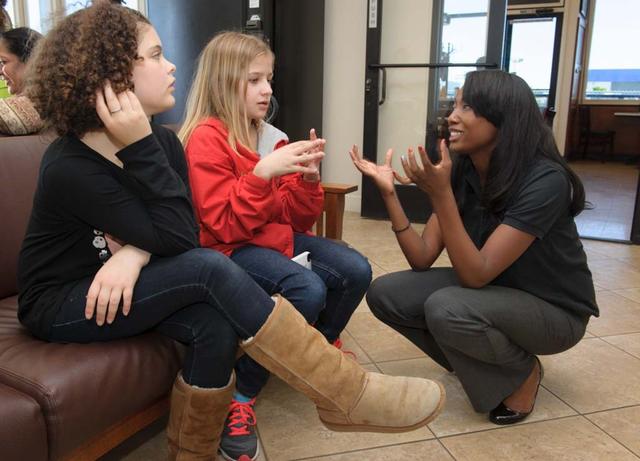

Women Fly it forward event at Hiller Aviation. Aisha Bowe (right) with Ames Navigation, Guidance & Control Systems Branch reaches out to Julia Smith (left) and Taylor Grafstrom (center) about women in aviation.

Aeronautics Technical Seminar: Nhan Nguyen presents 'NASA Past and Present Research in Adaptive Flight Control and Technology Challenges'

Aeronautics Technical Seminar with Dennis Koehler, Vice President, Science Applications International Corporation (and former FAA executive) presenting 'Beyond the Technical: Procedural, Operational and Economic Factors 'POET' for NextGen Success
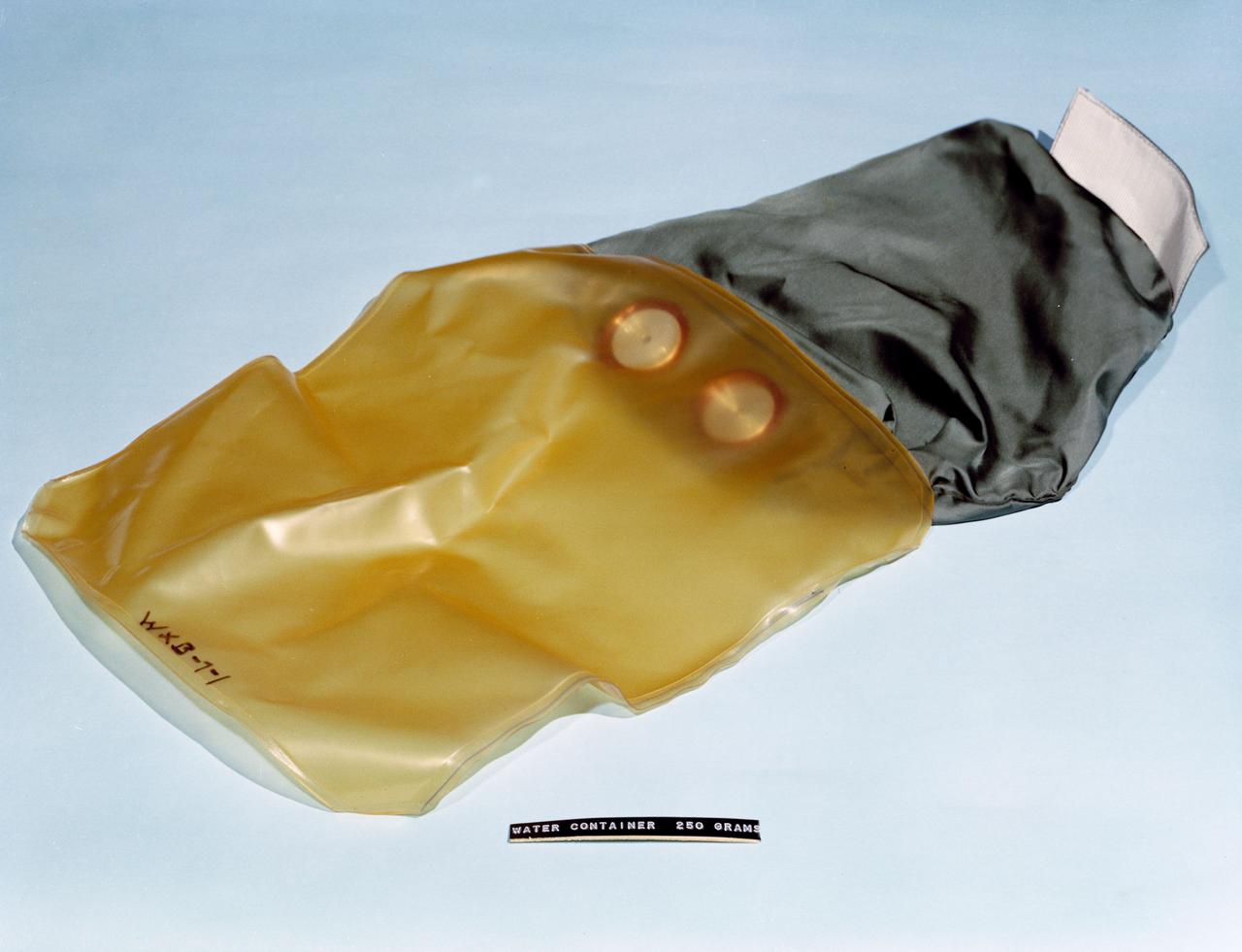
S62-06783 (1962) --- Component of Mercury astronauts survival equipment backpack - water container holding 250 grams when full. Photo credit: NASA
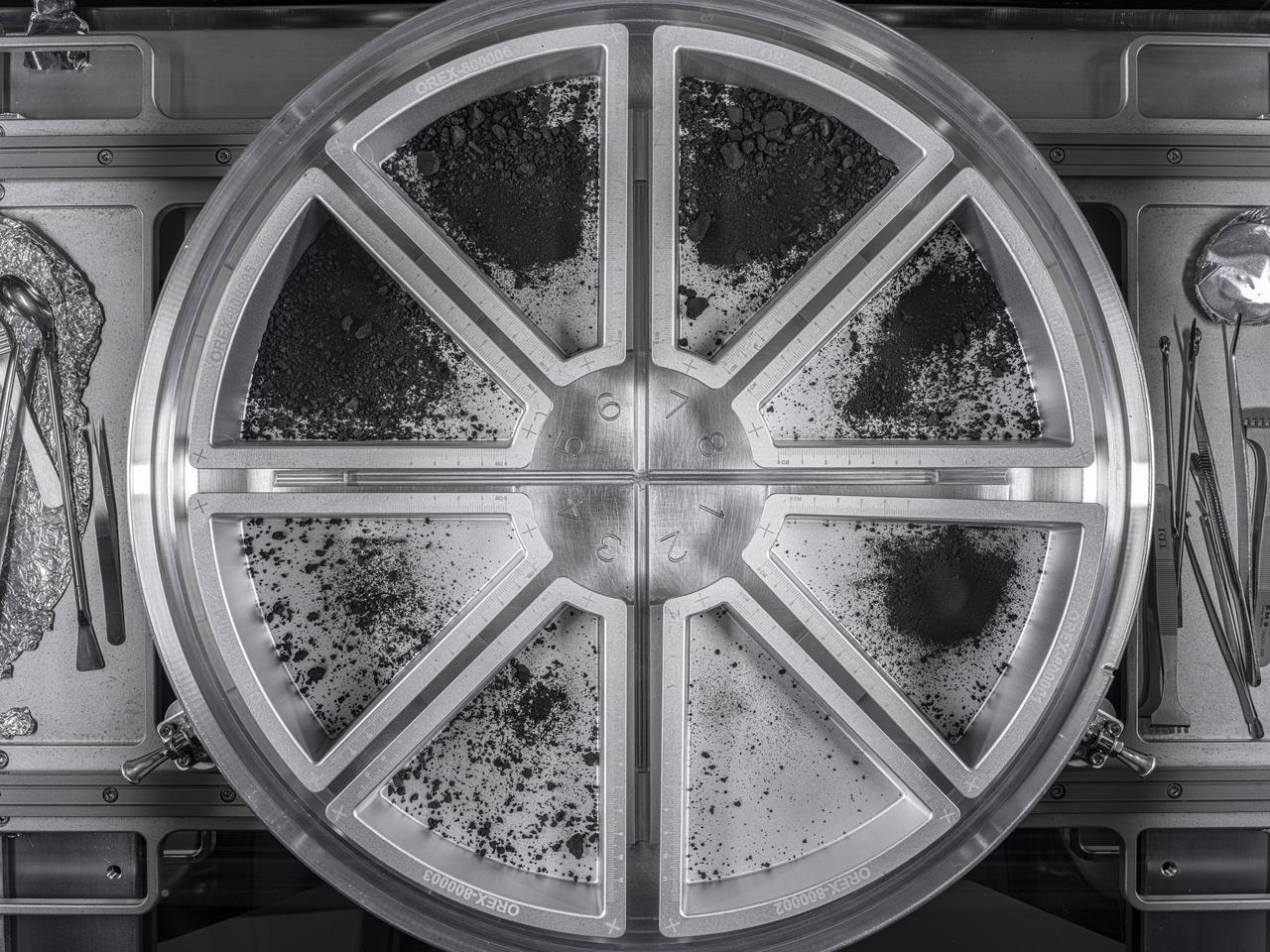

