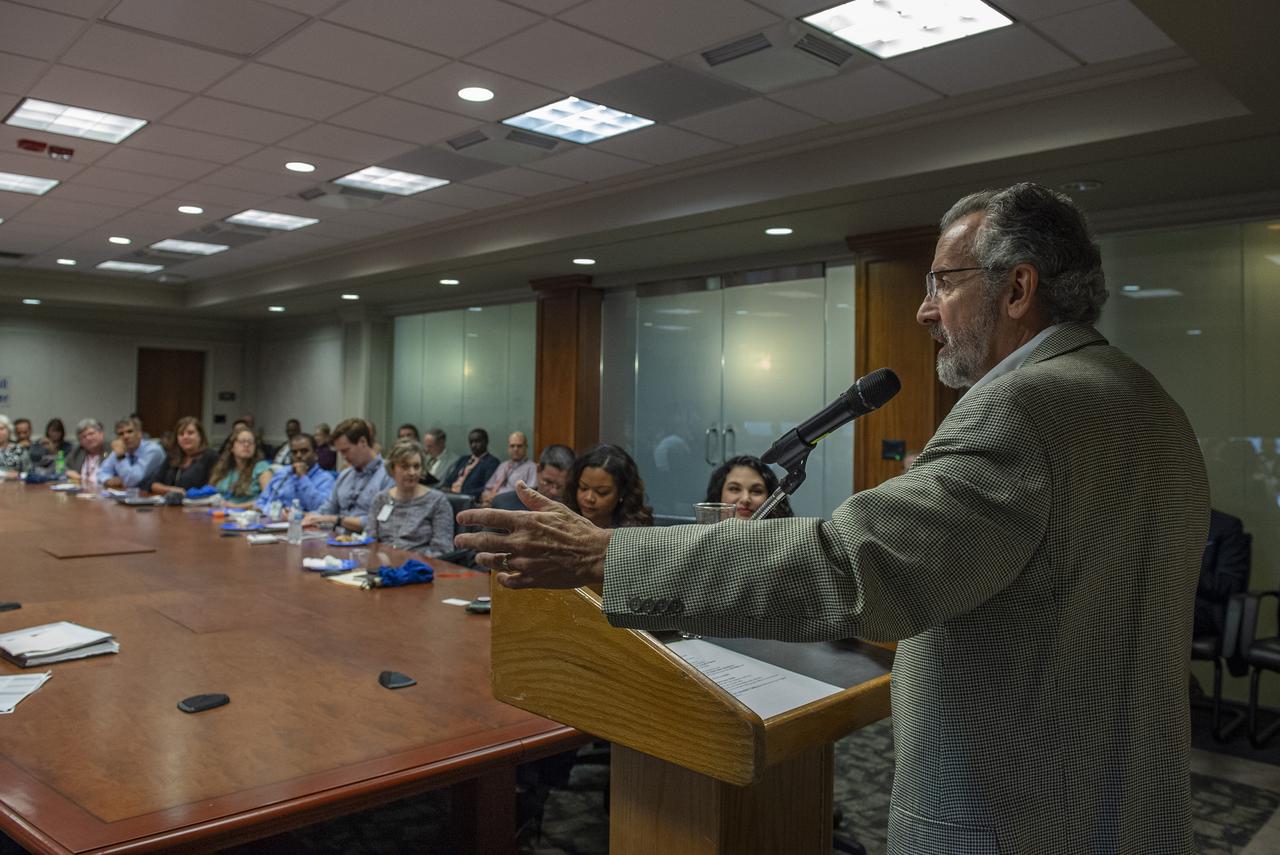

DR. PEDRO “PETE” RODRIGUEZ SPEAKS TO A FULL HOUSE AT HISPANIC MONTH LUNCH & LEARN EVENT ON “PAVING THE WAY TO MARS”, 10/30/19.
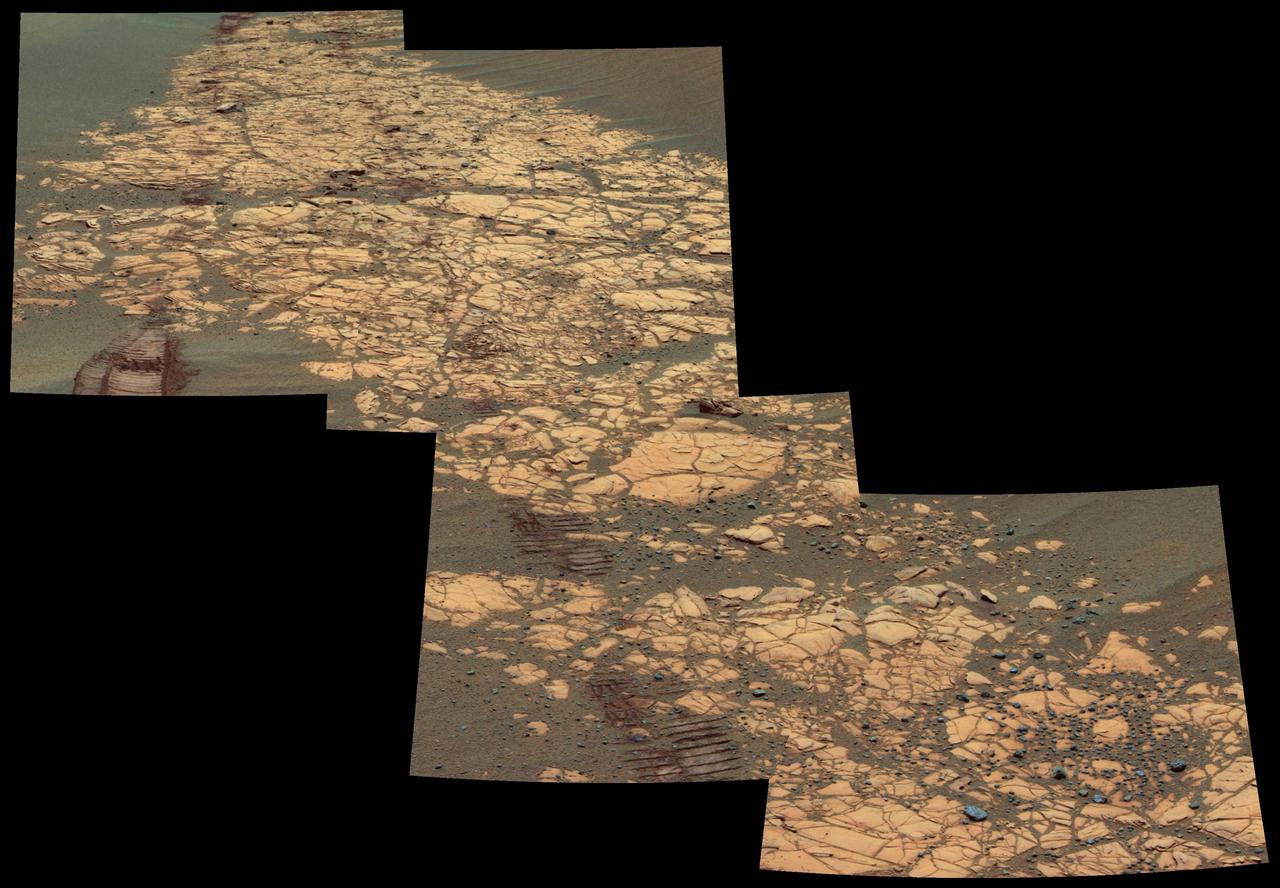

This view shows a portion of the outcrop named Bosque, including rover wheel tracks, fractured and finely-layered outcrop rocks and smaller, dark cobbles littered across the surface
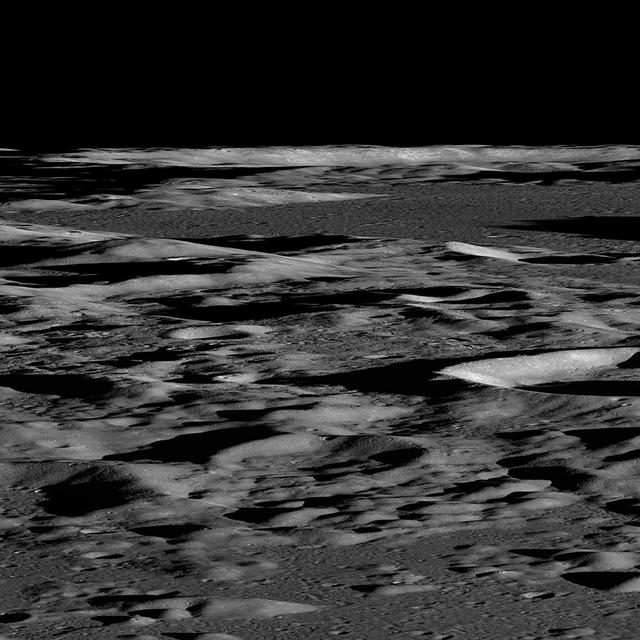

Several sequences were acquired by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter looking across the illuminated limb to quantify scattered light.

This frame from an animation shows a simulated rover descending into Victoria Crater via the rock-paved slopes of an alcove informally named Duck Bay.
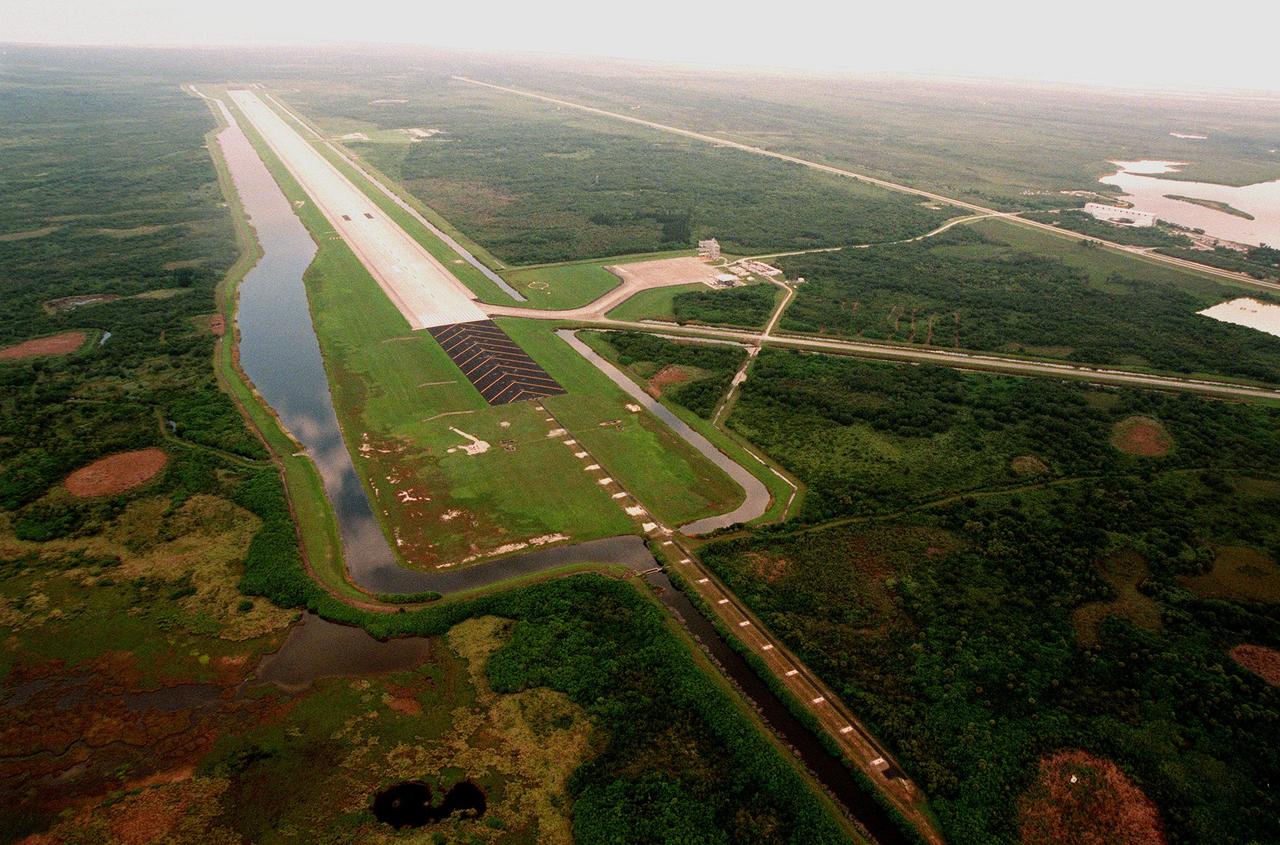

North of the Launch Complex 39 Area, the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) stretches to the northwest. One of the largest runways in the world, the runway is located 3.2 km (2 miles) northwest of the Vehicle Assembly Building and is 4,572 meters (15,000 ft) long and 91.4 meters (300 ft) wide -- about as wide as the length of a football field. It has 305 meters (1000 ft) of paved overruns at each end and the paving thickness is 40.6cm (15 in) at the center. The facility includes a 150 x 168-meter (490 ft x 550 ft) parking apron (at right) and a 3.2-km (2-mile) tow-way connecting it with the Orbiter Processing Facility.
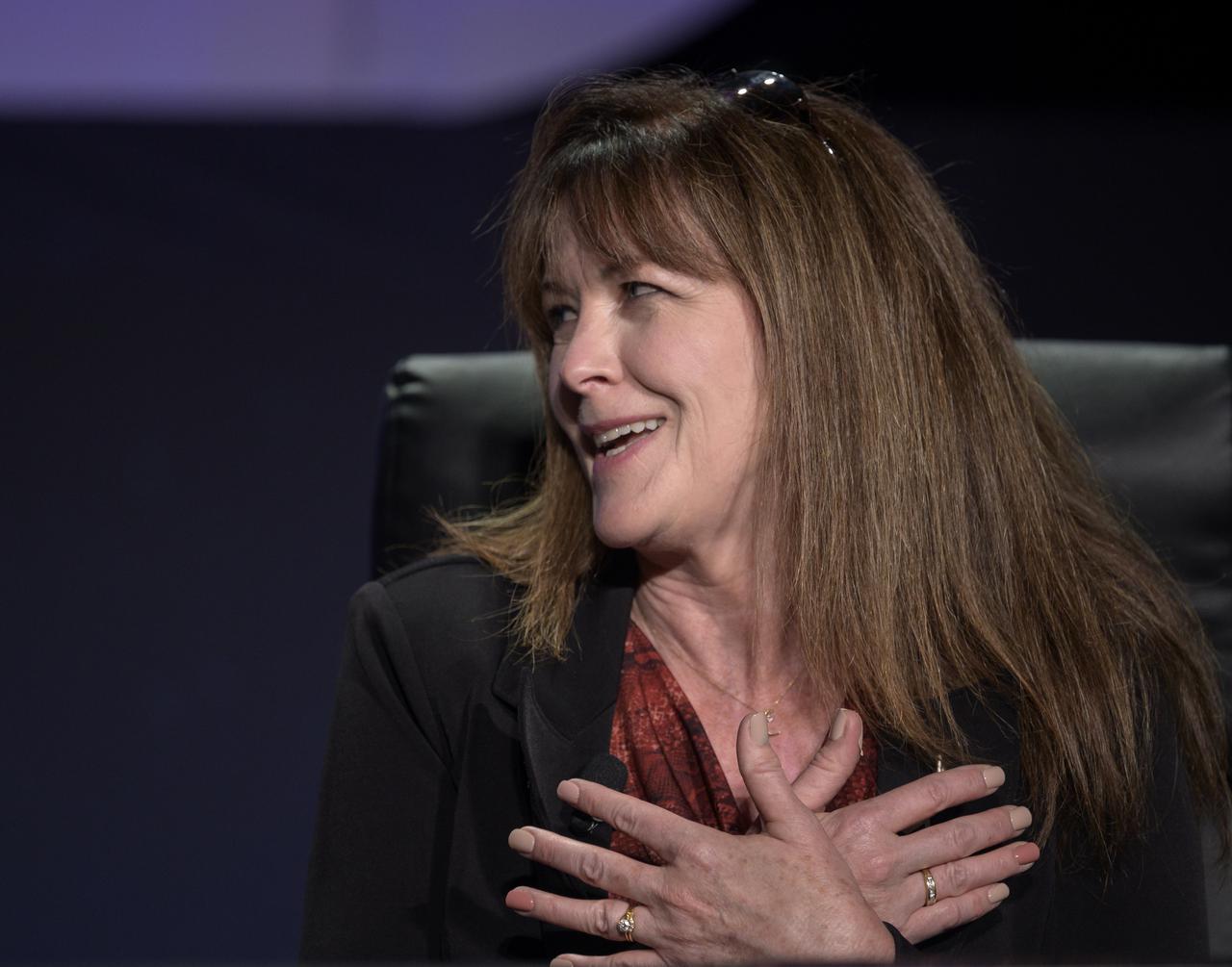

Executive Vice President, Sierra Space, Sierra Nevada Corporation, Janet Kavandi participates in a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
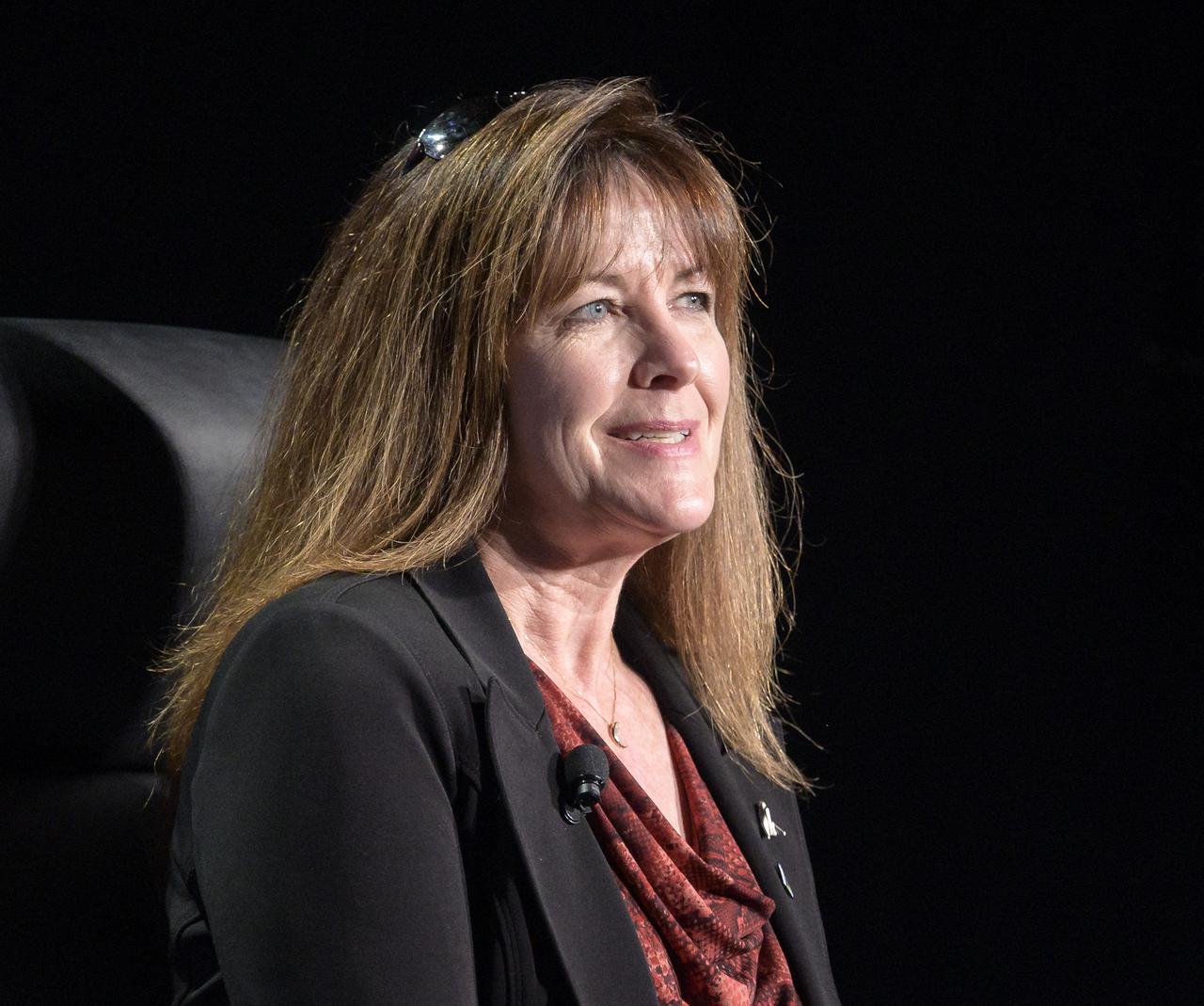

Executive Vice President, Sierra Space, Sierra Nevada Corporation, Janet Kavandi participates in a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
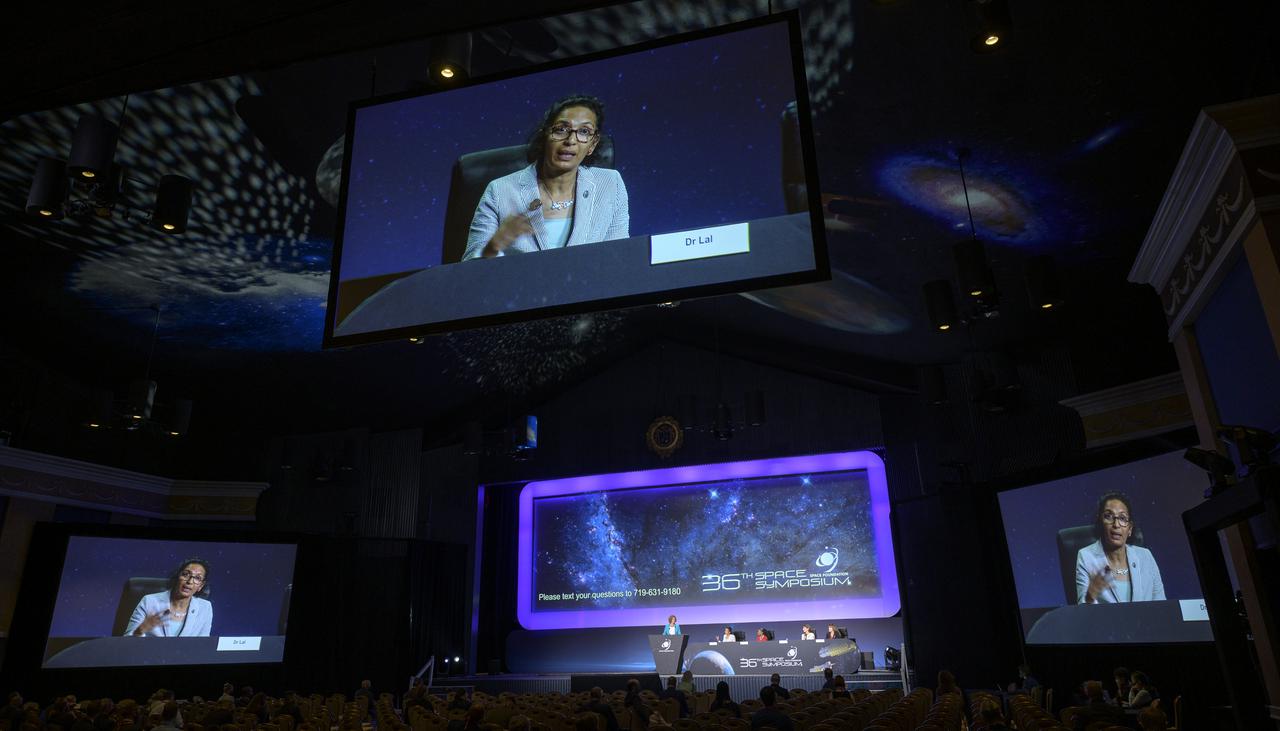

NASA Senior Advisor for Budget and Finance Bhavya Lal participates in a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
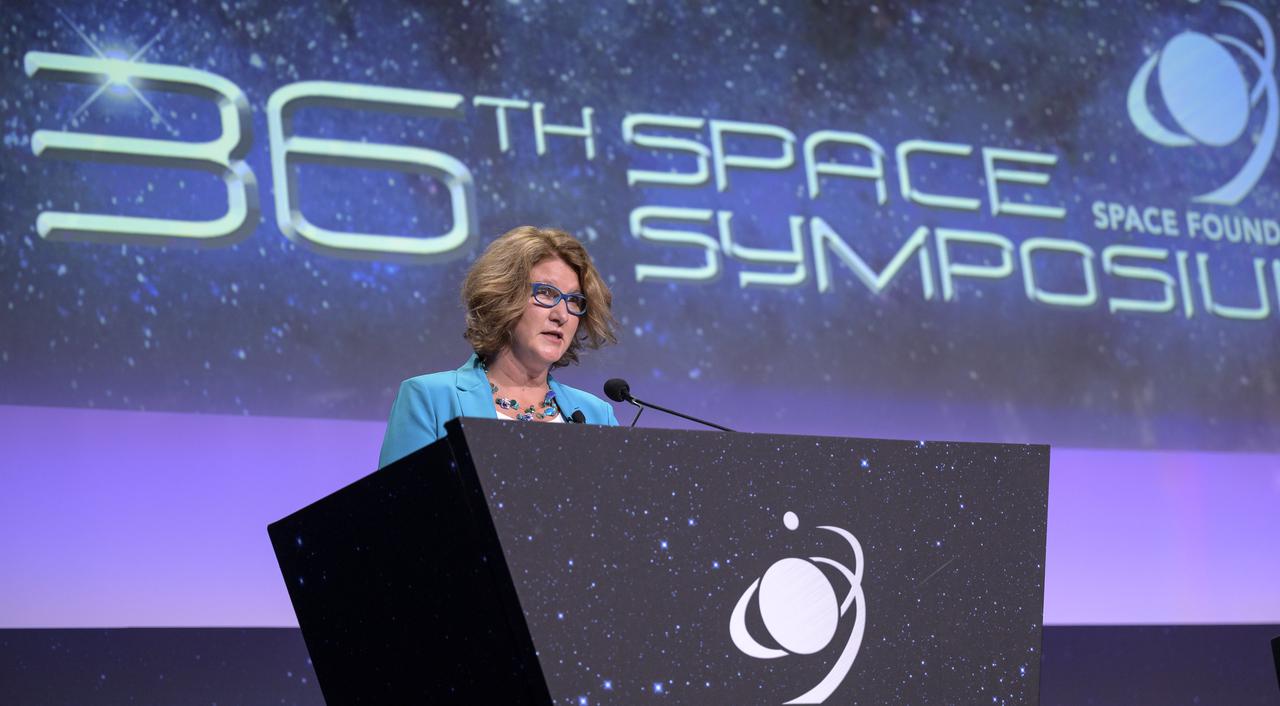

NASA Director of the Technology Demonstration Missions Program, Trudy Kortes moderates a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
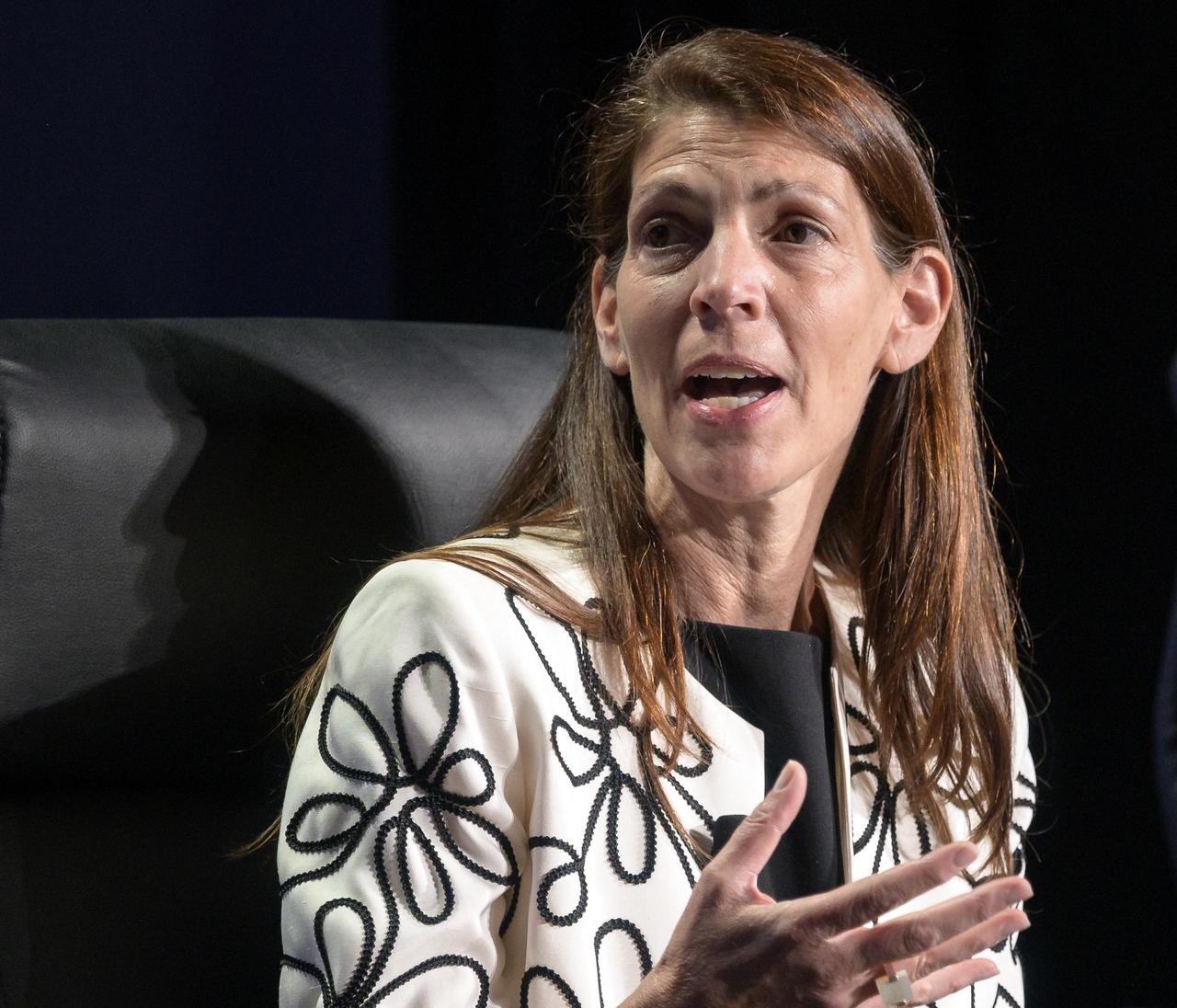

Vice President and General Manager, Commercial Civil Space, Lockheed Martin Space, Lisa Callahan participates in a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Artemis will light our way to Mars. The new Artemis identity draws bold inspiration from the Apollo program and forges its own path, showing how it will pursue lunar exploration like never before and pave the way to Mars.
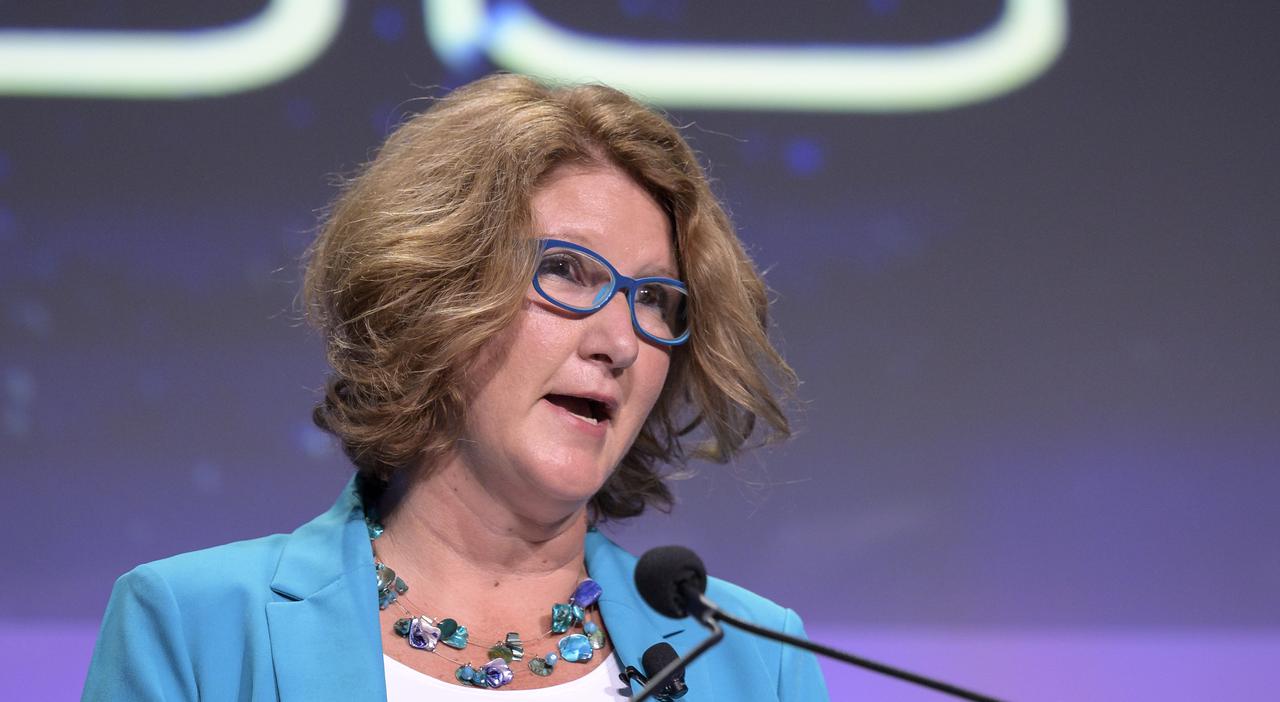

NASA Director of the Technology Demonstration Missions Program, Trudy Kortes moderates a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

This illustration shows NASA's Mars Perseverance rover on the surface of the Red Planet. Perseverance will search for signs of ancient microbial life. It will also characterize the planet's climate and geology, collect samples for future return to Earth and pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24346

art001e003069 (Dec. 11, 2022) On the day of its return to Earth, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured this image of the planet. The spacecraft splashed down at 12:40 p.m. EST Dec. 11, completing the Artemis I mission and paving the way for future Artemis missions to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon.

