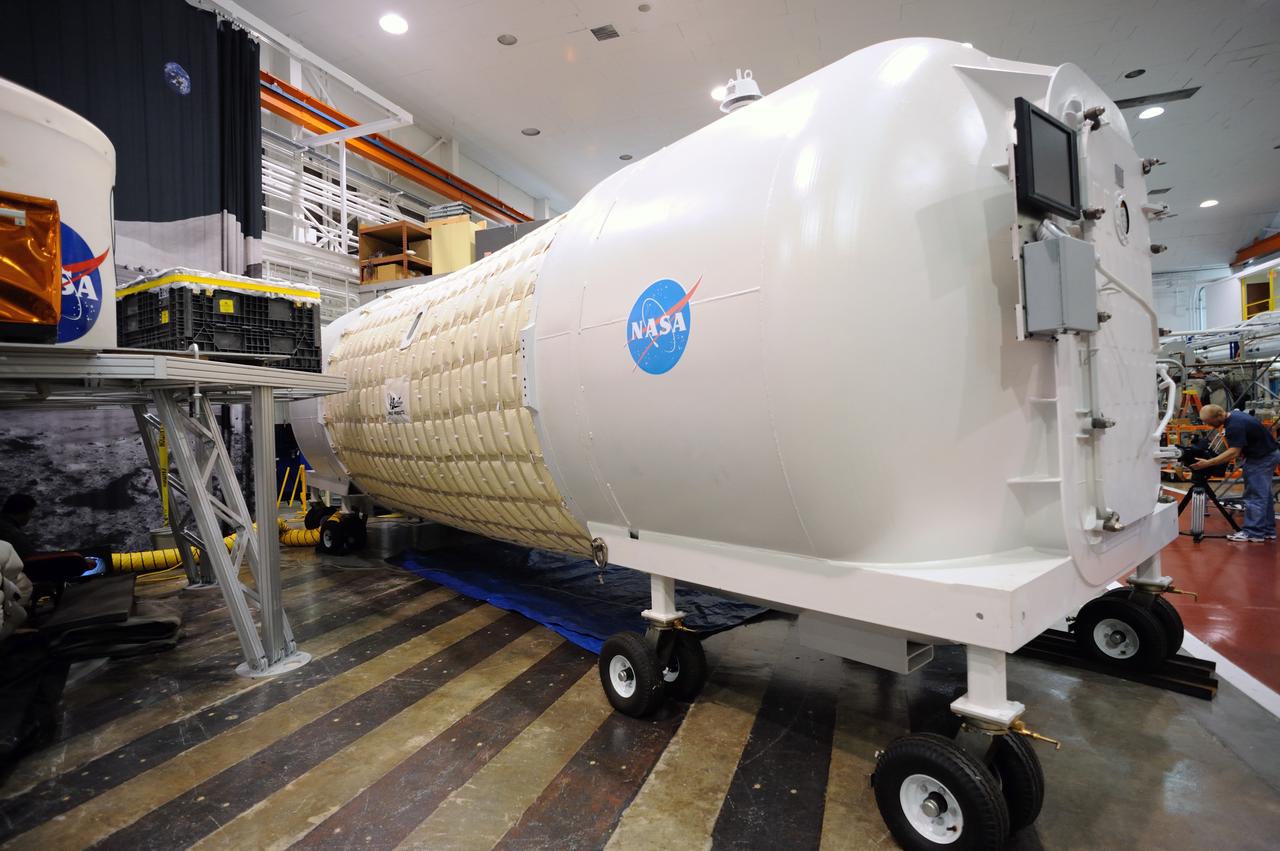

Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab).ILC Dover, under contract by NASA Langley Research Center, and in cooperation with NASA Johnson Space Center has designed and manufactured an expandable lunar habitat. This cylindrical habitat, or Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab) is a hybrid system with two hard end caps and a deployable softgoods section in the center.
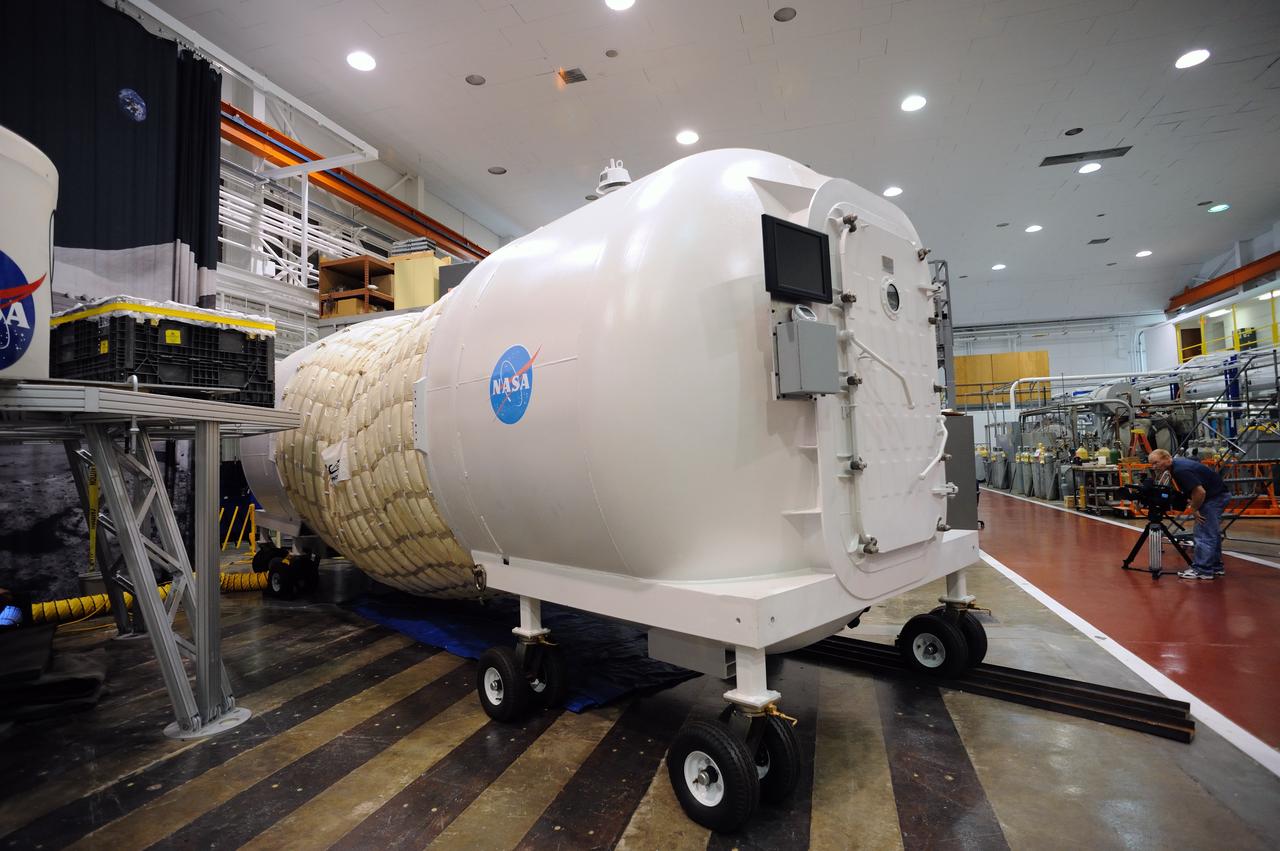

Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab).ILC Dover, under contract by NASA Langley Research Center, and in cooperation with NASA Johnson Space Center has designed and manufactured an expandable lunar habitat. This cylindrical habitat, or Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab) is a hybrid system with two hard end caps and a deployable softgoods section in the center.
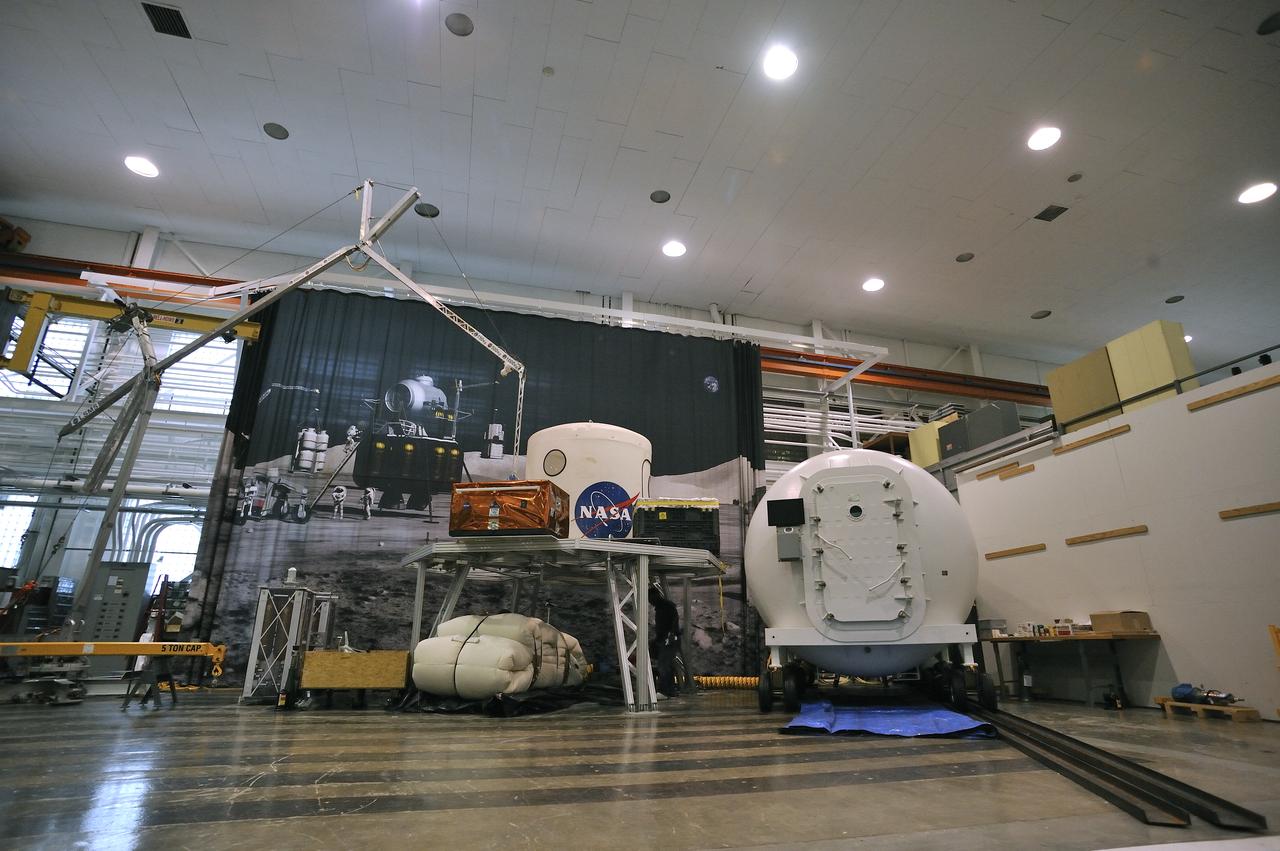

Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab).ILC Dover, under contract by NASA Langley Research Center, and in cooperation with NASA Johnson Space Center has designed and manufactured an expandable lunar habitat. This cylindrical habitat, or Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab) is a hybrid system with two hard end caps and a deployable softgoods section in the center.
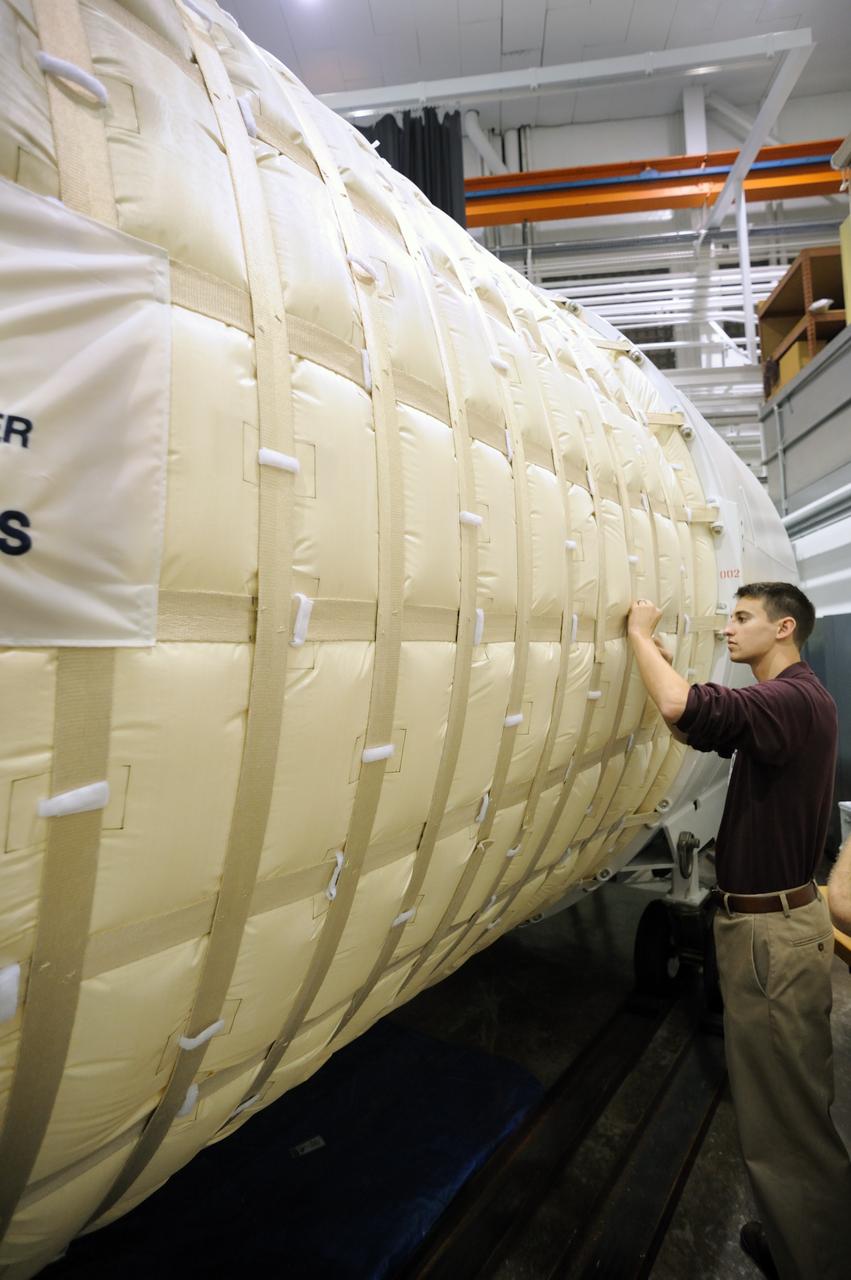

Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab).ILC Dover, under contract by NASA Langley Research Center, and in cooperation with NASA Johnson Space Center has designed and manufactured an expandable lunar habitat. This cylindrical habitat, or Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab) is a hybrid system with two hard end caps and a deployable softgoods section in the center.
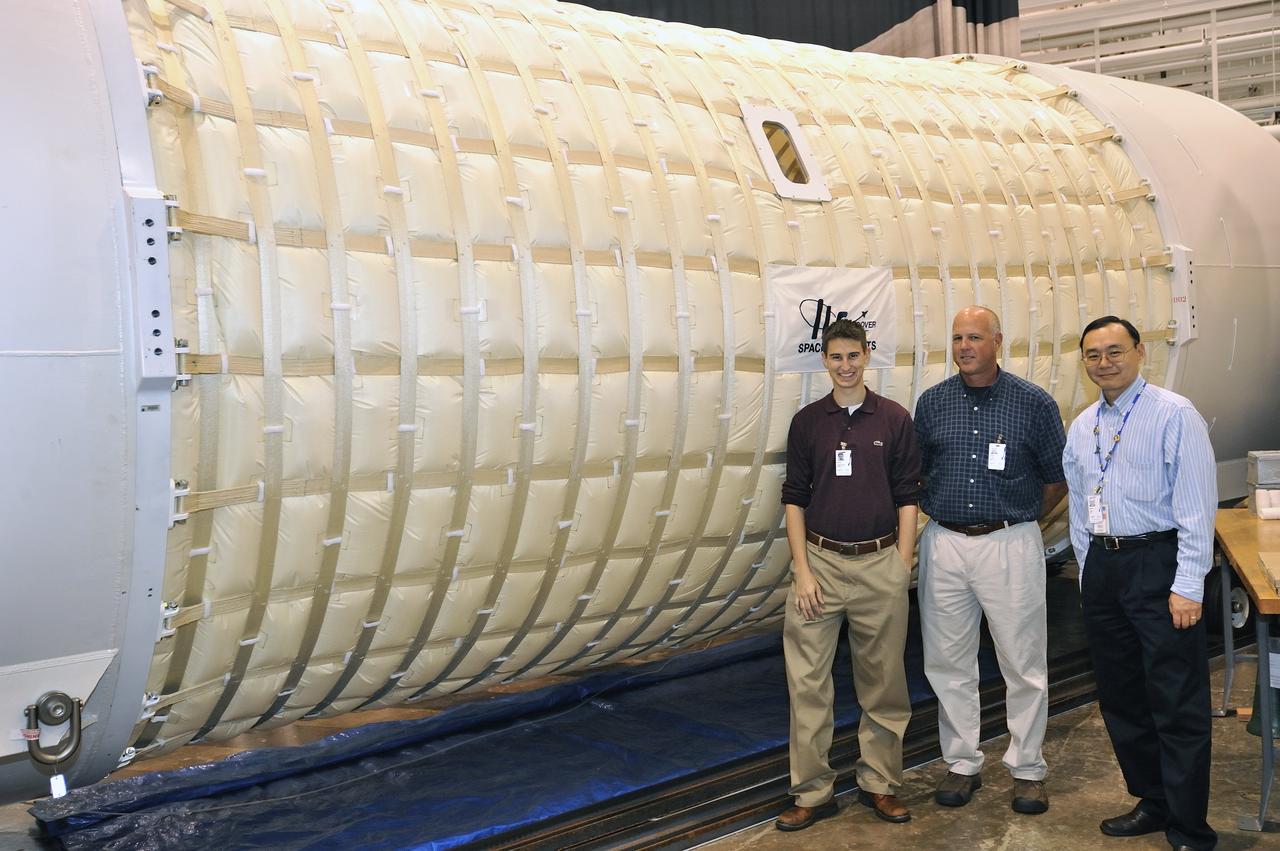

Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab).ILC Dover, under contract by NASA Langley Research Center, and in cooperation with NASA Johnson Space Center has designed and manufactured an expandable lunar habitat. This cylindrical habitat, or Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab) is a hybrid system with two hard end caps and a deployable softgoods section in the center.
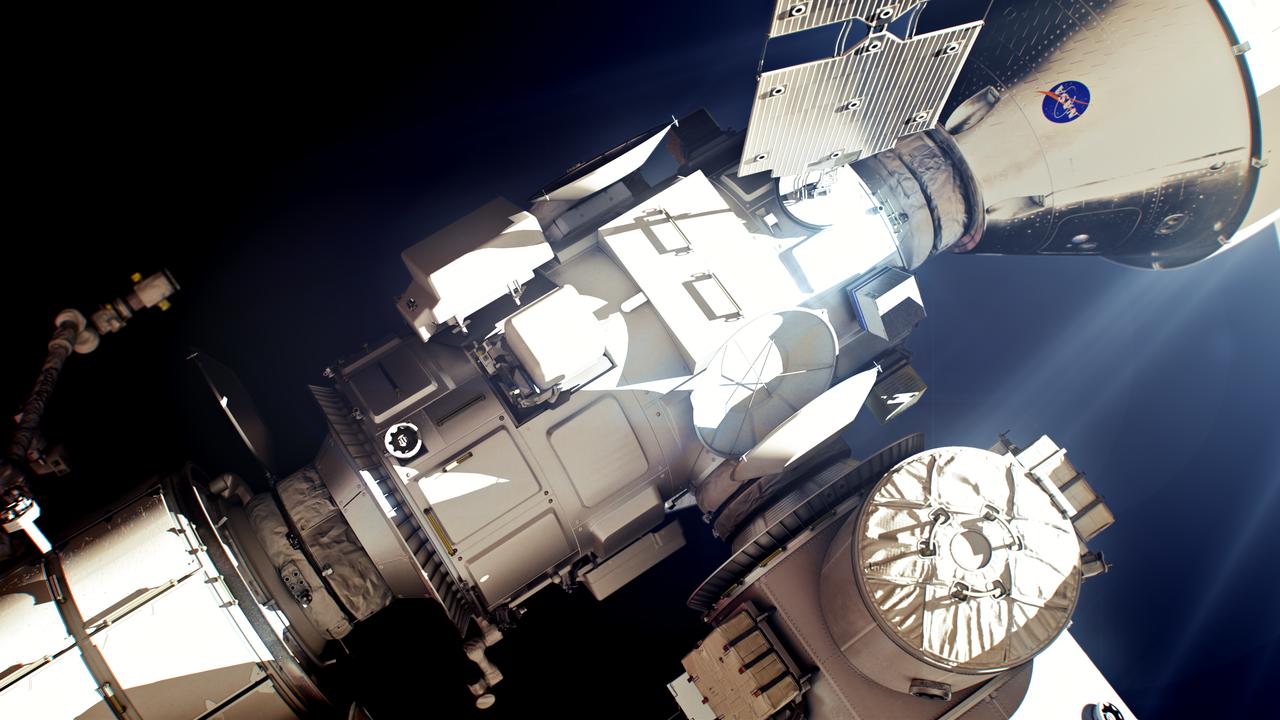

Gateway's International Habitat (I-Hab) module, provided by ESA, is one of two of the space station's habitation modules in addition to HALO. Astronauts will live, conduct science, and prepare for lunar surface missions inside I-Hab and HALO.

