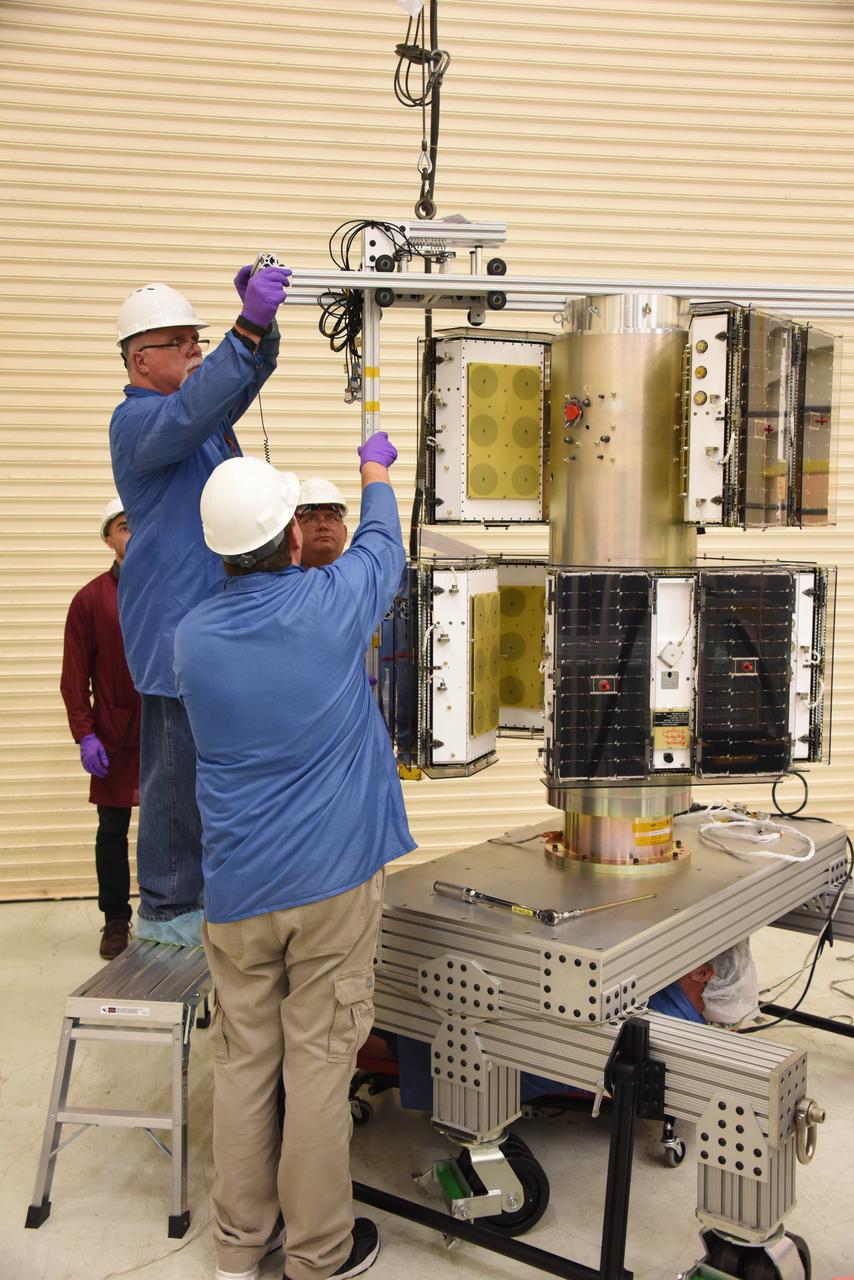

Technicians with Orbital ATK continue to install micro satellites on the deployment module for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
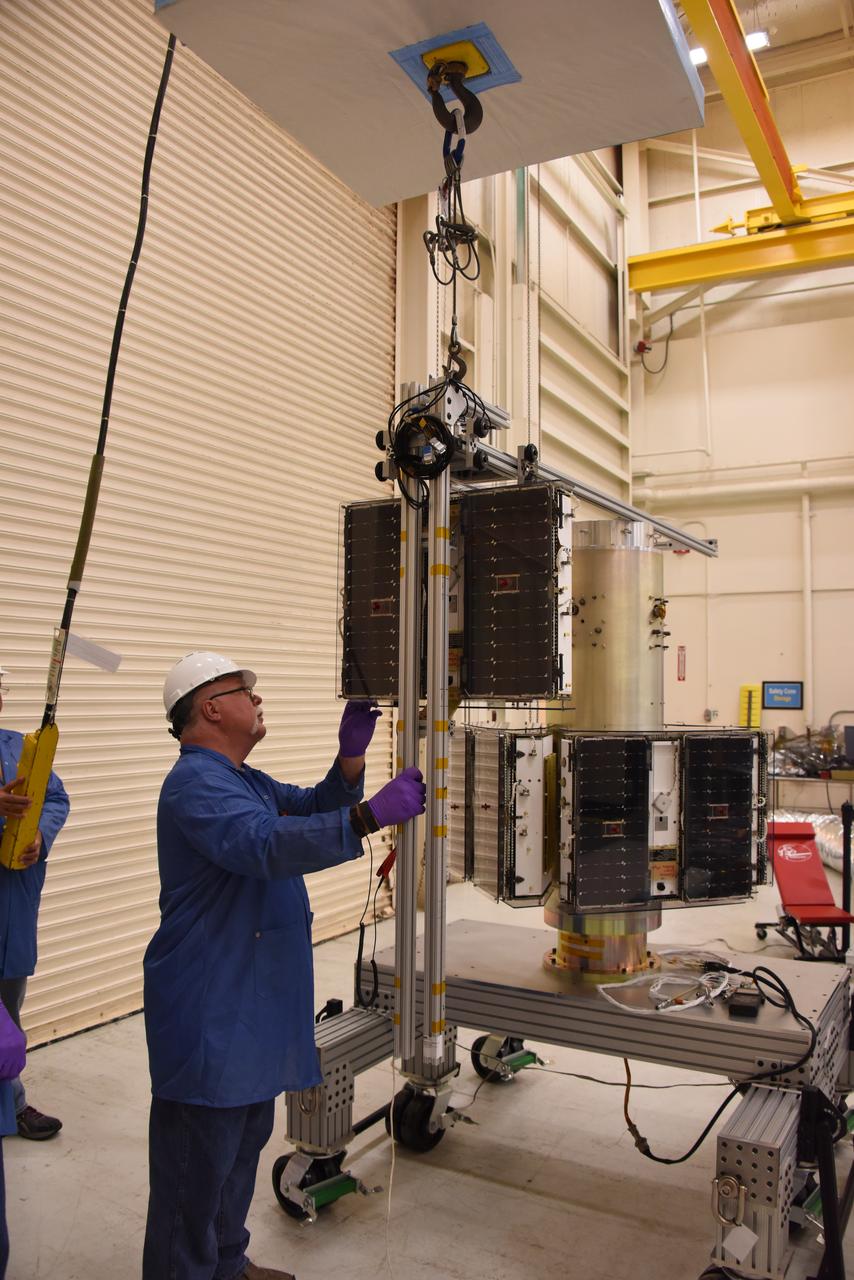

A technician with Orbital ATK prepares to install another micro satellite on the deployment module for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
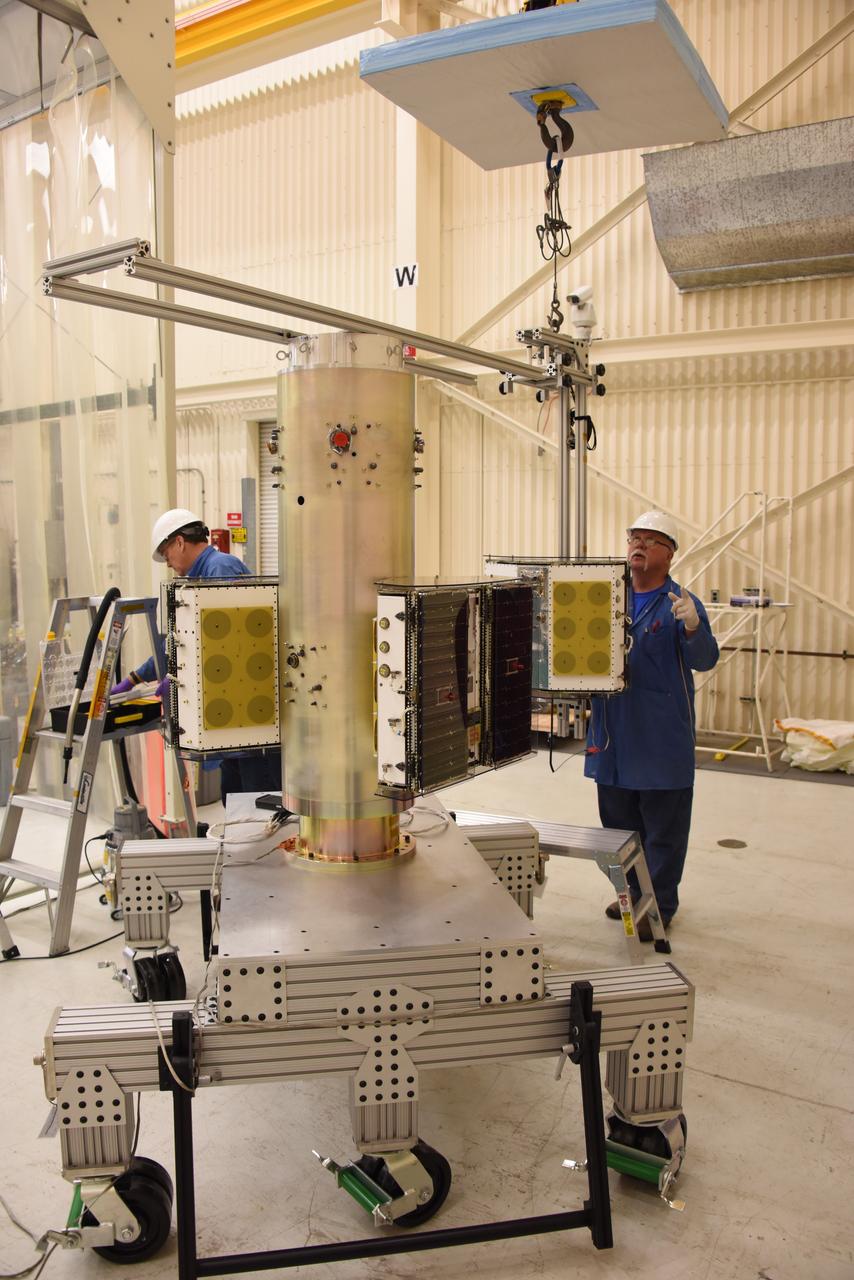

Technicians with Orbital ATK continue to install micro satellites on the deployment module for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
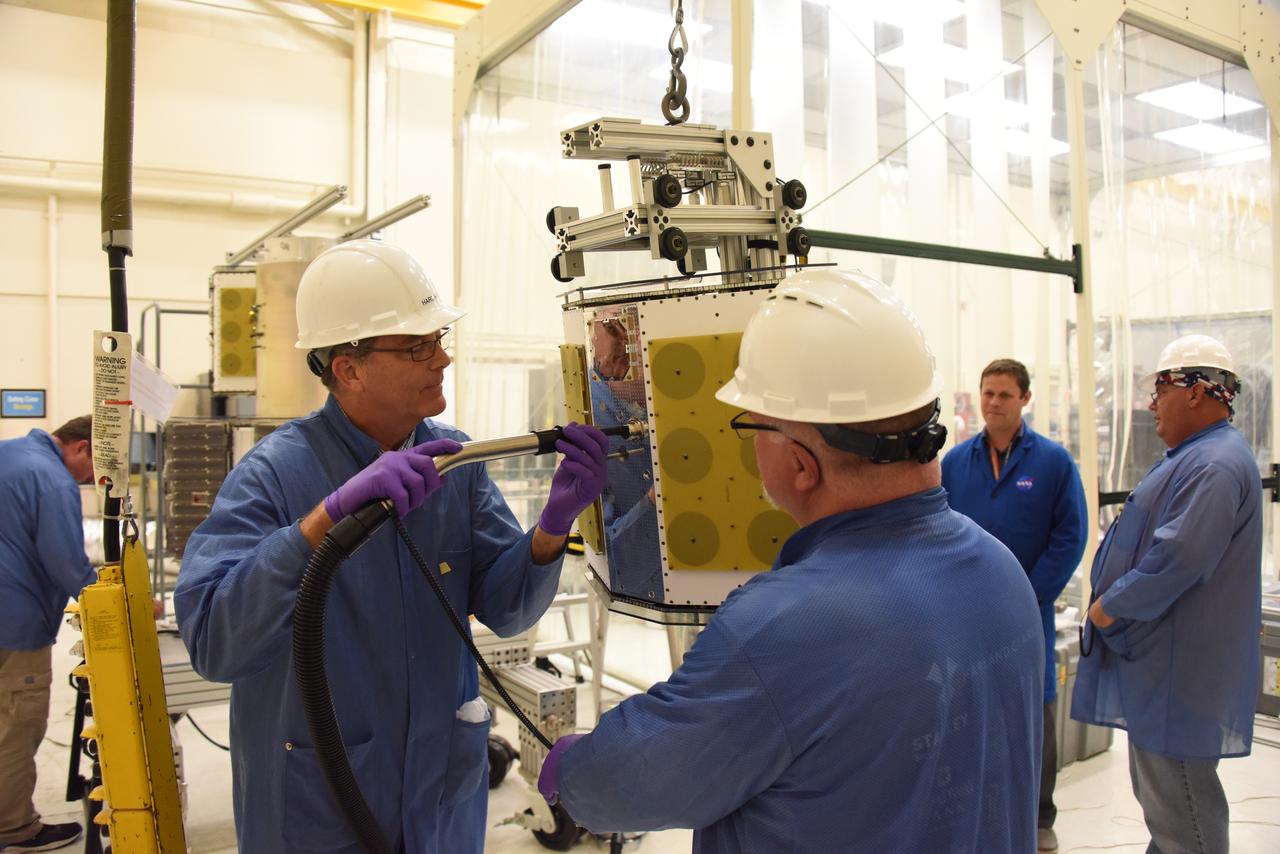

Technicians with Orbital ATK continue to install micro satellites on the deployment module for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
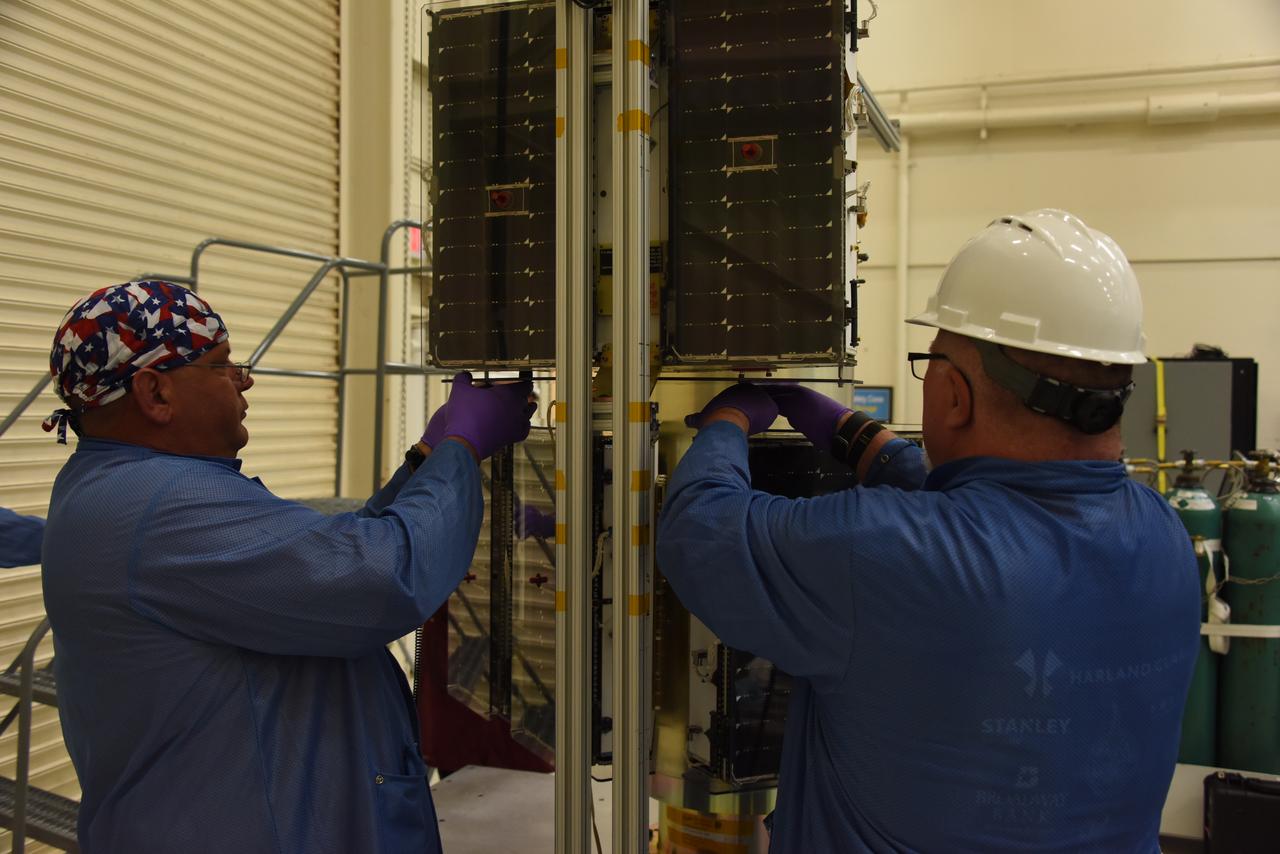

Technicians with Orbital ATK continue to install micro satellites on the deployment module for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
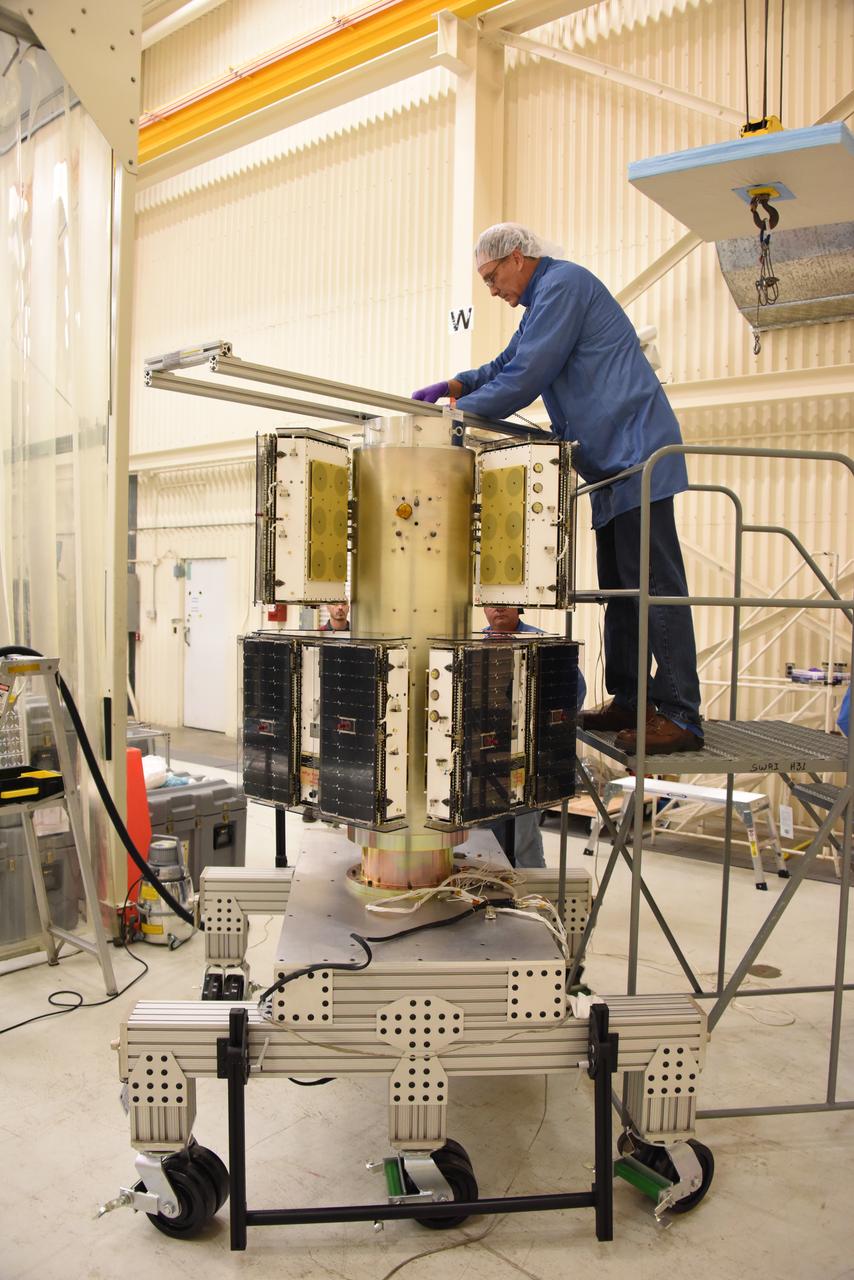

A technician with Orbital ATK checks the installation of the micro satellites on the deployment module for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
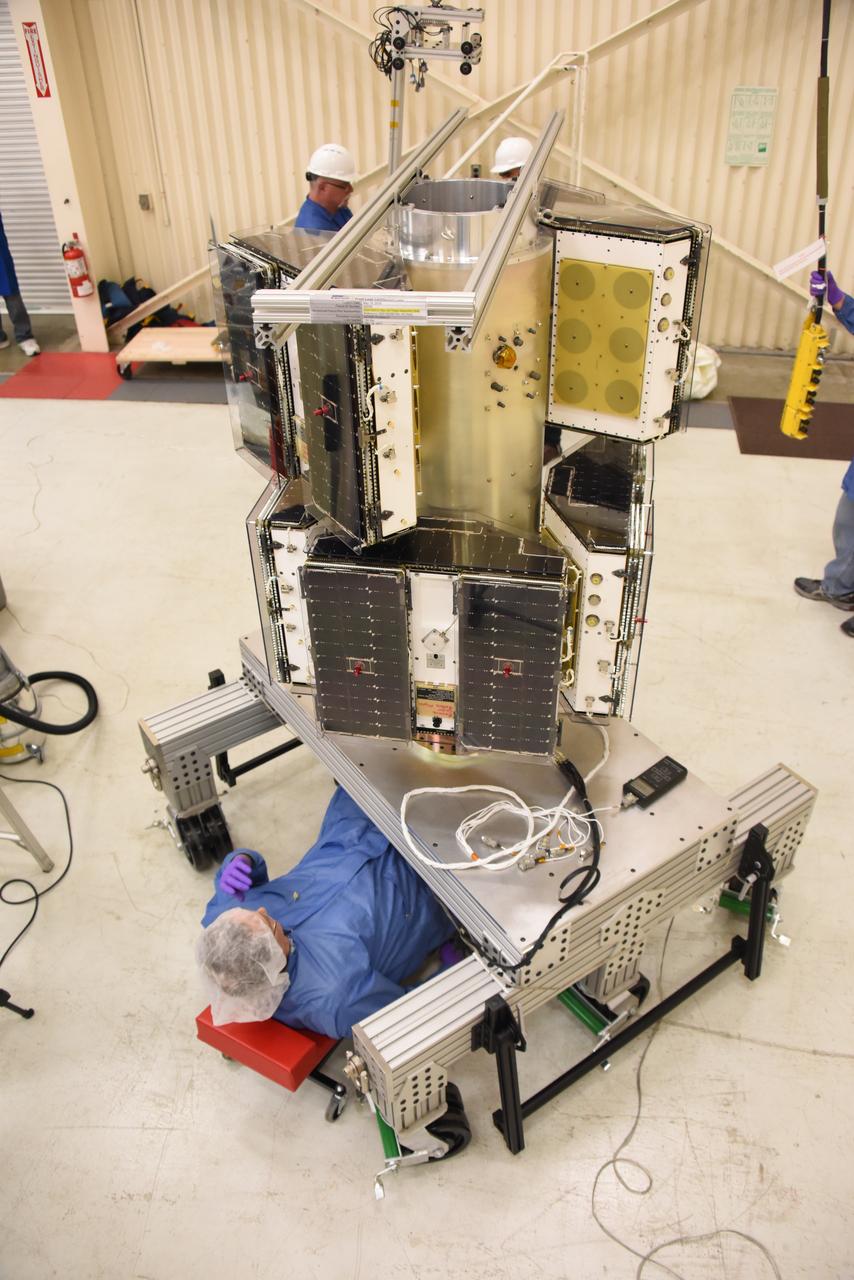
Technicians with Orbital ATK continue to install the micro satellites on the deployment module for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
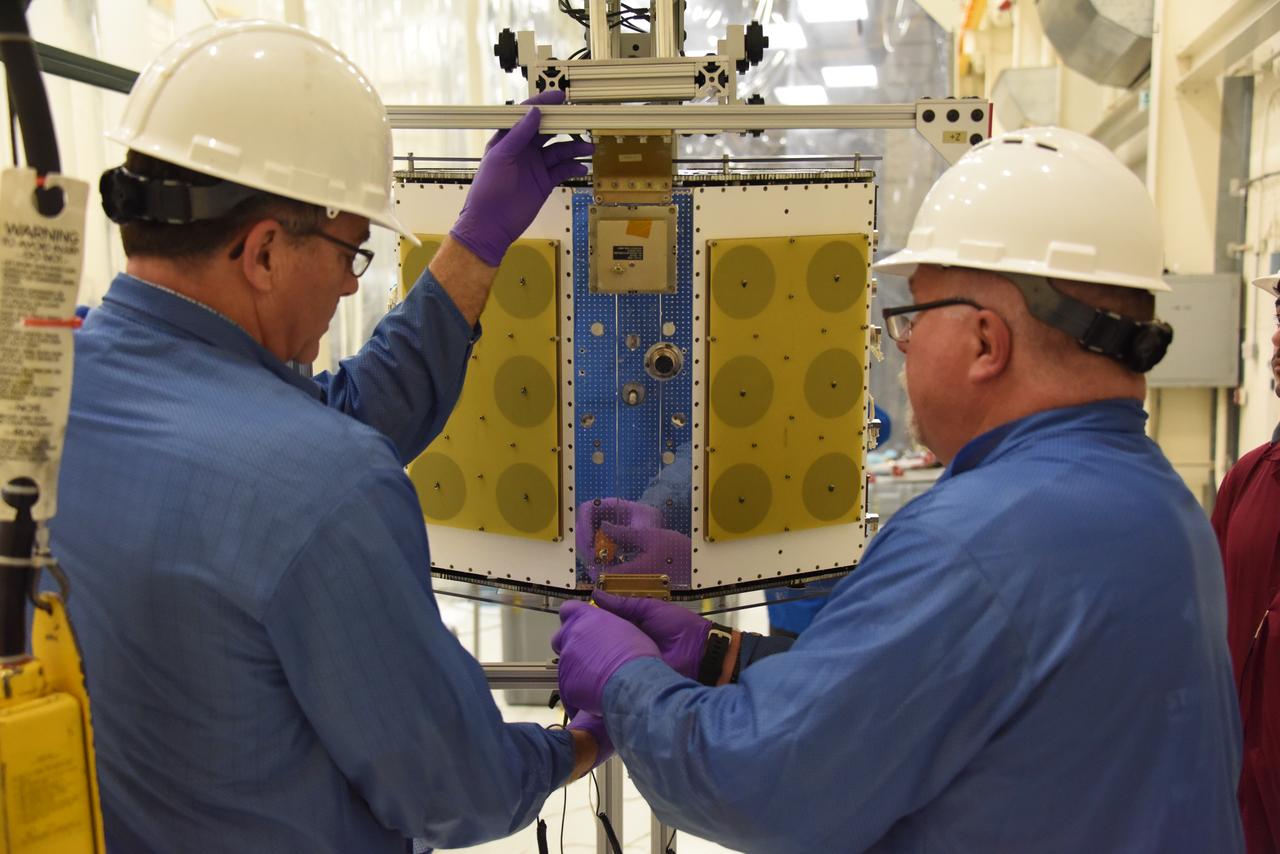

Technicians with Orbital ATK continue to install micro satellites on the deployment module for NASA’s Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. CYGNSS is being prepared at Vandenberg, and then will be transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket which will be attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.

Packaged in a protective container, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

Packaged in a protective container, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is about to be mated atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

Packaged in a protective container, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, arrives at Space Launch Complex 2 packaged in a protective container. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

JPSS-1 SpaceAt Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is mated atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.craft Transport to SLC-2; Lift and Mate to Delta II.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, is on its way to Space Launch Complex 2 packaged in a protective container. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

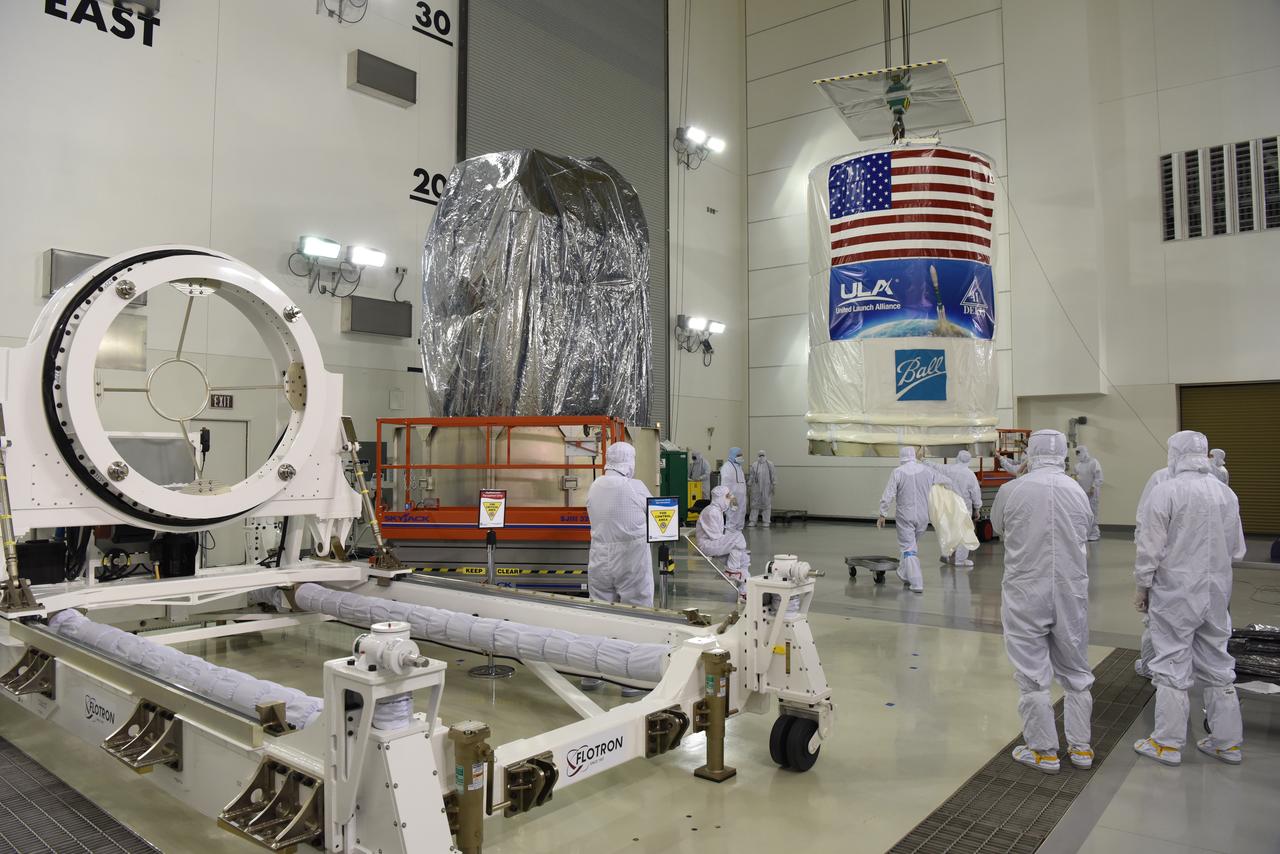
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is mated atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

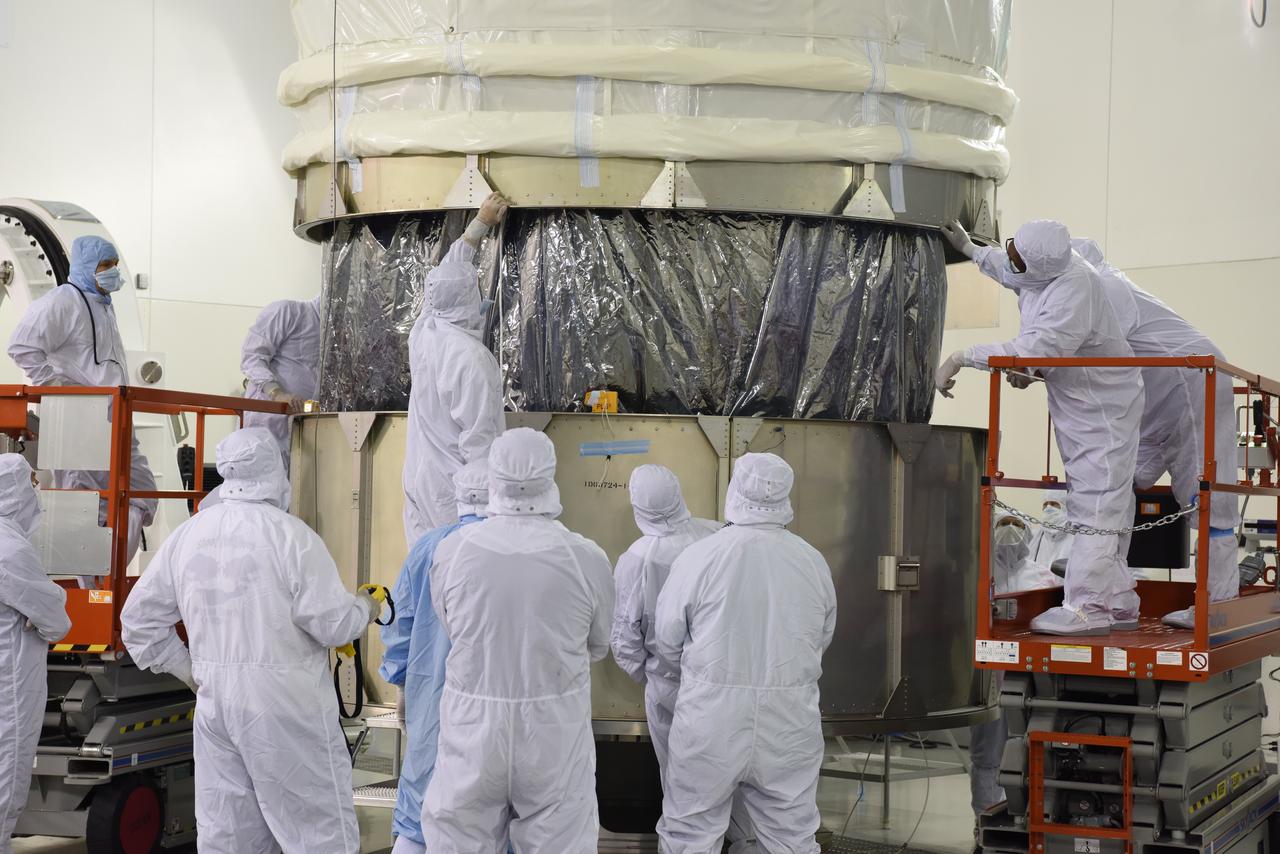
In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is prepared for departure in a protective container to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

