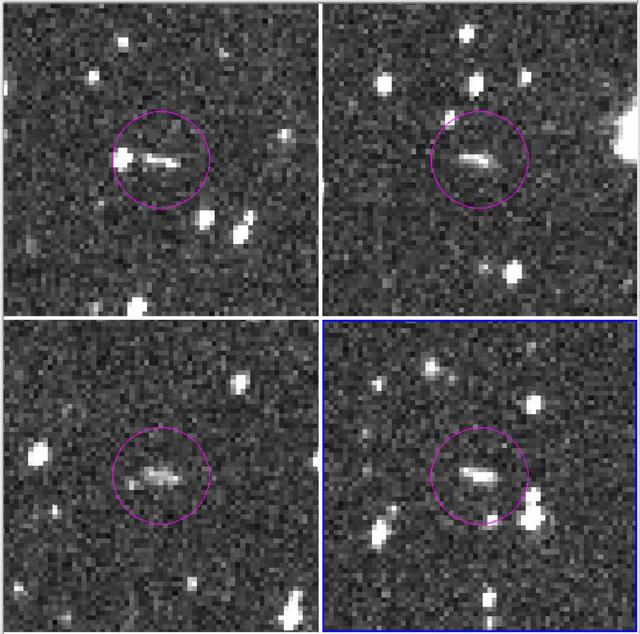

These are the discovery observations of asteroid 2018 LA from the Catalina Sky Survey, taken June 2, 2018. About eight hours after these images were taken, the asteroid entered Earth's atmosphere (about 9:44 a.m. PDT, 12:44 p.m. EDT, 16:44 UTC, 6:44 p.m. local Botswana time), and disintegrated in the upper atmosphere near Botswana, Africa. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22468
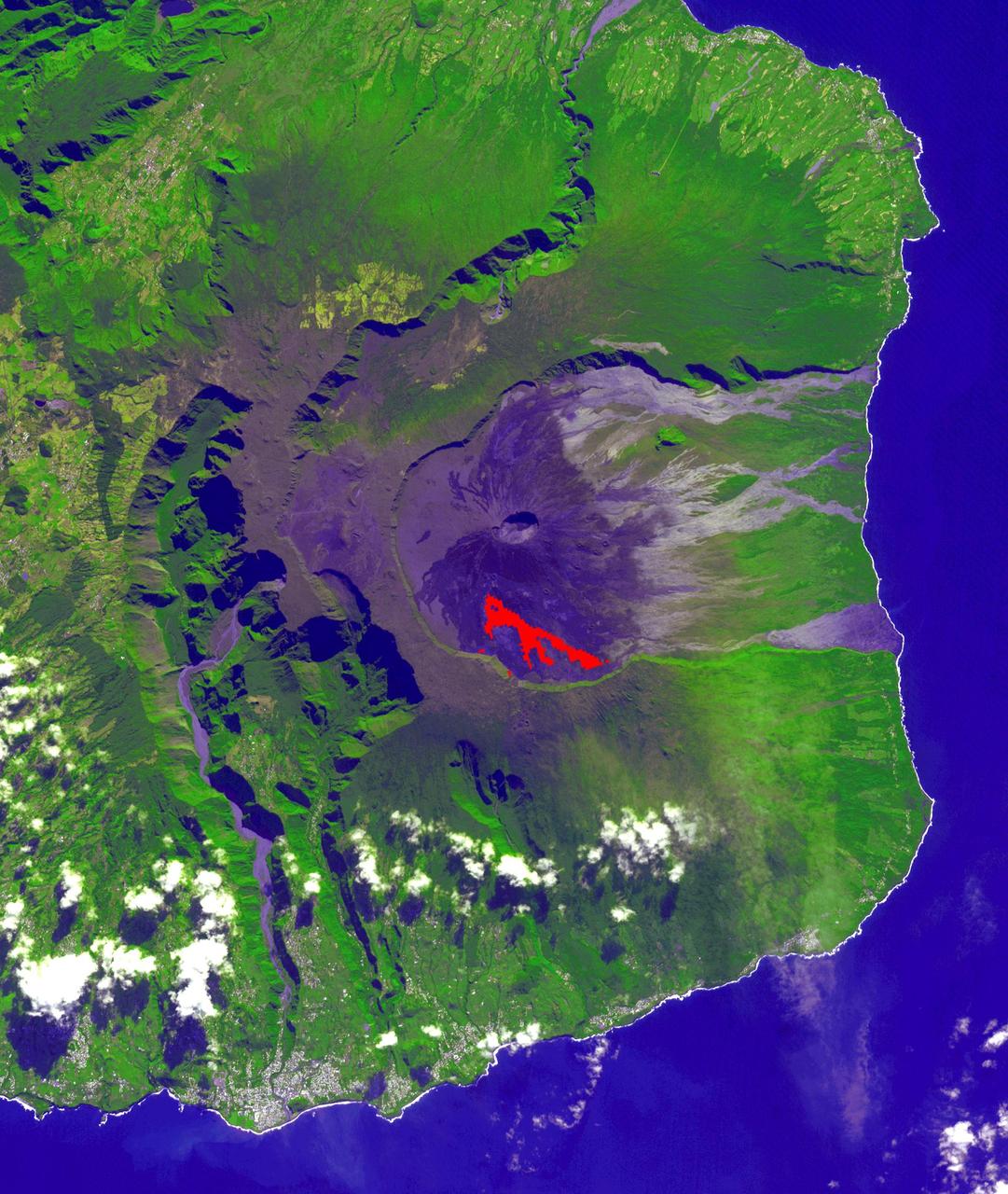
In July, 2018 an eruption began from Piton de la Fournaise volcano on Reunion Island in the western Indian Ocean. Activity continued through November, when these ASTER data were acquired. More than 150 eruptions have occurred since the 17th century. The active flow, derived from the thermal infrared band, is shown in red. The background is a pre-eruption image. The background image was acquired July 16, 2018, and the thermal image on November 1, 2018. The images cover an area of 18 miles by 21 miles (28.9 by 34.2 kilometers), and in the area of 21.3 degrees south, 55.8 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22755
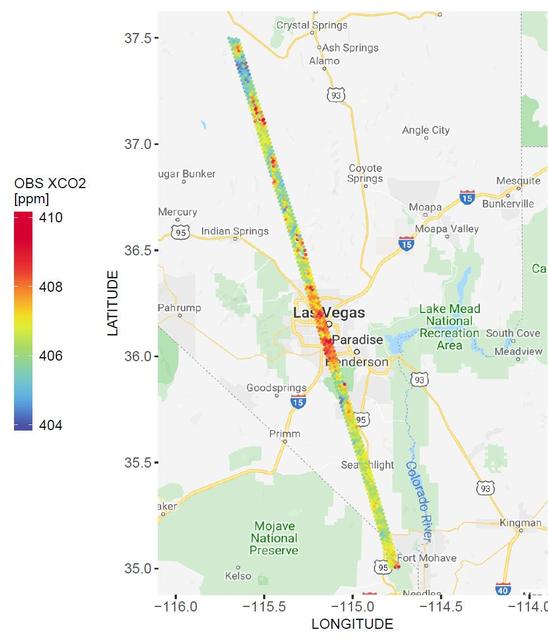
A spatial map of the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) present in columns of the atmosphere below NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite as it flew over Las Vegas on Feb. 8, 2018. Warmer colors over the city center indicate higher amounts of carbon dioxide. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23781
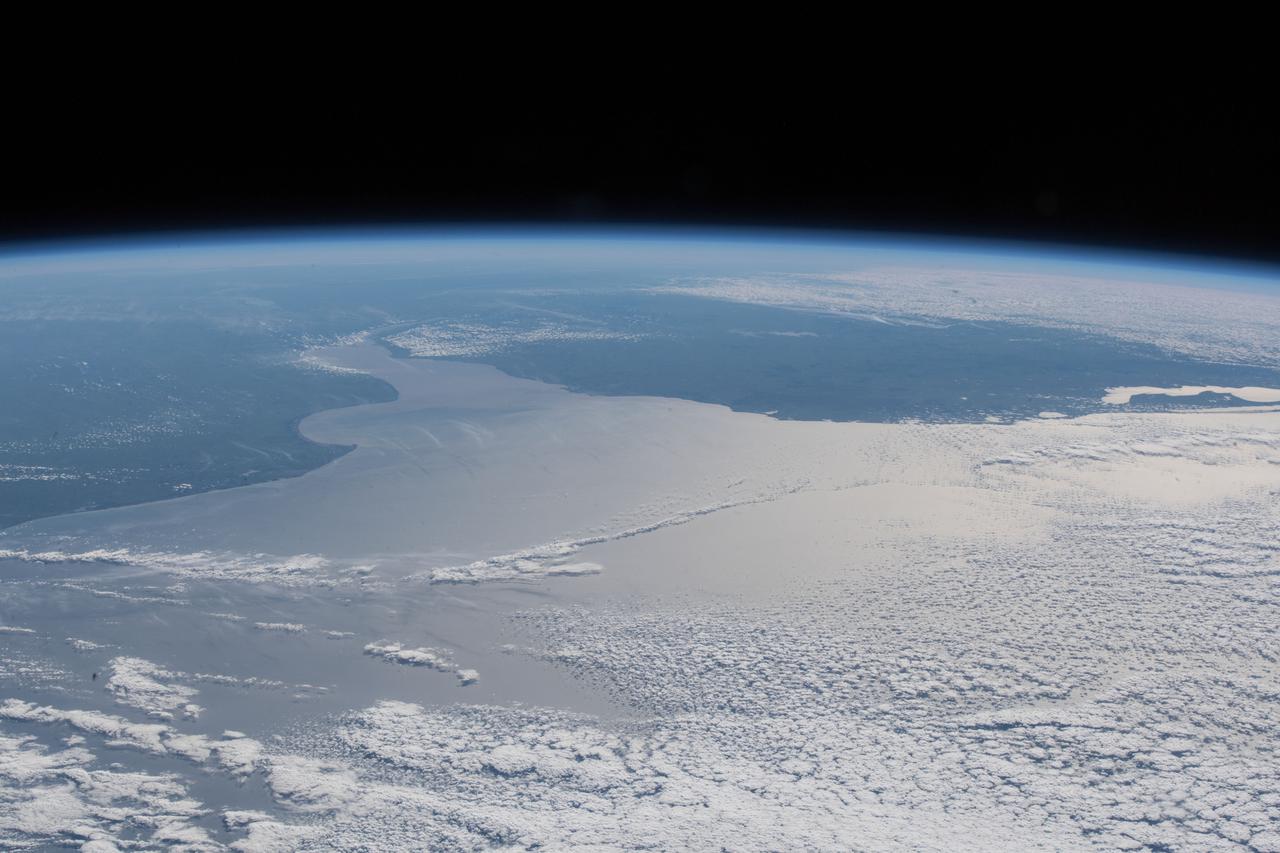

iss055e070222 (May 12, 2018) --- The Rio de la Plata and the Atlantic coasts of Argentina, Uruguay and Brazil are pictured from the International Space Station.
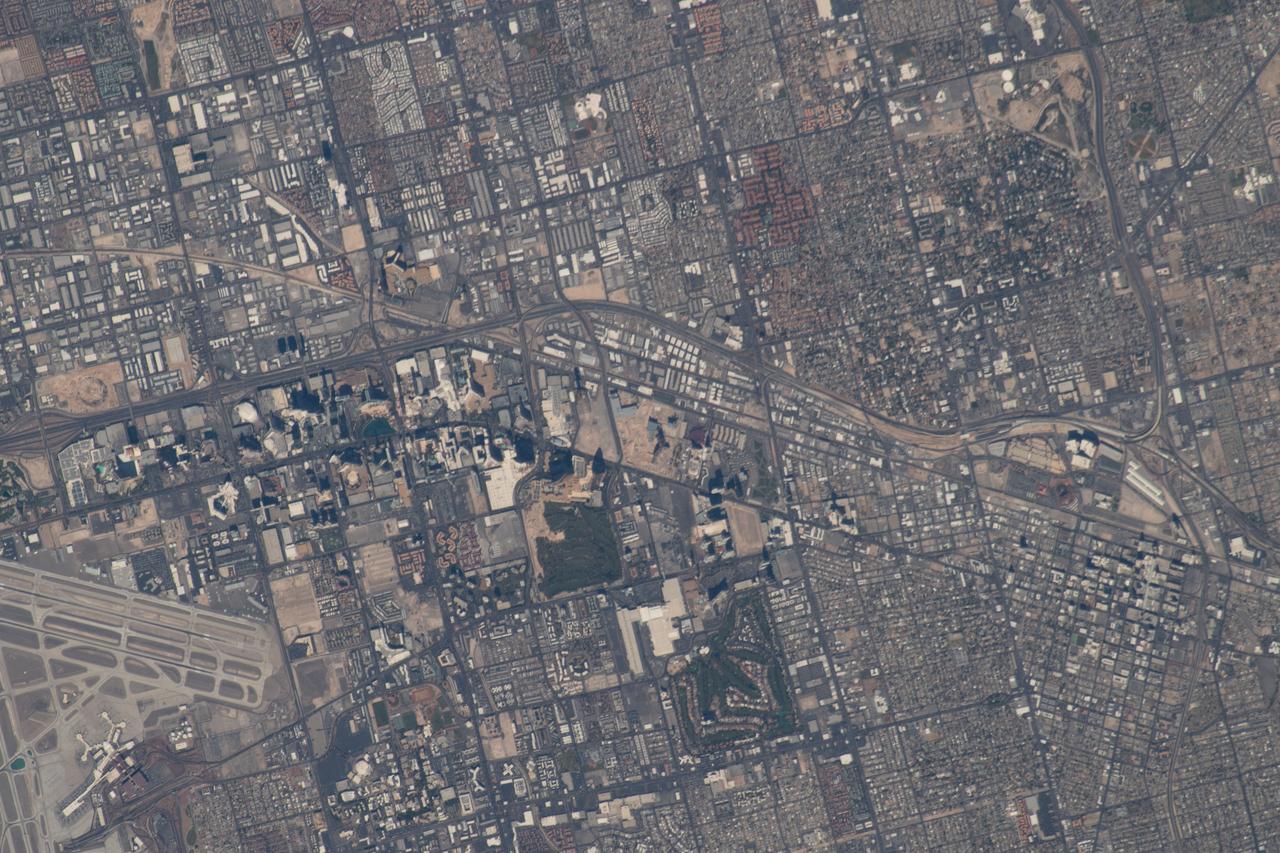

iss056e032756 (June 20, 2018) --- From left to right (true orientation is from south to north along Interstate 15) in this photograph are McCarran International Airport and downtown Las Vegas, Nev.
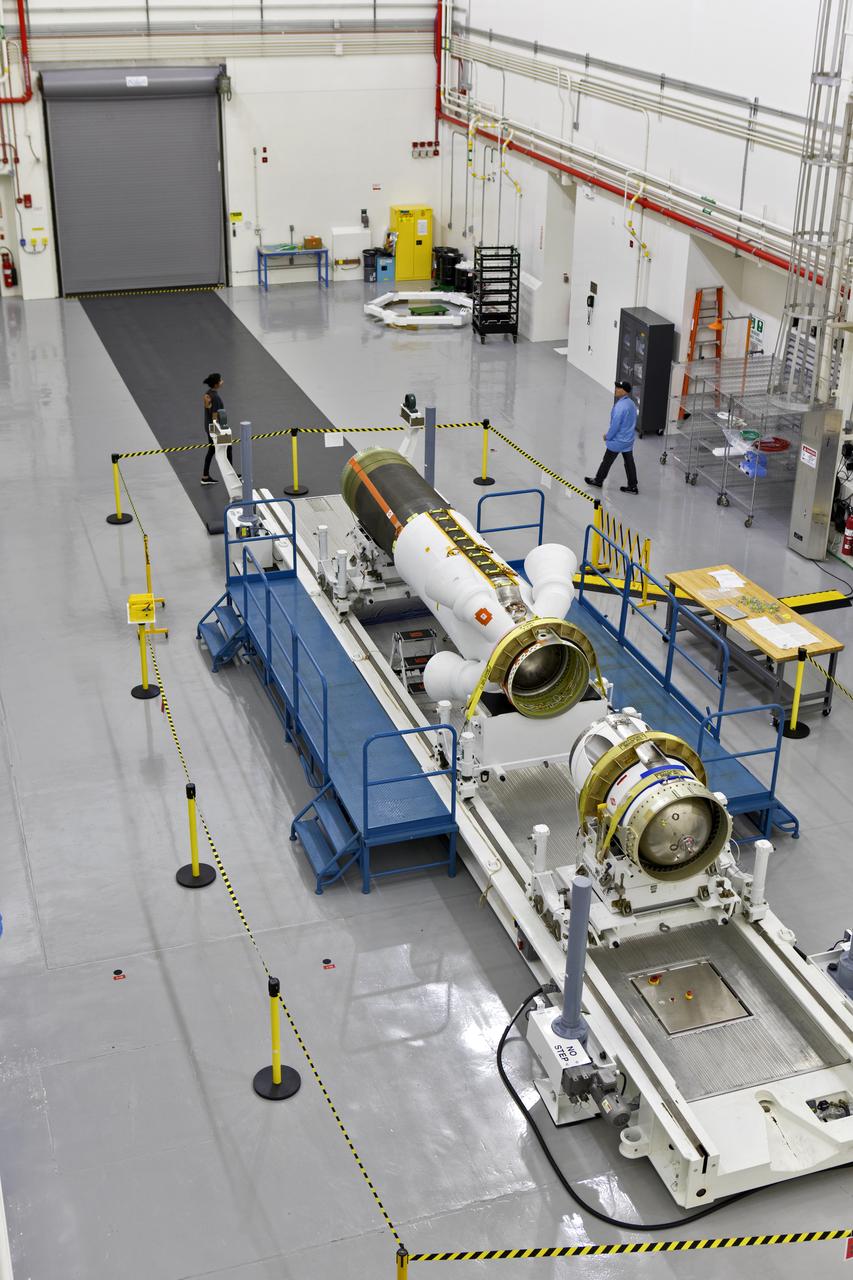

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
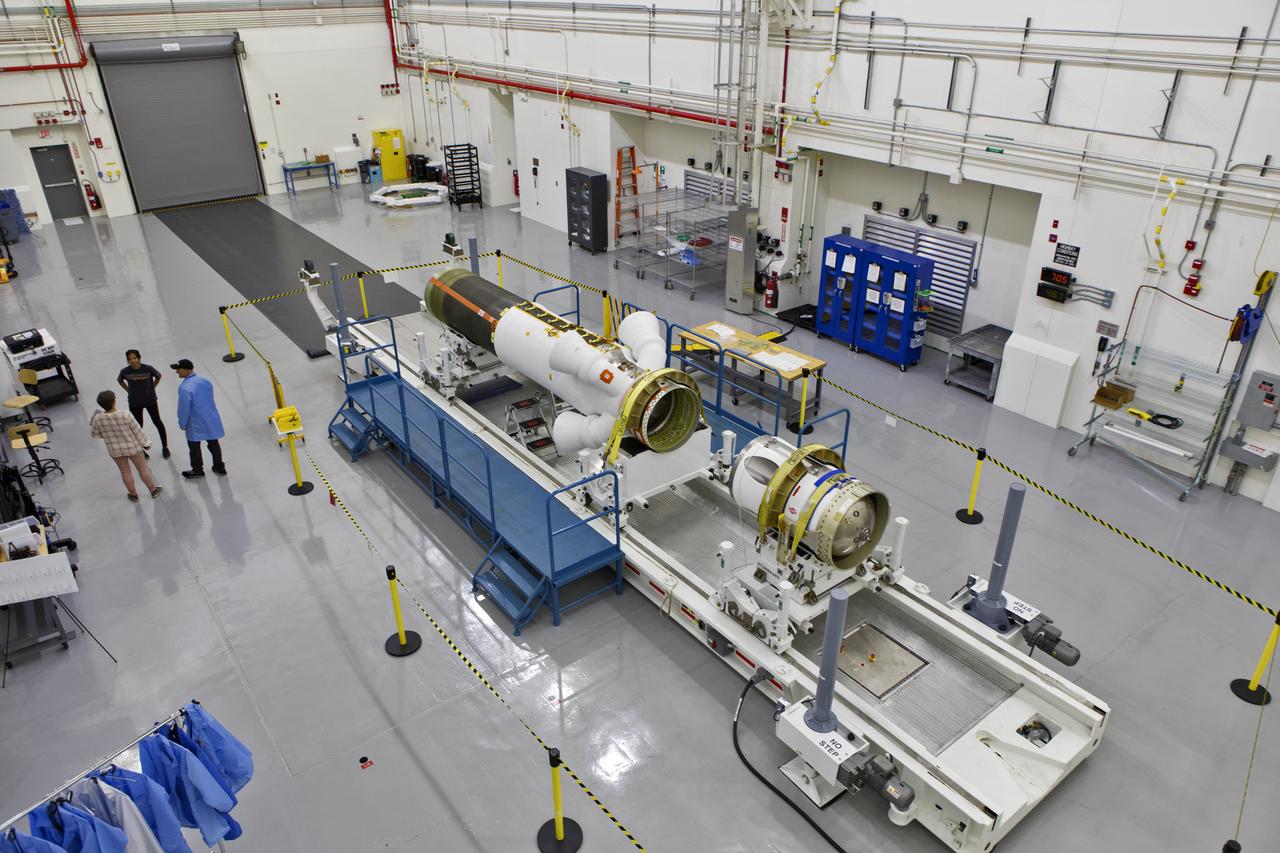

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
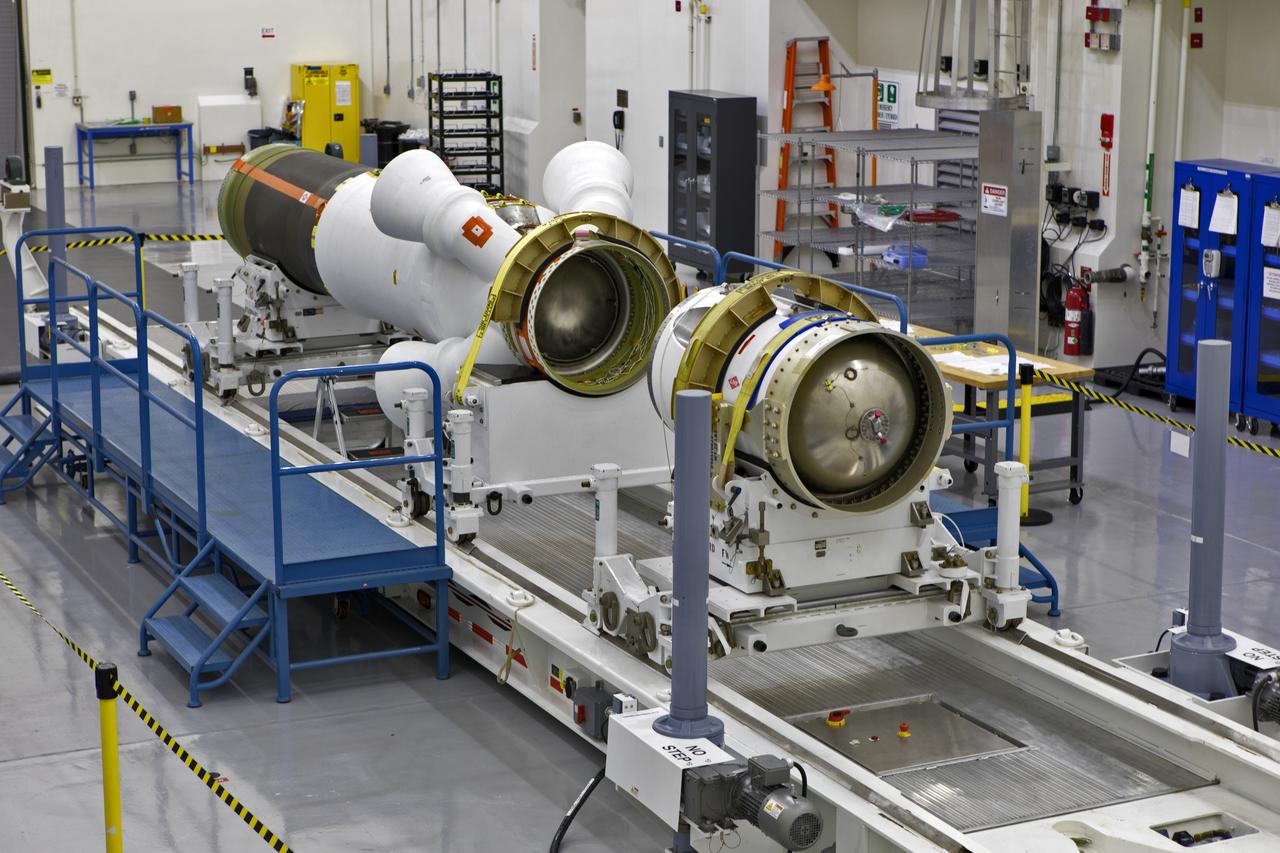

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
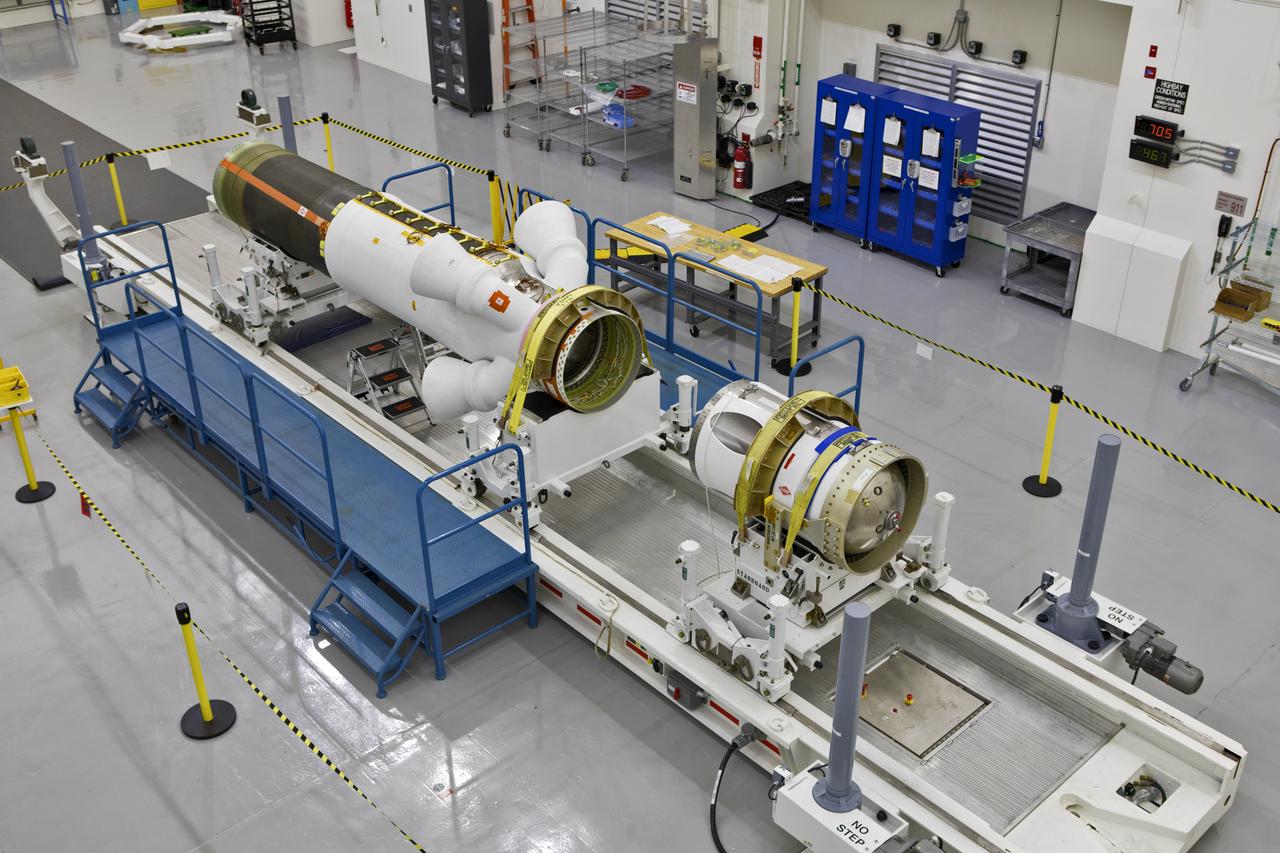

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
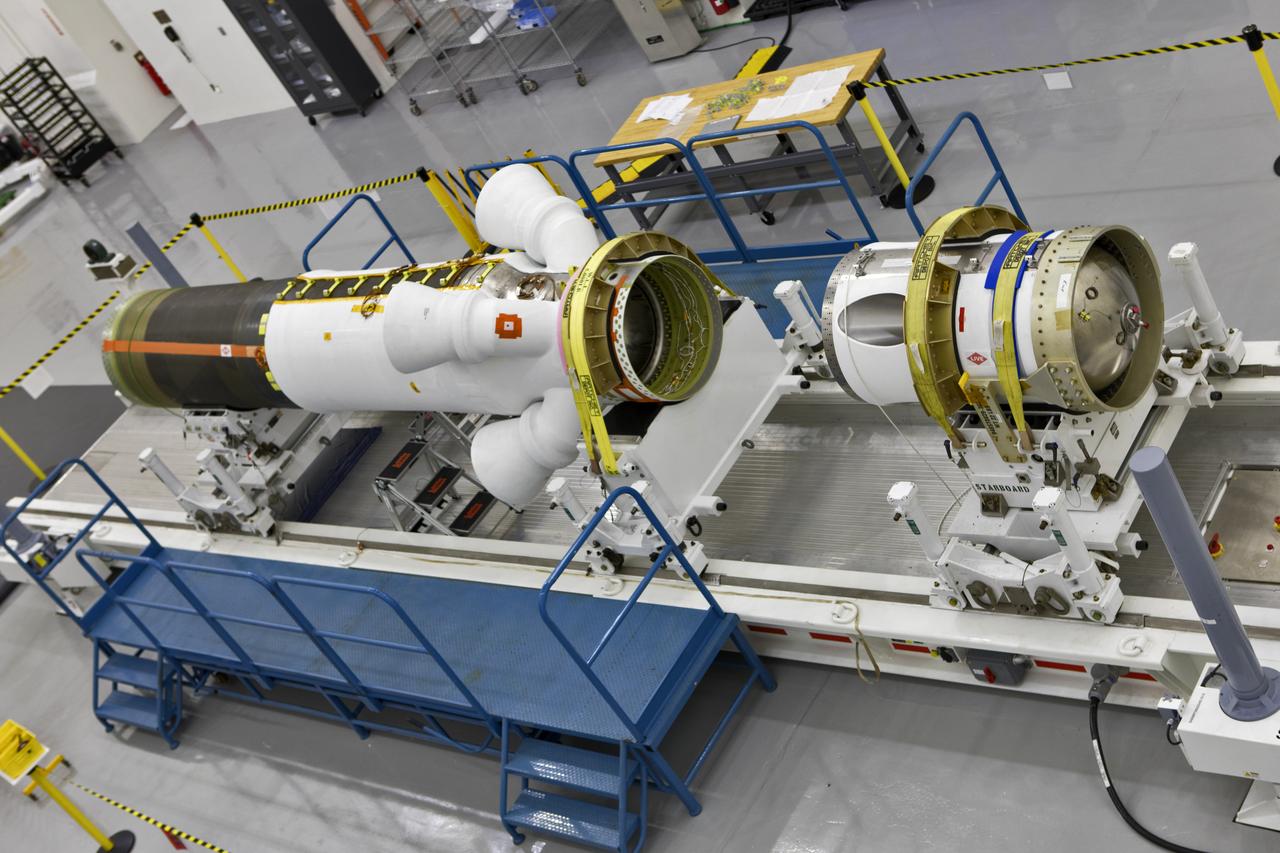

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
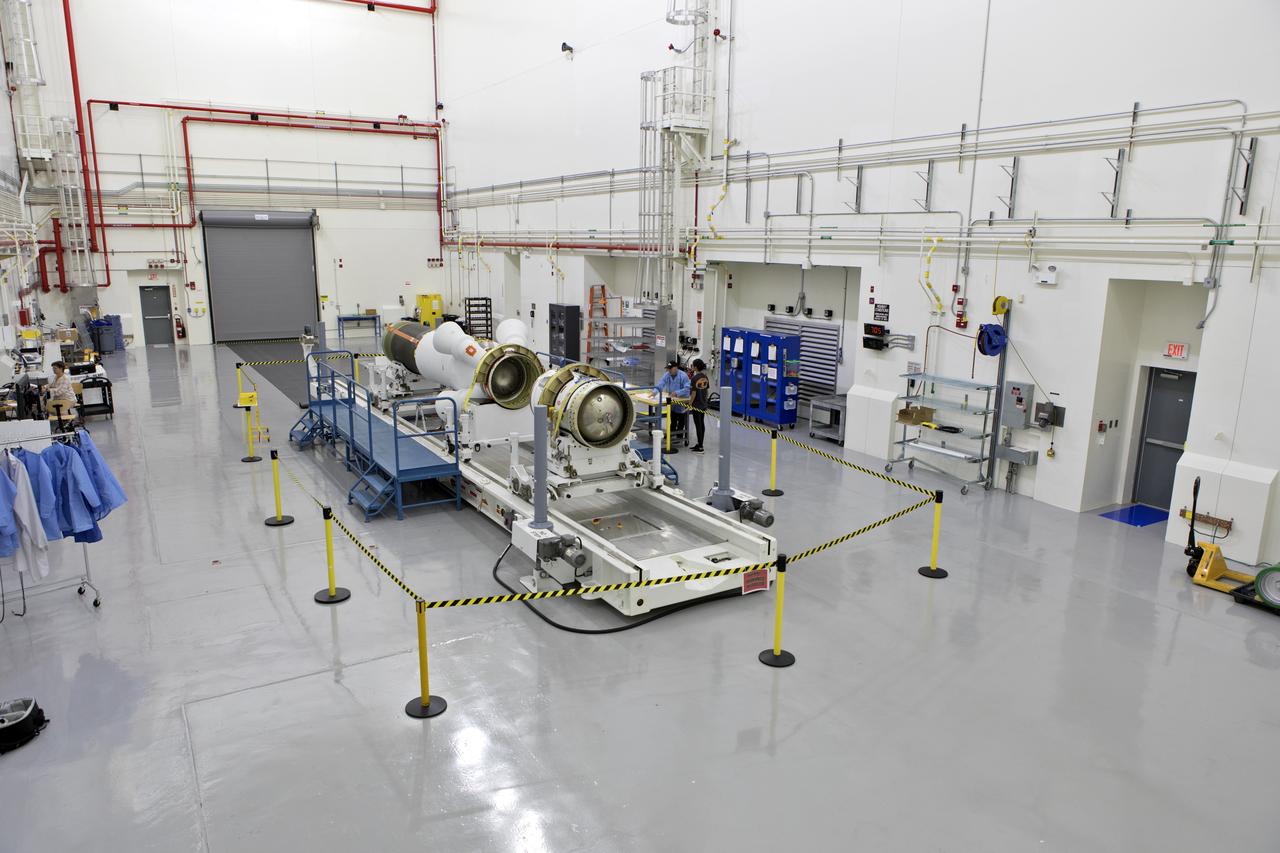

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
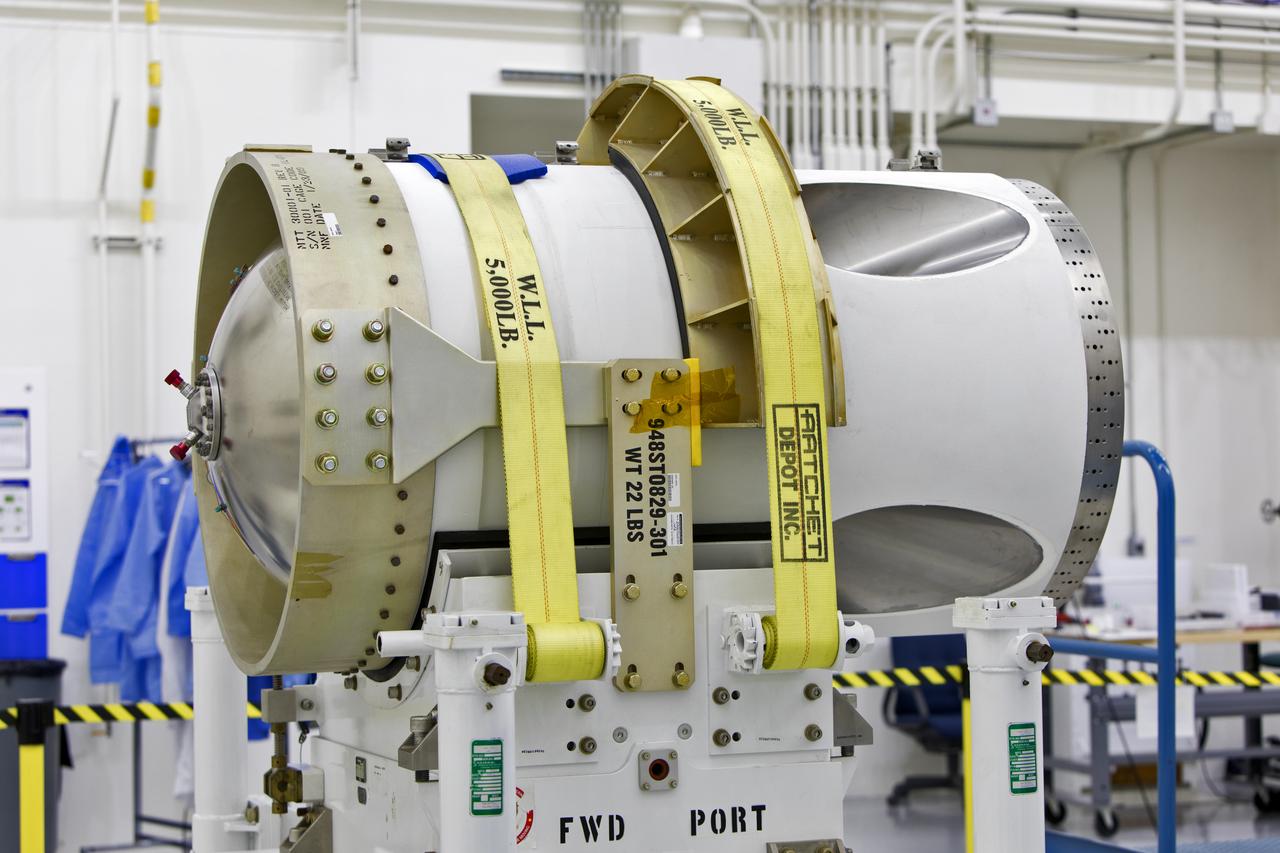
The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
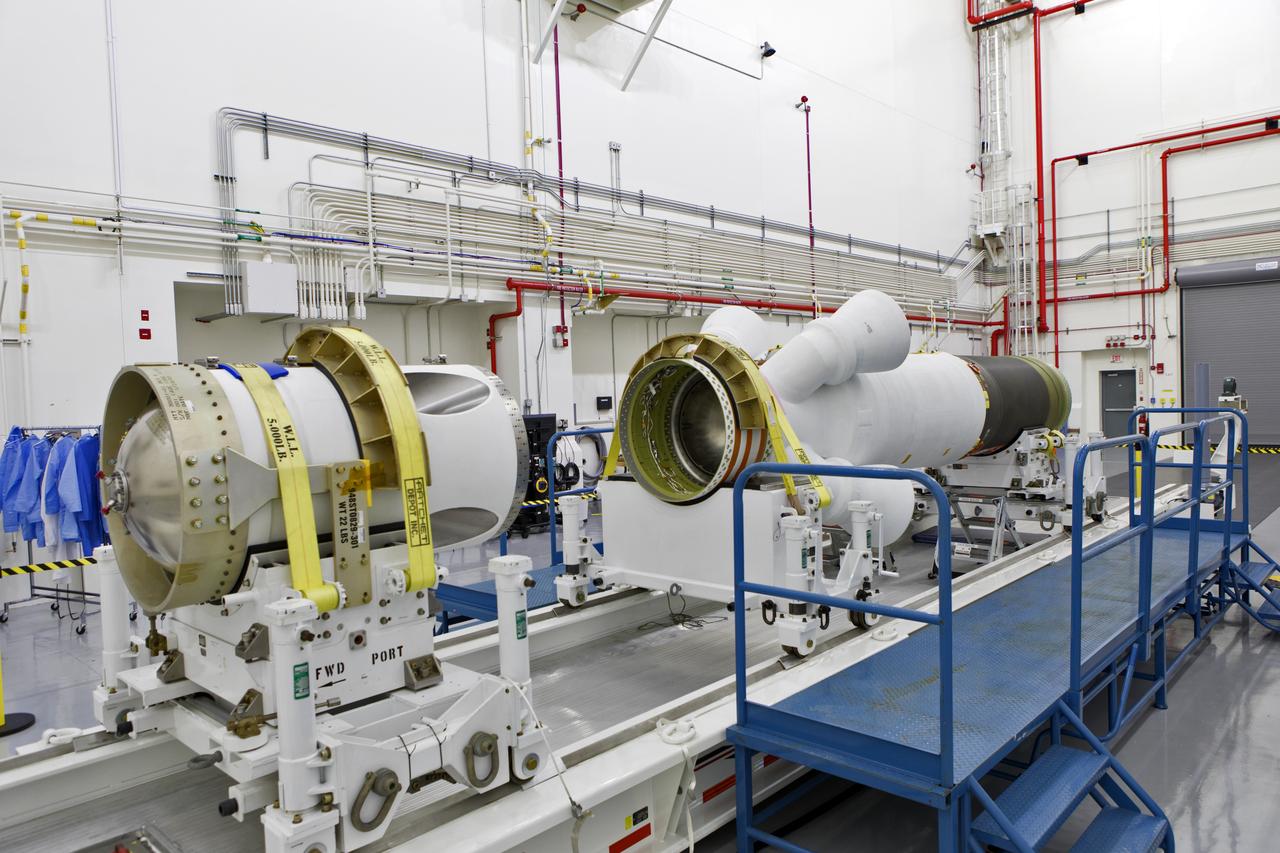

