
Celebrating the 4th with Tchaikovsky

The sun emitted a significant solar flare, peaking at 5:40 p.m. EDT on Oct. 24, 2014. The flare erupted from a particularly large active region -- labeled AR 12192 -- on the sun that is the largest in 24 years. This is the fourth substantial flare from this active region since Oct. 19. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/giant-sunspot-erupts-with-4th-substantial-flare" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/giant-sunspot-erupts-with-4t...</a>

Photographic documentation showing the Nassau Bay July 4th parade honoring George Abbey as "Citizen of the Year." View is of Mr. George Abbey, wearing a cowboy hat, in the back of a car.

Twin Peaks are modest-size hills to the southwest of NASA Mars Pathfinder landing site. They were discovered on the first panoramas taken by the IMP camera on the 4th of July, 1997. 3D glasses are necessary to identify surface detail.

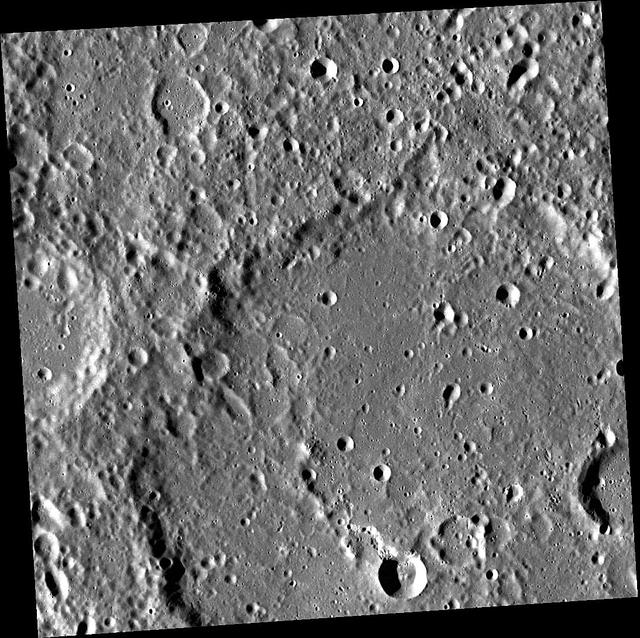
On July 4th the Narrow Angle Camera onboard NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter scanned its way towards the north pole at an altitude of 187 km, brushing past the crater Rozhdestvenskiy W.

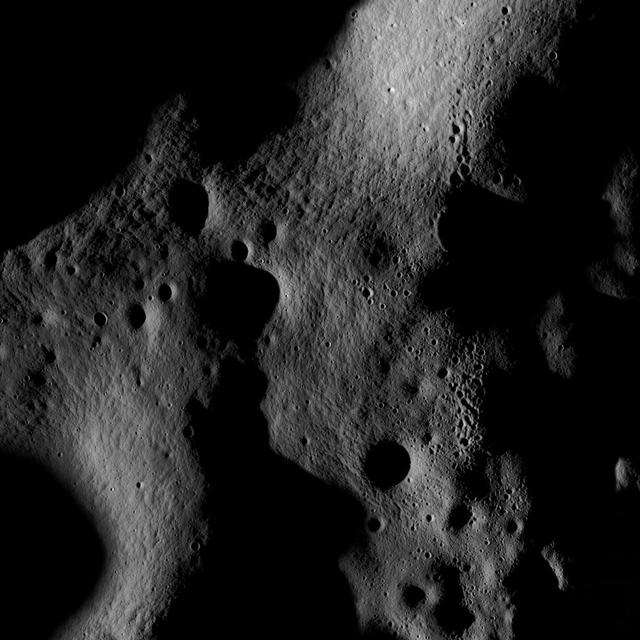
The large crater extending out the left side of this image is Praxiteles. Named for the ancient Greek sculptor of the 4th century BC, Praxiteles crater was first observed by Mariner 10.

Nova Stars are essentially giant fusion reactions occurring in the vacuum of space. Because stars have so much mass, they possess powerful gravitational force—but they don’t collapse because of the outward force generated by nuclear fusion, continually converting hydrogen atoms to helium. Sometimes stars begin orbiting each other, forming a binary star system. Typically this involves a white dwarf star and a red giant. Orbiting the red giant like a moon, the dwarf star rips matter from its companion until it essentially gags on the excess, coughing hot gas and radiation into space. This dramatic phenomenon is relatively common, and the white dwarf is not destroyed in the resulting nova. To learn more about x-ray emissions, read about NASA’s Chandra mission: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/chandra/main/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/chandra/main/</a> --- Original caption: In Hollywood blockbusters, explosions are often among the stars of the show. In space, explosions of actual stars are a focus for scientists who hope to better understand their births, lives, and deaths and how they interact with their surroundings. Using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, astronomers have studied one particular explosion that may provide clues to the dynamics of other, much larger stellar eruptions. A team of researchers pointed the telescope at GK Persei, an object that became a sensation in the astronomical world in 1901 when it suddenly appeared as one of the brightest stars in the sky for a few days, before gradually fading away in brightness. Today, astronomers cite GK Persei as an example of a “classical nova,” an outburst produced by a thermonuclear explosion on the surface of a white dwarf star, the dense remnant of a Sun-like star. Read Full Article: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/chandra/mini-supernova-explosion-could-have-big-impact.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/chandra/mini-supernova-explosi...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
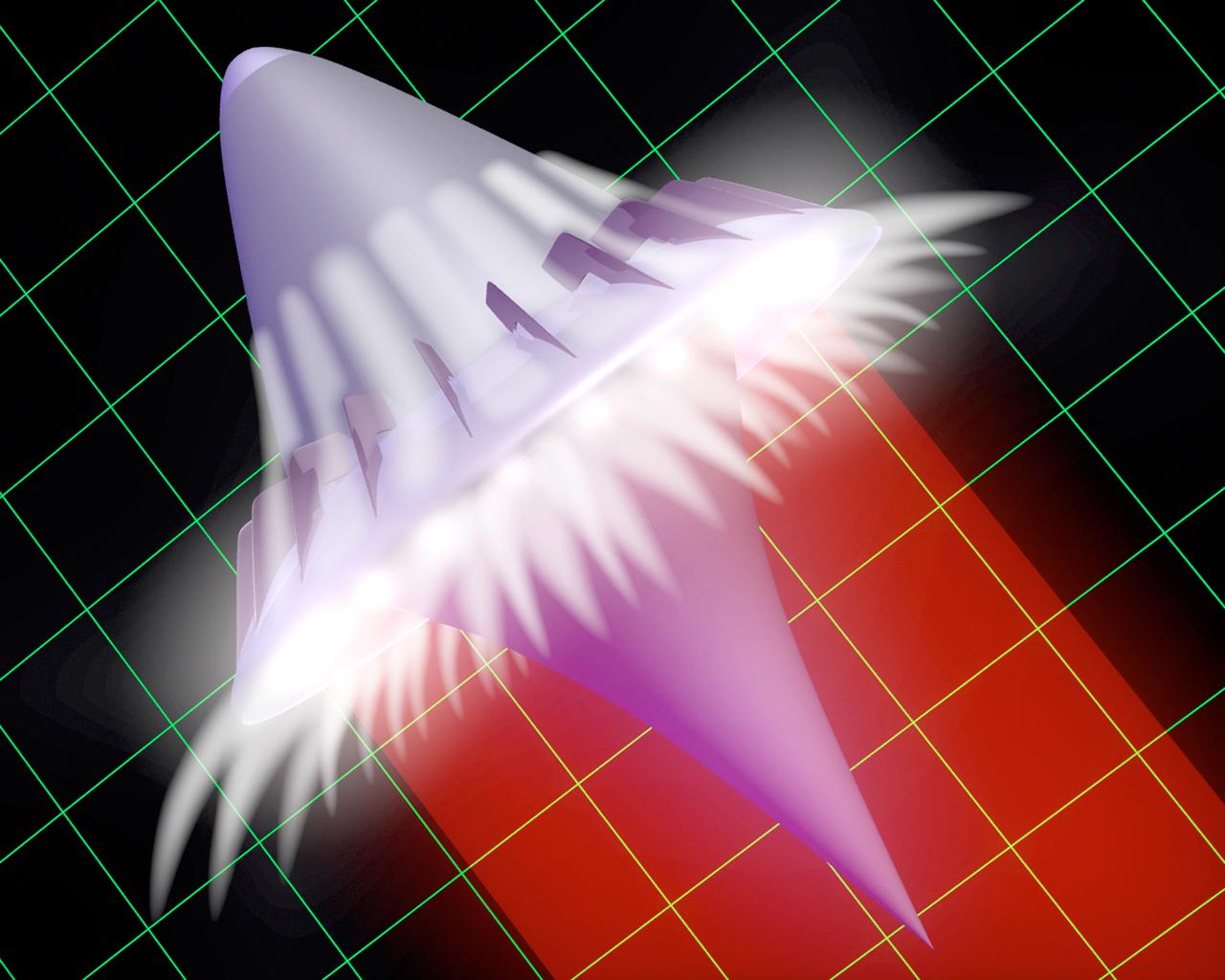

It is predicted that by the year 2040, there will be no distinction between a commercial airliner and a commercial launch vehicle. Fourth Generation Reusable Launch Vehicles (RLVs) will be so safe and reliable that no crew escape system will be necessary. Every year there will be in excess of 10,000 flights and the turn-around time between flights will be just hours. The onboard crew will be able to accomplish a launch without any assistance from the ground. Provided is an artist's concept of these fourth generation space vehicles.
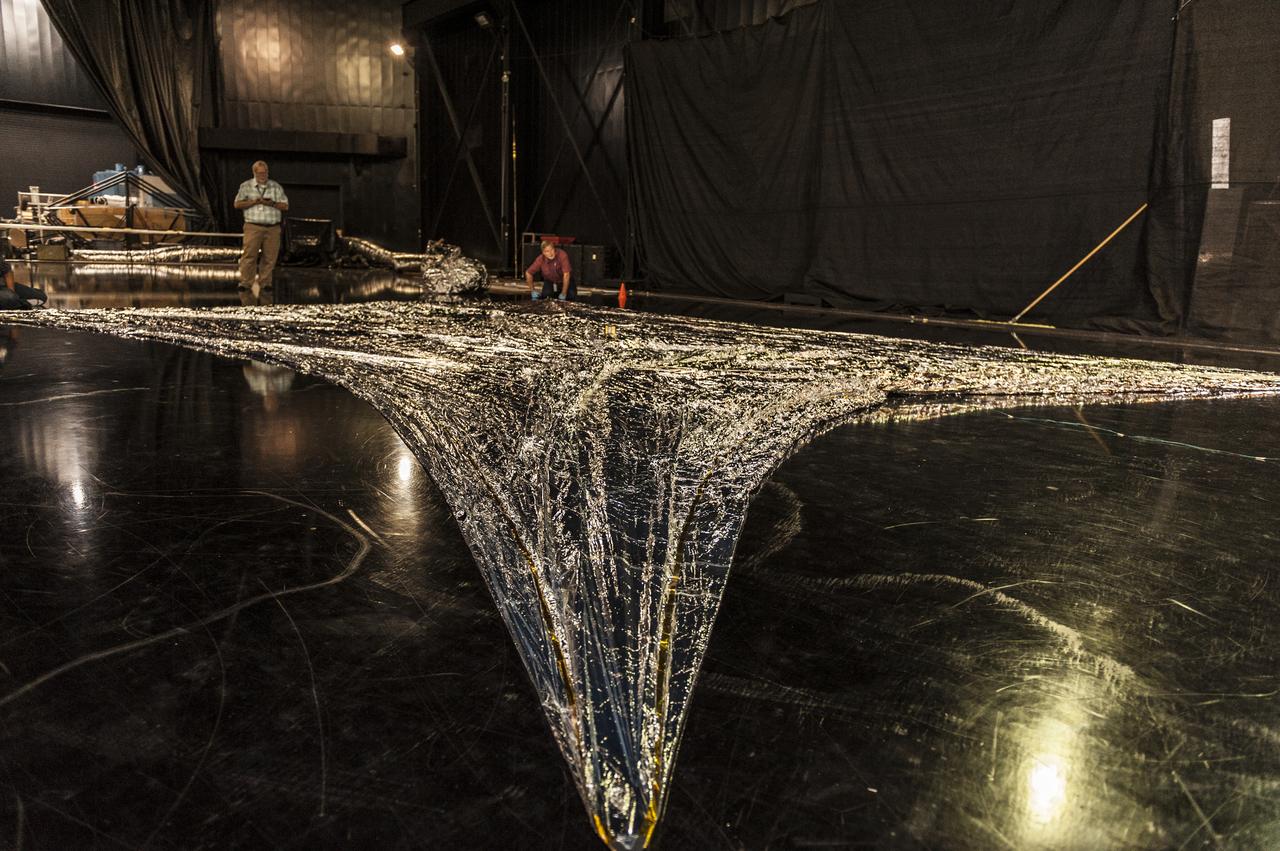

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
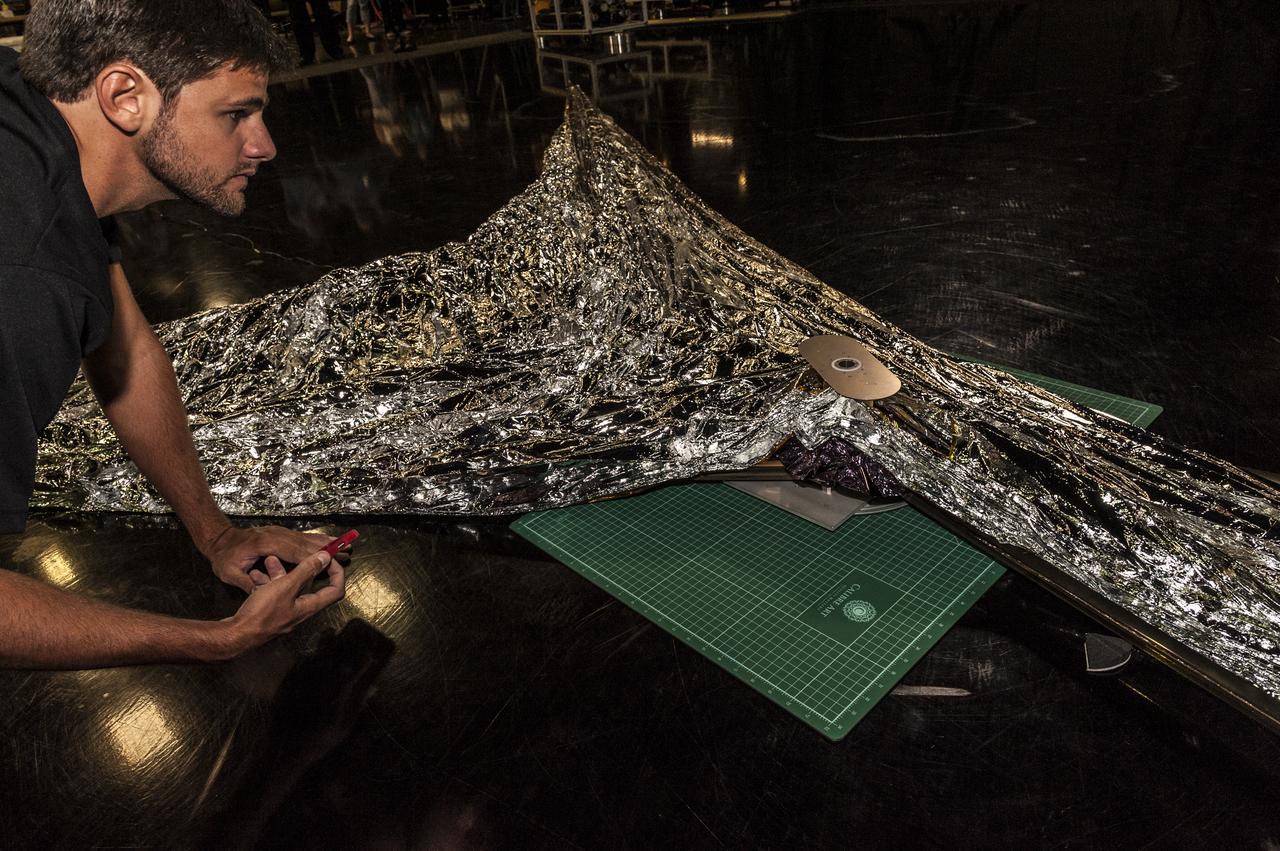

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
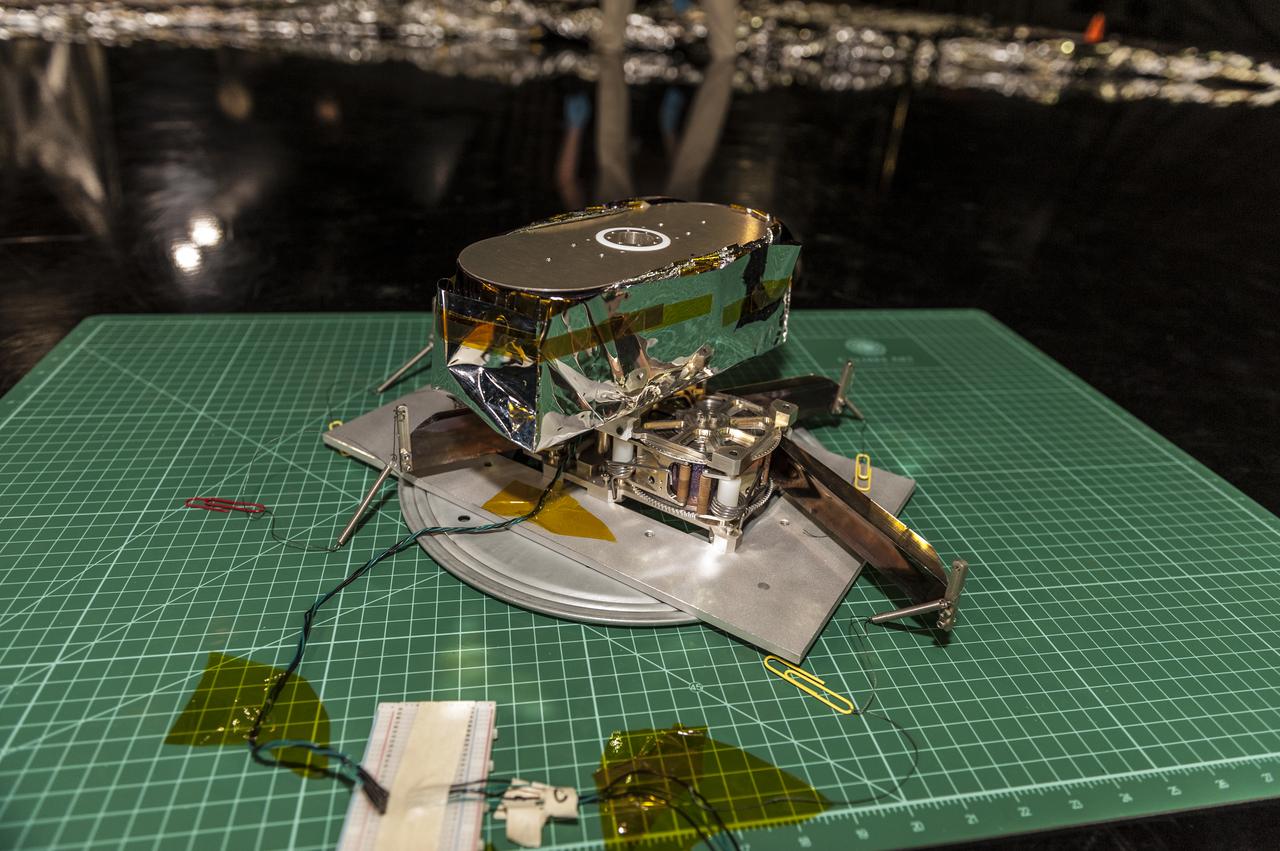
NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
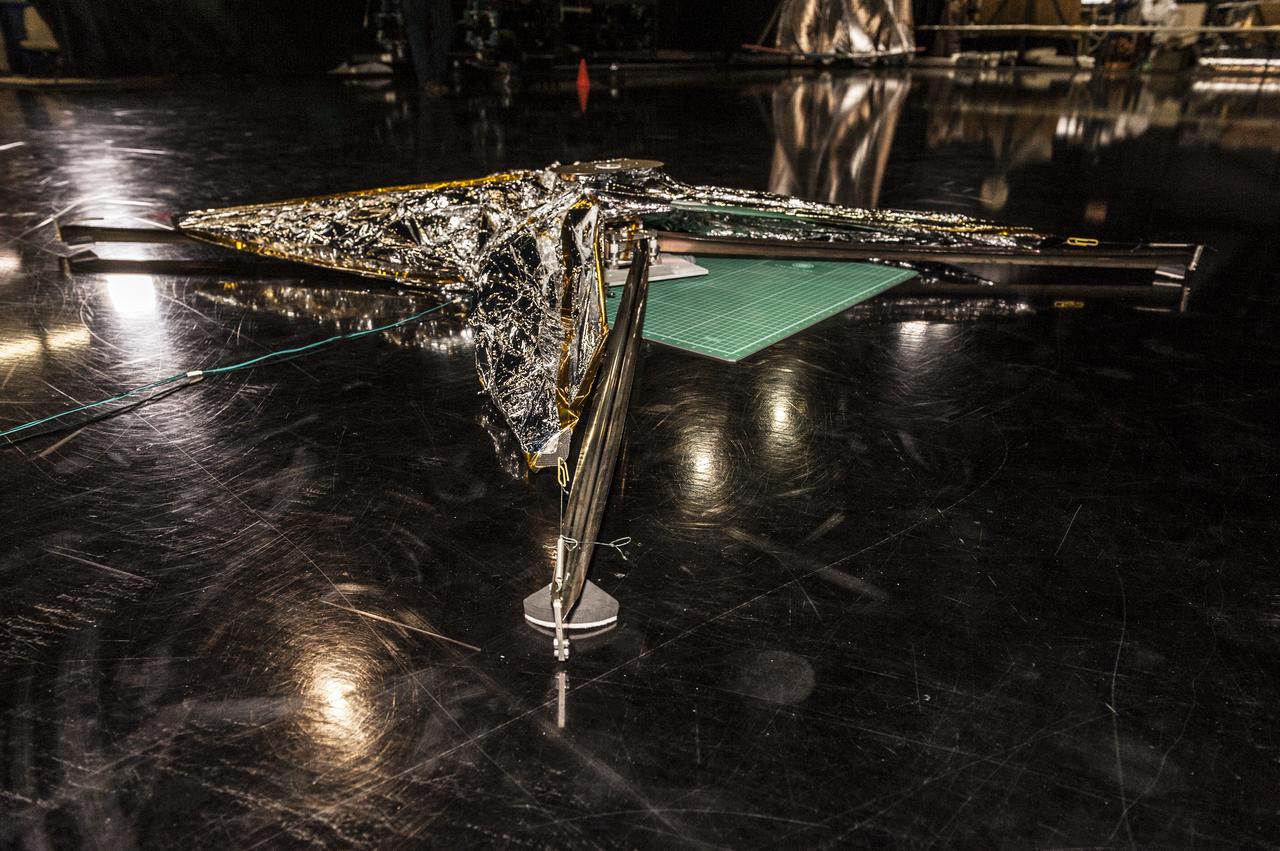

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
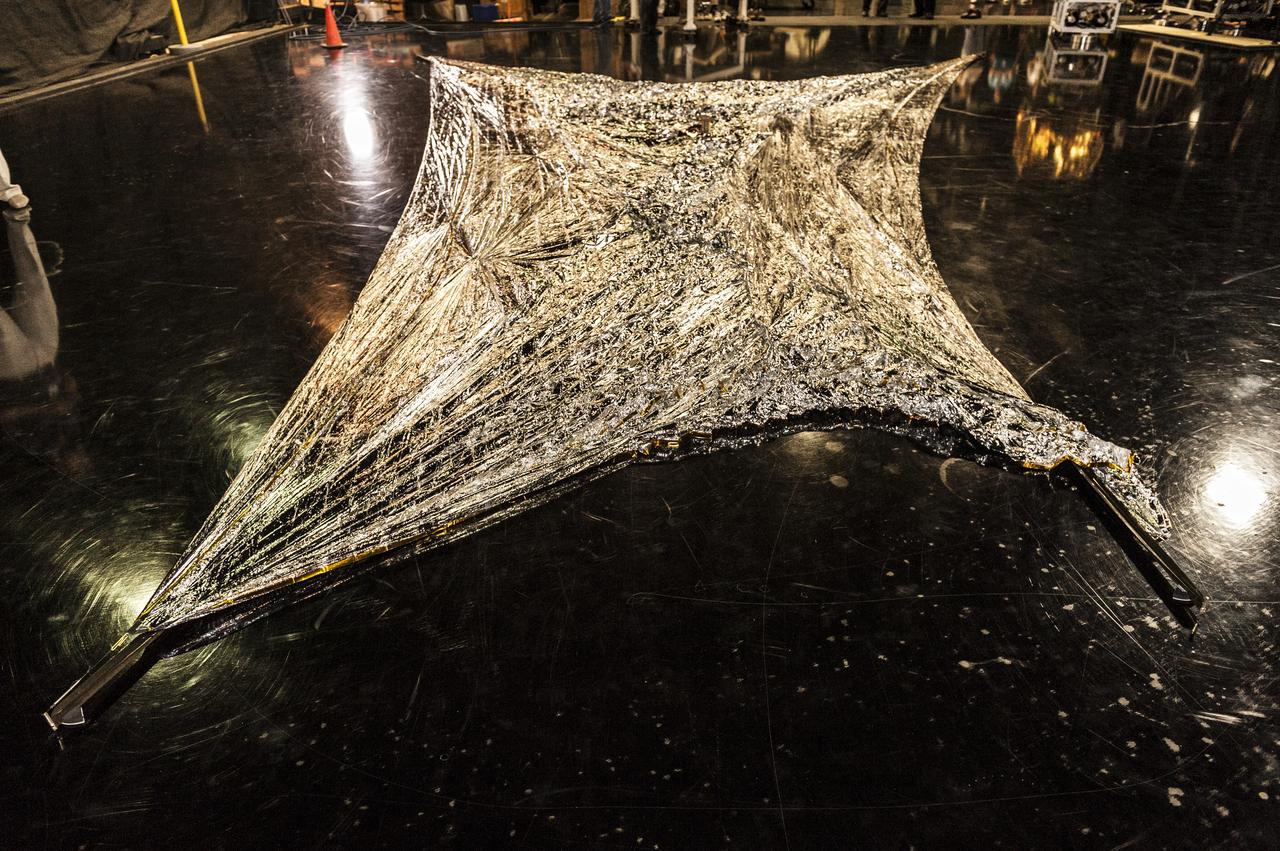

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
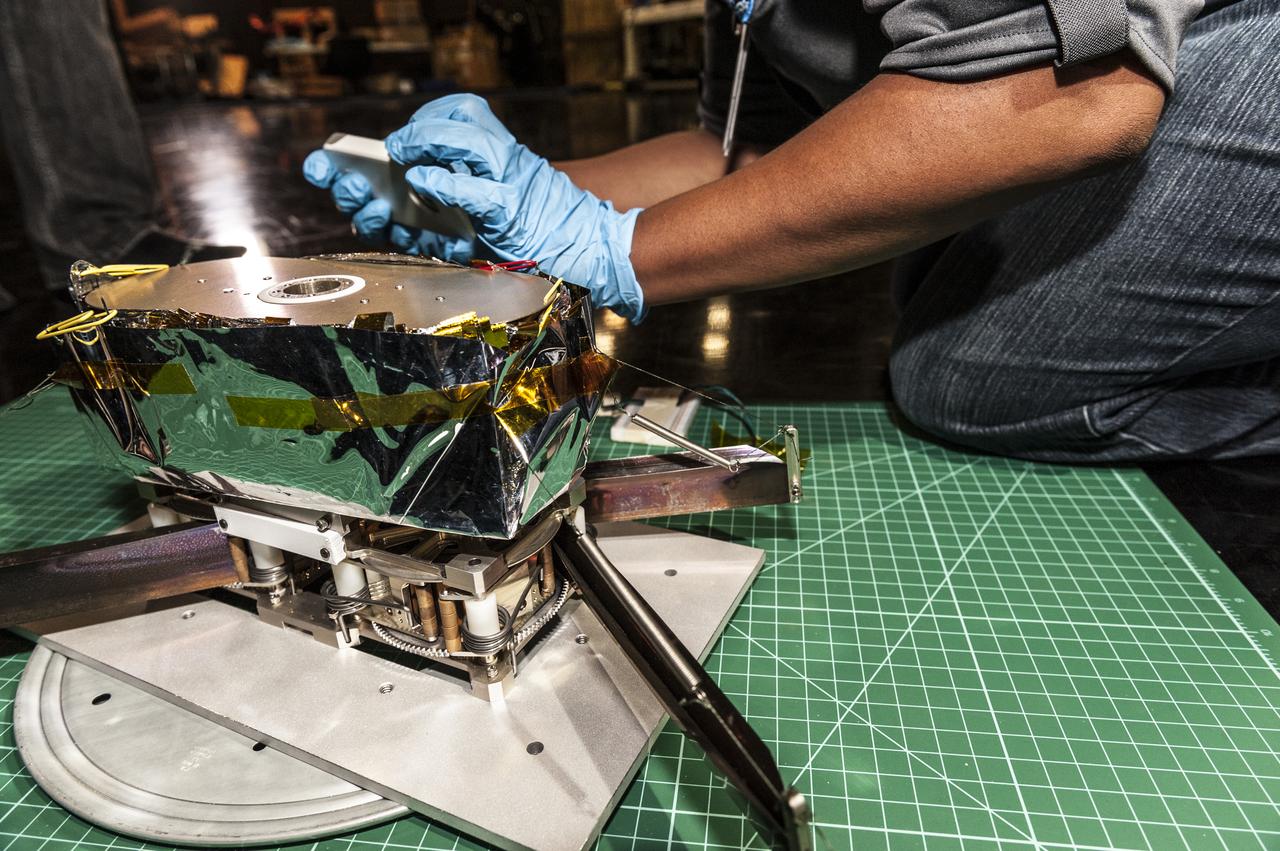

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
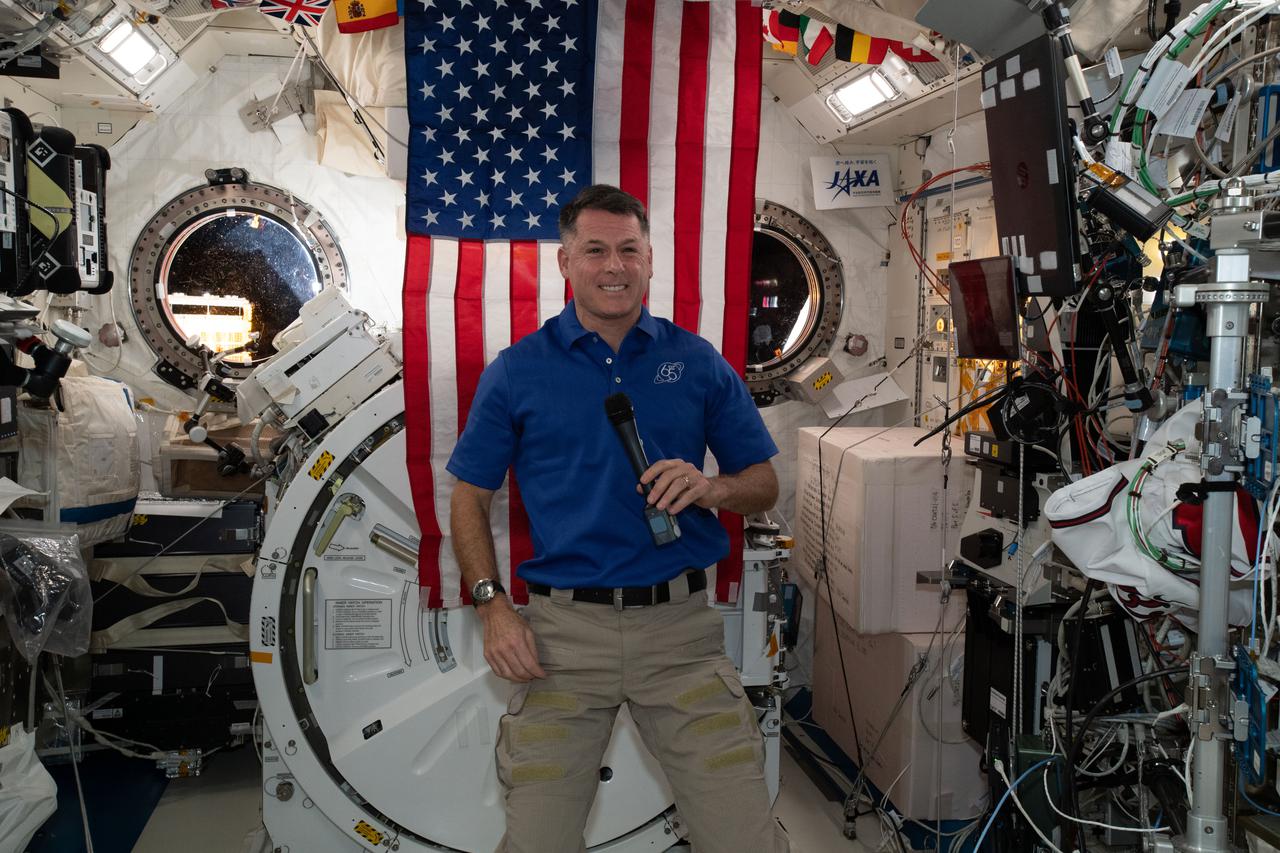

iss065e156102 (July 4, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough is pictured inside the Kibo laboratory module with the U.S. flag behind him on the July the 4th Independence Day holiday.
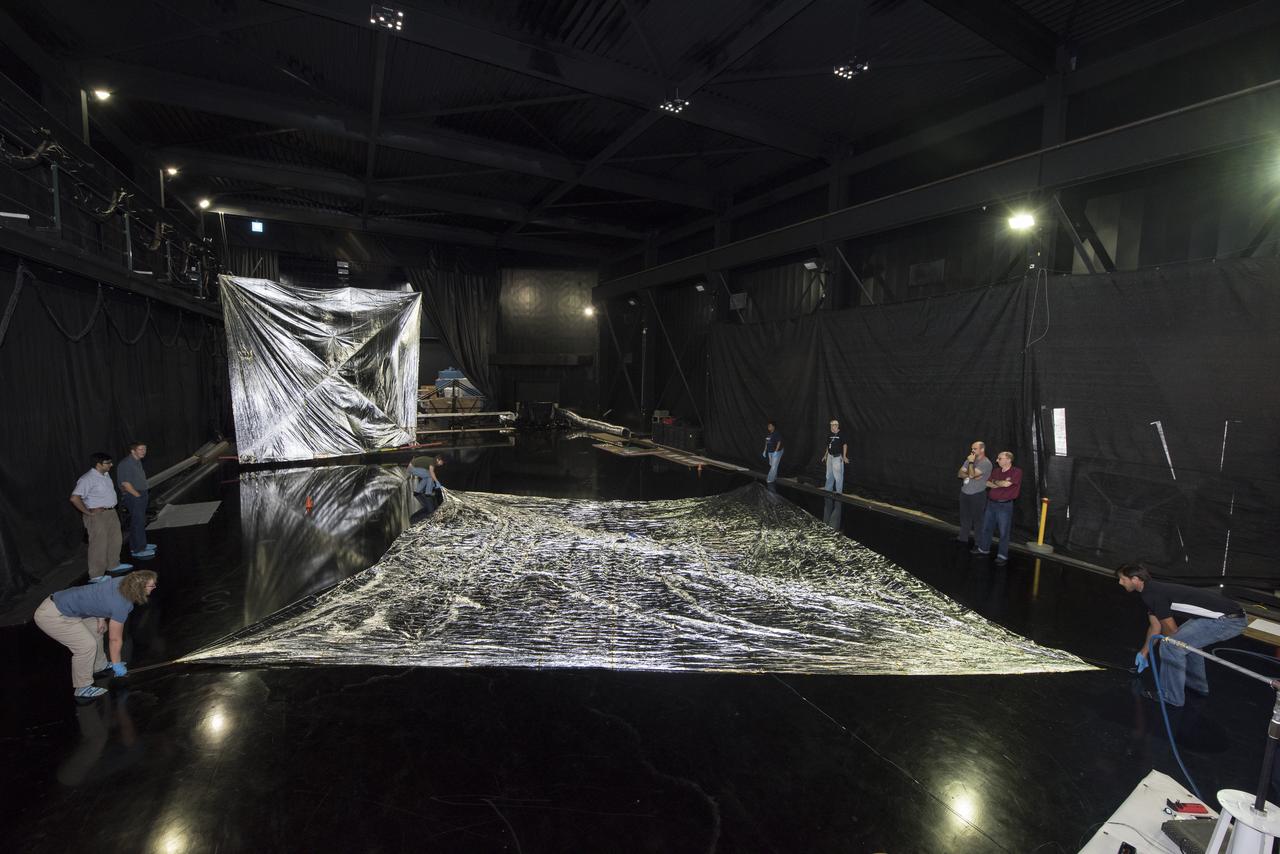

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
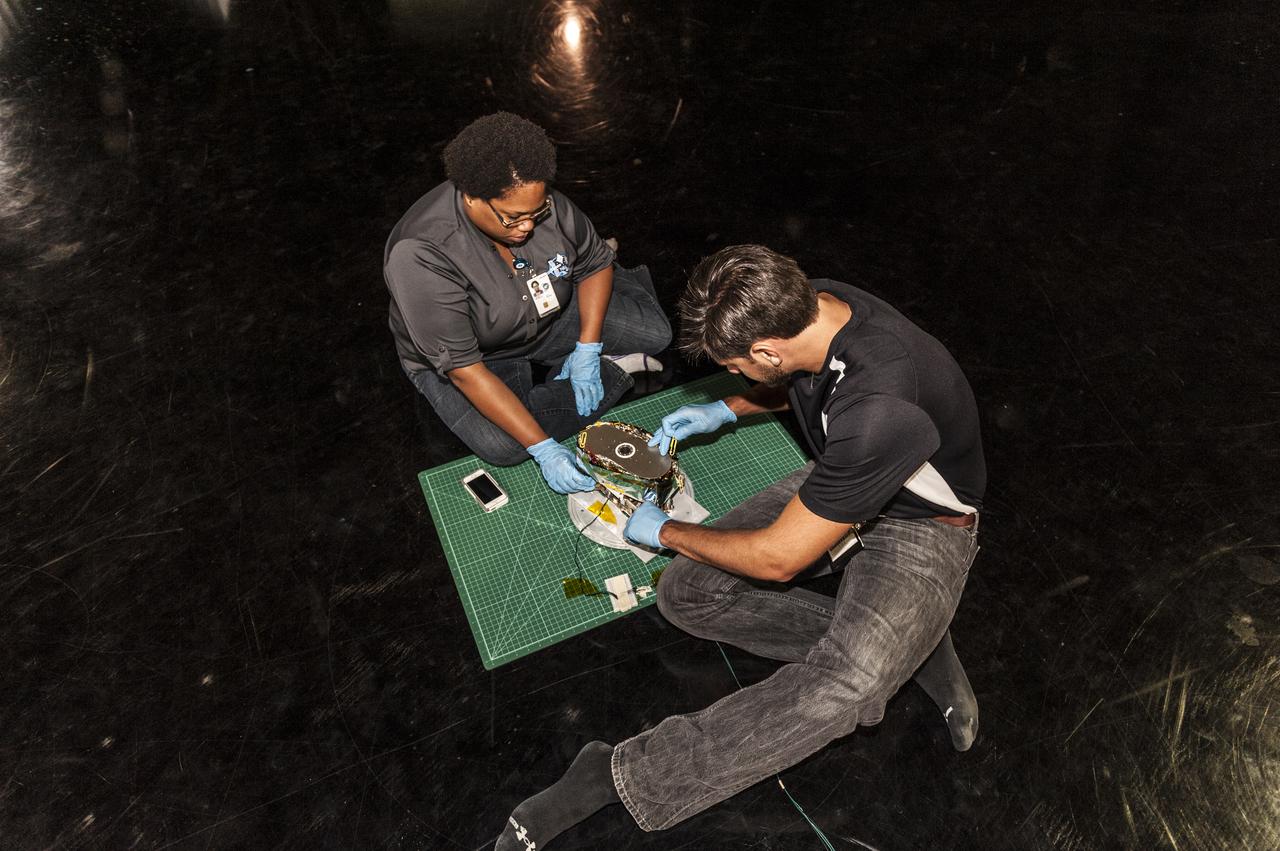

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
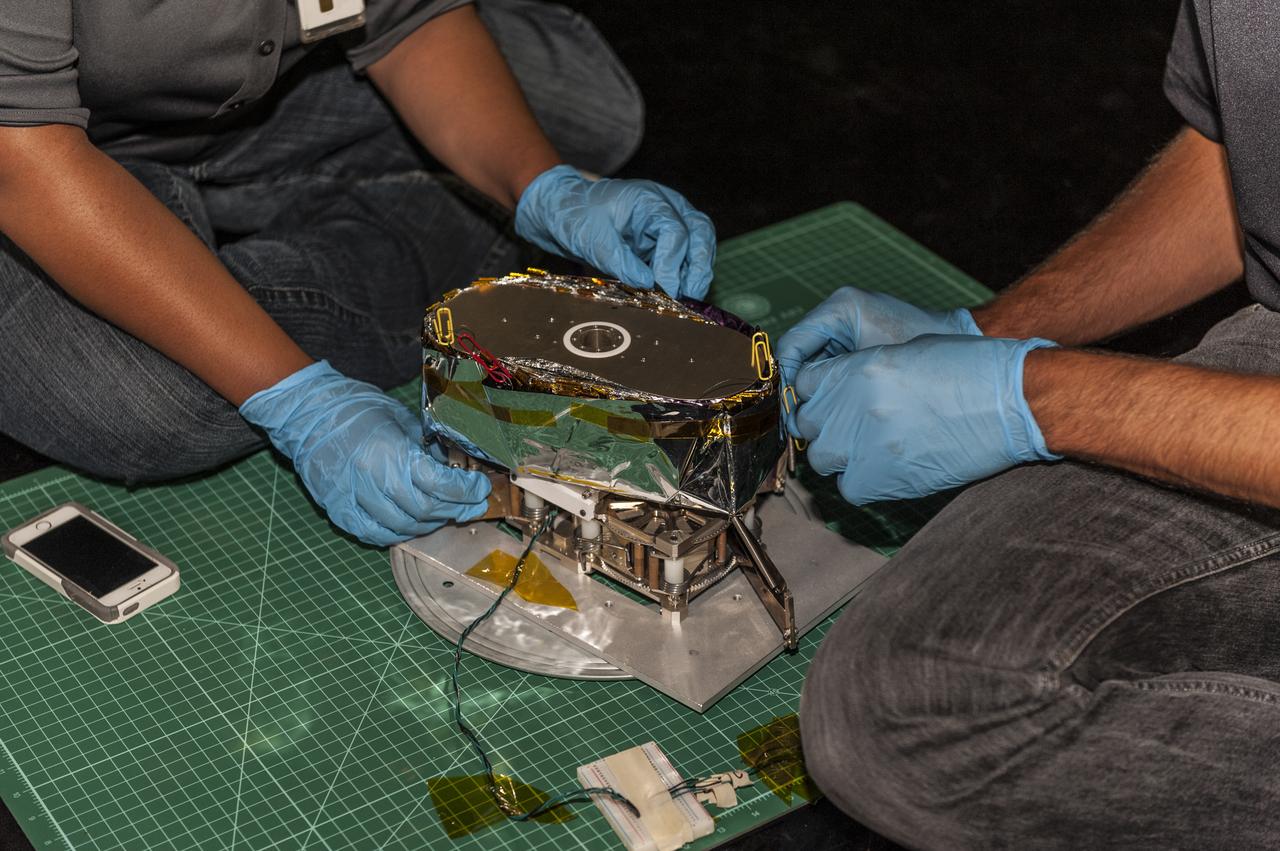

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
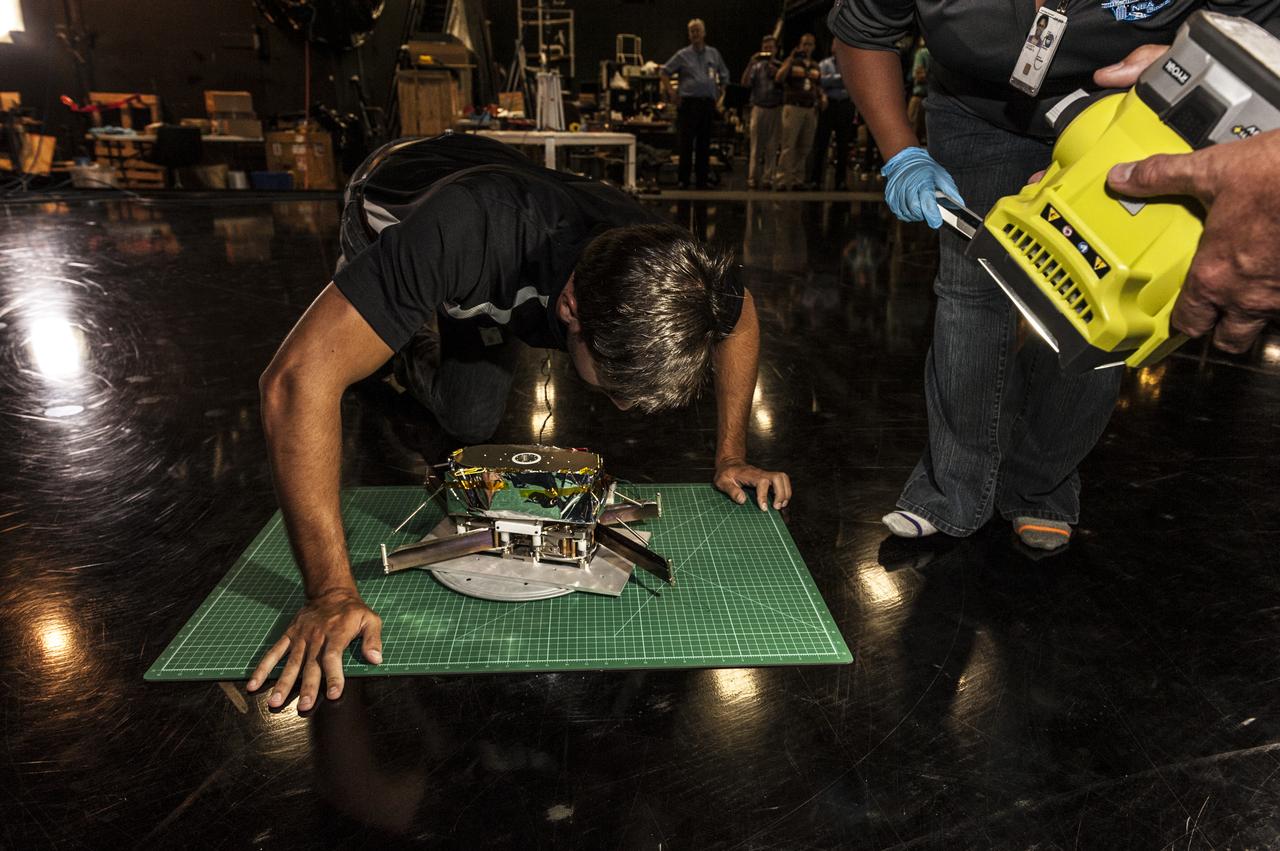

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
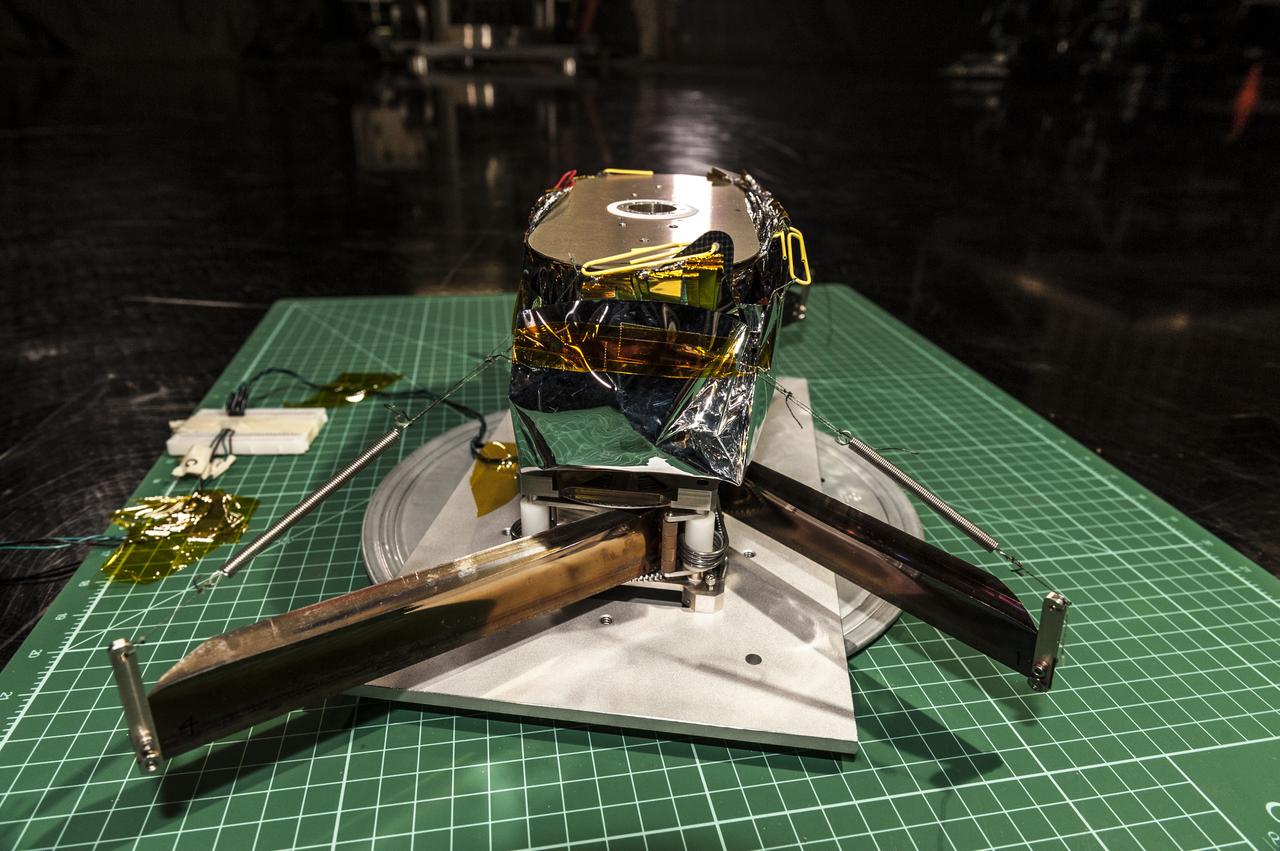

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
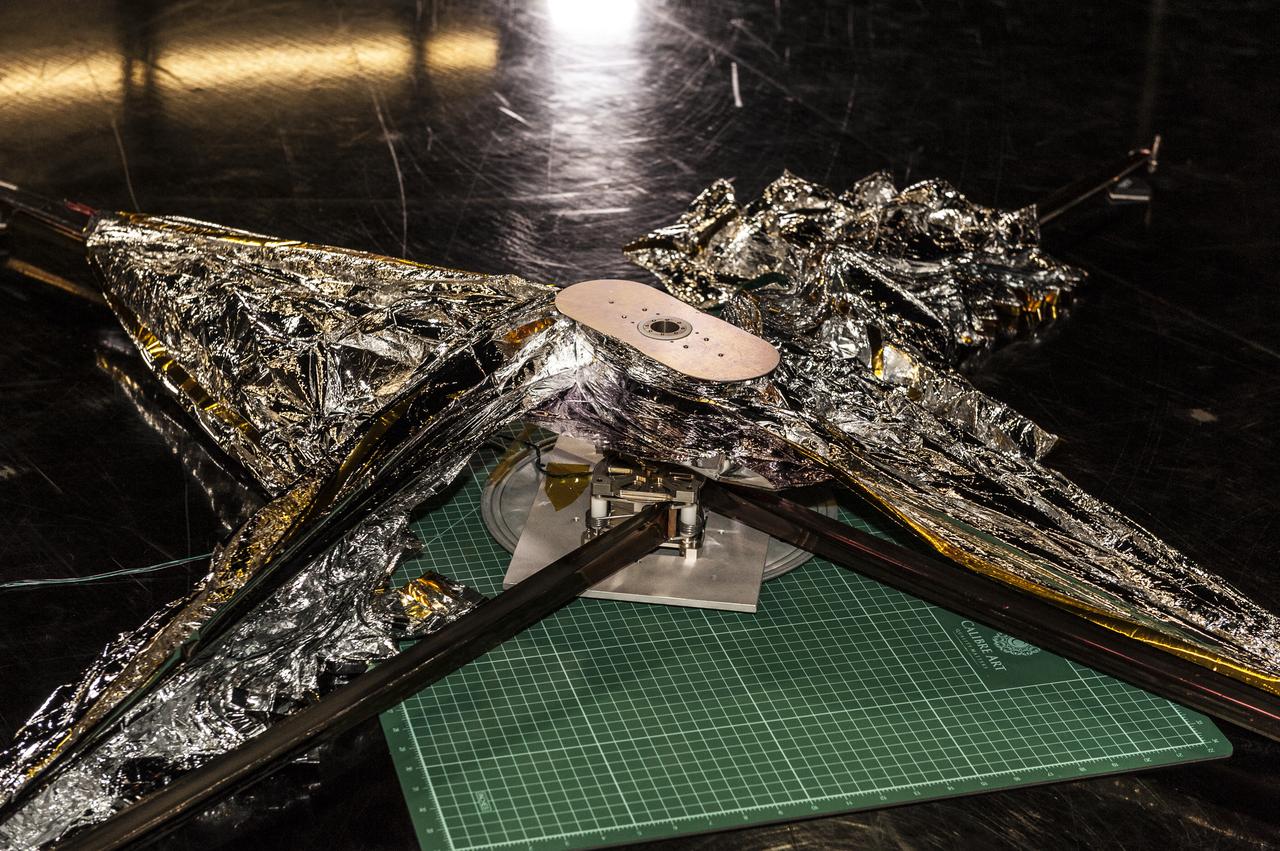
NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016

NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
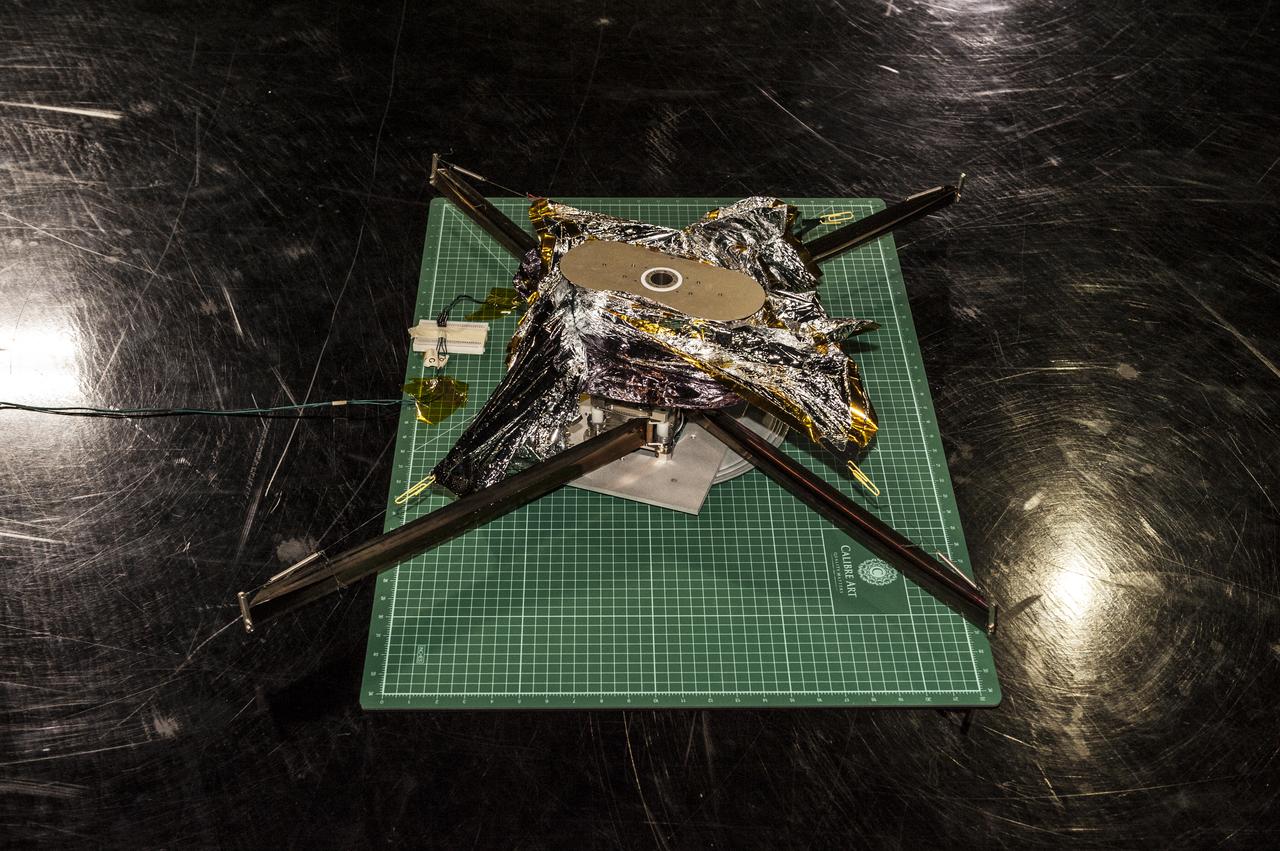
NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016
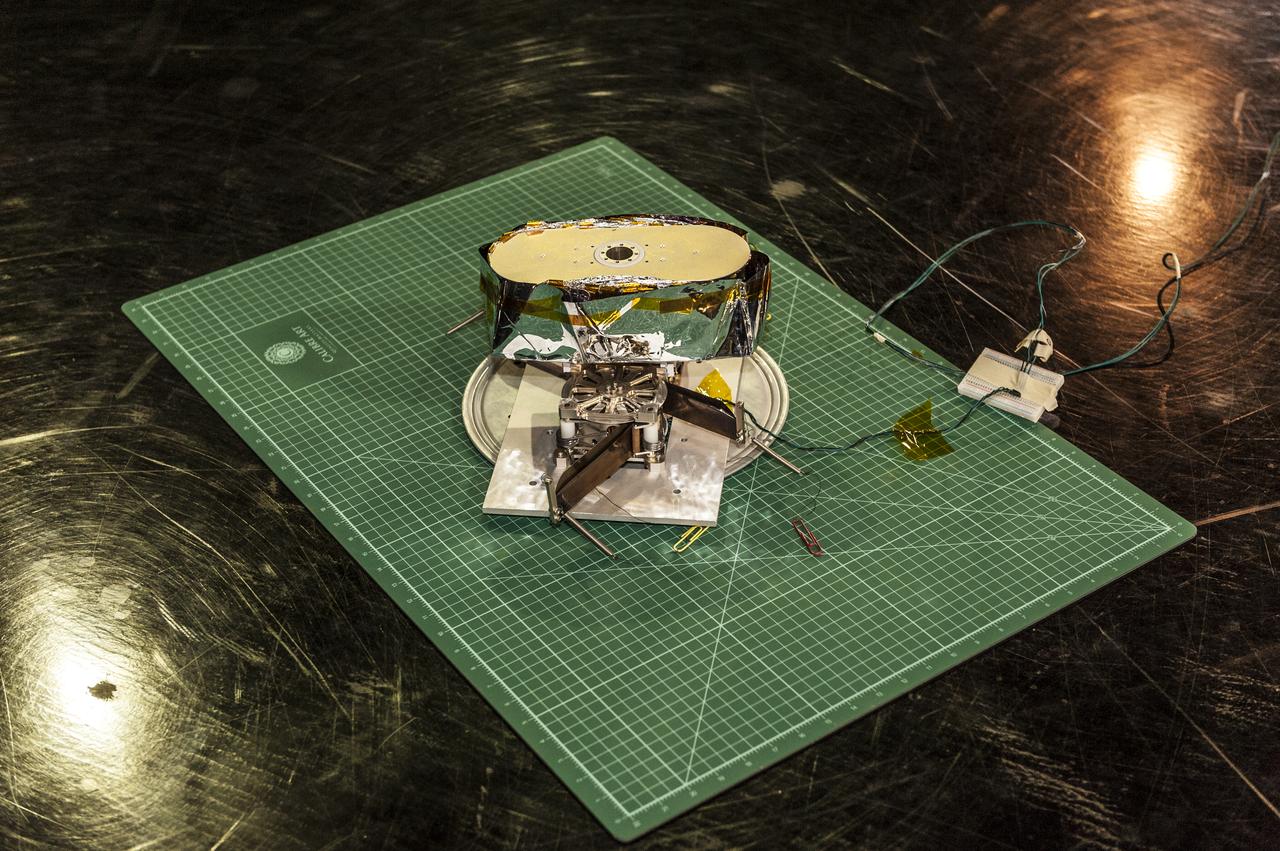
NEAR EARTH ASTEROID (NEA) SAIL TEAM PERFORMING A DEPLOYMENT OF THE FLIGHT-LIKE ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT UNIT SOLAR SAIL. THE SAIL WAS MANUFACTURED AT NEXOLVE (HSV, AL) AND DEPLOYED FOR THE FIRST TIME AT MSFC ON AUGUST 4TH, 2016

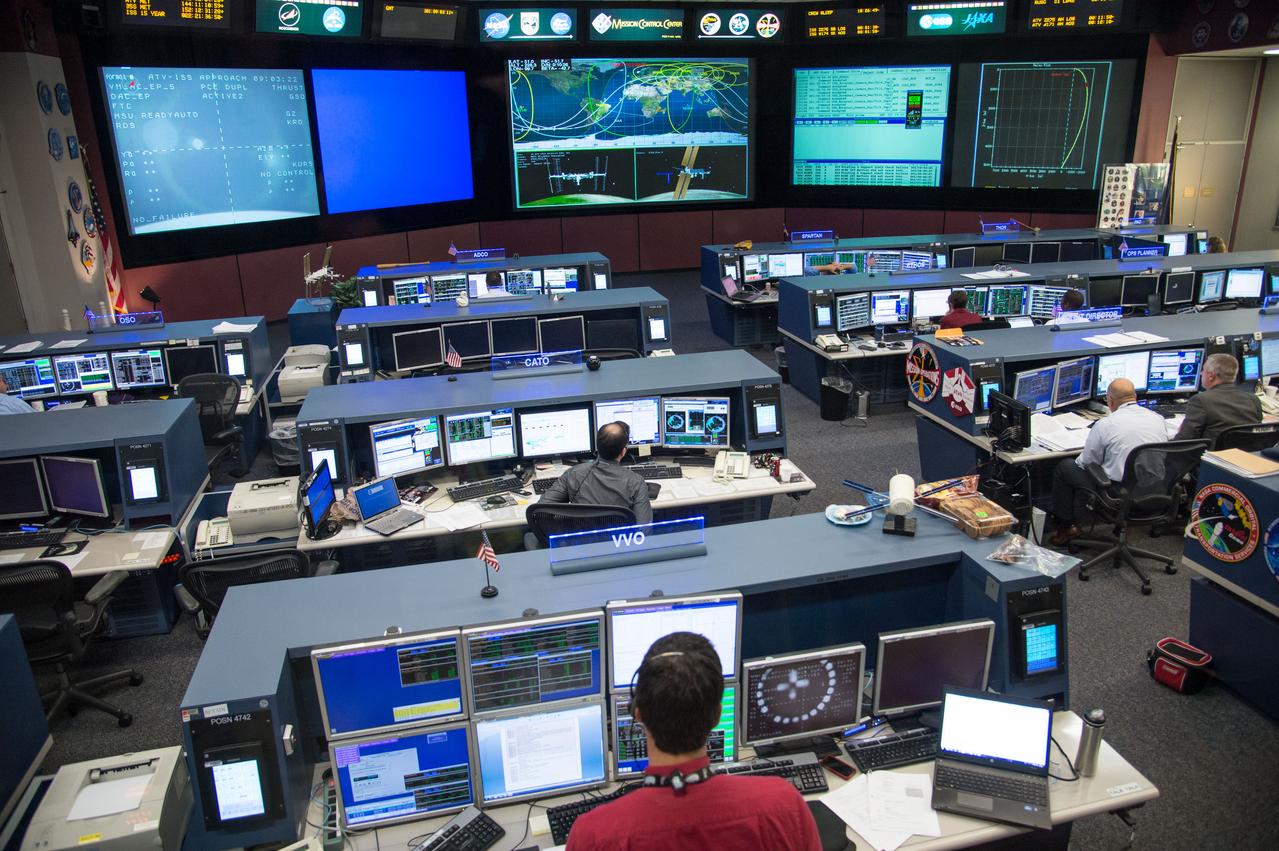
Photographic coverage of Expedition 37 flight controllers on console with Flight Director's Jerry Jason and Tony Ceccacci during the undocking of Europe's 4th Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) from the International Space Station. Photo Date: October 28, 2013. Location: Building 30 - FCR1. Photographer: Robert Markowitz

Photographic coverage of Expedition 37 flight controllers on console with Flight Director's Jerry Jason and Tony Ceccacci during the undocking of Europe's 4th Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) from the International Space Station. Photo Date: October 28, 2013. Location: Building 30 - FCR1. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
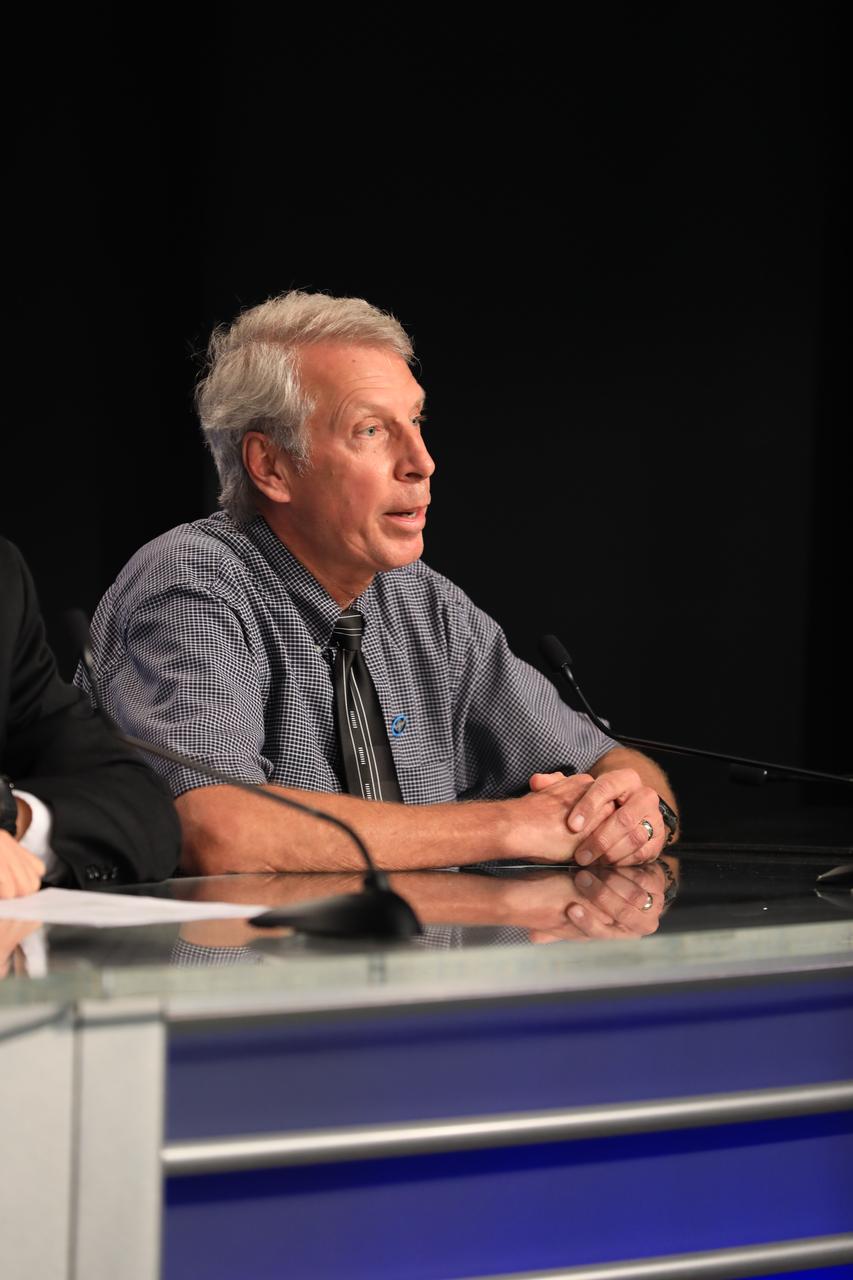

Clay Flinn, launch weather officer, 4th Weather Squadron, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, speaks to members of the news media during a Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) prelaunch news conference in the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium in Florida.
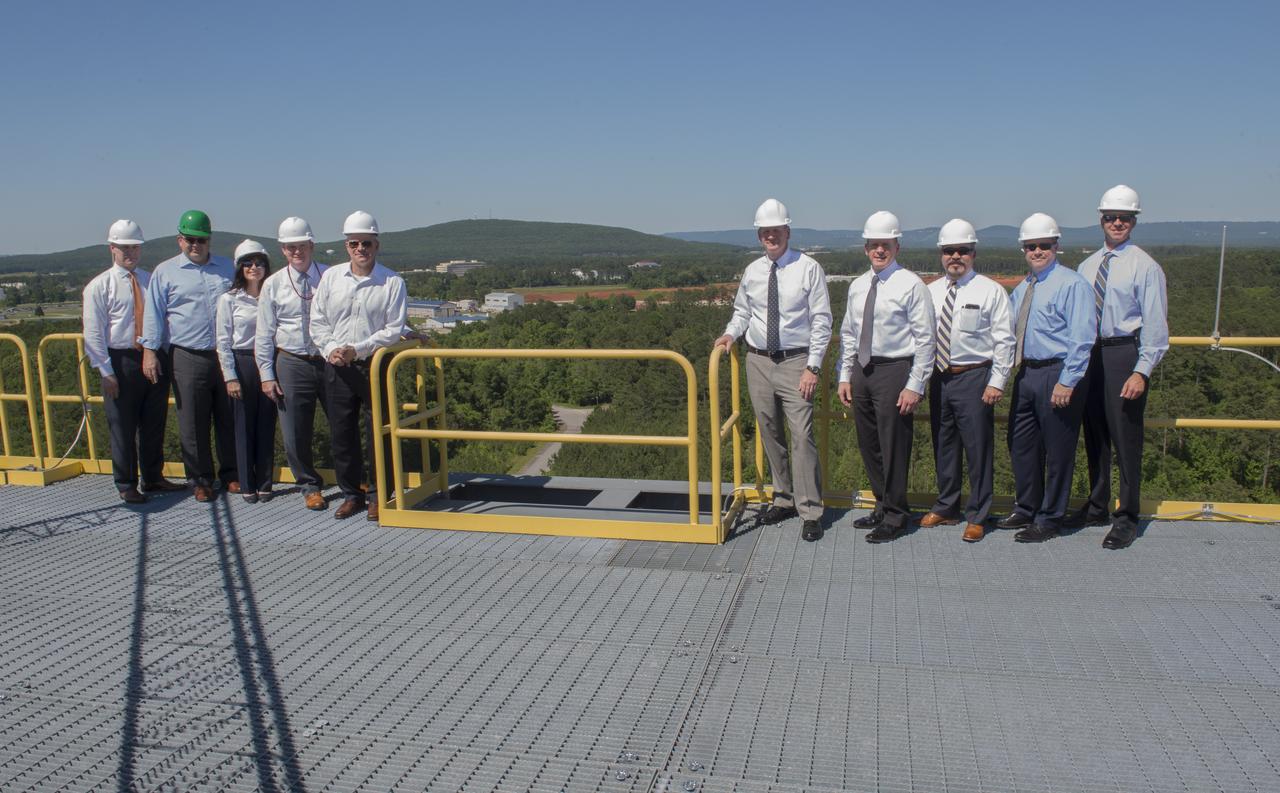

MSFC Director Todd May, (green hard hat), poses with FBI Associate Deputy Director Paul Abbate, (4th from right), and agents atop SLS Test Stand 4693 with view toward land being cleared for FBI complex.
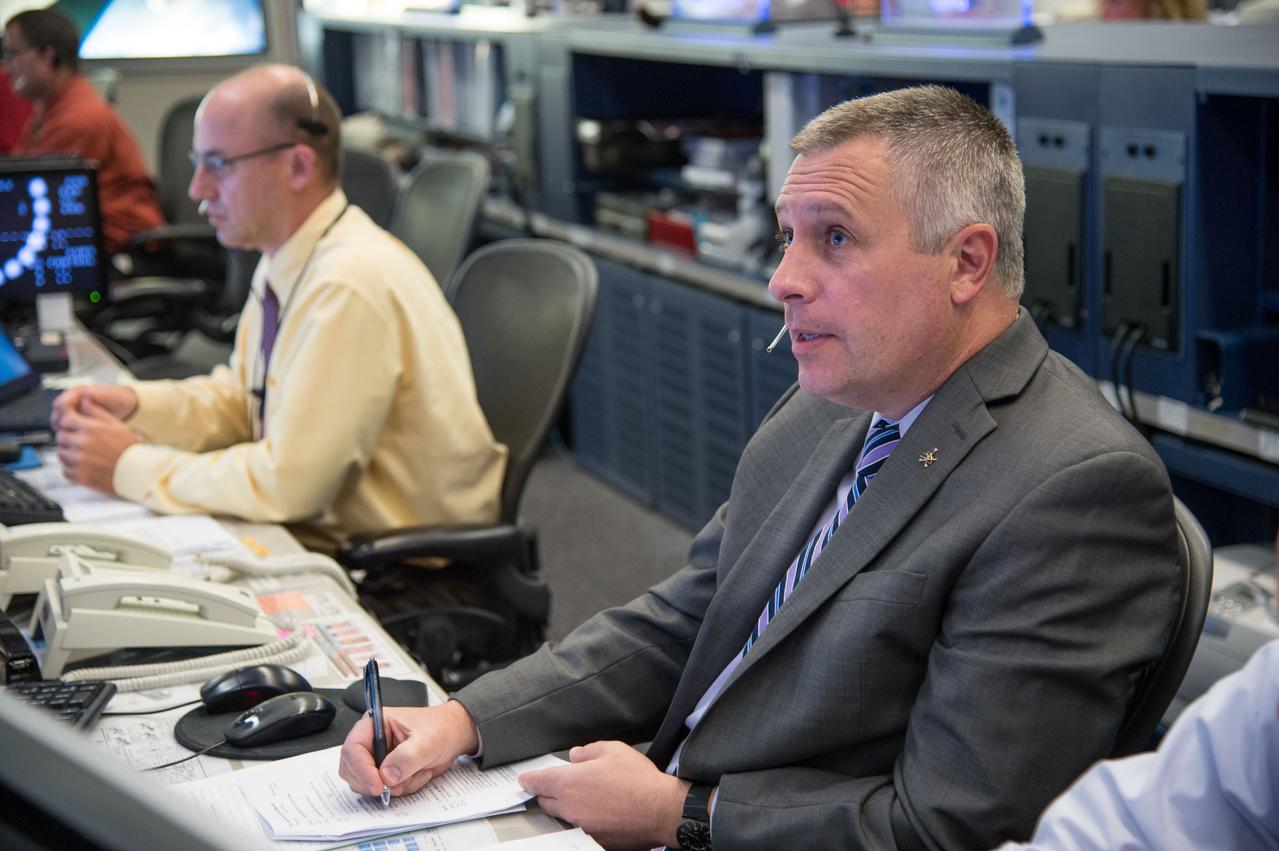

Photographic coverage of Expedition 37 flight controllers on console with Flight Director's Jerry Jason and Tony Ceccacci during the undocking of Europe's 4th Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) from the International Space Station. Photo Date: October 28, 2013. Location: Building 30 - FCR1. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
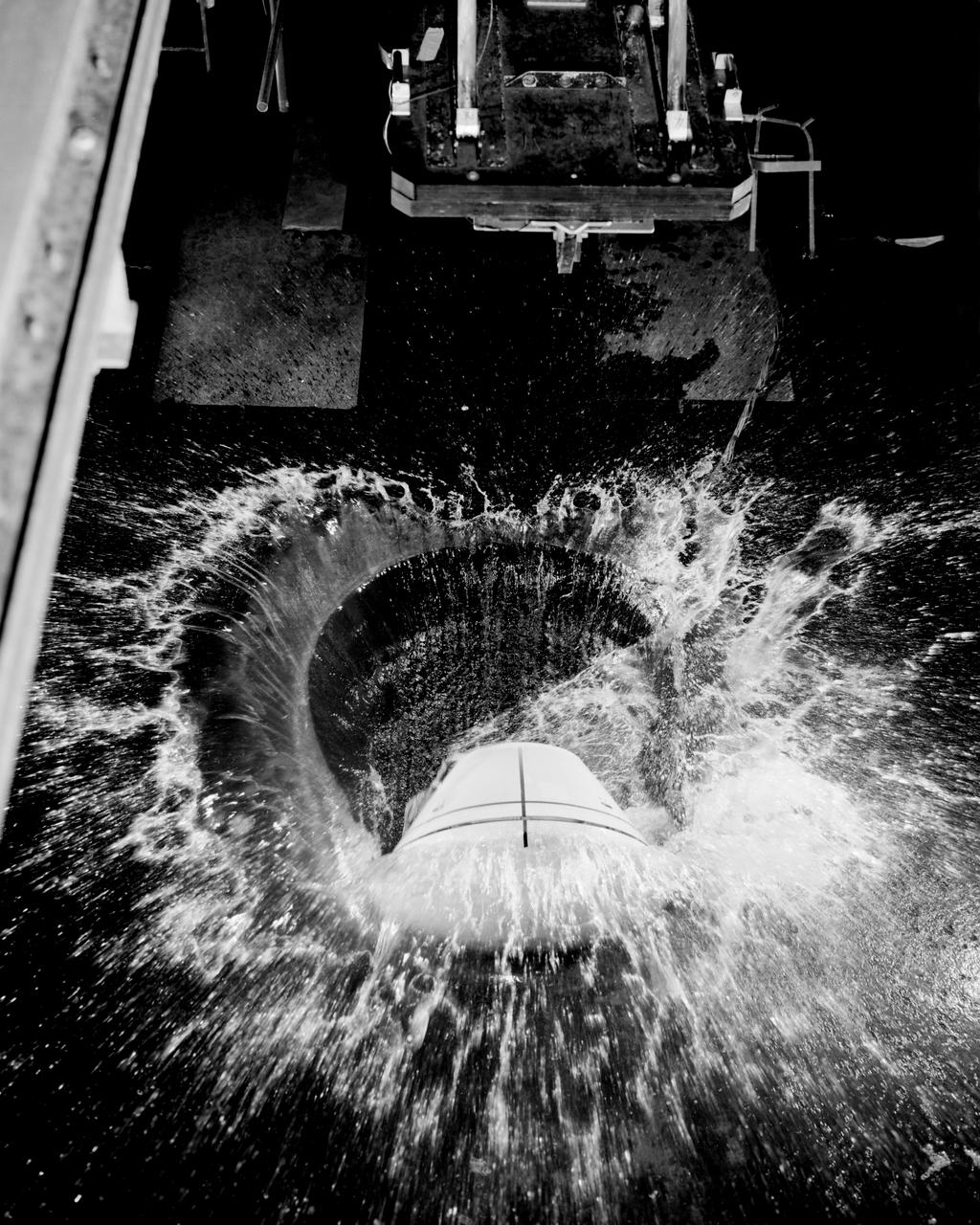

1/4th Scale Model of Apollo - Impact Structures Facility Launched from an overhead pendulum device, this Apollo spacecraft was tested in the Impact Structures Facility to determine water-landing characteristics. -- Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication (page 91), by James Schultz.
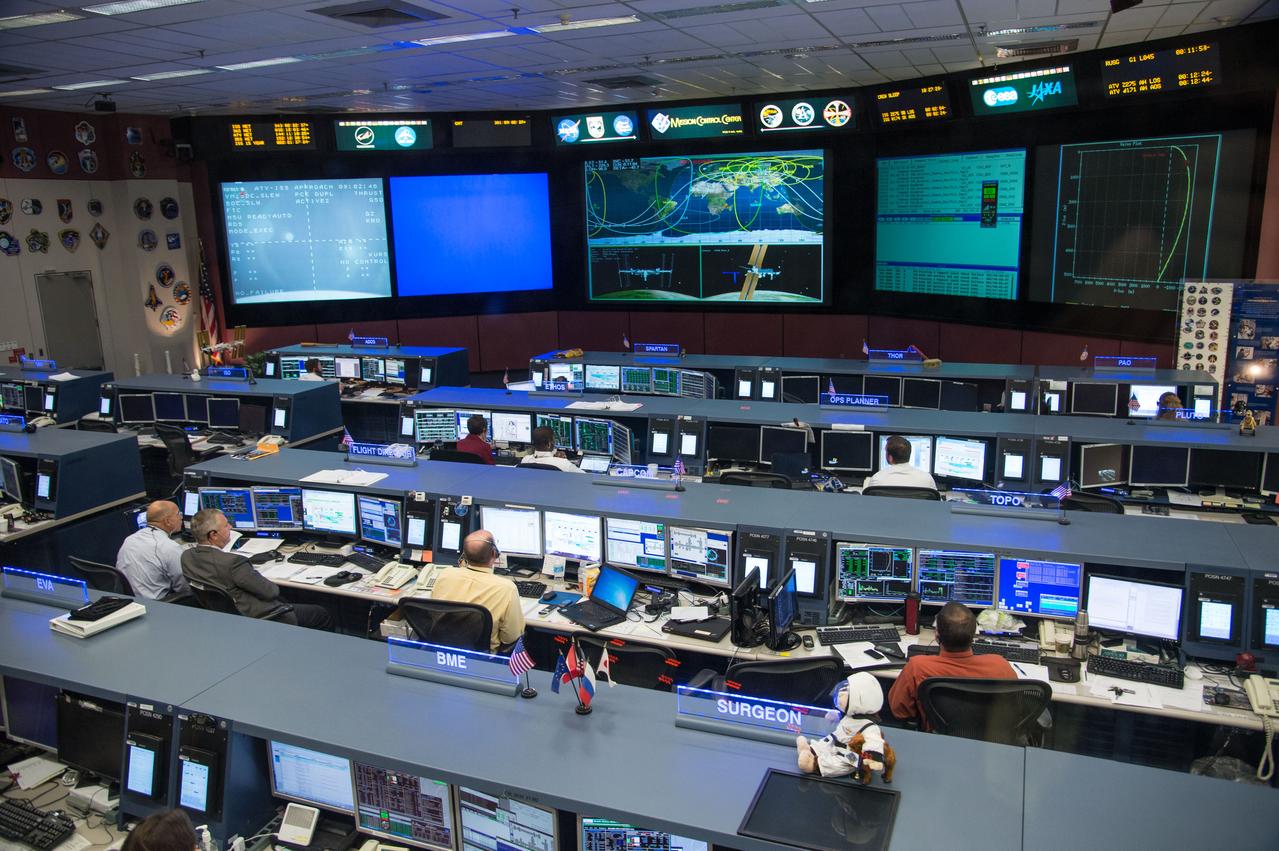

Photographic coverage of Expedition 37 flight controllers on console with Flight Director's Jerry Jason and Tony Ceccacci during the undocking of Europe's 4th Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) from the International Space Station. Photo Date: October 28, 2013. Location: Building 30 - FCR1. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
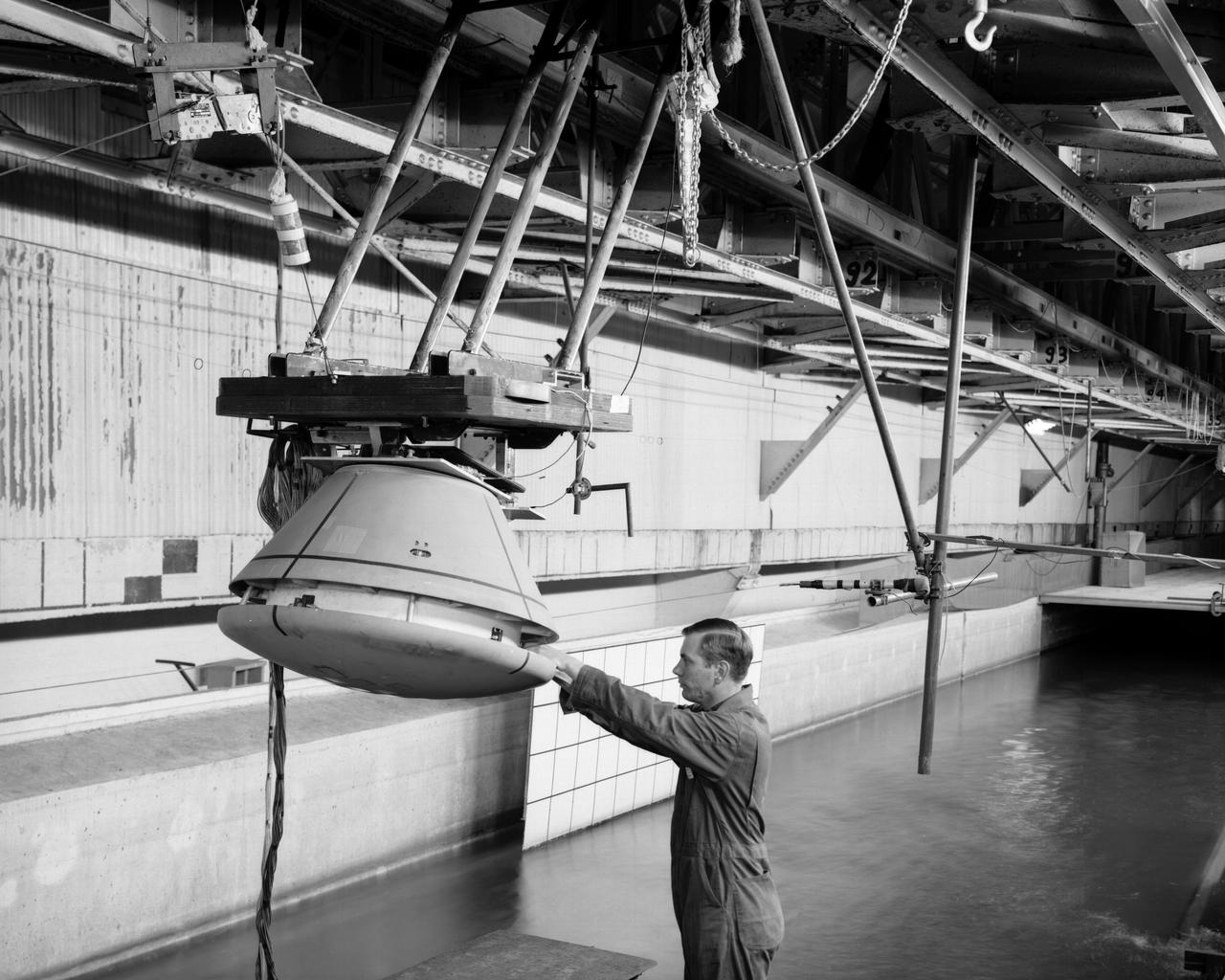

1/4th Scale Model of Apollo - Impact Structures Facility Launched from an overhead pendulum device, this Apollo spacecraft was tested in the Impact Structures Facility to determine water-landing characteristics. -- Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication (page 91), by James Schultz.

Photographic coverage of Expedition 37 flight controllers on console with Flight Director's Jerry Jason and Tony Ceccacci during the undocking of Europe's 4th Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) from the International Space Station. Photo Date: October 28, 2013. Location: Building 30 - FCR1. Photographer: Robert Markowitz

Photographic coverage of Expedition 37 flight controllers on console with Flight Director's Jerry Jason and Tony Ceccacci during the undocking of Europe's 4th Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) from the International Space Station. Photo Date: October 28, 2013. Location: Building 30 - FCR1. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
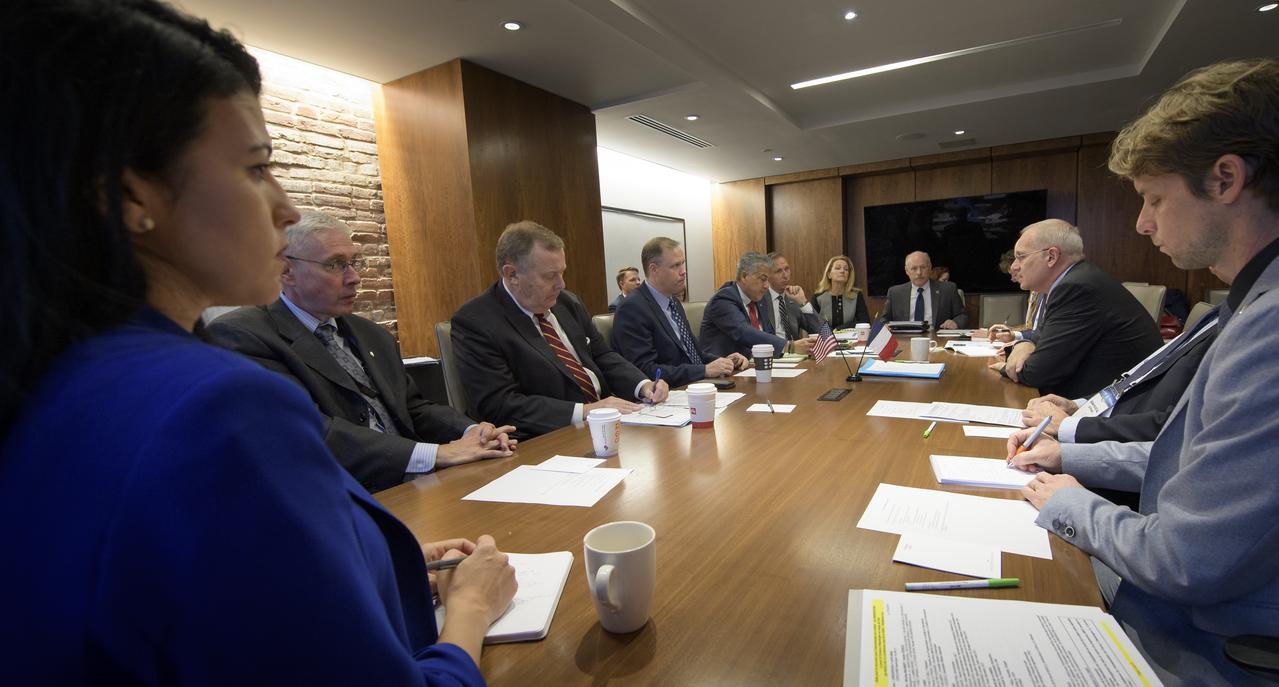

Jean-Yves Le Gall, President of the Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), 2nd from right, talks with NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, 4th from left, during a meeting at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Thursday, Oct. 24, 2019, in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
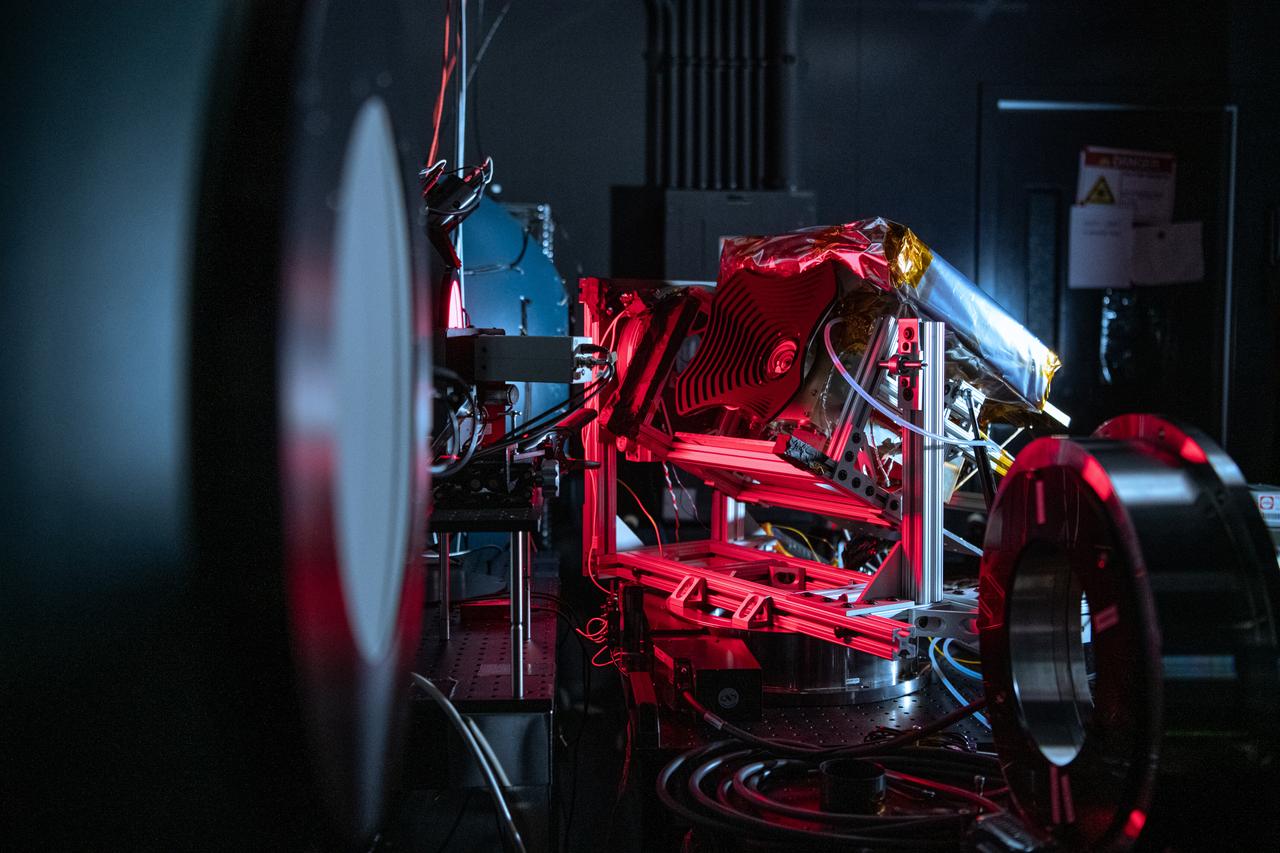

The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument undergoes calibration testing after at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on October 4th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute.
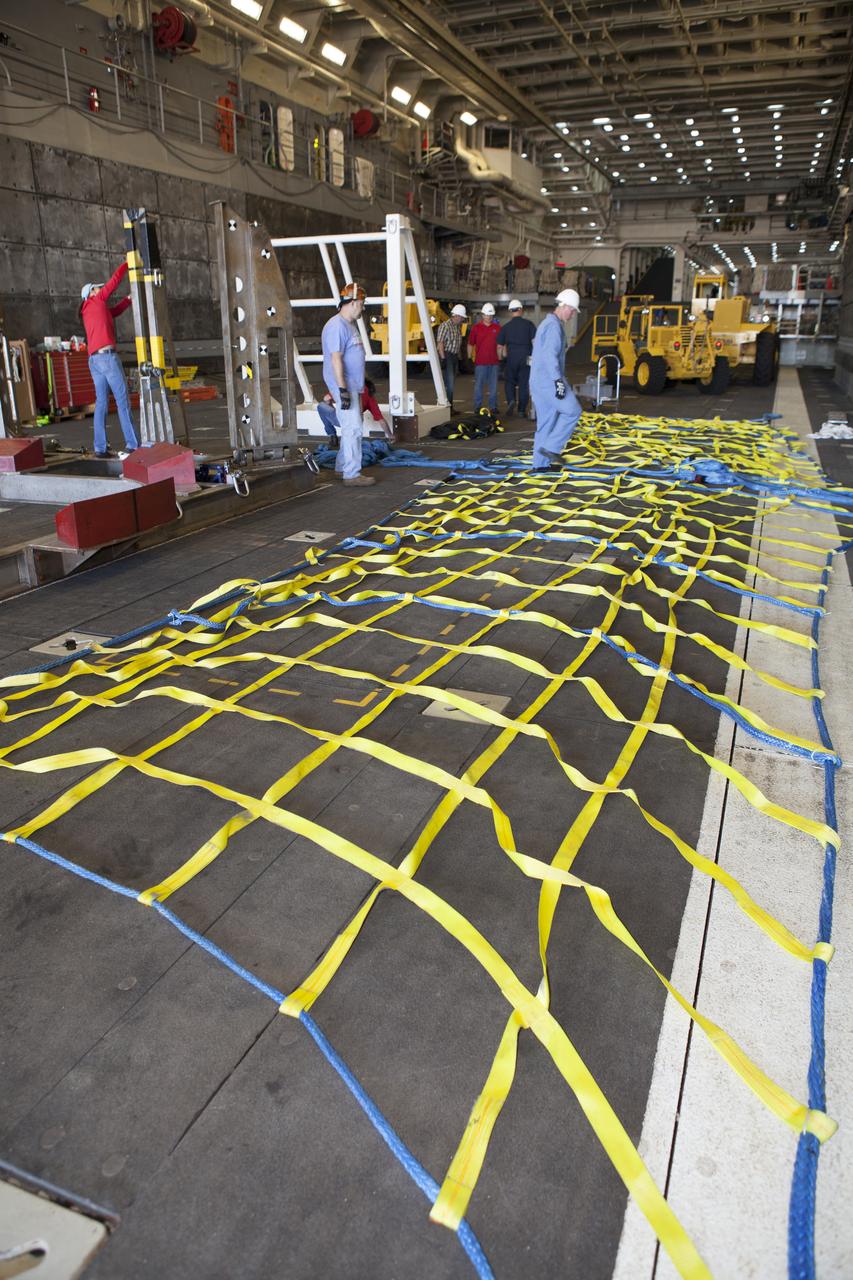

Ground support equipment is being secured in the well deck of the USS Anchorage at Naval Base San Diego in California. The equipment will be used during recovery of the Orion crew module after its first flight test. Before launch of Orion on a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel will head out to sea in the USS Anchorage and the USNS Salvor, a salvage ship, and wait for splashdown of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program will lead the recovery efforts. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
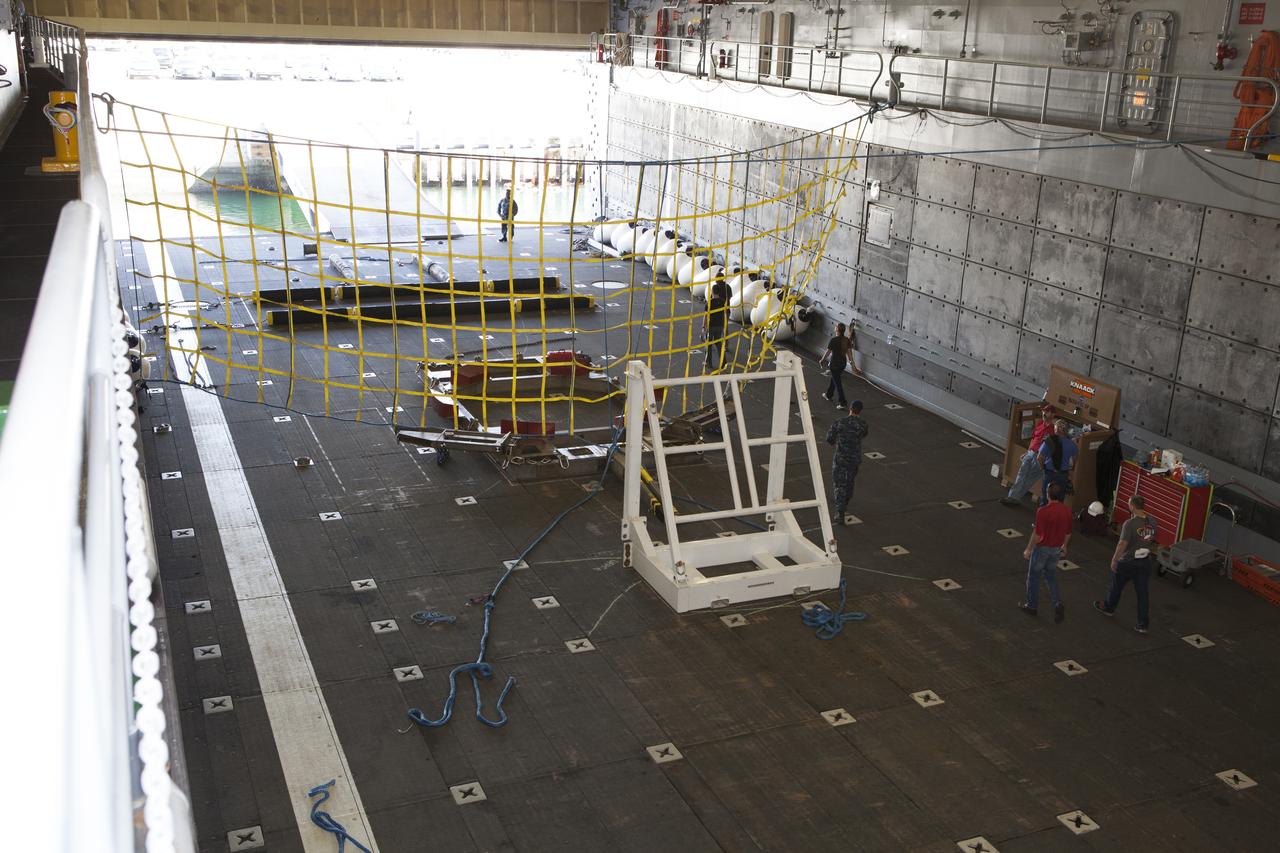

The Orion handling fixture and other ground support equipment is secured in the well deck of the USS Anchorage at Naval Base San Diego in California. The equipment will be used during recovery of the Orion crew module after its first flight test. Before launch of Orion on a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel will head out to sea in the USS Anchorage and the USNS Salvor, a salvage ship, and wait for splashdown of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program will lead the recovery efforts. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
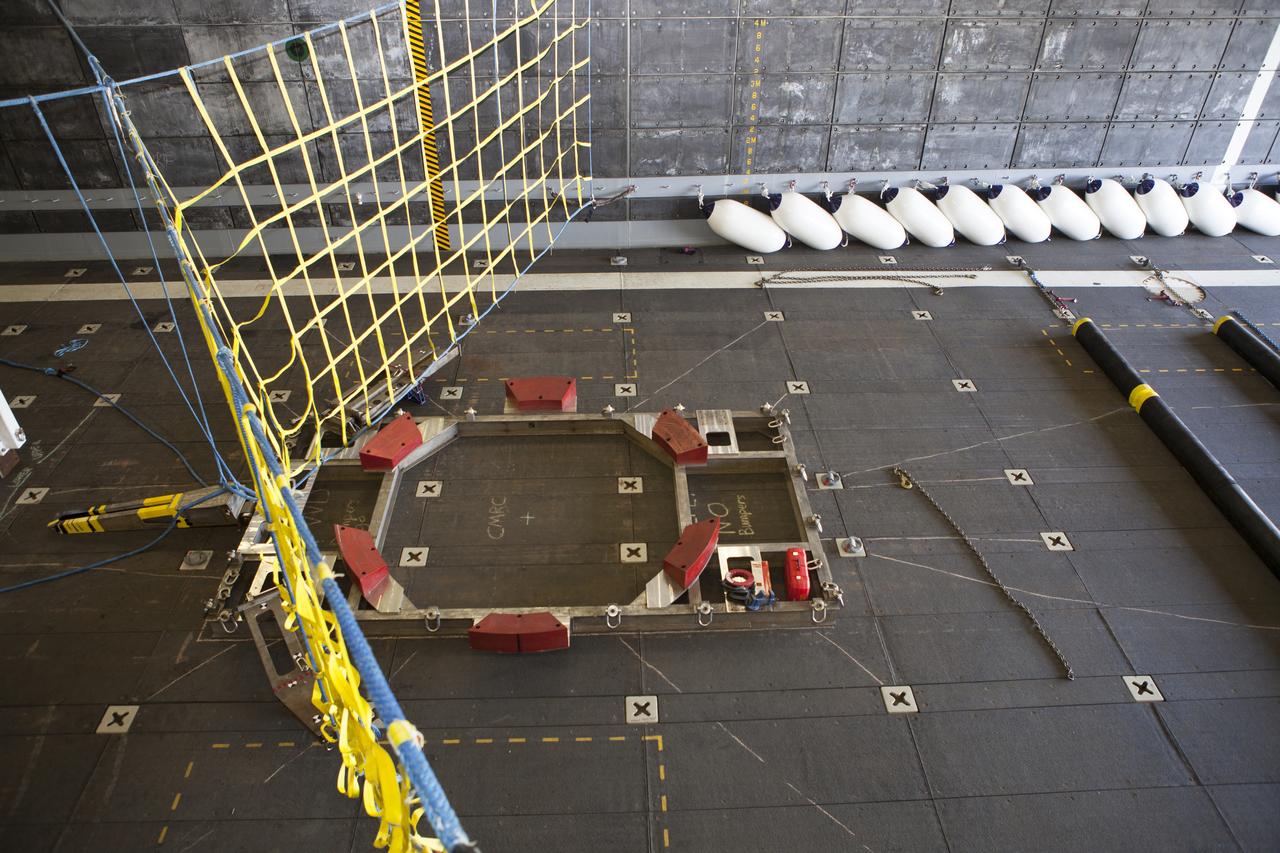

Ground support equipment is secured in the well deck of the USS Anchorage at Naval Base San Diego in California. The equipment will be used during recovery of the Orion crew module after its first flight test. Before launch of Orion on a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel will head out to sea in the USS Anchorage and the USNS Salvor, a salvage ship, and wait for splashdown of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program will lead the recovery efforts. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
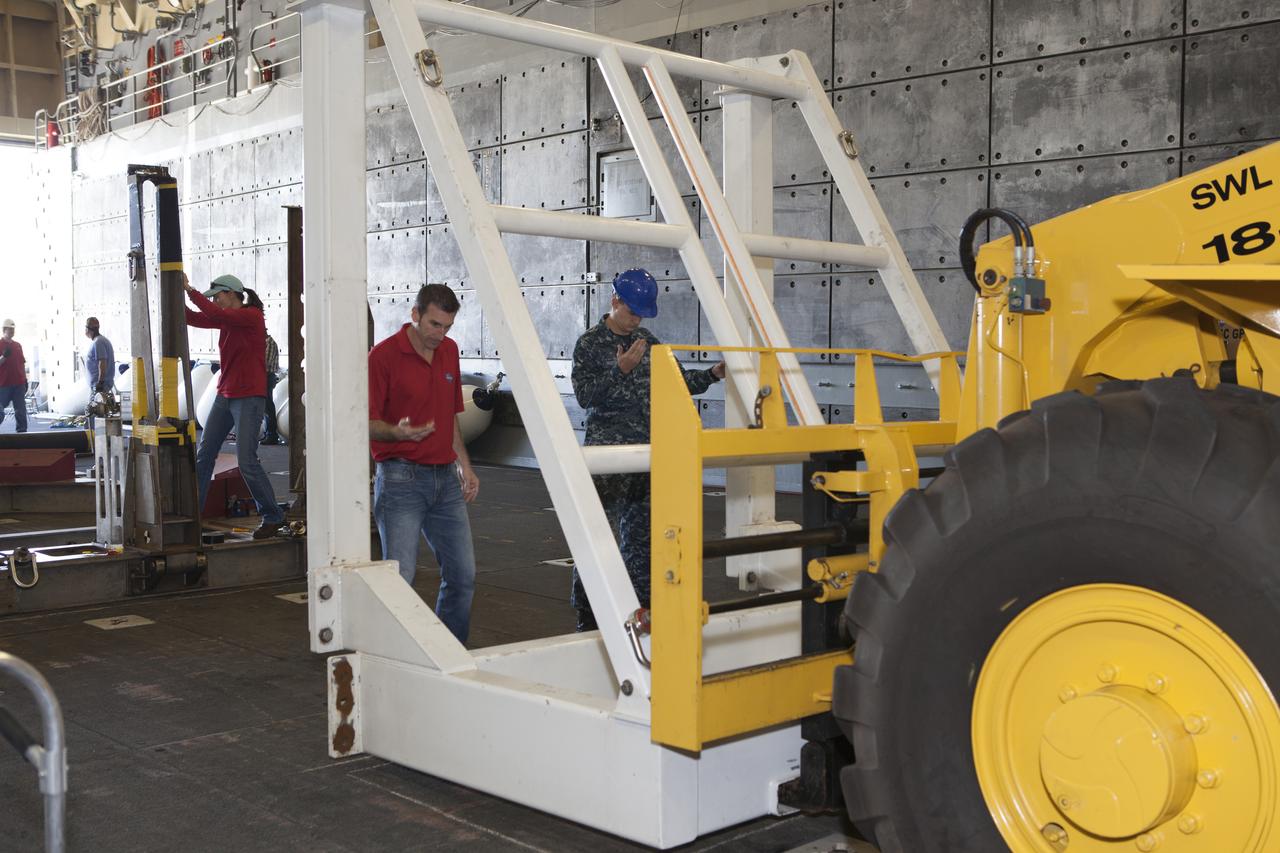

A forklift is used to set the Orion handling fixture down in the well deck of the USS Anchorage at Naval Base San Diego in California. The fixture and other ground support equipment will be used during recovery of the Orion crew module after its first flight test. Before launch of Orion on a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel will head out to sea in the USS Anchorage and the USNS Salvor, a salvage ship, and wait for splashdown of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program will lead the recovery efforts. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
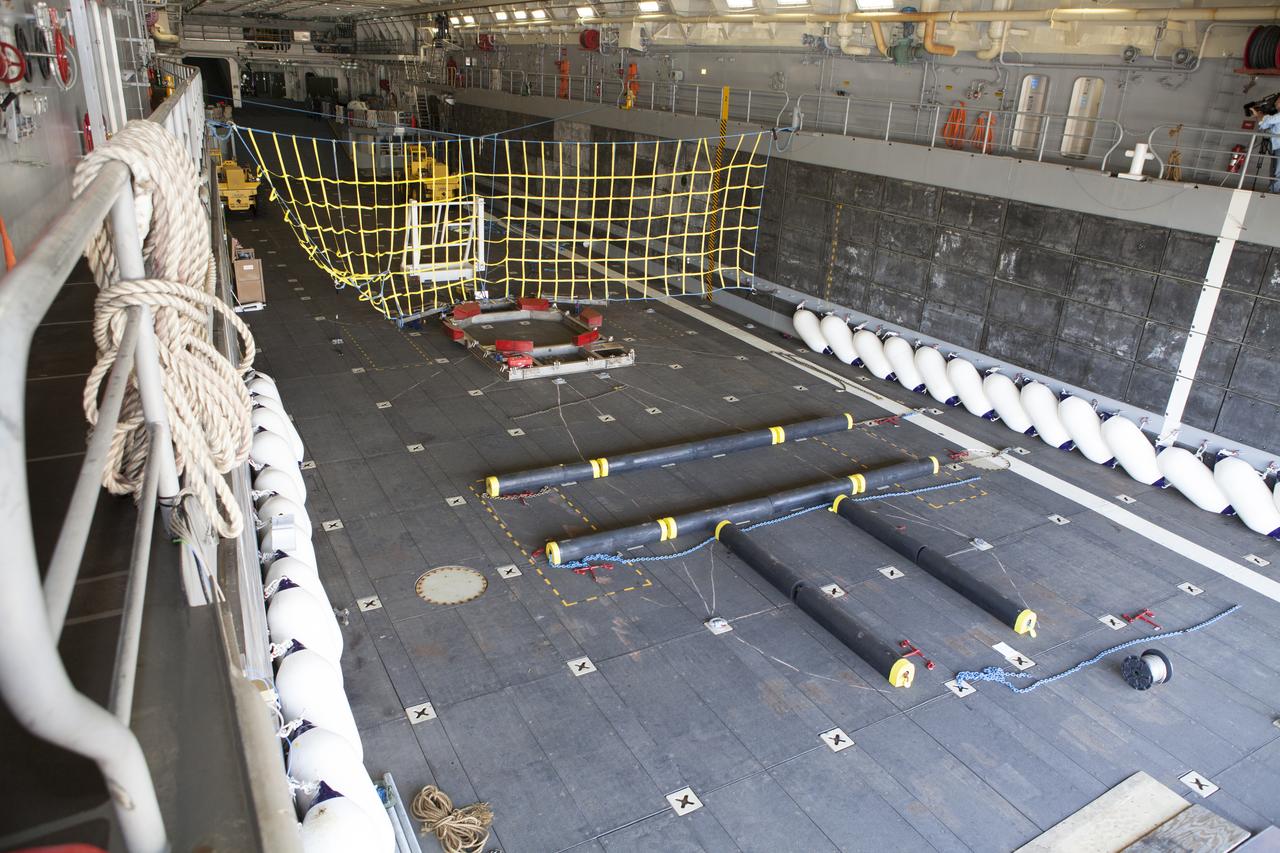

The Orion handling fixture, special bumpers and other ground support equipment are secured in the well deck of the USS Anchorage at Naval Base San Diego in California. The equipment will be used during recovery of the Orion crew module after its first flight test. Before launch of Orion on a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel will head out to sea in the USS Anchorage and the USNS Salvor, a salvage ship, and wait for splashdown of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program will lead the recovery efforts. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
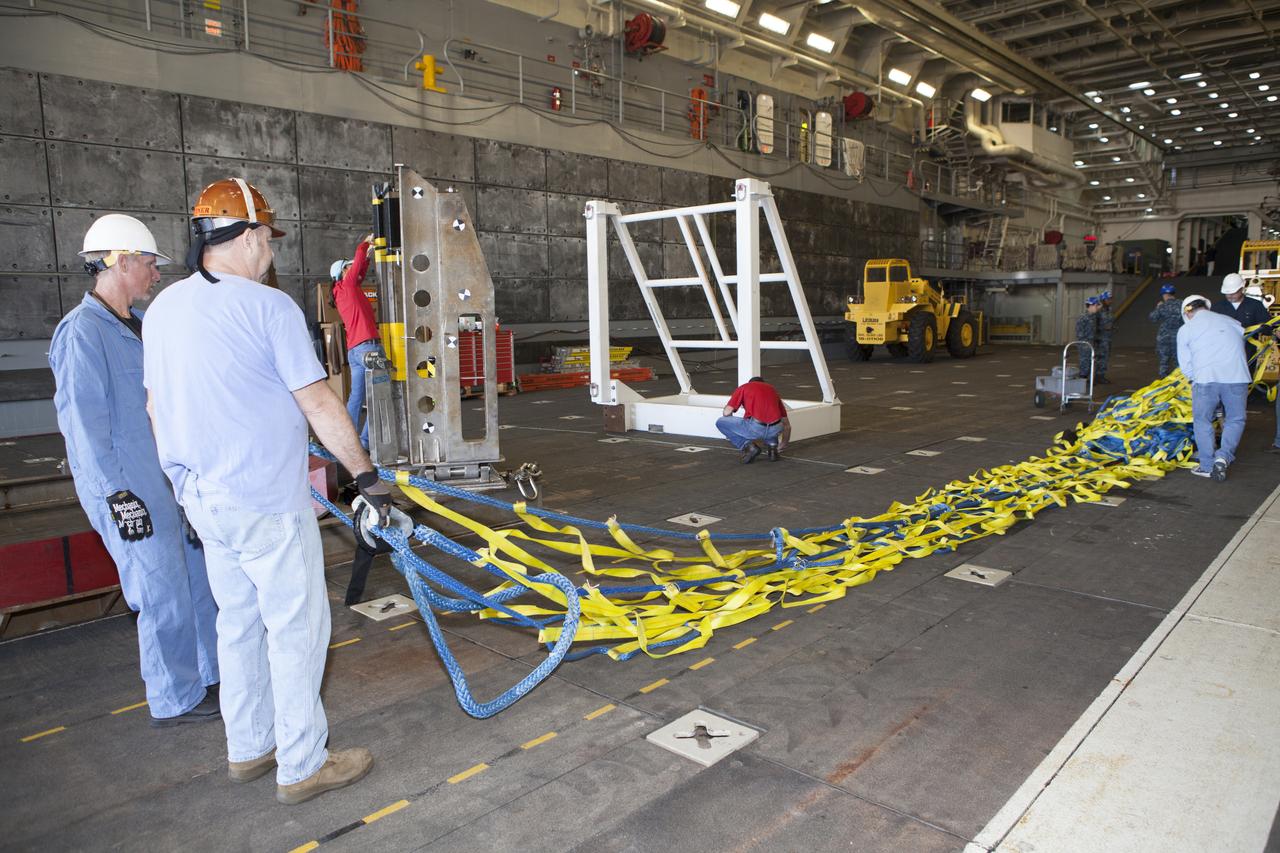

Ground support equipment is being secured in the well deck of the USS Anchorage at Naval Base San Diego in California. The equipment will be used during recovery of the Orion crew module after its first flight test. Before launch of Orion on a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel will head out to sea in the USS Anchorage and the USNS Salvor, a salvage ship, and wait for splashdown of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program will lead the recovery efforts. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
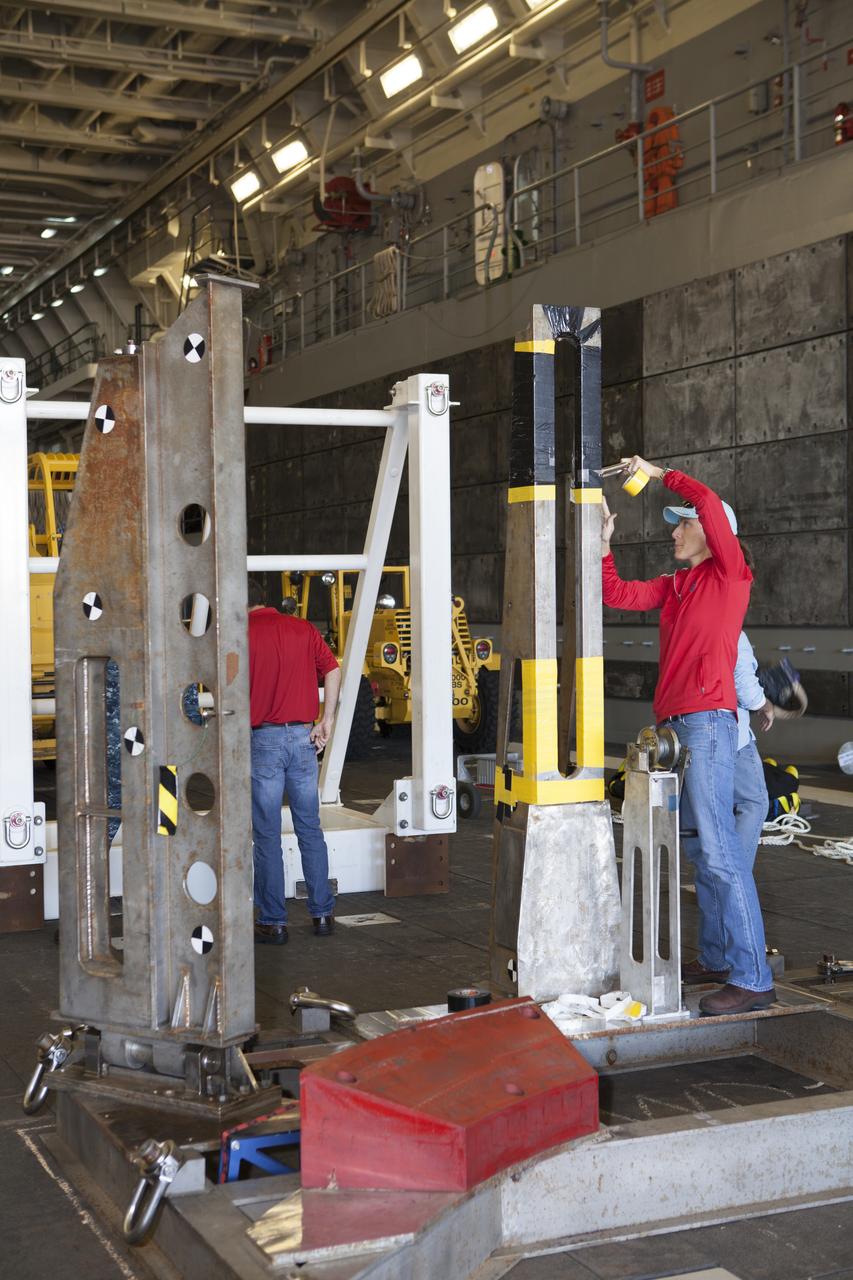

Ground support equipment is being secured in the well deck of the USS Anchorage at Naval Base San Diego in California. The equipment will be used during recovery of the Orion crew module after its first flight test. Before launch of Orion on a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel will head out to sea in the USS Anchorage and the USNS Salvor, a salvage ship, and wait for splashdown of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program will lead the recovery efforts. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
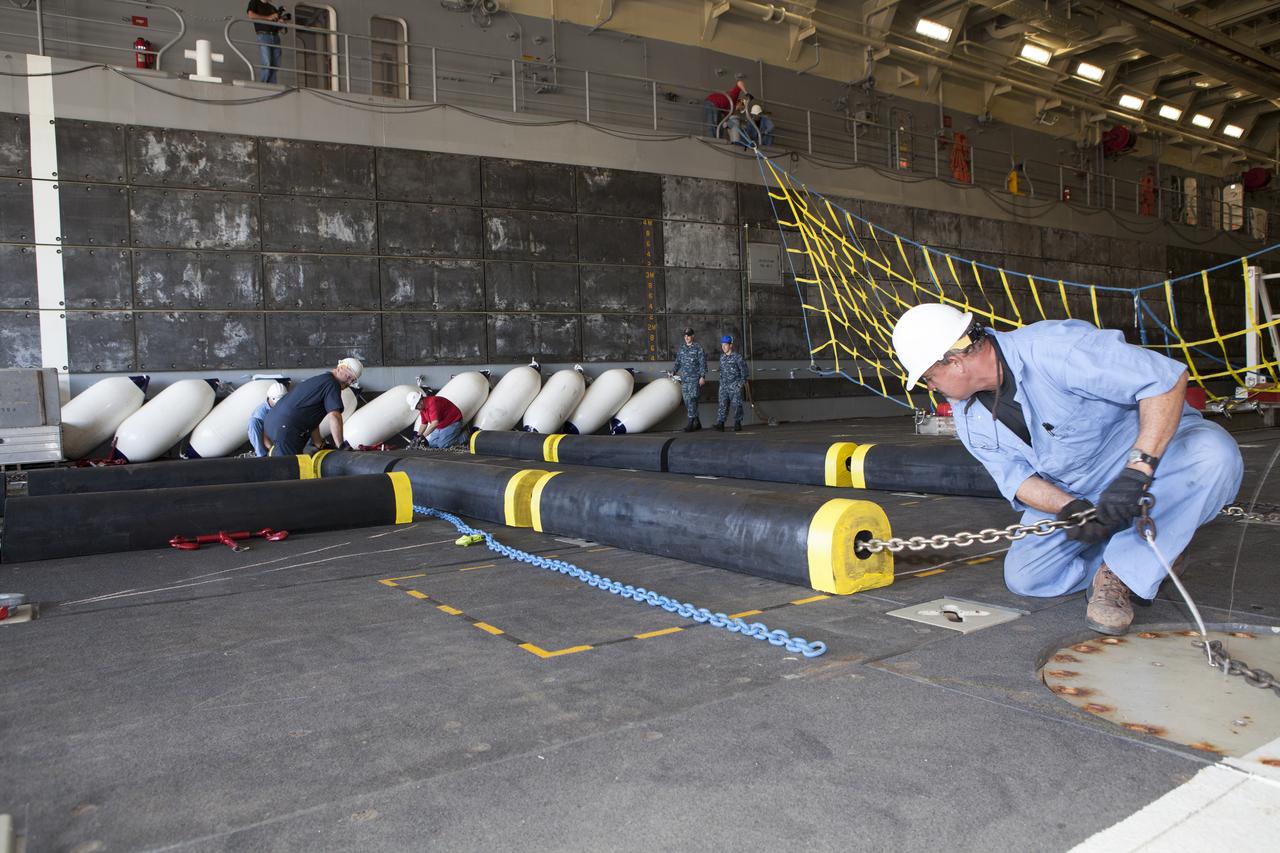

Ground support equipment is being secured in the well deck of the USS Anchorage at Naval Base San Diego in California. The equipment will be used during recovery of the Orion crew module after its first flight test. Before launch of Orion on a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel will head out to sea in the USS Anchorage and the USNS Salvor, a salvage ship, and wait for splashdown of the Orion crew module in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program will lead the recovery efforts. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
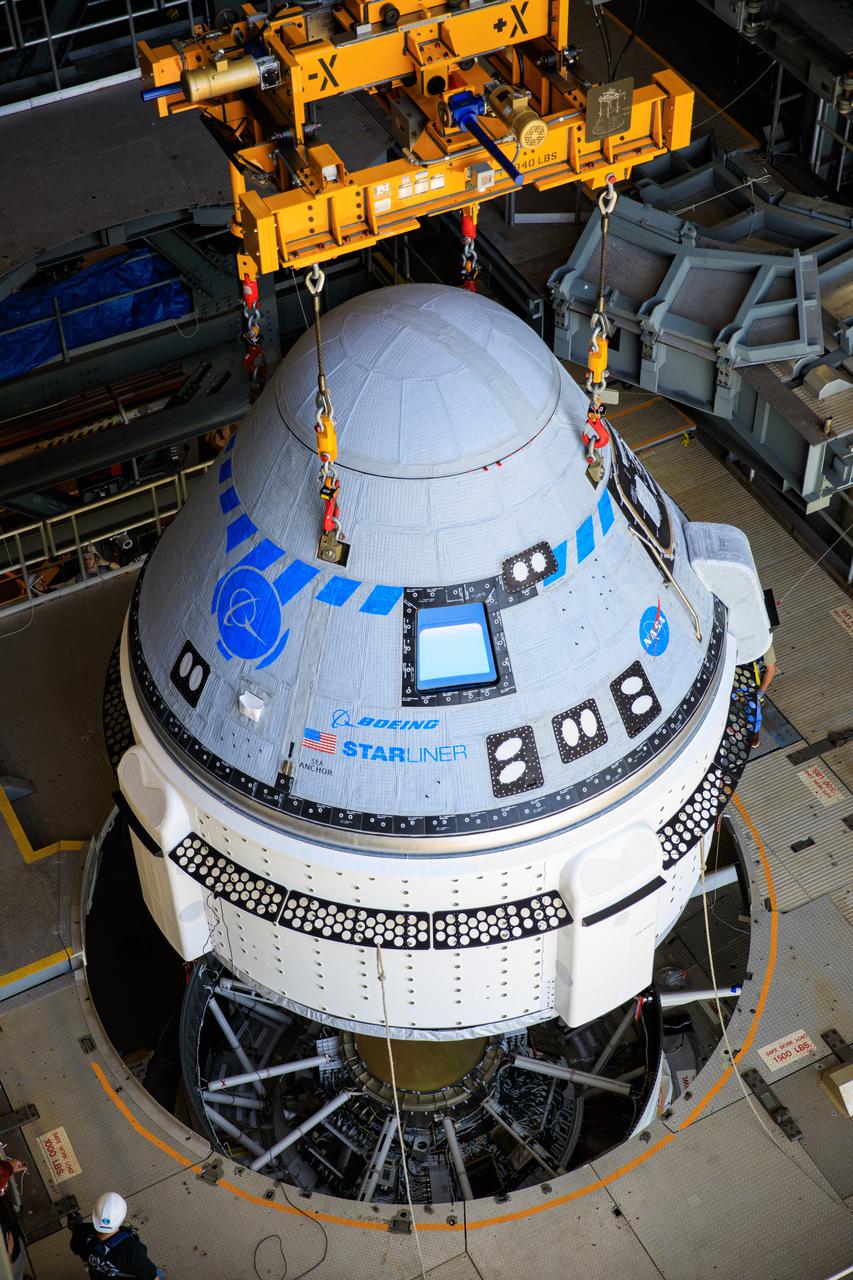

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
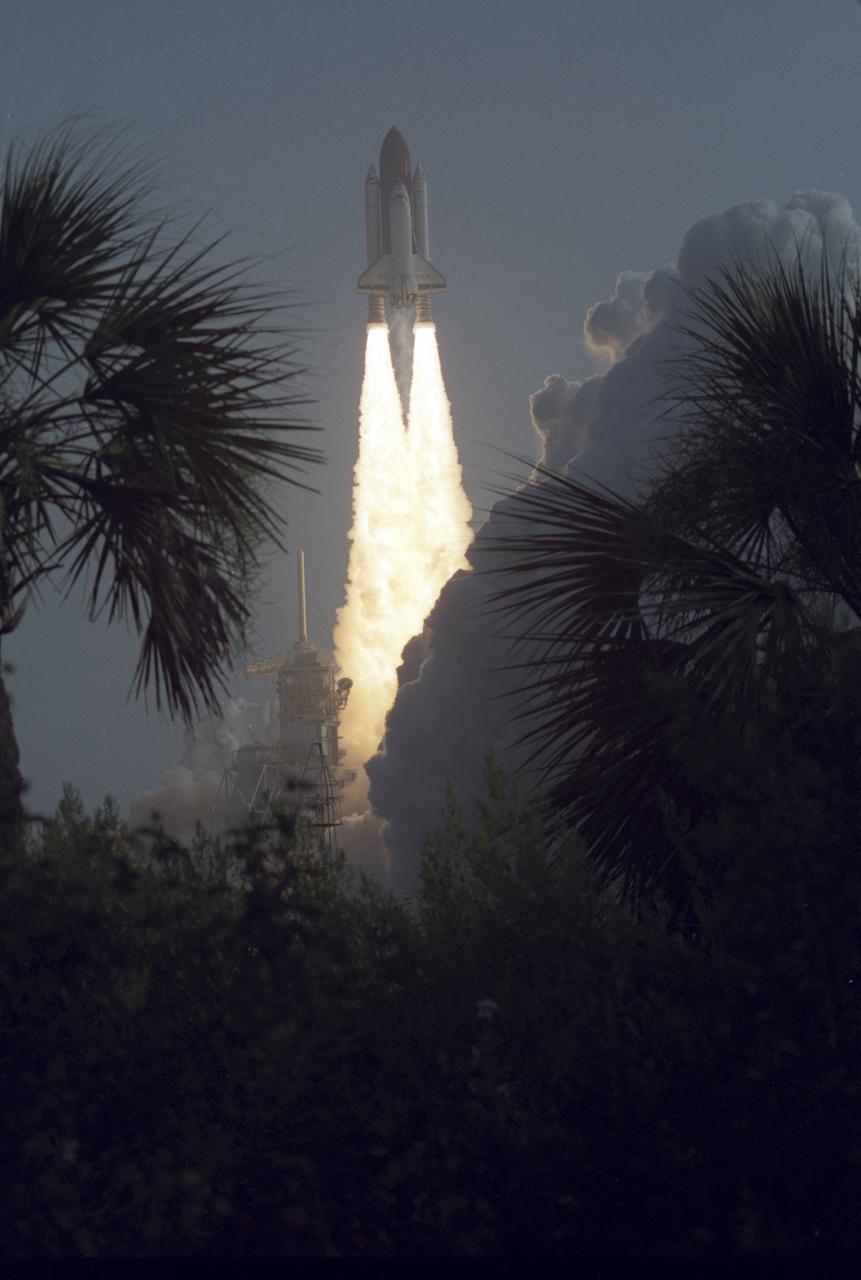

On August 8, 1989, the 4th mission dedicated to the Department of Defense (DOD), STS-28, lifted off from Kennedy Space Center’s (KSC) launch pad 39B. The five day mission included a crew of five: Richard N. (Dick) Richards, pilot; Brewster H. Shaw, commander; and mission specialists David C. Leestma, Mark N. Brown, and James C. (Jim) Adamson.
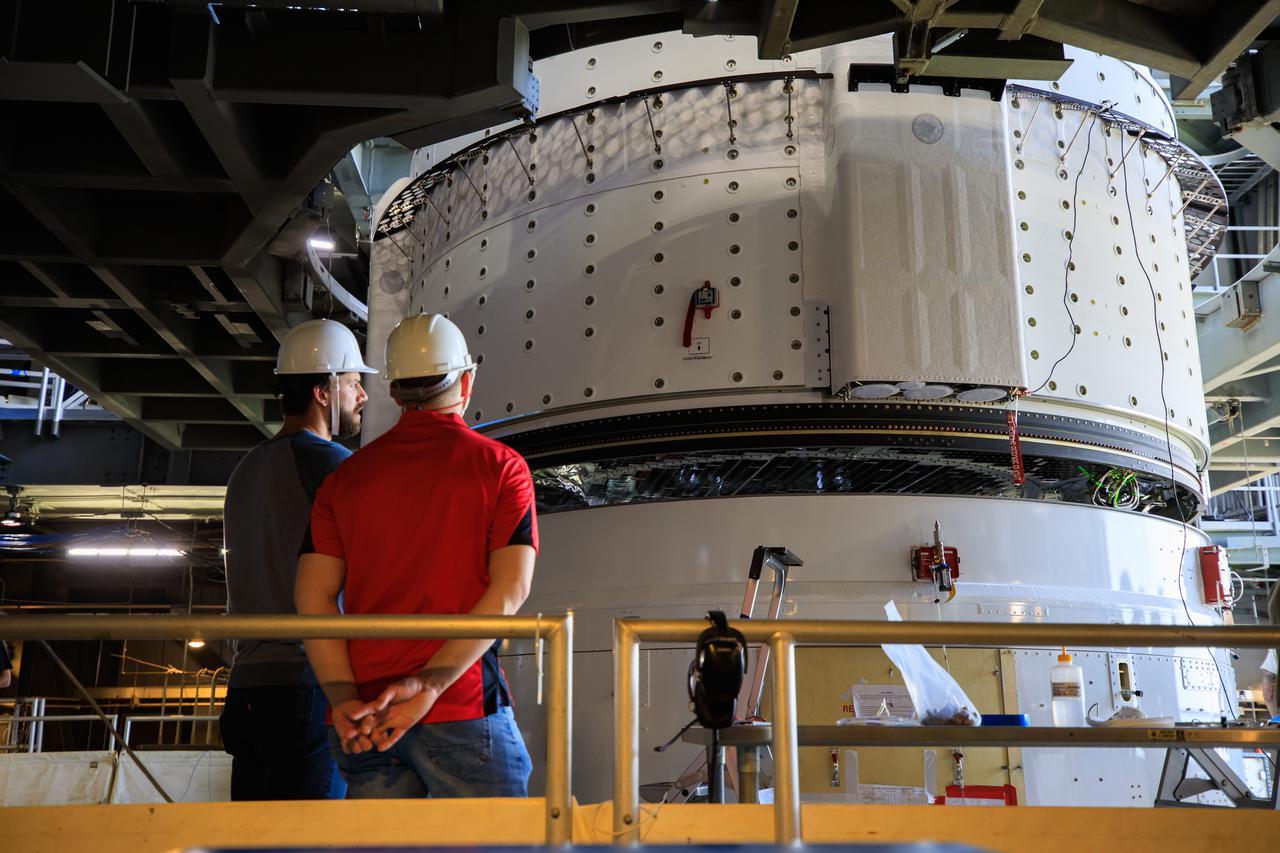
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
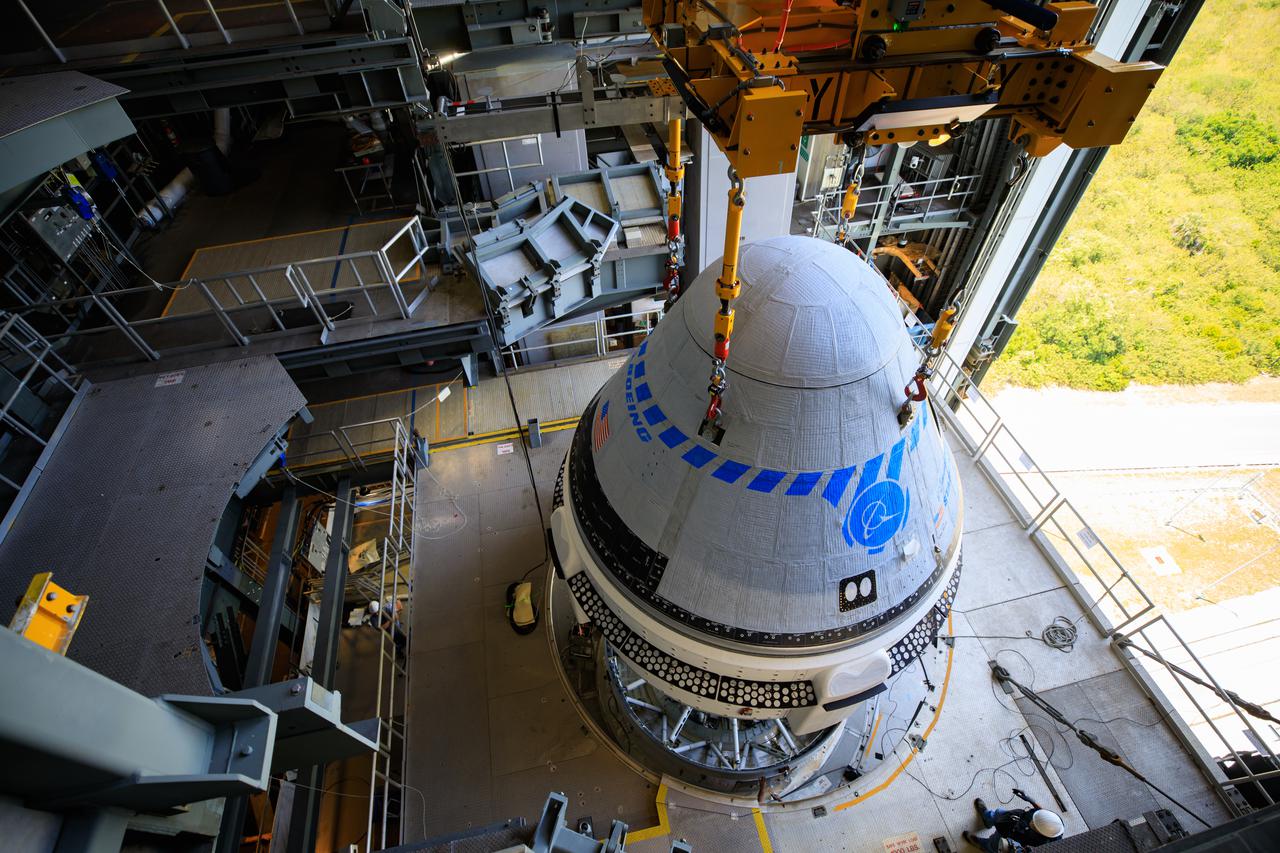
The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.
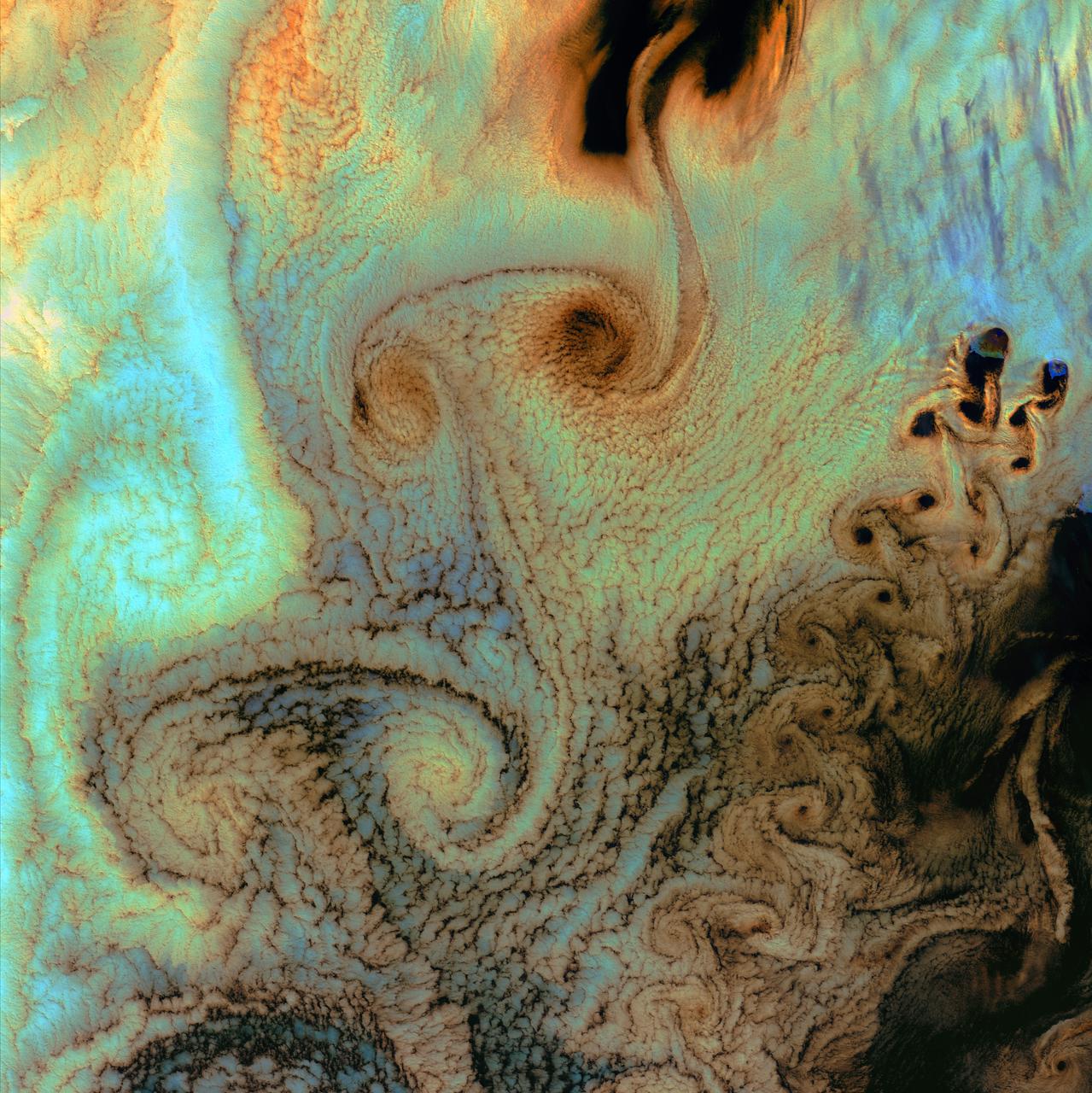
July 4th, 2002: Description: As air flows over and around objects in its path, spiraling eddies, known as Von Karman vortices, may form. The vortices in this image were created when prevailing winds sweeping east across the northern Pacific Ocean encountered Alaska’s Aleutian Islands. Source: Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a>
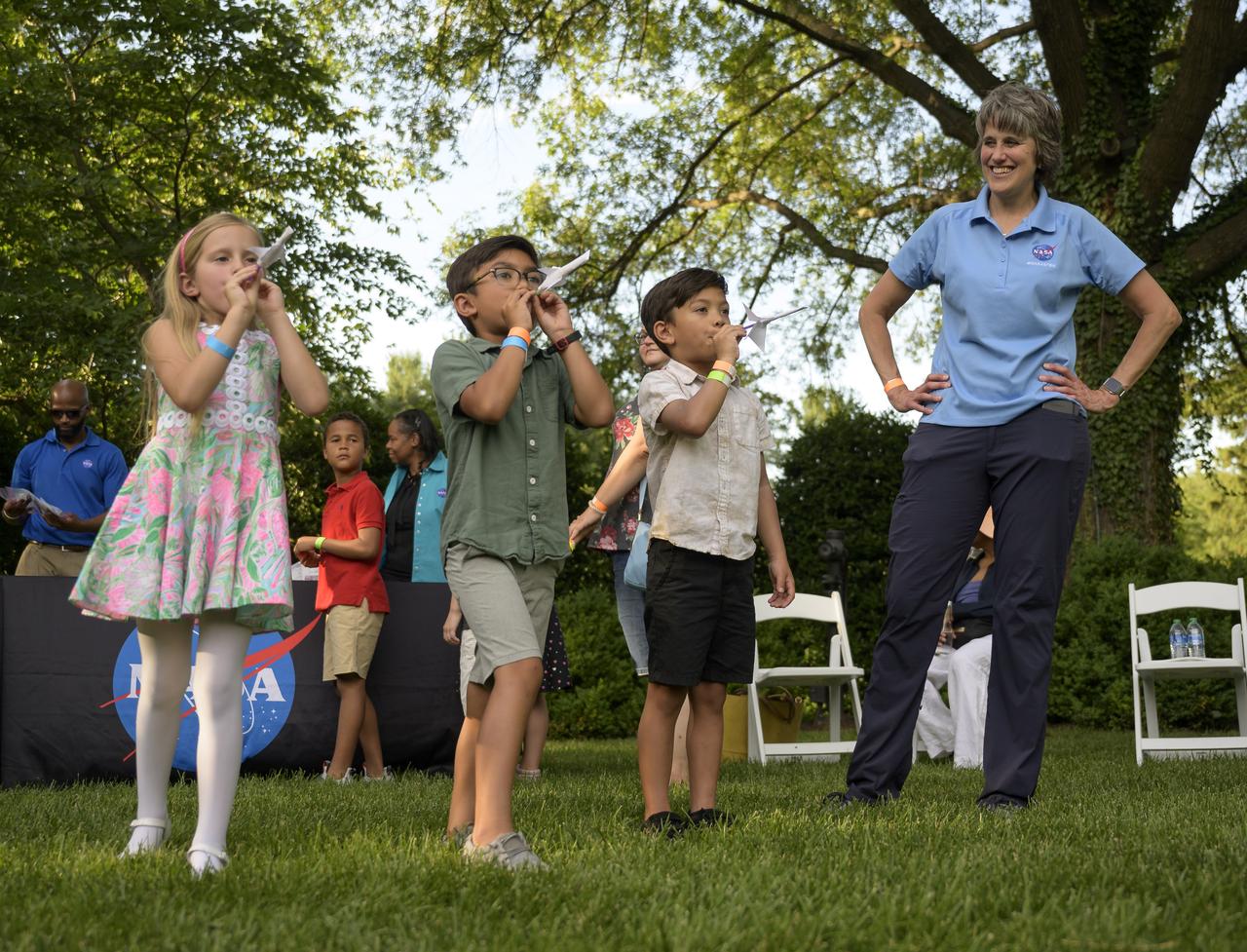
Cindy Hasselbring, NASA K-12 Education Advisor at NASA’s Office of STEM Engagement, works hands-on STEM activities with students from 4th-8th grade on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
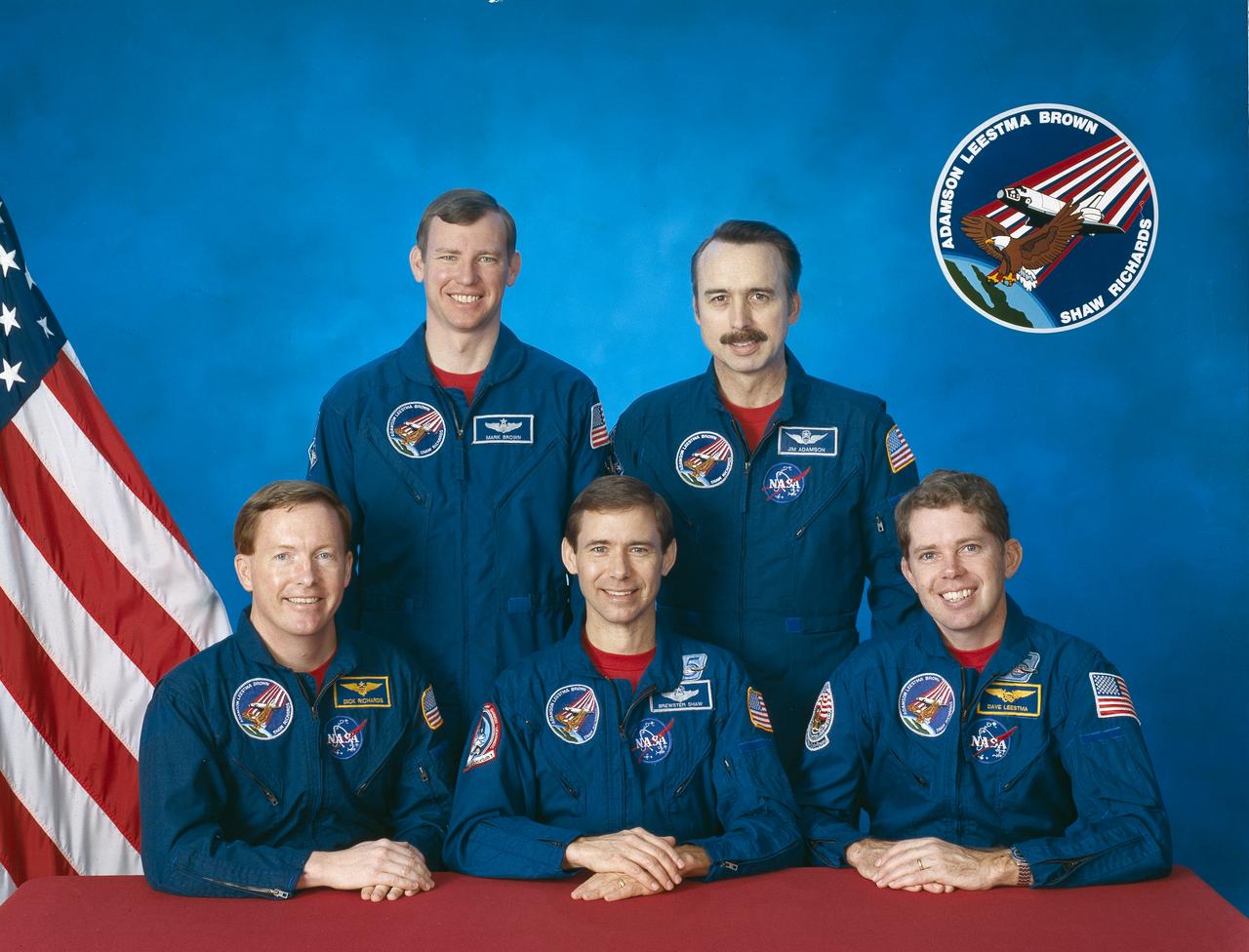

Five astronauts composed the STS-28 crew. Seated from left to right are Richard N. (Dick) Richards, pilot; Brewster H. Shaw, commander; and David C. Leestma, mission specialist 2. Standing, from left to right , are Mark N. Brown, mission specialist 3; and James C. (Jim) Adamson, mission specialist 1. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on August 8, 1989, the STS-28 mission was the 4th mission dedicated to the Department of Defense.
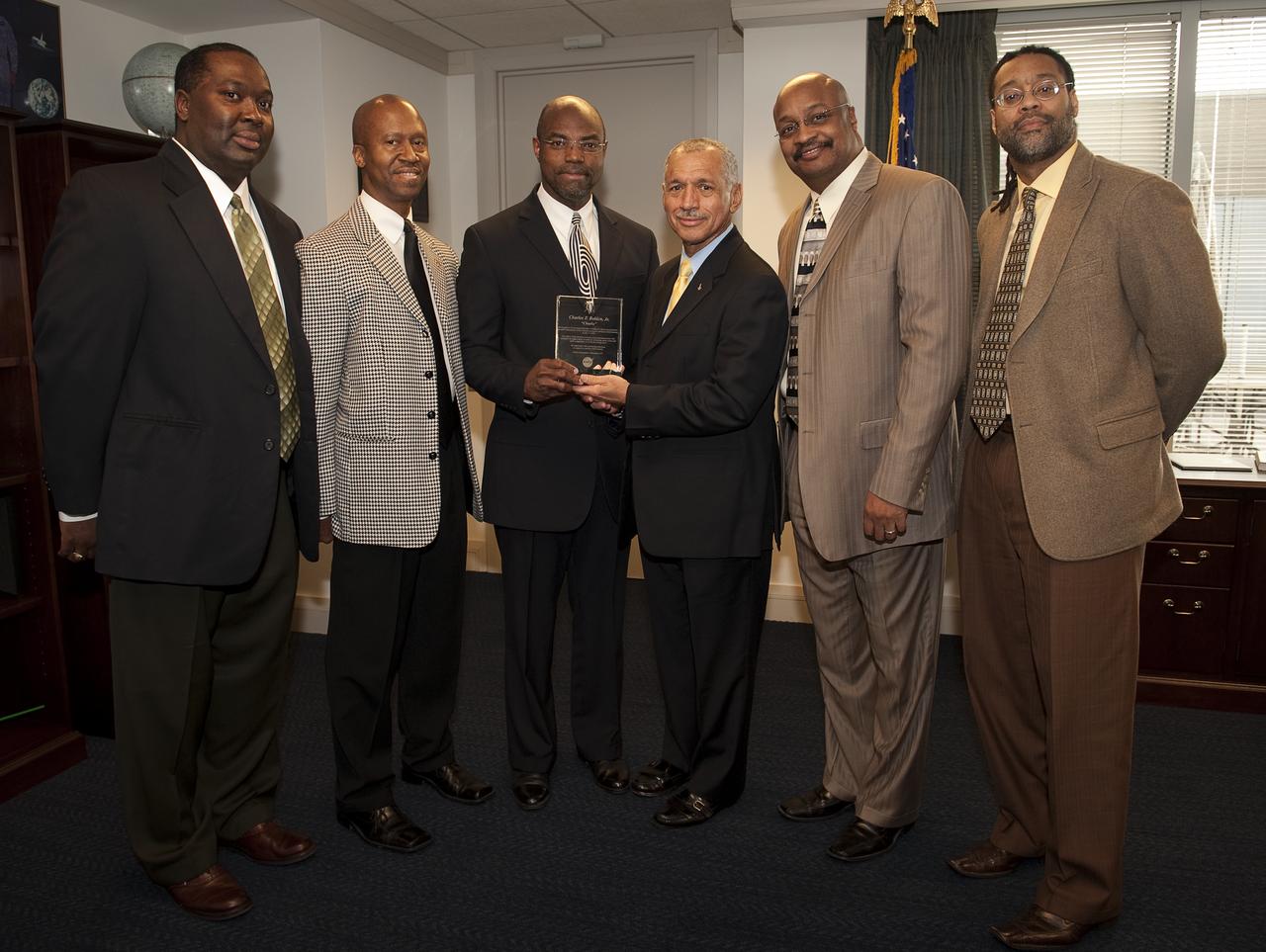

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, 4th from left, is presented a plaque in honor of him becoming the 12th NASA Administrator by NASA Headquarters members of his fraternity, Omega Psi Phi: from left, Andrew Hubbard, Clinton Green, Carl Person, Dwayne Brown, and Elbert Cox, right. Omega Psi Phi Fraternity, Inc. was founded at Howard University on Nov. 17, 1911. The phrase “friendship is essential to the soul," is the fraternity’s motto. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis on August 2, 1991, the STS-43 mission’s primary payload was the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite 5 (TDRS-5) attached to an Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), which became the 4th member of an orbiting TDRS cluster. The flight crew consisted of five astronauts: John E. Blaha, commander; Michael A. Baker, pilot; Shannon W. Lucid, mission specialist 1; James C. Adamson, mission specialist 2; and G. David Low, mission specialist 3.
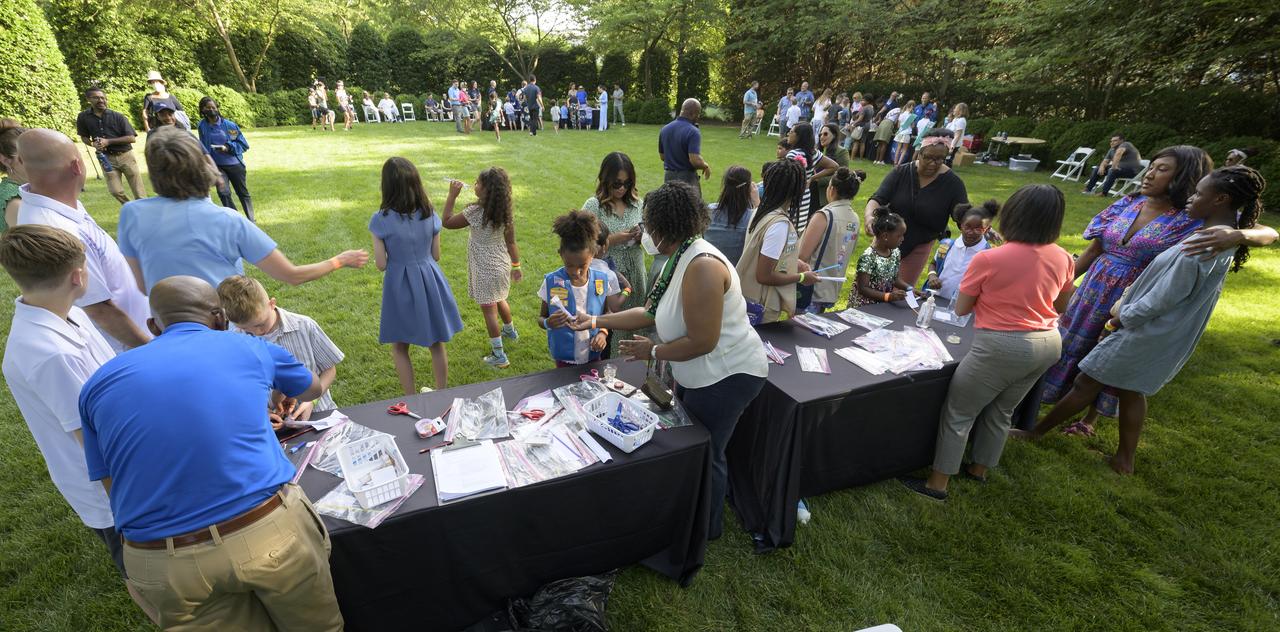

NASA astronauts and volunteers work hands-on STEM activities with students from 4th-8th grade on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
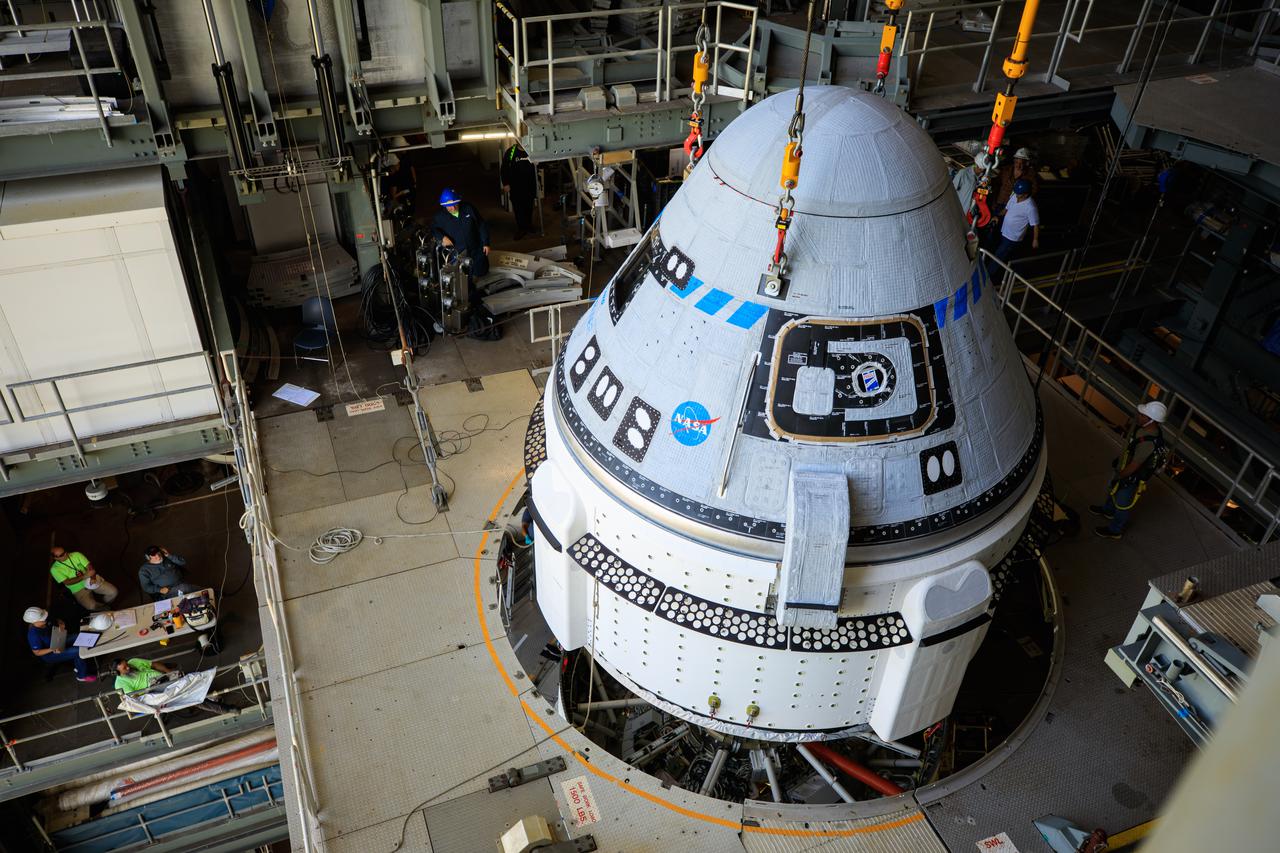

The Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft is lifted at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex-41 at Florida's Cape Canaveral Space Force Station on May 4th, 2022. Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for Boeing's second Orbital Flight Test (OFT-2) to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The spacecraft rolled out from Boeing's Commercial Crew and Cargo Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center earlier in the day.

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, 4th from left, along with Cadet First Class Grant Schlichting, left, Cadet Second Class Colt Crowson, and Cadet First Class Gavin Ross listen to Col Douglas “Beaker” Wickert, right, during a tour of the aeronautics lab at the United States Air Force Academy, Wednesday, Aug. 25, 2021, north of Colorado Springs, Colorado. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
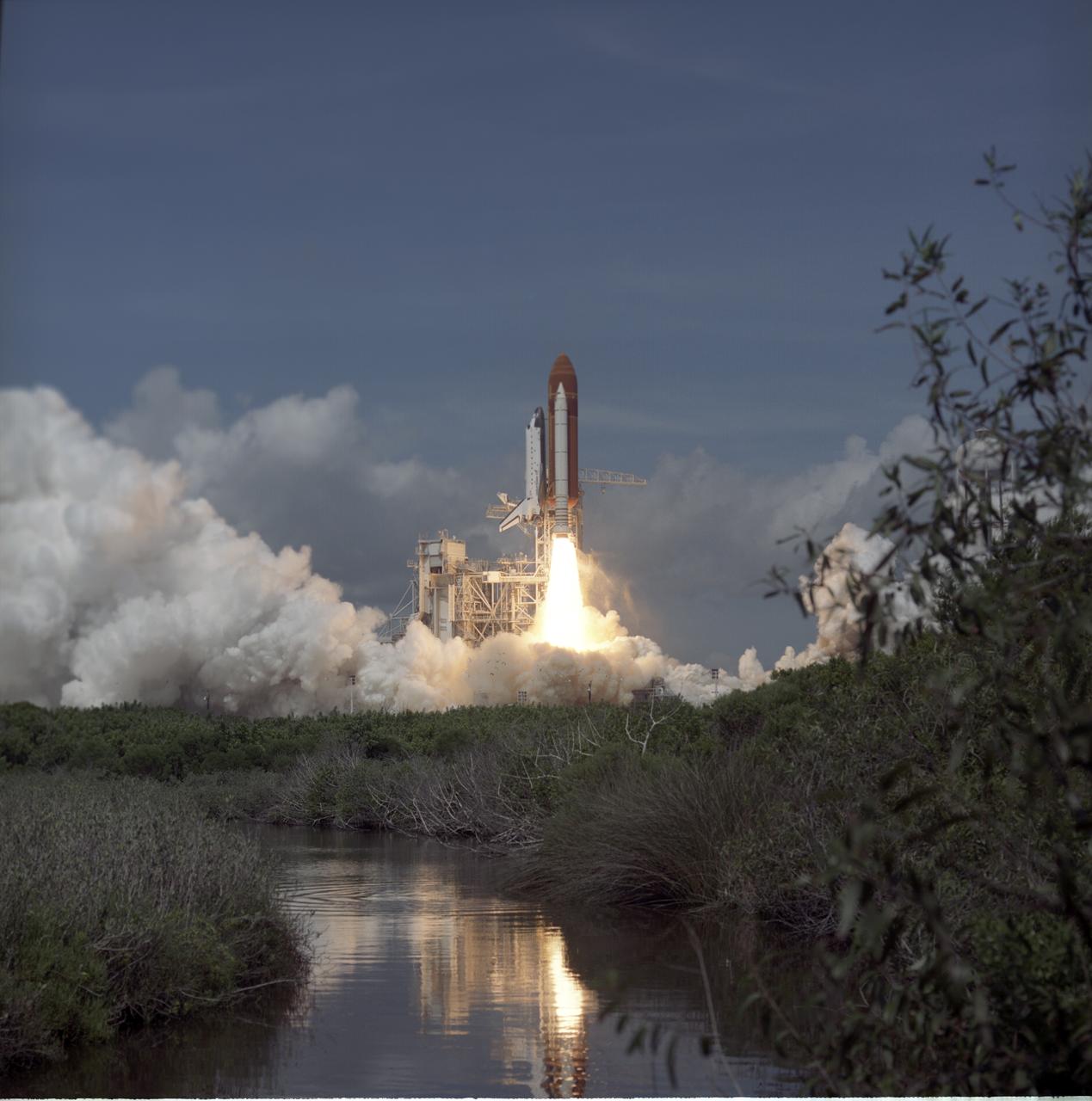

Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis on August 2, 1991, the STS-43 mission’s primary payload was the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite 5 (TDRS-5) attached to an Inertial Upper Stage (IUS), which became the 4th member of an orbiting TDRS cluster. The flight crew consisted of 5 astronauts: John E. Blaha, commander; Michael A. Baker, pilot; Shannon W. Lucid, mission specialist 1; James C. Adamson, mission specialist 2; and G. David Low, mission specialist 3.
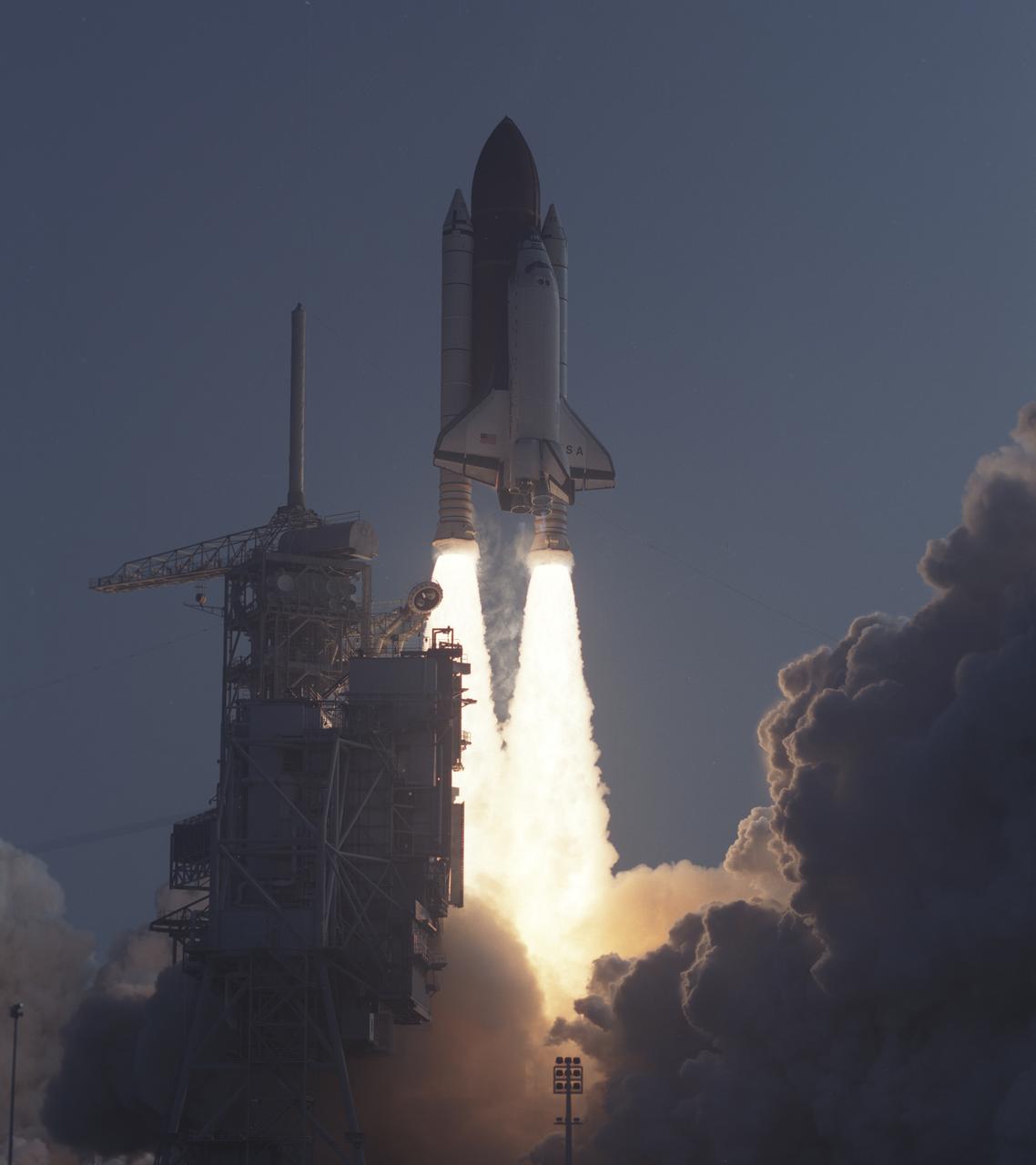

On August 8, 1989, the 4th mission dedicated to the Department of Defense (DOD), STS-28, lifted off from Kennedy Space Center’s (KSC) launch pad 39B. The five day mission included a crew of five: Richard N. (Dick) Richards, pilot; Brewster H. Shaw, commander; and mission specialists David C. Leestma, Mark N. Brown, and James C. (Jim) Adamson.
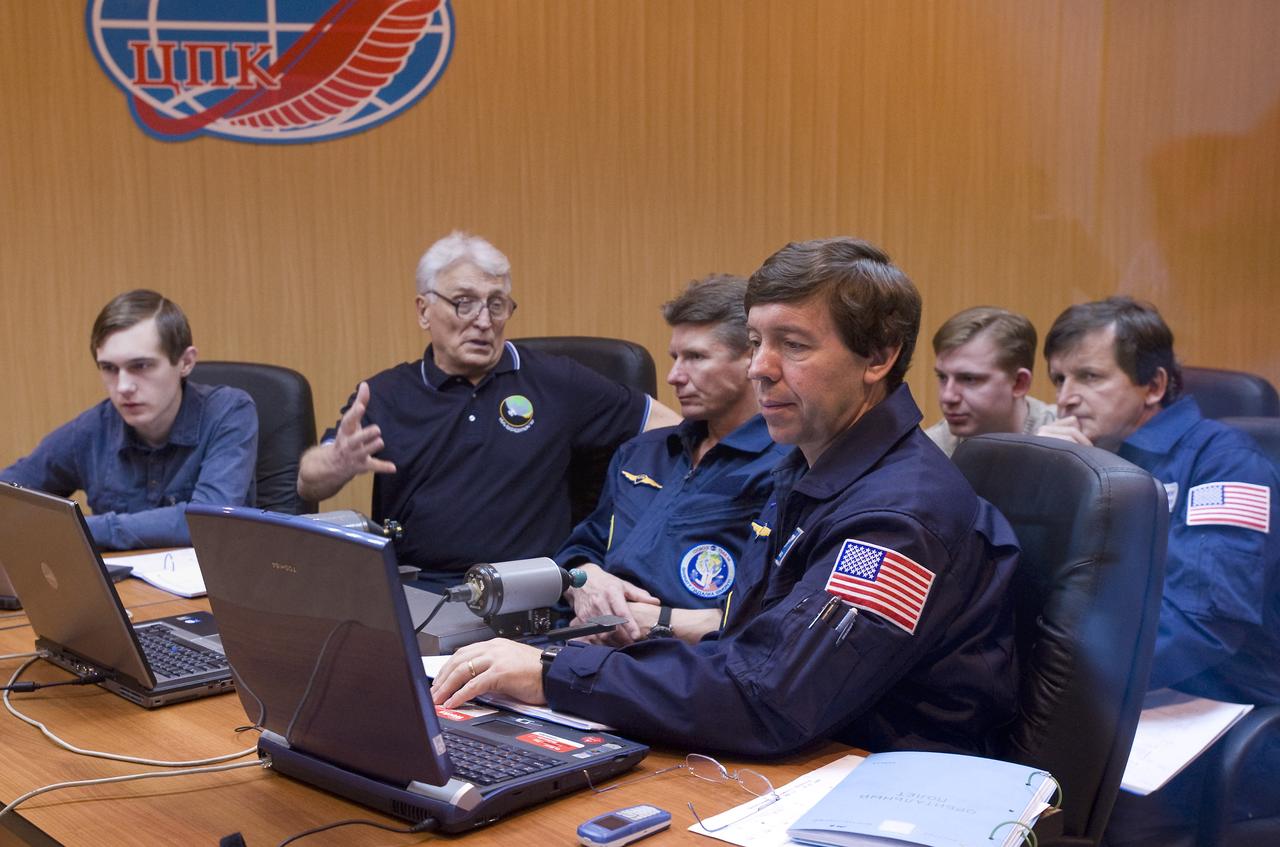

Expedition 19 Commander Gennady I. Padalka, 3rd from left, Flight Engineer Michael R. Barratt, 4th from left, and Spaceflight Participant Charles Simonyi, far right, along with cosmonaut instructors are seen through a quarantine windowed room as they participate in Soyuz rendezvous and docking training at the Cosmonaut Hotel, Saturday, March 21, 2009 in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. (Photo Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls)
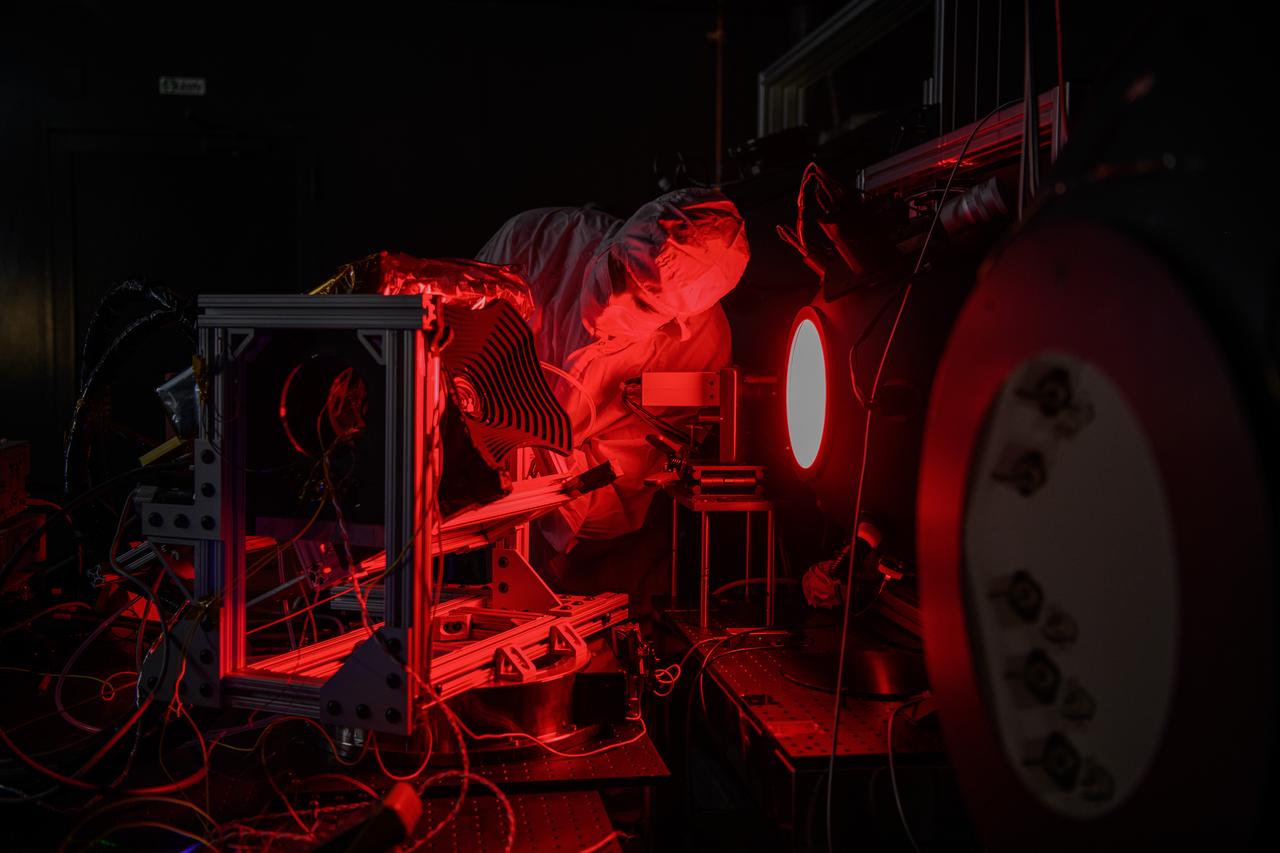

An engineer inspects the The Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter #2 (HARP2) instrument during calibration testing after at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt Maryland on October 4th, 2022. HARP2 is one of three instruments on NASA's Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) observatory, it was designed and built by UMBC's Earth and Space Institute.

NASA Kennedy Space Center's Associate Director Kelvin Manning, center, signs a license agreement with the President and CEO of ecoSPEARS, which allows the company to commercially sell a soil remediation technology developed by a research team at Kennedy. The technology, known as Sorbent Polymer Extraction And Remediation System, is designed to capture and remove polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) from contaminated sediments in waterways and wetlands.
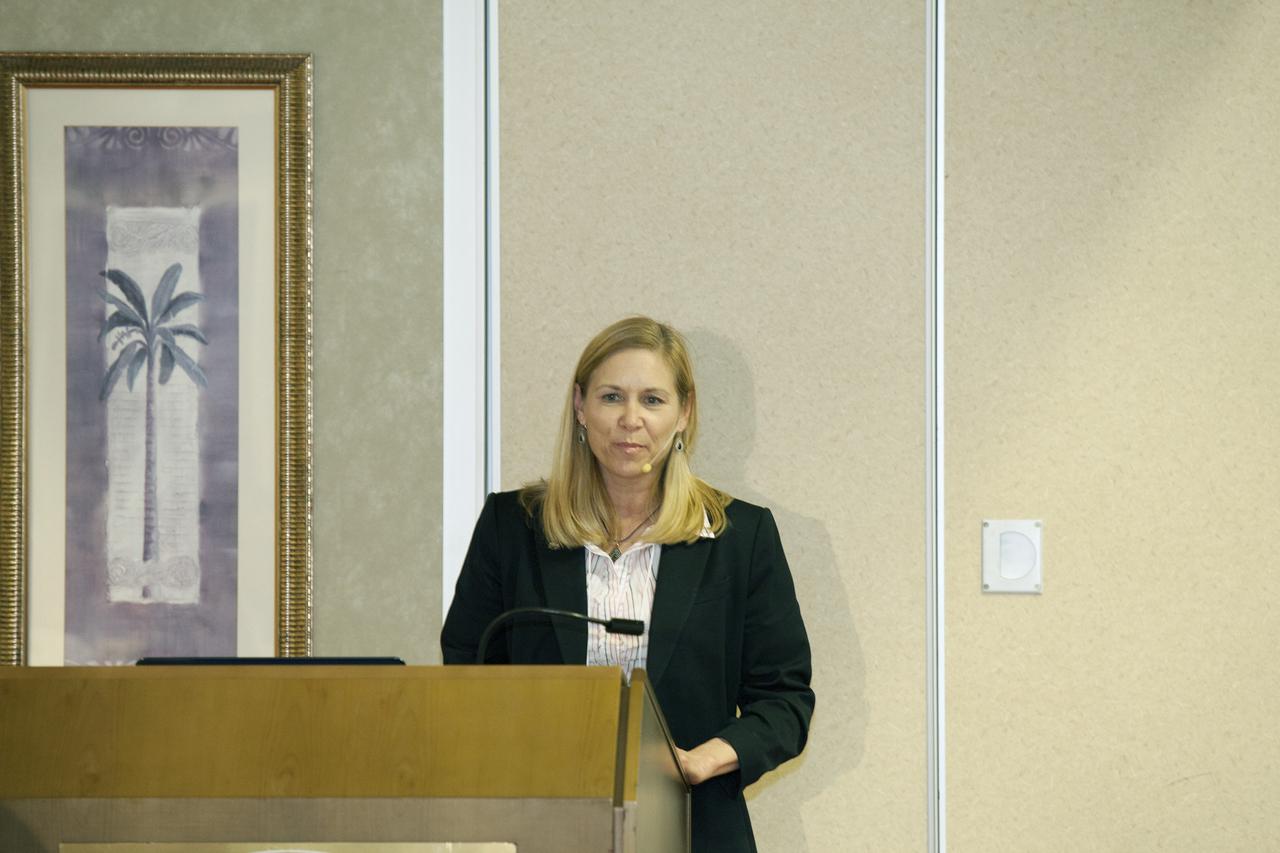

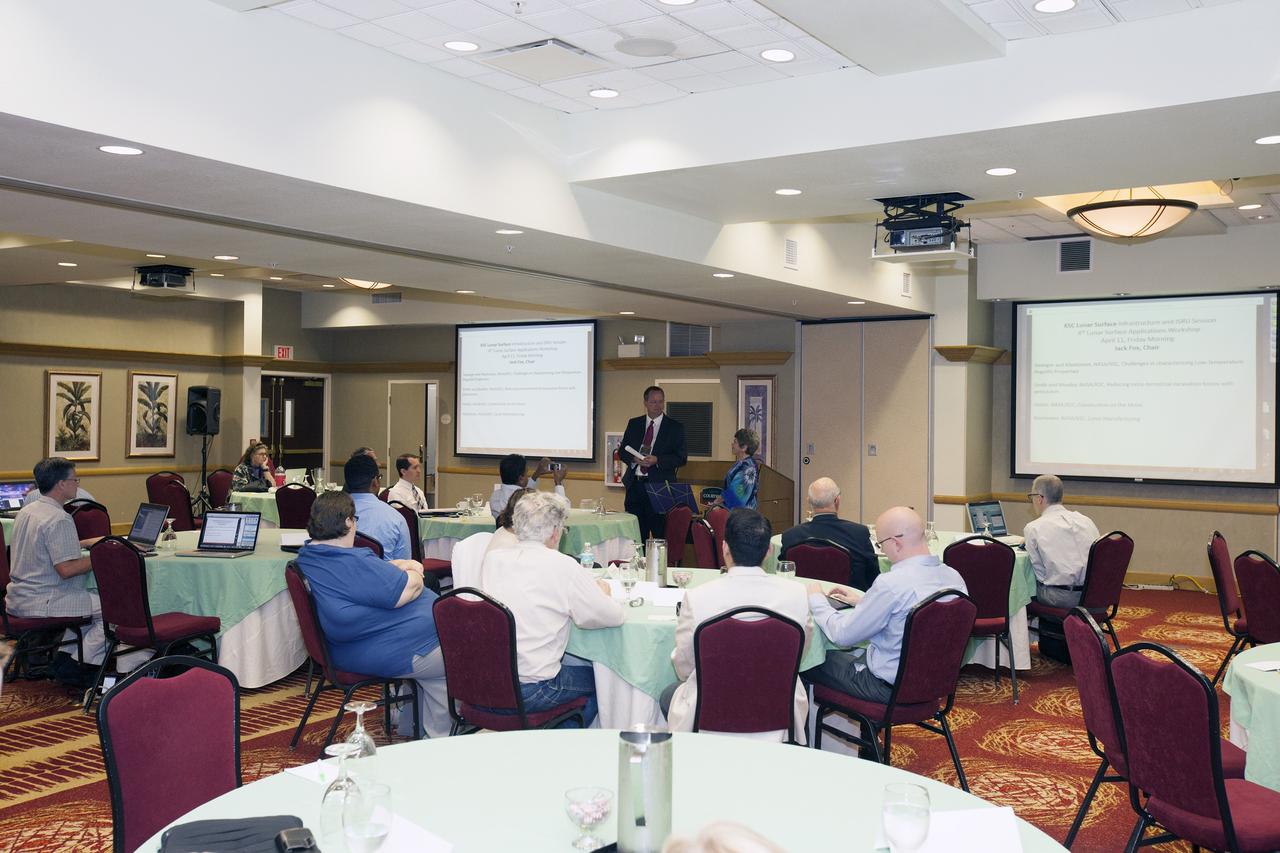
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Janet Petro, deputy director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

A "Hidden Figures Way" street sign is seen at the corner of 4th and E Street SW across from the NASA Headquarters building following a dedication ceremony, Wednesday, June 12, 2019 in Washington, DC. The 300 block of E Street SW in front of the NASA Headquarters building was designated as "Hidden Figures Way" to honor Katherine Johnson, Dorothy Vaughan, Mary Jackson and all women who have dedicated their lives to honorably serving their country, advancing equality, and contributing to the space program of the United States. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
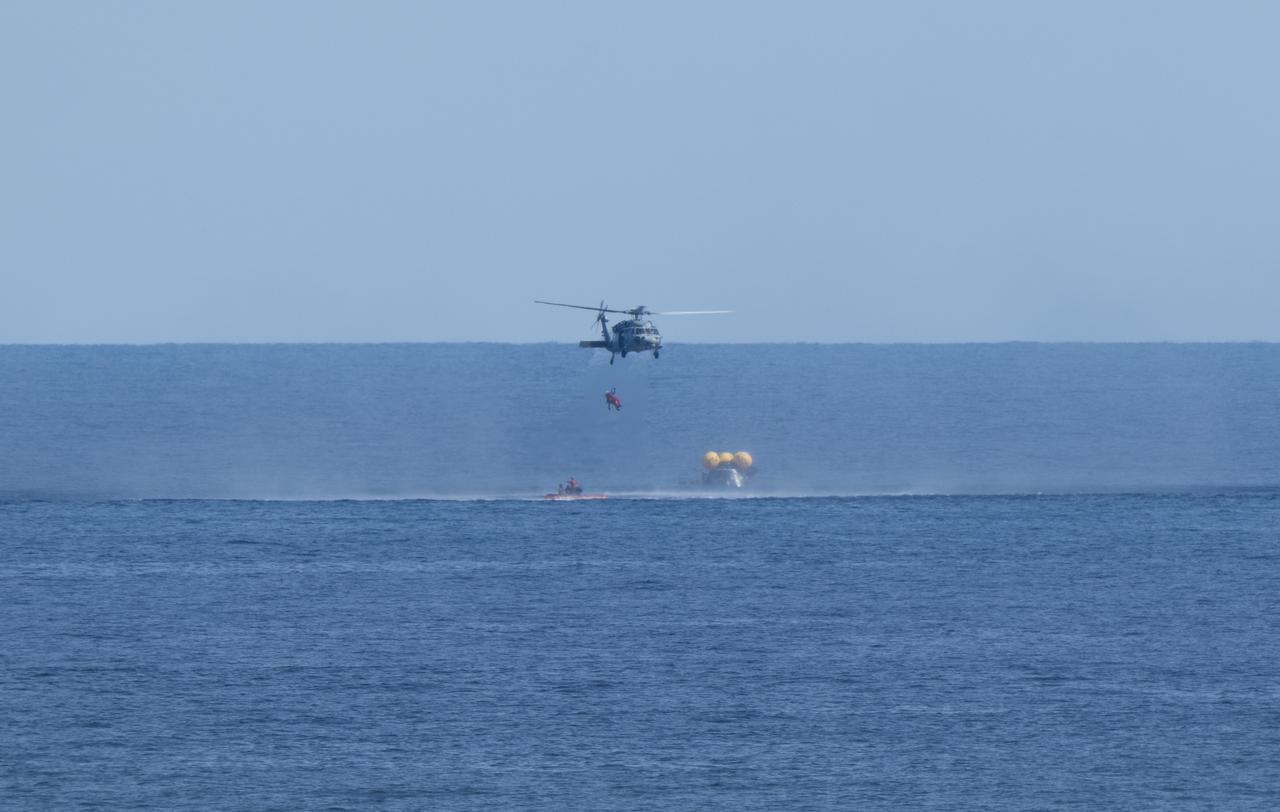

A Navy MH-60 Seahawk from Helicopter Sea Combat Squadron (HSC) 23 is seen as it lifts ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Luca Parmitano as teams practice Artemis recovery operations during Underway Recovery Test-12 onboard USS Somerset off the coast of California, Thursday, March 27, 2025. During the test, NASA and Department of Defense teams are practicing to ensure recovery procedures are validated as NASA plans to send the Artemis II astronauts around the Moon and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky) 4th lift
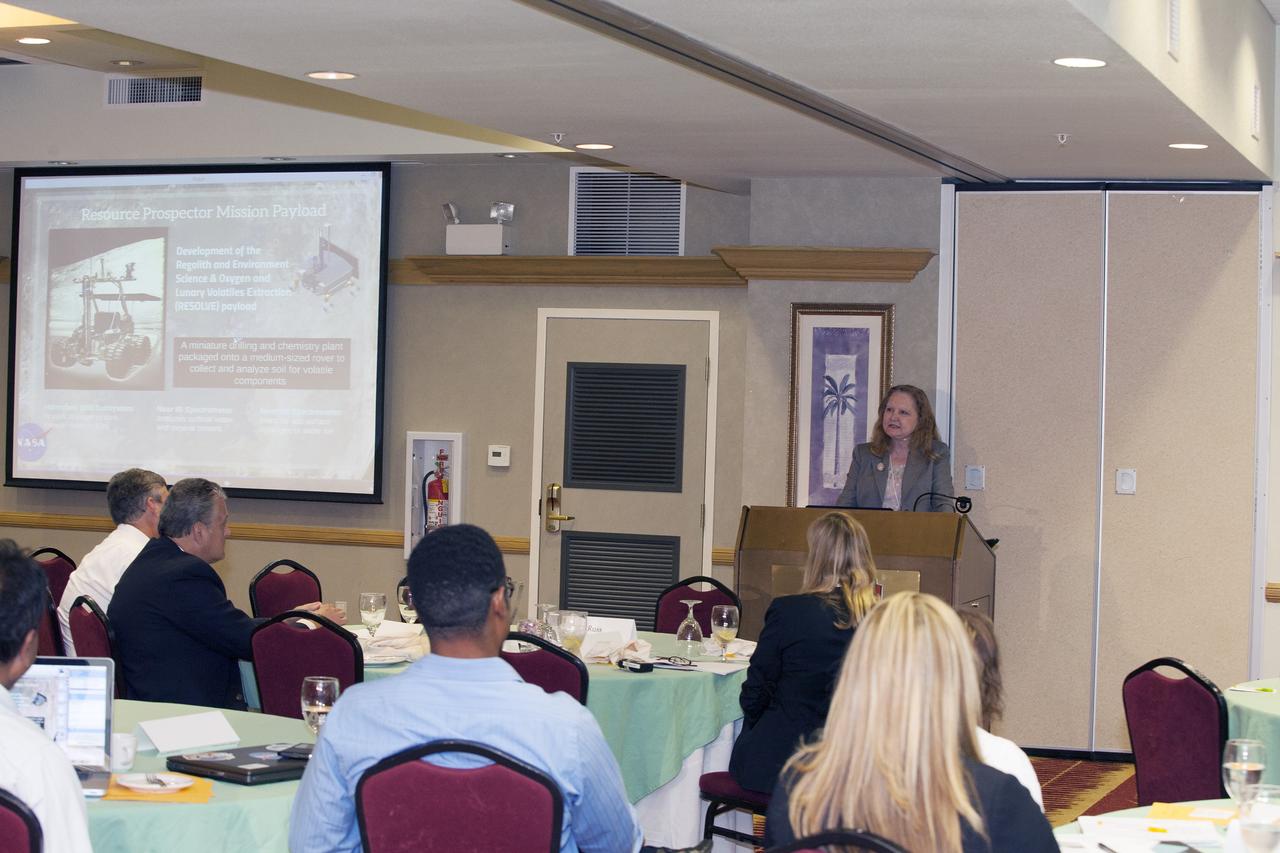

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Karen Thompson, NASA's chief technologist at the Kennedy Space Center, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Janet Petro, deputy director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
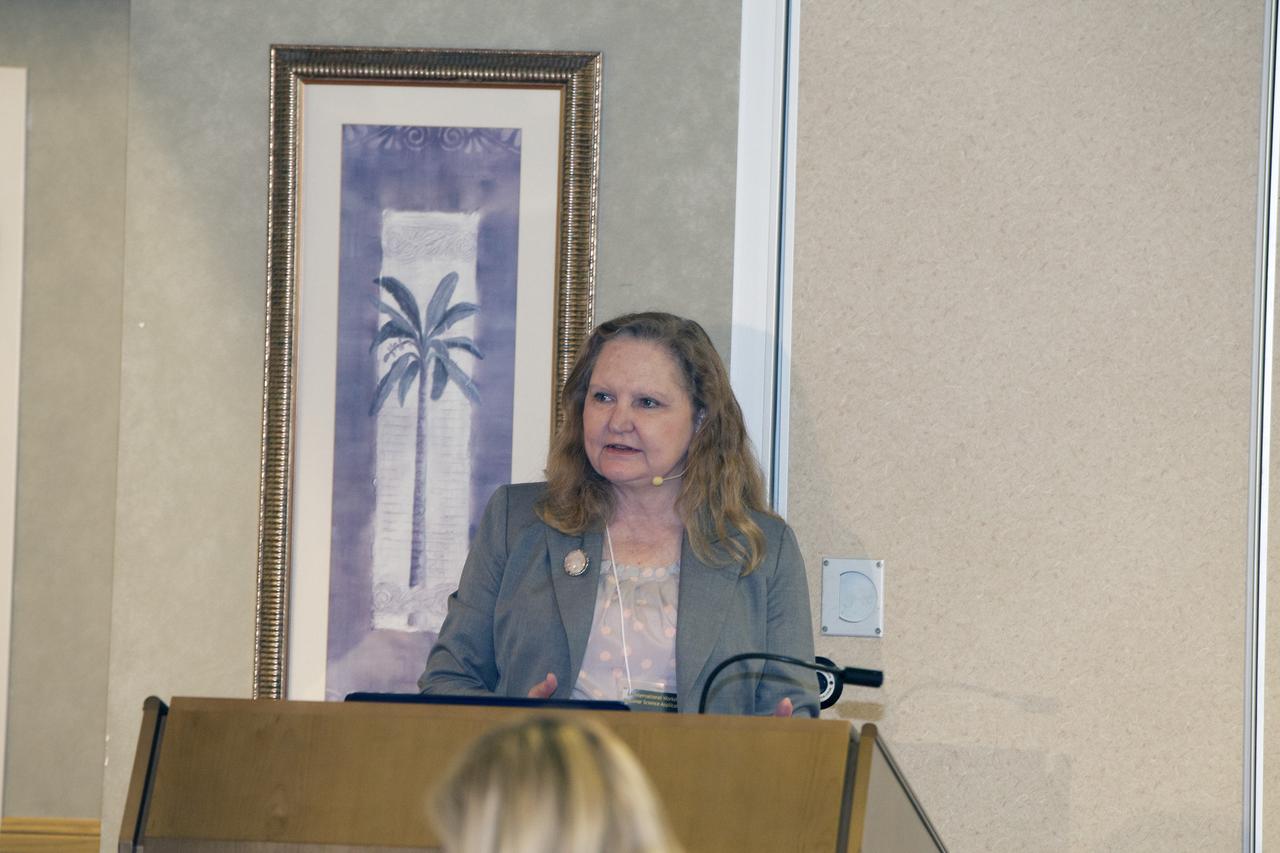

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Karen Thompson, NASA's chief technologist at the Kennedy Space Center, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
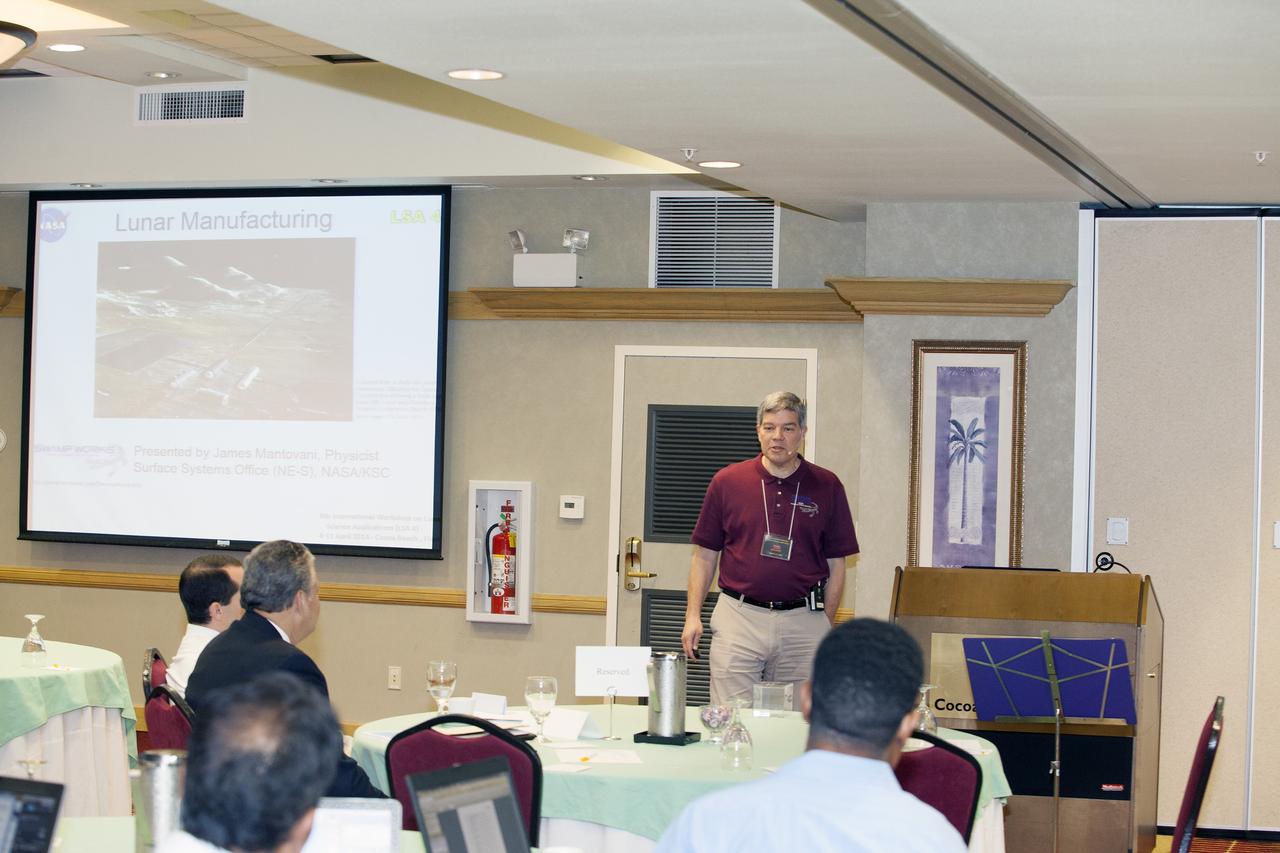

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., James Mantovani of the NASA Surface Systems Office at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
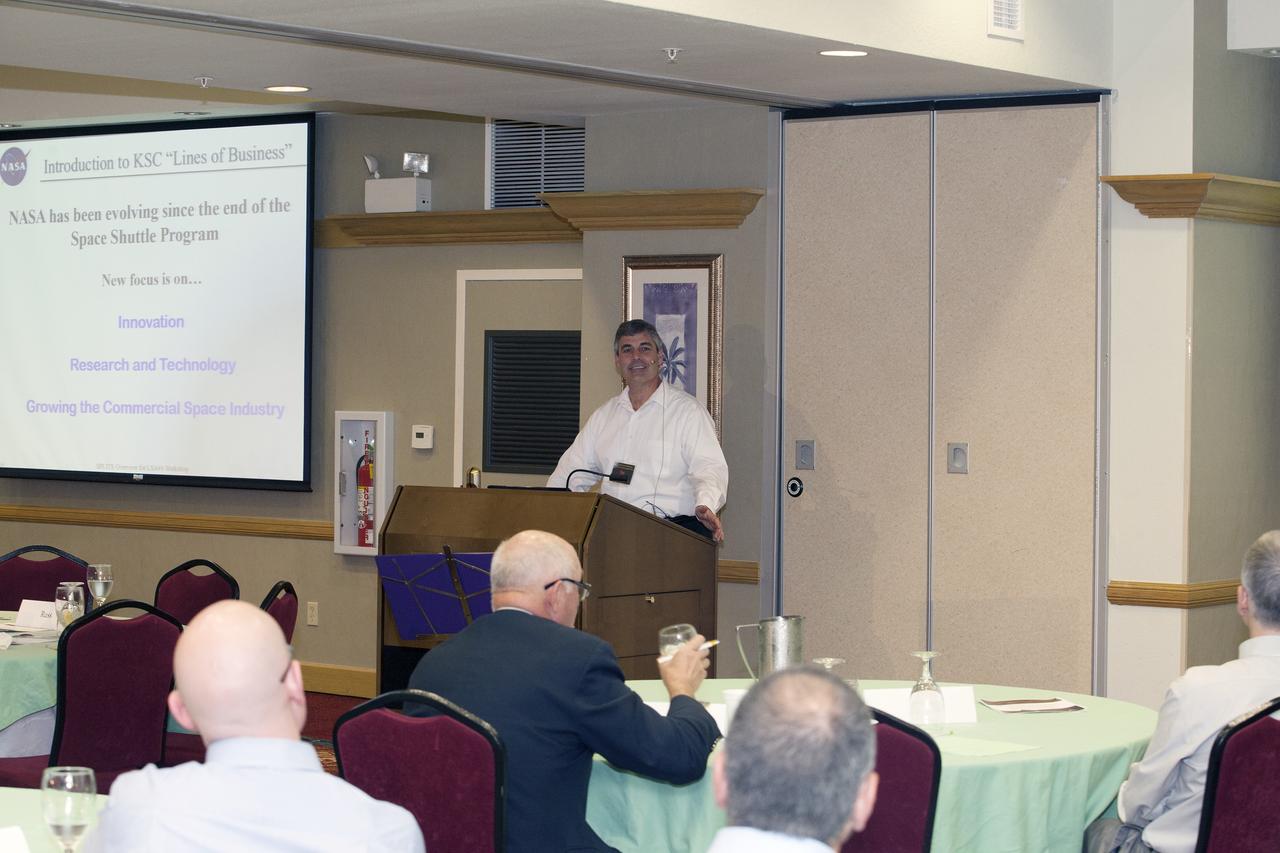

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Greg Clements, chief of Kennedy's Control and Data Systems Division and lead for the Engineering and Technology's Small Payload Integrated Testing Services, or SPLITS, line of business, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
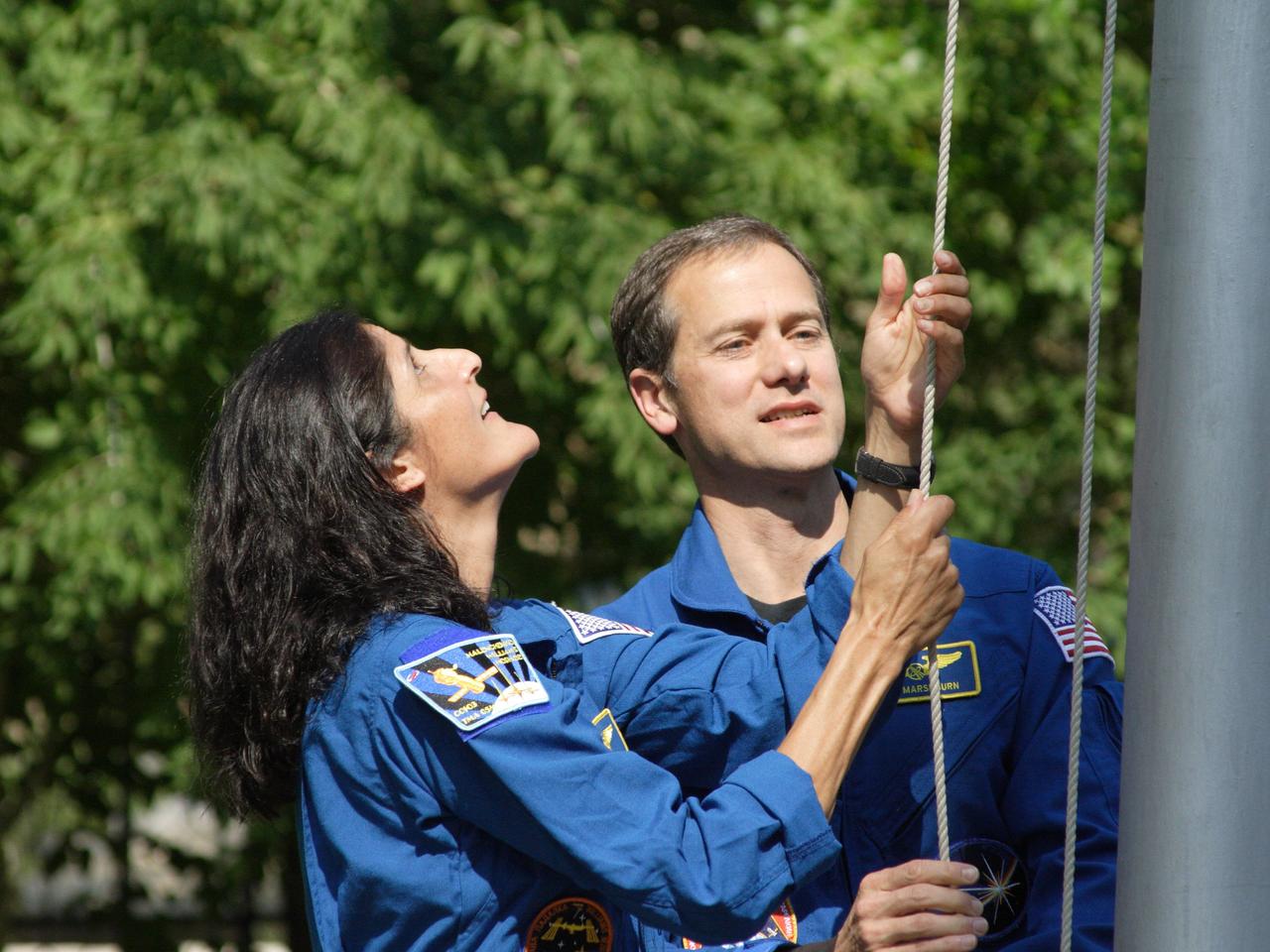

Outside their Cosmonaut Hotel crew quarters in Baikonur, Kazakhstan, Expedition 32 prime crew member Flight Engineer Sunita Williams of NASA (left) and backup Flight Engineer Tom Marshburn of NASA (right) raise the Stars and Stripes on the 4th of July, 2012 in a traditional flag-raising ceremony that was part of the pre-launch activities leading up to the launch of the next crew to the International Space Station. Williams, Soyuz Commander Yuri Malenchenko and Flight Engineer Aki Hoshide of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency will launch to the station July 15 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in their Soyuz TMA-05M spacecraft. NASA/Victor Zelentsov

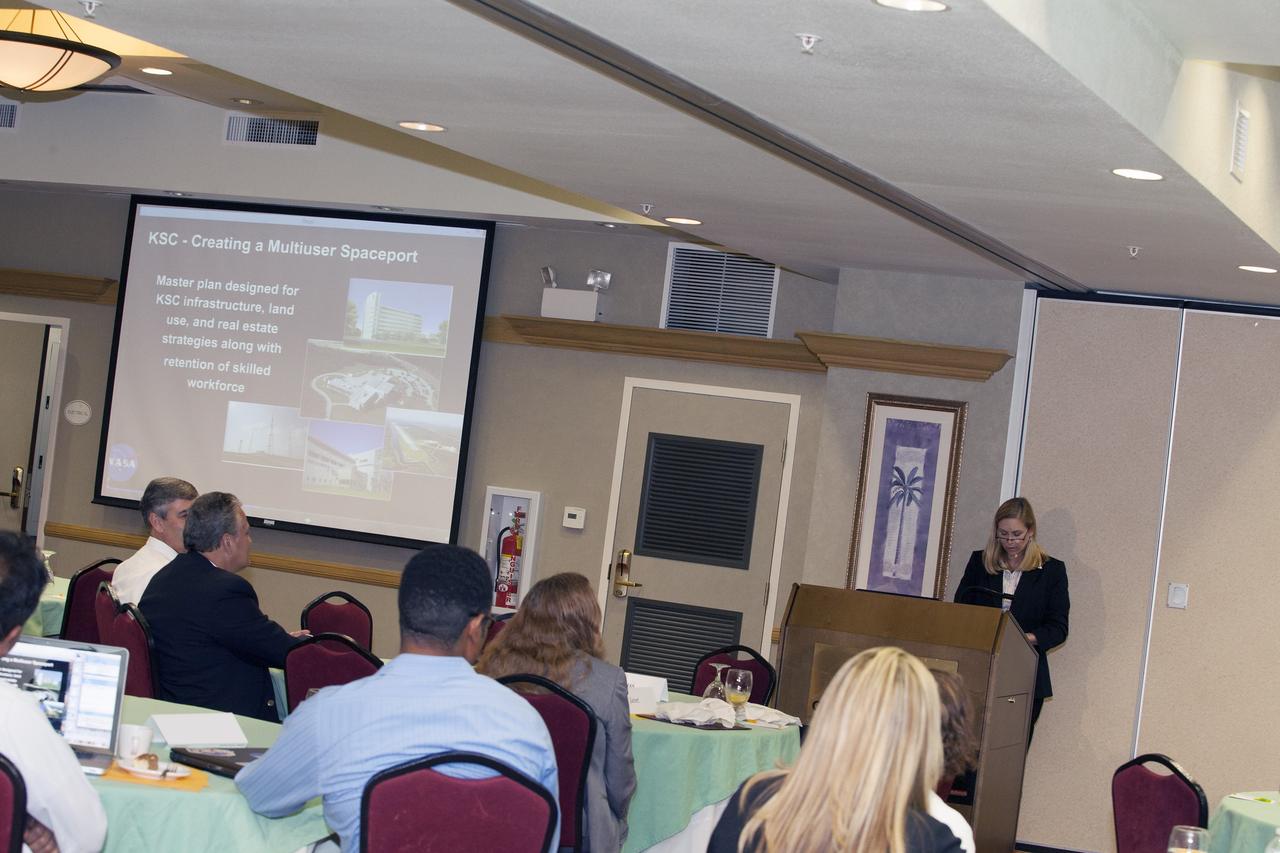
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Janet Petro, deputy director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

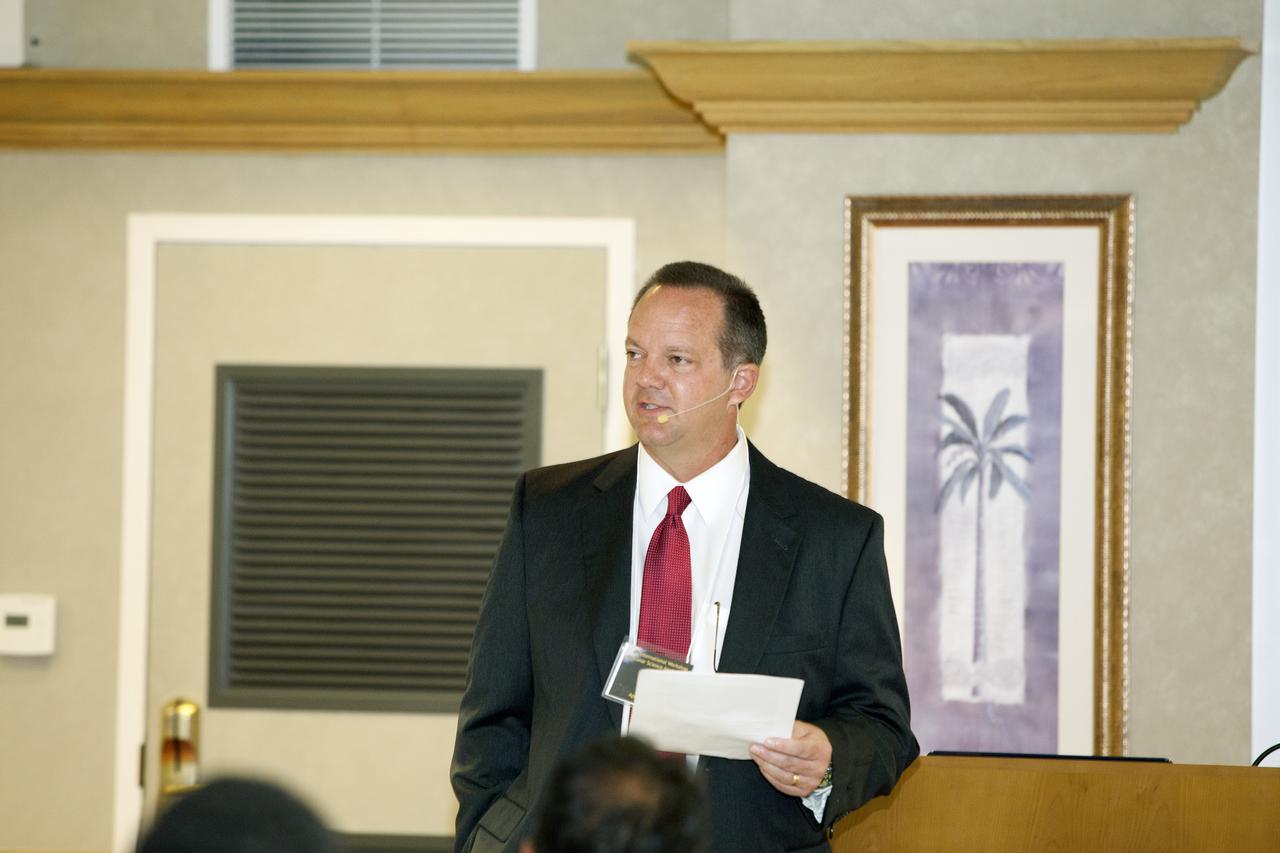
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Tom Engler, deputy director of Center Planning and Development at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
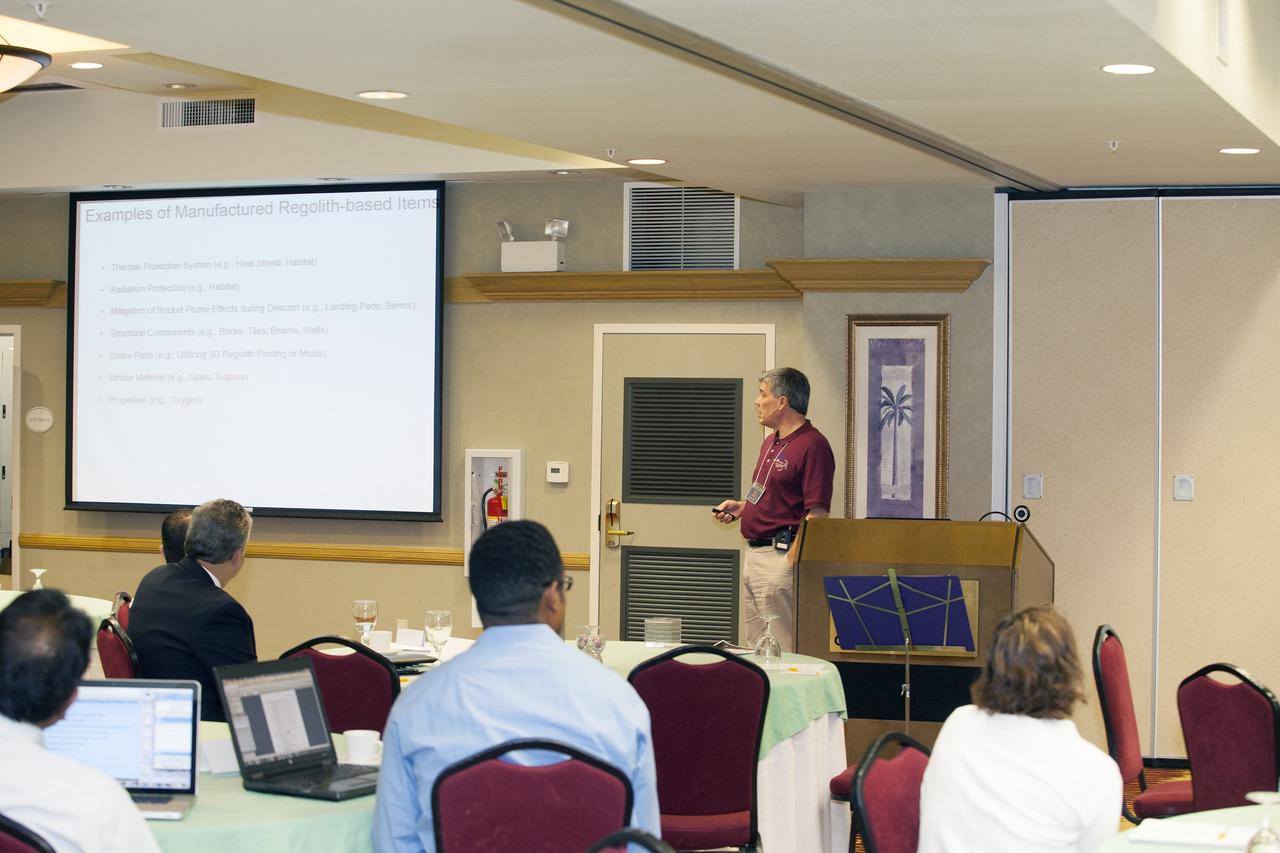

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., James Mantovani of the NASA Surface Systems Office at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Tom Engler, deputy director of Center Planning and Development at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
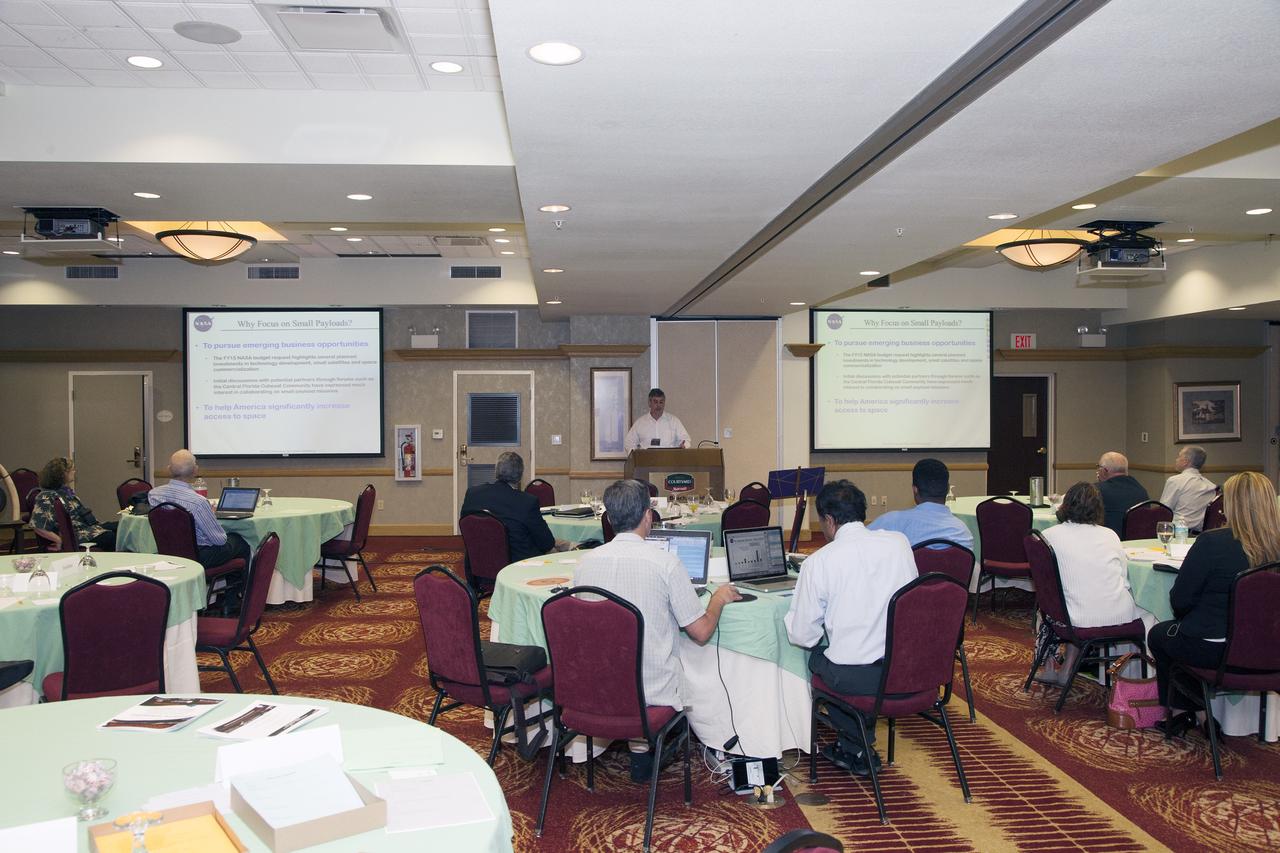

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Greg Clements, chief of Kennedy's Control and Data Systems Division and lead for the Engineering and Technology's Small Payload Integrated Testing Services, or SPLITS, line of business, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
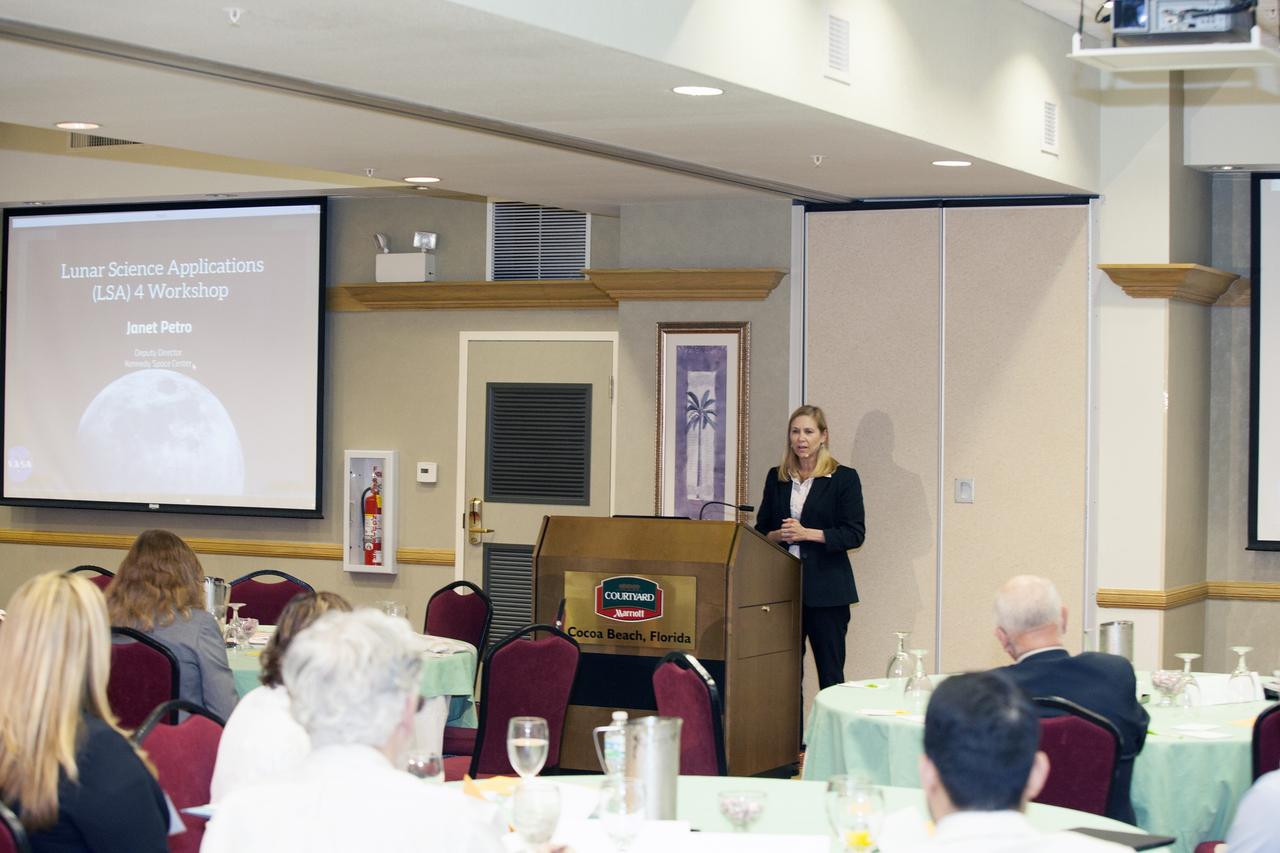

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Marriott Courtyard Hotel in Cocoa Beach, Fla., Janet Petro, deputy director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center, speaks to participants in the 4th International Workshop on Lunar and Planetary Compact and Cryogenic Science and Technology Applications. Scientists, engineers and entrepreneurs interested in research on the moon and other planetary surfaces, recently participated in the Workshop. Taking place April 8-11, 2014, the event was designed to foster collaborative work among those interested in solving the challenges of building hardware, software and businesses interested in going back to the moon and exploring beyond. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
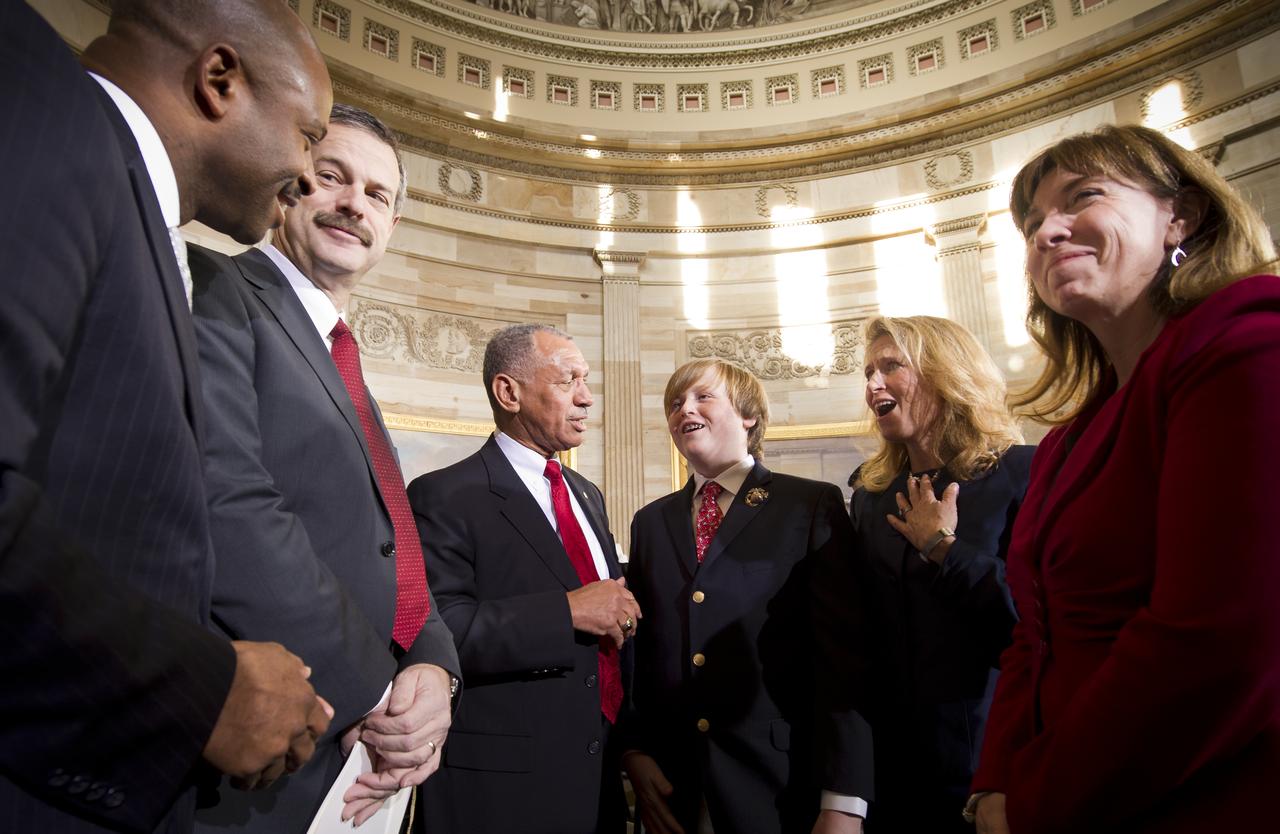

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden. 3rd from left, introduces Edward Moore Kennedy III, 4th from left, to NASA Astronaut Leland Melvin, left, and former NASA Astronaut Scott Altman, 2nd from left, as Edward's mother Kiki Kennedy, wife of Edward M Kennedy Jr. and NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver, right, look on at an event recognizing the 50th anniversary of the inauguration of John F. Kennedy as president of the United States, Thursday, Jan. 20, 2001 at the U.S. Capitol rotunda. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
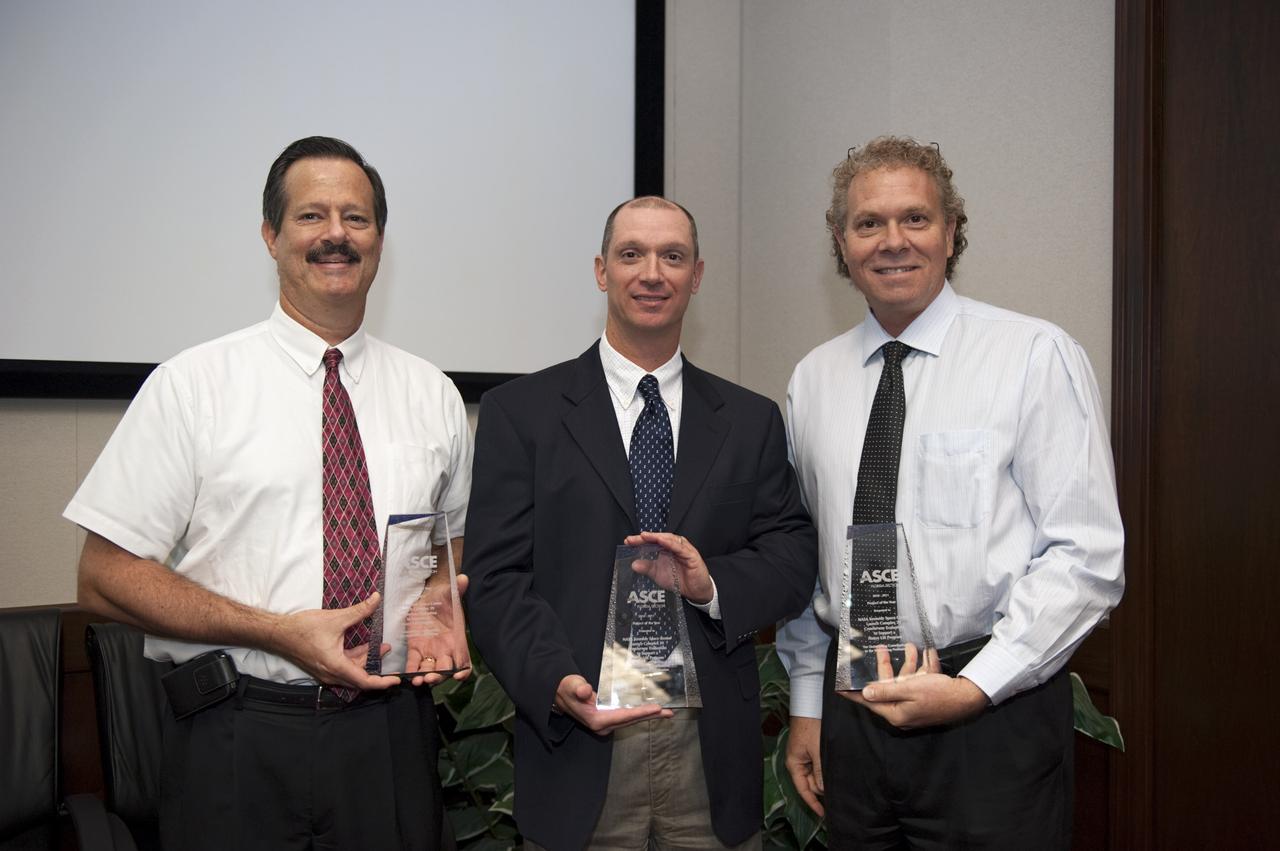

American Society Civil Enginner (ASCE) Project of Year Award Presentation
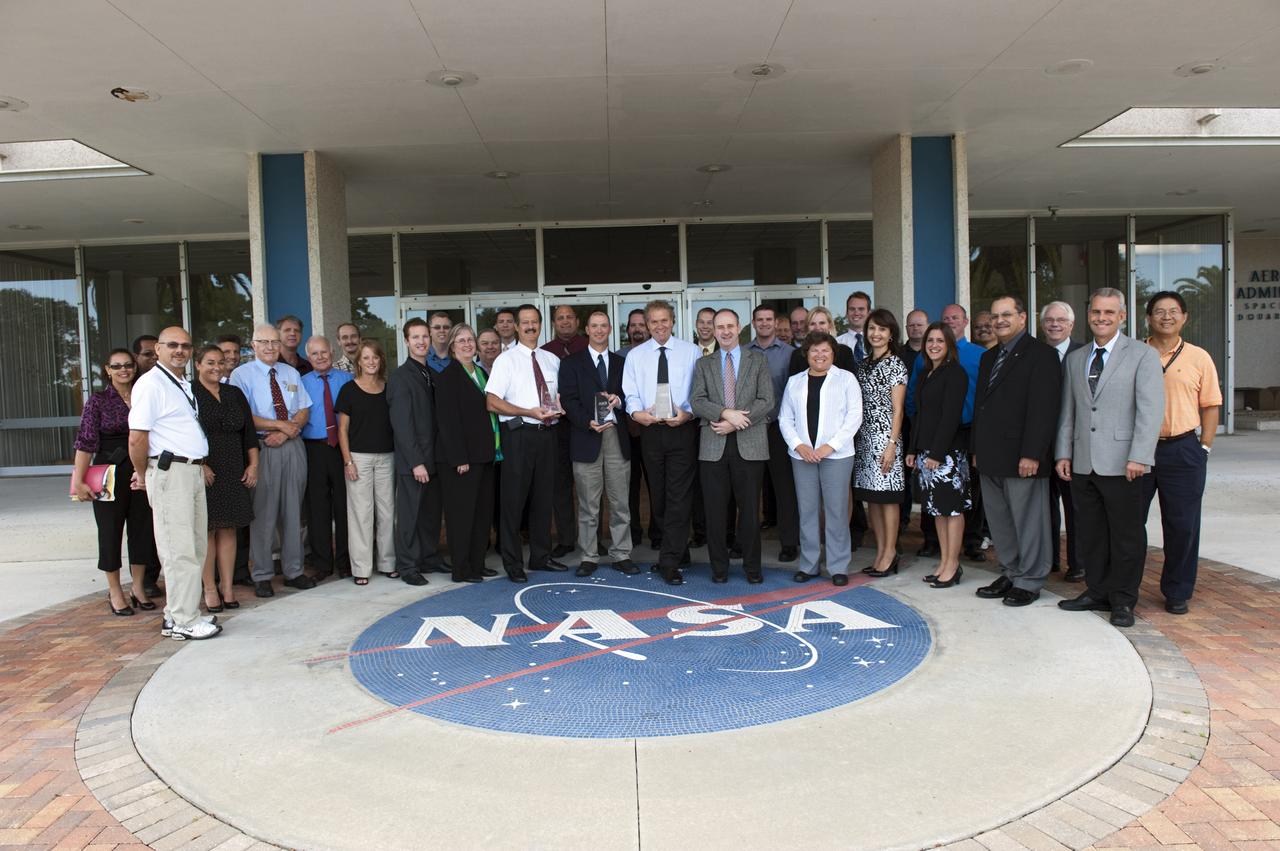

American Society Civil Enginner (ASCE) Project of Year Award Presentation
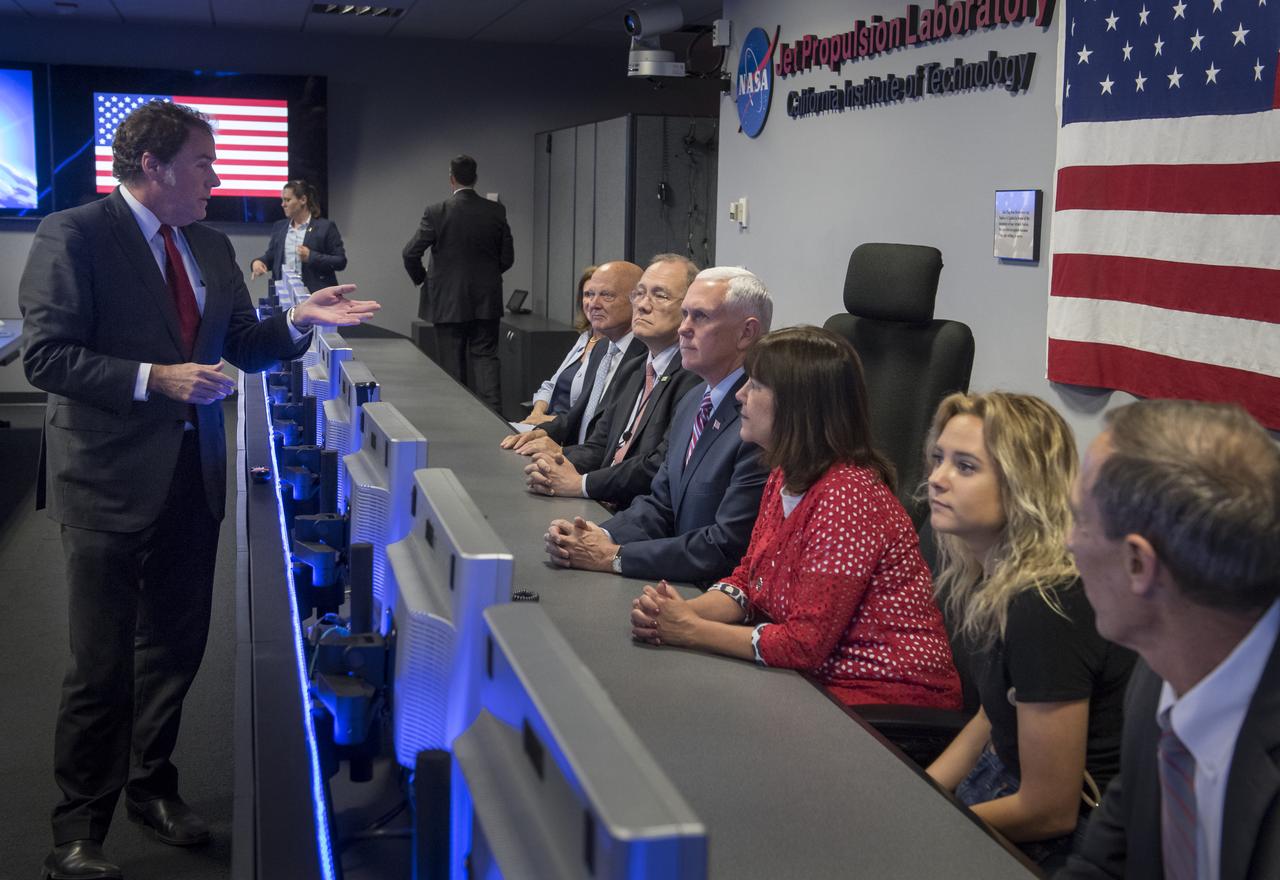

JPL Director Michael Watkins, left, explains the history of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the use of the Mission Support Area to Vice President Mike Pence, seated 4th from left, during a tour of JPL, Saturday, April 28, 2018 in Pasadena, California. Joining the Vice President was, JPL Distinguished Visiting Scientist and Spouse of UAG Chairman James Ellis, Elisabeth Pate-Cornell, left, UAG Chairman, Admiral (Ret) James Ellis, Executive Director of the National Space Council Scott Pace, wife of Mike Pence, Karen Pence, daughter of Mike Pence, Charlotte Pence, and JPL Deputy Director Lt. Gen. (Ret) Larry James. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA and industry leaders participate in a Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R), prelaunch news conference in the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium in Florida. NASA and industry leaders include: Michael Curie, of NASA Communications; Stephen Volz, assistant administrator for satellite and information services, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA's); Greg Mandt, GOES-R system program director, NOAA; Sandra Smalley, director, Joint Agency Satellite Division, NASA Headquarters; Omar Baez, launch director, NASA Kennedy; Scott Messer, program manager, NASA Missions, United Launch Alliance; and Clay Flinn, launch weather officer, 4th Weather Squadron, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
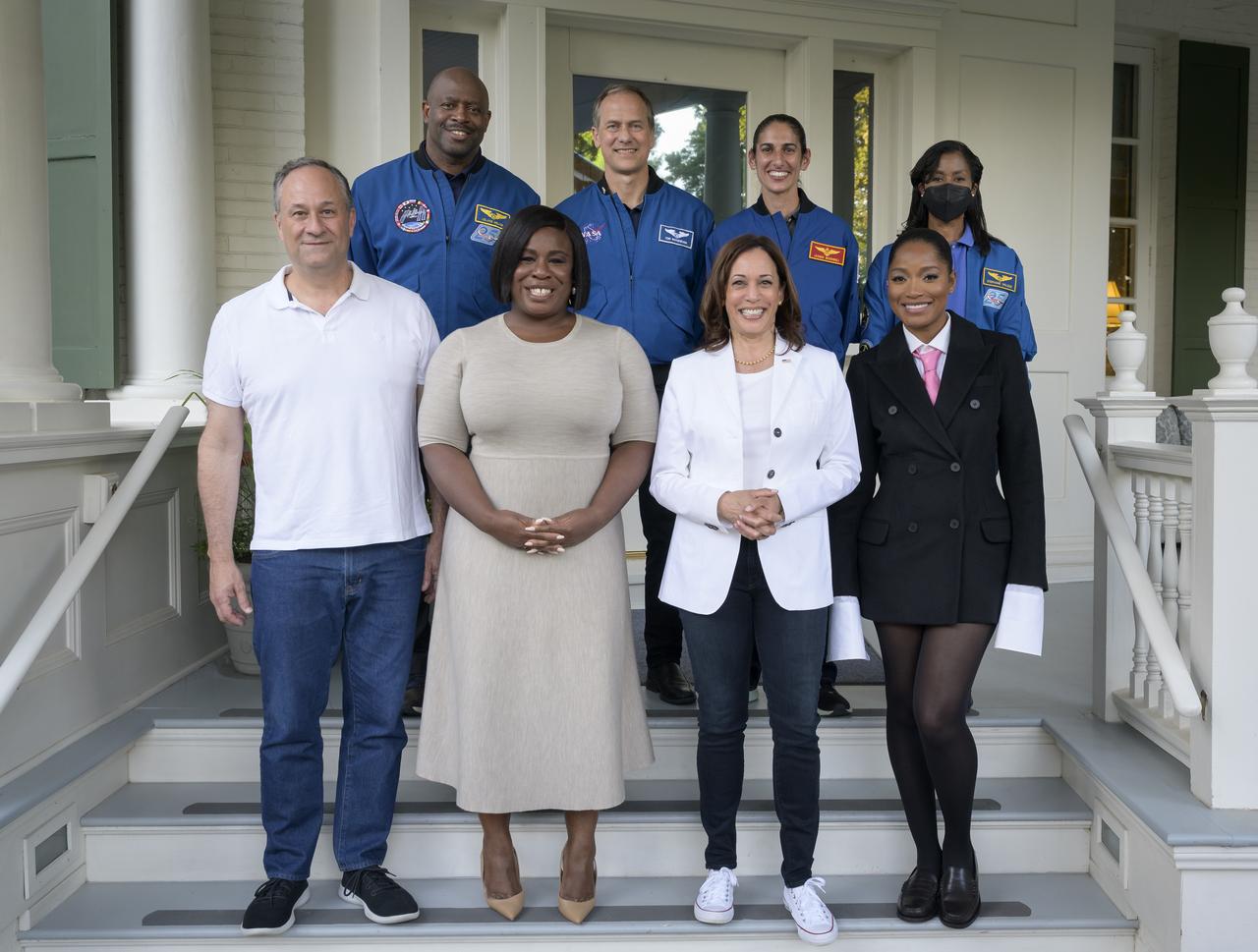

Vice President Kamala Harris and Second Gentleman Doug Emhoff pose for a group photo with Former NASA astronaut Leland Melvin, back left, NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn, Jasmin Moghbeli, and Stephanie Wilson, back right, along with American actress Uzo Aduba, and American actress Keke Palmer, bottom right, after they met with students from 4th-8th grade to work hands-on STEM activities on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
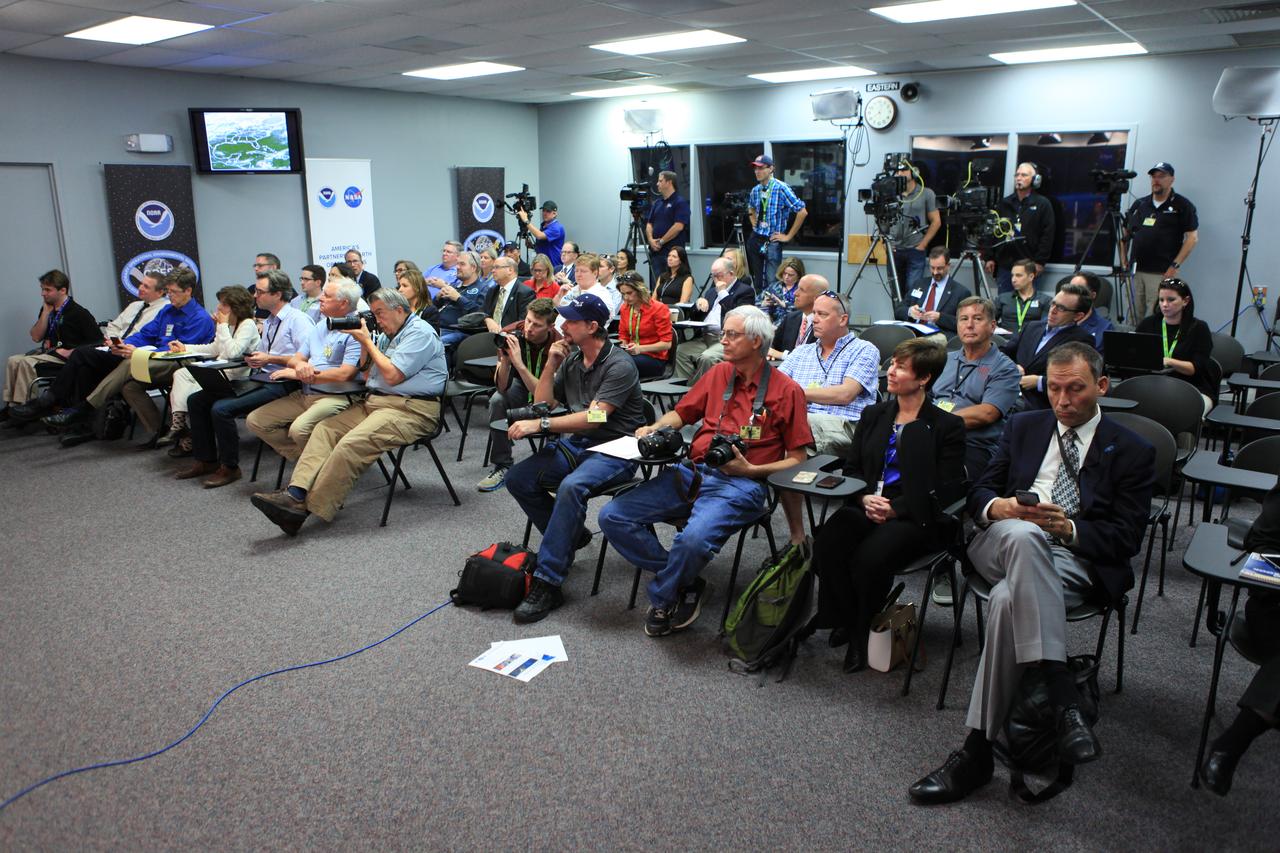

Members of the news media attend a Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) prelaunch news conference in the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium in Florida. NASA and industry leaders include: Michael Curie, of NASA Communications; Stephen Volz, assistant administrator for satellite and information services, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA's); Greg Mandt, GOES-R system program director, NOAA; Sandra Smalley, director, Joint Agency Satellite Division, NASA Headquarters; Omar Baez, launch director, NASA Kennedy; Scott Messer, program manager, NASA Missions, United Launch Alliance; and Clay Flinn, launch weather officer, 4th Weather Squadron, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
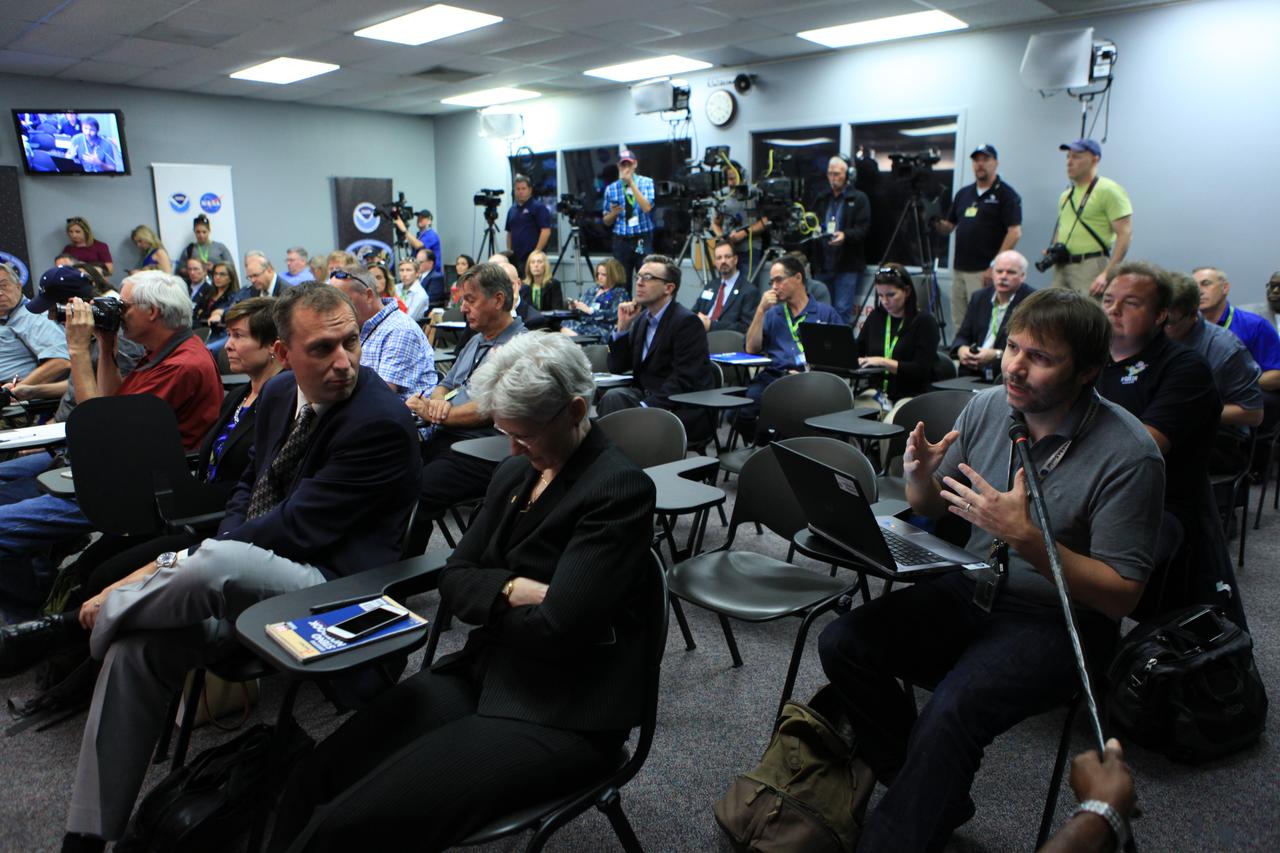

Members of the news media attend a Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) prelaunch news conference in the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium in Florida. NASA and industry leaders include: Michael Curie, of NASA Communications; Stephen Volz, assistant administrator for satellite and information services, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA's); Greg Mandt, GOES-R system program director, NOAA; Sandra Smalley, director, Joint Agency Satellite Division, NASA Headquarters; Omar Baez, launch director, NASA Kennedy; Scott Messer, program manager, NASA Missions, United Launch Alliance; and Clay Flinn, launch weather officer, 4th Weather Squadron, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
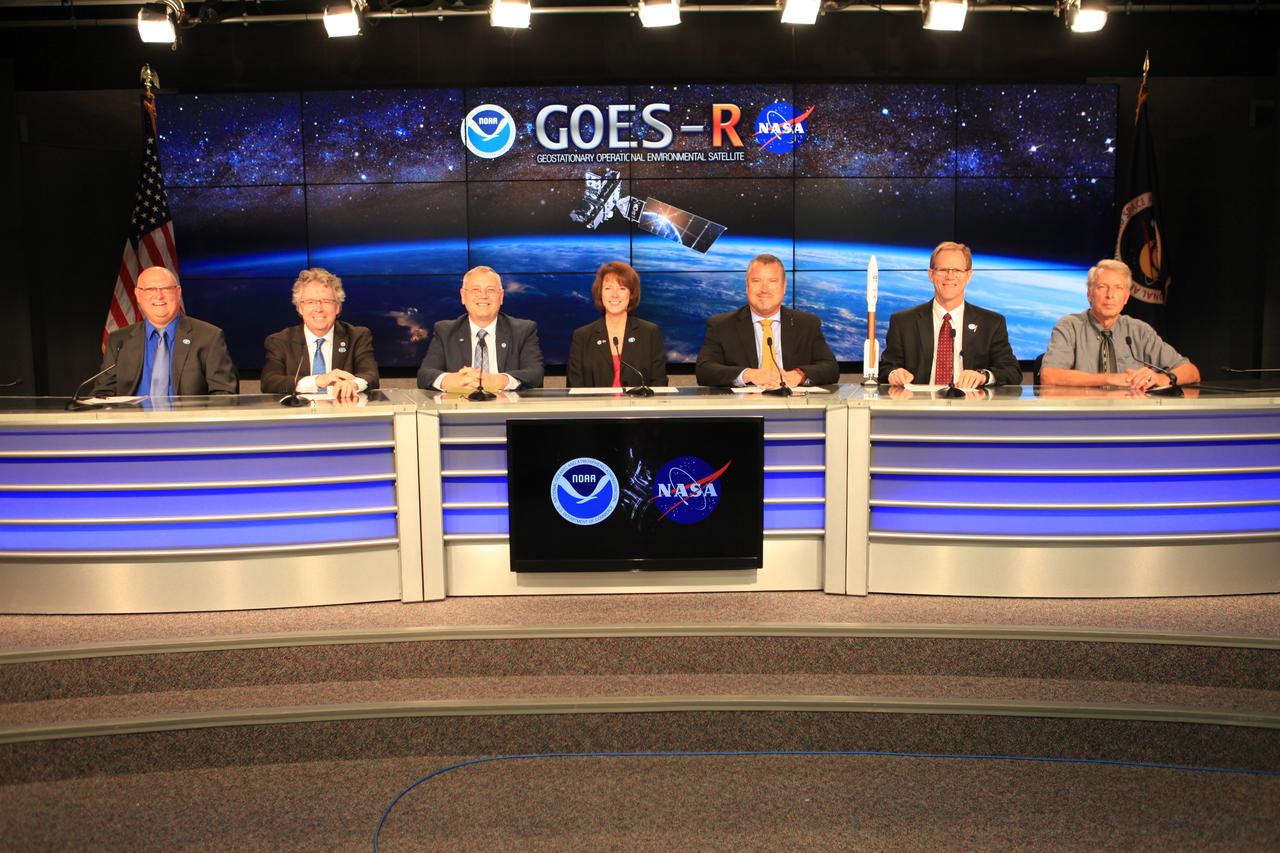

NASA and industry leaders participate in a Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R), prelaunch news conference in the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium in Florida. NASA and industry leaders include: Michael Curie, of NASA Communications; Stephen Volz, assistant administrator for satellite and information services, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA's); Greg Mandt, GOES-R system program director, NOAA; Sandra Smalley, director, Joint Agency Satellite Division, NASA Headquarters; Omar Baez, launch director, NASA Kennedy; Scott Messer, program manager, NASA Missions, United Launch Alliance; and Clay Flinn, launch weather officer, 4th Weather Squadron, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
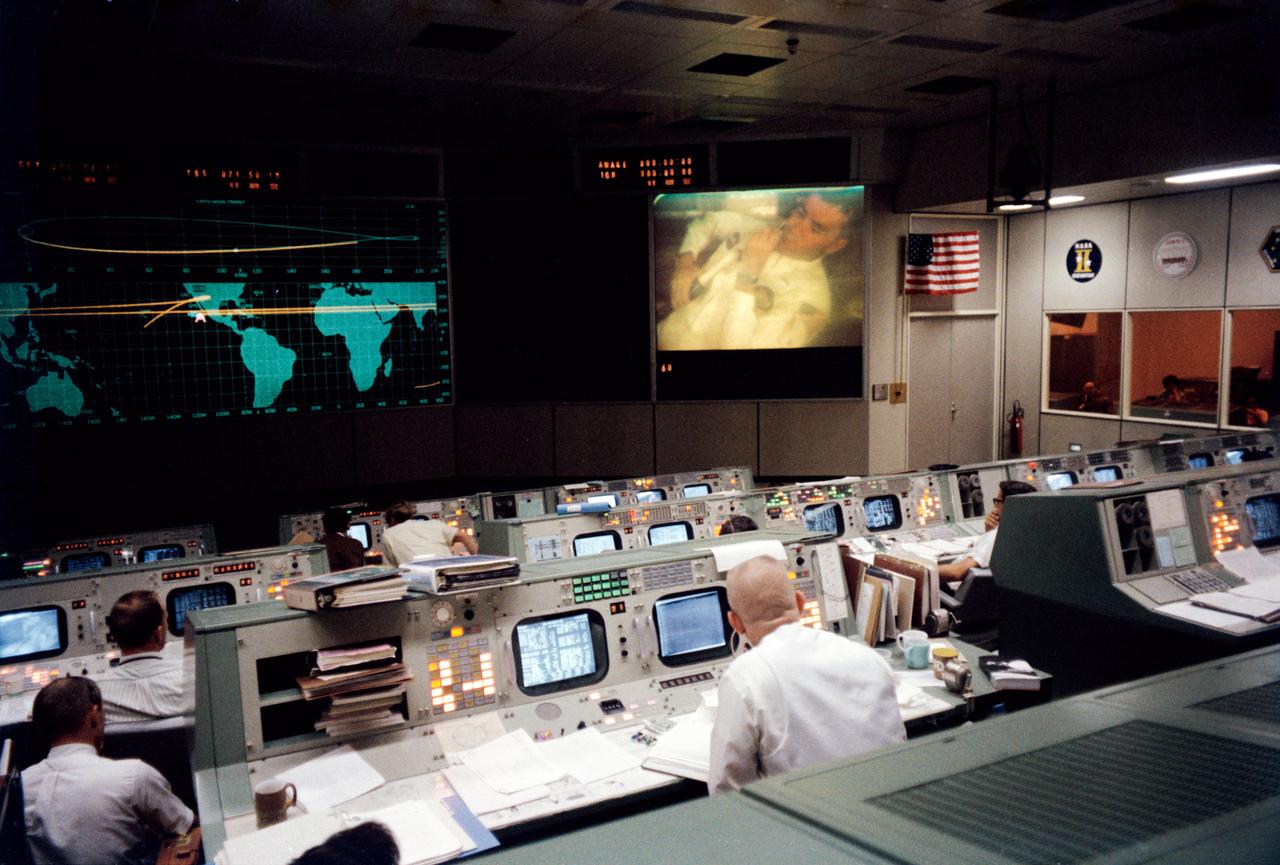

S70-35139 (13 April 1970) --- Overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC) at Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), during the fourth television transmission from the Apollo 13 mission in space. Eugene F. Kranz (foreground, back to camera), one of four Apollo 13 flight directors, views the large screen at front of MOCR, astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, is seen on the screen. The fourth TV transmission from the Apollo 13 mission was on the evening of April 13, 1970.
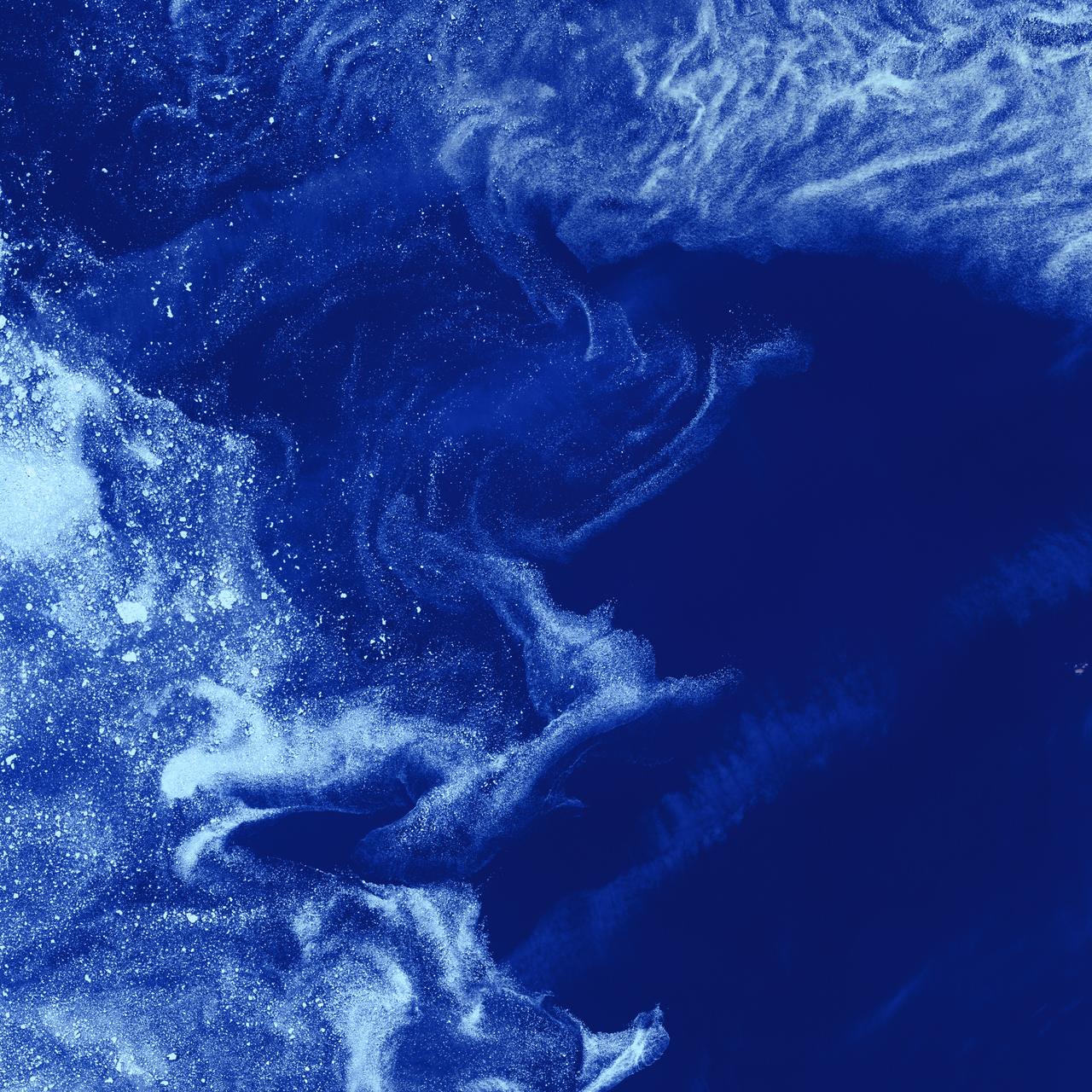
Ice Stars - August 4th, 2002 Description: Like distant galaxies amid clouds of interstellar dust, chunks of sea ice drift through graceful swirls of grease ice in the frigid waters of Foxe Basin near Baffin Island in the Canadian Arctic. Sea ice often begins as grease ice, a soupy slick of tiny ice crystals on the ocean's surface. As the temperature drops, grease ice thickens and coalesces into slabs of more solid ice. Credit: USGS/NASA/Landsat 7 To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to: <a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
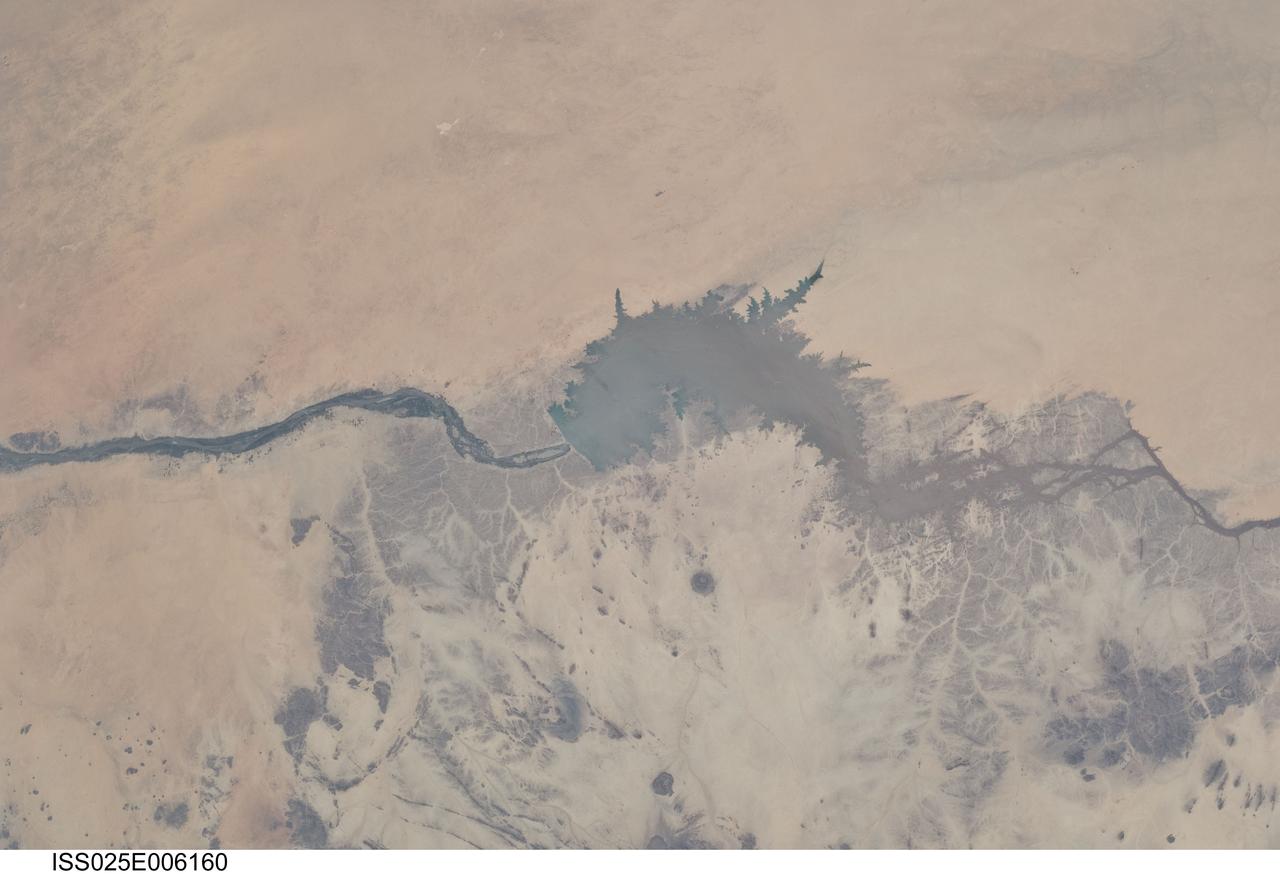

ISS025-E-006160 (5 Oct. 2010) --- Merowe Dam, Nile River and the Republic of the Sudan are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 25 crew member on the International Space Station. The Merowe Dam is located near the 4th cataract of the Nile River, in the Nubian Desert of the northeastern Republic of the Sudan (also known as Sudan). The dam was built to generate hydroelectric power—electricity intended to further industrial and agricultural development of the country. This photograph illustrates the current extent of the reservoir filling behind the dam; the final spill gate was closed in 2008. The Merowe Dam is located approximately 350 kilometers (215 miles) to the northwest of Sudan’s capital, Khartoum. The nearest settlement downstream of the dam is Karima. Following Sudan’s independence from Egypt and the United Kingdom in 1956, allocation and control of Nile River water was divided between Egypt and Sudan by the Nile Waters Treaty signed in 1959. Today, other countries within the Nile basin—including Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda—are seeking more equitable allocation and utilization of the water and recently (2010) signed a new water use pact challenging the 1959 treaty. Beyond the issues of water rights, several local tribes will be displaced by the planned 170 kilometer-long reservoir, and the flooded region contains significant but little-studied archeological sites. The Sudanese government has a resettlement program in place for the tribes. A variety of international institutions have been conducting “salvage” or “rescue” archeological surveys since 1999. Such rescue surveys seek to preserve as much information as possible from sites that will be destroyed or otherwise made inaccessible (in this case by flooding).
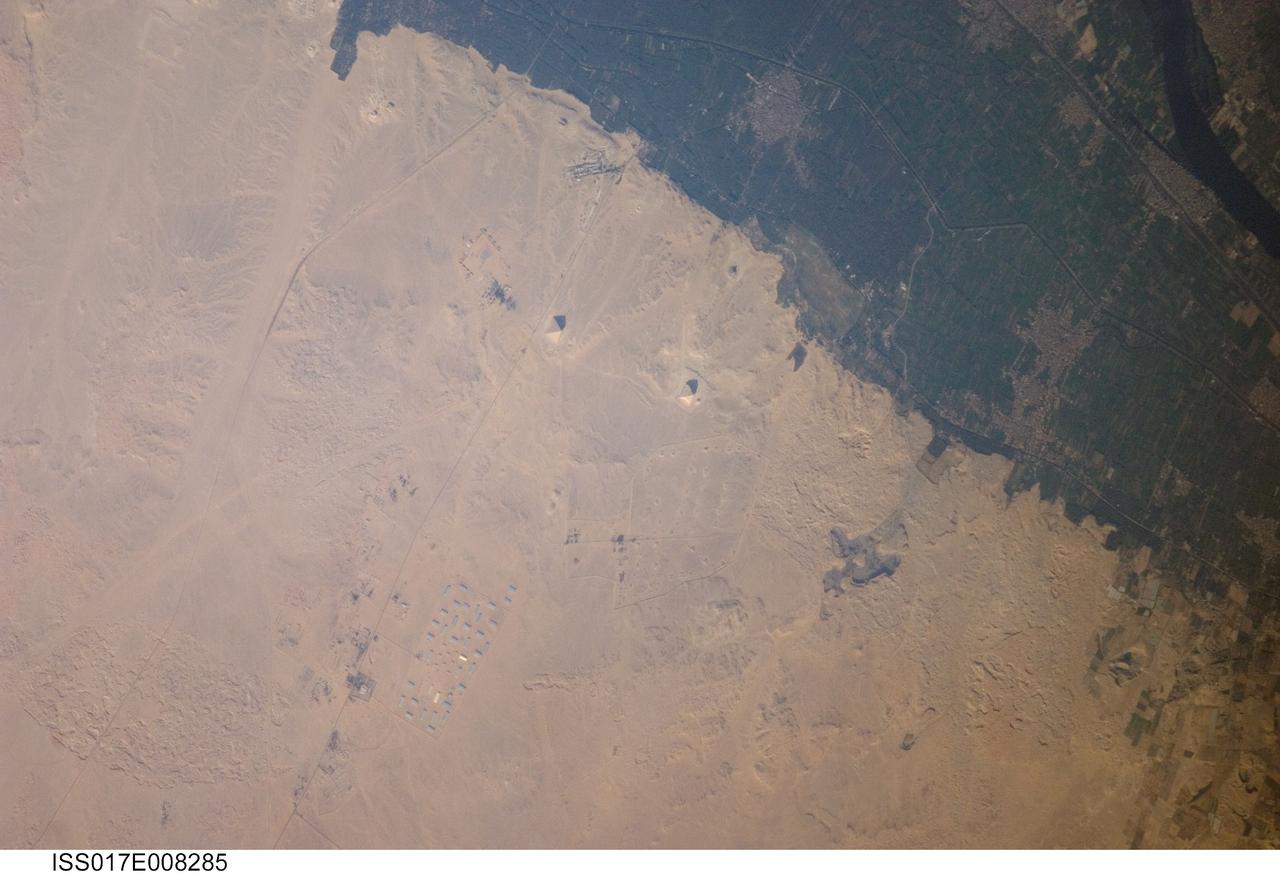

ISS017-E-008285 (30 May 2008) --- Pyramids of Dashur, Egypt are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 17 crewmember on the International Space Station. While the pyramids of Giza are perhaps the most famous, there are several other ancient Egyptian royal necropolis ("city of the dead") sites situated along the Nile River and its delta. One of these sites is located near the village of Dashur (upper right). The gray-brown built area of Dashur is surrounded by green agricultural land of the Nile Delta, which forms a distinct boundary with the tan desert to the west. It is in the desert that the monuments of the ancient rulers of Egypt are found. Several monuments are visible in this image, including the large Red and Bent Pyramids built by Snofru, first king of the 4th Dynasty that lasted from 2575-2465 BC. Other visible monuments include the pyramid complexes of Amenemhat III and Sesostris III, both kings of the 12th Dynasty (1991-1783 BC). Both of these complexes are poorly preserved, due both to unstable ground conditions, and dismantling of the limestone blocks forming the outer pyramid casings during later historical periods. The Bent Pyramid (lower right) is so called as the slope of the outer face was lessened halfway through construction, leading to a distinctive "bent" profile -- explanations for why this was done include decreasing the mass of the pyramid to prevent collapse, or to reduce the work necessary to complete it. The Red Pyramid to the north (center) was built after the Bent Pyramid, and is named for the coloration of the building stone at the structure's core. An irregular dark feature to the southeast of the Bent Pyramid is not a shadow cast by a monument; it is an irrigation feature extending into the desert.
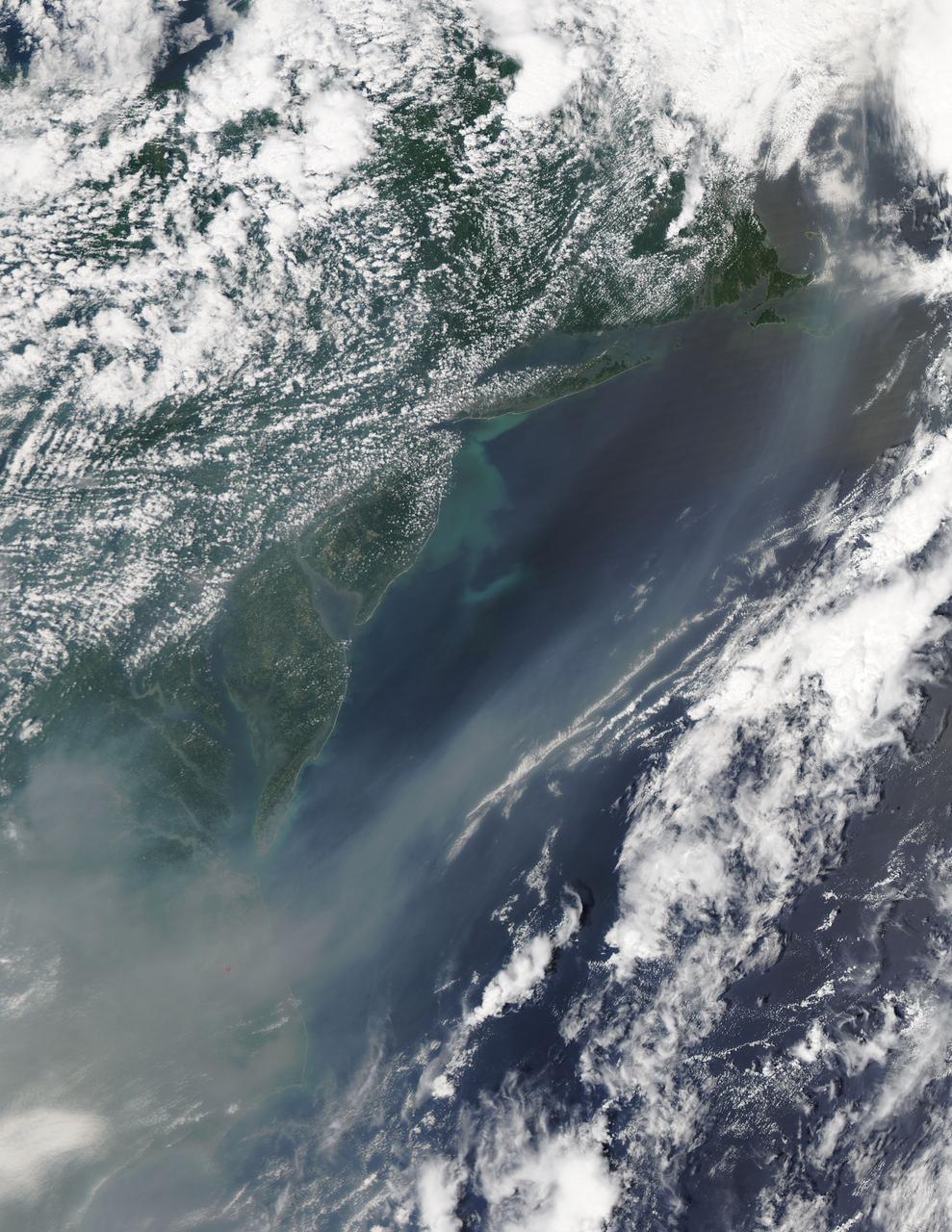

The smoke from the Canadian wildfires that was in the middle of the U.S. on June 30 has drifted its way to the East Coast obscuring parts of the coast from New Jersey to North Carolina. Images taken on June 30 showed the smoke covering states from Minnesota to Tennessee. The jet stream has pushed the smoke along so that by July 1 it reached the U.S. East Coast. Residents of the area will get a preview of July 4th fireworks with redder than usual sunrises and sunsets due to particulates in the air. This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite on July 1, 2015. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
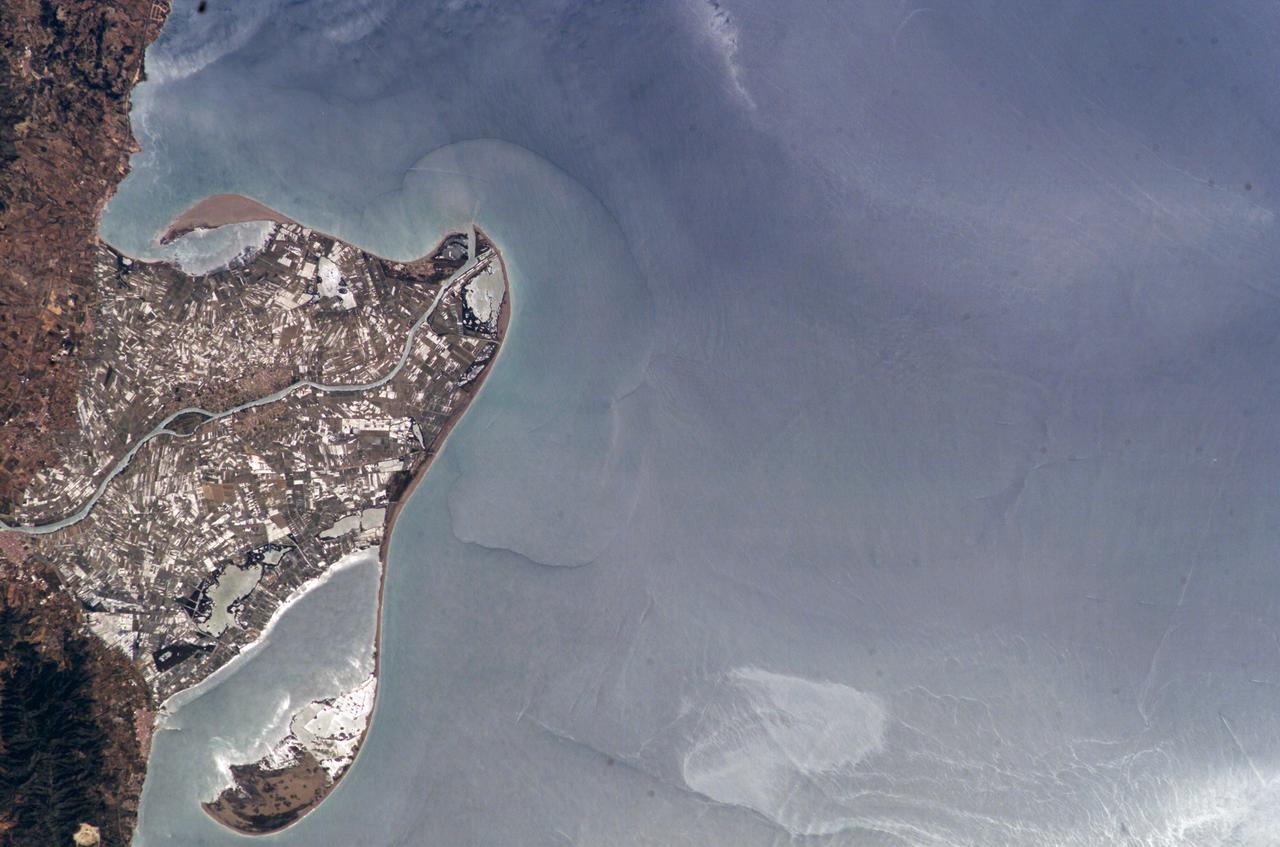

ISS009-E-09985 (3 June 2004) --- The Ebro River Delta, located along the eastern coast of Spain, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 9 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). Taken in partial sun glint, this view defines the Ebro’s fresh water lens— the water density boundary between the upper layer of fresh water issuing from the Ebro River mouth and the saltier, denser Mediterranean Sea water. According to NASA geologists studying the ISS imagery, diversion and impoundment of the Ebro River upstream has led to a decrease in water and sediment delivery to the delta. This decrease has led to increased erosion in some areas to the northeast of El Fangar Bay and along the southwestern shoreline of the delta. The Ebro River Delta is one of the largest wetland areas in the western Mediterranean region. The Ebro delta has grown rapidly—the historical rate of growth of the delta is demonstrated by the city of Amposta. This city was a seaport in the 4th Century, and is now located well inland from the current Ebro river mouth. The rounded form of the delta attests to the balance between sediment deposition by the Ebro River and removal of this material by wave erosion. The modern delta is in intensive agricultural use for rice, fruit, and vegetables. White polygonal areas to the north and south of the Ebro River are paddy fields. The Ebro delta also hosts numerous beaches, marshes, and saltpans that provide habitat for over 300 species of birds. A large part of the delta was designated as Parc Natural del Delta de l'Ebre (Ebre Delta National Park) in 1983. A network of canals and irrigation ditches constructed by both agricultural and conservation groups are helping to maintain the ecologic and economic resources of the Ebro Delta.

This montage depicts the flight crew patches for the manned Apollo 7 thru Apollo 17 missions. The Apollo 7 through 10 missions were basically manned test flights that paved the way for lunar landing missions. Primary objectives met included the demonstration of the Command Service Module (CSM) crew performance; crew/space vehicle/mission support facilities performance and testing during a manned CSM mission; CSM rendezvous capability; translunar injection demonstration; the first manned Apollo docking, the first Apollo Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA), performance of the first manned flight of the lunar module (LM); the CSM-LM docking in translunar trajectory, LM undocking in lunar orbit, LM staging in lunar orbit, and manned LM-CSM docking in lunar orbit. Apollo 11 through 17 were lunar landing missions with the exception of Apollo 13 which was forced to circle the moon without landing due to an onboard explosion. The craft was,however, able to return to Earth safely. Apollo 11 was the first manned lunar landing mission and performed the first lunar surface EVA. Landing site was the Sea of Tranquility. A message for mankind was delivered, the U.S. flag was planted, experiments were set up and 47 pounds of lunar surface material was collected for analysis back on Earth. Apollo 12, the 2nd manned lunar landing mission landed in the Ocean of Storms and retrieved parts of the unmanned Surveyor 3, which had landed on the Moon in April 1967. The Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) was deployed, and 75 pounds of lunar material was gathered. Apollo 14, the 3rd lunar landing mission landed in Fra Mauro. ALSEP and other instruments were deployed, and 94 pounds of lunar materials were gathered, using a hand cart for first time to transport rocks. Apollo 15, the 4th lunar landing mission landed in the Hadley-Apennine region. With the first use of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), the crew was bale to gather 169 pounds of lunar material. Apollo 16, the 5th lunar landing mission, landed in the Descartes Highlands for the first study of highlands area. Selected surface experiments were deployed, the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph was used for first time on the Moon, and the LRV was used for second time for a collection of 213 pounds of lunar material. The Apollo program came to a close with Apollo 17, the 6th and final manned lunar landing mission that landed in the Taurus-Littrow highlands and valley area. This mission hosted the first scientist-astronaut, Schmitt, to land on the Moon. The 6th automated research station was set up, and 243 ponds of lunar material was gathered using the LRV.
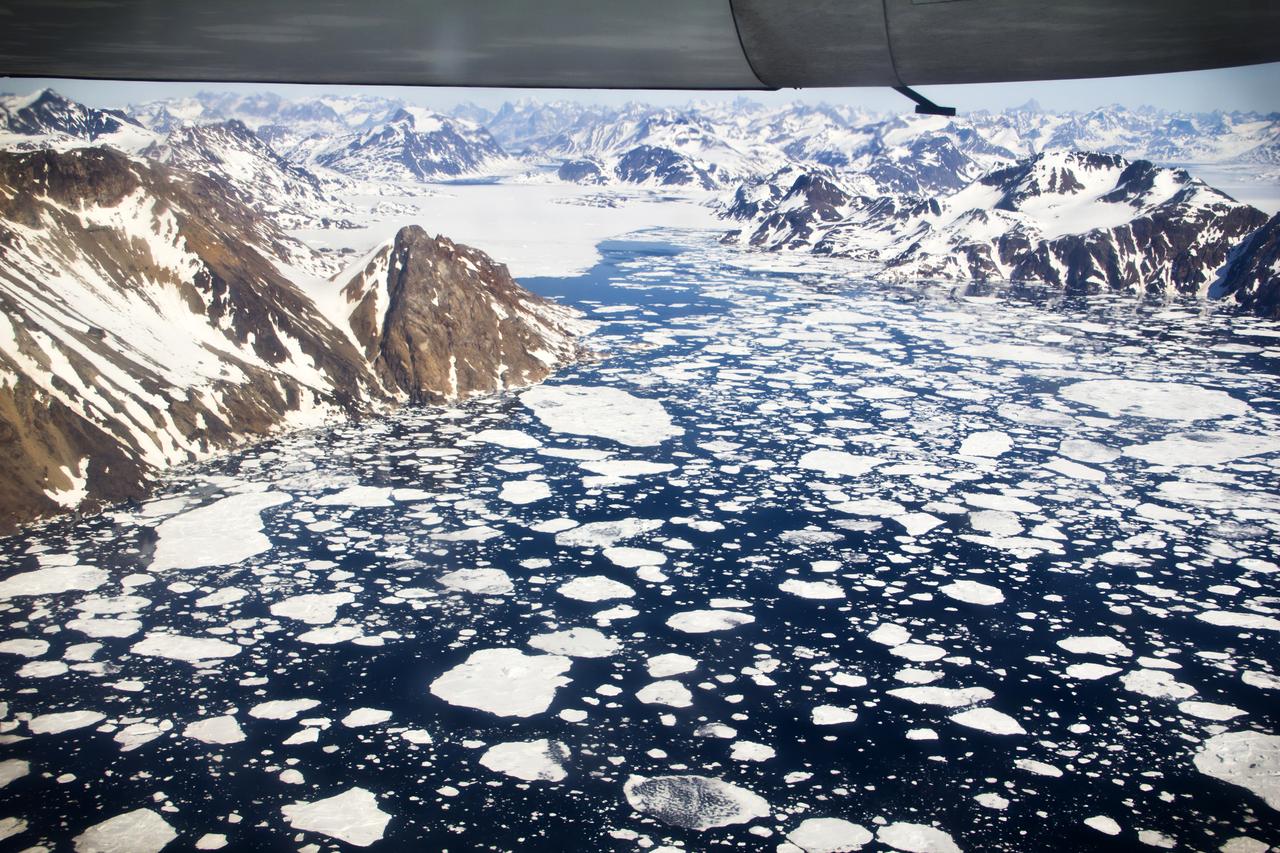

GPM "Let it Snow" Photo Contest Winners The Global Precipitation Measurement mission is happy to announce the top ten winners of the "Let It Snow" photo competition. Thank you to everyone who submitted their best pictures of winter. From January 7th through February 4th 2013, over 1,000 photos were submitted via Flickr and Instagram (see the Flickr submissions here: <a href="http://bit.ly/VVEubh" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/VVEubh</a>). We loved all of your entries and thoroughly appreciate your participation. About this image: Kulusuk Icebergs, by Andrew Bossi Location: On approach to the airstrip at Kulusuk, Greenland, located on the east coast. The flight departed out of Reykjavík, Iceland. How this Photo Was Taken: "My write-up of the day covers things in decent detail. Basically my vacation was focused on Scandinavia and hadn't even considered Greenland, but while traveling around Iceland I'd become aware that day trips were offered and I leapt at the opportunity. This approach was my first sight of Greenland. While I've seen plenty of glaciers and mountains, I'd never seen anything like this - it started with endless fields of ice amid the deep blue sea, and some minutes later a wall of frozen rock rose up from the horizon. I'd never seen anything so beautiful. I think my camera's shutter was snapping almost endlessly right up until we landed. The landing itself was an experience, as our tiny plane descended between the mountains -- rockfaces just outside each window -- and set down on a gravel runway." About Photographer Steven Sandner: More info about this photo: <a href="http://intentionallylost.blogspot.com/2011/06/gl-kulusuk.htm" rel="nofollow">intentionallylost.blogspot.com/2011/06/gl-kulusuk.htm</a> <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/thisisbossi/">www.flickr.com/photos/thisisbossi/</a> <a href="http://twitter.com/thisisbossi" rel="nofollow">twitter.com/thisisbossi</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Fireworks shows are not just confined to Earth’s skies. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has captured a spectacular fireworks display in a small, nearby galaxy, which resembles a July 4th skyrocket. A firestorm of star birth is lighting up one end of the diminutive galaxy Kiso 5639. The dwarf galaxy is shaped like a flattened pancake, but because it is tilted edge-on, it resembles a skyrocket, with a brilliant blazing head and a long, star-studded tail. Kiso 5639 is a rare, nearby example of elongated galaxies that occur in abundance at larger distances, where we observe the universe during earlier epochs. Astronomers suggest that the frenzied star birth is sparked by intergalactic gas raining on one end of the galaxy as it drifts through space. “I think Kiso 5639 is a beautiful, up-close example of what must have been common long ago,” said lead researcher Debra Elmegreen of Vassar College, in Poughkeepsie, New York. “The current thinking is that galaxies in the early universe grow from accreting gas from the surrounding neighborhood. It’s a stage that galaxies, including our Milky Way, must go through as they are growing up.” Observations of the early universe, such as Hubble’s Ultra-Deep Field, reveal that about 10 percent of all galaxies have these elongated shapes, and are collectively called “tadpoles.” But studies of the nearby universe have turned up only a few of these unusual galaxies, including Kiso 5639. The development of the nearby star-making tadpole galaxies, however, has lagged behind that of their peers, which have spent billions of years building themselves up into many of the spiral galaxies seen today. Elmegreen used Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 to conduct a detailed imaging study of Kiso 5639. The images in different filters reveal information about an object by dissecting its light into its component colors. Hubble’s crisp resolution helped Elmegreen and her team analyze the giant star-forming clumps in Kiso 5639 and determine the masses and ages of the star clusters. The international team of researchers selected Kiso 5639 from a spectroscopic survey of 10 nearby tadpole galaxies, observed with the Grand Canary Telescope in La Palma, Spain, by Jorge Sanchez Almeida and collaborators at the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias. The observations revealed that in most of those galaxies, including Kiso 5639, the gas composition is not uniform. The bright gas in the galaxy’s head contains fewer heavier elements (collectively called “metals”), such as carbon and oxygen, than the rest of the galaxy. Stars consist mainly of hydrogen and helium, but cook up other “heavier” elements. When the stars die, they release their heavy elements and enrich the surrounding gas. “The metallicity suggests that there has to be rather pure gas, composed mostly of hydrogen, coming into the star-forming part of the galaxy, because intergalactic space contains more pristine hydrogen-rich gas,” Elmegreen explained. “Otherwise, the starburst region should be as rich in heavy elements as the rest of the galaxy.” Hubble offers a detailed view of the galaxy’s star-making frenzy. The telescope uncovered several dozen clusters of stars in the galaxy’s star-forming head, which spans 2,700 light-years across. These clusters have an average age of less than 1 million years and masses that are three to six times larger than those in the rest of the galaxy. Other star formation is taking place throughout the galaxy but on a much smaller scale. Star clusters in the rest of the galaxy are between several million to a few billion years old. “There is much more star formation going on in the head than what you would expect in such a tiny galaxy,” said team member Bruce Elmegreen of IBM’s Thomas J. Watson’s Research Center, in Yorktown Heights, New York. “And we think the star formation is triggered by the ongoing accretion of metal-poor gas onto a part of an otherwise quiescent dwarf galaxy.” Hubble also revealed giant holes peppered throughout the galaxy’s starburst head. These cavities give the galaxy’s head a Swiss-cheese appearance because numerous supernova detonations – like firework aerial bursts – have carved out holes of rarified superheated gas. The galaxy, located 82 million light-years away, has taken billions of years to develop because it has been drifting through an isolated “desert” in the universe, devoid of much gas. What triggered the starburst in such a backwater galaxy? Based on simulations by Daniel Ceverino of the Center for Astronomy at Heidelberg University in Germany, and other team members, the observations suggest that less than 1 million years ago, Kiso 5639’s leading edge encountered a filament of gas. The filament dropped a large clump of matter onto the galaxy, stoking the vigorous star birth. Debra Elmegreen expects that in the future other parts of the galaxy will join in the star-making fireworks show. “Galaxies rotate, and as Kiso 5639 continues to spin, another part of the galaxy may receive an infusion of new gas from this filament, instigating another round of star birth,” she said. The team’s results have been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. Other team members include Casiana Munoz-Tunon and Mercedes Filho (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Canary Islands), Jairo Mendez-Abreu (University of St. Andrews, United Kingdom), John Gallagher (University of Wisconsin-Madison), and Marc Rafelski (NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C.
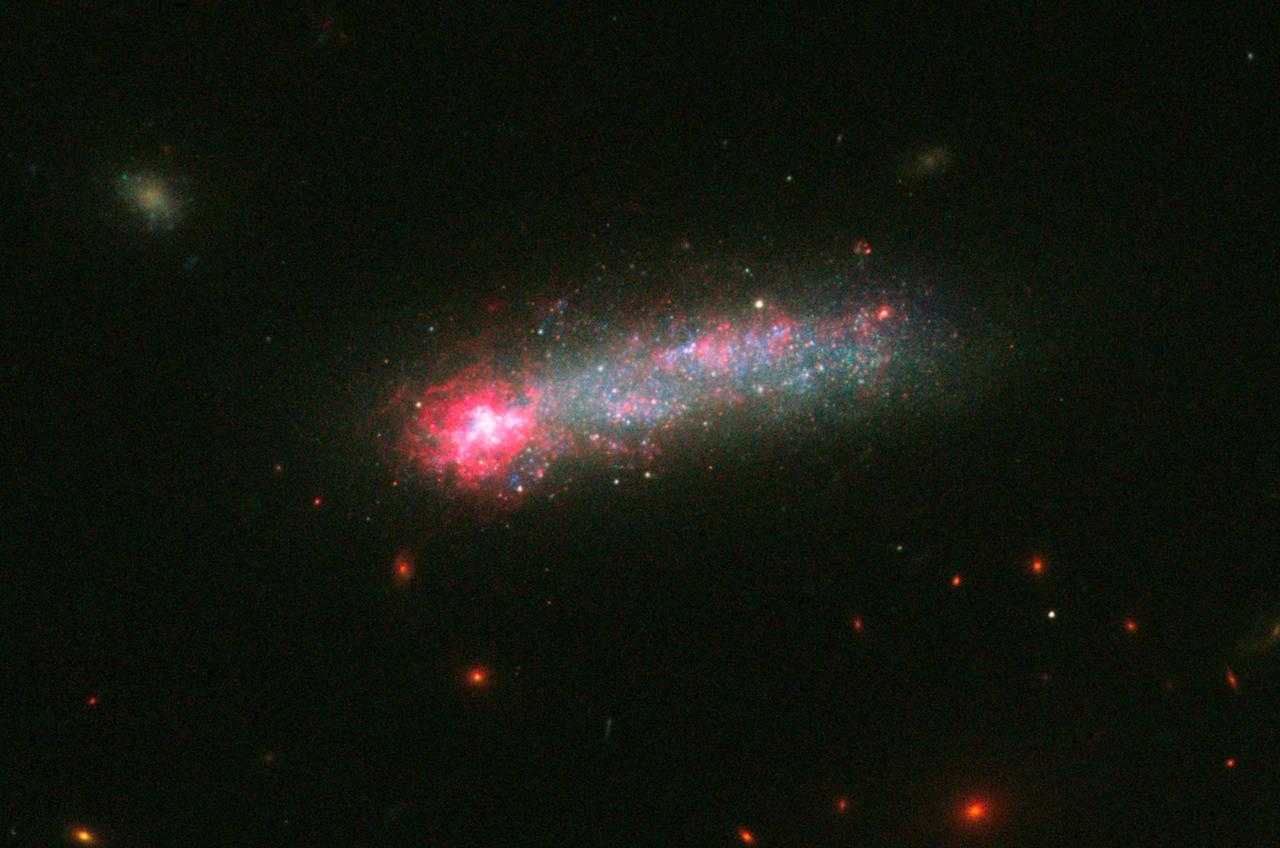

Fireworks shows are not just confined to Earth’s skies. NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has captured a spectacular fireworks display in a small, nearby galaxy, which resembles a July 4th skyrocket. A firestorm of star birth is lighting up one end of the diminutive galaxy Kiso 5639. The dwarf galaxy is shaped like a flattened pancake, but because it is tilted edge-on, it resembles a skyrocket, with a brilliant blazing head and a long, star-studded tail. Kiso 5639 is a rare, nearby example of elongated galaxies that occur in abundance at larger distances, where we observe the universe during earlier epochs. Astronomers suggest that the frenzied star birth is sparked by intergalactic gas raining on one end of the galaxy as it drifts through space. “I think Kiso 5639 is a beautiful, up-close example of what must have been common long ago,” said lead researcher Debra Elmegreen of Vassar College, in Poughkeepsie, New York. “The current thinking is that galaxies in the early universe grow from accreting gas from the surrounding neighborhood. It’s a stage that galaxies, including our Milky Way, must go through as they are growing up.” Observations of the early universe, such as Hubble’s Ultra-Deep Field, reveal that about 10 percent of all galaxies have these elongated shapes, and are collectively called “tadpoles.” But studies of the nearby universe have turned up only a few of these unusual galaxies, including Kiso 5639. The development of the nearby star-making tadpole galaxies, however, has lagged behind that of their peers, which have spent billions of years building themselves up into many of the spiral galaxies seen today. Elmegreen used Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3 to conduct a detailed imaging study of Kiso 5639. The images in different filters reveal information about an object by dissecting its light into its component colors. Hubble’s crisp resolution helped Elmegreen and her team analyze the giant star-forming clumps in Kiso 5639 and determine the masses and ages of the star clusters. The international team of researchers selected Kiso 5639 from a spectroscopic survey of 10 nearby tadpole galaxies, observed with the Grand Canary Telescope in La Palma, Spain, by Jorge Sanchez Almeida and collaborators at the Instituto de Astrofisica de Canarias. The observations revealed that in most of those galaxies, including Kiso 5639, the gas composition is not uniform. The bright gas in the galaxy’s head contains fewer heavier elements (collectively called “metals”), such as carbon and oxygen, than the rest of the galaxy. Stars consist mainly of hydrogen and helium, but cook up other “heavier” elements. When the stars die, they release their heavy elements and enrich the surrounding gas. “The metallicity suggests that there has to be rather pure gas, composed mostly of hydrogen, coming into the star-forming part of the galaxy, because intergalactic space contains more pristine hydrogen-rich gas,” Elmegreen explained. “Otherwise, the starburst region should be as rich in heavy elements as the rest of the galaxy.” Hubble offers a detailed view of the galaxy’s star-making frenzy. The telescope uncovered several dozen clusters of stars in the galaxy’s star-forming head, which spans 2,700 light-years across. These clusters have an average age of less than 1 million years and masses that are three to six times larger than those in the rest of the galaxy. Other star formation is taking place throughout the galaxy but on a much smaller scale. Star clusters in the rest of the galaxy are between several million to a few billion years old. “There is much more star formation going on in the head than what you would expect in such a tiny galaxy,” said team member Bruce Elmegreen of IBM’s Thomas J. Watson’s Research Center, in Yorktown Heights, New York. “And we think the star formation is triggered by the ongoing accretion of metal-poor gas onto a part of an otherwise quiescent dwarf galaxy.” Hubble also revealed giant holes peppered throughout the galaxy’s starburst head. These cavities give the galaxy’s head a Swiss-cheese appearance because numerous supernova detonations – like firework aerial bursts – have carved out holes of rarified superheated gas. The galaxy, located 82 million light-years away, has taken billions of years to develop because it has been drifting through an isolated “desert” in the universe, devoid of much gas. What triggered the starburst in such a backwater galaxy? Based on simulations by Daniel Ceverino of the Center for Astronomy at Heidelberg University in Germany, and other team members, the observations suggest that less than 1 million years ago, Kiso 5639’s leading edge encountered a filament of gas. The filament dropped a large clump of matter onto the galaxy, stoking the vigorous star birth. Debra Elmegreen expects that in the future other parts of the galaxy will join in the star-making fireworks show. “Galaxies rotate, and as Kiso 5639 continues to spin, another part of the galaxy may receive an infusion of new gas from this filament, instigating another round of star birth,” she said. The team’s results have been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. Other team members include Casiana Munoz-Tunon and Mercedes Filho (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Canary Islands), Jairo Mendez-Abreu (University of St. Andrews, United Kingdom), John Gallagher (University of Wisconsin-Madison), and Marc Rafelski (NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland). The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C. For images and more information about Kiso 5639 and Hubble, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2016/23" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2016/23</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> Image credit: NASA, ESA, and D. Elmegreen (Vassar College) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>