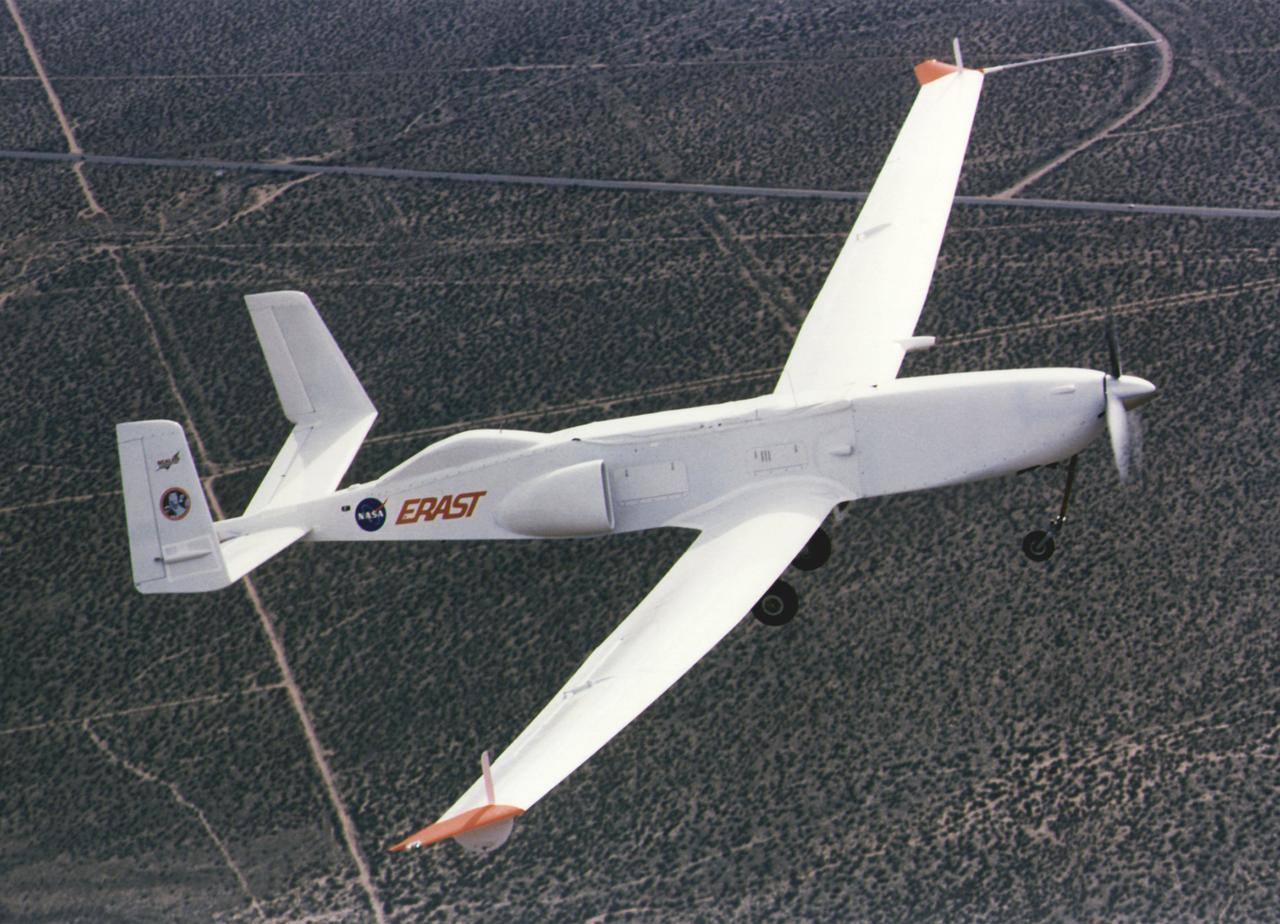

ERAST Demonstrator 2 (D-2) in flight
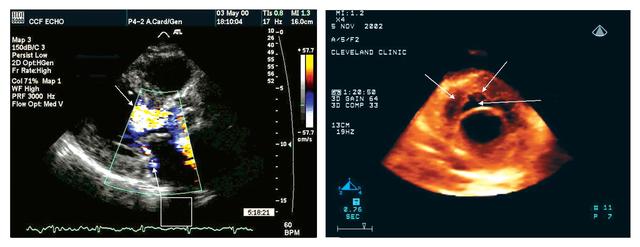
Echocardiography uses sound waves to image the heart and other organs. Developing a compact version of the latest technology improved the ease of monitoring crew member health, a critical task during long space flights. NASA researchers plan to adapt the three-dimensional (3-D) echocardiogram for space flight. The two-dimensional (2-D) echocardiogram utilized in orbit on the International Space Station (ISS) was effective, but difficult to use with precision. A heart image from a 2-D echocardiogram (left) is of a better quality than that from a 3-D device (right), but the 3-D imaging procedure is more user-friendly.
2-D Flow
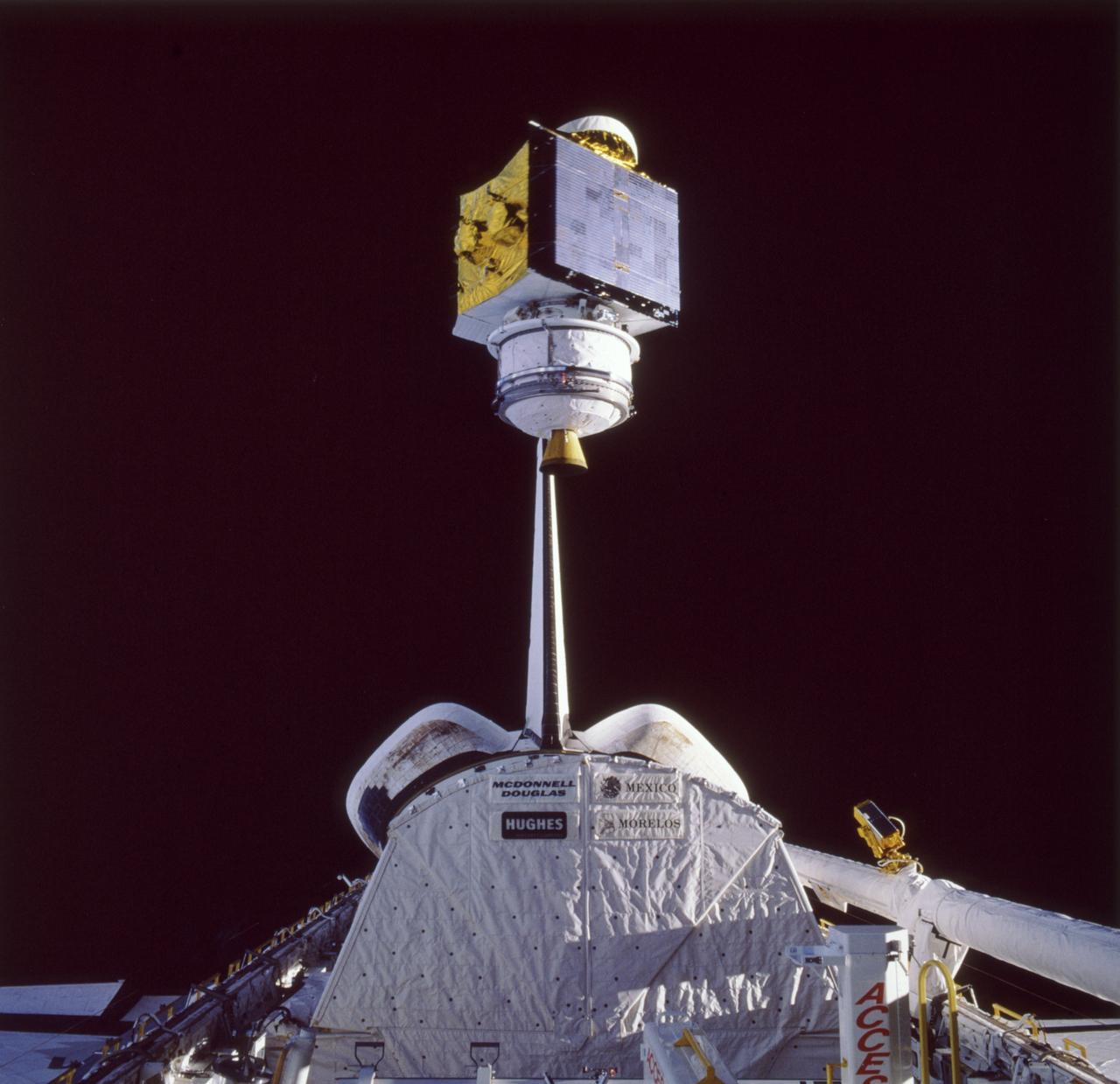

In this photograph the SATCOM KU-2 satellite attached to a Payload Assist Module-D (PAM-D) is being released from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis during STS-61B, the 23rd Shuttle Mission. The PAM-D is an upper stage system used to deploy payloads to a required orbit unattainable by the spacecraft. SATCOM KU-2 is an RCA communication satellite and was launched on November 26, 1985.
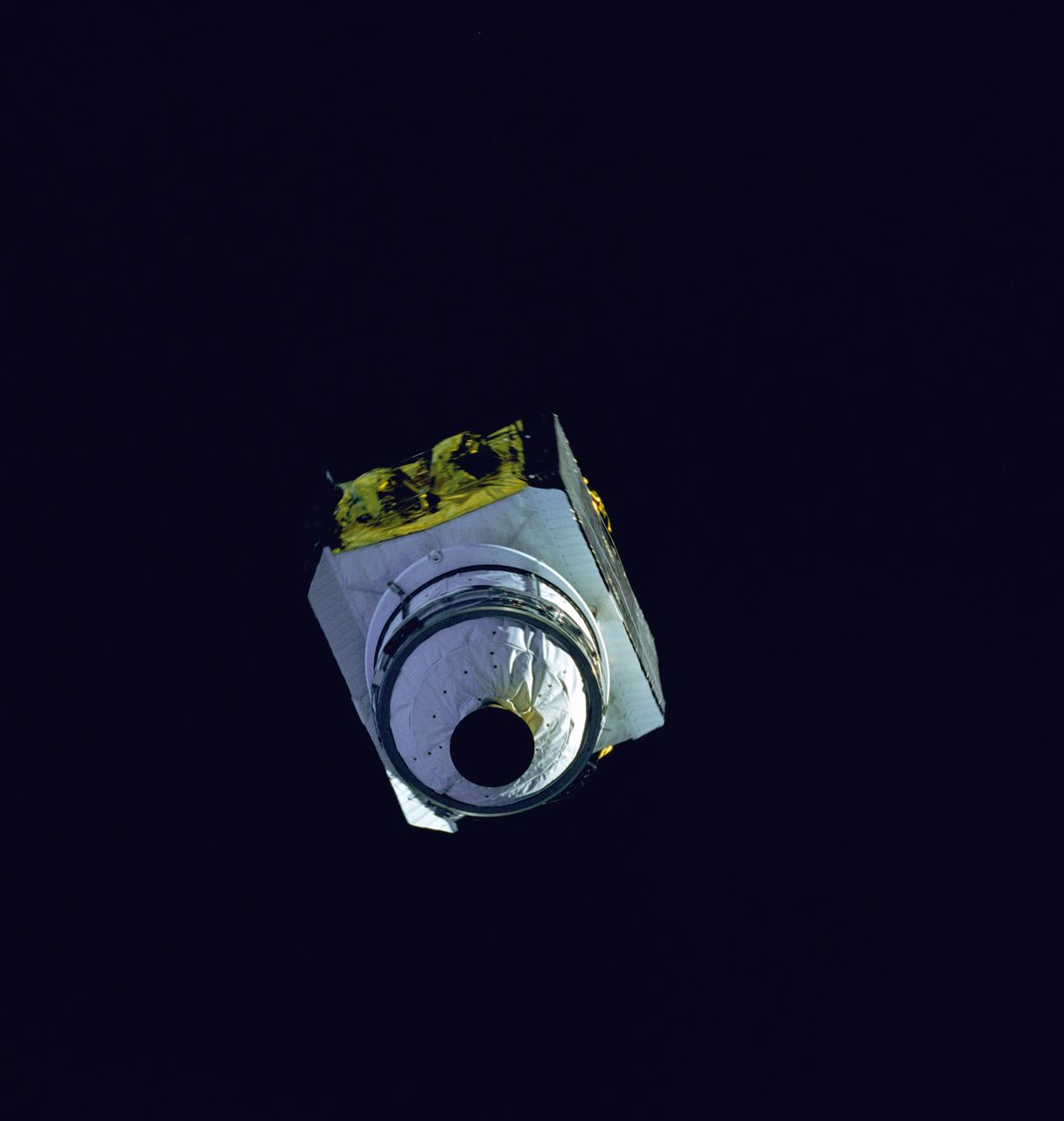

This image of the free-flying SATCOM KU-2 satellite, still attached to a Payload Assist Module-D (PAM-D), was photographed during STS-61B, the 23rd Space Shuttle mission. The SATCOM KU-2 is an RCA communication satellite and was launched on November 26, 1985, aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis. The PAM-D is an upper stage system used to deploy payloads to a required orbit unattainable by the launch vehicle.
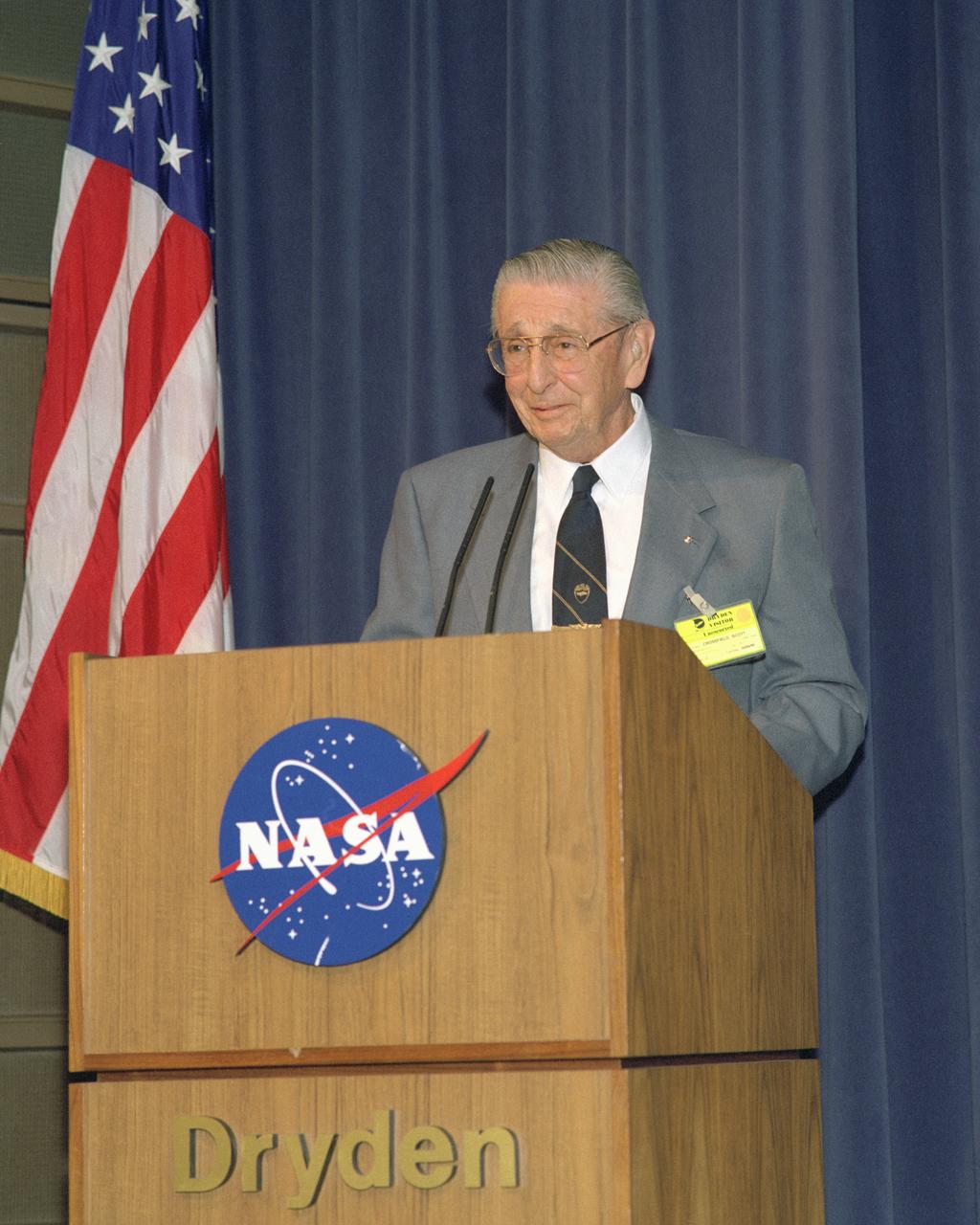

Former NACA test pilot Scott Crossfield at the 1998 "Men of Mach 2" symposium, an event celebrating his work in the 1950's on the D-558-II Skyrocket aircraft.
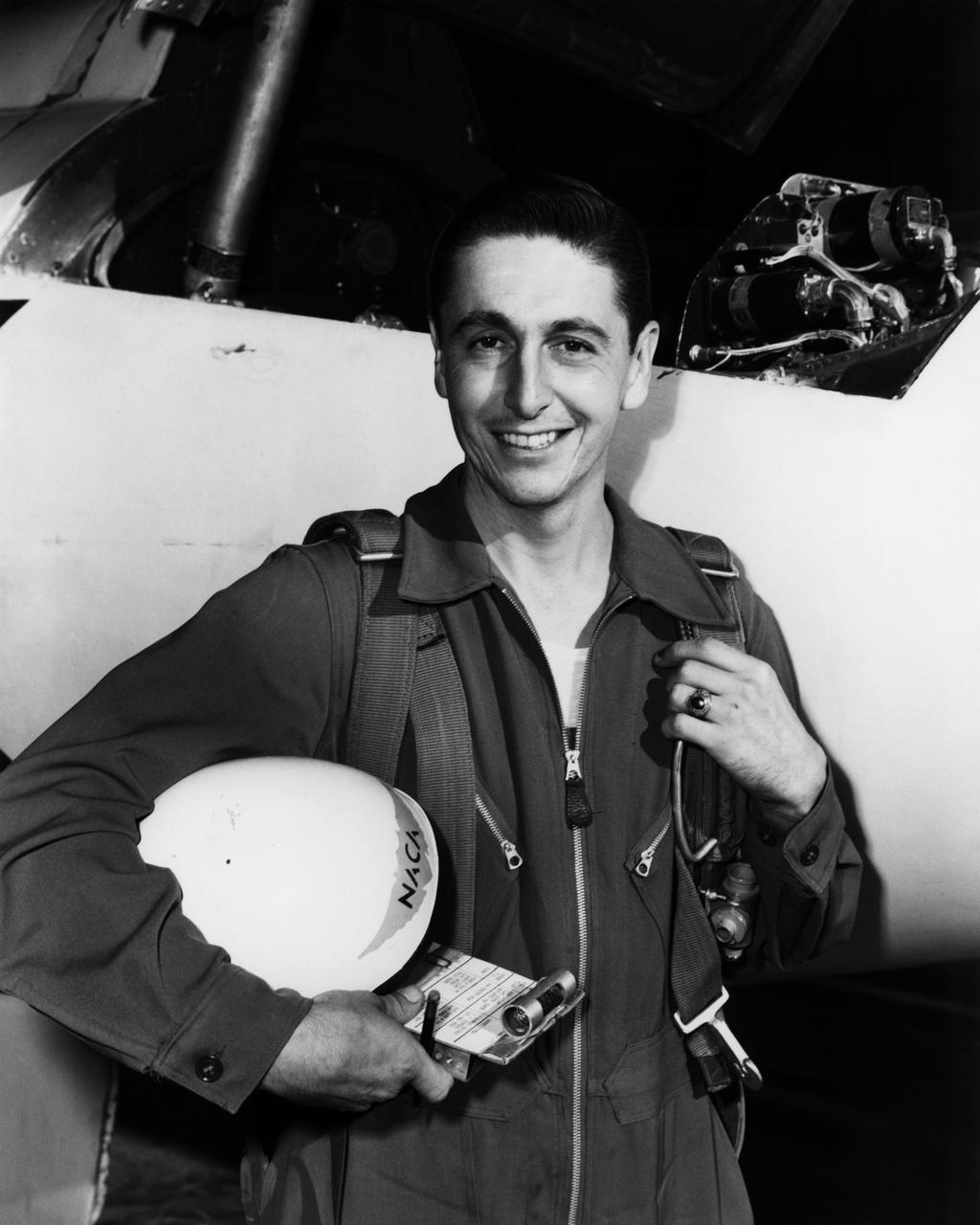

NACA pilot A. Scott Crossfield next to the D-558-2 after first Mach 2 flight.
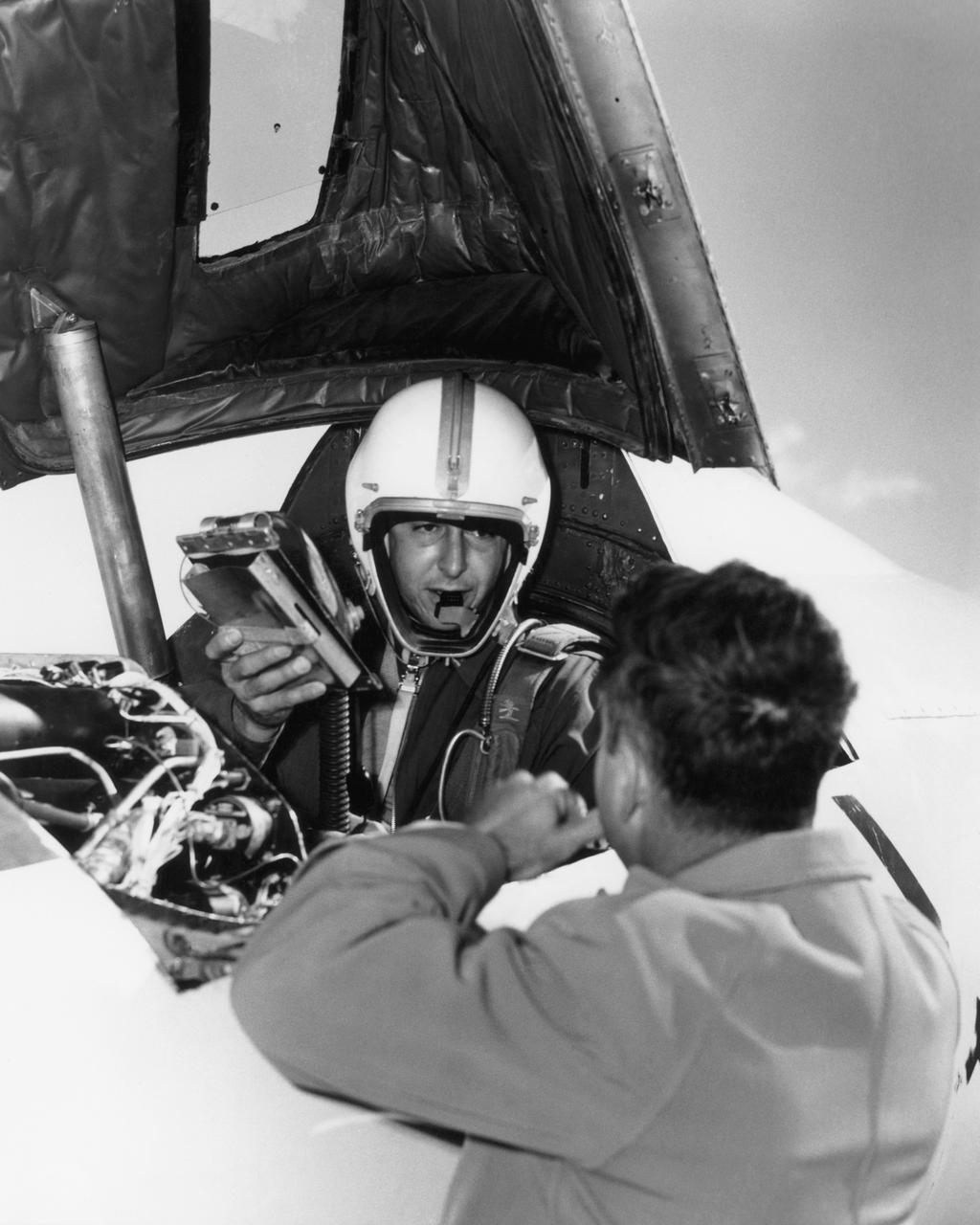

Scott Crossfield in cockpit of the Douglas D-558-2 after first Mach 2 flight.
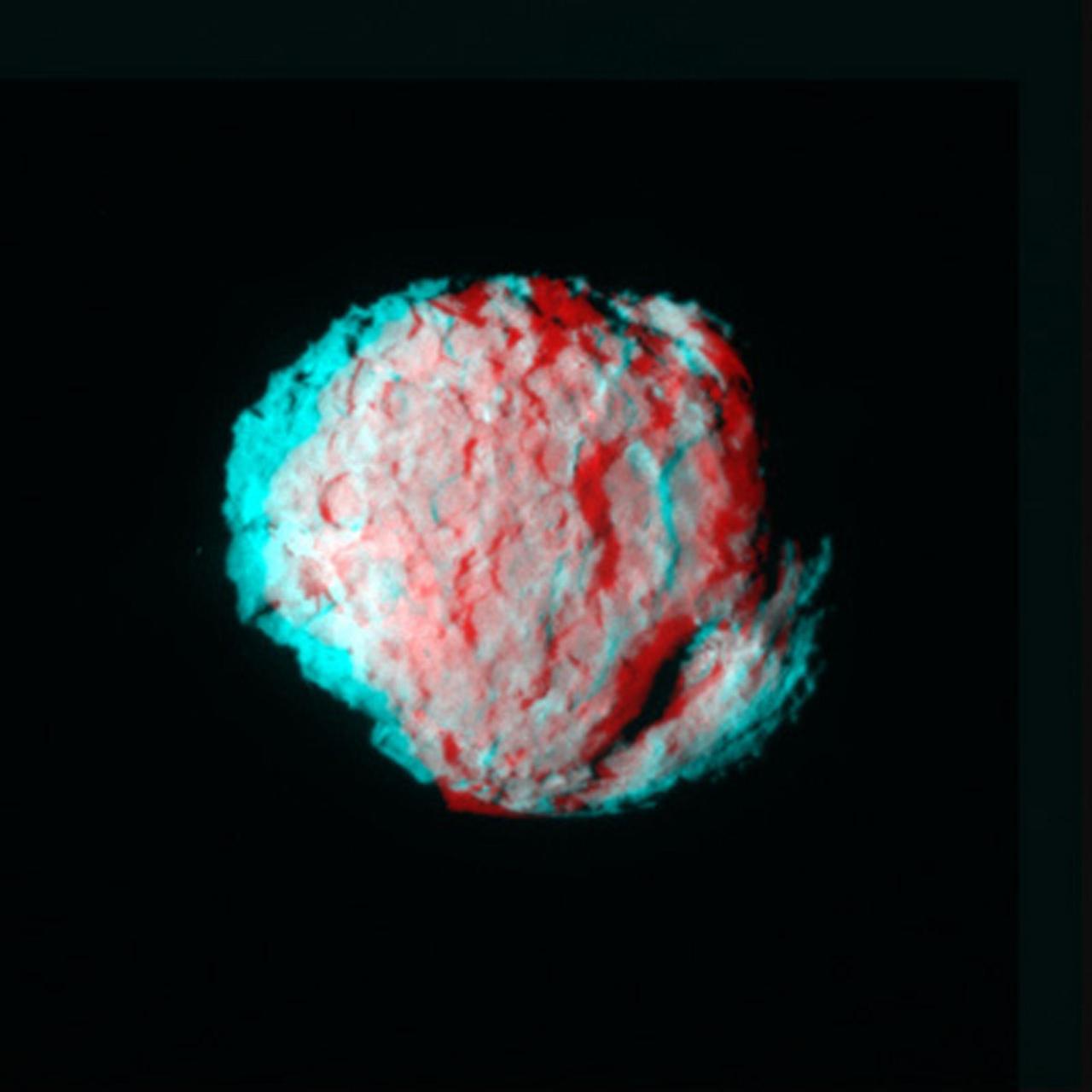
NASA Stardust Navigation Camera captured this anaglyph of the comet Wild 2. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.

Scott Crossfield talks to newsmen in front of NACA South Base hangar after his first flight to Mach 2 in the Douglas D-558-2.
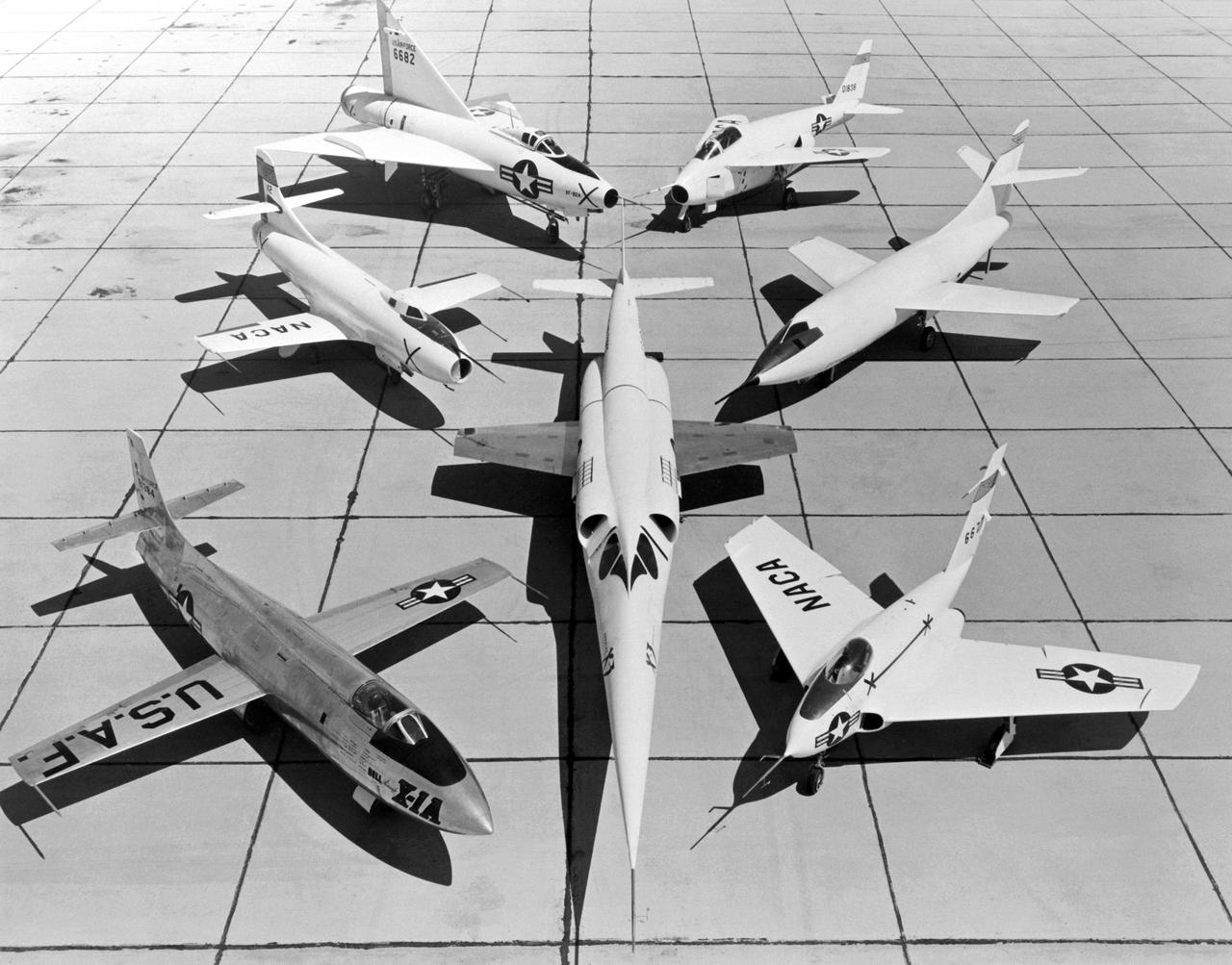

A 1953 photo of some of the research aircraft at the NACA High-Speed Flight Research Station (now known as the the Dryden Flight Research Center). The photo shows the X-3 (center) and, clockwise from left: X-1A (Air Force serial number 48-1384), the third D-558-1 (NACA tail number 142), XF-92A, X-5, D-558-2, and X-4.
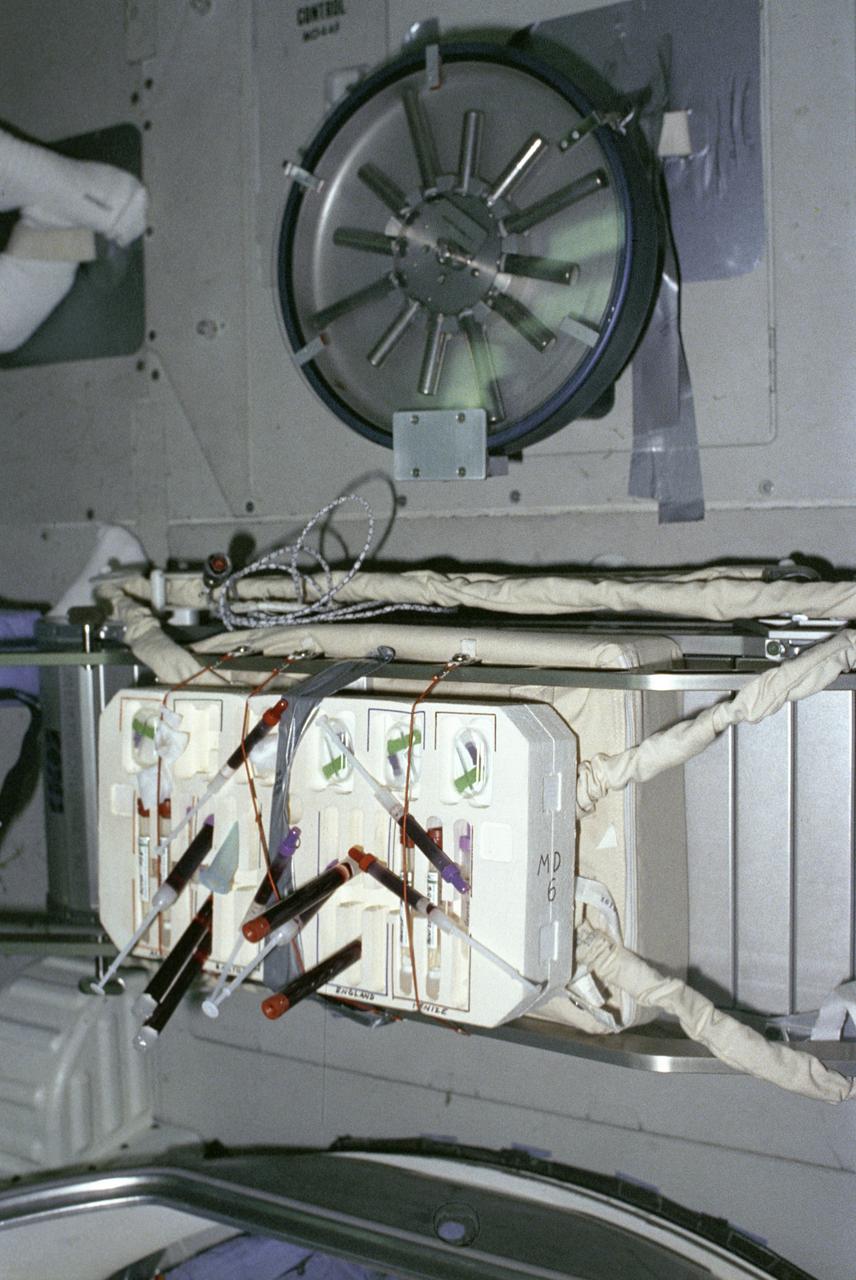
While instruments on the pallets in the payload bay observed the universe, biological experiments were performed in the middeck of the Shuttle Orbiter Challenger. Studying life processes in a microgravity environment can shed new light on the functioning of biological systems on Earth. These investigations can also help us understand how living organisms react to prolonged weightlessness. One such experiment was the vitamin D metabolites and bone demineralization experiment. This investigation measured the vitamin d metabolite levels of crew members to gain information on the cause of bone demineralization and mineral imbalance that occur during prolonged spaceflight as well as on Earth. Research into the biochemical nature of vitamin D has shown that the D-metabolites play a major role in regulating the body's calcium and phosphorus levels. One major function of the most biologically active vitamin D metabolite is to regulate the amount of calcium absorbed from the diet and taken out of bones. This investigation had two phases. The first was the developmental phase, which included extensive testing before flight, and the second, or final phase, involved the postflight analysis of the crew's blood samples. This photograph shows a blood draw test kit and centrifuge used for the experiment aboard the Spacelab-2. Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibilities of all Spacelab missions.
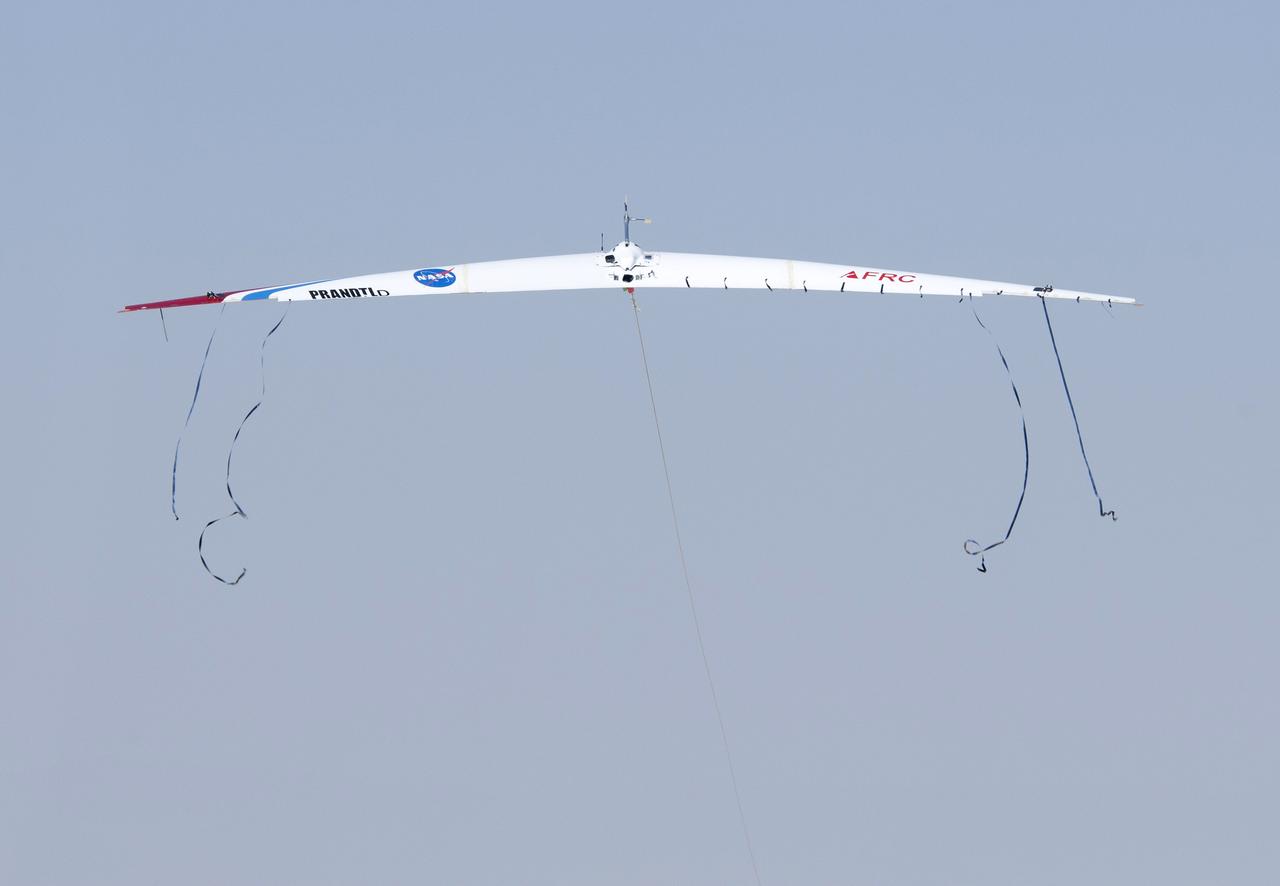

