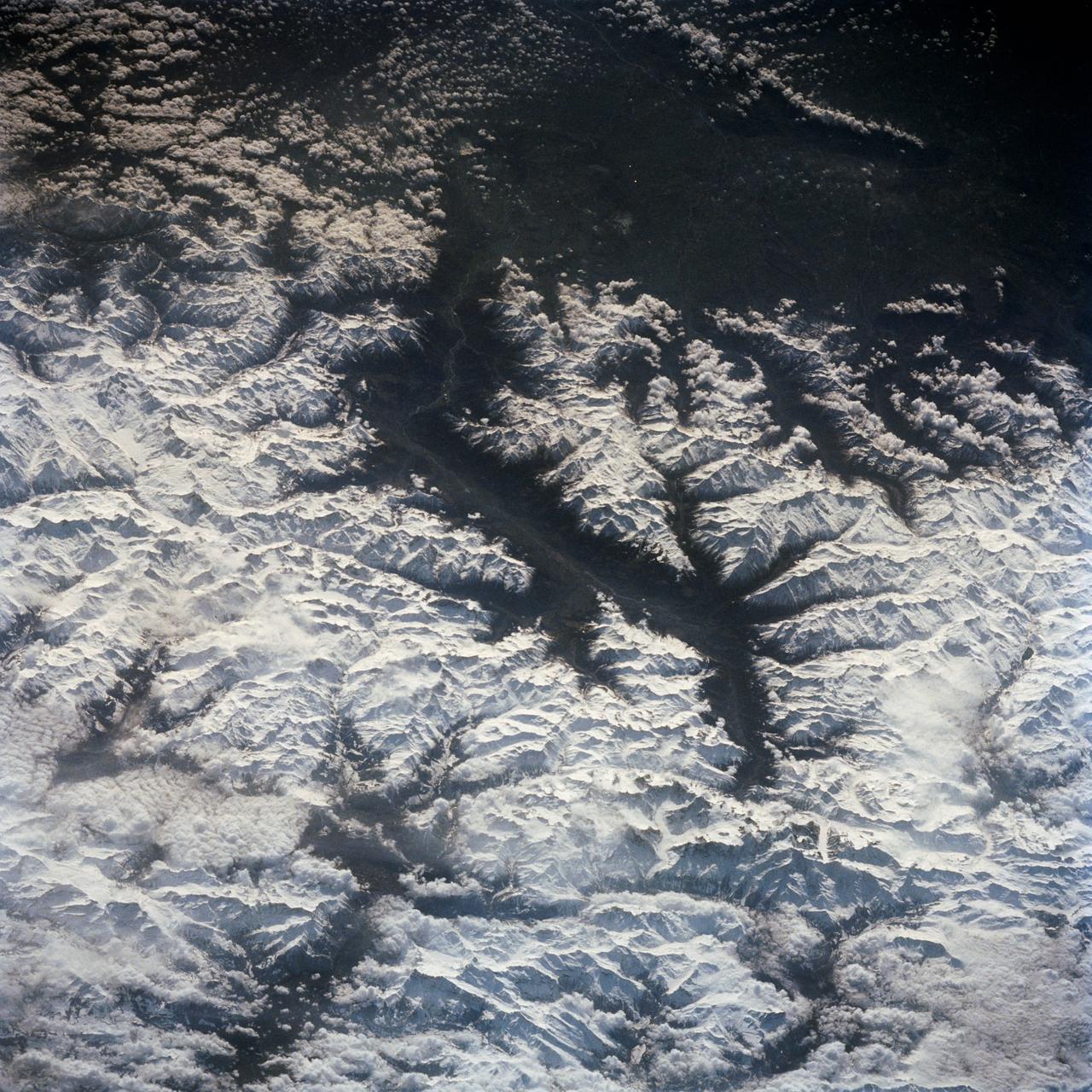

In this southeast looking view, Mont Blanc, on the French/Italian border, (48.0N, 4.5E) the highest mountain peak in all of Europe, is just below and right of center (below the end of the prominent valley of the Aosta River, in the center of the photo. The rivers flow out of the Alps into Italy toward Turin. Chamonix, the famous resort town and center of Alpine mountain climbing, lies in the valley just below Mont Blanc.
