
S69-18569 (February 1969) --- The insignia of the Apollo 9 space mission. The crew consist of astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. The NASA insignia design for Apollo flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced.
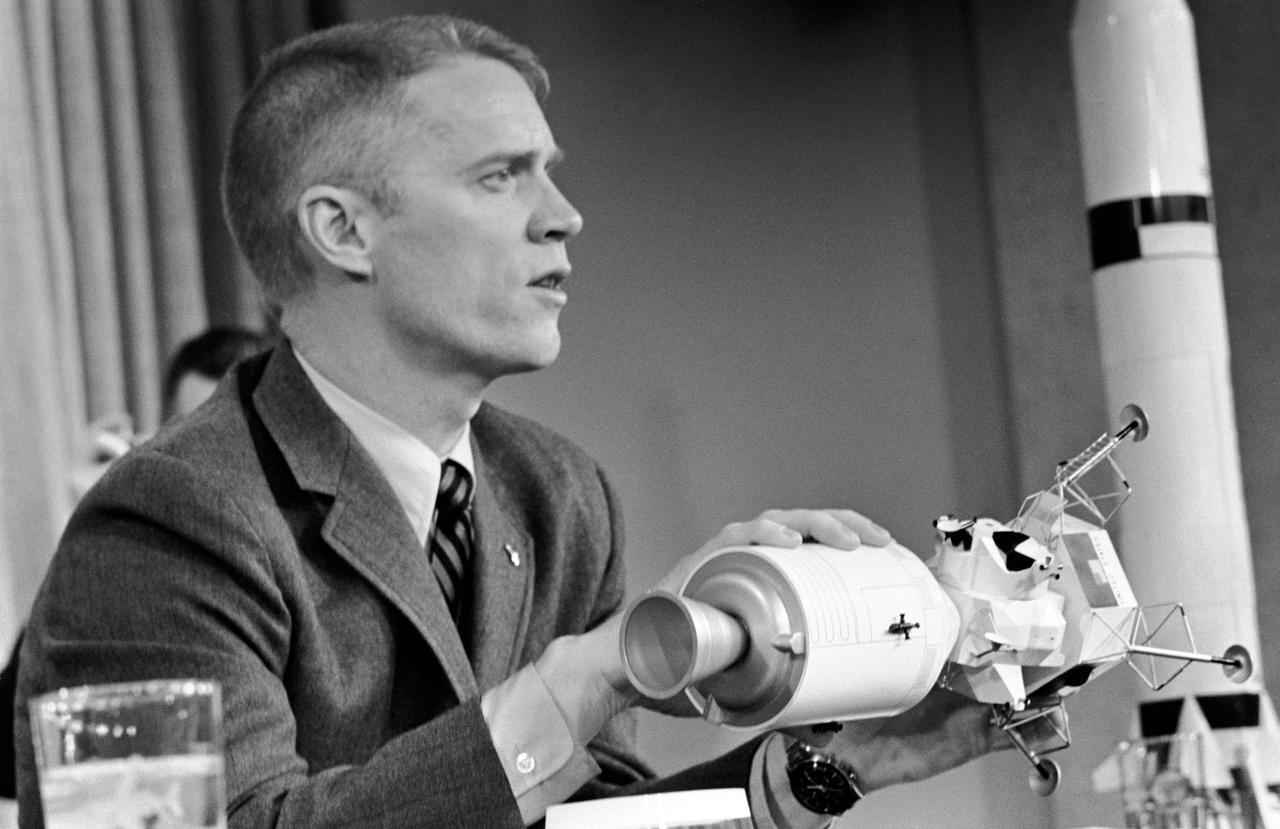

S69-17615 (25 Jan. 1969) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot of the Apollo 9 prime crew, participates in a press conference at the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. Grumman is the contractor to NASA for the Lunar Module. Schweickart is holding a model of a docked Lunar Module/Command and Service Modules. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
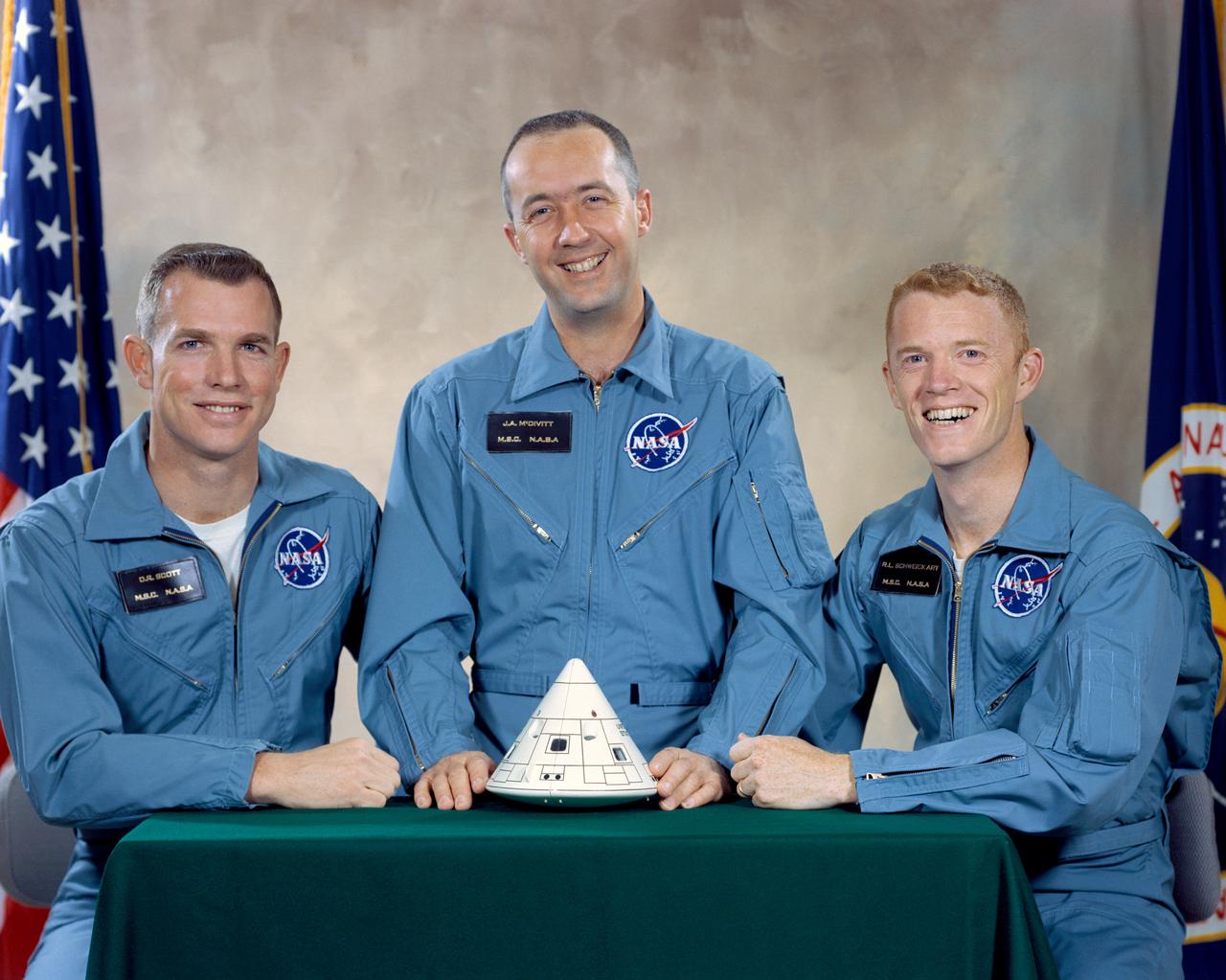

S66-30237 (March 1966) --- These three astronauts have been named as the prime crew of the Apollo 9 mission. They are (left to right) David R. Scott, command module pilot; James A. McDivitt, commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot.
![S68-56621 (18 Dec. 1968) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew of the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space mission. Left to right, are James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot: and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 launch is scheduled no earlier than February 28, 1969. In the background is the Apollo 8 space vehicle on Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, which was launched on December 21, 1968. (Gaseous liquid oxygen is venting from the vehicle’s first [S-1C] stage during a countdown demonstration test). McDivitt holds a U.S. flag.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/S68-56621/S68-56621~medium.jpg)
S68-56621 (18 Dec. 1968) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew of the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space mission. Left to right, are James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot: and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 launch is scheduled no earlier than February 28, 1969. In the background is the Apollo 8 space vehicle on Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, which was launched on December 21, 1968. (Gaseous liquid oxygen is venting from the vehicle’s first [S-1C] stage during a countdown demonstration test). McDivitt holds a U.S. flag.

S69-17590 (18 Dec. 1968) --- These three astronauts are the prime crew of the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/ Lunar Module 3/ Saturn 504) space mission. Left to right, are James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot.
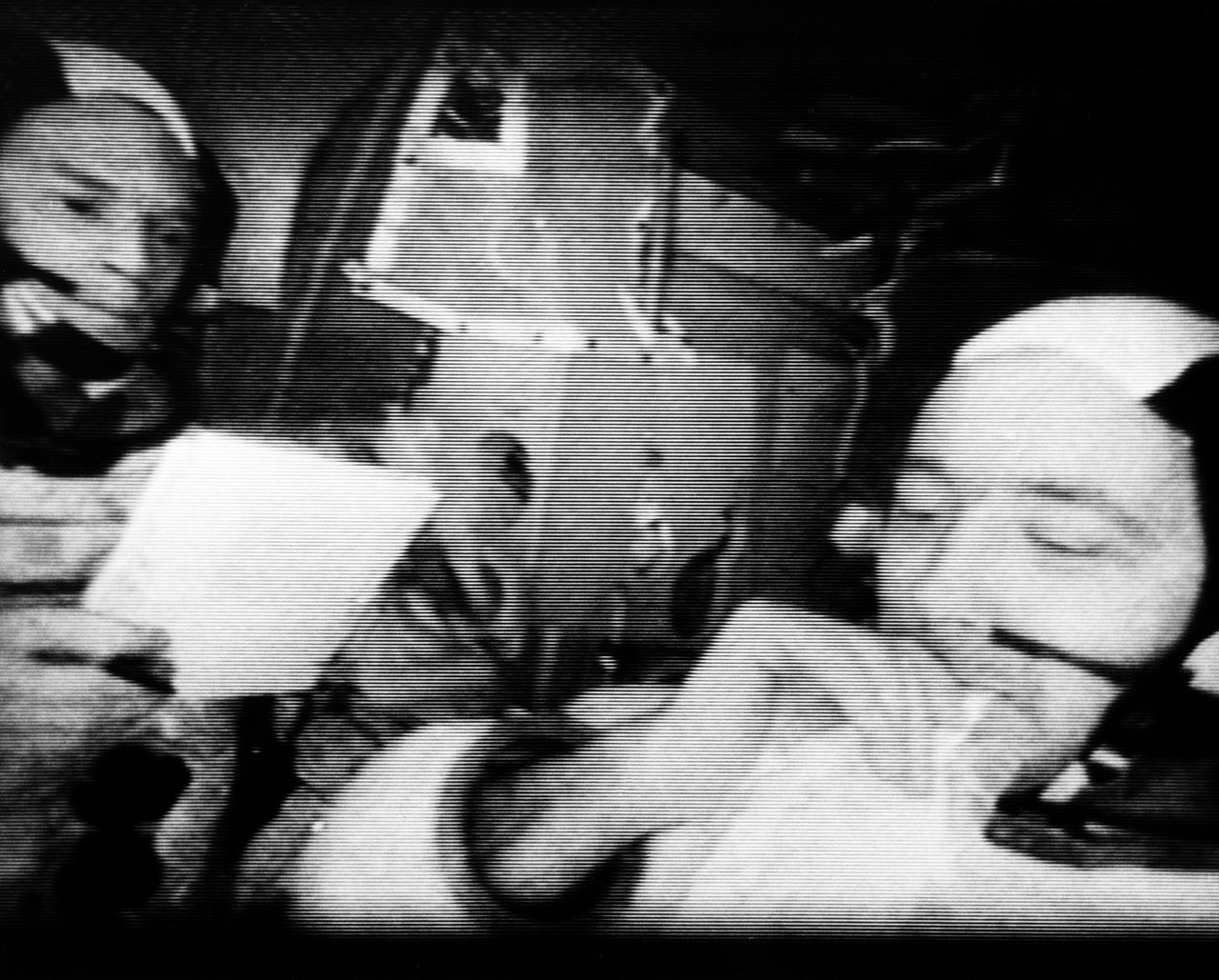
S69-26698 (March 1969) --- A photograph from a live television transmission from Apollo 9. This view shows the interior of the Lunar Module "Spider." Astronaut James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, is in right foreground. In left background is astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. At this moment Apollo 9 was orbiting Earth with the Command Module docked nose-to-nose with the Lunar Module. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module "Gumdrop" while the other two astronauts checked out the Lunar Module.
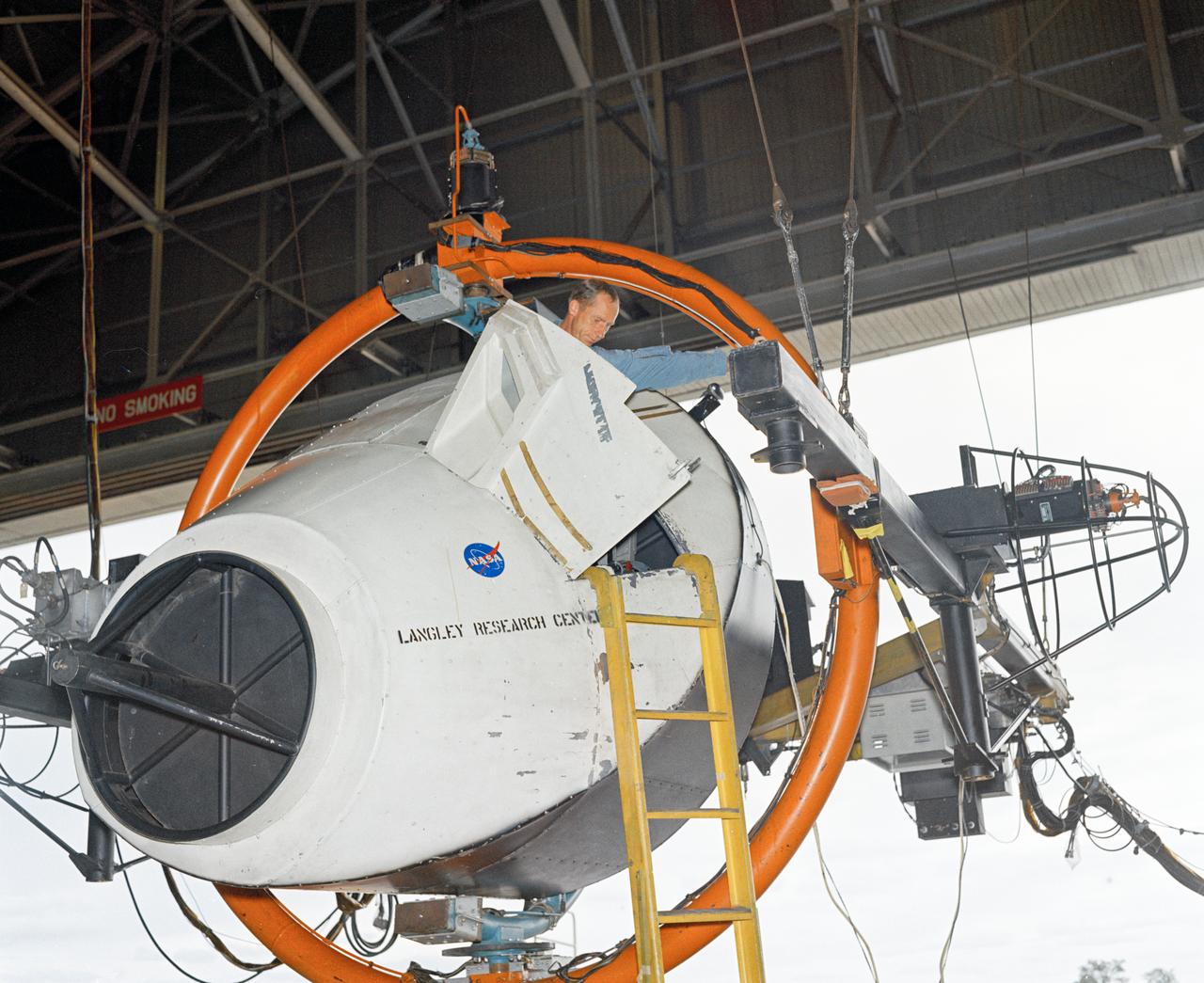

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
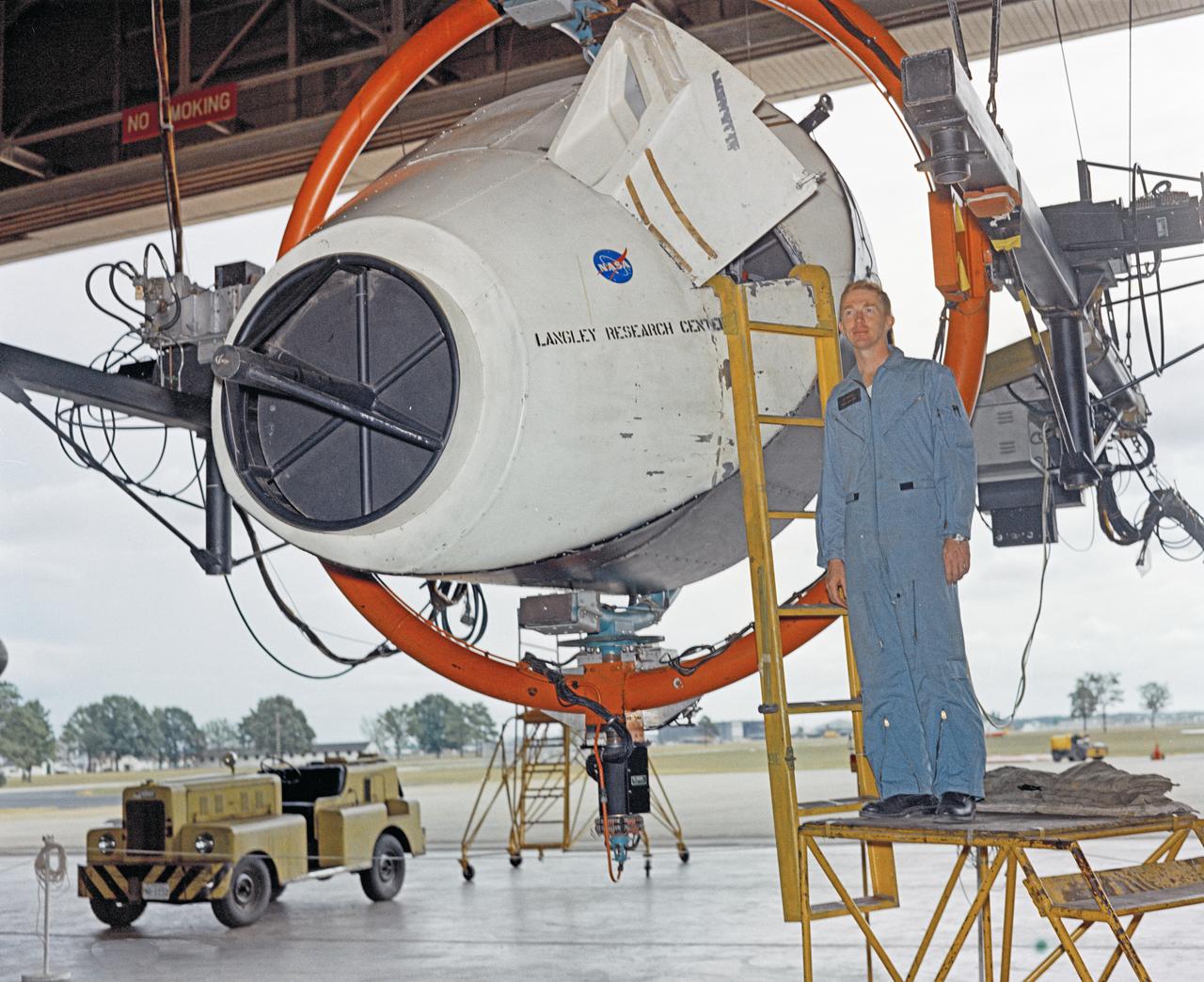

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
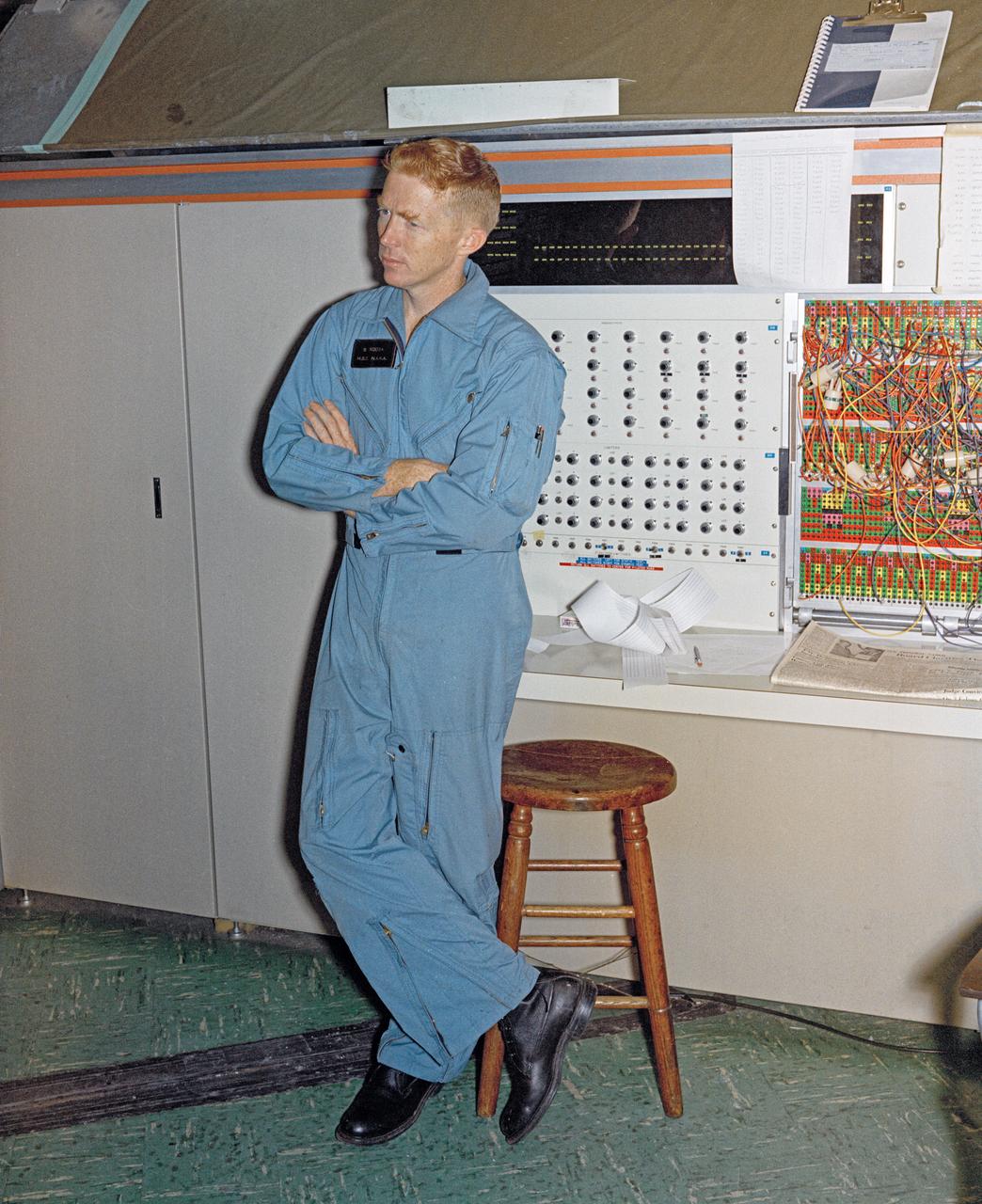

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
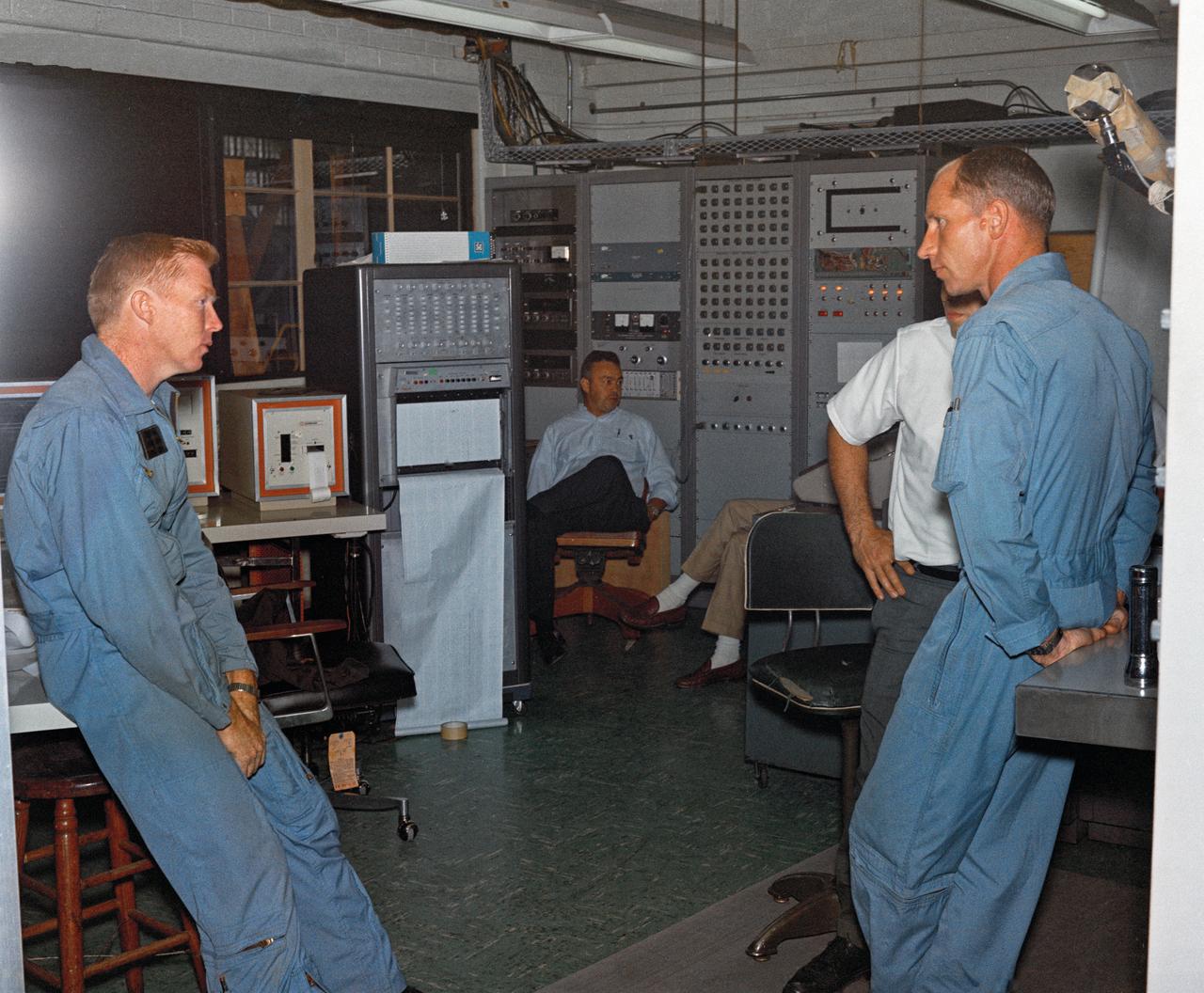

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
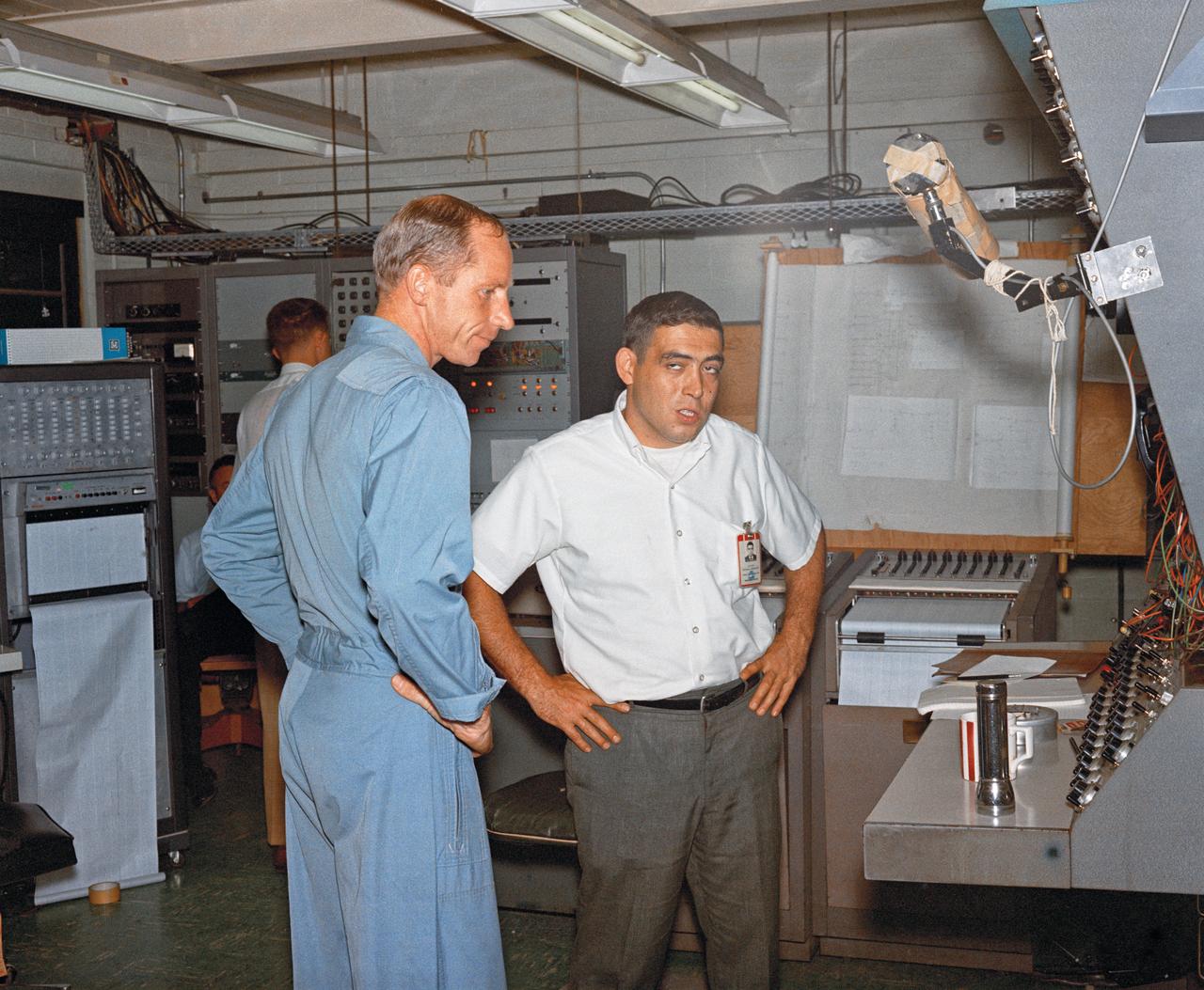

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
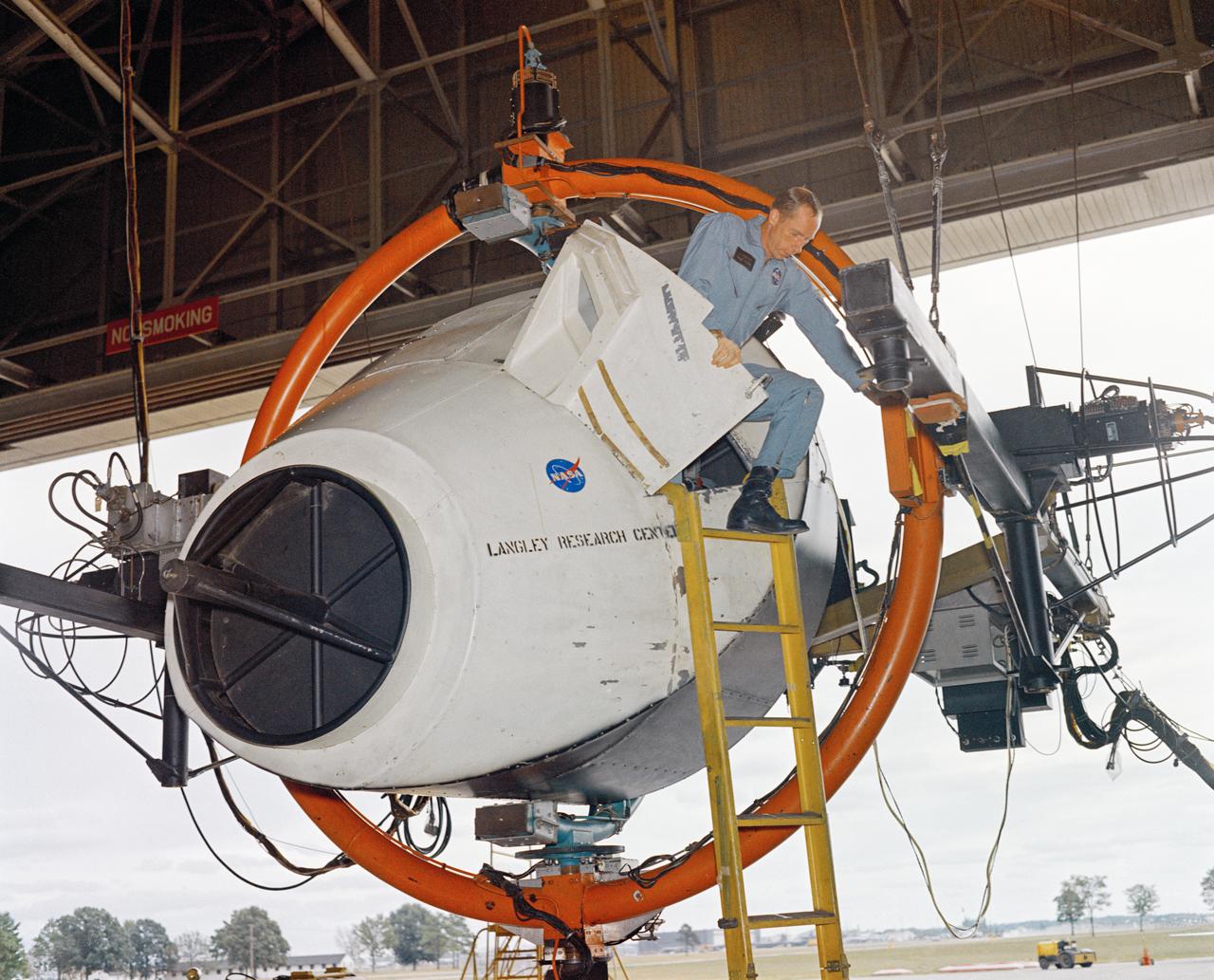

