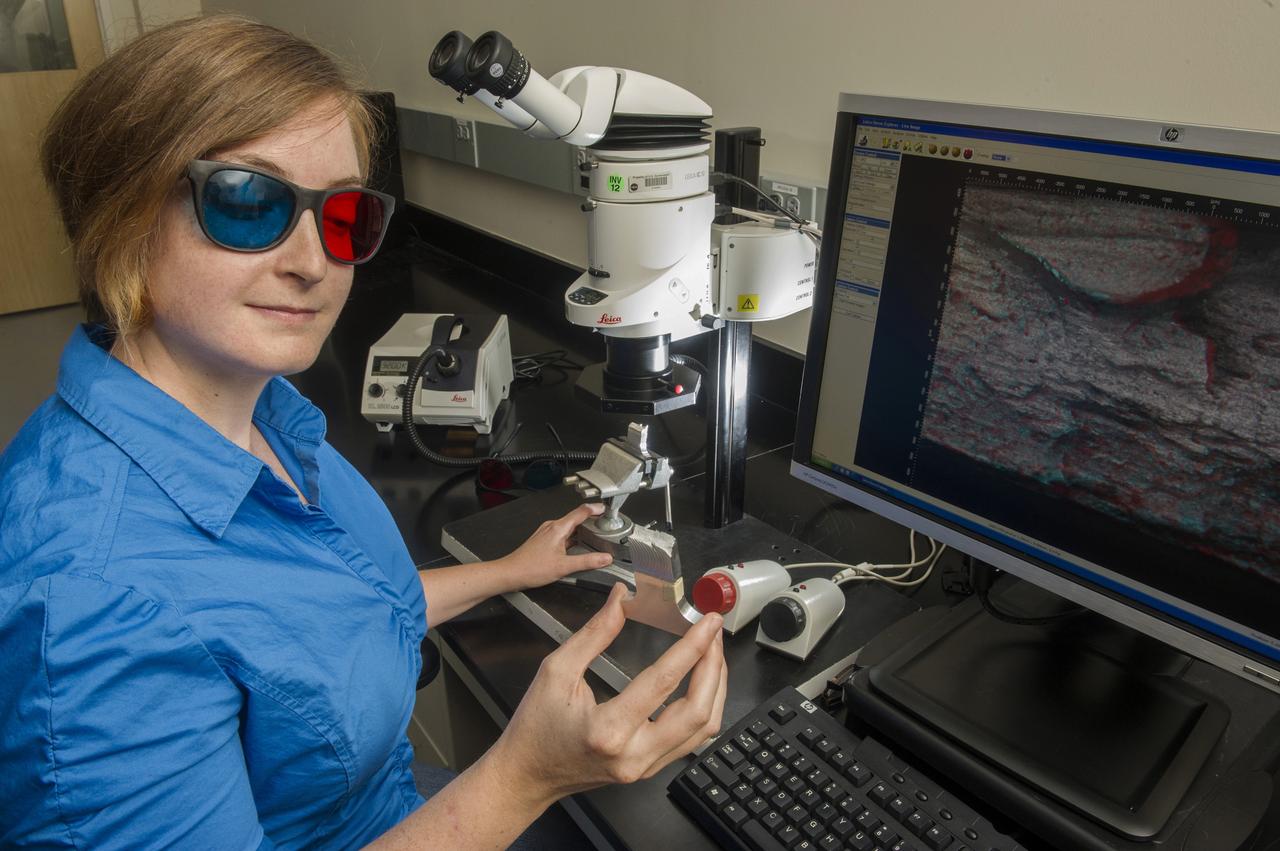

ELLEN RABENBERG, EM31, FAILURE ANALYSIS AND METALLURGY BRANCH, DIAGNOSTICS TEAM MEMBER WITH 3D MICROSCOPE
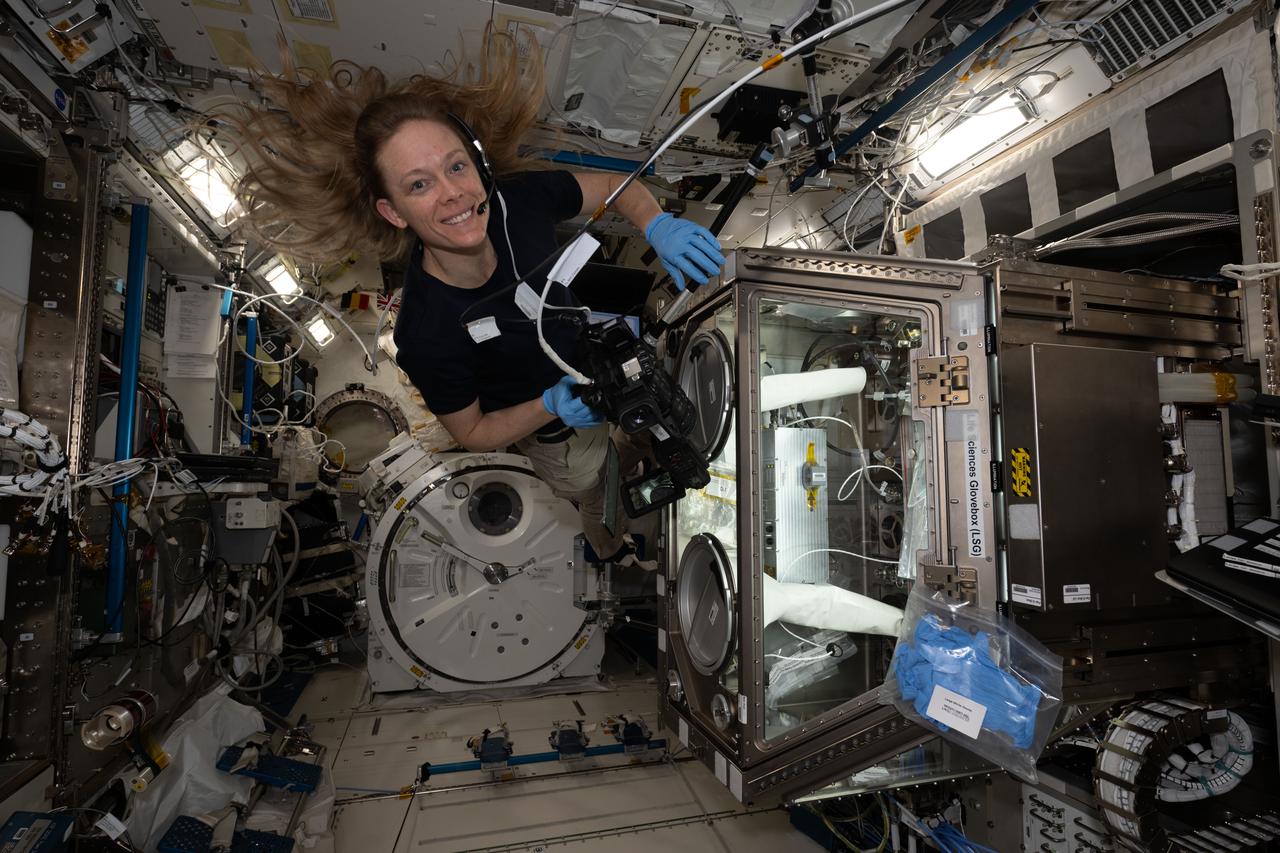

iss073e0134904 (June 5, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers works inside the Kibo laboratory module to test imaging operations of a 3D research microscope, also known as the Extant Life Volumetric Imaging System, or ELVIS. The specialized 3D imaging device, located in Kibo's Life Science Glovebox, could be used to monitor water quality, detect potentially infectious organisms, and study liquid mixtures and microorganisms in space and on Earth.
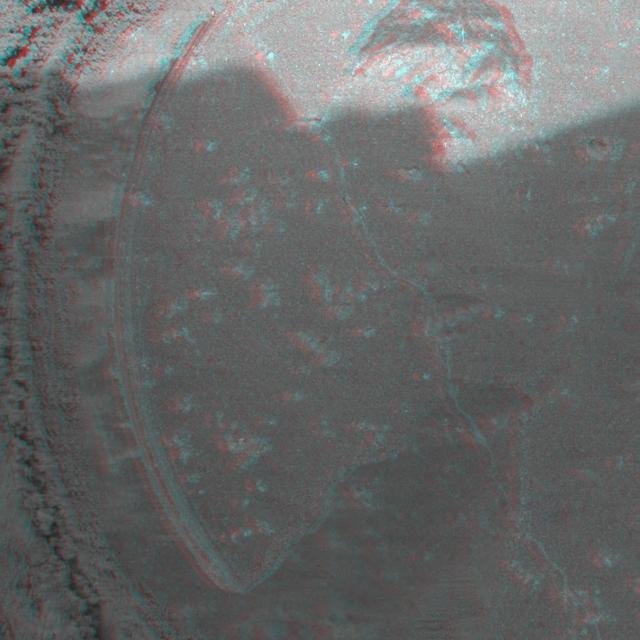
This 3D anaglyph, from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit, shows a microscopic image taken of the rock called Adirondack. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.