The streamers on the Prandtl-D No. 2 as it is launched illustrate how aerodynamic forces are maximized as birds overlap wingtips when flying in formation.
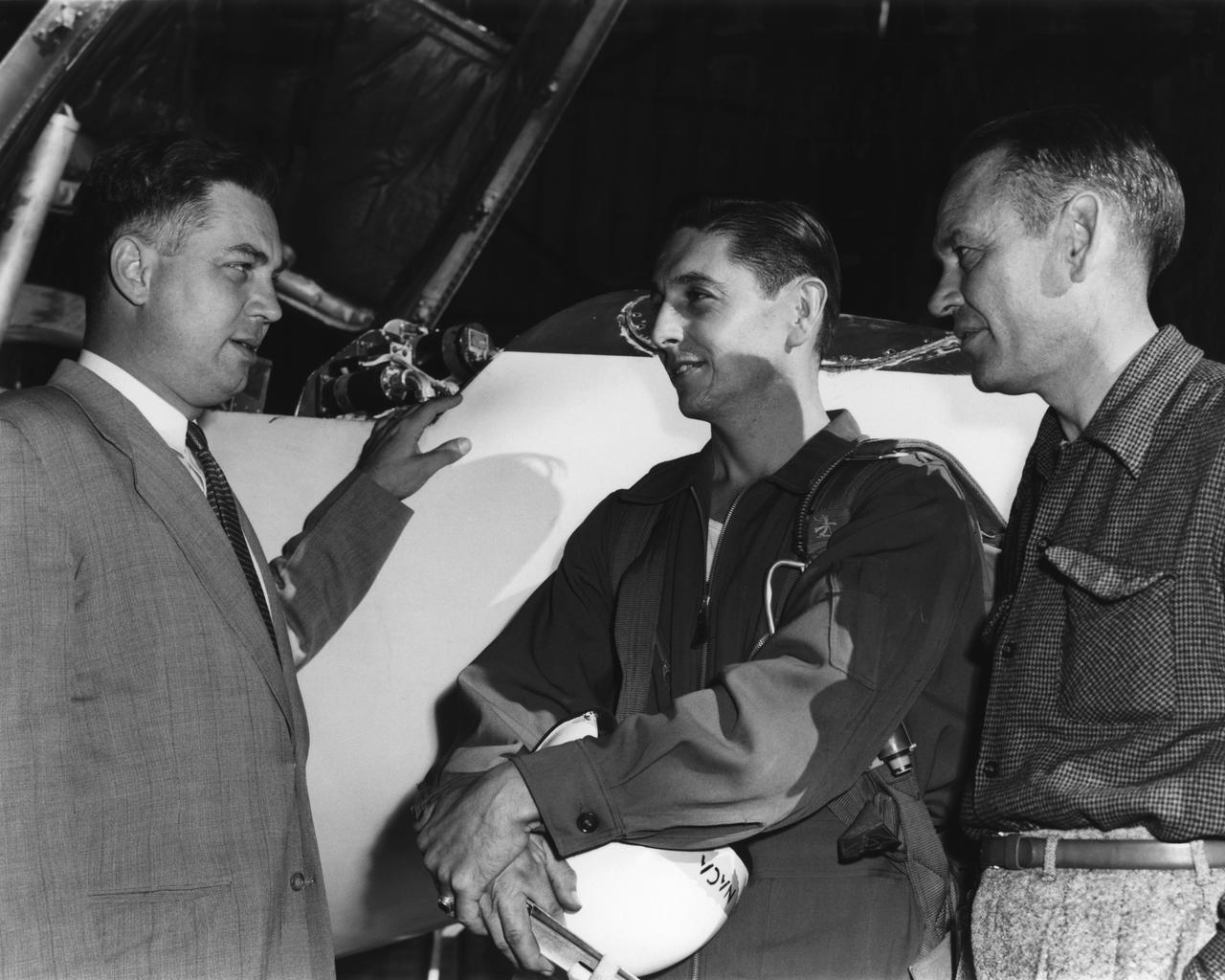

High-Speed Research Station Director Walter C. Williams, NACA pilot A. Scott Crossfield, and Director of Flight Operations Joe Vensel in front of the Douglas D-558-2 after the first Mach 2 flight.
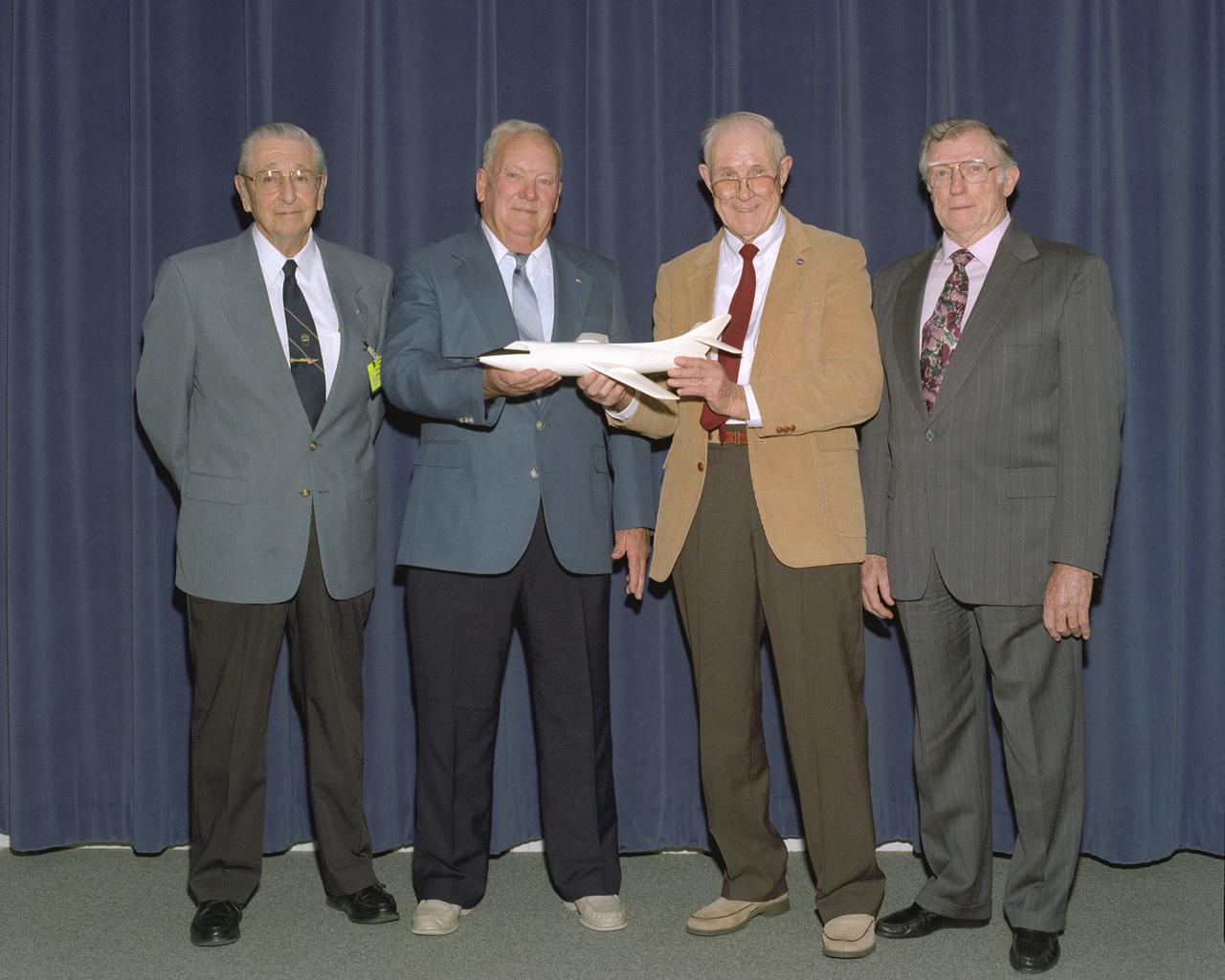

Former NACA test pilots Scott Crossfield, Stan Butchart, Robert Champine, and John Griffith gathered at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center for the "Men of Mach 2" symposium, an event celebrating their work in the 1950's on the D-558-II Skyrocket aircraft.
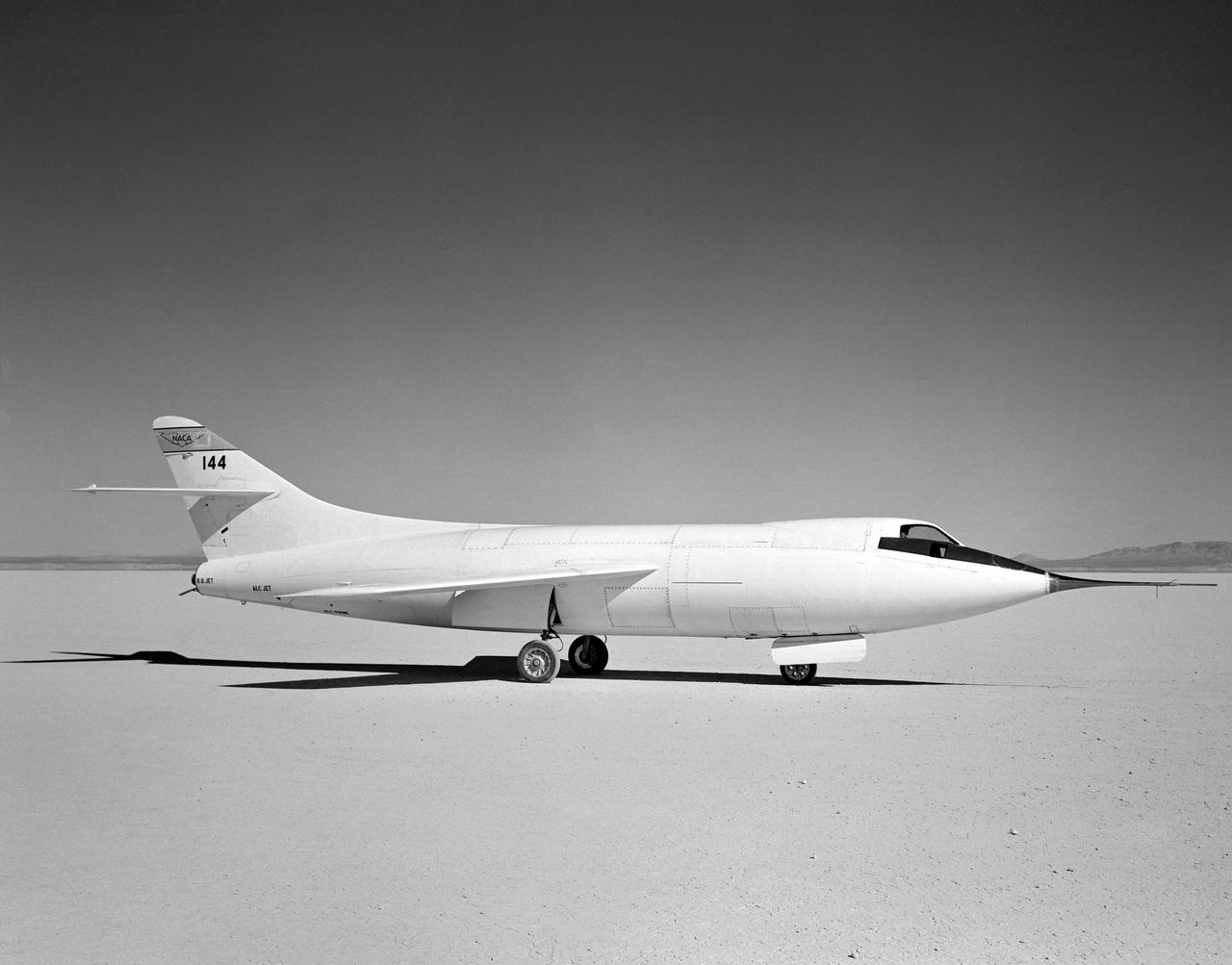

D-558-2 Aircraft on lakebed
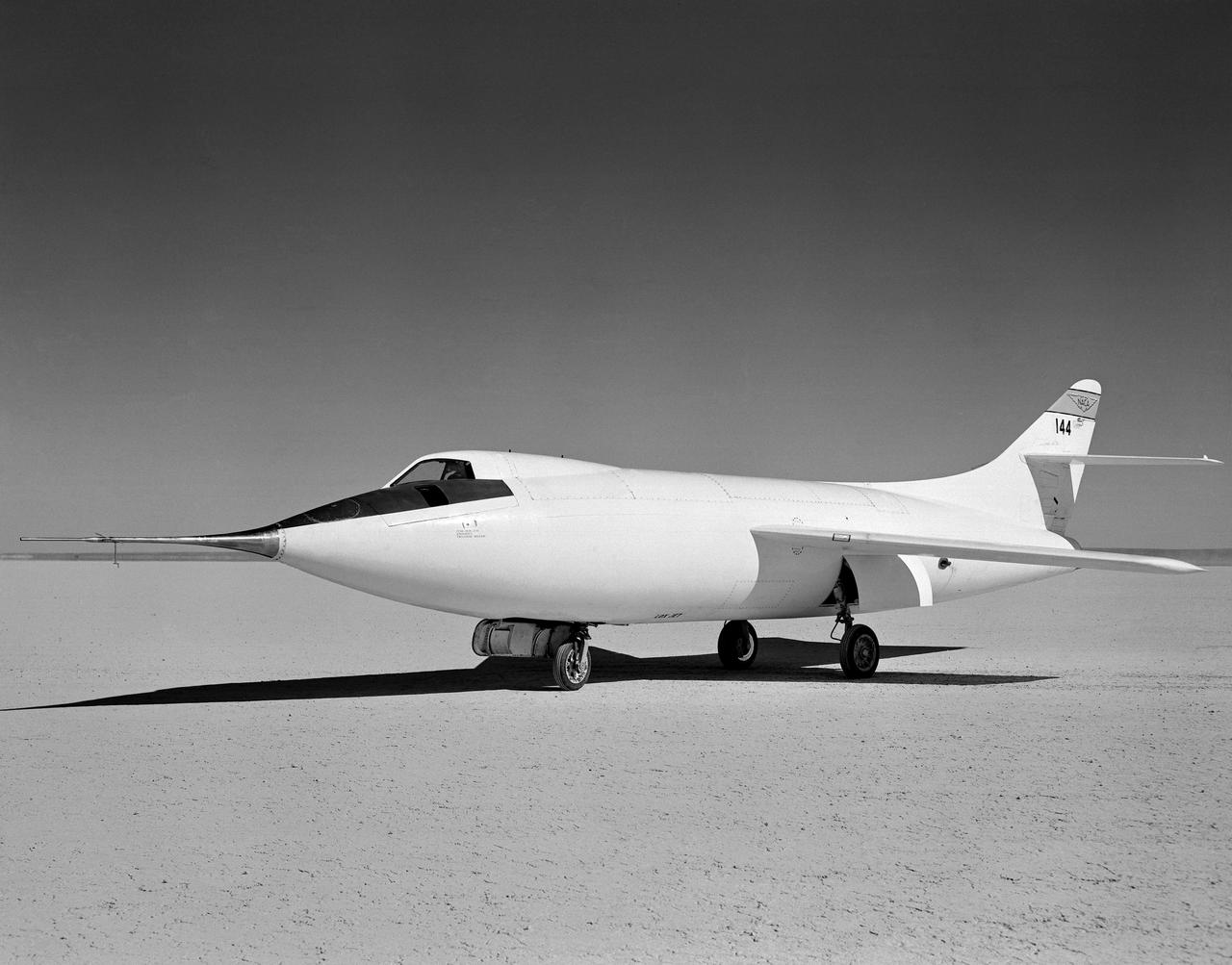

D-558-2 Aircraft on lakebed
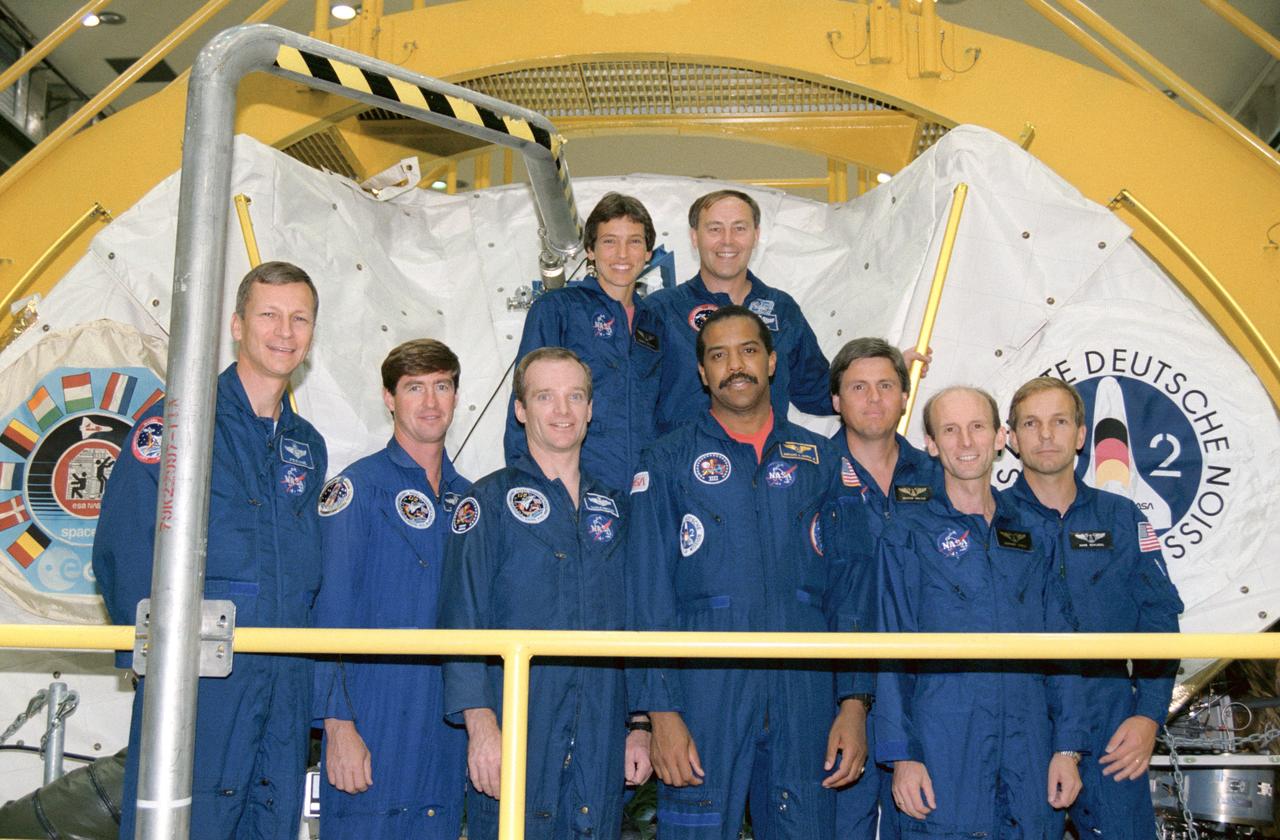

S92-49373 (8 Dec 1992) --- The seven prime flight crewmembers and two alternates assigned to support the STS-55\Spacelab D-2 mission pose with their science module. Left to right (front) are Steven R. Nagel, Terence T. (Tom) Henricks, Charles J. Precourt, Bernard A. Harris Jr., Ulrich Walter, Gerhard Thiele and Hans Schlegel; and (back) Renate Brummer and Jerry L. Ross. Nagel is mission commander; Henricks, pilot; and Ross, payload commander. Harris and Precourt will serve as mission specialists. Walter and Schlegel are scheduled to represent the DLR as payload specialists for the mission, while Brummer and Thiele will serve as alternates and fill supportive roles on the ground. The crew was photographed during a tour of the science module before its integration at Kennedy Space Center (KSC).
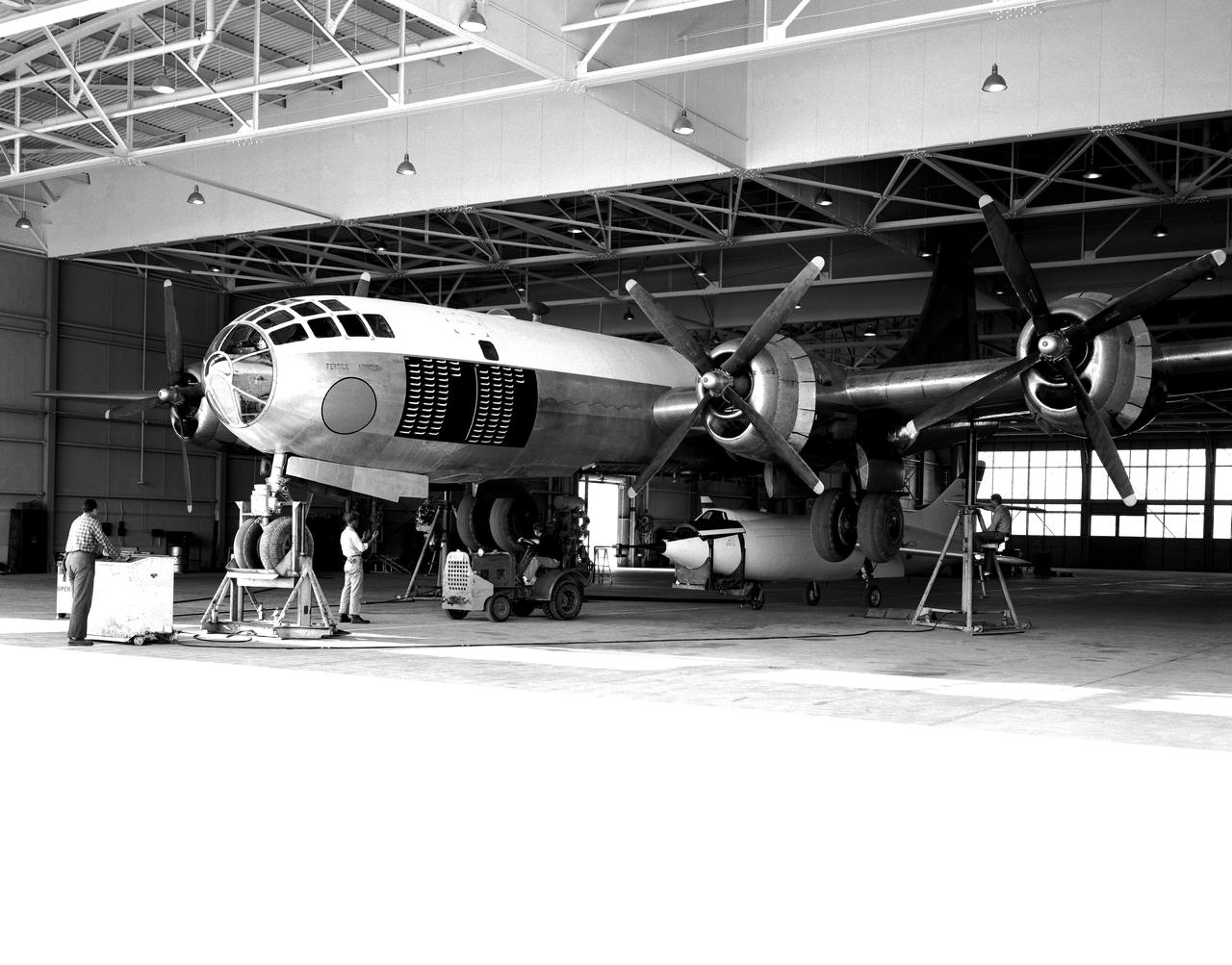

D-558-2 being mounted to P2B-1S launch aircraft in hangar.
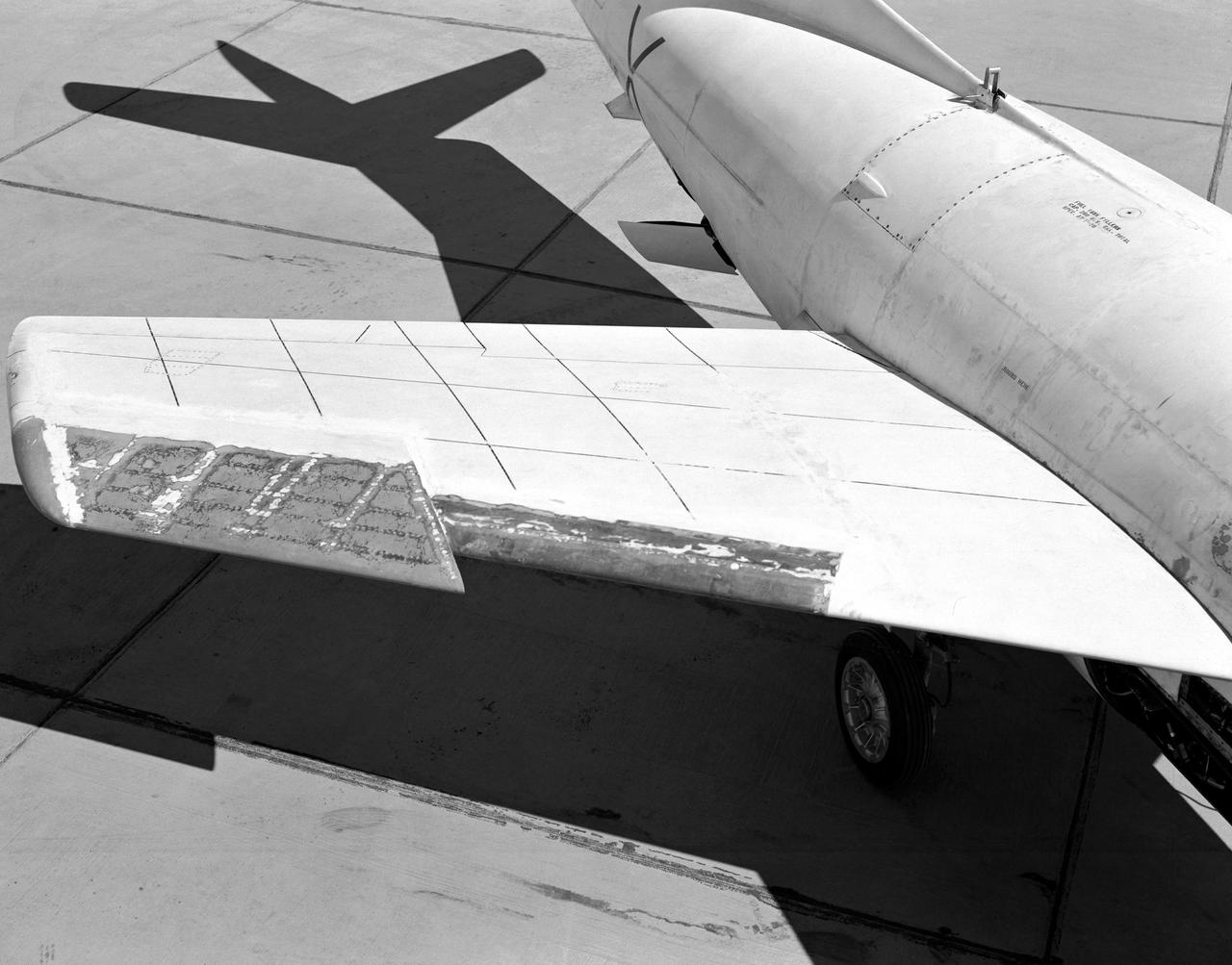

Wing chord extension on D-558-2

NASA Curiosity Mars rover recorded this stereo view of various rock types at waypoint called the Kimberley shortly after arriving at the location on April 2, 2014. You need 3-D glasses to view this image.
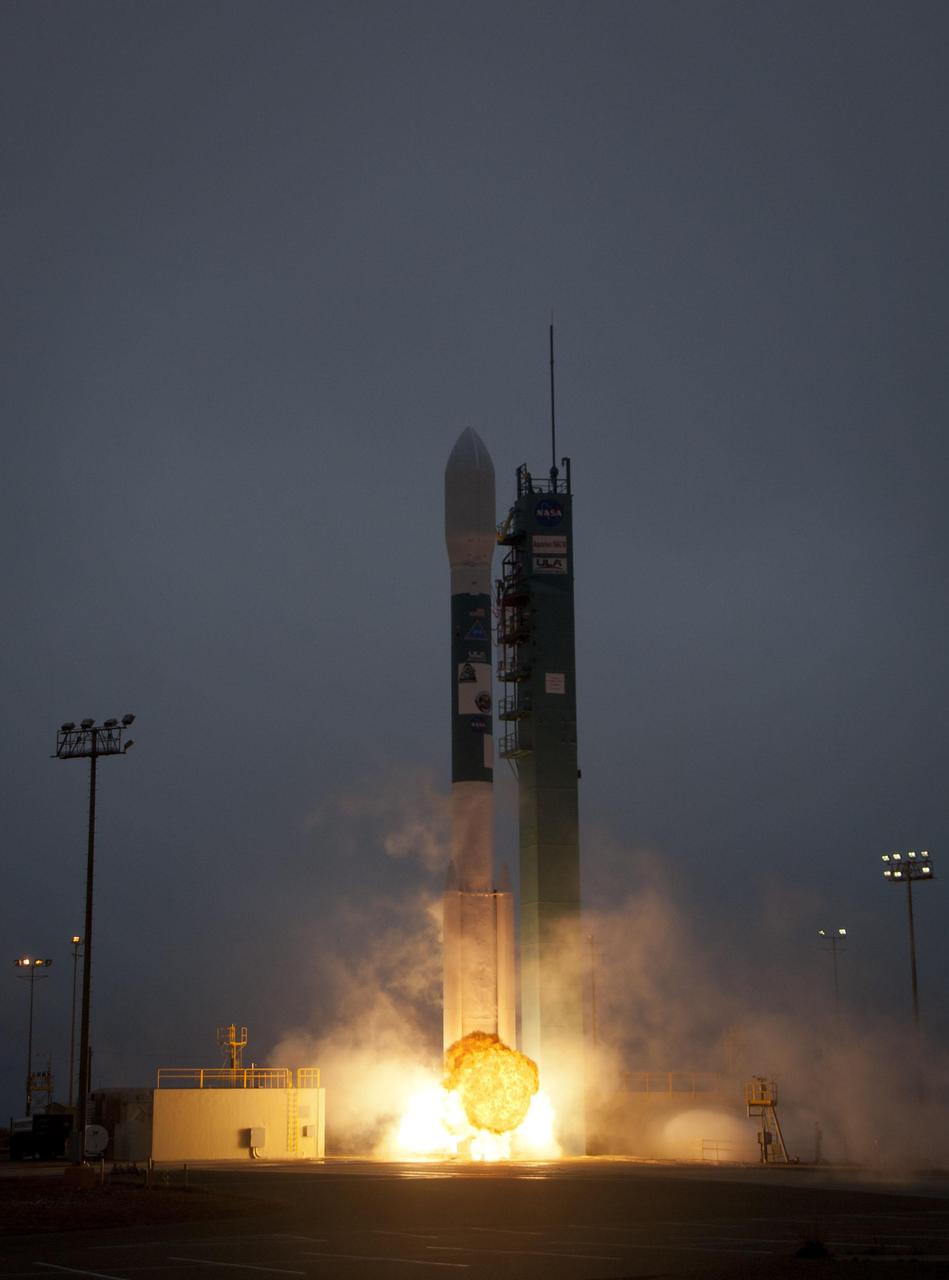

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011.
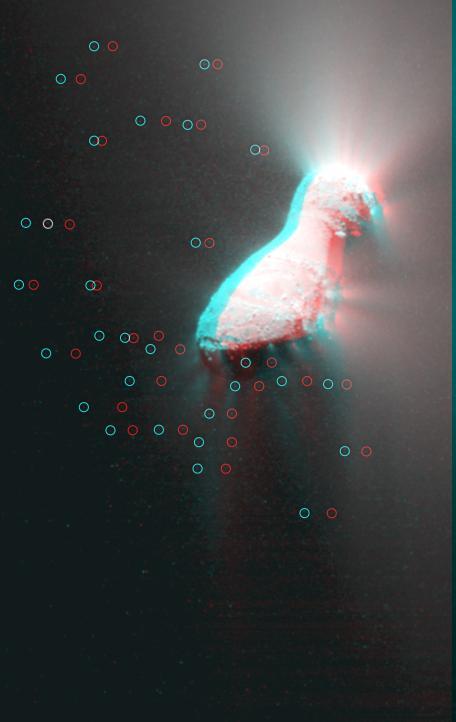
This 3-D image shows the region where NASA Deep Impact mission sent a probe into the surface of comet Tempel 1 in 2005. This picture was taken six years after the Deep Impact collision. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
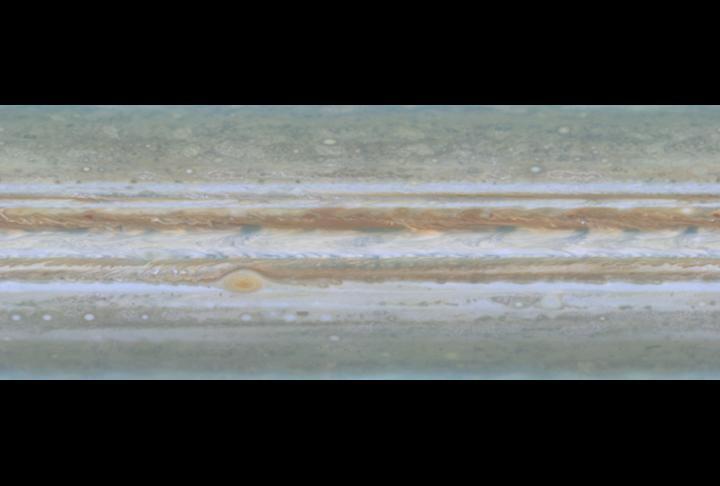

NASA Cassini spacecraft took narrow-angle images of Jupiter outer atmosphere, showing the giant planet as if it were constantly bathed in sunlight.
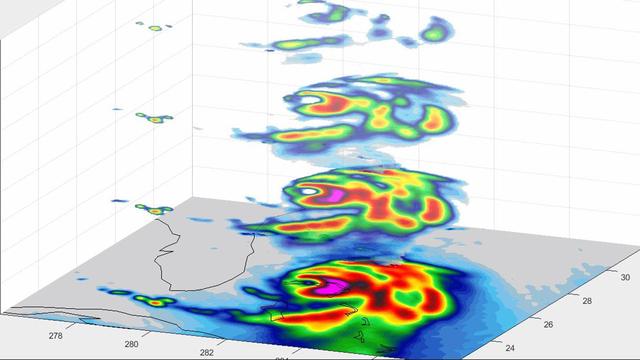
In this animation, TEMPEST-D — a weather-observing satellite the size of a cereal box — captured imagery of Hurricane Dorian off the coast of Florida at 2 a.m. EDT on Sep. 3, 2019 (11 p.m. PDT on Sept. 2, 2019). At a vantage point 250 miles (400 kilometers) above the storm, the CubeSat used its miniaturized radio-wave-based instrument to see through the clouds, revealing different depths of the hurricane with areas with heavy rainfall and moisture being pulled into the storm. The green colors indicate moisture spiraling into the storm's center, and the yellow, red and pink areas correspond to the most intense rainfall. TEMPEST-D — short for Temporal Experiment for Storms and Tropical Systems Demonstration — is an experiment in shrinking weather satellites to a size that makes them inexpensive enough to produce in multiples. The goal is eventual real-time storm coverage with many small satellites that can track storms around the world. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23431