Photo Date: 11/14/2023 Location: Turin, Italy Subject: ESA International Habitat (I-HAB) Photo Credit: ESA/Stephane Corvaja
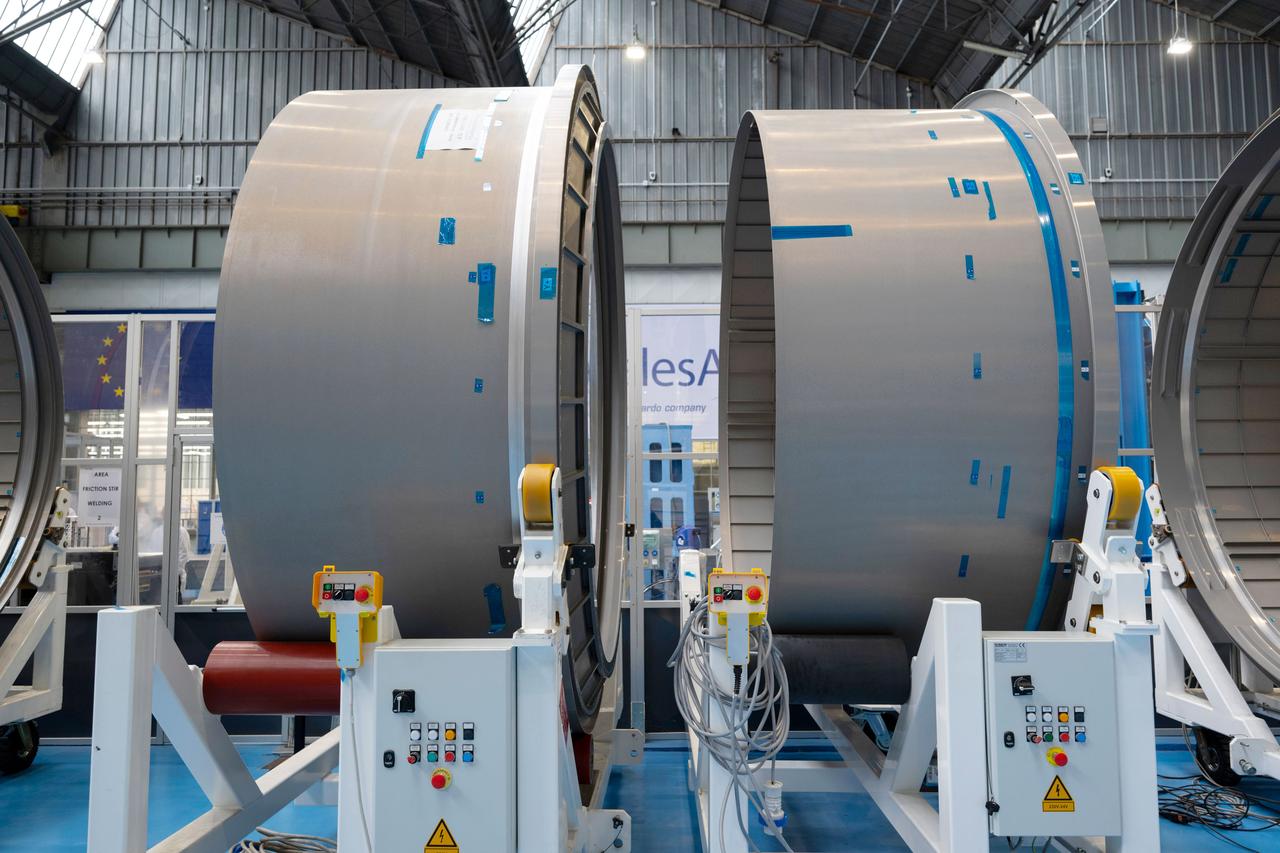

Photo Date: 11/14/2023 Location: Turin, Italy Subject: ESA International Habitat (I-HAB) Photo Credit: ESA/Stephane Corvaja
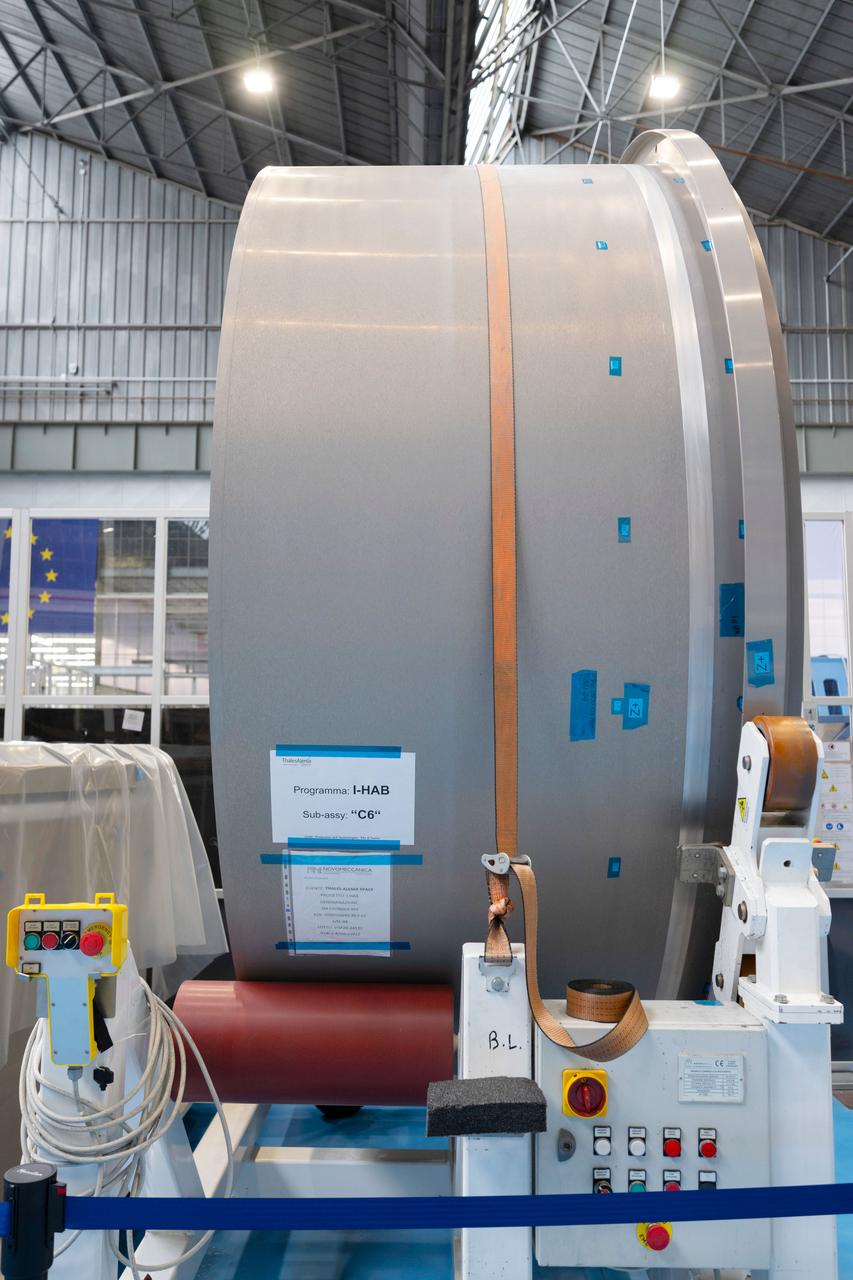

Photo Date: 11/14/2023 Location: Turin, Italy Subject: ESA International Habitat (I-HAB) Photo Credit: ESA/Stephane Corvaja
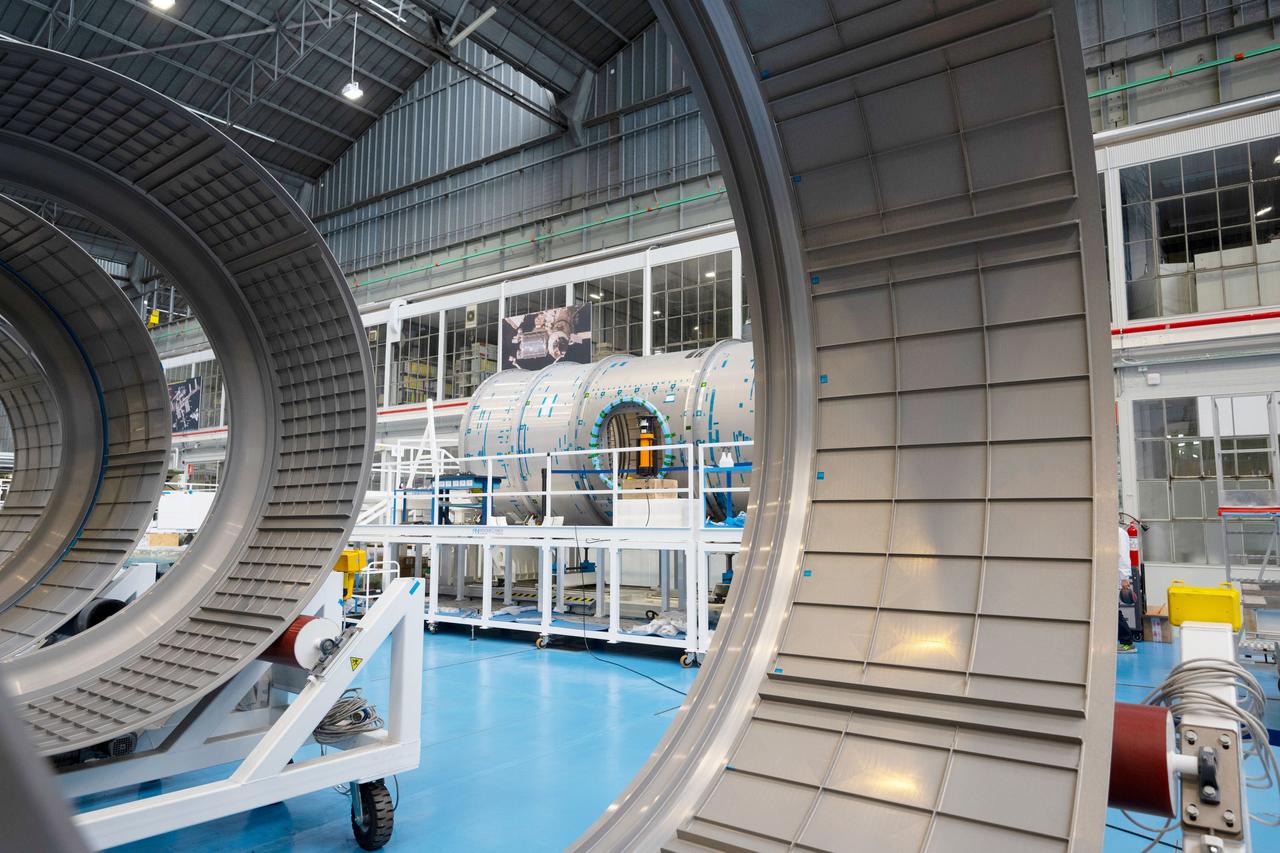

Photo Date: 11/14/2023 Location: Turin, Italy Subject: ESA International Habitat (I-HAB) Photo Credit: ESA/Stephane Corvaja
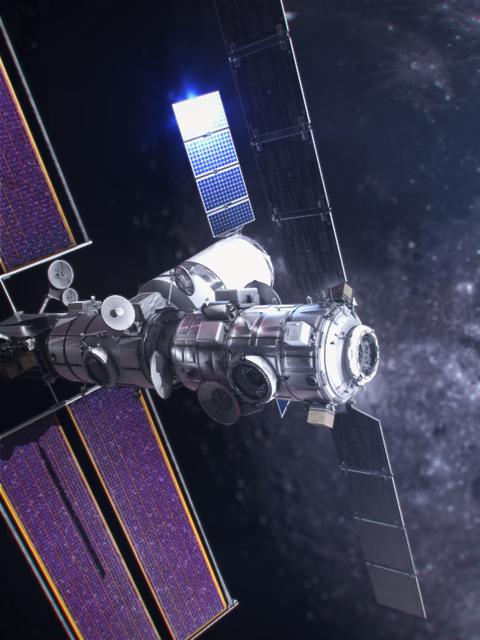

Astronauts will enter Gateway for the first time during the Artemis IV mission when the crewed Orion spacecraft will deliver the International Habitation (I-Hab) module to the space station.
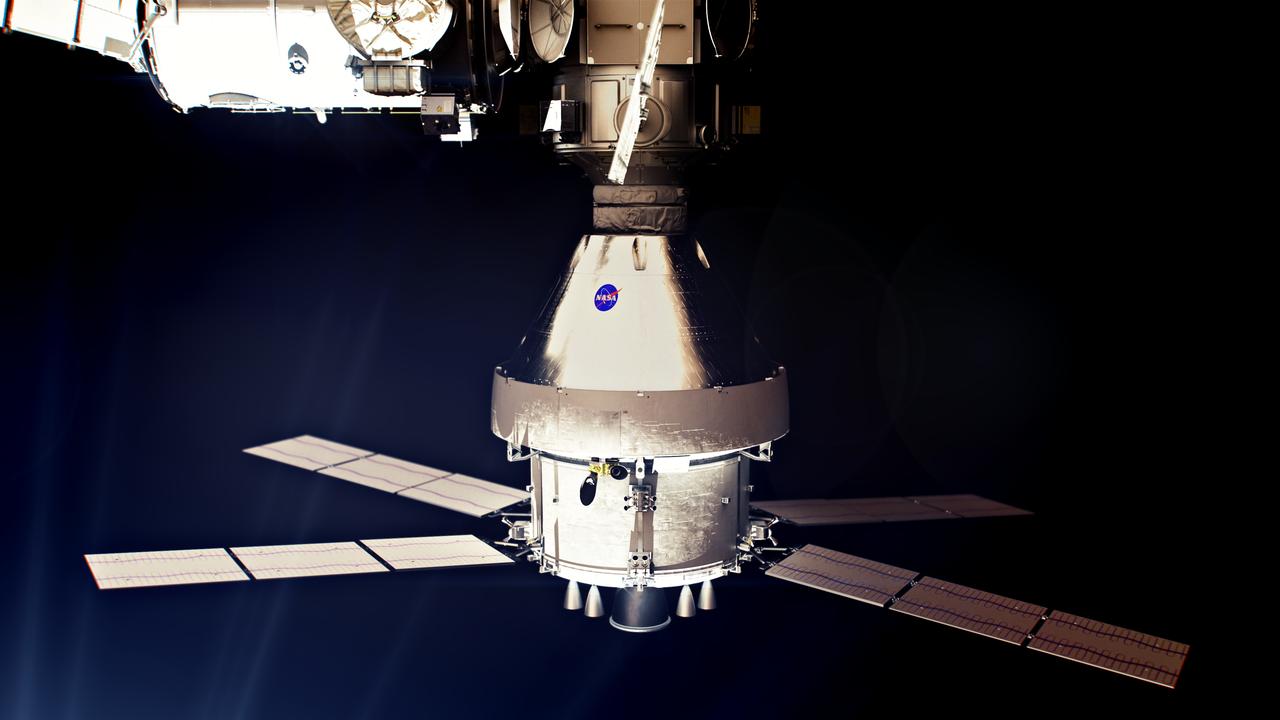
The Orion spacecraft docked to the Gateway space station. Orion will visit Gateway for the first time on the Artemis IV mission when astronauts will use it to deliver the International Habitat (I-Hab) module to Gateway. Orion will return to Gateway to deliver additional elements on Artemis V and VI.
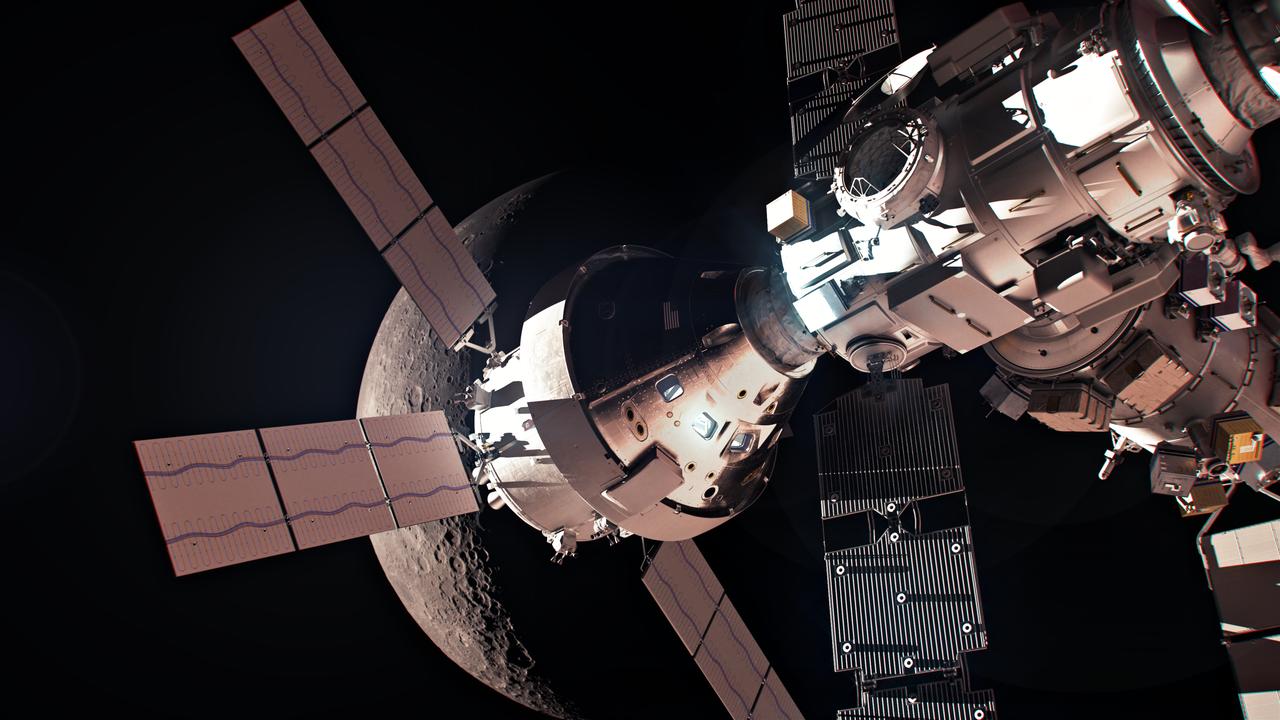