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
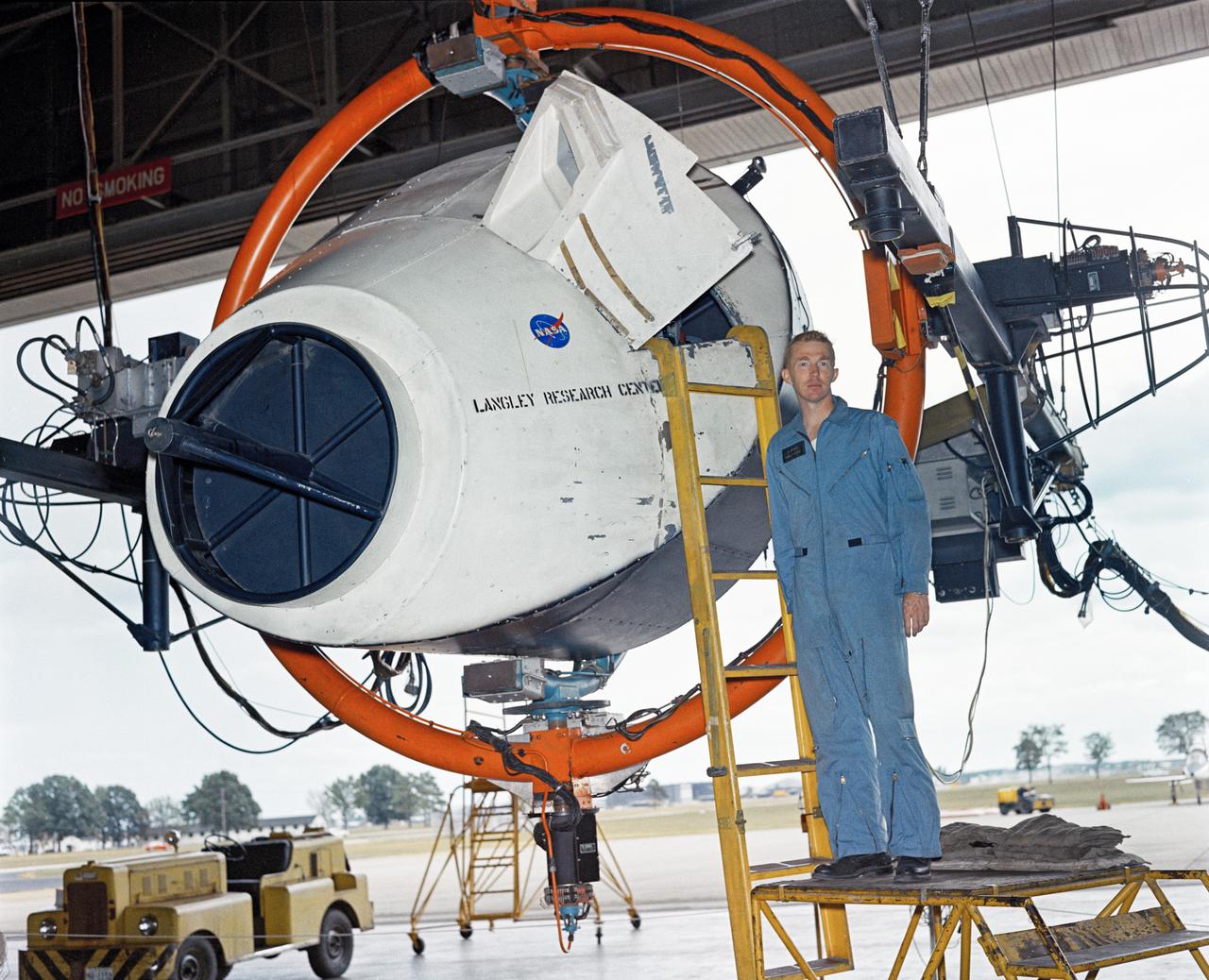

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
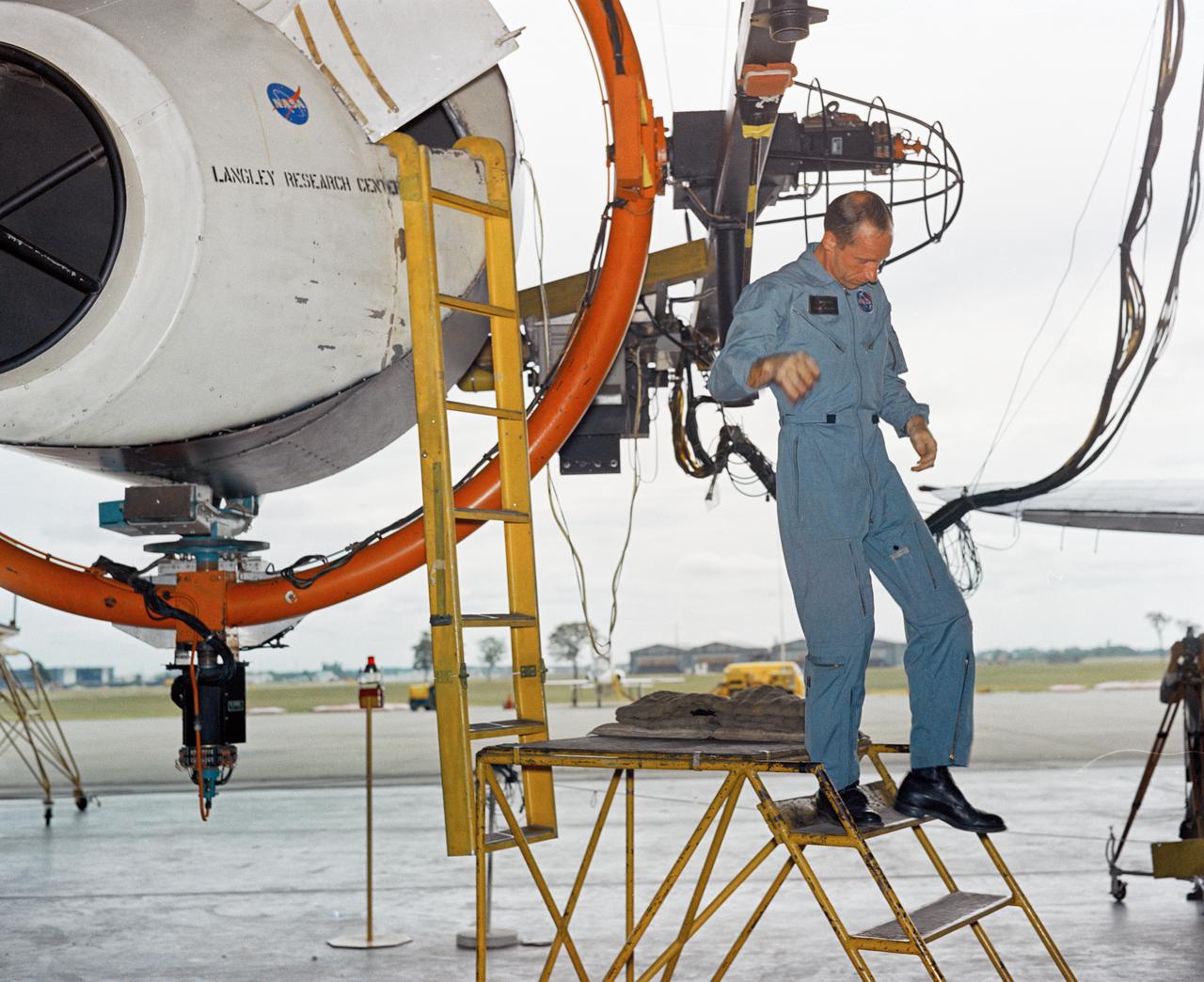

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
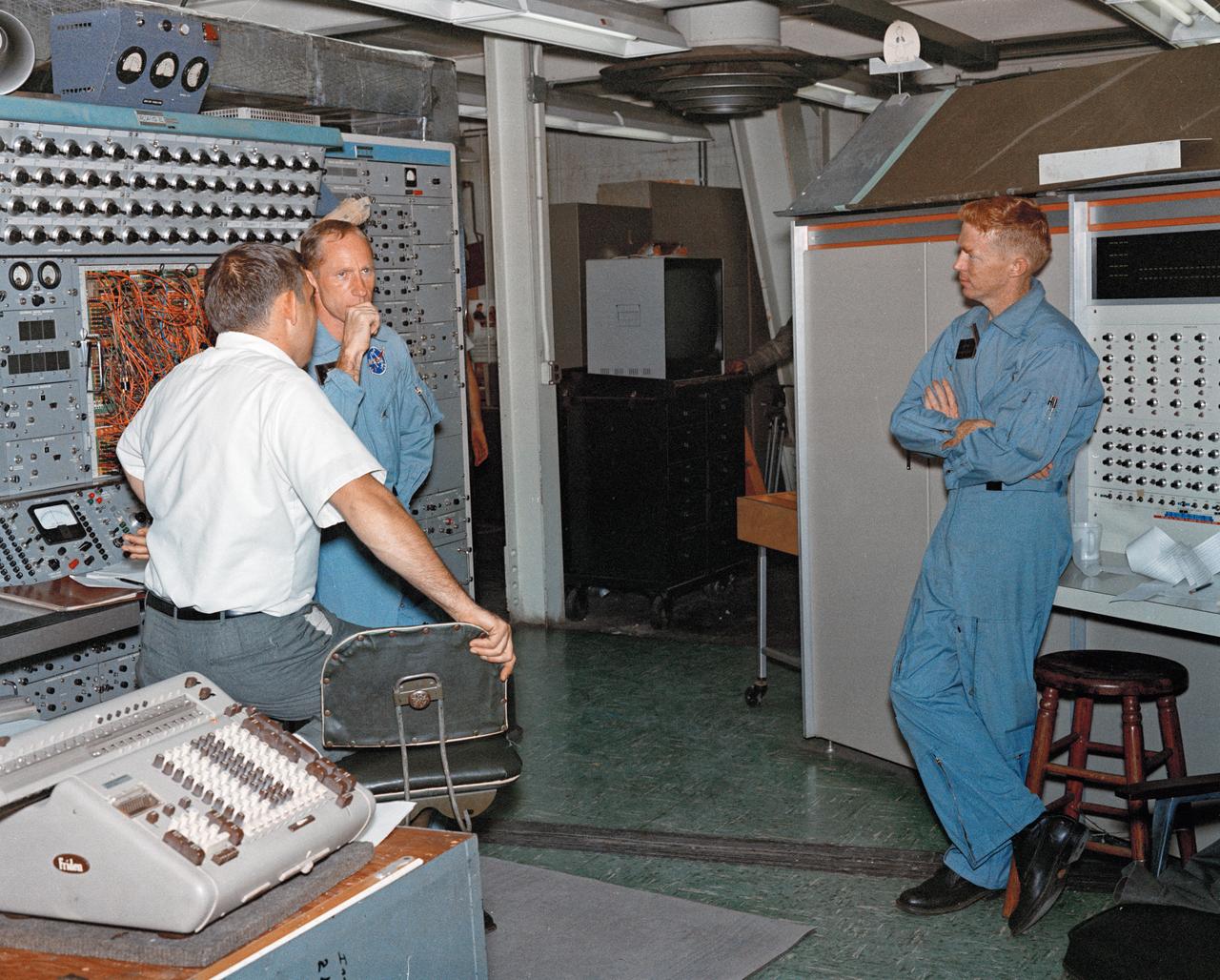

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
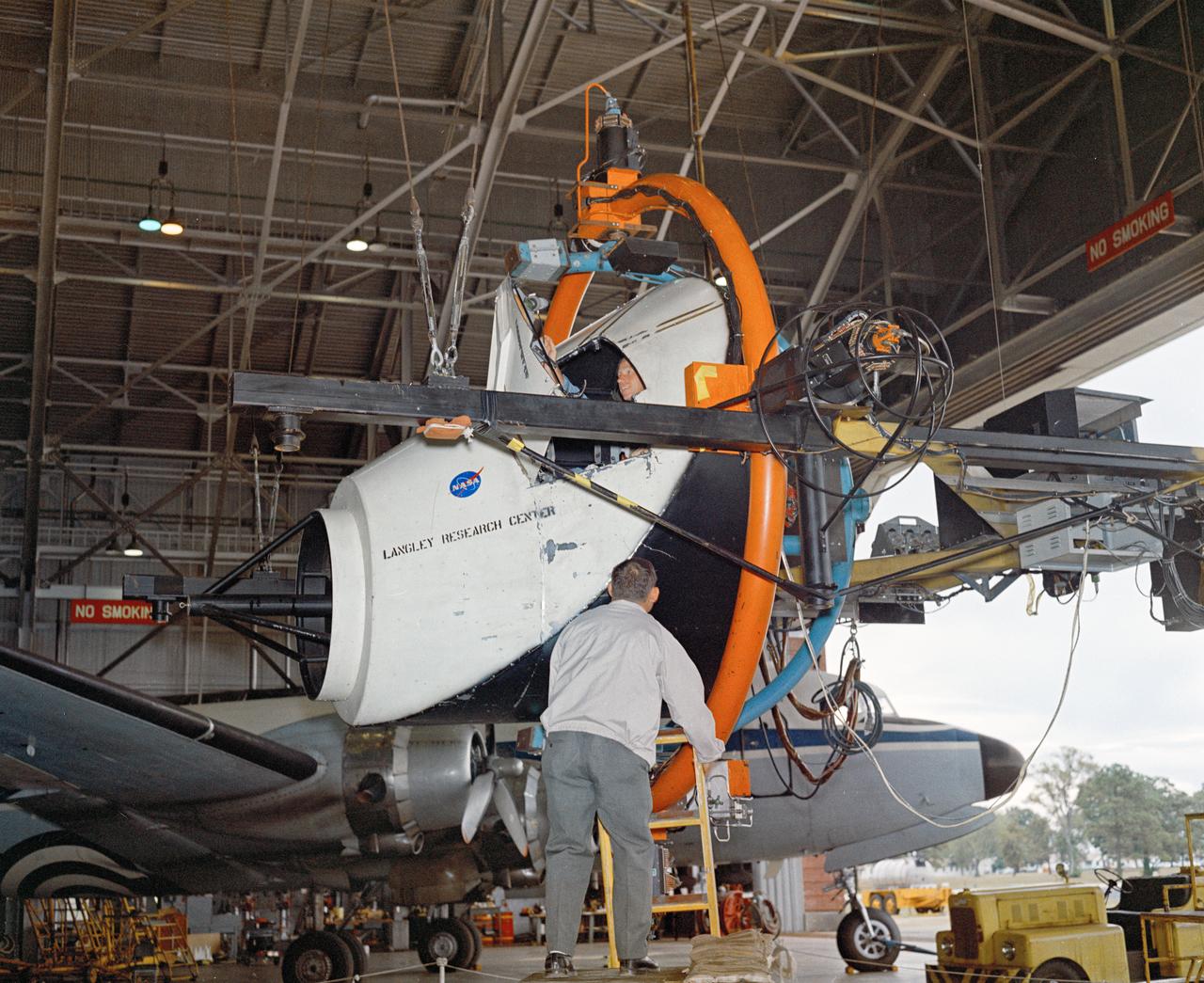

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
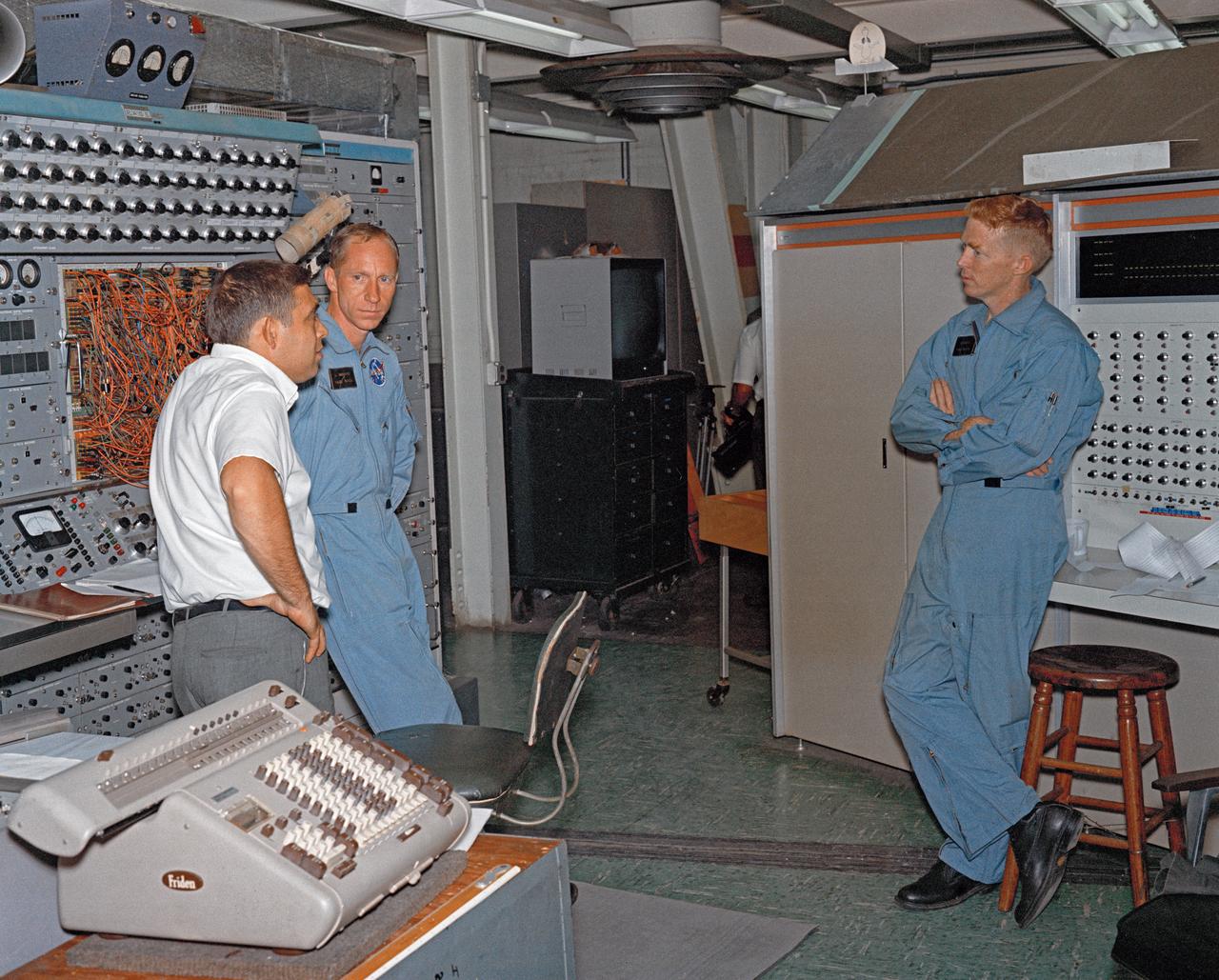

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
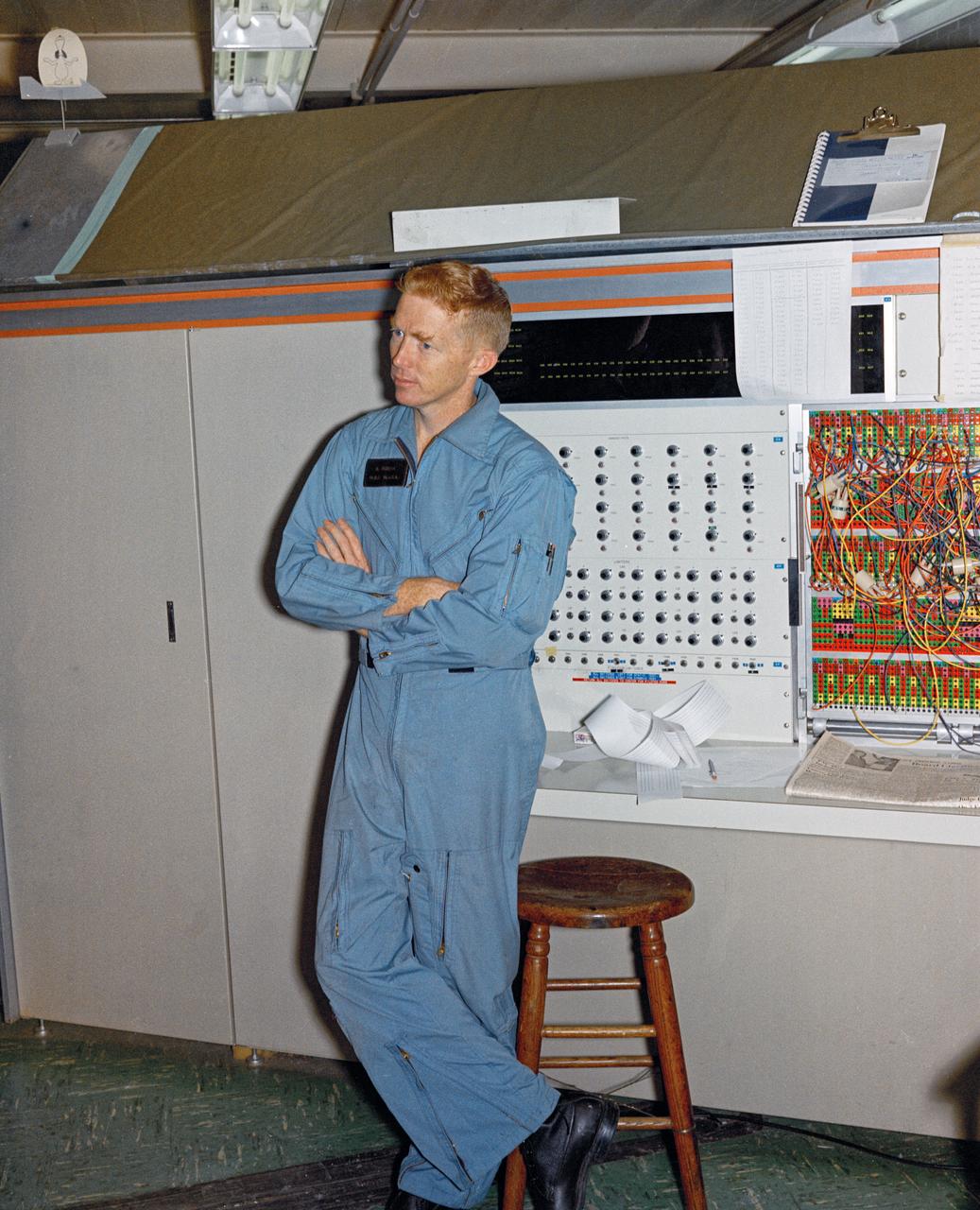

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
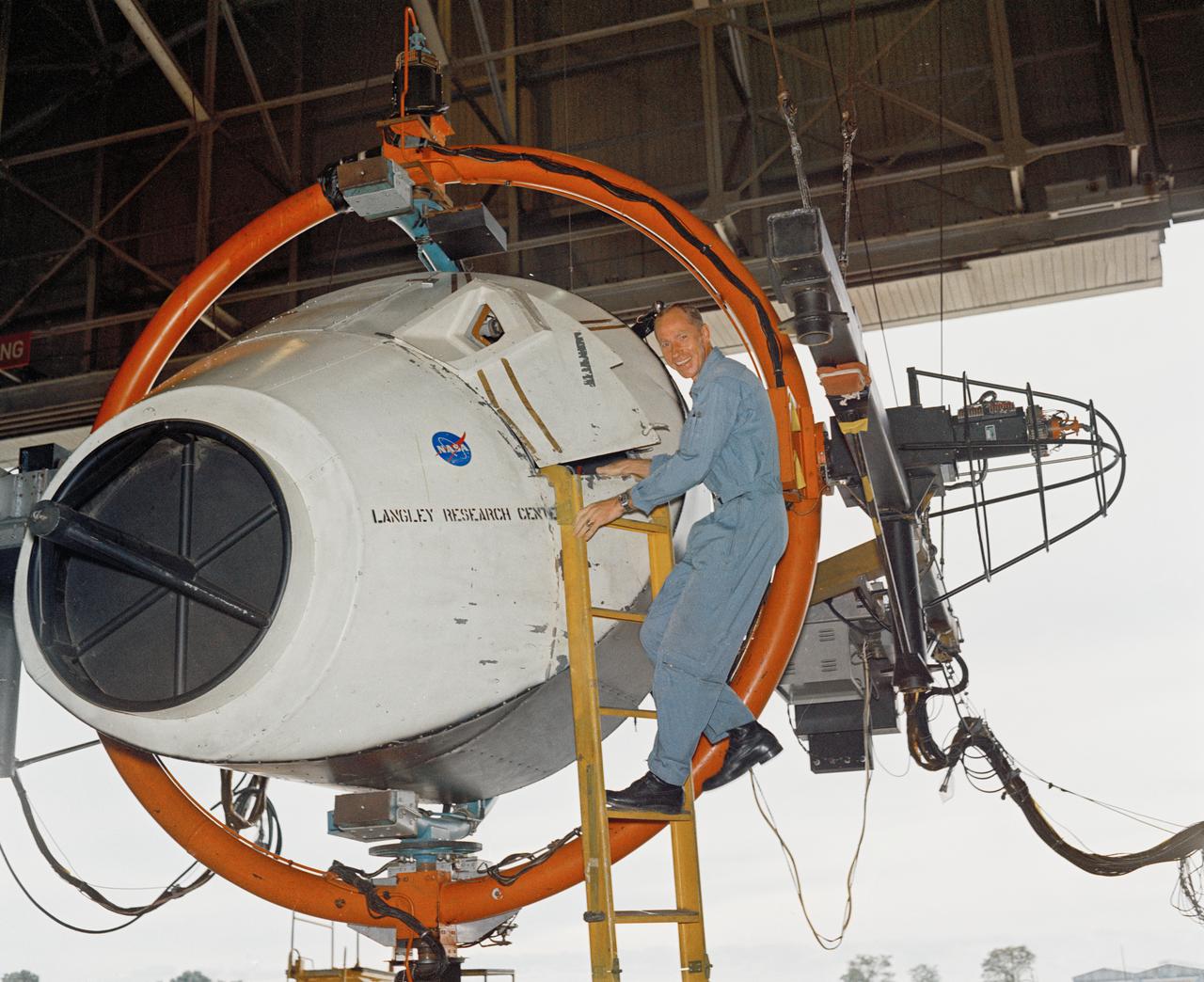

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
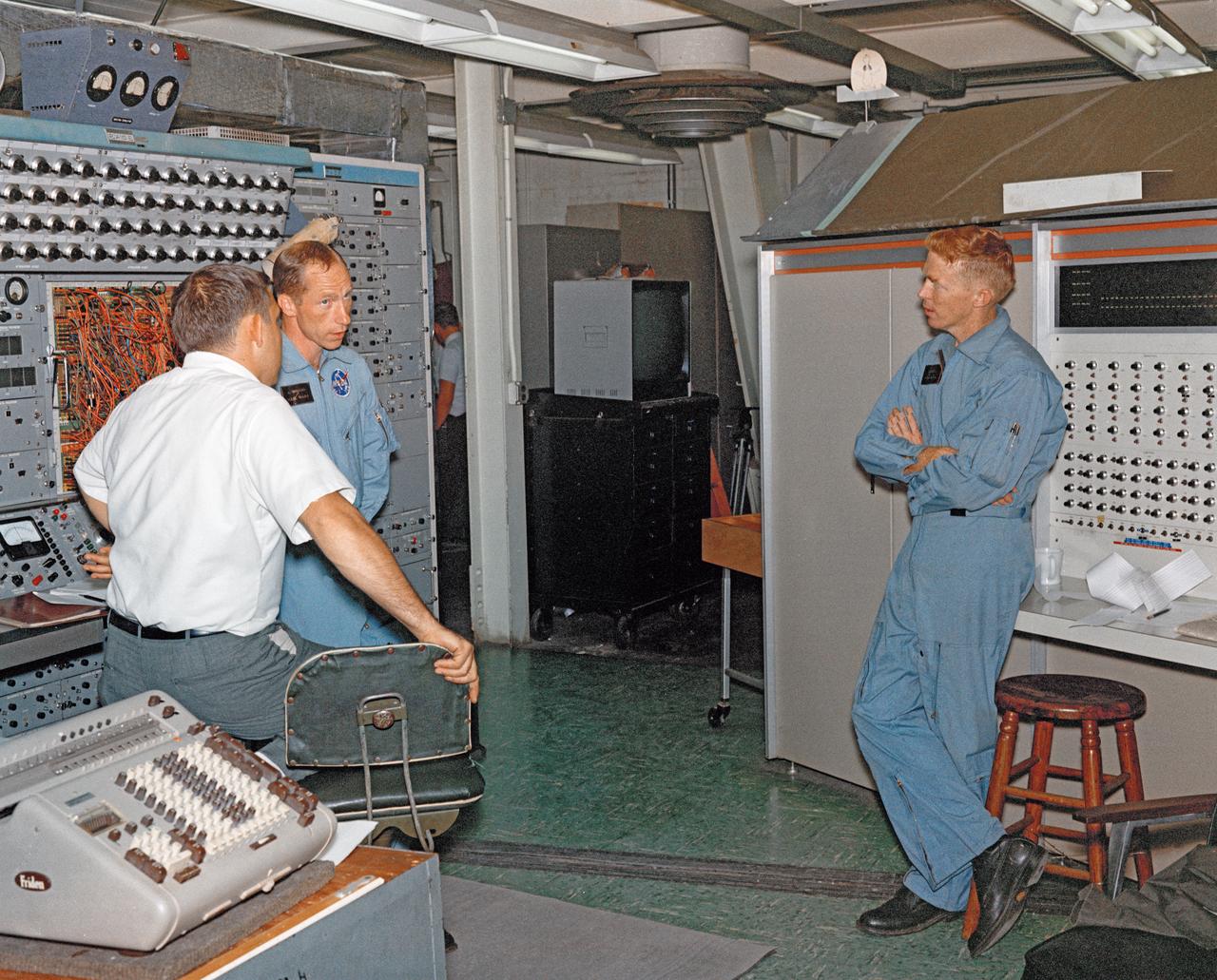

Astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, and Alfred M. Worden training a tRendezvous Docking Simulator NASA Langley. Worden was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He served as a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight and as backup command module pilot for the Apollo 12 flight. Colonel Roosa was one of the 19 astronauts selected by NASA in April 1966. He was a member of the astronaut support crew for the Apollo 9 flight.
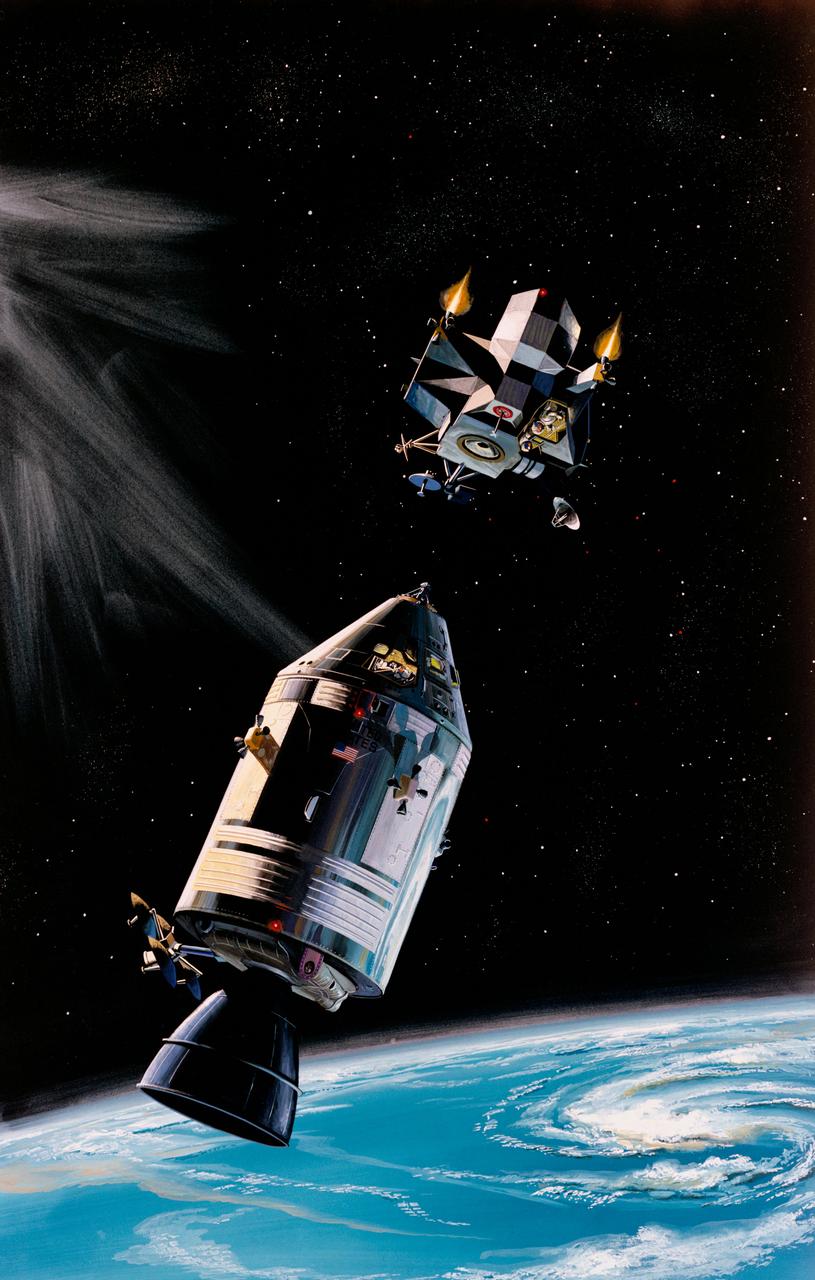

S69-18546 (February 1969) --- North American Rockwell artist's concept illustrating the docking of the Lunar Module ascent stage with the Command and Service Modules during the Apollo 9 mission. The two figures in the Lunar Module represent astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The figure in the Command Module represents astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.

