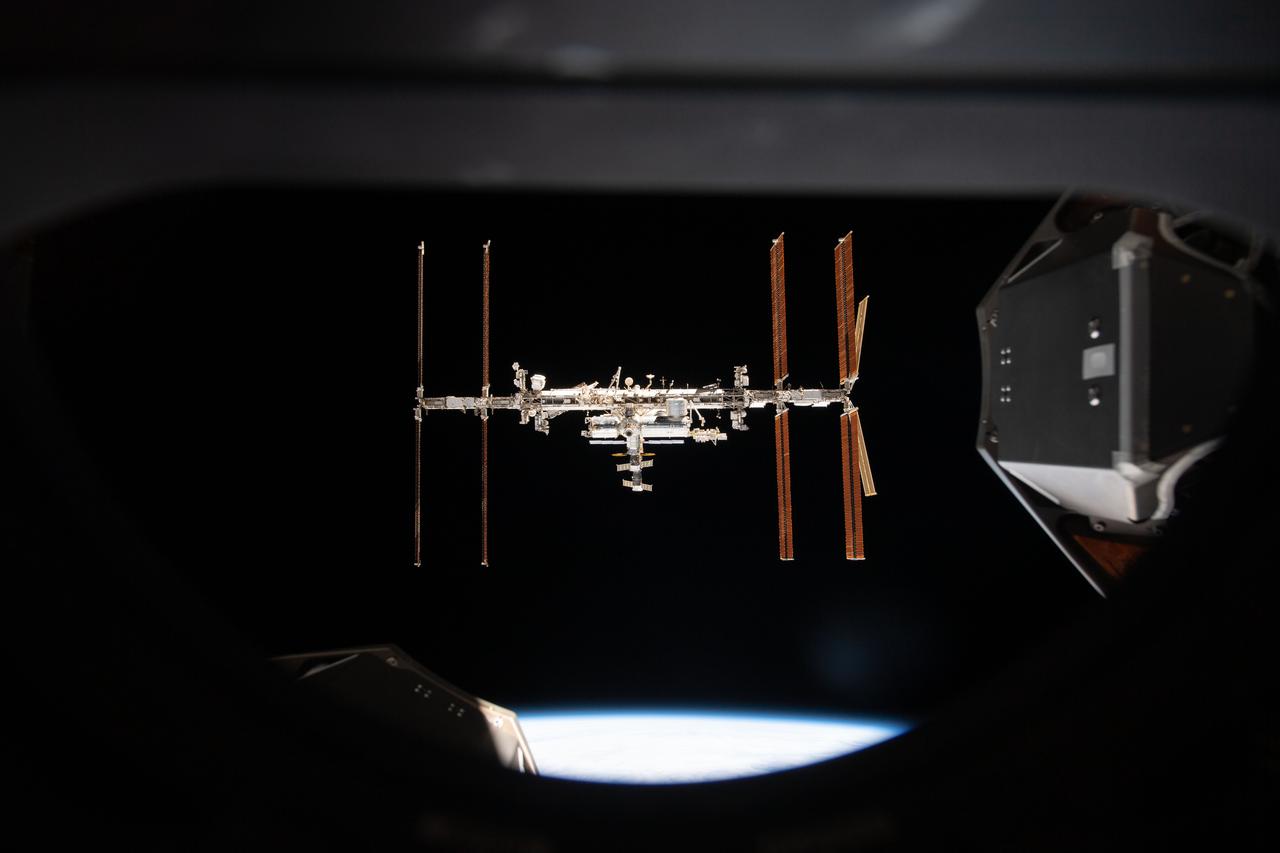
iss066e080907 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station is pictured from inside a window aboard the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021.
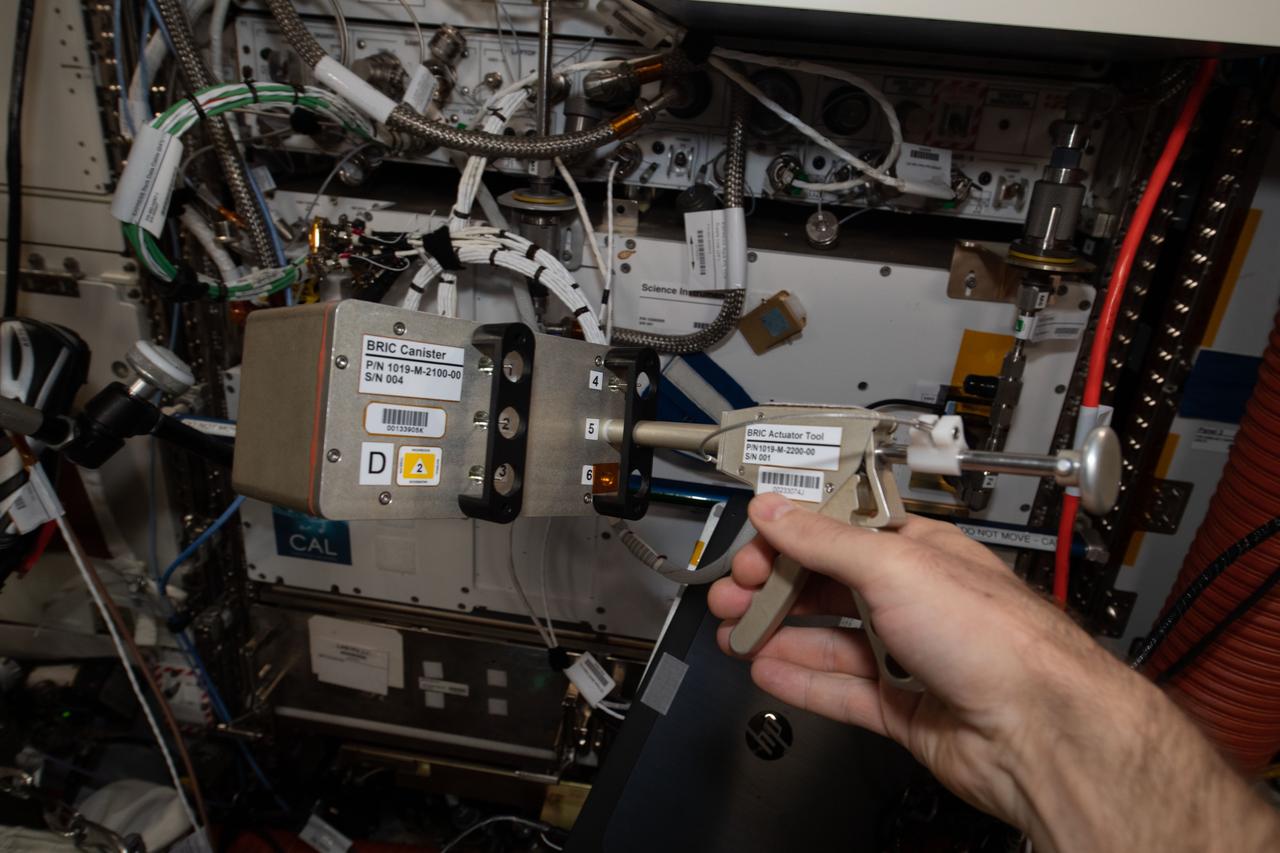

iss065e094066 (6/9/2021) --- A close-up view of the a BRIC-24 Canister and actuator tool. Biological Research In Canisters-24 (BRIC-24) tests how space affects organelle contacts and vacuole fusion in plants, systems that may be important for plant gravity sensing and response. Vacuoles are organelles in plant cells that have important functions.
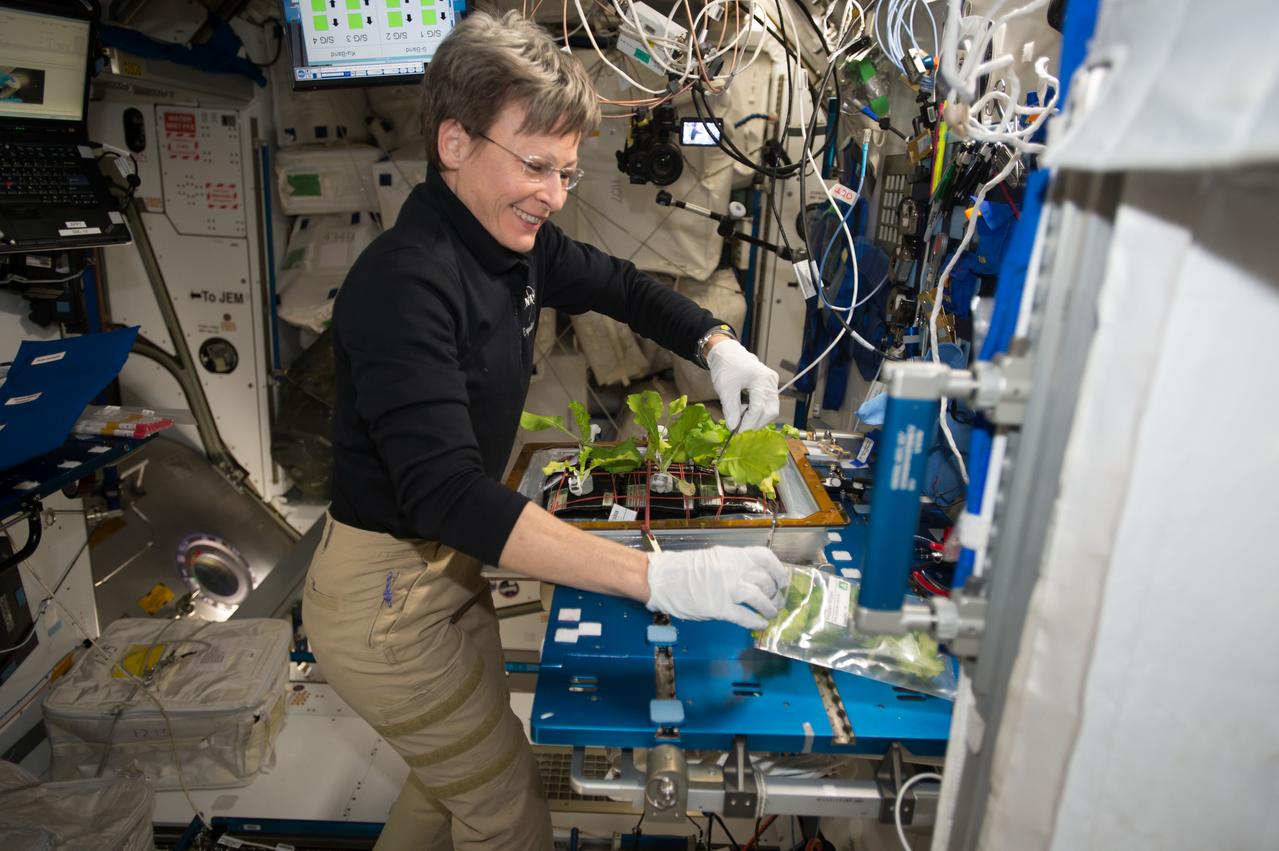

iss050e050335 (2/17/2017) --- NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson during harvesting and cleaning of VEG-03, in the Node 2. Organisms grow differently in space, from single-celled bacteria to plants and humans. But future long-duration space missions will require crew members to grow their own food, so understanding how plants respond to microgravity is an important step toward that goal. Veg-03 uses the Veggie plant growth facility to cultivate a type of cabbage, which is harvested in orbit with samples returned to Earth for testing.
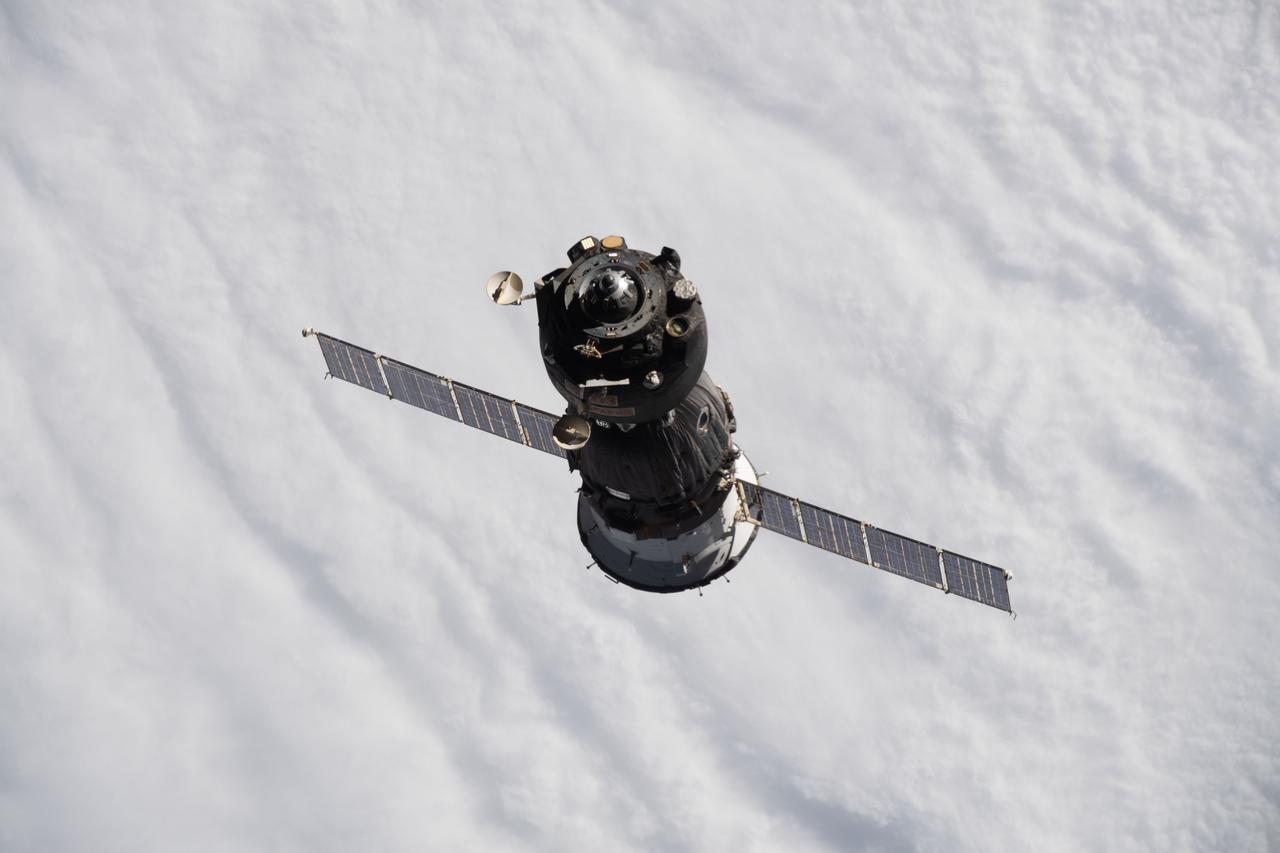

