
S66-36742 (1966) --- This is the insignia for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Apollo 1 mission, the first manned Apollo flight. Crew members are astronauts Virgil I. Grissom, Edward H. White II and Roger B. Chaffee. The NASA insignia design for Apollo flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced. EDITOR'S NOTE: The three astronauts lost their lives in a fire during a simulation on the launch pad on Jan. 27, 1967.
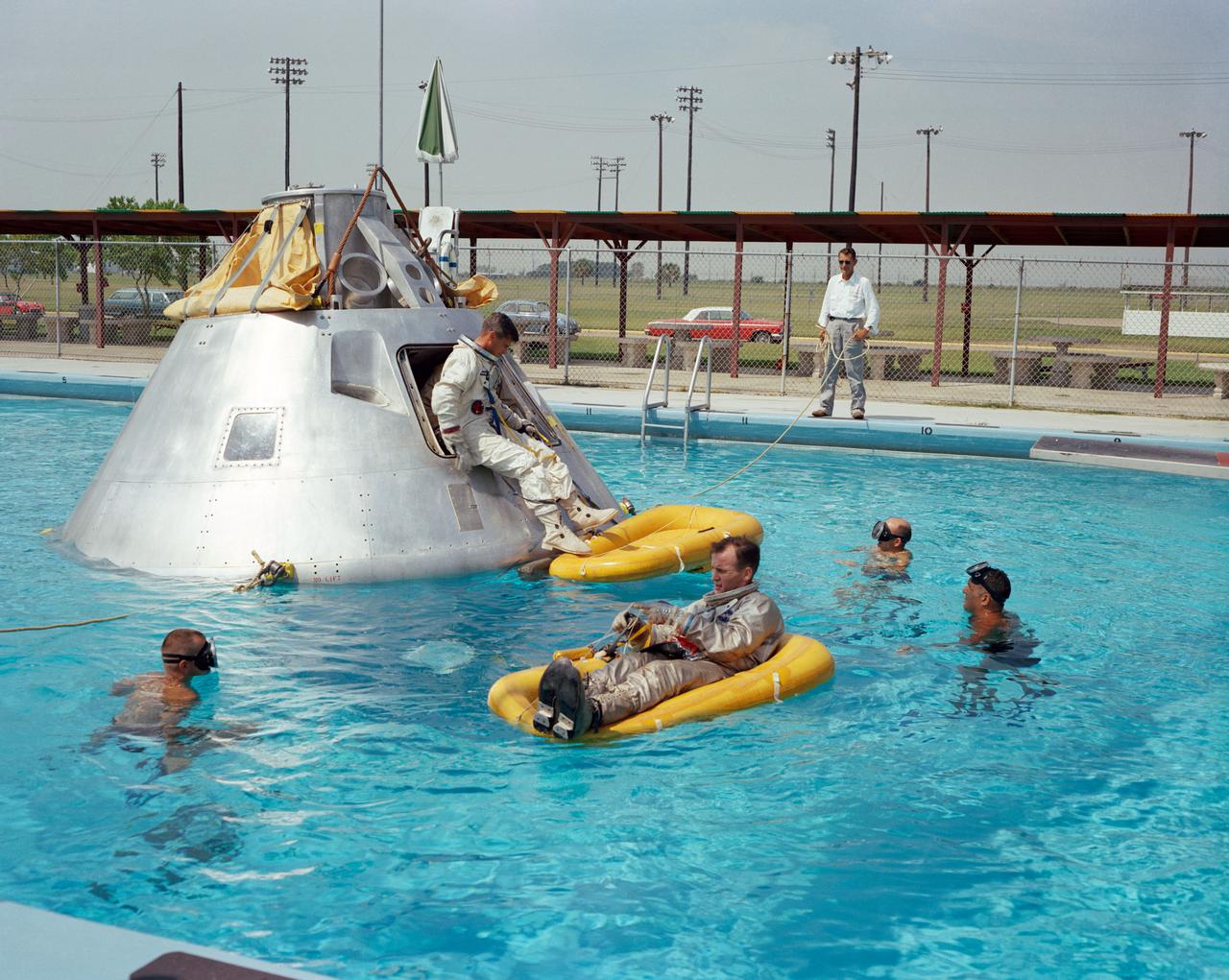

S66-51583 (June 1966)--- Prime crew members announced by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the first manned Apollo 1 space flight practice water egress procedures in a swimming pool at Ellington Air Force Base (EAFB), Houston, Texas. Astronaut Edward H. White II rides life raft in the foreground. Astronaut Roger B. Chaffee sits in hatch of the boilerplate model of the spacecraft. Astronaut Virgil I. Grissom, third member of the crew, waits inside the spacecraft.
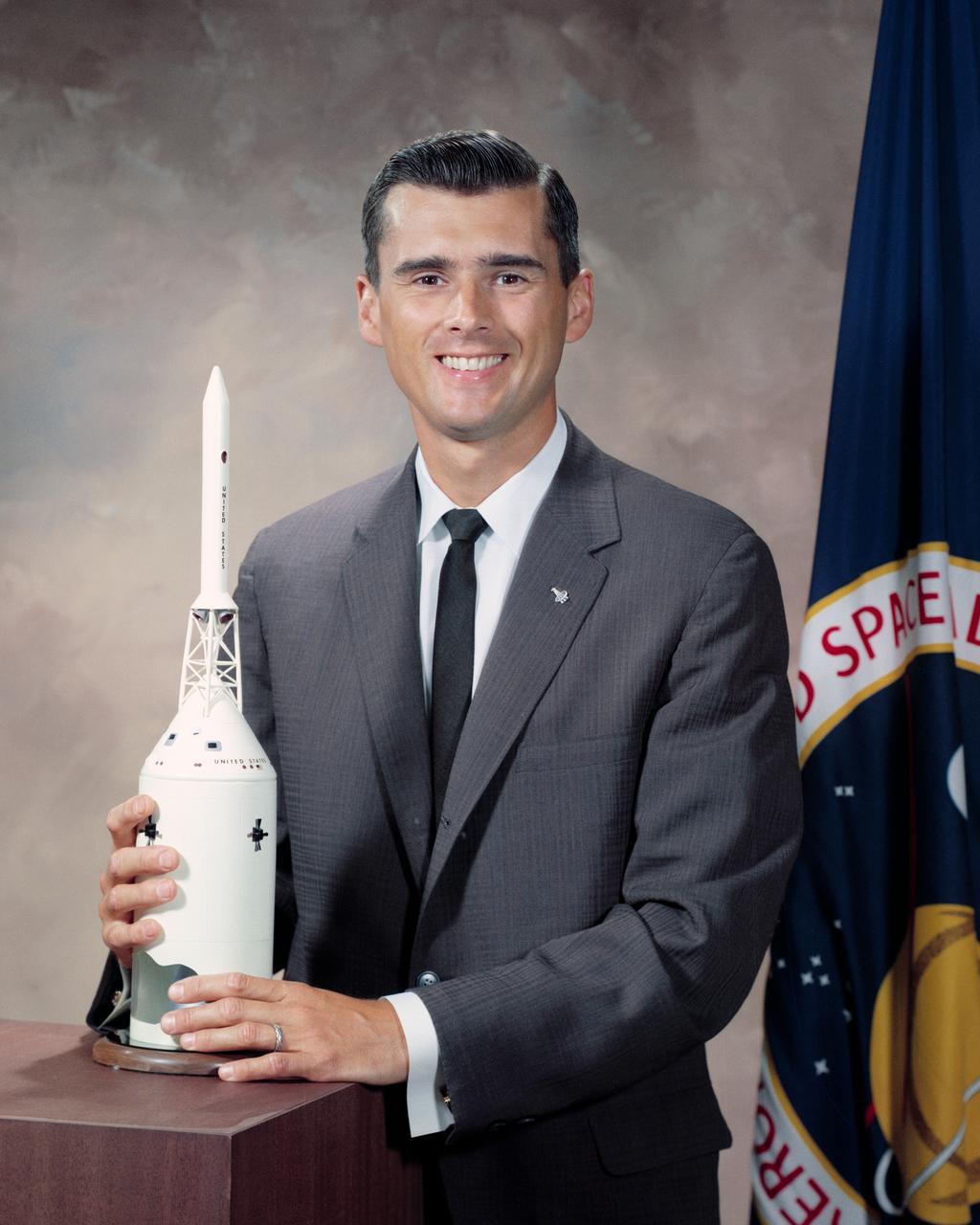

S64-31447 (10 Sept. 1964) --- Astronaut Roger B. Chaffee Editor's Note: Astronaut Chaffee died in the Apollo/Saturn 204 fire accident at Cape Canaveral, Florida, on Jan. 27, 1967, along with astronauts Virgil I. Grissom and Edward H. White II.
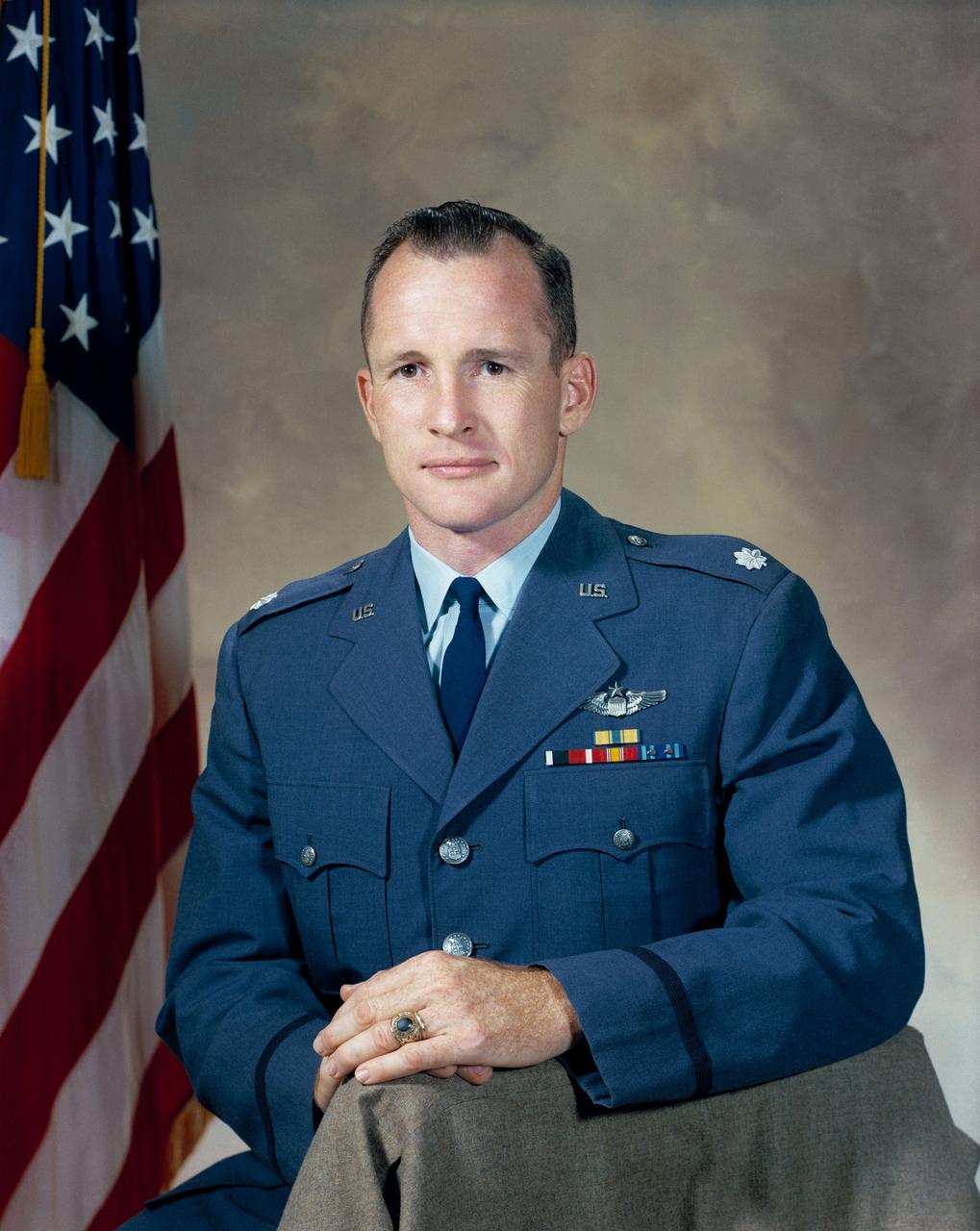

S66-35219 (1966) --- Astronaut Edward H. White II (United States Air Force Lieutenant Colonel), Gemini 4 pilot. Editor's Note: Since this portrait was taken astronaut White lost his life on Jan. 27, 1967, in the Apollo 1/Saturn 204 fire at Cape Kennedy, KSC, Florida.
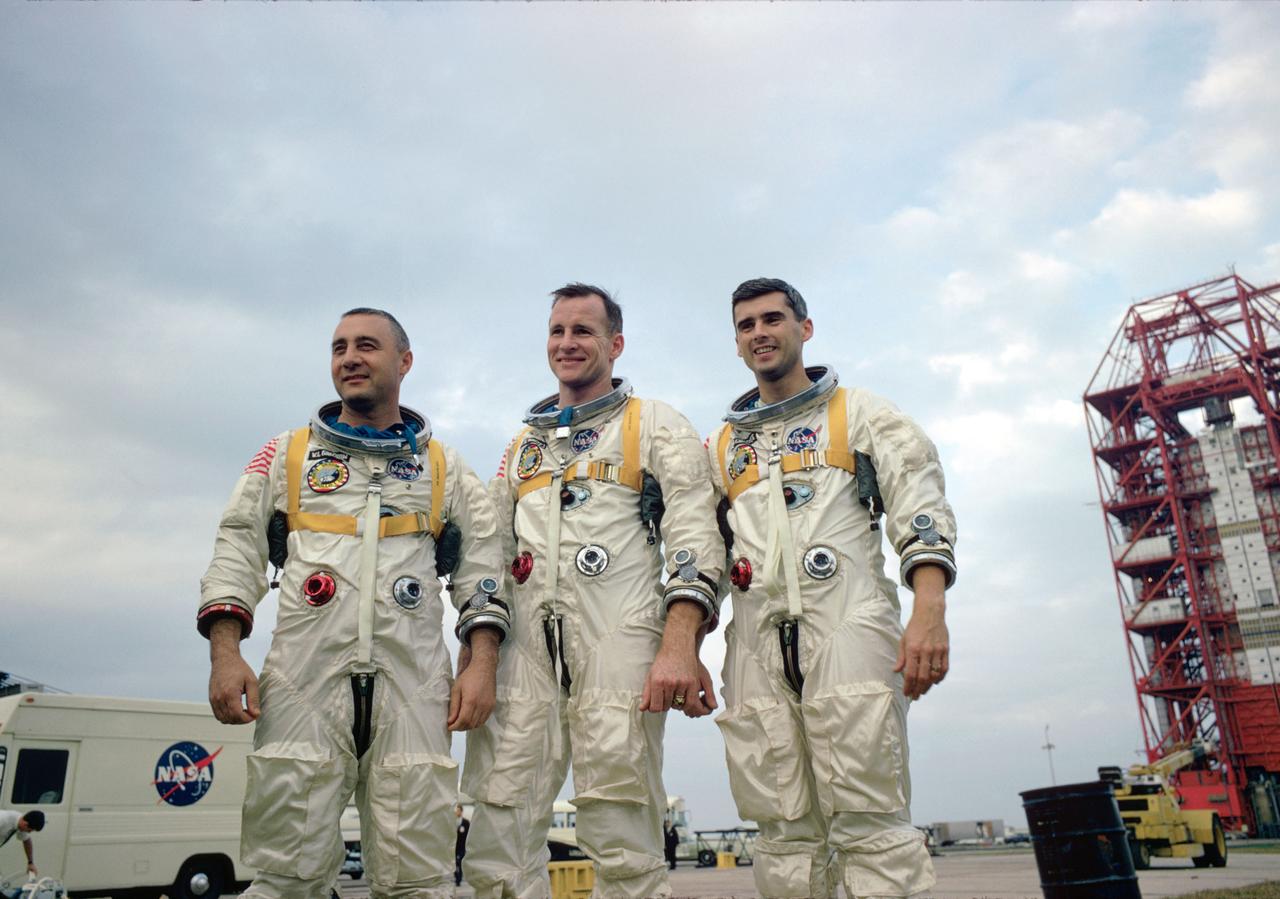

S67-19770 (January 1967) --- The prime crew of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) first manned Apollo Space Flight, named on March 21, 1966, are pictured during training in Florida. Left to right are astronauts Virgil I. Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee.
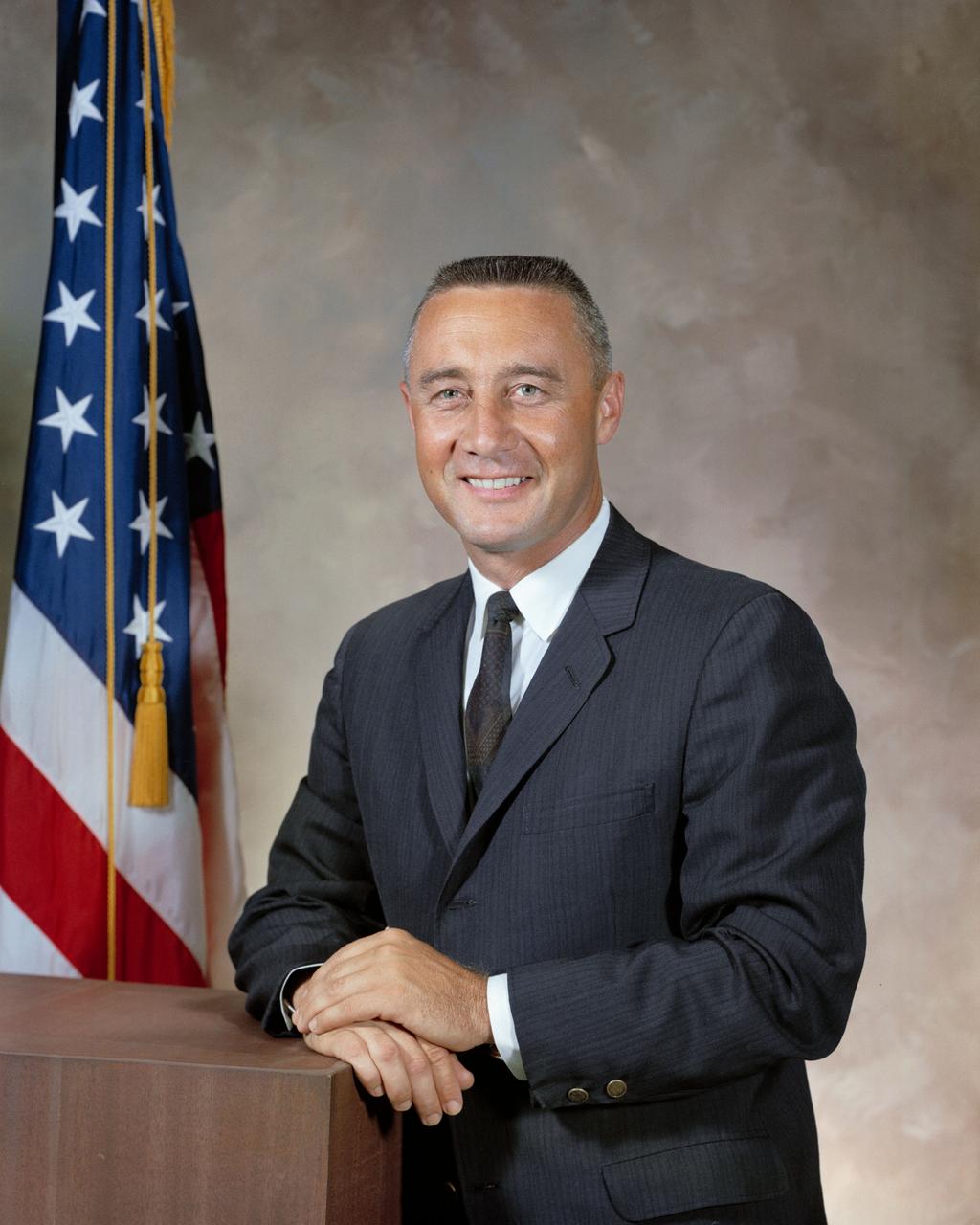

S64-32343 (10 Sept. 1964) --- Astronaut Virgil I. Grissom Editor's Note: Grissom, one of the Original Seven or Mercury astronauts, lost his life in the Apollo 204 fire at Cape Kennedy on Jan. 27, 1967, along with astronauts Edward H. White II and Roger B. Chaffee.
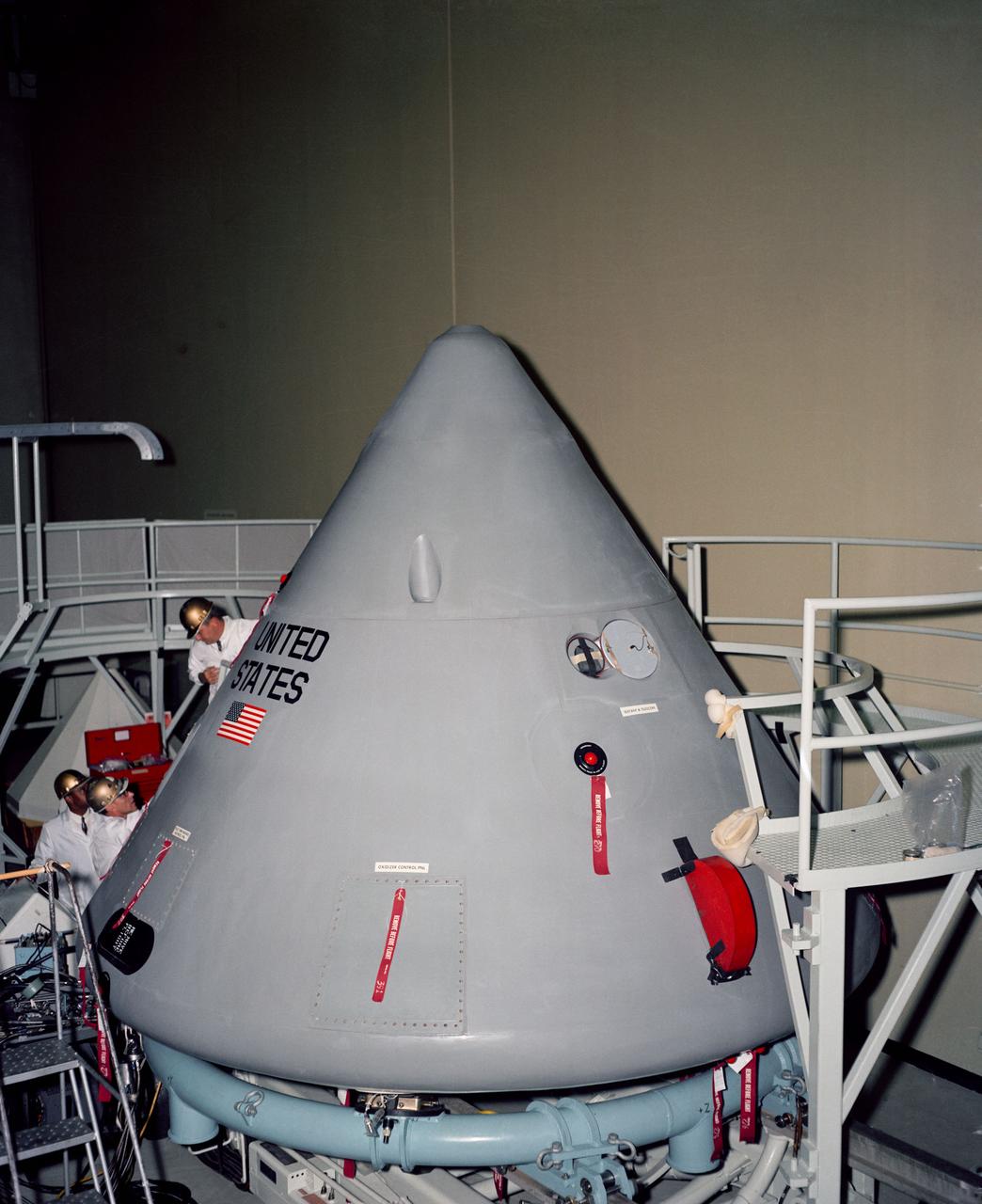

S66-53655 (1966) --- High angle view of Apollo Spacecraft 012 Command Module looking toward +Z axis during pre-shipping operations in south air lock of Systems Integration and Checkout Facility.
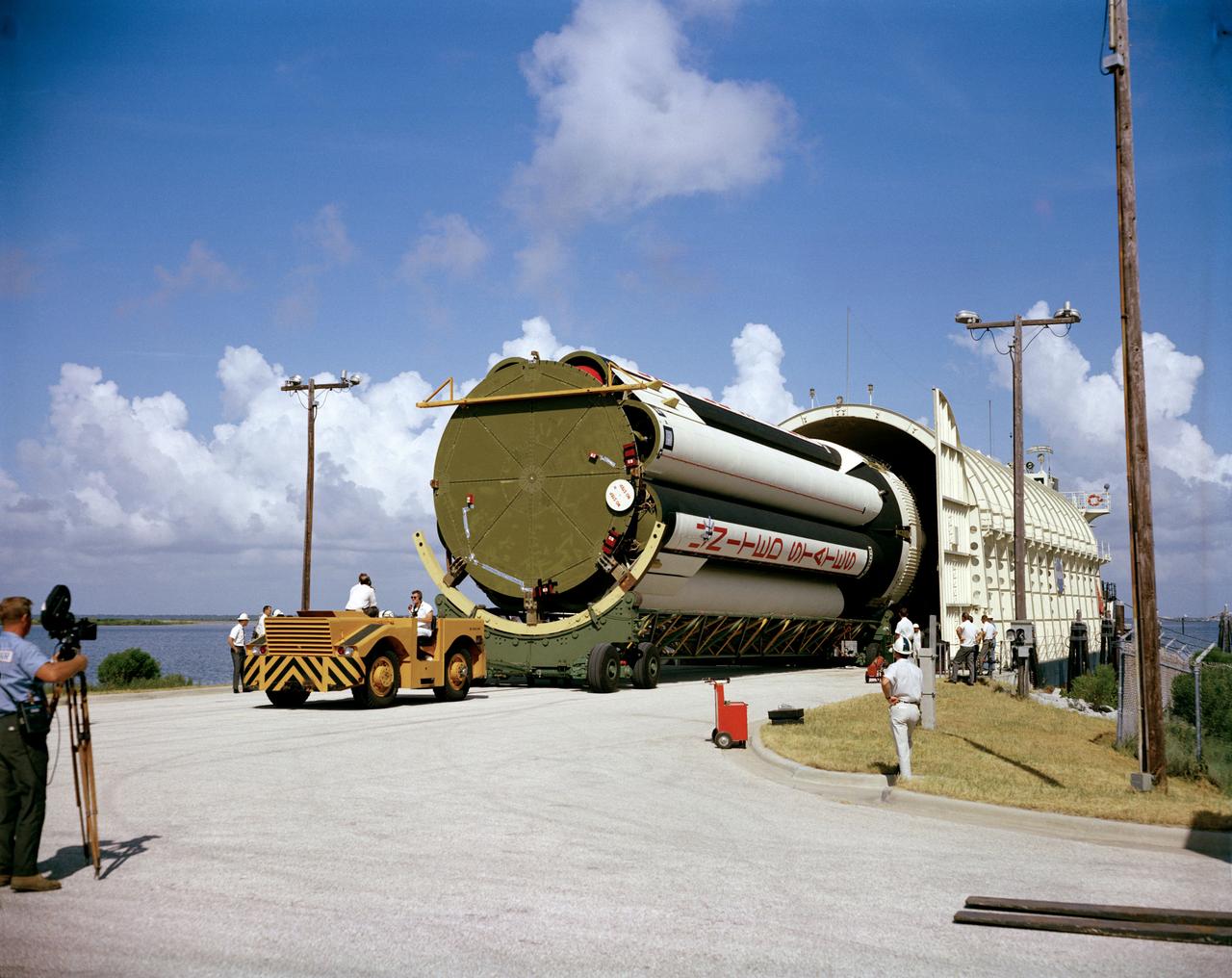

S66-50152 (1966) --- A stage of the uprated Saturn 1 launch vehicle unloaded from NASA barge Promise after arrival at Cape Kennedy. Launch vehicle for Apollo/Saturn 204 mission.
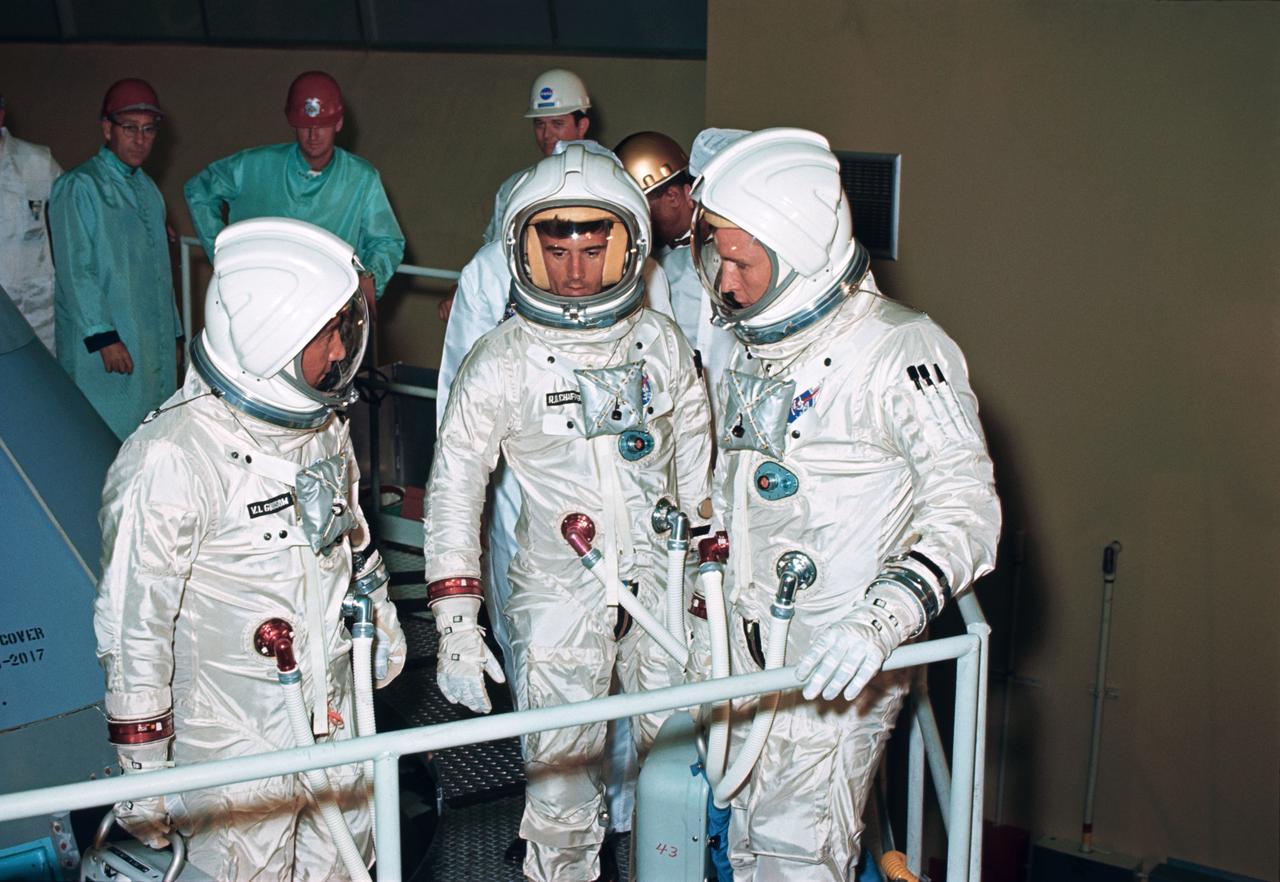

S66-49181 (August 1966) --- The three crew members for the Apollo-Saturn 204 (AS-204) mission check out the couch installation on the Apollo Command Module (CM) at North American's Downey facility. Left to right in their pressurized space suits are astronauts Virgil I. Grissom, Roger B. Chaffee and Edward H. White II. Editor's Note: The three astronauts died in a fire on the launch pad, Jan. 27, 1967.
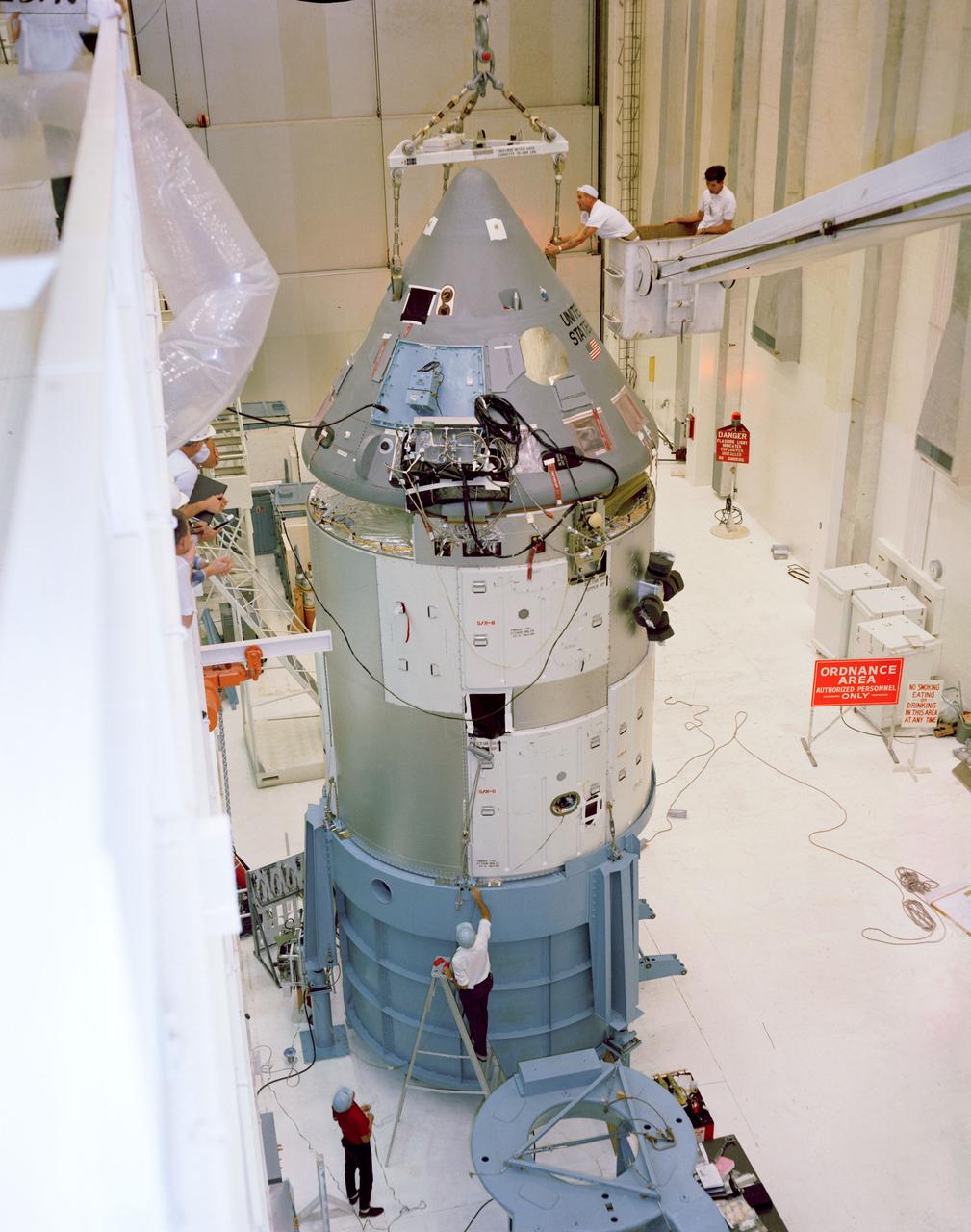

S67-15717 (1967) --- Apollo Spacecraft 012 Command/Service Module is moved from H-134 to east stokes for mating to the Saturn Lunar Module Adapter No. 05 in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building. S/C 012 will be flown on the Apollo/Saturn 204 mission.
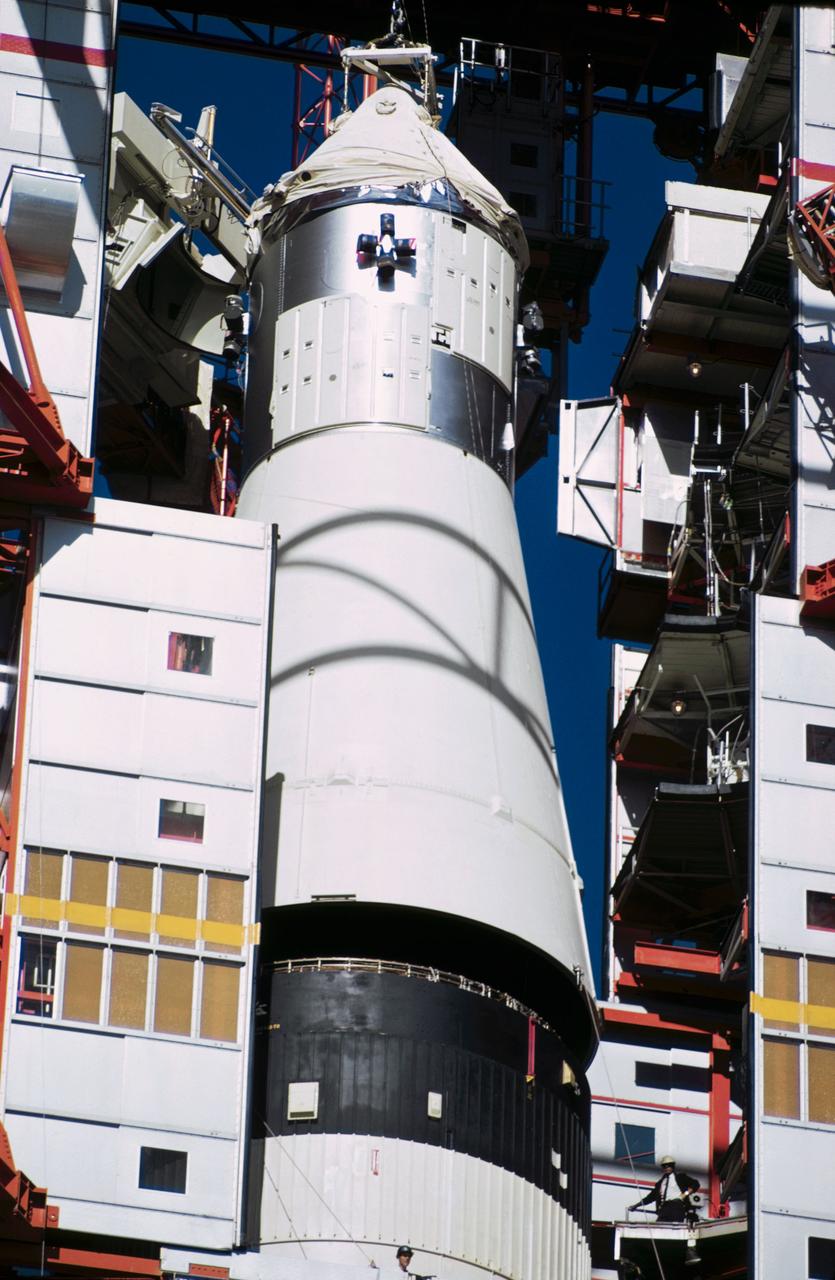

S67-17042 (1967) --- Apollo Spacecraft 012 is hoisted to the top of the gantry at Pad 34 during the Apollo/Saturn Mission 204 erection. S/C 012 will be mated with the uprated Saturn I launch vehicle.
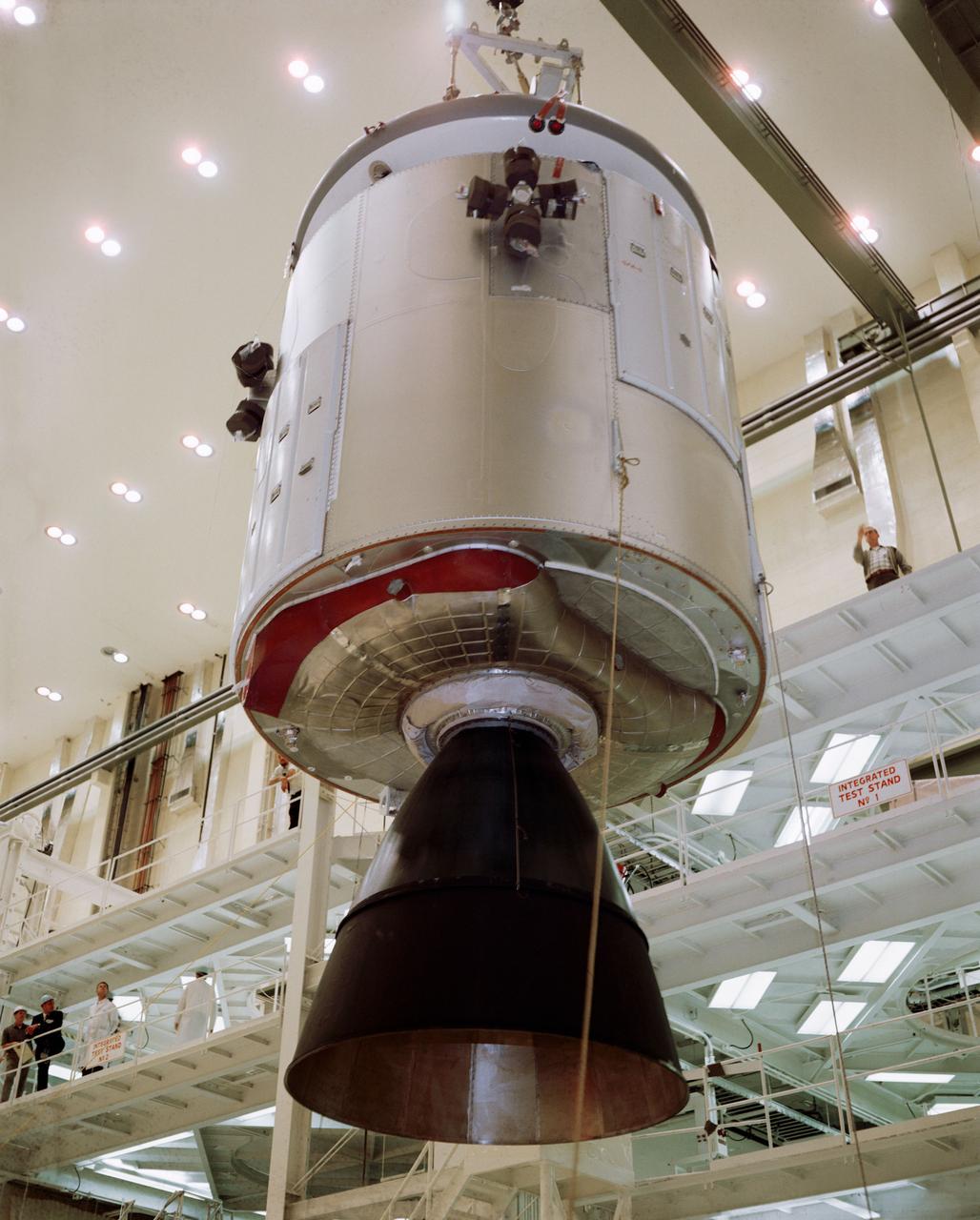