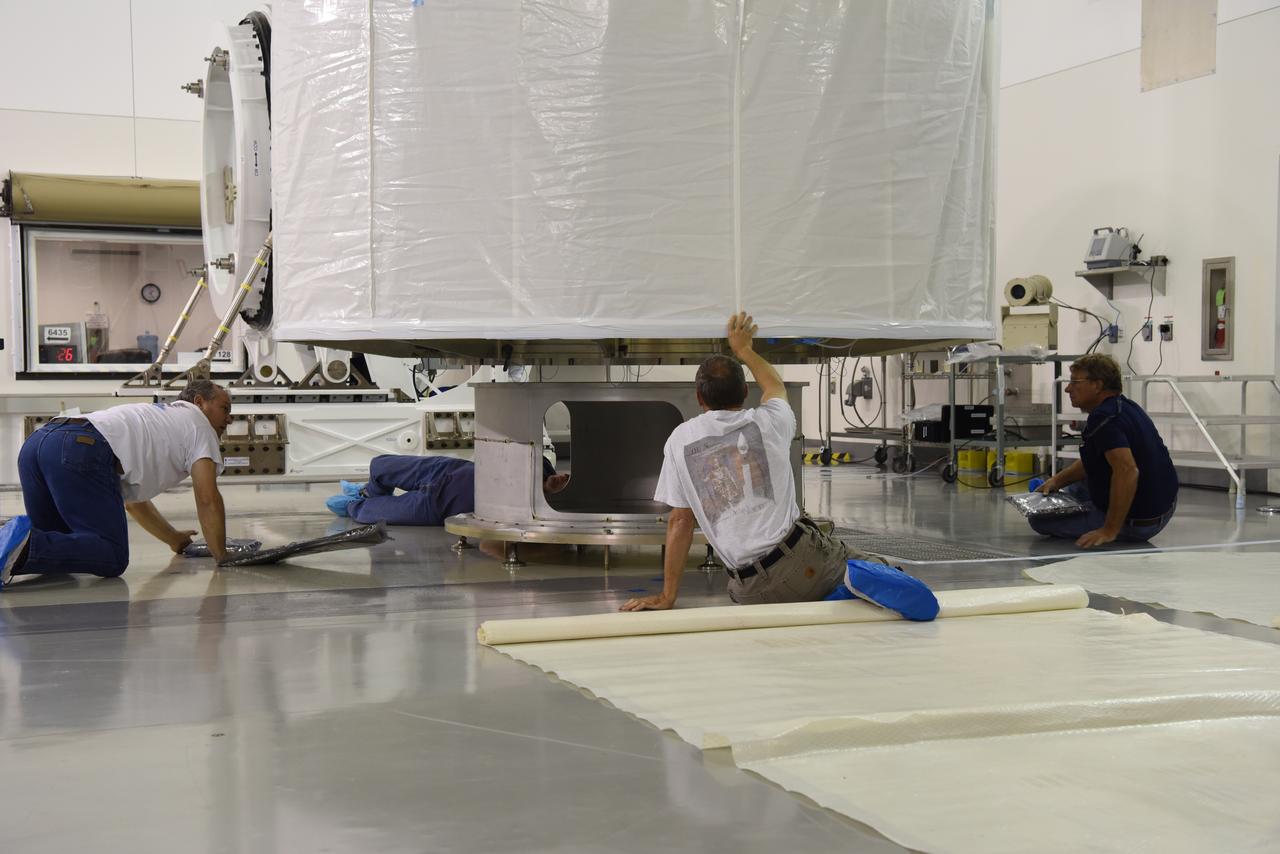
In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers place the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft in a protective container. It then will be mounted on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

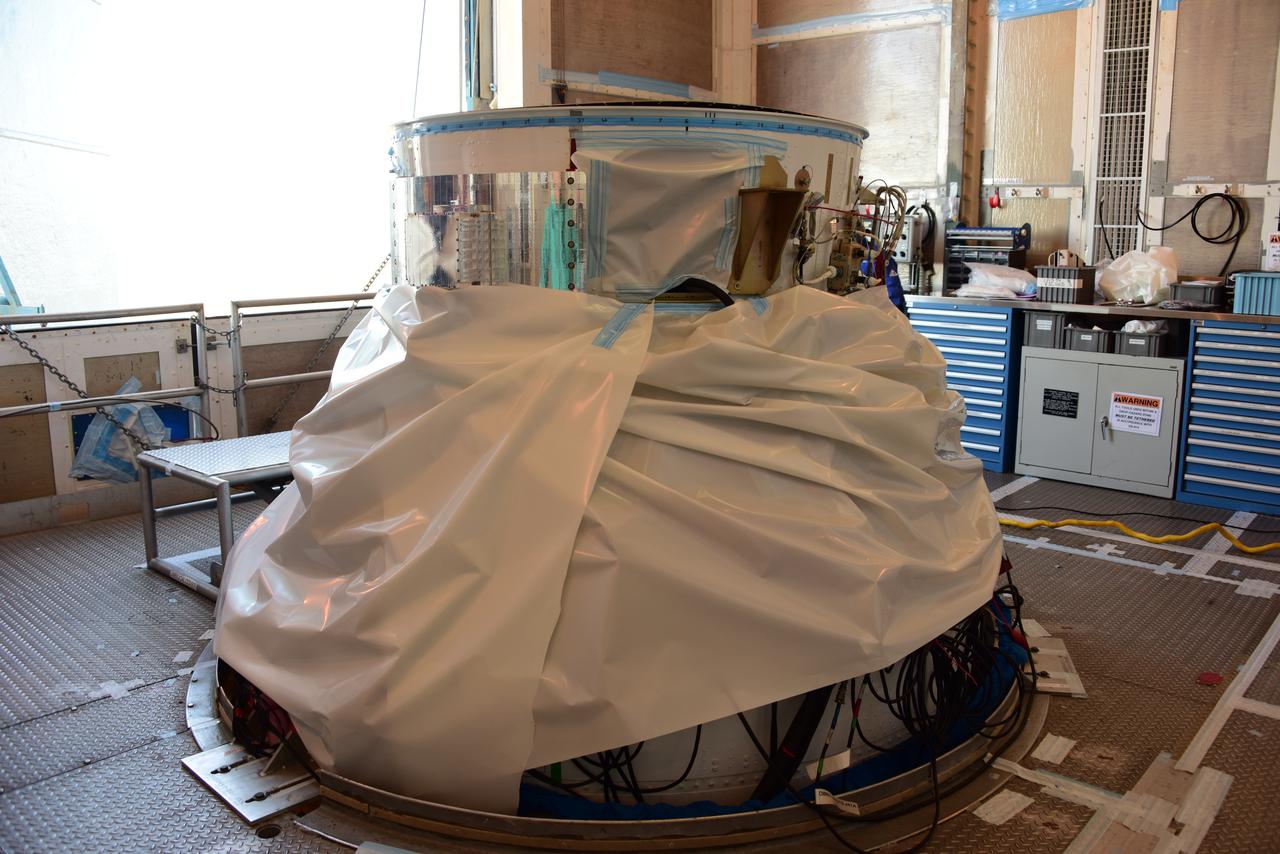
In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is wrapped in a protective covering prior to technicians and engineers placing it in a protective container. It then will be mounted on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is wrapped in a protective covering prior to technicians and engineers placing it in a protective container. It then will be mounted on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.
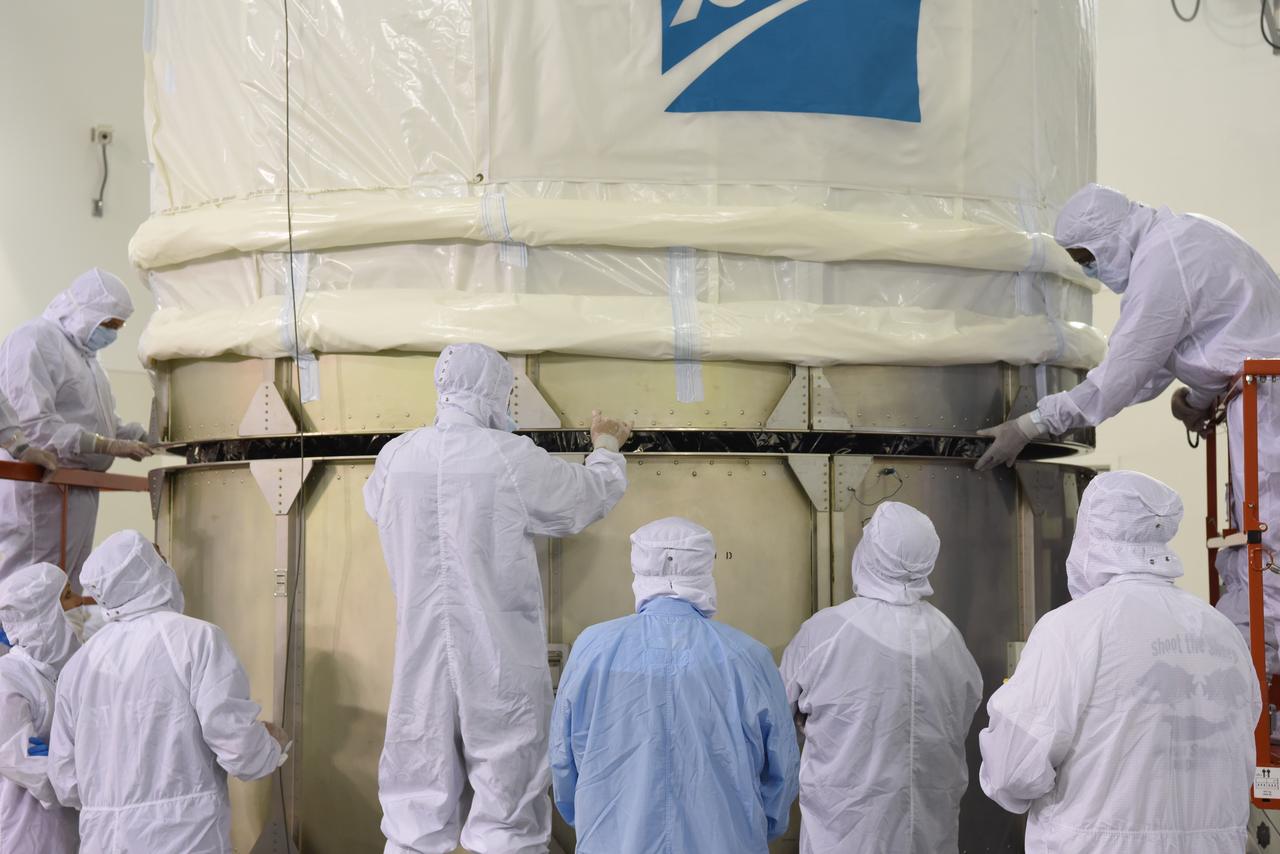

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers place the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft in a protective container. It then will be mounted on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is prepared for placing it in a protective container, then mounting on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers have placed the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft in a protective container. It then will be mounted on a transport trailer for its move from the Astrotech Processing Facility to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft departs the Astrotech Processing Facility in a protective container on its way to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

Packaged in a protective container, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is about to be lifted and mated atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

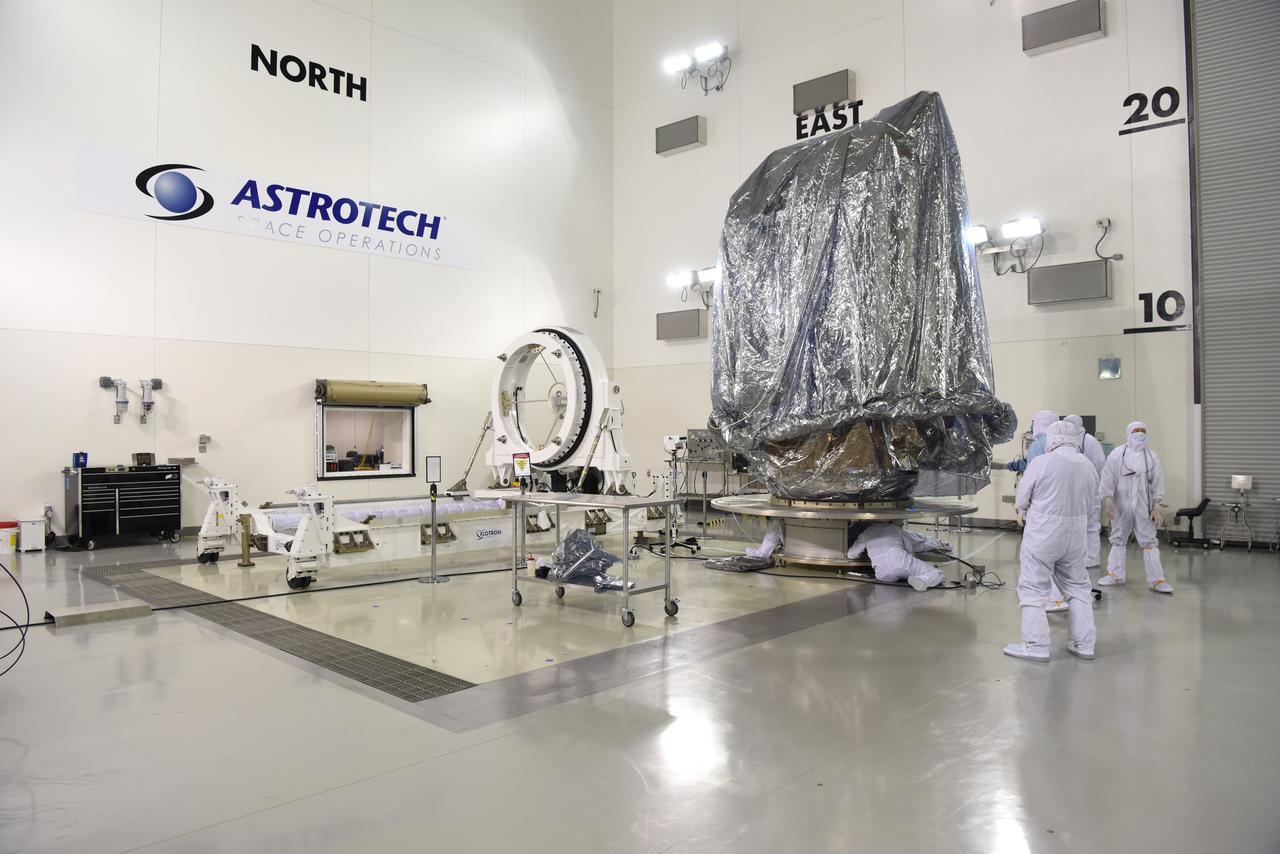
In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is prepared for placing it in a protective container, then mounting on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, arrives at Space Launch Complex 2 packaged in a protective container. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex.
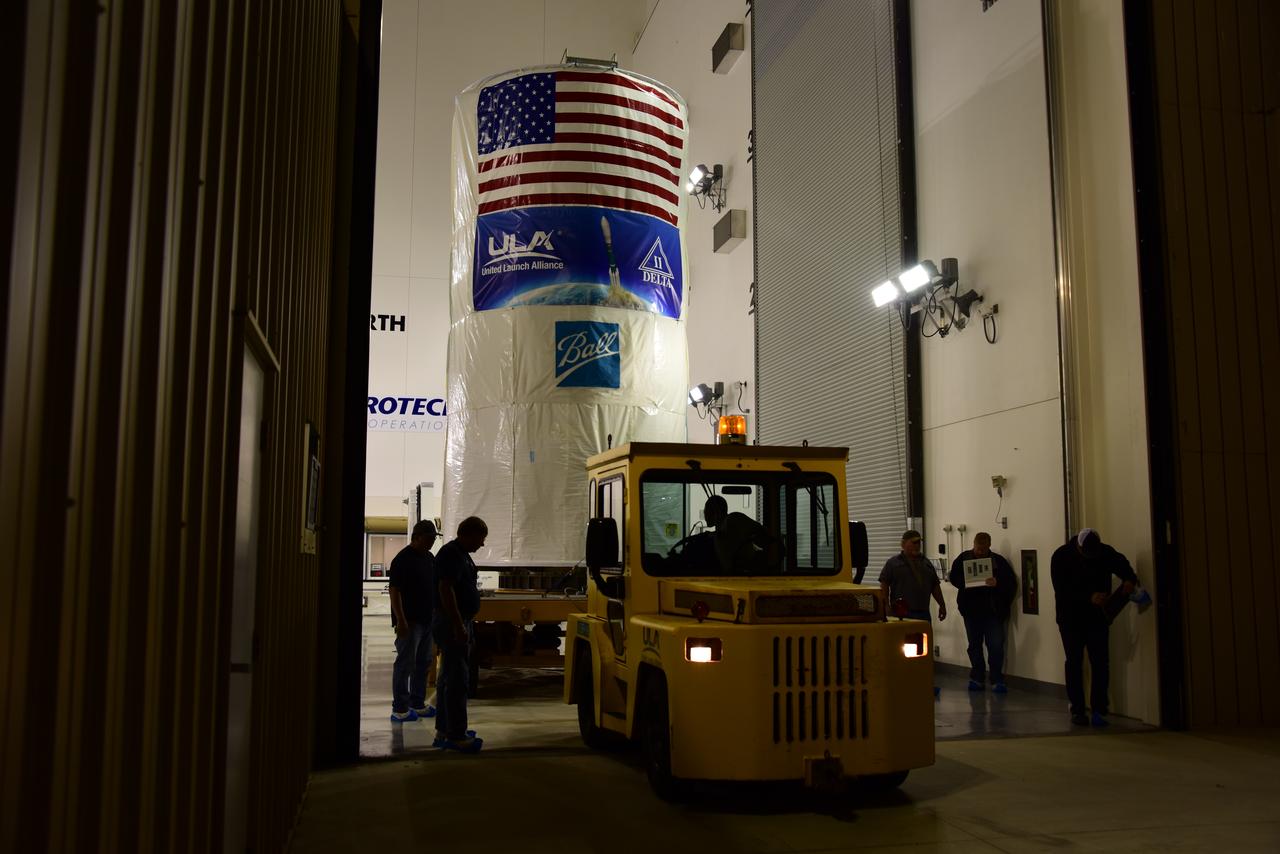

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft departs the Astrotech Processing Facility in a protective container on its way to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

A view of the Pacific coast at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. At the West Coast launch site, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is being prepared for liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.
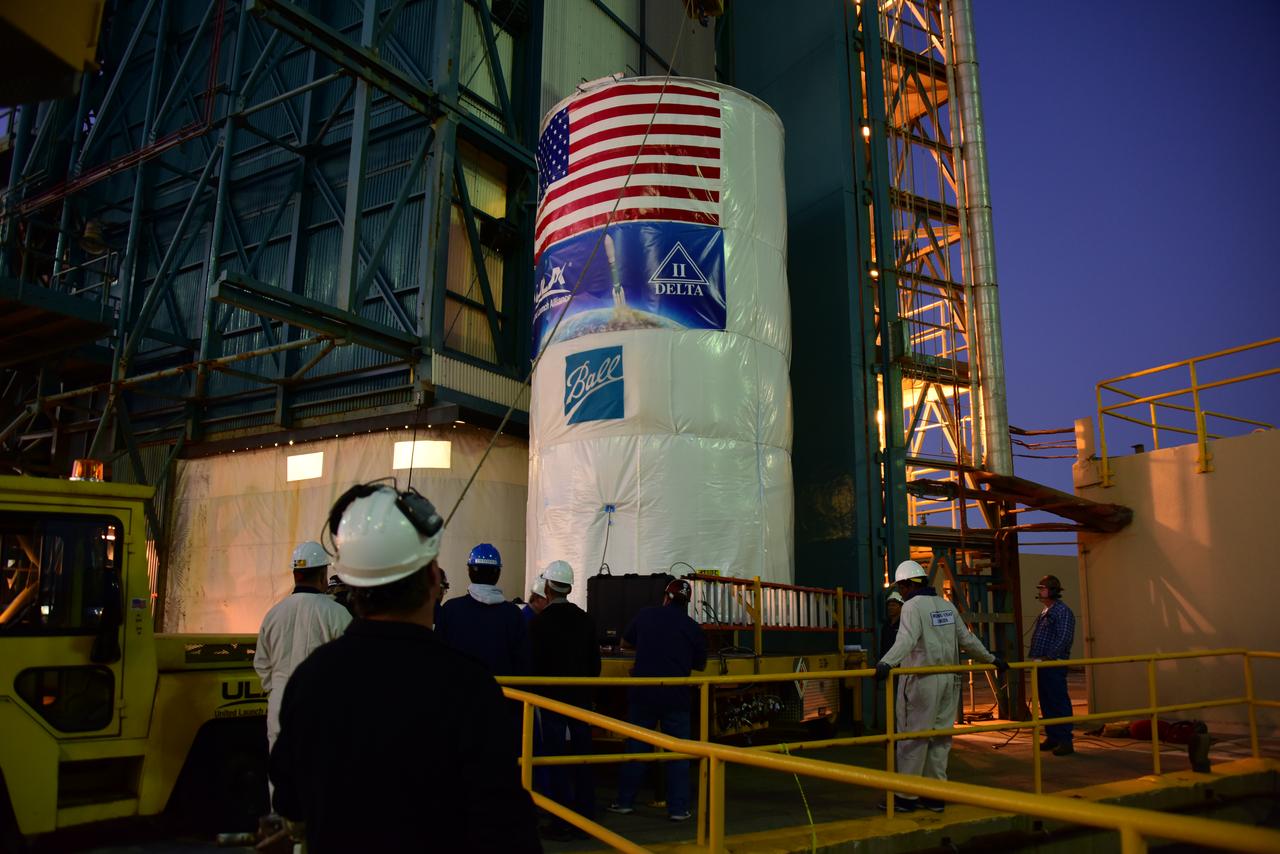

Packaged in a protective container, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is about to be lifted and mated atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, arrives at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020, aboard an Antonov cargo aircraft. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

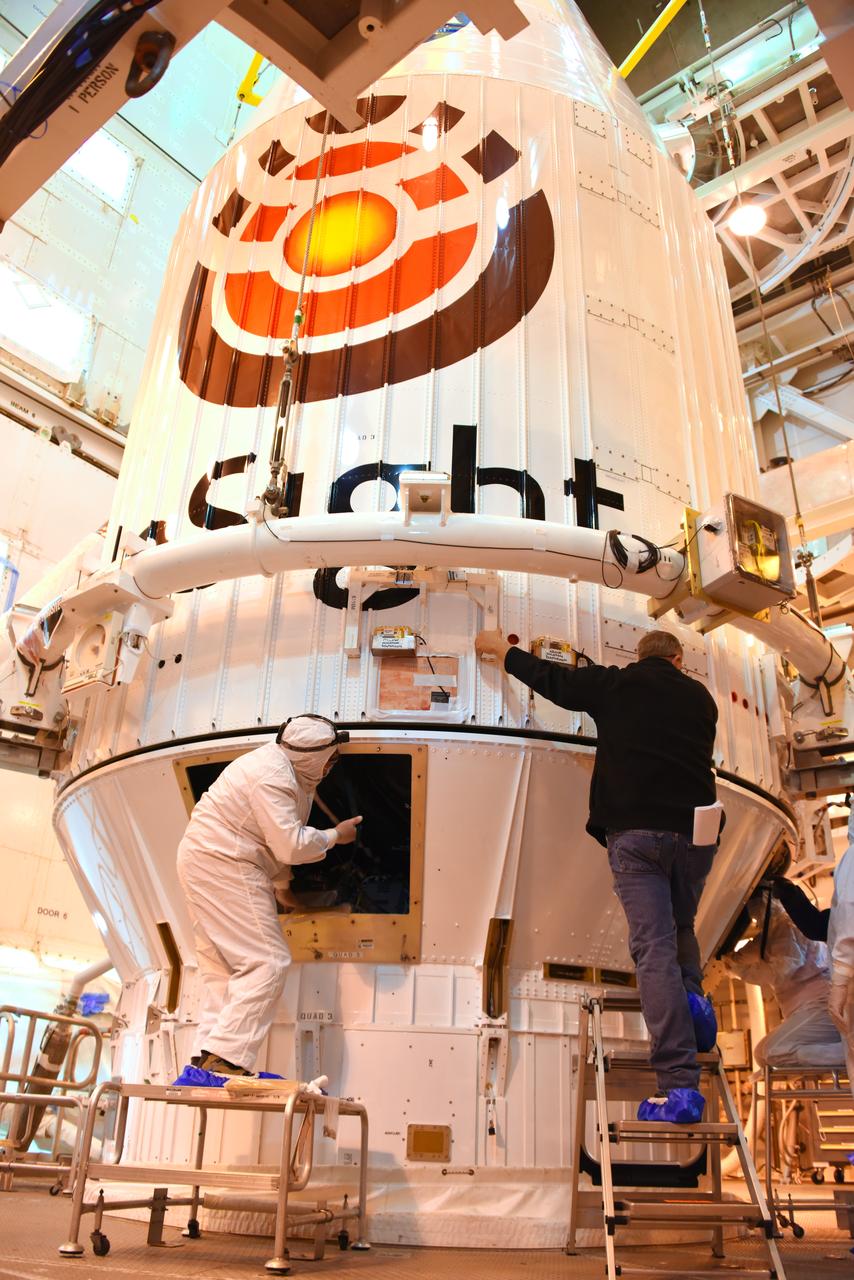
In the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander is encapsulated in its payload fairing. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.
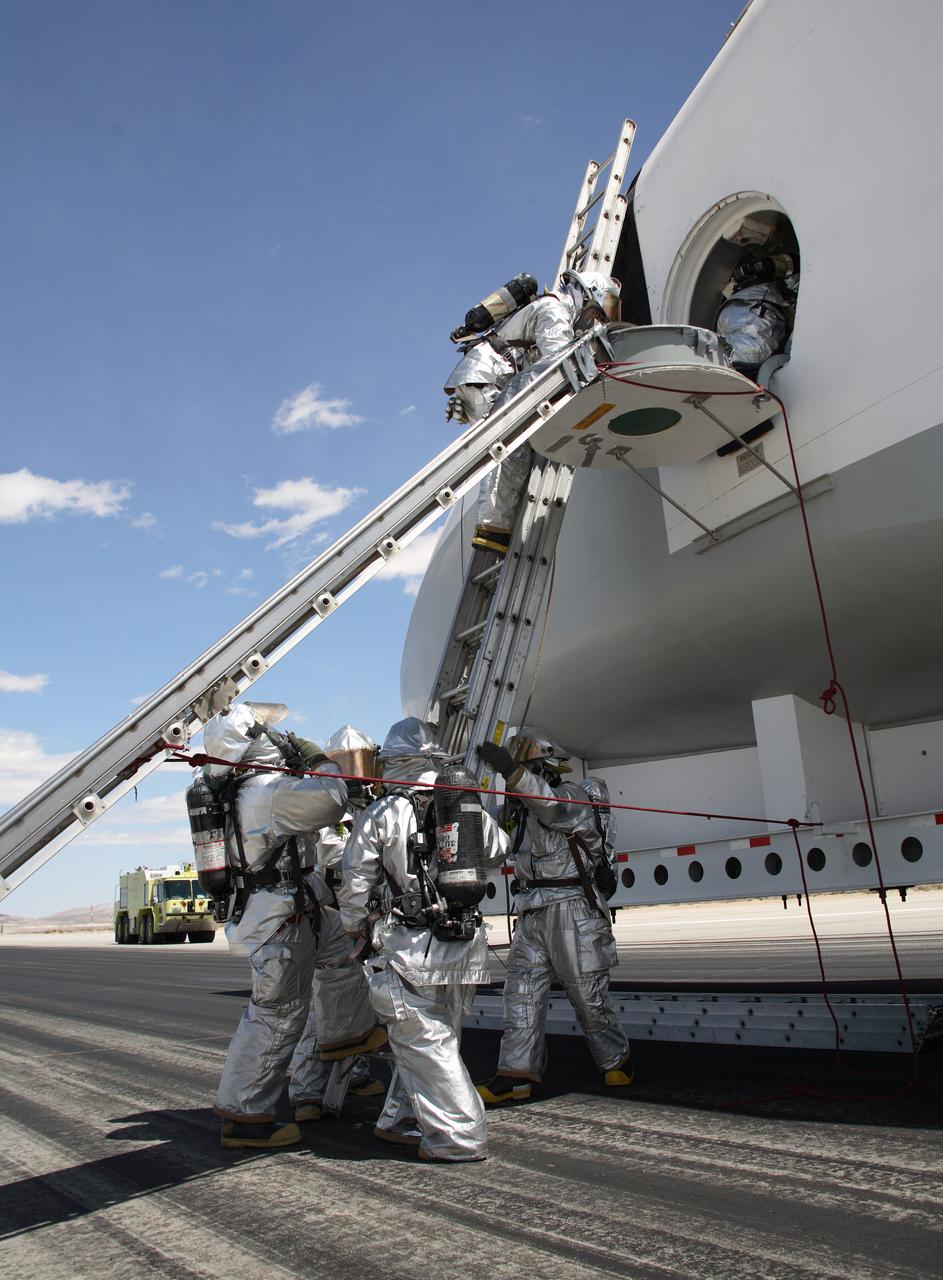

Air Force fire/rescue crew enter the space shuttle cabin mockup hatch to evacuate the shuttle crew during a shuttle rescue training exercise at Edwards AFB. (USAF photo # 070505-F-1287F-118)

In the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers encapsulate NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander in its payload fairing. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.
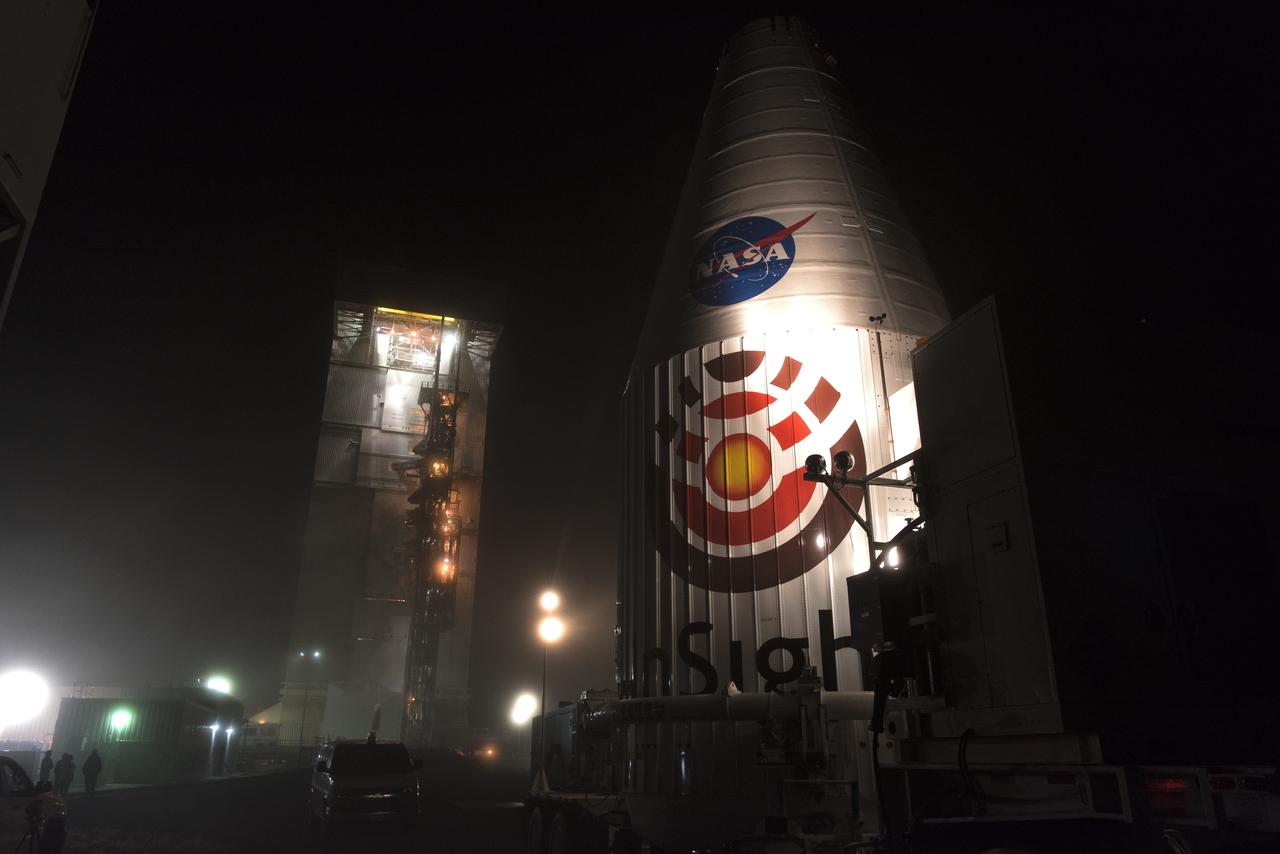

