
S68-26668 (June 1968) --- The official emblem of Apollo 7, the first manned Apollo space mission. The crew will consist of astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr., Donn F. Eisele, and Walter Cunningham. The NASA insignia design for Apollo flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for the official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced.

AS07-04-1586 (20 Oct. 1968) --- Astronaut Walter Cunningham, Apollo 7 lunar module pilot, writes with space pen as he is photographed performing flight tasks on the ninth day of the Apollo 7 mission. Note the 70mm Hasselblad camera film magazine just above Cunningham's right hand floating in the weightless (zero gravity) environment of the spacecraft.

AS07-04-1583 (11-22 Oct. 1968) --- Astronaut Donn F. Eisele, Apollo 7 command pilot, is photographed during the Apollo 7 mission.

AS07-04-1584 (11-22 Oct. 1968) --- Astronaut Walter Cunningham, Apollo 7 lunar module pilot, is photographed during the Apollo 7 mission.
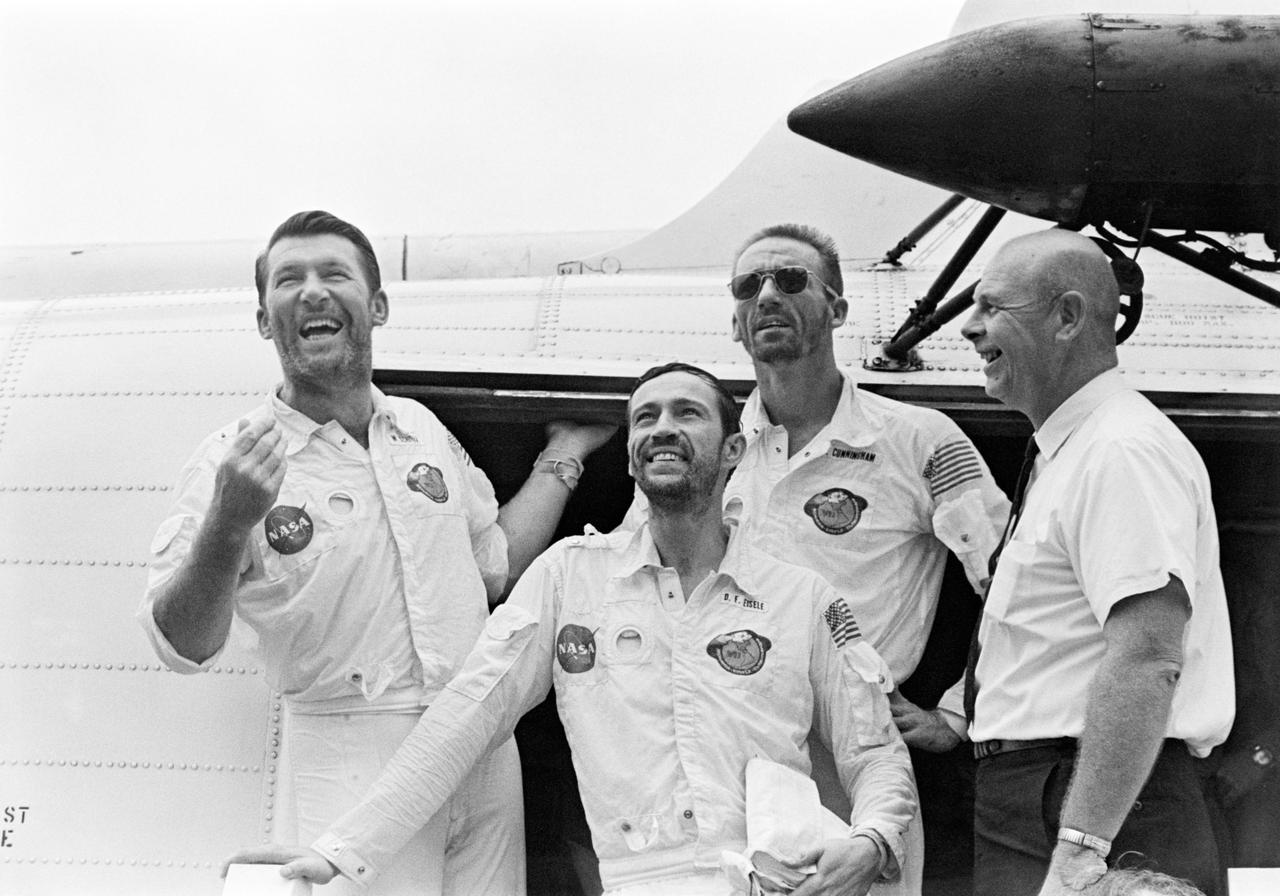

S68-52542 (22 Oct. 1968) --- The Apollo 7 crew arrives aboard the USS Essex, the prime recovery ship for the mission. Left to right, are astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr., commander; Donn F. Eisele, command module pilot; Walter Cunningham, lunar module pilot; and Dr. Donald E. Stullken, NASA Recovery Team Leader from the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Landing and Recovery Division. The crew is pausing in the doorway of the recovery helicopter.
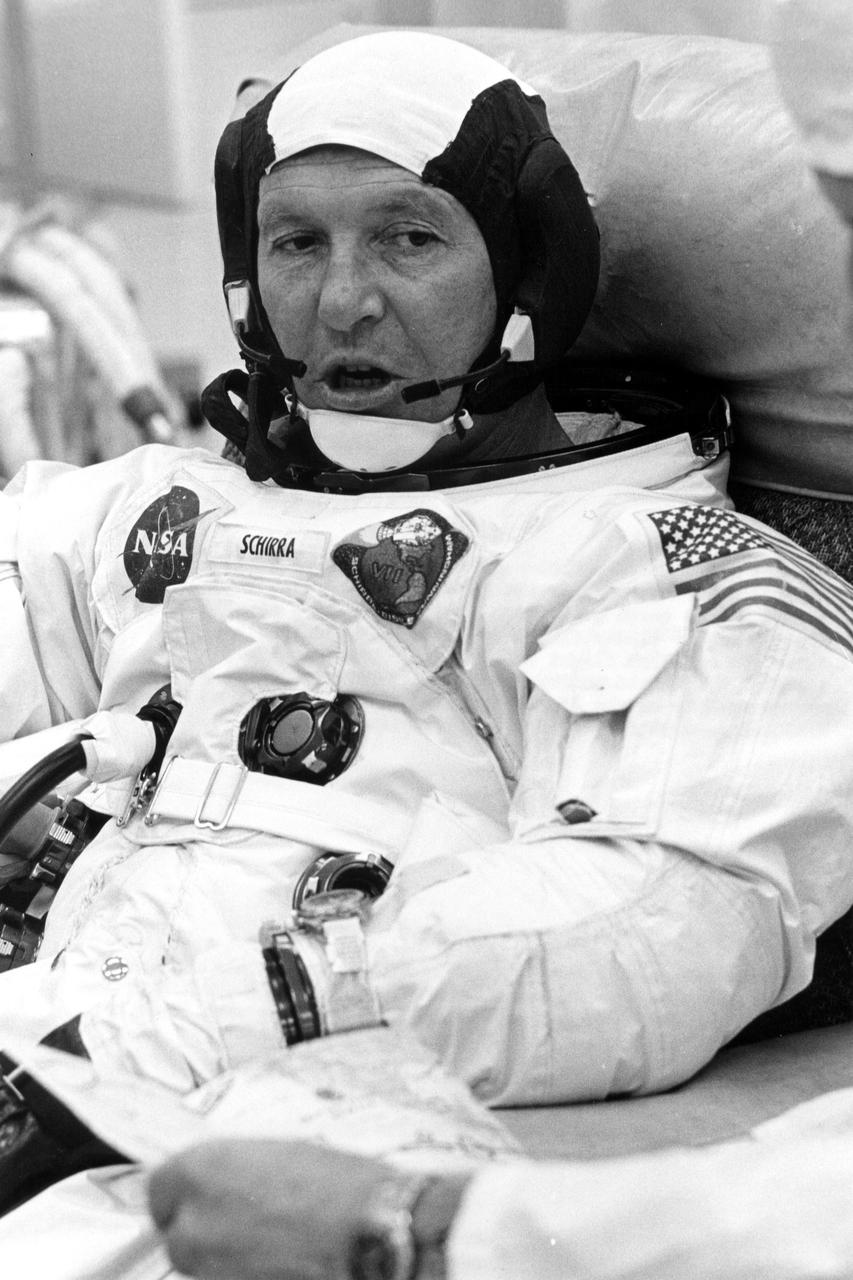

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astsronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr. relaxes prior to boarding the Apollo 7 spacecraft, which rocketed into Earth orbit from Cape Kennedy this morning. Purpose of the 11-day flight is to qualify the Apollo spacecraft for a future flight to the moon. Other Apollo 7 pilots are Donn Eisele and Walter Cunningham. This is the first manned mission of the Apollo series. It is conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
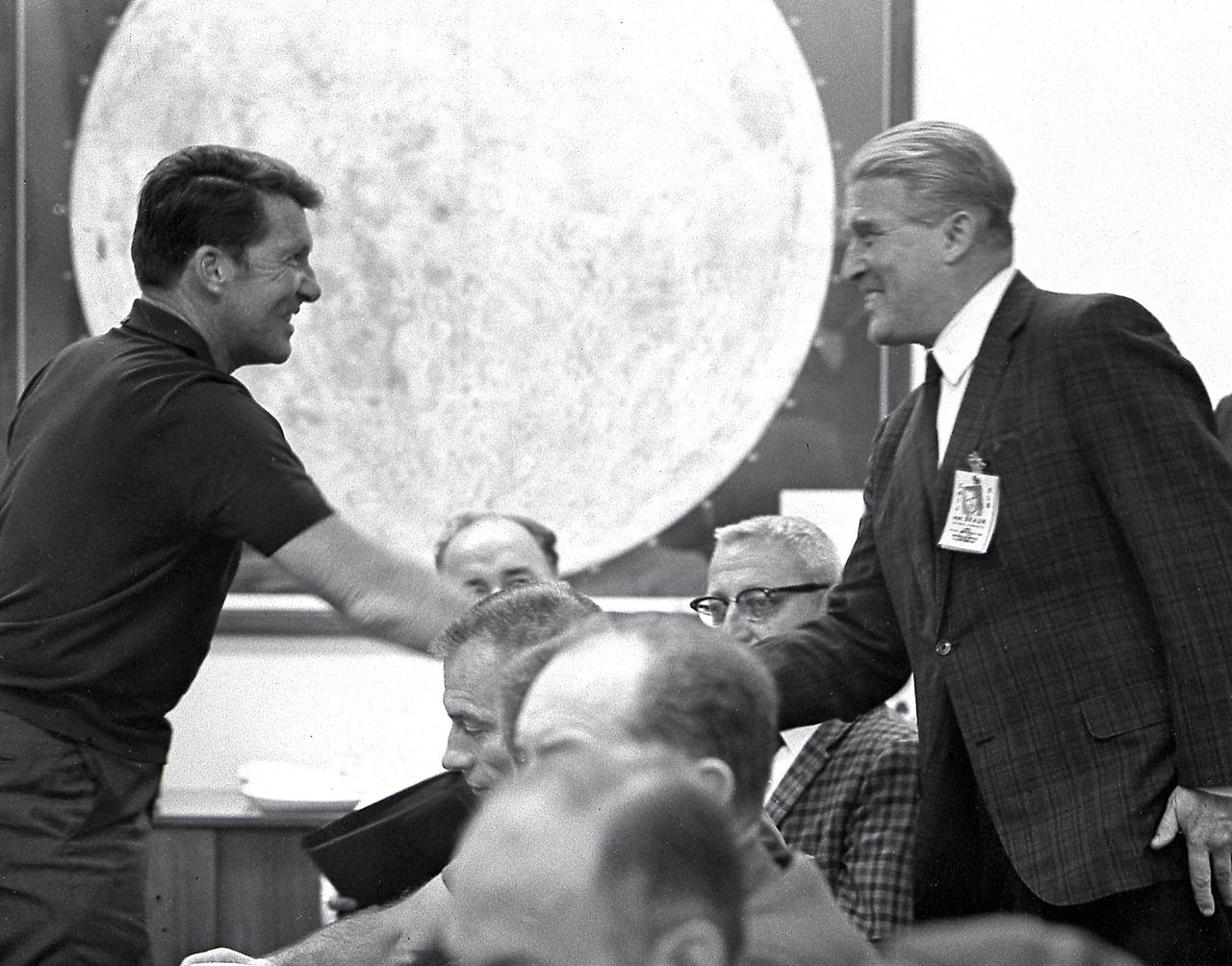

Dr. von Braun, Director of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), greets Commander of Apollo 7 mission, Walter M. Schirra, Jr., during the mission briefing at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The Apollo 7 mission, boosted by a Saturn IB launch vehicle on October 11, 1968, was the first flight of the Apollo spacecraft with crew. Other crew members were Astronaut Donn Eisele and Astronaut Walter Cunningham.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Astronaut Donn F. Eisele adjusts communications carrier prior to the start of an 11-day Earth orbital mission in the Apollo 7 spacecraft. The communications carrier contains microphones and earphones. Flying with Eisele aboard Apollo 7 are astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr. and Walter Cunningham. Purpose of the flight, conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, is to qualify the Apollo spacecraft for a future flight to the moon.
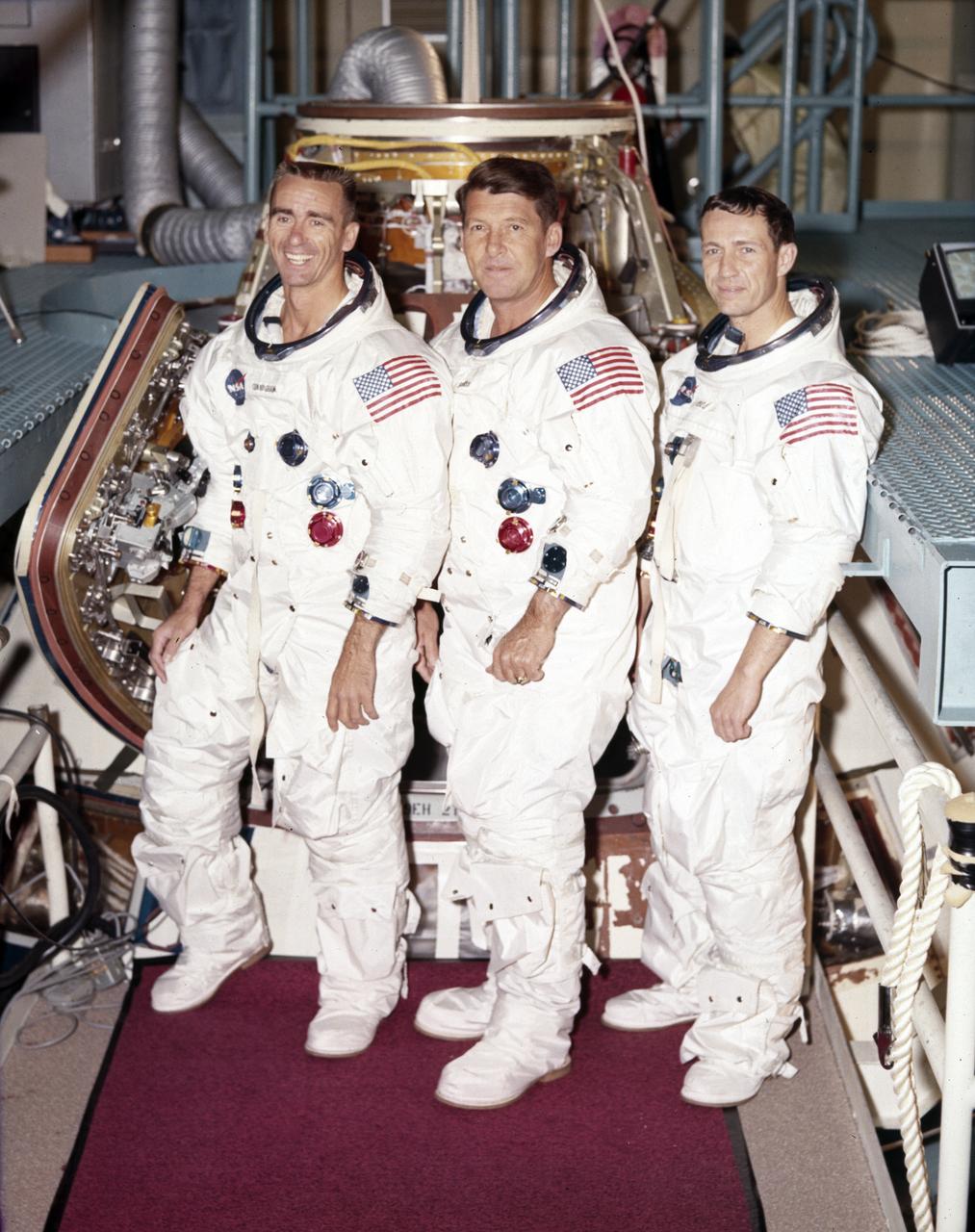

Pictured left to right, in the Apollo 7 Crew Portrait, are astronauts R. Walter Cunningham, Lunar Module pilot; Walter M. Schirra, Jr., commander; and Donn F. Eisele, Command Module Pilot. The Apollo 7 mission, boosted by a Saturn IB launch vehicle on October 11, 1968, was the first manned flight of the Apollo spacecraft.
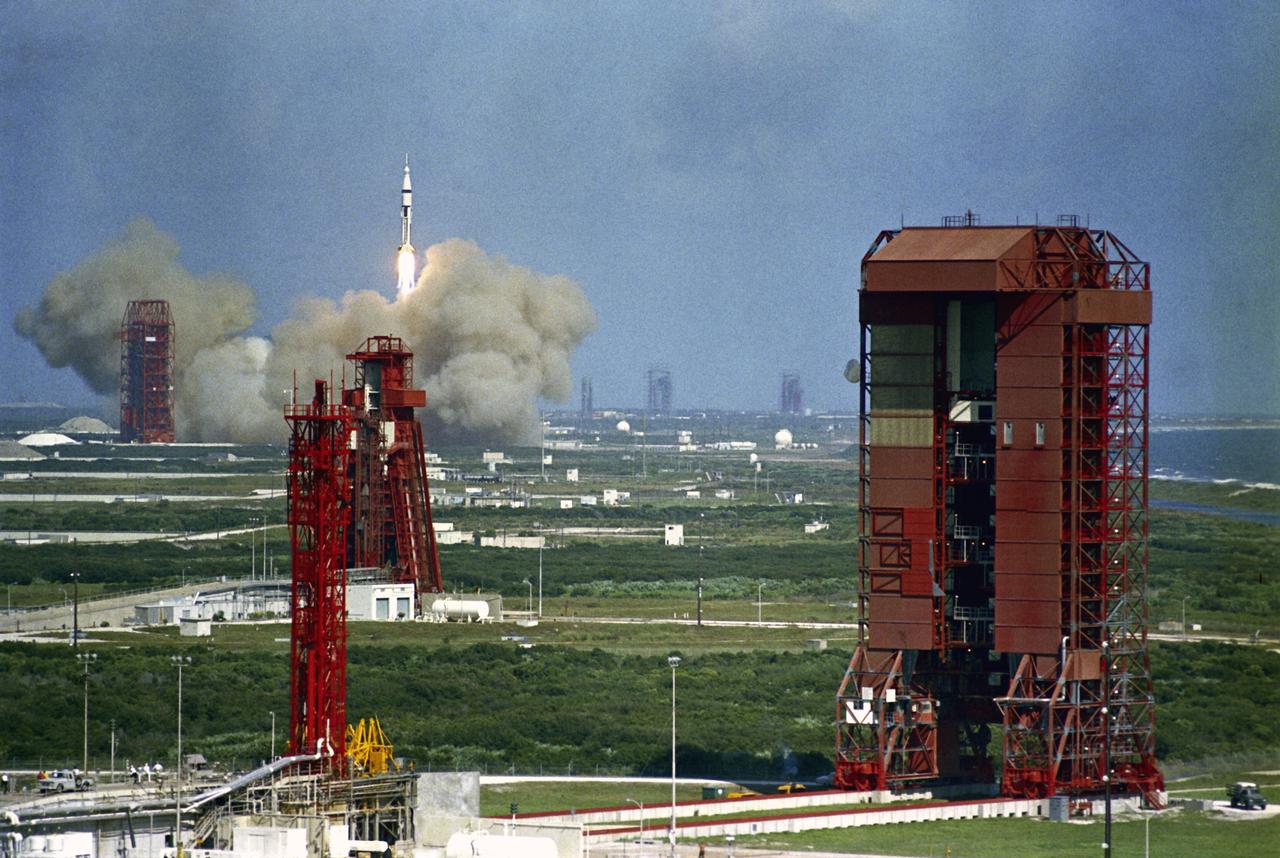

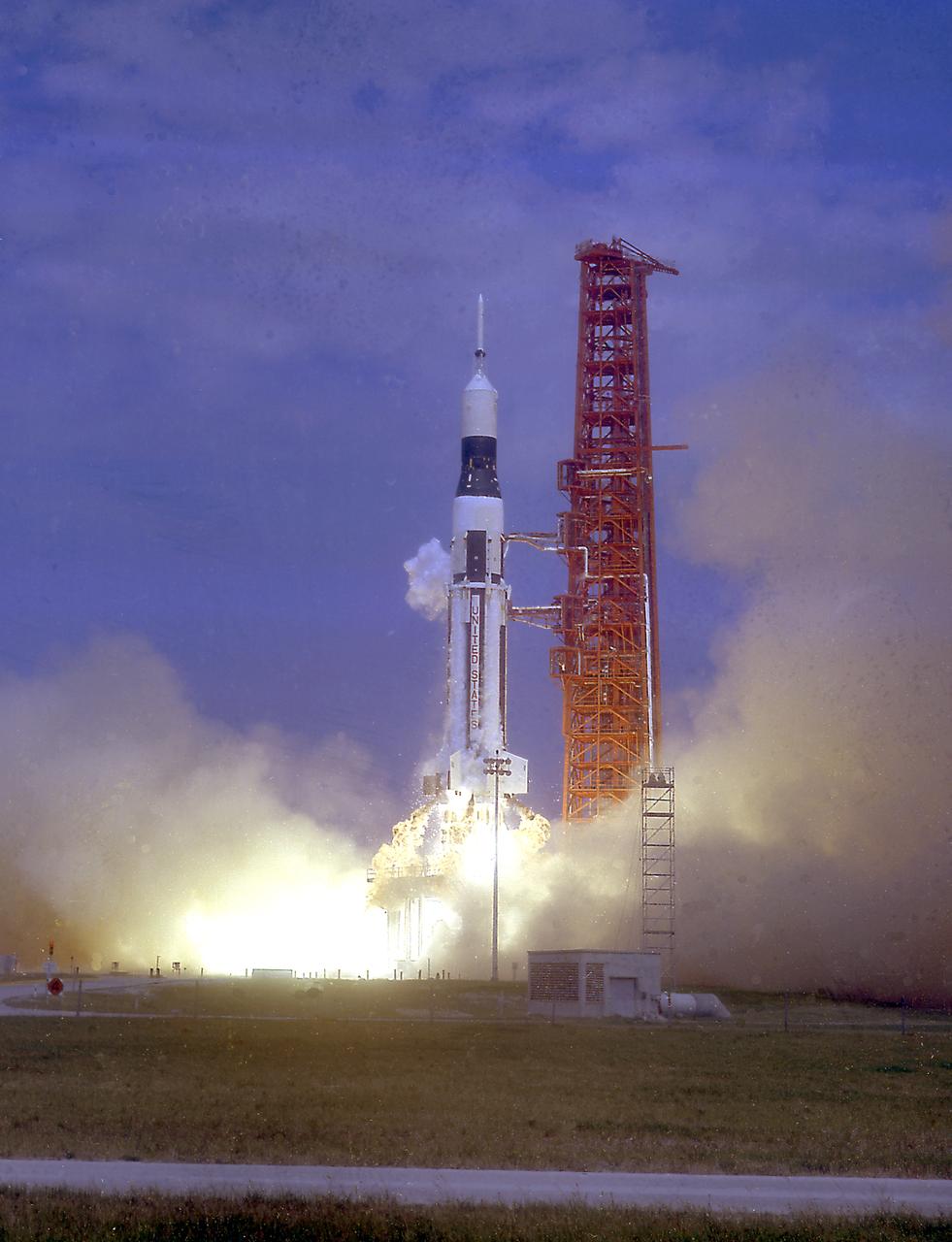
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The Apollo 7 spacecraft, atop a Saturn IB rocket, lifts off from Complex 34, Cape Kennedy, at 11:03 a.m. EDT. The spacecraft achieved orbit to begin an 11-day mission. The flight is intended to qualify Apollo for a manned flight to the moon. Photo credit: NASA
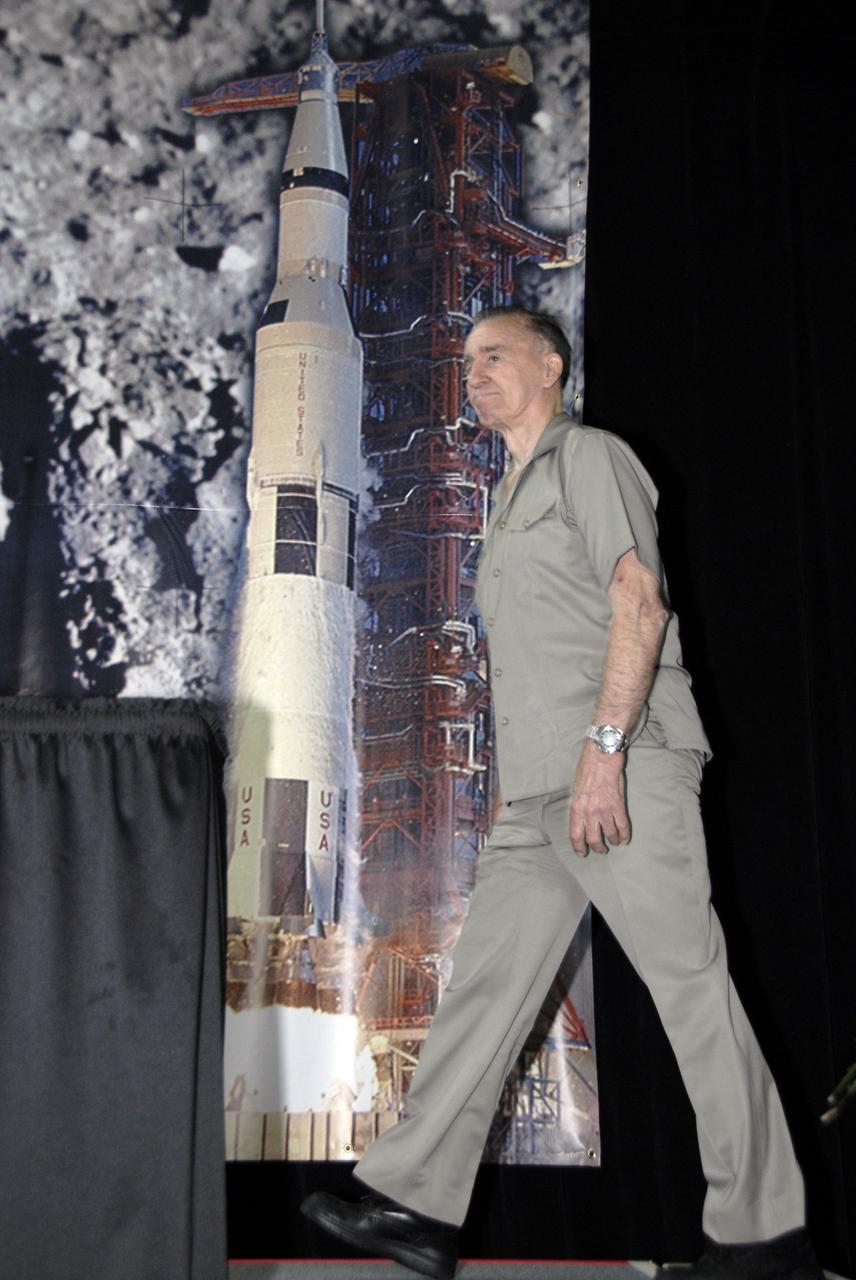

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo astronaut Walt Cunningham is introduced during NASA's 40th Anniversary of Apollo Celebration of the July 1969 launch and landing on the moon. Cunningham was joined by seven others involved in the program. Cunningham occupied the lunar module pilot seat for the 11-day flight of Apollo 7--the first manned flight test of the third-generation United States spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

AS-205, the fifth Saturn IB launch vehicle developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), lifts off from Cape Canaveral, Florida on the first marned Apollo-Saturn mission, Apollo 7. Primary mission objectives included demonstration of the Apollo crew (Walter Schirra, Don Eisele, and Walter Cunningham) capabilities and the Command/Service Module rendezvous capability. In all, nine Saturn IB flights were made, ending with the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in July 1975.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo astronaut Walt Cunningham shares his experiences with an eager crowd gathered for NASA's 40th Anniversary of Apollo Celebration of the July 1969 launch and landing on the moon. Cunningham occupied the lunar module pilot seat for the 11-day flight of Apollo 7--the first manned flight test of the third-generation United States spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
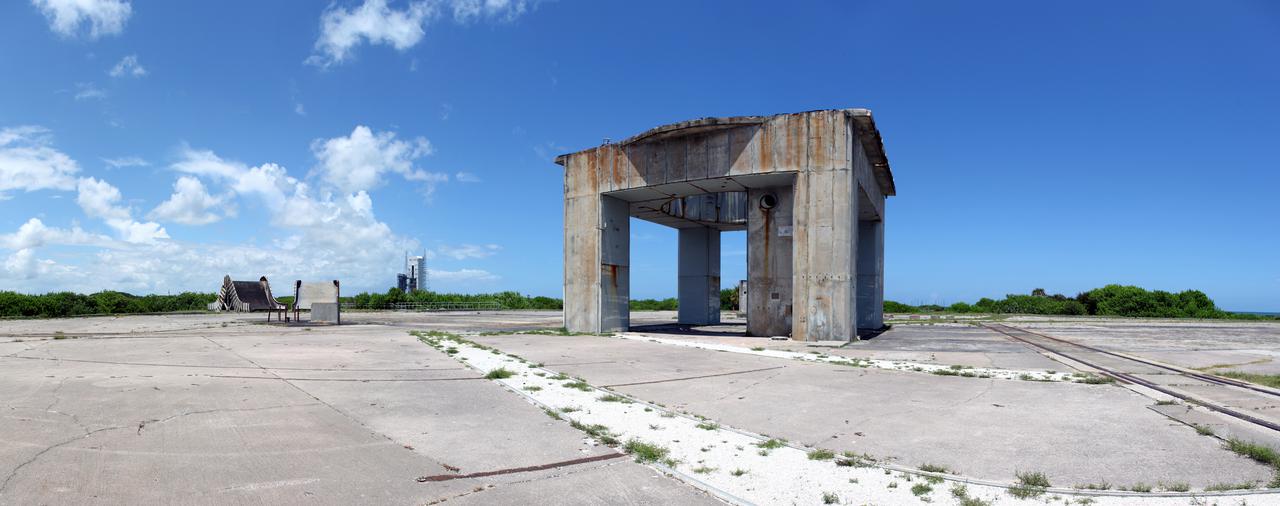

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida stands the Launch Complex-34 launch platform. During the Apollo Program, Complex-34 was the site of the first Saturn I and Saturn IB launches, as well as the tragic fire in which the Apollo 1 astronauts lost their lives. Apollo 7, the first crewed Apollo flight, was the last to launch from Complex-34. Subsequent Apollo mission launched from NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39. Photo credit: NASA_Frankie Martin
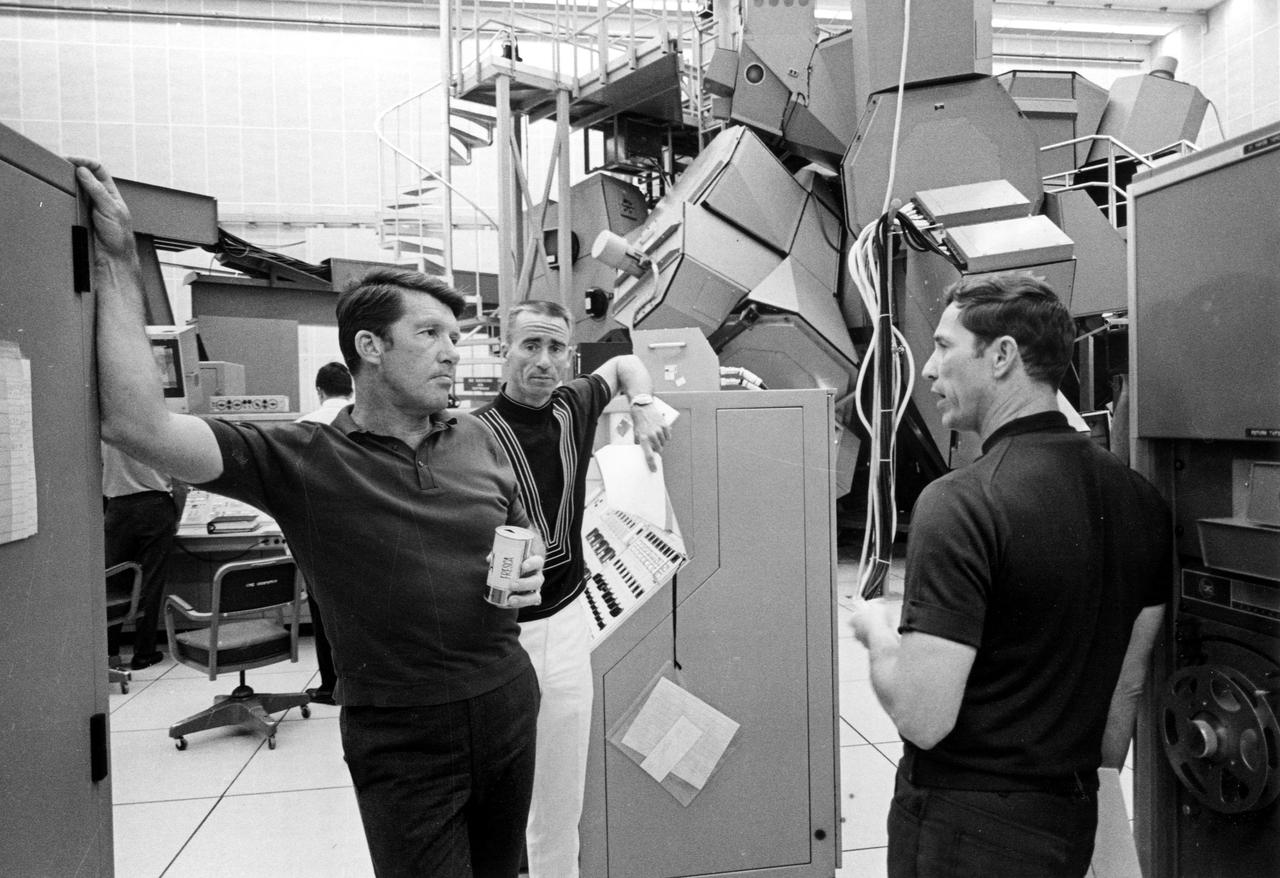

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Apollo 7 astronauts, left to right, Walter Schirra, Walter Cunningham and Donn Eisele pause during a practice mission yesterday within Kennedy Space Center's Flight Crew Training Building. The trio spent several hours in the Apollo mission simulator, rear, in preparation for their upcoming mission. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration's first manned Apollo flight is scheduled to begin no earlier than Oct. 11, 1968.
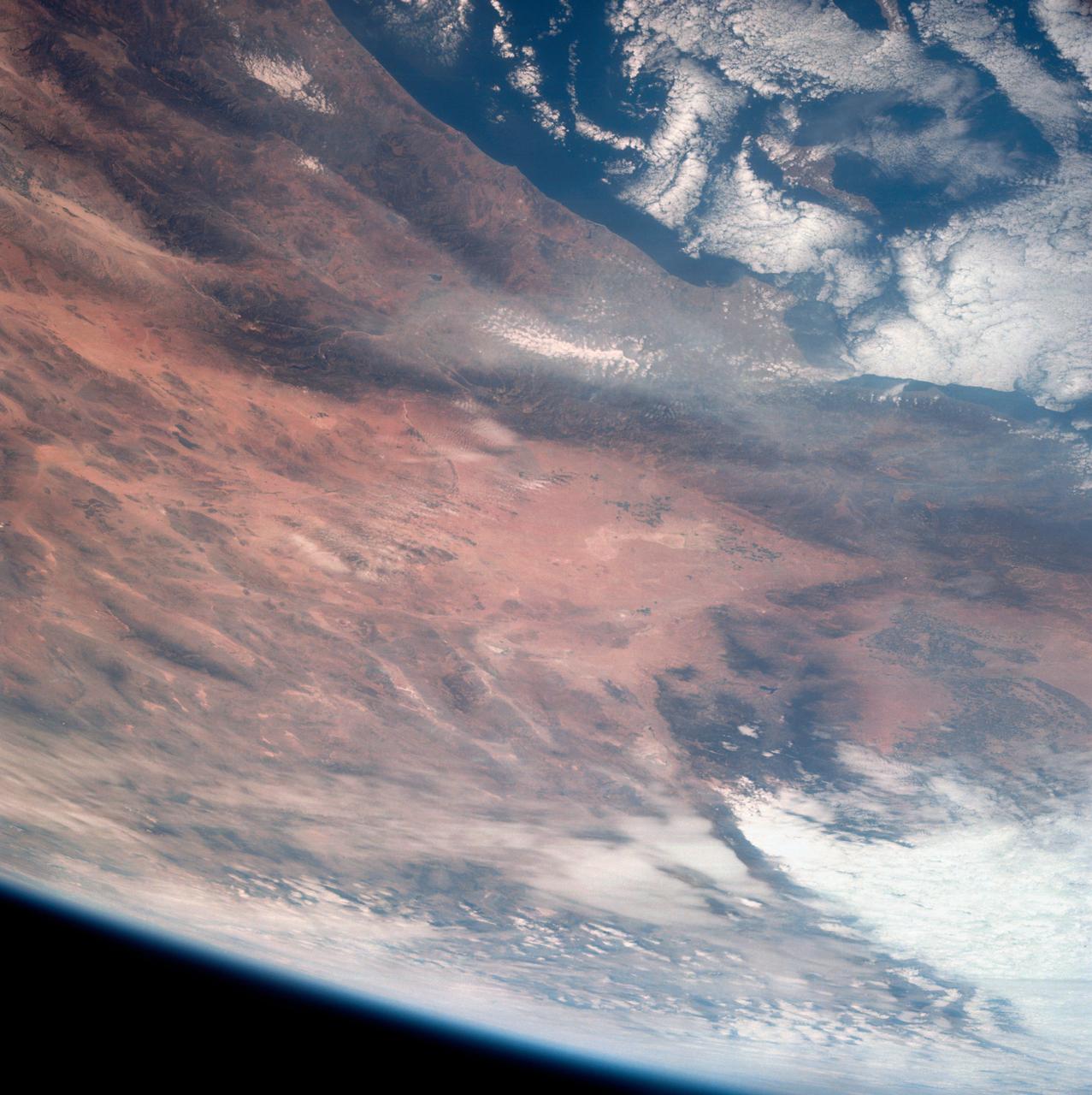

This view of southern California as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 18th revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 124 nautical miles. The coast of California can be seen from Point Mugu southward to Oceanside. Santa Catalina can be seen below the off shore clouds. Details of the Los Angeles area are obscured by pollution which extends from Banning westard for 100 miles to beyond Malibu. In the upper portion of the photograph can be seen (left to right) the San Joaquin Valley beyond Bakersfield, the Techachapi Mountains, the Sierra Nevada, Owens Valley, Death Valley and the Mojave Desert.