S69-19794 (February 1969) --- Composite of two artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the third day of the Apollo 9 mission, including crew transfer and Lunar Module system evaluation. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
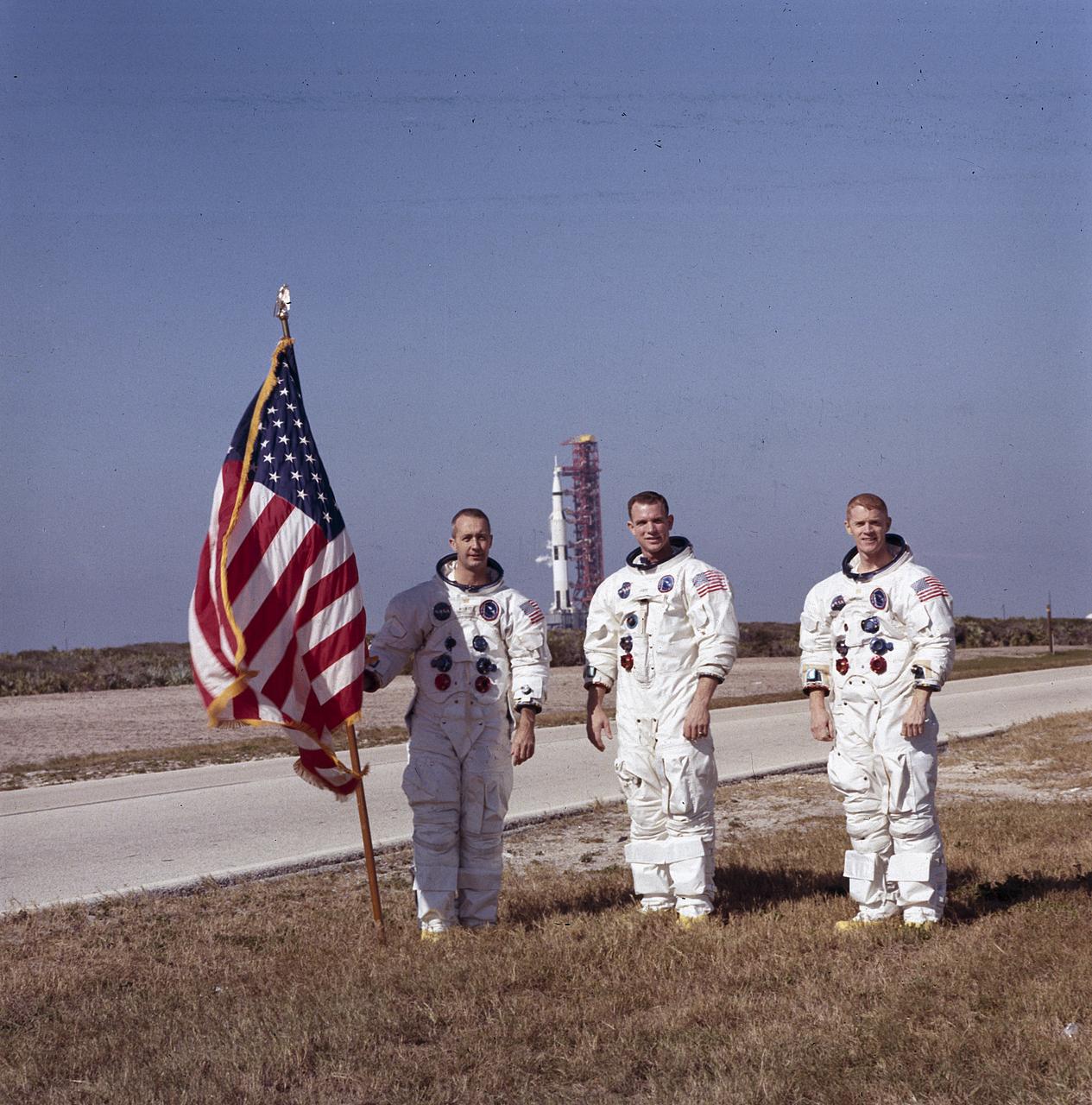

Pictured from left to right, the Apollo 9 astronauts, James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart, pause in front of the Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle that would launch the Apollo 8 crew. The launch of the Apollo 9 (Saturn V launch vehicle, SA-504) took place on March 3, 1968. The Apollo 9 spacecraft, in the lunar mission configuration, was tested in Earth orbit. The mission was designed to rehearse all the steps and reproduce all the events of the Apollo 11 mission with the exception of the lunar touchdown, stay, and liftoff. The command and service modules, and the lunar module were used in flight procedures identical to those that would later take similar vehicles to the Moon, and a landing. The flight mechanics, mission support systems, communications, and recording of data were tested in a final round of verification. Astronauts Scott and Schweickart conducted Extravehicular Activity during this mission.

Physicist Brian Cox serves as the moderator for a panel discussion with Apollo astronauts during the Apollo 11 50th Gala on July 16, 2019. The gala, presented by Northrop Grumman, was held inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. From left, are Apollo 9 astronaut Rusty Schweichart, Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins, Apollo 16 astronaut Charlie Duke, and Apollo Flight Director Gerry Griffin.
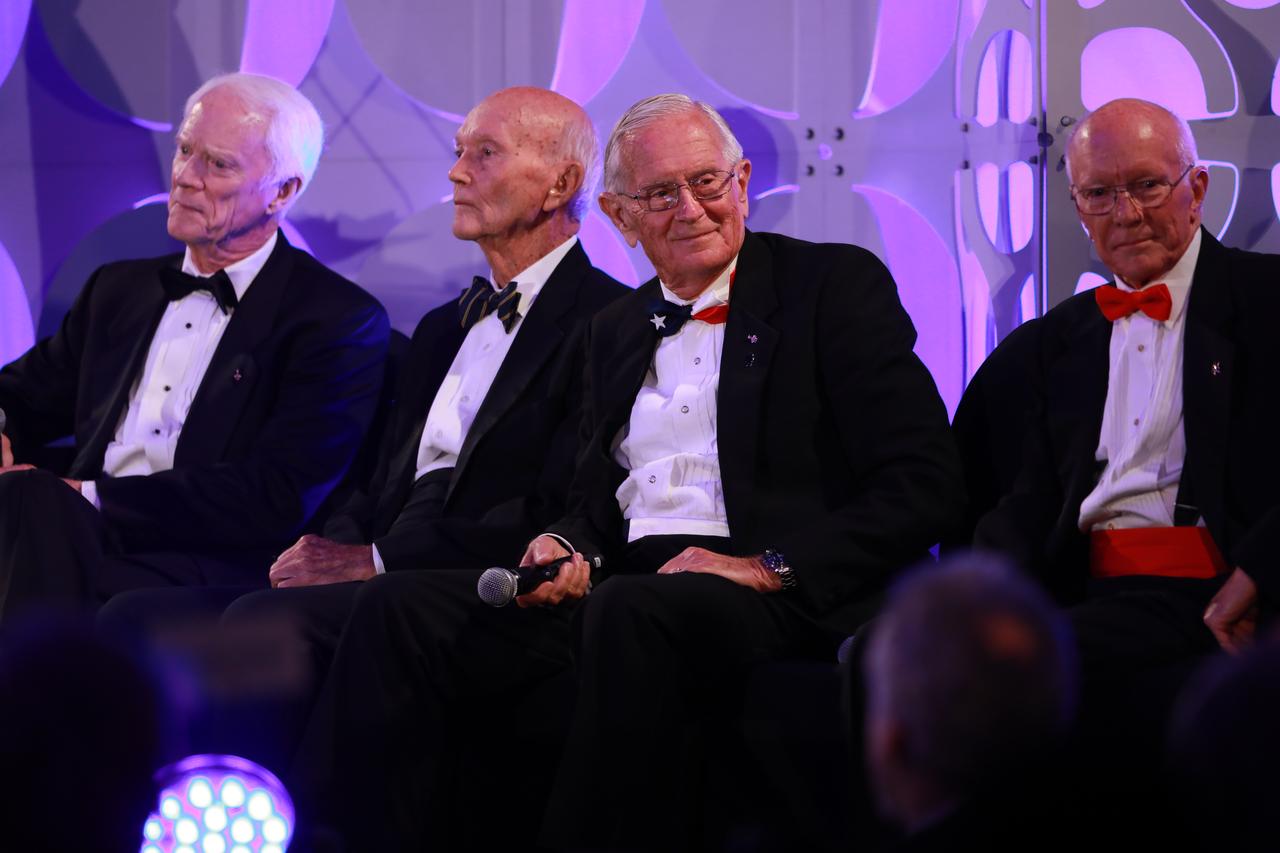

A panel discussion with Apollo astronauts took place during the Apollo 11 50th Gala, present by Northop Grumman, inside the Apollo/Saturn V Center at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on July 16, 2019. From left, are Apollo 9 astronaut Rusty Schweickart, Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins, Apollo 16 astronaut Charlie Duke, and Apollo Flight Director Gerry Griffin.

This photograph shows an early moment of the first test flight of the Saturn V vehicle for the Apollo 4 mission, photographed by a ground tracking camera, on the morning of November 9, 1967. This mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmarned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield.
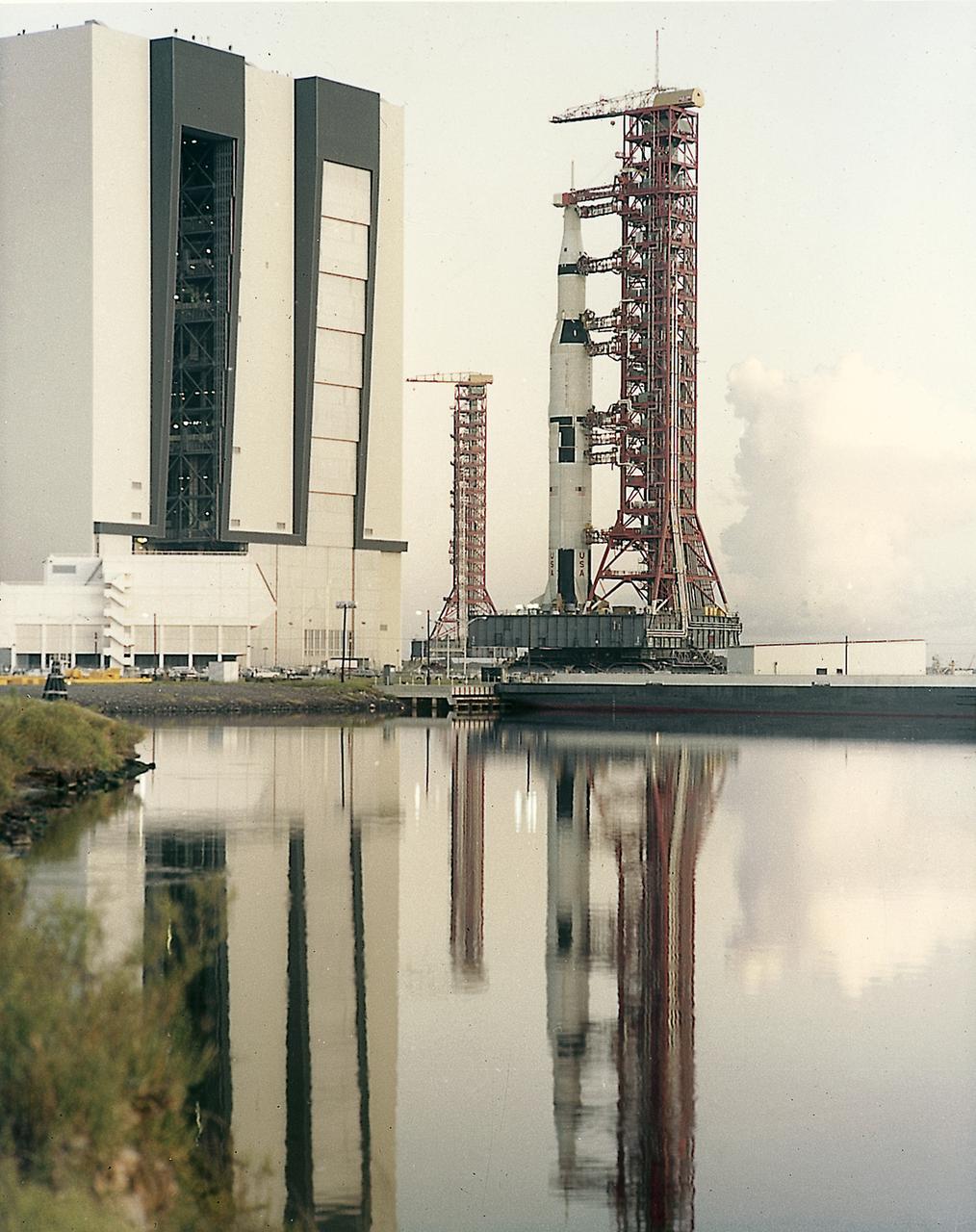

This picture shows the Saturn V vehicle (AS-501), for the Apollo 4 mission on the Crawler Transporter Vehicle. It was rolled out from the Vehicle Assembly Building and slowly (1 mph) moved to the launch pad at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.

This photograph depicts the Saturn V vehicle (SA-501) for the Apollo 4 mission in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). After the completion of the assembly operation, the work platform was retracted and the vehicle was readied to rollout from the VAB to the launch pad. The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.
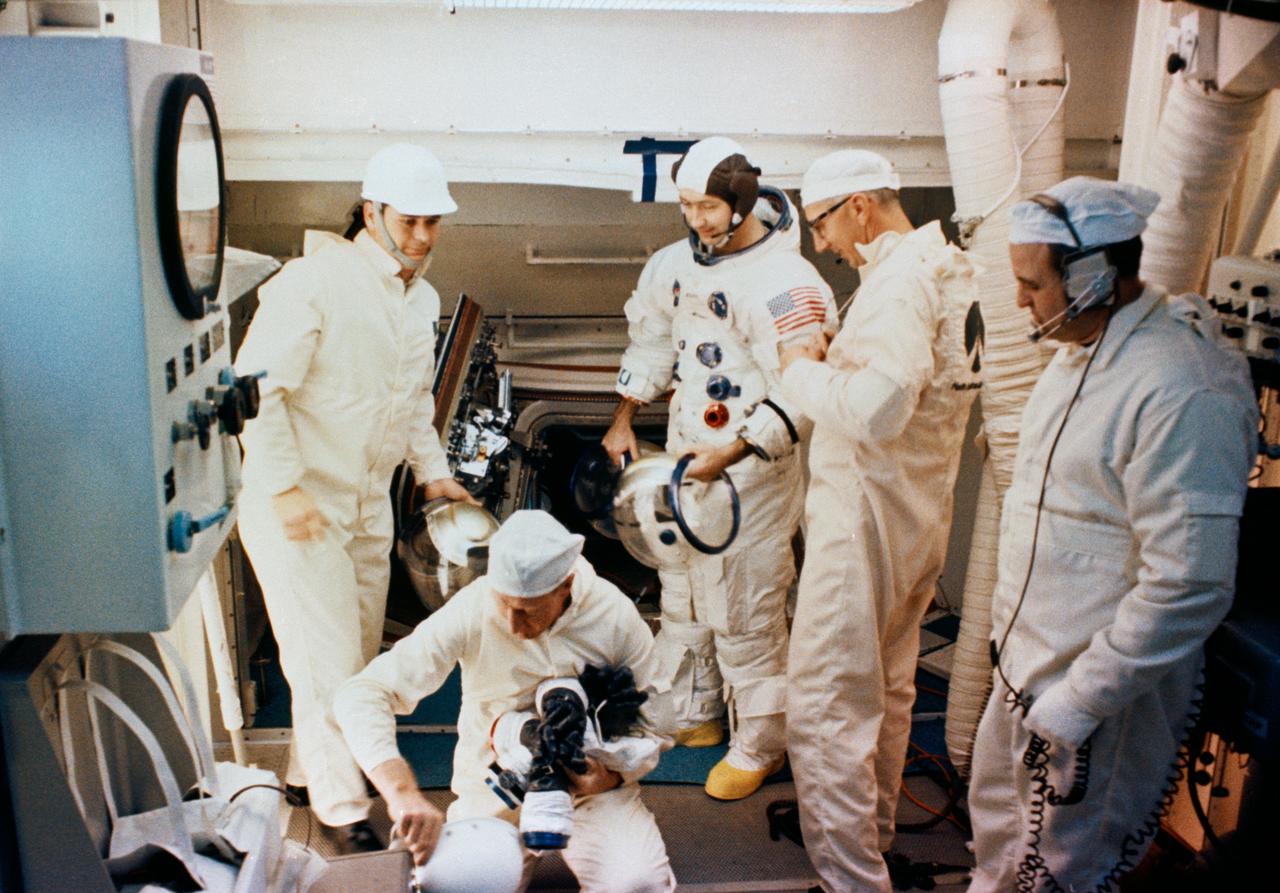

S69-25884 (23 Feb. 1969) --- Interior view of the white room atop Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, during Apollo 9 Countdown Demonstration Test activity. Standing next to spacecraft hatch is astronaut James A. McDivitt, commander. Also, taking part in the training exercise were astronauts David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 will be the second manned Saturn V mission.
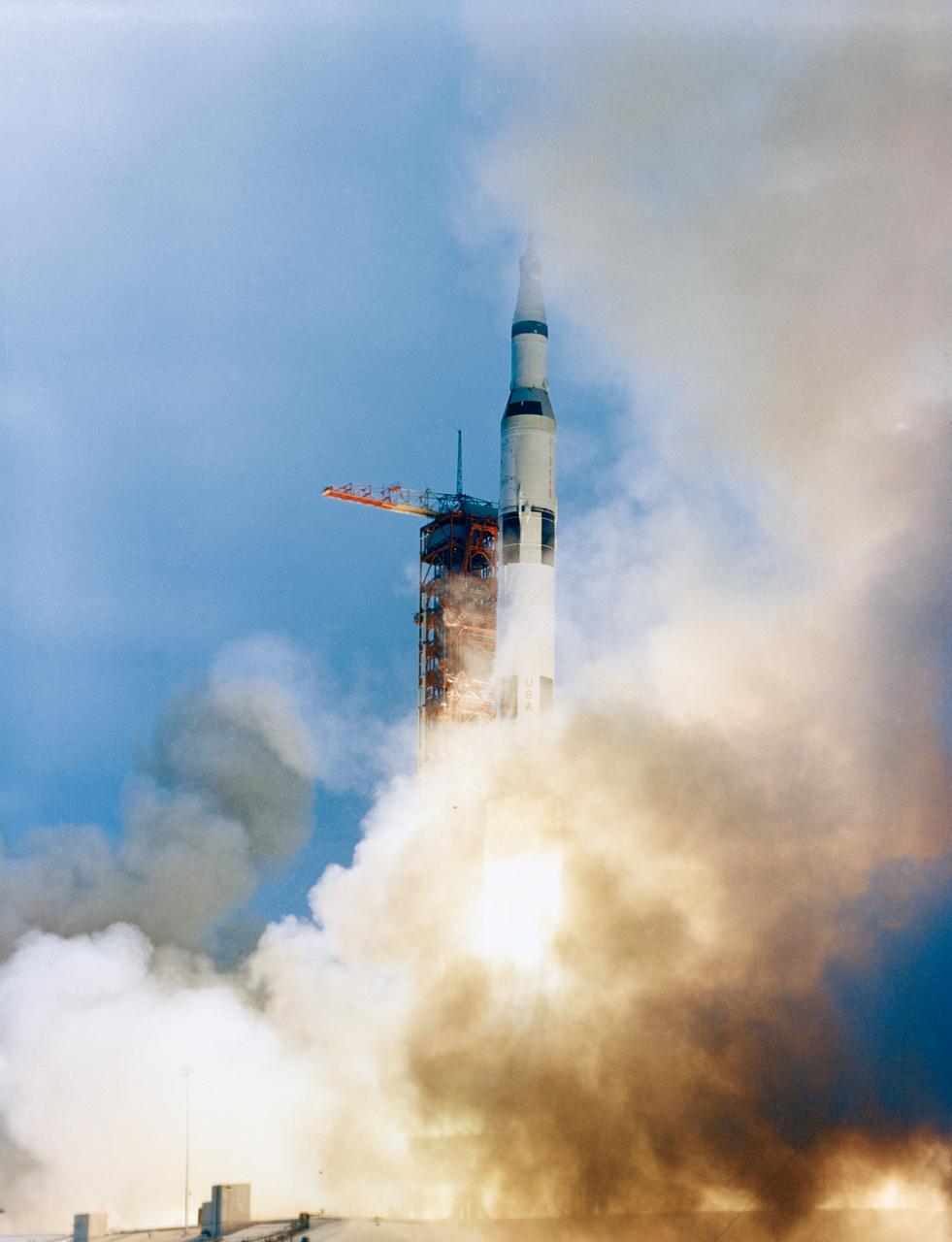

S69-25864 (3 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 is the second manned Saturn V mission.
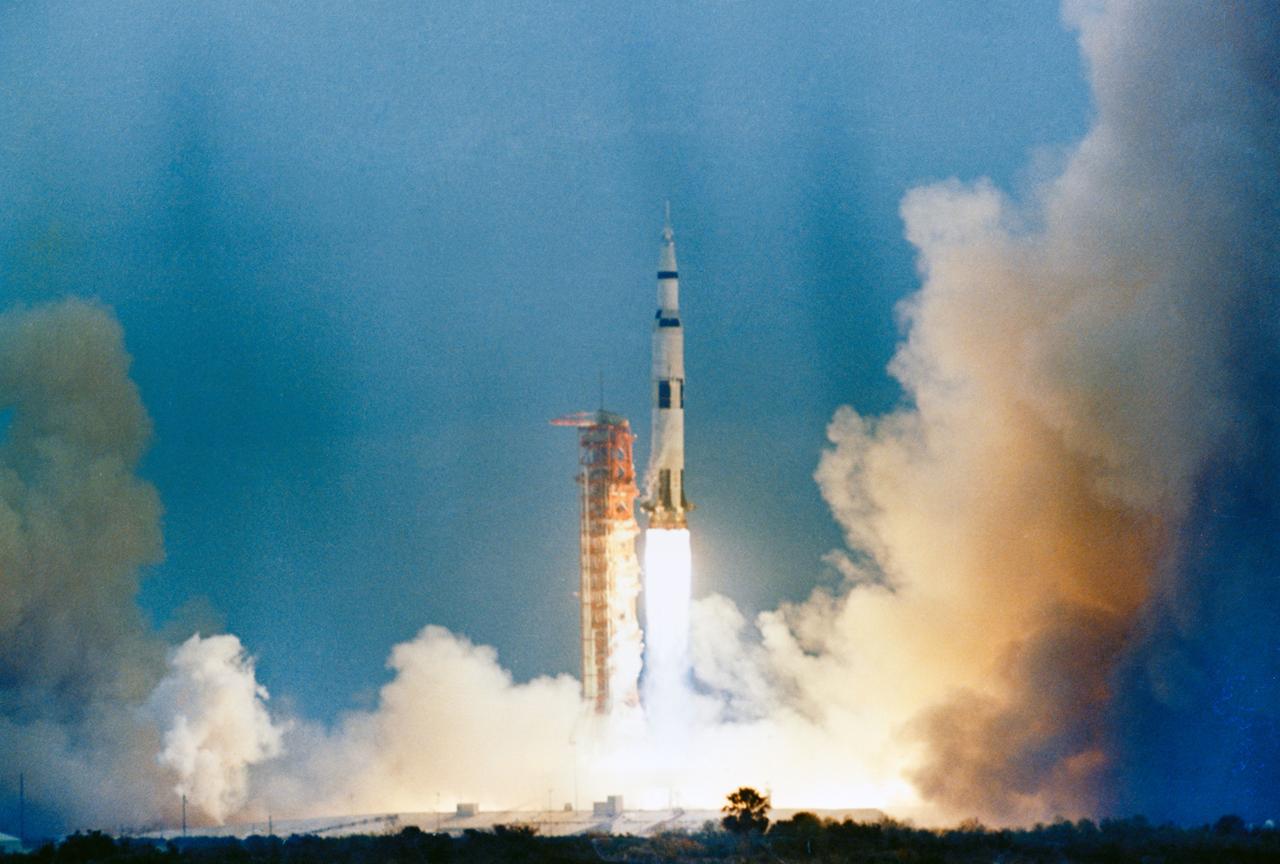

S69-25861 (3 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/ Saturn 504) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 is the second manned Saturn V mission.
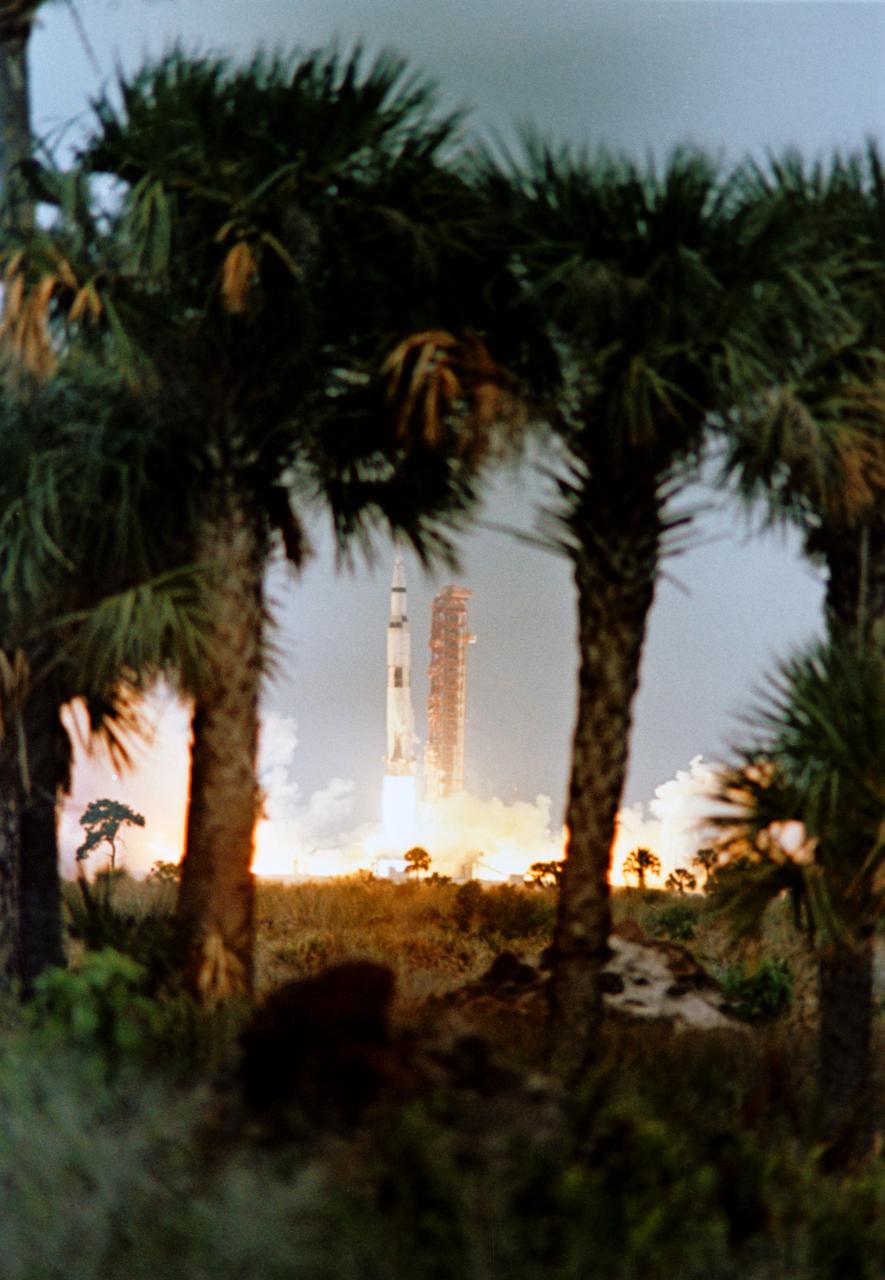

S69-25862 (3 March 1969) --- Framed by palm trees in the foreground, the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/ Saturn 504) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC) at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969. Aboard the spacecraft are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight. Apollo 9 is the second manned Saturn V mission.