Image for NASA Document NASA-TN-D-56. Equipment Used In Investigation. Document Title: An investigation to determine conditions under which downwash from VTOL aircraft will start surface erosion from various types of terrain Figure 2. Equipment Used In Investigation
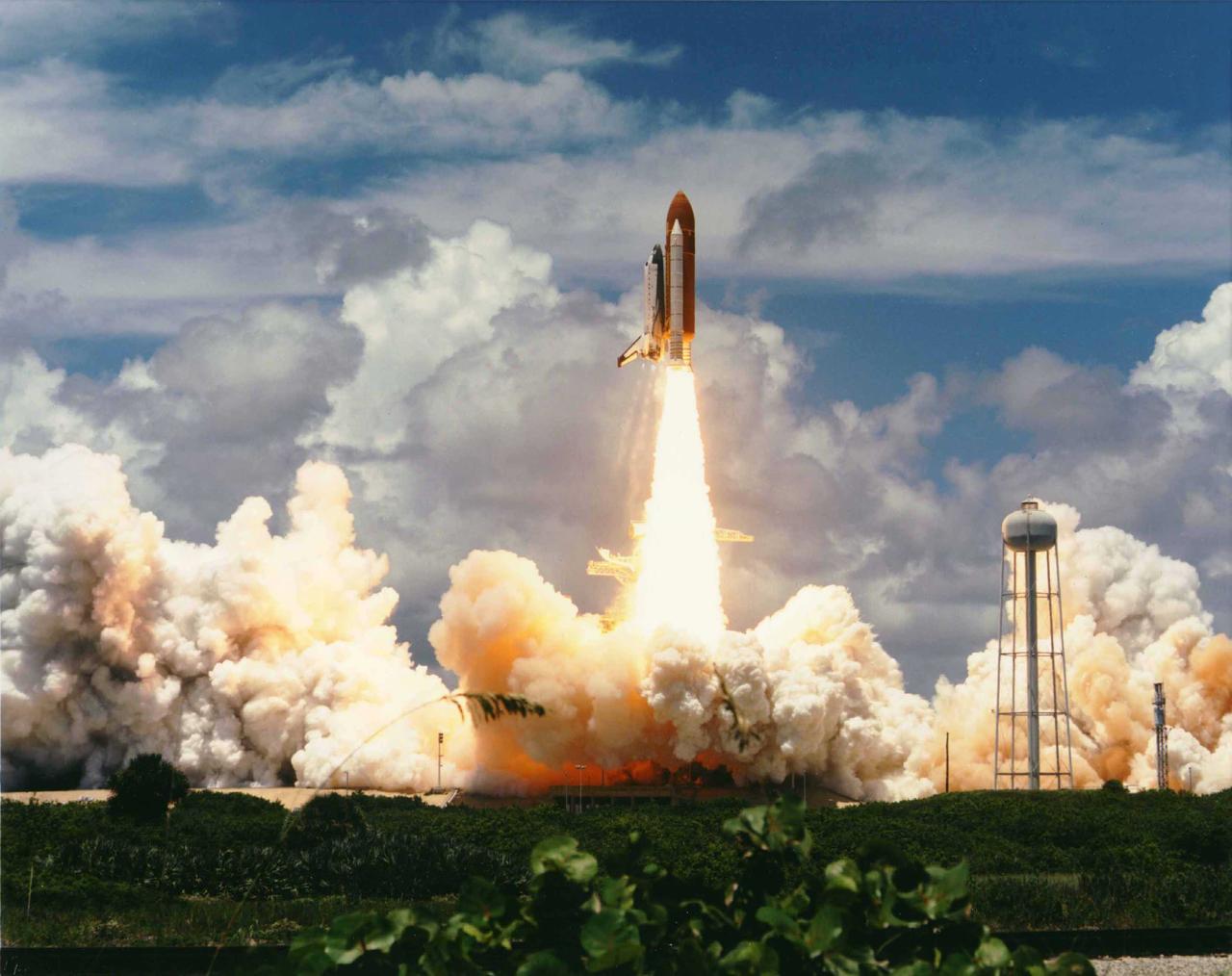

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The second International Microgravity Laboratory-2 (IML-2) is off to an ontime start as the Space Shuttle Columbia lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at 12:43:00 p.m. EDT. On board are a crew of seven and more than 80 investigations developed by more than 200 scientists from 13 countries. The IML-2 complement includes materials science, bioprocessing, space and radiation biology, and human physiology experiments that will be carried out over the course of the 14-day flight. The commander of Space Shuttle Mission STS-65 is Robert D. Cabana. James D. Halsell Jr. is the pilot; the payload commander is Richard J. Hieb; the three mission specialists are Carl E. Walz, Leroy Chiao and Donald A. Thomas. Dr. Chiaki Mukai, representing NASDA, the National Space Development Agency of Japan, is the payload specialist. Mukai becomes the first Japanese woman to fly into space.
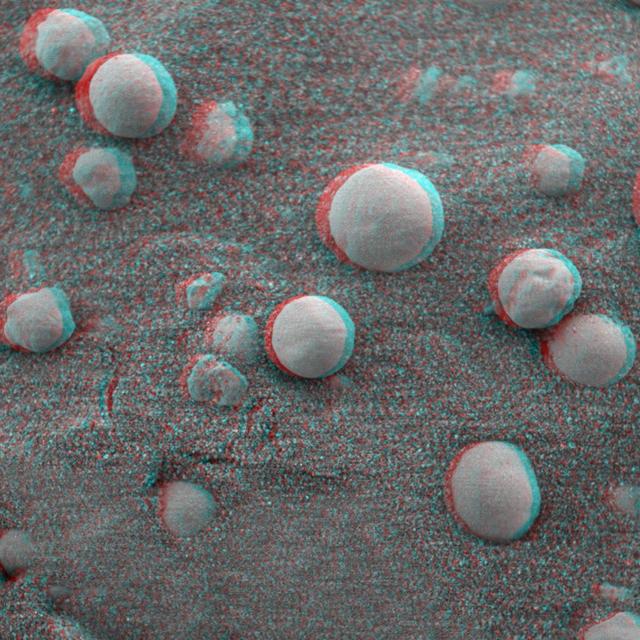
This 3-D anaglyph, from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit, shows a microscopic image taken of soil featuring round, blueberry-shaped rock formations on the crater floor at Meridiani Planum, Mars. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
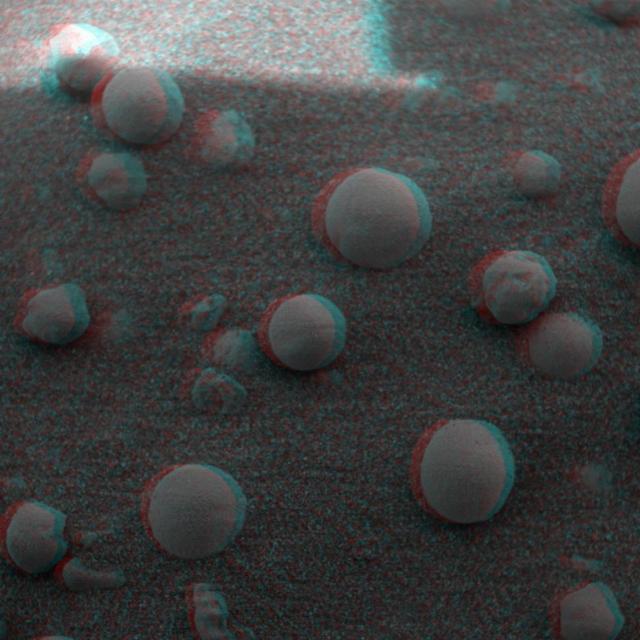
This 3-D anaglyph, from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit, shows a microscopic image taken of soil featuring round, blueberry-shaped rock formations on the crater floor at Meridiani Planum, Mars. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
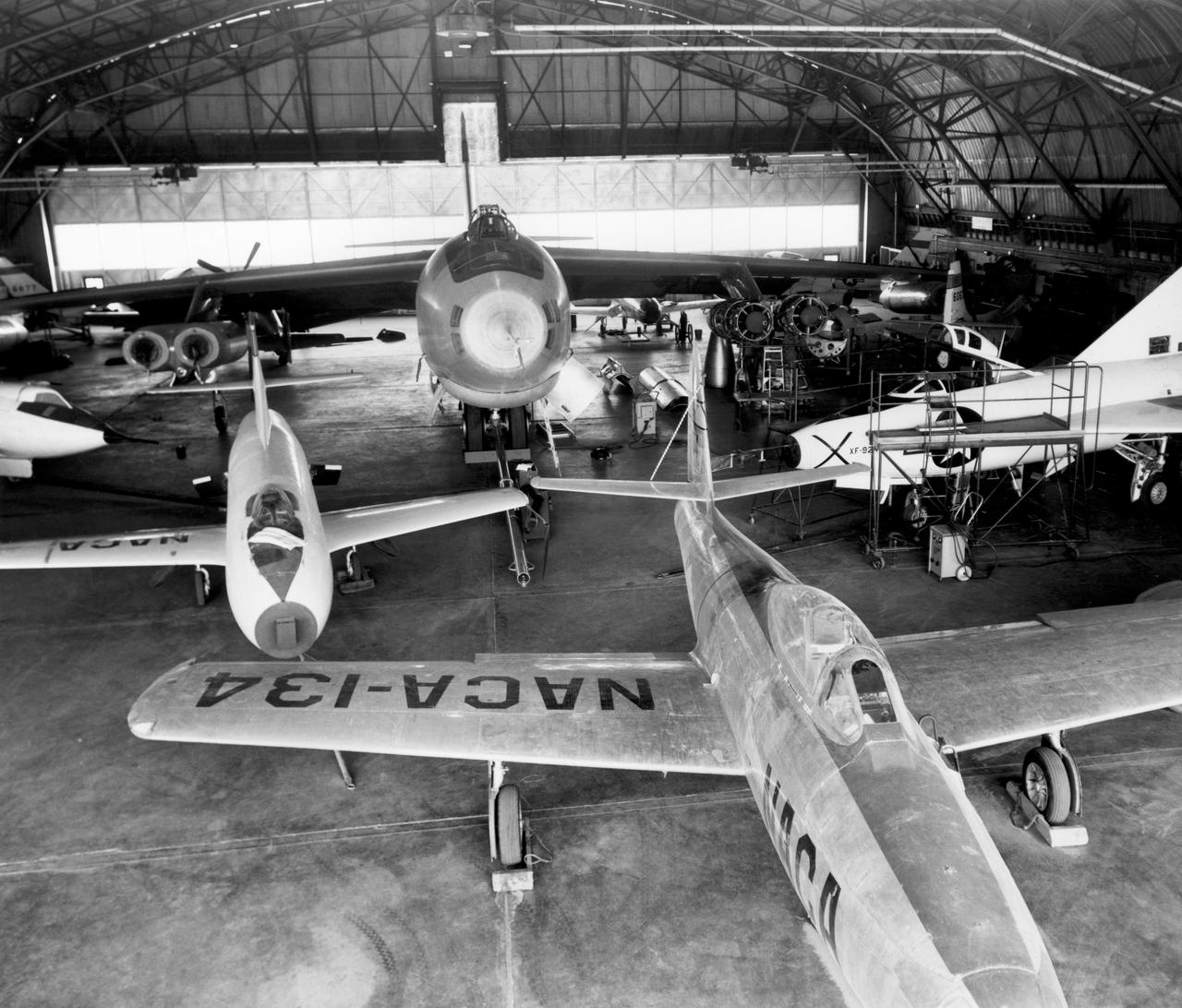

In the center foreground of this 1953 hangar photo is the YF-84A (NACA 134/Air Force 45-59490) used for vortex generator research. It arrived on November 28, 1949, and departed on April 21, 1954. Beside it is the third D-558-1 aircraft (NACA 142/Navy 37972). This aircraft was used for a total of 78 transonic research flights from April 1949 to June 1954. It replaced the second D-558-1, lost in the crash which killed Howard Lilly. Just visible on the left edge is the nose of the first D-558-2 (NACA 143/Navy 37973). Douglas turned the aircraft over to NACA on August 31, 1951, after the contractor had completed its initial test flights. NACA only made a single flight with the aircraft, on September 17, 1956, before the program was cancelled. In the center of the photo is the B-47A (NACA 150/Air Force 49-1900). The B-47 jet bomber, with its thin, swept-back wings, and six podded engines, represented the state of the art in aircraft design in the early 1950s. The aircraft undertook a number of research activities between May 1953 and its 78th and final research flight on November 22, 1957. The tests showed that the aircraft had a buffeting problem at speeds above Mach 0.8. Among the pilots who flew the B-47 were later X-15 pilots Joe Walker, A. Scott Crossfield, John B. McKay, and Neil A. Armstrong. On the right side of the B-47 is NACA's X-1 (Air Force 46-063). The second XS-1 aircraft built, it was fitted with a thicker wing than that on the first aircraft, which had exceeded Mach 1 on October 14, 1947. Flight research by NACA pilots indicated that this thicker wing produced 30 percent more drag at transonic speeds compared to the thinner wing on the first X-1. After a final flight on October 23, 1951, the aircraft was grounded due to the possibility of fatigue failure of the nitrogen spheres used to pressurize the fuel tanks. At the time of this photo, in 1953, the aircraft was in storage. In 1955, the aircraft was extensively modified, becoming the X-1E. In front o
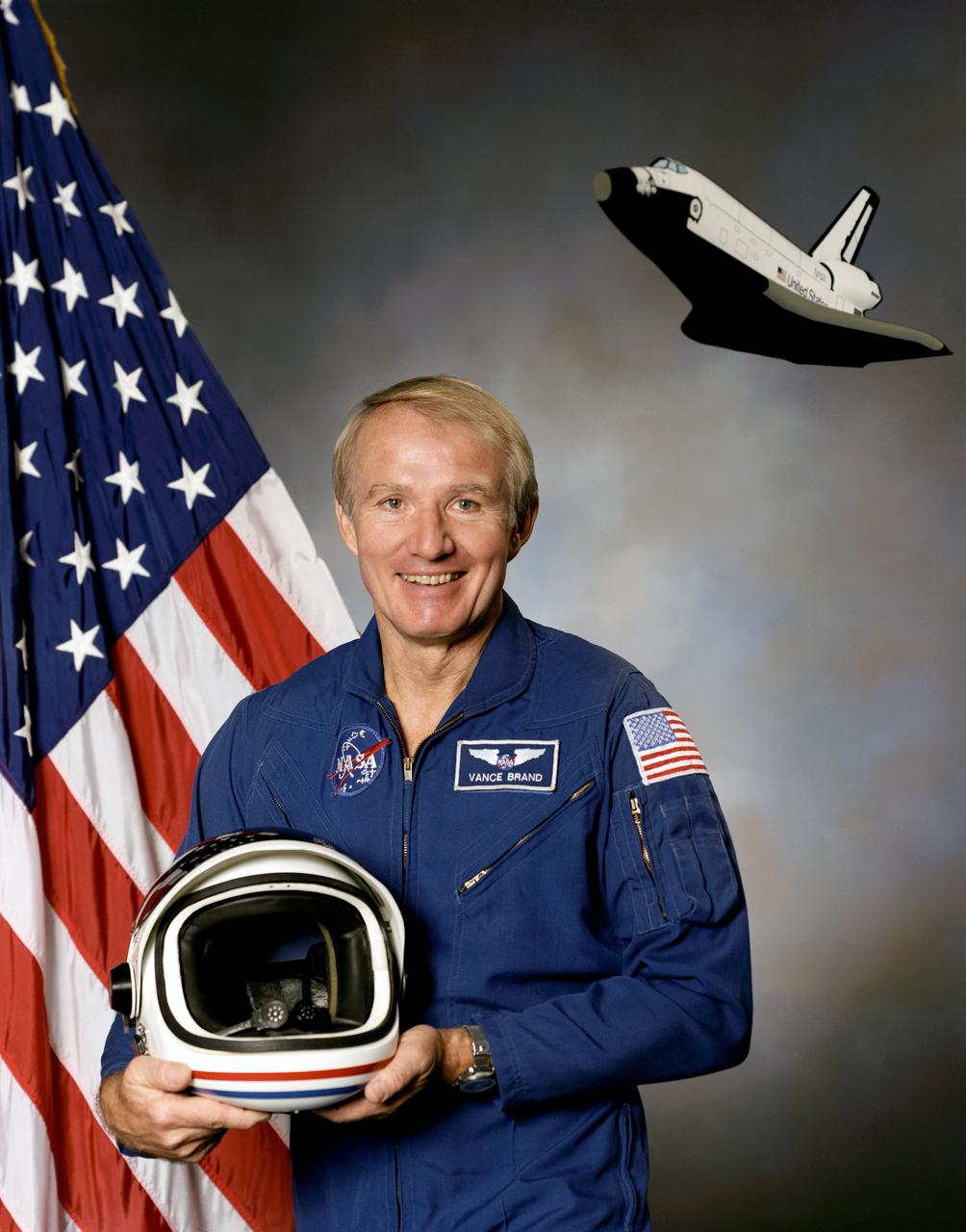

S86-38100 (2 Oct. 1986) --- Astronaut Vance D. Brand.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s liquid oxygen tank structural test article was manufactured and stacked in June 2019 at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. To construct the test article, Boeing technicians at Michoud moved the liquid oxygen tank to the Vertical Assemby Building stacking and integration area. Here, they added simulators to mimic the two structures that connect to the tank, the intertank and the forward skirt. This structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket is structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will be shipped on the Pegasus barge to NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Hunstville, Alabama, where it will undergo a series of tests that simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond. The flight liquid oxygen tank along with the liquid hydrogen tank supplies more than 500,000 gallons of propellant to the core stages four RS-25 engines, which produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help send the SLS rocket to space.
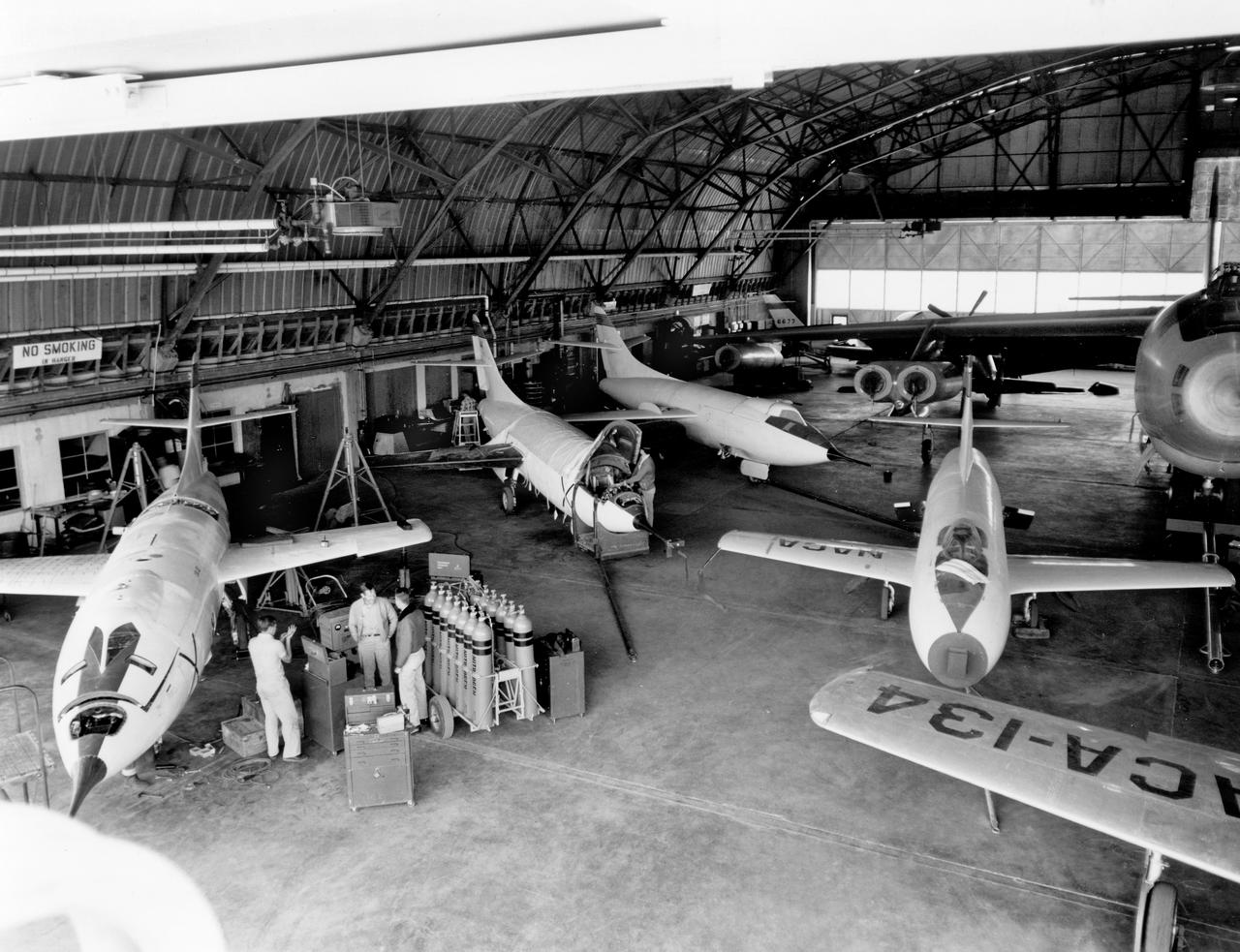

The aircraft in this 1953 photo of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) hangar at South Base of Edwards Air Force Base showed the wide range of research activities being undertaken. On the left side of the hangar are the three D-558-2 research aircraft. These were designed to test swept wings at supersonic speeds approaching Mach 2. The front D-558-2 is the third built (NACA 145/Navy 37975). It has been modified with a leading-edge chord extension. This was one of a number of wing modifications, using different configurations of slats and/or wing fences, to ease the airplane's tendency to pitch-up. NACA 145 had both a jet and a rocket engine. The middle aircraft is NACA 144 (Navy 37974), the second built. It was all-rocket powered, and Scott Crossfield made the first Mach 2 flight in this aircraft on November 20, 1953. The aircraft in the back is D-558-2 number 1. NACA 143 (Navy 37973) was also carried both a jet and a rocket engine in 1953. It had been used for the Douglas contractor flights, then was turned over to the NACA. The aircraft was not converted to all-rocket power until June 1954. It made only a single NACA flight before NACA's D-558-2 program ended in 1956. Beside the three D-558-2s is the third D-558-1. Unlike the supersonic D-558-2s, it was designed for flight research at transonic speeds, up to Mach 1. The D-558-1 was jet-powered, and took off from the ground. The D-558-1's handling was poor as it approached Mach 1. Given the designation NACA 142 (Navy 37972), it made a total of 78 research flights, with the last in June 1953. In the back of the hangar is the X-4 (Air Force 46-677). This was a Northrop-built research aircraft which tested a swept wing design without horizontal stabilizers. The aircraft proved unstable in flight at speeds above Mach 0.88. The aircraft showed combined pitching, rolling, and yawing motions, and the design was considered unsuitable. The aircraft, the second X-4 built, was then used as a pilot traine
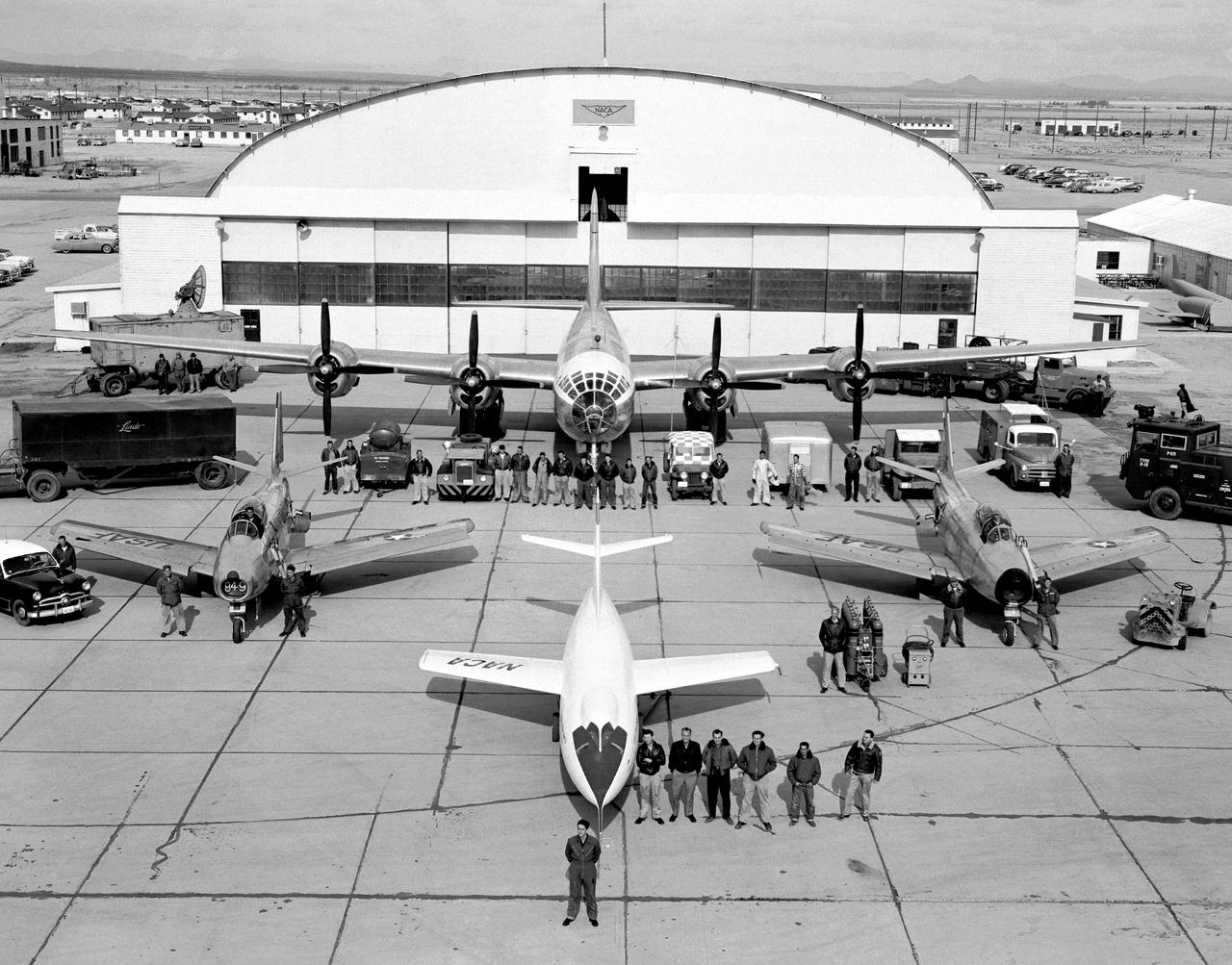

These people and this equipment supported the flight of the NACA D-558-2 Skyrocket at the High-Speed Flight Station at South Base, Edwards AFB. Note the two Sabre chase planes, the P2B-1S launch aircraft, and the profusion of ground support equipment, including communications, tracking, maintenance, and rescue vehicles. Research pilot A. Scott Crossfield stands in front of the Skyrocket.
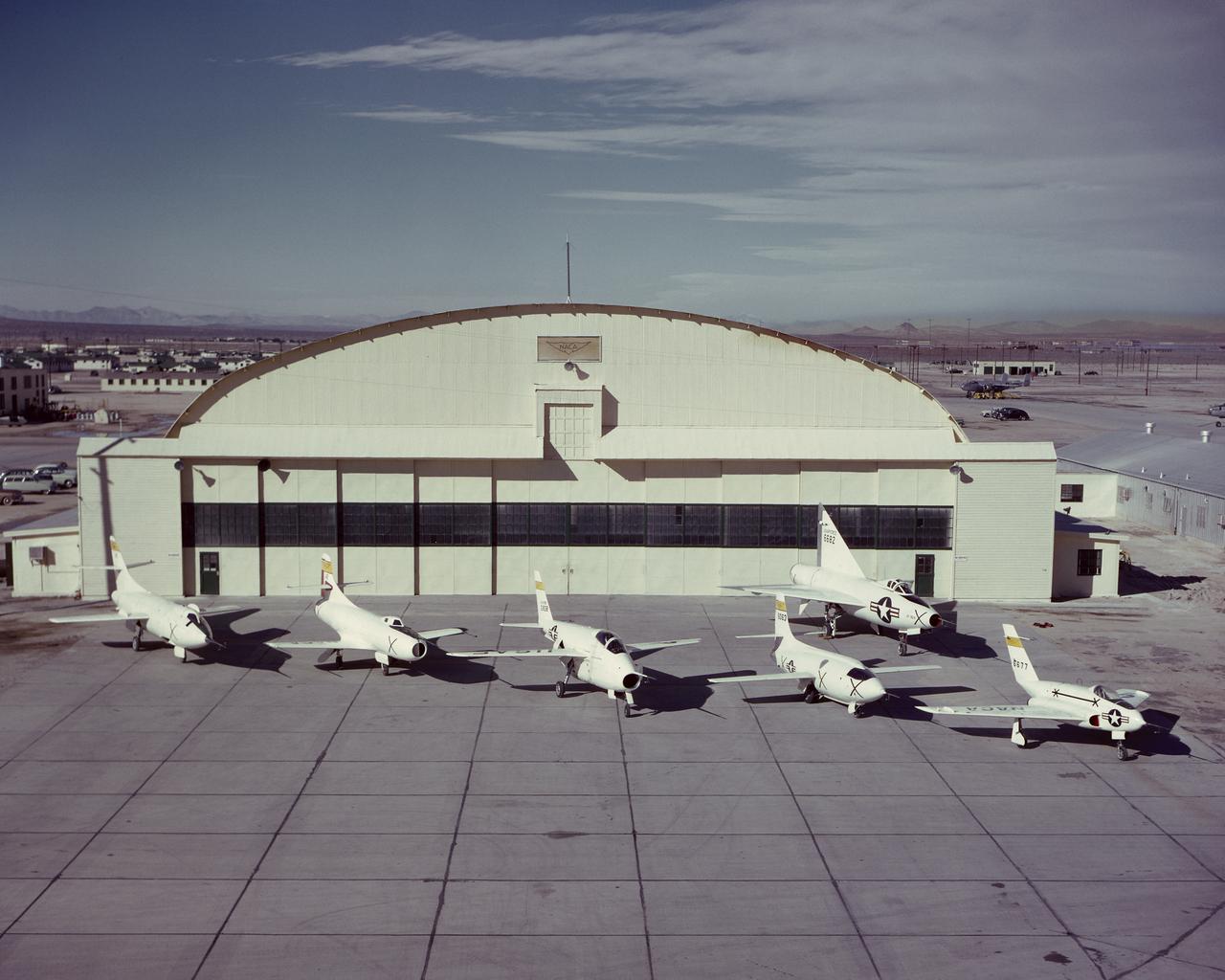

NACA X-Planes on South Base ramp. Northrop X-4, Bell X-1, Bell X-5, Douglas D-558-1, Douglas D-558-2. Back row Convair XF-92A. March 30, 1952
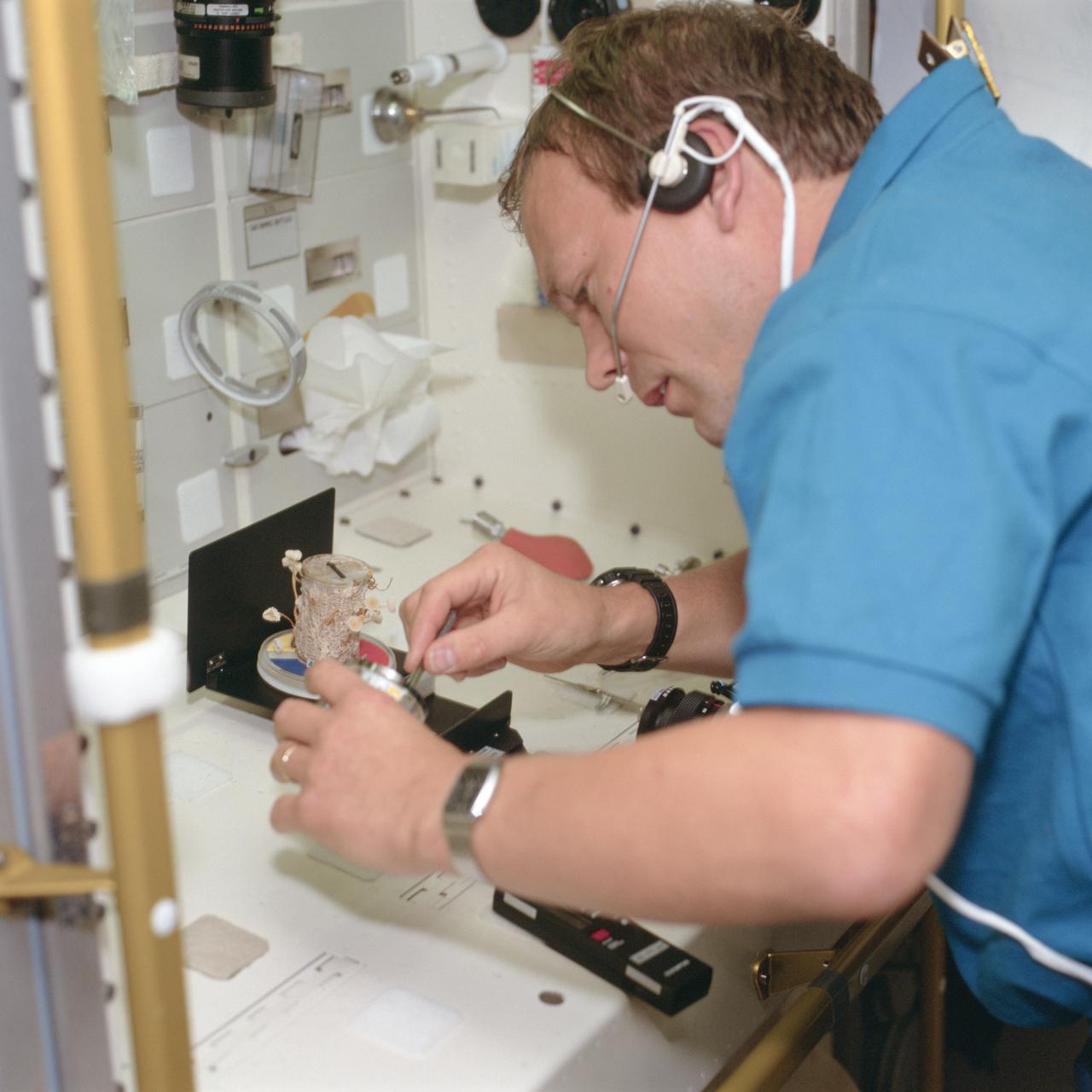

STS055-106-037 (26 April-6 May 1993) --- Hans Schlegel works with a fungi experiment in the Spacelab D-2 Science Module onboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Schlegel was one of two payload specialists representing the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DLR) on the 10-day Spacelab D-2 mission.
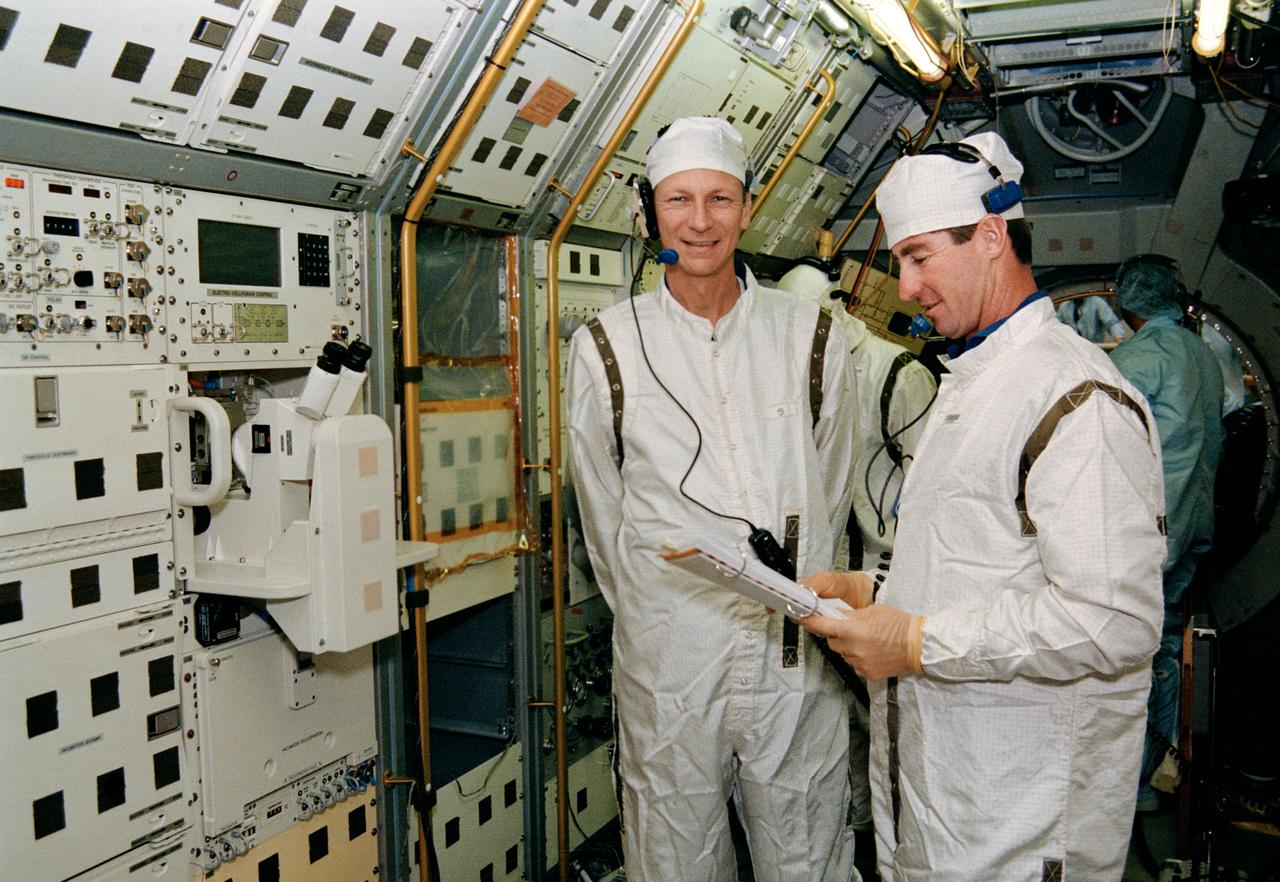