Director of the Program Management Office at MSI STEM Research and Development Consortium (MSRDC), Latonia Jones participates in a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
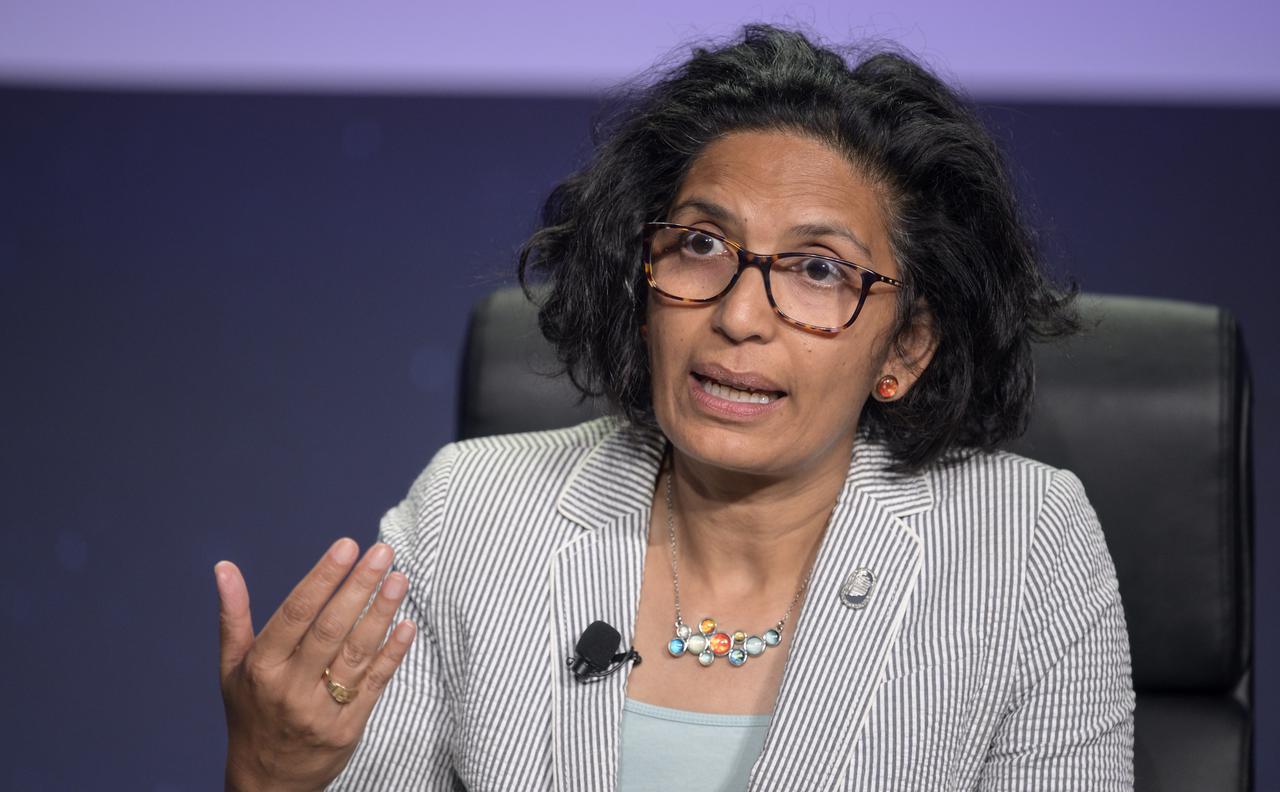

NASA Senior Advisor for Budget and Finance Bhavya Lal participates in a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

This illustration shows NASA's Mars Perseverance rover on the surface of the Red Planet. Perseverance will search for signs of ancient microbial life. It will also characterize the planet's climate and geology, collect samples for future return to Earth and pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24343
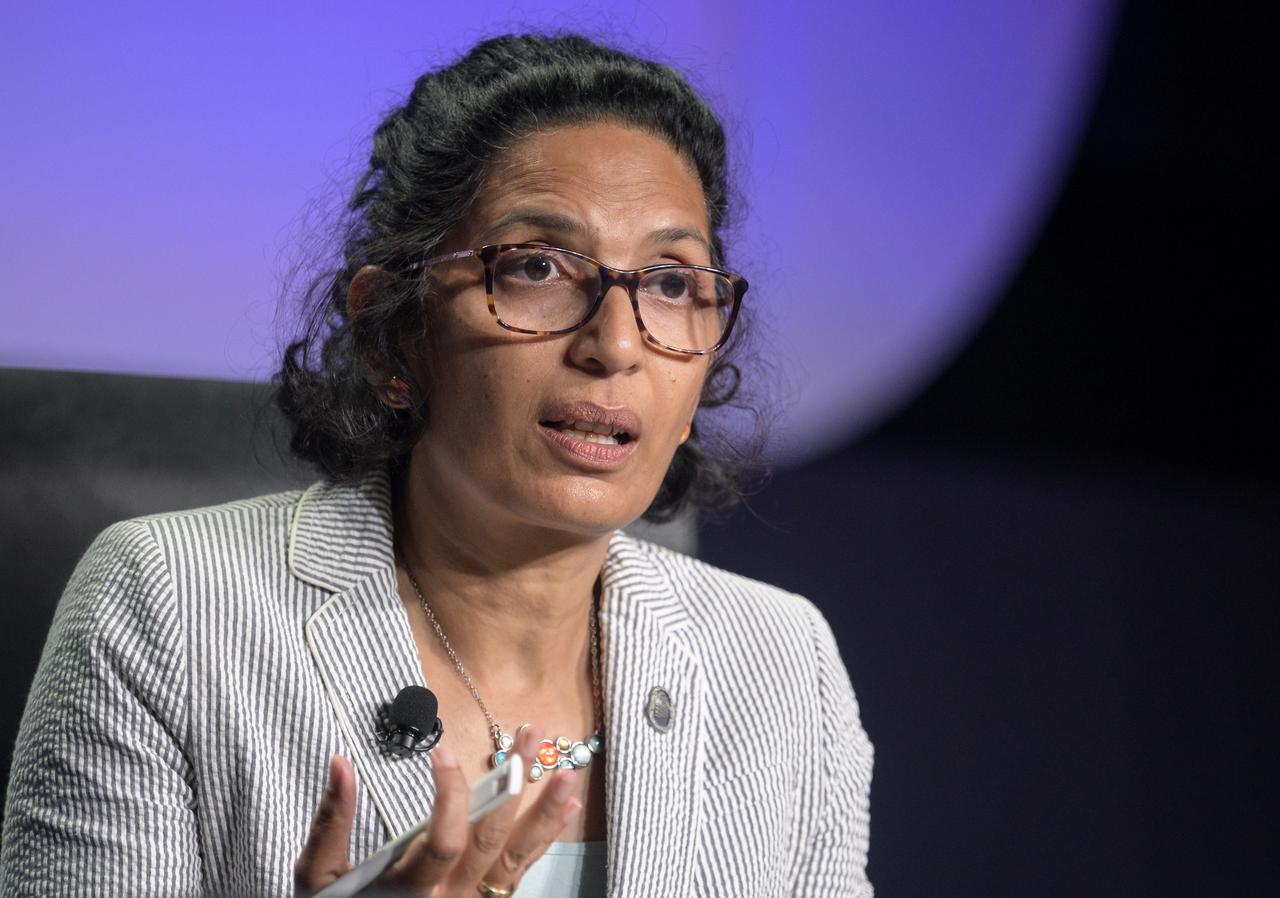

NASA Senior Advisor for Budget and Finance Bhavya Lal participates in a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
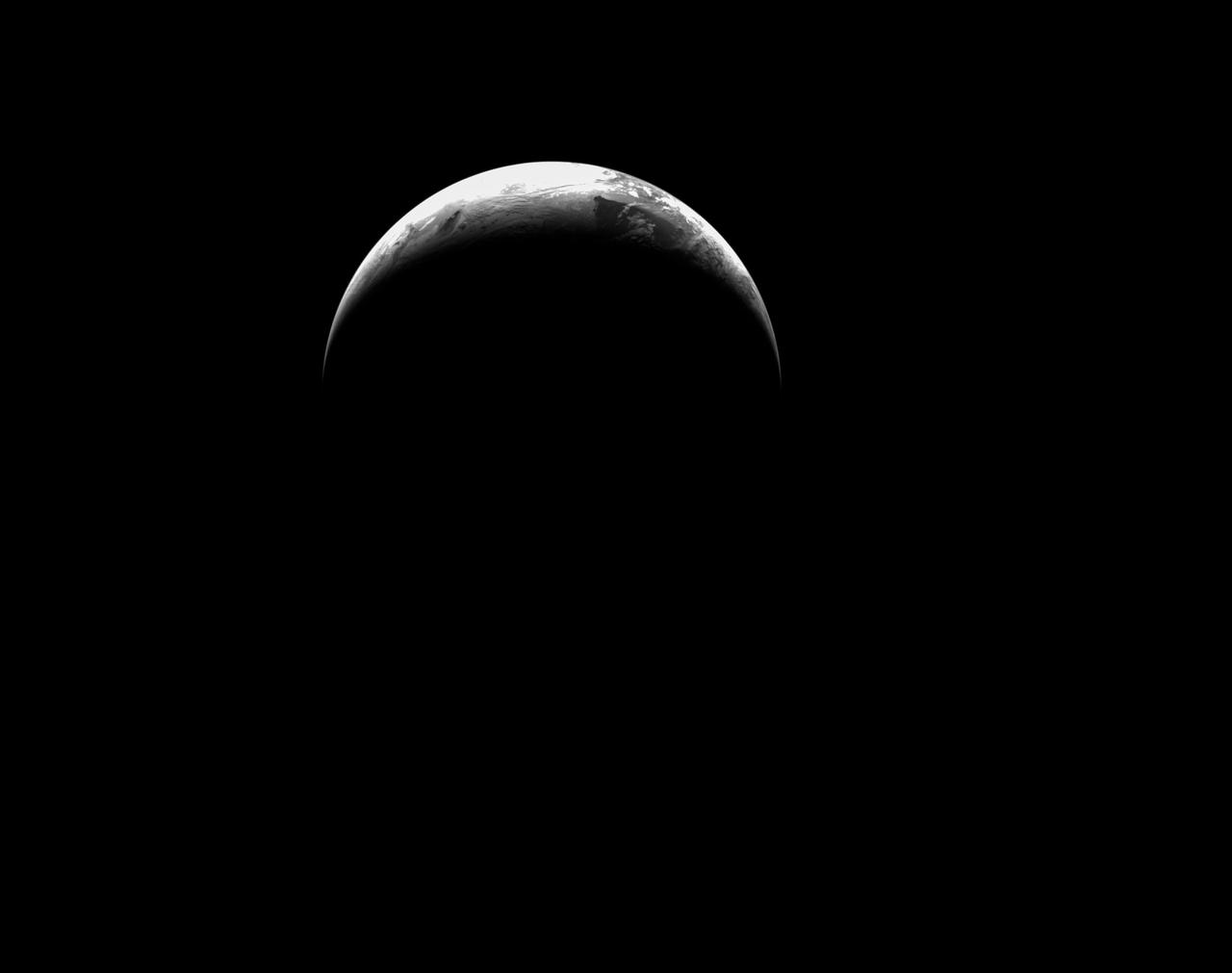

art001e003070 (Dec. 11, 2022) On the day of its return to Earth, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured this image of the planet. The spacecraft splashed down at 12:40 p.m. EST Dec. 11, completing the Artemis I mission and paving the way for future Artemis missions to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon.
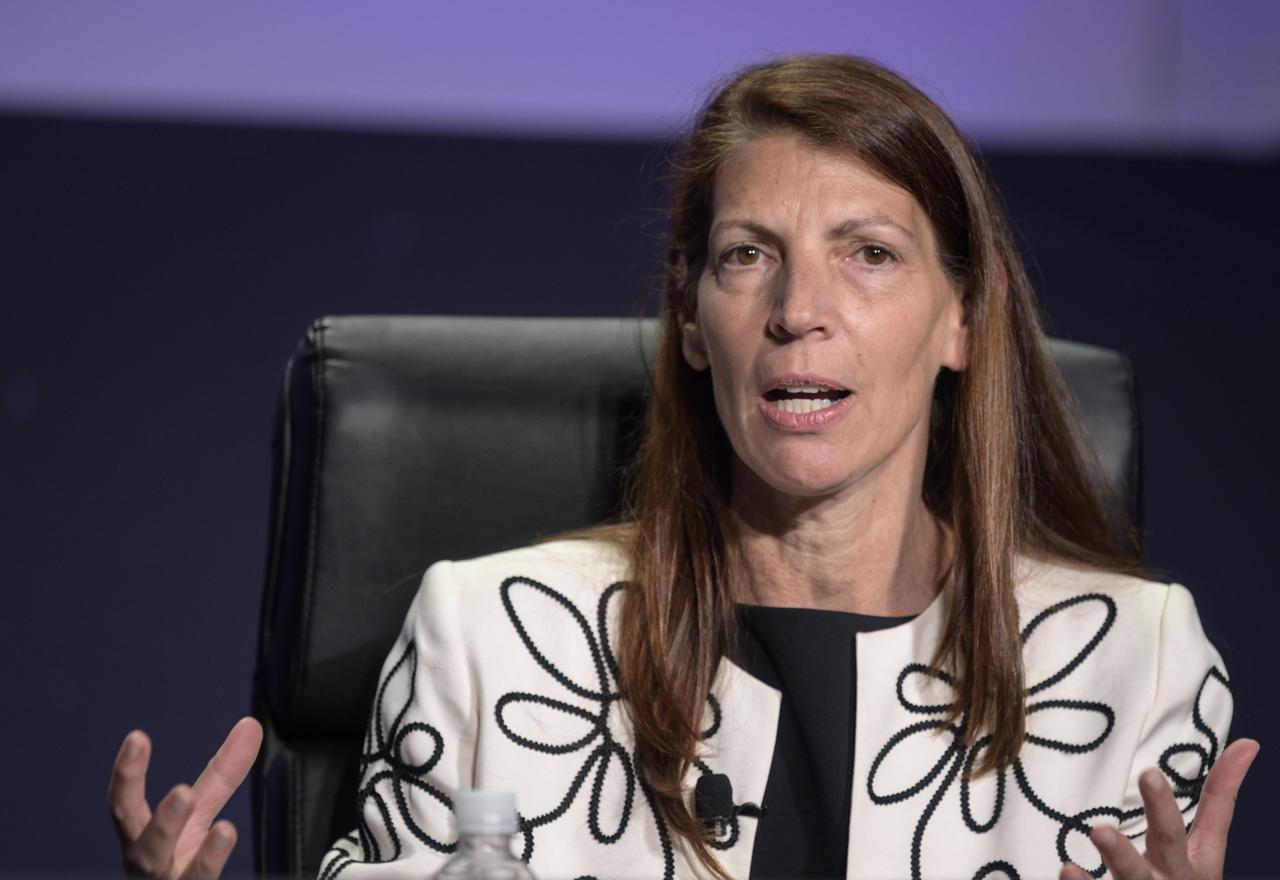

Vice President and General Manager, Commercial Civil Space, Lockheed Martin Space, Lisa Callahan participates in a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
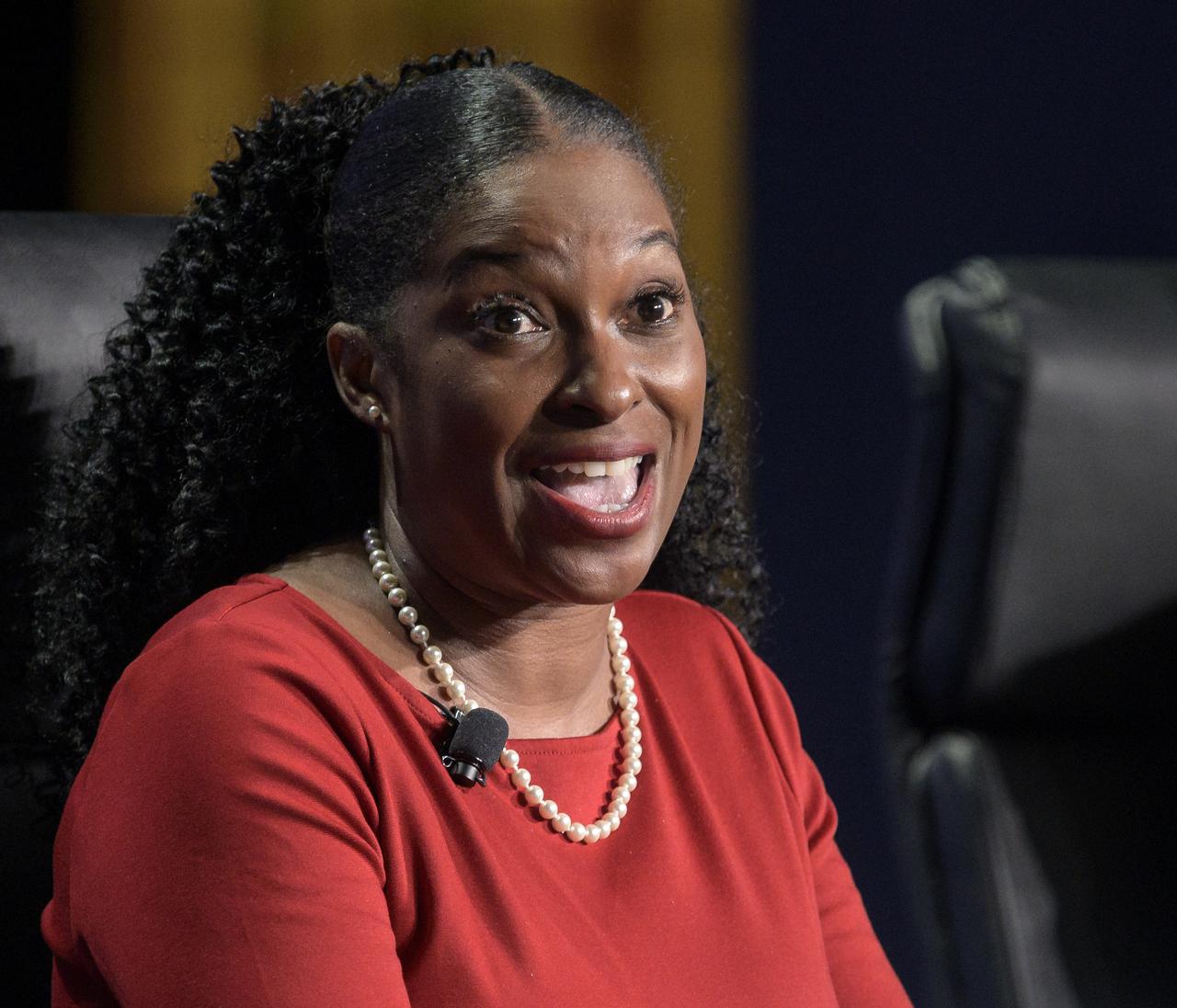

Director of the Program Management Office at MSI STEM Research and Development Consortium (MSRDC), Latonia Jones participates in a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
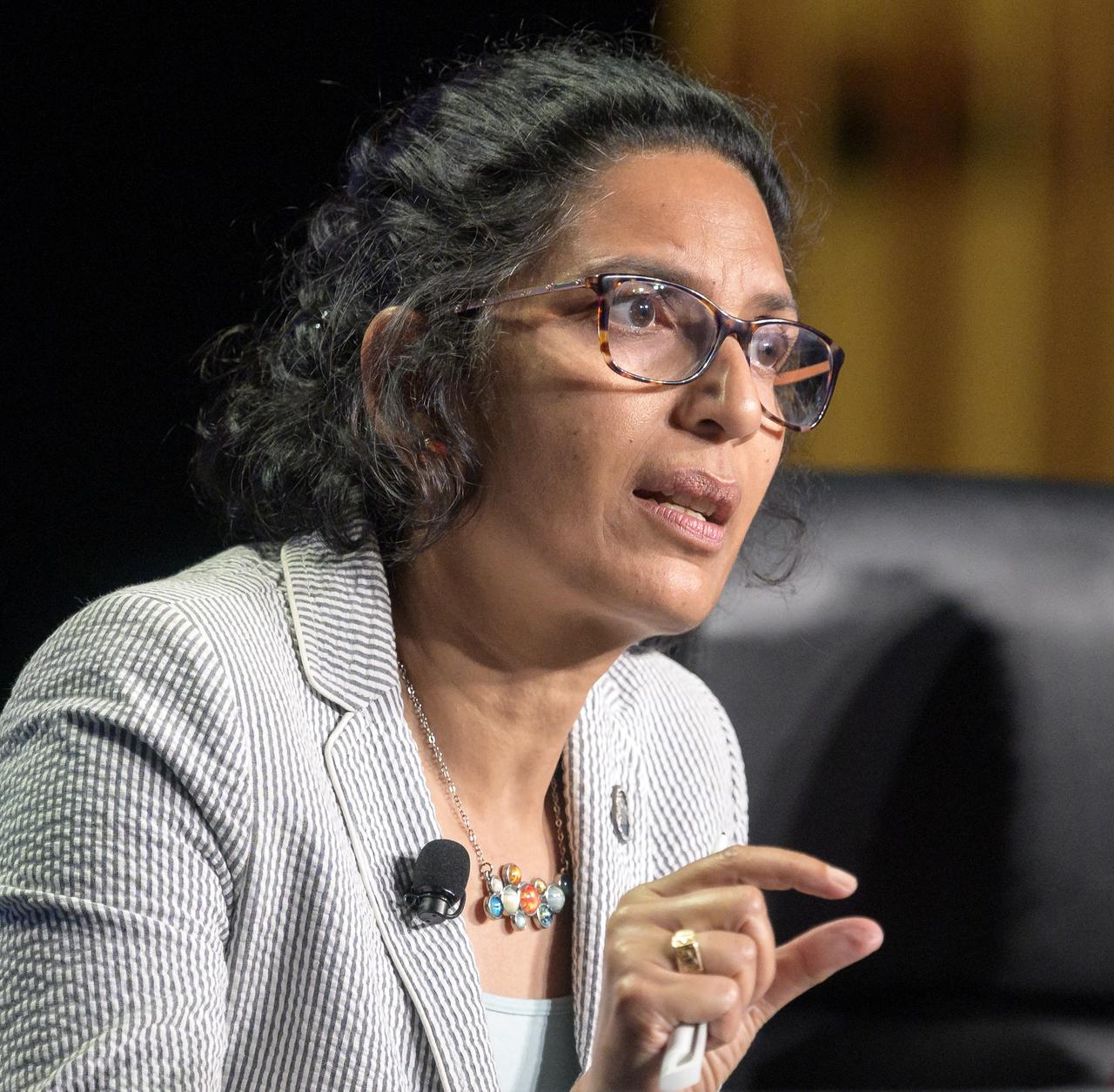

NASA Senior Advisor for Budget and Finance Bhavya Lal participates in a panel discussion titled “Technology Drives Exploration: Paving the Next Era of Space Exploration” during the 36th Space Symposium, Thursday, Aug. 26, 2021, in Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
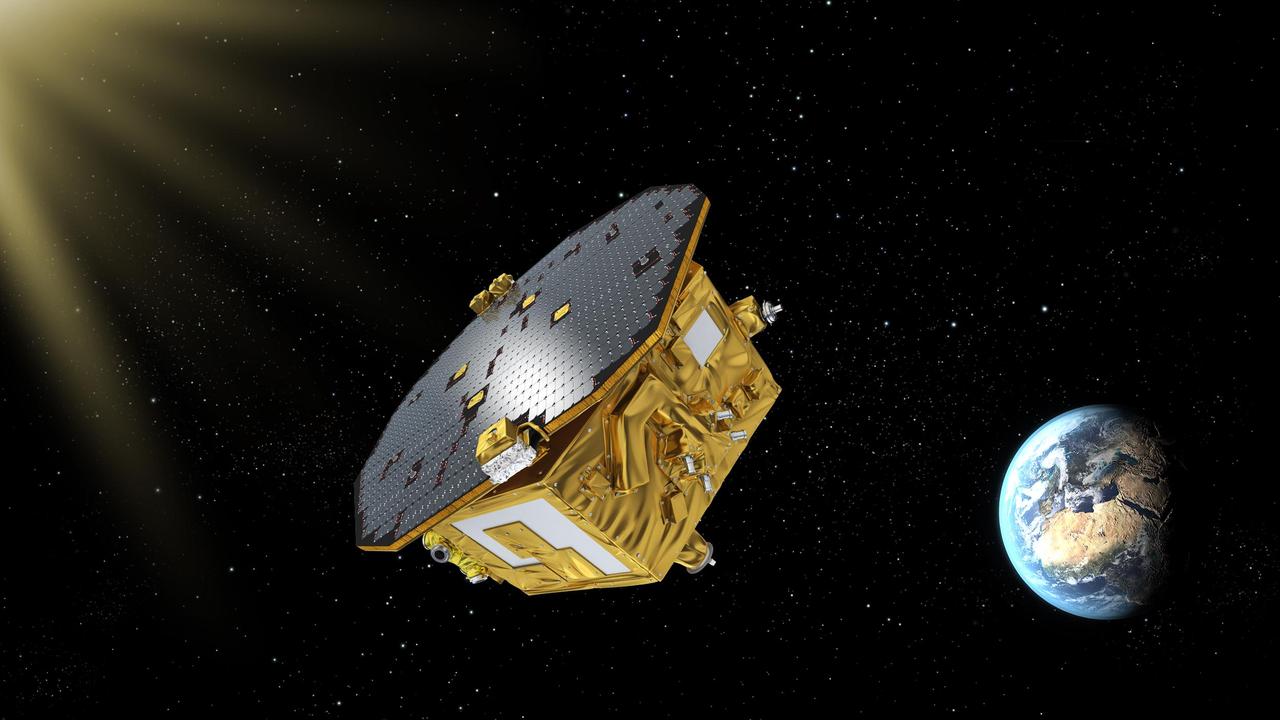

This artist's concept shows ESA's LISA Pathfinder spacecraft, which launched on Dec. 3, 2015, from Kourou, French Guiana, will help pave the way for a mission to detect gravitational waves. LISA Pathfinder, led by the European Space Agency (ESA), is designed to test technologies that could one day detect gravitational waves. Gravitational waves, predicted by Einstein's theory of general relativity, are ripples in spacetime produced by any accelerating body. But the waves are so weak that Earth- or space-based observatories would likely only be able to directly detect such signals coming from massive astronomical systems, such as binary black holes or exploding stars. Detecting gravitational waves would be an important piece in the puzzle of how our universe began. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20196
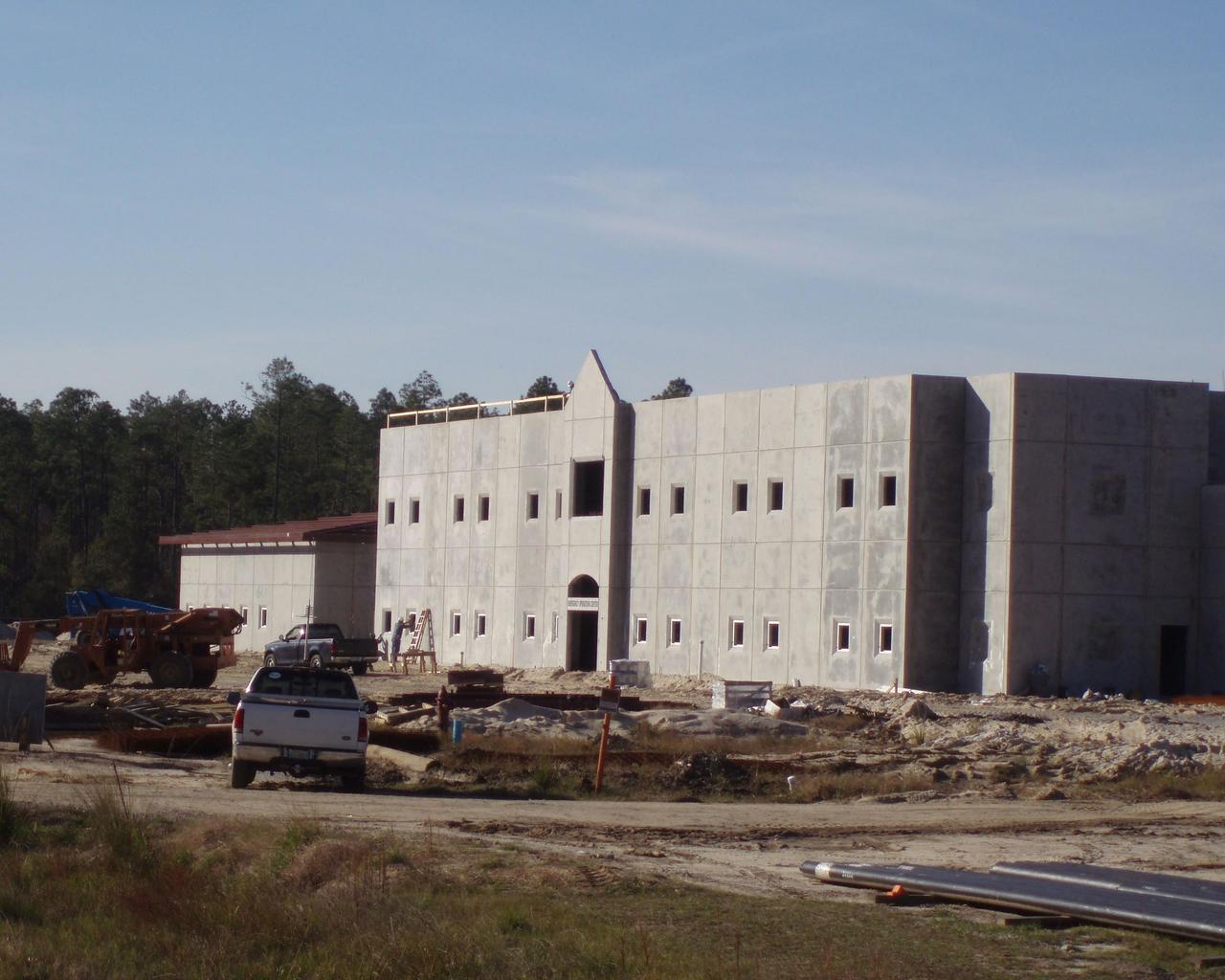

Work on Stennis Space Center's new Emergency Operations Center is progressing on schedule, according to Robert Perkins, construction manager with Jacobs Technology. At the turn of the New Year, construction contractors had completed the pervious paving for the north and west parking lots. Part of the facility's `green' design, pervious paving allows water to pass through and be absorbed directly into the ground below, preventing erosion from runoff. Through January, workers concentrated on installing the roof, sprinkler piping and overhead cable trays for electrical and communication lines. The next step will be interior work, erecting wallboard and installing electrical equipment. Perkins said NASA seeks to earn a Silver LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) Rating for the project's environmentally-friendly and sustainable design, construction and operation. The facility has a projected completion date of February 2009.
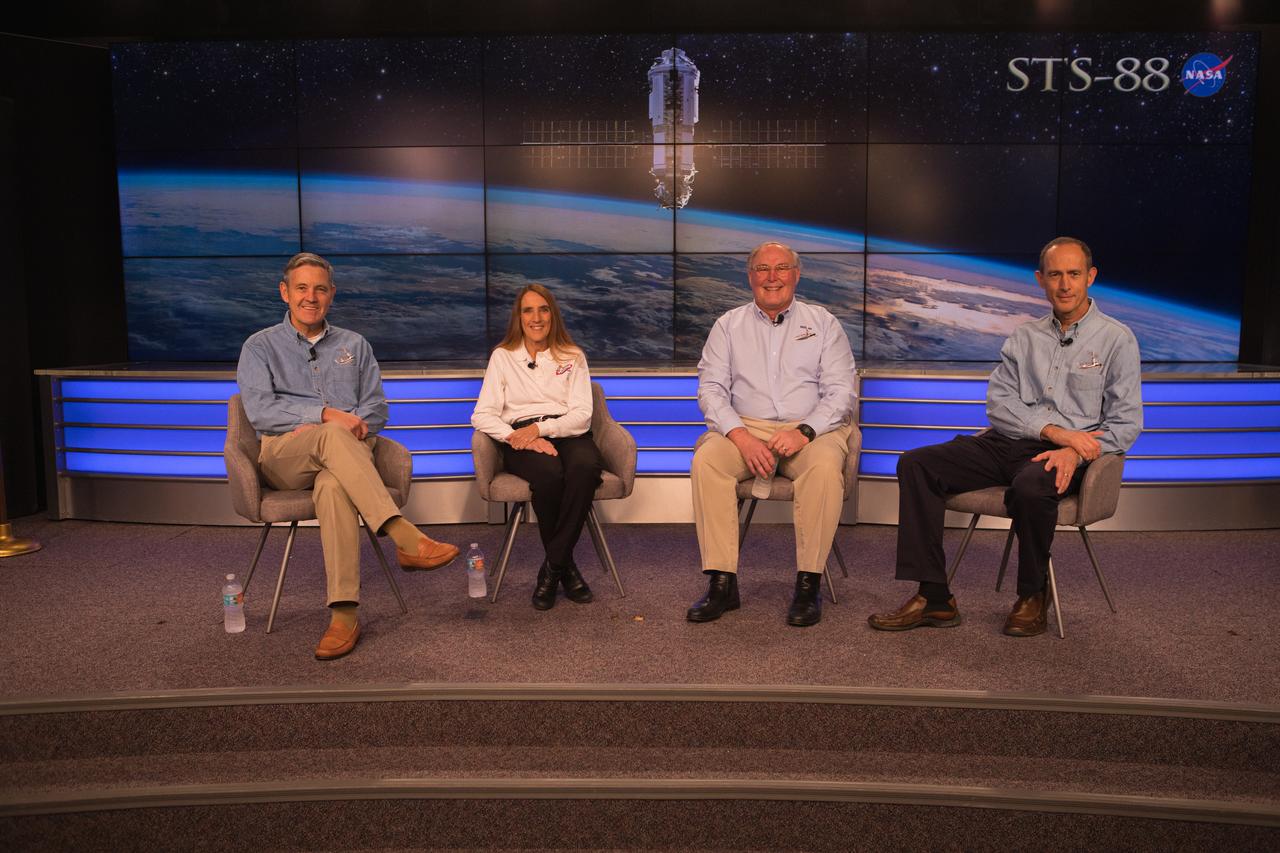

From left, Kennedy Space Center Director and STS-88 commander Bob Cabana, along with STS-88 mission specialists Nancy Currie-Gregg, Jerry Ross and Jim Newman, are recognized Dec. 10, 2018, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a 20th anniversary celebration of the first International Space Station assembly mission. The STS-88 mission paved the way for humans to live and work on the space station.

