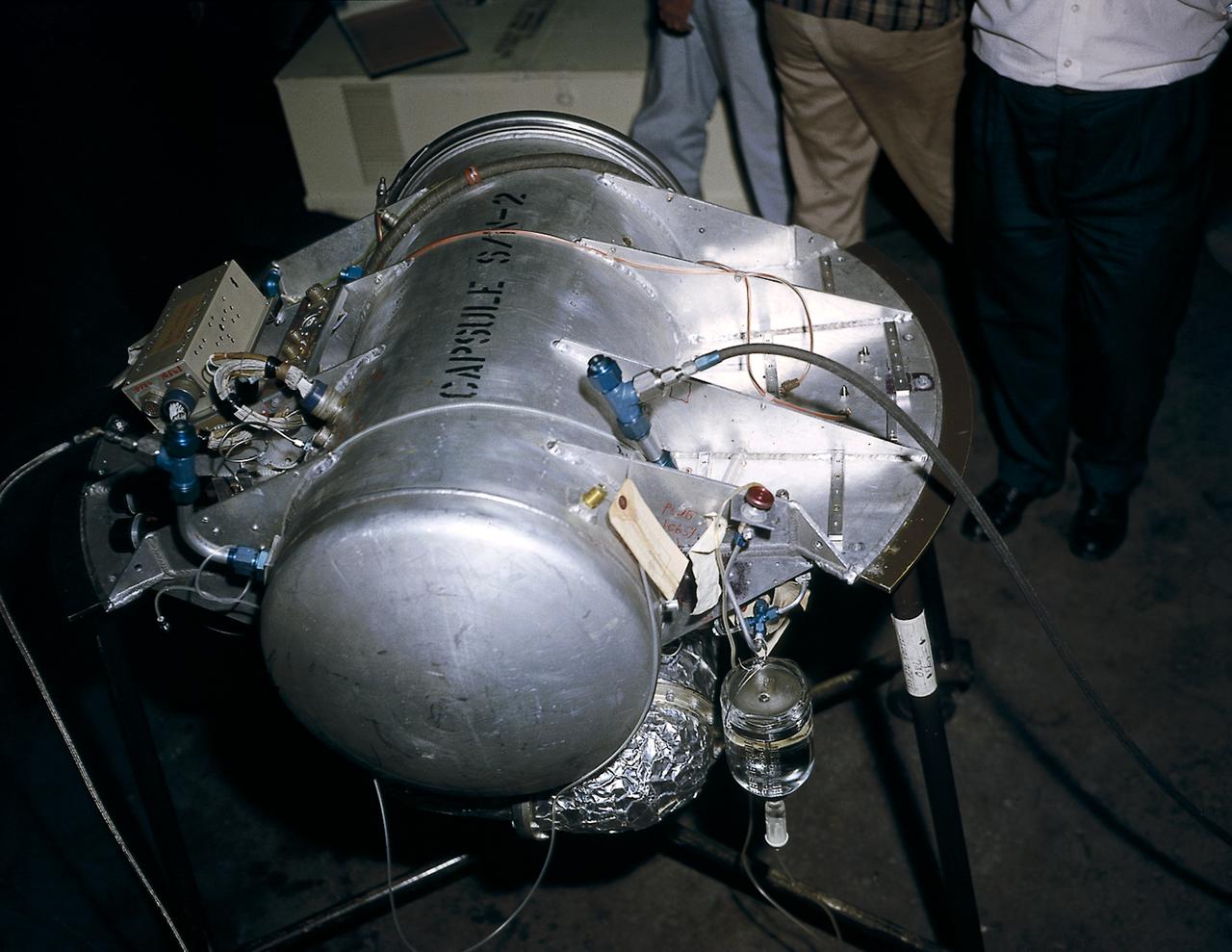
The capsule ready to be installed in the nose cone of Jupiter, AM-18, for pre-flight test, May 18, 1959. The capsule carried monkeys, Baker and Able, as the payload of AM-18 mission
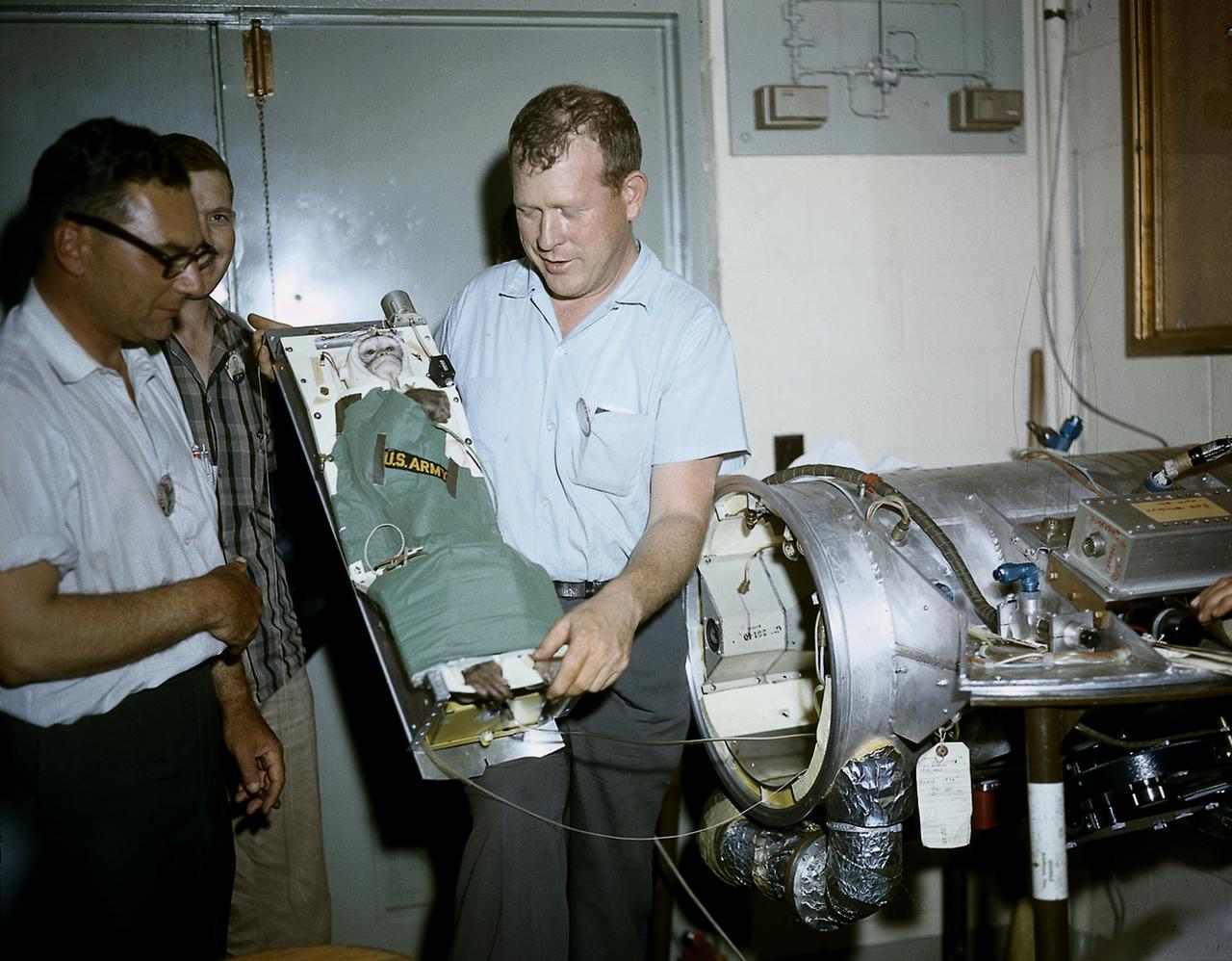

A squirrel monkey, Able, is being ready for placement into a capsule for a preflight test of Jupiter, AM-18 mission. AM-18 was launched on May 28, 1959 and also carried a rhesus monkey, Baker, into suborbit.
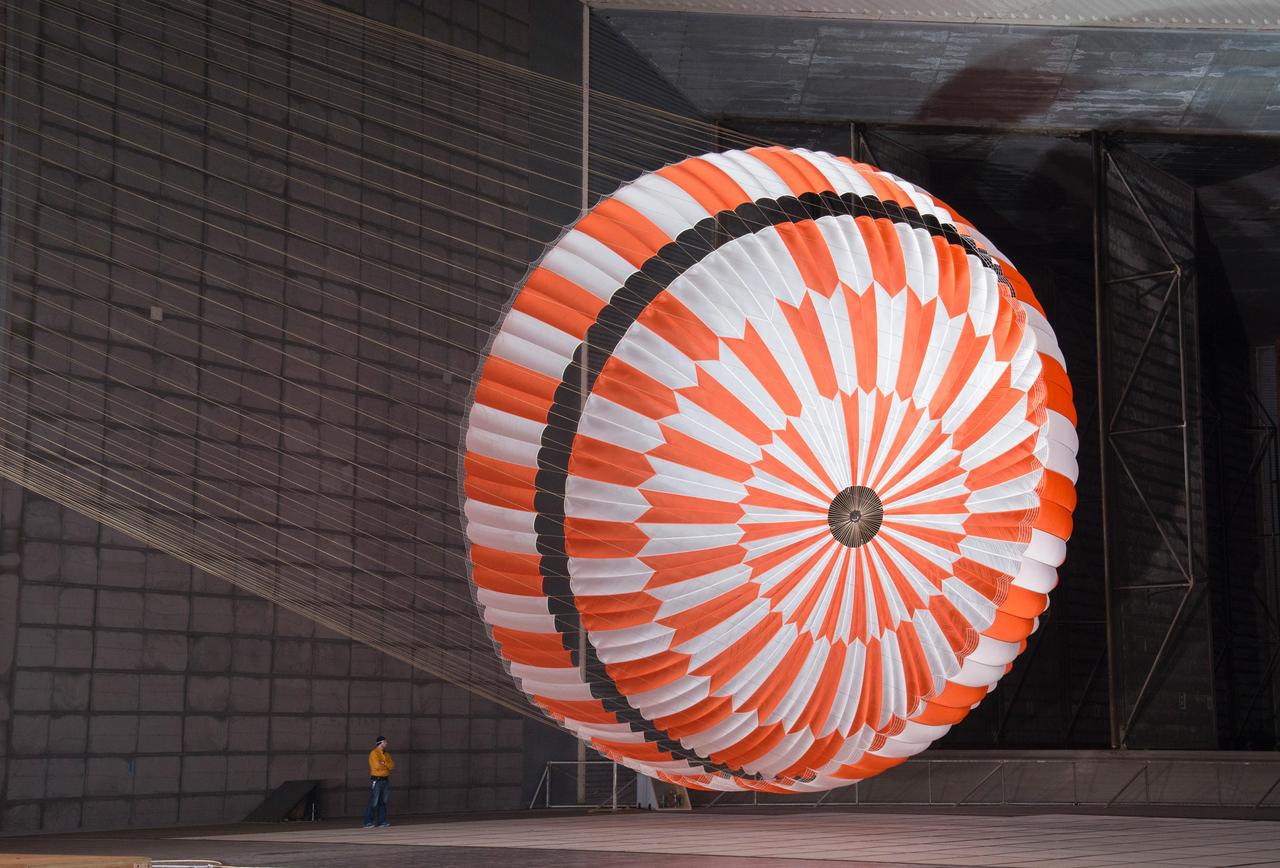

In this June 2017 photo, the supersonic parachute design that will land NASA's Perseverance rover on Mars on Feb. 18, 2021, undergoes testing in a wind tunnel at NASA's Ames Research Center in California's Silicon Valley. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23916
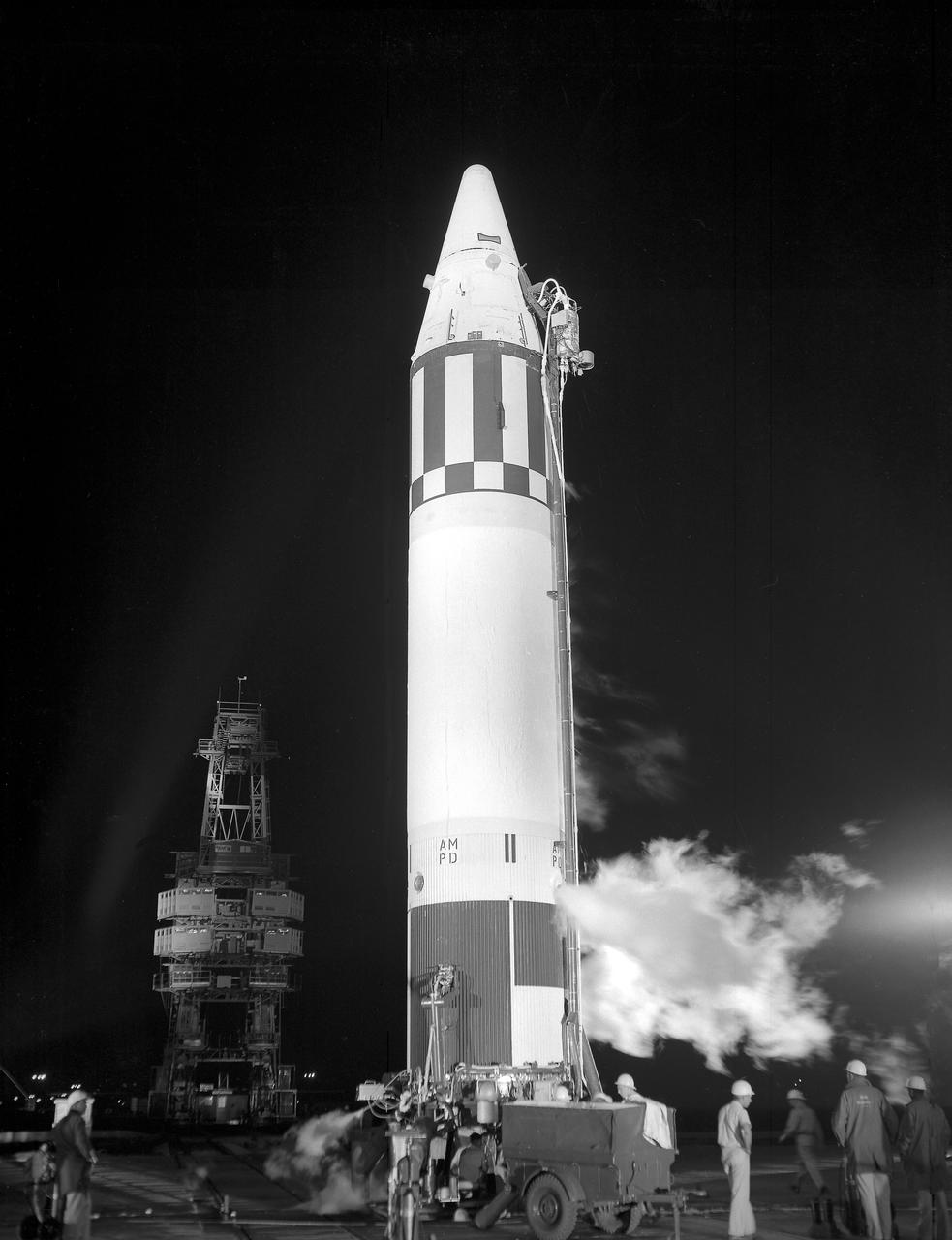

Jupiter (AM-18), suborbital primate flight with Able and Baker as its payload, being ready for launch, May 28, 1959
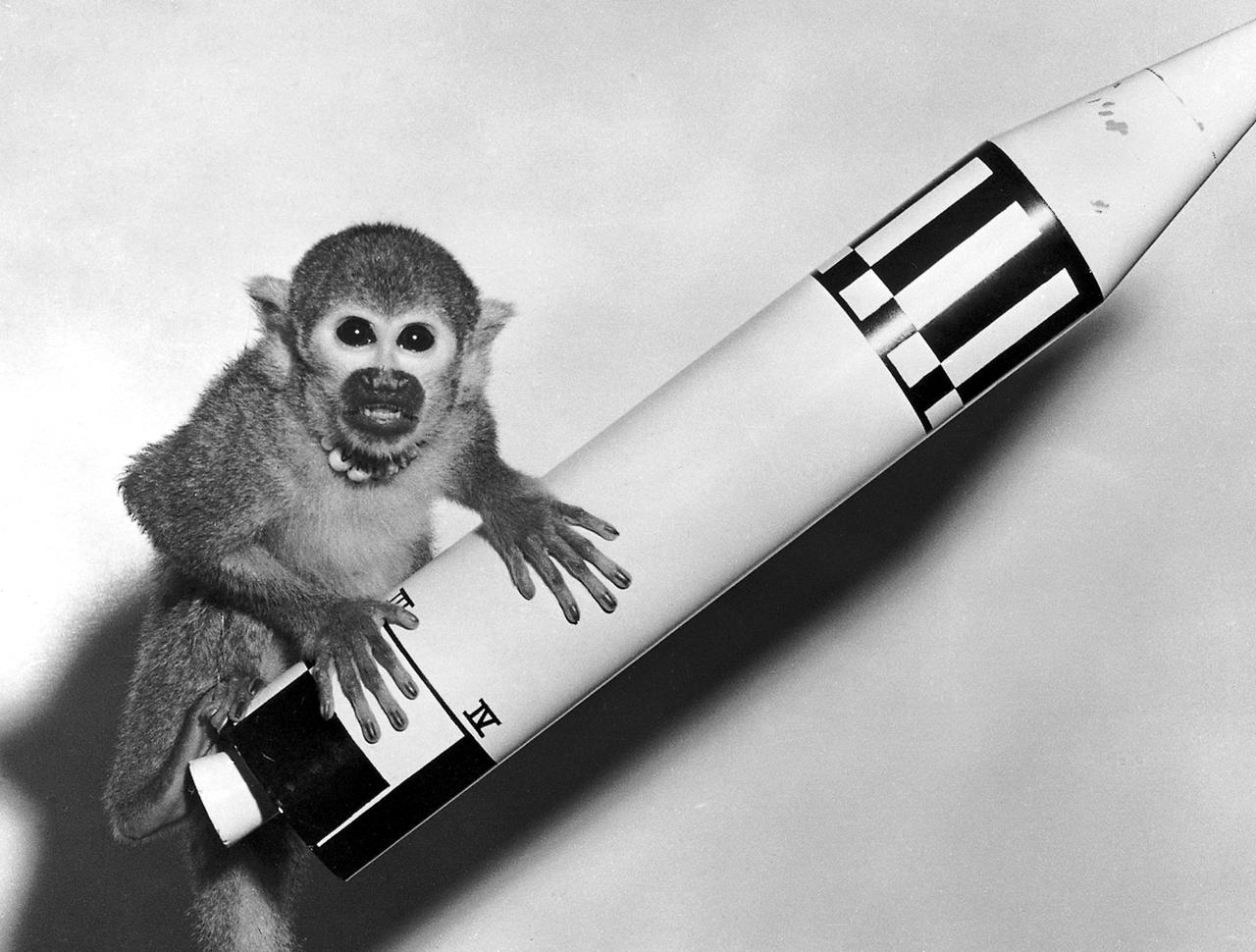

Monkey Baker, payload of Jupiter (AM-18), poses on a model of the Jupiter vehicle, May 29, 1959
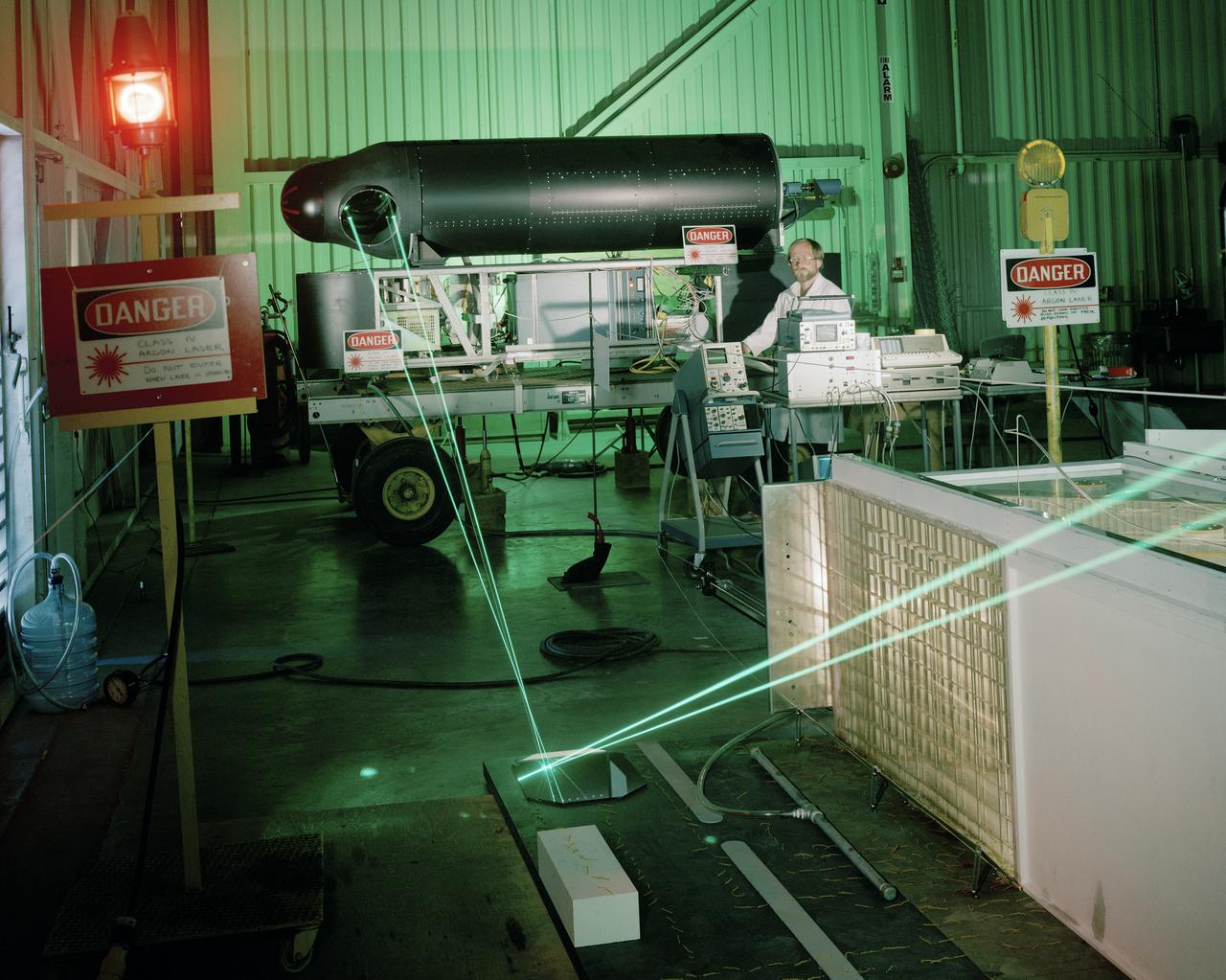
40x80x120 Foot Wind Tunnel at NASA's Ames Research Center Laser Velocimeter (LV) Long Range System. Requesting Organization: Low Speed Aircraft Photographed on May 18, 1983
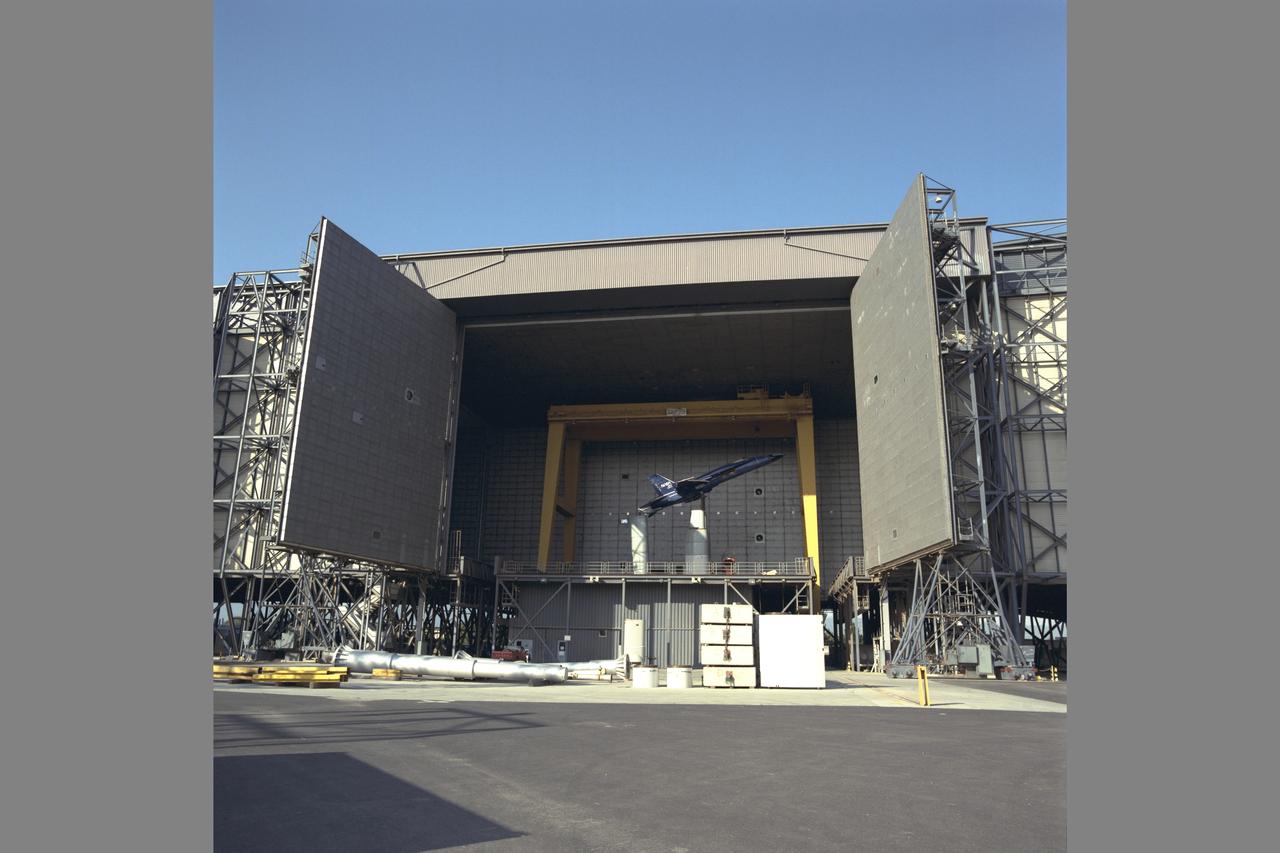

