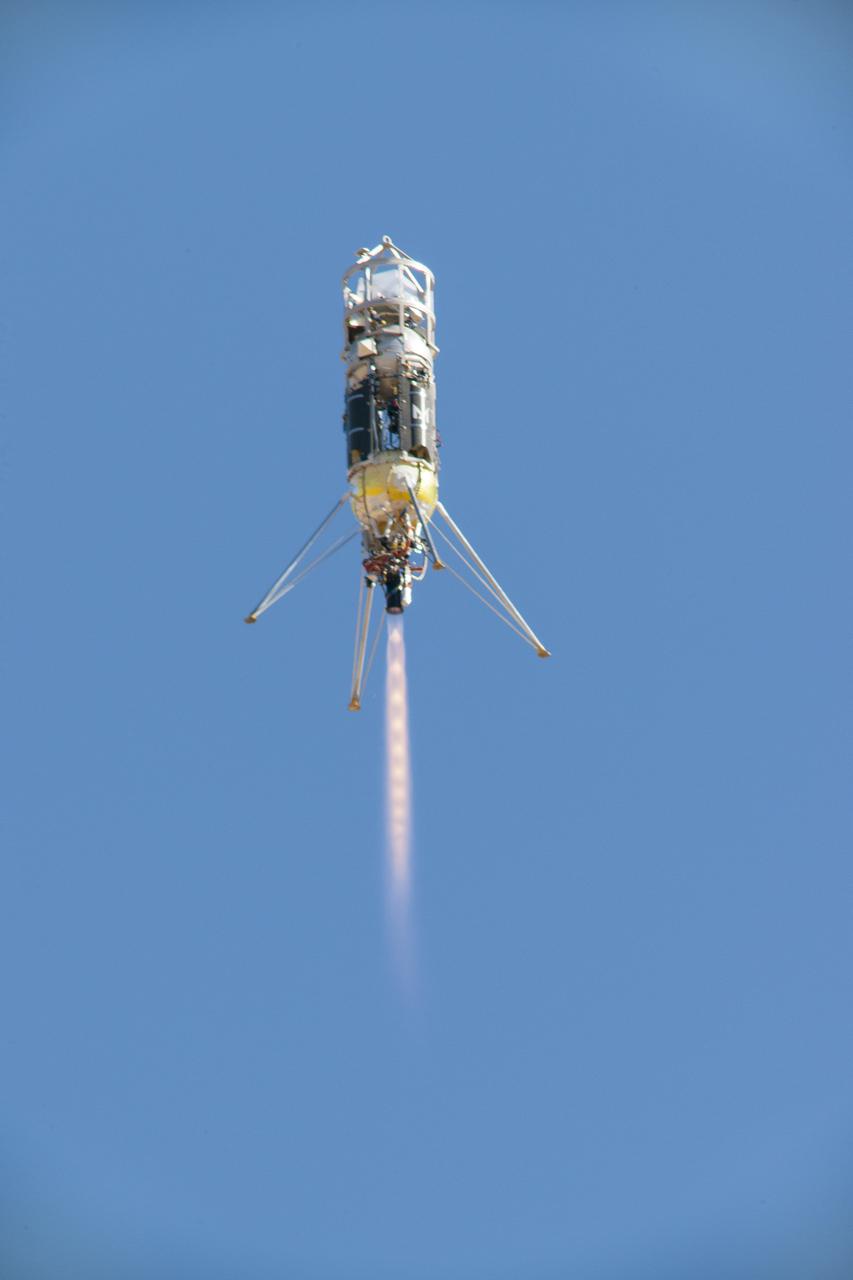

Masten rocket, Xodiac, launches out of Mojave Air and Space Port carrying JHU APL electromagnetic field measurement experiment.

Engineers at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, inspect the propulsion module of NASA's Europa Clipper spacecraft. In 2022, this major piece of hardware, designed and built at APL, will ship to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California for assembly, test, and launch operations (ATLO). With an internal global ocean under a thick layer of ice, Jupiter's moon Europa may have the potential to harbor existing life. The Europa Clipper spacecraft will swoop around Jupiter on an elliptical path, dipping close to the moon on each flyby to collect data. Understanding Europa's habitability will help scientists better understand how life developed on Earth and the potential for finding life beyond our planet. Europa Clipper is set to launch in 2024. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24783

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory speaks about the Kuiper Belt during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

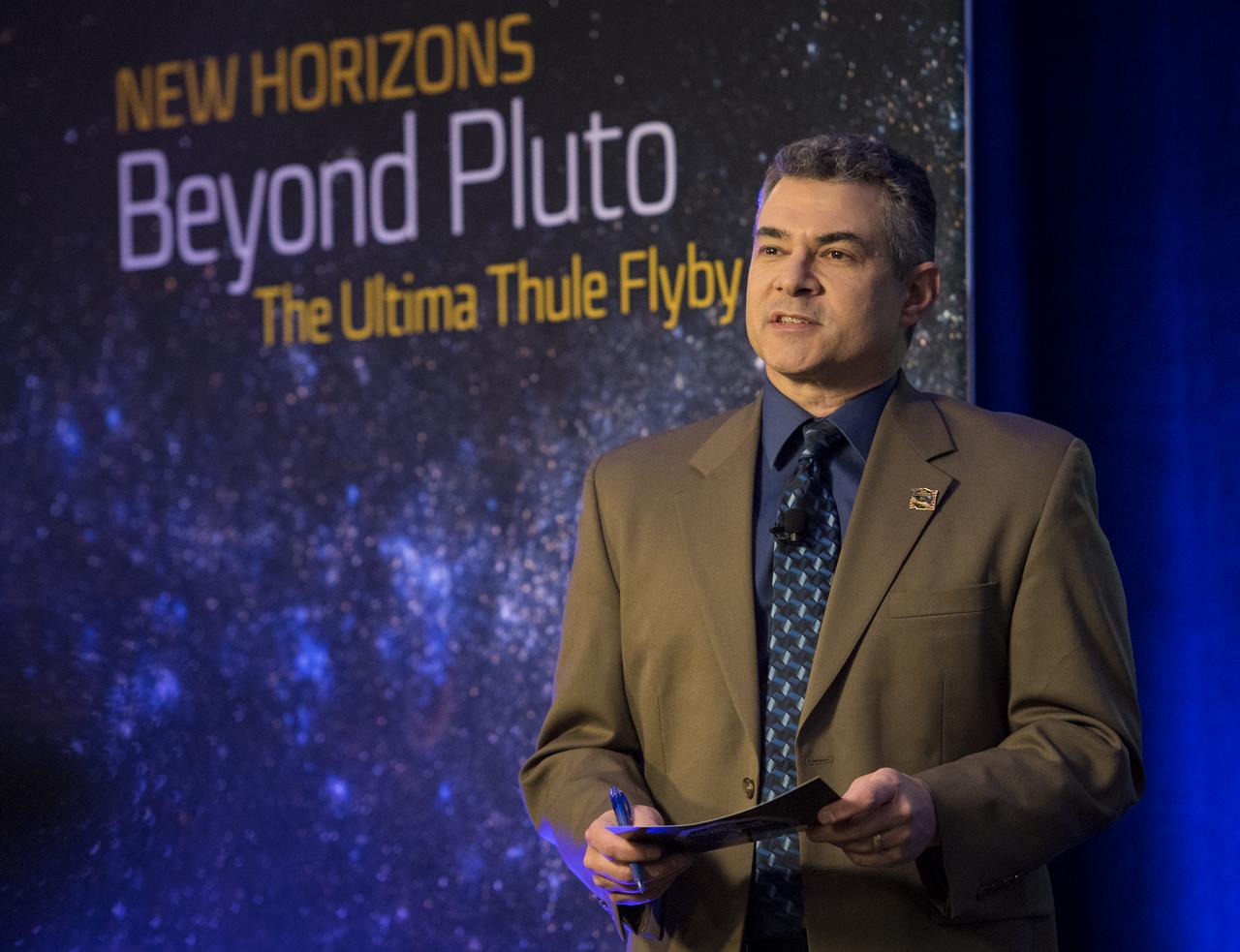
New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, speaks at a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory speaks about the Kuiper Belt during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory speaks about the Kuiper Belt during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
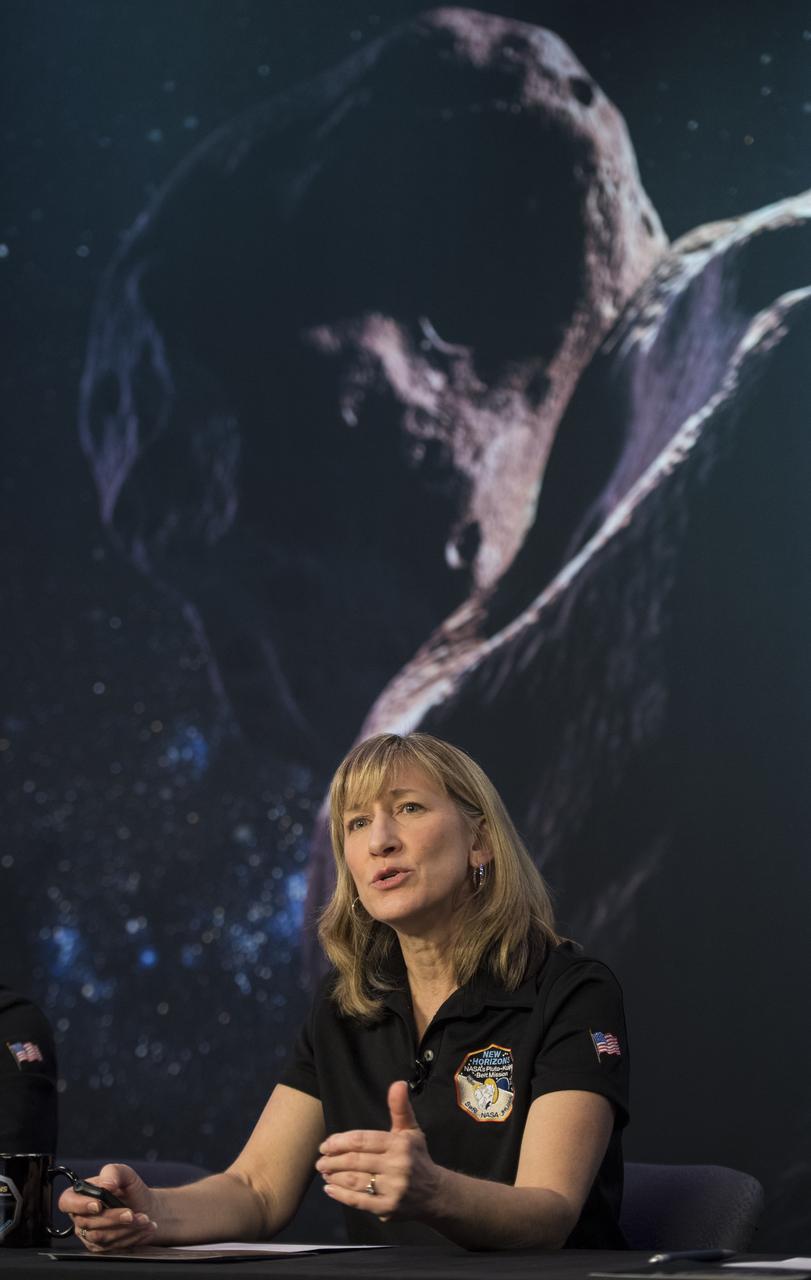

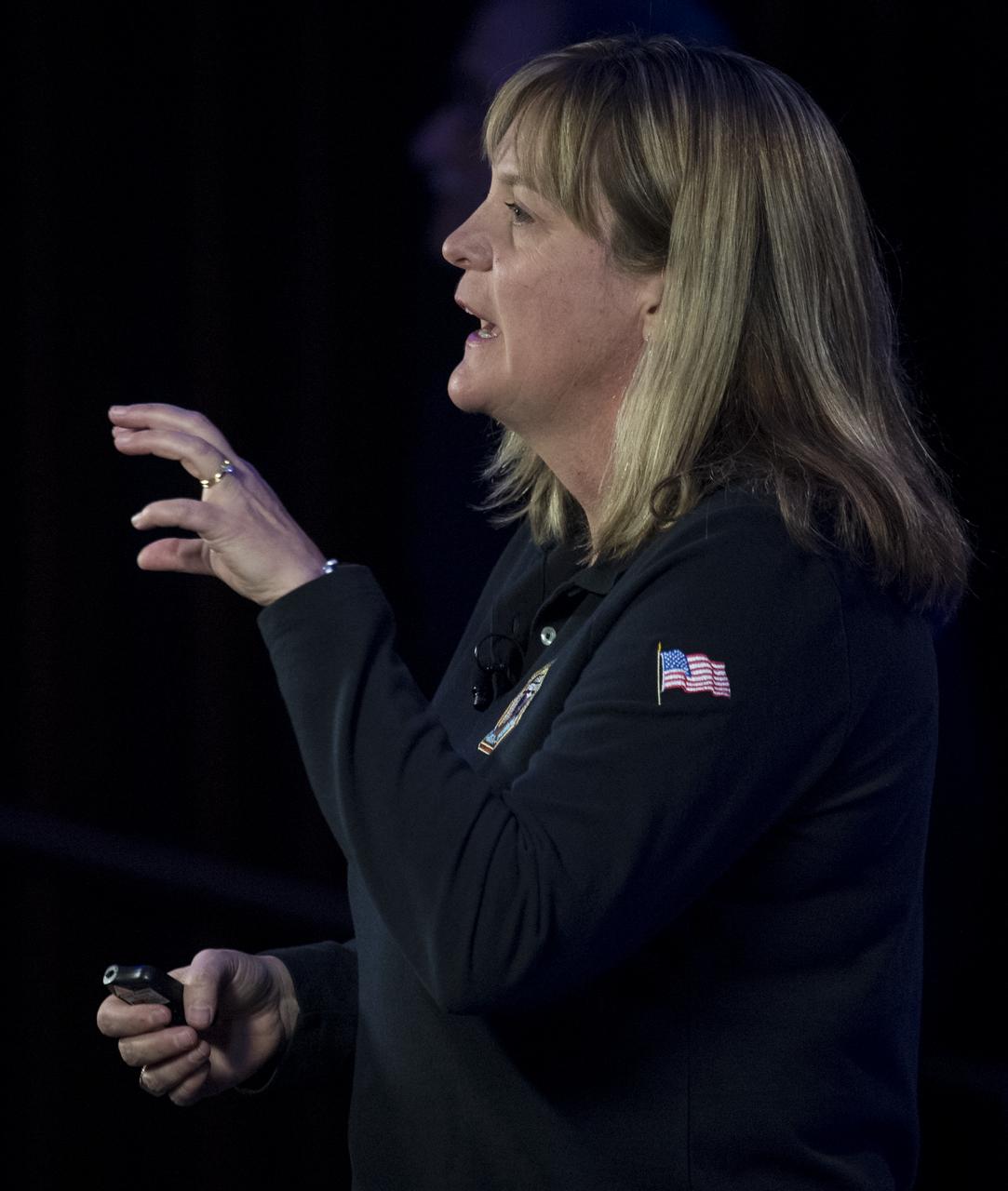
New Horizons project manager Helene Winters of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks at a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
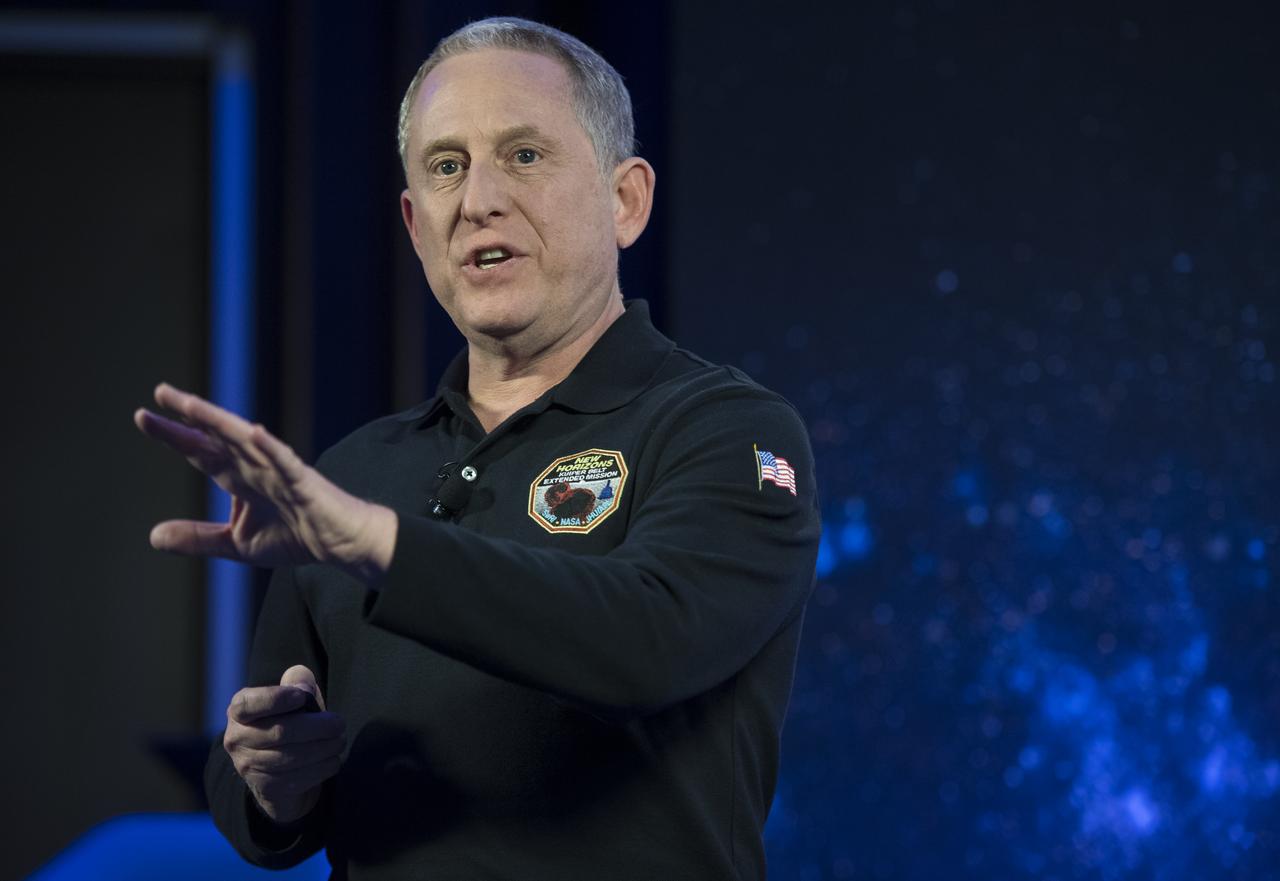

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, speaks during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project manager Helene Winters of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
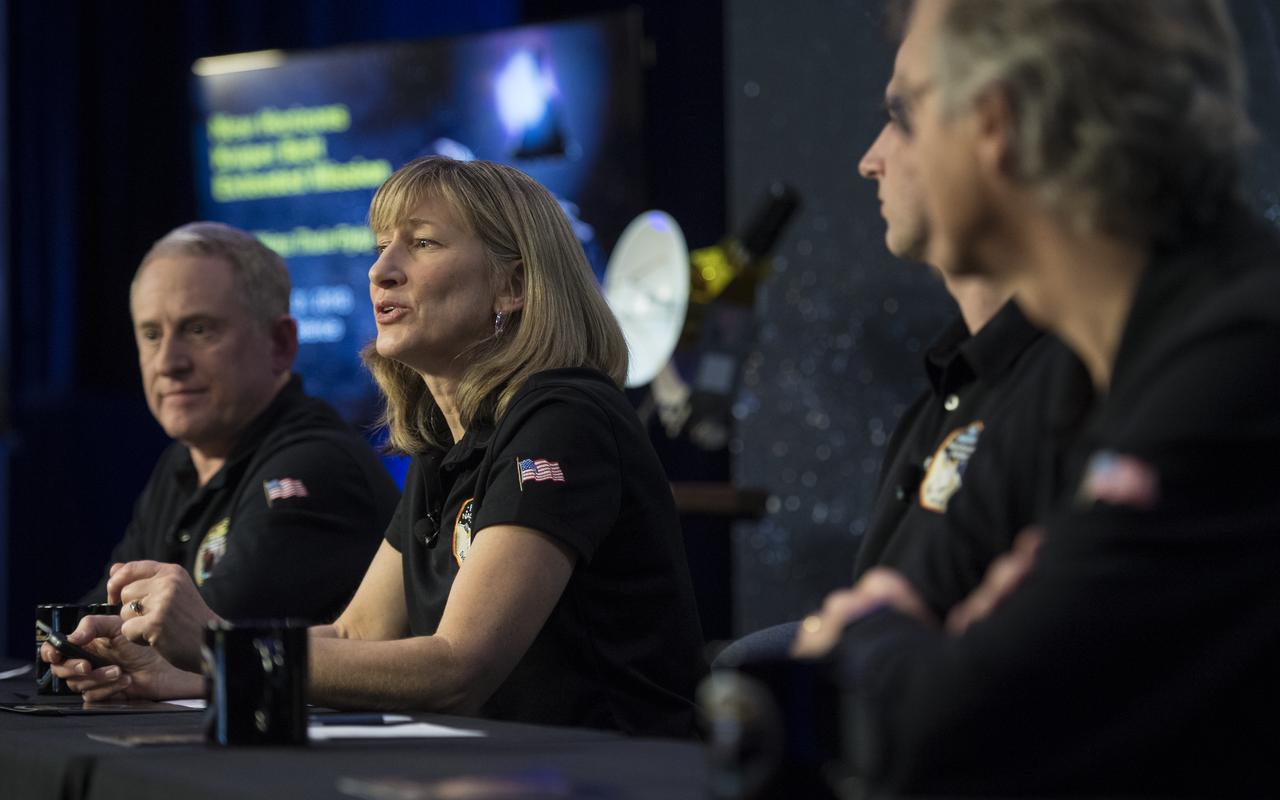

New Horizons project manager Helene Winters of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks at a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
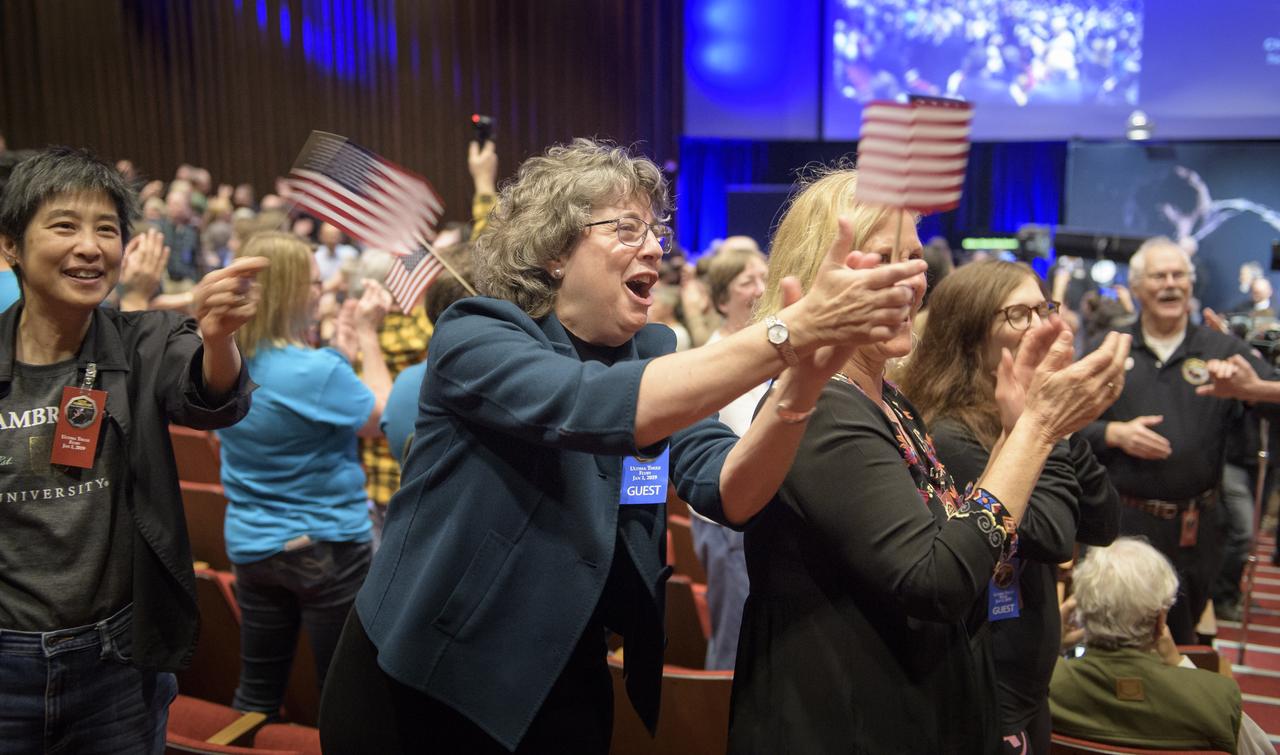

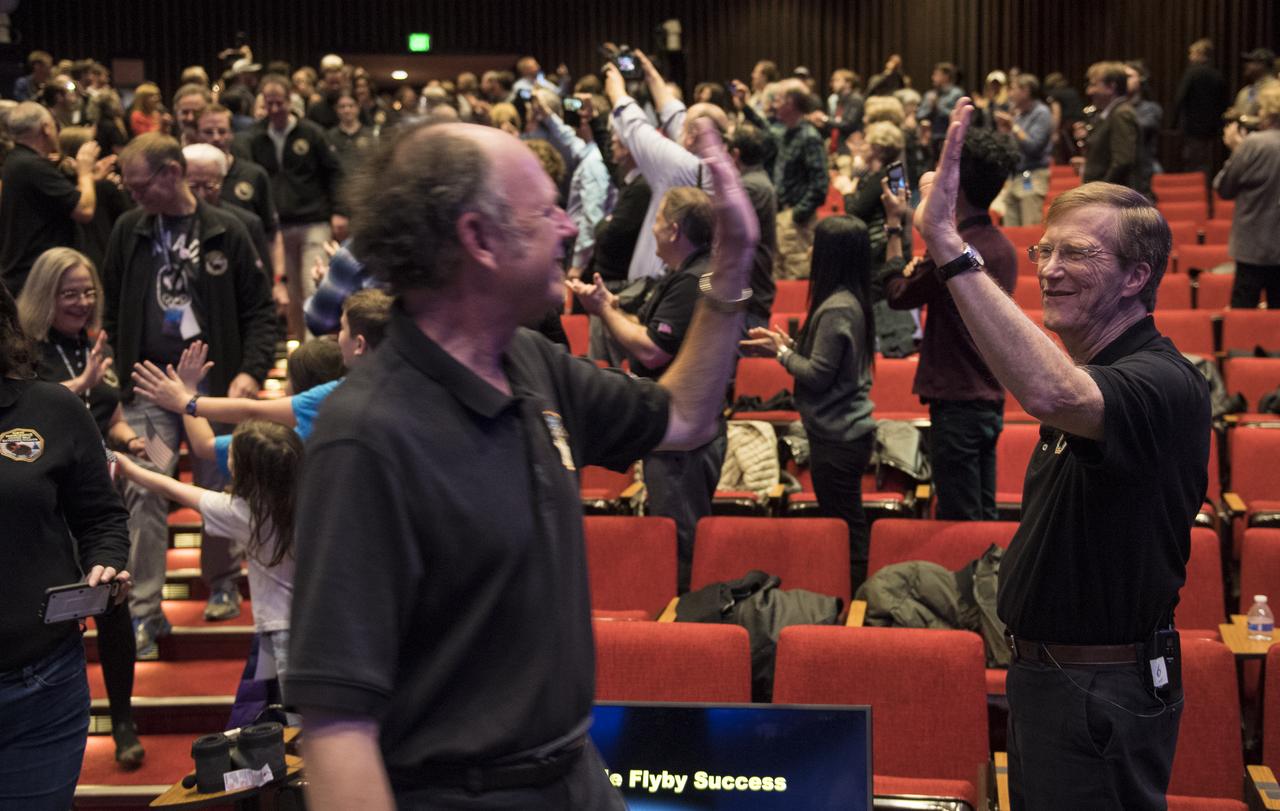
Guests congratulate New Horizons team members after they received signals from the New Horizons spacecraft that it is healthy and it collected data during the fly of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
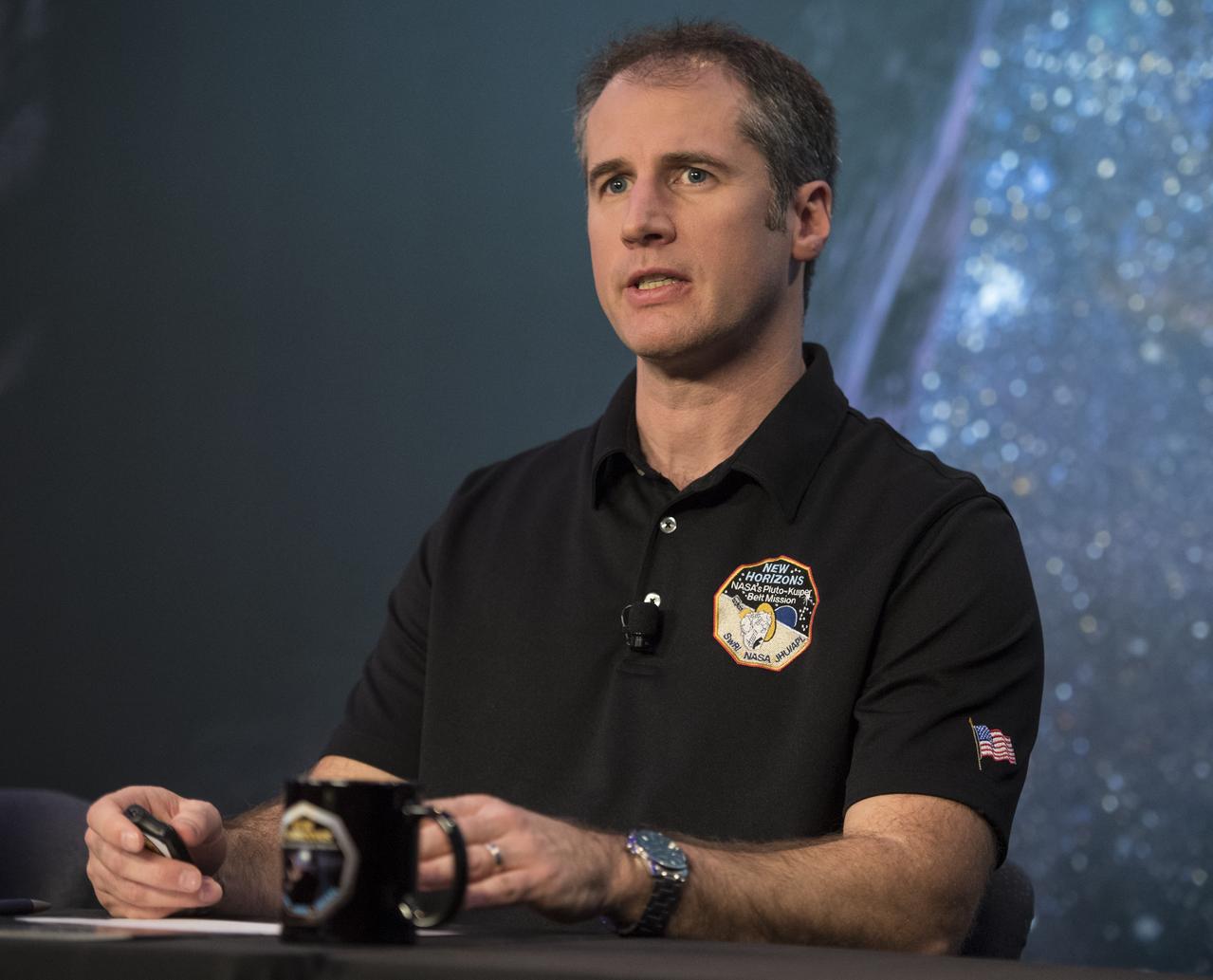