S67-15704 (3 Jan. 1967) --- Transfer of Apollo Spacecraft 012 Command/Service Module (CSM) for mating with the Saturn Lunar Module (LM) Adapter No.05 in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building. Spacecraft 012 will be flown on the Apollo/Saturn 1 (204) mission. Photo credit: NASA
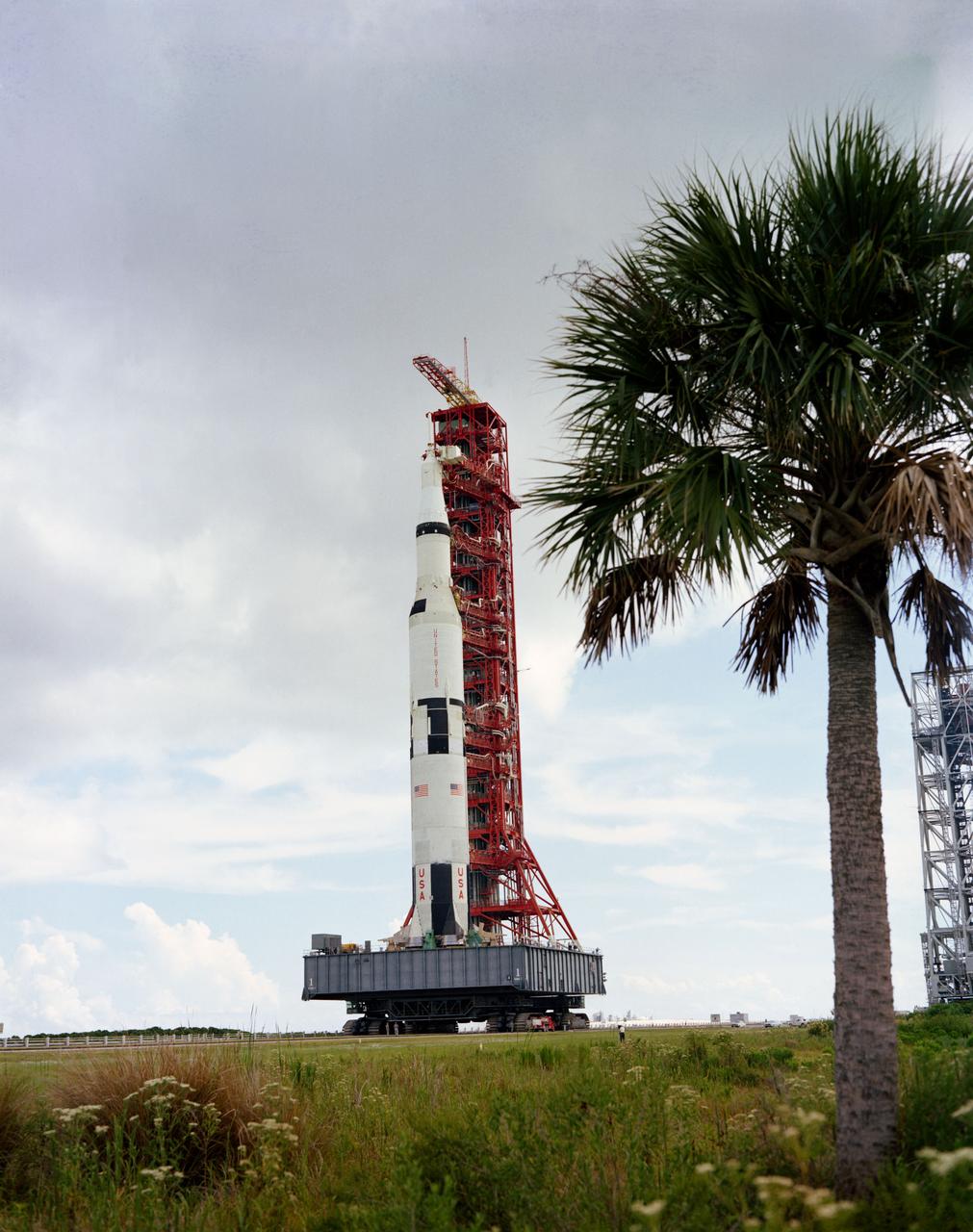

S67-43595 (26 Aug. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) stack and its mobile launch tower atop a crawler-transporter moving from the Vehicle Assembly Building toward Pad A, Launch Complex 39.
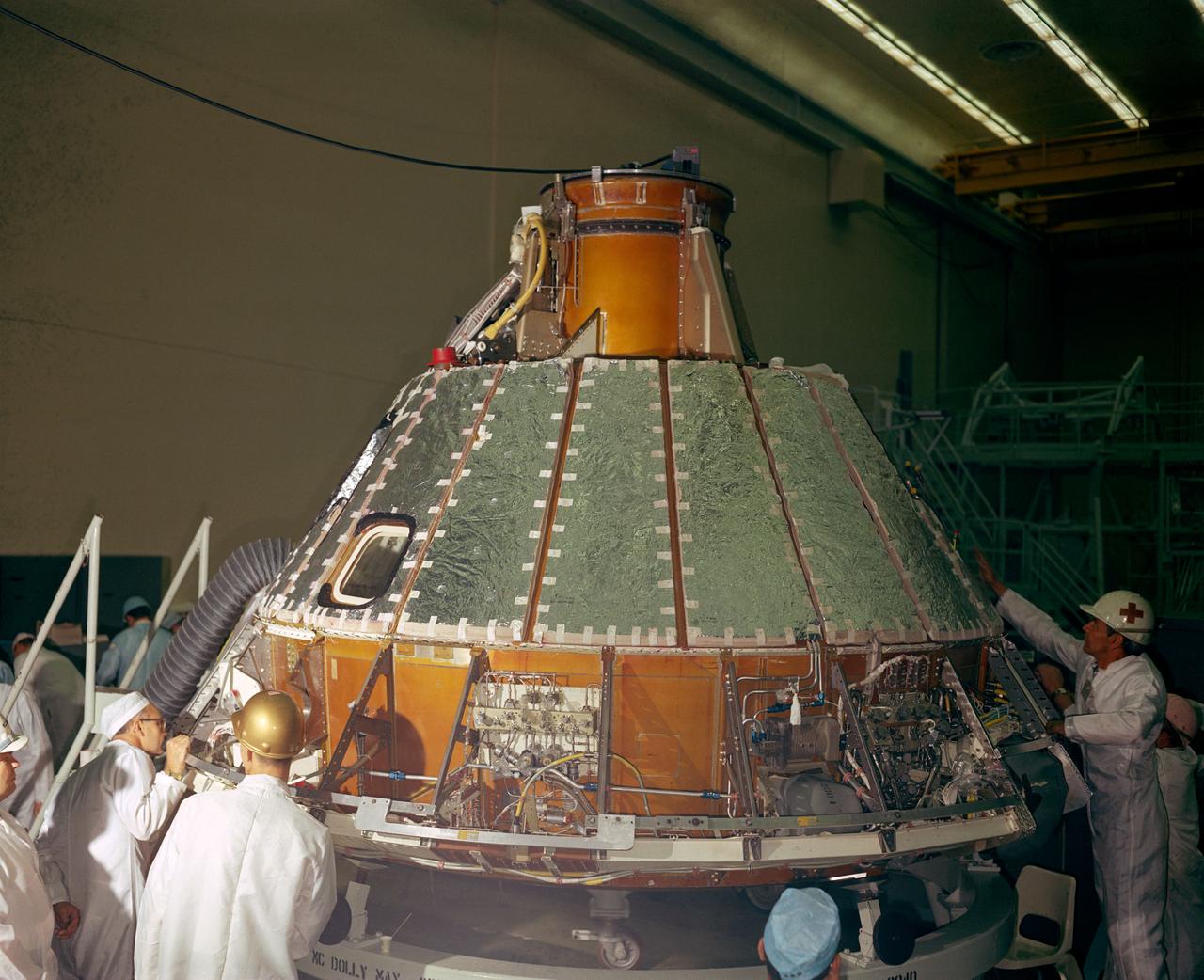

S66-41852 (1966) --- Spacecraft 012 looking toward -Y axis during installation of heat shield. Note uprighting system compressor in aft bay, at right, and Reaction Control System (RCS) valve module panel, center of photo.
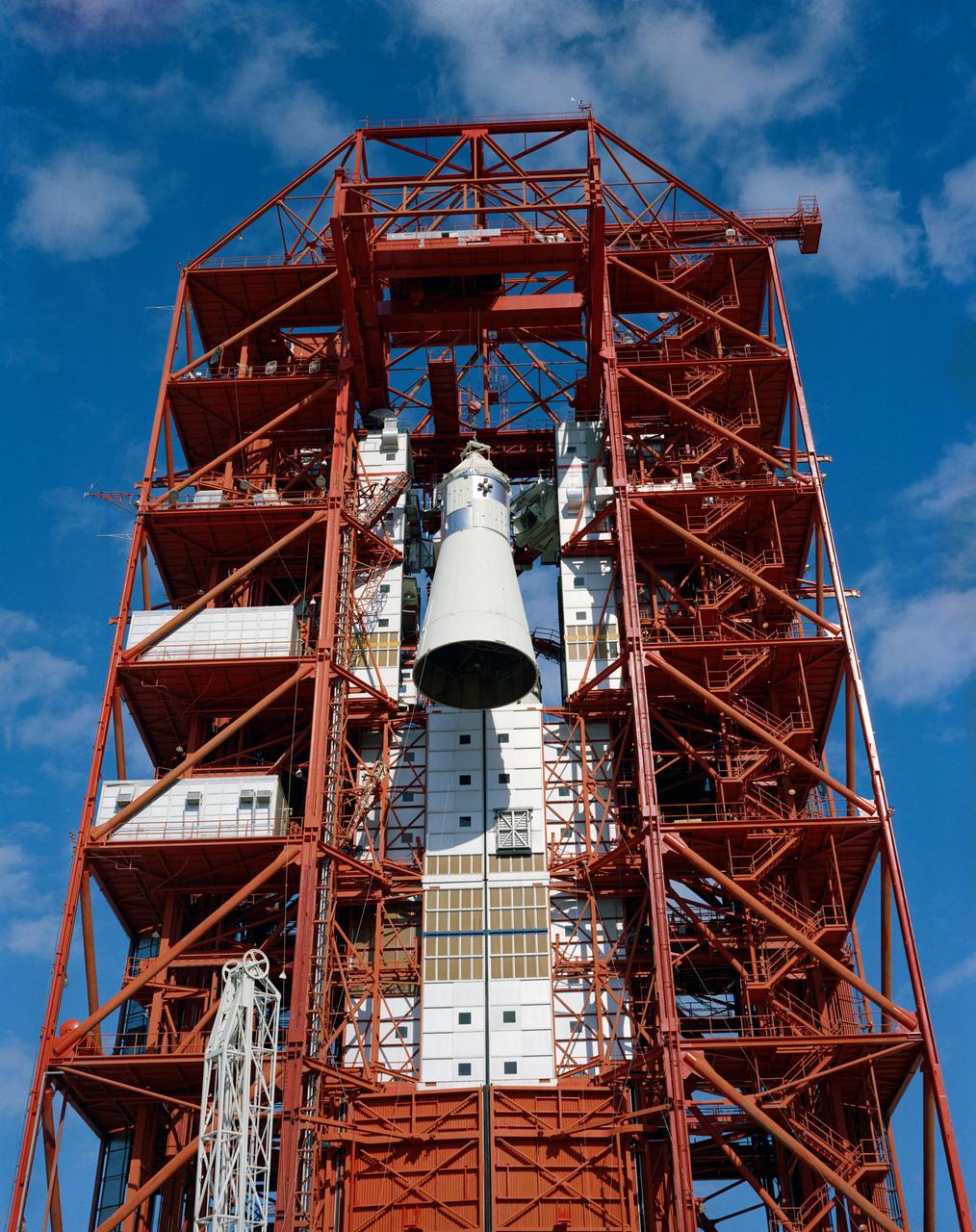

S67-15885 (1967) --- Apollo Spacecraft 012 is hoisted to the top of the gantry at Pad 34 during the Apollo/Saturn Mission 204 erection.
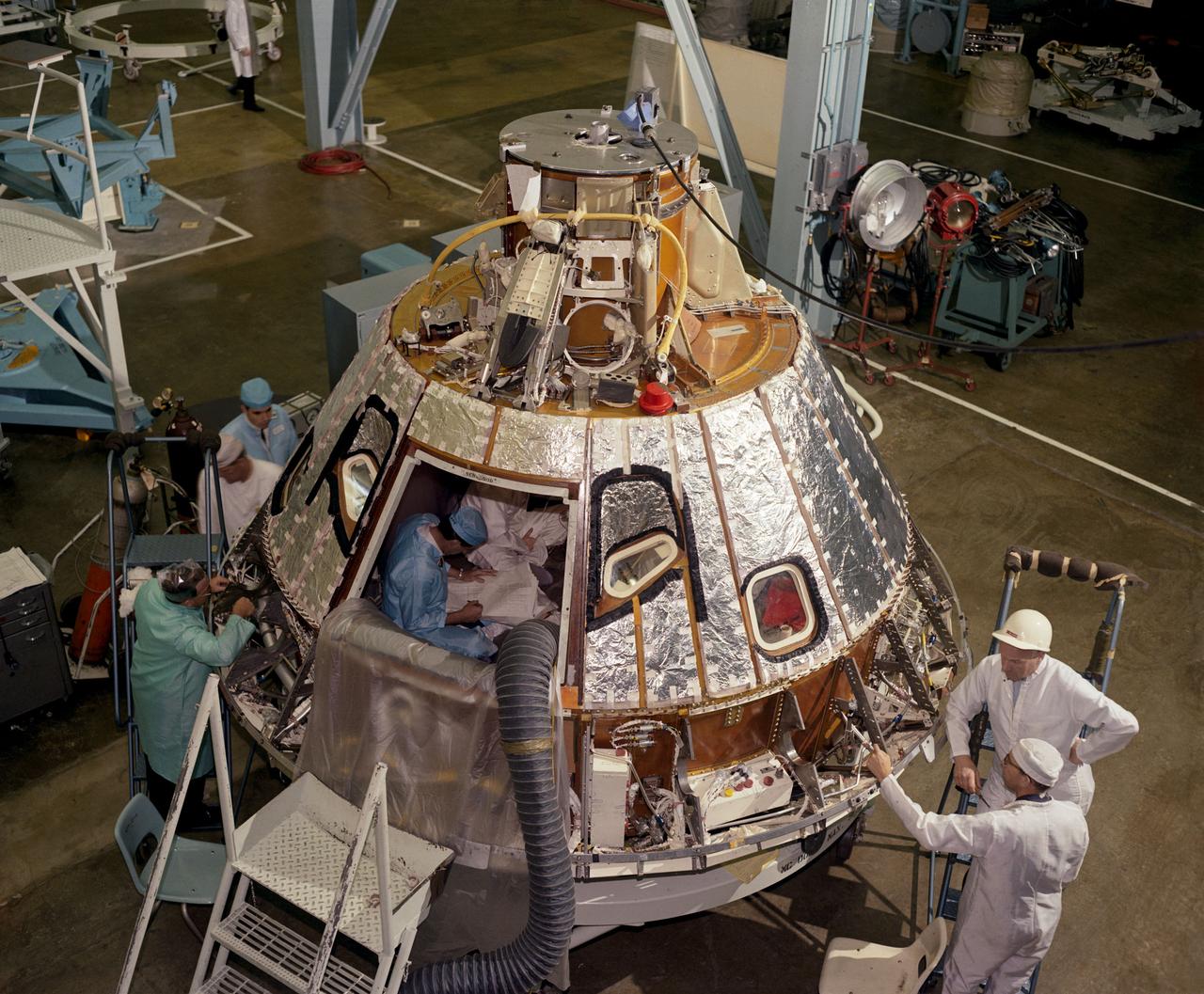
S66-41851 (1966) --- High angle view of Spacecraft 012 Command Module, looking toward -Z axis, during preparation for installation of the crew compartment heat shield, showing mechanics working on aft bay.

S67-43593 (26 Aug. 1967) --- The completely assembled Apollo Saturn 501 launch vehicle mated to the Apollo spacecraft 017 on Launch Complex 39A, Kennedy Space Center. The fully assembled vehicle was transported to the launch complex on the crawler.
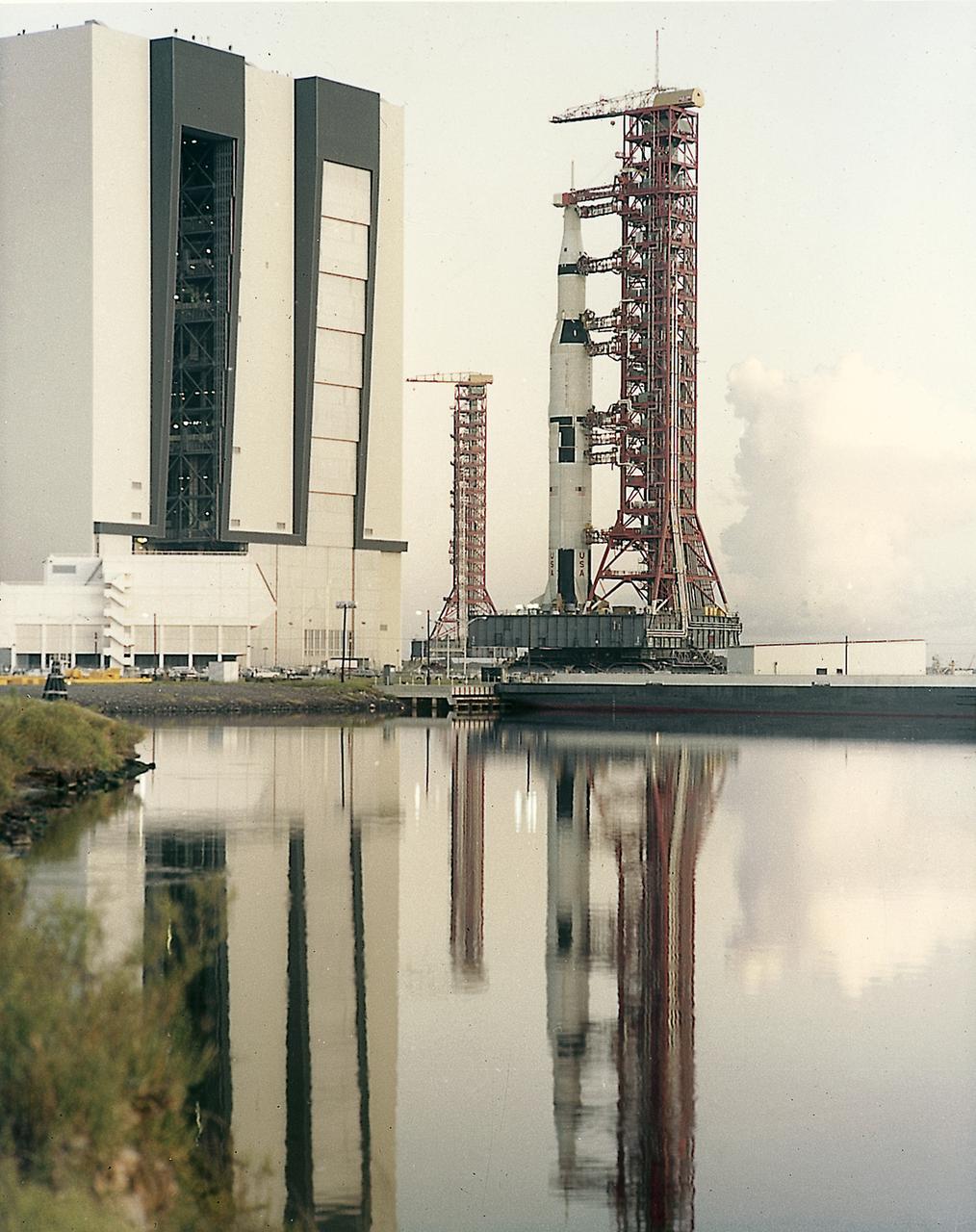

This picture shows the Saturn V vehicle (AS-501), for the Apollo 4 mission on the Crawler Transporter Vehicle. It was rolled out from the Vehicle Assembly Building and slowly (1 mph) moved to the launch pad at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.
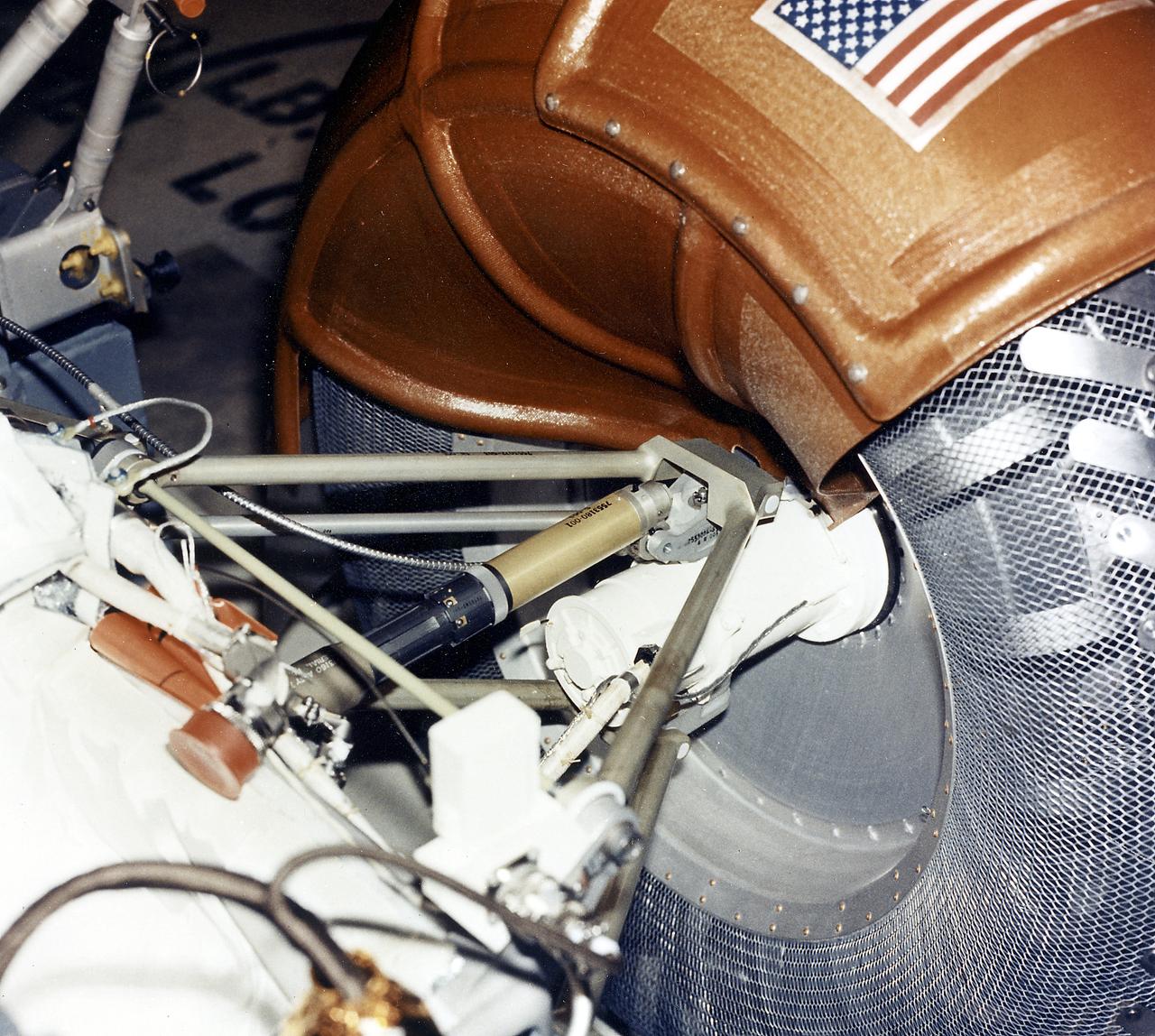
This is a close-up inboard view of a left front wheel of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 1. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater Range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
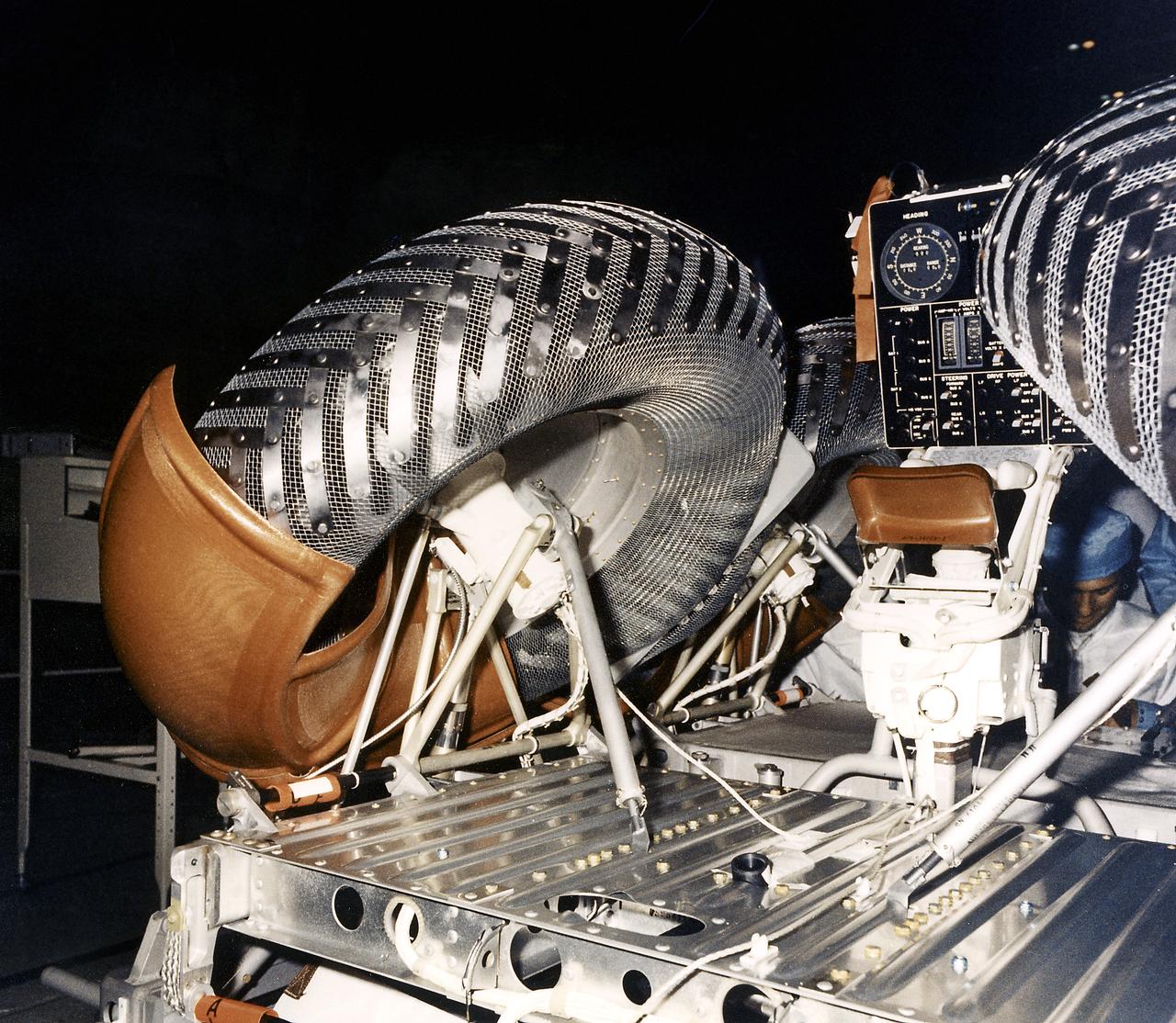
This is a close-up view of a right rear wheel strut of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 1. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
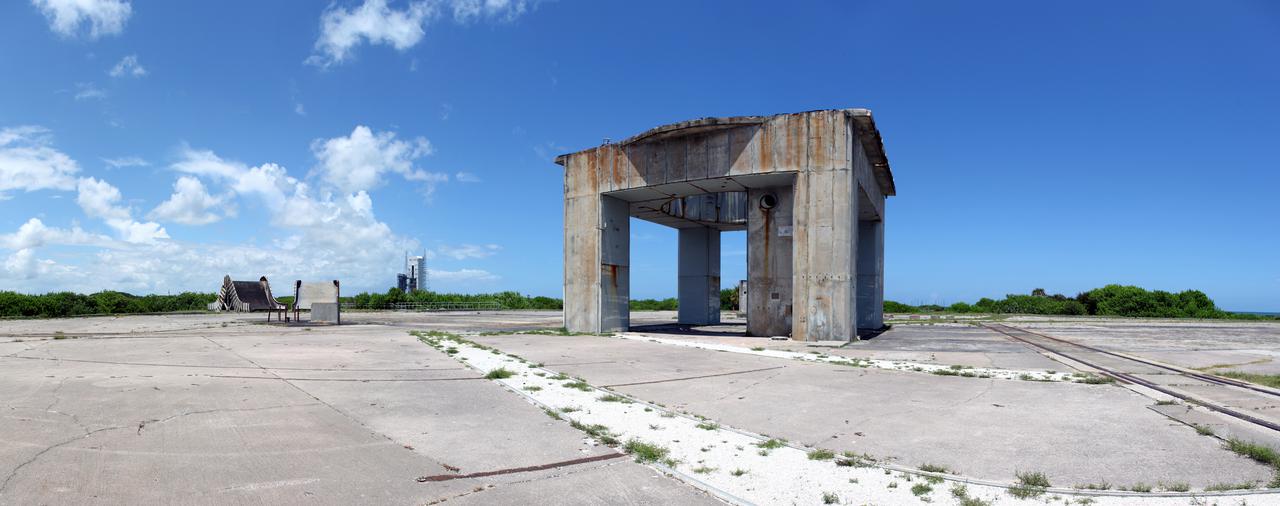

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida stands the Launch Complex-34 launch platform. During the Apollo Program, Complex-34 was the site of the first Saturn I and Saturn IB launches, as well as the tragic fire in which the Apollo 1 astronauts lost their lives. Apollo 7, the first crewed Apollo flight, was the last to launch from Complex-34. Subsequent Apollo mission launched from NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39. Photo credit: NASA_Frankie Martin
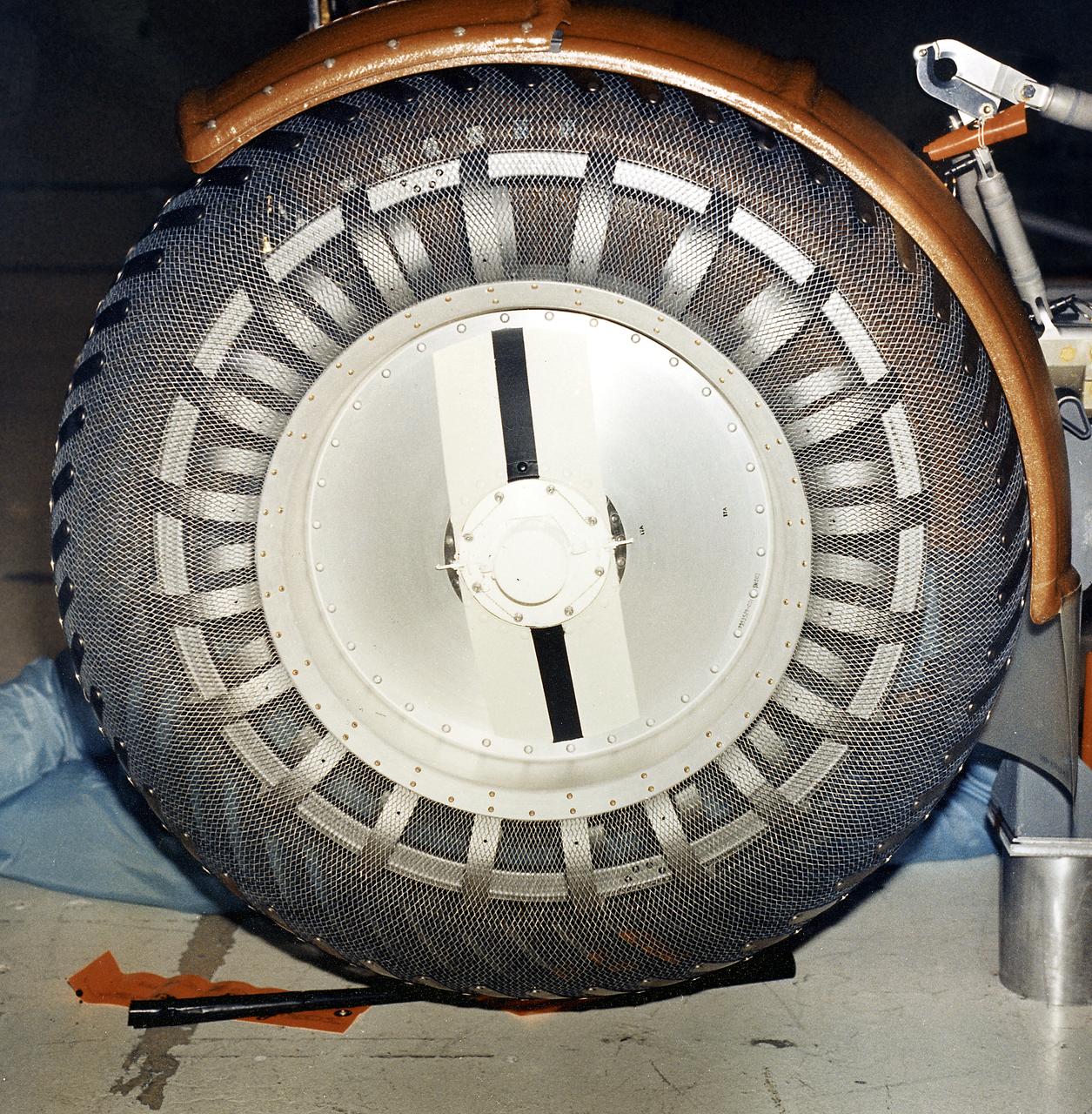

This is a close-up view of a left front wheel of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) No. 1. The LRV was built to give Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration. It was an open-space and collapsible vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and camera. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions; Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17. It was built by the Boeing Company under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.

Workmen at the Kennedy Space Center position the nose cone for the 204LM-1, an unmanned Apollo mission that tested the Apollo Lunar Module (LM) in Earth orbit. Also known as Apollo 5, the spacecraft was launched on the fourth Saturn IBC launch vehicle. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IBC utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine a larger booster and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.

Workmen at the Kennedy Space Center position the nose cone for the 204LM-1, an unmanned Apollo mission that tested the Apollo Lunar Module (LM) in Earth orbit. Also known as Apollo 5, the spacecraft was launched on the fourth Saturn IBC launch vehicle. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IBC utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine a larger booster and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.

Originally devised to observe Saturn stage separation during Apollo flights, Marshall Space Flight Center's Miniature Television Camera, measuring only 4 x 3 x 1 1/2 inches, quickly made its way to the commercial telecommunications market.
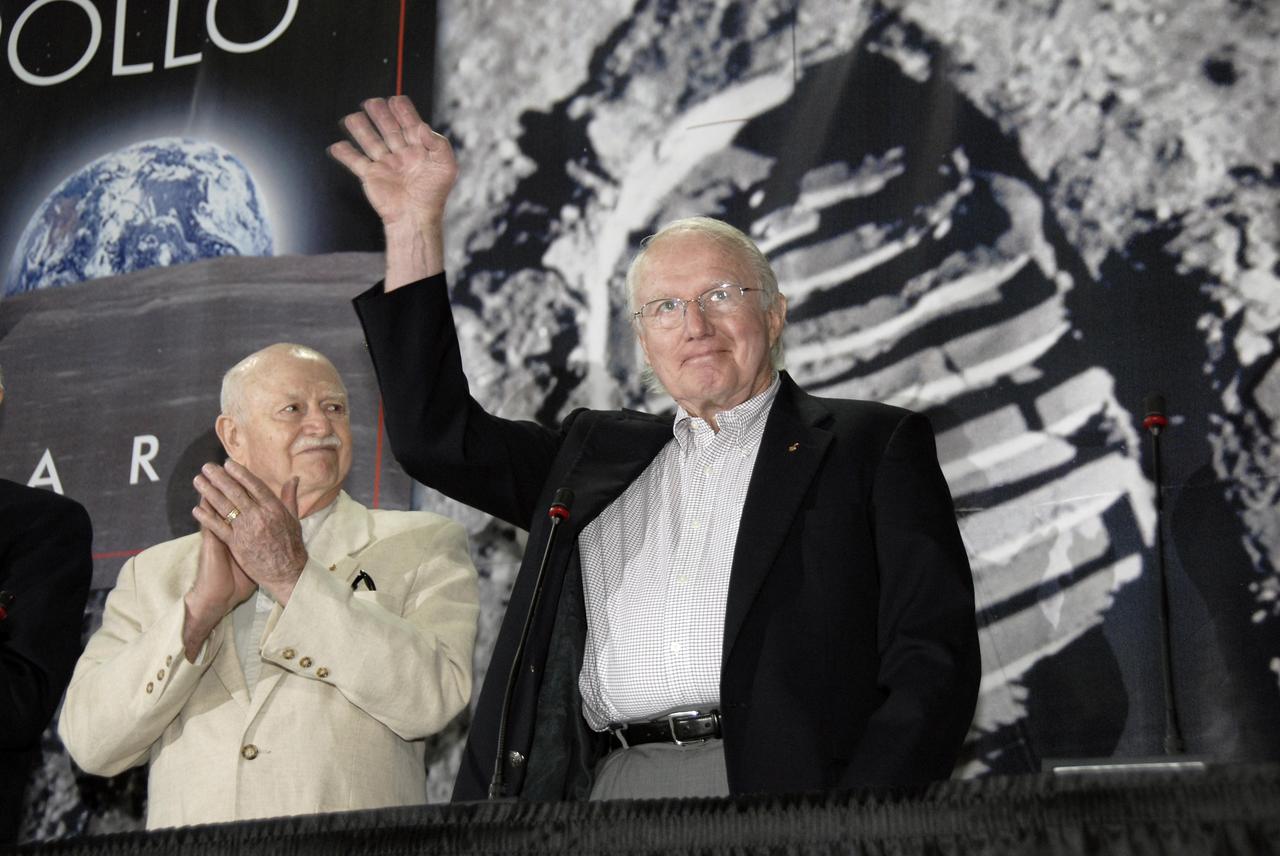

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo astronaut Gerald Carr (right) joins Vance Brand (left) and six other Apollo astronauts for NASA's 40th Anniversary of Apollo Celebration of the July 1969 launch and landing on the moon. Carr served as CAPCOM for the Apollo 8 and 12 flights, and was involved in the development and testing of the lunar roving vehicle which was used on the lunar surface by Apollo flight crews. He also was commander of Skylab 4 launched in 1973 on the third and final manned visit to the Skylab Orbital Workshop. It was the longest manned flight (84 days, 1 hour, 15minutes) in history at that date. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
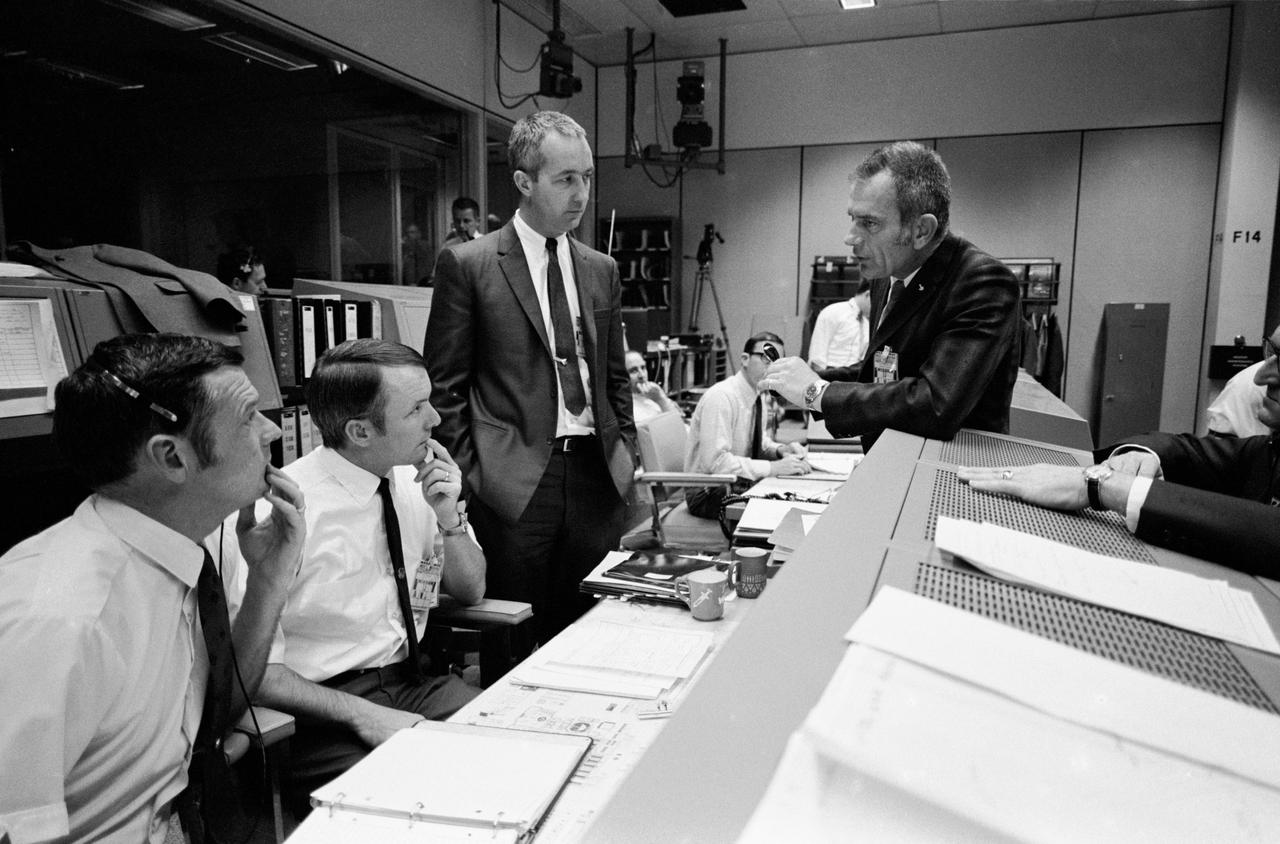