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
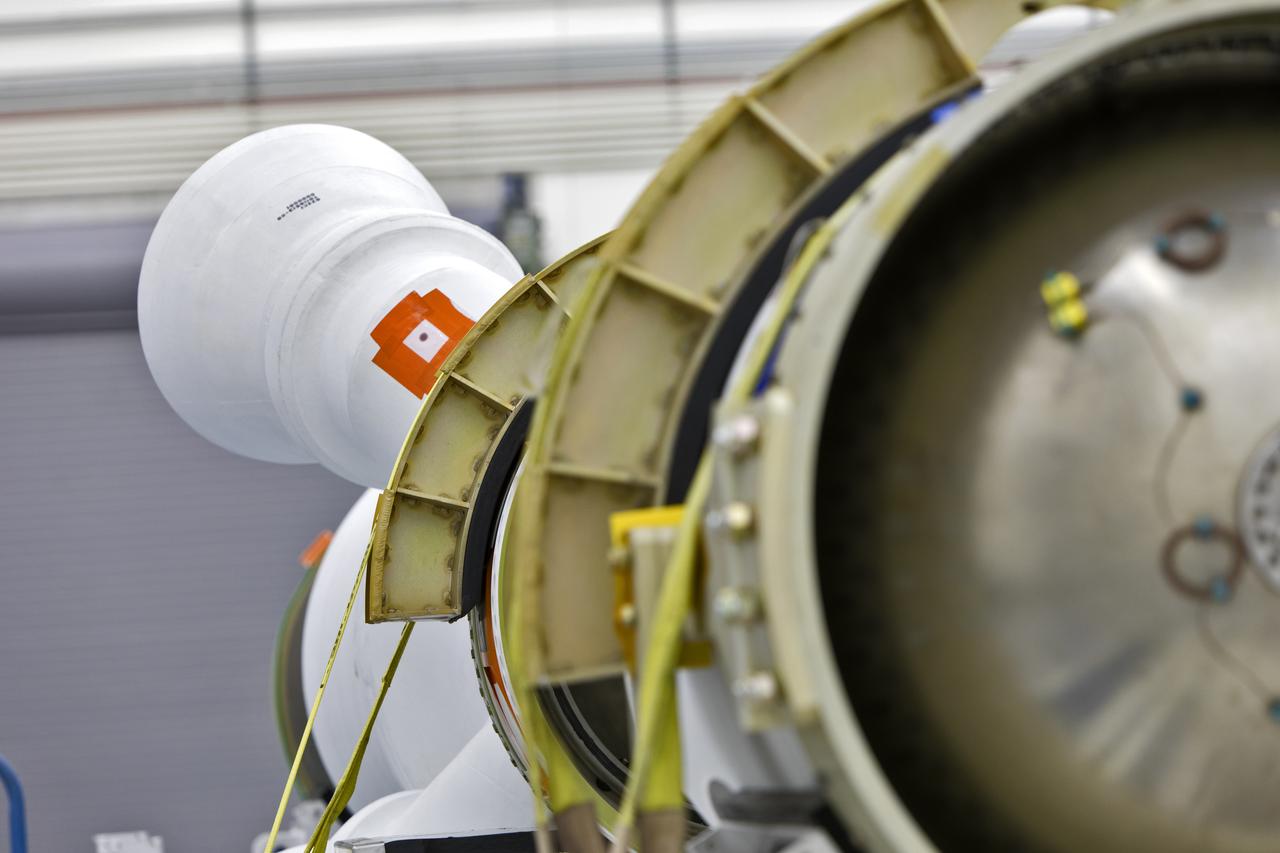

The jettison motor for Orion’s Launch Abort System (LAS) is shown inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The motor, which arrived at Kennedy on Sept. 10, 2018, will be stored in the LASF until processing for a full-stress test of the LAS called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. Designed and built by NASA and Lockheed Martin, the LAS will protect astronauts if a problem arises during launch by pulling the spacecraft away from a failing rocket. The jettison motor is one of three solid propellant rocket motors in the LAS (the abort motor and attitude control motor are the other two). The jettison motor will pull the LAS away from the crew module, allowing Orion’s parachutes to deploy and the spacecraft to safely land in the ocean.
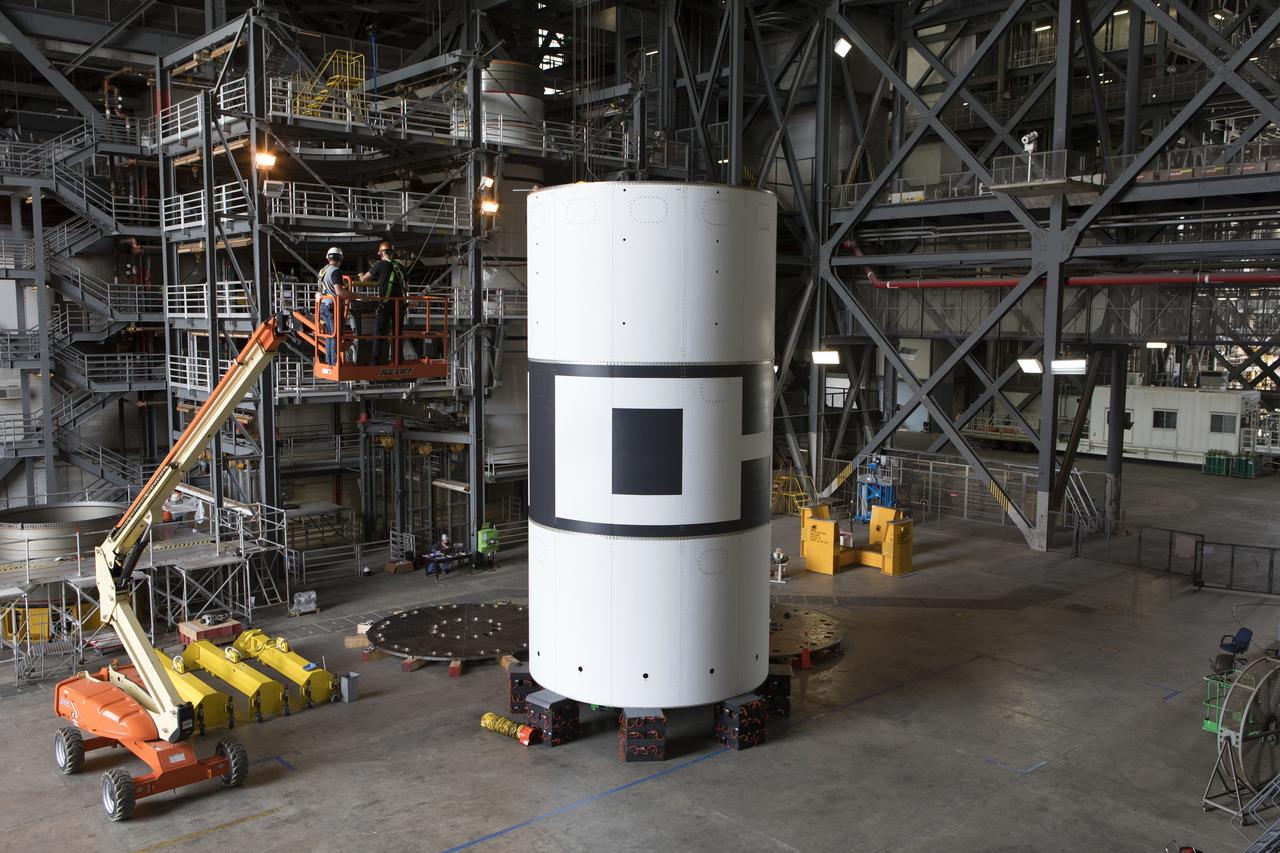

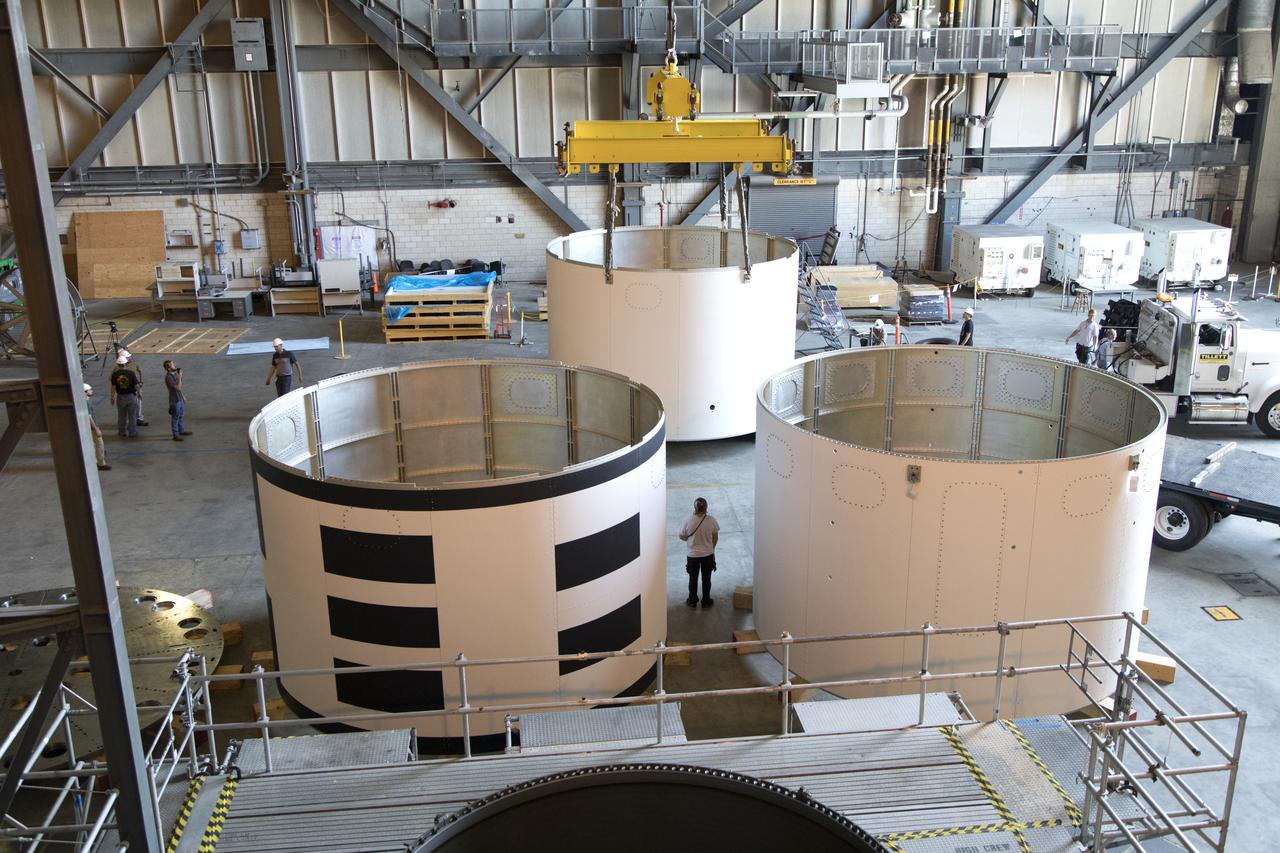
The aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) are stacked in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Aug. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshells are being prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
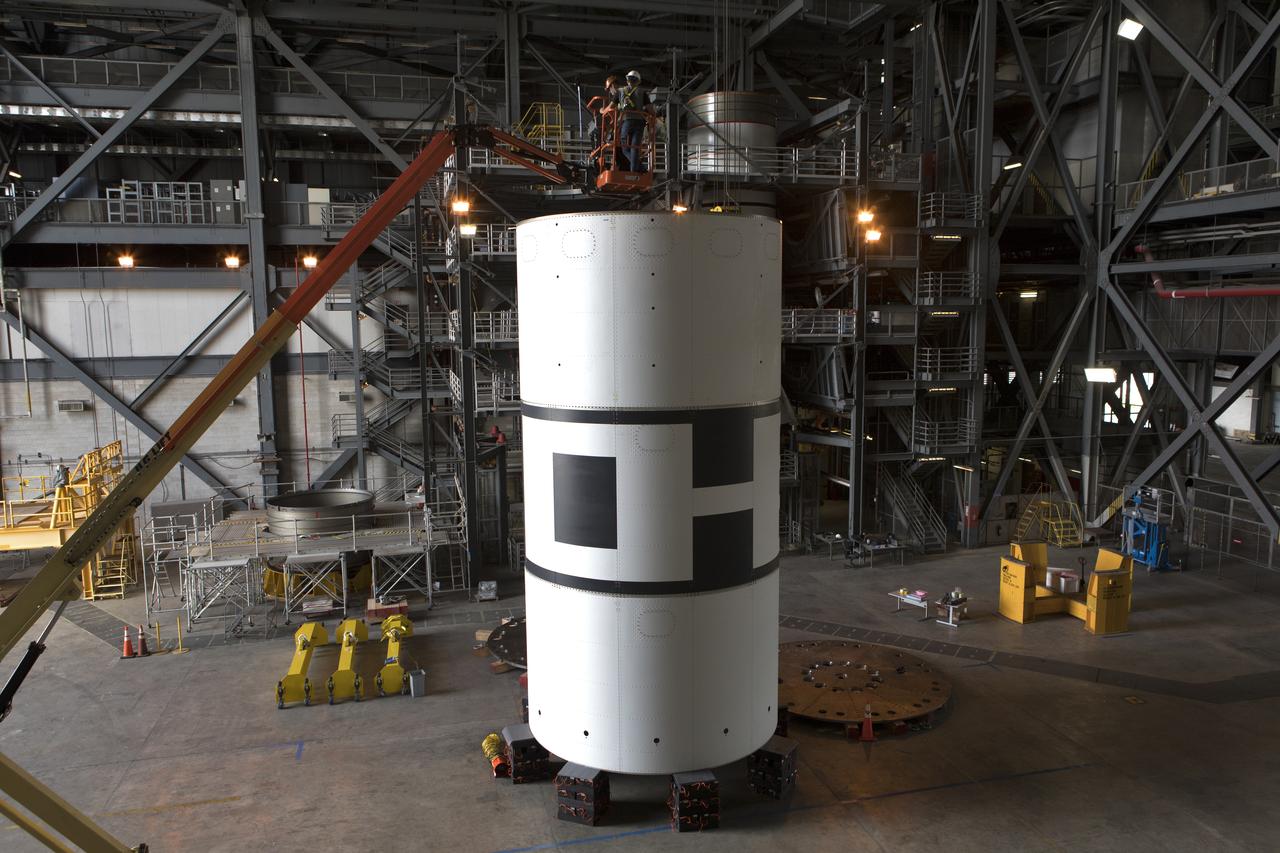

The aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) are being stacked in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Aug. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshells are being prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
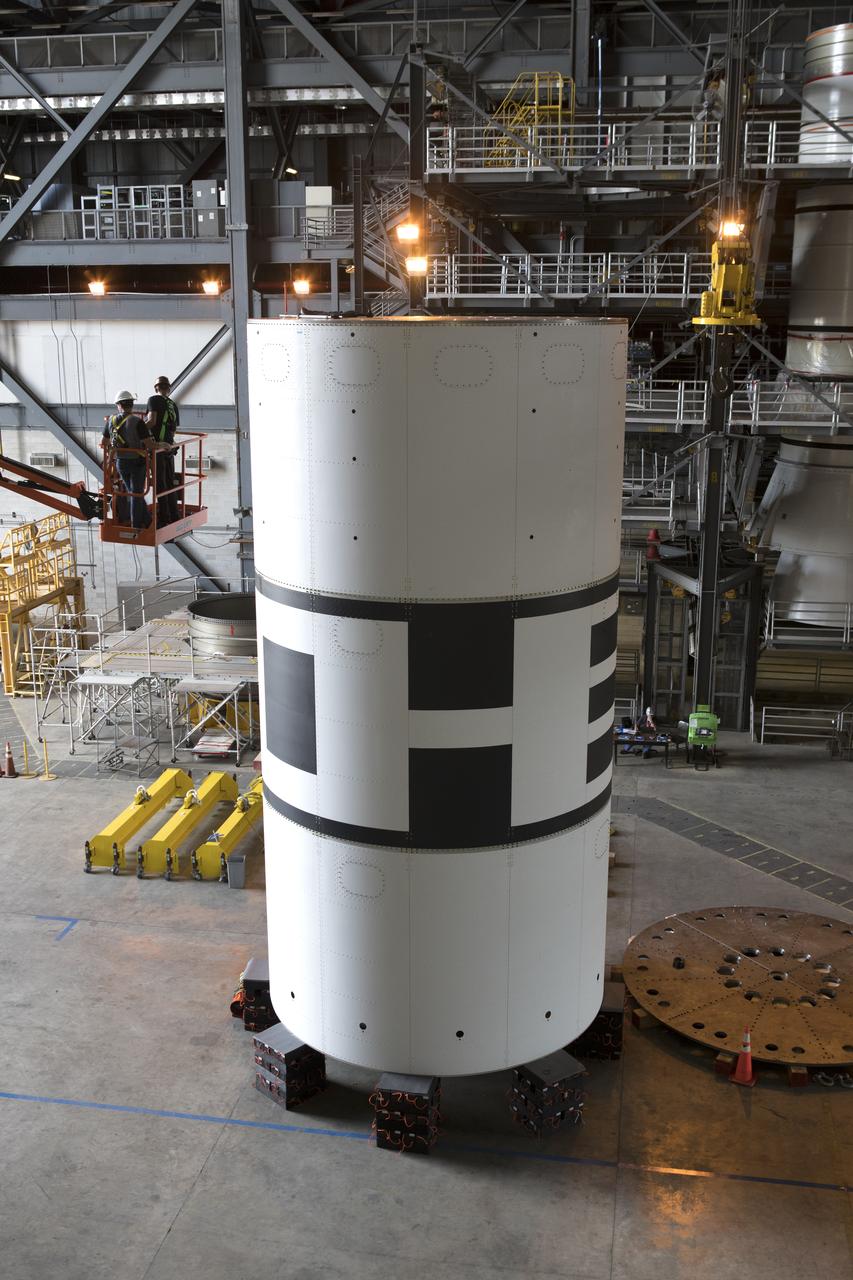
The aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) are being stacked in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Aug. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshells are being prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
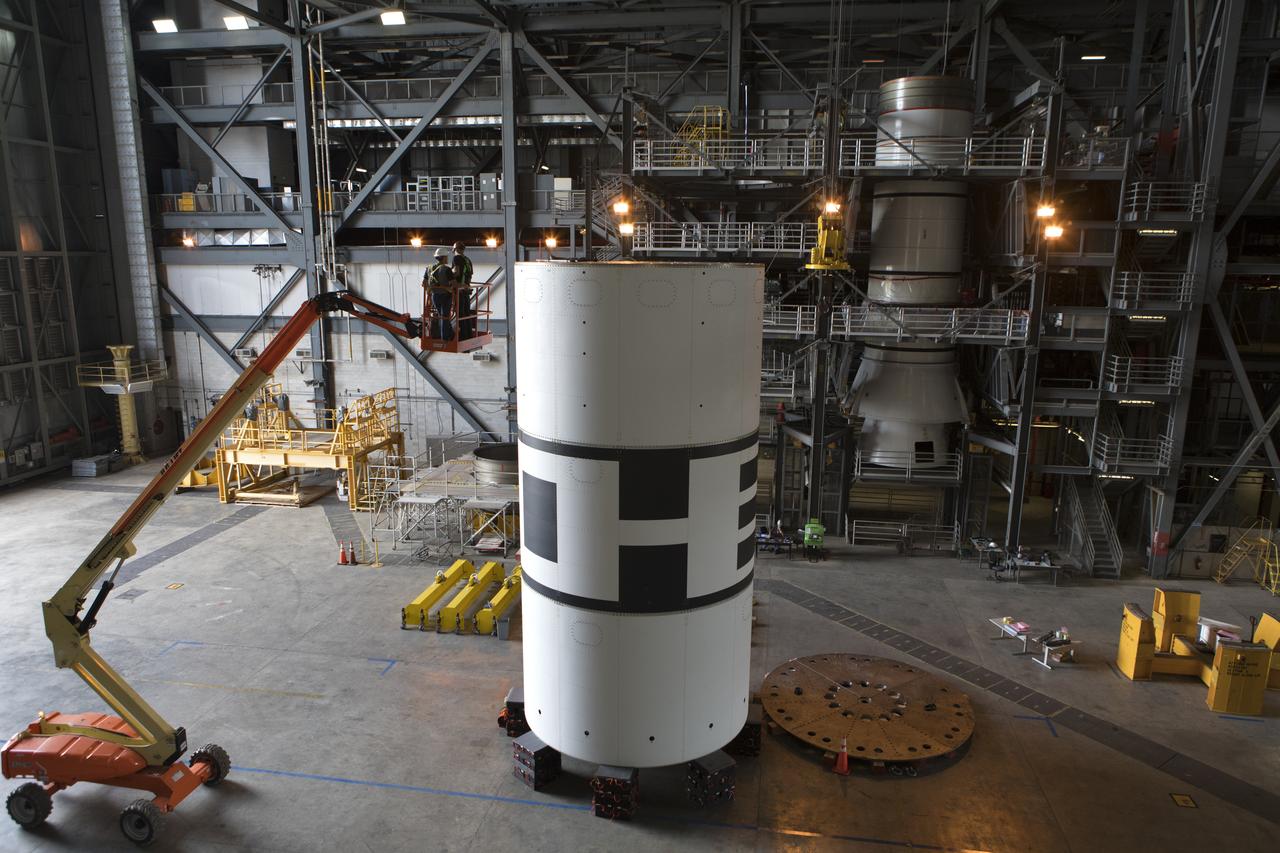

The aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) are being stacked in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Aug. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshells are being prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
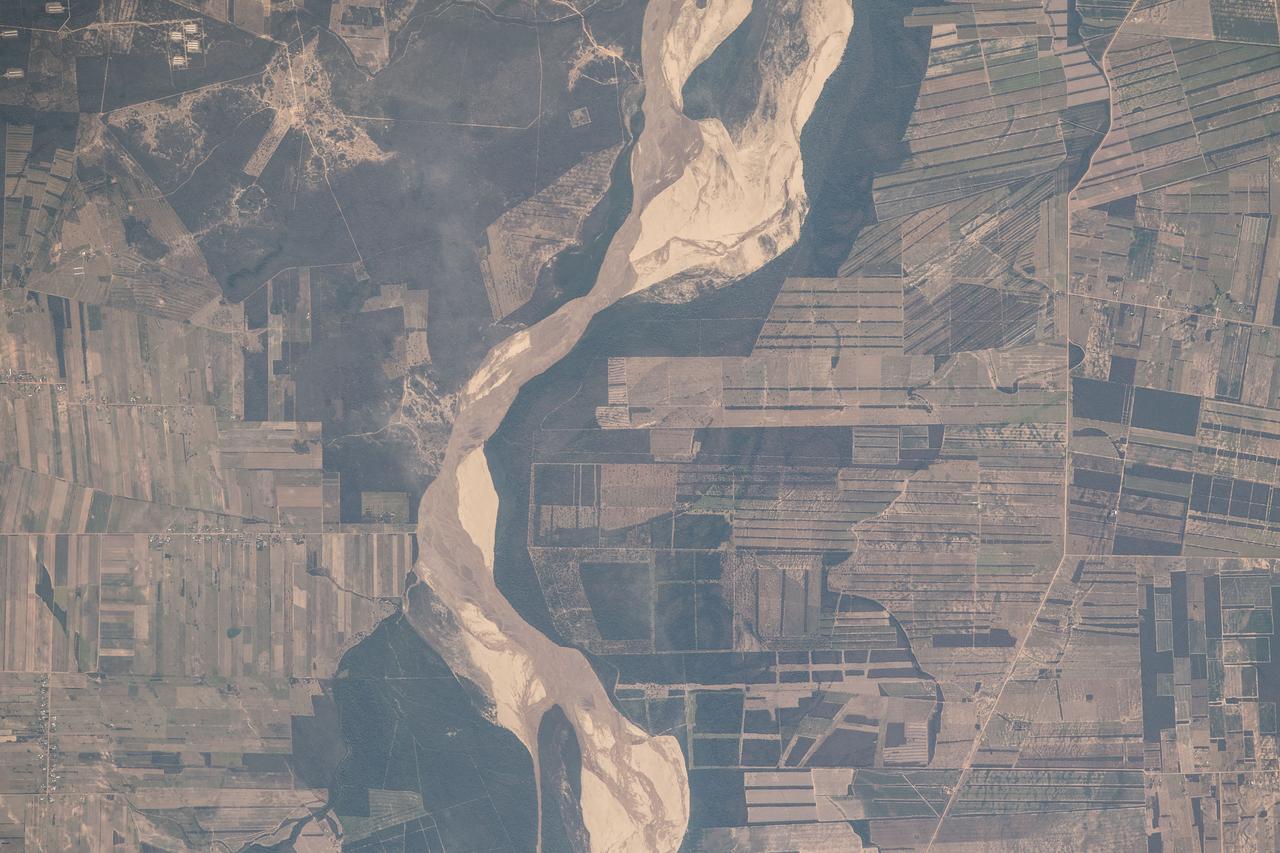

iss056e094532 (July 10, 2018) --- This portion of Bolivia's Rio Grande is about 27 miles east of downtown Santa Cruz de la Sierra, the country's largest city. The river in the Amazon Basin and the sub-tropical climate support navigation, fishing and agriculture.

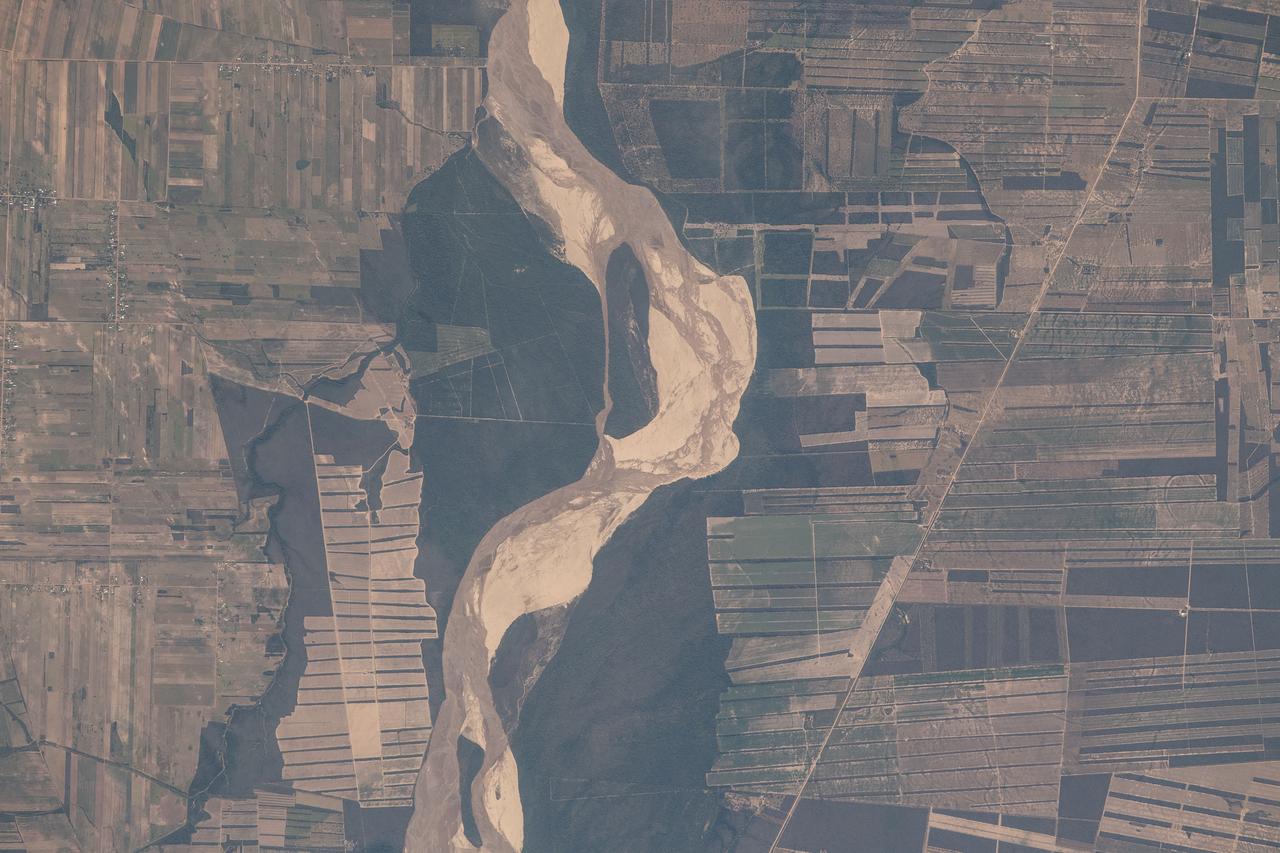
iss056e094533 (July 10, 2018) --- This portion of Bolivia's Rio Grande is about 27 miles east of downtown Santa Cruz de la Sierra, the country's largest city. The river in the Amazon Basin and the sub-tropical climate support navigation, fishing and agriculture.

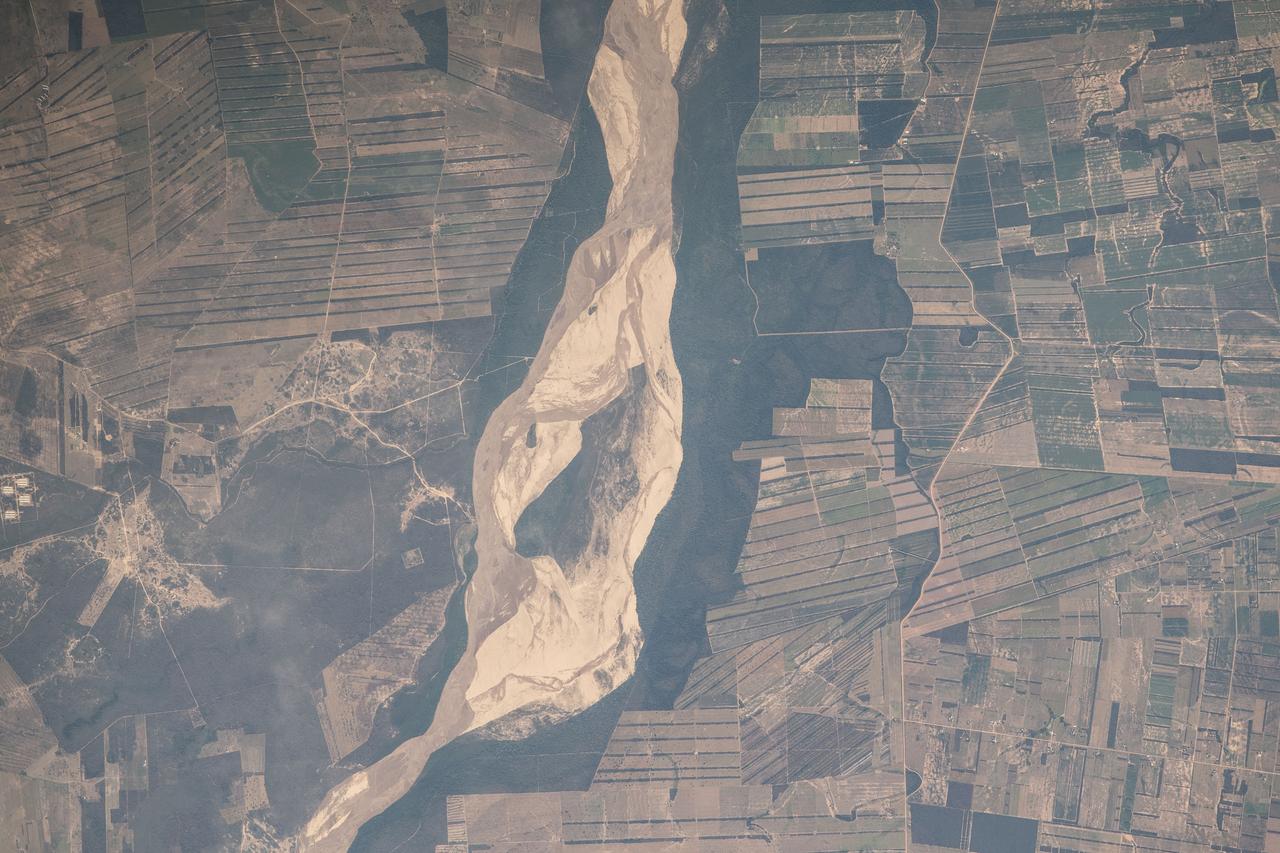
iss056e094531 (July 10, 2018) --- This portion of Bolivia's Rio Grande in the Amazon Basin is about 27 miles east of downtown Santa Cruz de la Sierra, the country's largest city. The river and the region's sub-tropical climate support navigation, fishing and agriculture.
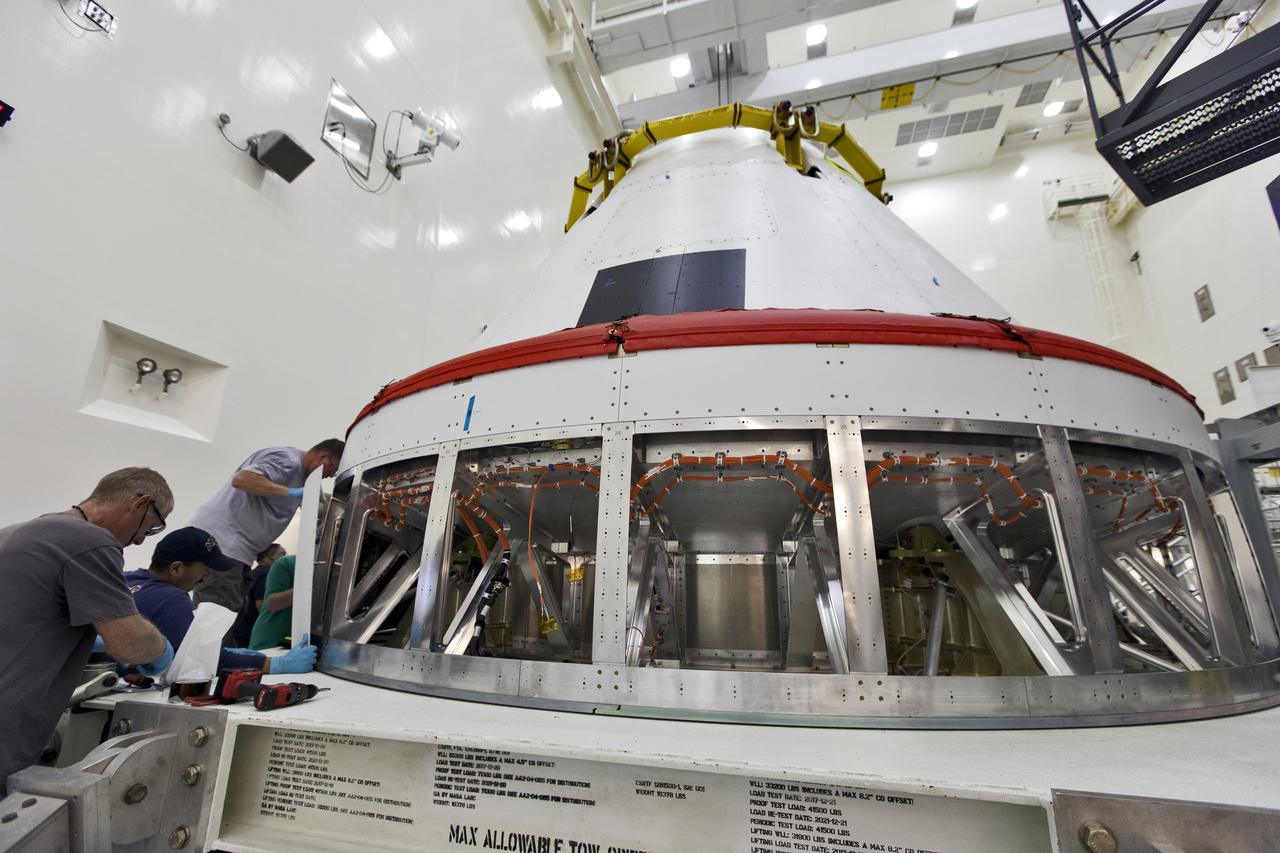