This 3D anaglyph, from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit, shows a microscopic image taken of the rock called Adirondack. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
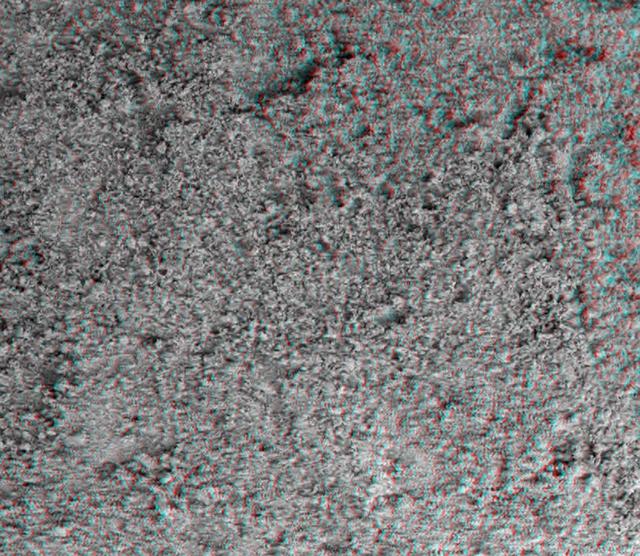
This image taken by the microscopic imager on NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit shows the powdery soil of Mars in 3-D. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
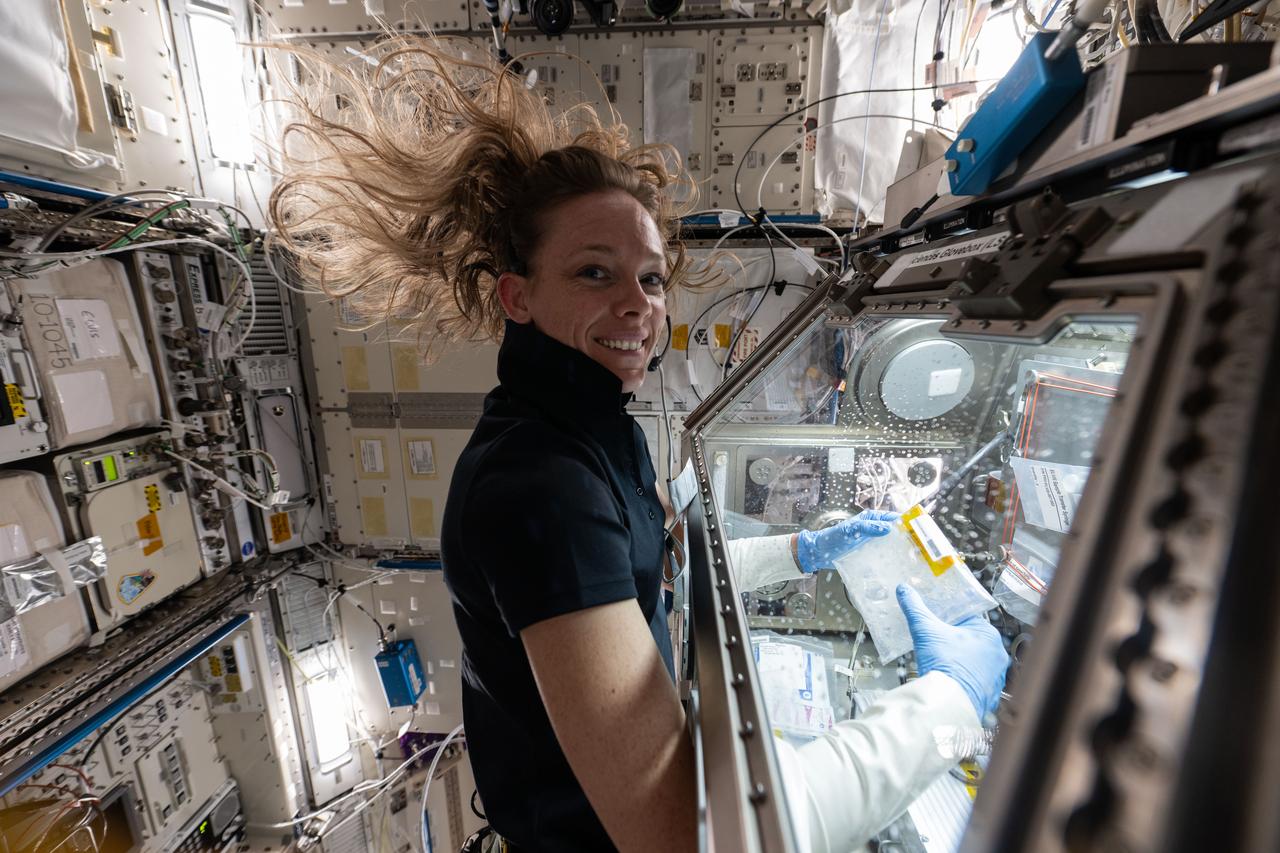

iss073e0025978 (May 9, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers works in the Kibo laboratory module's Life Sciences Glovebox processing bacteria samples before viewing them inside a 3D imaging microscope called Extant Life Volumetric Imaging System, or ELVIS. The technology demonstration may enable applications for monitoring water quality, detecting infectious organisms on spacecraft, and researching colloids (suspensions of particles in a liquid) and microorganisms in microgravity.

iss073e0027806 (May 10, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Anne McClain works in the Kibo laboratory module's Life Sciences Glovebox processing bacteria samples before viewing them inside a 3D imaging microscope called Extant Life Volumetric Imaging System, or ELVIS. The technology demonstration may enable applications for monitoring water quality, detecting infectious organisms on spacecraft, and researching colloids (suspensions of particles in a liquid) and microorganisms in microgravity.
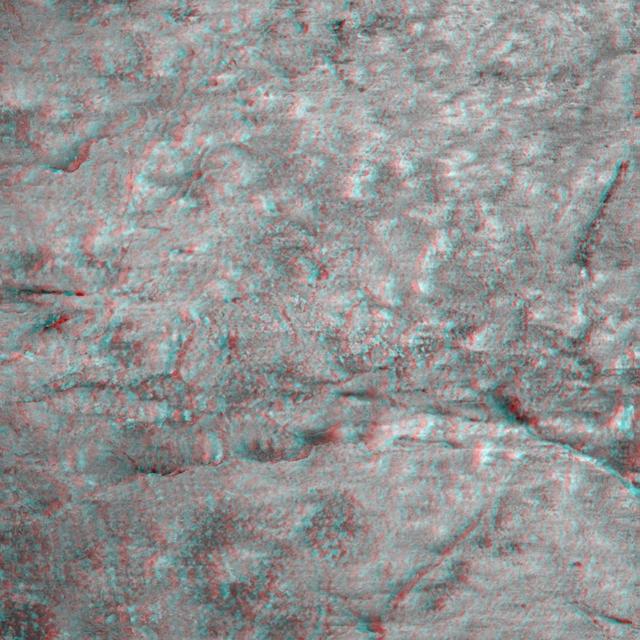
This 3-D image taken by the microscopic imager on NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity shows a close-up of the center of the rock abrasion tool hole, ground into Bounce. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