F-18 being installed in the NASA Ames Full-scale Aerodynamic Complex (NFAC) 80x120_foot wind tunnel test section for High Alpha Test-823 Phase II
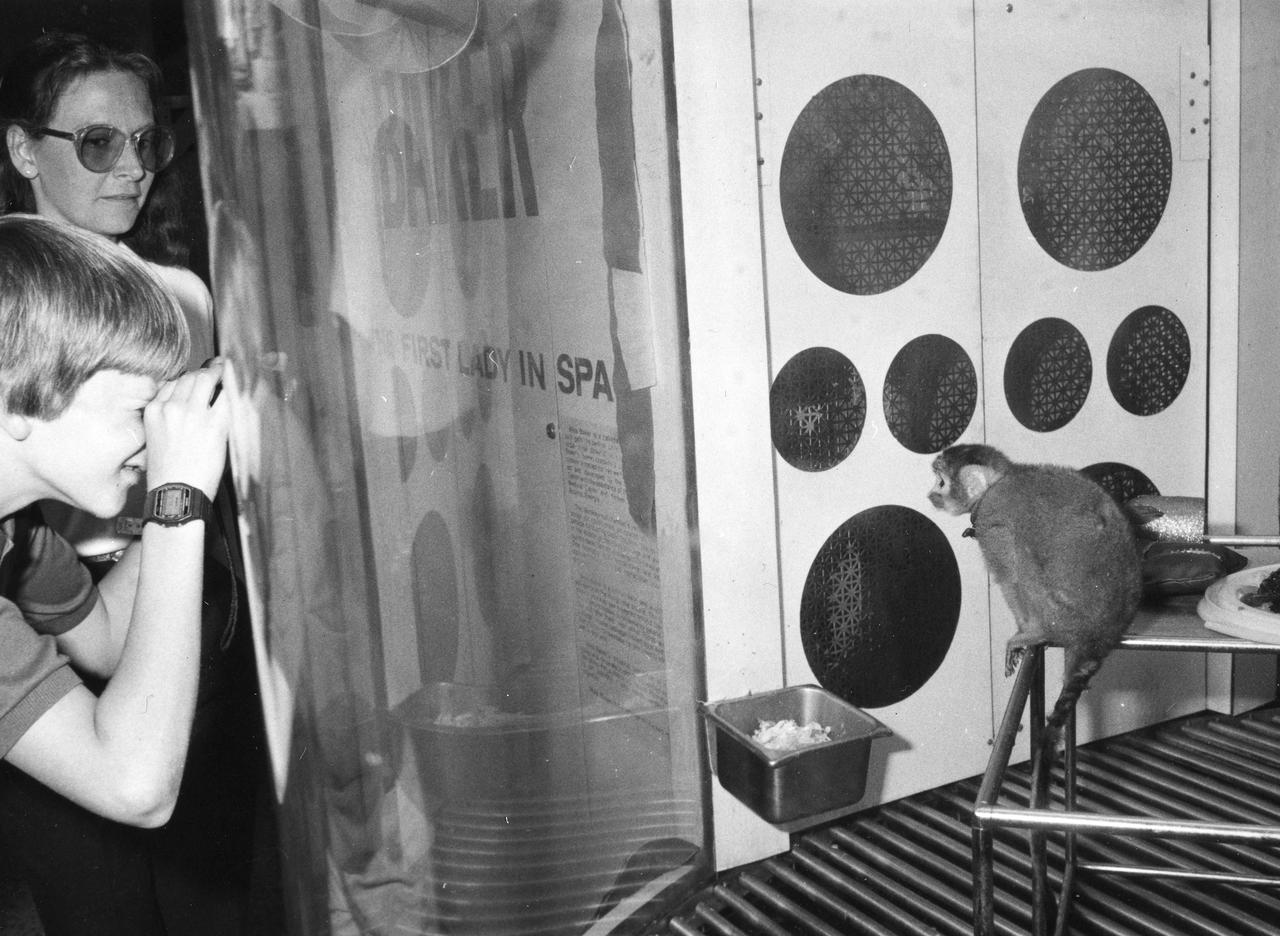

Miss Baker, a squirrel monkey who made a historical flight aboard the Jupiter (AM-18) in May 1959, is seen here in her viewing area where she resided at the U.S. Space and Rocket Center.
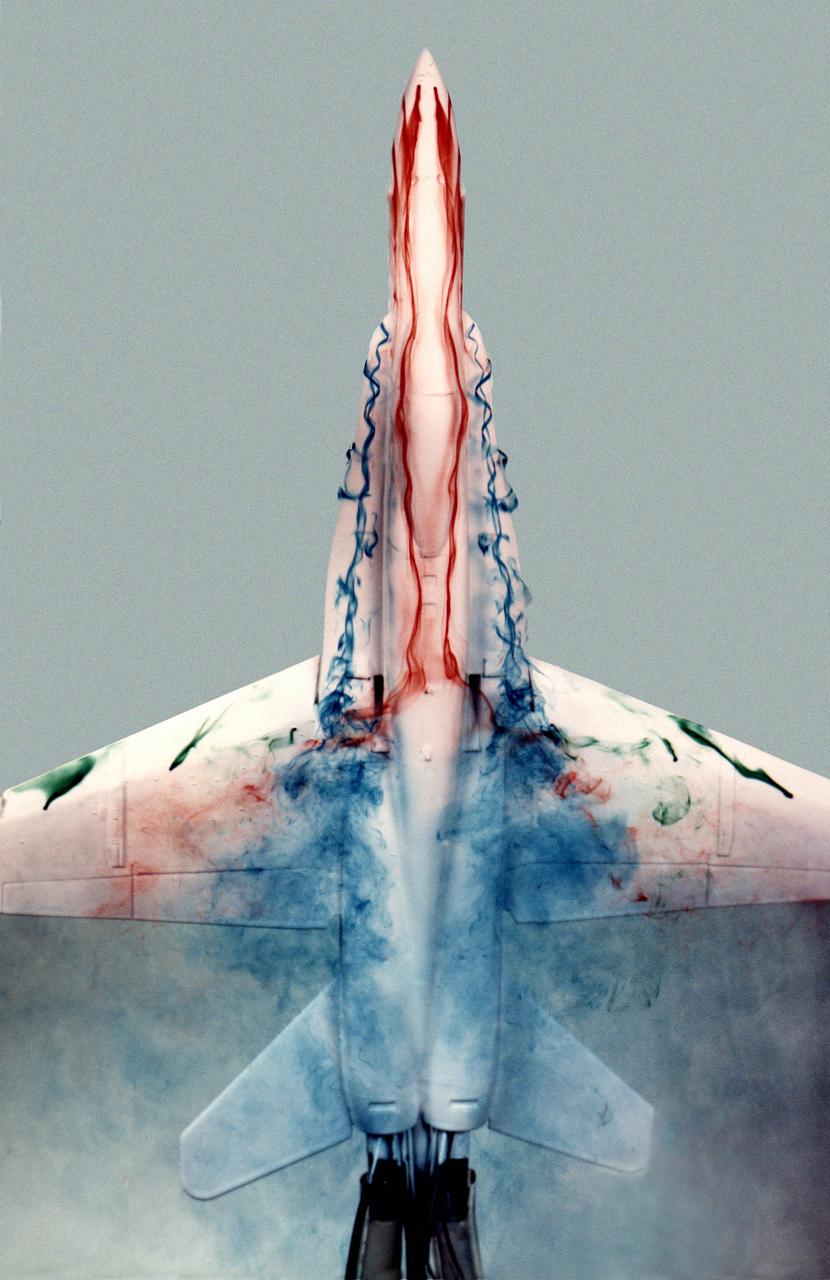
This image shows a plastic 1/48-scale model of an F-18 aircraft inside the "Water Tunnel" more formally known as the NASA Dryden Flow Visualization Facility. Water is pumped through the tunnel in the direction of normal airflow over the aircraft; then, colored dyes are pumped through tubes with needle valves. The dyes flow back along the airframe and over the airfoils highlighting their aerodynamic characteristics. The aircraft can also be moved through its pitch axis to observe airflow disruptions while simulating actual flight at high angles of attack. The Water Tunnel at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, CA, became operational in 1983 when Dryden was a Flight Research Facility under the management of the Ames Research Center in Mountain View, CA. As a medium for visualizing fluid flow, water has played a significant role. Its use dates back to Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519), the Renaissance Italian engineer, architect, painter, and sculptor. In more recent times, water tunnels have assisted the study of complex flows and flow-field interactions on aircraft shapes that generate strong vortex flows. Flow visualization in water tunnels assists in determining the strength of vortices, their location, and possible methods of controlling them. The design of the Dryden Water Tunnel imitated that of the Northrop Corporation's tunnel in Hawthorne, CA. Called the Flow Visualization Facility, the Dryden tunnel was built to assist researchers in understanding the aerodynamics of aircraft configured in such a way that they create strong vortex flows, particularly at high angles of attack. The tunnel provides results that compare well with data from aircraft in actual flight in another fluid-air. Other uses of the tunnel have included study of how such flight hardware as antennas, probes, pylons, parachutes, and experimental fixtures affect airflow. The facility has also been helpful in finding the best locations for emitting smoke from flight vehicles for flow vi

R4D-6 (Bu. No. 99827 NACA 18, NASA 701). TAKE-OFF MONITOR TEST, EDWARDS AIR FORCE BASE. Gunsight Tracking and Guidance and Control Displays. Note: Used in publication in Flight Research at Ames; 57 Years of Development and Validation of Aeronautical Technology NASA SP-1998-3300 fig 76

ISS027-E-032216 (18 May 2011) --- This close-up view of the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) in space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay was provided by an Expedition 27 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-134 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
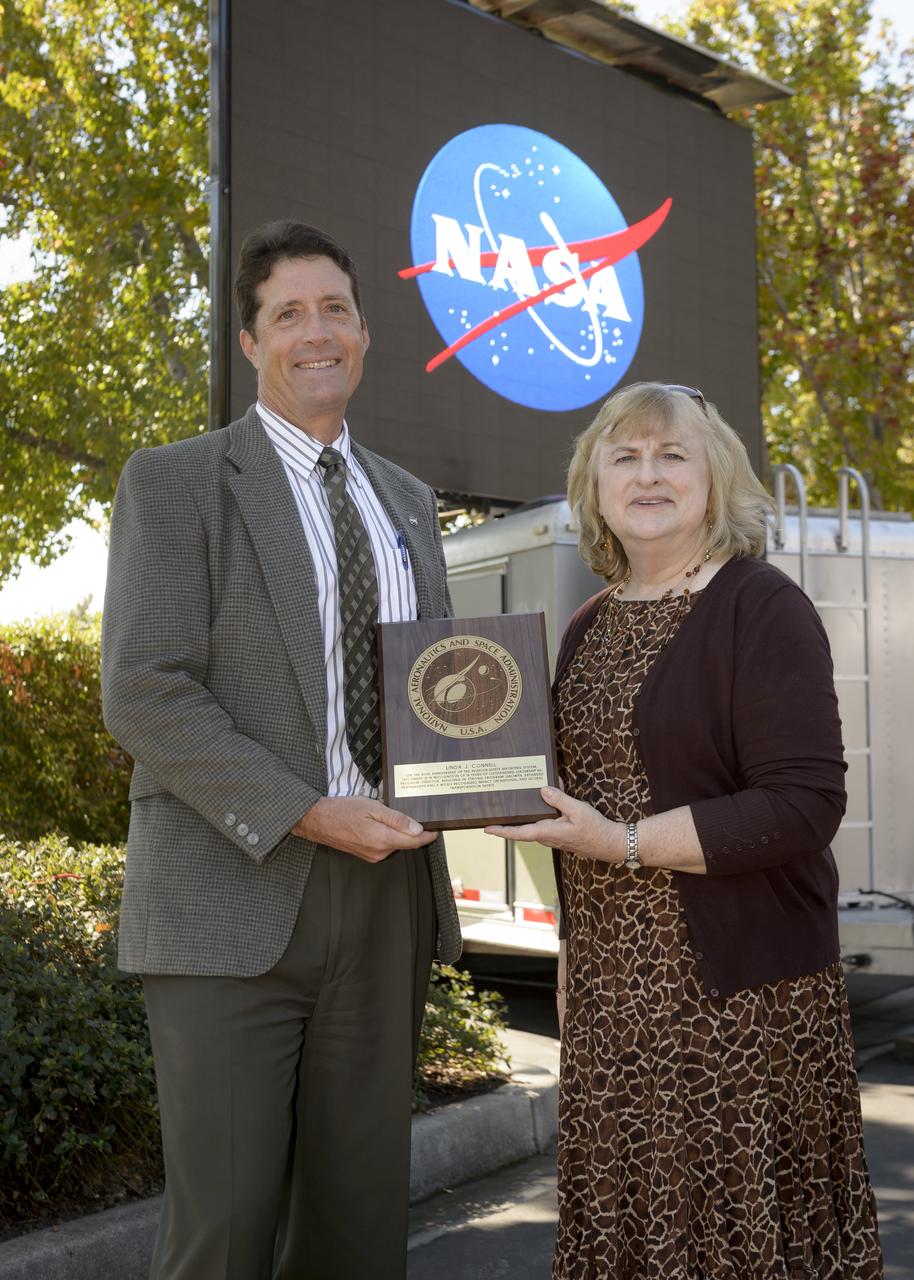

Avation Safety Reporting System (ASRS) 40th Anniversary lunch and open house at the Sunnyvale office. Thomas A Edwards, Deputy Center Director NASA Ames (Left), presents a plaque On the anniversary of the aviation safety reporting system, this award is in recognition of 18 years of outstanding leadership as Program Director, resulting in strong program growth, expanded partnership and a widely recognized impact on National and Global transportation safety. Presented to Linda J. Connell, ASRS Program Director (Right)
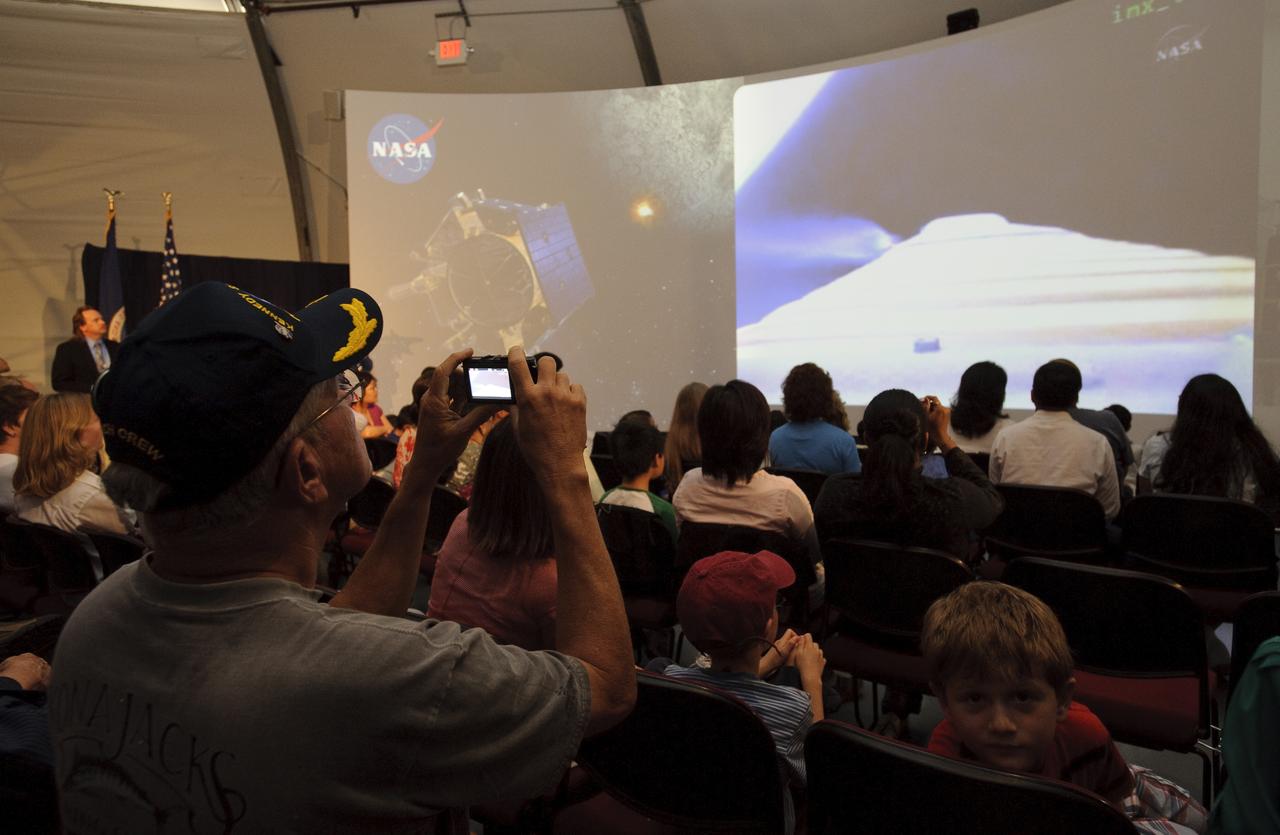

LCROSS launch public viewing event held at Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA NRP tenant Ecliptic Enterprises Corporation is playing a crucial role in the LCROSS (Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite) mission to search for the signature of water, a lunar resource that can be used for future human exploration, at the Moon’s rugged South Pole. Ecliptic’s signature product, RocketCam™, transmitted video from three camera perspectives of the picture-perfect launch from Cape Canaveral aboard an ATLAS V rocket on June 18. RocketCam™, a family of onboard imaging systems
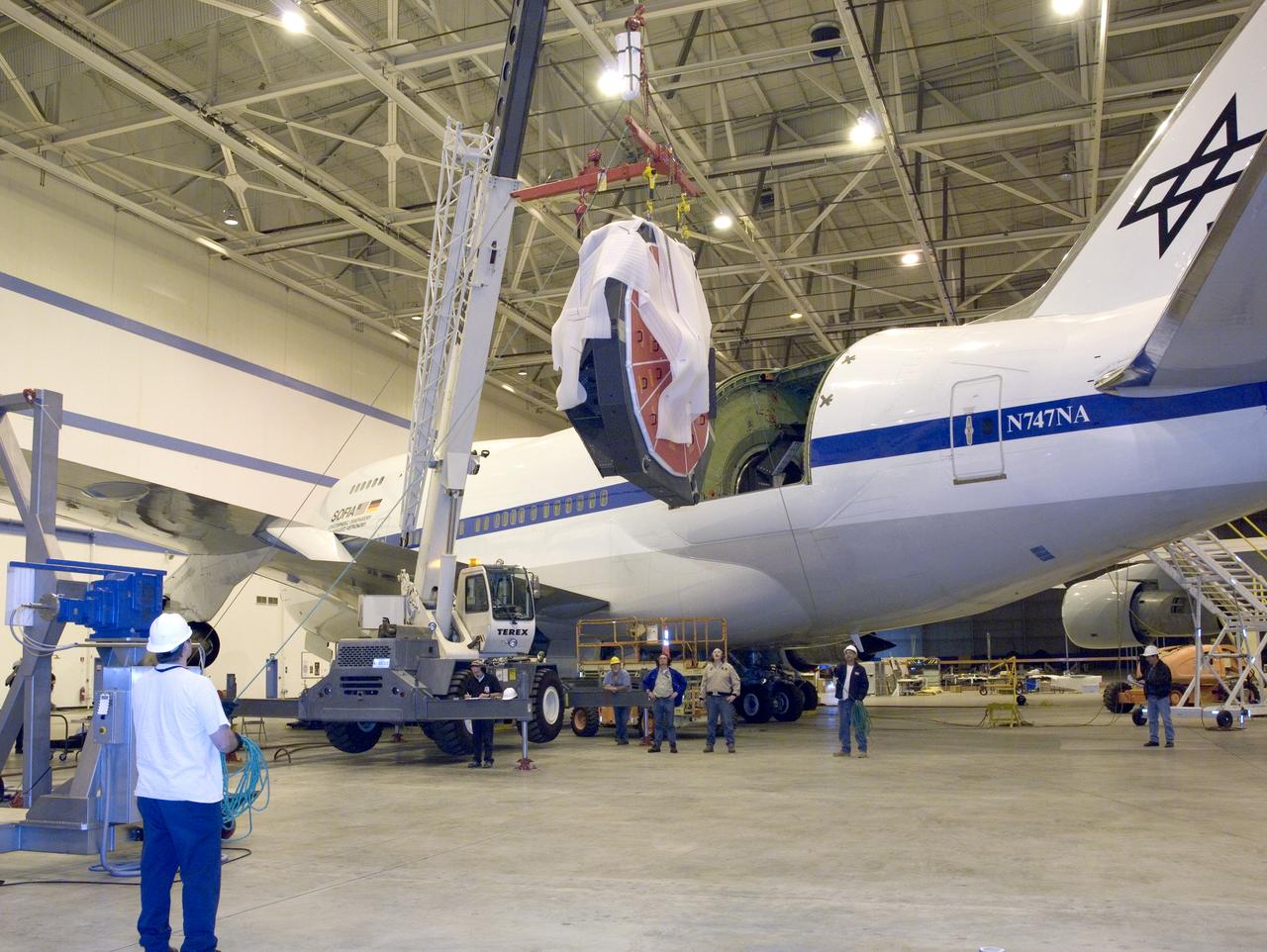