The greater New Orleans area, including portions of Louisiana and Mississippi, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 120th revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 95 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 190 hours and 45 minutes. The largest body of water in the picture is Lake Pontchartrain. The Mississippi River is clearly visible as it meanders past New Orleans. Note highway network, and 25-mile causeway across lake.
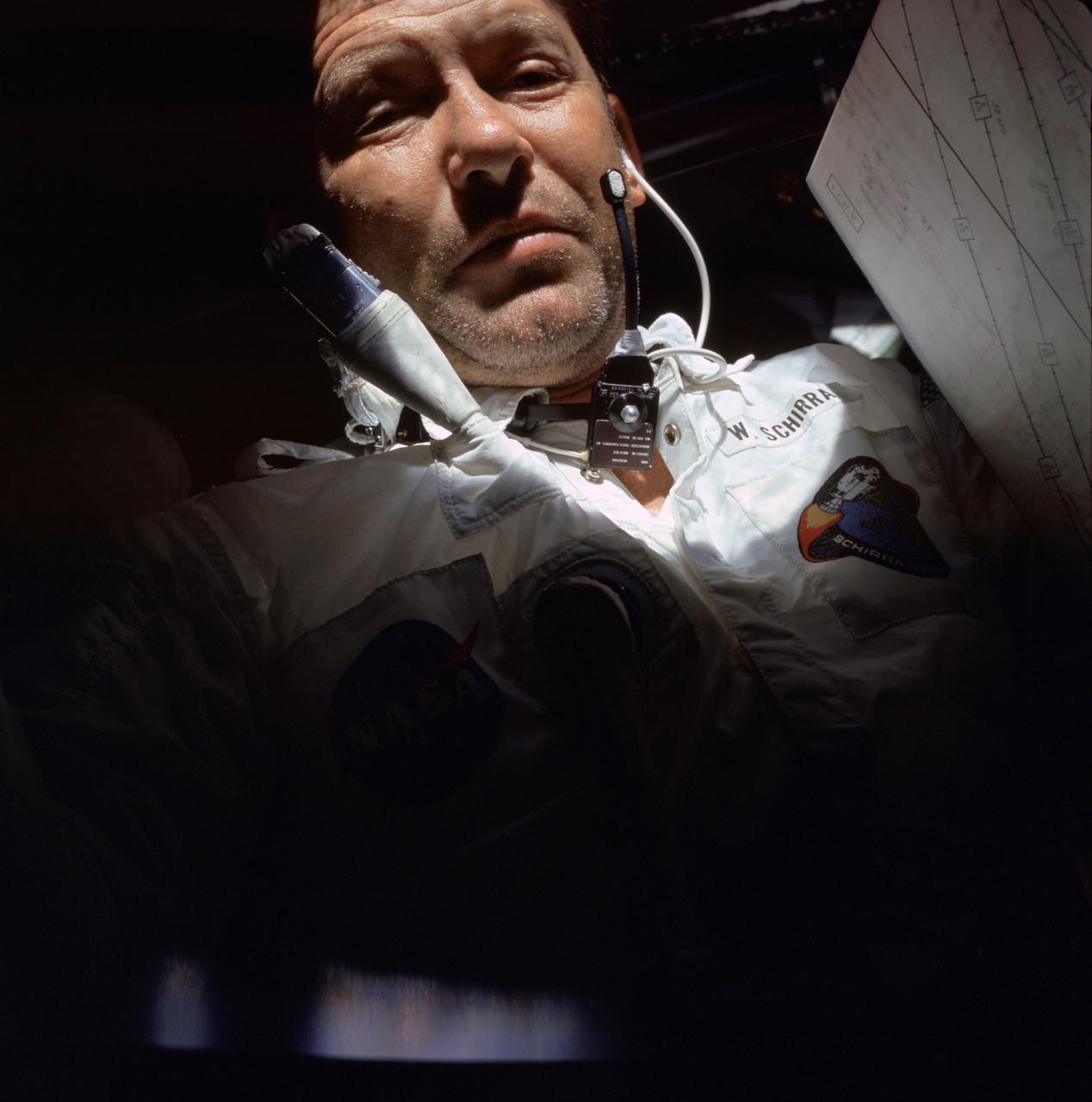

AS07-04-1582 (11-22 Oct. 1968) --- Astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr., Apollo 7 commander, is photographed during the Apollo 7 mission.
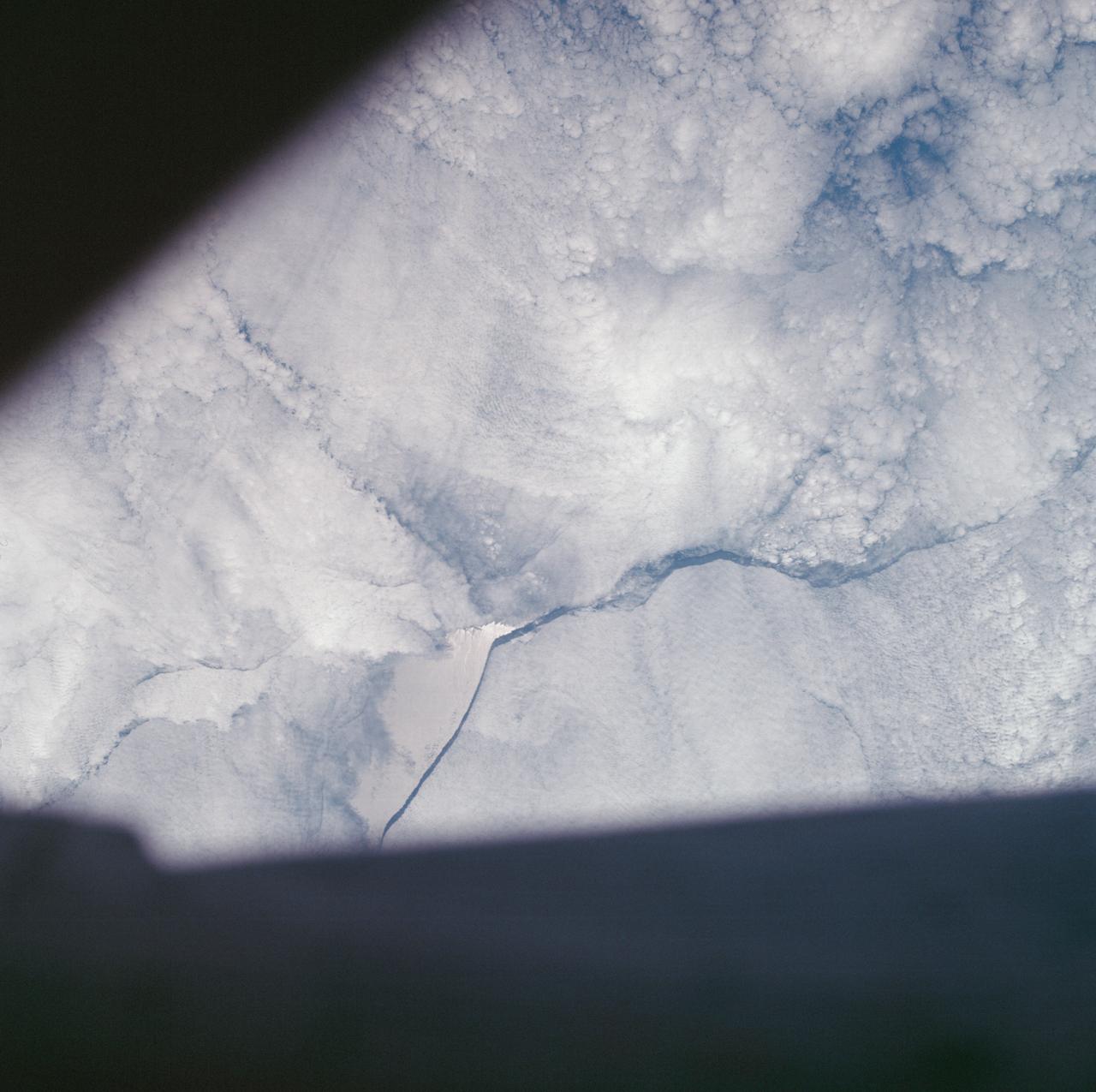

AS07-05-1644 (13 Oct. 1968) --- Remarkable cloud patterns as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 34th revolution of Earth. Note break in two adjacent decks of strato-cumulus cloud formations. Sea can be seen through holes in clouds.
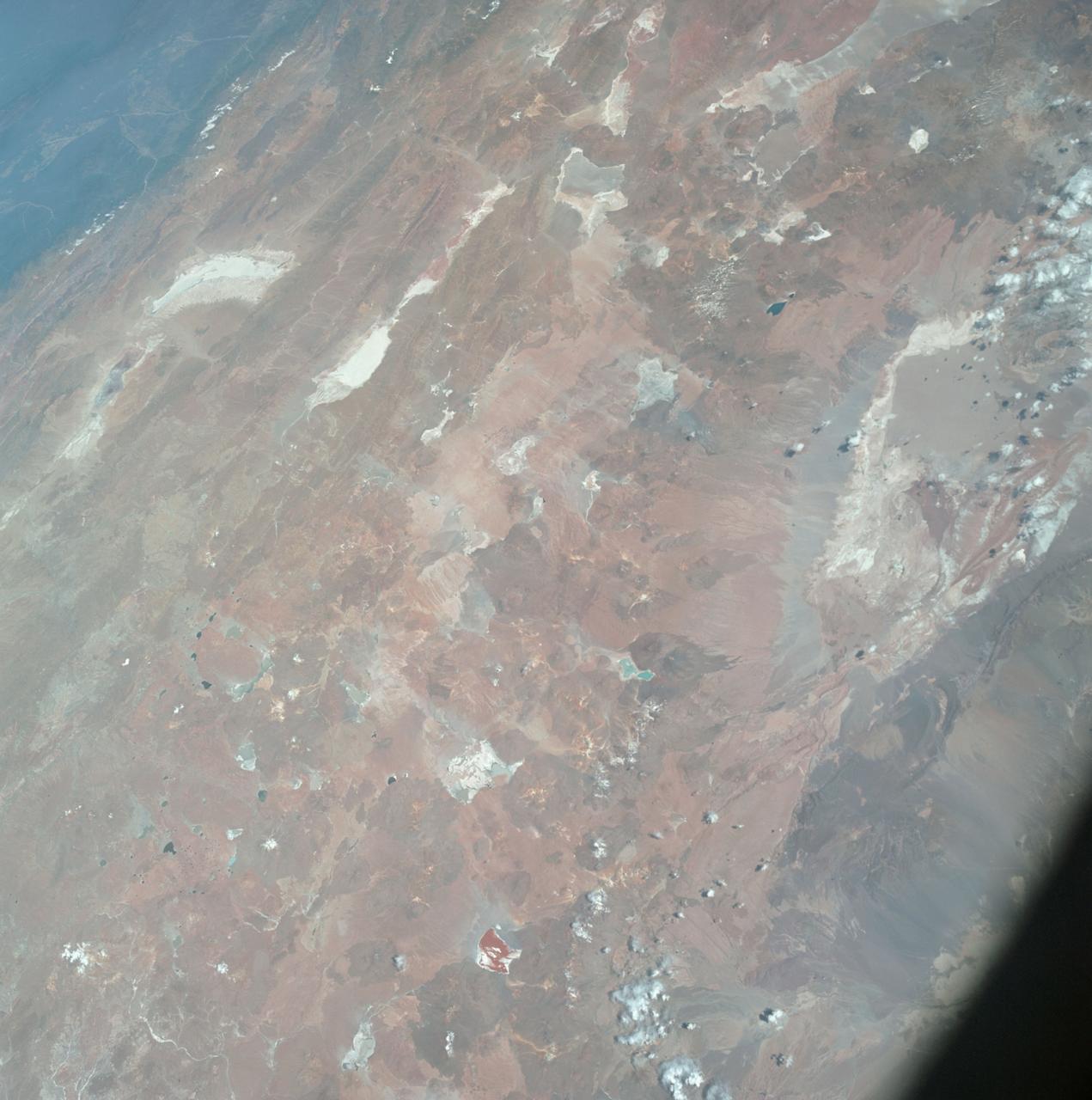

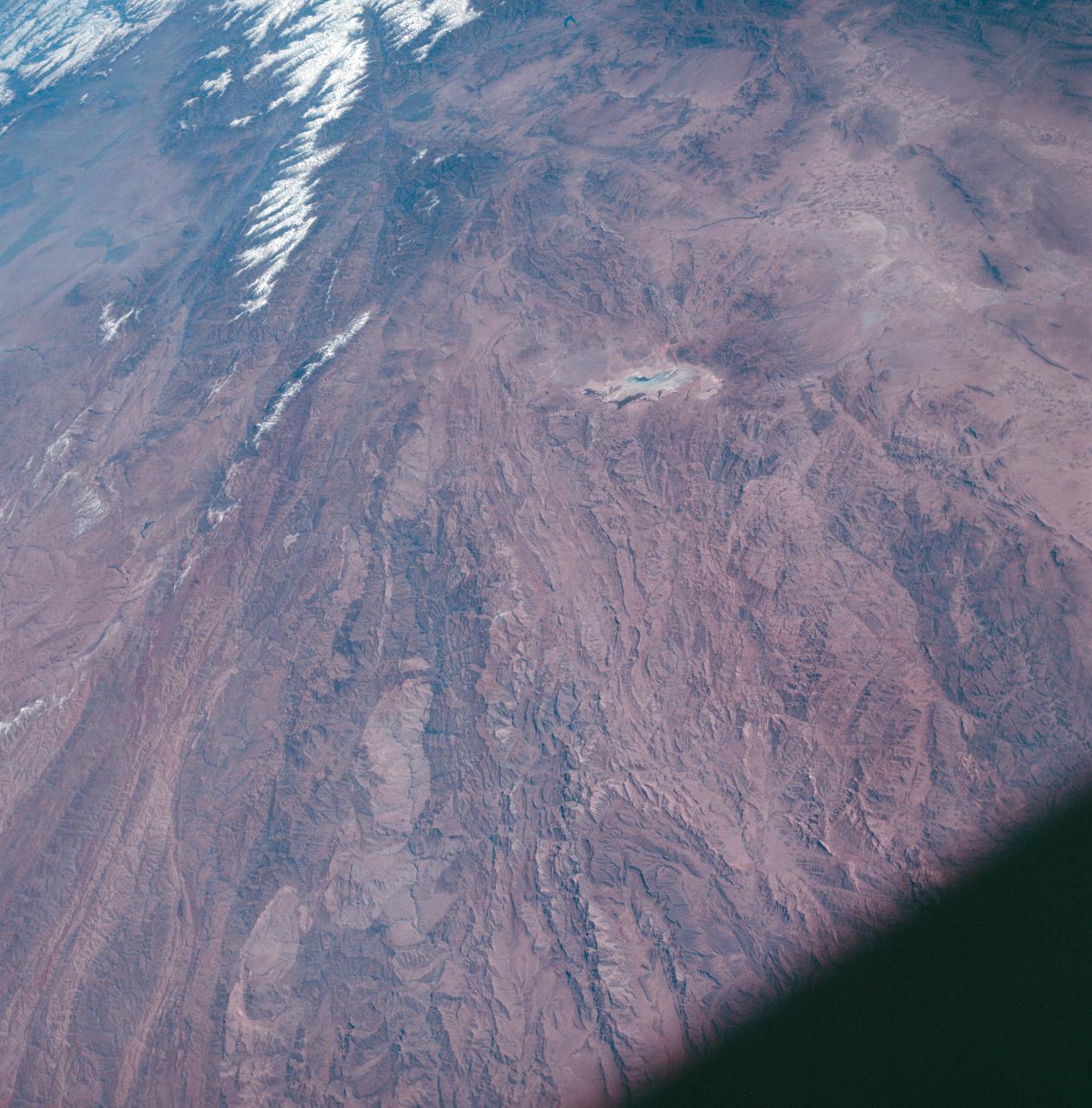
AS07-04-1593 (21 Oct. 1968) --- This Earth observation photograph shows Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Salar de Atacama, the Andes Mountains, and Gran Chaco. The coordinates for the center of this photograph are 23.00 degrees south and 67.30 degrees west, taken at an altitude of 175 miles during the 154th revolution around Earth. The crew consisted of astronauts Walter M. Schirra, Donn F. Eisele and Walter Cunningham.
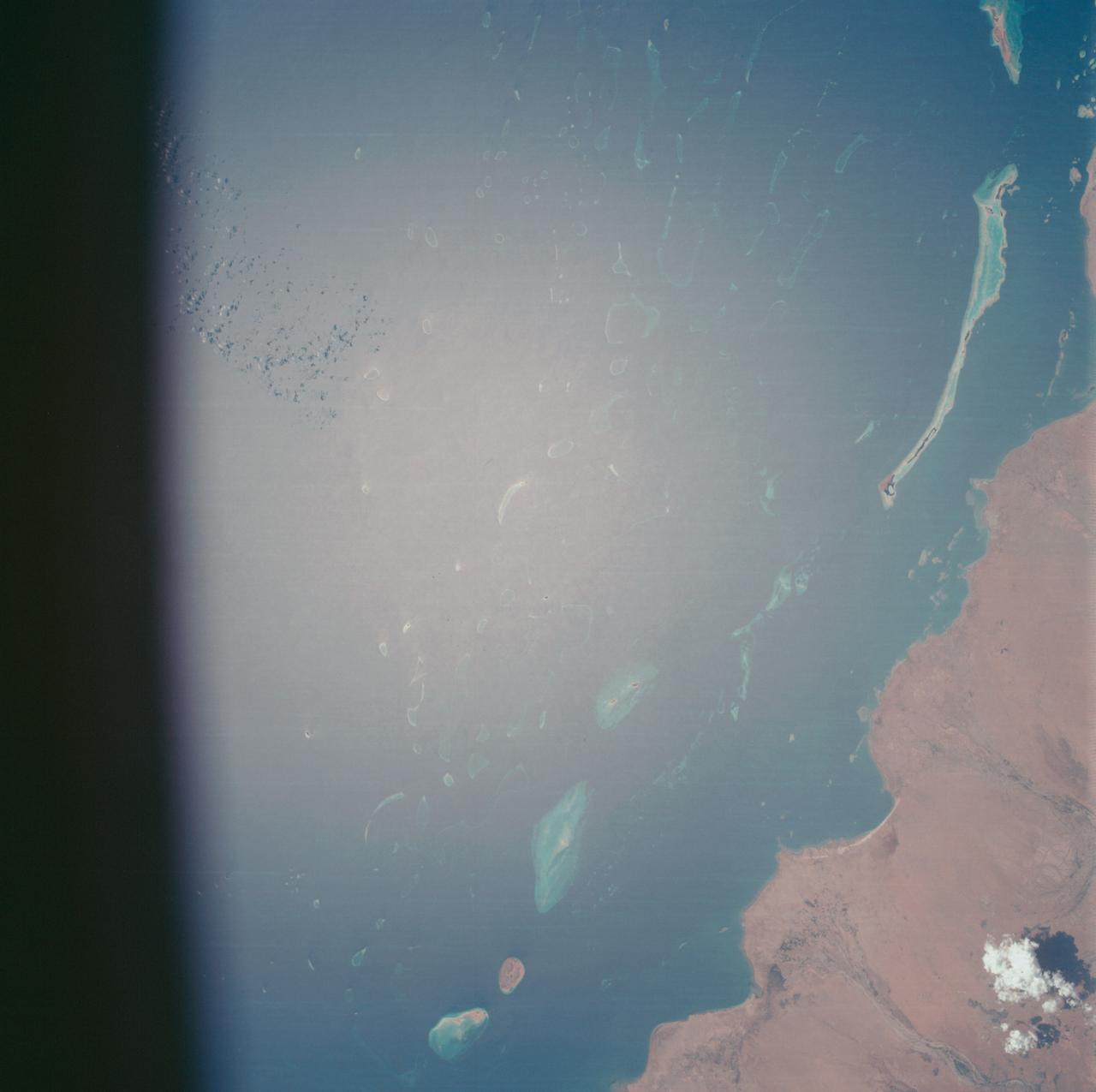

AS07-07-1774 (15 Oct. 1968) --- Red Sea coastal area of Saudi Arabia as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 58th revolution of Earth. This picture shows extent of coral reefs in the Red Sea. Photographed from an altitude of 88 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 91 hours and 17 minutes.
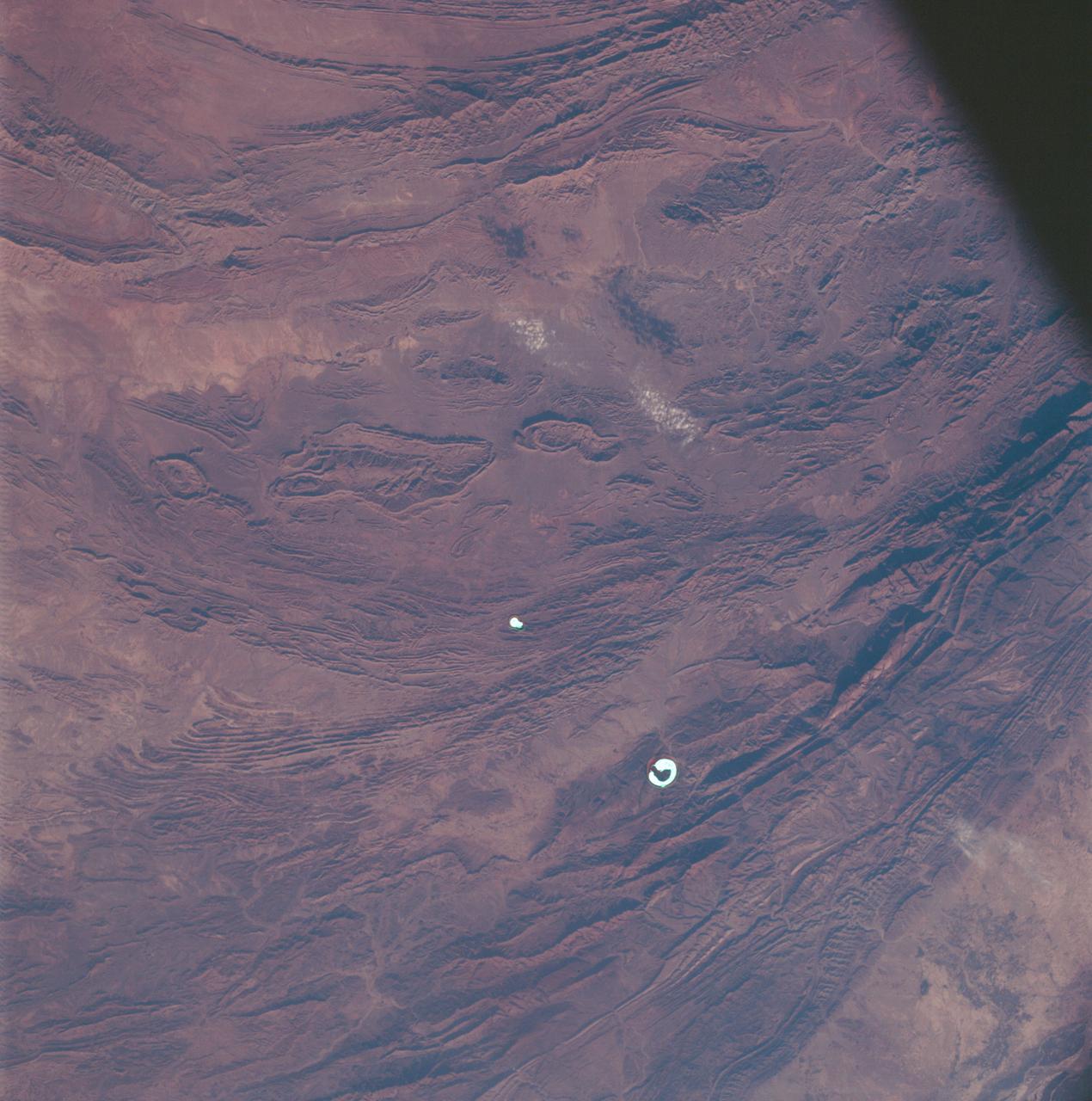

AS07-07-1832 (15 Oct. 1968) --- Toba, Kakar, Fort Sandeman, Sulaiman Range area in (West) Pakistan, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 84th revolution of Earth. Note geological features such as folded mountain structures, anticlines and synclines. Photographed from an altitude of 108 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 132 hours and 30 minutes.
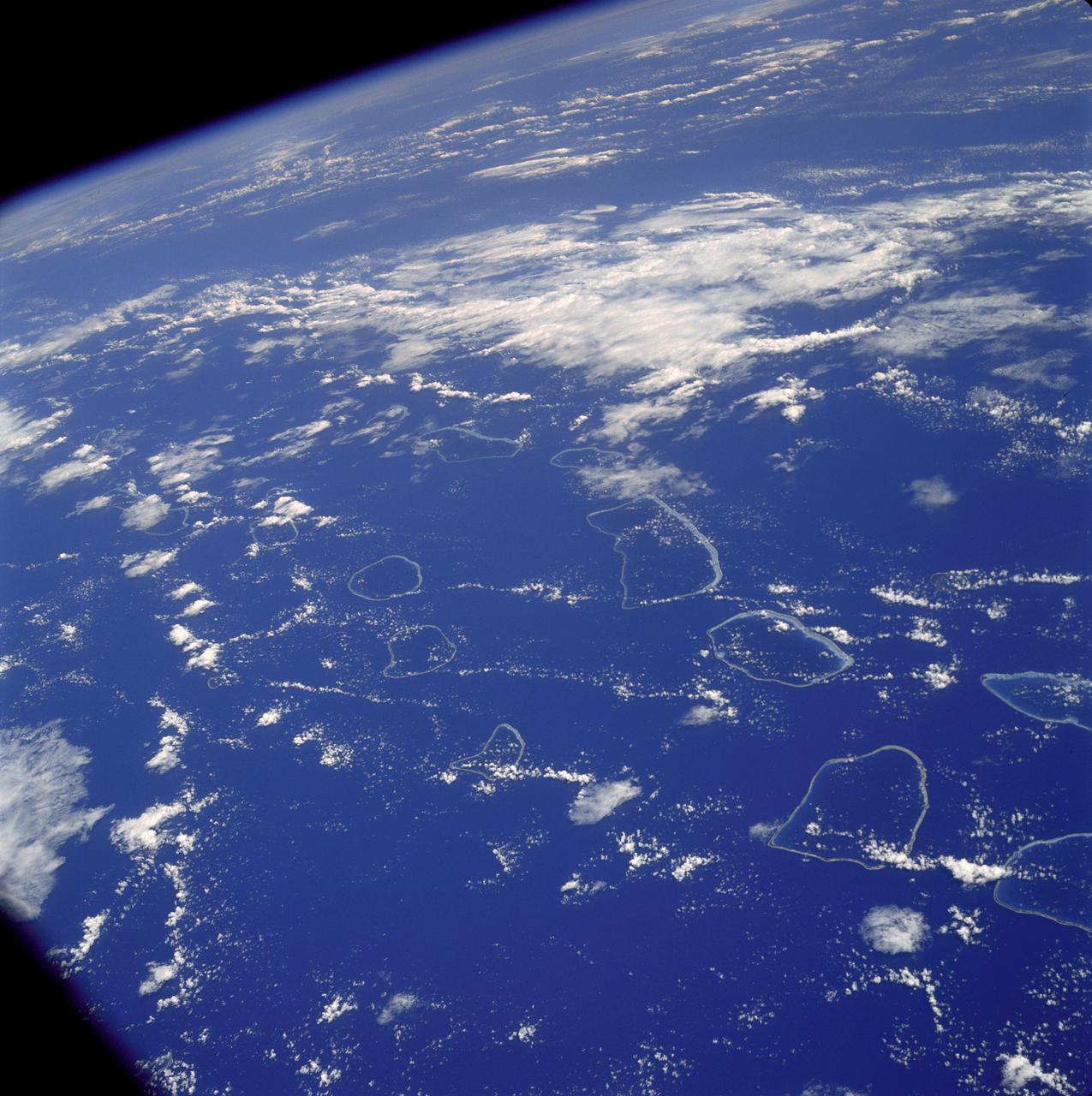

AS07-04-1590 (20 Oct. 1968) --- Tuamotu Archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, looking southwest, as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 141st revolution of Earth. The photograph was taken from an altitude of 110 nautical miles, at a ground elapsed time of 224 hours and 18 minutes.
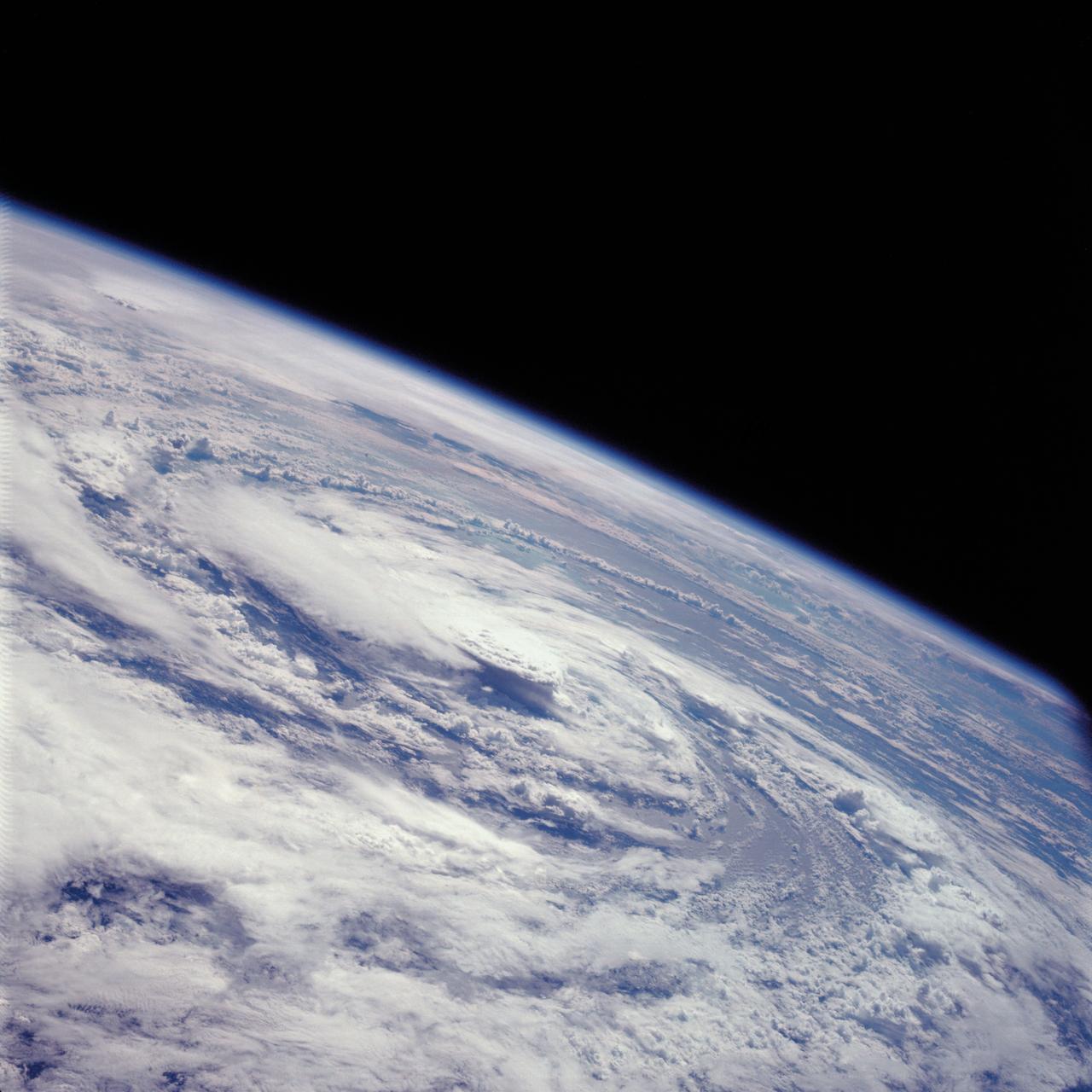

AS07-07-1877 (17 Oct. 1968) --- Hurricane Gladys, Gulf of Mexico, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 91st revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 99 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 144 hours and 27 minutes.
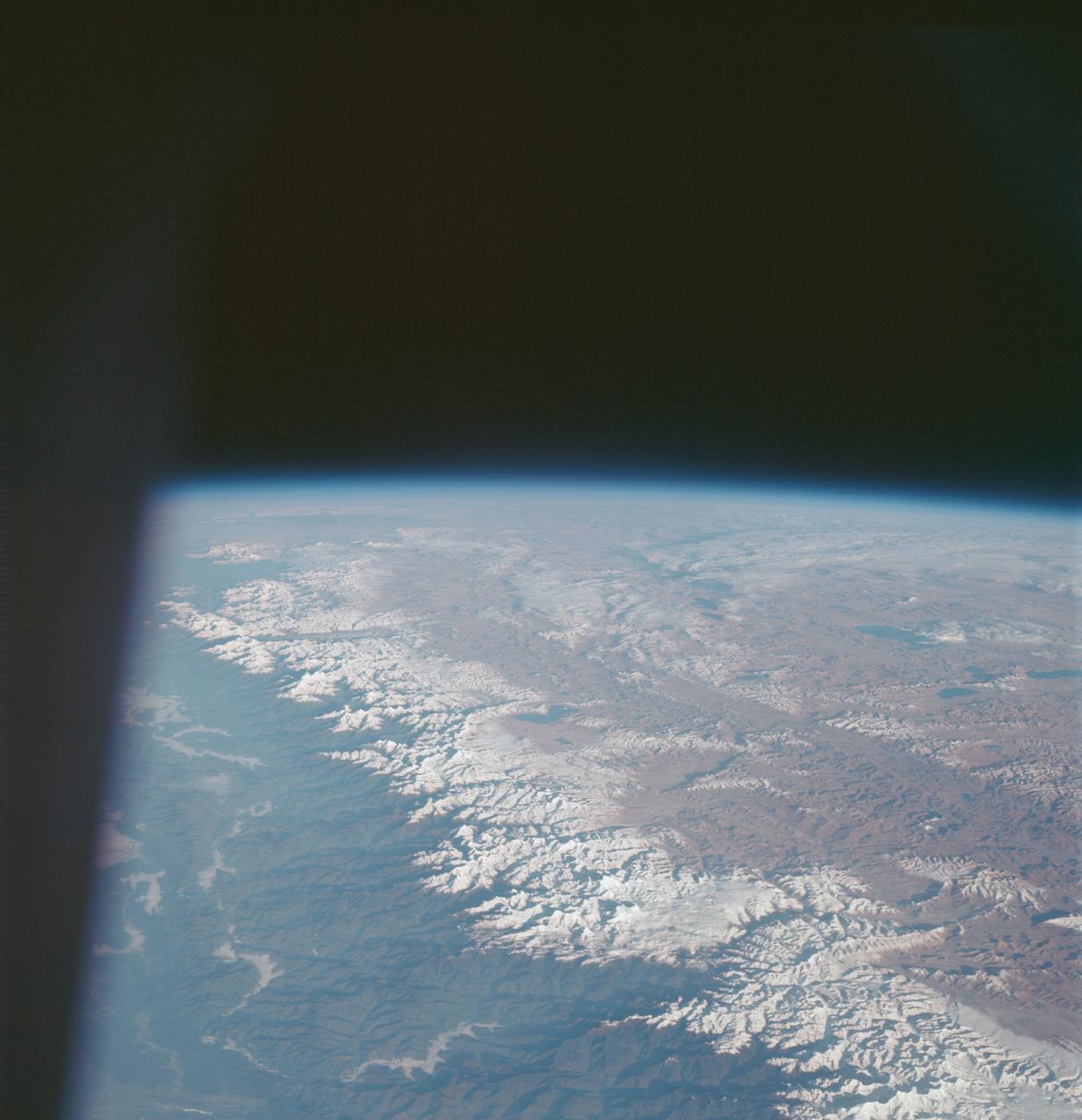

AS7-07-1748 (15 Oct. 1968) --- The world's dozen peaks which reach a height of greater than five miles above sea level are seen in this photograph from the Apollo 7 spacecraft at an altitude of approximately 130 nautical miles. The 29,028 ft. high Mount Everest is at lower center. On the central horizon can be seen the 28,250 ft. high Mount Godwin-Austen (K-2) some 800 miles northwest of Mount Everest. In the lower right, Mount Kanchenjunga rises 28,208 ft. to separate Nepal from Sikkim. The snow line on the peaks was at 17,500 ft. In the upper right the lake-studded highlands of Tibet are visible.

AS07-04-1600 (20 Oct. 1968) --- Astronaut Donn F. Eisele, Apollo 7 command module pilot, smiles through a heavy growth of beard as he is photographed during a momentary pause on the ninth day of the Apollo 7 mission.