Workers remove cover plates from a mock Orion crew module inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 6, 2018. The crew module will be used during a full stress test of the Launch Abort System (LAS), called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and the 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space.
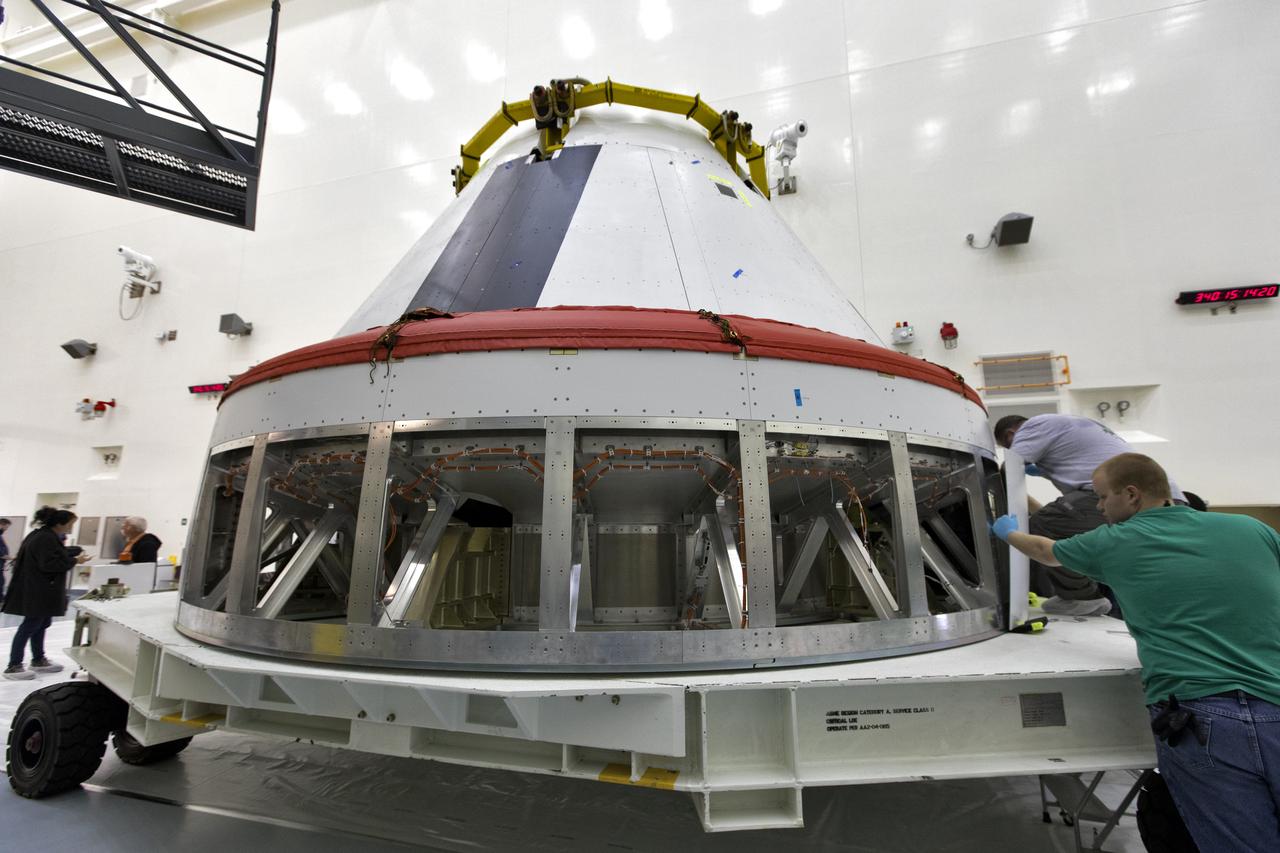

Workers remove cover plates from a mock Orion crew module inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 6, 2018. The crew module will be used during a full stress test of the Launch Abort System (LAS), called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the Northrop Grumman booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and the 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space.
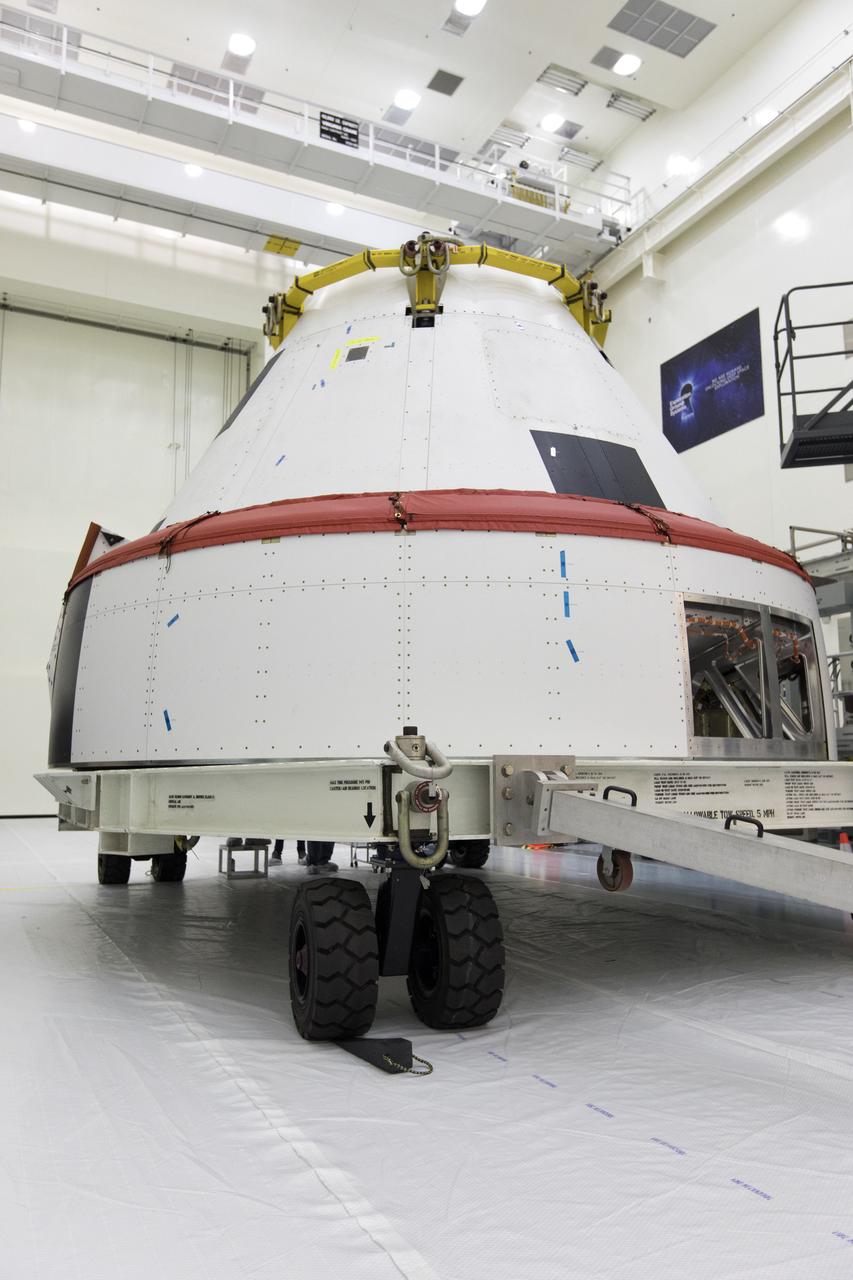

A mock Orion crew module is inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 6, 2018. The crew module will be used during a full stress test of the Launch Abort System (LAS), called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the Northrop Grumman booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and the 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space.
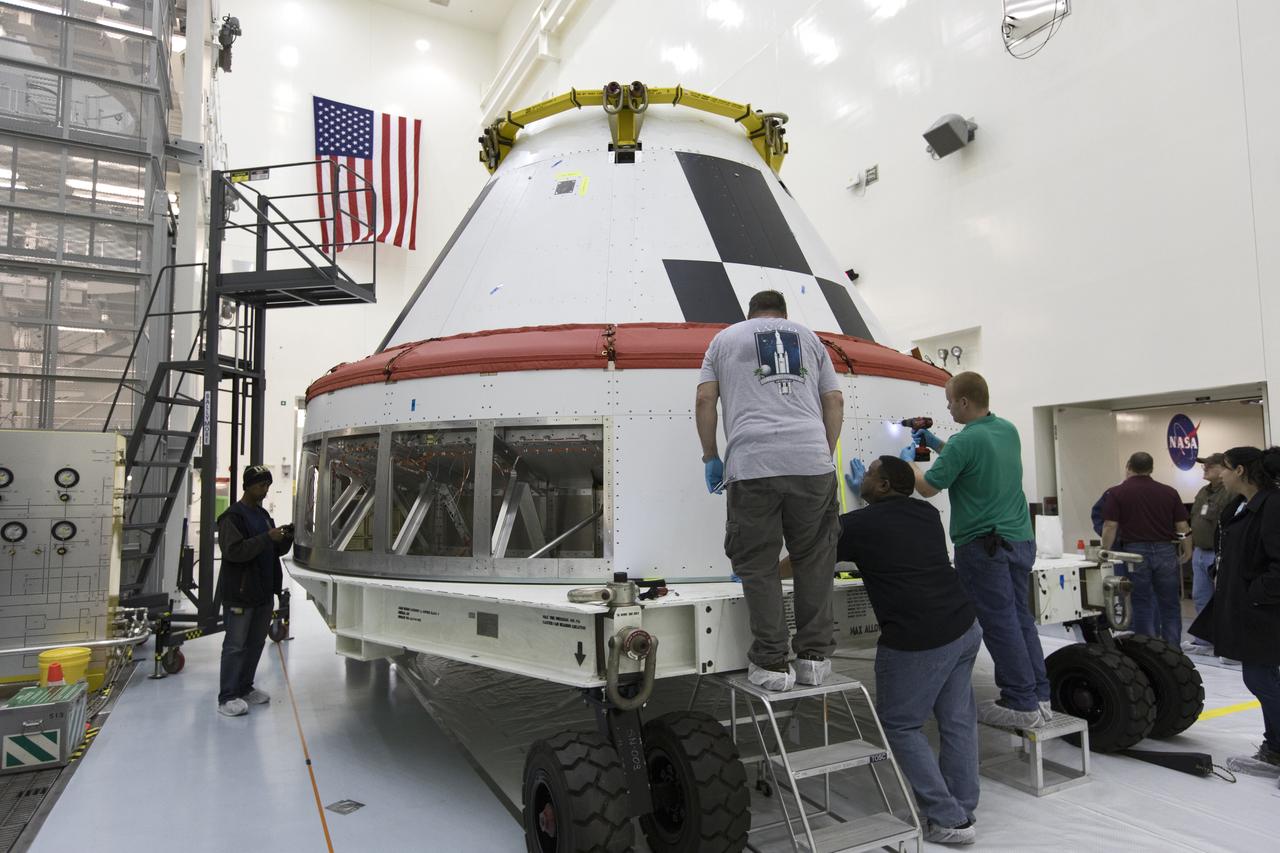

Workers remove cover plates from a mock Orion crew module inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 6, 2018. The crew module will be used during a full stress test of the Launch Abort System (LAS), called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the Northrop Grumman booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and the 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space.
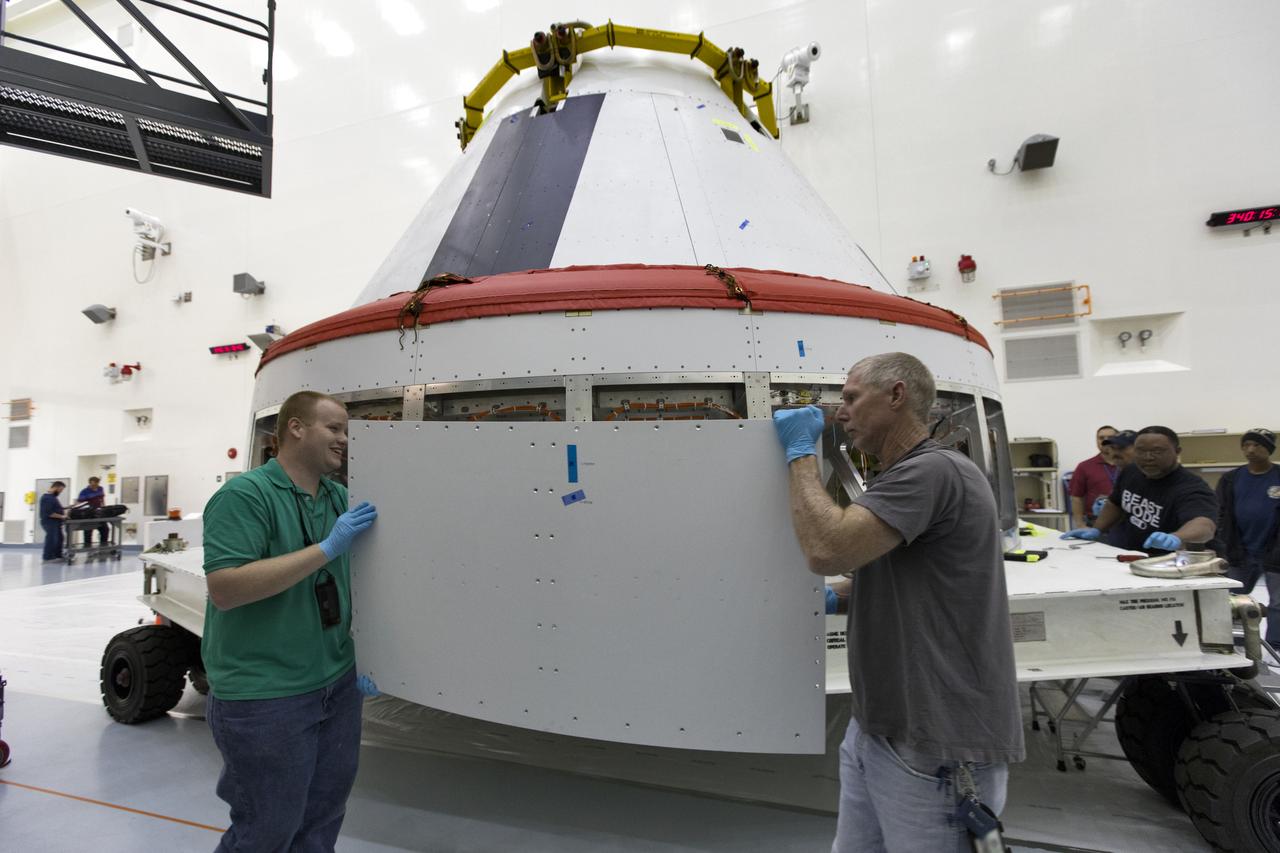

Workers remove cover plates from a mock Orion crew module inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 6, 2018. The crew module will be used during a full stress test of the Launch Abort System (LAS), called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the Northrop Grumman booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and the 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space.
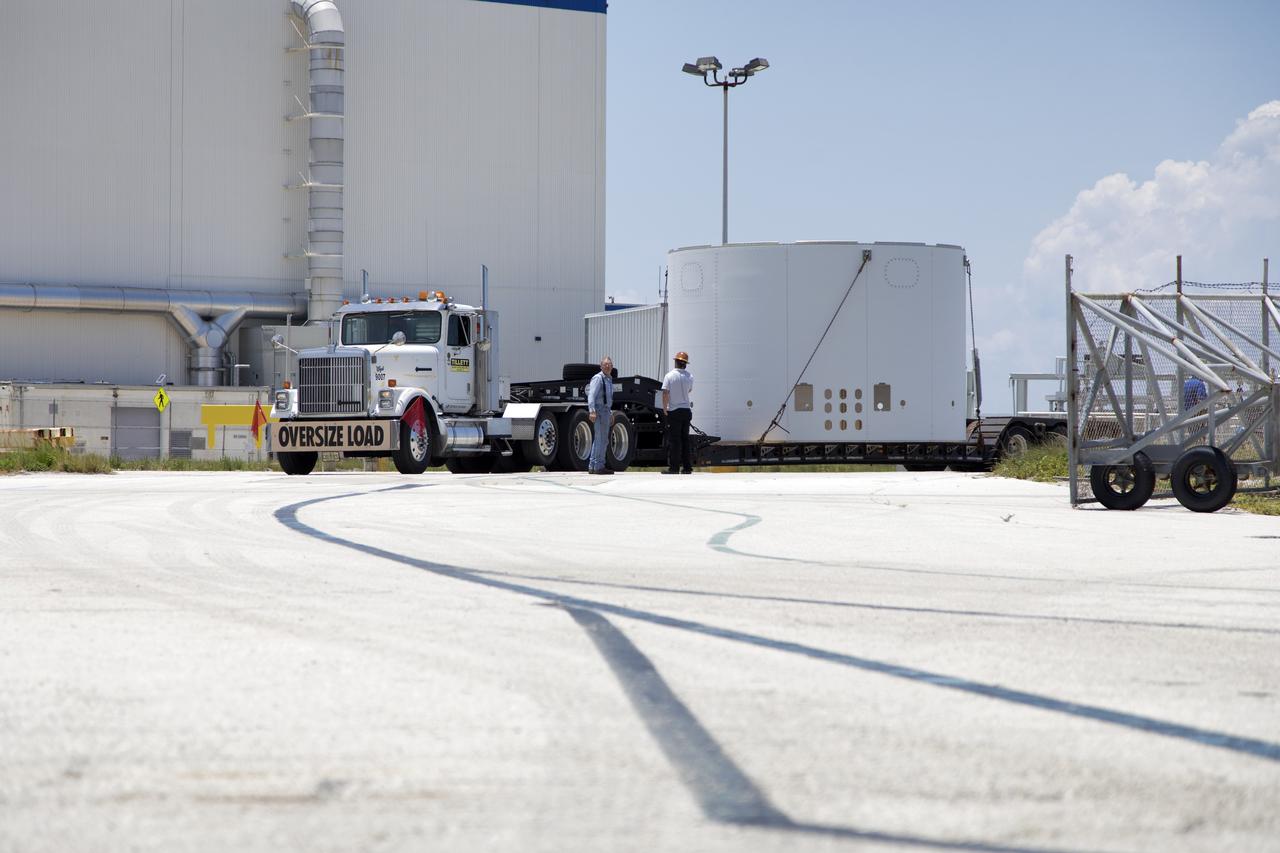

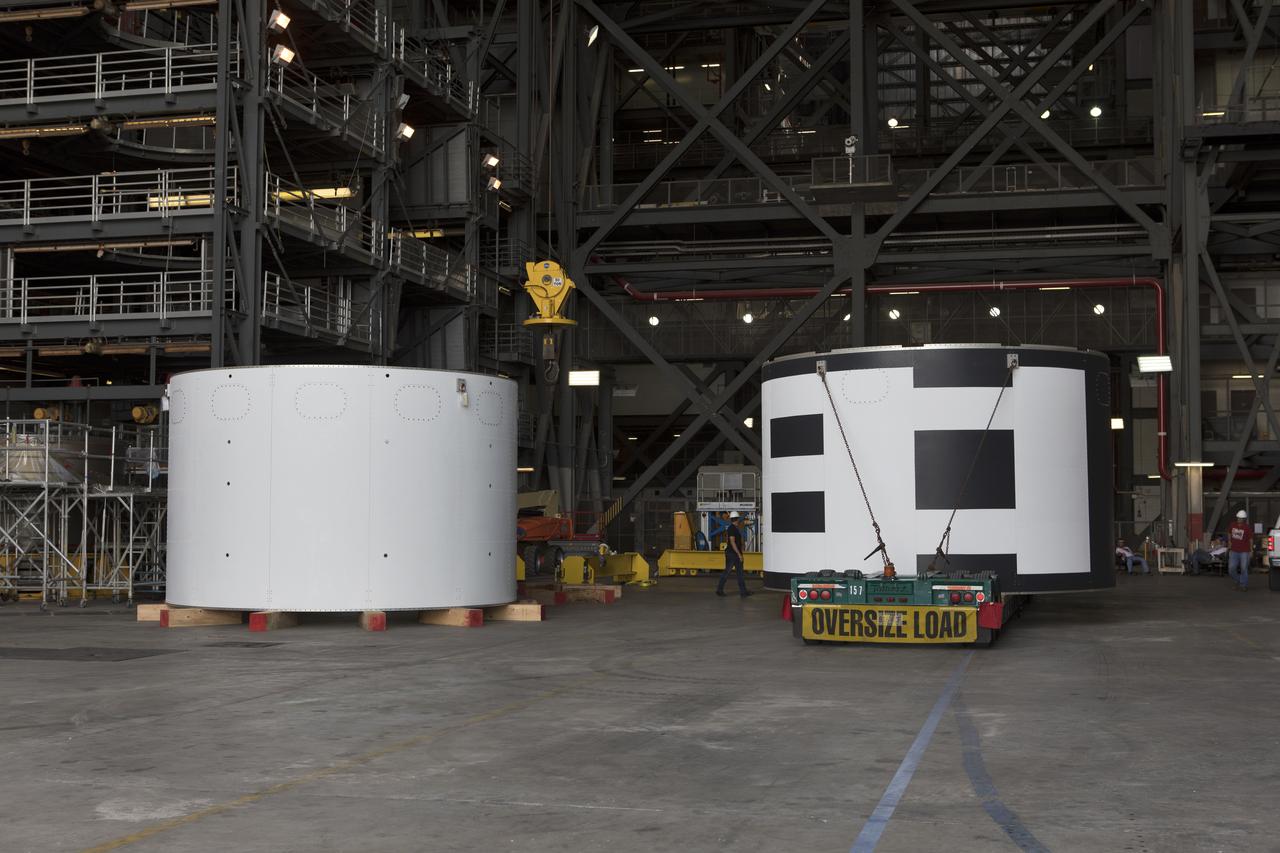
The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by truck on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.

The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is lifted by crane in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. The aeroshell will be lowered onto slats. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.

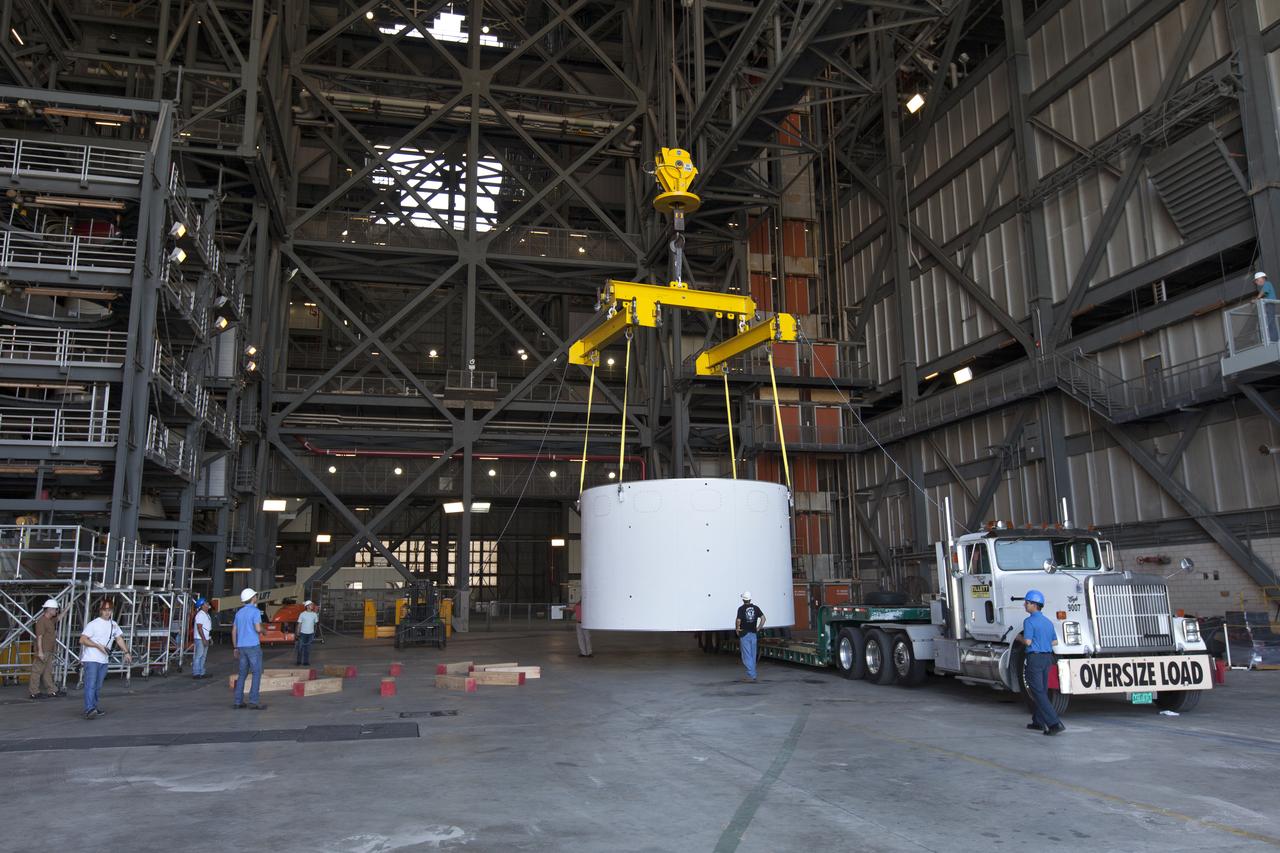
The second of three aeroshells, at right, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
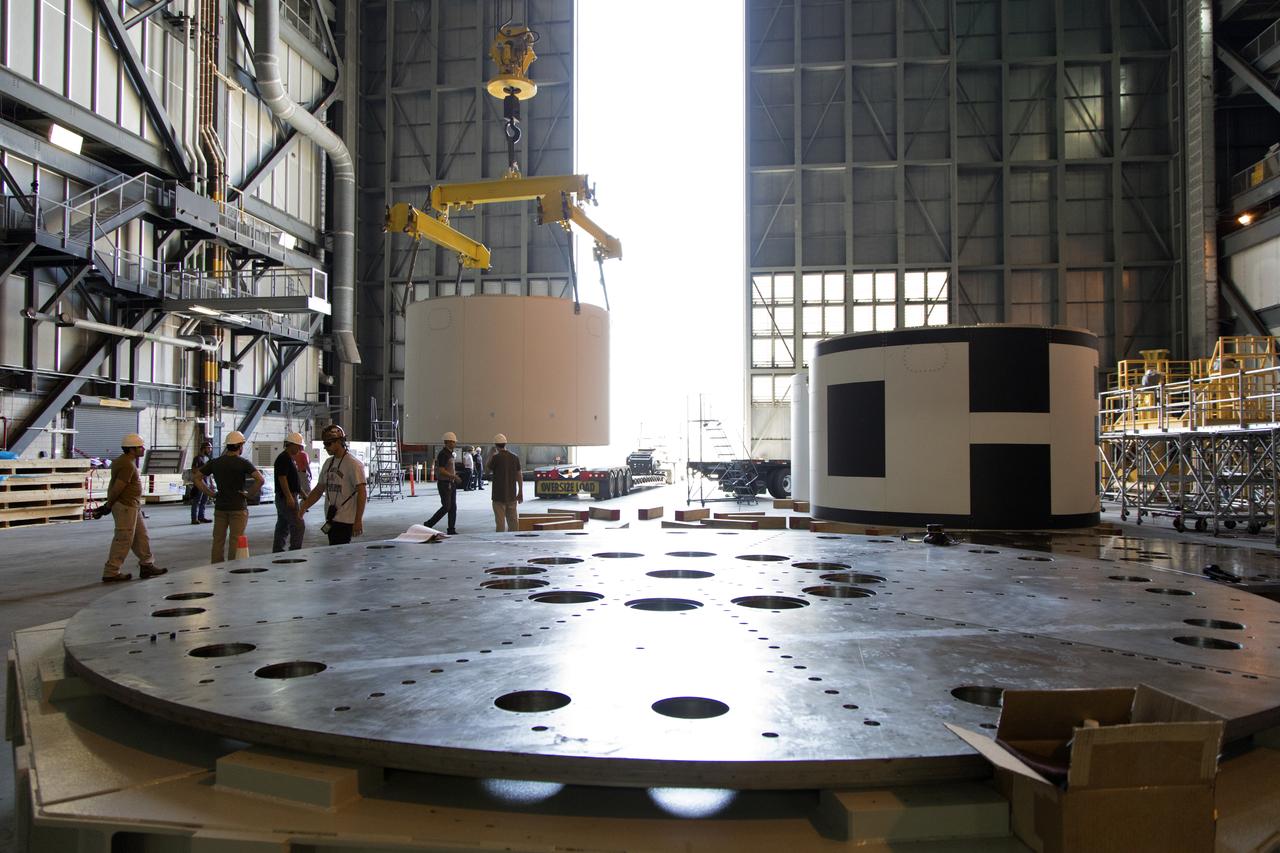

The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is lifted by crane and will be lowered onto slats in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.

The first of three aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by truck and is offloaded in High Bay 4 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 19, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
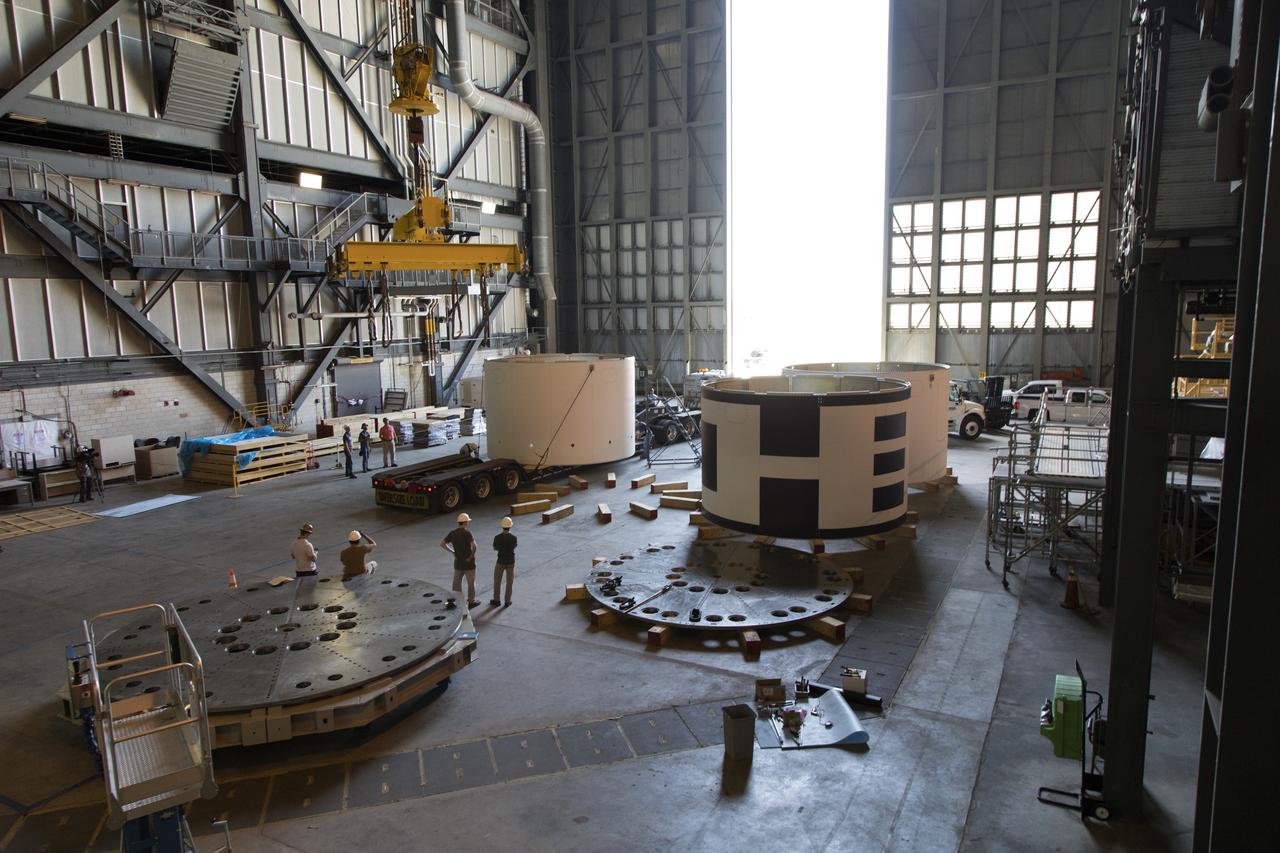

The third and final aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
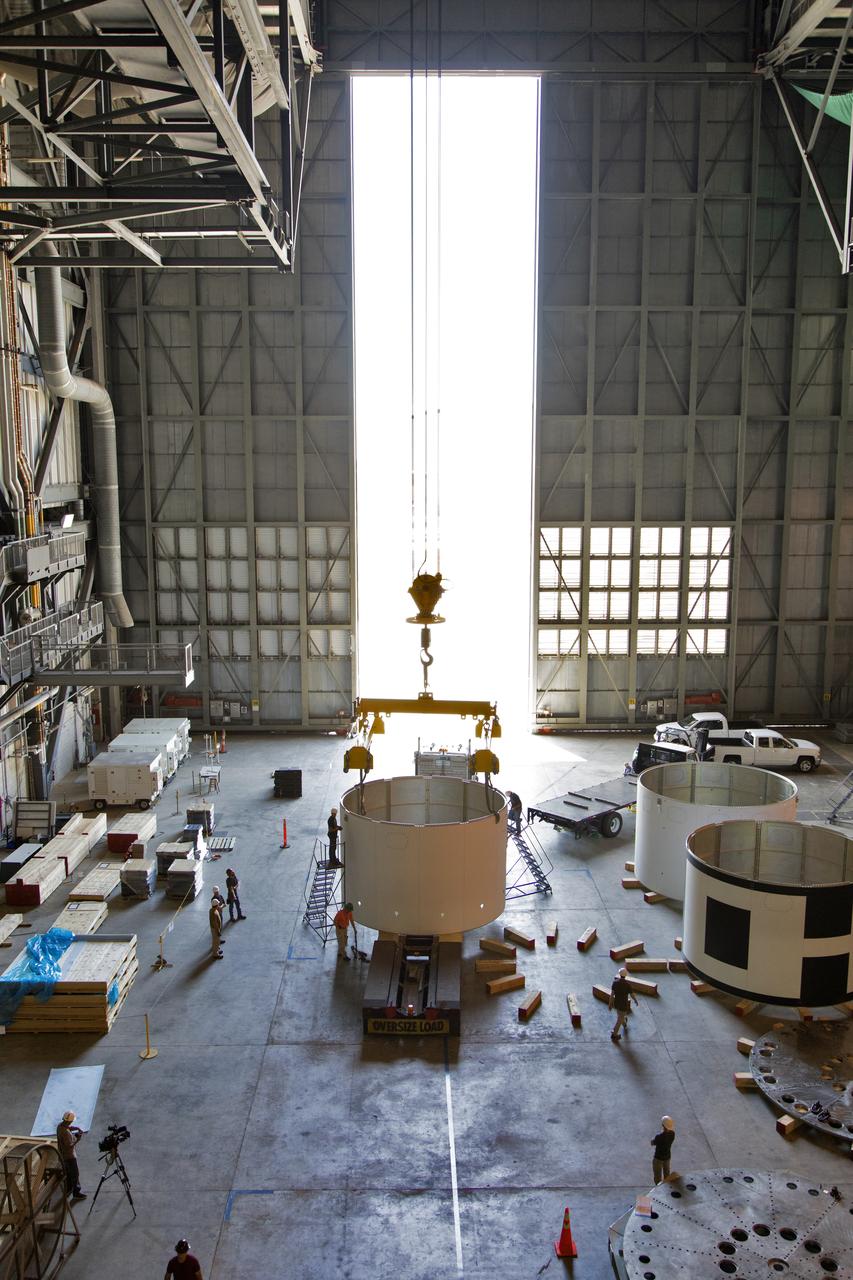