S93-29830 (4 Nov 1992) --- Inside the Spacelab D-2 module in the Operations and Checkout Building high bay, STS-55 Mission Commander Steven R. Nagel (left) and Pilot Terence T. Henricks are participating in a mission sequence test to check out experiment steps and procedures which will be conducted on-orbit. Spacelab D-2, the second German Spacelab, is scheduled to fly on space shuttle mission STS-55 in 1993.
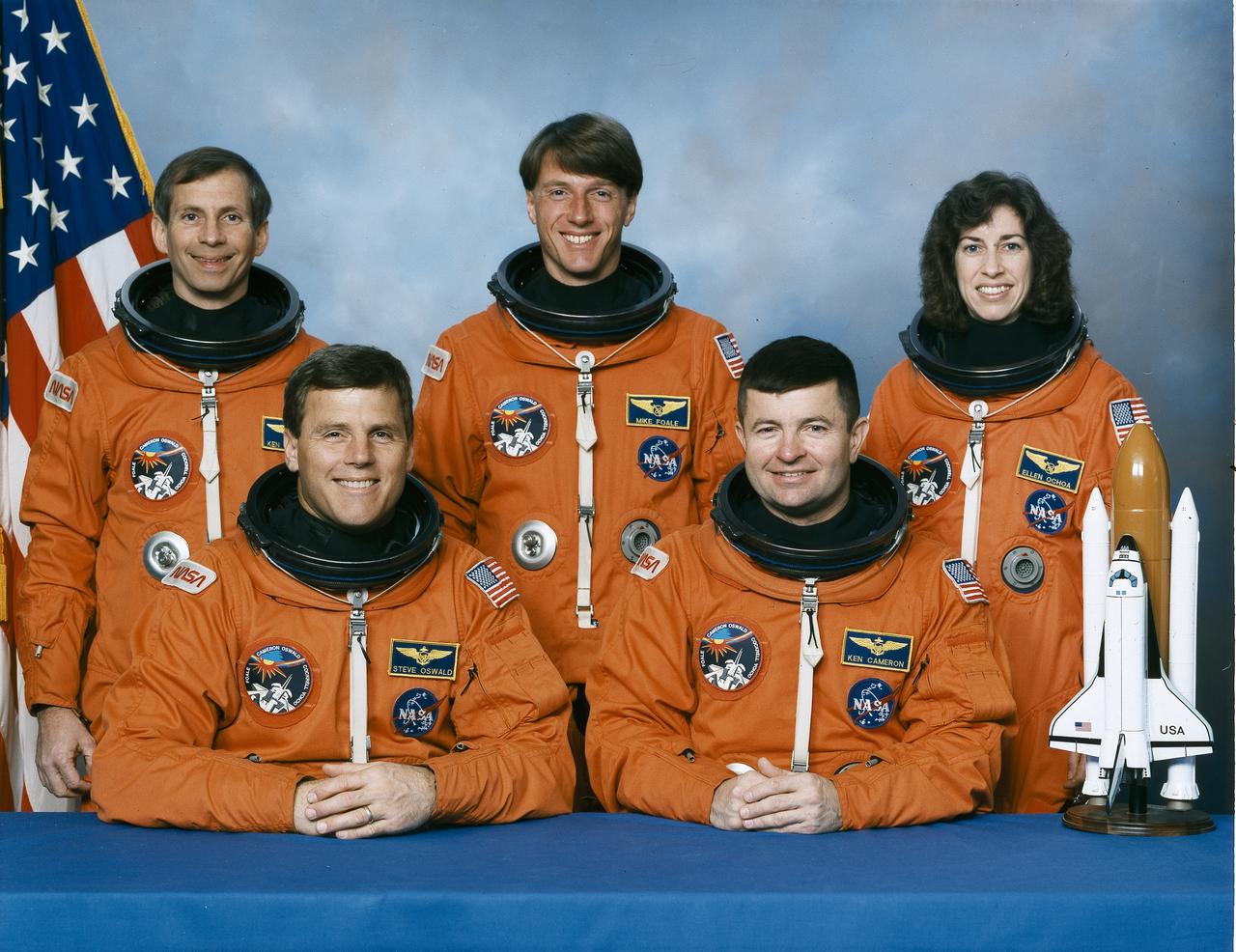

The STS-56 crew portrait includes five astronauts. Seated from the left are Stephen S. Oswald, pilot; and Kenneth D. Cameron, commander. Standing, from the left, are mission specialists Kenneth D. Cockrell, C. Michael Foal, and Ellen Ochoa. The crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 8, 1993 at 1:29:00 am (EDT) with the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science-2 (ATLAS-2) as the primary payload.
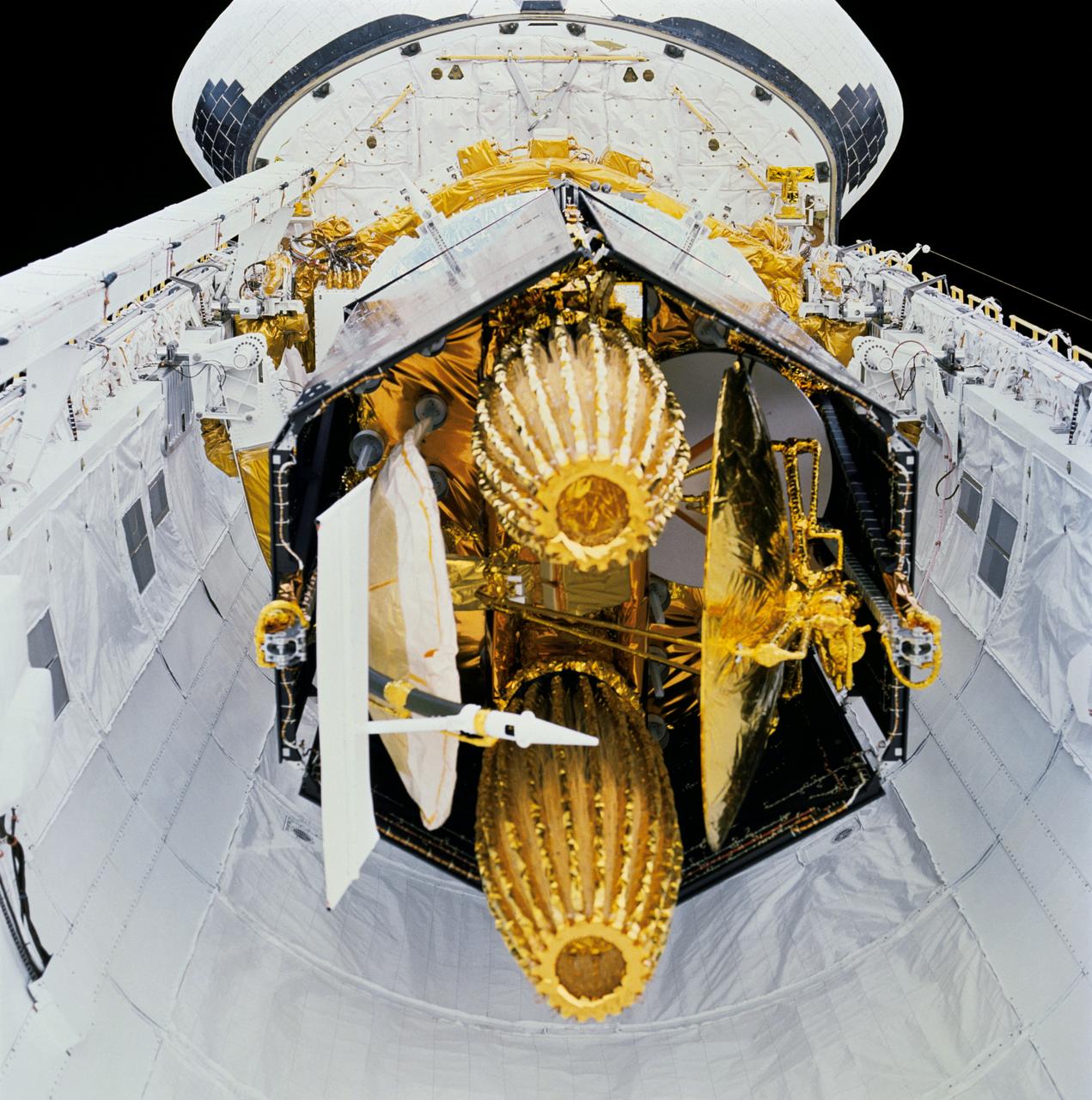

STS029-71-000AE (13-18 March 1989) --- STS-29 onboard view shows Space Shuttle Discovery's payload bay with tracking and data relay satellite D (TDRS-D) in stowed, pre-deployment position. In this head-on view, TDRS-D stowed components including single access #1 and #2, solar cell panels, SGL, S-Band omni antenna, and C-Band antenna are visible. TDRS-D rests in airborne support equipment (ASE) forward cradle and aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA). Discovery's aft bulkhead and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods are visible in the background.
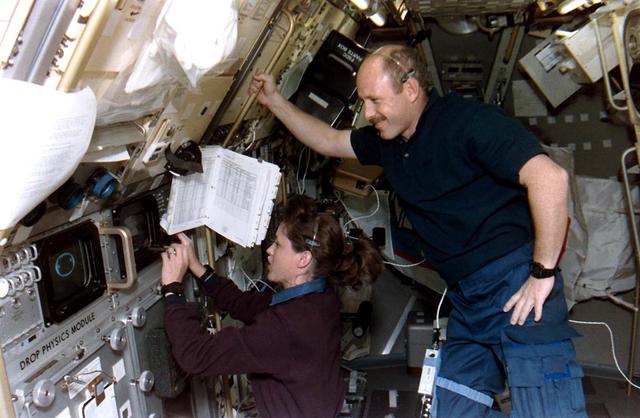

Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander, works at the Drop Physics Module (DPM) on the portside of the science module supporting the U.S. Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2). Astronaut Kerneth D. Bowersox, mission commander, looks on.
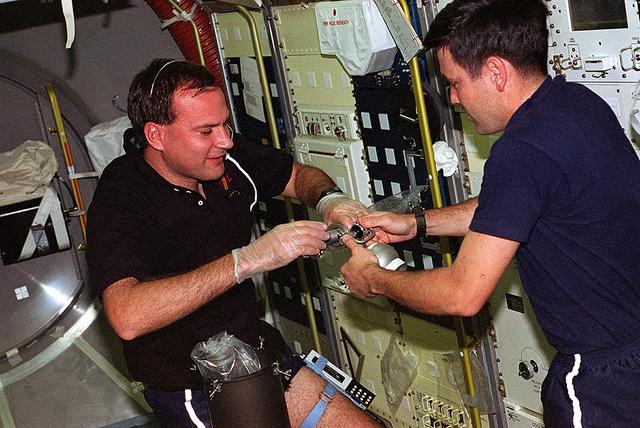

Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-65) onboard photo of Payload specialist Richard J. Hieb (right) and Shuttle Pilot James D. Halsell Jr. working on experiments in the Spacelab in the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
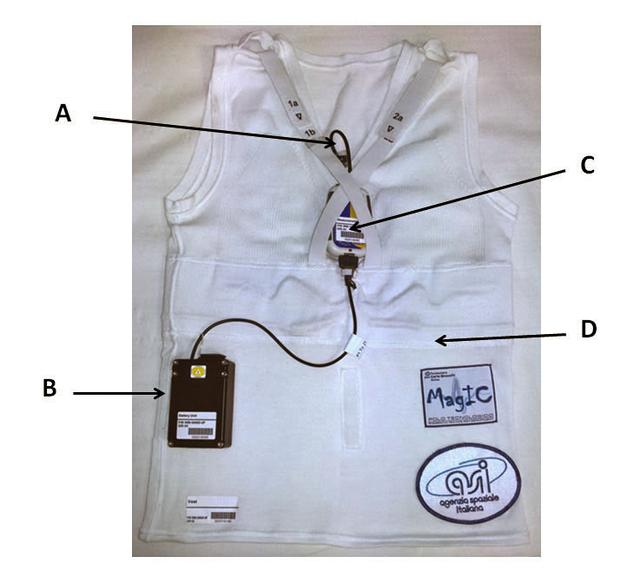
jsc2021e009422 (3/2/2021) --- A preflight view of the MagIC-Space payload. A=Thermometer probe; B= Battery Pack; C= Measurement Unit; D=Vest of the Wearable Monitoring Facility. Image courtesy of Marco Di Rienzo ©
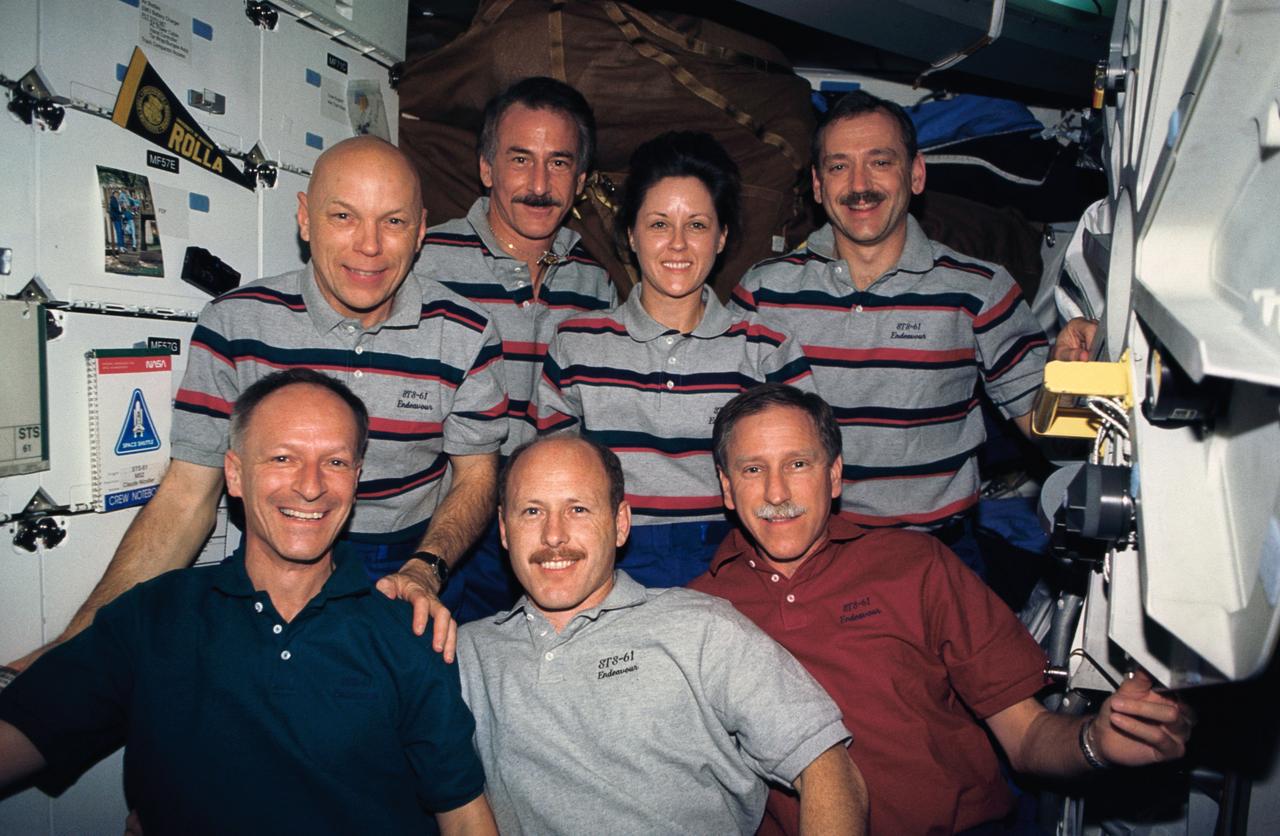

STS061-11-004 (2-13 Dec 1993) --- Traditional inflight portrait for the crew of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. On the front row are the three crew members who assisted from inside the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cabin throughout the five space walks. They are, left to right, Swiss scientist Claude Nicollier, mission specialist, along with astronauts Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot; and Richard O. Covey, mission commander. Back row -- all space walkers on this flight -- are astronauts F. Story Musgrave, payload commander; Jeffrey A. Hoffman, Kathryn D. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers, all mission specialists.
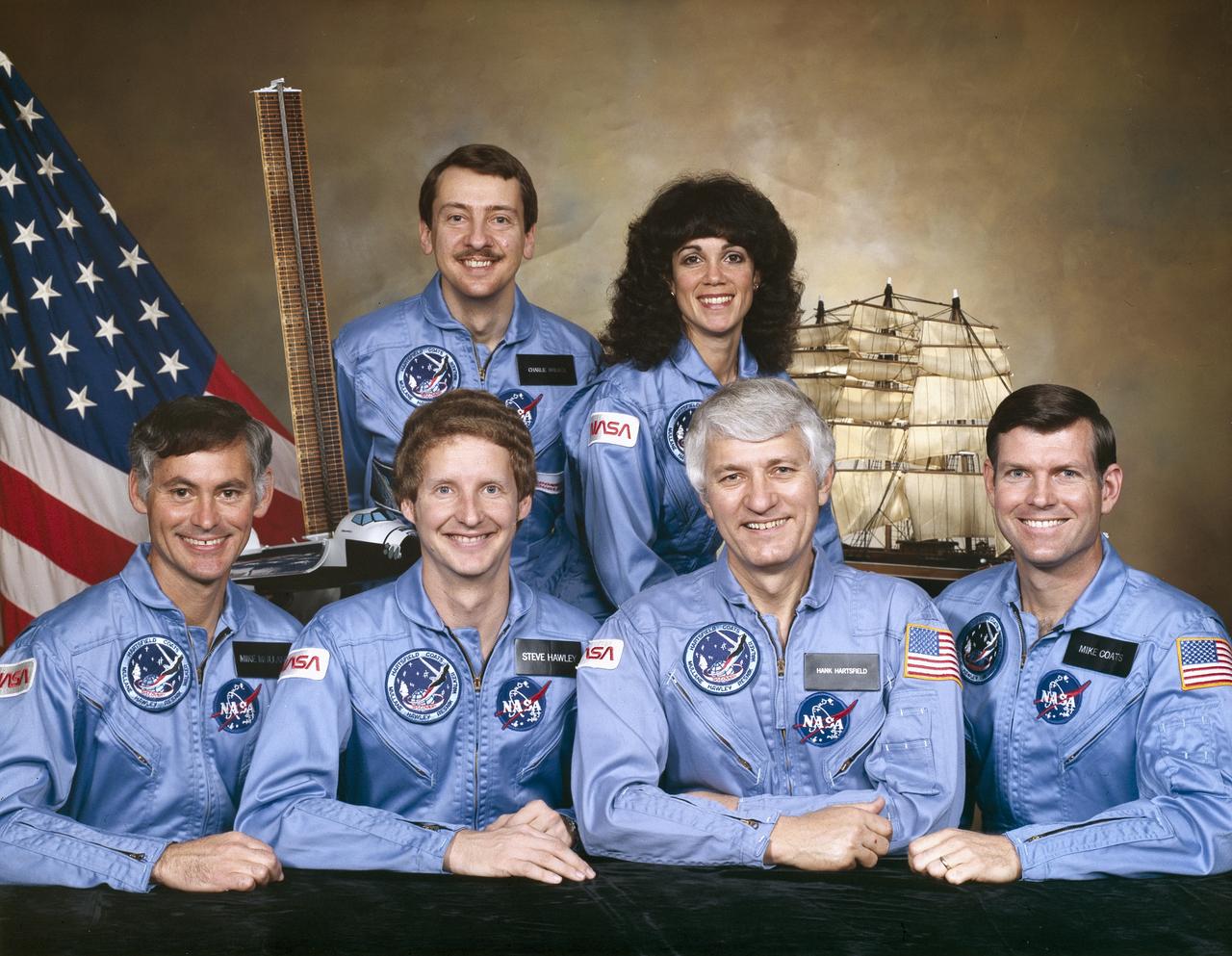

The crew assigned to the STS-41D mission included (seated left to right) Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, mission specialist; Steven A. Hawley, mission specialist; Henry W. Hartsfield, commander; and Michael L. (Mike) Coats, pilot. Standing in the rear are Charles D. Walker, payload specialist; and Judith A. (Judy) Resnik, mission specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery August 30, 1984 at 8:41:50 am (EDT), the STS-41D mission deployed three satellites: the Satellite Business System SBS-D; the SYCOM IV-2 (also known as LEASAT-2); and the TELSTAR.
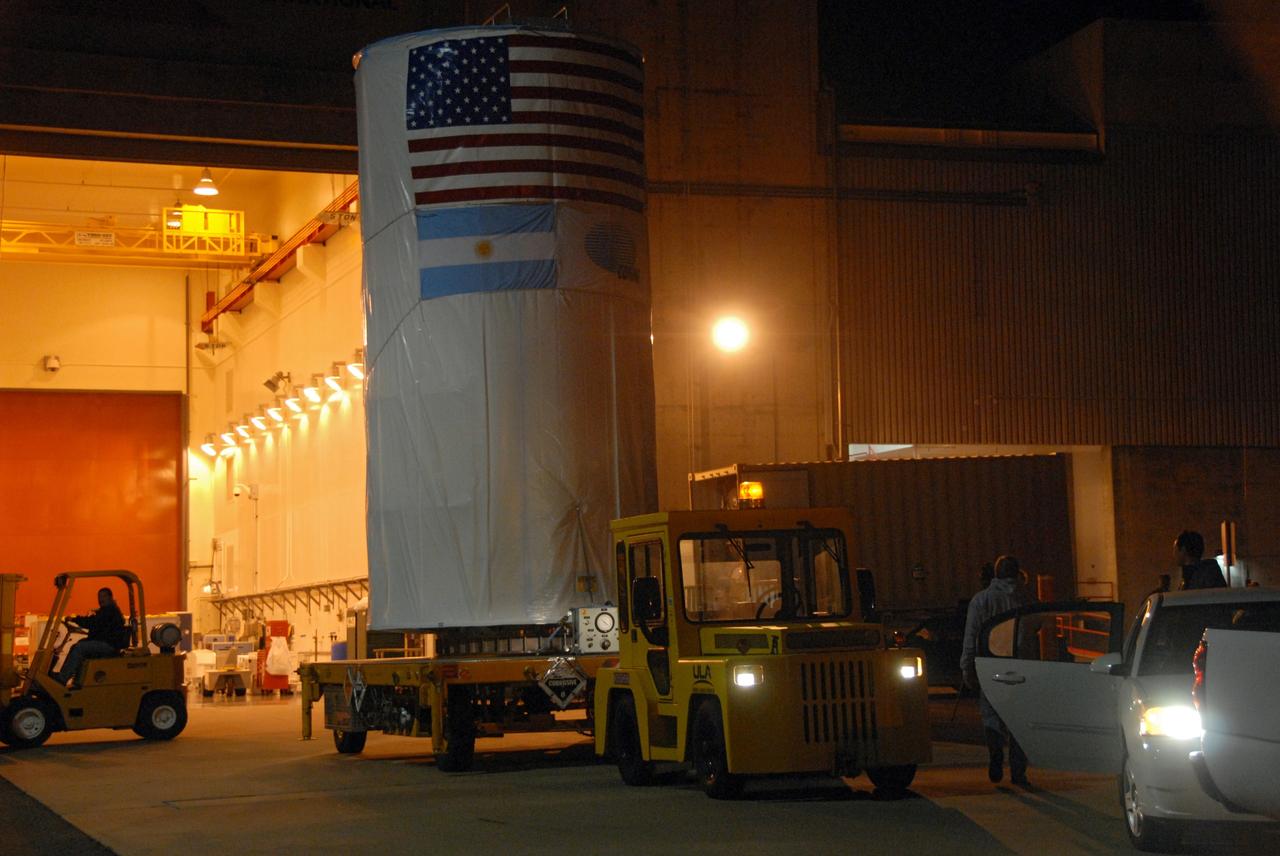

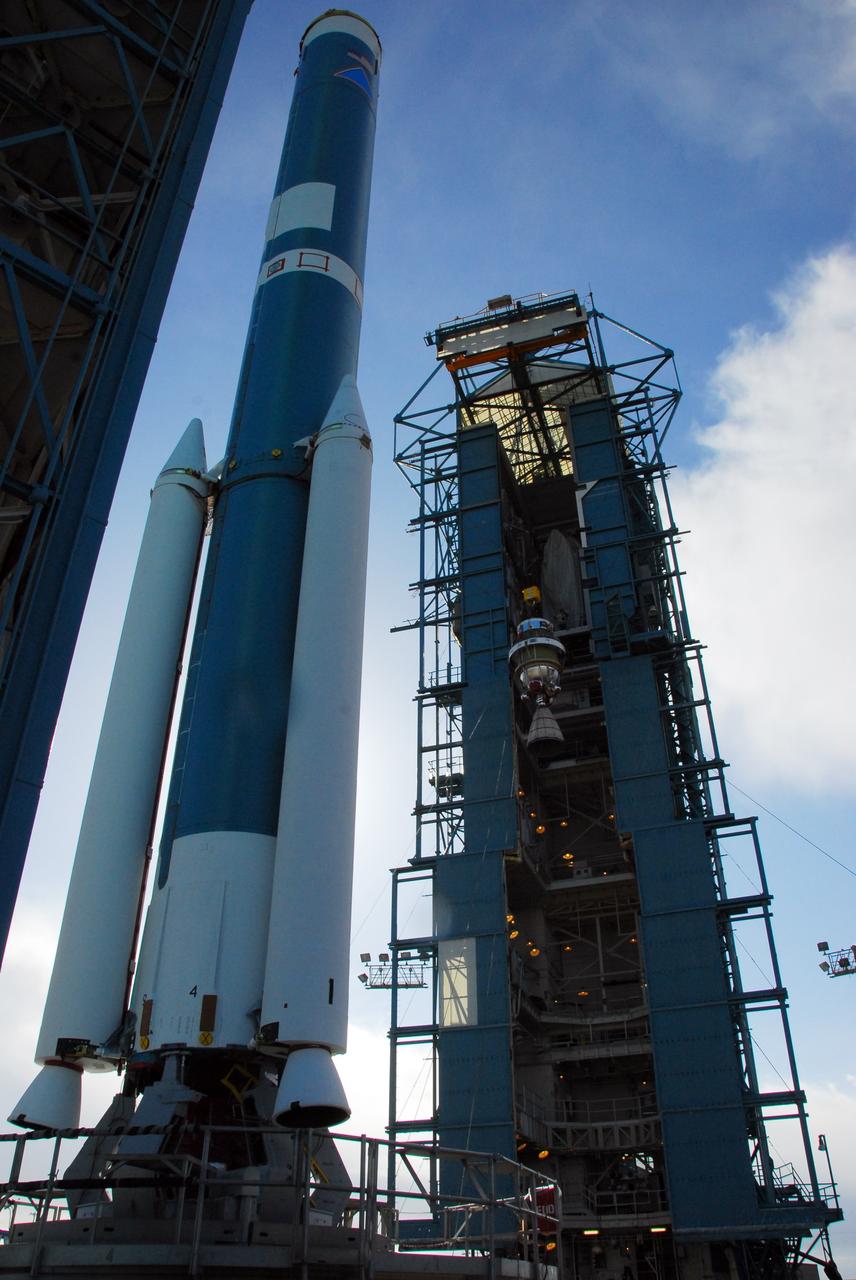
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft, secured inside its payload transportation canister, is being transferred to NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. There, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
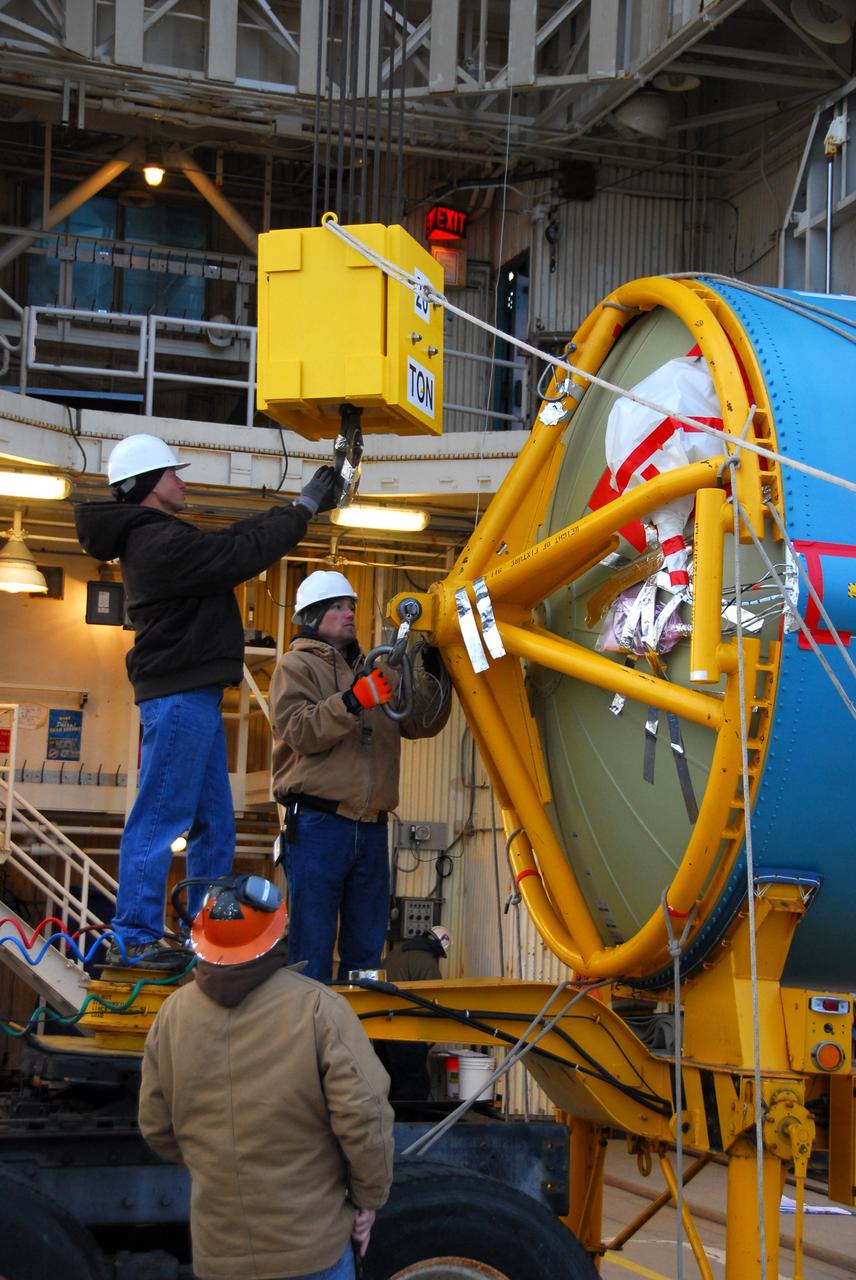

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers prepare the first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into low Earth orbit, for its vertical lift into the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, on its three-year mission, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
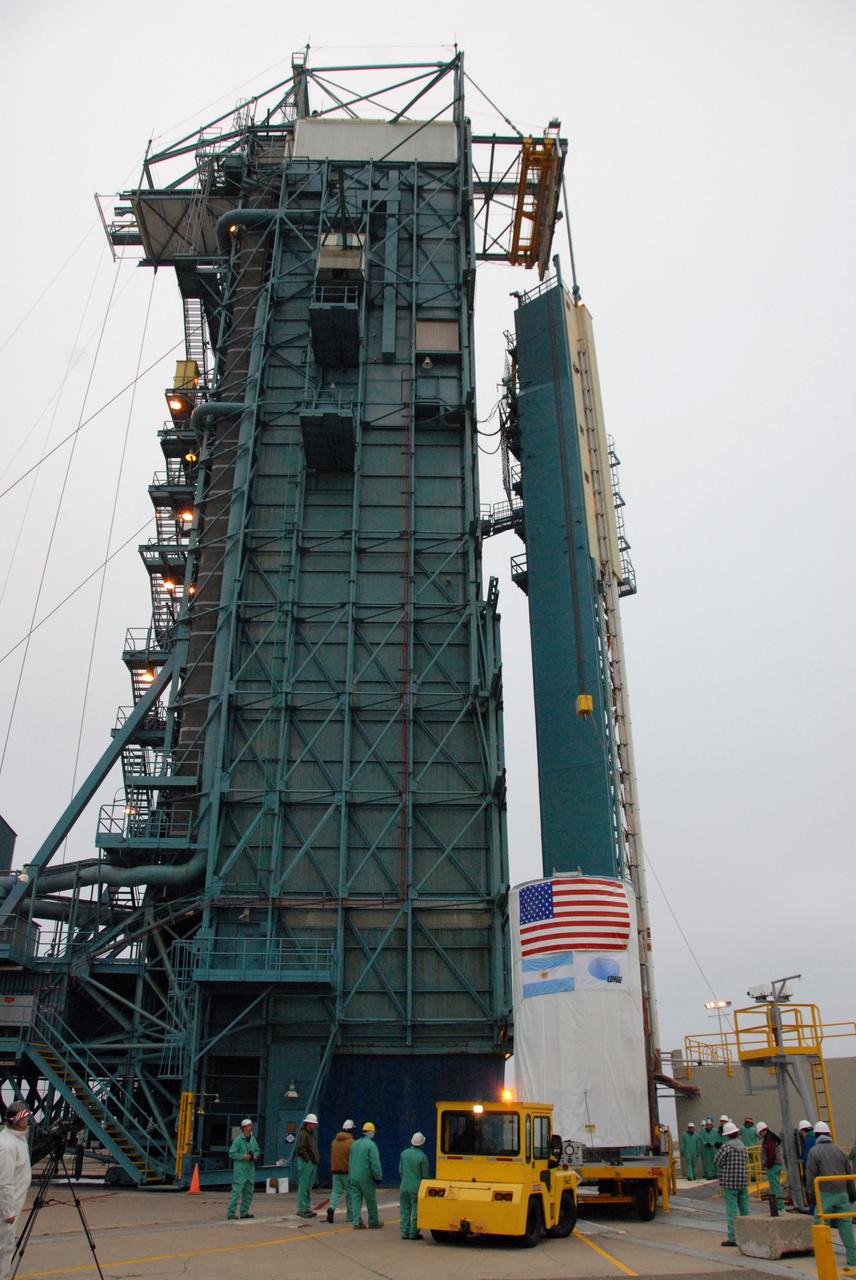

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers attach an overhead crane to the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft, secured inside its payload transportation canister, for lifting into the mobile service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. There, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- With the aid of an overhead crane, workers lift the first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into low Earth orbit, into the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, on its three-year mission, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