S70-35369 (16 April 1970) --- Discussion in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) dealing with the Apollo 13 crewmen during their final day in space. From left to right are Glynn S. Lunney, Shift 4 flight director; Gerald D. Griffin, Shift 2 flight director; astronaut James A. McDivitt, manager, Apollo Spacecraft Program, MSC; Dr. Donald K. Slayton, director of Flight Crew Operations, MSC; and Dr. Willard R. Hawkins, M.D., Shift 1 flight surgeon.
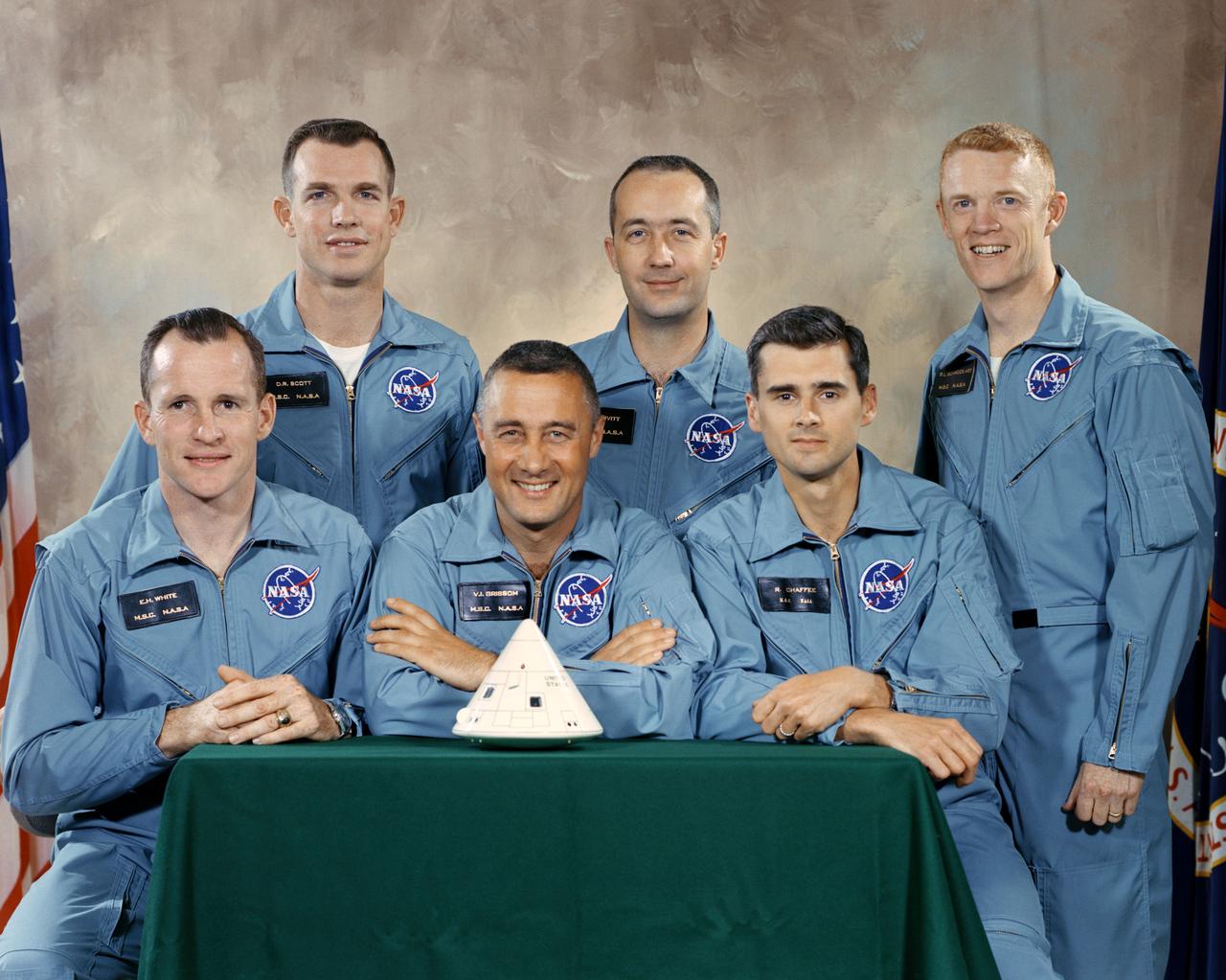

S66-30238 (1 April 1966) --- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has named these astronauts as the prime crew of the first manned Apollo Space Flight. Left to right, are Edward H. White II, command module pilot; Virgil I. Grissom, mission commander; and Roger B. Chaffee, lunar module pilot. On the second row are the Apollo 1 backup crew members, astronauts David R. Scott, James A. McDivitt and Russell L. Schweickart. EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronauts Grissom, White and Chaffee lost their lives in a Jan. 27, 1967 fire in the Apollo CM during testing at Cape Canaveral. McDivitt, Scott and Schweickart later served as crewmembers for the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission, which was one of the important stair-step missions leading up to the Apollo 11 manned lunar landing mission of July 1969.
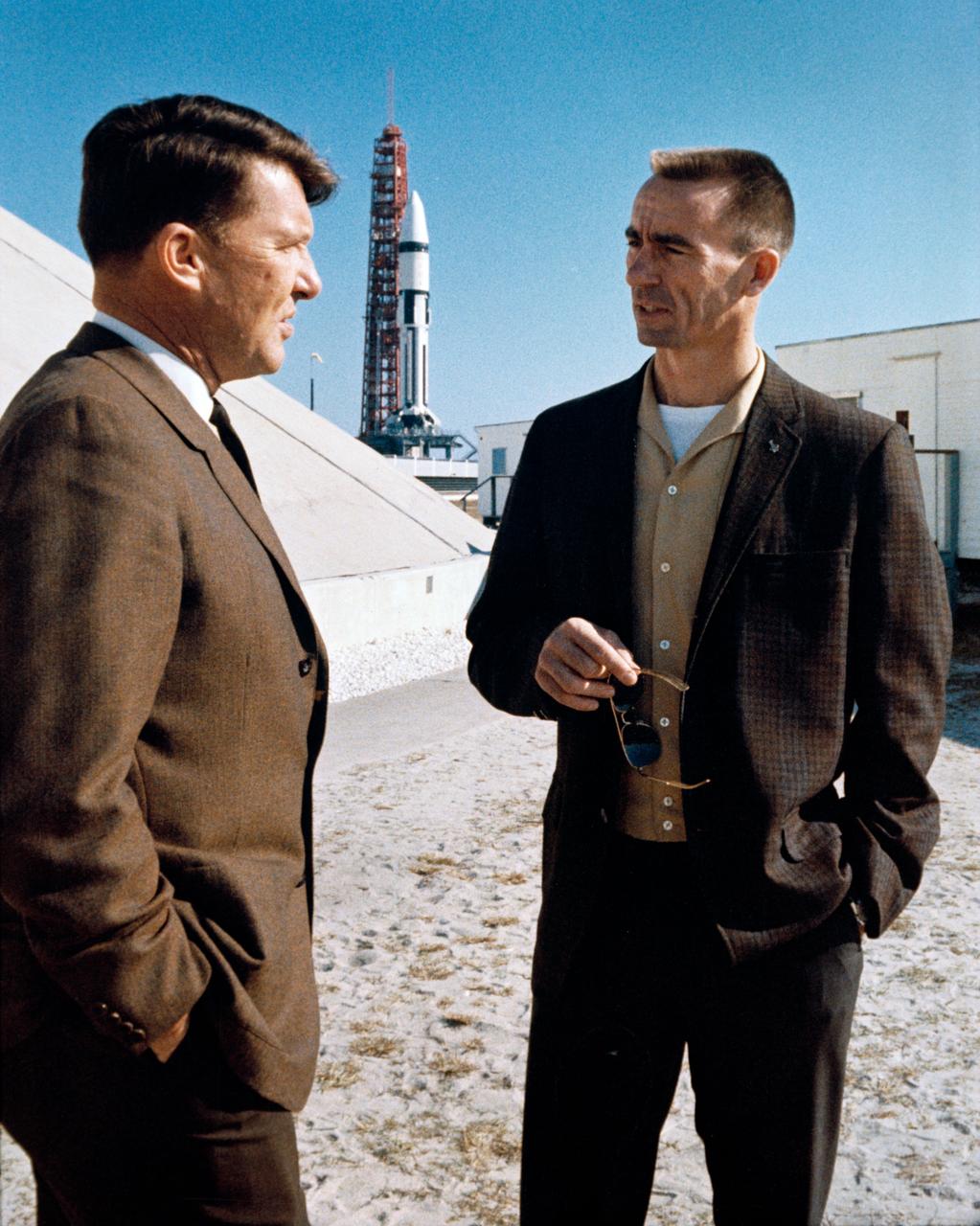

S68-18700 (22 Jan. 1968) --- Two prime crew members of the first manned Apollo space flight were present at Cape Kennedy for the launch of the Apollo V (LM-1/Saturn 204) unmanned space mission. On left is astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr.; and on right is astronaut R. Walter Cunningham. In background is the Apollo V stack at Launch Complex 37 ready for launch.
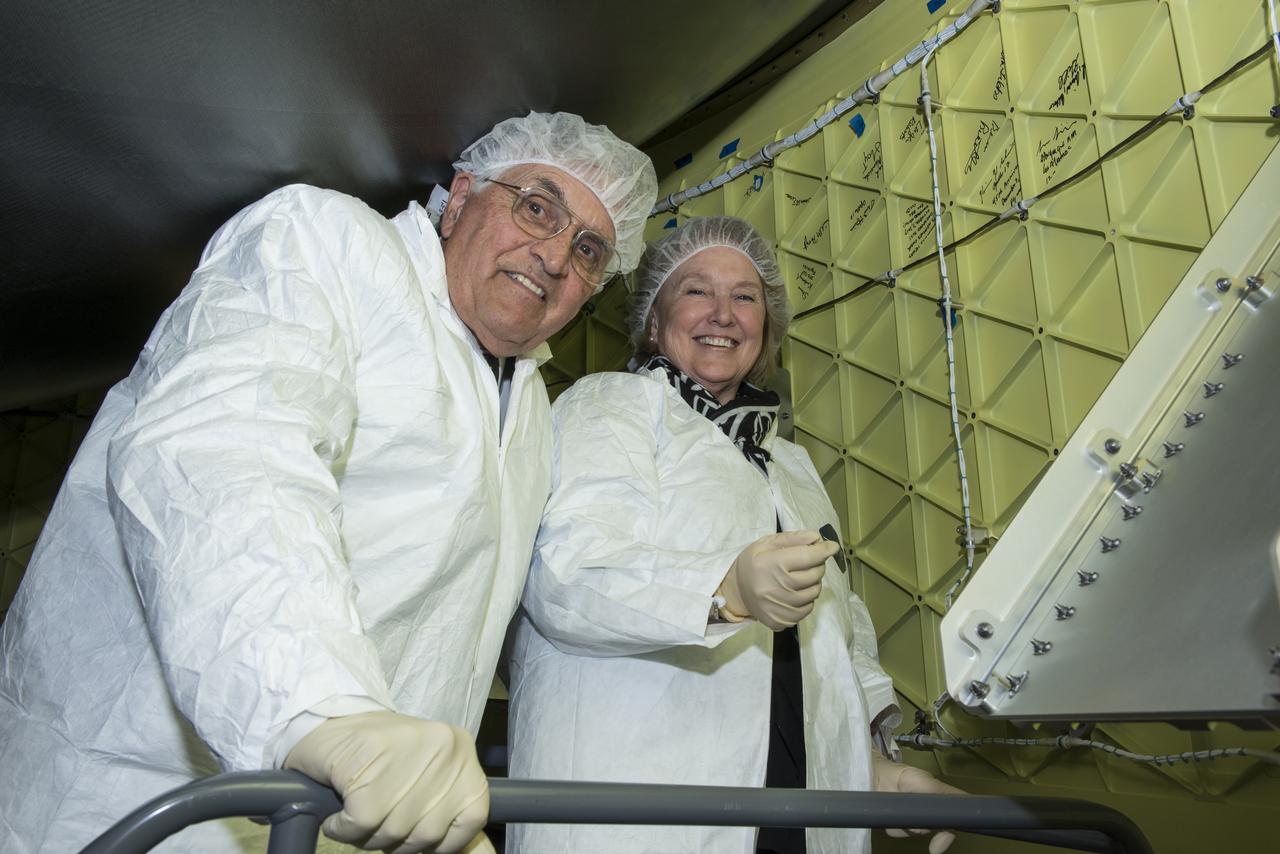

Apollo 17 astronaut Harrison Schmitt and his wife, Teresa, toured the Orion Stage Adapter while at Marshall and signed it before its flight on Exploration Mission-1 in late 2019
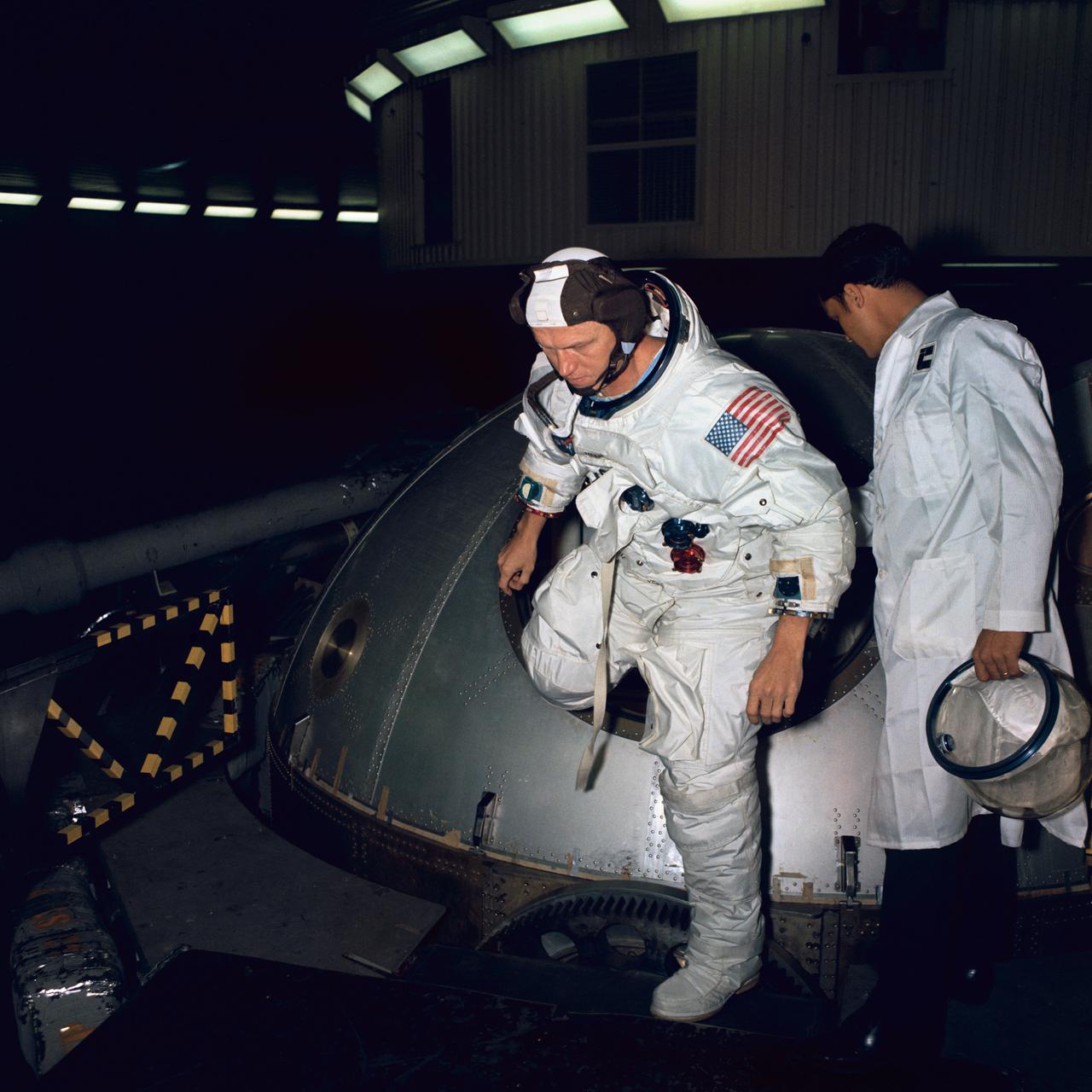

S68-53186 (1 Nov. 1968) --- Astronaut Frank Borman, Apollo 8 commander, egresses the gondola in Building 29 after centrifuge training in the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Flight Acceleration Facility (FAF).
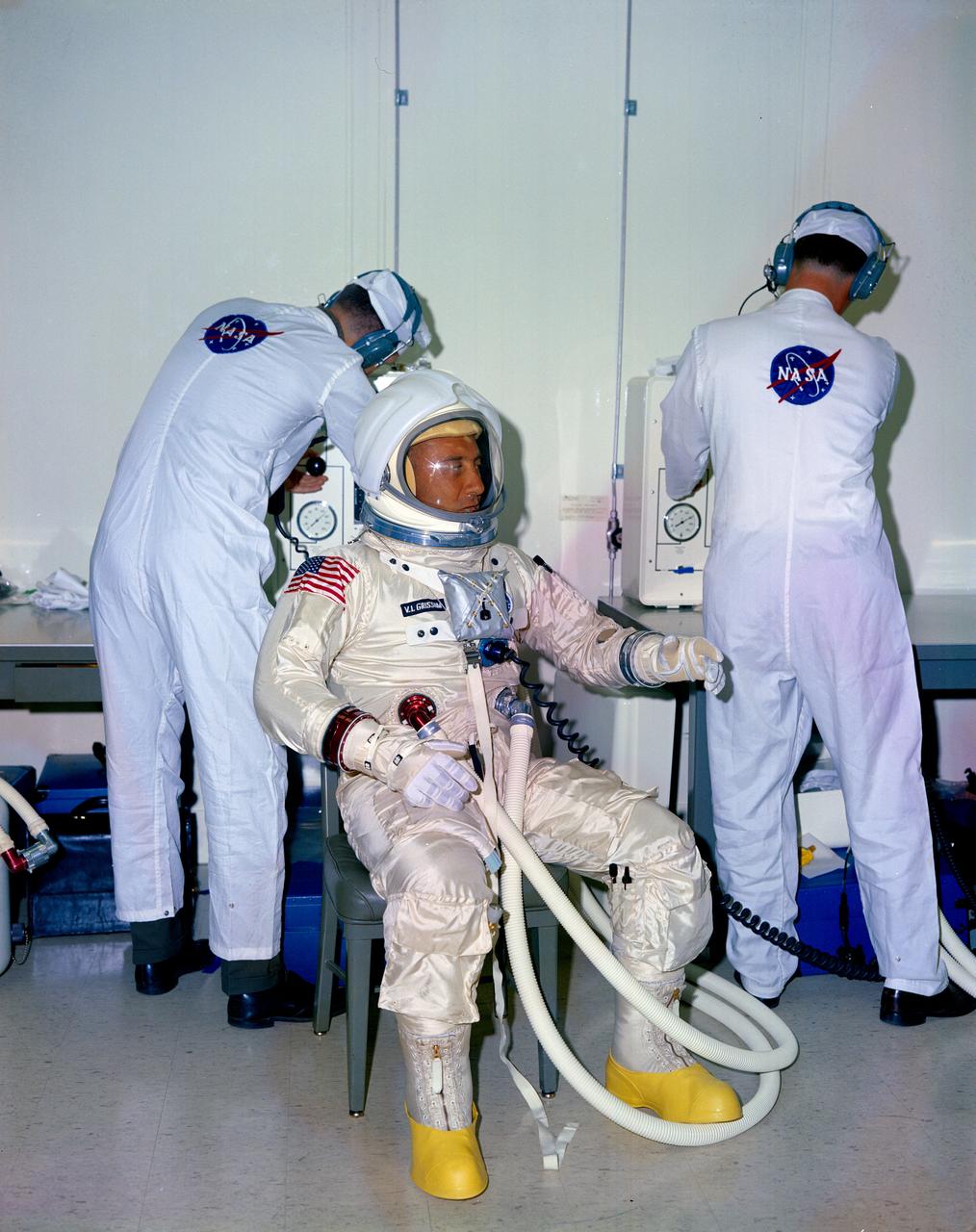

S66-58023 (1966) --- NASA suit technicians assist astronaut Virgil I. Grissom during suiting operations prior to tests at the Kennedy Space Center.
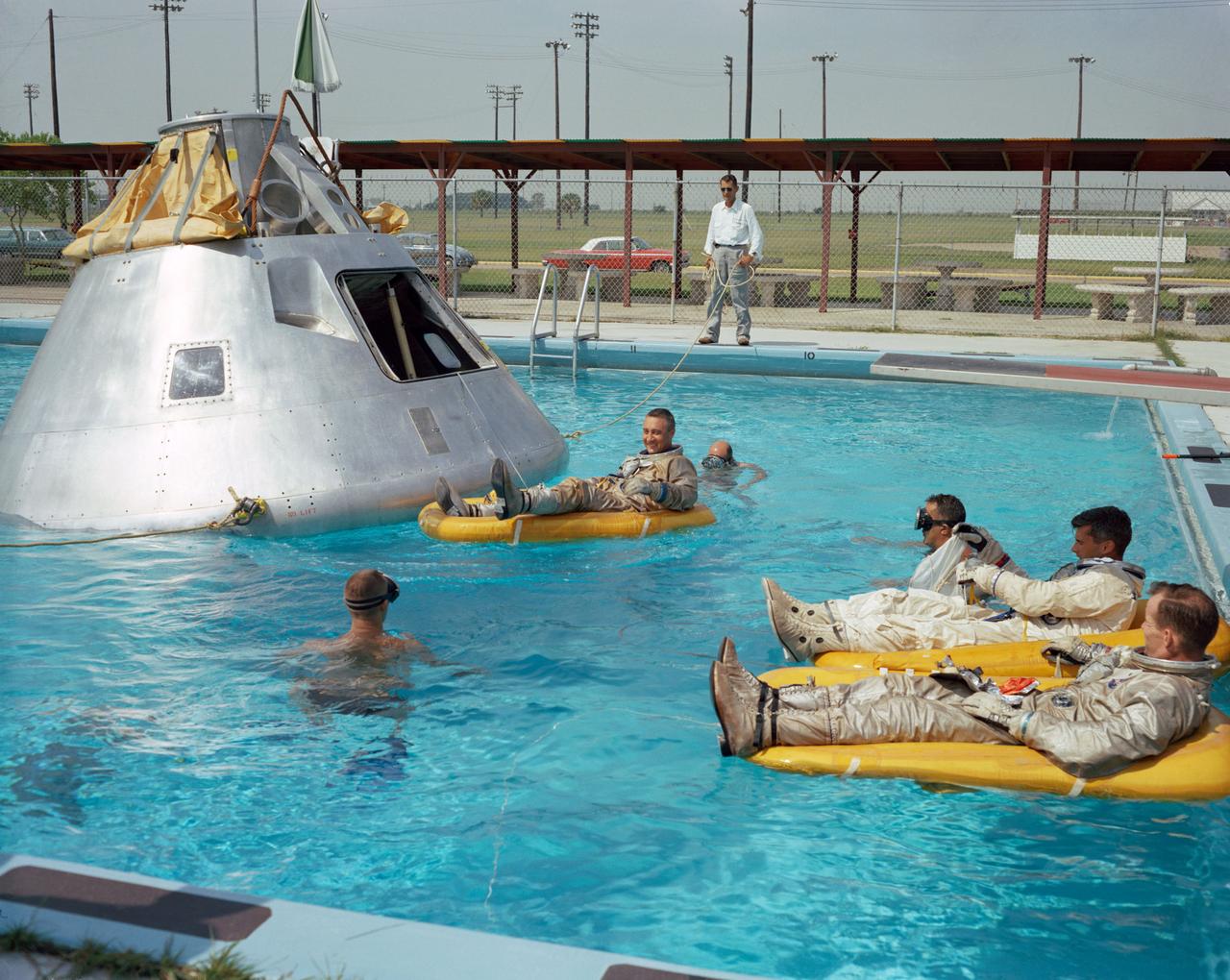

S66-51581 (June 1966) --- Prime crew for the first manned Apollo mission practice water egress procedures with full scale boilerplate model of their spacecraft. In the water at right is astronaut Edward H. White (foreground) and astronaut Roger B. Chaffee. In raft near the spacecraft is astronaut Virgil I. Grissom. NASA swimmers are in the water to assist in the practice session that took place at Ellington AFB, near the Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston.
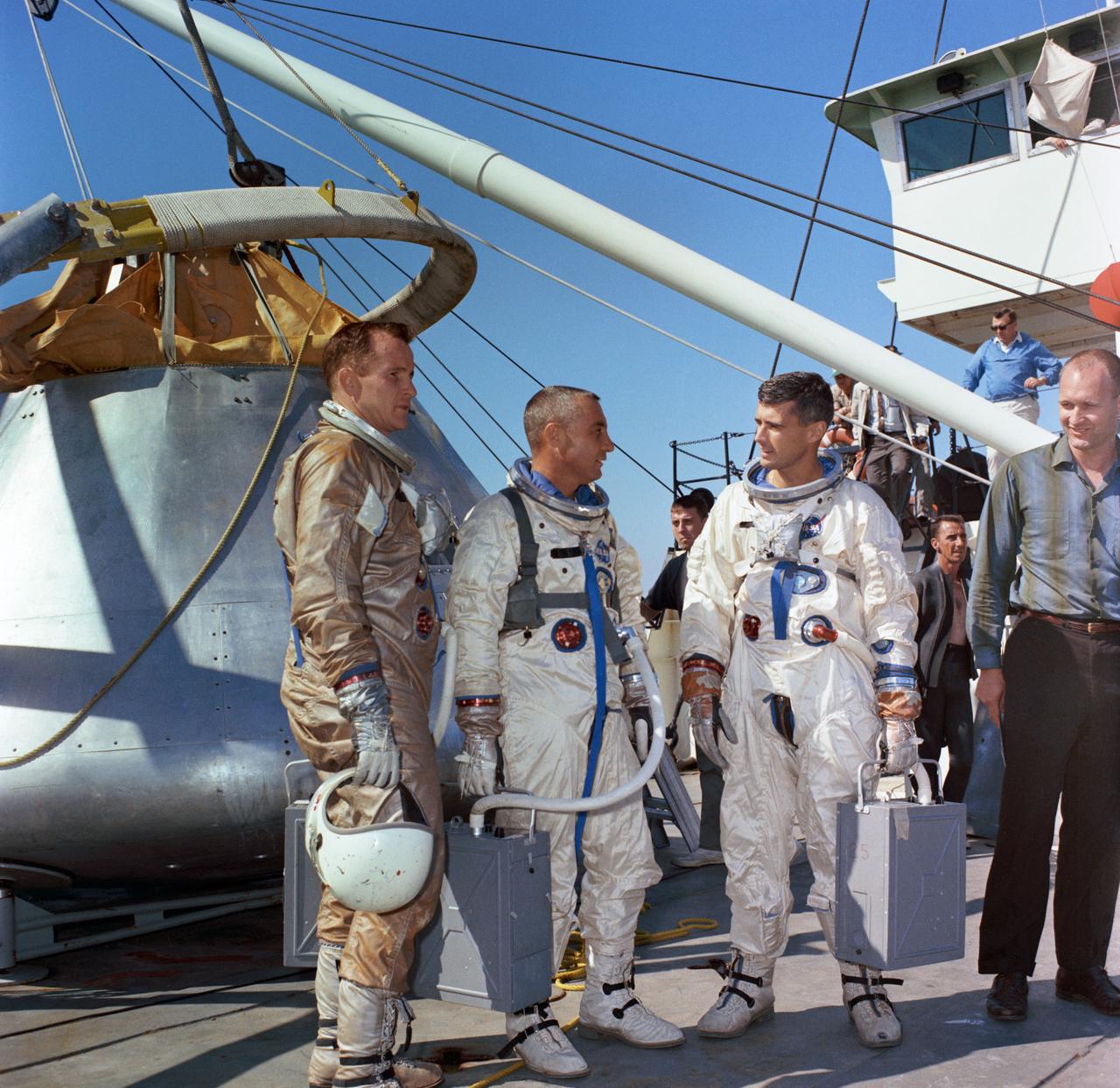

S66-58501 (27 Oct. 1966) --- The prime crew of the first manned Apollo Space Flight, Apollo/Saturn (AS) mission 204, is suited up aboard the NASA Motor Vessel Retriever (MVR) in preparation for Apollo water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. Left to right, are astronauts Edward H. White II, senior pilot; Virgil I. Grissom, command pilot; and Roger B. Chaffee, pilot.

Workmen at the Kennedy Space Center hoist the Saturn Lunar Module (LM) Adapter into position during assembly of the 204LM-1, an unmanned Apollo mission that tested the Apollo Lunar Module in Earth orbit. Also known as Apollo 5, the spacecraft was launched on the fourth Saturn IB launch vehicle. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine a larger booster and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.
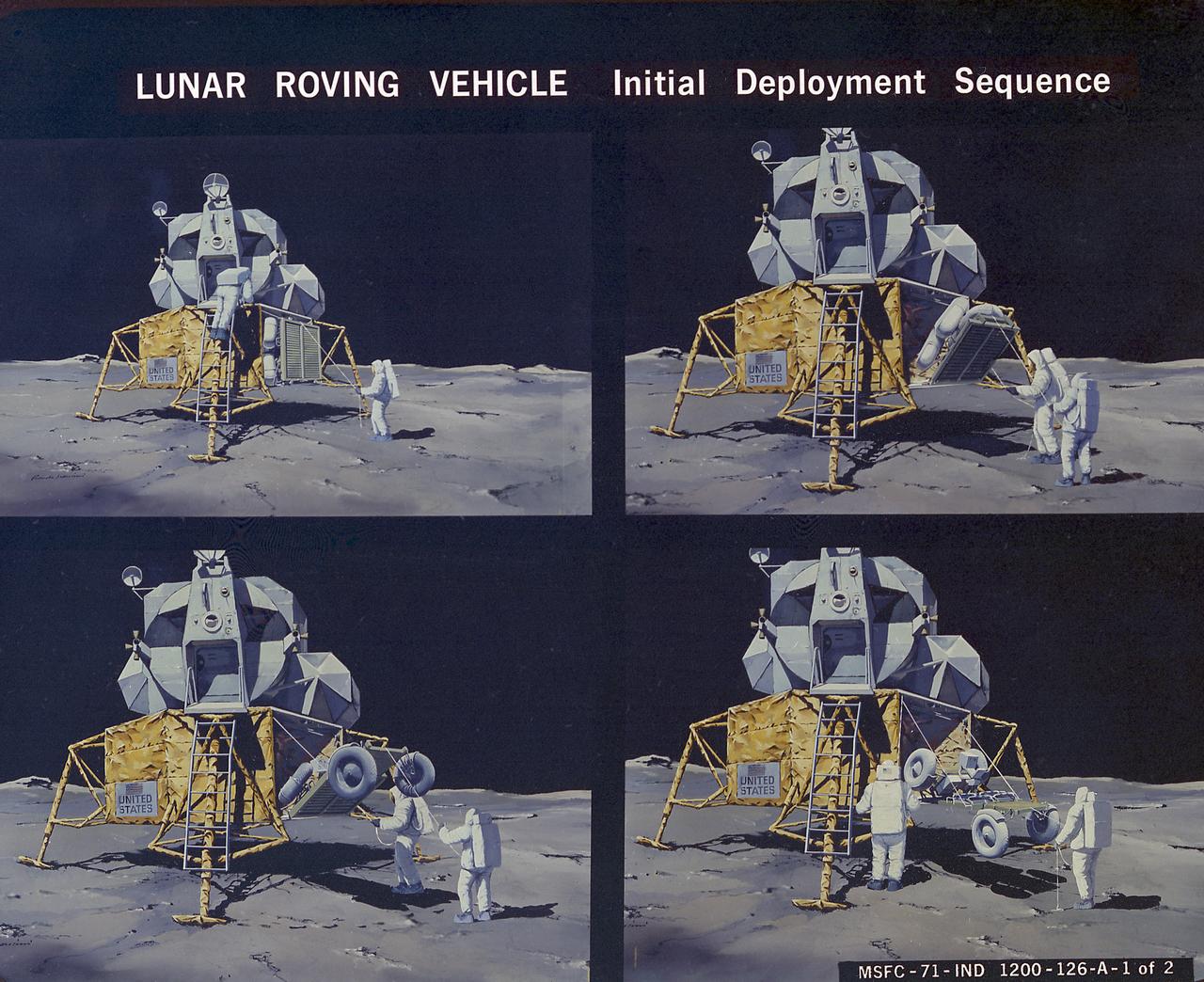
This artist's concept illustrates the deployment sequence of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Moon. The LRV was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
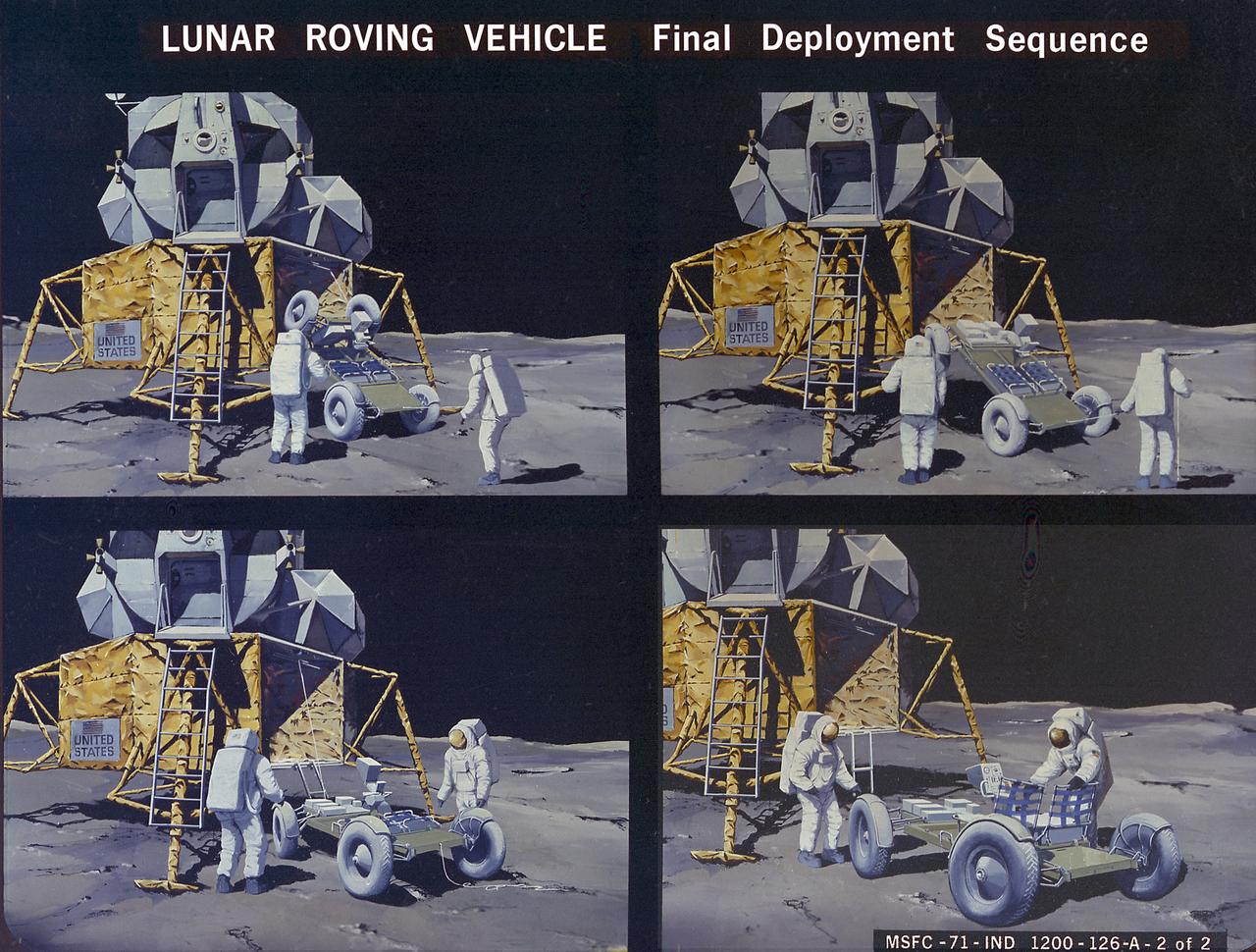
This artist's concept illustrates the deployment sequence of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Moon. The LRV was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.

The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
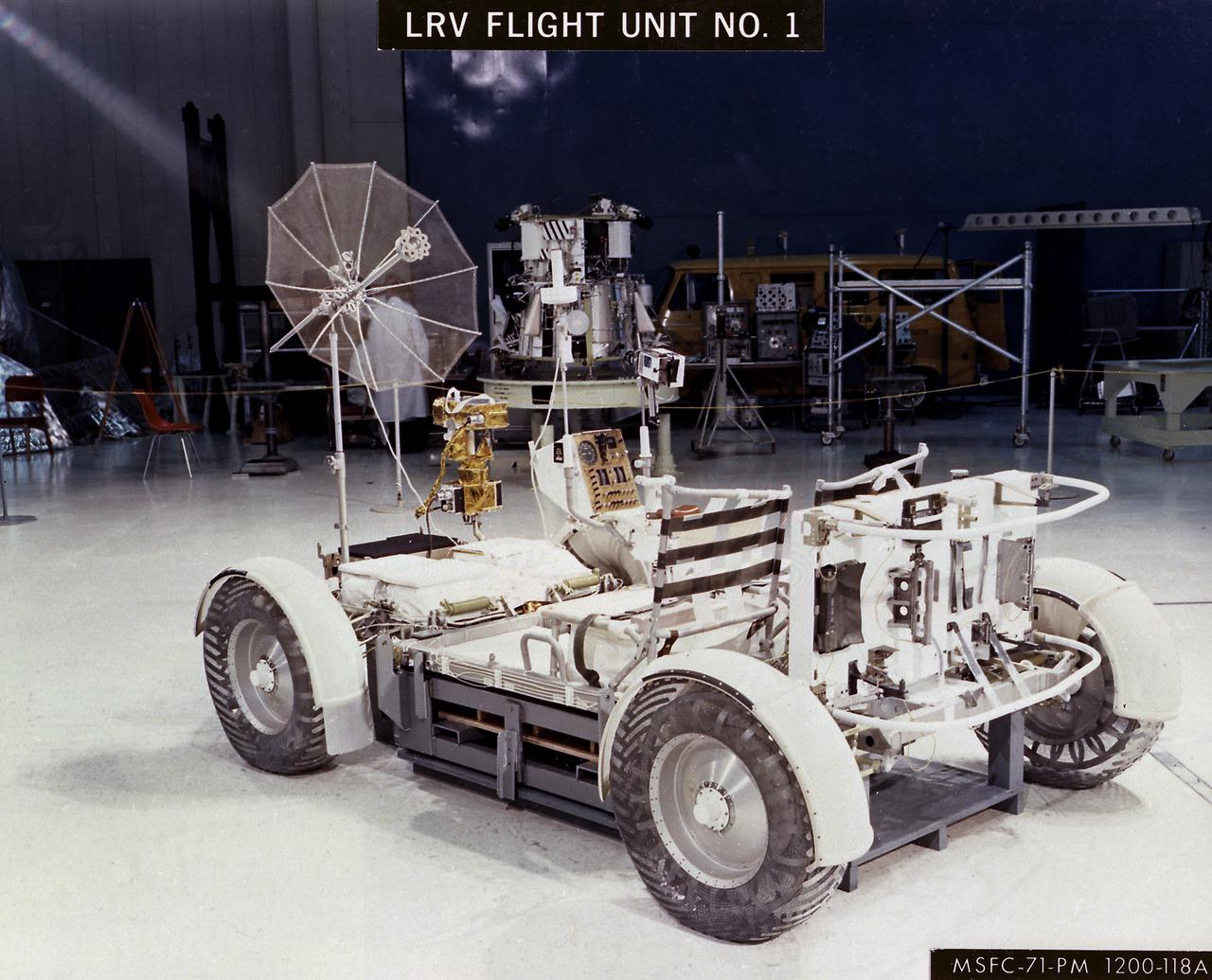
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crews to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
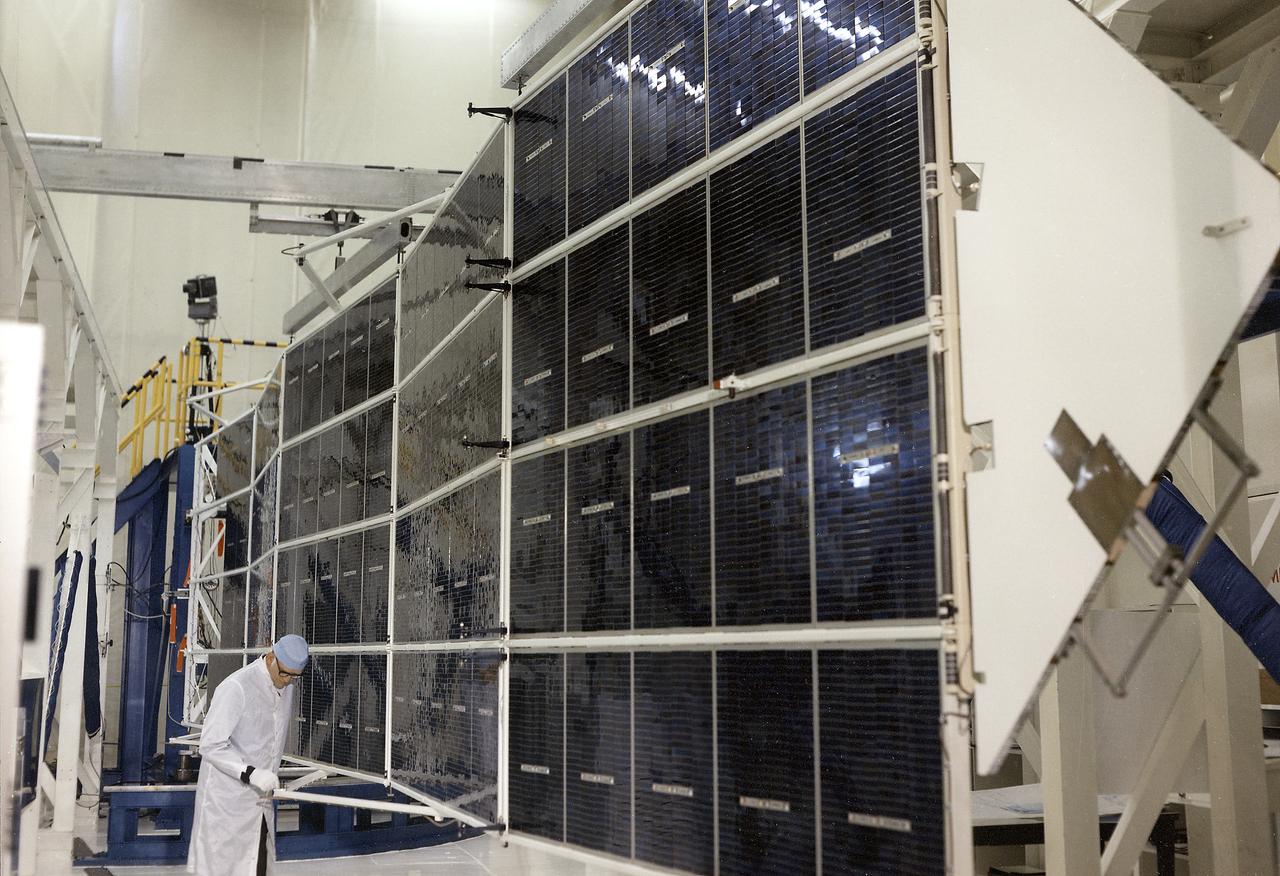

The Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), one of four major components comprising Skylab, was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. Power to operate the ATM's instruments and experiments was collected by four solar arrays, capable of producing up to 1.1 kilowatts of electricity. This is a photograph of the ATM Solar Array flight unit 1 in the deployed position.