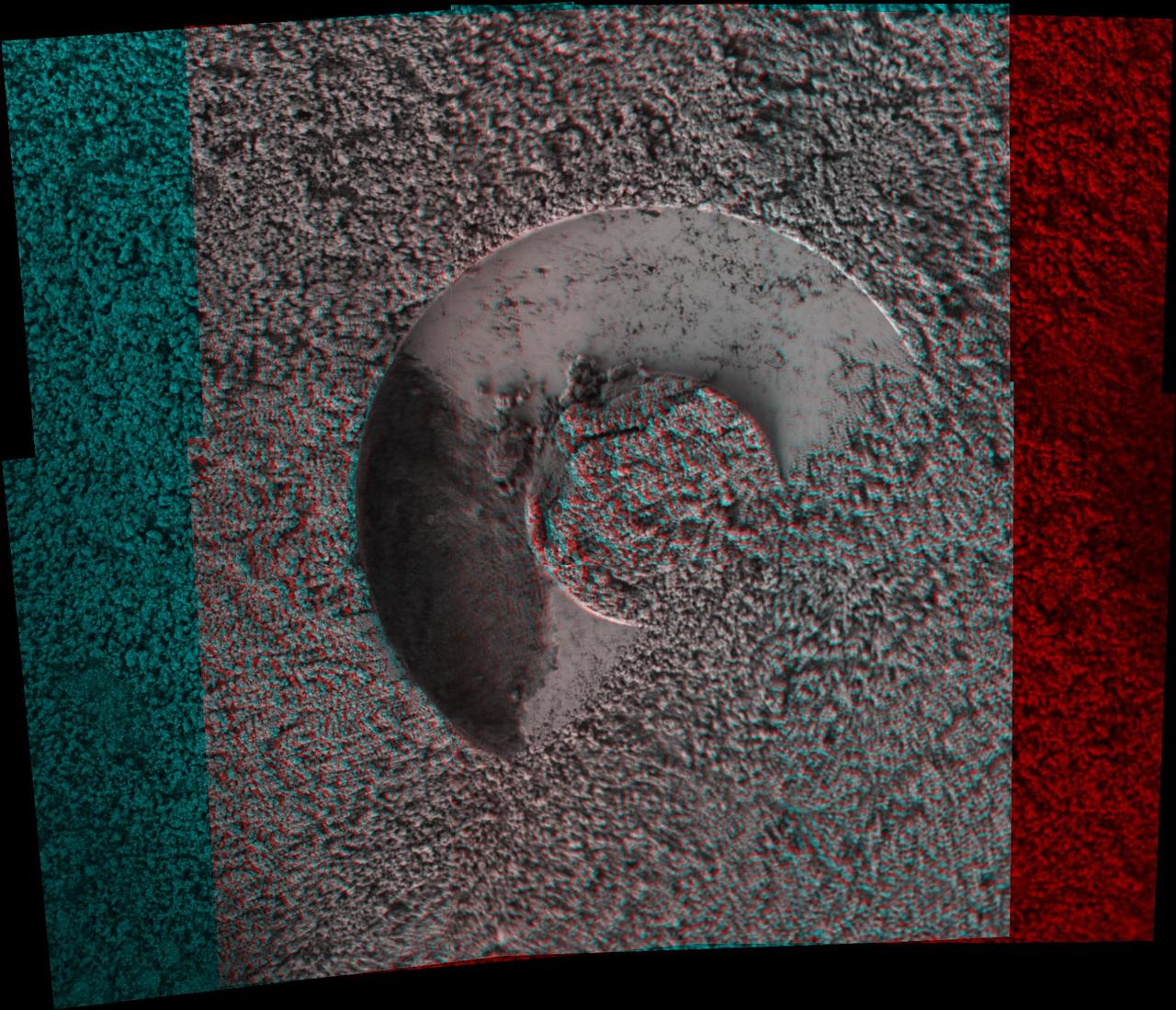
NASA Mars Exploration Rover microscopic imager onboard Spirit revealed a gap less than half an inch in the imprint left behind in the soil. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
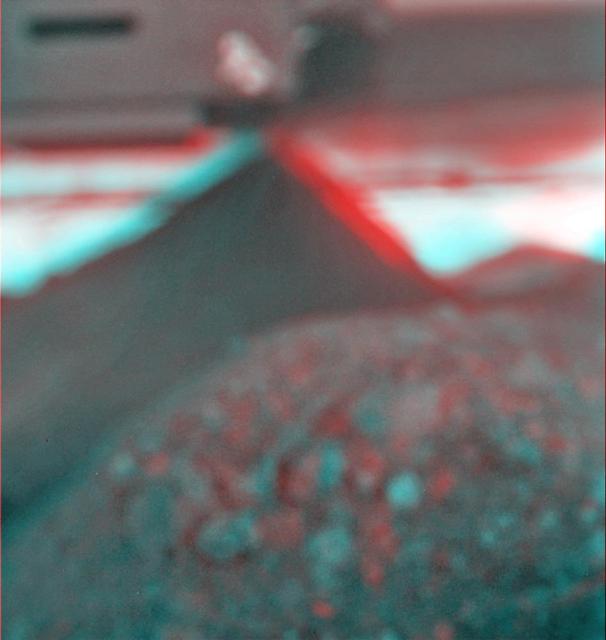

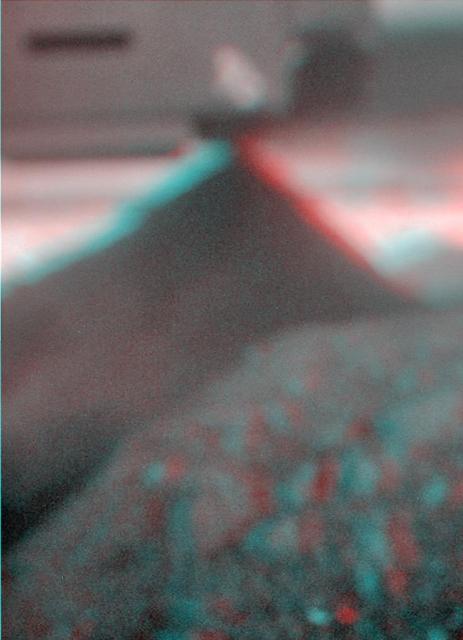
This stereo view combines a pair of images taken two months apart by the microscopic imager on NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
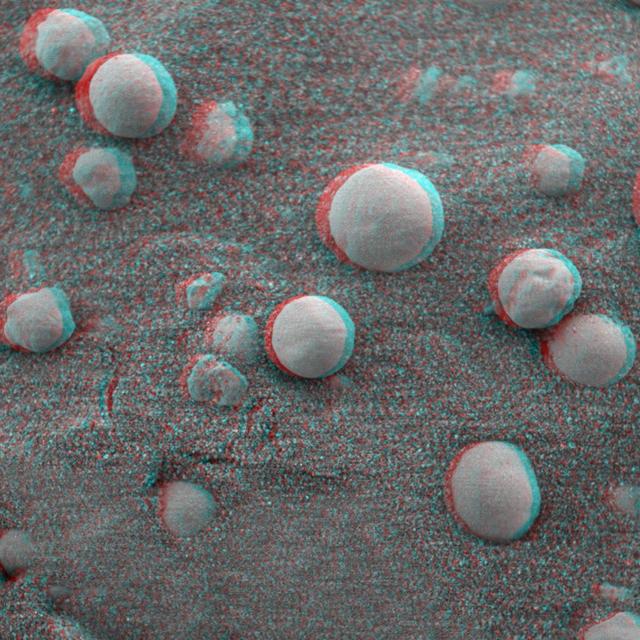
This 3-D anaglyph, from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit, shows a microscopic image taken of soil featuring round, blueberry-shaped rock formations on the crater floor at Meridiani Planum, Mars. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
This 3-D anaglyph, from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit, shows a microscopic image taken of soil featuring round, blueberry-shaped rock formations on the crater floor at Meridiani Planum, Mars. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
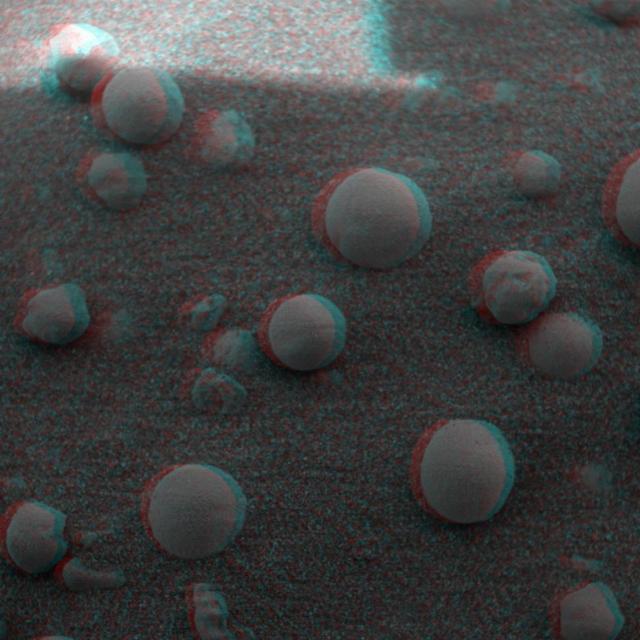
This stereo view combines a pair of images taken by the microscopic imager on NASA Mars Exploration Rover Spirit during the 1,925th Martian day sol of Spirit mission on Mars June 2, 2009. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
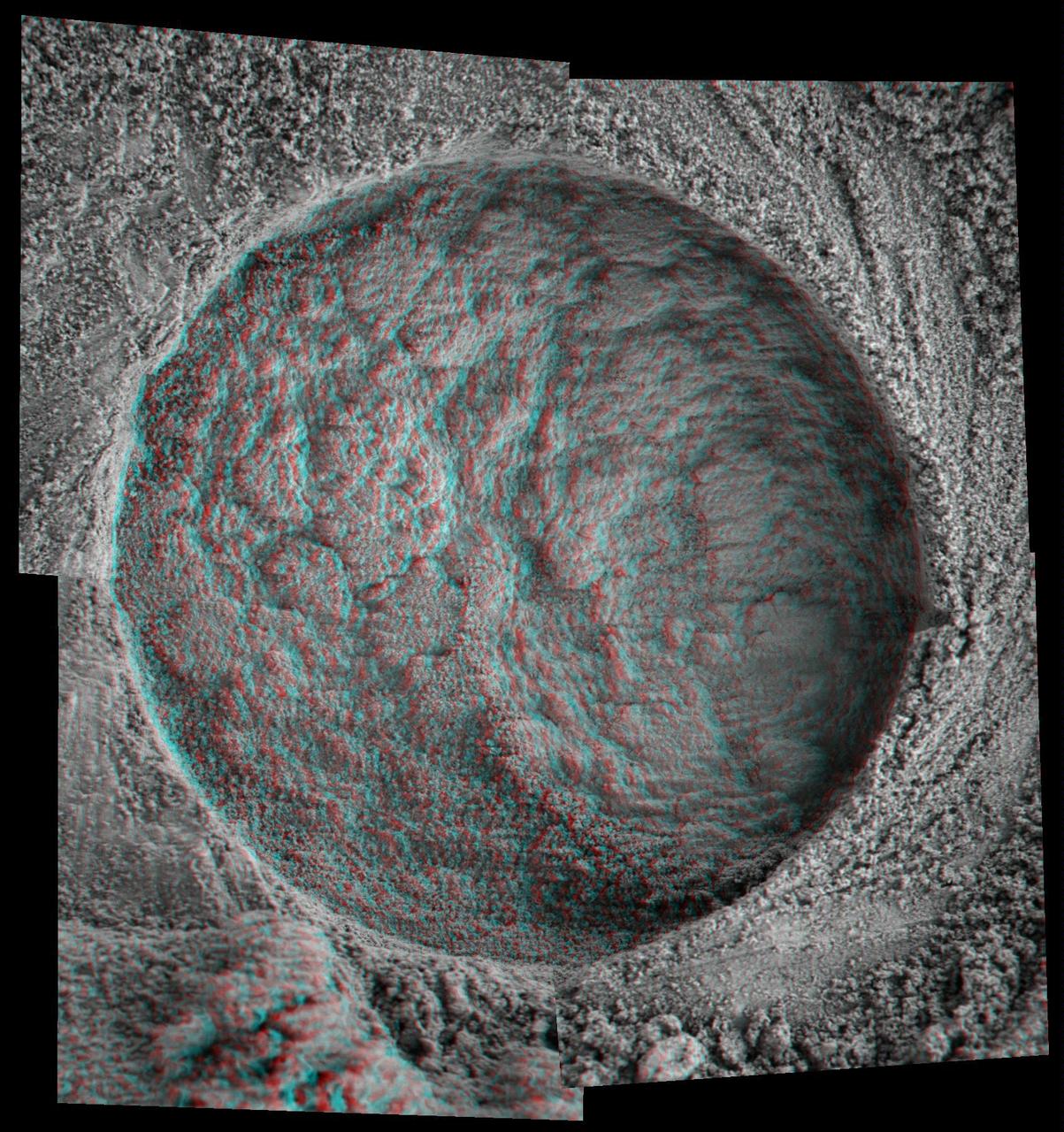
This 3-D, microscopic imager mosaic of a target area on a rock called Diamond Jenness was taken after NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity ground into the surface with its rock abrasion tool for a second time. 3D glasses are necessary.