iss066e001124 (Oct. 17, 2021) --- The Soyuz MS-18 crew ship, carrying Soyuz Commander Oleg Novitskiy and spaceflight participants Yulia Peresild and Klim Shipenko, is pictured departing the vicinity of the International Space Station as both spacecraft were orbiting 263 miles above the Sea of Okhotsk.
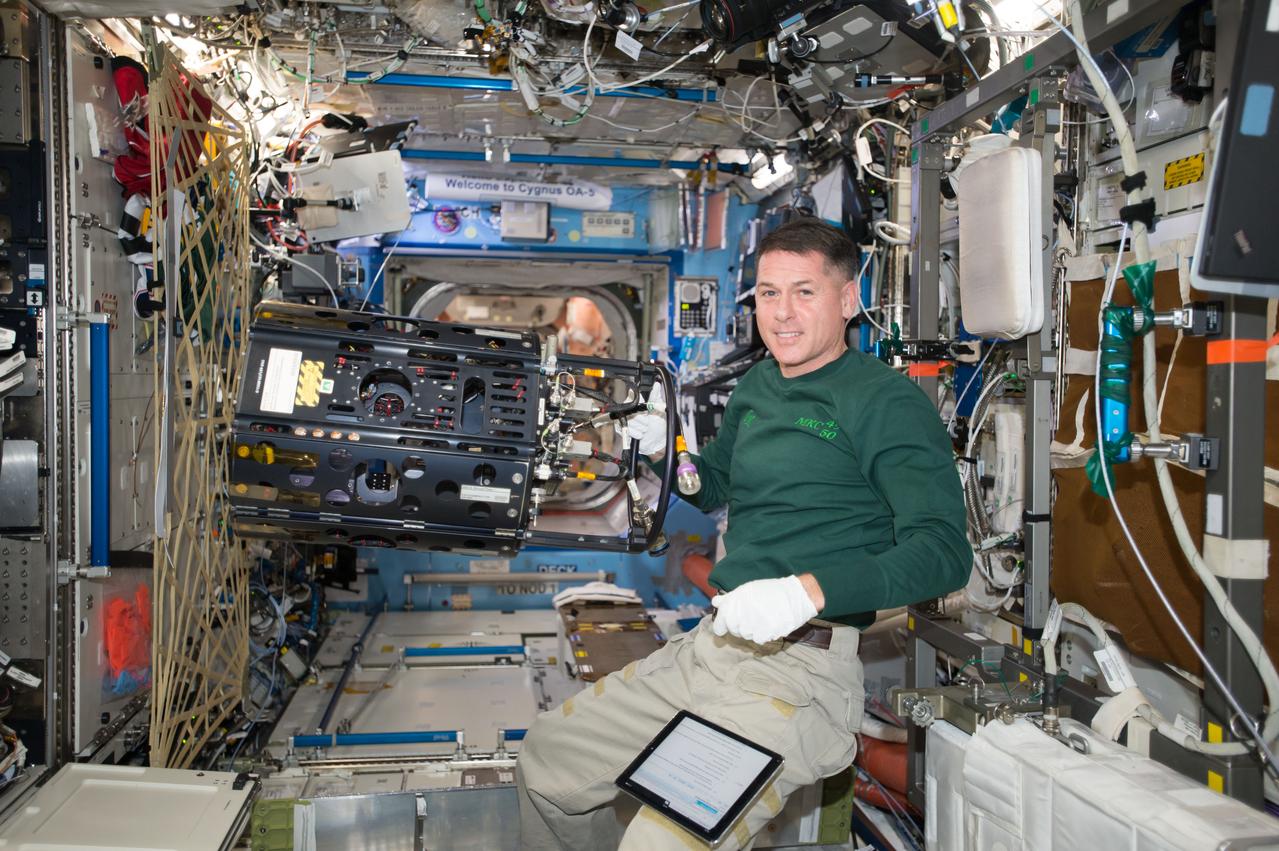

iss050e034393 (1/18/2017) --- NASA astronaut Shane Kimbrough during Combustion Integration Rack (CIR) Multi-user Droplet Combustion Apparatus (MDCA) Troubleshooting in the U.S. Laboratory. MDCA was removed from the CIR Combustion Chamber and spring fastener was repaired. The CIR is used to perform combustion experiments in microgravity. The CIR can be reconfigured easily on orbit to accommodate a variety of combustion experiments.
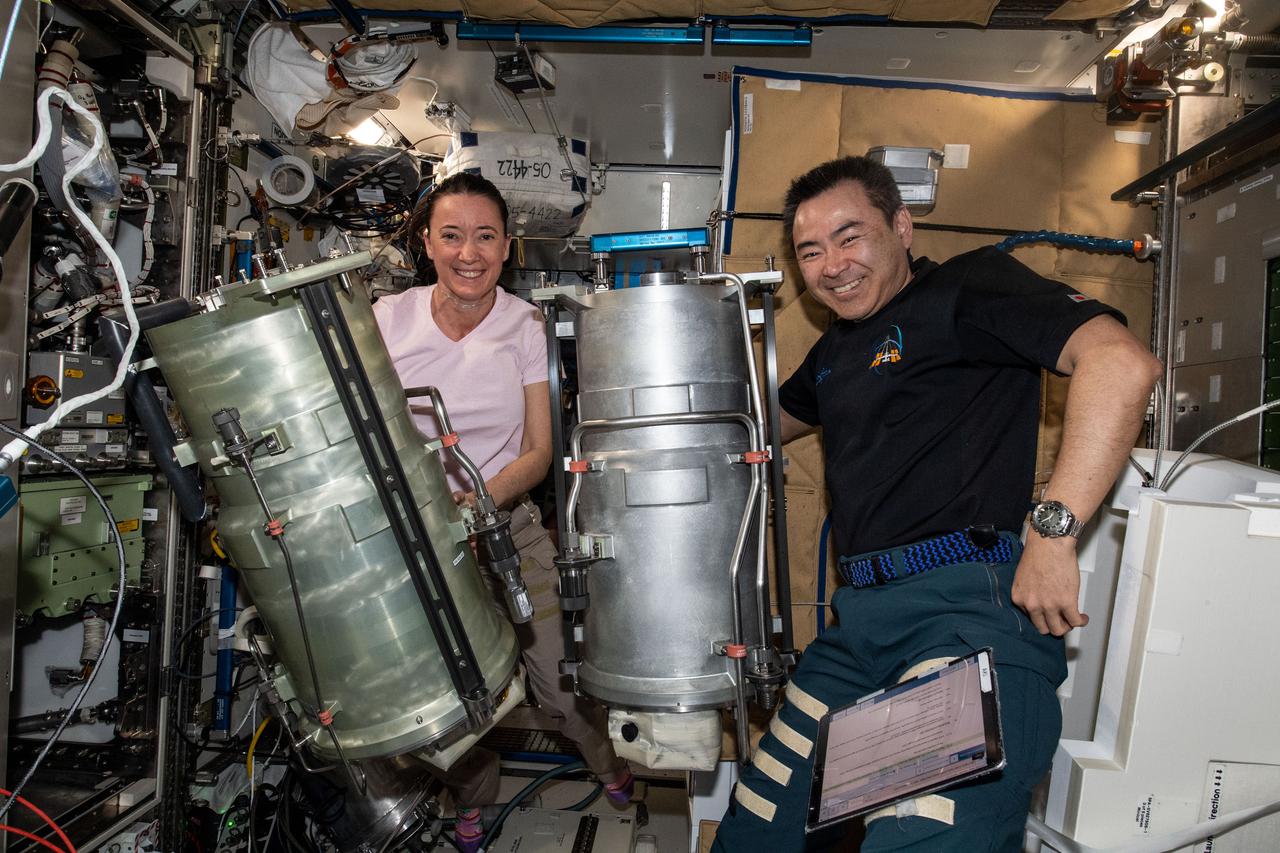

iss066e003308 (Oct. 20, 2021) --- Expedition 66 Flight Engineers Megan McArthur of NASA and Akihiko Hoshide of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) replace components and flush contaminants inside the Tranquility module's U.S. oxygen generation system.
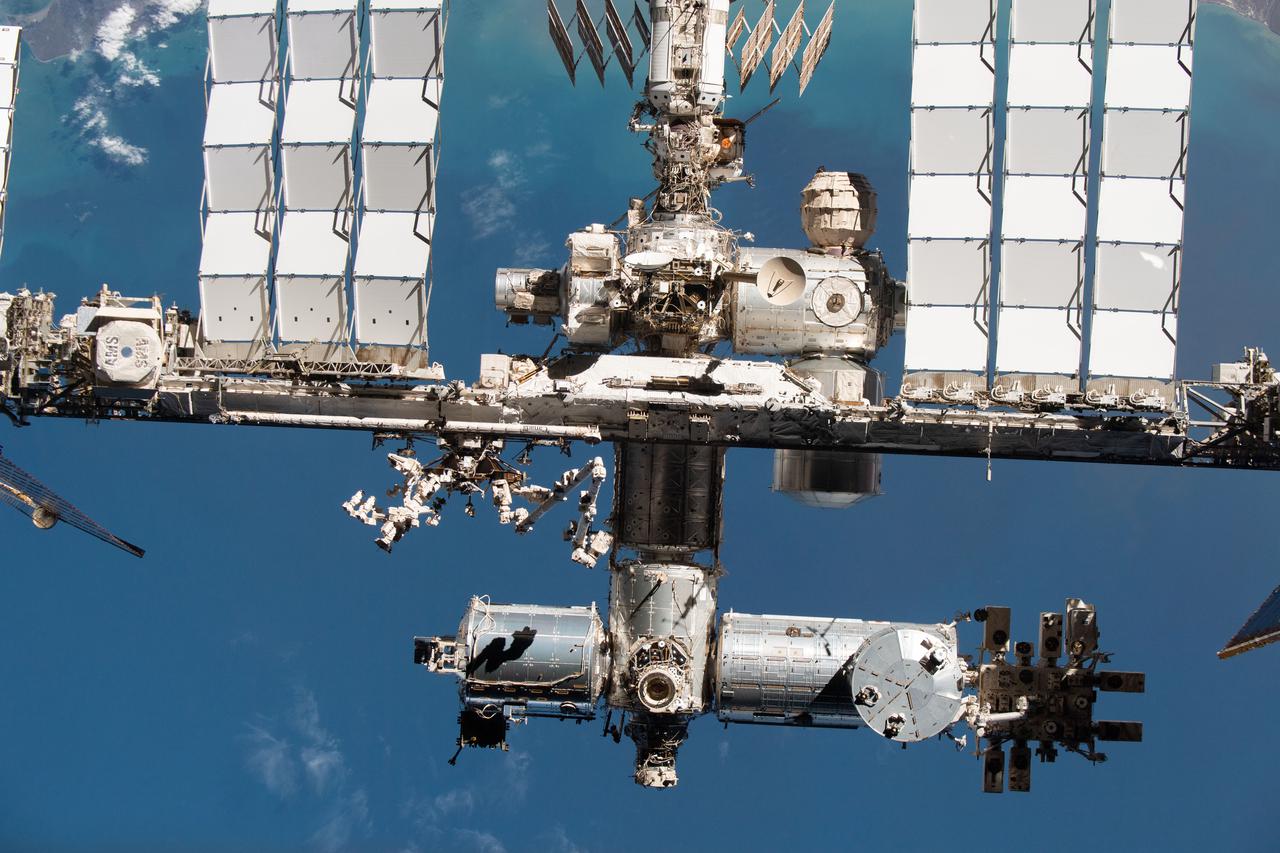

iss066e079170 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station's U.S. segment and portions of the Russian segment are pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021. In addition to the modules where astronauts live and work, several external structures are visible including large white radiators extending from its integrated truss structure and the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS-02) seen on the far left.
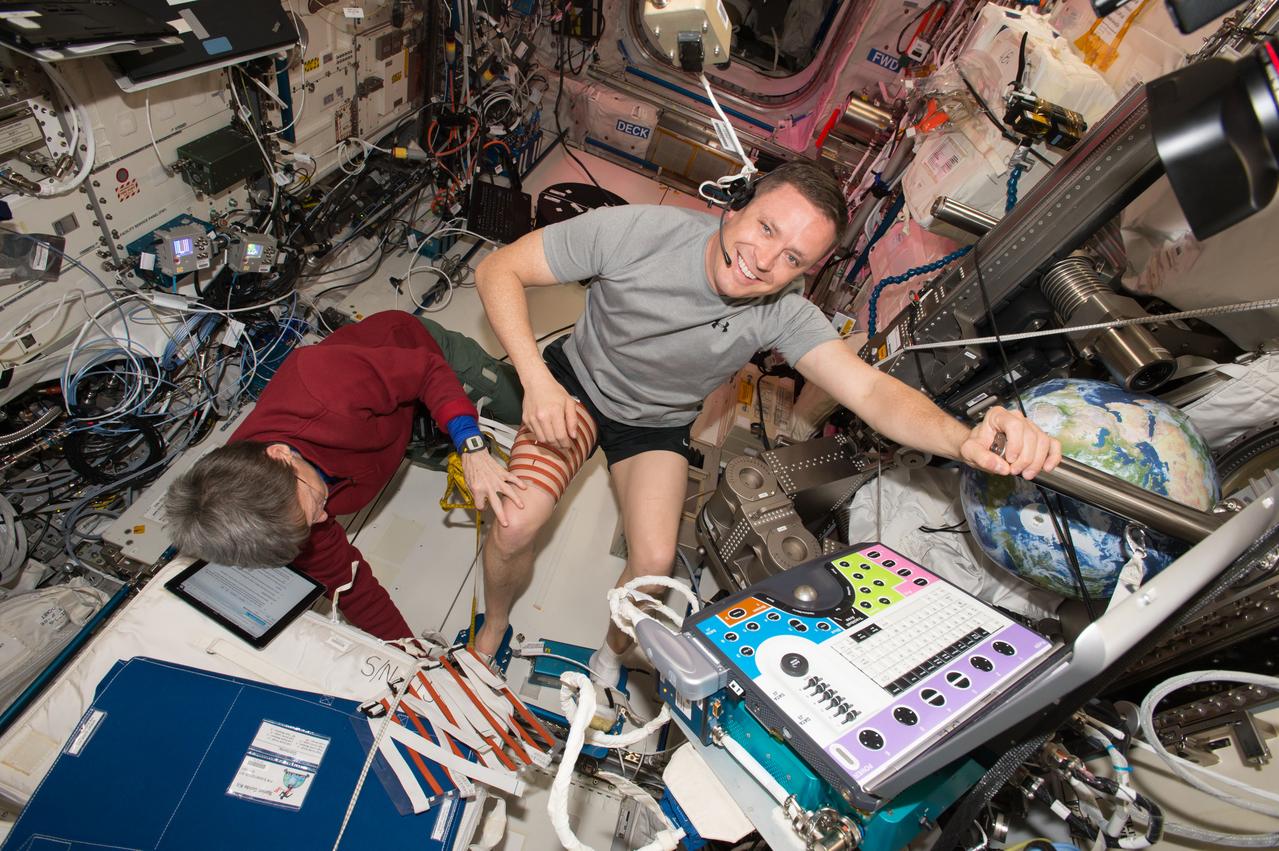