The Orion spacecraft docked to the Gateway space station. Orion will visit Gateway for the first time on the Artemis IV mission when astronauts will use it to deliver the International Habitat (I-Hab) module to Gateway. Orion will return to Gateway to deliver additional elements on Artemis V and VI.
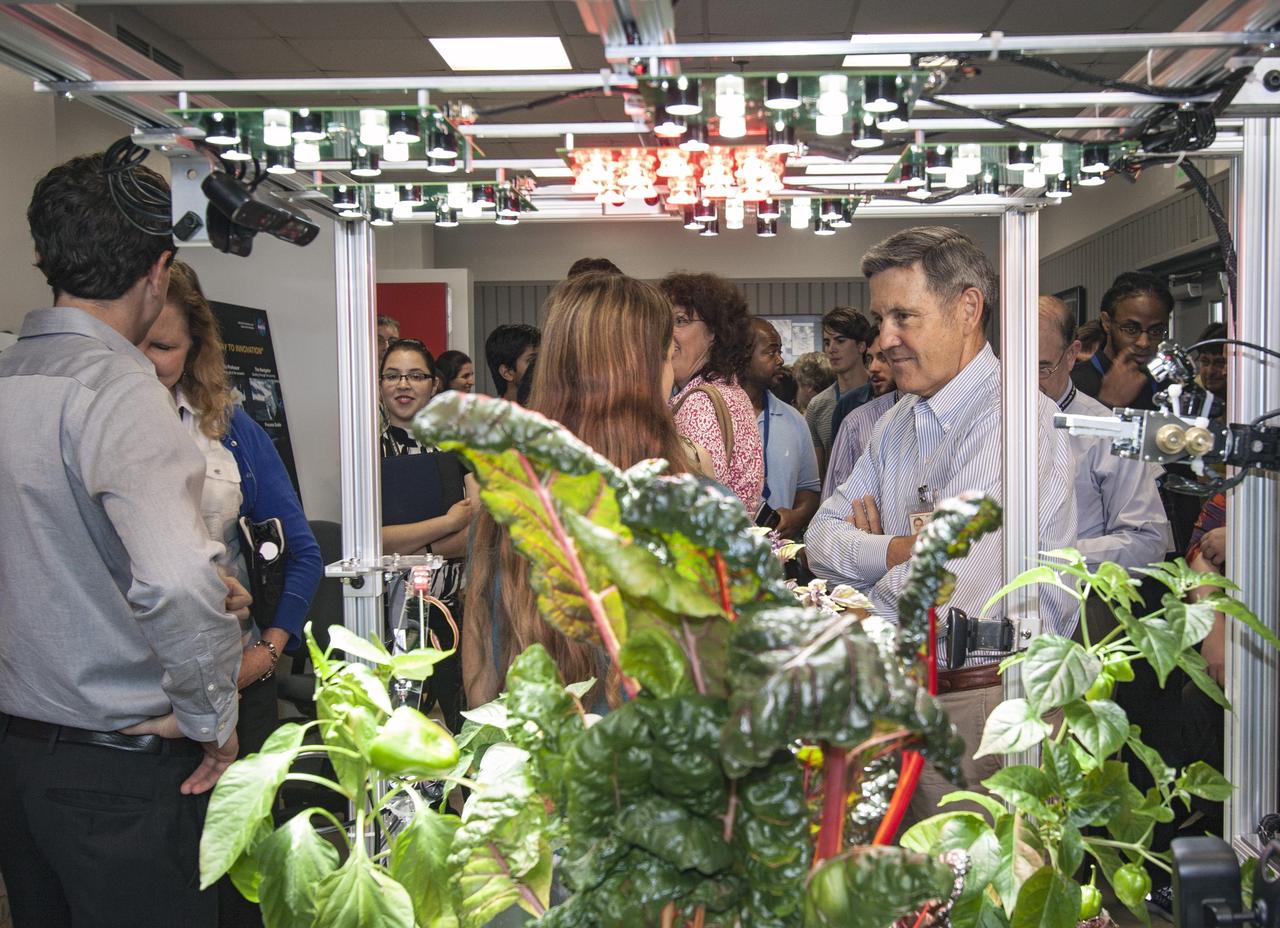

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana listens as a student from University of Colorado describes a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants, both for consumption as well as the benefit of oxygen-carbon dioxide cycling. Considerations range from monitoring and nutrient supply to selection of plants and autonomy. The activity is part of the eXploration Habitat, or X-Hab, Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
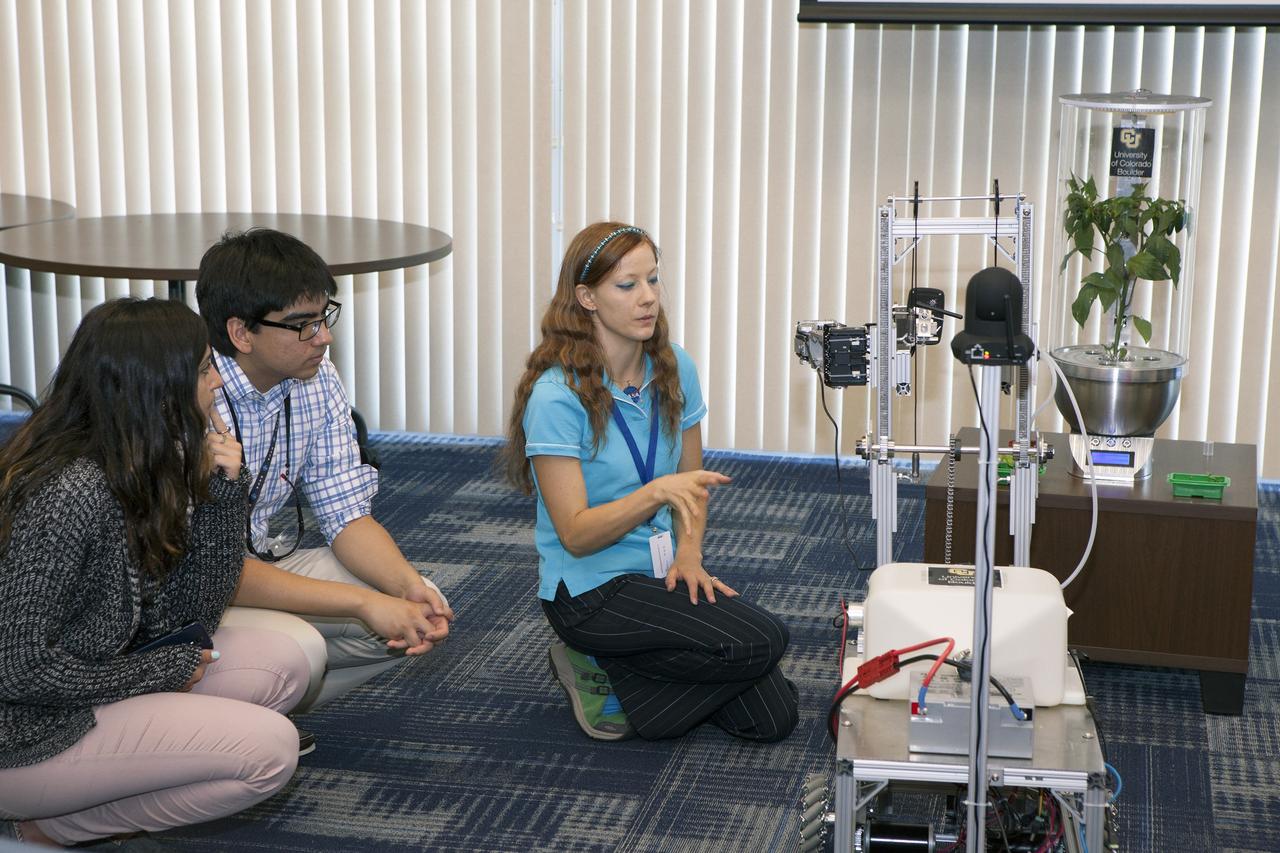
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Heather Hava, who is working on a doctorate in aerospace engineering sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder, describes a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, which could tend to plants grown in one of the SmartPots, or SPOTS seen on the right. The system is being developed by the graduate students participating in the eXploration HABitat X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
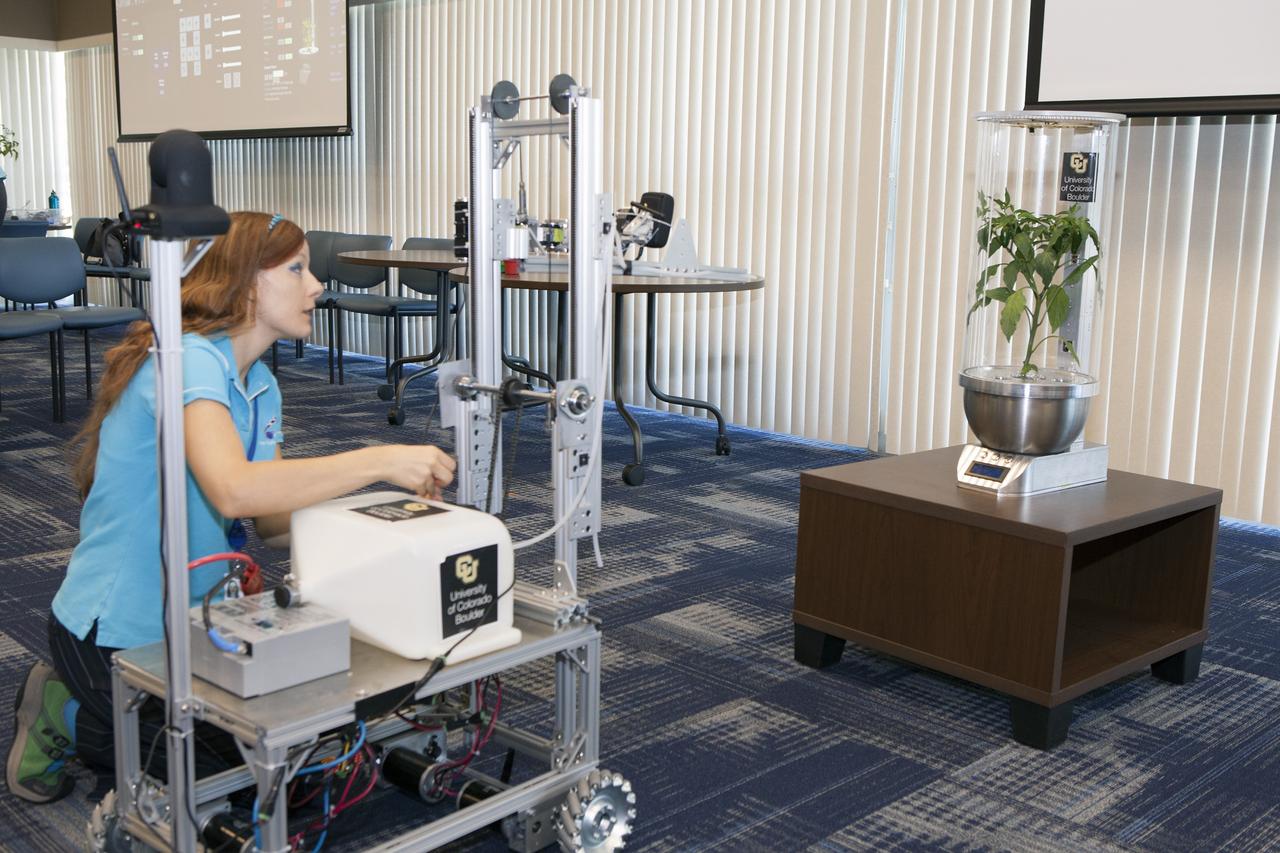

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Heather Hava, who is working on a doctorate in aerospace engineering sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder, makes adjustments on a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, which could tend to plants grown in one of the SmartPots, or SPOTS seen on the right. The system is being developed by the graduate students participating in the eXploration HABitat X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
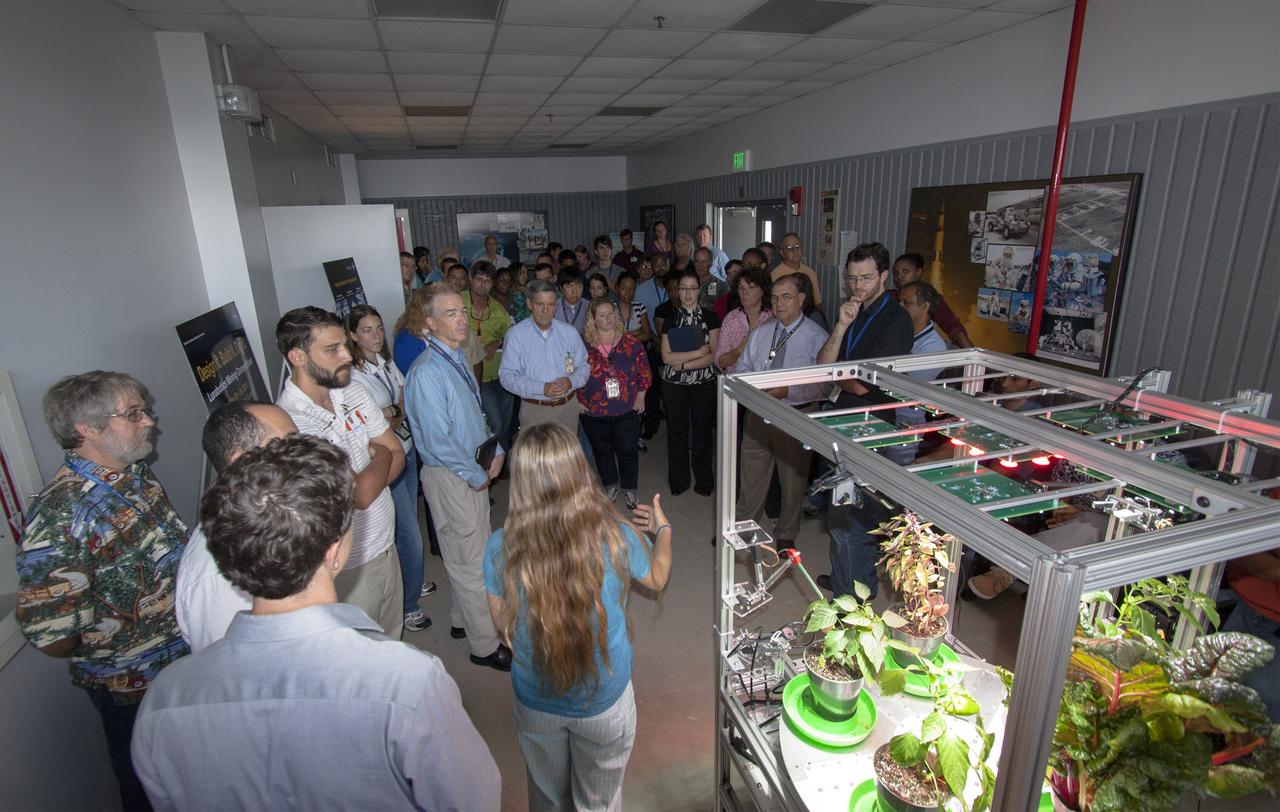

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students from University of Colorado describe a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants, both for consumption as well as the benefit of oxygen-carbon dioxide cycling. Considerations range from monitoring and nutrient supply to selection of plants and autonomy. The activity is part of the eXploration Habitat, or X-Hab, Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
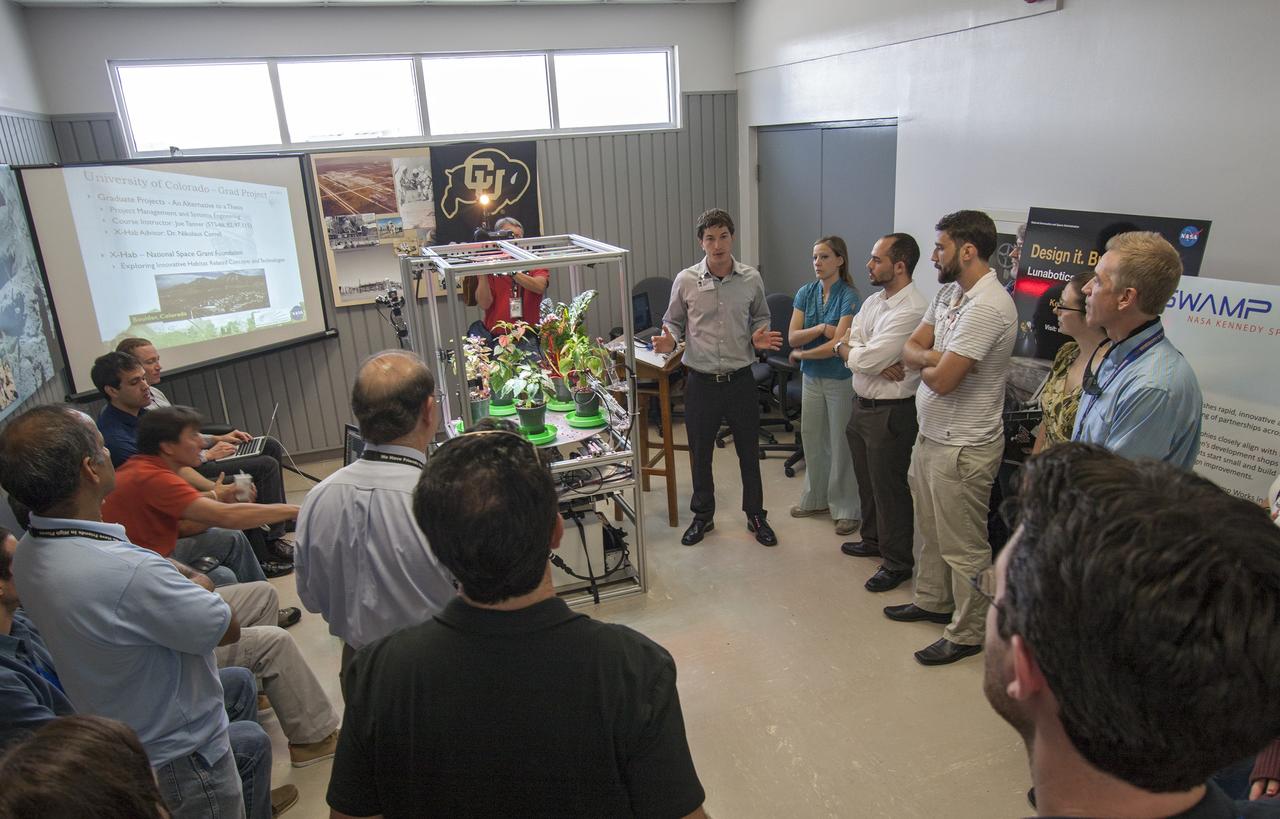

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students from University of Colorado describe a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants, both for consumption as well as the benefit of oxygen-carbon dioxide cycling. Considerations range from monitoring and nutrient supply to selection of plants and autonomy. The activity is part of the eXploration Habitat, or X-Hab, Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
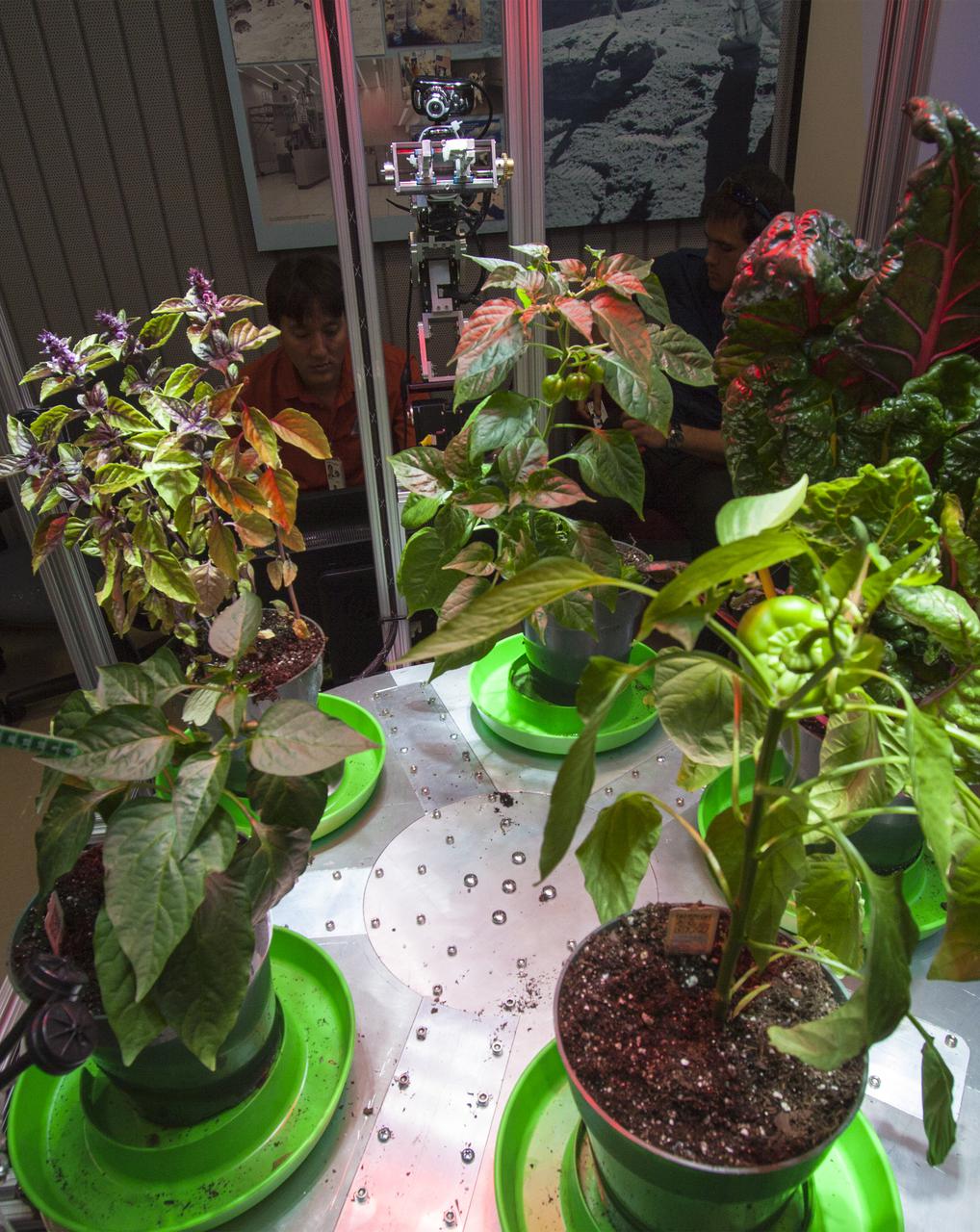