A view of eight sample trays containing the final material from asteroid Bennu. The dust and rocks were poured into the trays from the top plate of the Touch-and-Go Sample Acquisition Mechanism (TAGSAM) head. 51.2 grams were collected from this pour, bringing the final mass of asteroid sample to 121.6 grams. Credit: NASA/Erika Blumenfeld & Joseph Aebersold

Directors Colloquium: Dr Charles Beichman, NExSci Caltech/JPL presents 'Using JWST's Near-IR Camera to observe the Universe from 10 AU to Z>10'.
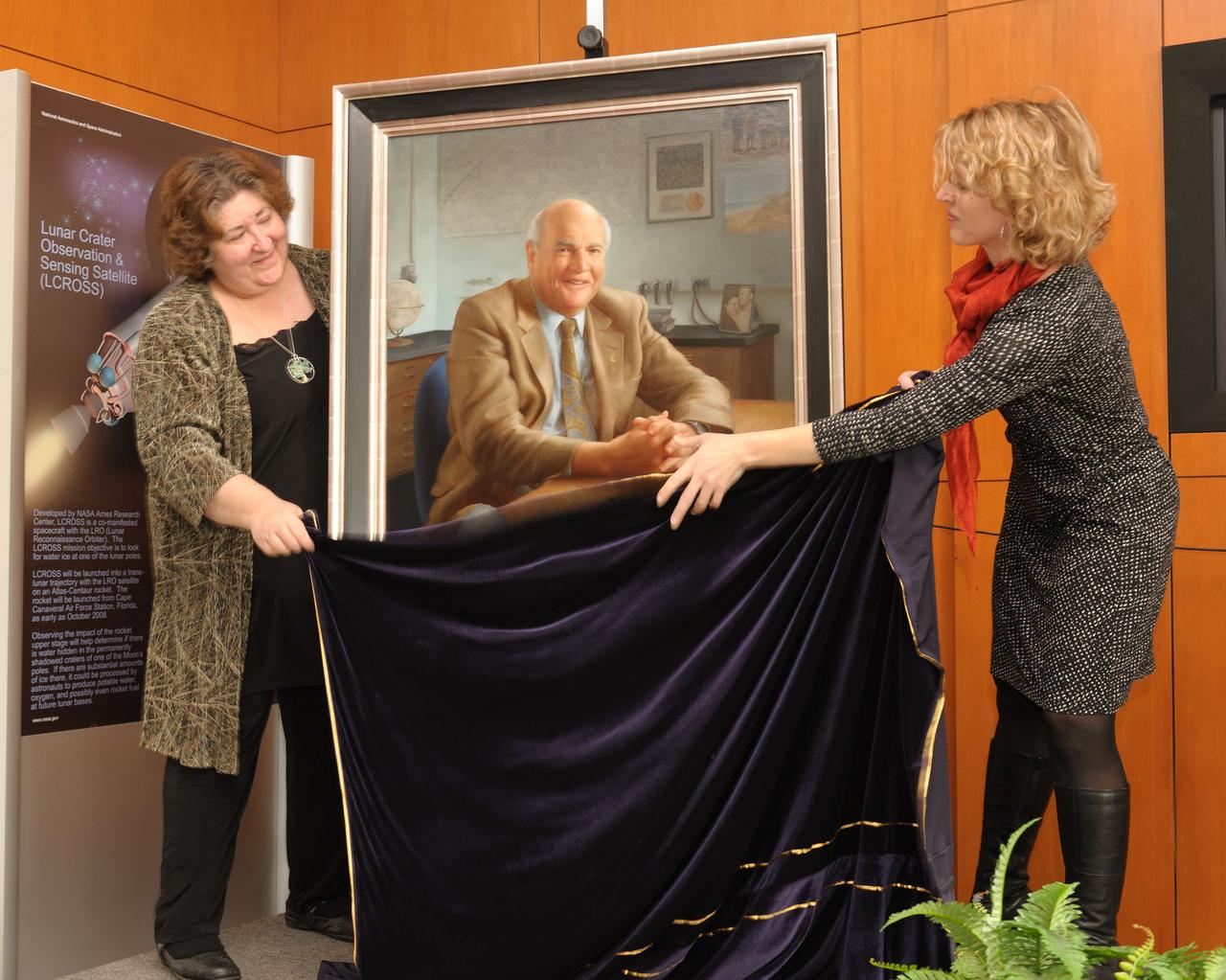

Dr. Brauch Blumberg portrait unveiling ceremony held at the Syverston Auditorium (N-201) NASA Ames Researc Center, Moffett Field, CA. Lynn Harper and Estelle Dotson (of NASA Astrobilolgy Institute) unveil portrait.

Dr. Brauch Blumberg portrait unveiling ceremony held at the Syverston Auditorium (N-201) NASA Ames Researc Center, Moffett Field, CA. From left Mrs. Jean Blumberg, Dolores Beasley, NASA stand by the Brauch Blumberg portrait with artist Elizabeth Zanzinger on right.
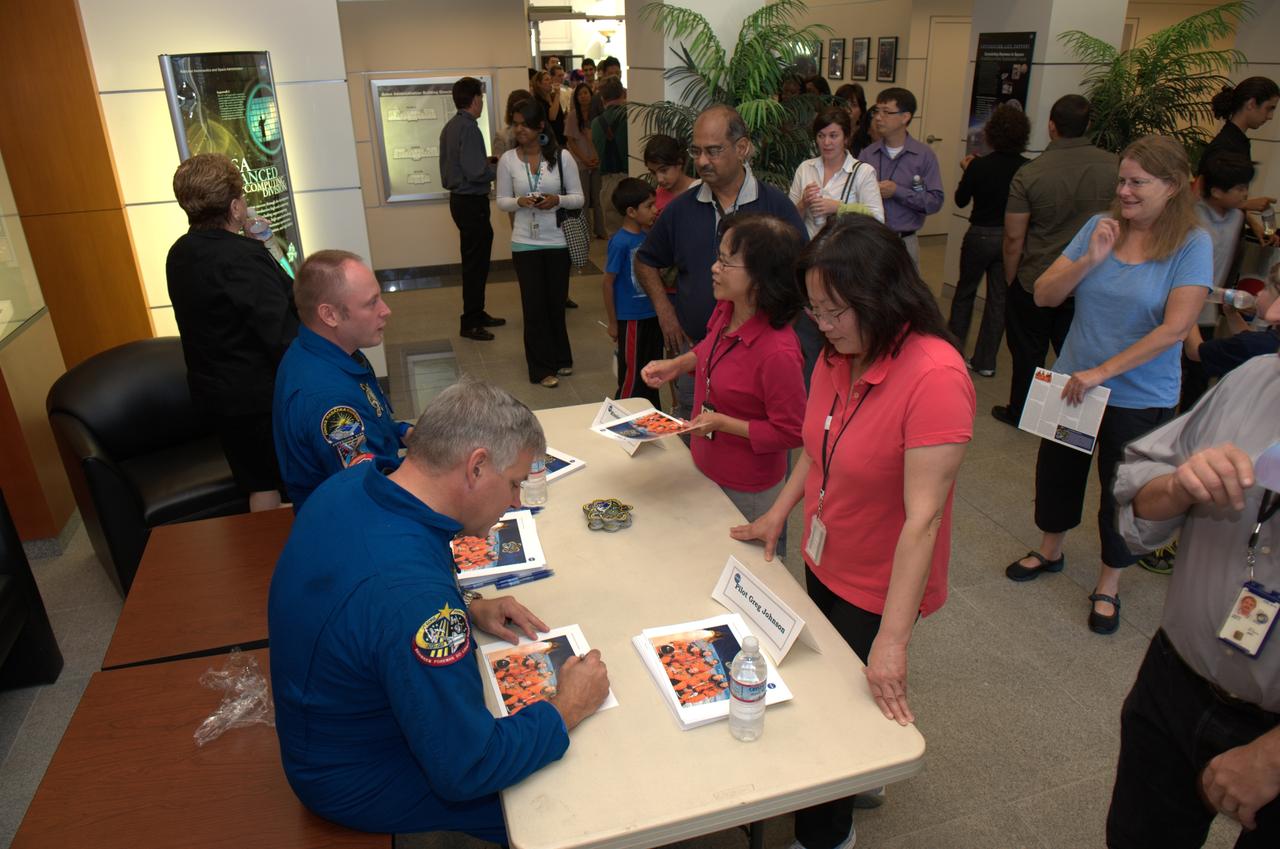