Fred Pelletier, lead of the project navigation team at KinetX Inc. in Simi Valley, California, speaks at a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, speaks during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, speaks about the flyby of Ultima Thule during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
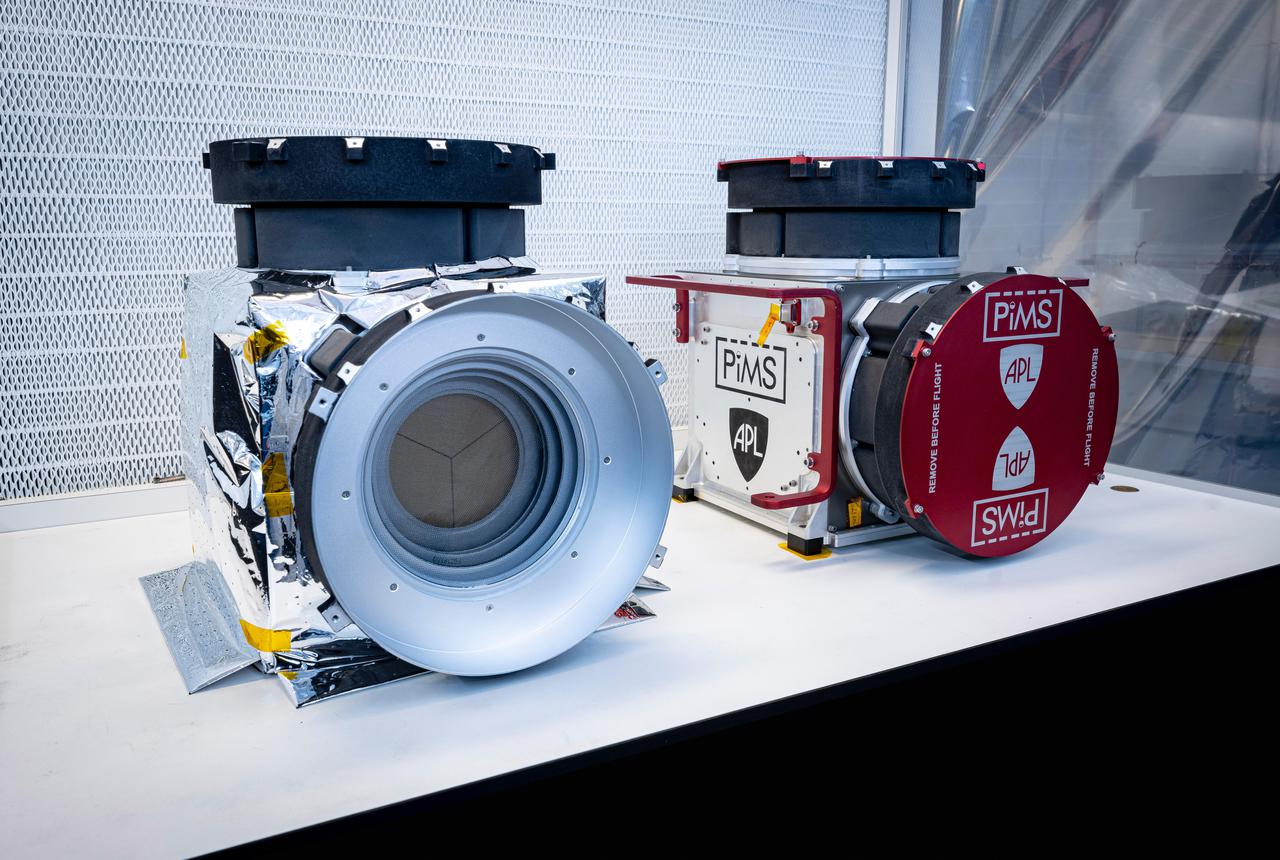

Included in the payload of science instruments for NASA's Europa Clipper is the Plasma Instrument for Magnetic Sounding (PIMS). Scientists will use PIMS to study the characteristics of plasma around Europa to better understand the moon's ice shell thickness, ocean depth, and ocean salinity. Built by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, PIMS is made up of two instruments, each with two identical sensors called Faraday cups that will measure the plasmas, or electrically charged gases, in Europa's ionosphere and Jupiter's magnetosphere. Pictured in a clean room at APL are the recently assembled Faraday cup sensors and instrument housings in two configurations. On the left is the final flight hardware, with insulating thermal blankets installed; on the right is a test configuration that protects sensitive hardware for transportation. With an internal global ocean twice the size of Earth's oceans combined, Europa may have the potential to harbor life. NASA's Europa Clipper spacecraft will swoop around Jupiter on an elliptical path, dipping close to the moon on each flyby to collect data. Understanding Europa's habitability will help scientists better understand how life developed on Earth and the potential for finding life beyond our planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24327
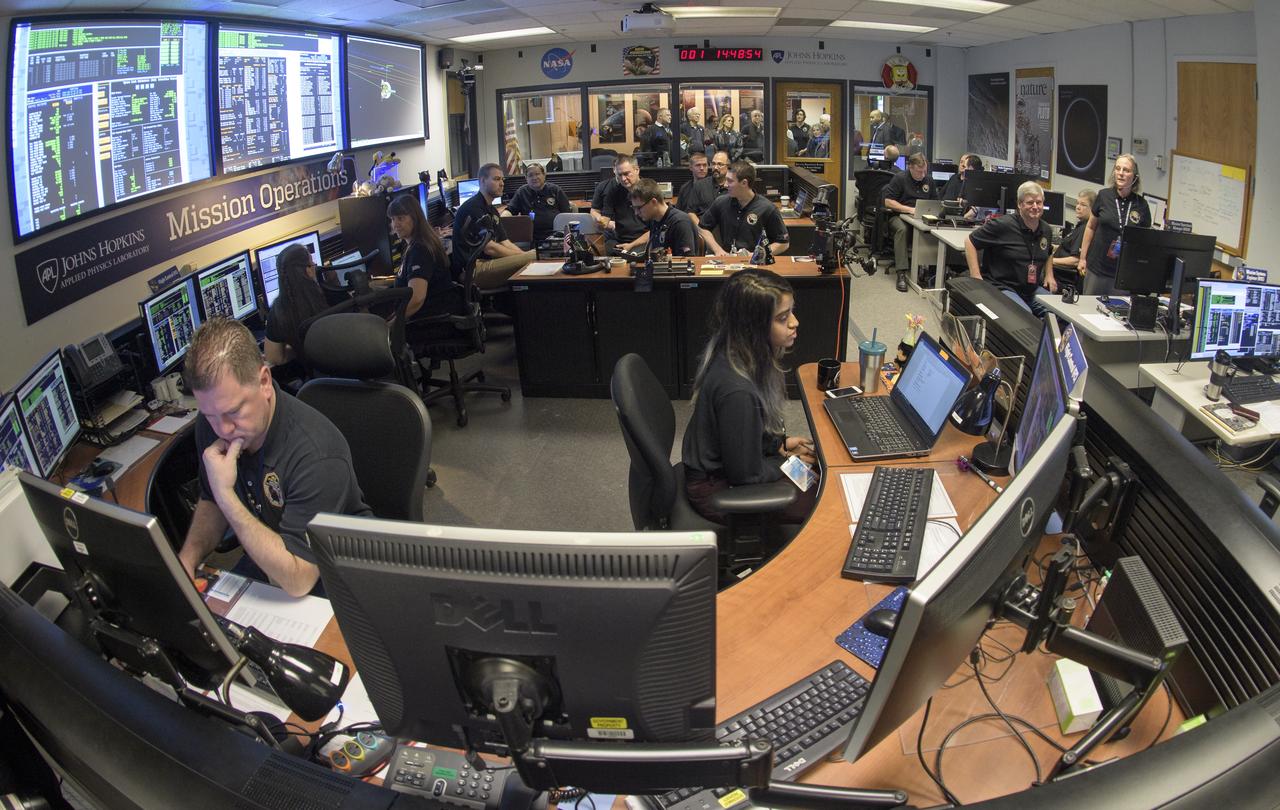

New Horizons team members wait for a signal from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
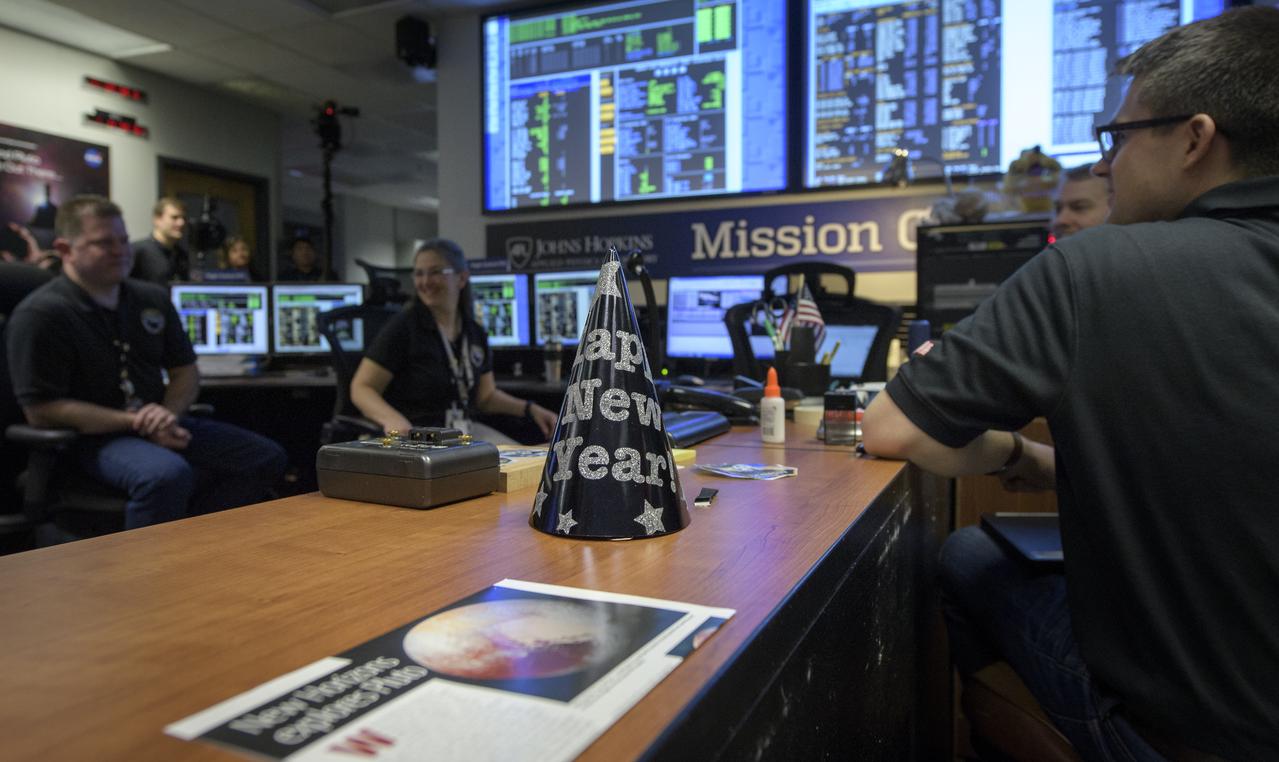

New Horizons team members wait for a signal from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
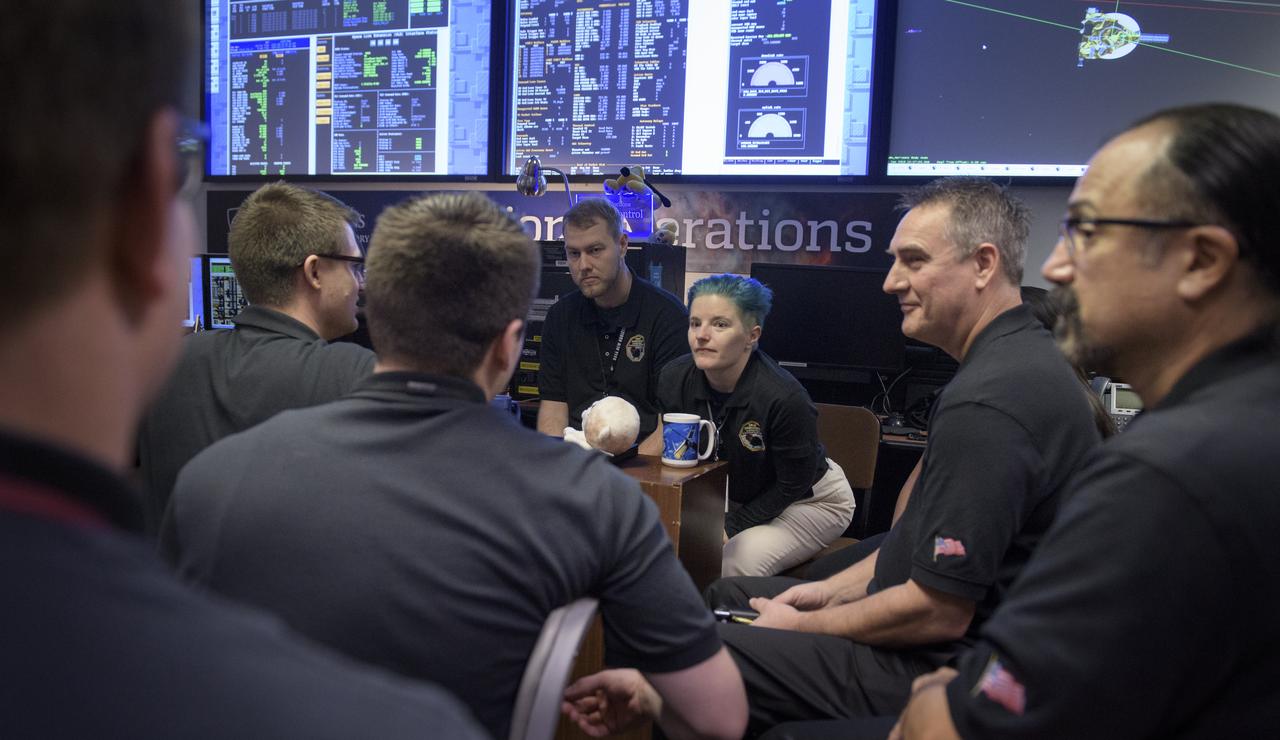

New Horizons team members wait for a signal from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
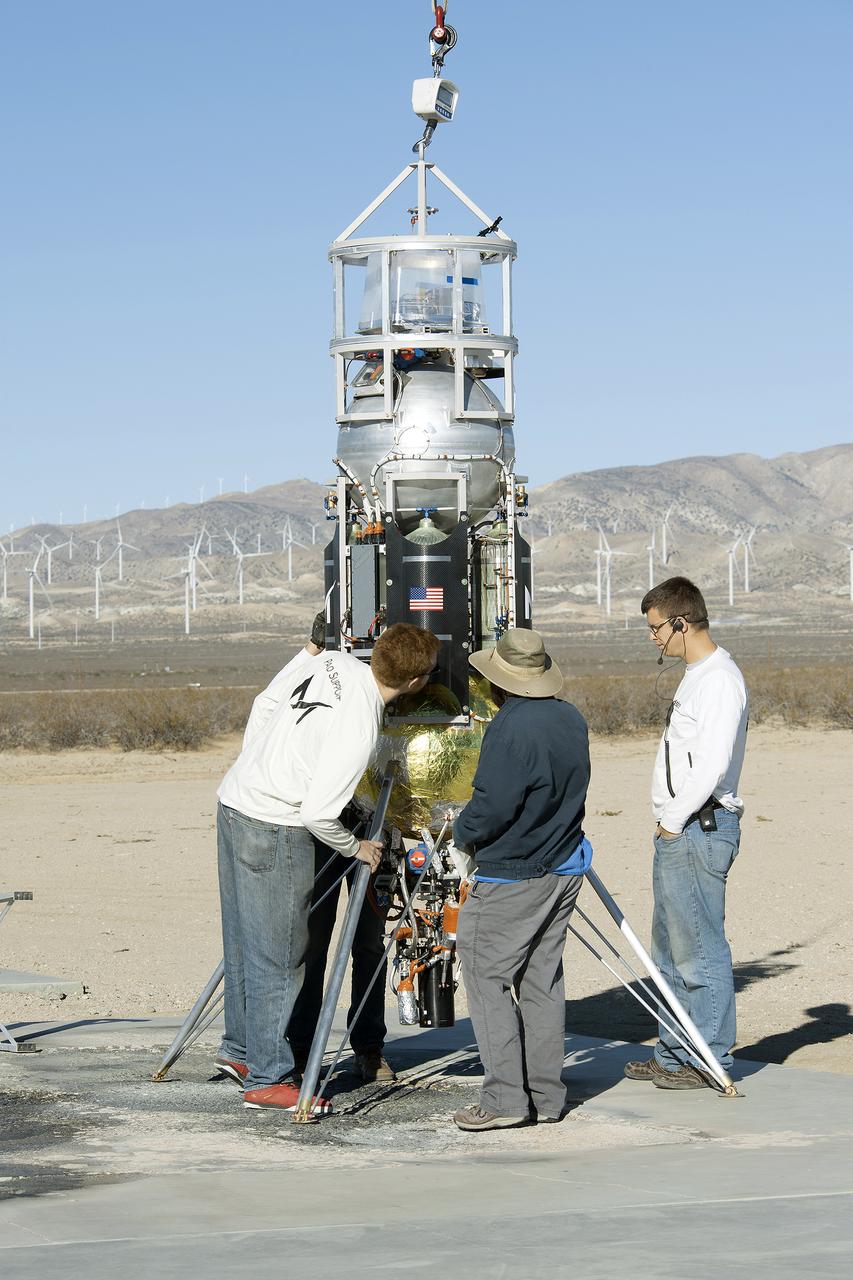

From left to right Masten employees, Luke Farrell, Richard Garcia and intern Alex Drozda employees prepare Xodiac rocket to flight test JHU APL technology.
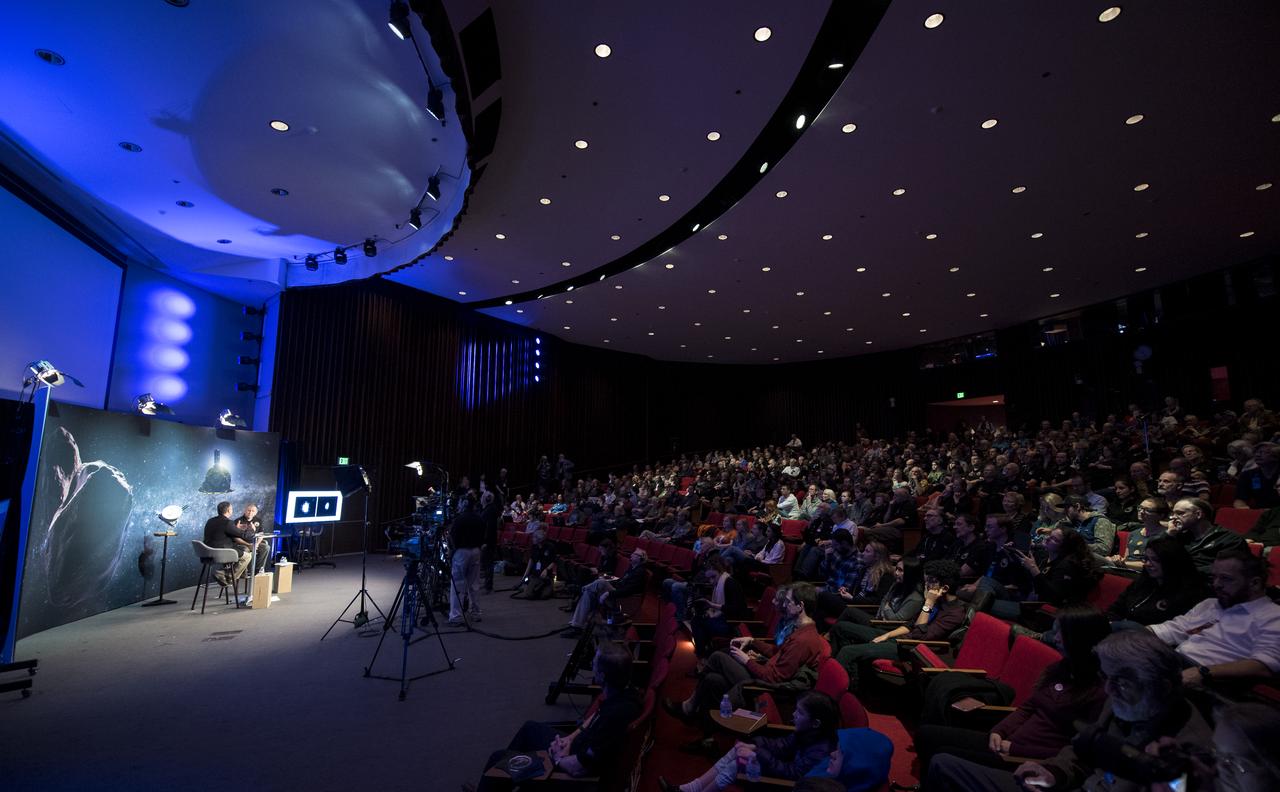

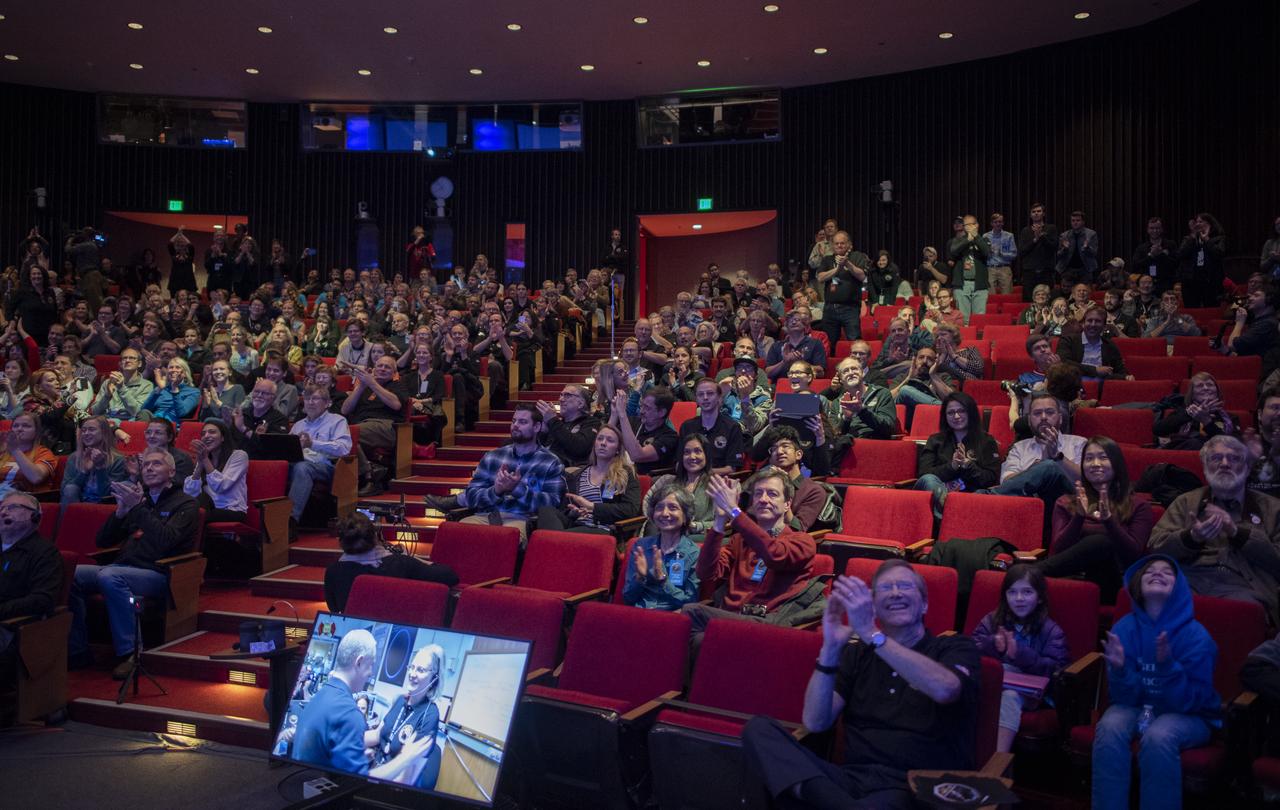
New Horizons team members and guests watch a live feed of the Mission Operations Center (MOC) as the team waits to receive confirmation from the spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
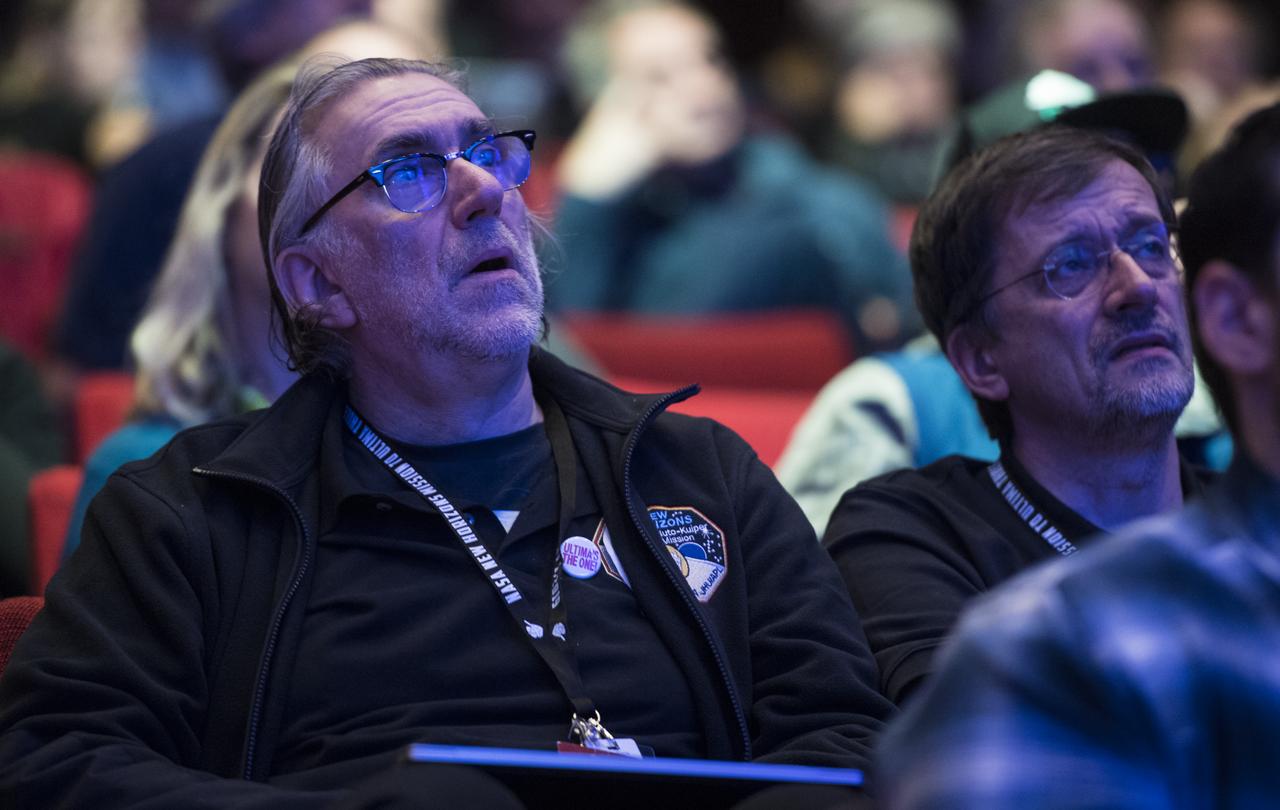

New Horizons team members and guests watch a live feed of the Mission Operations Center (MOC) as the team waits to receive confirmation from the spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
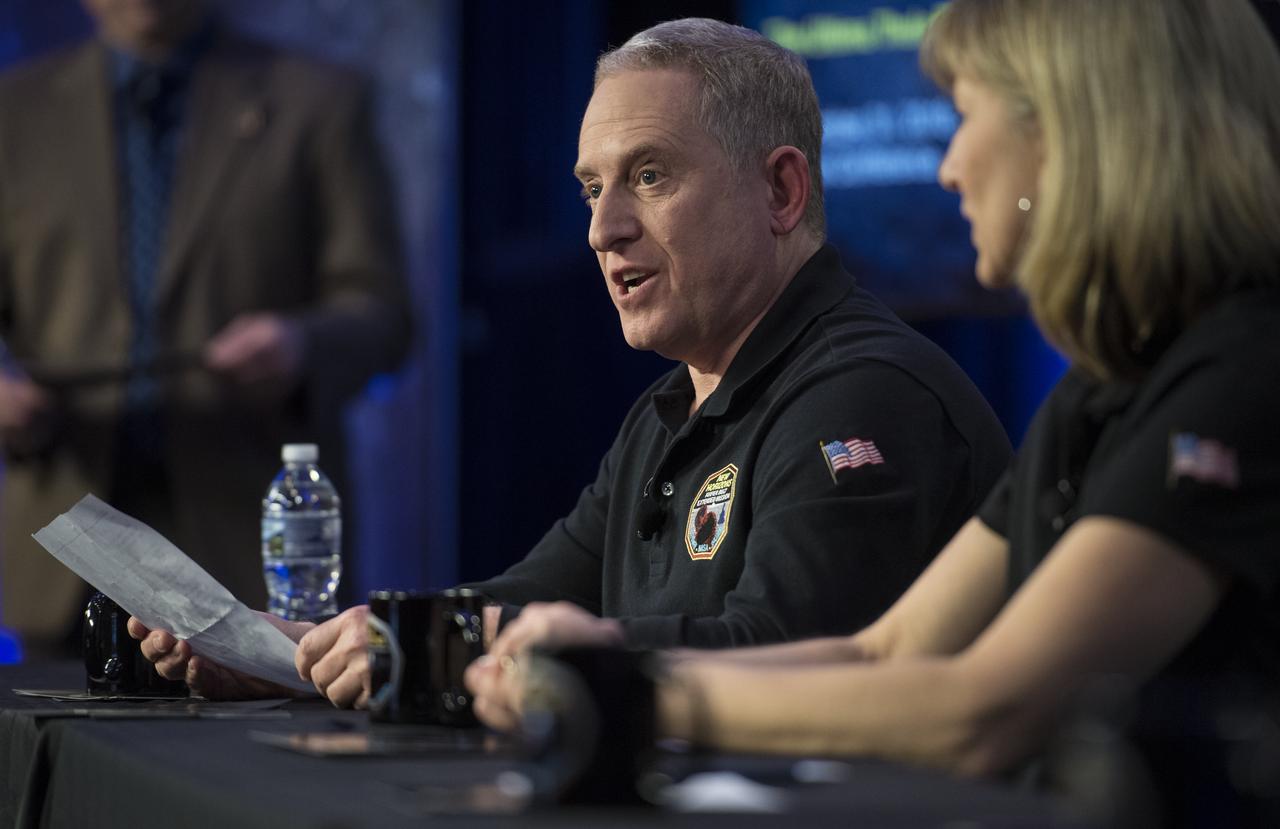

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, reads an e-mail sent by Associate Administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen during a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Michael Ryschkewitsch,head of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Space Exploration Sector, is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons team members and guests watch a live feed of the Mission Operations Center (MOC) as the team waits to receive confirmation from the spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO speaks during a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Mike Buckley, senior public information officer at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