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students from University of Colorado demonstrated a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants, both for consumption as well as the benefit of oxygen-carbon dioxide cycling. Considerations range from monitoring and nutrient supply to selection of plants and autonomy. The activity is part of the eXploration Habitat, or X-Hab, Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http:__www.nasa.gov_exploration_technology_deep_space_habitat_xhab_ Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
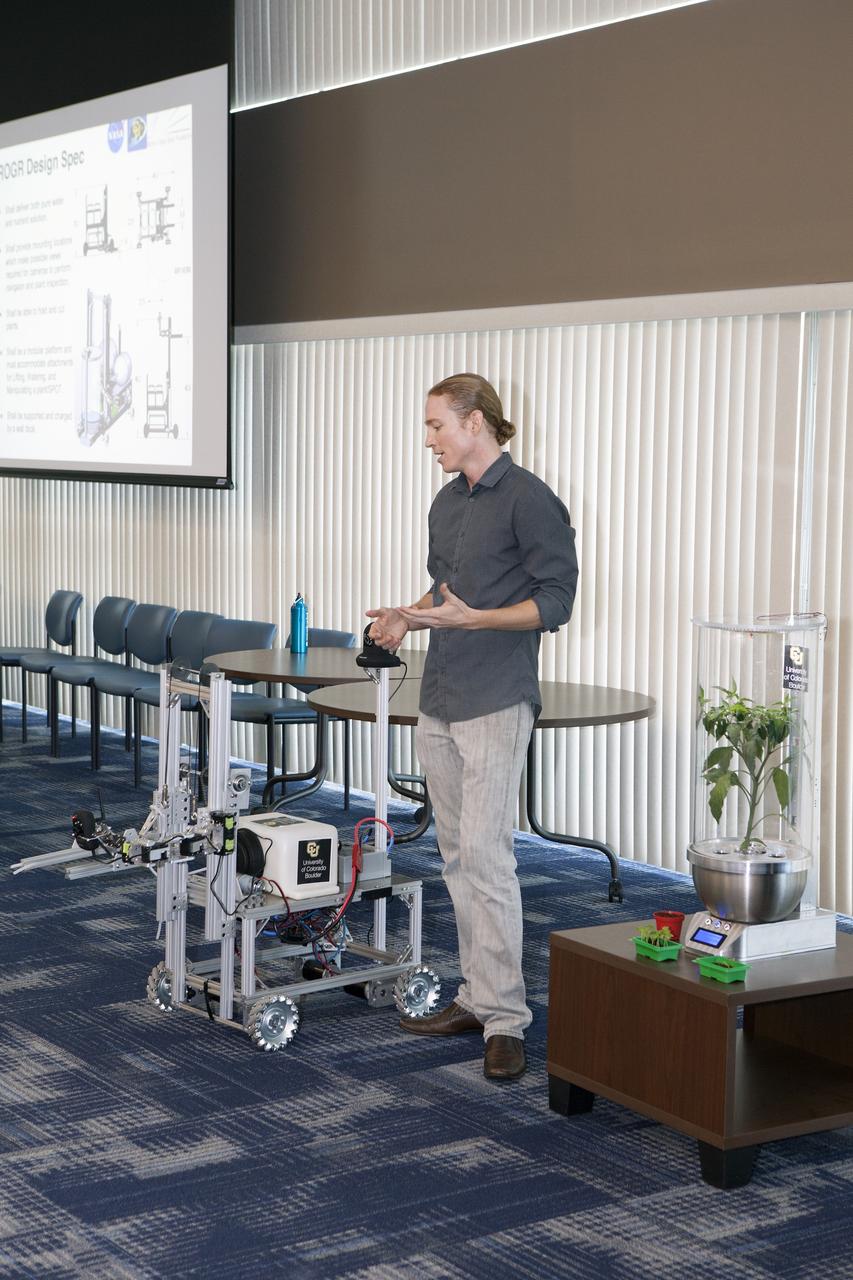

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Daniel Zukowski, a University of Colorado Boulder graduate student, describes a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, which could tend to plants grown in one of the SmartPots, or SPOTS, seen on the right. The system is being developed by the graduate students participating in the eXploration HABitation X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
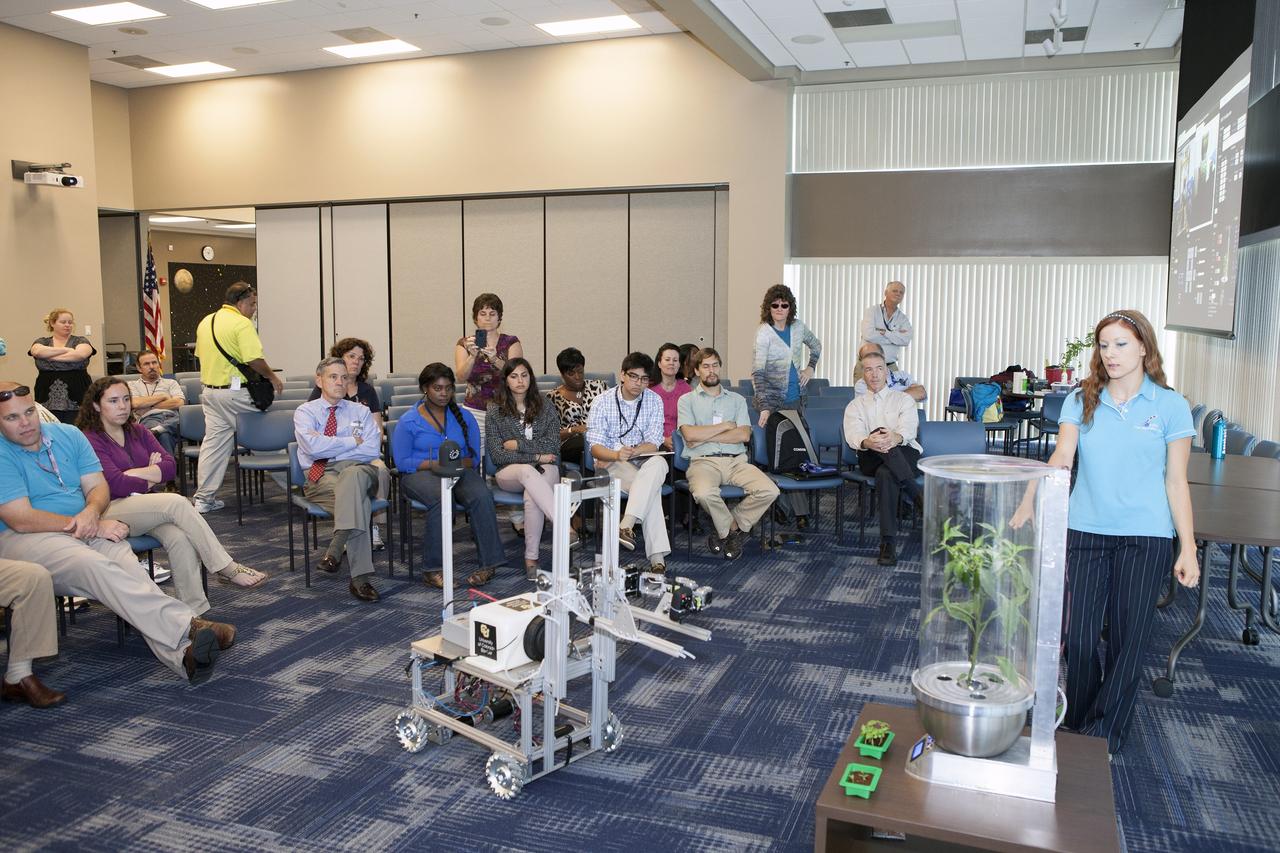

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Heather Hava, right, who is working on a doctorate in aerospace engineering sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder, describes a computerized SmartPot, or SPOT, which could be used to grow plants in a deep-space habitat. The SPOTs could be tended by a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, seen on the left. The system is being developed by the graduate students participating in the eXploration HABitat X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
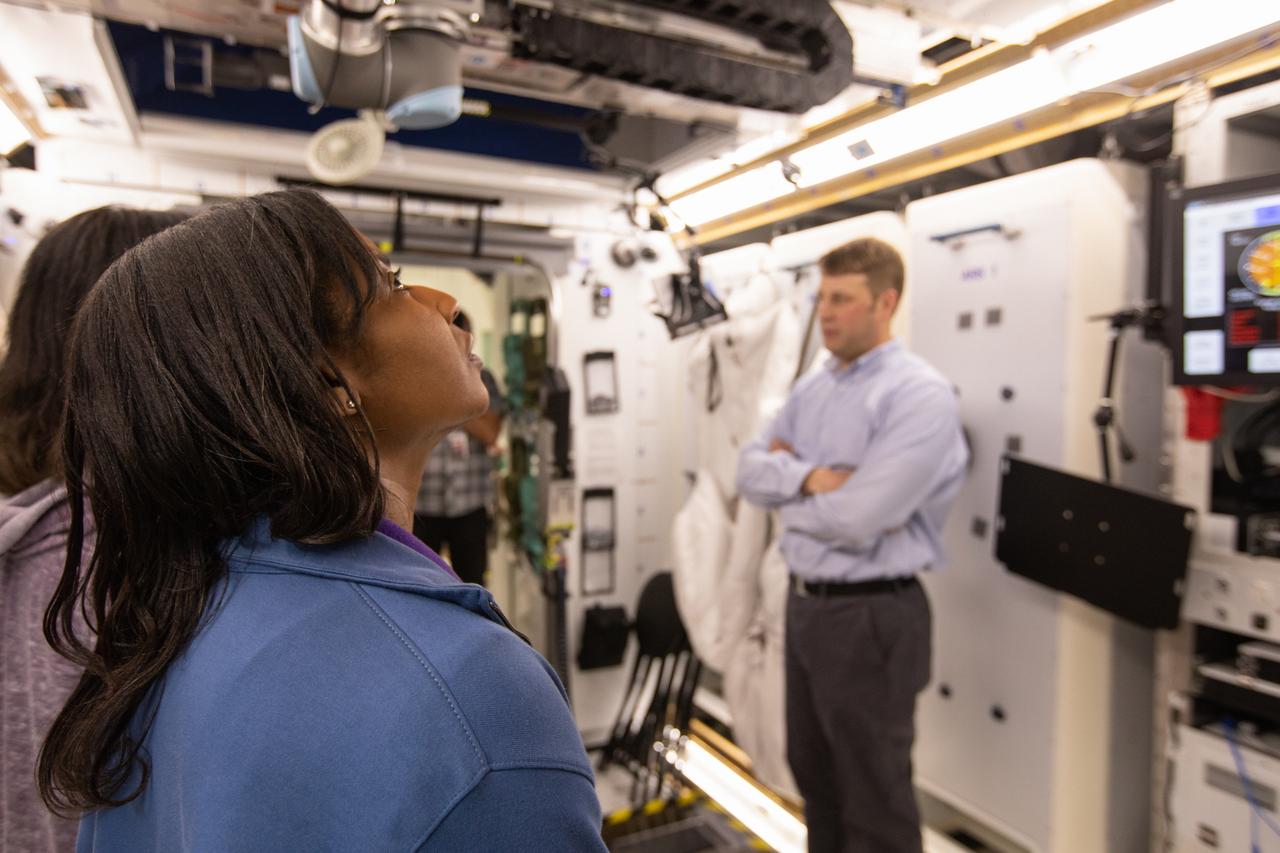

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, at left is astronaut Stephanie Wilson. To her left, partially hidden is astronaut Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.

NASA astronaut Raja Chari climbs through a hatch of Lockheed Martin’s deep space habitat ground prototype at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2019. Chari is one of the astronauts helping engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Astronauts provide important design perspective as they may one day live and work aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. To date, five habitat prototypes have been developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP. Lockheed Martin was the first to turn their habitat over to NASA for testing. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
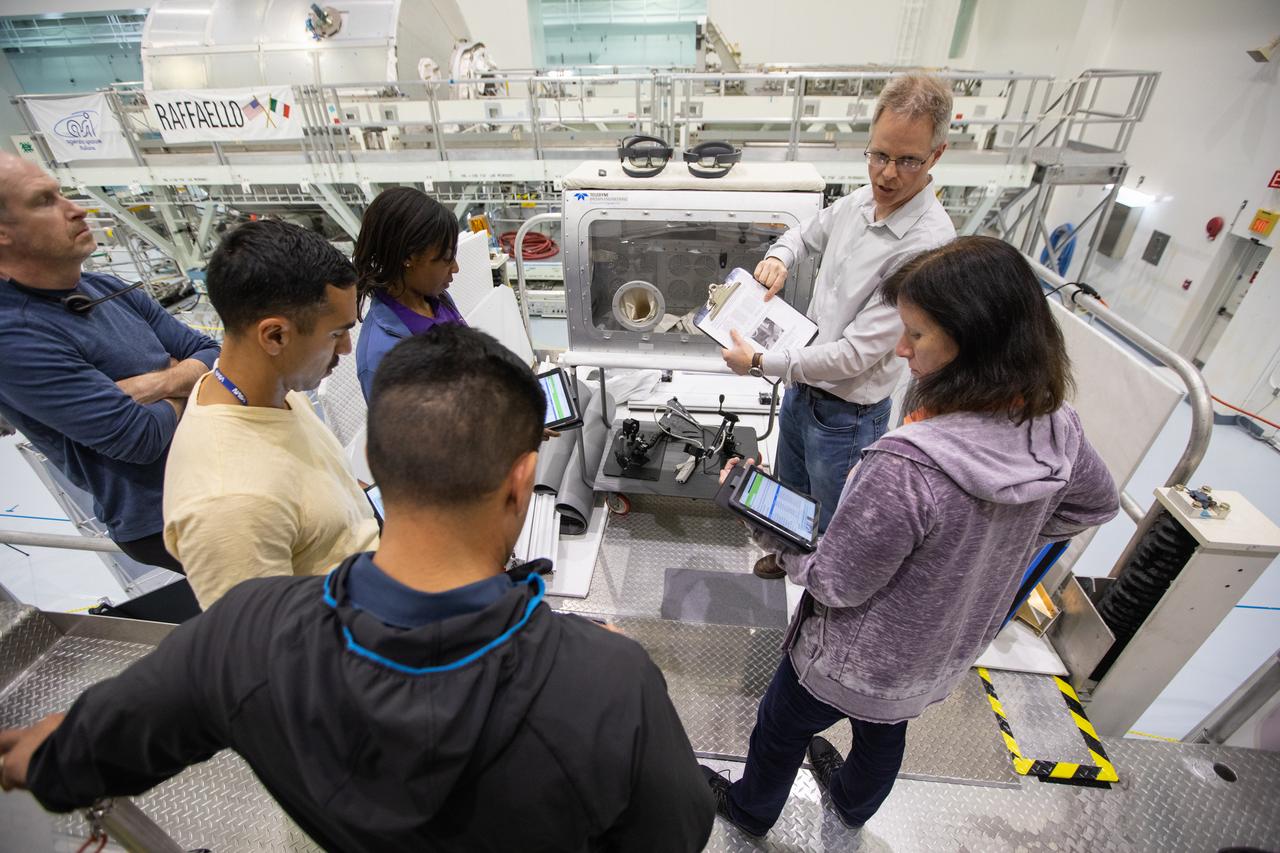

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the Space Station Processing Facility on March 26, 2019, from far left is astronaut Frank Rubio. In front of him, are Raja Chari and Stephanie Wilson. At right is astronaut Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
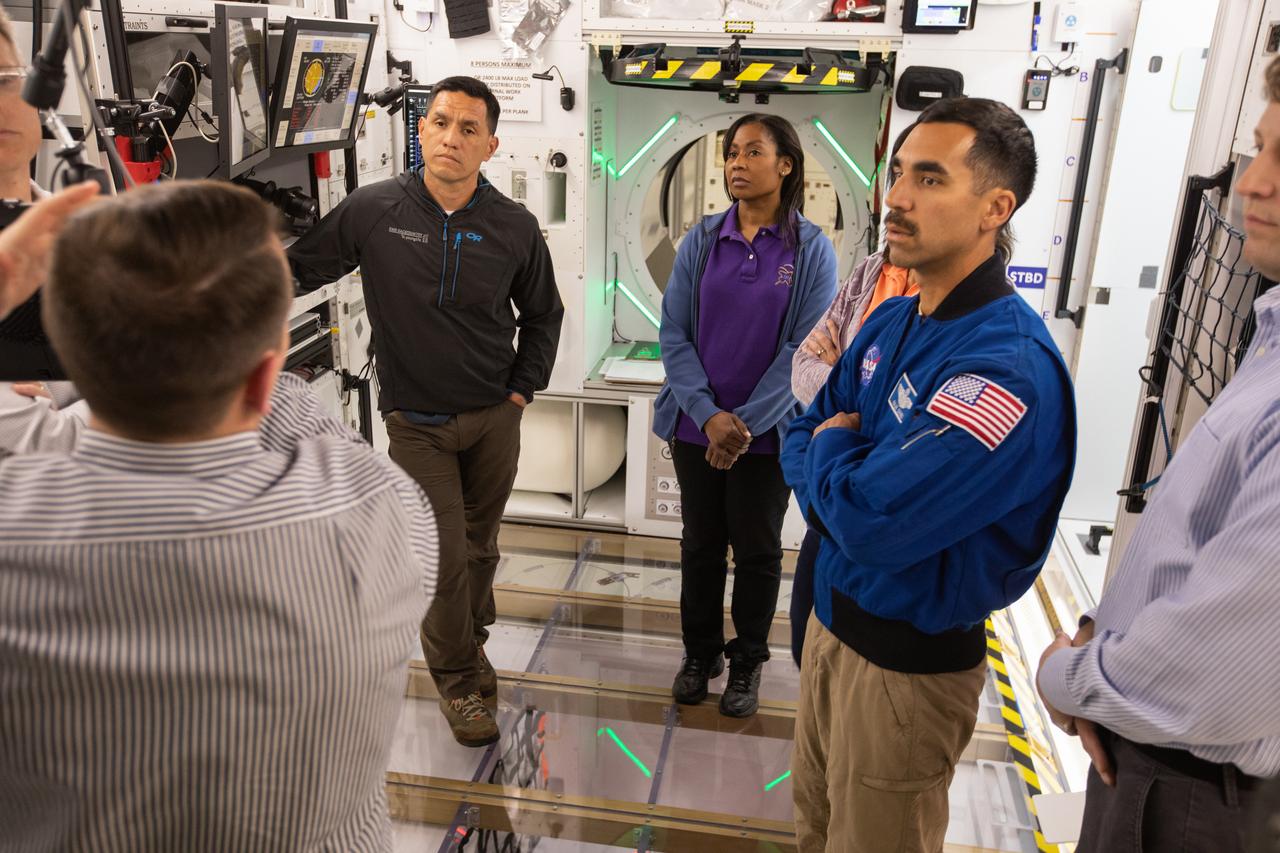