Pilot Greg Johnson and Mission Specialist Mike Fincke of Space Shuttle Endeavour's final mission STS-134 come to Ames Research Center to share their experiences, answer questions and sign autographs during a afternoon with the staff.
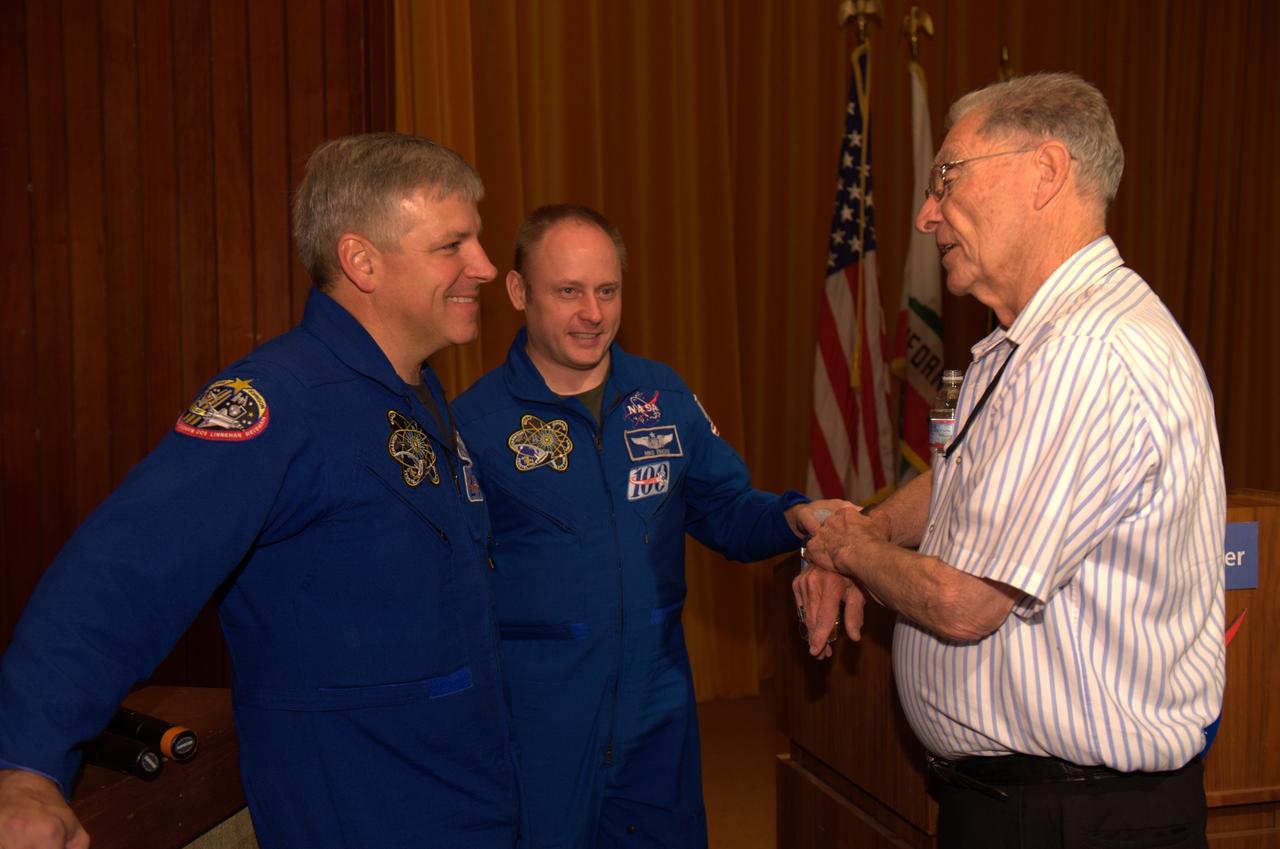

Pilot Greg Johnson and Mission Specialist Mike Fincke of Space Shuttle Endeavour's final mission STS-134 come to Ames Research Center to share their experiences, answer questions and sign autographs during a afternoon with the staff. With John W. 'Jack' Boyd on right.

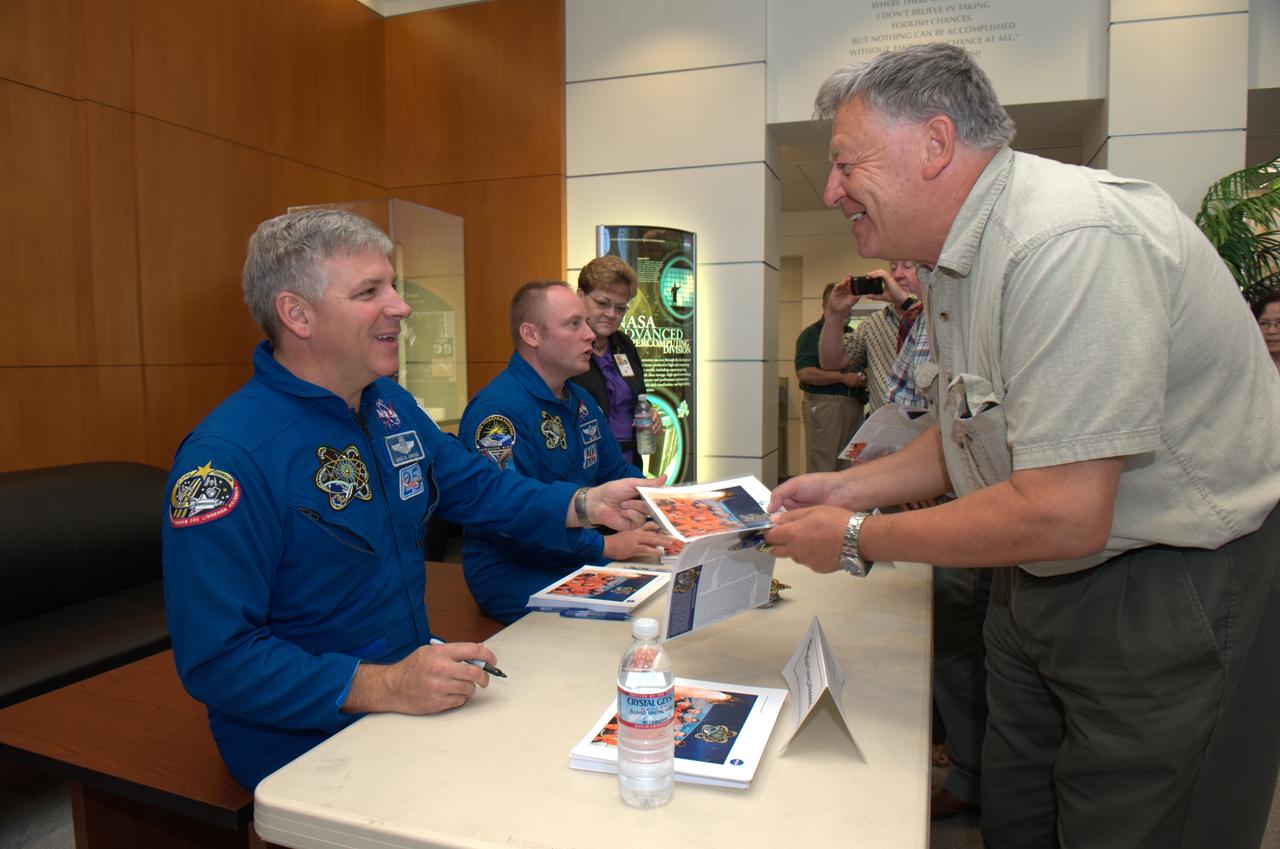
STS-135 Space Shuttle's final crew of Astronauts Ferguson, Hurley, Magnus and Walheim visit Ames for a mission/project briefing and with a meet and greet of Ames personnel,
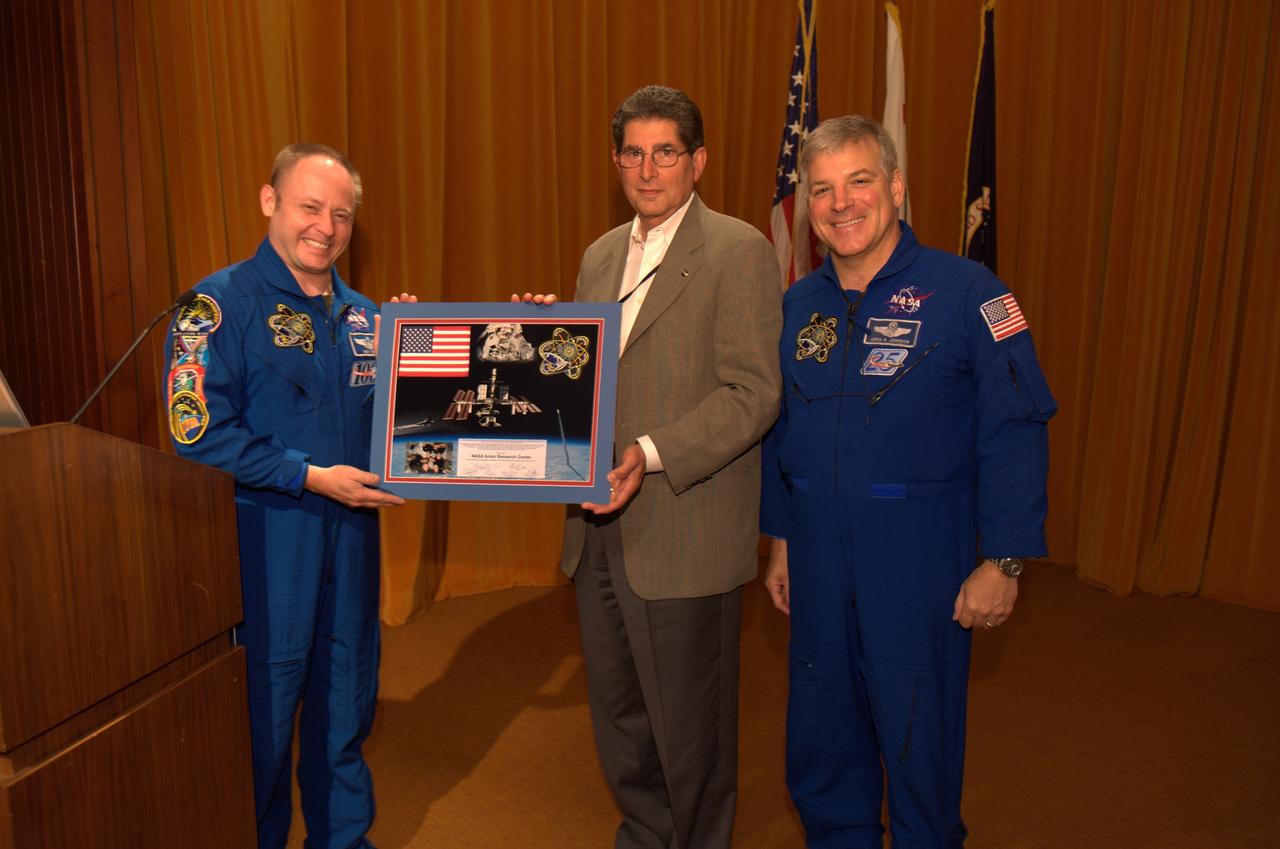

Pilot Greg Johnson and Mission Specialist Mike Fincke of Space Shuttle Endeavour's final mission STS-134 come to Ames Research Center to share their experiences, answer questions and sign autographs during a afternoon with the staff. Astronauts Johnson and Fincke present photo to Ames Associate Director Steve Zornetzer.