A serving tray with signatures from the NASA Perseverance Mars rover team is seen in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
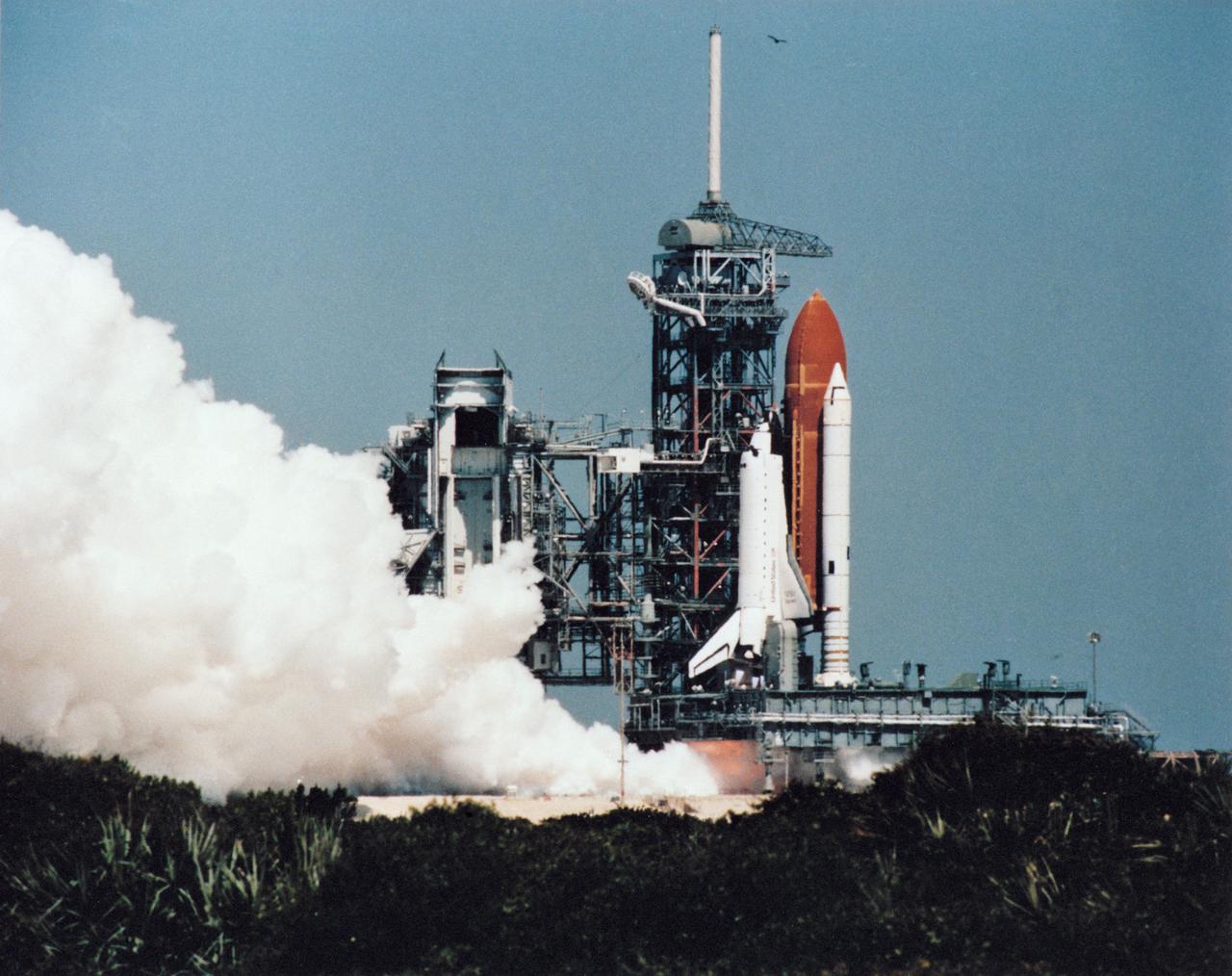

S84-35325 (2 June 1984) --- The Flight Readiness Firing (FRF) for NASA's 41-D spaceflight was completed on June 2, 1984 to pave the way for launch of the Discovery's seven-day mission later this month. Making its first flight, the orbiter will be mated to the same two solid rocket boosters (SRB) and external tank (ET) seen here.
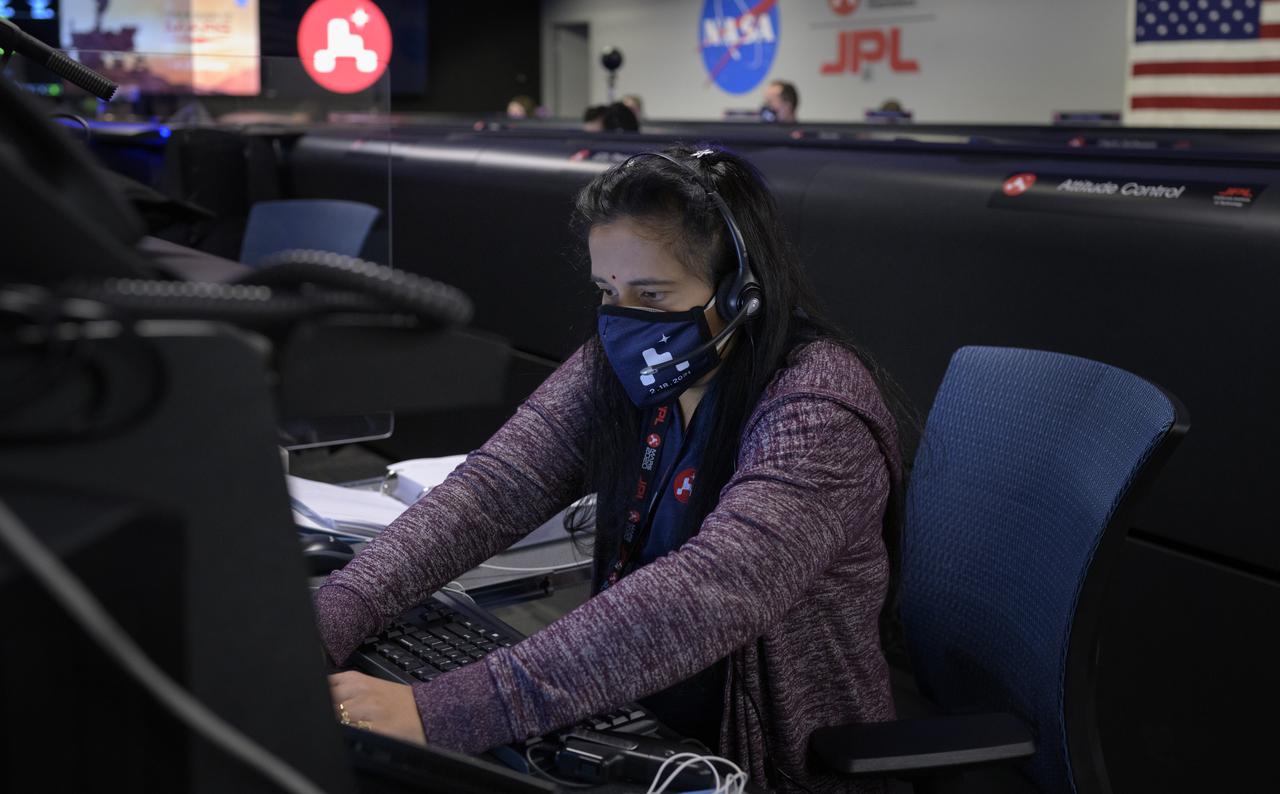

Perseverance Mars rover mission commentator and guidance, navigation, and controls operations Lead Swati Mohan studies data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
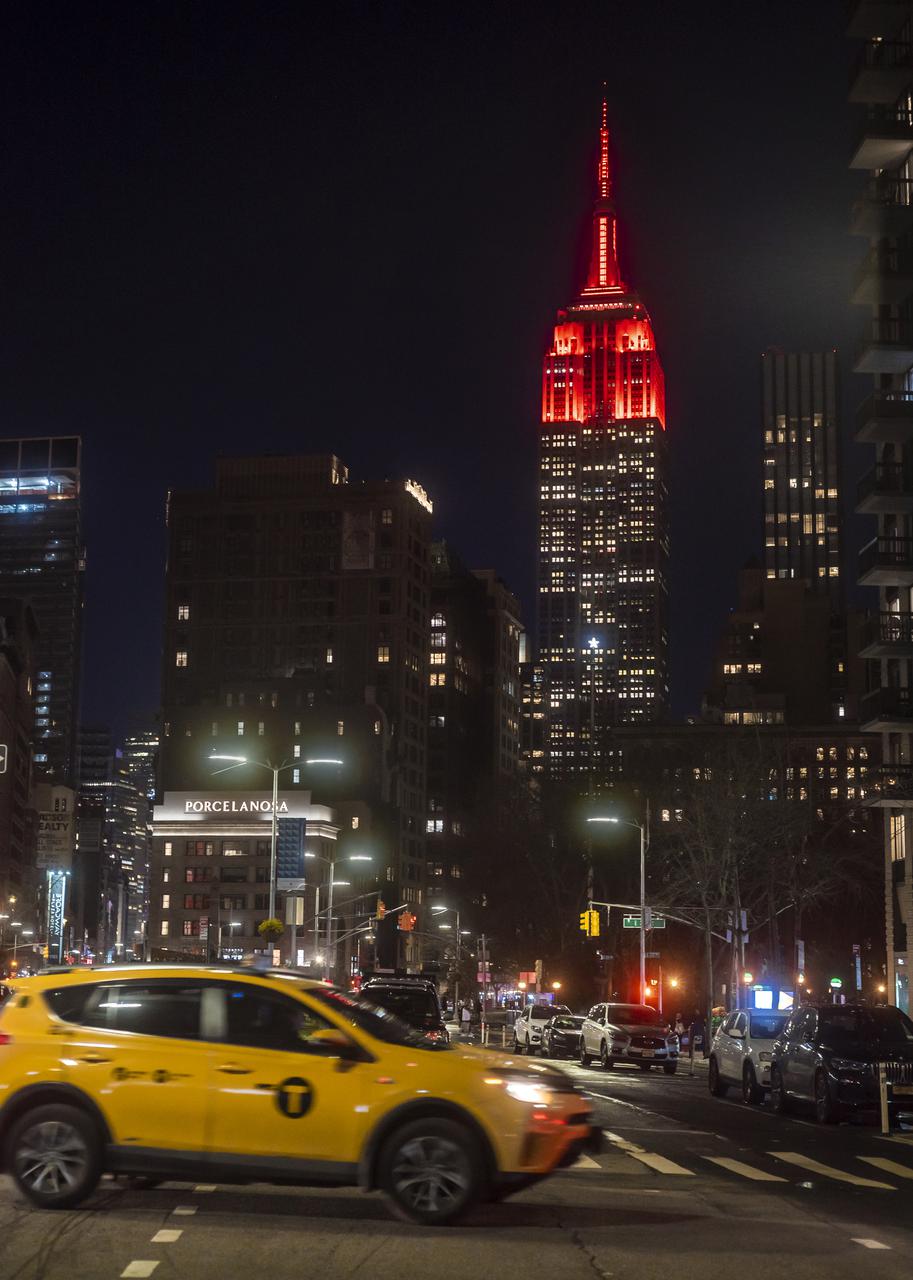

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
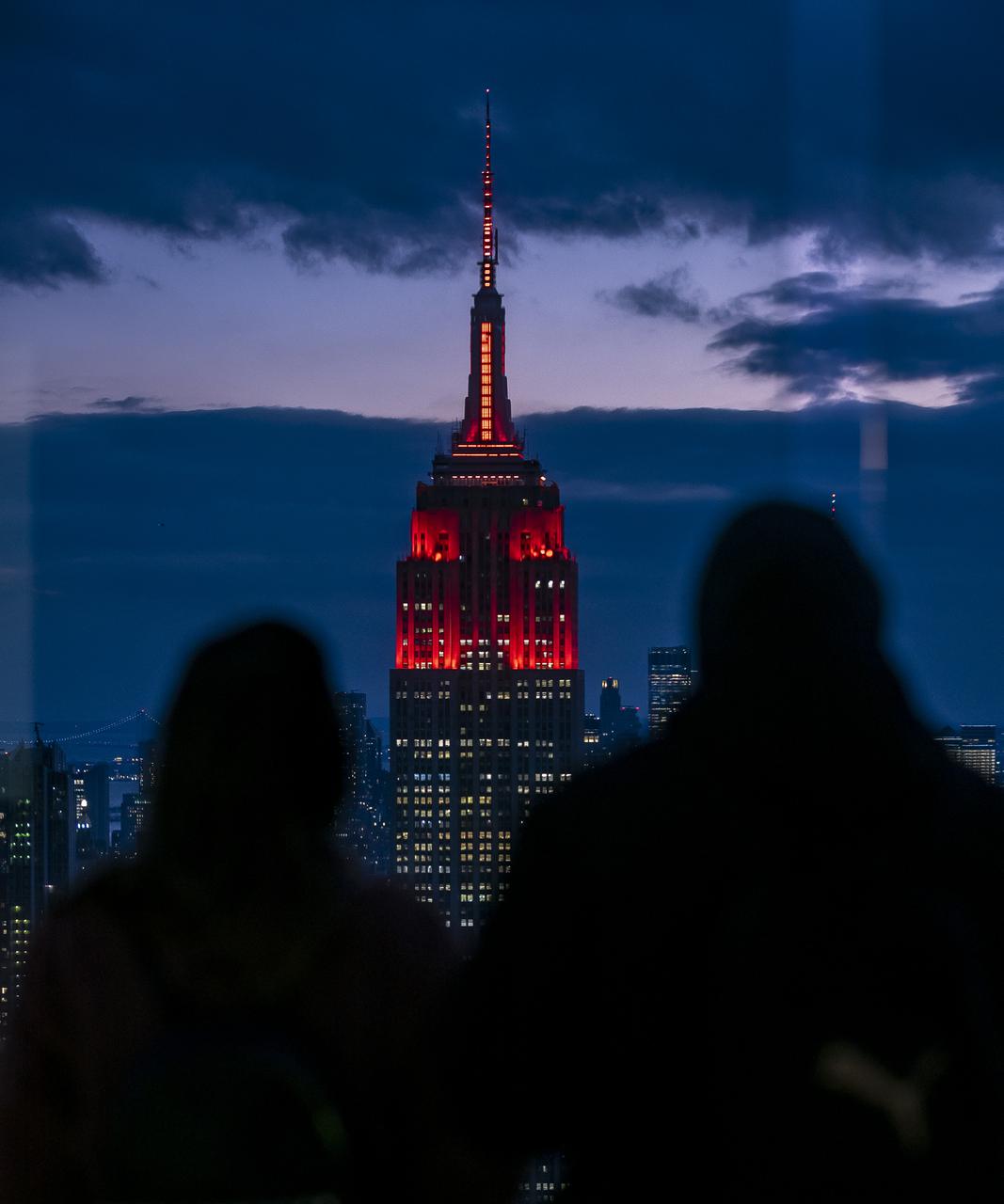

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
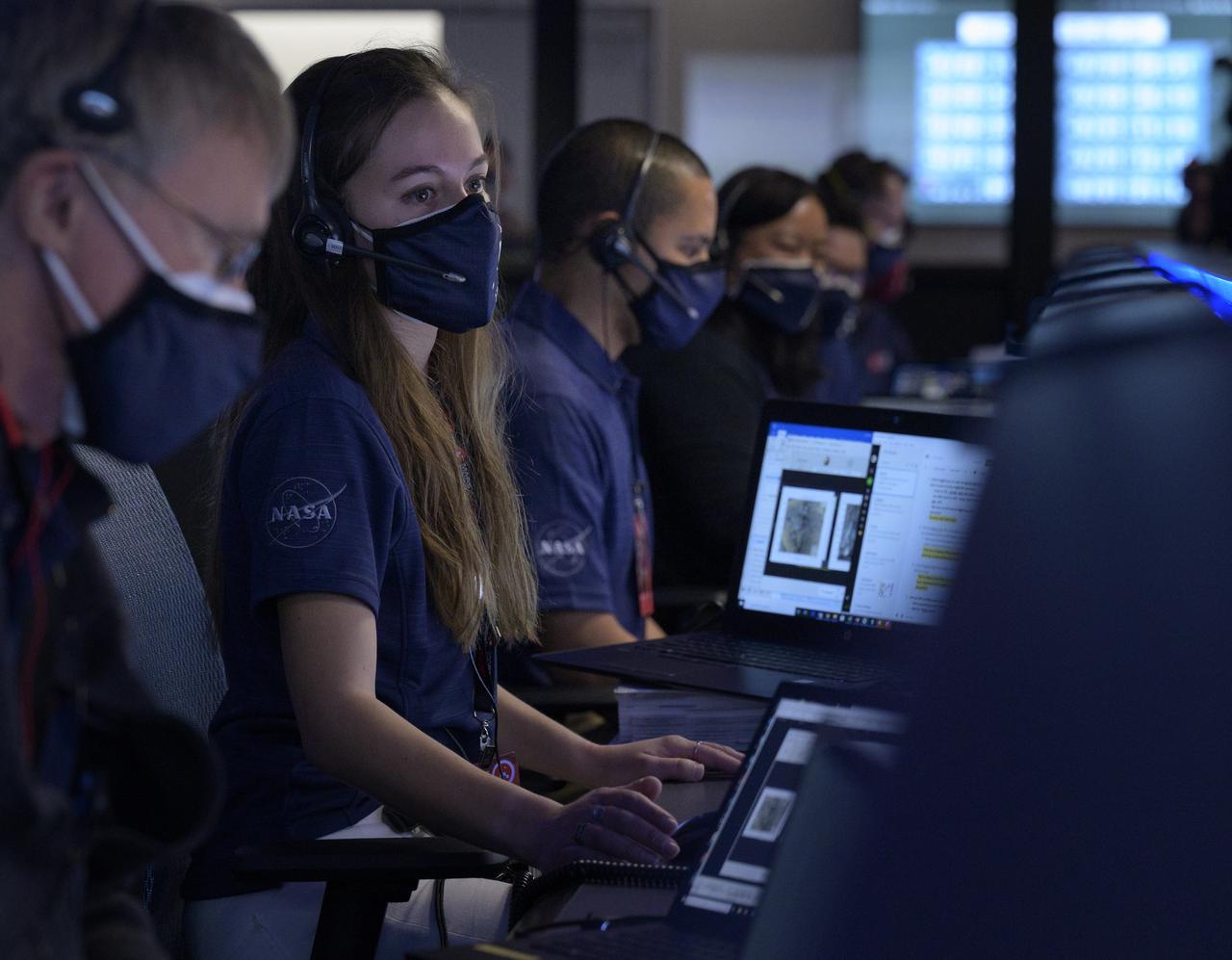

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A NASA Mars Rover Landing banner is seen on the One Times Square video board as NASA's Perseverance rover begins its descent towards the surface of Mars, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
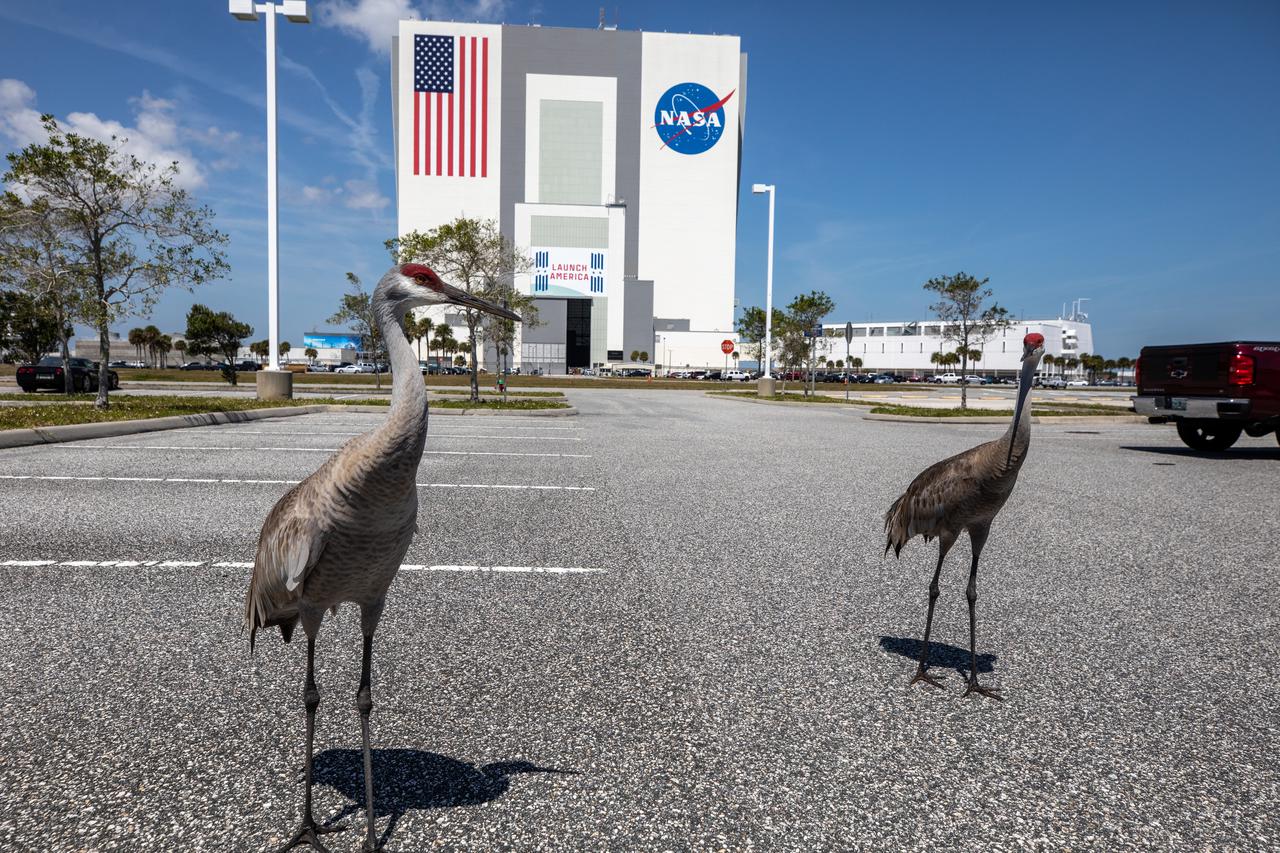

A pair of sandhill cranes explore a paved parking area near the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2021. Kennedy shares space with the Merritt Island National Wildlife refuge, which is home to more than 1,000 species of plants, 117 species of fish, 68 amphibians and reptiles, 330 birds, and 31 different mammals. The refuge provides a favorable environment for the cranes as it contains shallow freshwater habitats for nesting, along with a variety of vegetation and prey to feed on.
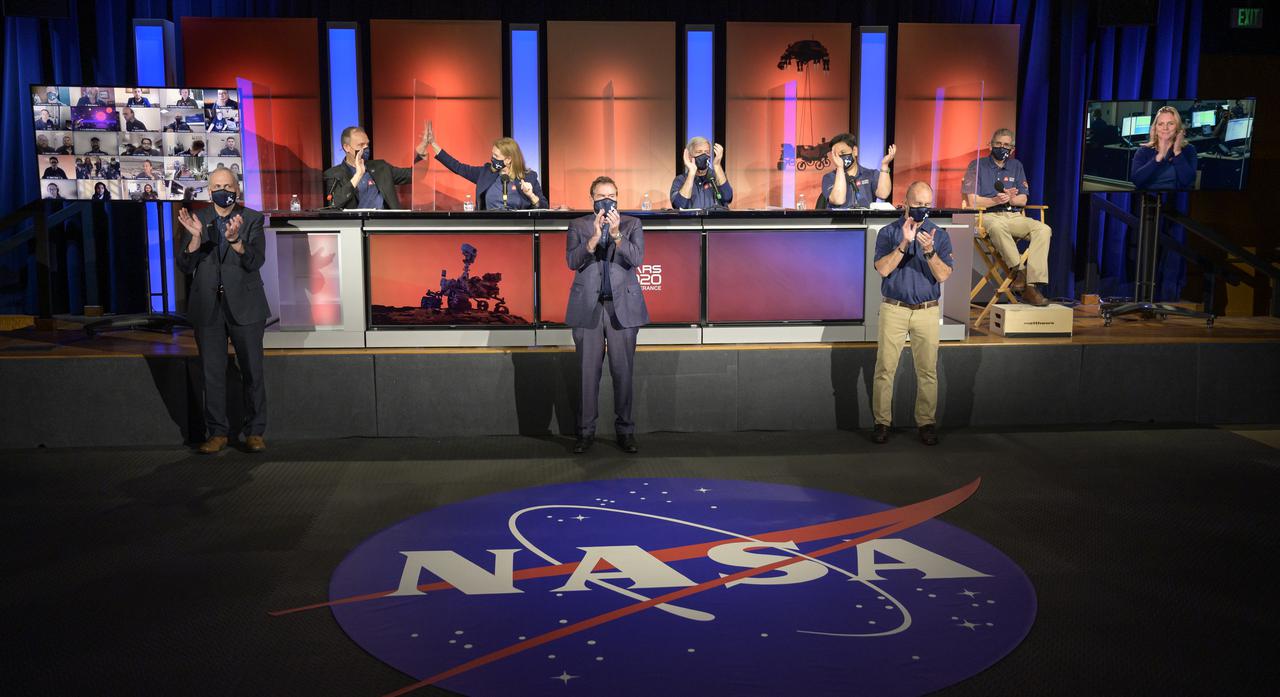

NASA Perseverance rover mission management and scientist celebrate a successful landing on Mars at the start of a post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
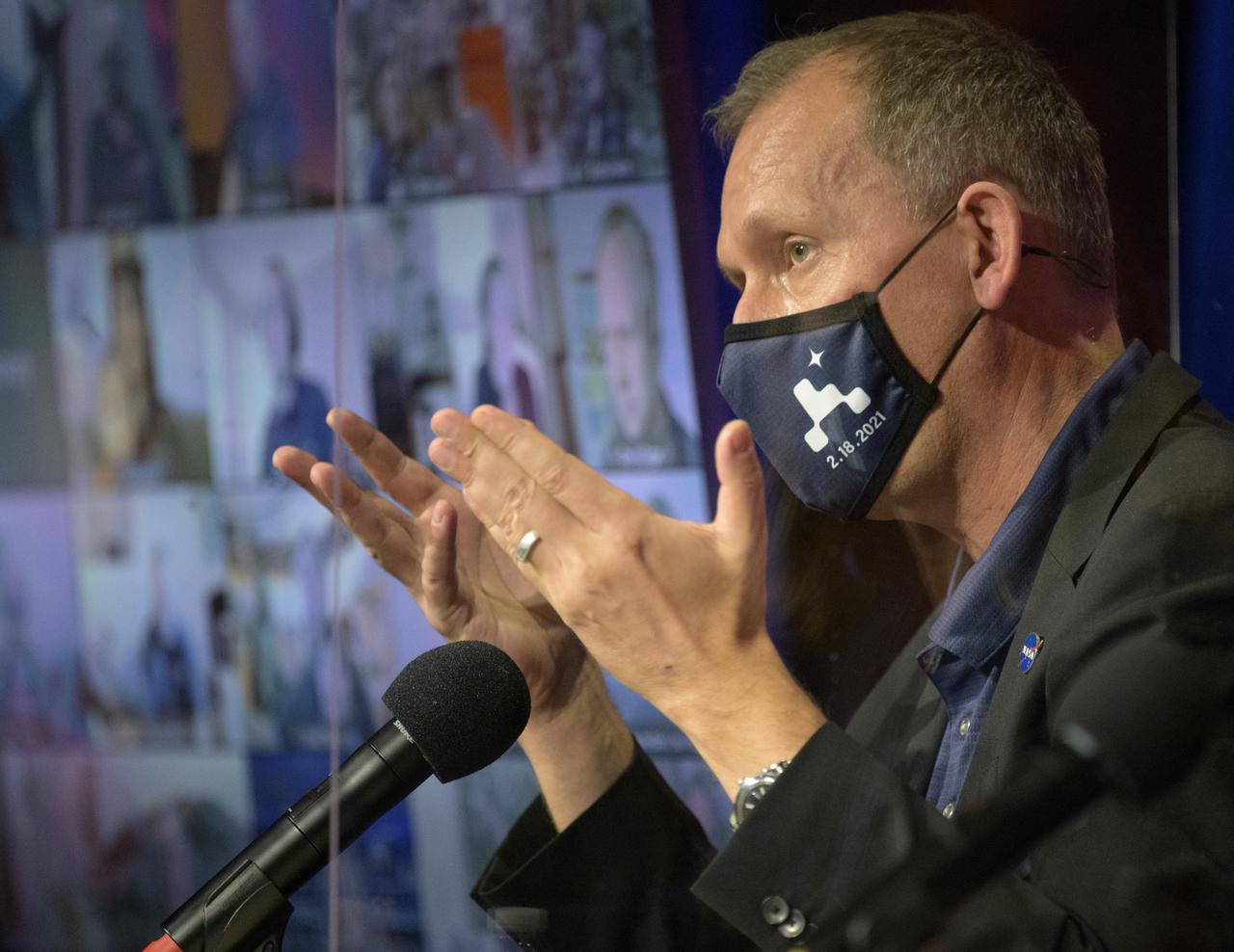

Associate Administrator of NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
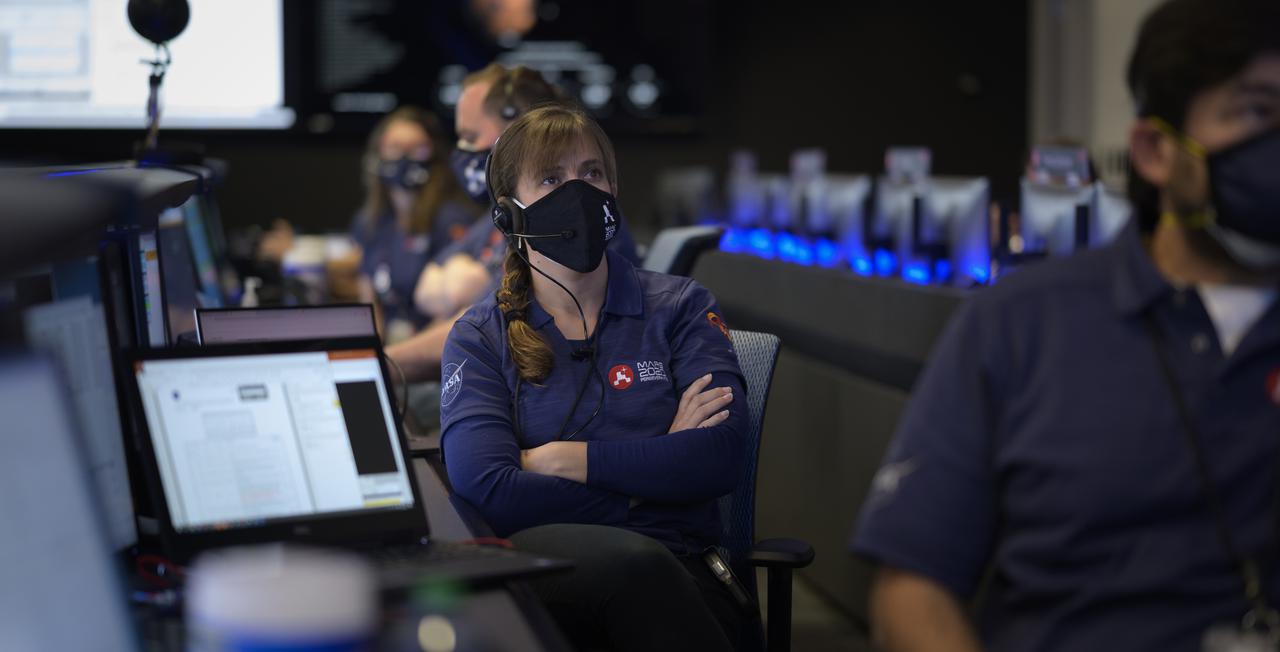

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team confer and study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine asks commercial companies to help get the agency back to the Moon as quickly as possible during an ‘industry day', Tuesday, May 8, 2018 held at NASA Headquarters in Washington. NASA is calling for commercial proposals for delivering instruments, experiments, and other small payloads to the surface of the Moon as early as next year. This solicitation is part of a broader Exploration Campaign that will pave the way for a human return to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
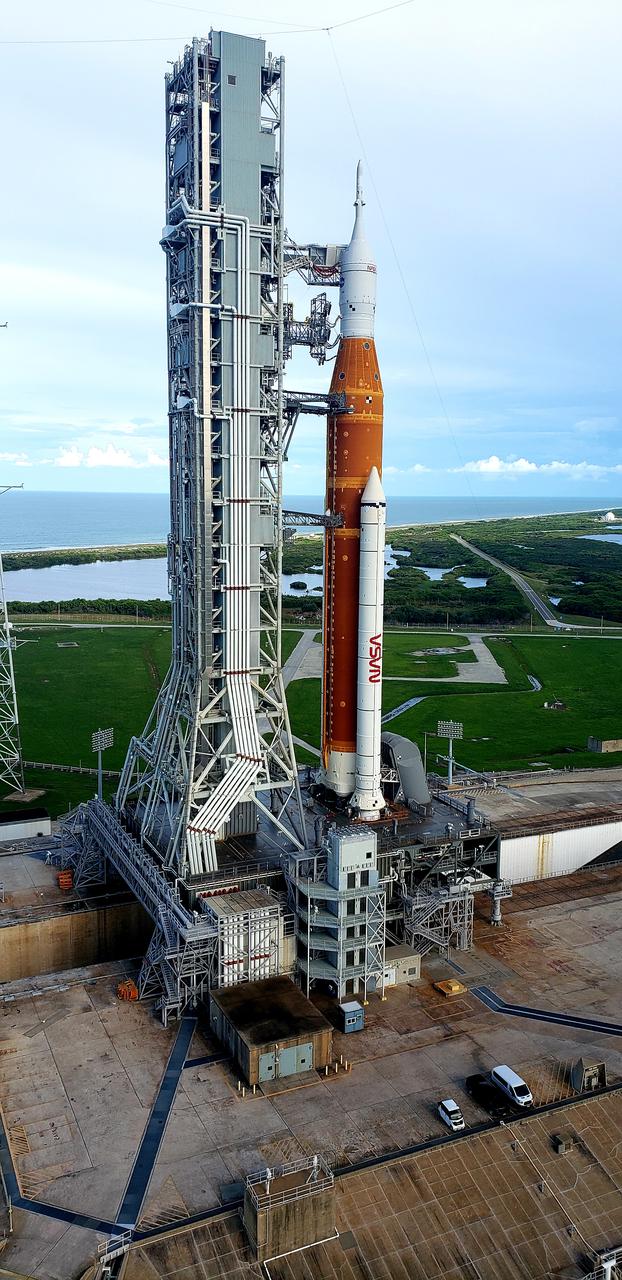