S69-19792 (February 1969) --- Composite of six artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the first day of the Apollo 9 mission, including flight crew preparation, orbital insertion, 103 nautical mile orbit, separation, docking, and docked Service Propulsion System burn. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
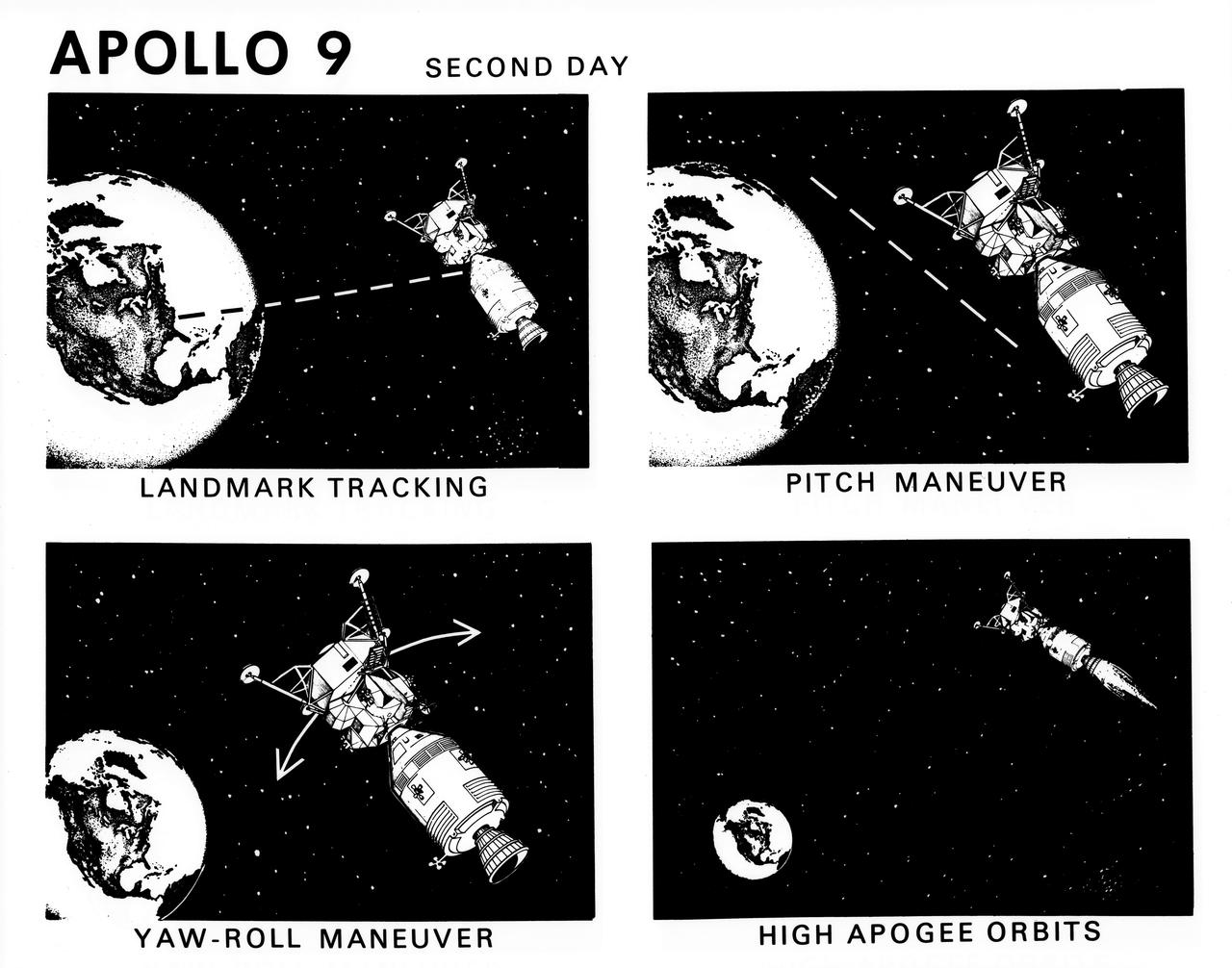
S69-19793 (February 1969) --- Composite of six artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the first day of the Apollo 9 mission, including flight crew preparation, orbital insertion, 103 nautical mile orbit, separation, docking, and docked Service Propulsion System burn. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
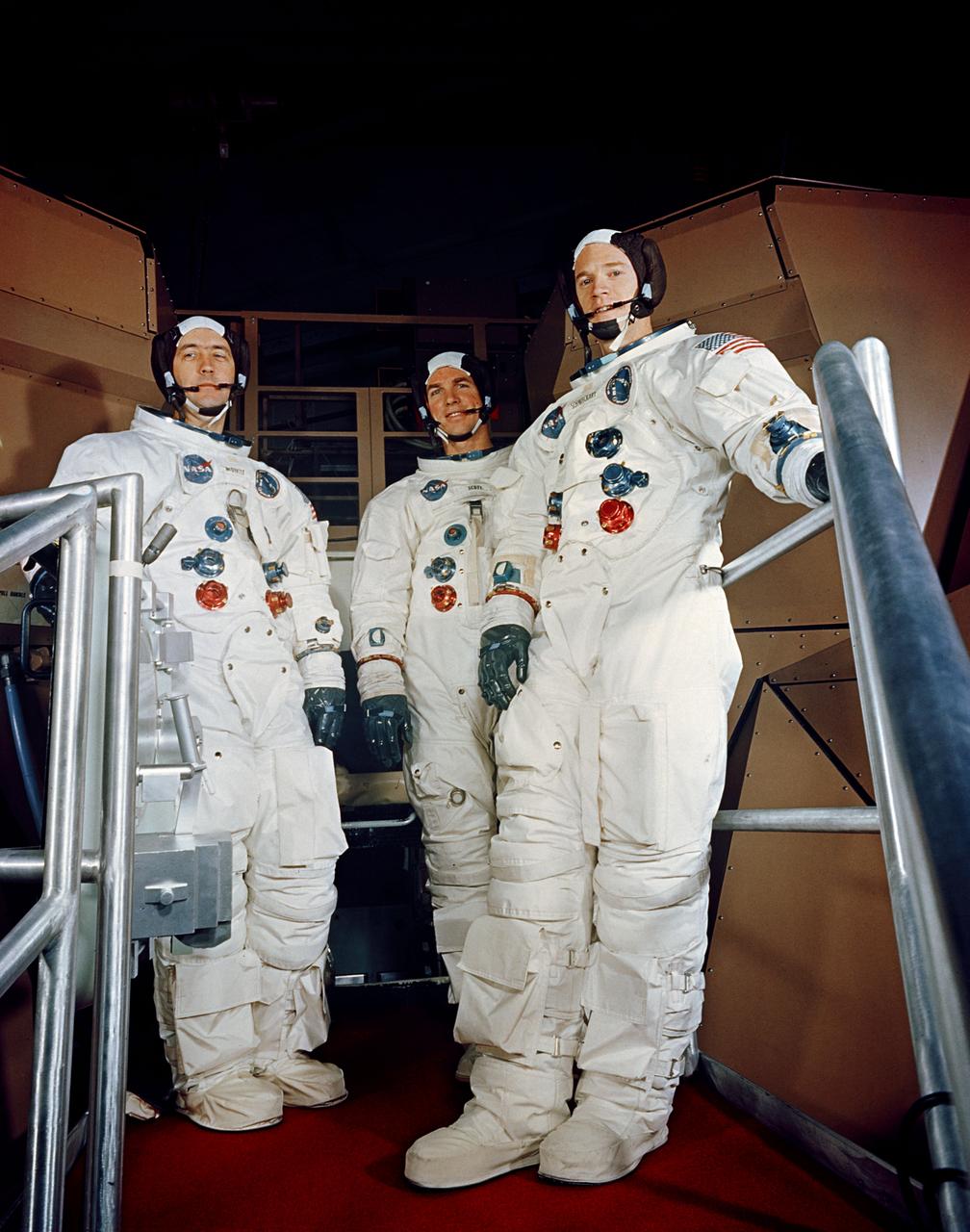

S69-19983 (17 Feb. 1969) --- The Apollo 9 crew is shown suited up for a simulated flight in the Apollo Mission Simulator at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Left to right are astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot.
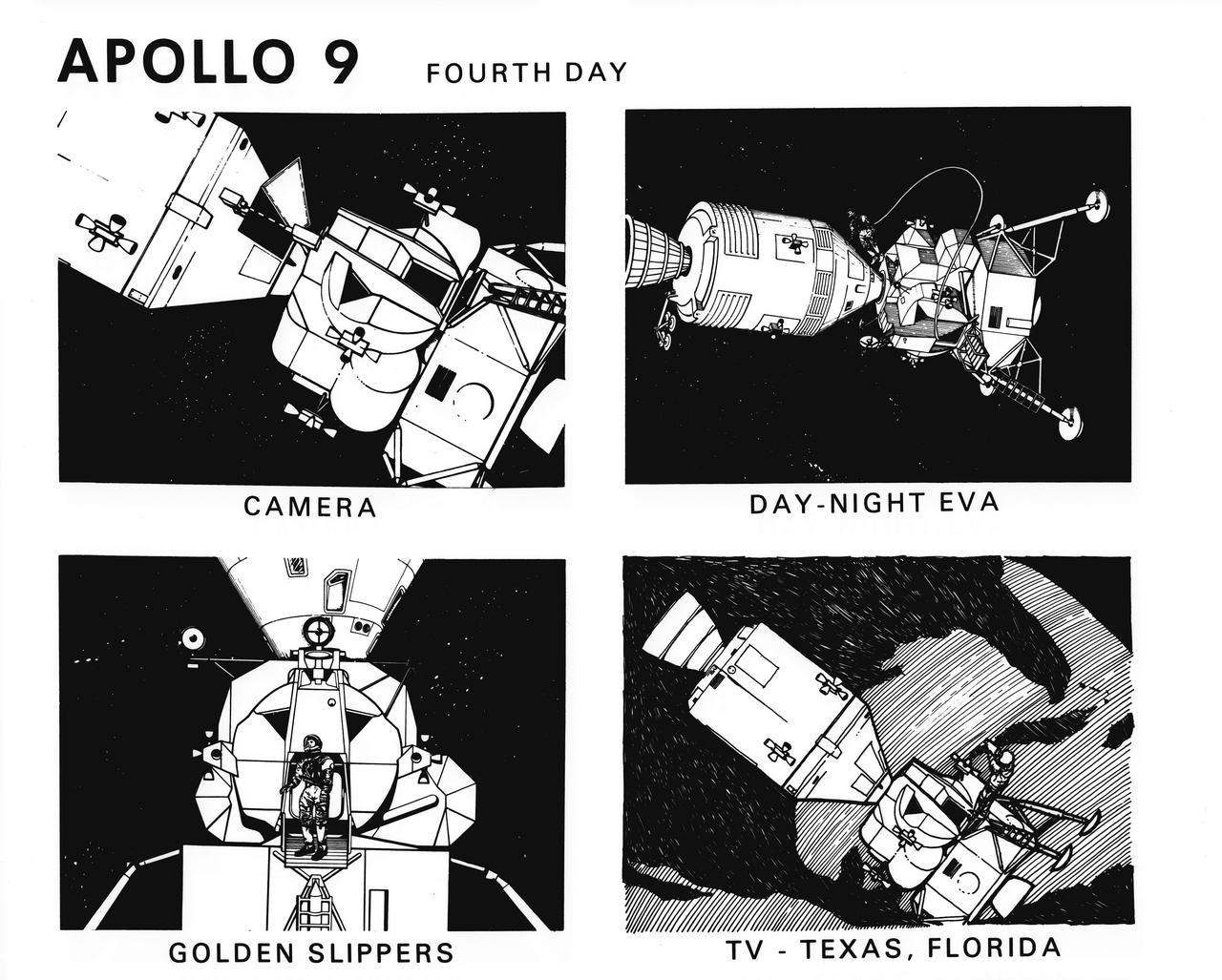
S69-19795 (February 1969) --- Composite of four artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 mission, including use of camera, day-night extravehicular activity, use of golden slippers, and television over Texas and Florida. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
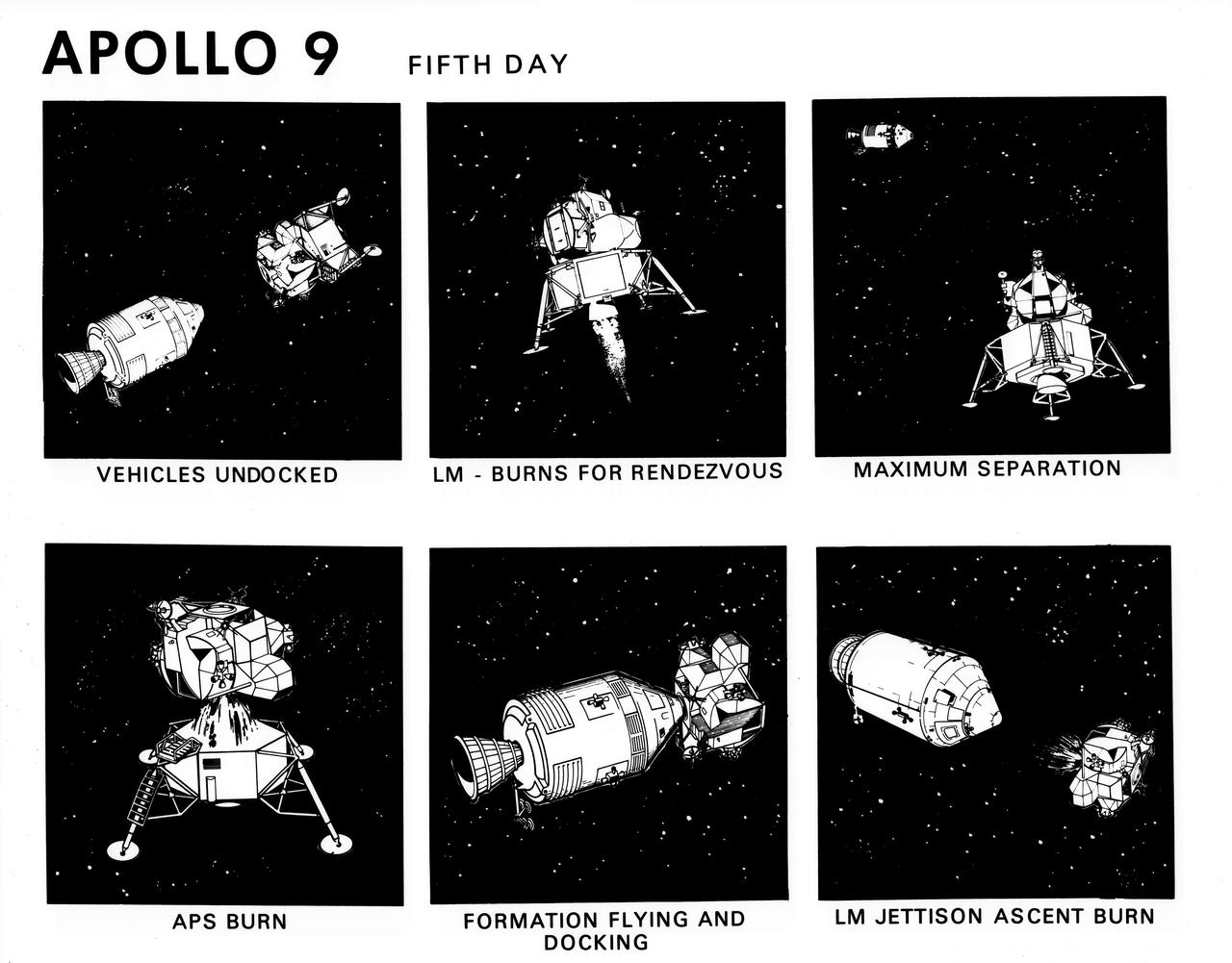
S69-19796 (February 1969) --- Composite of six artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 mission, including vehicles undocked, Lunar Module burns for rendezvous, maximum separation, ascent propulsion system burn, formation flying and docking, and Lunar Module jettison ascent burn. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
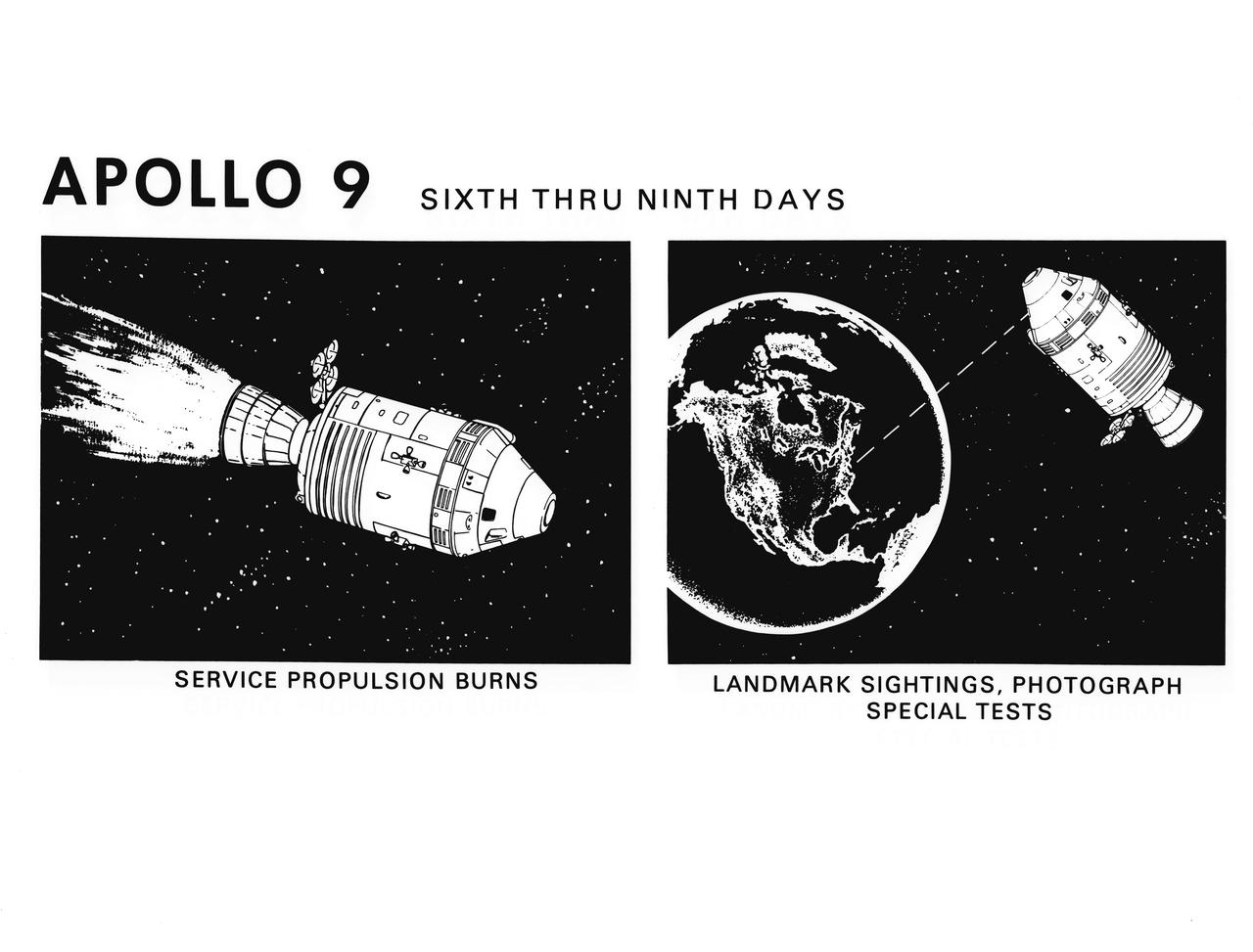
S69-19797 (February 1969) --- Composite of two artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities from the sixth through the ninth day of the Apollo 9 mission, including service propulsion system burns, and landmark sightings, photograph special tests. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.
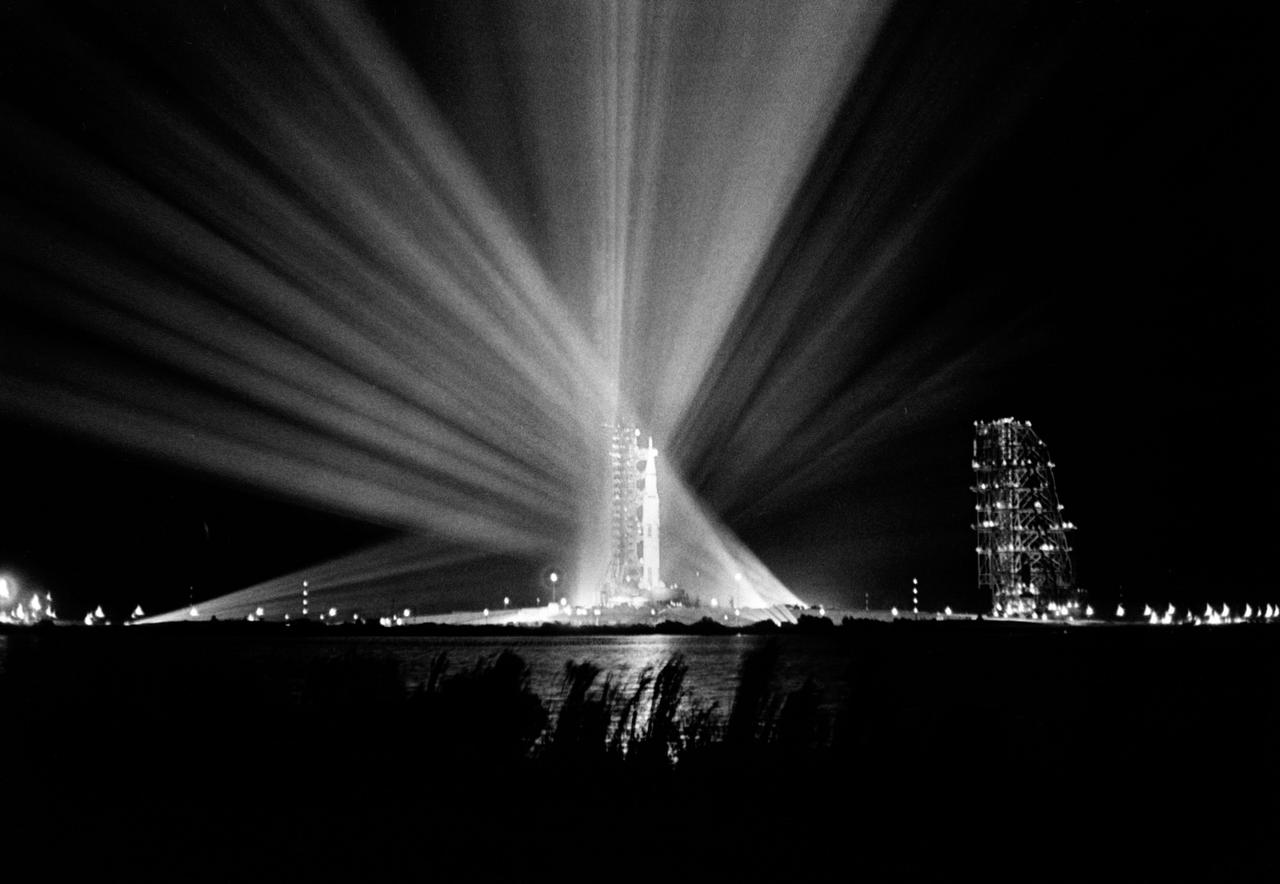

S69-25879 (23 Feb. 1969) --- Nighttime view of the 363-feet-high Apollo 9 space vehicle at Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, during preparations for the scheduled 10-day Earth-orbital space mission. The crew of the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space flight will be astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart.

S69-19798 (February 1969) --- Composite of three artist's concepts illustrating key events, tasks and activities on the tenth day of the Apollo 9 mission, including Command Module and Service Modules separation, re-entry, and Atlantic splashdown. The Apollo 9 mission will evaluate spacecraft lunar module systems performance during manned Earth-orbital flight.

S67-49969 (9 Nov. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The liftoff of the huge 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was at 7:00:01 a.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967. The successful objectives of the Apollo 4 Earth-orbital unmanned space mission obtained included (1) flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, subsystem operation, emergency detection subsystem operation, and (2) evaluation of the Apollo Command Module heat shield under conditions encountered on return from a moon mission.
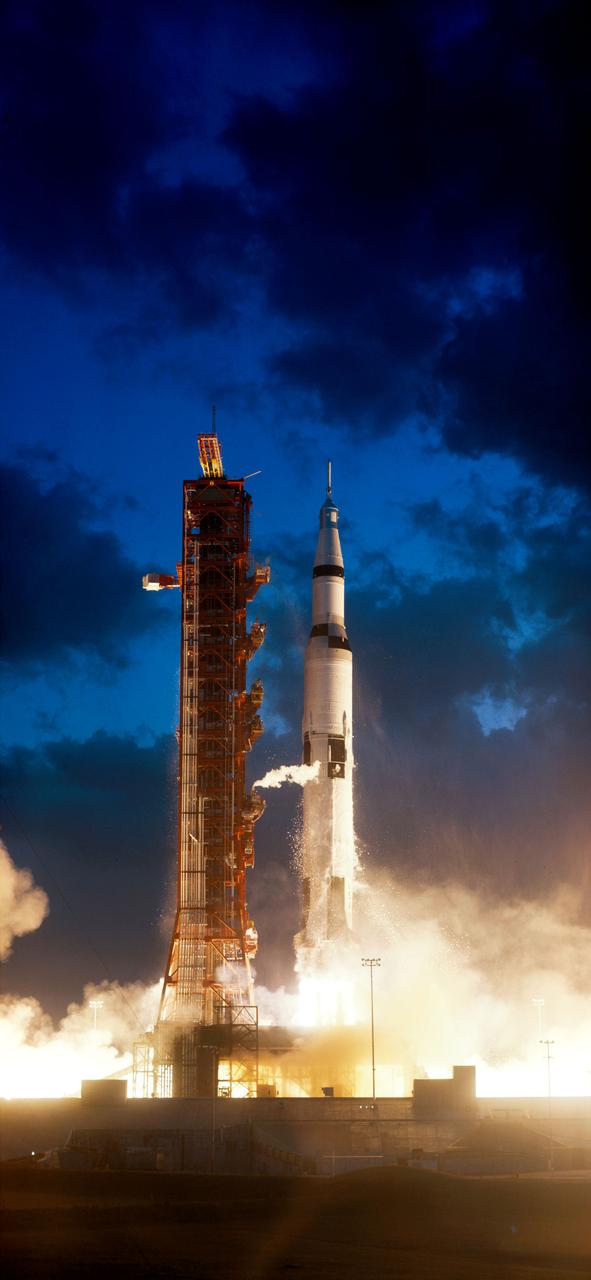

S67-50903 (9 Nov. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The liftoff of the huge 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was at 7:00:01 a.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967. The successful objectives of the Apollo 4 Earth-orbital unmanned space mission obtained included (1) flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, subsystem operation, emergency detection subsystem, and (2) evaluation of the Apollo Command Module heat shield under conditions encountered on return from a moon mission.
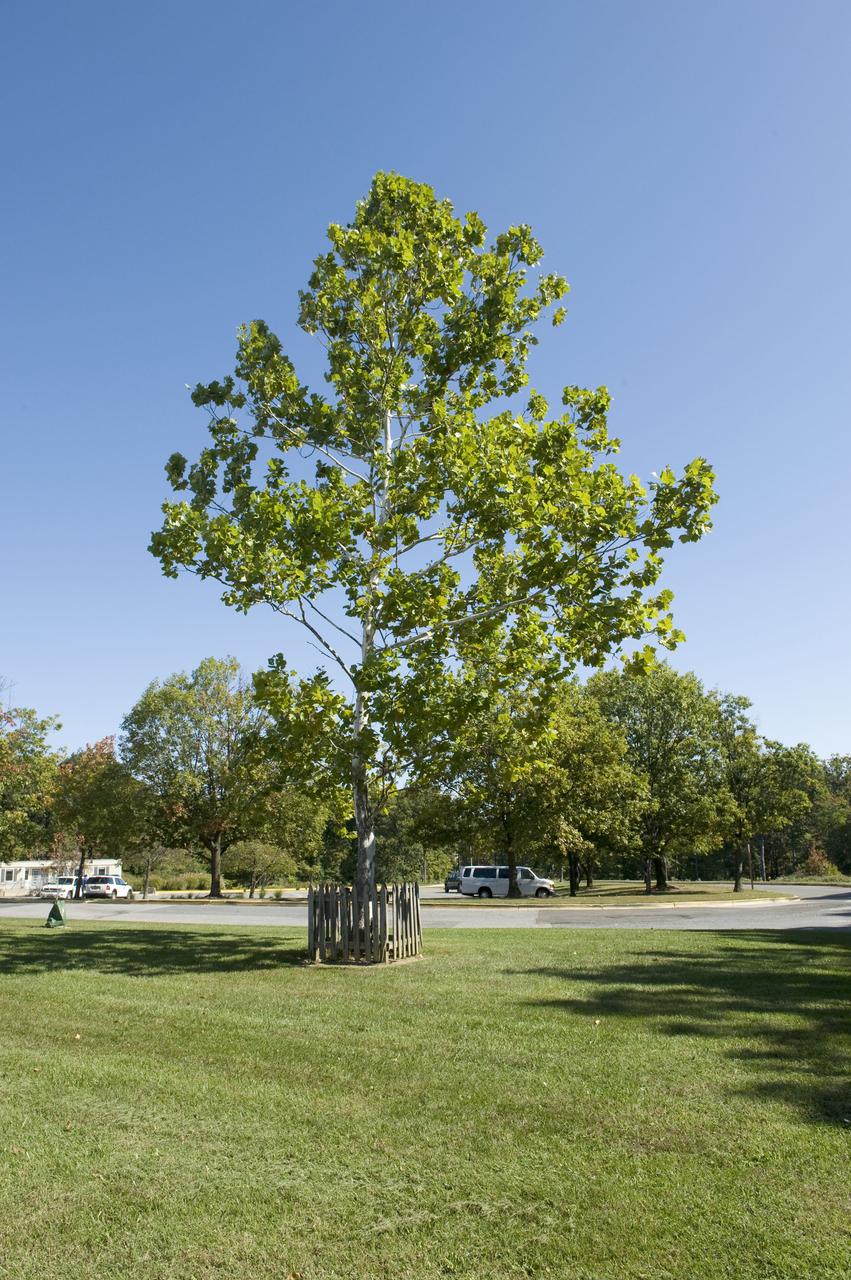

The "Moon Tree" in front of the Visitor Center at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. This sycamore was planted at the visitor center on June 9, 1977, and grew from a seed carried to the Moon aboard Apollo 14.
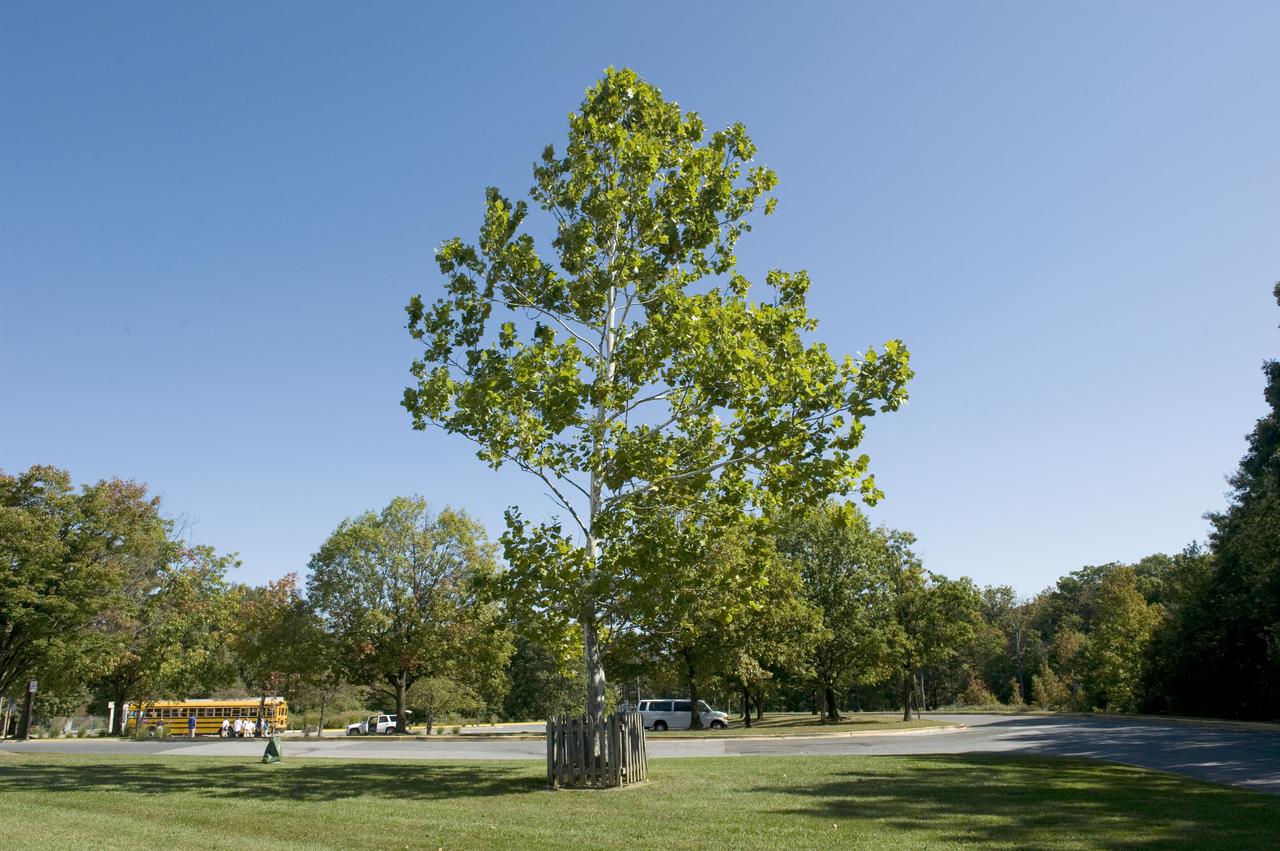

The "Moon Tree" in front of the Visitor Center at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. This sycamore was planted at the visitor center on June 9, 1977, and grew from a seed carried to the Moon aboard Apollo 14.
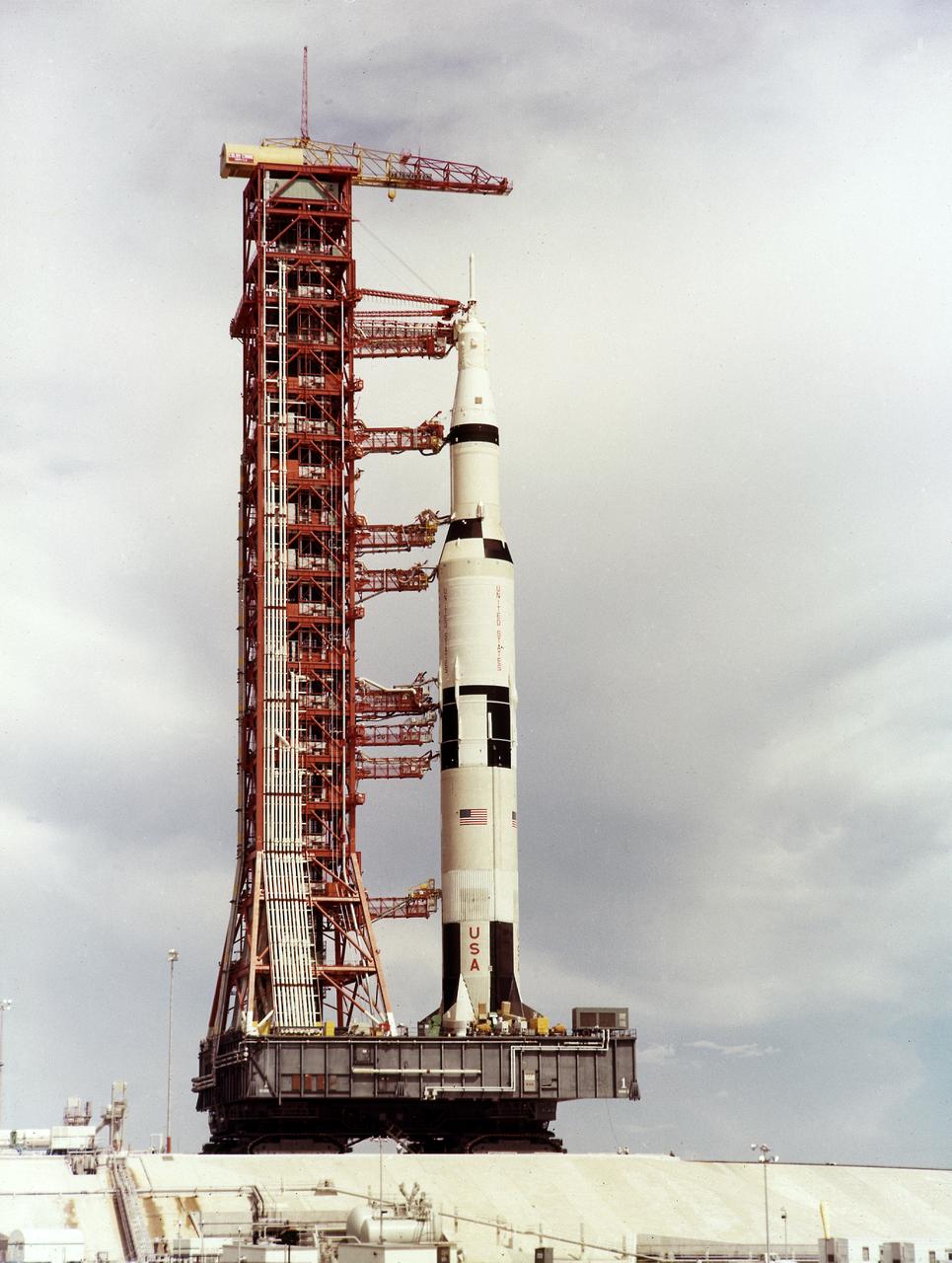
This is a view of the the first test flight of the Saturn V vehicle (SA-501) at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) launch complex 39A, awaiting the scheduled launch on November 9, 1967. Designated as Apollo 4, this mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield.