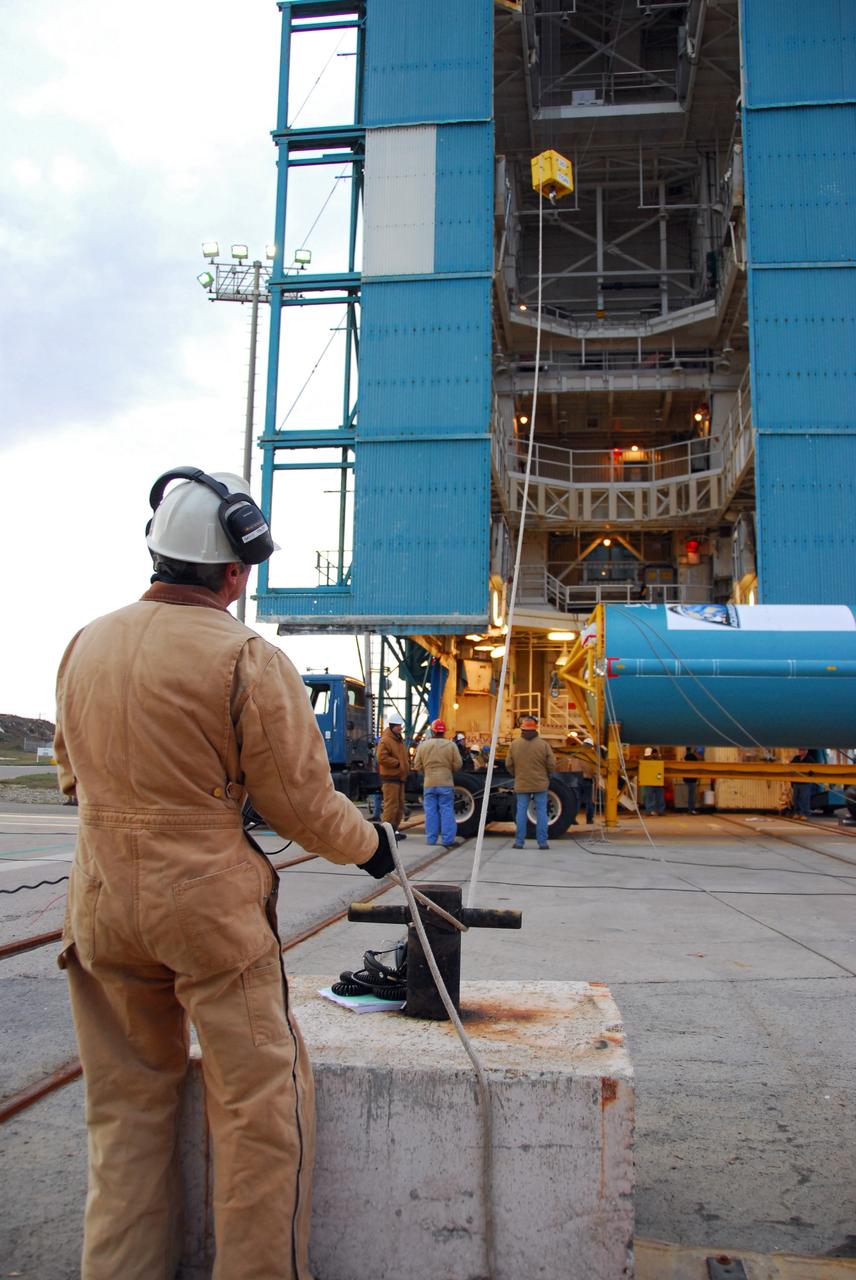
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers using an overhead crane lower the United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage motor toward the first stage for mating at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

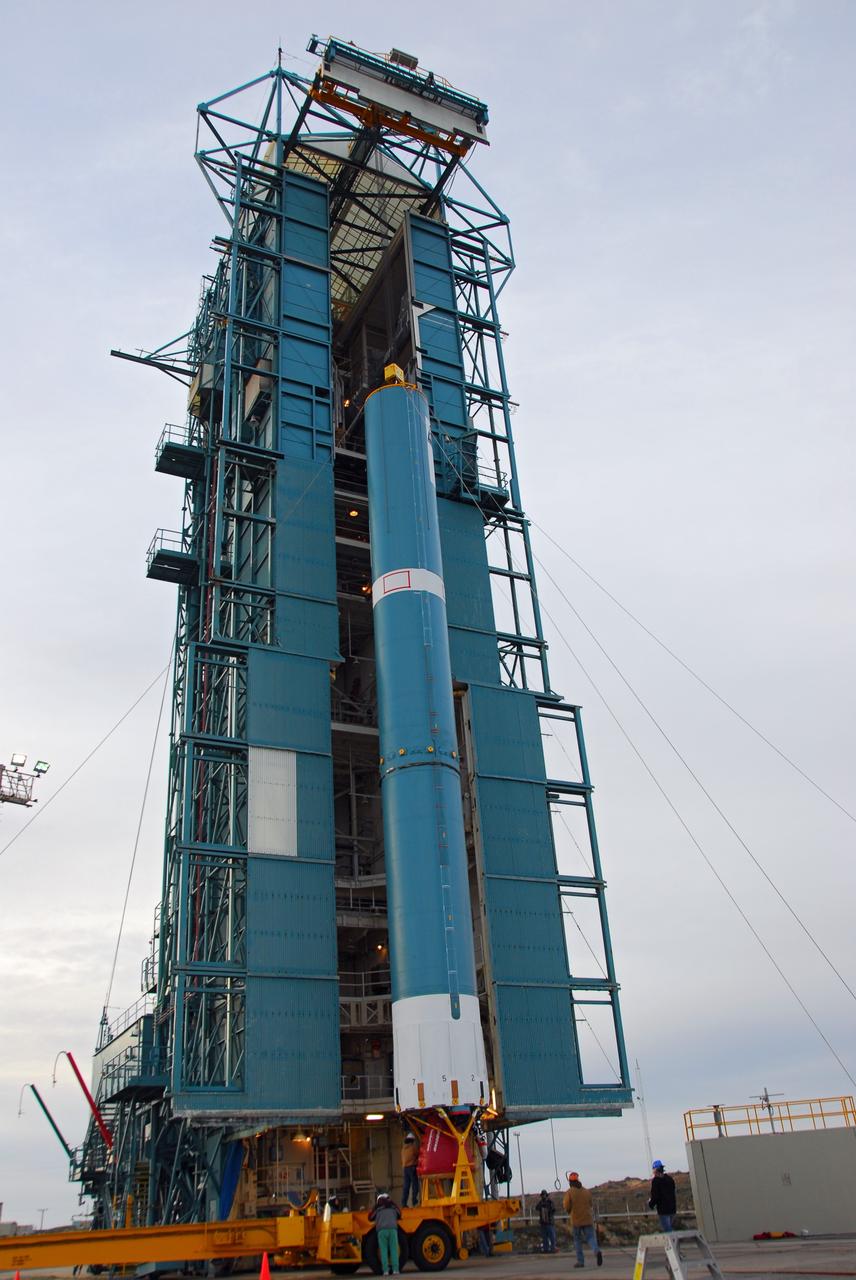
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into low Earth orbit is being prepared for its vertical lift into the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, on its three-year mission, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
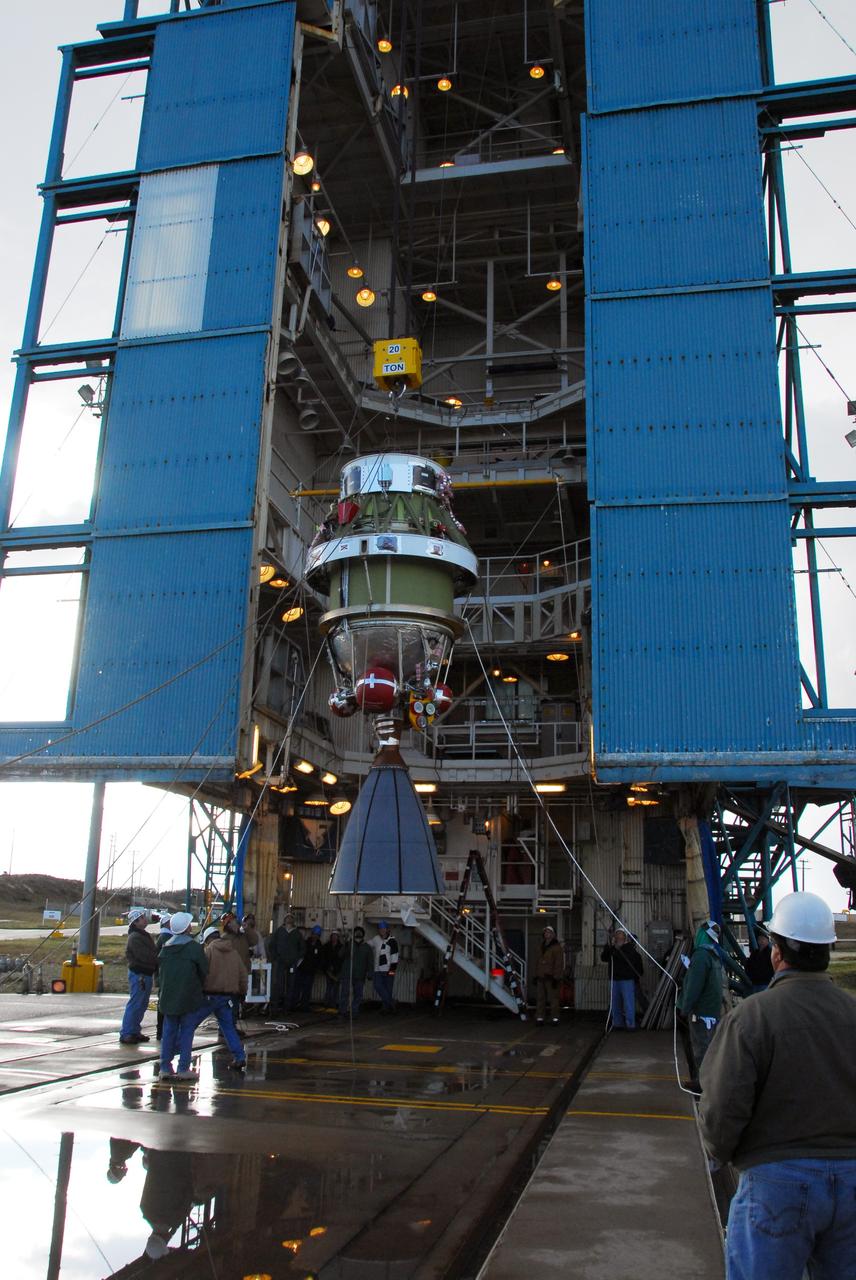

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- With the help of an overhead crane workers lift the United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage motor to the top of the service tower for mating with the first stage at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- An overhead crane lifts the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft, secured inside its payload transportation canister, into the mobile service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. There, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
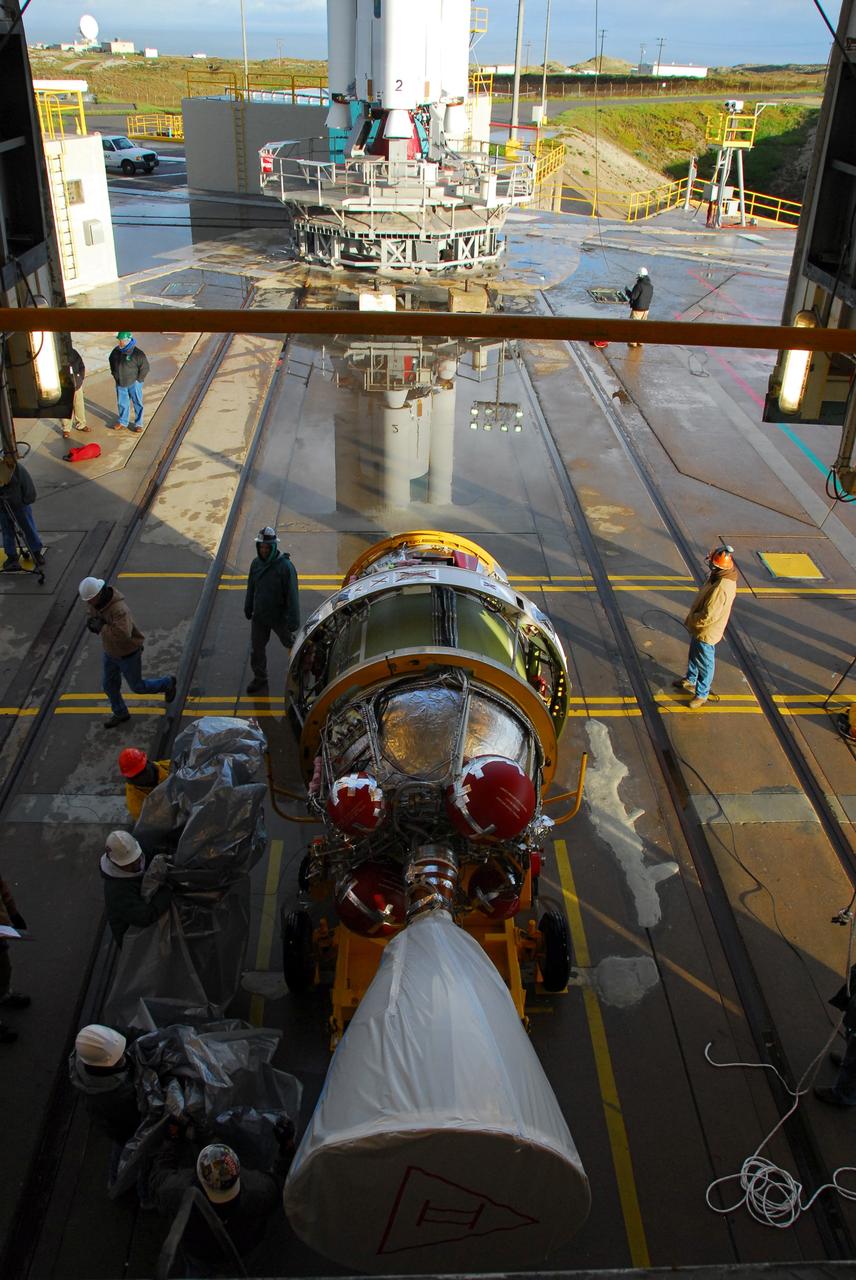
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers remove the payload transportation canister from the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft, after it was lifted into the mobile service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. There, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- With the help of an overhead crane workers lift the United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage motor to the top of the service tower for mating with the first stage at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers prepare the United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage motor for lifting into the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
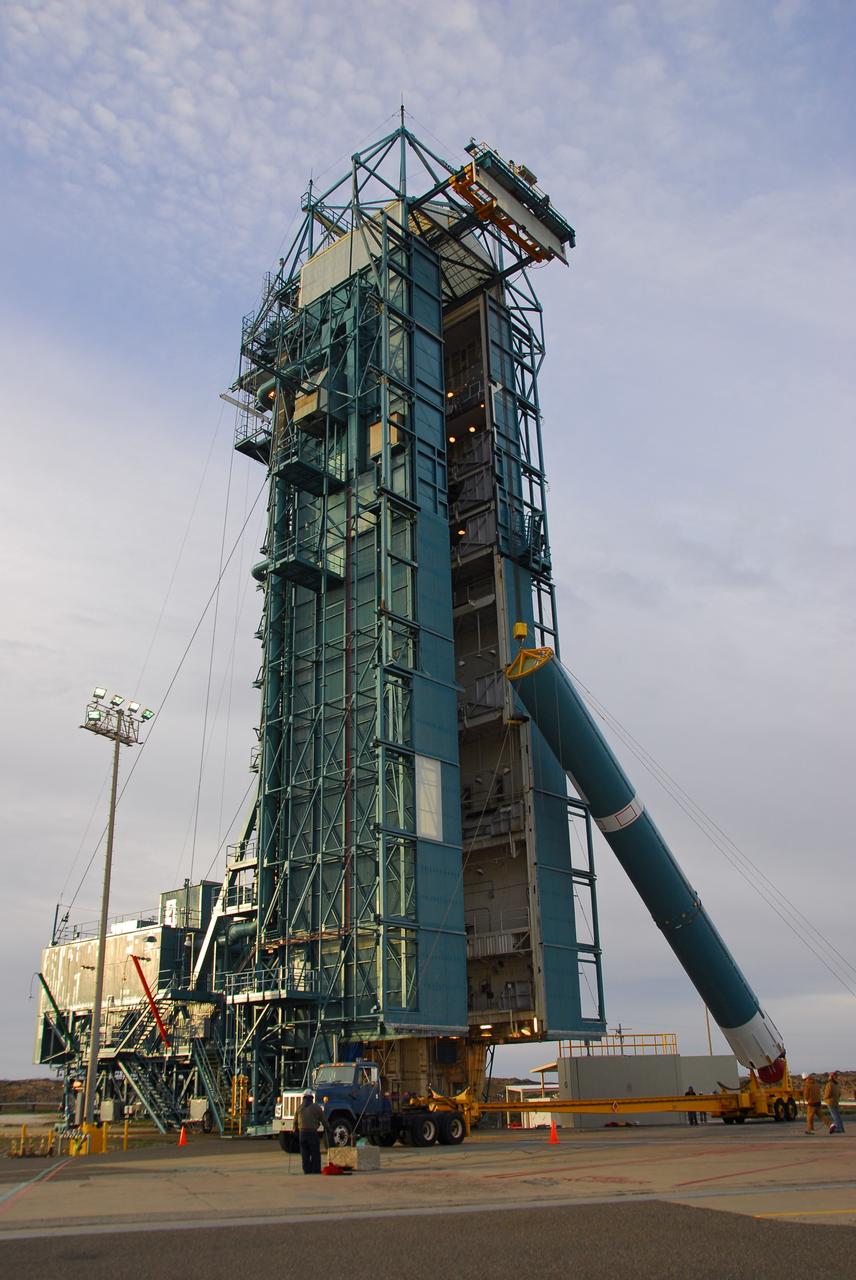

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- With the aid of an overhead crane, workers lift the first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into low Earth orbit, into the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, on its three-year mission, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
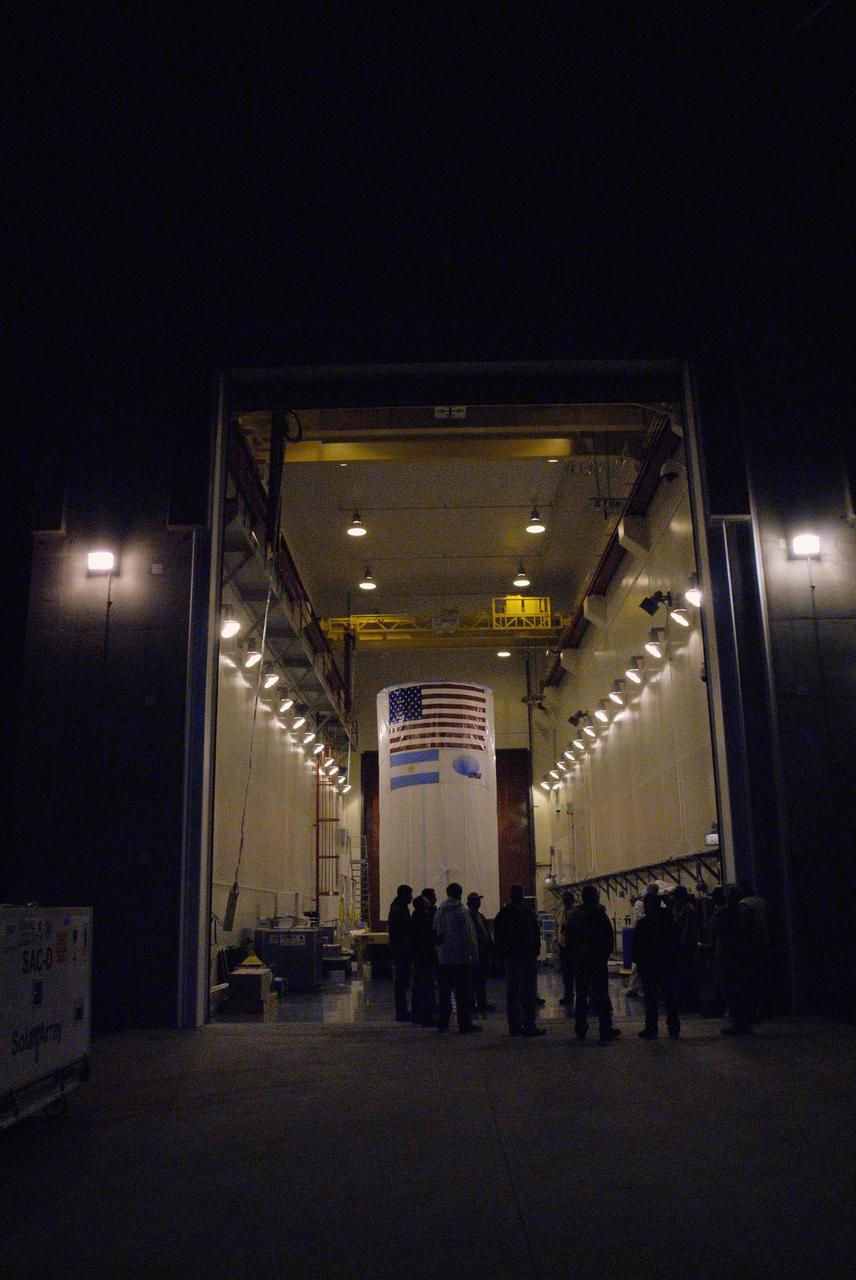

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft is secured inside its payload transportation canister for transfer to NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. There, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft, secured inside its payload transportation canister, is being transferred to NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. There, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
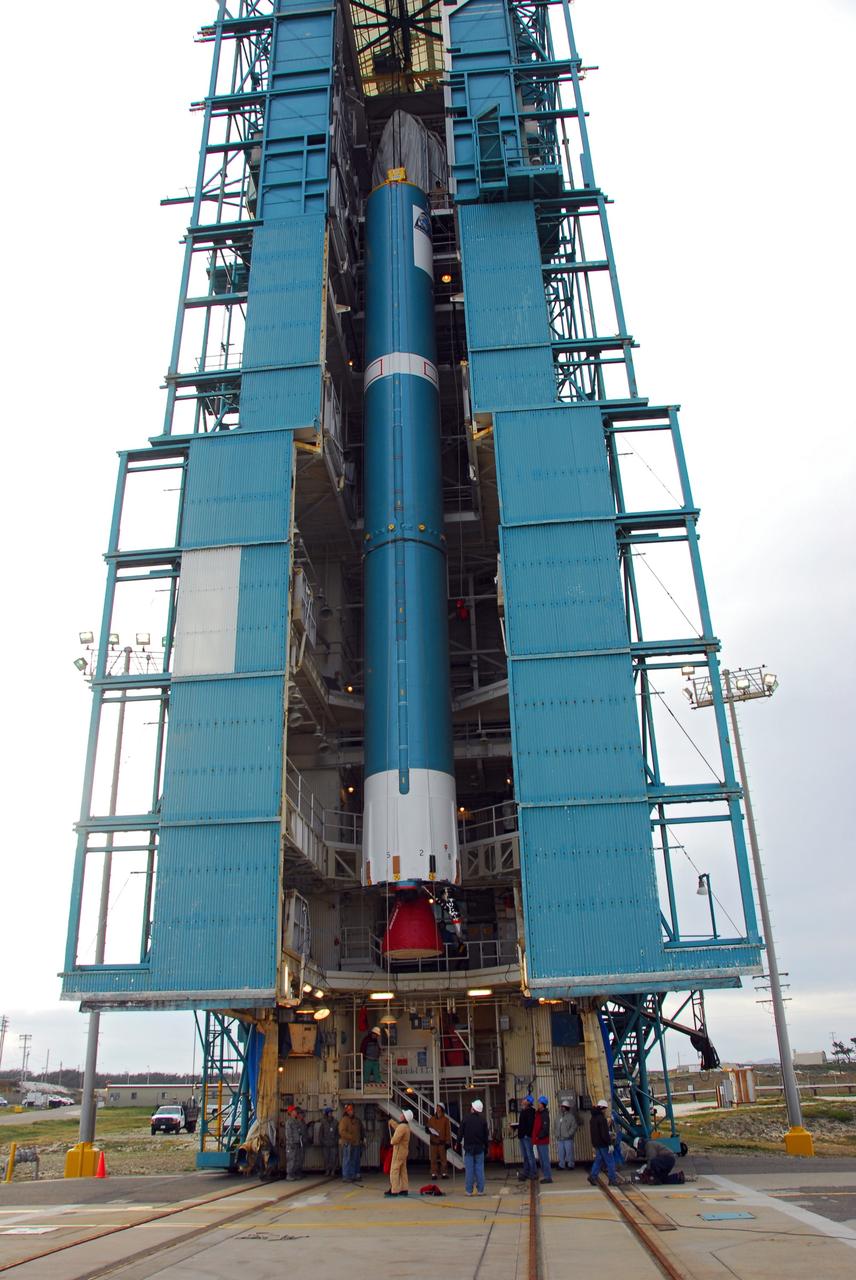

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- With the aid of an overhead crane, workers guide the first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into low Earth orbit, into the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, on its three-year mission, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- With the aid of an overhead crane, workers guide the first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into low Earth orbit, into the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, on its three-year mission, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry the Aquarius/SAC-D satellite into low Earth orbit arrives to the launch pad at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built primary instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, on its three-year mission, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
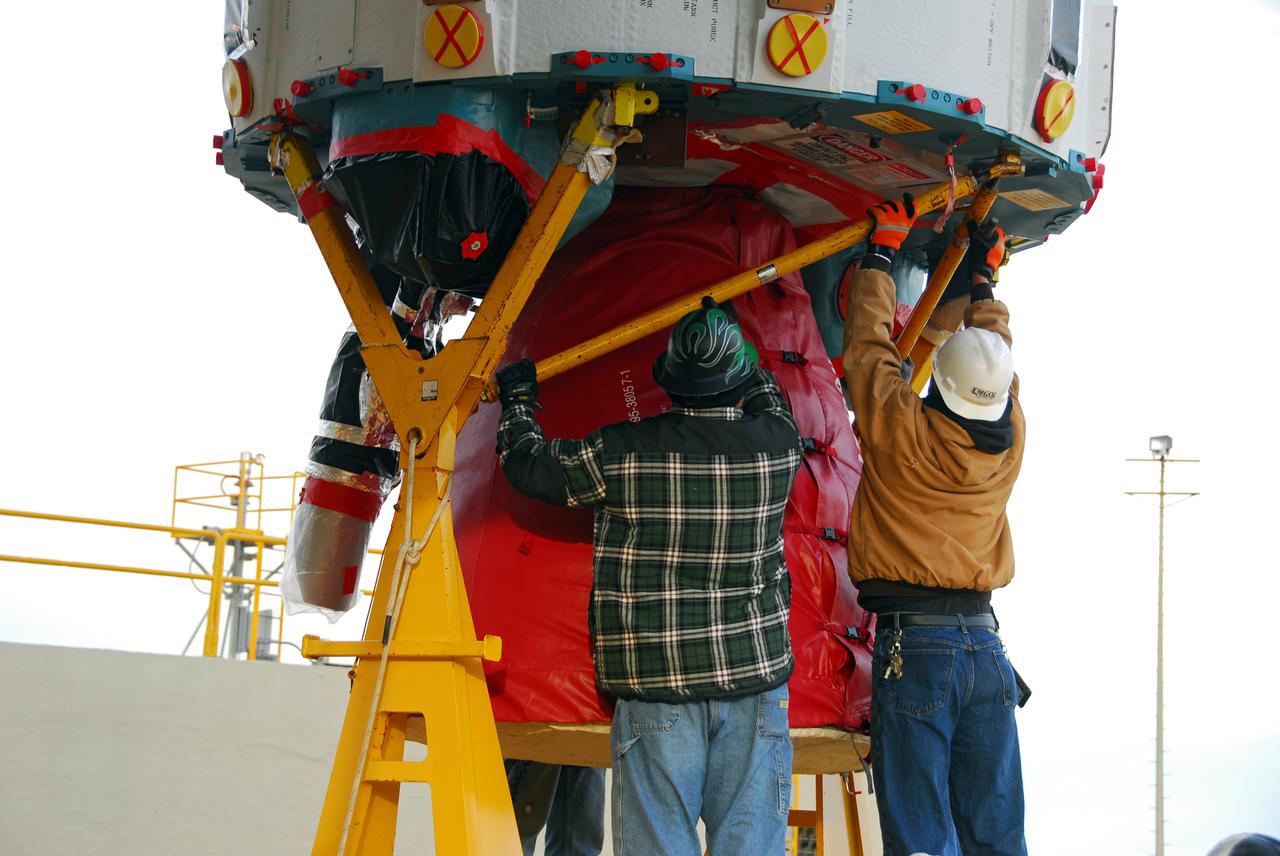

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers guide the first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry the Aquarius_SAC-D spacecraft into low Earth orbit onto the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, on its three-year mission, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes. Photo credit: NASA_VAFB
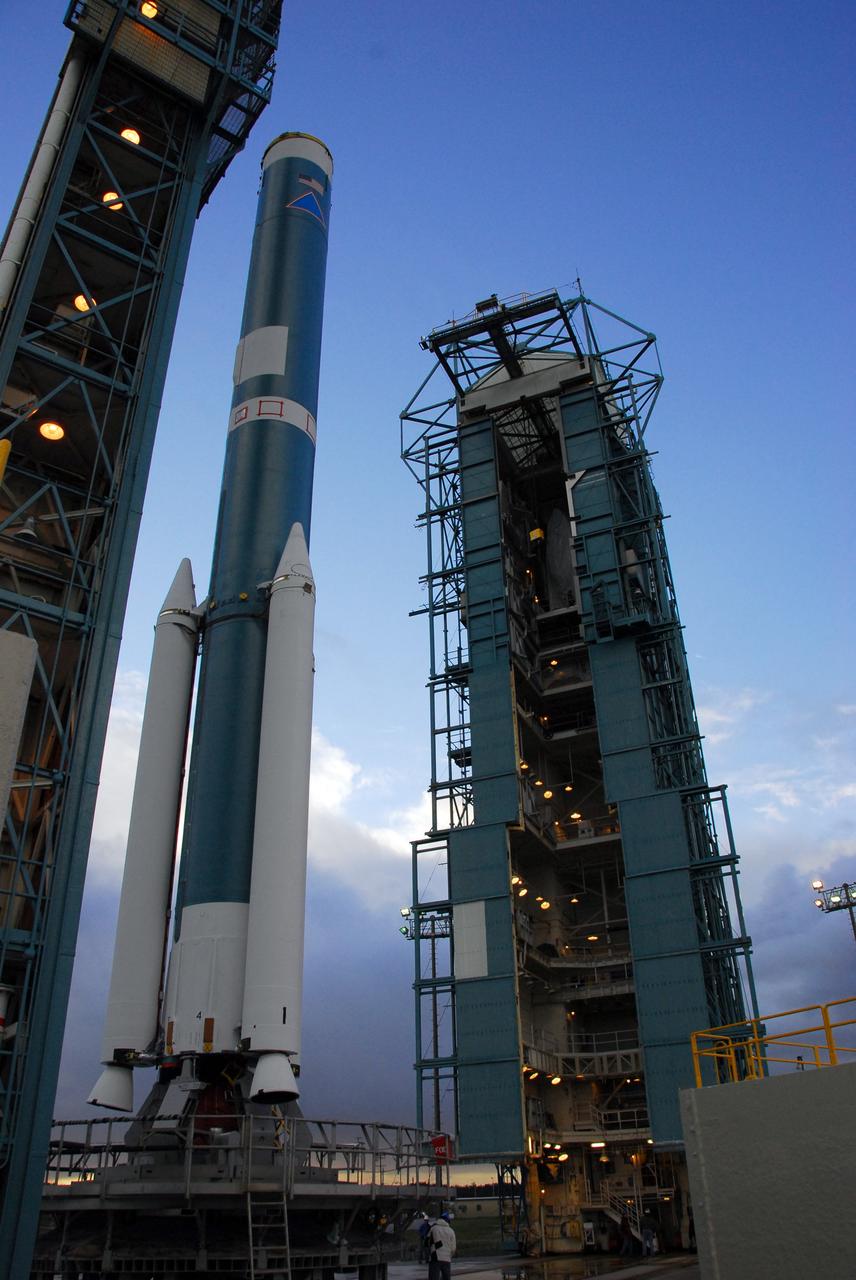

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is moved away from the service tower as workers prepare to lift the second stage to the top of the tower for mating with the first stage at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
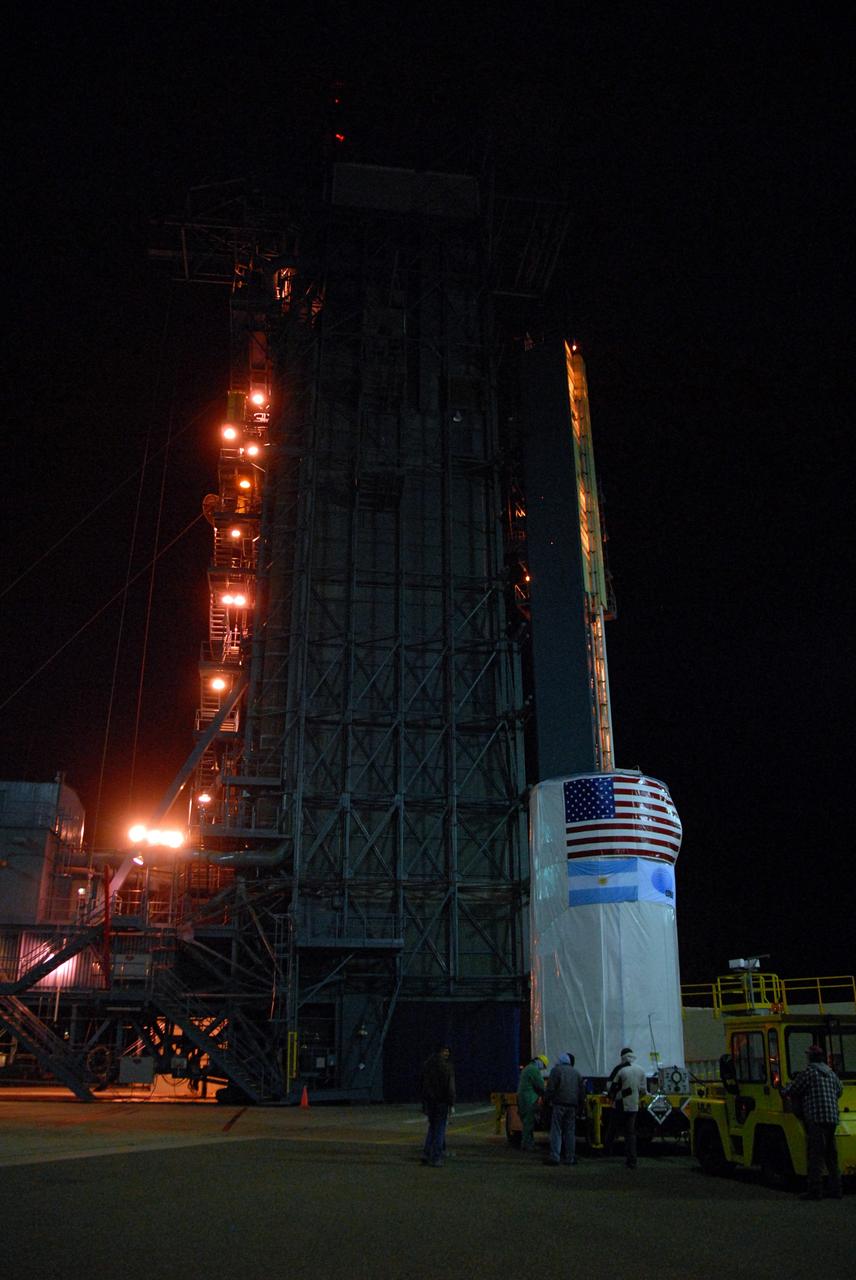

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft, secured inside its payload transportation canister, has been delivered to NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. There, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
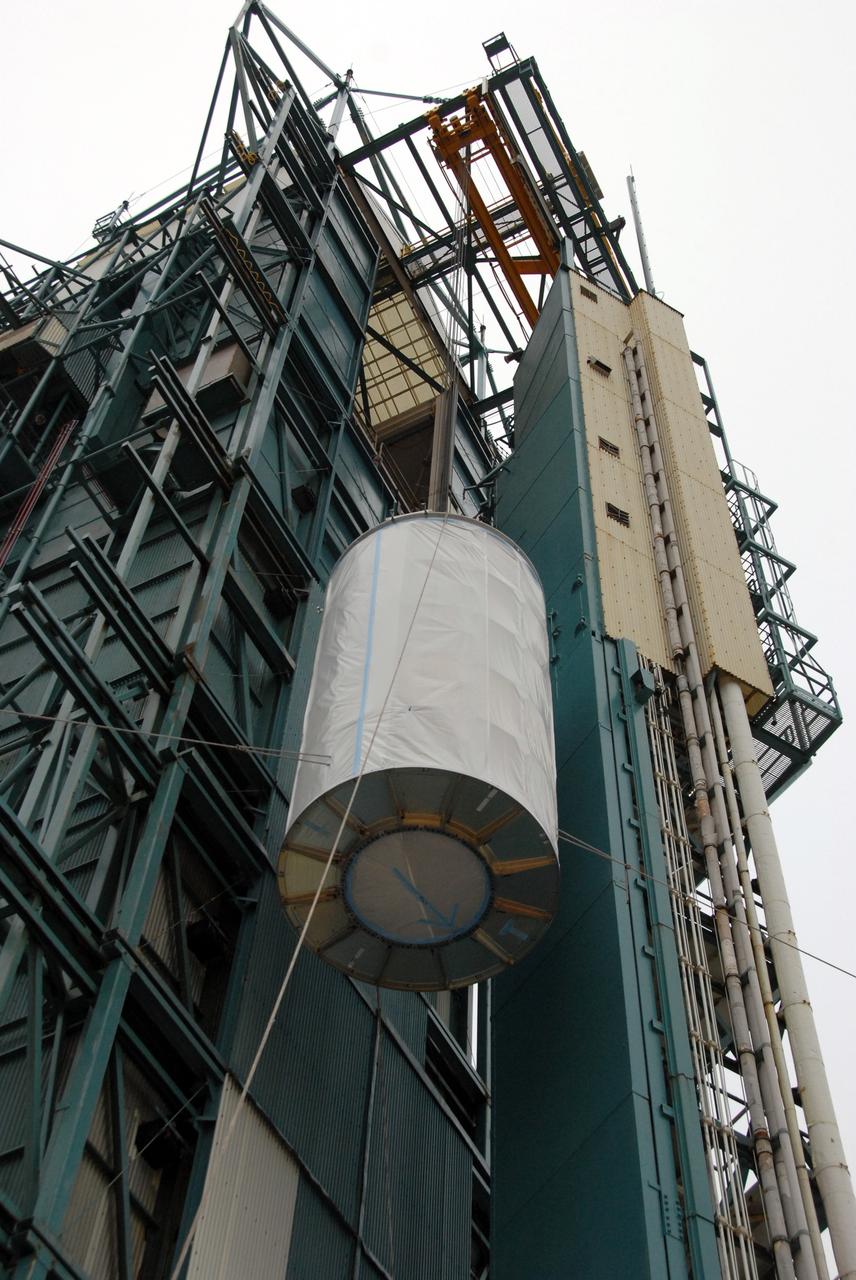