The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. Technicians prepare the aeroshell to be lifted off of the flatbed truck and transferred to slats. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
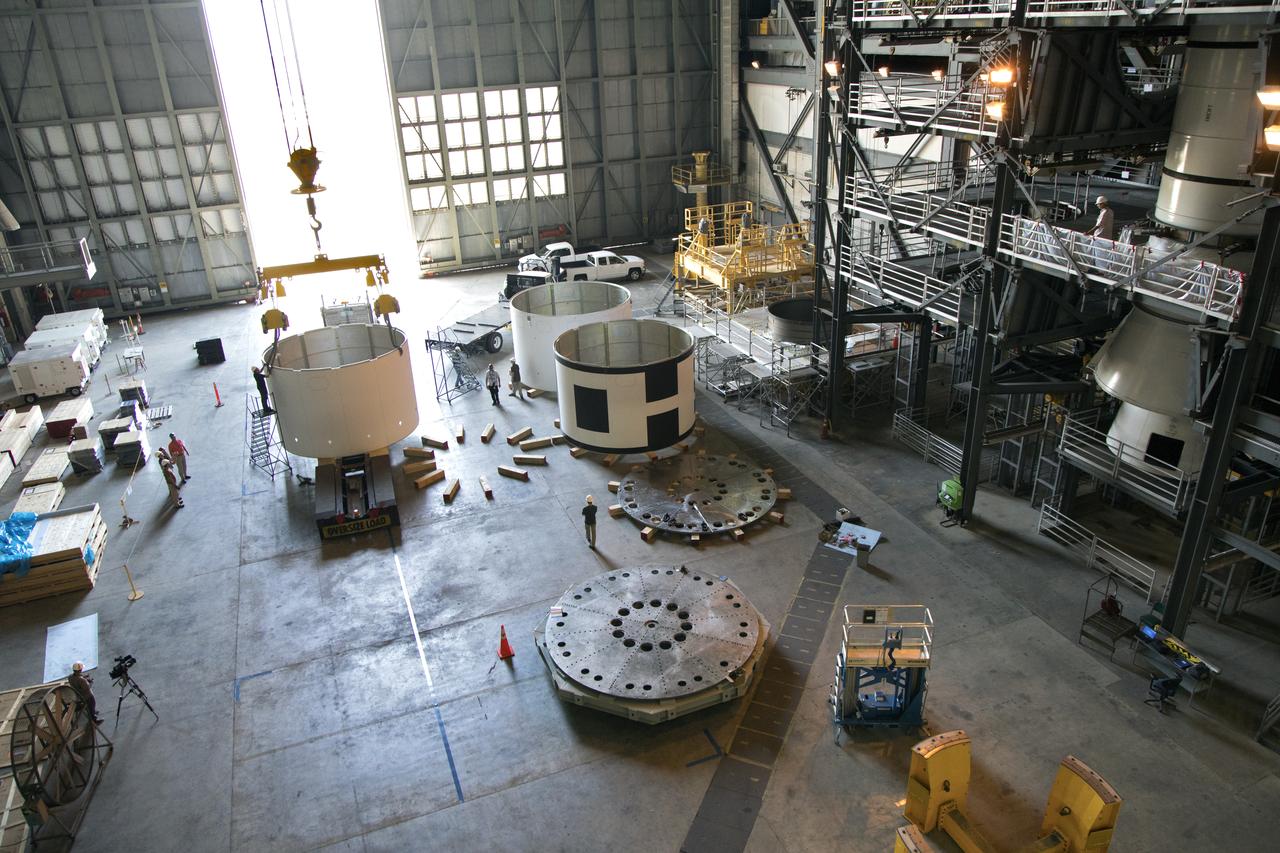
The third and final aeroshell, at left, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. Technicians prepare the aeroshell to be lifted off of the flatbed truck and transferred to slats. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
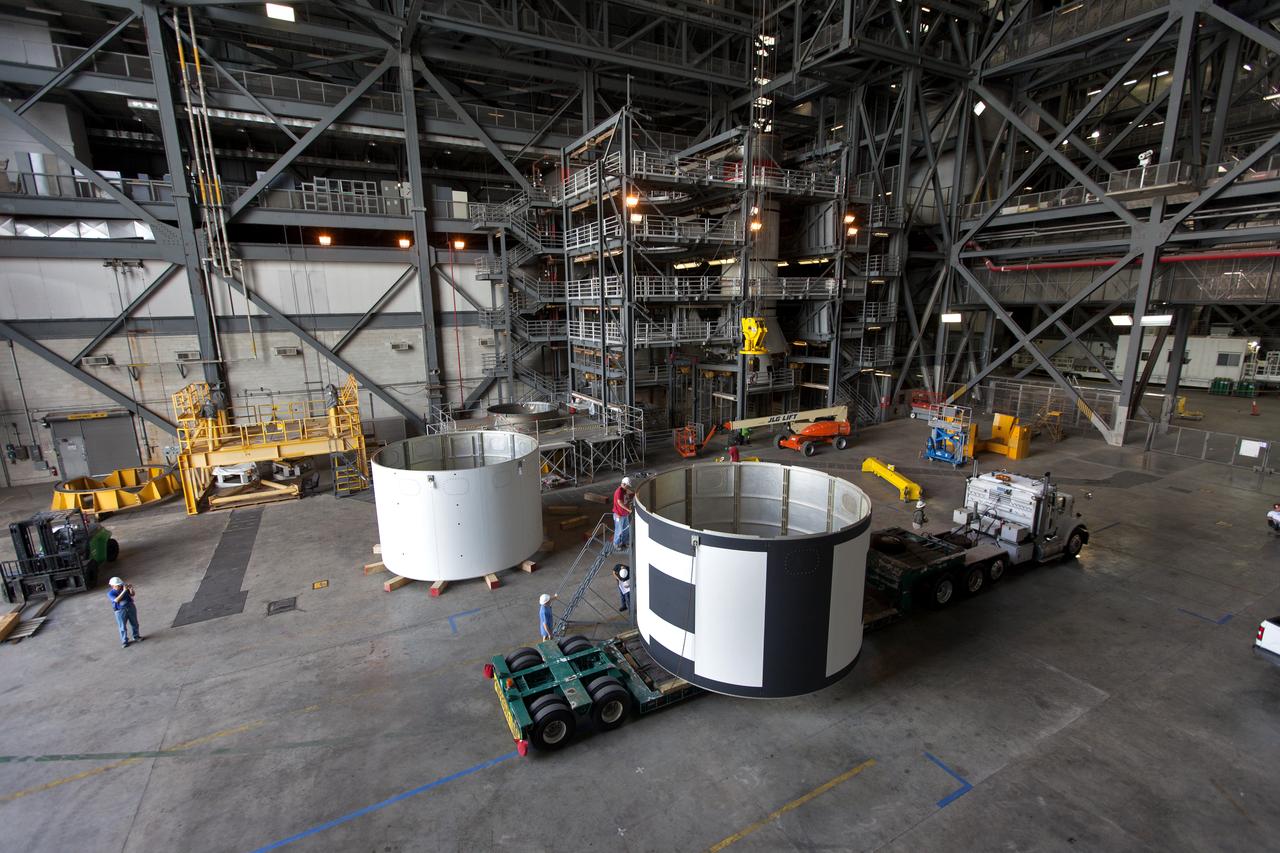

The second of three aeroshells, at right, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
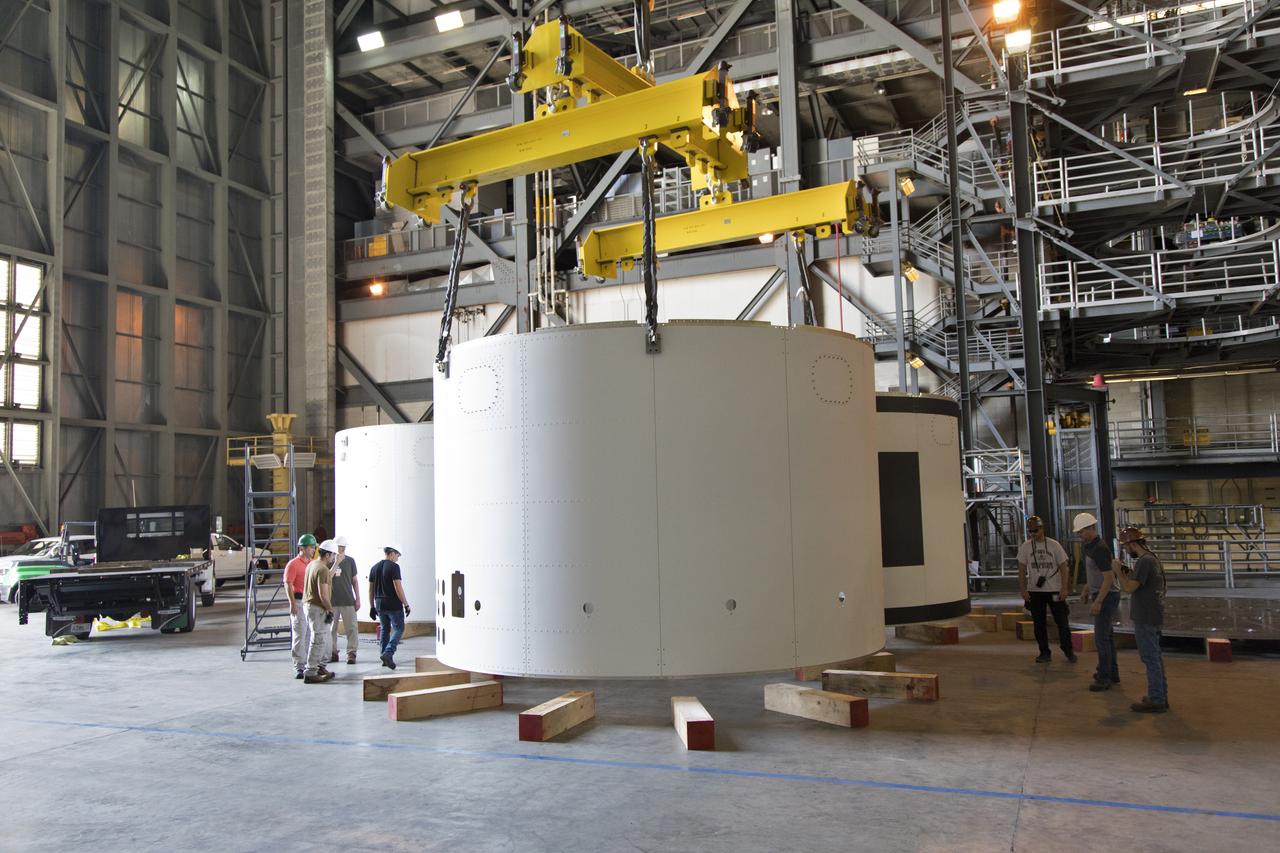

A crane lowers the third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) onto slats in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
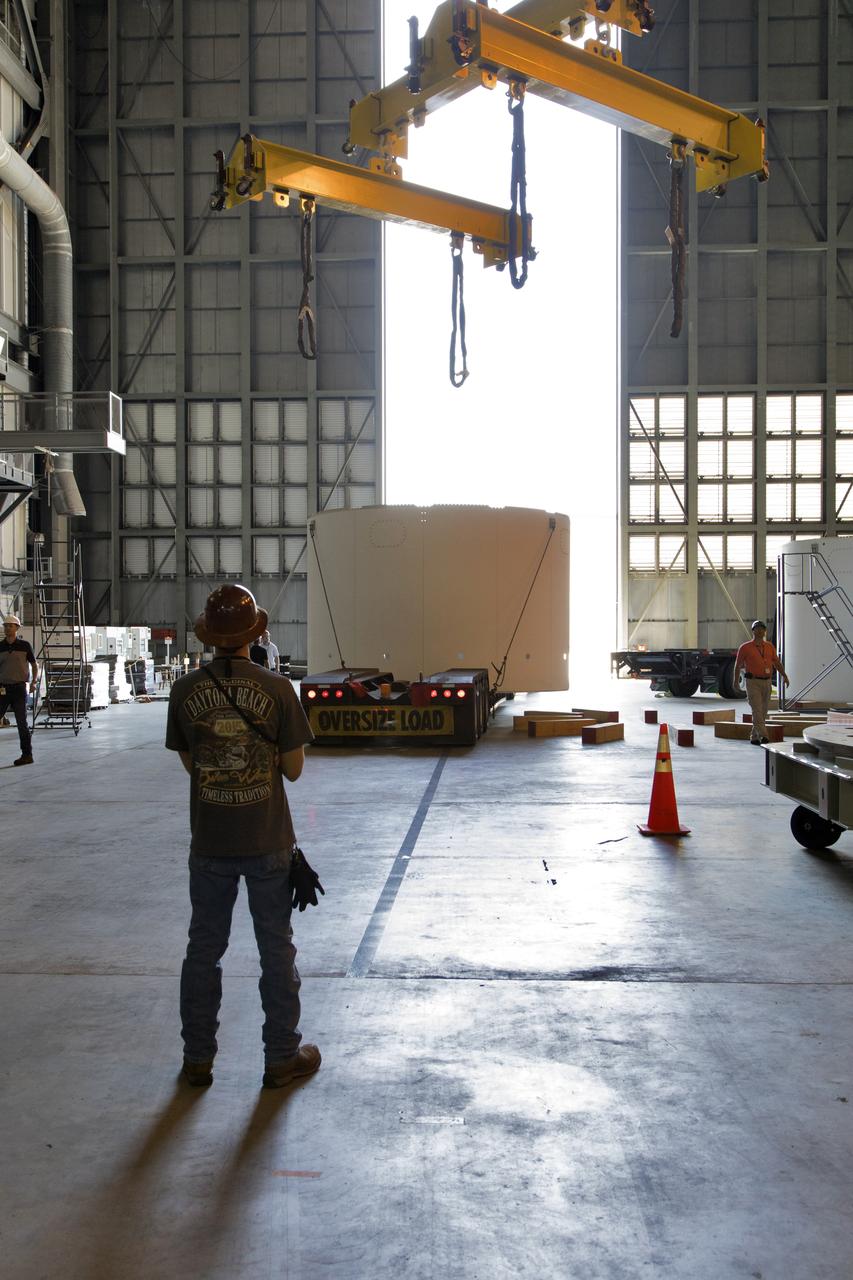

The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
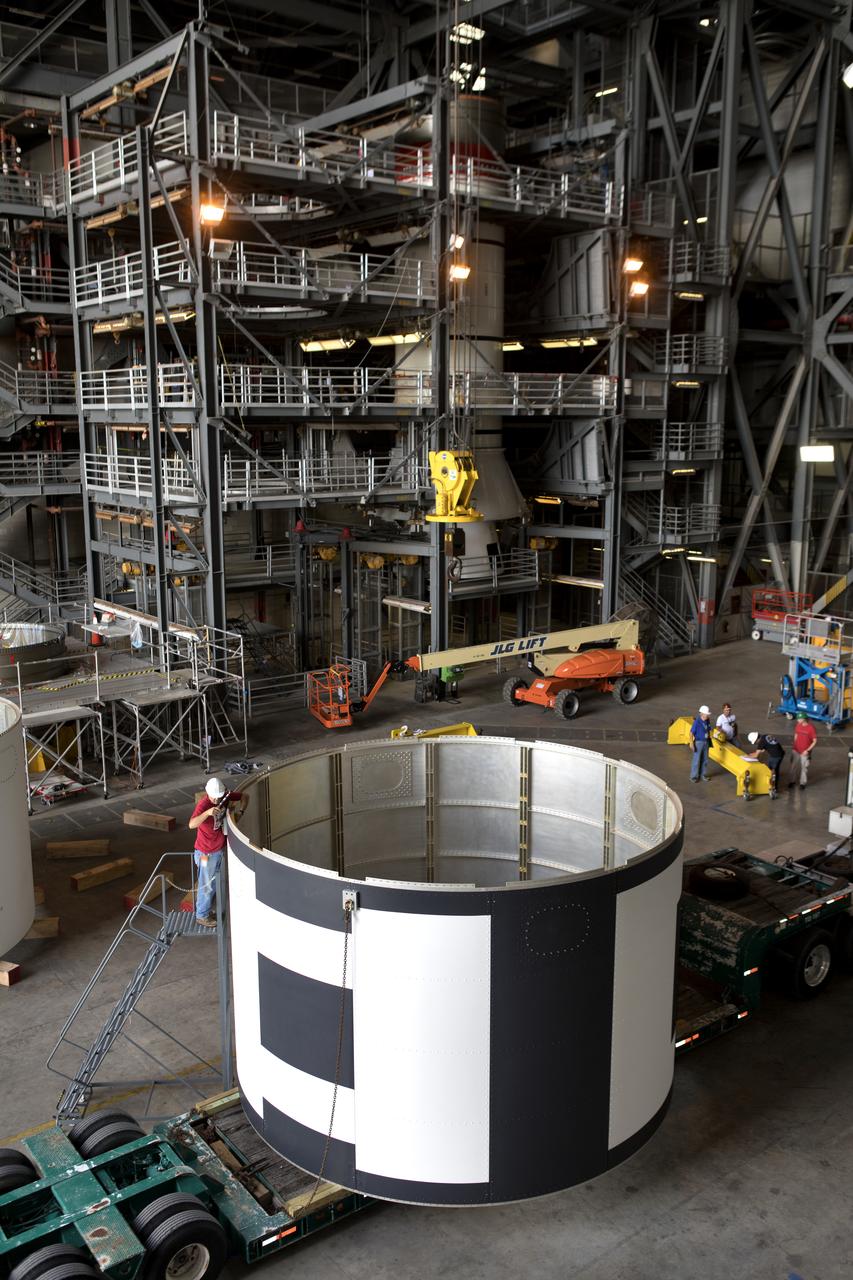

The second of three aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island, and will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.

The first of three aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is lowered onto wooden blocks in High Bay 4 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 19, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
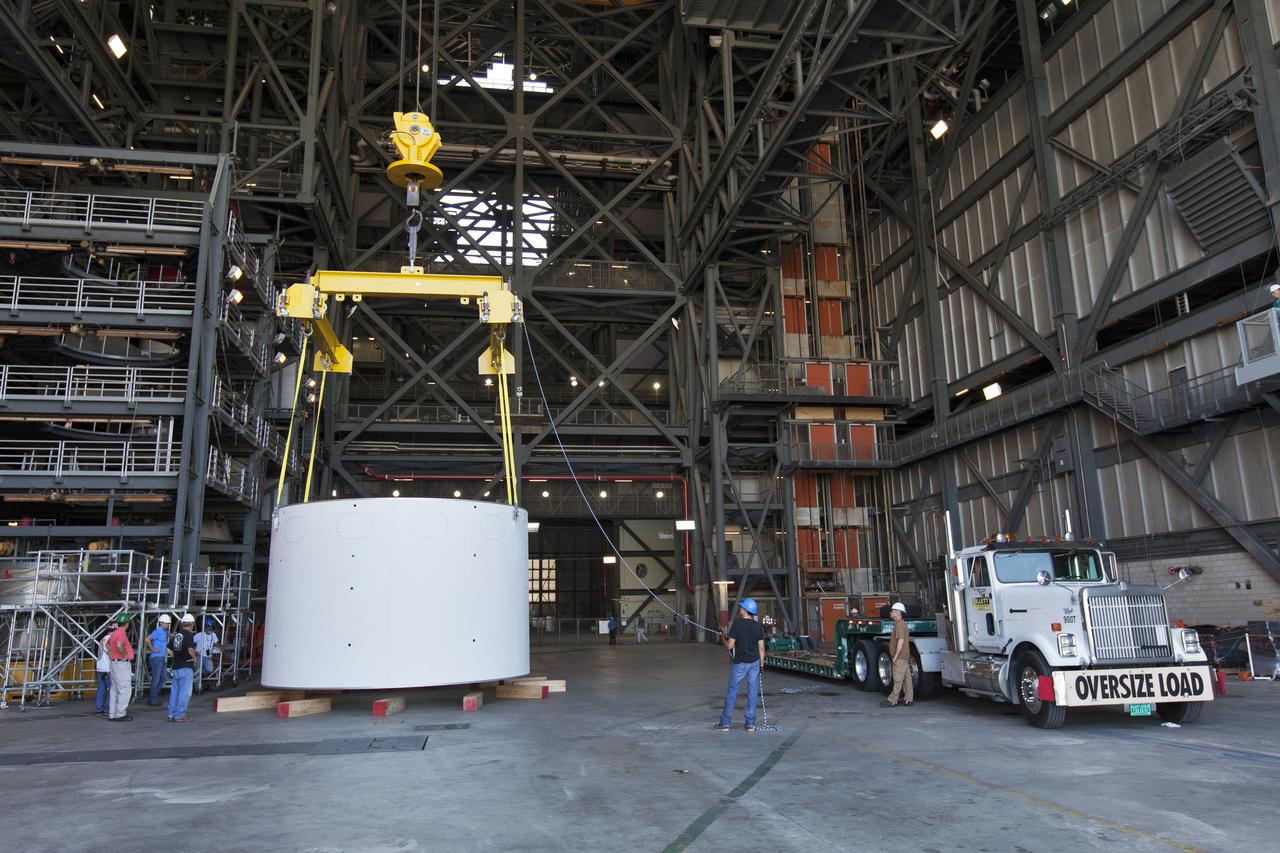

The first of three aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is offloaded from its transport truck by crane in High Bay 4 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 19, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
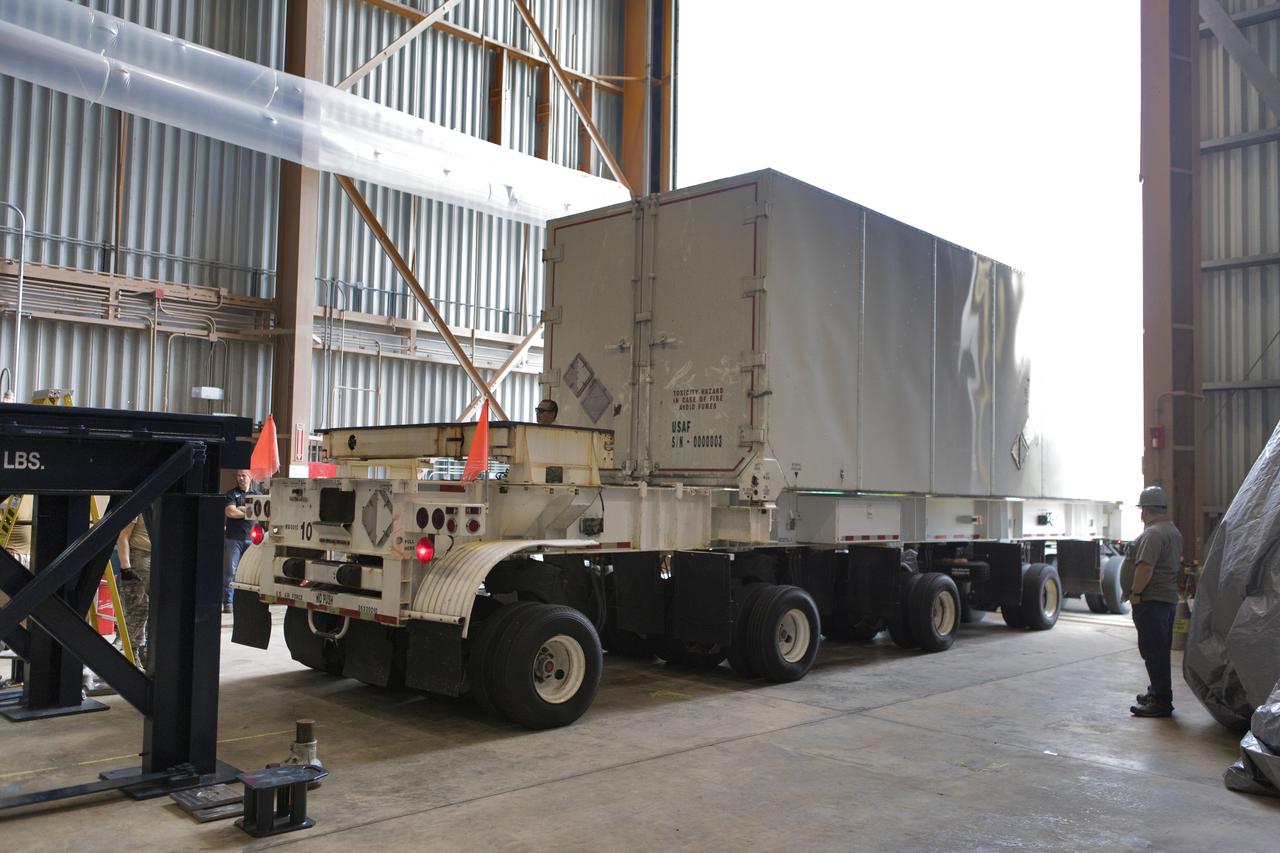

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

The second of three aeroshells, at right, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) was lifted up from a flatbed truck and secured in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
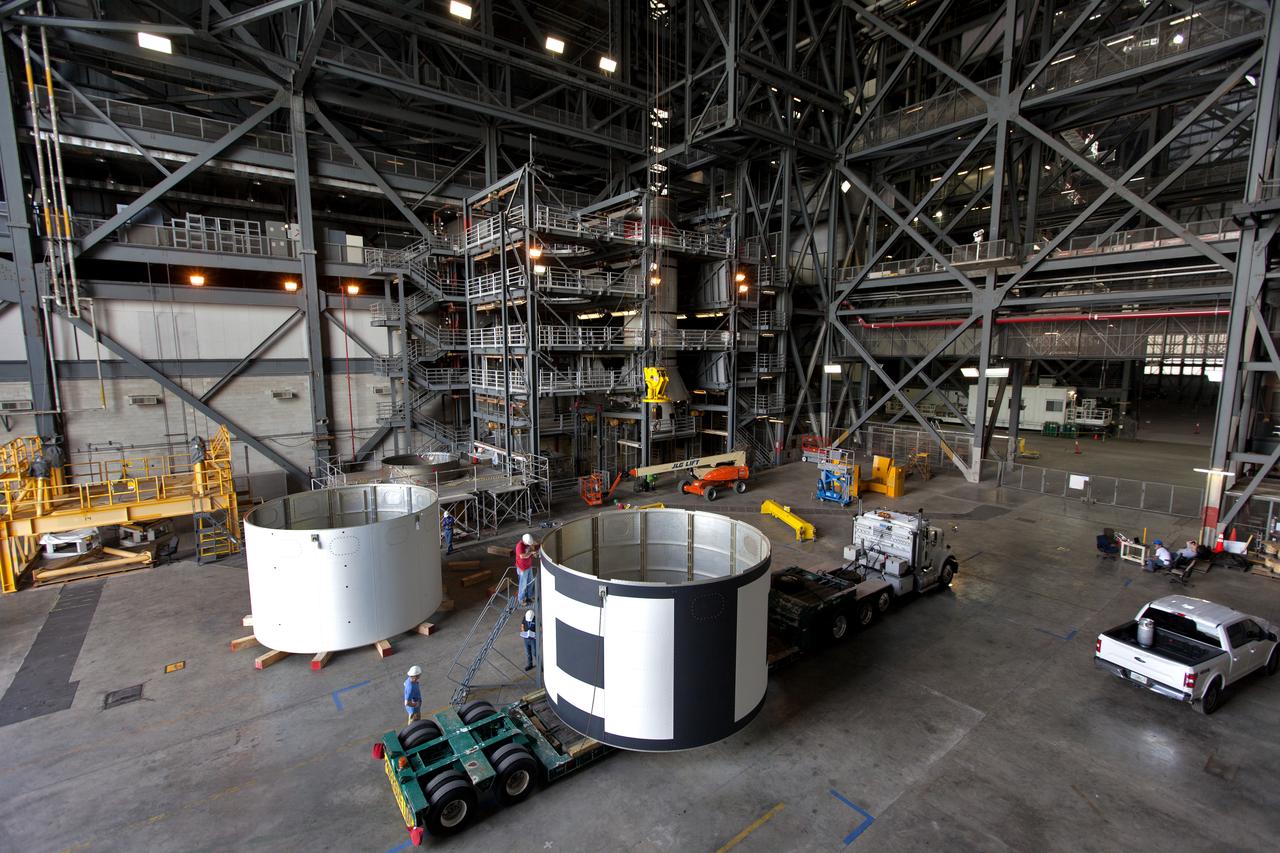

The second of three aeroshells, at right, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
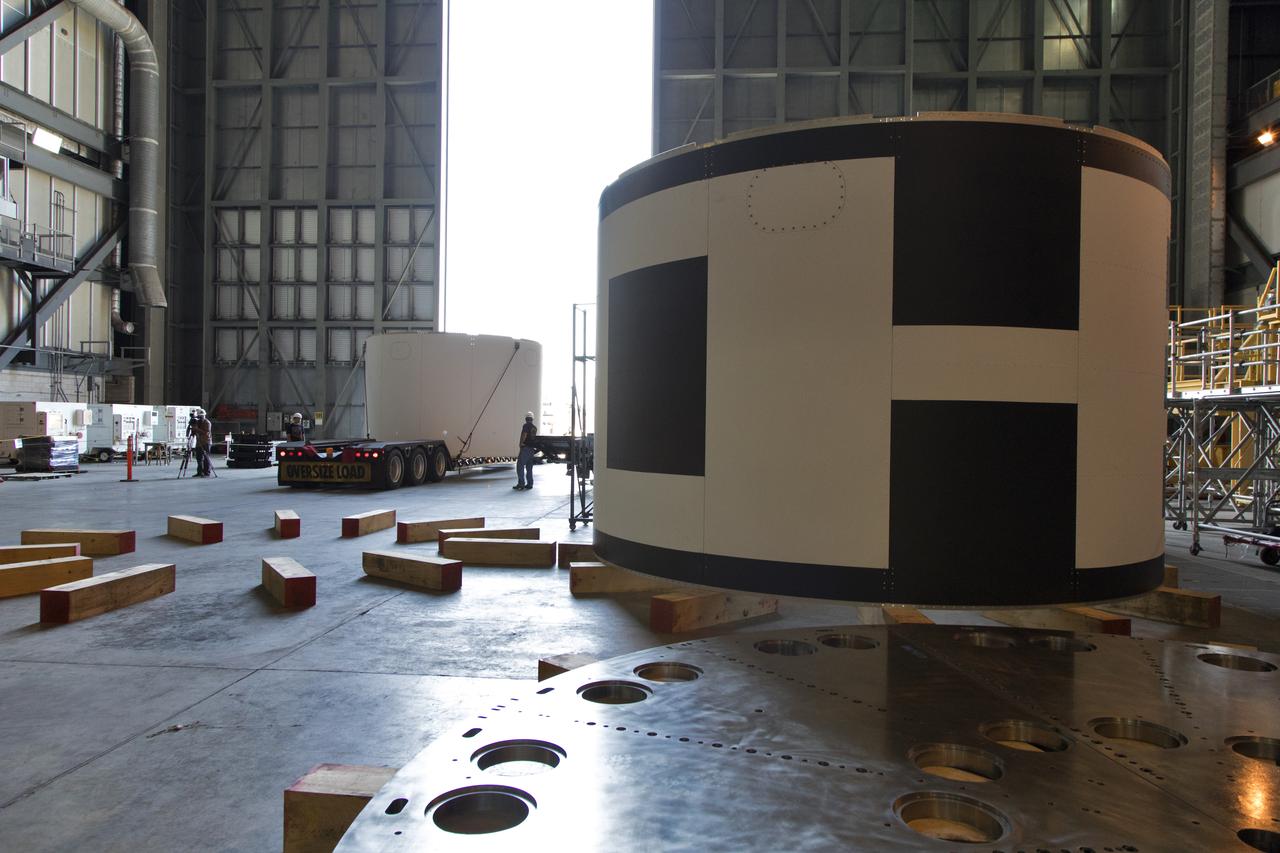

The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
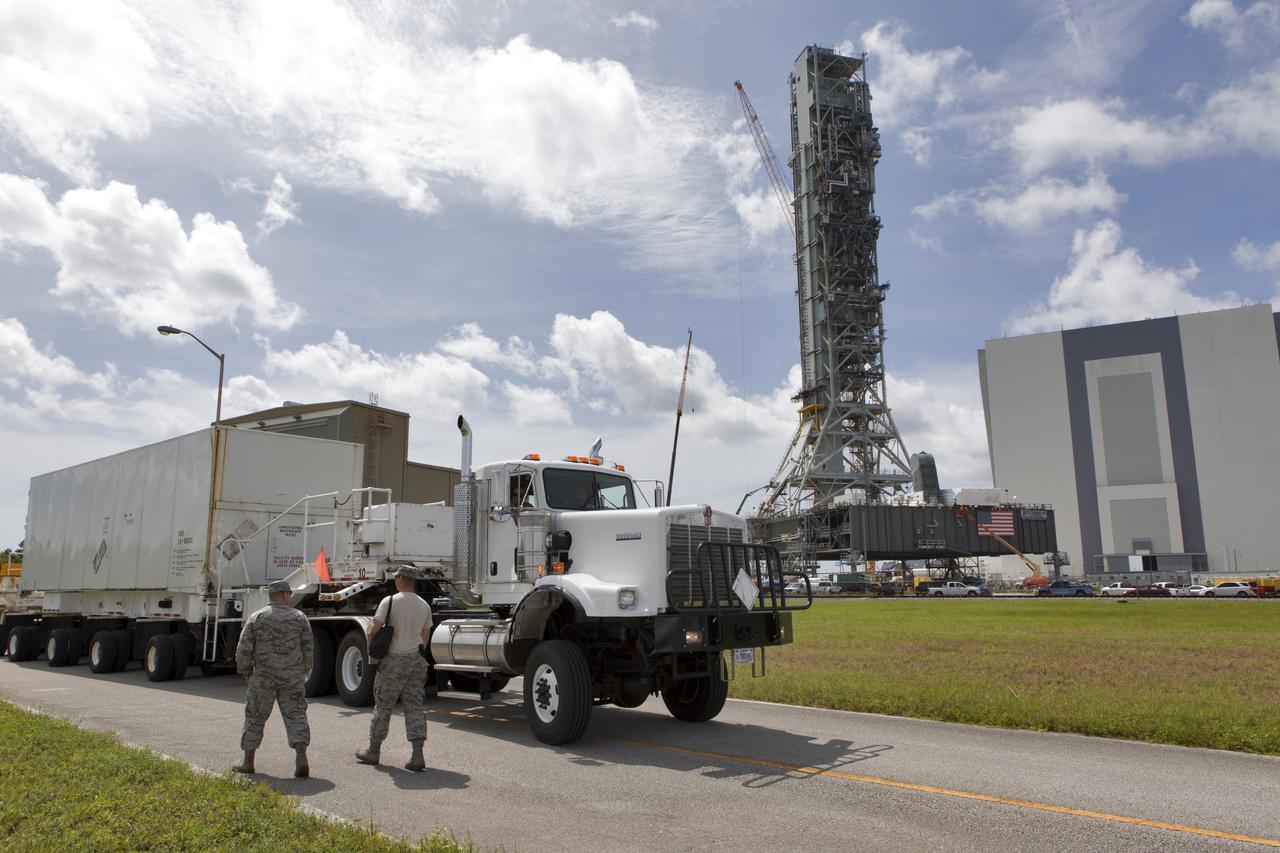

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
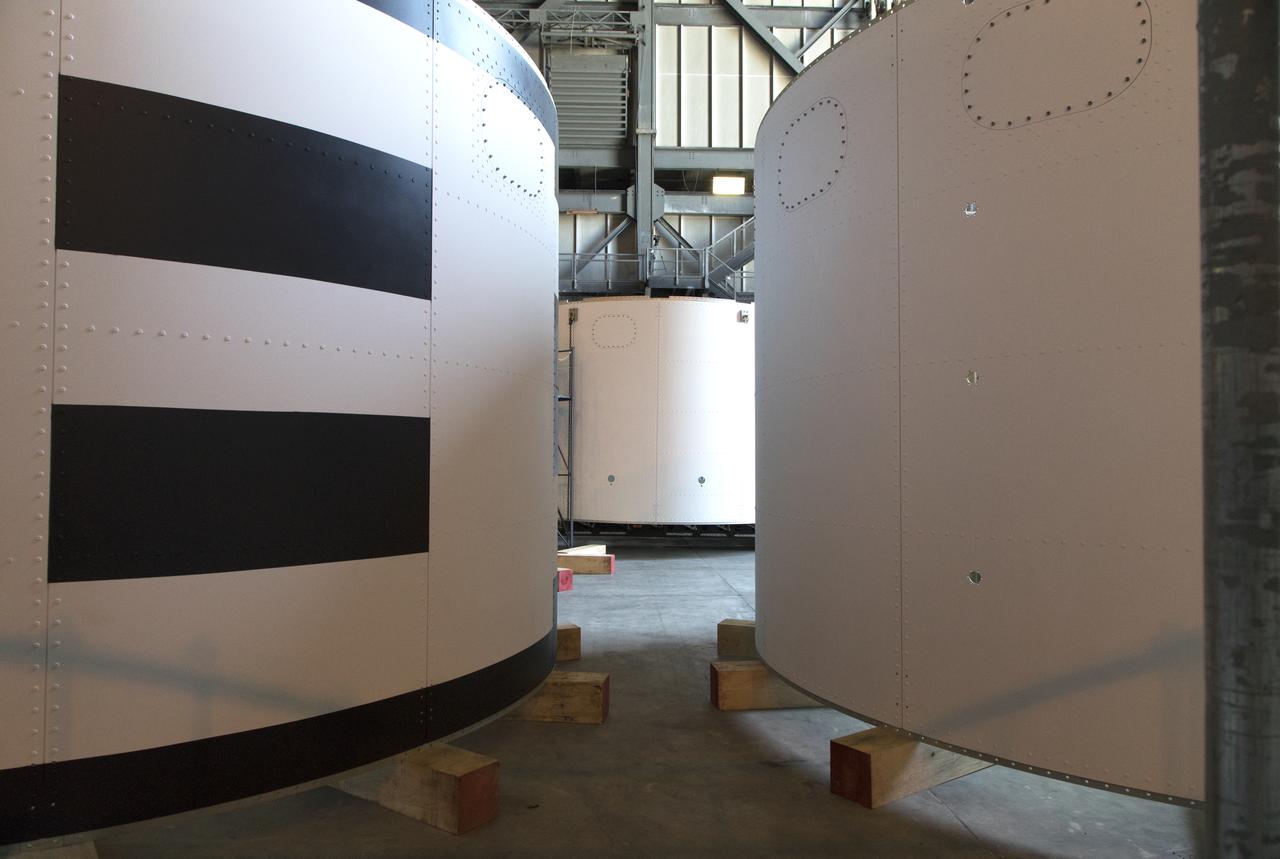

The third and final aeroshell, center in back, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell arrived by truck from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and placed on slats in the high bay. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
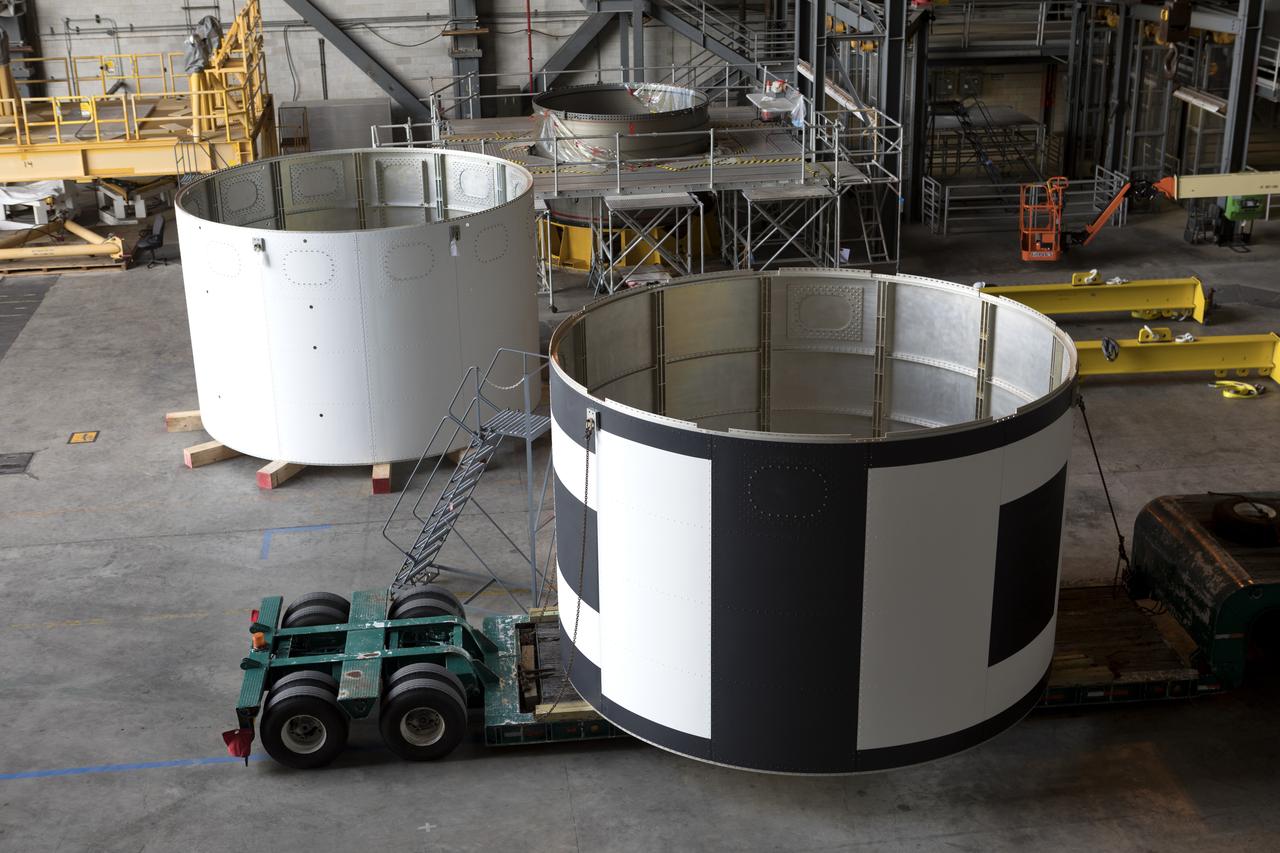