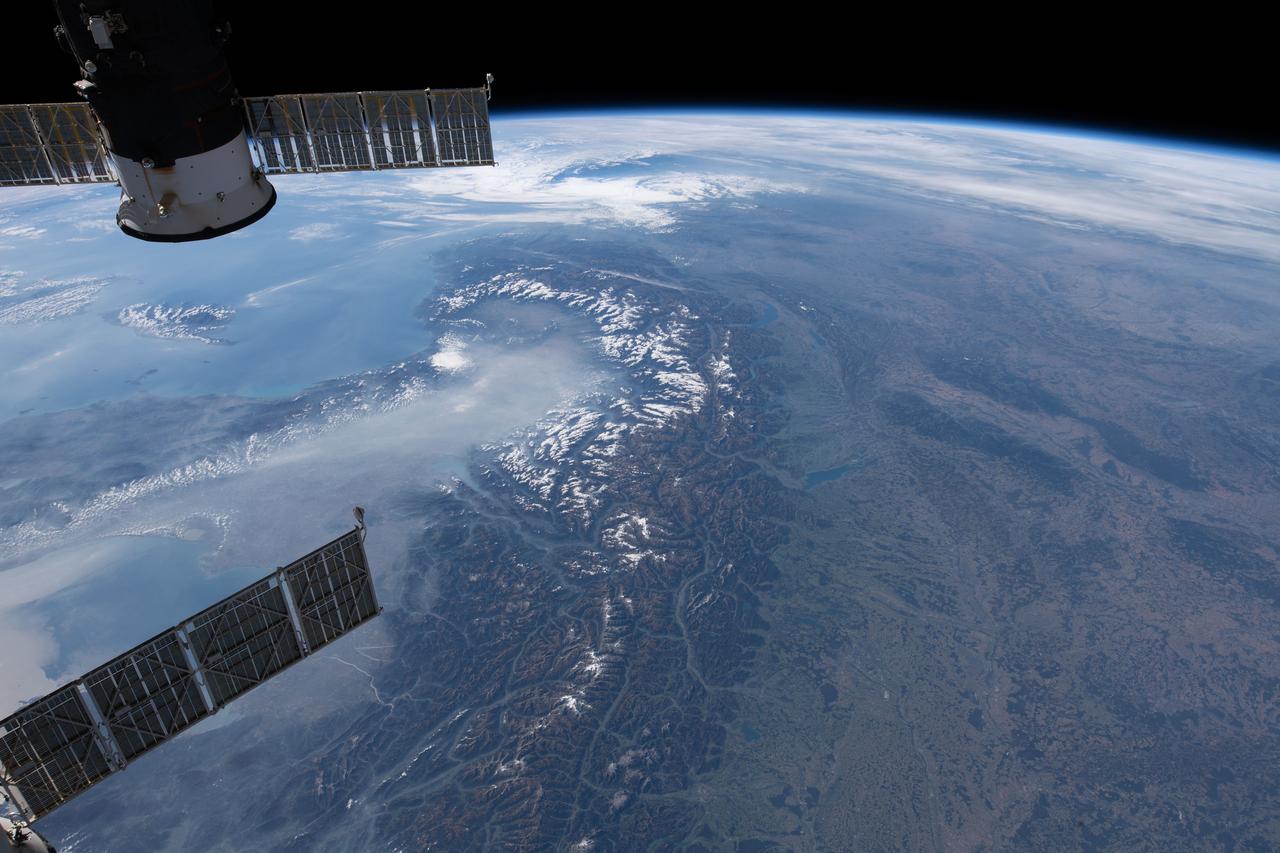

iss057e051220 (Oct. 13, 2018) --- The International Space Station was orbiting 256 miles above central Europe when this photograph was taken of the Swiss Alps mountain range and the Mediterranean coasts of Italy and France.
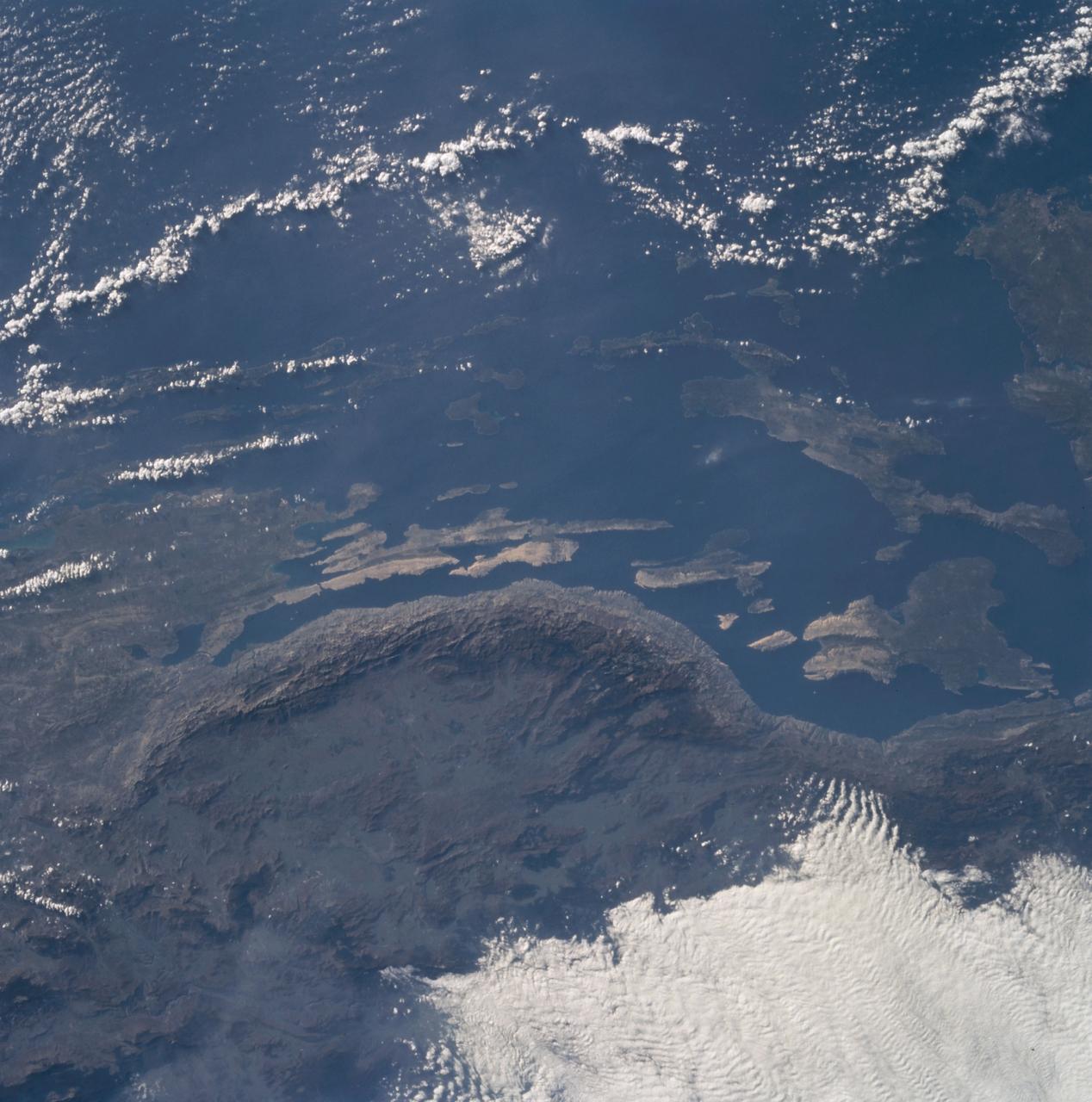

The Adriatic coast of Bosnia-Herzegovina and Croatia is centered at approximately 44.5 degrees north and 15.0 degrees east. North is at the bottom of the frame. The town of Bihac is located under the cloud layer in the center left of the frame. The terrain is composed of limestone and the geomorphic term "karst" is named after the city in the area. The Velebit Mountains form the ruggedd coast in the center of the frame.
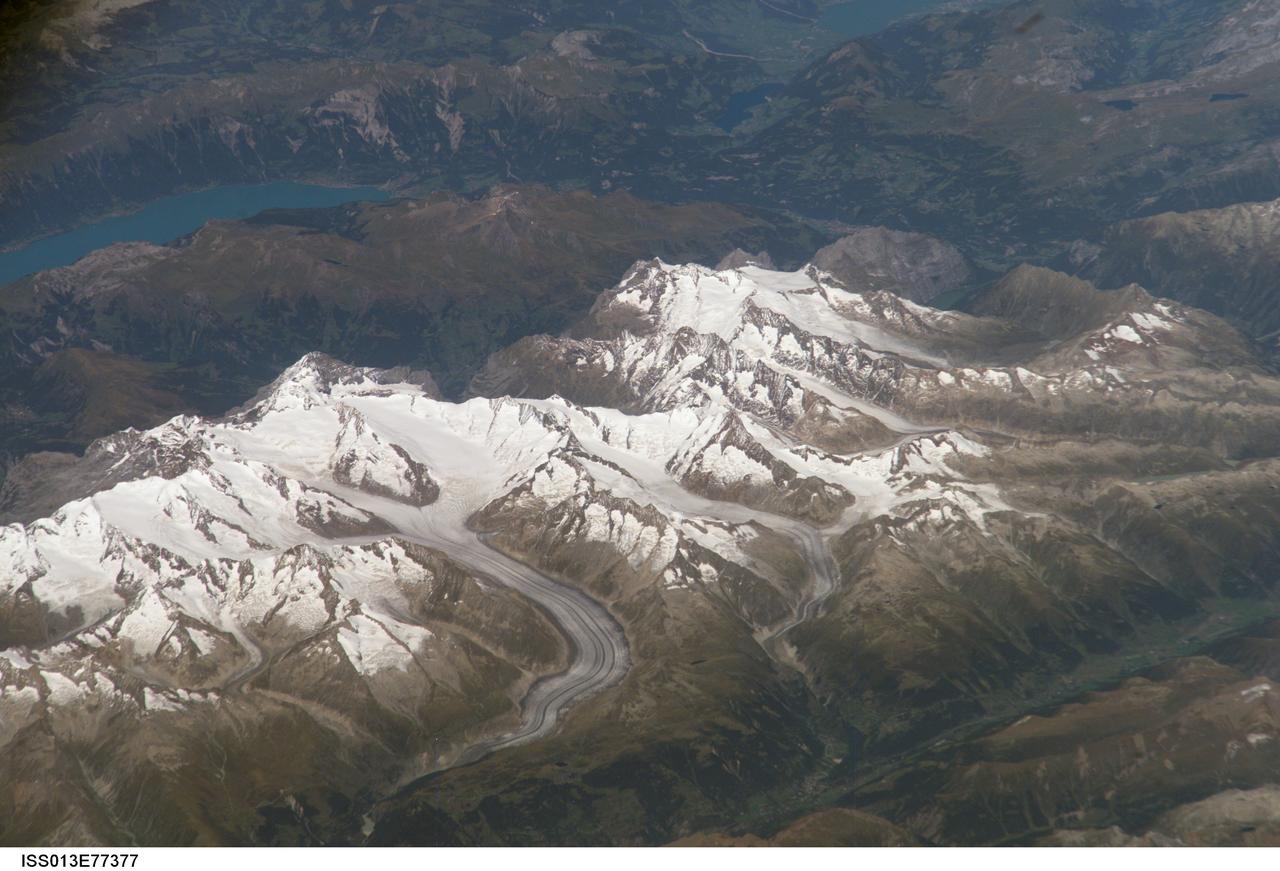

ISS013-E-77377 (5 Sept. 2006) --- Bernese Alps, Switzerland is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember onboard the International Space Station. The formidable mountain system of the Alps stretches across much of central Europe, with seven countries claiming portions of the mountains within their borders (Germany, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Austria, and Slovenia). The glacial landscape of the Bernese Alps, located in southwestern Switzerland, is well illustrated by this view. The image was taken by a crewmember looking north-northwest while the station was located over the Mediterranean