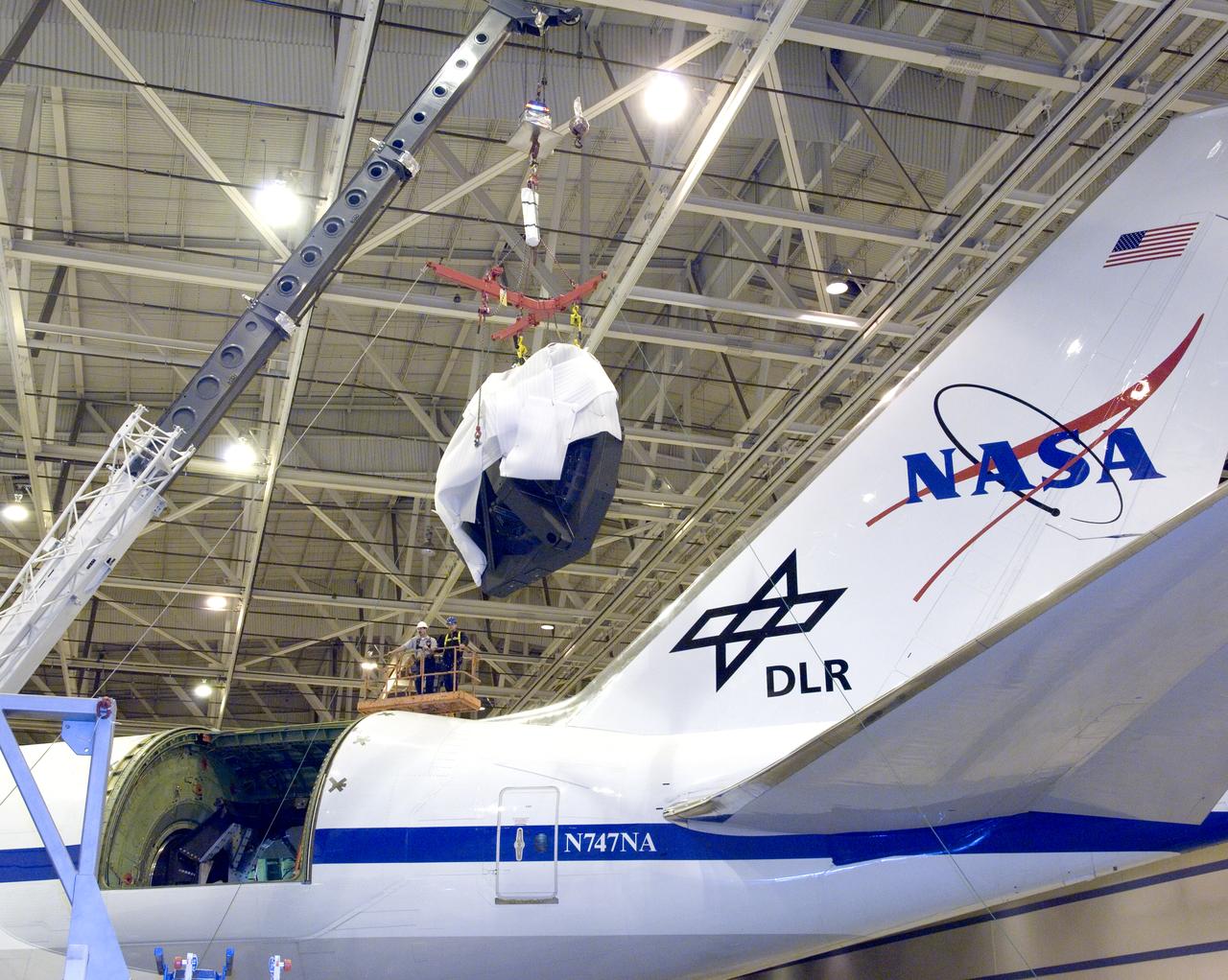
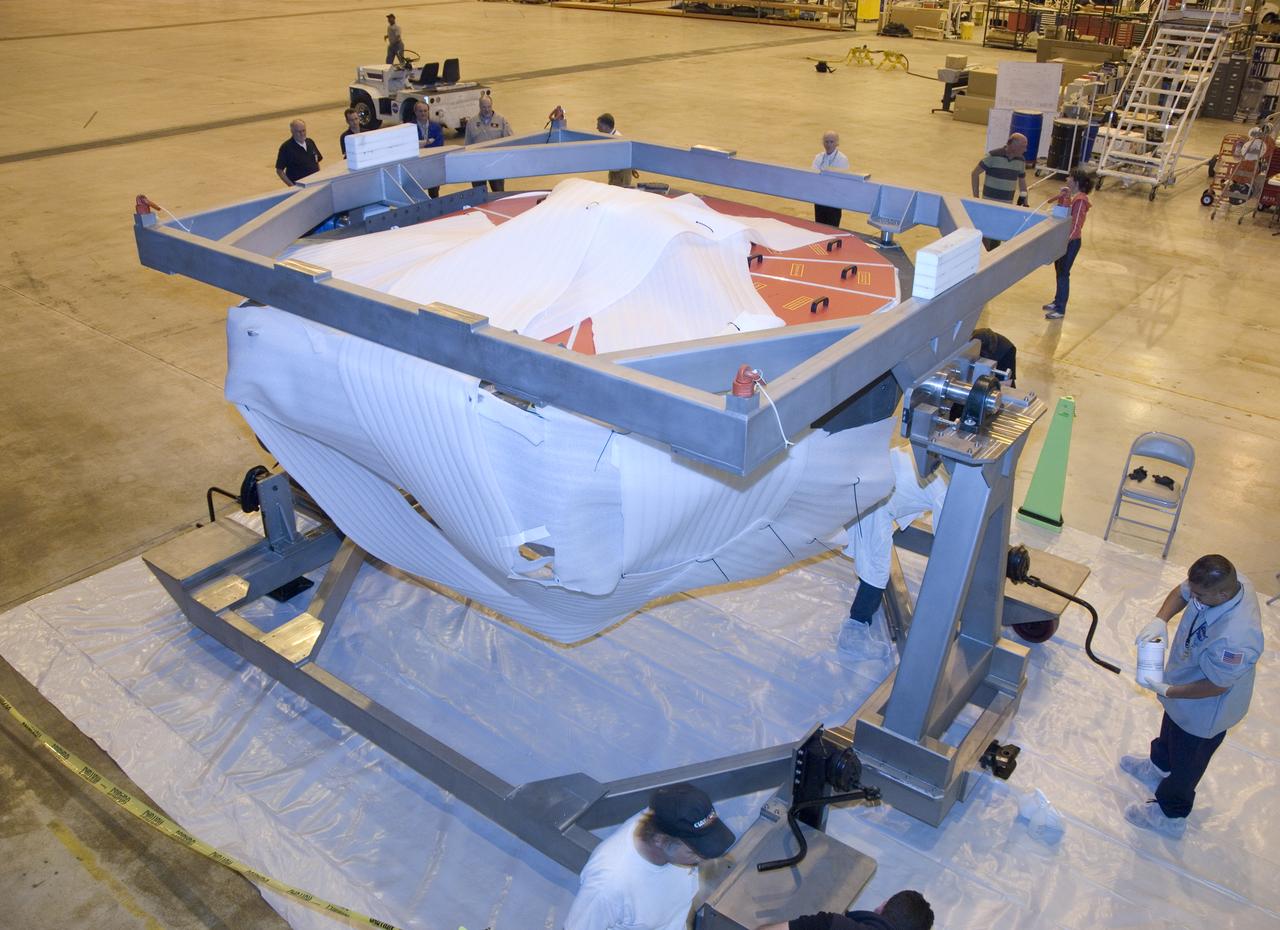
Technicians at the NASA Dryden Aircraft Operations Facility in Palmdale, Calif., removed the German-built primary mirror assembly from the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, April 18, 2008 in preparation for the final finish coating of the mirror. A precision crane lifted the more than two-ton mirror assembly from its cavity in the rear fuselage of the highly modified Boeing 747SP. The assembly was then secured in its transport dolly and moved to a clean room where it was prepared for shipment to NASA Ames Research Center at Moffett Field near Mountain View, Calif. where it would receive its aluminized finish coating before being re-installed in the SOFIA aircraft.
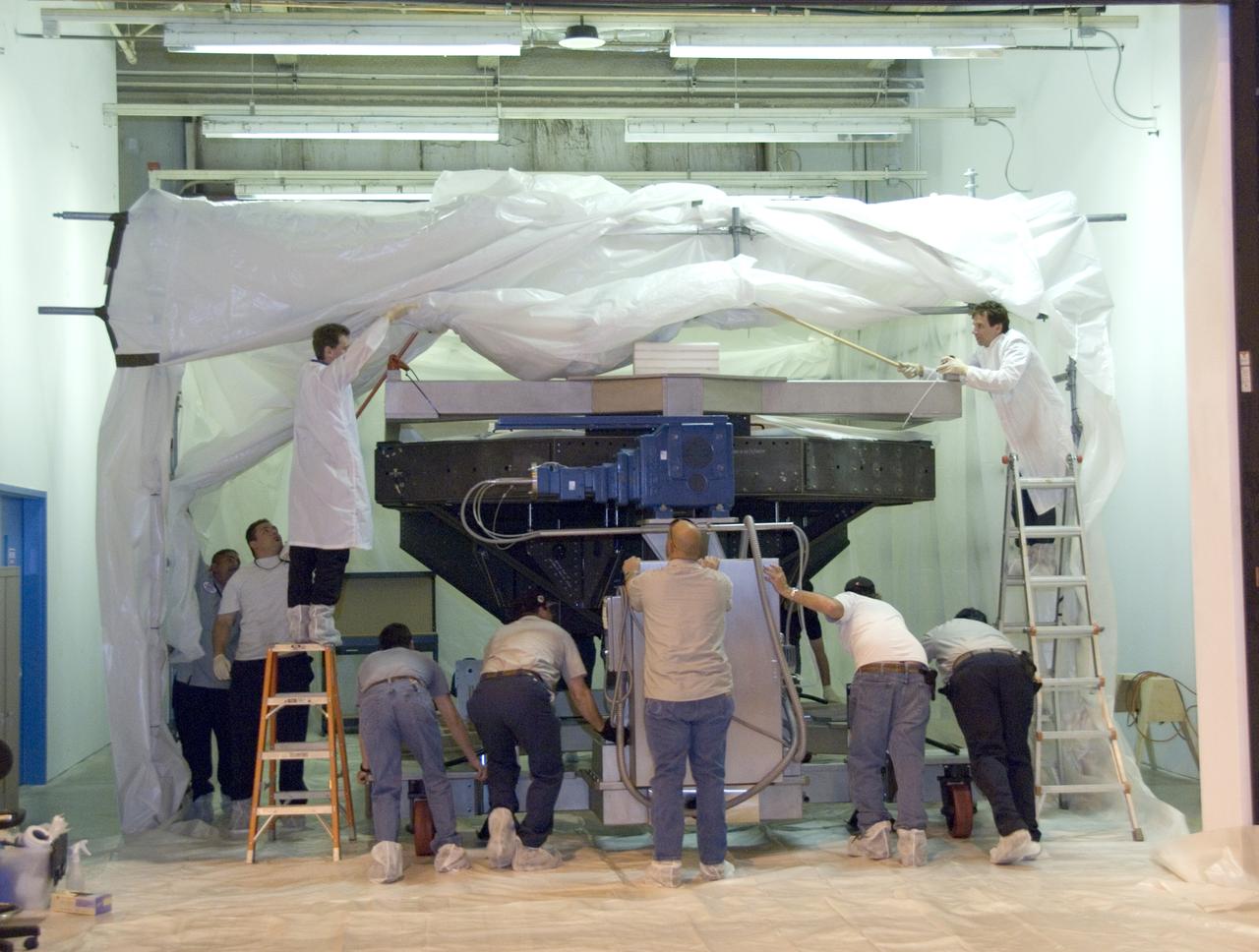

Technicians at the NASA Dryden Aircraft Operations Facility in Palmdale, Calif., removed the German-built primary mirror assembly from the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, April 18, 2008 in preparation for the final finish coating of the mirror. A precision crane lifted the more than two-ton mirror assembly from its cavity in the rear fuselage of the highly modified Boeing 747SP. The assembly was then secured in its transport dolly and moved to a clean room where it was prepared for shipment to NASA Ames Research Center at Moffett Field near Mountain View, Calif. where it would receive its aluminized finish coating before being re-installed in the SOFIA aircraft.
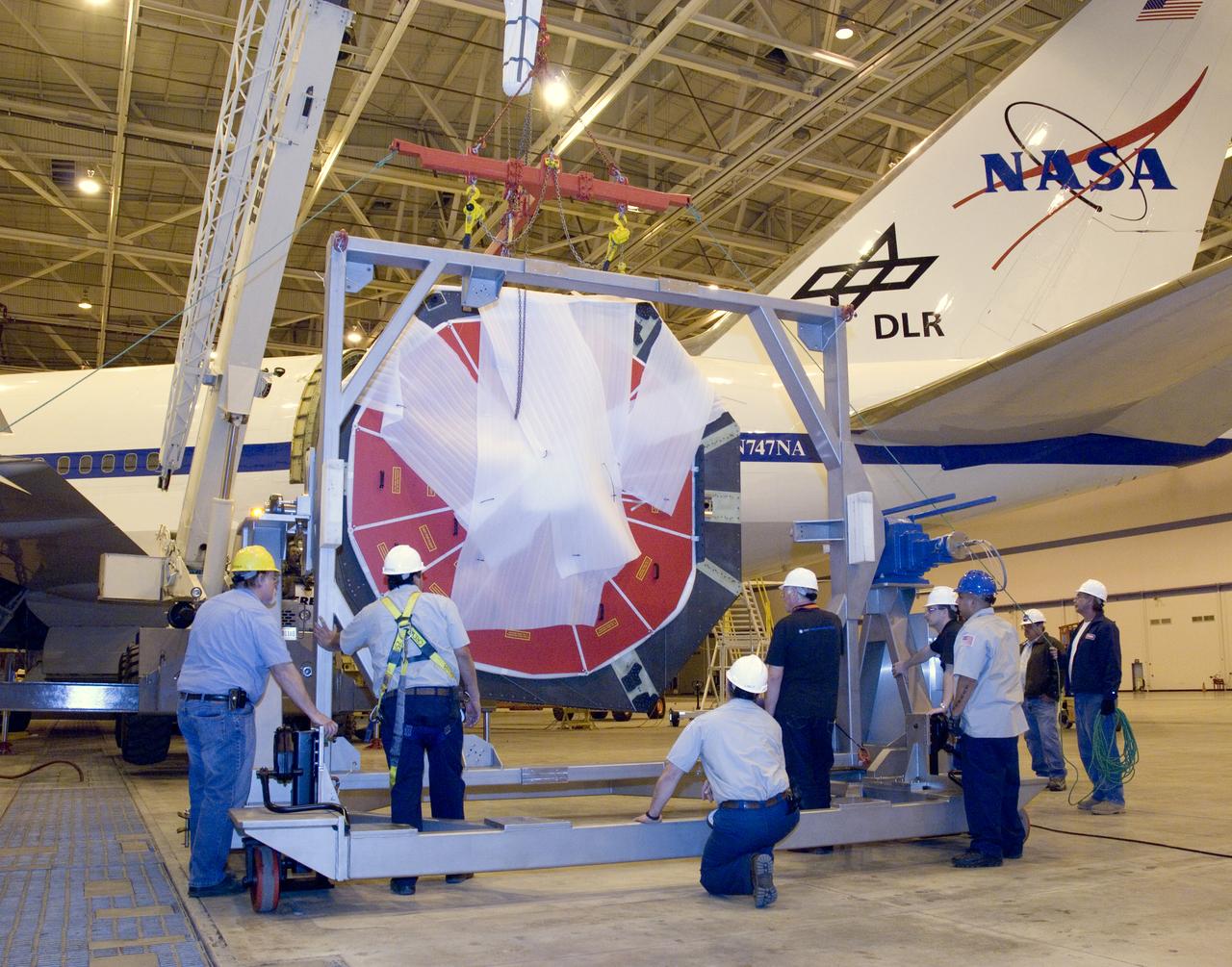

Technicians at the NASA Dryden Aircraft Operations Facility in Palmdale, Calif., removed the German-built primary mirror assembly from the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, April 18, 2008 in preparation for the final finish coating of the mirror. A precision crane lifted the more than two-ton mirror assembly from its cavity in the rear fuselage of the highly modified Boeing 747SP. The assembly was then secured in its transport dolly and moved to a clean room where it was prepared for shipment to NASA Ames Research Center at Moffett Field near Mountain View, Calif. where it would receive its aluminized finish coating before being re-installed in the SOFIA aircraft.

Technicians at the NASA Dryden Aircraft Operations Facility in Palmdale, Calif., removed the German-built primary mirror assembly from the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, April 18, 2008 in preparation for the final finish coating of the mirror. A precision crane lifted the more than two-ton mirror assembly from its cavity in the rear fuselage of the highly modified Boeing 747SP. The assembly was then secured in its transport dolly and moved to a clean room where it was prepared for shipment to NASA Ames Research Center at Moffett Field near Mountain View, Calif. where it would receive its aluminized finish coating before being re-installed in the SOFIA aircraft.

ISS027-E-032085 (18 May 2011) --- This close-up view of the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) in space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay was provided by an Expedition 27 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-134 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The station crew member used a digital still camera with an 800mm focal length, as the two spacecraft were approximately 600 feet (180 meters) apart.

Technicians at the NASA Dryden Aircraft Operations Facility in Palmdale, Calif., removed the German-built primary mirror assembly from the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA, April 18, 2008 in preparation for the final finish coating of the mirror. A precision crane lifted the more than two-ton mirror assembly from its cavity in the rear fuselage of the highly modified Boeing 747SP. The assembly was then secured in its transport dolly and moved to a clean room where it was prepared for shipment to NASA Ames Research Center at Moffett Field near Mountain View, Calif. where it would receive its aluminized finish coating before being re-installed in the SOFIA aircraft.
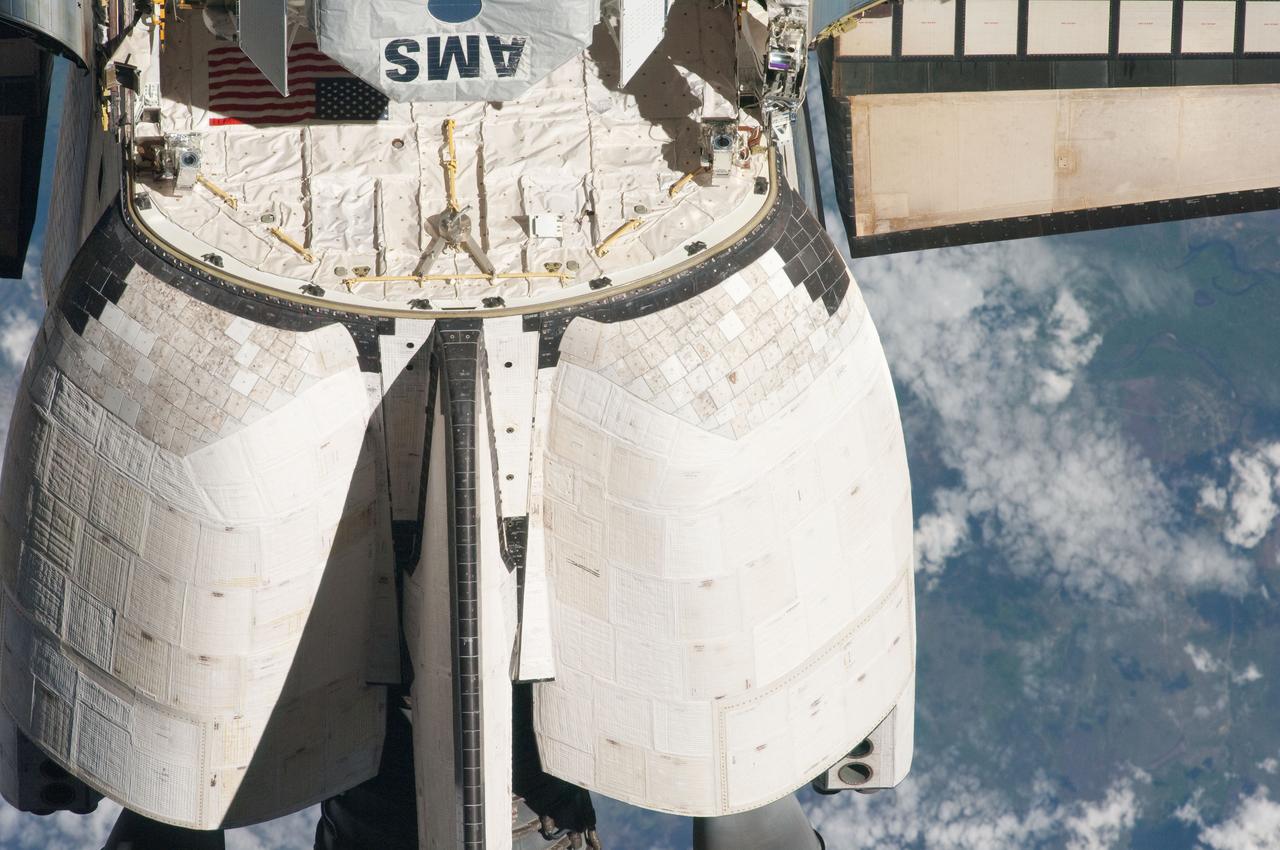