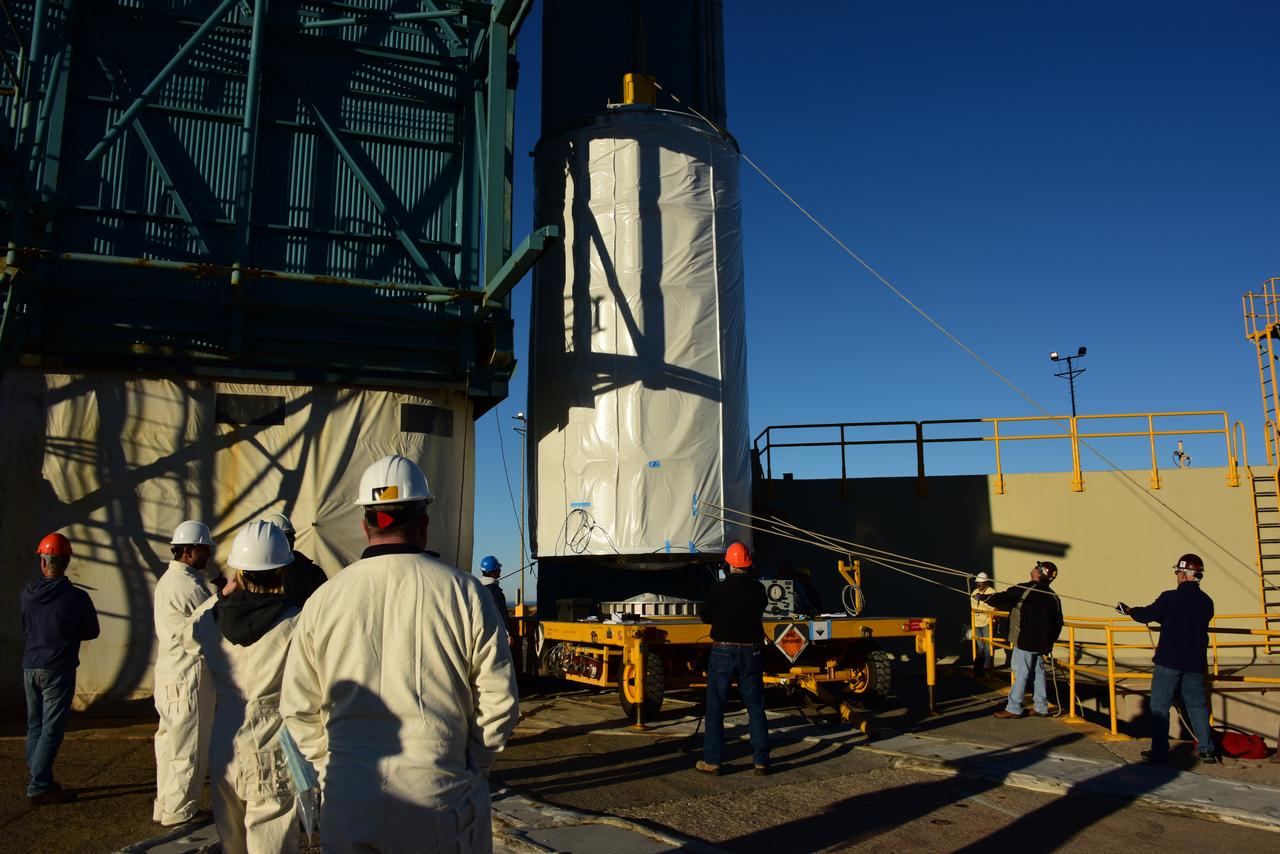
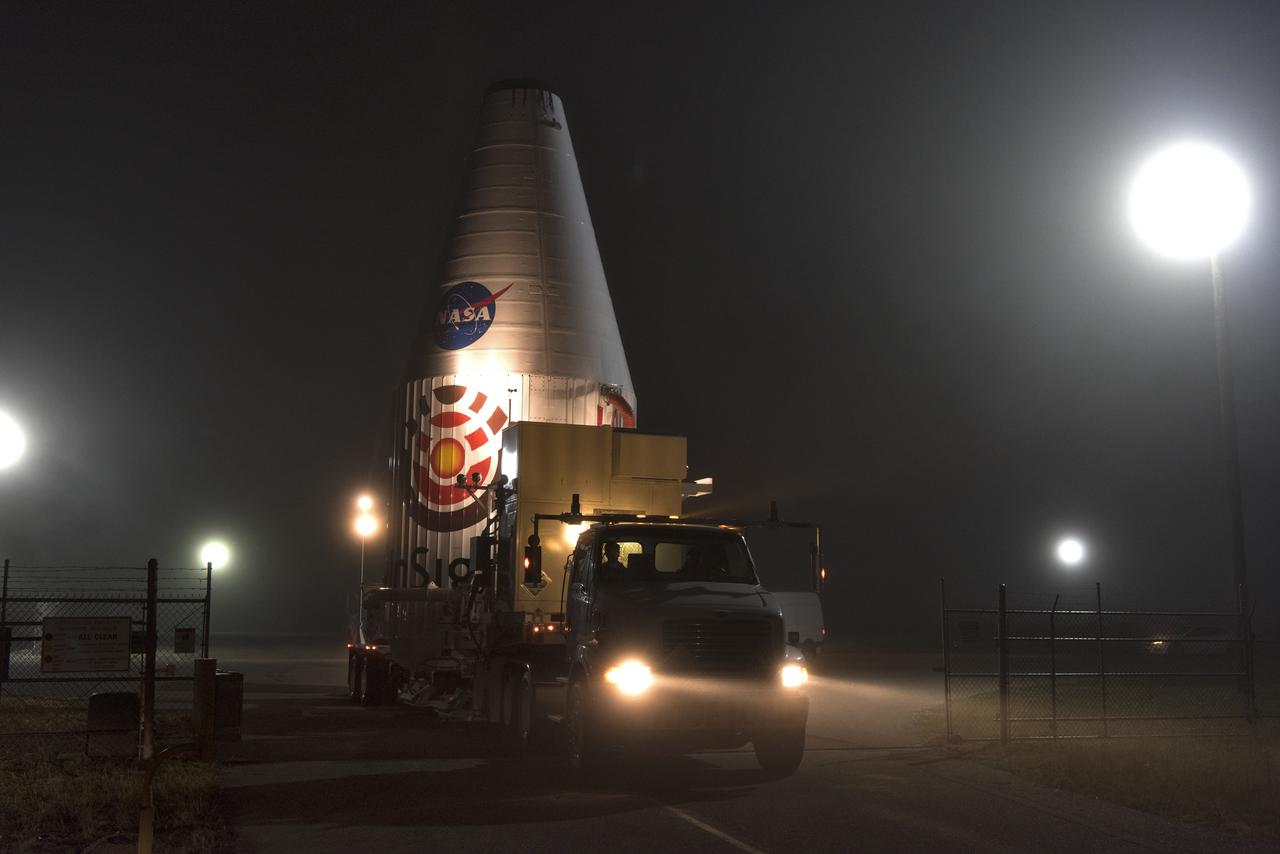
Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander is transported to Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.

Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander is transported to Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.
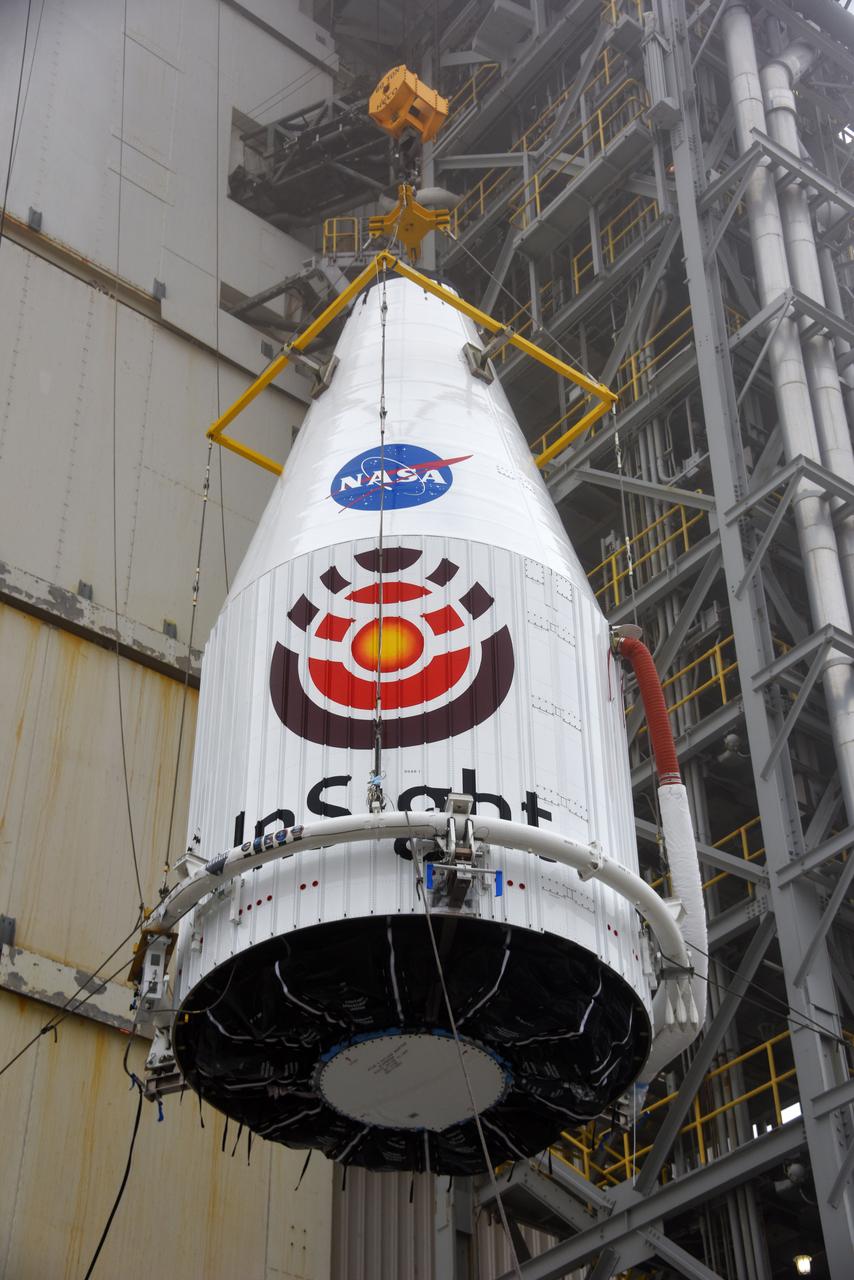

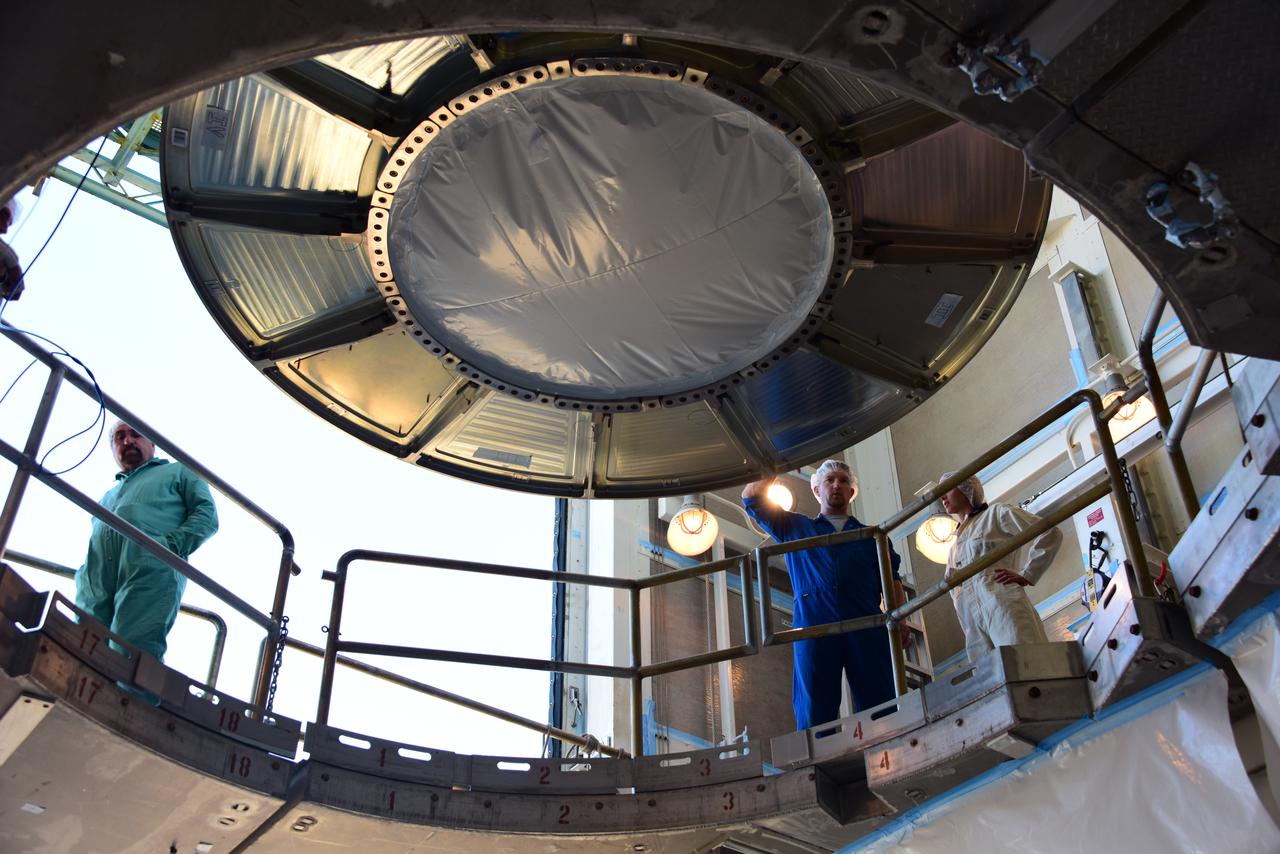
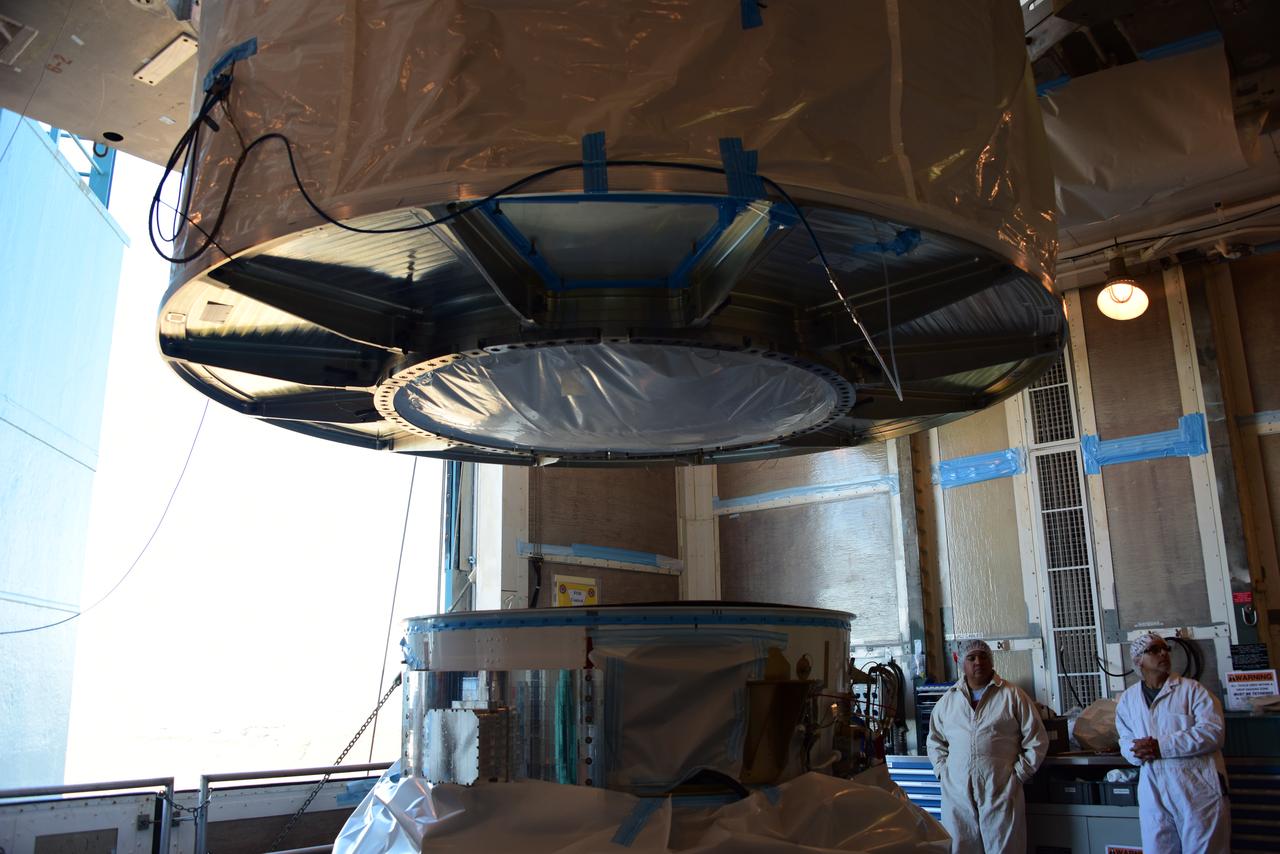
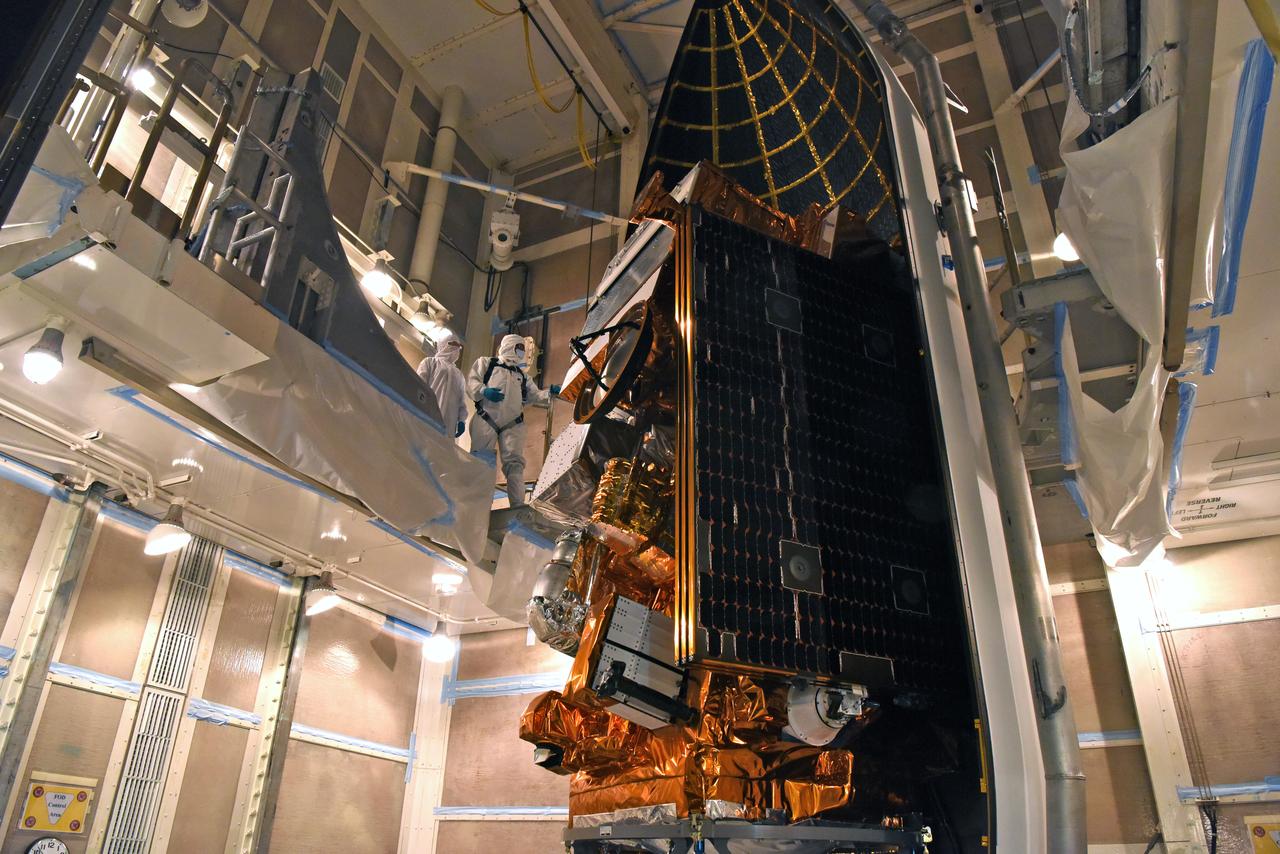
At Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane is used to lift NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.
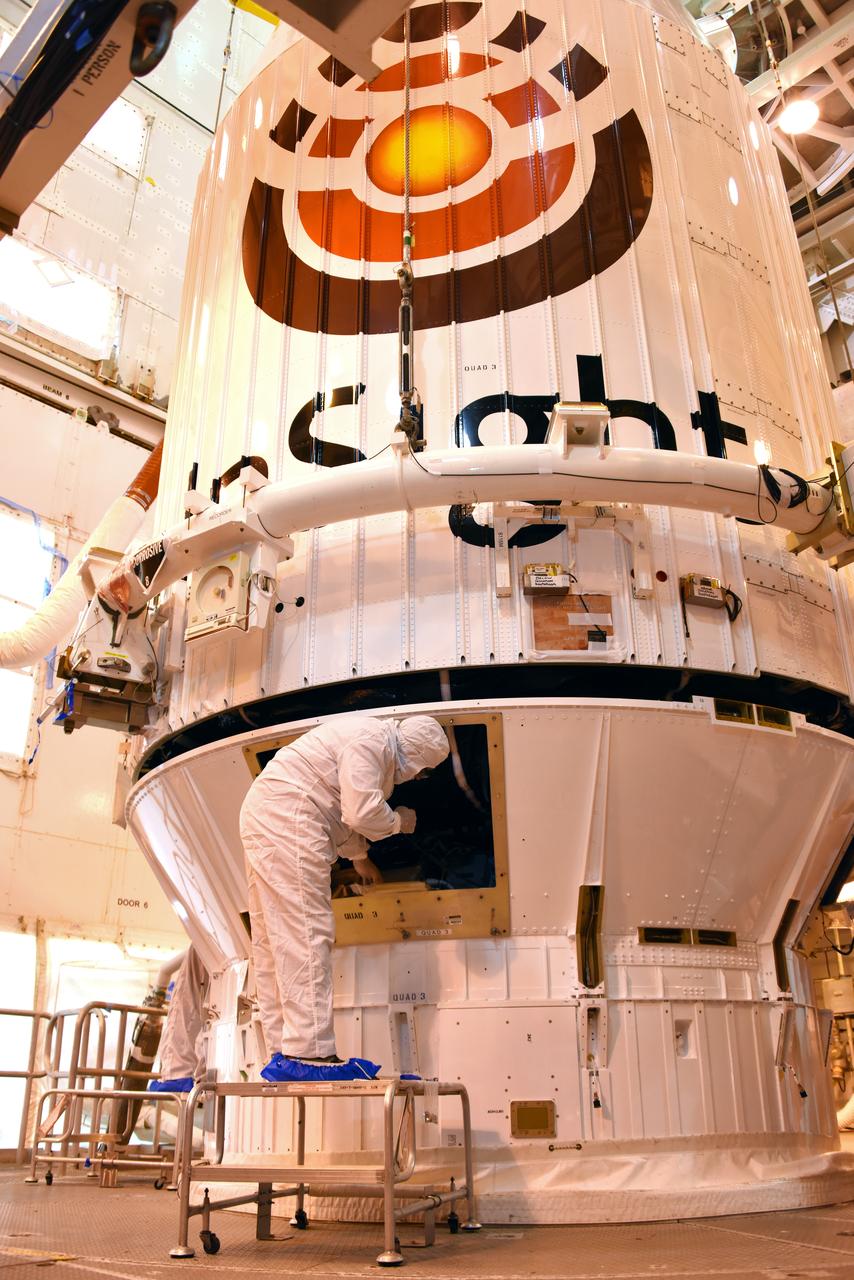

At Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers position NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.

Encapsulated in its payload fairing NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander is prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.
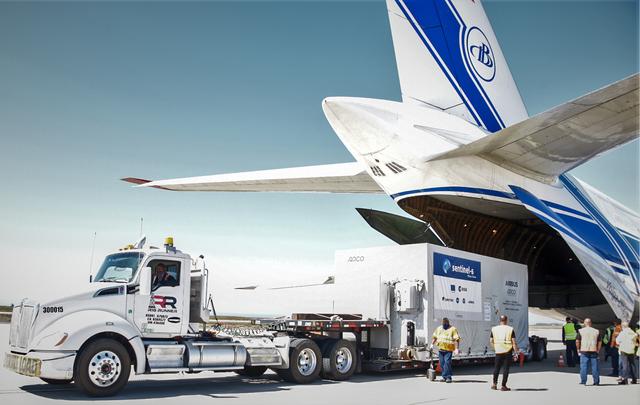

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, arrives at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020, aboard an Antonov cargo aircraft. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
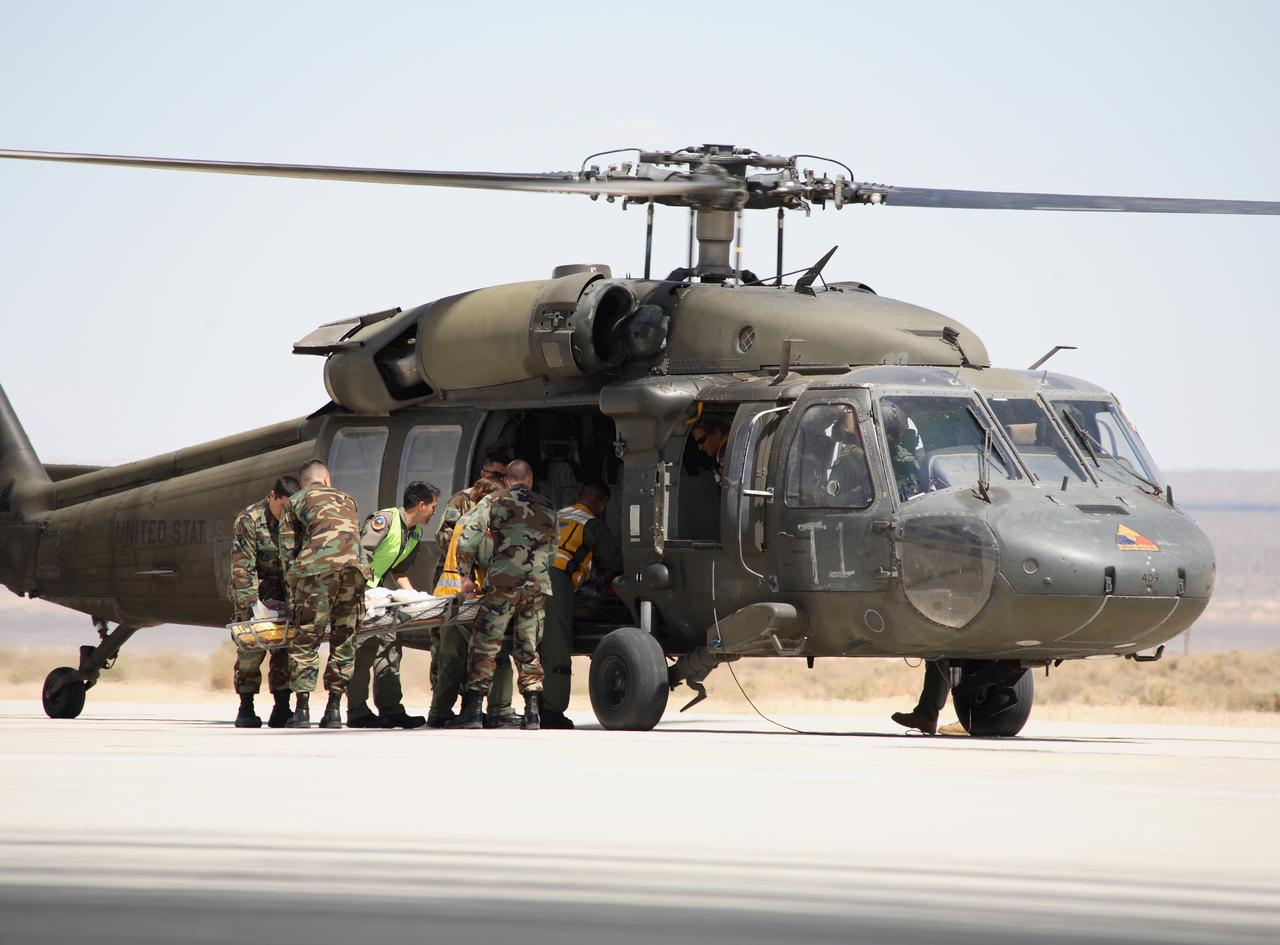

Air Force rescue team members load the volunteer "injured astronaut" on a stretcher into a Blackhawk helicopter for evacuation to a hospital during the exercise. (USAF photo # 070505-F-1287F-166)
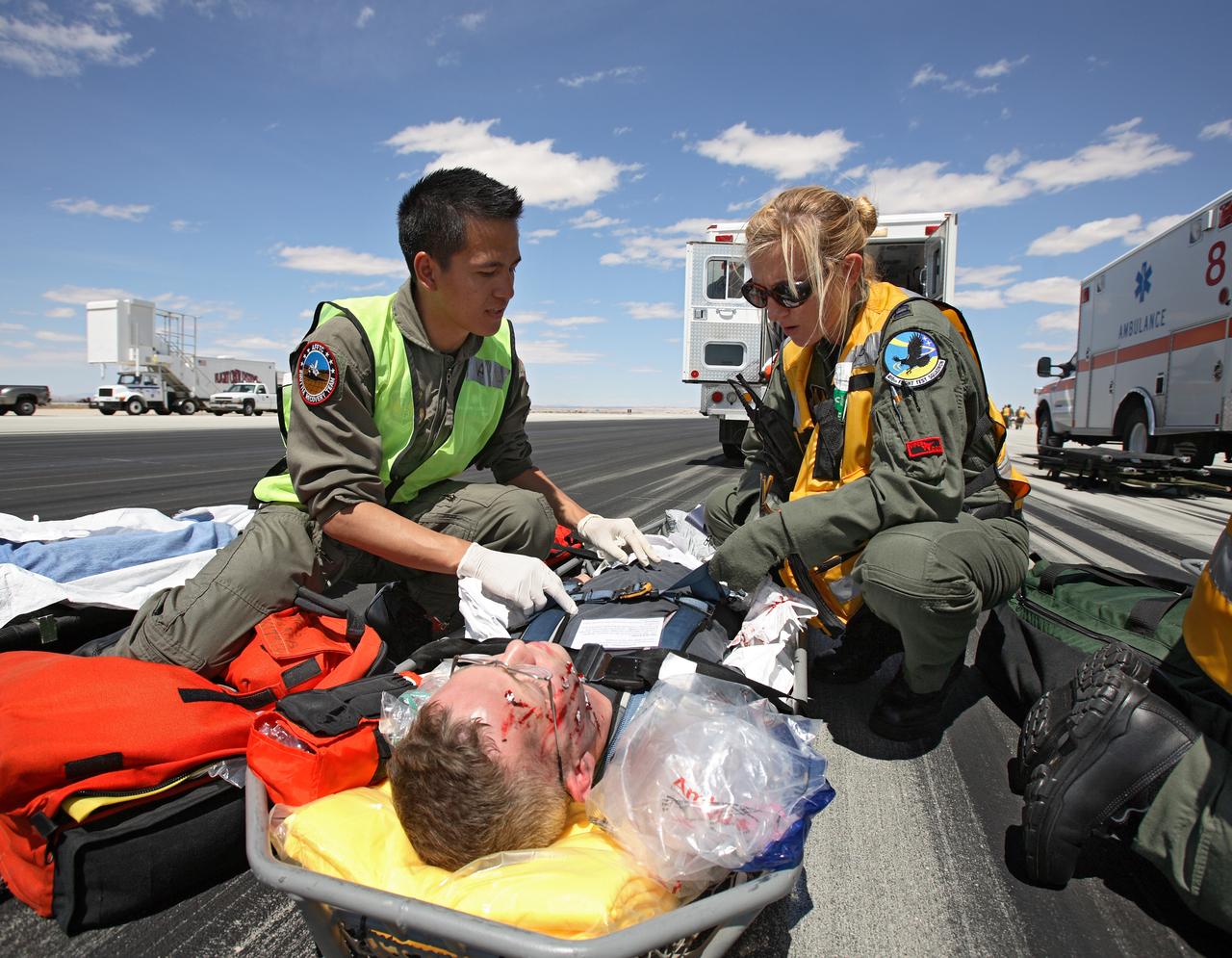

Complete with makeup to simulate facial injuries, a volunteer "astronaut" is tended to by aeromedical rescue staff after evacuation from the shuttle mockup. (USAF photo # 070505-F-1287F-145)

In the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers encapsulate NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander in its payload fairing. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.

At Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers position NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.
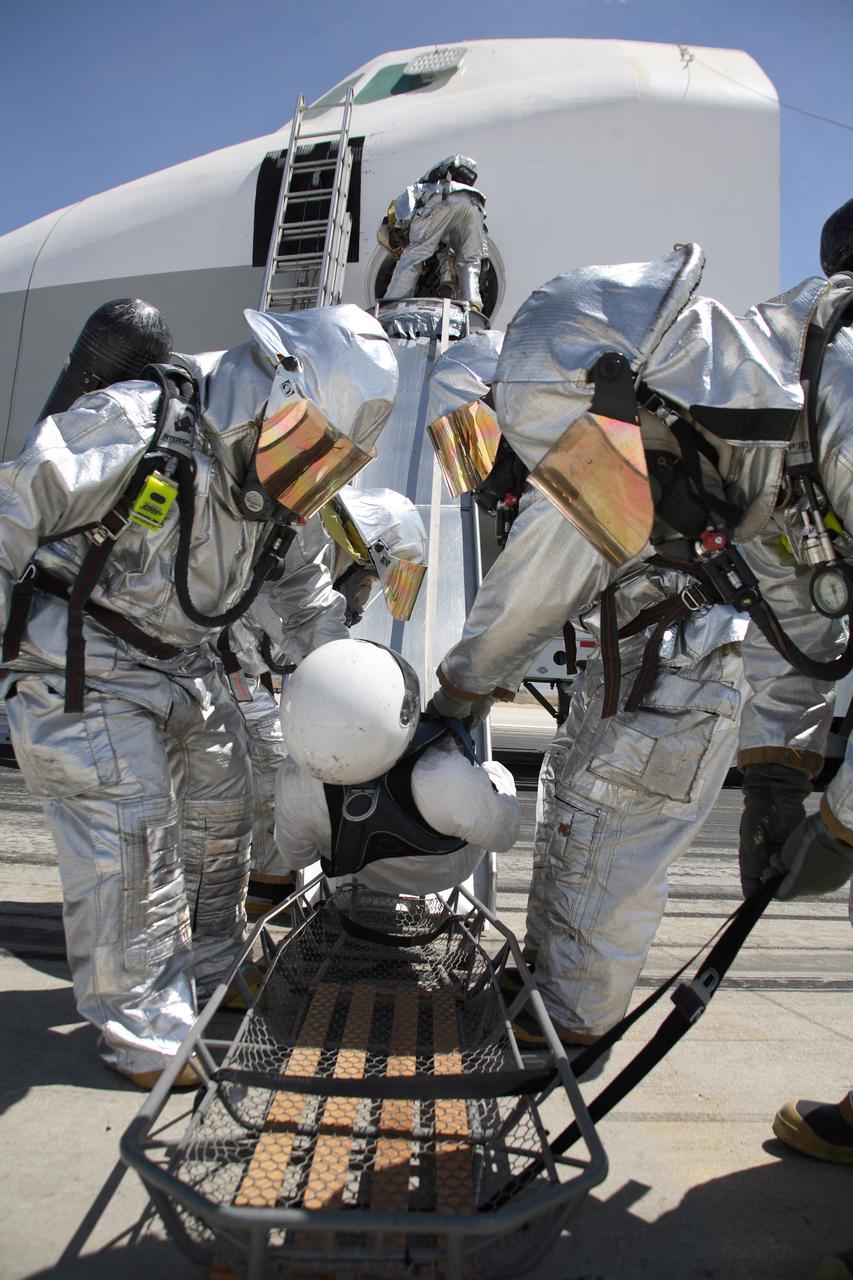

Air Force fire/rescue crew place a volunteer "injured astronaut" on a stretcher after exiting the shuttle cabin mockup during the training exercise. (USAF photo # 070505-F-1287F-126)
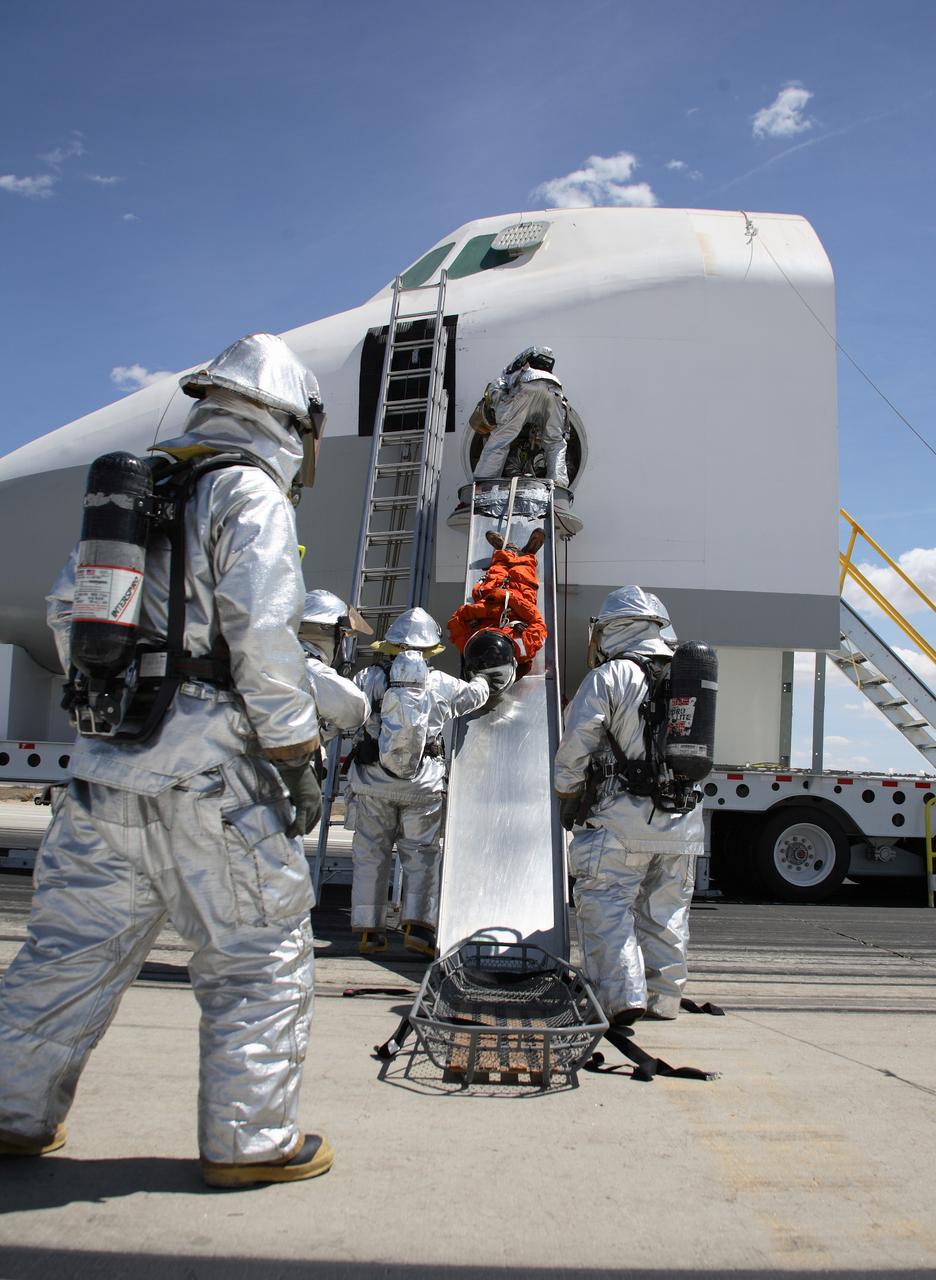

Clad in thermal protection suits, fire/rescue crew aid a volunteer "Injured astronaut" to a head-first ride down the exit slide from the shuttle cabin mockup. (USAF photo # 070505-F-1287F-132)

Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander is transported to Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.

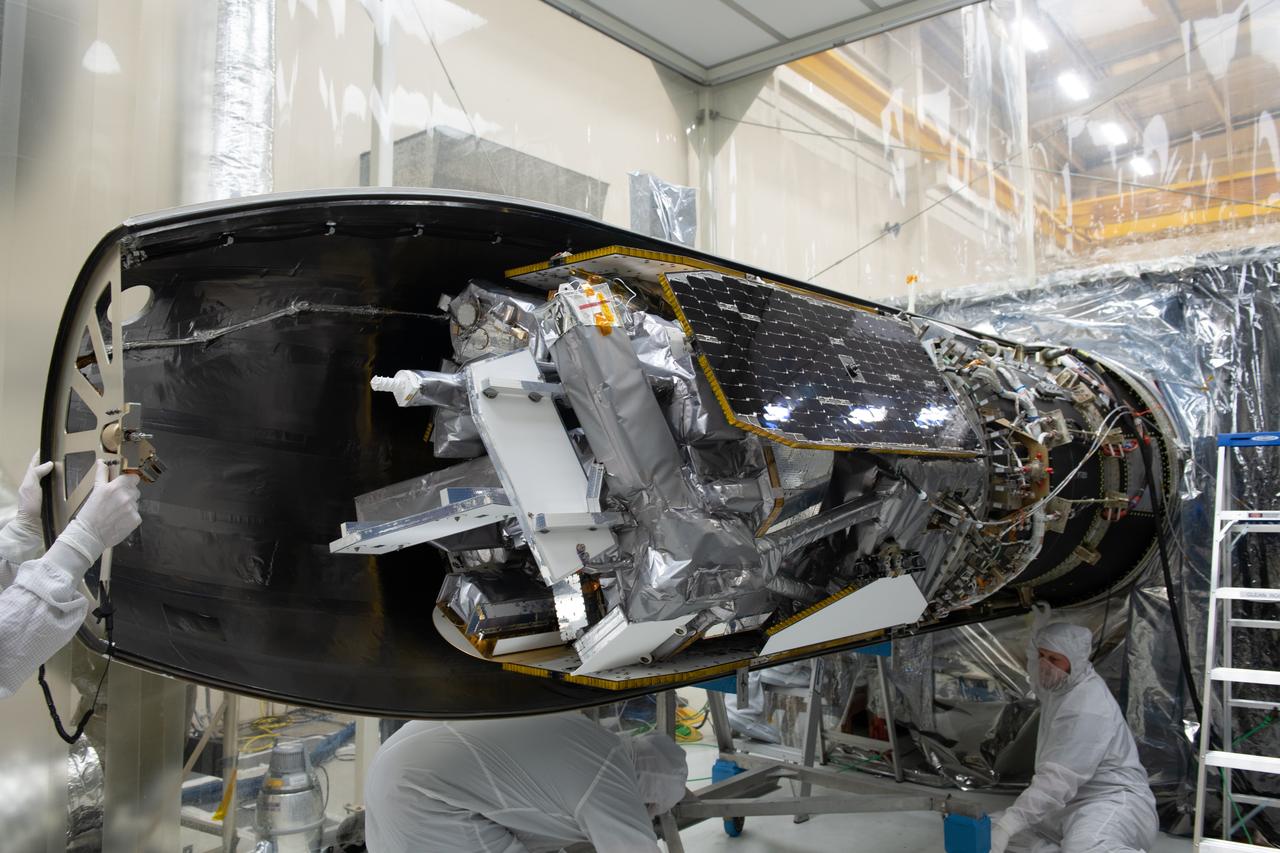
Encapsulated in its payload fairing, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, Mars lander is transported to Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. InSight will be the first mission to look deep beneath the Martian surface. It will study the planet's interior by measuring its heat output and listen for marsquakes. The spacecraft will use the seismic waves generated by marsquakes to develop a map of the planet’s deep interior. The resulting insight into Mars’ formation will provide a better understanding of how other rocky planets, including Earth, were created. InSight is scheduled for liftoff May 5, 2018.

The starboard side of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket’s payload fairing has been installed around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 17, 2019. ICON launched on the Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
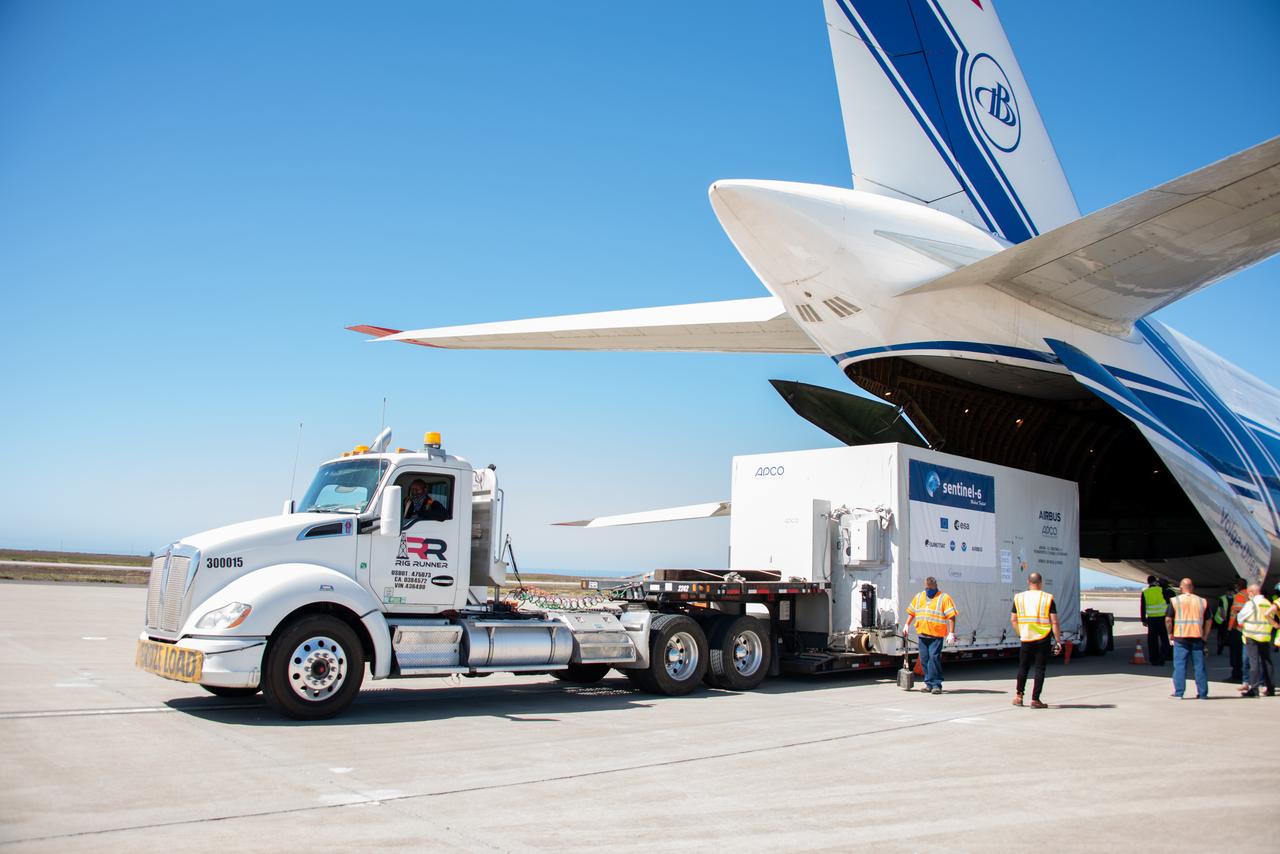

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, is placed on a transport vehicle after the spacecraft’s arrival at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California aboard a Antonov cargo aircraft, Sept. 24, 2020. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
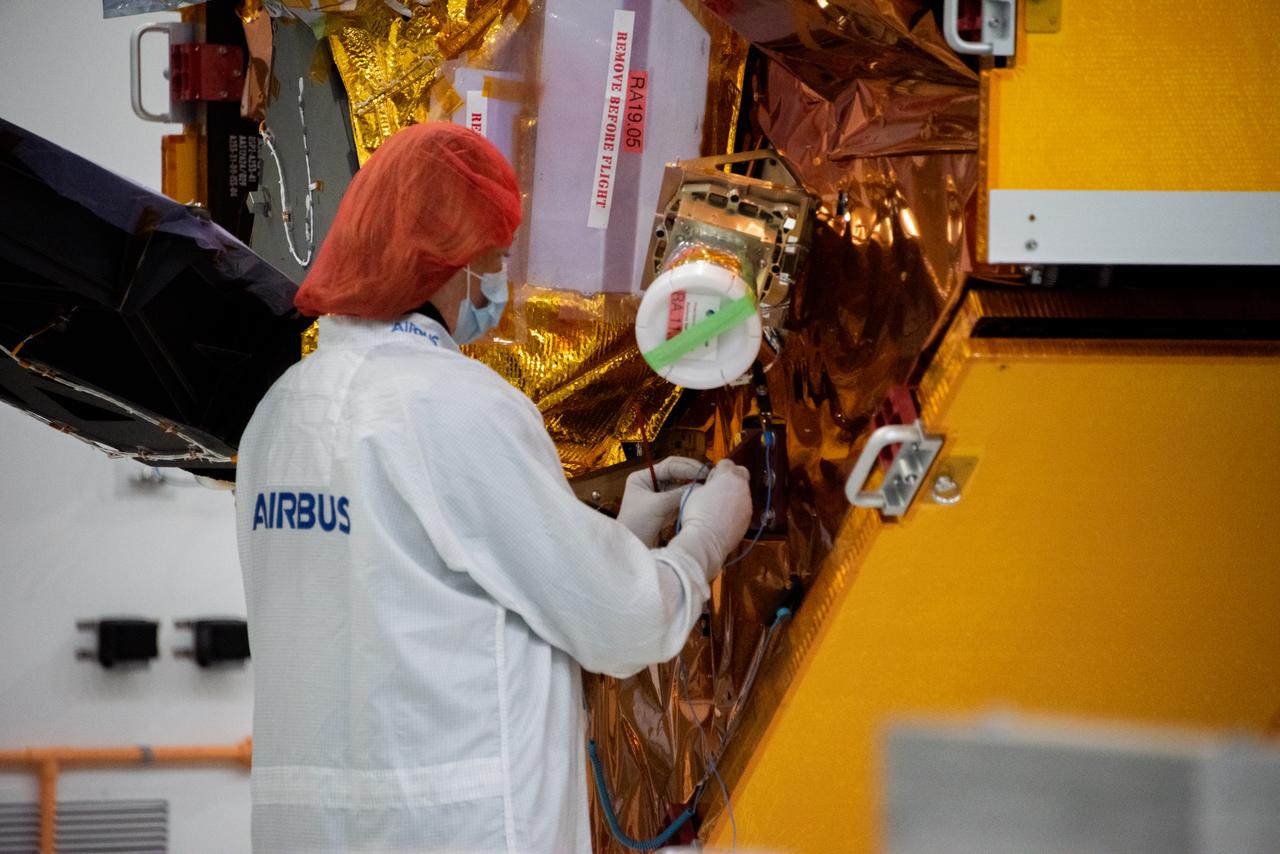

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
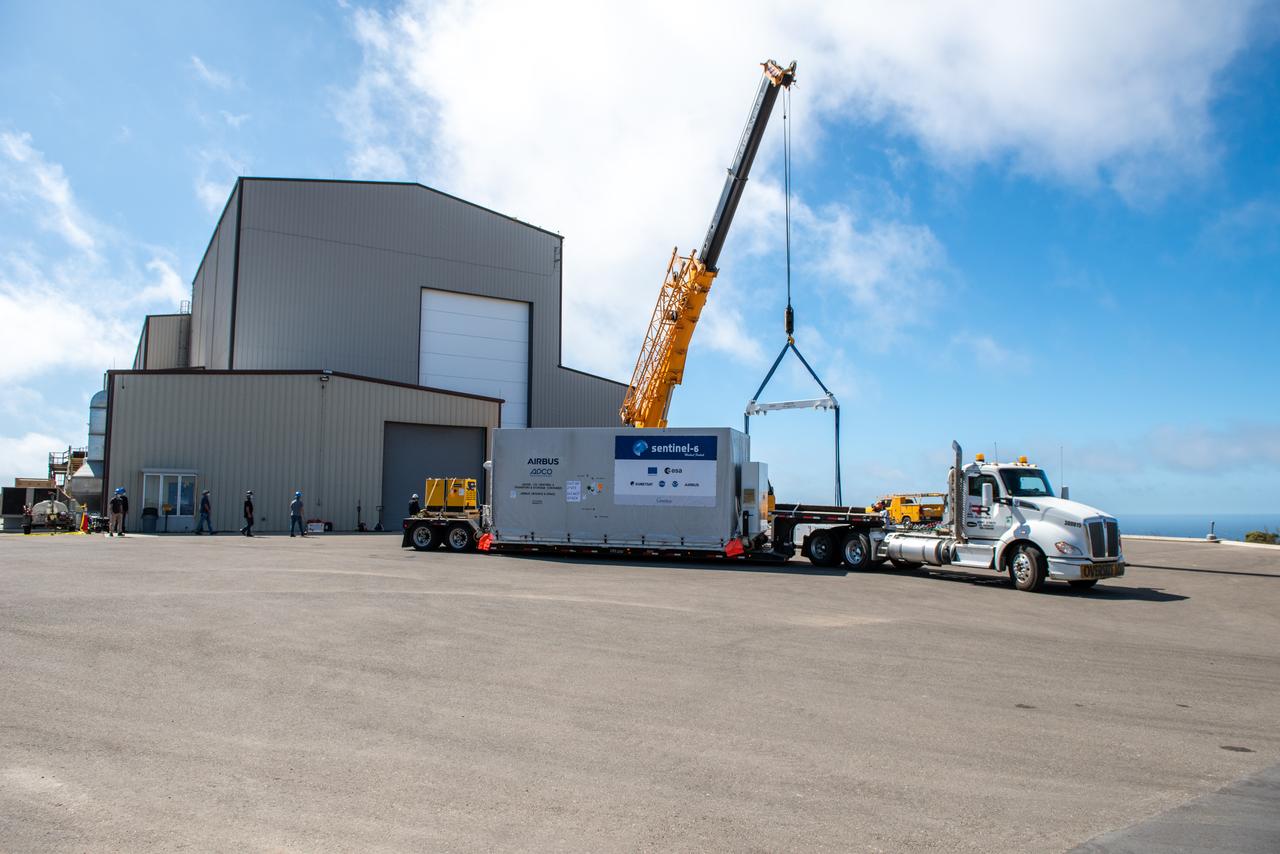

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

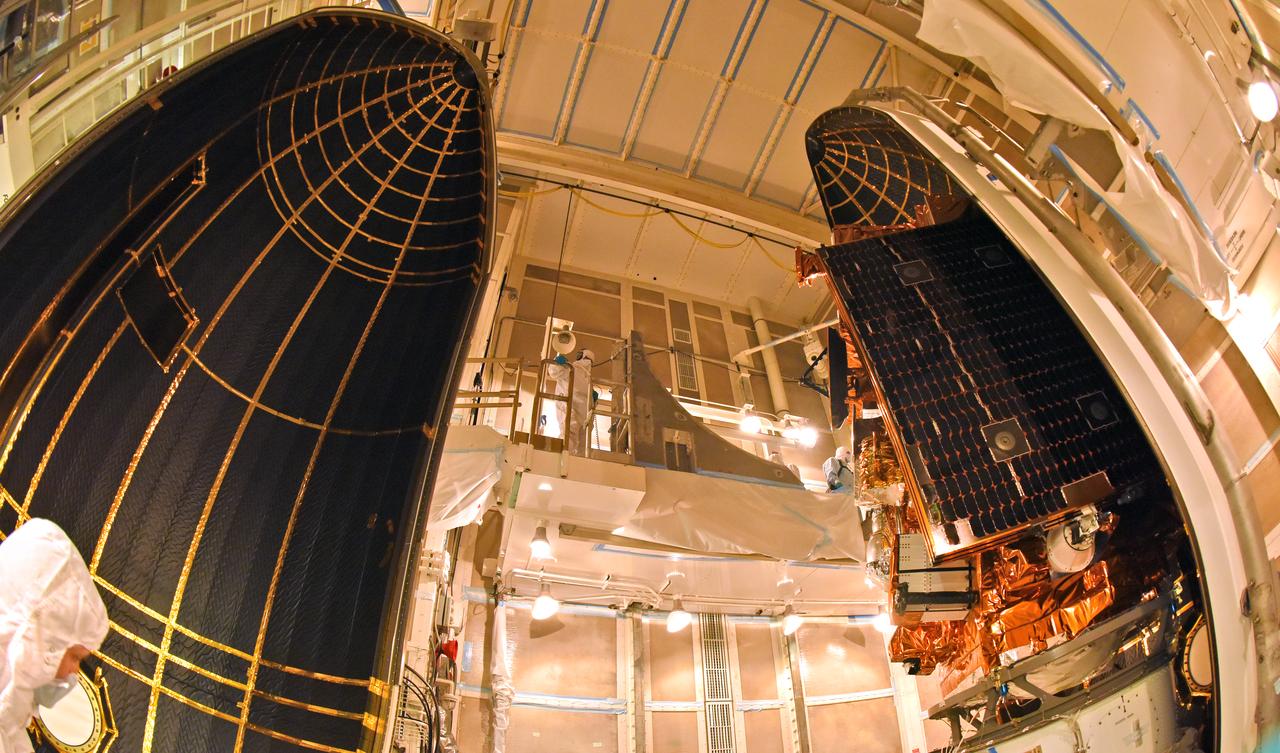
Technicians extend the solar array on NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) during a deployment test inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 10, 2019. ICON will launch on a Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
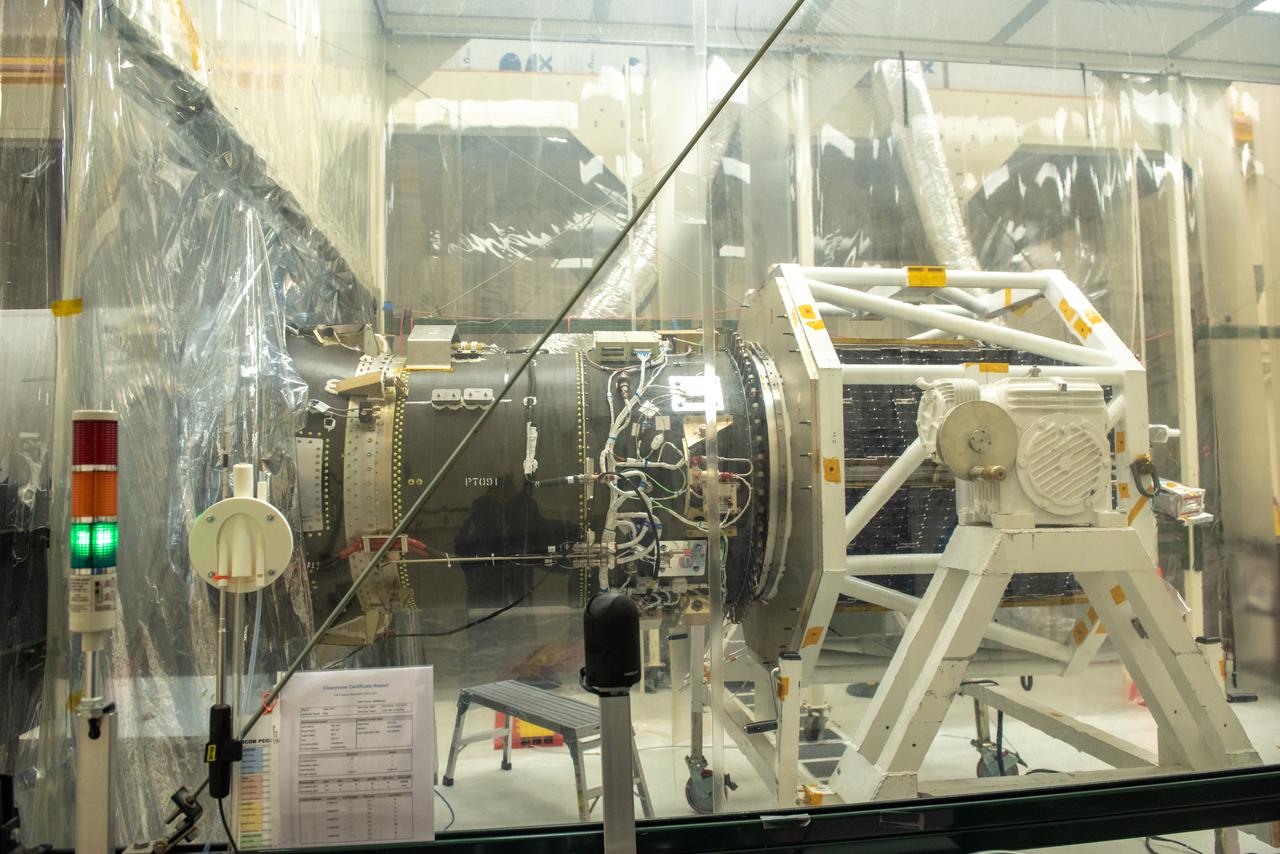
NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is attached to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 10, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
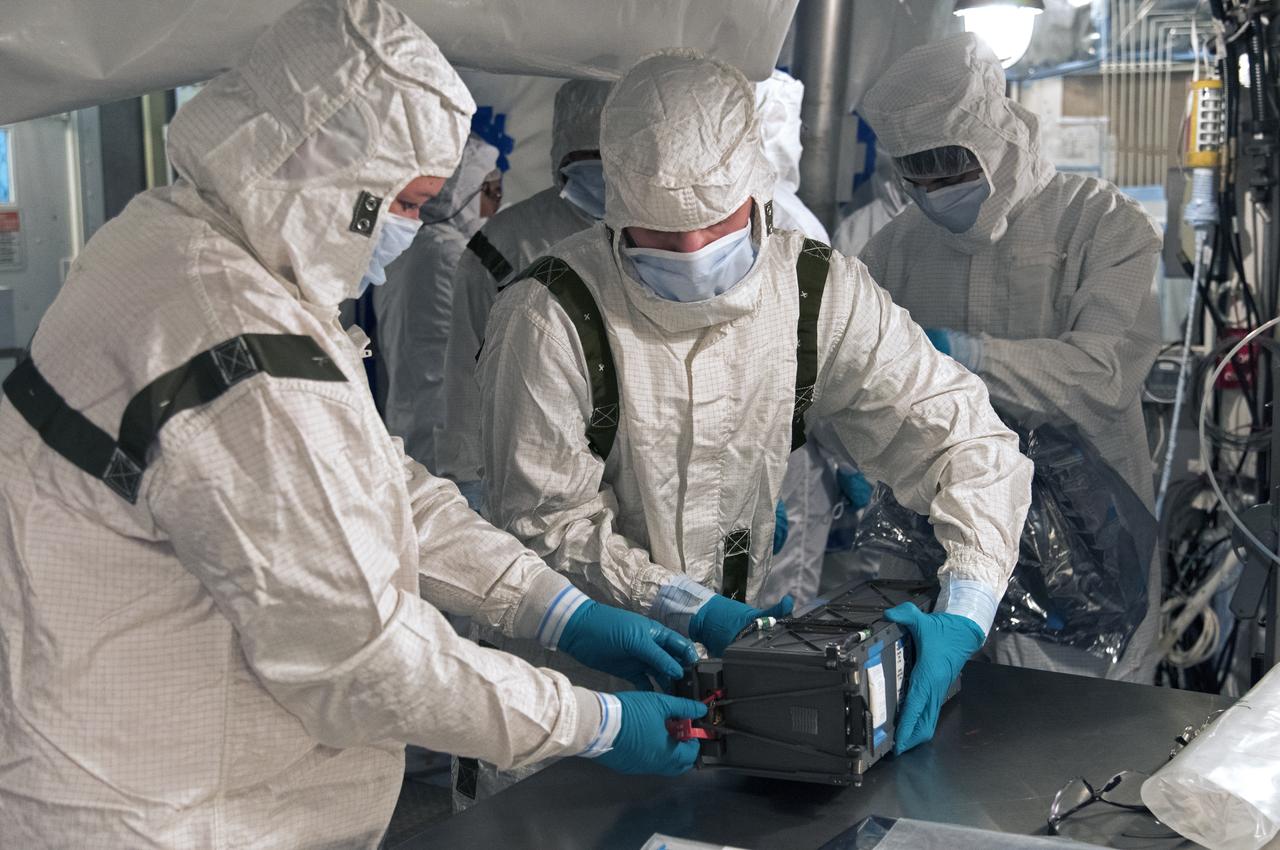

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container for installation on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is installed on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare to install a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, begins rollout from Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
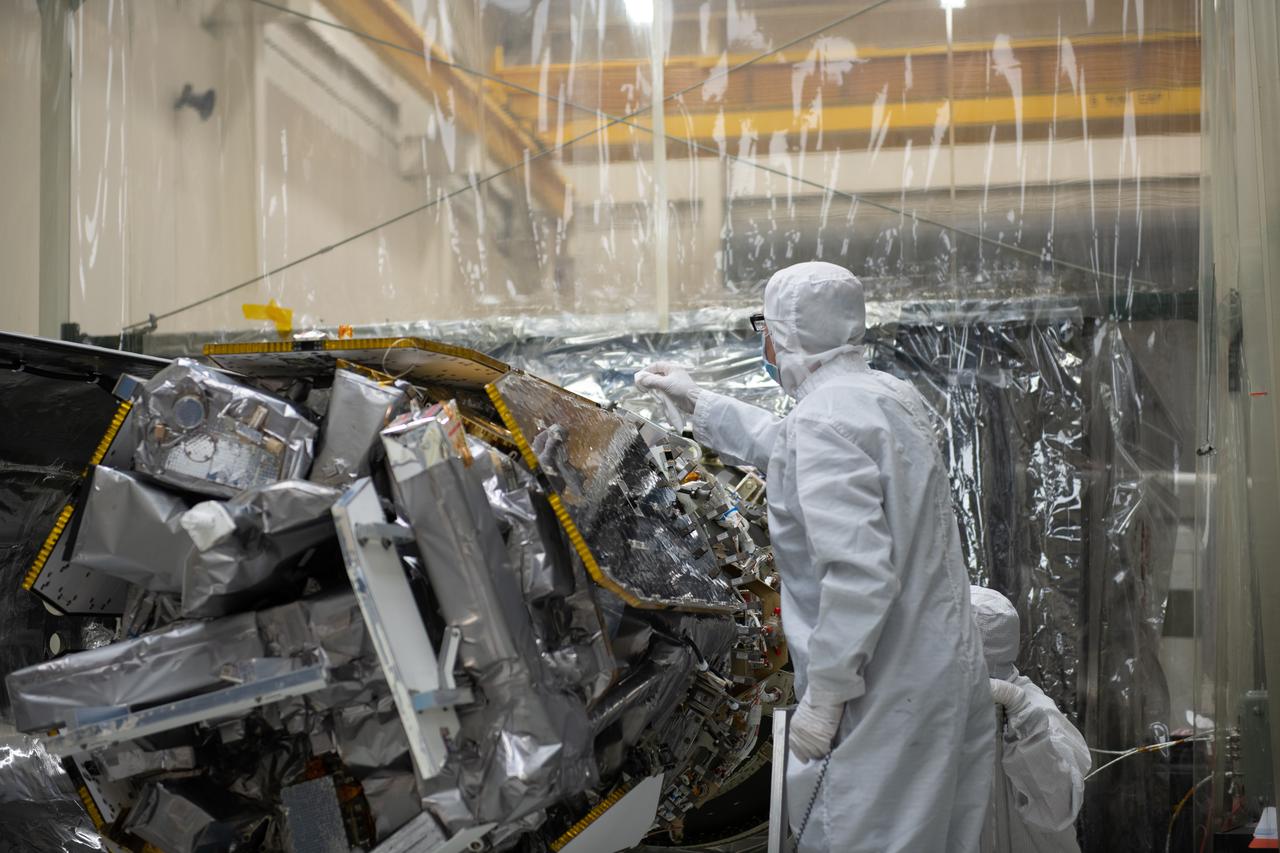