Sea between Corsica and Italy -- this oblique viewing angle imparts a sense of perspective to the image. This type of viewing angle complements more nadir (downward)--viewing imagery of the region. Three of the higher peaks of the central Alps are visible--Jungfrau (4,158 meters), Moench (4,089 meters), and Eiger (3,970 meters). To the east and south of the Jungfrau is the Aletsch Glacier, clearly marked by dark medial moraines extending along the glacier's length parallel to the valley axis. The moraines are formed from rock and soil debris collected along the sides of three mountain glaciers located near the Jungfrau and Moench peaks -- as these flowing ice masses merge to form the Aletsch Glacier, the debris accumulates in the middle of the glacier and is carried along the flow direction. According to geologists, Lake Brienz to the northwest was formed by the actions of both glacial ice and the flowing waters of the Aare and Lutschine rivers, and has a maximum depth of 261 meters. The lake has a particularly fragile ecosystem, as demonstrated by the almost total collapse of the whitefish population in 1999. Possible causes for the collapse, according to the scientists, include increased water turbidity associated with upstream hydropower plant operations, and reduction of phosphorus (a key nutrient for lake algae, a basic element of the local food web) due to water quality concerns.

ISS012-E-11144 (11 Dec. 2005) --- Sierra Nevada, Spain is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 12 crew member on the International Space Station. According to scientists, the Sierra Nevada, part of the Betic Cordillera of southern Spain, was formed during the Alpine Orogeny (or mountain-building event) that also formed the European Alps to the east and the Atlas Mountains of northern Africa across the Mediterranean Sea to the south. The Sierra as observed today formed during the Tertiary Period (65 to 1.8 million years ago) during collision of the African and Eurasian continental plates. The former Tethys Sea also closed during this time period, the scientists say, and the Mediterranean Sea is the largest surviving remnant basin of the ancient Tethys. The Sierra Nevada in the Granada province of Spain is perhaps the southernmost skiing location in all of Europe. Veleta Peak, at an elevation of 3,398 meters above sea level, is a popular destination for skiers and snowboarders. The rapid transition from lofty ski runs to Mediterranean beaches within a few hours’ drive has made the Sierra Nevada region popular for both outdoor and urban tourism. This photograph depicts the Veleta Peak region of the range and illustrates the sharp contrast between the snow capped mountains, adjacent dry lowlands to the west and north, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south.