AS07-05-1652 (13 Oct. 1968) --- Pacific coast area of southwestern Mexico, State of Guerrero, from Acapulco to Tecoanapa, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 34th revolution of Earth. Photographed from an altitude of 125 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 54 hours and 10 minutes. Much cloud cover in area.
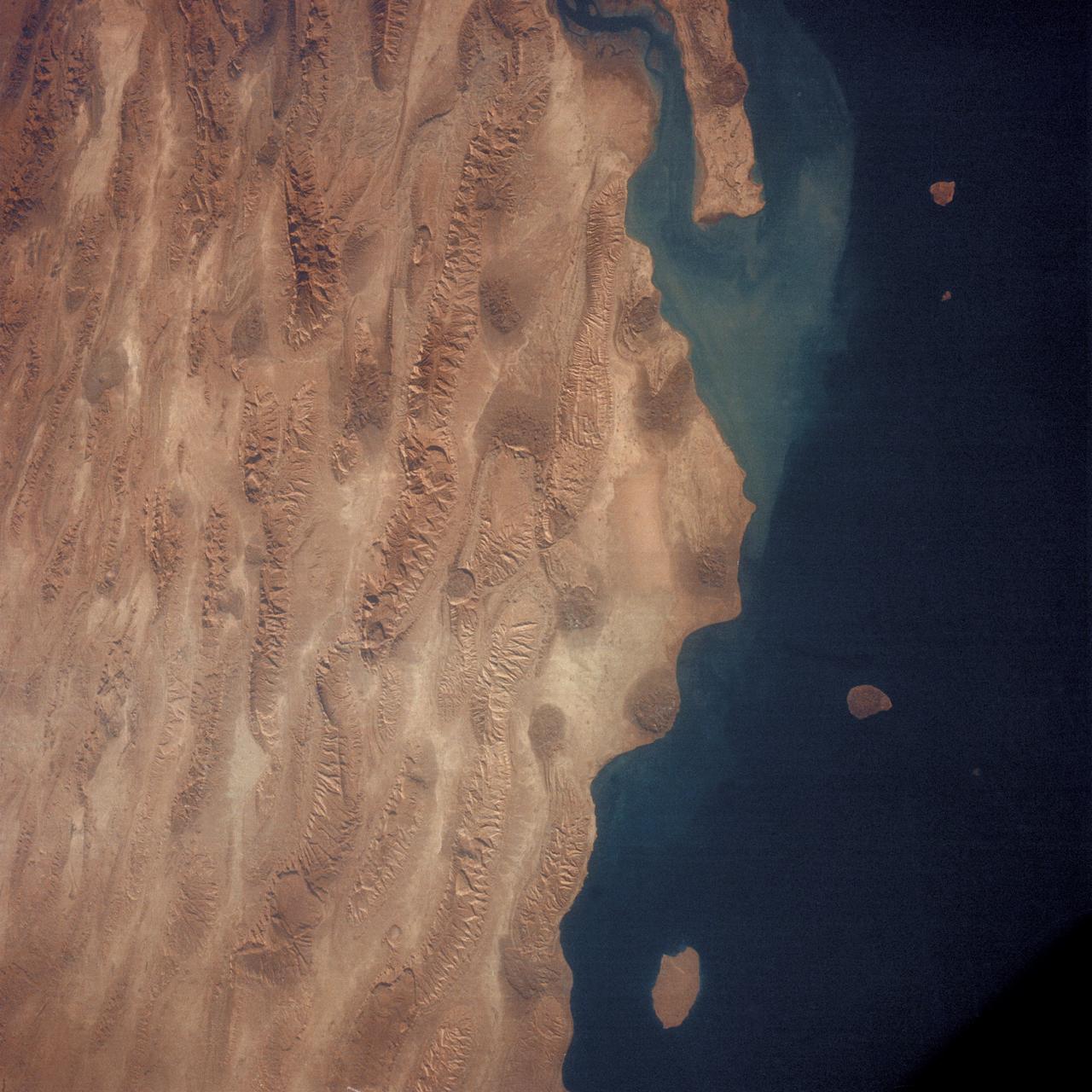

AS7-05-1615 (12 Oct. 1968) --- Persian Gulf coastal area of Iran, Qeshm Island, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 24th revolution of Earth. Photographed from an altitude of approximately 130 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 37 hours and 23 minutes.
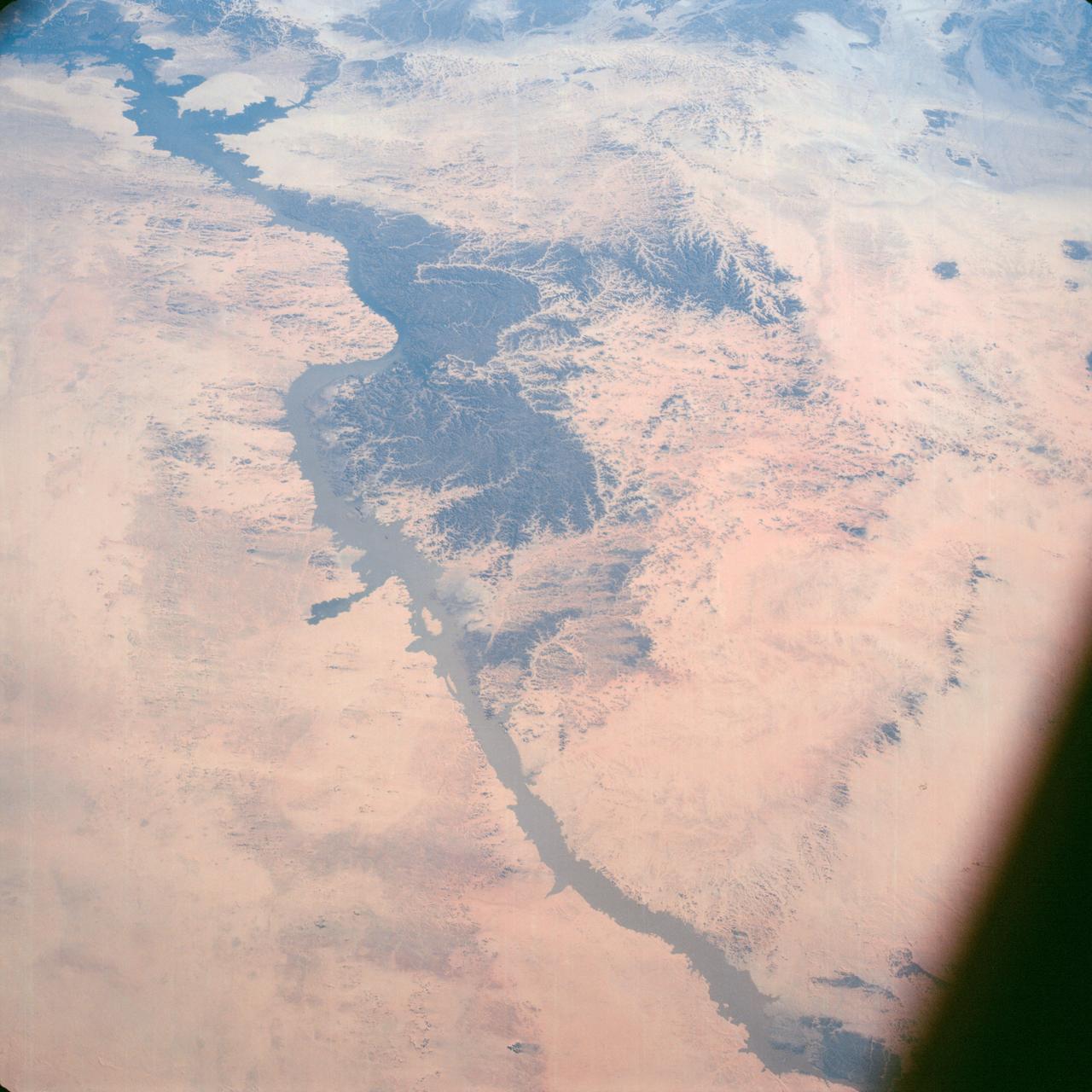

Lake Nasser on the Nile River in southeastern United Arab Republic (Egypt) as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 10th revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 130 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 14 hours and 56 minutes. Lake Nasser was created by the contruction of the Aswan Dam on the Nile.
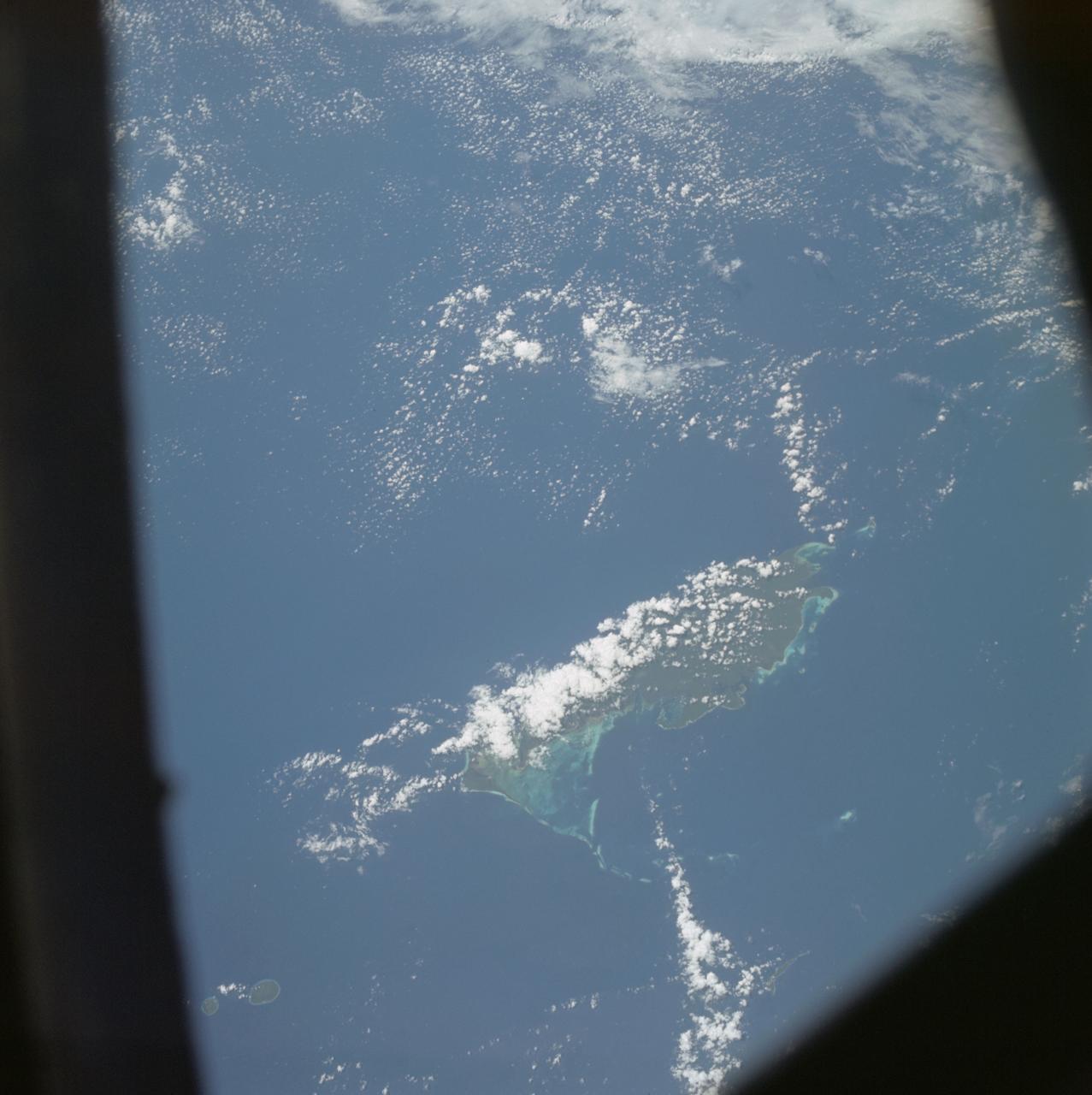

AS07-04-1609 (21 Oct. 1968) --- Woodlark Island in the Solomon Sea, east of New Guinea and northeast of Australia, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 158th revolution of Earth. Photographed from an altitude of 140 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 251 hours and 21 minutes.

AS7-07-1741 (14 Oct. 1968) --- Island of Oahu, State of Hawaii, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 51st revolution of Earth. Photographed from an altitude of 122 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 81 hours. Diamond Head and Pearl Harbor are clearly visible.
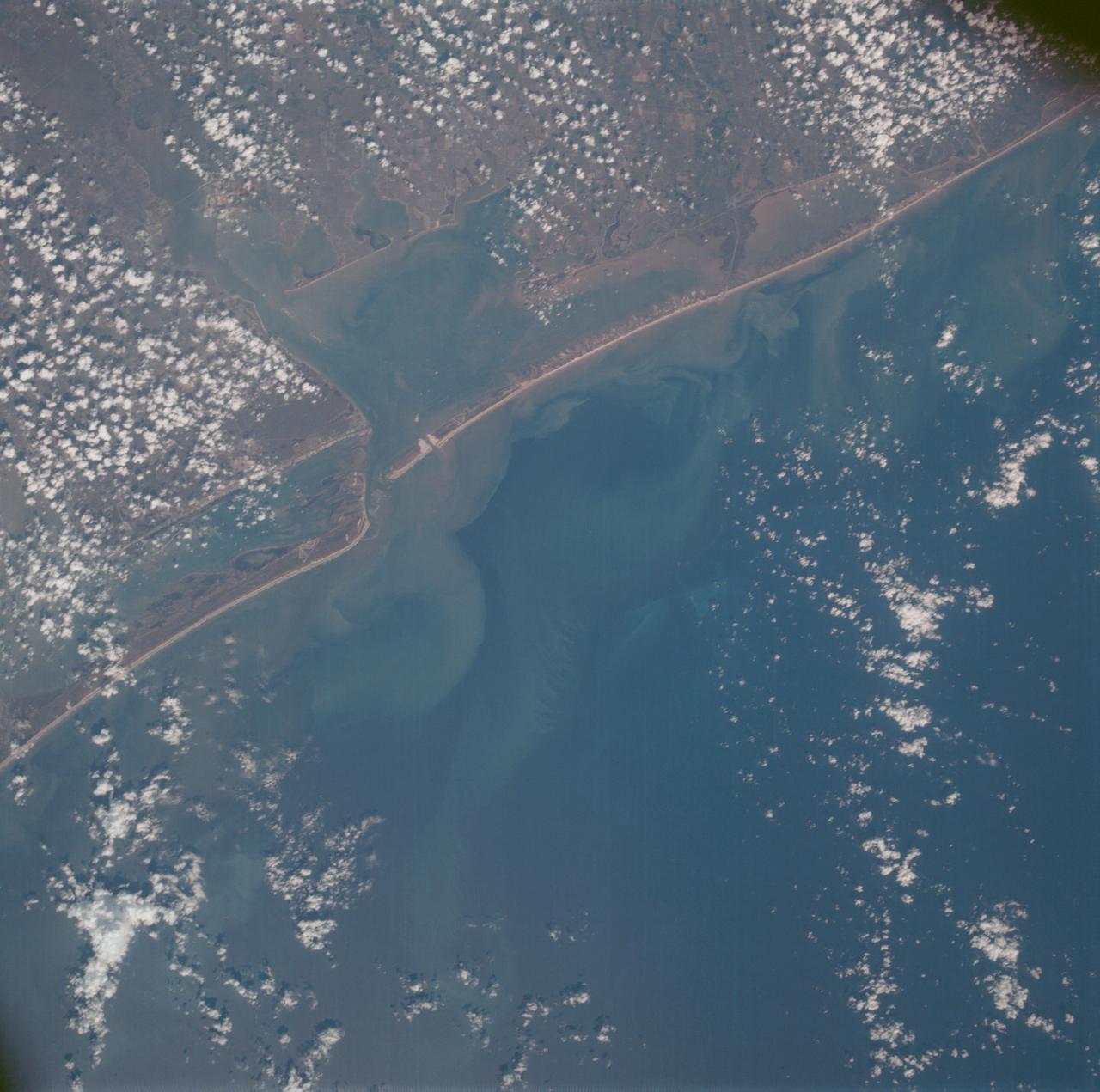

AS07-07-1800 (15 Oct. 1968) --- Matagorda Bay area on the Gulf Coast of Texas as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 62nd revolution of Earth. Photographed from an altitude of 90 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 98 hours and 38 minutes.

AS7-05-1667 (13 Oct. 1968) --- Kabul, Afghanistan area as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 39th revolution of Earth. Photographed from an altitude of 127 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 61 hours and 20 minutes. Also, visible in picture are the Panjshir River and the Koh-i-Baba Mountains.
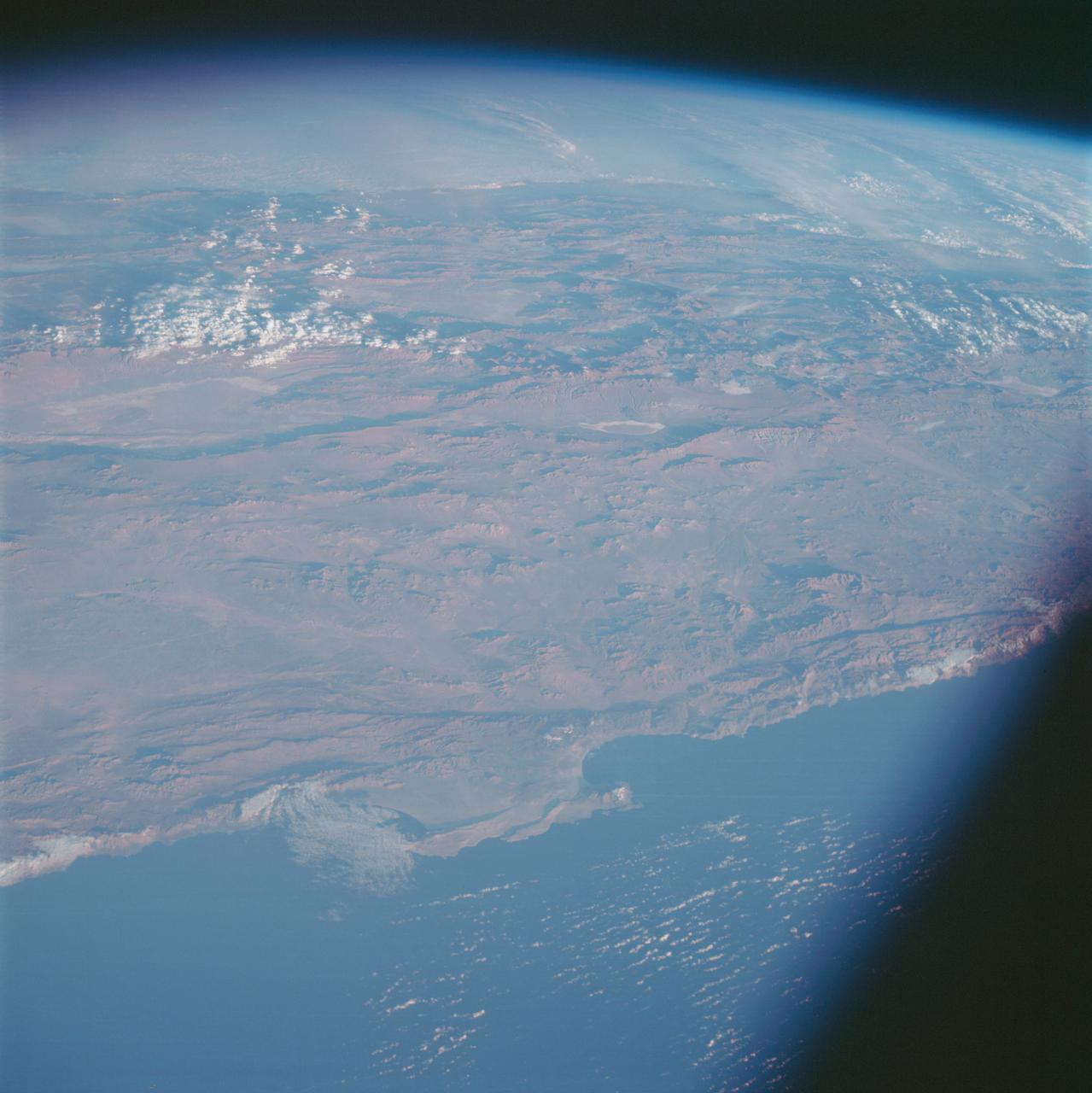

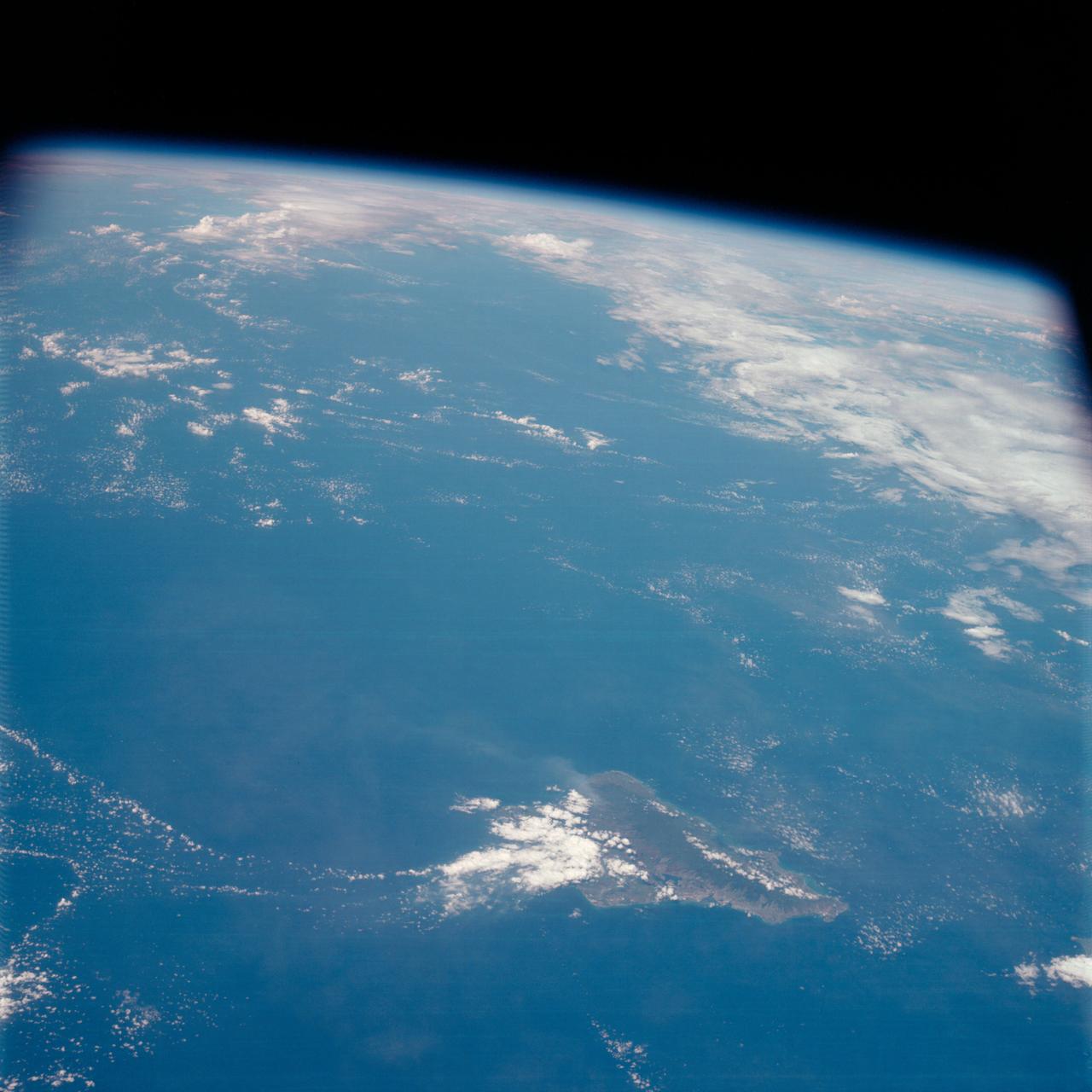
AS07-07-1826 (17 Oct. 1968) --- This view of South America was photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 81st revolution of Earth from an altitude of 120 nautical miles. The port city of Antofagasta, Chile, is located in the half-moon shaped bay in the lower left portion of the picture. Beyond the coast is the Andean peak of Llullaillaco Volcano which rises 22,000 feet above sea level. At left center is the Chuquicamata copper mines located near Coloma. At the center of the photo, behind the large salt lake and atop a 19,000 foot high volcano, the countries of Bolivia, Argentina, and Chile meet at a common point. Below the clouds in the upper portion of the photo are the Great Plains known as the Gran Chaco.
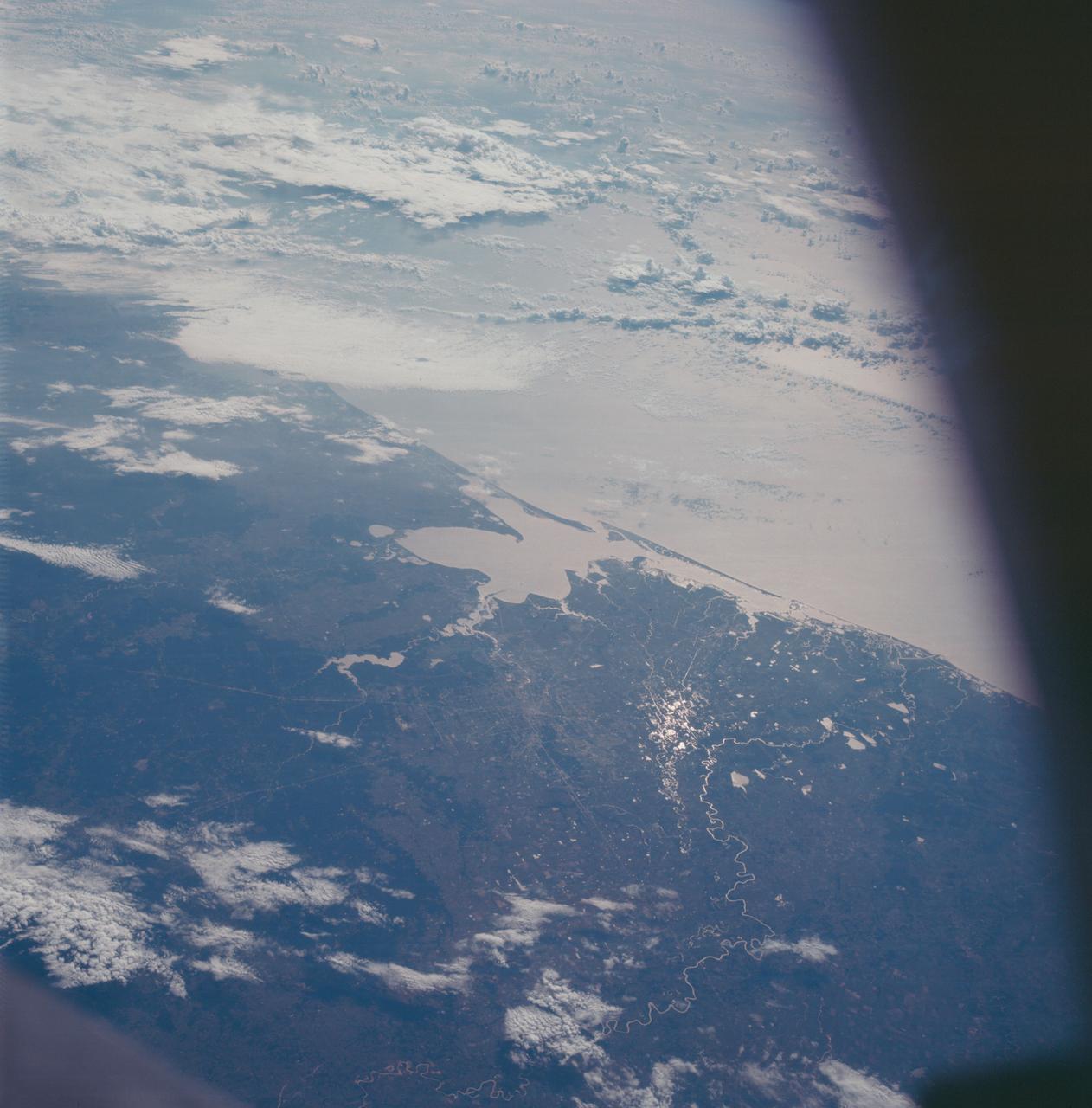

AS07-07-1872 (11-22 Oct. 1968) --- The Houston, Texas, and Gulf Coast area, looking southeast, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft at an altitude of 101 nautical miles. This photograph was made during the spacecraft's 91st revolution of Earth, at ground elapsed time of 144 hours and 26 minutes. The morning sun causes a spectacular reflection on water surfaces such as the Gulf of Mexico, Galveston Bay, Buffalo Bayou, and the Brazos River, and causes a unique reflection in the canals and rice fields west of Alvin. Some of the landmarks visible in this picture include highways and freeways, the Astrodome, the new Intercontinental Airport, and the Manned Spacecraft Center.
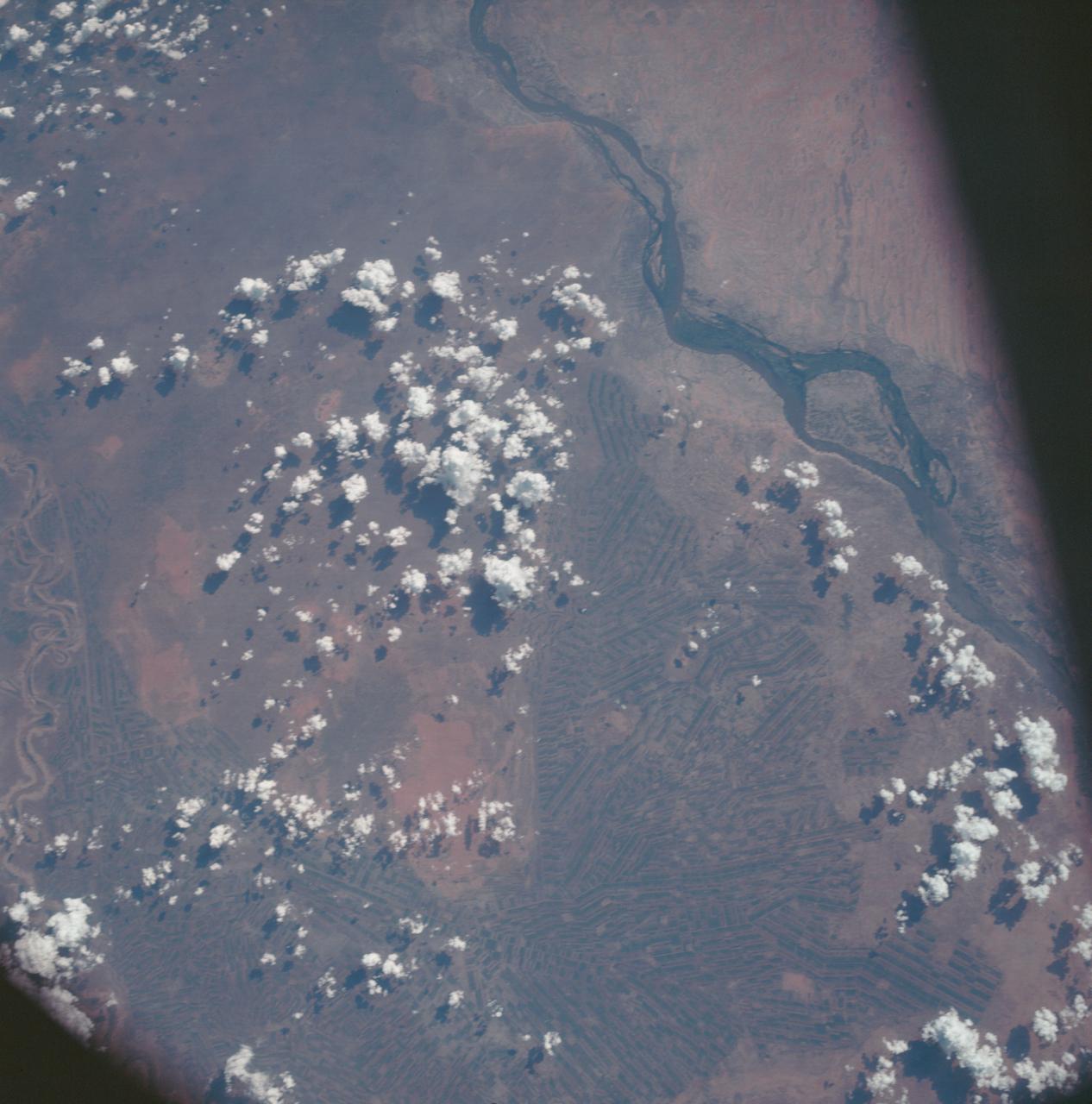

AS7-06-1718 (14 Oct. 1968) --- Sudan, showing White Nile and Blue Nile rivers below Khartoum, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 44th revolution of Earth. Photographed from an altitude of approximately 130 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 69 hours and 10 minutes. Note quilted-patchwork effect created by irrigated cultivated land.
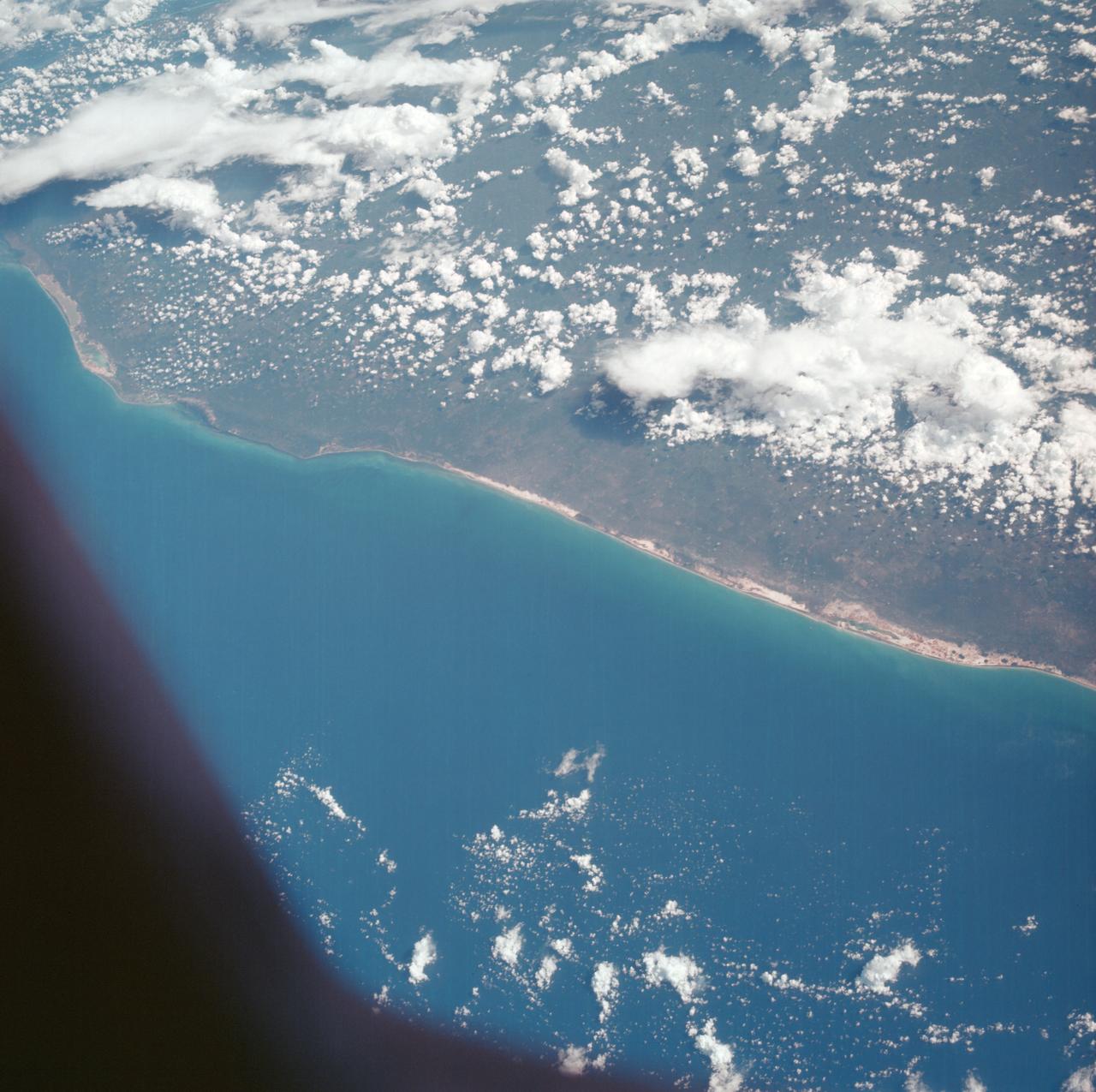

AS07-05-1635 (13 Oct. 1968) --- Gulf of Mexico, coast of Yucatan, Mexico, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 33rd revolution of Earth. Note road leading to city of Merida which is under cloud cover. Photographed from an altitude of 123 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 52 hours and 37 minutes.