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- An overhead crane lifts the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft, secured inside its payload transportation canister, into the mobile service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. There, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
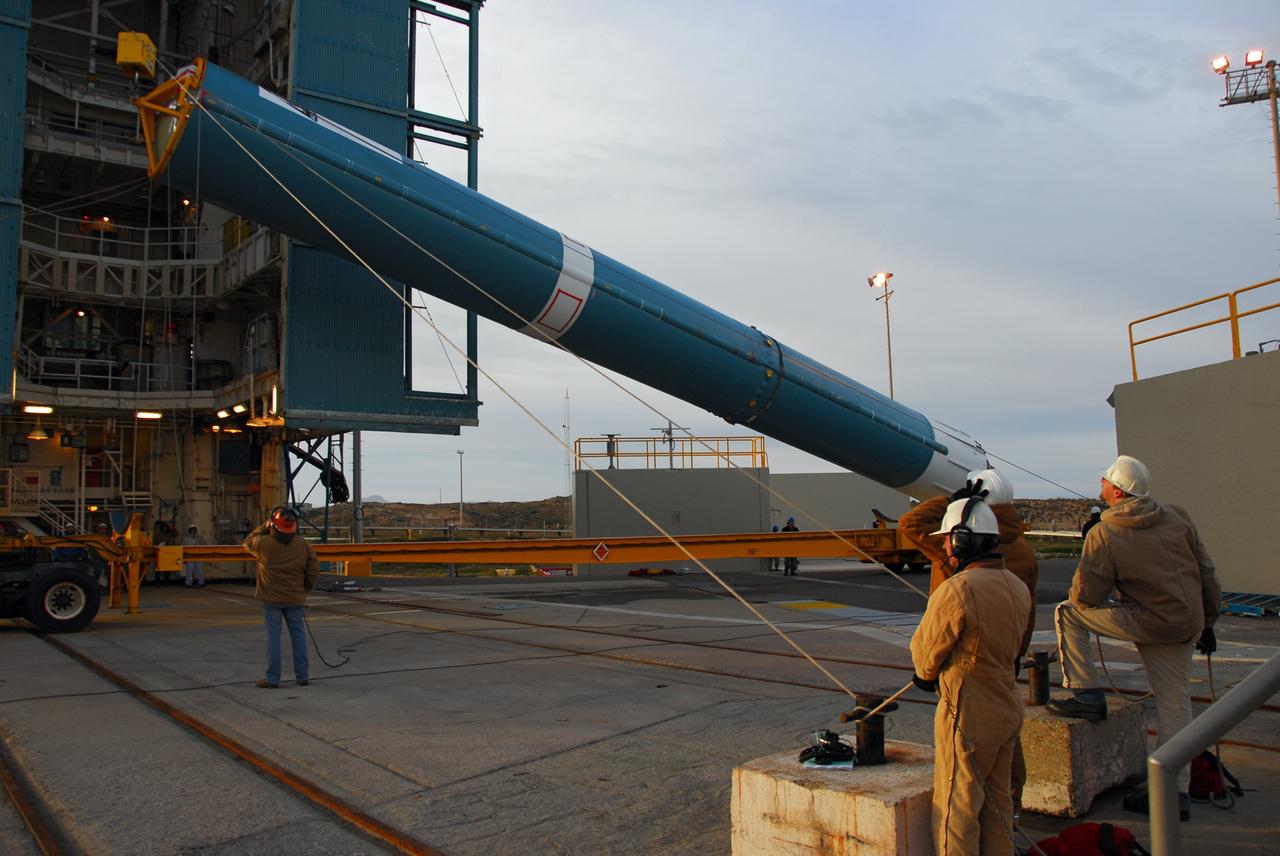

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- With the aid of an overhead crane, workers lift the first stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will carry the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft into low Earth orbit, into the service tower at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II in preparation for the targeted June launch. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, on its three-year mission, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
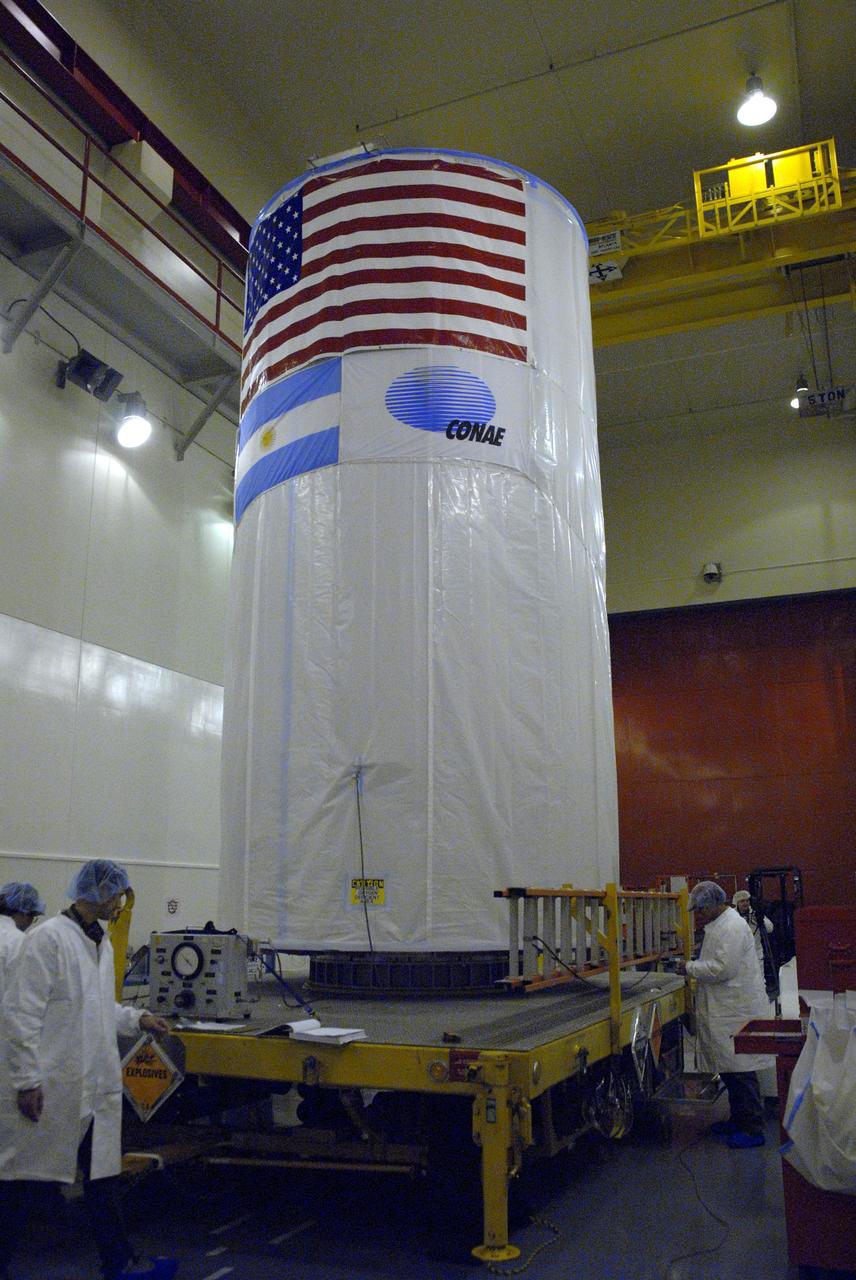

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft is secured inside its payload transportation canister for transfer to NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. There, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
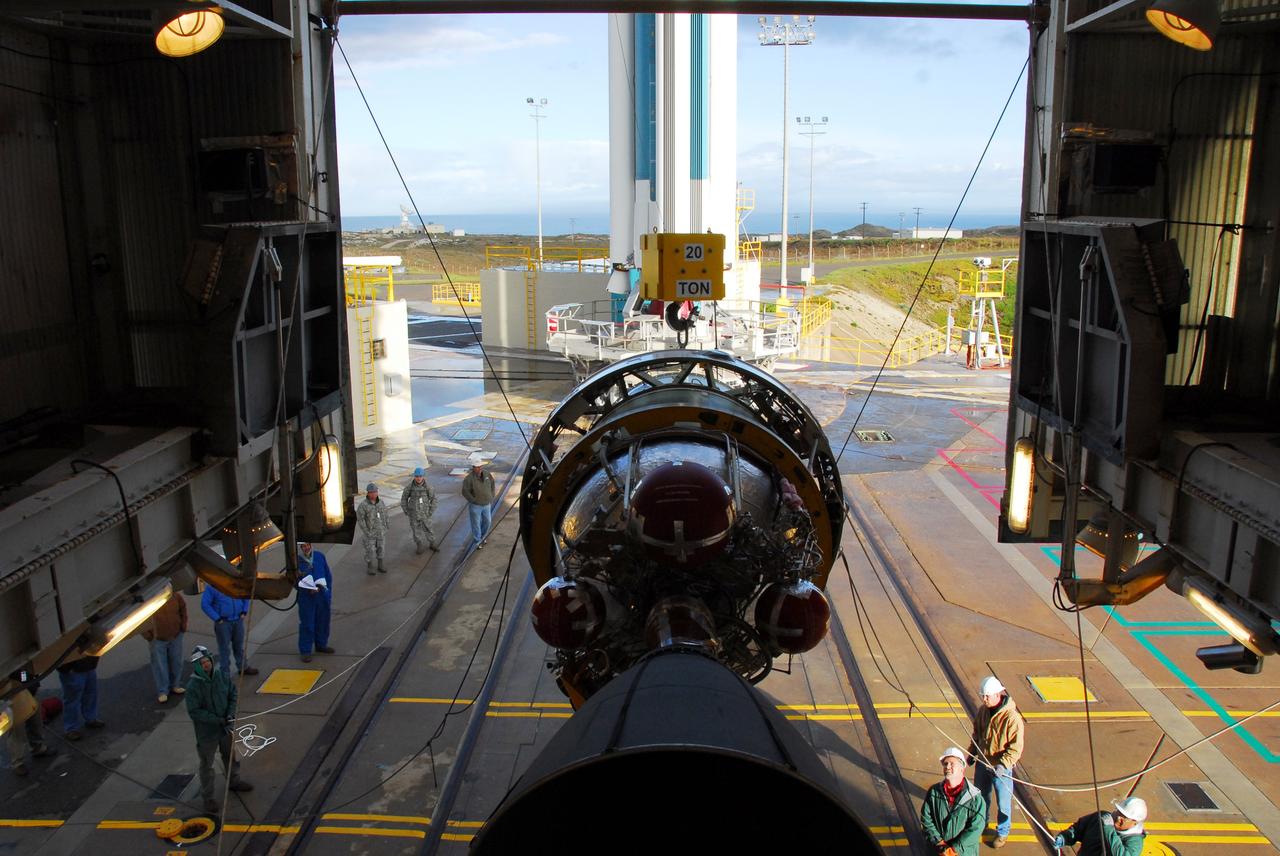

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Workers attach cables from an overhead crane to the United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage motor for mating to the first stage at NASA's Space Launch Complex-2 (SLC-2) at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Following final tests, the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft will be integrated to the Delta II launch vehicle in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
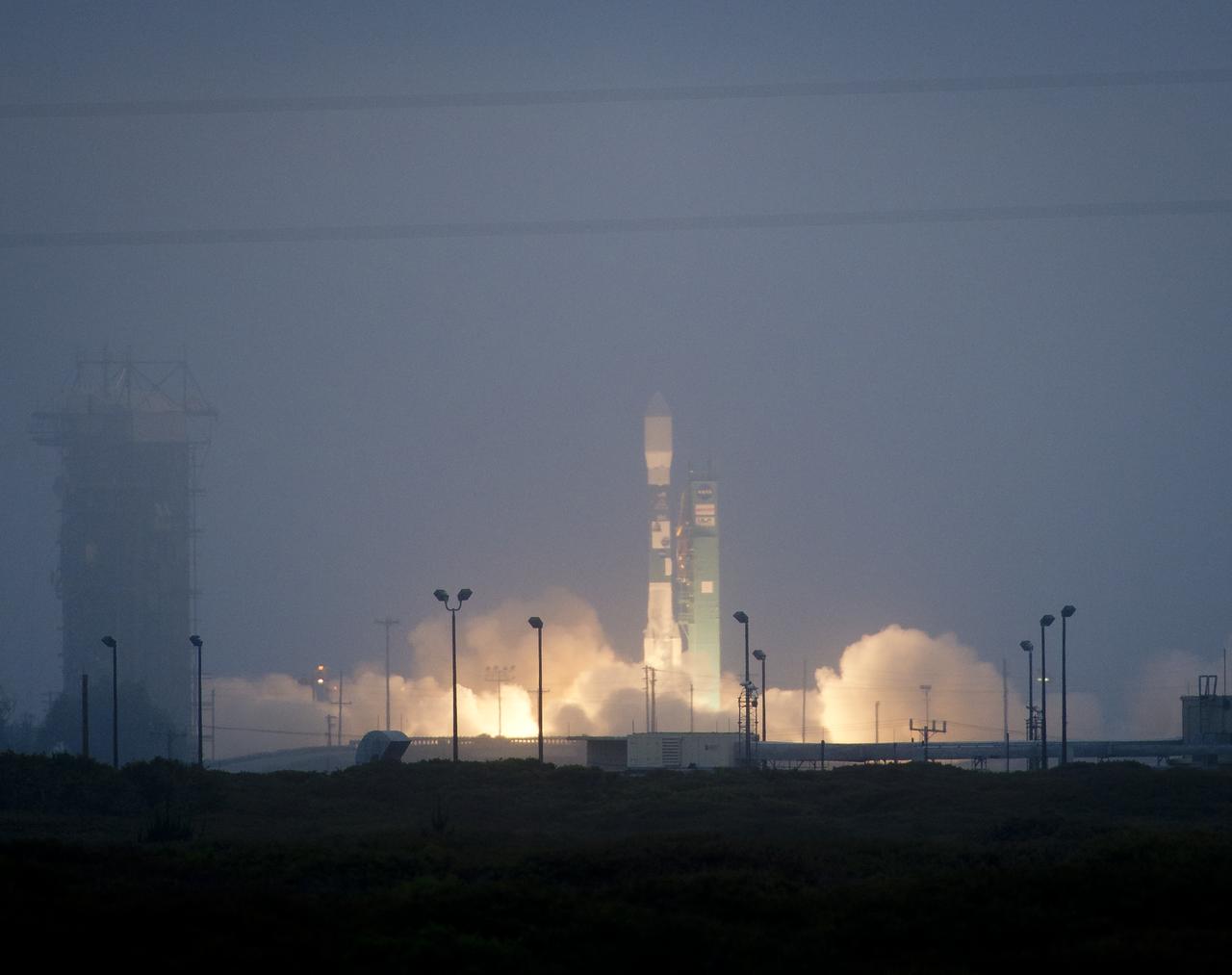

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission, set to launch June 10, will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
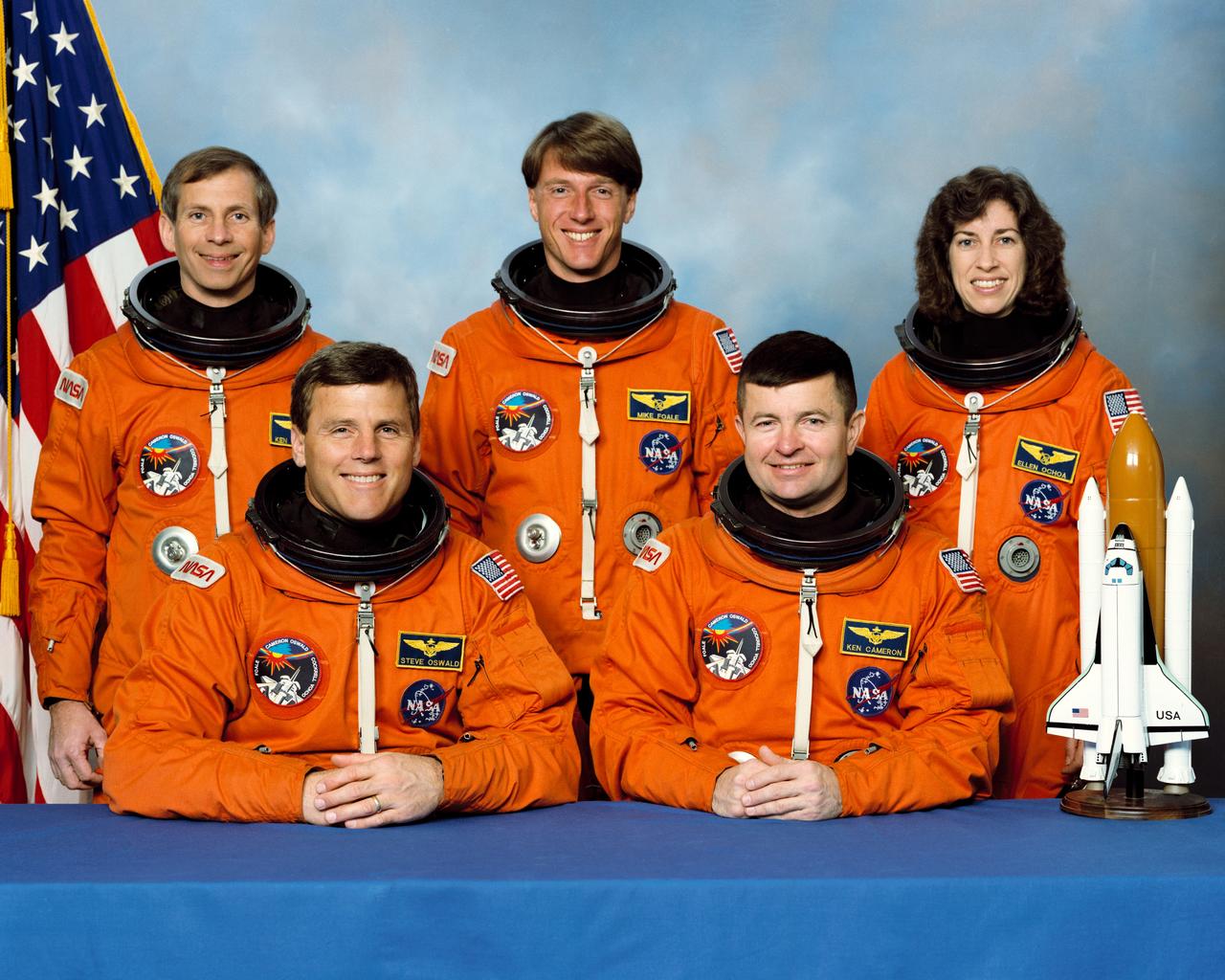

STS056-S-002 (January 1993) --- The five NASA astronauts assigned to fly aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery for the STS-56\Atlas-2 mission are pictured in training versions of their partial-pressure launch and entry garments. Left to right are astronauts Kenneth D. Cockrell, Steven S. Oswald, C. Michael Foale, Kenneth D. Cameron and Ellen Ochoa. Cameron is mission commander; Oswald, pilot; while the other three will serve as mission specialists.
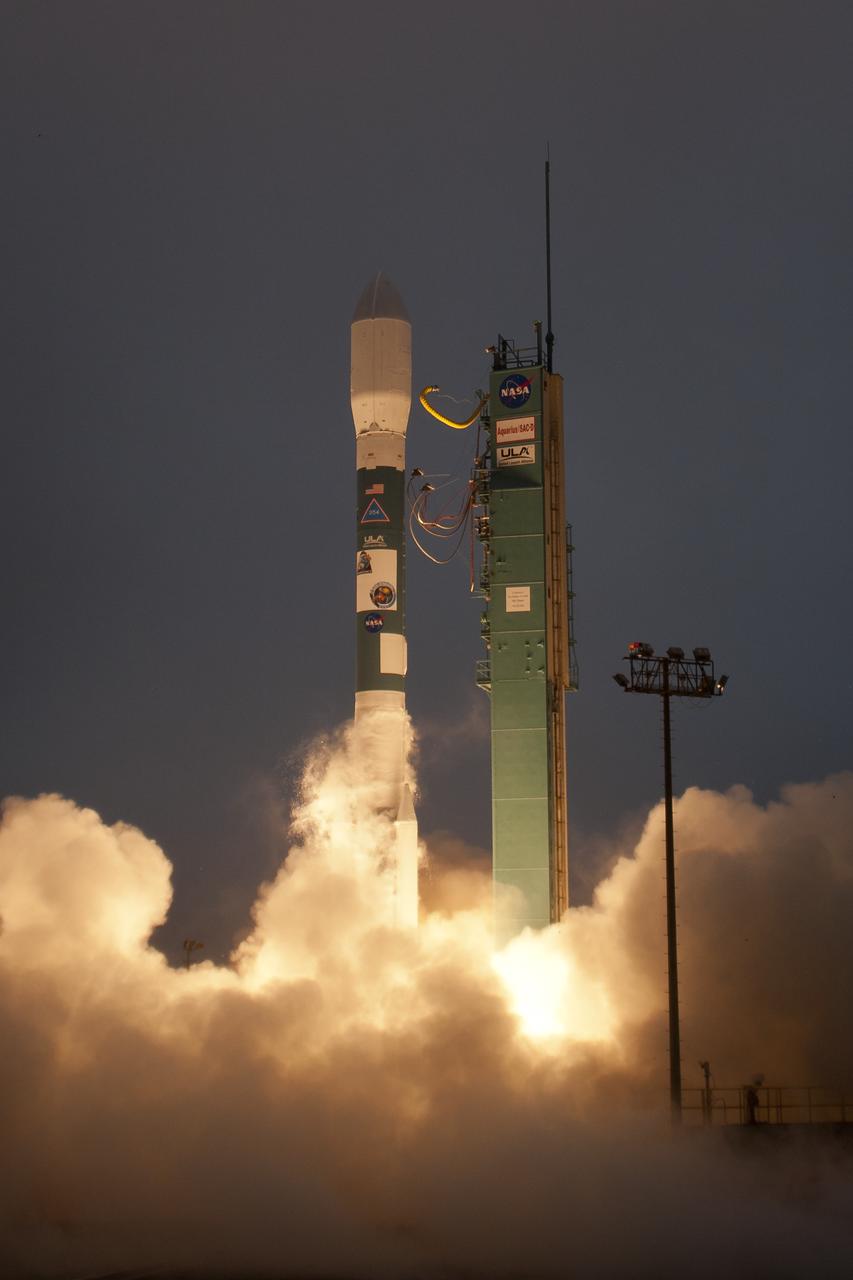

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
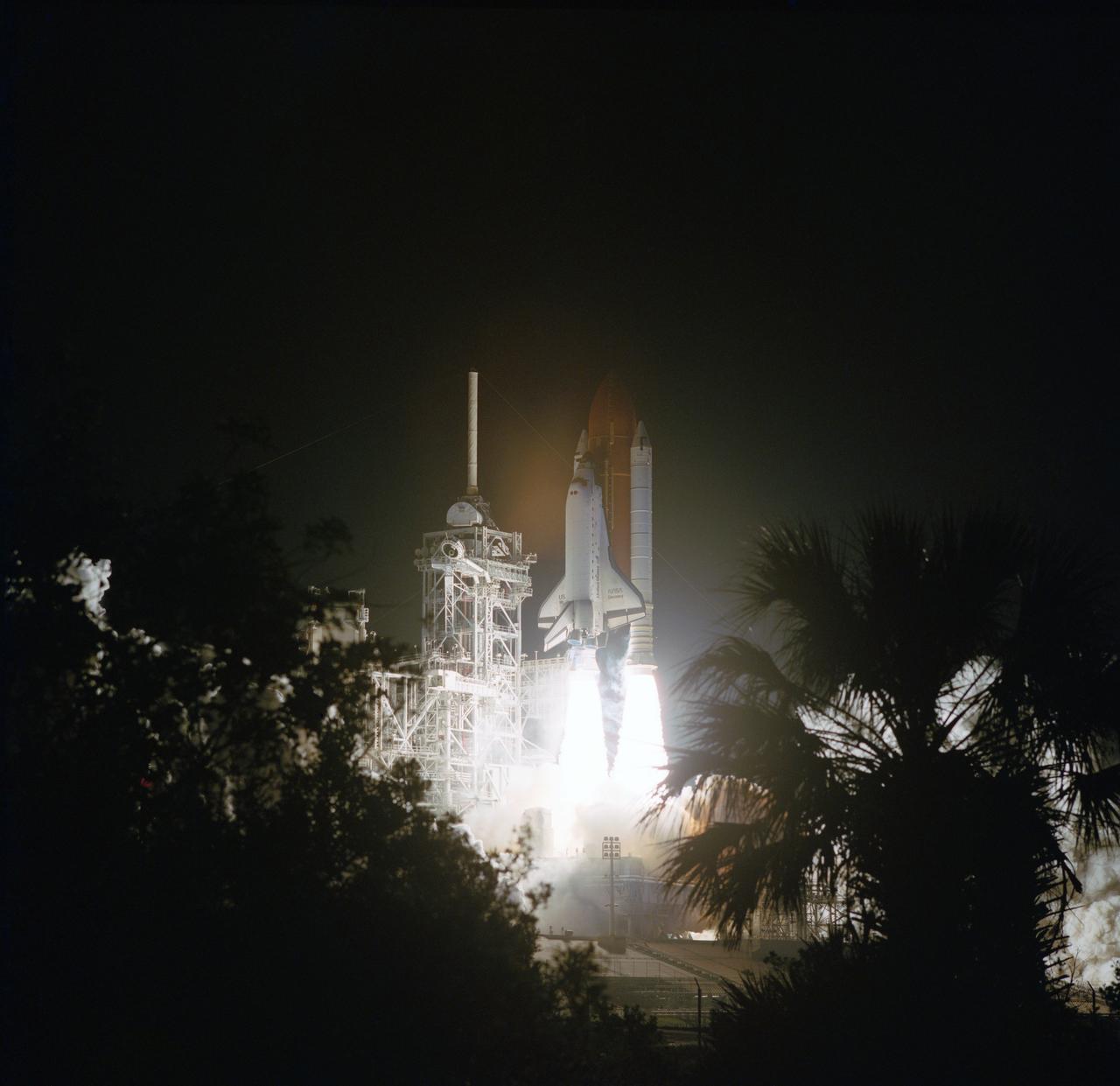

STS056-S-052 (8 April 1993) --- A nocturnal scene shows the Space Shuttle Discovery leaving the Launch Pad to begin the Atlas-2 mission in Earth-orbit. Launch occurred at 1:29 a.m. (EDT), April 8. Onboard were astronauts Kenneth D. Cameron, Stephen S. Oswald, C. Michael Foale, Kenneth D. Cockrell and Ellen Ochoa.
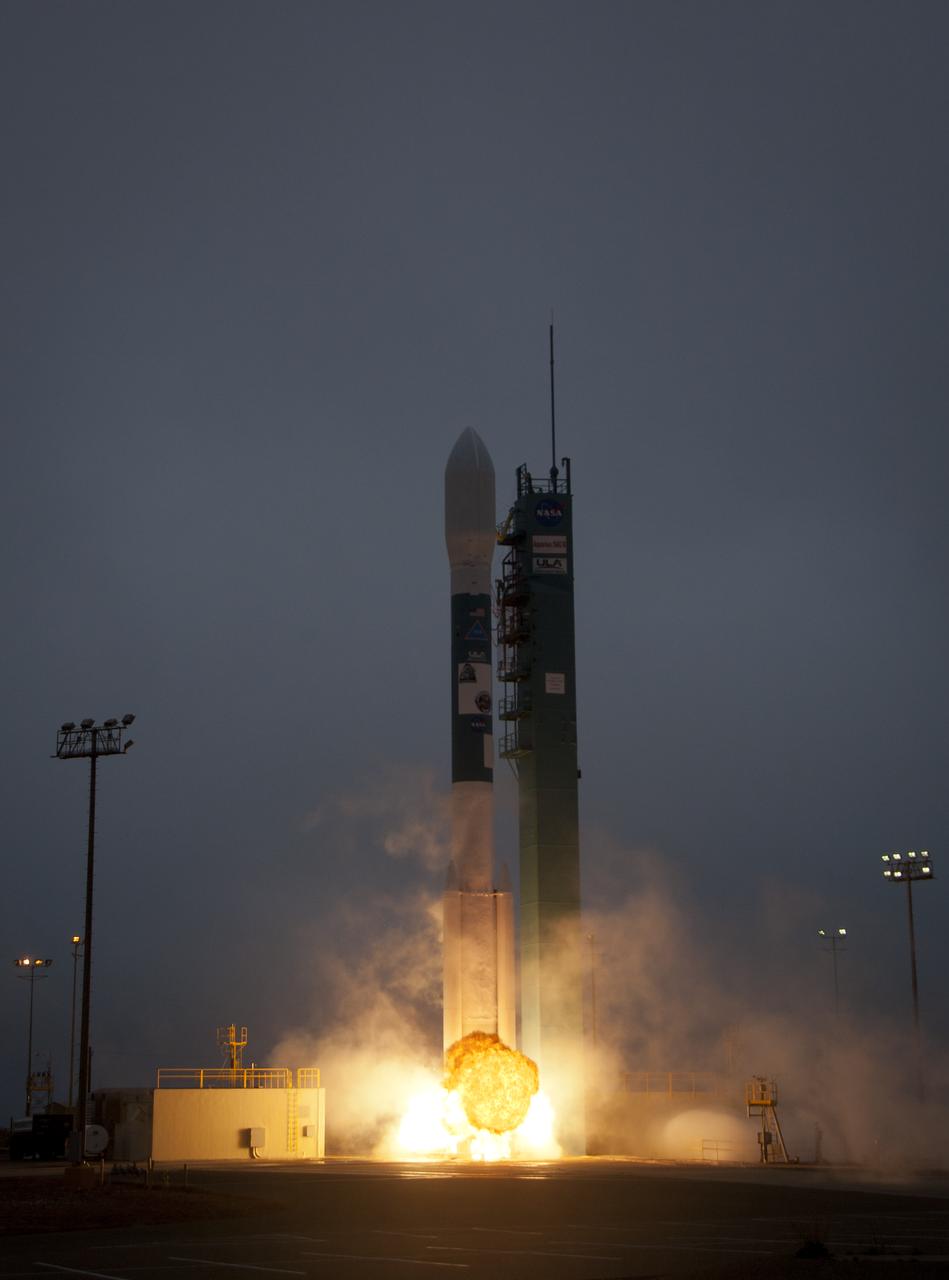

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
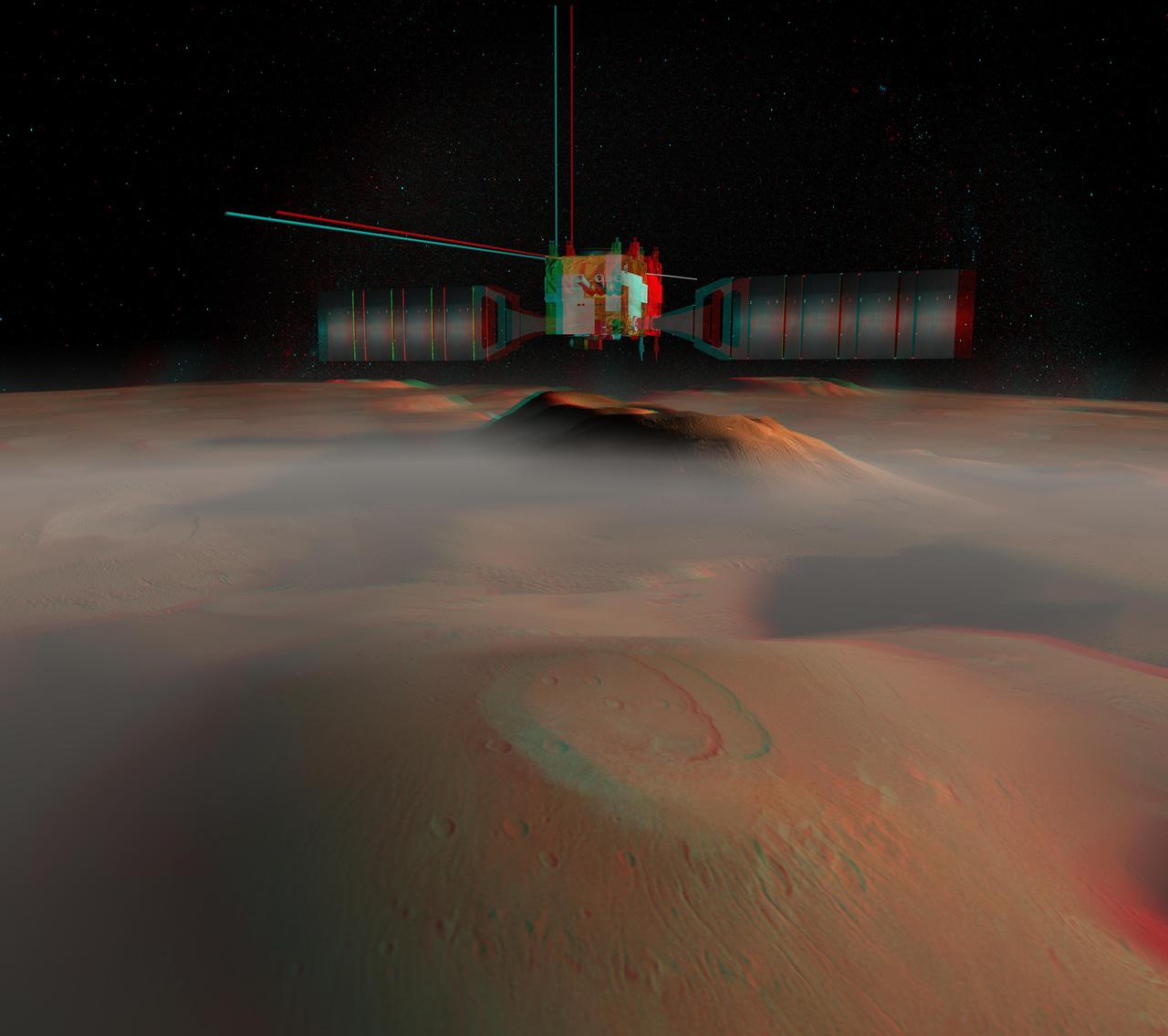
The European Space Agency's Mars Express spacecraft is depicted in orbit around Mars in this artist's concept stereo illustration. The spacecraft was launched June 2, 2003, from Baikonur, Kazakhstan, on a journey to arrive at Mars in December 2003. This red-blue anaglyph artwork can be viewed in 3-D on your computer monitor or in color print form by wearing red-blue (cyan) 3-D glasses. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04803
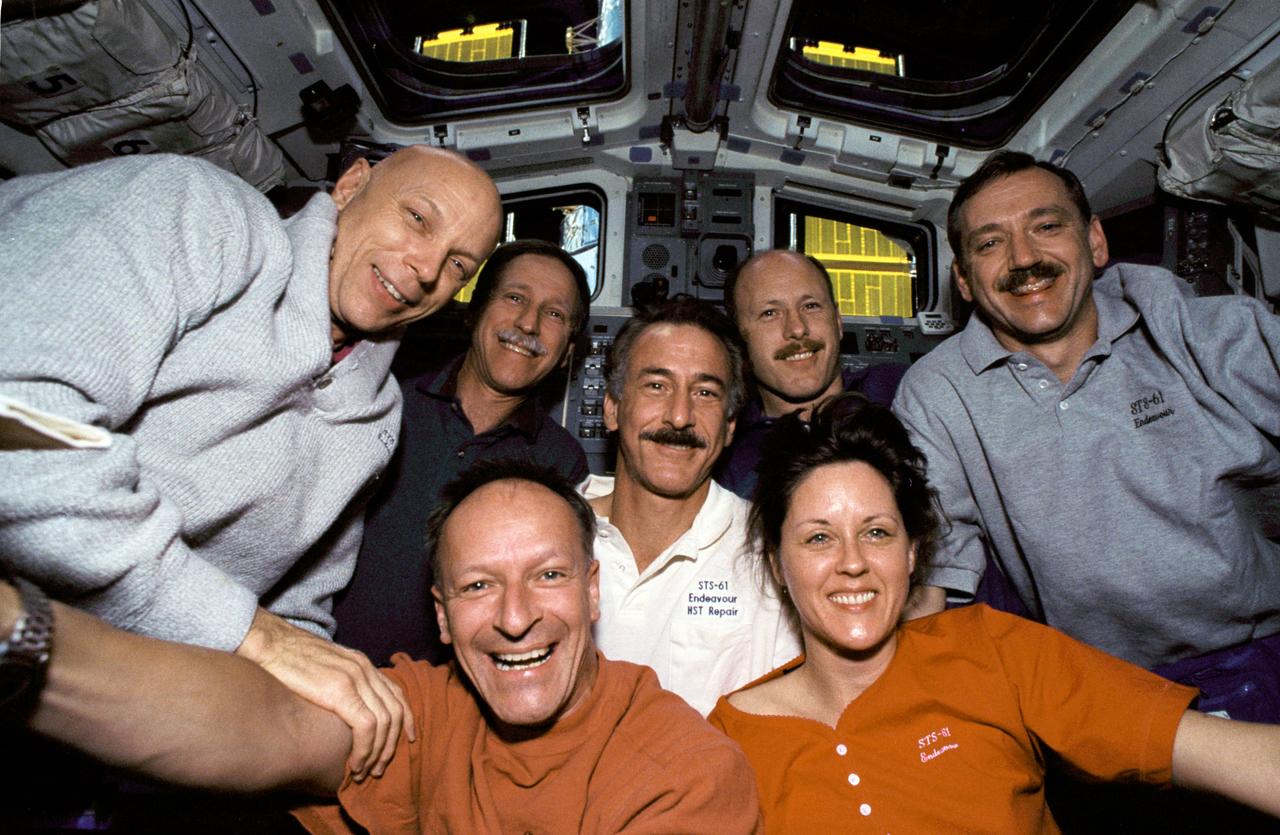