S67-49969 (9 Nov. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The liftoff of the huge 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was at 7:00:01 a.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967. The successful objectives of the Apollo 4 Earth-orbital unmanned space mission obtained included (1) flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, subsystem operation, emergency detection subsystem operation, and (2) evaluation of the Apollo Command Module heat shield under conditions encountered on return from a moon mission.
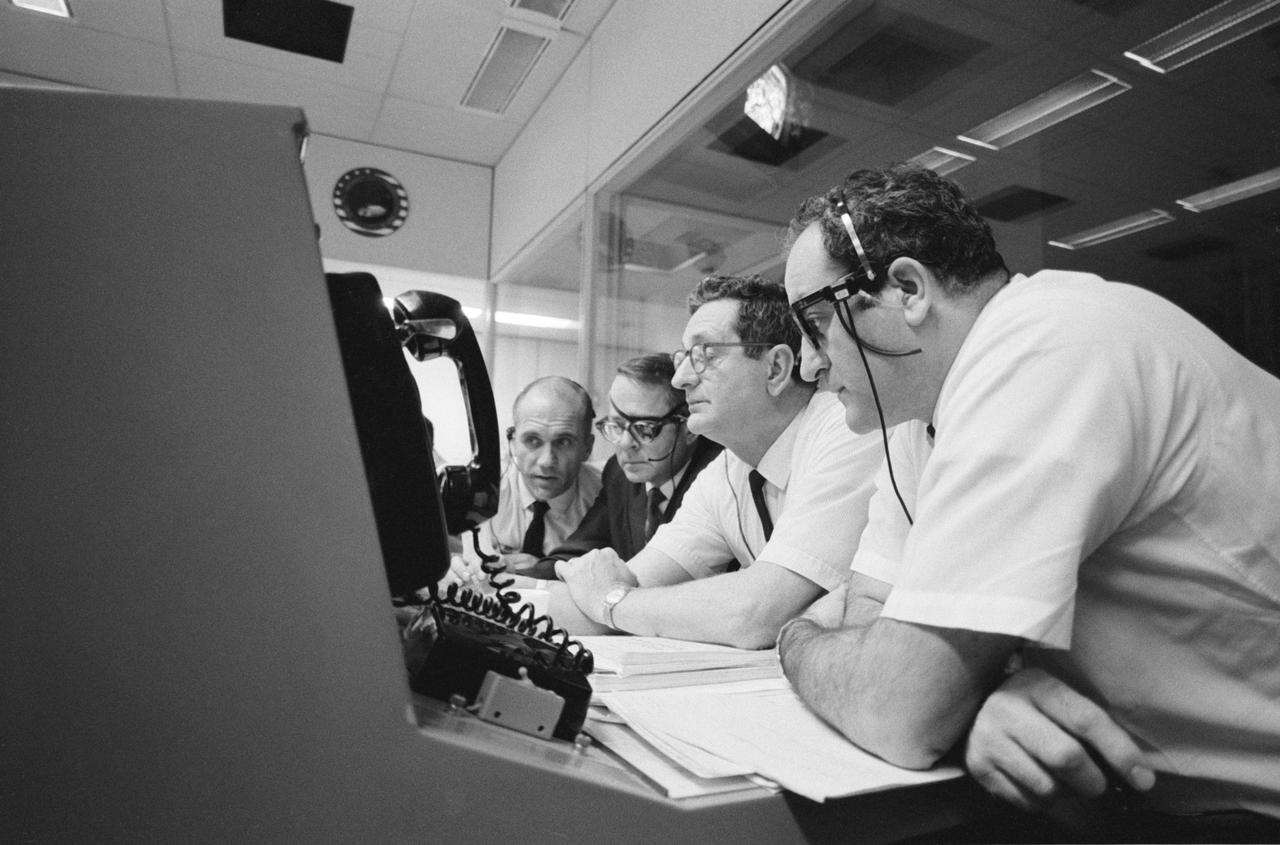

S70-35096 (16 April 1970) --- As the problem-plagued Apollo 13 crewmen entered their final 24 hours in space, several persons important to the mission remained attentive at consoles in the Mission Operations Control Room of the Mission Control Center at Manned Spacecraft Center. Among those monitoring communications and serving in supervisory capacities were these four officials from National Aeronautics and Space Administration Headquarters, Washington, D.C.: (from left) Thomas H. McMullen, Office of Manned Space Flight, who served as Shift 1 mission director; Dale Myers, associate administrator, Manned Space Flight; Chester M. Lee of the Apollo Program Directorate, OMSF, Apollo 13 mission director; and Dr. Rocco A. Petrone, Apollo program director, OMSF.
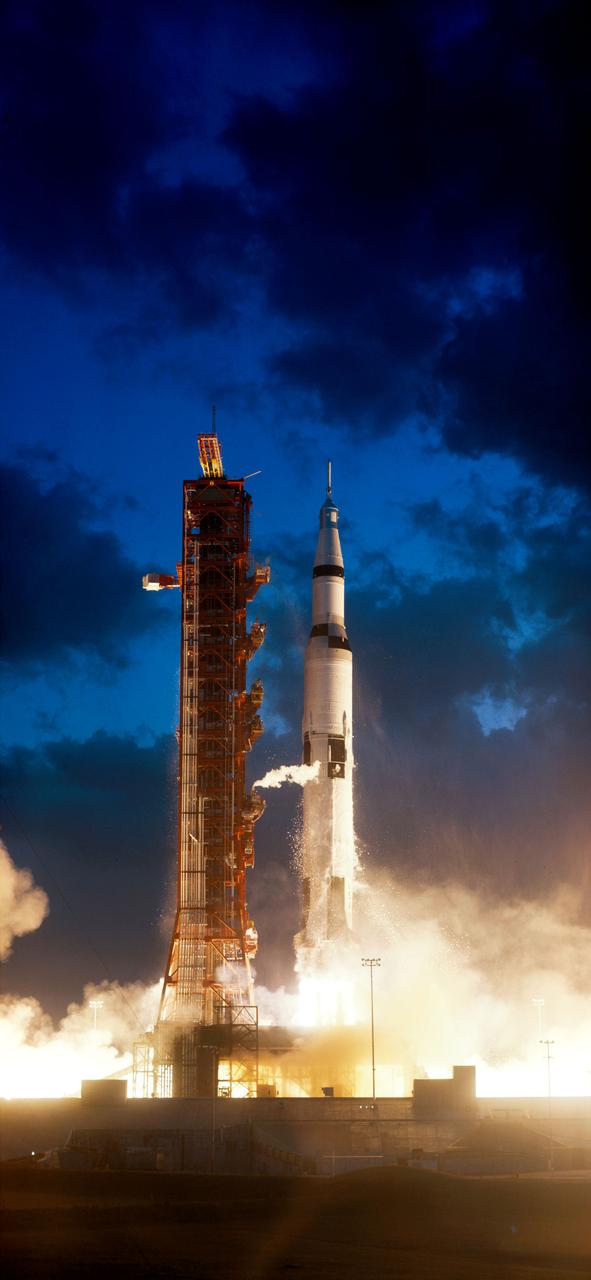

S67-50903 (9 Nov. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The liftoff of the huge 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was at 7:00:01 a.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967. The successful objectives of the Apollo 4 Earth-orbital unmanned space mission obtained included (1) flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, subsystem operation, emergency detection subsystem, and (2) evaluation of the Apollo Command Module heat shield under conditions encountered on return from a moon mission.

S68-19459 (22 Jan. 1968) --- The Apollo 5 (LM-1/Saturn 204) unmanned space mission was launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 37 at 5:48:09 p.m. (EST), Jan. 22, 1968. The Lunar Module-1 payload was boosted into Earth orbit by a launch vehicle composed of a Saturn IB first stage and a Saturn S-IVB second stage. The Apollo lunar module's first flight test was called a complete success. Ascent and descent propulsion systems and the ability to abort a lunar landing and return to orbit were demonstrated.

S68-19460 (22 Jan. 1968) --- The Apollo 5 (LM-1/Saturn 204) unmanned space mission was launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 37 at 5:48:09 p.m. (EST), Jan. 22, 1968. The Lunar Module-1 payload was boosted into Earth orbit by a launch vehicle composed of a Saturn IB first stage and a Saturn S-IVB second stage. The Apollo lunar module's first flight test was called a complete success. Ascent and descent propulsion systems and the ability to abort a lunar landing and return to orbit were demonstrated.
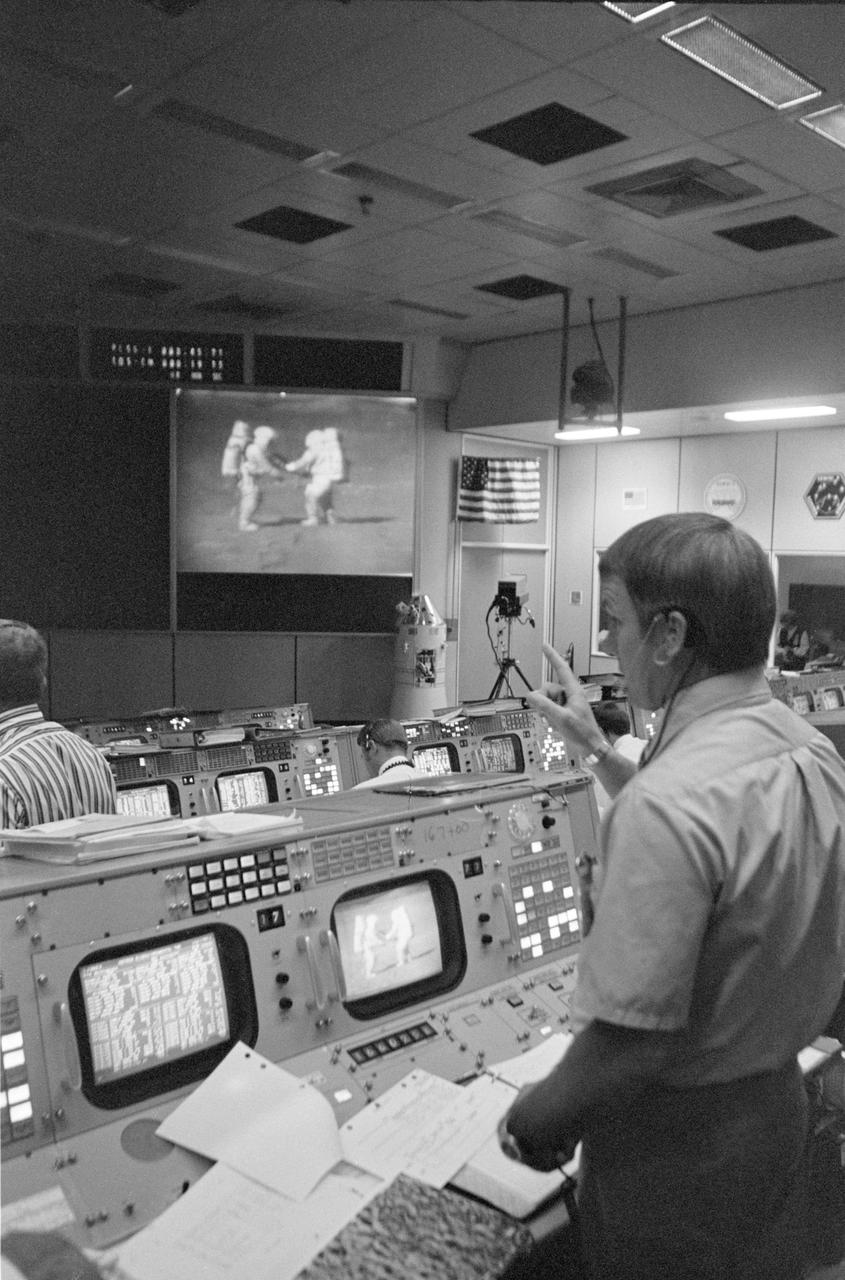

S71-41852 (2 Aug. 1971) --- Gerald D. Griffin, foreground, stands near his console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) during Apollo 15's third extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. Griffin is Gold Team (Shift 1) flight director for the Apollo 15 mission. Astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin can be seen on the large screen at the front of the MOCR as they participate in sample-gathering on the lunar surface.
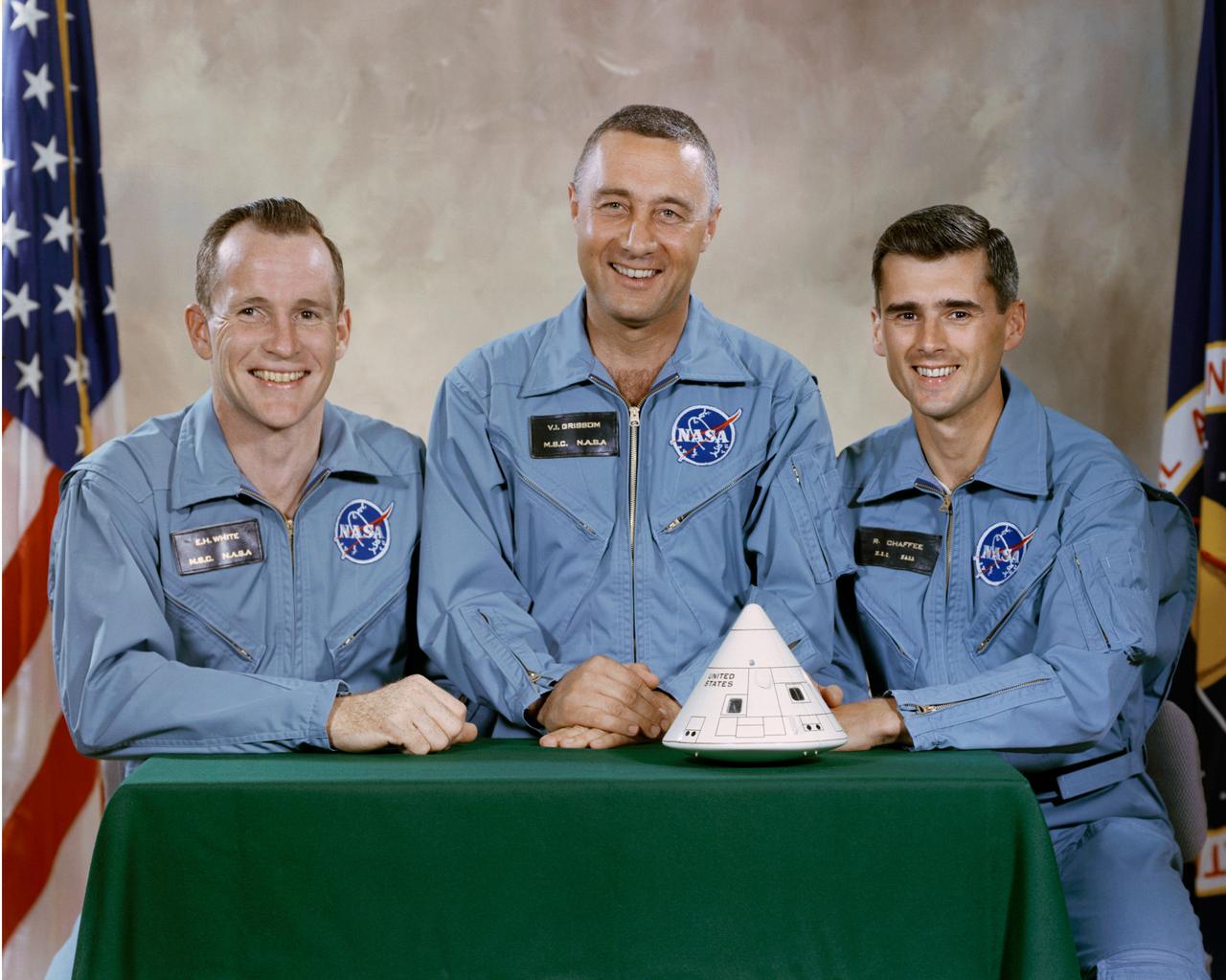

S66-30236 (1 April 1966) --- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has named these astronauts as the prime crew of the first manned Apollo Space Flight. Left to right, are Edward H. White II, command module pilot; Virgil I. Grissom, mission commander; and Roger B. Chaffee, lunar module pilot. Editor's Note: Astronauts Grissom, White and Chaffee lost their lives in a Jan. 27, 1967 fire in the Apollo Command Module (CM) during testing at the launch facility.
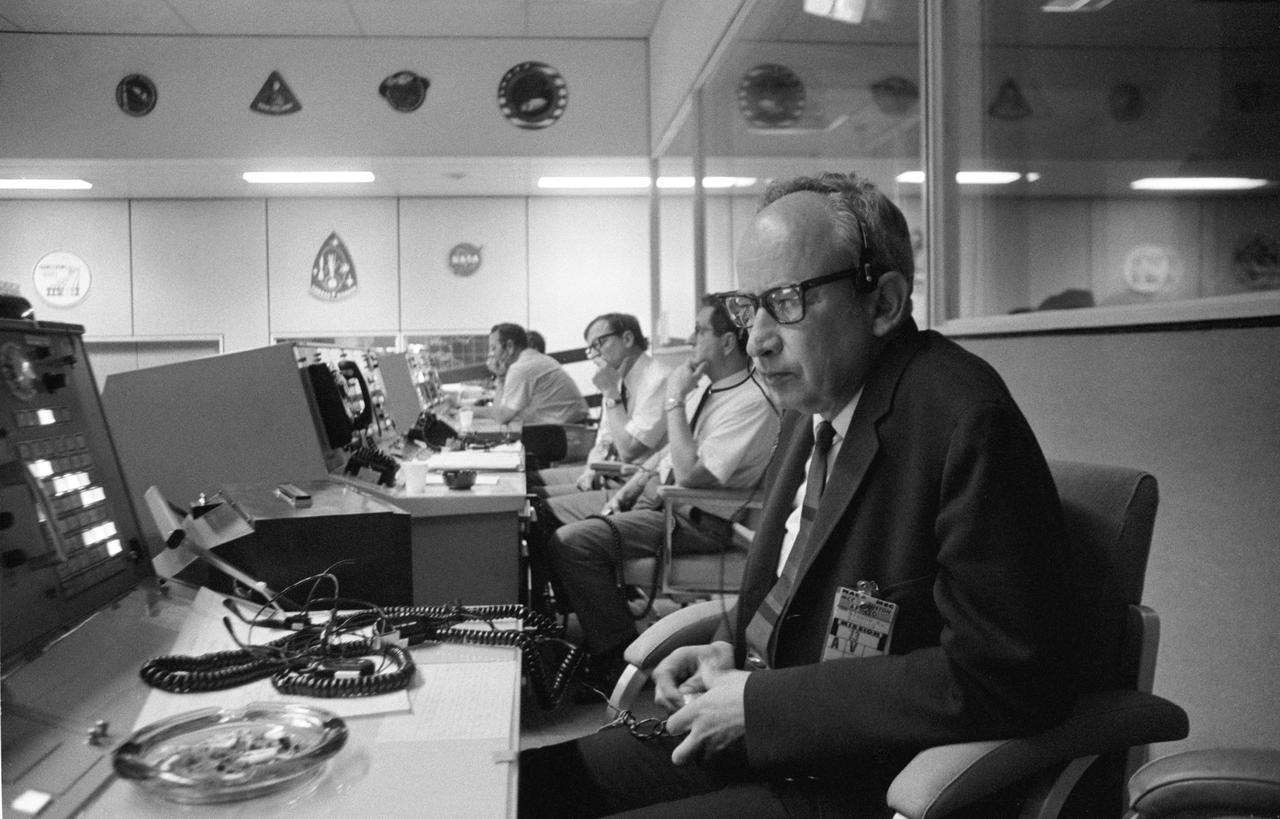

S70-34627 (11 April 1970) --- Sigurd A. Sjoberg, director of flight operations, at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), views the Apollo 13 liftoff from a console in the MSC Mission Control Center (MCC), Building 30. Apollo 13 lifted off at 1:13 p.m. (CST) April 11, 1970. Photo credit: NASA
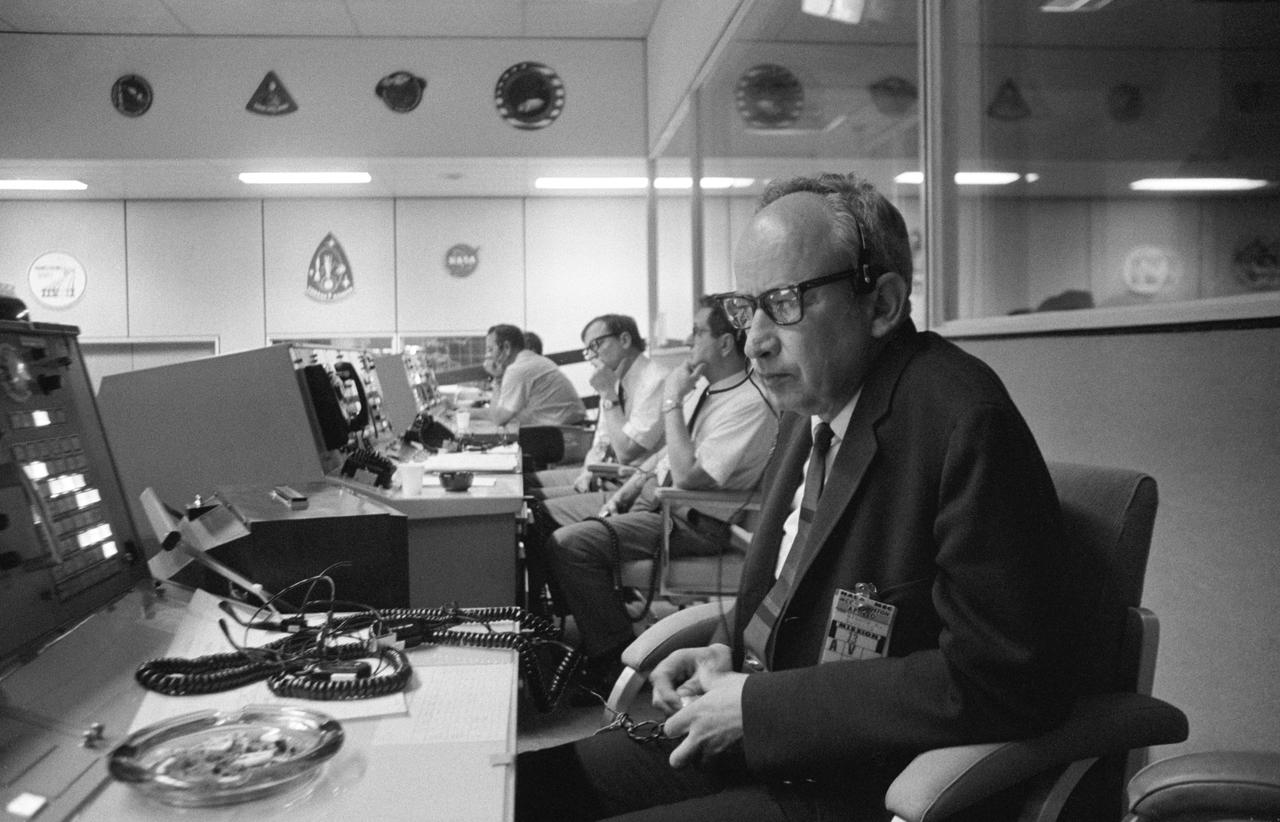

S70-34627 (11 April 1970) --- Sigurd A. Sjoberg, director of flight operations, at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), views the Apollo 13 liftoff from a console in the MSC Mission Control Center (MCC), Building 30. Apollo 13 lifted off at 1:13 p.m. (CST) April 11, 1970. Photo credit: NASA
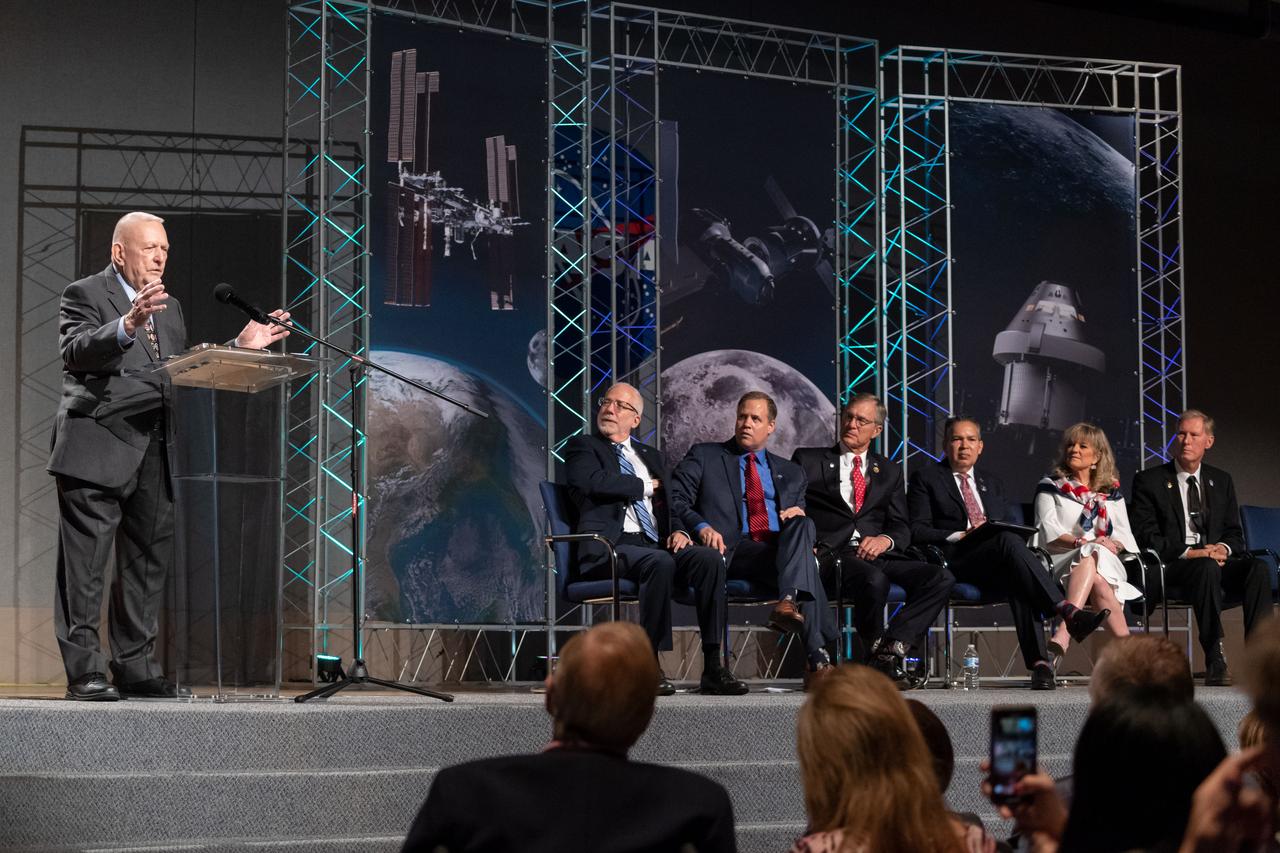

jsc2019e036696 (June 28, 2019) – Apollo 11 flight director Gene Kranz talks to grand opening visitors in NASA Johnson Space Center’s Teague Auditorium. NASA’s Johnson Space Center reopened the fully restored Apollo Mission Control Center with a grand opening and ribbon cutting event with NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine on June 28. The room now is reconfigured to its Apollo-era condition. Many of the items in the restored room are original pieces from 1969 that were found or donated, and the missing items were replicated to ensure walking into the viewing room would feel like taking a step back in time. The restoration team used old photographs, footage, documents and interviews and discussions with Apollo veterans to set everything in its proper place, including coffee mugs, clothing articles and ashtrays. Beginning July 1, the Apollo Mission Control Center will become part of daily tours at Johnson hosted by Space Center Houston.
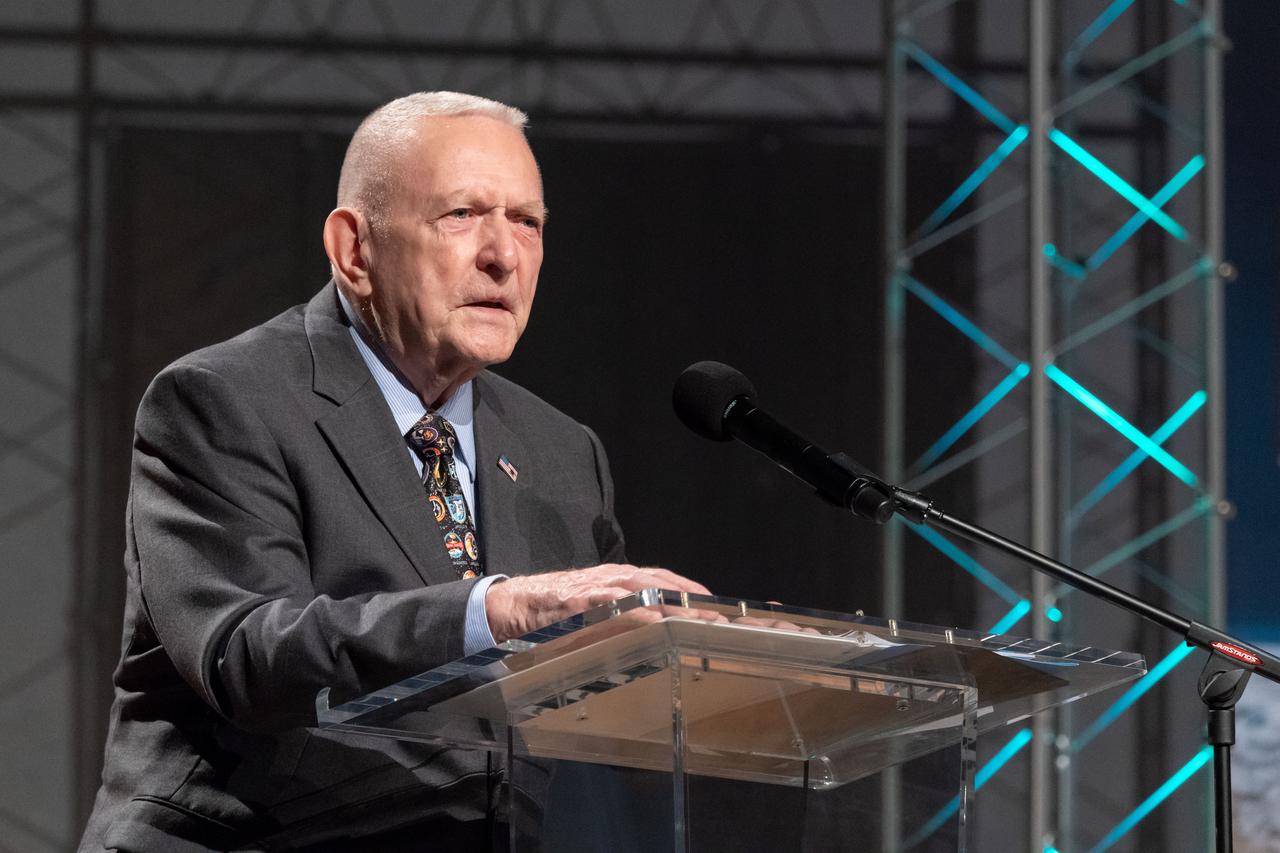

jsc2019e036695 (June 28, 2019) – Apollo 11 flight director Gene Kranz talks to grand opening visitors in NASA Johnson Space Center’s Teague Auditorium. NASA’s Johnson Space Center reopened the fully restored Apollo Mission Control Center with a grand opening and ribbon cutting event with NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine on June 28. The room now is reconfigured to its Apollo-era condition. Many of the items in the restored room are original pieces from 1969 that were found or donated, and the missing items were replicated to ensure walking into the viewing room would feel like taking a step back in time. The restoration team used old photographs, footage, documents and interviews and discussions with Apollo veterans to set everything in its proper place, including coffee mugs, clothing articles and ashtrays. Beginning July 1, the Apollo Mission Control Center will become part of daily tours at Johnson hosted by Space Center Houston.
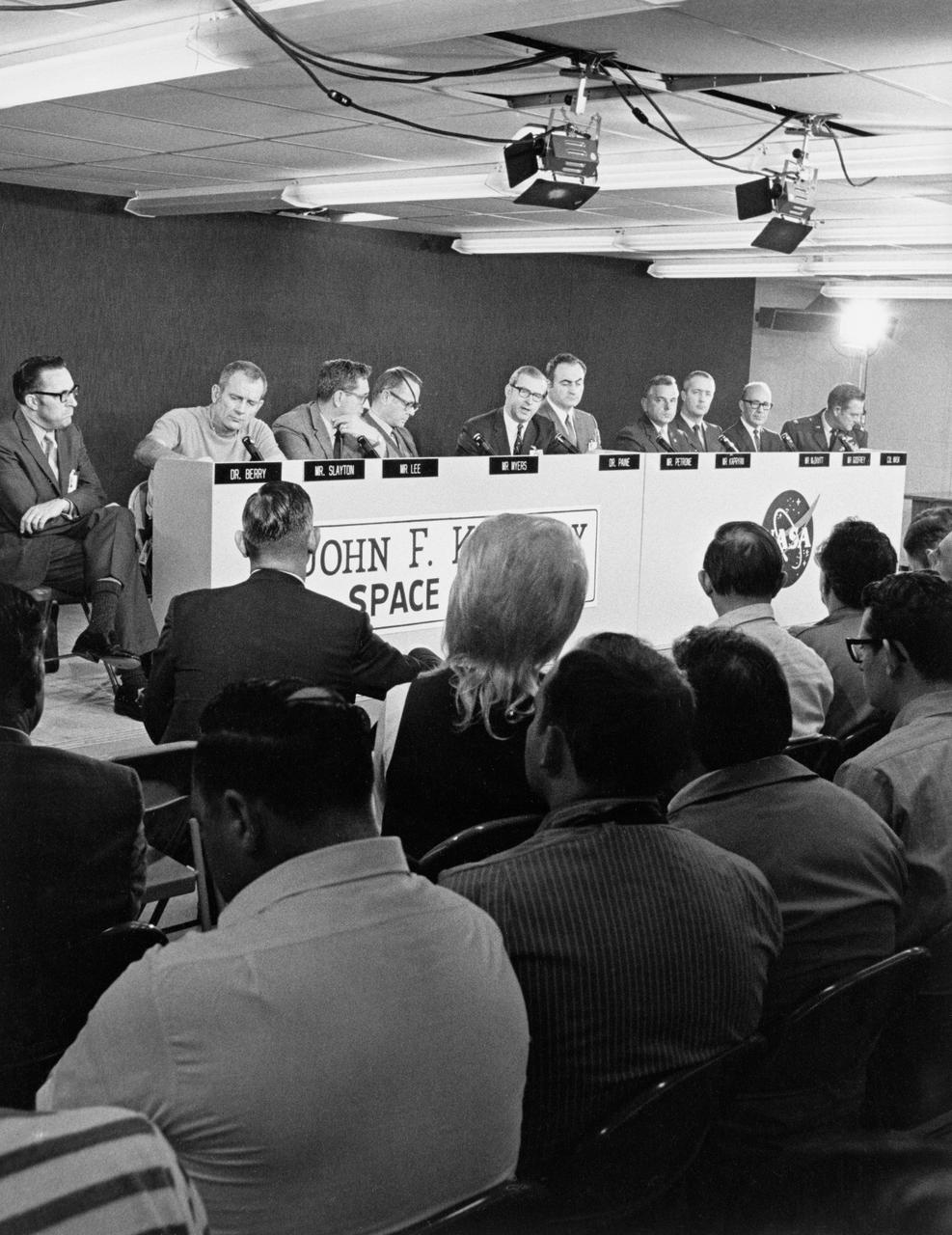

S70-36782 (10 April 1970) --- Several NASA and military officials (background at dais) meet the press on April 10, 1970, during a scheduled a T-1 prelaunch briefing for the Apollo 13 mission in the Apollo News Center at the Kennedy Space Center. The briefing participants, from the left, are Dr. Charles A. Berry, Director, Medical Research and Operations Directorate, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC); Dr. Donald K. (Deke) Slayton, director of flight crew operations, MSC; Chester M. Lee of the Apollo Program Directorate, Office Manned Space Flight (OMSF),NASA Hq. and Apollo 13 Mission Director; Dale Myers, Associate Administrator, OMSF,NASA Hq.; Dr. Thomas O. Paine, NASA Administrator; Dr. Rocco A. Petrone, Apollo Program Director, OMSF,NASA Hq.; Walter J. Kapryan, NASA's Director of Launch Operations; James A. McDivitt, Manager of the Apollo Spacecraft Program Office; Roy E. Godfrey, Manager, Saturn Program Office; and Col. Kenneth J. Mask, USAF, DOD Manned Space Flight Support Office. Photo credit: NASA
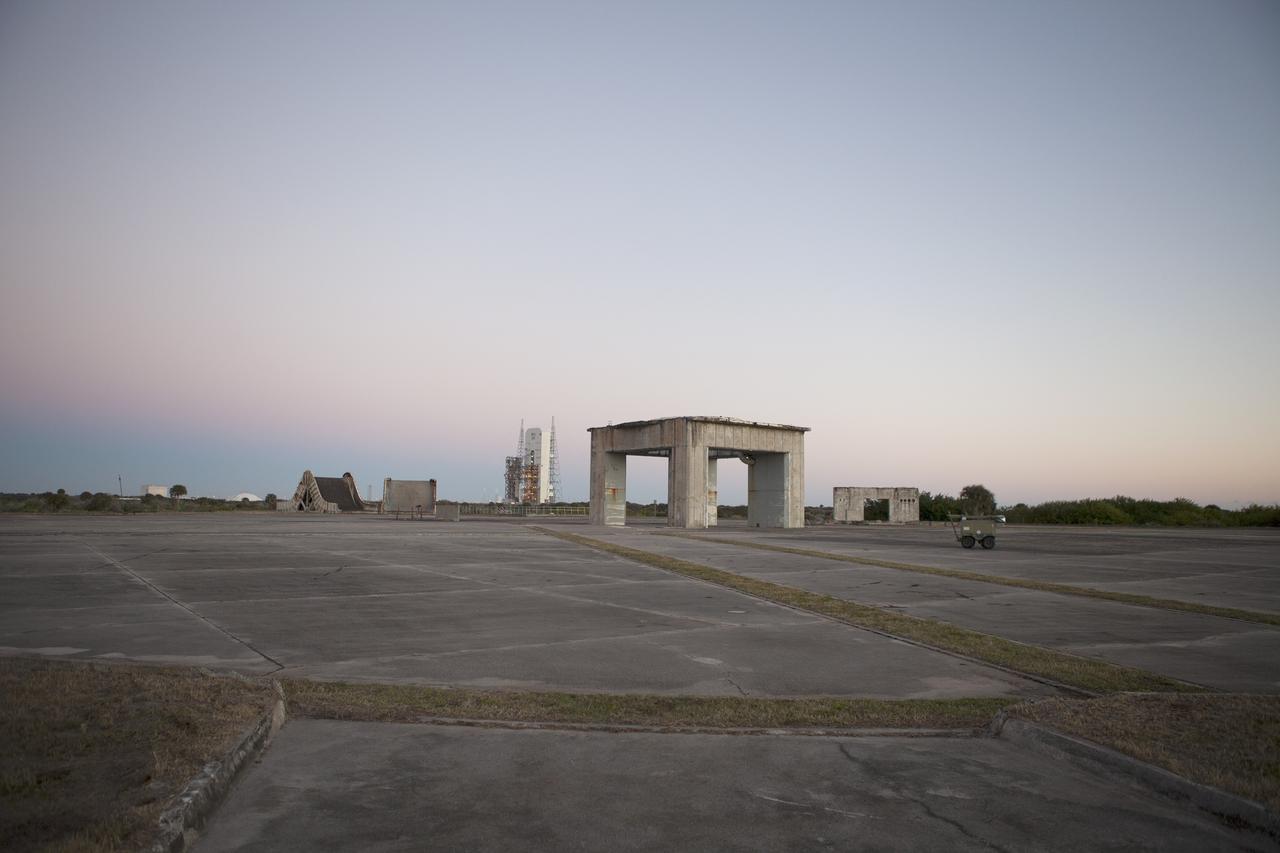