iss051e037012 (May 3, 2017) --- Flight engineer Jack Fischer dons Thigh and Calf Guides in preparation for Ultrasound 2 operations for the Integrated Resistance and Aerobic Training Study (Sprint) experiment. He is assisted by Commander Peggy Whitson. Image was taken in the Columbus European Laboratory.
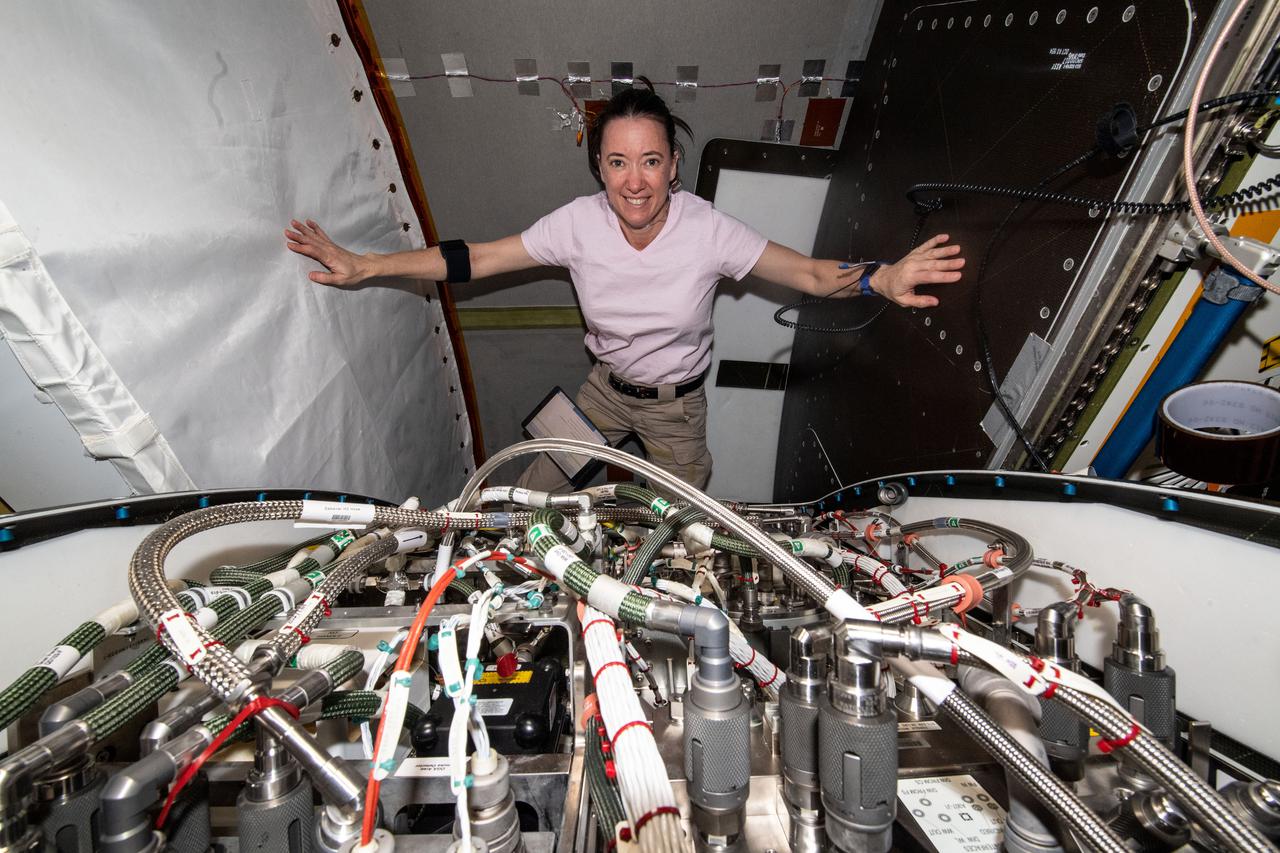

iss066e003338 (Oct. 20, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur replaces components and flushes contaminants inside the Tranquility module's U.S. oxygen generation system.
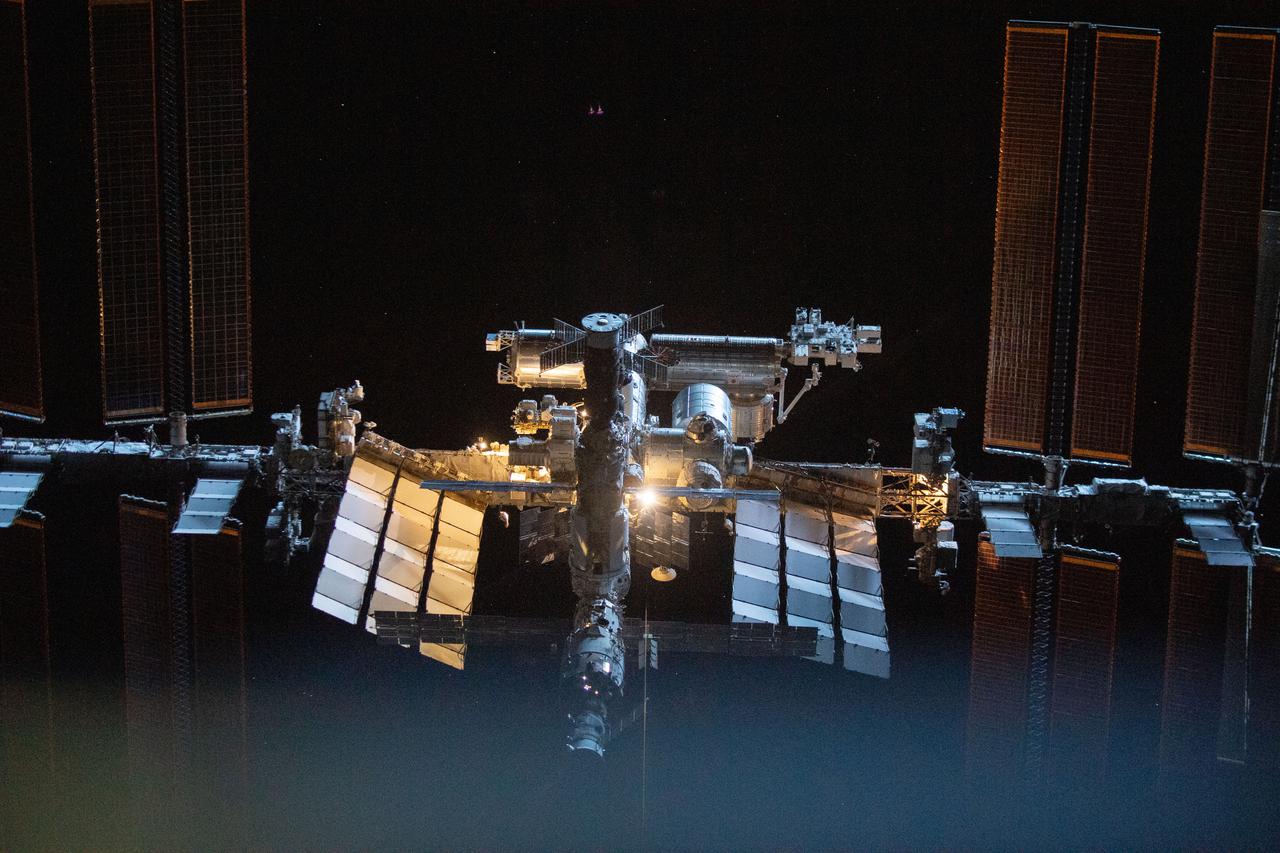

iss066e080166 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021.
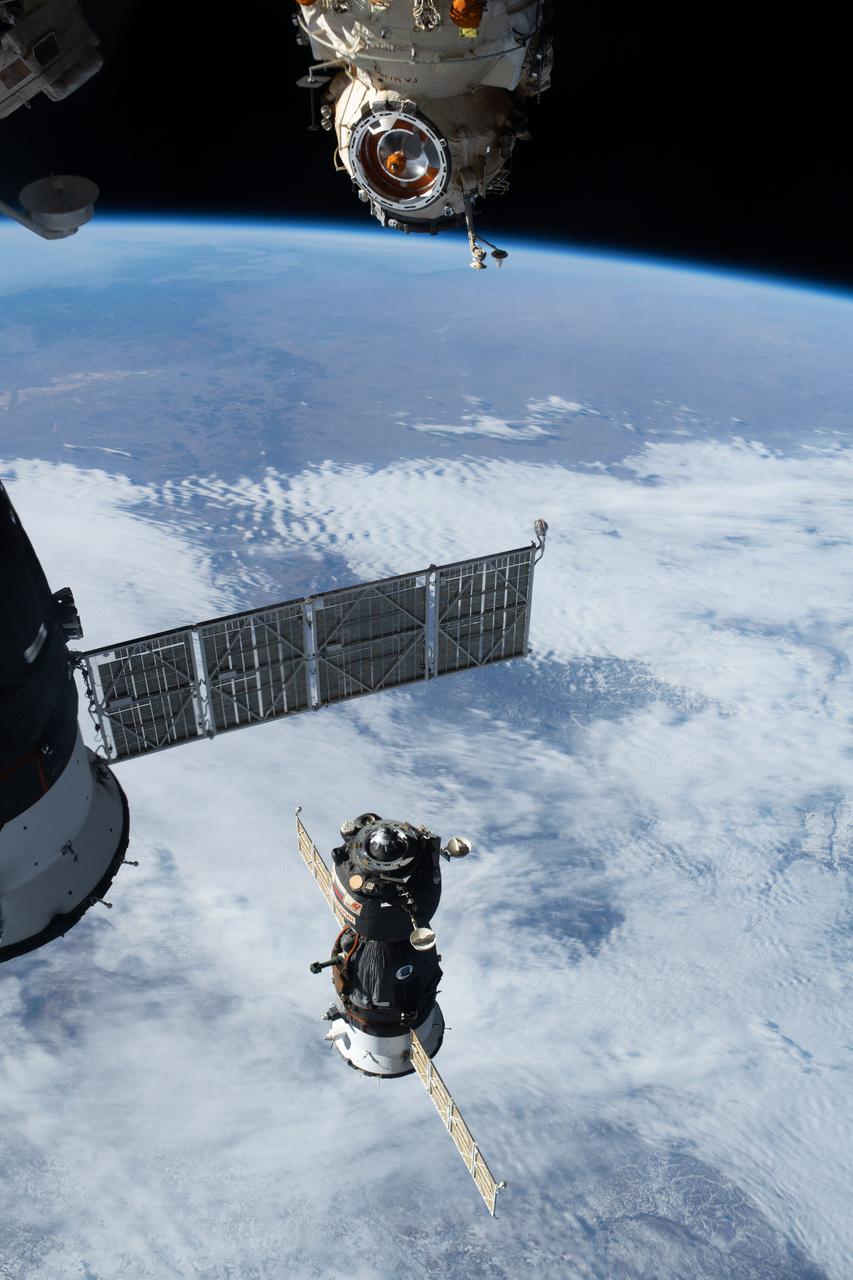

iss066e000920 (Oct. 17, 2021) --- The Soyuz MS-18 crew ship undocks from the Nauka multipurpose laboratory module and departs the International Space Station as both spacecraft were orbiting 263 miles above the eastern China-Russia border.
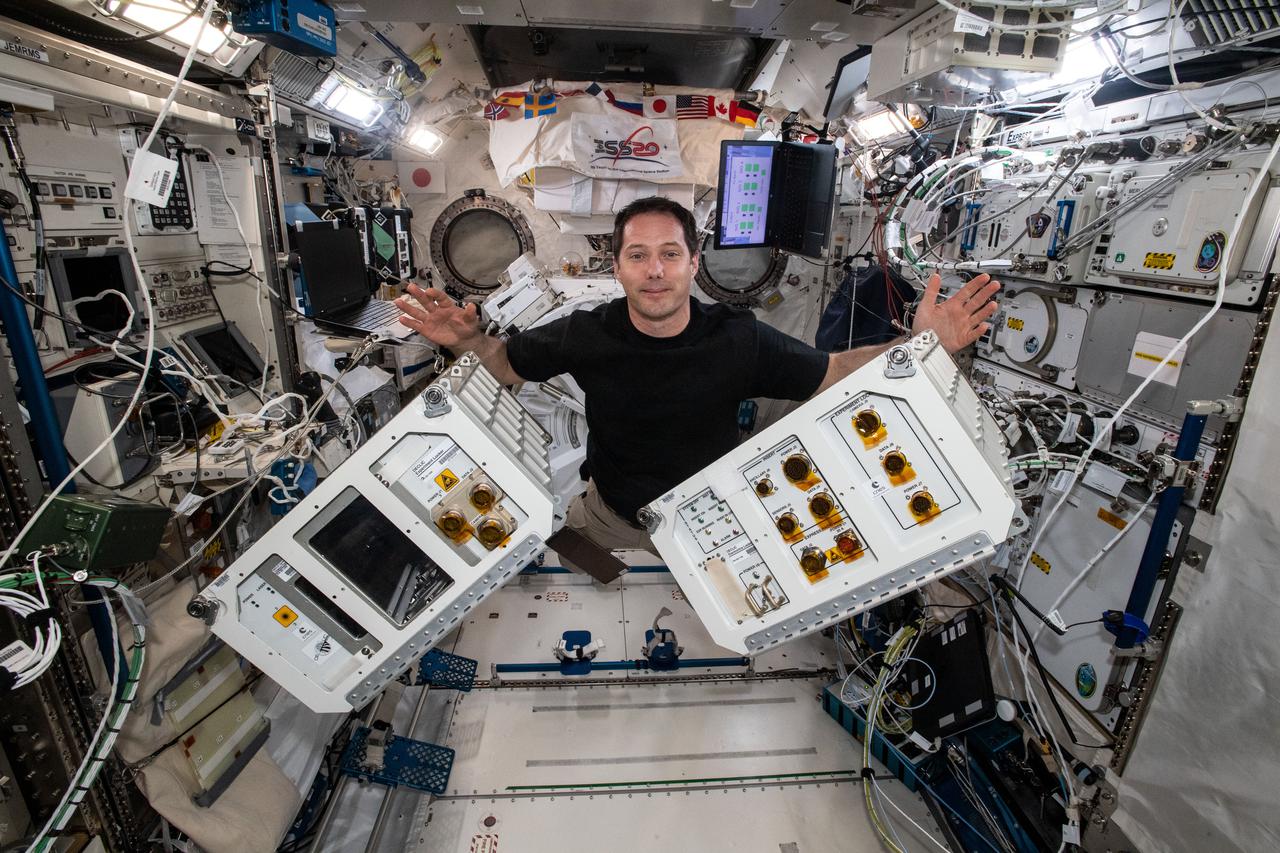