A close-up view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 15, 2022. A portion of the umbilical connections are in view, as well as the crew access arm. Artemis I is the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
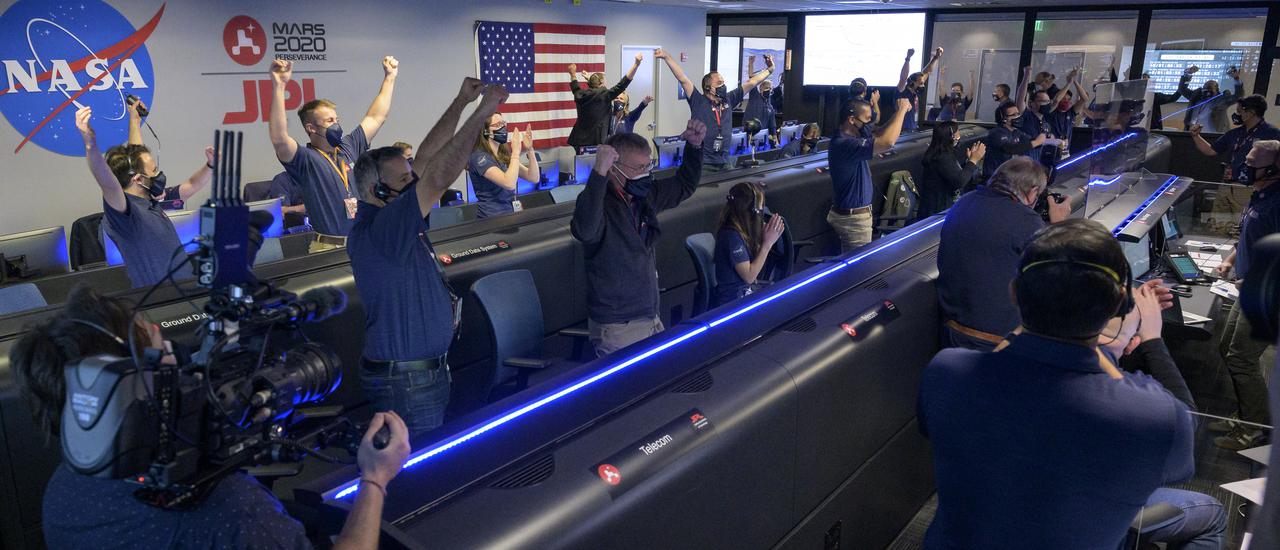

Members of NASA’s Perseverance rover team react in mission control after receiving confirmation the spacecraft successfully touched down on Mars, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
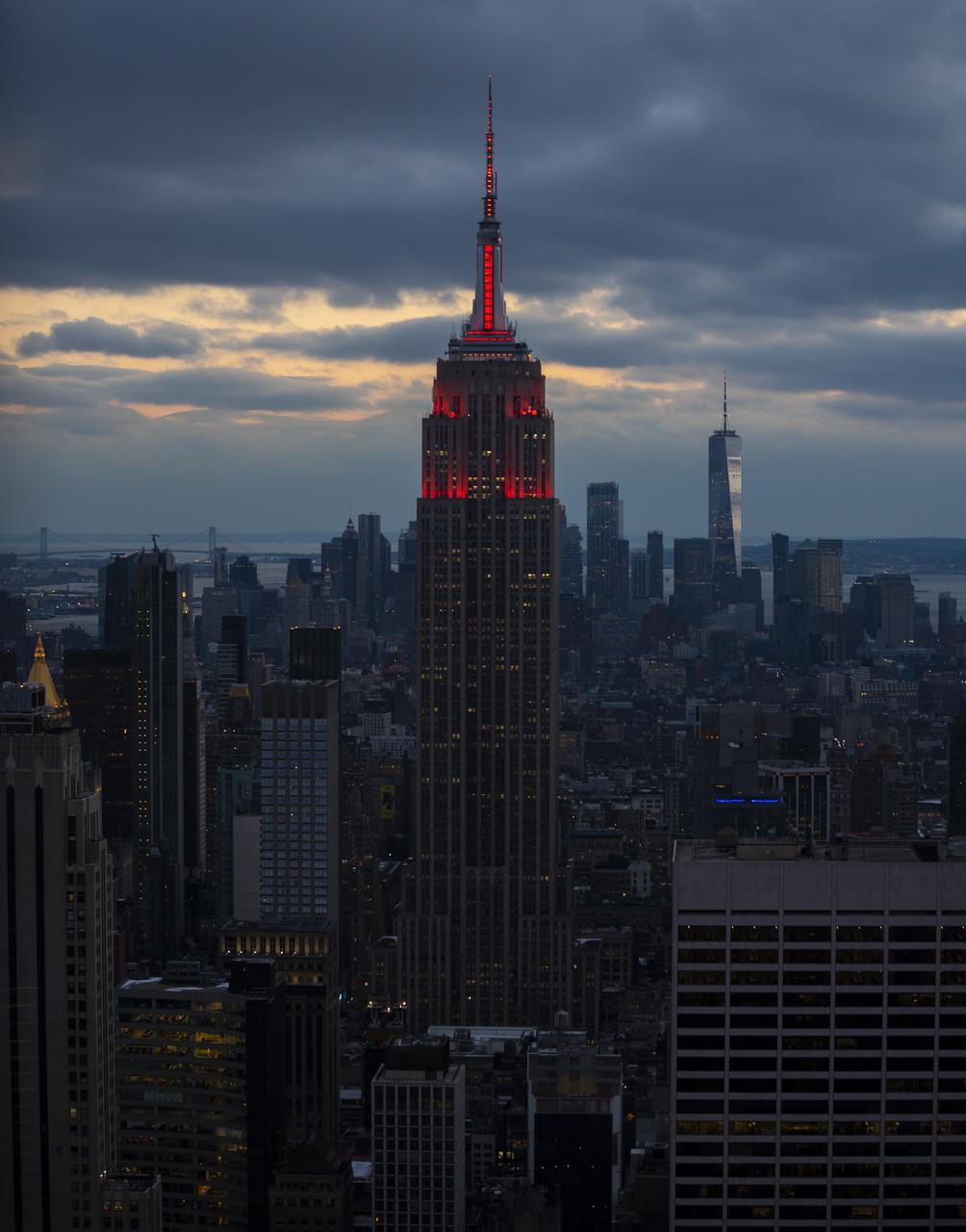

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
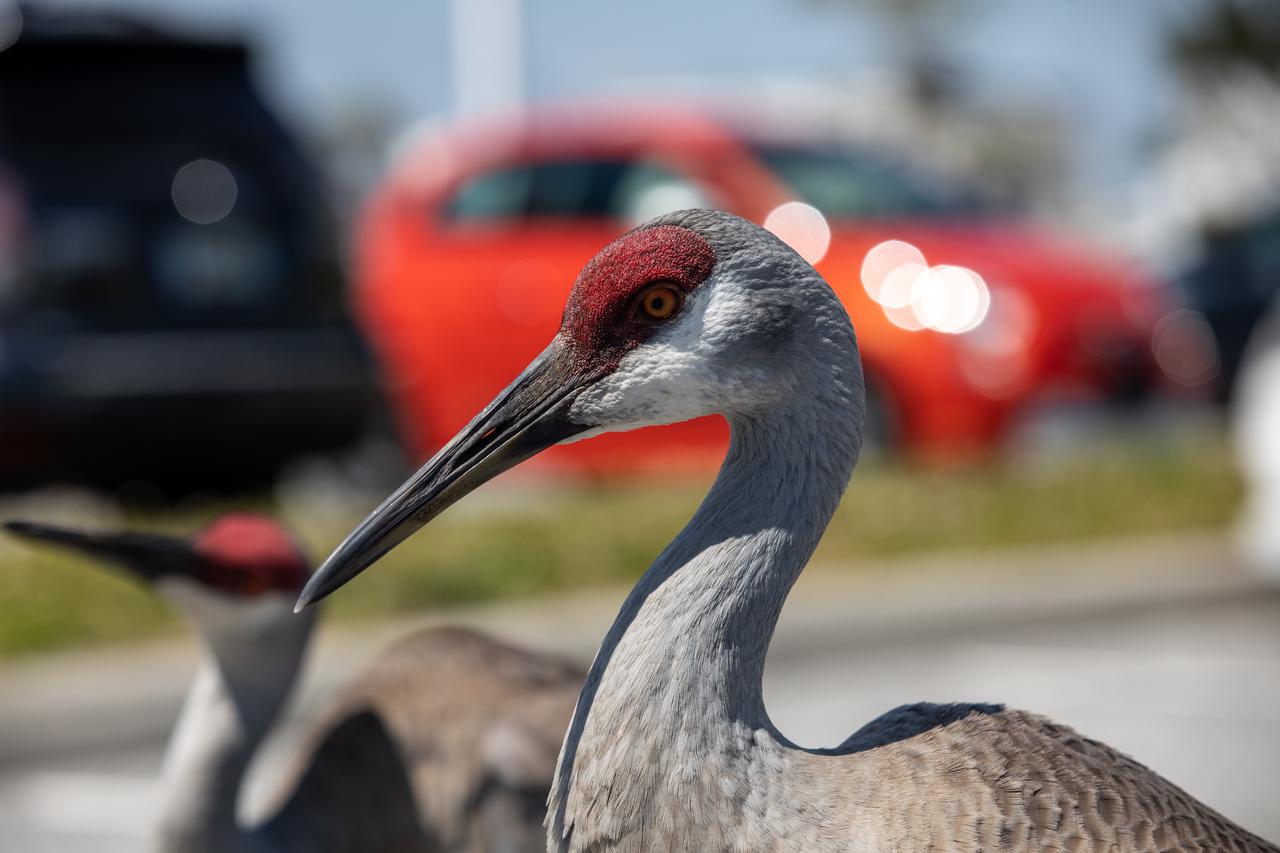

A pair of sandhill cranes explore a paved parking area at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2021. Kennedy shares space with the Merritt Island National Wildlife refuge, which is home to more than 1,000 species of plants, 117 species of fish, 68 amphibians and reptiles, 330 birds, and 31 different mammals. The refuge provides a favorable environment for the cranes as it contains shallow freshwater habitats for nesting, along with a variety of vegetation and prey to feed on.

Artemis II NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman greets Exploration Ground Systems team members inside the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building during a visit to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 7, 2023. The approximately 10-day Artemis II flight will test NASA’s foundational human deep space exploration capabilities, the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, for the first time with astronauts and will pave the way for lunar surface missions, including landing the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon.

A view of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, during sunrise on Jan. 19, 2022. Inside the VAB, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft are stacked in High Bay 3 in preparation for the agency’s Artemis I mission. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
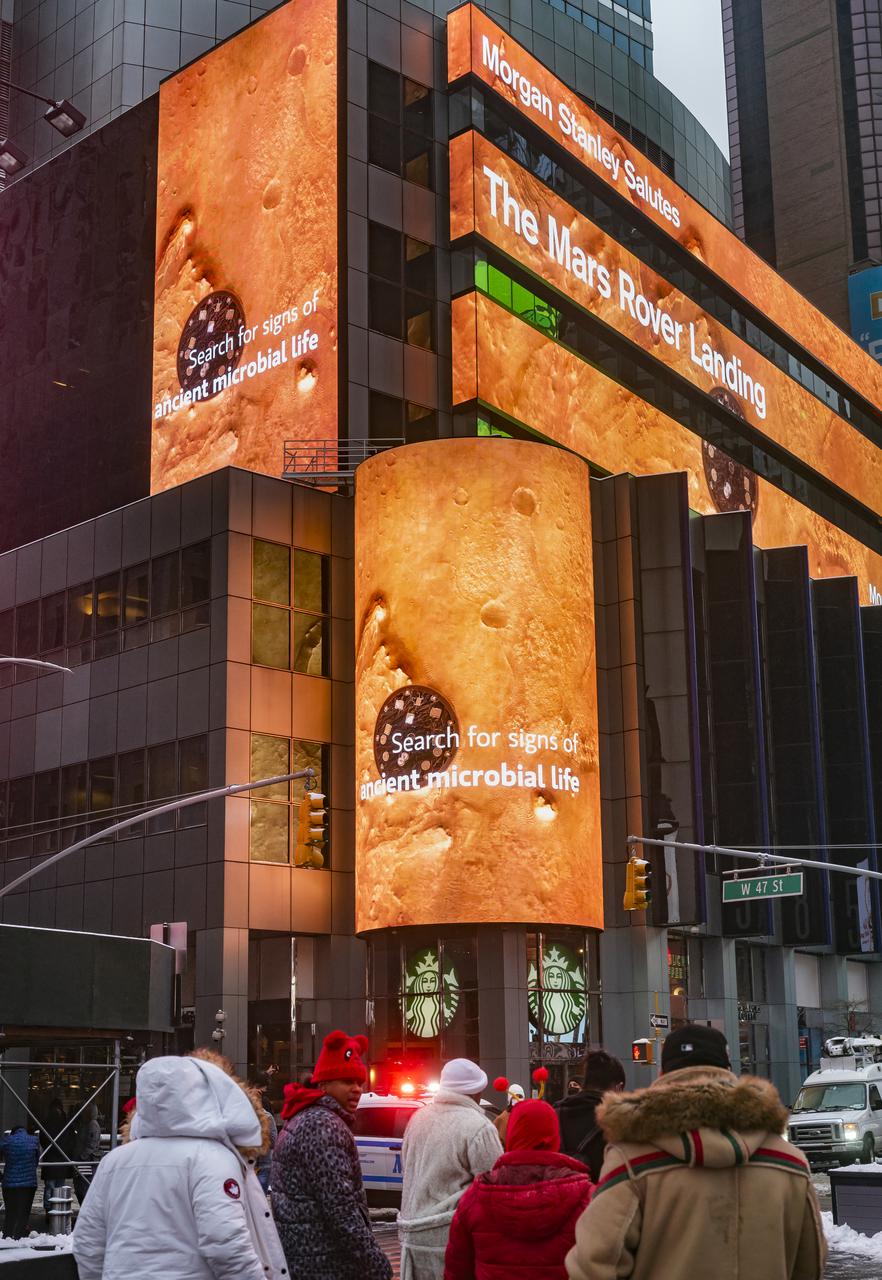

A NASA Mars Rover Landing banner is seen on the Morgan Stanley video board as NASA's Perseverance rover completes its descent towards the surface of Mars, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
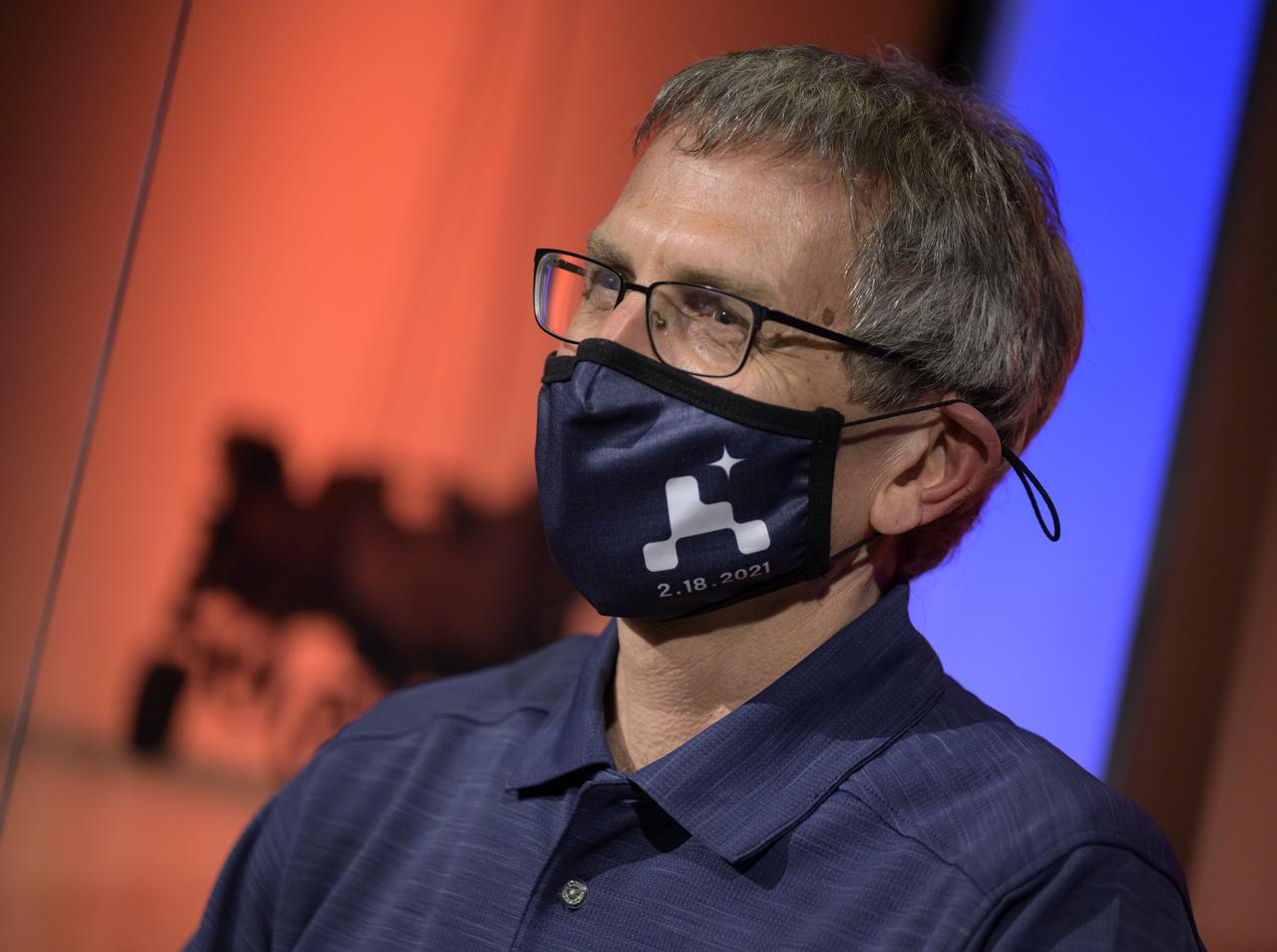

Perseverance project scientist, Caltech, Pasadena, California, Ken Farley, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
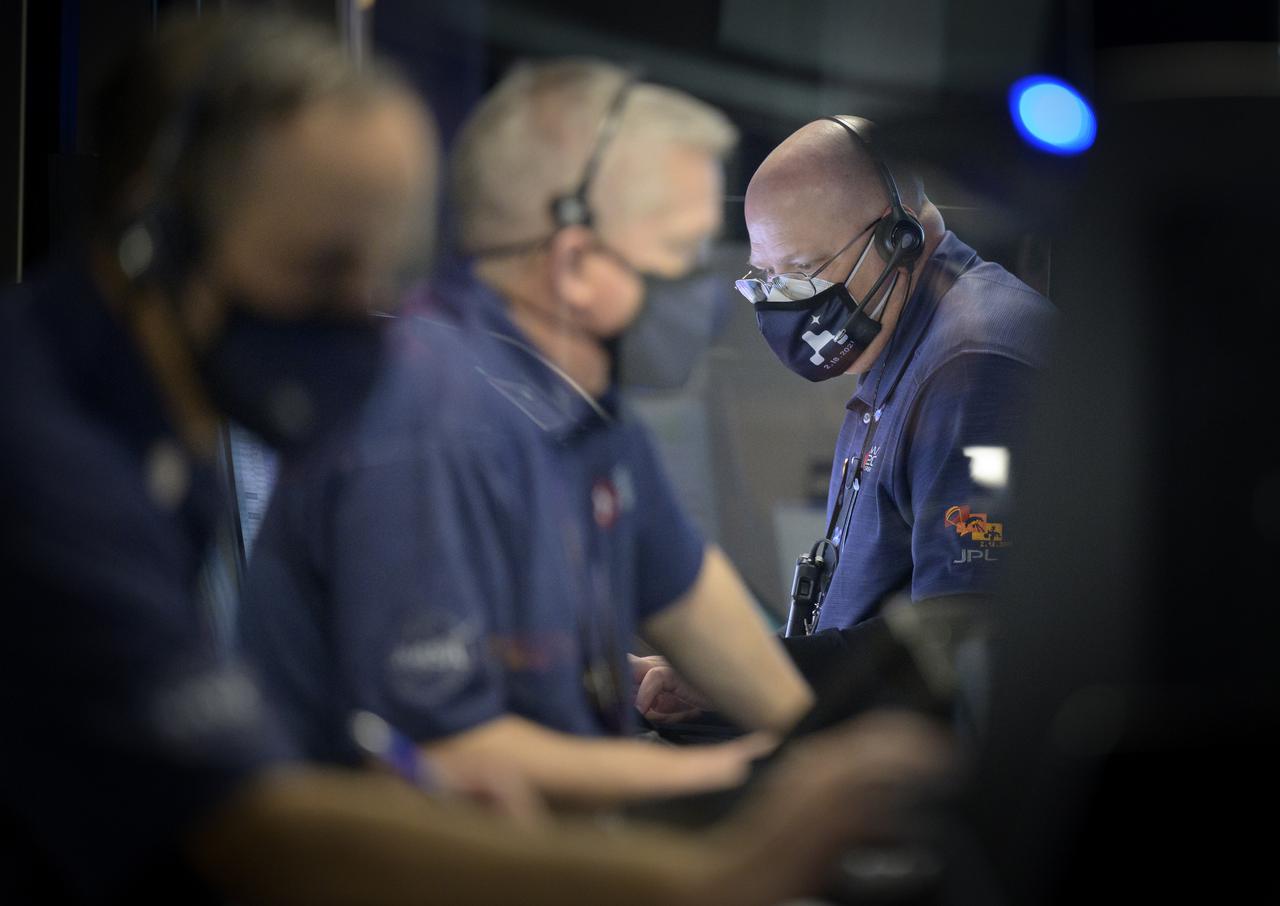

Bob Lineaweaver, right, and other members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The Mars 2020 Perseverance rover's astrobiology mission will search for signs of ancient microbial life. It will also characterize the planet's climate and geology, collect samples for future return to Earth and pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet. The mission is part of a larger program that includes missions to the Moon as a way to prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Charged with returning astronauts to the Moon by 2024, NASA will establish a sustained human presence on and around the Moon by 2028 through NASA's Artemis lunar exploration plans. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23920
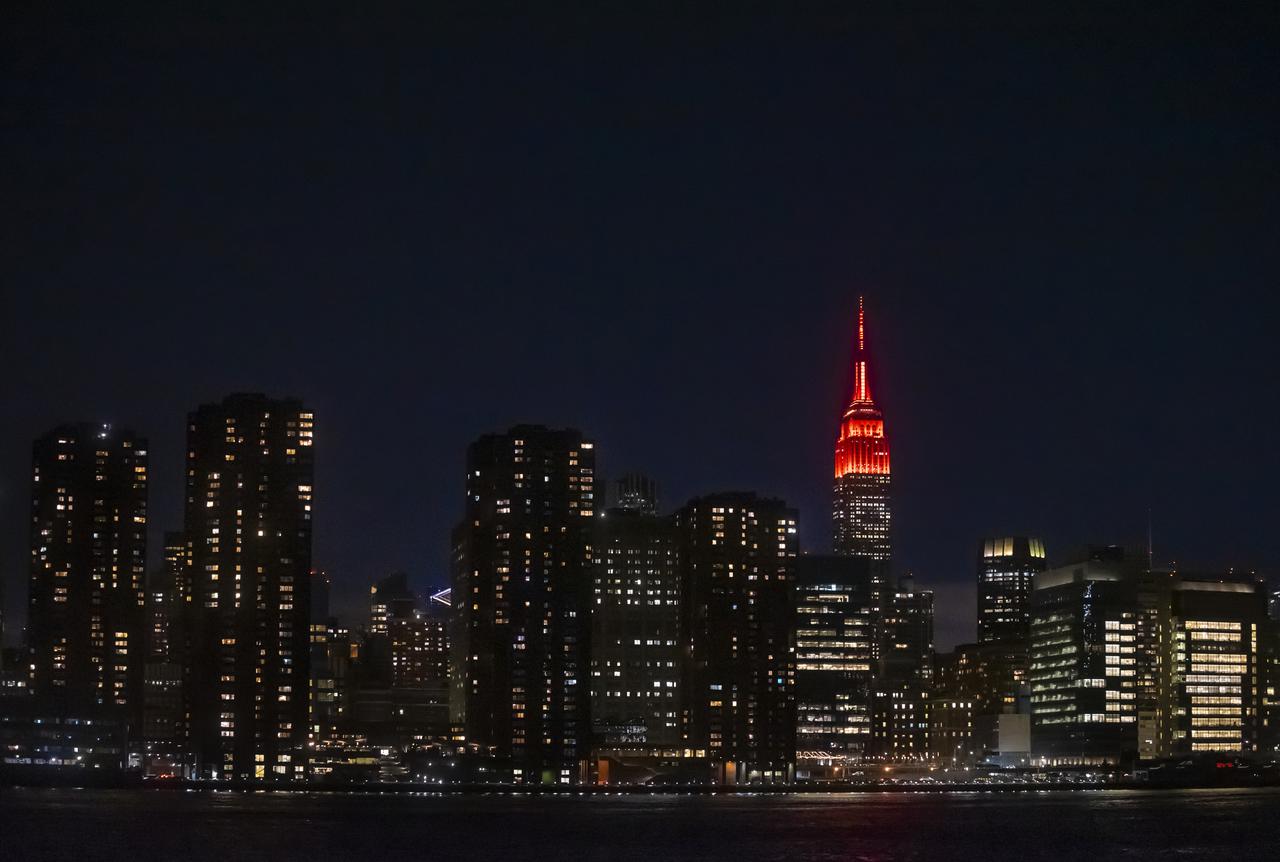

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
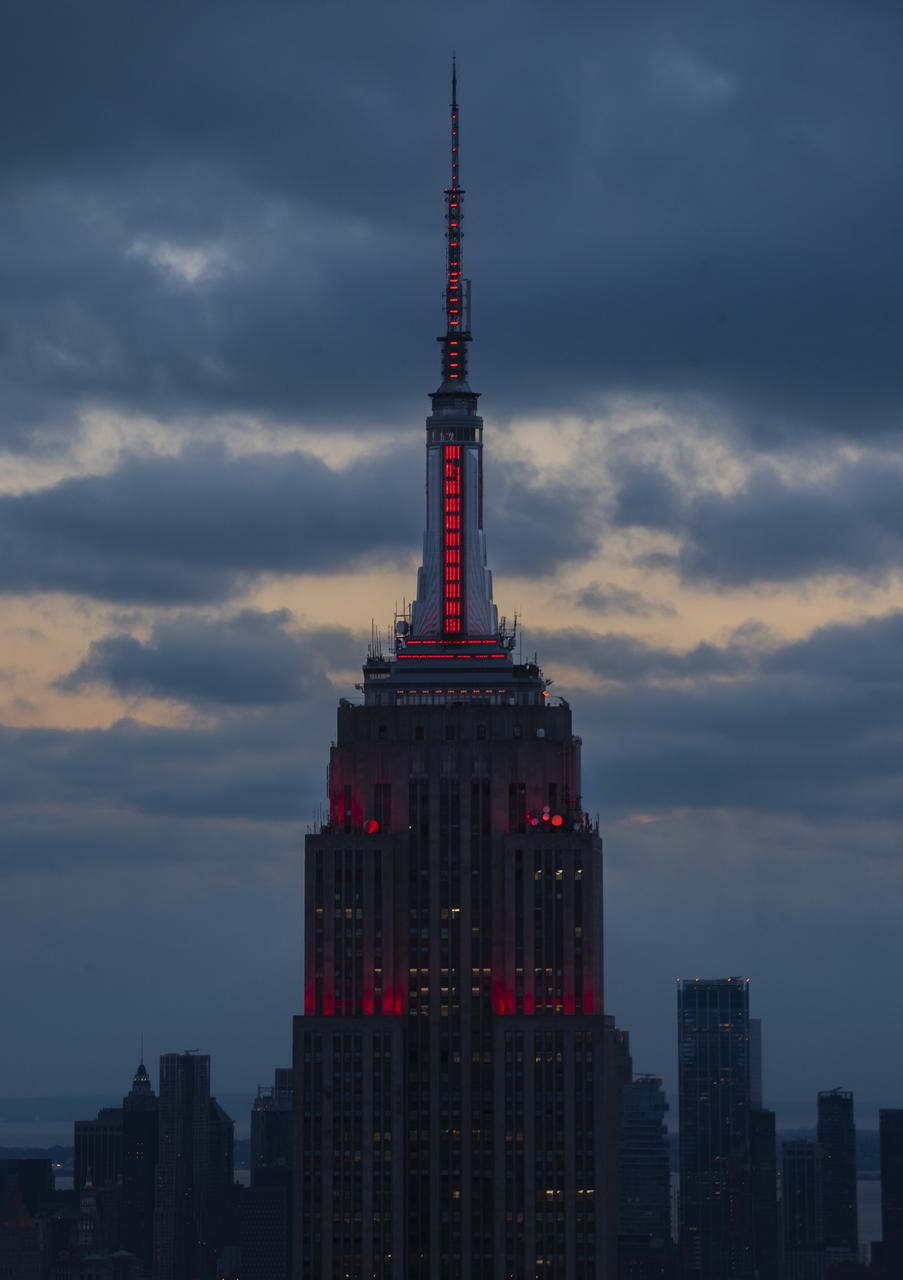

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
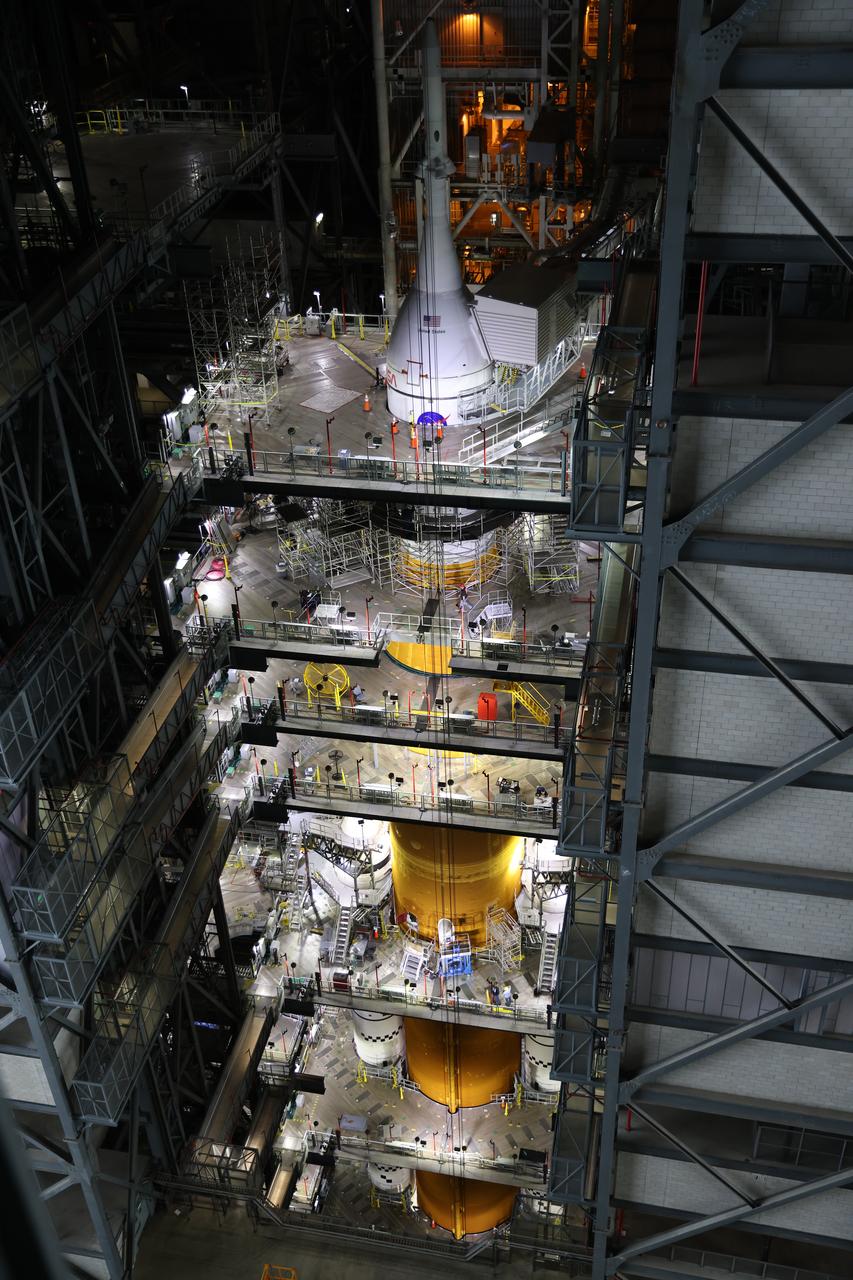