S68-48788 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The Apollo 7/Saturn IB space vehicle is launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 34 at 11:03 a.m. (EDT), Oct. 11, 1968. Apollo 7 (Spacecraft 101/Saturn 205) is the first of several manned flights aimed at qualifying the spacecraft for the half-million-mile round trip to the moon. Aboard the Apollo spacecraft are astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr., commander; Donn F. Eisele, command module pilot; and Walter Cunningham, lunar module pilot. (Tracking antenna on left and pad service structure on right)
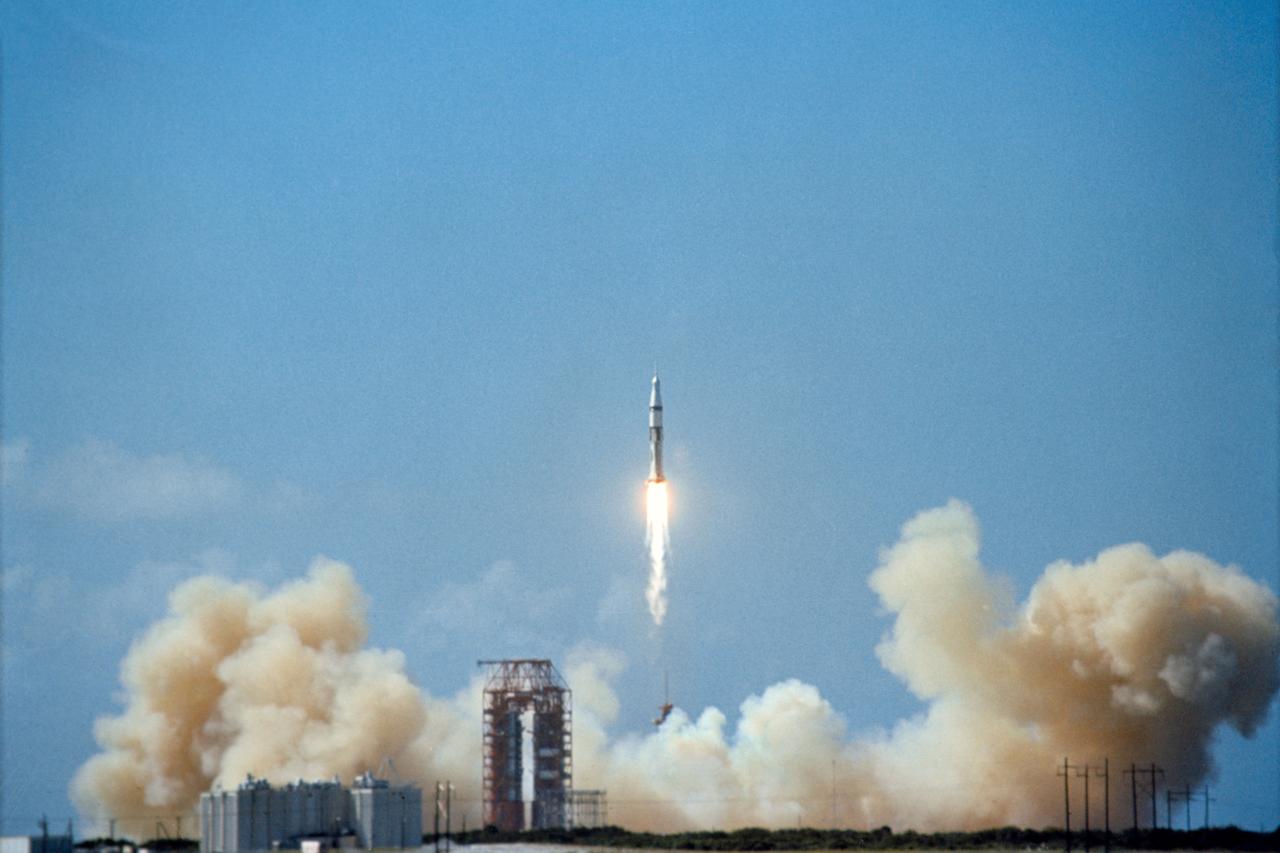

S68-48666 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The Apollo 7/Saturn IB space vehicle is launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 34 at 11:03 a.m. (EDT), Oct. 11, 1968. Apollo 7 (Spacecraft 101/Saturn 205) is the first of several manned flights aimed at qualifying the spacecraft for the half-million-mile round trip to the moon. Aboard the Apollo spacecraft are astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr., commander; Donn F. Eisele, command module pilot; and Walter Cunningham, lunar module pilot.
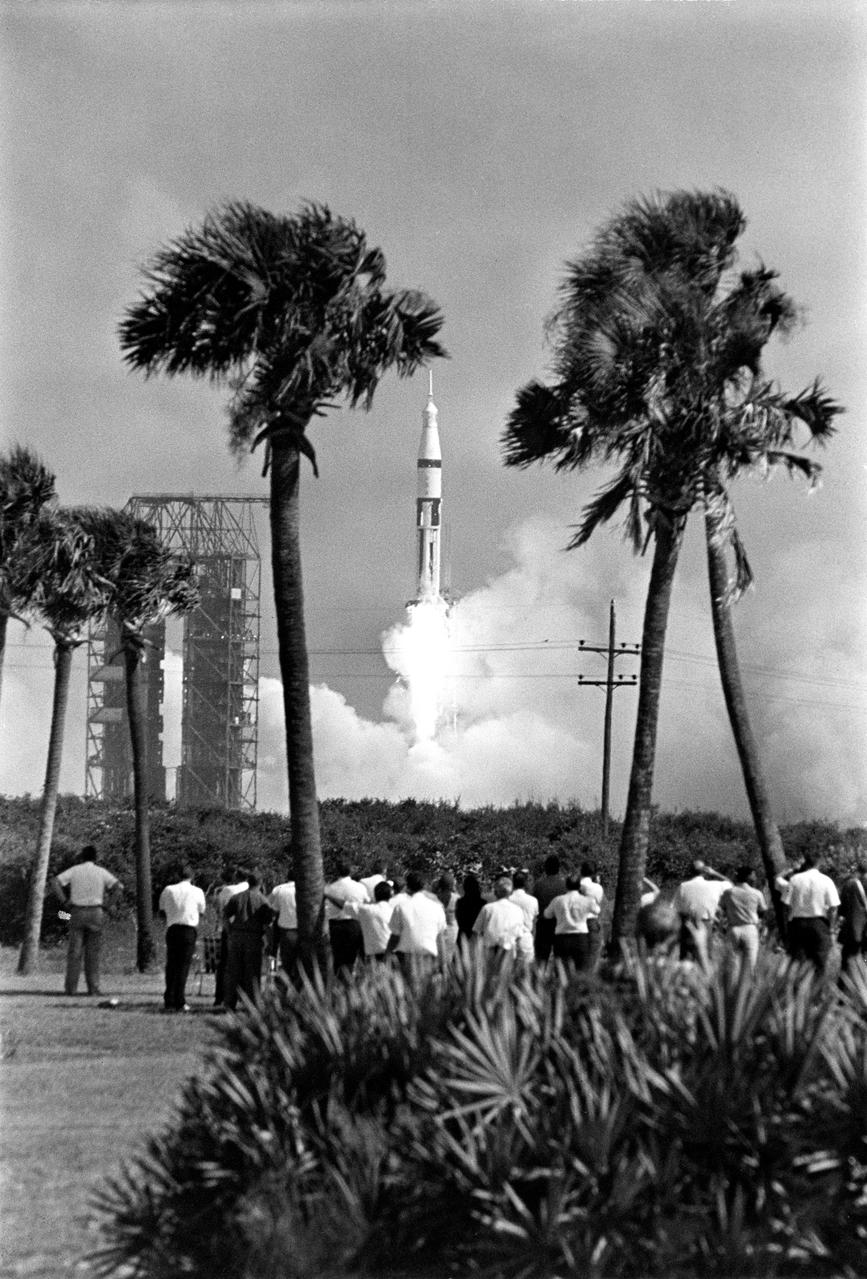

S68-48662 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The Apollo 7/Saturn IB space vehicle is launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 34 at 11:03 a.m. (EDT), Oct. 11, 1968. Apollo 7 (Spacecraft 101/Saturn 205) is the first of several manned flights aimed at qualifying the spacecraft for the half-million mile round trip to the moon. Aboard the Apollo spacecraft are astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr., commander; Donn F. Eisele, command module pilot; and Walter Cunningham, lunar module pilot. (This view is framed by palm trees on either side).
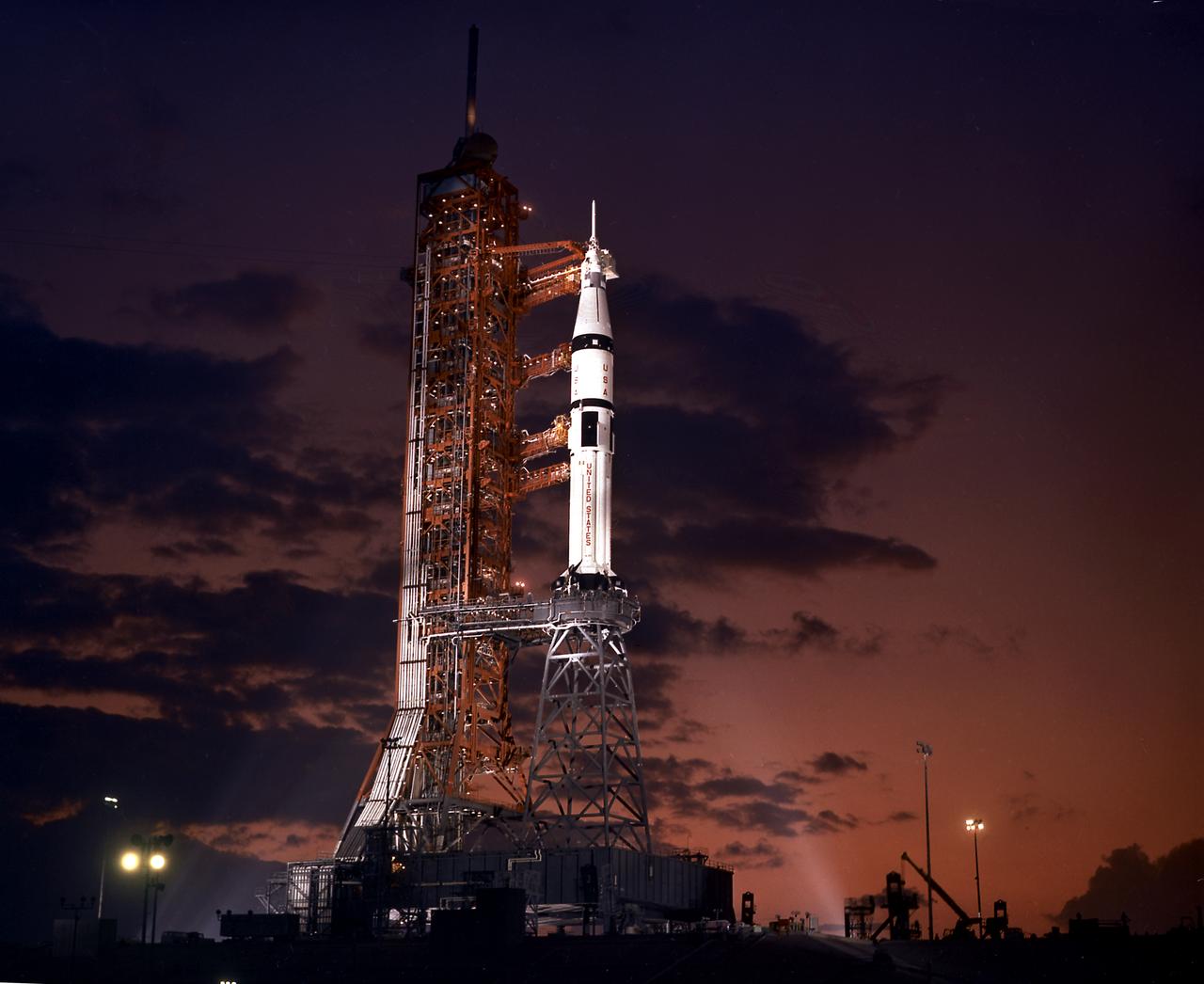

SA-210 Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) awaits the launch scheduled on July 15, 1975 on the launch pad at the Kennedy Space Center, the ASTP mission with astronauts Thomas Stafford, Vance Brand, and Donald "Deke" Slayton. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project .

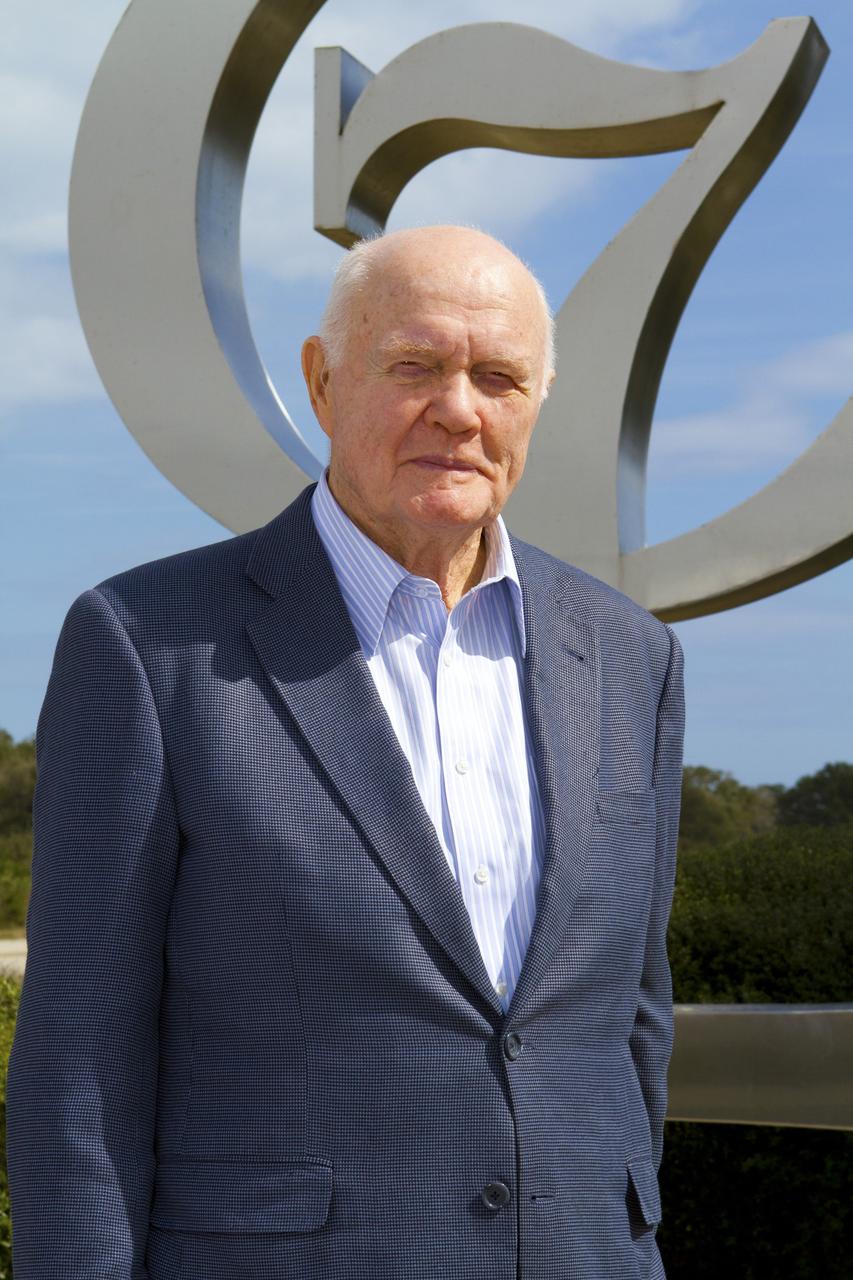
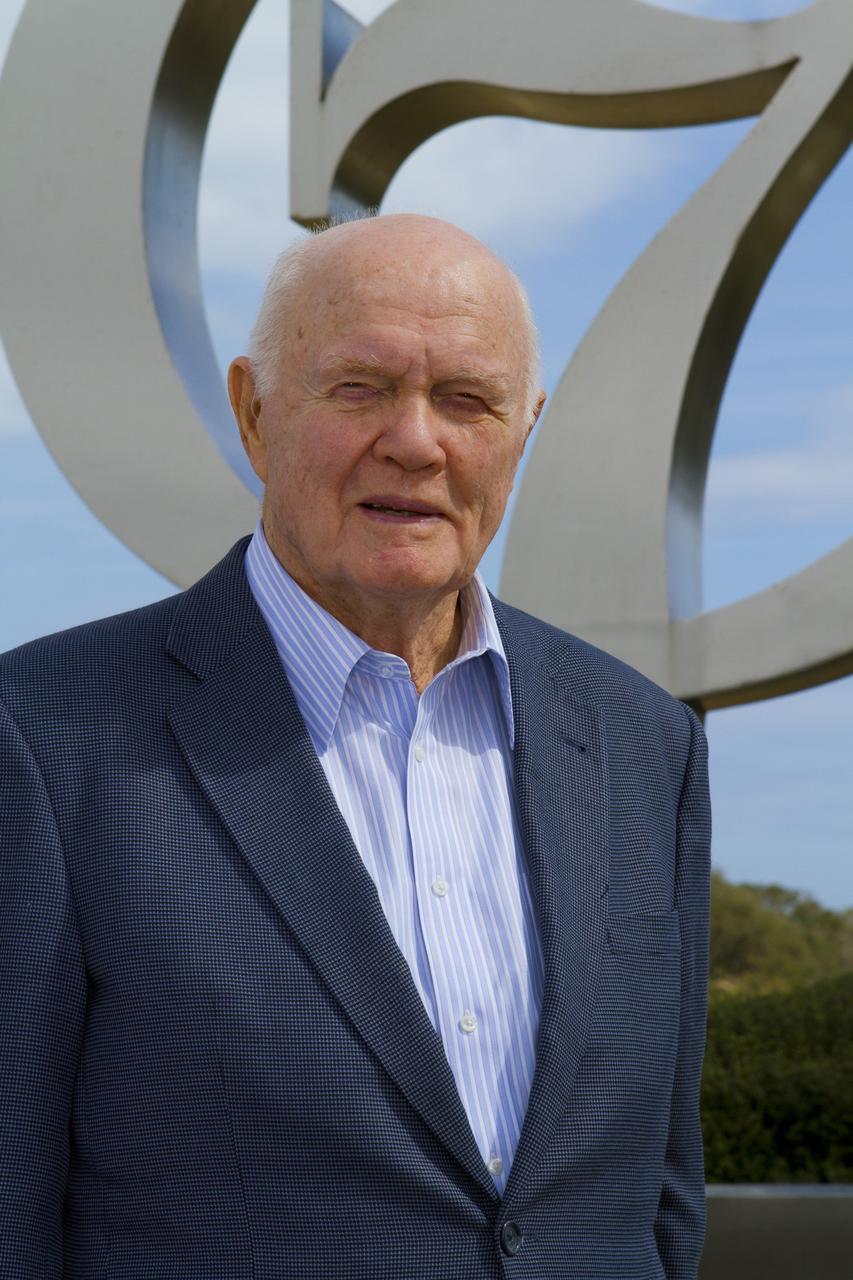
A memorial wreath is placed in the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida following a ceremony honoring the memory of former Apollo astronaut Walter Cunningham. The ceremony was held Jan. 9, 2023. Cunningham was the lunar module pilot for Apollo 7 – the first crewed flight test of the Apollo spacecraft – where he tested maneuvers necessary for docking and lunar orbit rendezvous. He passed away Jan. 3 at the age of 90.

A photo of former Apollo astronaut Walter Cunningham is displayed during a memorial ceremony at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ceremony was held Jan. 9, 2023, at the Heroes and Legends exhibit within the Astronaut Hall of Fame at the center’s visitor complex. Cunningham was the lunar module pilot for Apollo 7 – the first crewed flight test of the Apollo spacecraft – where he tested maneuvers necessary for docking and lunar orbit rendezvous. He passed away Jan. 3 at the age of 90.

Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, speaks during a memorial ceremony honoring former Apollo astronaut Walter Cunningham. The ceremony was held Jan. 9, 2023, at the Heroes and Legends exhibit within the Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Florida spaceport’s visitor complex. Cunningham was the lunar module pilot for Apollo 7 – the first crewed flight test of the Apollo spacecraft – where he tested maneuvers necessary for docking and lunar orbit rendezvous. He passed away Jan. 3 at the age of 90.
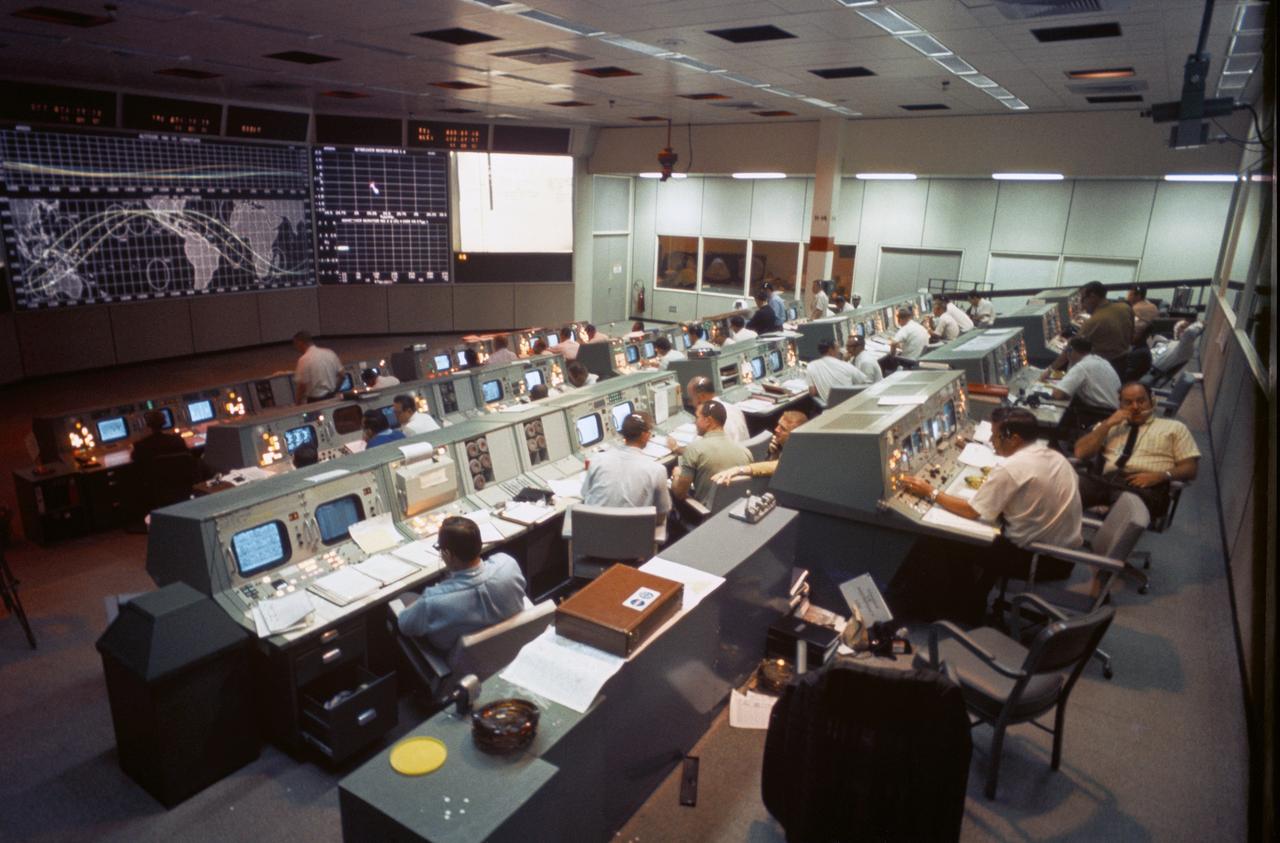

Overall view of activity in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center, Bldg 30, on the first day of the Apollo 7 space mission.
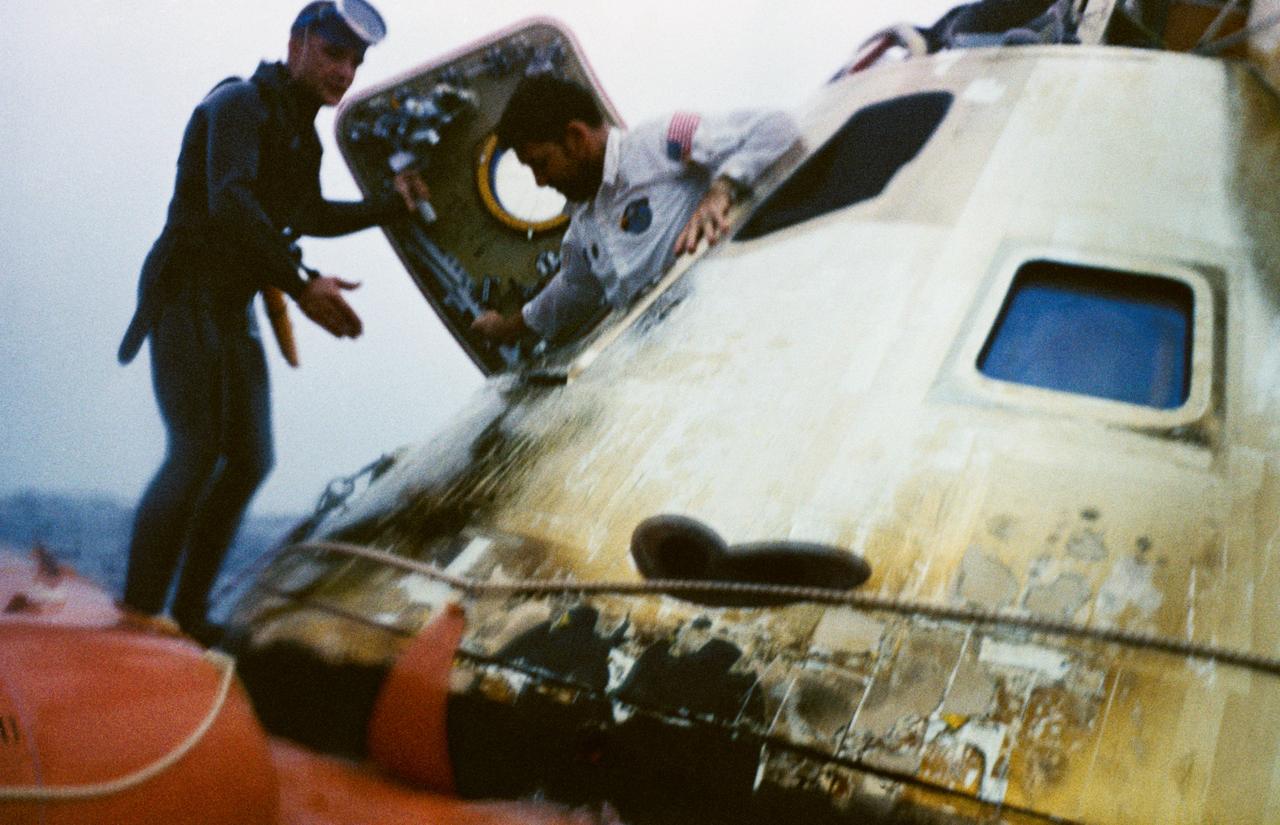

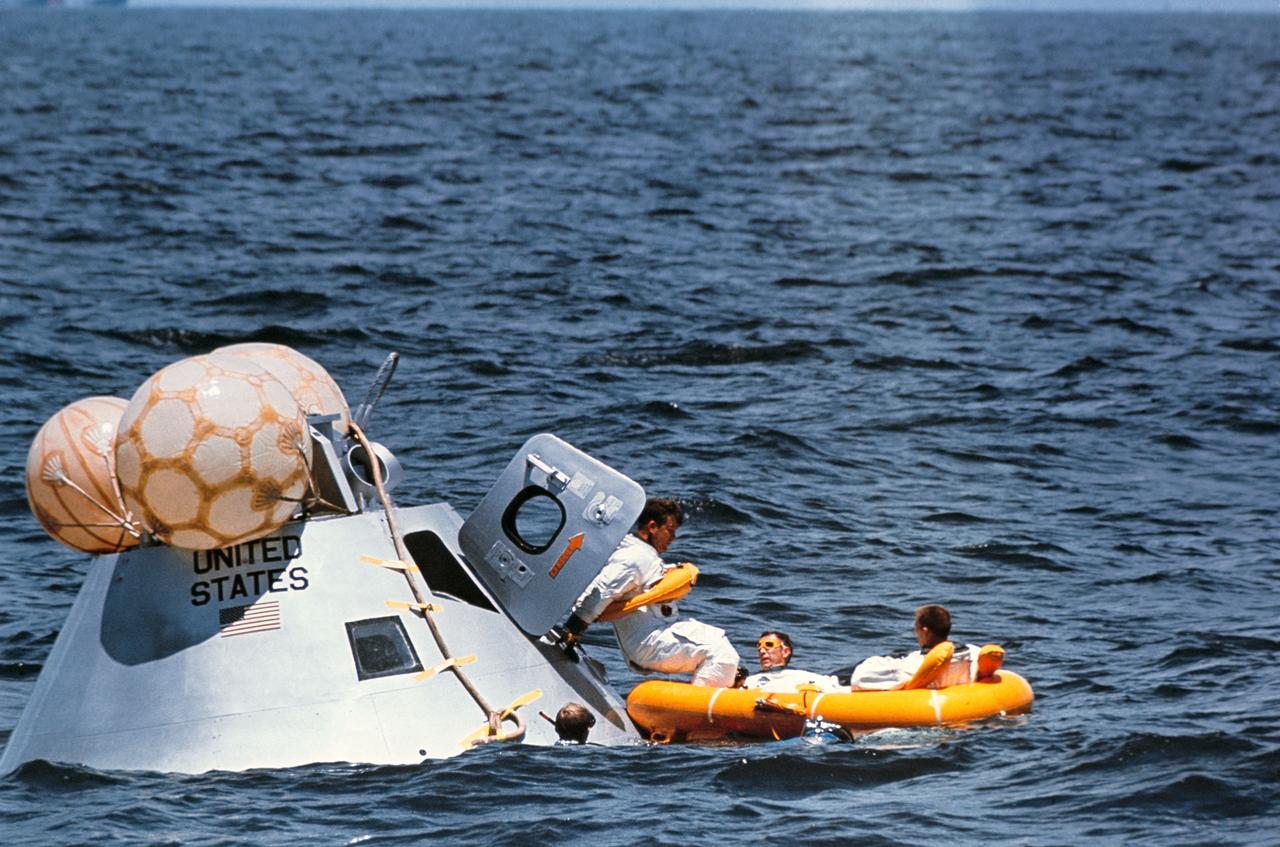
Astronaut Walter M. Schirra, Jr., Apollo 7 commander, egresses the spacecraft during recovery operations in the Atlantic. He is assisted by a member of the U.S. Navy frogman team. The Apollo 7 spacecraft splashed down at 7:11 a.m., October 22, 1968, approximately 200 nautical miles south-southwest of Bermuda.
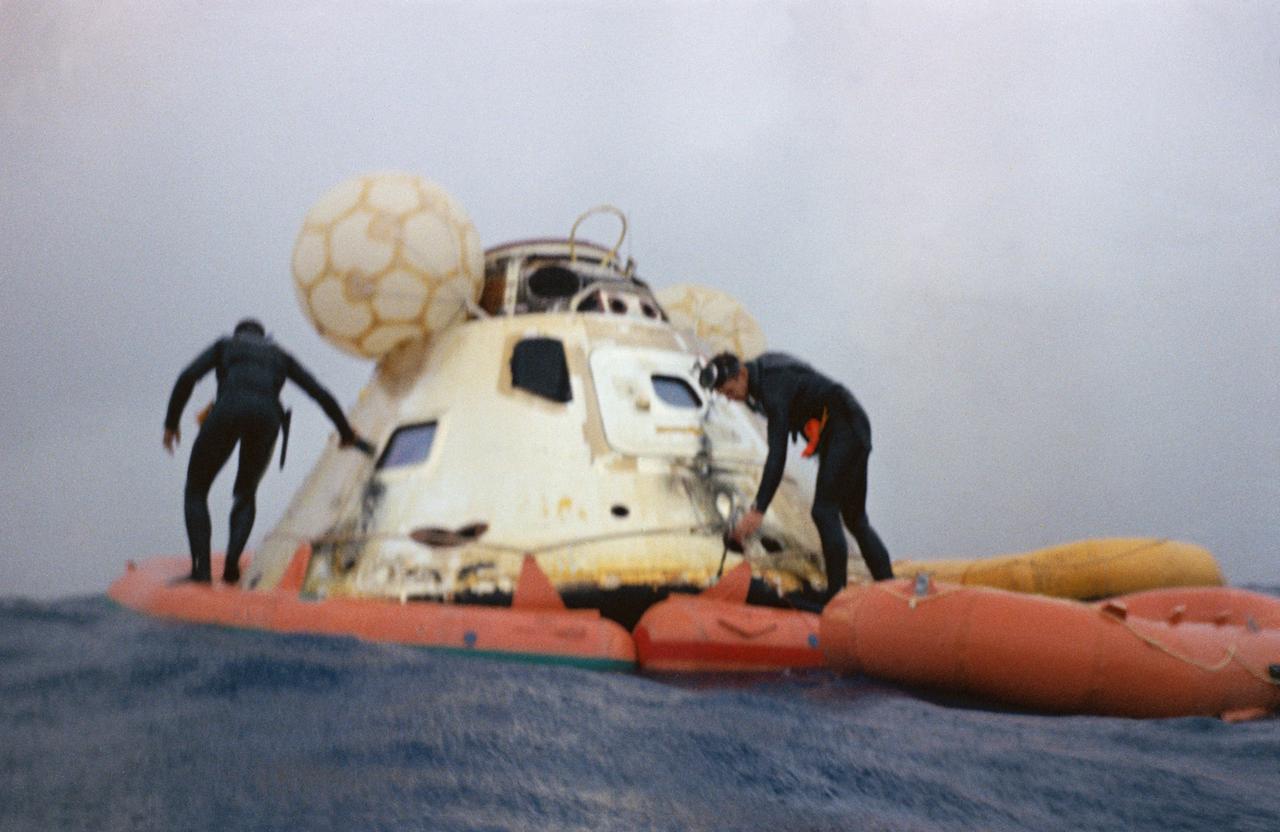

U.S. Navy frogmen attach a flotation collar to the Apollo 7 command module during recovery operations in the Atlantic. The Apollo 7 spacecraft splashed down at 7:11 a.m., October 22, 1968, approximately 200 nautical miles south-southwest of Bermuda.
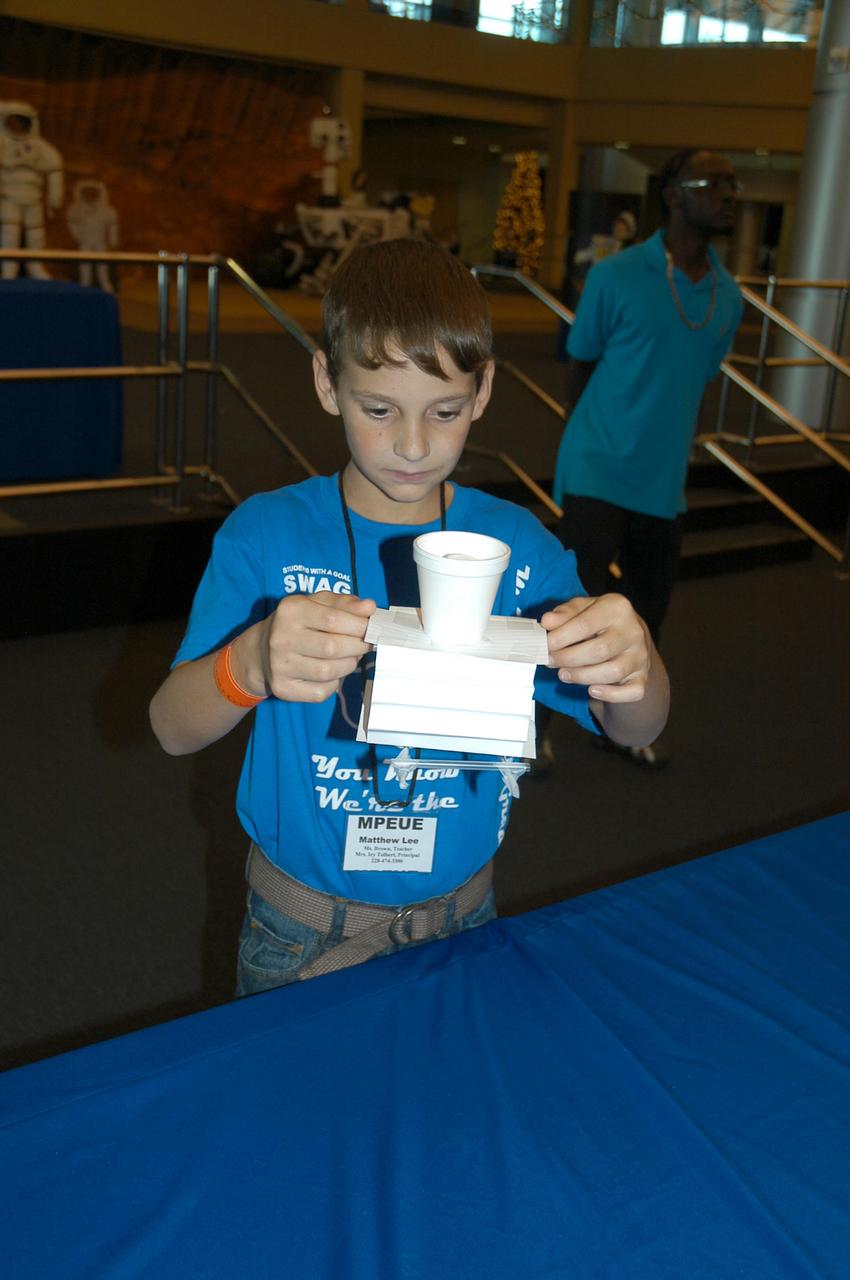