iss065e442803 (10/7/2021) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet gathers fluid physics and materials research hardware inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. Device for the Study of Critical Liquids and Crystallization (DECLIC) is a multi-user facility developed by the agency Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (French Space Agency, CNES) and flown in collaboration with NASA. It is designed to support experiments in the fields of fluid physics and materials science. Special inserts allow researchers to study both ambient temperature critical point fluids and high temperature super-critical fluids. Another class of insert studies the dynamics and morphology of the fronts that form as a liquid material solidifies.
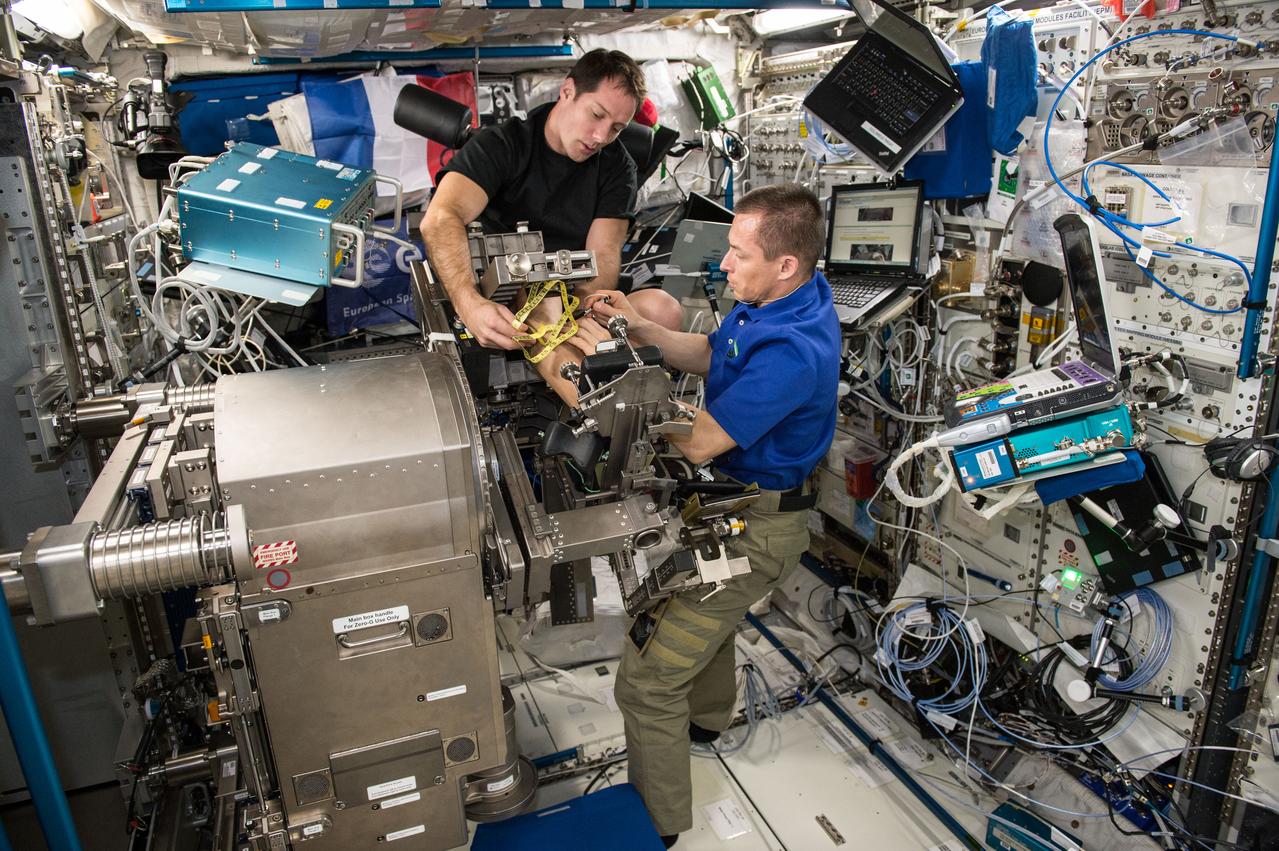

iss050e012389 (11/29/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) Thomas Pesquet and Cosmonaut Sergei Ryzhikov during the setup phase of the Sarcolab-3 Experiment in the Columbus Module. Myotendinous and Neuromuscular Adaptation to Long-term Spaceflight (Sarcolab) investigates the adaptation and deterioration of the soleus, or calf muscle, where it joins the Achilles tendon, which links it to the heel and carries loads from the entire body. Muscle fiber samples are taken from crew members before and after flight, and analyzed for changes in structural and chemical properties.
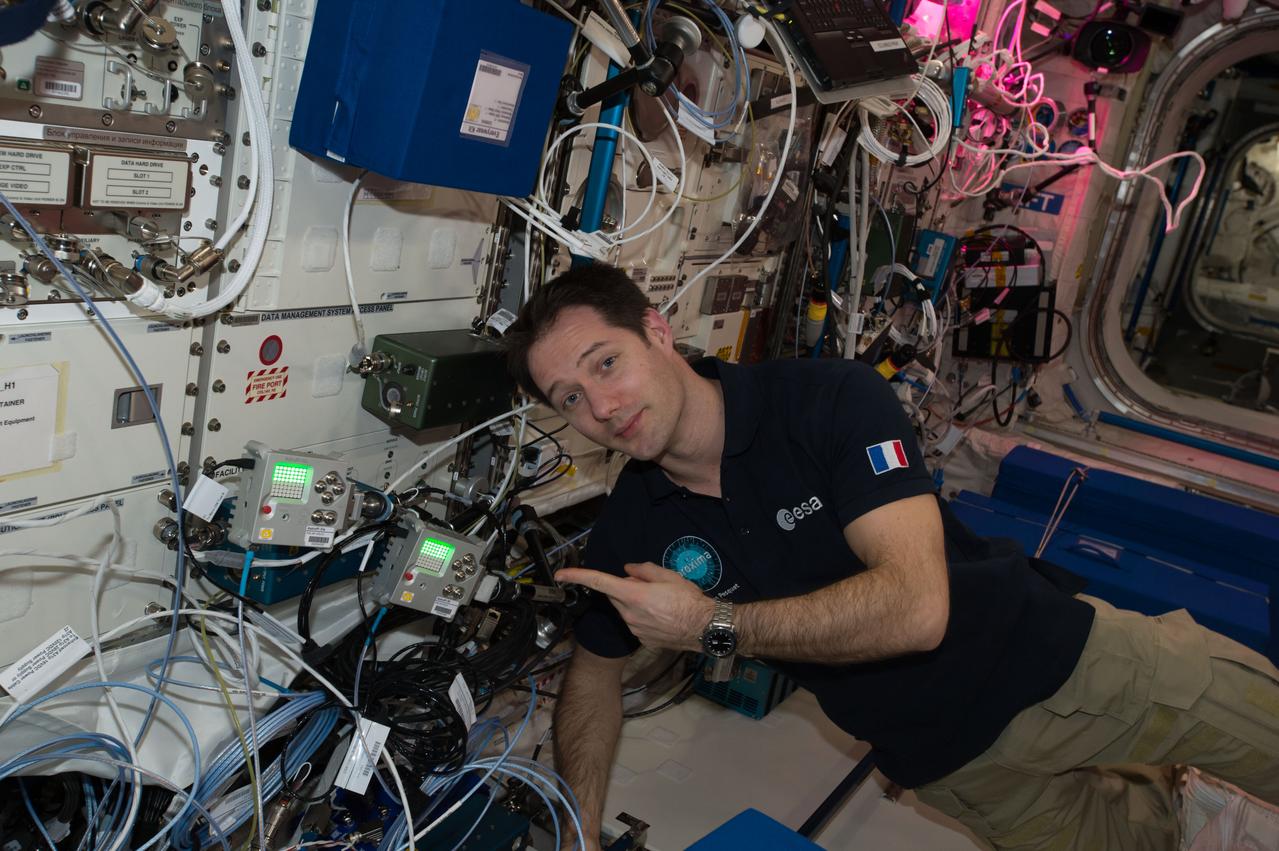

iss051e029182 (4/27/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet poses for a photo next to AstroPi Raspberry Pi computers equipped with Visual and Infrared Cameras. Image was taken in the Columbus European Laboratory. The activities related to this project are intended to encourage and strengthen the teaching of computing and coding curriculums, and through this stimulate the curiosity of students and motivate them towards further study of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) subjects.
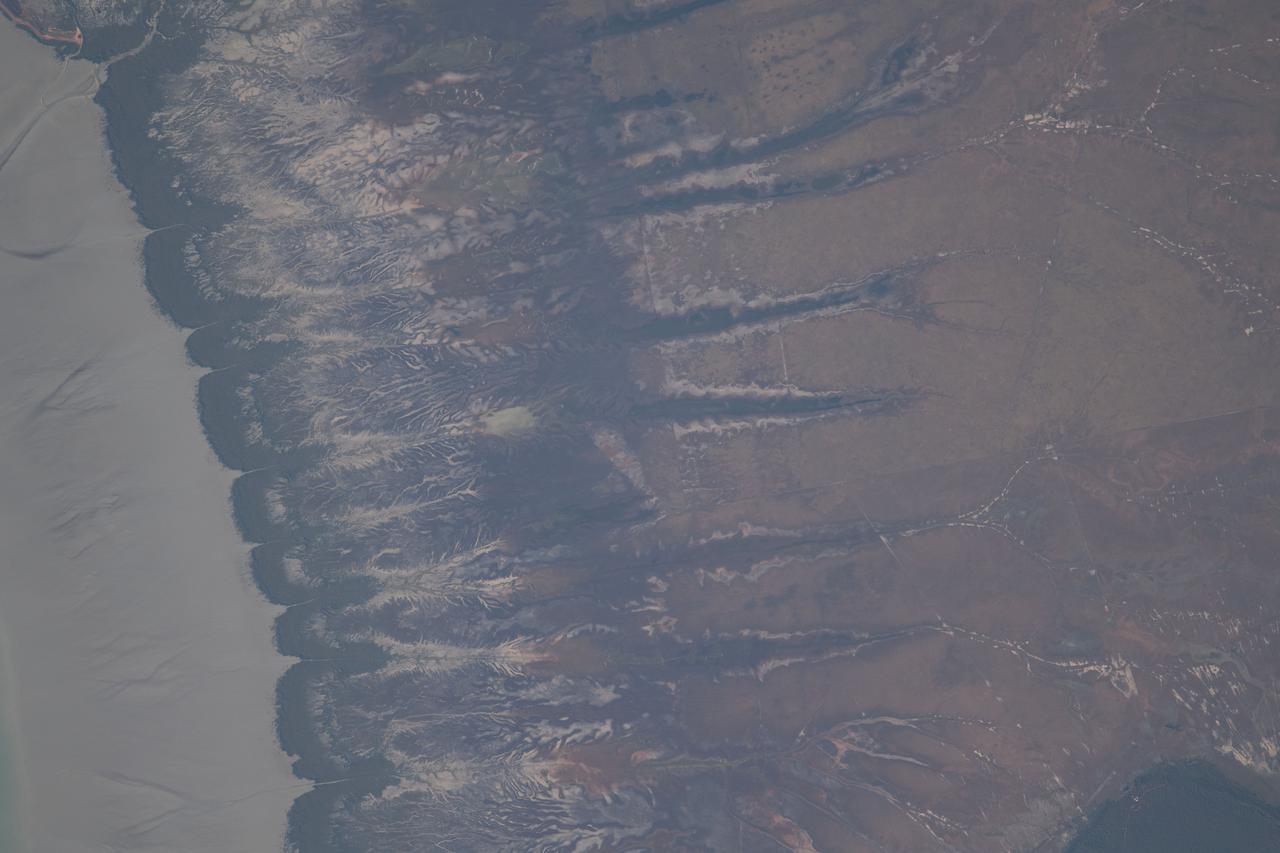

iss065e046509 (May 14, 2021) --- A portion of Western Australia off the coast of the Indian Ocean is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 265 miles above.
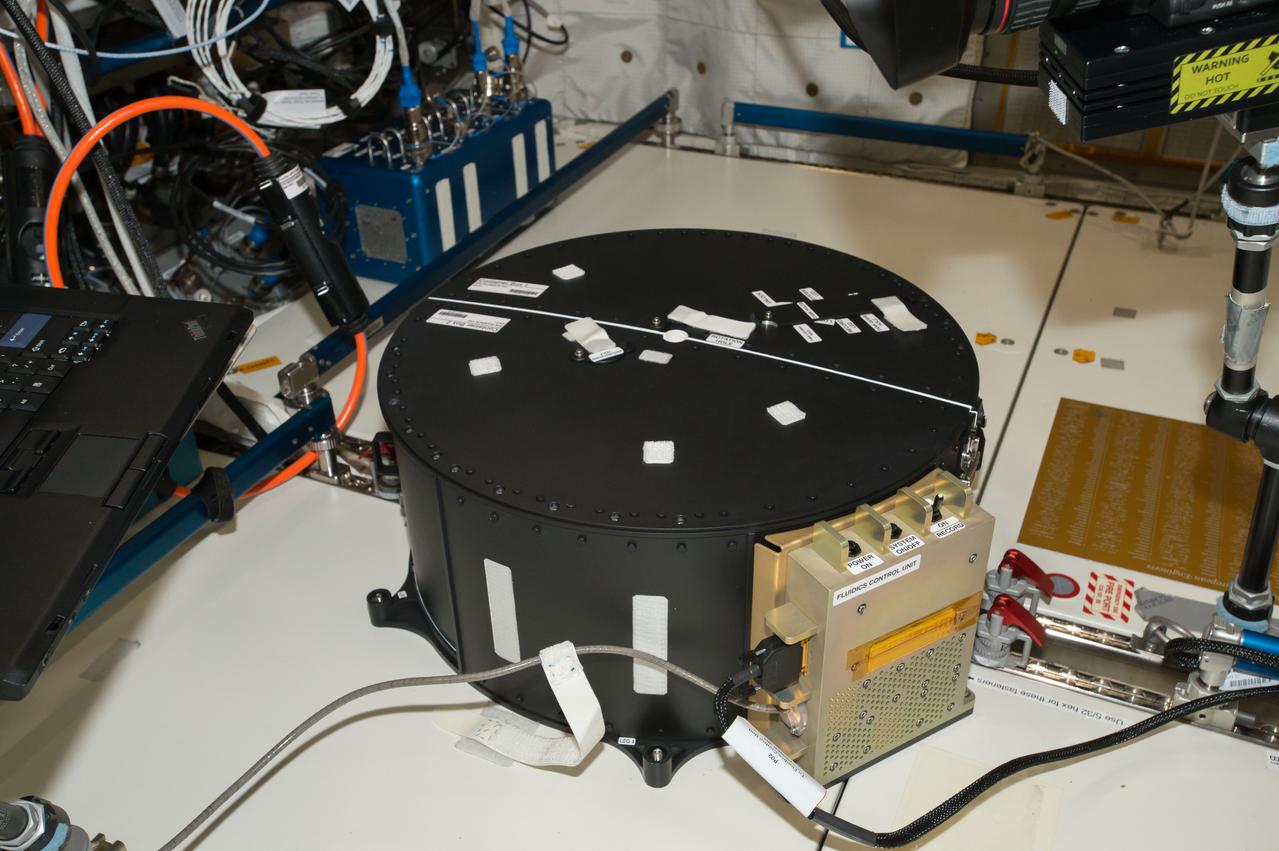