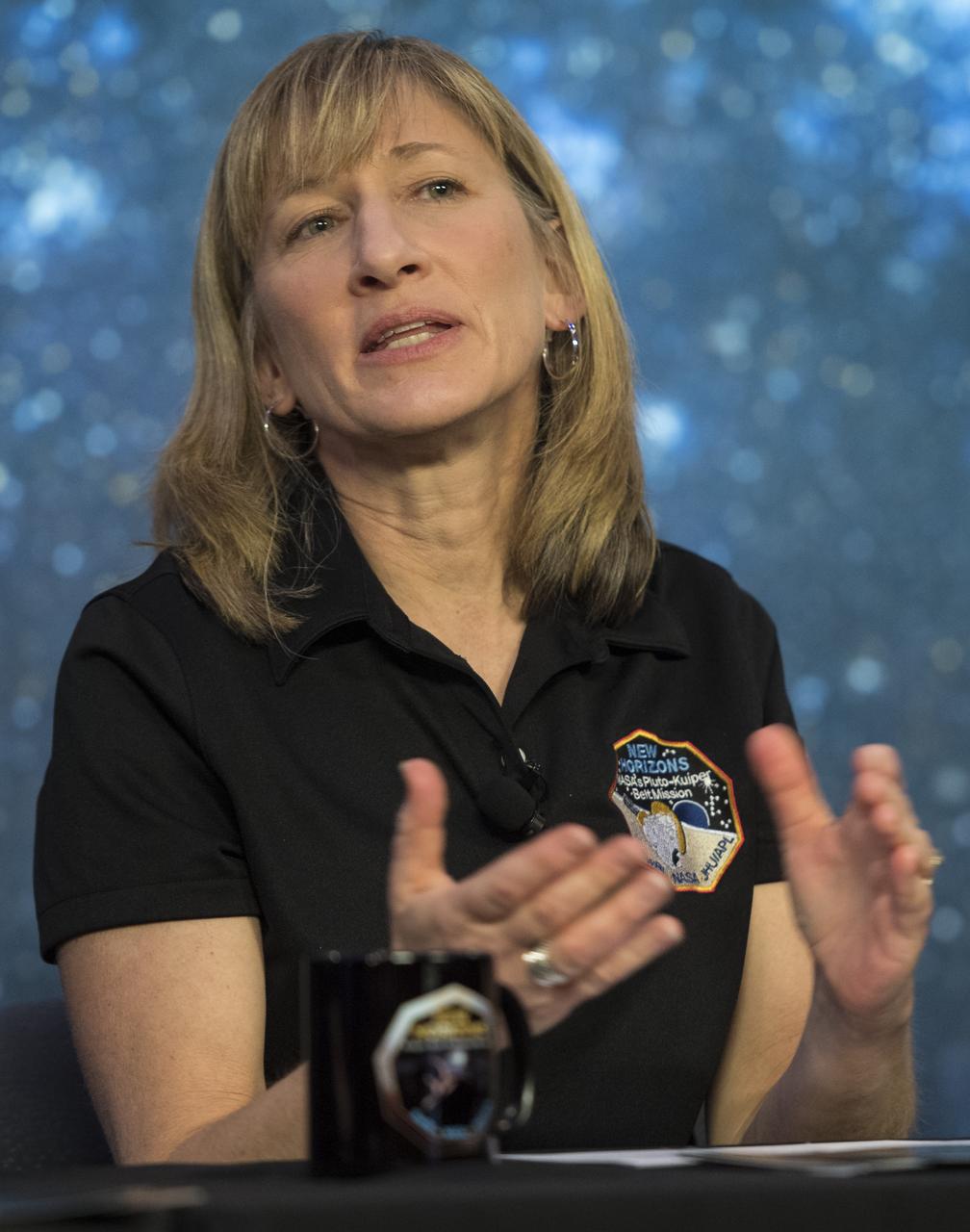
New Horizons co-investigator Cathy Olkin of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) speaks about Kuiper Belt object MU69, Ultima Thule, during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
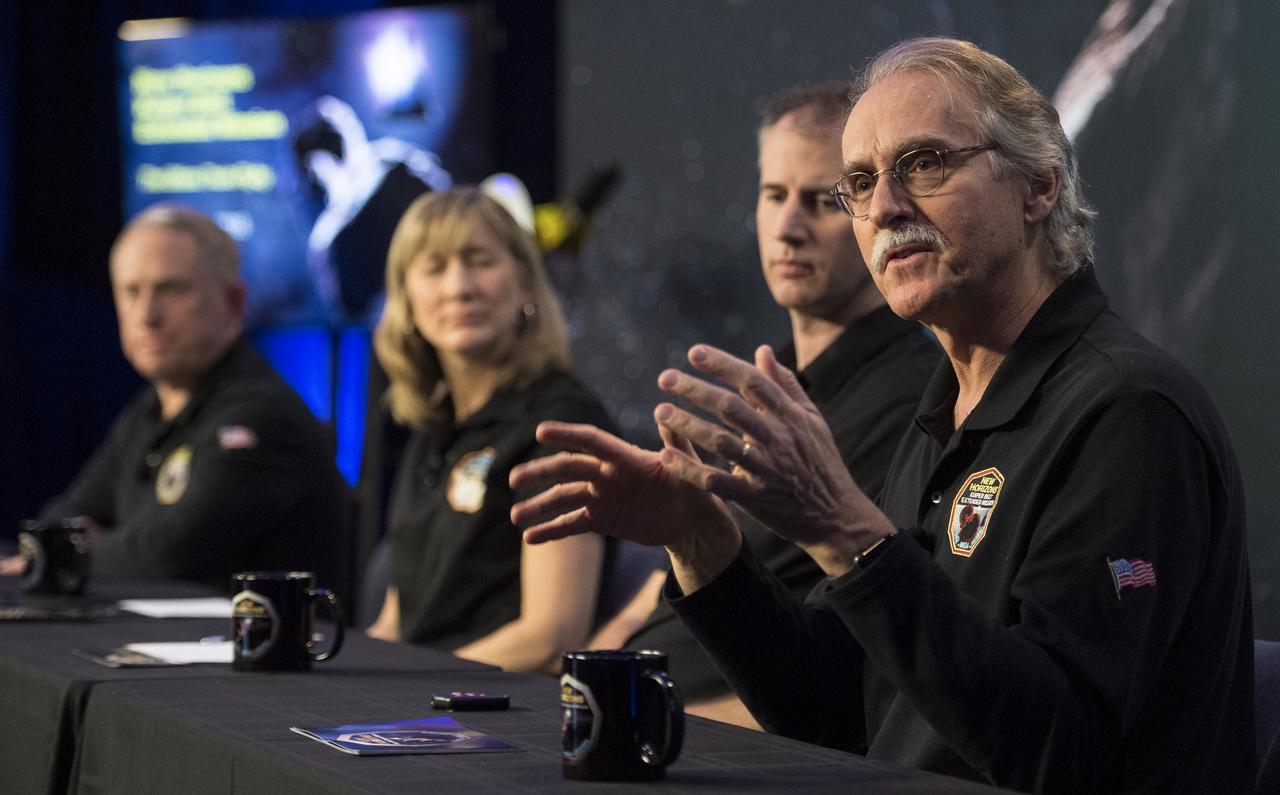

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO speaks during a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
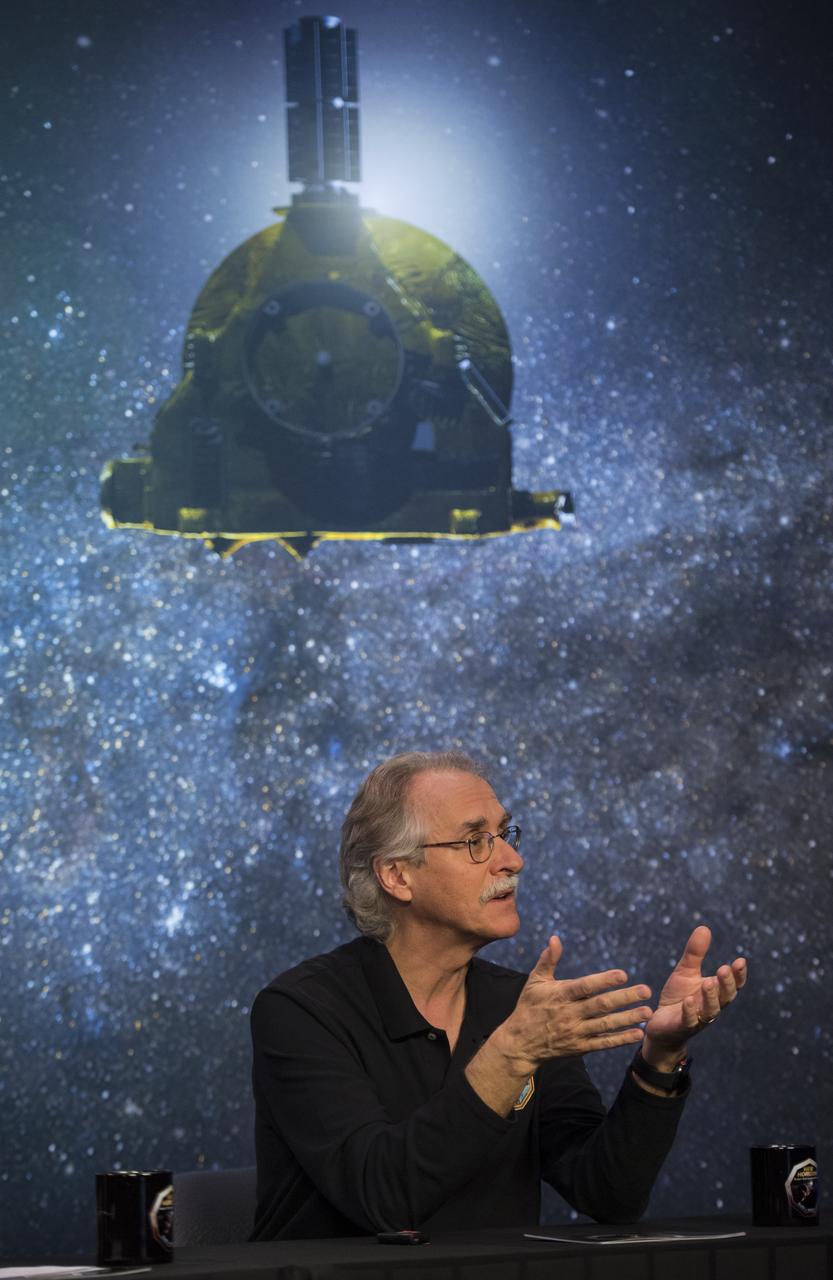

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO speaks during a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
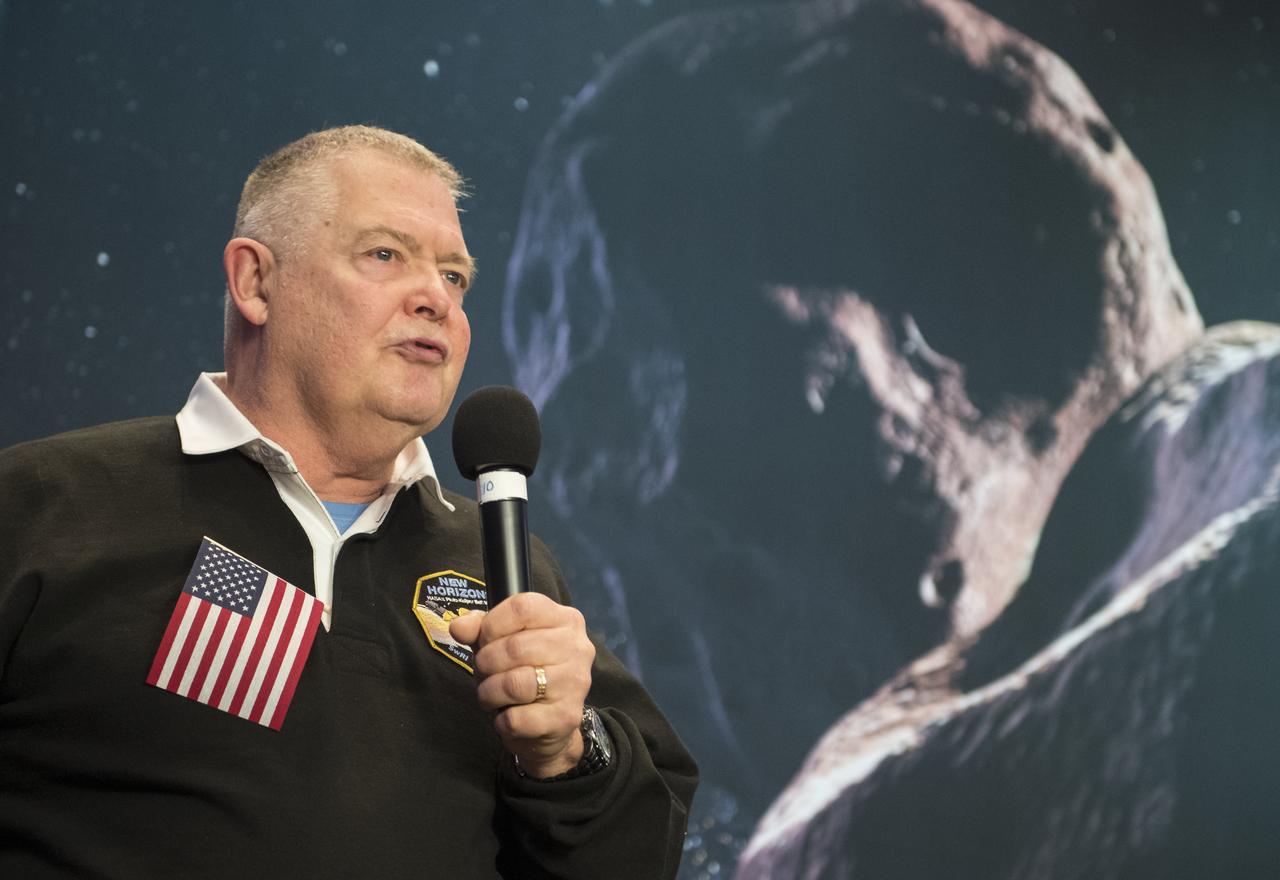
Michael Ryschkewitsch,head of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Space Exploration Sector, is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen before a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, right, speaks during a press conference prior to the flyby about the first images received from the New Horizons spacecraft of Ultima Thule that were captured on Dec. 30 as the spacecraft was 1.2 million miles away from Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
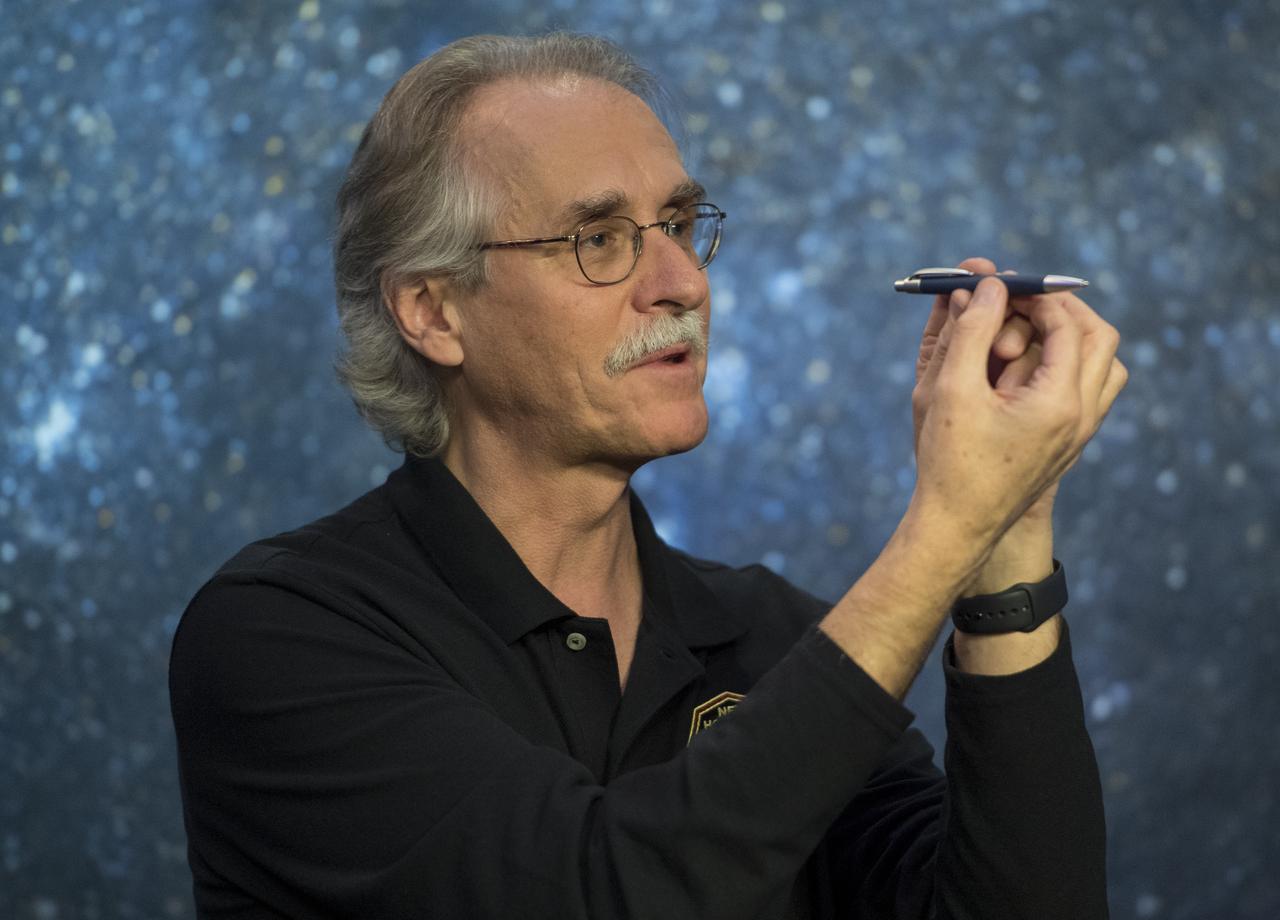

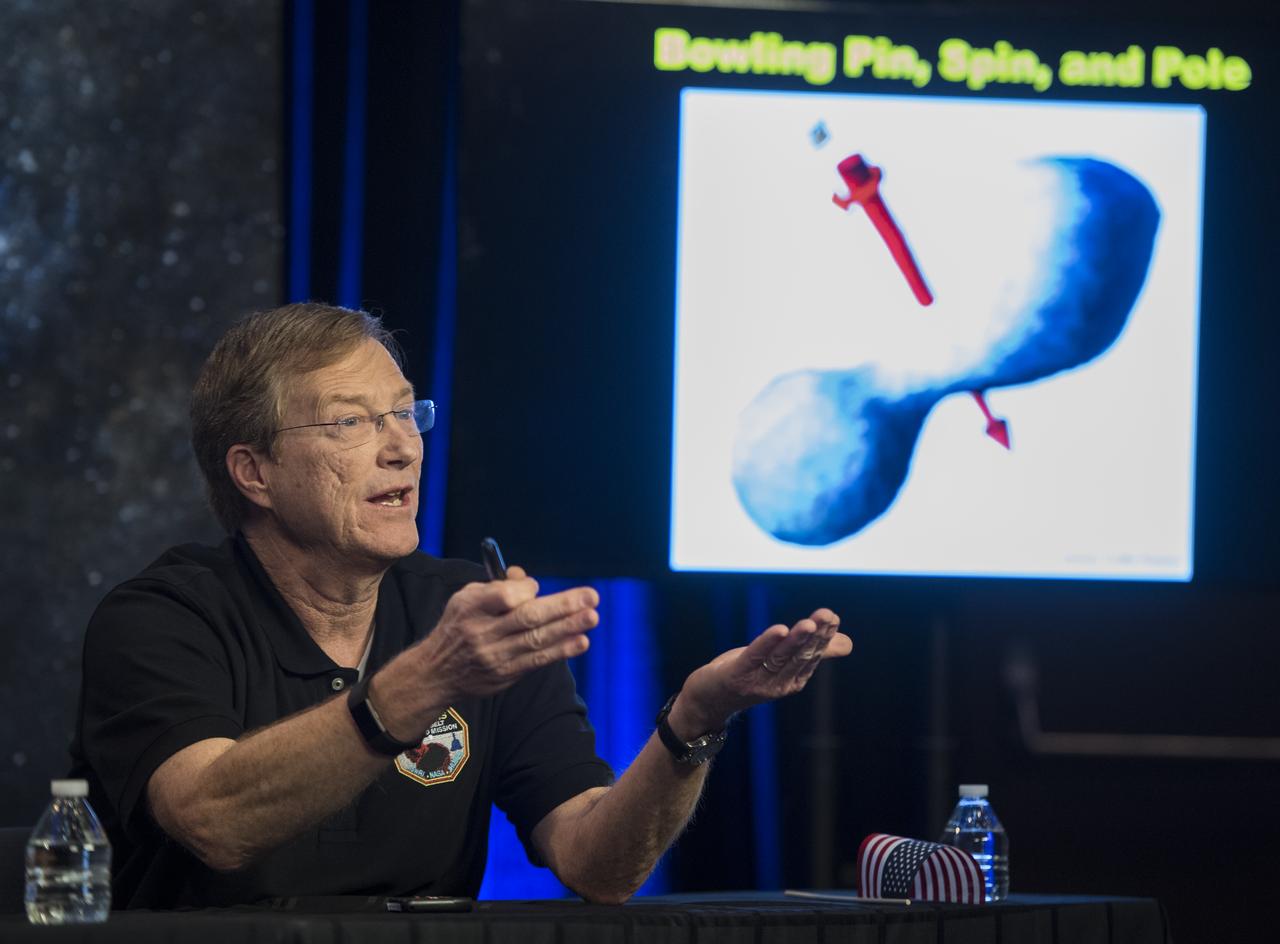
New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, uses a pen to demonstrate how Ultima Thule might be rotating during a press conference prior to the flyby of the Kuiper Belt object by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
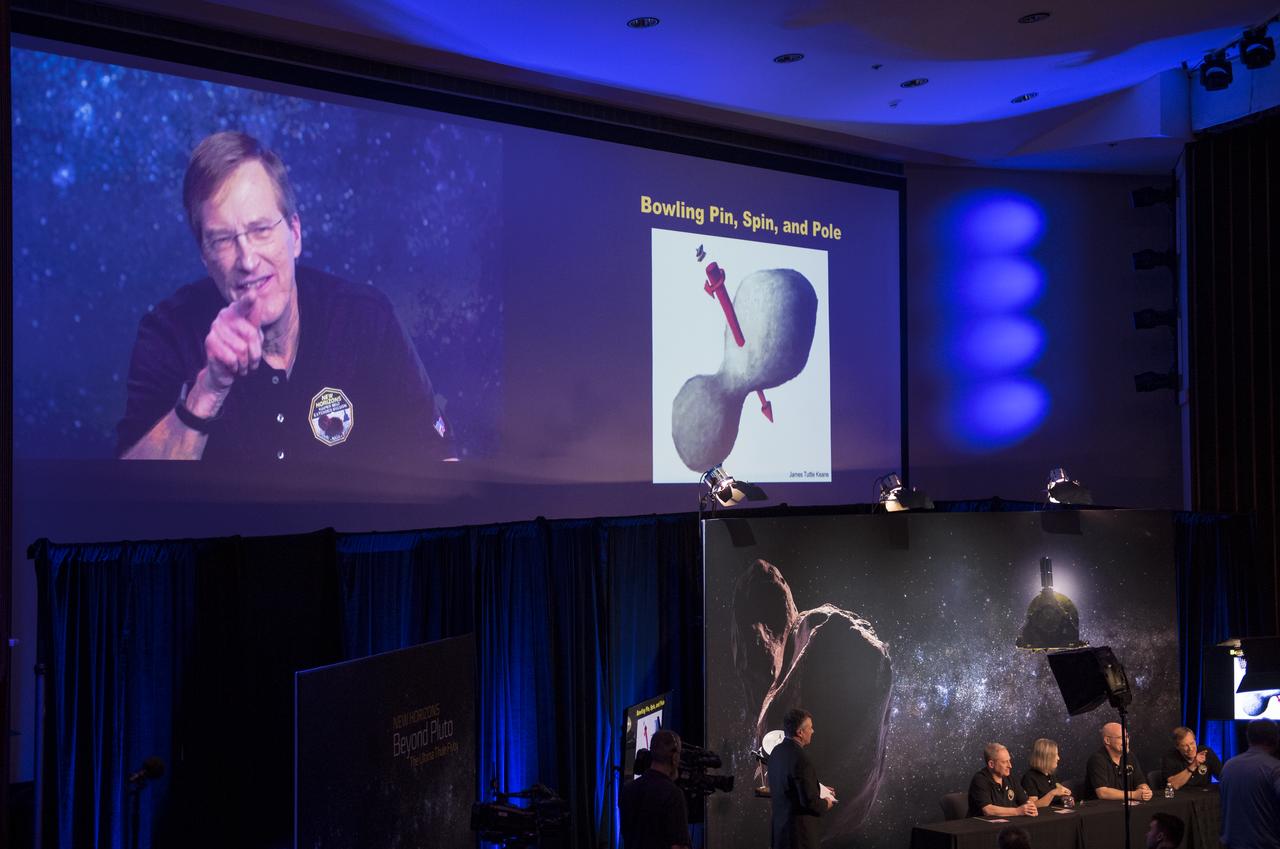

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks about new data received from the New Horizons spacecraft during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
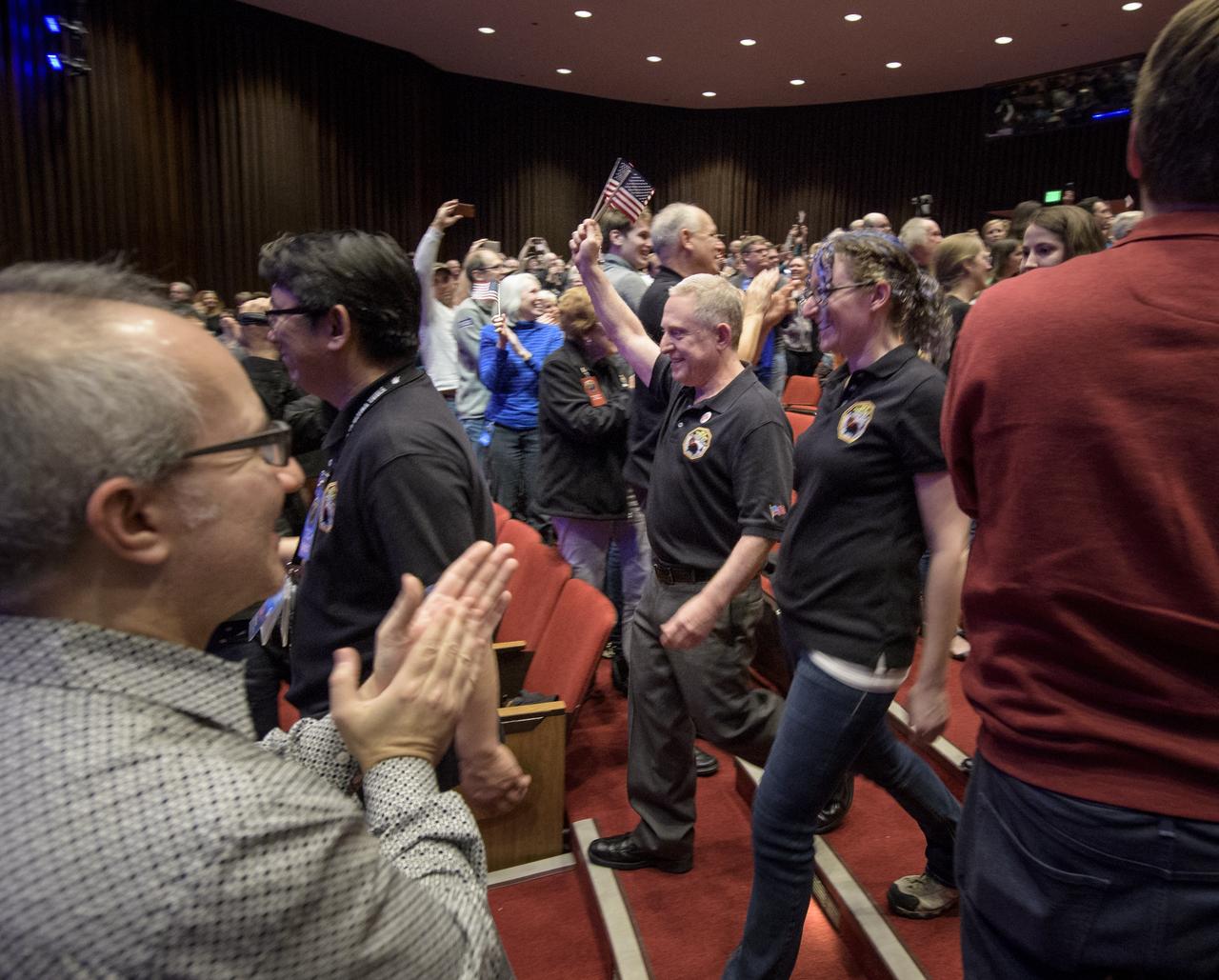

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, along with other mission team members, waves American flags as he enters the main auditorium for a press conference, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. The New Horizons team received signals from the spacecraft that it is healthy and it collected data during the fly of Ultima Thule. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons project manager Helene Winters of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks during a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator Cathy Olkin of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) speaks about Kuiper Belt object MU69, Ultima Thule, during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Mike Buckley, senior public information office at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks at the beginning of a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
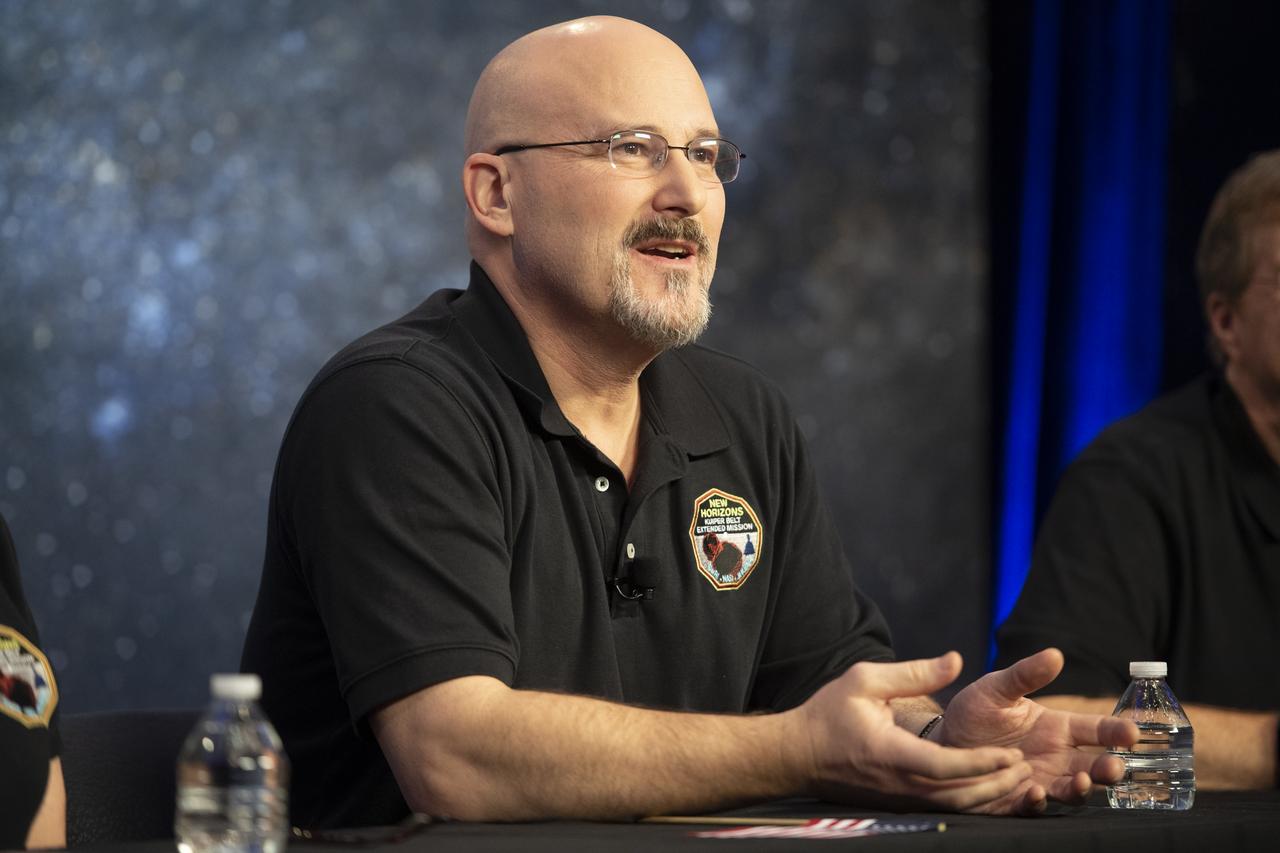

New Horizons mission systems engineer Chris Hersman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory high-fives a New Horizons team member after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
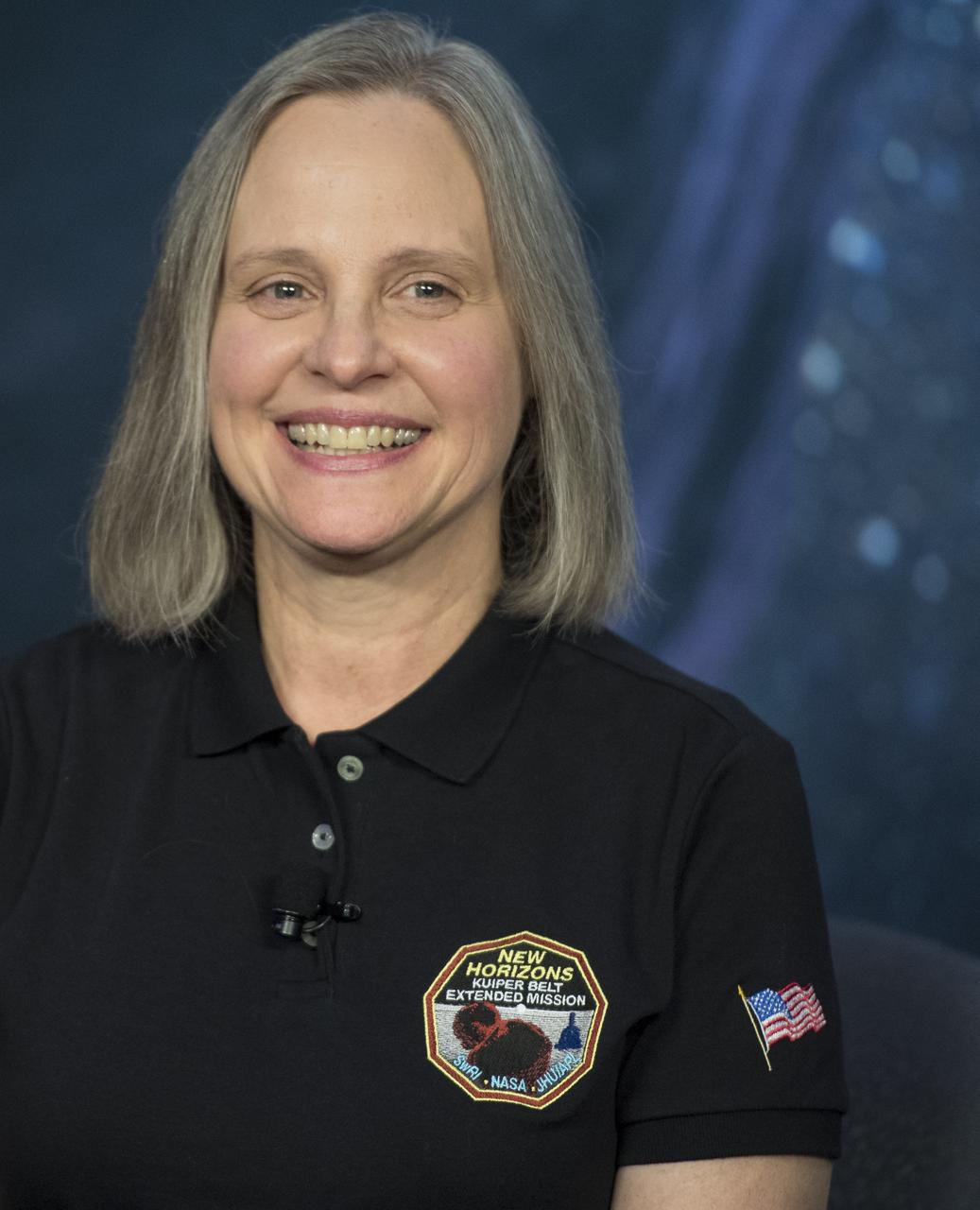