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The past intersects with the future on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. In the foreground is what remains of historic Launch Pad 34 in the distance behind it is Space Launch Complex 37 whence NASA's Orion spacecraft made its first flight test. On this day in 1967, a fire erupted on the Pad 34 during a preflight test, taking the lives of the Apollo 1 crew, NASA astronauts Virgil Grissom, Edward White and Roger Chaffee. To learn more about Apollo 1 and the crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/apollo/missions/apollo1.html. To learn more about Orion, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/orion/. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
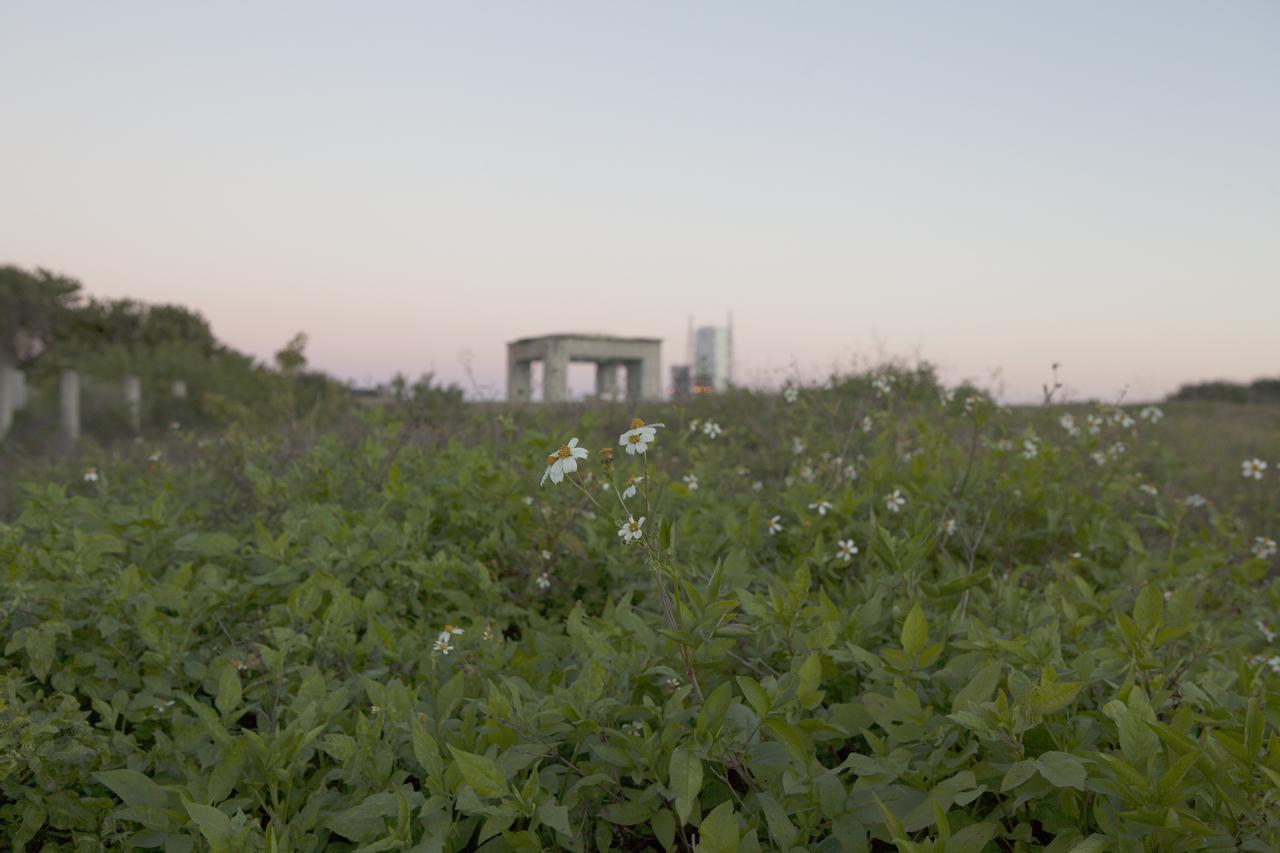

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The past intersects with the future on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. In the foreground is what remains of historic Launch Pad 34 in the distance behind it is Space Launch Complex 37 whence NASA's Orion spacecraft made its first flight test. On this day in 1967, a fire erupted on the Pad 34 during a preflight test, taking the lives of the Apollo 1 crew, NASA astronauts Virgil Grissom, Edward White and Roger Chaffee. To learn more about Apollo 1 and the crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/apollo/missions/apollo1.html. To learn more about Orion, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/orion/. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
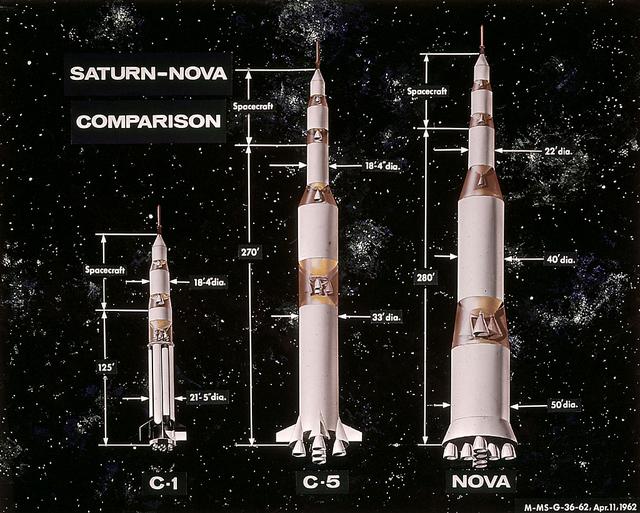

In this 1962 artist's concept , a proposed Nova rocket, shown at right, is compared to a Saturn C-1, left, and a Saturn C-5, center. The Marshall Space Flight Center directed studies of Nova configuration from 1960 to 1962 as a means of achieving a marned lunar landing with a direct flight to the Moon. Various configurations of the vehicle were examined, the largest being a five-stage vehicle using eight F-1 engines in the first stage. Although the program was effectively cancelled in 1962 when NASA planners selected the lunar-orbital rendezvous mode, the proposed F-1 engine was eventually used to propel the first stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle in the Apollo Program.
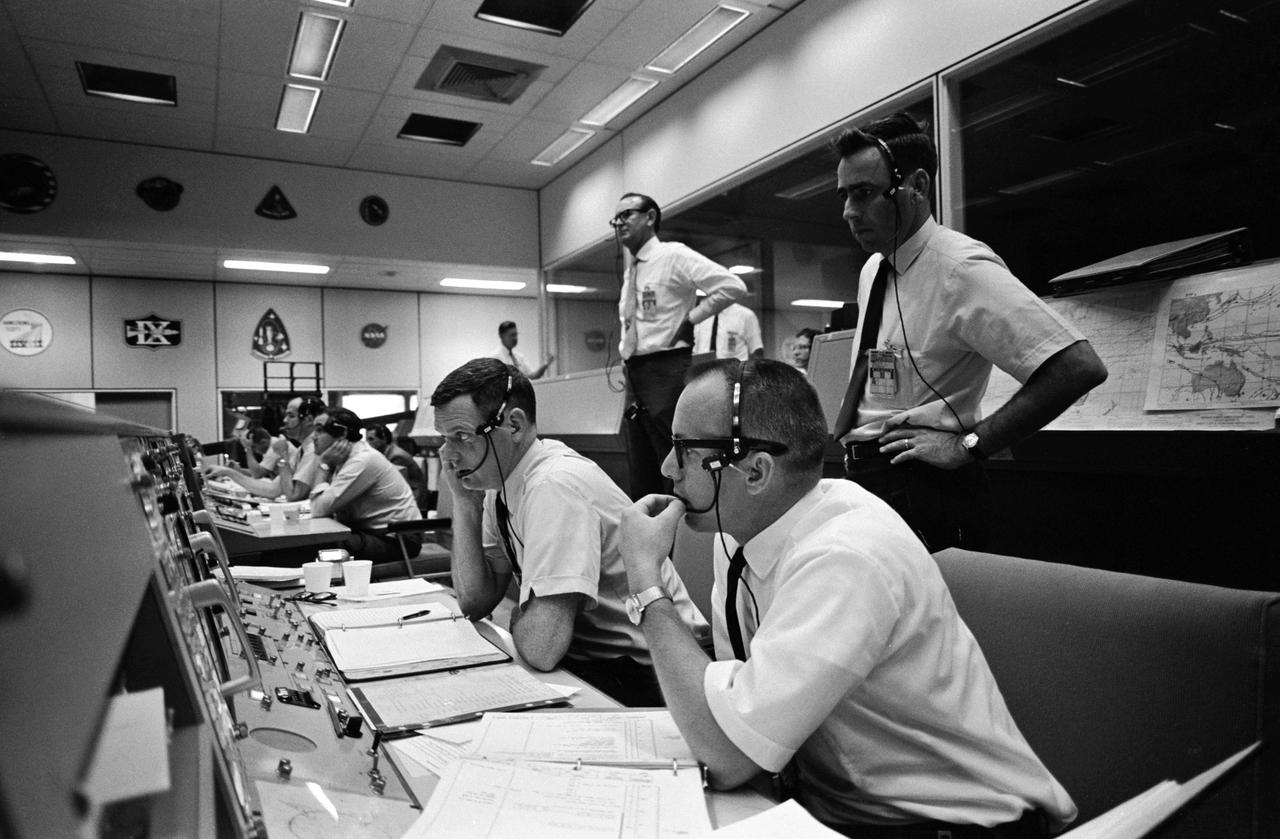

S69-34038 (18 May 1969) --- View of activity at the flight director's console in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center, Building 30, on the first day of the Apollo 10 lunar orbit mission. Seated are Gerald D. Griffin (foreground) and Glynn S. Lunney, Shift 1 (Black Team) flight directors. Milton L. Windler, standing behind them, is the flight director of Shift 2 (Maroon Team). In the center background, standing, is Dr. Christopher C. Kraft Jr., MSC Director of Flight Operations.
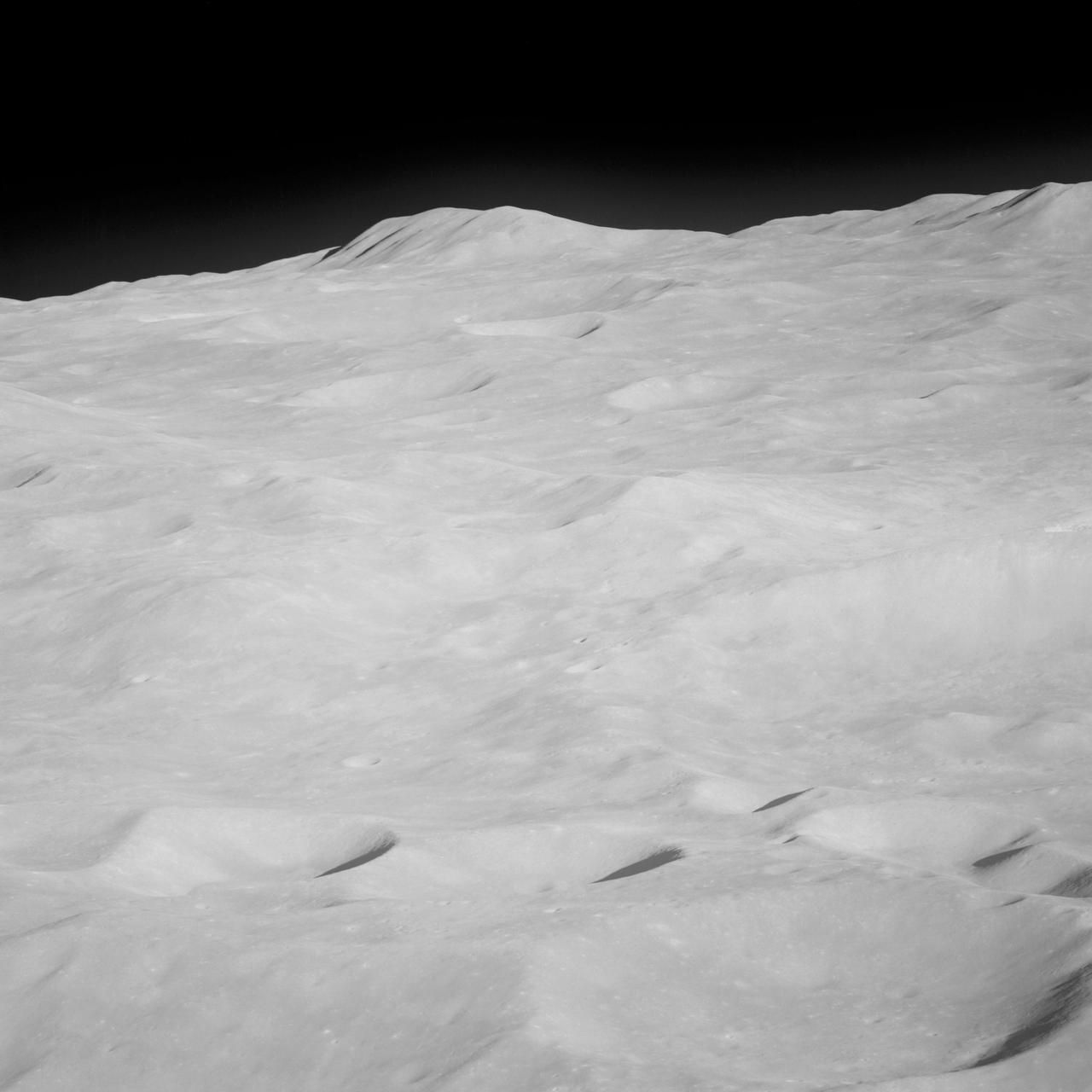

Apollo 8,Moon, Latitude 15 degrees South,Longitude 170 degrees West. Camera Tilt Mode: High Oblique. Direction: Southeast. Sun Angle 17 degrees. Original Film Magazine was labeled E. Camera Data: 70mm Hasselblad; F-Stop: F-5.6; Shutter Speed: 1/250 second. Film Type: Kodak SO-3400 Black and White,ASA 40. Other Photographic Coverage: Lunar Orbiter 1 (LO I) S-3. Flight Date: December 21-27,1968.
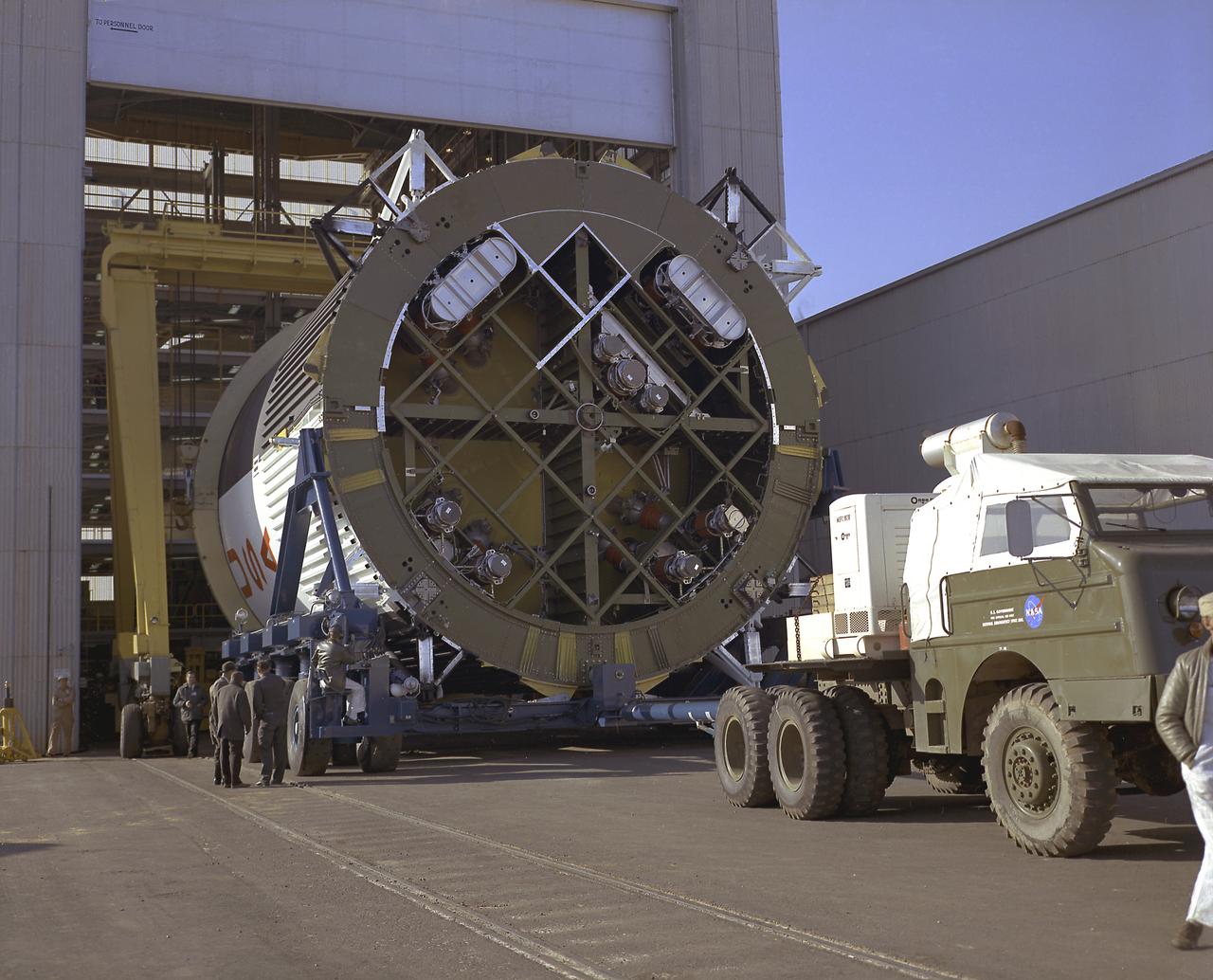

This photograph shows the fuel tank assembly for the Saturn V S-IC (first) stage being transported to the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705 for mating to the liquid oxygen (LOX) tank. The fuel tank carried kerosene (RP-1) as its fuel. The S-IC stage used five F-1 engines, that used kerosene and liquid oxygen as propellant and each engine provided 1,500,000 pounds of thrust. This stage lifted the entire vehicle and Apollo spacecraft from the launch pad.
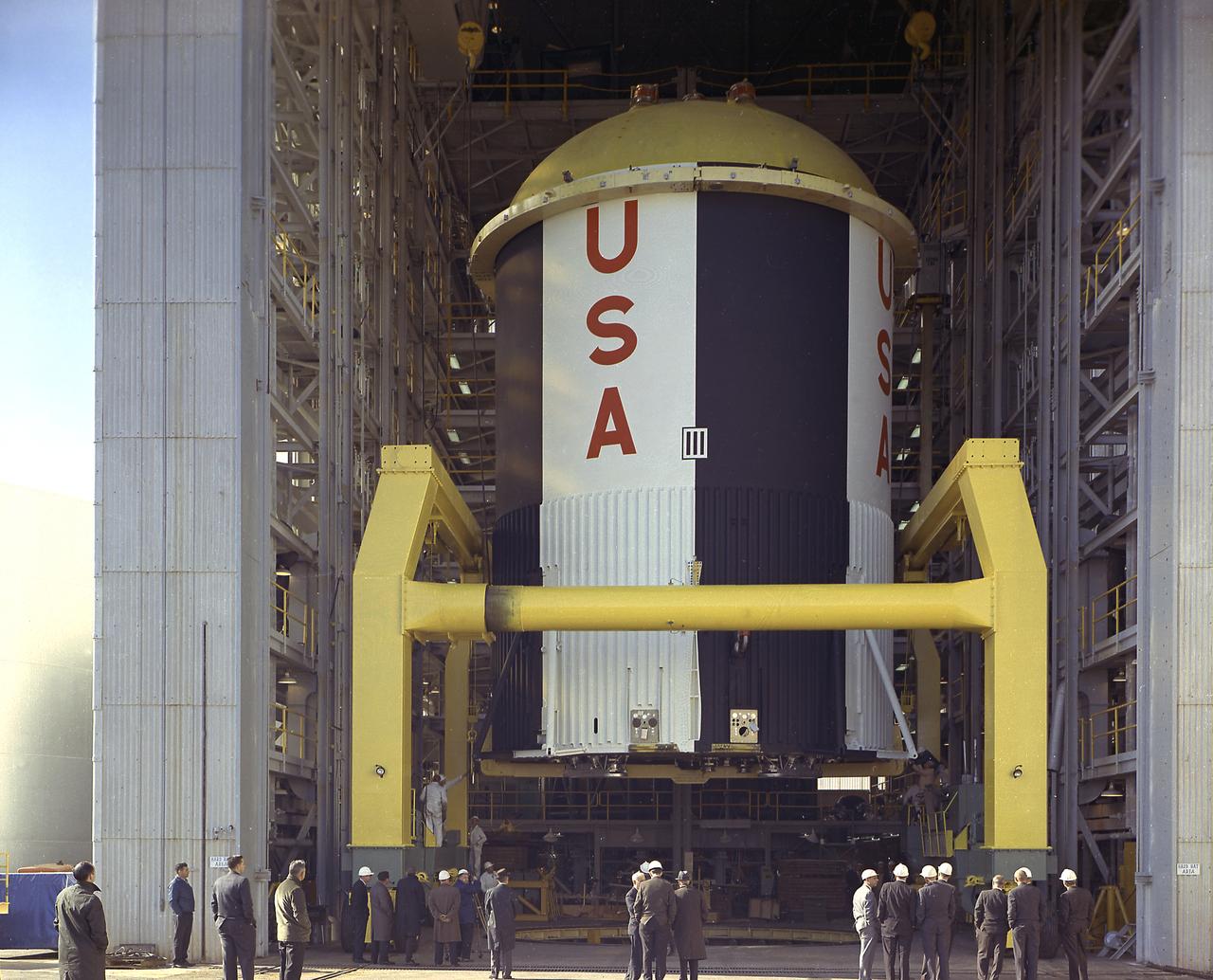
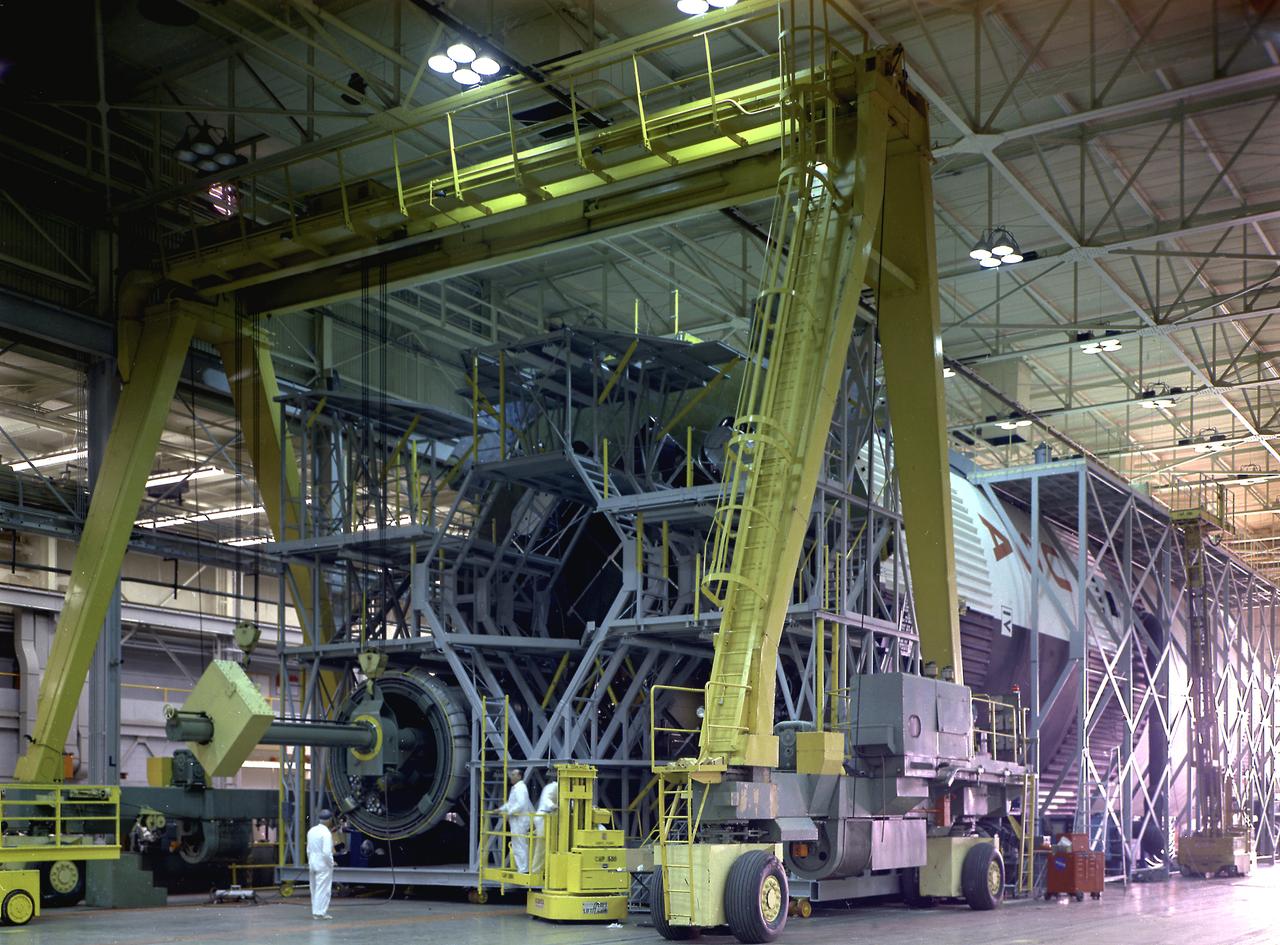
The fuel tank assembly of the Saturn V S-IC (first) stage supported with the aid of a C frame on the transporter was readied to be transported to the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705. The fuel tank carried kerosene (RP-1) as its fuel. The S-IC stage utilized five F-1 engines that used kerosene and liquid oxygen as propellant and each engine provided 1,500,000 pounds of thrust. This stage lifted the entire vehicle and Apollo spacecraft from the launch pad.
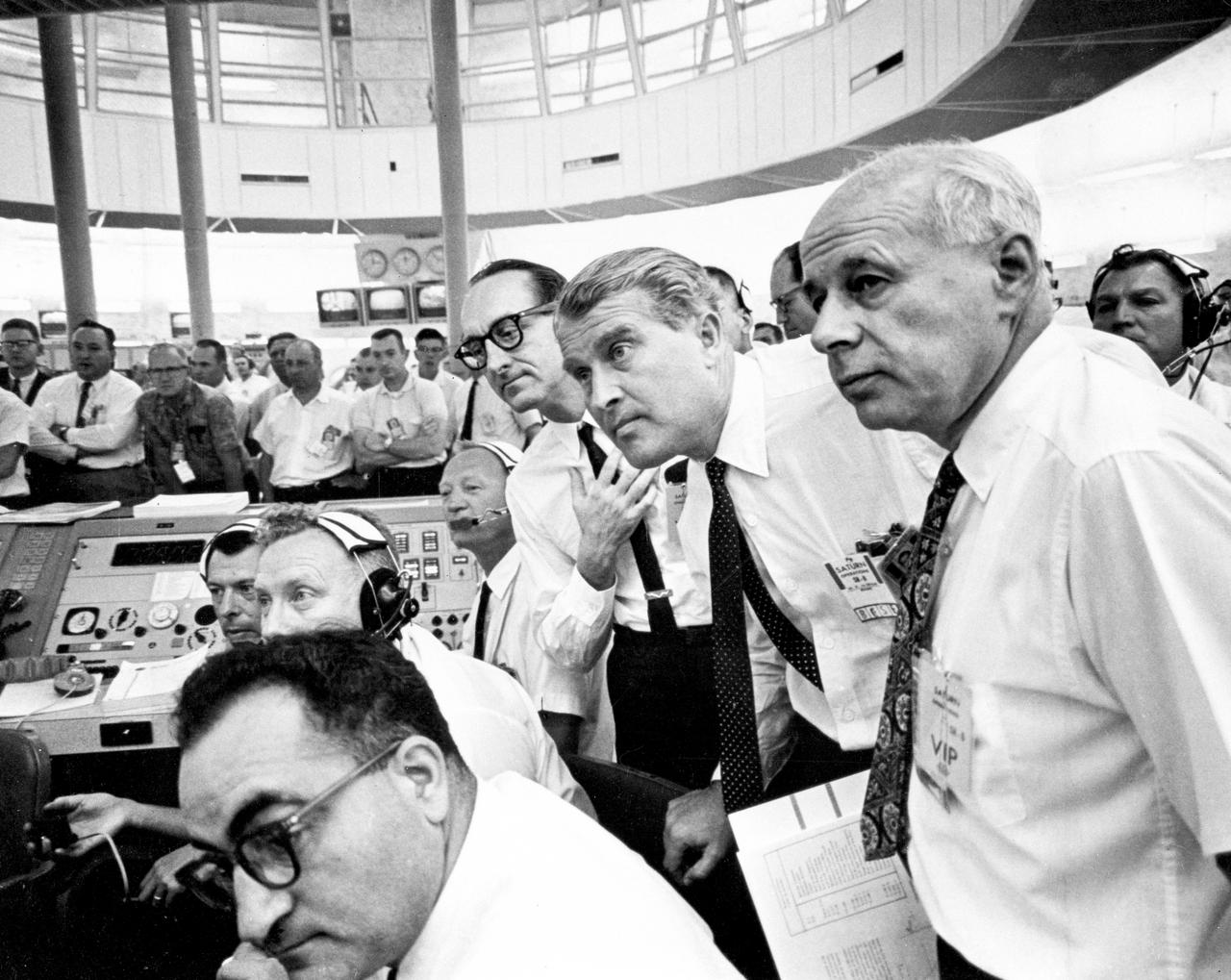

This photograph depicts an intense moment during the SA-6 launch at the Firing Room. Dr. von Braun, Director of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is at center; to his left is Dr. George Mueller, Associate Director for Marned Space Flight; and far right is Dr. Eberhard Rees, Director for Research and Development, MSFC. The SA-6, the sixth flight of the Saturn 1 vehicle, launched a S-IV stage (a second stage) and an Apollo boilerplate spacecraft.
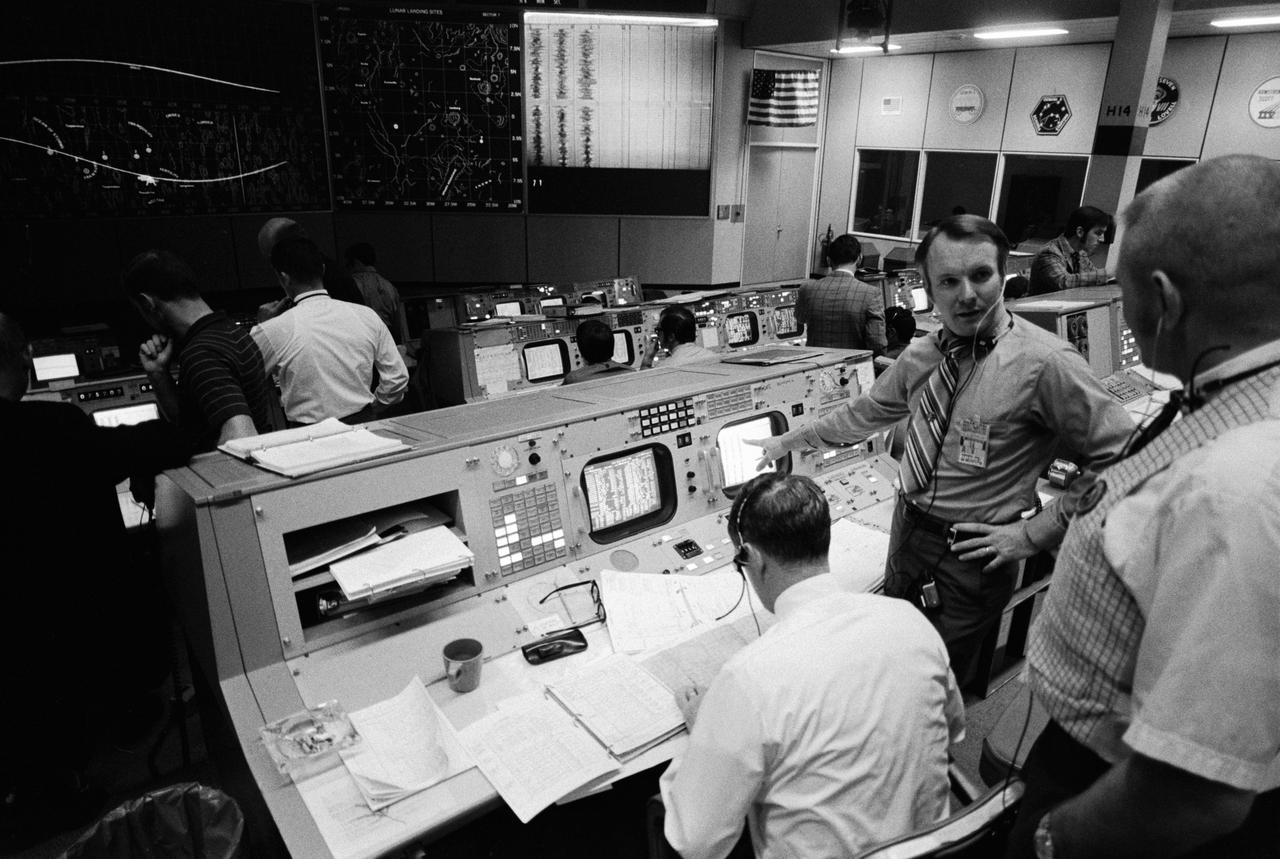

S71-17610 (4 Feb. 1971) --- Partial view of activity in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center at the time the Apollo 14 S-IVB stage impacted on the lunar surface. The flight director's console is in the foreground. Eugene F. Kranz, chief of the MSC Flight Control Division, is in the right foreground. Seated at the console is Glynn S. Lunney, head of the Flight Director Office, Flight Control Division. Facing the camera is Gerald D. Griffin, flight director of the Third (Gold) Team. A seismic reading from the impact can be seen in the center background. The S-IVB impacted on the lunar surface at 1:40:54 a.m. (CST), Feb. 4, 1971, about 90 nautical miles south-southwest of the Apollo 12 passive seismometer. The energy release was comparable to 11 tons of TNT.

This artist's concept illustrates the Module Nova concept - Solid C-3 Basis. From 1960 to 1962, the Marshall Space Flight Center considered the Nova launch vehicle as a means to achieve a marned lunar landing with a direct flight to the Moon. Various configurations of the vehicle were examined. The latest configuration was a five-stage vehicle using eight F-1 engines in the first stage. Although the program was canceled after NASA planners selected the lunar/orbital rendezvous mode, the proposed F-1 engine would eventually be used in the Apollo Program to propel the first stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle.

This artist's concept illustrates the Module Nova concept - Solid C-3 Basis. From 1960 to 1962, the Marshall Space Flight Center considered the Nova launch vehicle as a means to achieve a marned lunar landing with a direct flight to the Moon. Various configurations of the vehicle were examined. The latest configuration was a five-stage vehicle using eight F-1 engines in the first stage. Although the program was canceled after NASA planners selected the lunar/orbital rendezvous mode, the proposed F-1 engine would eventually be used in the Apollo Program to propel the first stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle.

On Dec. 1, 2014, Milt Heflin briefs the Orion recovery team on board the U.S. Navy's USS Anchorage, which will be used to retrieve Orion after it splashes down in the Pacific Ocean following Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) on Dec. 4. Heflin began his 46-year-long NASA career as part of the team that recovered the Apollo capsules from the Pacific. Now retired from NASA, he is acting as a consultant for the Orion team through Red Canyon Software, Inc. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

S68-18733 (22 Jan. 1968) --- Dr. Robert R. Gilruth (right), MSC Director, sits with Dr. Christopher C. Kraft Jr., MSC director of flight operations, at his flight operations director console in the Mission Control Center, Building 30, during the Apollo 5 (LM-1/Saturn 204) unmanned space mission.
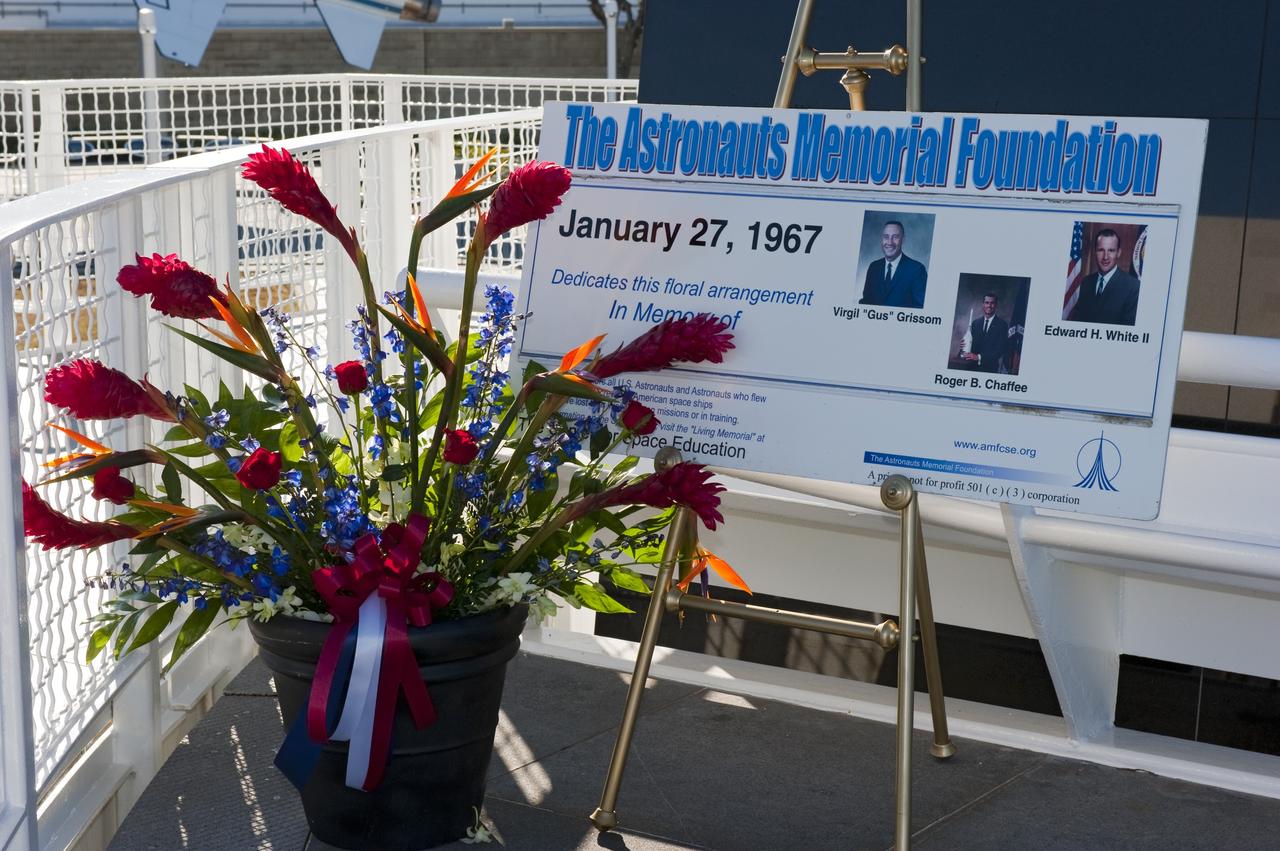