In a view from above, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Artemis I are in High Bay 3 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 3, 2022. Work platforms surround the SLS and Orion stack. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
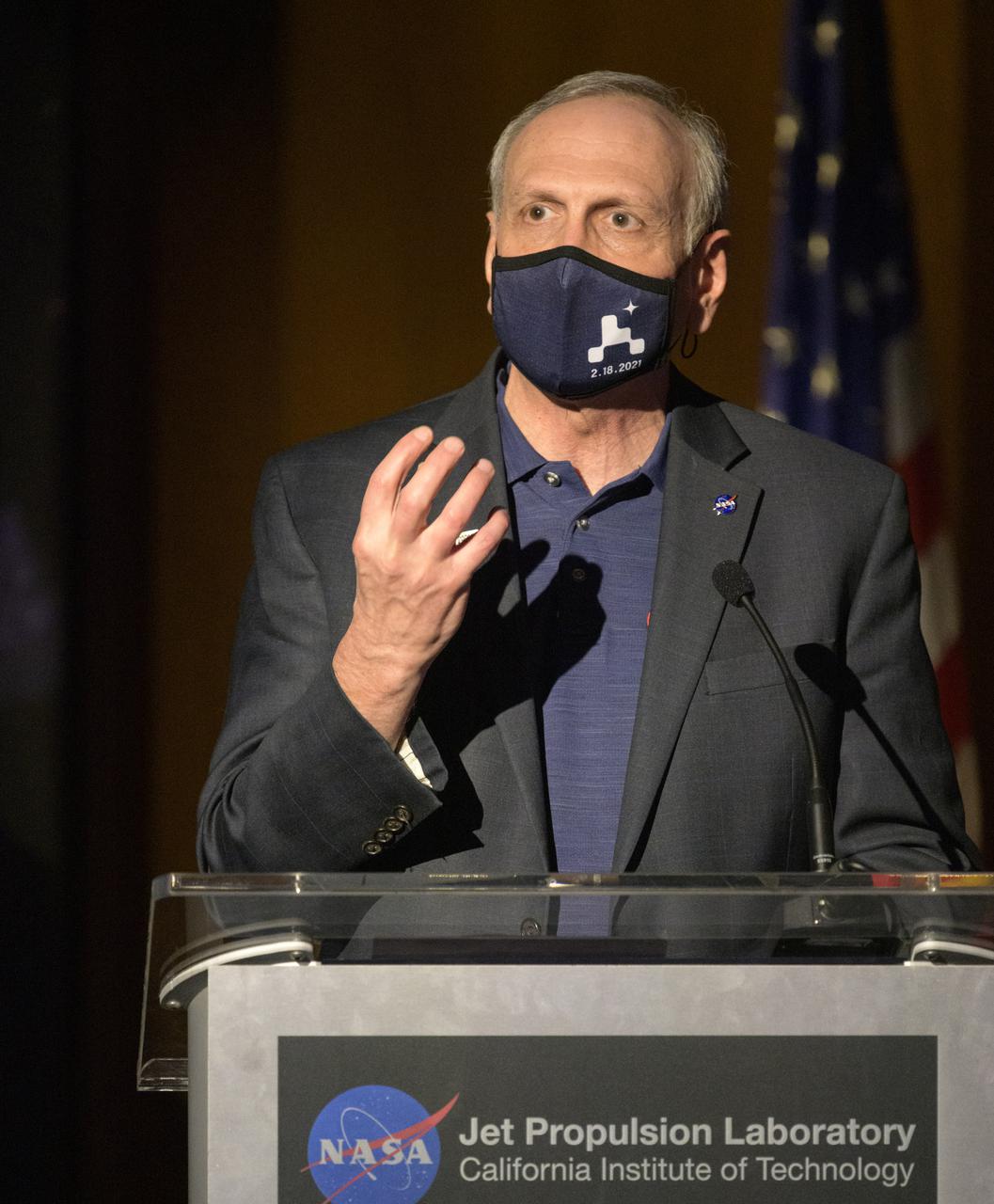

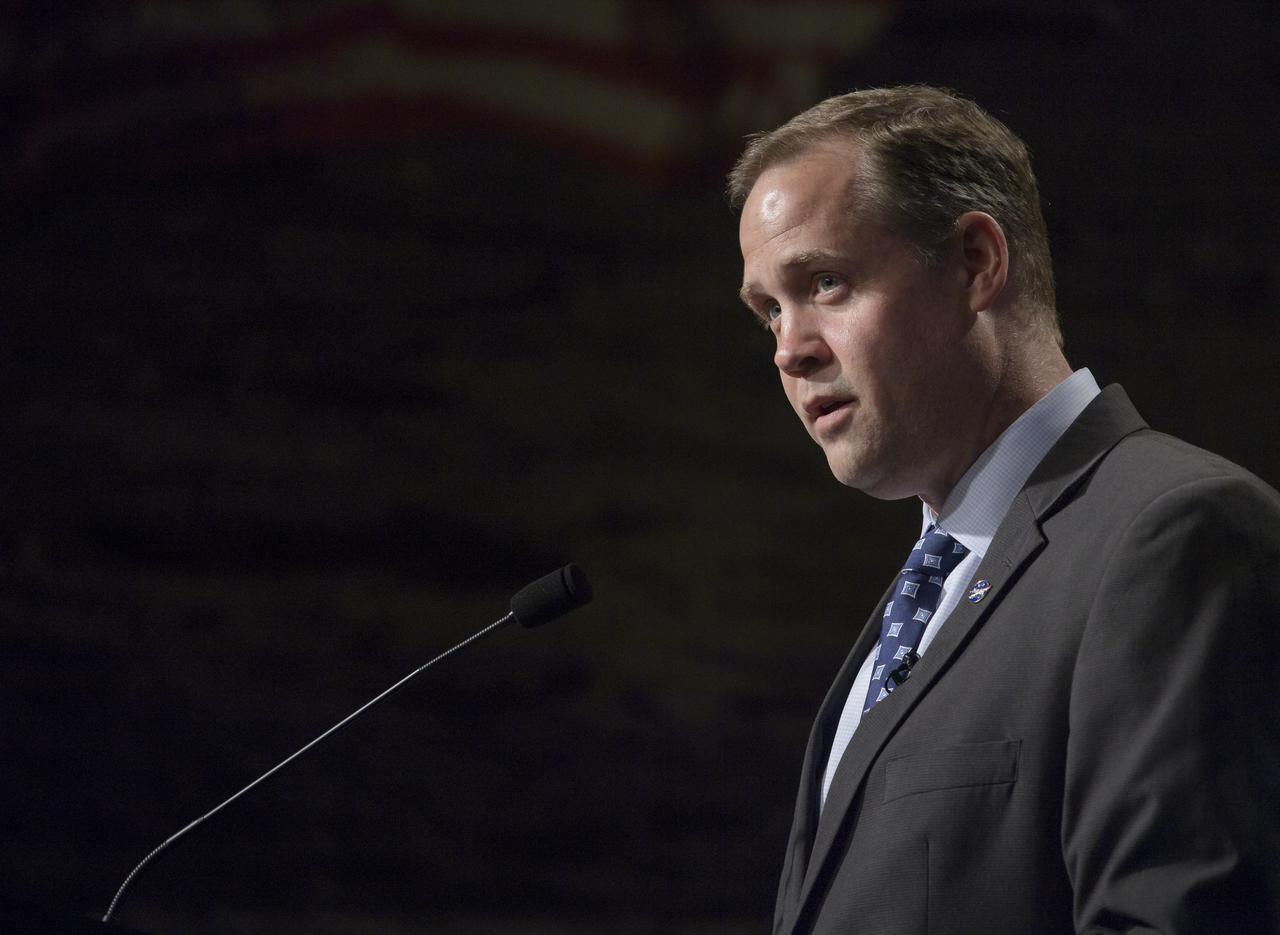
Acting NASA Administrator Steve Jurczyk gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
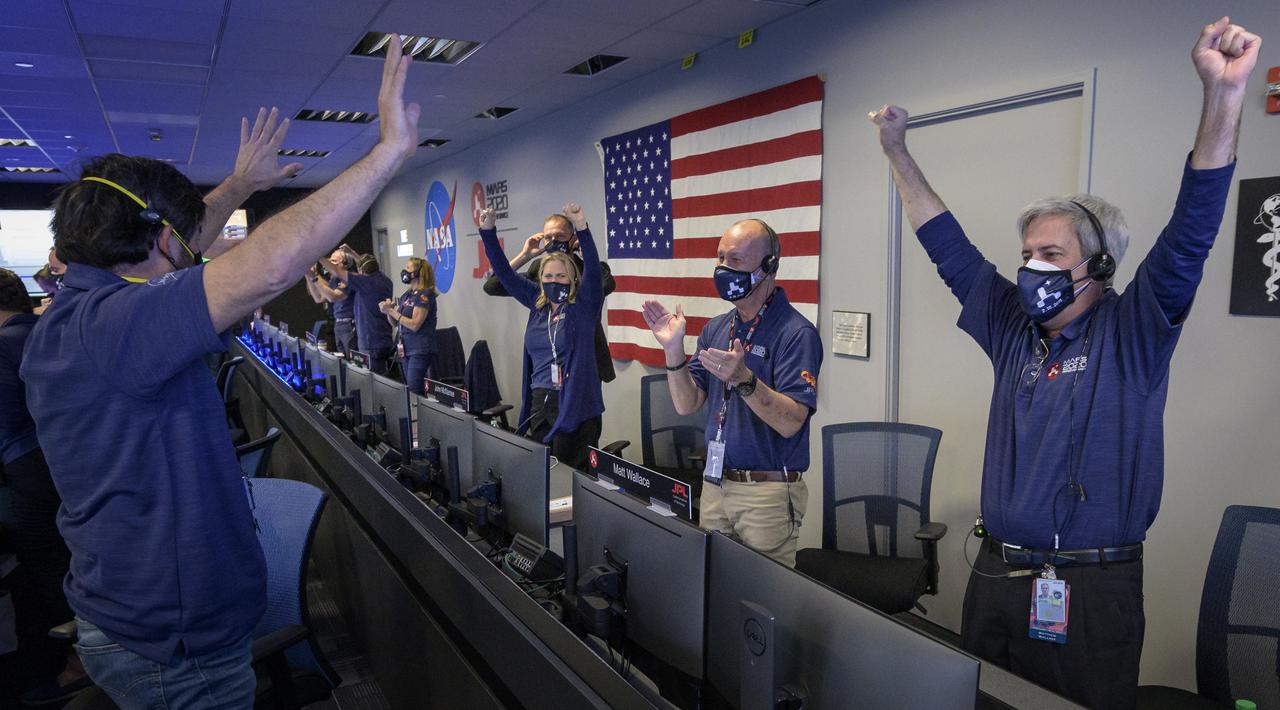

Members of NASA’s Perseverance rover team react in mission control after receiving confirmation the spacecraft successfully touched down on Mars, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
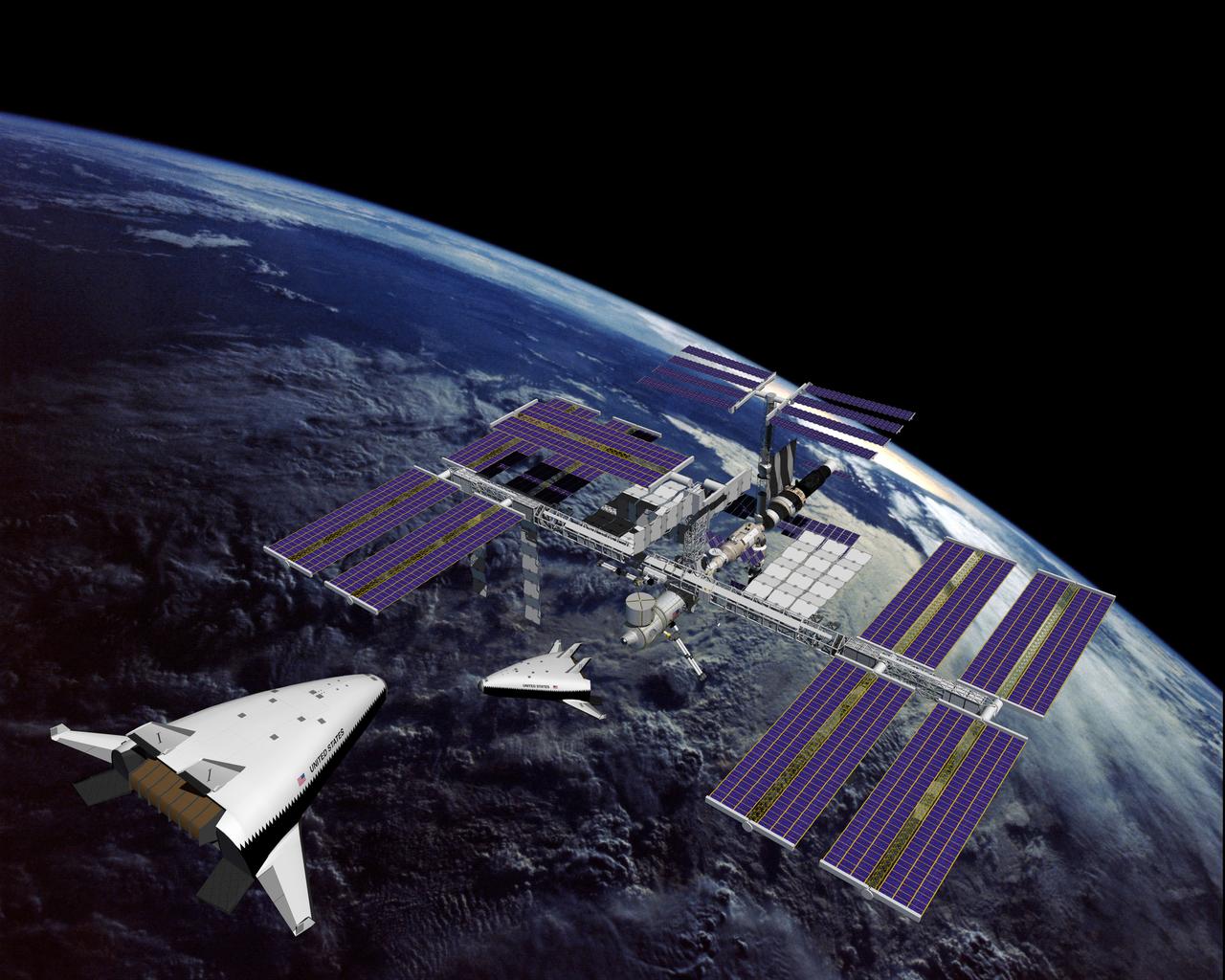

This is an artist's concept of the completely operational International Space Station being approached by an X-33 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV). The X-33 program was designed to pave the way to a full-scale, commercially developed RLV as the flagship technology demonstrator for technologies that would lower the cost of access to space. It is unpiloted, taking off vertically like a rocket, reaching an altitude of up to 60 miles and speeds between Mach 13 and 15, and landing horizontally like an airplane. The X-33 program was cancelled in 2001.
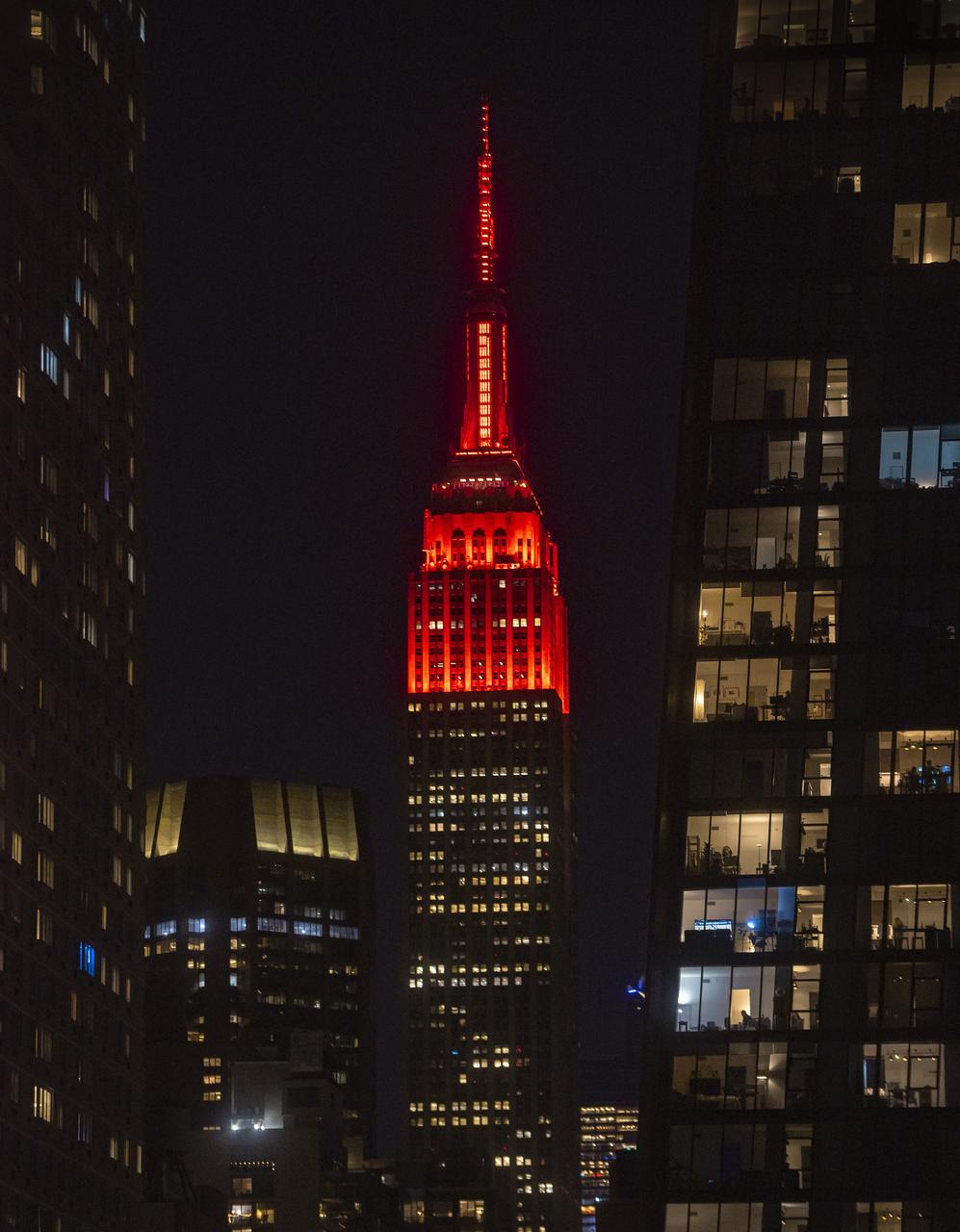

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
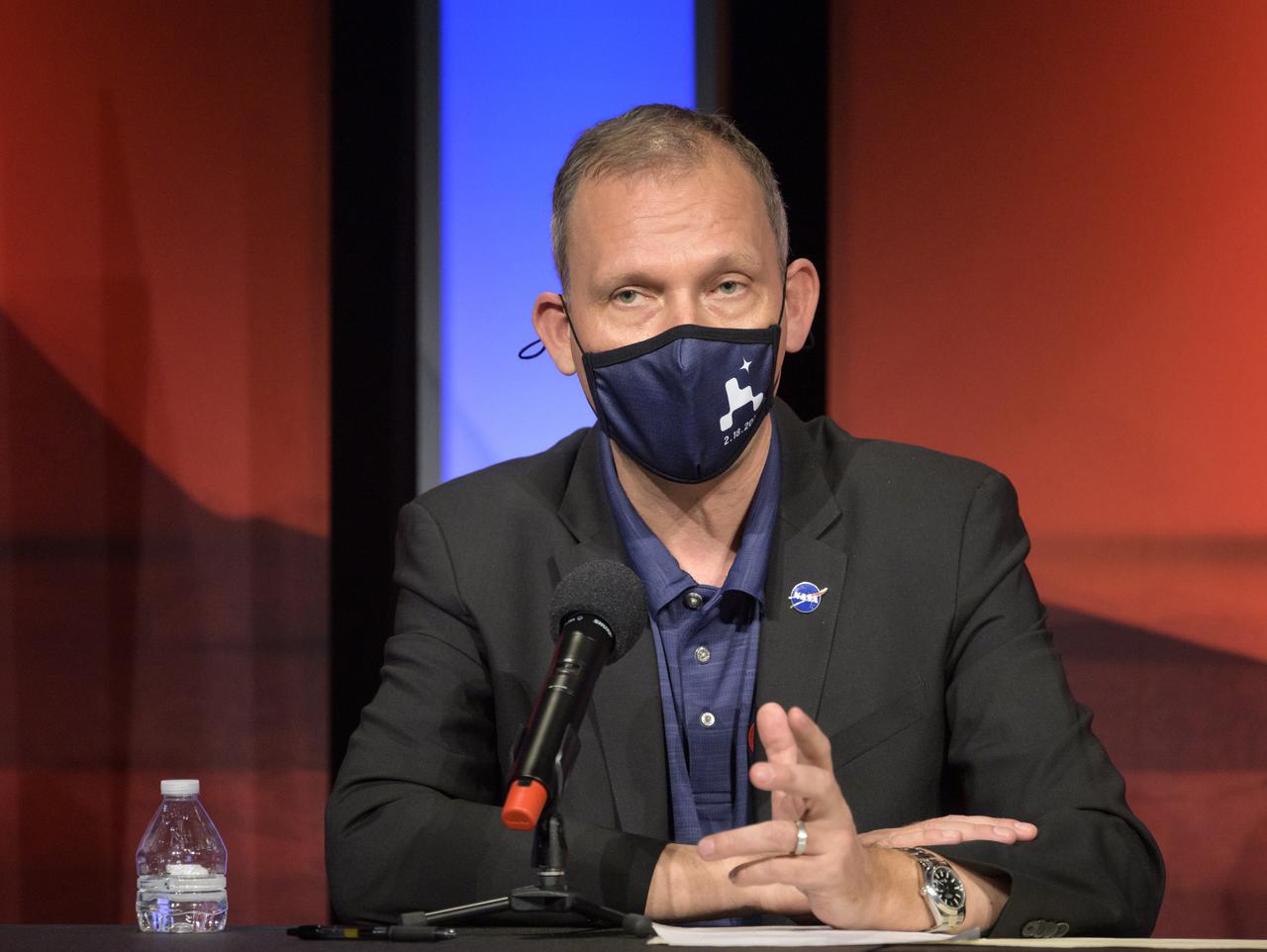

Associate Administrator of NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
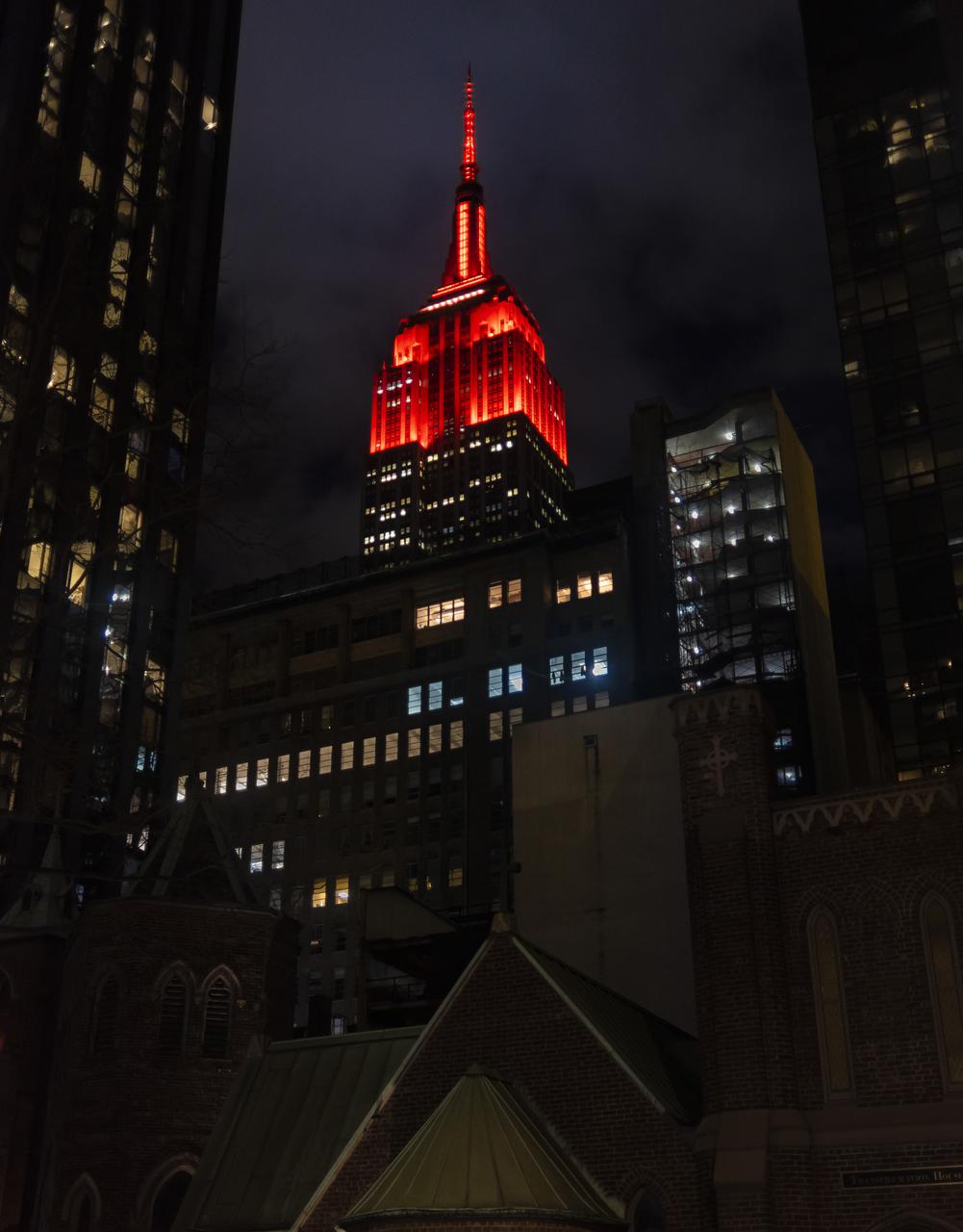

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)

A sandhill crane explores a paved parking area near the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 24, 2021. Kennedy shares space with the Merritt Island National Wildlife refuge, which is home to more than 1,000 species of plants, 117 species of fish, 68 amphibians and reptiles, 330 birds, and 31 different mammals. The refuge provides a favorable environment for sandhill cranes as it contains shallow freshwater habitats for nesting, along with a variety of vegetation and prey to feed on.
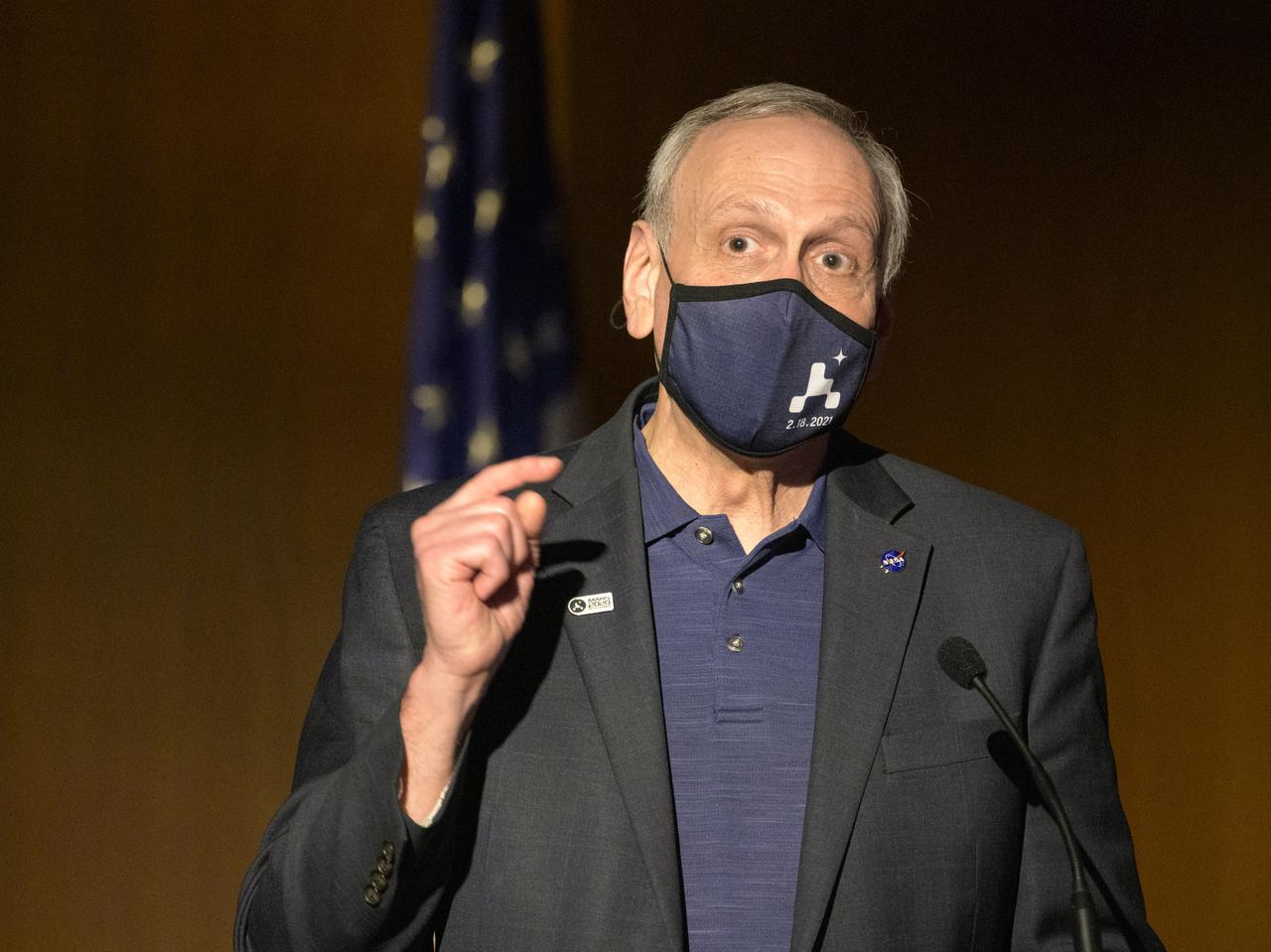

Acting NASA Administrator Steve Jurczyk gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
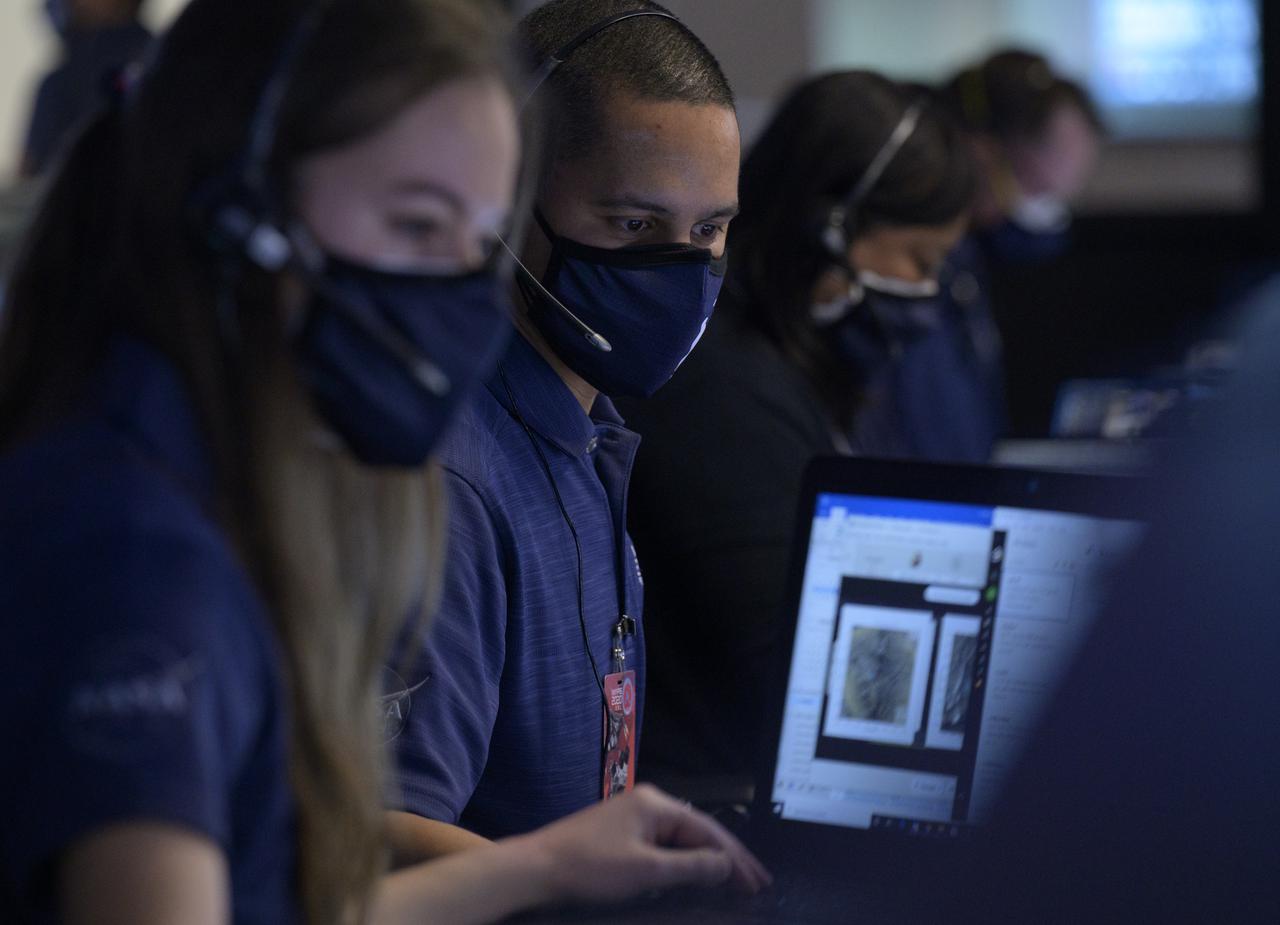

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
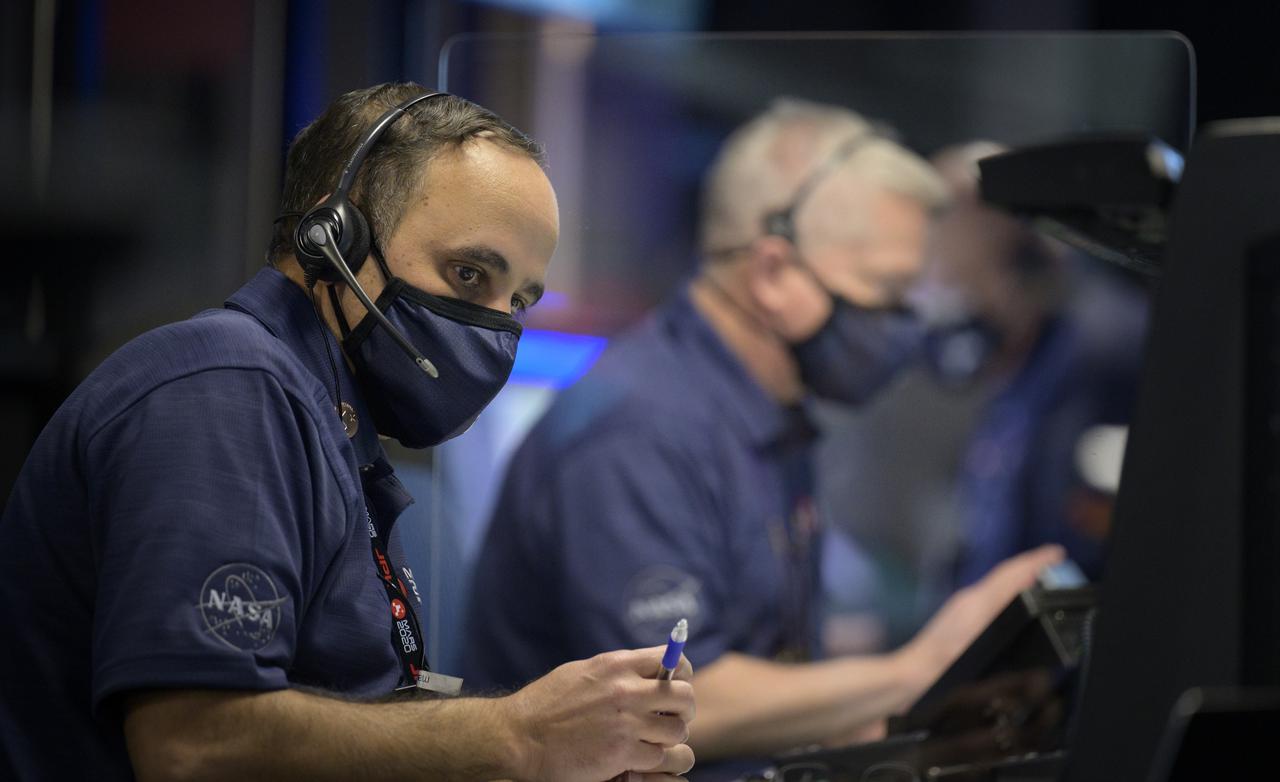