iss051e034001 (5/2/2017) --- Documentation of the Container Box attached to the COL1D1-D2 Seat Track during the first run of the Fluid Dynamics in Space (FLUIDICS) experiment. Image was taken in the Columbus European Laboratory. The FLUIDICS investigation evaluates the Center of Mass (CoM) position regarding a temperature gradient on a representation of a fuel tank. The observation of capillary wave turbulence on the surface of a fluid layer in a low-gravity environment can provide insights into measuring the existing volume in a sphere.
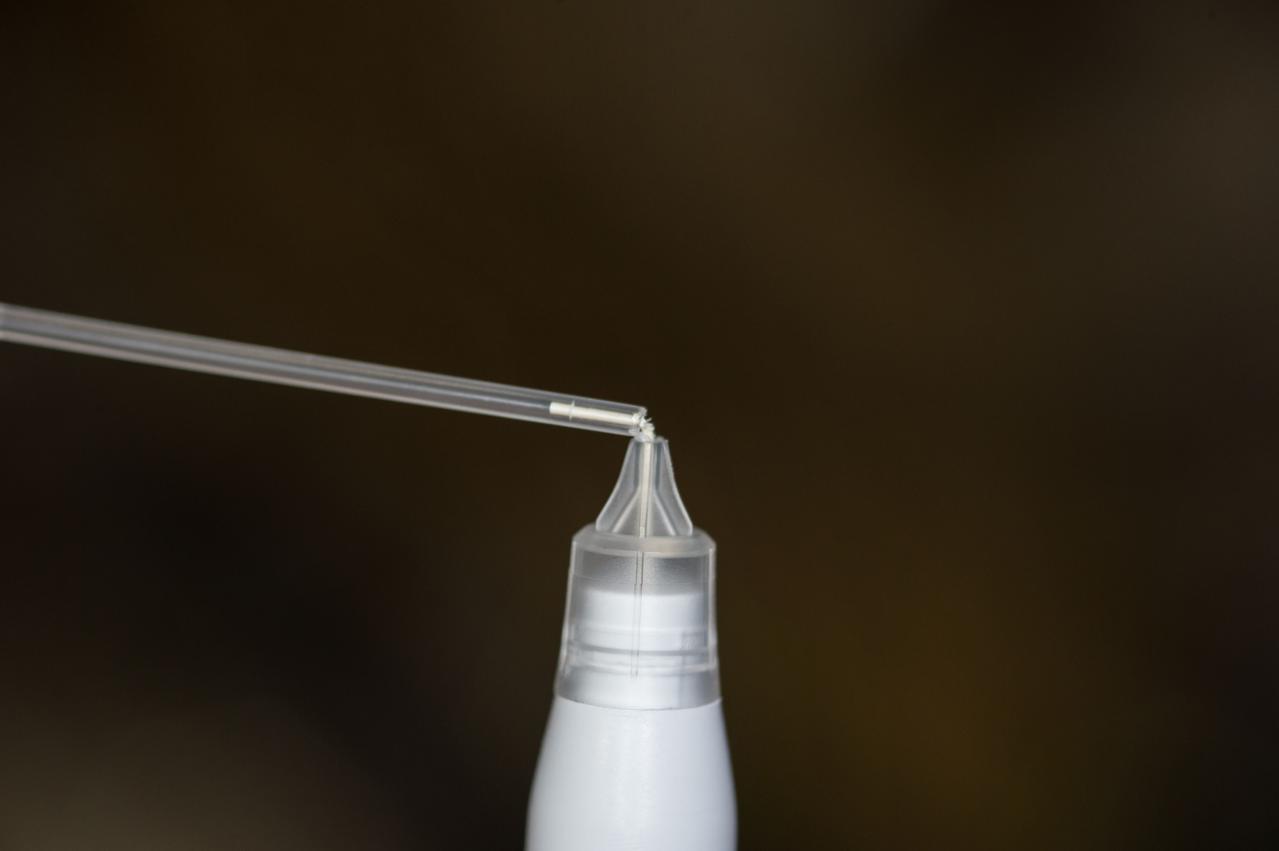
iss051e041912 (5/13/2017) --- Photo documentation of a broken pipette that was to be used to dispense water droplets into the Electrowetting Drawer of ExPRESS (Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station) Rack 8 for the Passive Thermal Flight Experiment. The Advanced Passive Thermal eXperiment (APTx) tests three advanced thermal management technologies. It demonstrates the in-space performance of each, an important step toward improving these technologies for use on future space exploration missions.
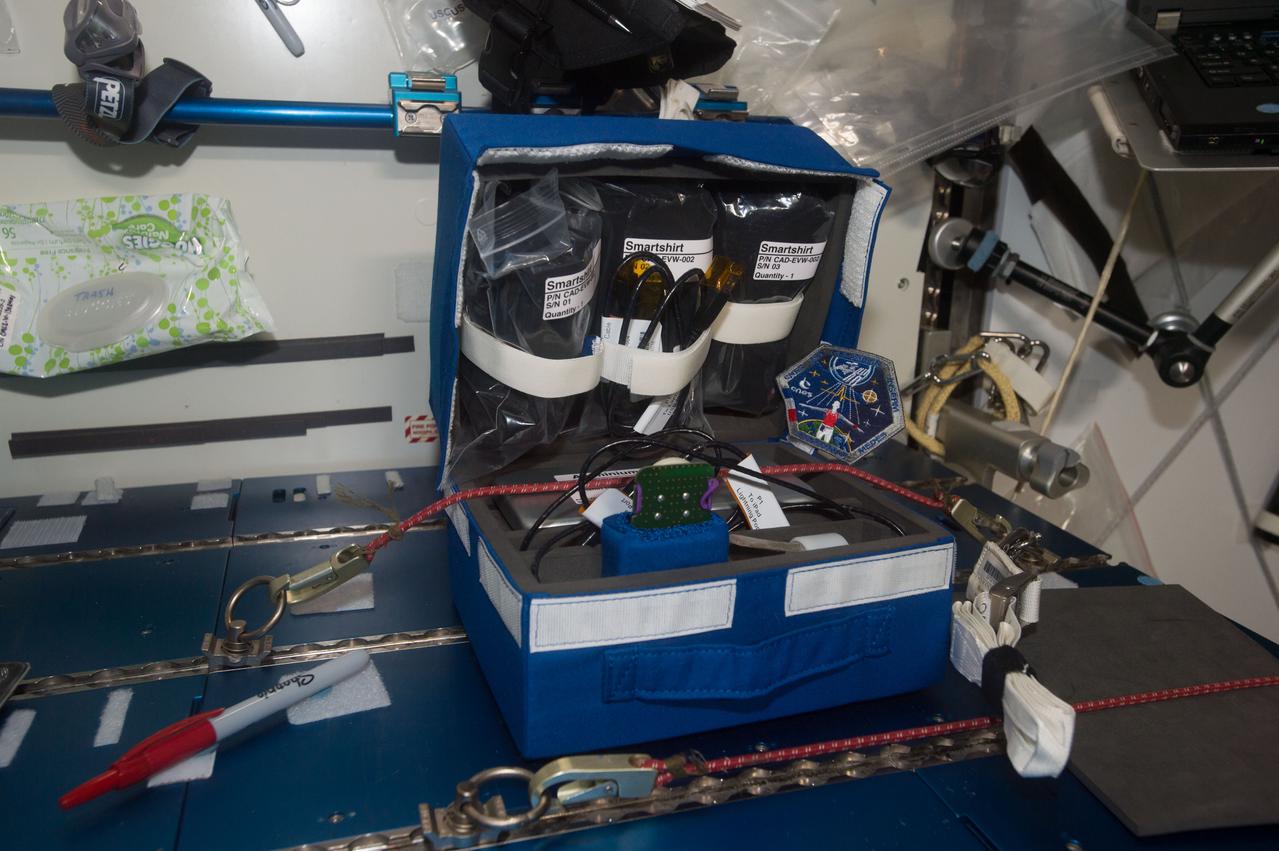

iss050e014794 (12/6/2016) --- View of Smartshirts within Cargo Transfer Bag (CTB). The EveryWear system is an ambulatory data collection system making use of wearable sensors connected to a station iPad itself wirelessly synchronized with ground. This easy-use system should demonstrate extensive physiology data collection for both science and medical follow-up purpose by improving usability for the astronauts.
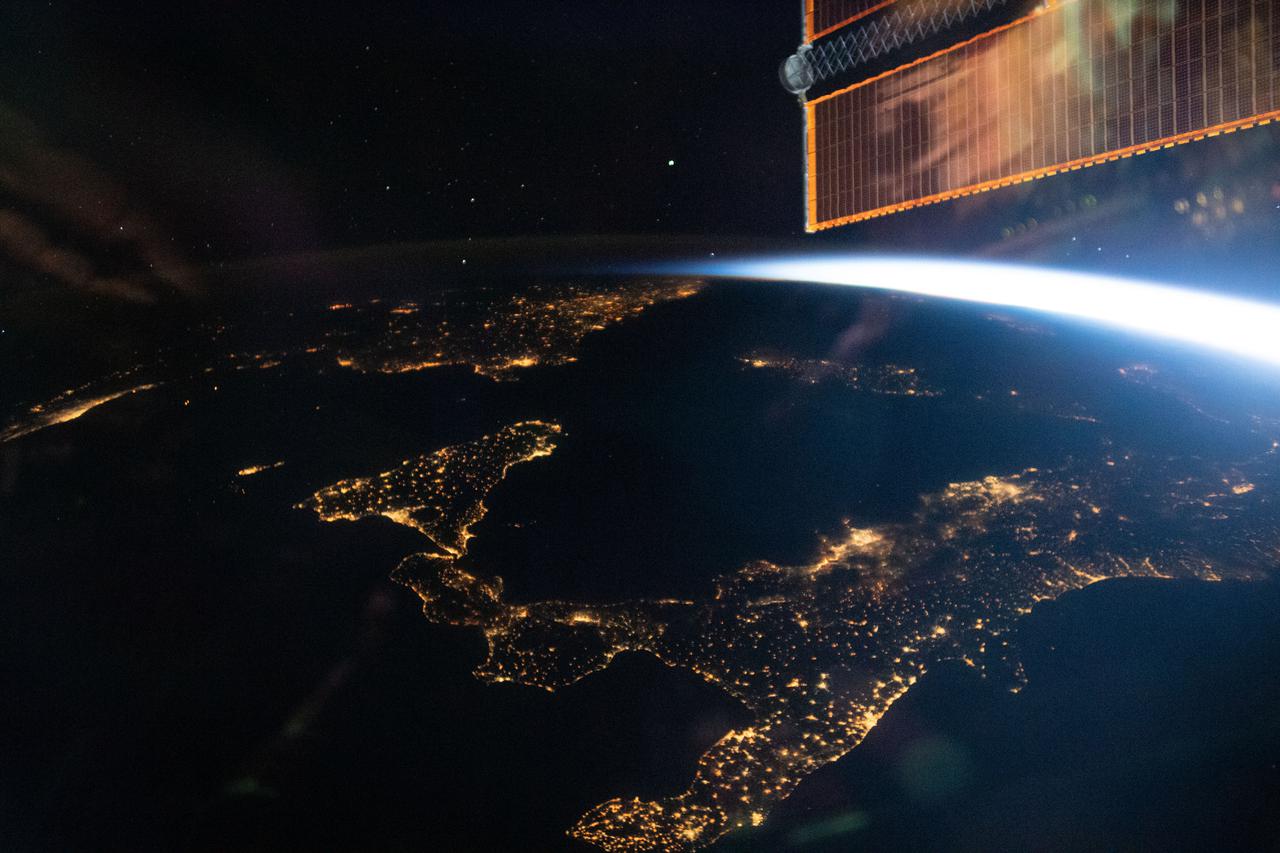

iss065e045974 (May 13, 2021) --- The night lights of Italy are prominent as the International Space Station soared 262 miles above southern Europe during an orbital twilight.

iss050e016760 (12/17/2016) --- View of Aquapad Containment Boxes. Photo was taken during Expedition 50.
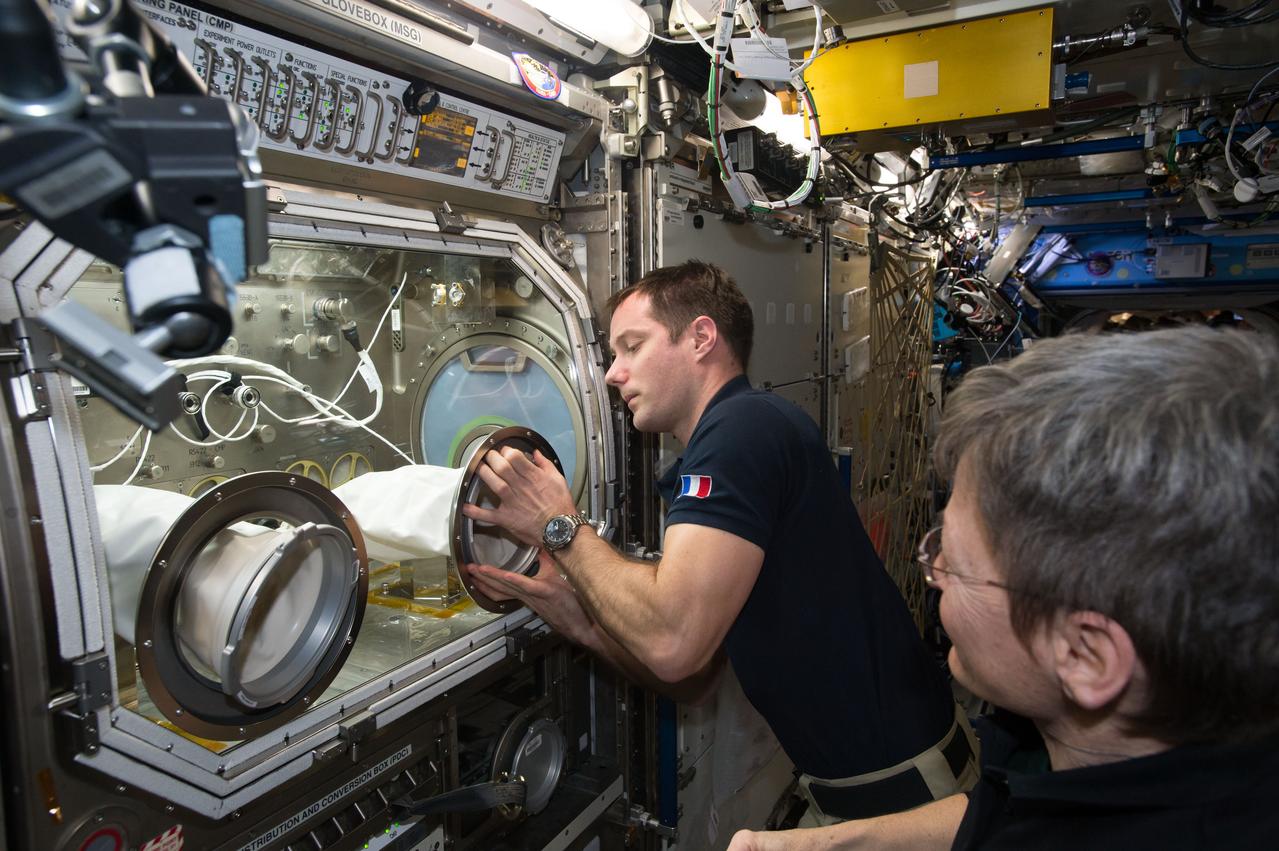