STS061-05-031 (2-13 Dec 1993) --- With the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) berthed in Endeavour's cargo bay, crew members for the STS-61 mission pause for a crew portrait on the flight deck. Left to right are F. Story Musgrave, Richard O. Covey, Claude Nicollier, Jeffrey A. Hoffman, Kenneth D. Bowersox, Kathryn C. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers.
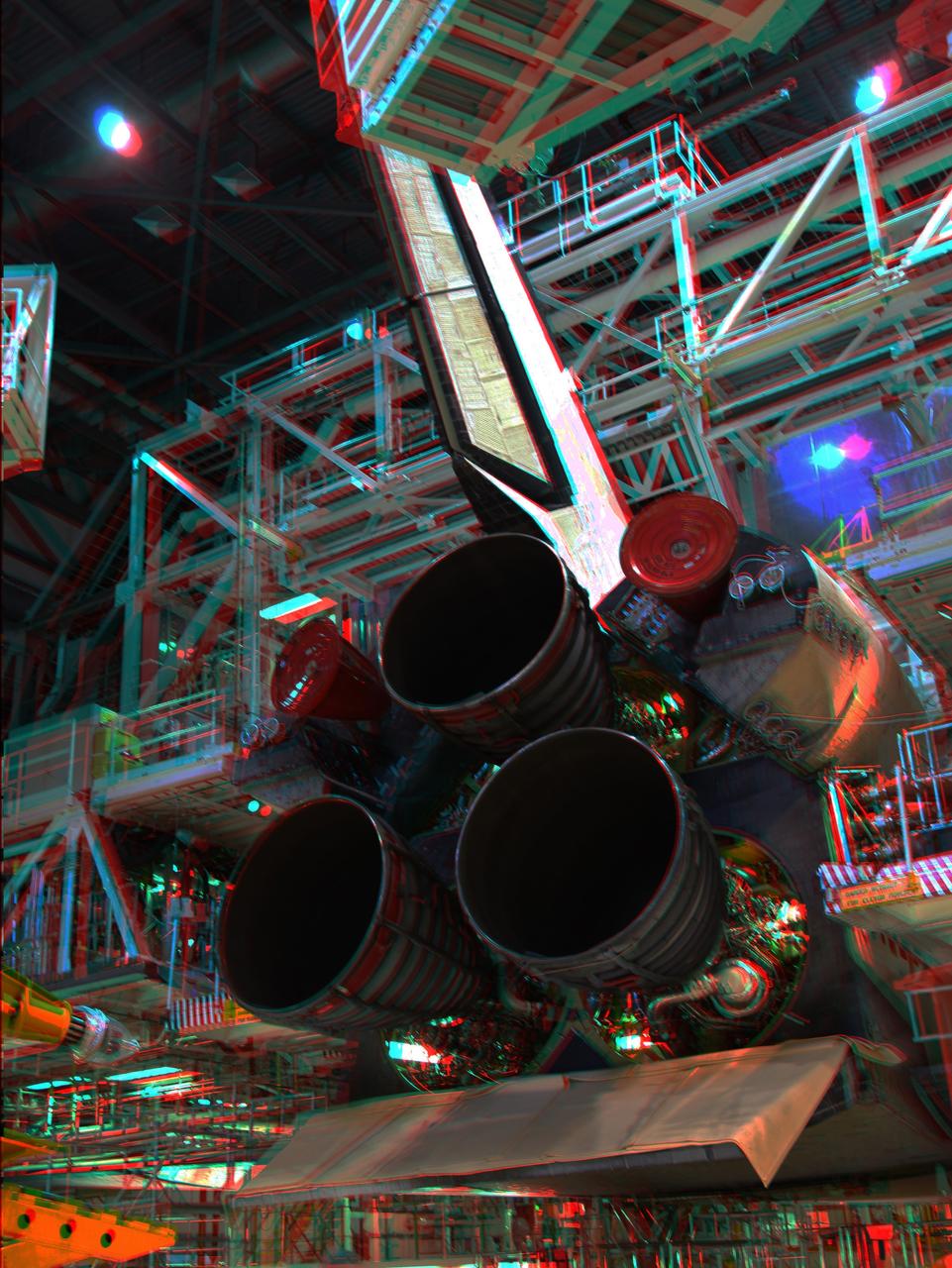

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, this 3-D image shows space shuttle Discovery's main engines before removeal for cleaning and inspection. The work is part of the spacecraft's transition and retirement processing and is expected to help rocket designers build next-generation spacecraft and prepare the shuttle for future public display. To view this image, use green and magenta 3-D glasses. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
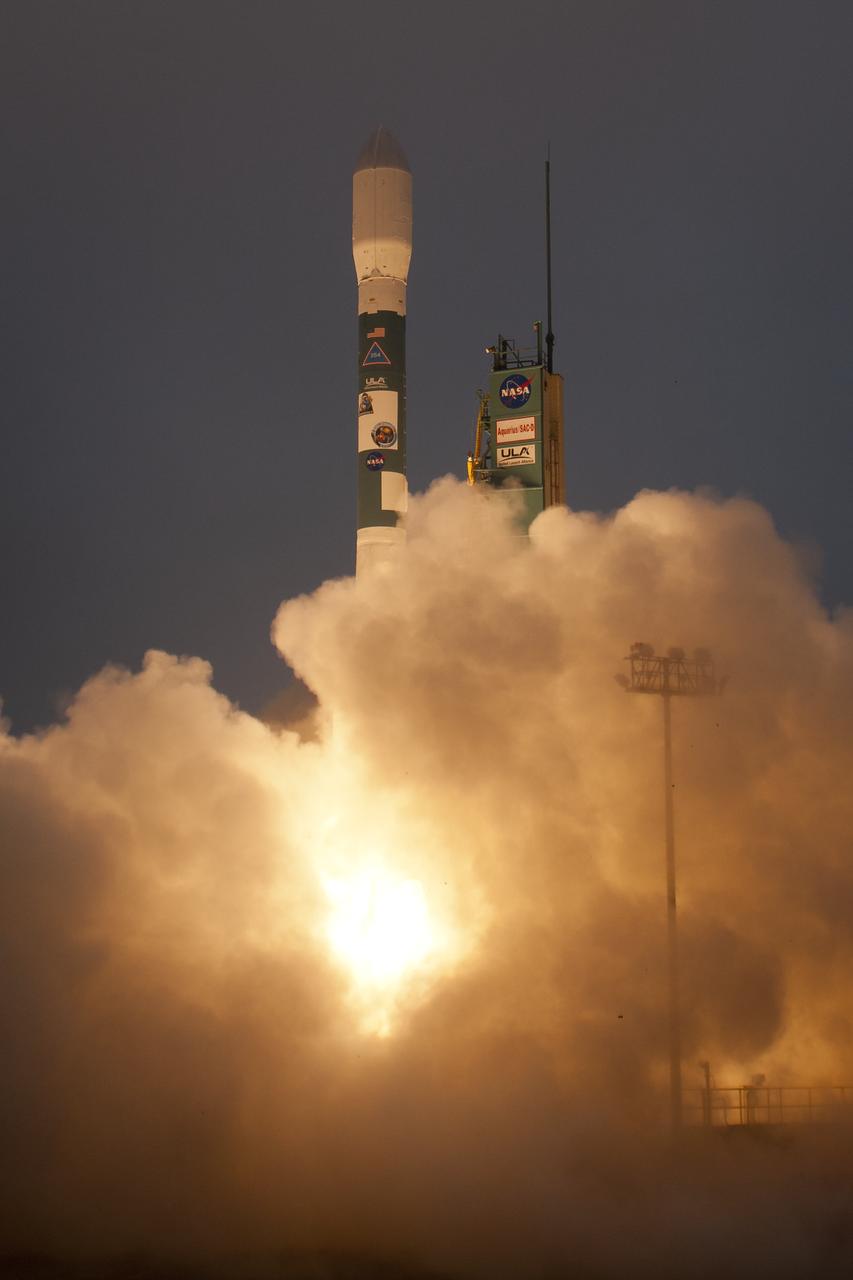

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
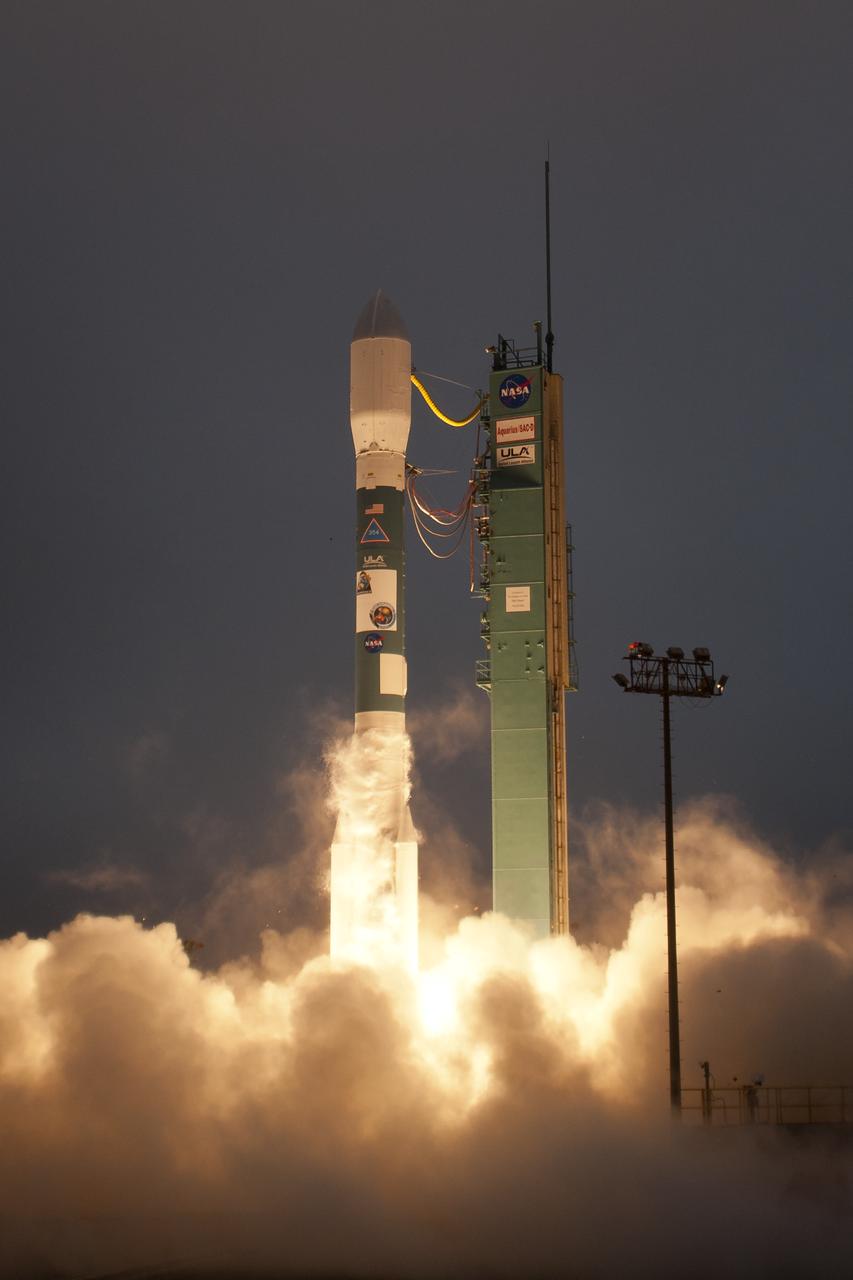

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
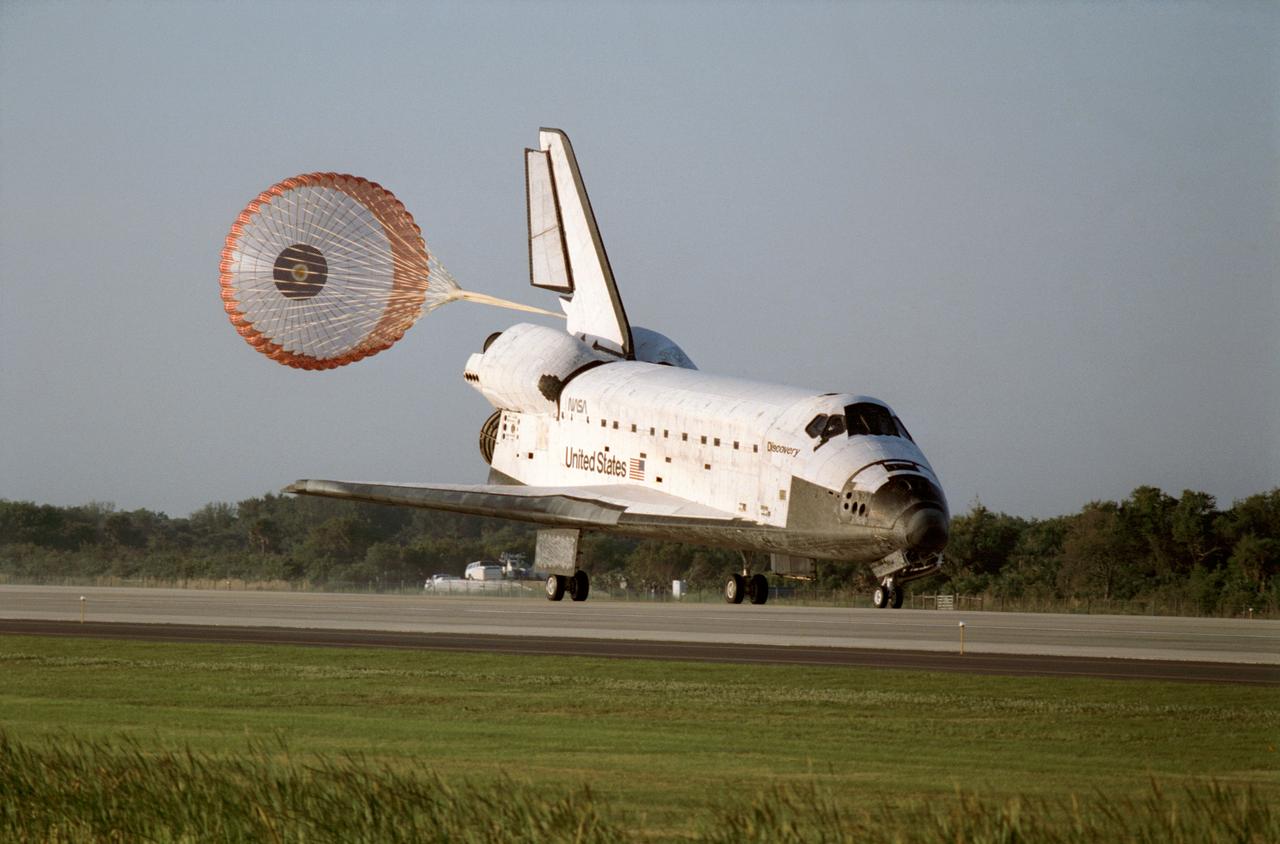

STS056-S-098 (17 April 1993) --- The drag chute is deployed following landing of the Space Shuttle Discovery on the Shuttle landing facility at the Kennedy Space Center to complete the STS-56\Atlas 2 mission. Touchdown occurred at 7:37 a.m. (EDT). Onboard the spacecraft were astronauts Kenneth D. Cameron, commander; Stephen S. Oswald, pilot; and C. Michael Foale, Ellen Ochoa and Kenneth D. Cockrell, mission specialists.
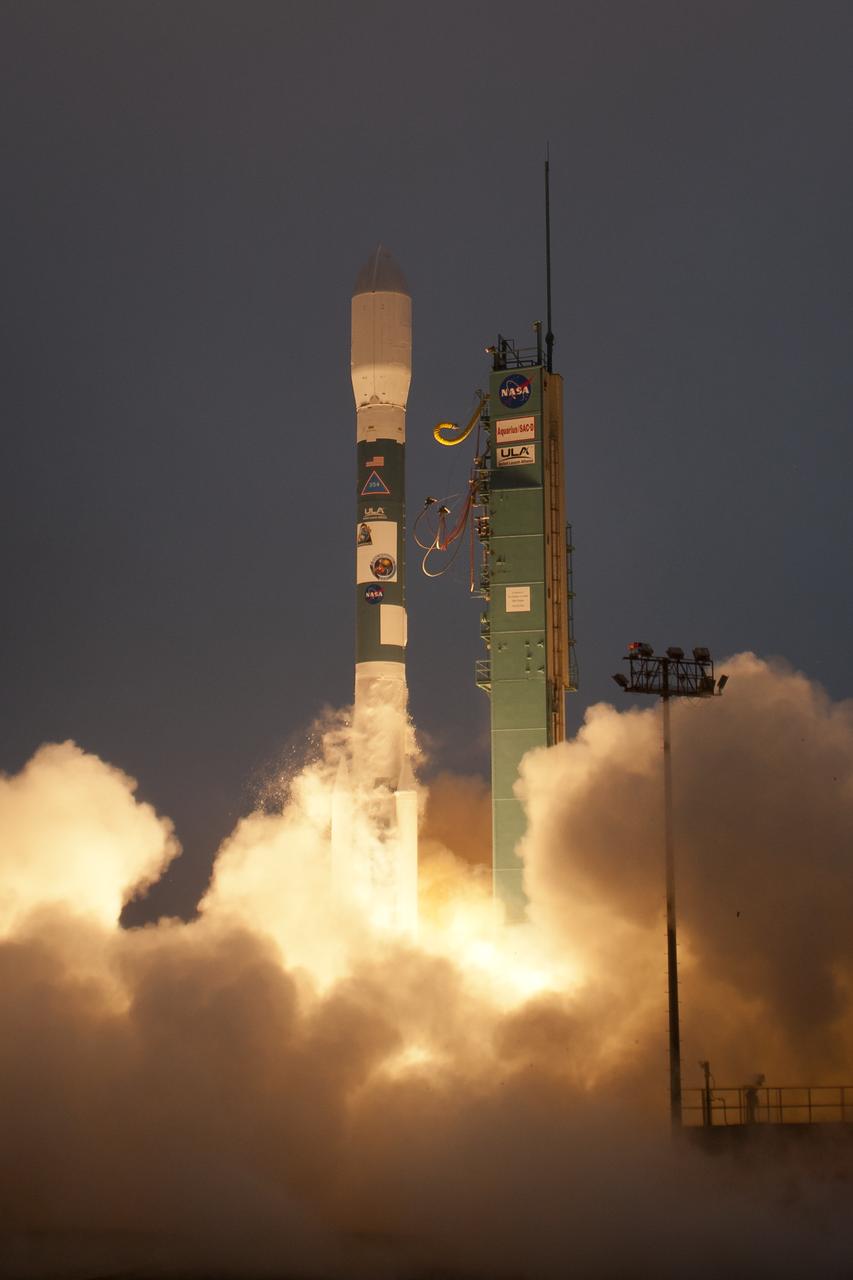

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
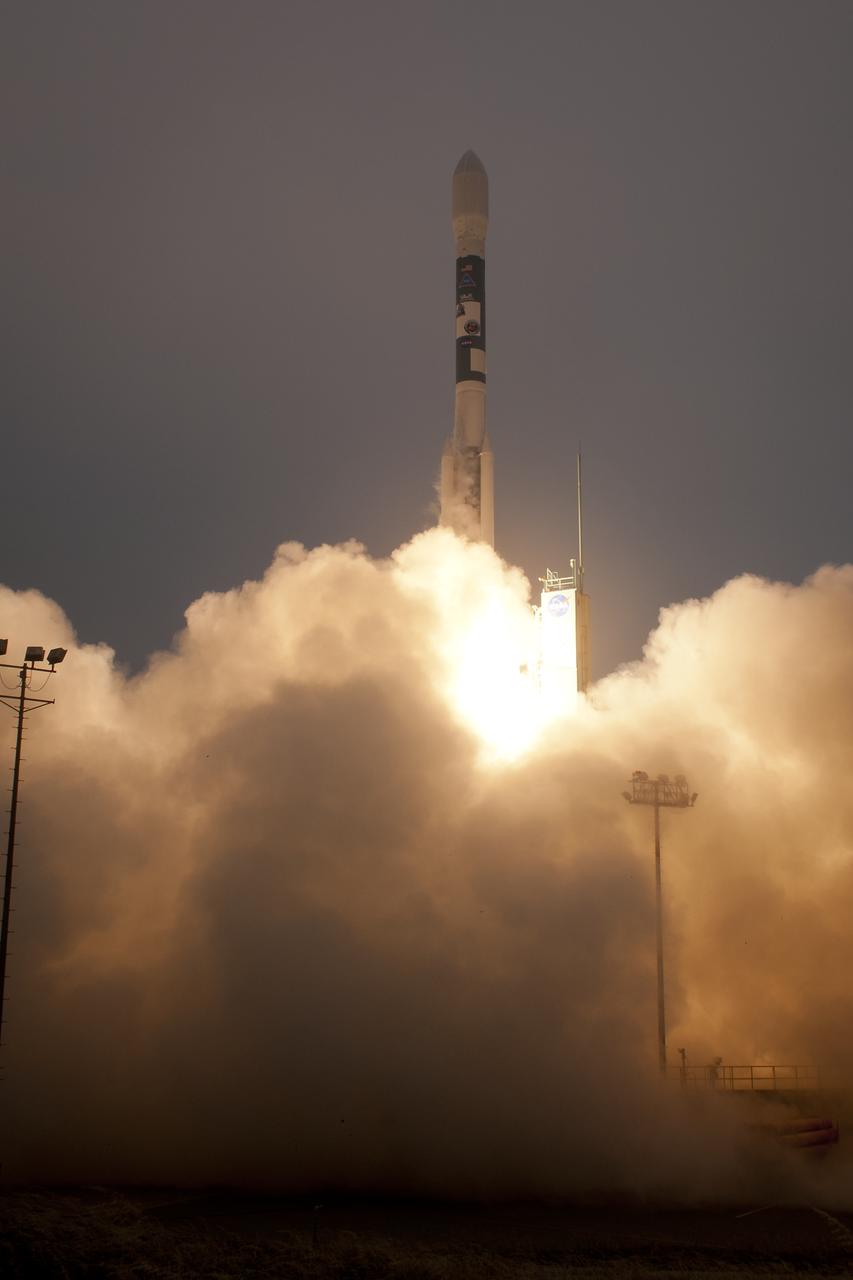

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
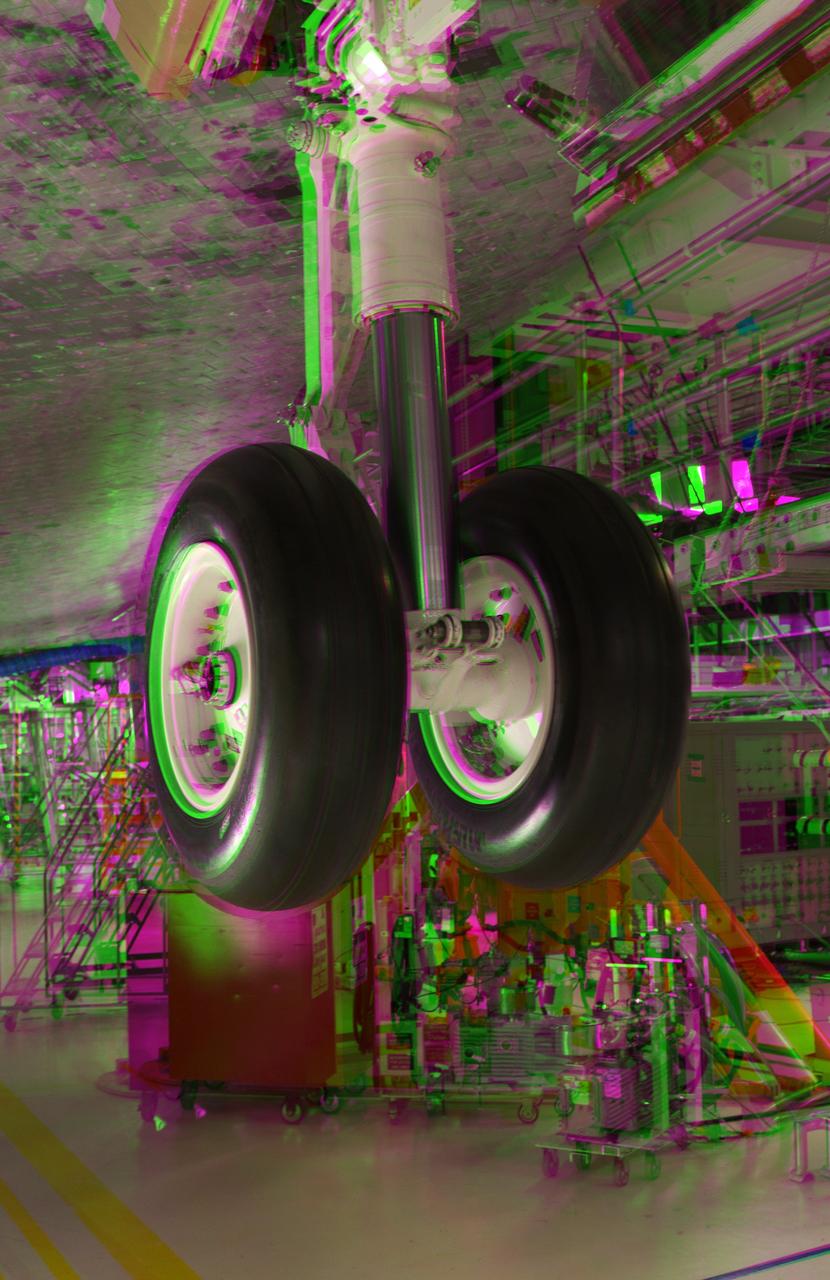

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This 3-D image was taken in Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, after crews installed the final tire on space shuttle Discovery. This is part of the spacecraft's transition and retirement processing and work performed on Discovery is expected to help rocket designers build next-generation spacecraft and prepare the shuttle for future public display. To view this image, use green and magenta 3-D glasses. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
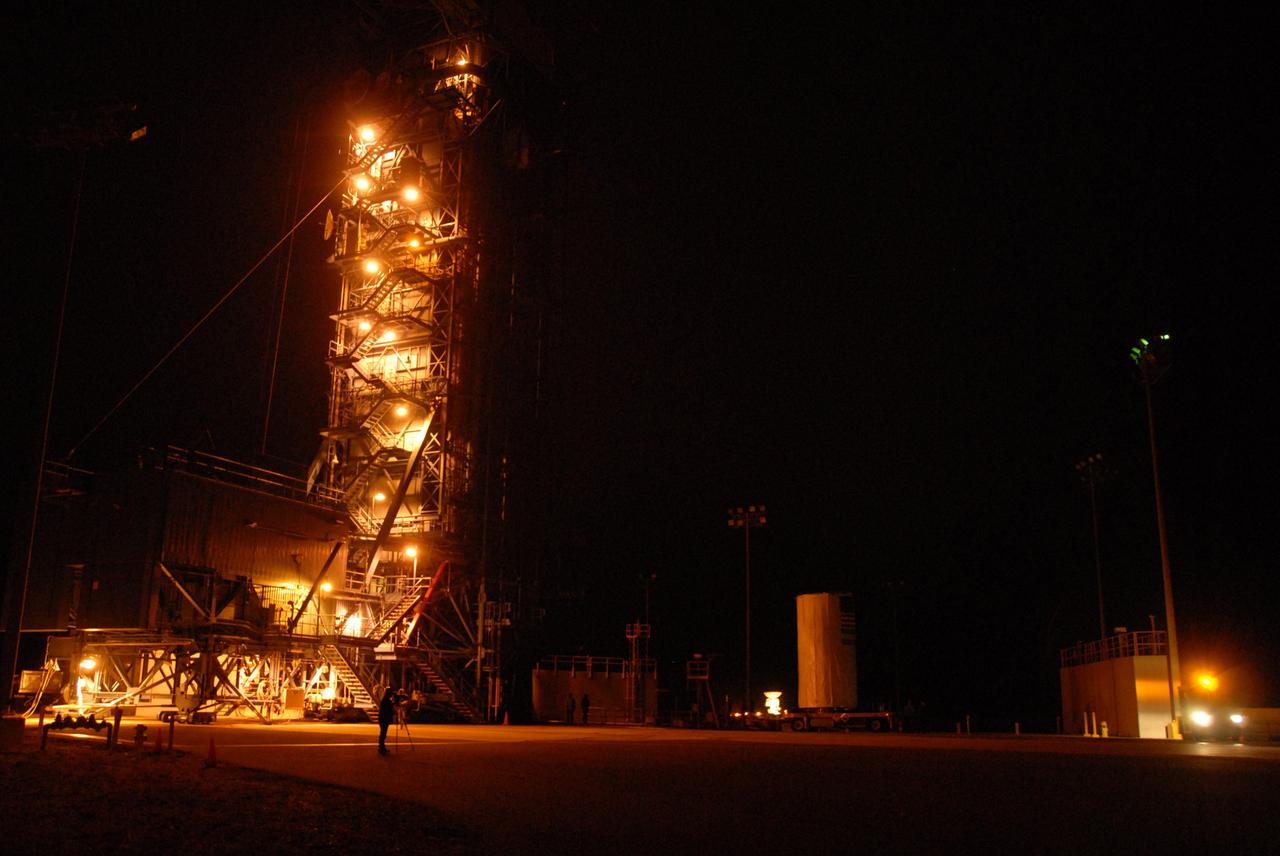

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- The Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft, secured inside its payload transportation canister, has been delivered to Space Launch Complex-2. There, the spacecraft will be integrated to a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in preparation for the targeted June liftoff. Aquarius, the NASA-built instrument on the SAC-D spacecraft, will provide new insights into how variations in ocean surface salinity relate to fundamental climate processes on its three-year mission. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
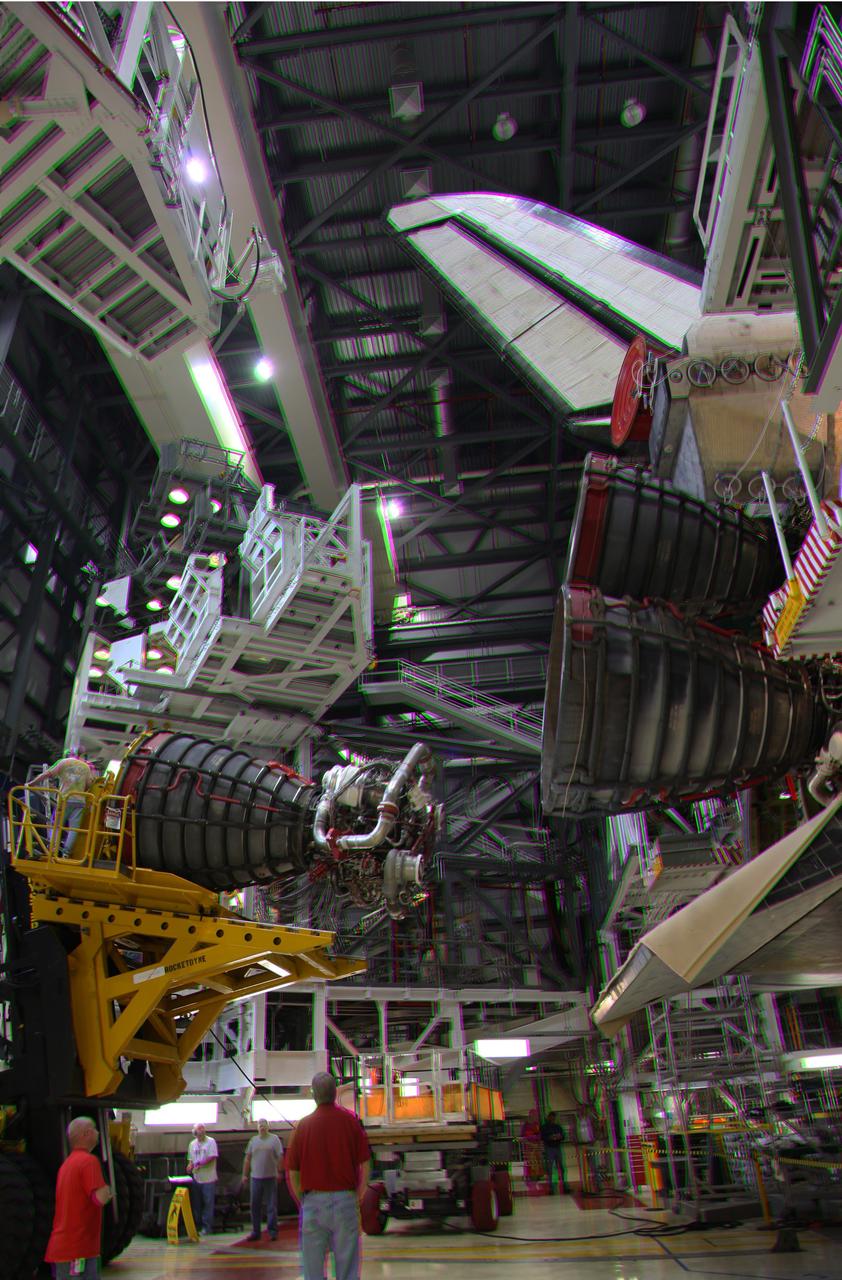

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a 3-D image of crews in Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida using a Hyster forklift to lower one of space shuttle Discovery's main engines after removal for cleaning and inspection. This is part of the spacecraft's transition and retirement processing and work performed on Discovery is expected to help rocket designers build next-generation spacecraft and prepare the shuttle for future public display. To view this image, use green and magenta 3-D glasses. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
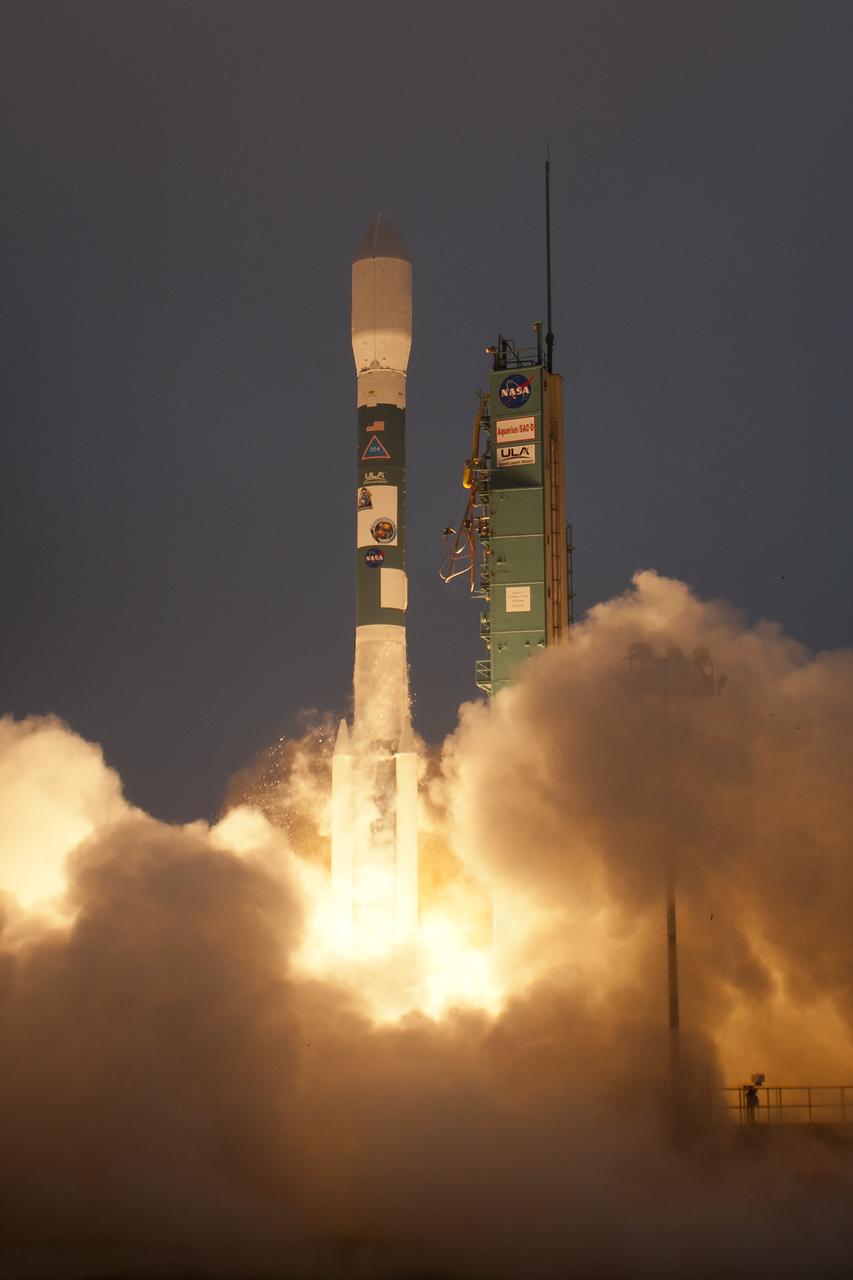

A Delta II rocket launches with the Aquarius/SAC-D spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Friday, June 10, 2011. The joint U.S./Argentinian Aquarius/Satélite de Aplicaciones Científicas (SAC)-D mission will map the salinity at the ocean surface, information critical to improving our understanding of two major components of Earth's climate system: the water cycle and ocean circulation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
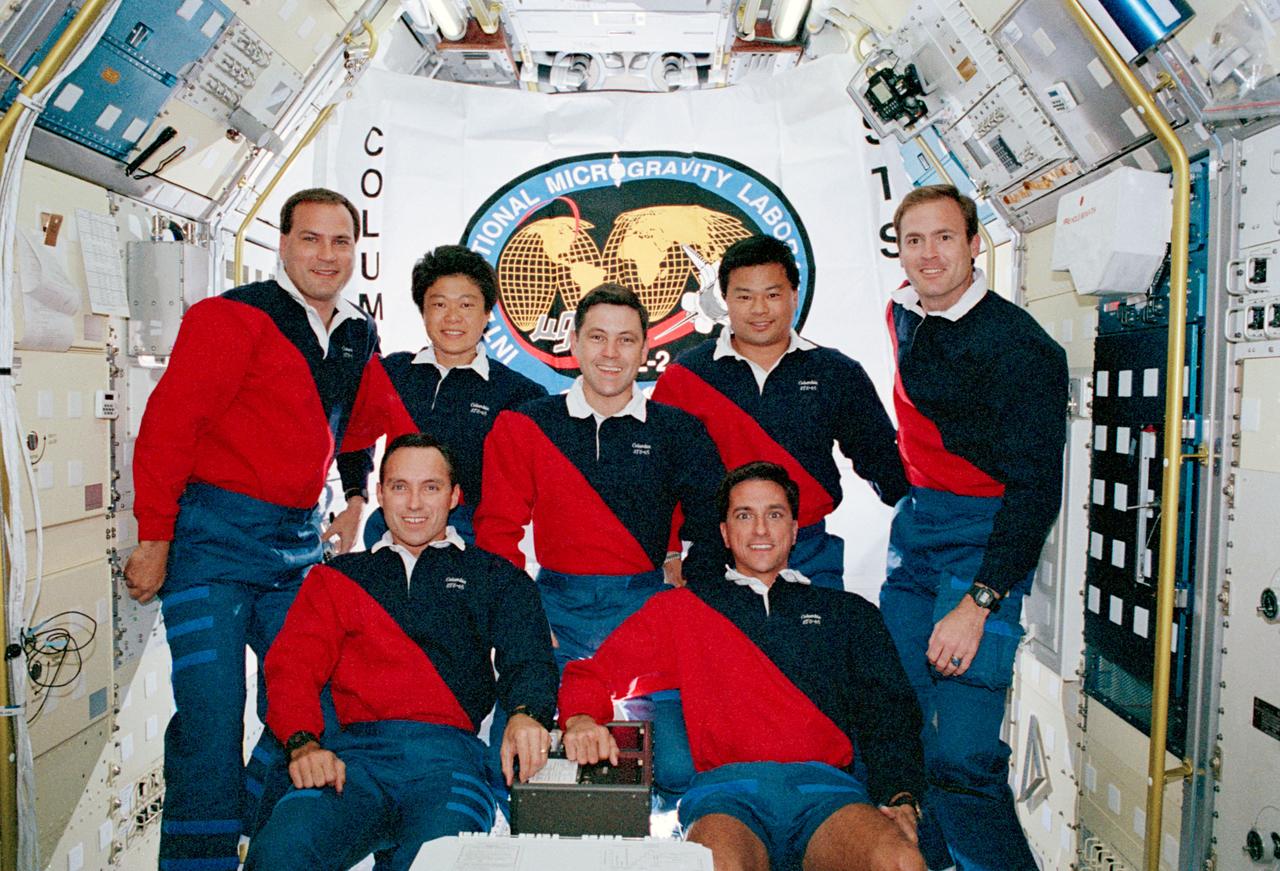

In the spacelab science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, the seven crewmembers pose for the traditional onboard (inflight) crew portrait. Displayed in the background is a flag with the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) insignia and Columbia inscribed along the edge. In the front row (left to right) are Mission Specialist (MS) Carl E. Walz and MS Donald A. Thomas. Behind them (left to right) are Payload Commander (PLC) Richard J. Hieb, Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, Commander Robert D. Cabana, MS Leroy Chiao, and Pilot James D. Halsell, Jr. Mukai represents the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan. Crewmembers are wearing their mission polo shirts for the portrait. Inside this module, the crew conducted experiments in support of the IML-2 mission.