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Flowers lay at the foot of the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida before a Day of Remembrance wreath laying ceremony to honor members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The floral arrangement is dedicated to the Apollo 1 crew members Virgil "Gus" Grissom, Roger B. Chaffee and Edward H. White II. The memorial honors 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
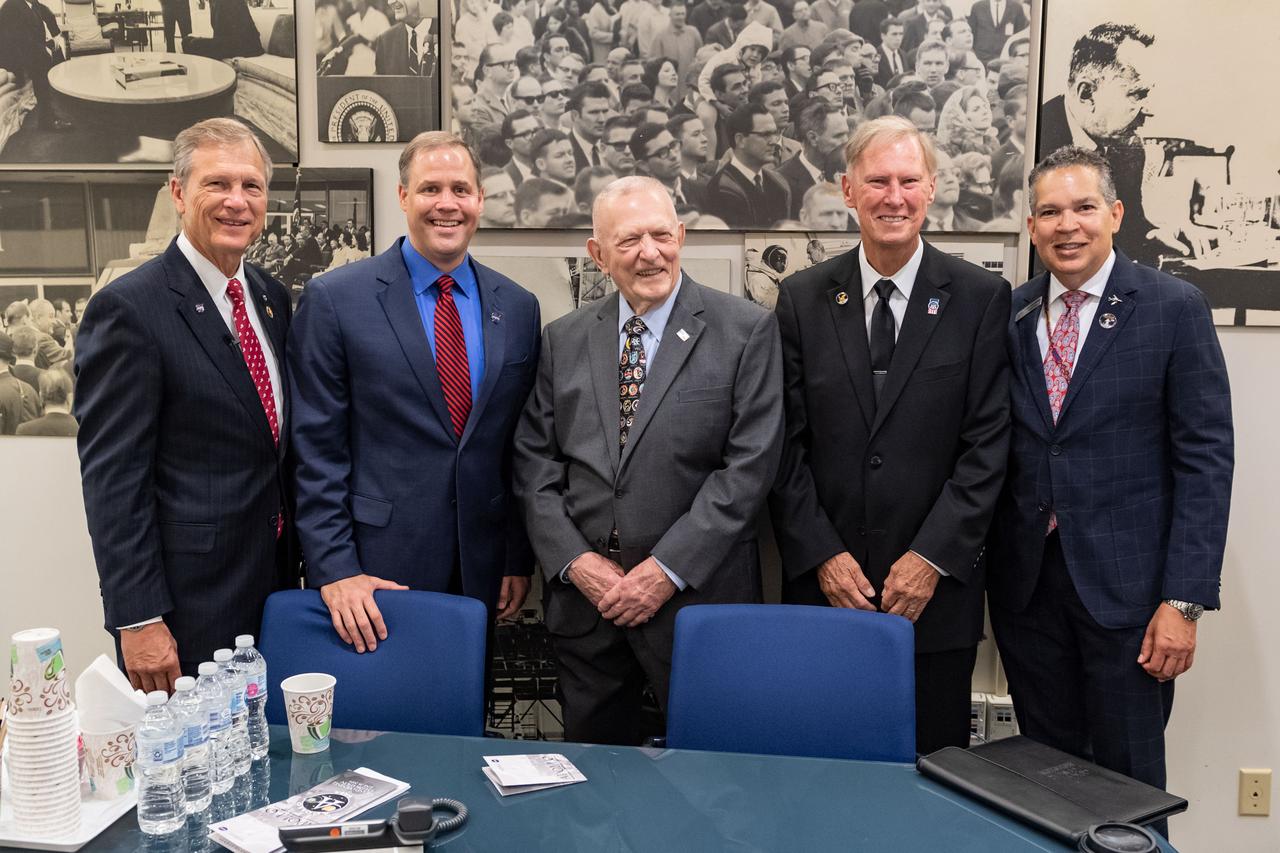

jsc2019e036671 (June 28, 2019) – Apollo 11 flight director Gene Kranz is surrounded by grand opening participants (from left) U.S. Rep. Brian Babin, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, Kranz, Advisory Council on Historic Preservation’s Chairman Milford Wayne Donaldson and Space Center Houston CEO William Harris in the visitors in NASA Johnson Space Center’s Teague Auditlorium. NASA’s Johnson Space Center reopened the fully restored Apollo Mission Control Center with a grand opening and ribbon cutting event with NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine on June 28. The room now is reconfigured to its Apollo-era condition. Many of the items in the restored room are original pieces from 1969 that were found or donated, and the missing items were replicated to ensure walking into the viewing room would feel like taking a step back in time. The restoration team used old photographs, footage, documents and interviews and discussions with Apollo veterans to set everything in its proper place, including coffee mugs, clothing articles and ashtrays. Beginning July 1, the Apollo Mission Control Center will become part of daily tours at Johnson hosted by Space Center Houston.
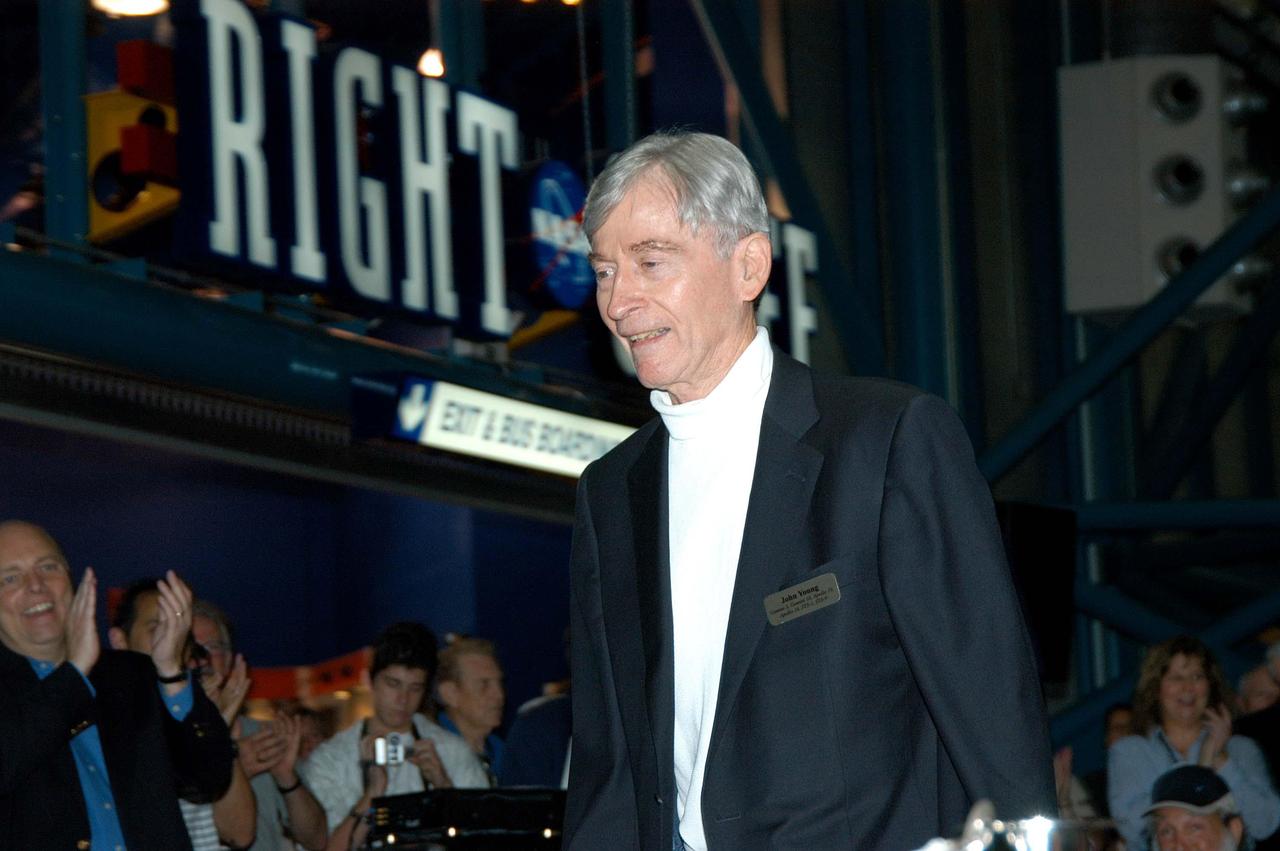

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Before the induction ceremony of five space program heroes into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame, astronaut John Young is warmly greeted as he is introduced as a previous inductee. Co-holder of a record for the most space flights, six, he flew on Gemini 3 and 10, orbited the Moon on Apollo 10, walked on the Moon on Apollo 16, and commanded two space shuttle missions, STS-1 and STS-9. Young currently serves as associate director, technical, at Johnson Space Center. The induction ceremony was held at the Apollo/Saturn V Center at KSC. New inductees are Richard O. Covey, commander of the Hubble Space Telescope repair mission; Norman E. Thagard, the first American to occupy Russia’s Mir space station; the late Francis R. "Dick" Scobee, commander of the ill-fated 1986 Challenger mission; Kathryn D. Sullivan, the first American woman to walk in space; and Frederick D. Gregory, the first African-American to command a space mission and the current NASA deputy administrator. The U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame opened in 1990 to provide a place where space travelers could be remembered for their participation and accomplishments in the U.S. space program. The five inductees join 52 previously honored astronauts from the ranks of the Gemini, Apollo, Skylab, Apollo-Soyuz, and Space Shuttle programs.
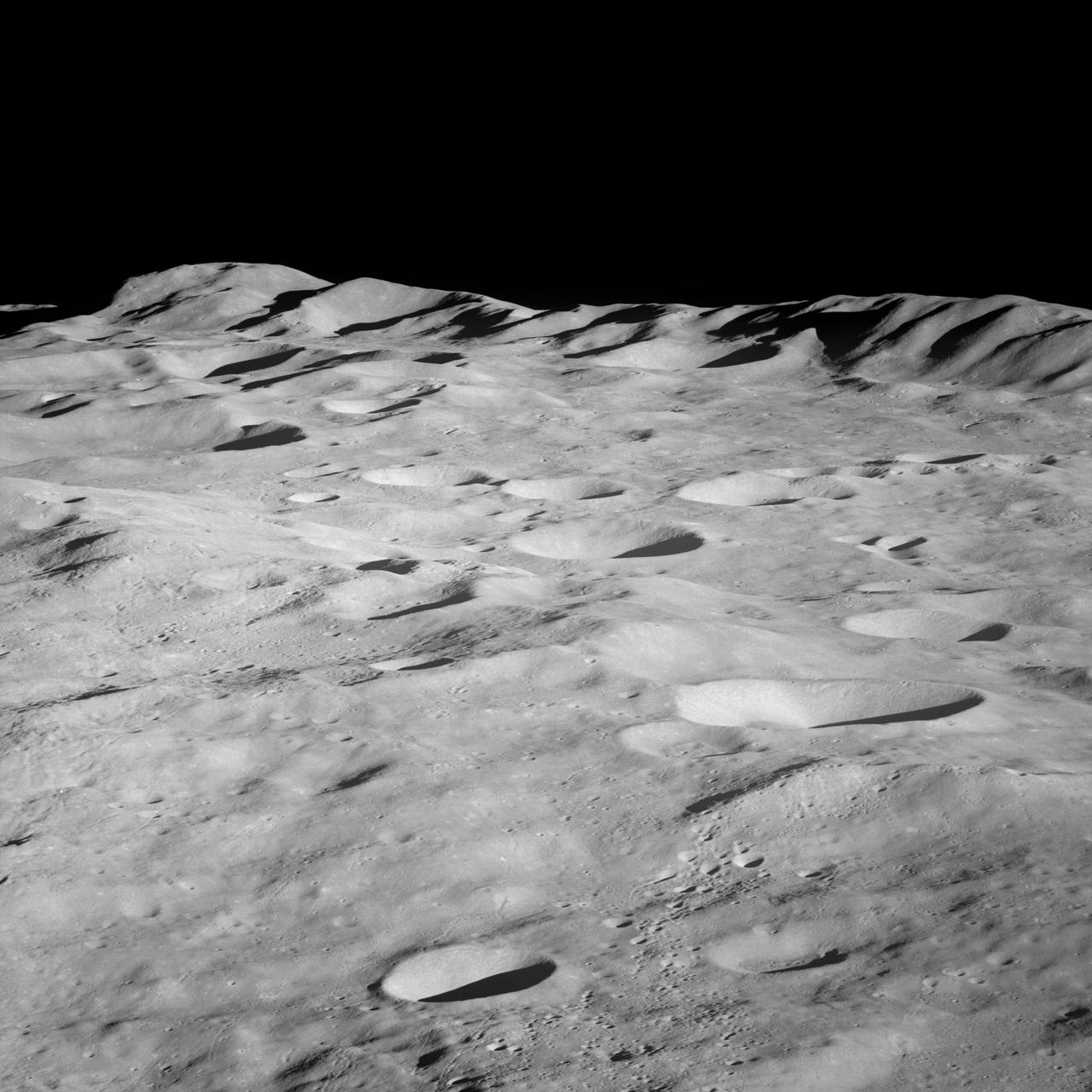

Apollo 8,Moon,Target of Opportunity (T/O) 10, Various targets. Latitude 18 degrees South,Longitude 163.50 degrees West. Camera Tilt Mode: High Oblique. Direction: South. Sun Angle 12 degrees. Original Film Magazine was labeled E. Camera Data: 70mm Hasselblad; F-Stop: F-5.6; Shutter Speed: 1/250 second. Film Type: Kodak SO-3400 Black and White,ASA 40. Other Photographic Coverage: Lunar Orbiter 1 (LO I) S-3. Flight Date: December 21-27,1968.
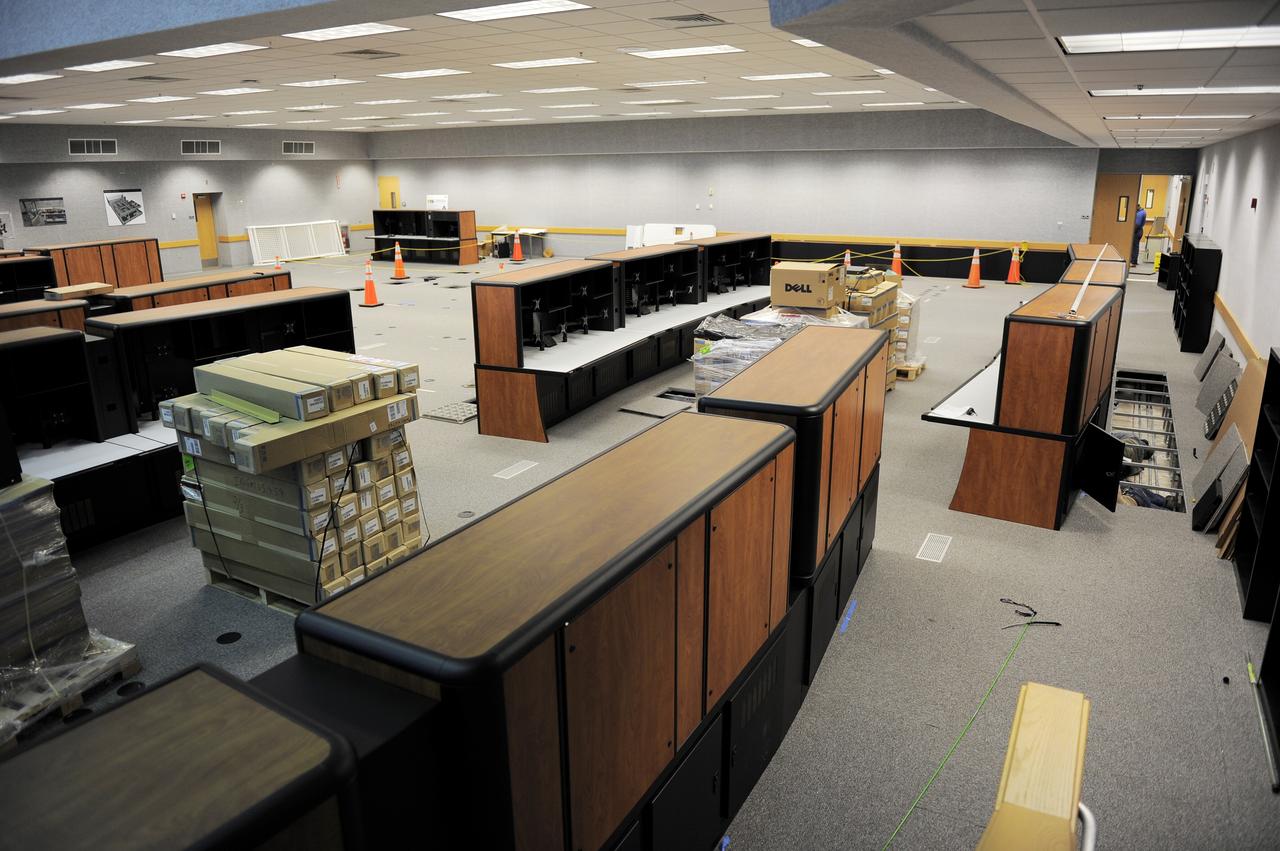

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, remodeling for launches of future human spaceflight vehicles takes place in the Launch Control Center's Young-Crippen Firing Room. Known as Firing Room 1 in the Apollo era, it was re-named as a tribute to the Space Shuttle Program's first crewed mission, STS-1, which was flown by Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen in April 1981. The firing room most recently was set up to support the Ares I-X flight test in Oct. 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
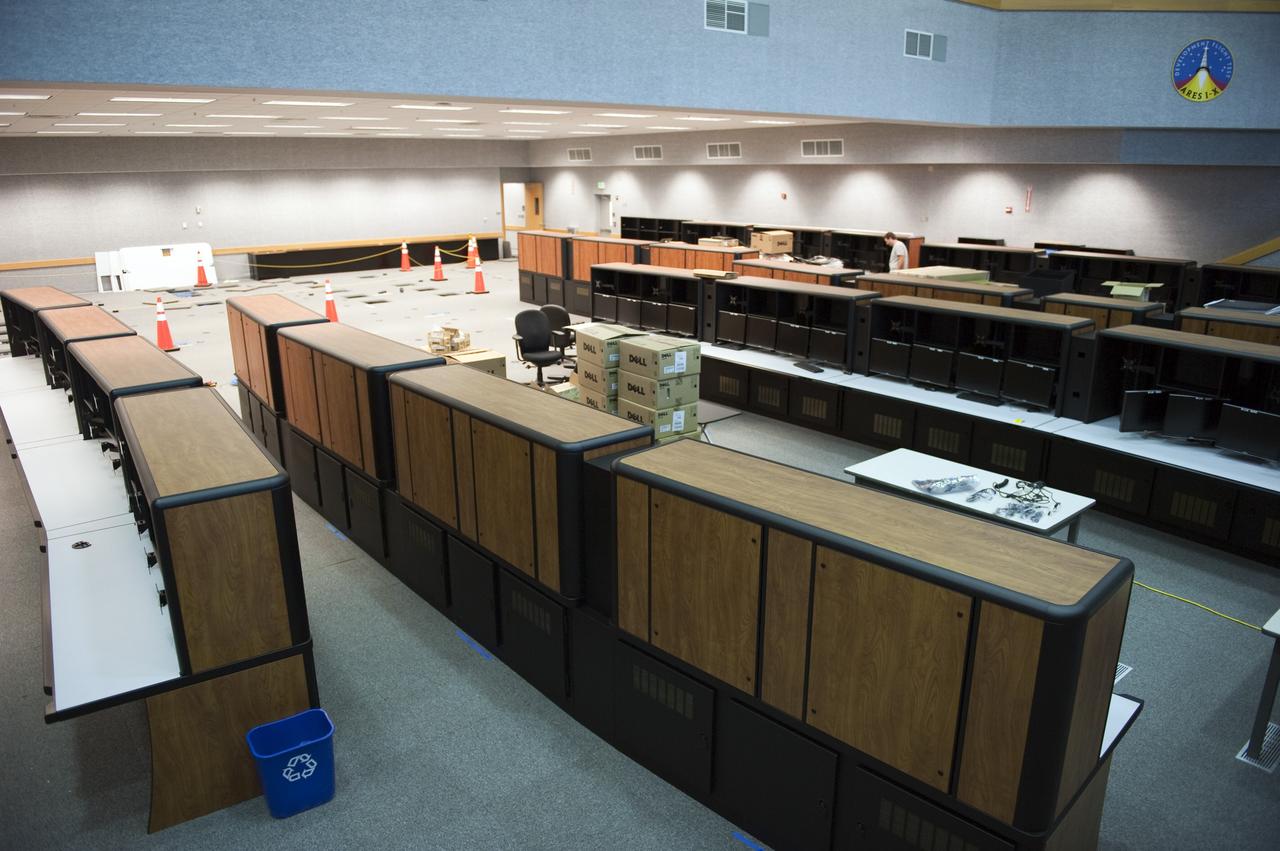

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, remodeling for launches of future human spaceflight vehicles takes place in the Launch Control Center's Young-Crippen Firing Room. Known as Firing Room 1 in the Apollo era, it was re-named as a tribute to the Space Shuttle Program's first crewed mission, STS-1, which was flown by Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen in April 1981. The firing room most recently was set up to support the Ares I-X flight test in Oct. 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, remodeling for launches of future human spaceflight vehicles takes place in the Launch Control Center's Young-Crippen Firing Room. Known as Firing Room 1 in the Apollo era, it was re-named as a tribute to the Space Shuttle Program's first crewed mission, STS-1, which was flown by Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen in April 1981. The firing room most recently was set up to support the Ares I-X flight test in Oct. 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, remodeling for launches of future human spaceflight vehicles takes place in the Launch Control Center's Young-Crippen Firing Room. Known as Firing Room 1 in the Apollo era, it was re-named as a tribute to the Space Shuttle Program's first crewed mission, STS-1, which was flown by Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen in April 1981. The firing room most recently was set up to support the Ares I-X flight test in Oct. 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, remodeling for launches of future human spaceflight vehicles continues in the Launch Control Center's Young-Crippen Firing Room. Consoles already have been rewired for the comprehensive upgrade and are now being outfitted with new computers and monitors. Known as Firing Room 1 in the Apollo era, it was re-named as a tribute to the Space Shuttle Program's first crewed mission, STS-1, which was flown by Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen in April 1981. The firing room most recently was set up to support the Ares I-X flight test in Oct. 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
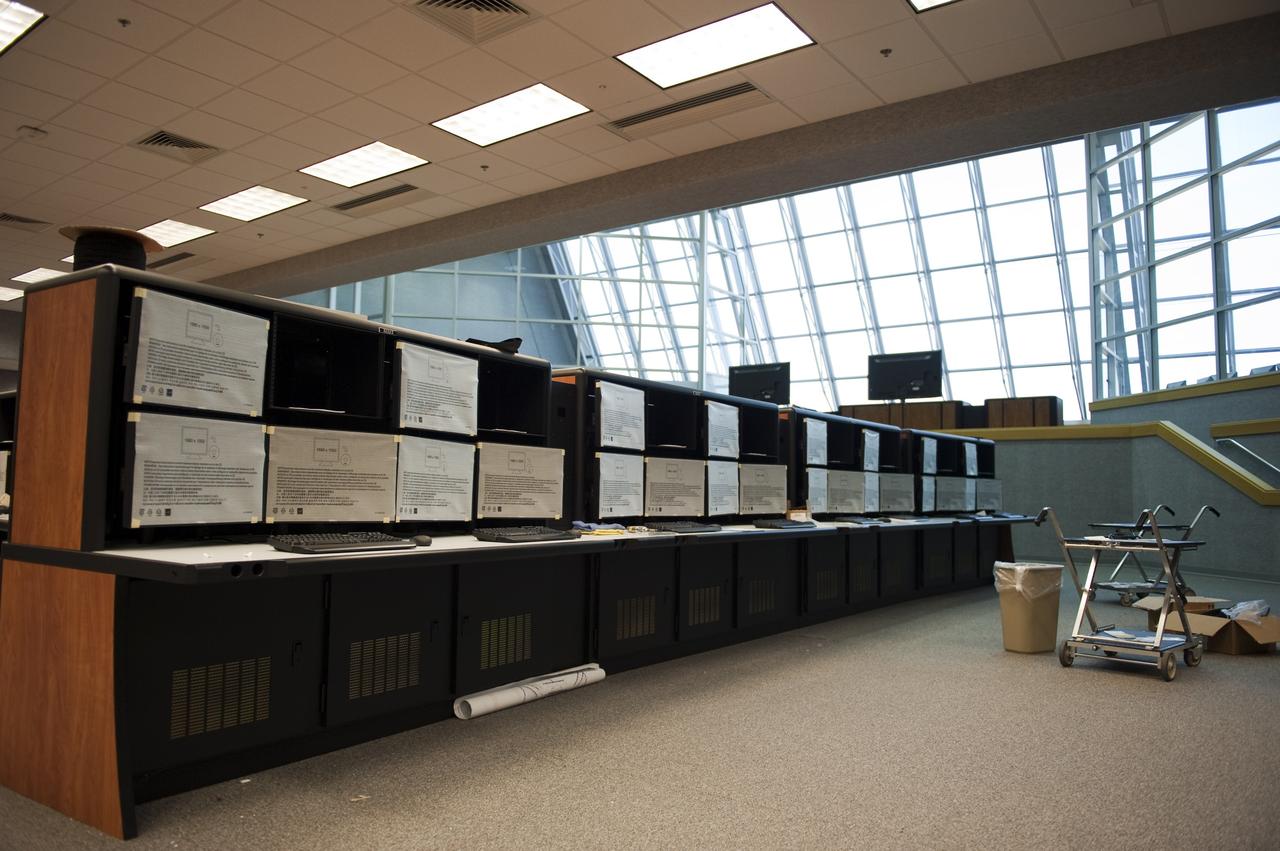

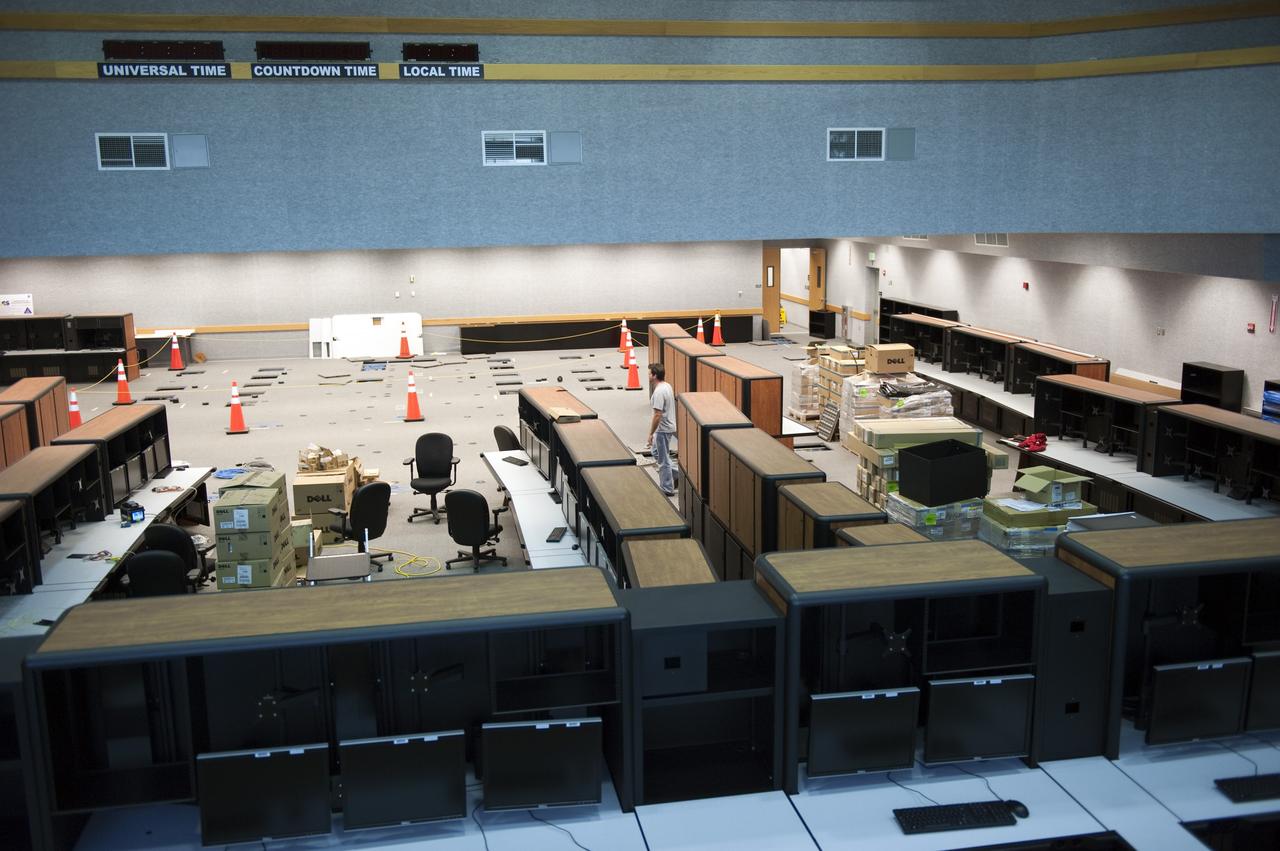
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, remodeling for launches of future human spaceflight vehicles continues in the Launch Control Center's Young-Crippen Firing Room. Consoles already have been rewired for the comprehensive upgrade and are now being outfitted with new computers and monitors. Known as Firing Room 1 in the Apollo era, it was re-named as a tribute to the Space Shuttle Program's first crewed mission, STS-1, which was flown by Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen in April 1981. The firing room most recently was set up to support the Ares I-X flight test in Oct. 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
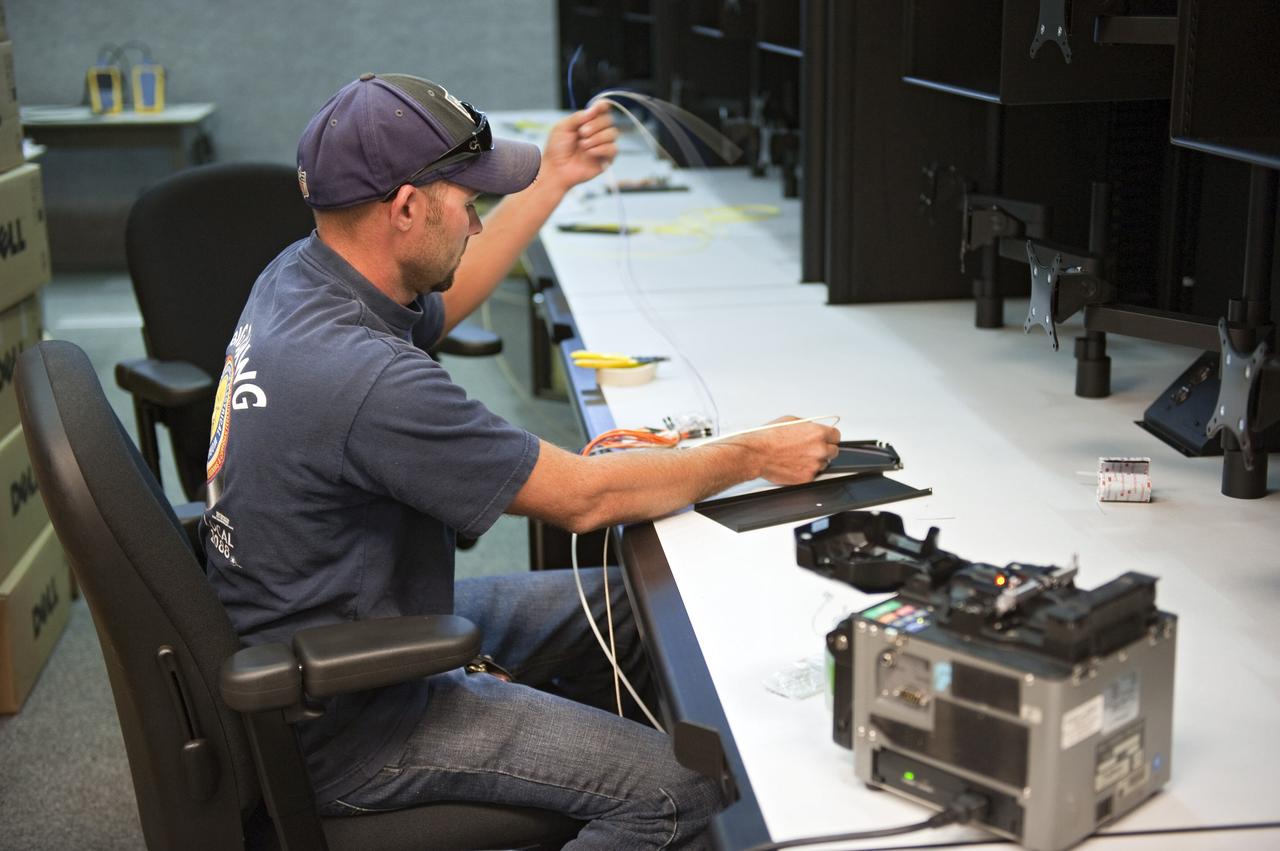

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, rewiring of consoles and remodeling for launches of future human spaceflight vehicles take place in the Launch Control Center's Young-Crippen Firing Room. Known as Firing Room 1 in the Apollo era, it was re-named as a tribute to the Space Shuttle Program's first crewed mission, STS-1, which was flown by Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen in April 1981. The firing room most recently was set up to support the Ares I-X flight test in Oct. 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
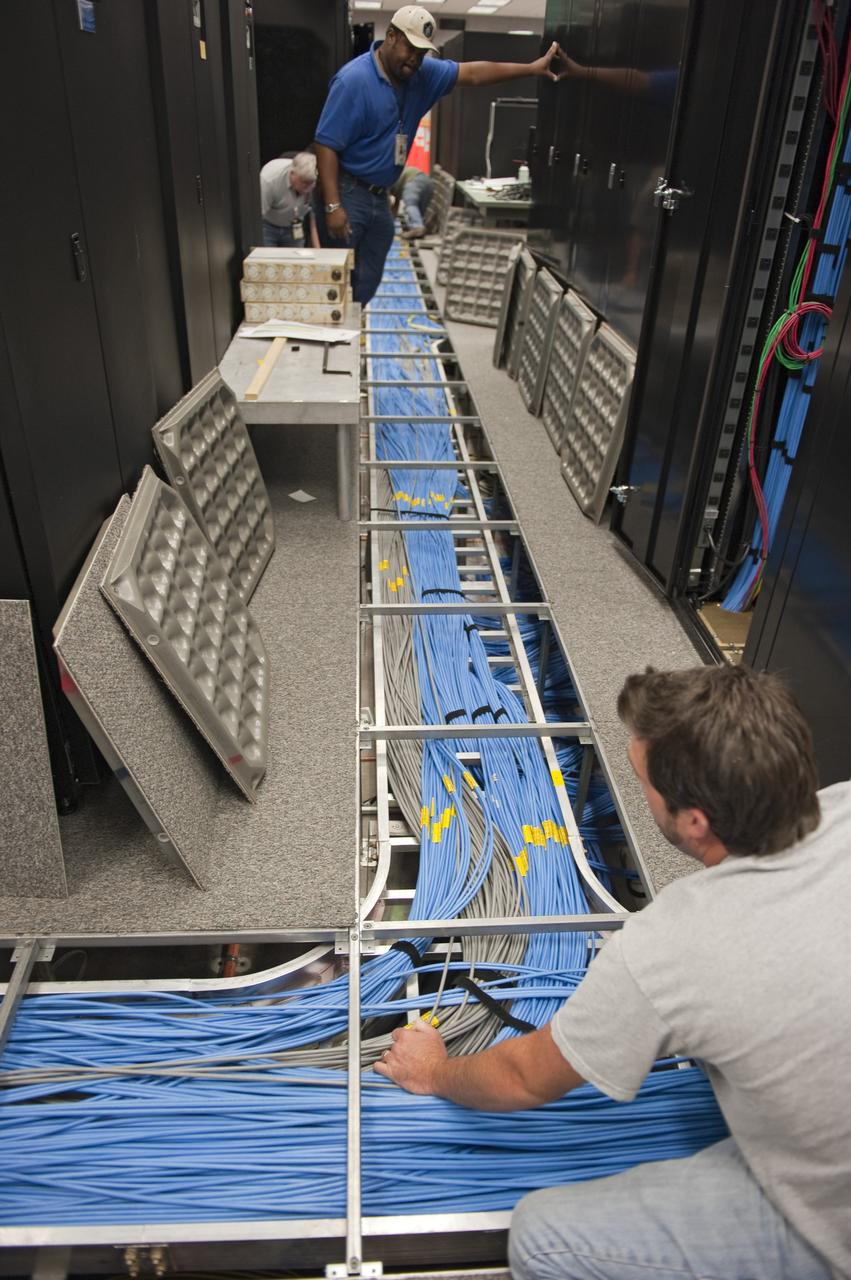

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, rewiring and remodeling for launches of future human spaceflight vehicles take place in the Launch Control Center's Young-Crippen Firing Room. Known as Firing Room 1 in the Apollo era, it was re-named as a tribute to the Space Shuttle Program's first crewed mission, STS-1, which was flown by Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen in April 1981. The firing room most recently was set up to support the Ares I-X flight test in Oct. 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
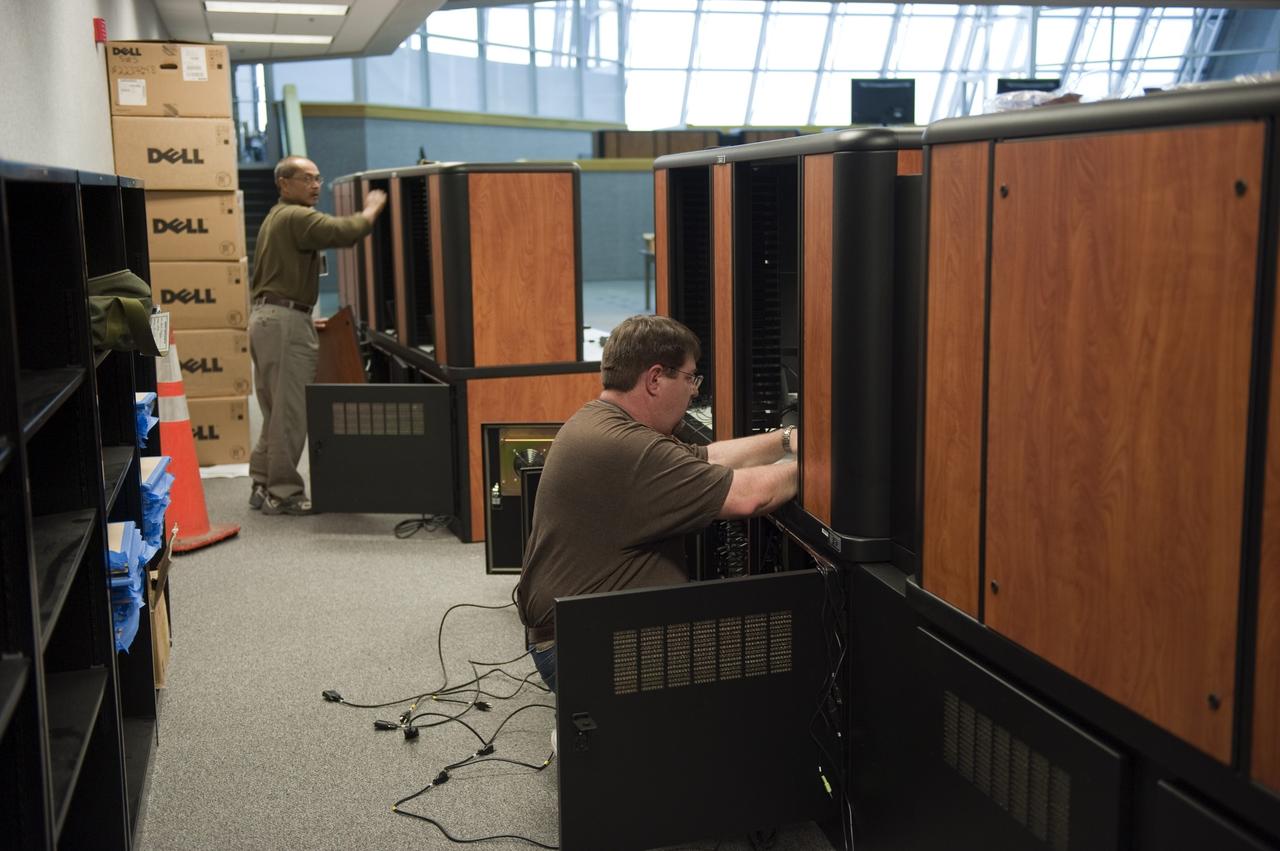