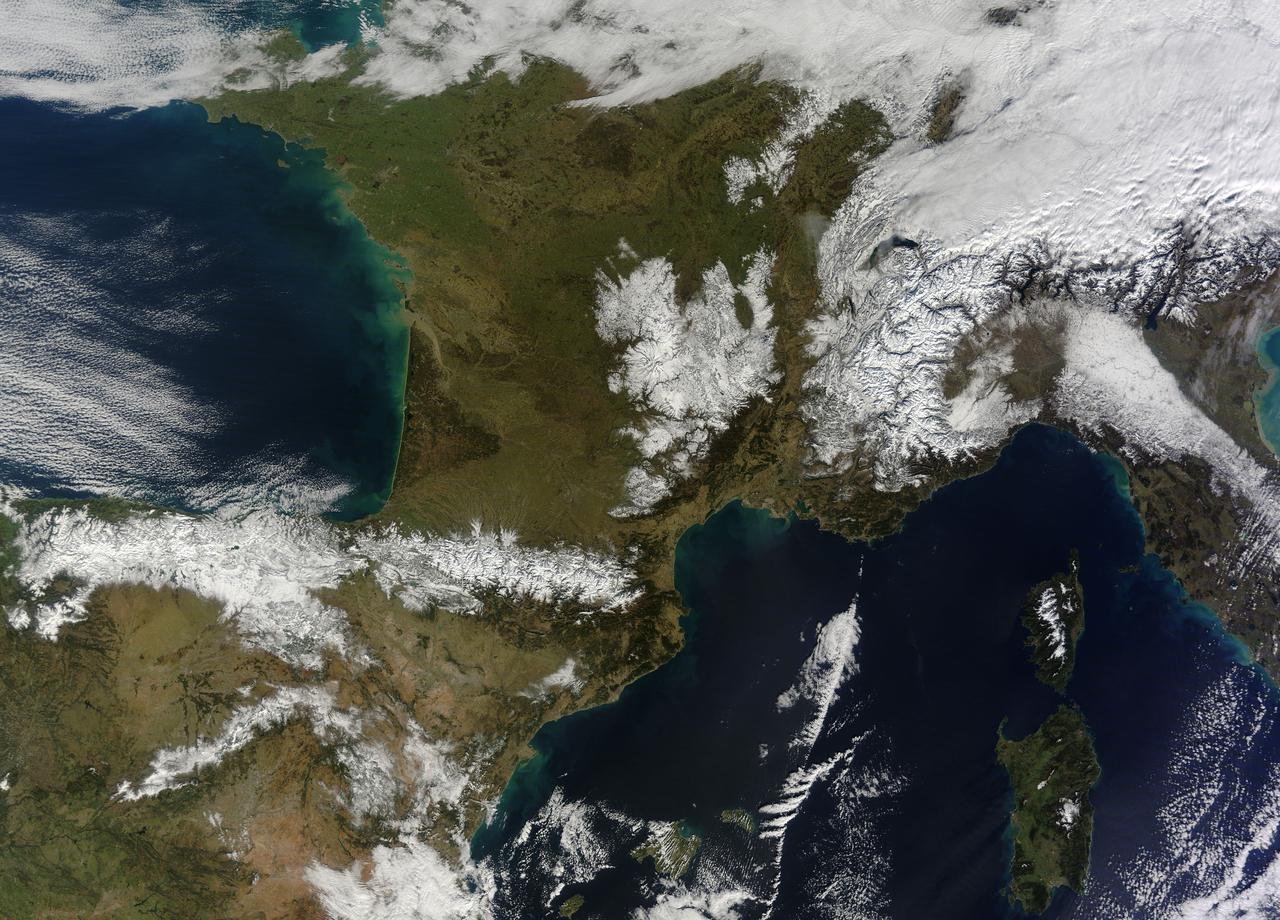

In February 2015, New England was not alone in dealing with the wrath of Old Man Winter. Thick snow blanketed mountain ranges in southwestern Europe after a winter storm pushed through the region in early February. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this true-color image of the snow-covered peaks of the Cantabrian Mountains, the Pyrenees, the Alps, and Massif Central on February 9, 2015. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
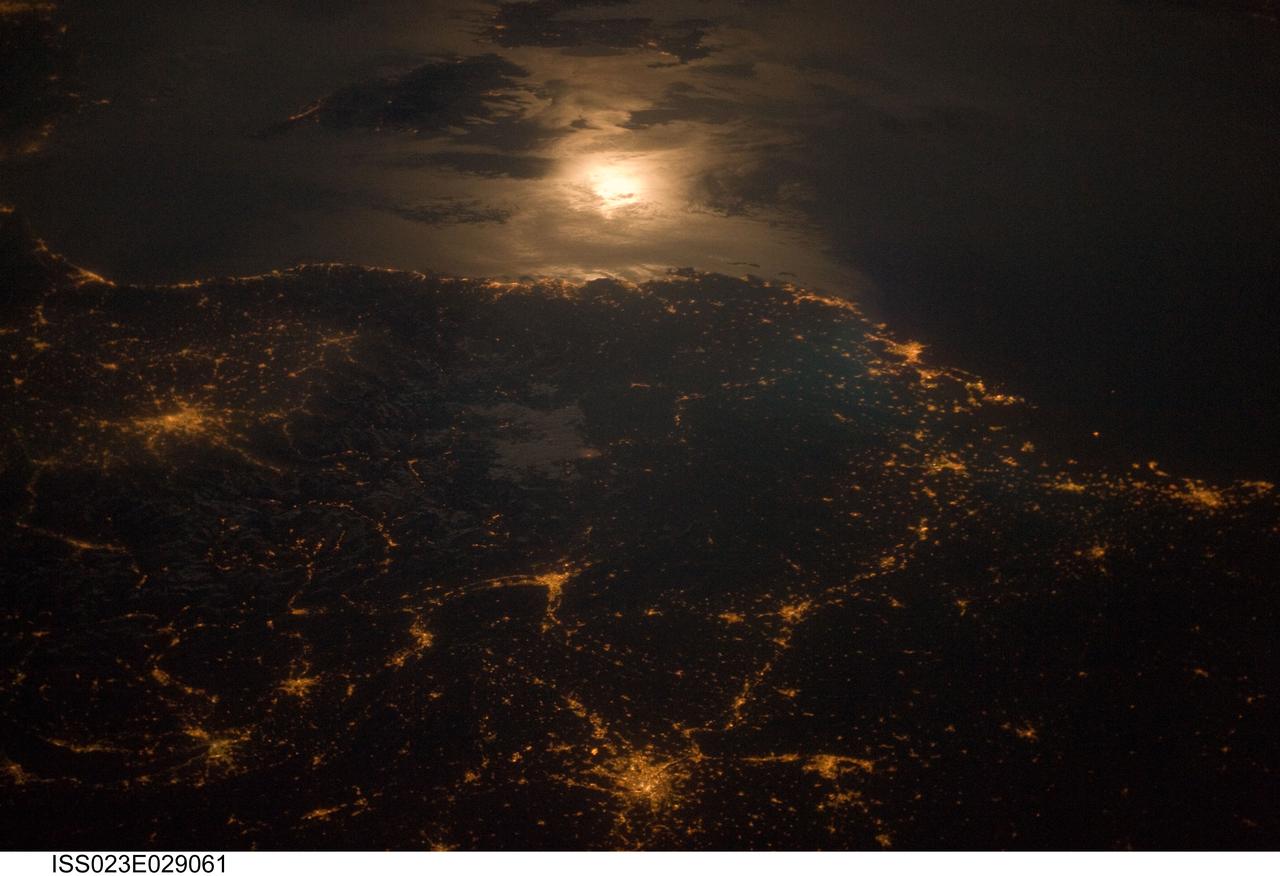

ISS023-E-029061 (28 April 2010) --- City lights at night along the France-Italy border, Europe are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 23 crew member on the International Space Station (ISS). The brightly lit metropolitan areas of Torino (Italy), Lyon, and Marseille (both in France) stand out amidst numerous smaller urban areas in this dramatic photograph. The image captures the night time appearance of the France-Italy border area between the mountainous Alps to the north (not shown) and the island of Corsica in the Ligurian Sea to the south (top). The full moon reflects brightly on the water surface and also illuminates the tops of low patchy clouds over the border (center). This image was taken by an ISS crew member at approximately 11:55 p.m. local time when the station was located over the France-Belgium border near Luxembourg. Crew members orbiting Earth frequently collect images that include sunglint, or sunlight that reflects off a water surface at such an angle that it travels directly back towards the observer. Sunglint typically lends a mirror-like appearance to the water surface. During clear sky conditions reflected light from the moon can produce the same effect (moon glint) as illustrated in this view. The observer was looking towards the southeast at an oblique viewing angle at the time the image was taken; in other words, looking outwards from the ISS, not straight down towards Earth.