ISS027-E-032241 (18 May 2011) --- This view of the aft portion of the space shuttle Endeavour, including the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) in the payload bay, was provided by an Expedition 27 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-134 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
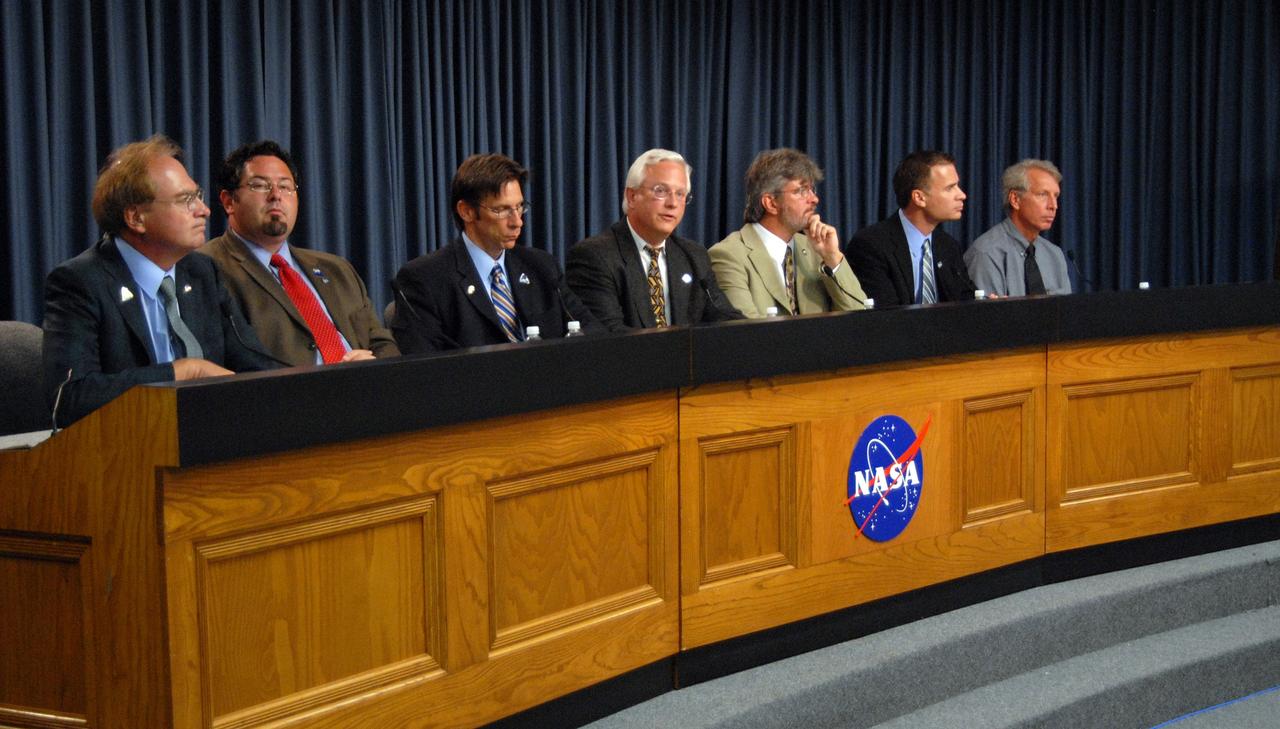

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A prelaunch press conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida provided news about a new date, June 18, for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter/Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LRO/LCROSS, launch. On the dais are, from left, NASA Public Affairs Officer George Diller, who moderated; Todd May, program manager of the Lunar Precursor Robotic Program at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala.; Chuck Dovale, NASA launch director at Kennedy; Vernon Thorp, program manager of NASA Missions with United Launch Alliance; Craig Tooley, the LRO project Manager at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.; Daniel Andrews, the LCROSS project manager at NASA's Ames Research Center at Moffett Field, Calif.; and Clay Flinn, the Atlas V launch weather officer of the 45th Weather Squadron at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The LRO and LCROSS launch was moved to June 18 to accommodate space shuttle Endeavour's June 17 liftoff on the STS-127 mission. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
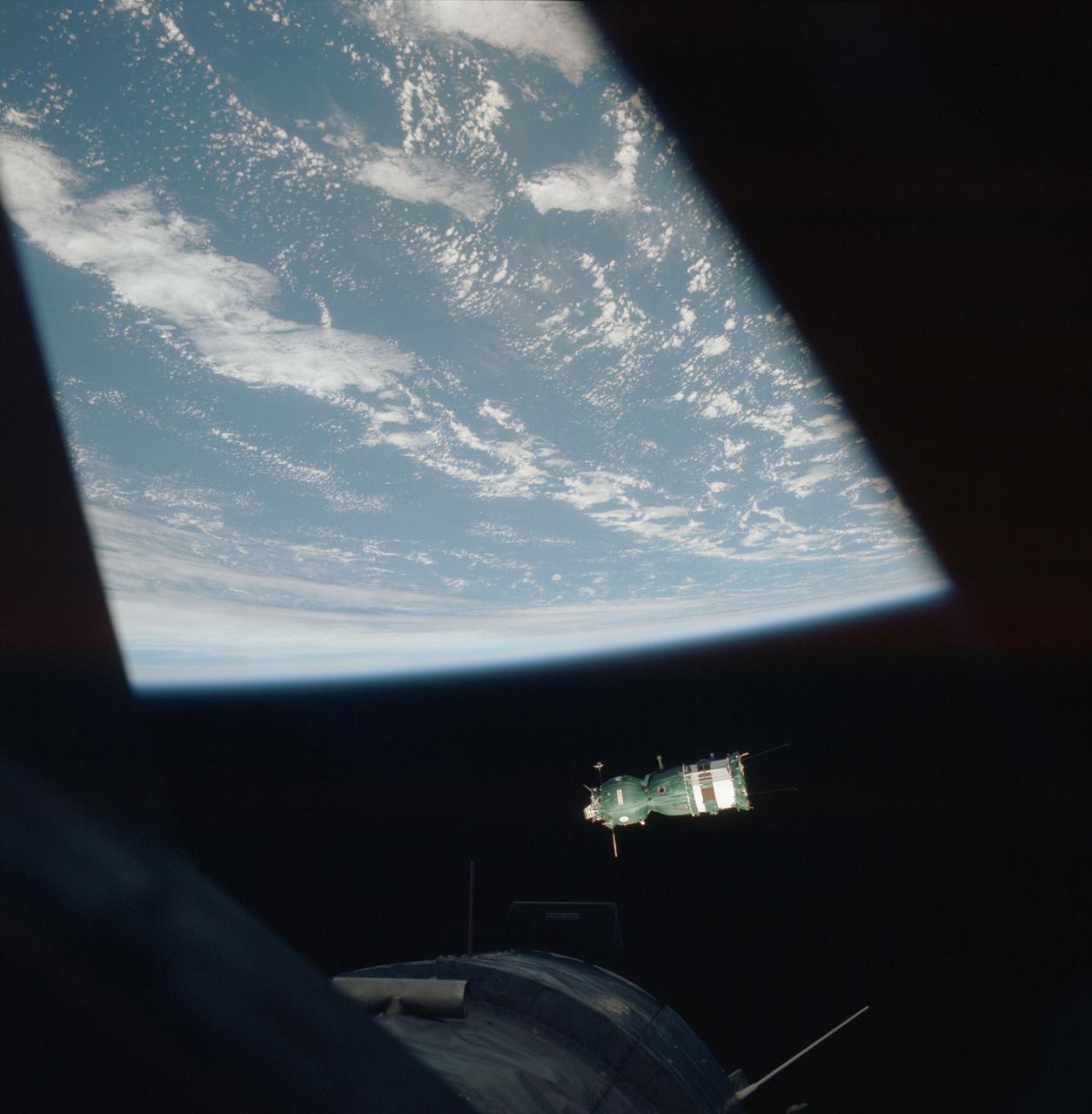

AST-02-093 (18 July 1975) --- This scene photographed with a hand-held 70mm camera from a rendezvous window of the American Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit shows the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft contrasted against a black-sky background with Earth's horizon below. The three major components of the Soyuz are the spherical-shaped Orbital Module (OM), the bell-shaped Descent Vehicle (DV) and the cylindrical-shaped instrument Assembly Module (AM). The docking system on the Orbital Module was specially designed to interface with the docking system on the Apollo's Docking Module (DM). The DM is visible very faintly at the bottom of the picture. The ASTP astronauts and cosmonauts visited each other's spacecraft while the Soyuz and Apollo were docked in Earth orbit for two days.
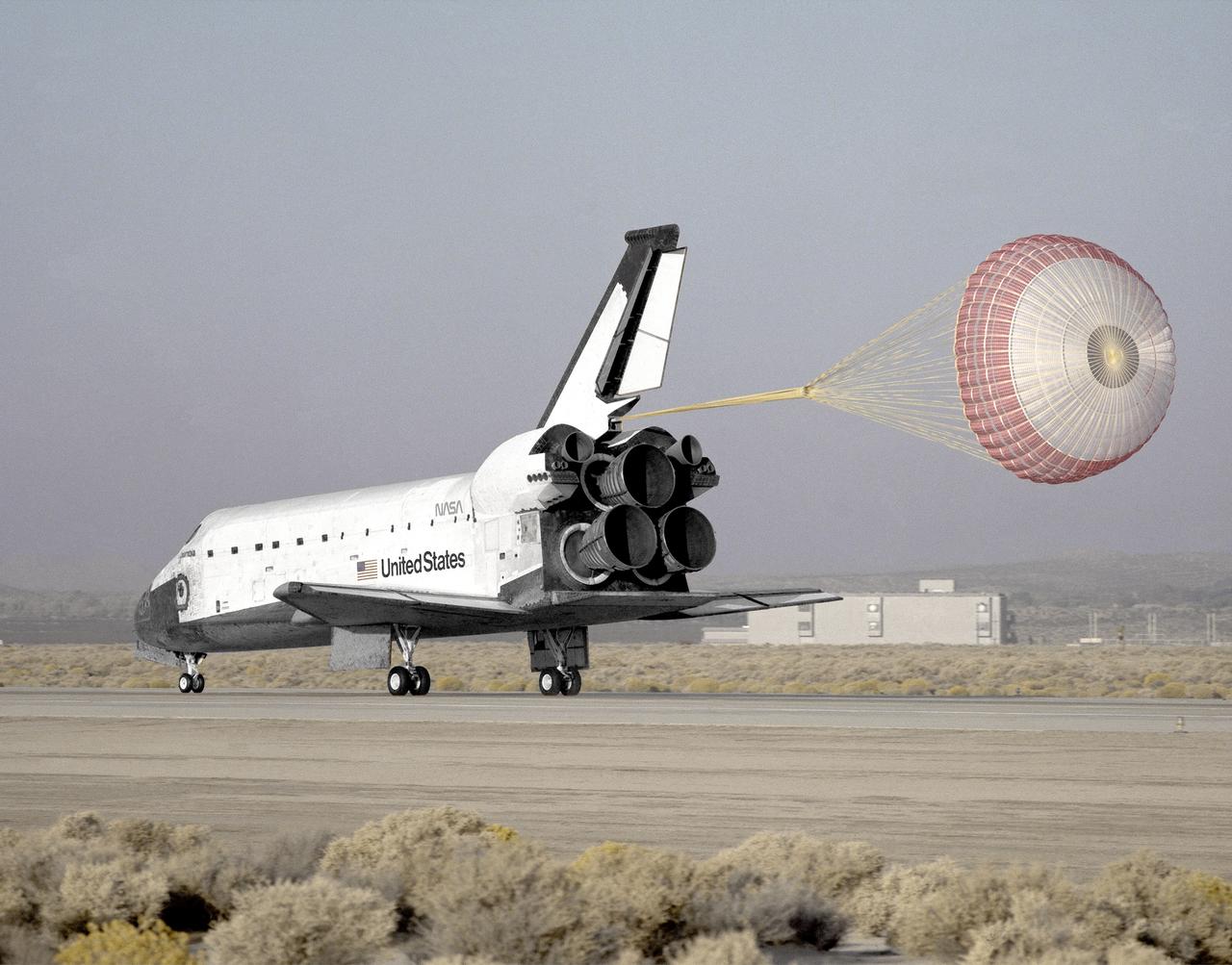

A drag chute slows the space shuttle Columbia as it rolls to a perfect landing concluding NASA's longest mission at that time, STS-58, at the Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later redesignated the Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, with a 8:06 a.m. (PST) touchdown 1 November 1993 on Edward's concrete runway 22. The planned 14 day mission, which began with a launch from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 7:53 a.m. (PDT), October 18, was the second spacelab flight dedicated to life sciences research. Seven Columbia crewmembers performed a series of experiments to gain more knowledge on how the human body adapts to the weightless environment of space. Crewmembers on this flight included: John Blaha, commander; Rick Searfoss, pilot; payload commander Rhea Seddon; mission specialists Bill MacArthur, David Wolf, and Shannon Lucid; and payload specialist Martin Fettman.
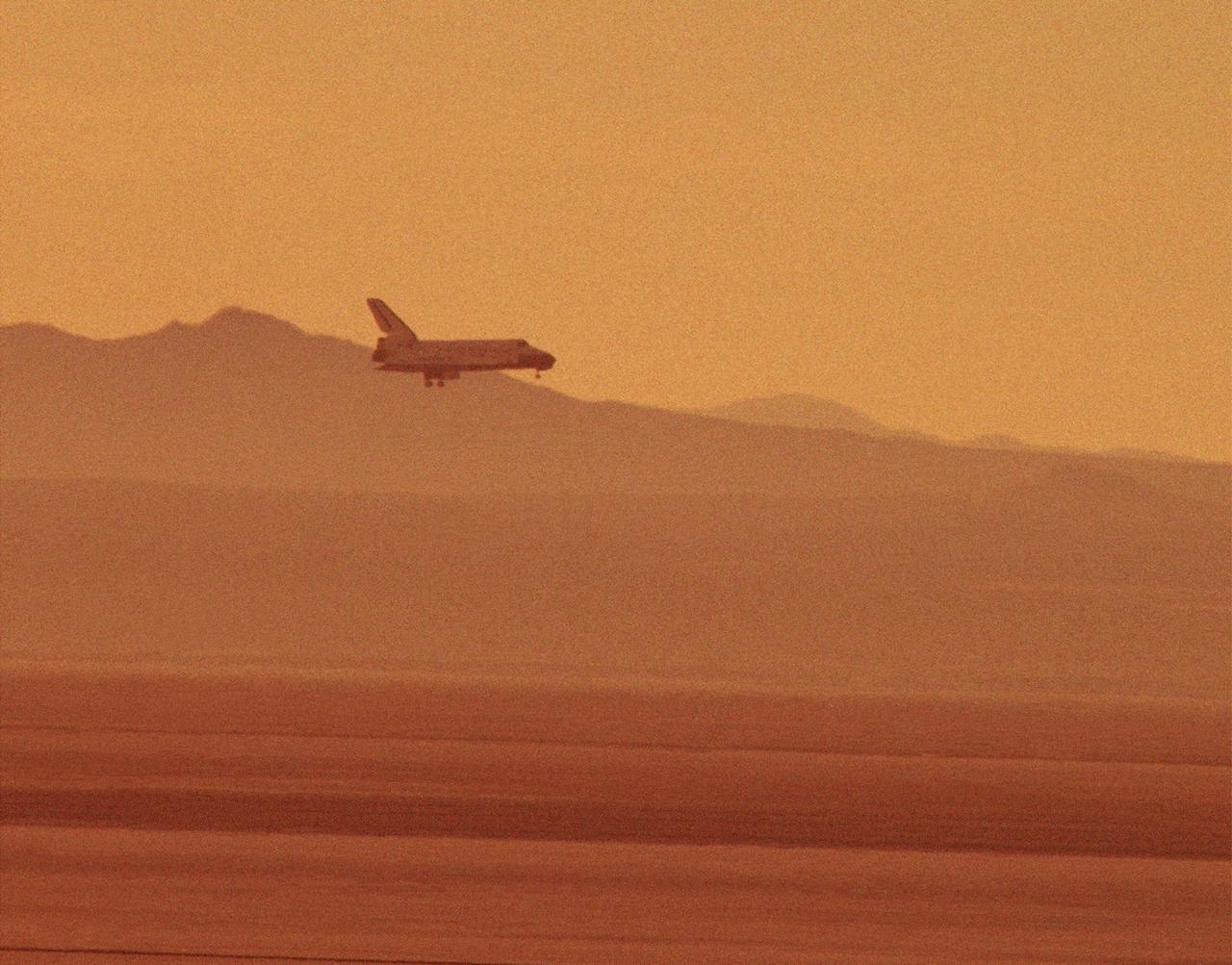

The STS-29 Space Shuttle Discovery mission approaches for a landing at NASA's then Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility, Edwards AFB, California, early Saturday morning, 18 March 1989. Touchdown was at 6:35:49 a.m. PST and wheel stop was at 6:36:40 a.m. on runway 22. Controllers chose the concrete runway for the landing in order to make tests of braking and nosewheel steering. The STS-29 mission was very successful, completing the launch a Tracking and Data Relay communications satellite, as well as a range of scientific experiments. Discovery's five man crew was led by Commander Michael L. Coats, and included pilot John E. Blaha and mission specialists James P. Bagian, Robert C. Springer, and James F. Buchli.
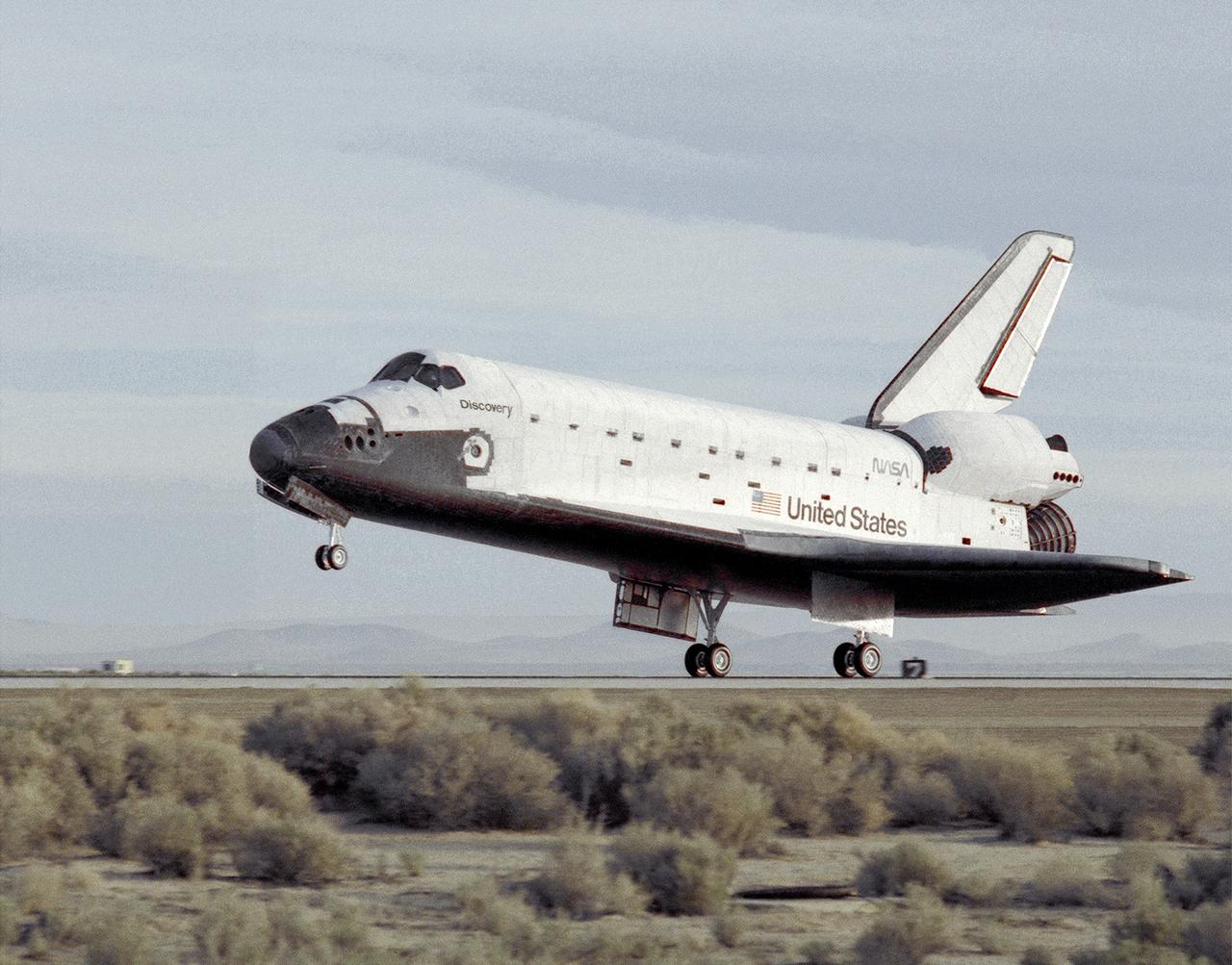