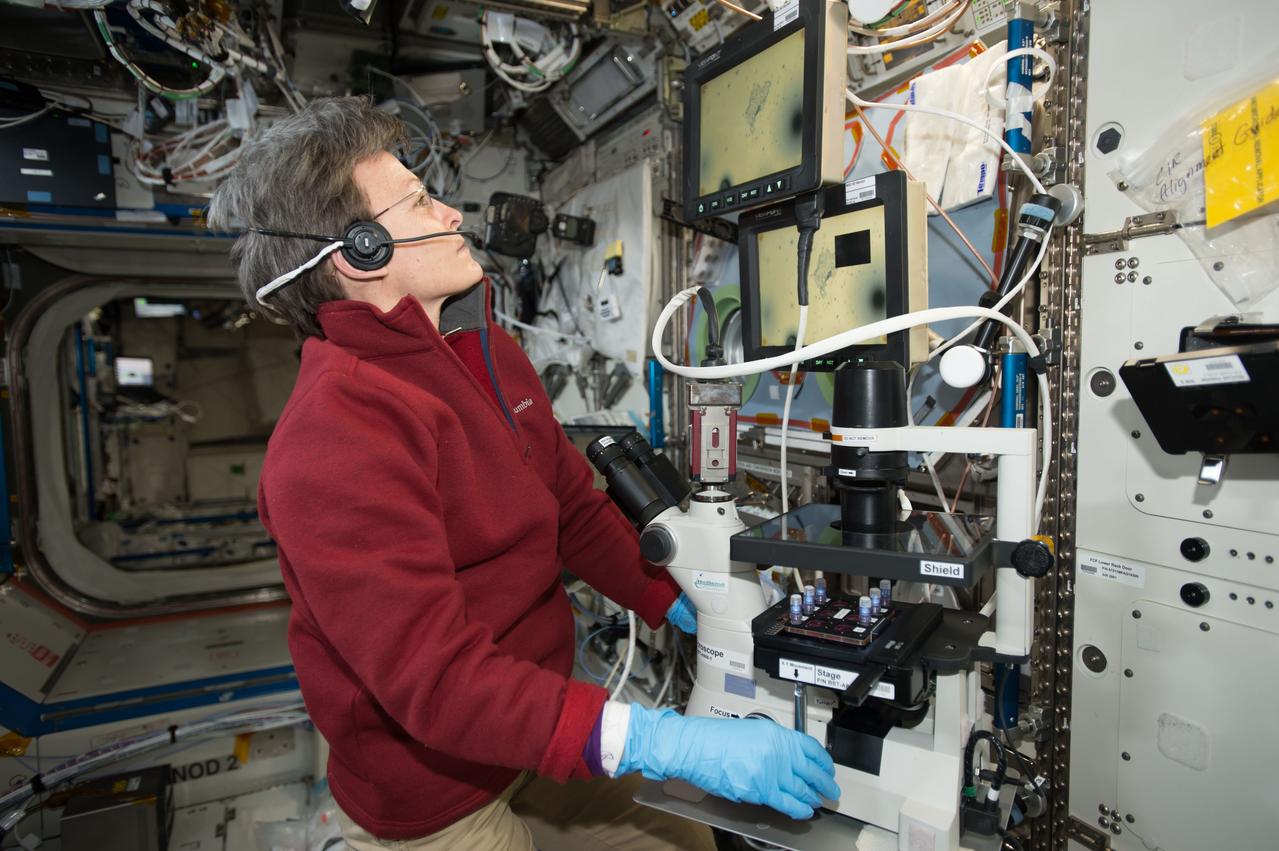

iss052e014201 (7/11/2017) --- NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson uses a microscope to view Magnetic 3D Biocells. This investigation uses magnetized cells and tools to make it easier to handle cells and cultures and to improve the reproducibility of experiments.
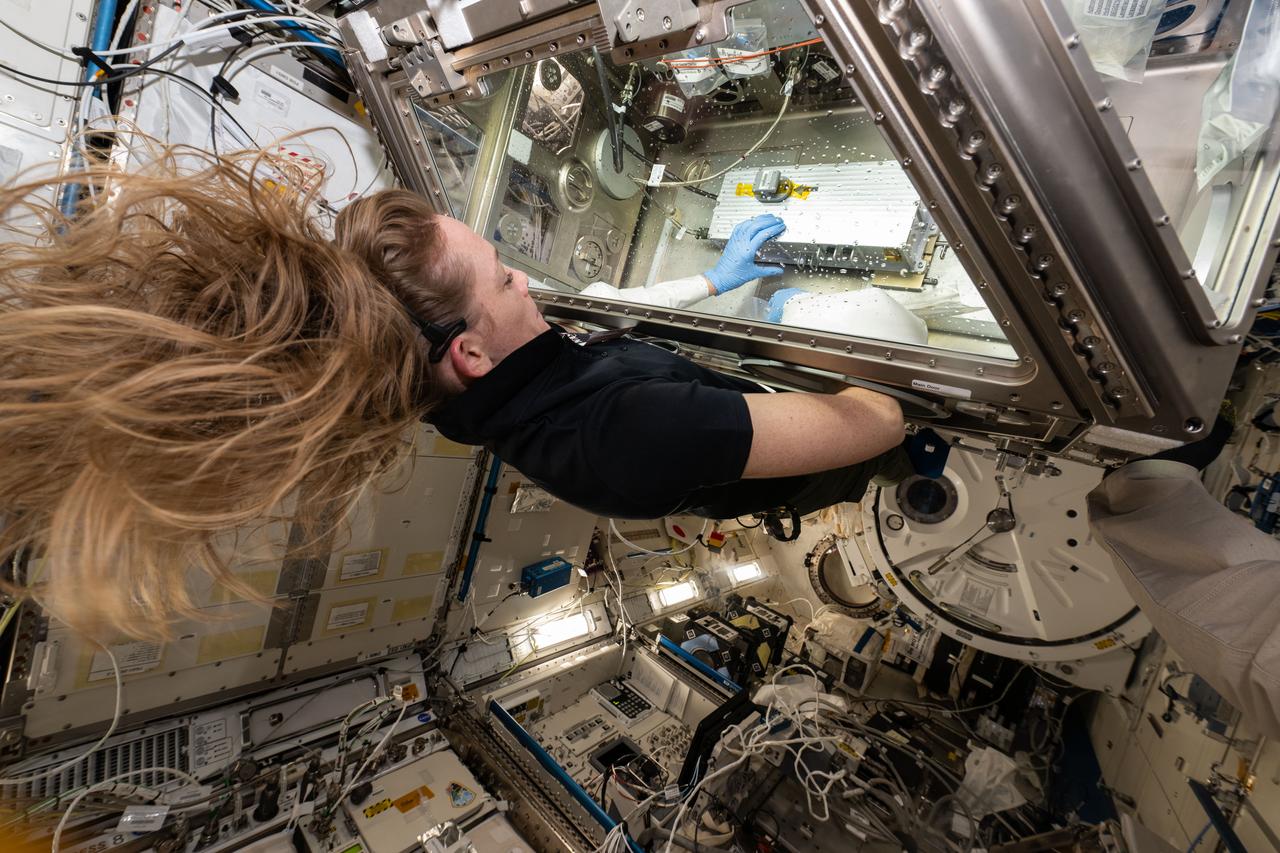

iss073e0025988 (5/9/2025) --- NASA astronaut Nichole Ayers works with the ELVIS investigation at the Life Sciences Glovebox (LSG), aboard the Kibo module of the International Space Station. Extant Life Volumetric Imaging System (ELVIS) is a microscope for 3D imaging of objects as small as bacteria, with the goal of making the technology available to anyone studying microscopic motion in space.