Matthew Lee from Escatawpa Elementary School in Moss Point, Miss., builds a lunar lander model during an activity at INFINITY Science Center, a NASA visitors center, on Dec. 7. NASA hosted two days of activities at the facility to celebrate the Apollo 17 flight to the moon in 1972, the final manned lunar mission of the Apollo Program
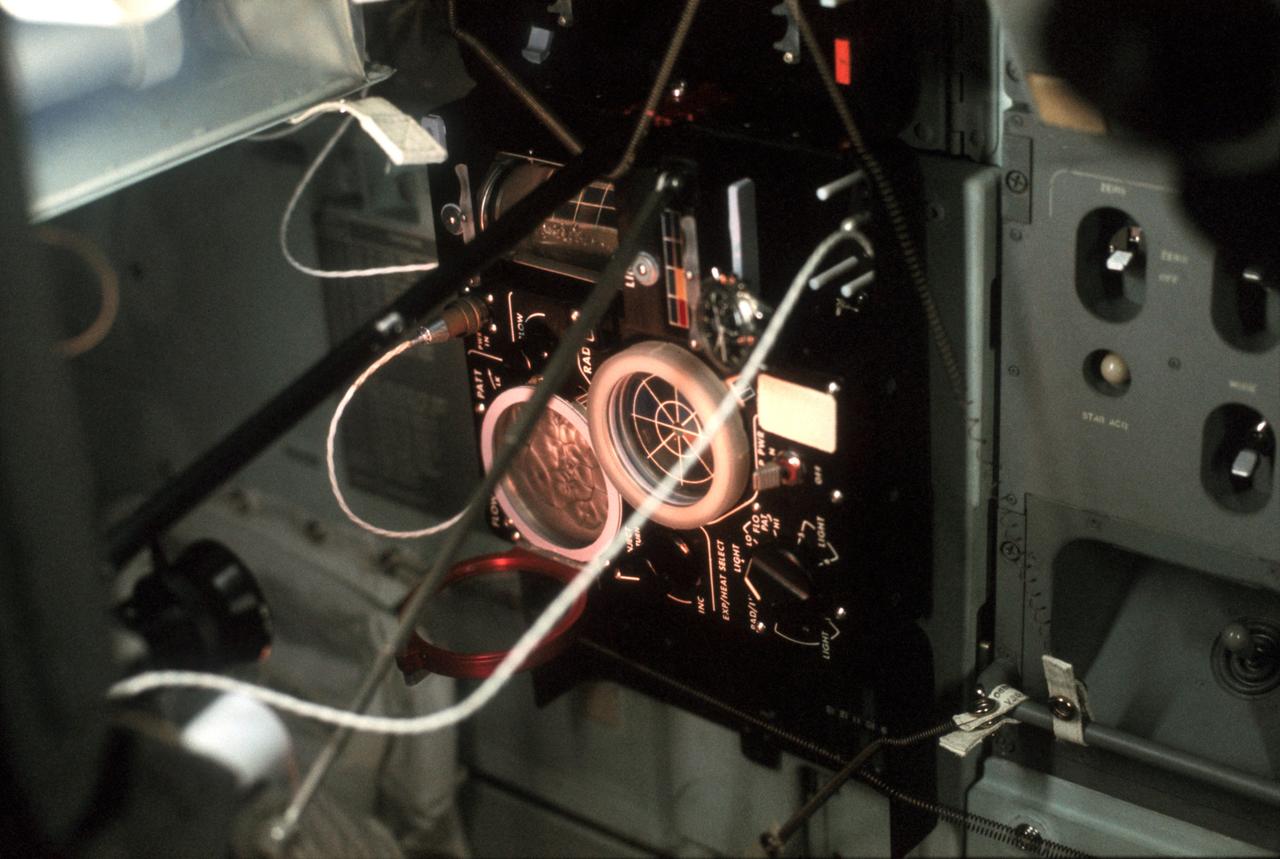
AS17-162-24063 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- A close-up view of the equipment used for the Heat Flow and Convection Experiment, an engineering and operational test and demonstration carried out aboard the Apollo 17 command module during the final lunar landing mission in NASA's Apollo program. Three test cells were used in the demonstration for measuring and observing fluid flow behavior in the absence of gravity in space flight. Data obtained from such demonstrations will be valuable in the design of future science experiments and for manufacturing processes in space.
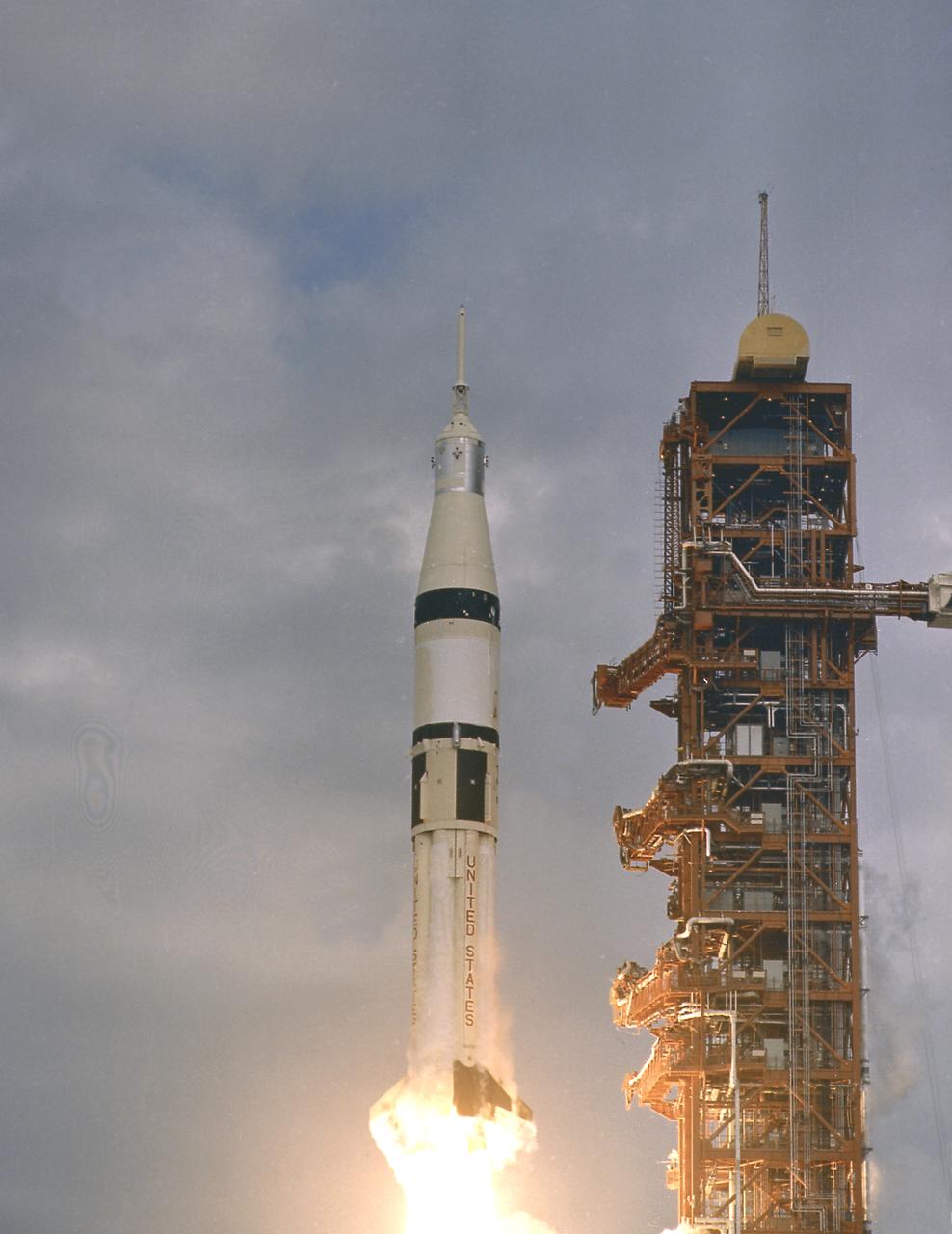
SA-206 lifts off from Kennedy Space Center's launch complex 39B, in Florida, on May 25, 1973, for the first manned Skylab mission (SL-2) with astronauts Pete Conrad, Joseph Kerwin, and Paul Weitz. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP).
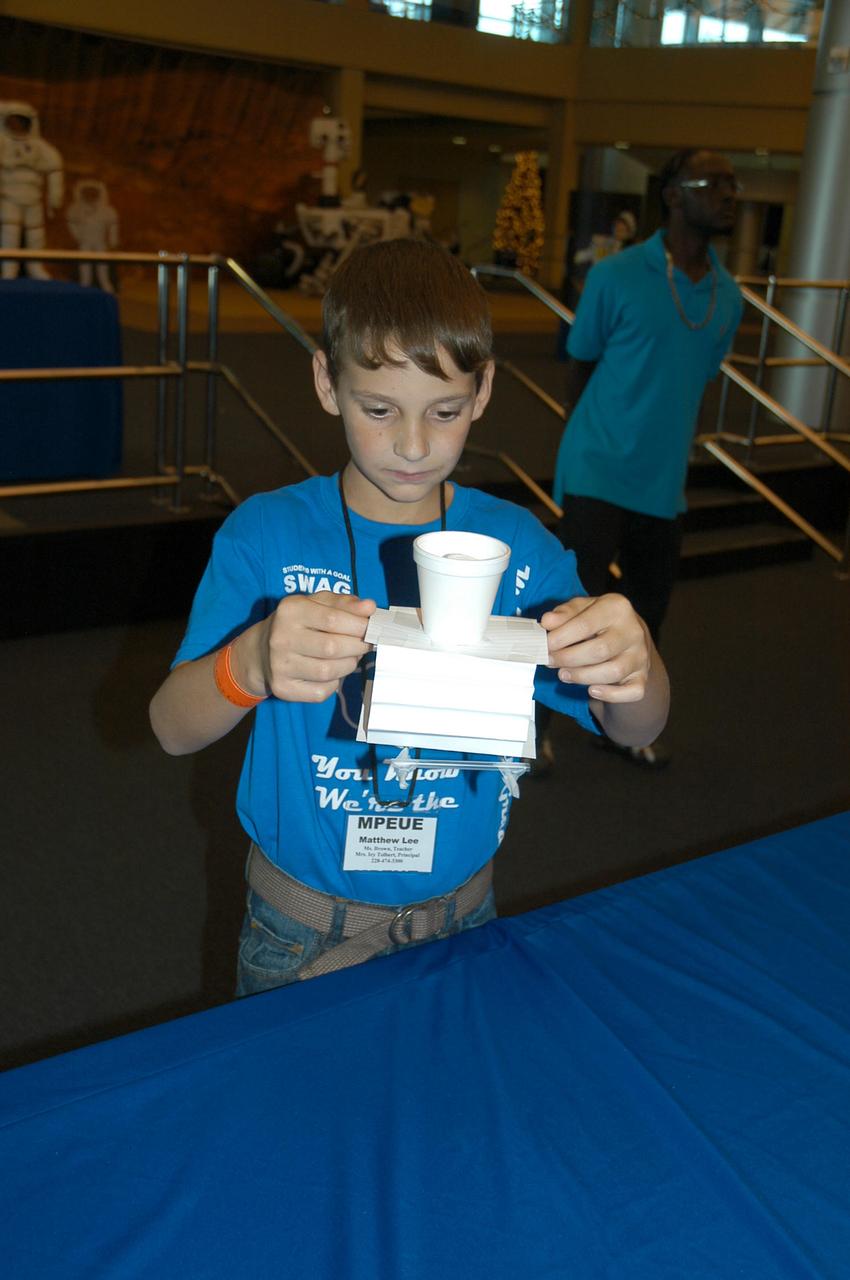

Matthew Lee from Escatawpa Elementary School in Moss Point, Miss., builds a lunar lander model during an activity at INFINITY Science Center, a NASA visitors center, on Dec. 7. NASA hosted two days of activities at the facility to celebrate the Apollo 17 flight to the moon in 1972, the final manned lunar mission of the Apollo Program.
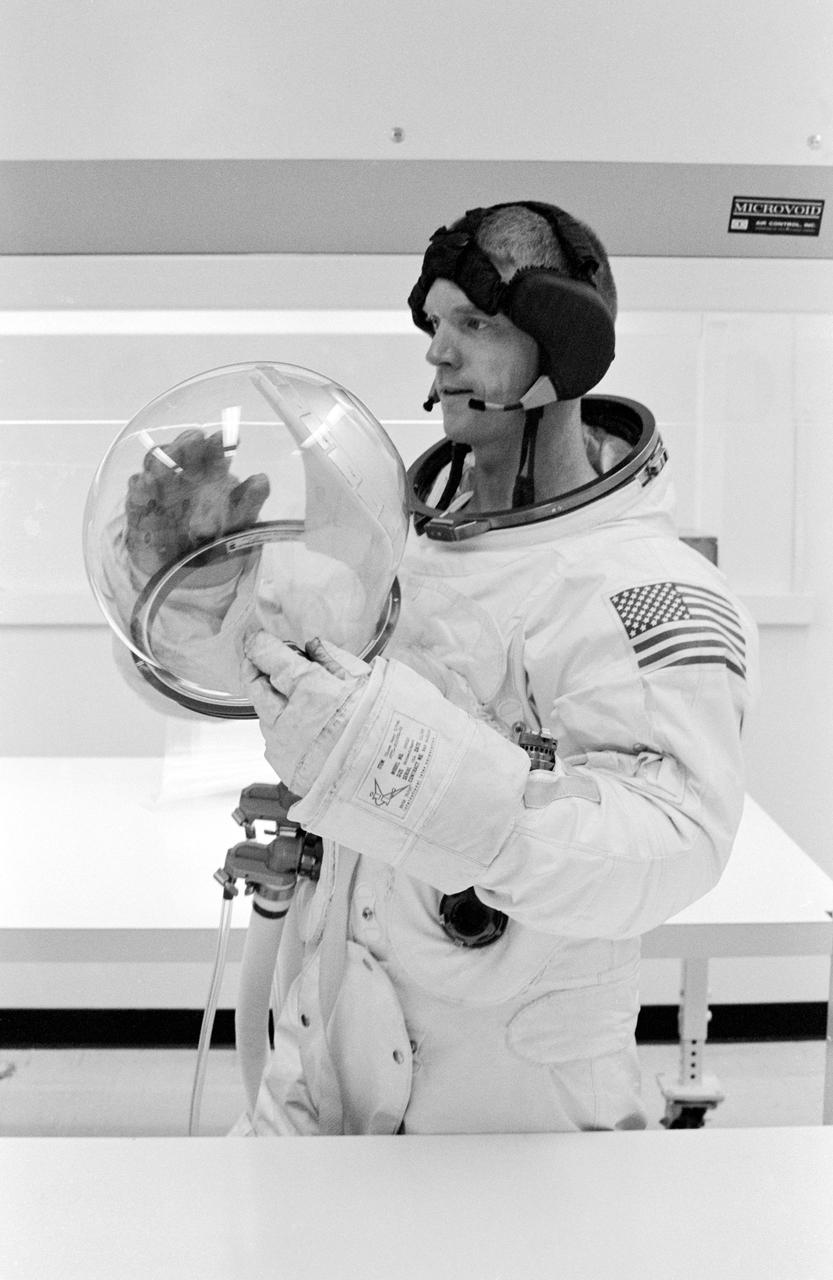

S68-38051 (29 June 1968) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart suits up to participate in an altitude verification test of the Apollo Portable Life Support System flight unit in Crew Systems Division's 8-ft altitude chamber in Building 7.
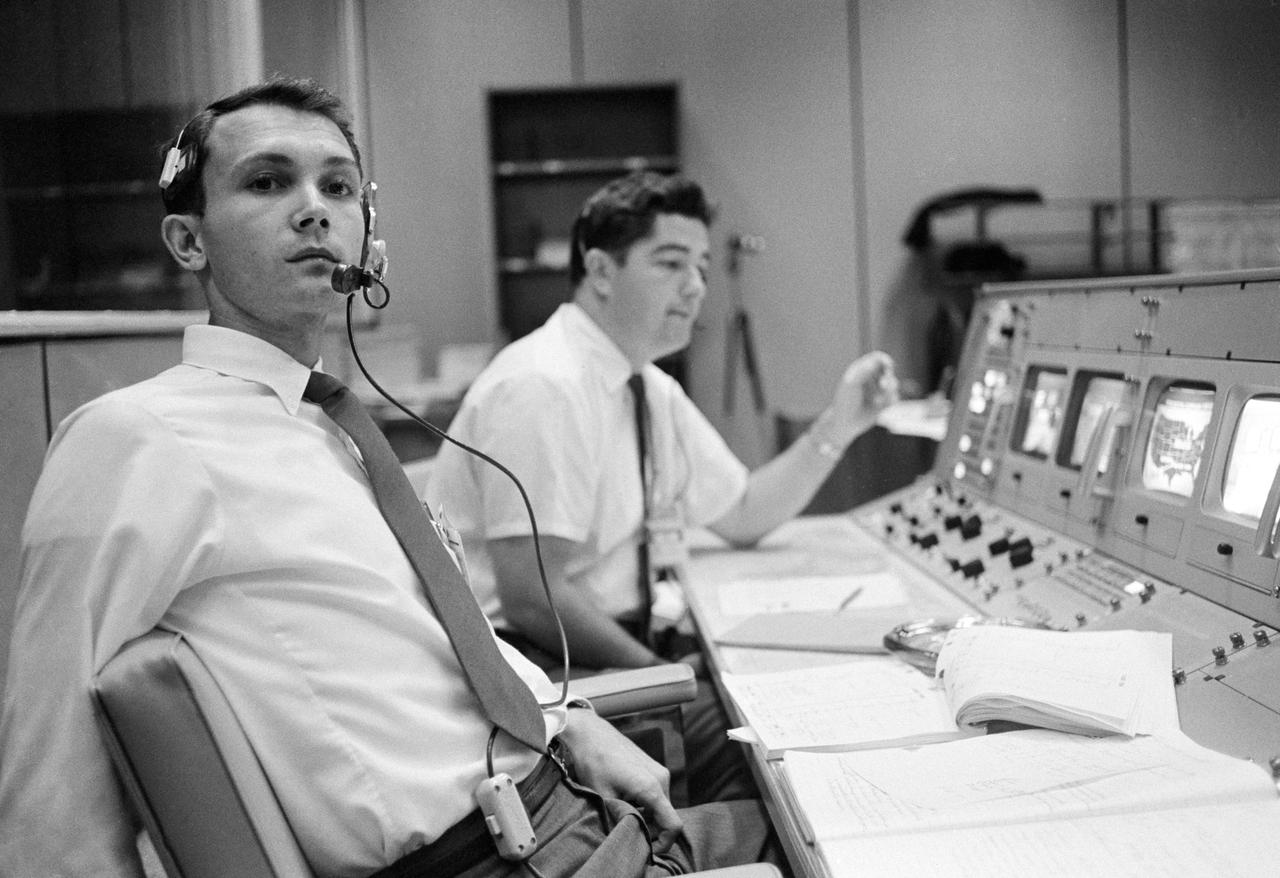

S68-50696 (October 1968) --- Public Affairs Office (PAO) commentator Douglas K. Ward (foreground) is pictured at his console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center at NASA's Johnson Space Center during the flight of Apollo 7. Photo credit: NASA
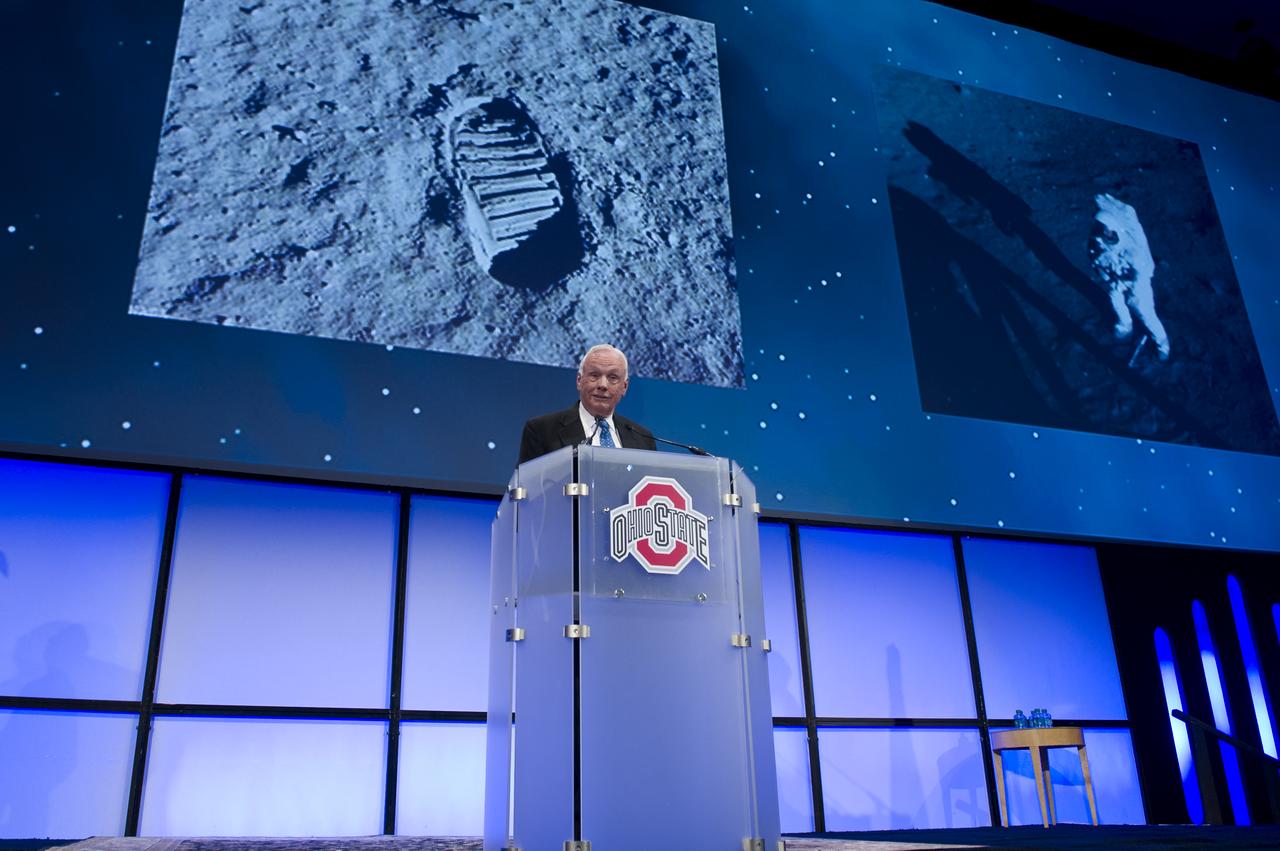

Apollo 11 Astronaut Neil Armstrong speaks during a celebration dinner at Ohio State University honoring the 50th anniversary of John Glenn's historic flight aboard Friendship 7 Monday, Feb. 20, 2012, in Columbus, Ohio. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
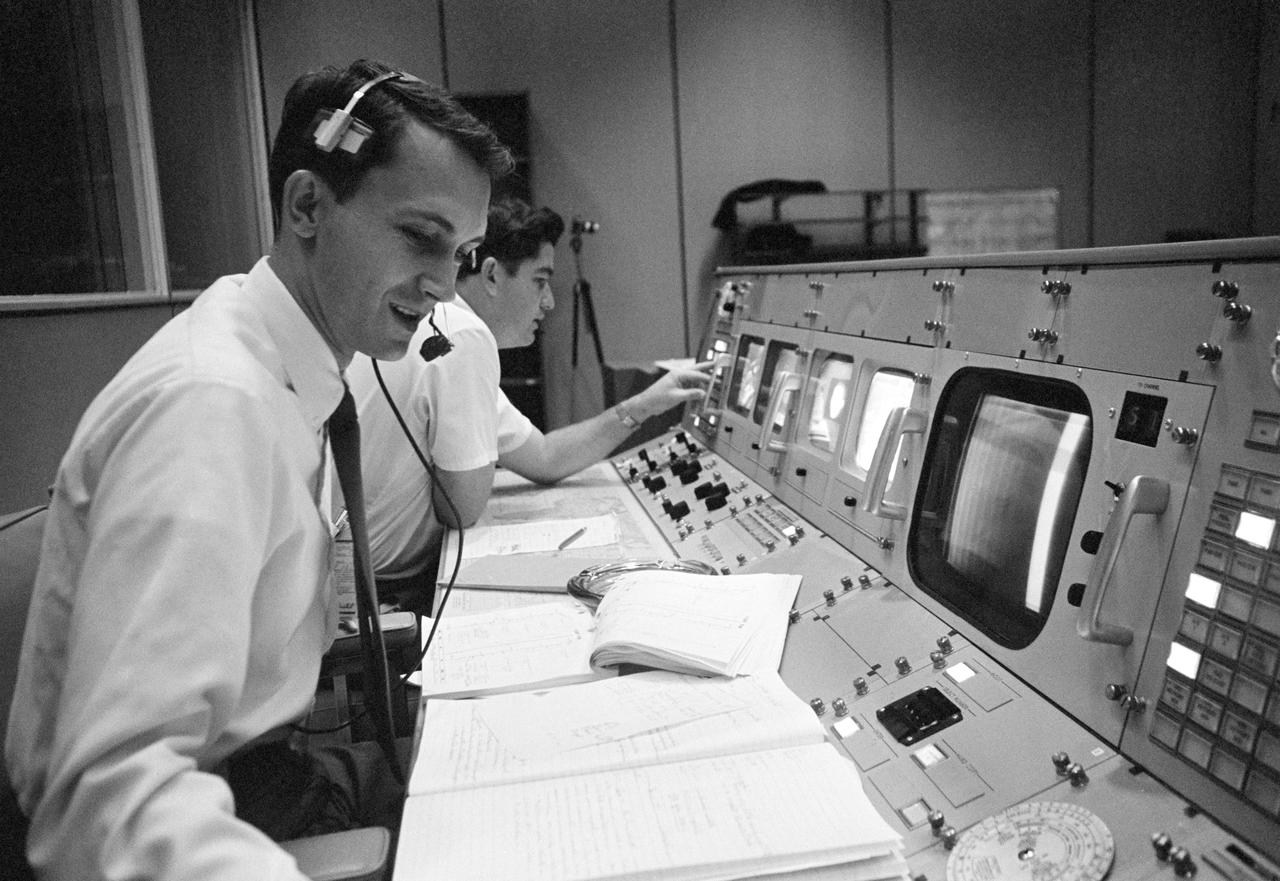

S68-50684 (October 1968) --- Public Affairs Office (PAO) commentator Douglas K. Ward is pictured at his console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center at NASA's Johnson Space Center during the flight of Apollo 7. Photo credit: NASA
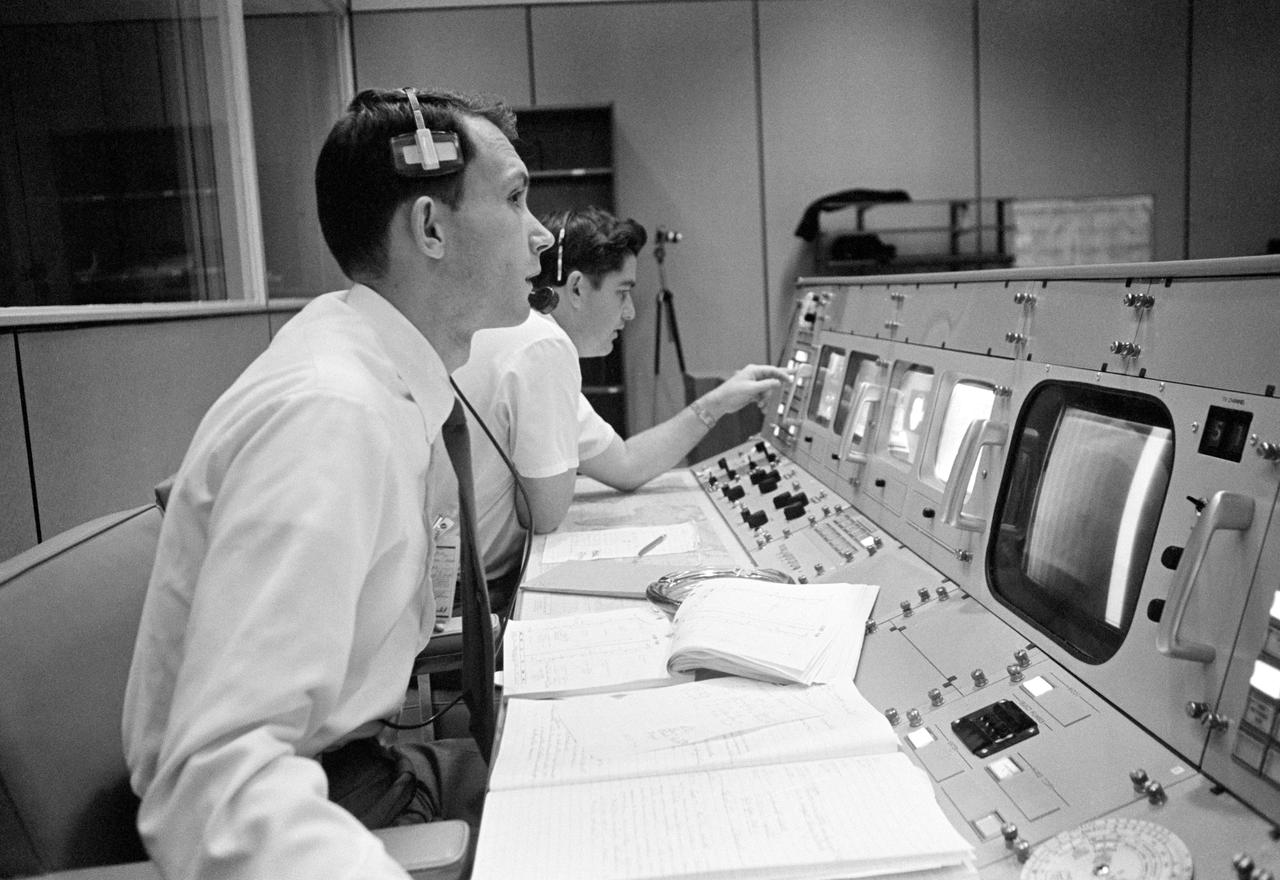

S68-50682 (October 1968) --- Public Affairs Office (PAO) commentator Douglas K. Ward is pictured at his console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center at NASA's Johnson Space Center during the flight of Apollo 7. Photo credit: NASA
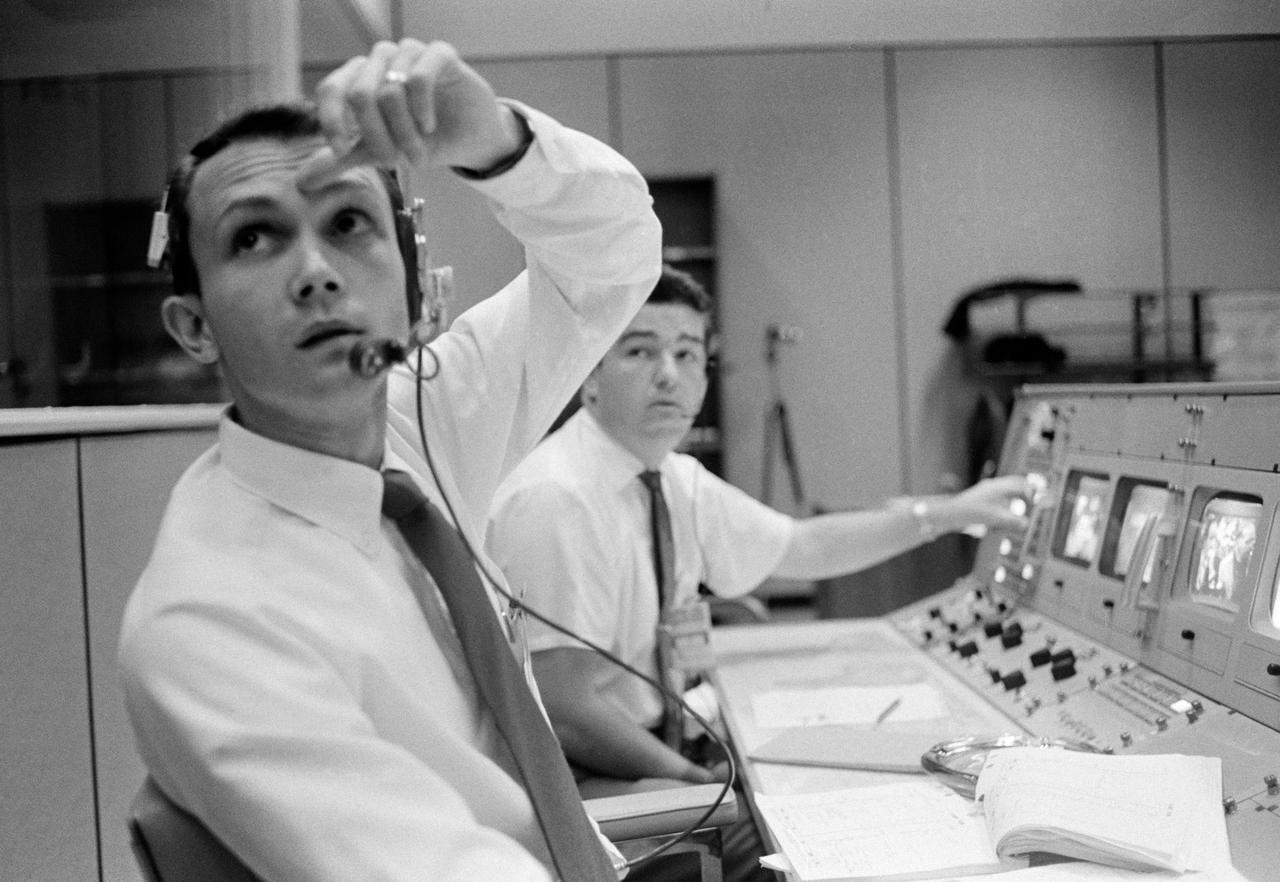

S68-50695 (October 1968) --- Public Affairs Office (PAO) commentator Douglas K. Ward is pictured at his console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center at NASA's Johnson Space Center during the flight of Apollo 7. Photo credit: NASA
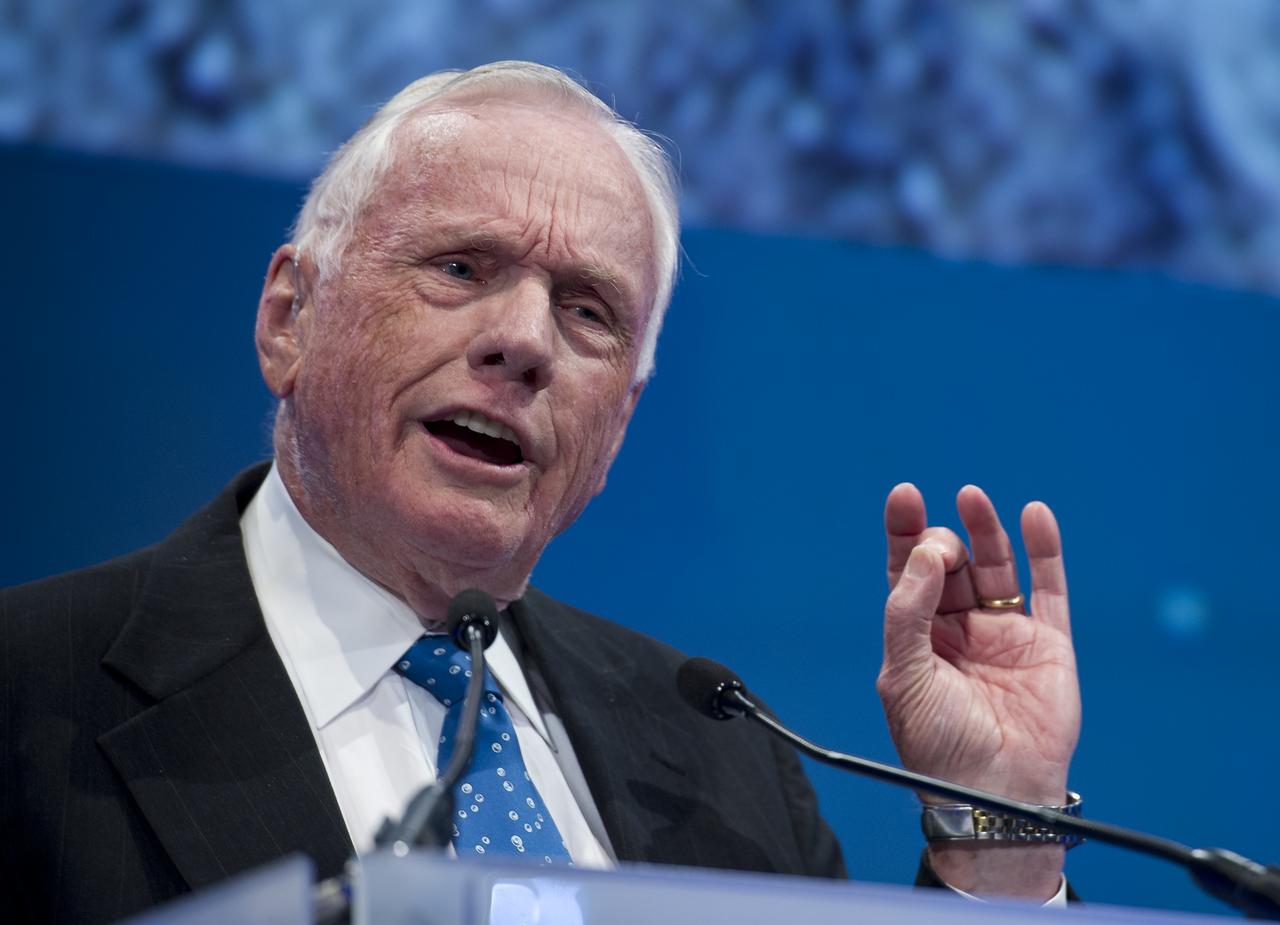

Apollo 11 Astronaut Neil Armstrong speaks during a celebration dinner at Ohio State University honoring the 50th anniversary of John Glenn's historic flight aboard Friendship 7 Monday, Feb. 20, 2012, in Columbus, Ohio. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Lisa Schott, vice chairman of the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, speaks during a memorial ceremony honoring former Apollo astronaut Walter Cunningham at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ceremony was held Jan. 9, 2023, at the Heroes and Legends exhibit within the Astronaut Hall of Fame at the spaceport’s visitor complex. Cunningham was the lunar module pilot for Apollo 7 – the first crewed flight test of the Apollo spacecraft – where he tested maneuvers necessary for docking and lunar orbit rendezvous. He passed away Jan. 3 at the age of 90.

S67-49969 (9 Nov. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The liftoff of the huge 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was at 7:00:01 a.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967. The successful objectives of the Apollo 4 Earth-orbital unmanned space mission obtained included (1) flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, subsystem operation, emergency detection subsystem operation, and (2) evaluation of the Apollo Command Module heat shield under conditions encountered on return from a moon mission.