iss050e042167 (2/13/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) Thomas Pesquet and NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson setting up the Microgravity Expanded Stem Cells (MESC) Life Science Ancillary Hardware (LSAH) in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG). Microgravity Expanded Stem Cells cultivates human stem cells aboard the International Space Station (ISS) for use in clinical trials to evaluate their use in treating disease.
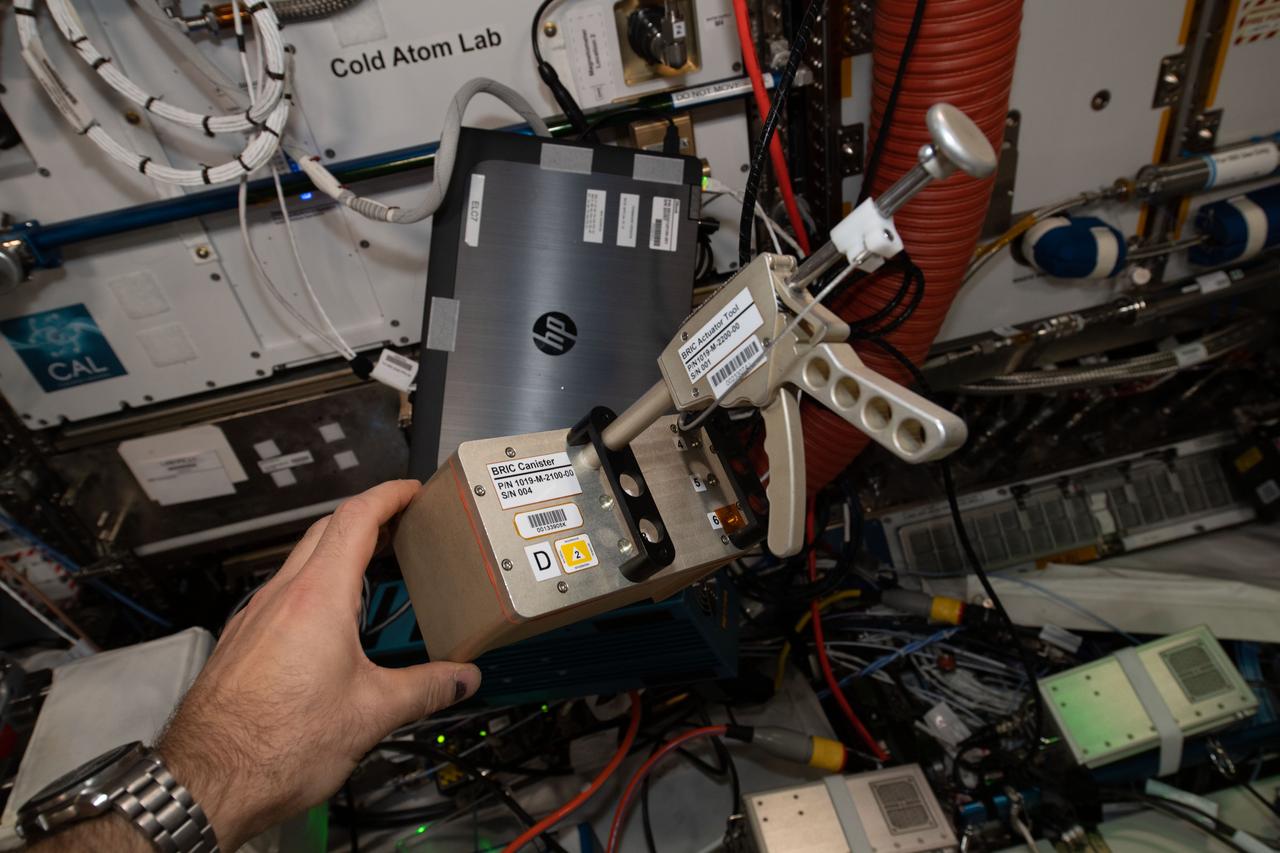

iss065e094062 (6/9/2021) --- A close-up view of the a BRIC-24 Canister and actuator tool. Biological Research In Canisters-24 (BRIC-24) tests how space affects organelle contacts and vacuole fusion in plants, systems that may be important for plant gravity sensing and response. Vacuoles are organelles in plant cells that have important functions.
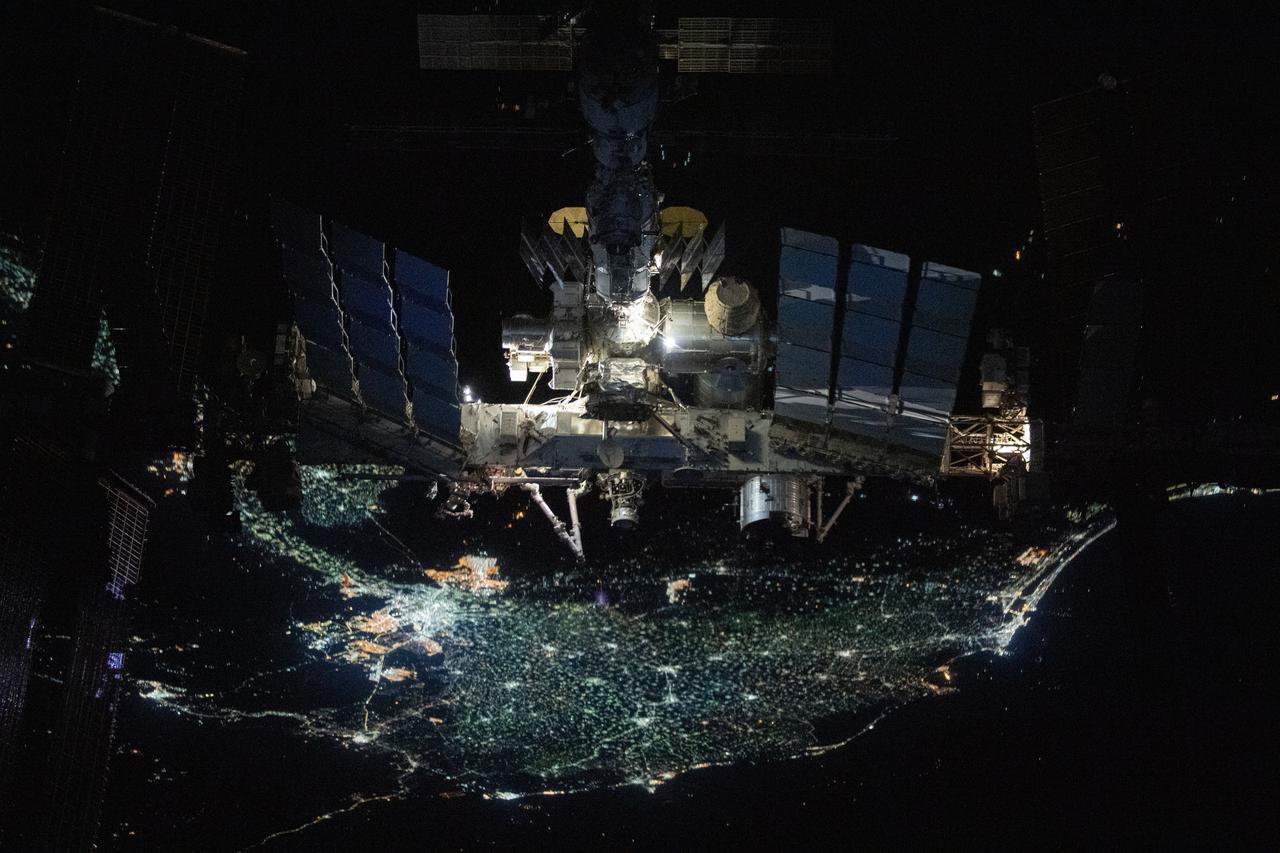

iss066e080034 (Nov. 8, 2021) -- The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021. The orbital complex was flying over 250 miles above the Nile Delta in Egypt when this photograph was taken.
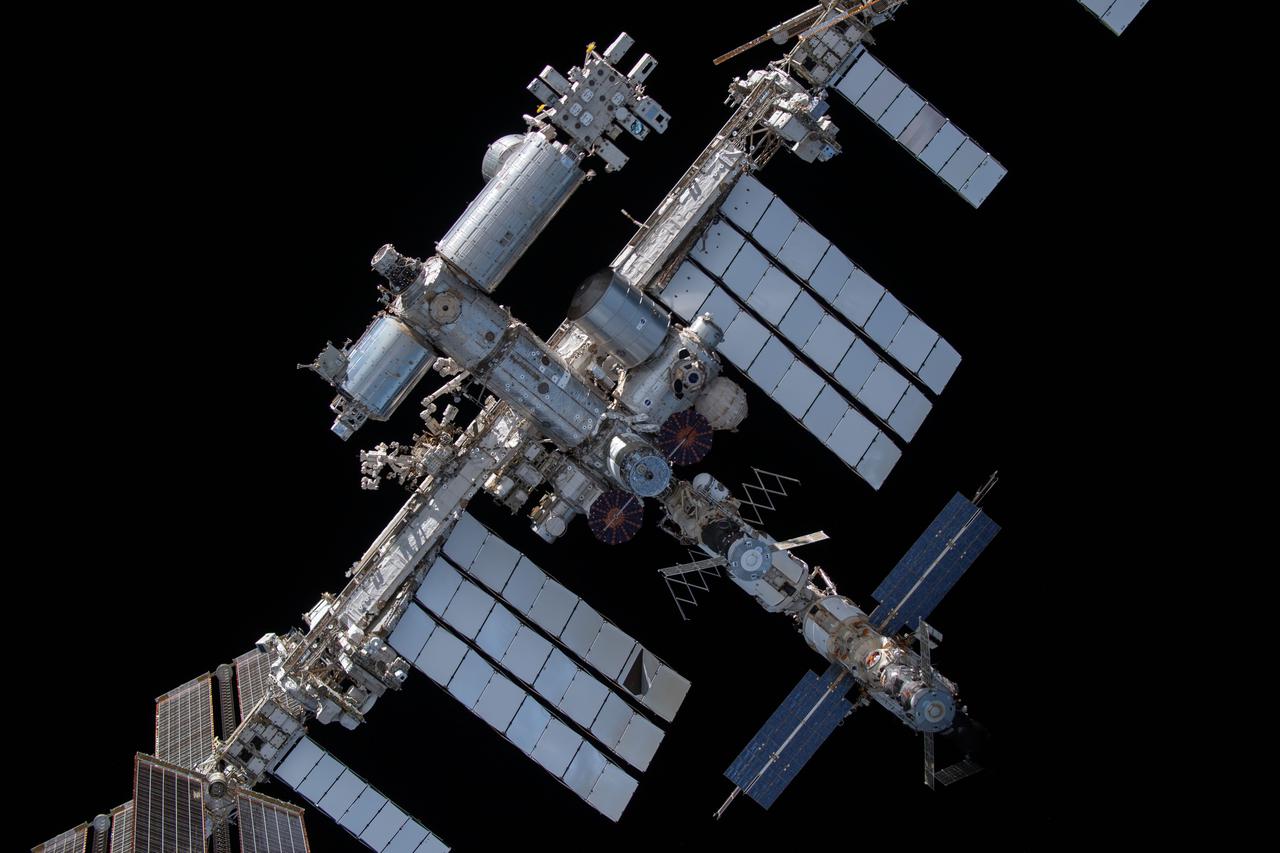

iss066e080432 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021.
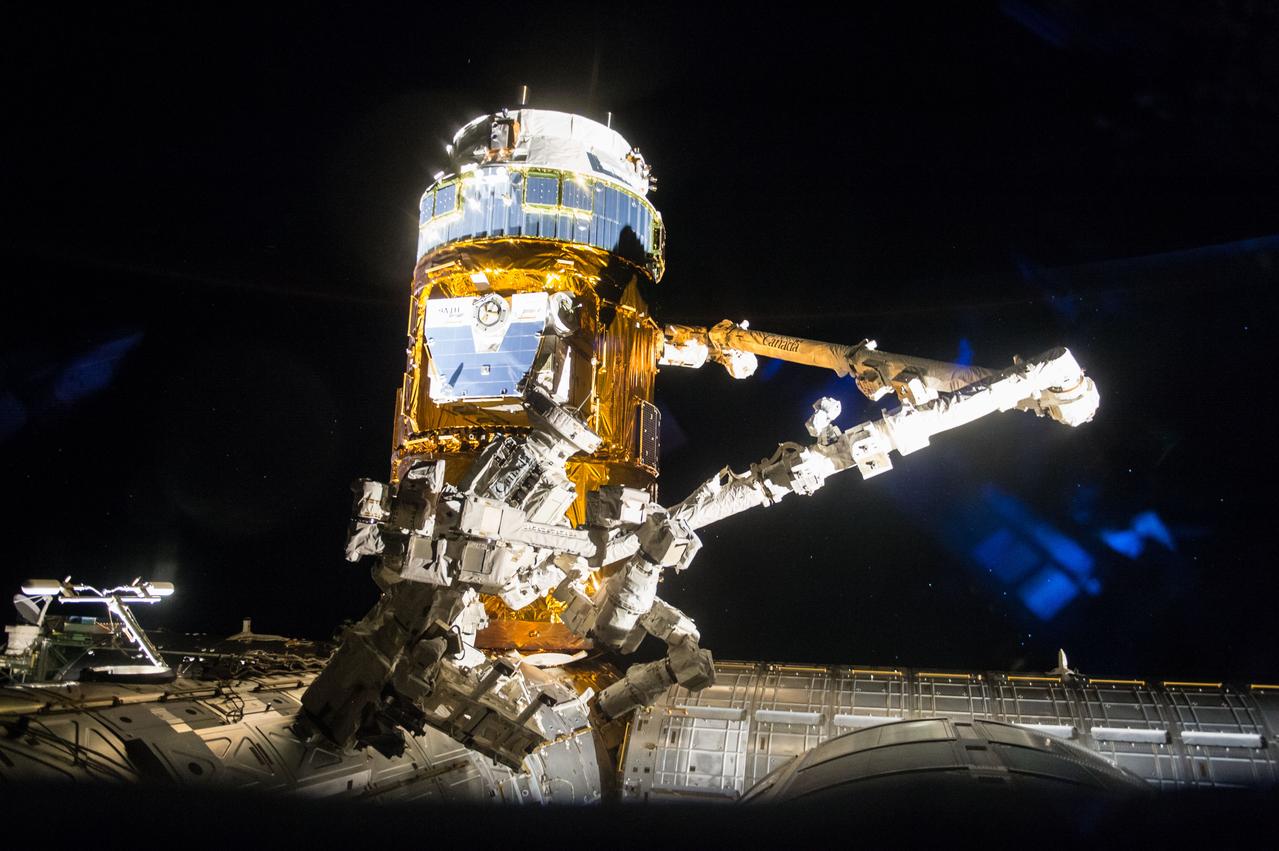