New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
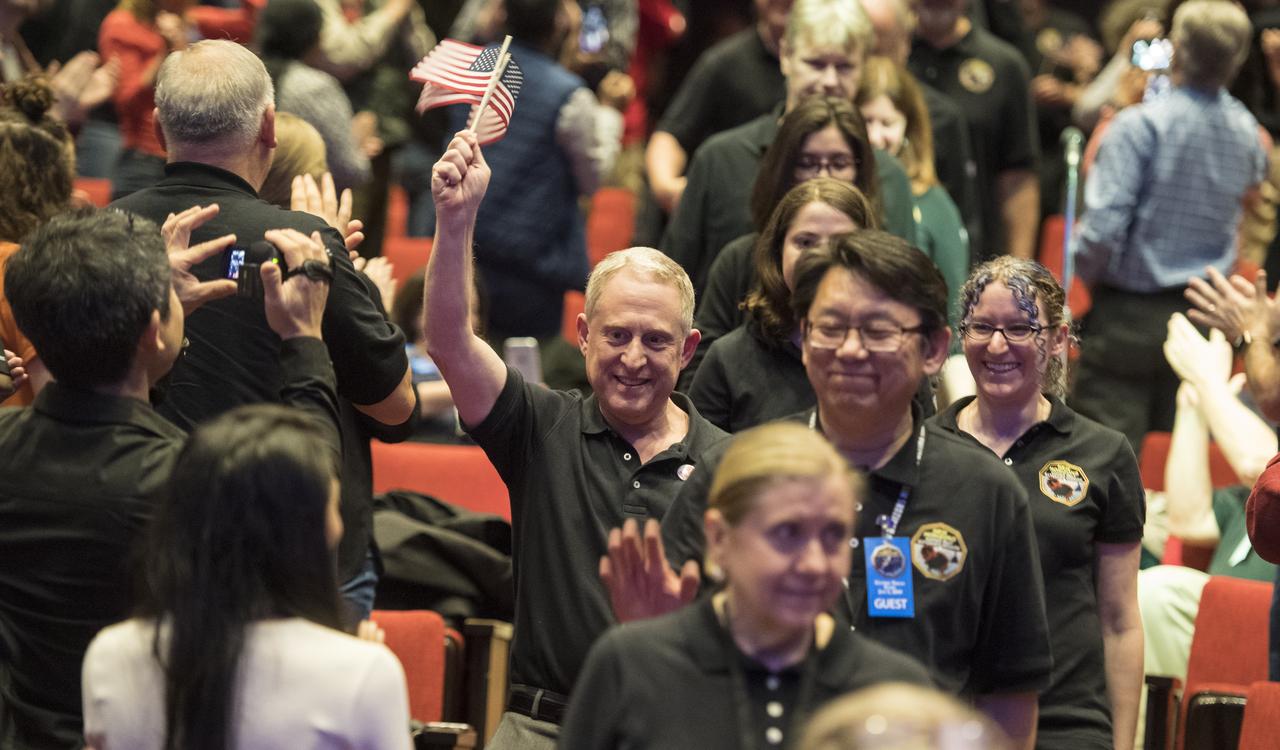

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, is seen with New Horizons team members as they enter the auditorium prior to a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
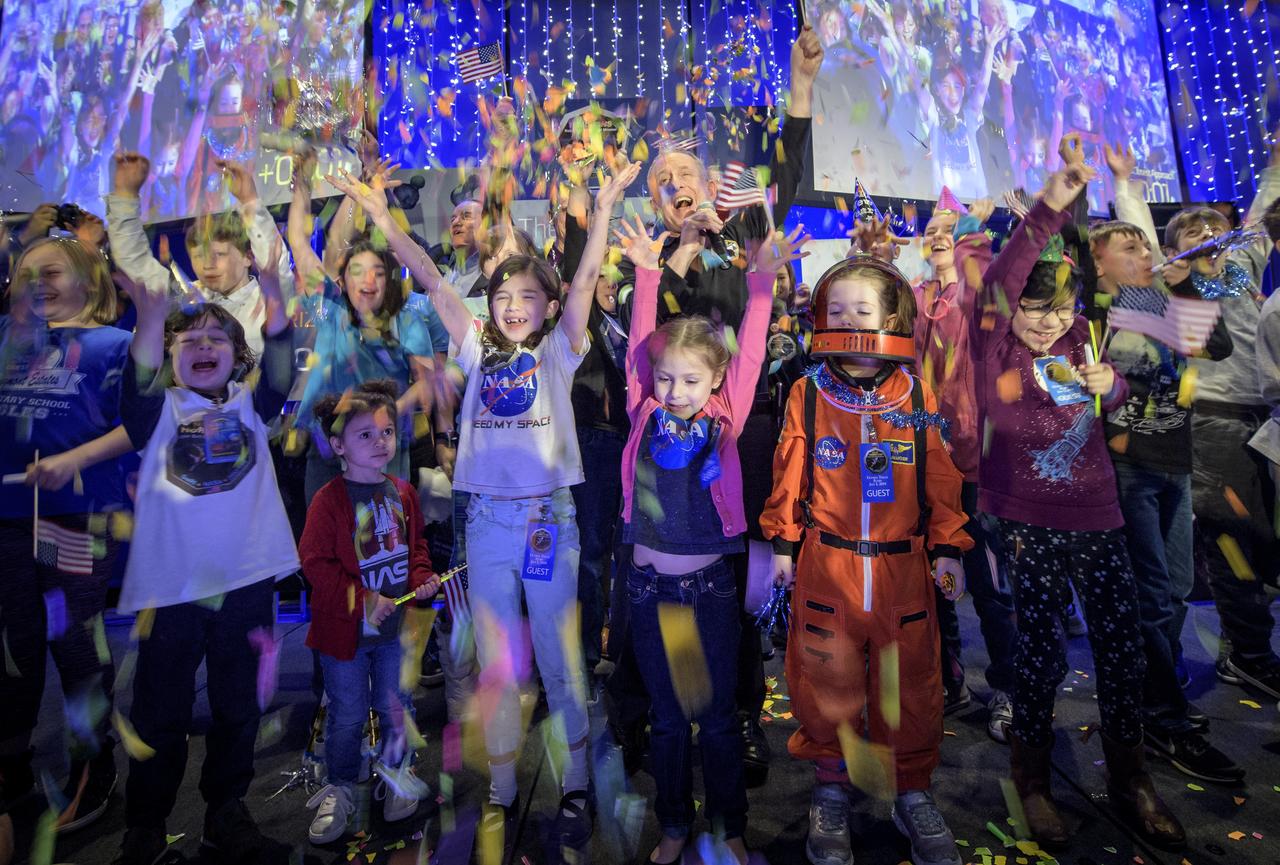

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, center, celebrates with school children at the moment the spacecraft was planned to reach its closest approach to Kuiper Belt object Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
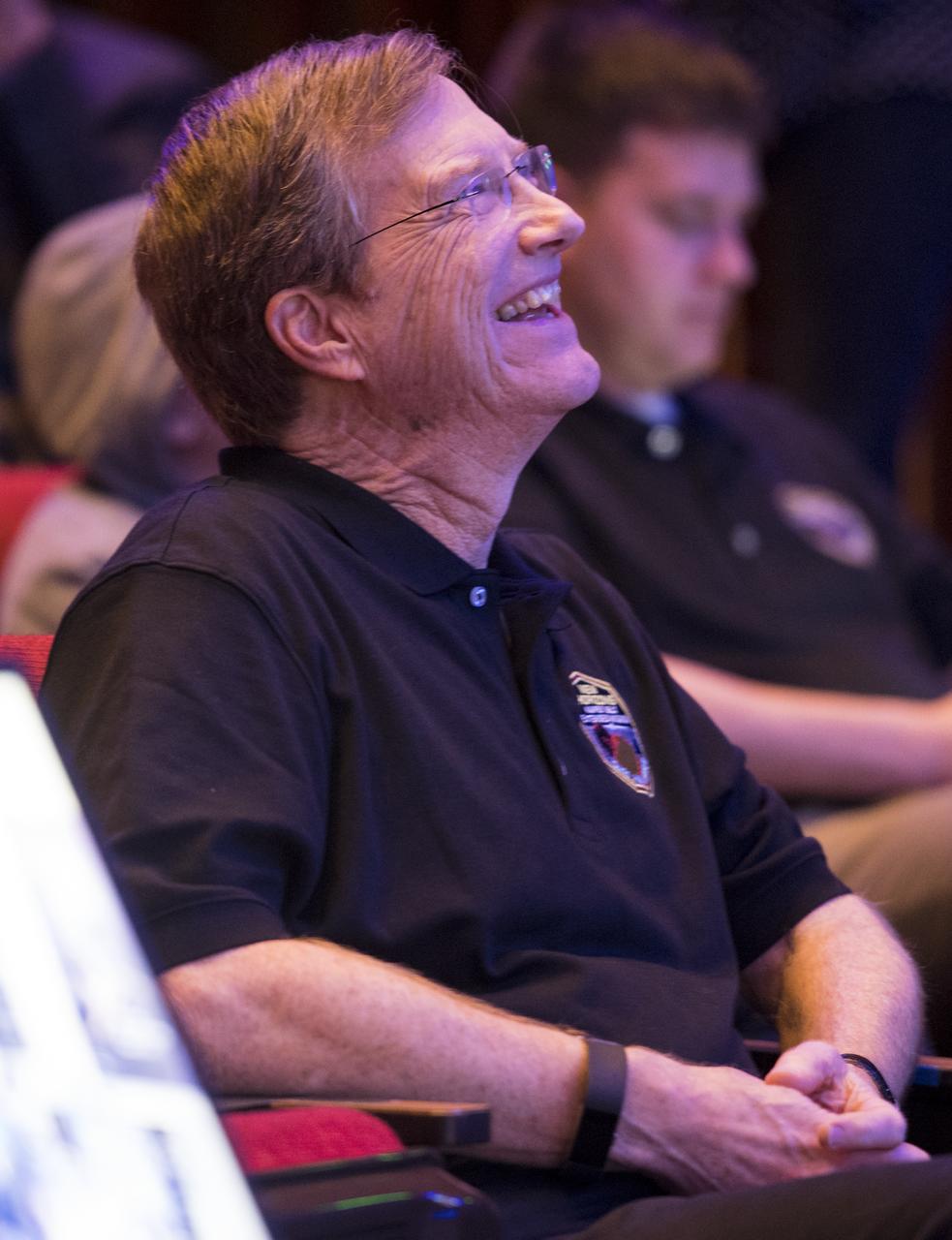

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory watches a live feed of the Mission Operations Center (MOC) as the team waits to receive confirmation from the spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
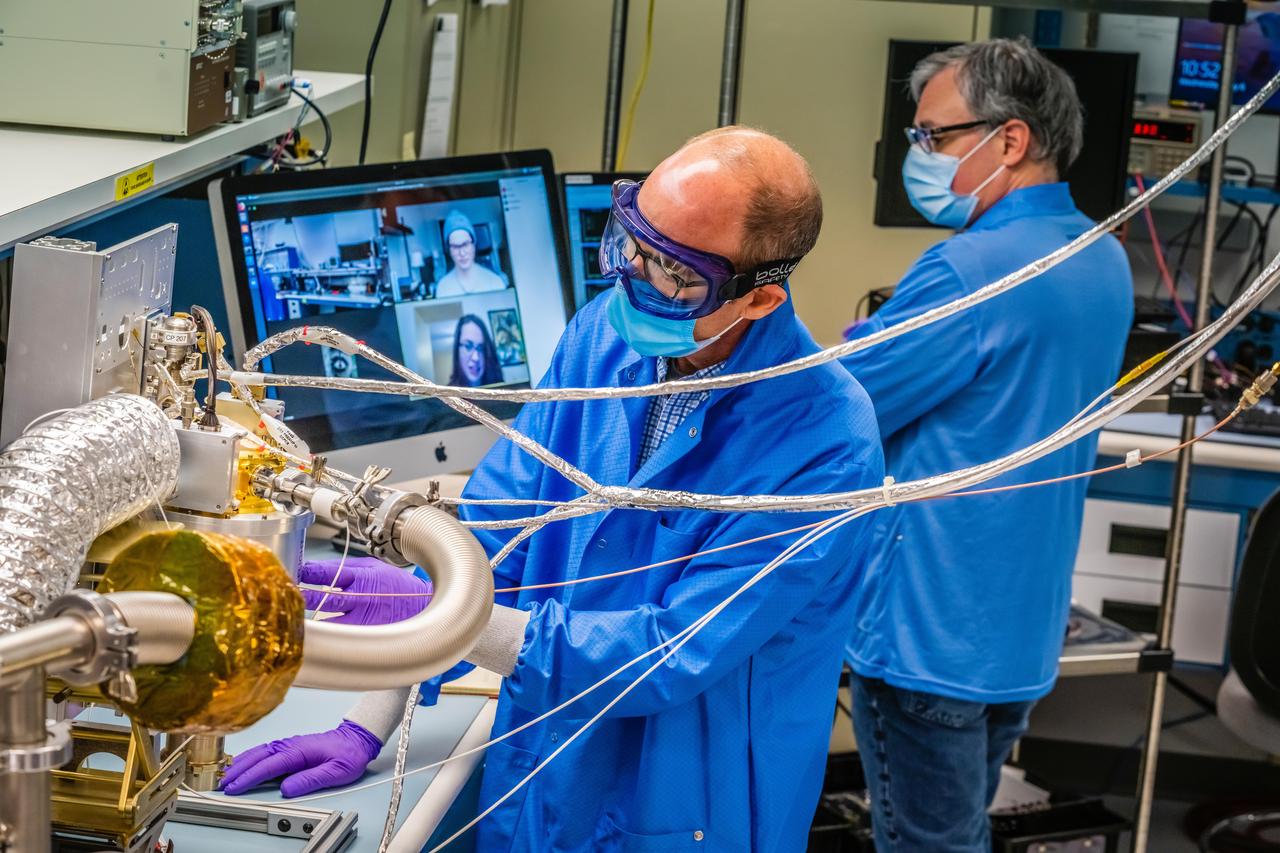

Engineers at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, continue to make progress on Psyche's spectrometer while observing COVID-19 safety procedures. Engineers John Goldsten (left) and Sam Fix work on the Gamma Ray/Neutron Spectrometer (GRNS) instrument that will launch aboard the Psyche spacecraft in 2022 to detect, measure and map the asteroid Psyche's elemental composition. The instrument's team at APL moved the majority of its work to video conferencing, which has enabled the team to whittle operations down to requiring just one or two staff members on campus once or twice a week. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23880
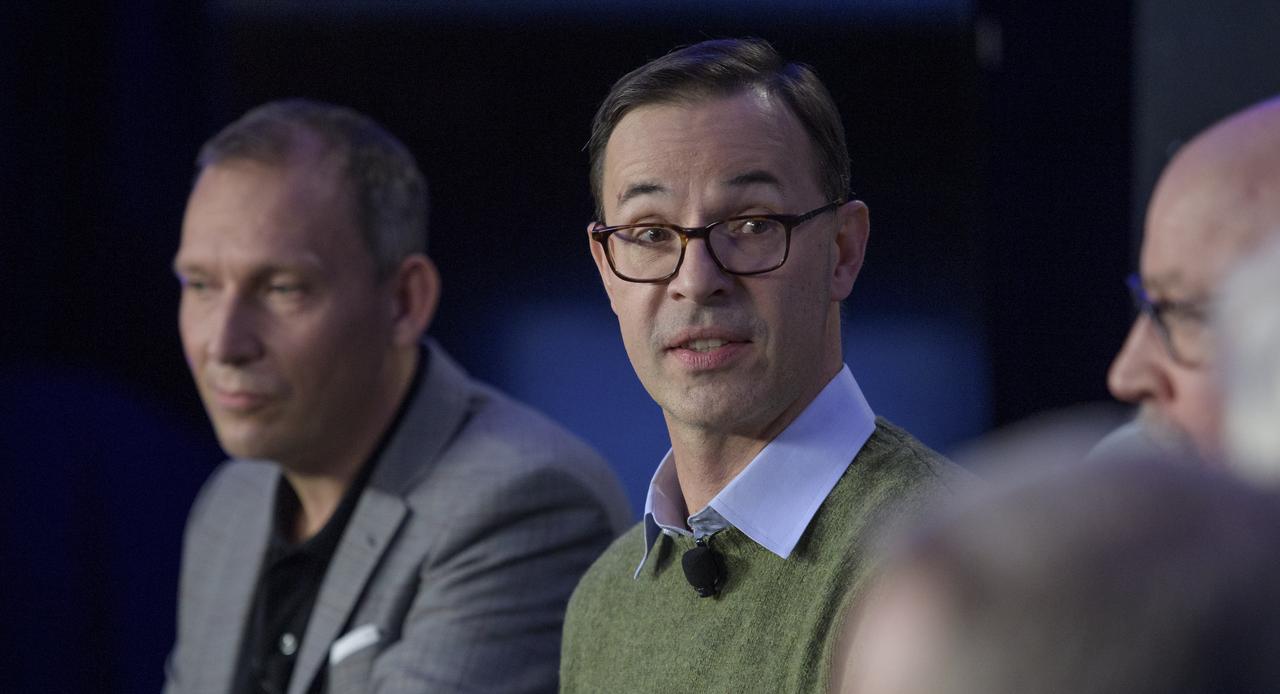

Olivier Barnouin (US Instrument Scientist, Johns Hopkins University/APL) discusses the OSIRIS-REx mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
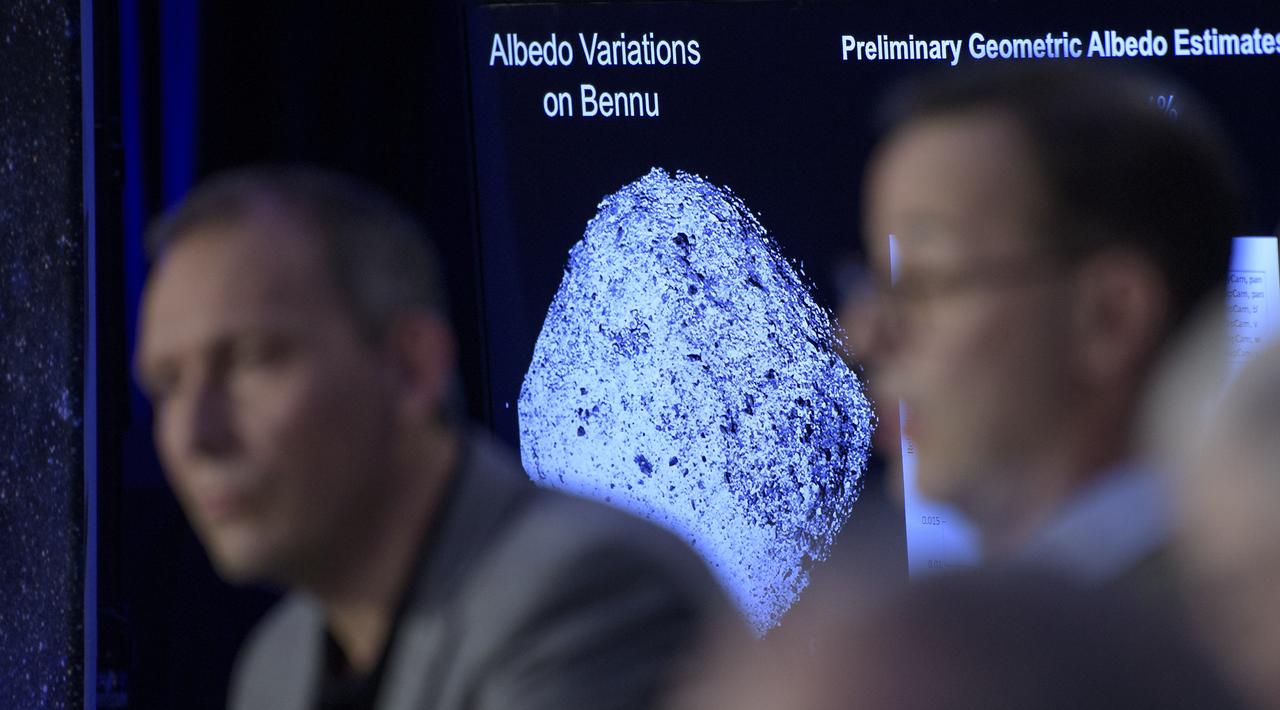

An image of asteroid Bennu is shown as Olivier Barnouin (US Instrument Scientist, Johns Hopkins University/APL) discusses the OSIRIS-REx mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
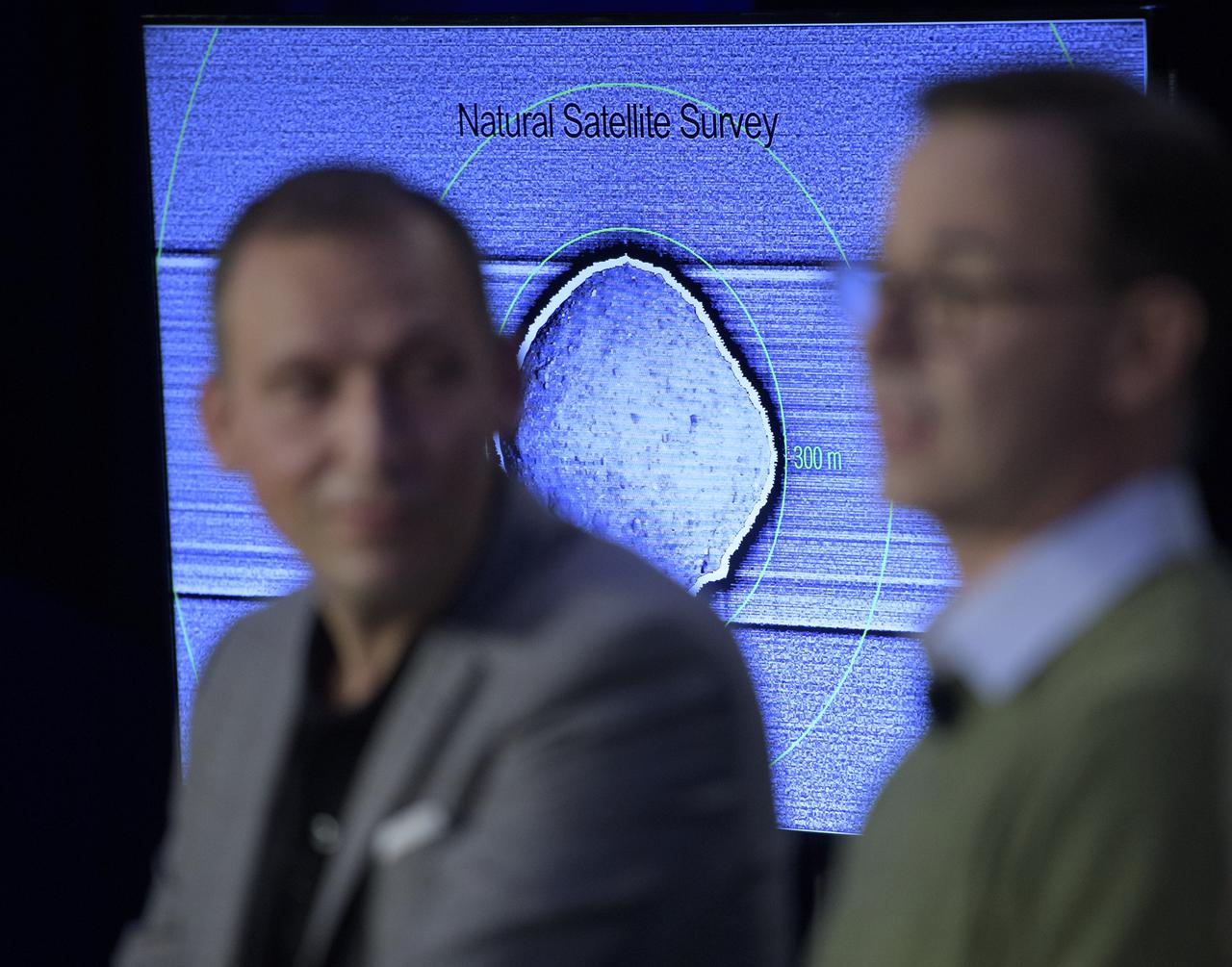

An image of asteroid Bennu is shown as Olivier Barnouin (US Instrument Scientist, Johns Hopkins University/APL) discusses the OSIRIS-REx mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
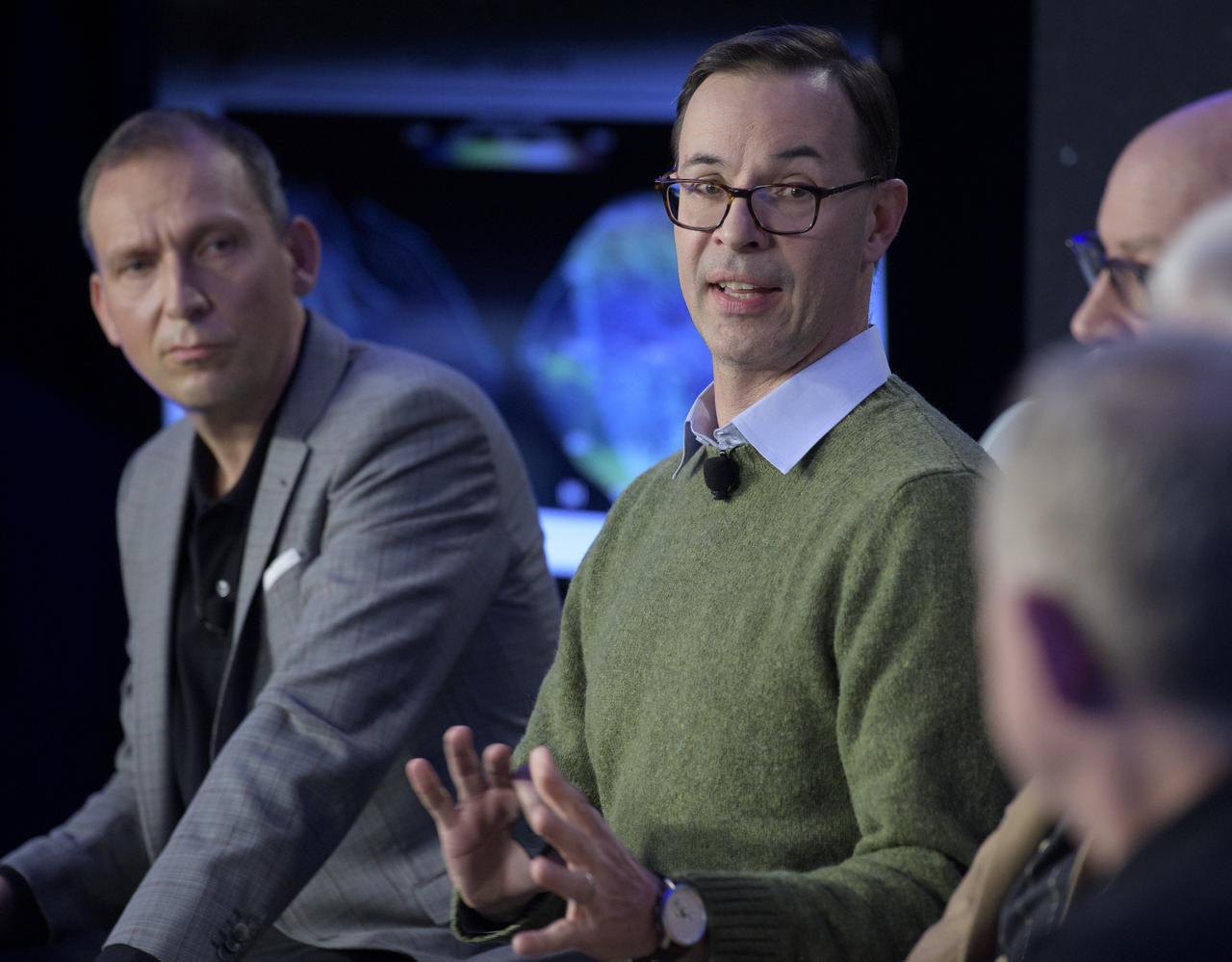

Olivier Barnouin (US Instrument Scientist, Johns Hopkins University/APL) discusses the OSIRIS-REx mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A New Horizons Pluto flyby coffee mug is seen as team members wait for a signal from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
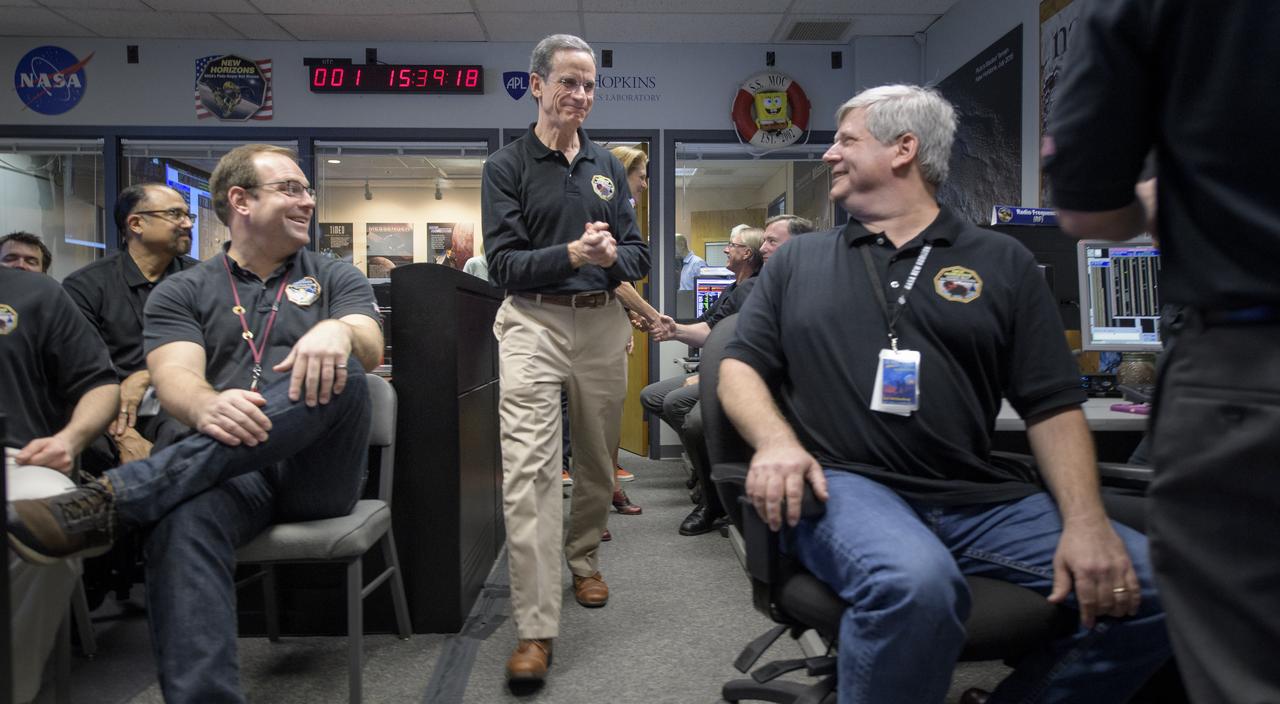