S67-50903 (9 Nov. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The liftoff of the huge 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was at 7:00:01 a.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967. The successful objectives of the Apollo 4 Earth-orbital unmanned space mission obtained included (1) flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, subsystem operation, emergency detection subsystem, and (2) evaluation of the Apollo Command Module heat shield under conditions encountered on return from a moon mission.
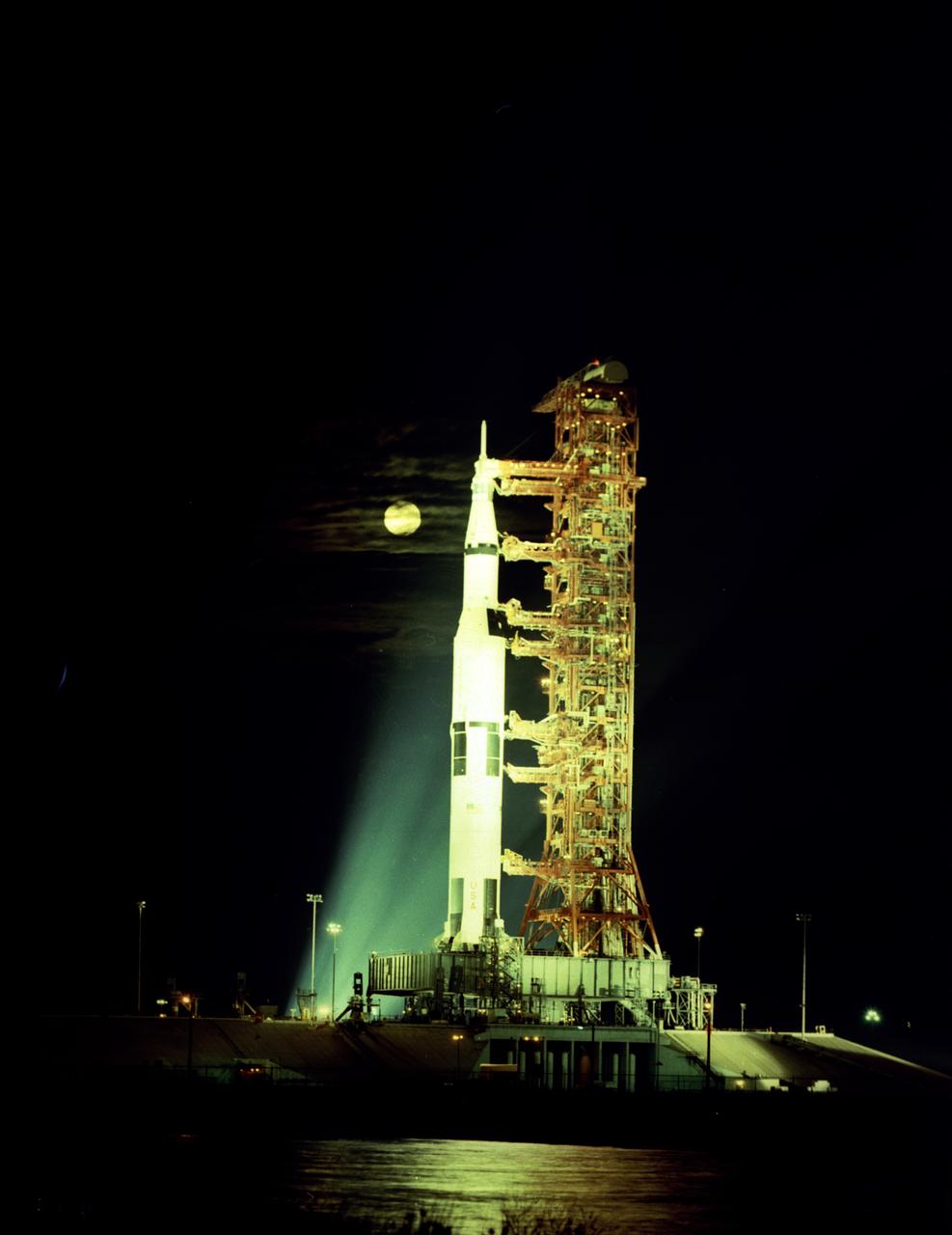

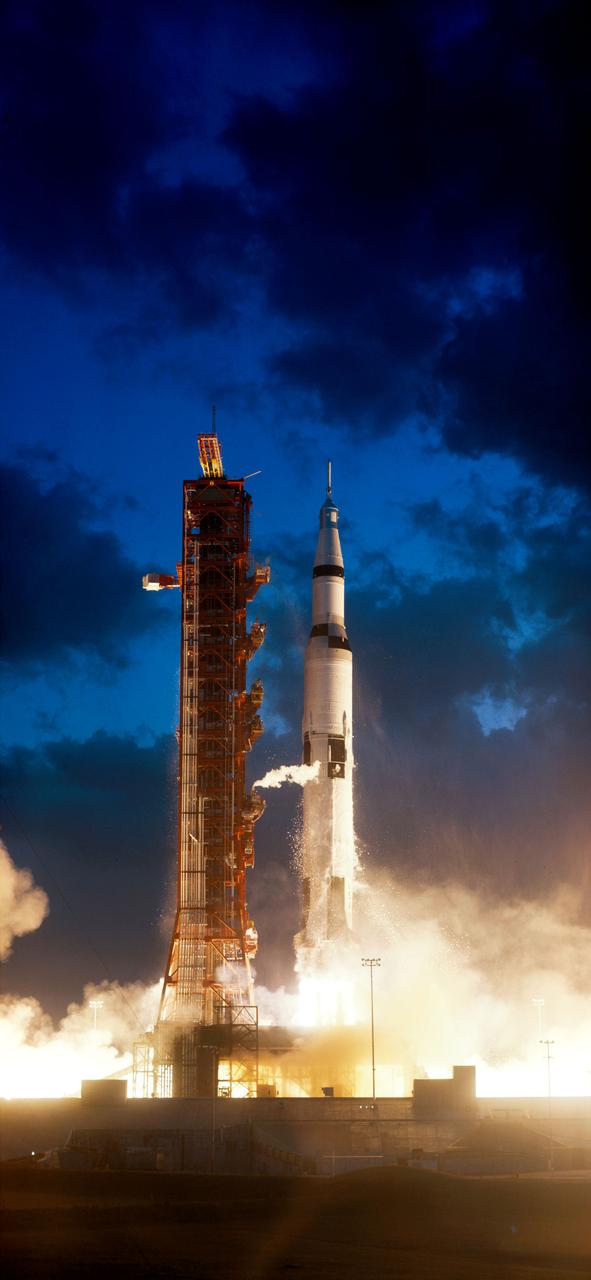
This is a breathtaking moonlit view of Apollo 17 on the Launch Pad at Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC). The seventh and last manned lunar landing and return to Earth mission, the Apollo 17, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Mission Commander Eugene A. Cernan, Lunar Module pilot Harrison H. Schmitt, and Command Module pilot Ronald E. Evans, lifted off on December 7, 1972. The basic objective of the Apollo 17 mission was to sample basin-rim highland material and adjacent mare material, and investigate the geological evolutionary relationship between these two major units. The mission marked the longest Apollo mission, 504 hours, and the longest lunar surface stay time, 75 hours, which allowed the astronauts to conduct an extensive geological investigation. They collected 257 pounds (117 kilograms) of lunar samples with the use of the Marshall Space Flight Center designed Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The mission ended on December 19, 1972

This montage depicts the flight crew patches for the manned Apollo 7 thru Apollo 17 missions. The Apollo 7 through 10 missions were basically manned test flights that paved the way for lunar landing missions. Primary objectives met included the demonstration of the Command Service Module (CSM) crew performance; crew/space vehicle/mission support facilities performance and testing during a manned CSM mission; CSM rendezvous capability; translunar injection demonstration; the first manned Apollo docking, the first Apollo Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA), performance of the first manned flight of the lunar module (LM); the CSM-LM docking in translunar trajectory, LM undocking in lunar orbit, LM staging in lunar orbit, and manned LM-CSM docking in lunar orbit. Apollo 11 through 17 were lunar landing missions with the exception of Apollo 13 which was forced to circle the moon without landing due to an onboard explosion. The craft was,however, able to return to Earth safely. Apollo 11 was the first manned lunar landing mission and performed the first lunar surface EVA. Landing site was the Sea of Tranquility. A message for mankind was delivered, the U.S. flag was planted, experiments were set up and 47 pounds of lunar surface material was collected for analysis back on Earth. Apollo 12, the 2nd manned lunar landing mission landed in the Ocean of Storms and retrieved parts of the unmanned Surveyor 3, which had landed on the Moon in April 1967. The Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) was deployed, and 75 pounds of lunar material was gathered. Apollo 14, the 3rd lunar landing mission landed in Fra Mauro. ALSEP and other instruments were deployed, and 94 pounds of lunar materials were gathered, using a hand cart for first time to transport rocks. Apollo 15, the 4th lunar landing mission landed in the Hadley-Apennine region. With the first use of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), the crew was bale to gather 169 pounds of lunar material. Apollo 16, the 5th lunar landing mission, landed in the Descartes Highlands for the first study of highlands area. Selected surface experiments were deployed, the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph was used for first time on the Moon, and the LRV was used for second time for a collection of 213 pounds of lunar material. The Apollo program came to a close with Apollo 17, the 6th and final manned lunar landing mission that landed in the Taurus-Littrow highlands and valley area. This mission hosted the first scientist-astronaut, Schmitt, to land on the Moon. The 6th automated research station was set up, and 243 ponds of lunar material was gathered using the LRV.

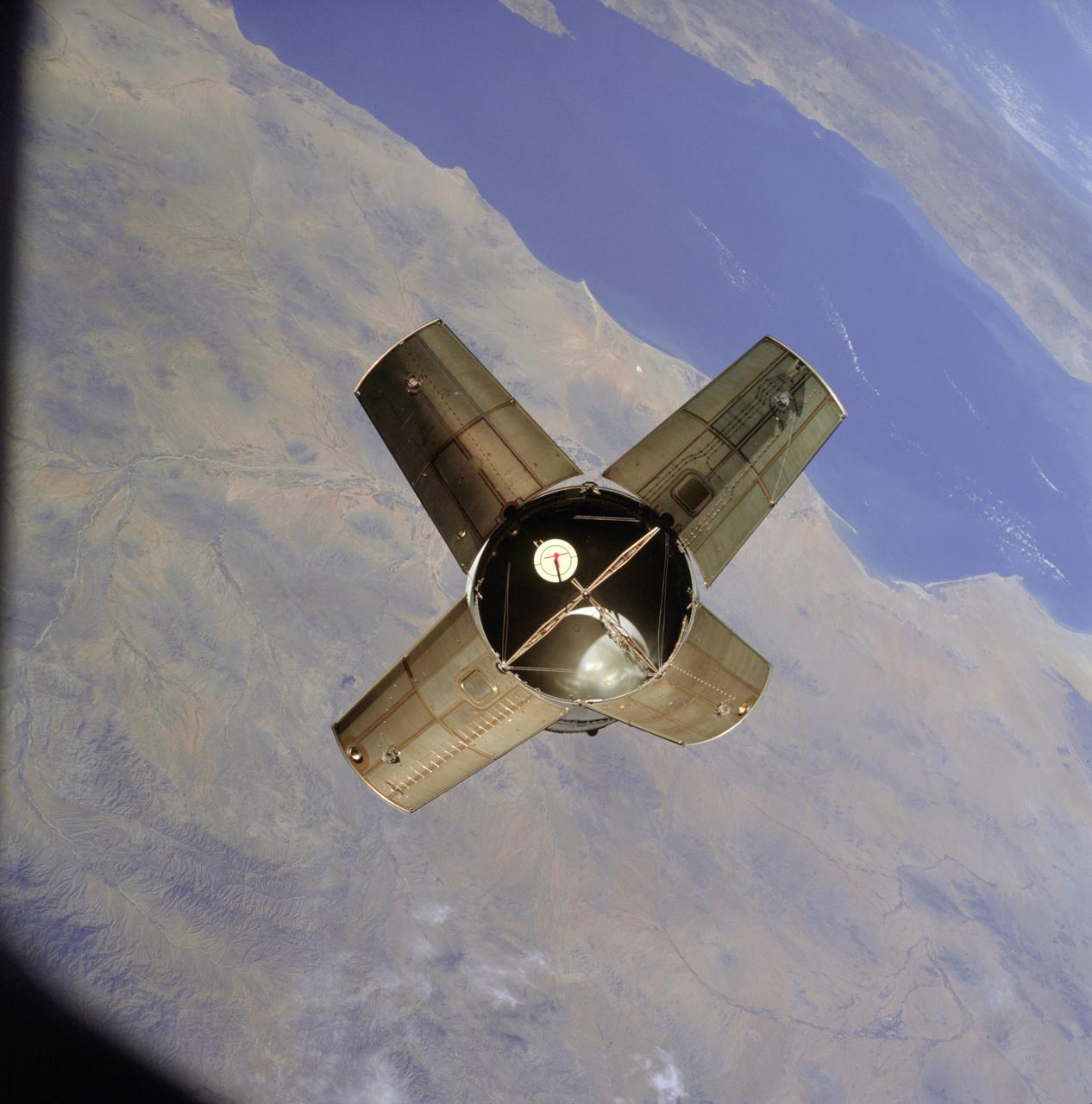
AS07-03-1538 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers. This photograph was taken during Apollo 7's second revolution of Earth. Earth below has heavy cloud cover. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the Saturn IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the lunar module for docking during lunar missions.
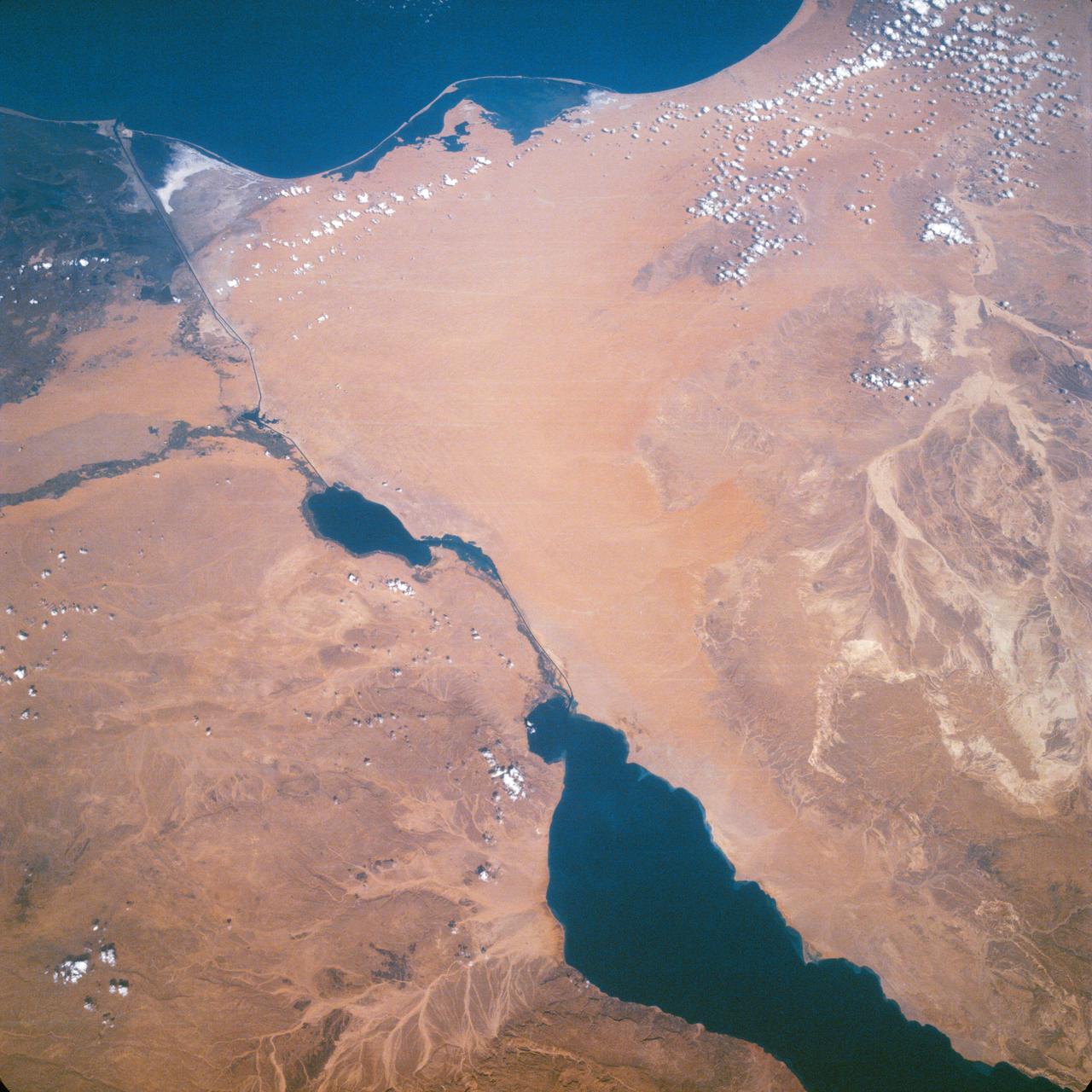

Suez Canal, Gulf of Suez, Sinai Peninsula, United Arab Republic (Egypt), Mediterranean Sea, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 13th revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 126 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 19 hours and 42 minutes.

AS07-03-1531 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers. This photograph was taken over Sonora, Mexico, during Apollo 7's second revolution of Earth. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the Saturn IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the lunar module for docking during lunar missions.
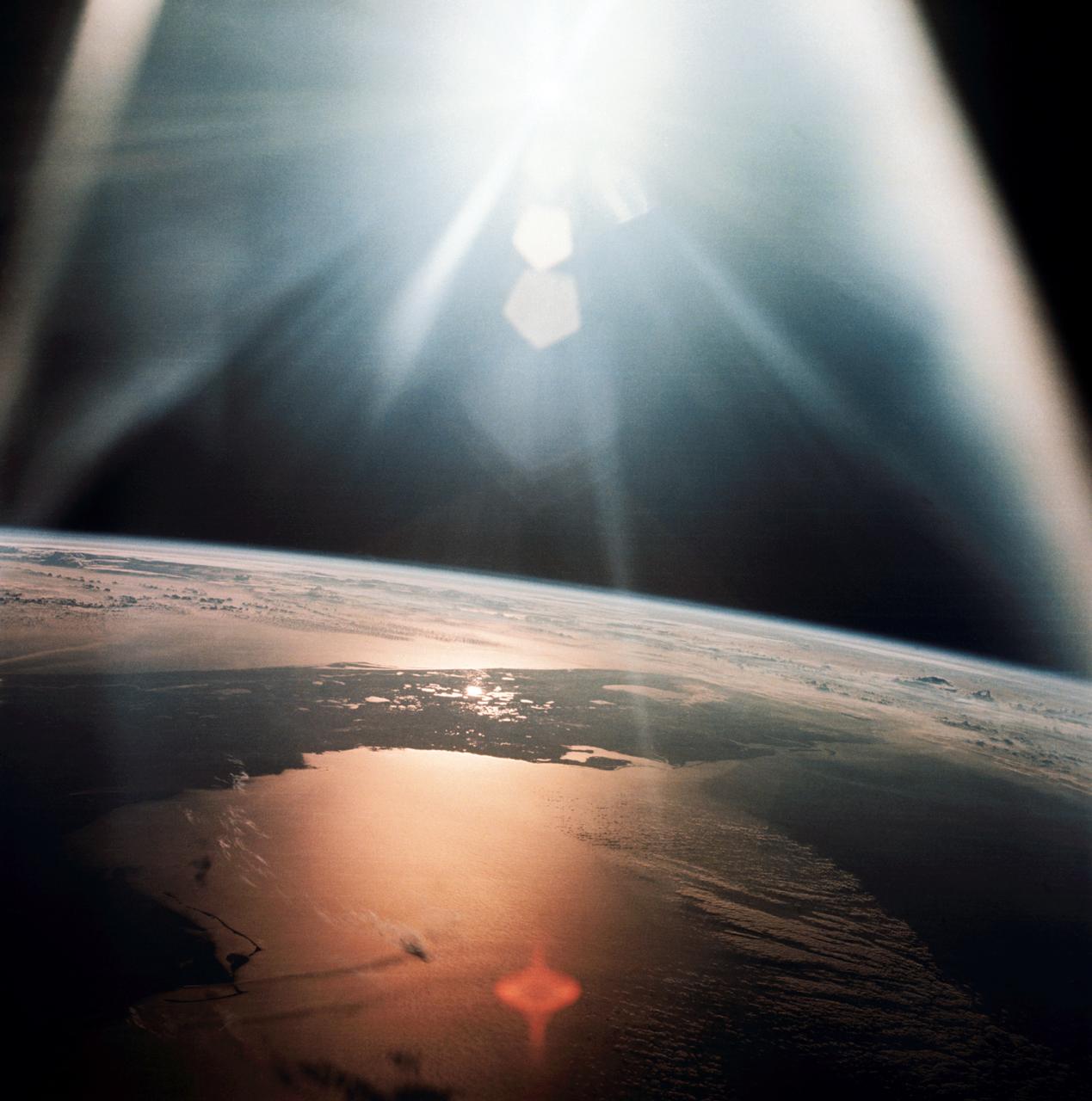

AS07-08-1933 (20 Oct. 1968) --- The morning sun reflects on the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft at an altitude of 120 nautical miles above Earth. Most of Florida peninsula appears as a dark silhouette. This photograph was made during the spacecraft's 134th revolution of Earth, some 213 hours and 19 minutes after liftoff.
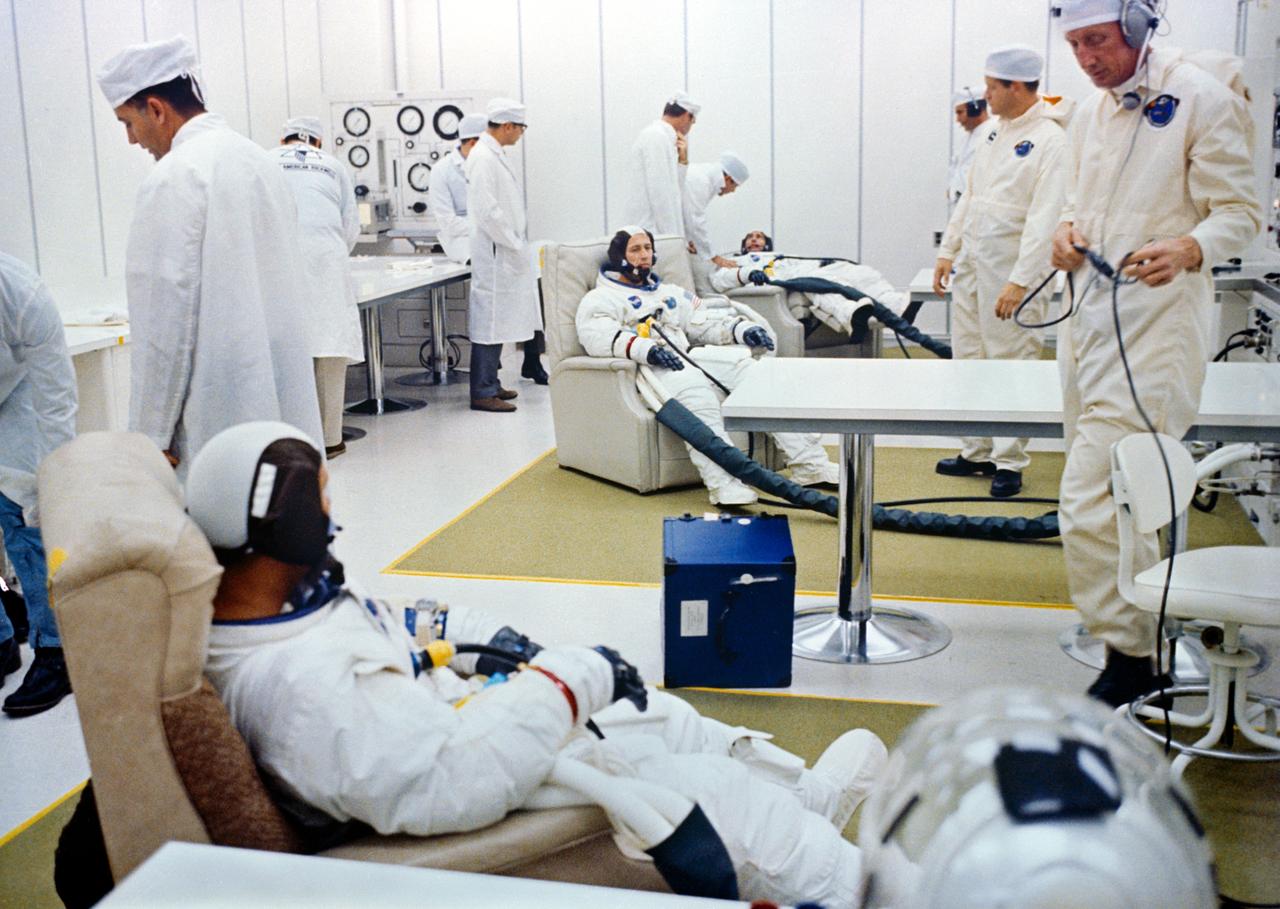
The Apollo 7 prime crew goes through suiting up operations in the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building during the Apollo 7 prelaunch countdown. From front to rear, are Astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr., commander; Donn F. Eisele, command module pilot; and Walter Cunningham, lunar module pilot.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Apollo 7 astronauts Donn F. Eisele, foreground, and Walter Cunningham, rear, undergo spacesuit checks today prior to their Earth orbital mission with Walter M. Schirra Jr., not shown. The three space pilots lifted off atop a Saturn 1B space vehicle from Cape Kennedy's Launch Complex 34 at 11:03 a.m. EDT, Oct. 11, 1968. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration's first manned Apollo flight is designed to verify spacecraft systems for future lunar voyages.
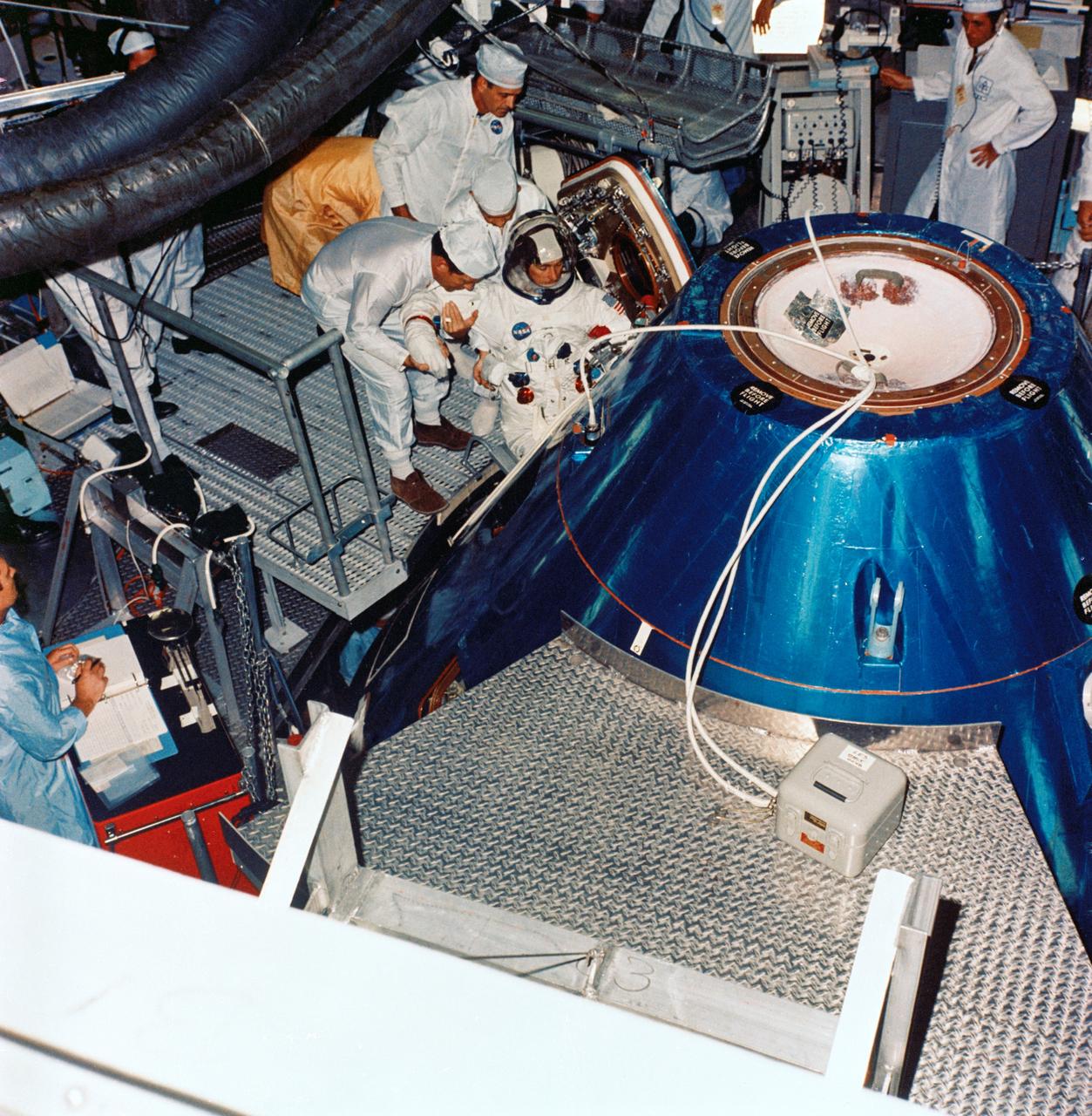
S68-40875 (5 July 1968) --- Astronaut John W. Young, Apollo 7 backup command module pilot, ingresses Apollo Spacecraft 101 Command Module during simulated altitude runs at the Kennedy Space Center's Pad 34.
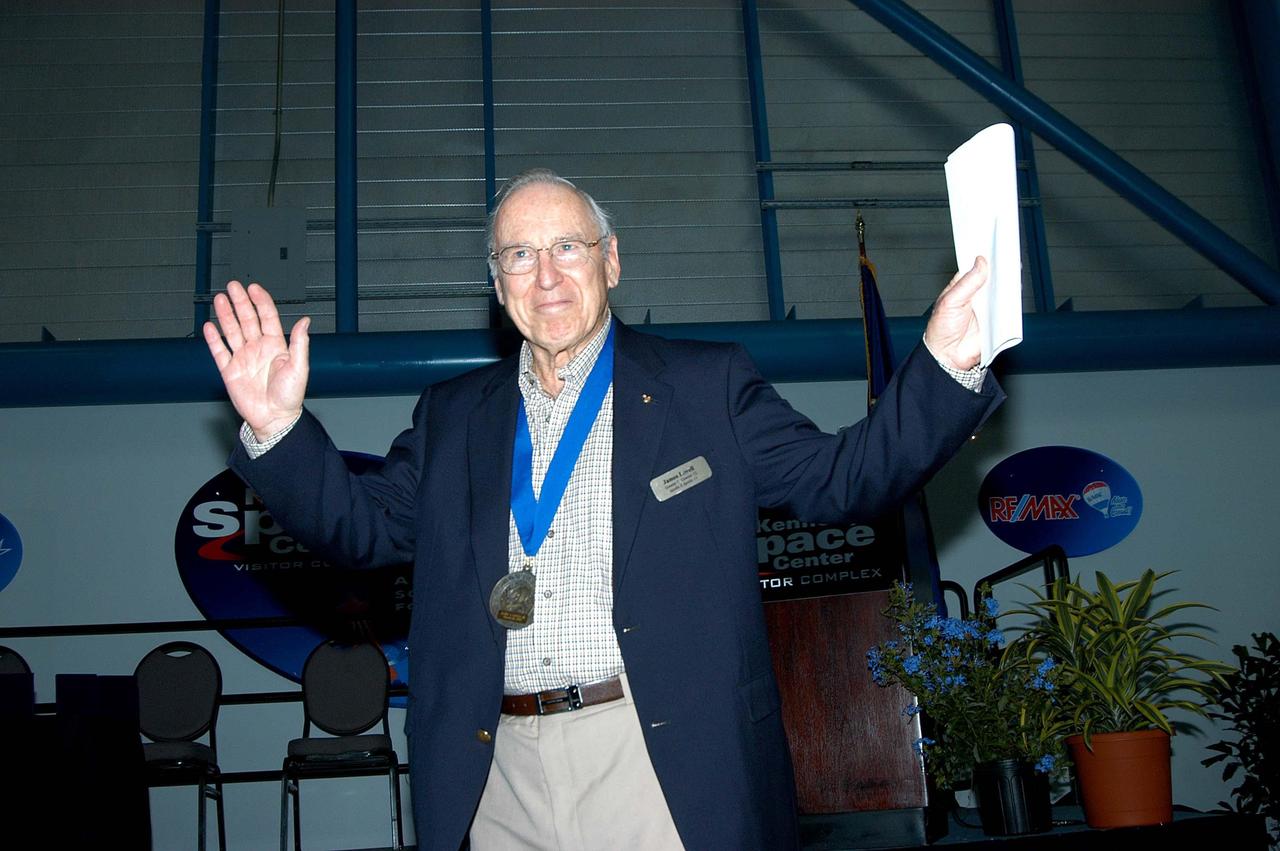

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Former astronaut Jim Lovell acknowledges the applause as he is introduced as a previous inductee into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame. He and other Hall of Fame members were present for the induction of five new space program heroes into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame: Richard O. Covey, commander of the Hubble Space Telescope repair mission; Norman E. Thagard, the first American to occupy Russia’s Mir space station; the late Francis R. "Dick" Scobee, commander of the ill-fated 1986 Challenger mission; Kathryn D. Sullivan, the first American woman to walk in space; and Frederick D. Gregory, the first African-American to command a space mission and the current NASA deputy administrator. Lovell piloted Gemini 7, commanded Gemini 12, orbited the Moon on Apollo 8 and commanded the aborted Apollo 13 moon flight. The induction ceremony was held at the Apollo/Saturn V Center at KSC. The U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame opened in 1990 to provide a place where space travelers could be remembered for their participation and accomplishments in the U.S. space program. The five inductees join 52 previously honored astronauts from the ranks of the Gemini, Apollo, Skylab, Apollo-Soyuz, and Space Shuttle programs.
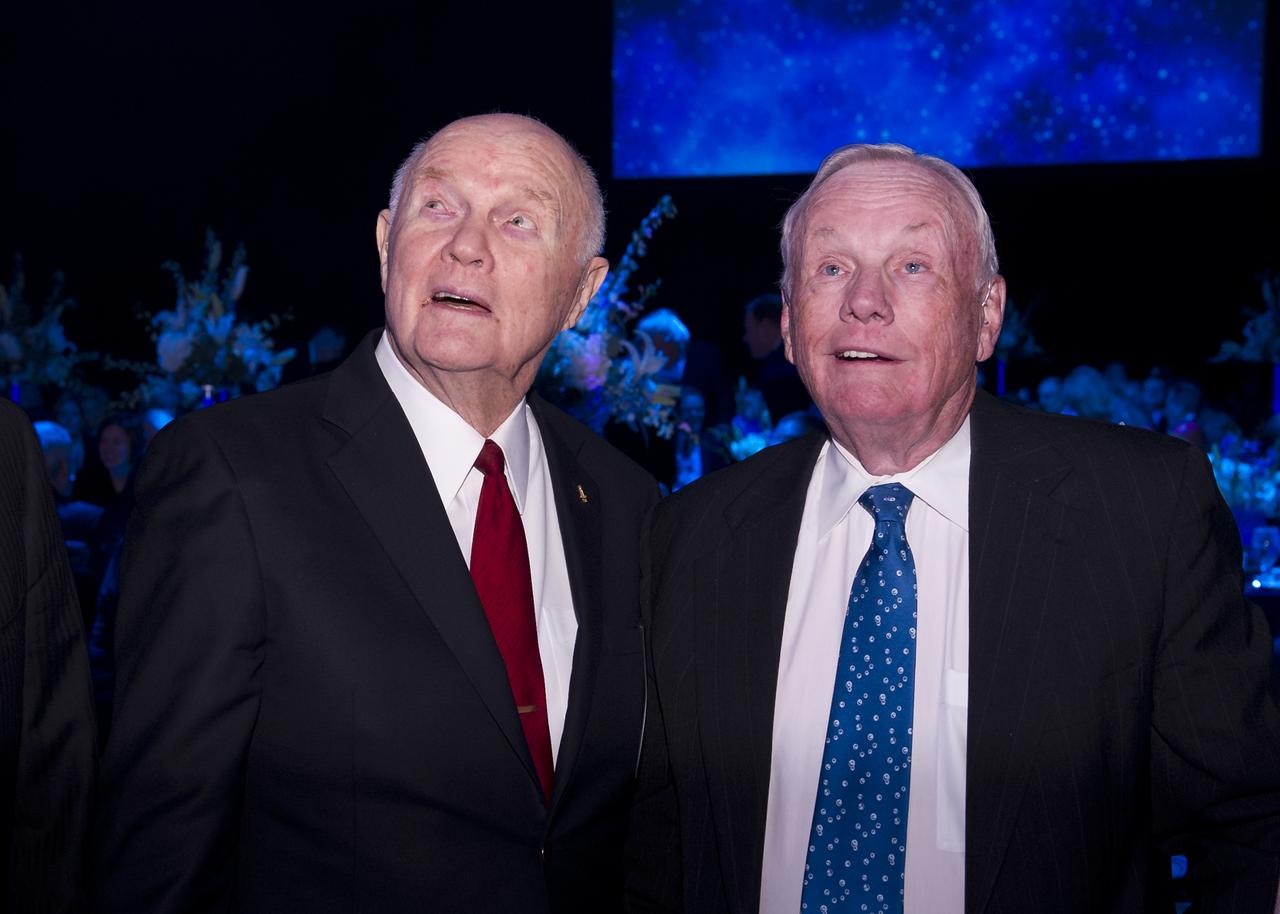

Sen. John Glenn, left, and Apollo 11 Astronaut Neil Armstrong are seen prior to the start of a dinner at Ohio State University that honored the 50th anniversary of John Glenn's historic flight aboard Friendship 7 Monday, Feb. 20, 2012, in Columbus, Ohio. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
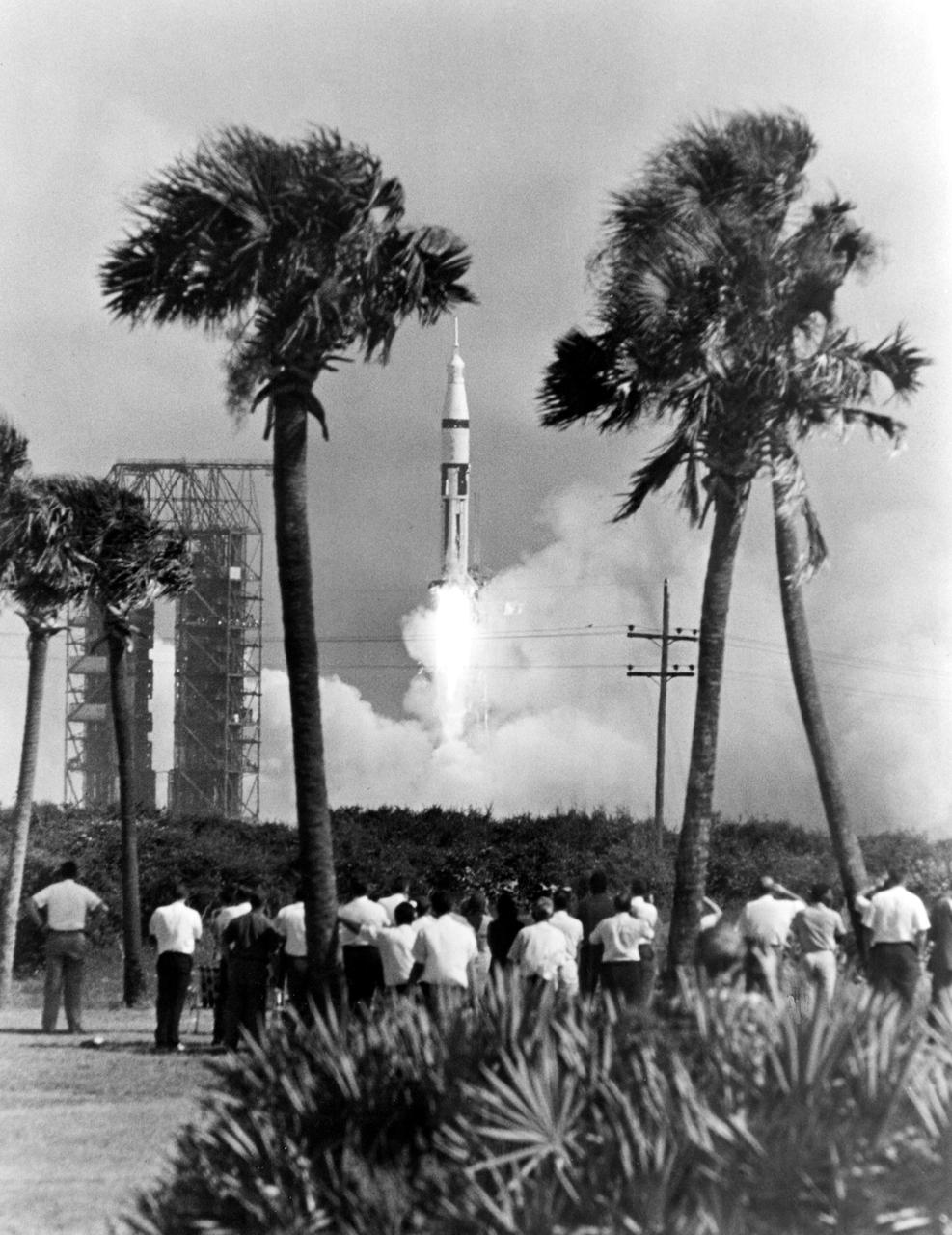

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers at Cape Kennedy watched a 224-foot-high Saturn 1B space vehicle lift off today from Complex 34 carrying Apollo 7 astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr., Donn F. Eisele and Walter Cunningham at the start of their scheduled 11-day Earth orbital flight.