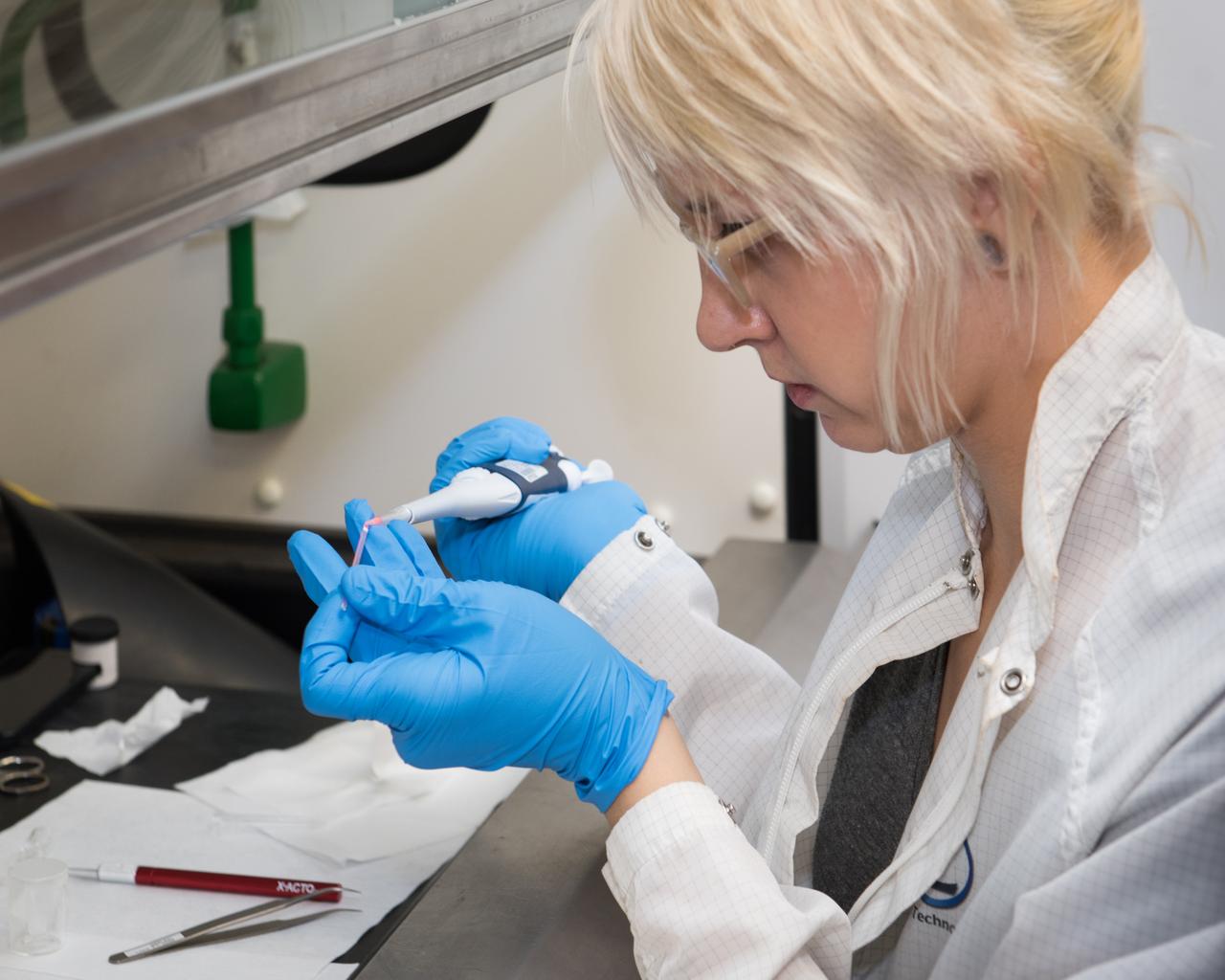

Deena Dombrosky (Zin Technologies Engineer) is shown here filling a Procter & Gamble (P & G) sample that will be used in ground-testing as NASA prepares for their experiment on the International Space Station (ISS). The sample particles are the size of the wavelength of light and they are dyed orange/pink to glow when illuminated with the laser light enabling a confocal microscope to produce 3D images. The P & G experiment will improve product stabilizers that extend product shelf life. This has the added advantage of leading to more compact environmentally friendly containers.
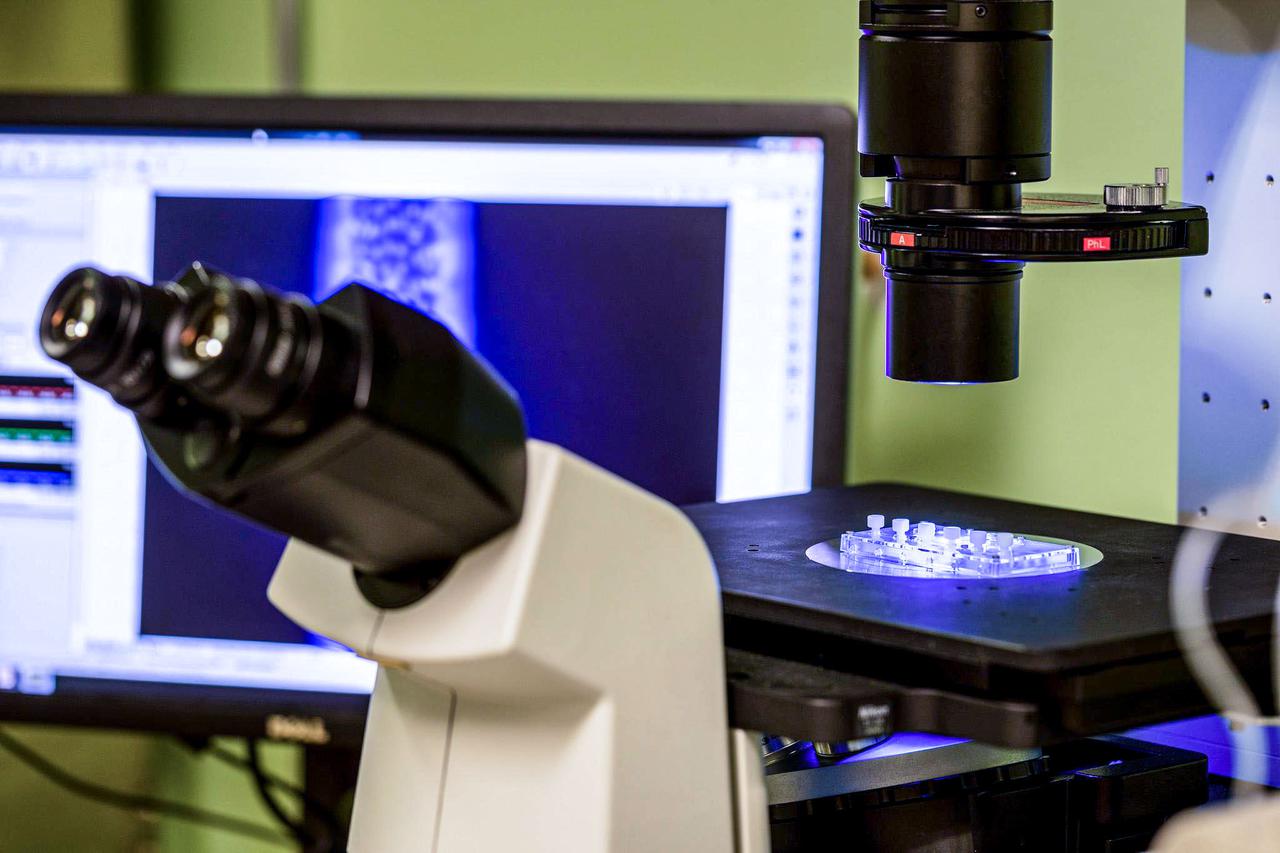
jsc2021e019397 (5/19/2021) --- The Nortis Organ Chip under a microscope in the laboratory of Edward Kelly in the University of Washington Department of Pharmaceutics. The image on the screen in the background shows a kidney cell tubule. Effects of Microgravity on the Structure and Function of Proximal and Distal Tubule MPS (Kidney Cells-02) uses a 3D kidney cell model or chip to study the effects of microgravity on formation of microcrystals in kidney tubules. Image courtesy of Alex Levine (UW School of Pharmacy).
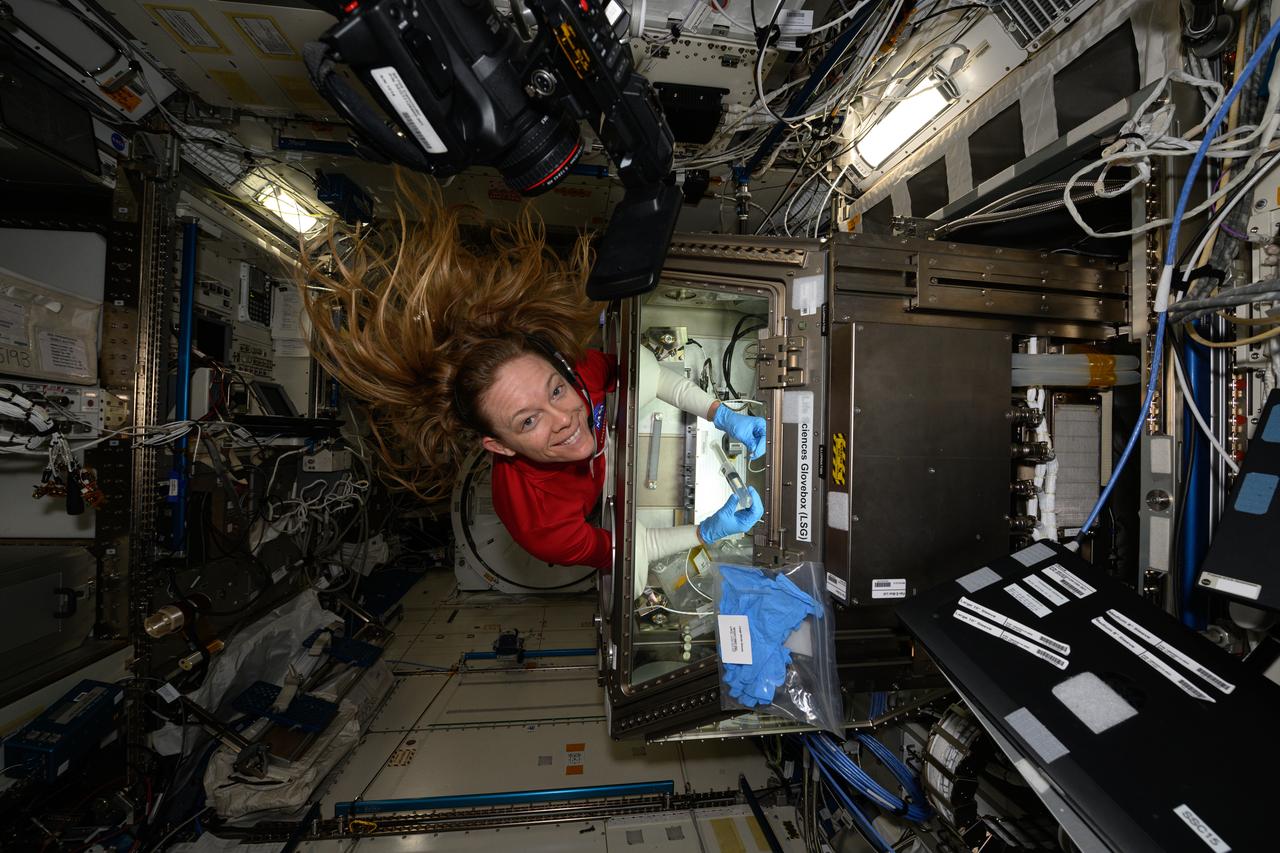

iss073e0118821 (May 30, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers conducts research operations inside the Kibo laboratory module's Life Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. Ayers was processing samples of deep-sea bacteria to test a specialized 3D microscope for its ability to monitor water quality, detect potentially infectious organisms, and study liquid mixtures and microorganisms in space and on Earth.