A memorial wreath is placed in the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida following a ceremony honoring the memory of former Apollo astronaut Walter Cunningham. The ceremony was held Jan. 9, 2023. Cunningham was the lunar module pilot for Apollo 7 – the first crewed flight test of the Apollo spacecraft – where he tested maneuvers necessary for docking and lunar orbit rendezvous. He passed away Jan. 3 at the age of 90.

A photo of former Apollo astronaut Walter Cunningham is displayed during a memorial ceremony at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ceremony was held Jan. 9, 2023, at the Heroes and Legends exhibit within the Astronaut Hall of Fame at the center’s visitor complex. Cunningham was the lunar module pilot for Apollo 7 – the first crewed flight test of the Apollo spacecraft – where he tested maneuvers necessary for docking and lunar orbit rendezvous. He passed away Jan. 3 at the age of 90.

Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, speaks during a memorial ceremony honoring former Apollo astronaut Walter Cunningham. The ceremony was held Jan. 9, 2023, at the Heroes and Legends exhibit within the Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Florida spaceport’s visitor complex. Cunningham was the lunar module pilot for Apollo 7 – the first crewed flight test of the Apollo spacecraft – where he tested maneuvers necessary for docking and lunar orbit rendezvous. He passed away Jan. 3 at the age of 90.
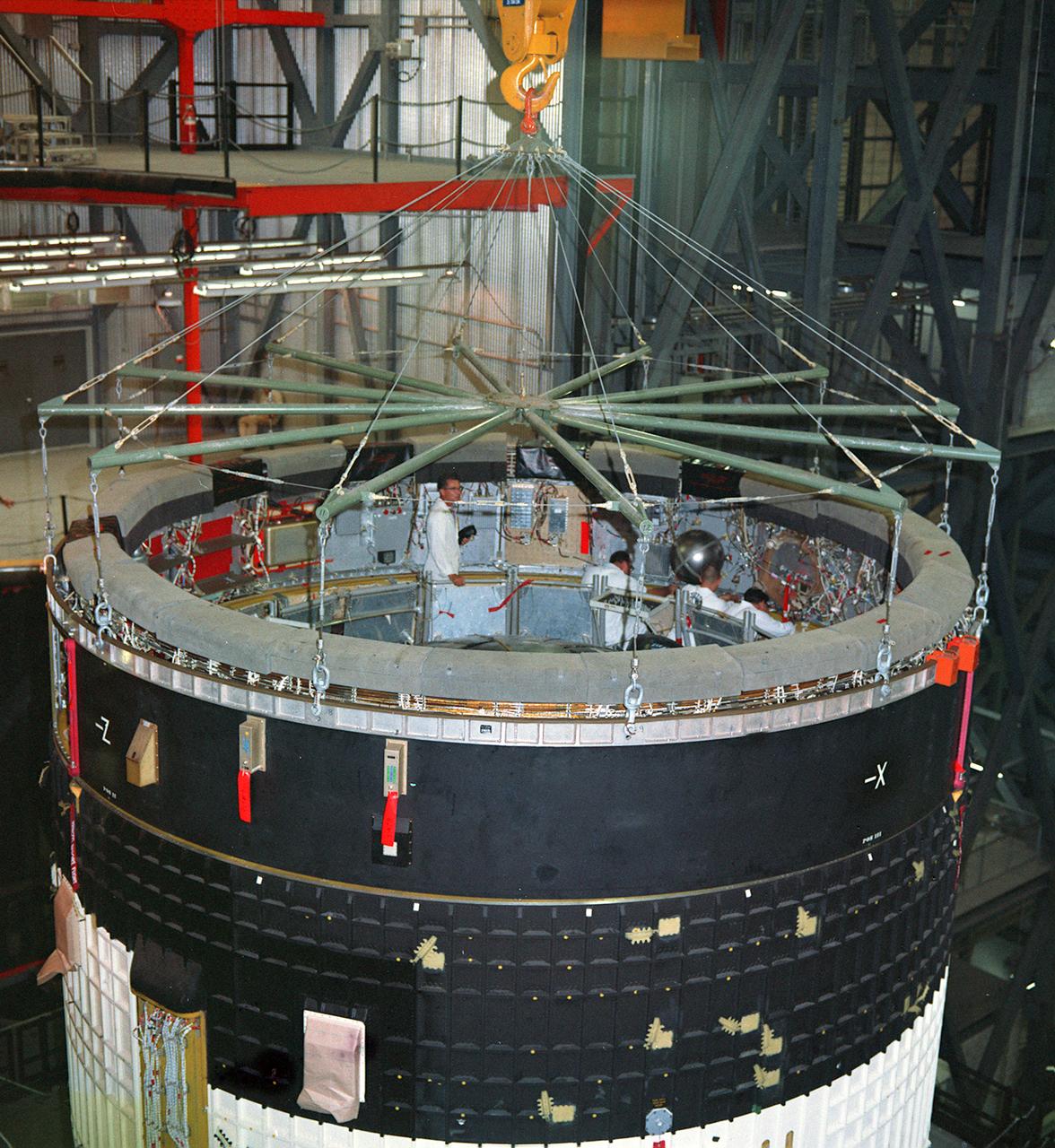

This photograph was taken during the final assembly operation of the Saturn V launch vehicle for the Apollo 4 (SA 501) mission. The instrument unit (IU) was mated atop the S-IC/S-II assembly in the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay at the Kennedy Space Center. The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.
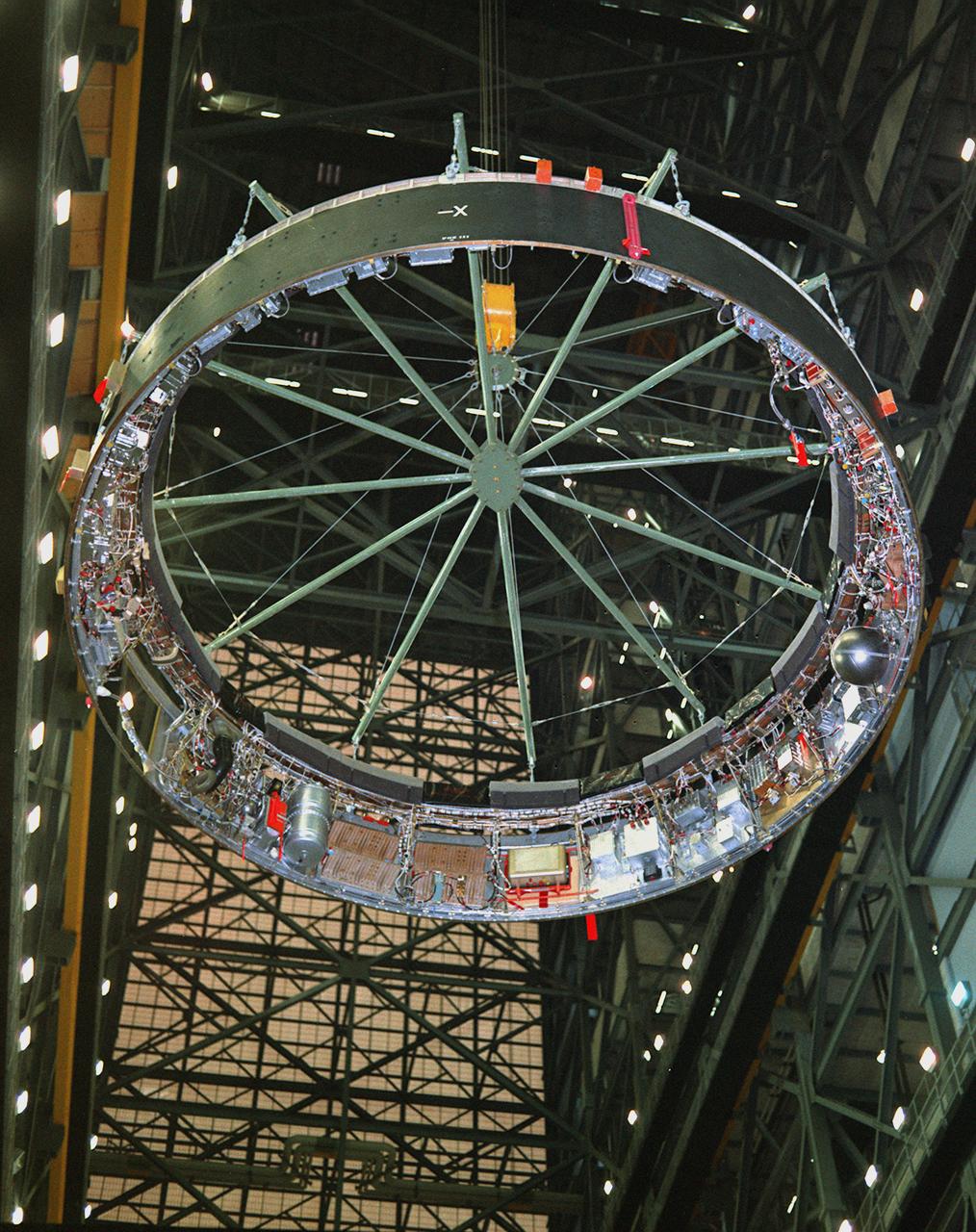

This photograph was taken during the final assembly operation of the Saturn V launch vehicle for the Apollo 4 (SA 501) mission. The instrument unit (IU) was hoisted to be mated to the S-IC/S-II assembly in the Vehicle Assembly Building high bay at the Kennedy Space Center. The Apollo 4 mission was the first launch of the Saturn V launch vehicle. Objectives of the unmanned Apollo 4 test flight were to obtain flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, and subsystems operation including testing of restart of the S-IVB stage, and to evaluate the Apollo command module heat shield. The Apollo 4 was launched on November 9, 1967 from KSC.
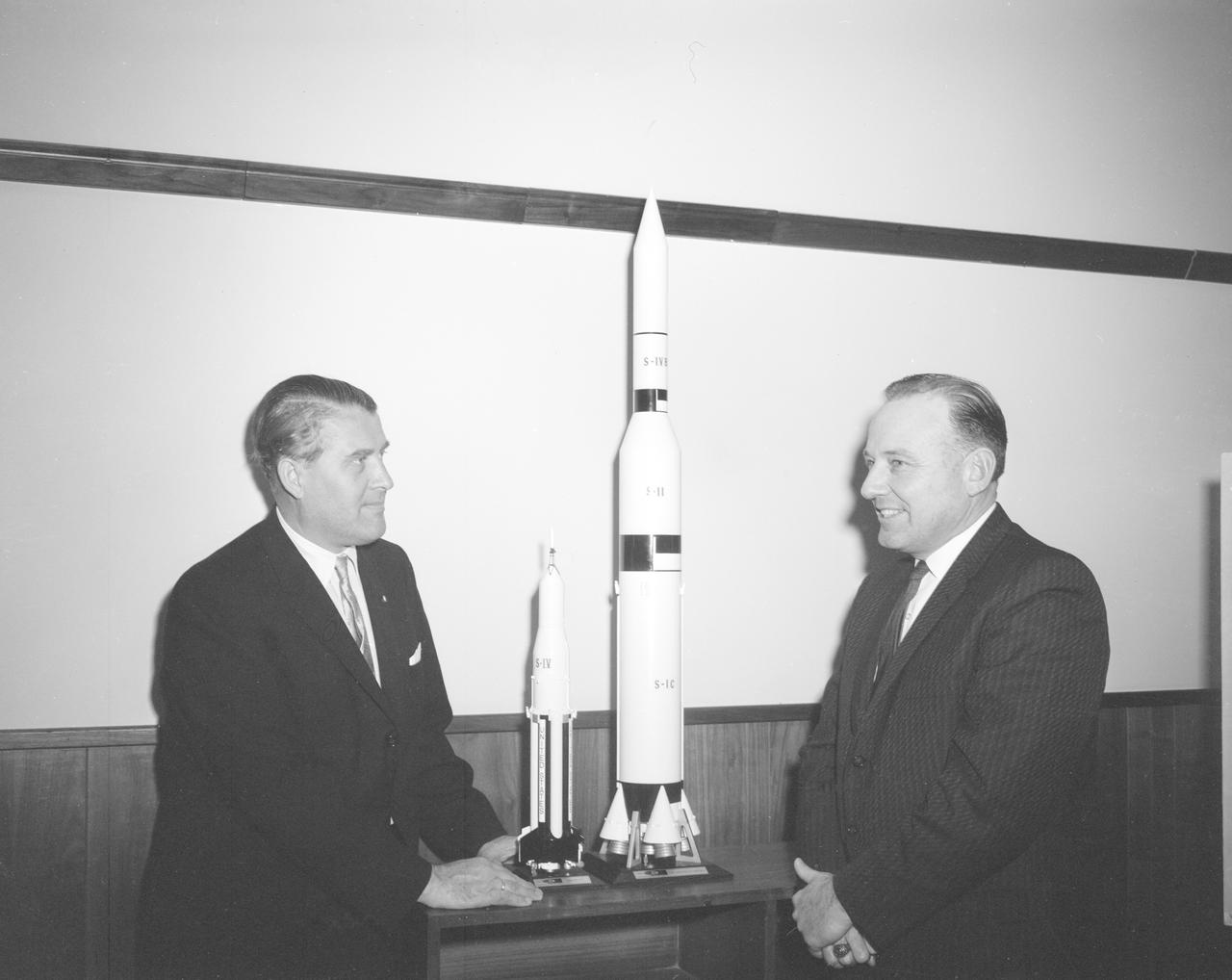

The members of the House Committee on Science and Astronautics visited the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on March 9, 1962 to gather firsthand information of the nation’s space exploration program. The congressional group was composed of members of the Subcommittee on Manned Space Flight. The subcommittee was briefed on MSFC’s manned space efforts earlier in the day and then inspected mockups of the Saturn I Workshop and the Apollo Telescope Mount, two projects developed by MSFC for the post-Apollo program. In this photograph, MSFC Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun and Joe Waggoner, Democratic representative of Louisiana, discuss Apollo models.
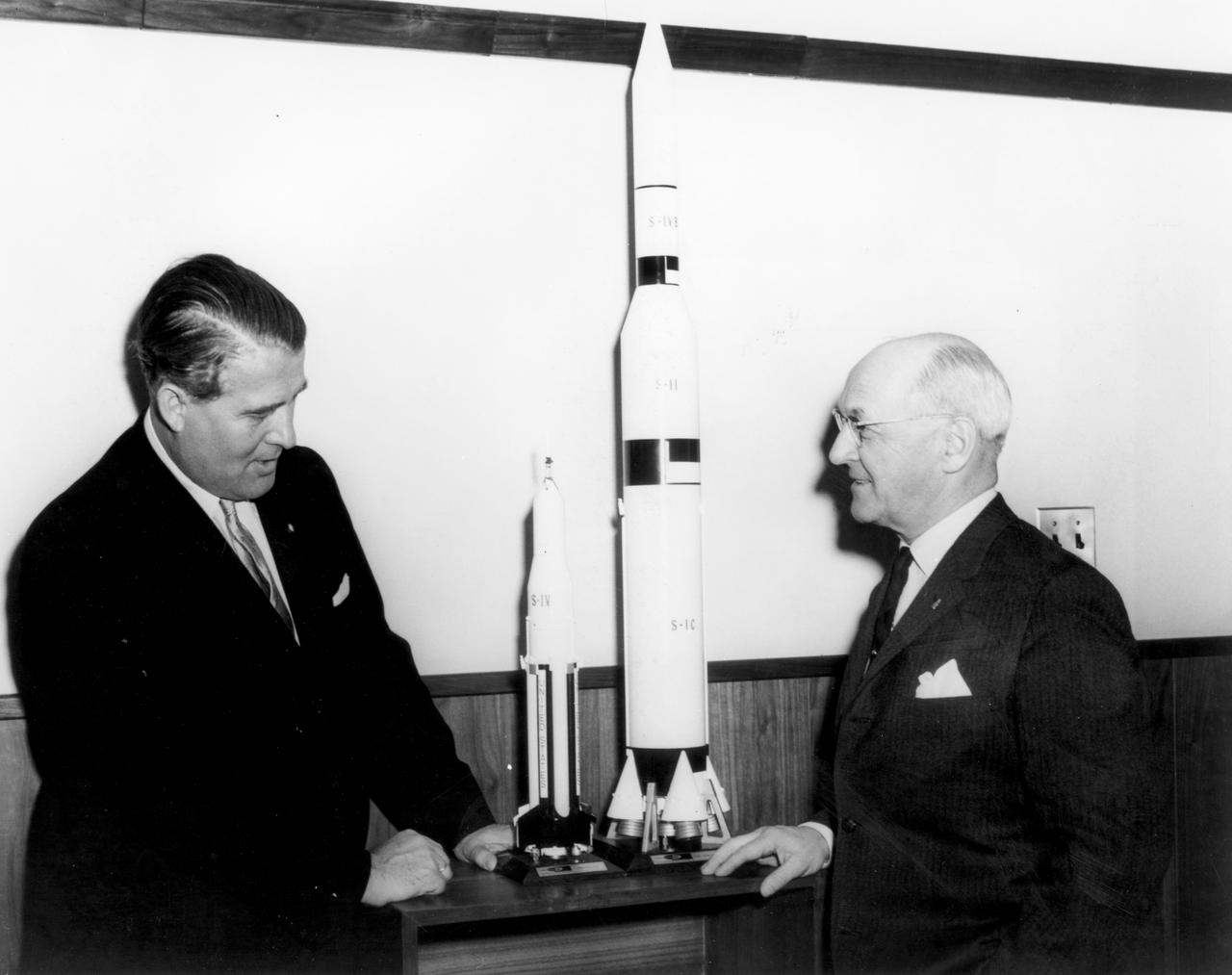

The members of the House Committee on Science and Astronautics visited the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on March 9, 1962 to gather firsthand information of the nation’s space exploration program. The congressional group was composed of members of the Subcommittee on Manned Space Flight. The subcommittee was briefed on MSFC’s manned space efforts earlier in the day and then inspected mockups of the Saturn I Workshop and the Apollo Telescope Mount, two projects developed by MSFC for the post-Apollo program. In this photograph, MSFC Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun and R. Walter Riehlman, Republican representative of New York, discuss Apollo models.
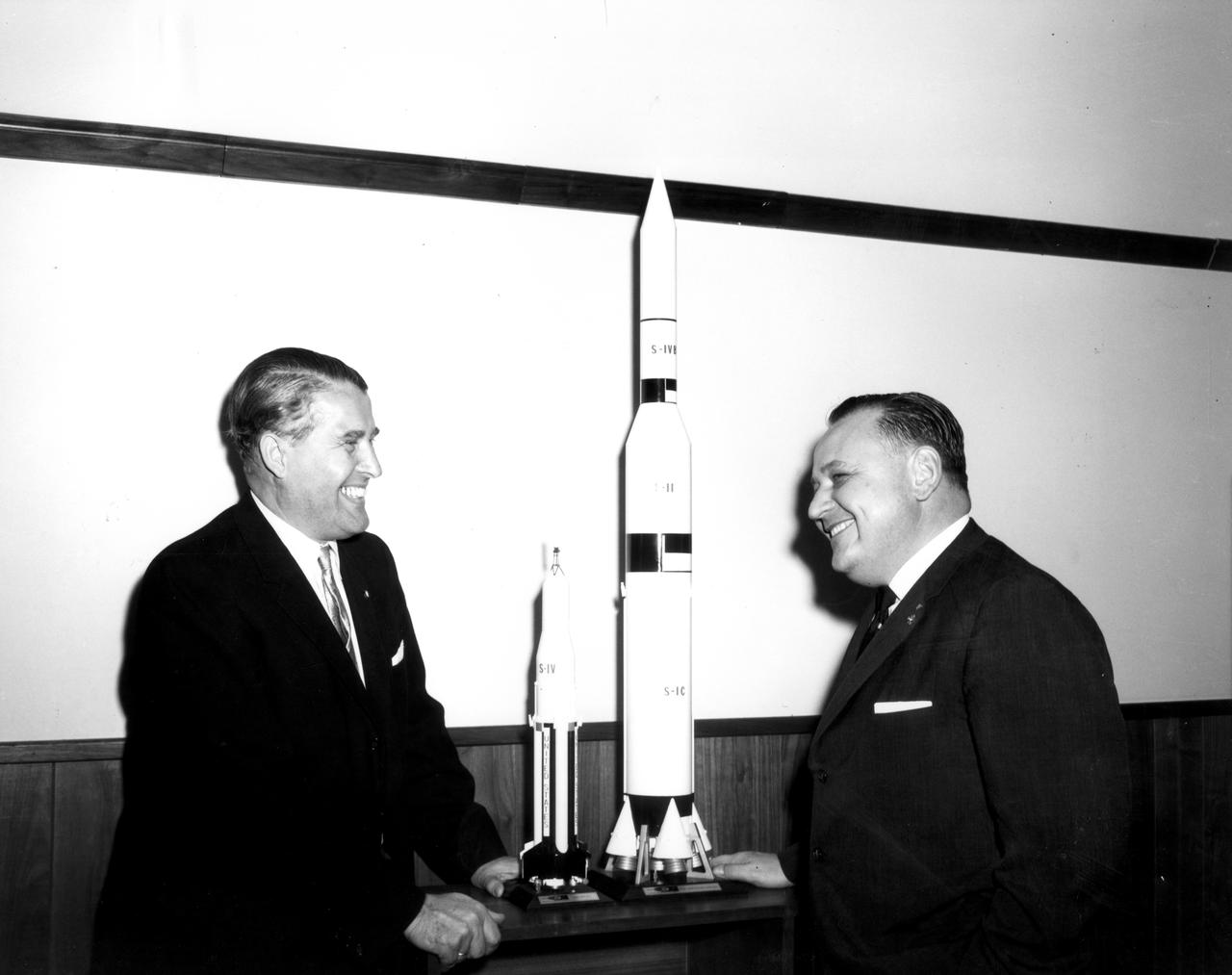

The members of the House Committee on Science and Astronautics visited the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on March 9, 1962 to gather firsthand information of the nation’s space exploration program. The congressional group was composed of members of the Subcommittee on Manned Space Flight. The subcommittee was briefed on MSFC’s manned space efforts earlier in the day and then inspected mockups of the Saturn I Workshop and the Apollo Telescope Mount, two projects developed by MSFC for the post-Apollo program. In this photograph, MSFC Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun and Richard L. Roudebush, Republican representative of Indiana, discuss Apollo models.
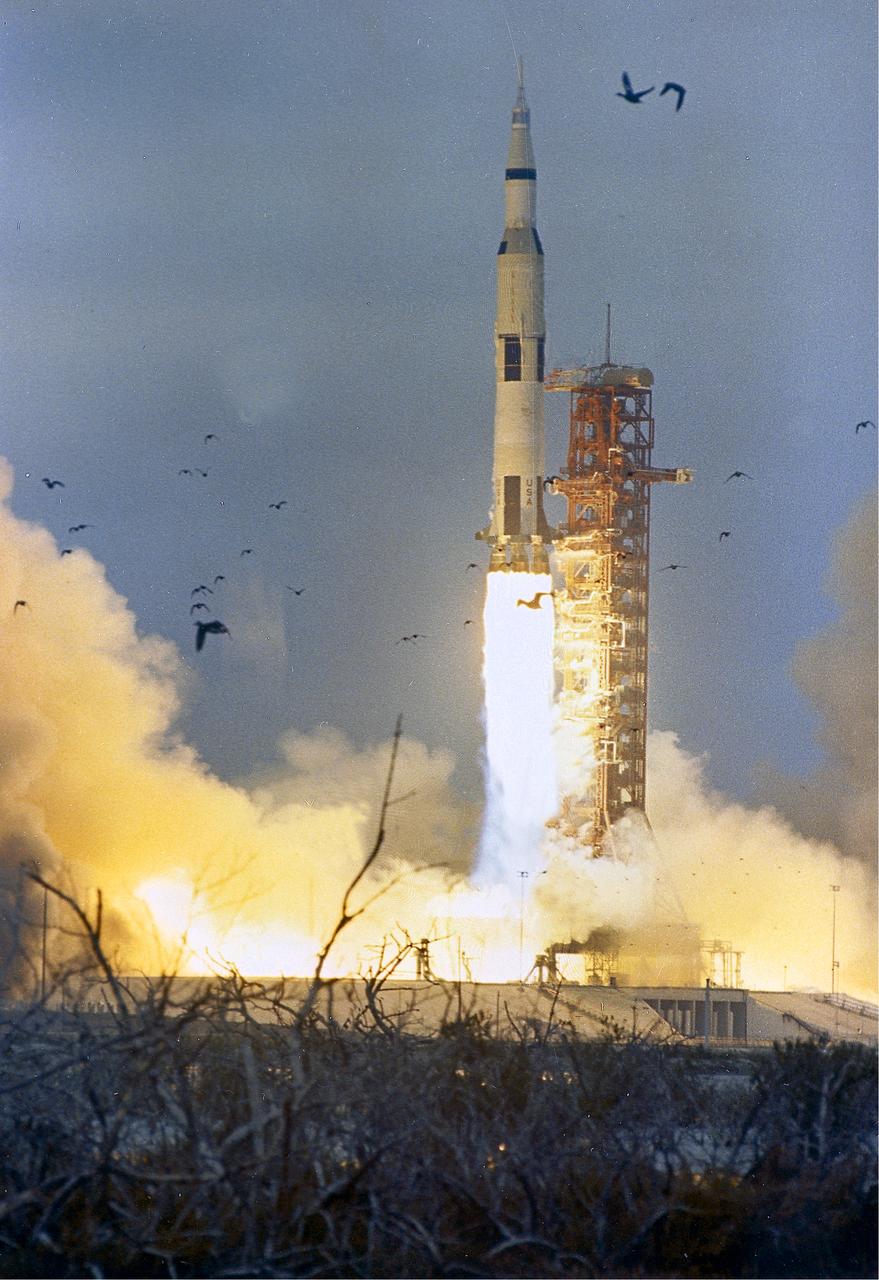

The launch of the Apollo 9 (Saturn V launch vehicle, SA-504), with astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart, took place on March 3, 1968. The Apollo 9 spacecraft, in the lunar mission configuration, was tested in Earth orbit. The mission was designed to rehearse all the steps and reproduce all the events of the Apollo 11 mission with the exception of the lunar touchdown, stay, and liftoff. The command and service modules, and the lunar module were used in flight procedures identical to those that would later take similar vehicles to the Moon, and a landing. The flight mechanics, mission support systems, communications, and recording of data were tested in a final round of verification. Astronauts Scott and Schweickart conducted Extravehicular Activity during this mission.
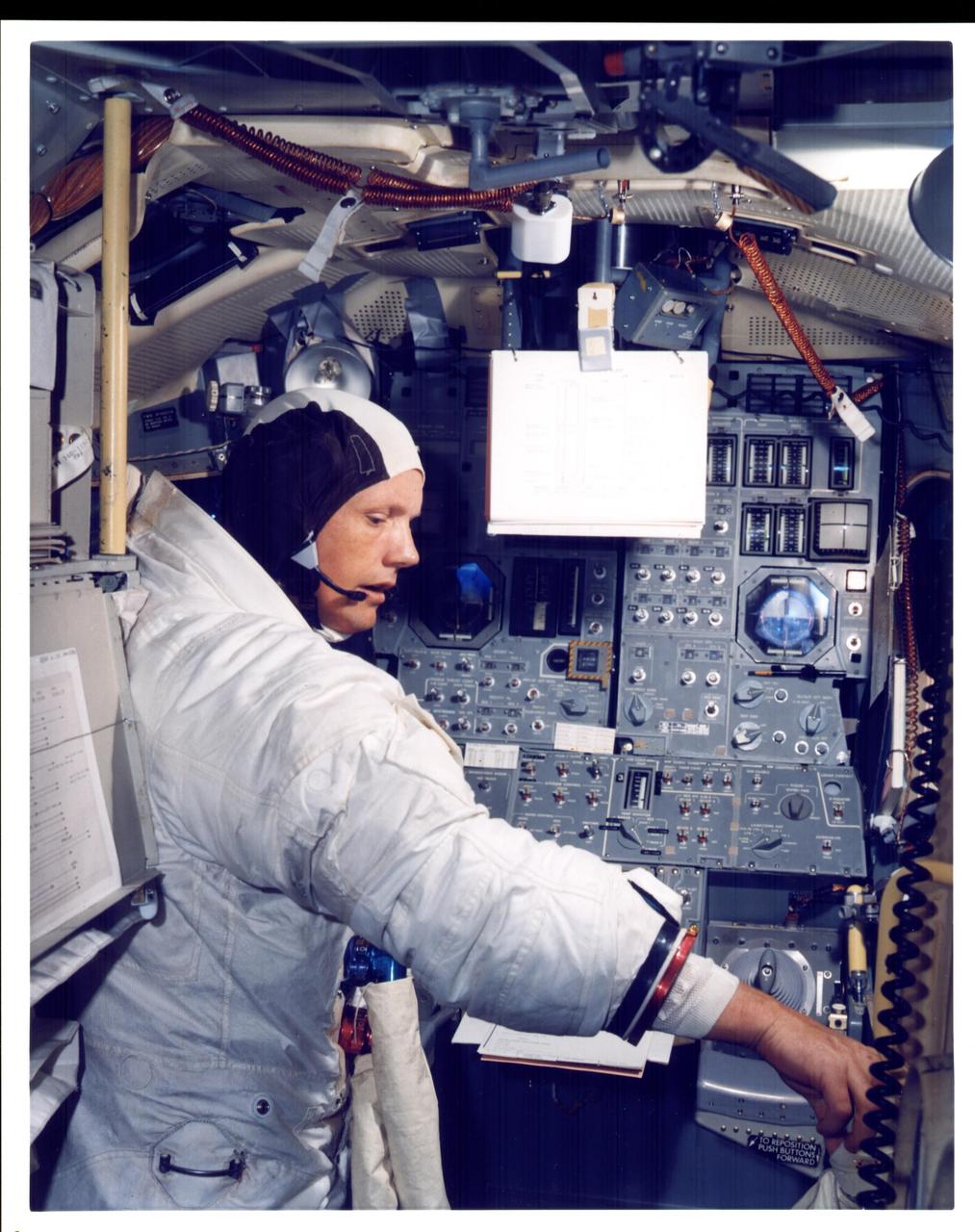