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, from left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Stephanie Wilson and Raja Chari. Partially in view next to Chari is astronaut Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
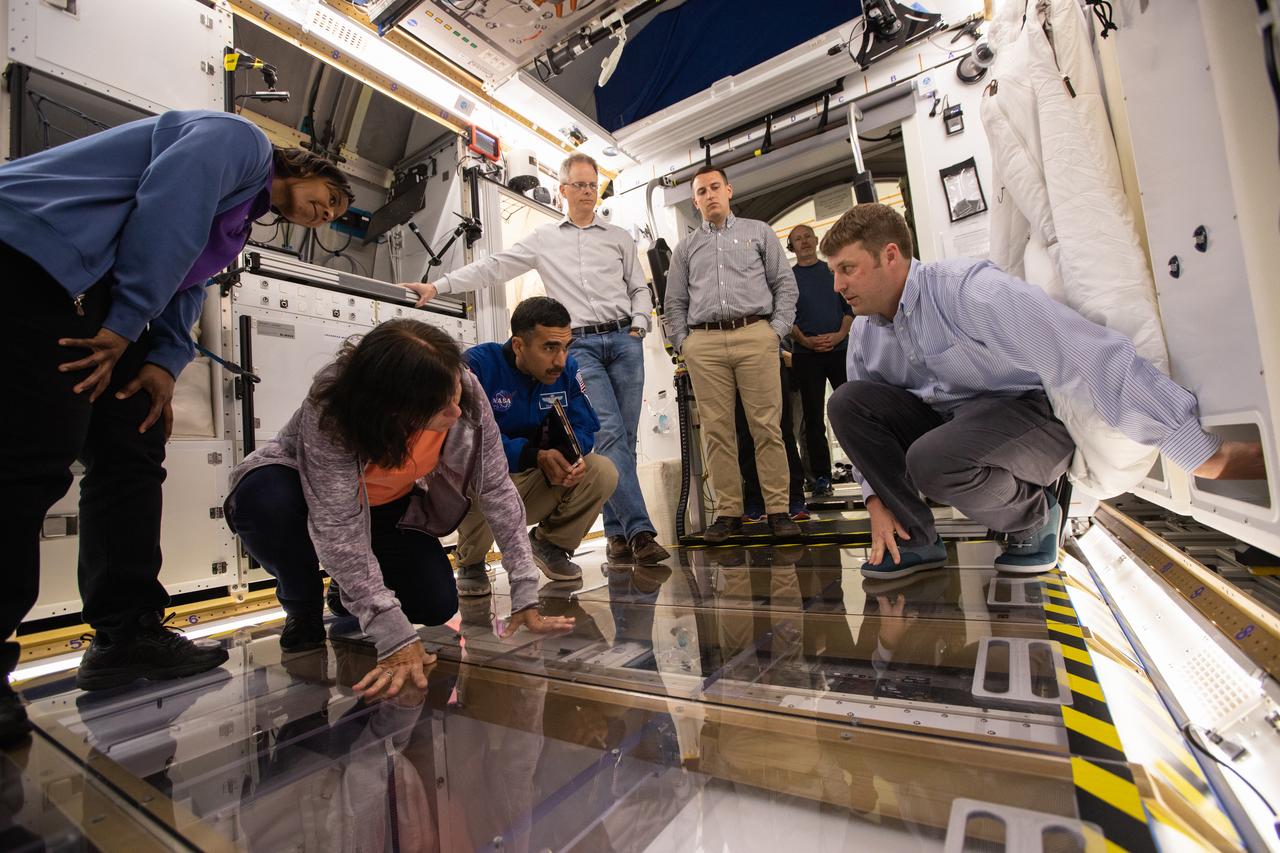

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, from left are astronauts Stephanie Wilson, Shannon Walker and Raja Chari. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
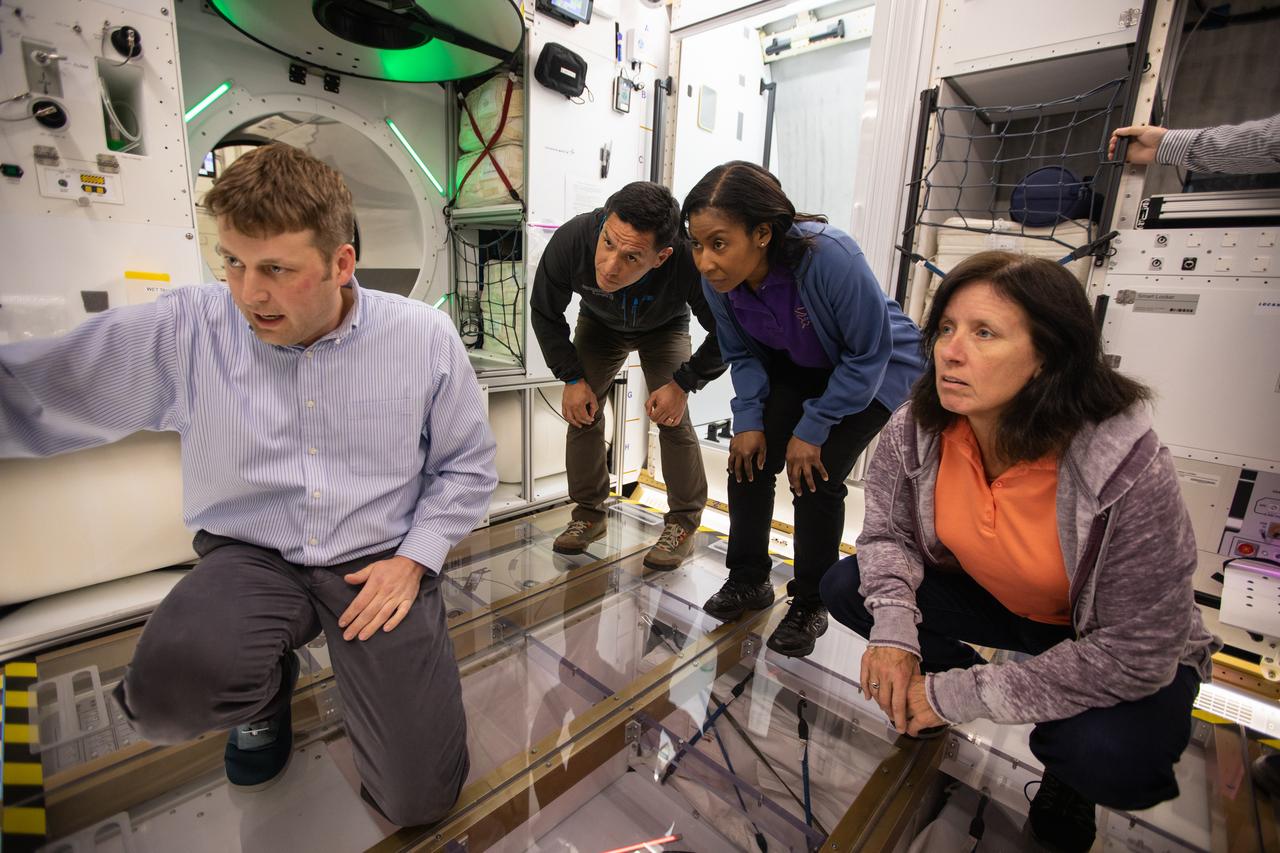

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, in back from left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Stephanie Wilson and Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
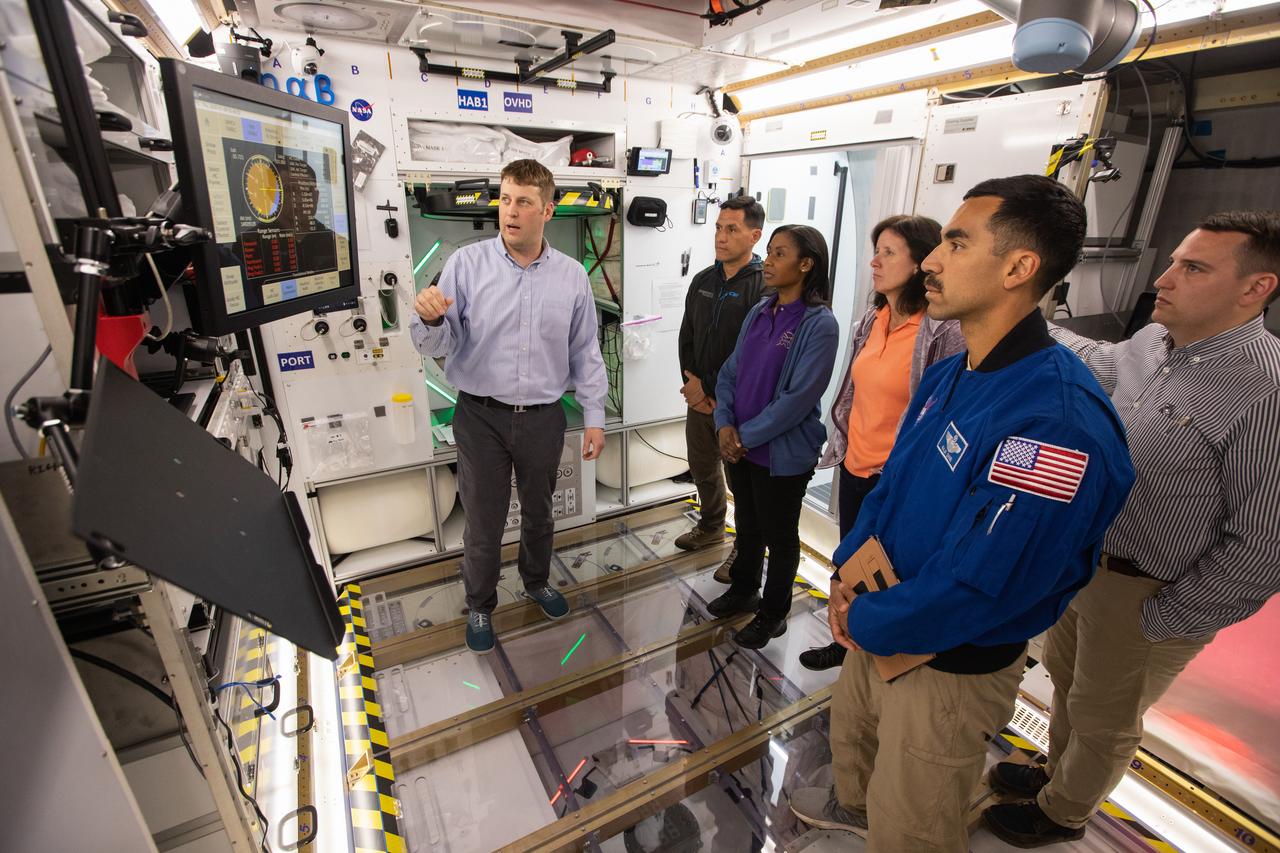

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, beginning second from left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Raja Shari, Stephanie Wilson and Shannon Walker. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
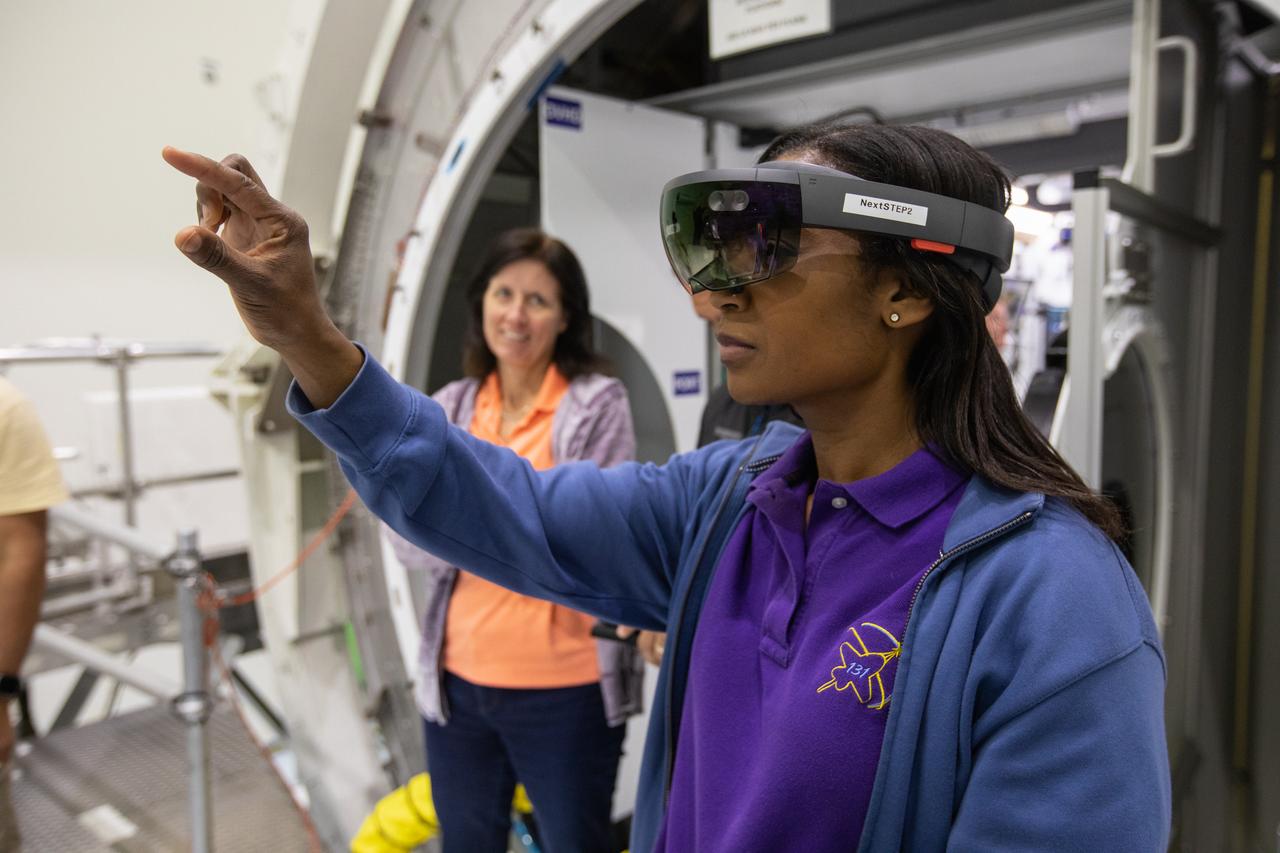

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the Space Station Processing Facility on March 26, 2019, from left are astronauts Shannon Walker and Stephanie Wilson. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
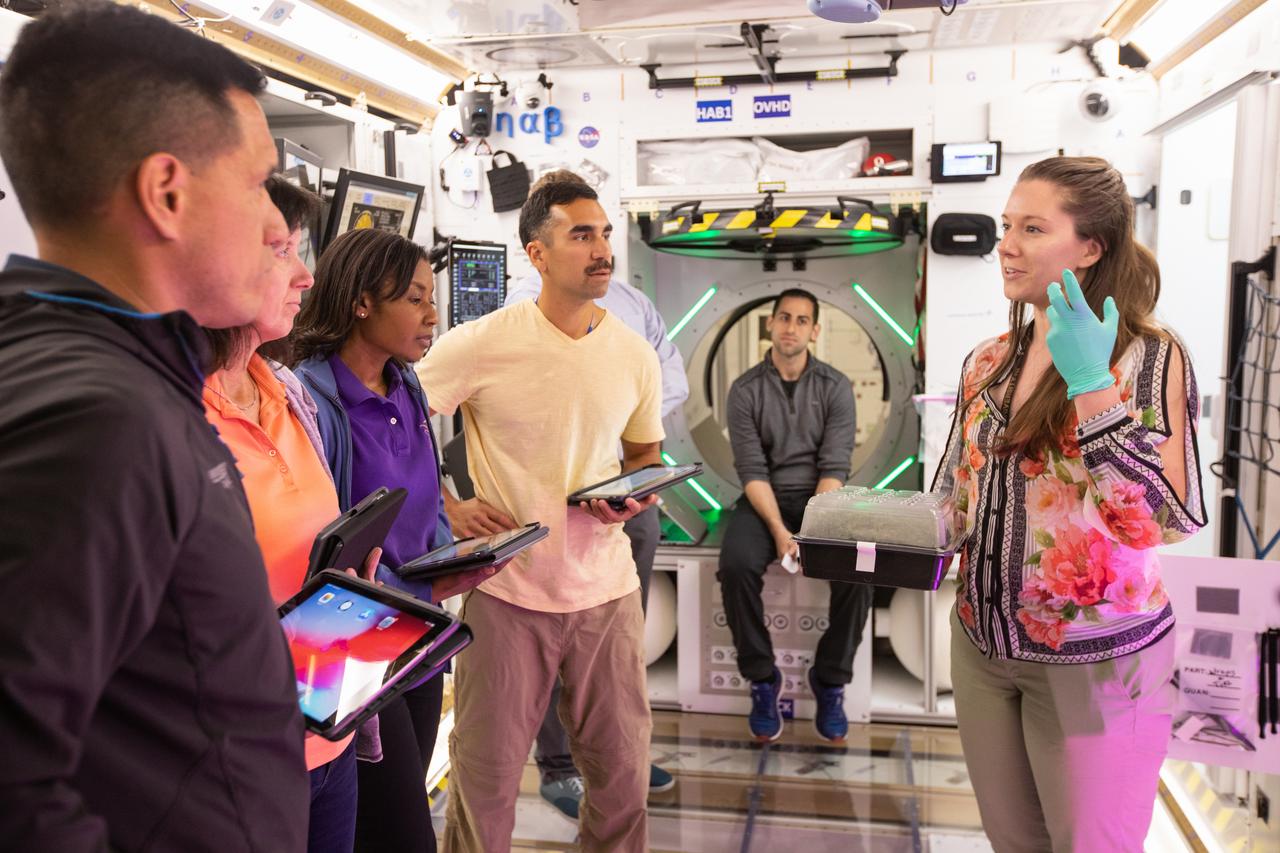

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, from far left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Shannon Walker, Stephanie Wilson and Raja Chari. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
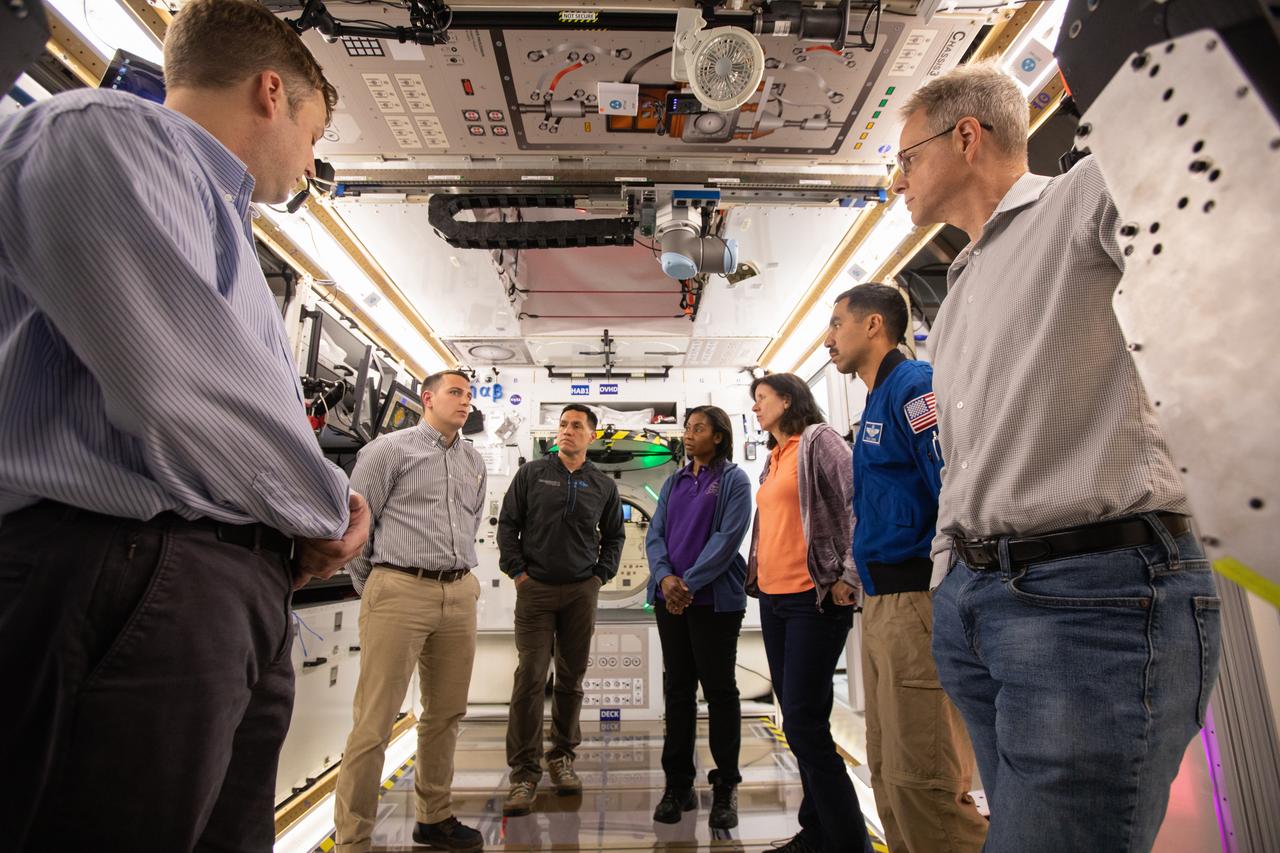