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, remodeling for launches of future human spaceflight vehicles continues in the Launch Control Center's Young-Crippen Firing Room. Consoles already have been rewired for the comprehensive upgrade and are now being outfitted with new computers and monitors. Known as Firing Room 1 in the Apollo era, it was re-named as a tribute to the Space Shuttle Program's first crewed mission, STS-1, which was flown by Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen in April 1981. The firing room most recently was set up to support the Ares I-X flight test in Oct. 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
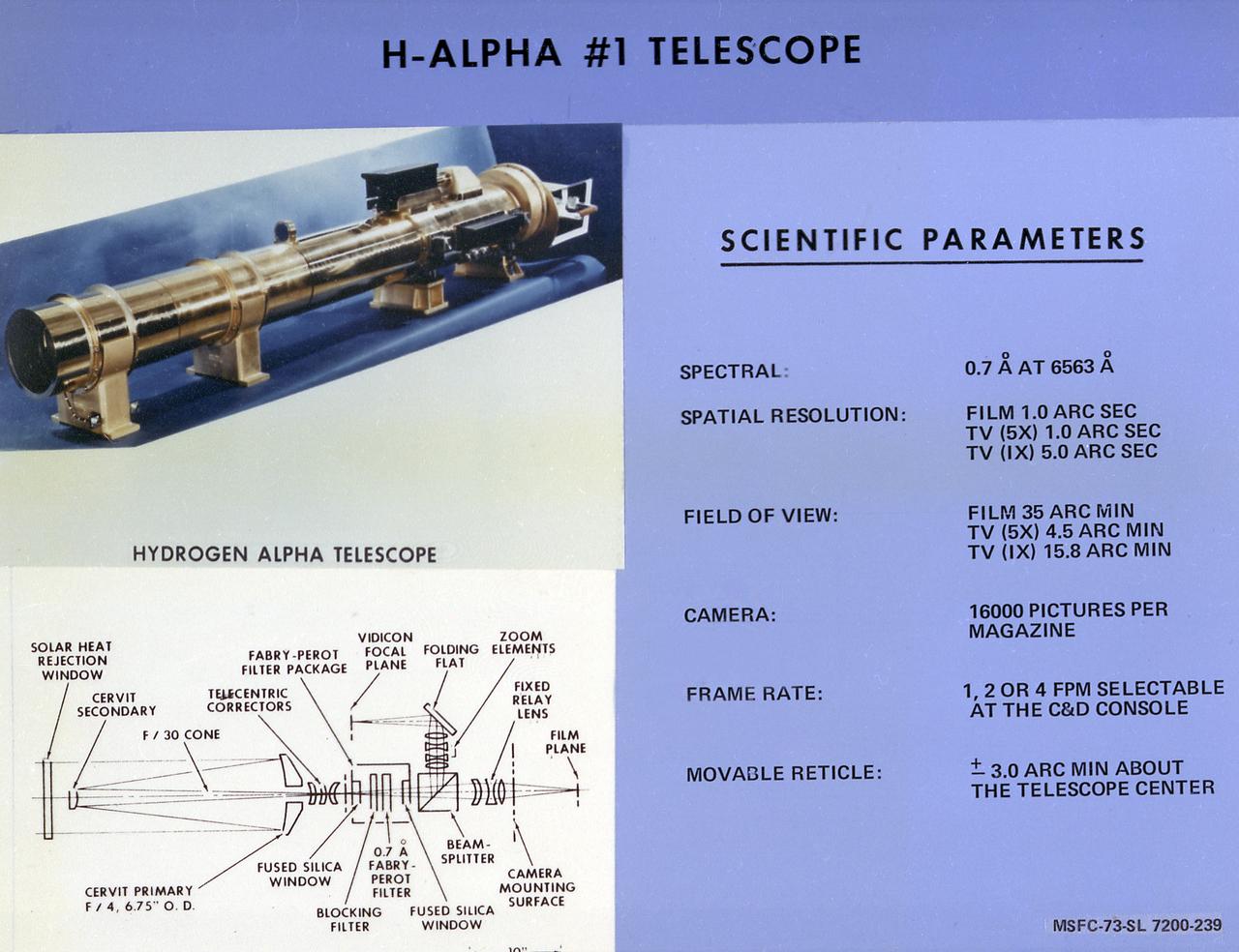
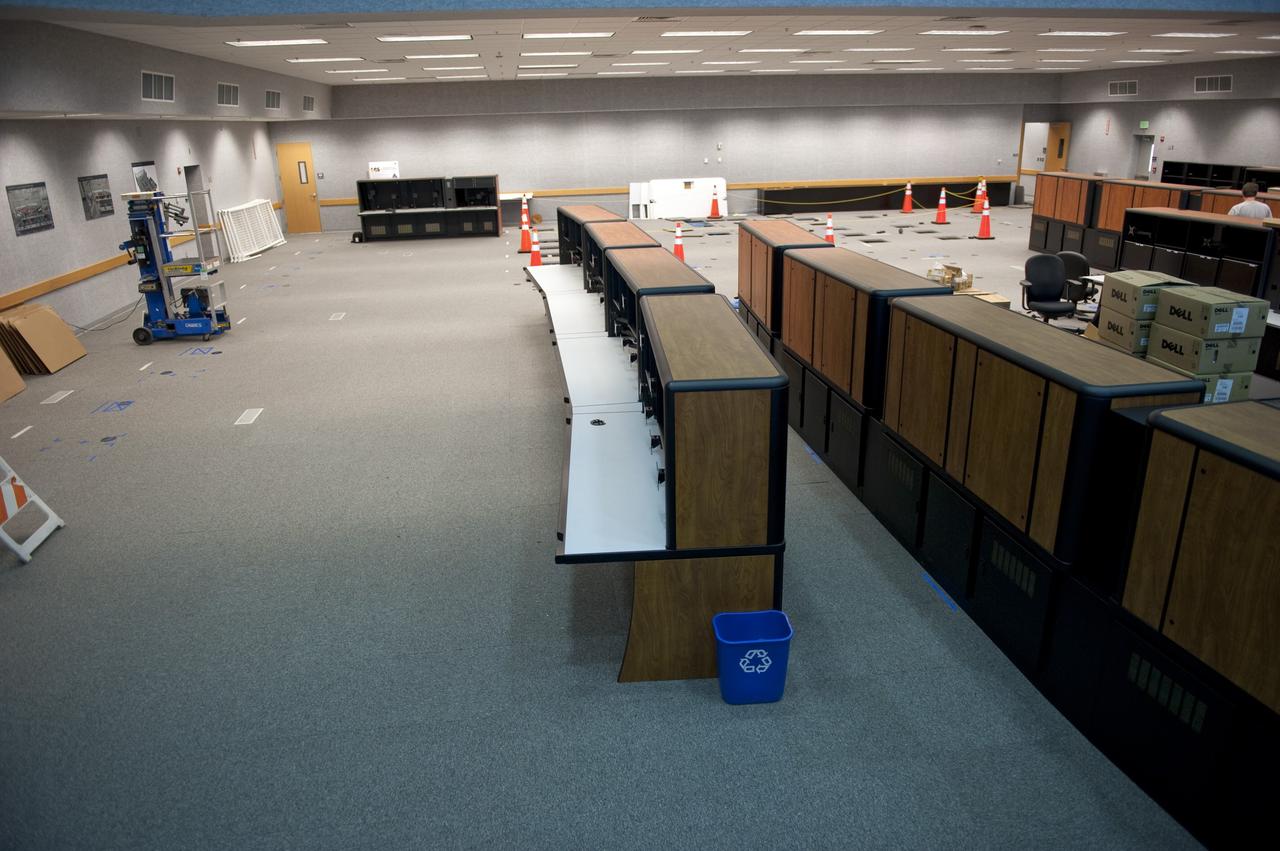
This chart describes the Hydrogen-Alpha (H-Alpha) #1 Telescope, one of eight major solar study facilities on the Skylab Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM). There were two H-Alpha telescopes on the ATM that were used primarily to point the ATM and keep a continuous photographic record during the solar observation periods. Both telescopes gave the Skylab astronauts a real-time picture of the Sun in the red light of the H-Alpha spectrum through a closed-circuit television. The H-Alpha #1 Telescope provided simultaneous photographic and ultraviolet (UV) pictures, while the #2 Telescope operated only in the TV mode. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development of the H-Alpha Telescopes.
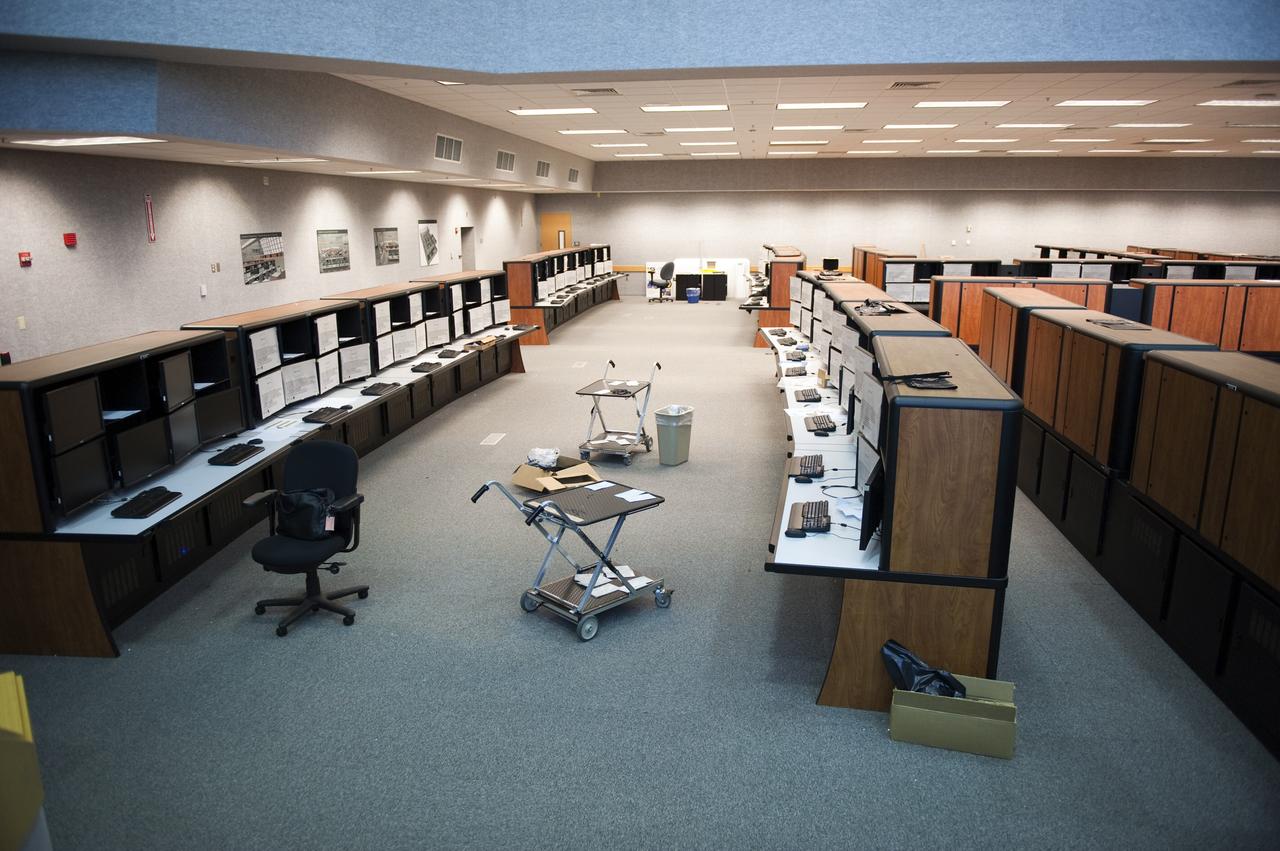

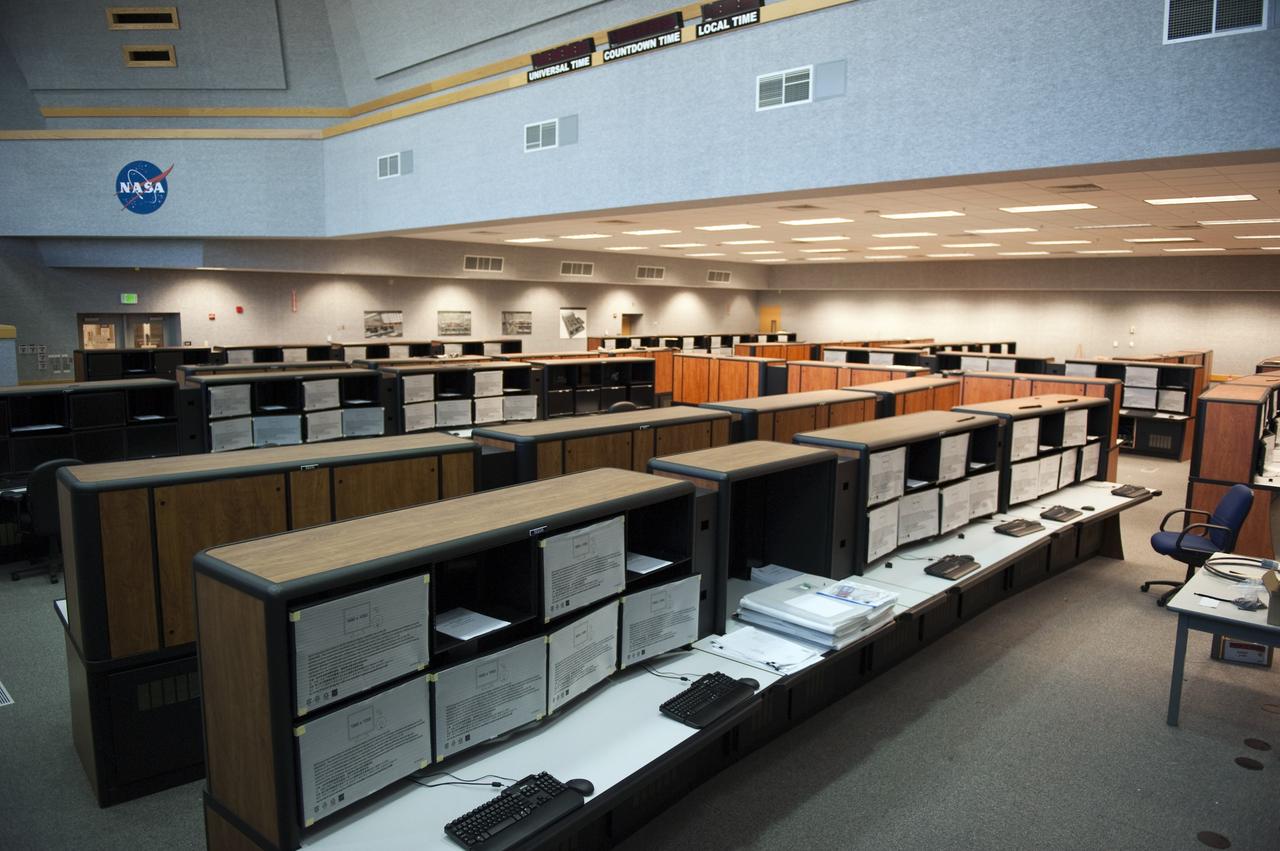
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, remodeling for launches of future human spaceflight vehicles continues in the Launch Control Center's Young-Crippen Firing Room. Consoles already have been rewired for the comprehensive upgrade and are now being outfitted with new computers and monitors. Known as Firing Room 1 in the Apollo era, it was re-named as a tribute to the Space Shuttle Program's first crewed mission, STS-1, which was flown by Commander John Young and Pilot Robert Crippen in April 1981. The firing room most recently was set up to support the Ares I-X flight test in Oct. 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
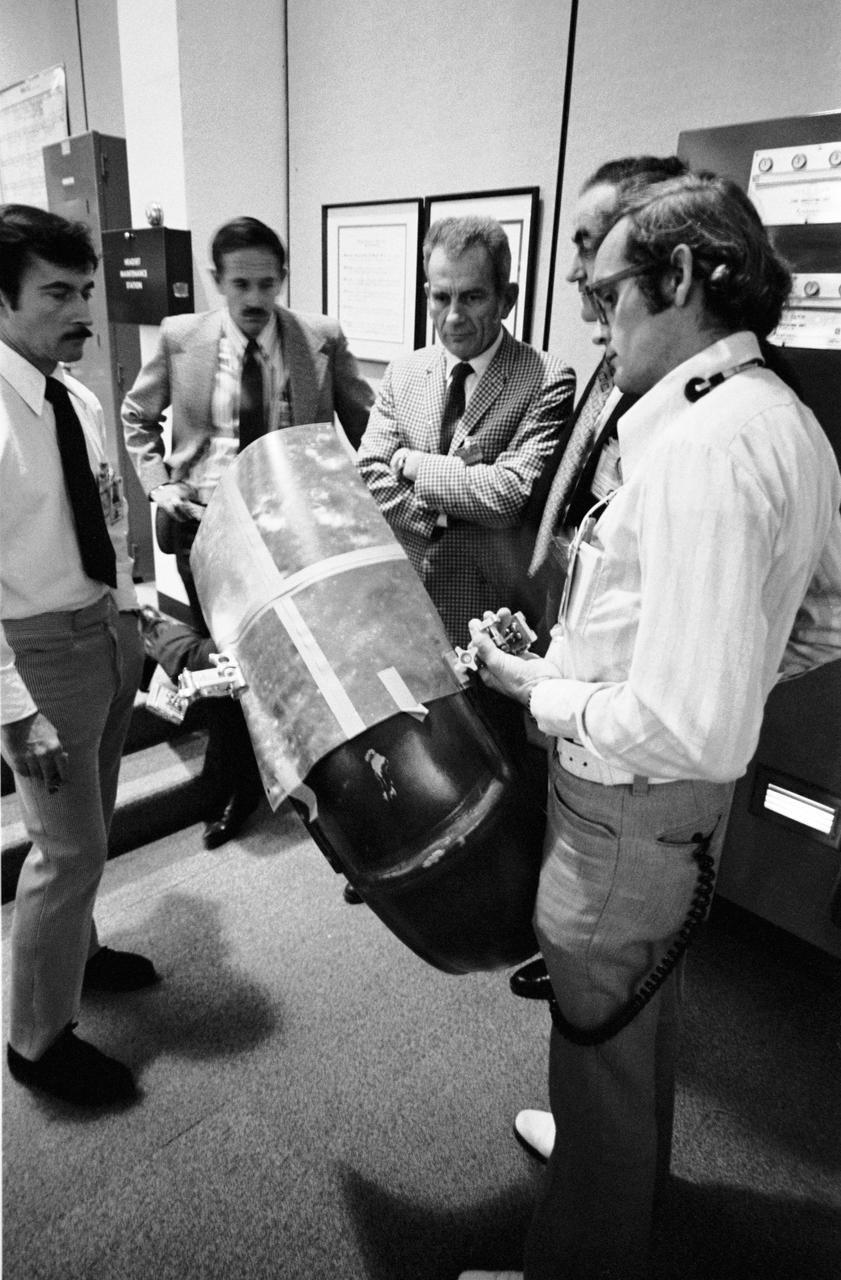

S72-55170 (11 Dec. 1972) --- These five men in the Mission Control Center ponder the solution to the problem of the damage to the right rear fender of the Apollo 17 Lunar Roving Vehicle at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. During the first lunar surface extravehicular activity a hammer got underneath the fender and a part of it was knocked off. Astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt were reporting a problem with lunar dust because of the damaged fender. They sought some way to repair the broken fender. Clockwise are astronauts John W. Young and Charles M. Duke Jr., two Apollo 17 CAPCOM; Donald K. Slayton, director of flight crew operations at MSC; Dr. Roco A. Petrone, Apollo program director, Office of Manned Space Flight, NASA HQ; and Ronald V. Blevins, an EVA-1 flight controller with General Electric. They are looking over a makeshift repair arrangement which uses lunar maps and clamps from the optical alignment telescope lamp, a repair suggestion made by astronaut Young. The suggestion was relayed to Cernan and Schmitt and the repair made at the beginning of EVA-2. The problem was solved satisfactorily.
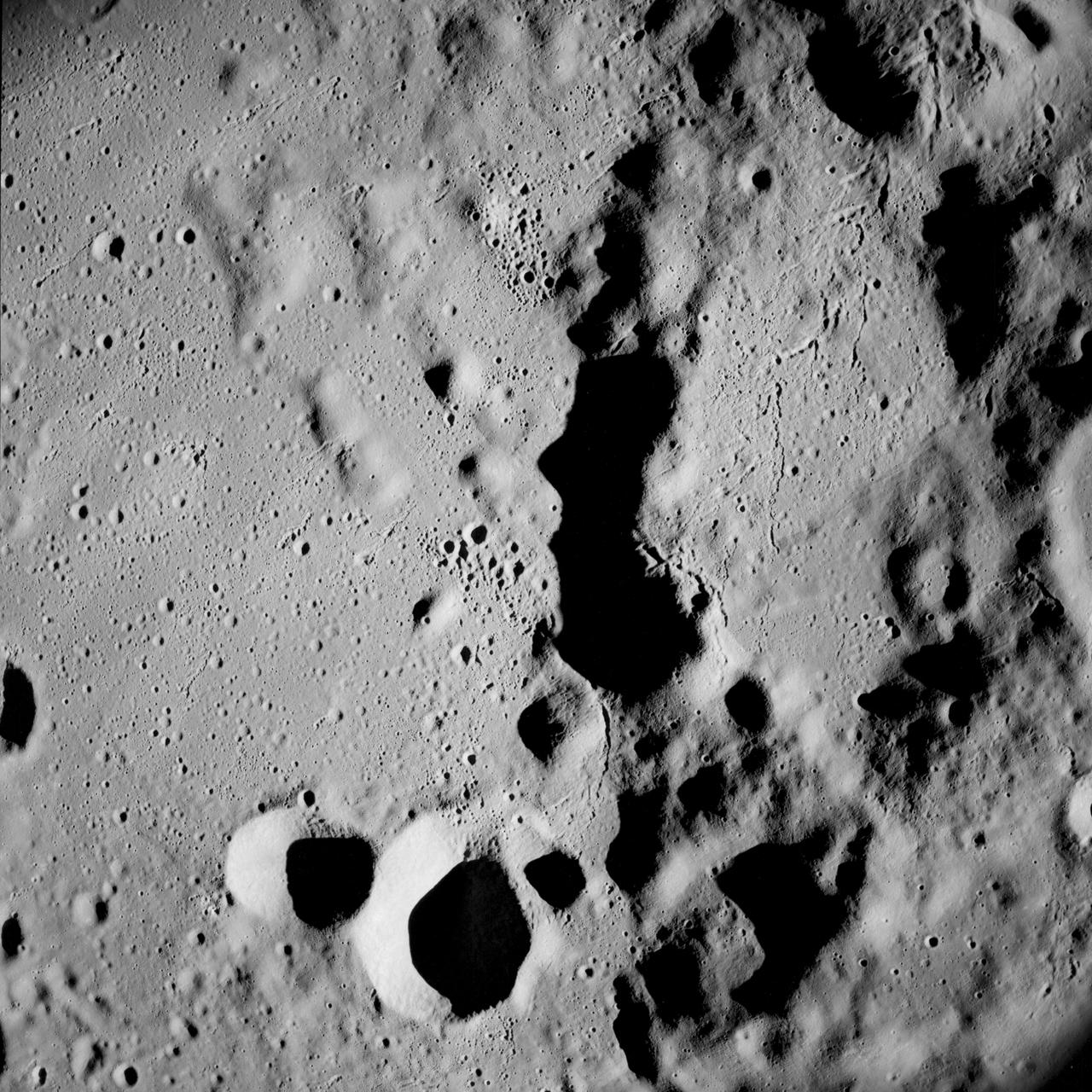

Apollo 8,Farside of Moon. Image taken on Revolution 4. Camera Tilt Mode: Vertical Stereo. Sun Angle: 13. Original Film Magazine was labeled D. Camera Data: 70mm Hasselblad. Lens: 80mm; F-Stop: F/2.8; Shutter Speed: 1/250 second. Film Type: Kodak SO-3400 Black and White,ASA 40. Flight Date: December 21-27,1968.
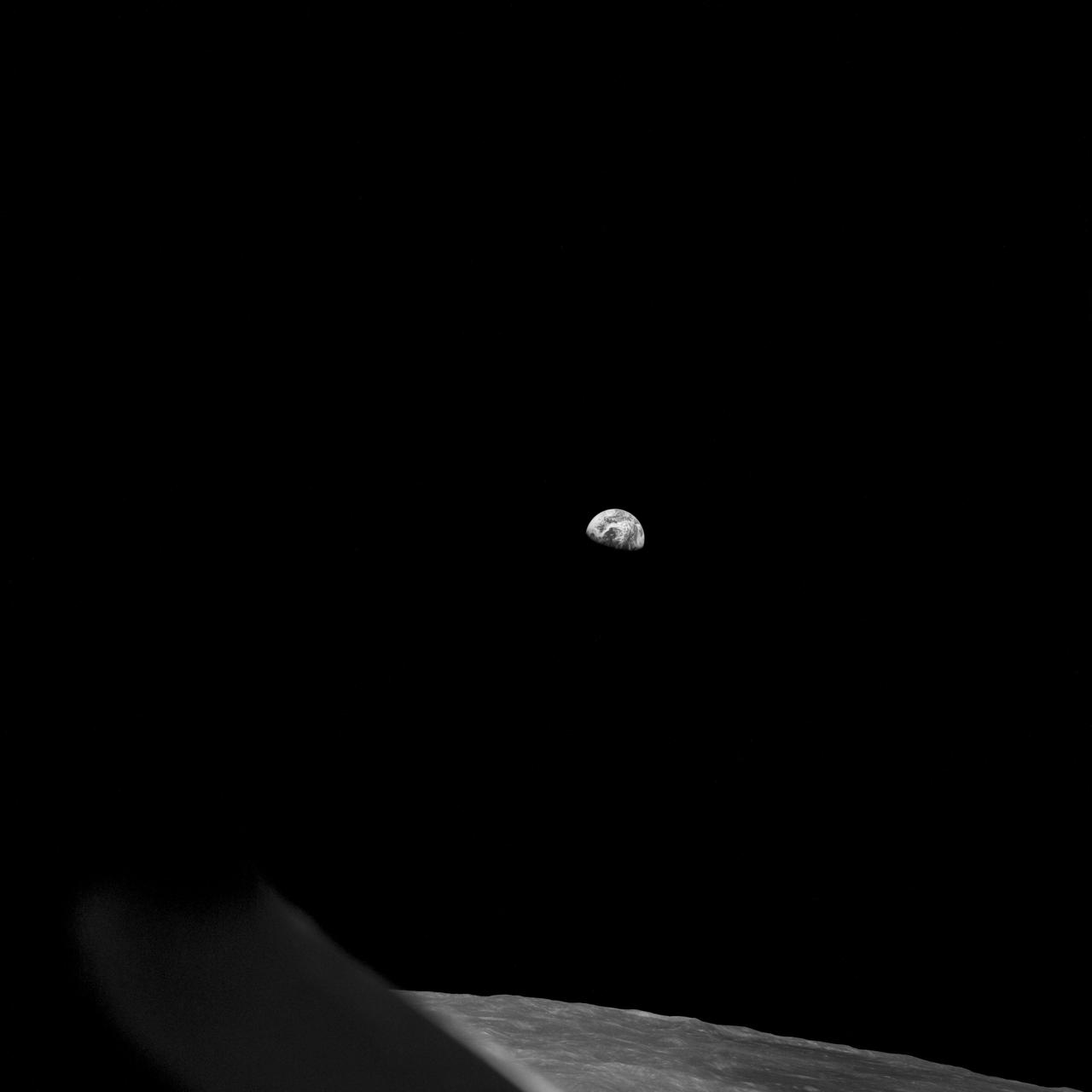

Apollo 8,Earth and Lunar Horizon. Image taken on Revolution 10 during Transearth Injection (TEI). Original Film Magazine was labeled D. Camera Data: 70mm Hasselblad. Lens: 80mm; F-Stop: F/11; Shutter Speed: 1/250 second. Film Type: Kodak SO-3400 Black and White,ASA 40. Flight Date: December 21-27,1968.

The fuel tank assembly of the Saturn V S-IC (first) stage is readied to be mated to the liquid oxygen tank at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The fuel tank carried kerosene as its fuel. The S-IC stage utilized five F-1 engines that used kerosene and liquid oxygen as propellant. Each engine provided 1,500,000 pounds of thrust. This stage lifted the entire vehicle and Apollo spacecraft from the launch pad.

Engineers and technicians at the Marshall Space Flight Center were installing an F-I engine on the Saturn V S-IC (first) stage thrust structure in building 4705. The S-IC (first) stage used five F-1 engines that produced a total thrust of 7,500,000 pounds as each engine produced 1,500,000 pounds of thrust. The S-IC stage lifted the Saturn V vehicle and Apollo spacecraft from the launch pad.
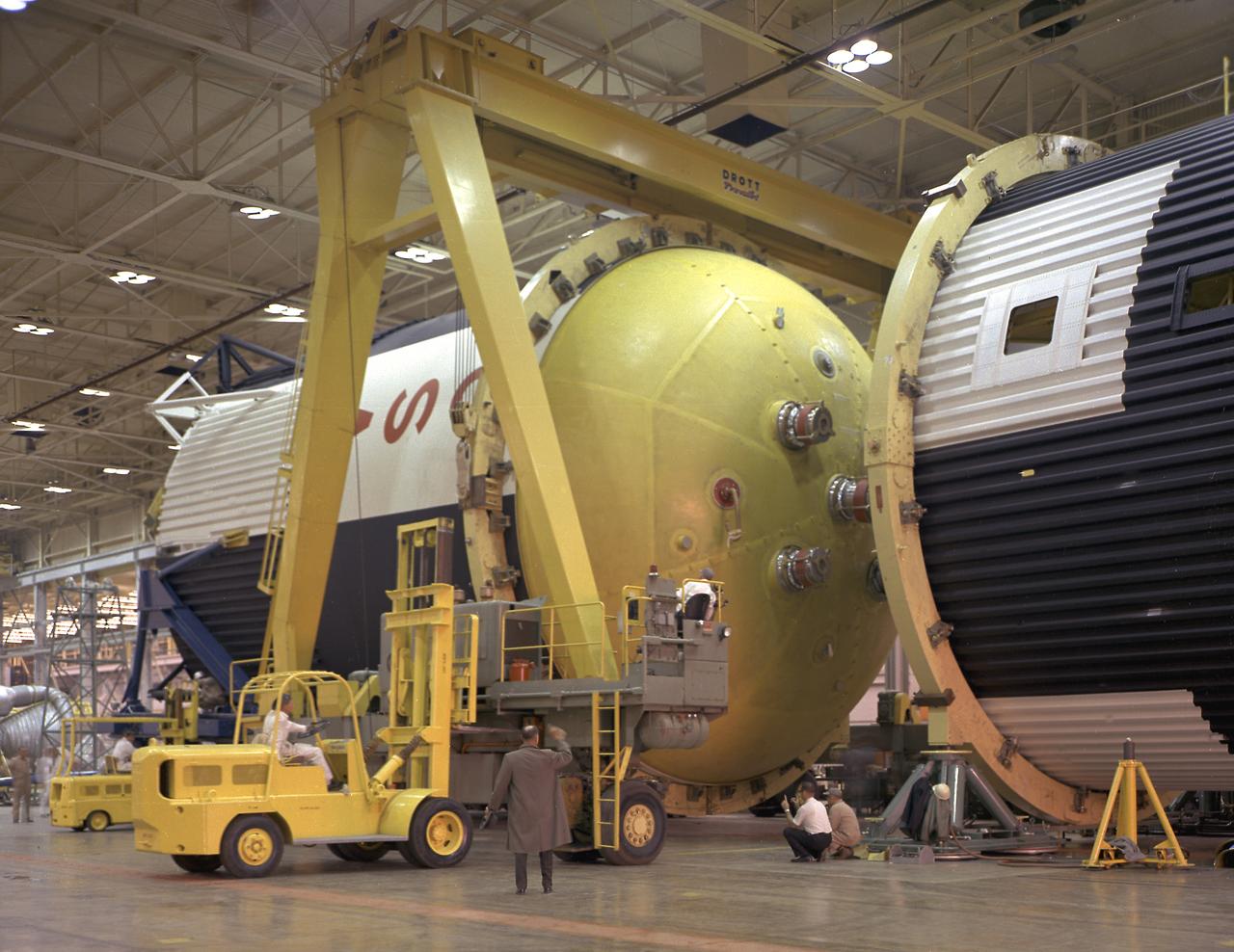

This photograph shows how the fuel tank assembly and the liquid oxygen tank for the Saturn V S-IC (first) stage are placed side by side prior to commencement of the mating of the two stages in the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705. The fuel tank carried kerosene as its fuel. The S-IC stage used five F-1 engines, that used kerosene and liquid oxygen as propellant and each engine provided 1,500,000 pounds of thrust. This stage lifted the entire vehicle and Apollo spacecraft from the launch pad.
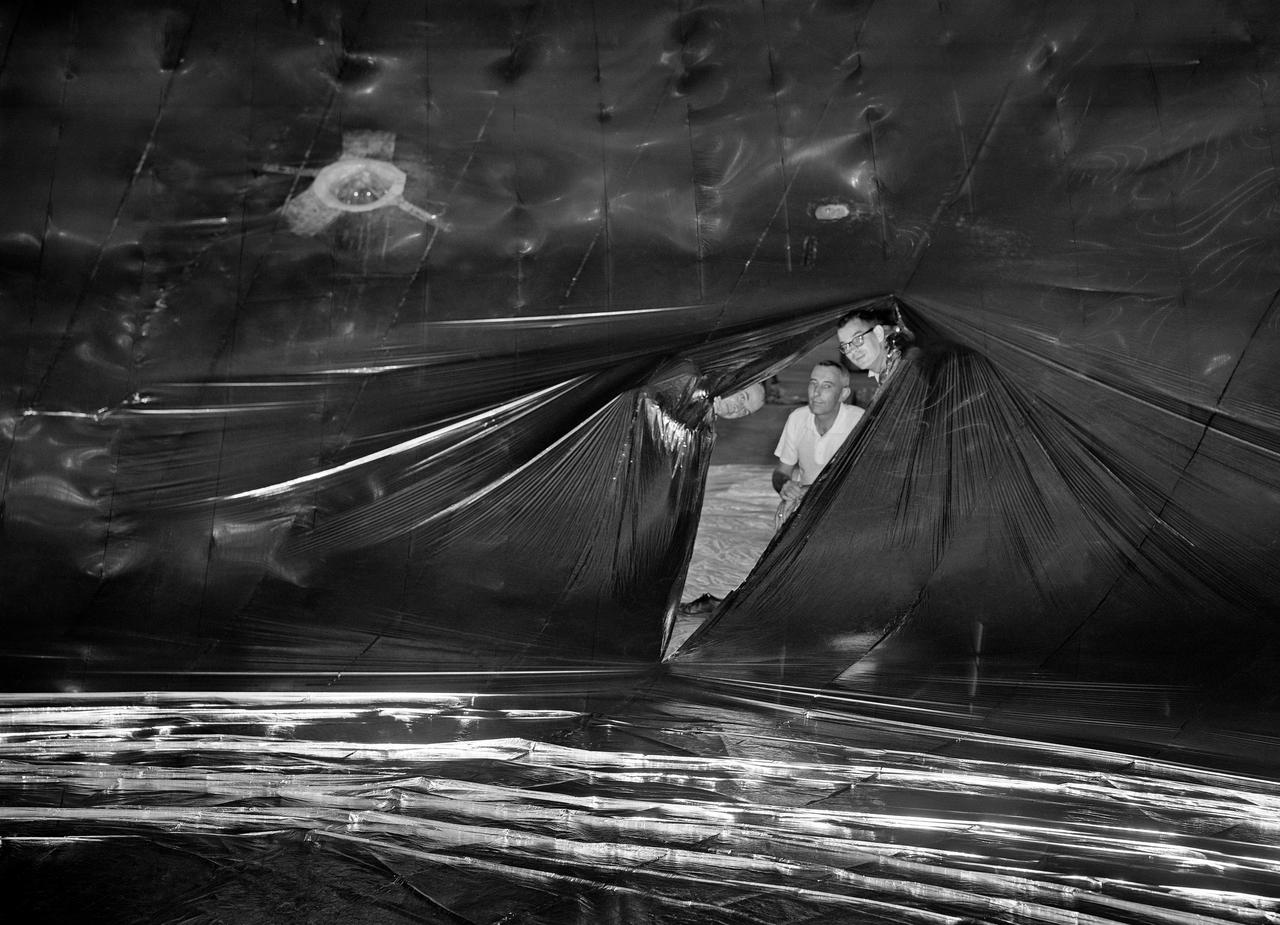

Inflation Tests of the Echo 1 Satellite in Weeksville, N.C. 1958-L-03603 Image Langley engineers Edwin Kilgore (center), Norman Crabill (right) and an unidentified man take a peek inside the vast balloon during inflation tests. Page. 183 Space Flight Revolution NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo. NASA SP-4308.
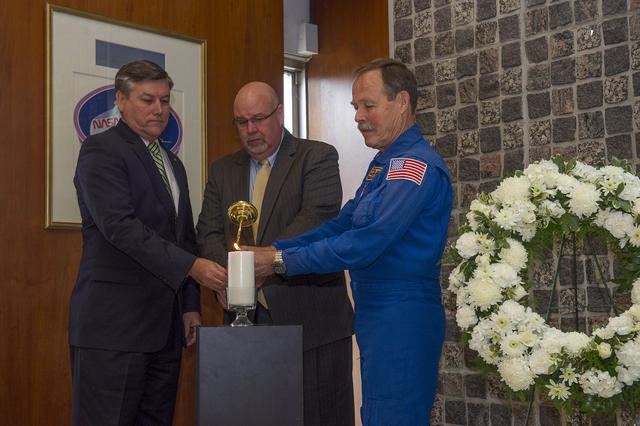

LIGHTING A MEMORIAL CANDLE DURING THE JAN. 29 DAY OF REMEMBRANCE OBSERVANCE AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER ARE, FROM LEFT, PATRICK SCHEUERMANN, MARSHALL DIRECTOR; JOHN HONEYCUTT, DEPUTY MANAGER OF THE SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM; AND RETIRED ASTRONAUT ROBERT “HOOT” GIBSON. THE CEREMONY IN BUILDING 4200 PAID TRIBUTE TO THE CREWS OF APOLLO 1 AND SPACE SHUTTLES CHALLENGER AND COLUMBIA, AS WELL AS OTHER NASA COLLEAGUES.
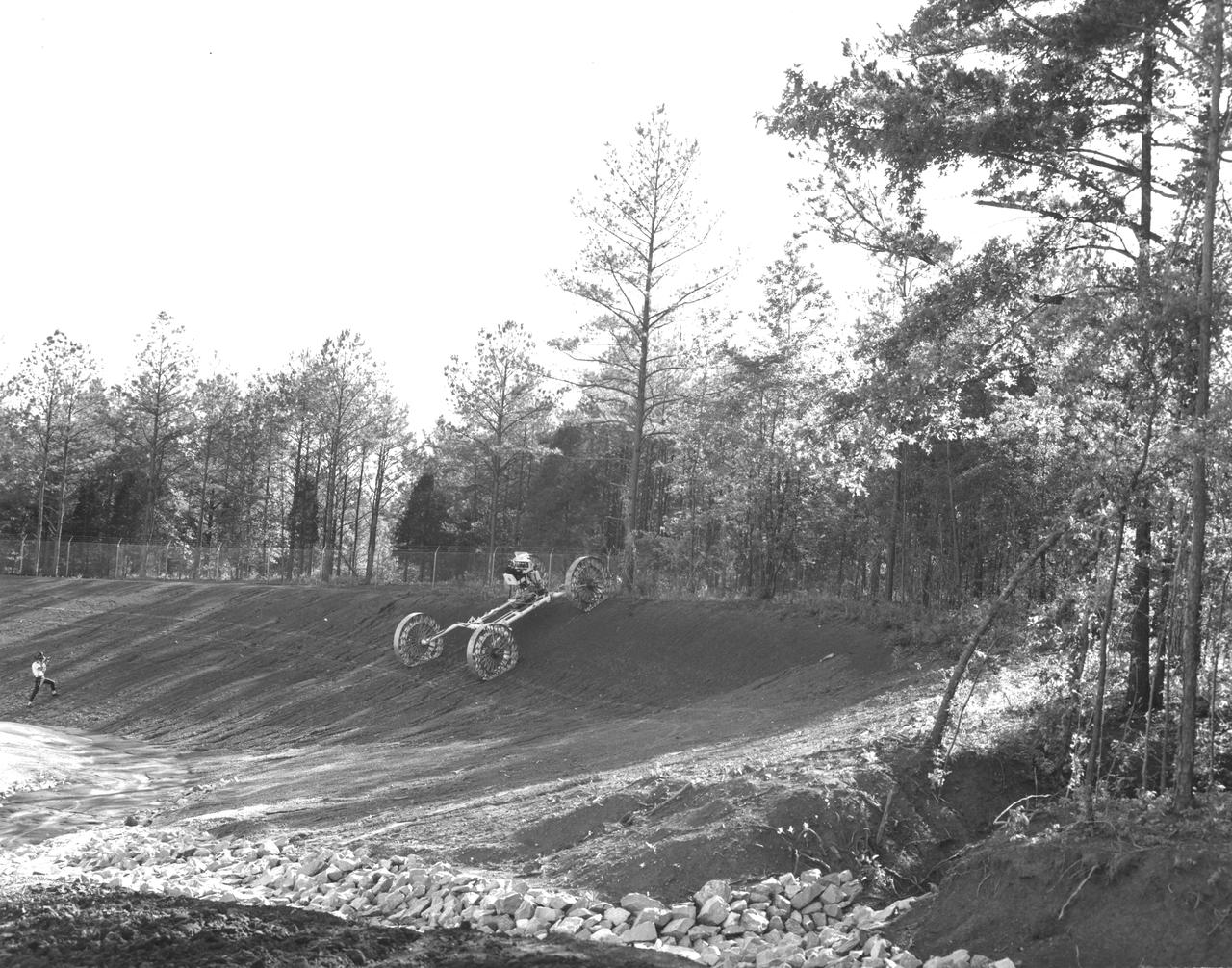

An engineer demonstrates a Mobility Test Article (MTA) at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This unit, weighing 1/6th as much as an actual vehicle, was built by the Bendix Corporation and was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
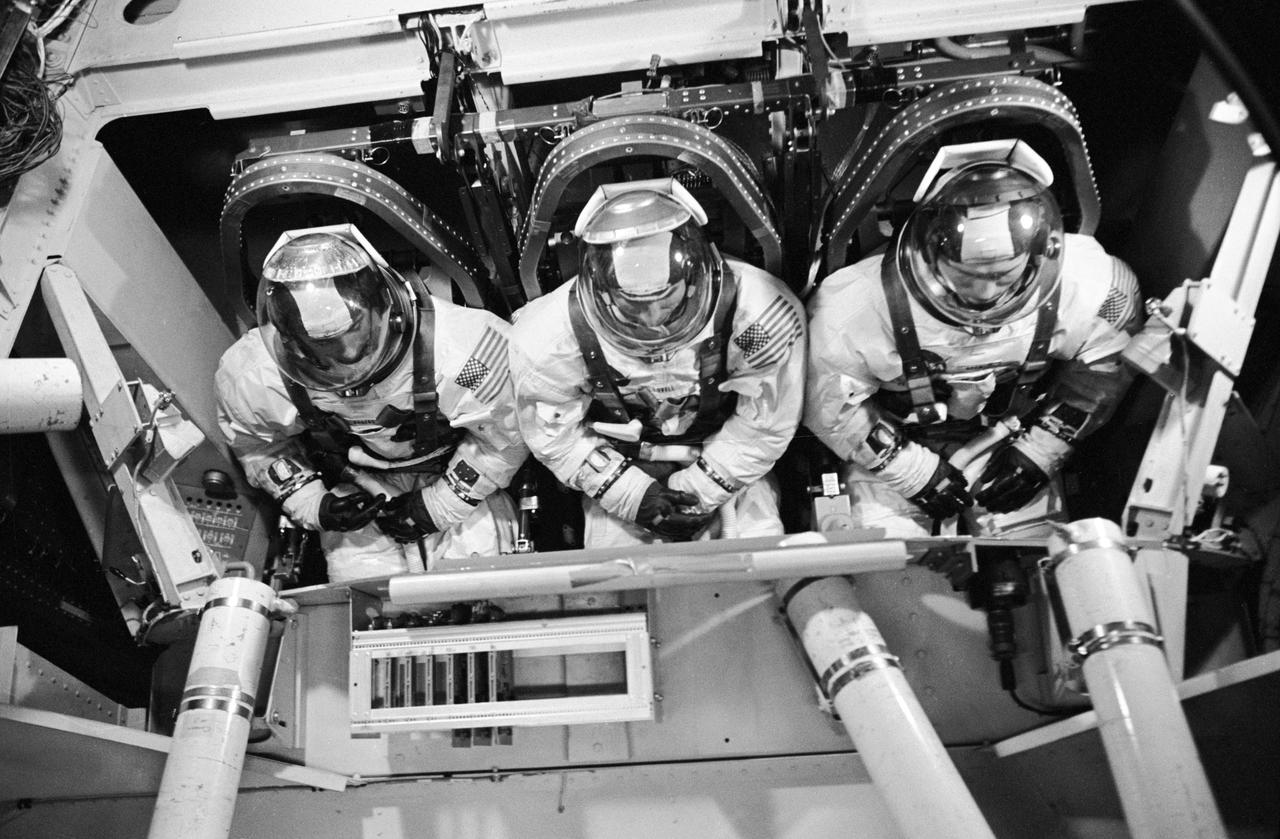