The STS-29 Space Shuttle Discovery mission lands at NASA's then Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility, Edwards AFB, California, early Saturday morning, 18 March 1989. Touchdown was at 6:35:49 a.m. PST and wheel stop was at 6:36:40 a.m. on runway 22. Controllers chose the concrete runway for the landing in order to make tests of braking and nosewheel steering. The STS-29 mission was very successful, completing the launch of a Tracking and Data Relay communications satellite, as well as a range of scientific experiments. Discovery's five-man crew was led by Commander Michael L. Coats, and included pilot John E. Blaha and mission specialists James P. Bagian, Robert C. Springer, and James F. Buchli.
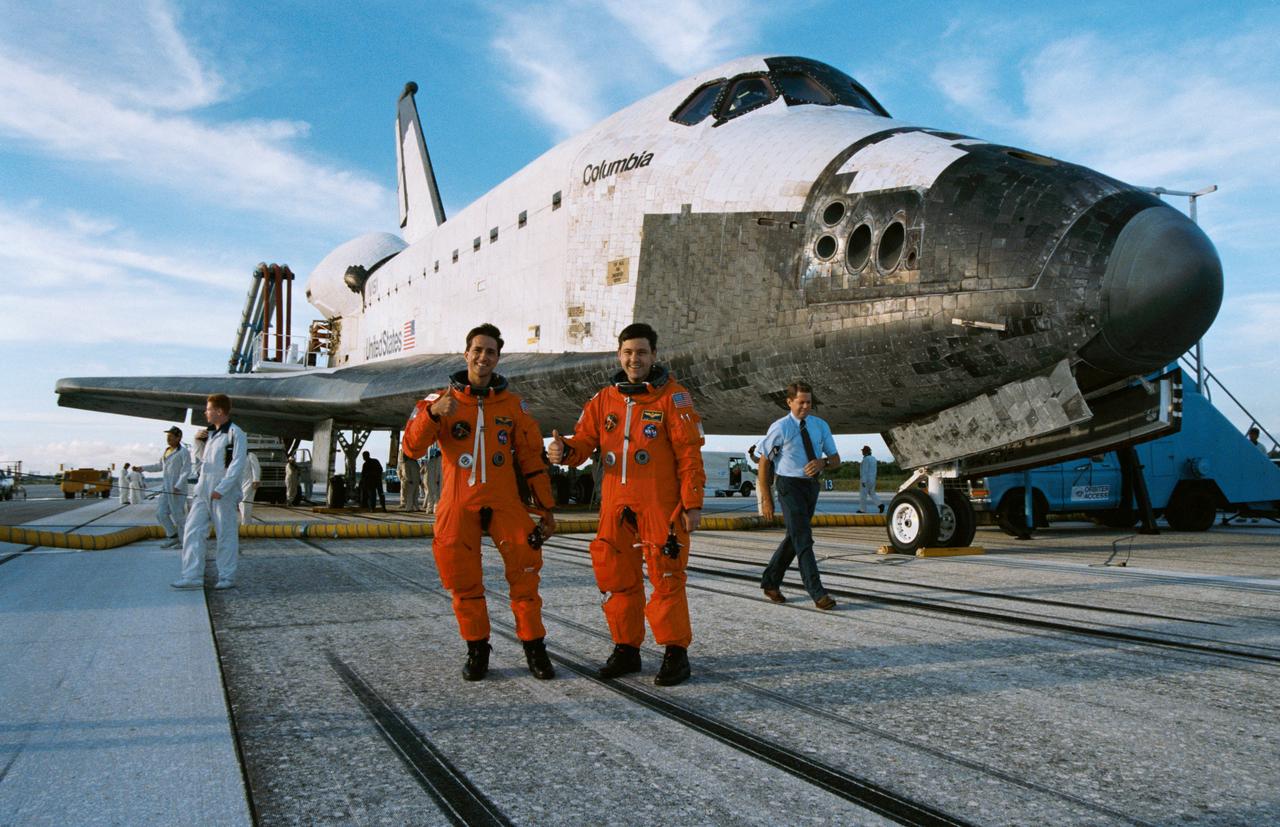

STS-65 Commander Robert D. Cabana (right) and Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas, wearing launch and entry suits (LESs), signal mission success with a "thumbs up" gesture as they stand in front of Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102. The two crewmembers are all smiles after OV-102's landing at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF). The two, along with four other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist, had just broken a Shuttle duration record as they ran almost 18 hours over two weeks in space in support of the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) mission. Landing occurred at 6:38 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). Mission duration was 14 days, 17 hours and 56 minutes. In the background, KSC personnel conduct postflight servicing of the vehicle.
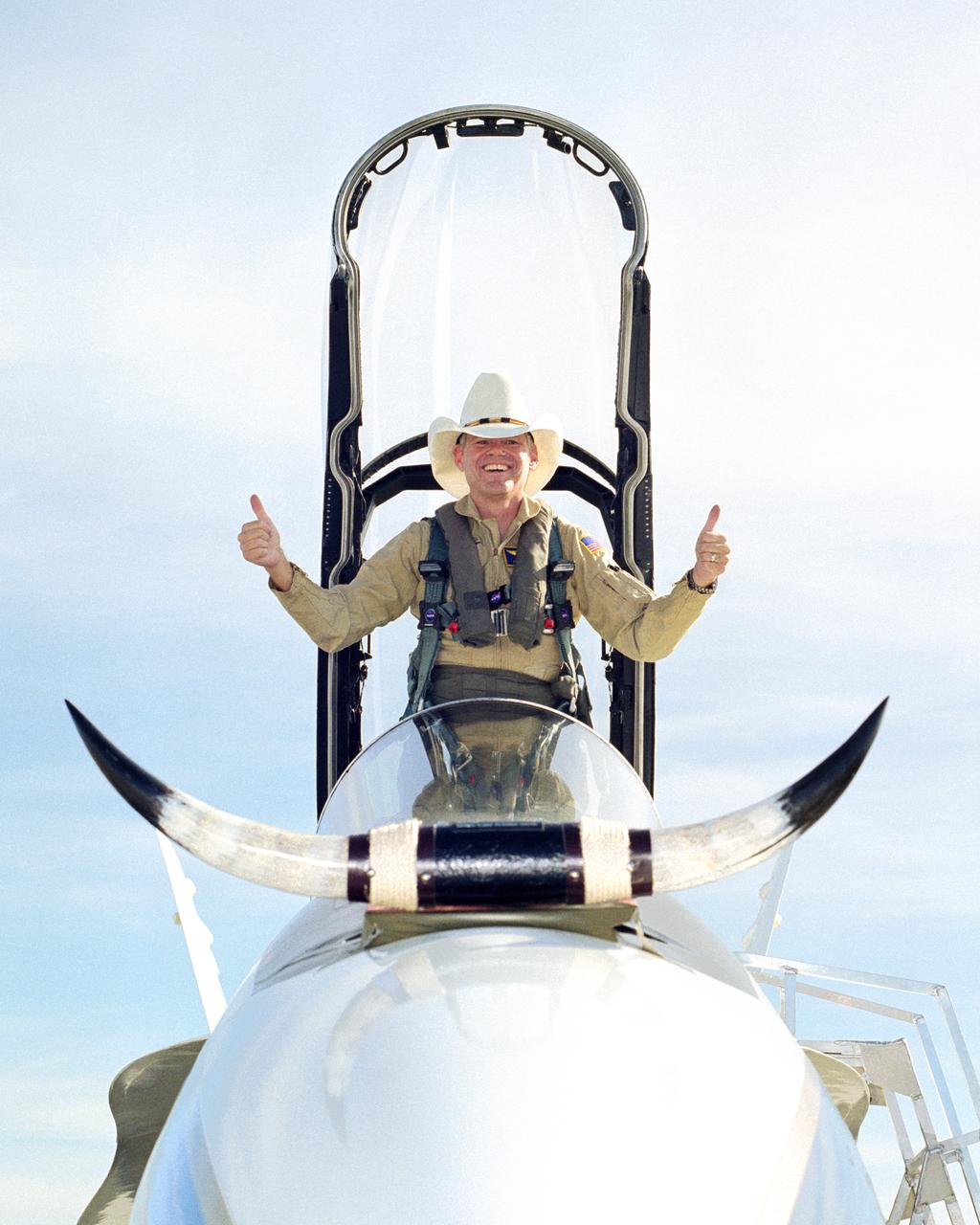

In a lighter mood, Ed Schneider gives a "thumbs-up" after his last flight at the Dryden Flight Research Center on September 19, 2000. Schneider arrived at the NASA Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility on July 5, 1982, as a Navy Liaison Officer, becoming a NASA research pilot one year later. He has been project pilot for the F-18 High Angle-of-Attack program (HARV), the F-15 aeronautical research aircraft, the NASA B-52 launch aircraft, and the SR-71 "Blackbird" aircraft. He also participated in such programs as the F-8 Digital Fly-By-Wire, the FAA/NASA 720 Controlled Impact Demonstration, the F-14 Automatic Rudder Interconnect and Laminar Flow, and the F-104 Aeronautical Research and Microgravity projects.
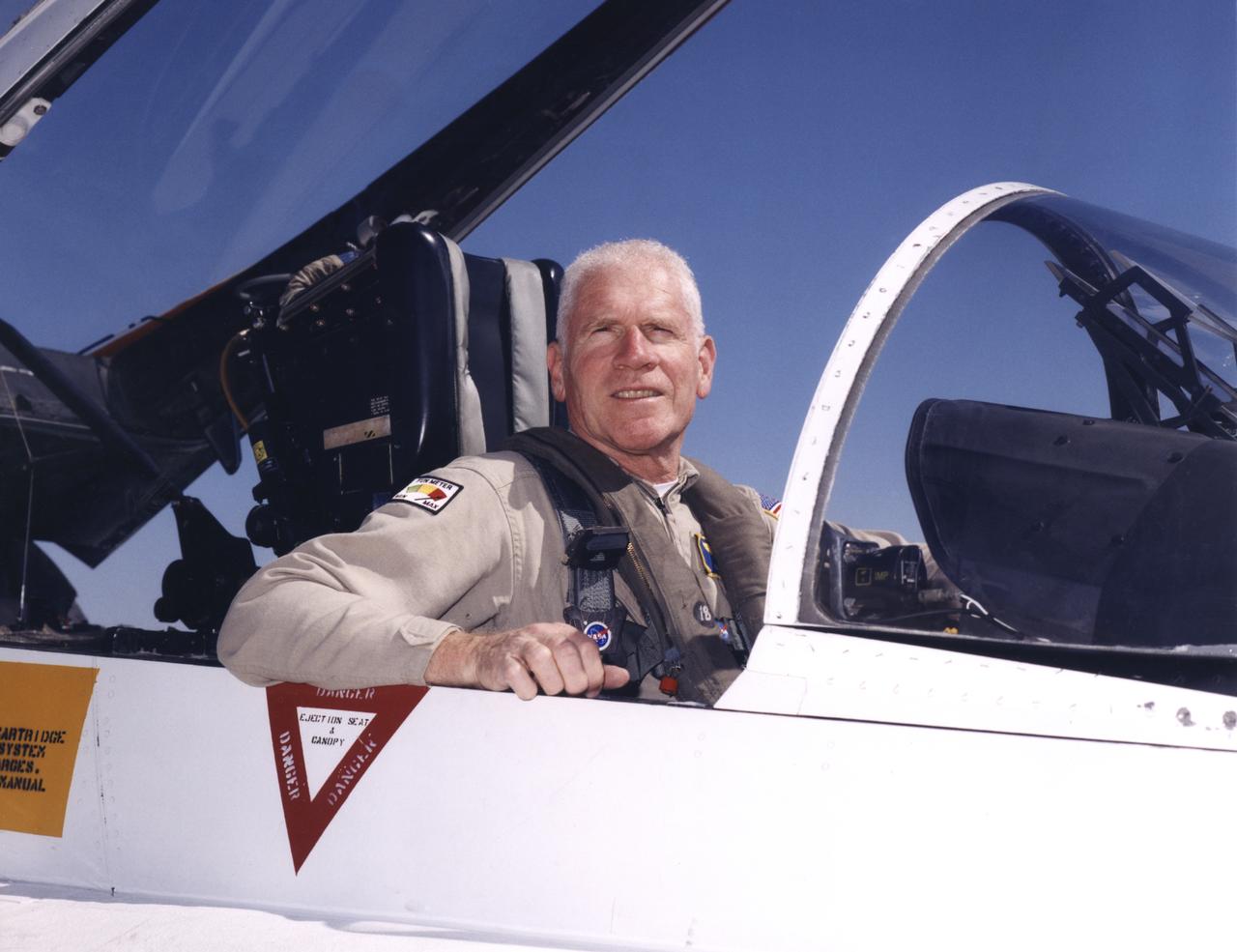

Edwin W. Lewis Jr. is a research pilot in the Airborne Science program, Flight Crew Branch, Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. He currently flies the DC-8, F/A-18, Lear Jet 24, King Air, and T-34C in support of Dryden's flight operations and is mentor pilot for the King Air and the Lear Jet. Prior to accepting this assignment Lewis was a pilot for eight years at NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, flying 10 different aircraft C-130B, DC-8-72, UH-1, SH-3, King Air, Lear 24, T-38A, T-39G and YO-3A in support of NASA flight missions. Lewis also flew the Kuiper Airborne Observatory (a modified civilian version of the Lockheed C-141 Starlifter). He was project pilot for Ames' 747 and T-38 programs. Lewis was born in New York City on May 19, 1936, and began flight training as a Civil Air Patrol cadet in 1951, ultimately earning his commercial pilot's certificate in 1958. He received a bachelor of arts degree in biology from Hobart College, Geneva, N.Y., and entered the U.S. Air Force through the Reserve Officer Training Corps. Following pilot training he was assigned to Moody Air Force Base, Ga., as an instructor pilot, for both the T-33 and T-37 aircraft. He served in Vietnam in 1965 and 1966, where he was a forward air controller, instructor and standardization/evaluation pilot, flying more than 1,000 hours in the O-1 "Bird Dog." Lewis separated from the regular Air Force and joined Pan American World Airways and the 129th Air Commando Group, California Air National Guard (ANG) based in Hayward, California. During his 18-year career with the California ANG he flew the U-6, U-10, C-119, HC-130 aircraft and the HH-3 helicopter. He retired as commander, 129th Air Rescue and Recovery Group, a composite combat rescue group, in the grade of colonel. During his 22 years as an airline pilot, he flew the Boeing 707, 727 and 747. He took early retirement from Pan American in 1989 to become a pilot with NASA.
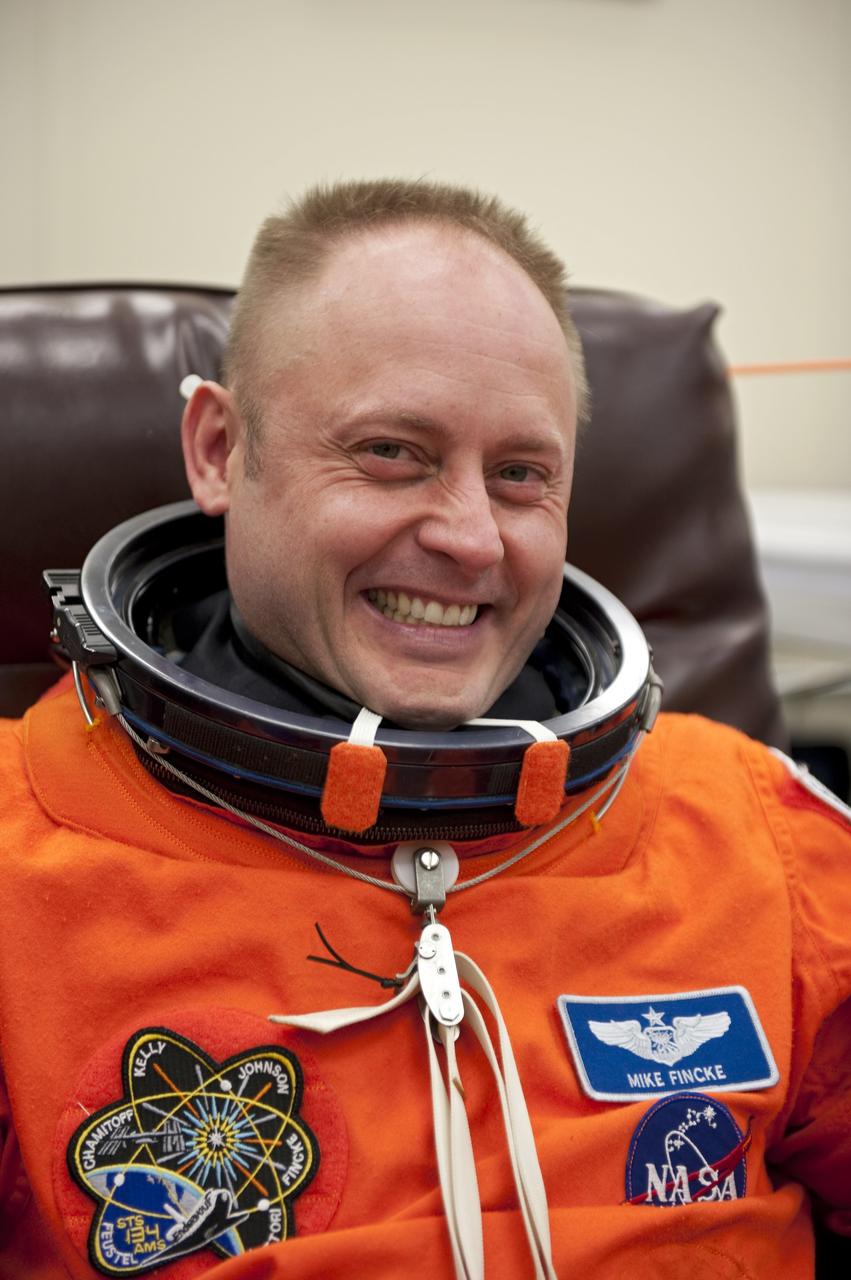

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour's STS-134 astronauts put on their launch-and-entry suits and check the fit of their helmets and gloves before heading to the Astrovan for the ride to Launch Pad 39A. Mission Specialist Michael Fincke, seen here, last served as a member of the Expedition 18 crew of the International Space Station in 2009. This will be Fincke's first flight aboard a space shuttle. STS-134 will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. May 16 at 8:56 a.m. will be the second launch attempt for Endeavour. The first attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
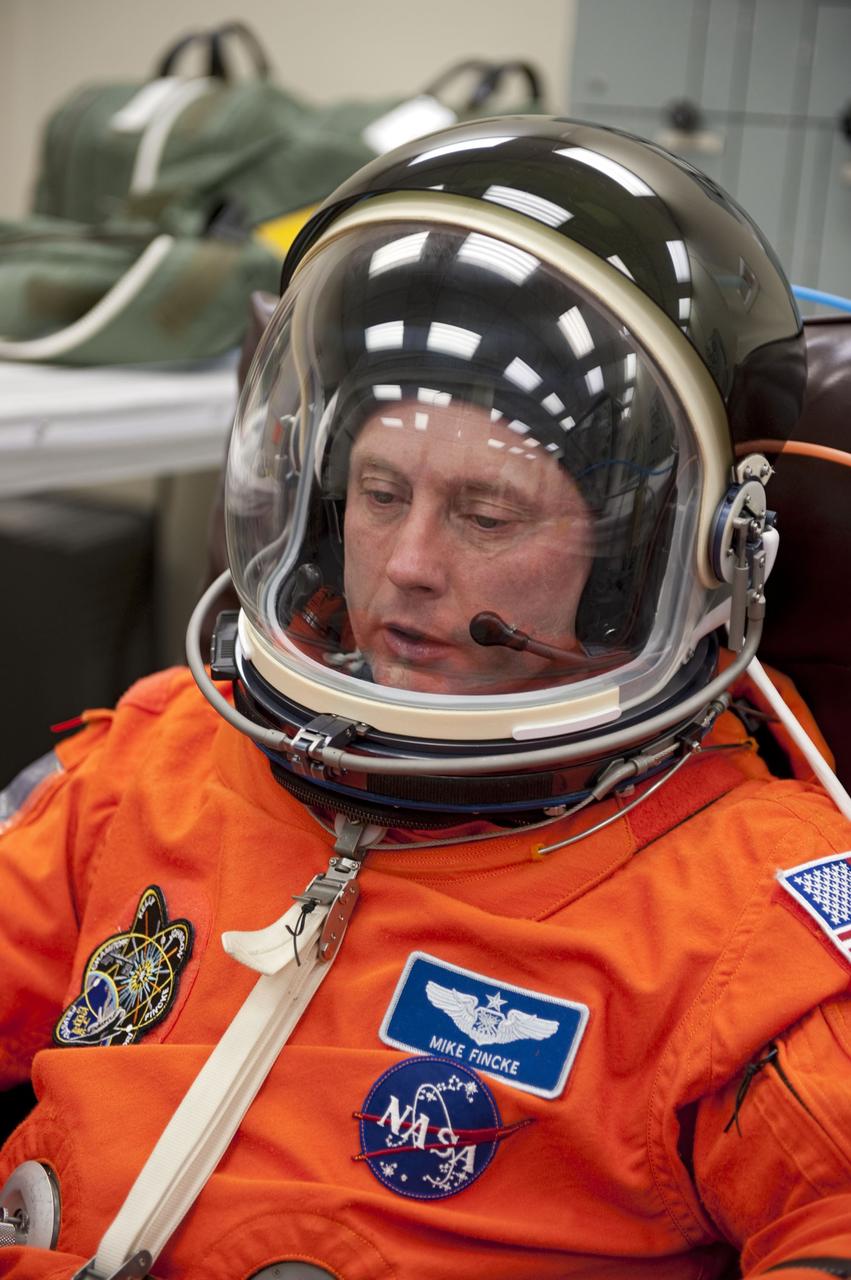

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour's STS-134 astronauts put on their launch-and-entry suits and check the fit of their helmets and gloves before heading to the Astrovan for the ride to Launch Pad 39A. Mission Specialist Michael Fincke, seen here, last served as a member of the Expedition 18 crew of the International Space Station in 2009. This will be Fincke's first flight aboard a space shuttle. STS-134 will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the space station. Endeavour was scheduled to launch at 3:47 p.m. on April 29, but that attempt was scrubbed for at least 72 hours while engineers assess an issue associated with the shuttle's Auxiliary Power Unit 1. STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
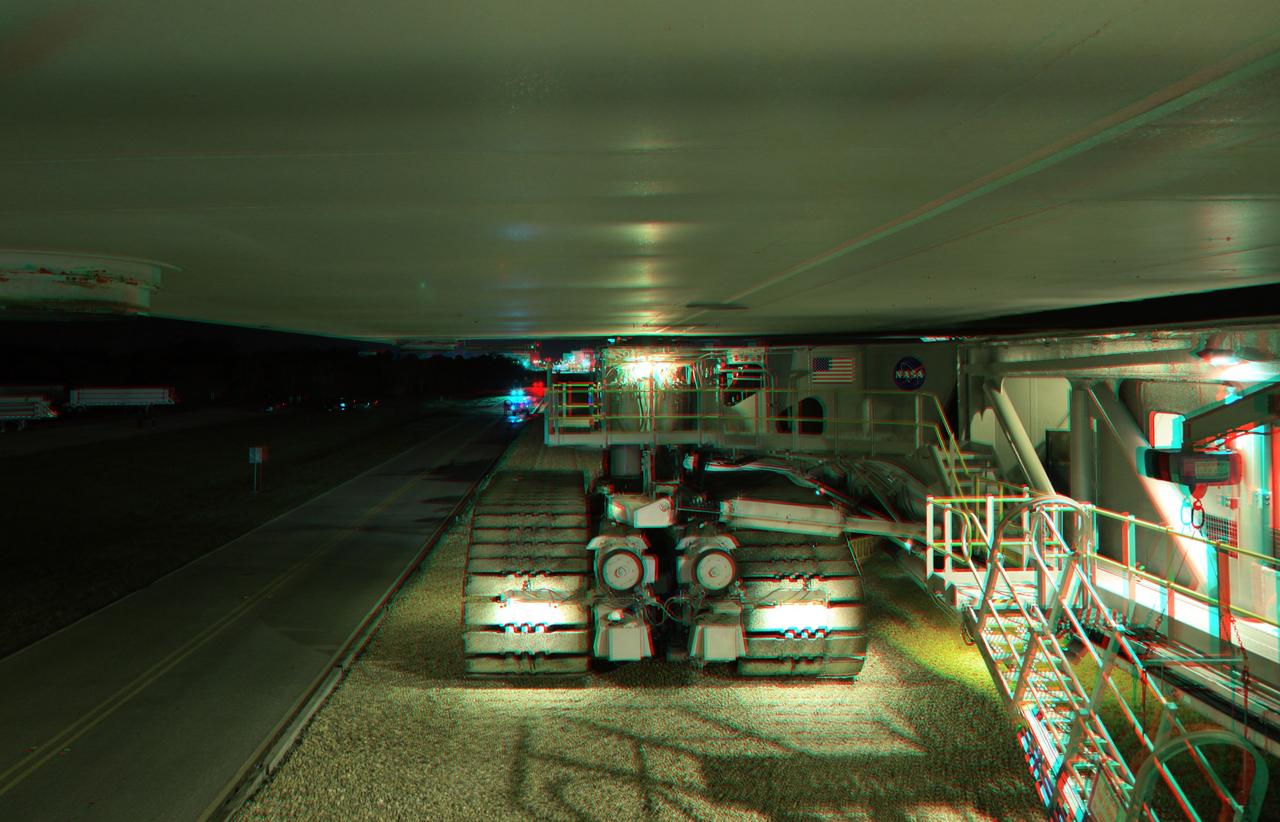