The second of three aeroshells, at right, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
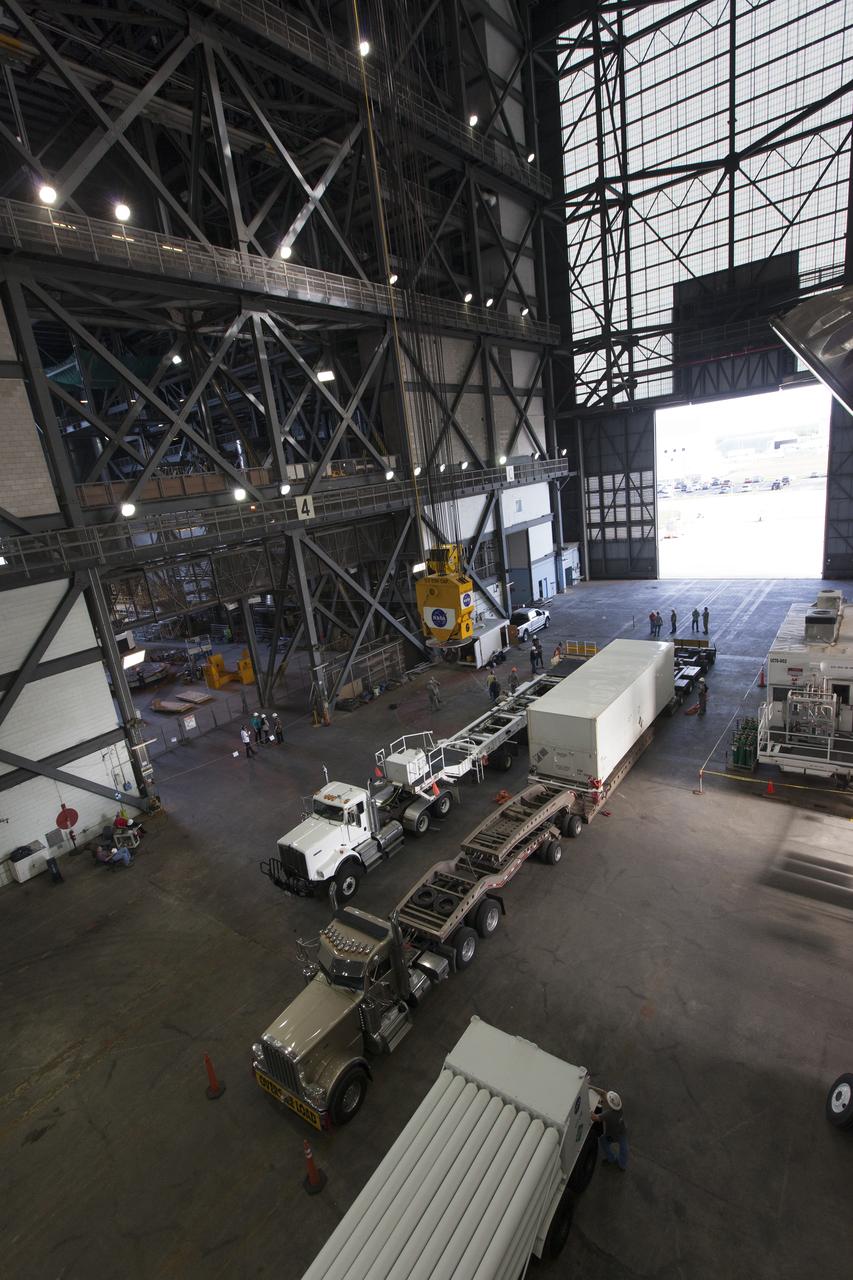

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
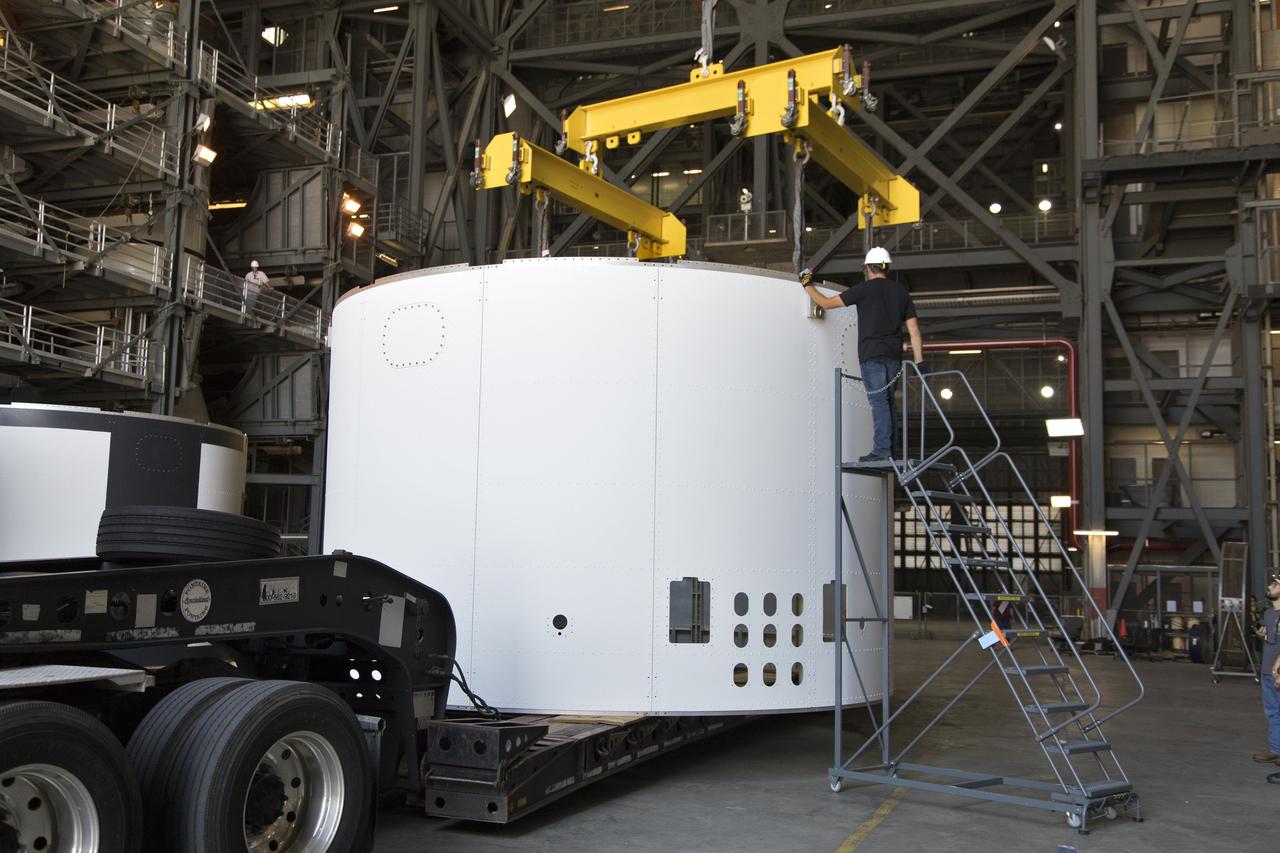

The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. A technician assists with crane attachment so that the aeroshell can be offloaded and placed on slats in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
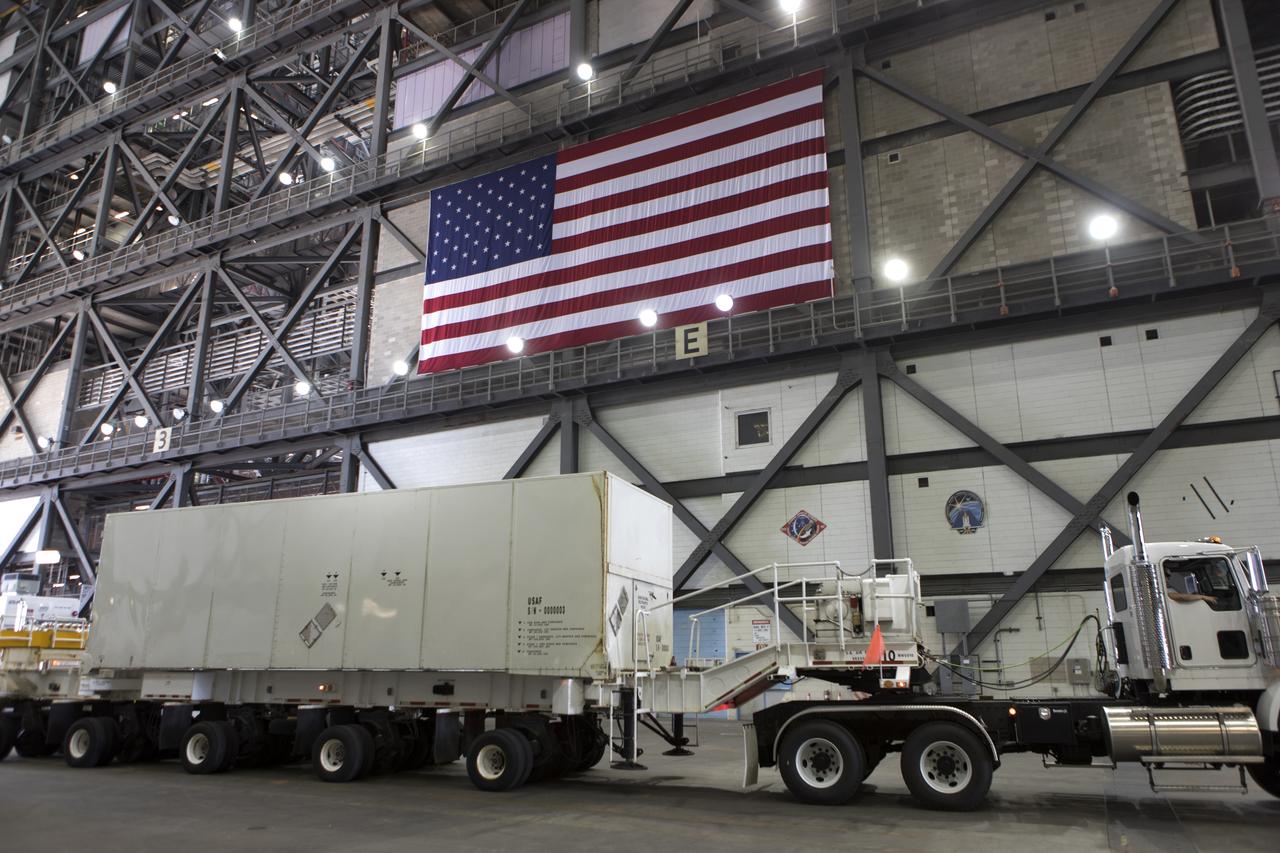

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) will be moved from the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
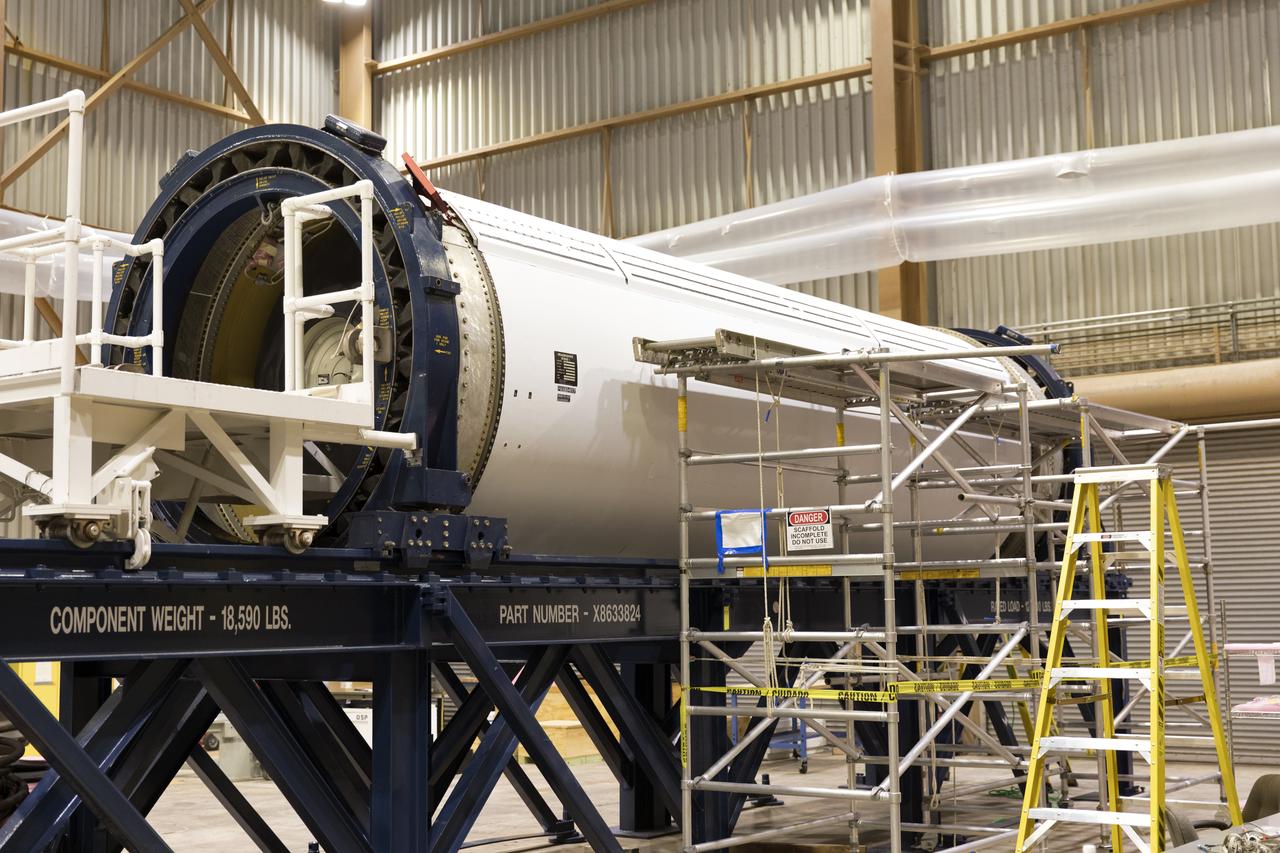

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
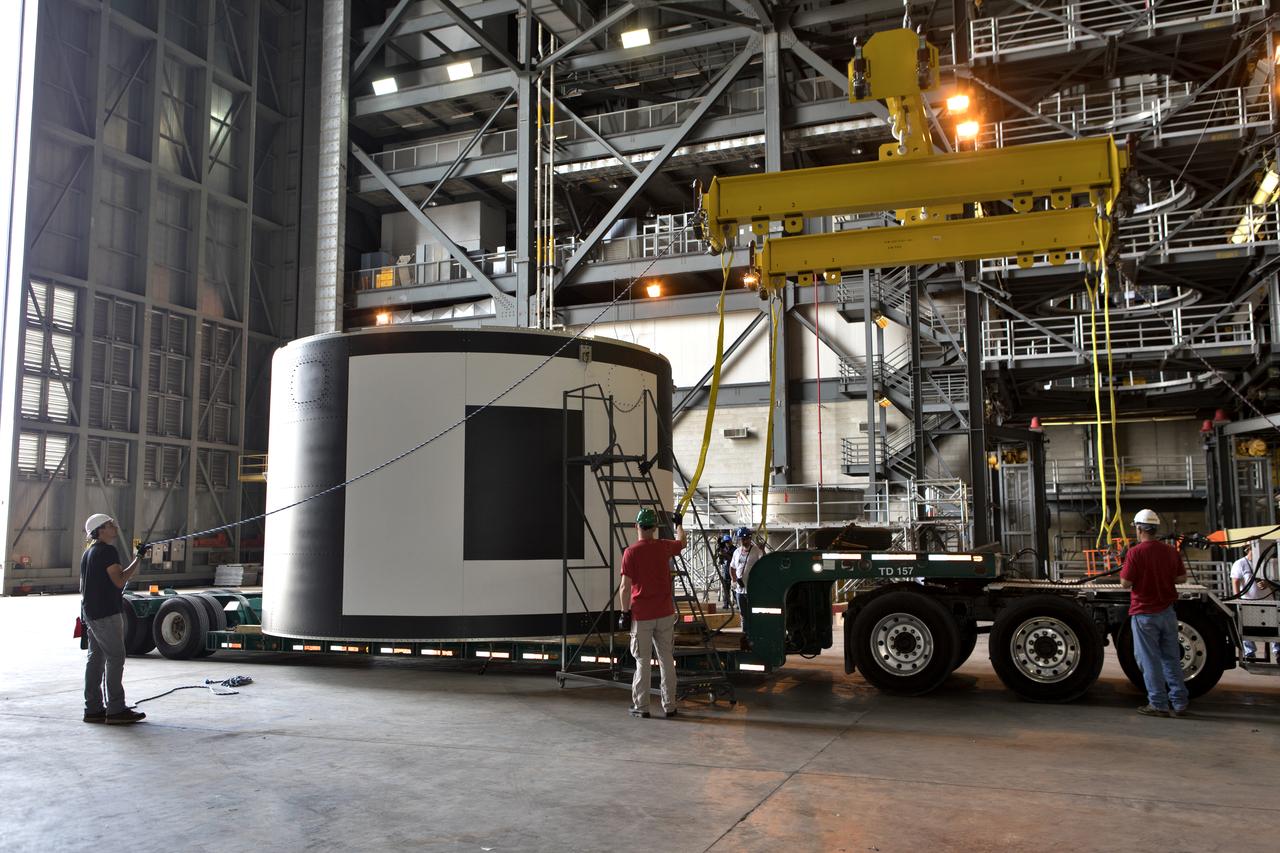

The second of three aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
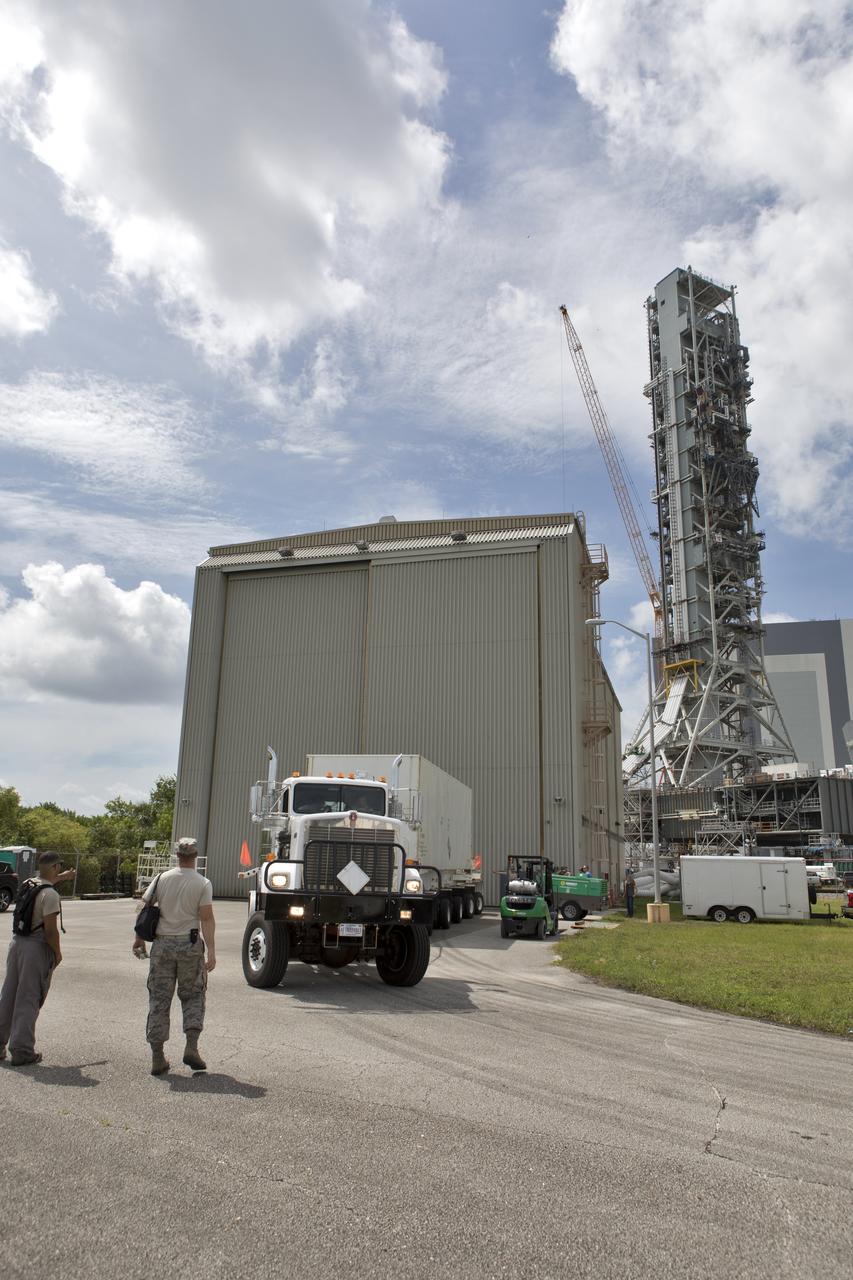

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
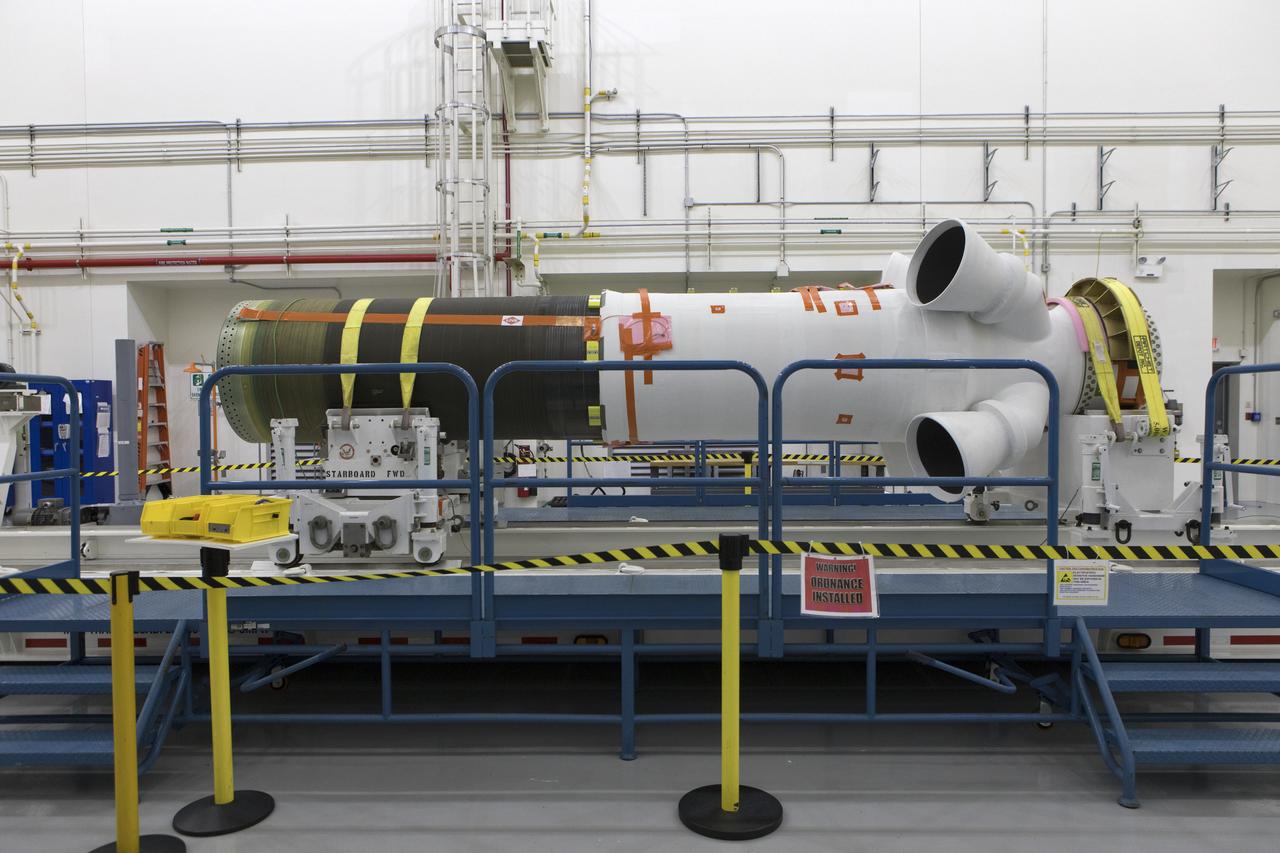

The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
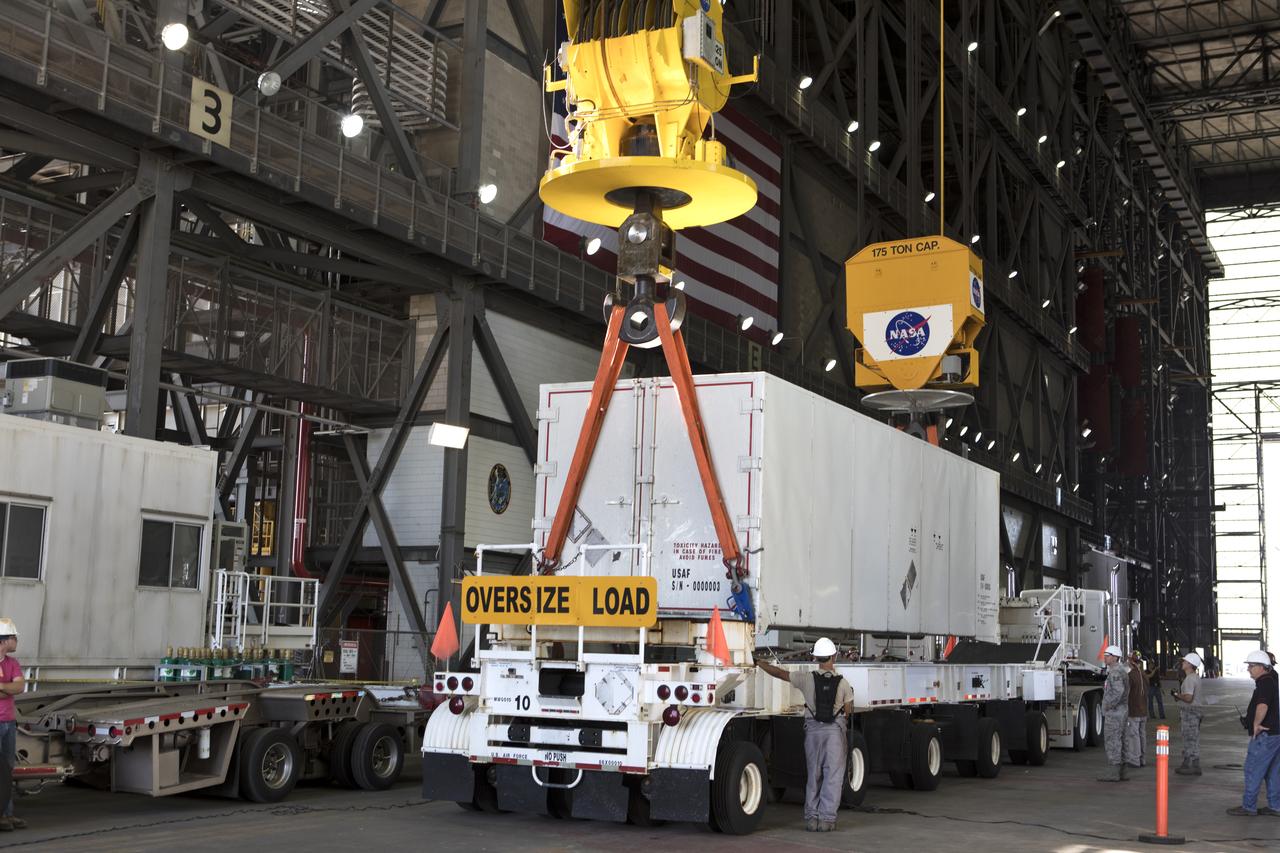

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside onto another transporter on July 20, 2018. The container will be moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
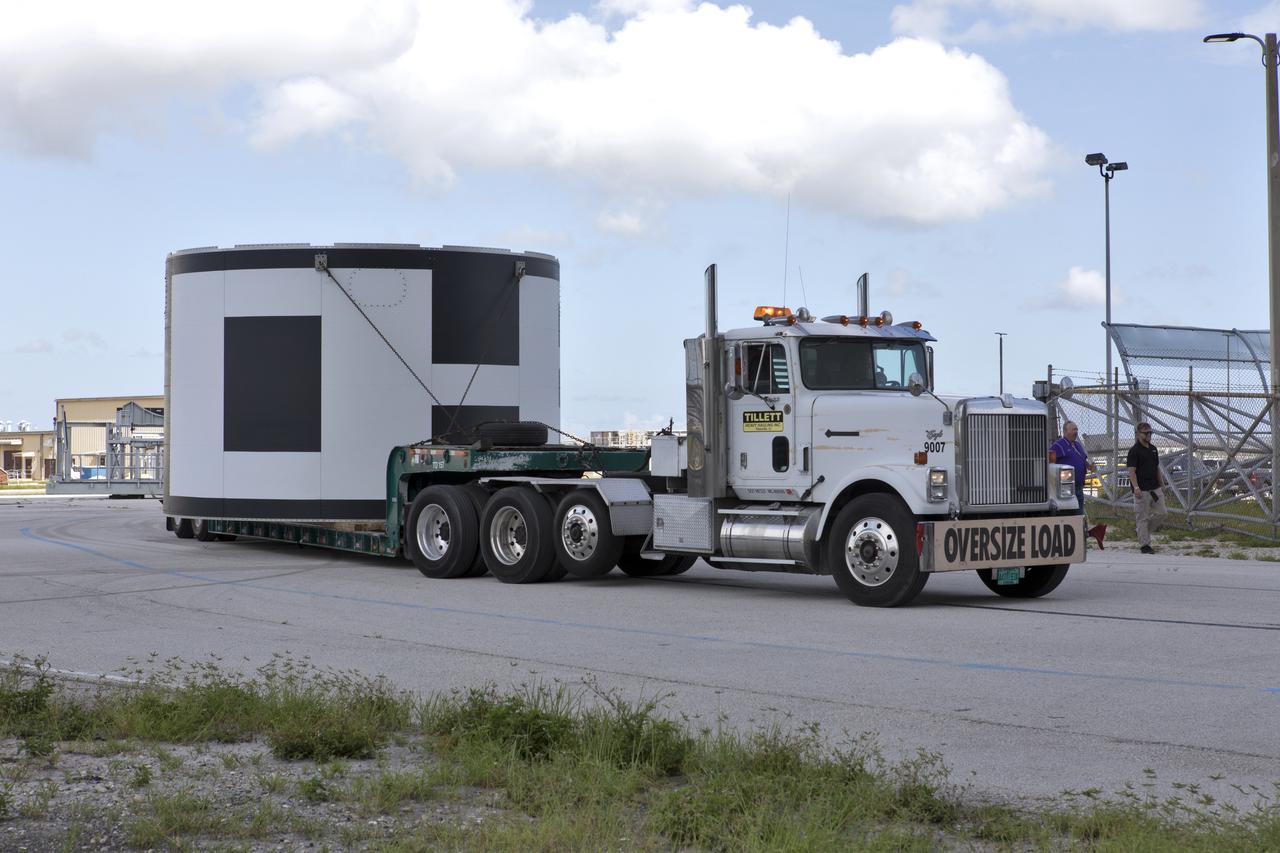

The second of three aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by truck at the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in High Bay 4. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
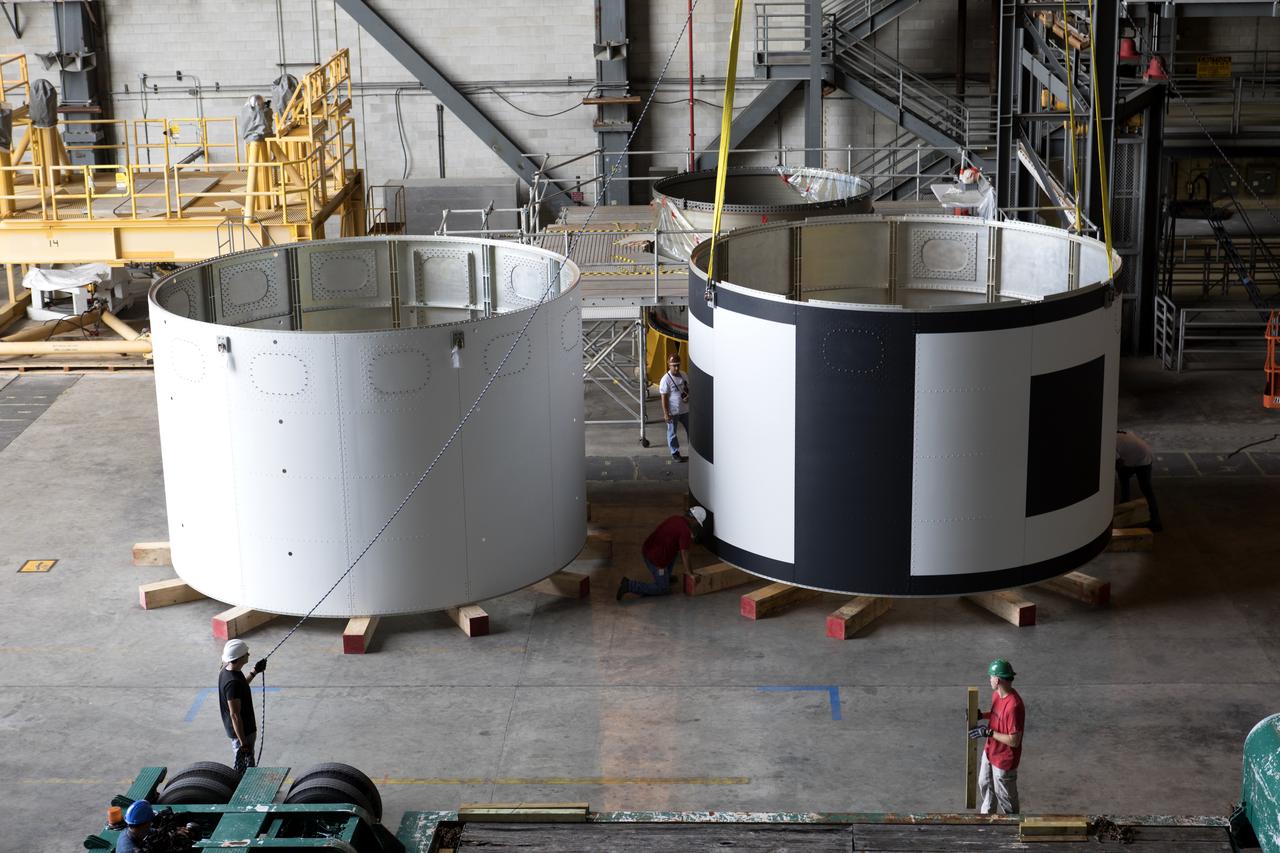
The second of three aeroshells, at right, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) was lifted up from a flatbed truck and secured in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
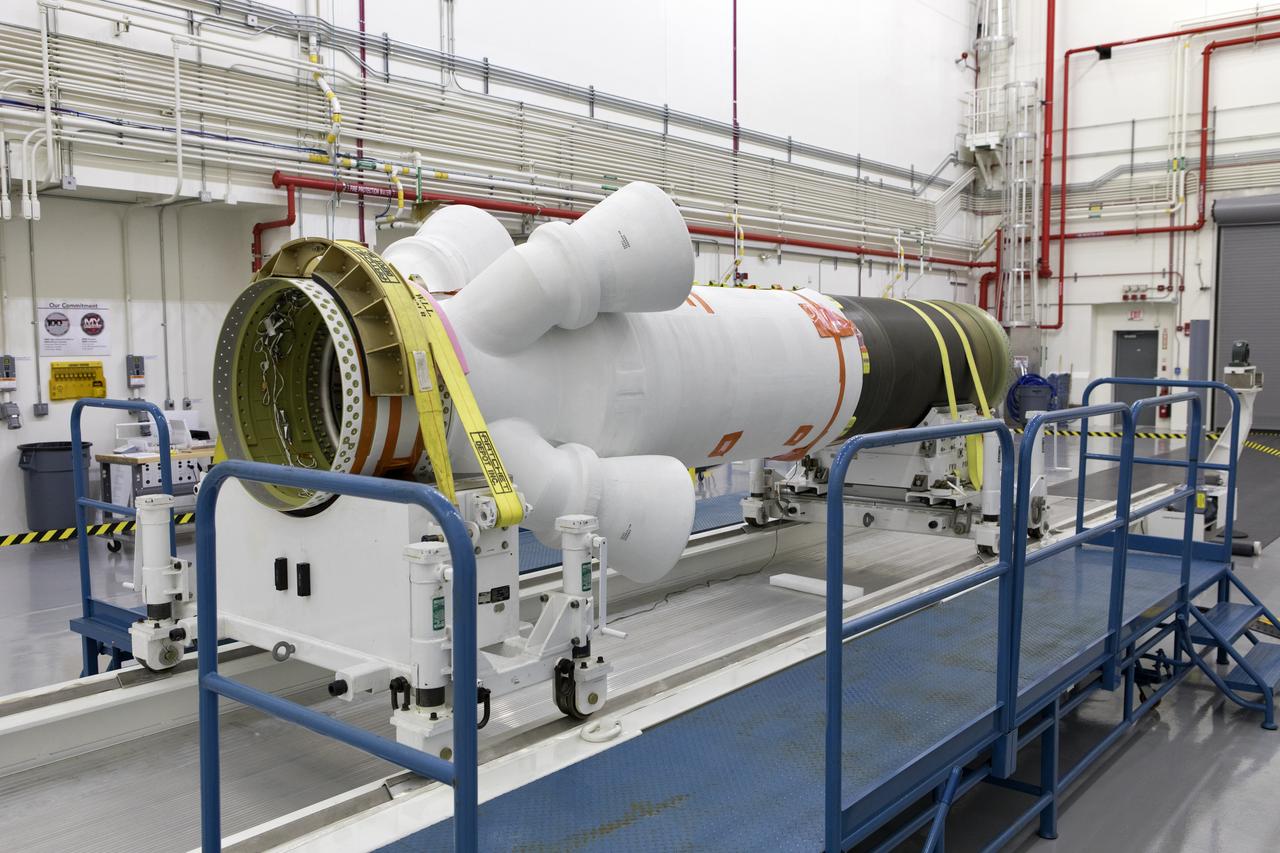