Pilot Greg Johnson and Mission Specialist Mike Fincke of Space Shuttle Endeavour's final mission STS-134 come to Ames Research Center to share their experiences, answer questions and sign autographs during a afternoon with the staff.
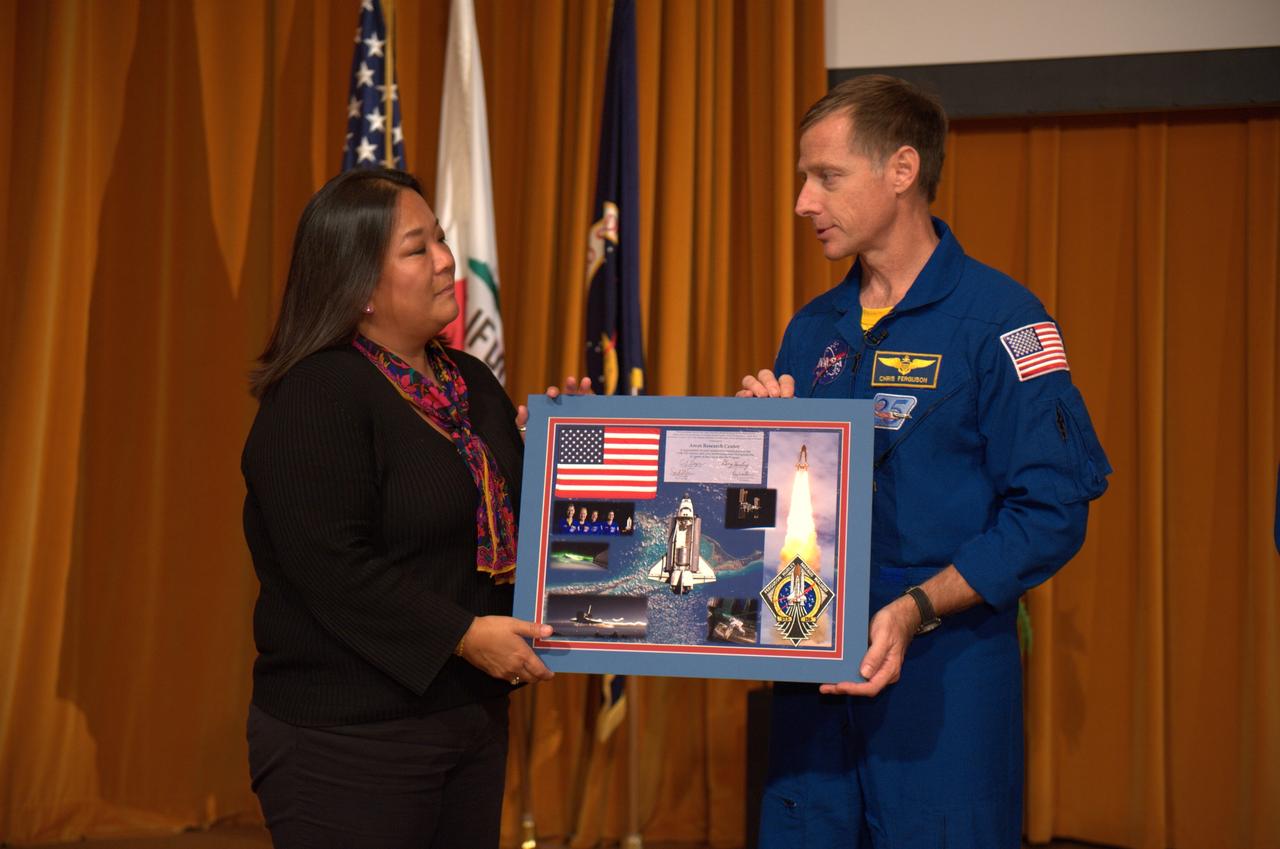

STS-135 Space Shuttle's final crew of Astronauts Ferguson, Hurley, Magnus and Walheim visit Ames for a mission/project briefing and with a meet and greet of Ames personnel. STS-135 Mission Commander Ferguson presents Deb Feng, Acting Deputy Center Director with a mission remembrance.
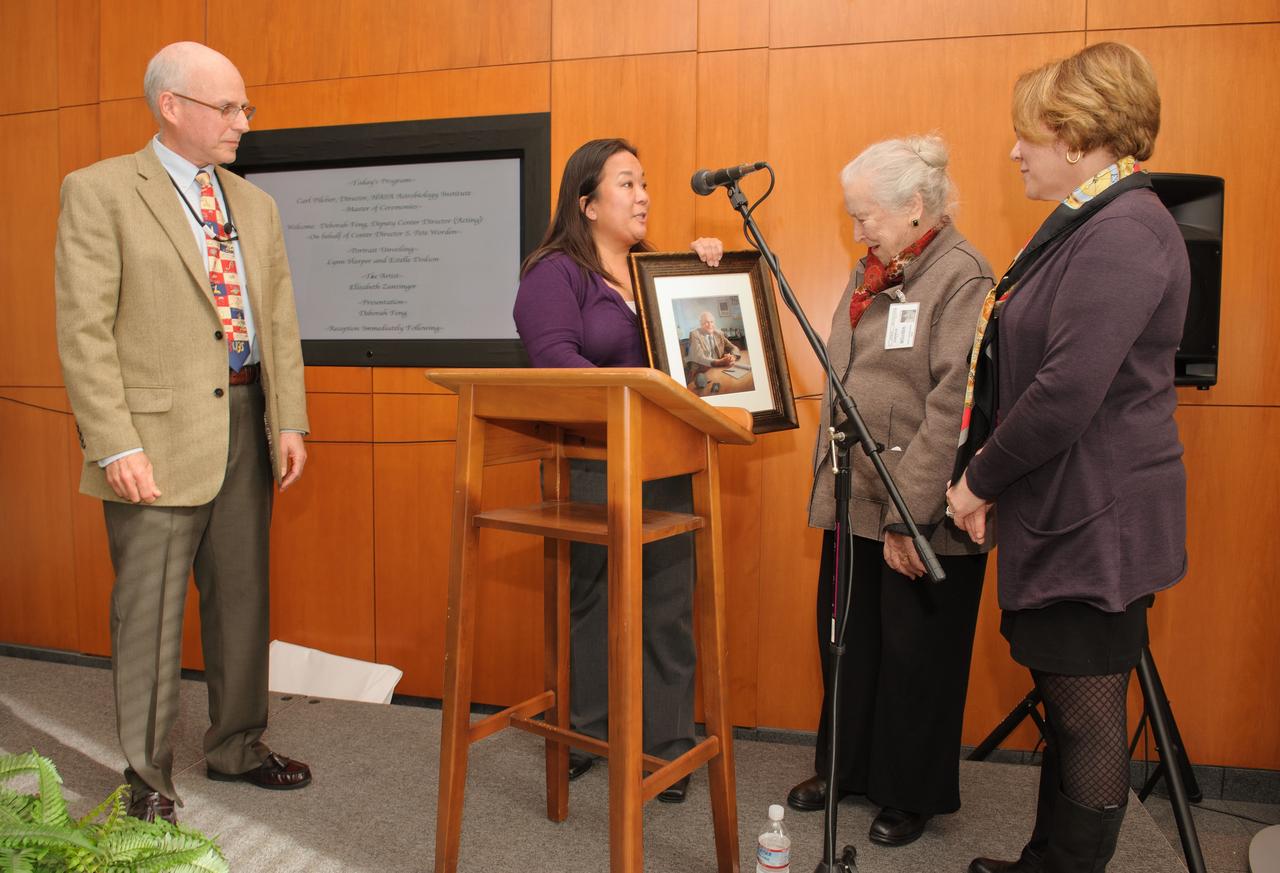