Apollo 7,Cumulus,alto-cumulus,cirrus clouds. Very high oblique. Cloud Cover 50%. Original film magazine was labeled S. Camera Data: Hasselblad 500-C; Lens: Zeiss Planar,F/2.8,80mm; Film Type: Kodak SO-121,Aerial Ektachrome; Filter: Wratten 2A. Flight Date: October 11-12. 1968.
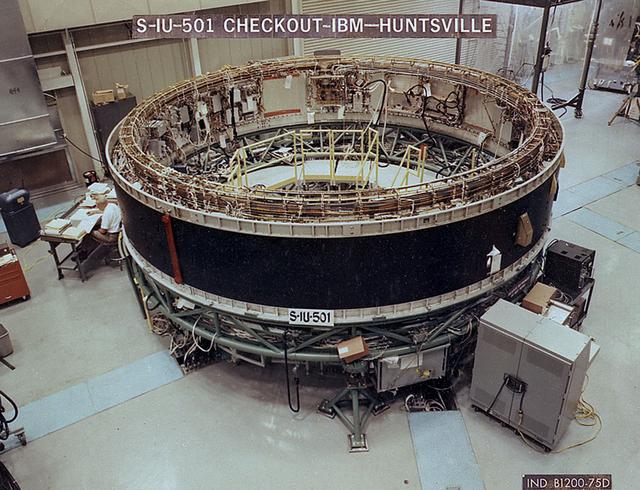
A technician checks the systems of the Saturn V instrument unit in a test facility in Huntsville. This instrument unit was flown aboard Apollo 4 on November 7, 1967, which was the first test flight of the Saturn V. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multi-stage, multi-engine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Mercury astronauts, John Glenn, left, and Scott Carpenter, talk to Mercury Project workers and other guests in the Astronaut Encounter Theater at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. The pair participated in 50th anniversary events at the launch site of Glenn's first orbital flight aboard NASA's Friendship 7 capsule, which launched Feb. 20, 1962, aboard an Atlas rocket. Glenn's launch aboard an Atlas rocket took with it the hopes of an entire nation and ushered in a new era of space travel that eventually led to Americans walking on the moon by the end of the 1960s. Glenn soon was followed into orbit by Carpenter, Walter Schirra and Gordon Cooper. Their fellow Mercury astronauts Alan Shepard and Virgil "Gus" Grissom flew earlier suborbital flights. Deke Slayton, a member of NASA's original Mercury 7 astronauts, was grounded by a medical condition until the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Mercury astronauts, John Glenn, left, and Scott Carpenter, talk to Mercury Project workers and other guests in the Astronaut Encounter Theater at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. The pair participated in 50th anniversary events at the launch site of Glenn's first orbital flight aboard NASA's Friendship 7 capsule, which launched Feb. 20, 1962, aboard an Atlas rocket. Glenn's launch aboard an Atlas rocket took with it the hopes of an entire nation and ushered in a new era of space travel that eventually led to Americans walking on the moon by the end of the 1960s. Glenn soon was followed into orbit by Carpenter, Walter Schirra and Gordon Cooper. Their fellow Mercury astronauts Alan Shepard and Virgil "Gus" Grissom flew earlier suborbital flights. Deke Slayton, a member of NASA's original Mercury 7 astronauts, was grounded by a medical condition until the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
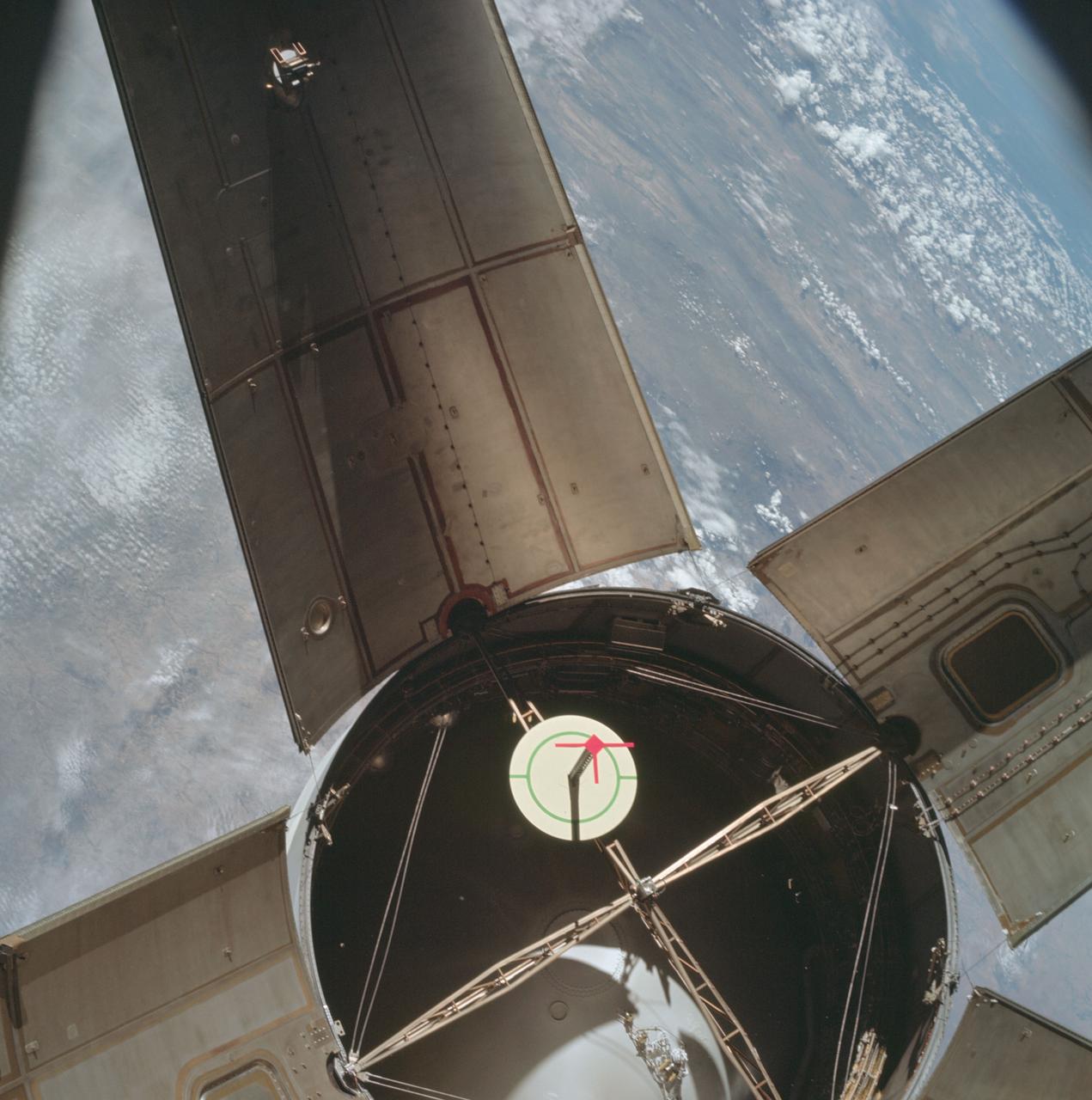

AS07-03-1535 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers at an altitude of 126 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of three hours, 11 minutes. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the Saturn IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the lunar module for docking during lunar missions. The spacecraft is directly over Odessa-Midland, Texas. The view between the two panels (area of large puffy clouds) extends southwest across Texas into the Mexican State of Chihuahua. The distance between the Apollo 7 spacecraft and the S-IVB is approximately 50 feet.
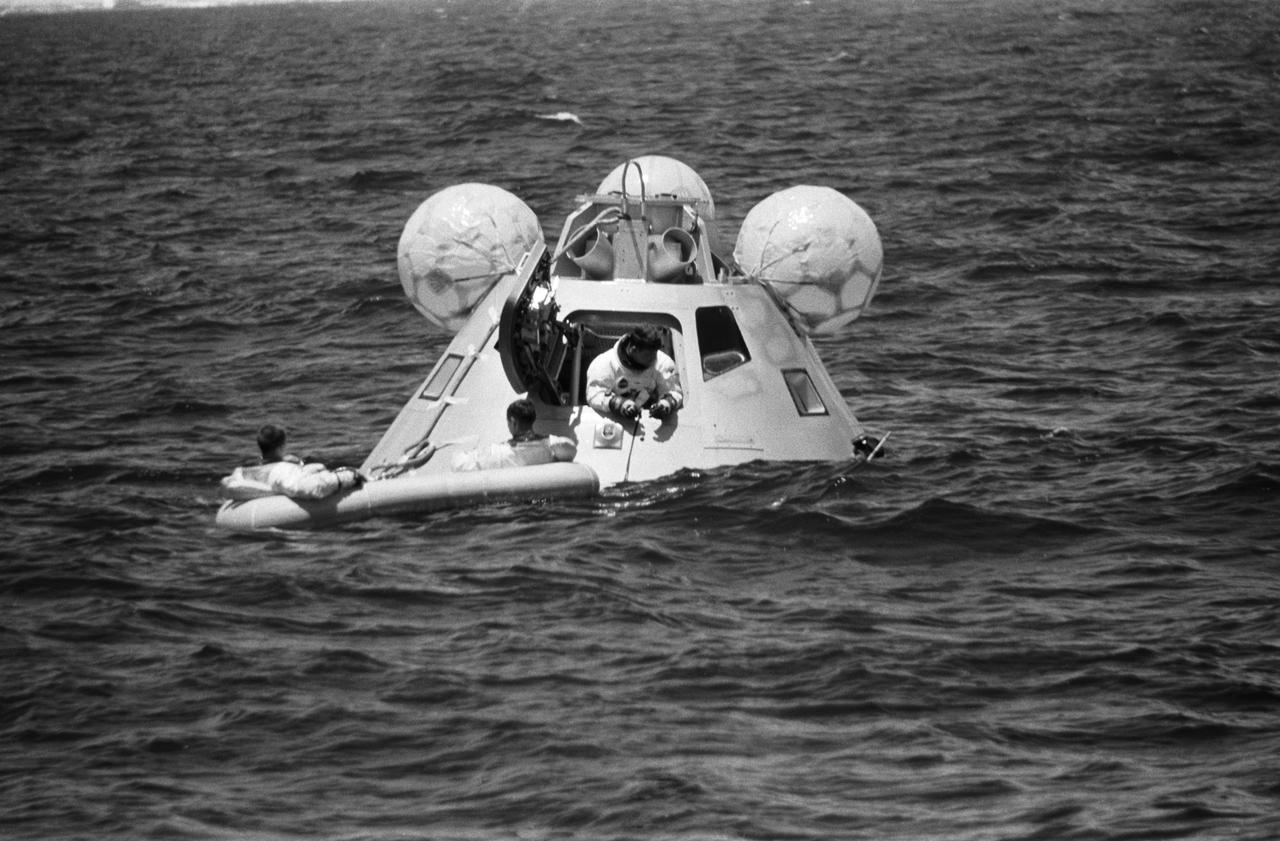

S68-42197 (5 Aug. 1968) --- The prime crew of the first manned Apollo space mission, Apollo 7, participates in water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. In hatch of the Apollo egress trainer (command module) is astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr. Sitting in life raft are astronauts Walter Cunningham (on left) and Donn F. Eisele. A team of MSC swimmers assisted with the training exercise. The inflated bags were used to upright the trainer prior to egress.

S68-46604 (5 Aug. 1968) --- The prime crew of the first manned Apollo mission (Spacecraft 101/Saturn 205) is seen in Apollo Command Module Boilerplate 1102 during water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. In foreground is astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr., in center is astronaut Donn F. Eisele, and in background is astronaut Walter Cunningham.

S68-46605 (5 Aug. 1968) --- The prime crew of the first manned Apollo mission (Spacecraft 101/Saturn 205) participates in water egress training in the Gulf of Mexico. Left to right, are astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr. (stepping into life raft), Donn F. Eisele, and Walter Cunningham. They have just egressed Apollo Command Module Boilerplate 1102, and are awaiting helicopter pickup. Inflated bags were used to upright the boilerplate. MSC swimmers assisted in the training exercise.
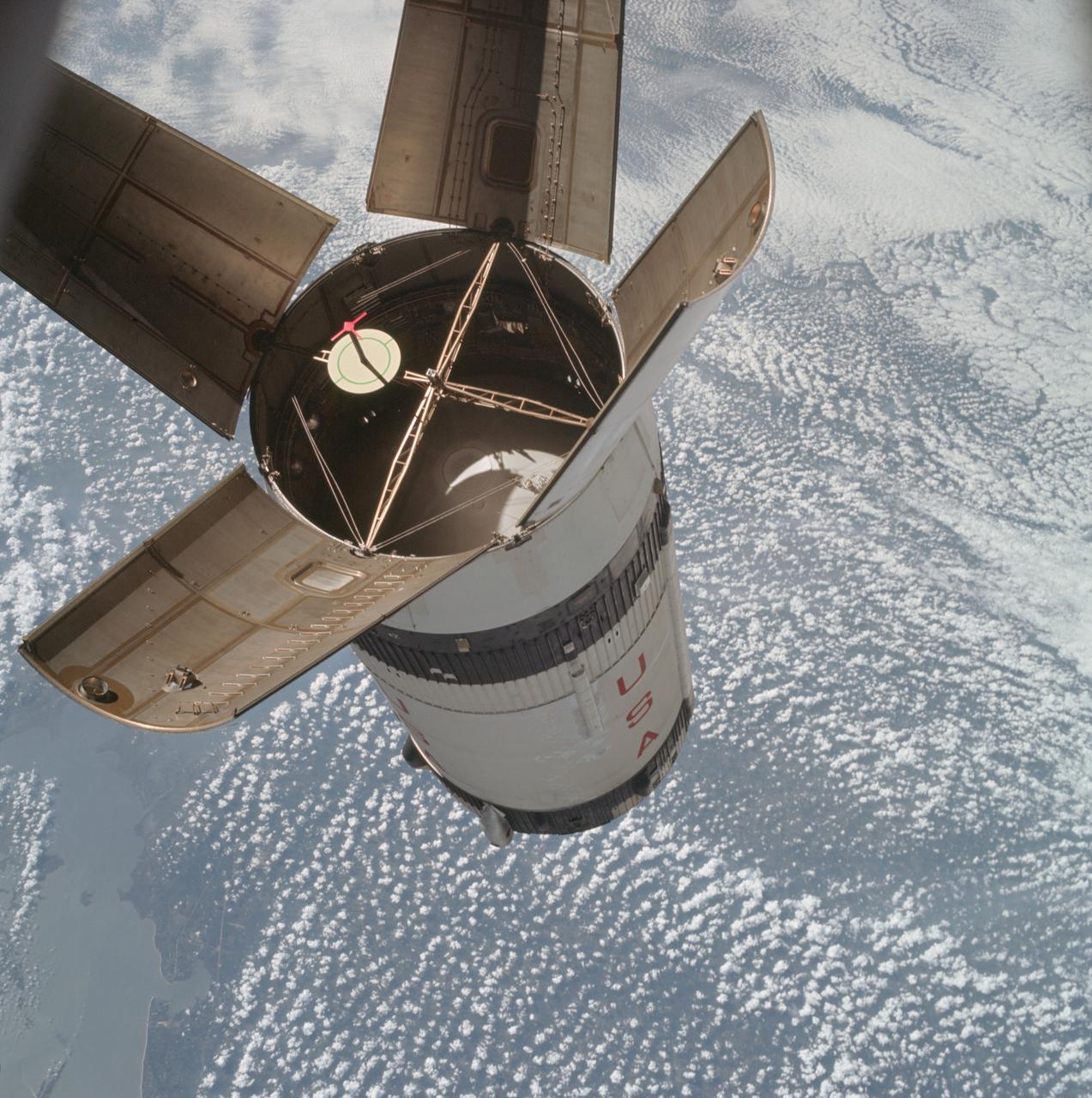

AS07-03-1541 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers. St. Louis Bay and Lake Borgne area just east of New Orleans is seen below. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the Saturn IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the lunar module for docking during lunar missions.
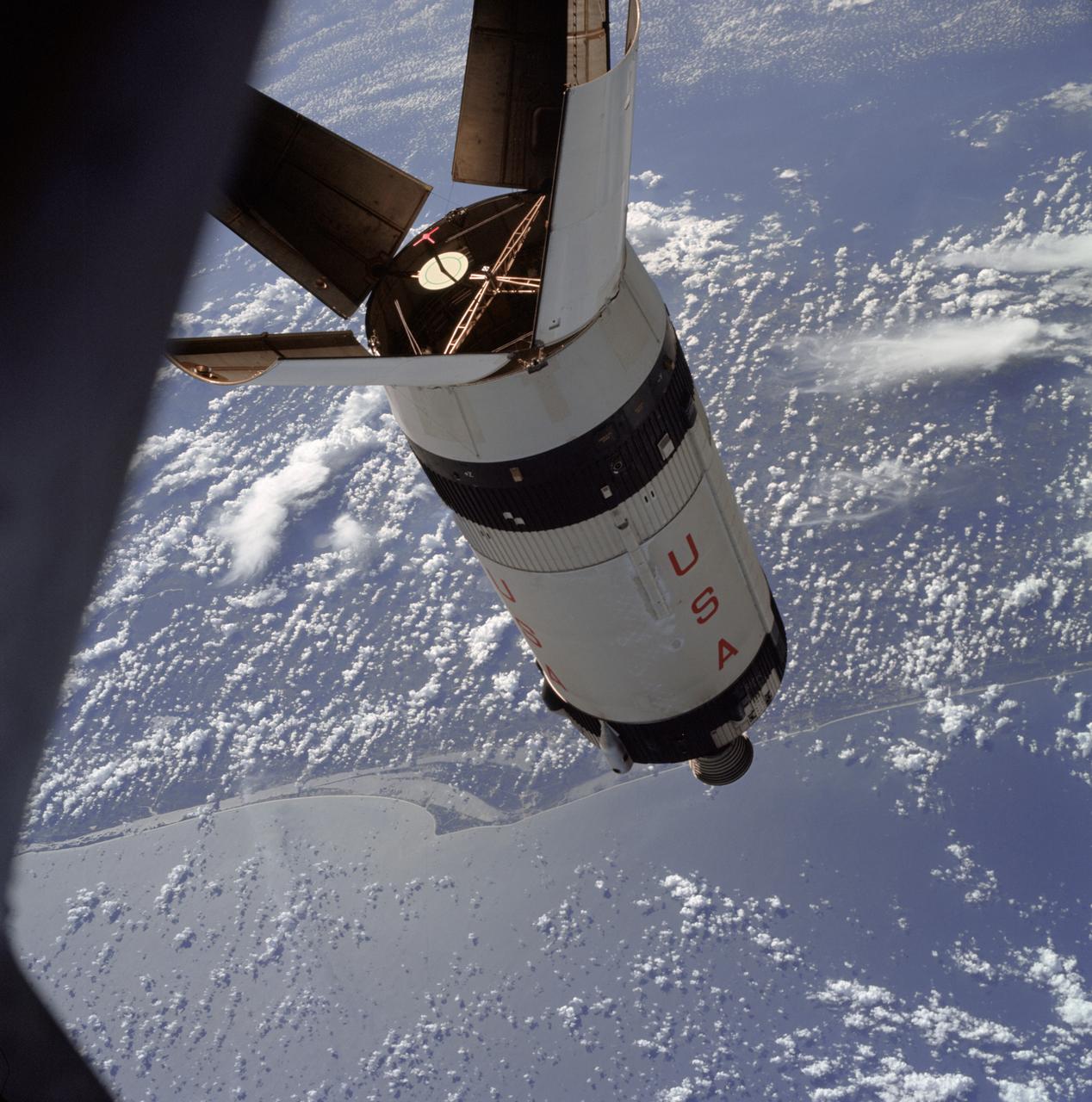

AS07-03-1545 (11 Oct. 1968) --- The expended Saturn S-IVB stage as photographed from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during transposition and docking maneuvers at an approximate altitude of 125 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of three hours and 16 minutes (beginning of third revolution). This view is over the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Cape Kennedy, Florida. The Florida coastline from Flagler Beach southward to Vero Beach is clearly visible in picture. Much of the Florida peninsula can be seen. Behind the open panels is the Gulf of Mexico. Distance between the Apollo 7 spacecraft and the S-IVB is approximately 100 feet. The round, white disc inside the open panels of the S-IVB is a simulated docking target similar to that used on the Lunar Module (LM) for docking during lunar missions.
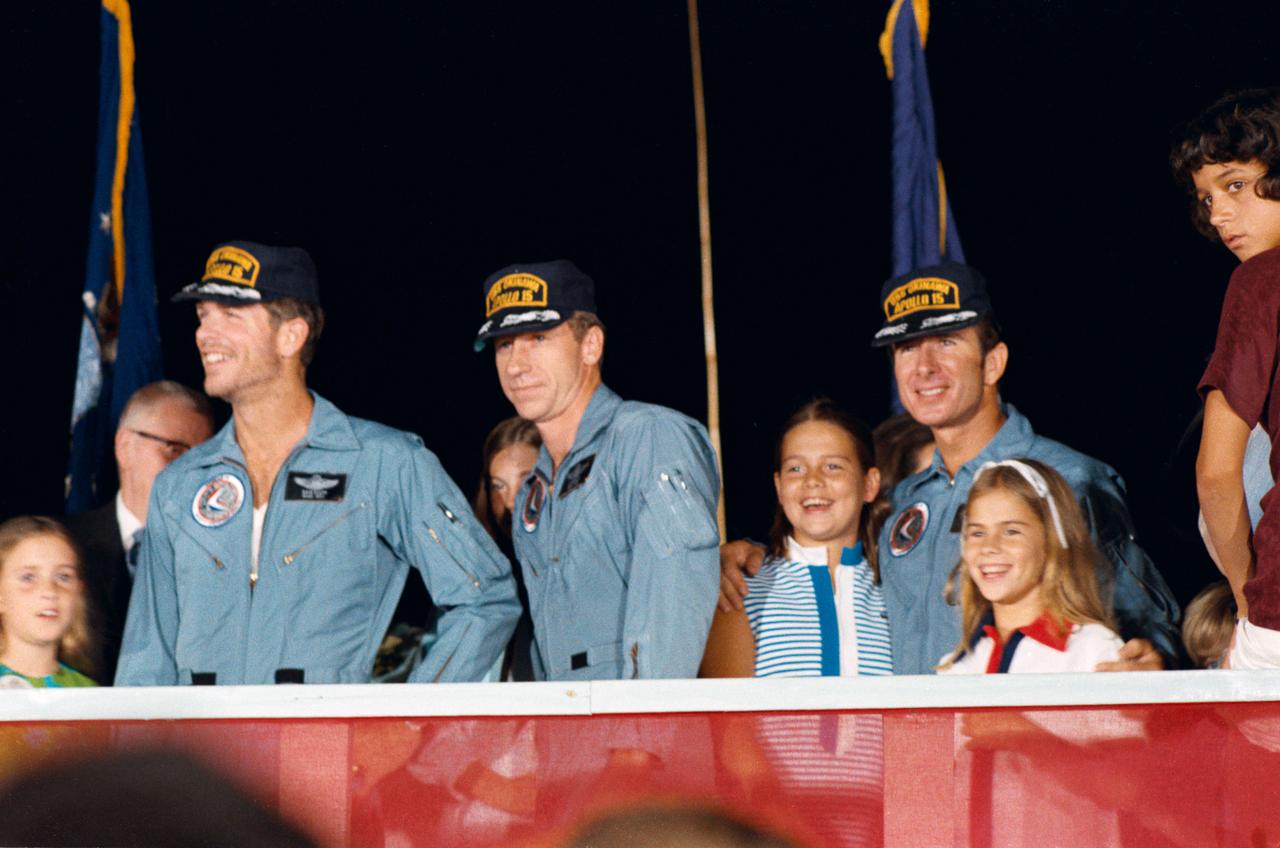

S71-43428 (8 Aug. 1971) --- The three crew men, of the highly successful Apollo 15 lunar landing mission, receive a warm welcome home at Ellington Air Force Base (EAFB), Houston, after an eight hour flight aboard a U.S. Air Force C-141 jet aircraft from Hawaii. Left to right, are astronauts David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. Apollo 15 splashdown in the mid-Pacific at 3:45 p.m. (CDT), Aug. 7, 1971, some 330 miles north of Honolulu. The C-141 landed at EAFB at 9 p.m. (CDT), Sunday, Aug. 8, 1971. Members of the astronauts' families identifiable in the picture are, left to right, Scott's daughter, Tracy; Worden's father, Merrill Worden; Worden's daughter, Merrill; and Irwin's two daughters, Joy and Jill.
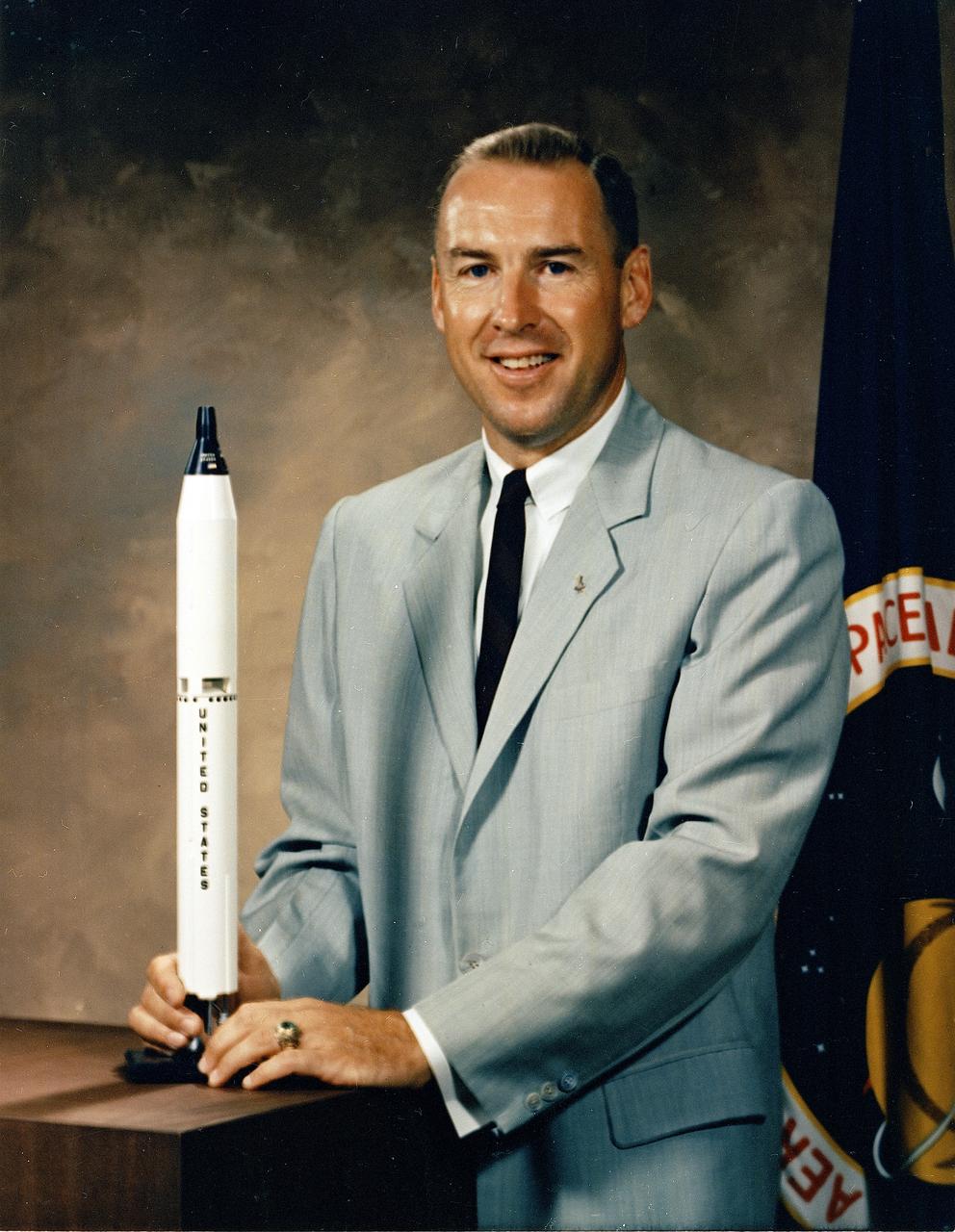

This is the official NASA portrait of astronaut James Lovell. Captain Lovell was selected as an Astronaut by NASA in September 1962. He has since served as backup pilot for the Gemini 4 flight and backup Commander for the Gemini 9 flight, as well as backup Commander to Neil Armstrong for the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. On December 4, 1965, he and Frank Borman were launched into space on the history making Gemini 7 mission. The flight lasted 330 hours and 35 minutes and included the first rendezvous of two manned maneuverable spacecraft. The Gemini 12 mission, commanded by Lovell with Pilot Edwin Aldrin, began on November 11, 1966 for a 4-day, 59-revolution flight that brought the Gemini program to a successful close. Lovell served as Command Module Pilot and Navigator on the epic six-day journey of Apollo 8, the first manned Saturn V liftoff responsible for allowing the first humans to leave the gravitational influence of Earth. He completed his fourth mission as Spacecraft Commander of the Apollo 13 flight, April 11-17, 1970, and became the first man to journey twice to the moon. The Apollo 13 mission was cut short due to a failure of the Service Module cryogenic oxygen system. Aborting the lunar course, Lovell and fellow crewmen, John L. Swigert and Fred W. Haise, working closely with Houston ground controllers, converted their lunar module, Aquarius, into an effective lifeboat that got them safely back to Earth. Captain Lovell held the record for time in space with a total of 715 hours and 5 minutes until surpassed by the Skylab flights. On March 1, 1973, Captain Lovell retired from the Navy and the Space Program.

This is the Apollo 17 insignia or logo. The seventh and last manned lunar landing and return to Earth mission, the Apollo 17, carried a crew of three astronauts: Harrison H. Schmitt, Lunar Module pilot; Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander; and Ronald E. Evans, Command Module pilot. Apollo 17 lifted off on December 7, 1972 from the Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC). Scientific objectives of the mission included geological surveying and sampling of materials and surface features in a preselected area of the Taurus-Littrow region, deploying and activating surface experiments, and conducting in-flight experiments and photographic tasks during lunar orbit and transearth coast (TEC). The objectives included deployed experiments such as the Apollo lunar surface experiment package (ALSEP) with a Heat Flow experiment, Lunar seismic profiling (LSP), Lunar surface gravimeter (LSG), Lunar atmospheric composition experiment (LACE) and Lunar ejecta and meteorites (LEAM). The mission also included Lunar Sampling and Lunar Orbital experiments. Biomedical experiments included the Biostack II and the BIOCORE experiments. The mission marked the longest Apollo mission, 504 hours, and the longest lunar surface stay time, 75 hours, which allowed the astronauts to conduct an extensive geological investigation. They collected 257 pounds (117 kilograms) of lunar samples with the use of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) designed Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The mission ended on December 19, 1972.
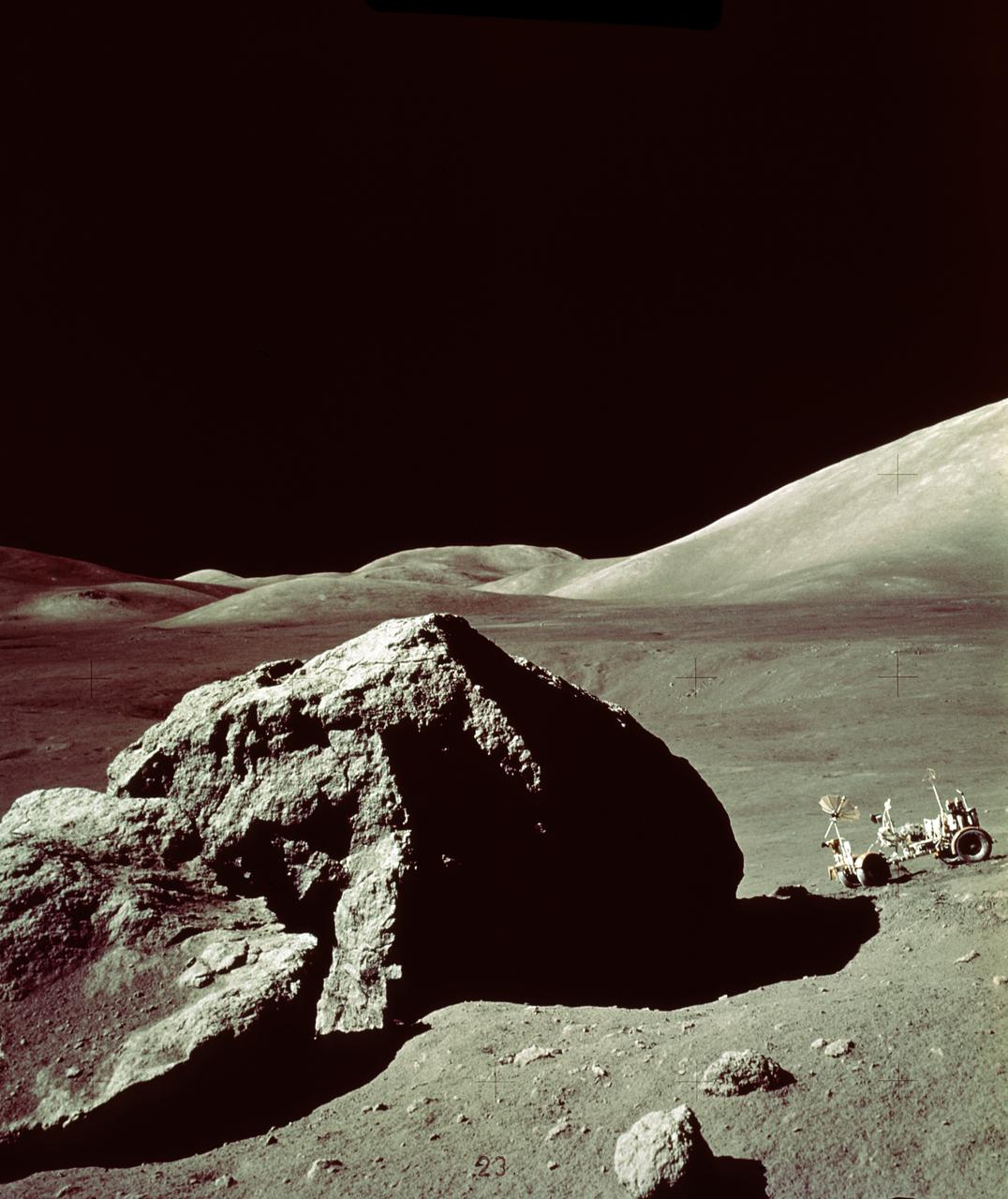

In this Apollo 17 onboard photo, a Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked beside a huge boulder near the Valley of Tourus-Litttrow on the lunar surface. The seventh and last manned lunar landing and return to Earth mission, the Apollo 17, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Mission Commander Eugene A. Cernan; Lunar Module pilot Harrison H. Schmitt; and Command Module pilot Ronald E. Evans, lifted off on December 7, 1972 from the Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC). Scientific objectives of the Apollo 17 mission included geological surveying and sampling of materials and surface features in a preselected area of the Taurus-Littrow region, deploying and activating surface experiments, and conducting in-flight experiments and photographic tasks during lunar orbit and transearth coast (TEC). These objectives included: Deployed experiments such as the Apollo lunar surface experiment package (ALSEP) with a Heat Flow experiment, Lunar seismic profiling (LSP), Lunar surface gravimeter (LSG), Lunar atmospheric composition experiment (LACE) and Lunar ejecta and meteorites (LEAM). The mission also included Lunar Sampling and Lunar orbital experiments. Biomedical experiments included the Biostack II Experiment and the BIOCORE experiment. The mission marked the longest Apollo mission, 504 hours, and the longest lunar surface stay time, 75 hours, which allowed the astronauts to conduct an extensive geological investigation. They collected 257 pounds (117 kilograms) of lunar samples with the use of the Marshall Space Flight Center developed LRV. The mission ended on December 19, 1972
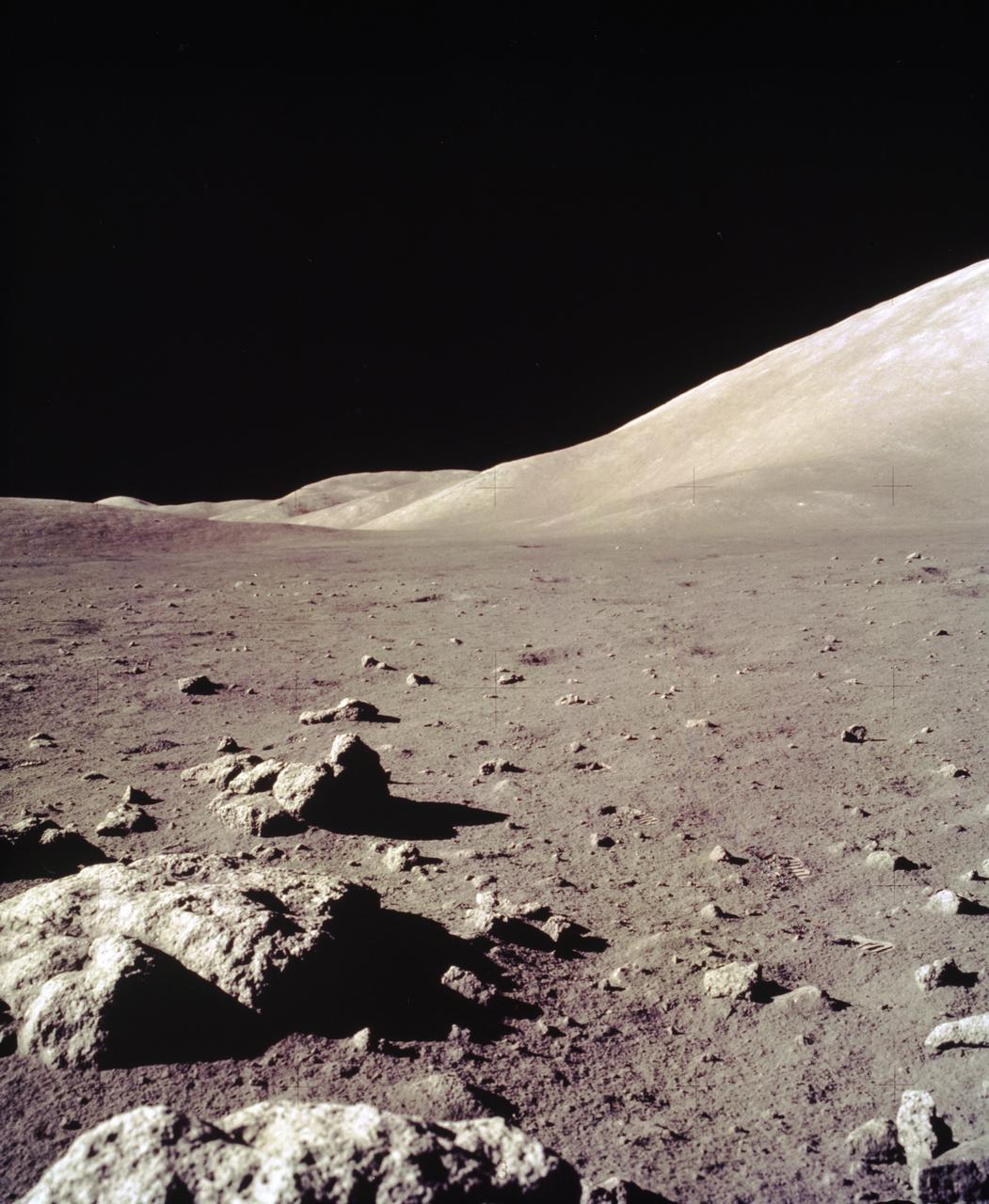