The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
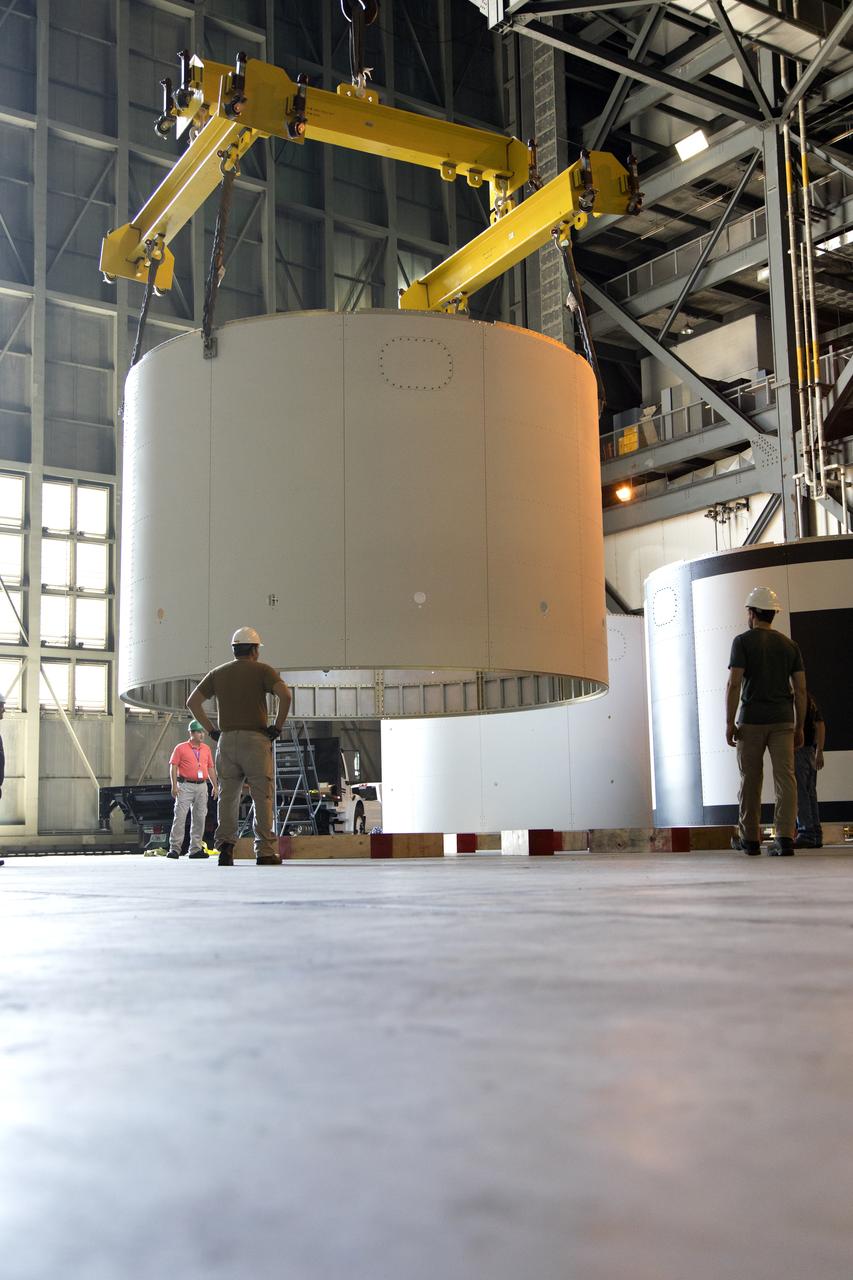

Technicians assist as a crane lowers the third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) onto slats in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
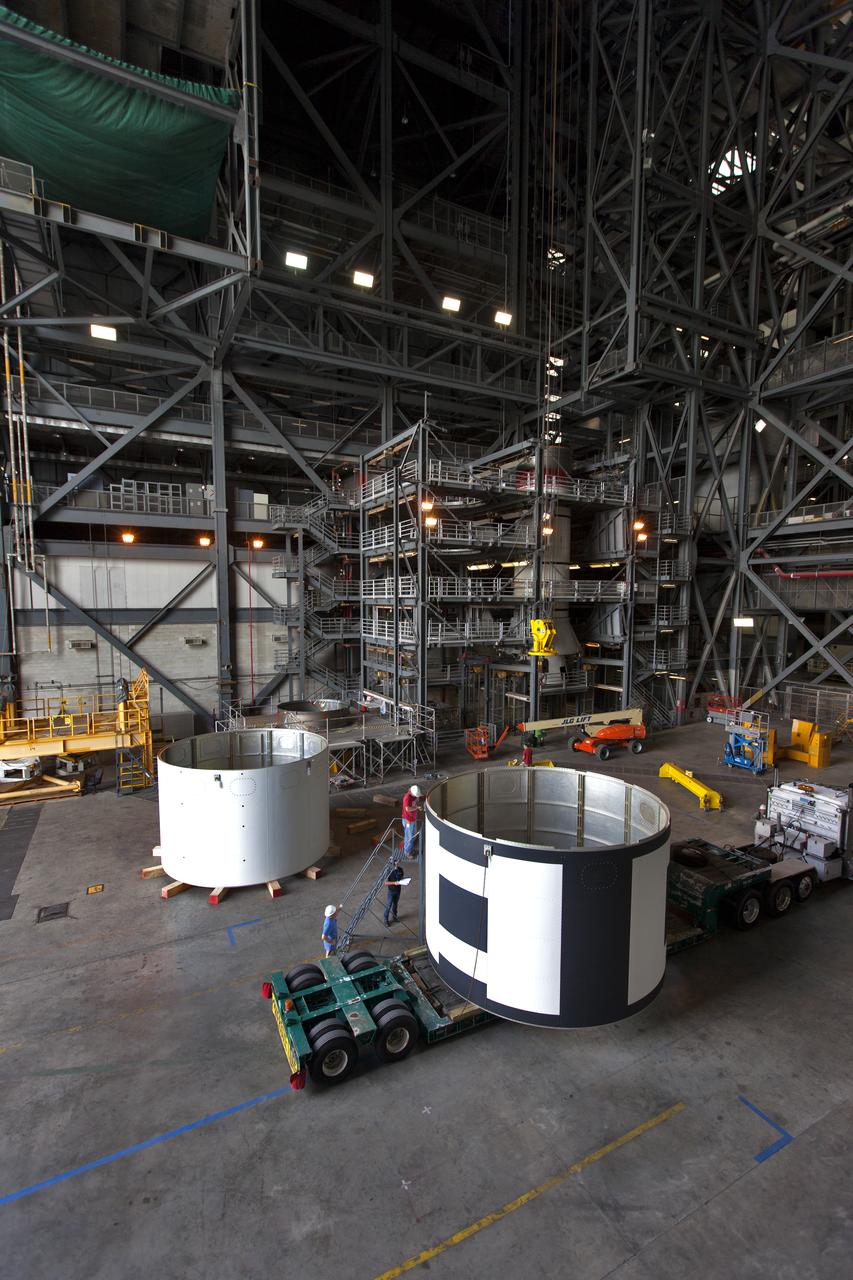

The second of three aeroshells, at right, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell arrived by truck from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
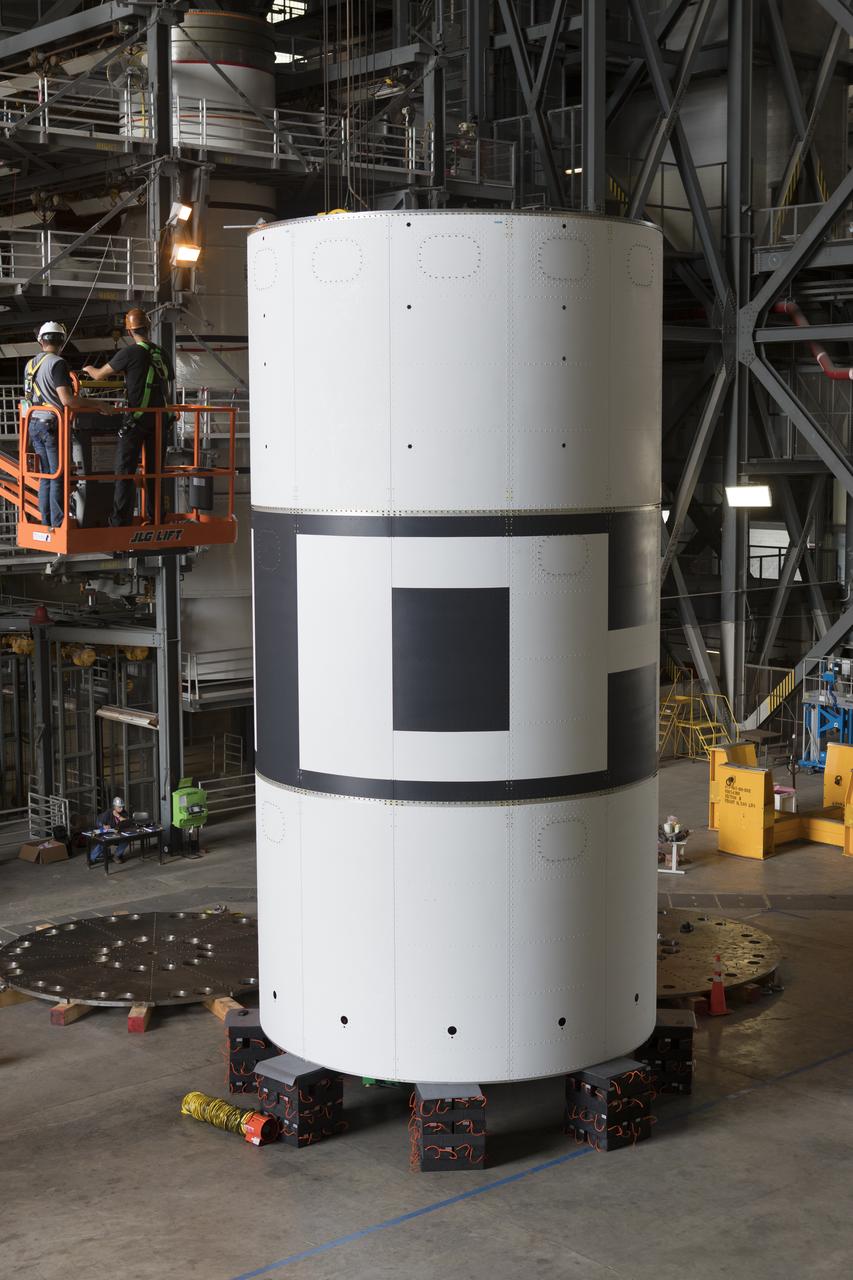

Technicians with Jacobs check the alignment during stacking of the aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Aug. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshells are being prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
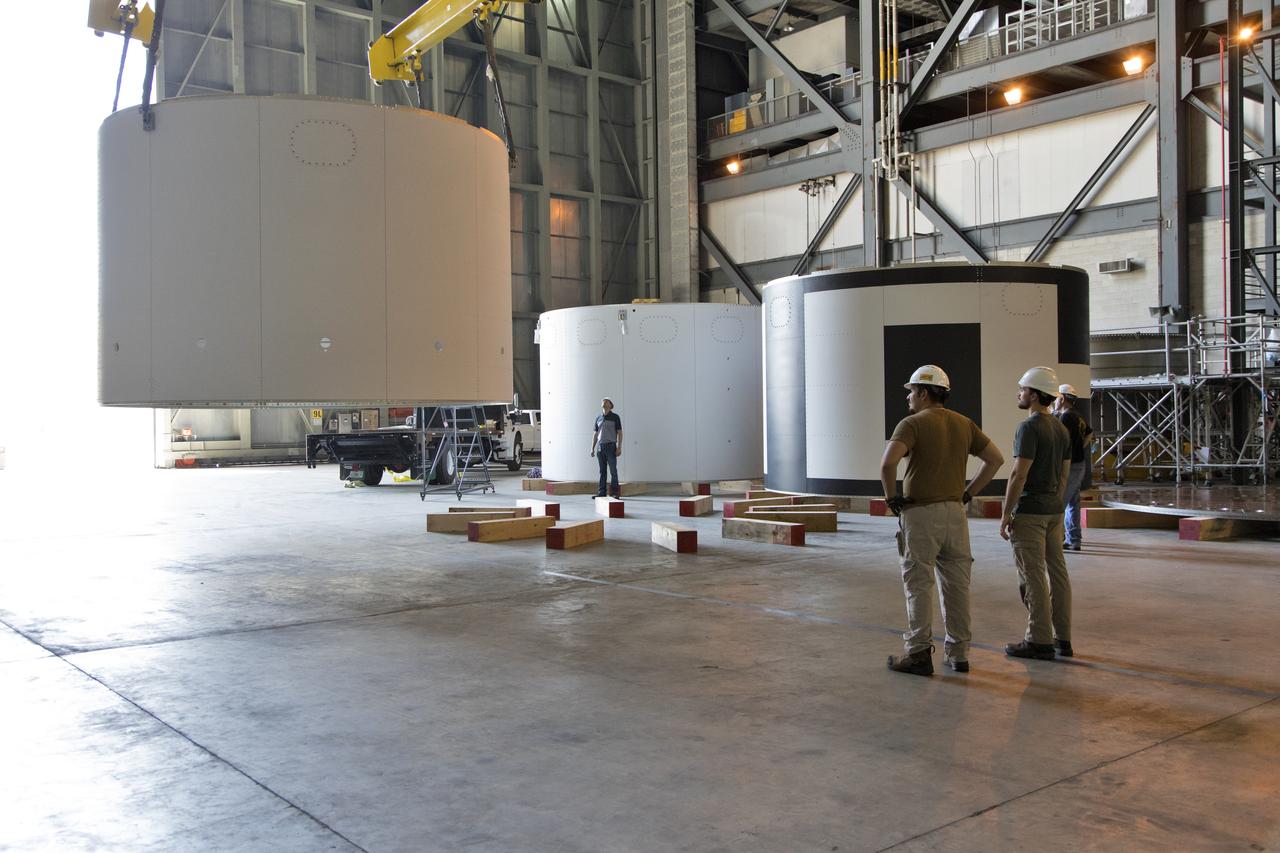

The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is lifted by crane in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
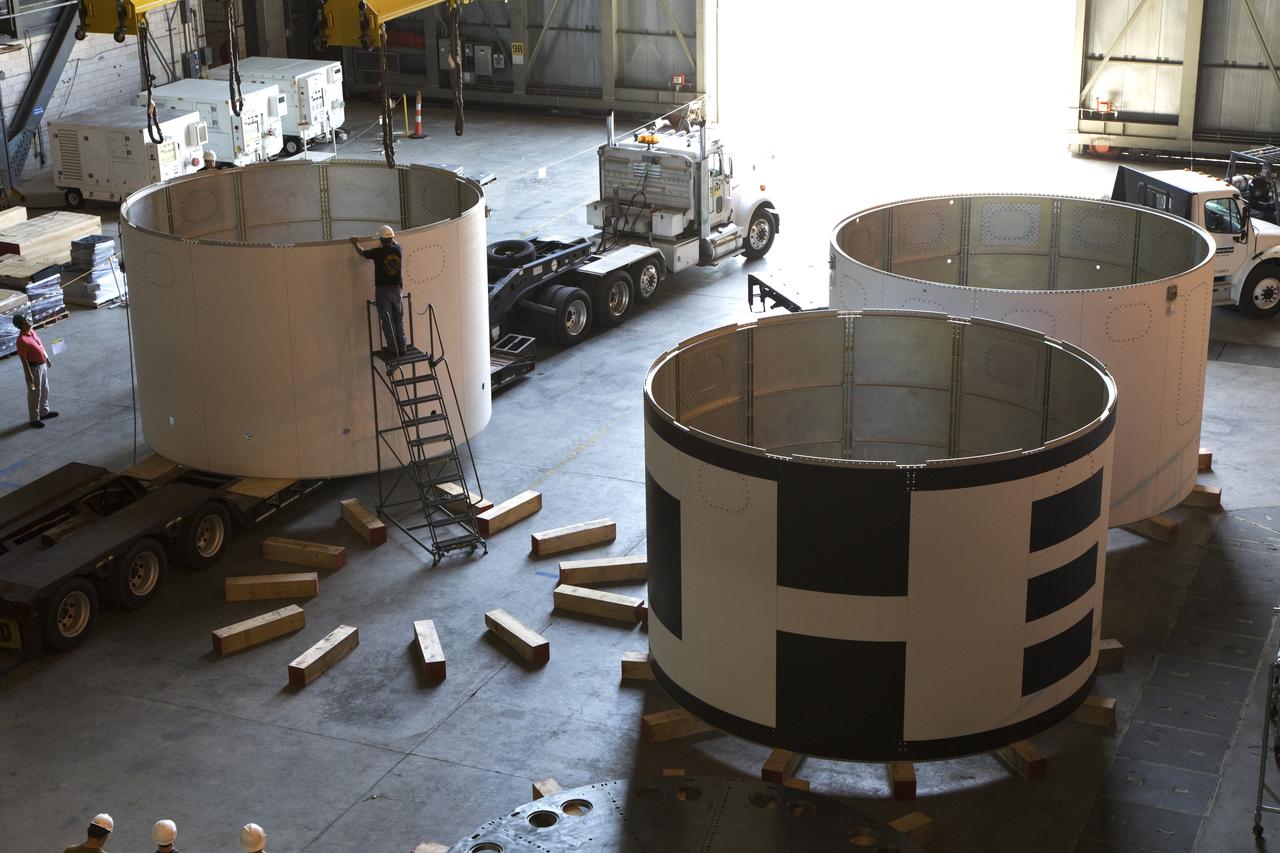

The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. Technicians prepare the aeroshell to be lifted off of the flatbed and transferred to slats. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
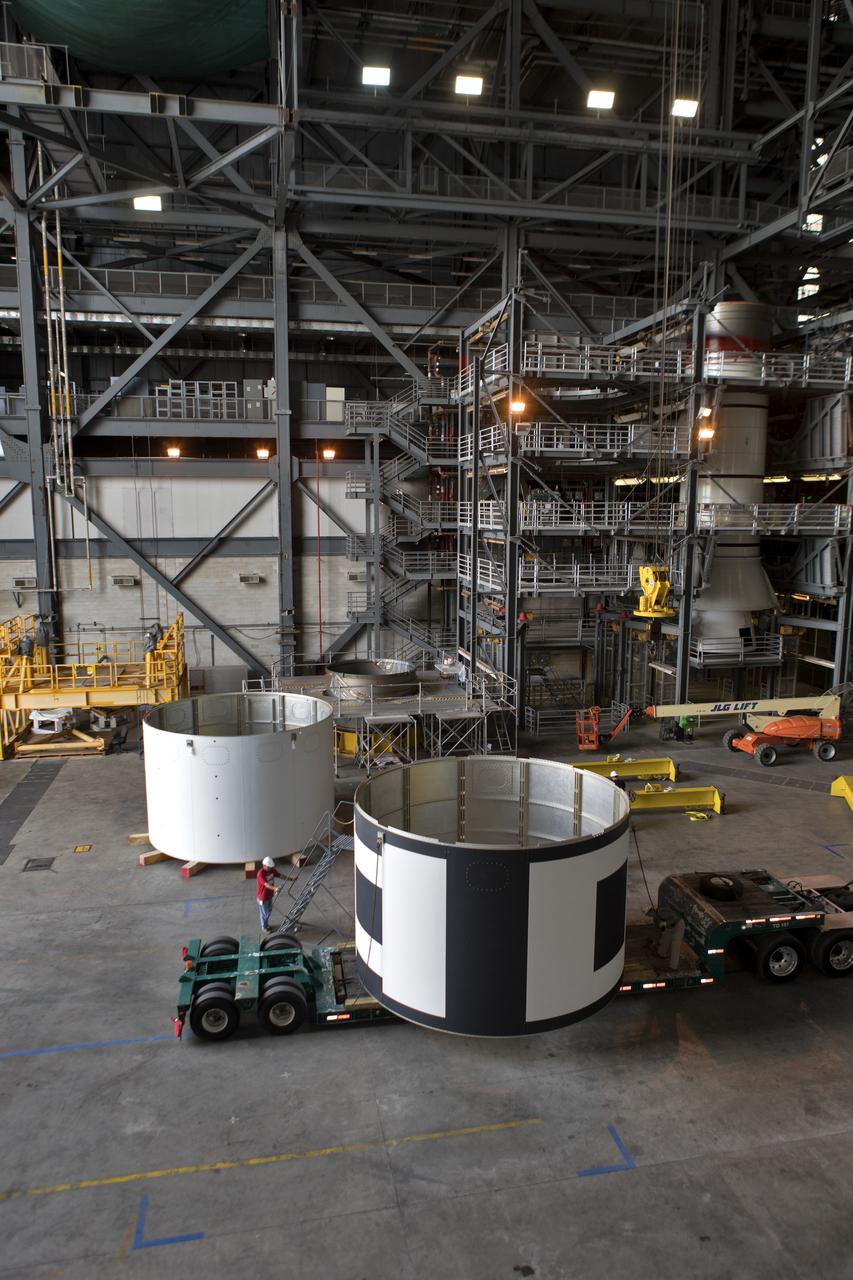

The second of three aeroshells, at right, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
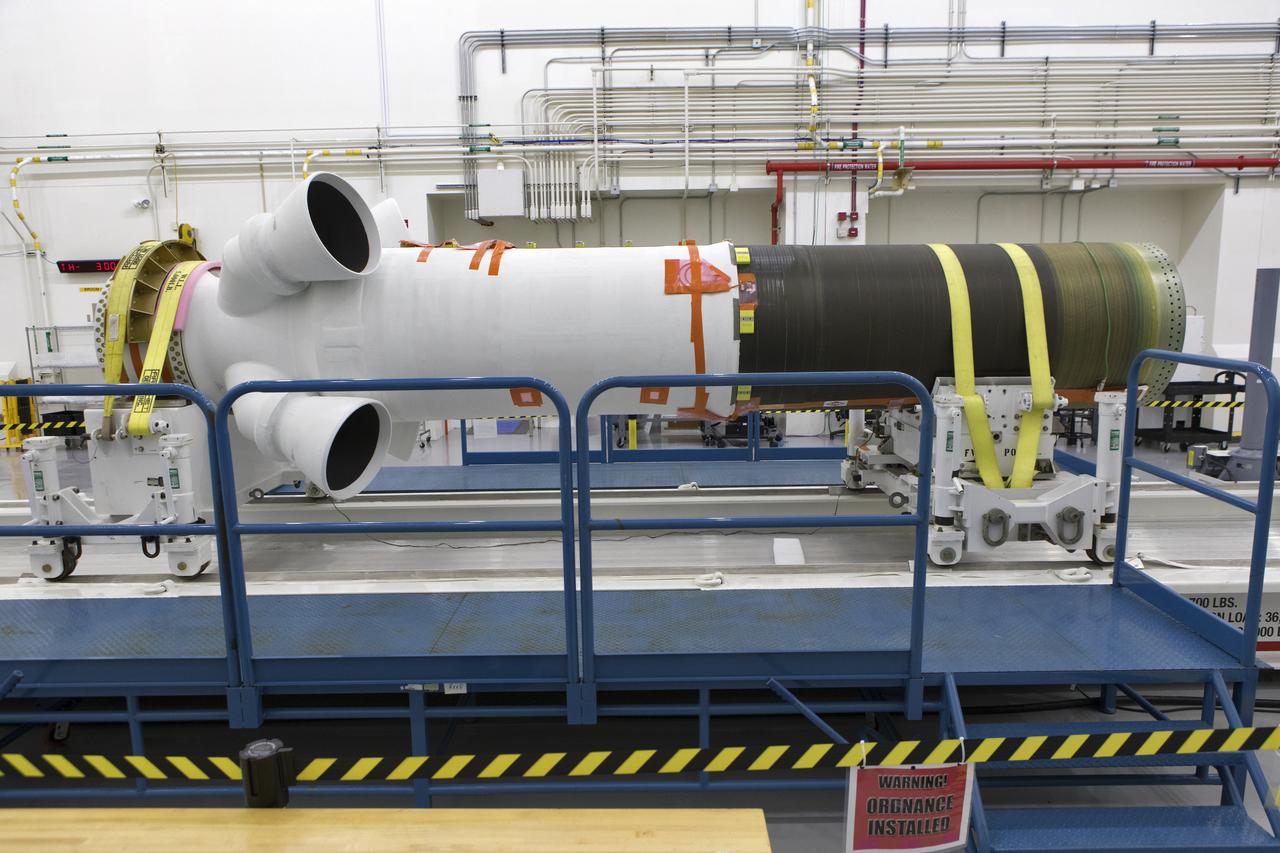
The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
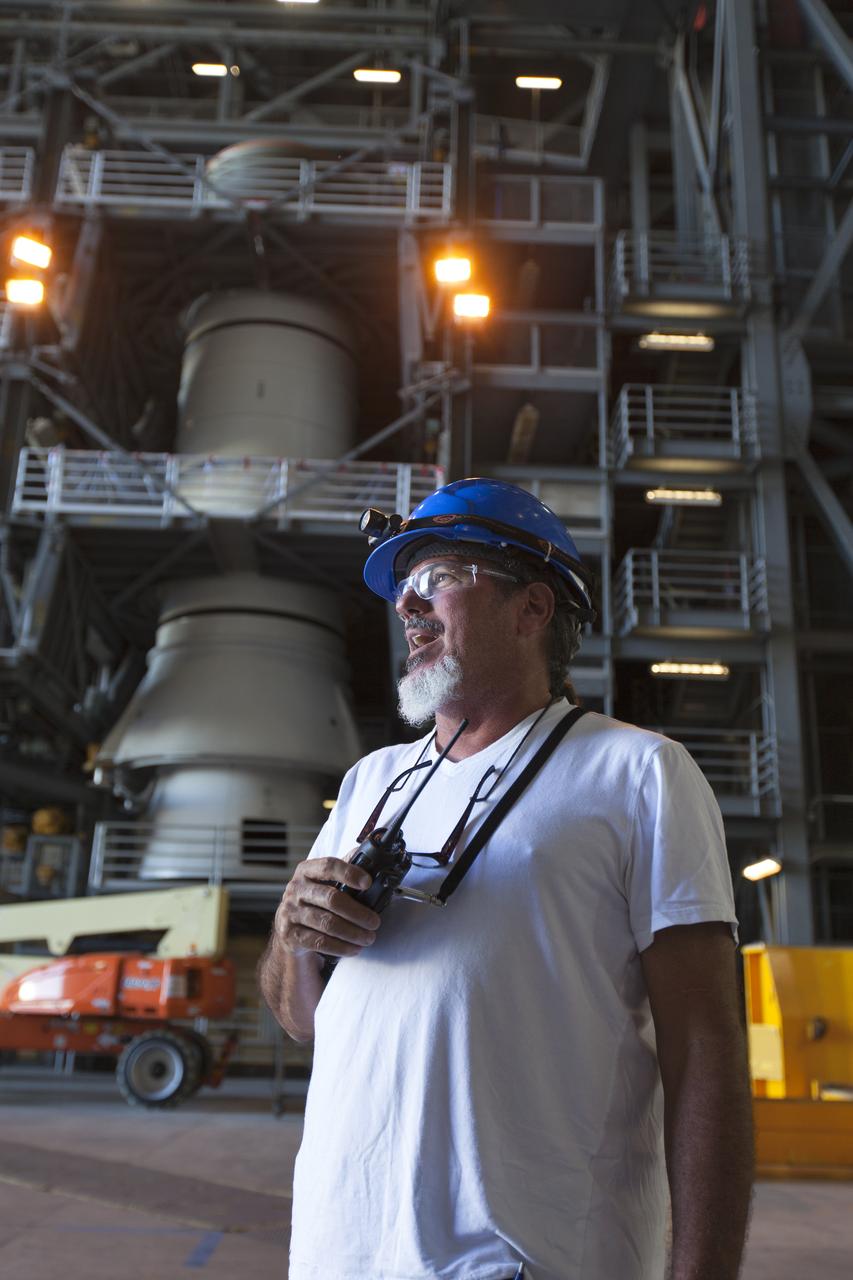

Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Anthony Sabatino, with Jacobs on the Test and Operations Support Contract, awaits arrival of the first of three aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) on June 19, 2018. The aeroshell is arriving by truck from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island and will be offloaded and secured in High Bay 4. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
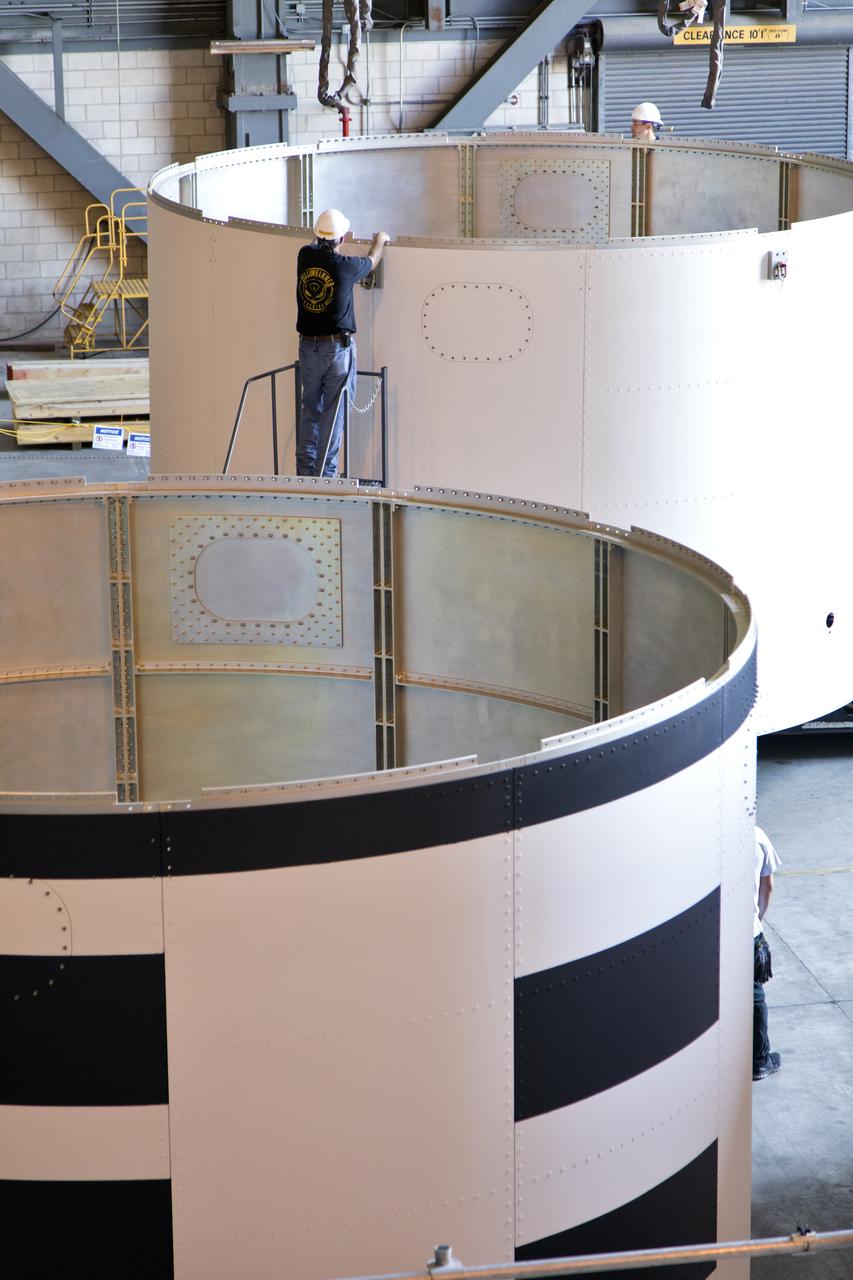

The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. Technicians prepare the aeroshell to be lifted off of the flatbed and transferred to slats. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
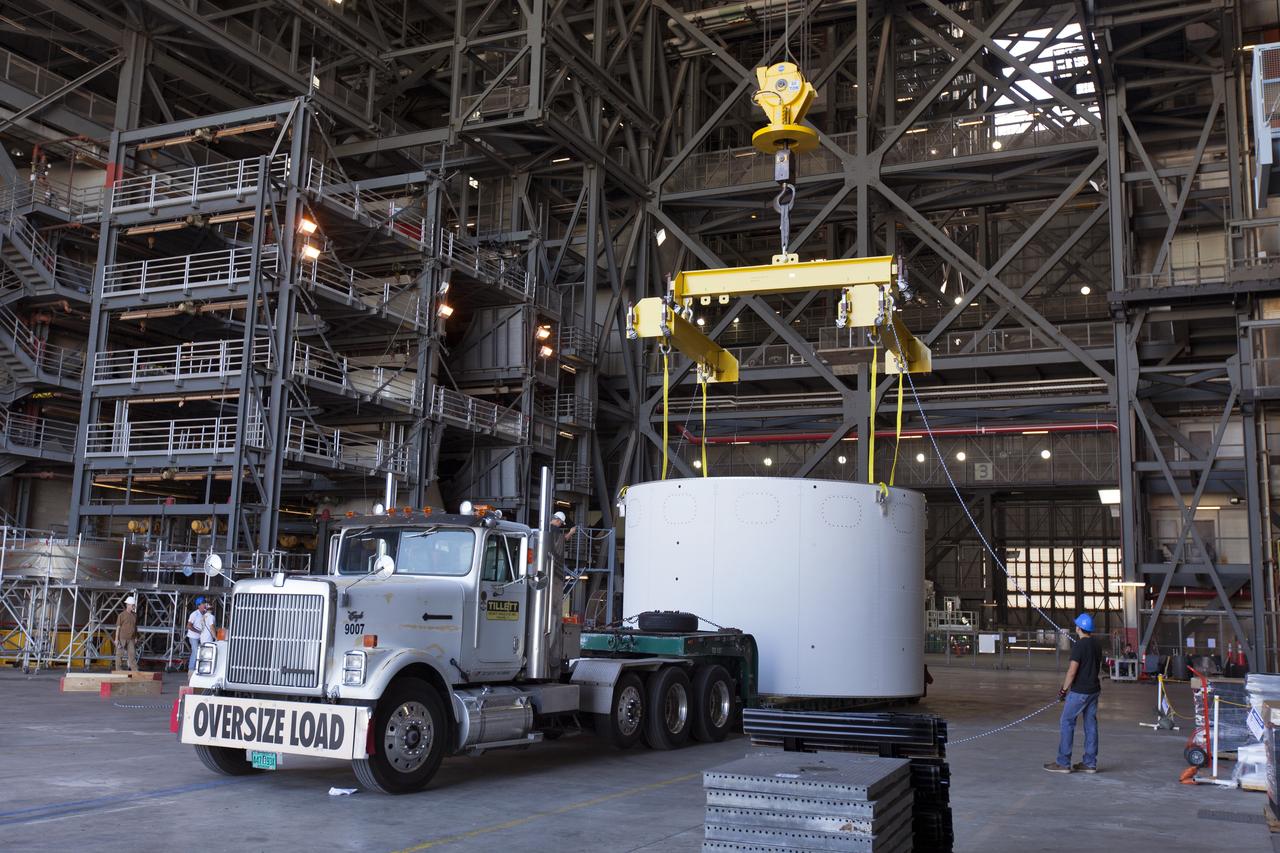

The first of three aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by truck in High Bay 4 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 19, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
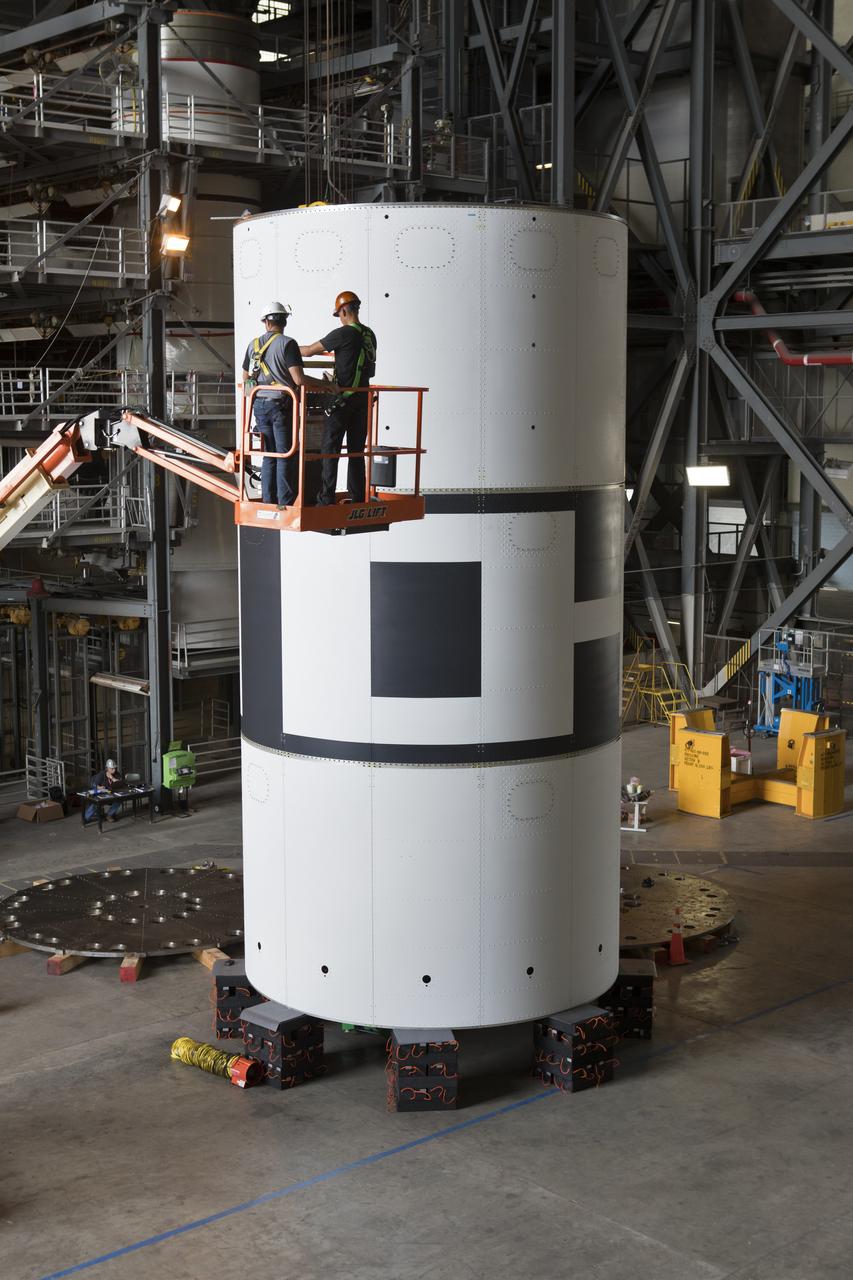