Technicians prepare to install the starboard side of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket’s payload fairing around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 17, 2019. ICON launched on the Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
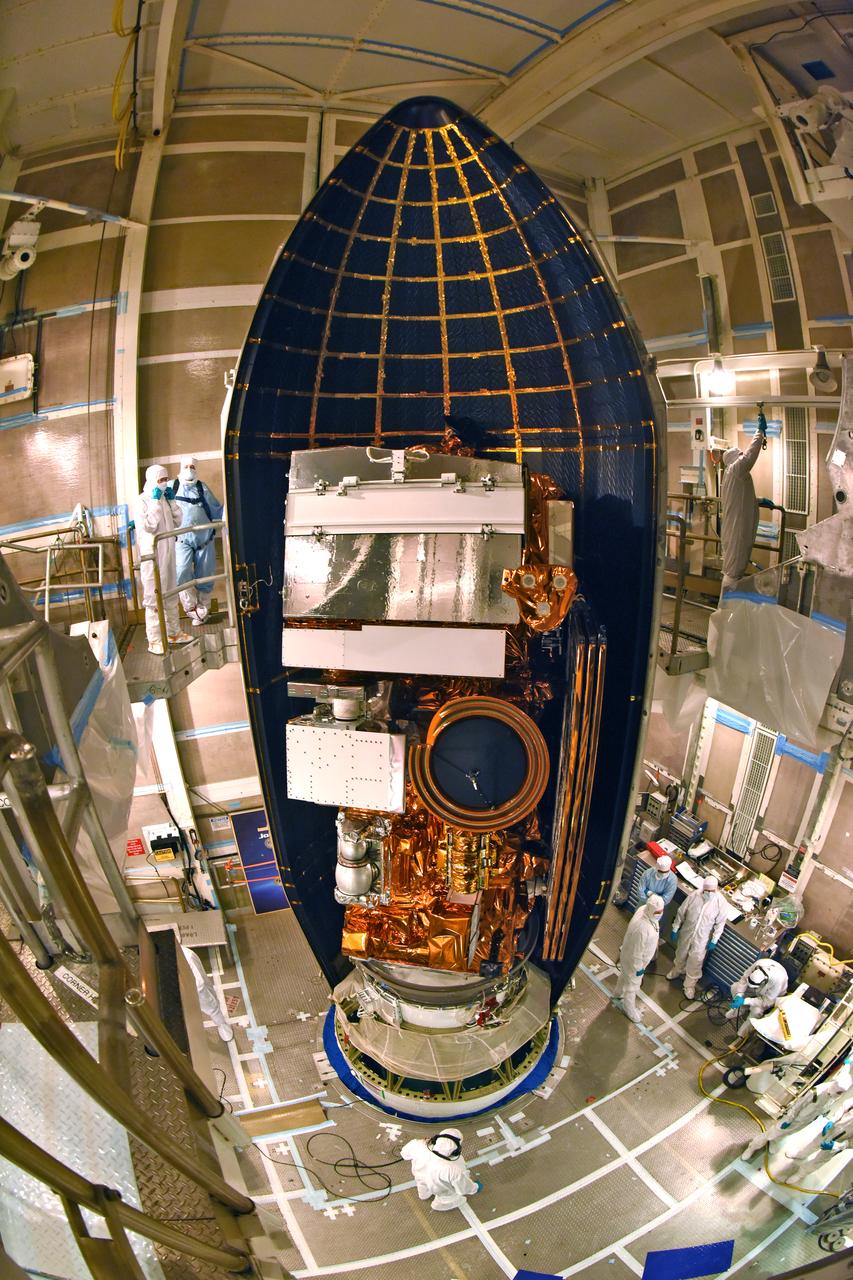
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, this wide angle view shows the payload fairing as it is installed encapsulating the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2 at 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
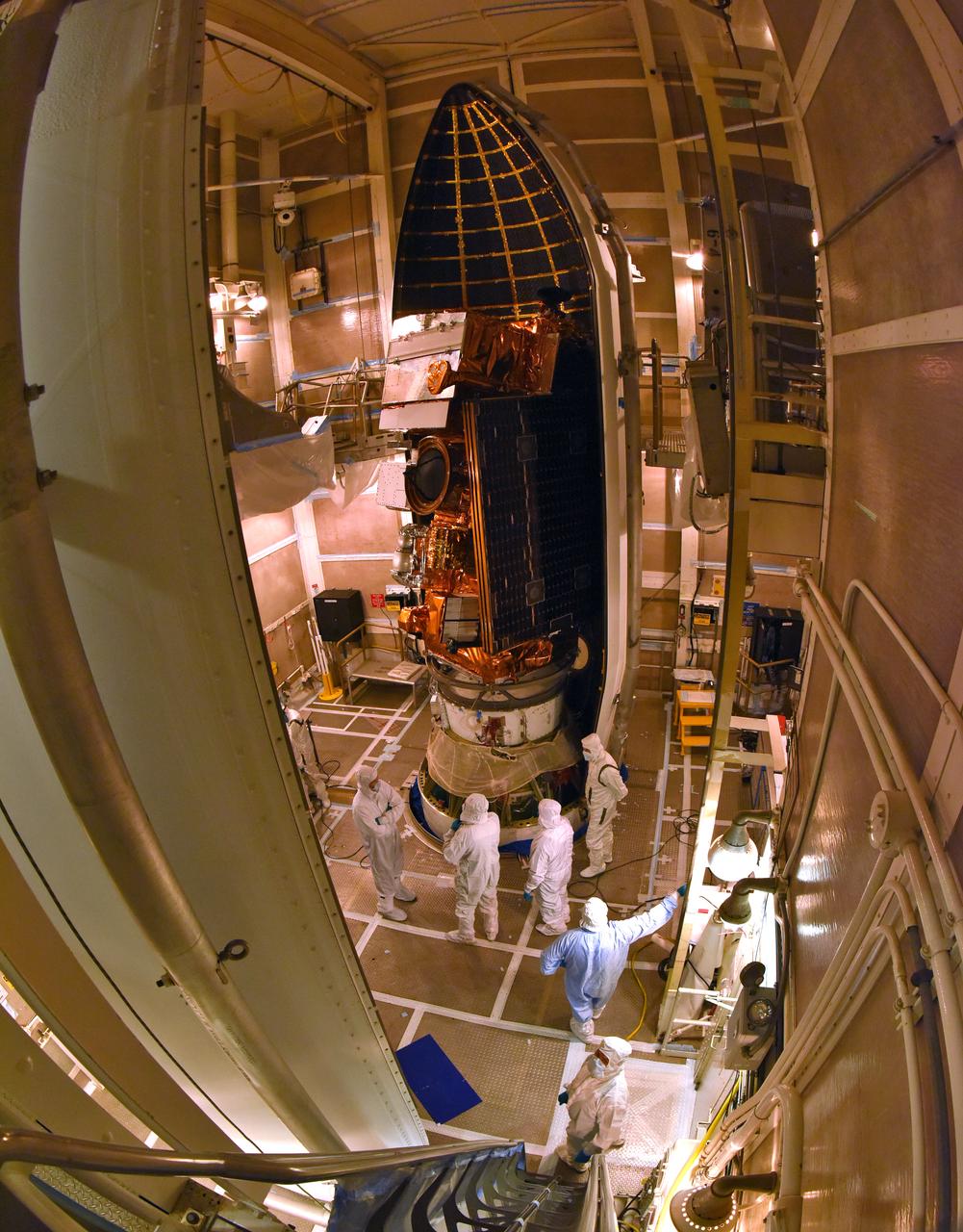

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, this wide angle view shows the payload fairing as it is installed encapsulating the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2 at 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
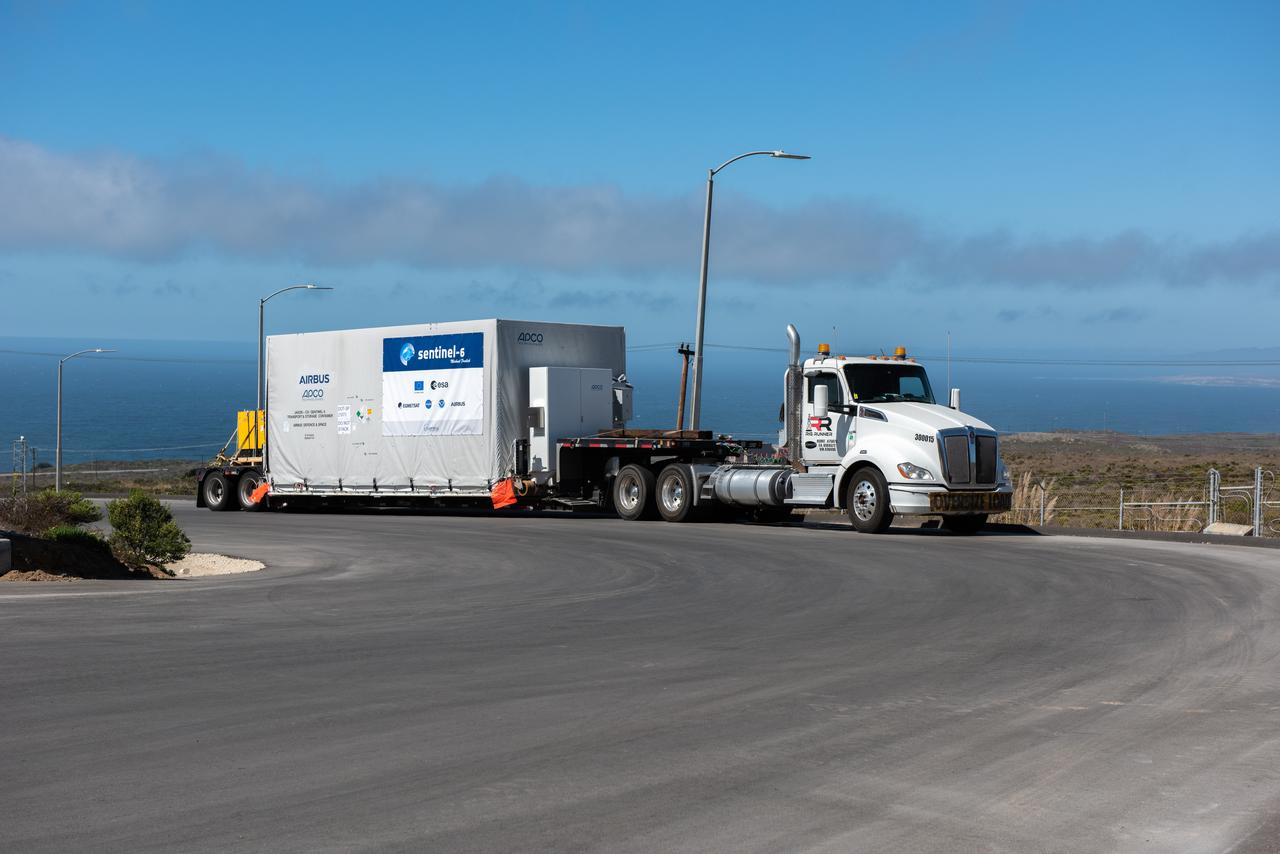

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
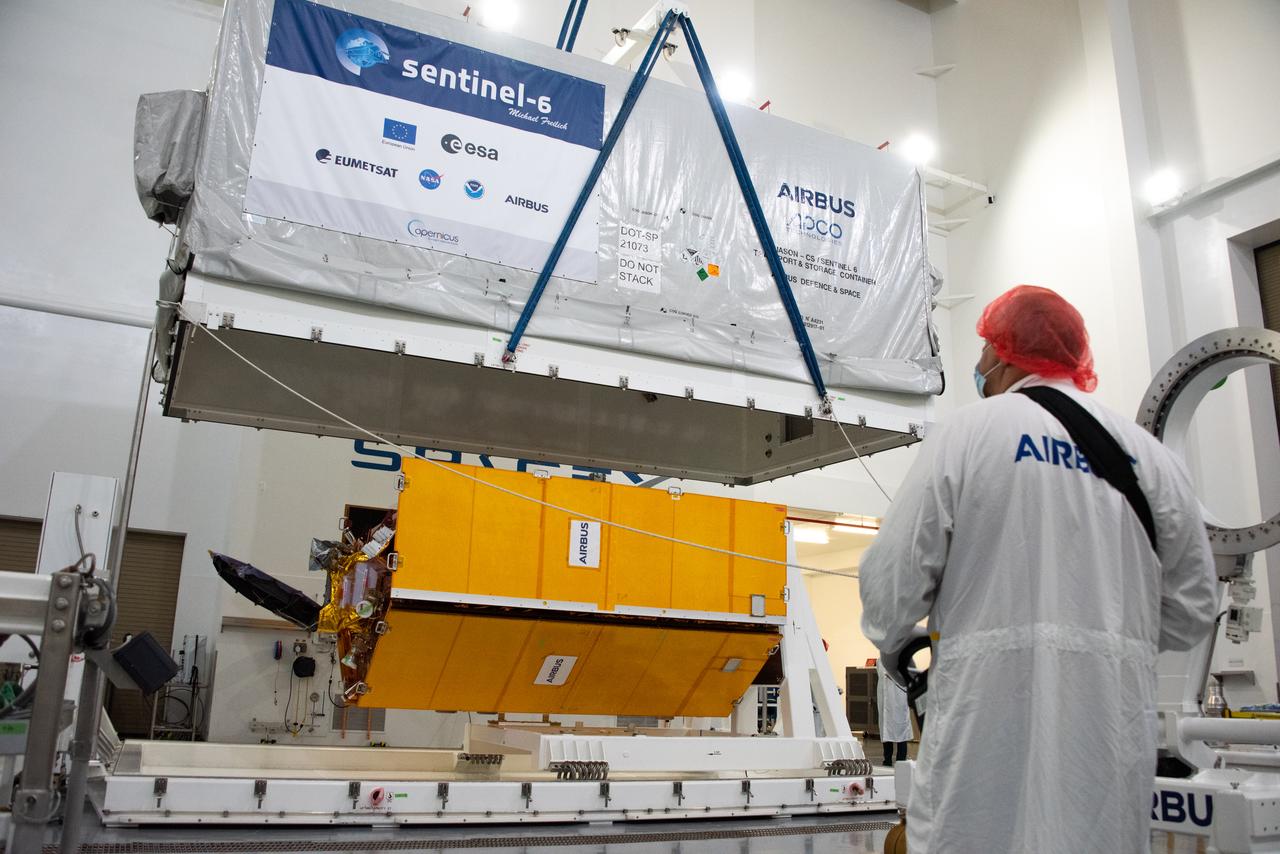

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
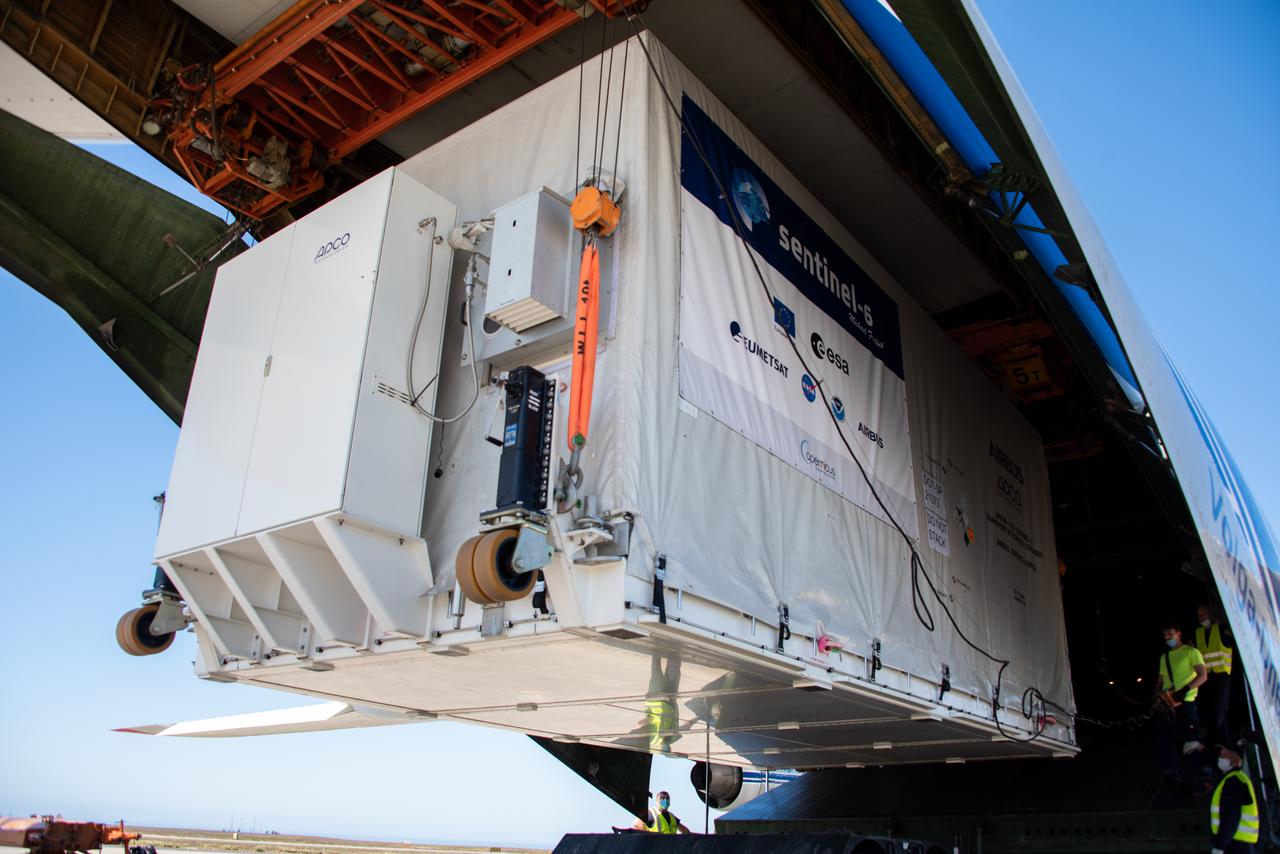

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, is offloaded from the Antonov cargo aircraft that delivered it to Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
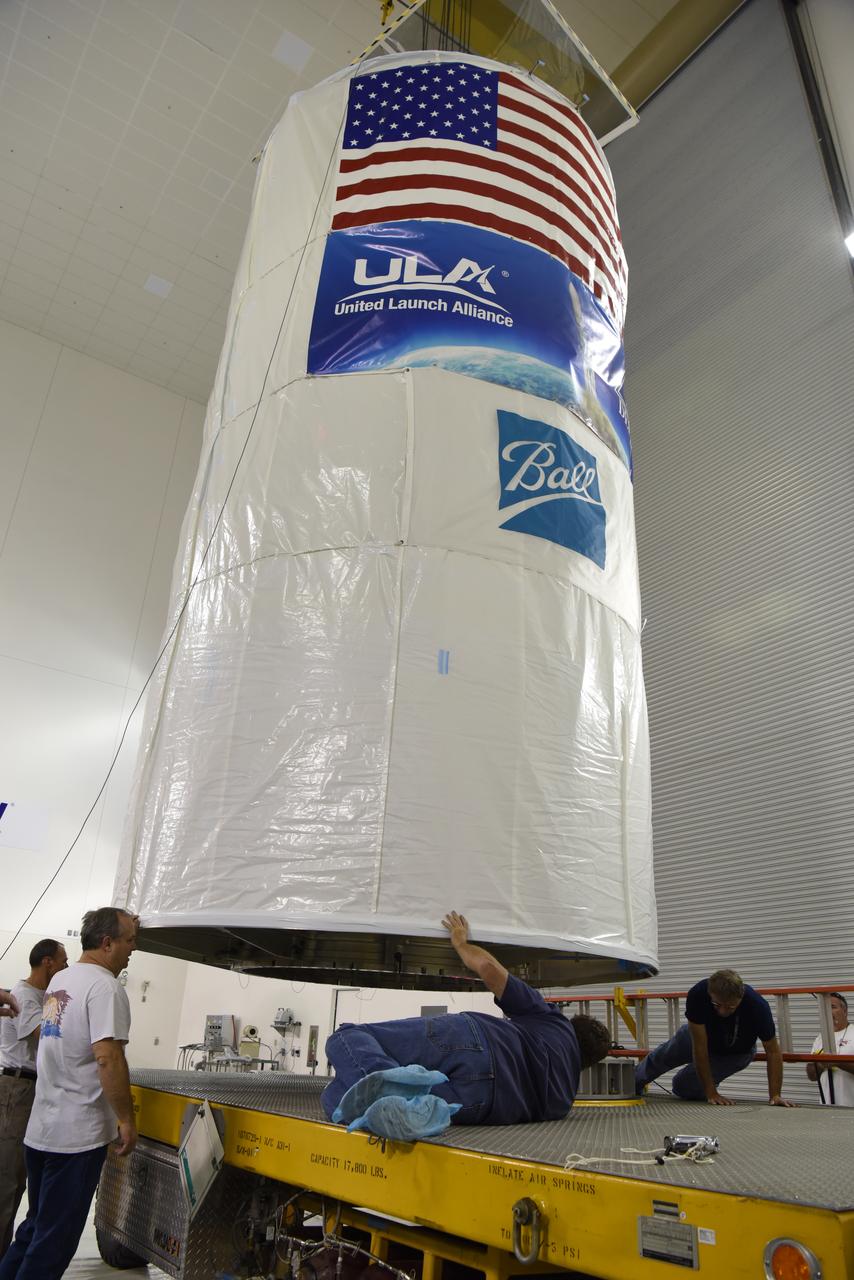

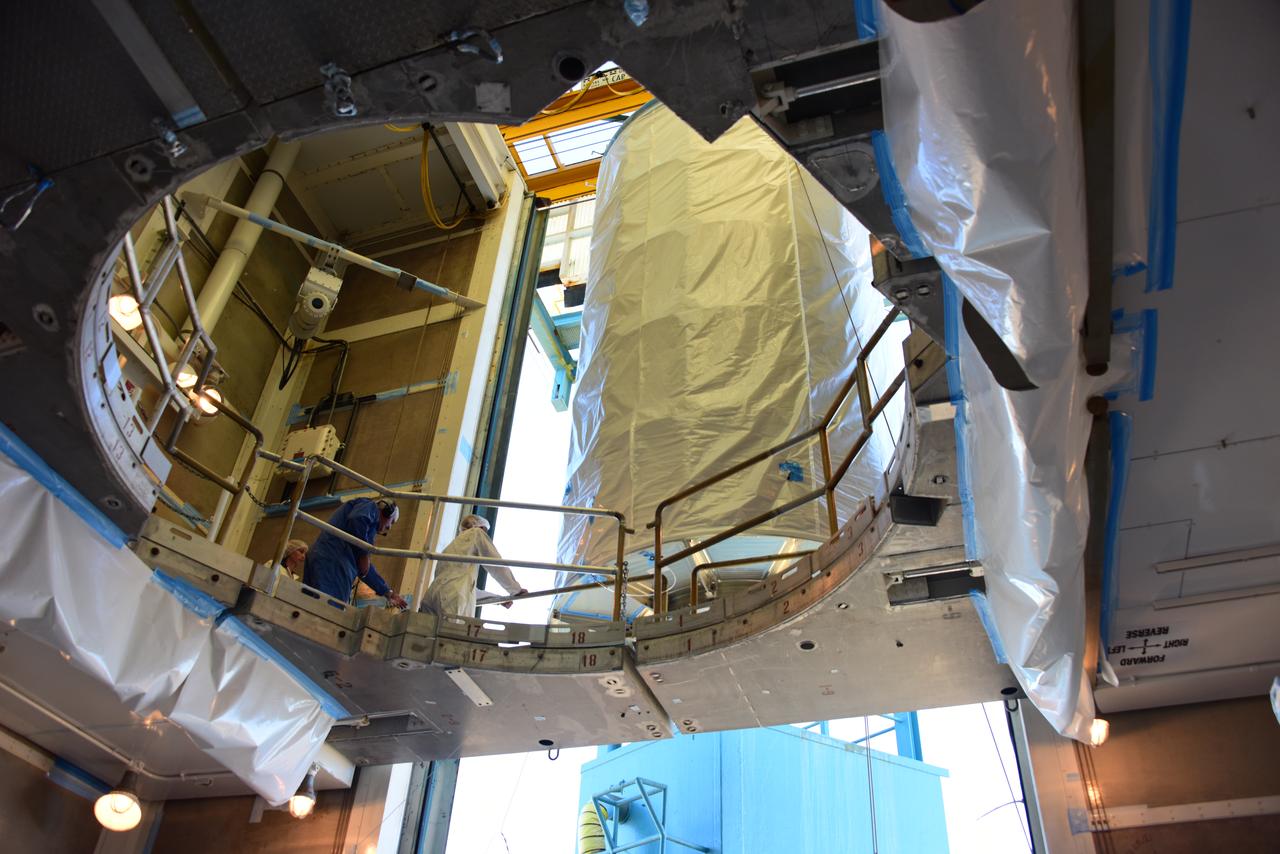
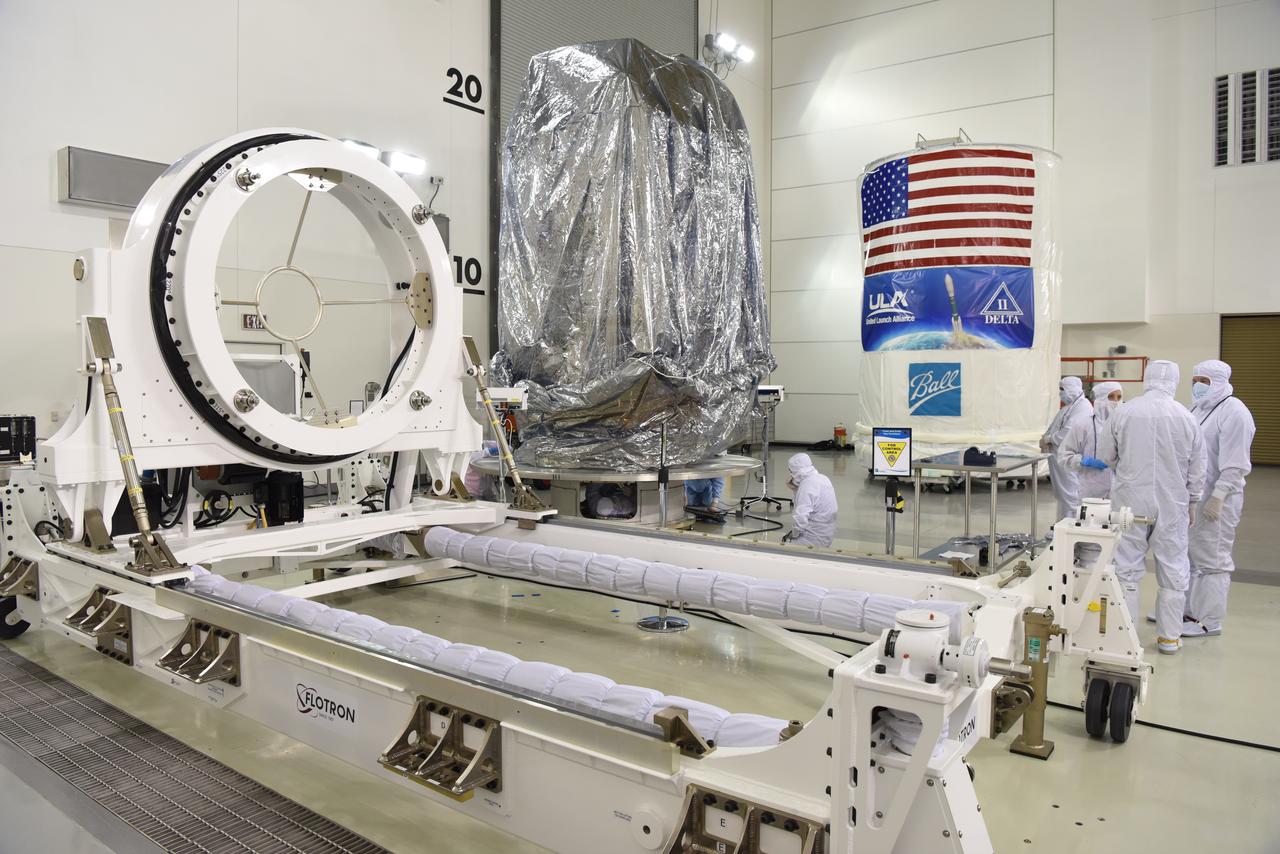
In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft in a protective container is placed on a transport trailer for the trip to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.
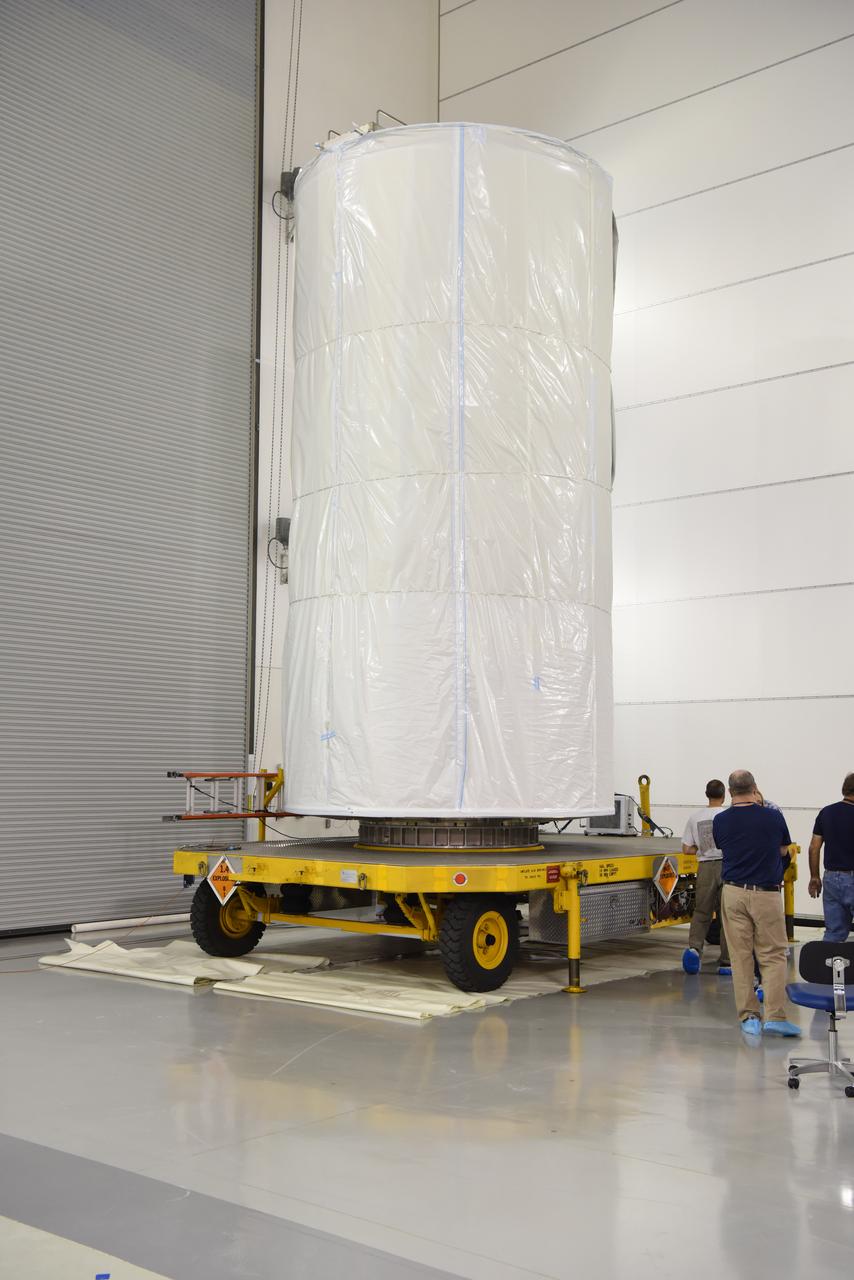

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft in a protective container is mounted on a transport trailer for the trip to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is wrapped in a protective covering prior to technicians and engineers placing it in a protective container. It then will be mounted on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