Dr. Brauch Blumberg portrait unveiling ceremony held at the Syverston Auditorium (N-201) NASA Ames Researc Center, Moffett Field, CA. From left, Carl Pilcher and Deb Feng present a copy of the painting to the Blumberg family.
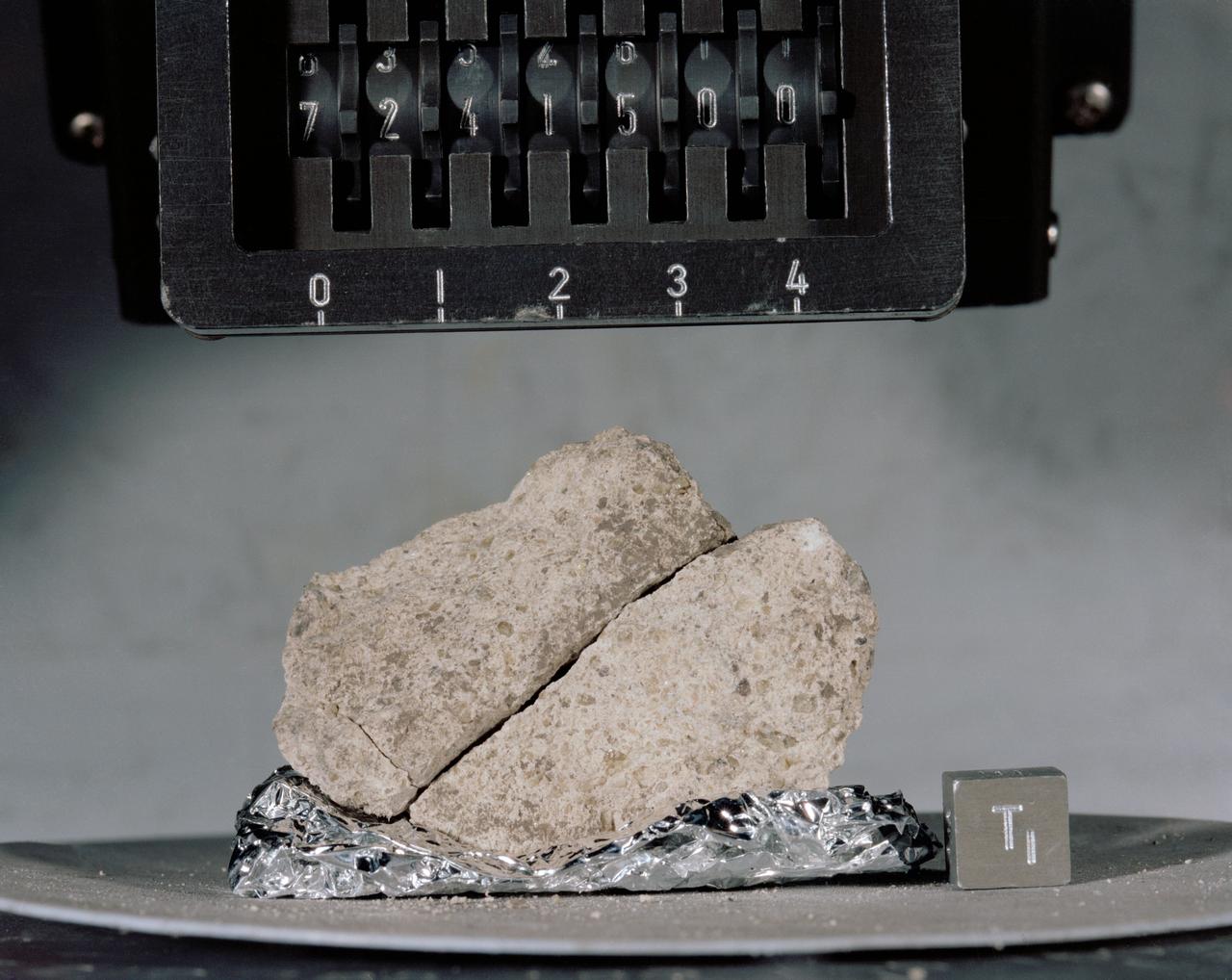

S73-16199 (December 1972) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar sample number 72415,0 which was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. This sample is a brecciated dunite clast weighing a little over 32 grams (about 1.14 ounces). This sample was collected at station 2 (South Massif) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA). IMPORTANT NOTE FOR CREDIT: The view was photographed by Karl Mills, Scientific Photo Arts, Berkeley, California.
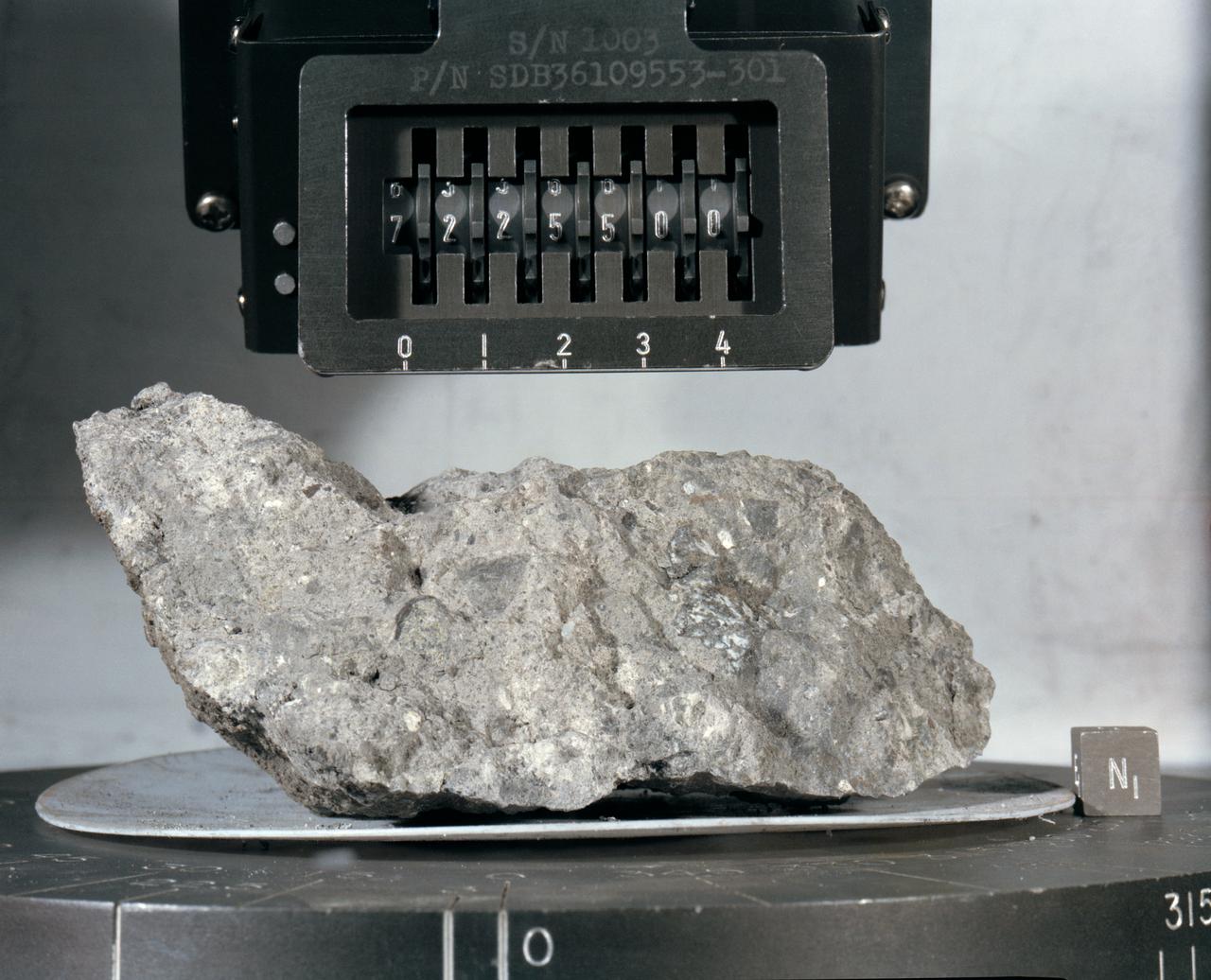

S73-16007 (December 1972) --- A "mug shot" of Apollo 17 lunar sample no. 72255 which was brought back from the lunar surface by the final team of Apollo astronauts. The rock weighs 461.2 grams and measures 2.5 x 9 x 10.5 centimeters. The light grey breccia is sub-rounded on all faces except the top and north sides.
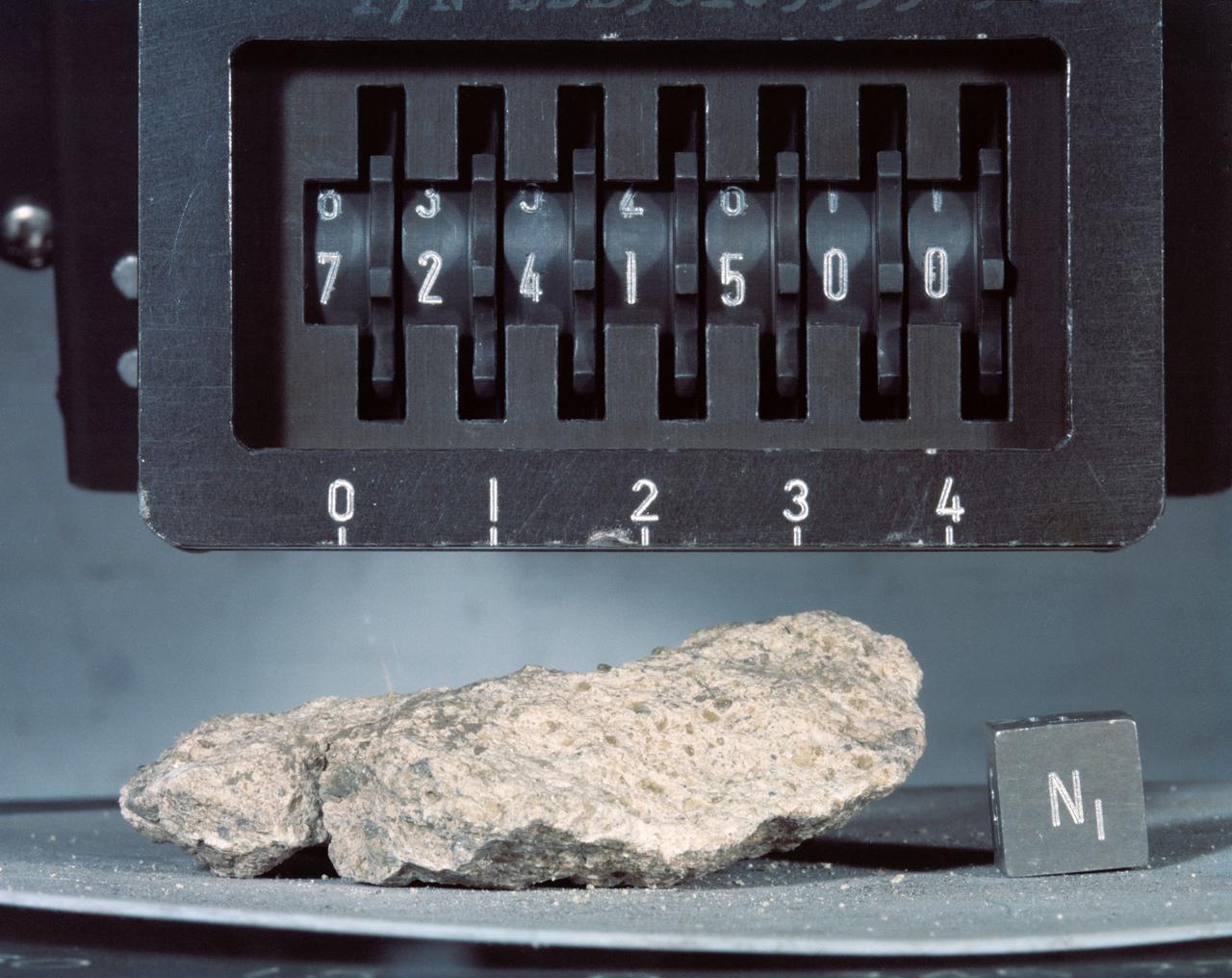