Technicians with Jacobs check the alignment during stacking of the aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Aug. 3, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshells are being prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
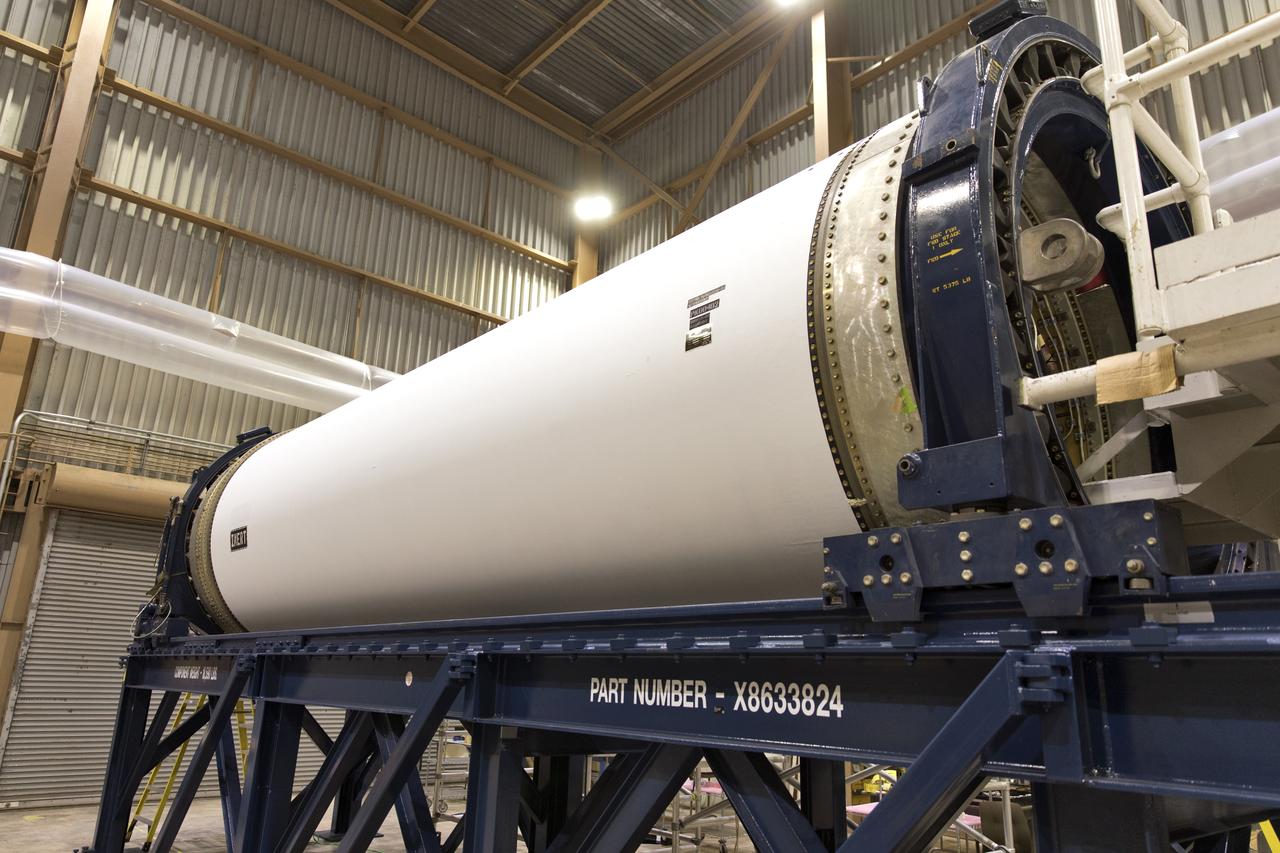

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
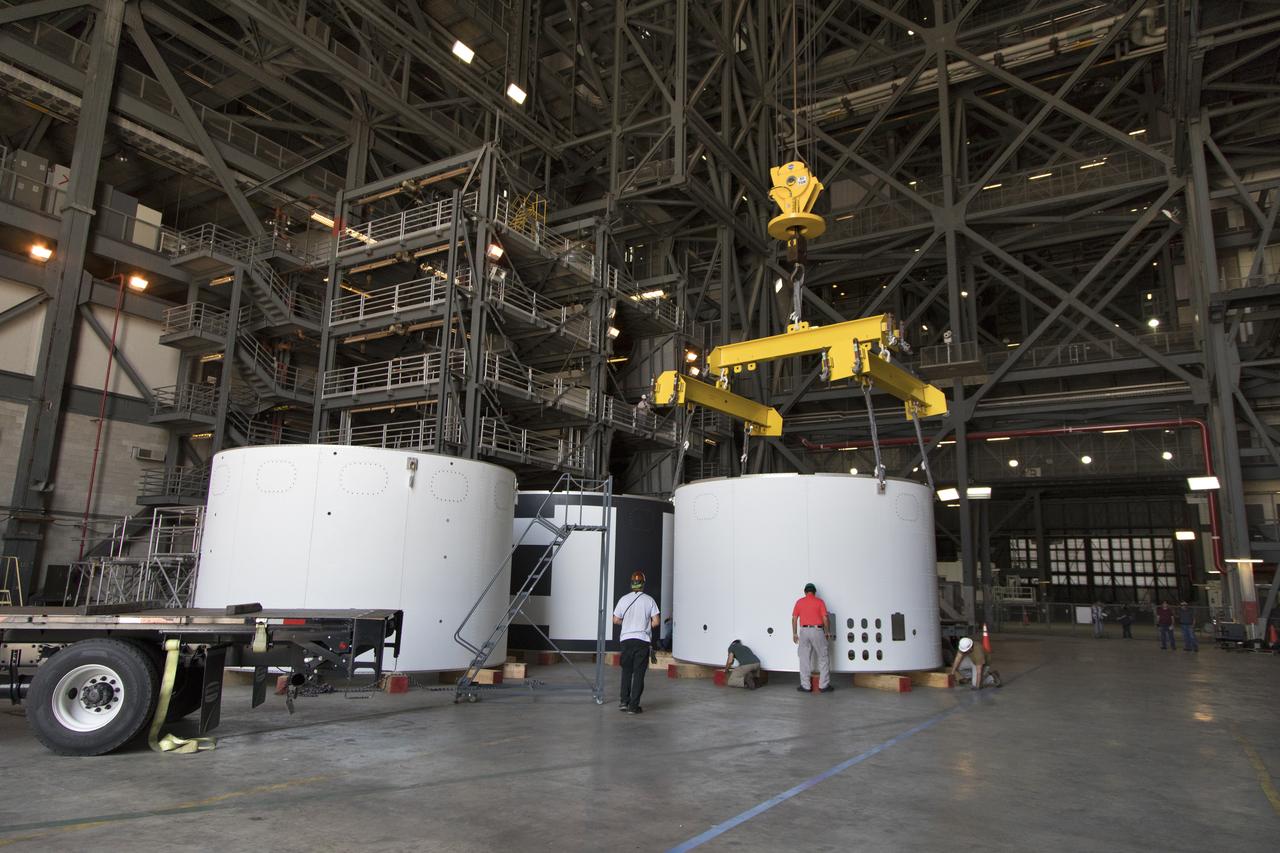

Technicians assist as a crane lowers the third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) onto slats in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
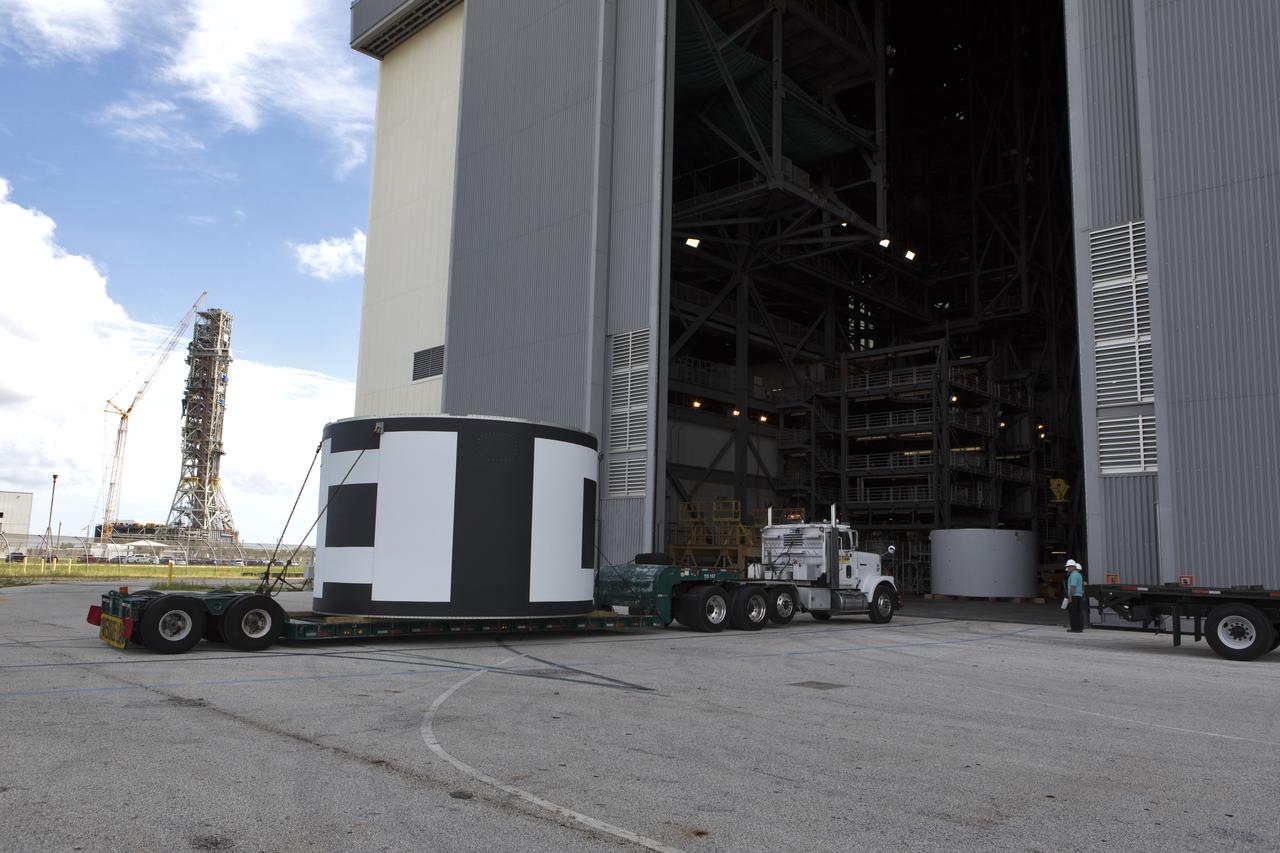

The second of three aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by truck at the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in High Bay 4. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
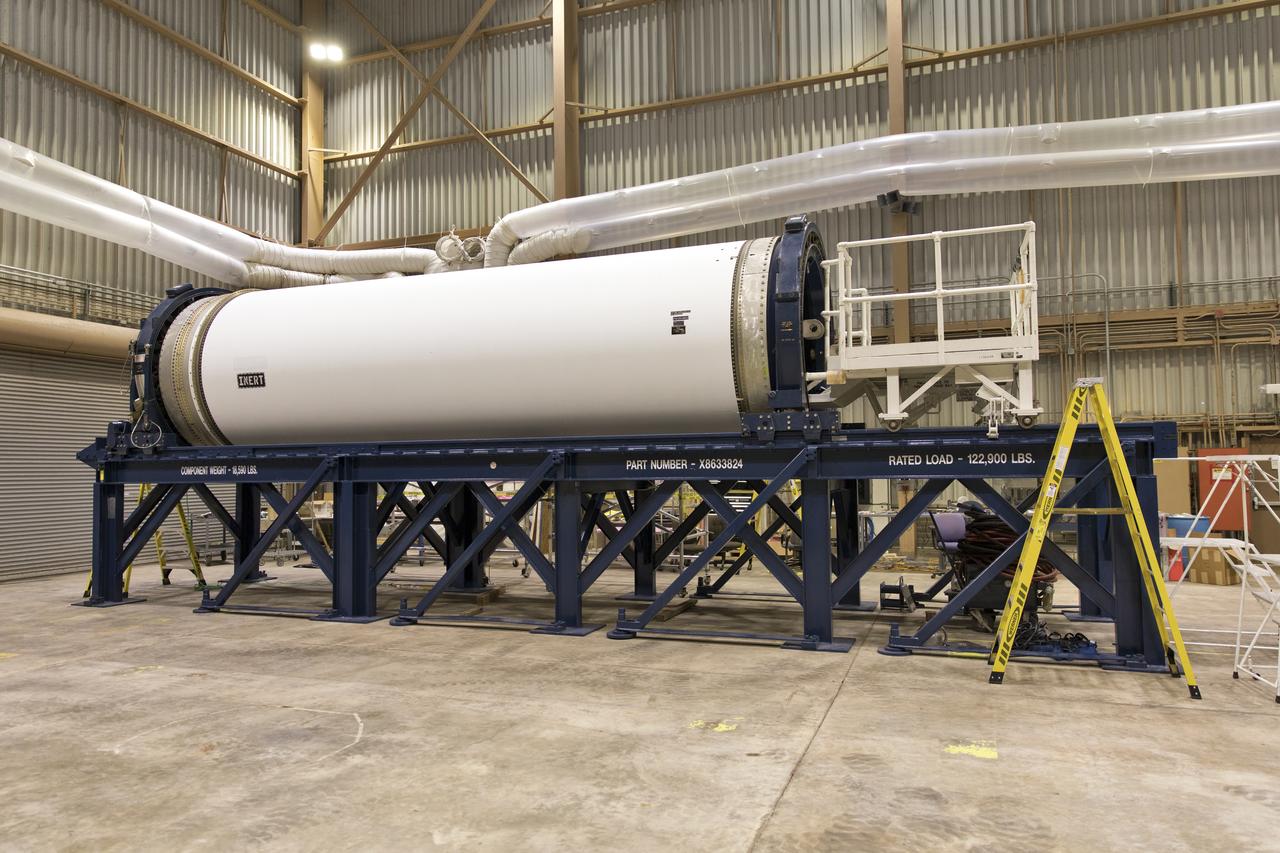

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
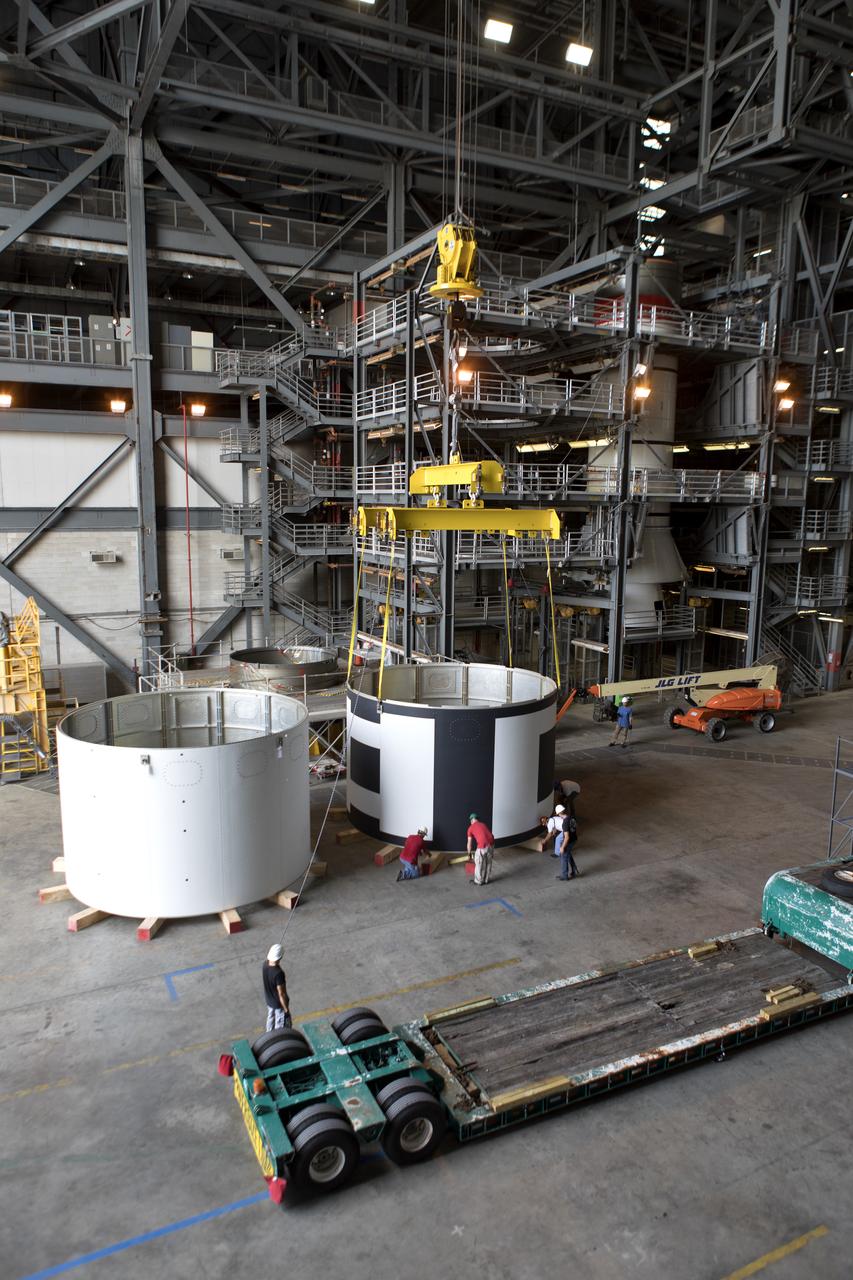

The second of three aeroshells, at right, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) was lifted up from a flatbed truck and secured in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 26, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
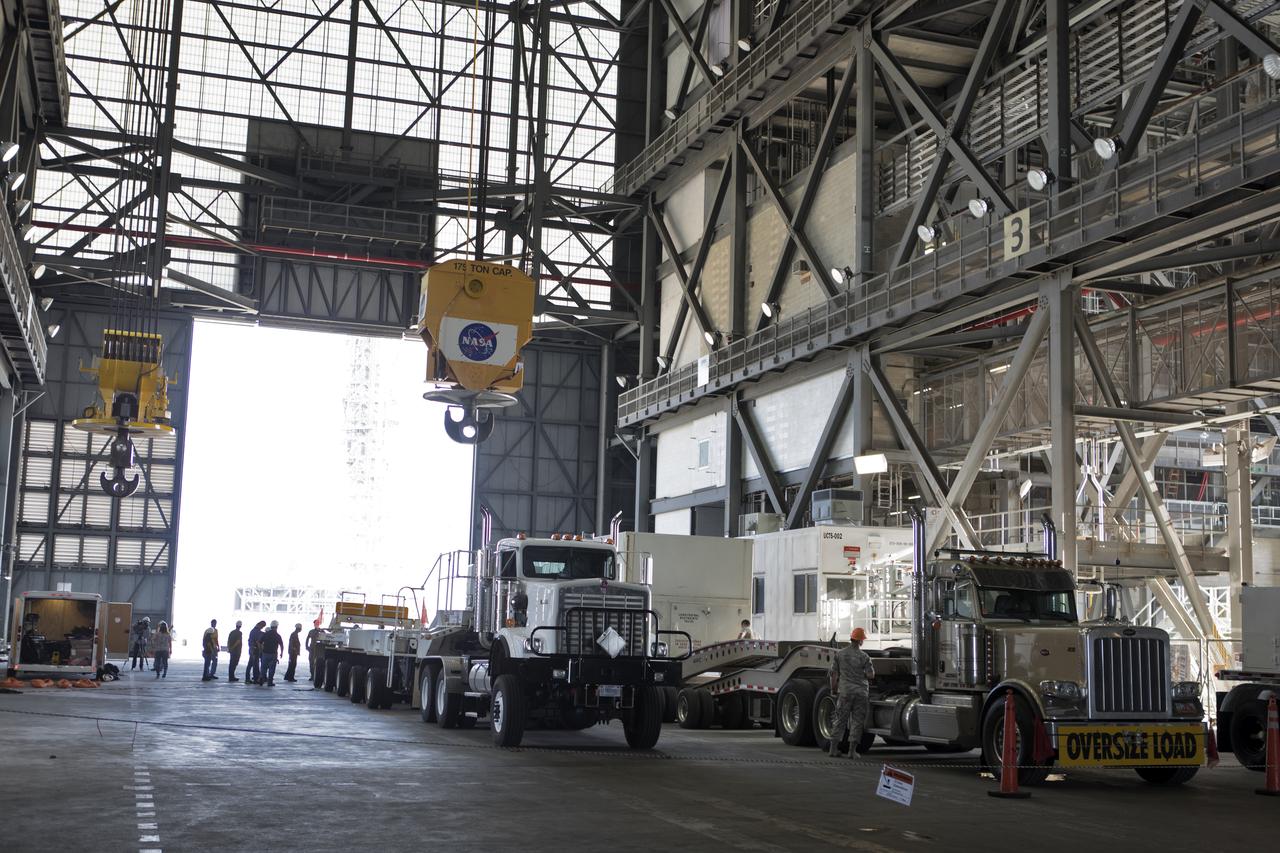

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
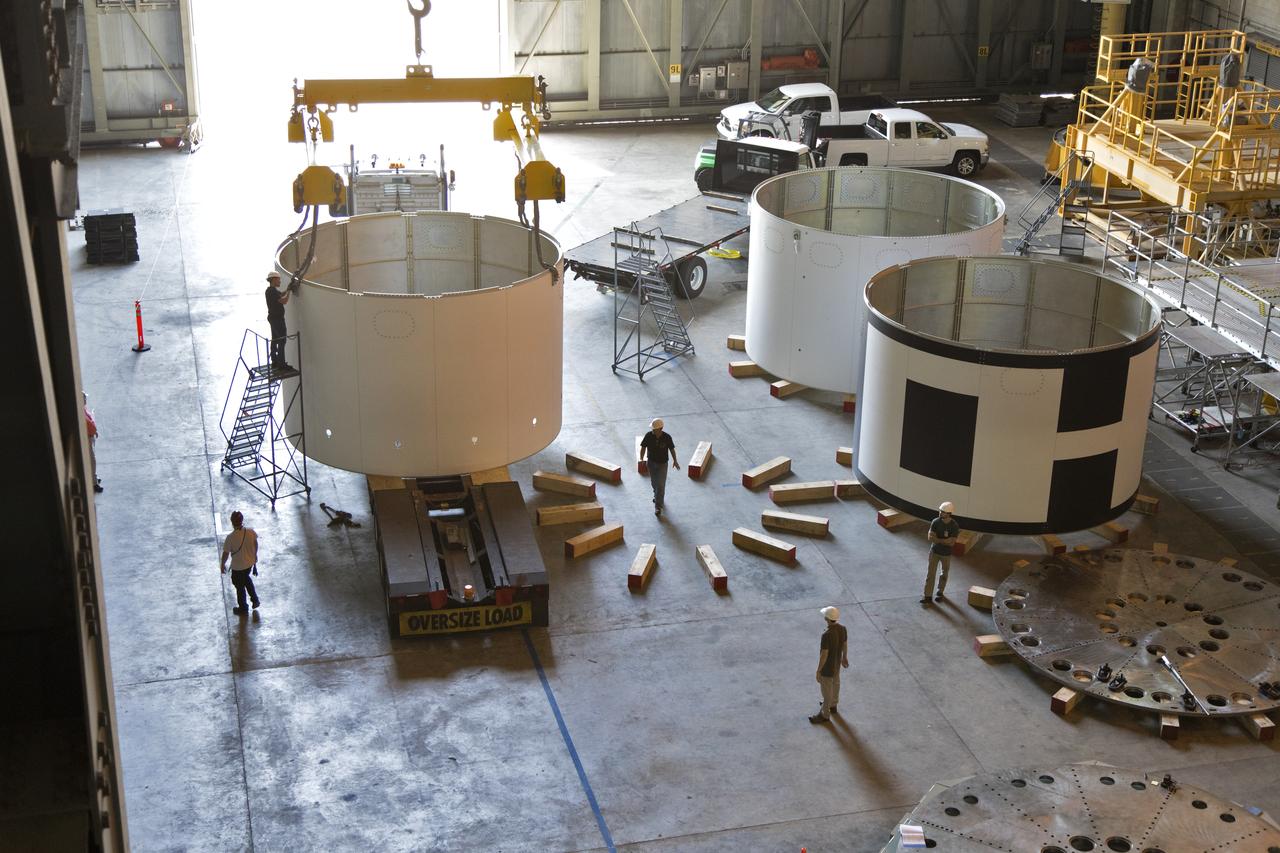

The third and final aeroshell, at left, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. Technicians prepare the aeroshell to be lifted off of the flatbed truck and transferred to slats. All three aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
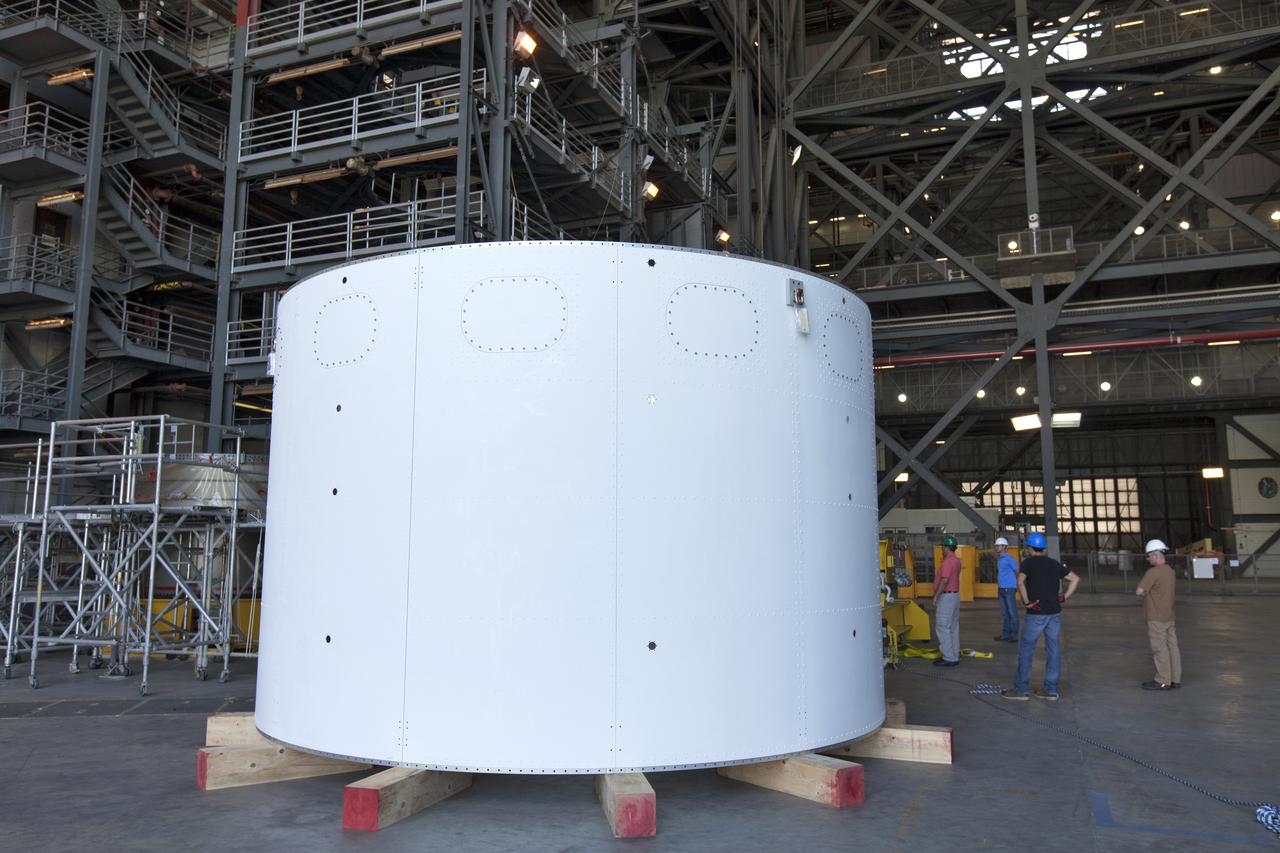

The first of three aeroshells for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is lowered onto wooden blocks in High Bay 4 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on June 19, 2018. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
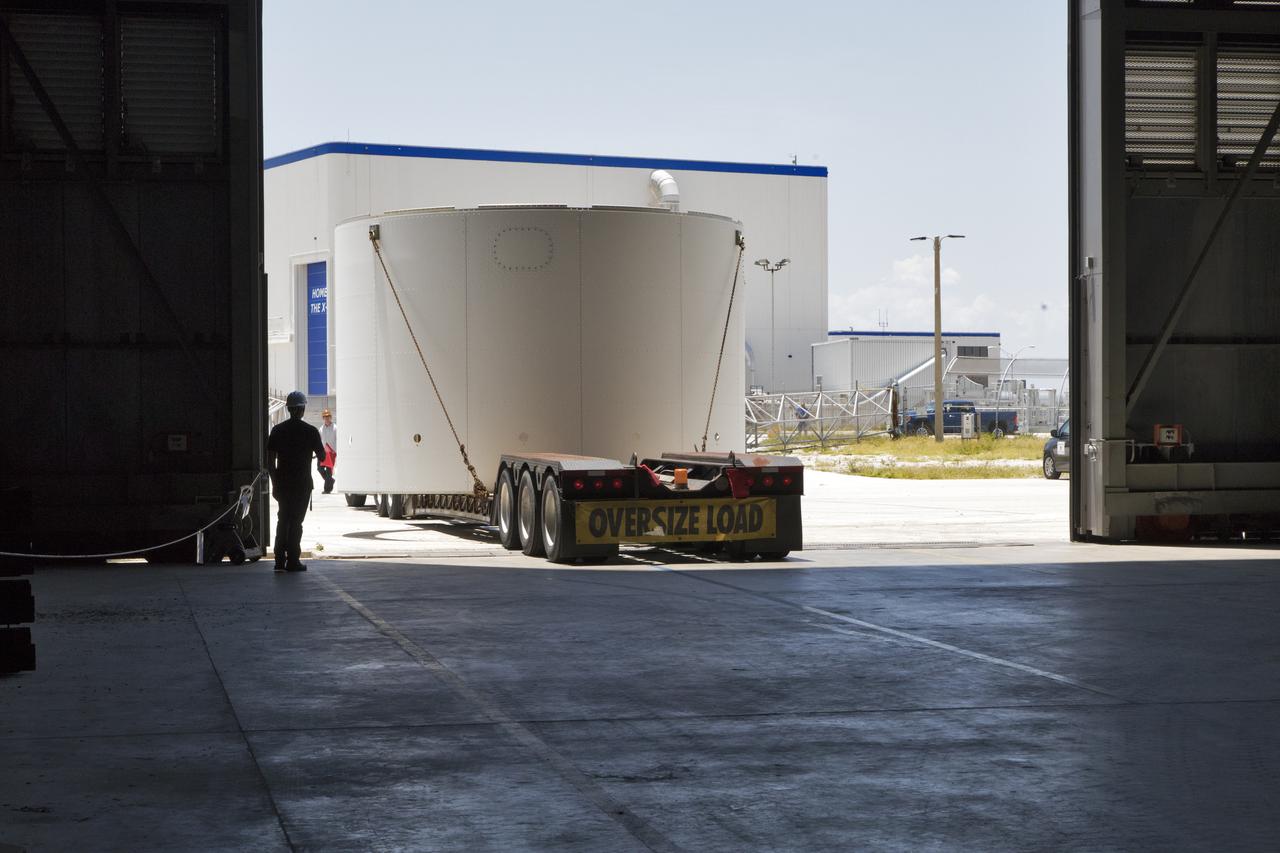

The third and final aeroshell for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by truck at the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in High Bay 4. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
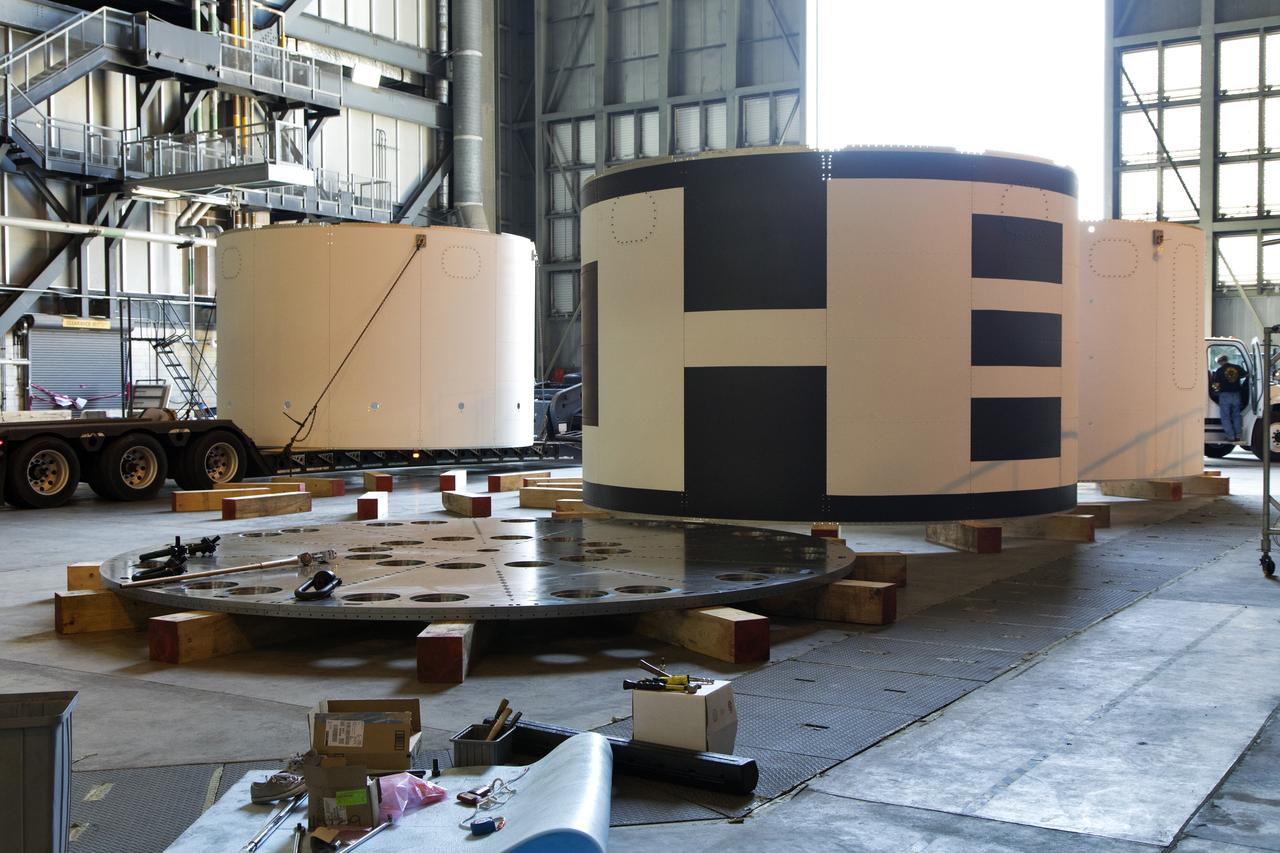

The third and final aeroshell, at left, for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in High Bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 12, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The aeroshell was shipped from EMF Inc. on nearby Merritt Island. It will be offloaded and secured in the high bay. The aeroshells will be stacked and prepared for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, a booster will launch from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1.
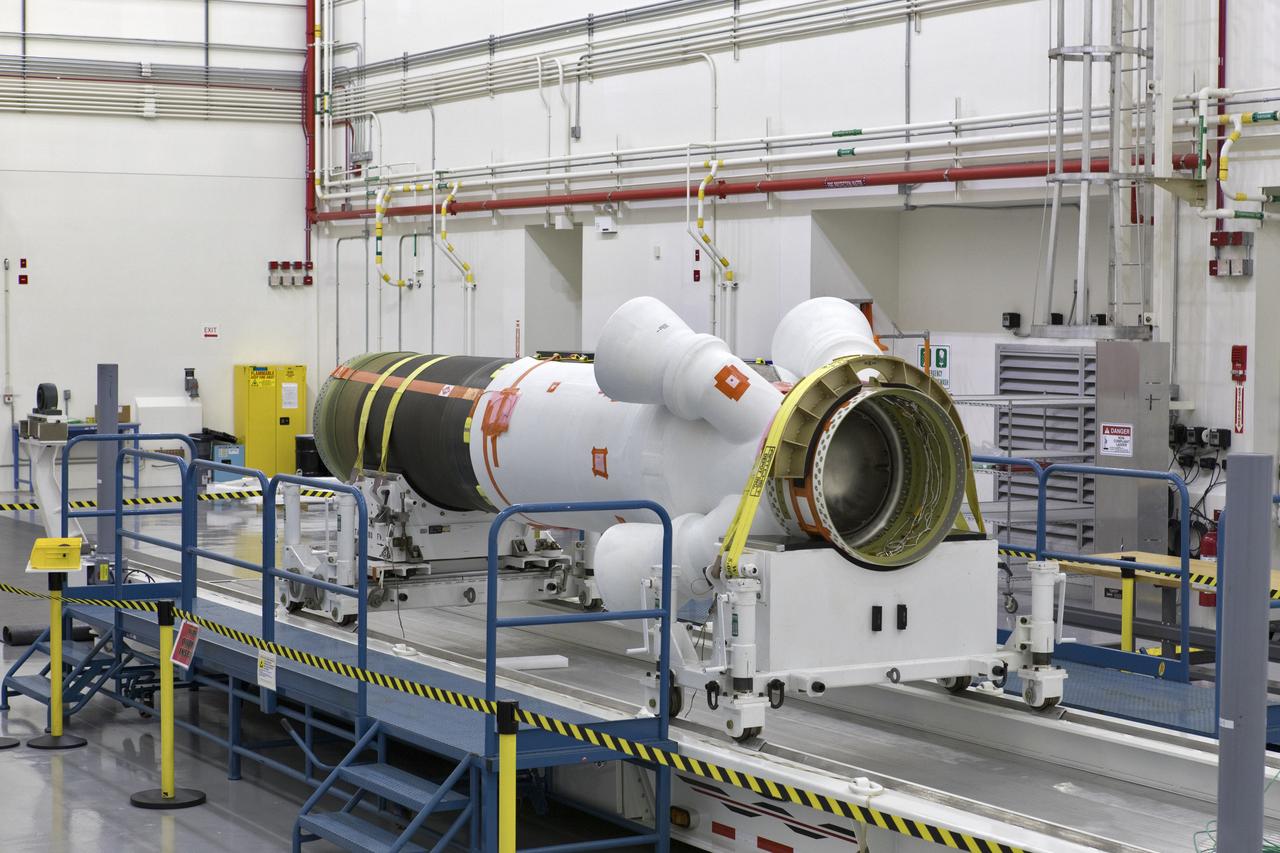

The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.

Members of the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test team perform a drop test of data recording devices about 10 miles off the coast of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 8, 2018. These devices, called Ejectable Data Recorders (EDRs), were tossed out of a helicopter hovering 5,000 feet over the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved by recovery boats. The AA-2 Flight Test team is evaluating how the systems in the devices react to elements encountered from the sky to the ocean. In April 2019, the EDRs will eject from the Orion test article during a scheduled test of the spacecraft’s Launch Abort System (LAS).

Helen Fricker, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, California, ICESat-2 science definition team member, speaks to members of the news media and social media participants during a prelaunch mission briefing for NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2), a mission to measure the changing height of Earth's ice, on Sept. 13, 2018 at Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB) in California. ICESat-2 will launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II, the rocket’s final mission, from Space Launch Complex 2 at VAFB. Launch is scheduled for 8:46 a.m. EDT (5:46 a.m. PDT).