Director of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Ralph Semmel celebrates with other mission team members after they received signals from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons missions managers including New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, behind door, wait for a signal from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
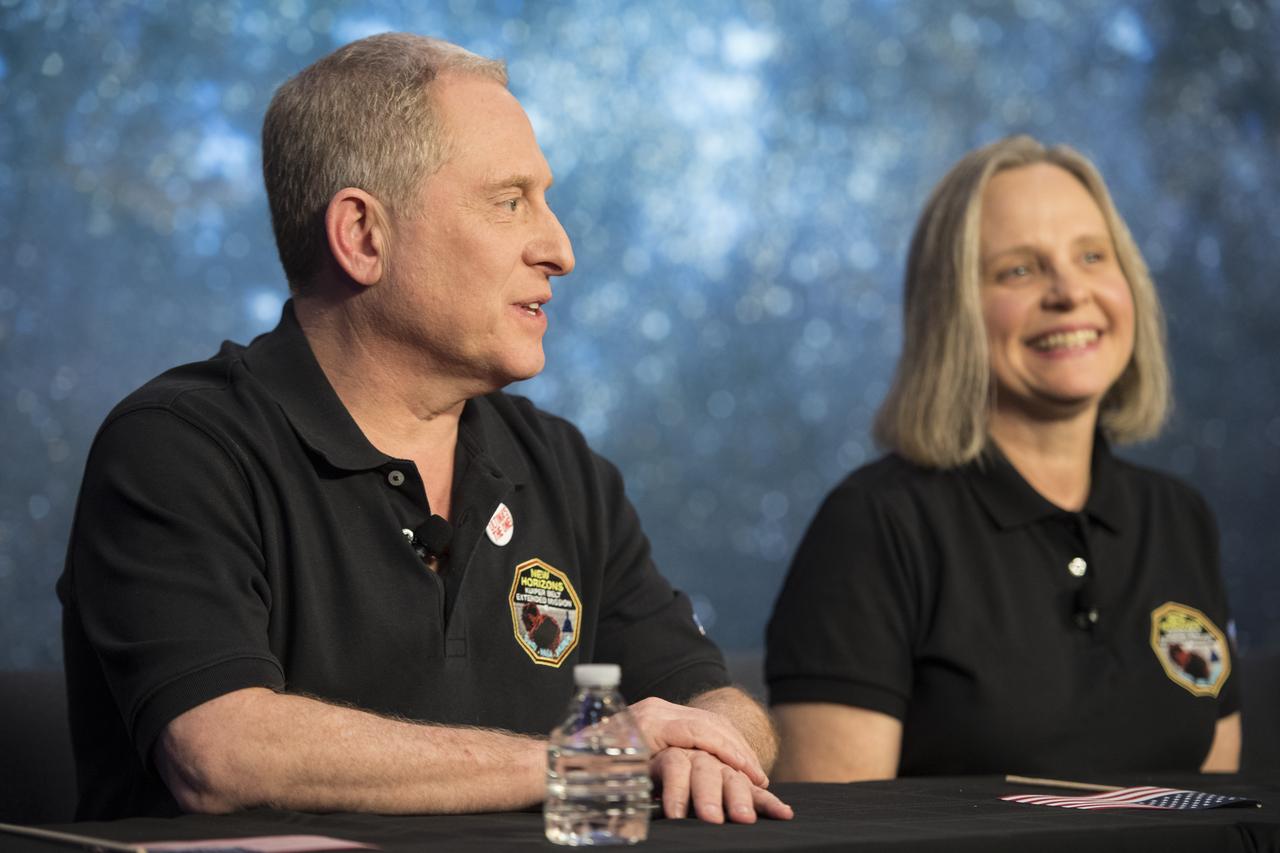

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO and New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory are seen on a television screen as New Horizons team members and guests cheer as the team receives confirmation from the spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
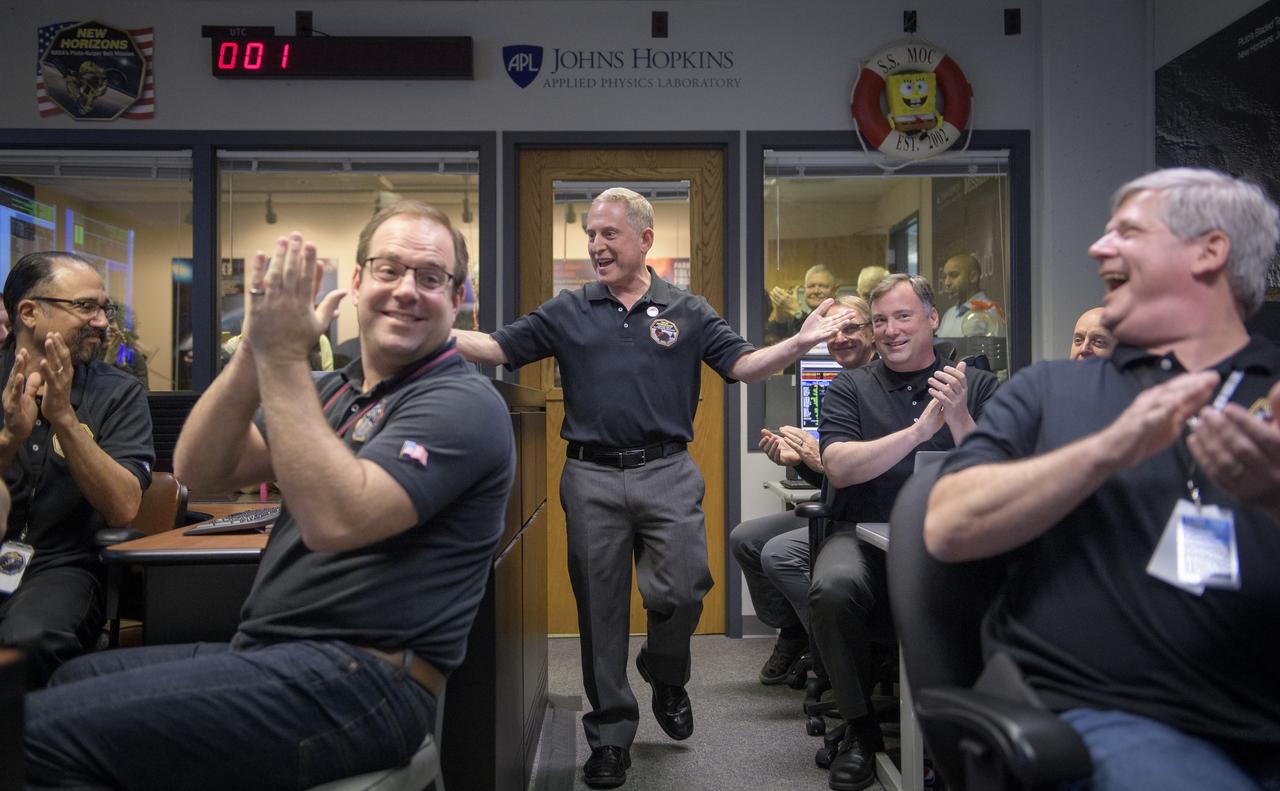

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, celebrates with other mission team members after they received signals from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
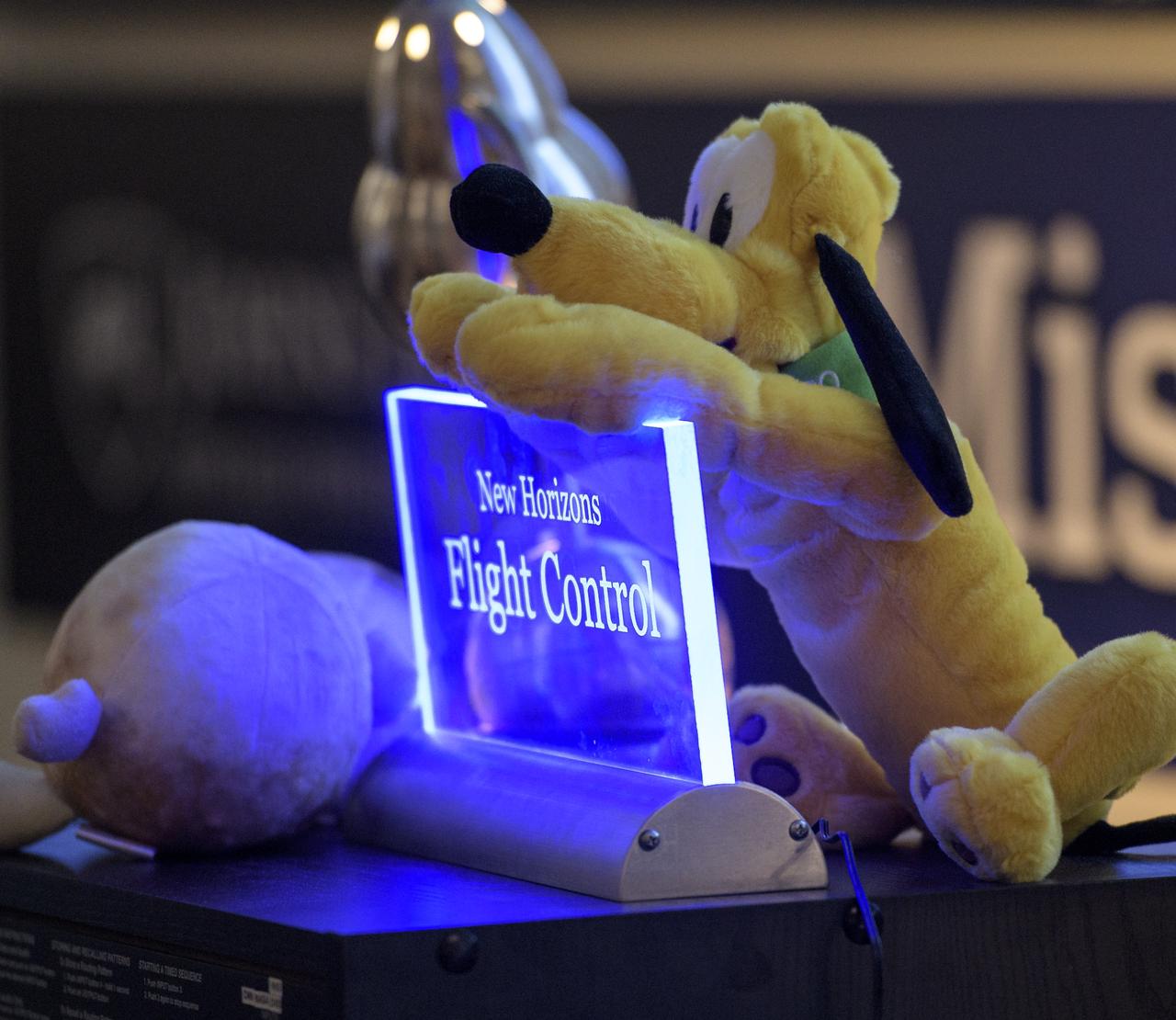

A sign marking the seat location of the New Horizons Flight Controller is seen as team members wait for a signal from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
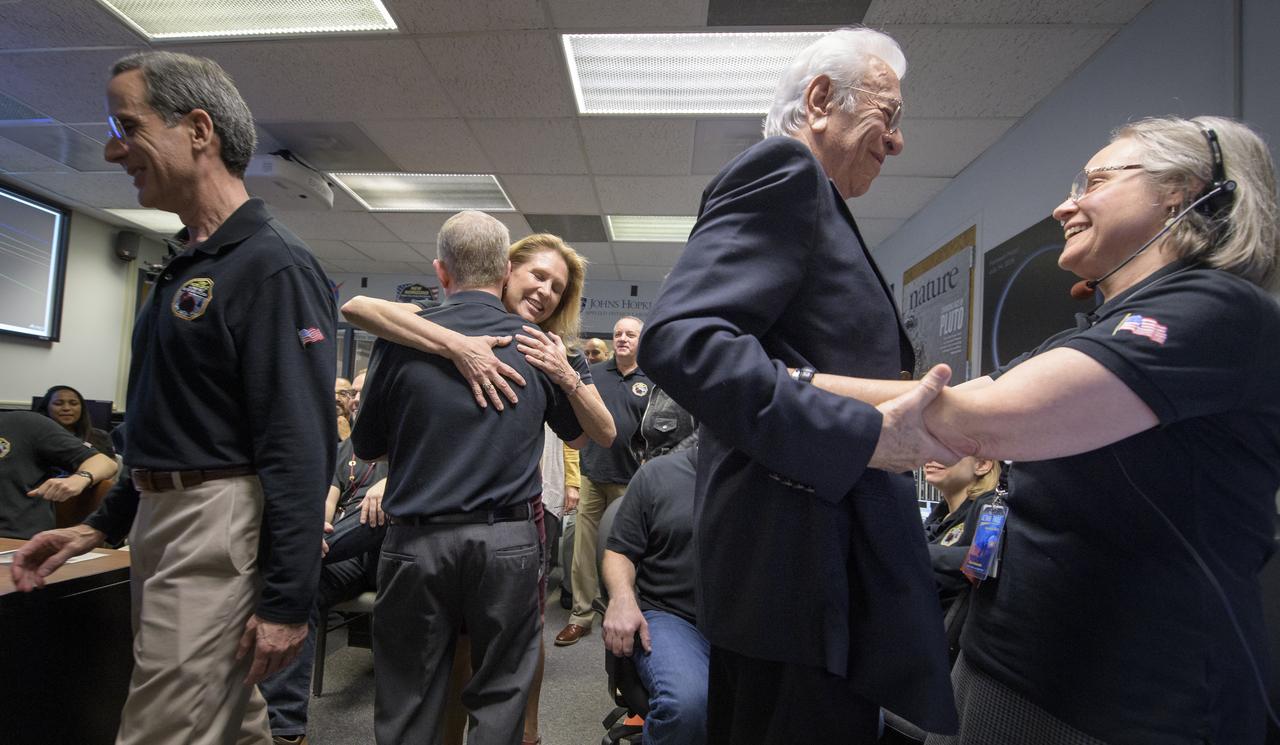

New Horizons mission managers rejoice after they received signals from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Pictured from left; Director of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Ralph Semmel: New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO: Acting director of Planetary Science at NASA Headquarters Lori Glaze: APL Space Department Head Emeritus Stamatios (Tom) Krimigis, and New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
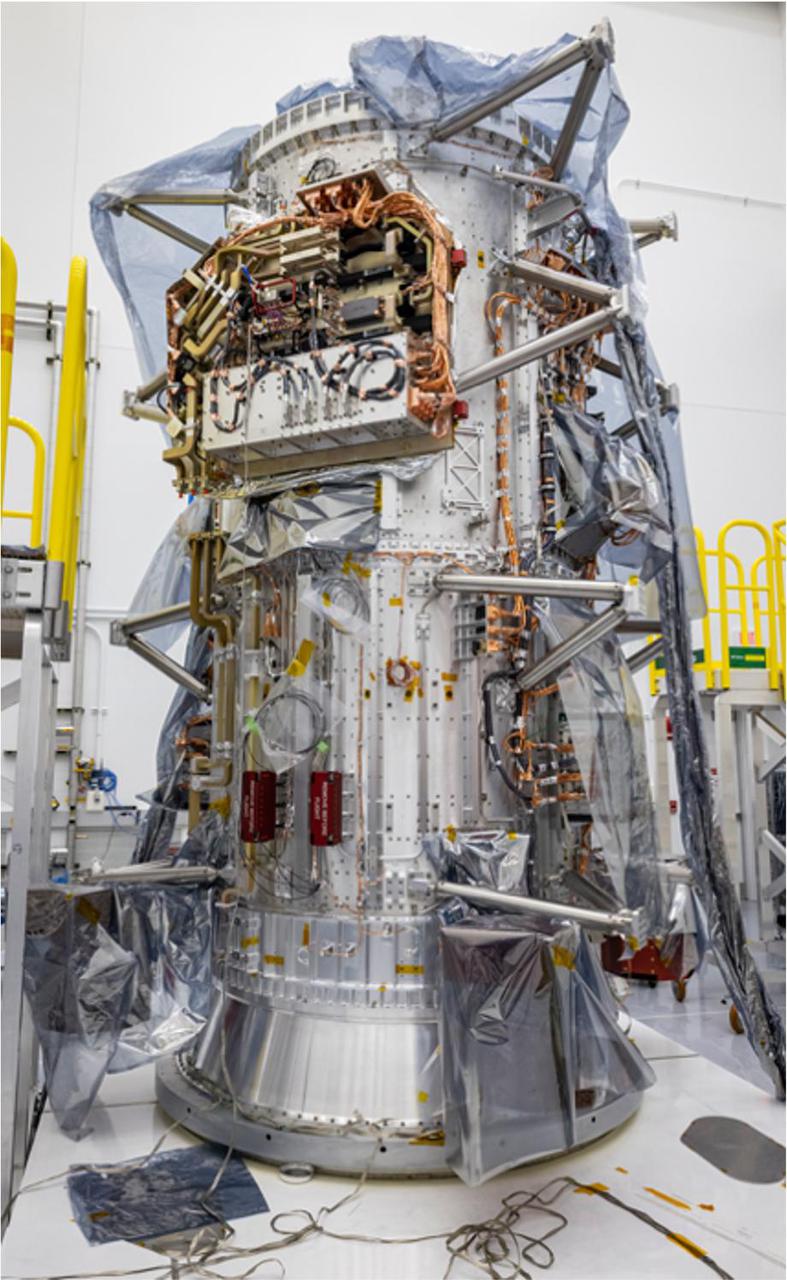

The propulsion module for NASA's Europa Clipper, the main body of the spacecraft, is nearing completion at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. The module consists of two stacked cylinders that stand almost 10 feet (3 meters) high and hold the propulsion tanks and rocket engines that will adjust and change Europa Clipper's trajectory once it leaves Earth's atmosphere on its path toward Jupiter's icy moon Europa. The propulsion module will be shipped to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California this spring. With an internal global ocean under a thick layer of ice, Jupiter's moon Europa may have the potential to harbor existing life. Europa Clipper will swoop around Jupiter in an elliptical orbit, dipping close to the moon on each flyby to collect data. Understanding Europa's habitability will help scientists better understand how life developed on Earth and the potential for finding life beyond our planet. Europa Clipper is set to launch in 2024. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24900
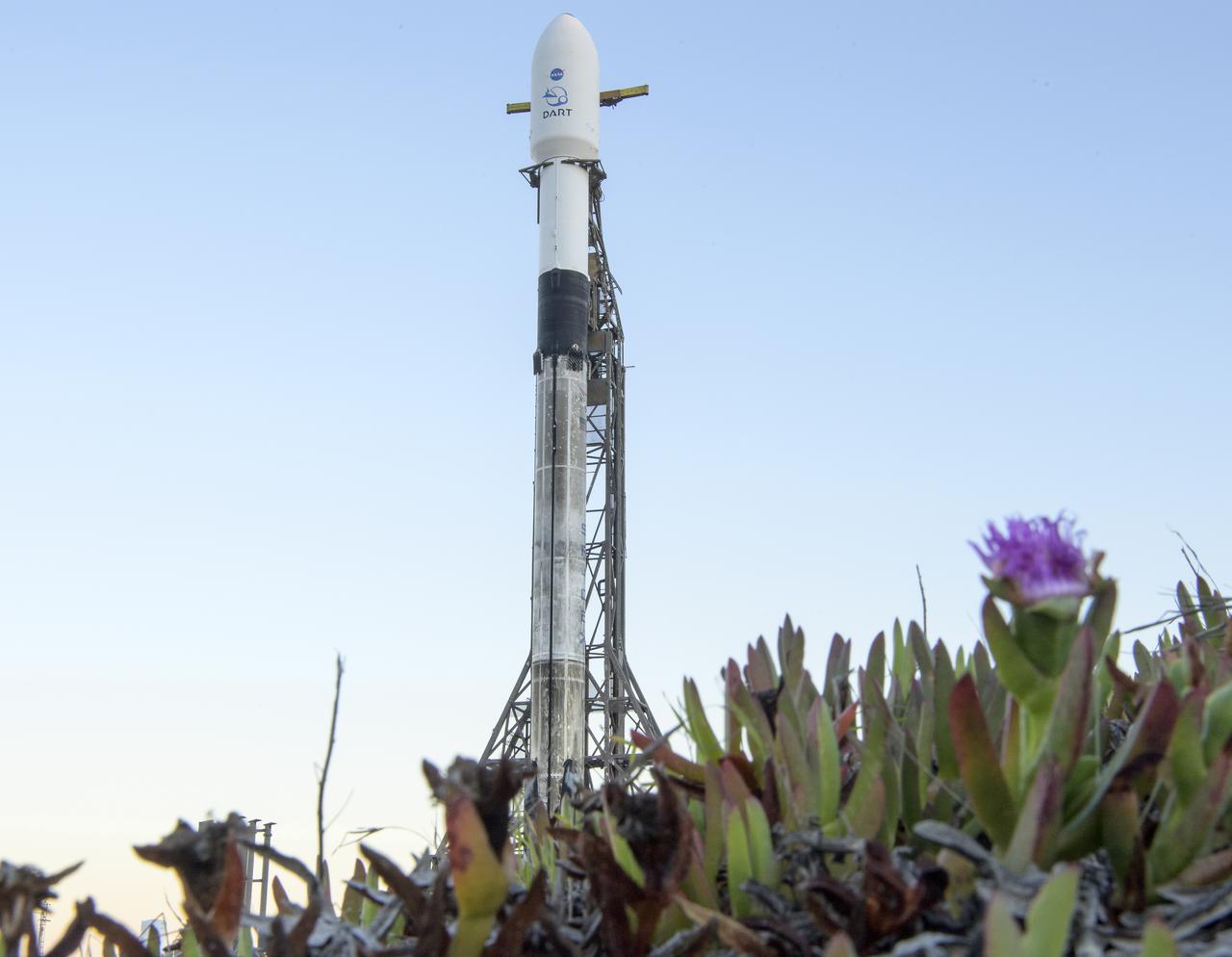

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
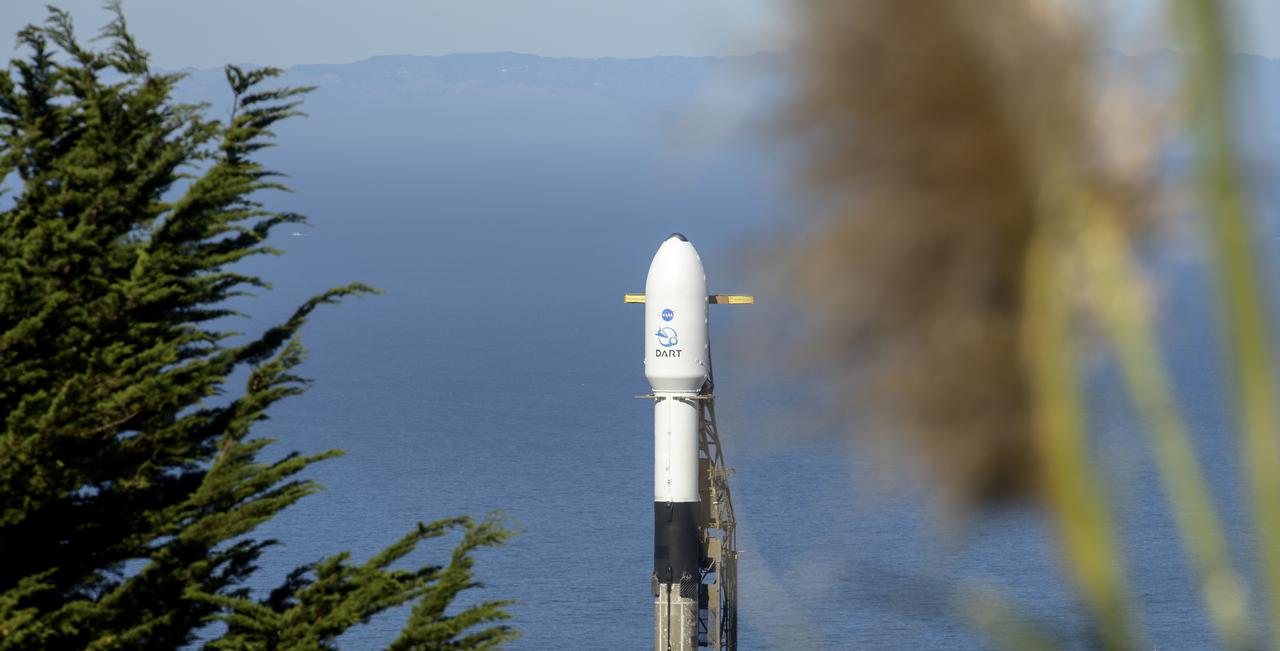

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
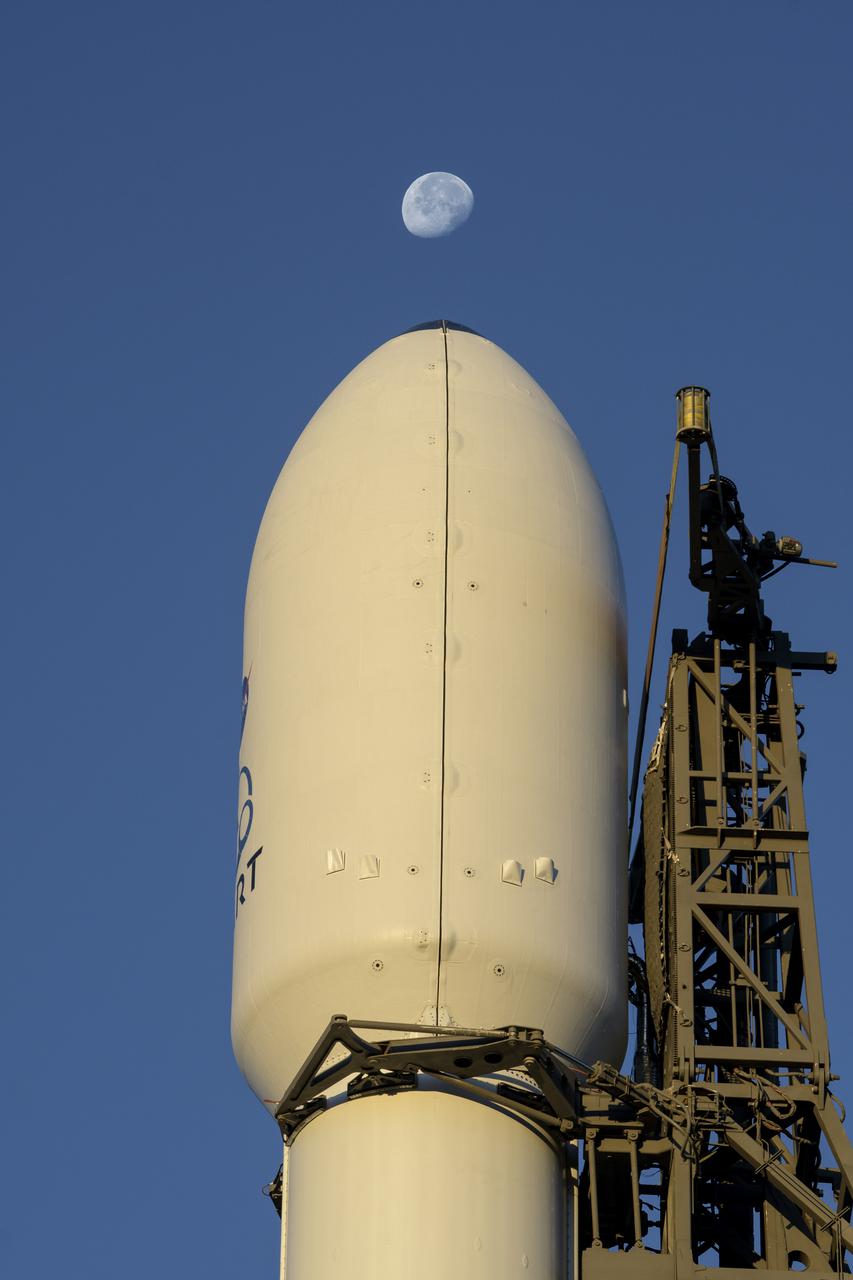

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
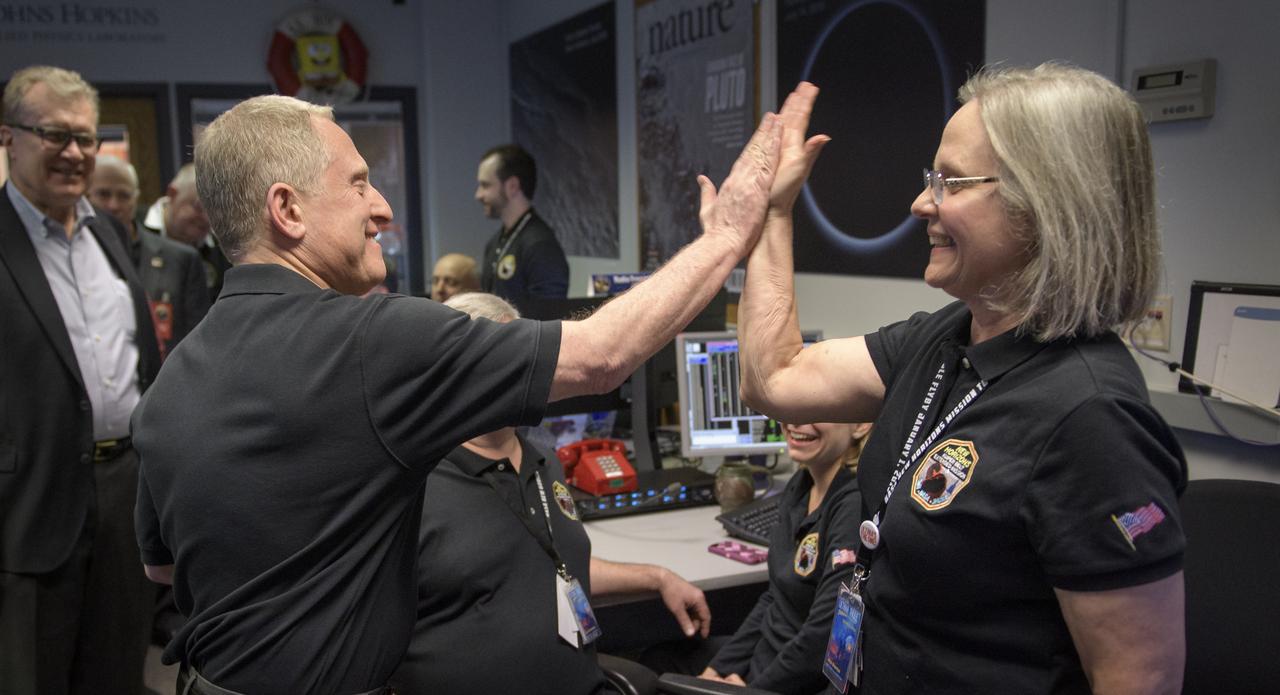

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, left gives a high five to New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory after the team received signals from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
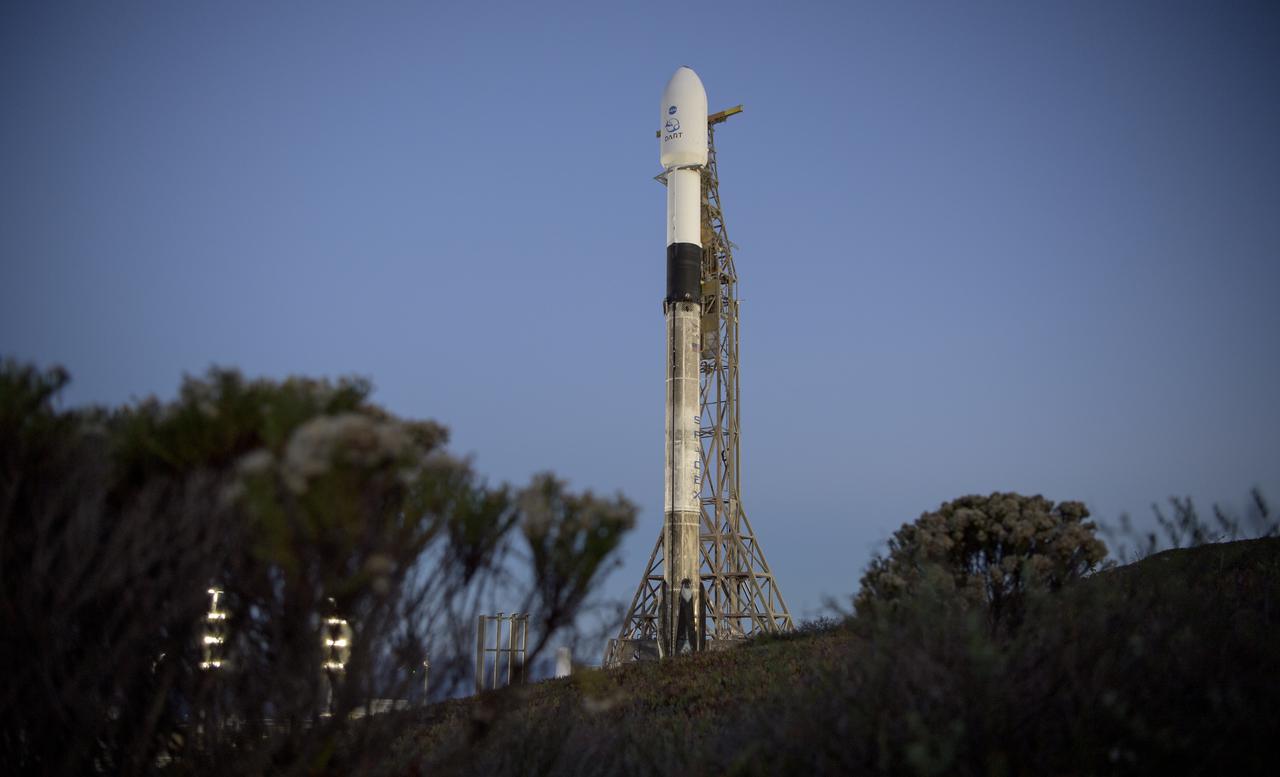