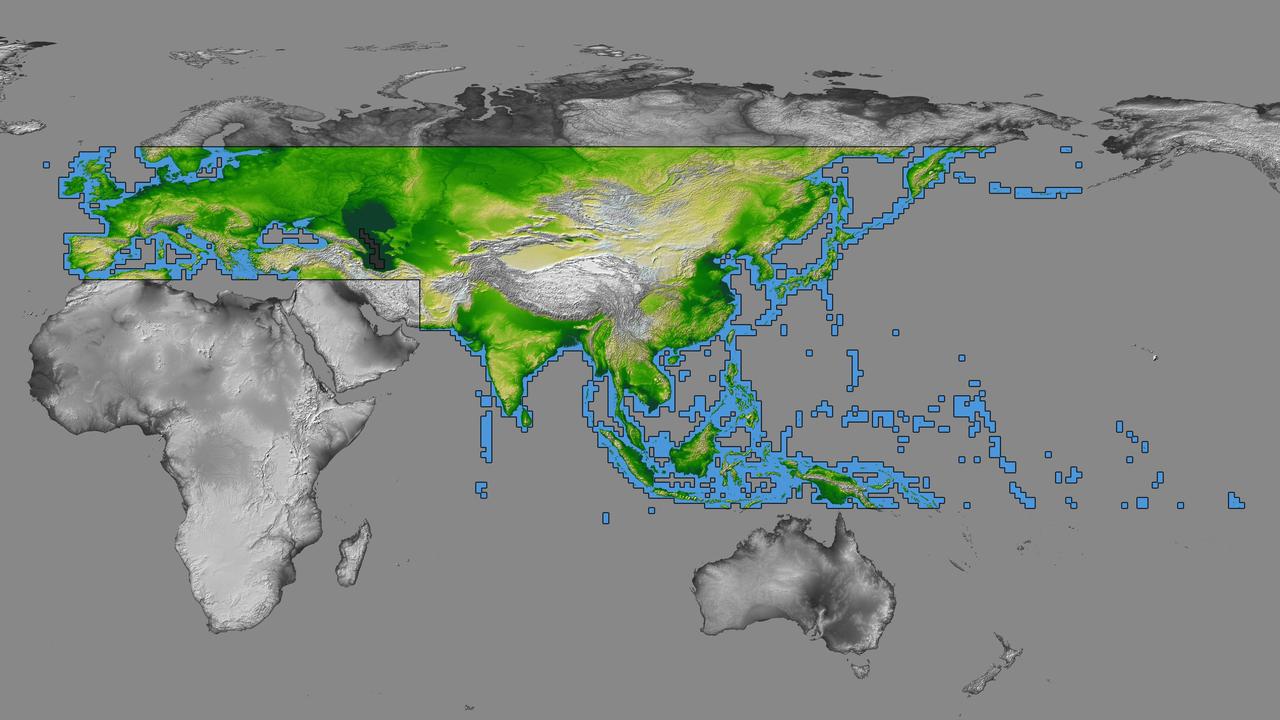
inal Caption Released with Image: The colored regions of this map show the extent of digital elevation data recently released by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). This release includes data for most of Europe and Asia plus numerous islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. SRTM flew on board the Space Shuttle Endeavour in February 2000 and used an interferometric radar system to map the topography of Earth's landmass between latitudes 56 degrees south and 60 degrees north. The data were processed into geographic "tiles," each of which represents one by one degree of latitude and longitude. A degree of latitude measures 111 kilometers (69 miles) north-south, and a degree of longitude measures 111 kilometers or less east-west, decreasing away from the equator. The data are being released to the public on a continent-by-continent basis. This Eurasia segment includes 5,940 tiles, more than a third of the total data set. Previous releases covered North America and South America. Forthcoming releases will include Africa-Arabia and Australia plus an "Islands" release for those islands not included in the continental releases. Together these data releases constitute the world's first high-resolution, near-global elevation model. The resolution of the publicly released data is three arcseconds (1/1,200 of a degree of latitude and longitude), which is about 90 meters (295 feet). European coverage in the current data release stretches eastward from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west, across the Alps and Carpathian Mountains, as well as the Northern European Plain, to the Ural and Caucasus Mountains bordering Asia. The Asian coverage includes a great diversity of landforms, including the Tibetan Plateau, Tarin Basin, Mongolian Plateau, and the mountains surrounding Lake Baikal, the world's deepest lake. Mt. Everest in the Himalayas, at 8,848 meters (29,029 feet) is the world's highest mountain. From India's Deccan Plateau, to Southeast Asia, coastal China, and Korea, various landforms place constraints upon land use planning for a great population. Volcanoes in the East Indies, the Philippines, Japan, and the Kamchatka Peninsula form the western part of the "Ring of Fire" around the Pacific Ocean. Many of these regions were previously very poorly mapped due to