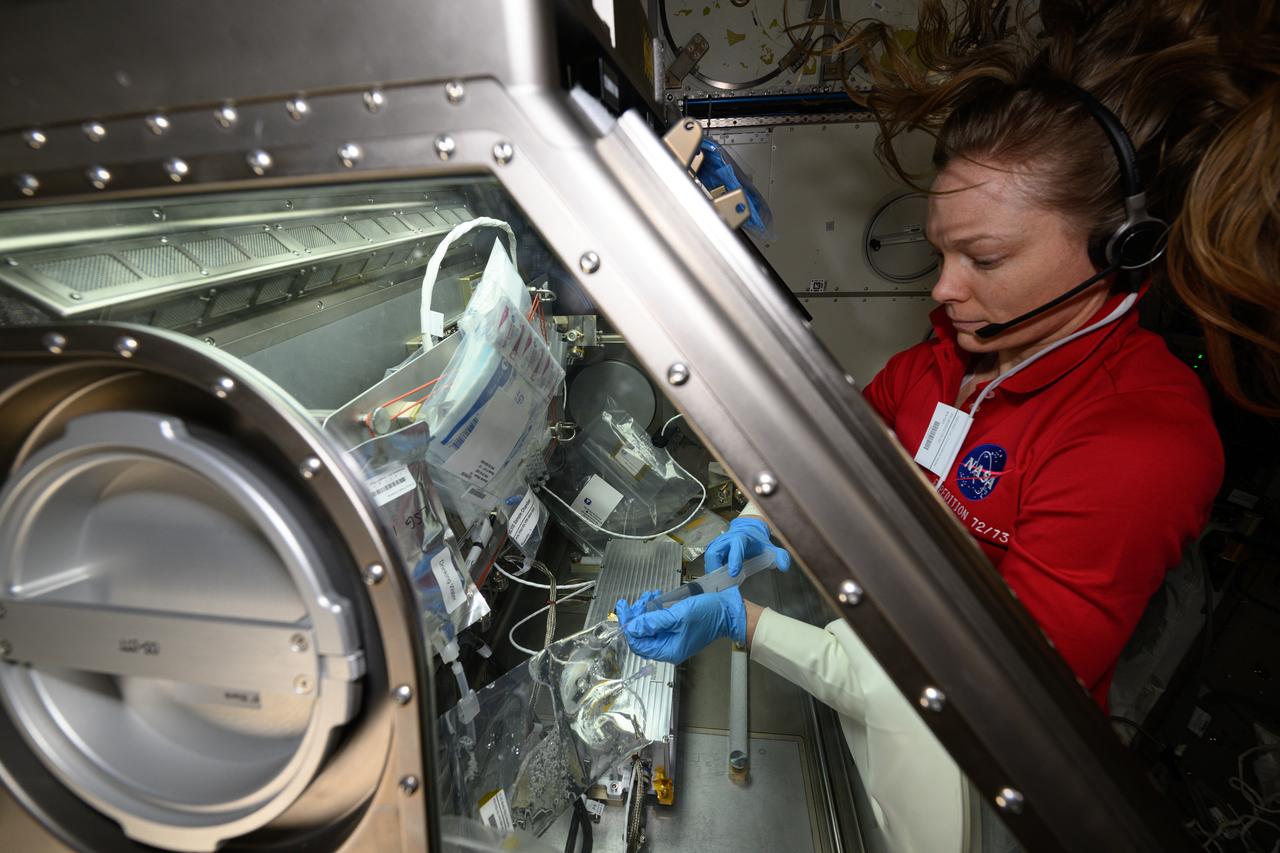

iss073e0118830 (May 30, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers conducts research operations inside the Kibo laboratory module's Life Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. Ayers was processing samples of deep-sea bacteria to test a specialized 3D microscope for its ability to monitor water quality, detect potentially infectious organisms, and study liquid mixtures and microorganisms in space and on Earth.
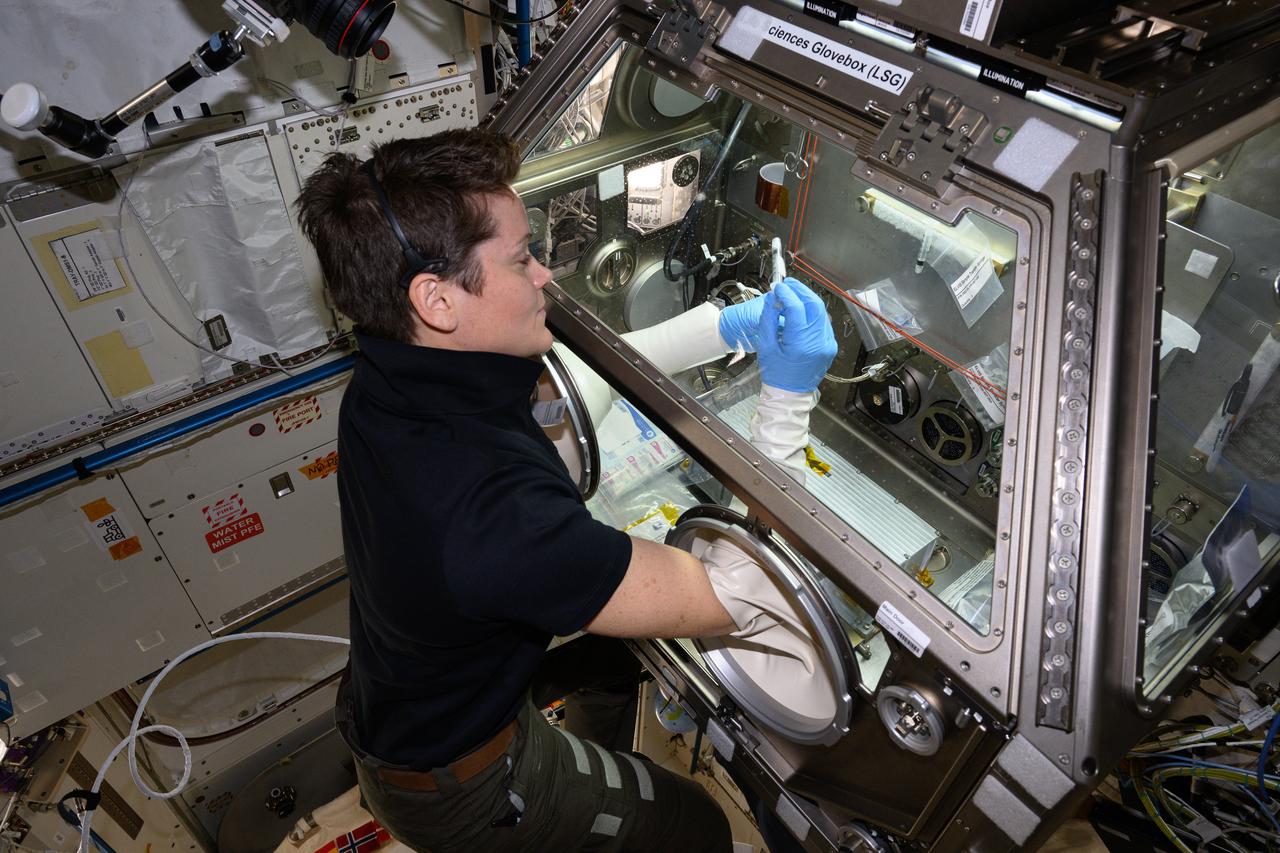

iss073e0027808 (May 10, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Anne McClain works in the Kibo laboratory module's Life Sciences Glovebox processing bacteria samples before viewing them inside a 3D imaging microscope called the Extant Life Volumetric Imaging System, or ELVIS. The technology demonstration may enable applications for monitoring water quality, detecting infectious organisms on spacecraft, and researching colloids (suspensions of particles in a liquid) and microorganisms in microgravity.