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
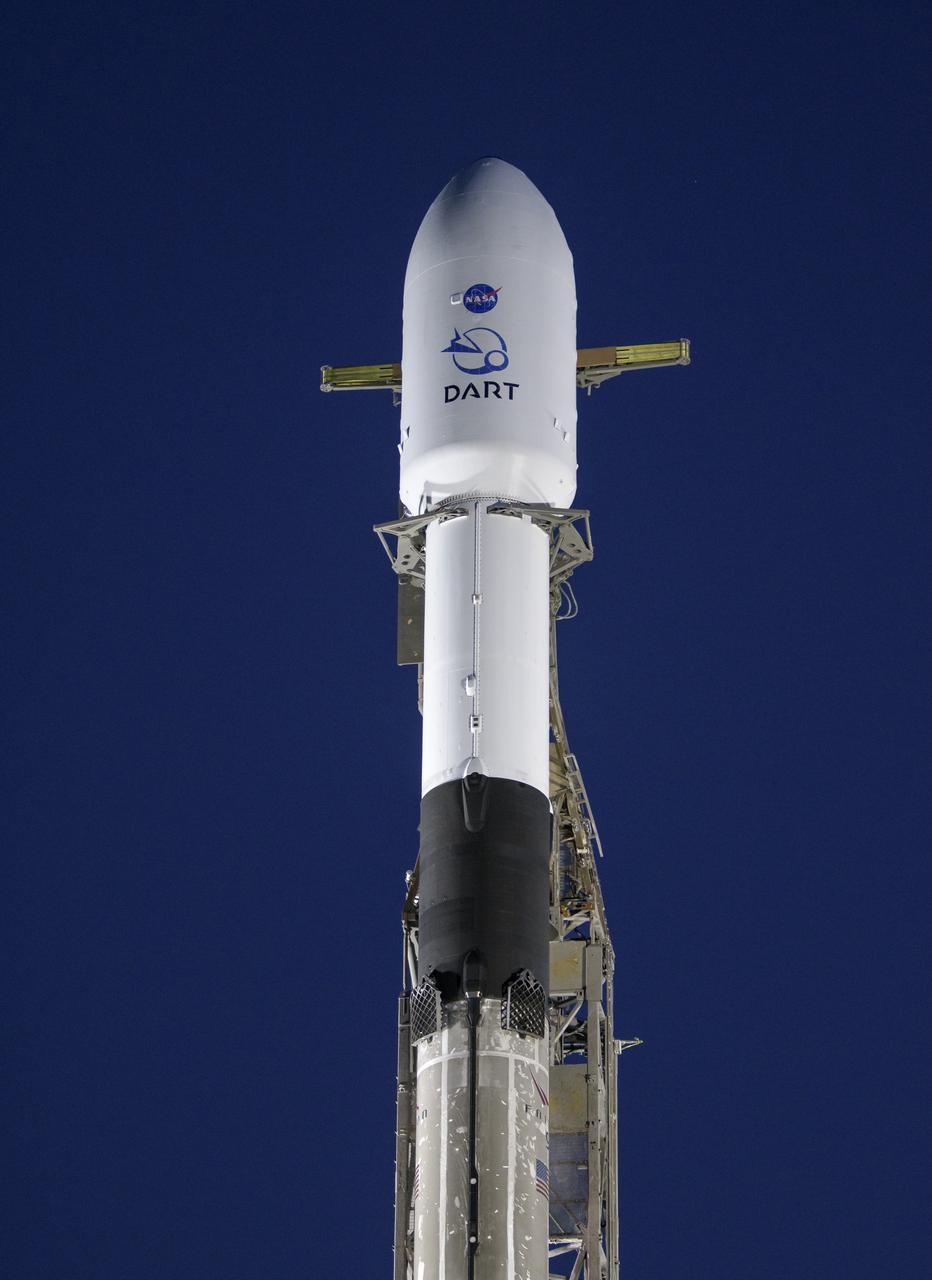

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
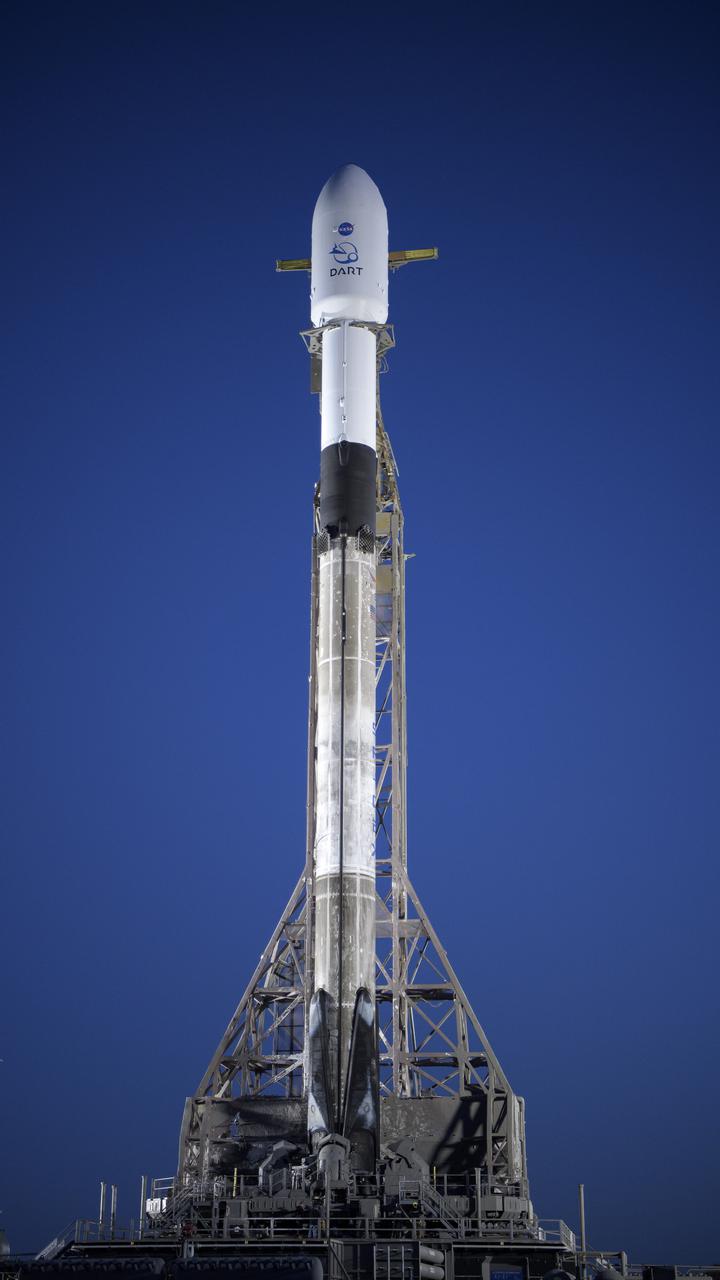

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
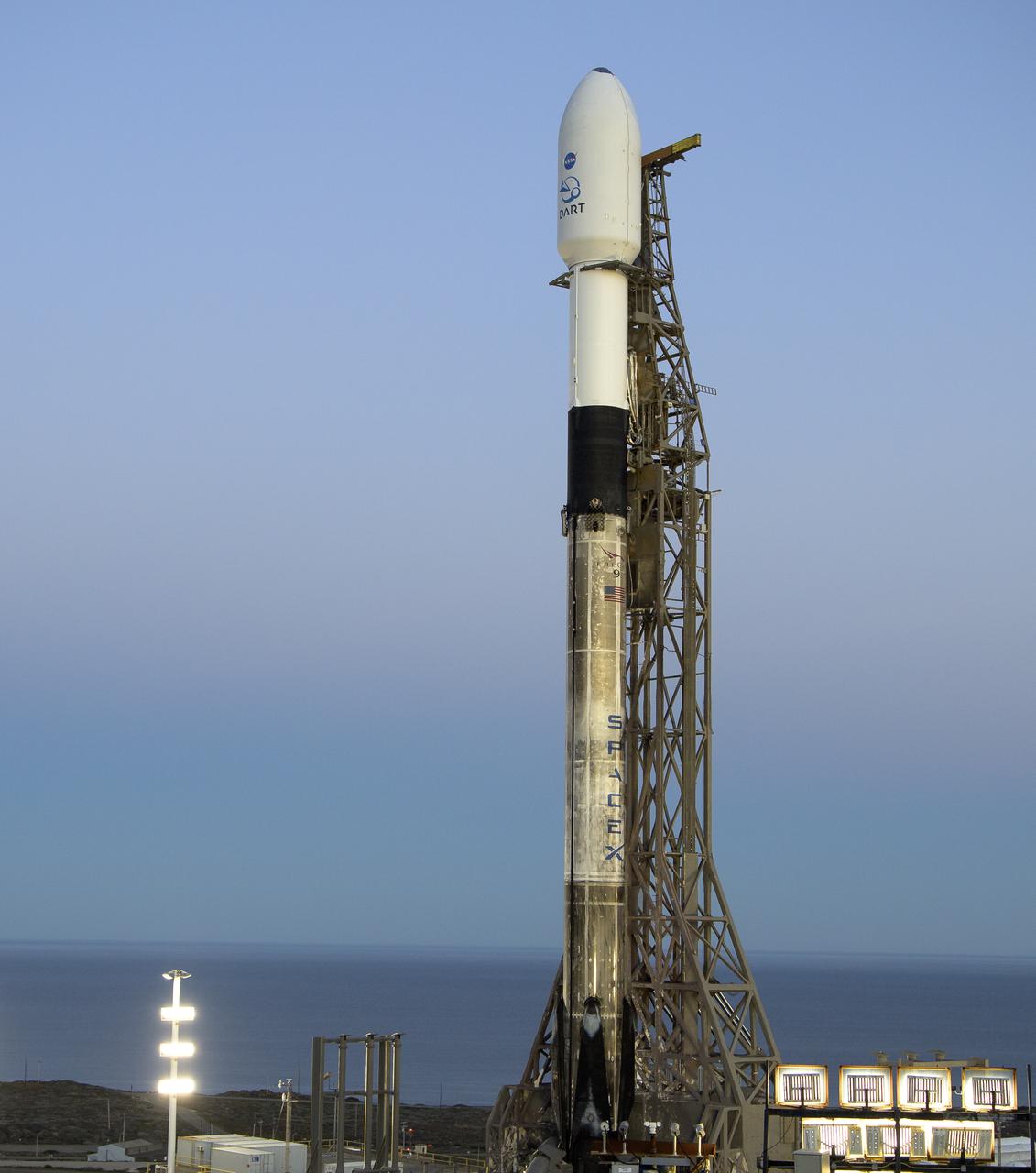

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
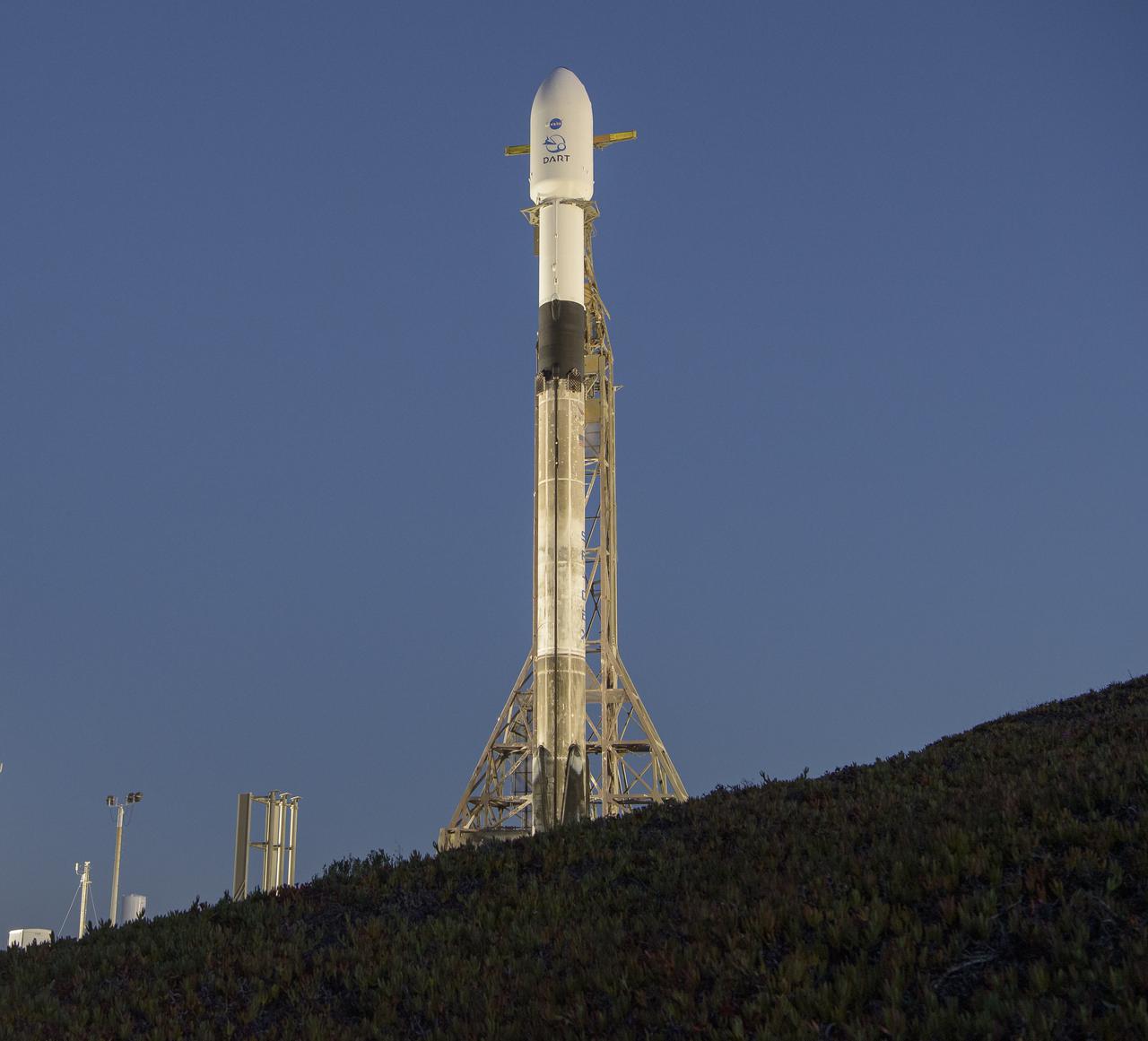

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
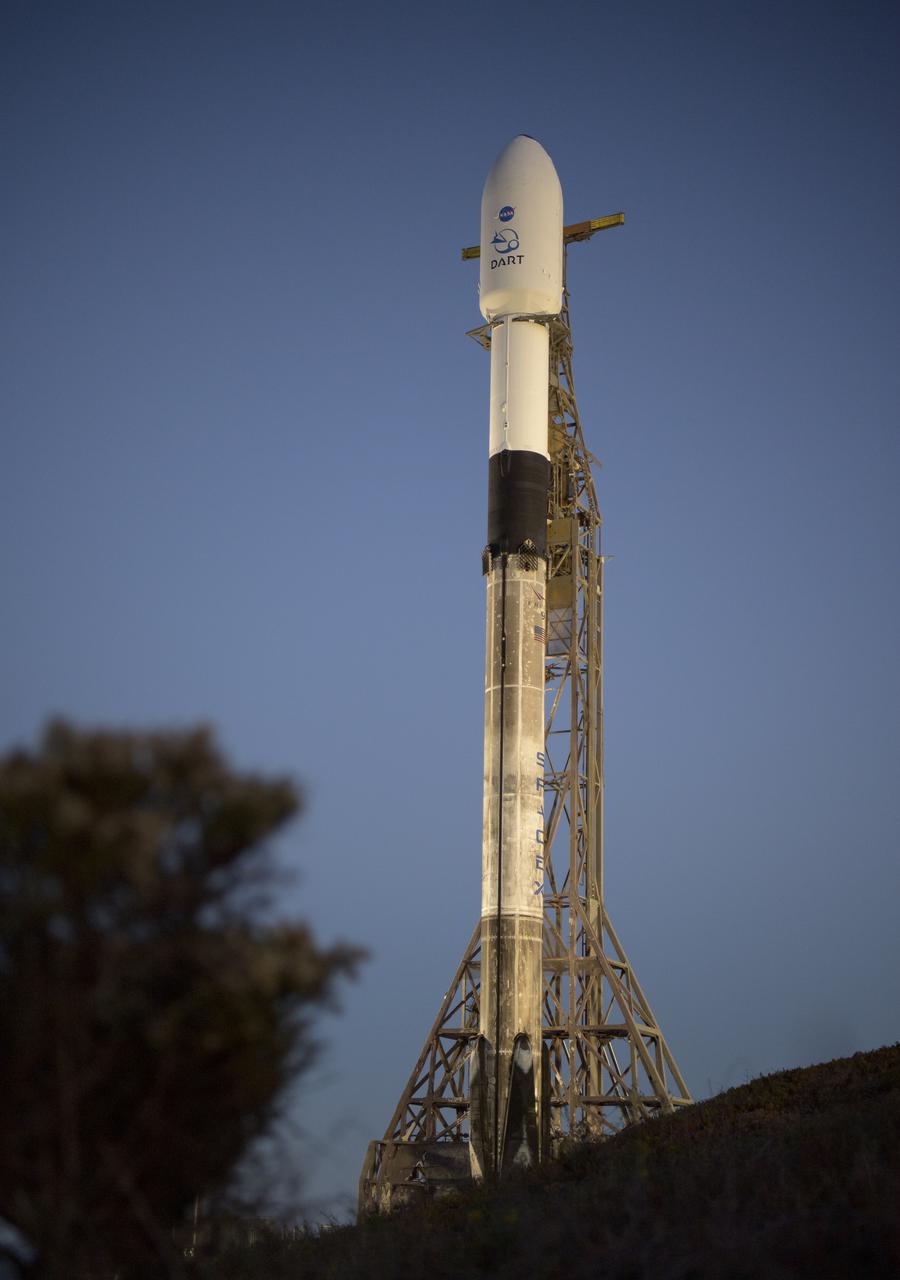

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
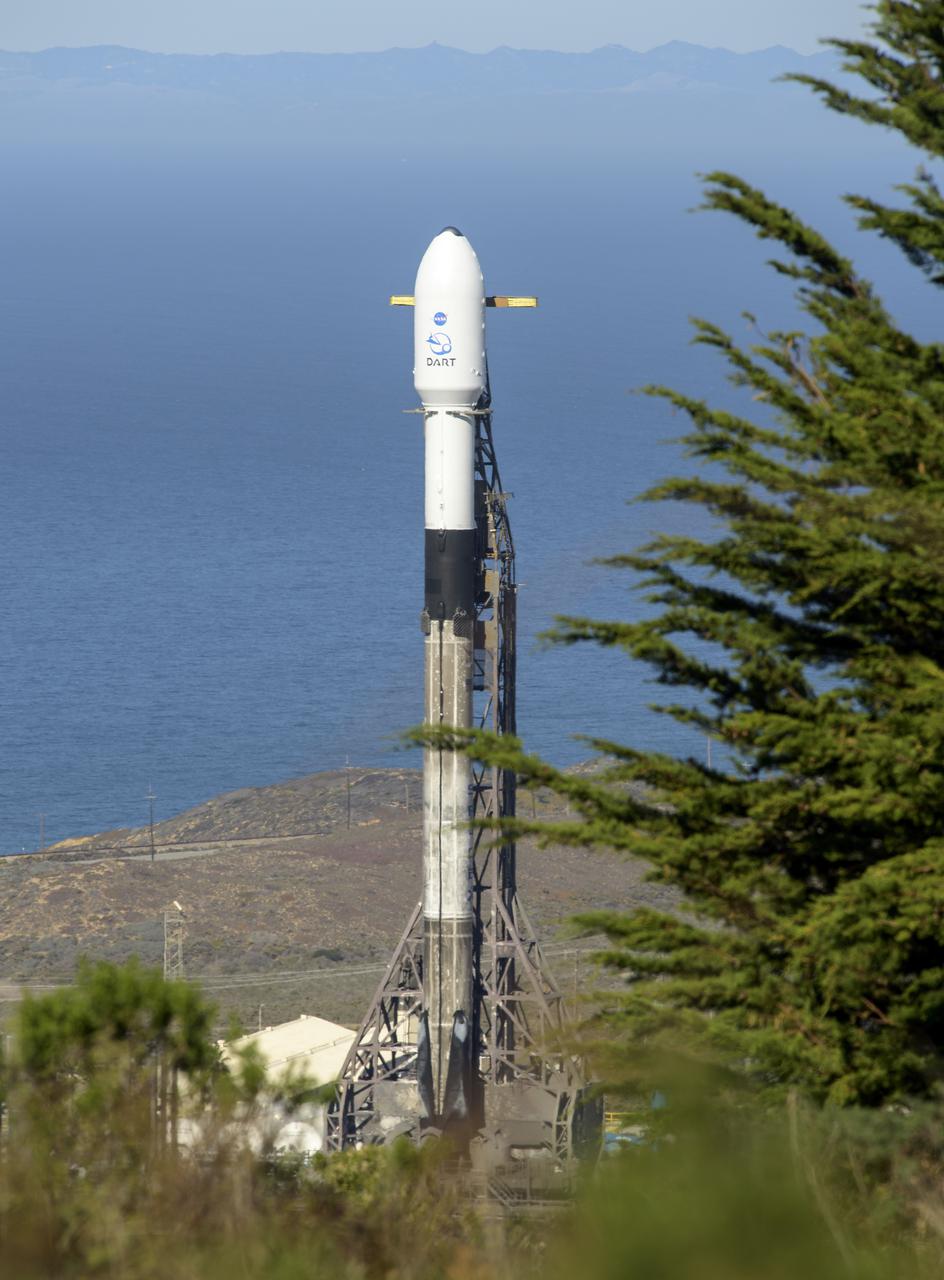

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons Mission Systems Engineer Chris Hersman, left, New Horizons Project Manager Helene Winters, and New Horizons Deputy Mission Systems Engineer Gabe Rogers, right, all of the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, wait for a signal from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
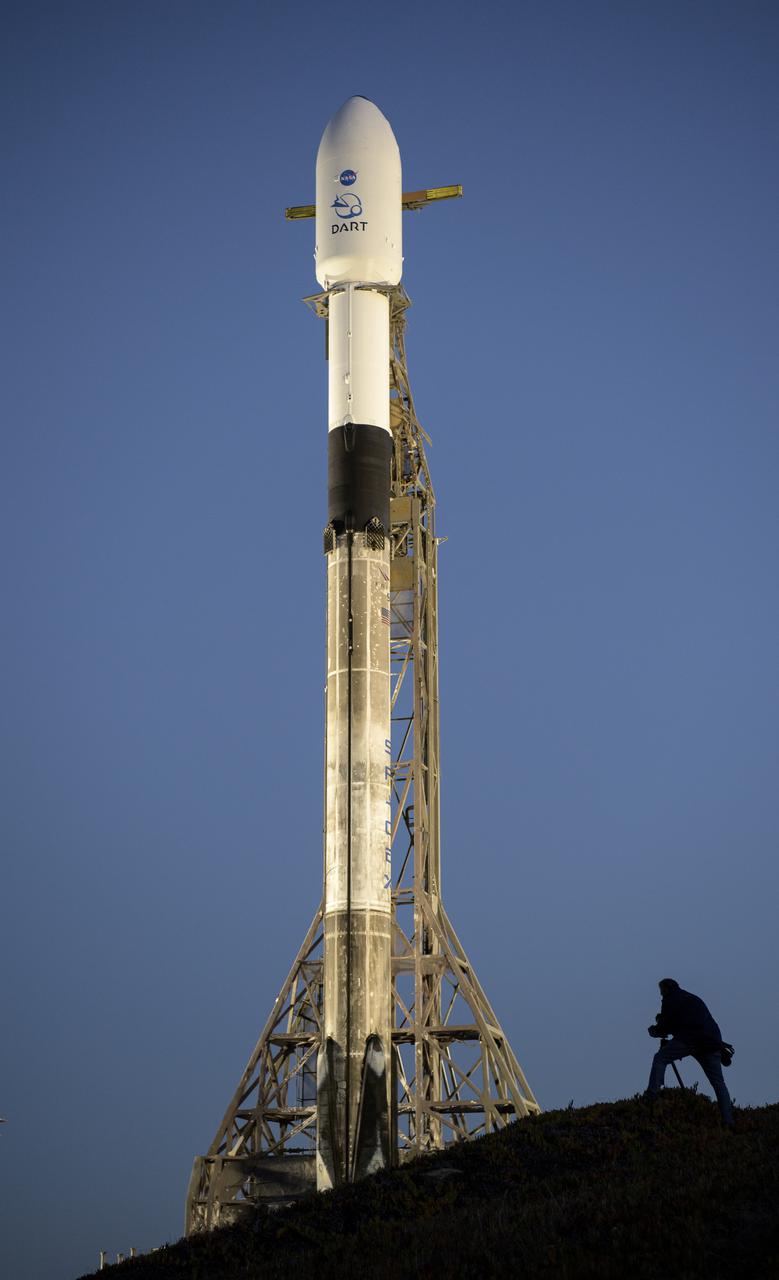

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
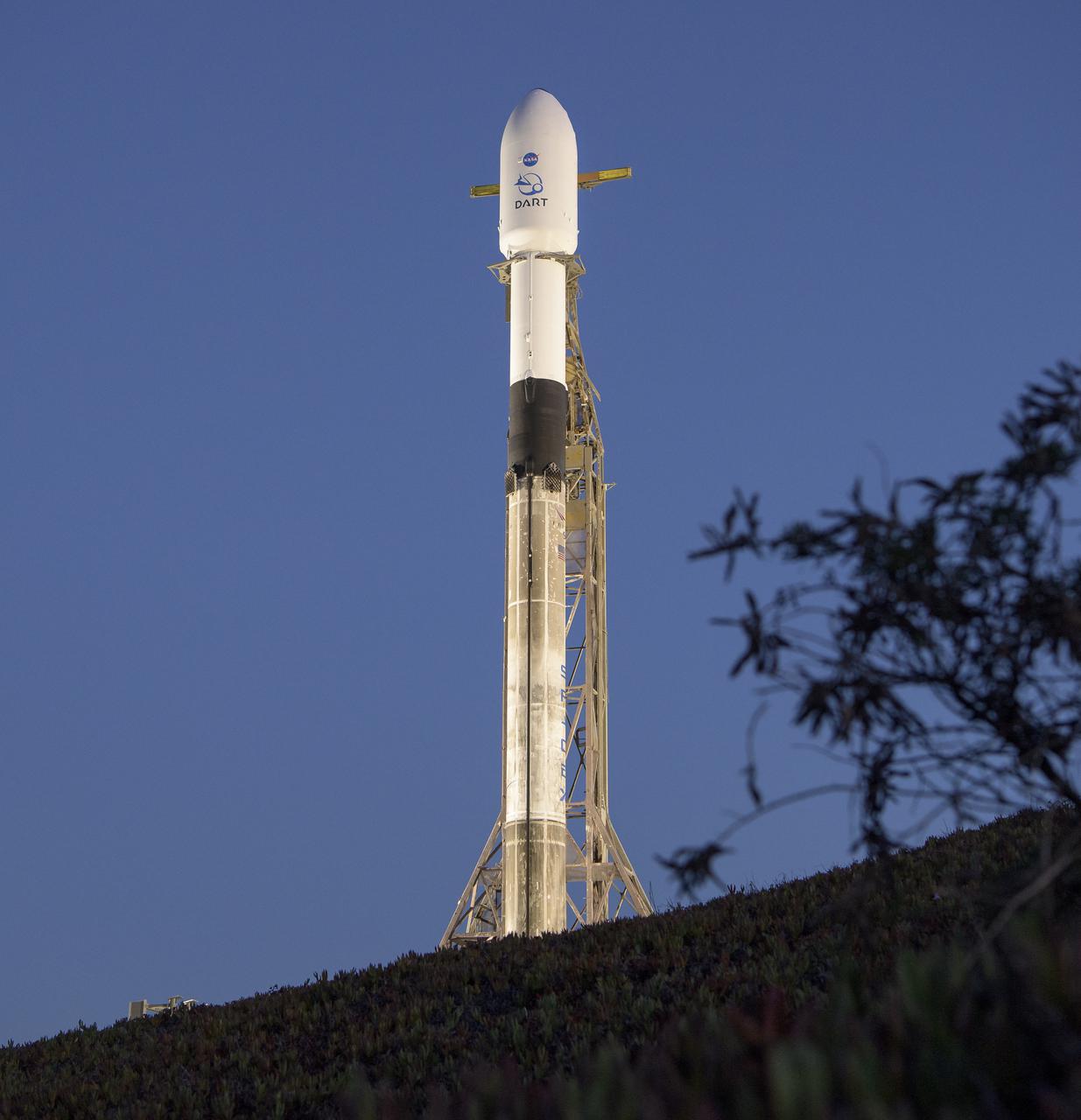

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
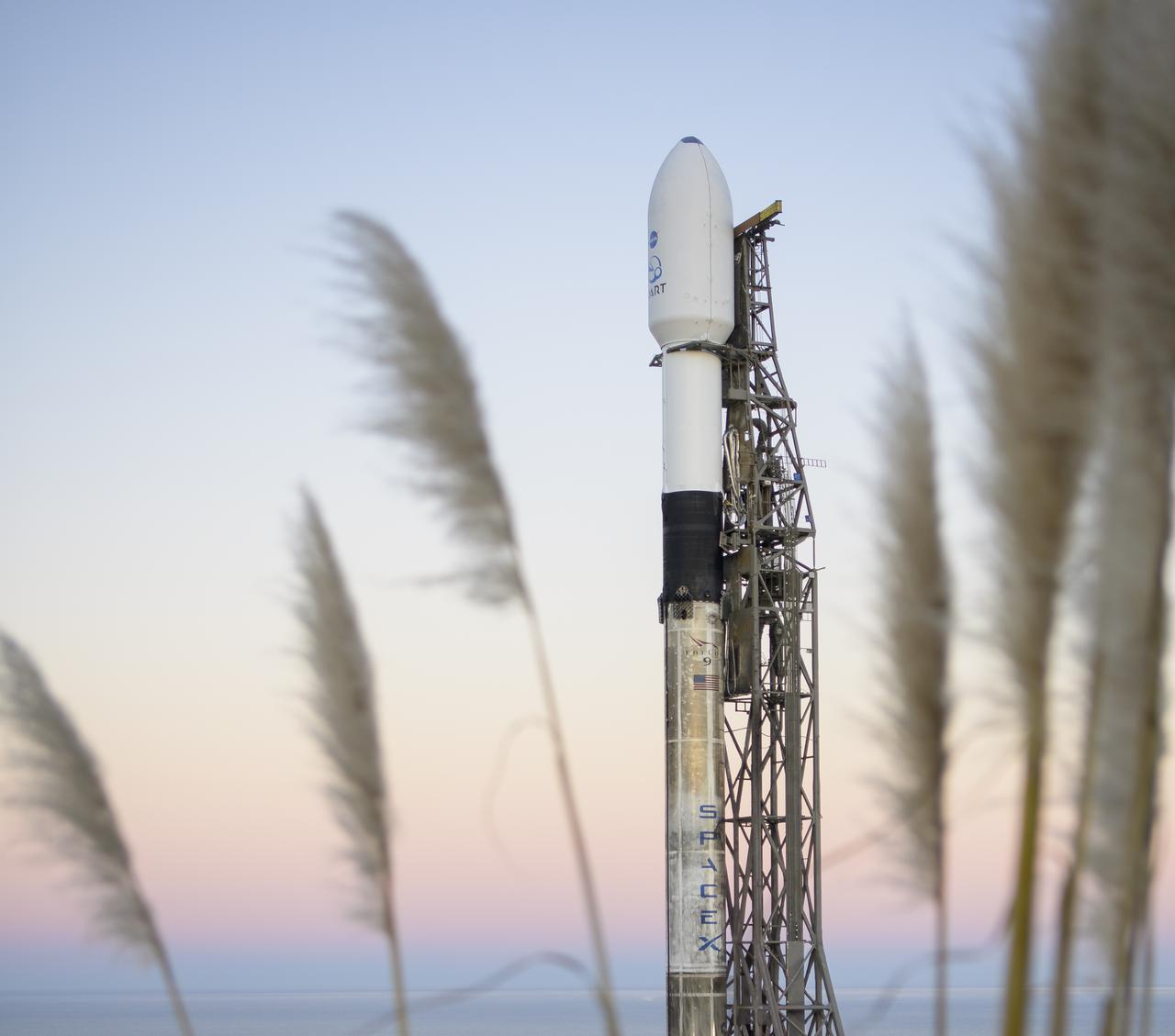