STS073-230-014 (20 October - 5 November 1995) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Bowersox, STS-73 mission commander, uses a camcorder to record United States Microgravity Laboratory 2 (USML-2) activities onboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. Nearby, astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, payload commander, prepares to open a supply chest to support one of many science experiments conducted by the seven-member crew during the 16-day USML-2 flight.

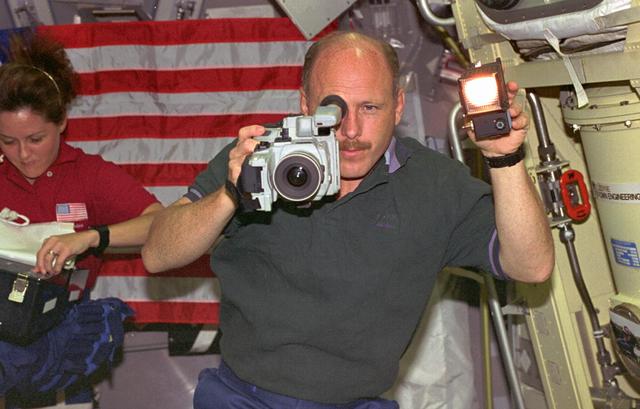
S106-E-5033 (9 September 2000) --- Astronaut Scott D. Altman, STS-106 pilot, is looking down at a checklist in this electronic still camera's (ESC) view, recorded during busy Flight Day 2 activity onboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Atlantis.

U.S. Rep. Gabrielle Giffords, D-Ariz., left, speaks with reitred astronaut Lt. Gen. Thomas Stafford prior to the start of a hearing before the House Subcommitte on Space and Aeronautics regarding Safety of Human Spaceflight on Capitol Hill, Wednesday, Dec. 2, 2009, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
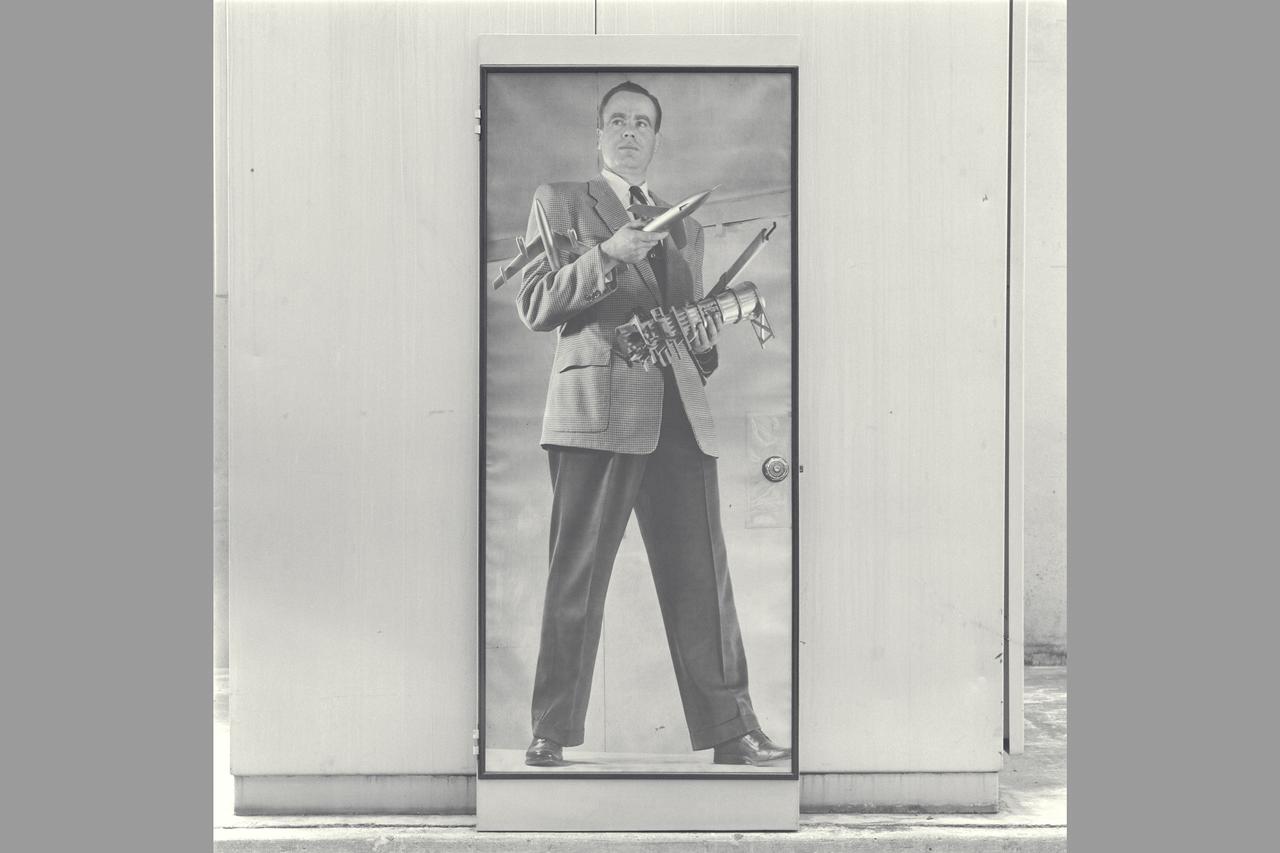

Historical Recruiting poster of Cleve E Voss holding model of B-47, Douglas D-558-2, 6x6ft w.t. & slide rule (on Display at Macy's San Francisco 1947 - 1950 ish) NOTE: Poster recovered from Voss's wife and copied from the (bedroom) door to which it had been adhered.
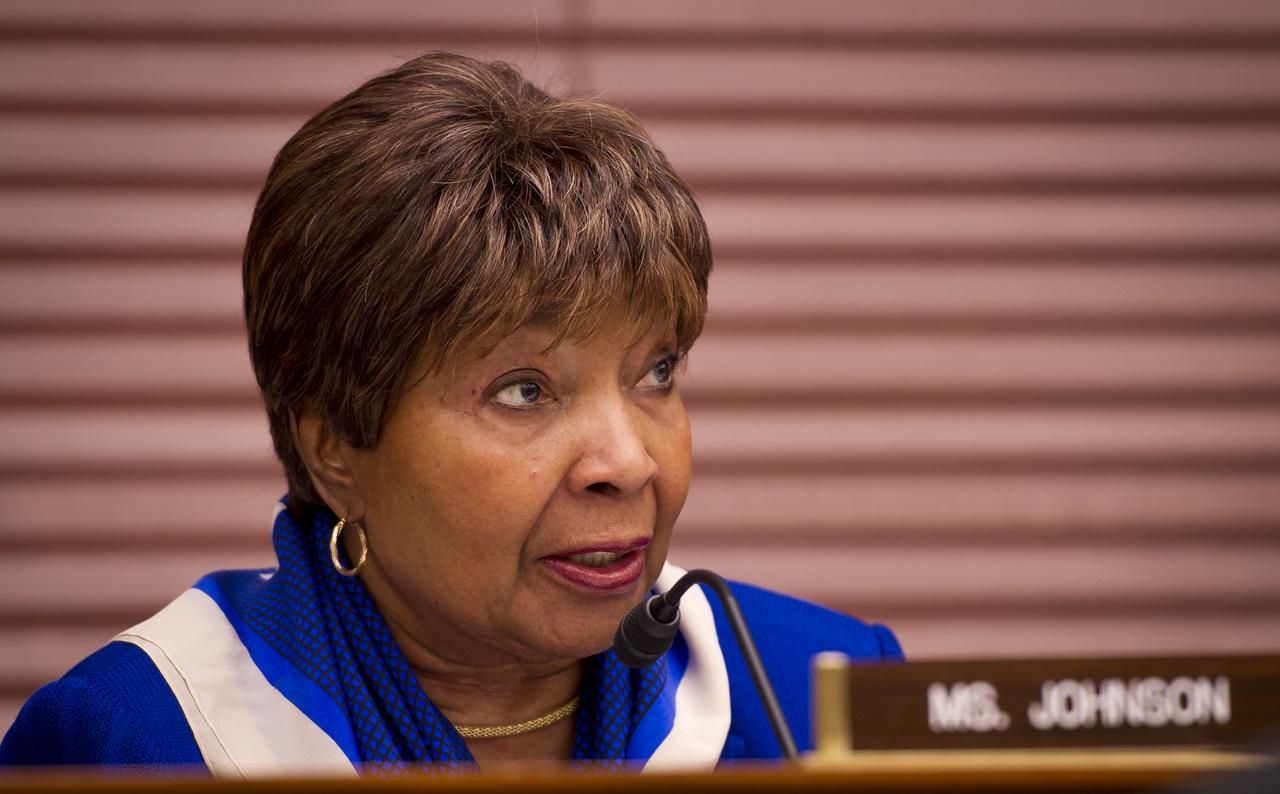

U.S. Rep. Eddie Bernice Johnson, D-Texas, questions NASA Administrator Charles Bolden during a House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology budget hearing, Wednesday, March 2, 2011 in the Rayburn House Office Building on Capitol Hill in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
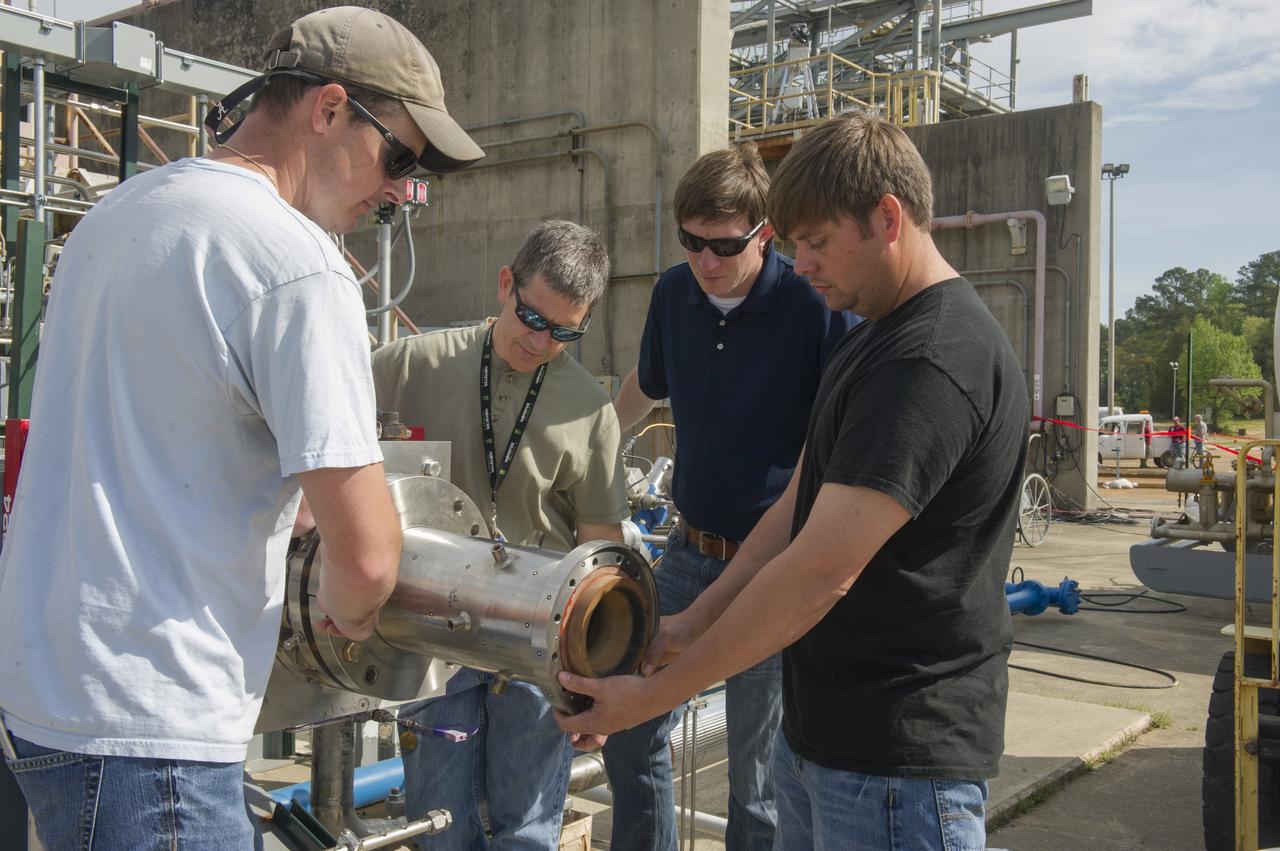

2. ENGINEERS AND TECHNICIANS PREPARE FOR AN UPCOMING HOT-FIRE TEST OF A ROCKET INJECTOR MANUFACTURED USING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING, OR 3-D PRINTING…(L TO R) WILLIE PARKER, INFOPRO TECHNICIAN, BRAD BULLARD, NASA, NICK CASE, NASA, AND RANDALL MCALLISTER, INFOPRO TECHNICIAN

STS113-E-05384 (2 December 2002) --- Astronaut James D. Wetherbee, STS-113 mission commander, adds the STS-113 patch to the growing collection of those representing Shuttle crews who have worked on the International Space Station (ISS). A location in the Unity node serves as one of the traditional posting sites for the patches.

Egress training of Orbiter Simulator, Bldg. 9A, (Technical Services Facility). S78-34922 - Fullerton & Brand, suited. 1. SHUTTLE - CREW TRAINING 2. VANCE D. BRAND - EGRESS TRAINING 3. CHARLES G. FULLERTON - EGRESS TRAINING JSC, HOUSTON, TX
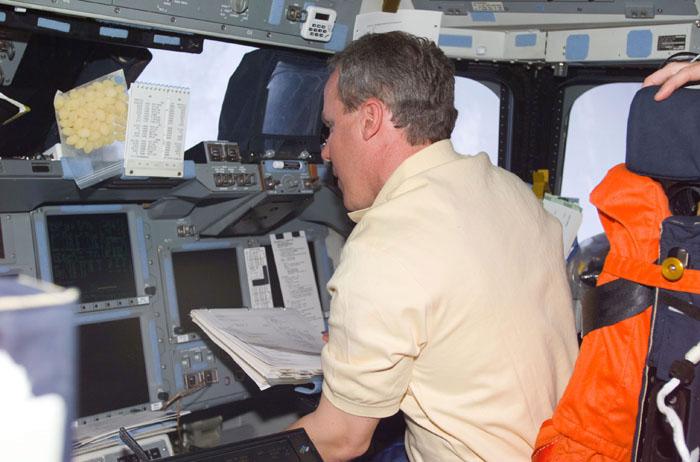

STS98-E-5027 (9 February 2001) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, temporarily mans the pilot's station on the flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis during STS-98 Flight Day 2 maneuvers. The photograph was recorded with a digital still camera.
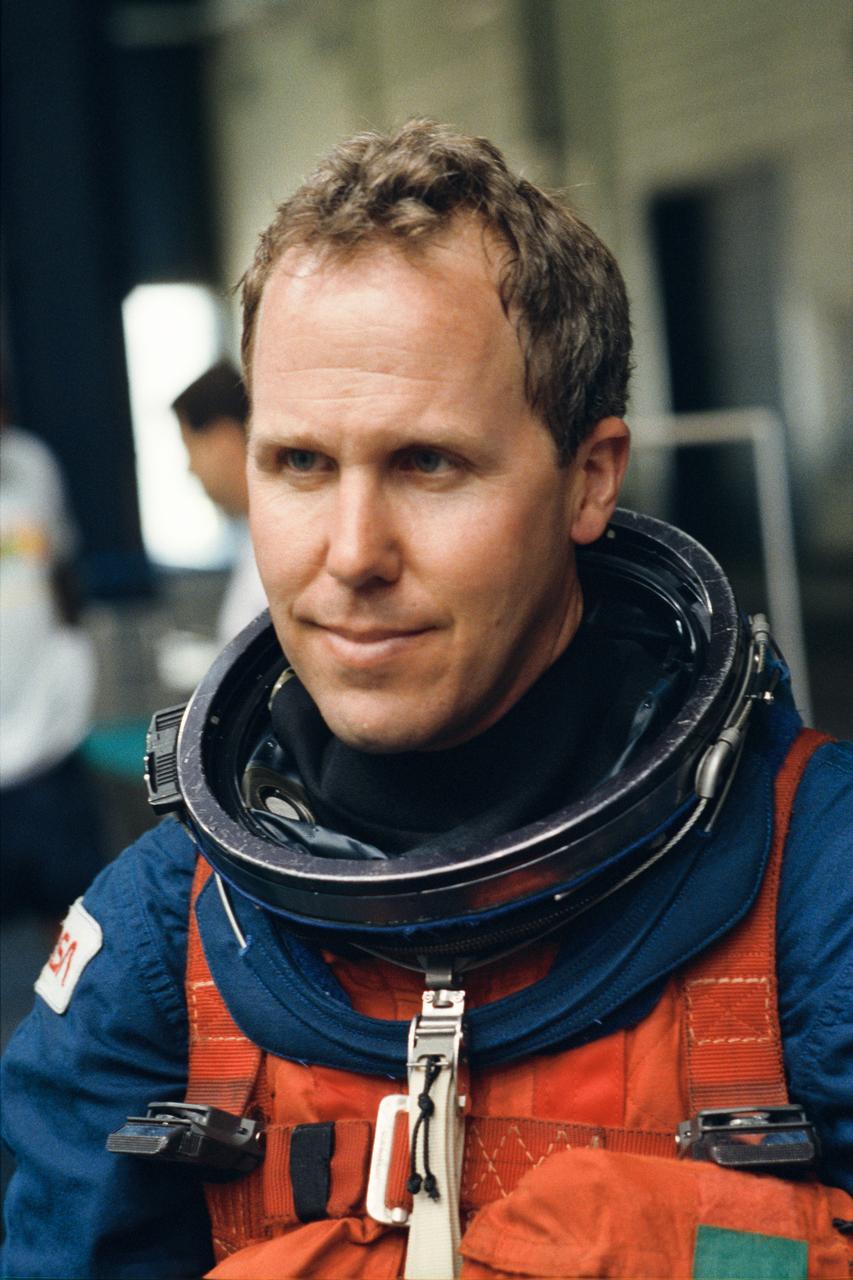

S93-43108 (2 June 1993) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Jones, mission specialist, takes a break during emergency bailout training at the Johnson Space Center's (JSC) Weightless Environment Training Facility (WET-F). Jones and five other NASA astronauts are scheduled to fly aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour next year.
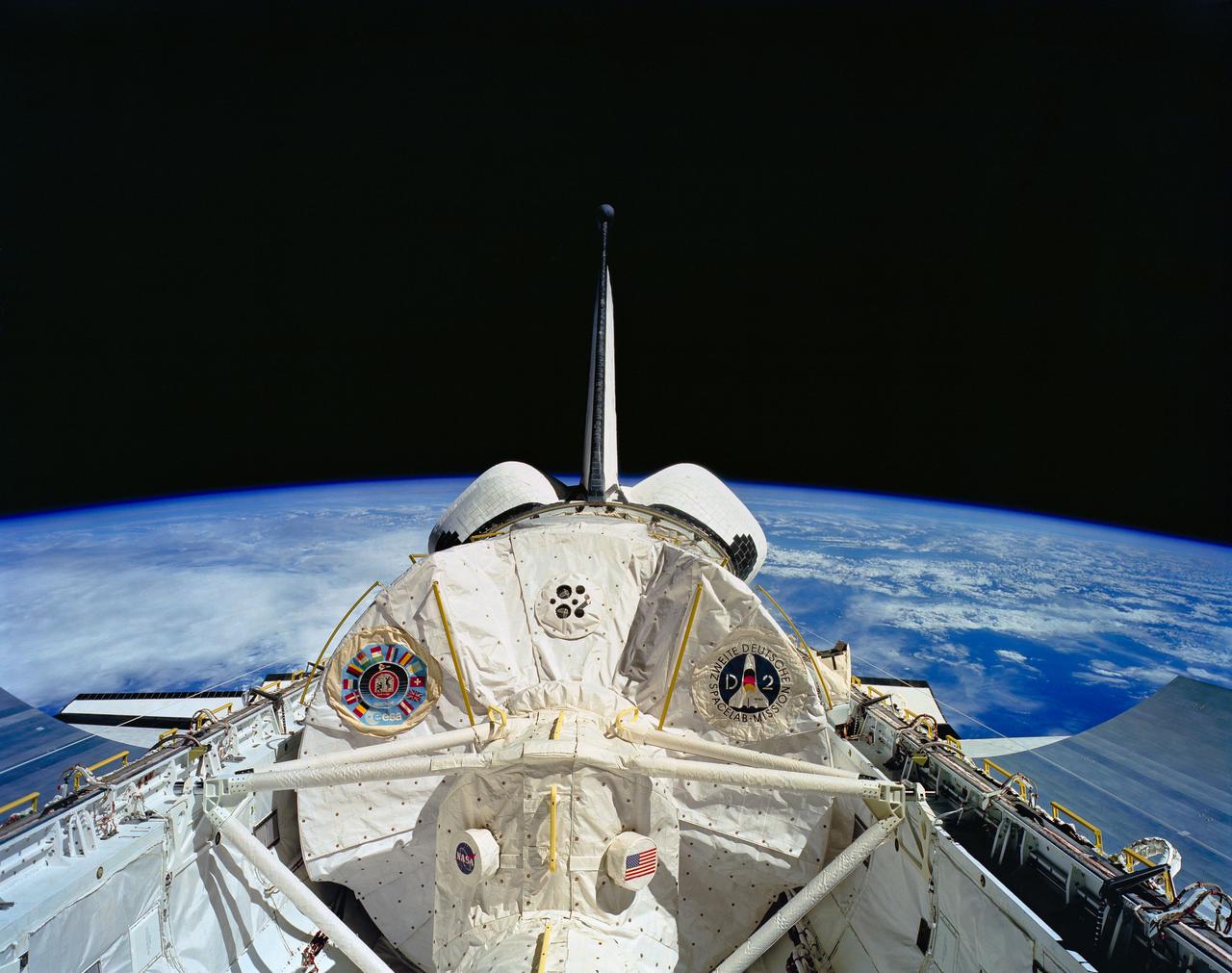

STS055-151B-189 (26 April-6 May 1993) --- Clouds over a wide span of ocean waters form the backdrop for this picture of the Spacelab D-2 Science Module in the Space Shuttle Columbia's cargo bay. A Linhof camera was aimed through the spacecraft's aft flight deck windows to record the scene.
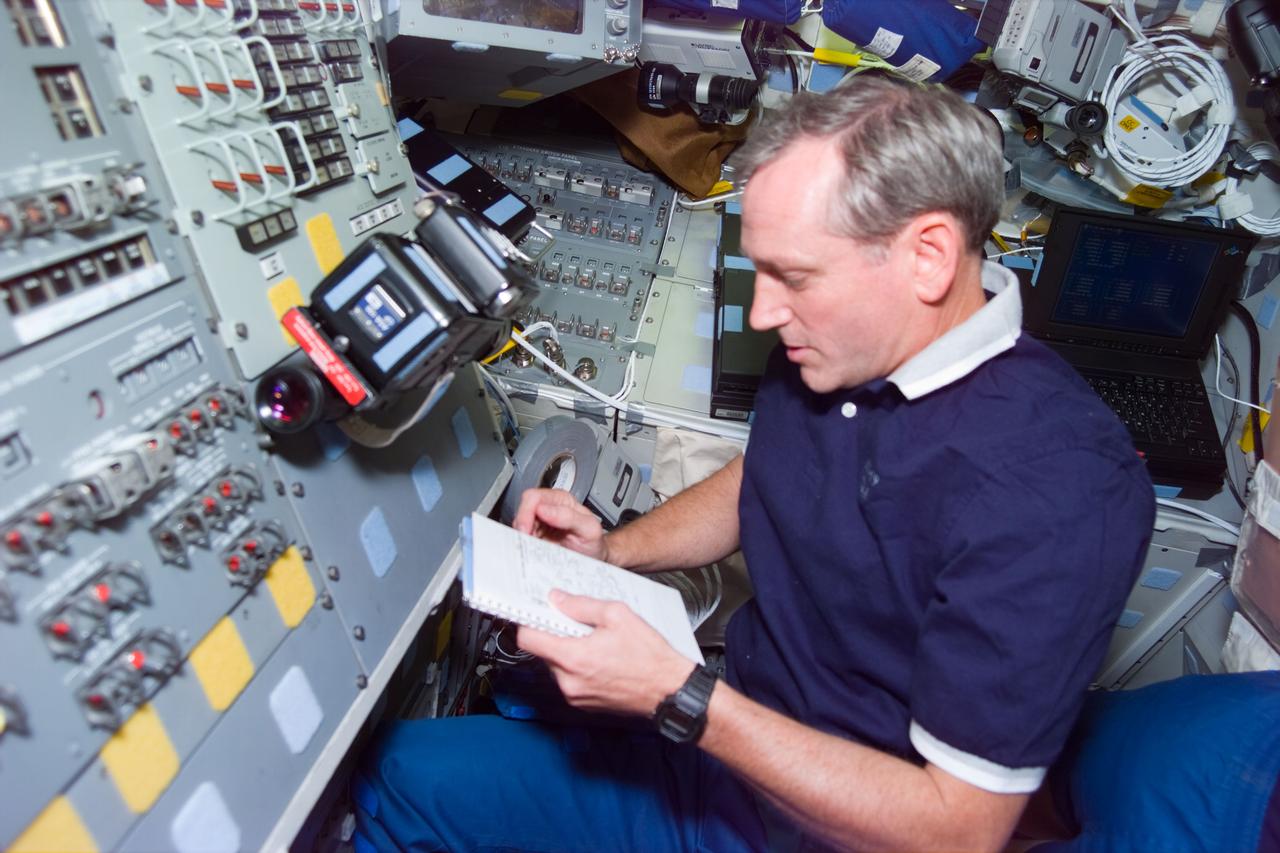

STS79-E-5013 (17 September 1996) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Akers, mission specialist, on the Space Shuttle Atlantis' flight deck soon after STS-79 crew begins its in-space activities, on Flight Day 2.
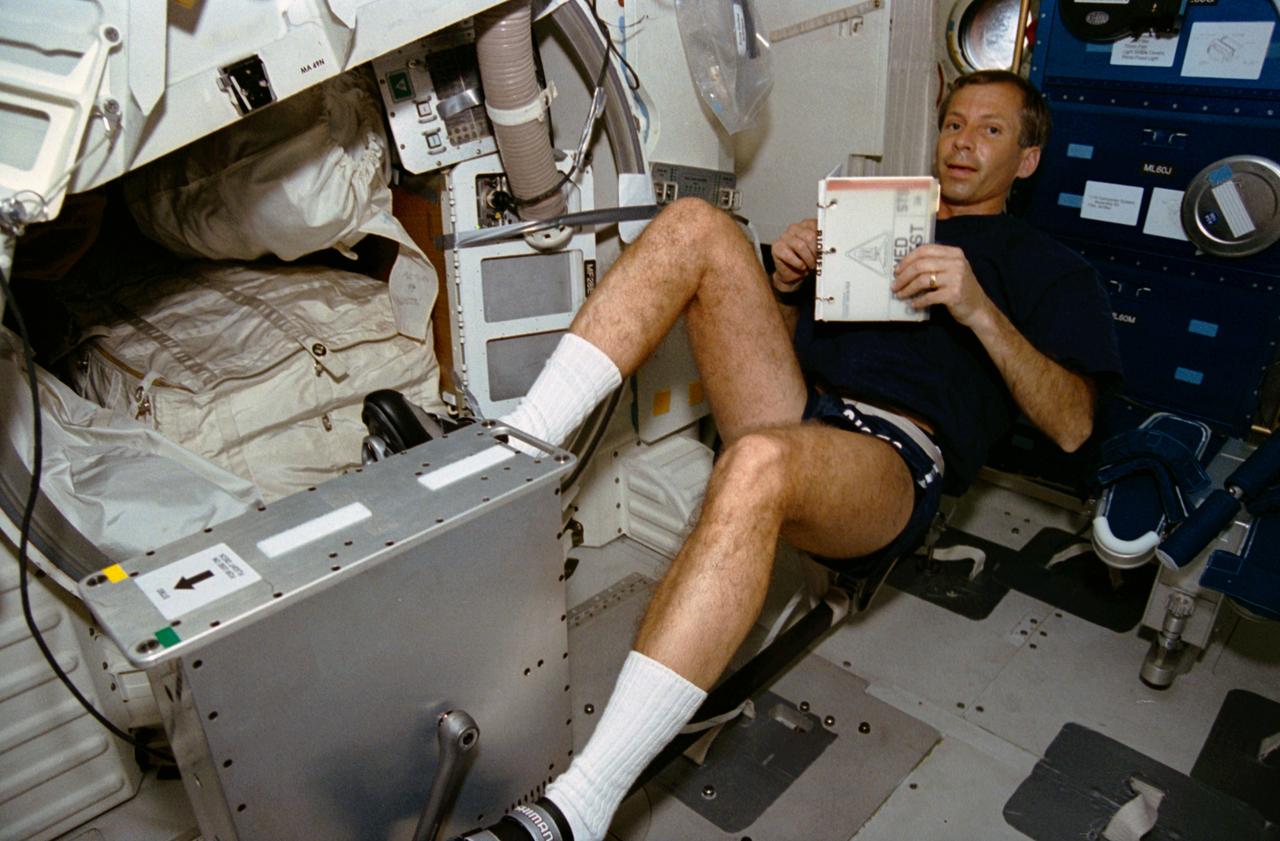

STS056-13-004 (8-17 April 1993) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Cockrell pedals the bicycle ergometer on Discovery's middeck. The mission specialist, along with four other NASA astronauts, spent nine days in space in support of the ATLAS 2 mission.
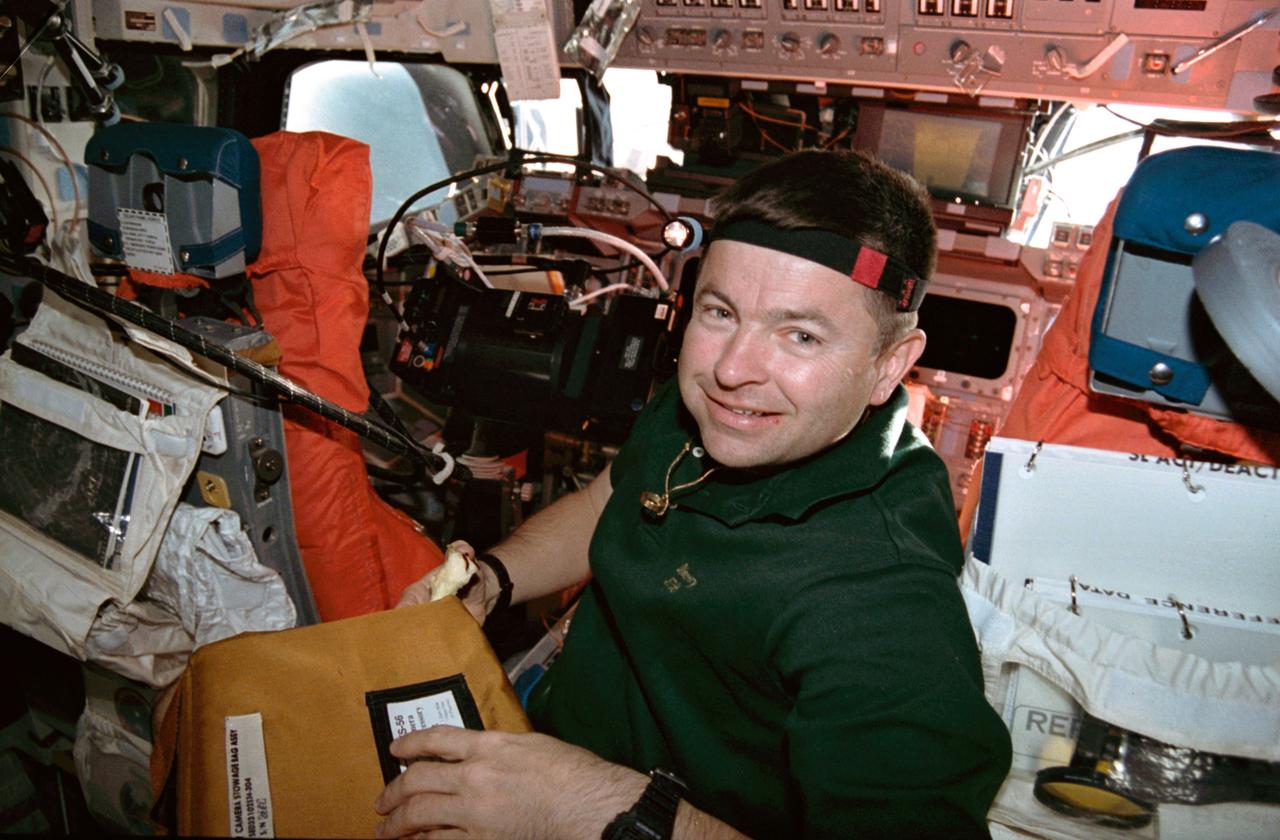

STS056-08-028 (8-17 April 1993) --- Astronaut Kenneth D. Cameron, mission commander, prepares to remove a camera before making exposures with it on Discovery's flight-deck. Cameron and four other NASA astronauts spent nine days in space supporting the Atlas 2 mission.