S68-53283 (1 Nov. 1968) --- The Apollo 8 prime crew is seen inside the gondola during centrifuge training in MSC's Flight Acceleration Facility, Building 29. Left to right, are astronauts William A. Anders, lunar module pilot, James A. Lovell Jr., command module pilot; and Frank Borman, commander. Photo credit: NASA
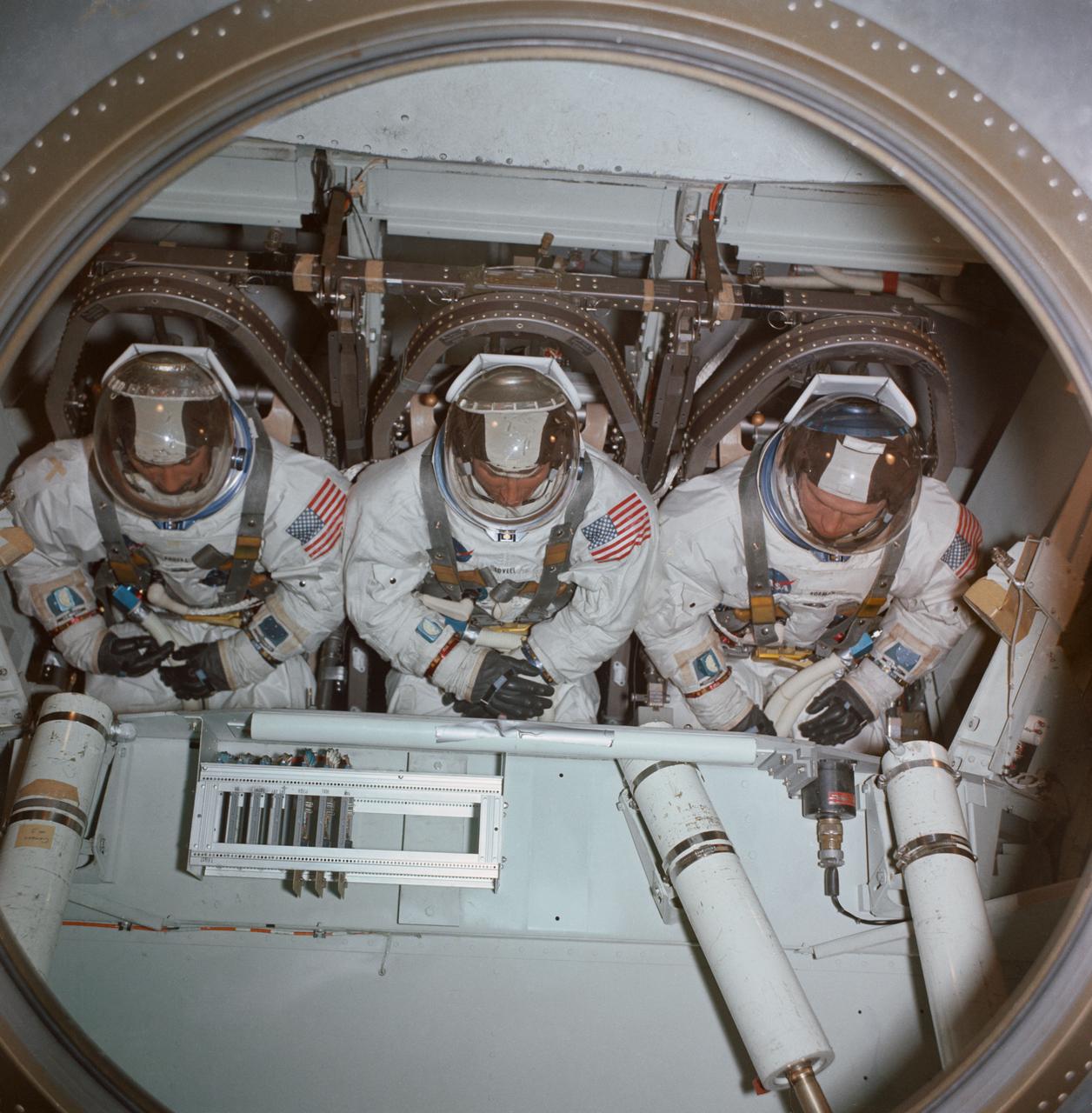

S68-53194 (1 Nov. 1968) --- The Apollo 8 prime crew inside the centrifuge gondola in Building 29 during centrifuge training in MSC's Flight Acceleration Facility. (View with crew lying on back) Left to right are astronauts William A. Anders, lunar module pilot; James A. Lovell Jr., command module pilot; and Frank Borman, commander. Photo credit: NASA
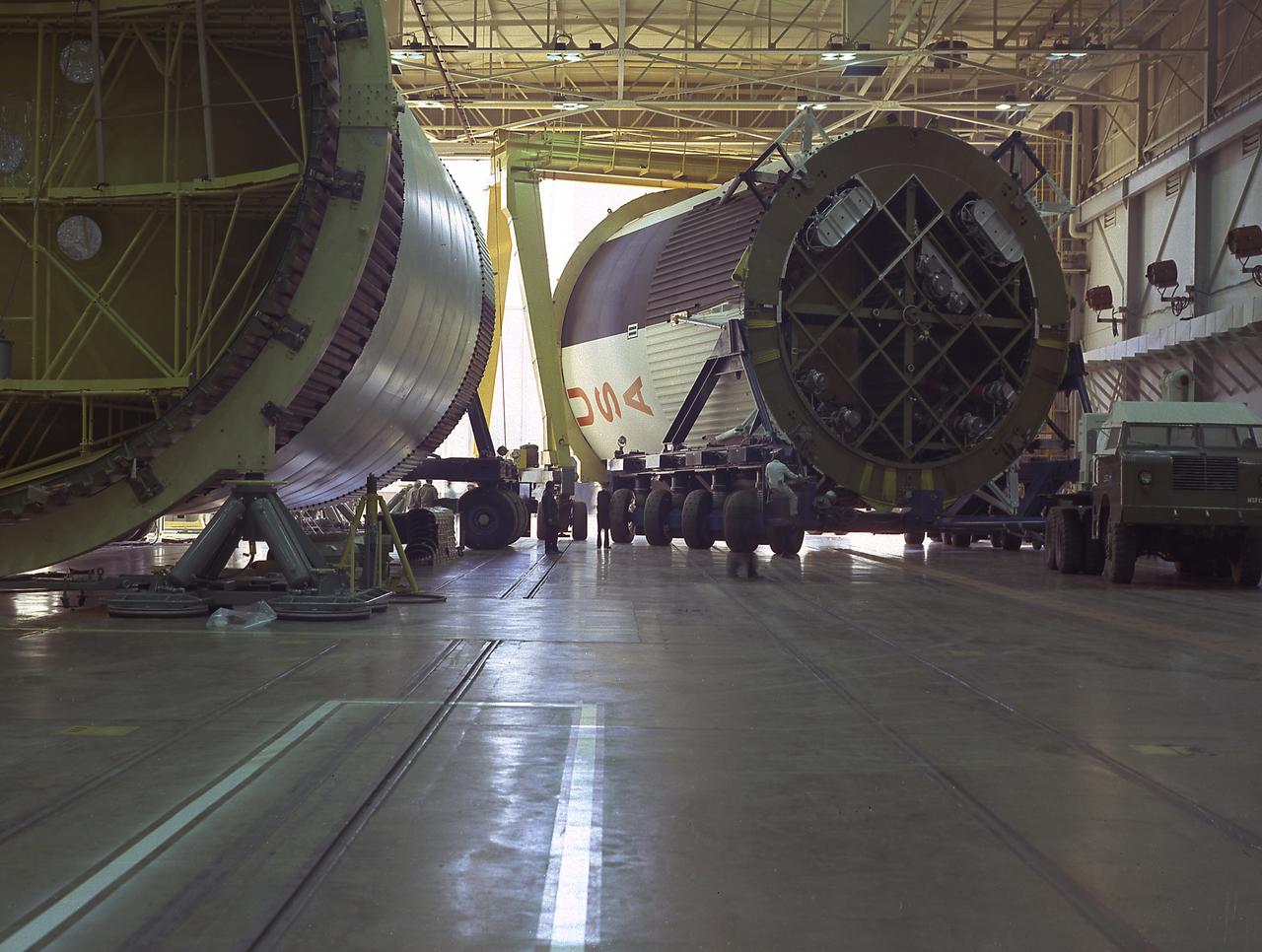

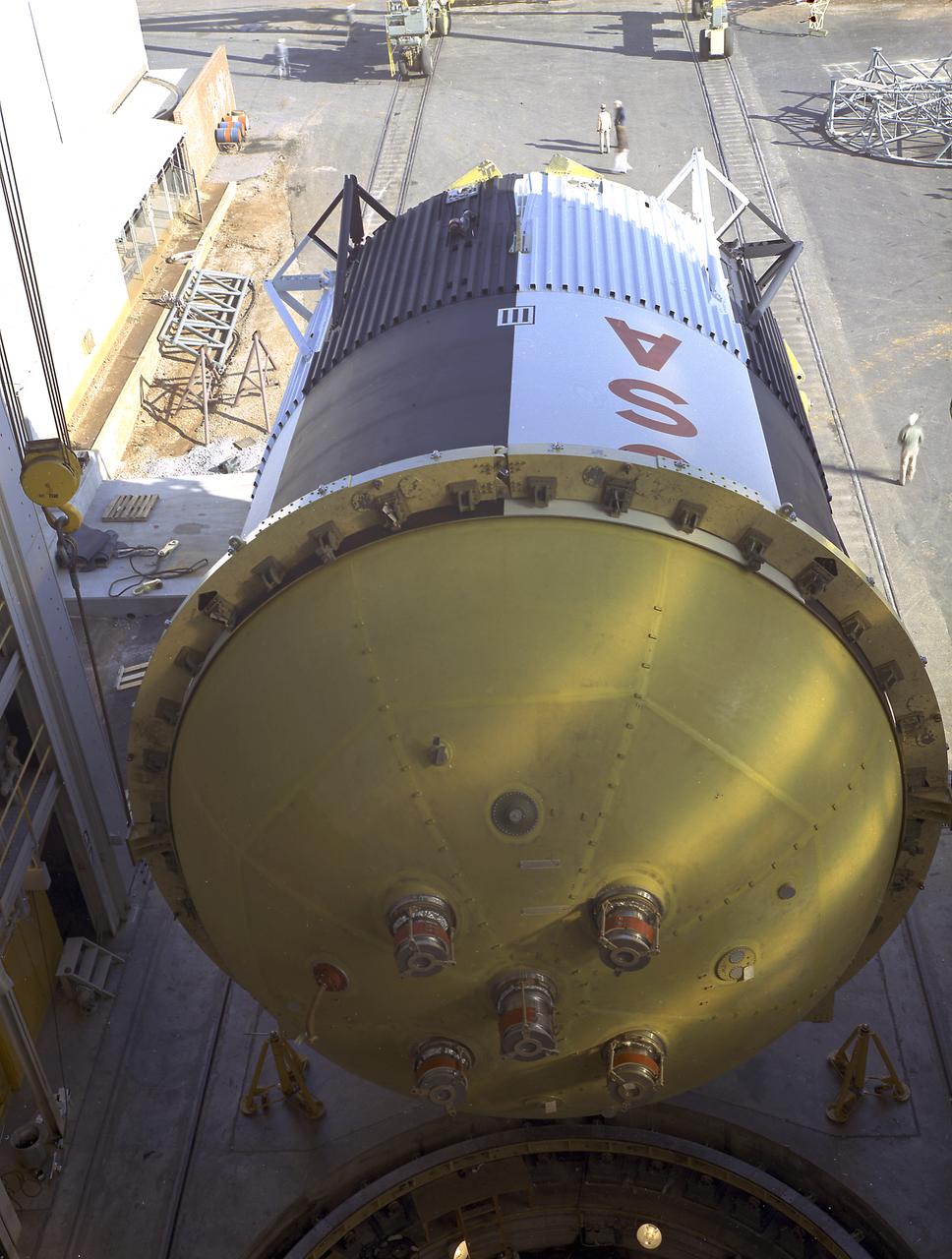
The fuel tank assembly for the Saturn V S-IC (first) stage arrived at the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4707, for mating to the liquid oxygen tank. The fuel tank carried kerosene as its fuel. The S-IC stage used five F-1 engines, that used kerosene and liquid oxygen as propellant and each engine provided 1,500,000 pounds of thrust. This stage lifted the entire vehicle and Apollo spacecraft from the launch pad.
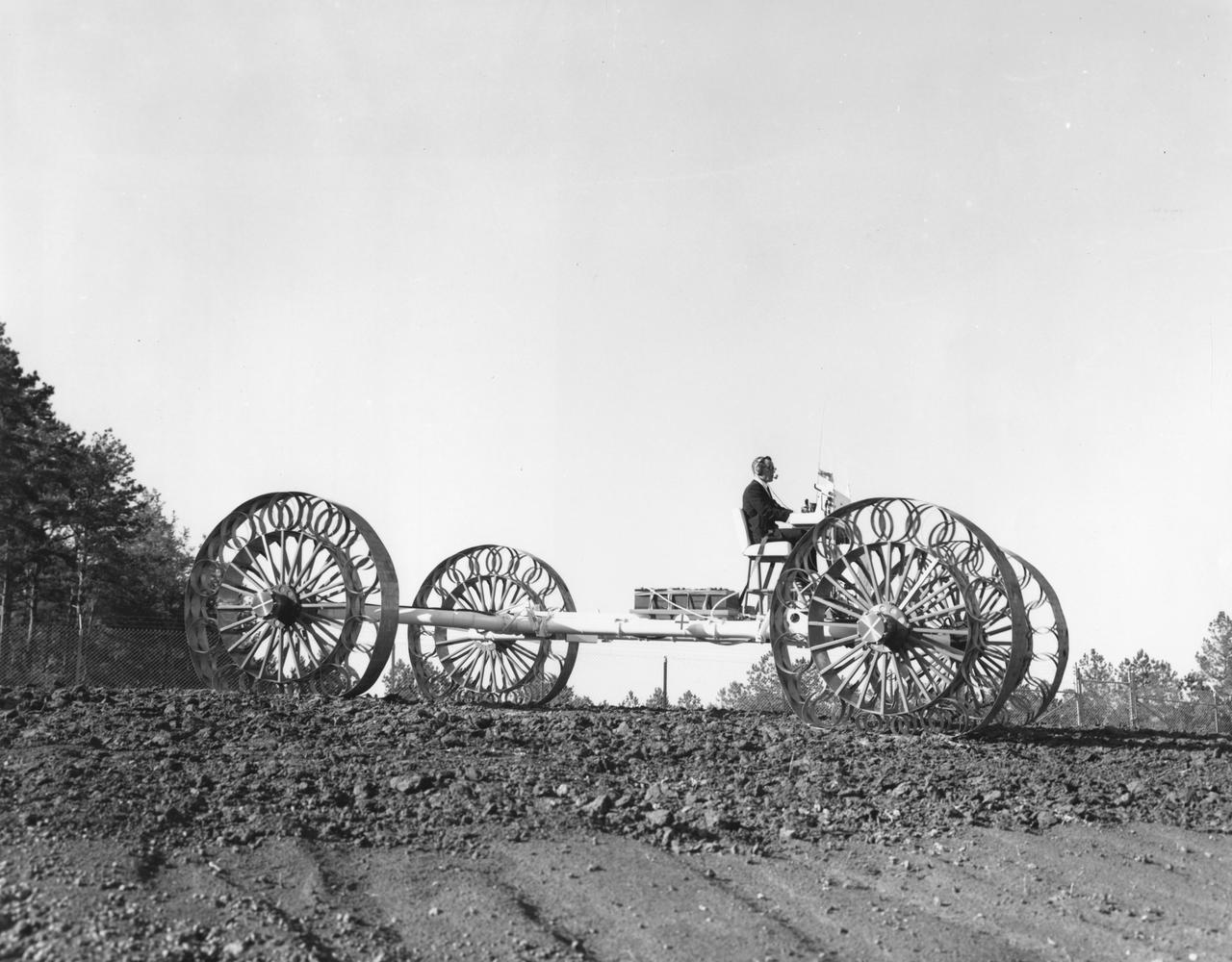

An engineer demonstrates a Mobility Test Article (MTA) at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This unit, weighing 1/6th as much as an actual vehicle, was built by the Bendix Corporation and was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
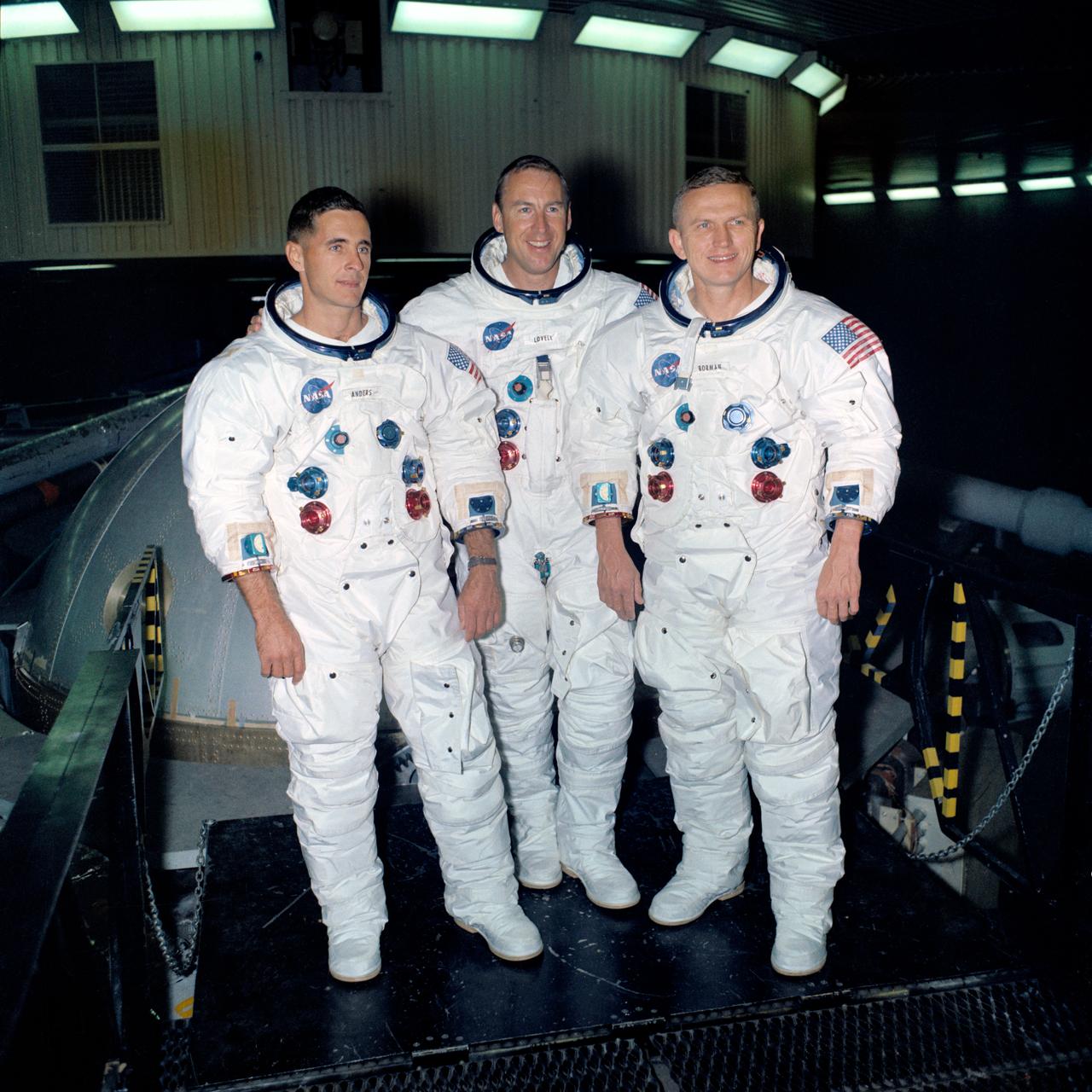

S68-53187 (1 Nov. 1968) --- The prime crew of the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission stands beside the gondola in Building 29 after suiting up for centrifuge training in the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Flight Acceleration Facility (FAF). Left to right, are astronauts William A. Anders, lunar module pilot; James A. Lovell Jr., command module pilot; and Frank Borman, commander.
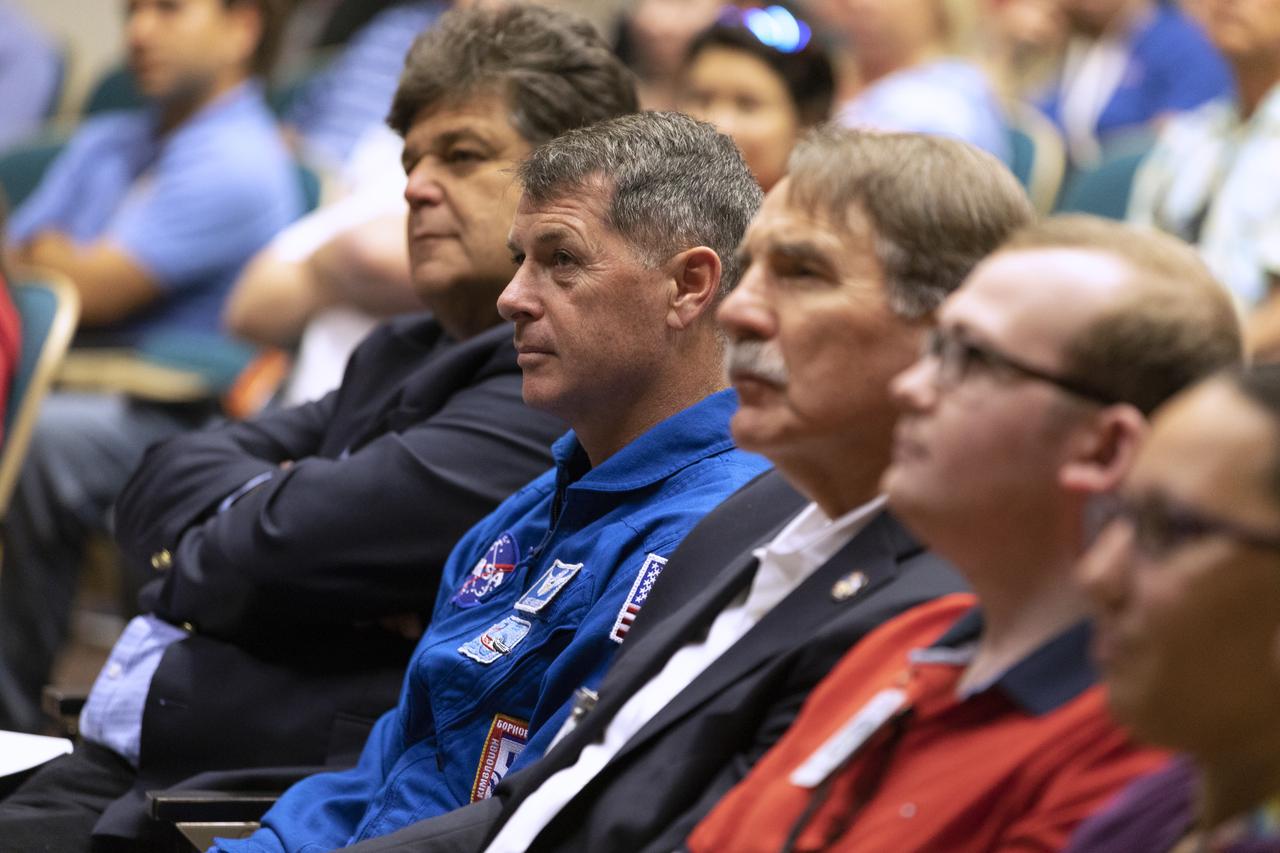

NASA astronaut Shane Kimbrough, blue flight suit, listens to a presentation in Kennedy Space Center’s Training Auditorium on April 12, 2019, during “Columbia: The Mission Continues,” an event organized by the Apollo Challenger Columbia Lessons Learned Program (ACCLLP). Kimbrough also was a speaker at the event, which is part of the Space Shuttle Columbia national tour and took place on the 38th anniversary of STS-1, the first orbital spaceflight of NASA’s Space Shuttle Program. The tour launched at Kennedy and will make its way to each of the 10 NASA centers.
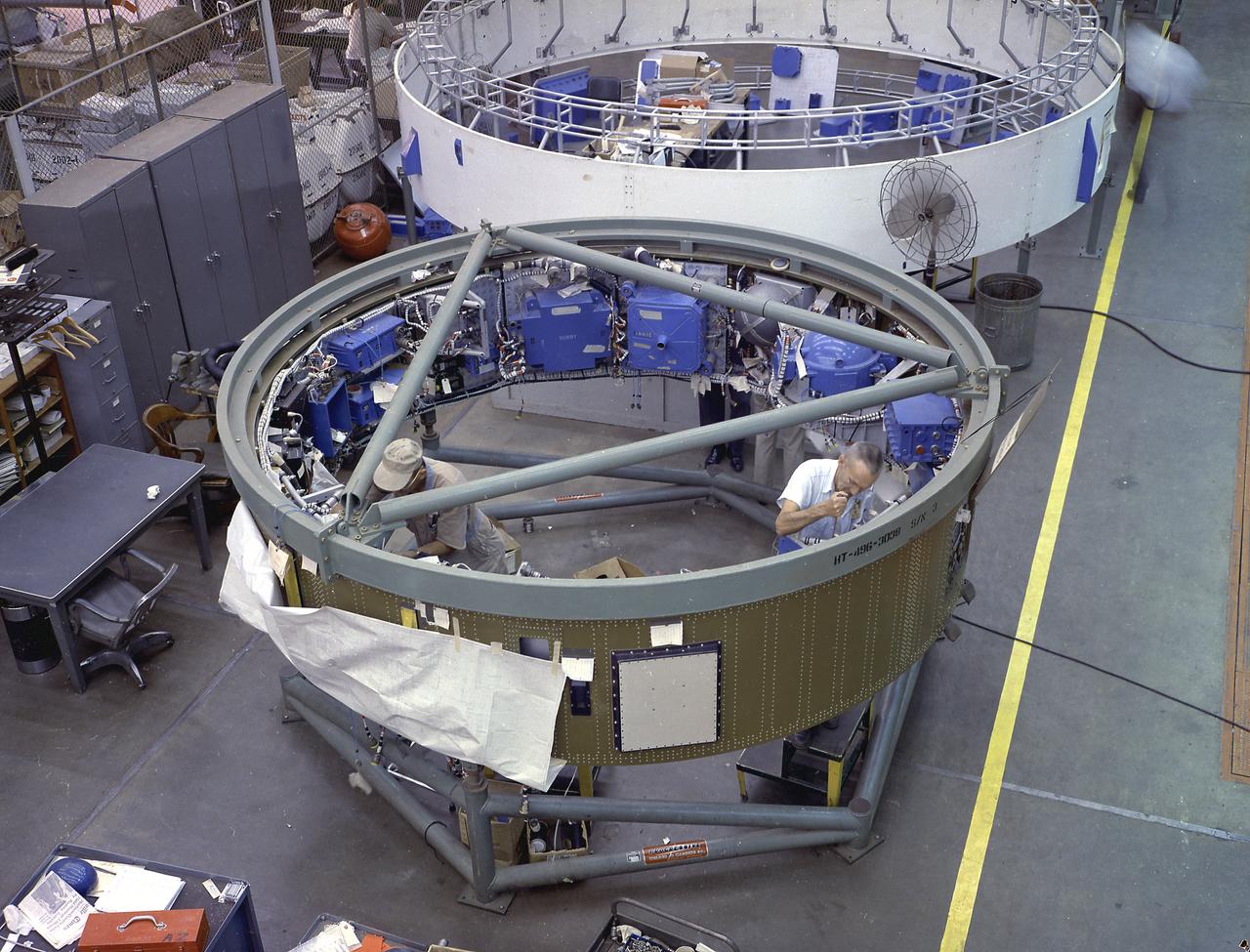
This image depicts a high angle view of technicians working on the instrument unit (IU) component assembly for the SA-8 mission in Marshall Space Flight Center's building 4705. A thin, circular structure, only 1-meter high and 7.6 meters in diameter, the IU was sandwiched between the S-IV and Apollo spacecraft. Packed inside were the computers, gyroscopes, and assorted black boxes necessary to keep the launch vehicle properly functioning and on its course.
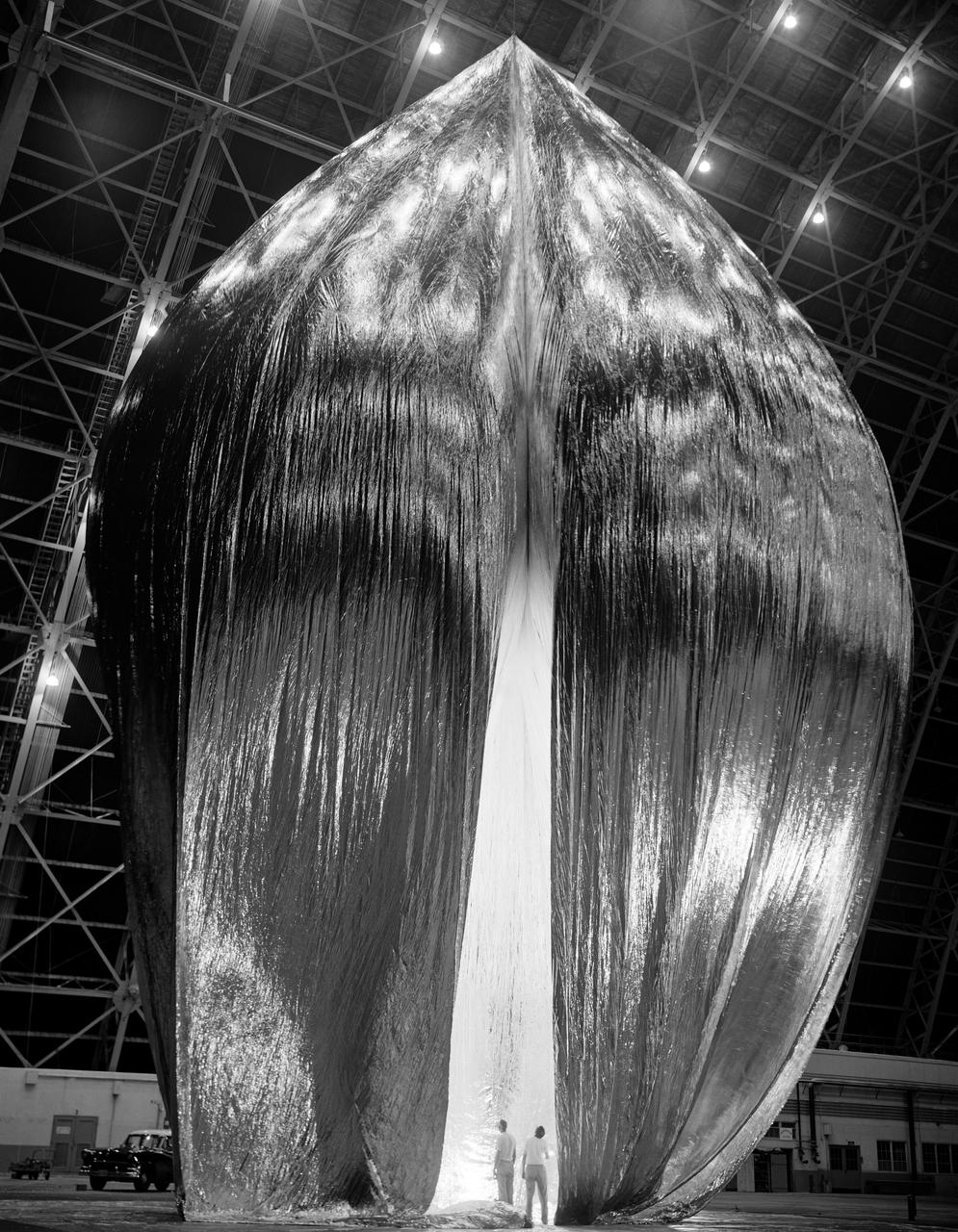

Inflation Tests of the Echo 1 Satellite in Weeksville, N.C. 1958-L-03603 Image Langley engineers Edwin Kilgore (center), Norman Crabill (right) and an unidentified man take a peek inside the vast balloon during inflation tests. Page. 183 Space Flight Revolution NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo. NASA SP-4308.
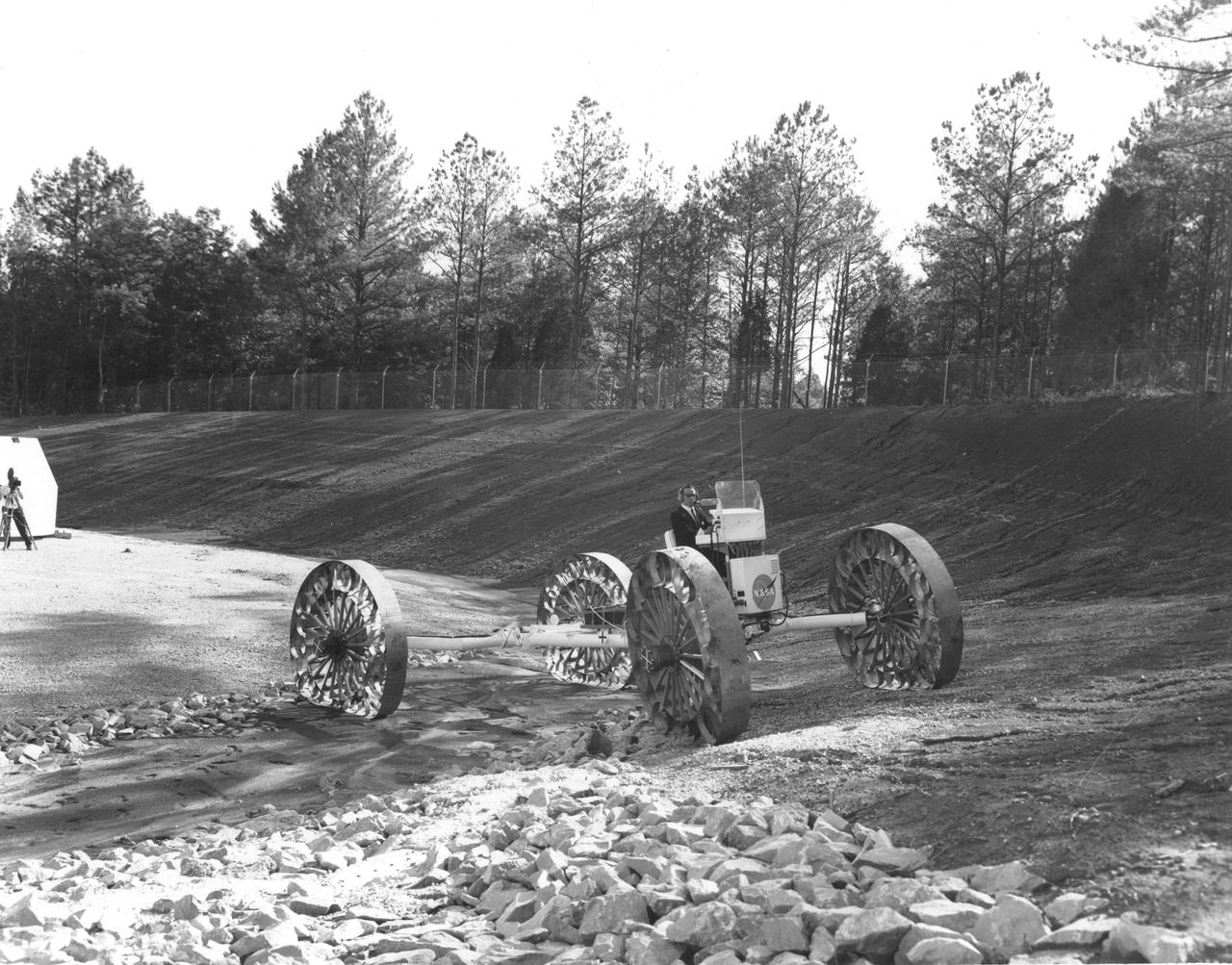

An engineer demonstrates a Mobility Test Article (MTA) at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as he crosses a soft clay strip onto rocky ground. This unit, weighing 1/6th as much as an actual vehicle, was built by the Bendix Corporation and was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the LRV, developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
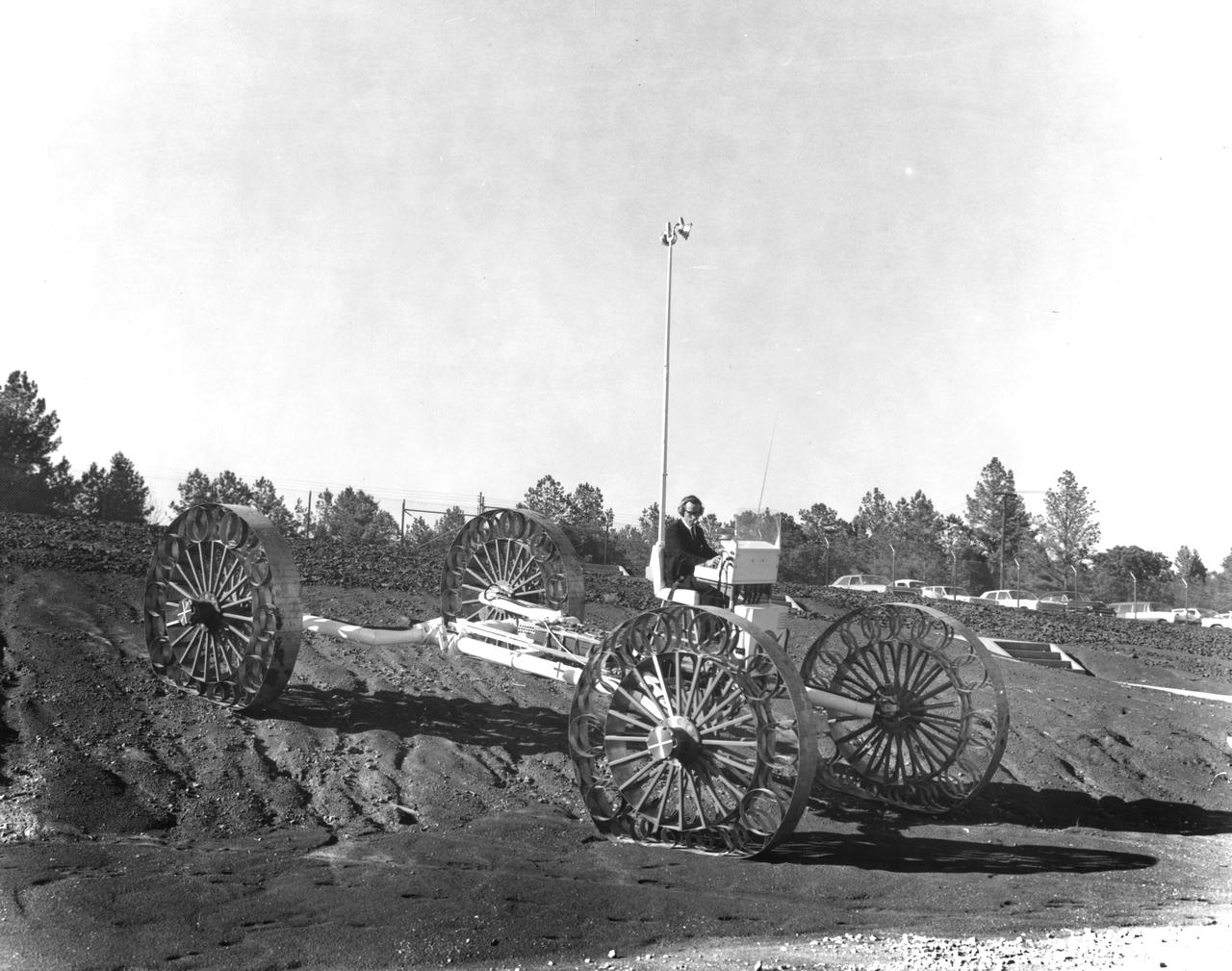

An engineer demonstrates a Mobility Test Article (MTA) at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as he goes down a slope onto soft earth. This unit, weighing 1/6th as much as an actual vehicle, was built by the Bendix Corporation and was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.
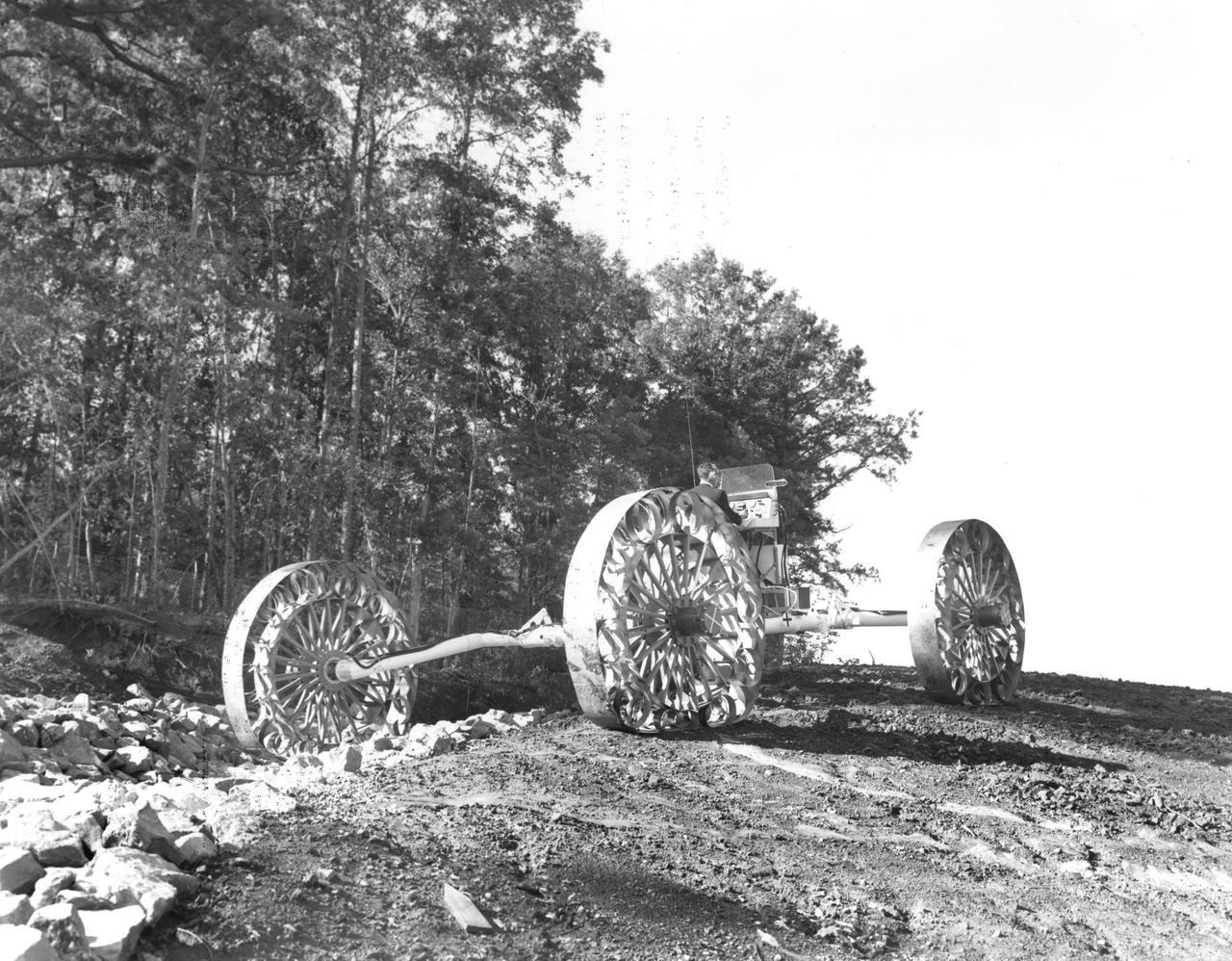

An engineer demonstrates a Mobility Test Article (MTA) at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This unit, weighing 1/6th as much as an actual vehicle, was built by the Bendix Corporation and was one of the concepts of a possible Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The data provided by the MTA helped in designing the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), developed under the direction of MSFC. The LRV was designed to allow Apollo astronauts a greater range of mobility during lunar exploration missions.