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, beginning third from left are astronauts Frank Rubio, Stephanie Wilson, Shannon Walker and Raja Chari. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
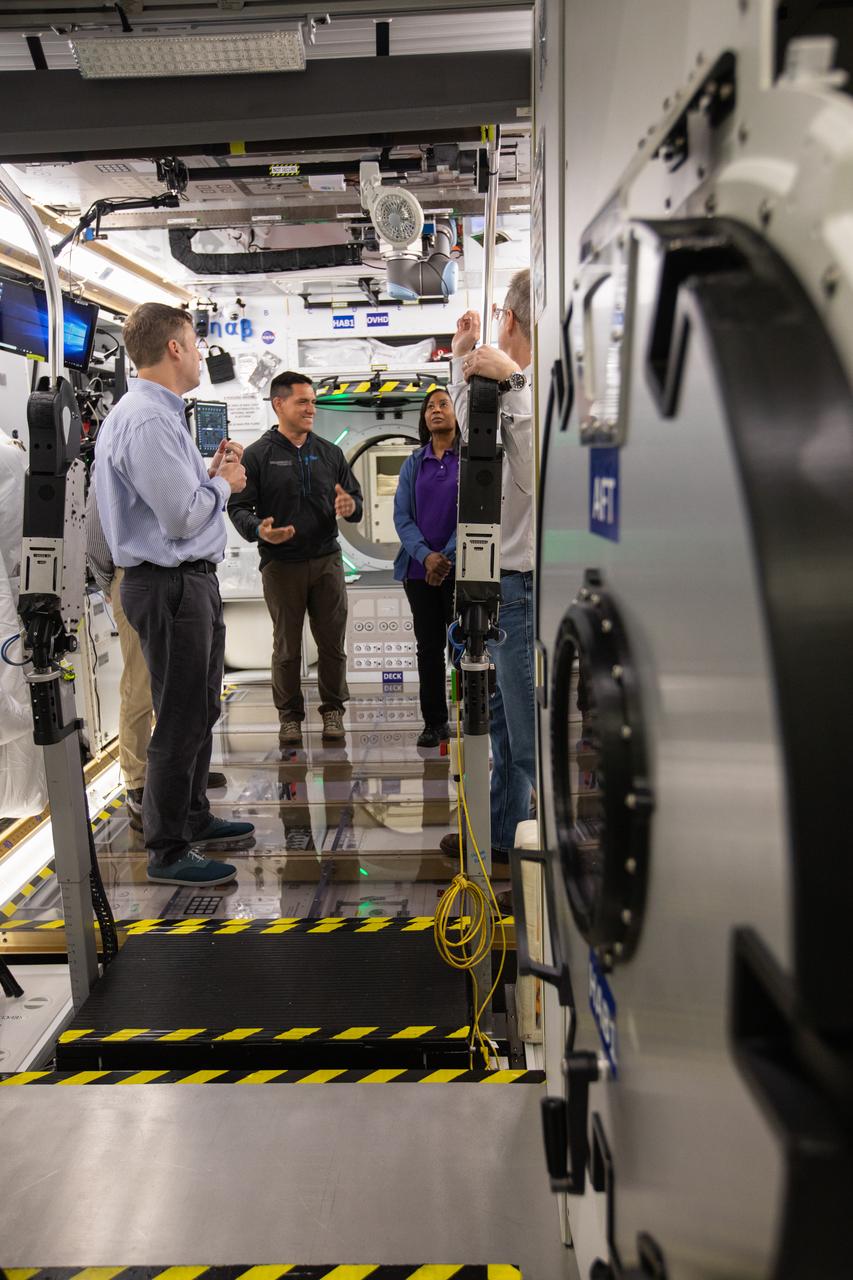

NASA began evaluating five habitat prototypes developed through NASA’s Next Space Exploration for Technologies Partnerships, or NextSTEP, to help engineers refine requirements for the design of an American-made deep space habitat for the Gateway. Lockheed Martin turned over its prototype to NASA, and testing began with crew on March 25, 2019, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pictured inside the habitat prototype on March 26, 2019, second from left is astronaut Frank Rubio. Next to him is astronaut Stephanie Wilson. Astronauts are participating in the evaluations to provide their perspectives as those who may one day live aboard the lunar outpost, which would be located about 250,000 miles from Earth. Ground prototypes developed by Bigelow Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, and Sierra Nevada Corporation will be tested in the future at various facilities across the country. A sixth company, NanoRacks, plans to develop a prototype as well.
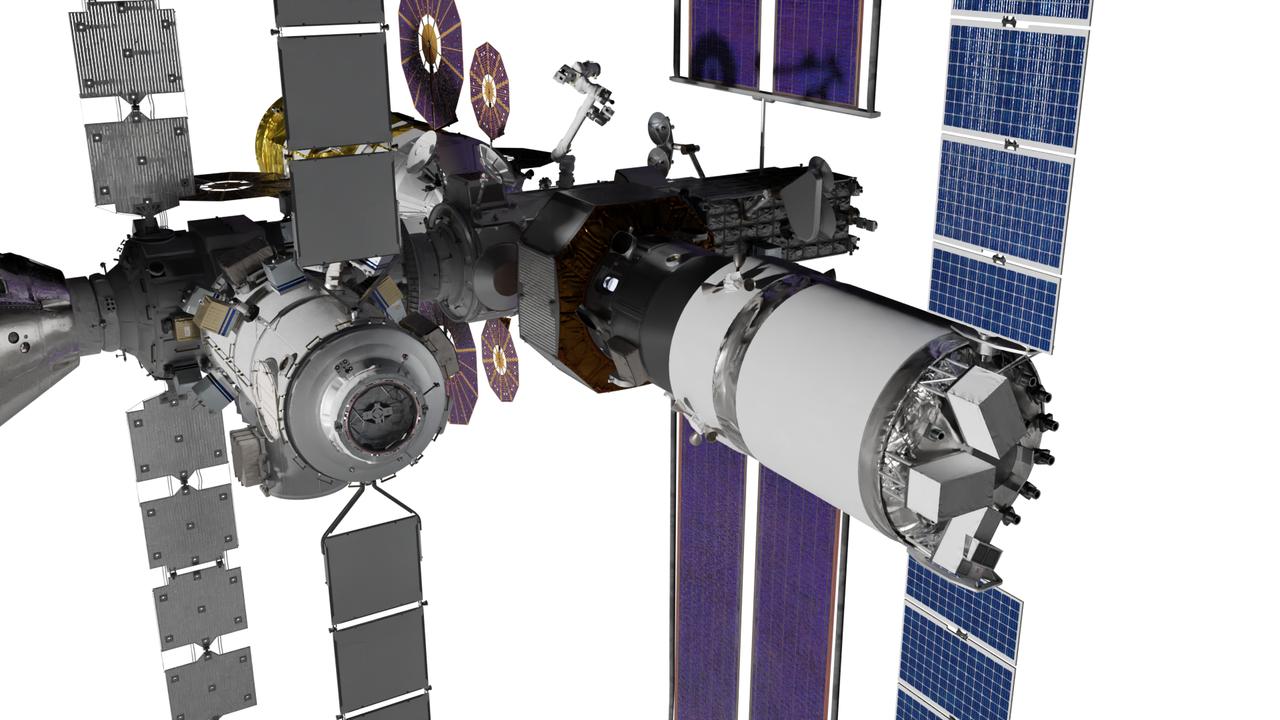
An artist’s rendering displays a configuration of the lunar-orbiting Gateway space station’s modules and visiting spacecraft. The core elements of Gateway consist of the Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) element, the Power and Propulsion Element (PPE), and Lunar I-Hab. Visiting vehicles include the Orion spacecraft, the Logistics Module, and the Human Landing System. Gateway is built in collaboration with NASA’s commercial and international partners to serve as a multiuse space port for lunar science as humanity’s first place to live and work in lunar orbit.
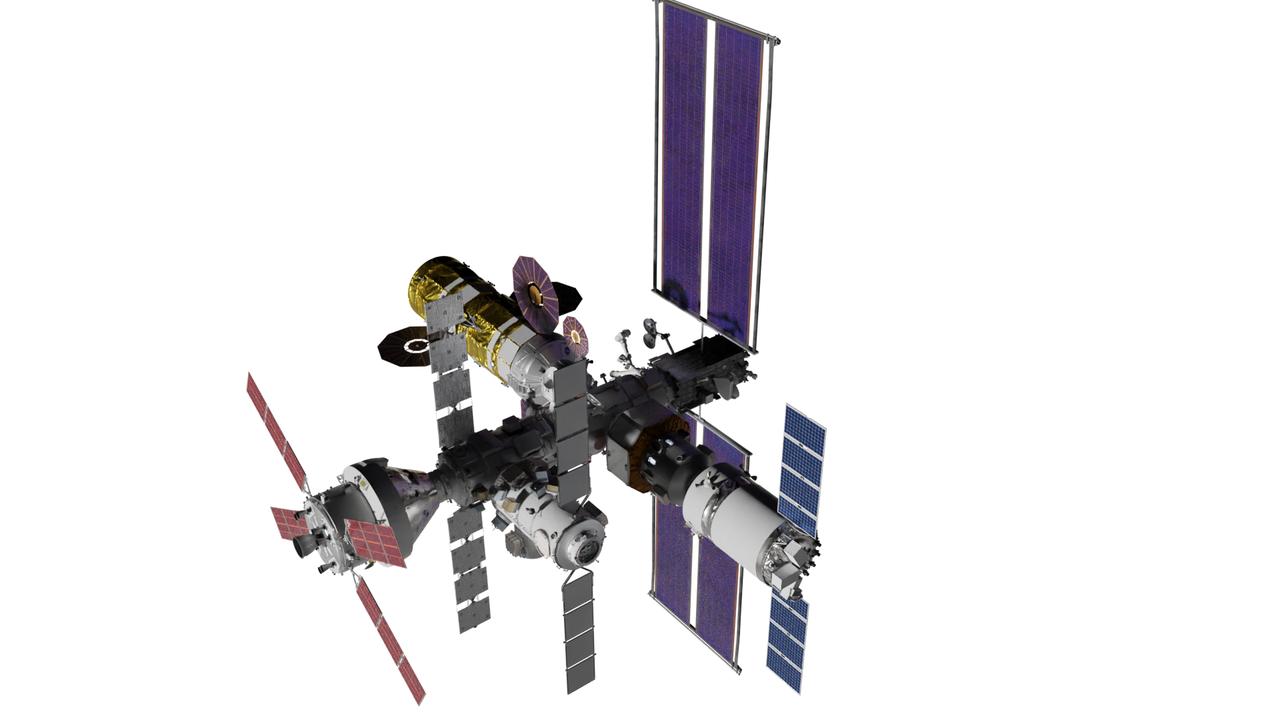

An artist’s rendering displays a configuration of the lunar-orbiting Gateway space station’s modules and visiting spacecraft. The core elements of Gateway consist of the Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) element, the Power and Propulsion Element (PPE), and Lunar I-Hab. Visiting vehicles include the Orion spacecraft, the Logistics Module, and the Human Landing System. Gateway is built in collaboration with NASA’s commercial and international partners to serve as a multiuse space port for lunar science as humanity’s first place to live and work in lunar orbit.
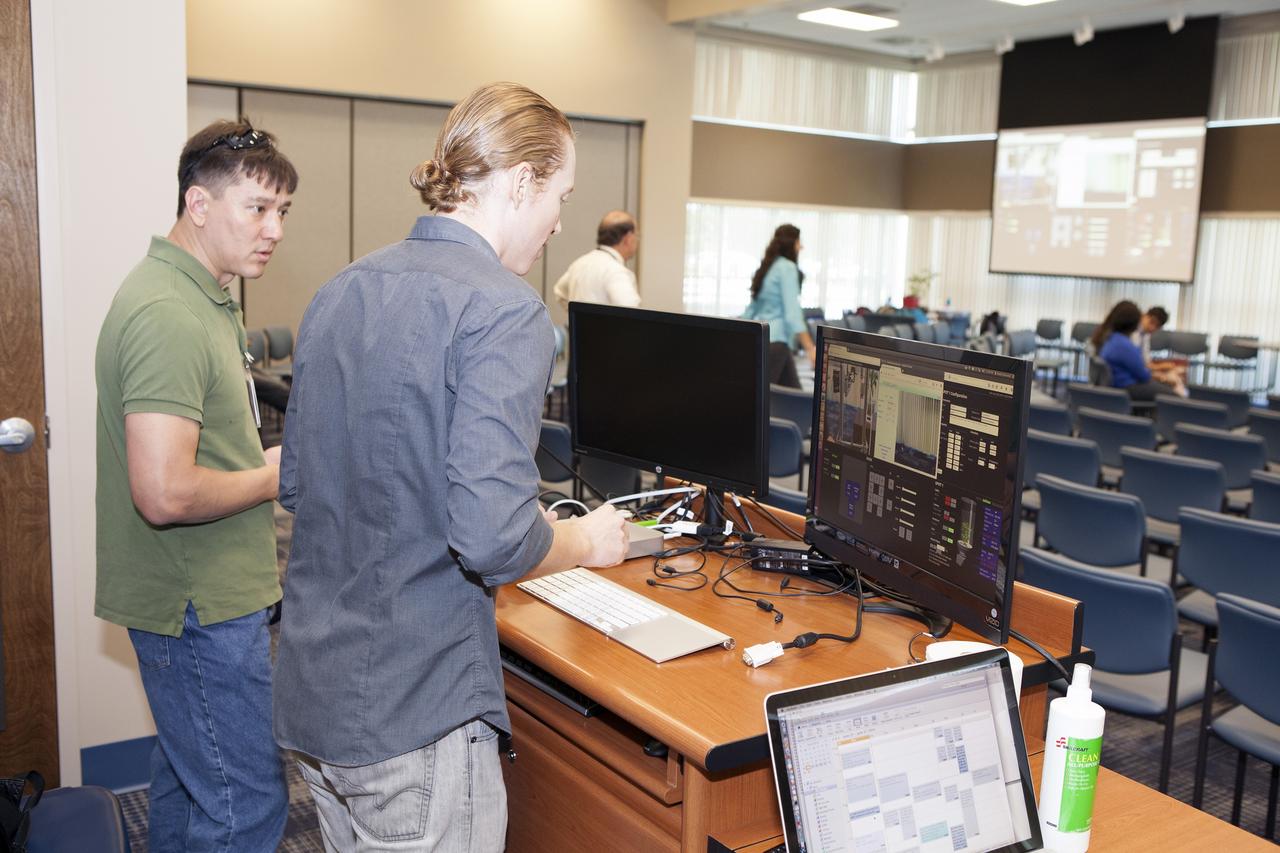

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students from the University of Colorado Boulder demonstrated a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants in a deep-space habitat. Daniel Zukowski, a University of Colorado Boulder graduate student, right, and Morgan Simpson of the NASA Ground Processing Directorate, check computer displays during a presentation of the team's entry in the eXploration HABitat X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. In their concept called "Plants Anywhere: Plants Growing in Free Habitat Spaces," their approach calls for robotically tended plants to be scattered in any available space in a deep-space habitat instead of an area set aside just for vegetation. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
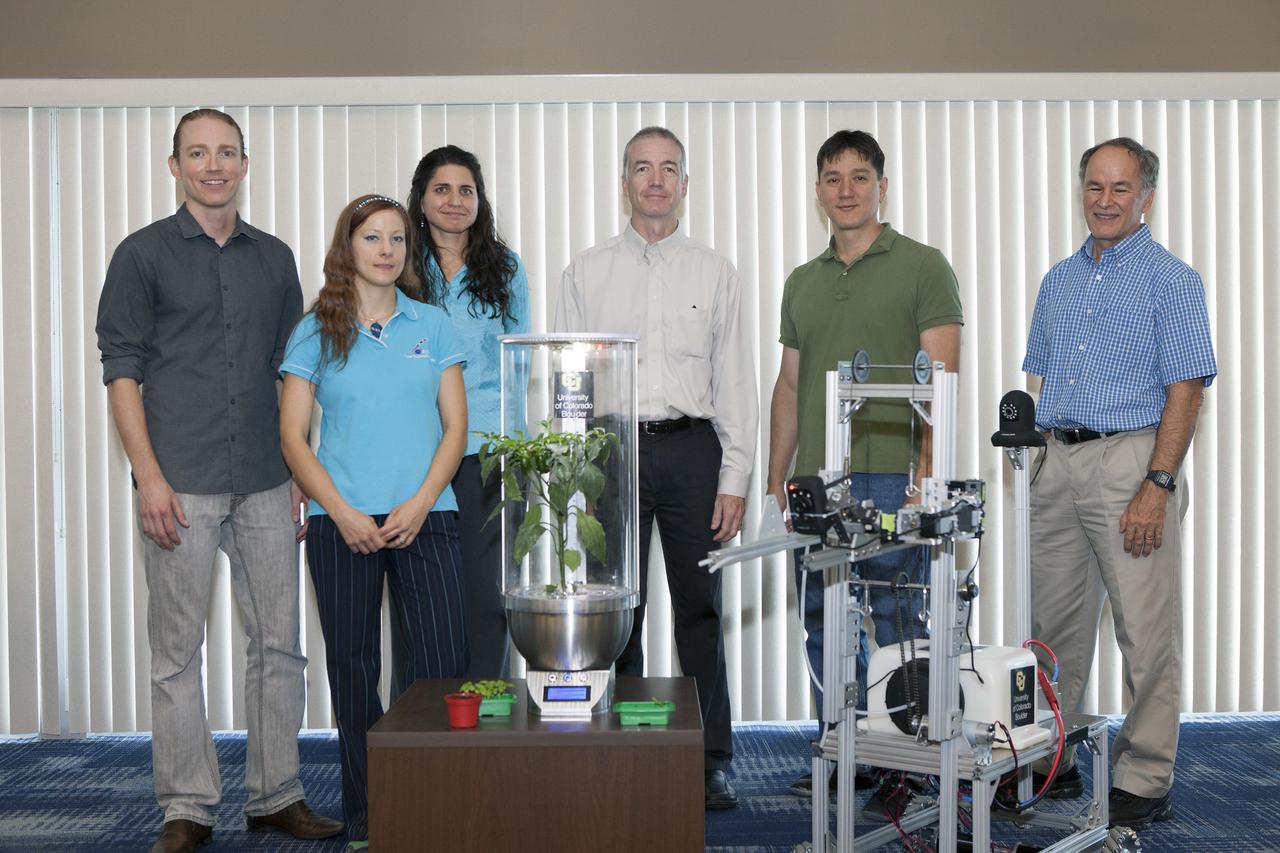

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, University of Colorado Boulder graduate students Heather Hava, far left, and Daniel Zukowski, second from the left, pose with a computerized SmartPot, or SPOT, which could be used to grow plants in a deep-space habitat. To the right of the SPOT is a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR. The system is being developed by the graduate students participating in the eXploration HABitat X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. From the left are Zukowski, Hava, Gioia Massa of the NASA International Space Station Ground Processing and Research Project Office, Tracy Gill of the NASA Center Planning and Development Directorate, Morgan Simpson of the NASA Ground Processing Directorate, and Ray Wheeler of the NASA Engineering and Technology Directorate. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
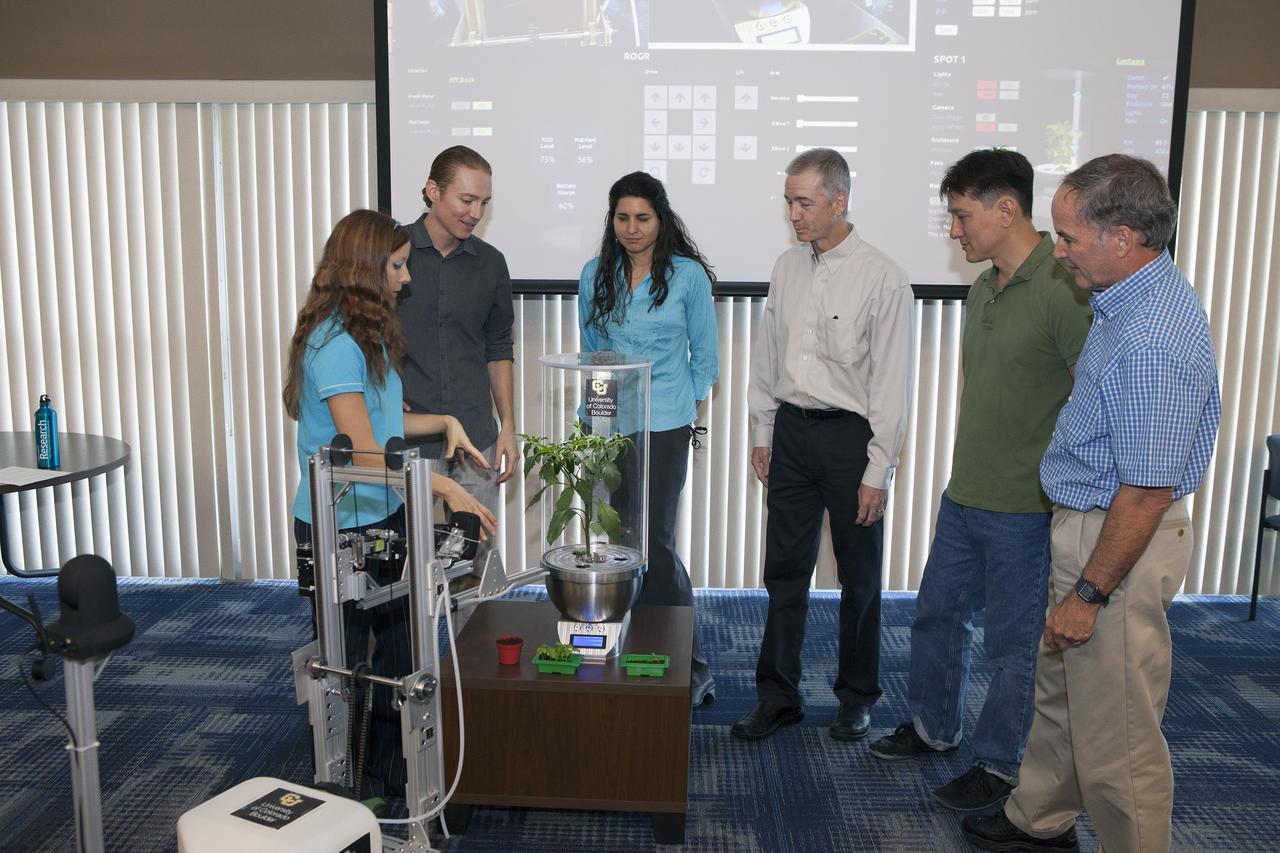