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a 3-D image of the crawler-transporter as it slowly hauls space shuttle Endeavour from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The gigantic tracked mover weighs about 18 million pounds with the space shuttle, two solid rocket boosters, external fuel tank and mobile launcher platform attached. It takes six to eight hours to complete the 3.4-mile trip along crushed Alabama river rock at a speed of about 1 mph. To view this image, use green and magenta 3-D glasses. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
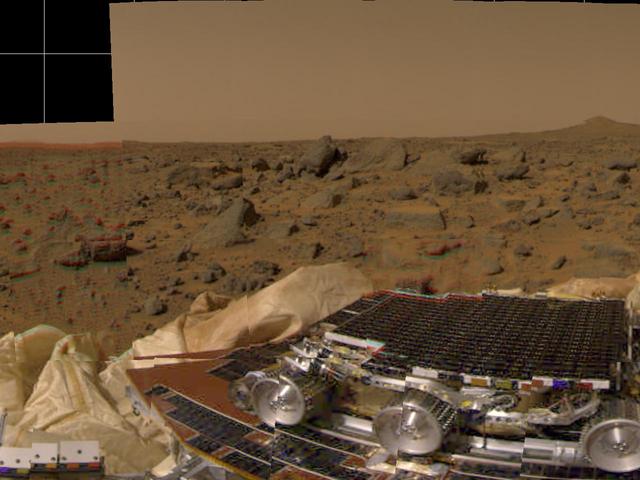

This picture from Mars Pathfinder was taken at 9:30 AM in the martian morning (2:30 PM Pacific Daylight Time), after the spacecraft landed earlier today (July 4, 1997). The Sojourner rover is perched on one of three solar panels. The rover is 65 cm (26 inches) long by 18 cm (7 inches) tall; each of its wheels is about 13 cm (5 inches) high. The white material to the left of the front of the rover is part of the airbag system used to cushion the landing. Many rocks of different of different sizes can be seen, set in a background of reddish soil. The landing site is in the mouth of an ancient channel carved by water. The rocks may be primarily flood debris. The horizon is seen towards the top of the picture. The light brown hue of the sky results from suspended dust. Pathfinder, a low-cost Discovery mission, is the first of a new fleet of spacecraft that are planned to explore Mars over the next ten years. Mars Global Surveyor, already en route, arrives at Mars on September 11 to begin a two year orbital reconnaissance of the planet's composition, topography, and climate. Additional orbiters and landers will follow every 26 months. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00608
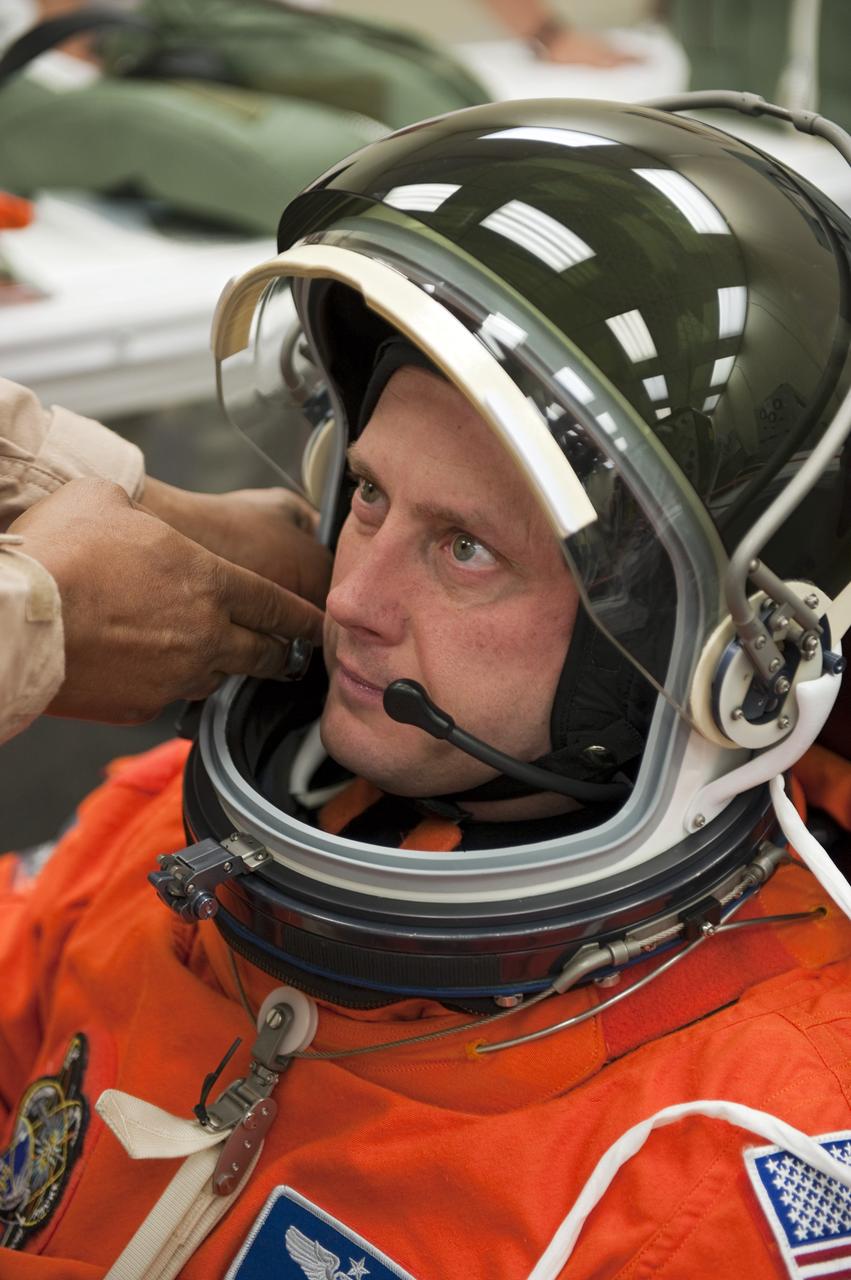

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour's STS-134 astronauts put on their launch-and-entry suits and check the fit of their helmets and gloves before heading to the Astrovan for the ride to Launch Pad 39A. Mission Specialist Michael Fincke, seen here, last served as a member of the Expedition 18 crew of the International Space Station in 2009. This will be Fincke's first flight aboard a space shuttle. STS-134 will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. May 16 at 8:56 a.m. will be the second launch attempt for Endeavour. The first attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
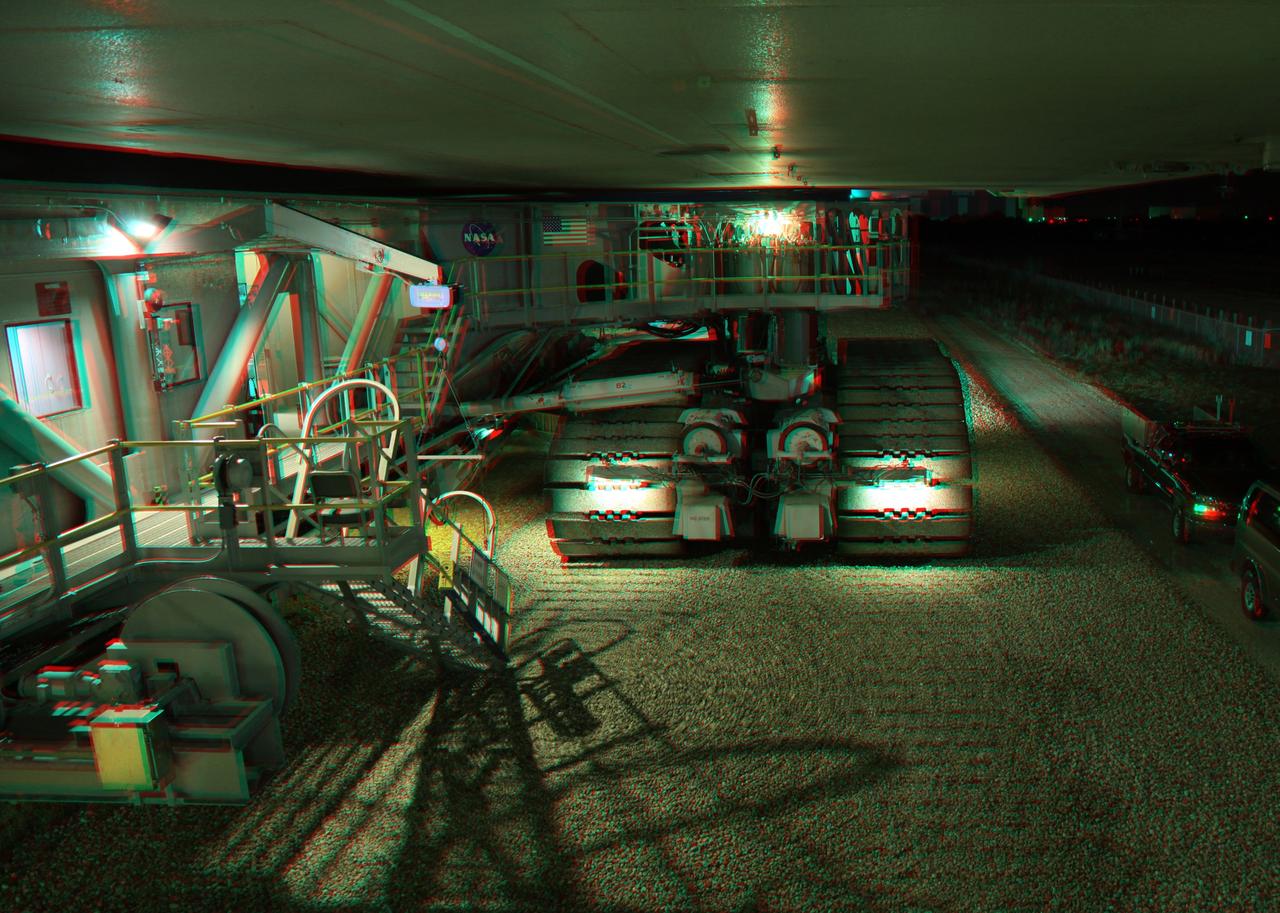
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- This is a 3-D image of the crawler-transporter as it slowly hauls space shuttle Endeavour from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The gigantic tracked mover weighs about 18 million pounds with the space shuttle, two solid rocket boosters, external fuel tank and mobile launcher platform attached. It takes six to eight hours to complete the 3.4-mile trip along crushed Alabama river rock at a speed of about 1 mph. To view this image, use green and magenta 3-D glasses. Endeavour and its six-member STS-134 crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank, additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper and micrometeoroid debris shields to the International Space Station. Endeavour's final launch is targeted for April 19 at 7:48 p.m. EDT. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
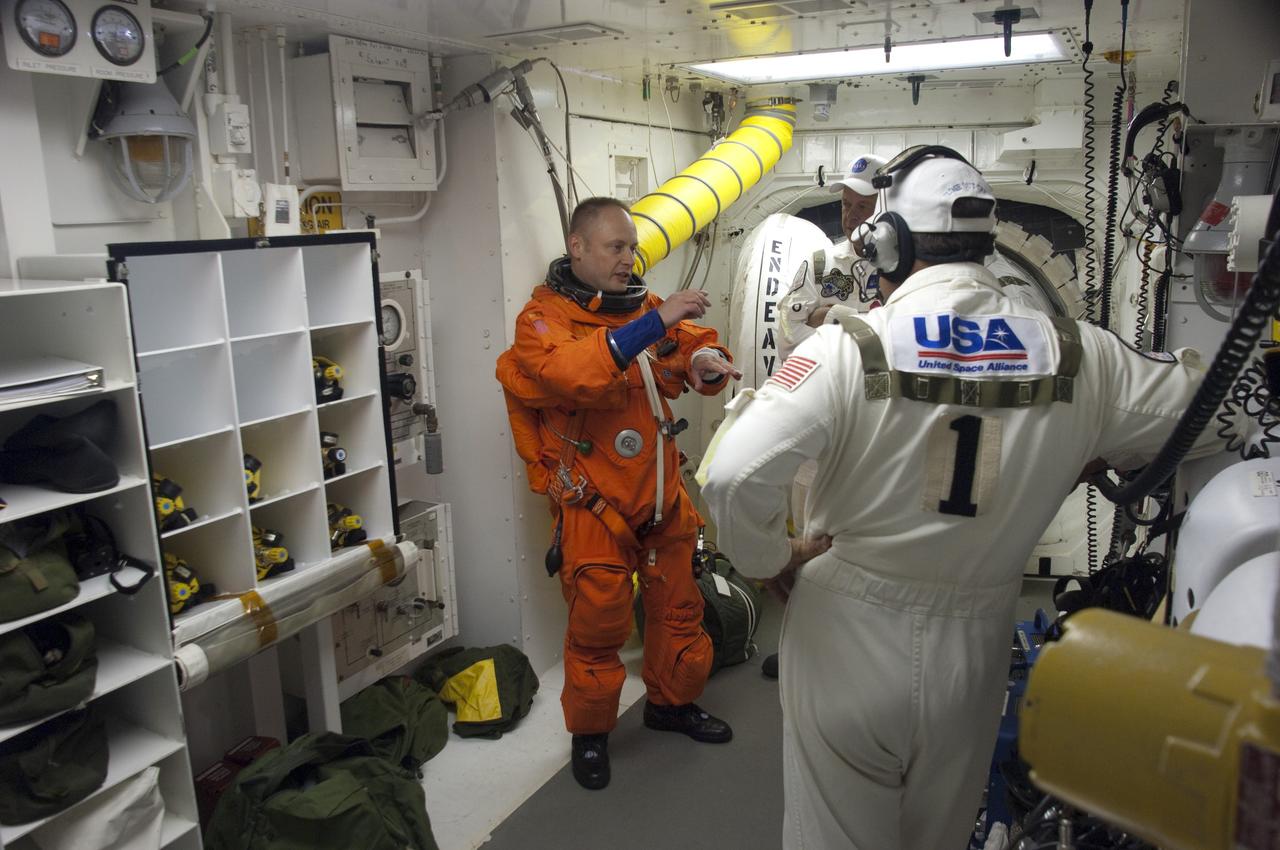

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the White Room at Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-134 Mission Specialist Michael Fincke prepares to board space shuttle Endeavour through the crew hatch in the background. Members of the Closeout Crew, in white uniforms, are there to assist astronauts with their launch-and-entry suits and the boarding process. Fincke last served as a member of the Expedition 18 crew of the International Space Station in 2009. This will be Fincke's first flight aboard a space shuttle. STS-134 will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), Express Logistics Carrier-3, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the International Space Station. May 16 at 8:56 a.m. will be the second launch attempt for Endeavour. The first attempt on April 29 was scrubbed because of an issue associated with a faulty power distribution box called the aft load control assembly-2 (ALCA-2). STS-134 will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
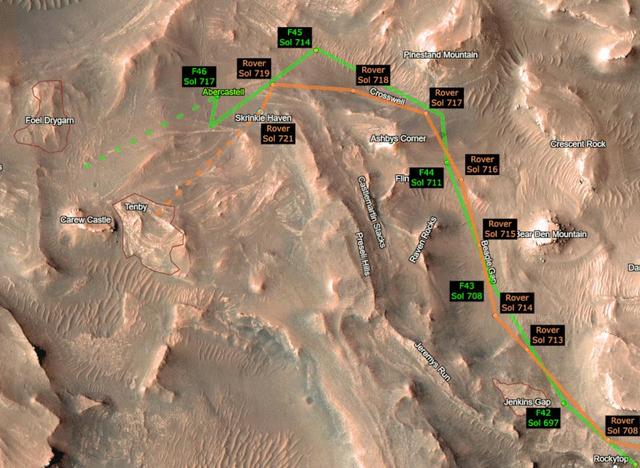
This animation shows the progress of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover and its Ingenuity Mars Helicopter as they make the climb up Jezero Crater's delta toward ancient river deposits. The helicopter's route is depicted in green, while the rover's progress is shown in orange. Black labels indicate which day, or sol, of the mission the rover and helicopter were on at each point. (Martian sols are counted from the date the Perseverance rover landed on Mars, Feb. 18, 2021). For the helicopter, the black labels also indicate which flight is shown; depicted here are Ingenuity's 42nd (F42) to 46th (F46) sorties. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which also manages the project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center in California's Silicon Valley, and NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity’s development. AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm, and SolAero also provided design assistance and major vehicle components. Lockheed Martin Space designed and manufactured the Mars Helicopter Delivery System. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25687
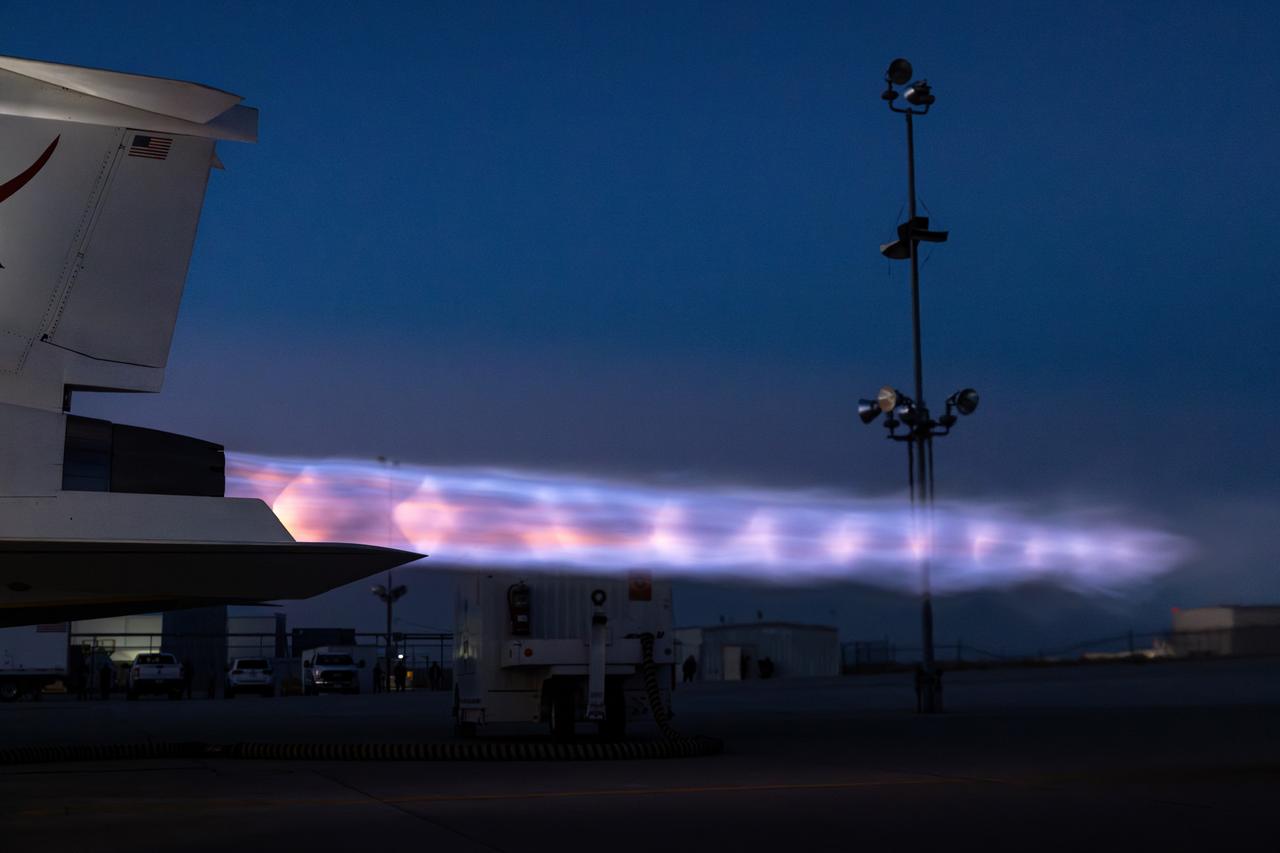

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.
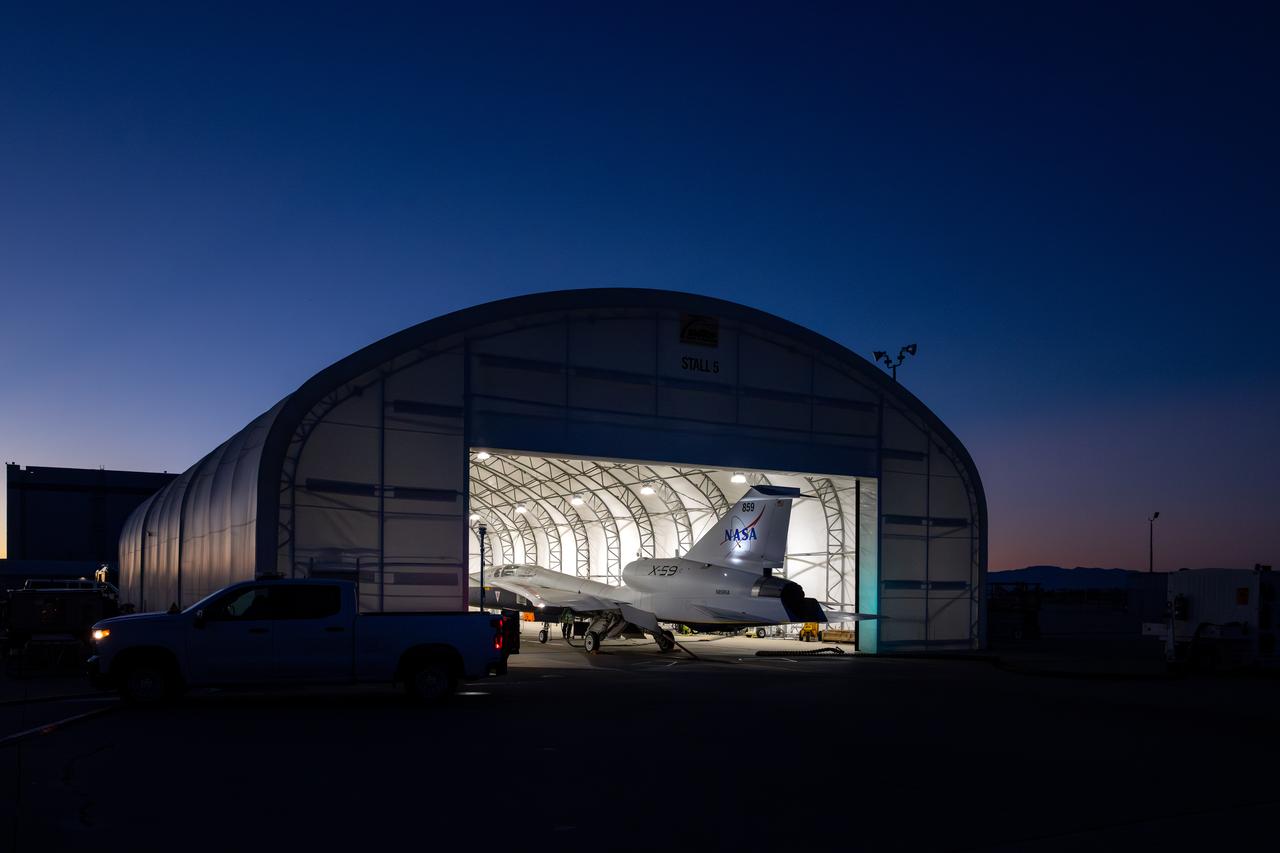

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits inside its run stall following maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the mission, designed to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land, addressing a key barrier to commercial supersonic travel.