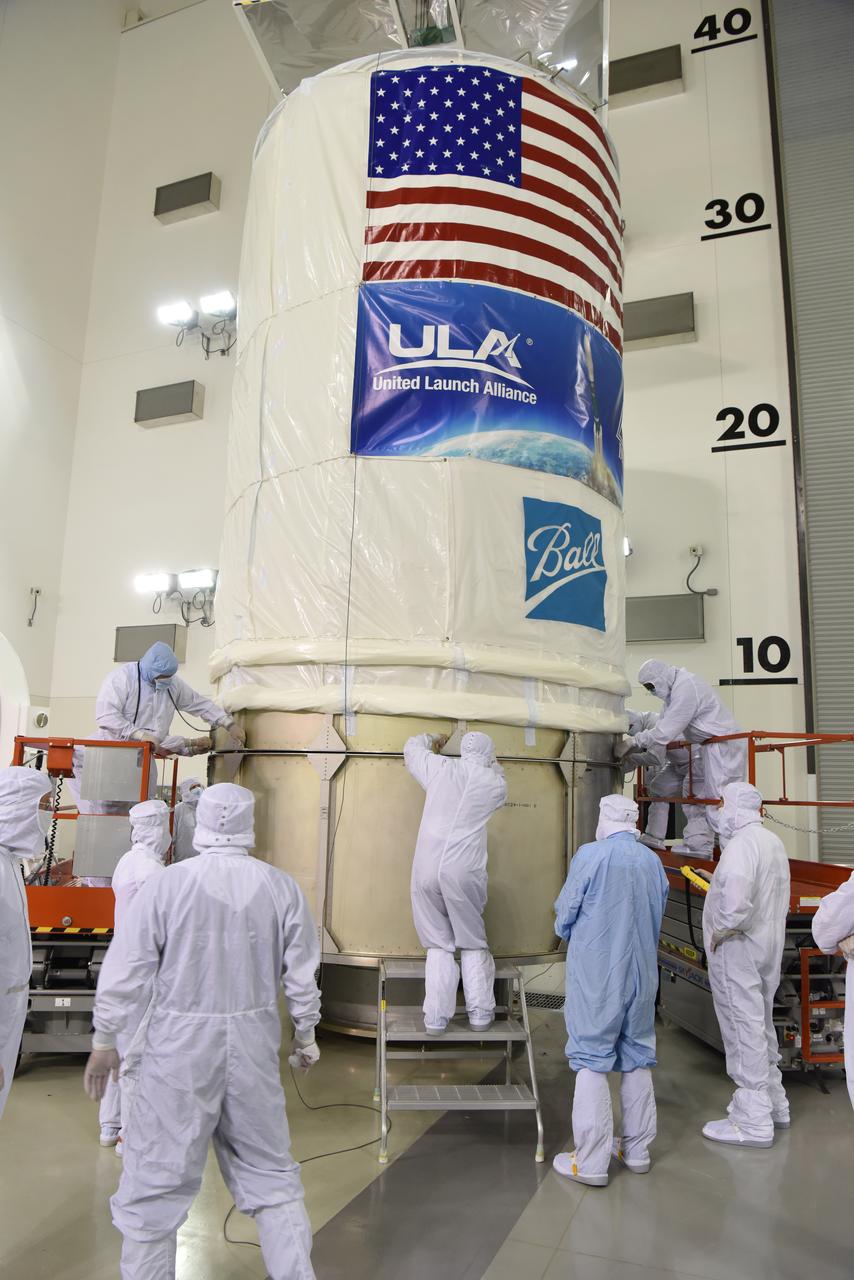
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, this wide angle view shows the payload fairing as it is installed encapsulating the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2 at 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers place the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft in a protective container. It then will be mounted on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is installed on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
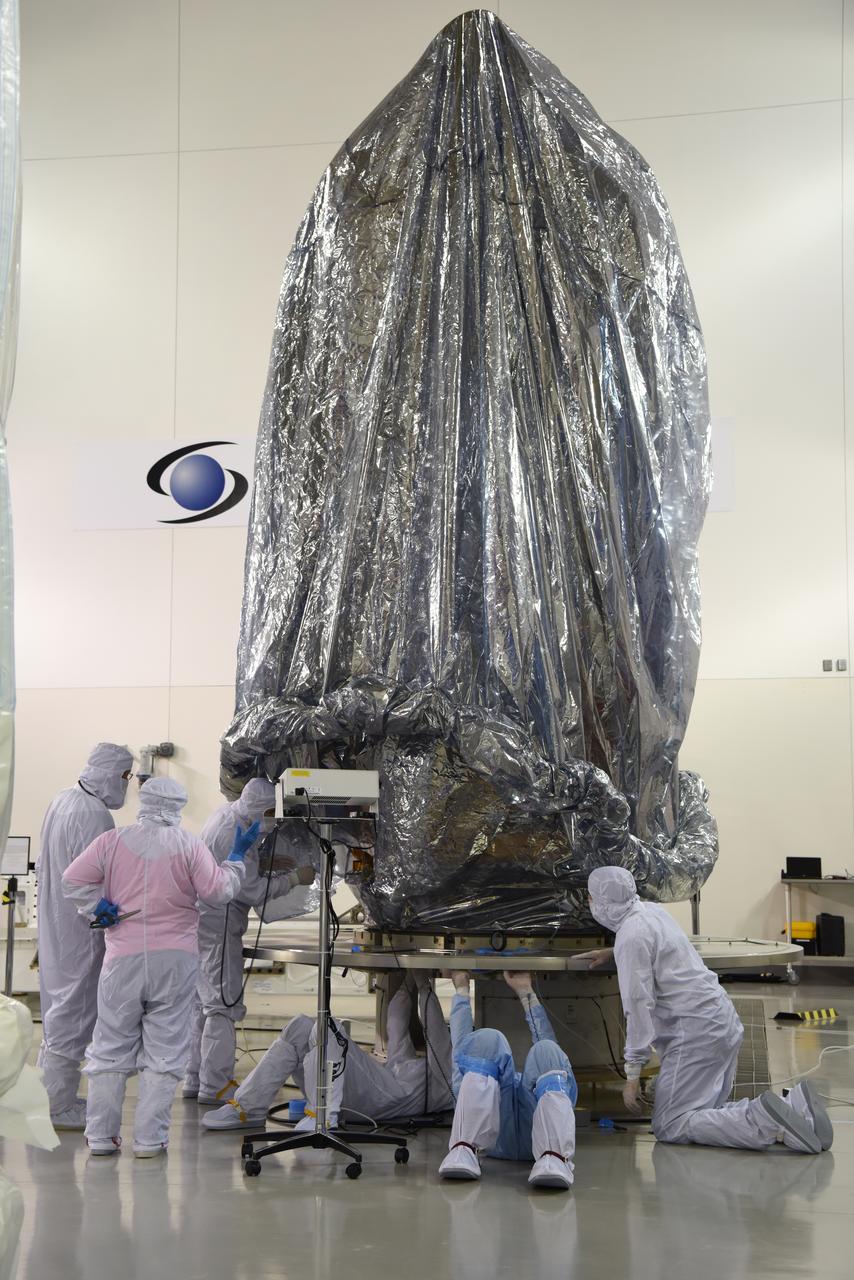

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is wrapped in a protective covering prior to being placed it in a protective container. It then will be mounted on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.
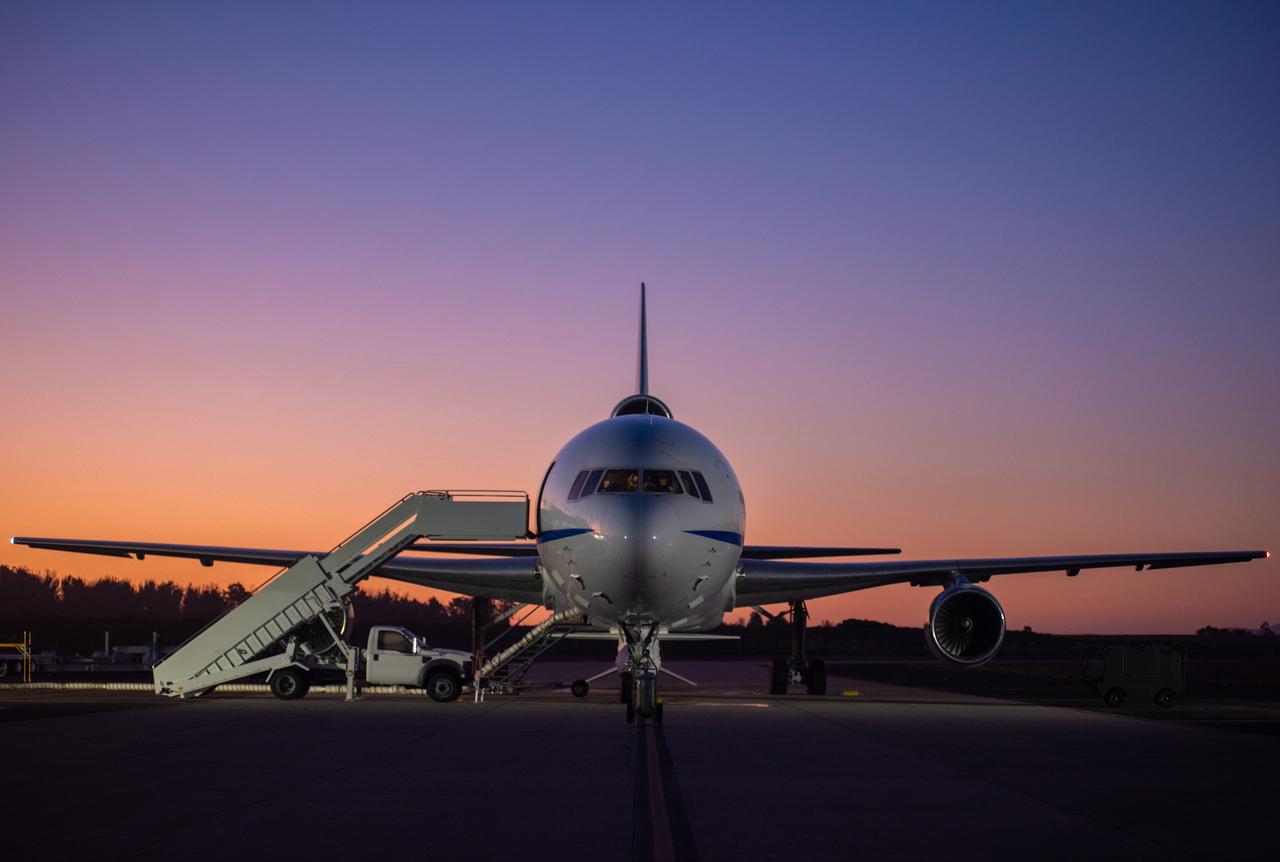

Backdropped by a twilight sky, Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer undergoes final preparations prior to its takeoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Oct. 1, 2019. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer is targeted to launch on Oct. 9, 2019, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
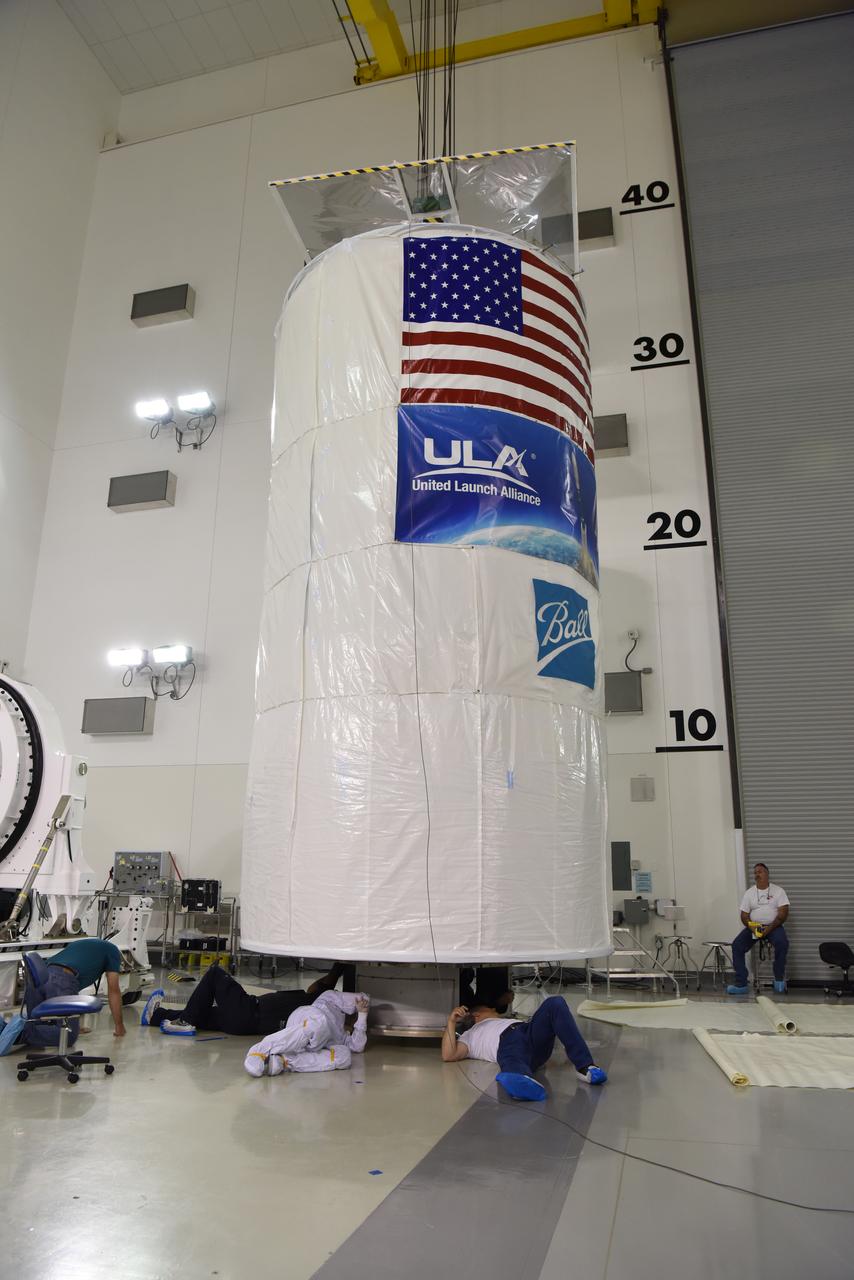

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is prepared for departure in a protective container to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.
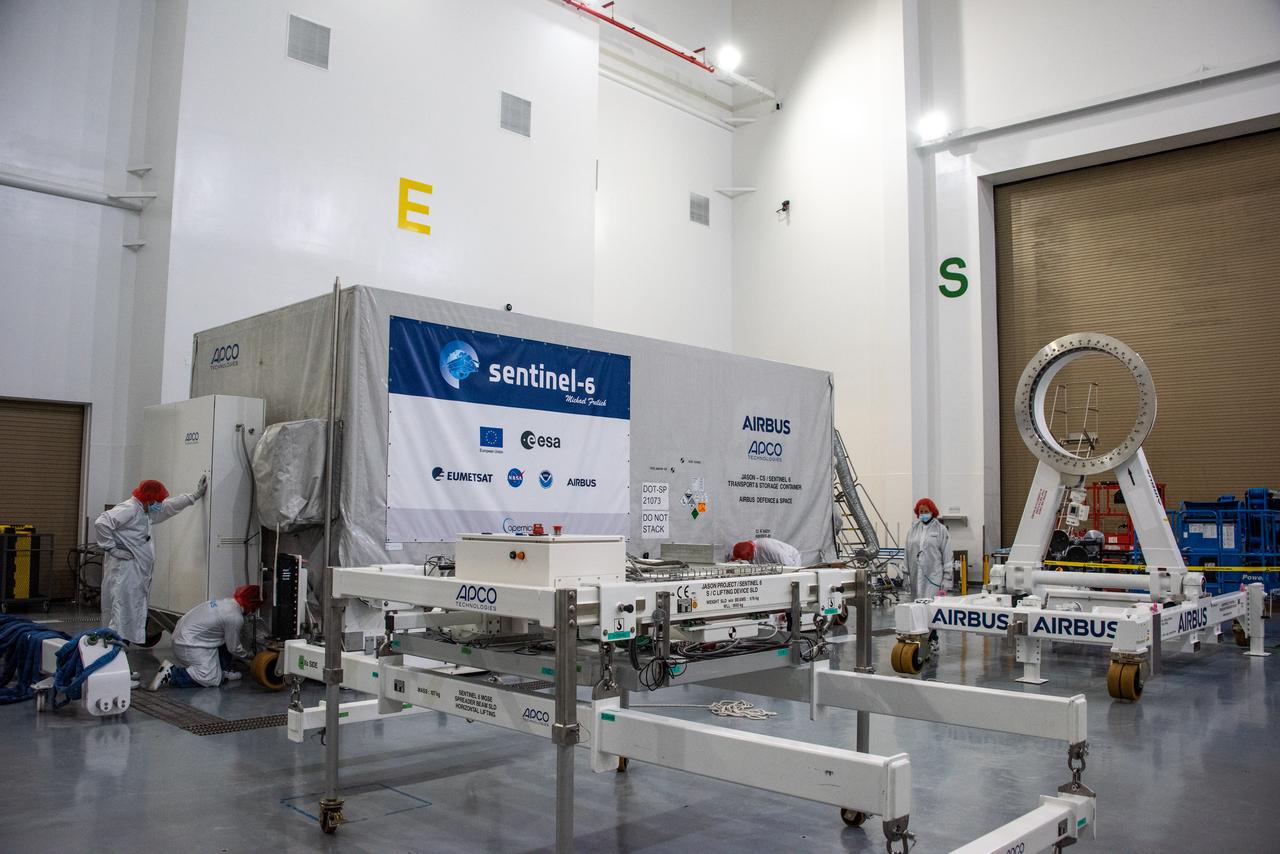

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers place the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft in a protective container. It then will be mounted on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.

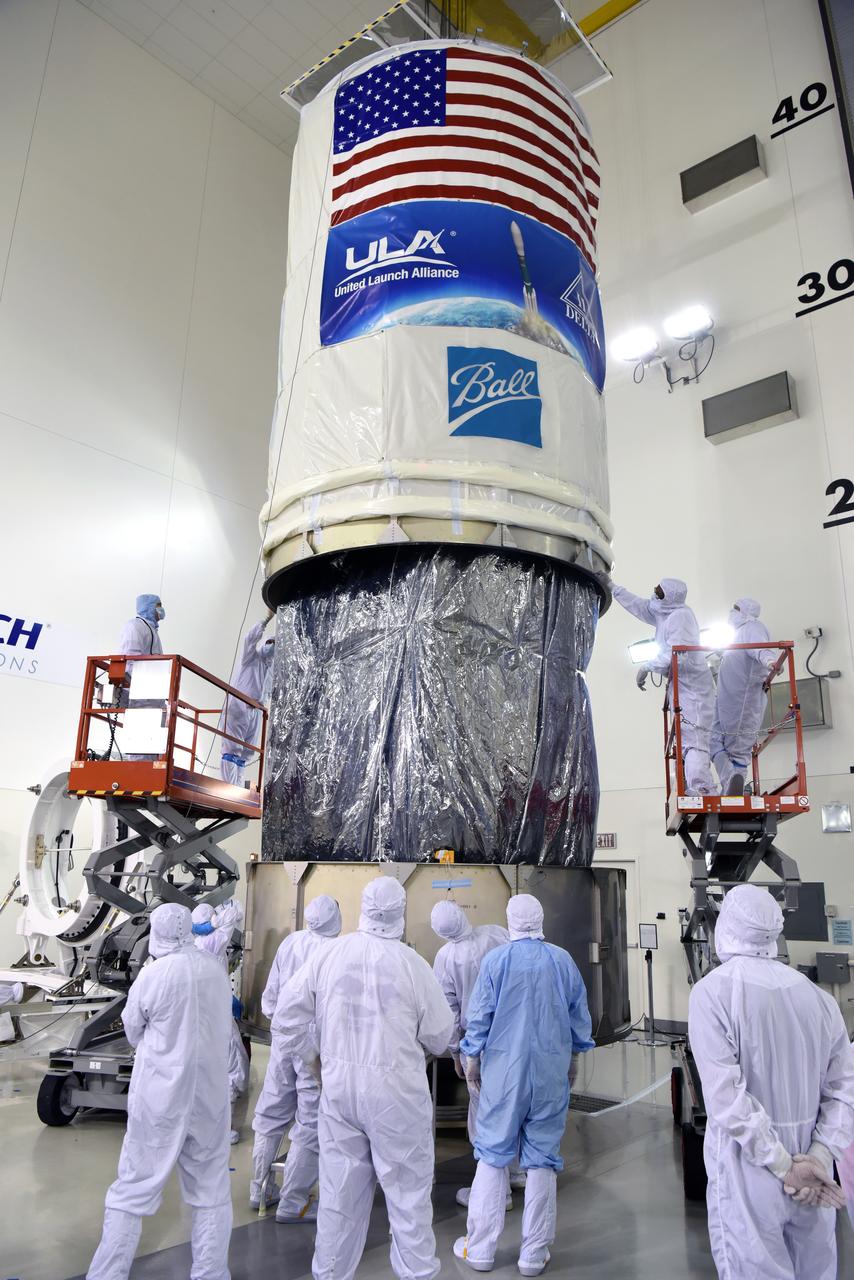
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the payload fairing is installed encapsulating the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2 at 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
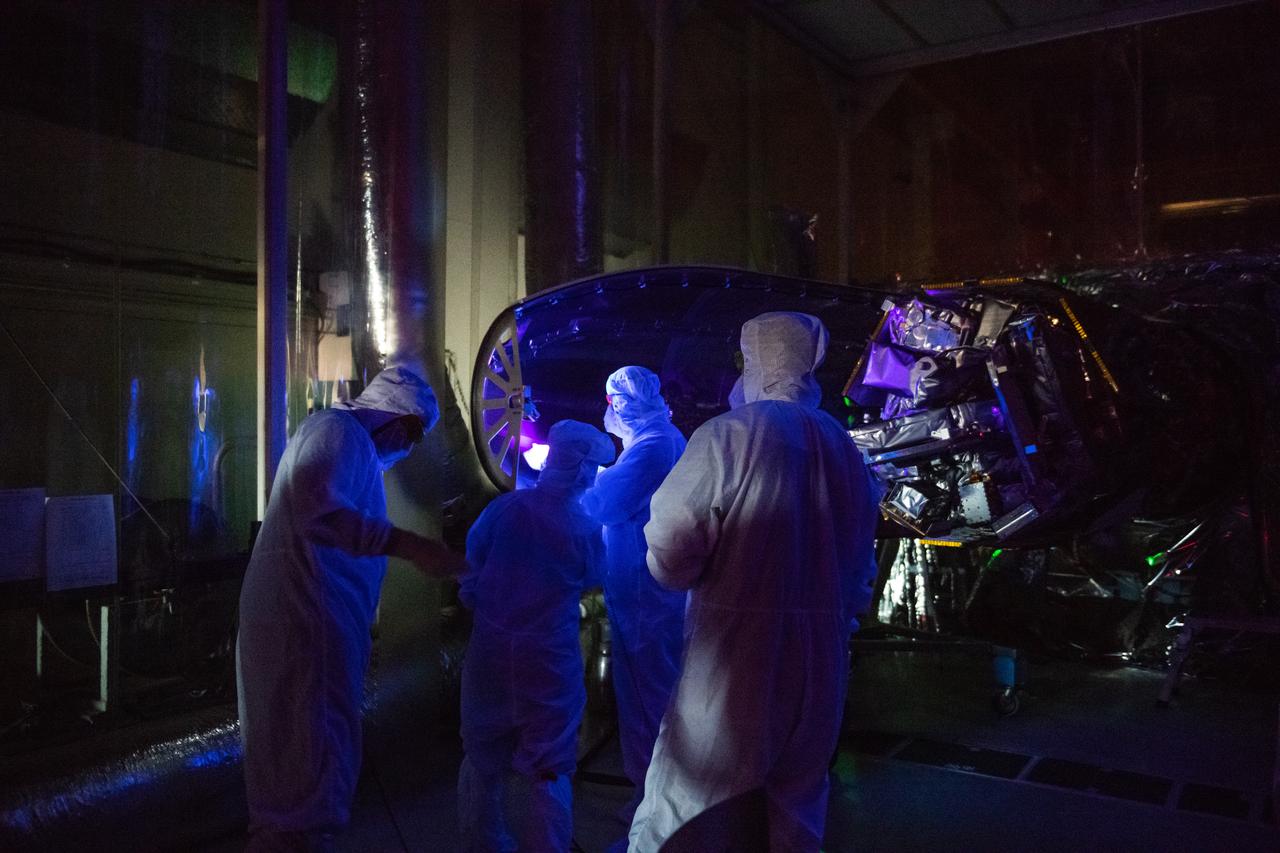
Technicians install the starboard side of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket’s payload fairing around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 17, 2019. ICON launched on the Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, is offloaded from the Antonov cargo aircraft that delivered it to Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
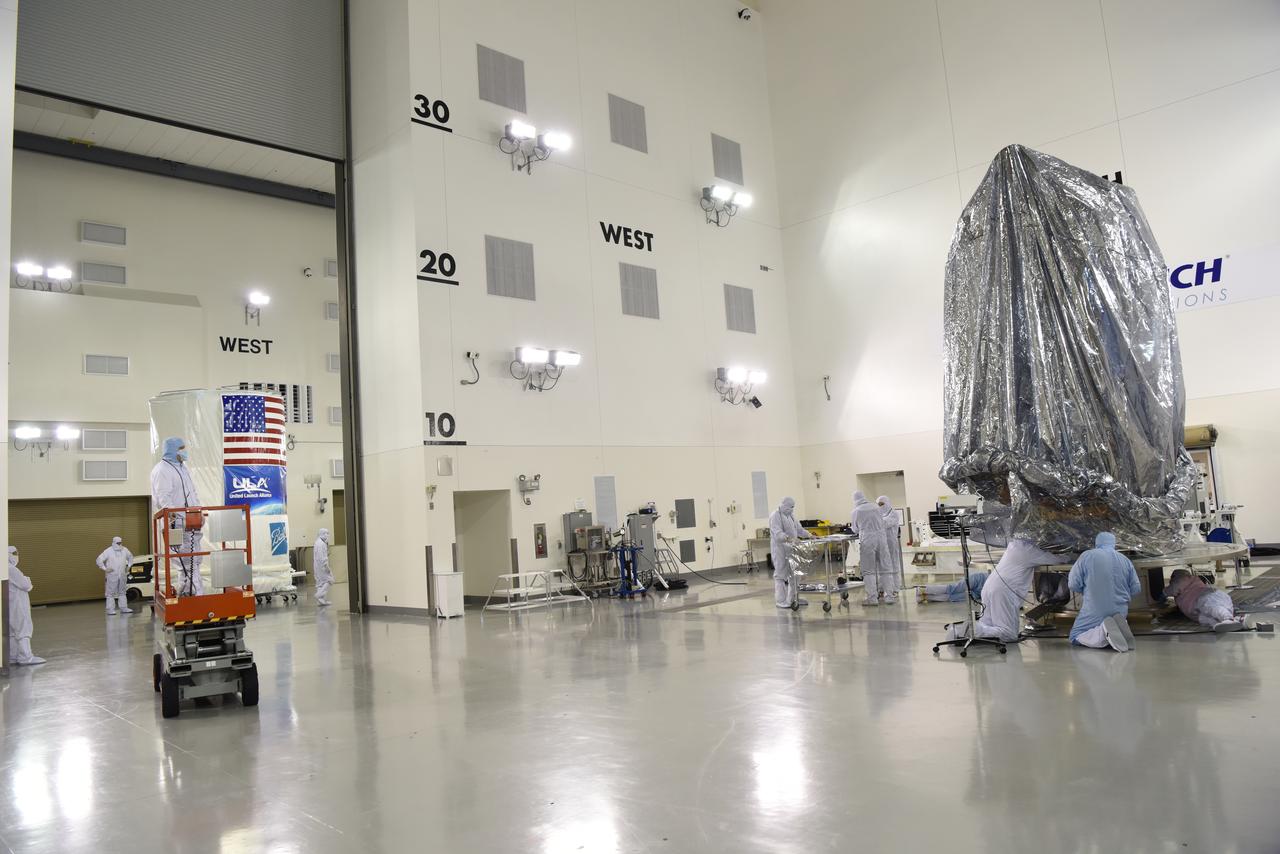

JPSS-1 Spacecraft Canning and Lift to Transport Trailer at the Astrotech facility located at Vandenberg Air Force Station in California.
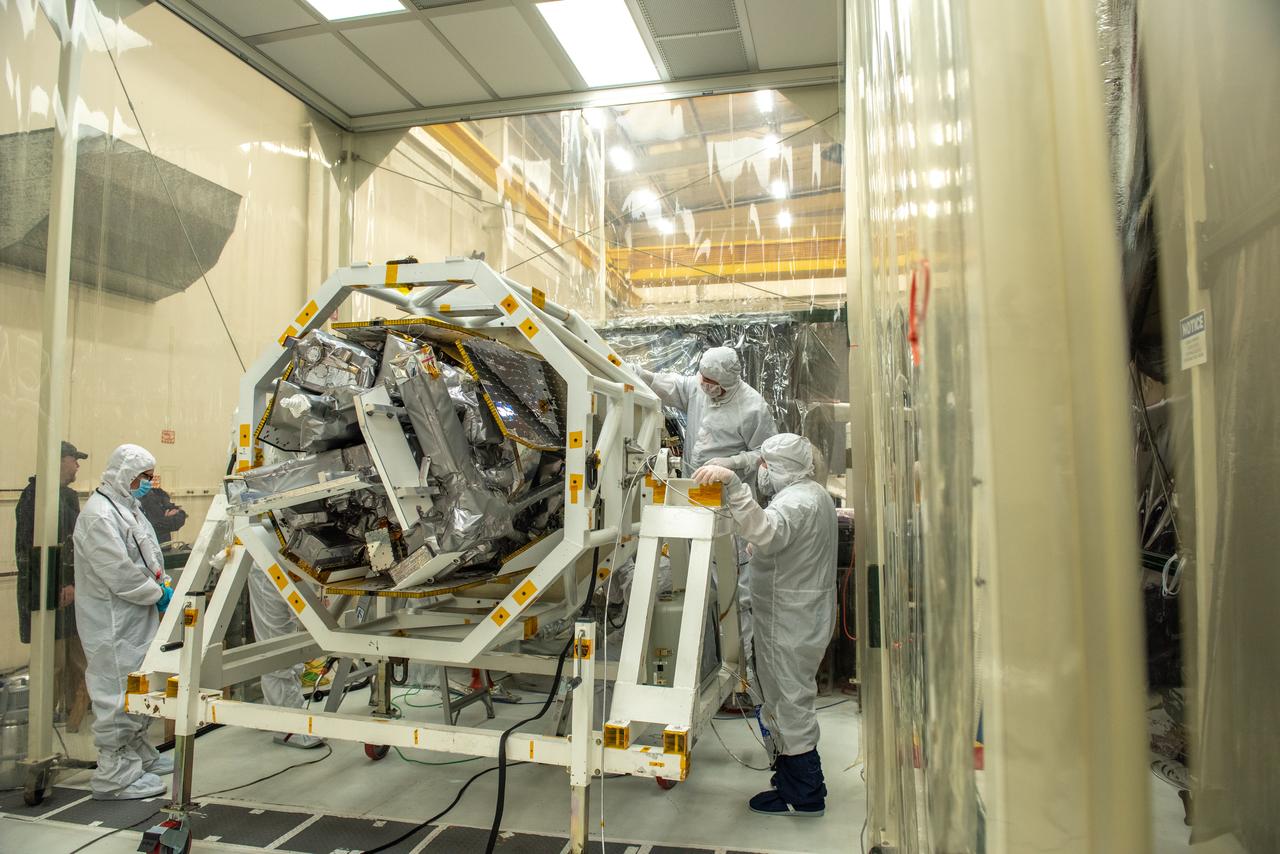

Technicians attach NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 10, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
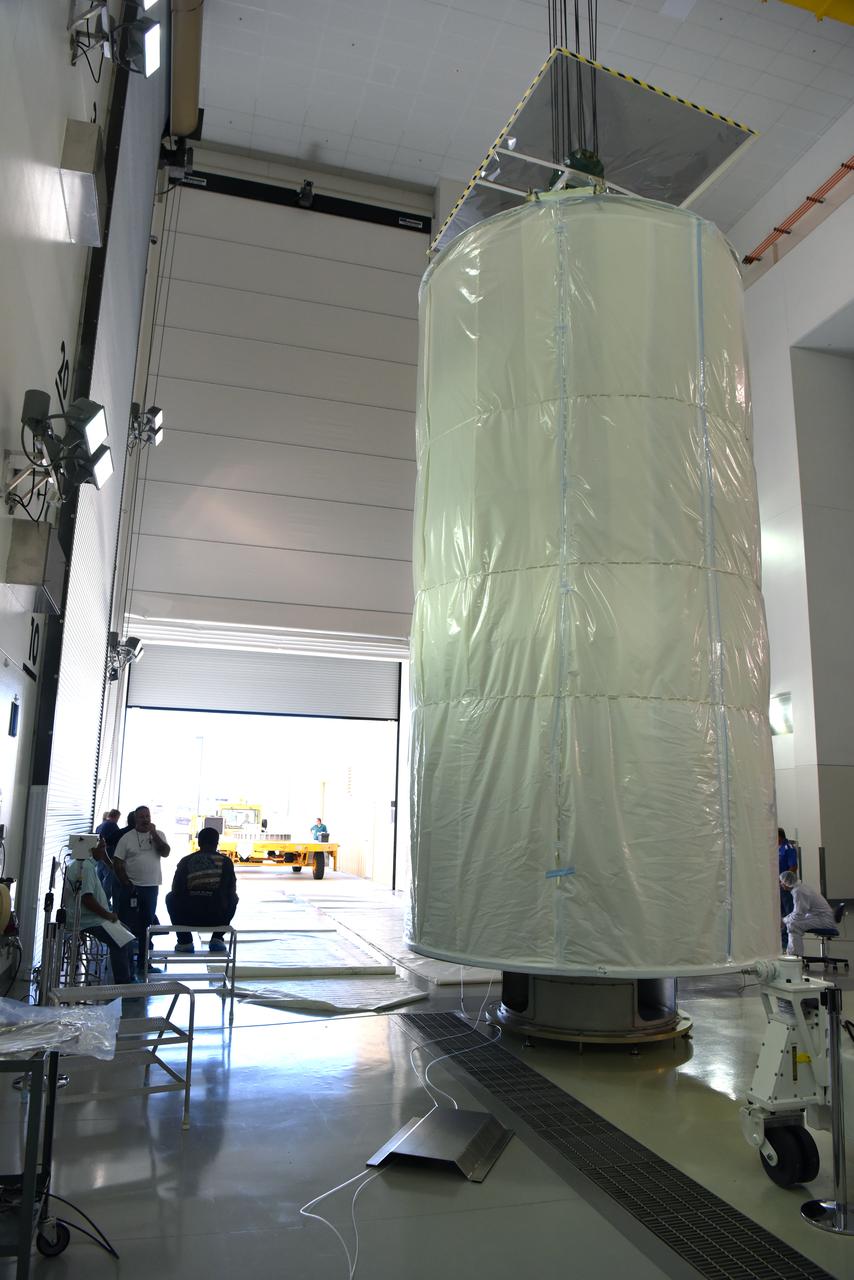

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft is prepared for departure in a protective container to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.
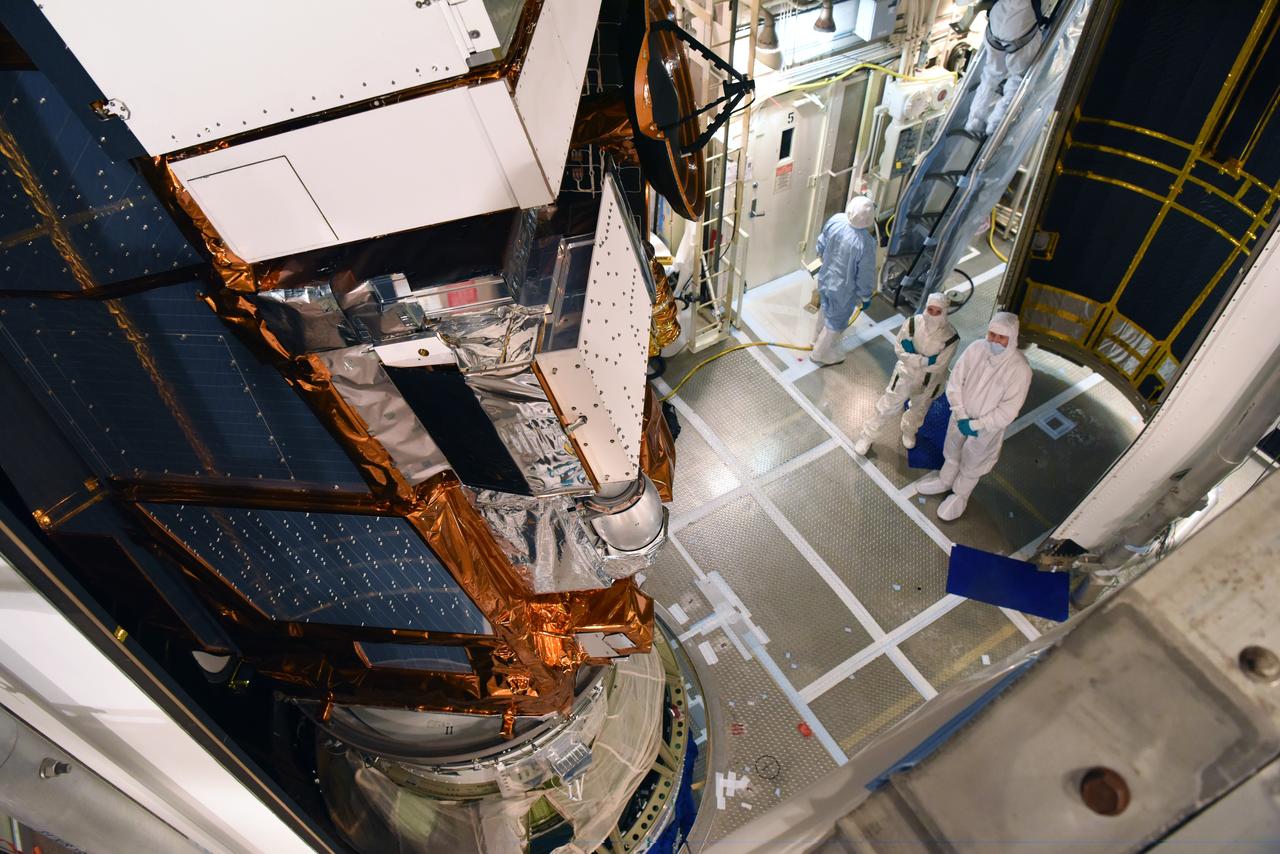