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, University of Colorado Boulder graduate students Heather Hava, far left, and Daniel Zukowski, second from the left, describe a computerized SmartPot, or SPOT, which could be used to grow plants in a deep-space habitat. The SPOTs could be tended by a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, seen on the left. The system is being developed by the graduate students participating in the eXploration HABitat X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge. From the left are Hava, Zukowski, Gioia Massa of the NASA International Space Station Ground Processing and Research Project Office, Tracy Gill of the NASA Center Planning and Development Directorate, Morgan Simpson of the NASA Ground Processing Directorate, and Ray Wheeler of the NASA Engineering and Technology Directorate. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
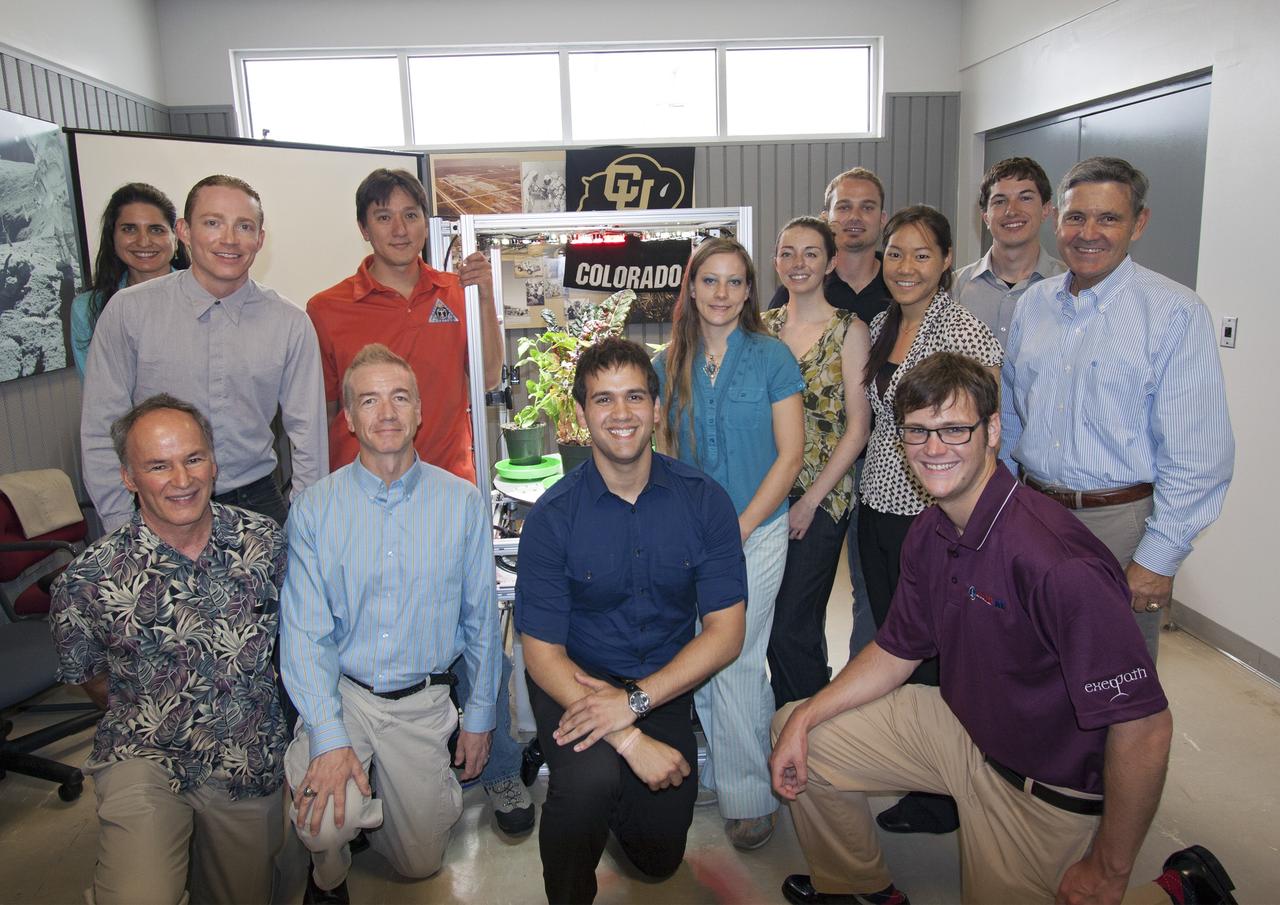

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students from University of Colorado are working with NASA mentors in developing a robotic capability for growing a variety of plants, both for consumption as well as the benefit of oxygen-carbon dioxide cycling. Considerations range from monitoring and nutrient supply to selection of plants and autonomy. The activity is part of the eXploration Habitat, or X-Hab, Academic Innovation Challenge. Standing, left to right, are Gioia Massa of the NASA ISS Ground Processing and Research Project Office, Daniel Zukowski, Morgan Simpson of the NASA Ground Processing Directorate, Heather Hava, Keira Havens, Matthew Carton, Christine Fanchiang, Jordan Holquist and Kennedy Director Bob Cabana. Kneeling, left to right, are Ray Wheeler of the NASA Engineering and Technology Directorate, Tracy Gill of the NASA Center Planning and Development Directorate, Scott Mishra and Robert Griffin Hale. Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in Science, Technology, Engineering and Math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
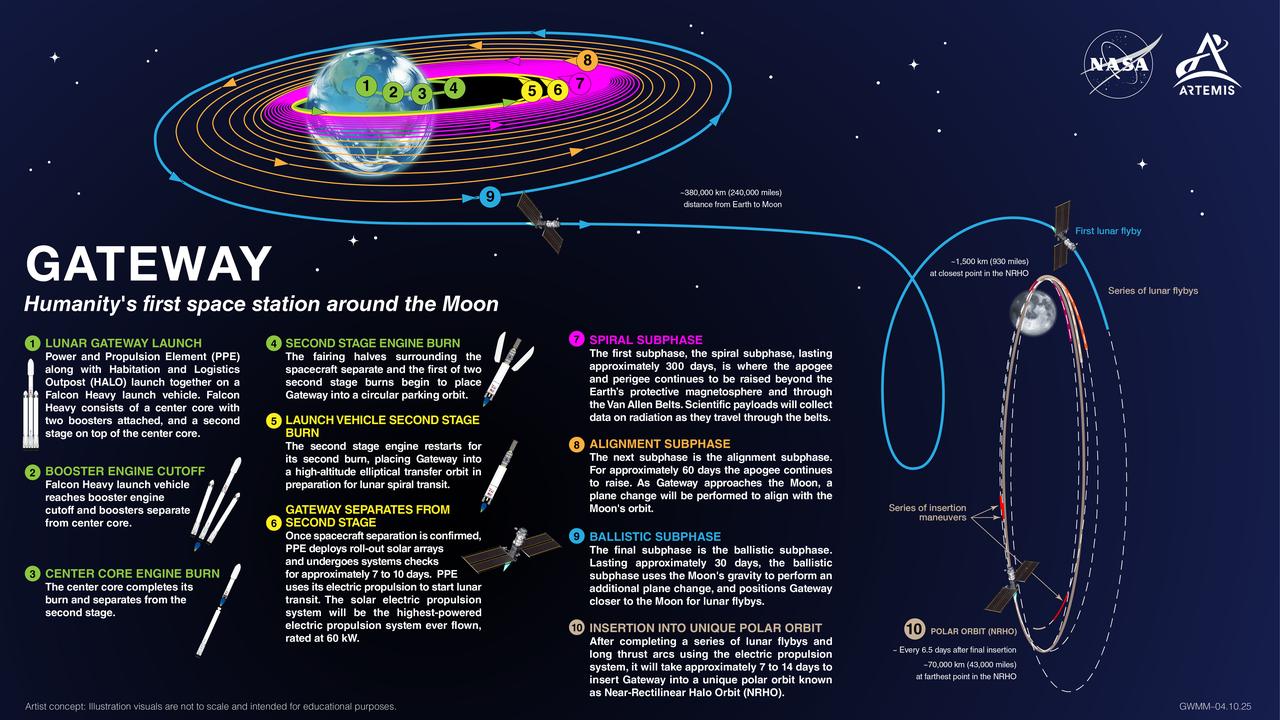
The Lunar Gateway Launch, mapped. Gateway's first elements, the Power and Propulsion Element and HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost), will launch together to lunar orbit, where they’ll set the stage for Artemis IV: the first Gateway assembly mission. During this milestone mission, the Artemis IV crew will deliver the European Space Agency's Lunar I-Hab, dock it to HALO, and enter the space station for the very first time. NASA is currently targeting a 2027 launch for HALO and the Power and Propulsion Element. This timeline allows for the roughly year-long journey to lunar orbit and ensures everything is in place ahead of Artemis IV.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Heather Hava, who is working on a doctorate in aerospace engineering sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder, makes adjustments on a Remotely Operated Gardening Rover, or ROGR, which could tend plants on a deep-space habitat. X-Hab Academic Innovation Challenge is a university-level activity designed to engage and retain students in science, technology, engineering and math, or STEM, disciplines. NASA will directly benefit from the effort by sponsoring the development of innovative habitat concepts from universities which may result in innovative ideas and solutions that could be applied to exploration habitats. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/technology/deep_space_habitat/xhab/ Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
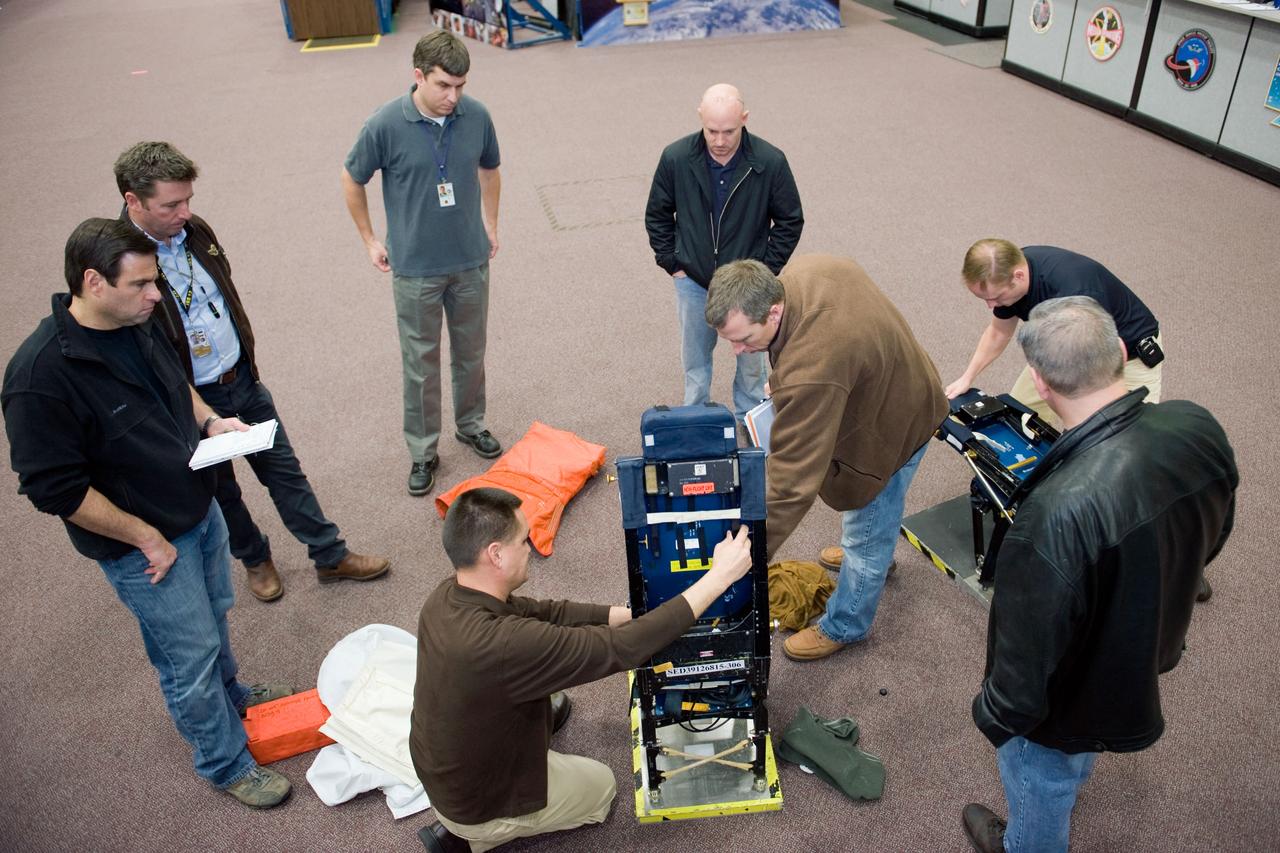

JSC2010-E-009595 (13 Jan. 2010) --- STS-134 crew members participate in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA?s Johnson Space Center. Pictured are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly (center right background), commander; Gregory H. Johnson (right foreground), pilot; Greg Chamitoff (left), Andrew Feustel (center right), Michael Fincke (right background) and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori (second left), all mission specialists. Crew trainer Adam Flagan (center foreground) assisted the crew members.
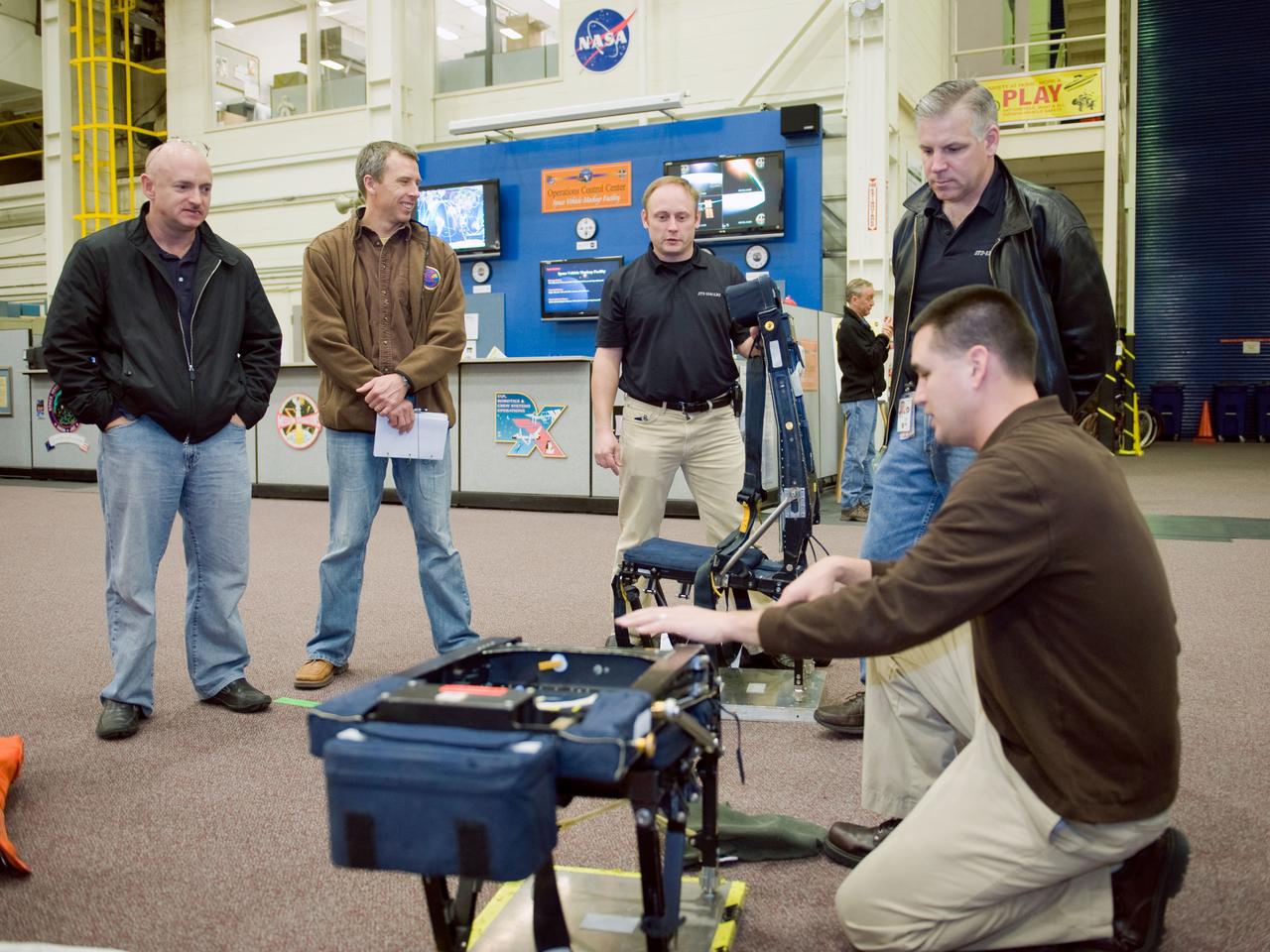

JSC2010-E-009597 (13 Jan. 2010) --- STS-134 crew members participate in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA?s Johnson Space Center. Pictured from the left are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, commander; Andrew Feustel, Michael Fincke, both mission specialists; and Gregory H. Johnson, pilot. Crew trainer Adam Flagan assisted the crew members.
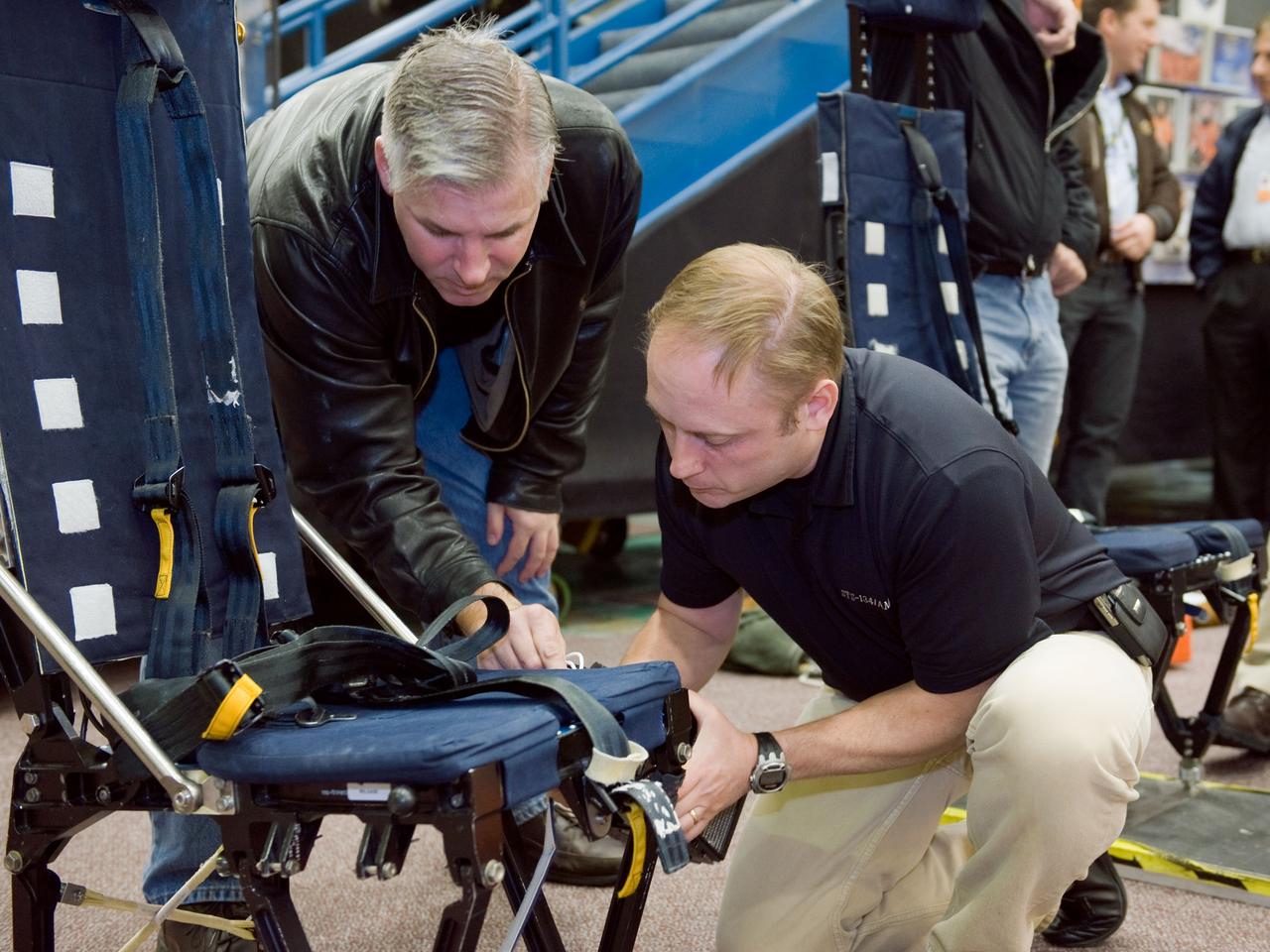