This view of the Lunar surface was taken during the Apollo 17 mission. The seventh and last manned lunar landing and return to Earth mission, the Apollo 17, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Mission Commander Eugene A. Cernan; Lunar Module pilot Harrison H. Schmitt; and Command Module pilot Ronald E. Evans, lifted off on December 7, 1972 from the Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC). Scientific objectives of the Apollo 17 mission included geological surveying and sampling of materials and surface features in a preselected area of the Taurus-Littrow region, deploying and activating surface experiments, and conducting in-flight experiments and photographic tasks during lunar orbit and transearth coast (TEC). These objectives included: Deployed experiments such as the Apollo lunar surface experiment package (ALSEP) with a Heat Flow experiment, Lunar seismic profiling (LSP), Lunar surface gravimeter (LSG), Lunar atmospheric composition experiment (LACE) and Lunar ejecta and meteorites (LEAM). The mission also included Lunar Sampling and Lunar orbital experiments. Biomedical experiments included the Biostack II Experiment and the BIOCORE experiment. The mission marked the longest Apollo mission, 504 hours, and the longest lunar surface stay time, 75 hours, which allowed the astronauts to conduct an extensive geological investigation. They collected 257 pounds (117 kilograms) of lunar samples with the use of the Marshall Space Flight Center designed Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The mission ended on December 19, 1972.
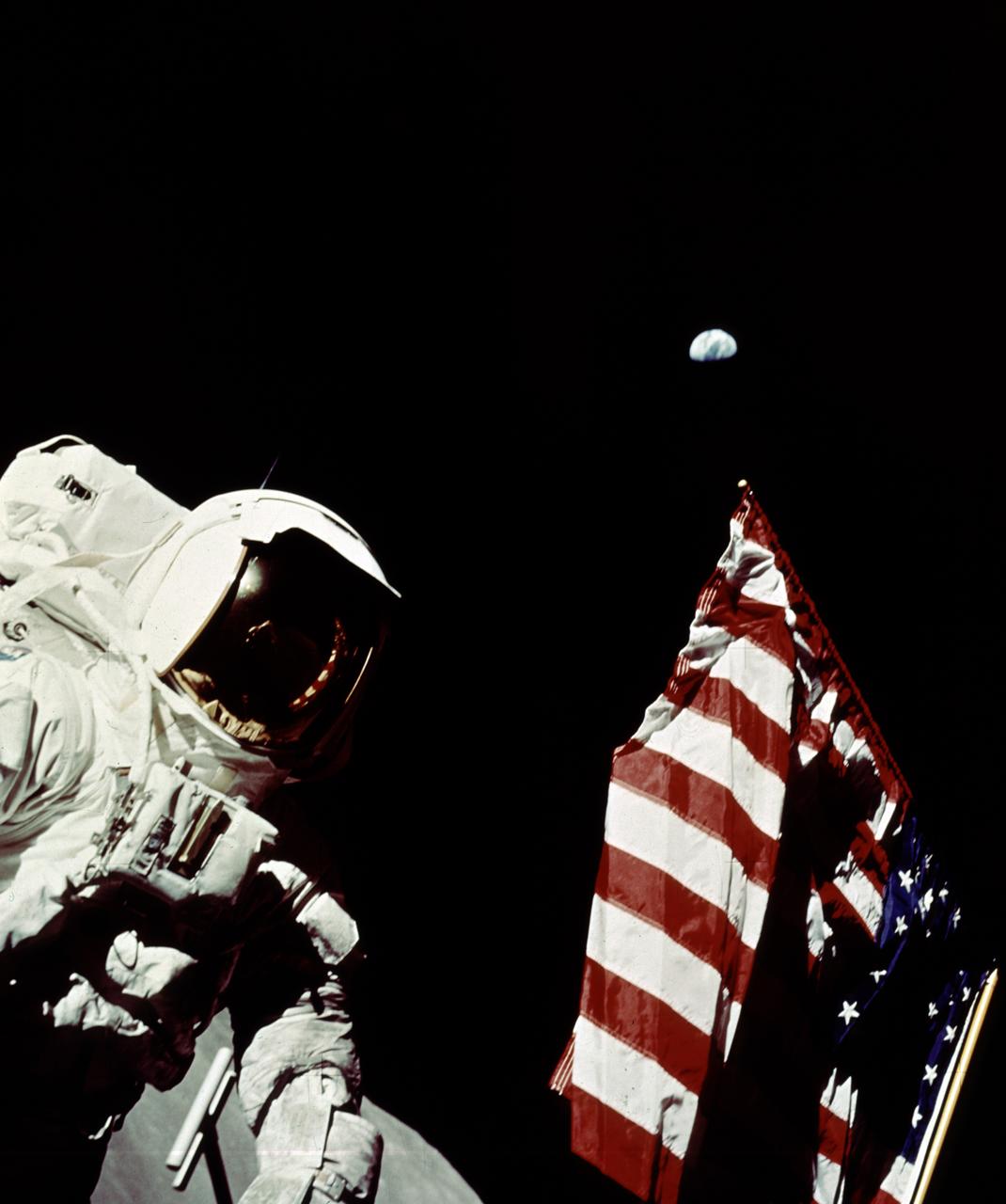

In this Apollo 17 onboard photo, Mission Commander Eugene A. Cernan adjusts the U.S. flag deployed upon the Moon. The seventh and last manned lunar landing and return to Earth mission, the Apollo 17, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Cernan; Lunar Module pilot Harrison H. Schmitt; and Command Module pilot Ronald E. Evans, lifted off on December 7, 1972 from the Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC). Scientific objectives of the Apollo 17 mission included geological surveying and sampling of materials and surface features in a preselected area of the Taurus-Littrow region, deploying and activating surface experiments, and conducting in-flight experiments and photographic tasks during lunar orbit and transearth coast (TEC). These objectives included: Deployed experiments such as the Apollo lunar surface experiment package (ALSEP) with a Heat Flow experiment, Lunar seismic profiling (LSP), Lunar surface gravimeter (LSG), Lunar atmospheric composition experiment (LACE) and Lunar ejecta and meteorites (LEAM). The mission also included Lunar Sampling and Lunar orbital experiments. Biomedical experiments included the Biostack II Experiment and the BIOCORE experiment. The mission marked the longest Apollo mission, 504 hours, and the longest lunar surface stay time, 75 hours, which allowed the astronauts to conduct an extensive geological investigation. They collected 257 pounds (117 kilograms) of lunar samples with the use of the Marshall Space Flight Center developed LRV. The mission ended on December 19, 1972
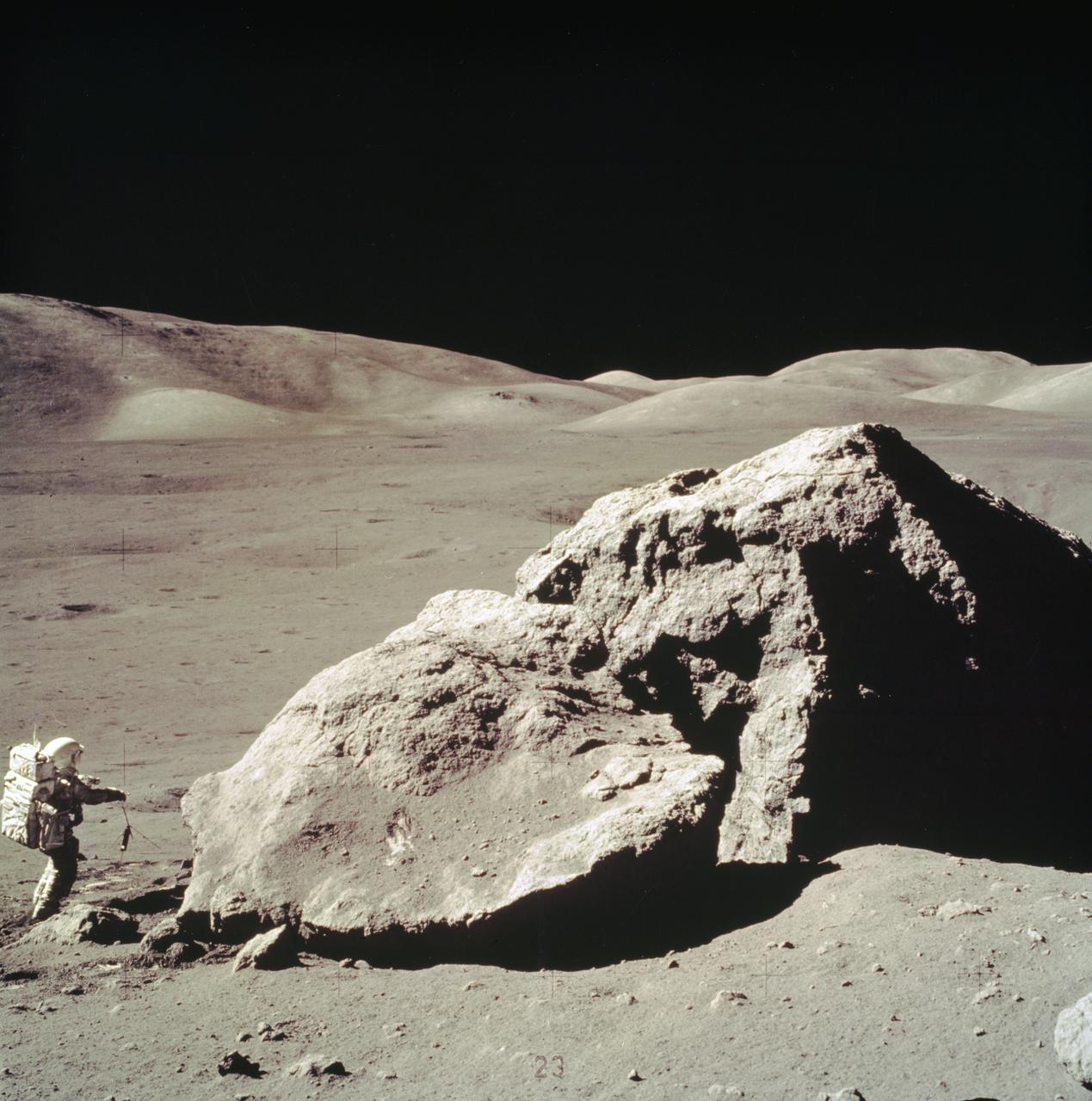

In this Apollo 17 onboard photo, Lunar Module pilot Harrison H. Schmitt collects rock samples from a huge boulder near the Valley of Tourus-Littrow on the lunar surface. The seventh and last manned lunar landing and return to Earth mission, the Apollo 17, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Schmitt; Mission Commander Eugene A. Cernan; and Command Module pilot Ronald E. Evans, lifted off on December 7, 1972 from the Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC). Scientific objectives of the Apollo 17 mission included geological surveying and sampling of materials and surface features in a preselected area of the Taurus-Littrow region, deploying and activating surface experiments, and conducting in-flight experiments and photographic tasks during lunar orbit and transearth coast (TEC). These objectives included: Deployed experiments such as the Apollo lunar surface experiment package (ALSEP) with a Heat Flow experiment, Lunar seismic profiling (LSP), Lunar surface gravimeter (LSG), Lunar atmospheric composition experiment (LACE) and Lunar ejecta and meteorites (LEAM). The mission also included Lunar Sampling and Lunar orbital experiments. Biomedical experiments included the Biostack II Experiment and the BIOCORE experiment. The mission marked the longest Apollo mission, 504 hours, and the longest lunar surface stay time, 75 hours, which allowed the astronauts to conduct an extensive geological investigation. They collected 257 pounds (117 kilograms) of lunar samples with the use of the Marshall Space Flight Center designed Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). The mission ended on December 19, 1972
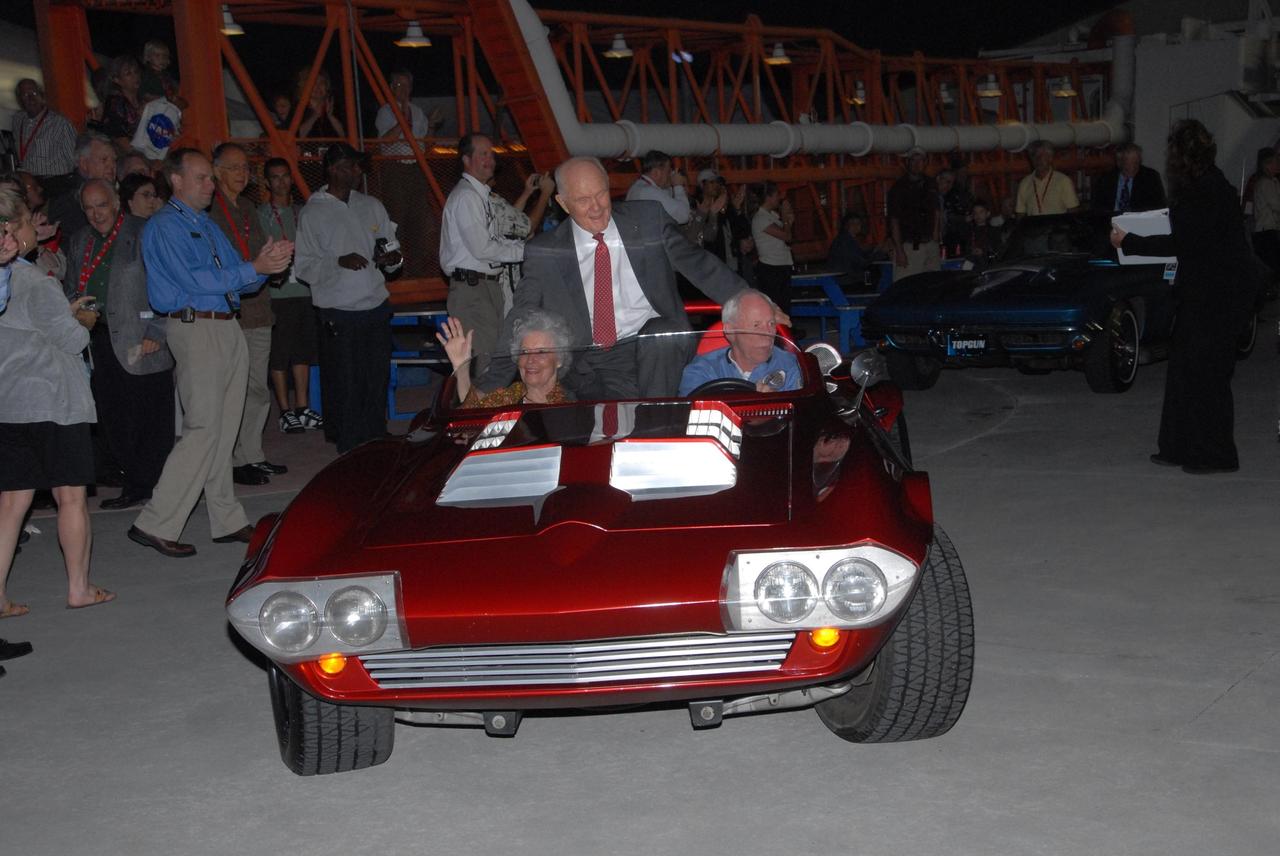

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In a cavalcade of veteran Apollo and Mercury astronauts, John Glenn rides in the back of a Corvette driven by Al Worden. On Feb. 20, 1962, John Glenn piloted the Mercury-Atlas 6 "Friendship 7" spacecraft on the first U.S. manned orbital mission. Worden was command module pilot for Apollo 15, July 26-Aug. 7, 1971. The astronauts were part of the World Space Expo, an event to commemorate humanity's first 50 years in space while looking forward to returning people to the moon and exploring beyond. Commemorating humanity's first 50 years in space while looking forward to returning people to the moon and exploring beyond, the expo showcased various panels, presentations and educational programs, as well as an aerial salute featuring the U.S. Air Force Thunderbirds, U.S. Air Force F-22 Raptor, U.S. Navy F-18 Super Hornet, U.S. Air Force F-15 Eagle, the P-51 Mustang Heritage Flight, and the U.S. Air Force 920th Rescue Wing, which was responsible for Mercury and Gemini capsule recovery. The U.S. Army Golden Knights also demonstrated precision skydiving. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Mercury astronaut John Glenn poses for a photo in front of the Project Mercury monument at Launch Complex-14 LC-14 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During events at the Cape and NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Glenn is marking the 50th anniversary of being the first American astronaut to orbit the Earth inside the Friendship 7 capsule on Feb. 20, 1962. Glenn's launch aboard an Atlas rocket took with it the hopes of an entire nation and ushered in a new era of space travel that eventually led to Americans walking on the moon by the end of the 1960s. Glenn soon was followed into orbit by Scott Carpenter, Walter Schirra and Gordon Cooper. Their fellow Mercury astronauts Alan Shepard and Virgil "Gus" Grissom flew earlier suborbital flights. Deke Slayton, a member of NASA's original Mercury 7 astronauts, was grounded by a medical condition until the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

The launch of the SA-7 (Saturn I Block II) was on September 18, 1964. The SA-7 mission was the second orbital flight of the S-IV stage (second stage) with the payload consisting of the Apollo command and service module's instrument unit. The Saturn I Block II vehicle had two live stages, and were basically in the two-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. While the tank arrangement and the engine patterns were the same, there were marked changes between the Block I and II versions. The first stage (S-I stage) was an improved version of the Block I S-I stage. The Block II S-1 stage had eight fins added for greater aerodynamic stability in the lower atmosphere.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Mercury astronaut John Glenn poses for a photo in front of the Project Mercury monument at Launch Complex-14 LC-14 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. During events at the Cape and NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Glenn is marking the 50th anniversary of being the first American astronaut to orbit the Earth inside the Friendship 7 capsule on Feb. 20, 1962. Glenn's launch aboard an Atlas rocket took with it the hopes of an entire nation and ushered in a new era of space travel that eventually led to Americans walking on the moon by the end of the 1960s. Glenn soon was followed into orbit by Scott Carpenter, Walter Schirra and Gordon Cooper. Their fellow Mercury astronauts Alan Shepard and Virgil "Gus" Grissom flew earlier suborbital flights. Deke Slayton, a member of NASA's original Mercury 7 astronauts, was grounded by a medical condition until the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project in 1975. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
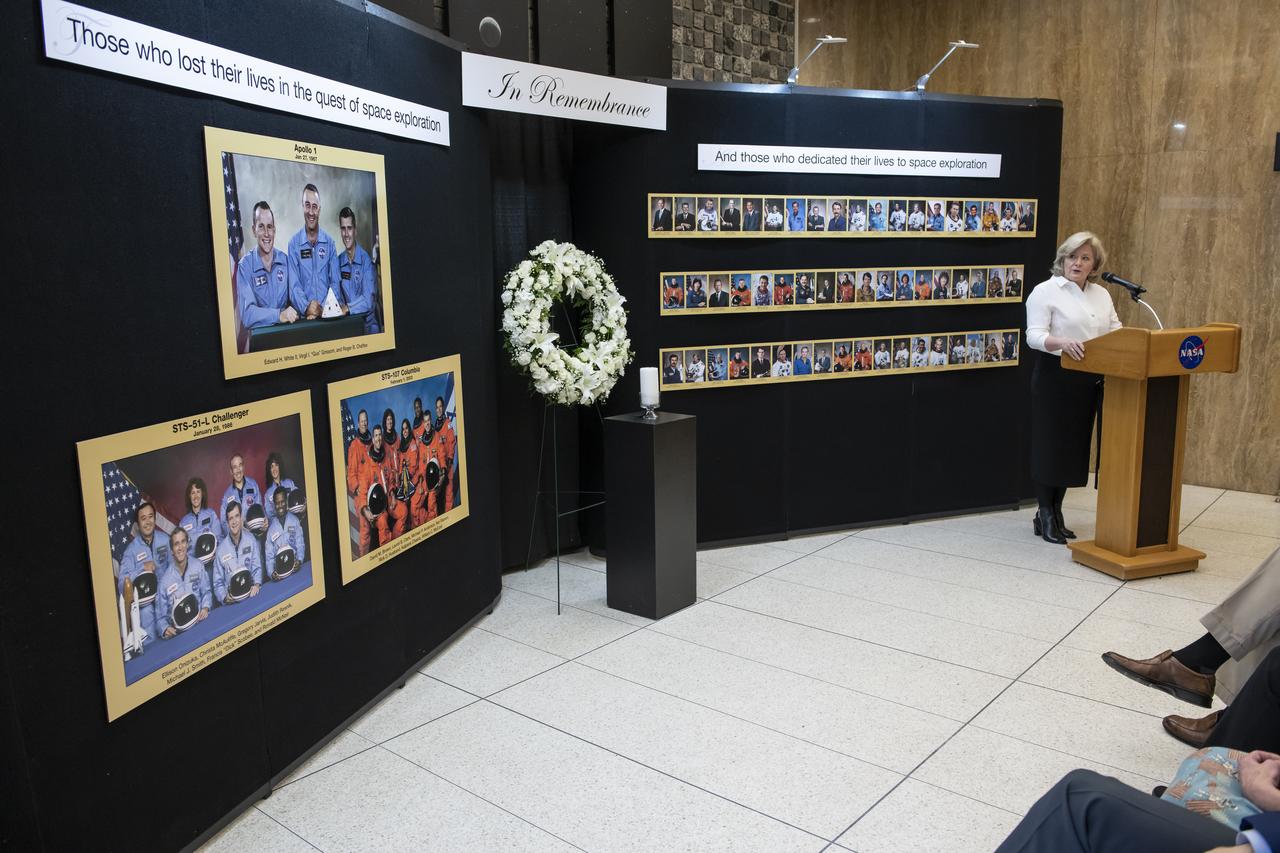

NASA Marshall Space Flight Center Director Jody Singer looks solemnly toward a display honoring the crews of space shuttle Columbia STS-107, space shuttle Challenger STS-51L and Apollo 1 during the center's Day of Remembrance ceremony Feb. 7. Singer, former astronaut Jan Davis, and Marshall Safety and Mission Assurance Directorate Director Rick Burt, spoke at the annual ceremony, which honors those who lost their lives in the quest of space exploration and those who dedicated their lives to space exploration. The ceremony concluded with Singer lighting a candle in memory of the honorees and a moment of silence led by Johnny Stephenson, director of the Office of Strategic Analysis & Communications.
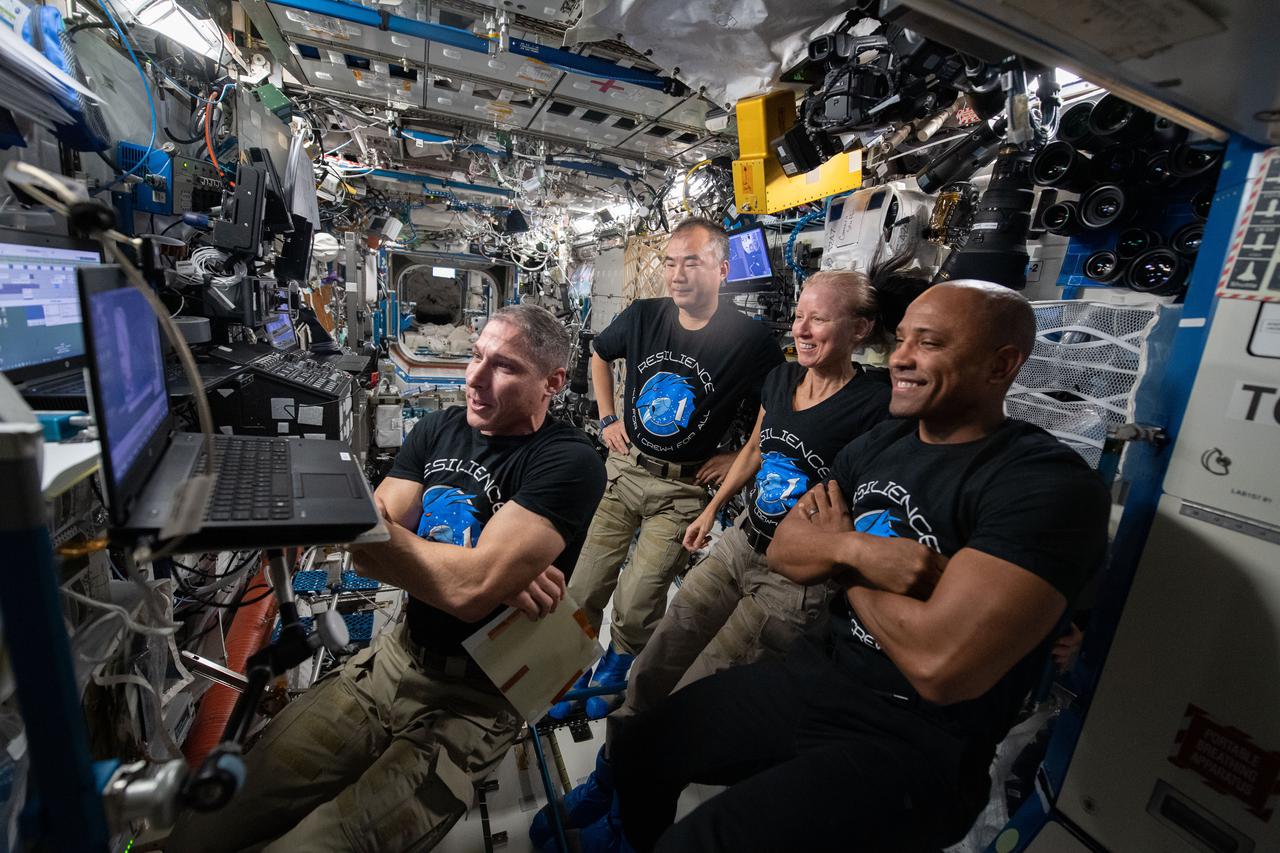

iss064e029574 (Feb. 7, 2021) --- Four Expedition 64 Flight Engineers, who are also the SpaceX Crew-1 astronauts, gather around a laptop computer to join a video conference with former NASA astronaut Edward Gibson, who along with his former Skylab-4 crewmates Gerald Carr and William Pogue, docked their Apollo crew ship to the Skylab space station on Nov. 16, 1973, 47 years to the day when the crew of the “Resilience” Crew Dragon spacecraft docked to the orbiting lab. From left are, Michael Hopkins of NASA, Soichi Noguchi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), and NASA astronauts Shannon Walker and Victor Glover.
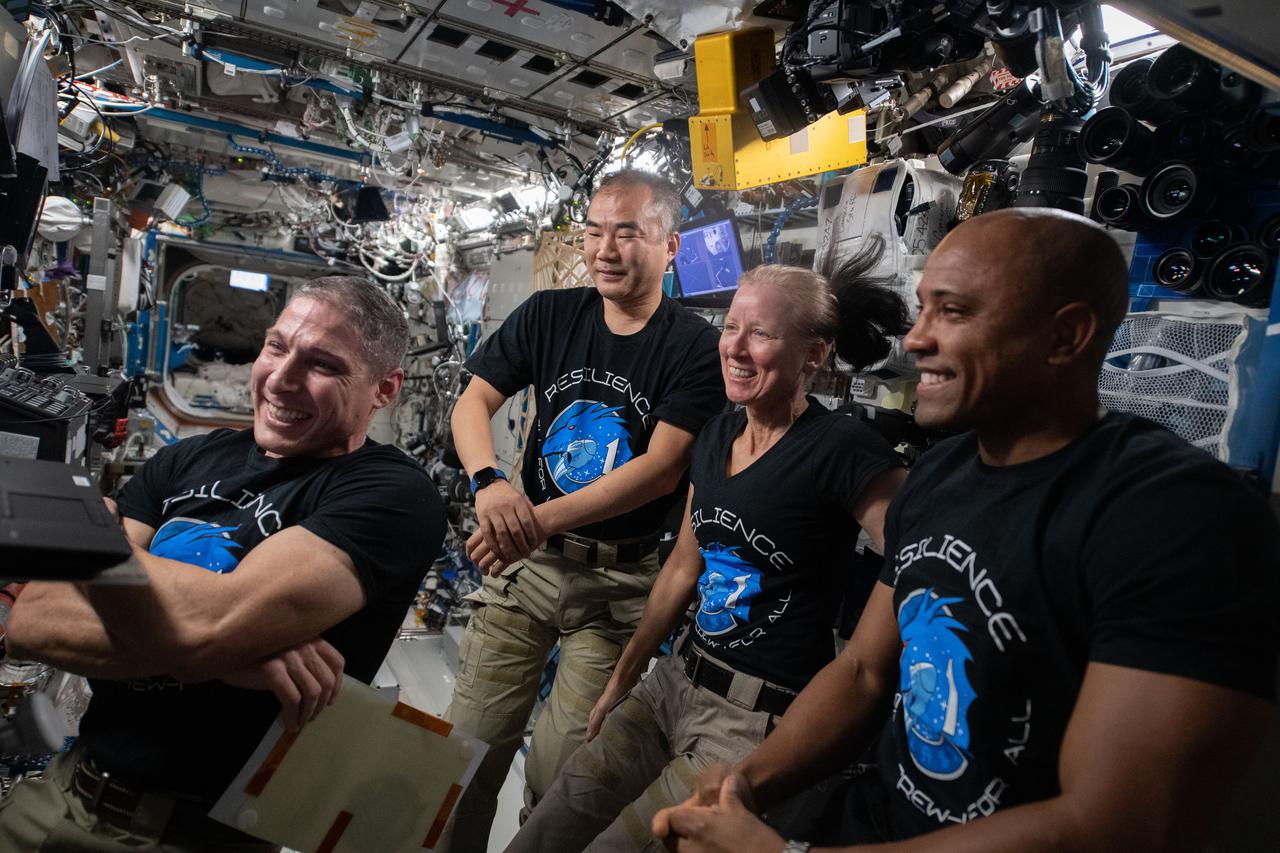

iss064e029583 (Feb. 7, 2021) --- Four Expedition 64 Flight Engineers, who are also the SpaceX Crew-1 astronauts, gather around a laptop computer to join a video conference with former NASA astronaut Edward Gibson, who along with his former Skylab-4 crewmates Gerald Carr and William Pogue, docked their Apollo crew ship to the Skylab space station on Nov. 16, 1973, 47 years to the day when the crew of the “Resilience” Crew Dragon spacecraft docked to the orbiting lab. From left are, Michael Hopkins of NASA, Soichi Noguchi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), and NASA astronauts Shannon Walker and Victor Glover.

The Ohio State University President E. Gordon Gee, left, Apollo 11 Astronaut Neil Armstrong, 2nd from left, Former space shuttle astronaut and former Under Secretary of the Air Force Dr. Ron Sega, and Captain Mark Kelly, commander of the space shuttle Endeavour’s final mission and husband of retired U.S. Representative Gabrielle Giffords, right, talk prior to a reception at Ohio State University honoring the 50th anniversary of John Glenn's historic flight aboard Friendship 7 Monday, Feb. 20, 2012, in Columbus, Ohio. Glenn was the first American to orbit Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
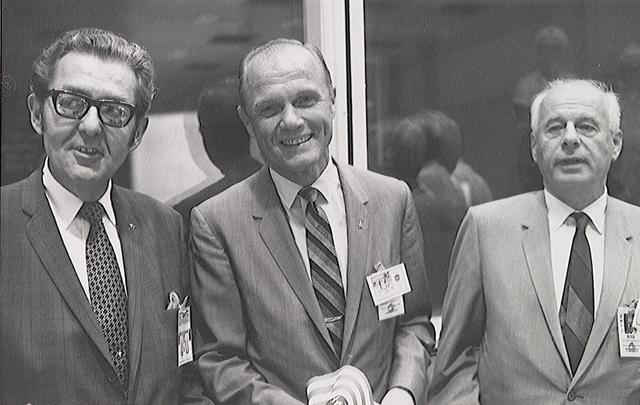

S69-44022 (7-24-69) --- On hand in Houston's mission control center to witness activity associated with the landing and recovery operations for the Apollo 11 mission were, from the left, Bob Kline, chief of the Mission Operations Procurement Branch at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC); astronaut John H. Glenn Jr.; and Eberhard Rees, deputy director of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). They were among a large number of personnel on hand in the MCC's mission operations control room (MOCR). Glenn holds one of the dozens of flags that were handed out for the return's celebration.
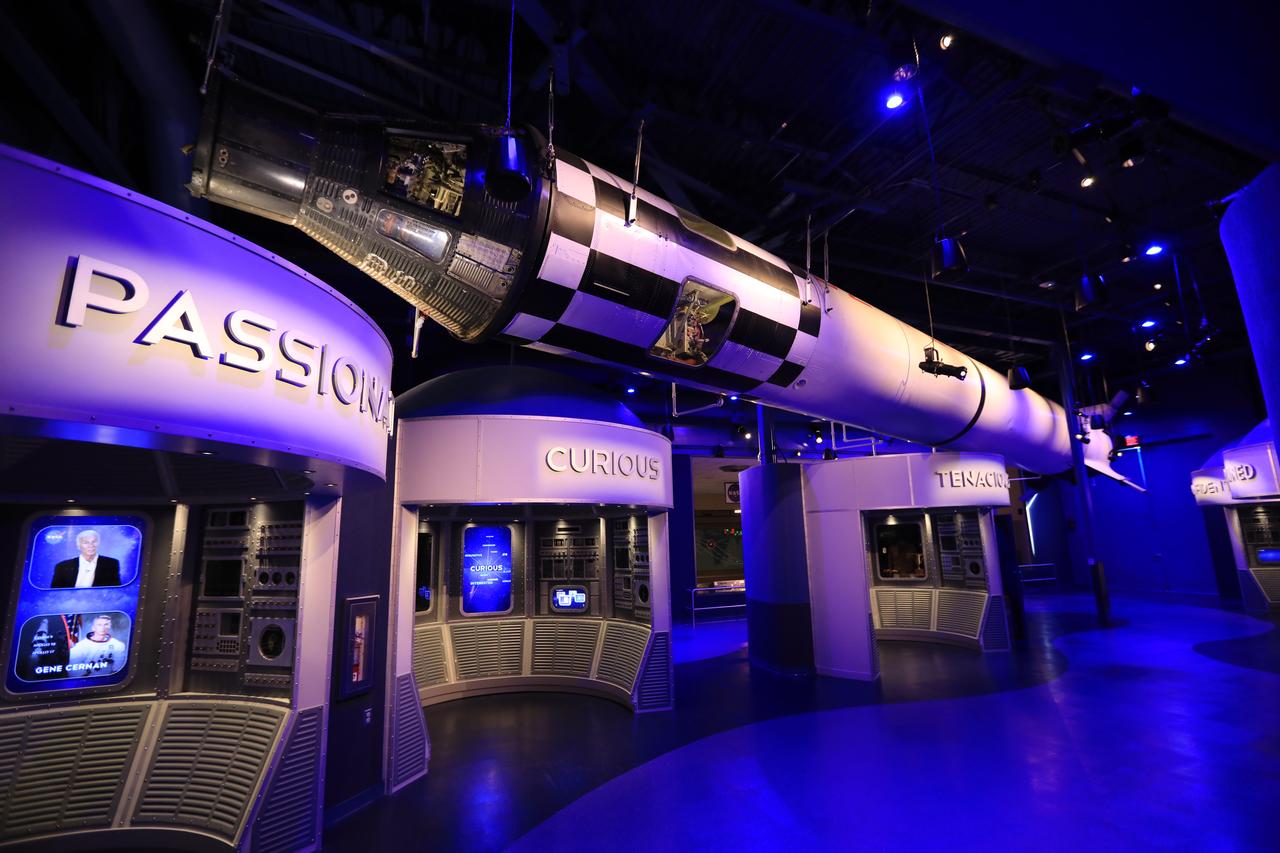

Inside the Heroes and Legends attraction at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, the Sigma 7 Mercury spacecraft in this exhibit was piloted by astronaut Wally Schirra during his six-orbit mission on Oct. 3, 1962. For display purposes, it is shown here attached to a Redstone launch vehicle like the one that boosted astronauts Alan Shepard and Gus Grissom on sub-orbital flights in 1961. Schirra's capsule was actually launched by the more powerful Atlas rocket in order to reach orbit. The new facility looks back to the pioneering efforts of Mercury, Gemini and Apollo. It sets the stage by providing the background and context for space exploration and the legendary men and women who pioneered the nation's journey into space.