iss050e036114 (1/27/2017) --- A view of H2 Transfer Vehicle (HTV) 6 at dawn. HTV-6, is the sixth flight of the H-II Transfer Vehicle, an unmanned cargo spacecraft launched to resupply the International Space Station. It was launched at 13:26:47 UTC on 9 December 2016 aboard H-IIB launch vehicle from Tanegashima Space Center.
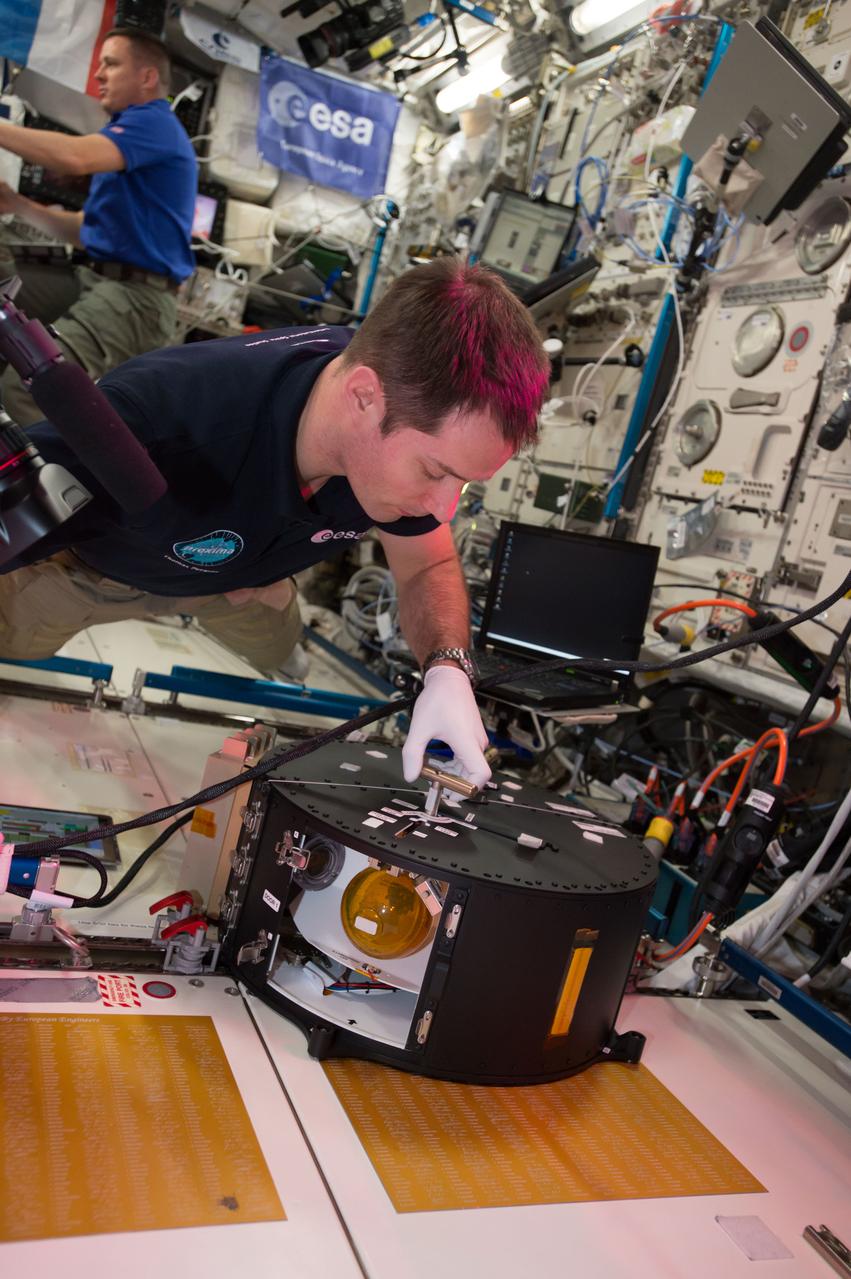

iss051e036148 (5/3/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet works with Fluid Dynamics in Space (FLUIDICS) hardware during the completion of experiment runs. FE Jack Fischer is visible in the background. Image was taken in the Columbus European Laboratory. The FLUIDICS investigation evaluates the Center of Mass (CoM) position regarding a temperature gradient on a representation of a fuel tank. The observation of capillary wave turbulence on the surface of a fluid layer in a low-gravity environment can provide insights into measuring the existing volume in a sphere.
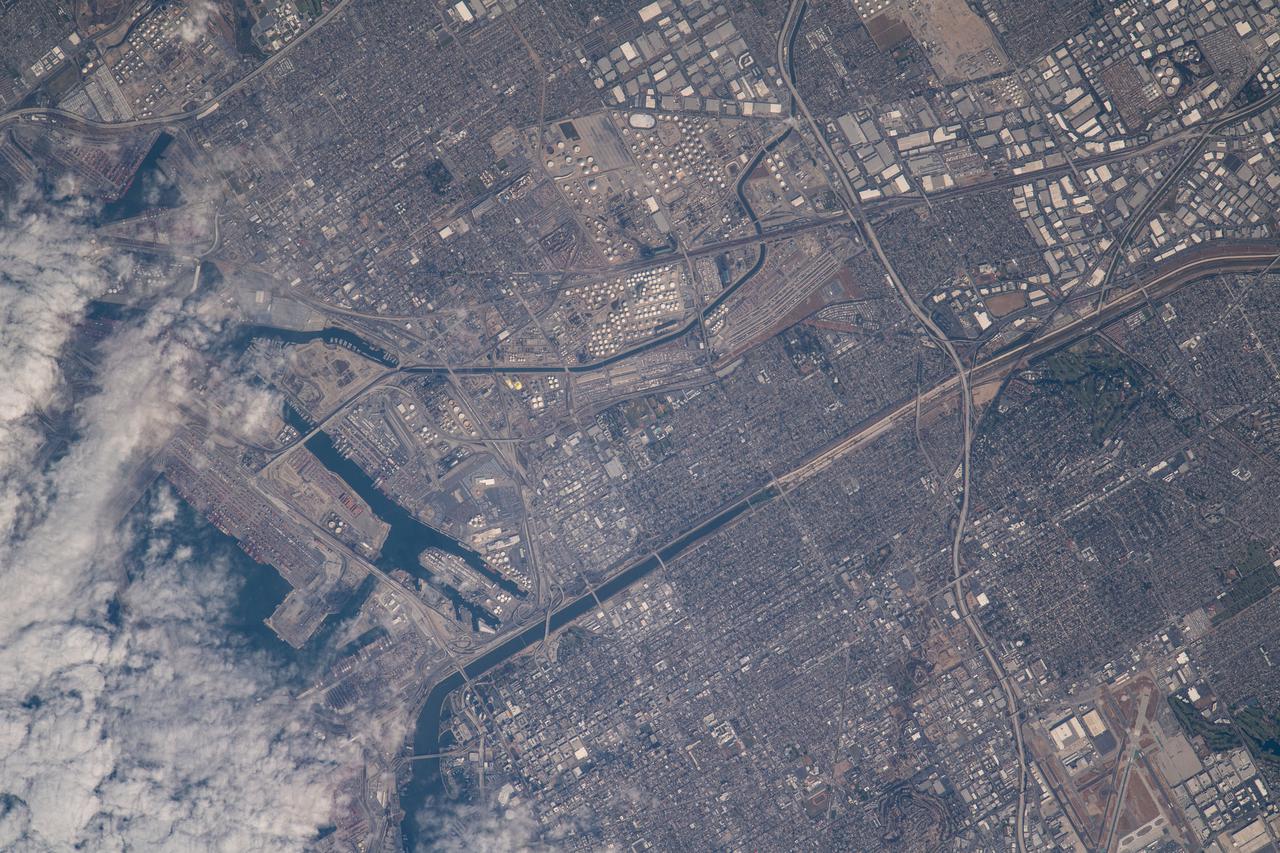

iss065e021010 (May 5, 2021) --- A cloud-covered Terminal Island and Long Beach south of Los Angeles, California, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 263 miles above the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego.
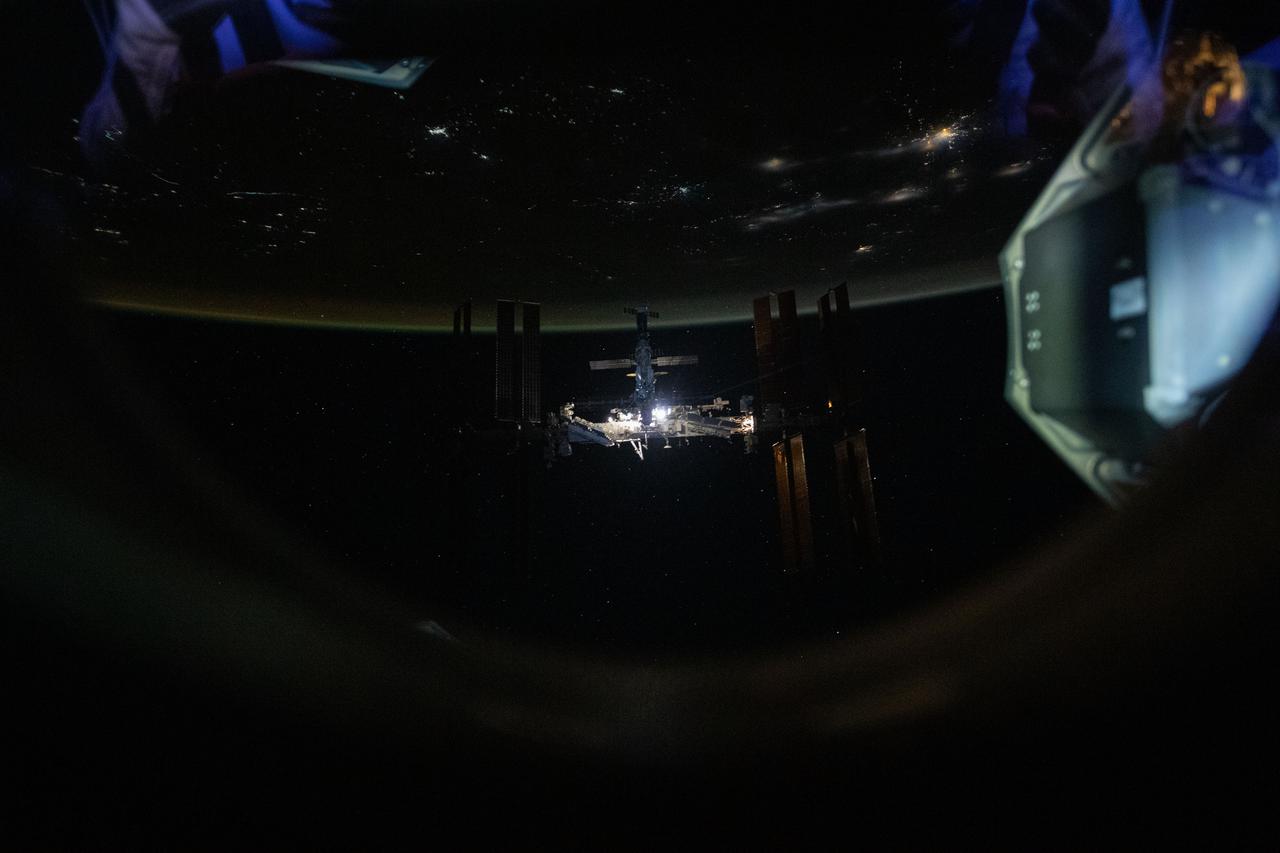

iss066e080097 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021. The orbital complex was flying 264 miles above the African nation of Mali when this photograph was taken.
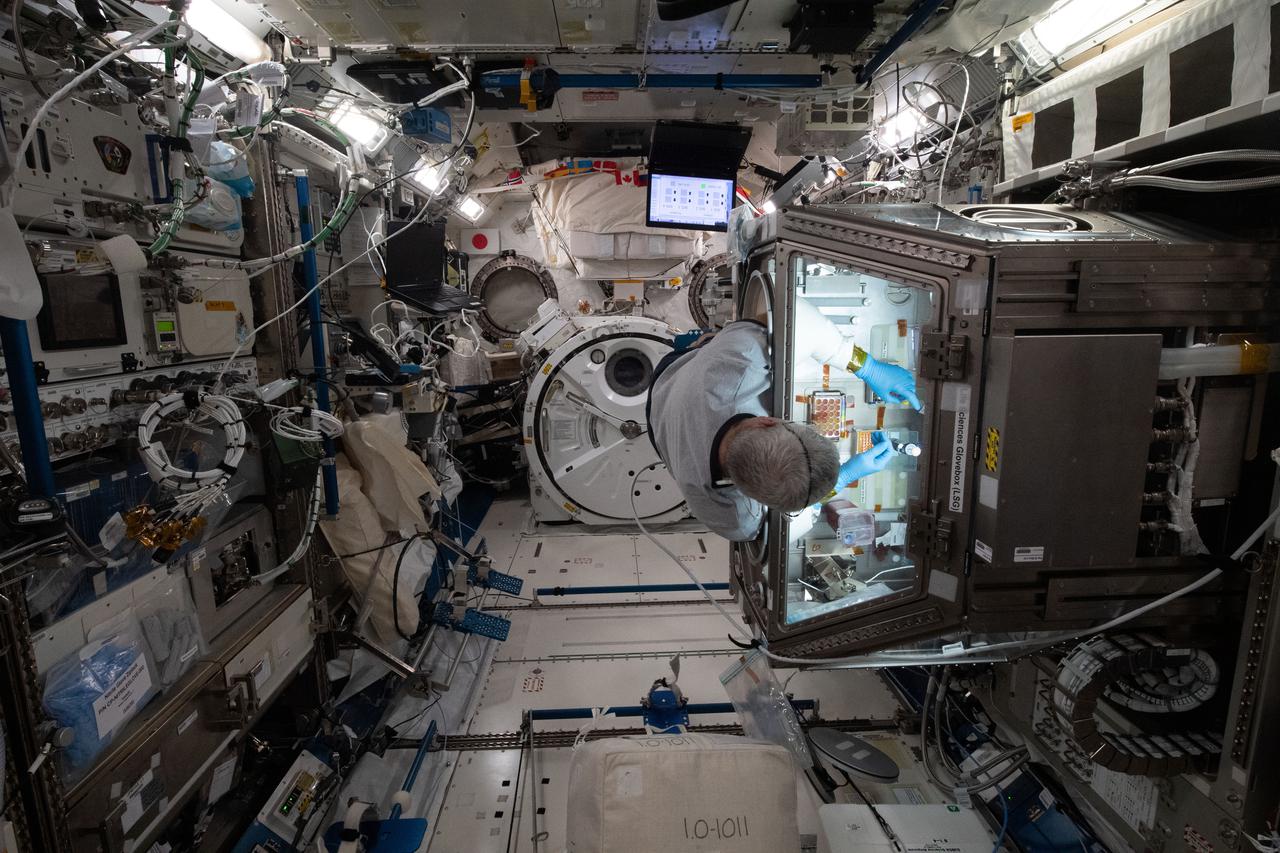