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Apollo 11 Commander Neil Armstrong is going through flight training in the lunar module simulator situated in the Flight Crew Training Building at KSC. Armstrong wil pilot the lunar module to a Moon landing on July 20, following launch from KSC at 9:32 a.m. July 16.
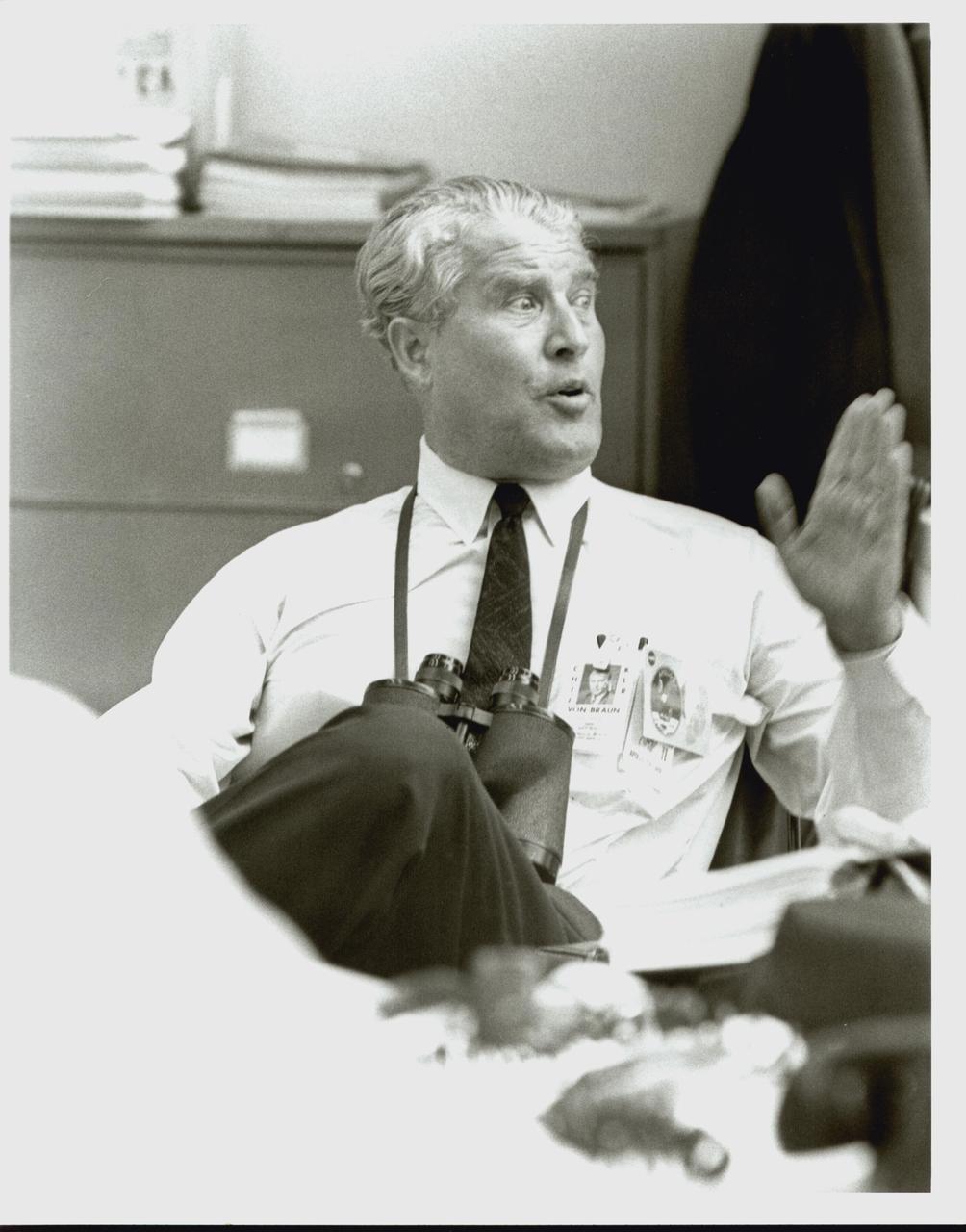
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Dr. Wernher von Braun, director of the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala., relaxes in the Launch Control Center at Kennedy Space Center after the successful launch of Apollo 11. This historic launch, the first manned landing on the Moon, began at 9:32 a.m. EDT today when the Apollo/Saturn V launch vehicle lifted off from Launch Complex 39A.
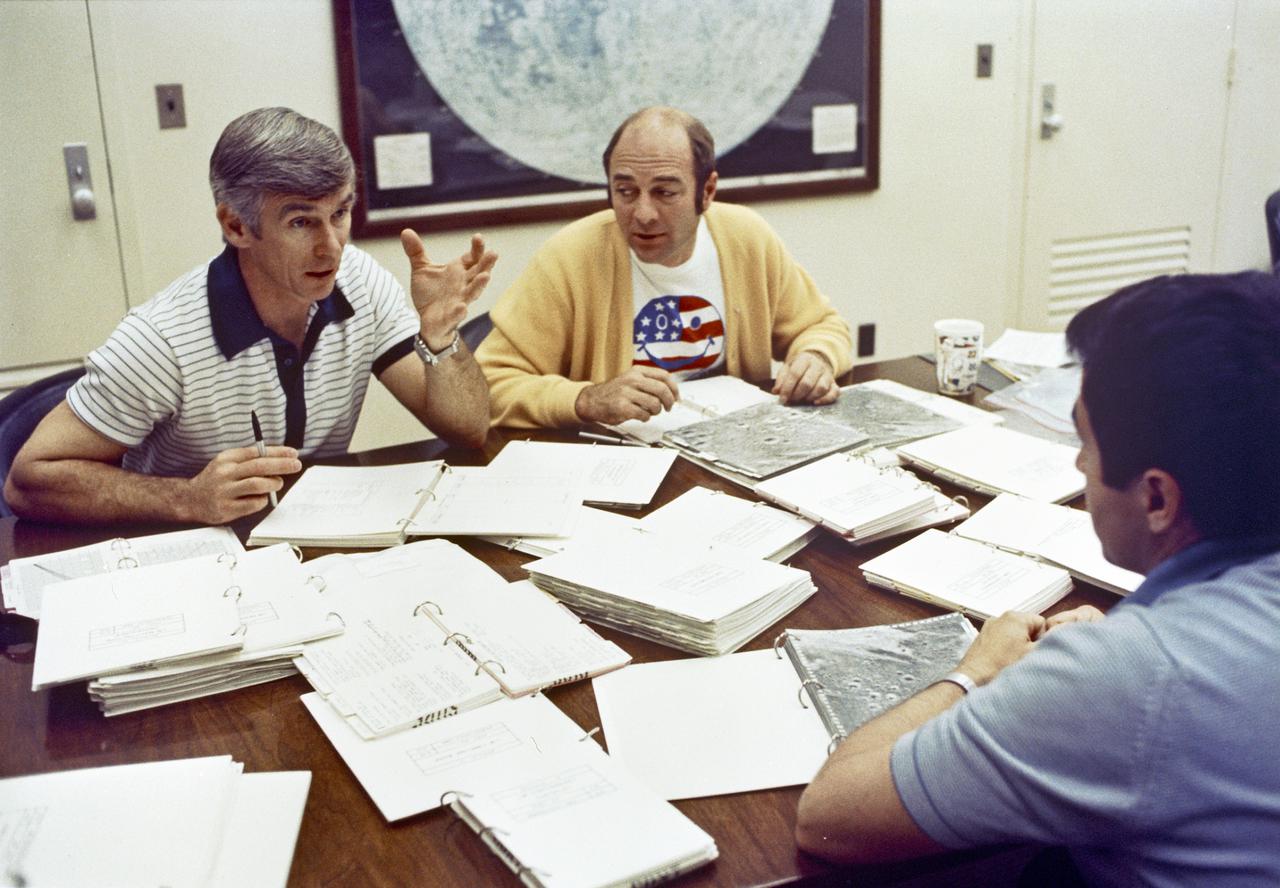

Apollo 17 Mission commander Eugene A. Cernan, left, reviews flight plan with crewmates Ronald E. Evans, center, and Harrison H. Schmitt in the astronaut's quarters. Evans will pilot the command module alone in lunar orbit while Cernan and Lunar Module Pilot Schmitt explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the Moon's surface. The launch of Apollo 17 is scheduled for December 6, 1972 at 9:53 p.m.
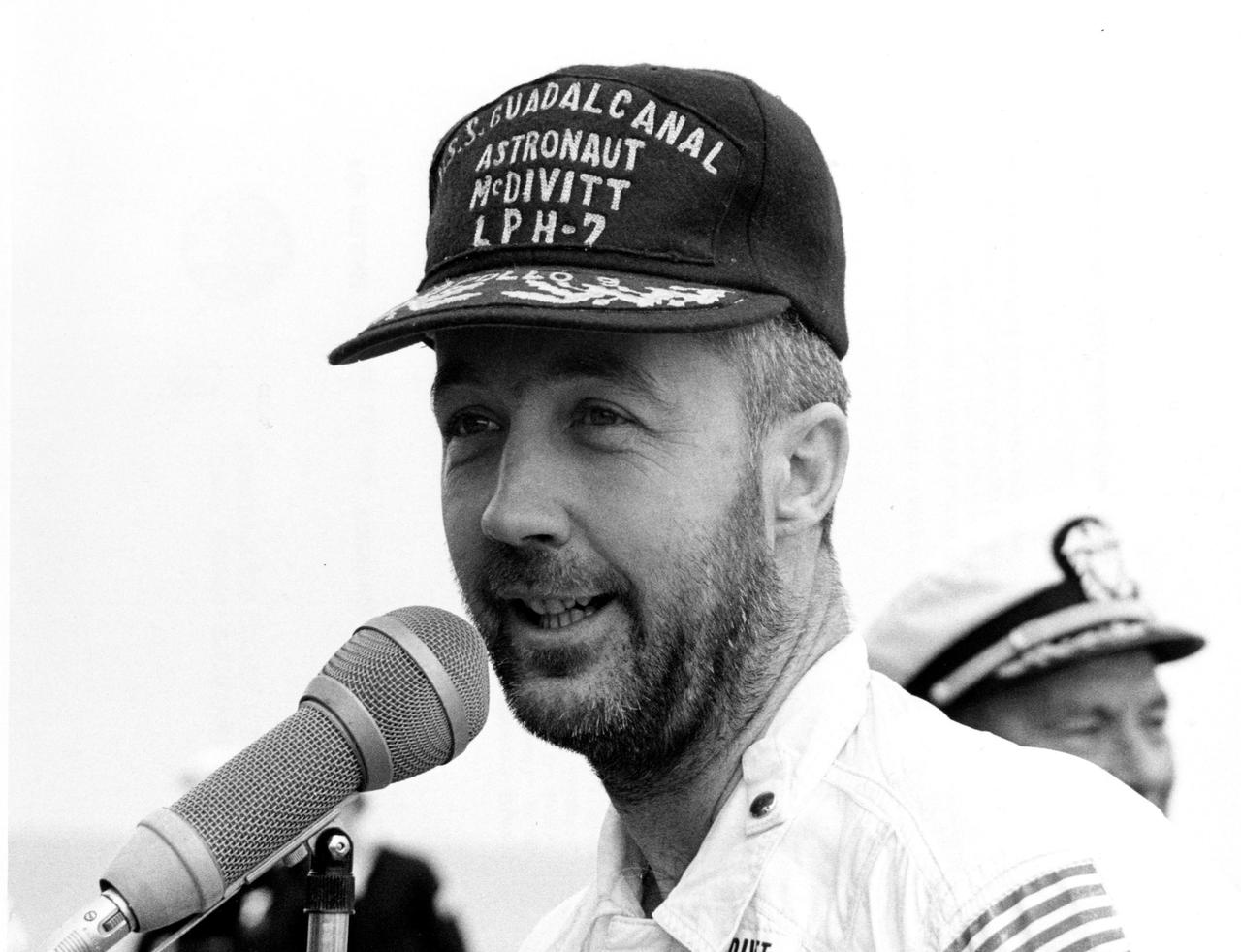

ABOARD THE USS GUADALCANAL -- Bearded Apollo 9 commander James A. McDivitt speaks to personnel aboard the USS Guadalcanal, prime recovery ship, an hour after he and astronauts David R. Scott and Russell L. Schweickart splashed down today in the Atlantic Ocean, 780 nautical miles southeast of Cape Kennedy. Their 10-day Earth orbital flight verified a lunar landing later this year. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration directs the Apollo program.
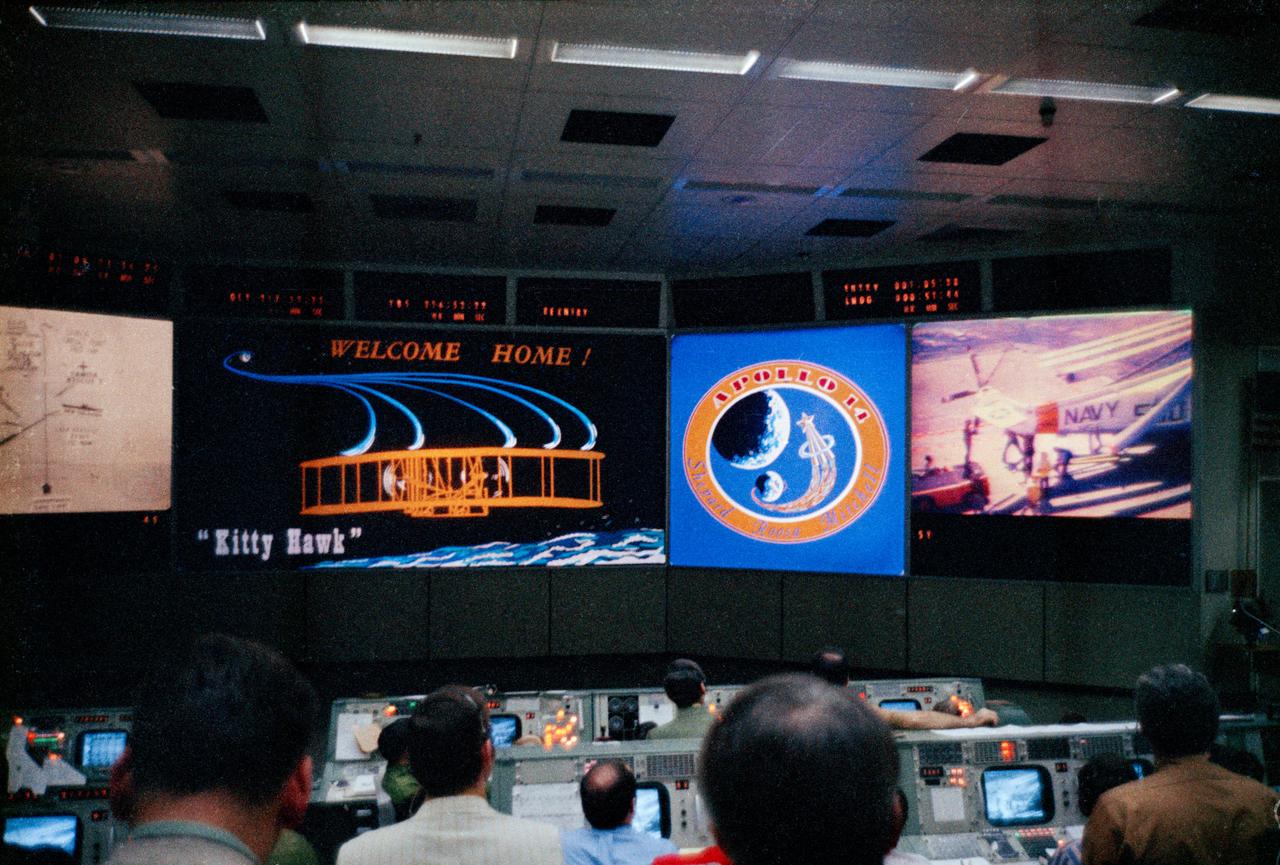

S71-18400 (9 Feb. 1971) --- Flight controllers in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) of the Mission Control Center (MCC) view a colorful display which signals the successful splashdown and recovery of the crew of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. The MOCR's large screen at right shows a television shot aboard the USS New Orleans, Apollo 14 prime recovery ship.

Lisa Schott, vice chairman of the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation, speaks during a memorial ceremony honoring former Apollo astronaut Walter Cunningham at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ceremony was held Jan. 9, 2023, at the Heroes and Legends exhibit within the Astronaut Hall of Fame at the spaceport’s visitor complex. Cunningham was the lunar module pilot for Apollo 7 – the first crewed flight test of the Apollo spacecraft – where he tested maneuvers necessary for docking and lunar orbit rendezvous. He passed away Jan. 3 at the age of 90.
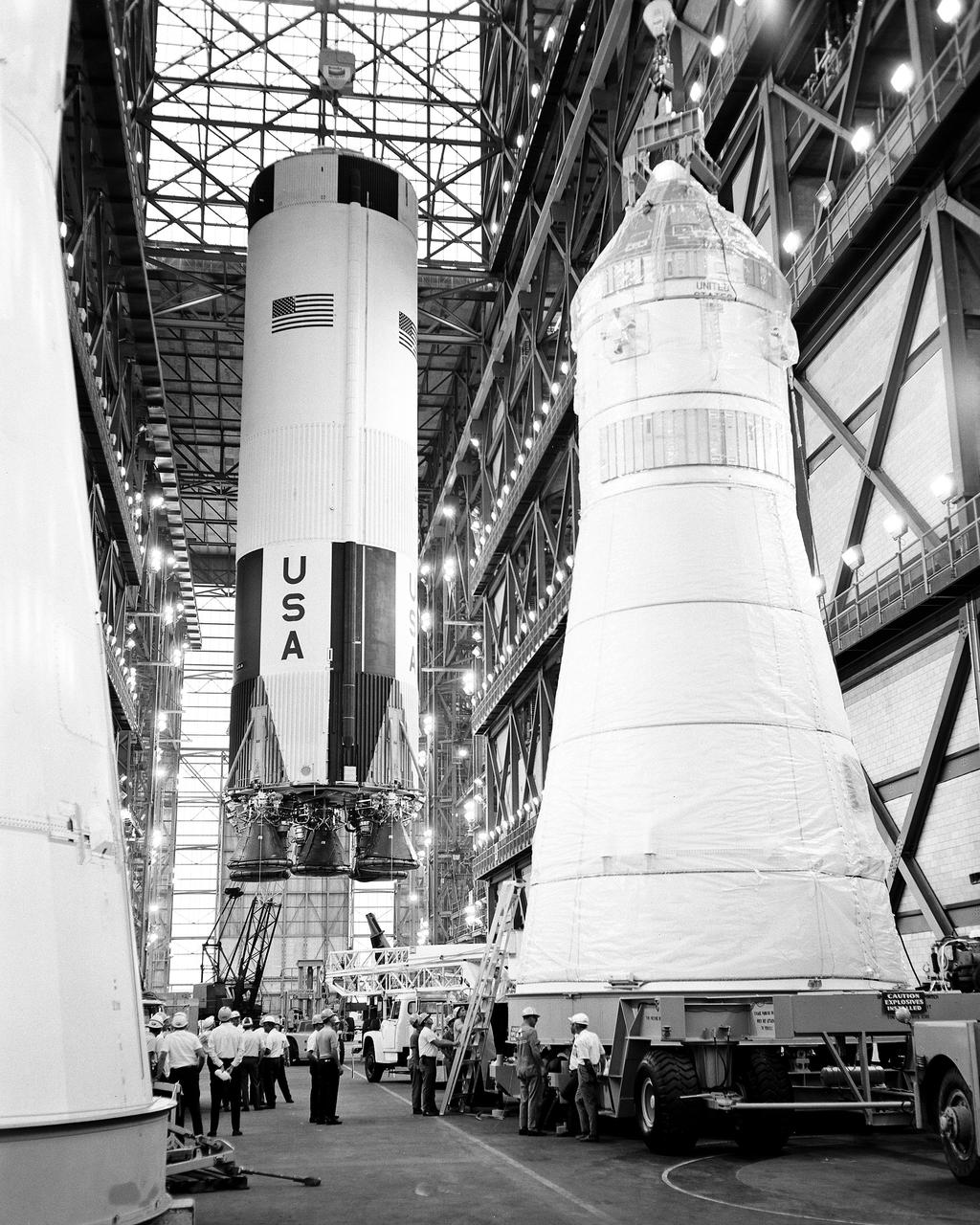

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The first stage of the Apollo 10 Saturn V space vehicle is hoisted above the transfer aisle in preparation for erection on a mobile launcher within High Bay 2 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. The erection of the 138-foot-long stage marked the first use of mobile launcher 3 and high bay 2. Apollo 10 will be piloted by astronauts Thomas Stafford, John Young and Eugene Cernan. In the foreground are the mated command, service and lunar modules the latter enclosed within the adapter for the Apollo 9 flight of James McDivitt, David Scott and Russel Schweickart. Photo credit: NASA
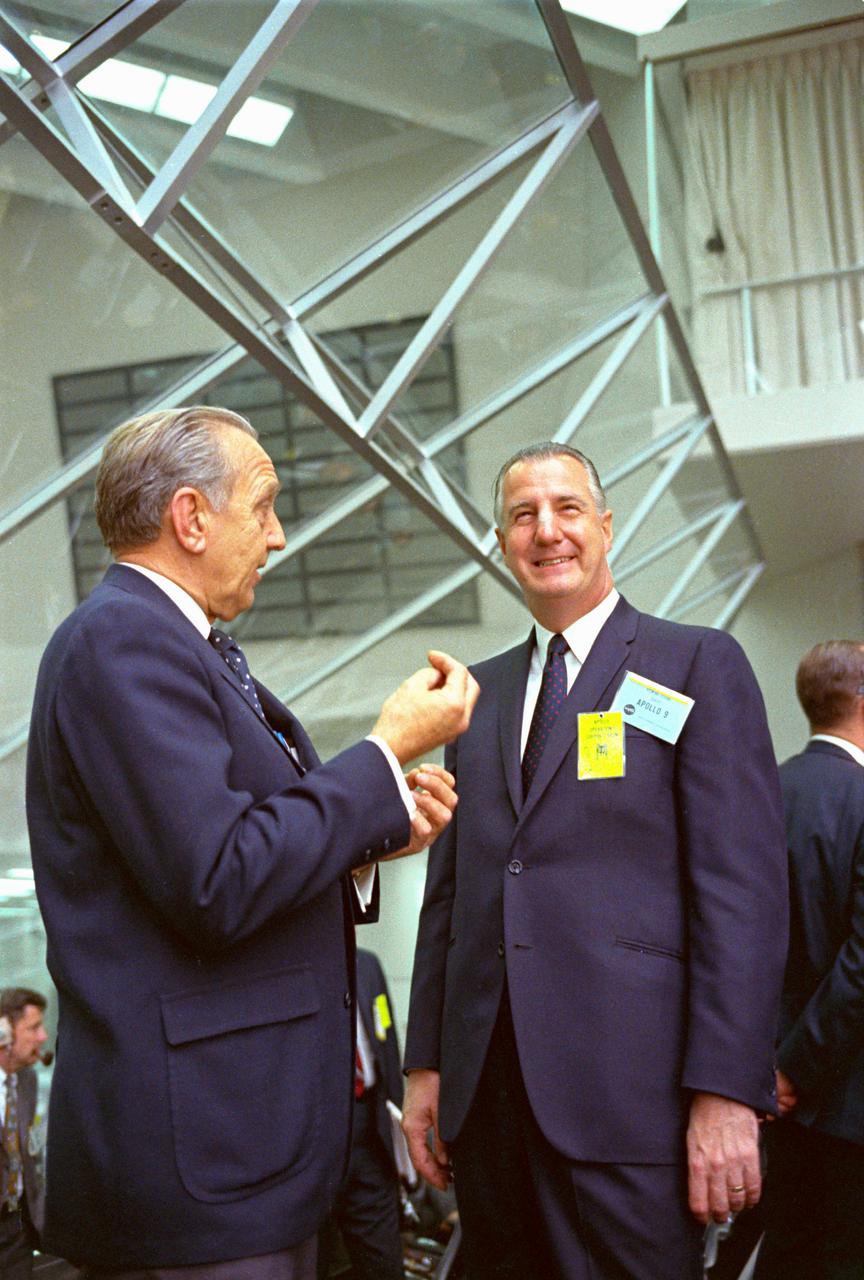

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Within the Launch Control Center, Vice President Spiro T. Agnew listens to Dr. Kurt H. Debus, director, Kennedy Space Center, explain highlights of the Apollo Program. The Vice President viewed the launch of Apollo 9 astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott and Russell L. Schweickart today. They were sent on a planned 10-day Earth orbital flight to put a lunar module spacecraft through extensive tests to qualify it for a possible manned lunar landing later this year. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration directs the Apollo Program.
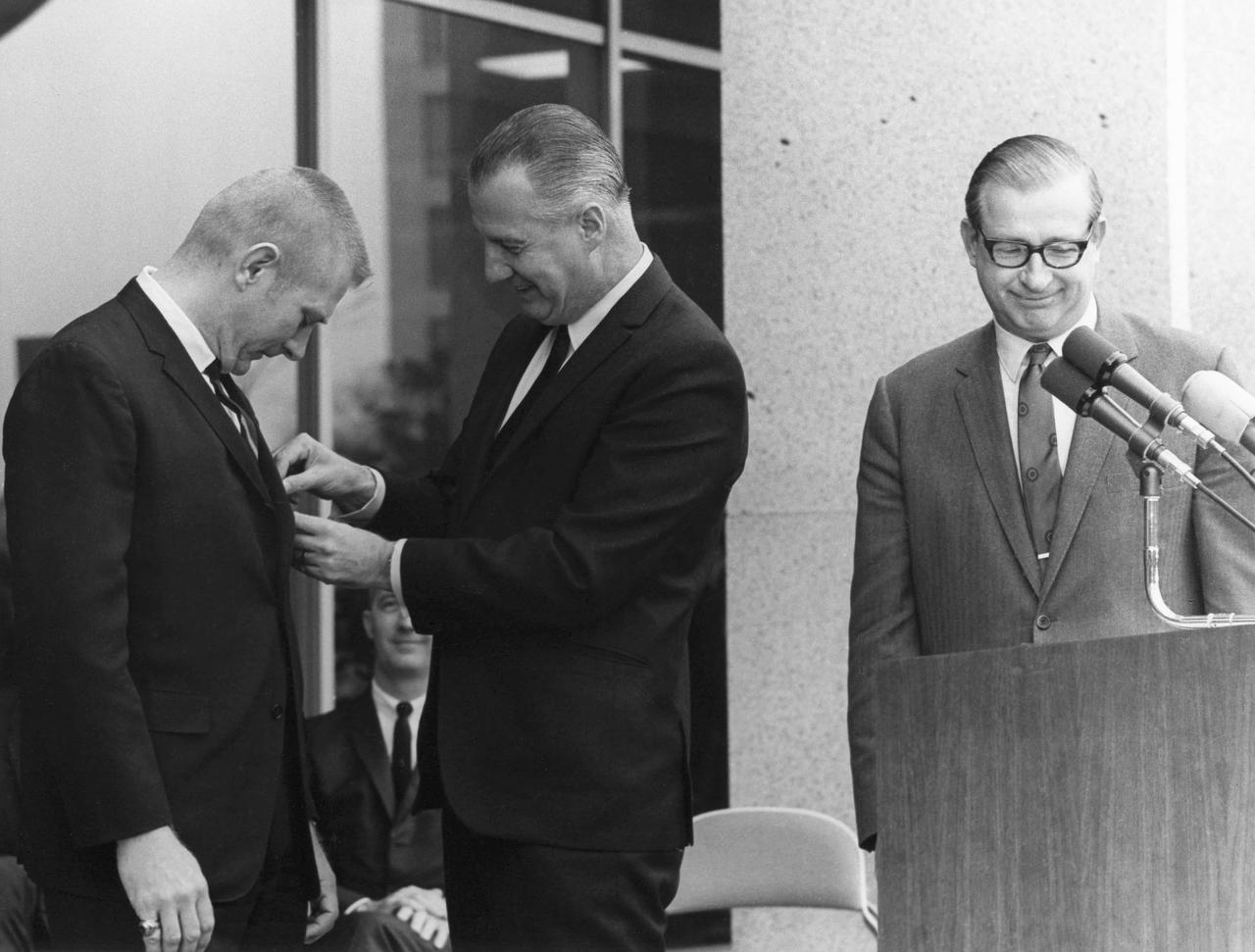

JSC2013-E-009914 (1969) -- Vice President Spiro Agnew pins Flight Director Eugene F. Kranz as NASA Administrator Thomas Paine and Apollo 9 Commander James A. McDivitt look on. Photo credit: NASA Hq. photo identification no. is 69-H-537
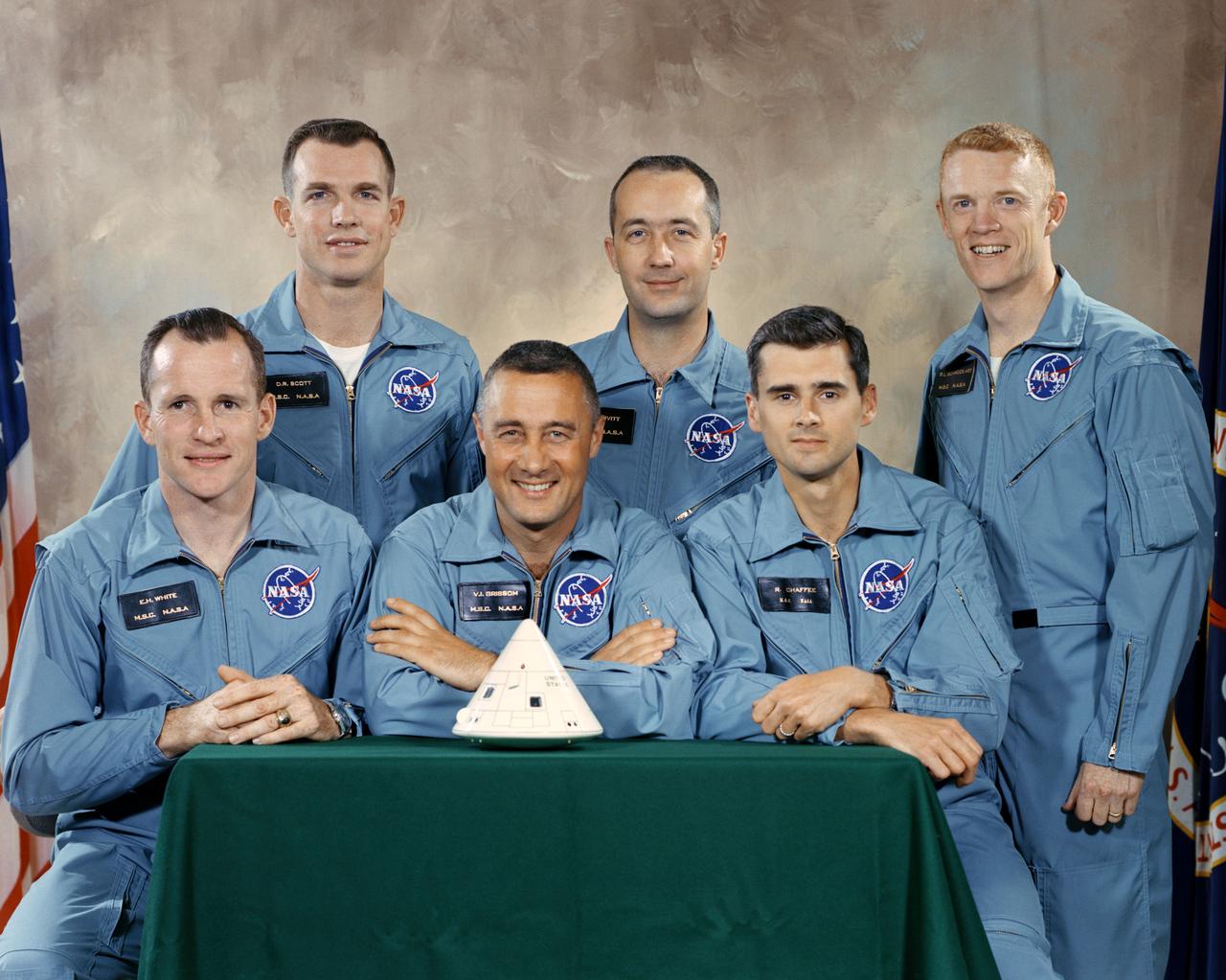

S66-30238 (1 April 1966) --- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has named these astronauts as the prime crew of the first manned Apollo Space Flight. Left to right, are Edward H. White II, command module pilot; Virgil I. Grissom, mission commander; and Roger B. Chaffee, lunar module pilot. On the second row are the Apollo 1 backup crew members, astronauts David R. Scott, James A. McDivitt and Russell L. Schweickart. EDITOR'S NOTE: Astronauts Grissom, White and Chaffee lost their lives in a Jan. 27, 1967 fire in the Apollo CM during testing at Cape Canaveral. McDivitt, Scott and Schweickart later served as crewmembers for the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission, which was one of the important stair-step missions leading up to the Apollo 11 manned lunar landing mission of July 1969.