S73-16198 (December 1972) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar sample number 72415,0 which was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. This sample is a brecciated dunite clast weighing a little over 32 grams (about 1.14 ounces). This sample was collected at station 2 (South Massif) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA).
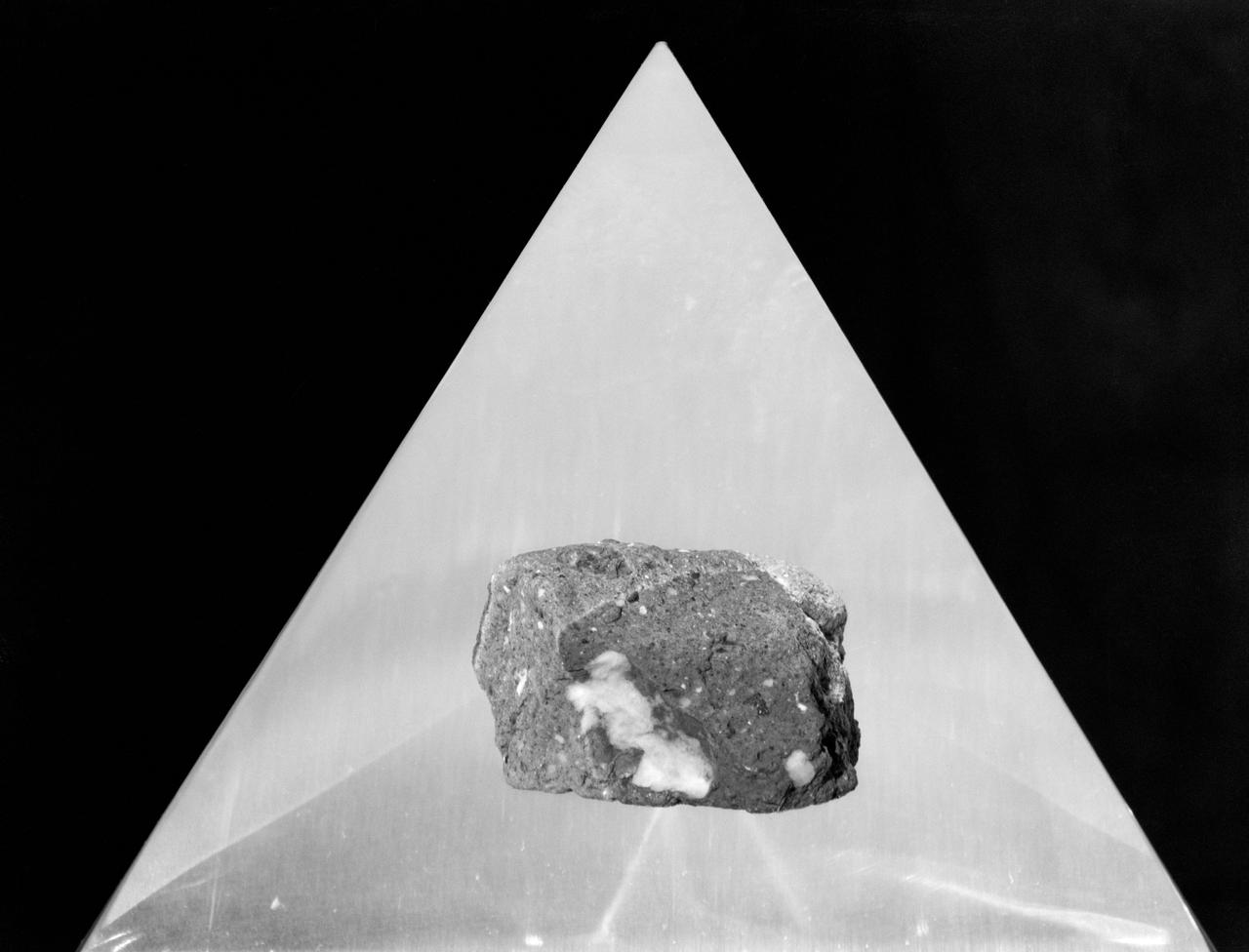

S75-23543 (April 1972) --- This Apollo 16 lunar sample (moon rock) was collected by astronaut John W. Young, commander of the mission, about 15 meters southwest of the landing site. This rock weighs 128 grams when returned to Earth. The sample is a polymict breccia. This rock, like all lunar highland breccias, is very old, about 3,900,000,000 years older than 99.99% of all Earth surface rocks, according to scientists. Scientific research is being conducted on the balance of this sample at NASA's Johnson Space Center and at other research centers in the United States and certain foreign nations under a continuing program of investigation involving lunar samples collected during the Apollo program.
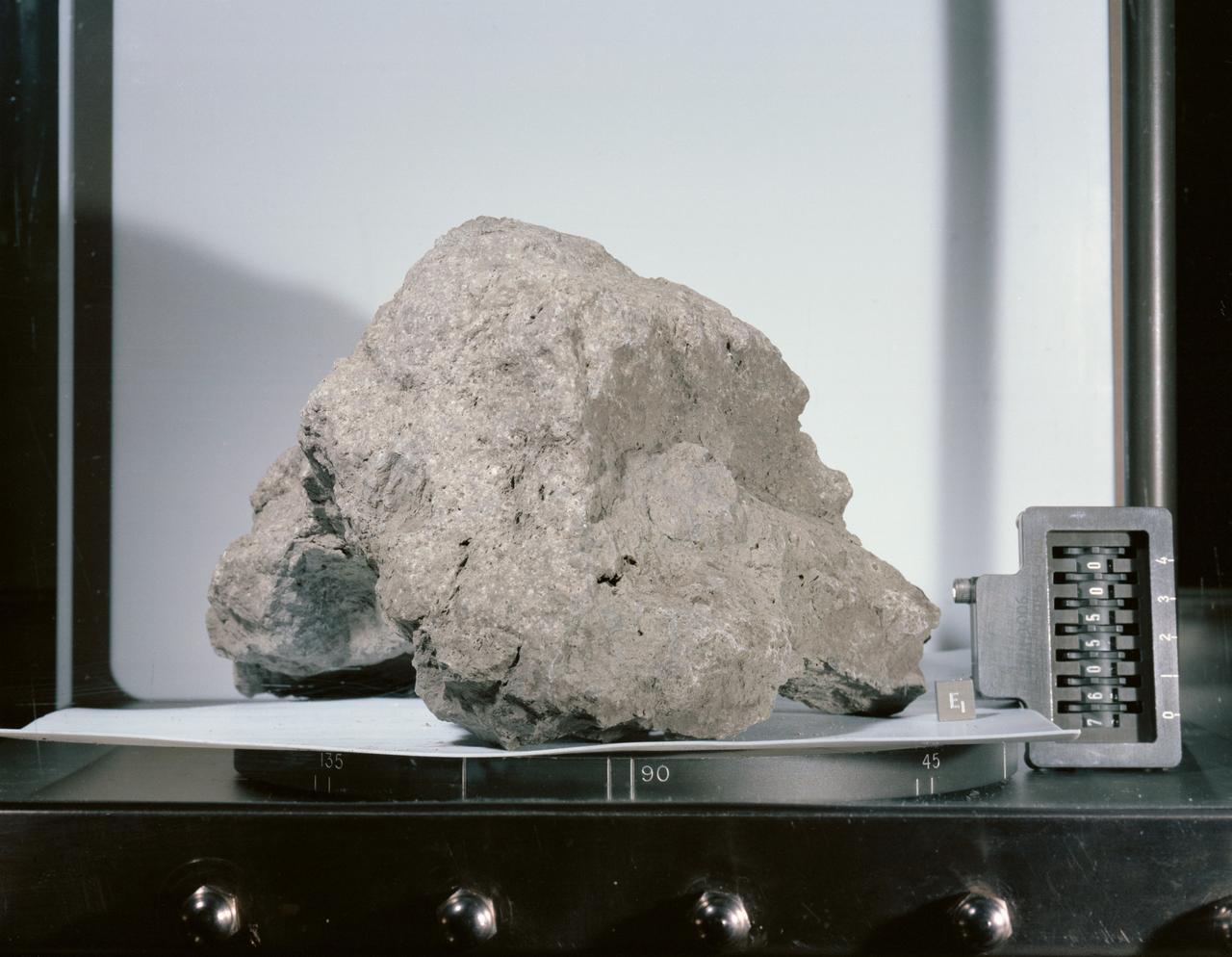