Perseverance flight director Magdy Bareh and other members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
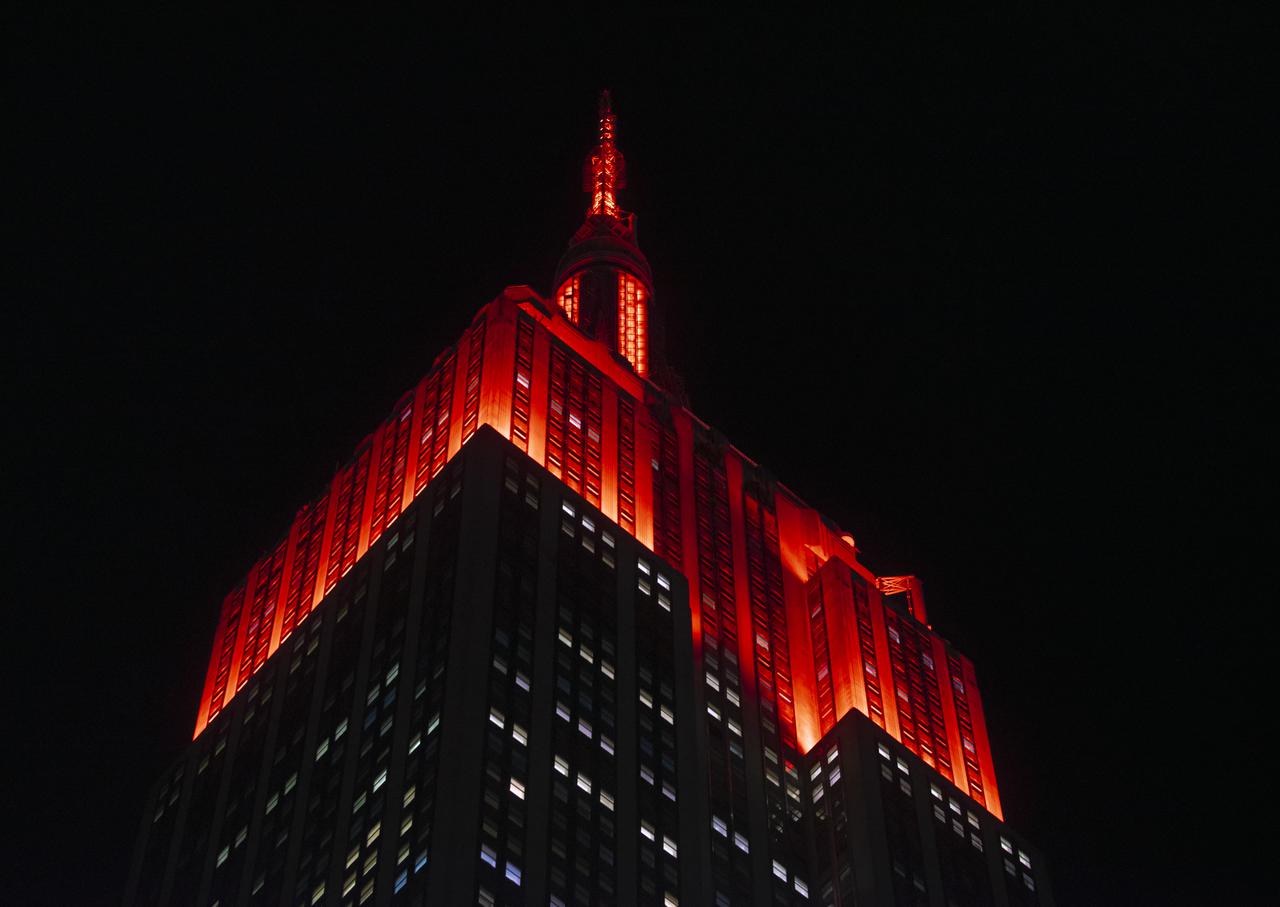

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
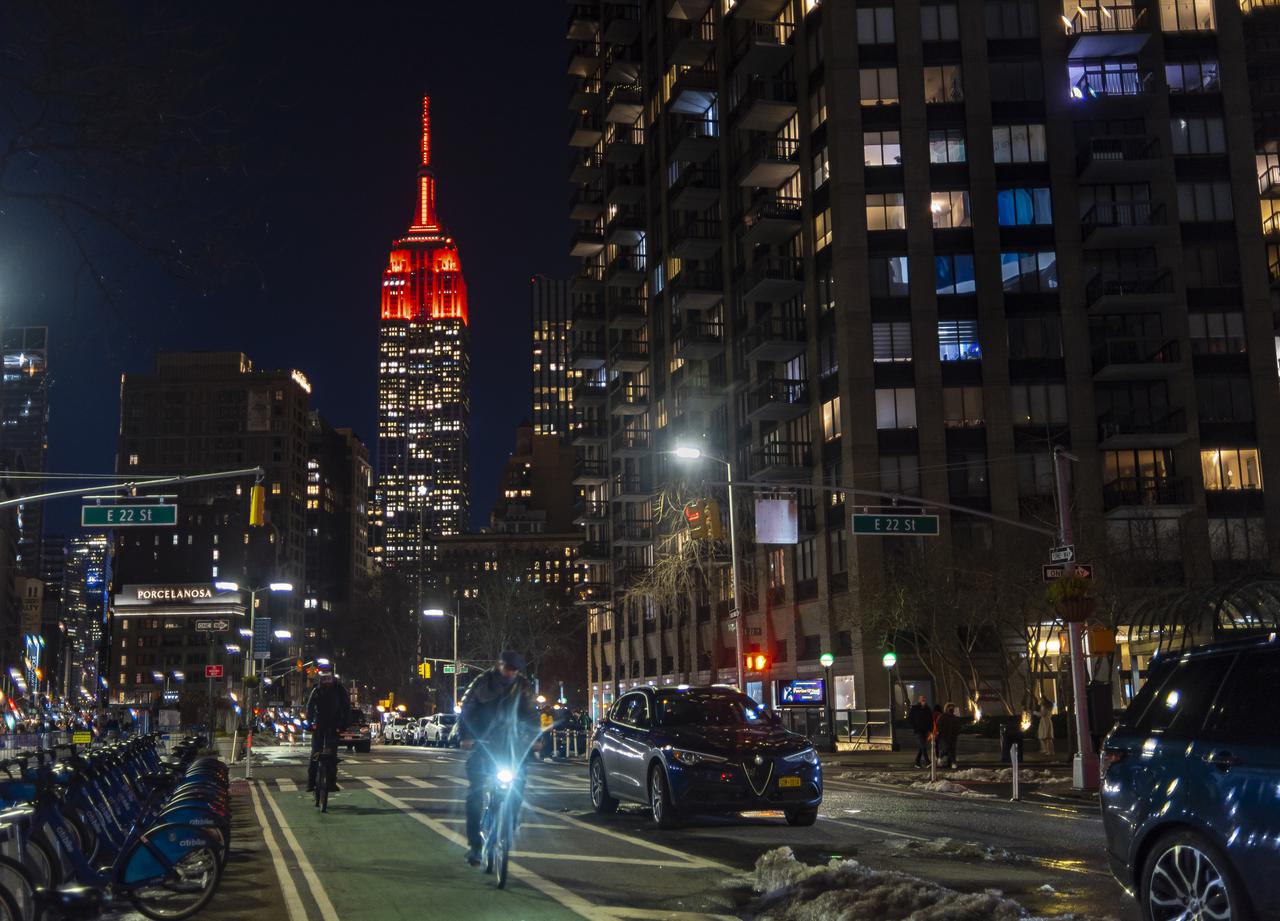

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
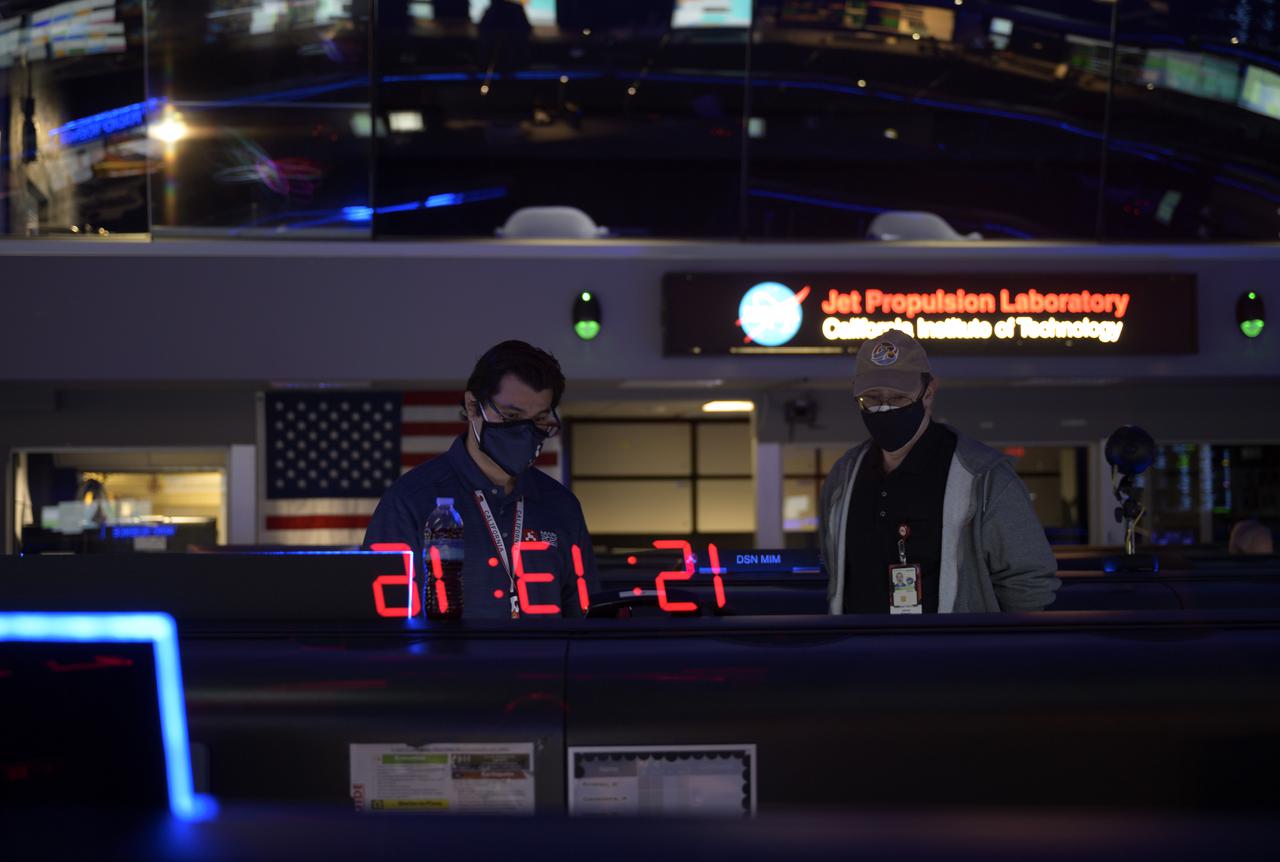

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
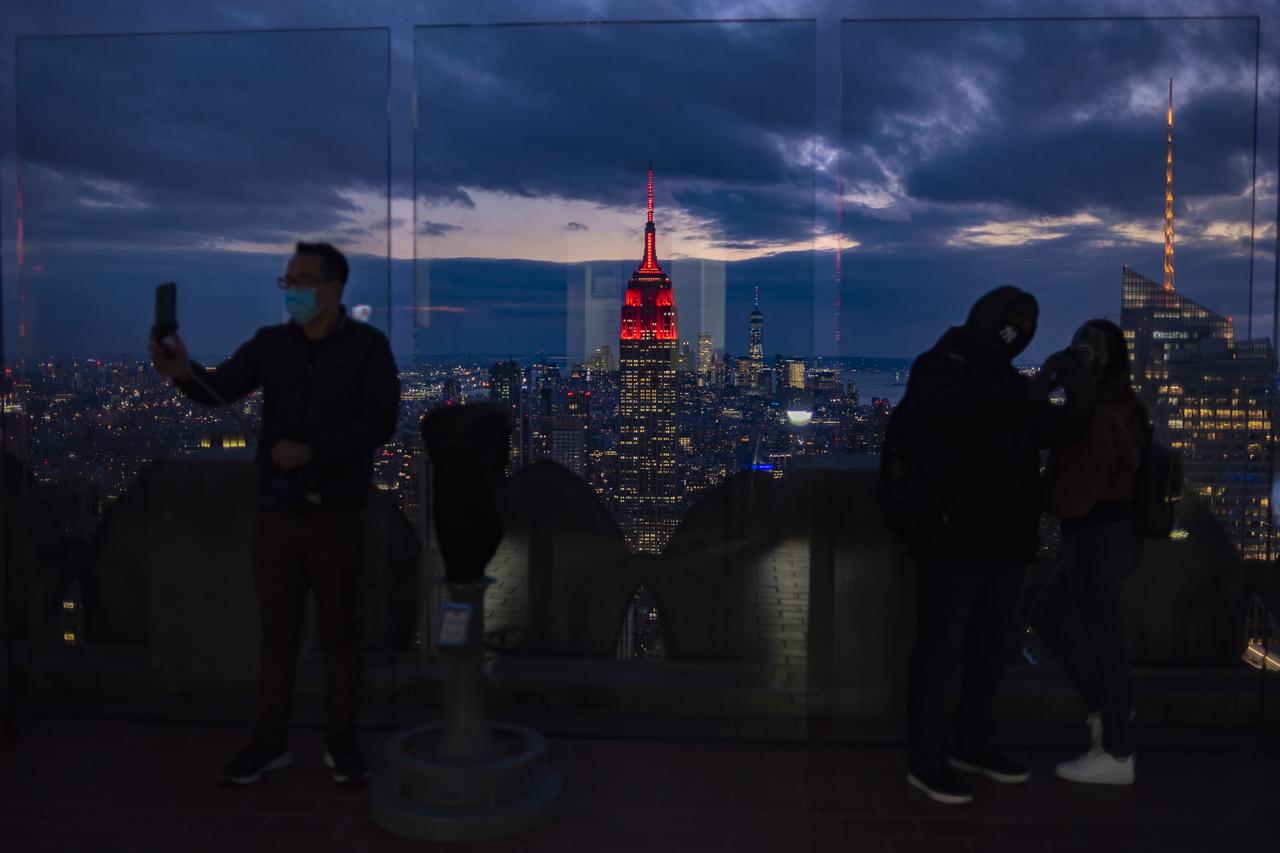

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
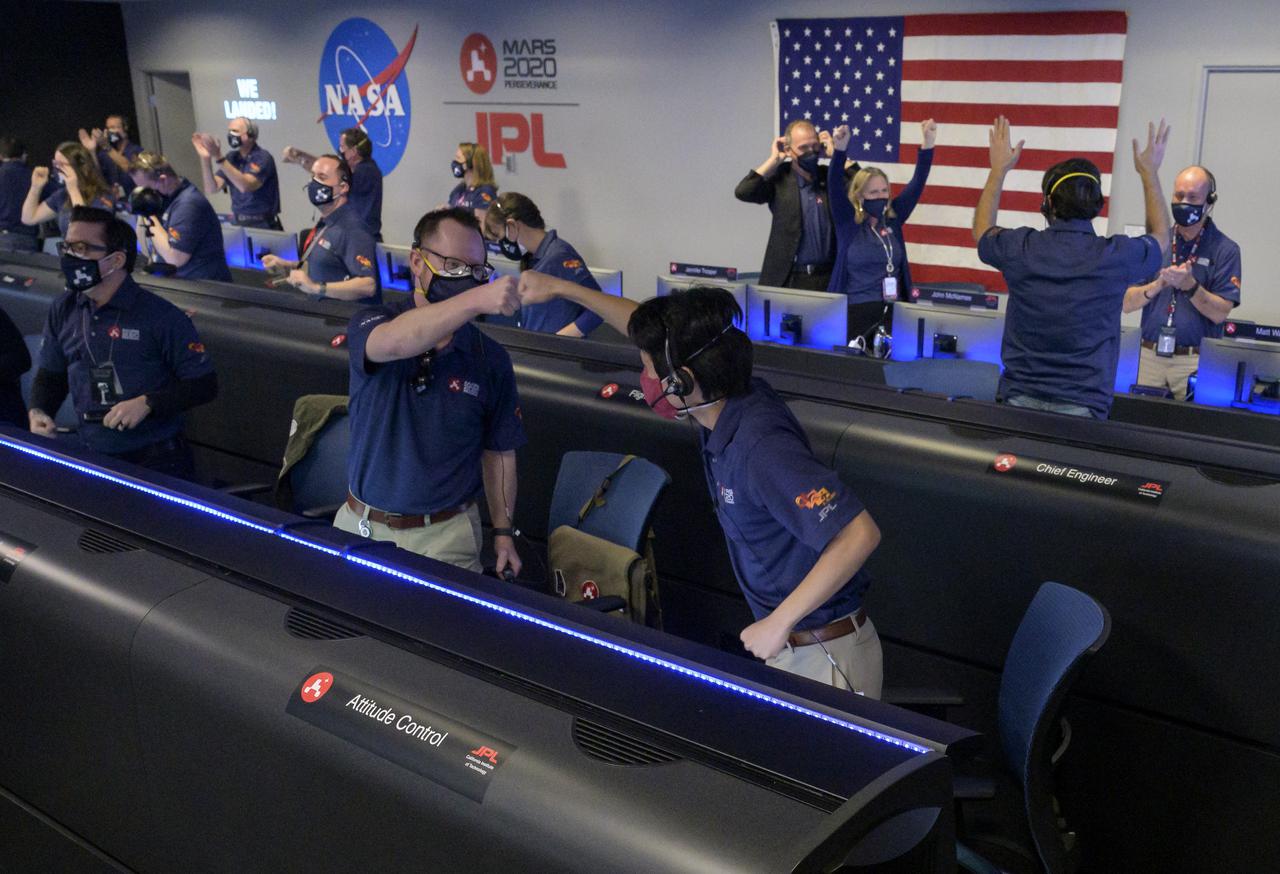

Members of NASA’s Perseverance rover team react in mission control after receiving confirmation the spacecraft successfully touched down on Mars, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
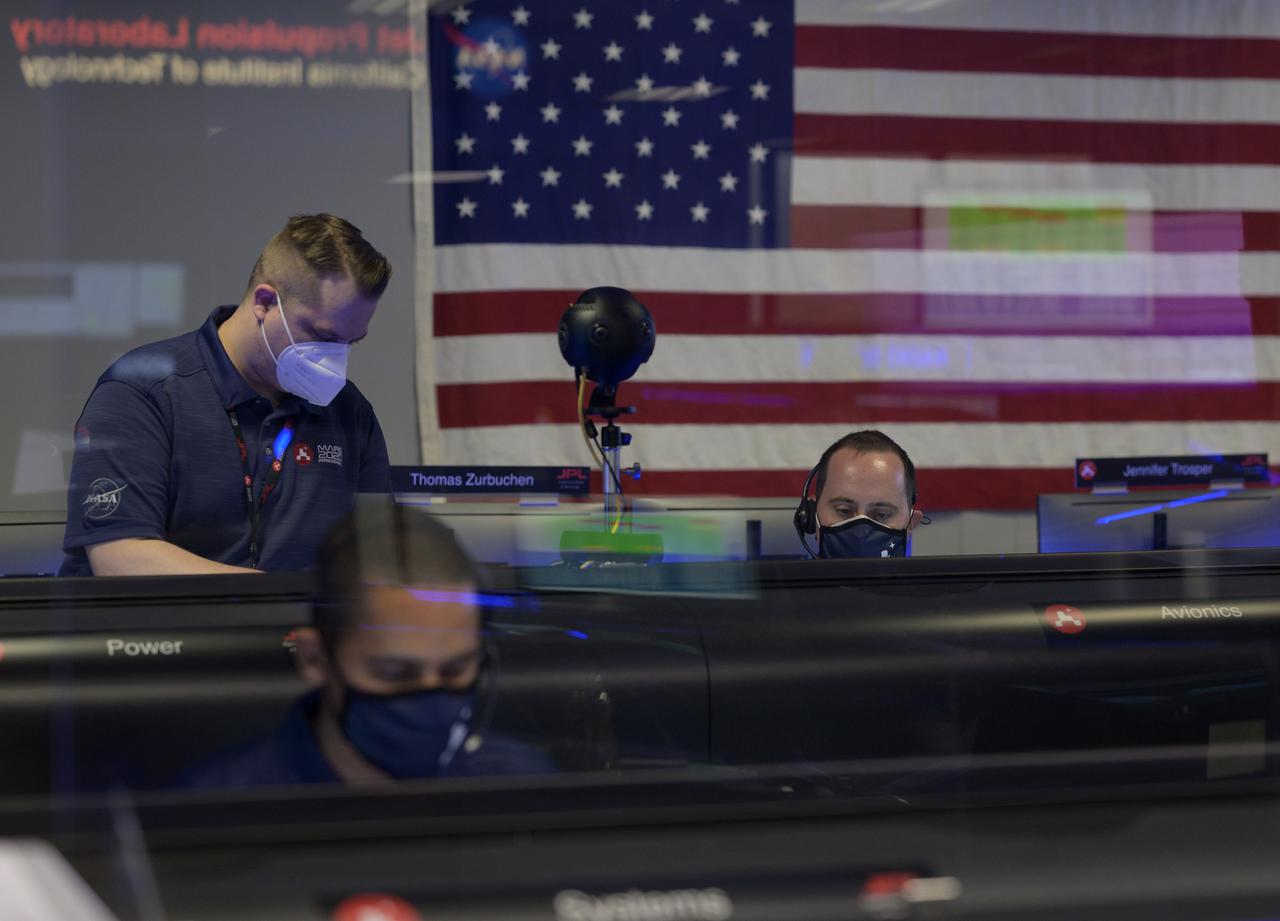

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
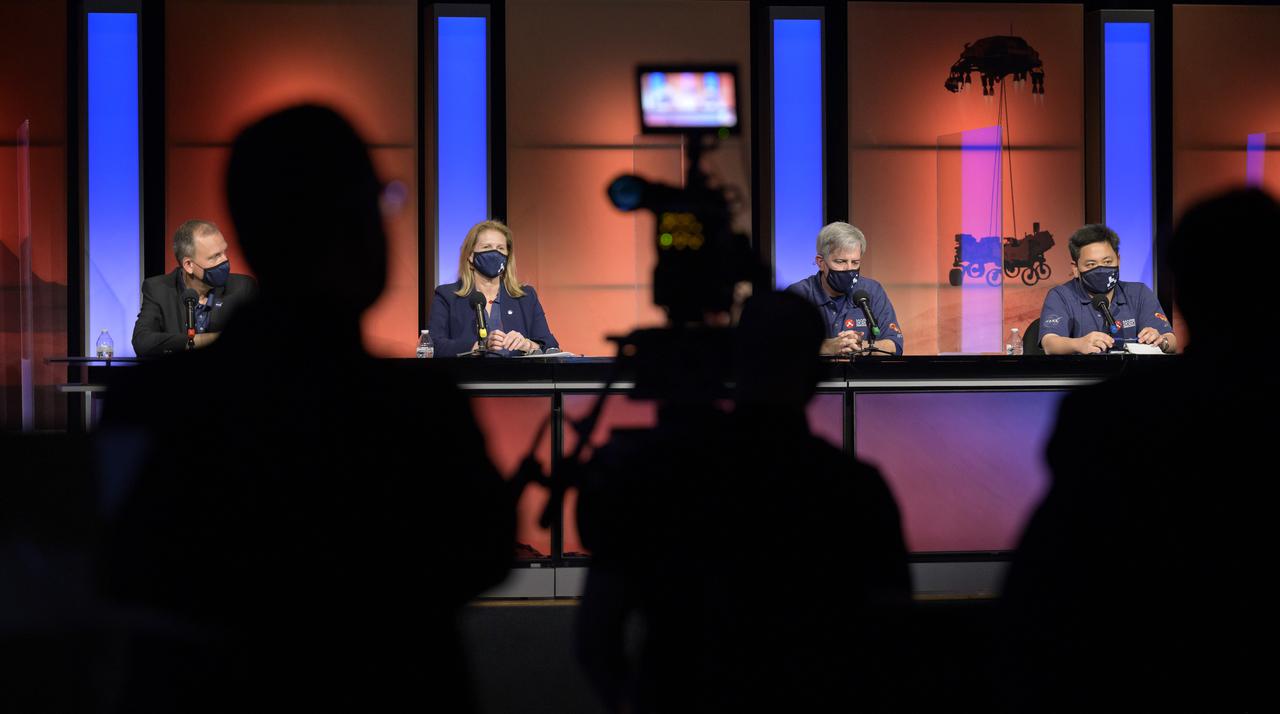

NASA Perseverance rover mission management and scientist celebrate a successful landing on Mars at the start of a post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
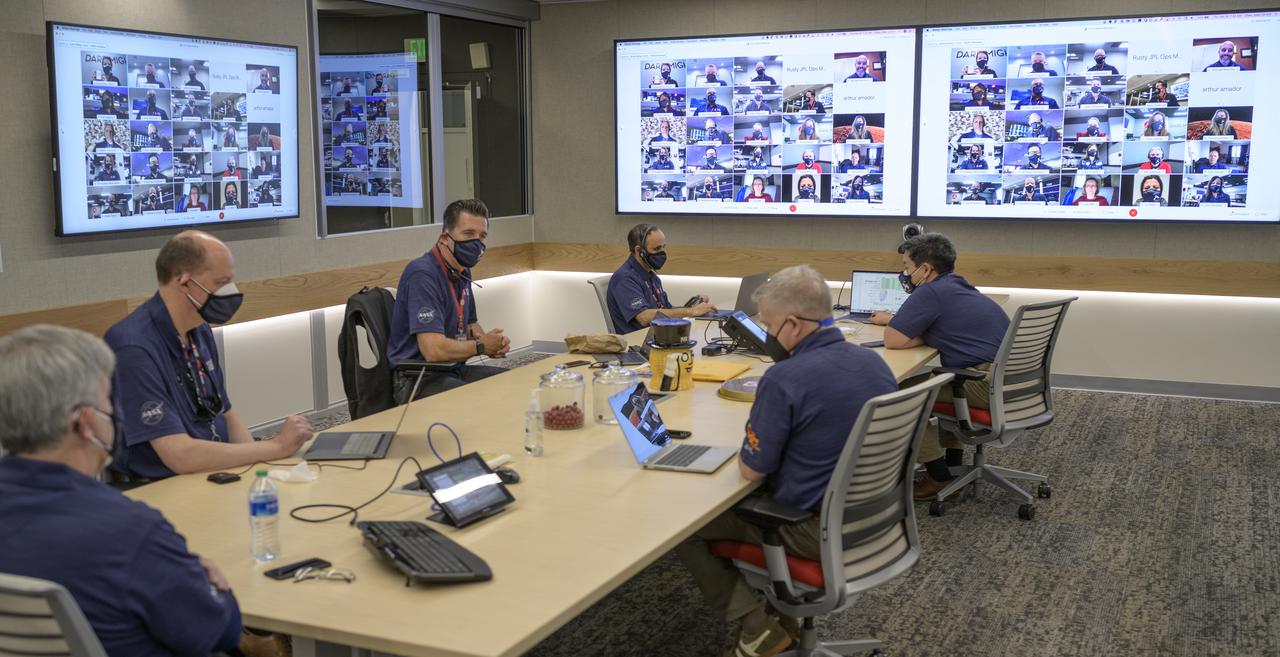

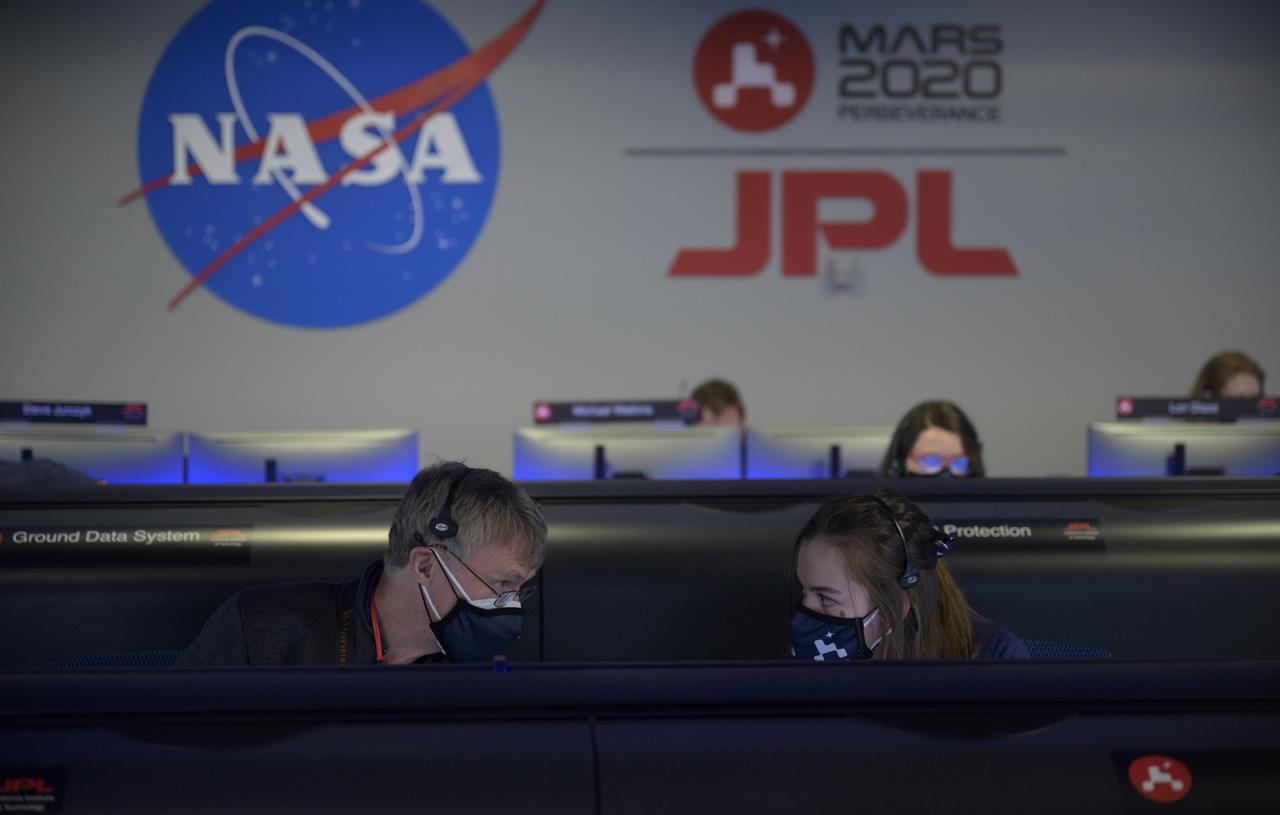
Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover management team meet via remote and in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
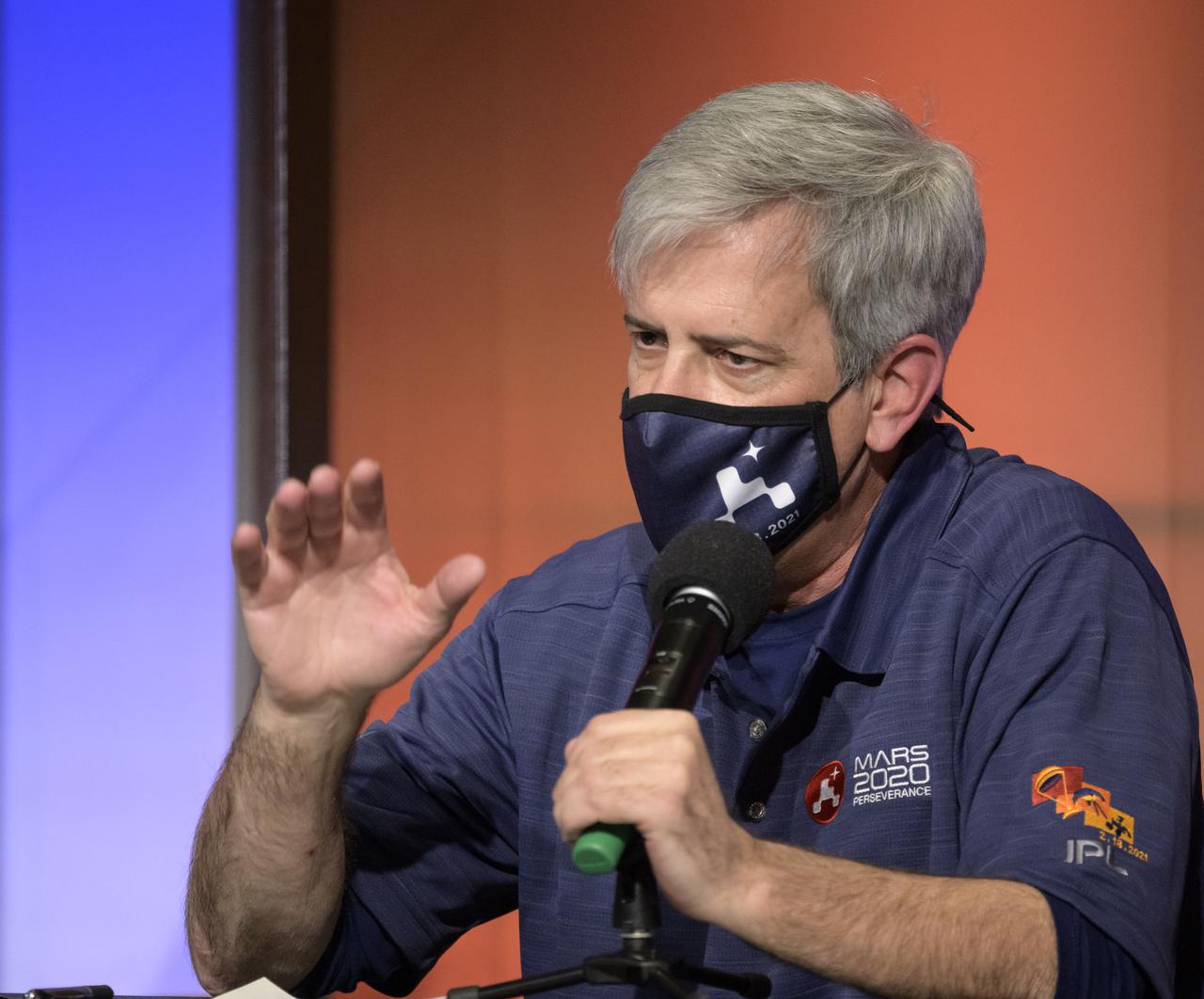