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the payload fairing is installed encapsulating the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2 at 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
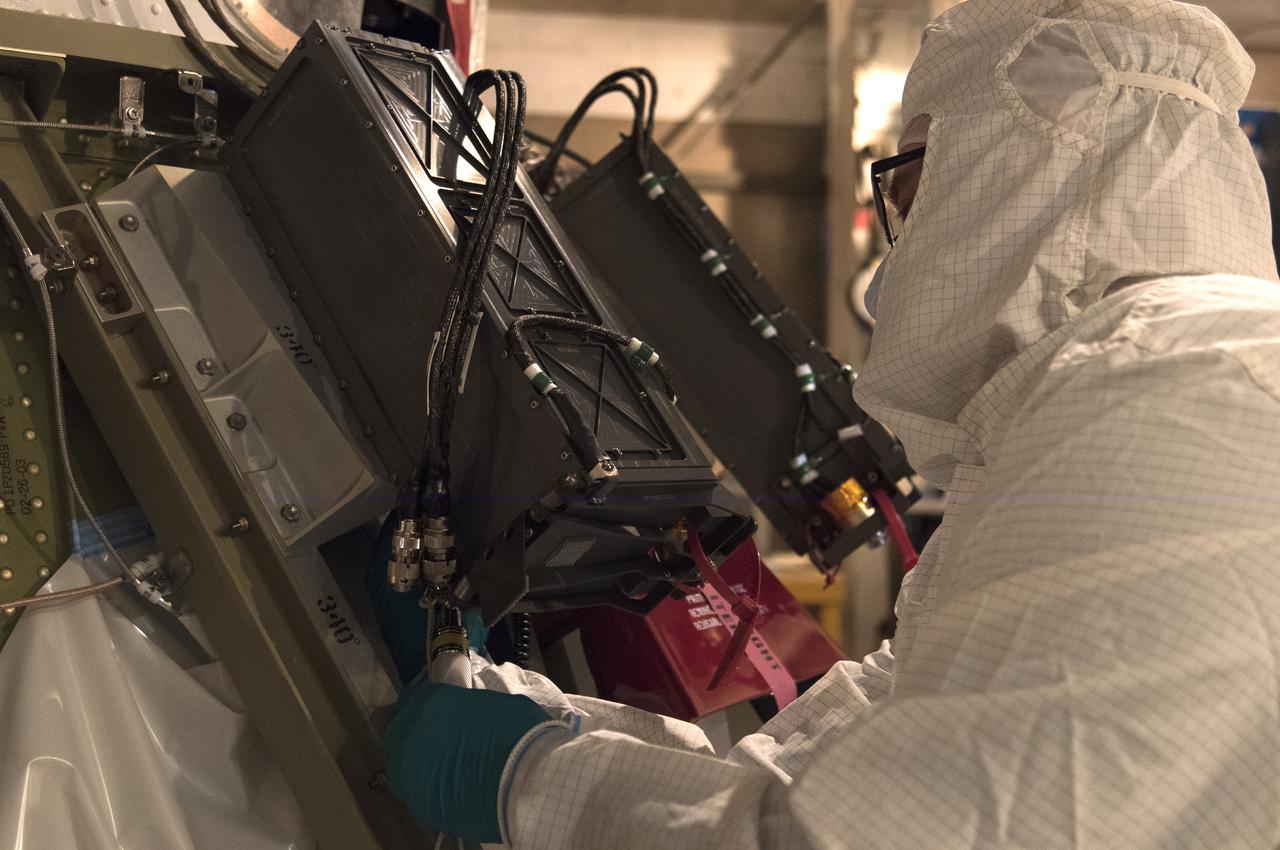

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is installed on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
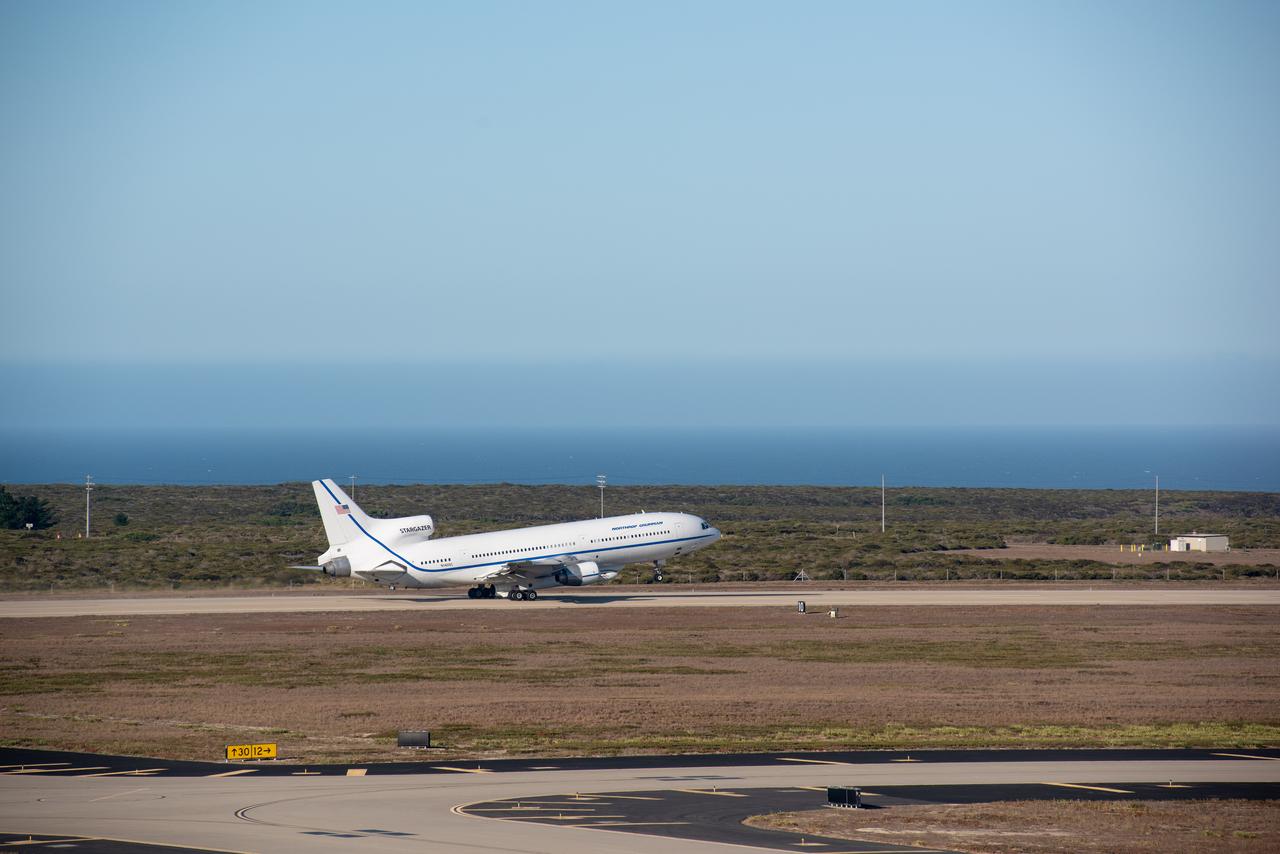

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Oct. 1, 2019. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer is targeted to launch on Oct. 9, 2019, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
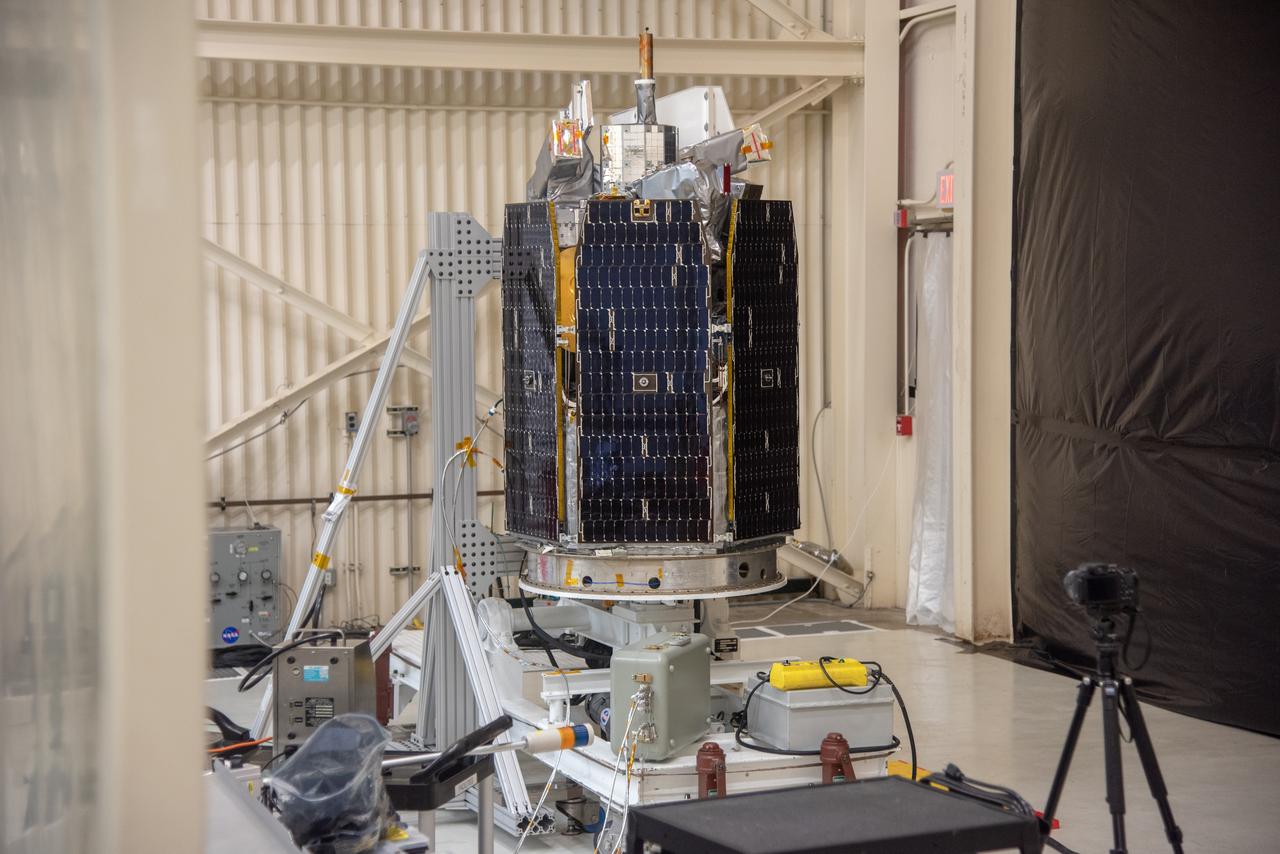

A solar array deployment test will begin on NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 10, 2019. ICON will launch on a Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

Technicians attach NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 10, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
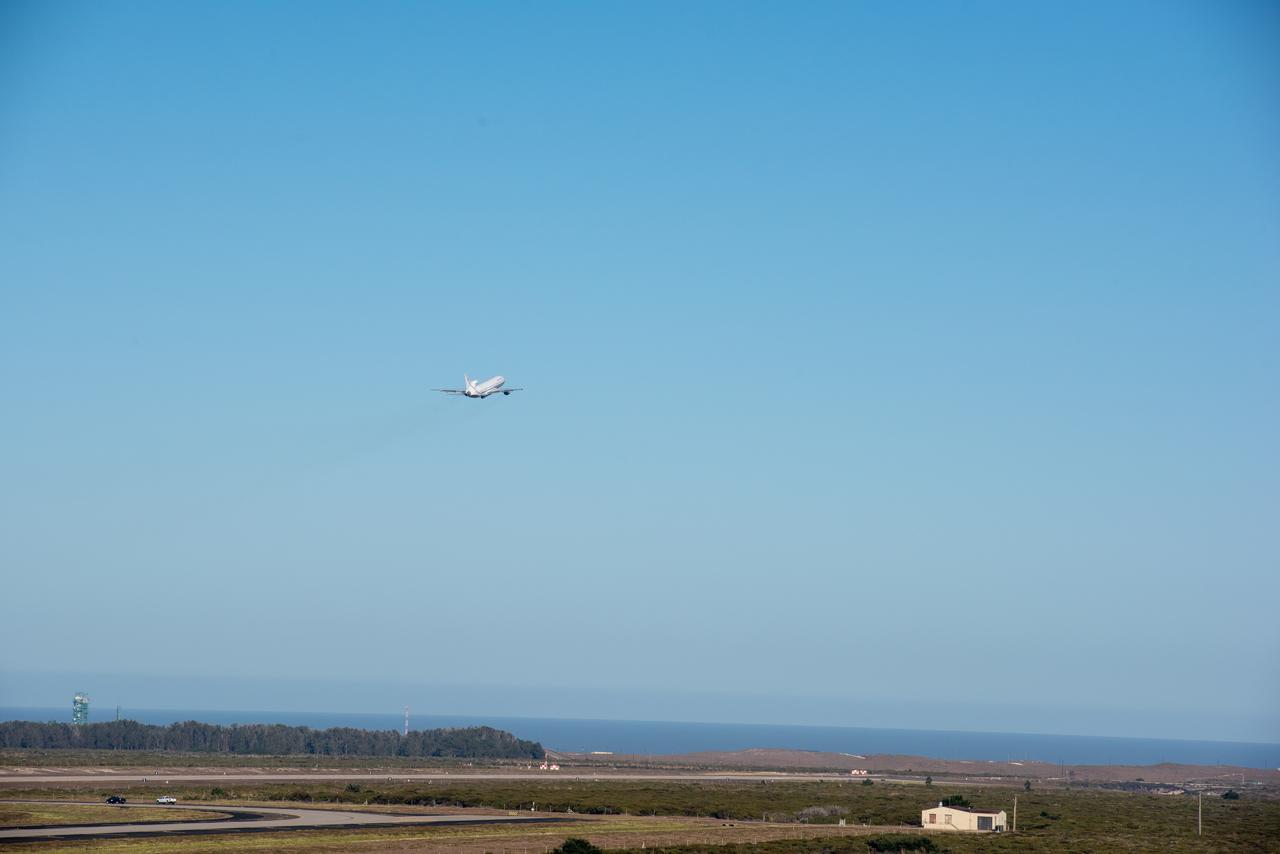

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Oct. 1, 2019. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer is targeted to launch on Oct. 9, 2019, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
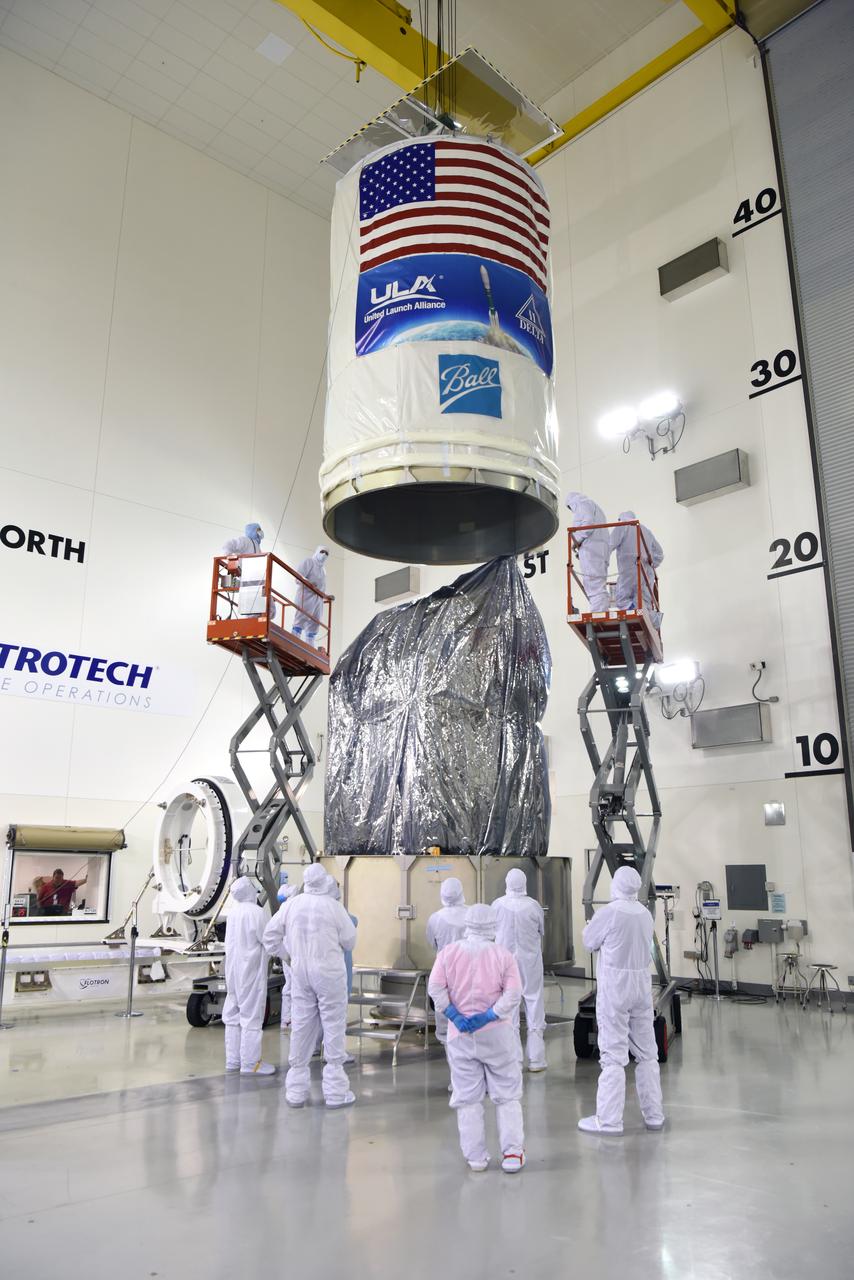

In the Astrotech Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers place the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft in a protective container. It then will be mounted on a transport trailer for its move to Space Launch Complex 2. At the pad, JPSS-1 will be lifted for mating atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2.
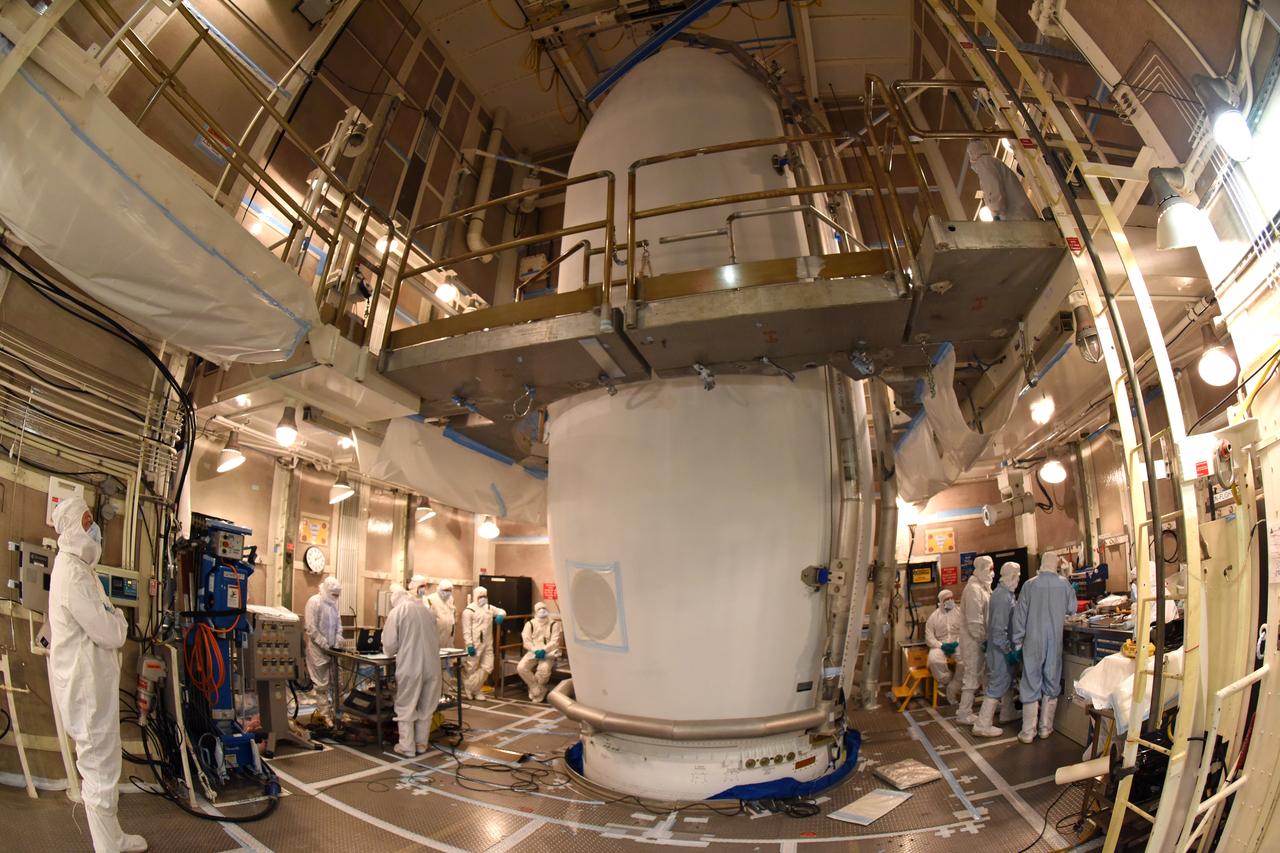

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the payload fairing is installed encapsulating the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket at Space Launch Complex 2. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2 at 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
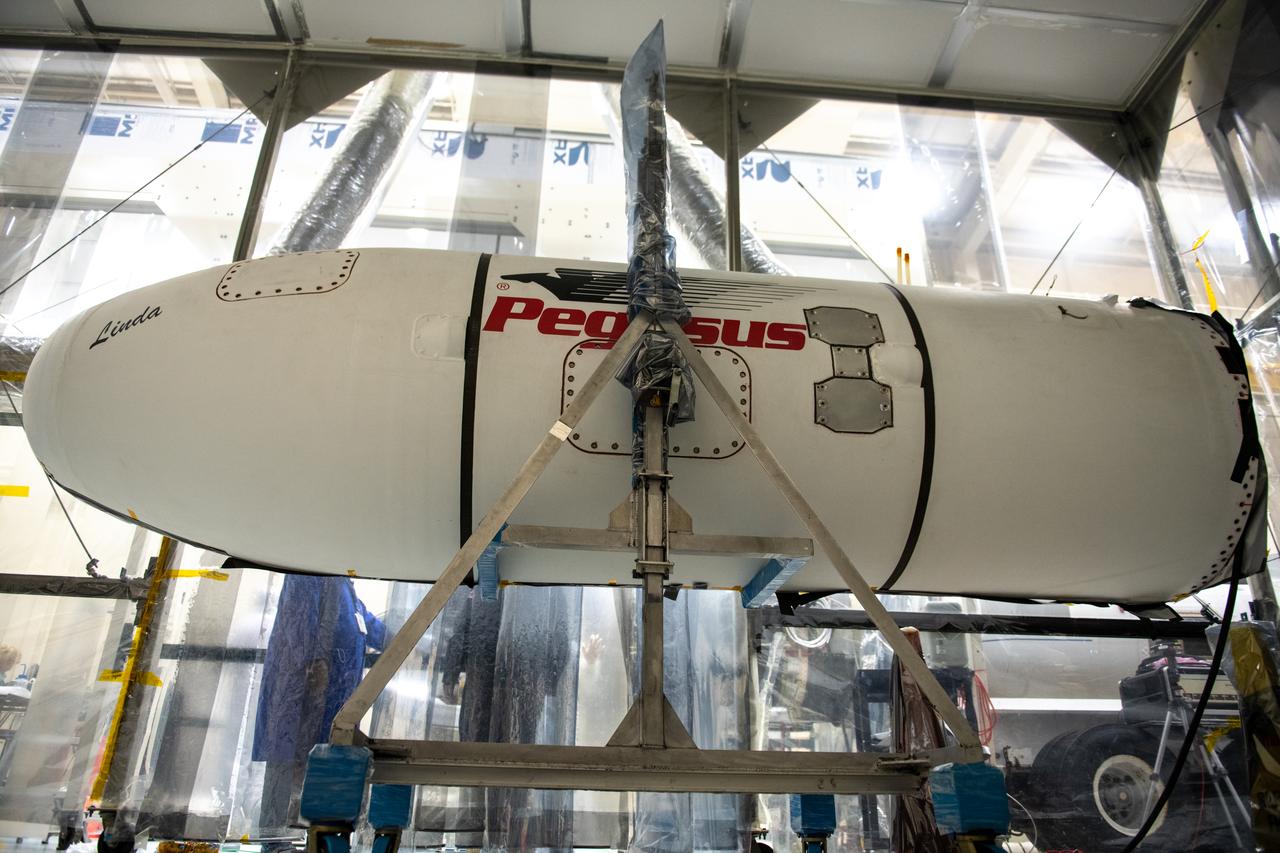

The starboard side of the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket’s payload fairing is ready for installation around NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 17, 2019. ICON launched on the Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
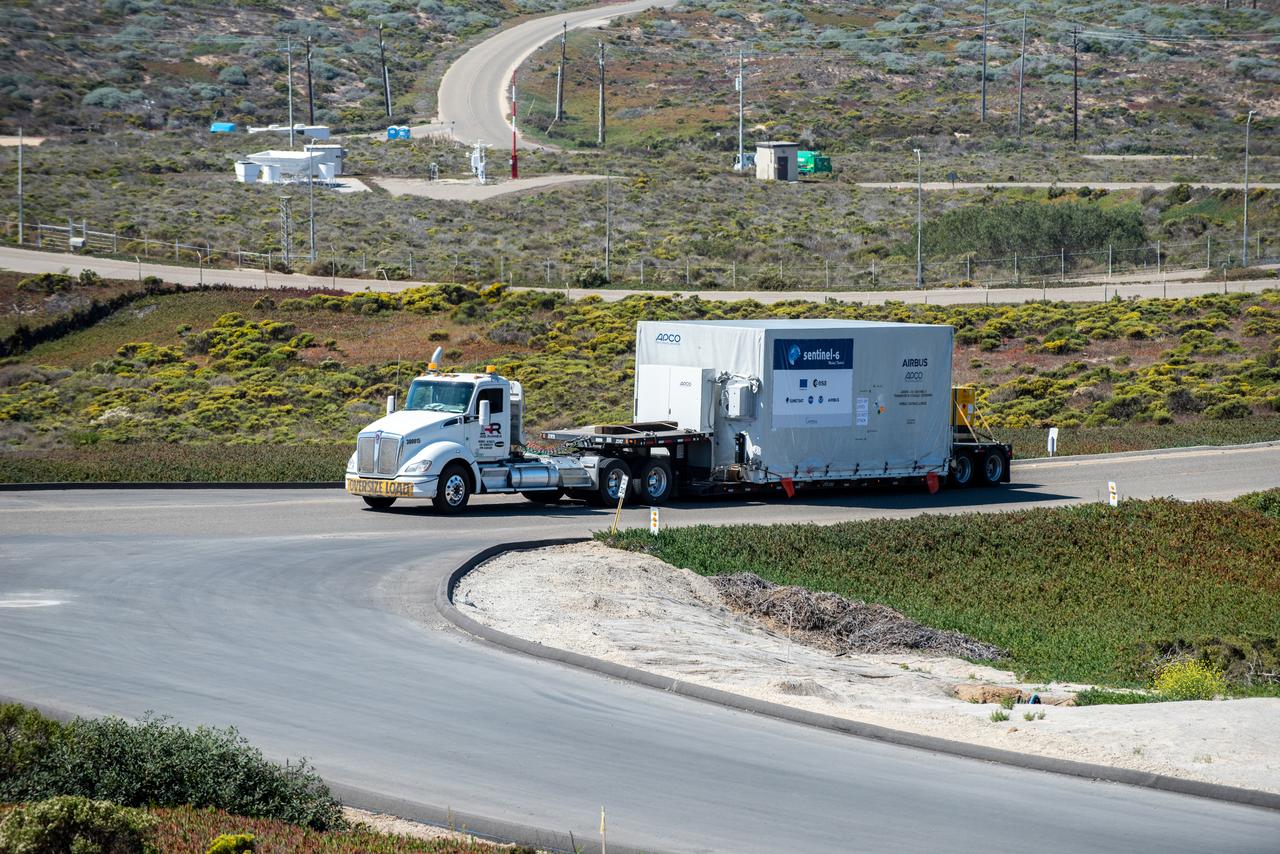

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
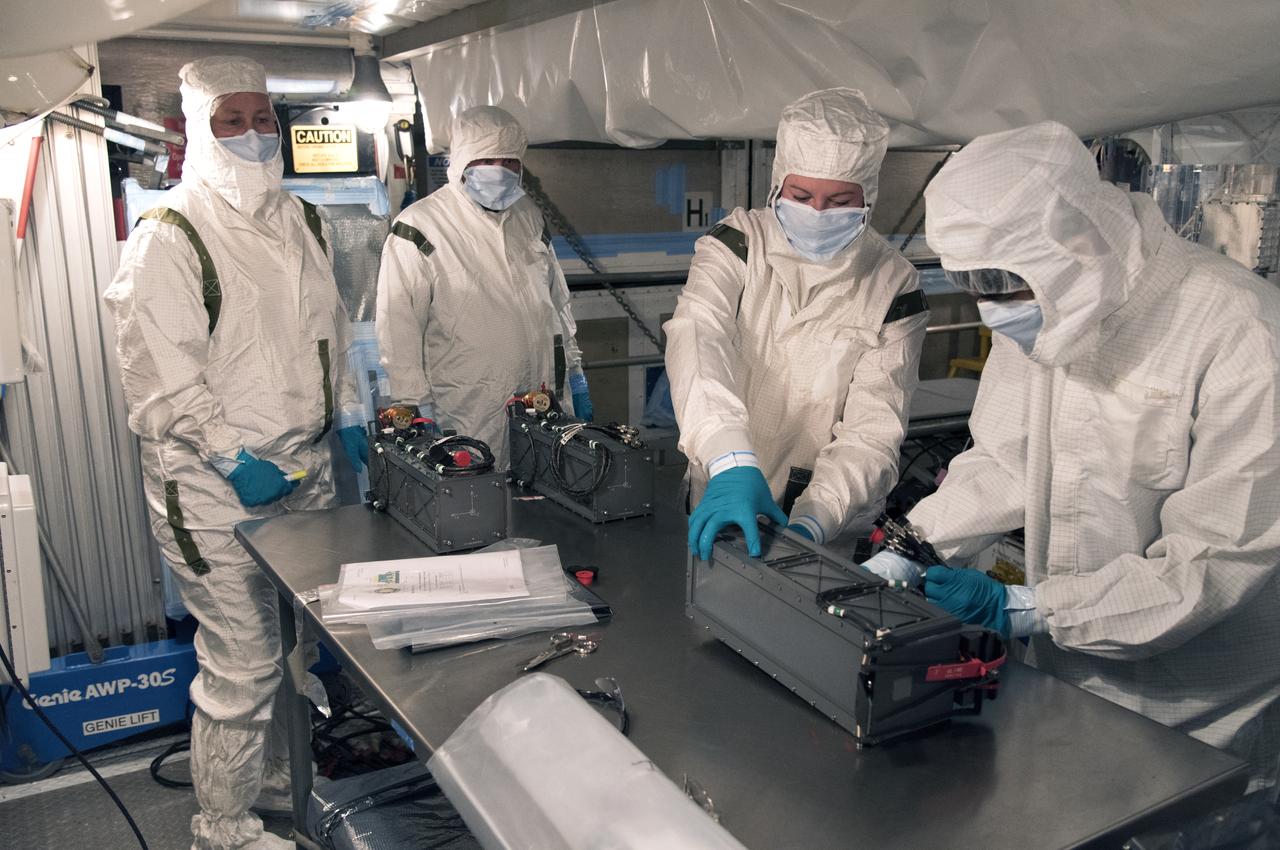