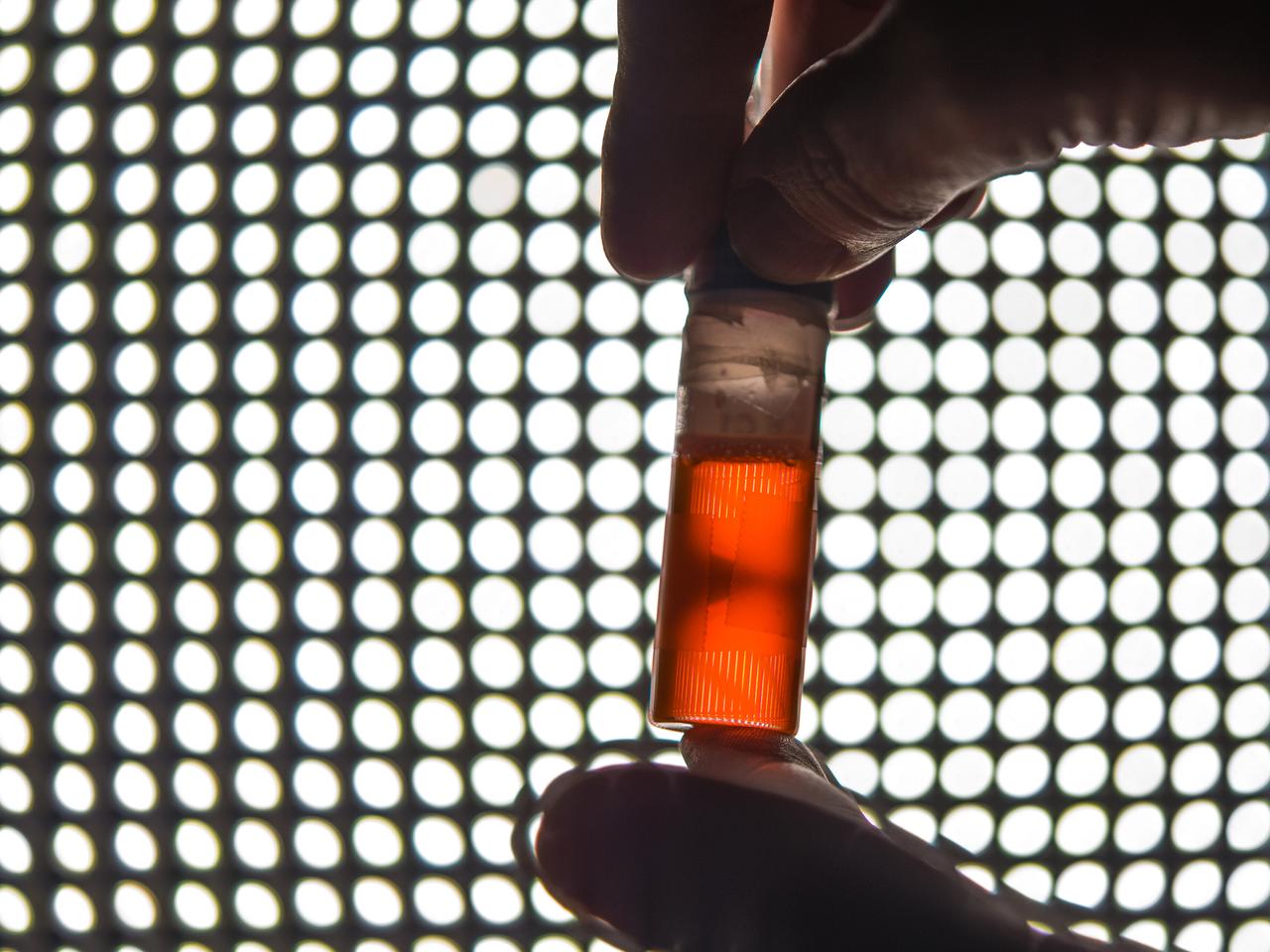

Ground testing for the first confocal Light Microscopy Microscope (LMM) Experiment. Procter and Gamble is working with NASA Glenn scientists to prepare for a study that examines product stabilizers in a microgravity environment. The particles in the tube glow orange because they have been fluorescently tagged with a dye that reacts to green laser lights to allow construction of a 3D image point by point. The experiment, which will be sent to the ISS later this year, will help P&G develop improved product stabilizers to extend shelf life and develop more environmentally friendly packaging.
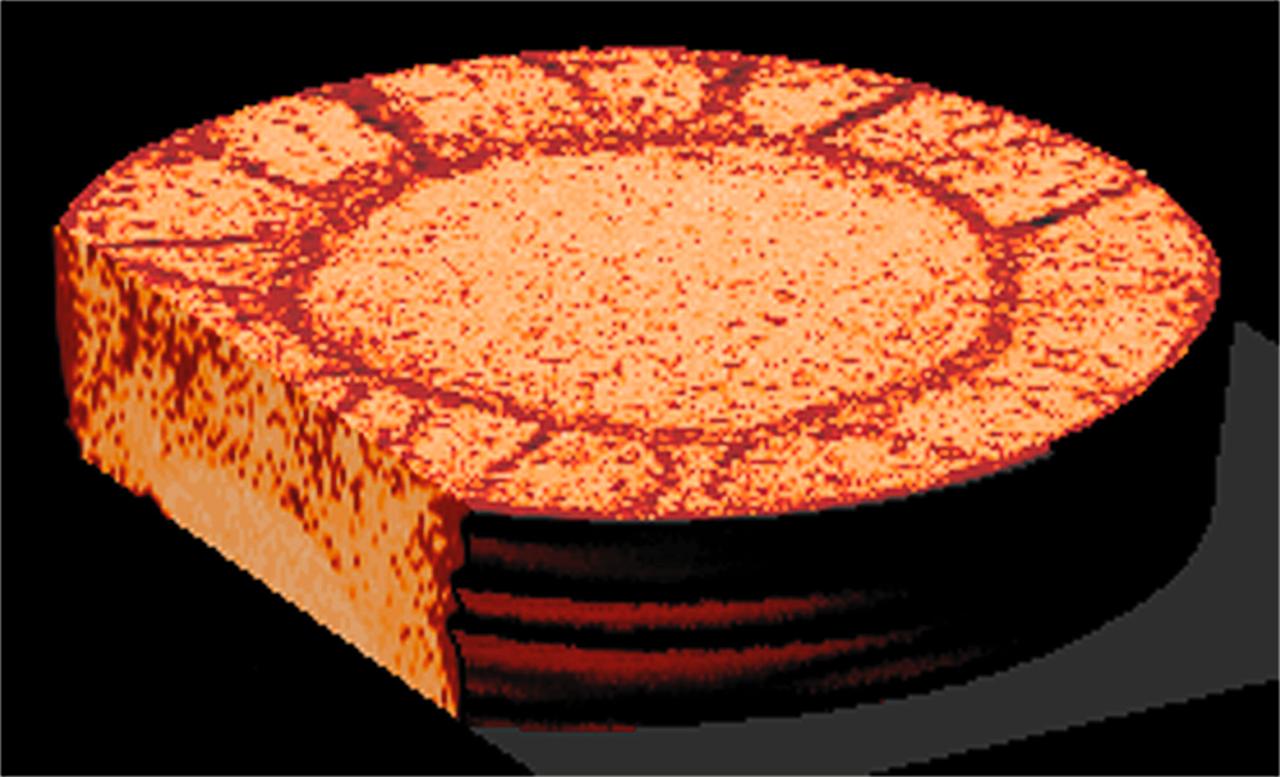
CT scans of the spcimens on STS-79 reveal internal cone-shaped features and radial patterns not seen in specimens processed on the ground. The lighter areas are the densest in these images. CT scans produced richly detailed images allowing scientists to build 3D models of the interior of the specimens that can be compared with microscopic examination of thin slices. This view is made from a series of horizontal slices. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditions that carnot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory and the University of Colorado at Boulder.
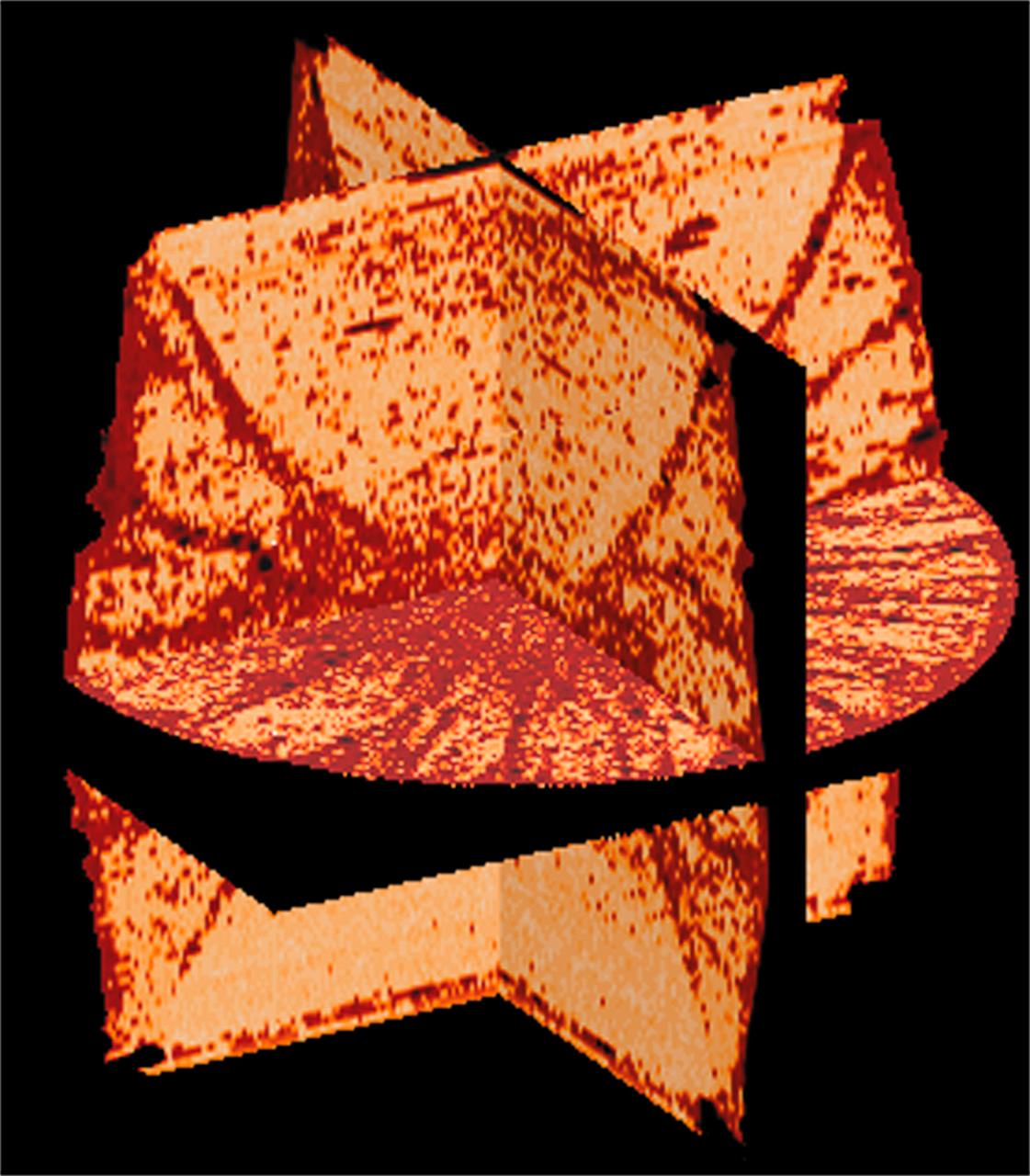
CT scans of the specimens on STS-79 reveal internal cone-shaped features and radial patterns not seen in specimens processed on the ground. The lighter areas are the densest in these images. CT scans produced richly detailed images allowing scientists to build 3D models of the interior of the specimens that can be compared with microscopic examination of thin slices. This view is made from three orthogonal slices. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditions that carnot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. (Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory and the University of Colorado at Boulder).
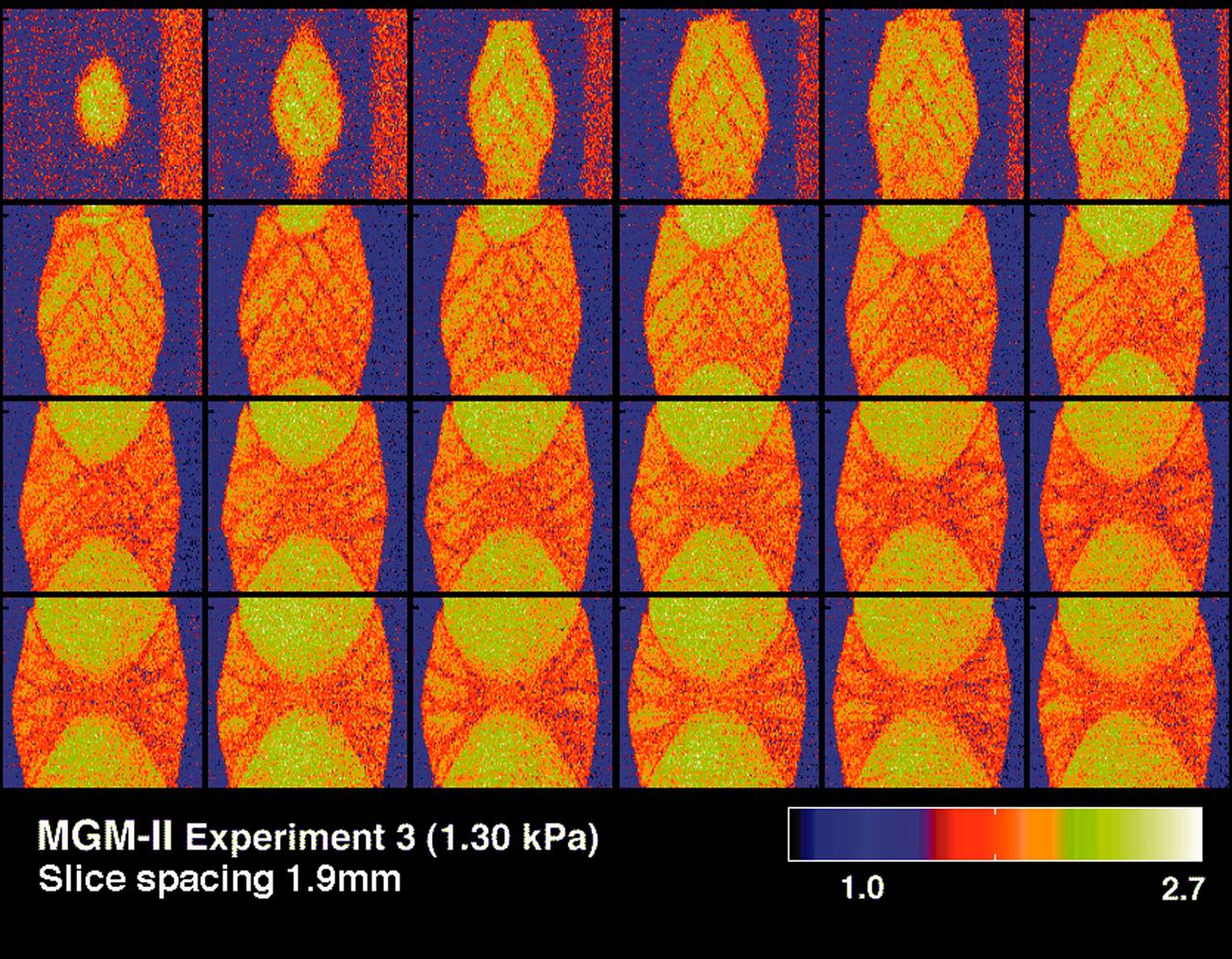
CT scans of the spcimens on STS-79 reveal internal cone-shaped features and radial patterns not seen in specimens processed on the ground. The lighter areas are the densest in these images. CT scans produced richly detailed images allowing scientists to build 3D models of the interior of the specimens that can be compared with microscopic examination of thin slices. These views depict vertical slices from side to middle of a flight specimen. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditions that carnot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory and the University of Colorado at Boulder.
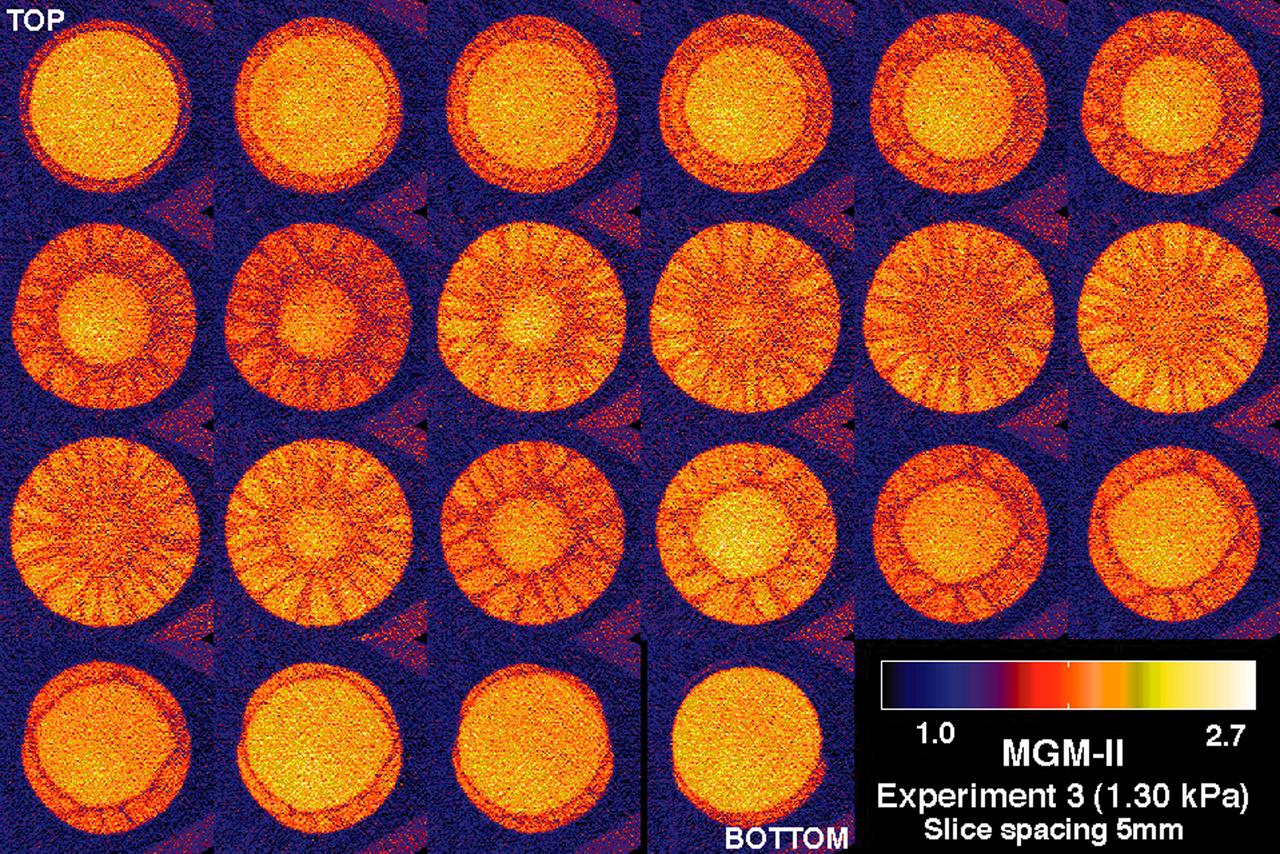
CT scans of the spcimens on STS-79 reveal internal cone-shaped features and radial patterns not seen in specimens processed on the ground. The lighter areas are the densest in these images. CT scans produced richly detailed images allowing scientists to build 3D models of the interior of the specimens that can be compared with microscopic examination of thin slices. This view depict horizontal slices from top to bottom of a flight specimen. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditions that carnot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory and the University of Colorado at Boulder.