S73-15713 (January 1973) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar rock sample No. 76055 being studied and analyzed in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. This tan-gray irregular, rounded breccia was among many lunar samples brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crew. The rock measures 18 x 20 x 25 centimeters (7.09 x 7.87 x 9.84 inches) and weighs 6,389 grams (14.2554 pounds). The rock was collected from the south side of the lunar roving vehicle while the Apollo 17 astronauts were at Station 7 (base of North Massif).
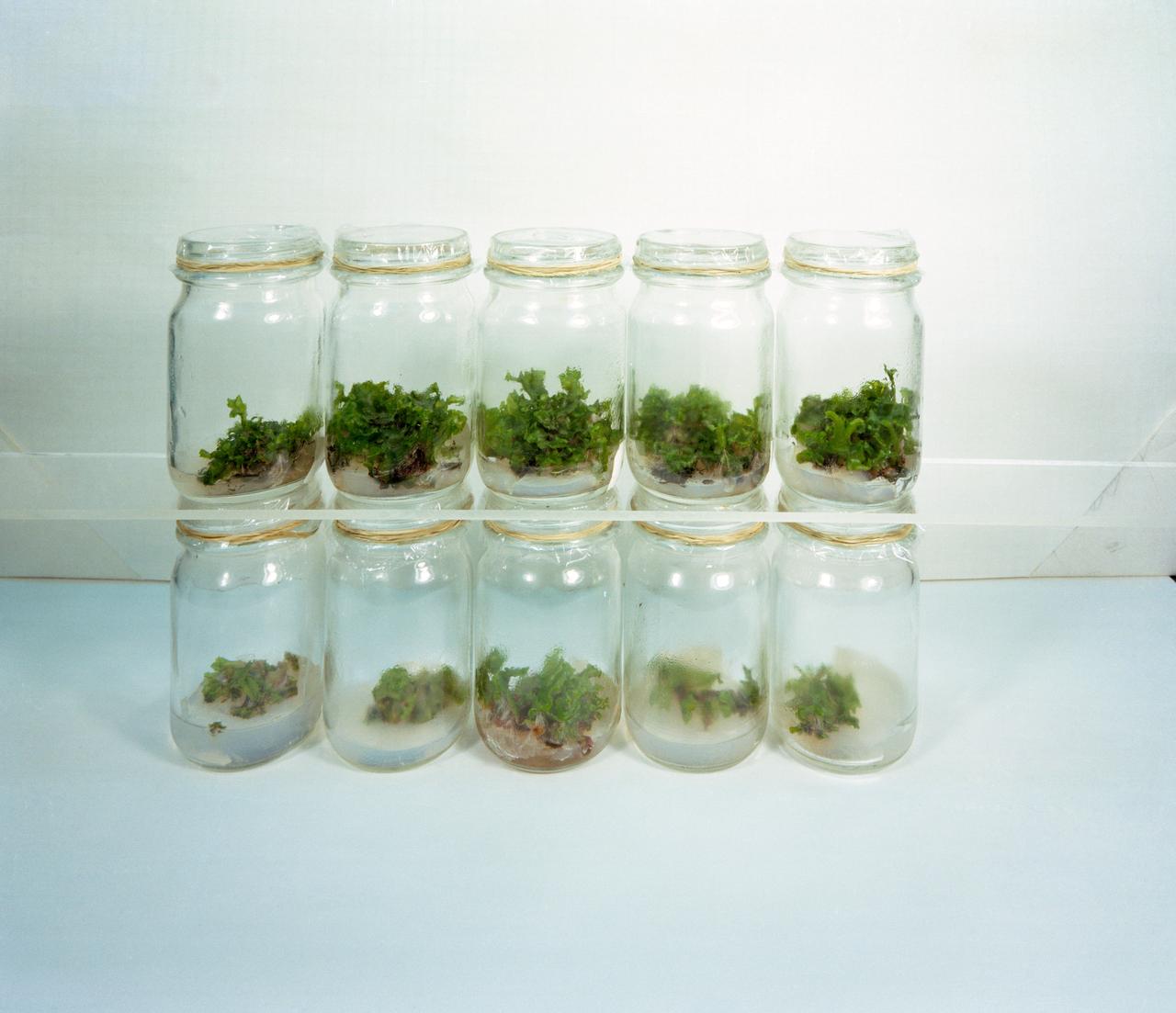

S69-53126 (30 Sept. 1969) --- A progress photograph of sample experiments being conducted in the Manned Spacecraft Center?s Lunar Receiving Laboratory with lunar material brought back to Earth by the crew of the Apollo 11 mission. Aseptic cultures of liverwort (Marchantia polymorpha) - a species of plant commonly found growing on rocks or in wooded areas - are shown in two rows of sample containers. Seven weeks or some 50 days prior to this photograph 0.22 grams of finely ground lunar material was added to each of the upper samples of cultures. The lower cultures were untreated, and a noted difference can be seen in the upper row and the lower one, both in color and size of the cultures.

MOXIE (Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment) was launched aboard NASA's Perseverance rover to test a technology for extracting oxygen from the Red Planet's carbon dioxide-rich atmosphere. Audio of MOXIE's air compressor at work on Mars was captured by the microphone on Perseverance's SuperCam instrument on May 27, 2021, the 96th day of the rover's mission. Since Perseverance landed on Mars in 2021, MOXIE generated a total of 122 grams of oxygen – about what a small dog breathes in 10 hours. At its most efficient, MOXIE was able to produce 12 grams of oxygen an hour – twice as much as NASA's original goals for the instrument – at 98% purity or better. On its final, 16th run, on Aug. 7, 2023, the instrument made 9.8 grams of oxygen. MOXIE successfully completed all of its technical requirements and was operated at a variety of conditions throughout a full Mars year, allowing the instrument's developers to learn a great deal about the technology. MOXIE produces molecular oxygen through an electrochemical process that separates one oxygen atom from each molecule of carbon dioxide pumped in from Mars' thin atmosphere. As these gases flow through the system, they're analyzed to check the purity and quantity of oxygen produced. While many of Perseverance's experiments are addressing primary science goals, MOXIE was focused on future human exploration. MOXIE served as the first-ever demonstration of technology that humans could use to survive on, and leave, the Red Planet. An oxygen-producing system could help future missions in various ways, but the most important of them would be as a source of rocket propellant, which would be required in industrial quantities to launch rockets with astronauts for their return trip home. Rather than bringing large quantities of oxygen with them to Mars, future astronauts could live off the land, using materials they find on the planet's surface to survive. This concept – called in-situ resource utilization, or ISRU – has evolved into a growing area of research. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Audio file available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26041

This image of the titanium nameplate on the robotic arm of NASA's Mars Perseverance rover was taken at a payload servicing facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center soon after being attached on March 4, 2020. The plate serves as rock and debris shield to protect a flexible cable that carries power and data from computers in the rover's body to actuators in the arm, as well as to the instruments and the drill in the turret. The laser-etched plate weighs 104 grams (3.7 ounces) and measures 17 inches long by 3.25 inches wide (43 centimeters long by 8.26 centimeters wide). The plate was cut using a waterjet, and the surface was coated with black thermal paint before a computer-guided laser generated the name "Perseverance" by ablating paint from the surface. (The video below shows the process, speeded up 3,000 times.) The nameplate was attached to the rover on March 4, 2020. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23766