persistent cloud cover or the inaccessibility of the terrain. Digital elevation data, such as provided by SRTM, are particularly in high demand by scientists studying earthquakes, volcanism, and erosion patterns for use in mapping and modeling hazards to human habitation. But the shape of Earth's surface affects nearly every natural process and human endeavor that occurs there, so elevation data are used in a wide range of applications. In this index map color-coding is directly related to topographic height, with green at the lower elevations, rising through yellow and tan, to white at the highest elevations. The large, very dark green feature in western Asia is the Caspian Sea, which is below sea level. Blue areas on the map represent water within the mapped tiles, each of which includes shorelines or islands. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03398
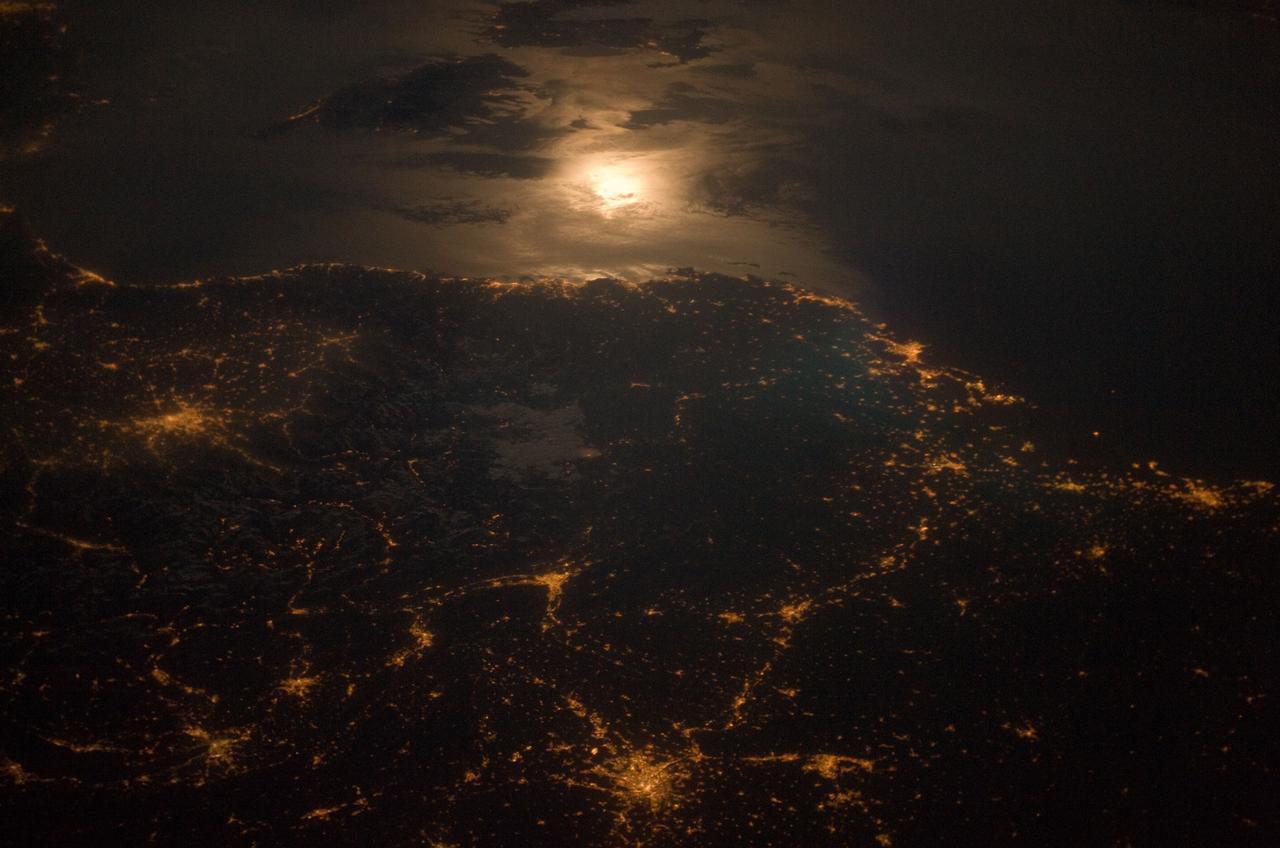

City lights at night along the France-Italy border, Europe are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 23 crew member on the International Space Station (ISS). The brightly lit metropolitan areas of Torino (Italy), Lyon, and Marseille (both in France) stand out amidst numerous smaller urban areas in this dramatic photograph. The image captures the night time appearance of the France-Italy border area between the mountainous Alps to the north (not shown) and the island of Corsica in the Ligurian Sea to the south (top). The full moon reflects brightly on the water surface and also illuminates the tops of low patchy clouds over the border (center). This image was taken by an ISS crew member at approximately 11:55 p.m. local time when the station was located over the France-Belgium border near Luxembourg. Crew members orbiting Earth frequently collect images that include sunglint, or sunlight that reflects off a water surface at such an angle that it travels directly back towards the observer. Sunglint typically lends a mirror-like appearance to the water surface. During clear sky conditions reflected light from the moon can produce the same effect (moon glint) as illustrated in this view. The observer was looking towards the southeast at an oblique viewing angle at the time the image was taken; in other words, looking outwards from the ISS, not straight down towards Earth. Credit: NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>