Mars 2020 Deputy Project Manager Matt Wallace, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams at Kennedy Space Center in Florida transported the fourth core stage engine section from the spaceport’s Space Systems Processing Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building in August 2025. The flight hardware will remain in the facility’s transfer aisle until teams lift the section into High Bay 2 for assembly and integration with the remaining core stage elements. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.
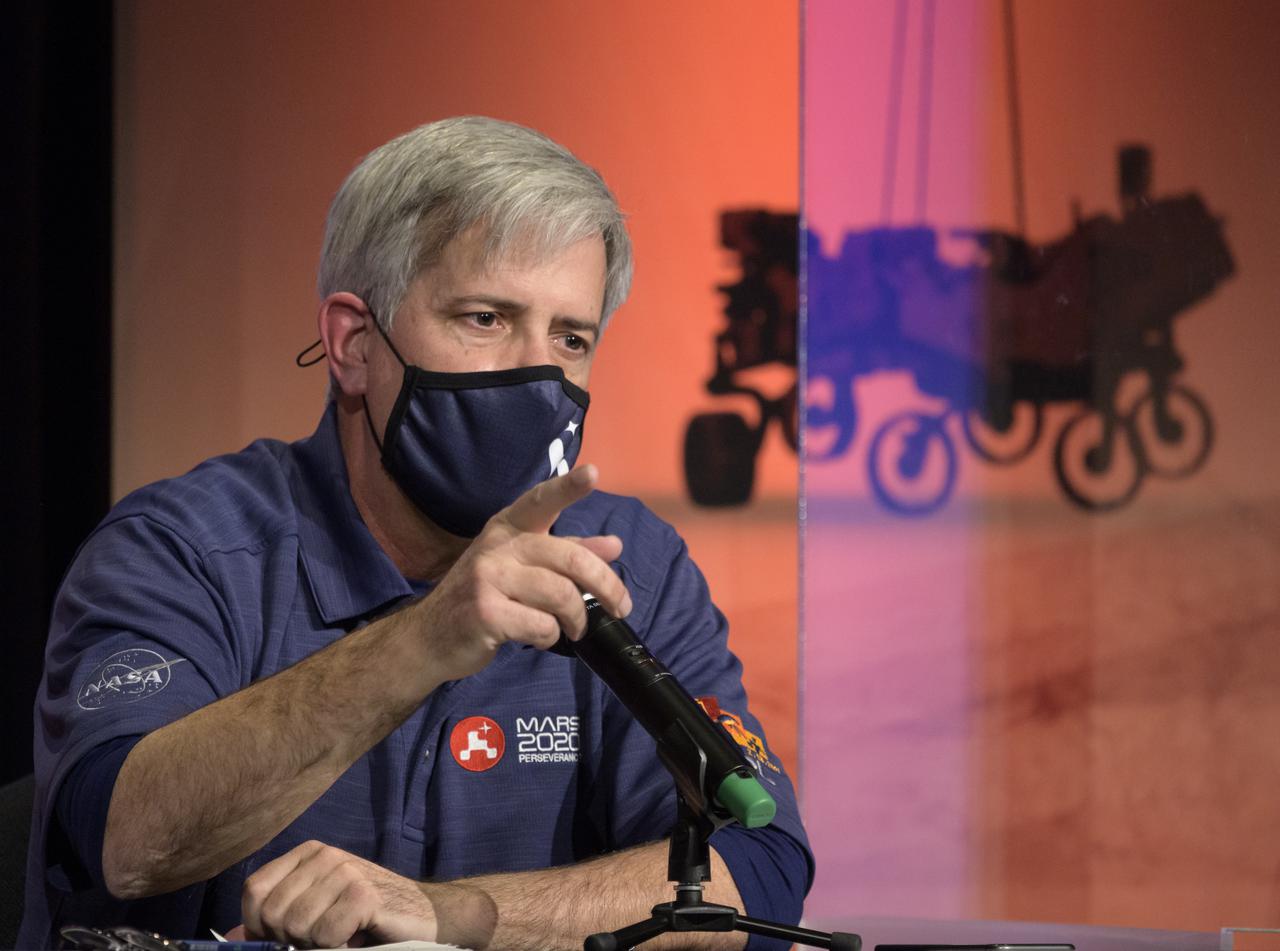

Mars 2020 Deputy Project Manager Matt Wallace, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
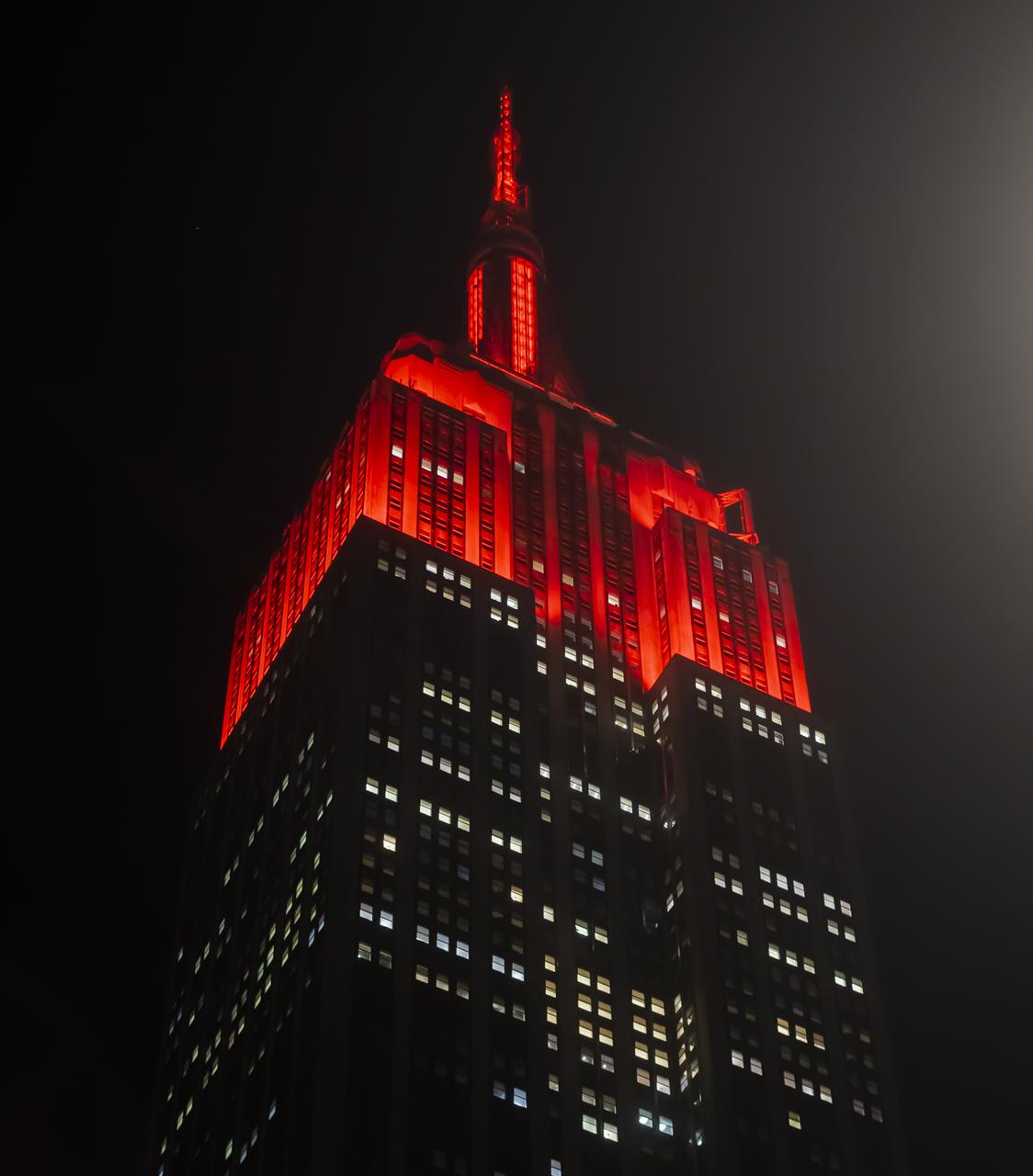

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
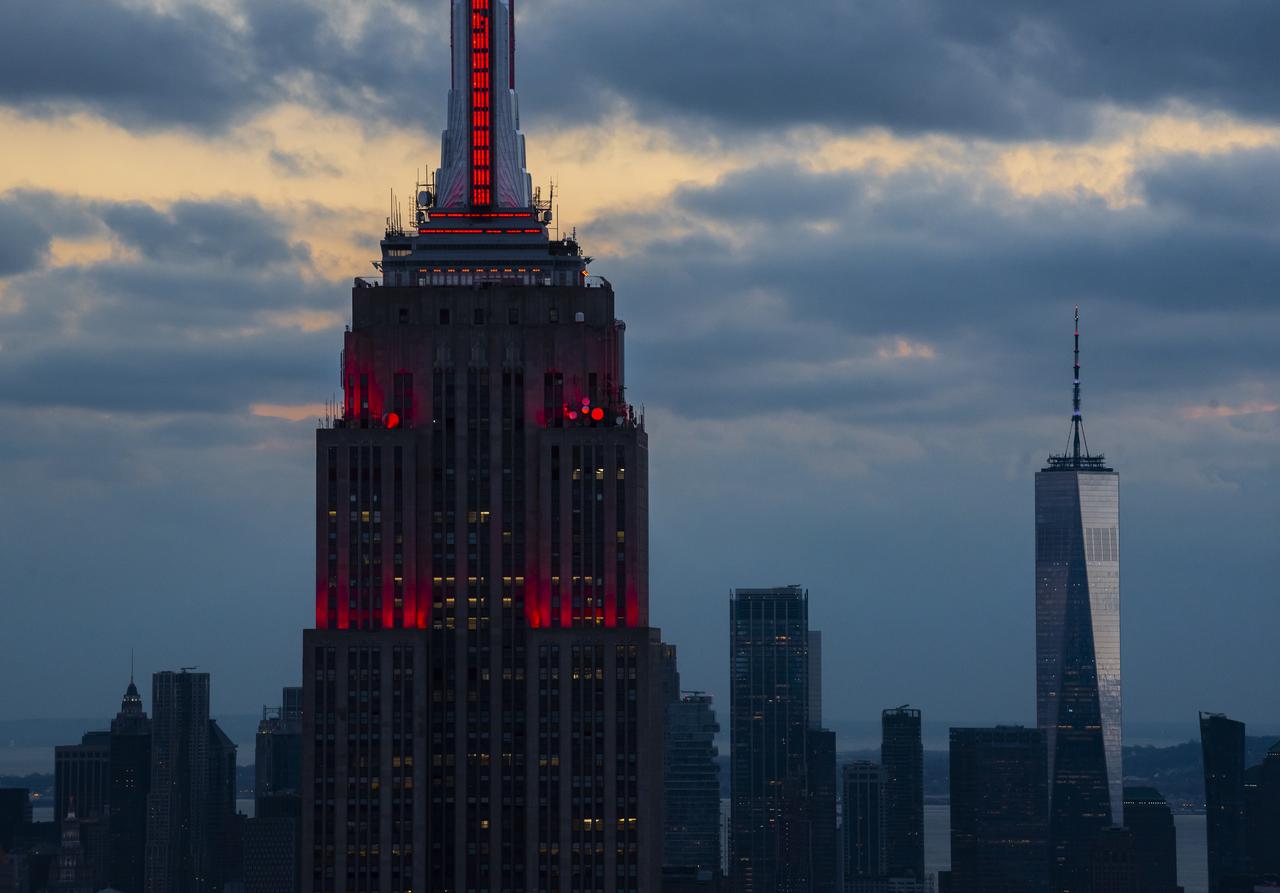

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)

A view of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, during sunrise on Jan. 19, 2022. Inside the VAB, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft are stacked in High Bay 3 in preparation for the agency’s Artemis I mission. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
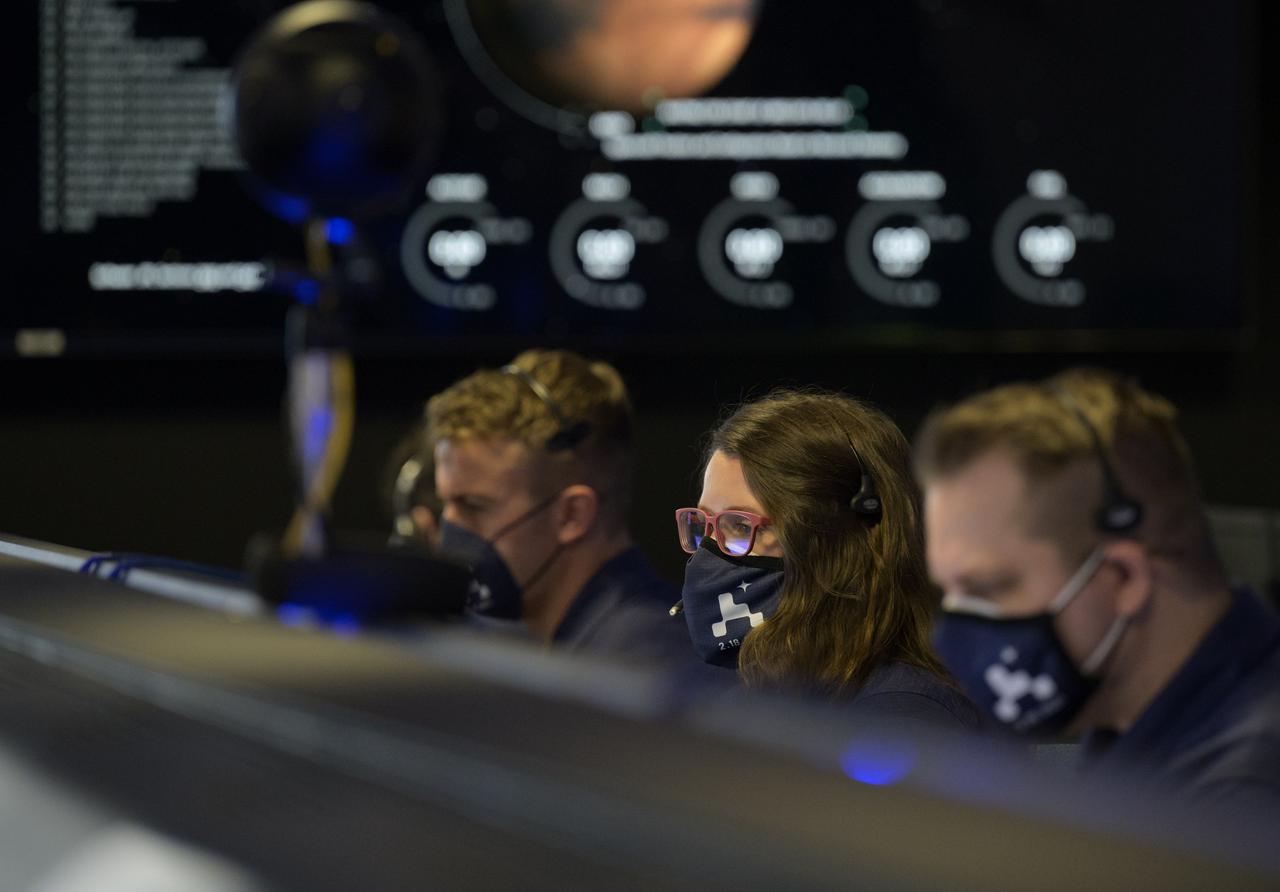

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

JPL Director Michael Watkins gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
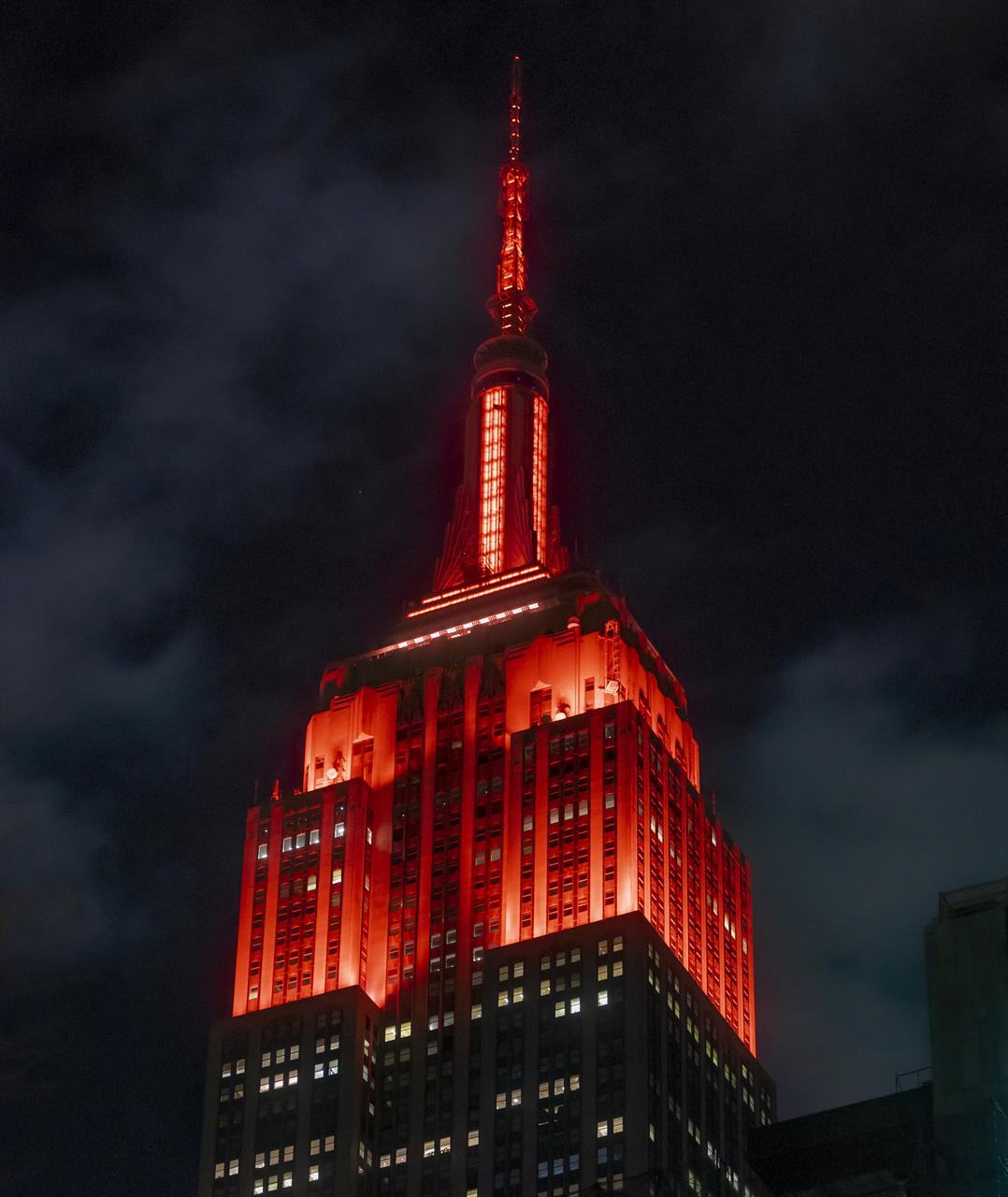

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)

A NASA Mars Rover Landing banner is seen on the Morgan Stanley video board as NASA's Perseverance rover begins its descent towards the surface of Mars, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
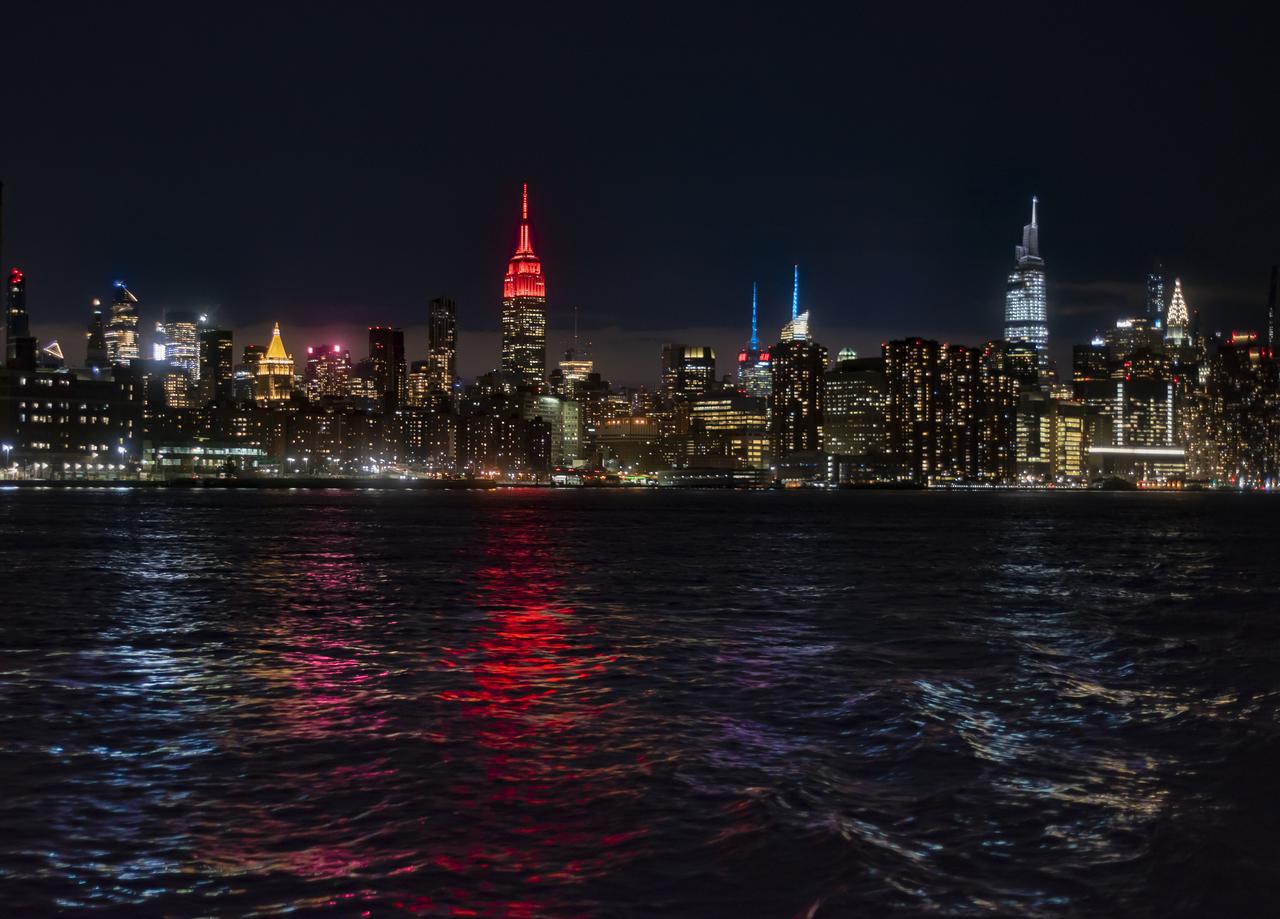

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)

Perseverance entry, descent, and landing phase lead Allen Chen, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
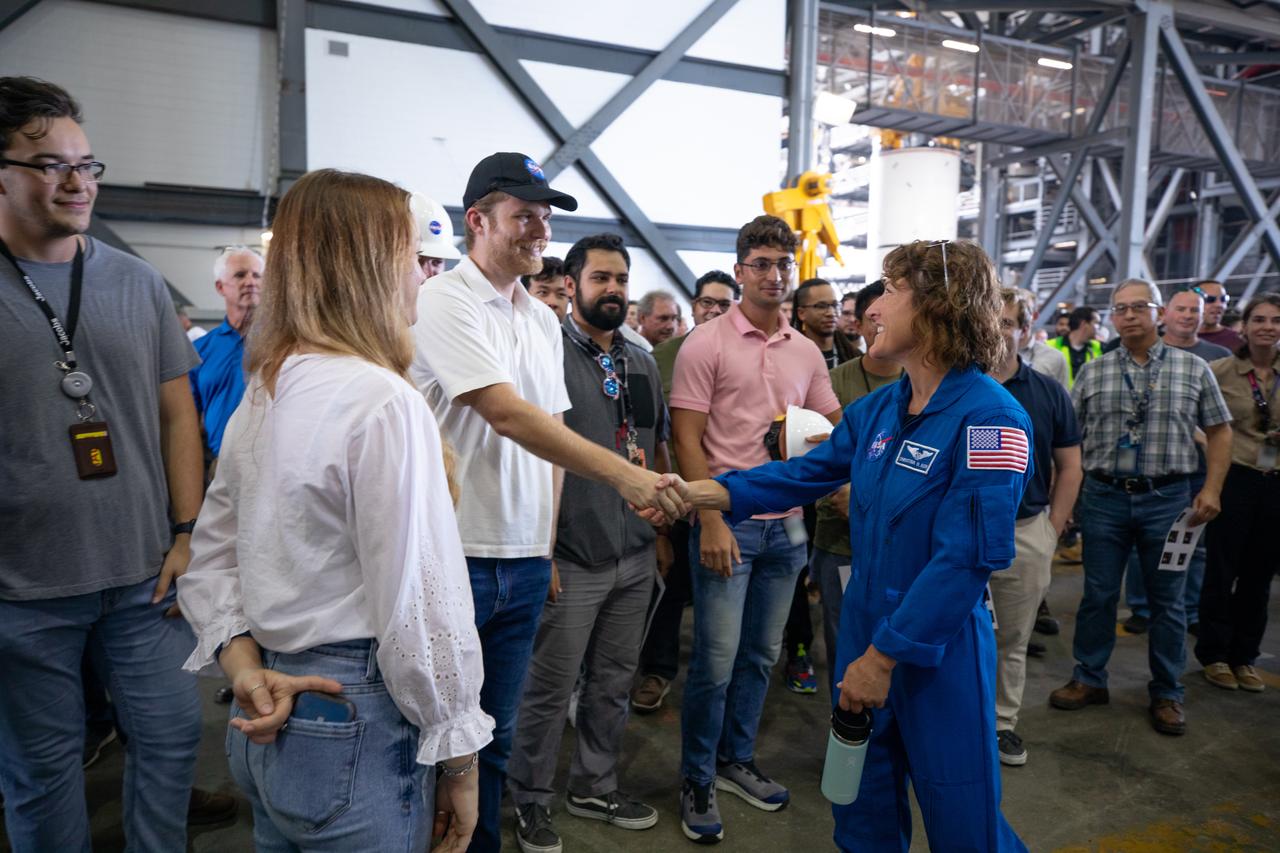

Artemis II NASA astronaut Christina Koch greets Exploration Ground Systems team members inside the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building during a visit to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 7, 2023. The approximately 10-day Artemis II flight will test NASA’s foundational human deep space exploration capabilities, the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, for the first time with astronauts and will pave the way for lunar surface missions, including landing the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon.
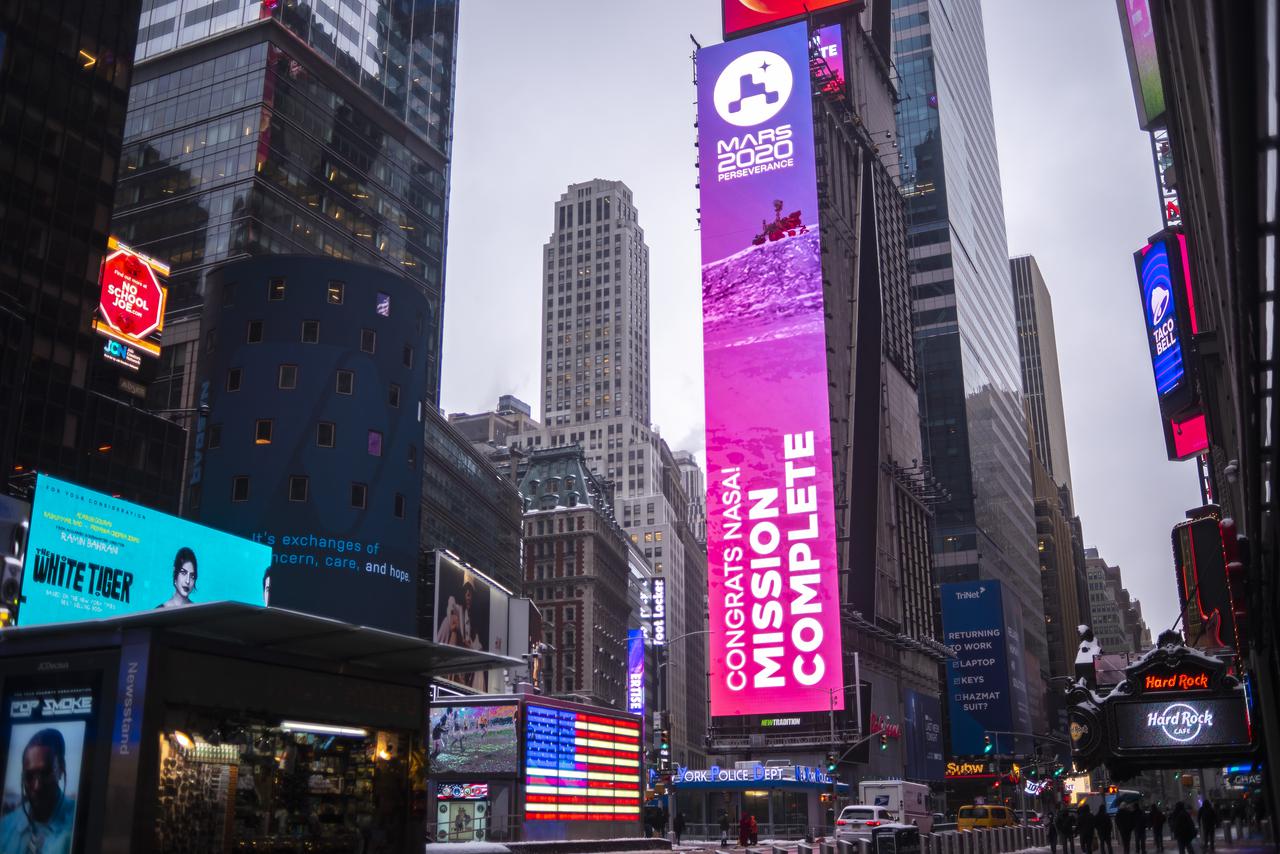

A NASA Mars Rover Landing banner is seen confirming the mission is complete on the One Times Square video board after NASA's Perseverance rover landed on the surface of Mars, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
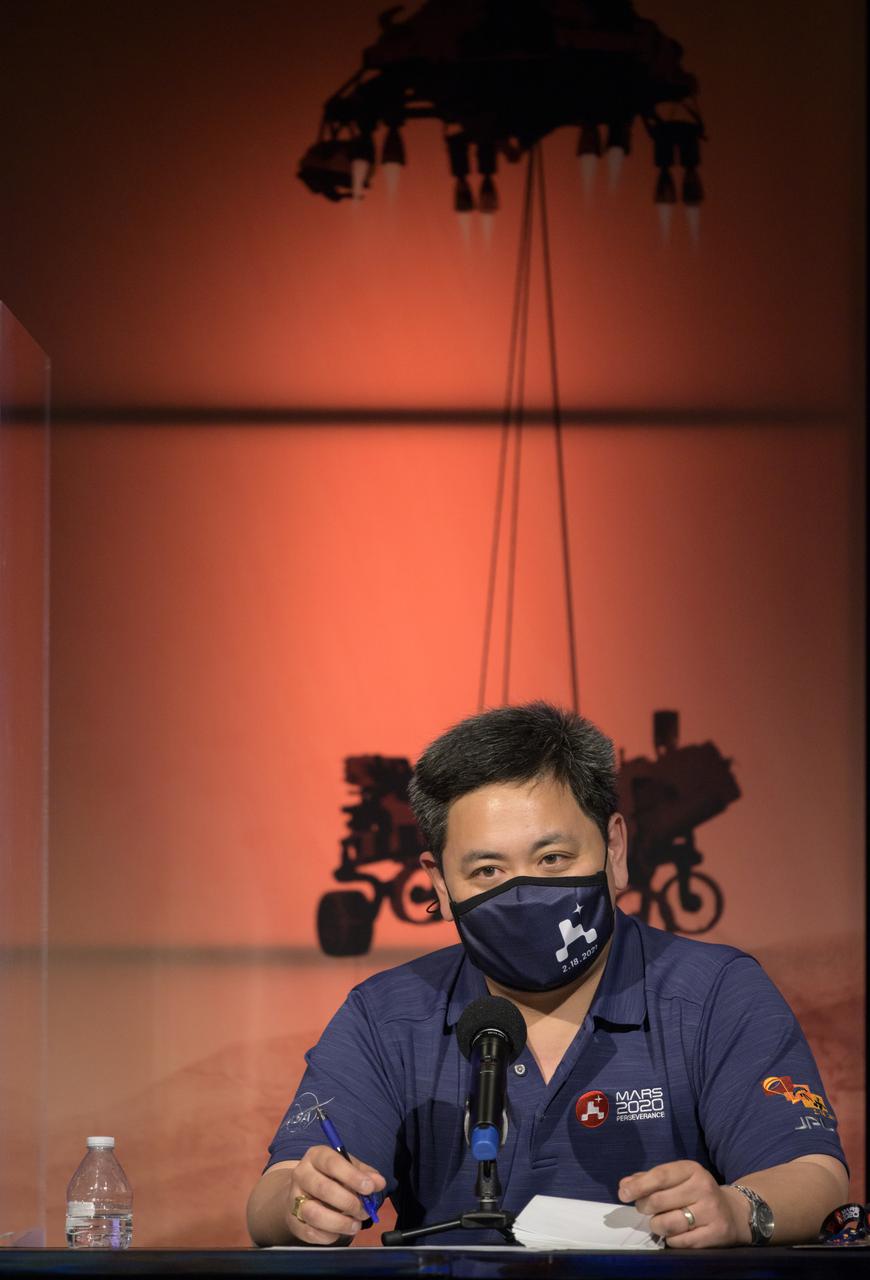