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
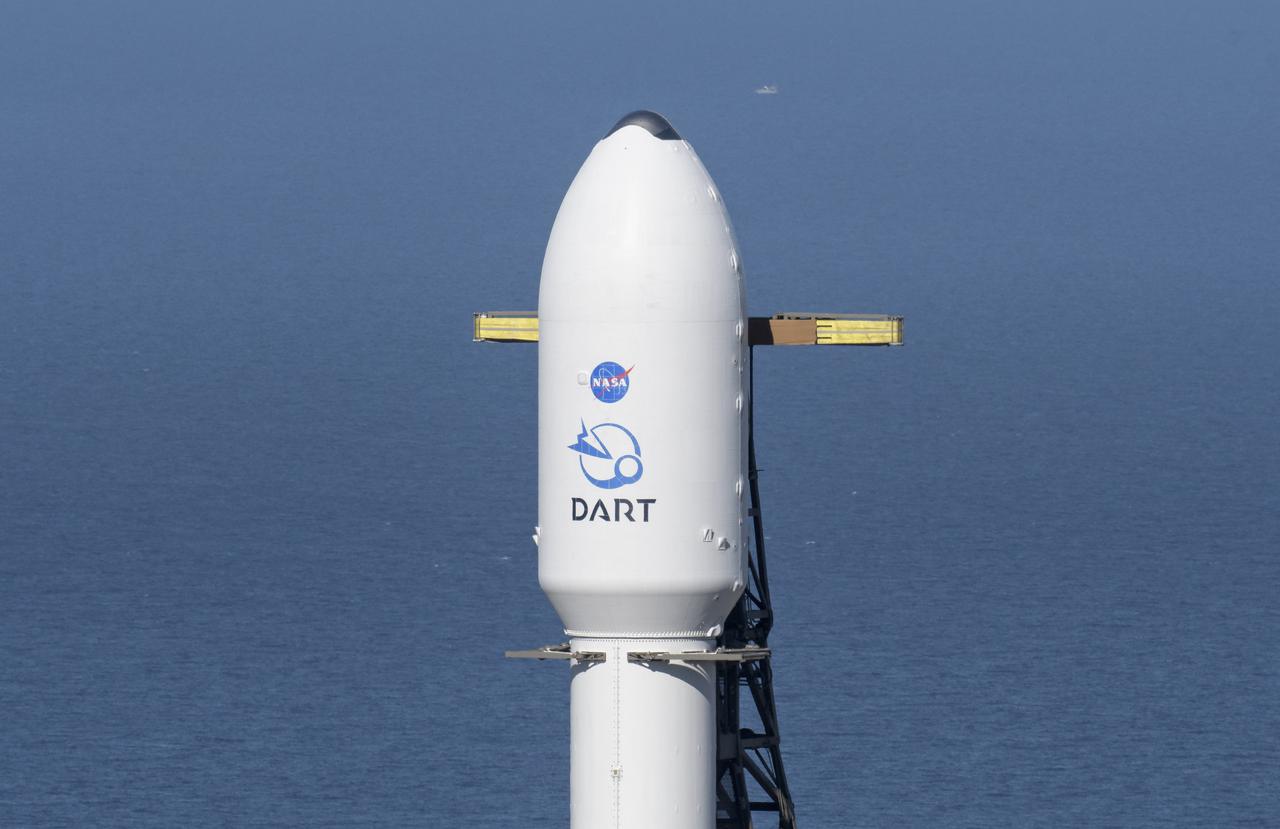

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
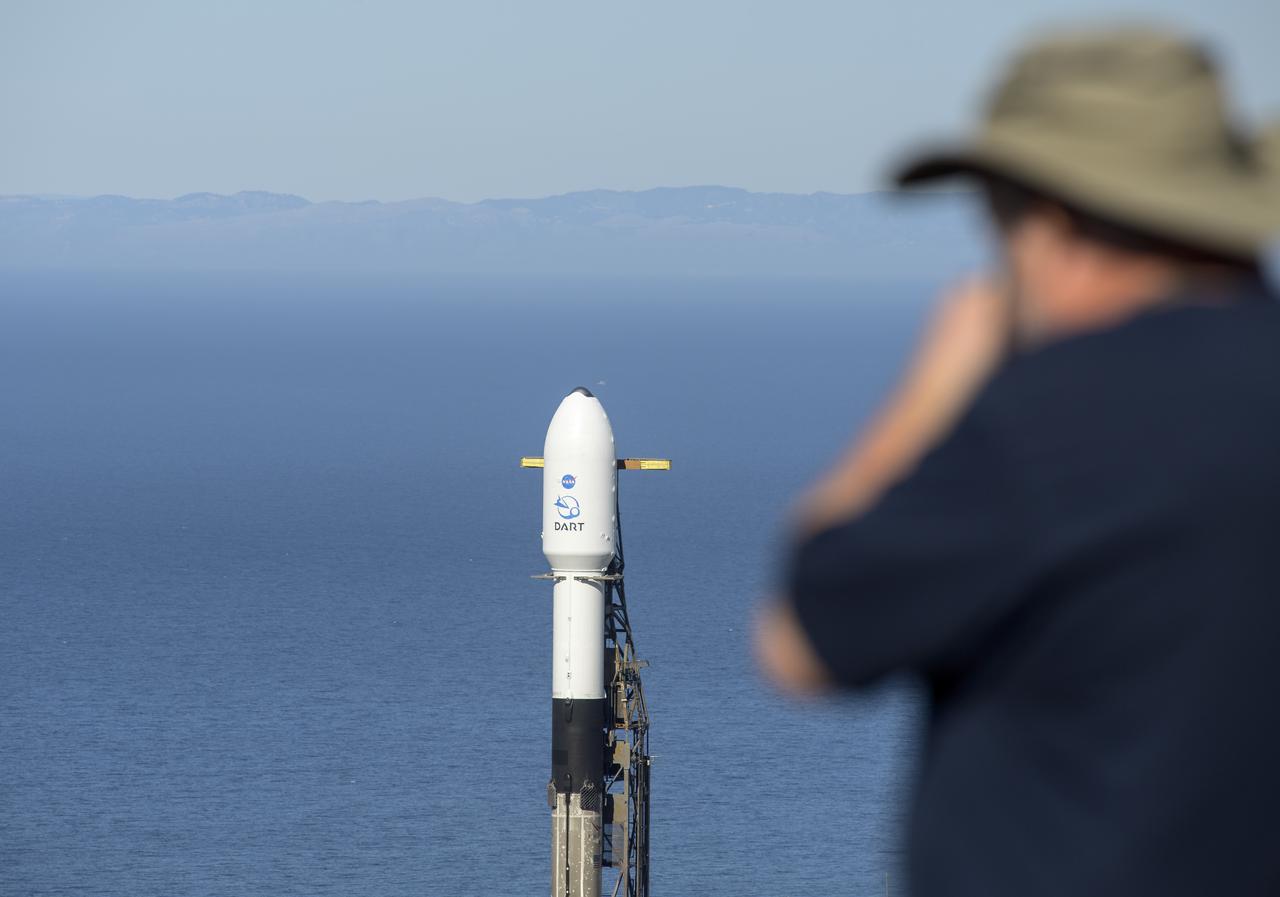

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
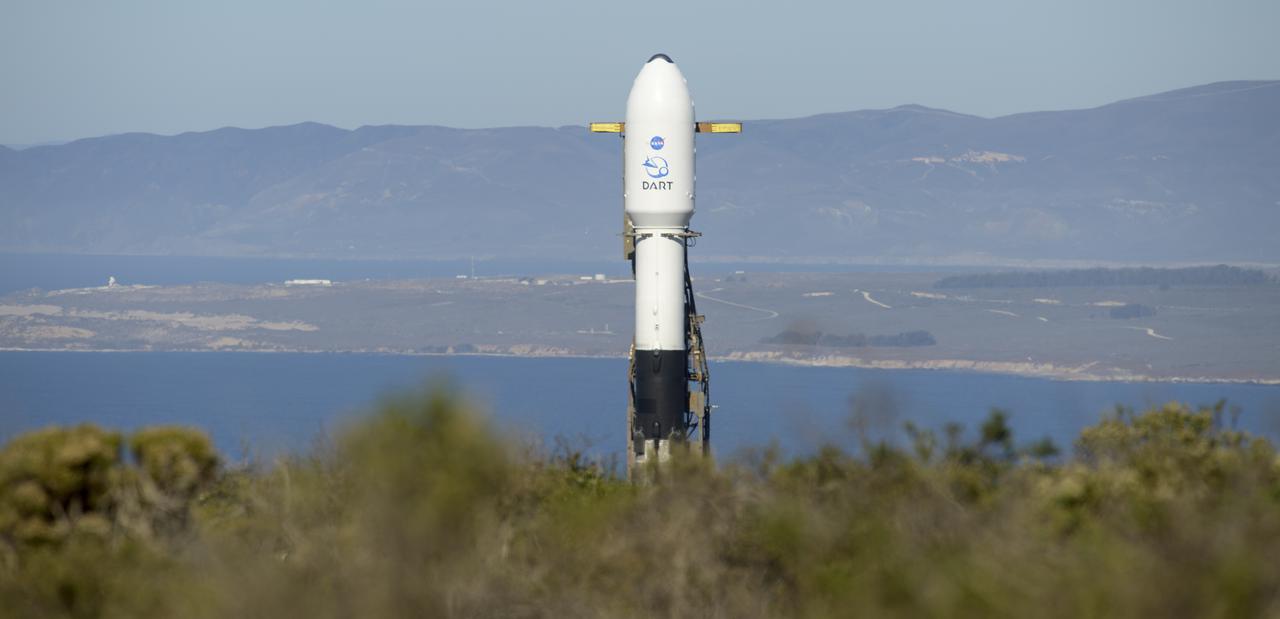

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
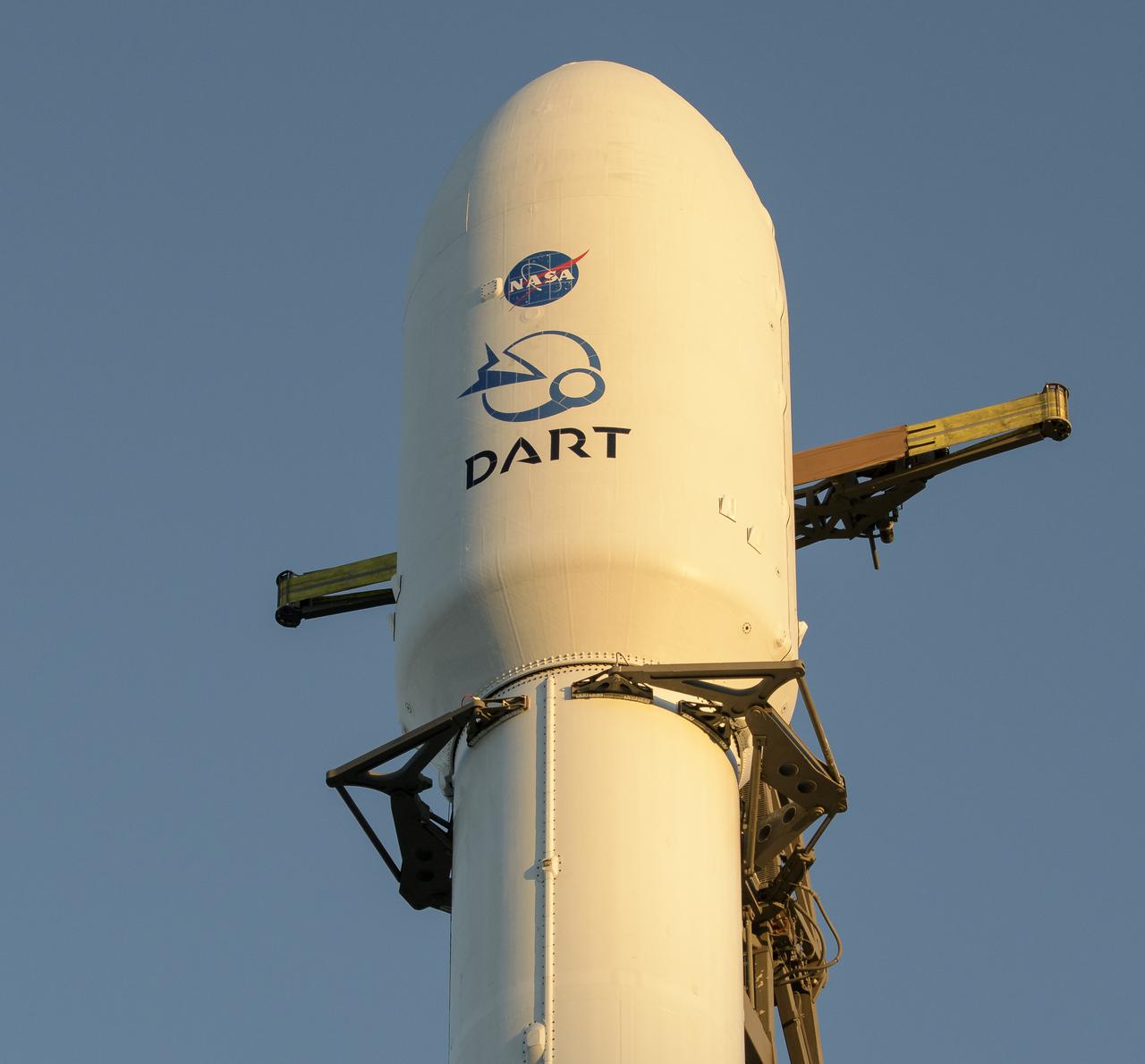

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
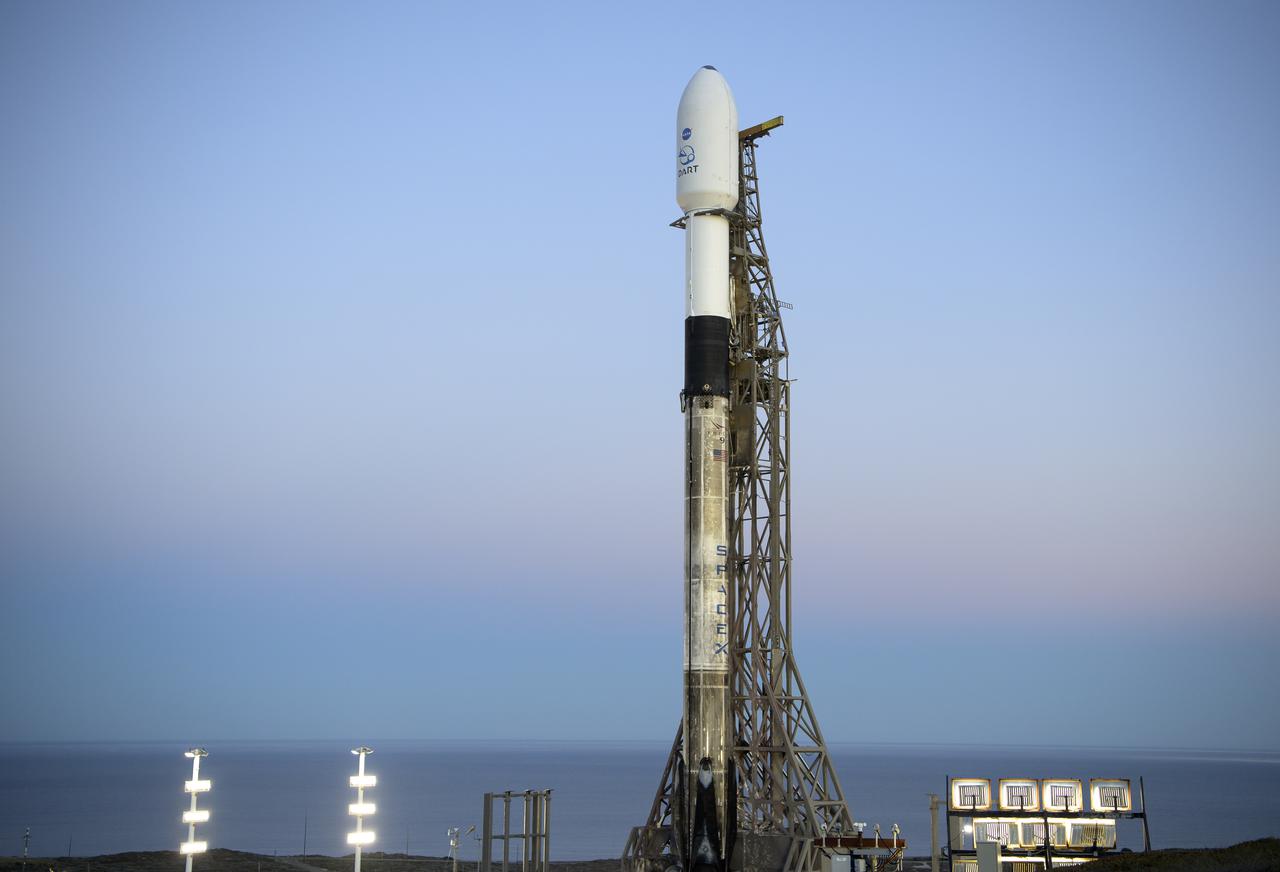

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen during sunrise, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by the Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
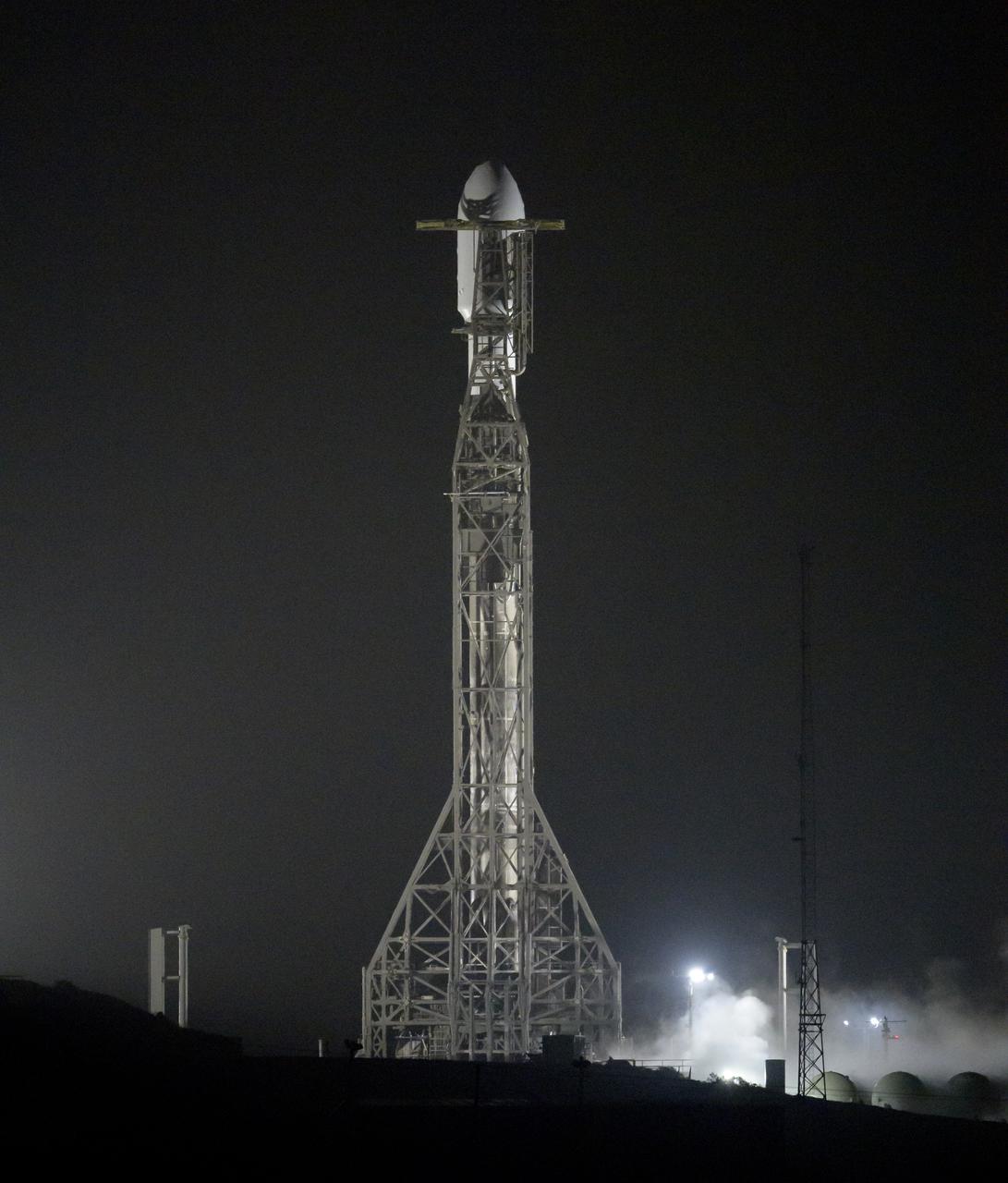

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, is seen ready for launch, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, at Space Launch Complex 4E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
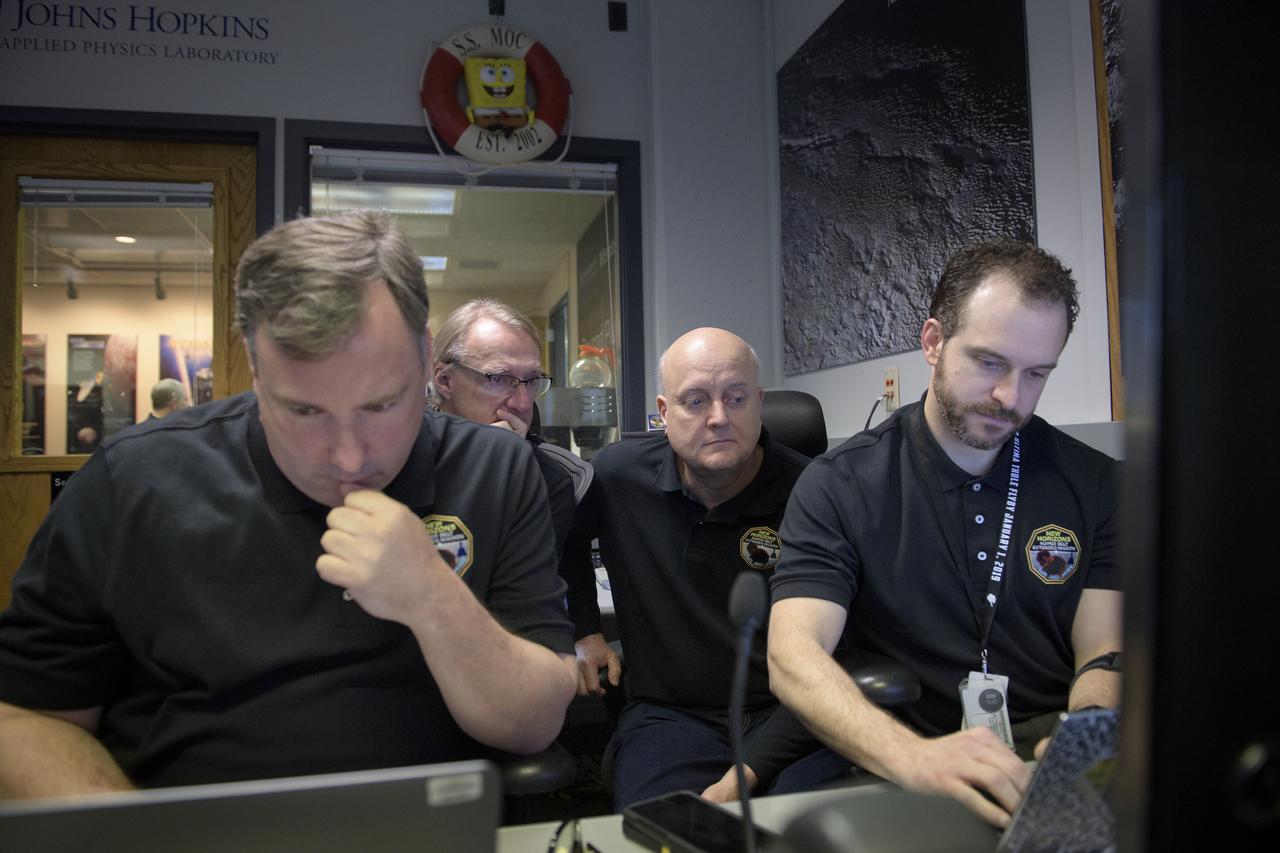

New Horizons mission managers: Chris DeBoy, left, Mark Kochte, Rick Shelton, and Michael Vincent, right, wait for a signal from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 in the Mission Operations Center at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Mike Buckley, senior public information officer at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, left, and New Horizons encounter mission manager Mark Holdridge of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, right, watch a live feed of the Mission Operations Center (MOC) along with guests and New Horizons team members as they wait to receive confirmation from the spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
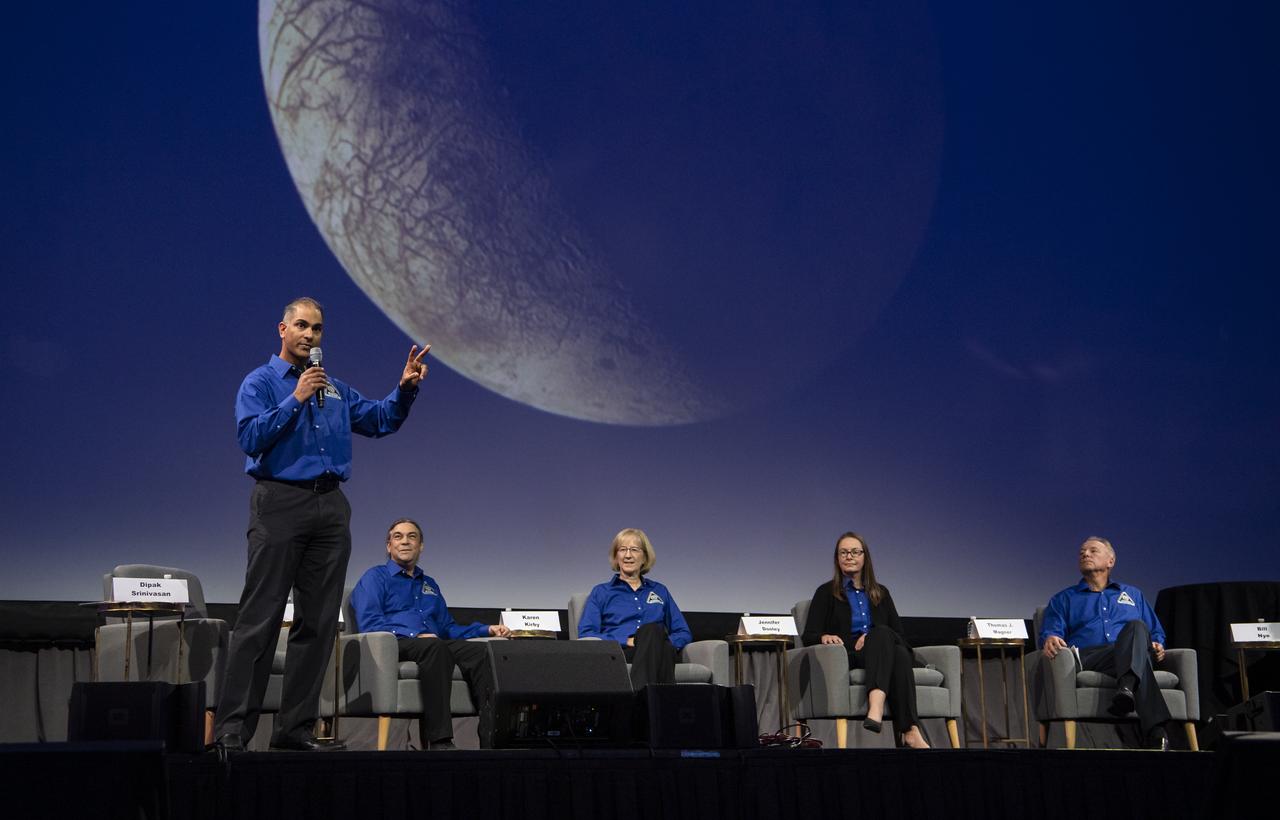

Dipak Srinivasan, Europa Clipper Telecommunications Manager, Johns Hopkins University, Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) moderates a panel titled, “Europa Clipper: Making a Mission to Understand Our Place in the Universe” with panelists, from left to right, Robert Pappalardo, Europa Clipper Project Scientist, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL); Karen Kirby, Europa Clipper Deputy Project System Engineer, APL; Jennifer Dooley, Europa Clipper Project Systems Engineer, JPL; Thomas Magner, Manager, APL; and Bill Nye, Chief Executive Officer, The Planetary Society, during the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Wednesday, Oct. 23, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Dipak Srinivasan, Europa Clipper Telecommunications Manager, Johns Hopkins University, Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), left, moderates a panel titled, “Europa Clipper: Making a Mission to Understand Our Place in the Universe” with panelists, from left to right, Robert Pappalardo, Europa Clipper Project Scientist, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL); Karen Kirby, Europa Clipper Deputy Project System Engineer, APL; Jennifer Dooley, Europa Clipper Project Systems Engineer, JPL; Thomas Magner, Manager, APL; and Bill Nye, Chief Executive Officer, The Planetary Society, during the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Wednesday, Oct. 23, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
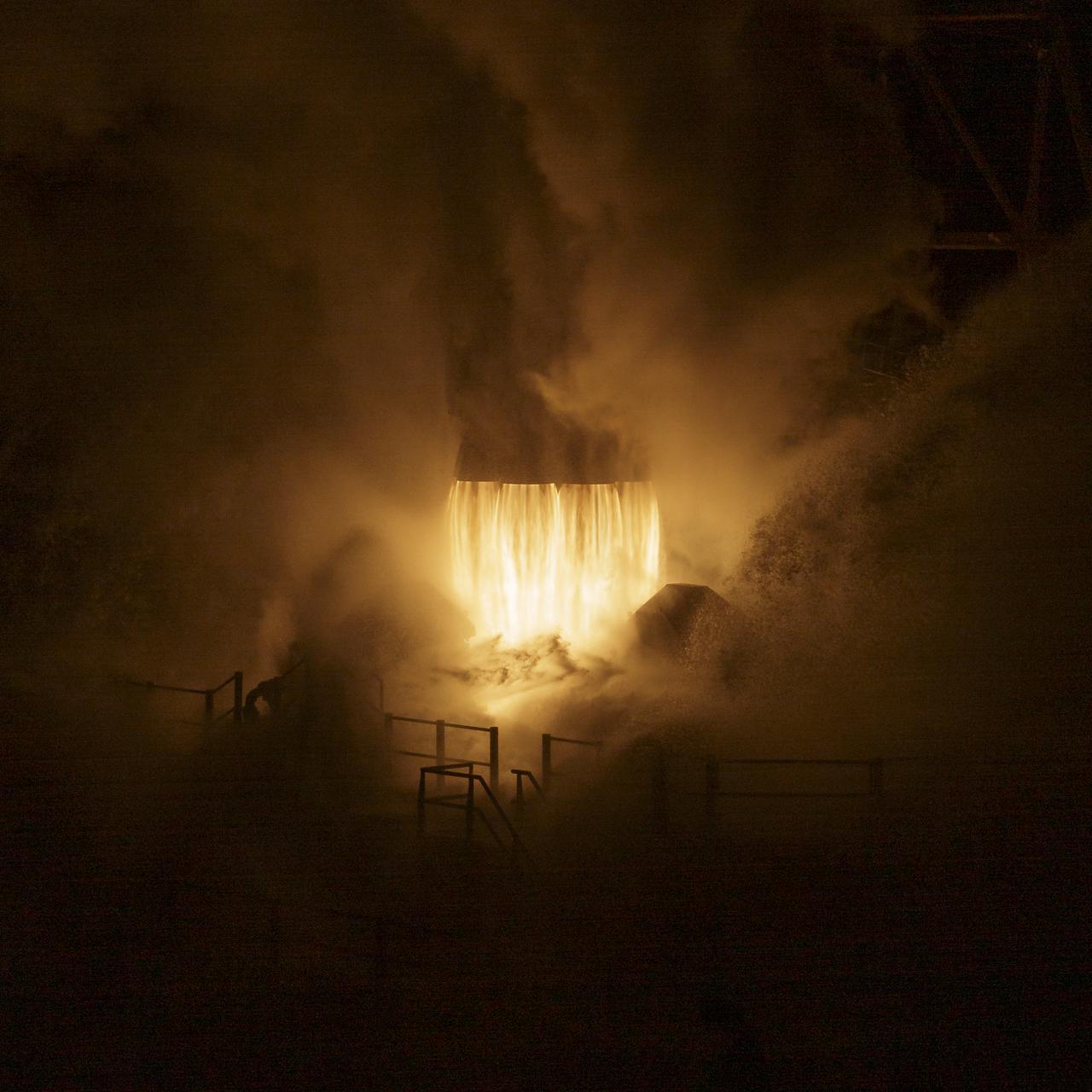