JSC2010-E-009599 (13 Jan. 2010) --- NASA astronauts Gregory H. Johnson (left), STS-134 pilot; and Michael Fincke, mission specialist, participate in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA?s Johnson Space Center.
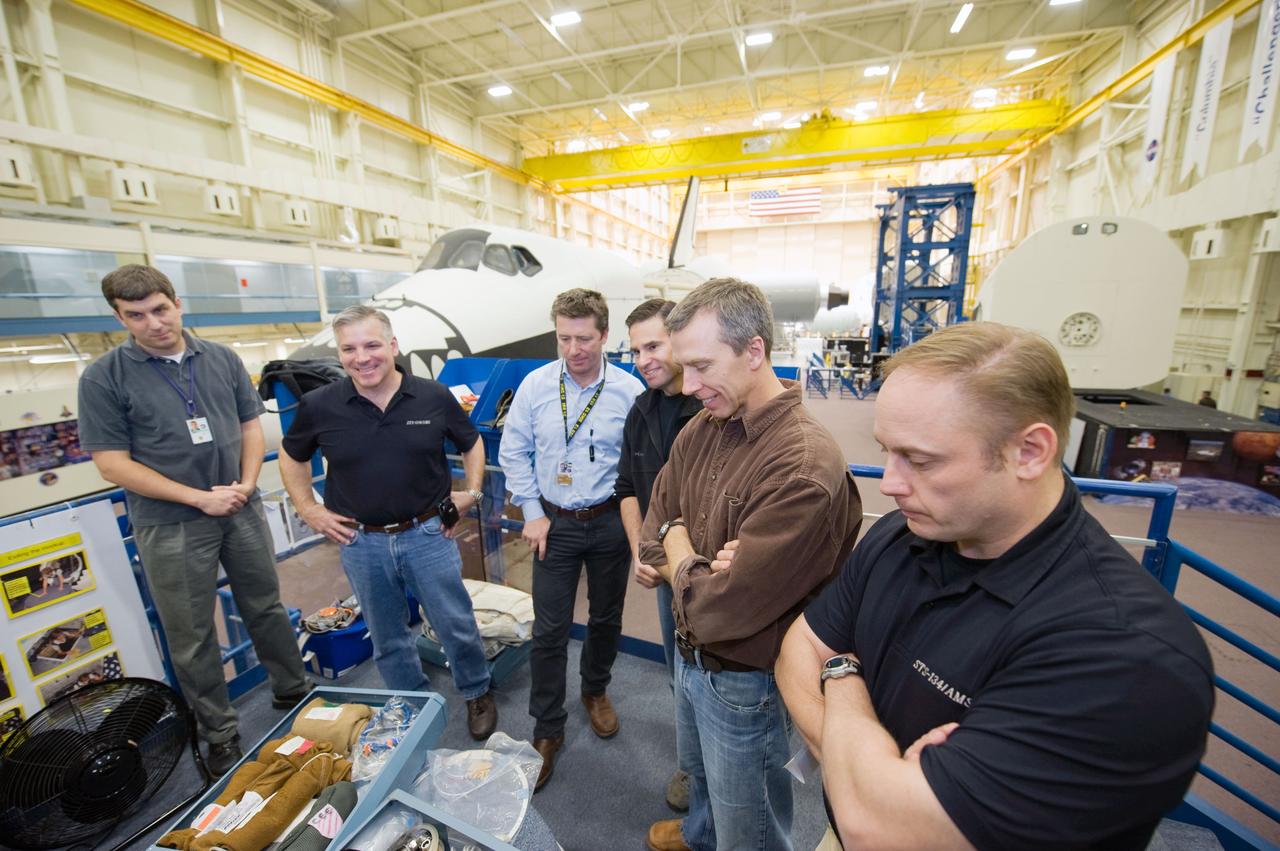

JSC2010-E-009602 (13 Jan. 2010) --- STS-134 crew members participate in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA?s Johnson Space Center. Pictured from the second left are NASA astronaut Gregory H. Johnson, pilot; European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, NASA astronauts Greg Chamitoff, Andrew Feustel and Michael Fincke, all mission specialists.
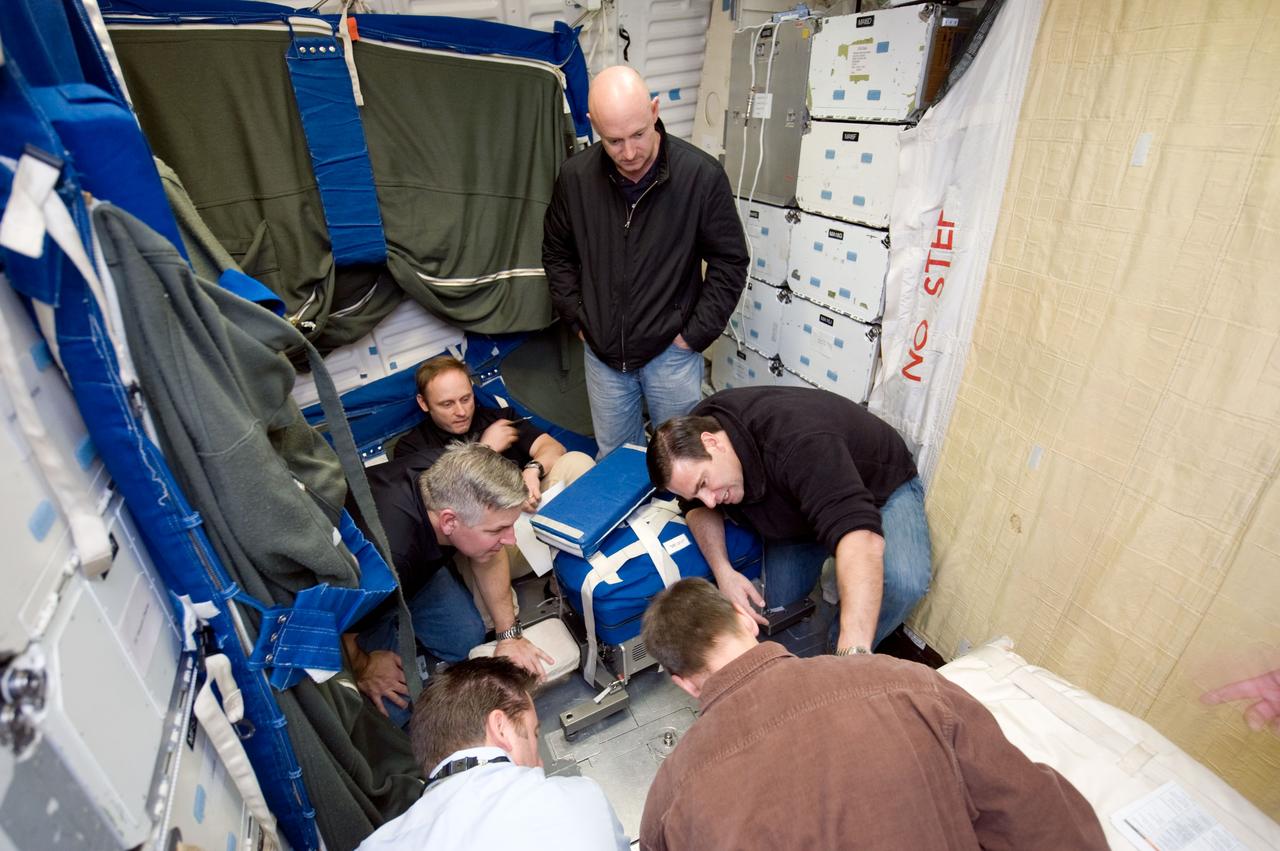

JSC2010-E-009605 (13 Jan. 2010) --- STS-134 crew members participate in a training session in a shuttle mock-up in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA's Johnson Space Center. Pictured are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly (standing), commander; Gregory H. Johnson (left), pilot; Michael Fincke (background), Greg Chamitoff (right), Andrew Feustel (right foreground) and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists.
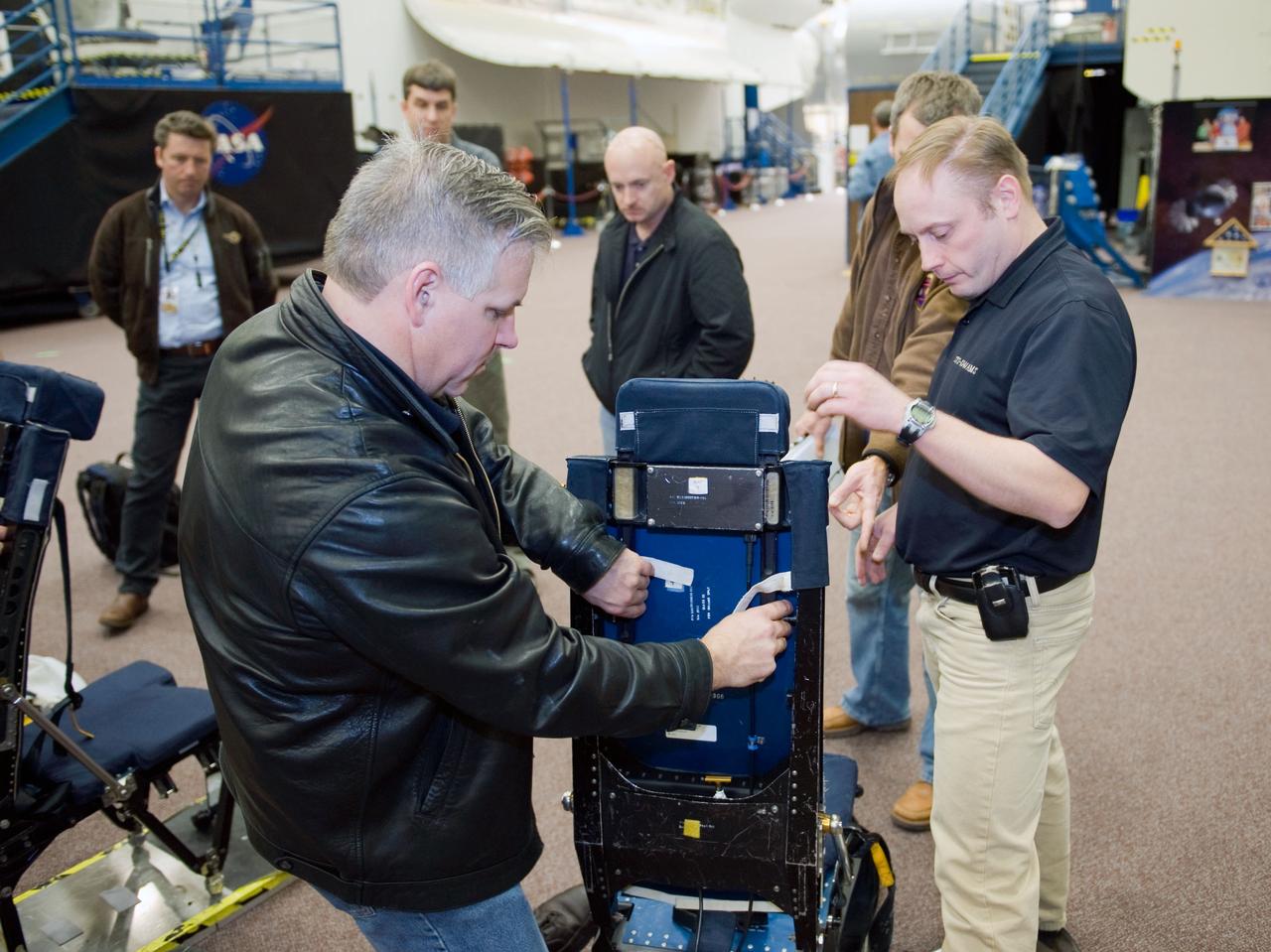

JSC2010-E-009596 (13 Jan. 2010) --- STS-134 crew members participate in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mock-up Facility at NASA?s Johnson Space Center. Pictured are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly (center background), commander; Gregory H. Johnson (left foreground), pilot; Michael Fincke (right foreground), Andrew Feustel (right background) and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori (left background), all mission specialists.
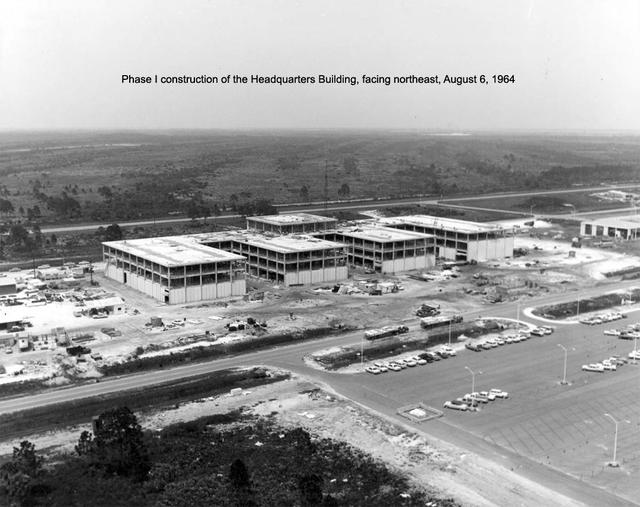

Aerial view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Exterior View of CIF

Interior View of CIF

Aerial view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior View of CIF

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Exterior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Aerial view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior View of CIF

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior View of CIF

Interior View of CIF

Exterior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior View of CIF

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Aerial view of KSC Headquarters Building

Aerial view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior View of CIF

Interior View of CIF

Aerial view of KSC Headquarters Building

Exterior View of CIF

Exterior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Exterior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior View of CIF

Exterior View of CIF

View of CIF Roof

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building
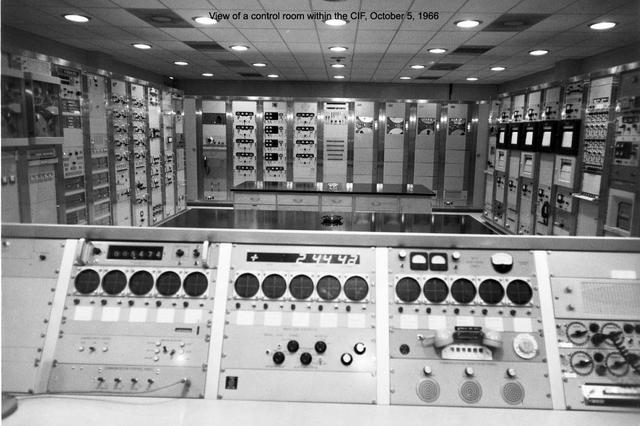

Interior View of CIF

Interior View of CIF

Interior View of CIF

Interior View of CIF

Interior View of CIF

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Exterior View of CIF

Interior View of CIF

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Exterior View of CIF
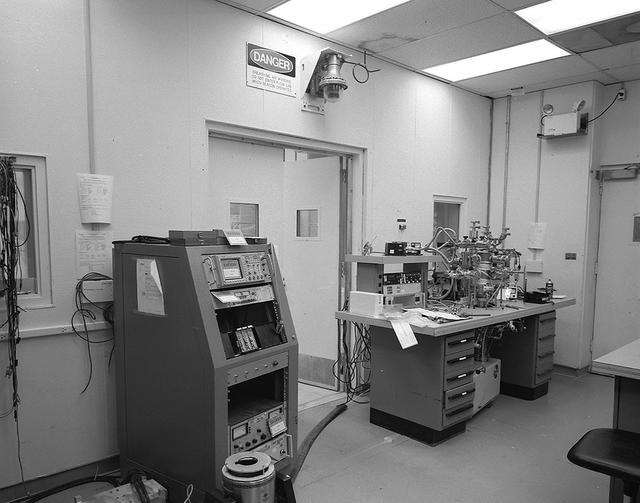

Interior View of CIF
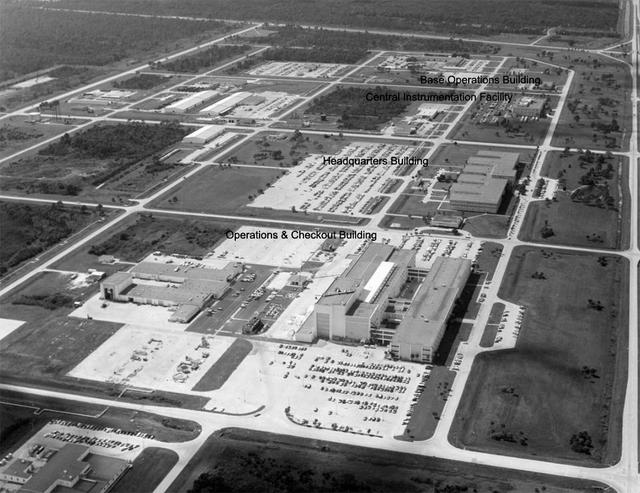

Aerial view of KSC Headquarters Building
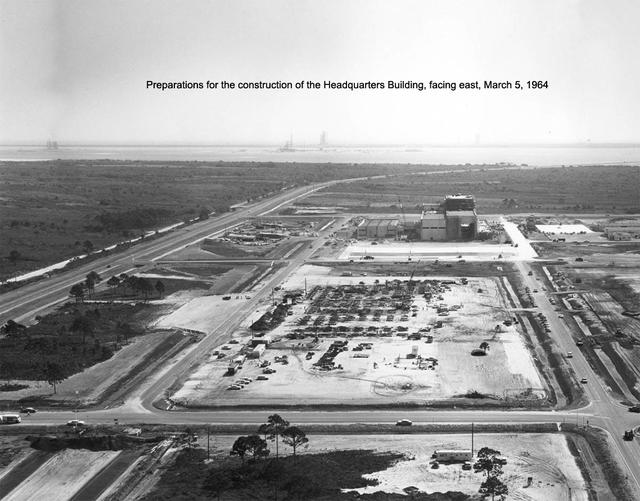

Aerial view of KSC Headquarters Building
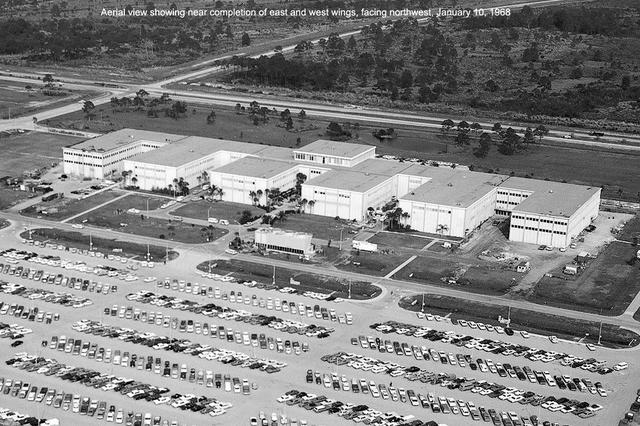

Aerial view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior View of CIF

Exterior View of CIF

Interior View of CIF

Exterior View of CIF

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Exterior View of CIF

Exterior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior view of KSC Headquarters Building

Interior View of CIF