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.
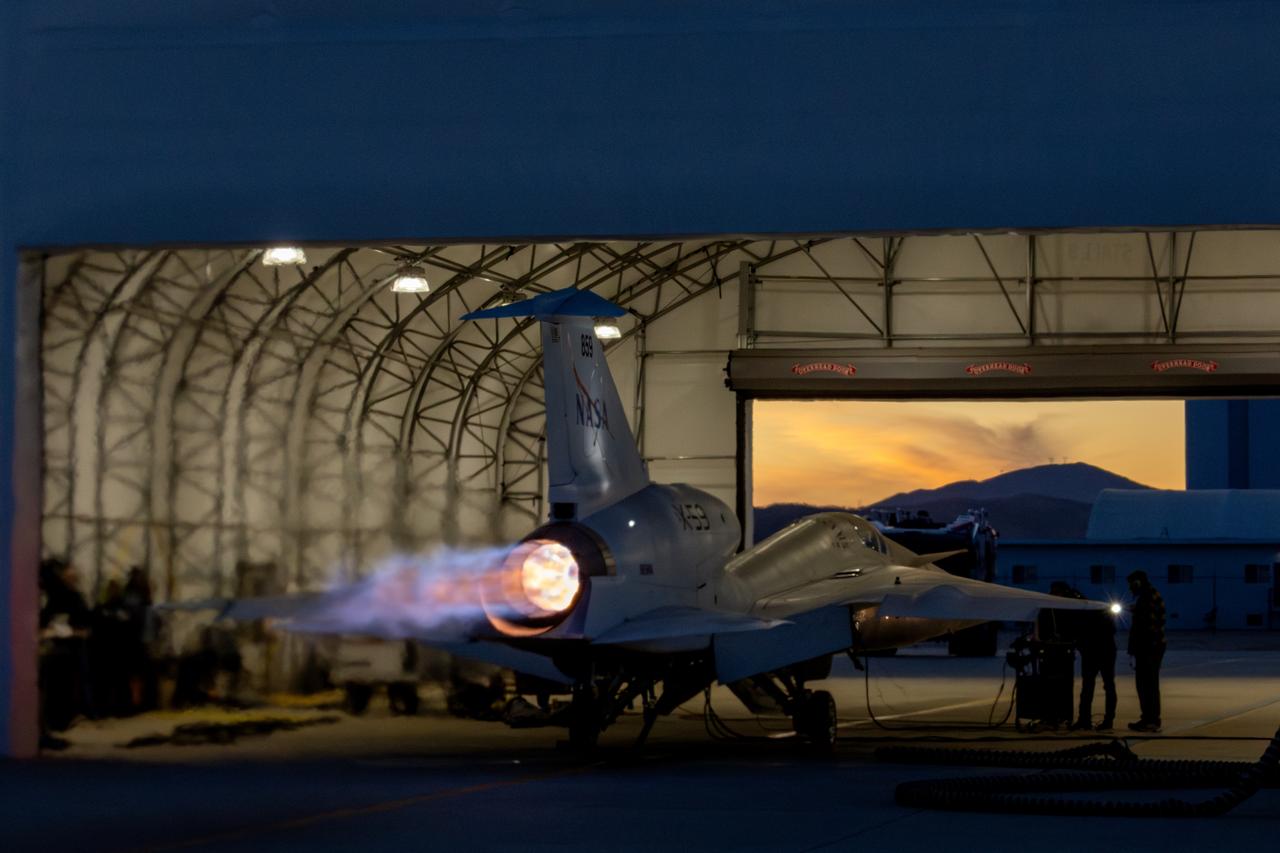

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.
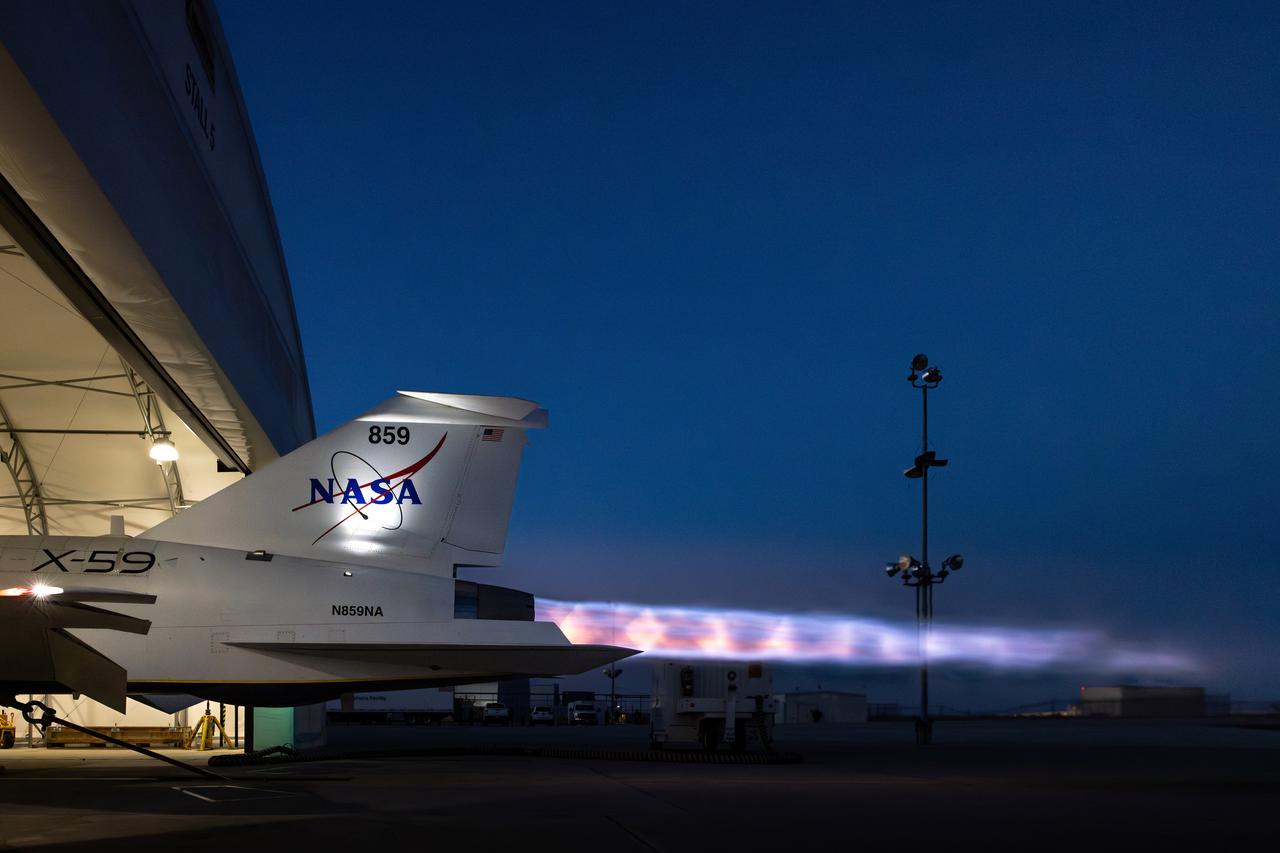

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.
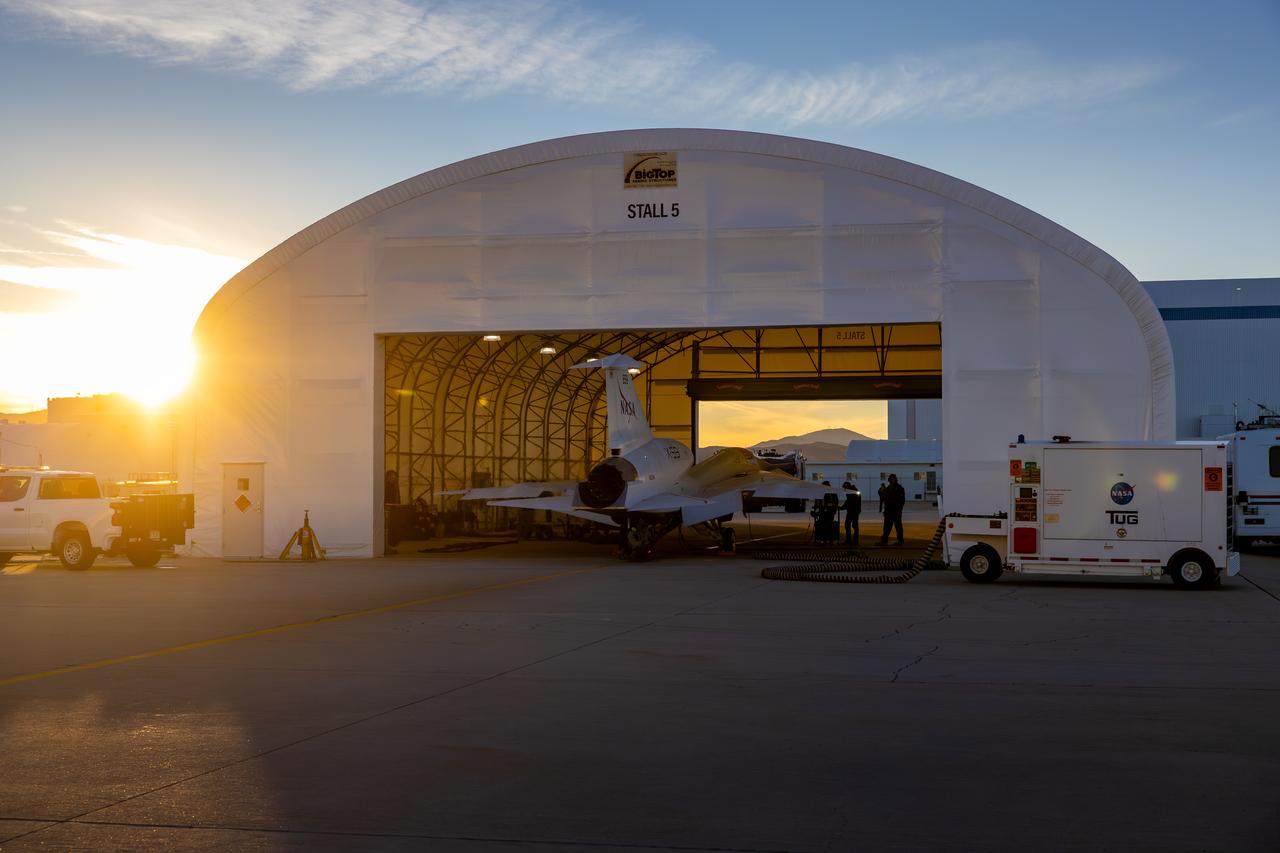

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits inside its run stall in preparation for maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Teams conduct final checks on the aircraft before its high-thrust engine runs. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission designed to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land, addressing a key barrier to commercial supersonic travel.
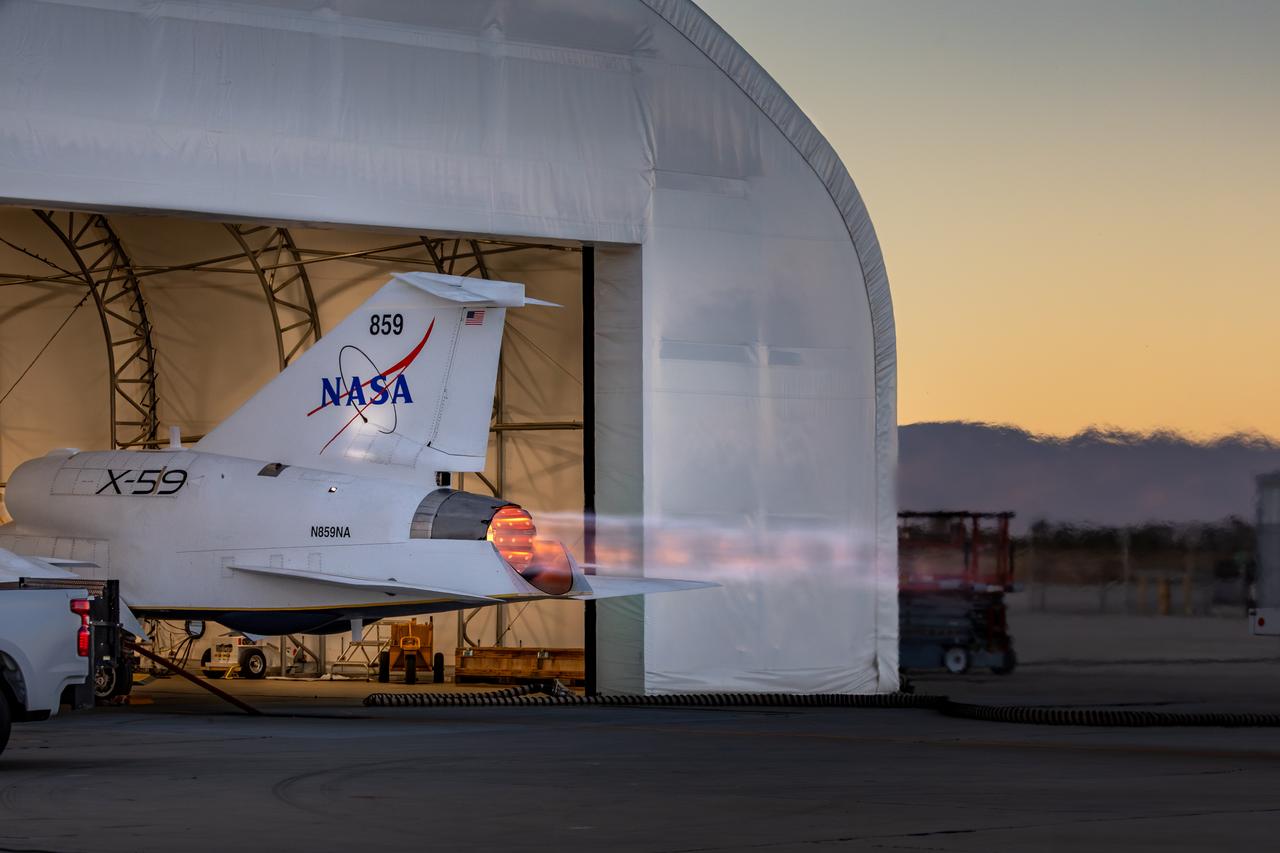

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.
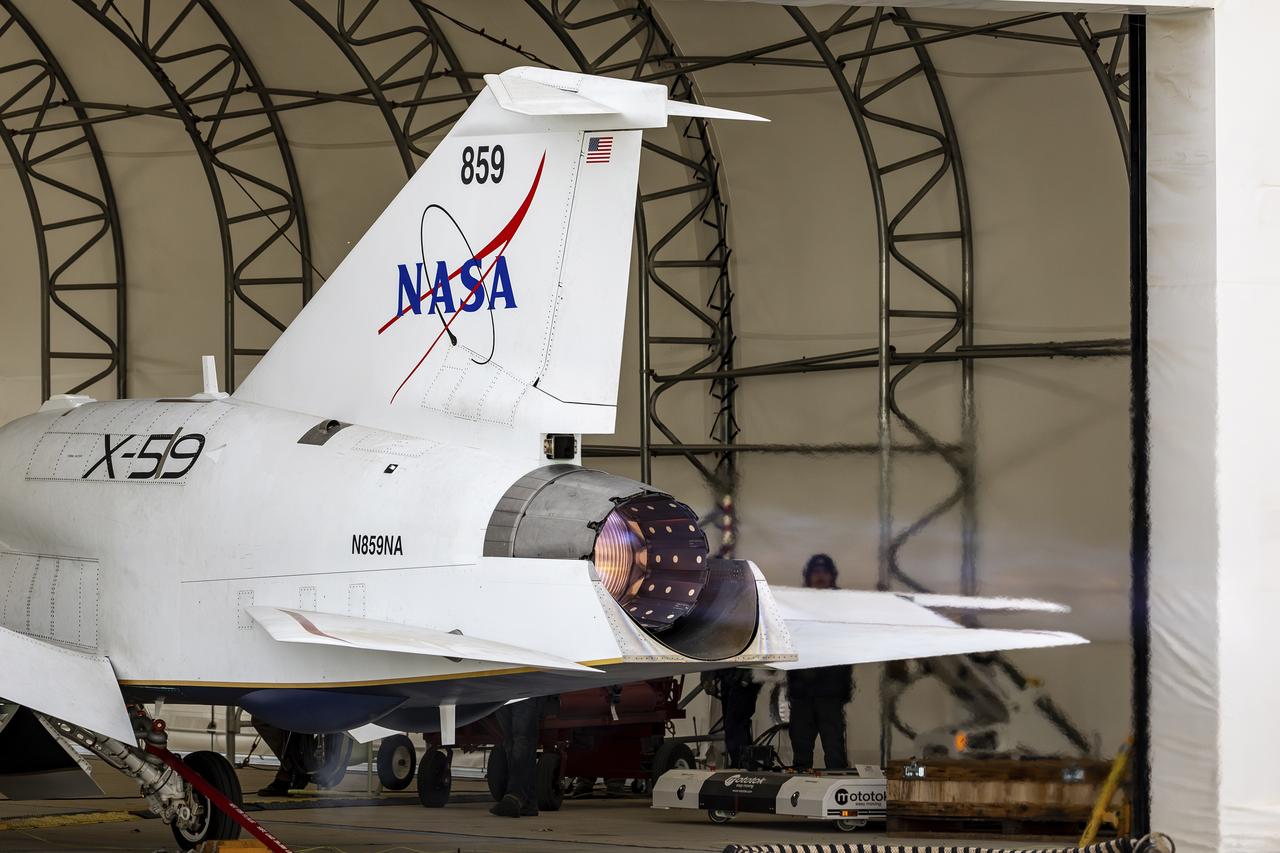

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft completed its first maximum afterburner test at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. This full-power test, during which the engine generates additional thrust, validates the additional power needed for meeting the testing conditions of the aircraft. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to overcome a major barrier to supersonic flight over land by reducing the noise of sonic booms.
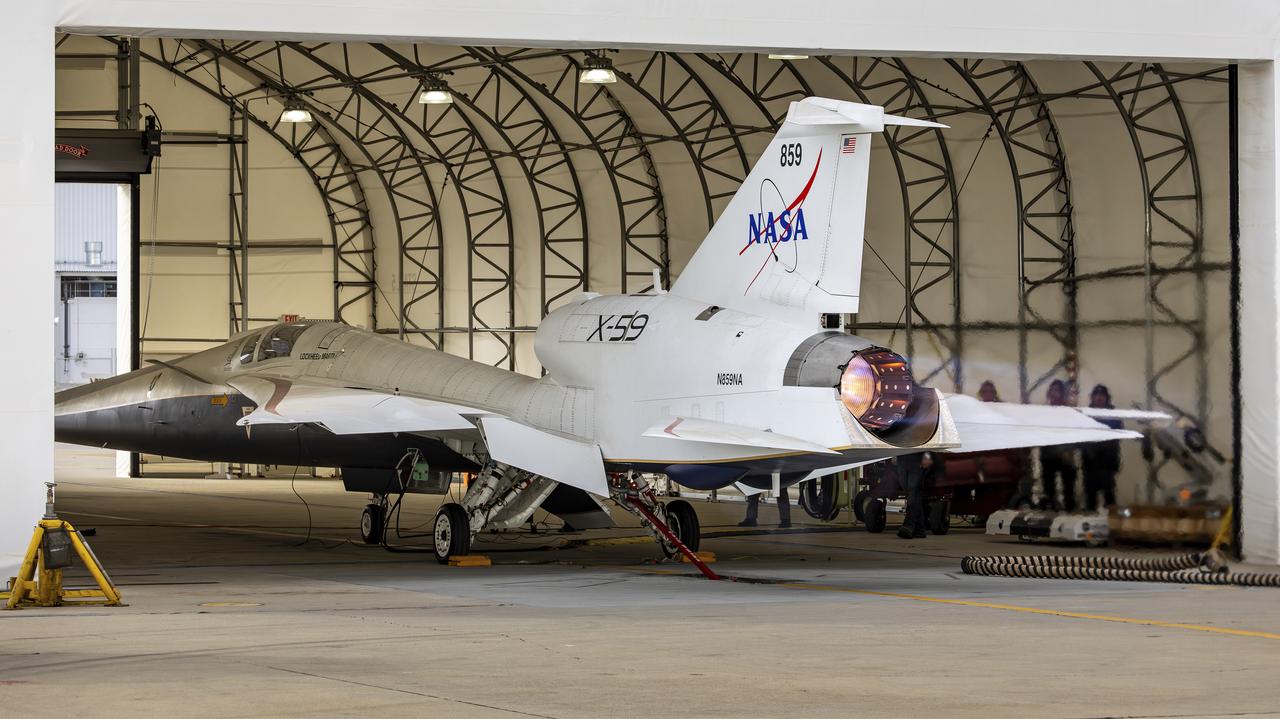