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
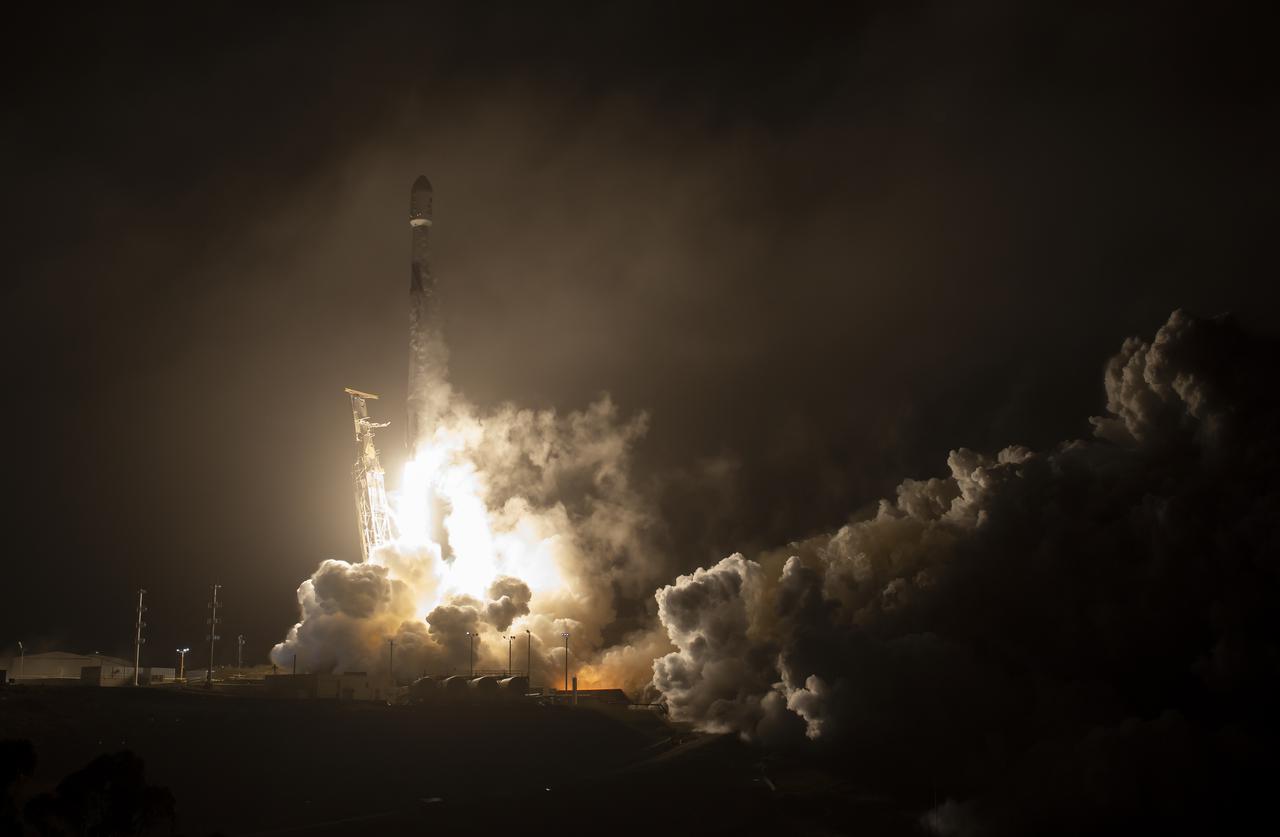

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
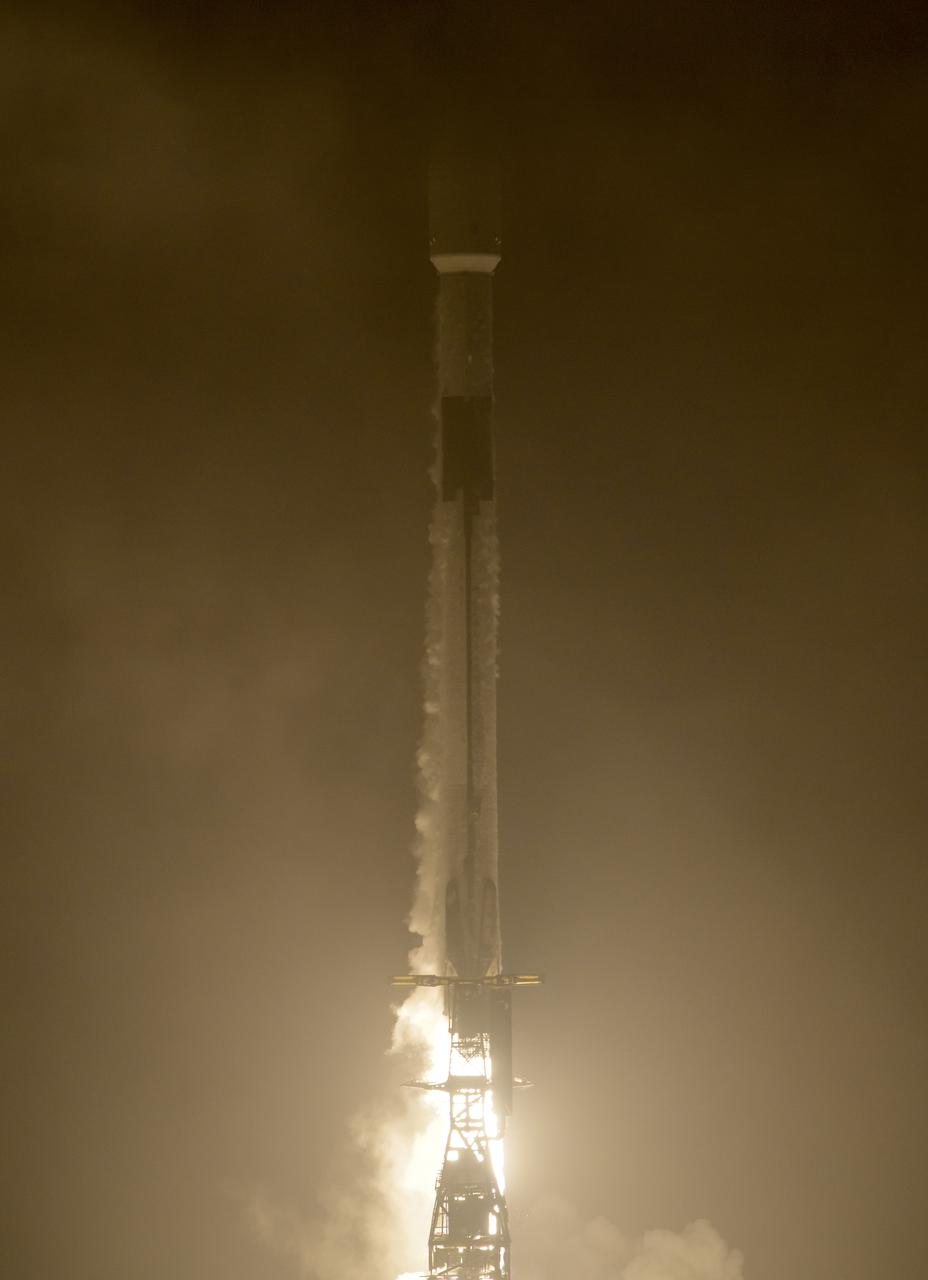

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
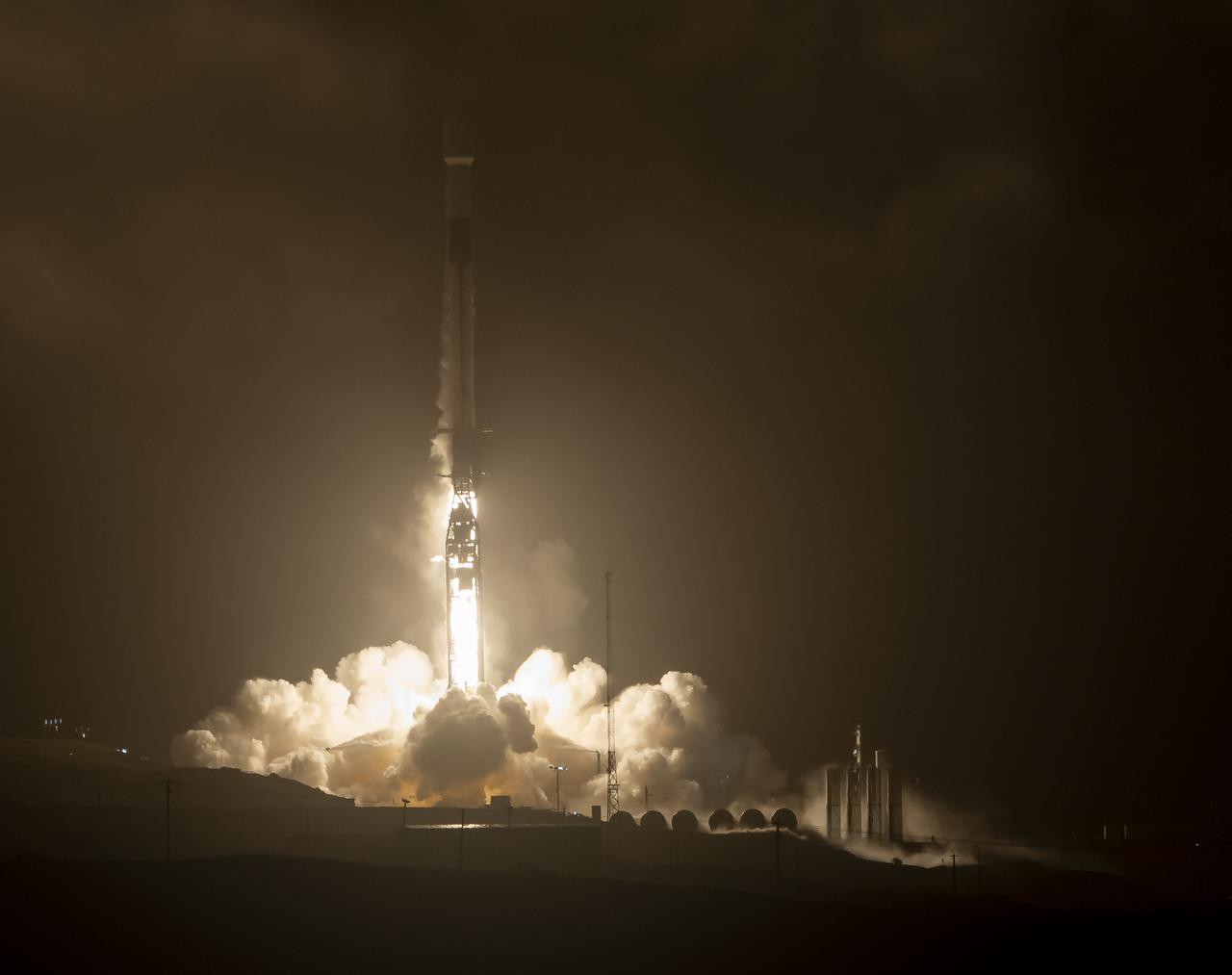

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
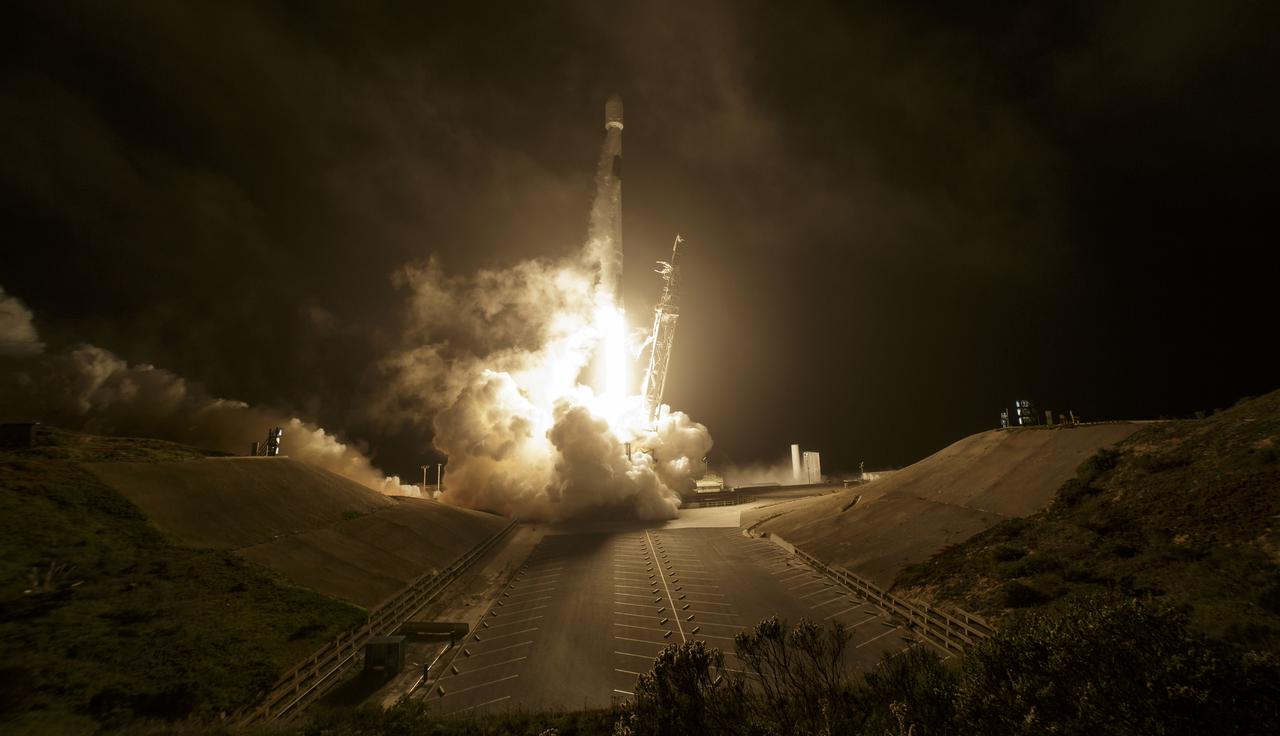

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
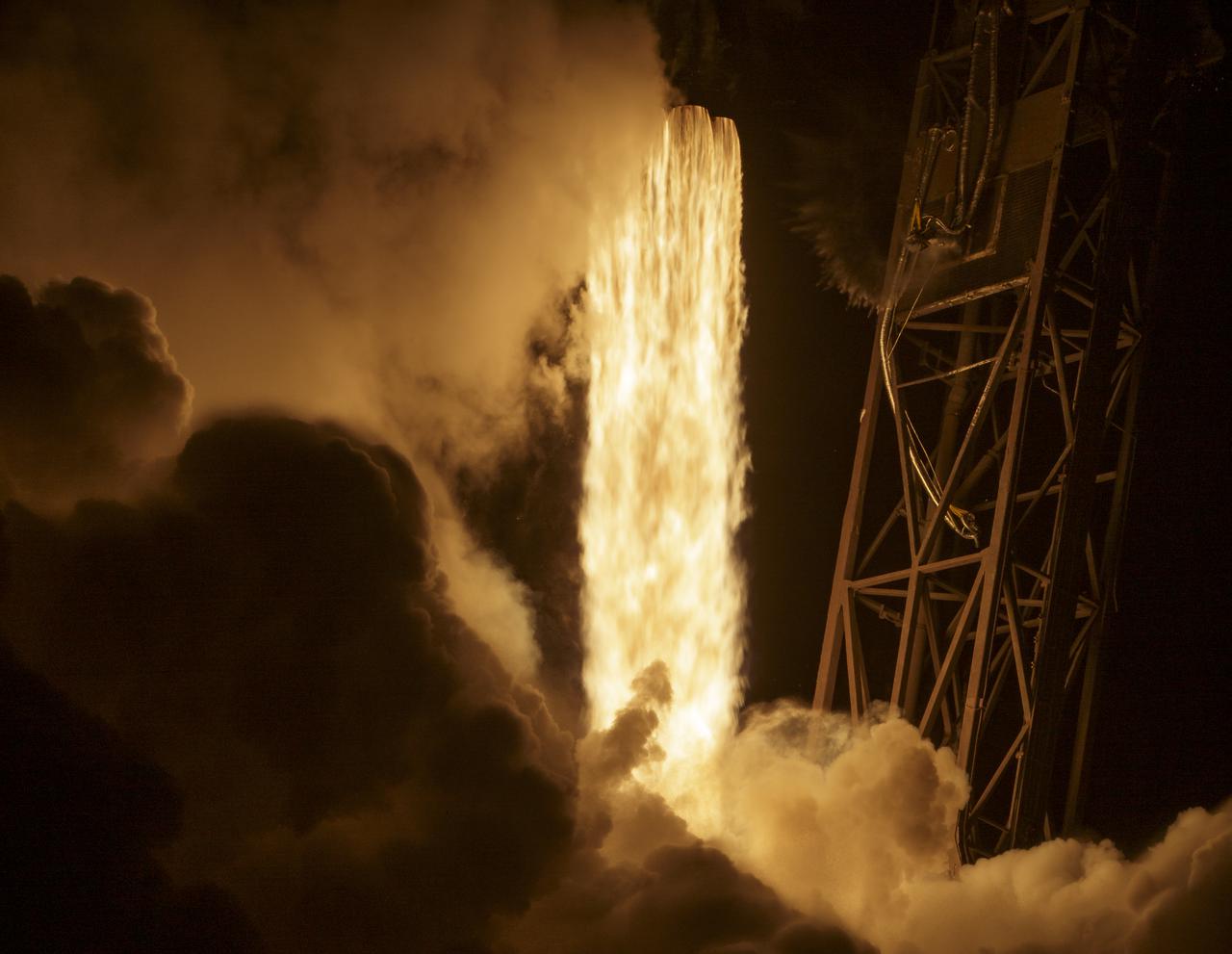

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
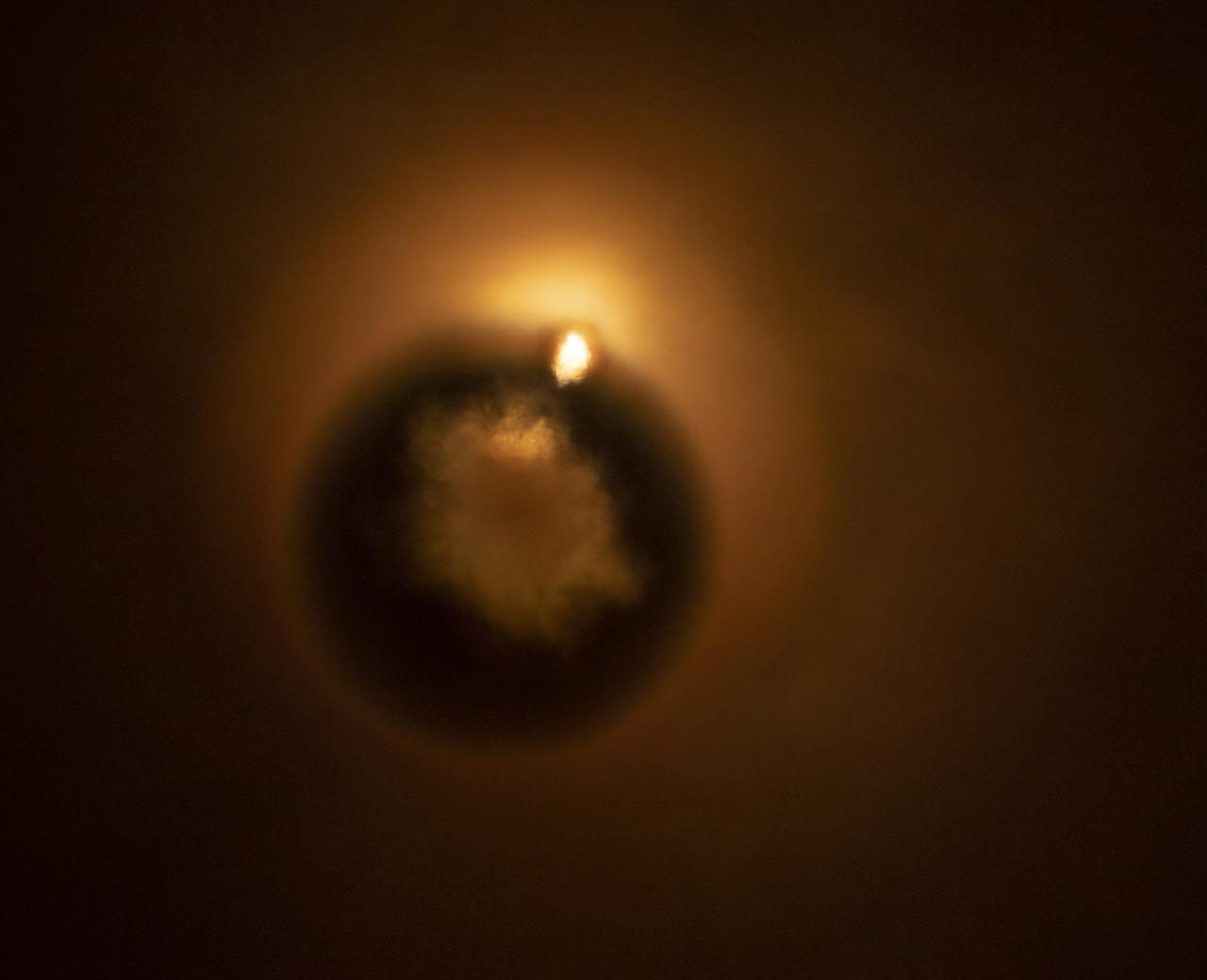
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, or DART, spacecraft onboard, Tuesday, Nov. 23, 2021, Pacific time (Nov. 24 Eastern time) from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. DART is the world’s first full-scale planetary defense test, demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection technology. The mission was built and is managed by Johns Hopkins APL for NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
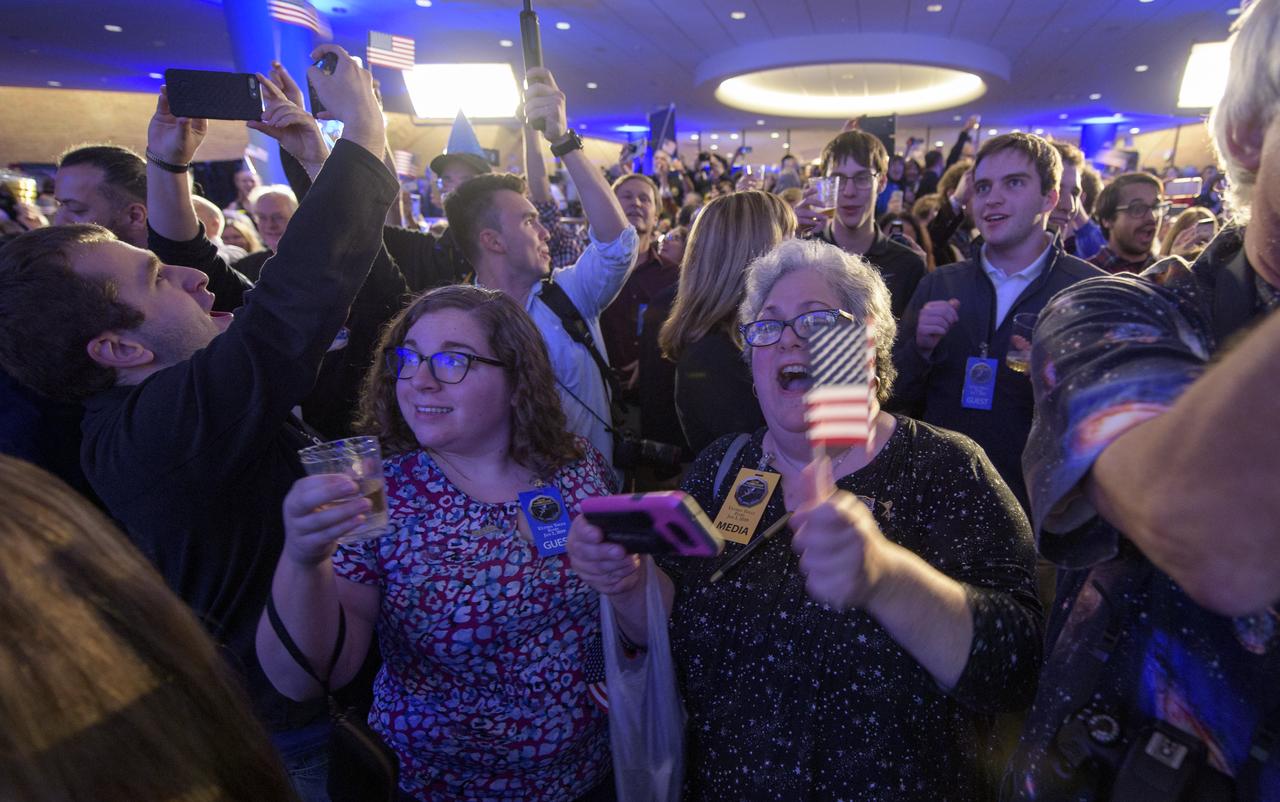

Guests celebrate New Years, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
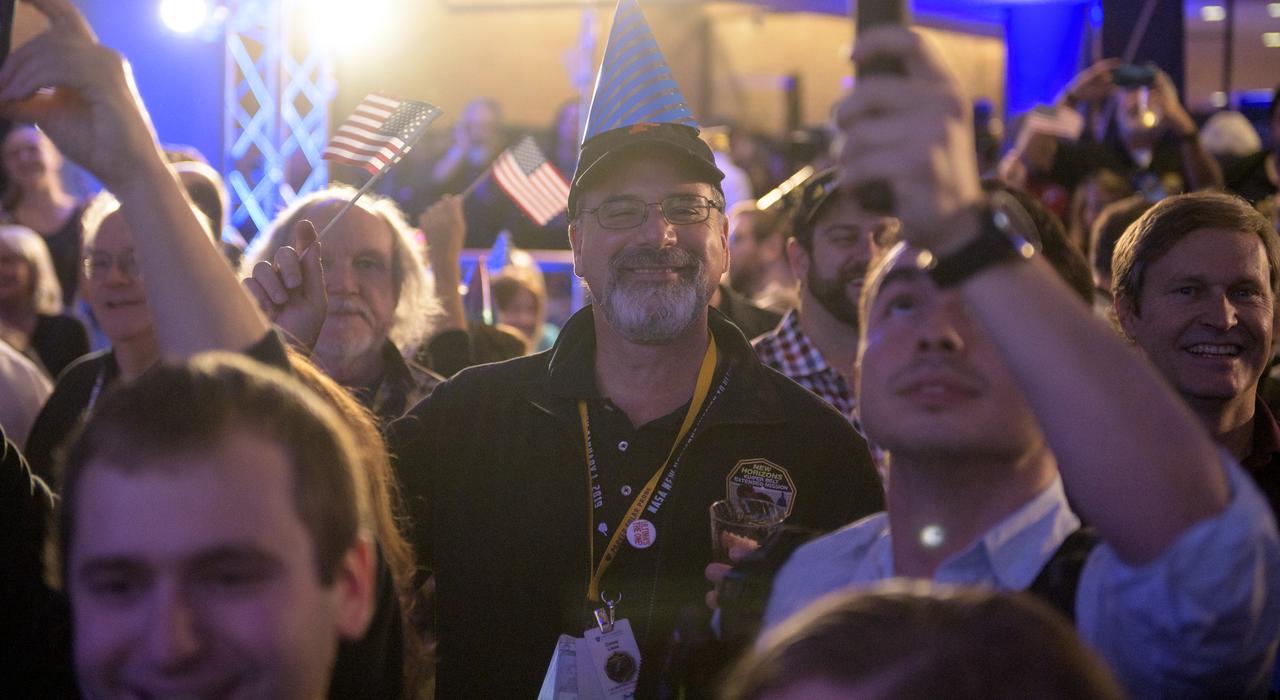

Guests celebrate New Years, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
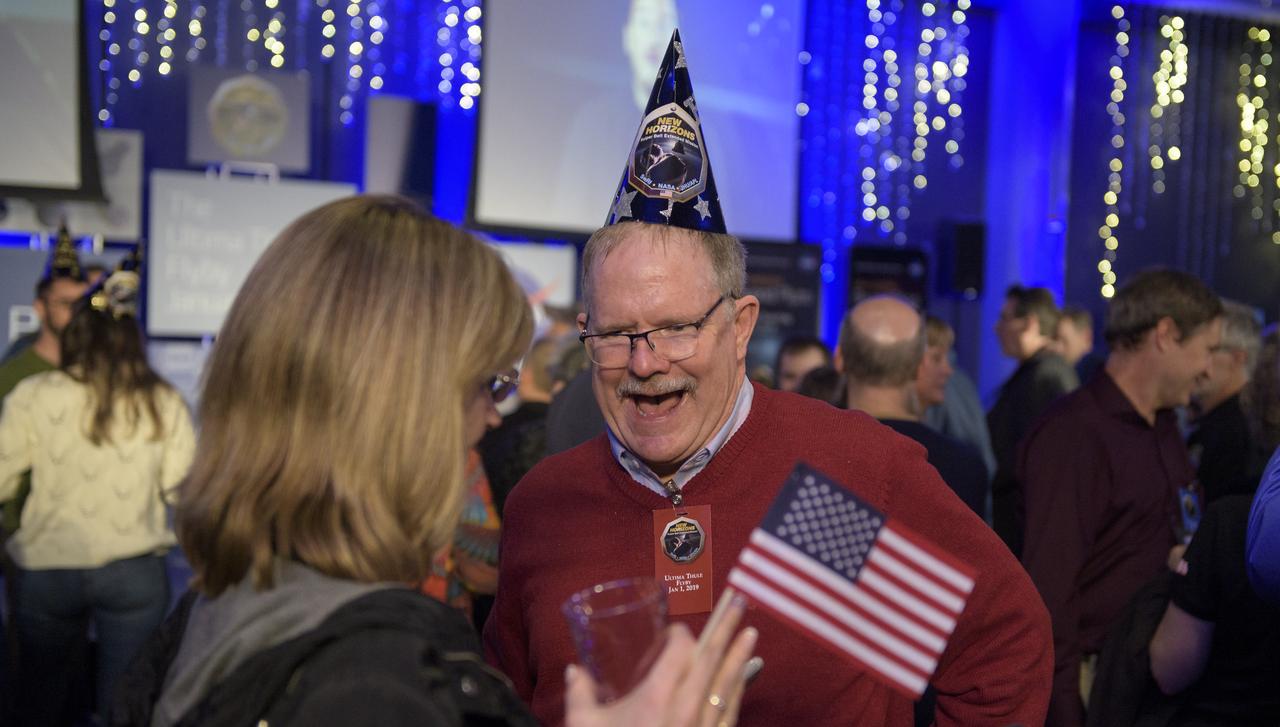

Guests celebrate New Years, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Musician Craig Werth introduces a song he made for the New Horizons mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
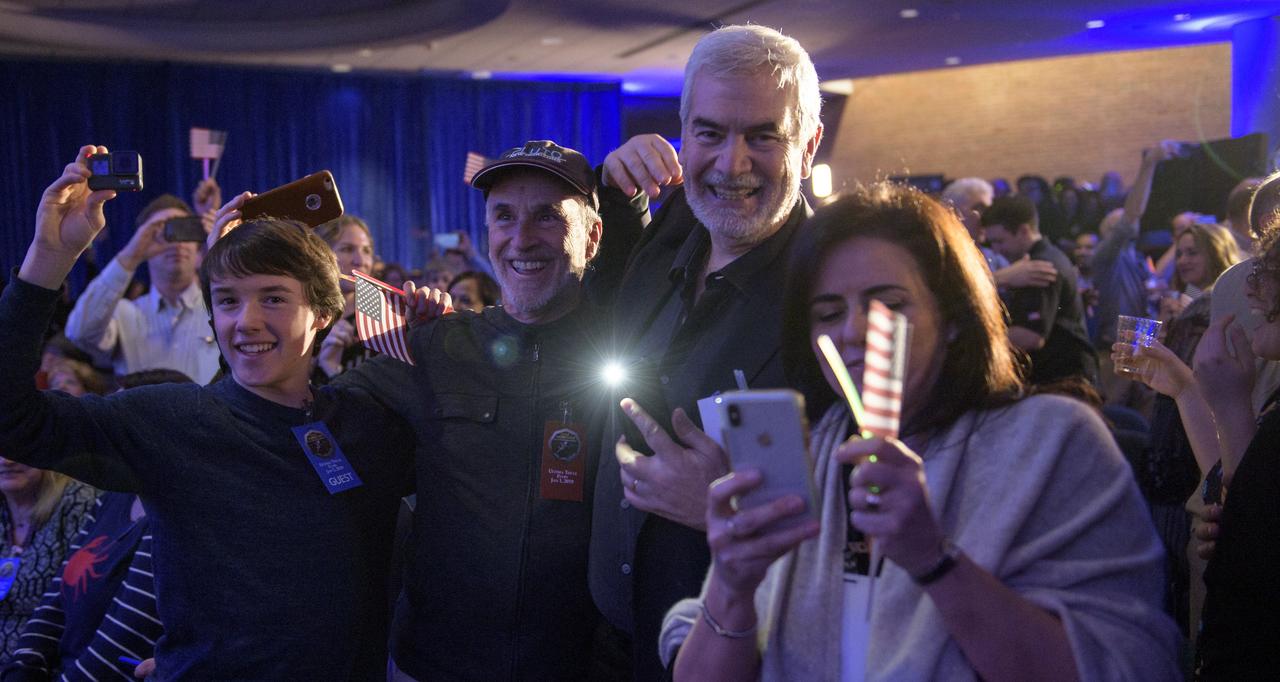

Guests celebrate New Years, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)