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container for installation on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
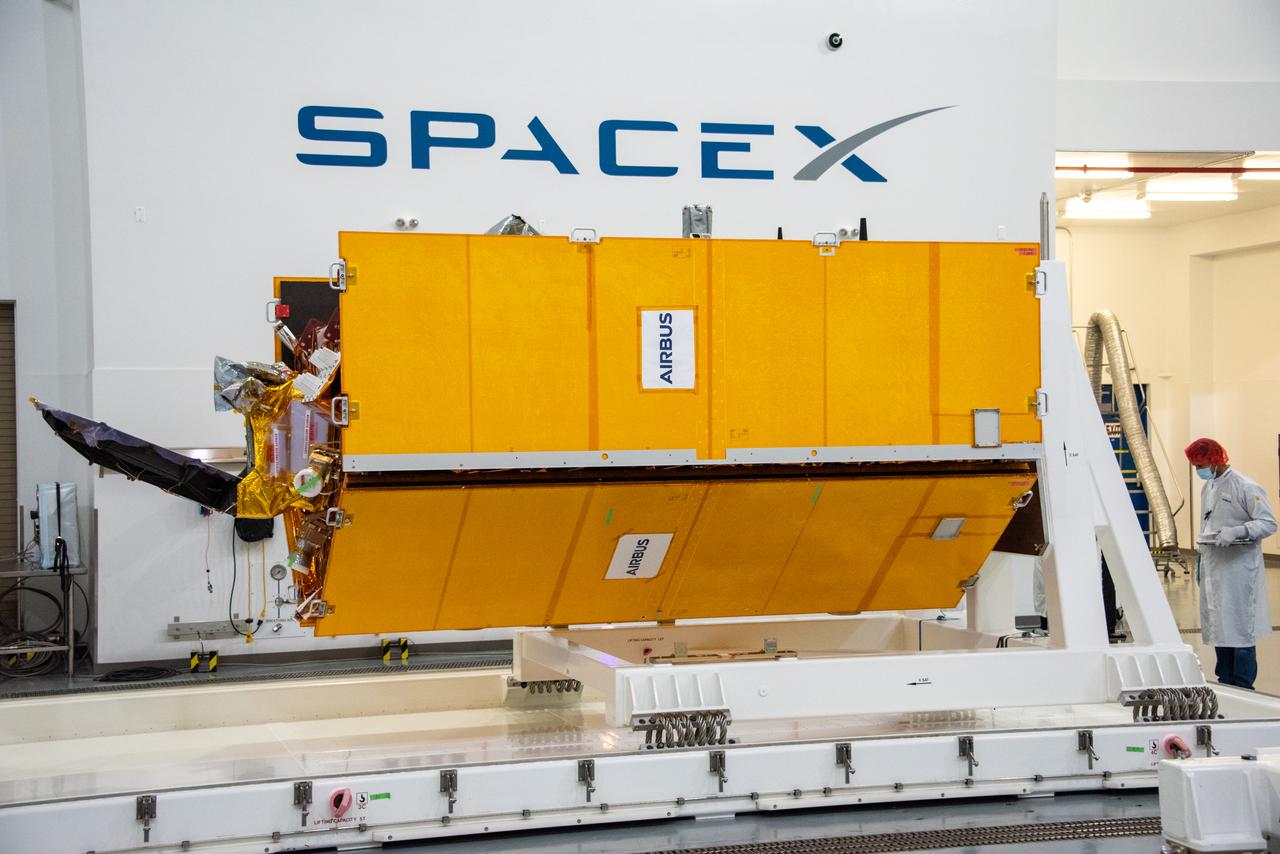

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
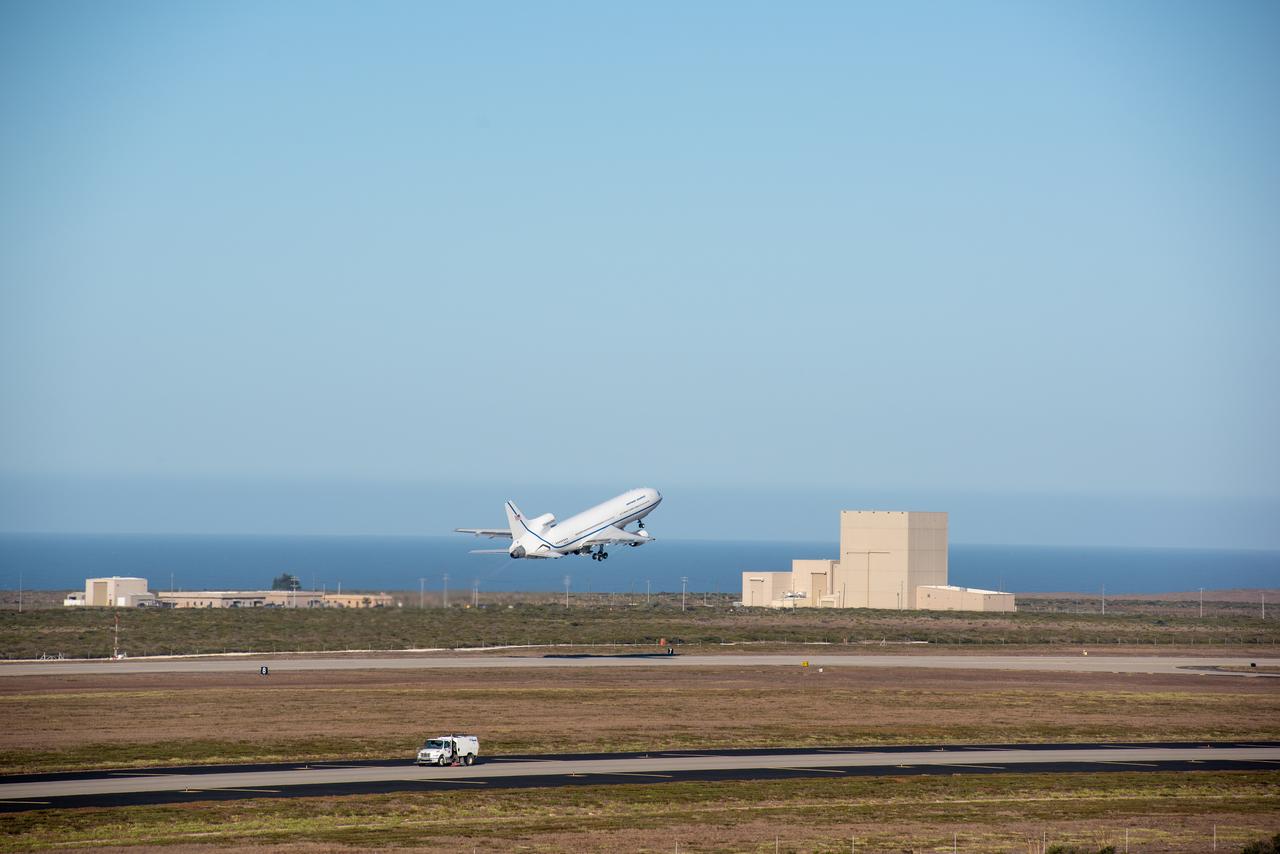

Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer takes off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Oct. 1, 2019. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer is targeted to launch on Oct. 9, 2019, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.
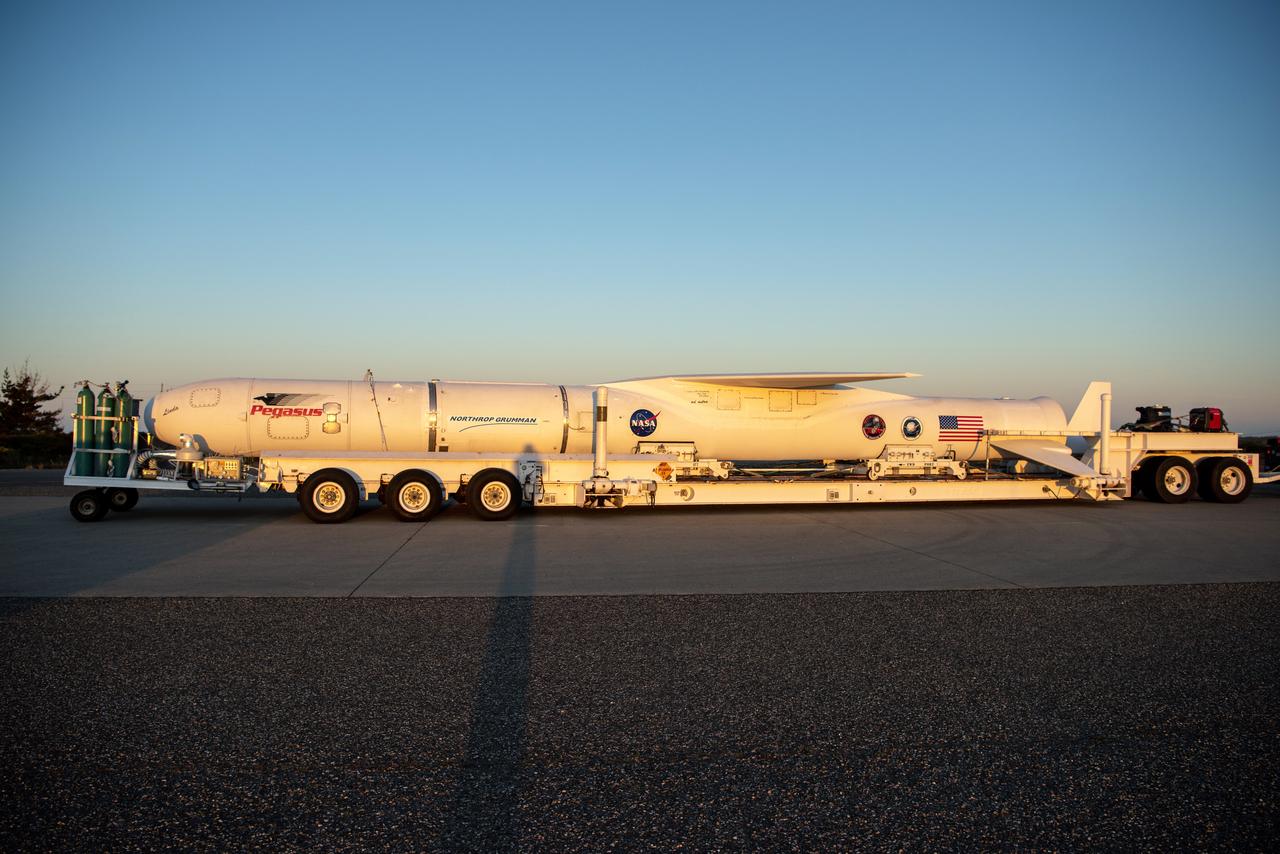

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, rolls out to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
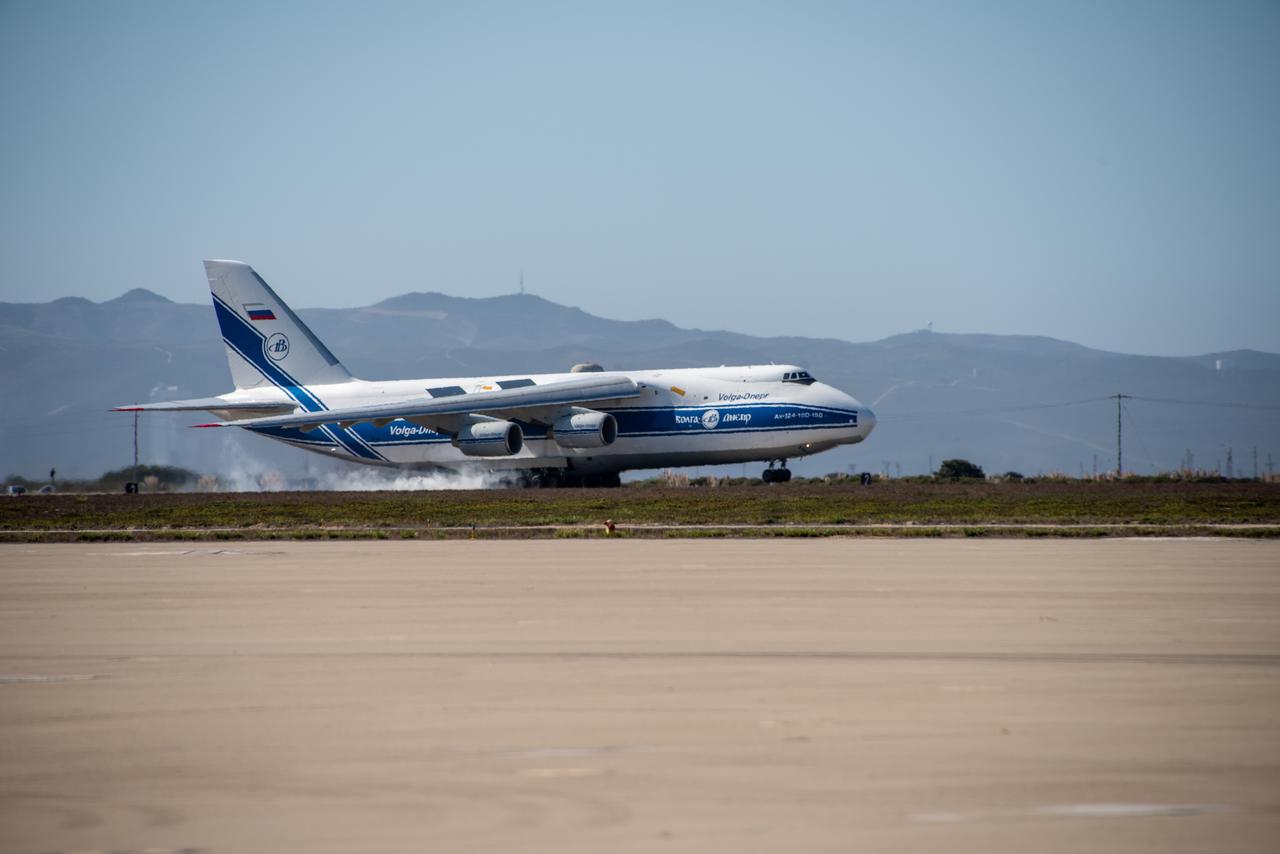

The Antonov cargo aircraft carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite touches down on the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
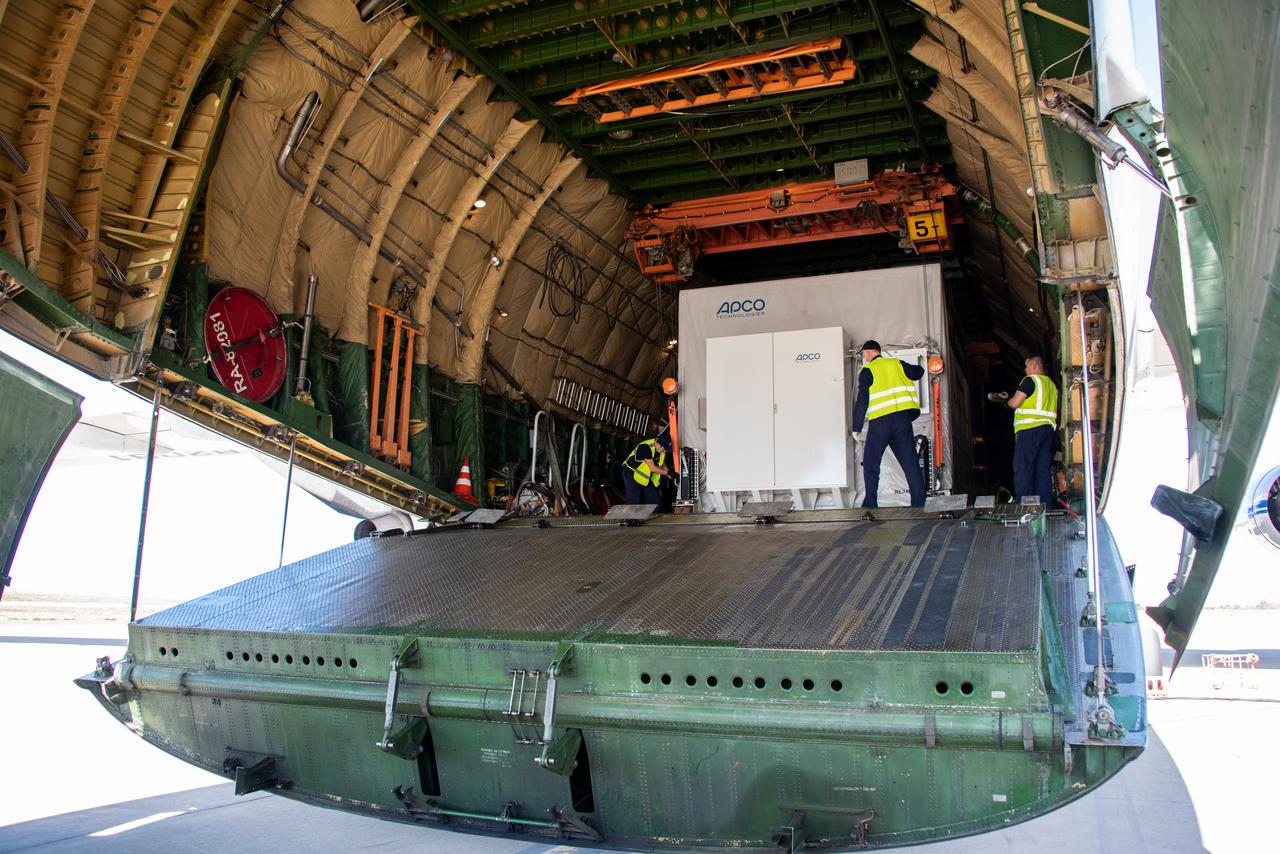

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, is visible inside the Antonov cargo aircraft that delivered it to Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
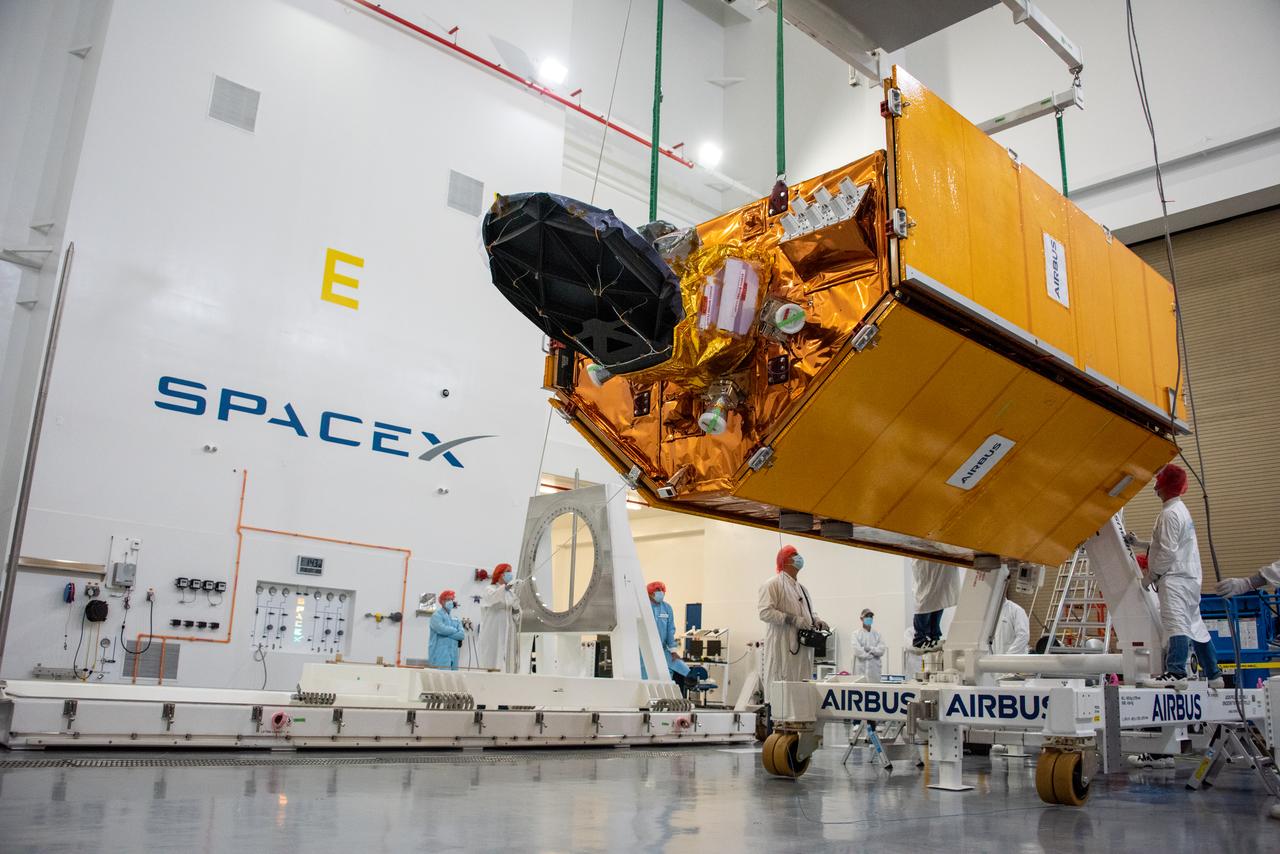

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
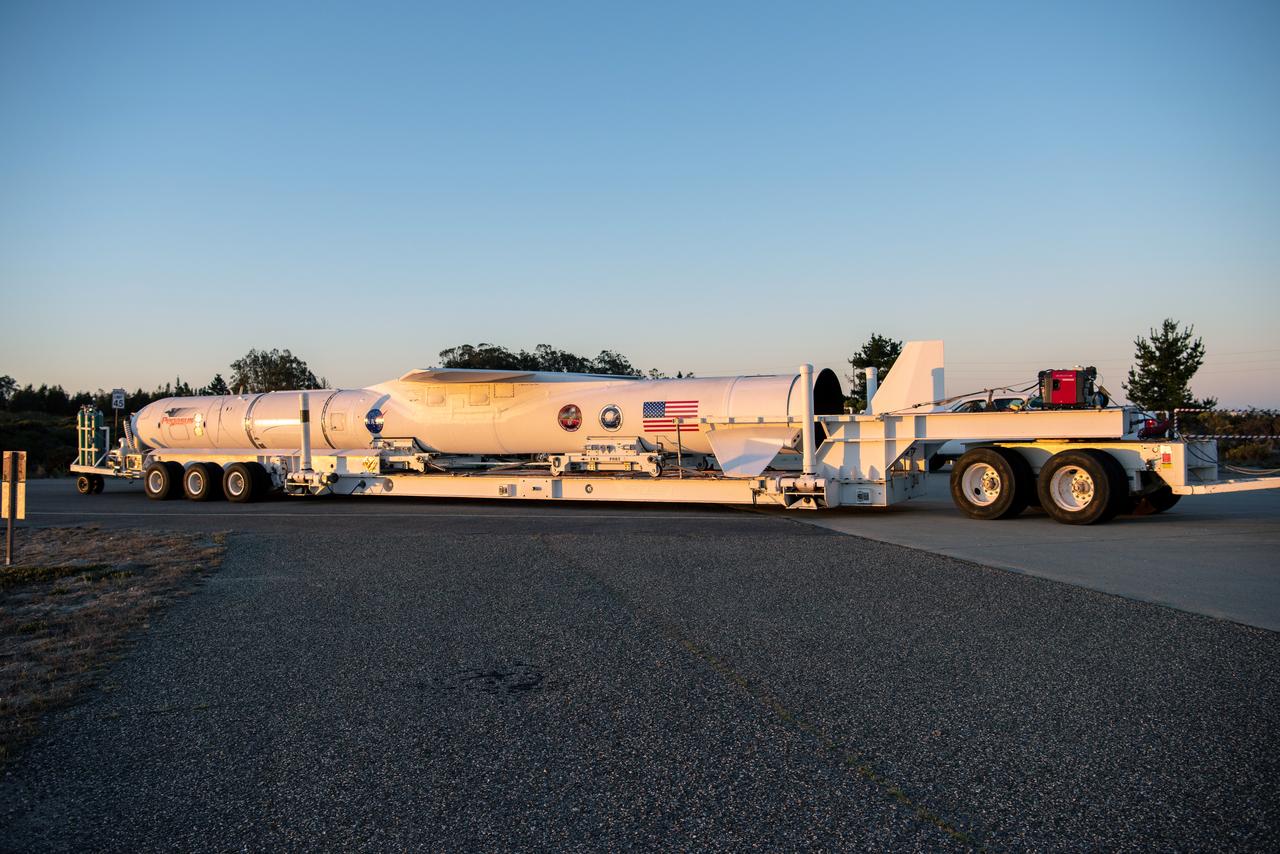

The Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, with NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) secured in its payload fairing, rolls out from Building 1555 to the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 25, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket will be attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft for the flight to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Florida. ICON will launch from the Skid Strip at CCAFS in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 10, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
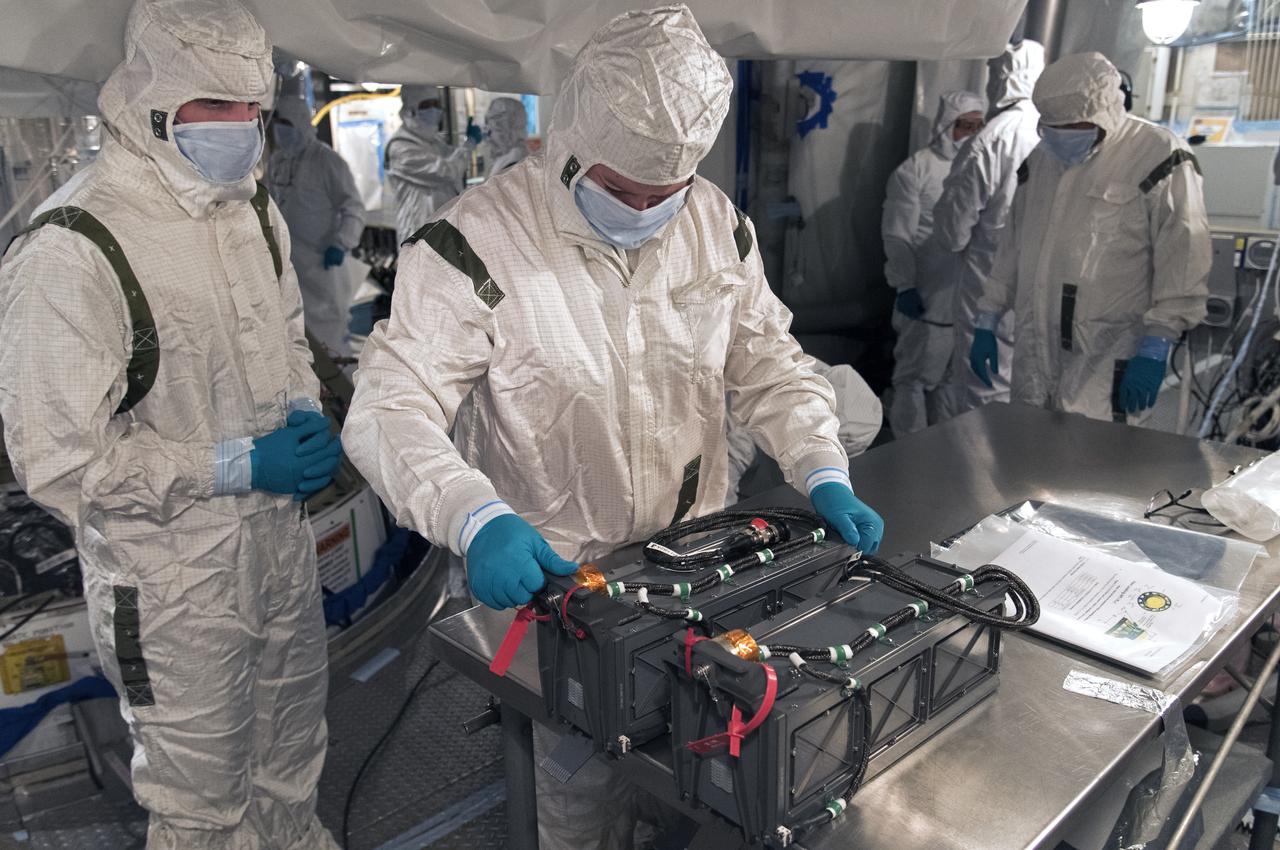

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container for installation on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
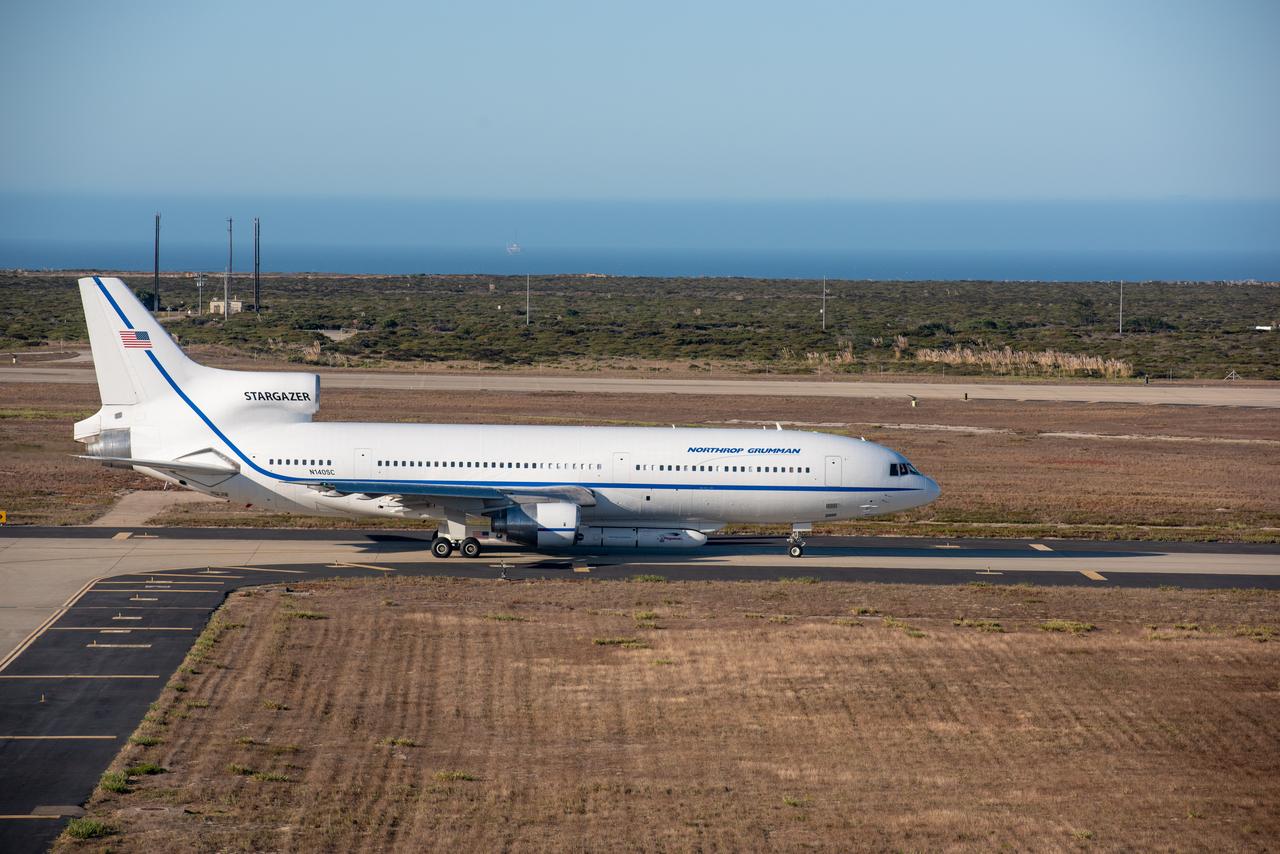

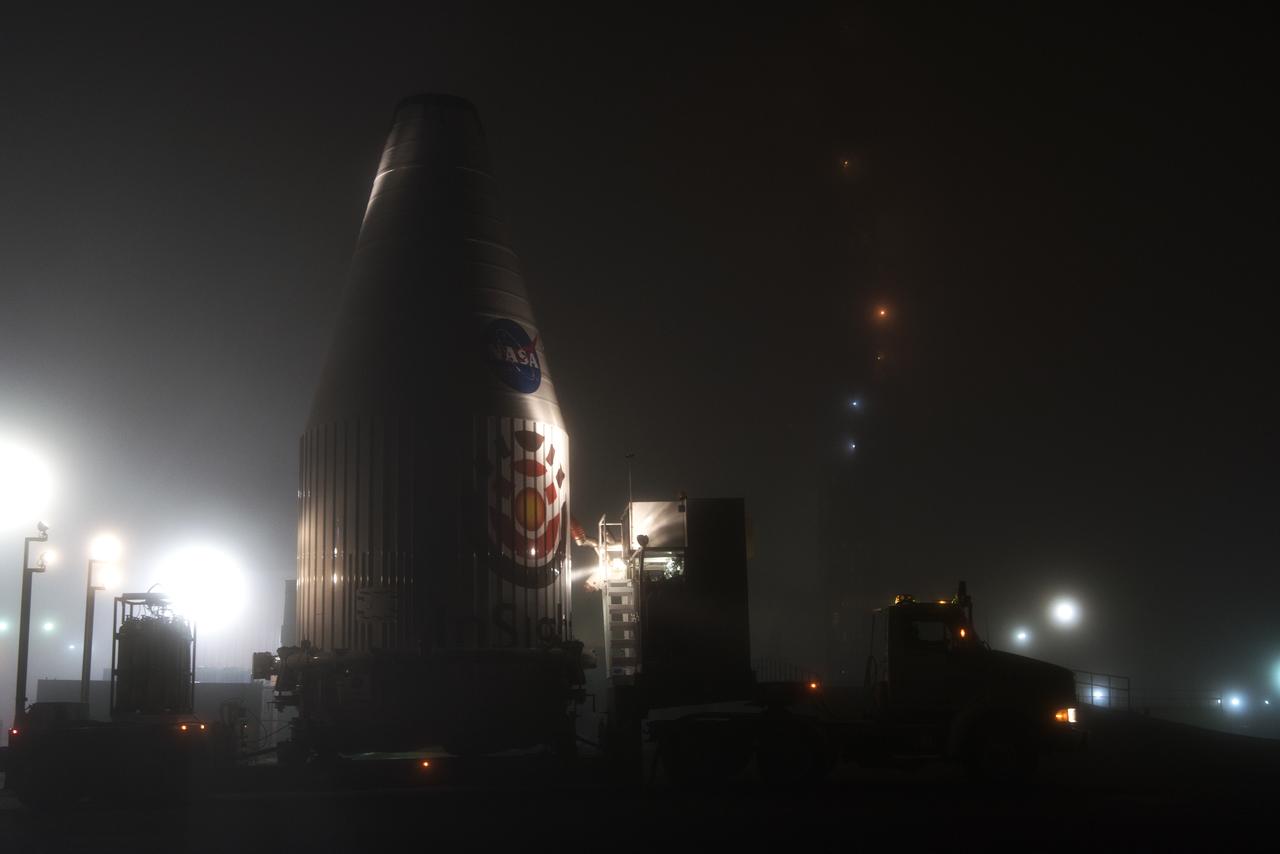
Northrop Grumman's L-1011 Stargazer awaits takeoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Oct. 1, 2019. The company's Pegasus XL rocket, containing NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON), is attached beneath the aircraft. The explorer is targeted to launch on Oct. 9, 2019, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above.