In the launch control center at Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC), Walter J. Kapryan, Director of Launch Operations (center), discusses an aspect of the Apollo 14 flight with Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC) Dr. Rocco A. Petrone, Apollo Program Director (right). The Apollo 14, carrying a crew of three astronauts: Mission commander Alan B. Shepard Jr., Command Module pilot Stuart A. Roosa, and Lunar Module pilot Edgar D. Mitchell, lifted off from launch complex 39A at KSC on January 31, 1971. It was the third manned lunar landing, the first manned landing in exploration of the lunar highlands, and it demonstrated pinpoint landing capability. The major goal of Apollo 14 was the scientific exploration of the Moon in the foothills of the rugged Fra Mauro region. The extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Shepard and Mitchell included setting up an automated scientific laboratory called Apollo Lunar Scientific Experiments Package (ALSEP), and collecting a total of about 95 pounds (43 kilograms) of Moon rock and soil for a geological investigation back on the Earth. Apollo 14 safely returned to Earth on February 9, 1971.
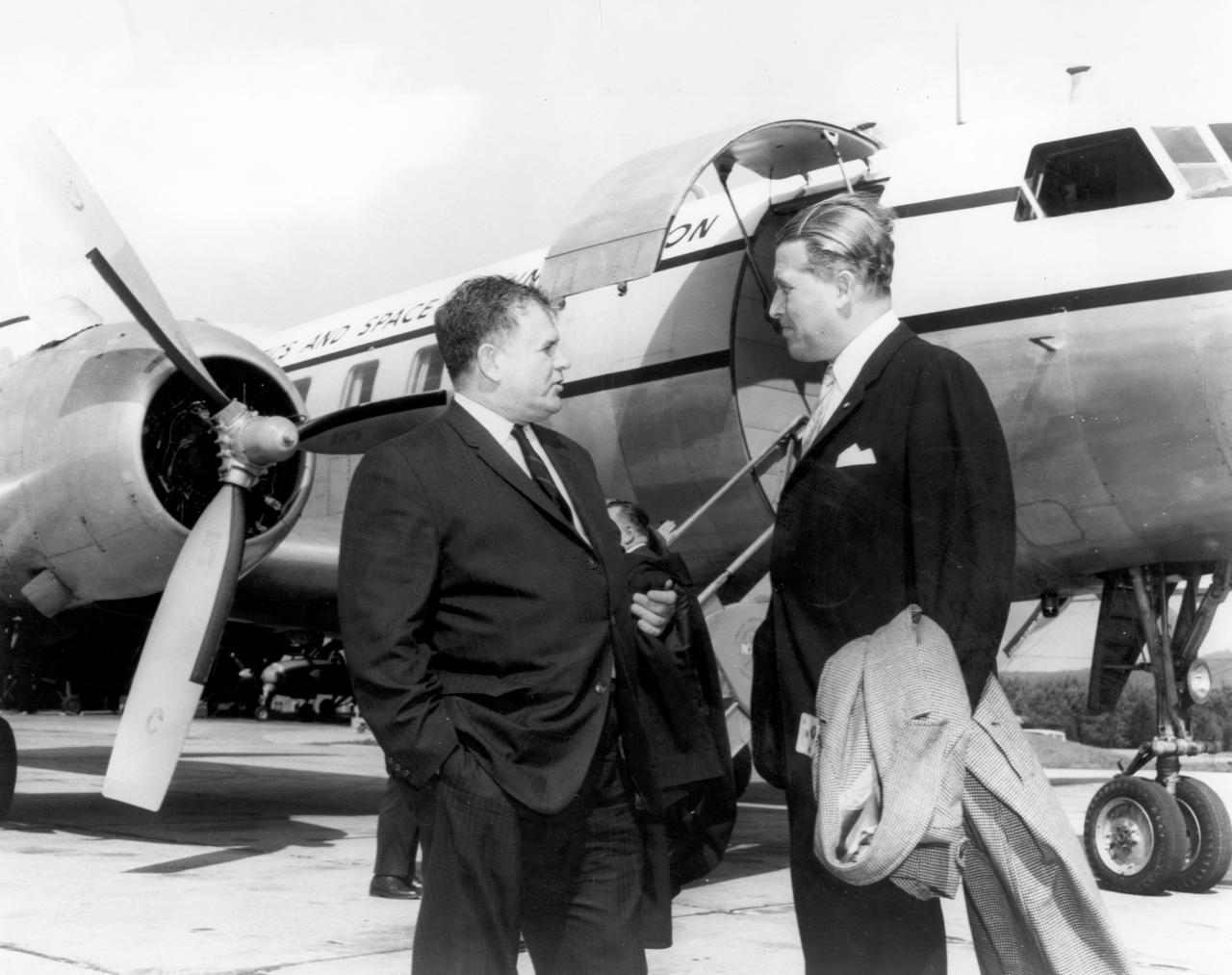

The members of the House Committee on Science and Astronautics visited the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on March 9, 1962 to gather firsthand information of the nation’s space exploration program. The congressional group was composed of members of the Subcommittee on Manned Space Flight. The subcommittee was briefed on MSFC’s manned space efforts earlier in the day and then inspected mockups of the Saturn I Workshop and the Apollo Telescope Mount, two projects developed by MSFC for the post-Apollo program. In this photograph, MSFC Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun, bids farewell to Texas Democratic Representative Olin E. Teague before departure at the Redstone Arsenal Airstrip.
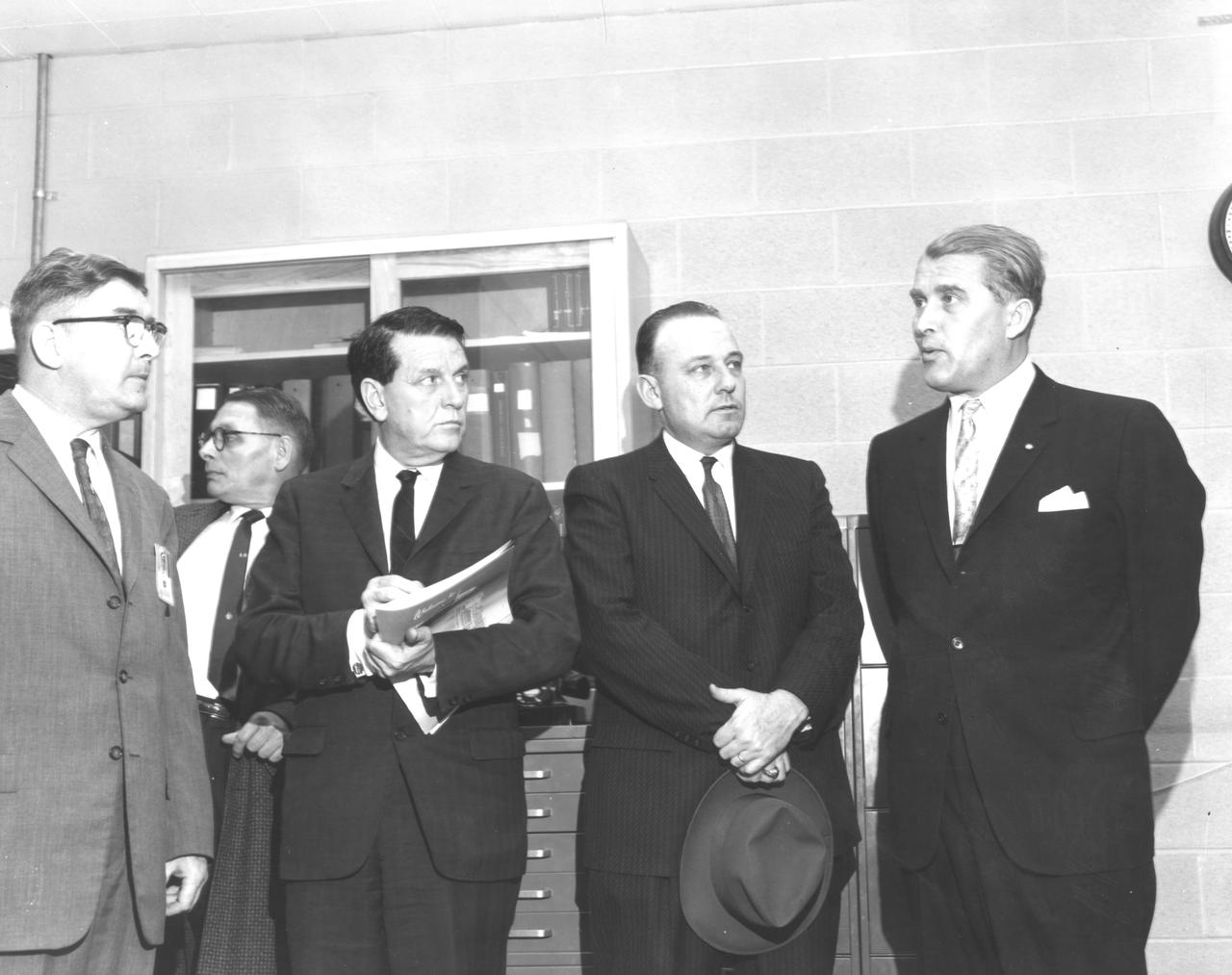

The members of the House Committee on Science and Astronautics visited the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on March 9, 1962 to gather firsthand information of the nation's space exploration program. The congressional group was composed of members of the Subcommittee on Manned Space Flight. They were briefed on MSFC's manned space efforts earlier in the day and then inspected mockups of the Saturn I Workshop and the Apollo Telescope Mount, two projects developed by MSFC for the post-Apollo program. Pictured left-to-right are Dieter Grau, MSFC; Konrad Dannenberg, MSFC; James G. Fulton, Republican representative for Pennsylvania; Joe Waggoner, Democratic representative for Louisiana; and Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director of MSFC.

AS04-01-580 (9 Nov. 1967) --- Earth as viewed from 10,000 miles. In 1969, the Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) unmanned test flight made a great ellipse around Earth as a test of the translunar motors and of the high speed entry required of a manned flight returning from the moon. A 70mm camera was programmed to look out a window toward Earth, and take a series of photographs from "high apogee". Coastal Brazil, Atlantic Ocean, West Africa, Antarctica, looking west. This photograph was made when the Apollo 4 spacecraft, still attached to the S-IVB (third) stage, was orbiting Earth at an altitude of 9,544 miles.
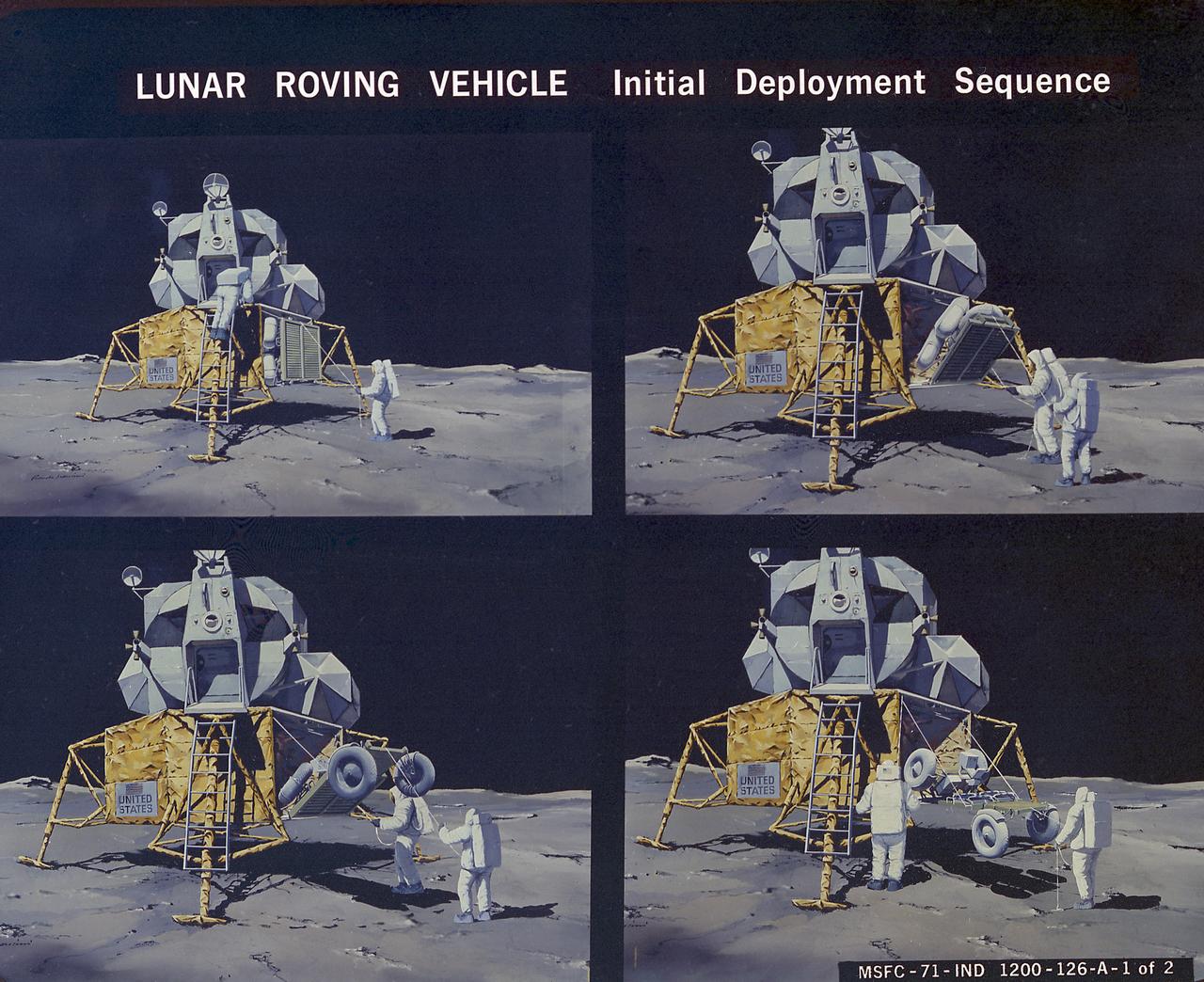
This artist's concept illustrates the deployment sequence of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Moon. The LRV was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
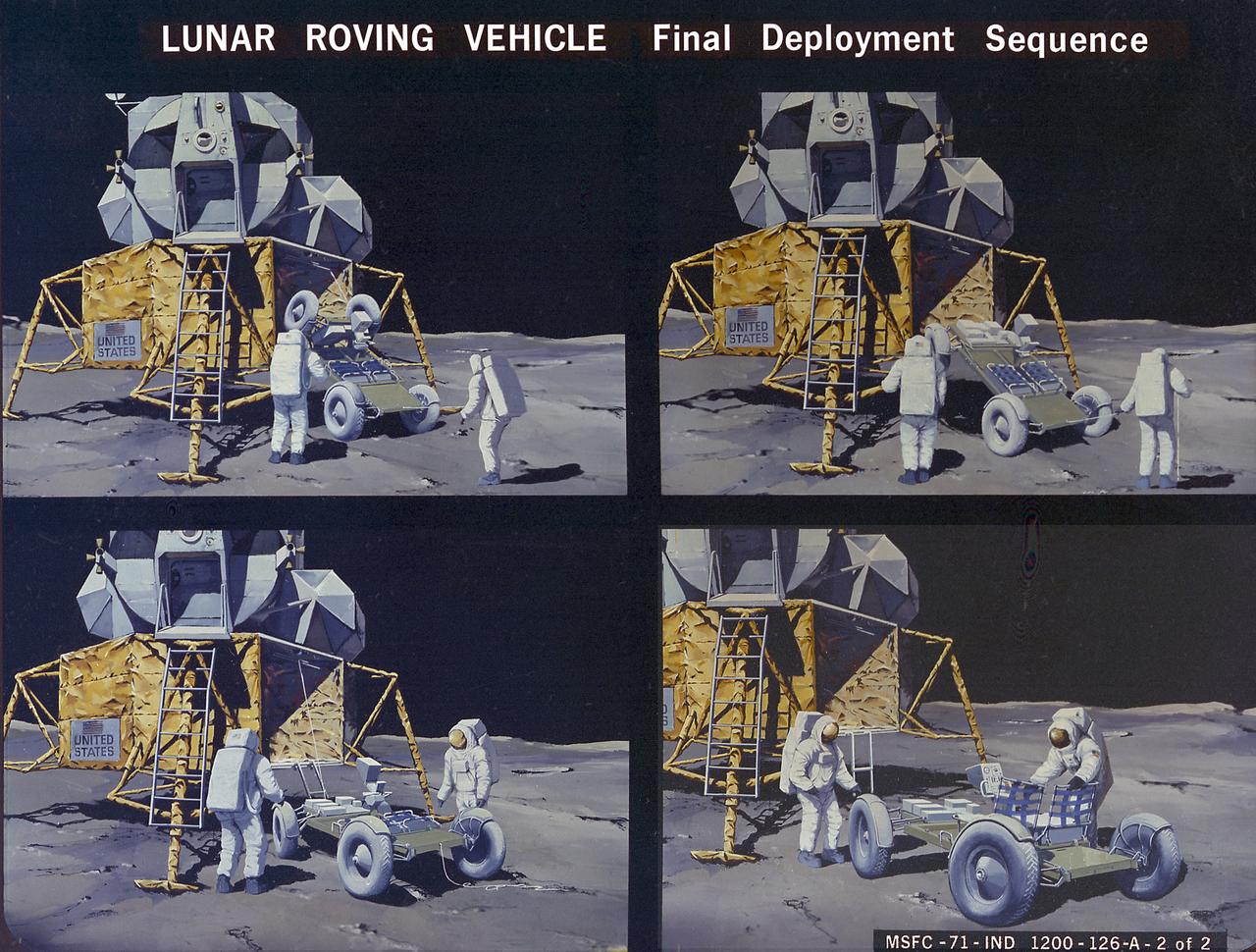
This artist's concept illustrates the deployment sequence of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the Moon. The LRV was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.

The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crew to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
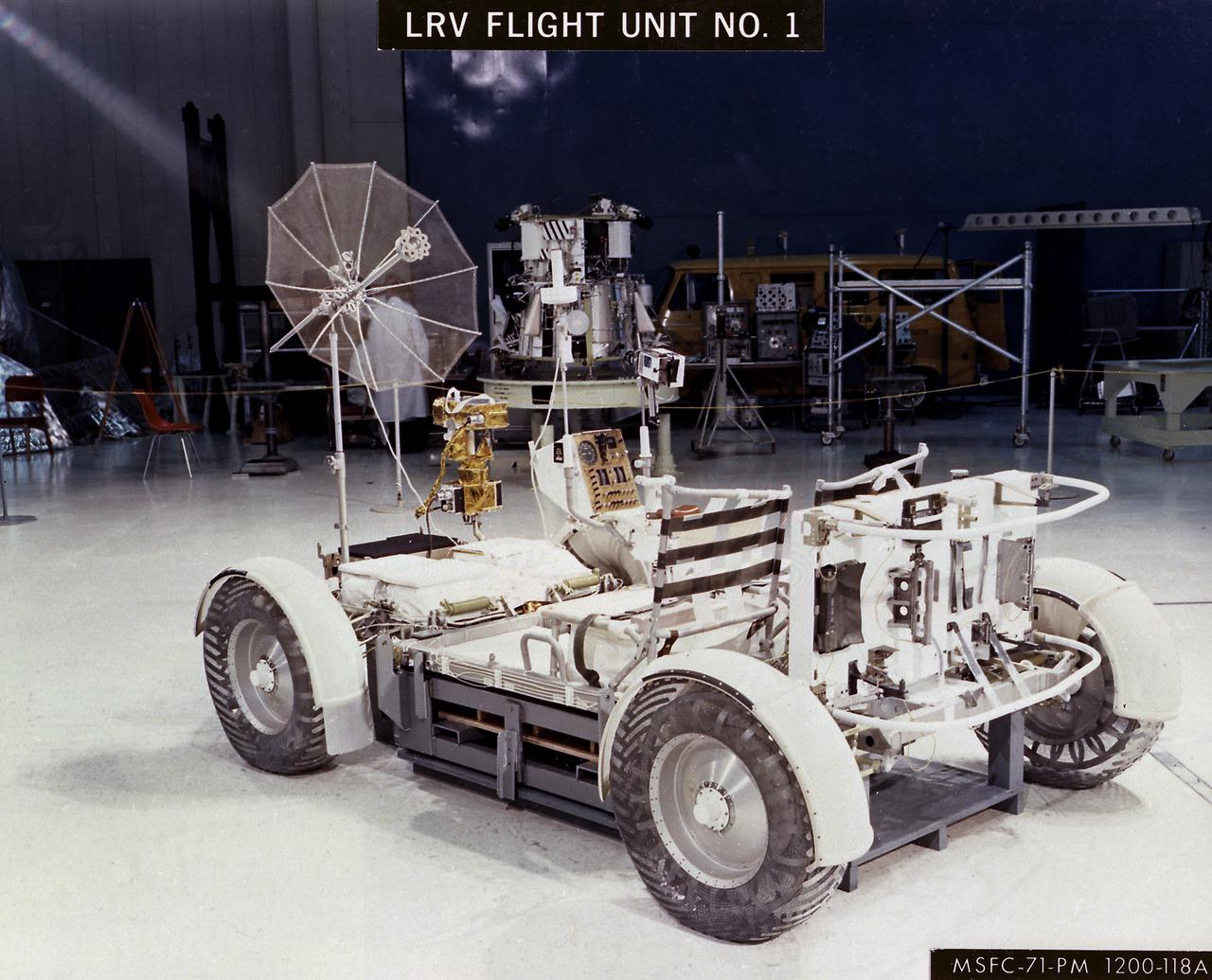
The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) was designed to transport astronauts and materials on the Moon. It was a collapsible open-space vehicle about 10 feet long with large mesh wheels, anterna, appendages, tool caddies, and cameras. Powered by two 36-volt batteries, it has four 1/4-hp drive motors, one for each wheel. The vehicle was designed to travel in forward or reverse, negotiate obstacles about 1 foot high, cross crevasses about 2 feet wide, and climb or descend moderate slopes. Its speed limit was about 9 miles (14 kilometers) per hour. An LRV was used on each of the last three Apollo missions (Apollo 15, Apollo 16, and Apollo 17) and permitted the crews to travel several miles from the Lunar Module. The LRV was designed, developed, and tested by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Plant in Kent, Washington.
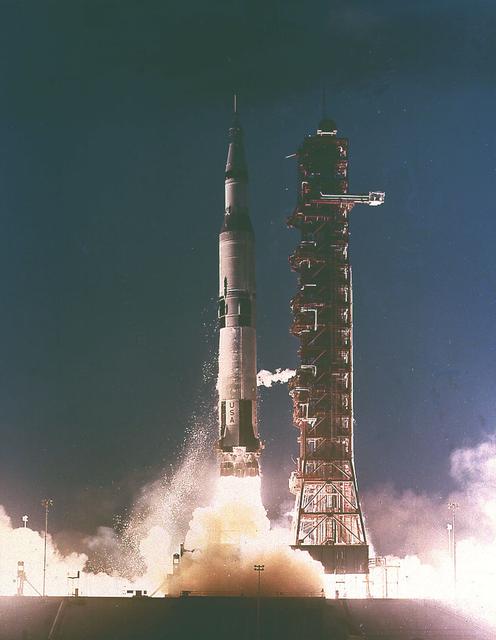
AS-501, the first flight of the Saturn V launch vehicle, takes flight from Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39A on November 9, 1967. The unmanned mission, also designated Apollo 4, marked the first test flight of the S-IC and S-II stages, developed for the Saturn program under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center.
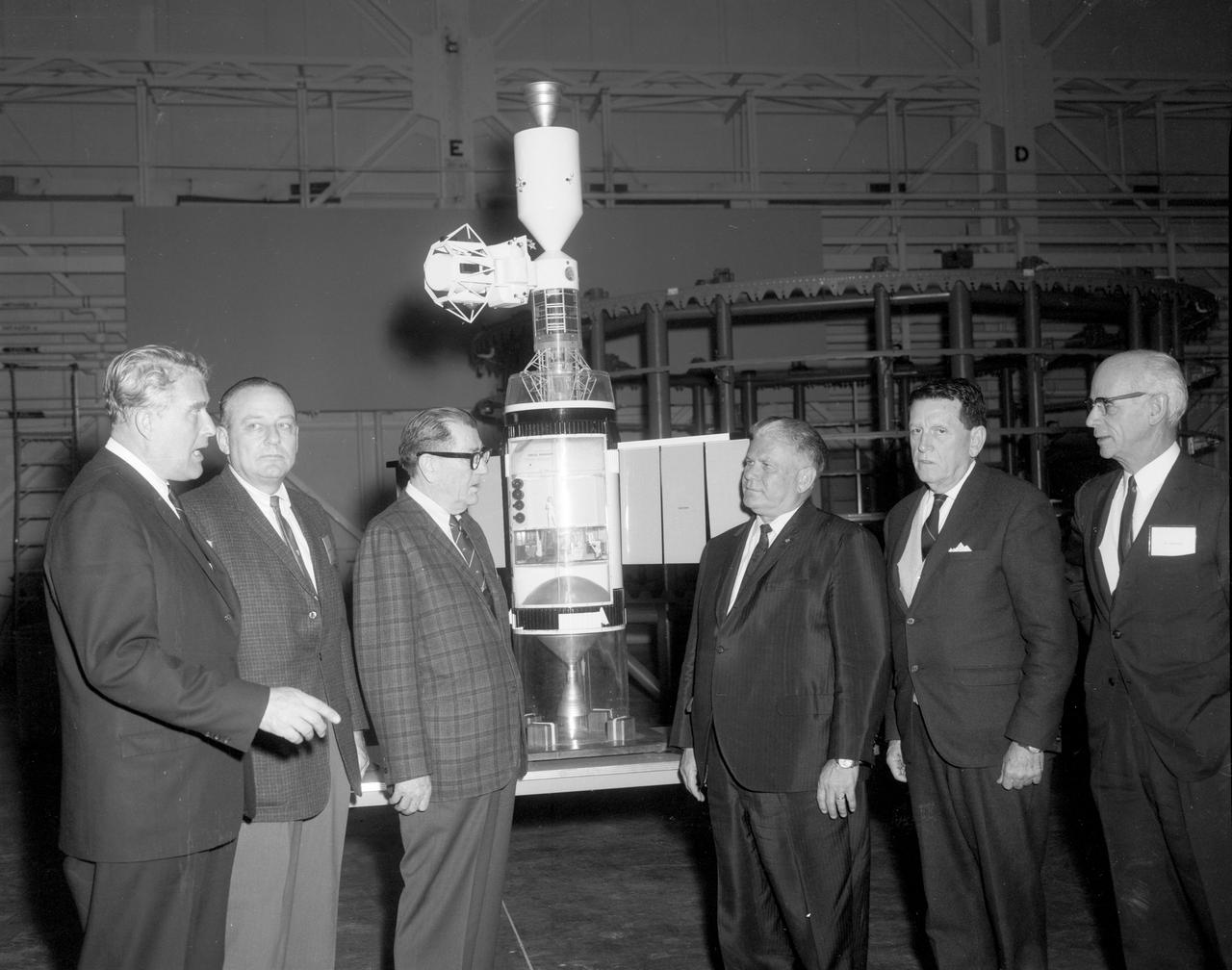

The members of the House Committee on Science and Astronautics visited the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on March 9, 1962 to gather firsthand information of the nation’s space exploration program. The congressional group was composed of members of the Subcommittee on Manned Space Flight. Standing at the Apollo Applications Program Cluster Model in building 4745 are (left-to-right): Dr. Wernher von Braun, MSFC; Congressman Joe D. Waggoner, Democratic representative of Louisiana; Congressman Earle Cabell, Democratic representative of Texas; Subcommittee Chairman Olin E. Teague, Democratic representative of Texas; Congressman James G. Fulton, Republican representative of Pennsylvania; and Dr. Ernst Stuhlinger, associate MSFC director for science. The subcommittee was briefed on MSFC’s manned space efforts earlier in the day and then inspected mockups of the Saturn I Workshop and the Apollo Telescope Mount, two projects developed by MSFC for the post-Apollo program.
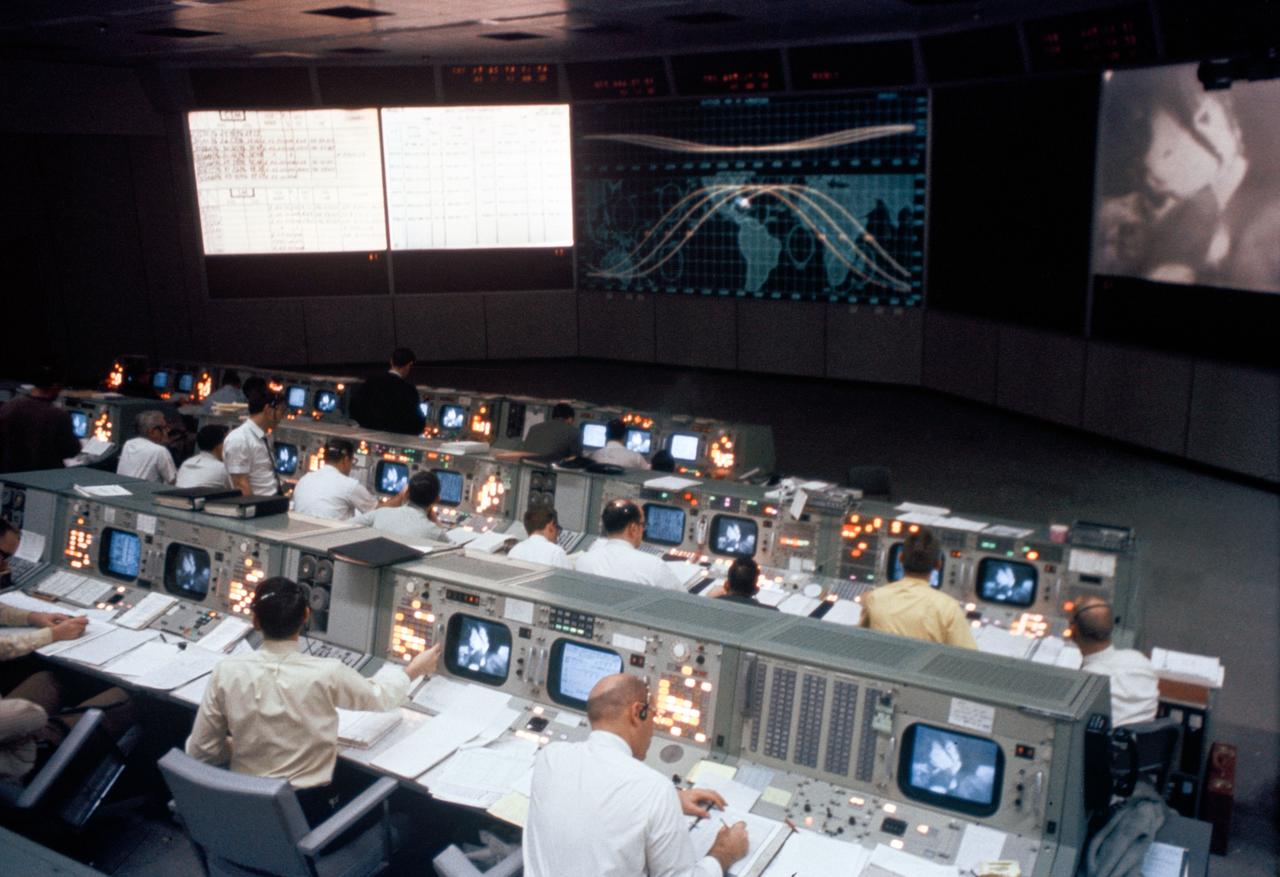

S69-26301 (March 1969) --- Overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center, Building 30, during the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. When this photograph was taken a live television transmission was being received from Apollo 9 as it orbited Earth.
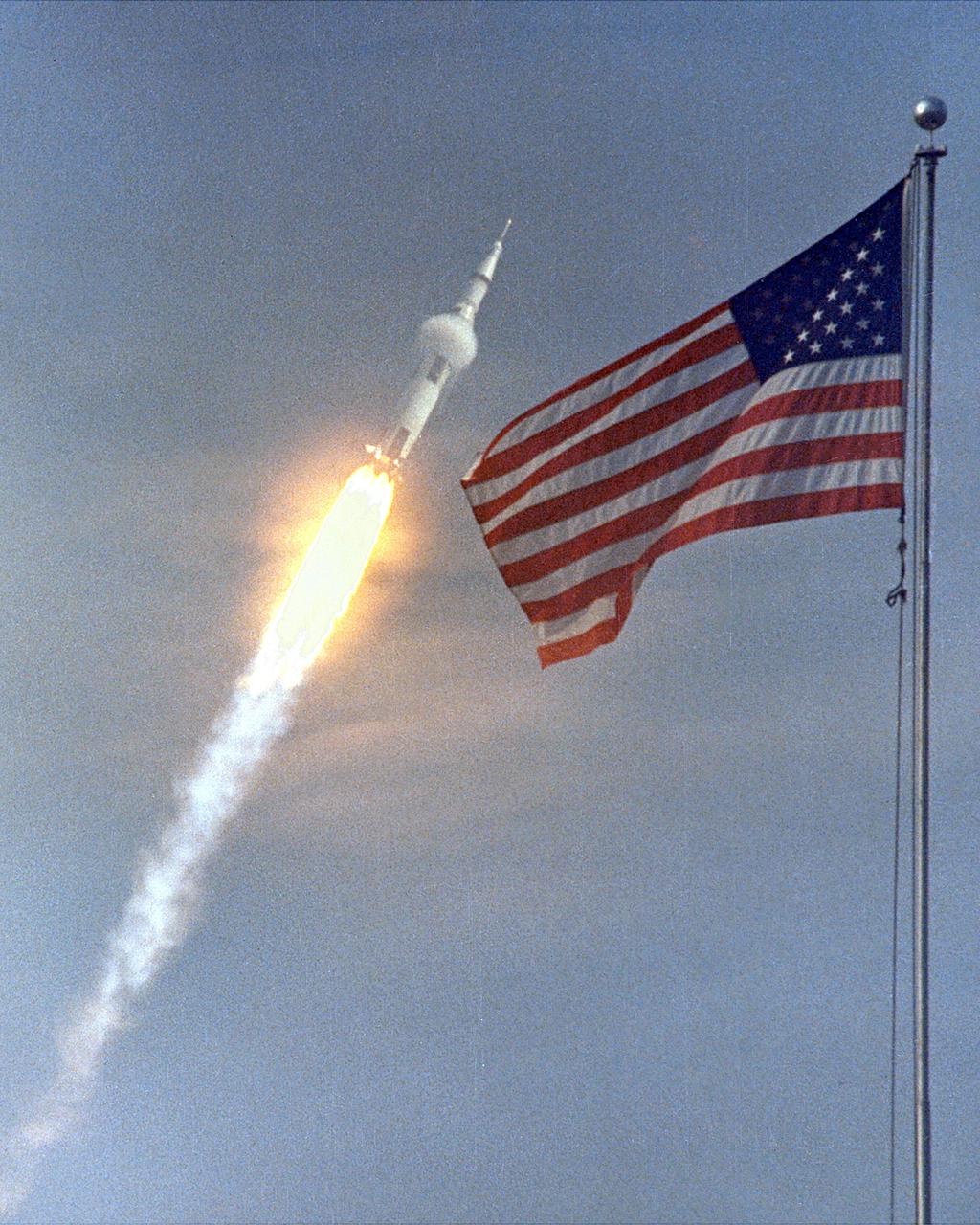
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The American Flag heralds the flight of Apollo 11, man's first lunar landing mission. This double exposure was made with a 1,000 mm lens. The photograph was taken from Cape Kennedy, adjacent to Kennedy Space Center, where Apollo 11 lifted off from pad 39A at 9:32 a.m. EDT. This image was imposed upon the image of hte flag, filmed a day earlier. In the photo, the rocket at an alititude of about 5,000 feet. A band of super-cold propellants seems to circle the rocket near its center. The effect is caused by the difference in temperature between the propellants and the atmosphere. Photo credit: NASA
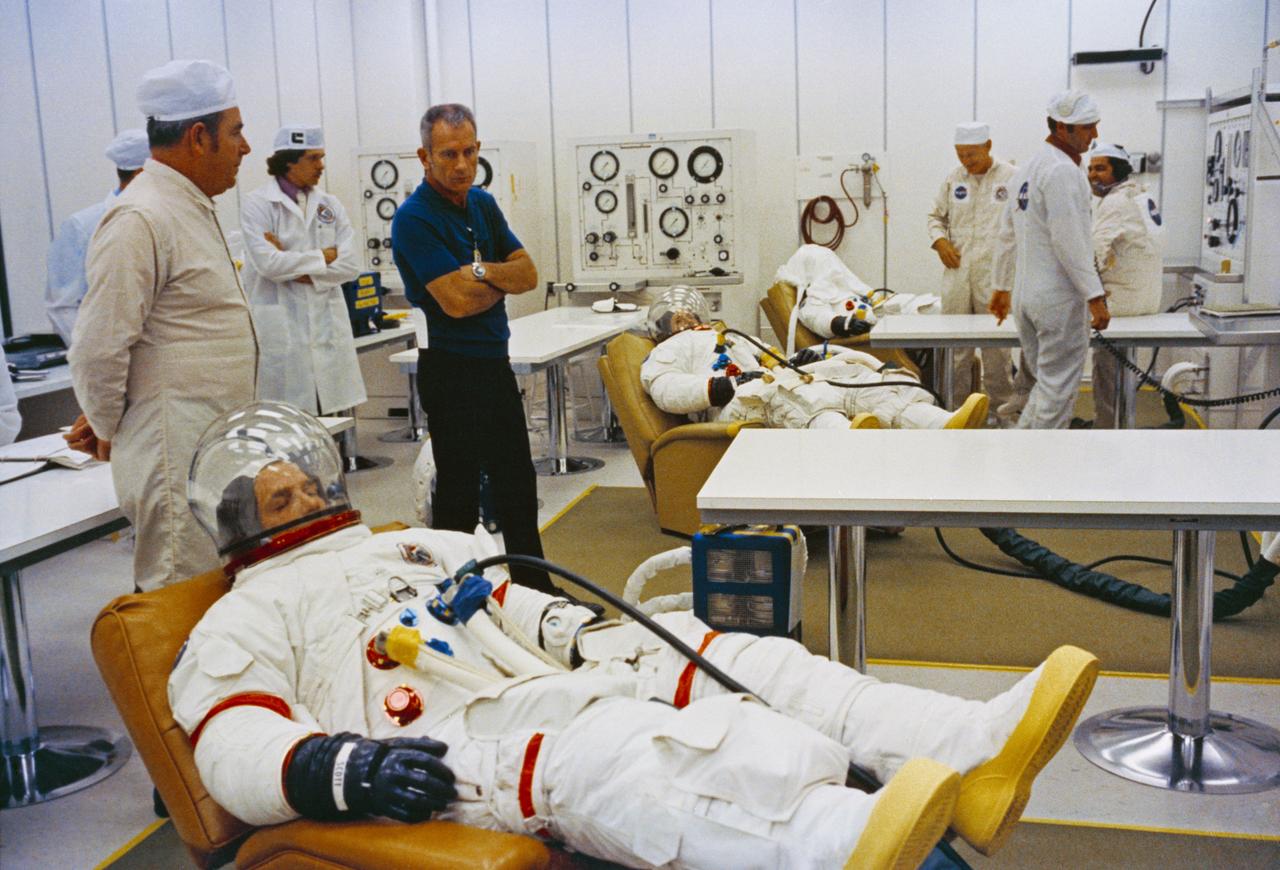

S71-41408 (26 July 1971) --- The three Apollo 15 astronauts go through suiting up operations in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Manned Spacecraft Operations Building (MSOB) during the Apollo 15 prelaunch countdown. They are David R. Scott (foreground), commander; Alfred M. Worden (center), command module pilot; and James B. Irwin (background), lunar module pilot. Minutes later the crew rode a special transport van over to Pad A, Launch Complex 39, where their spacecraft awaited them. With the crew was Dr. Donald (Deke) K. Slayton (wearing dark blue sport shirt), director of Flight Crew Operations, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The Apollo 15 space vehicle was launched at 9:34:00:79 a.m. (EDT), July 26, 1971, on a lunar landing mission.