Perseverance entry, descent, and landing phase lead Allen Chen, gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
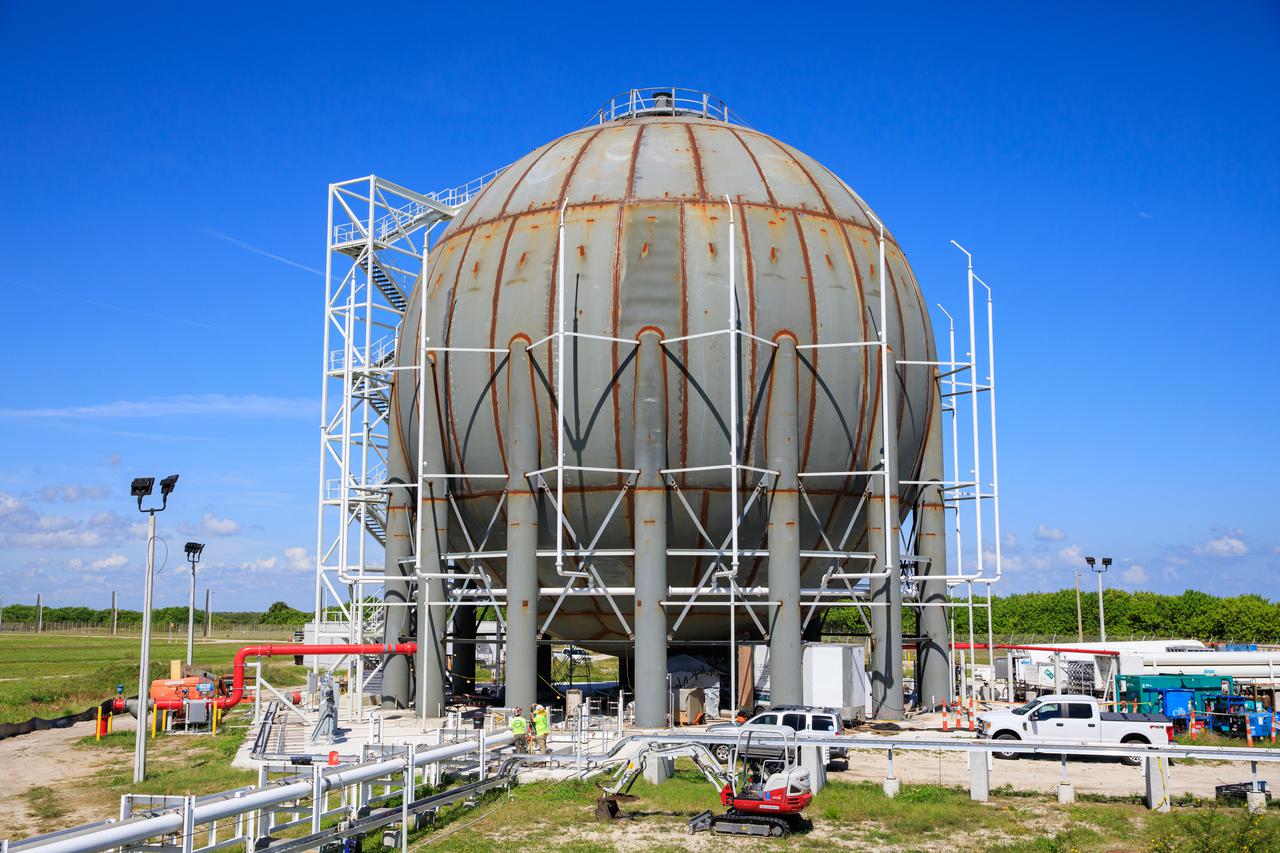

Seen here is a newly constructed liquid hydrogen (LH2) storage tank at Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 1, 2021. With construction now complete, teams will focus on painting the tank next. The storage tank, capable of holding 1.25 million gallons of LH2, will be used to support future Artemis missions to the Moon and, eventually, Mars. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, paving the way for a long-term presence in lunar orbit.
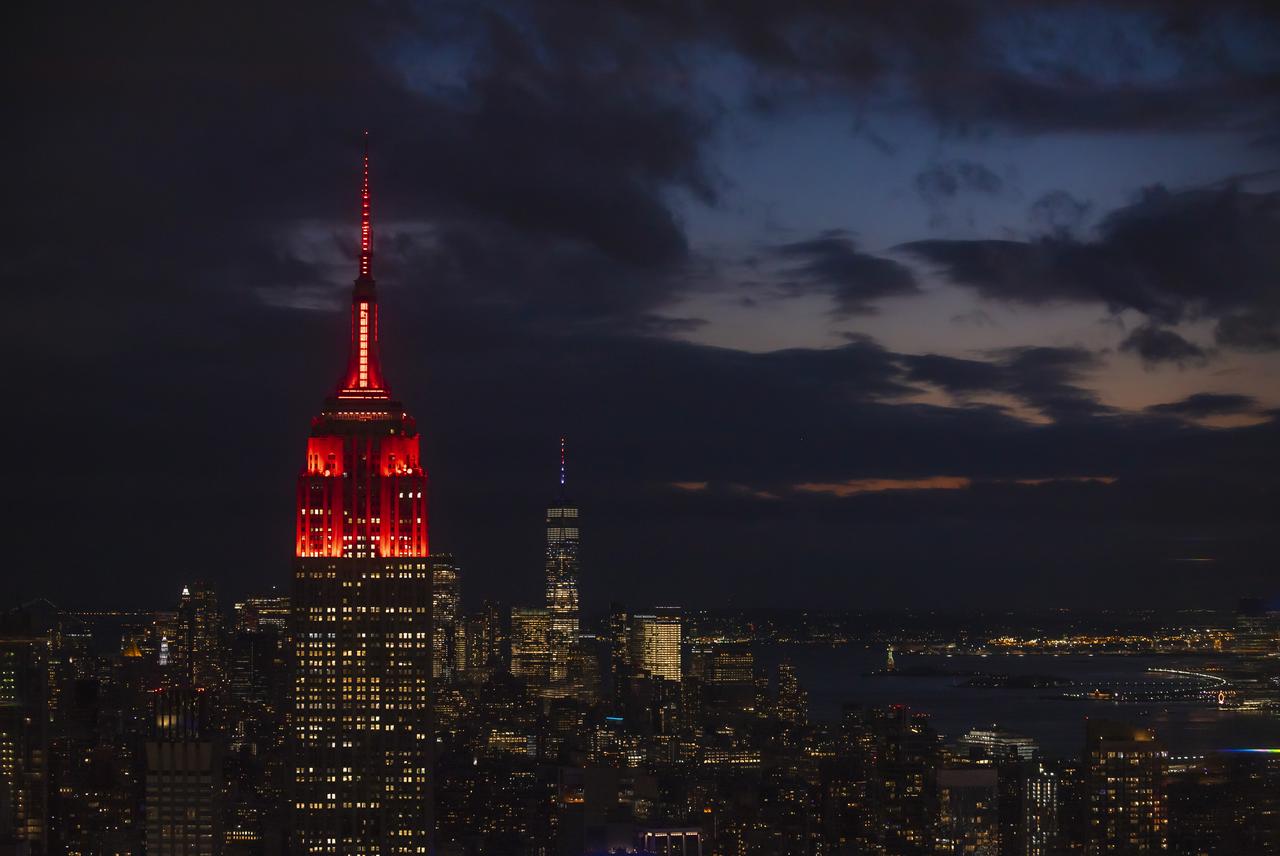

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)
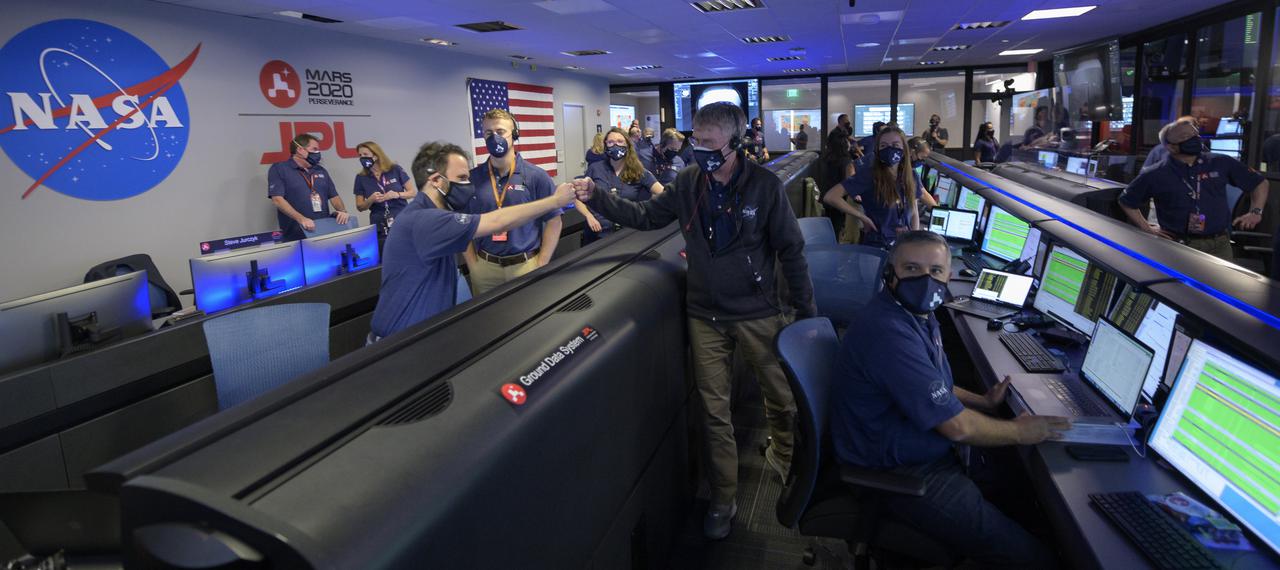

Members of NASA’s Perseverance rover team react in mission control after receiving confirmation the spacecraft successfully touched down on Mars, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
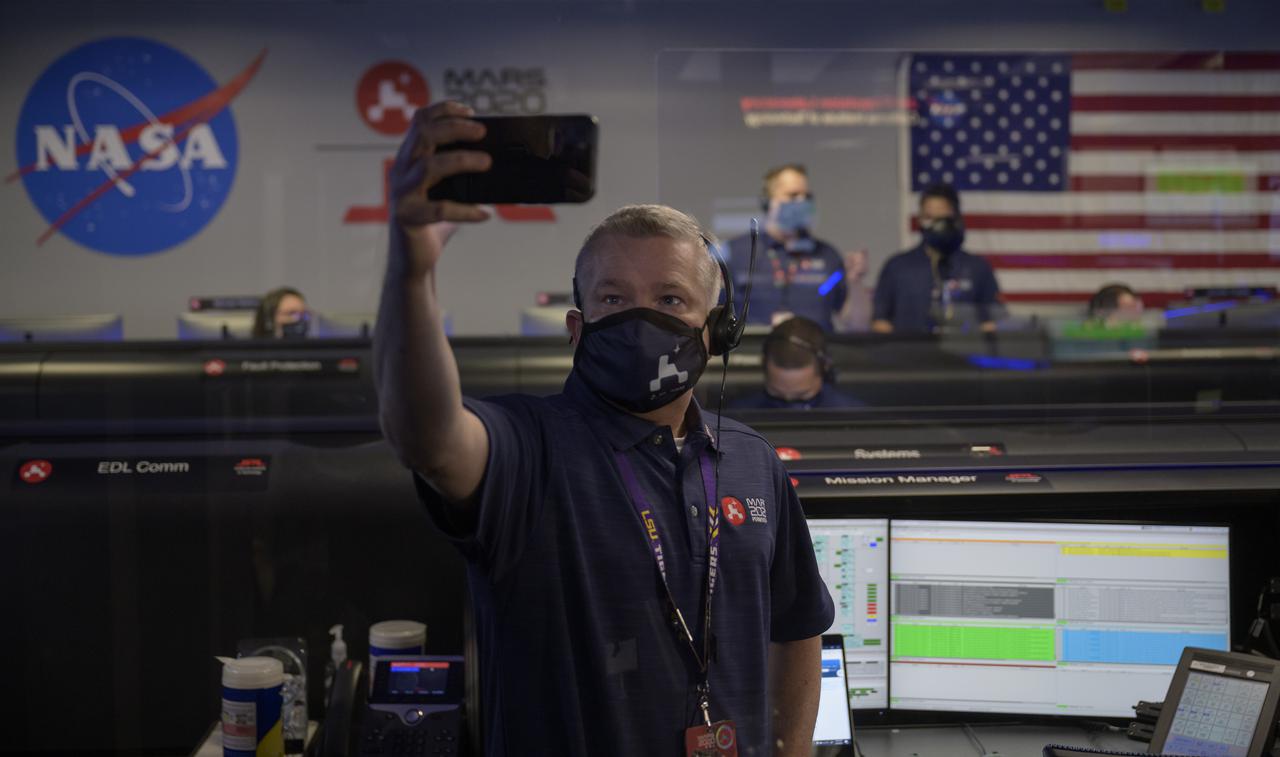

Perseverance mission manager Keith Comeaux takes a selfie as the NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team begins to settle in to track landing in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
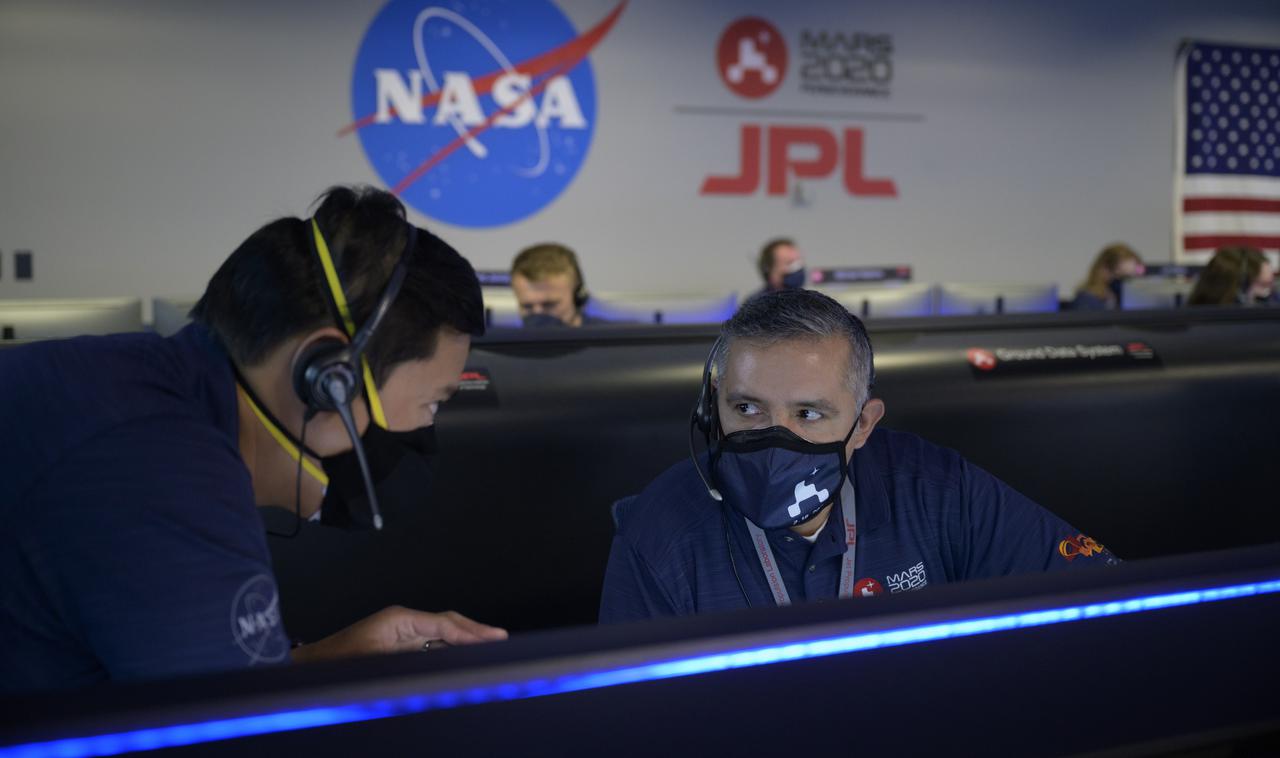

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team confer and study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
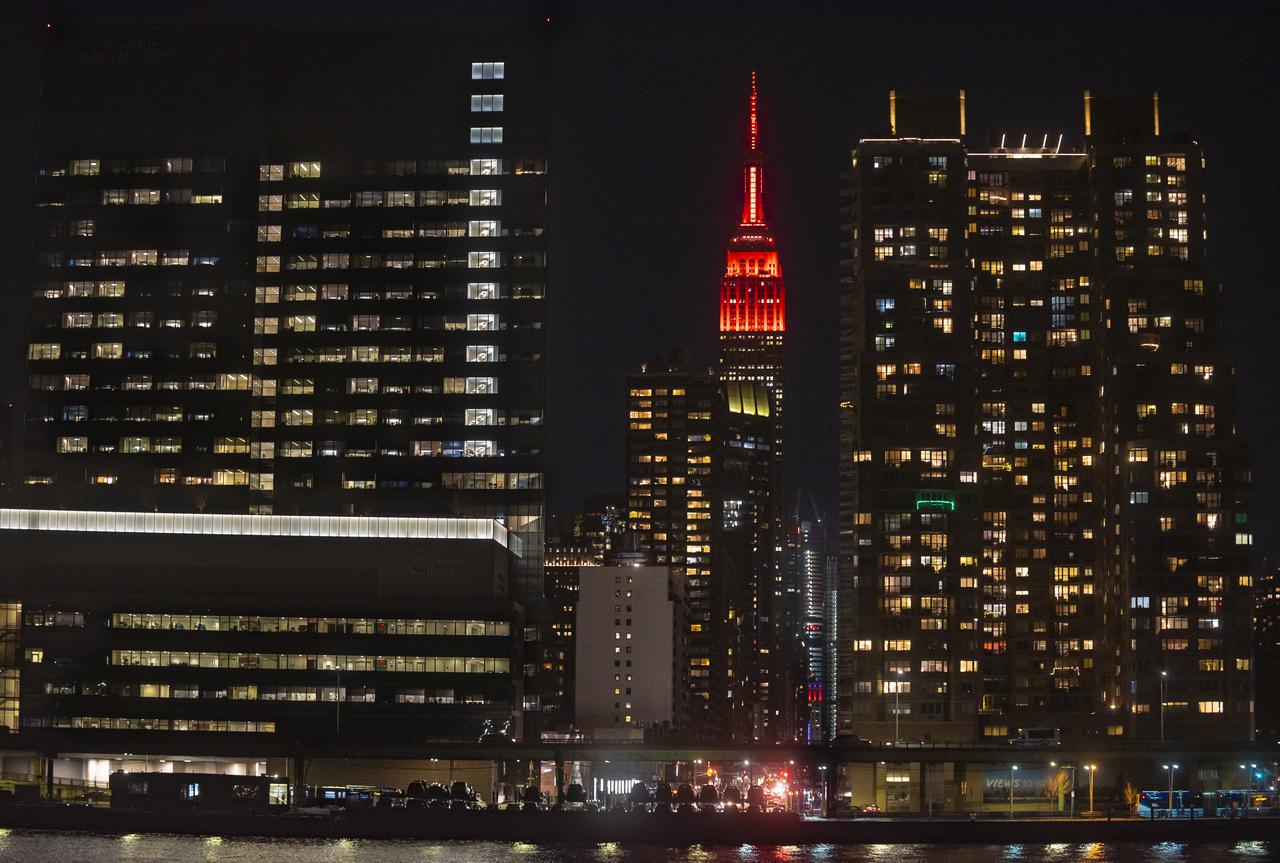

The Empire State Building is illuminated in red to celebrate this Thursday's scheduled landing on Mars of NASA's Perseverance rover, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021 in New York City. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emma Howells)

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team are seen reflected in a monitor in mission control as they await the spacecraft’s landing on Mars, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
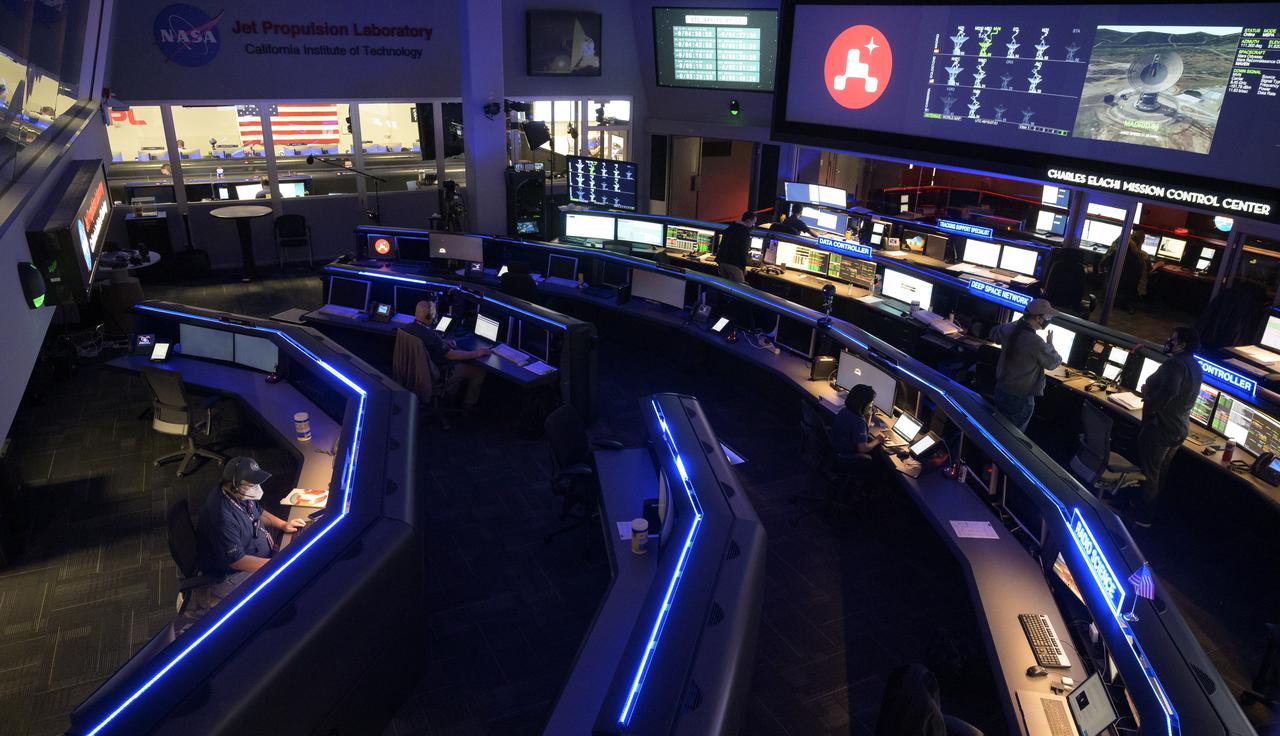

Members of NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover team study data on monitors in mission control, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
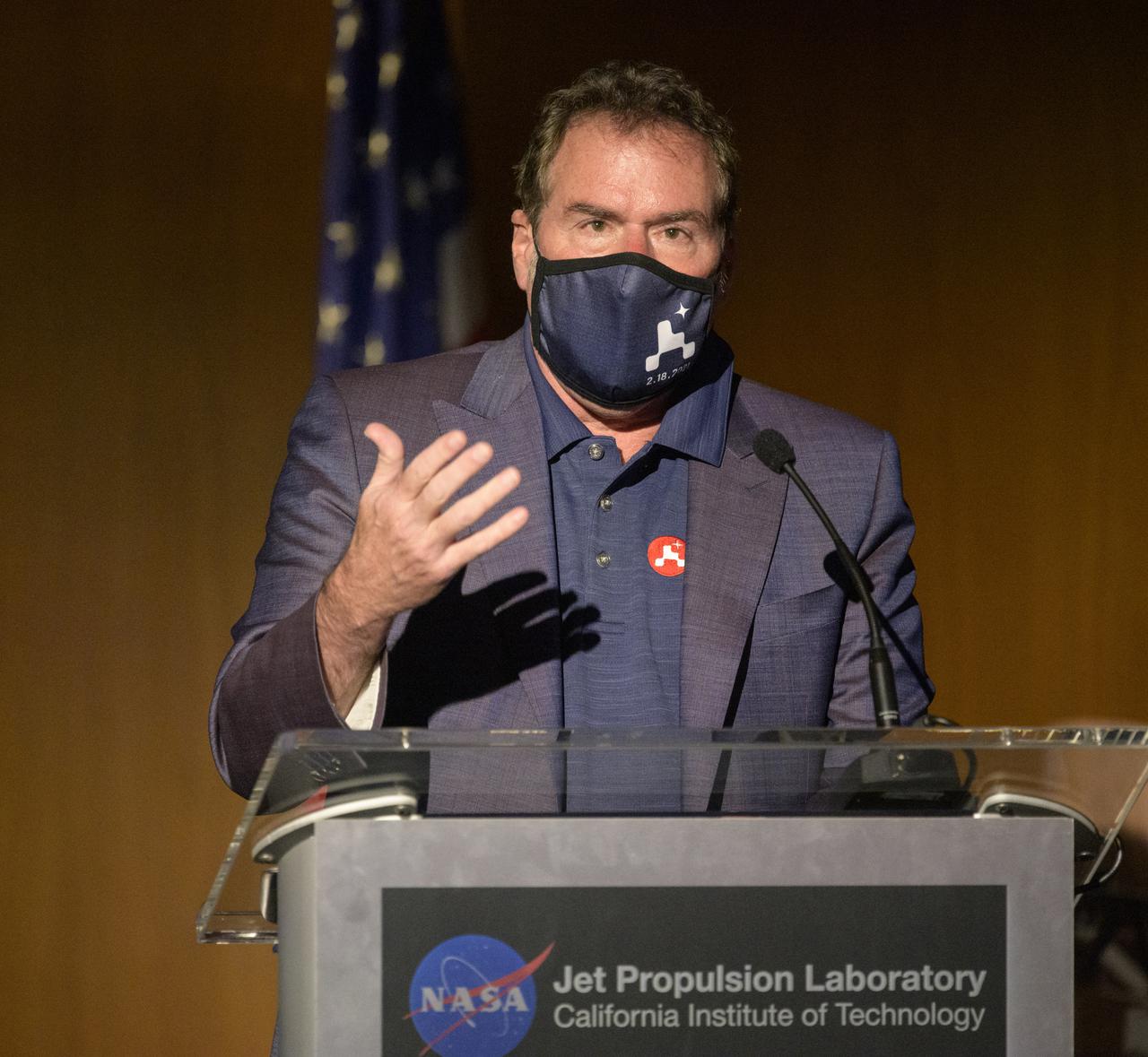

JPL Director Michael Watkins gives remarks during a NASA Perseverance rover mission post-landing update, Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.
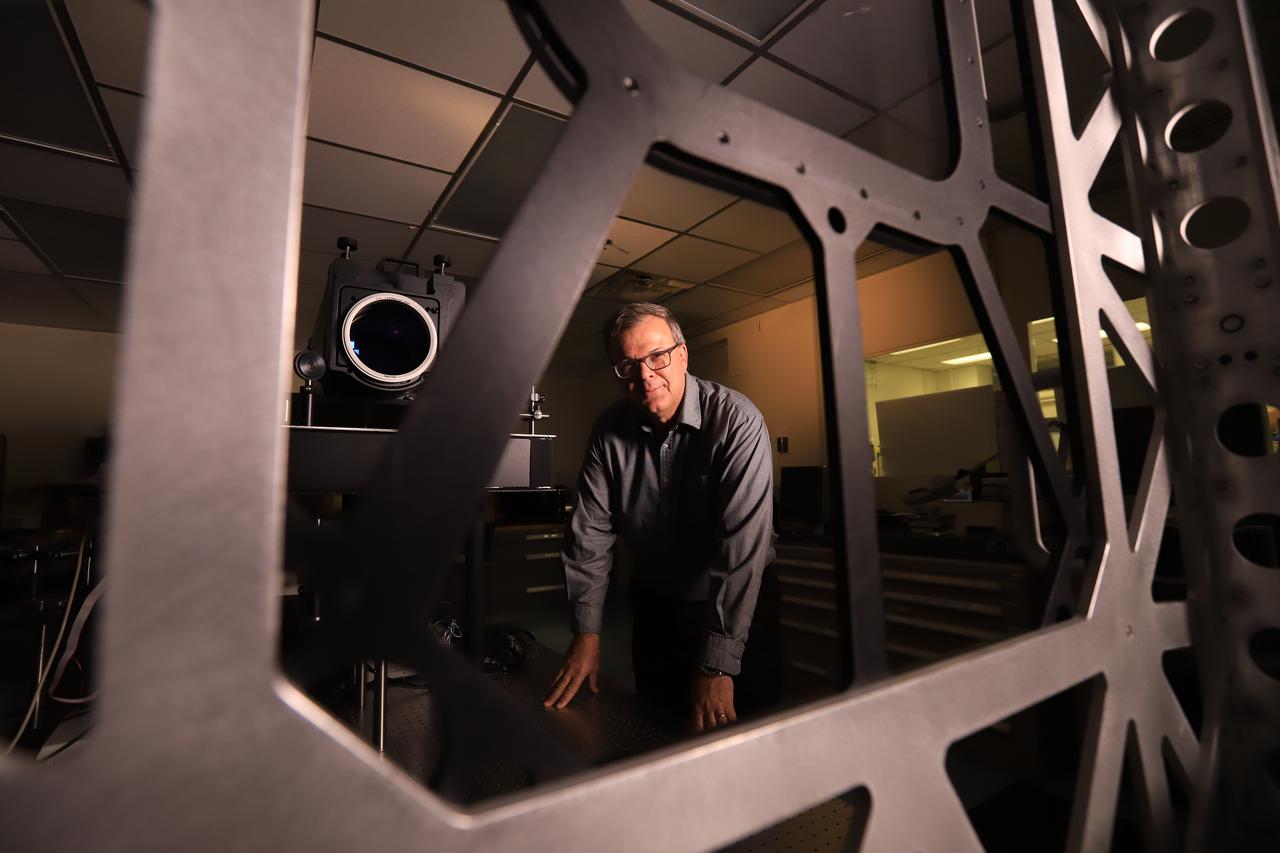
Mark Nurge, a physicist in Kennedy Space Center’s Applied Physics Lab, stands near a laser interferometer, which is used to determine if there are acceptable levels of distortion and imperfections in windows. Nurge recently completed optical metrology testing and evaluation of all flight windows on the Orion capsule for Artemis 1. The interferometer uses a laser source to do wavefront and transmission measurements, as well as evaluation of the color balance. Artemis 1 is an uncrewed flight that will pave the way for future crewed missions and enable future missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
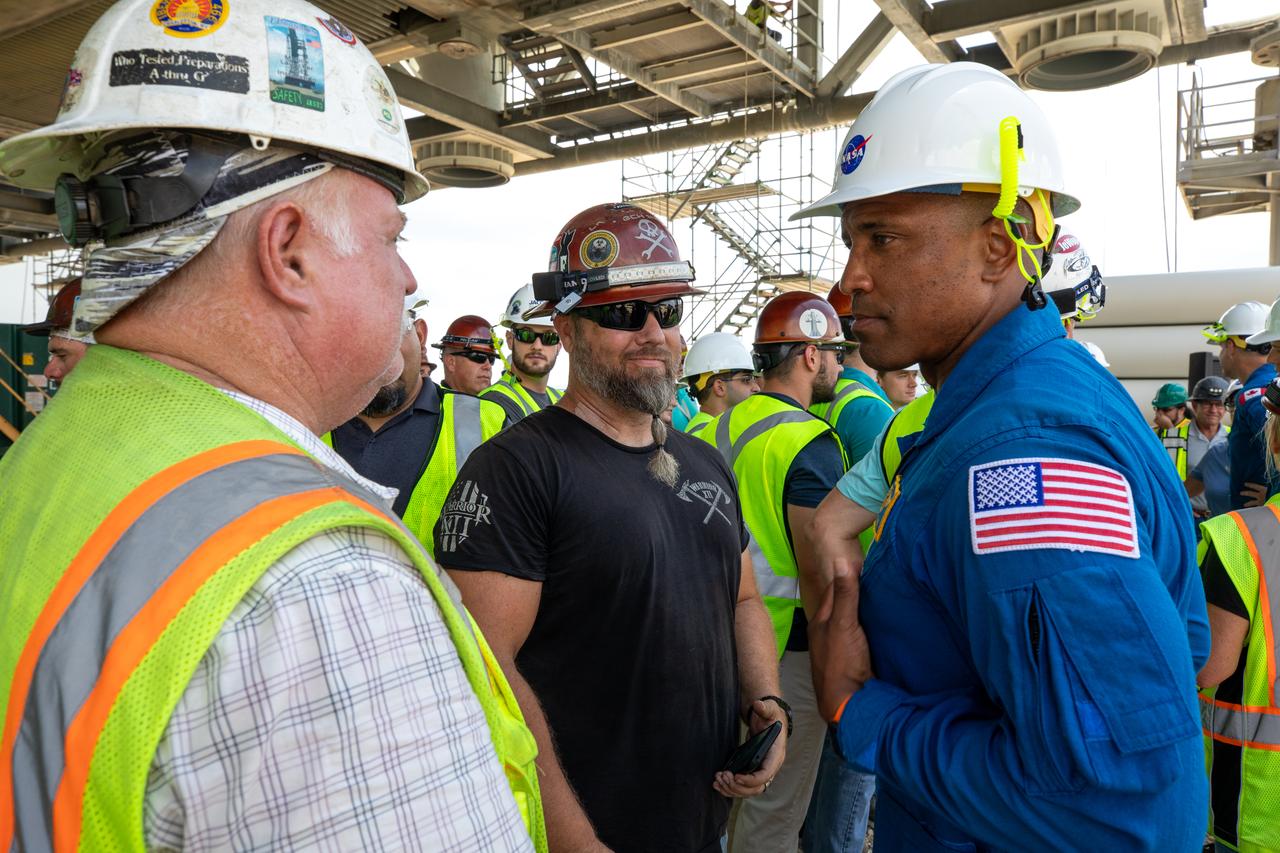

Artemis II NASA astronaut Victor Glover is seen with Exploration Ground Systems workers during a visit to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 7, 2023. The approximately 10-day Artemis II flight will test NASA’s foundational human deep space exploration capabilities, the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, for the first time with astronauts and will pave the way for lunar surface missions, including landing the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon.