
Complexity

Flow Complexity

Complex Surface
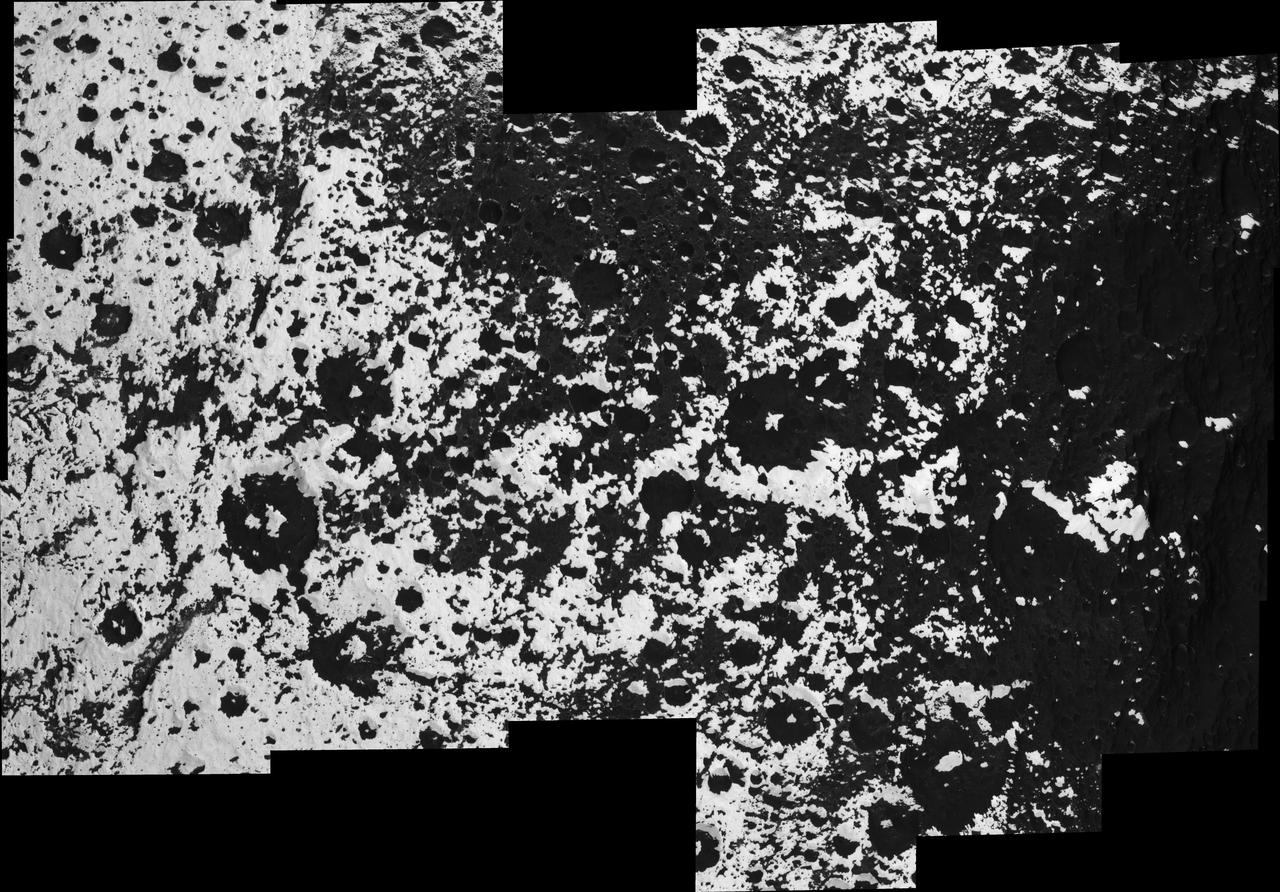
A Complex Transition

Titanic Complexity
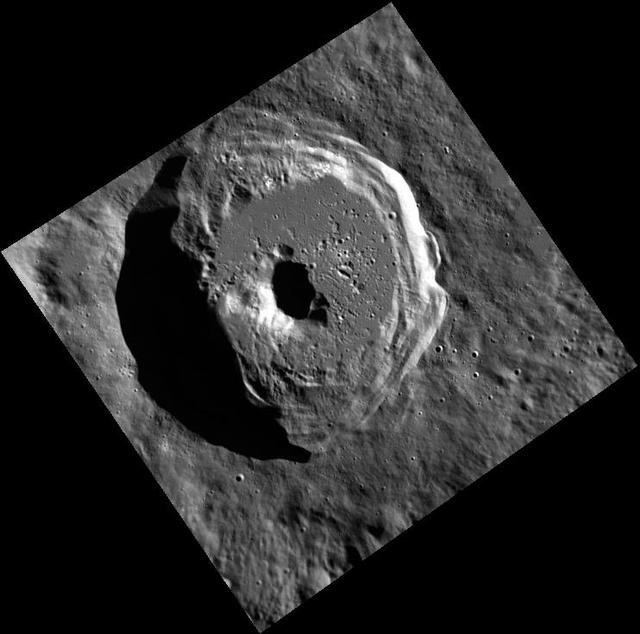
It a Complex World
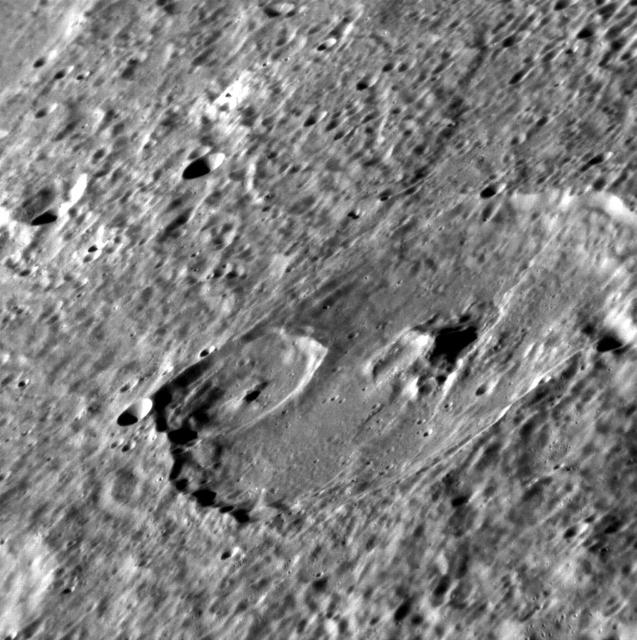

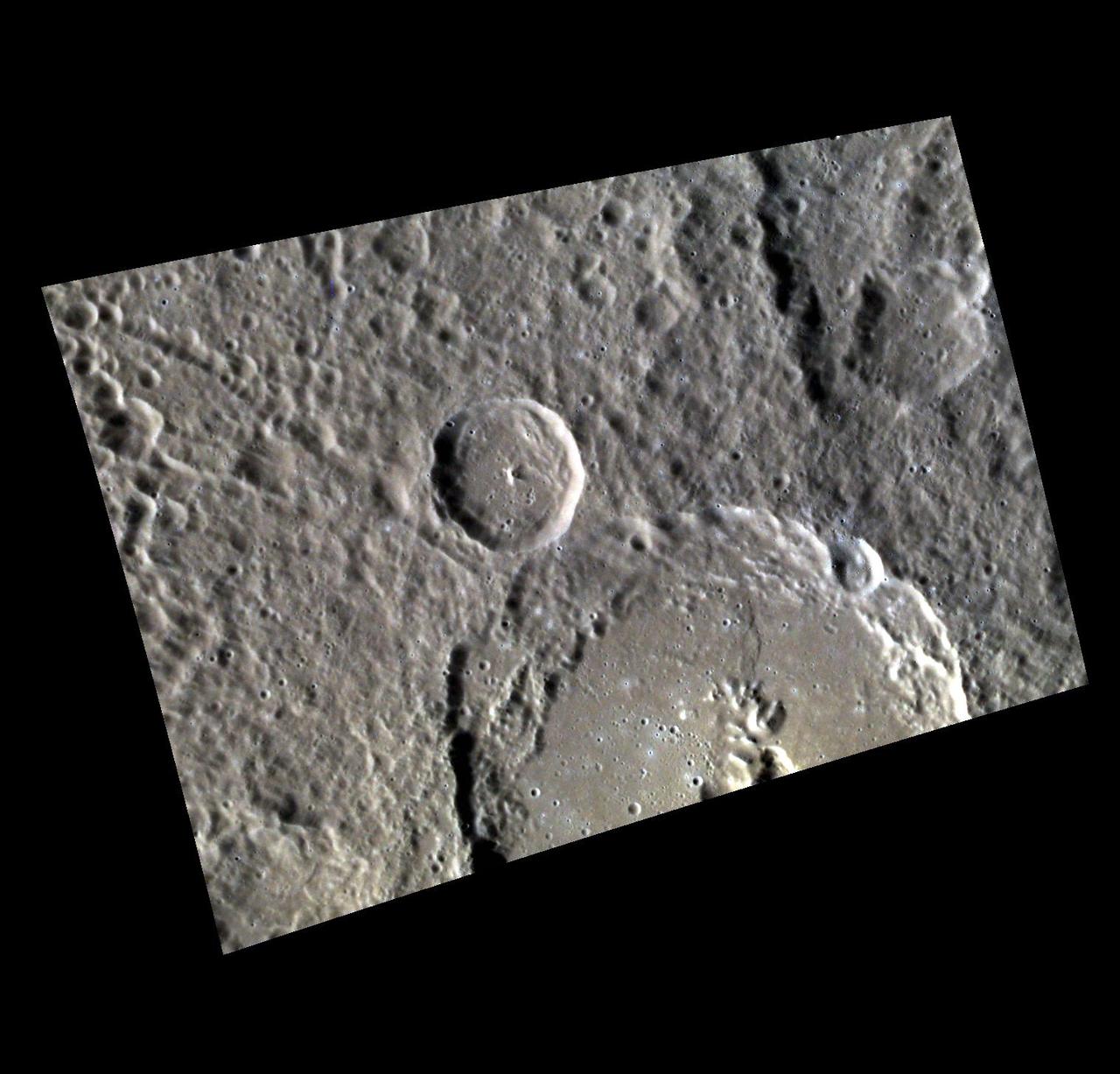
Complex Craters
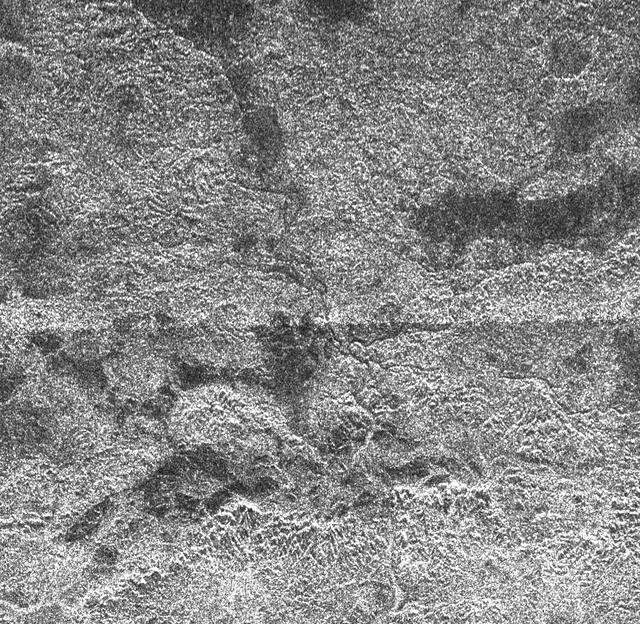

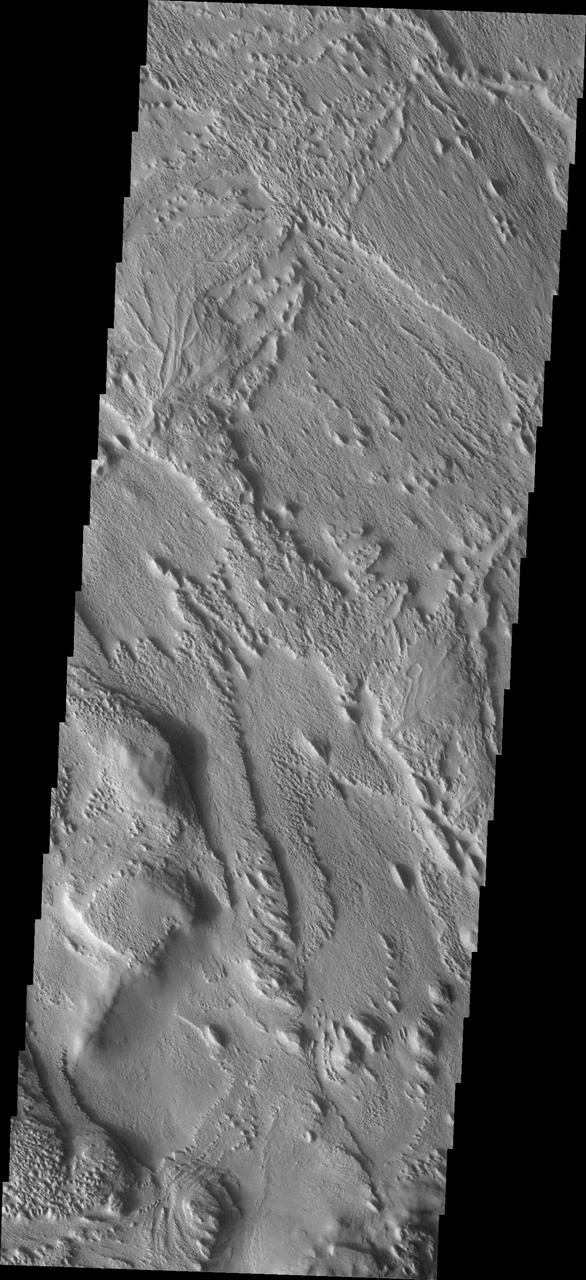
Complex Terrain
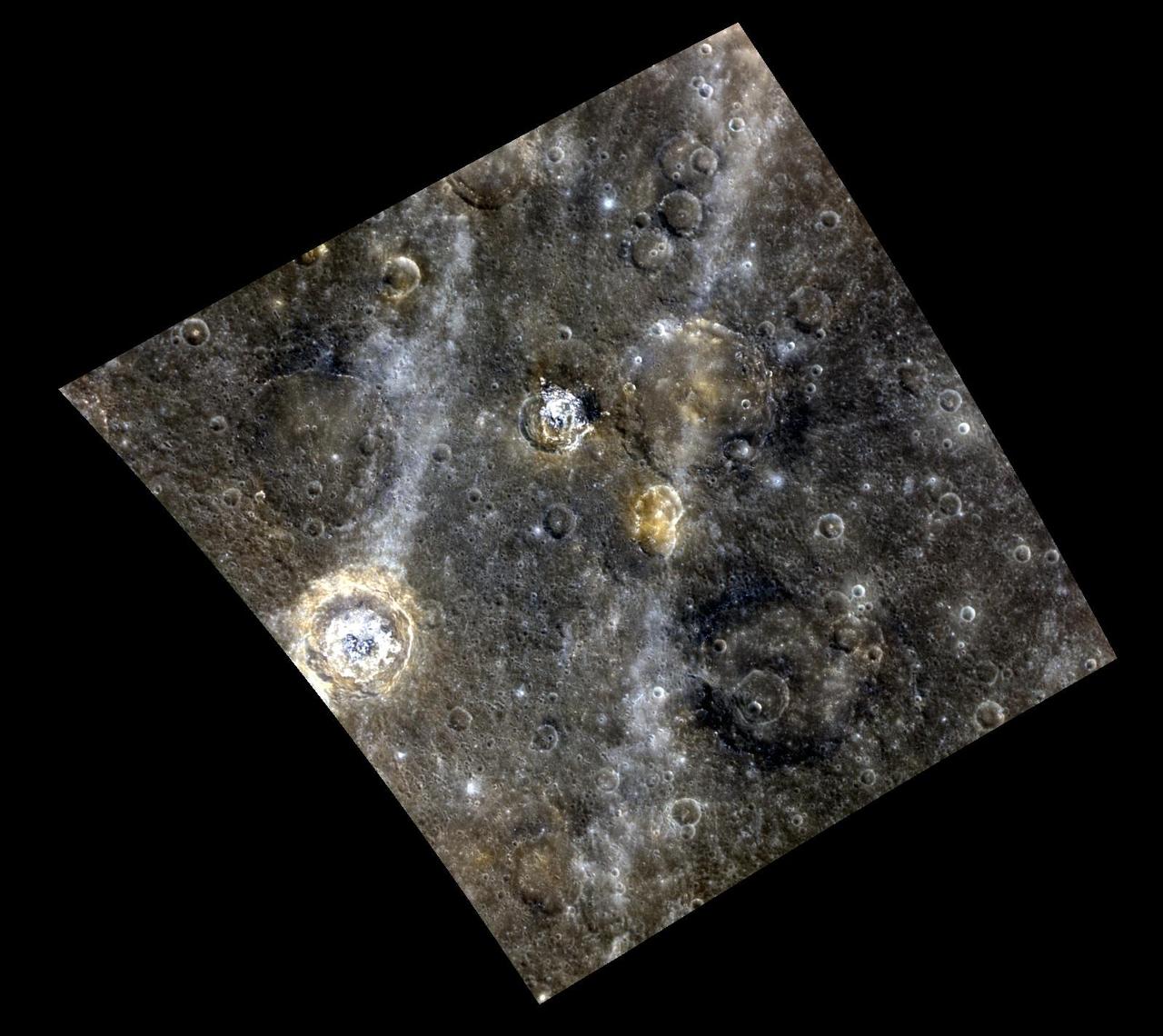
A Colorful Complex
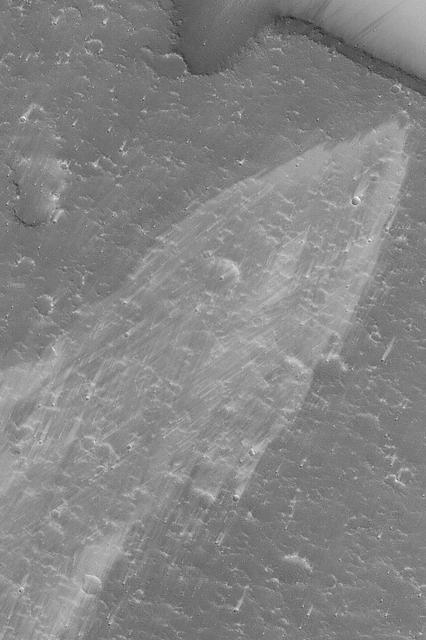

Complex Wind Streaks
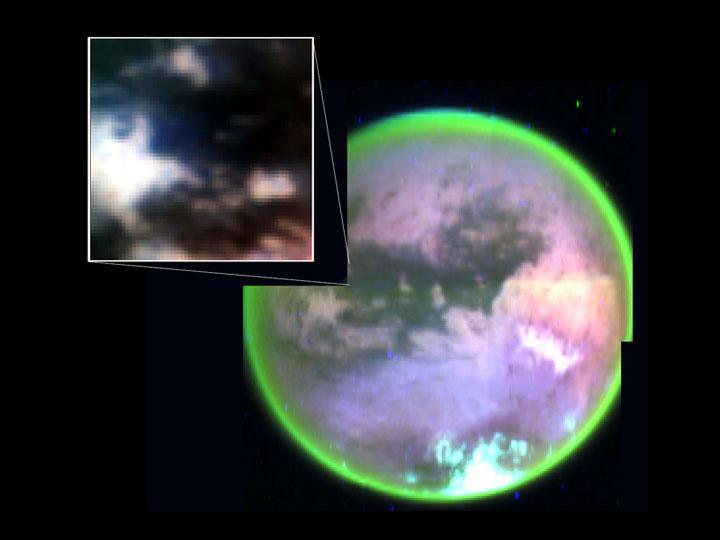

Titan Complex Surface
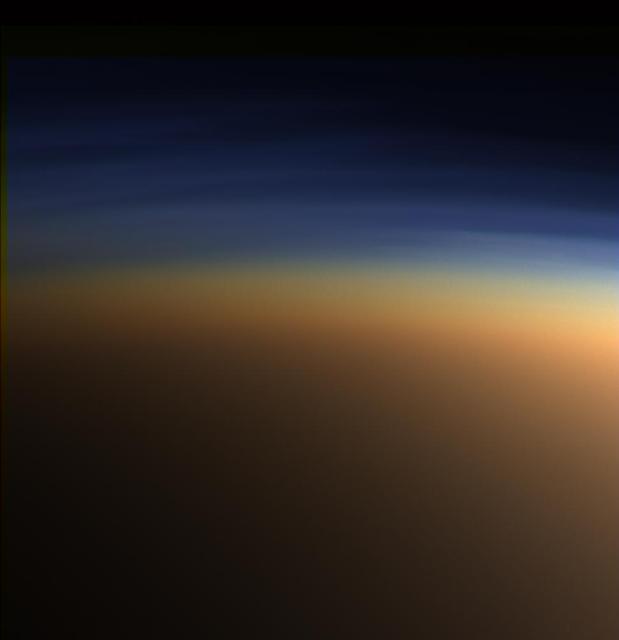

Titan: Complex Anti-greenhouse
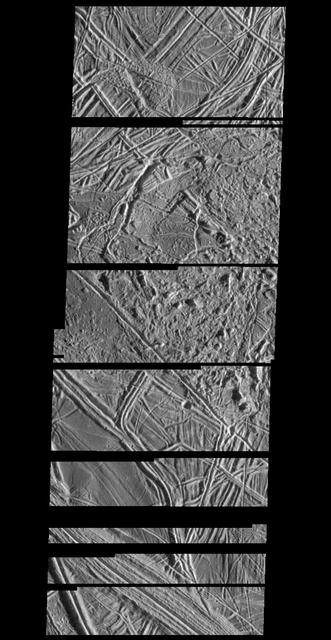
Structurally Complex Surface of Europa

The Complex Geology of Geddes Crater
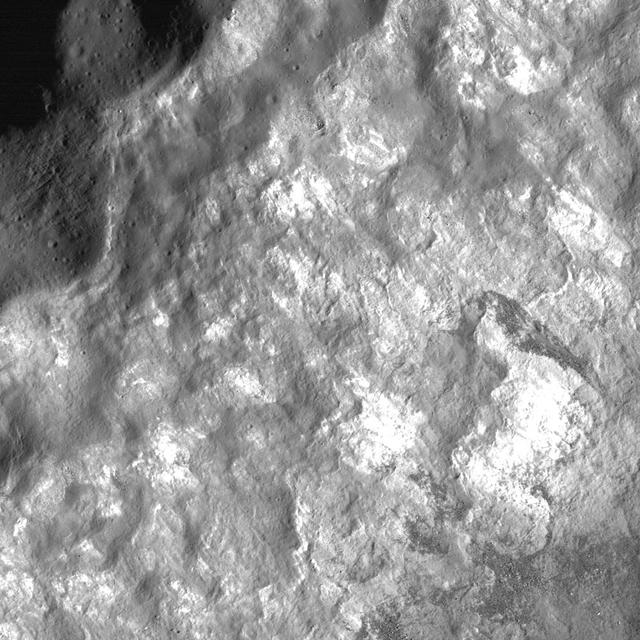

Not your Average Complex Crater
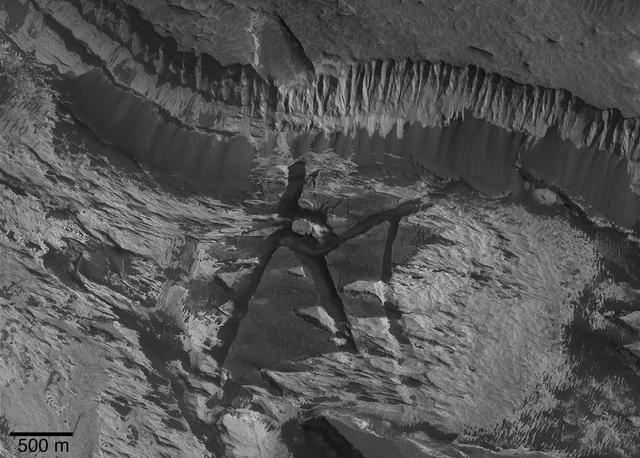

Aram Chaos Complexity
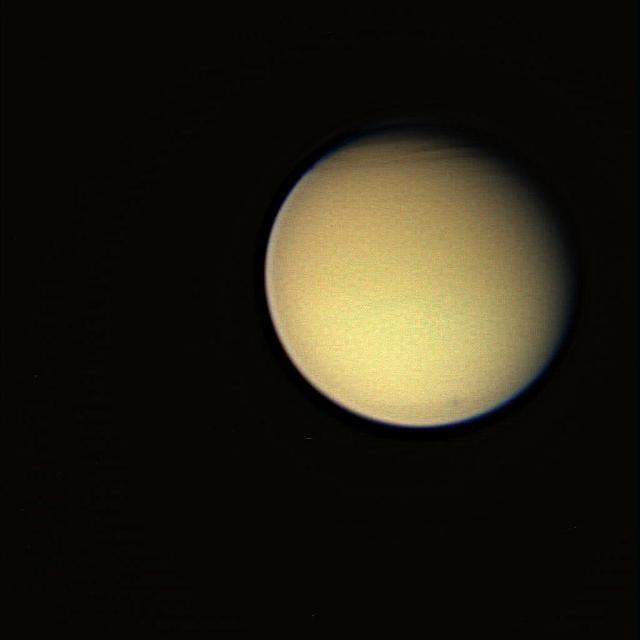

Titanic Complexity Color
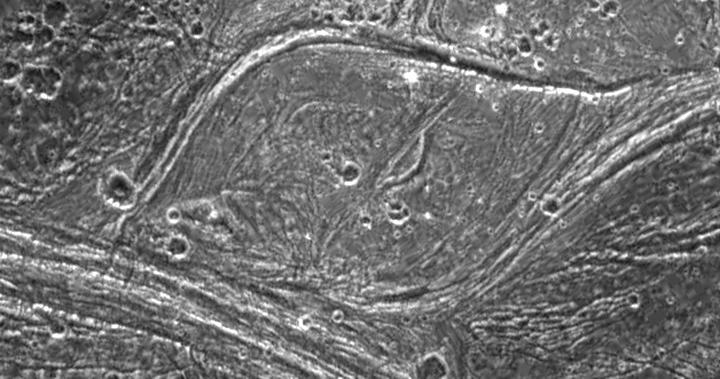
Complex Tectonism on Ganymede
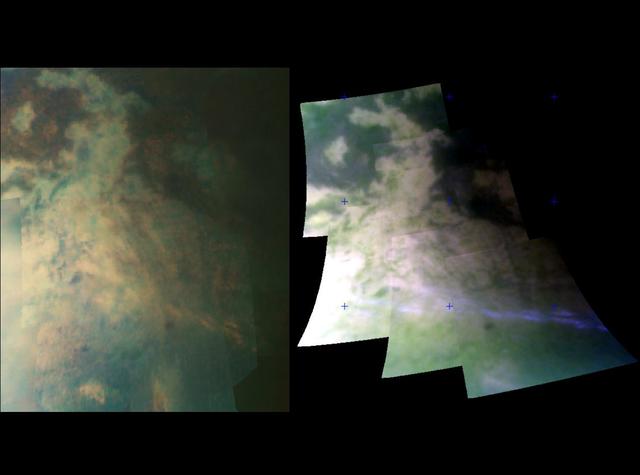
Large Tectonic Complex
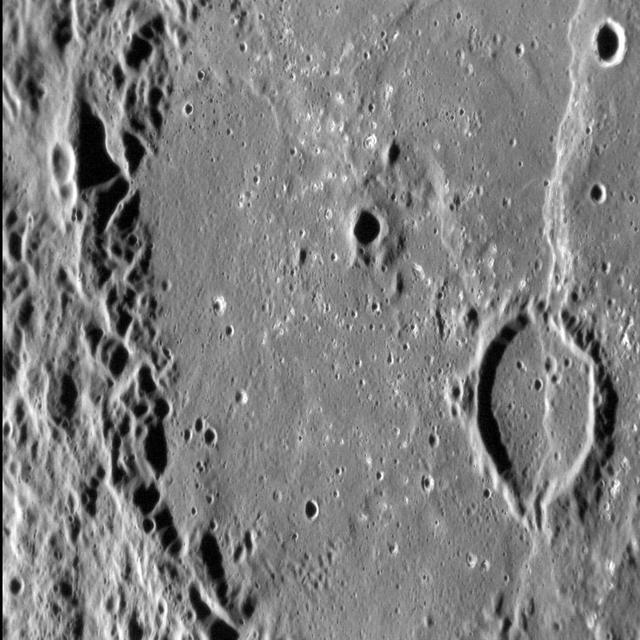

Dario Basin: Complex Cross-cuts
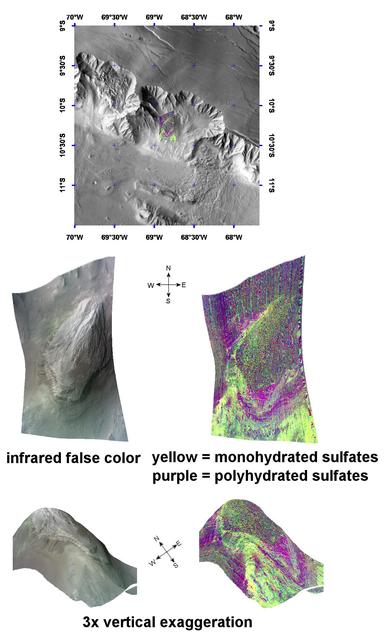
Complex Sulfate Deposits in Coprates Chasma
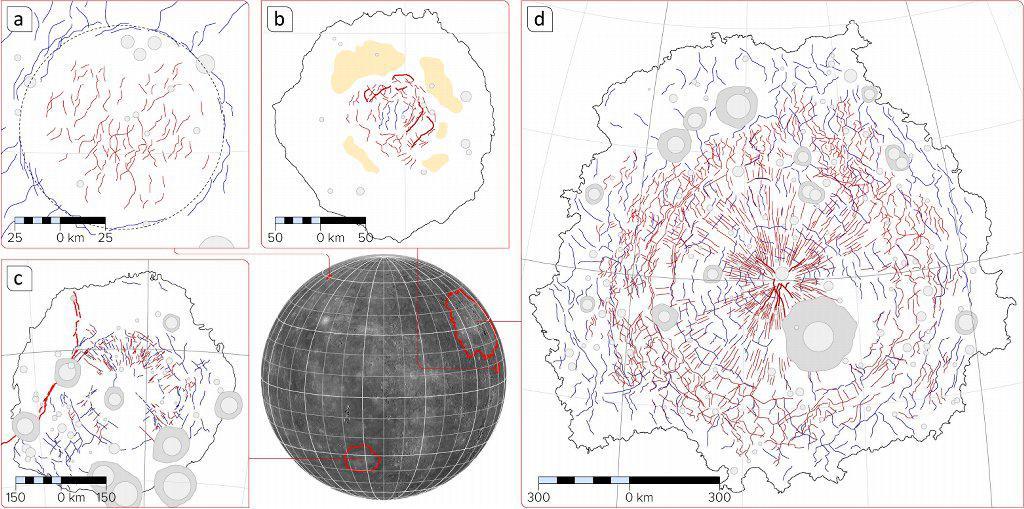
Tectonic Complexity in Mercury Impact Features
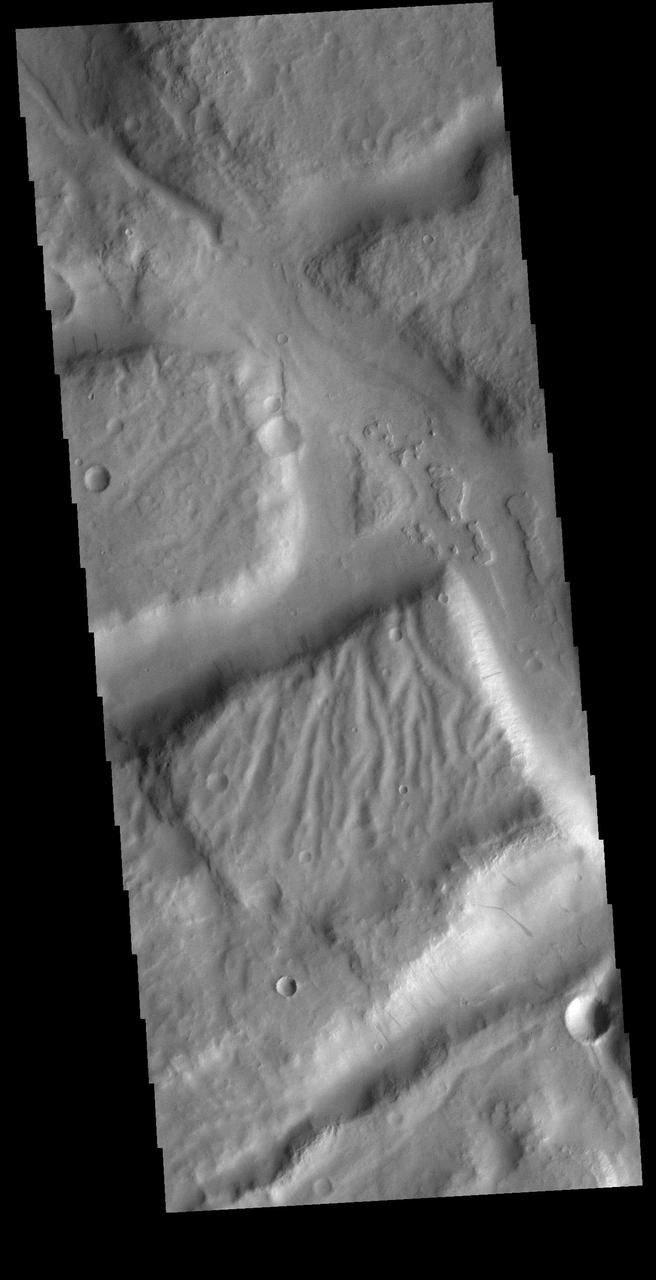

Today's VIS image shows a complex region of features in northern Terra Sirenum. Right angle valley intersections were created by tectonic forces, the tops of the mesas are dissected by channels and several cliff sides contain dark slope streaks. Orbit Number: 81952 Latitude: -7.86492 Longitude: 191.975 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-06-05 05:49 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24113
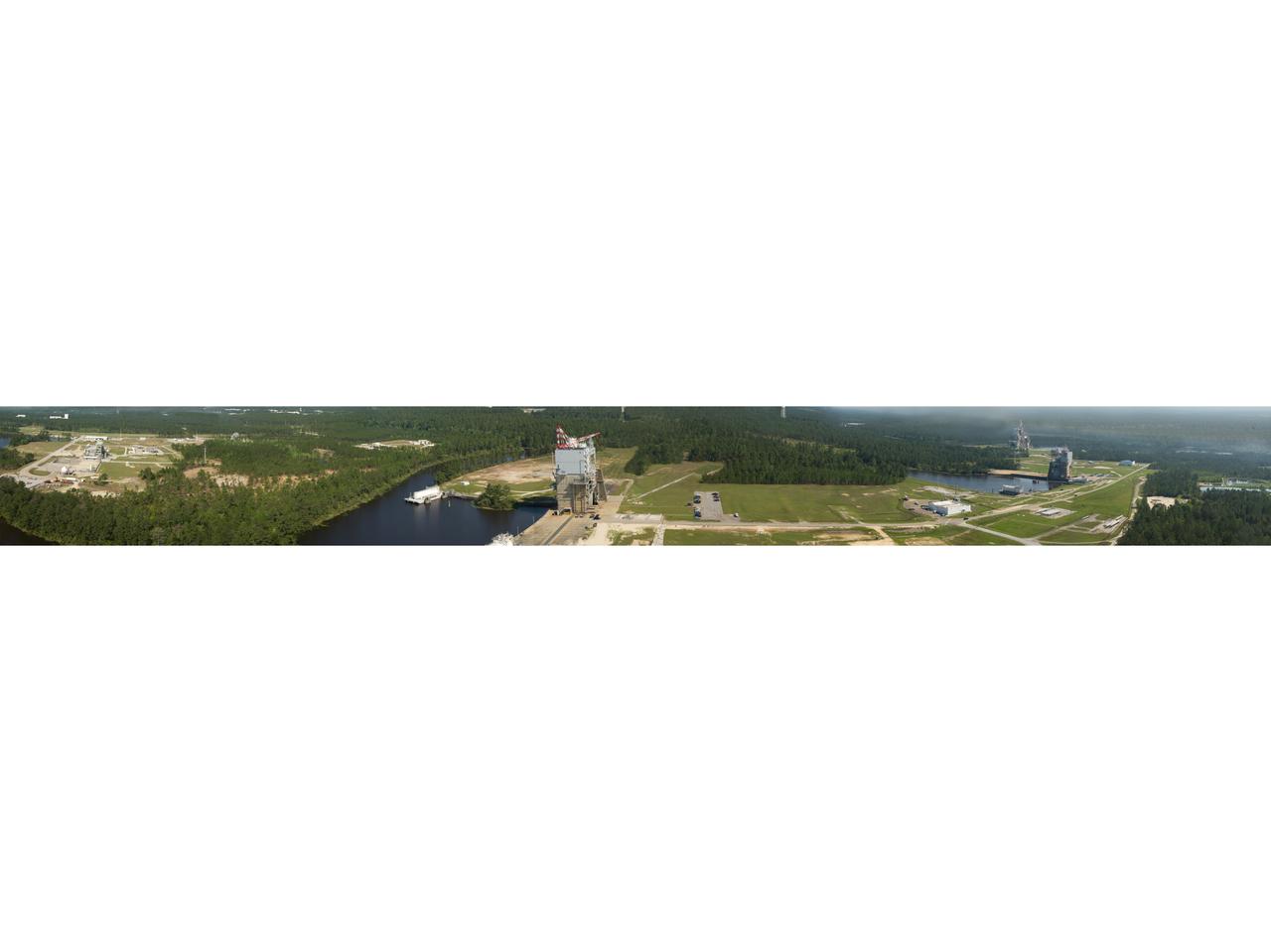

A photo taken from the top of the new A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center offers a panoramic view of the A, B and E test complexes at the south Mississippi facility.
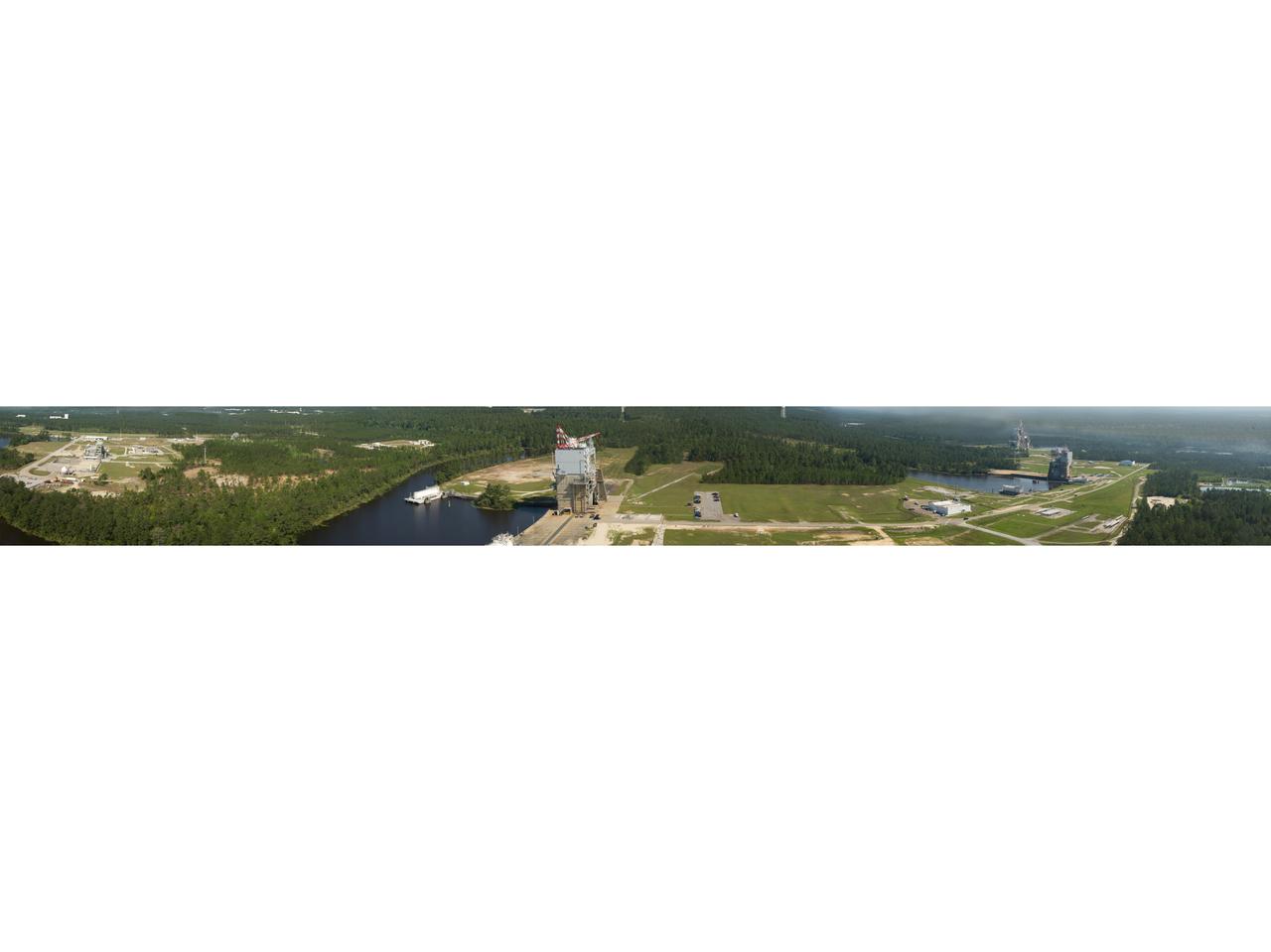

photo taken from the top of the new A-3 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center offers a panoramic view of the A, B and E test complexes at the south Mississippi faci
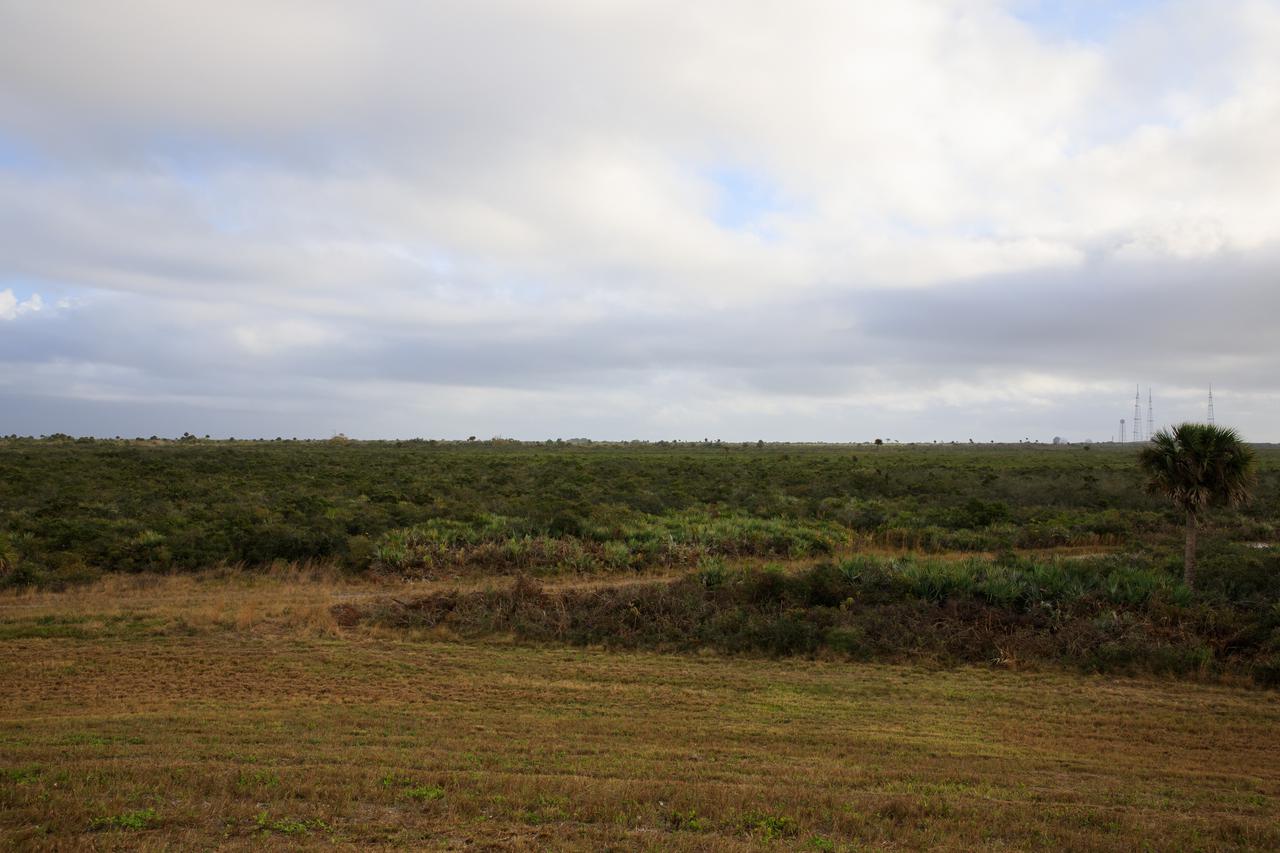

A view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 20, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.
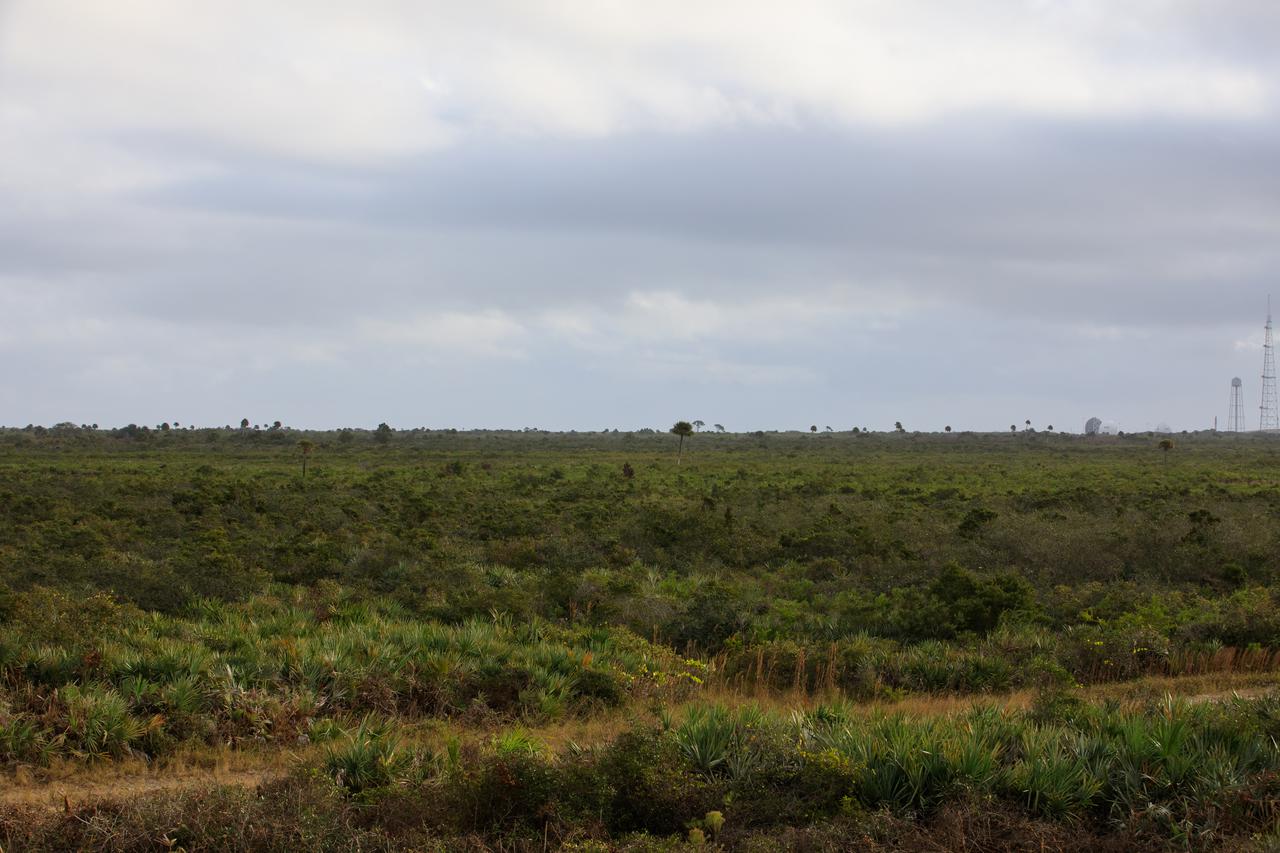

A view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 20, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.
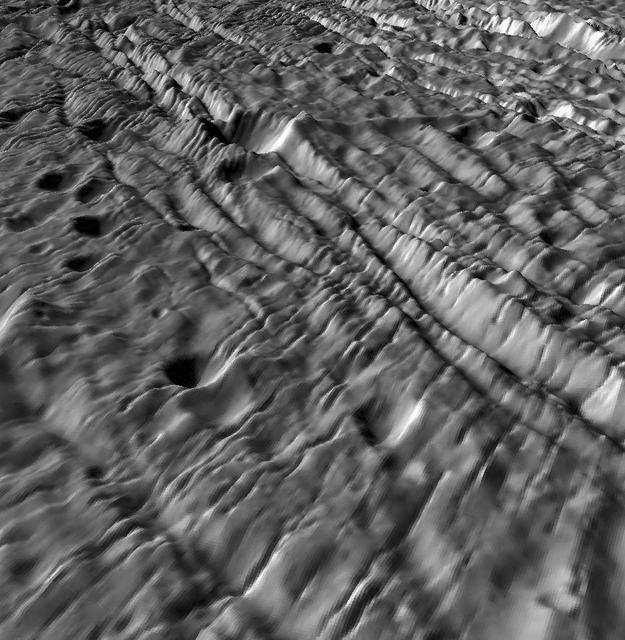

Ancient Cratered Terrains on Enceladus - A Complex Deformation History
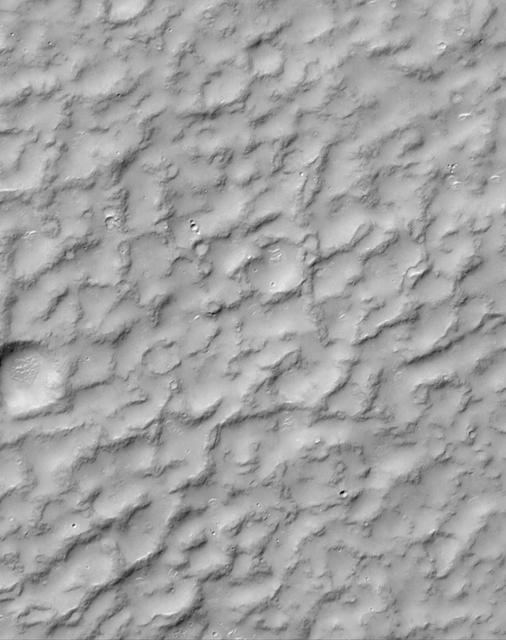

A Complex, Ridged Terrain in North Terra Cimmeria

Complex exposures of North Polar layered material
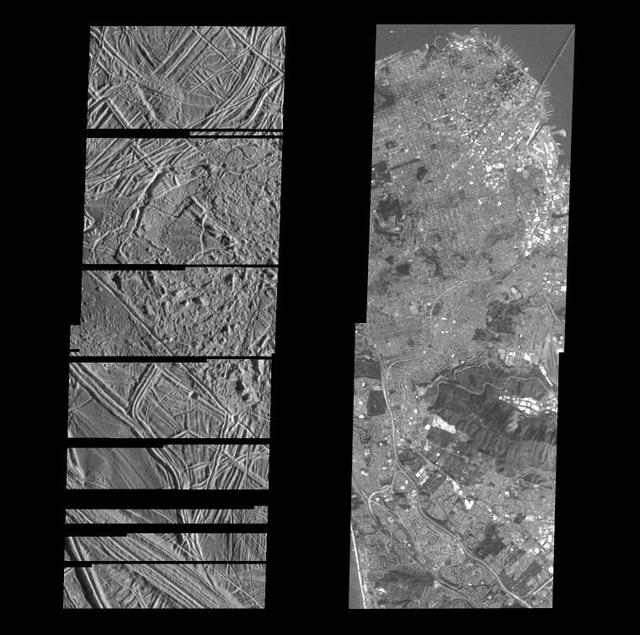
Structurally Complex Surface of Europa and similar scales on Earth
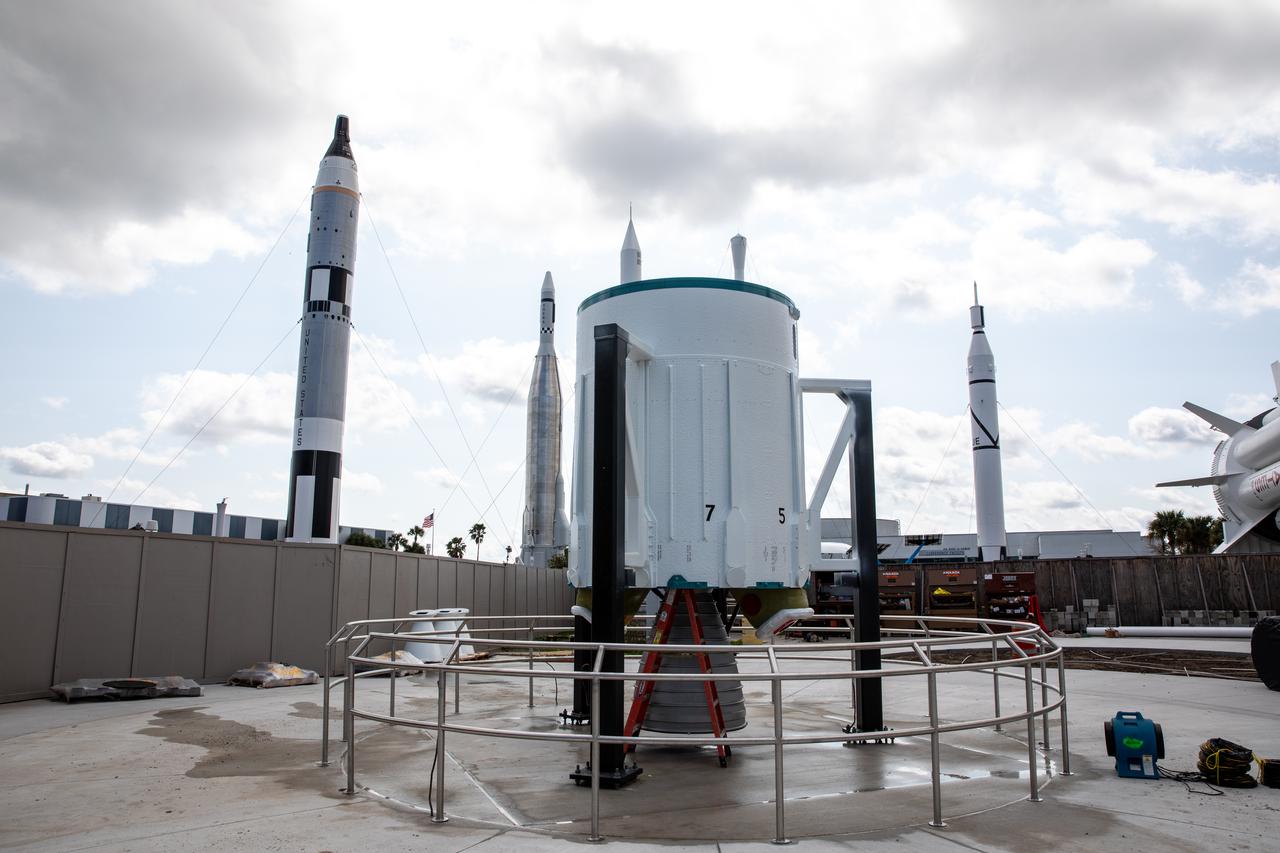

The last United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket joined the lineup of historic launch vehicles in the Rocket Garden at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, on March 3, 2021. The first segment was placed in its display area. The Delta II rocket was a workhorse for NASA and civilian scientists, the U.S. military, and commercial clients throughout its almost 30 years of service. Since its first launch in 1989, the Delta II has launched 154 successful missions. NASA’s Launch Services Program launched the ICESat-2 spacecraft on the final Delta II launch on Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
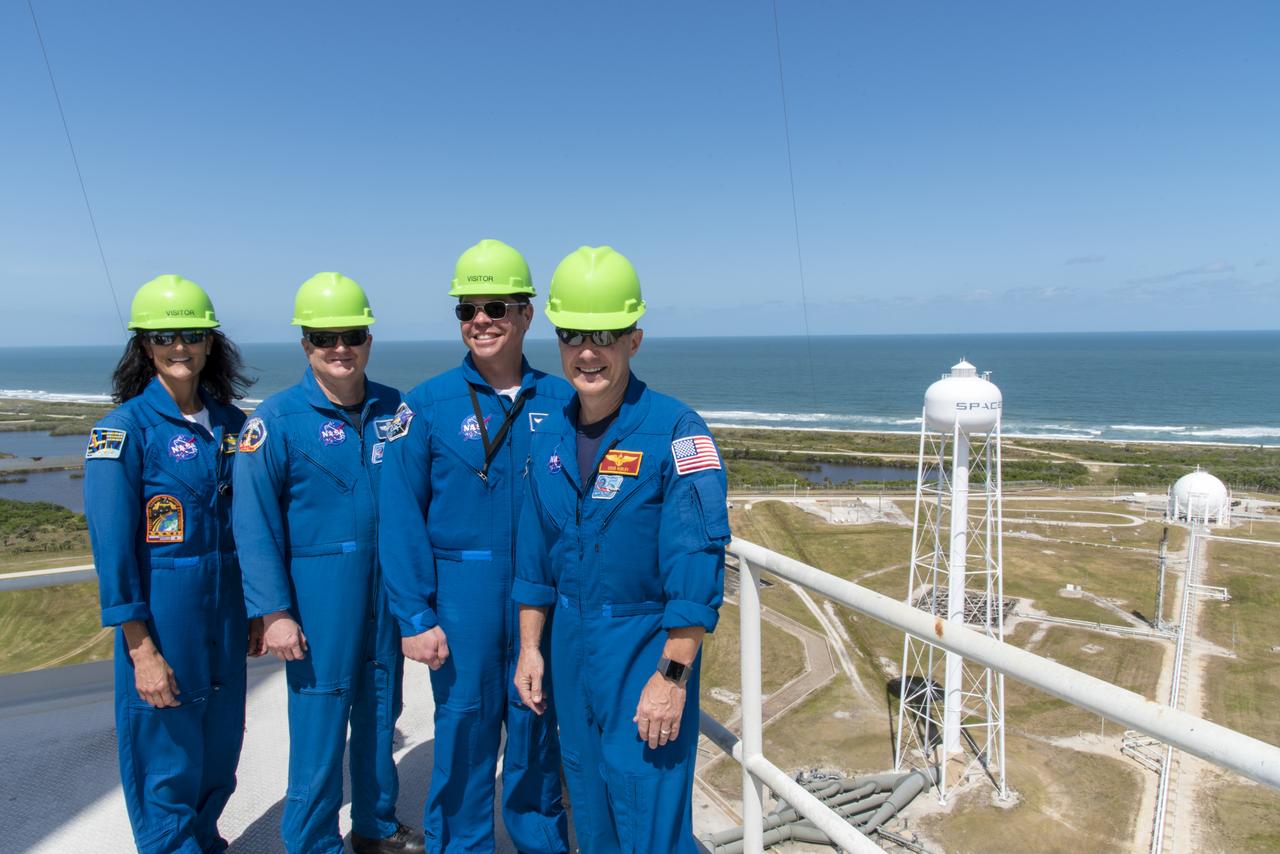

Commercial Crew Program astronauts, from the left, Suni Williams, Eric Boe, Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley take in the view from the top of Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy Space Center. The astronauts toured the pad for an up-close look at modifications that are in work for the SpaceX Crew Dragon flight tests. Tower modifications included l removal of the space shuttle era rotating service structure. Future integration of the crew access arm will allow for safe crew entry for launch and exit from the spacecraft in the unlikely event a pad abort is required.
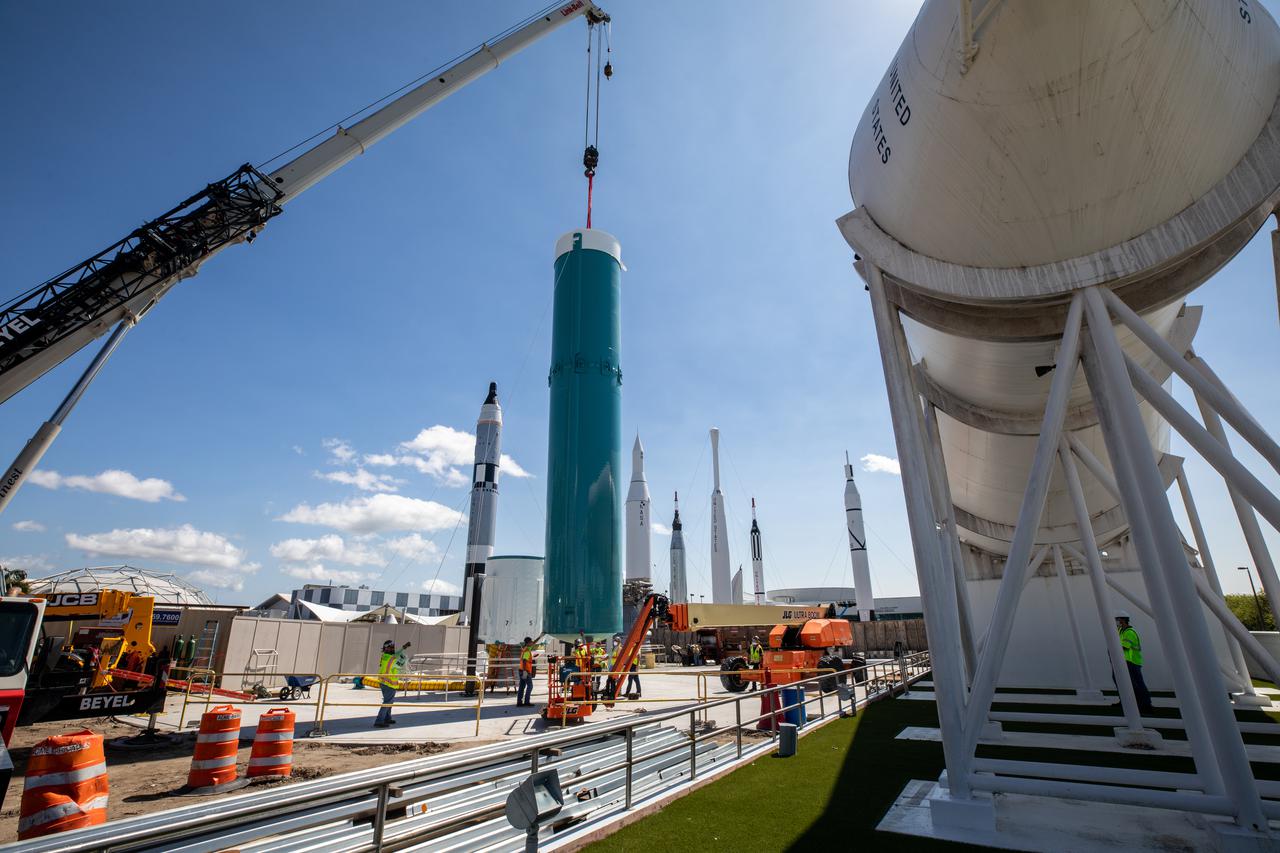

The last United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket joined the lineup of historic launch vehicles in the Rocket Garden at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, on March 3, 2021. Workers use a crane to stack the segments of the Delta II in its display area. The Delta II rocket was a workhorse for NASA and civilian scientists, the U.S. military, and commercial clients throughout its almost 30 years of service. Since its first launch in 1989, the Delta II has launched 154 successful missions. NASA’s Launch Services Program launched the ICESat-2 spacecraft on the final Delta II launch on Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
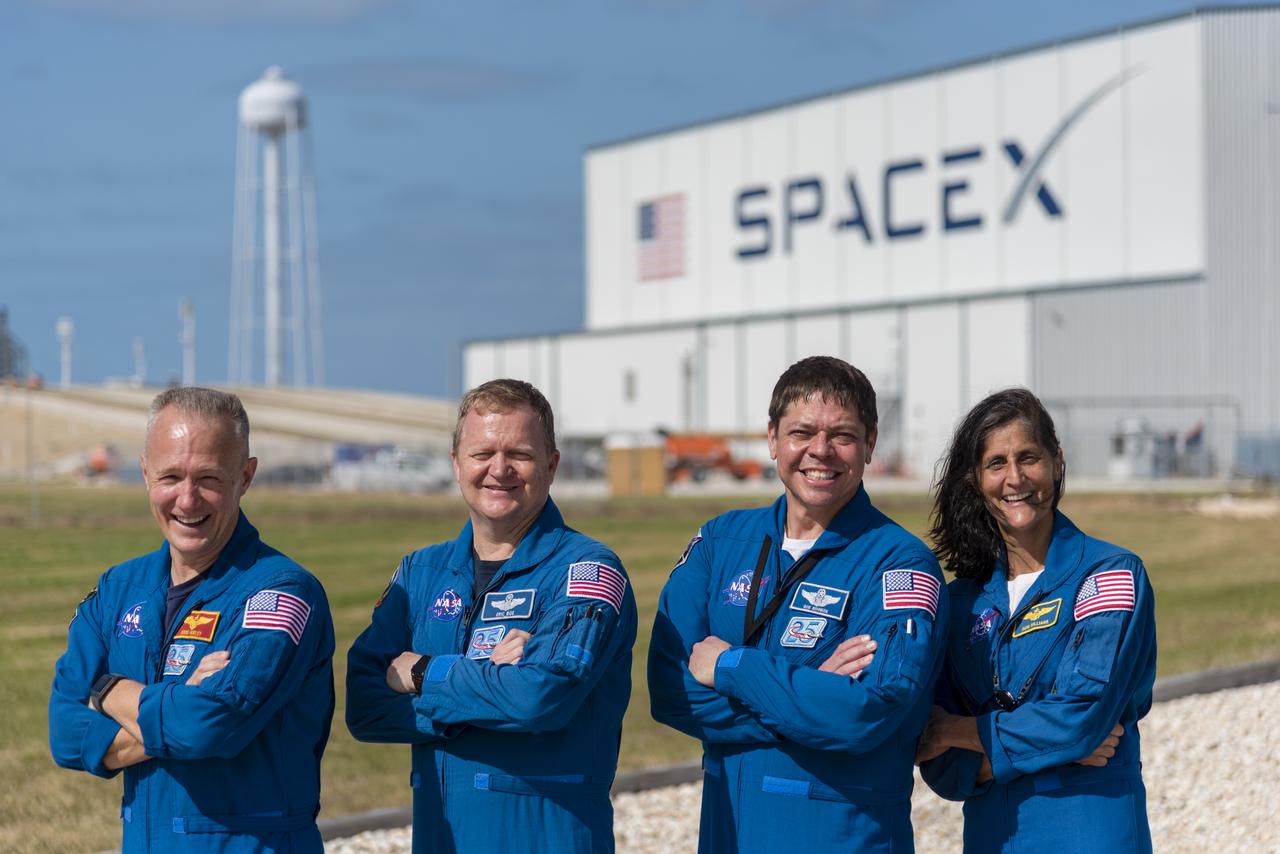

Commercial Crew Program astronauts, from the left Doug Hurley, Eric Boe, Bob Behnken and Suni Williams, pose just outside Launch Complex 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The astronauts toured the pad for an up-close look at modifications that are in work for the SpaceX Crew Dragon flight tests. The tower modifications included removal of the space shuttle era rotating service structure. Future integration of the crew access arm will allow for safe crew entry for launch and exit from the spacecraft in the unlikely event a pad abort is required.
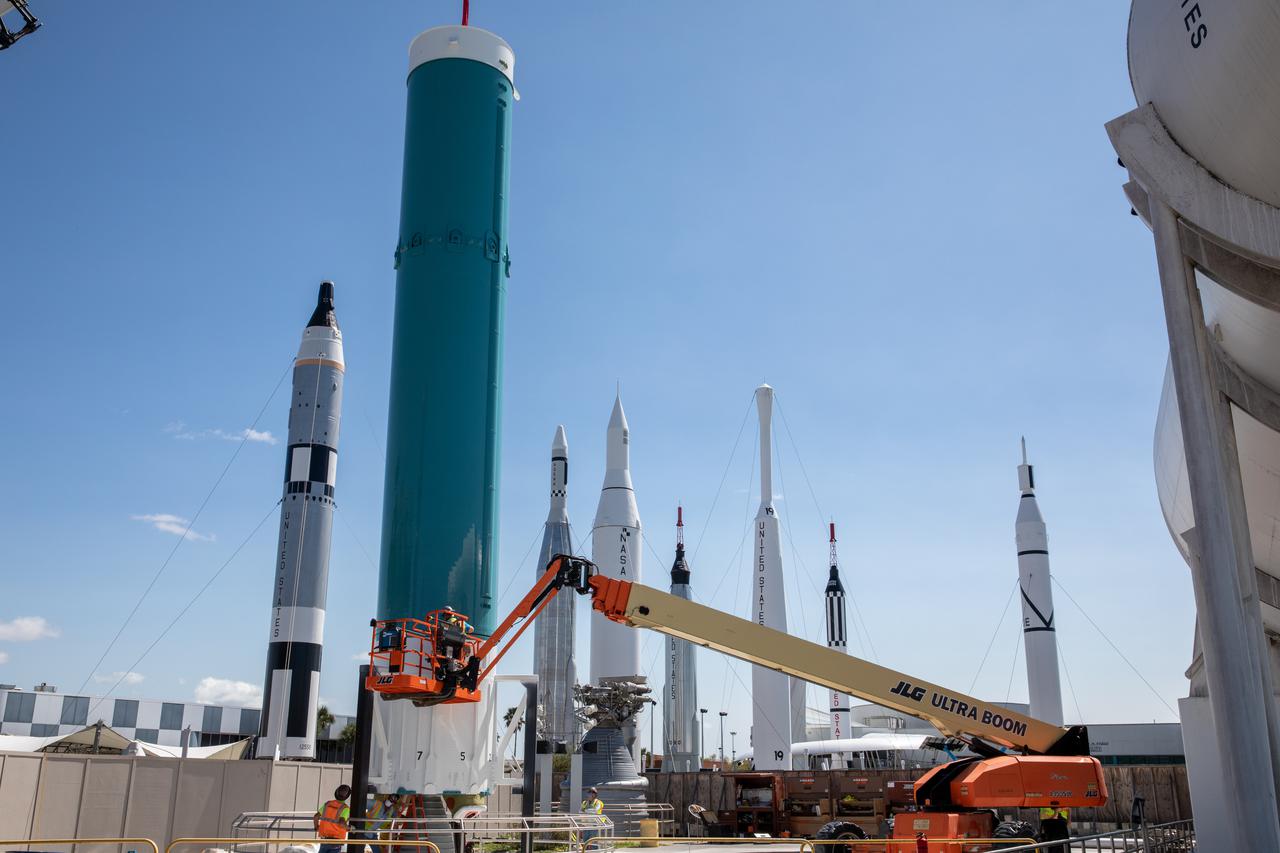

The last United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket joined the lineup of historic launch vehicles in the Rocket Garden at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, on March 3, 2021. Workers use a crane to stack the segments of the Delta II in its display area. The Delta II rocket was a workhorse for NASA and civilian scientists, the U.S. military, and commercial clients throughout its almost 30 years of service. Since its first launch in 1989, the Delta II has launched 154 successful missions. NASA’s Launch Services Program launched the ICESat-2 spacecraft on the final Delta II launch on Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.

The last United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket joined the lineup of historic launch vehicles in the Rocket Garden at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida, on March 3, 2021. Workers use a crane to lift a segment of the Delta II for stacking in its display area. The Delta II rocket was a workhorse for NASA and civilian scientists, the U.S. military, and commercial clients throughout its almost 30 years of service. Since its first launch in 1989, the Delta II has launched 154 successful missions. NASA’s Launch Services Program launched the ICESat-2 spacecraft on the final Delta II launch on Sept. 15, 2018, from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
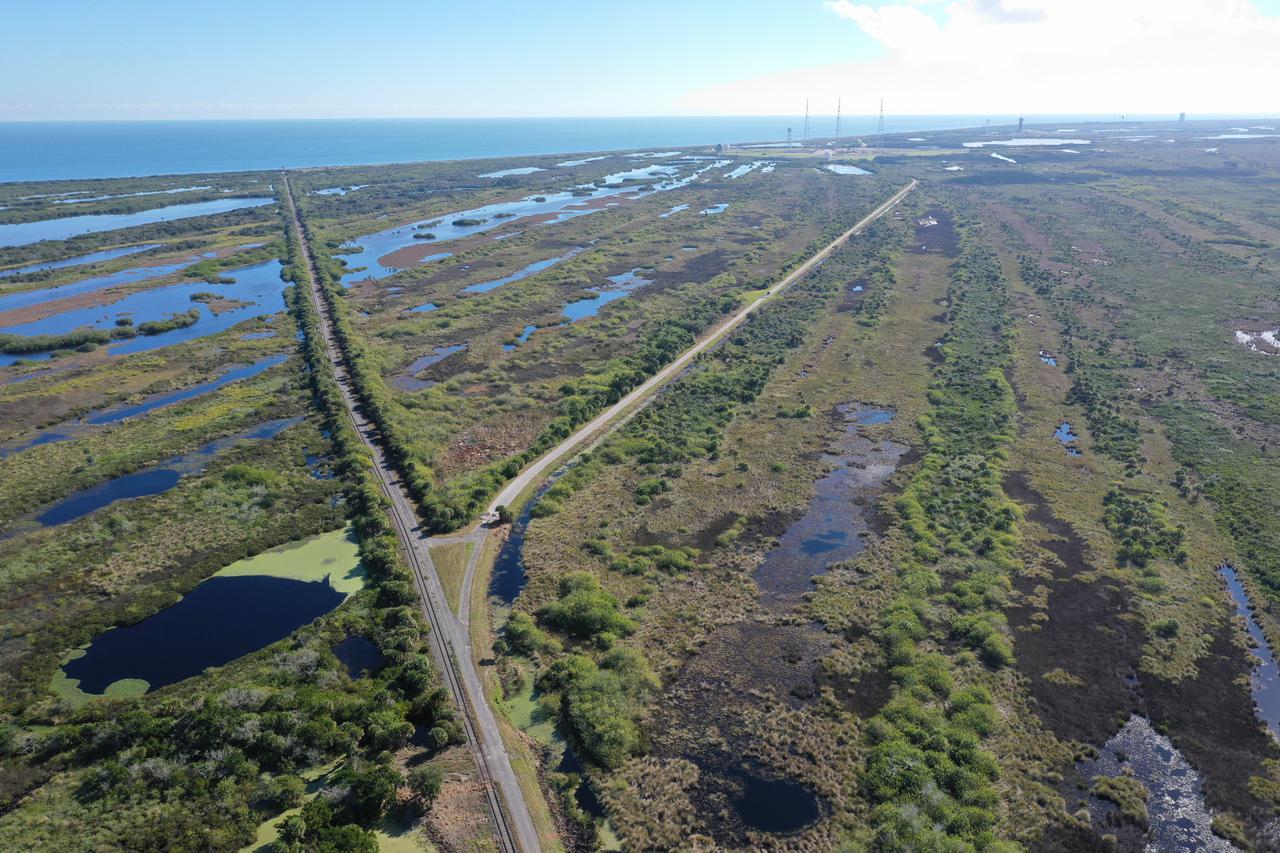

An aerial view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 28, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.
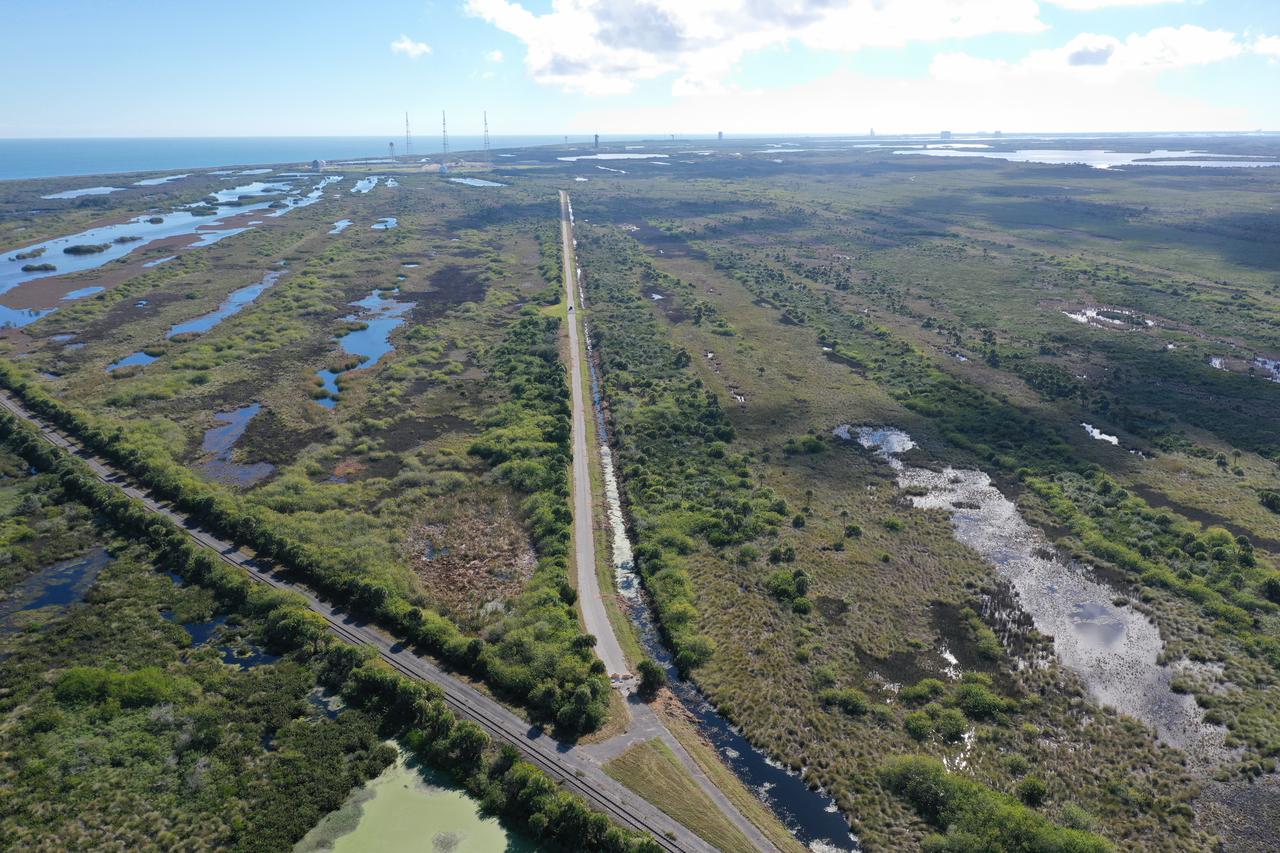

An aerial view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 28, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.
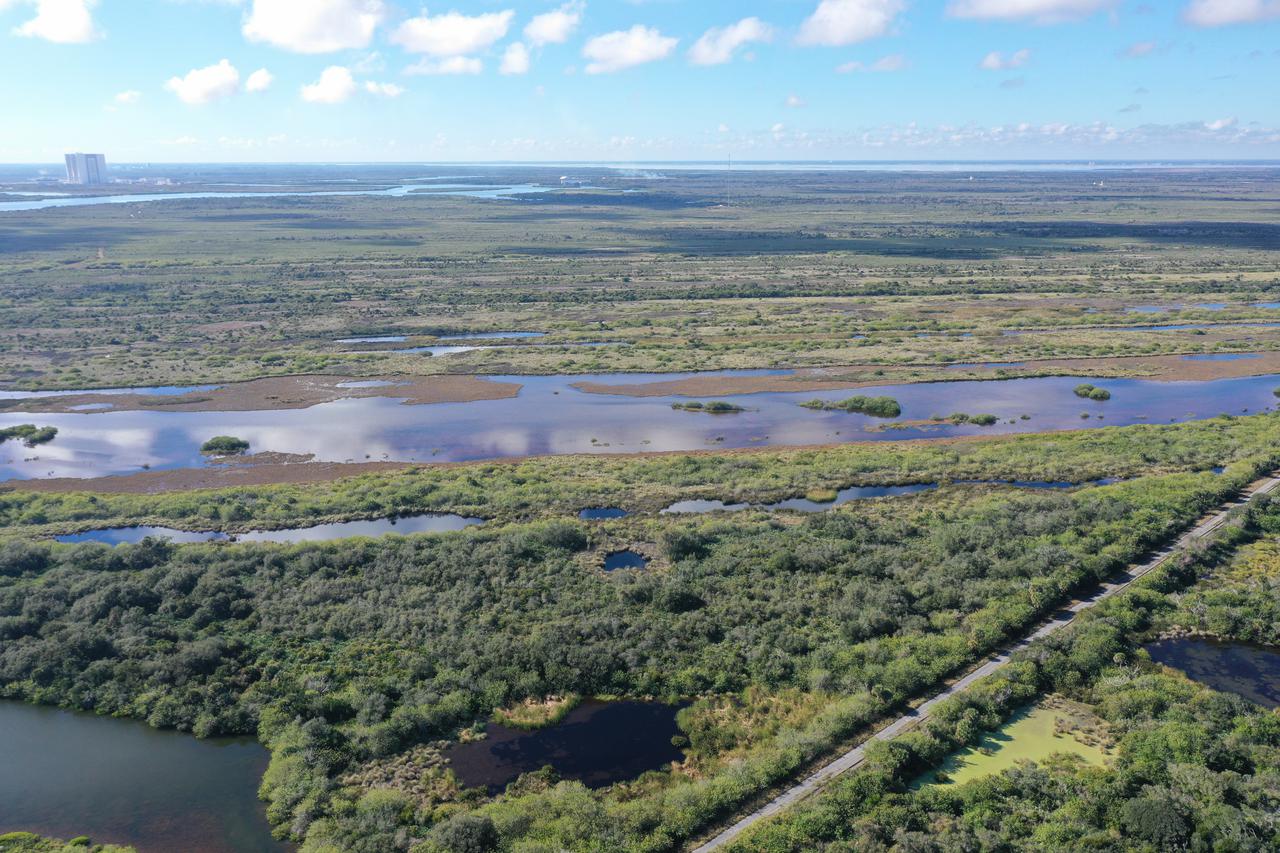

An aerial view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 28, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.

An aerial view of a proposed new launch site, Launch Complex 49, on Dec. 28, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In response to an inquiry from SpaceX, NASA is preparing to conduct environmental assessments to develop the proposed launch site. The 175-acre site, located north of Launch Complex 39B within the center’s security perimeter, would support the launch and landing of SpaceX’s Starship and Super Heavy launch vehicle. NASA and SpaceX are moving forward with the initial environmental assessment before concluding a potential agreement to develop the property.
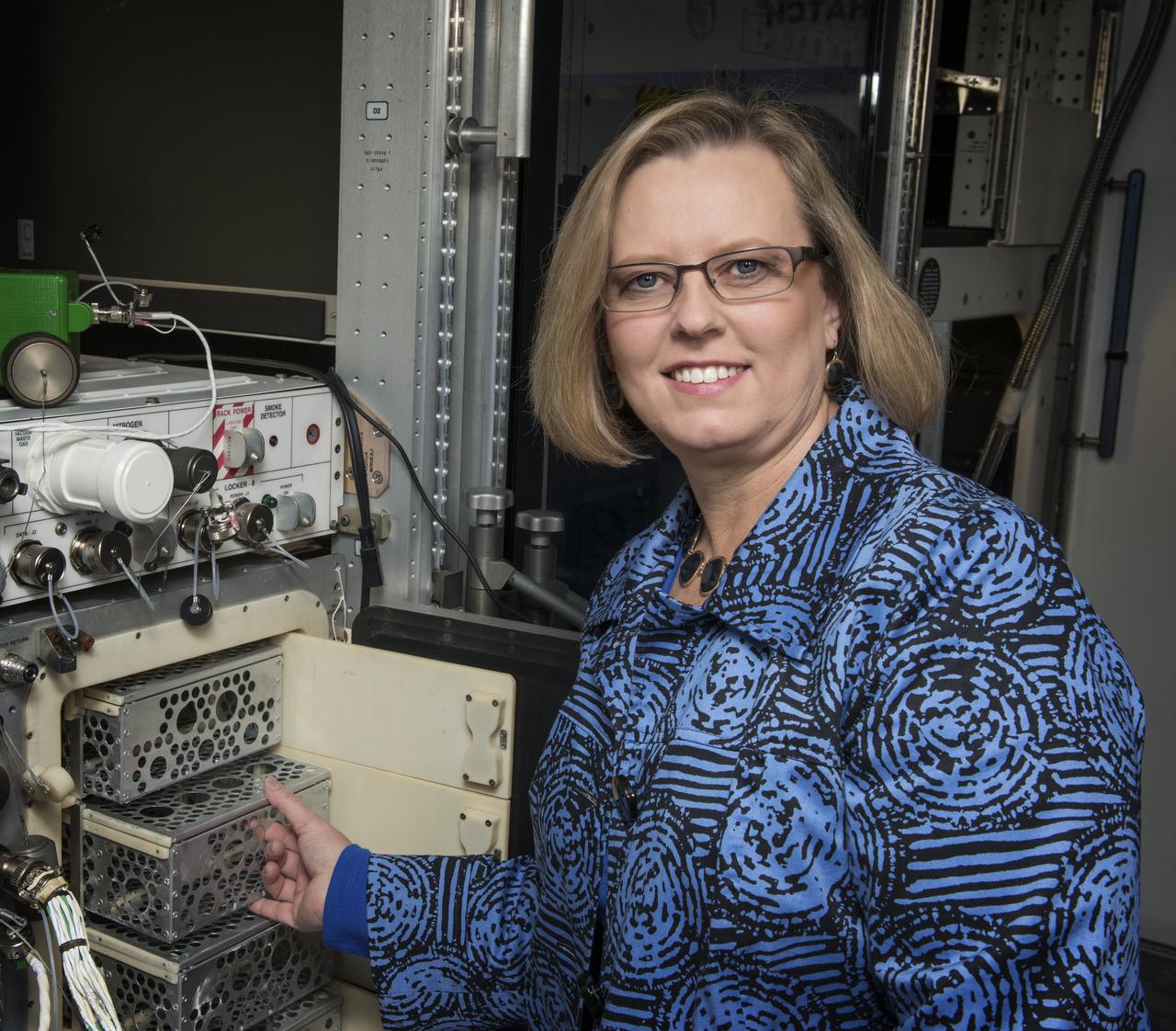
LISA SMITH, THE TRAINING TEAM LEAD IN MARSHALL'S MISSION OPERATIONS LAB, EXAMINES THE DRAWERS IN THE GLACIER MOCK-UP, A TRAINING VERSION OF A FREEZER ON THE INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION INSTALLED IN THE MARSHALL CENTER'S LABORATORY TRAINING COMPLEX
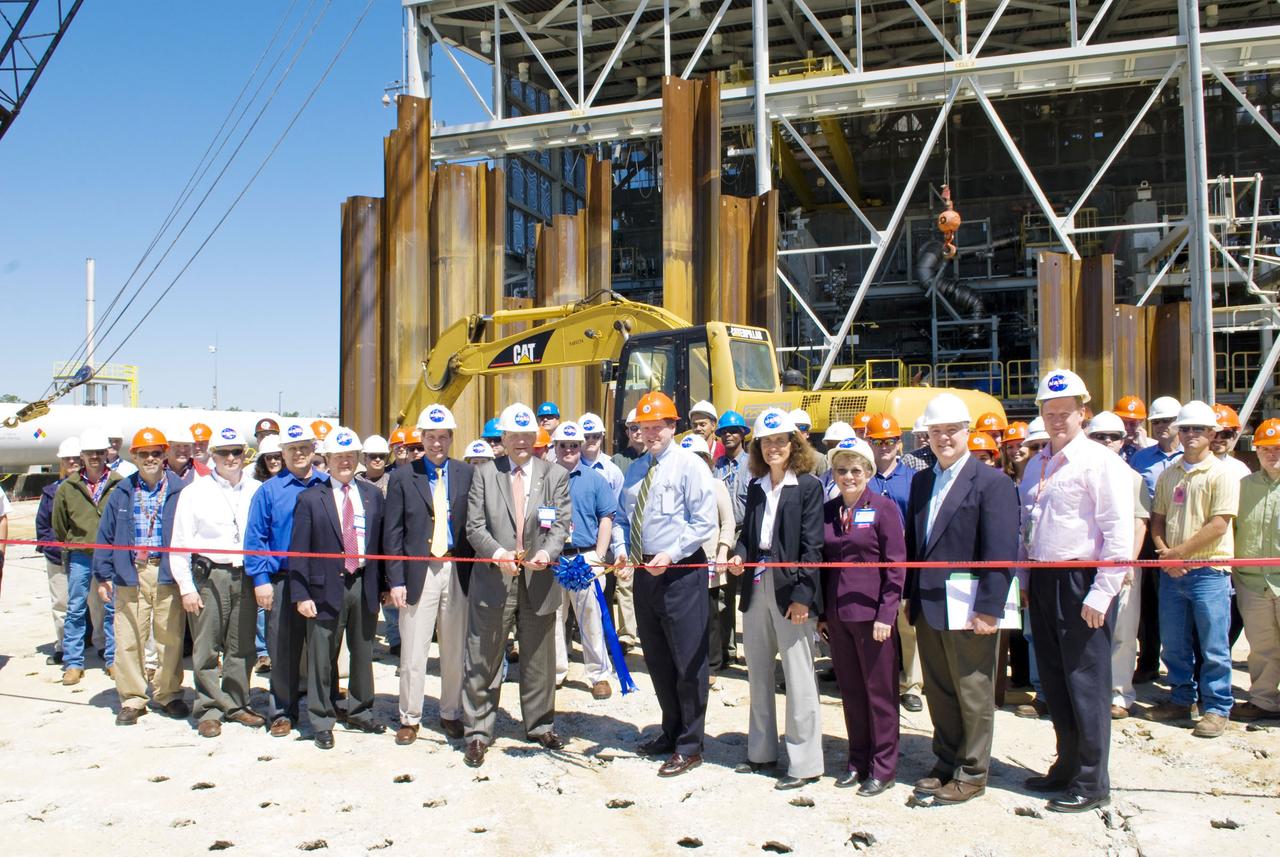

Representatives from NASA, Orbital Sciences Corp. and Aerojet participate in a ribbon-cutting ceremony for construction of a flame deflector trench at Stennis Space Center's E Test Complex. Participants included Orbital CEO J.R. Thompson (center, left) and Stennis Space Center Director Gene Goldman (center, right).
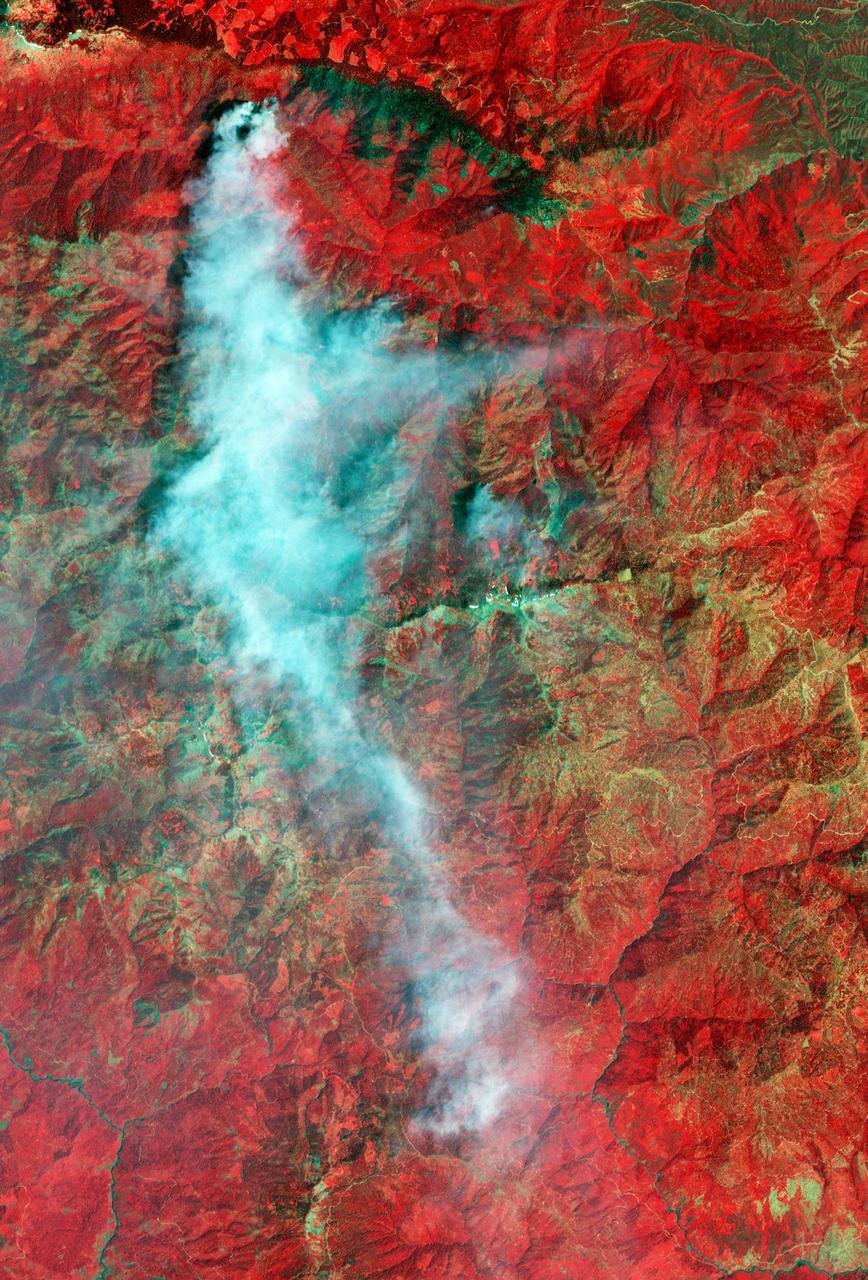

The Yolla Bolly Complex Wildland Fire was started on June 21, 2008 by a lightning strike. This image was acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft.
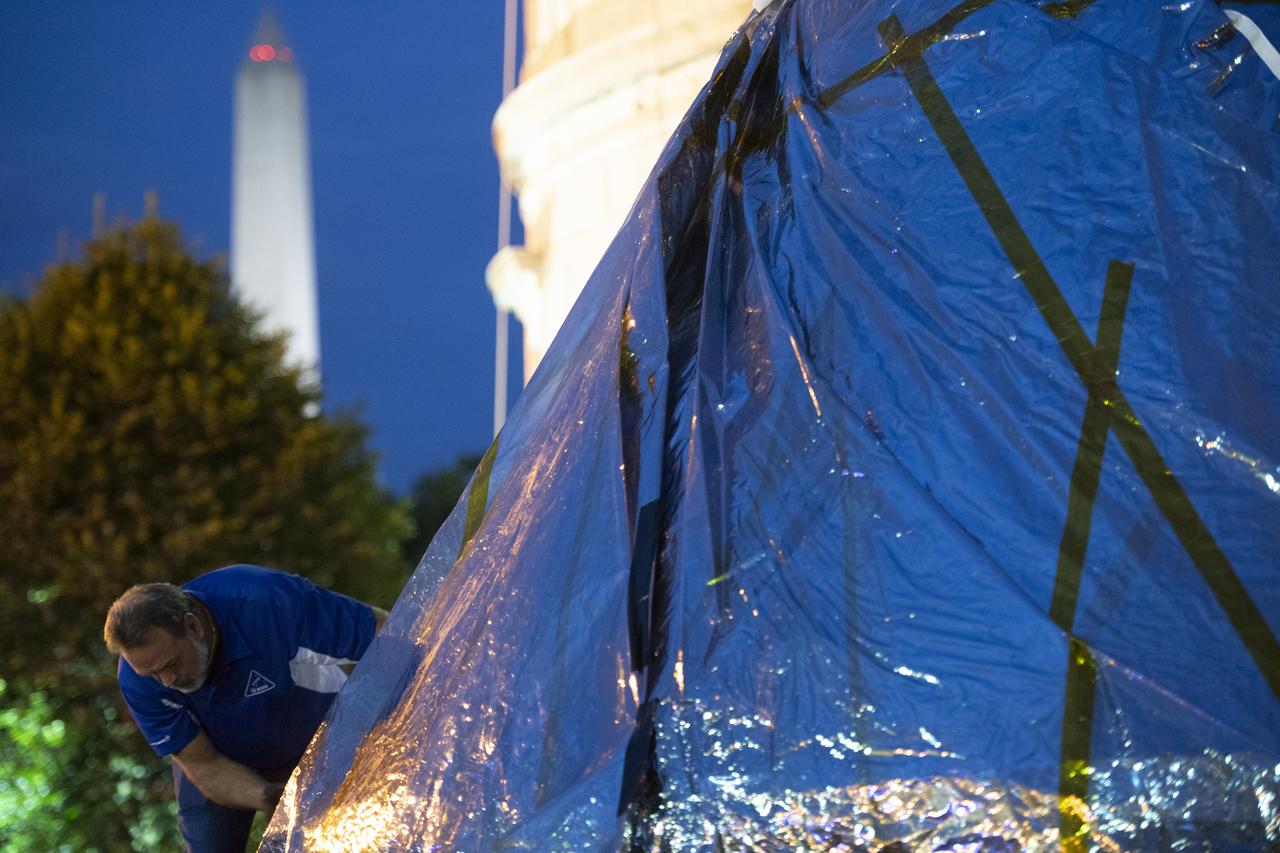

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
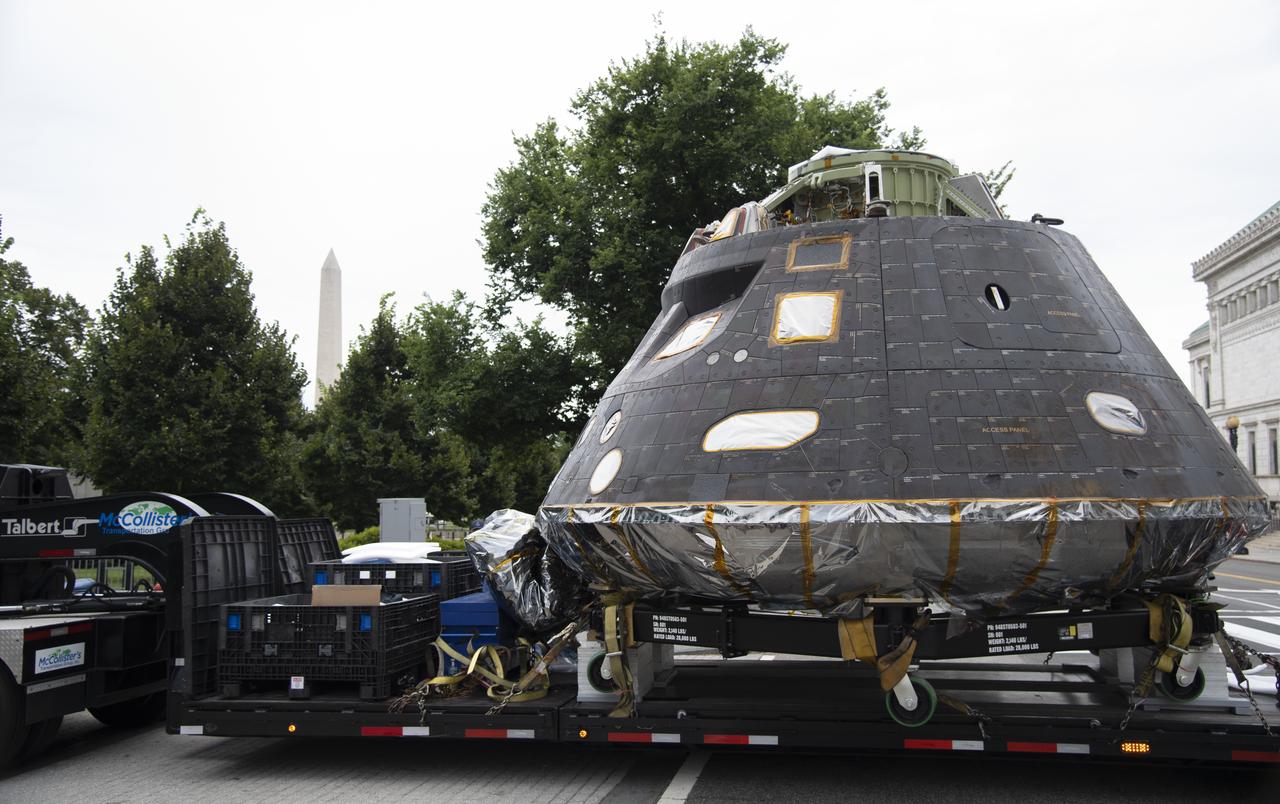

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
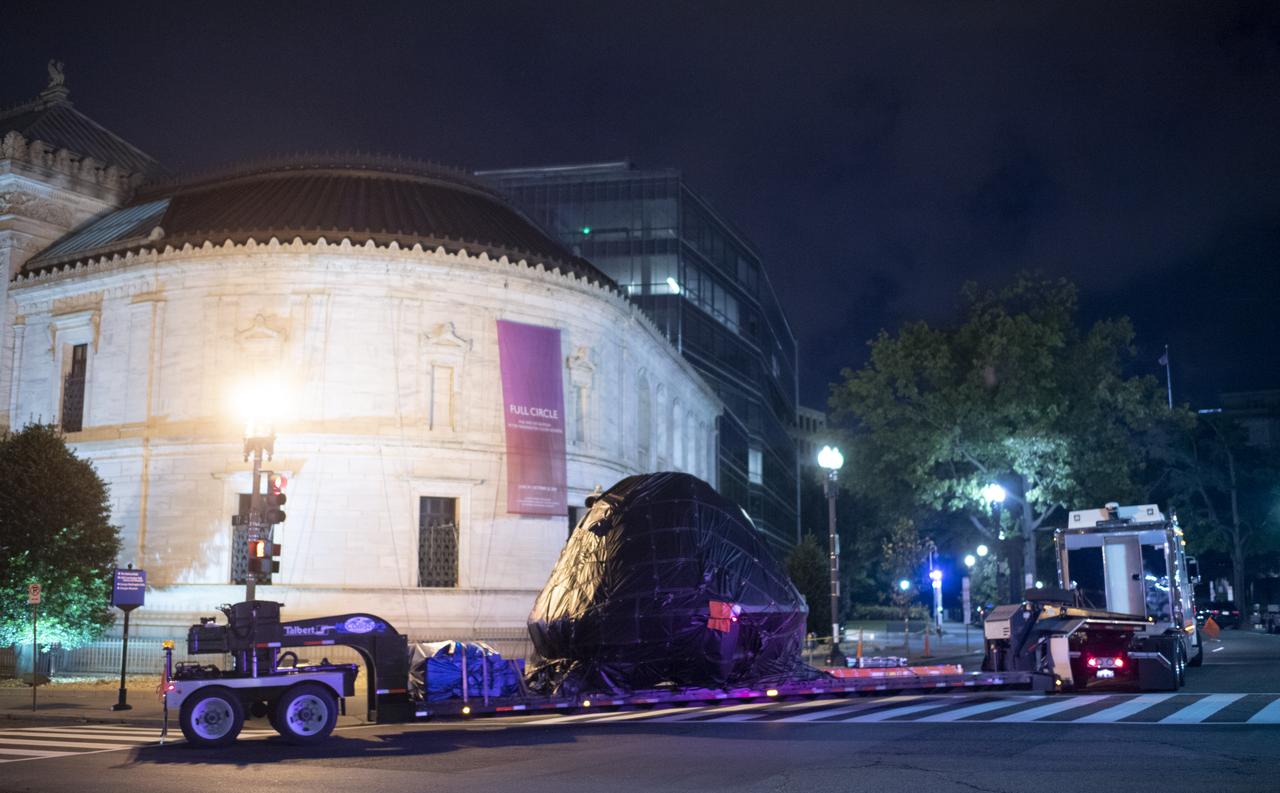

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
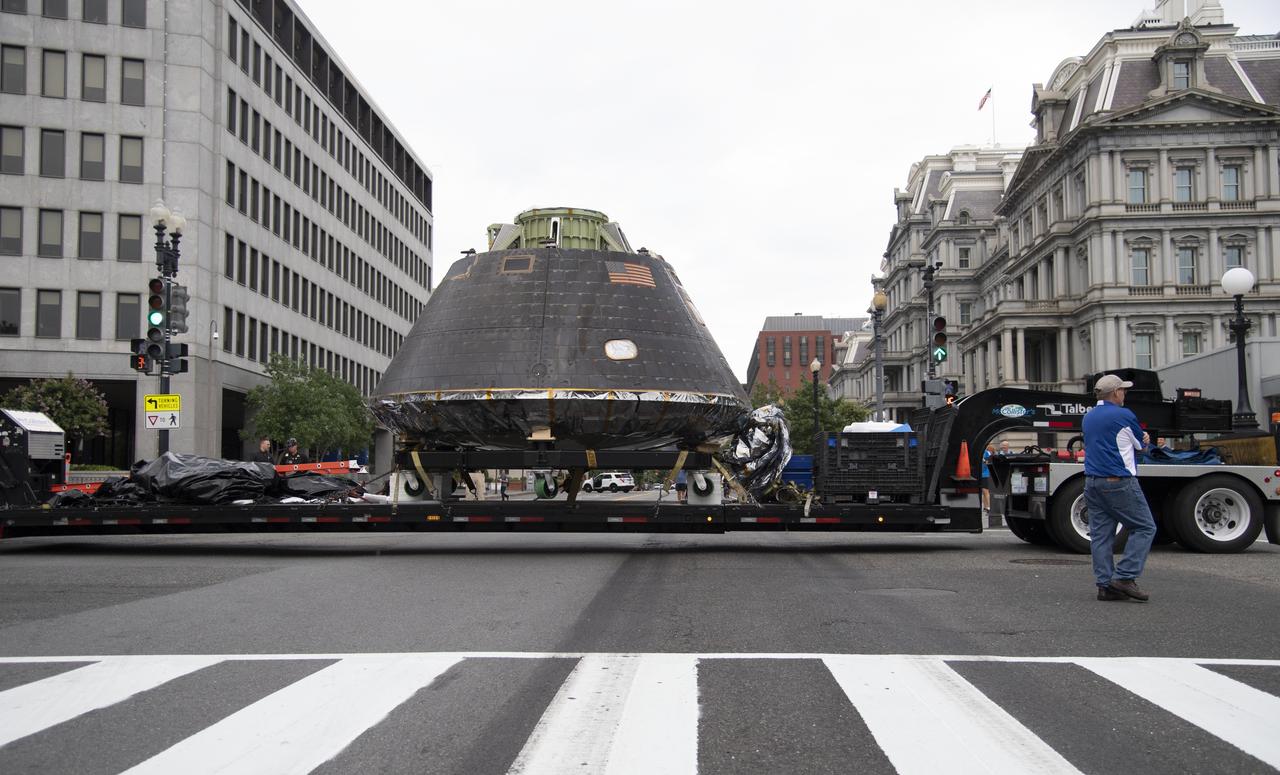

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
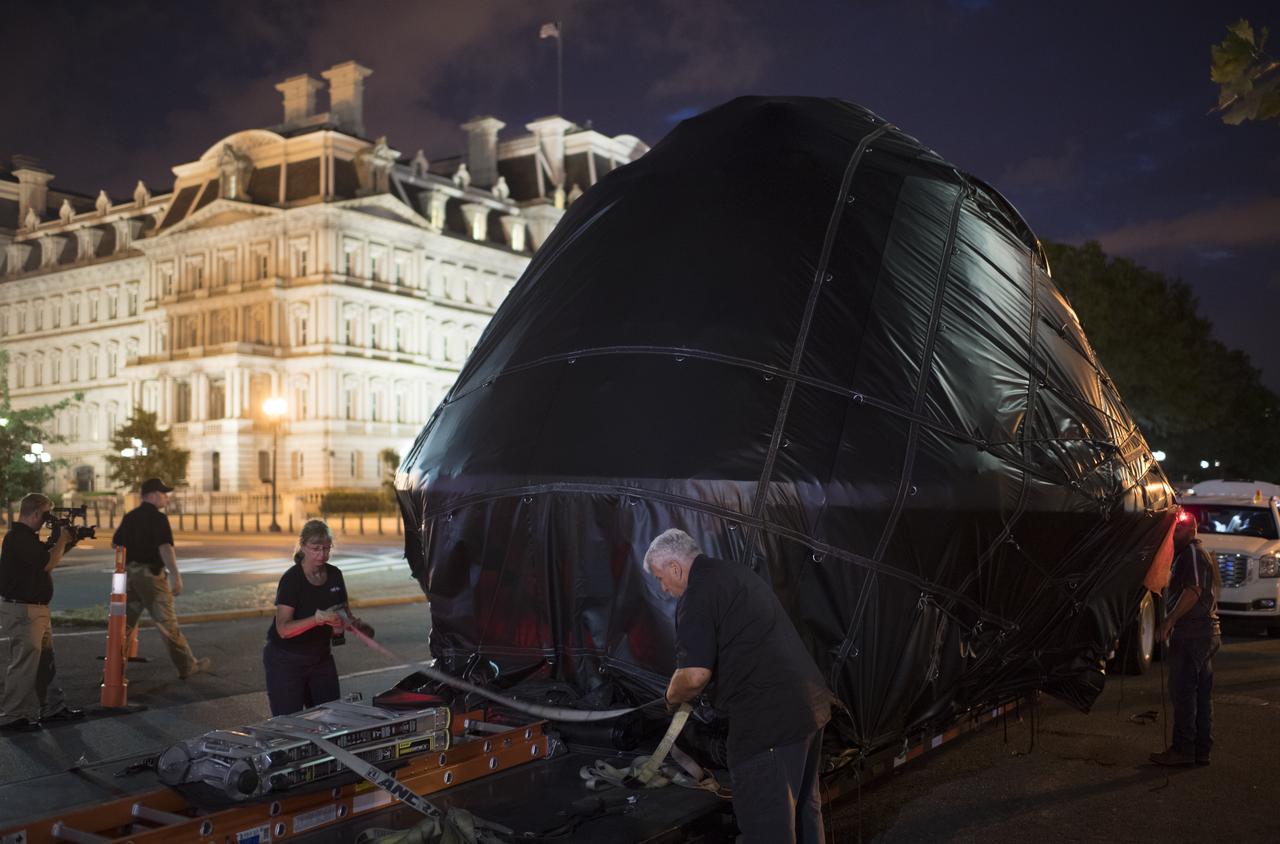

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it arrives at the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

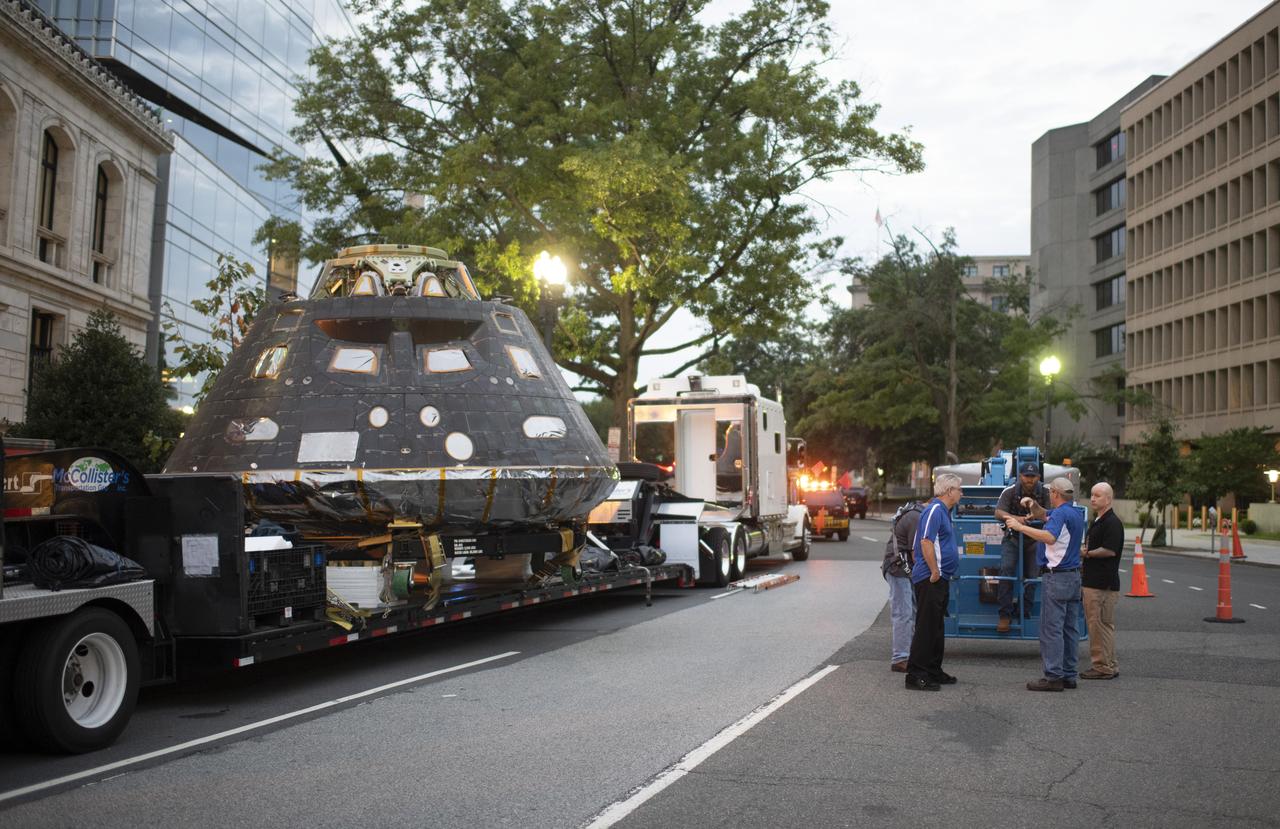
NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen after being uncovered in preparation for being moved onto the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
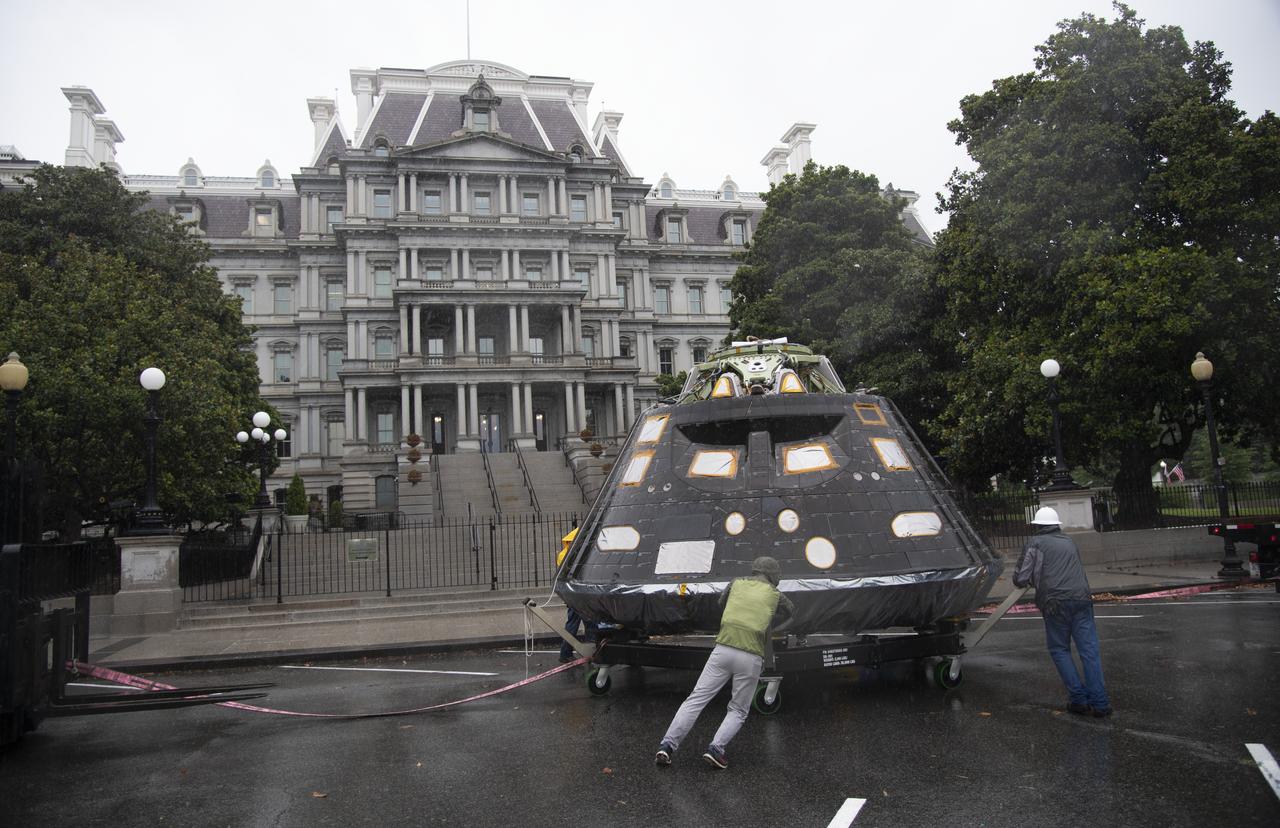

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen in front of the Eisenhower Executive Office Building on the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
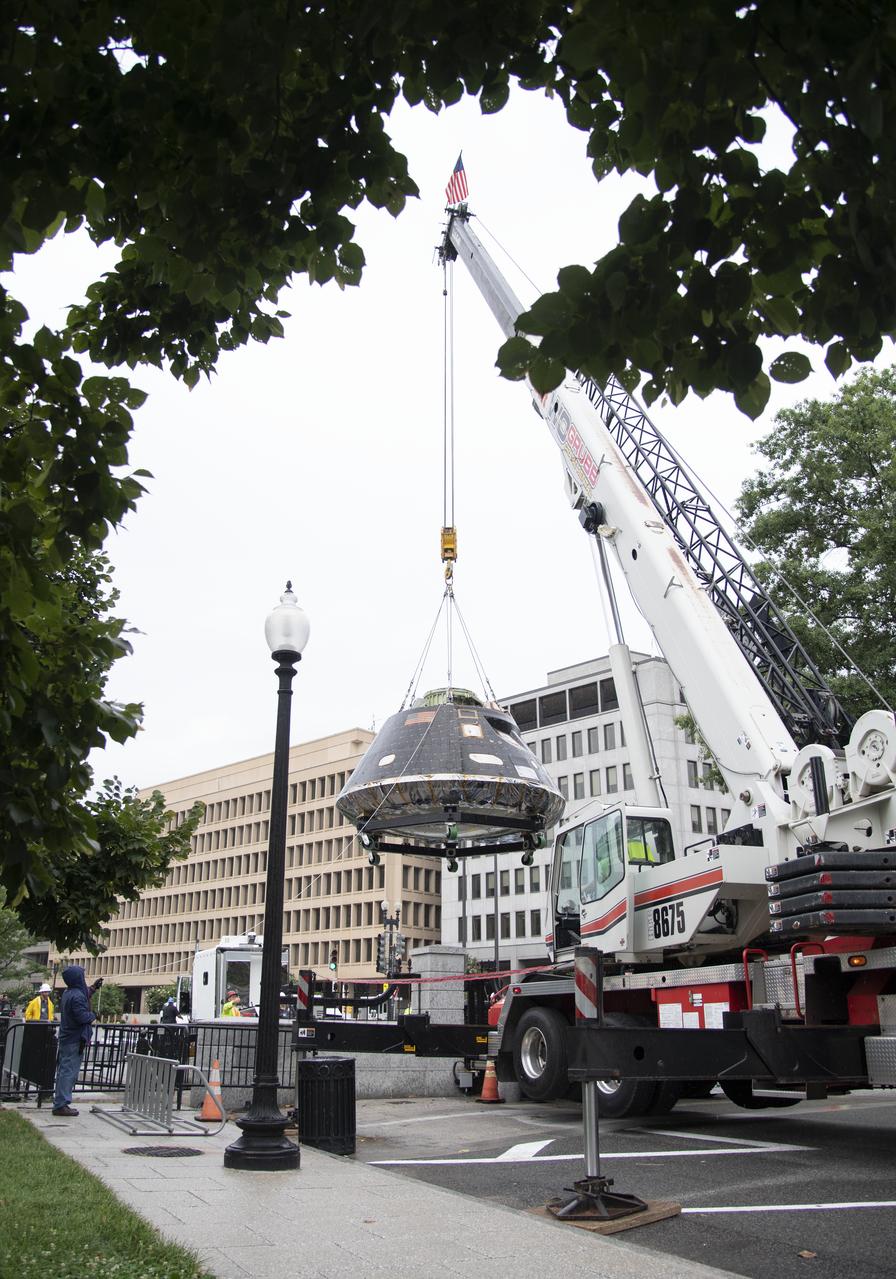

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it is lifted over a gate onto the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen as it is lifted over a gate onto the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
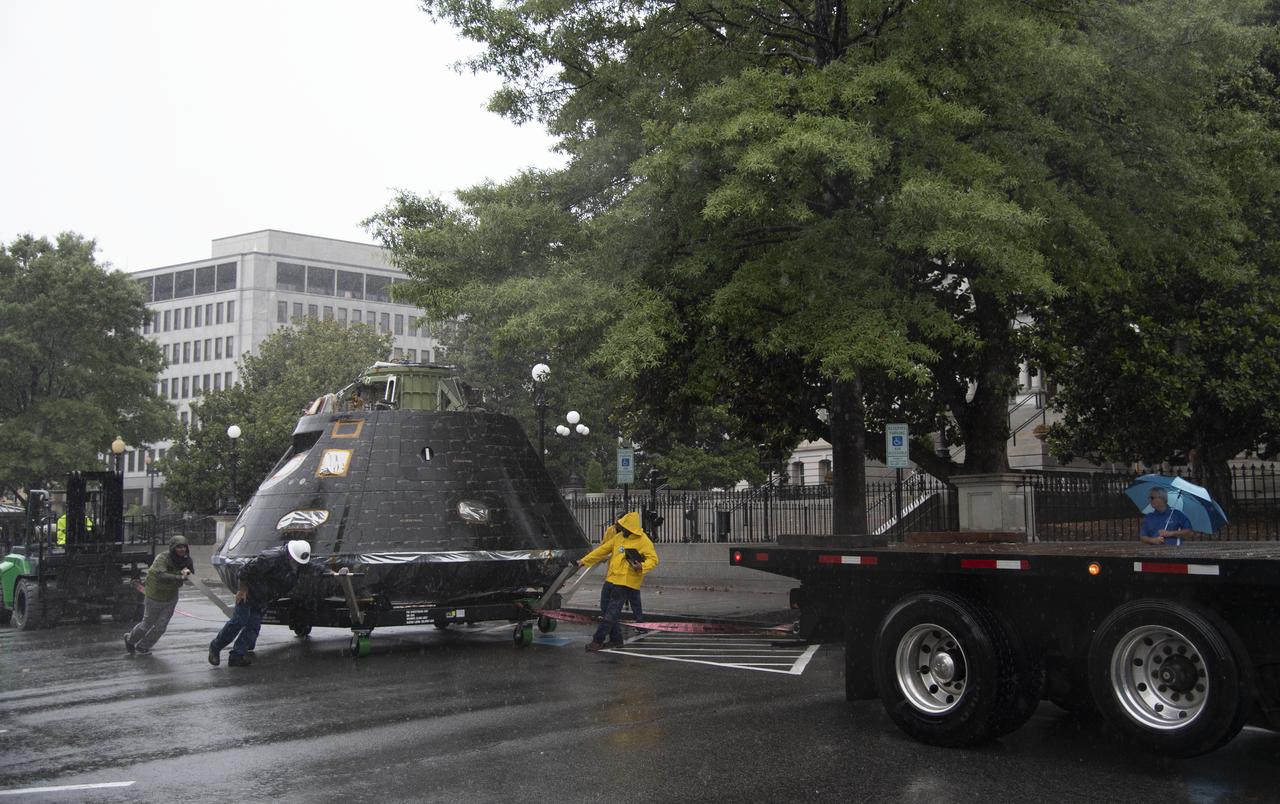

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen in front of the Eisenhower Executive Office Building on the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
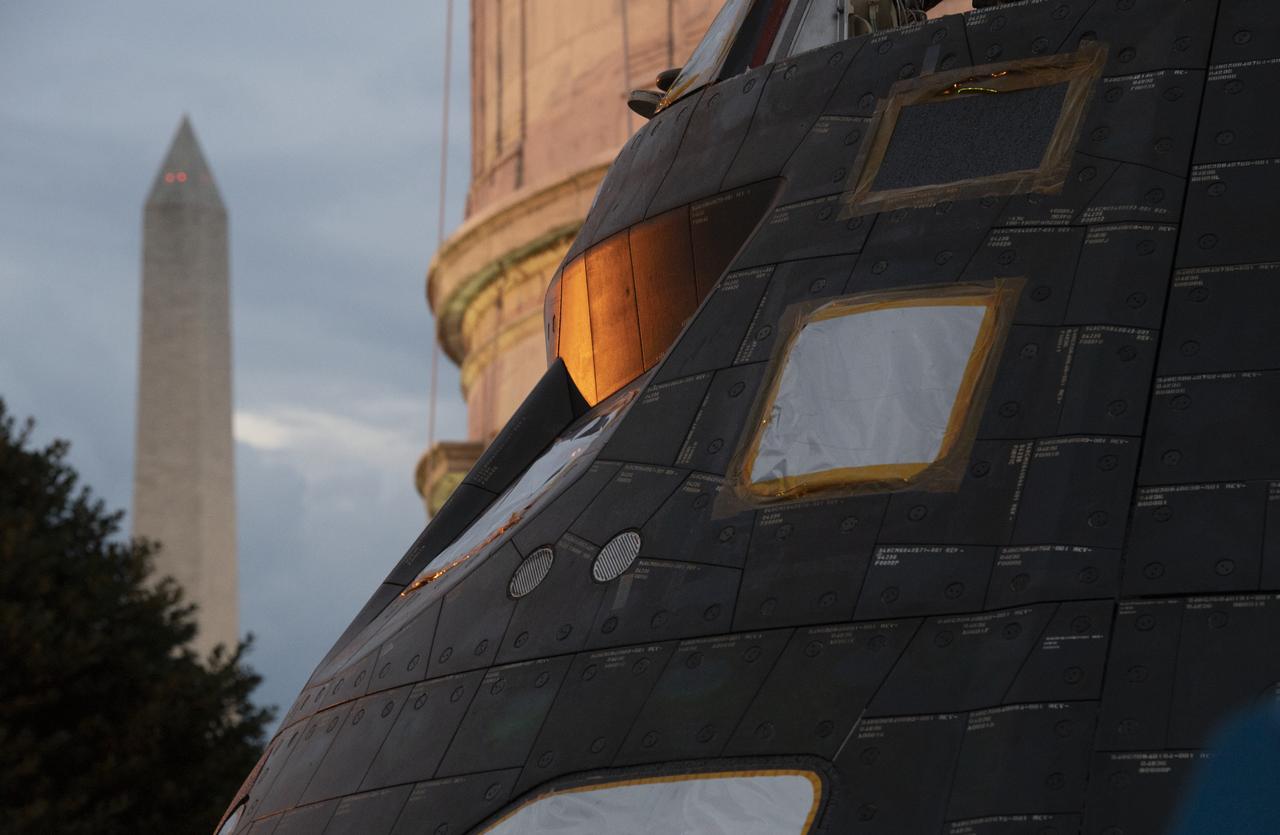

NASA's Orion spacecraft that flew Exploration Flight Test-1 on Dec. 5, 2014 is seen after being uncovered in preparation for being moved onto the White House complex, Saturday, July 21, 2018 in Washington, DC. Lockheed Martin, NASA’s prime contractor for Orion, began manufacturing the Orion crew module in 2011 and delivered it in July 2012 to NASA's Kennedy Space Center where final assembly, integration and testing was completed. More than 1,000 companies across the country manufactured or contributed elements to the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
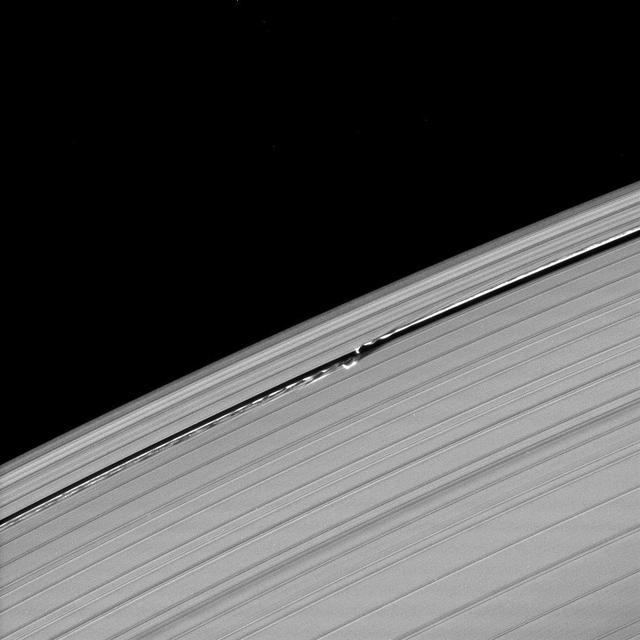

Waves in the edges of the Keeler gap in Saturn A ring, created by the embedded moon Daphnis, show considerable complexity in this image taken as Saturn approached its August 2009 equinox.

Part of the complex geologic history of icy Triton, Neptune largest satellite, is shown in this NASA Voyager 2 photo. The photo was received as part of a Triton-mapping sequence in 1989.
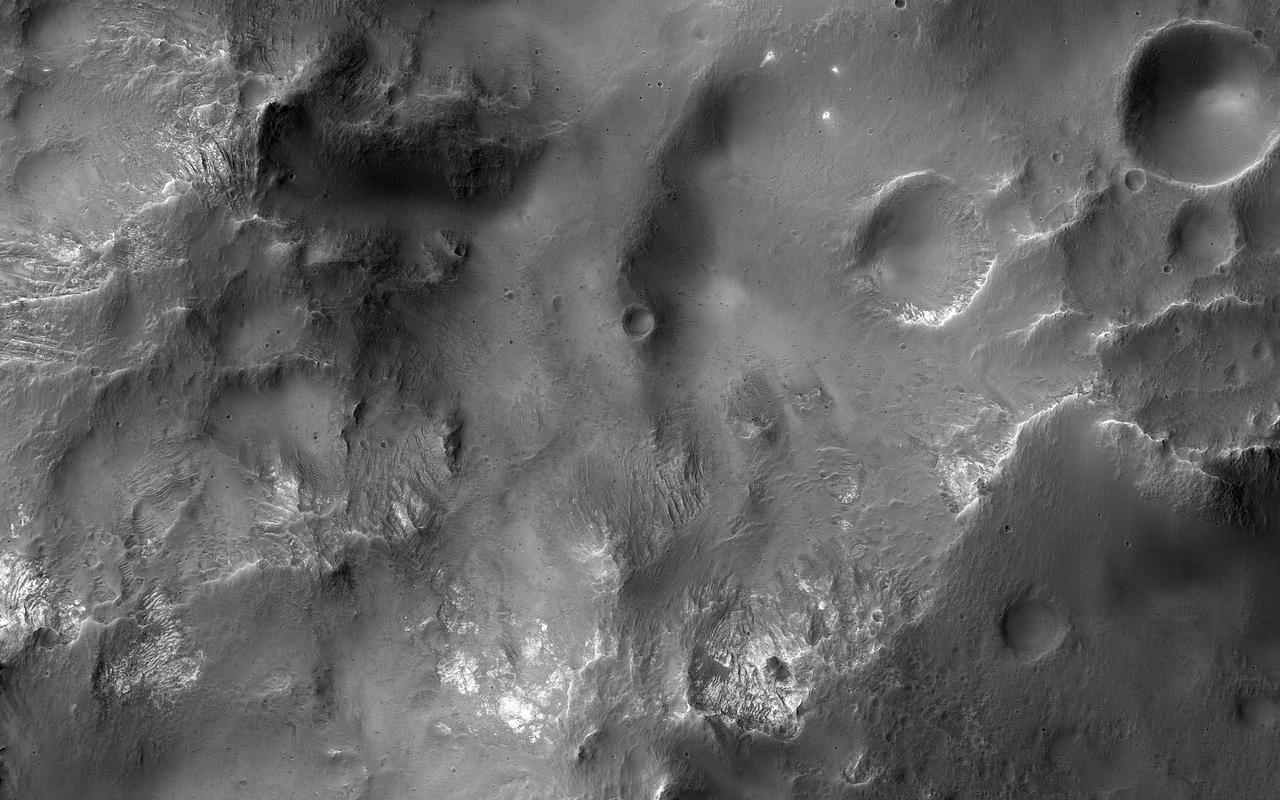

This image shows a cross-section of a complex crater in Terra Cimmeria. Starting in the center, we see a series of peaks with exposed bedrock. These peaks formed during the impact event when material that was originally several kilometers below the surface was uplifted and exposed. The impact also melted the rocks. This eventually cooled, forming the pitted materials that coat the crater floor around the uplift. The rim of the crater was unstable, and collapsed inwards to form terraces, and we see additional pitted materials between the terraces and the rim. Just outside the crater we can see dark-toned material that was excavated and thrown out after the impact. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23022
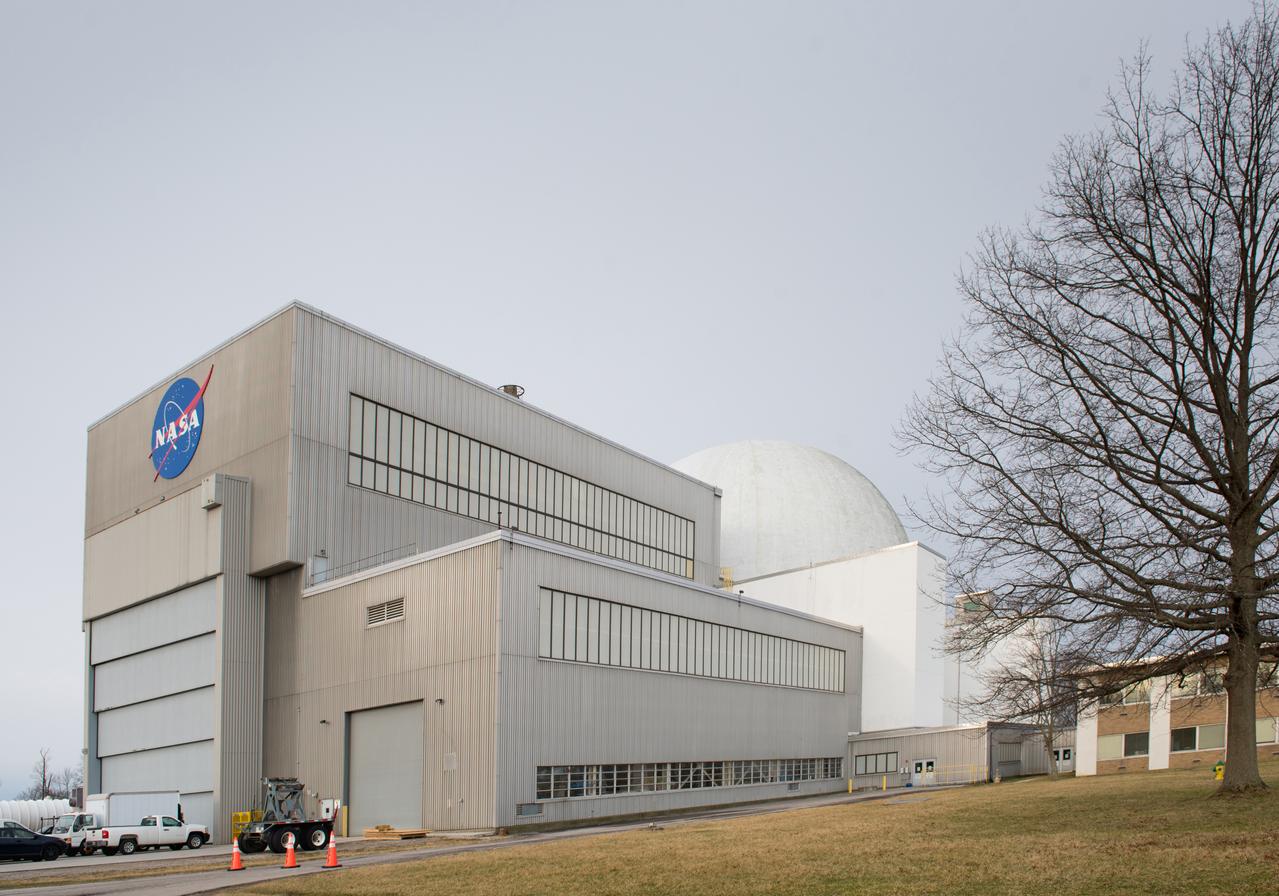

Space Environments Complex at Plum Brook Station
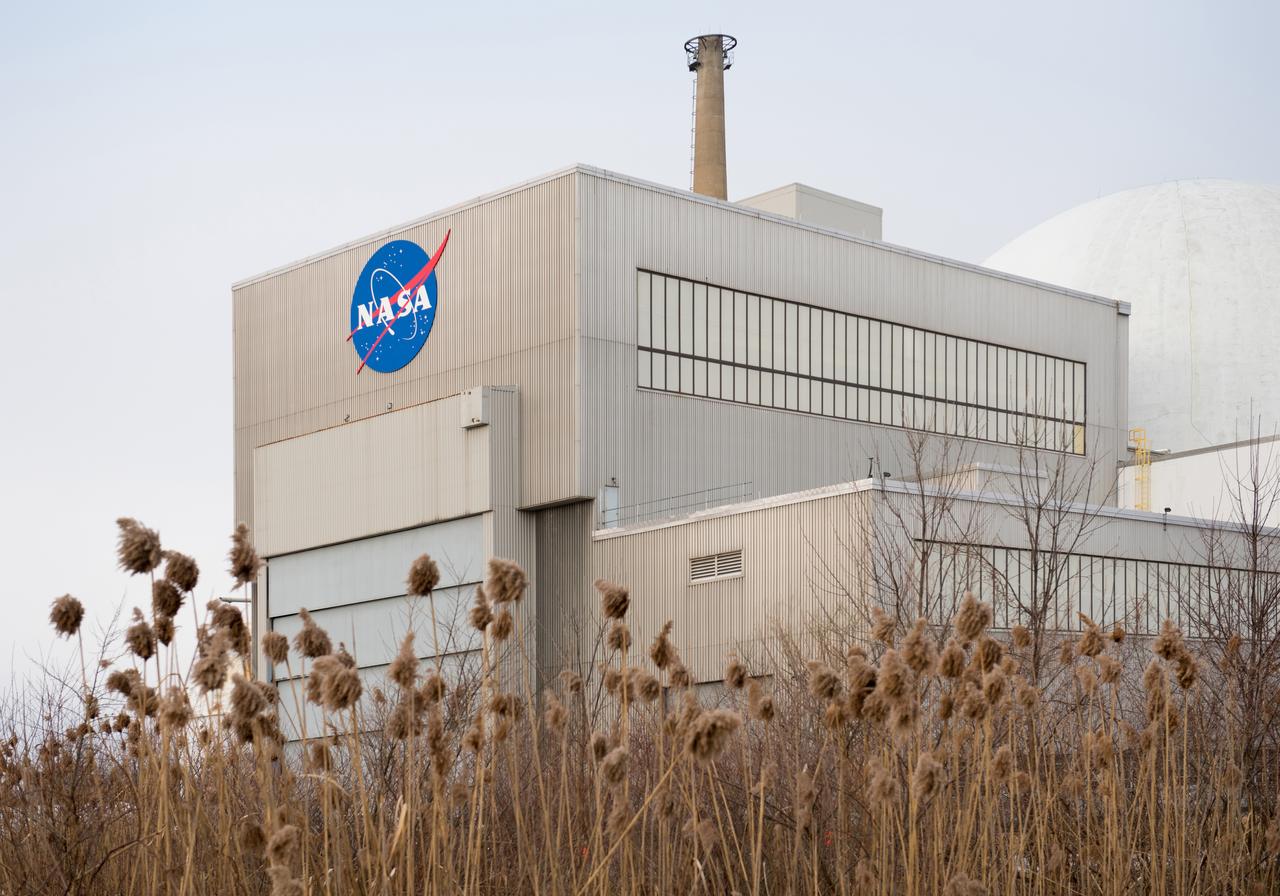

Space Environments Complex at Plum Brook Station

Space Environments Complex at Plum Brook Station
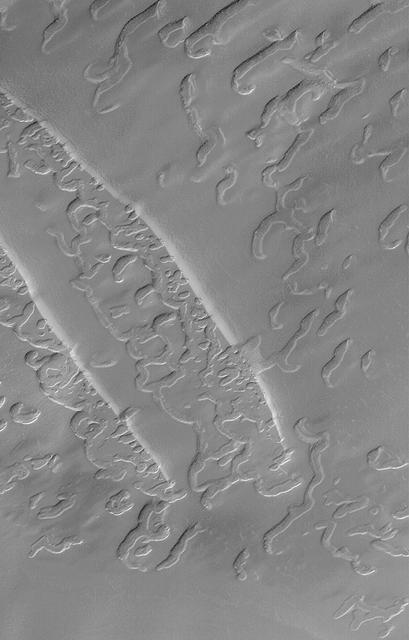
Complex Burial and Exhumation of South Polar Cap Pitted Terrain

Complex Floor Deposits Within Western Ganges Chasma, Valles Marineris
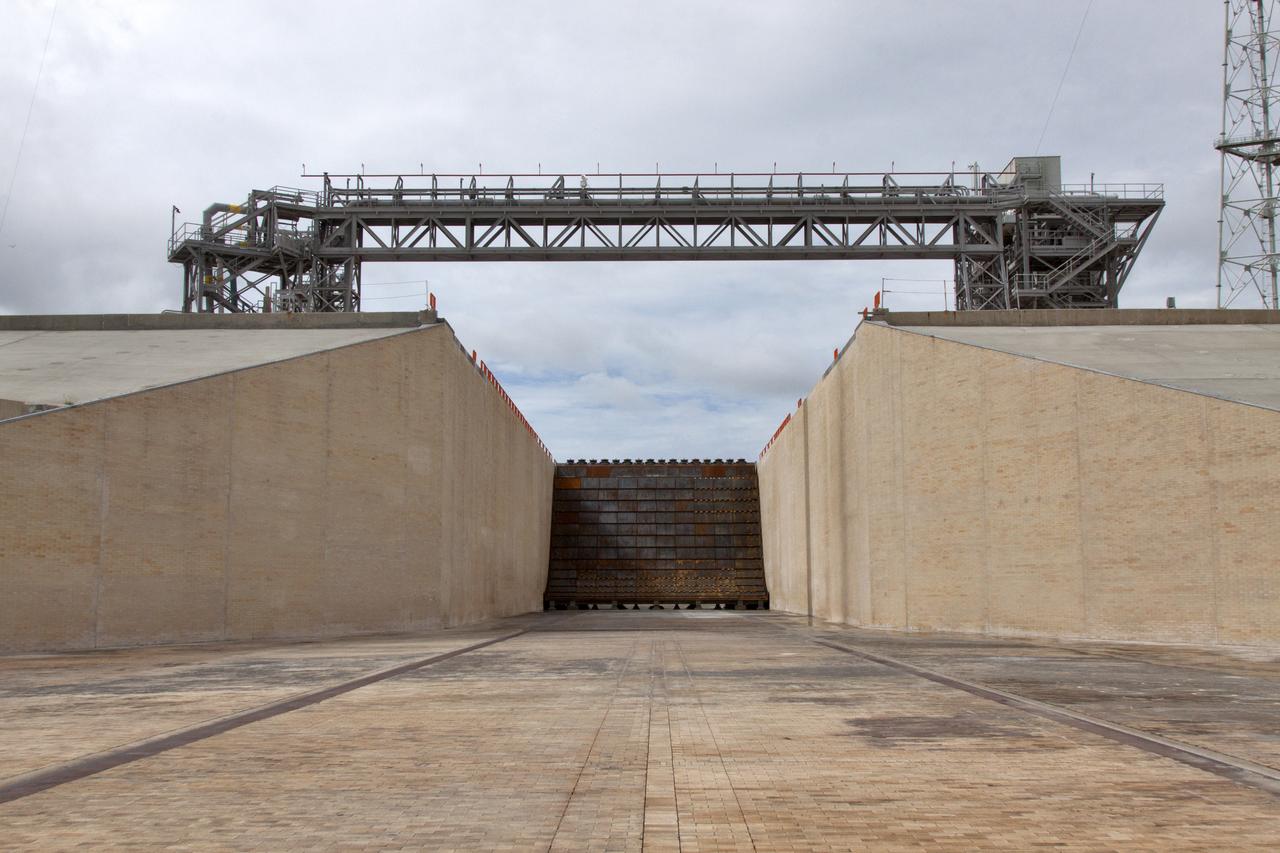

Construction is complete on the main flame deflector in the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The flame deflector will safely deflect the plume exhaust from NASA's Space Launch System rocket during launch. It will divert the rocket's exhaust, pressure and intense heat to the north at liftoff. The Exploration Ground Systems Program at Kennedy is refurbishing the pad to support the launch of the SLS rocket and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, and helping to transform the space center into a multi-user spaceport.
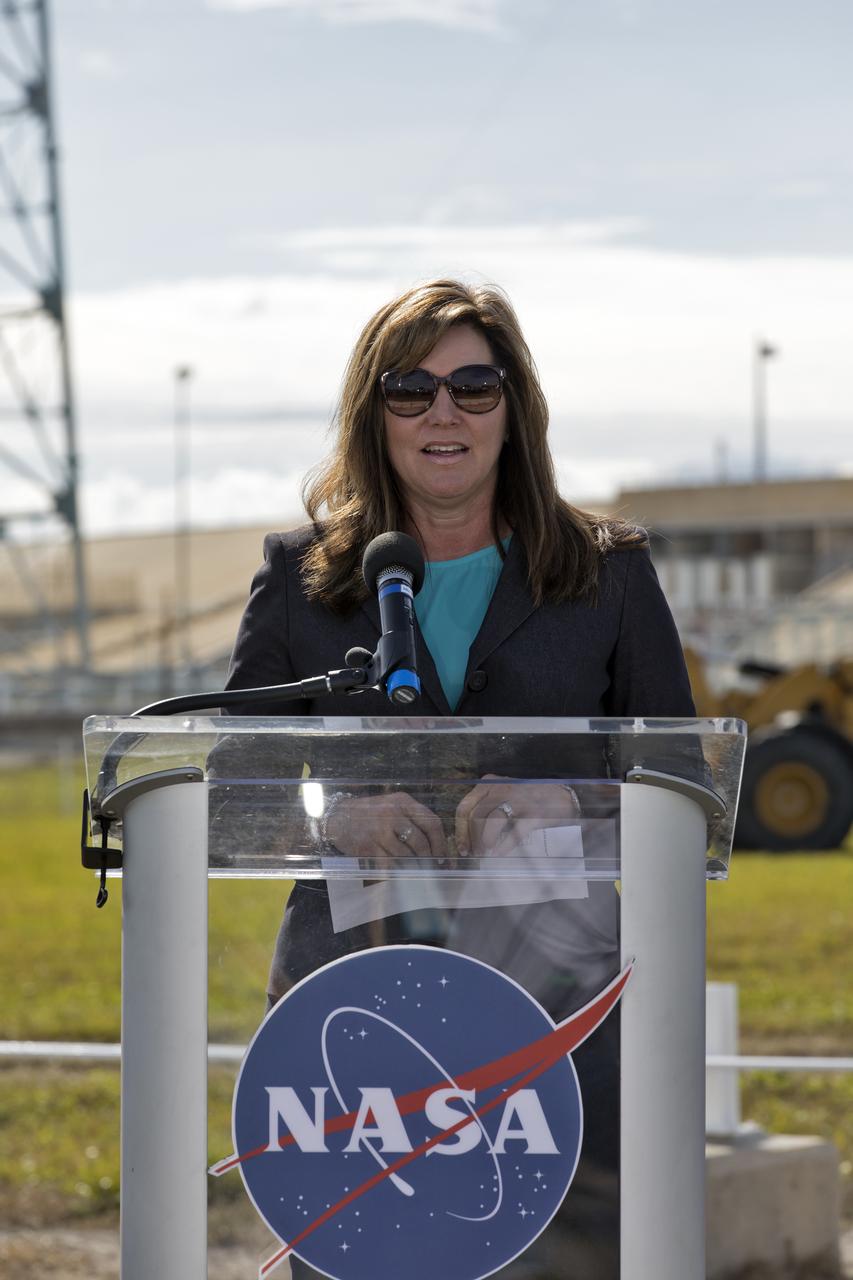

On Dec. 19, 2018, Jennifer Kunz, deputy program manager for Exploration Ground Systems, speaks during a groundbreaking ceremony for a new liquid hydrogen tank for Launch Complex 39B at the agency's Kennedy Space Center. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.
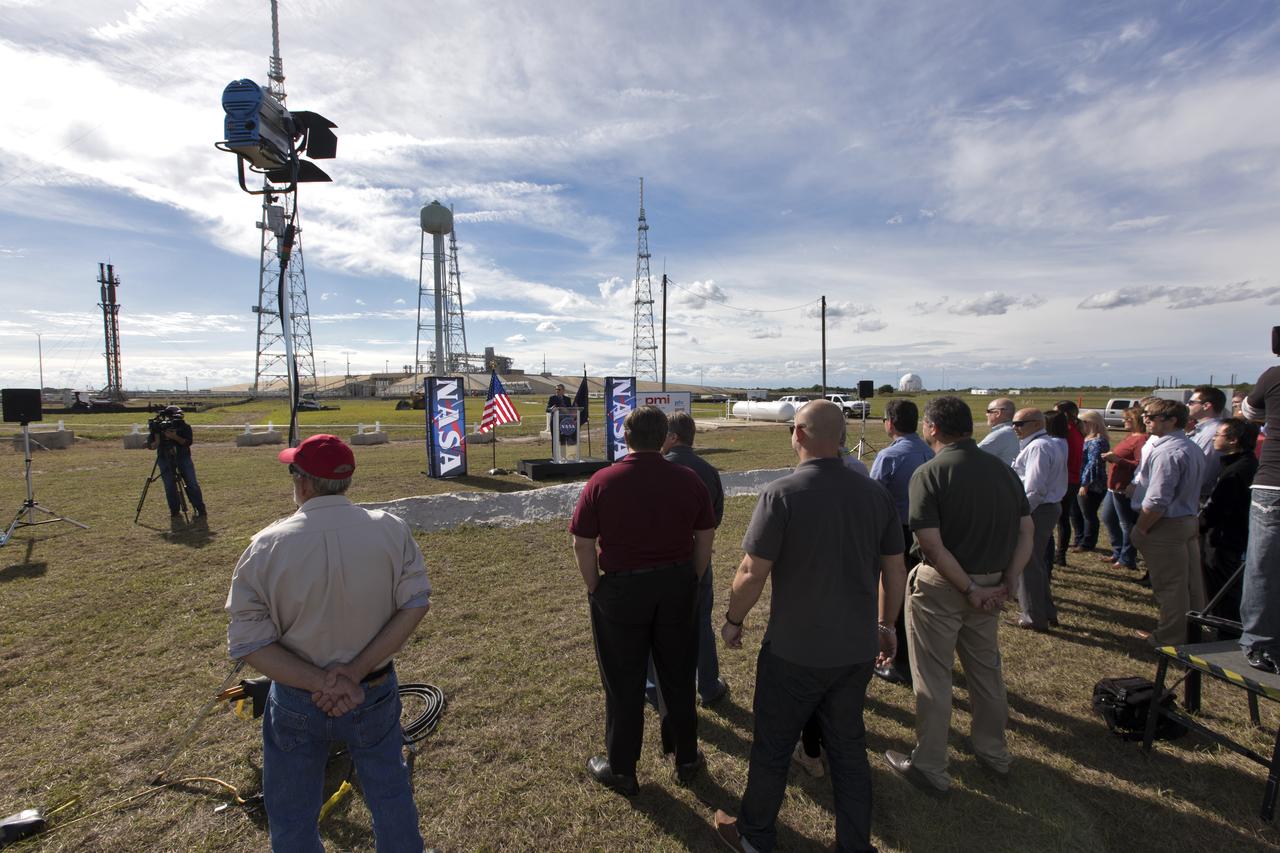

On Dec. 19, 2018, NASA and contractor managers gathered for a groundbreaking ceremony for a new liquid hydrogen tank for Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.

On Dec. 19, 2018, NASA Launch Director Charlie Blackwell-Thompson speaks during a groundbreaking ceremony for a new liquid hydrogen tank for Launch Complex 39B at the agency's Kennedy Space Center. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.
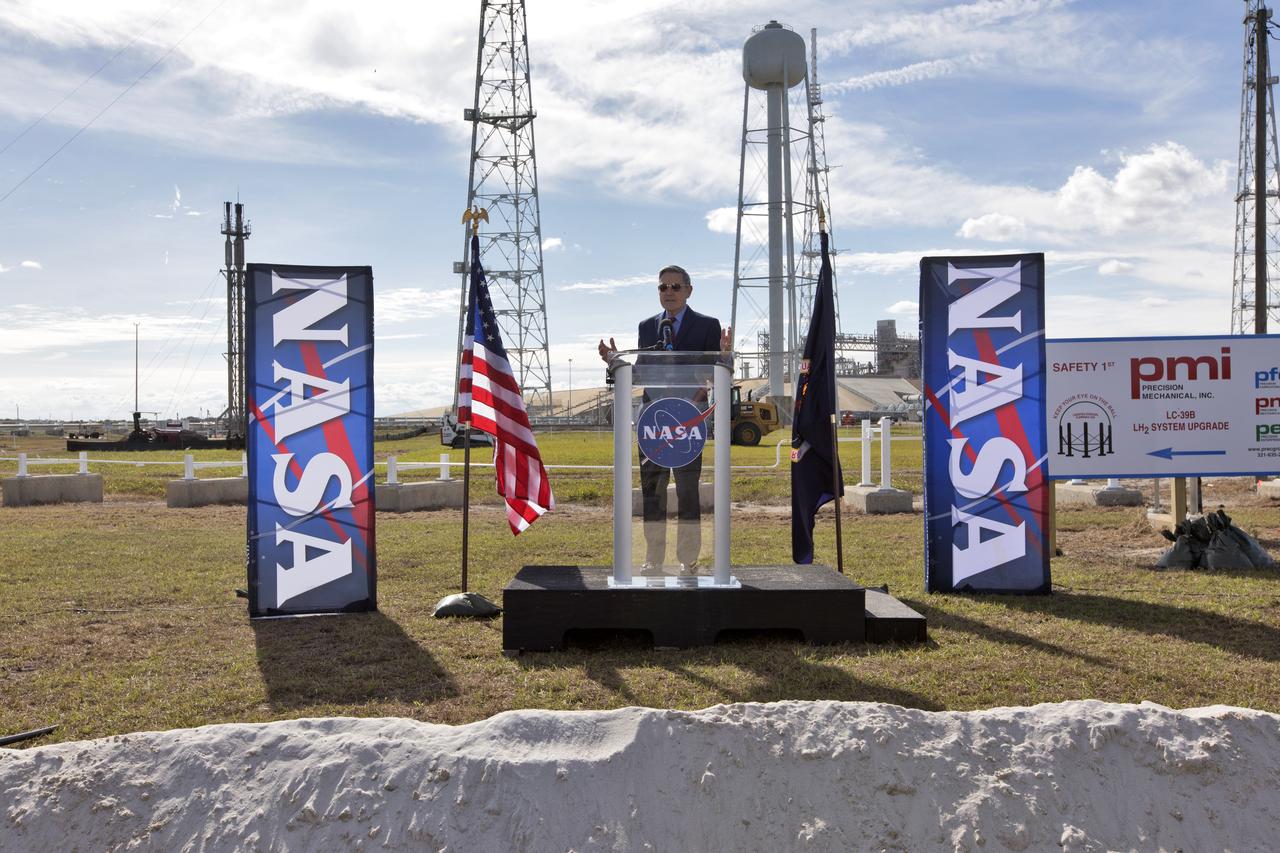

On Dec. 19, 2018, Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana speaks during a groundbreaking ceremony for a new liquid hydrogen tank for Launch Complex 39B at the space center. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.
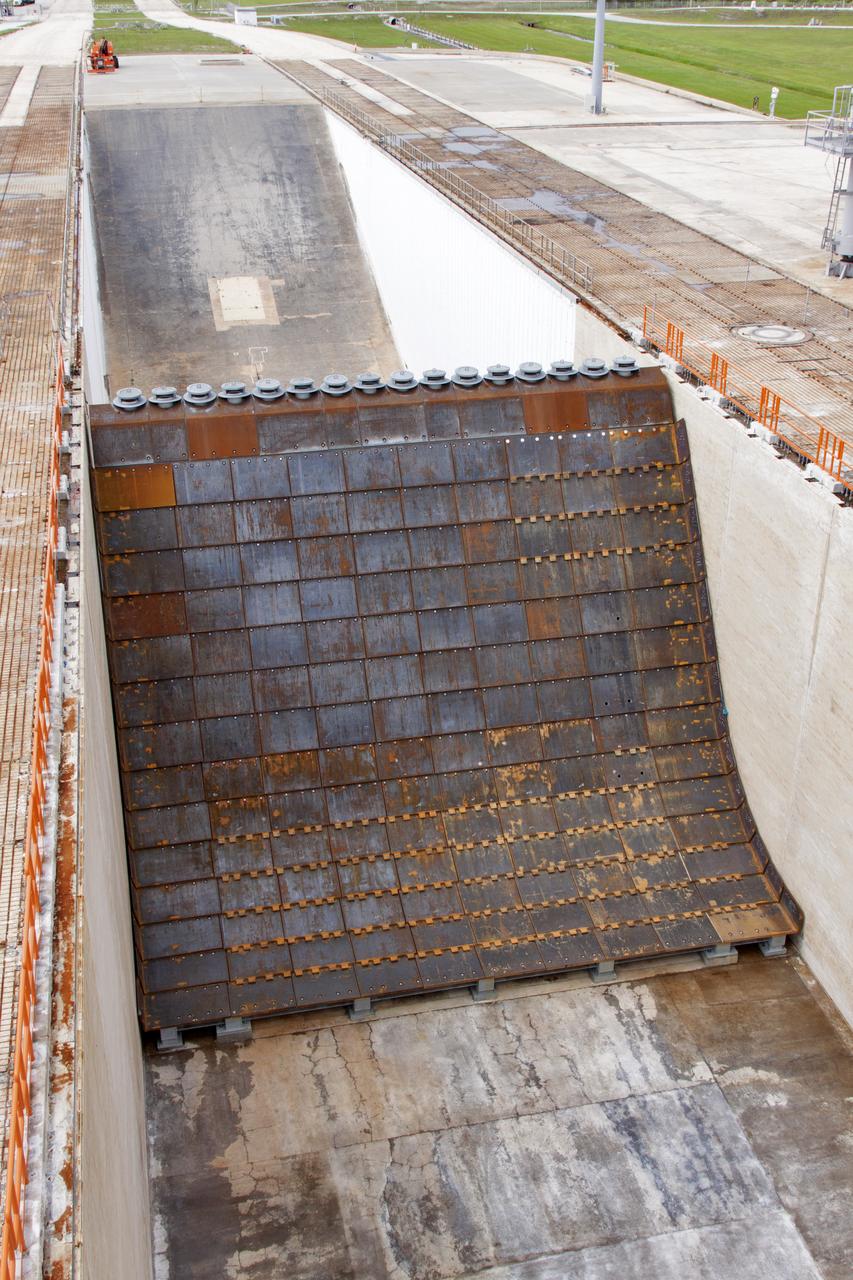

Construction is complete on the main flame deflector in the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The flame deflector will safely deflect the plume exhaust from NASA's Space Launch System rocket during launch. It will divert the rocket's exhaust, pressure and intense heat to the north at liftoff. The Exploration Ground Systems Program at Kennedy is refurbishing the pad to support the launch of the SLS rocket and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, and helping to transform the space center into a multi-user spaceport.
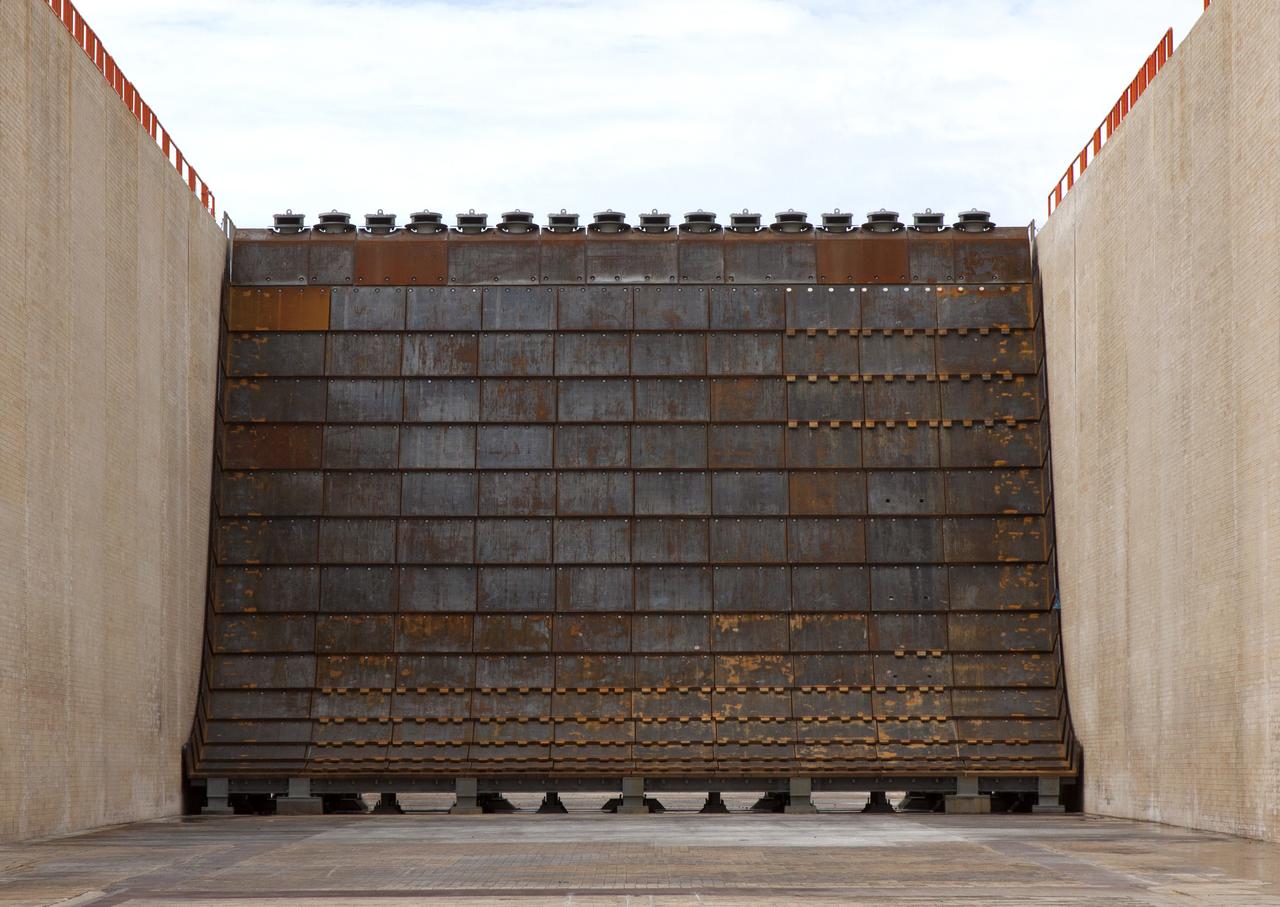

Construction is complete on the main flame deflector in the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The flame deflector will safely deflect the plume exhaust from NASA's Space Launch System rocket during launch. It will divert the rocket's exhaust, pressure and intense heat to the north at liftoff. The Exploration Ground Systems Program at Kennedy is refurbishing the pad to support the launch of the SLS rocket and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, and helping to transform the space center into a multi-user spaceport.

On Dec. 19, 2018, Bill Hill, deputy associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development at NASA Headquarters in Washington, speaks during a groundbreaking ceremony for a new liquid hydrogen tank for Launch Complex 39B at the agency's Kennedy Space Center. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.
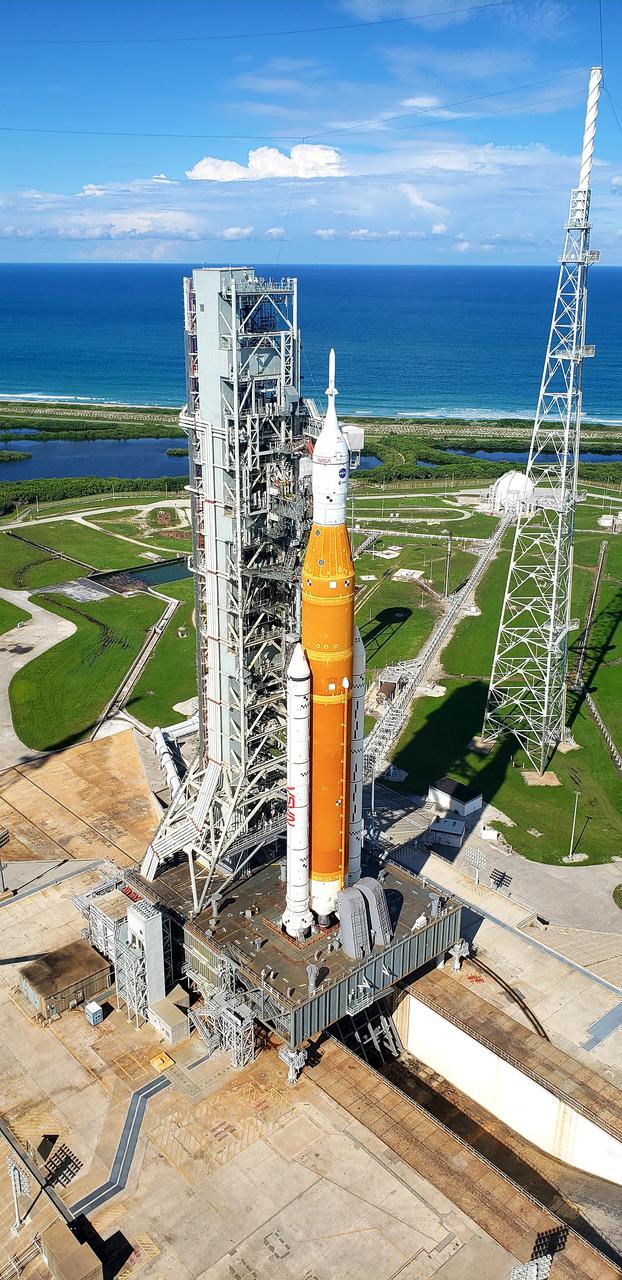

A view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 15, 2022. To the right is one of three lightning protection towers that surround the pad and protect the SLS and Orion from lightning strikes. Artemis I is the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
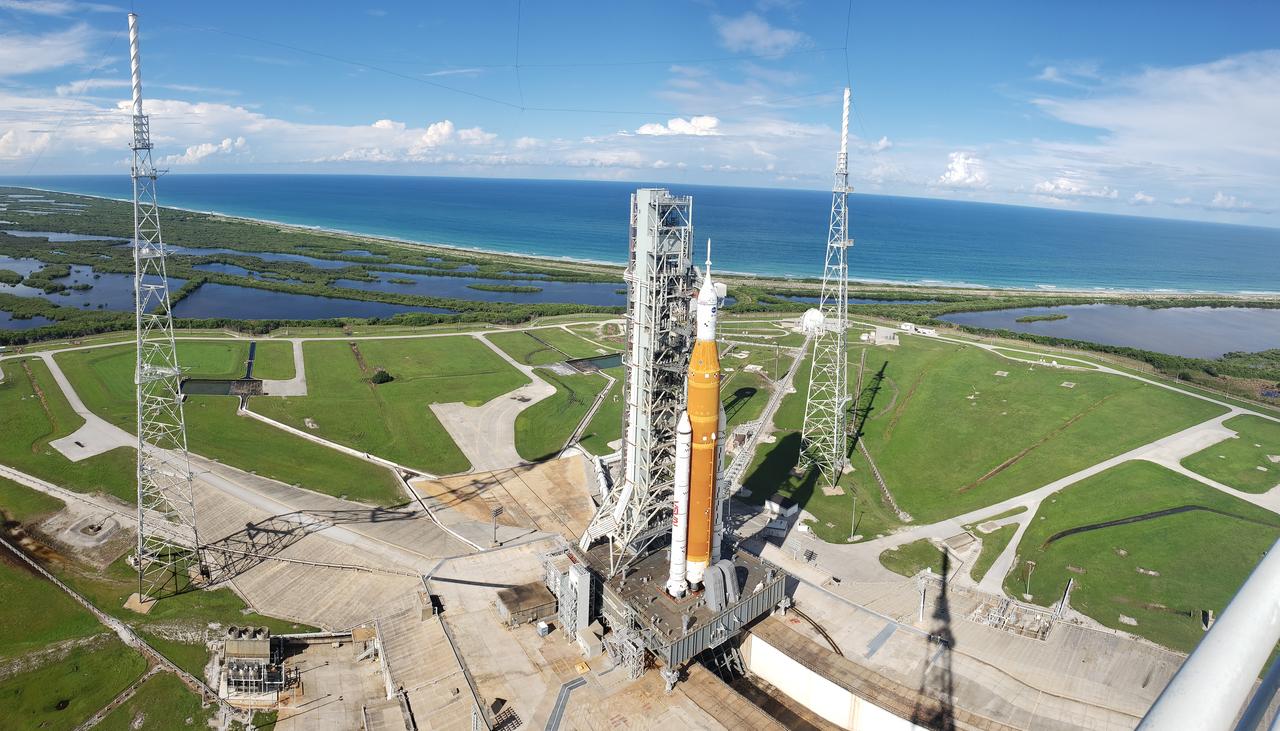

A view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 15, 2022. Also in view are two of the three lightning towers that surround the pad and protect the SLS and Orion from lightning strikes. Artemis I is the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
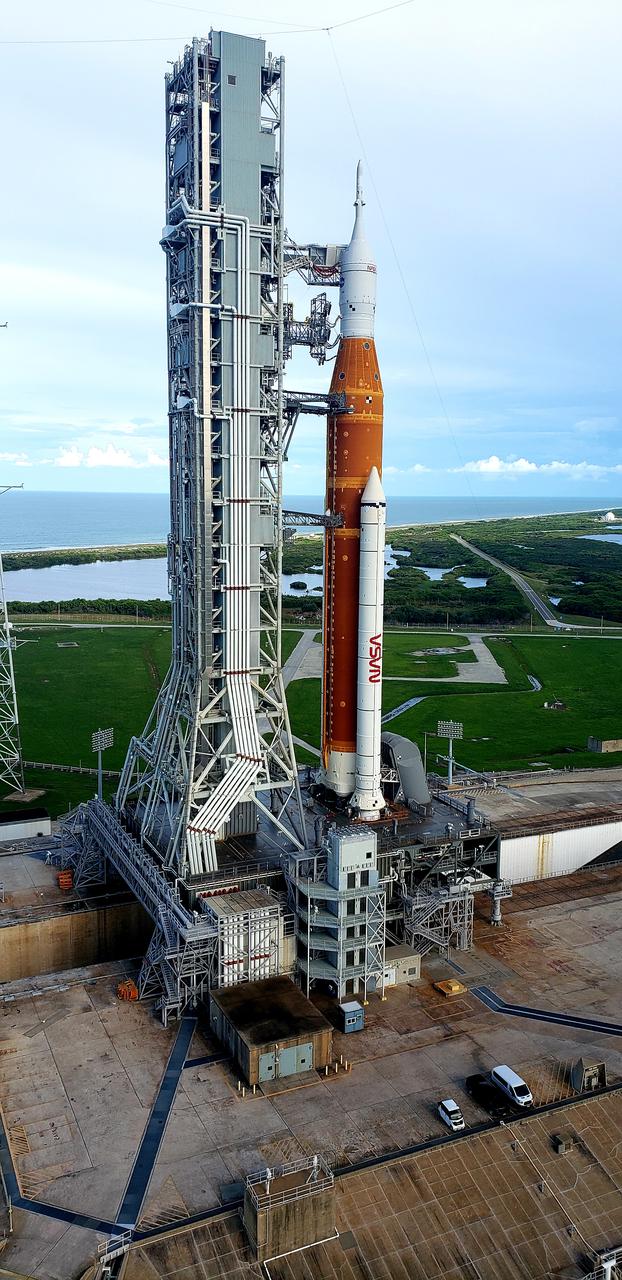

A close-up view of the Artemis I Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft atop the mobile launcher on Launch Pad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 15, 2022. A portion of the umbilical connections are in view, as well as the crew access arm. Artemis I is the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In future Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
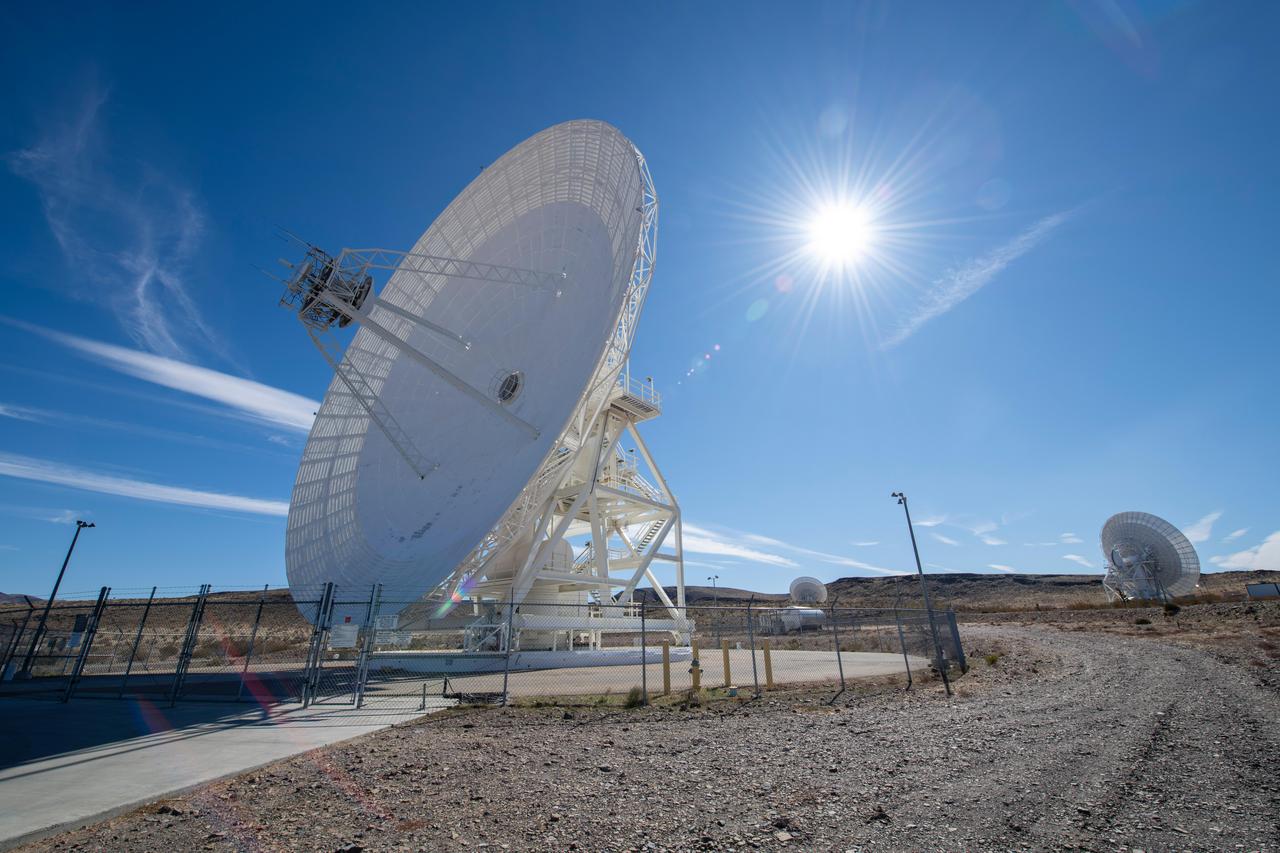

Antenna dishes at NASA's Deep Space Network complex in Goldstone, California, photographed on Feb. 11, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23214
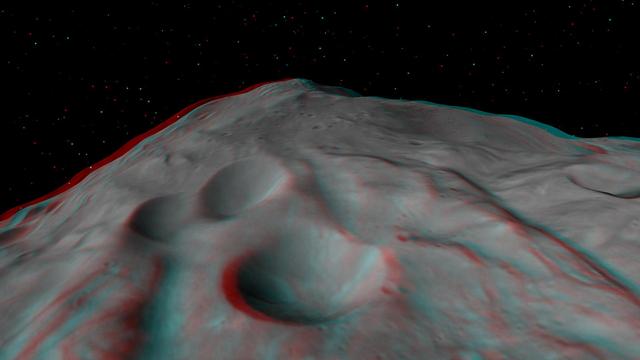
This anaglyph shows the central complex in asteroid Vesta Rheasilvia impact basin. The central complex about two and a half times taller than Mt. Everest. You need 3-D glasses to view this image.
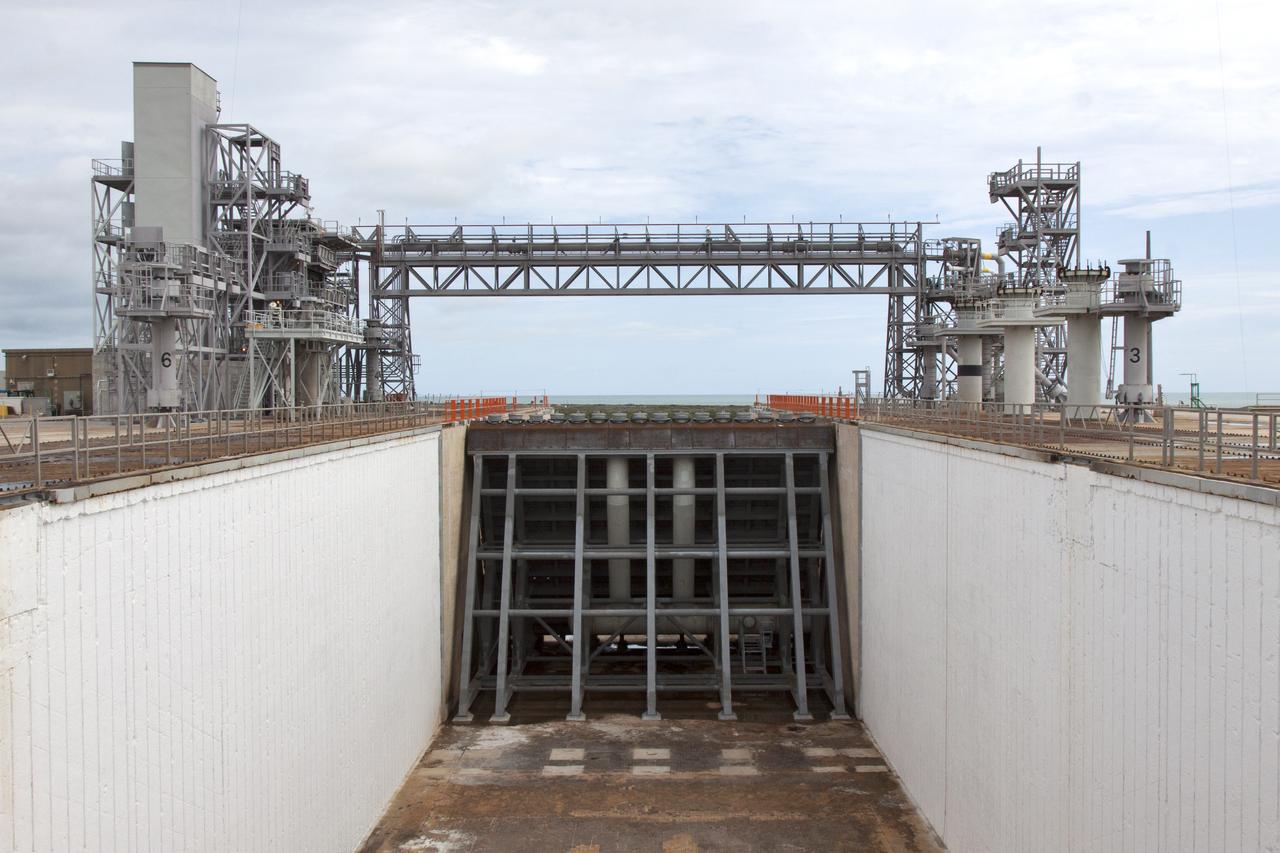

Construction is complete on the main flame deflector in the flame trench at Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The flame deflector will safely deflect the plume exhaust from NASA's Space Launch System rocket during launch. It will divert the rocket's exhaust, pressure and intense heat to the north at liftoff. In view is the south side of the main flame deflector. The Exploration Ground Systems Program at Kennedy is refurbishing the pad to support the launch of the SLS rocket and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, and helping to transform the space center into a multi-user spaceport.
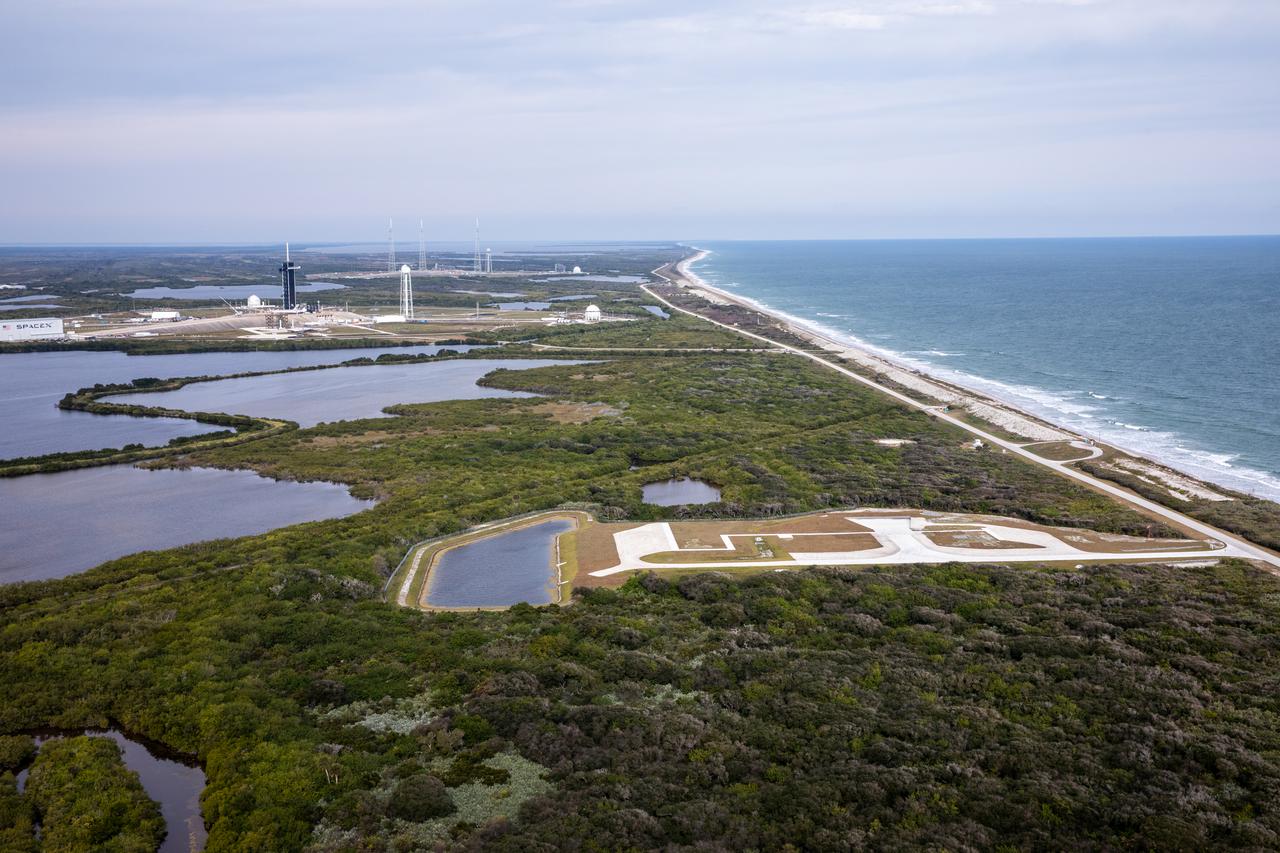

NASA Kennedy Space Center’s newest launch complex – Launch Complex 48 – is a dedicated site for small-class launch vehicles. The complex offers a “clean pad” concept, allowing companies to bring in their own resources and commodities for launch and, in turn, reducing their investment in launch pad infrastructure.
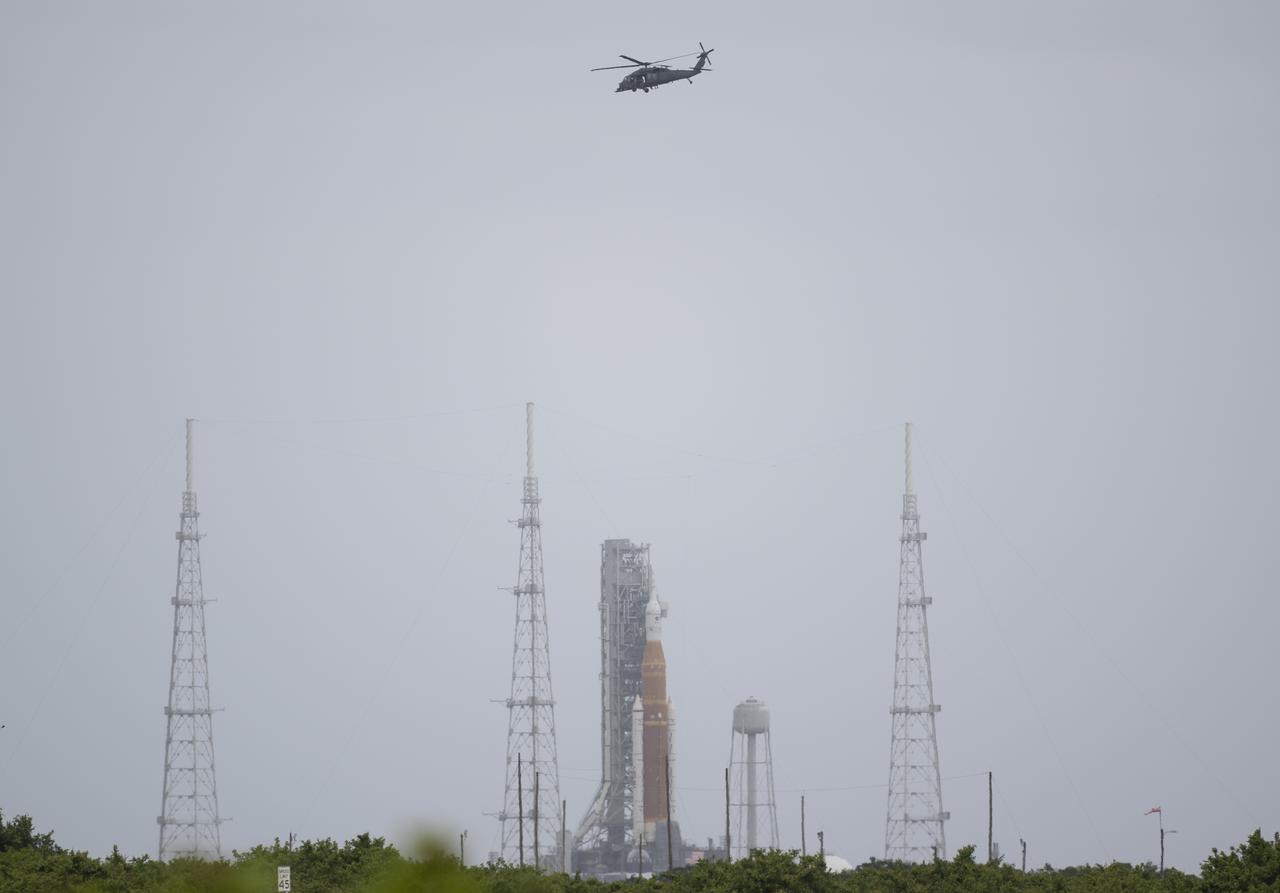

A helicopter is seen flying past NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard atop a mobile launcher at Launch Complex 39B, Thursday, April 21, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
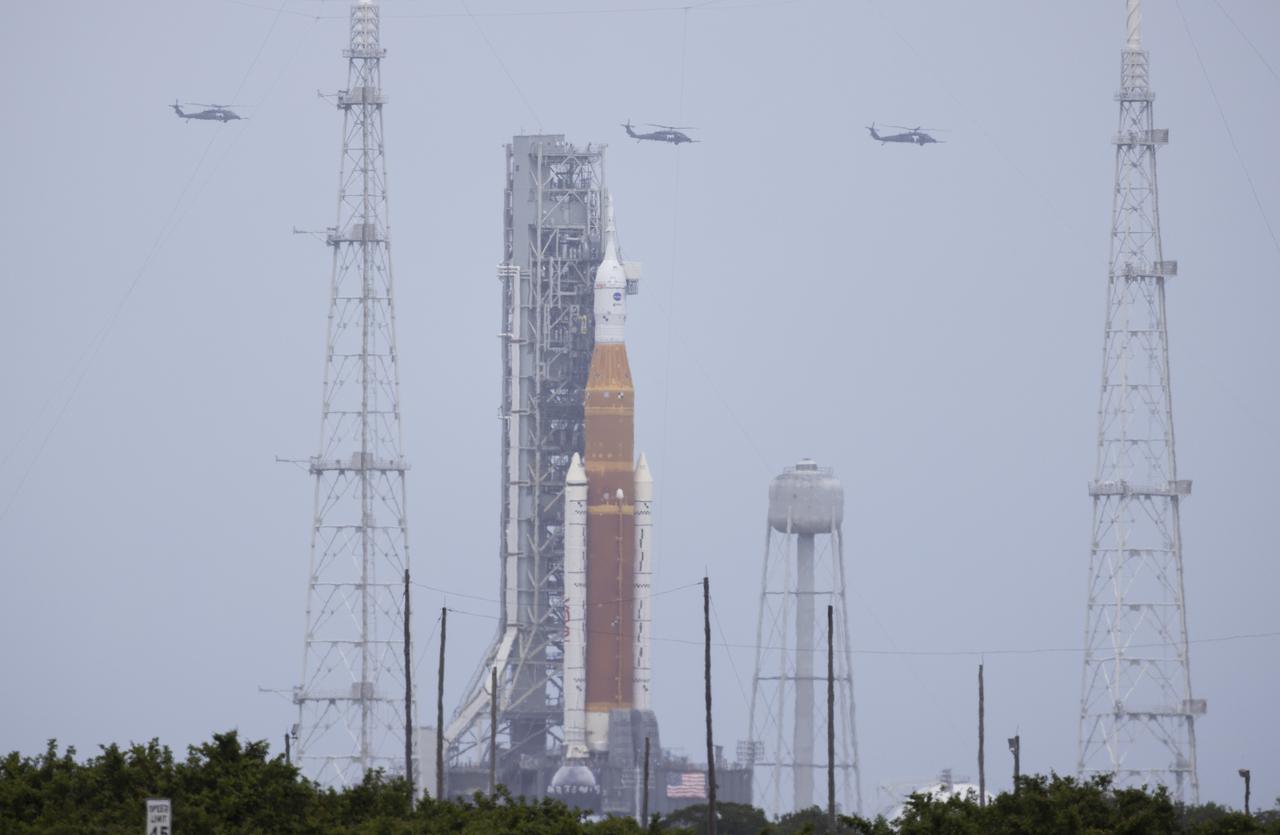

Three helicopters are seen flying past NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard atop a mobile launcher at Launch Complex 39B, Thursday, April 21, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

On August 29, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of wildfires burning in Idaho and Montana. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When the image was acquired, the moon was in its waxing gibbous phase, meaning it was more than half-lit, but less than full. Numerous hot spots from the Mustang Complex Fire are visible in northern Idaho. A plume of thick, billowing smoke streams west from the brightest fires near the Idaho-Montana border. The Halstead and Trinity Ridge fires are visible to the south. In addition to the fires, city lights from Boise and other smaller cities appear throughout the image. A bank of clouds is located west of the Mustang Complex, over southeastern Washington and northeastern Oregon. The Operational Line System (OLS)—an earlier generation of night-viewing sensors on the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites—was also capable of detecting fires at night. But the VIIRS “day-night band” is far better than OLS at resolving them. Each pixel of an VIIRS image shows roughly 740 meters (0.46 miles), compared to the 3-kilometer footprint (1.86 miles) on the OLS system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79754" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
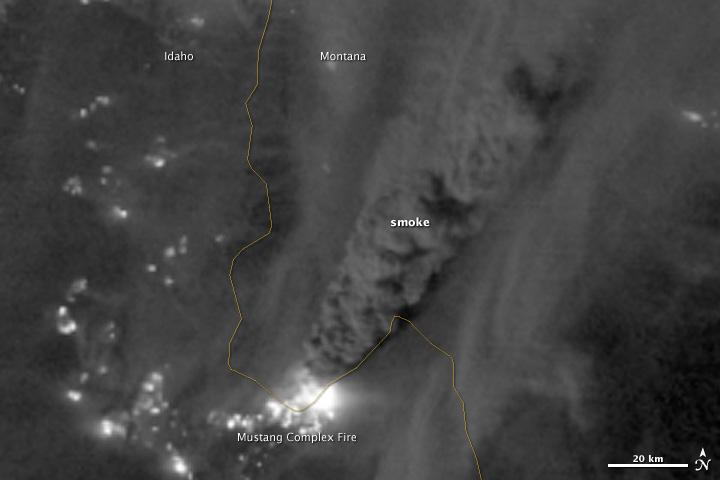

On August 29, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of wildfires burning in Idaho and Montana. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When the image was acquired, the moon was in its waxing gibbous phase, meaning it was more than half-lit, but less than full. Numerous hot spots from the Mustang Complex Fire are visible in northern Idaho. A plume of thick, billowing smoke streams west from the brightest fires near the Idaho-Montana border. The Halstead and Trinity Ridge fires are visible to the south. In addition to the fires, city lights from Boise and other smaller cities appear throughout the image. A bank of clouds is located west of the Mustang Complex, over southeastern Washington and northeastern Oregon. The Operational Line System (OLS)—an earlier generation of night-viewing sensors on the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites—was also capable of detecting fires at night. But the VIIRS “day-night band” is far better than OLS at resolving them. Each pixel of an VIIRS image shows roughly 740 meters (0.46 miles), compared to the 3-kilometer footprint (1.86 miles) on the OLS system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79754" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
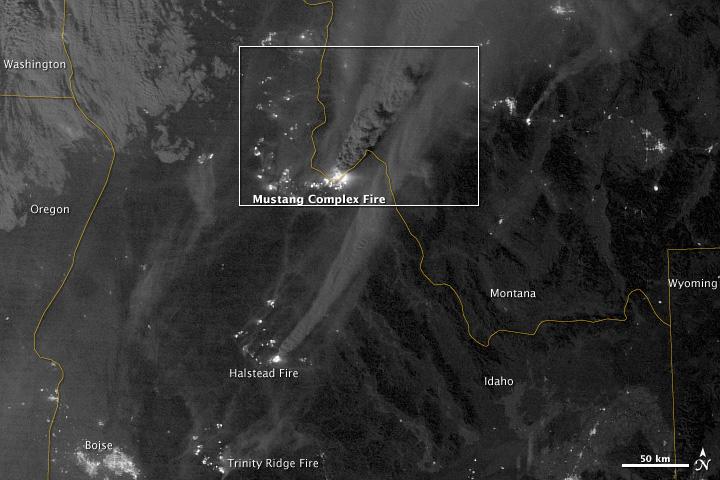
On August 29, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of wildfires burning in Idaho and Montana. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When the image was acquired, the moon was in its waxing gibbous phase, meaning it was more than half-lit, but less than full. Numerous hot spots from the Mustang Complex Fire are visible in northern Idaho. A plume of thick, billowing smoke streams west from the brightest fires near the Idaho-Montana border. The Halstead and Trinity Ridge fires are visible to the south. In addition to the fires, city lights from Boise and other smaller cities appear throughout the image. A bank of clouds is located west of the Mustang Complex, over southeastern Washington and northeastern Oregon. The Operational Line System (OLS)—an earlier generation of night-viewing sensors on the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites—was also capable of detecting fires at night. But the VIIRS “day-night band” is far better than OLS at resolving them. Each pixel of an VIIRS image shows roughly 740 meters (0.46 miles), compared to the 3-kilometer footprint (1.86 miles) on the OLS system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79754" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
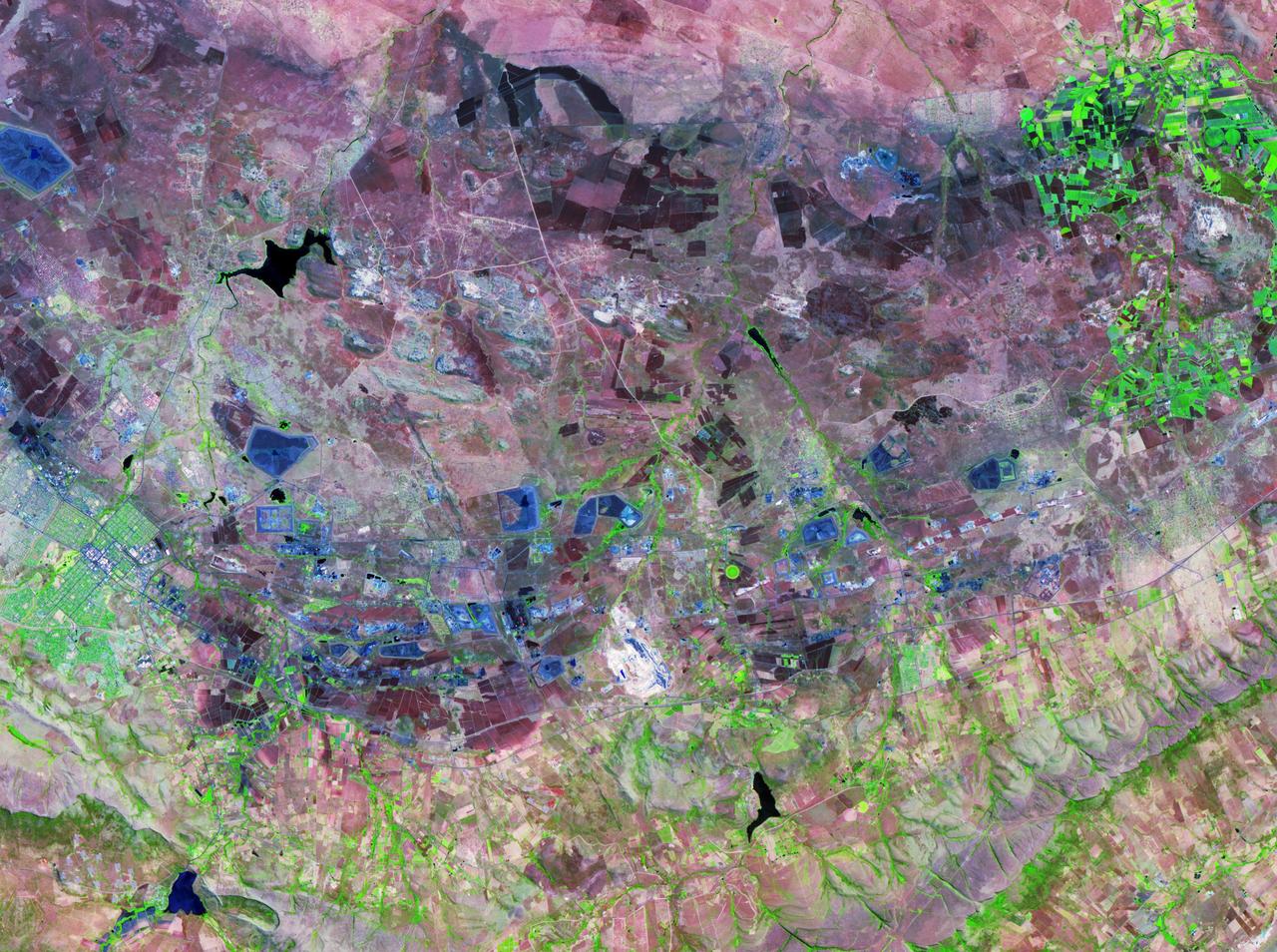

The Bushveld Igneous Complex BIC is a large layered igneous intrusion within the earth crust, exposed at the edge of the Transvaal Basin in South Africa. Numerous mines, tailings piles, and leach ponds are shown in blue.

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-6 astronauts make their way down the crew access arm to the Dragon spacecraft Endeavour. From left are Warren “Woody” Hoburg, pilot; and Stephen Bowen, spacecraft commander. Along with Sultan Alneyadi, UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and mission specialist; and Andrei Fedyaev, Roscosmos cosmonaut and mission specialist, they will launch to the International Space Station aboard the Crew Dragon Endeavour on a SpaceX Falcon 9. Launch was targeted for 1:45 a.m. EST on Feb. 27 from Launch Complex 39A, but was scrubbed for the day. Crew-6 is the sixth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the station, and the seventh flight of Dragon with people as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
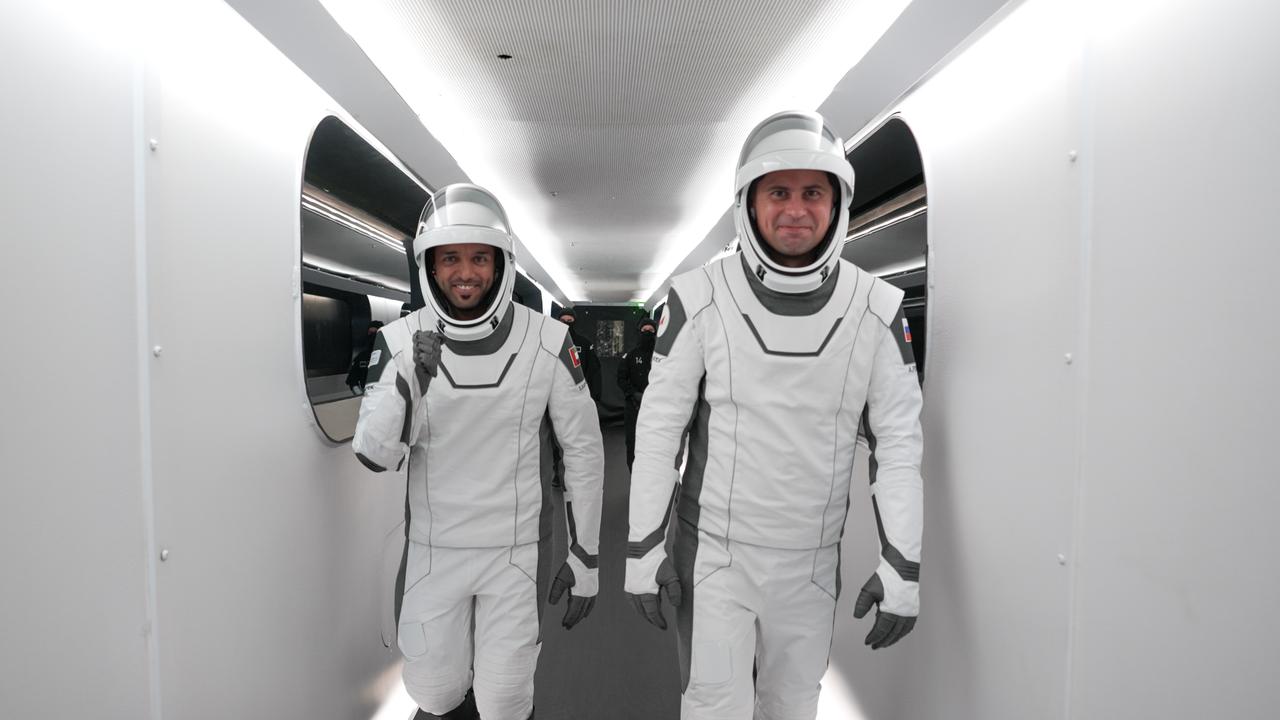

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-6 astronauts make their way down the crew access arm to the Dragon spacecraft Endeavour. From left are Sultan Alneyadi, UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and mission specialist; and Andrey Fedyaev, Roscosmos cosmonaut and mission specialist. Along with Stephen Bowen, spacecraft commander; and Warren “Woody” Hoburg, pilot, they will launch to the International Space Station aboard the Crew Dragon Endeavour on a SpaceX Falcon 9. Launch was targeted for 1:45 a.m. EST on Feb. 27 from Launch Complex 39A, but was scrubbed for the day. Crew-6 is the sixth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the station, and the seventh flight of Dragon with people as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
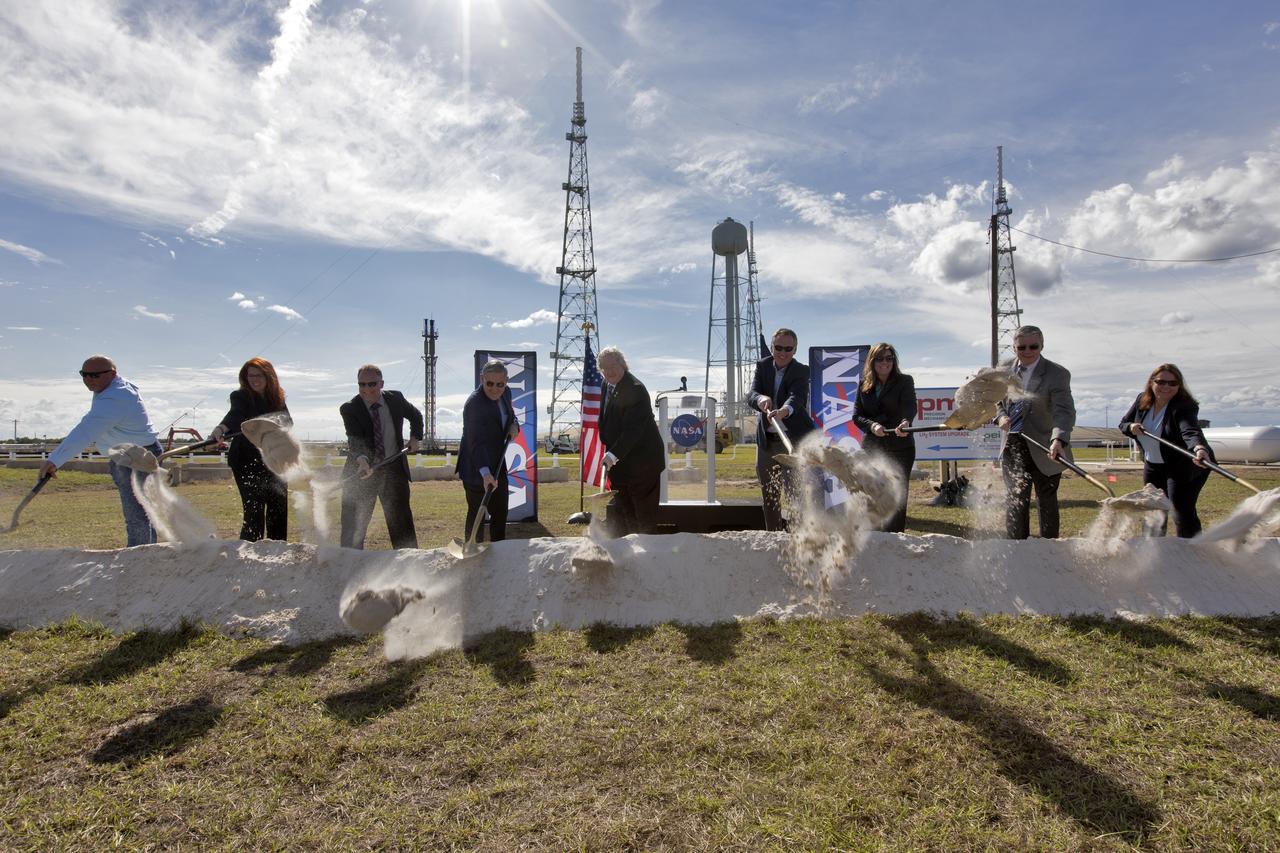

On Dec. 19, 2018, at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39B, agency and contractor managers break ground for a new liquid hydrogen tank. Participating, from the left, are Todd Gray, president of Precision Mechanical, prime contractor for the project; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, launch director; Shawn Quinn, director of Engineering; Bob Cabana, center director; Bill Hill, deputy associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development at NASA Headquarters in Washington; Mike Bolger, program manager for Exploration Ground Systems (EGS); Jennifer Kunz, deputy program manager for EGS, Andy Allen, general manager for Jacobs, NASA's Test and Operations Support Contractor; and Regina Spellman, launch pad senior project manager in EGS. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.
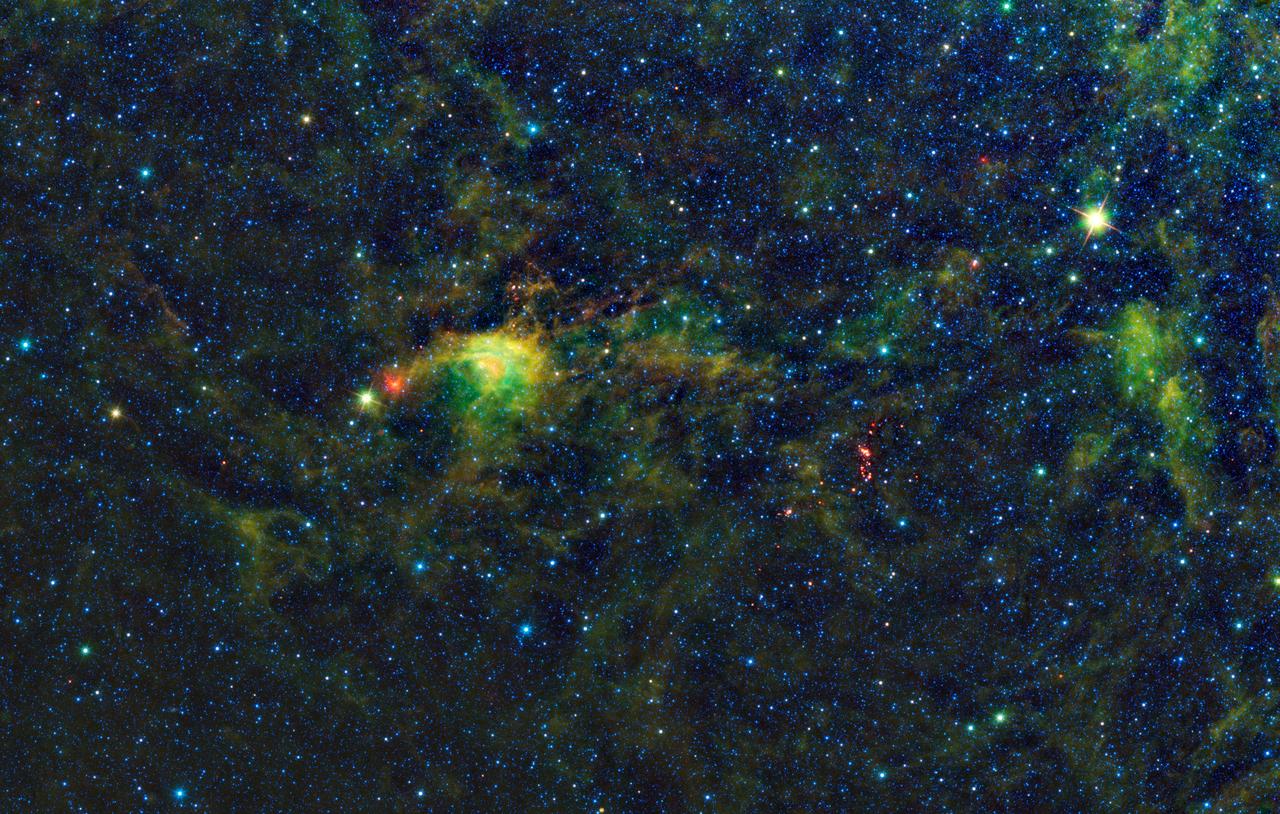

NASA Wide-Field Infrared Survey Explorer has uncovered a striking population of young stellar objects in a complex of dense, dark clouds in the southern constellation of Circinus.
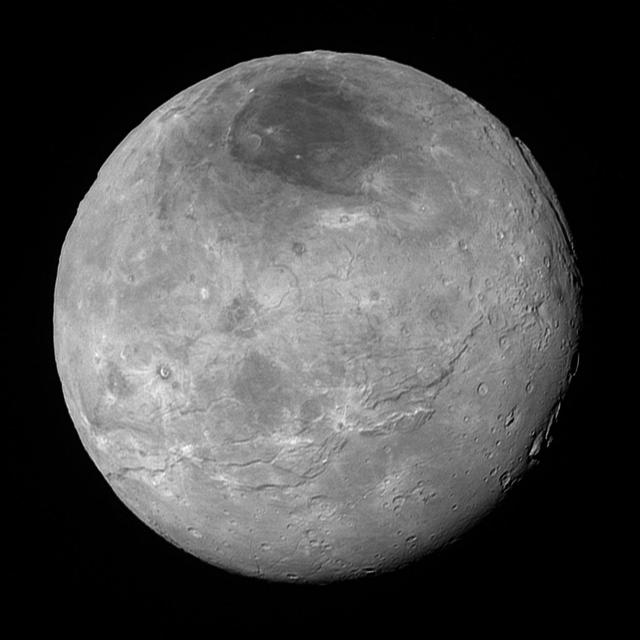

This image of Pluto's largest moon Charon, taken by NASA's New Horizons spacecraft 10 hours before its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015 from a distance of 290,000 miles (470,000 kilometers), is a recently downlinked, much higher quality version of a Charon image released on July 15. Charon, which is 750 miles (1,200 kilometers) in diameter, displays a surprisingly complex geological history, including tectonic fracturing; relatively smooth, fractured plains in the lower right; several enigmatic mountains surrounded by sunken terrain features on the right side; and heavily cratered regions in the center and upper left portion of the disk. There are also complex reflectivity patterns on Charon's surface, including bright and dark crater rays, and the conspicuous dark north polar region at the top of the image. The smallest visible features are 2.9 miles 4.6 kilometers) in size. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19932
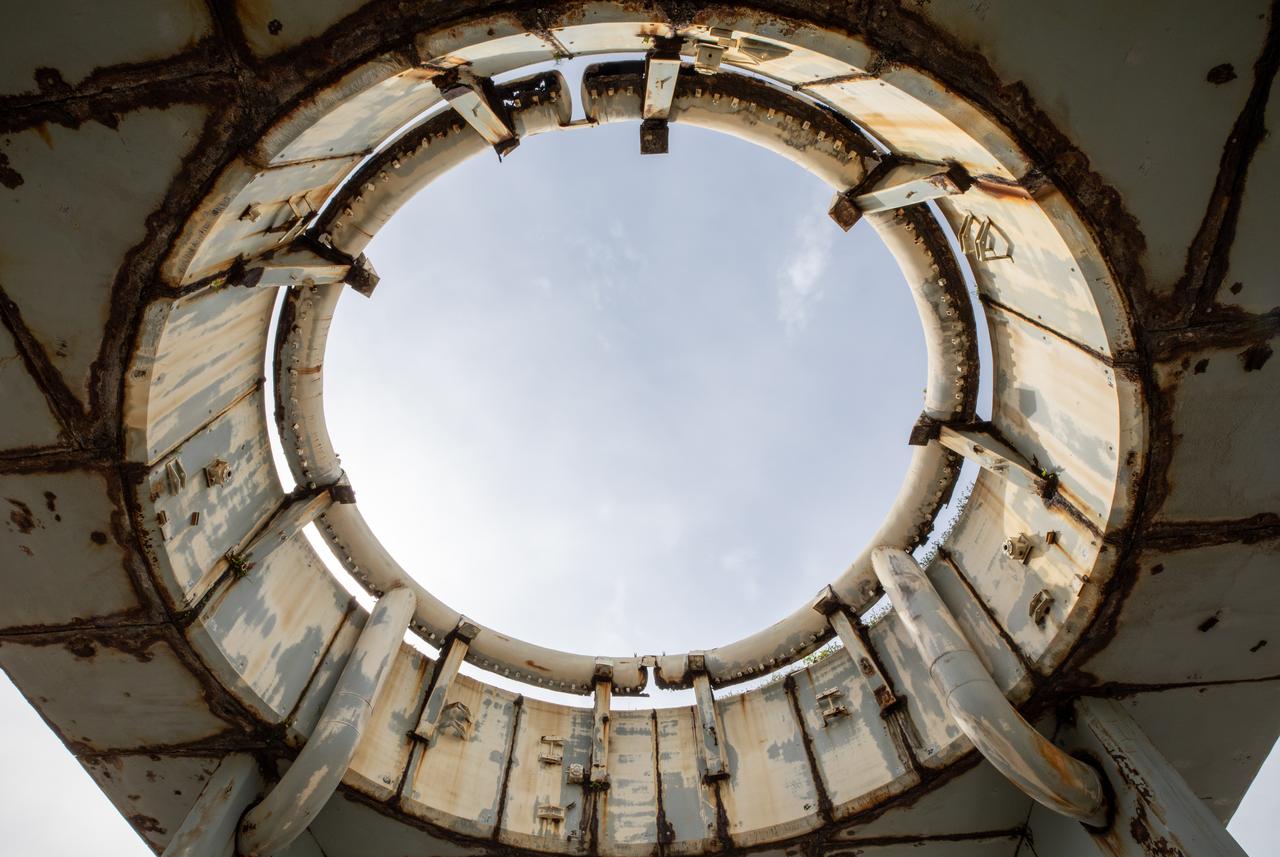

A view looking up from inside the launch pedestal still standing at Launch Complex 34 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 22, 2020. Work will soon begin to perform environmental contamination removal on the pedestal and the ground area surrounding the launch complex.
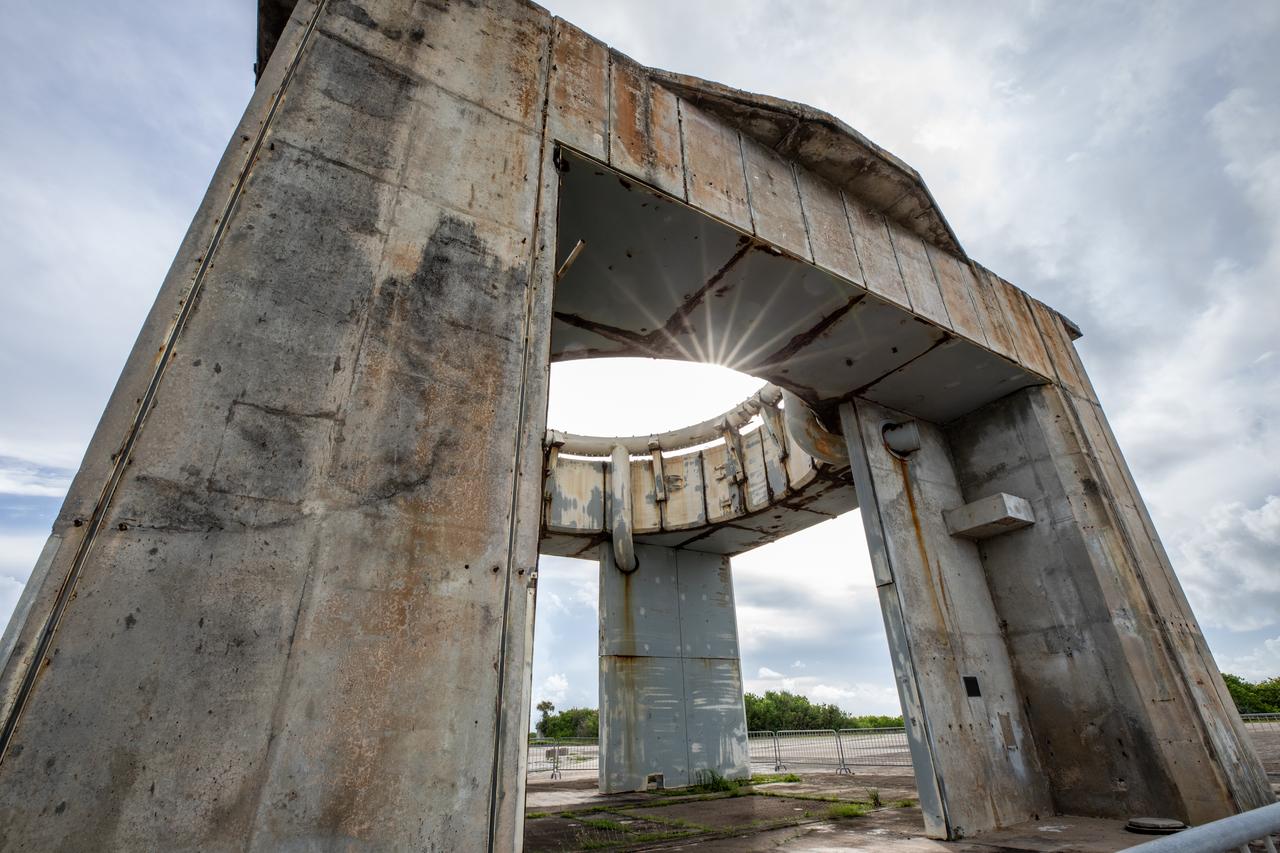

A close-up view of the launch pedestal still standing at Launch Complex 34 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 22, 2020. Work will soon begin to perform environmental contamination removal on the pedestal and the ground area surrounding the launch complex.
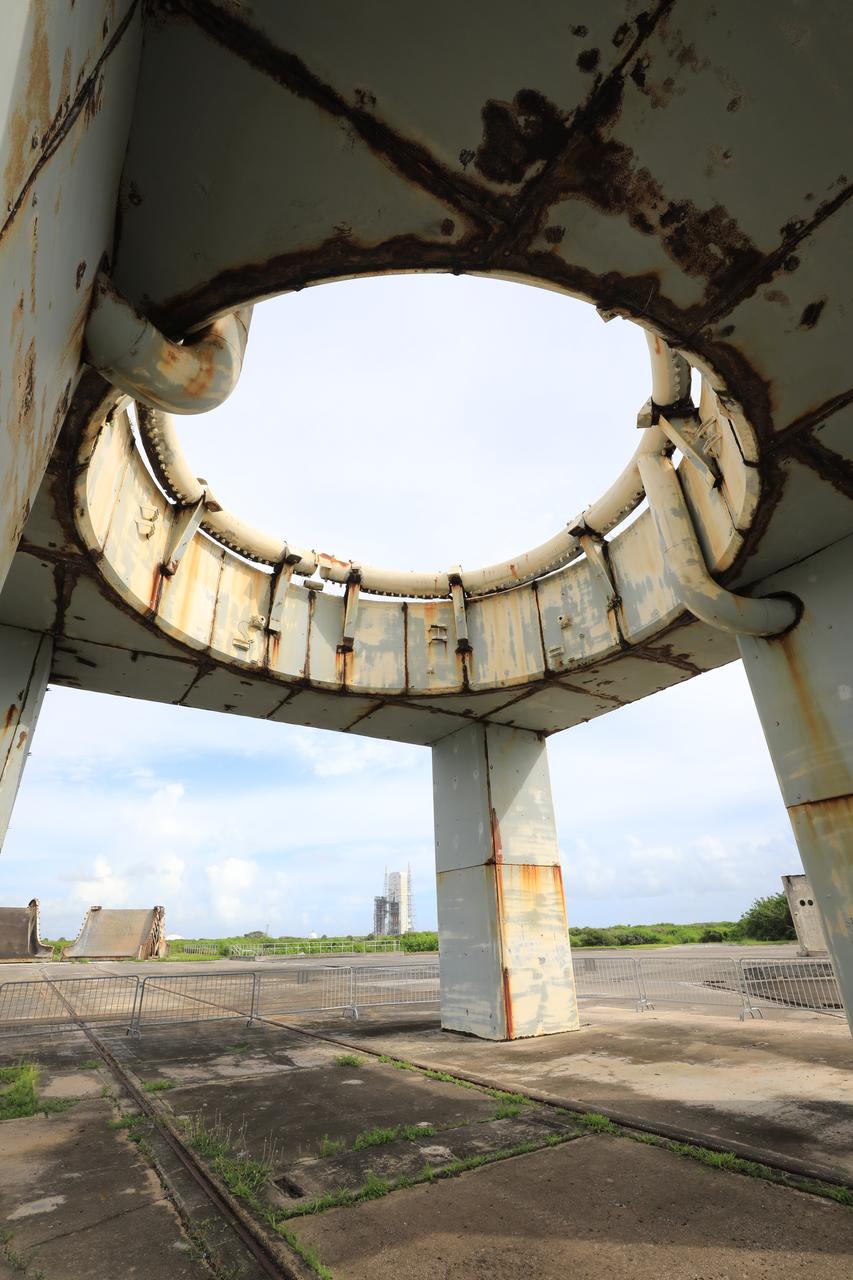

A view looking up from inside the launch pedestal still standing at Launch Complex 34 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 22, 2020. Work will soon begin to perform environmental contamination removal on the pedestal and the ground area surrounding the launch complex.
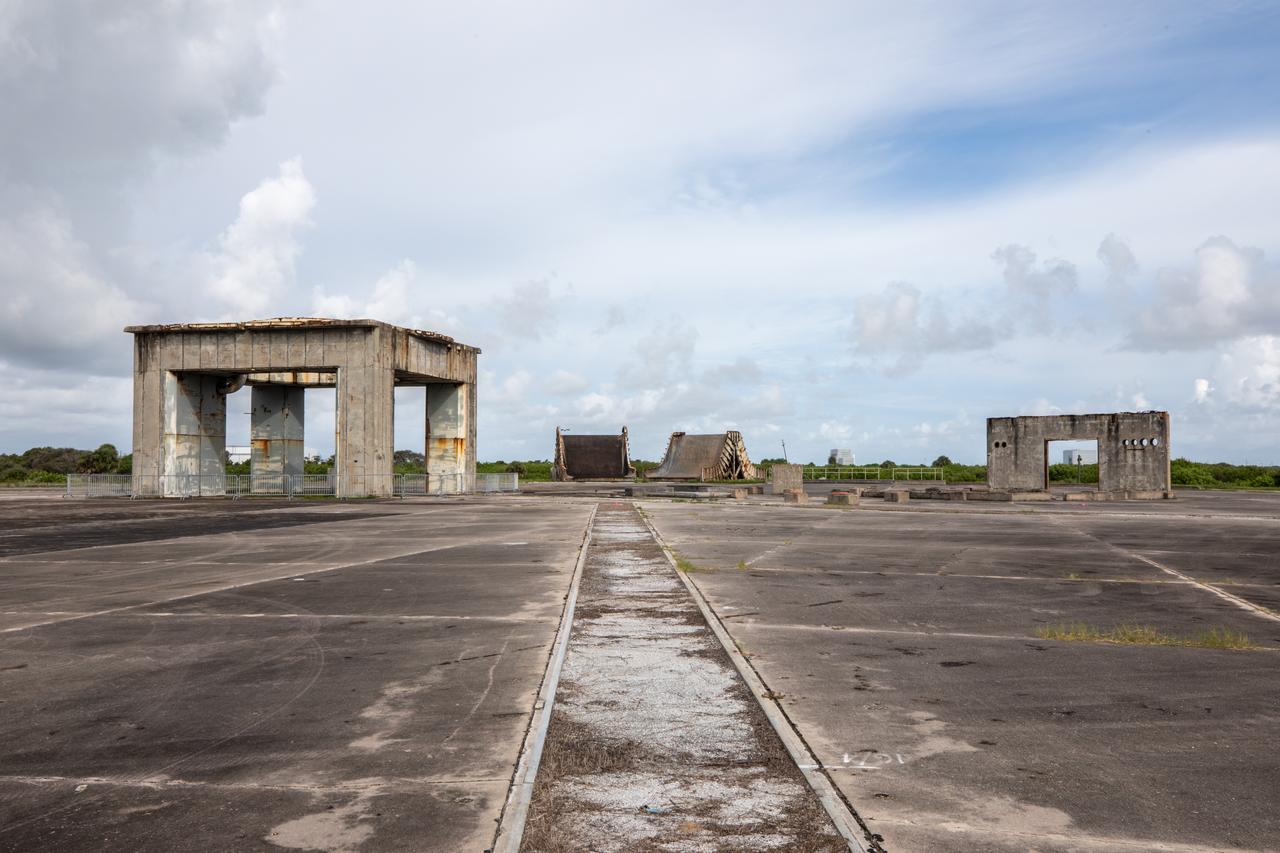

A view of the launch pedestal (at left) still standing at Launch Complex 34 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 22, 2020. In the background are two flame deflectors. Work will soon begin to perform environmental contamination removal on the pedestal and the ground area surrounding the launch complex.
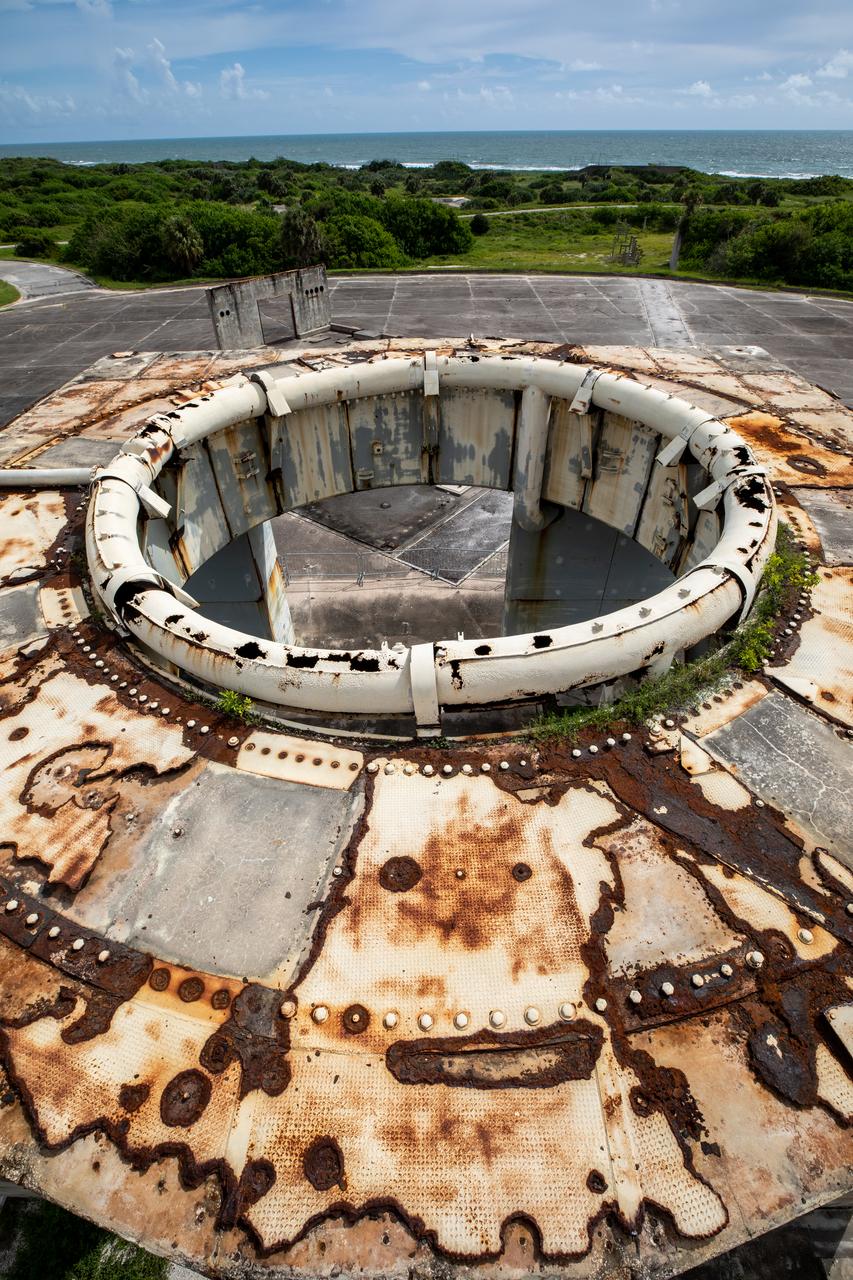

A view of the top of the launch pedestal still standing at Launch Complex 34 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 22, 2020. Work will soon begin to perform environmental contamination removal on the pedestal and the ground area surrounding the launch complex.
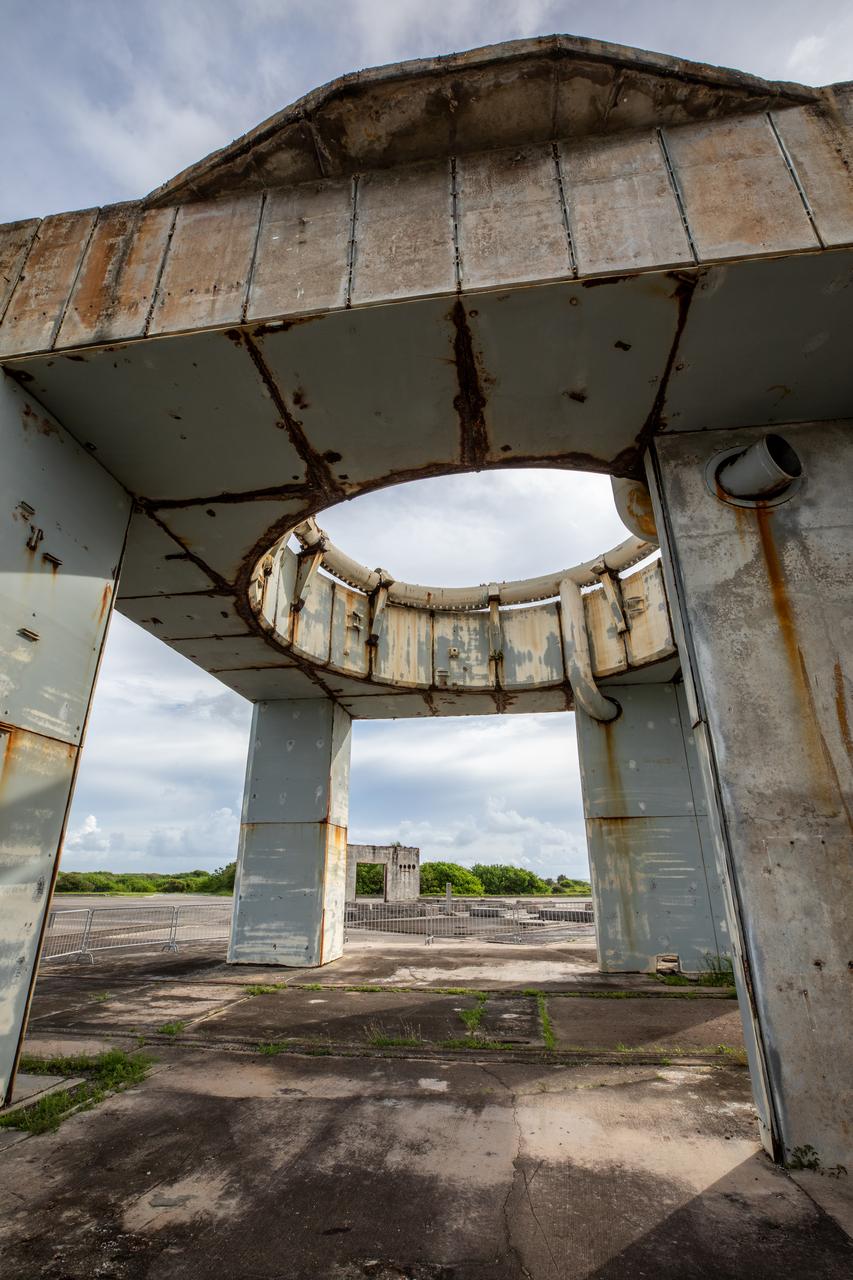

A close-up view of the launch pedestal still standing at Launch Complex 34 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 22, 2020. Work will soon begin to perform environmental contamination removal on the pedestal and the ground area surrounding the launch complex.

A close-up view of the historic marker on the launch pedestal still standing at Launch Complex 34 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 22, 2020. Work will soon begin to perform environmental contamination removal on the pedestal and the ground area surrounding the launch complex.
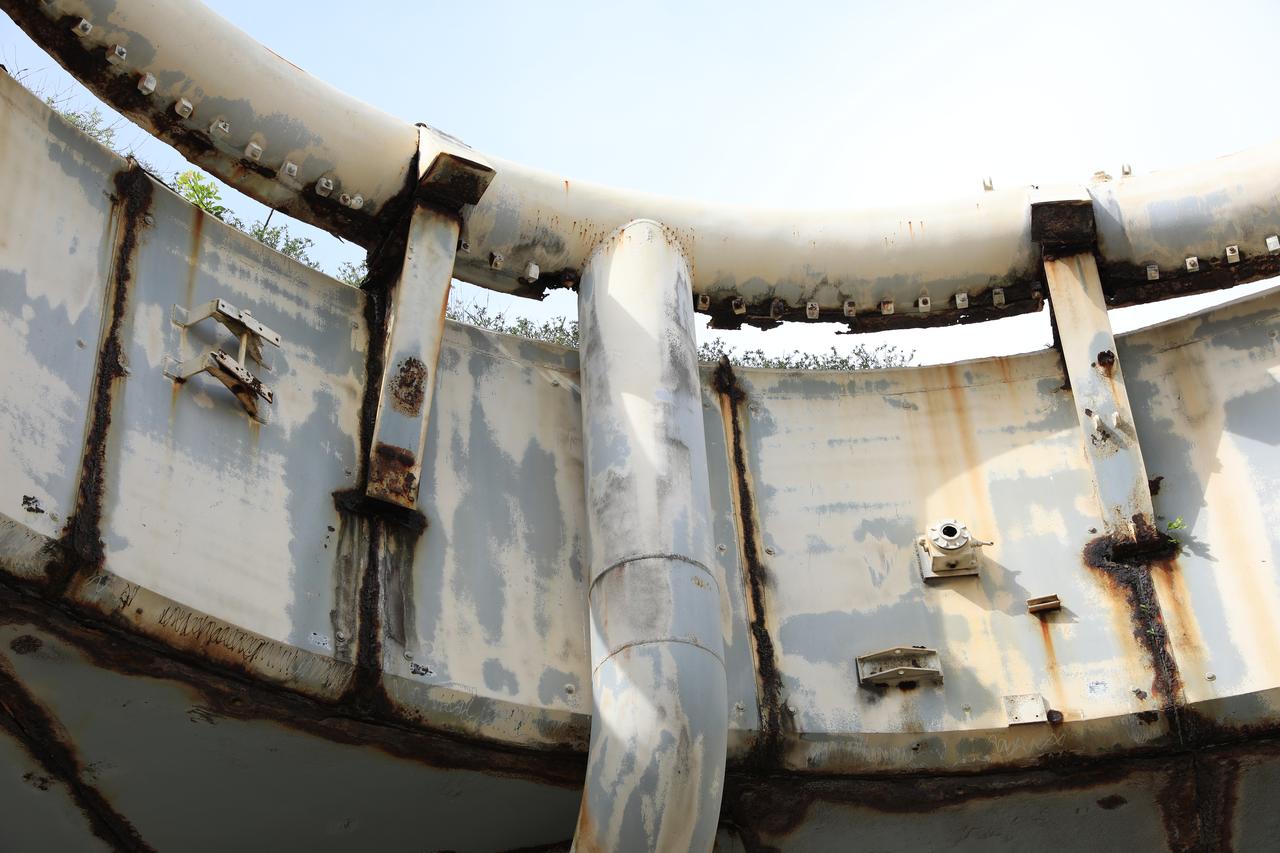

A view looking up from inside the launch pedestal still standing at Launch Complex 34 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 22, 2020. Work will soon begin to perform environmental contamination removal on the pedestal and the ground area surrounding the launch complex.
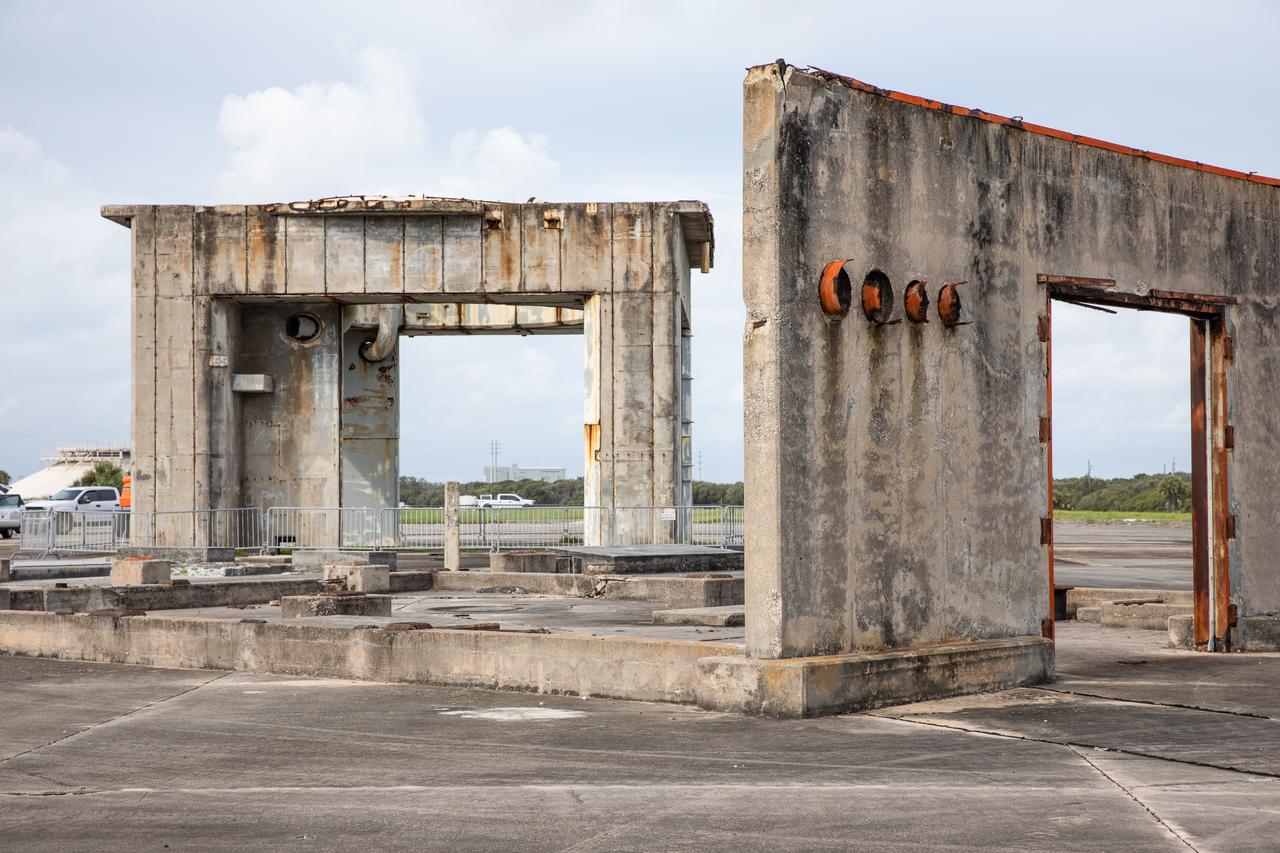

A close-up view of the launch pedestal and a support structure still standing at Launch Complex 34 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 22, 2020. Work will soon begin to perform environmental contamination removal on the pedestal and the ground area surrounding the launch complex.
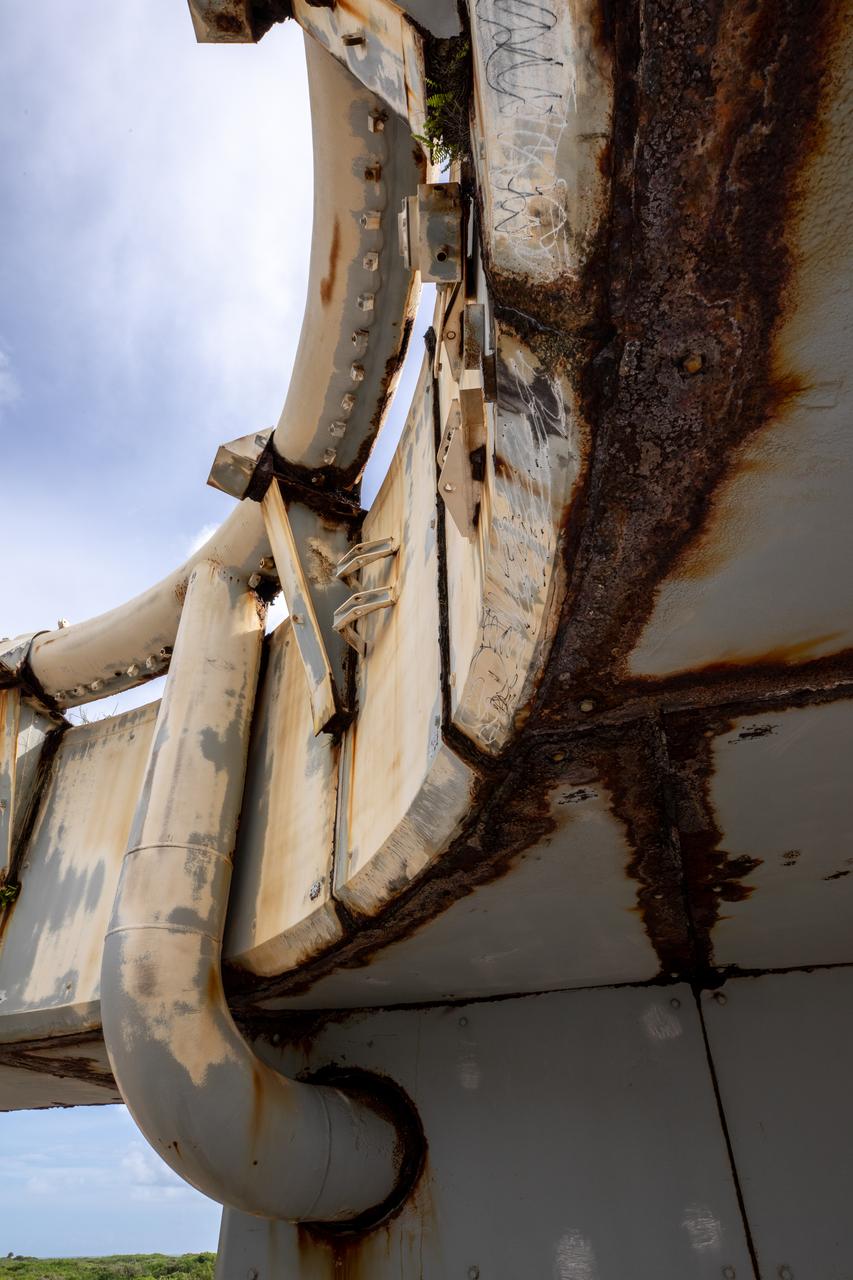

A close-up view of a portion of the launch pedestal still standing at Launch Complex 34 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on July 22, 2020. Work will soon begin to perform environmental contamination removal on the pedestal and the ground area surrounding the launch complex.