Members of JPL's assembly, test and launch operations team for NASA's Perseverance mission show appreciation for their newly named rover. The image was taken on March 4, 2020, at a payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The plate is actually a rock and debris shield, designed to protect a cable that carries power and data from computers in the rover's body to actuators in the arm, as well as to the rotary percussive drill and instruments in the turret. Weighing in at about 104 grams (3.7 ounces), the 17-inch-long by 3.25-inch-wide (43-centimeter-long by 8.26-centimeter-wide) plate was cut using a water jet. The surface was coated with black thermal paint before a computer-guided laser generated the name "Perseverance" by ablating paint off the surface. The nameplate was attached to the rover on March 4, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23767
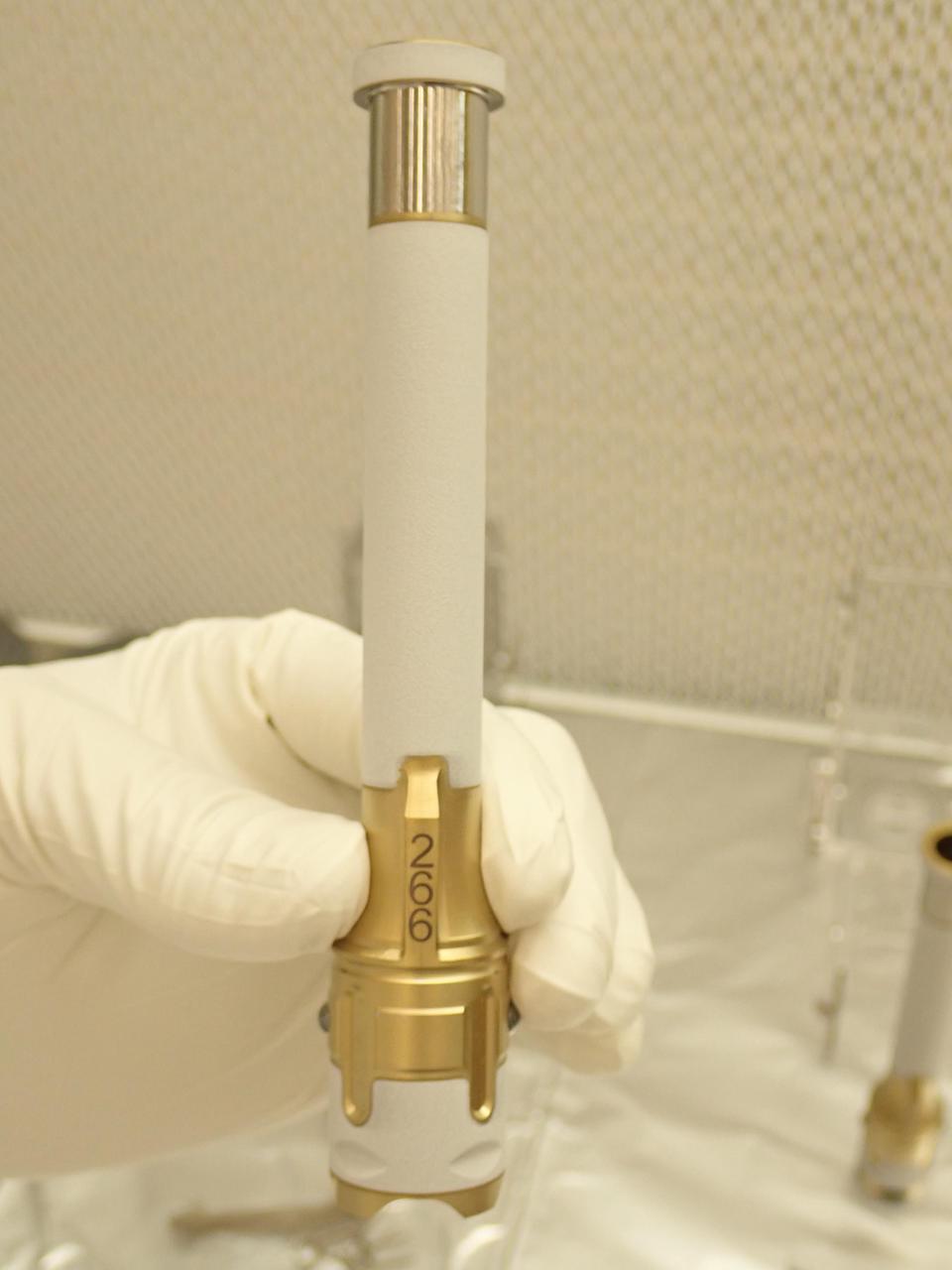

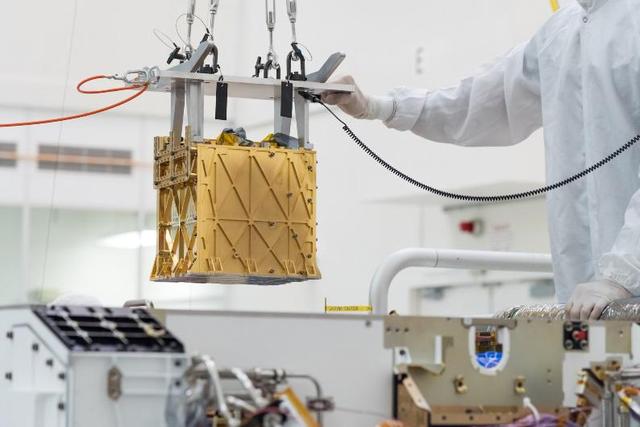
This image, taken in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, shows sample tube number 266, which was used to collect the first sample of Martian rock by NASA's Perseverance rover. The laser-etched serial number helps science team identify the tubes and their contents. Perseverance carries 43 sample tubes, 38 of which have been tasked to carry different samples from a variety of geologic units and surface materials. The other five are "witness tubes" that (prior to launch) were loaded with materials geared to capture molecular and particulate contaminants. They'll be opened one at a time on Mars to witness the ambient environment primarily near sample collection sites, so the science team can catalog any impurities that may have traveled with the tube from Earth or contaminants from the spacecraft that may be present during sample collection. Made chiefly of titanium, each sample tube for Perseverance weighs less than 2 ounces (57 grams) and is less than 6 inches long. . A white exterior coating guards against heating by the Sun potentially changing the chemical composition of the samples after Perseverance deposits the tubes on the surface of Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24808
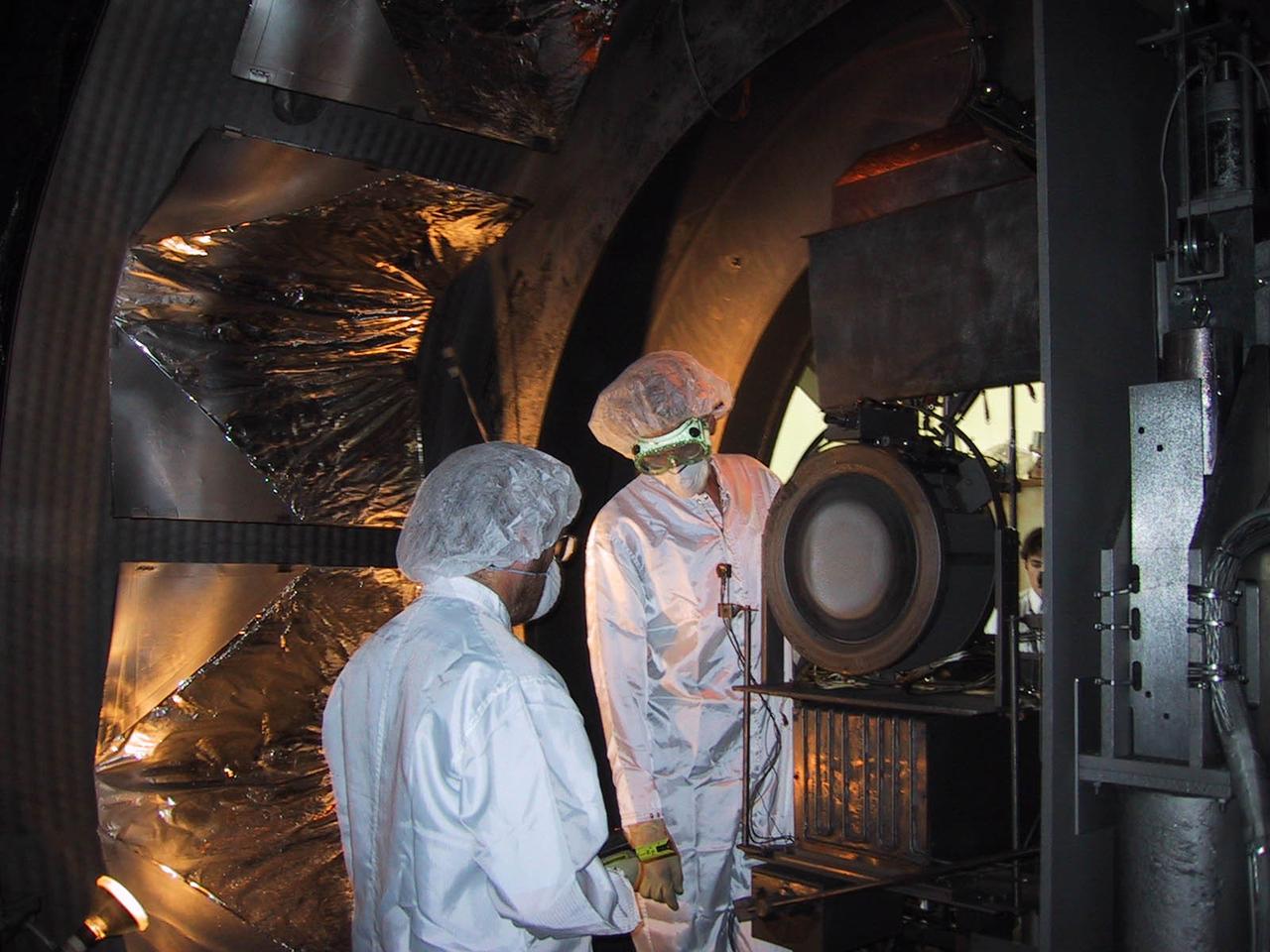

An ion thruster is removed from a vacuum chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The thruster, a spare engine from NASA's Deep Space 1 mission, with a designed life of 8,000 hours, ran for a record 30,352 hours (nearly 5 years) giving researchers the ability to observe its performance and wear at different power levels throughout the test. This information will be vital to future missions that use ion propulsion. Ion propulsion systems can be very lightweight, rurning on just a few grams of xenon gas a day. Xenon is the same gas that is found in photo flash bulbs. This fuel efficiency can lower launch vehicle costs. The successful Deep Space 1 mission featured the first use of an ion engine as the primary means of propulsion on a NASA spacecraft. NASA's next-generation ion propulsion efforts are implemented by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The program seeks to develop advanced propulsion technologies that will significantly reduce cost, mass, or travel times.