Members of the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test team perform a drop test of data recording devices about 10 miles off the coast of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 8, 2018. These devices, called Ejectable Data Recorders (EDRs), were tossed out of a helicopter hovering 5,000 feet over the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved by recovery boats. The AA-2 Flight Test team is evaluating how the systems in the devices react to elements encountered from the sky to the ocean. In April 2019, the EDRs will eject from the Orion test article during a scheduled test of the spacecraft’s Launch Abort System (LAS).

Members of the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test team perform a drop test of data recording devices about 10 miles off the coast of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 8, 2018. These devices, called Ejectable Data Recorders (EDRs), were tossed out of a helicopter hovering 5,000 feet over the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved by recovery boats. The AA-2 Flight Test team is evaluating how the systems in the devices react to elements encountered from the sky to the ocean. In April 2019, the EDRs will eject from the Orion test article during a scheduled test of the spacecraft’s Launch Abort System (LAS).

Members of the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test team perform a drop test of data recording devices about 10 miles off the coast of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 8, 2018. These devices, called Ejectable Data Recorders (EDRs), were tossed out of a helicopter hovering 5,000 feet over the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved by recovery boats. The AA-2 Flight Test team is evaluating how the systems in the devices react to elements encountered from the sky to the ocean. In April 2019, the EDRs will eject from the Orion test article during a scheduled test of the spacecraft’s Launch Abort System (LAS).
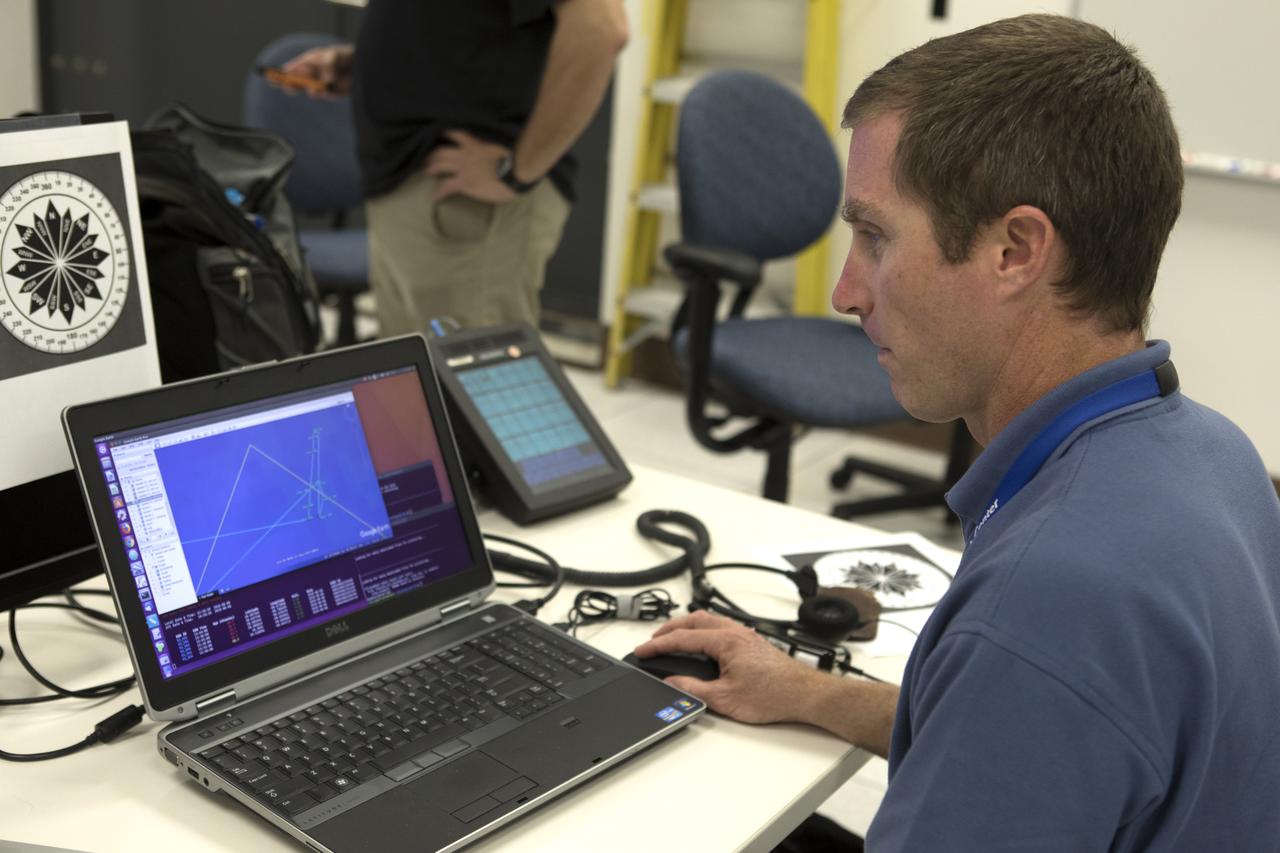

Members of the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test team perform a drop test of data recording devices about 10 miles off the coast of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 8, 2018. These devices, called Ejectable Data Recorders (EDRs), were tossed out of a helicopter hovering 5,000 feet over the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved by recovery boats. The AA-2 Flight Test team is evaluating how the systems in the devices react to elements encountered from the sky to the ocean. In April 2019, the EDRs will eject from the Orion test article during a scheduled test of the spacecraft’s Launch Abort System (LAS).
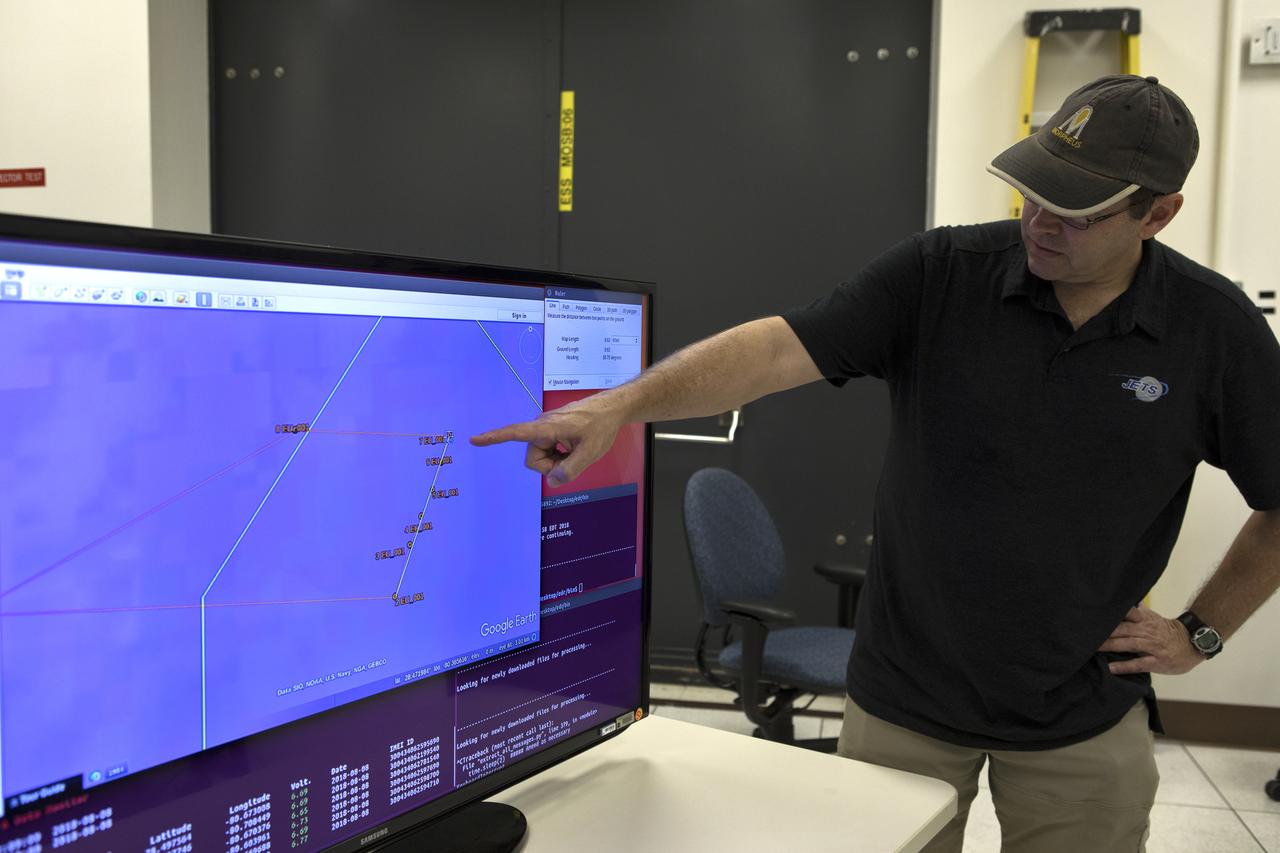

Members of the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test team perform a drop test of data recording devices about 10 miles off the coast of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 8, 2018. These devices, called Ejectable Data Recorders (EDRs), were tossed out of a helicopter hovering 5,000 feet over the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved by recovery boats. The AA-2 Flight Test team is evaluating how the systems in the devices react to elements encountered from the sky to the ocean. In April 2019, the EDRs will eject from the Orion test article during a scheduled test of the spacecraft’s Launch Abort System (LAS).
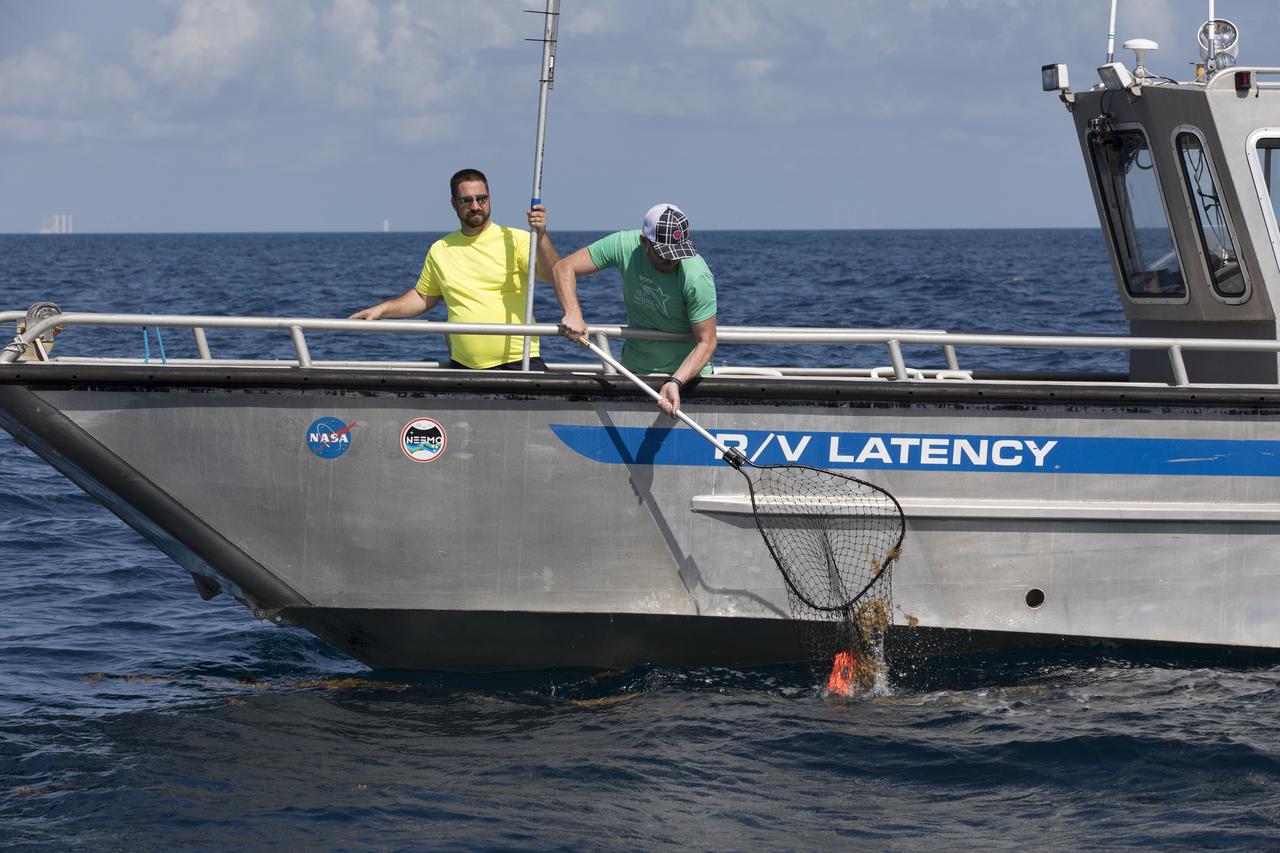

Members of the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test team perform a drop test of data recording devices about 10 miles off the coast of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 8, 2018. These devices, called Ejectable Data Recorders (EDRs), were tossed out of a helicopter hovering 5,000 feet over the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved by recovery boats. The AA-2 Flight Test team is evaluating how the systems in the devices react to elements encountered from the sky to the ocean. In April 2019, the EDRs will eject from the Orion test article during a scheduled test of the spacecraft’s Launch Abort System (LAS).

Members of the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test team perform a drop test of data recording devices about 10 miles off the coast of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 8, 2018. These devices, called Ejectable Data Recorders (EDRs), were tossed out of a helicopter hovering 5,000 feet over the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved by recovery boats. The AA-2 Flight Test team is evaluating how the systems in the devices react to elements encountered from the sky to the ocean. In April 2019, the EDRs will eject from the Orion test article during a scheduled test of the spacecraft’s Launch Abort System (LAS).

Members of the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test team perform a drop test of data recording devices about 10 miles off the coast of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 8, 2018. These devices, called Ejectable Data Recorders (EDRs), were tossed out of a helicopter hovering 5,000 feet over the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved by recovery boats. The AA-2 Flight Test team is evaluating how the systems in the devices react to elements encountered from the sky to the ocean. In April 2019, the EDRs will eject from the Orion test article during a scheduled test of the spacecraft’s Launch Abort System (LAS).

Members of the Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test team perform a drop test of data recording devices about 10 miles off the coast of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Aug. 8, 2018. These devices, called Ejectable Data Recorders (EDRs), were tossed out of a helicopter hovering 5,000 feet over the Atlantic Ocean and retrieved by recovery boats. The AA-2 Flight Test team is evaluating how the systems in the devices react to elements encountered from the sky to the ocean. In April 2019, the EDRs will eject from the Orion test article during a scheduled test of the spacecraft’s Launch Abort System (LAS).
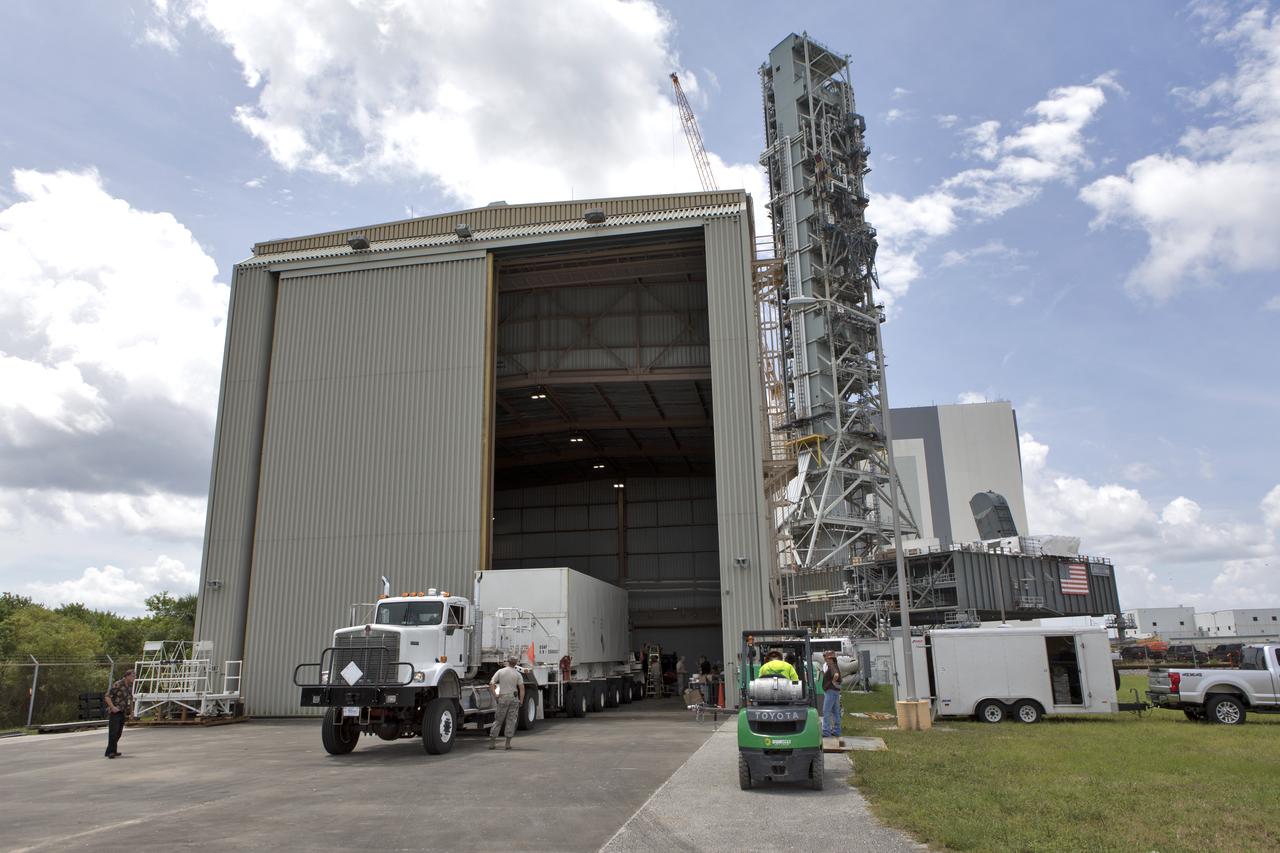

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
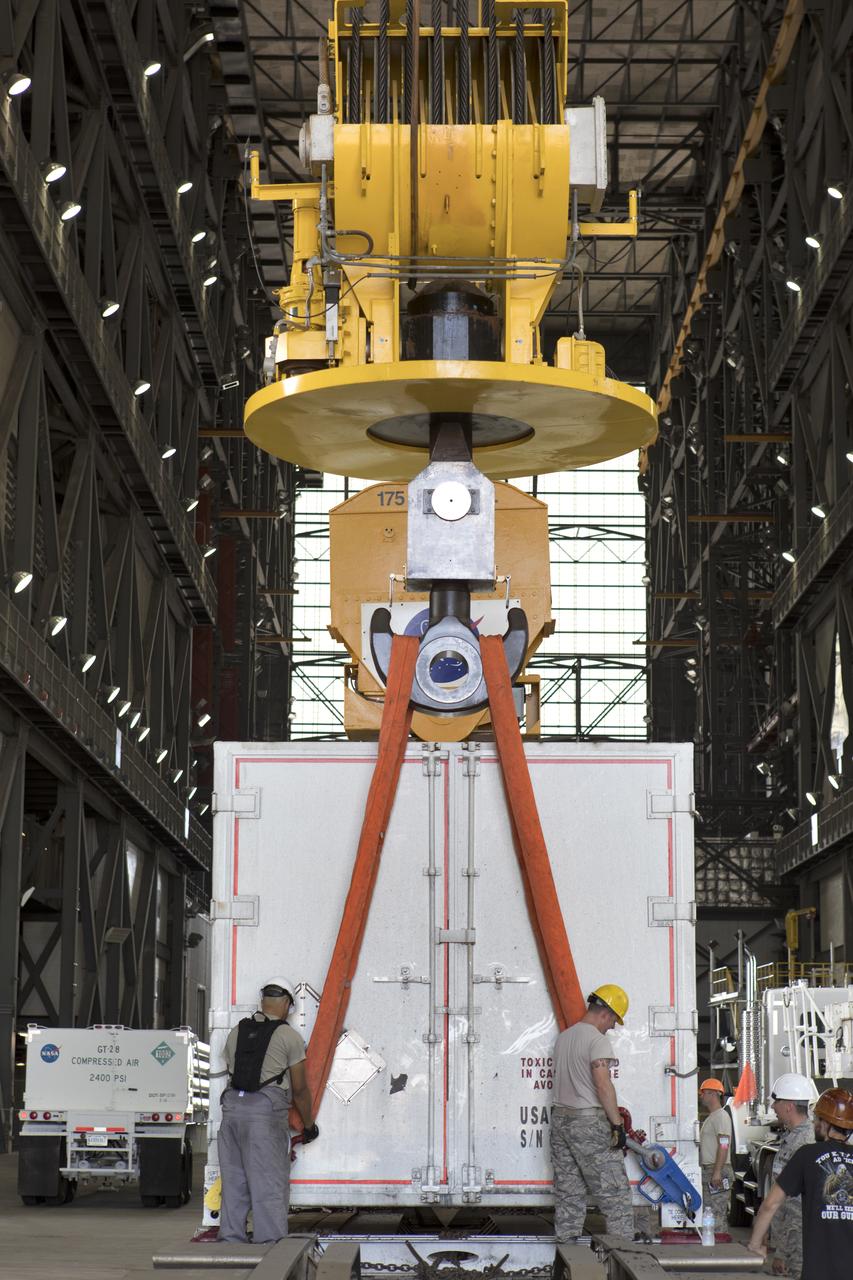

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jacob’s technicians on the Test Operations Support Contract attach a crane to a shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lifted and transferred to another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
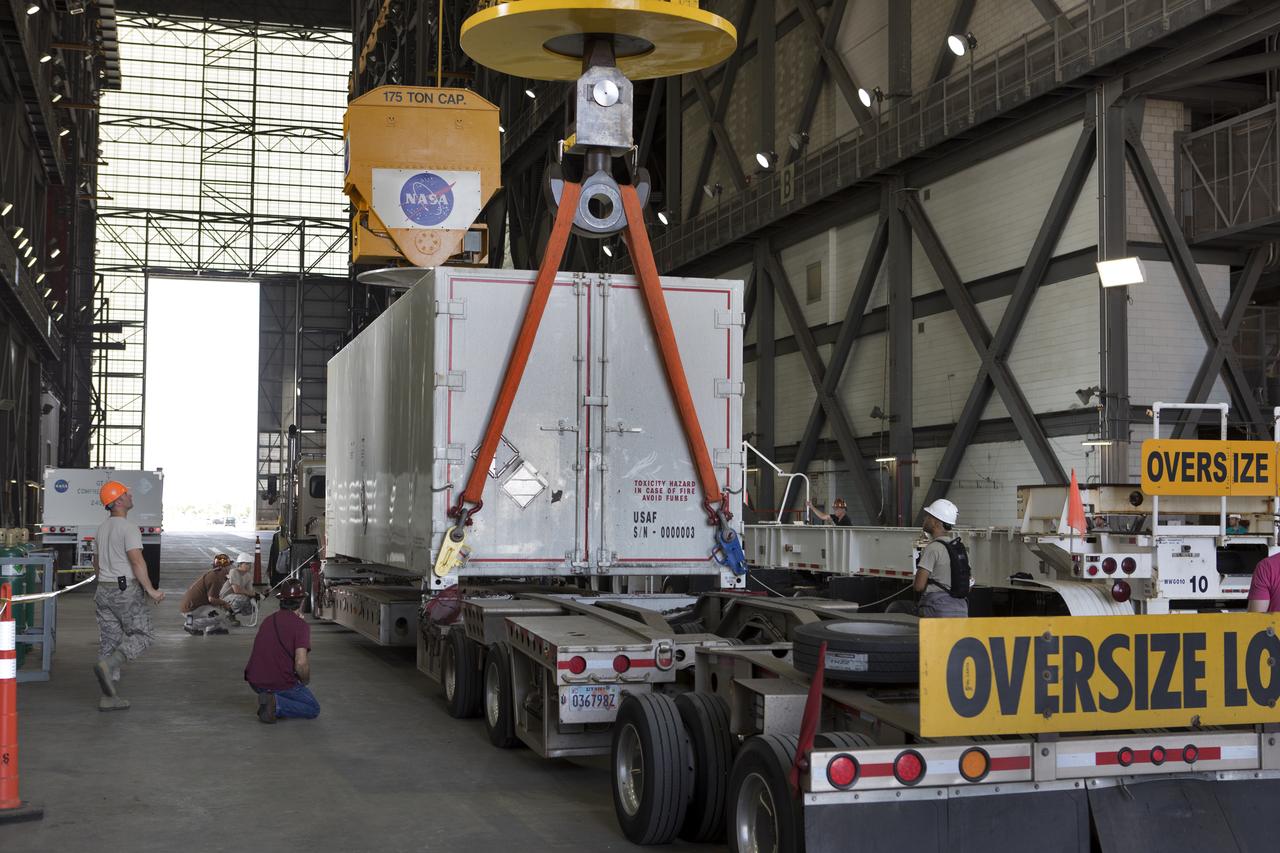

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jacob’s technicians attach a crane to a shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lifted and transferred to another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
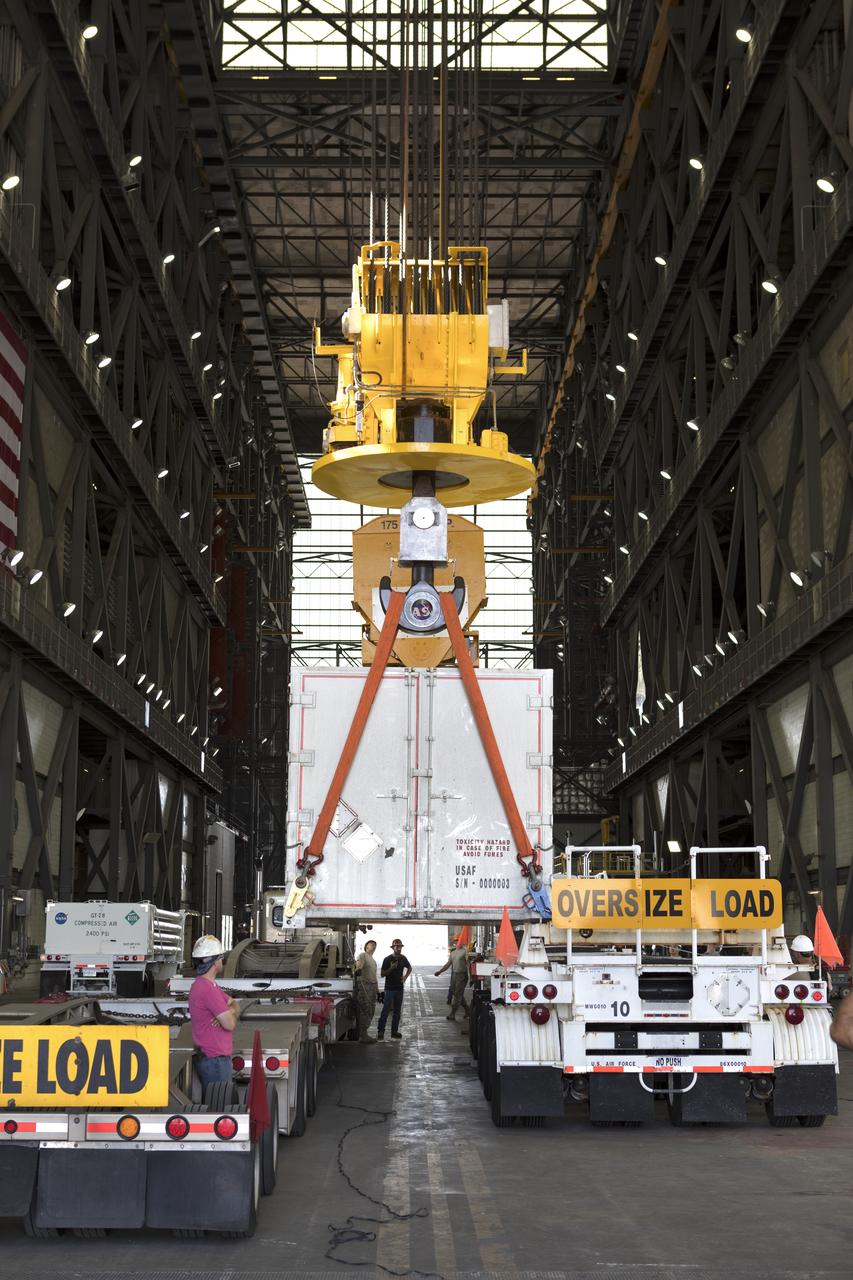

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to lift up the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lowered onto another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
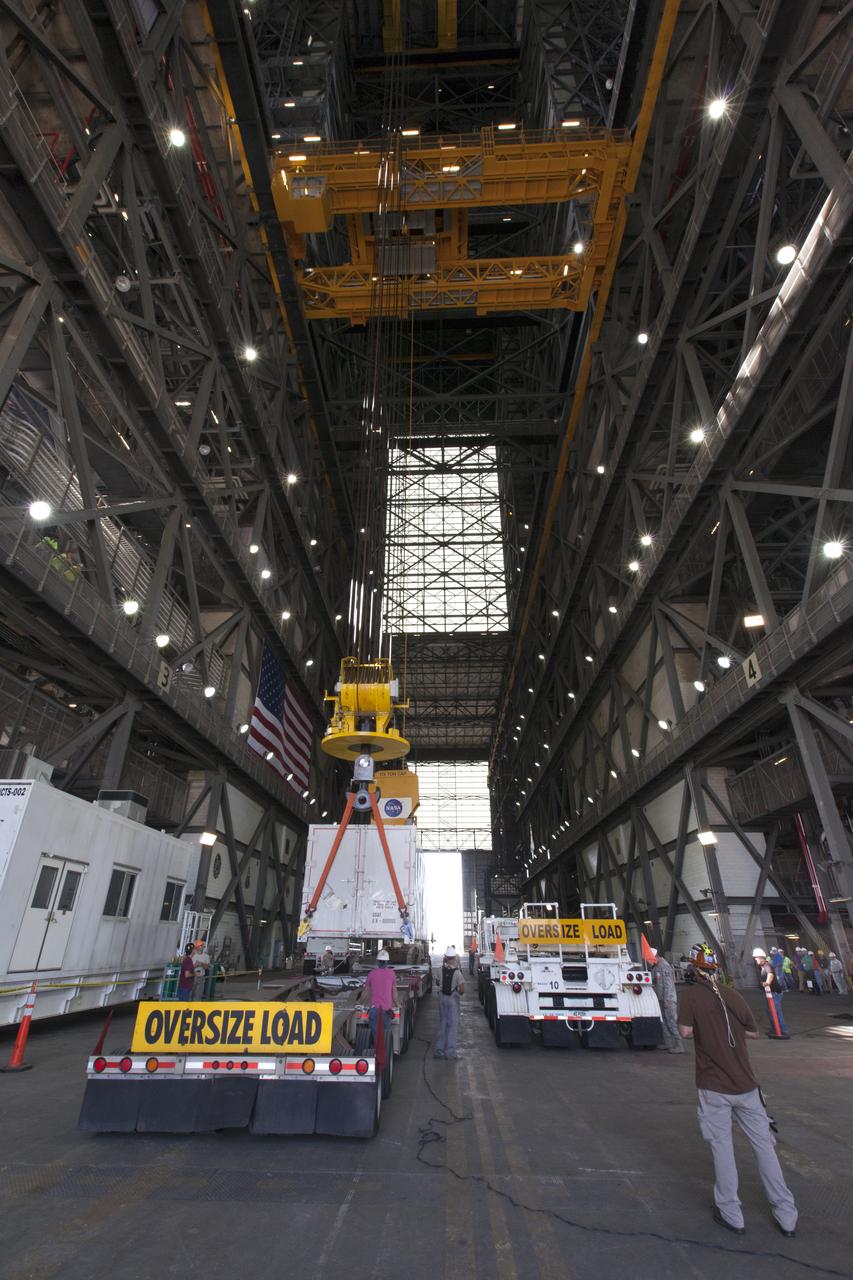

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to lift up a shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lifted and transferred to another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
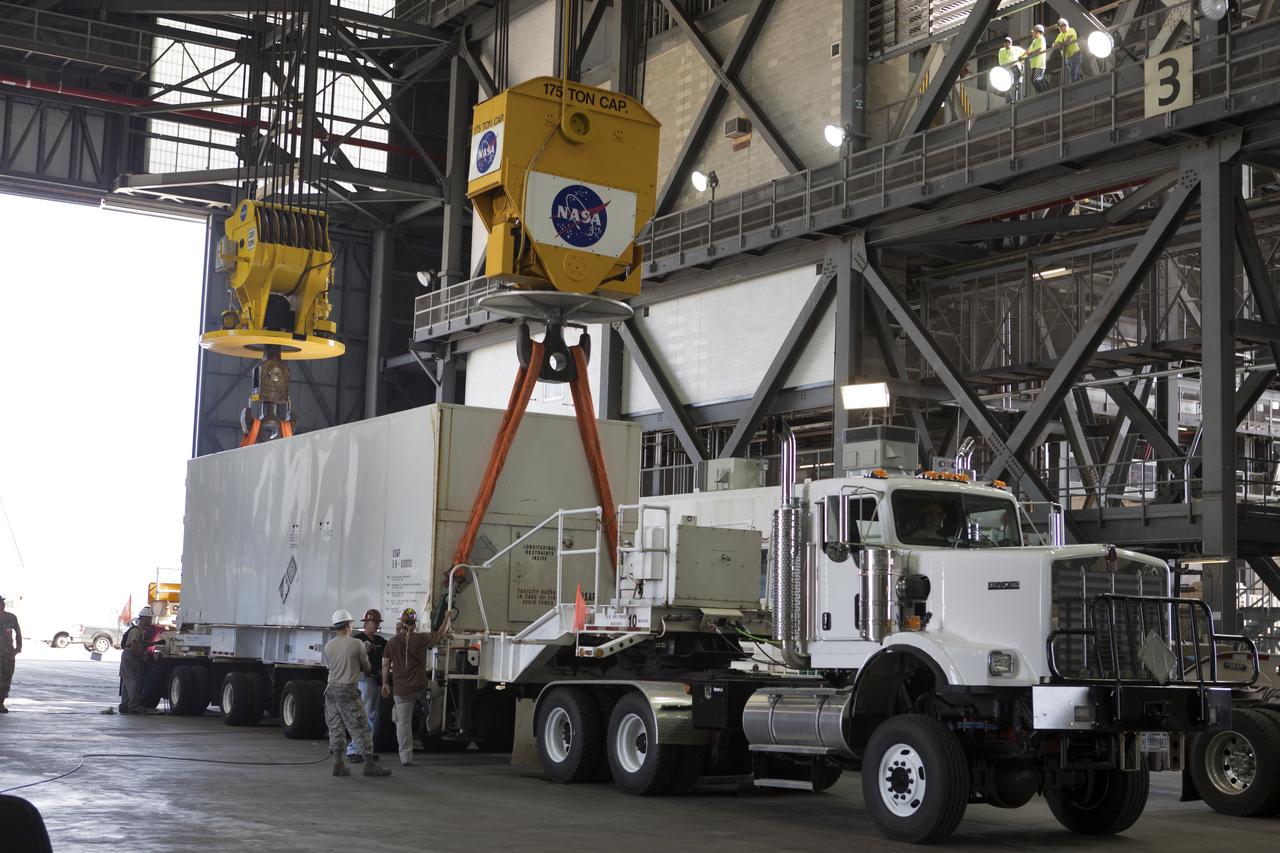

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane operated by Jacob’s technicians lowers the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside onto another transporter on July 20, 2018. The container will be moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
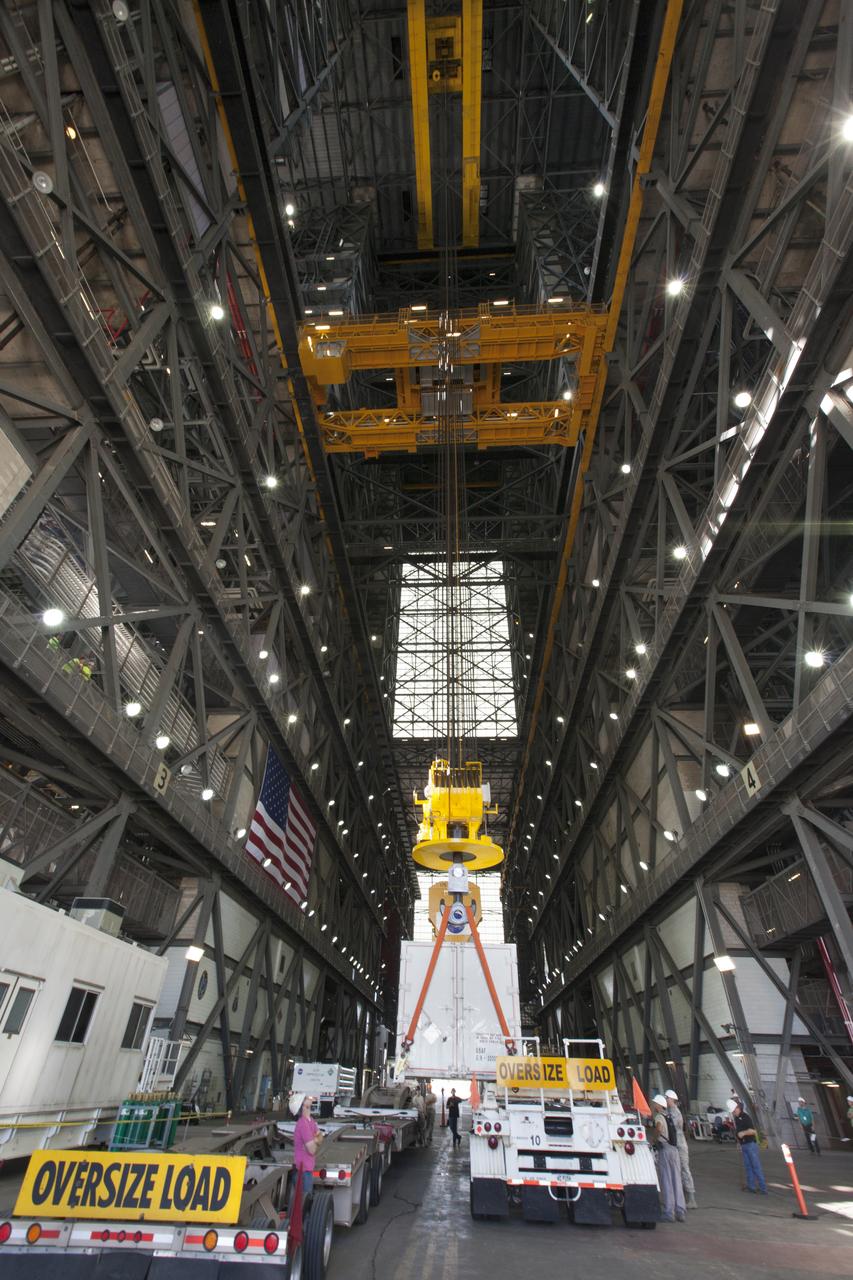

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to lift up the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lowered onto another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.