iss065e058810 (May 22, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei services donor cell samples inside the Kibo laboratory module's Life Science Glovebox. The samples for the Celestial Immunity study are compared to cell cultures harvested on Earth and may help scientists develop new vaccines and drugs to treat diseases on Earth.
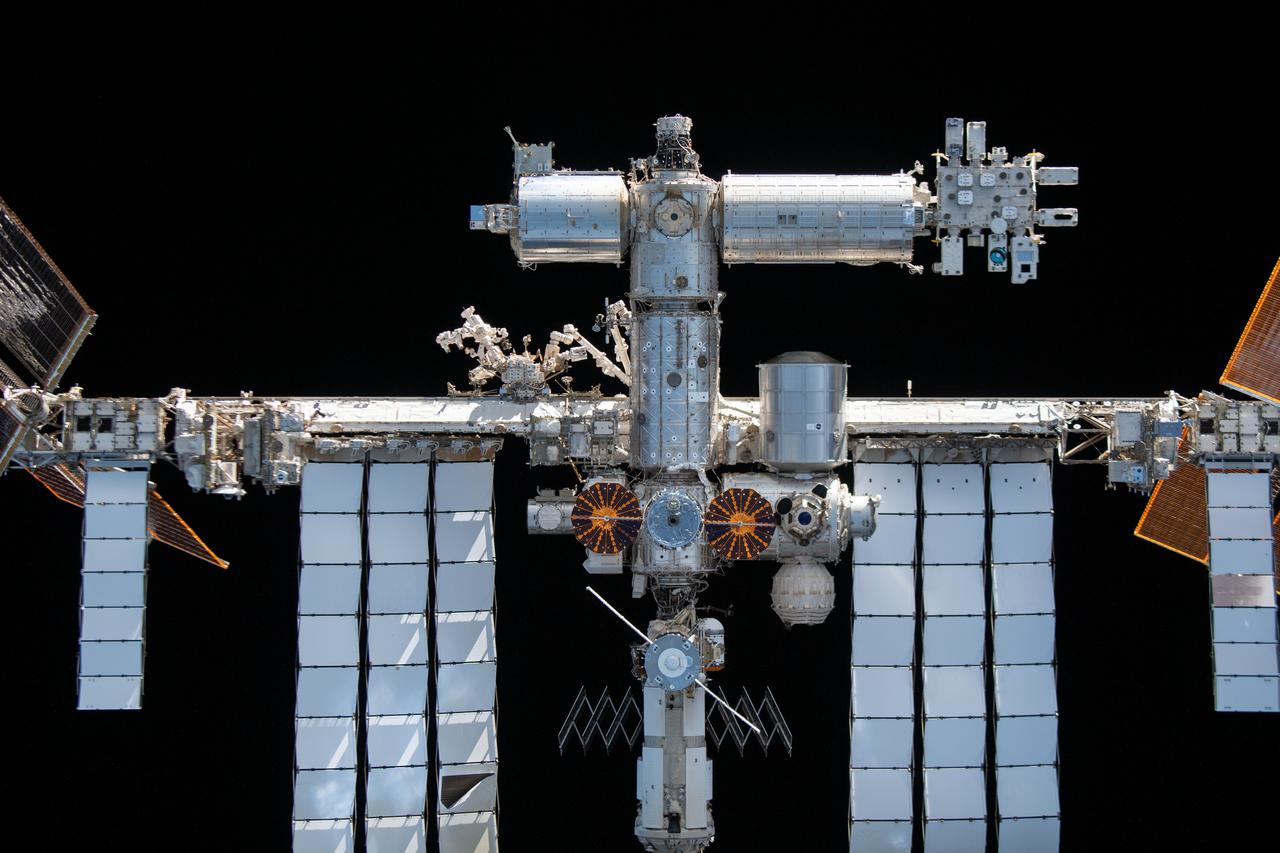
iss066e080382 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station's U.S. segment and portions of the Russian segment are pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021. Prominent at center in this view are the cymbal-shaped UltraFlex solar arrays of the Northrop Grumman Cygnus space freighter.
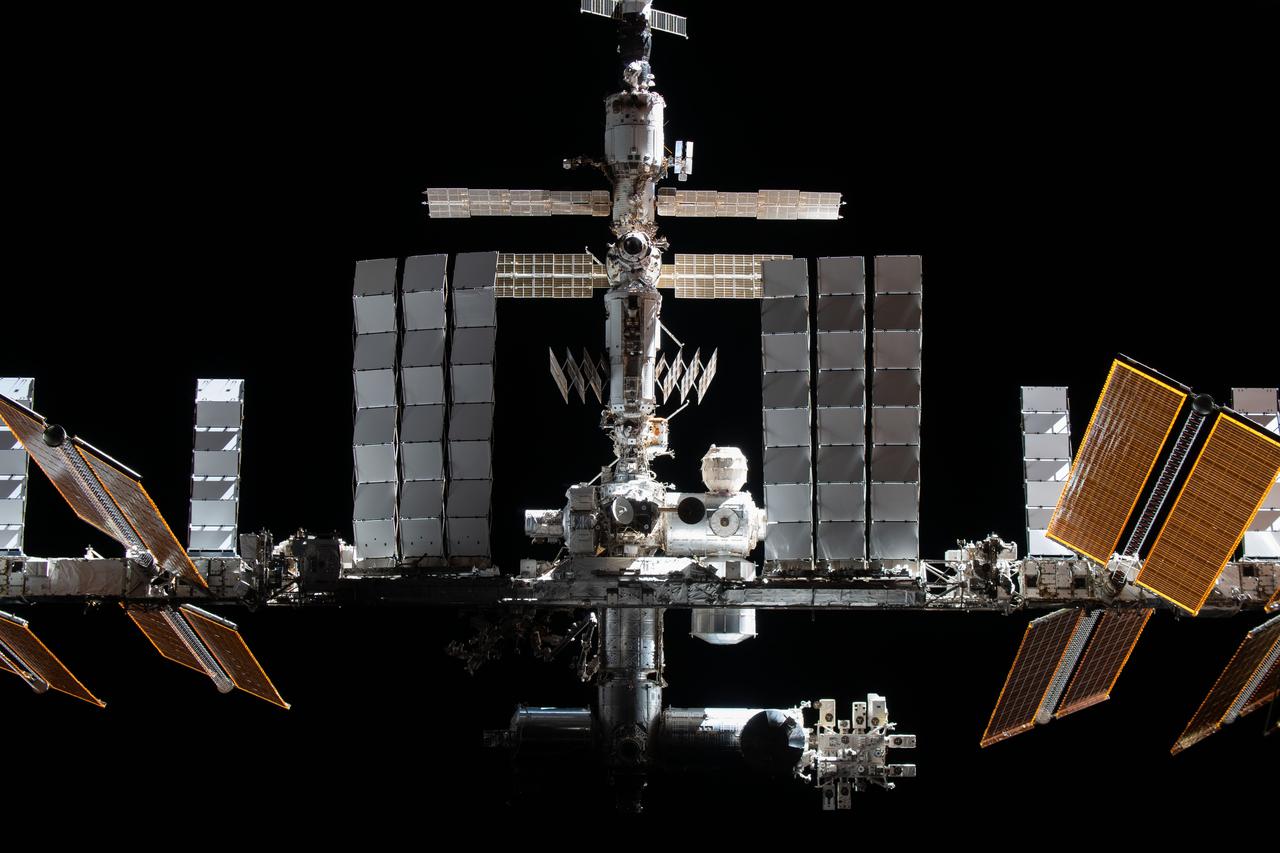
iss066e079893 (Nov. 8, 2021) --- The International Space Station is pictured from the SpaceX Crew Dragon Endeavour during a fly around of the orbiting lab that took place following its undocking from the Harmony module’s space-facing port on Nov. 8, 2021. This view shows the habitable volume of the station (modules arranged vertically through the center) along with white radiators used to dissipate heat and the large solar arrays used to generate electricity.
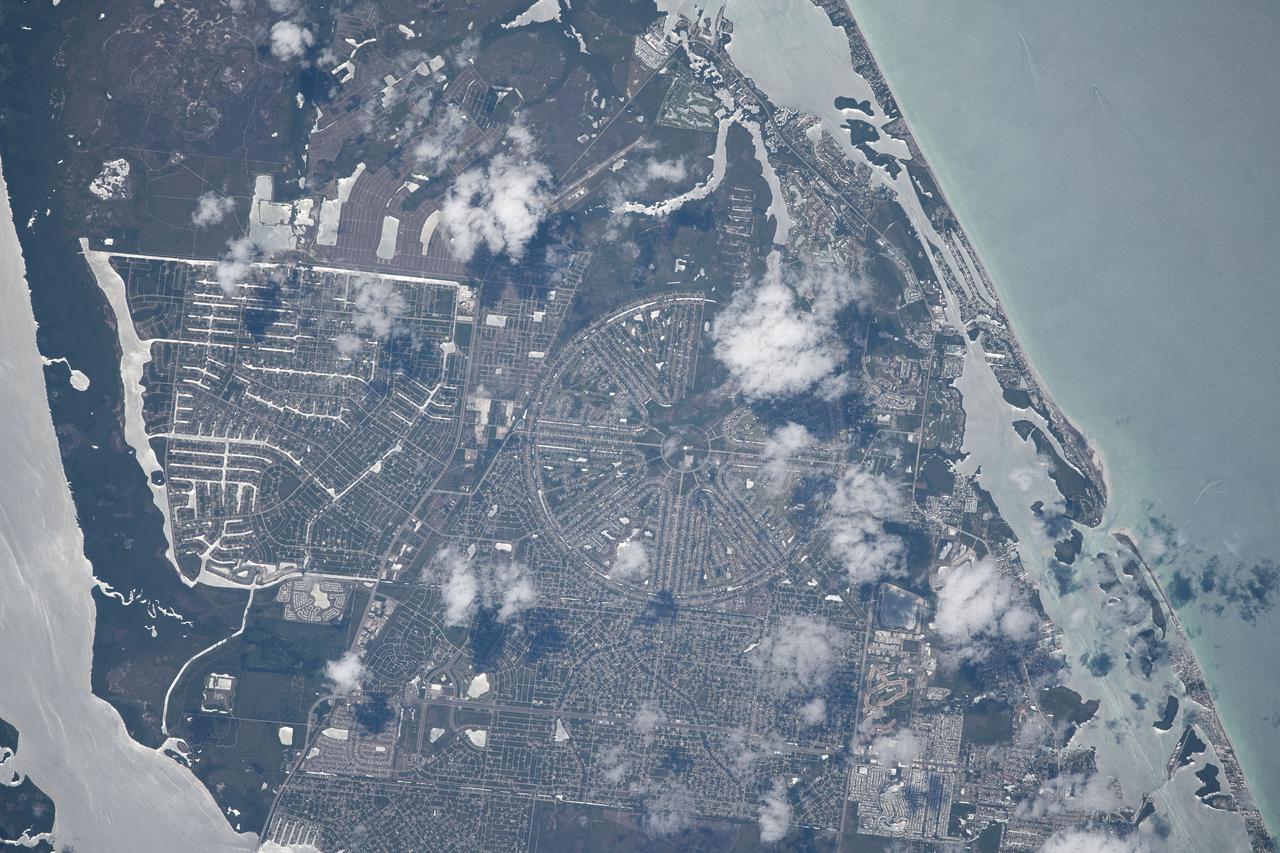

iss065e007903 (April 28, 2021) --- This portion of Englewood County, Florida, is on the Sunshine State's southern coast on the Gulf of Mexico. The International Space Station was orbiting 262 miles above on a southeastern trek at the time this photograph was taken.
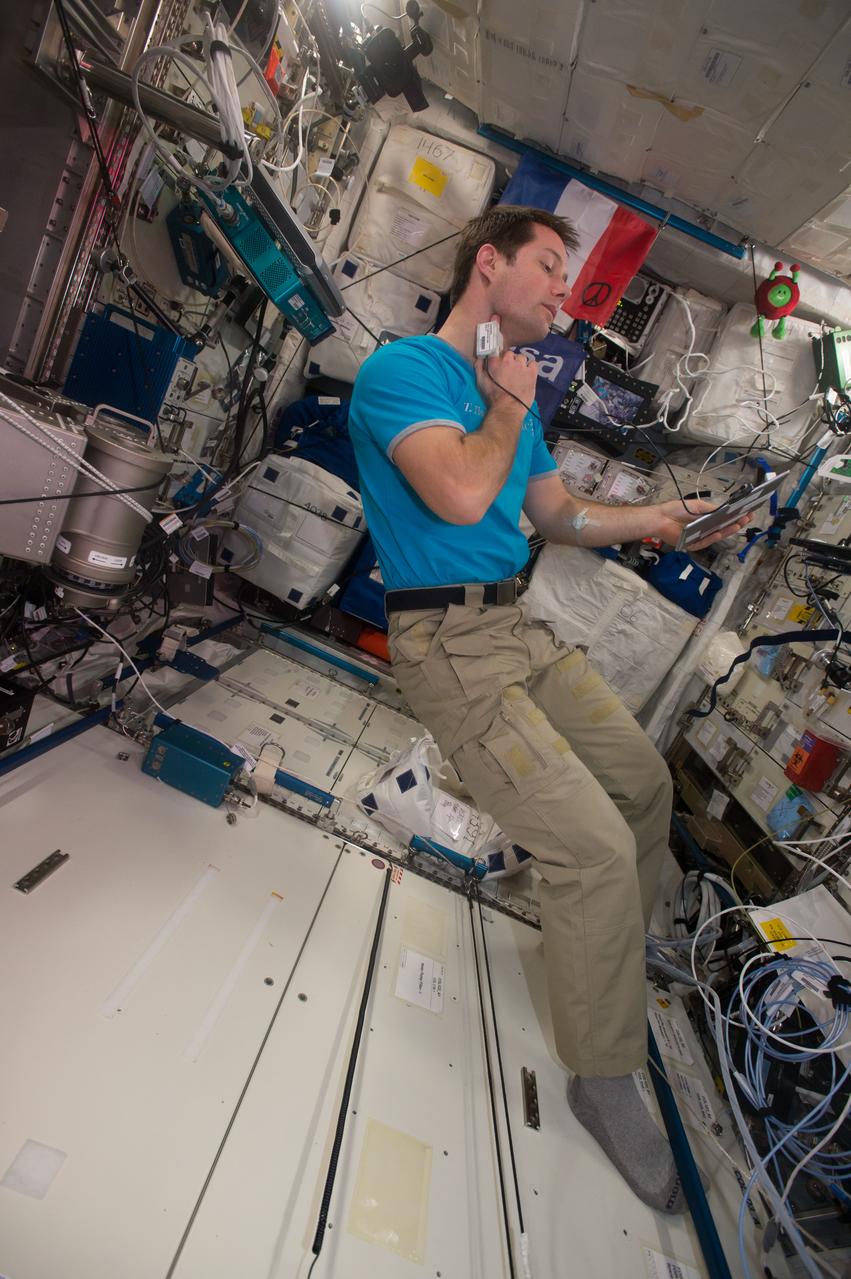

iss050e014804 (12/7/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) Thomas Pesquet wearing sensor (Tonometer) connected to iPad during EVERYWEAR experiment, in the Columbus Module. The EveryWear system is an ambulatory data collection system making use of wearable sensors connected to a station iPad itself wirelessly synchronized with ground. This easy-use system should demonstrate extensive physiology data collection for both science and medical follow-up purpose by improving usability for the astronauts.