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft completed its first maximum afterburner test at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. This full-power test, during which the engine generates additional thrust, validates the additional power needed for meeting the testing conditions of the aircraft. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to overcome a major barrier to supersonic flight over land by reducing the noise of sonic booms.
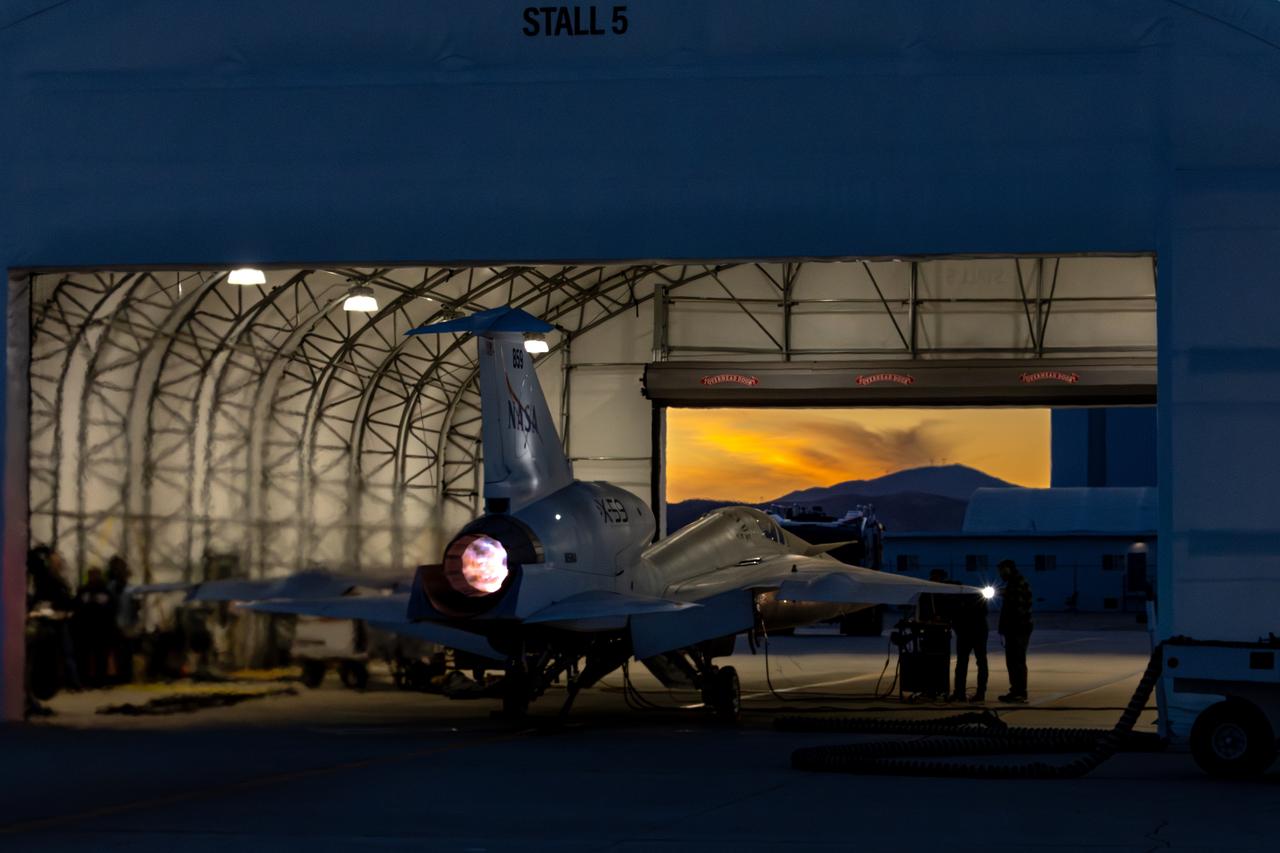

NASA’s X-59 lights up the night sky with its unique Mach diamonds, also known as shock diamonds, during maximum afterburner testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The test demonstrates the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight, advancing NASA’s Quesst mission.
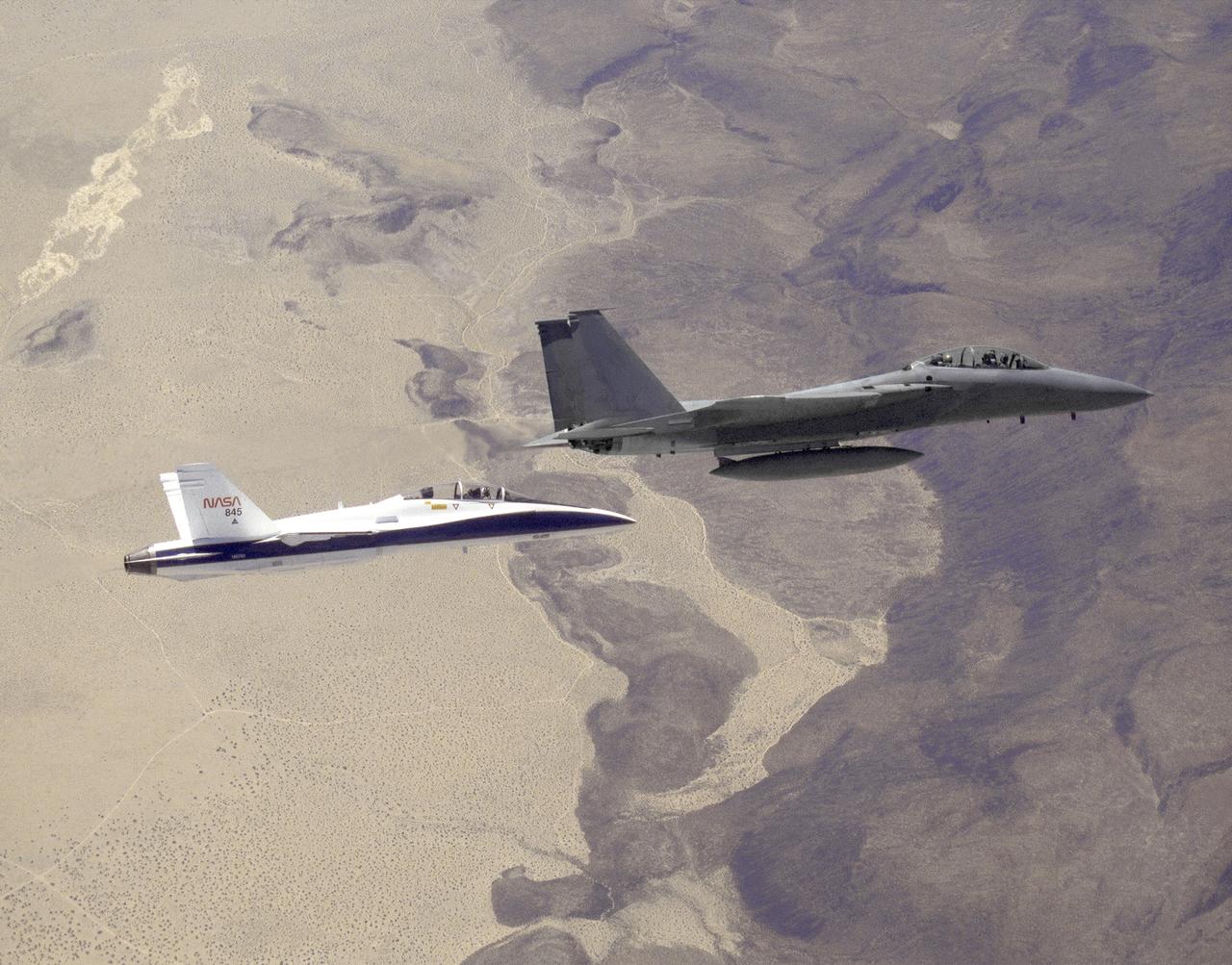

The three thrust-vectoring aircraft at Edwards, California, each capable of flying at extreme angles of attack, cruise over the California desert in formation during flight in March 1994. They are, from left, NASA's F-18 High Alpha Research Vehicle (HARV), flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center; the X-31, flown by the X-31 International Test Organization (ITO) at Dryden; and the Air Force F-16 Multi-Axis Thrust Vectoring (MATV) aircraft.
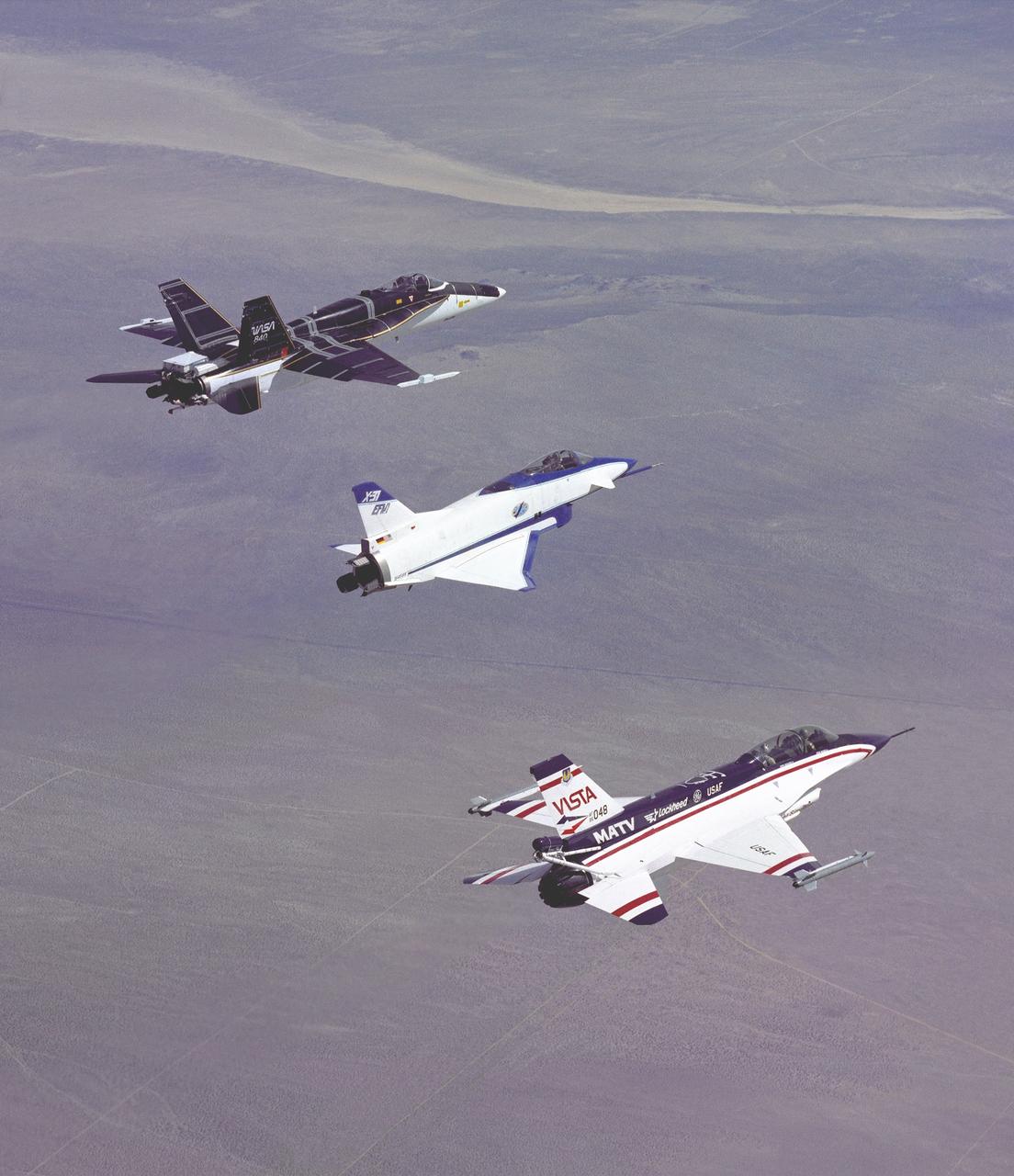

The three thrust-vectoring aircraft at Edwards, California, each capable of flying at extreme angles of attack, cruise over the California desert in formation during flight in March 1994. They are, from left, NASA's F-18 High Alpha Research Vehicle (HARV), flown by the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center; the X-31, flown by the X-31 International Test Organization (ITO) at Dryden; and the Air Force F-16 Multi-Axis Thrust Vectoring (MATV) aircraft.
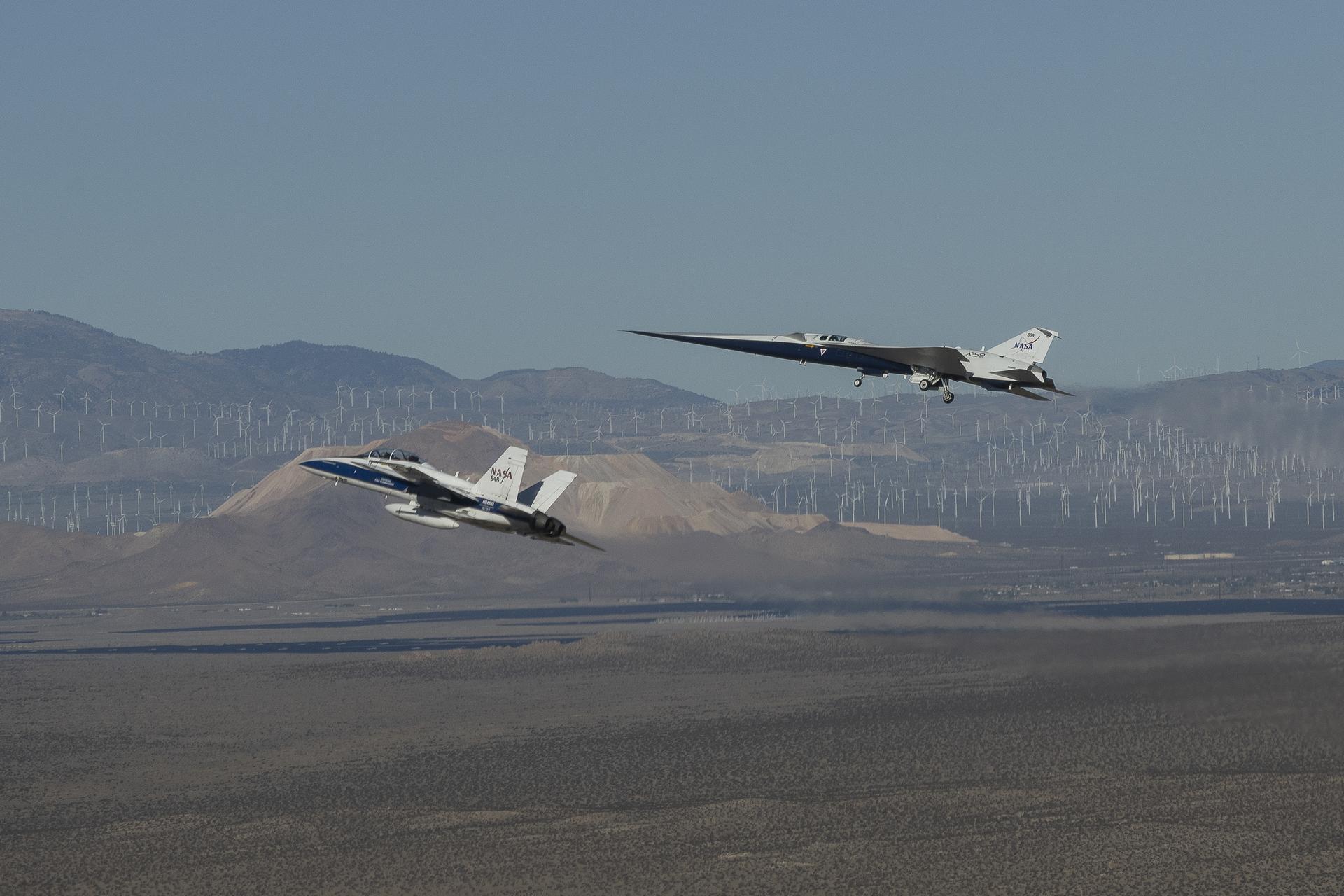

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft flies above Palmdale and Edwards, California, during its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025, accompanied by a NASA F/A-18 research aircraft. A NASA F-15 research aircraft (not pictured) captured the image as the X-59 traveled to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, where it will begin flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land.
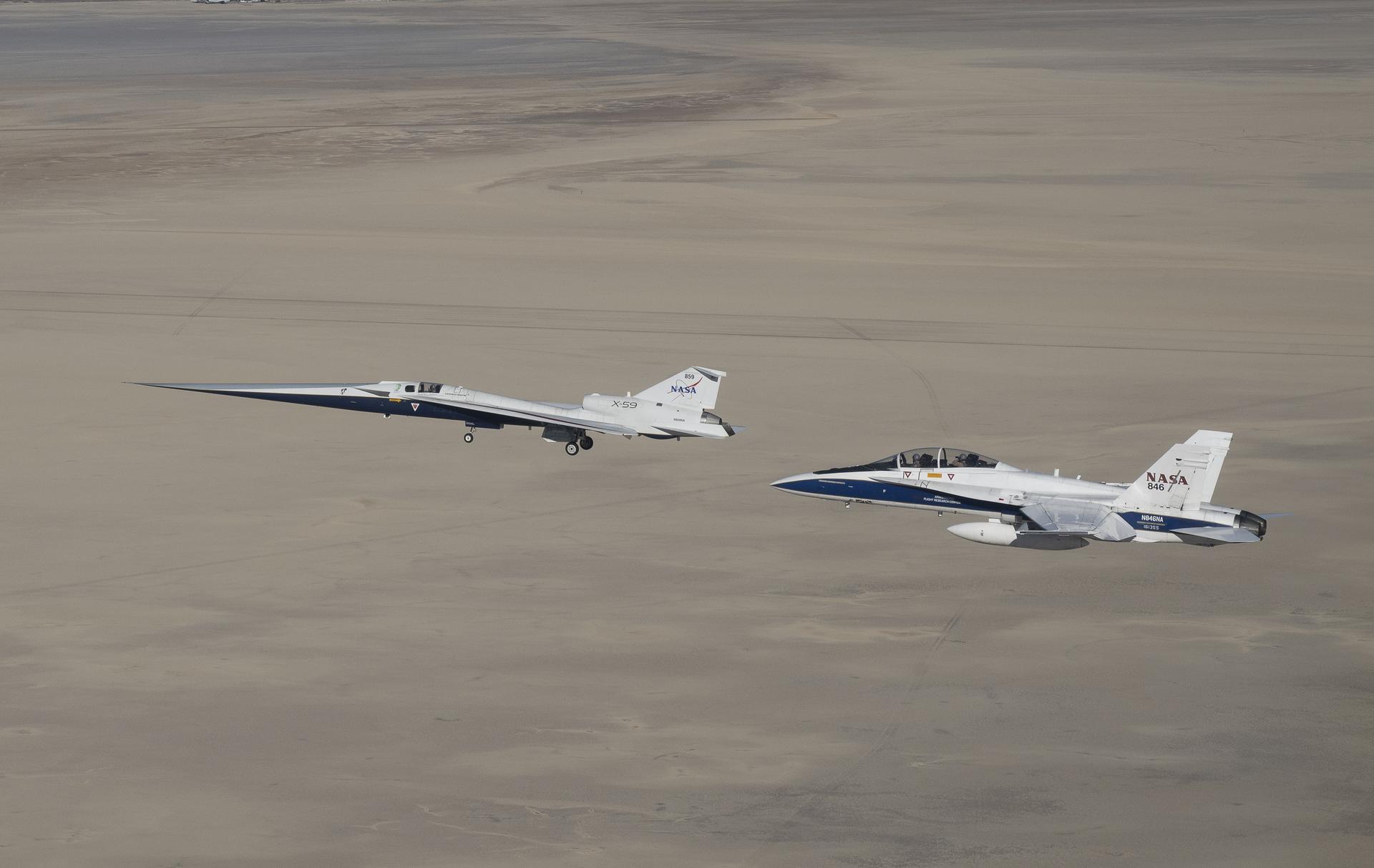

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft flies above Palmdale and Edwards, California, during its first flight Tuesday, Oct. 28, 2025, accompanied by a NASA F/A-18 research aircraft. A NASA F-15 research aircraft (not pictured) captured the image as the X-59 traveled to NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, where it will begin flight testing for NASA’s Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight over land.
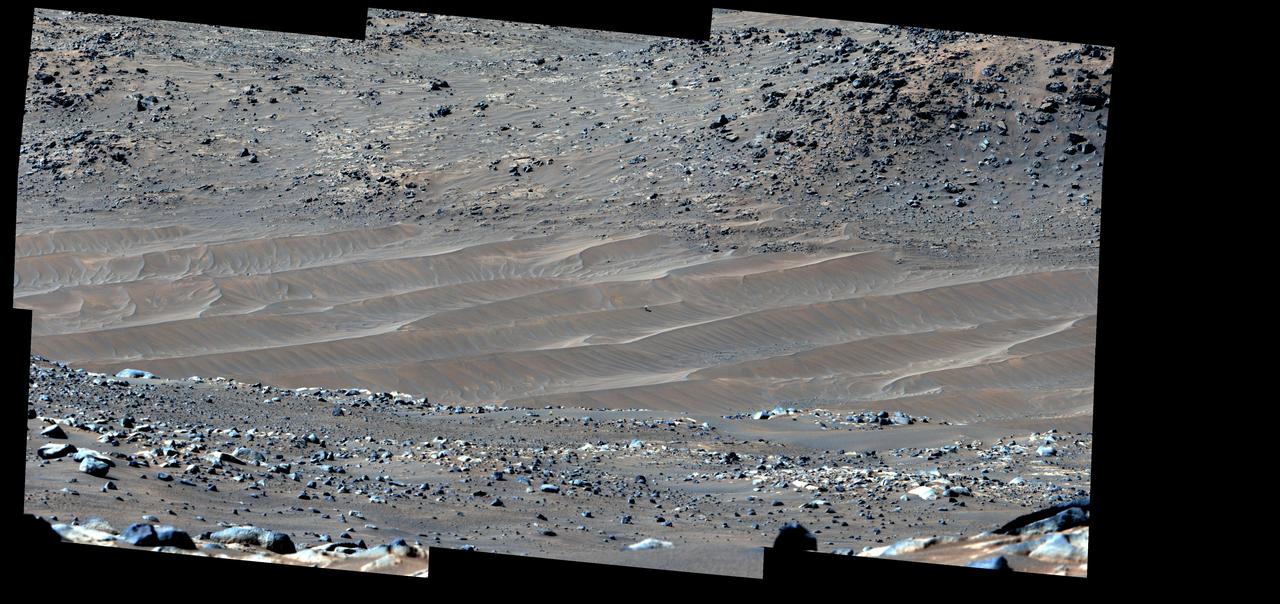

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this mosaic showing the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter at its final airfield on Feb. 4, 2024. The helicopter damaged its rotor blades during landing on its 72nd flight on Jan. 18, 2024. The Ingenuity team has nicknamed the spot where the helicopter completed its final flight "Valinor Hills" after the fictional location in J.R.R. Tolkien's fantasy novels, which include "The Lord of the Rings" trilogy. The six images that were stitched together to make up this mosaic were captured from about 1,475 feet (450 meters) away by the rover's Mastcam-Z imager. Shown here is an enhanced-color view that exaggerates subtle color differences in the scene to show more detail. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages the project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center in California's Silicon Valley and NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm, and SolAero also provided design assistance and major vehicle components. Lockheed Martin Space designed and manufactured the Mars Helicopter Delivery System. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26236