S70-30534 (9 March 1970) --- A Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV), piloted by astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., sets down on the runway at the conclusion of a test flight at Ellington Air Force Base. Lovell is the commander of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Lovell used the LLTV to practice lunar landing techniques in preparation for his scheduled mission. Lovell will be at the controls of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) when it lands on the moon in the highlands just north of Fra Mauro. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, will remain with the Apollo 13 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Lovell and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, descend in the LM to explore the moon. A hovering helicopter watches the LLTV landing.
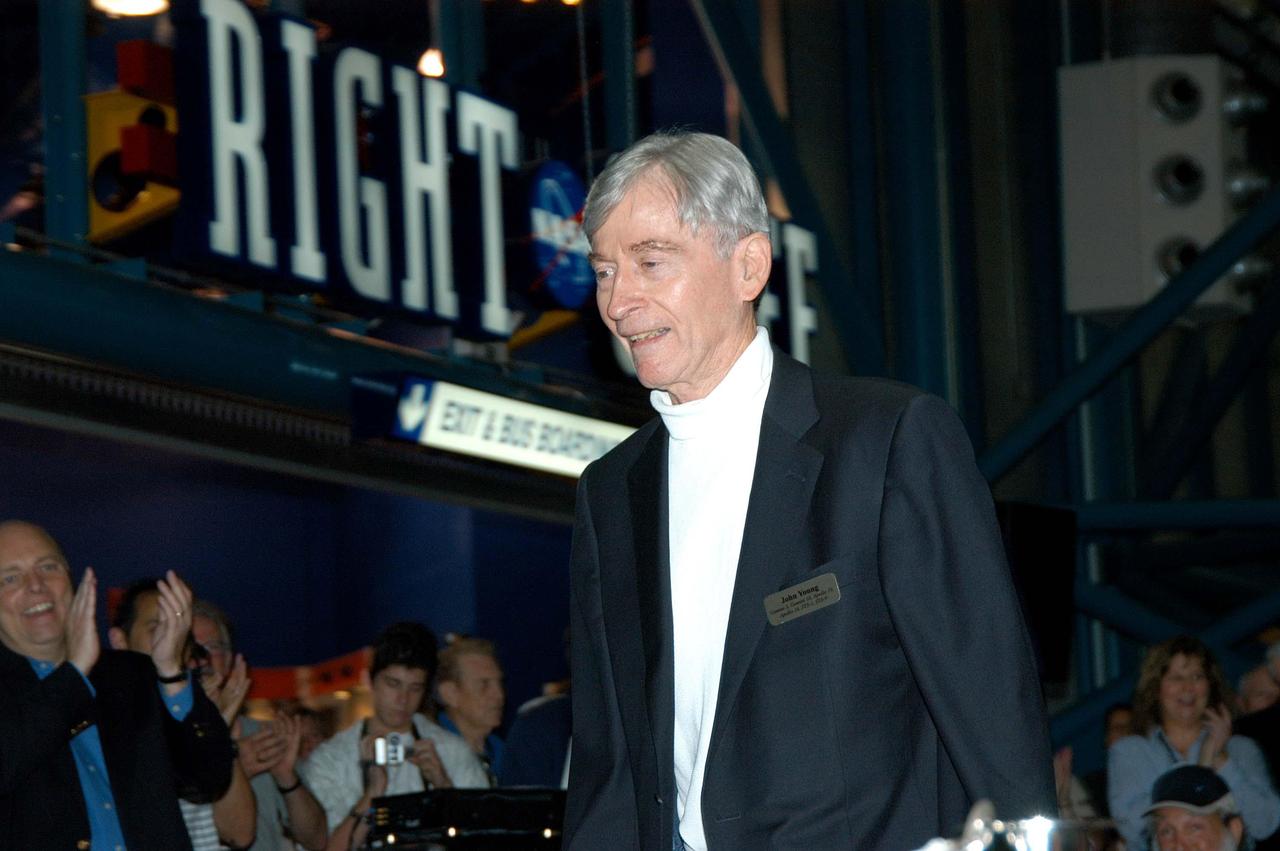

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Before the induction ceremony of five space program heroes into the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame, astronaut John Young is warmly greeted as he is introduced as a previous inductee. Co-holder of a record for the most space flights, six, he flew on Gemini 3 and 10, orbited the Moon on Apollo 10, walked on the Moon on Apollo 16, and commanded two space shuttle missions, STS-1 and STS-9. Young currently serves as associate director, technical, at Johnson Space Center. The induction ceremony was held at the Apollo/Saturn V Center at KSC. New inductees are Richard O. Covey, commander of the Hubble Space Telescope repair mission; Norman E. Thagard, the first American to occupy Russia’s Mir space station; the late Francis R. "Dick" Scobee, commander of the ill-fated 1986 Challenger mission; Kathryn D. Sullivan, the first American woman to walk in space; and Frederick D. Gregory, the first African-American to command a space mission and the current NASA deputy administrator. The U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame opened in 1990 to provide a place where space travelers could be remembered for their participation and accomplishments in the U.S. space program. The five inductees join 52 previously honored astronauts from the ranks of the Gemini, Apollo, Skylab, Apollo-Soyuz, and Space Shuttle programs.
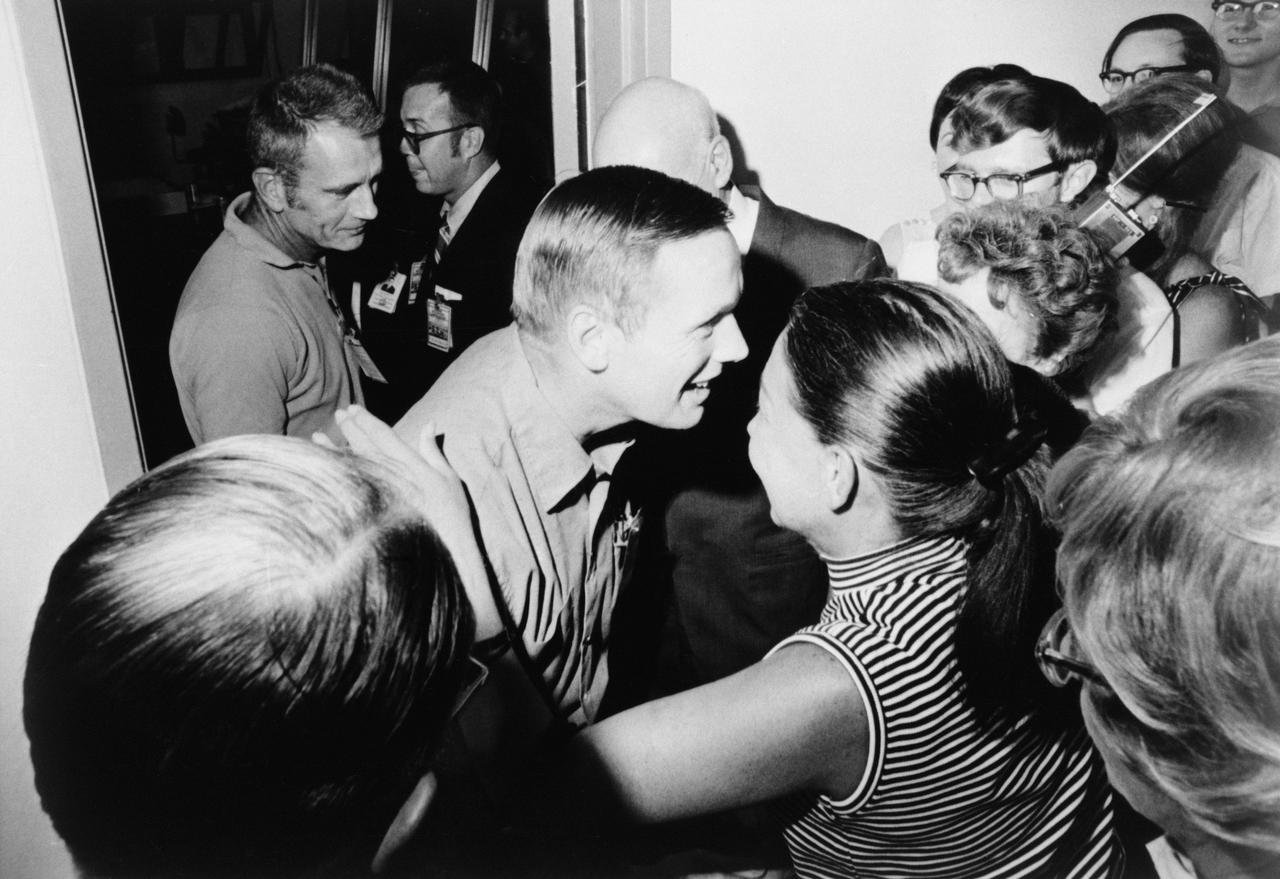

Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong (center), is greeted by friends in the crew reception area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory. Dr. Gilruth is pictured just to right of Armstrong. Donald K. Slayton, Director of Space Flight Crew Operations, is behind ArmstrongThe Apollo 11 crew left the crew reception area of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at 9 p.m., Aug. 10, 1969.
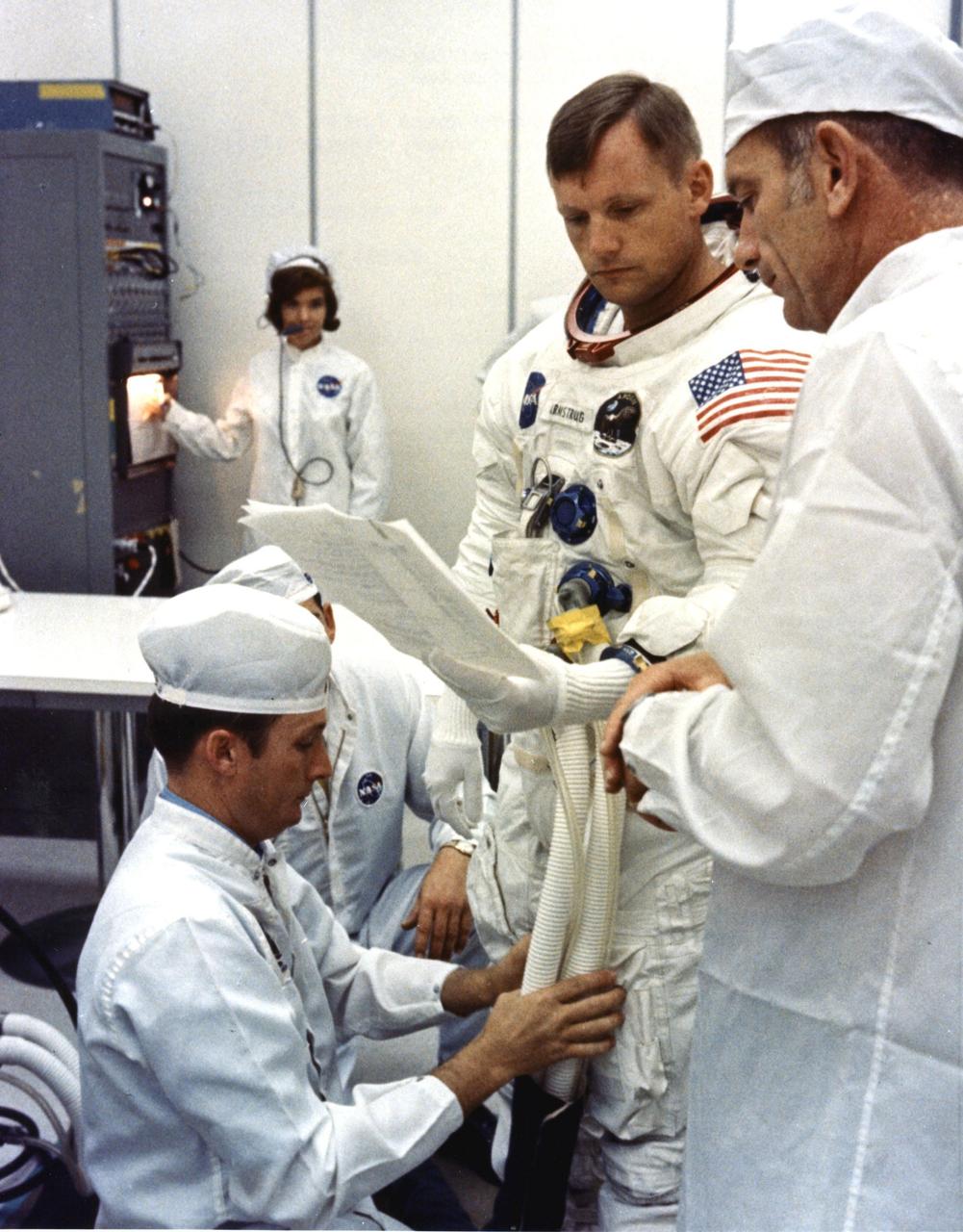

Apollo 11 Commander Neil Armstrong is looking over flight plans while being assisted by a spacesuit technician during suiting operations in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building (MSOB) prior to the astronauts' departure to Launch Pad 39A. The three astronauts, Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Neil A. Armstrong and Michael Collins will then board the Saturn V launch vehicle, scheduled for a 9:32 a.m. EDT liftoff, for the first manned lunar landing mission
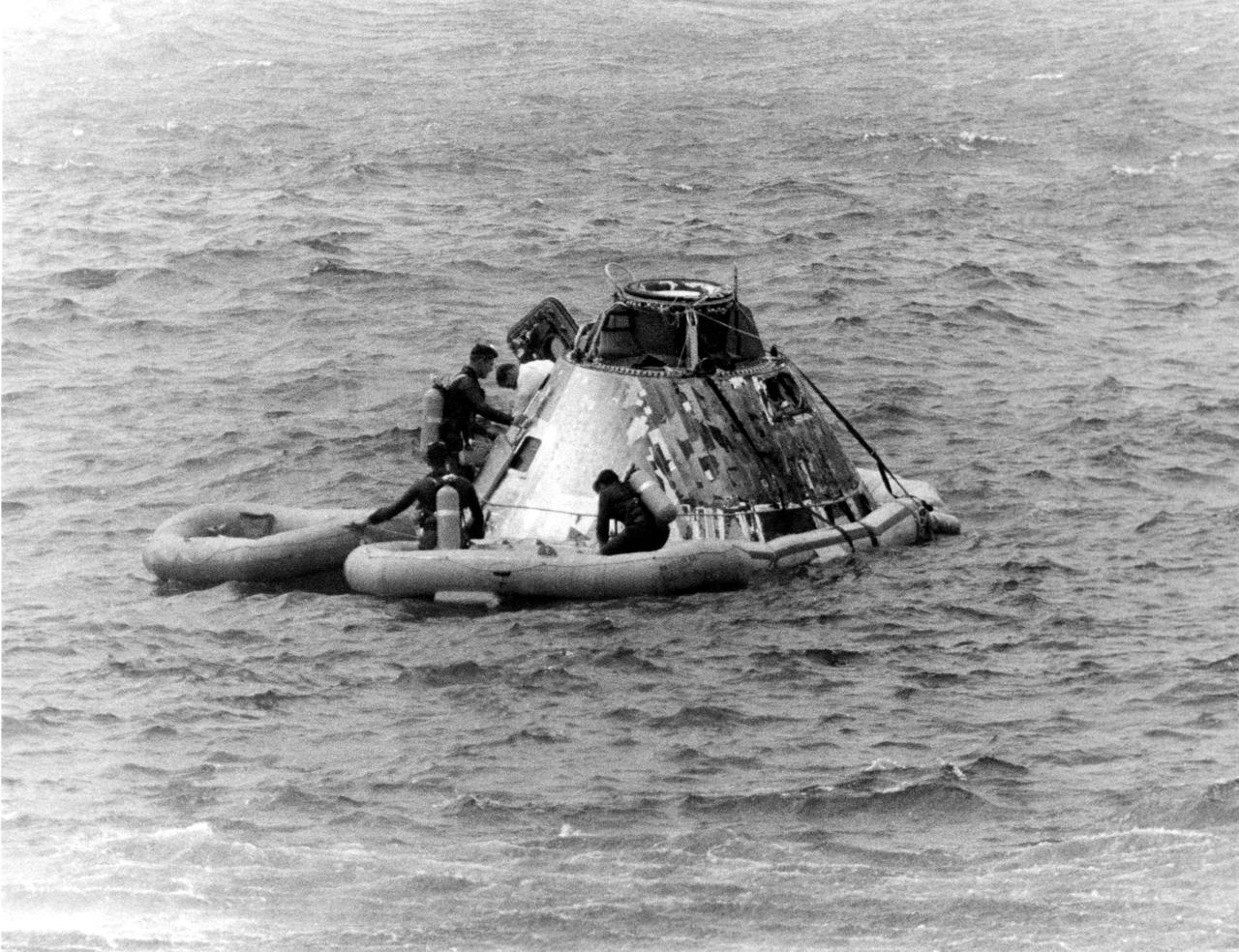

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Pararescueman helps Apollo 9 Command Module Pilot David R. Scott from the spacecraft today during recovery at completion of the 10-day Earth orbital flight with James A. McDivitt and Russell L. Schweickart, still in the spacecraft. The astronauts splashed down less than five miles from the USS Guadalcanal, prime recovery ship, at the beginning of their 152nd revolution. During the highly successful flight, they extensively tested the lunar module spacecraft, paving the way for a similar one to carry Americans to the Moon later this year. They were lalunched March 3 by an Apollo_Saturn V space vehicle from the Kennedy Space Center at the start of NASA's third manned mission using an Apollo spacecraft.
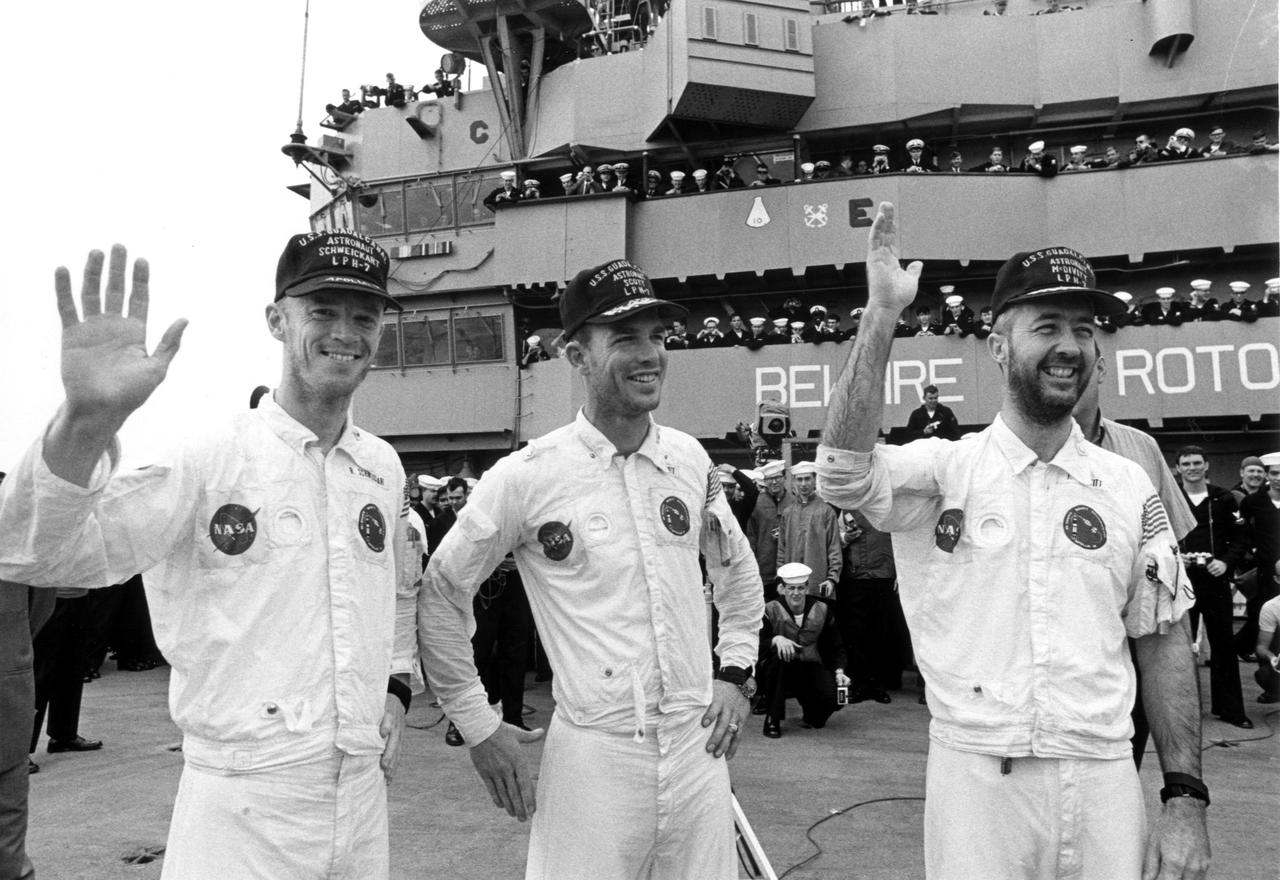

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Wearing flight caps presented to them by the crew of the USS Guadalcanal, bearded Apollo 9 astronauts (left to right) Russell L. Schweickart, David R. Scott and James A. McDivitt, wave to well-wishers aboard the recovery ship at the completion of their 10-day Earth orbital mission. Their spacecraft splashed down 780 nautical miles southeast of Cape Kennedy at 12:01 p.m. EST, March 13, 1969. During the textbook mission, the space pilots verified a lunar module spacecraft similar to the one that is to land Americans on the Moon later this year. Their flight began March 3 when they were launched by an Apollo_Saturn V rocket from the Kennedy Space Center. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration directs the Apollo program.
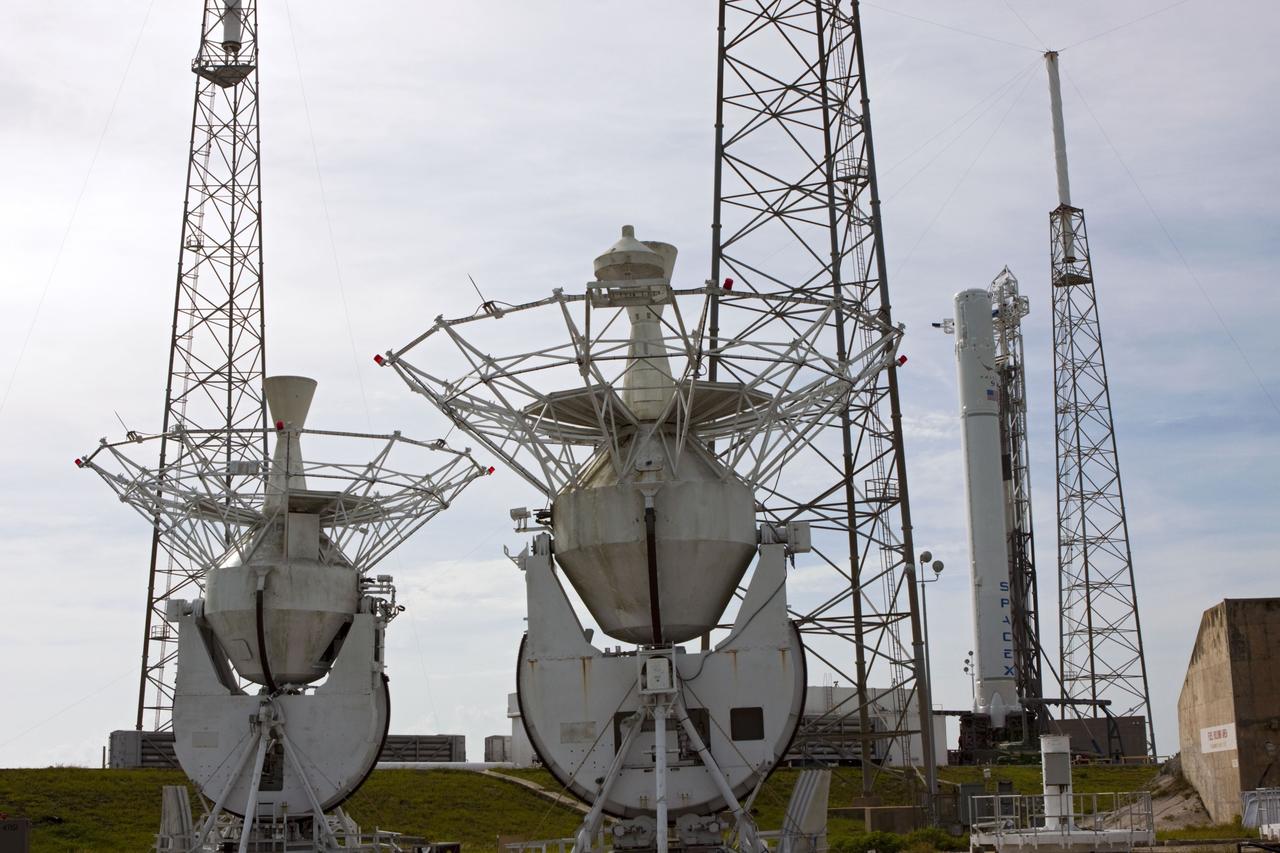

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Just prior to the wet dress rehearsal for the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, the frameworks of the former MILA tracking station S-band 9-meter tracking antennas are seen with the Falcon 9 rocket. These antennas were used by NASA during the Apollo and space shuttle programs. They are being re-purposed by SpaceX. The antennas will moved to another location, reassembled and refurbished for tracking during future SpaceX launches and missions. The SpaceX CRS contract with NASA provides for 12 cargo resupply missions to the station through 2015, the first of which is targeted to launch in October 2012.SpaceX became the first private company to berth a spacecraft with the space station in 2012 during its final demonstration flight under the Commercial Orbital Transportation Services, or COTS, program managed by NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

On July 3, 1974 NASA commemorated the 5th anniversary of the Apollo 11, first lunar landing mission, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Launch Pad 39, from which astronauts Neil Armstrong, Edwin Aldrin, and Michael Collins first embarked on their historic journey to the Moon, was dedicated as a national landmark. Apollo 11 was launched at 9:32 am on July 16, 1969 and made the first successful lunar landing July 20th. During the 45 minute ceremony, the three Apollo 11 astronauts unveiled this plaque which was placed at the launch site. Other participating dignitaries included Dr. James Fletcher and Dr. George H. Low, NASA Administrator and Deputy Administrator respectively; Florida Governor Rubin Askew; Senator frank E. Moss; Congressman Olin E. Teague, and Kurt Debus, KSC Director. Apollo 11 launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via a Saturn V launch which was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun.
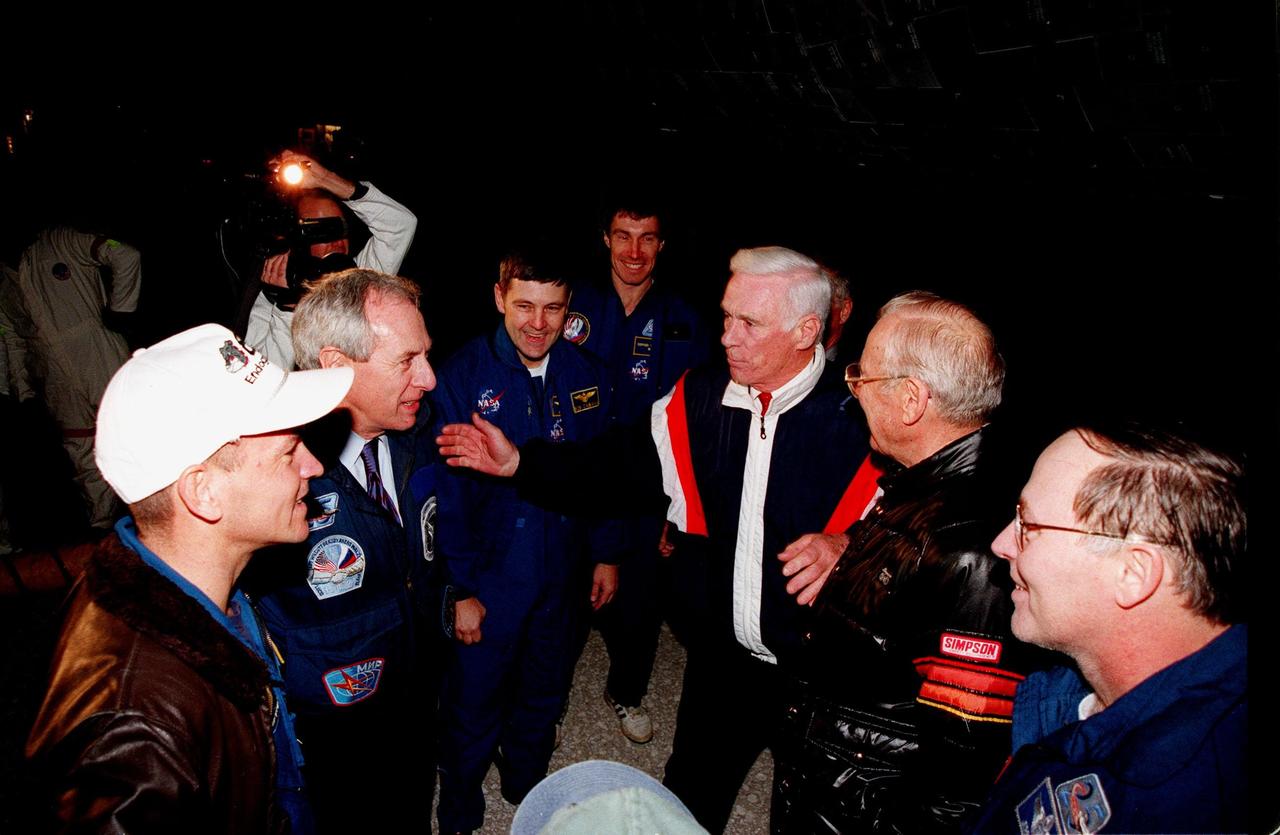

Following their touchdown on Runway 15 at 10:53:29 p.m. EST, STS-88 crew members are greeted by NASA Administrator Daniel Goldin and former astronauts Eugene A. Cernan and James A. Lovell Jr. From left are Pilot Frederick W. "Rick" Sturckow, Goldin , Commander Robert D. Cabana, Mission Specialist Sergei Konstantinovich Krikalev, Cernan, Lovell and Mission Specialist Jerry L. Ross. Cernan flew on Gemini 9, Apollo 10 and 17 and has more than 566 cumulative hours of space flight. Lovell flew on Gemini 7 and 12, Apollo 8 and 13. His cumulative hours of space flight are more than 715. On the 4.6-million-mile, nearly 12-day STS-88 mission, Endeavour carried the U.S.-built Unity connecting module to begin construction of the International Space Station. The crew successfully mated Unity with the Russian-built Zarya control module during three space walks. With this mission, Ross completed seven space walks totaling 44 hours and 9 minutes, more than any other American space walker. Newman moved into third place for U.S. space walks with a total of 28 hours and 27 minutes on four excursions
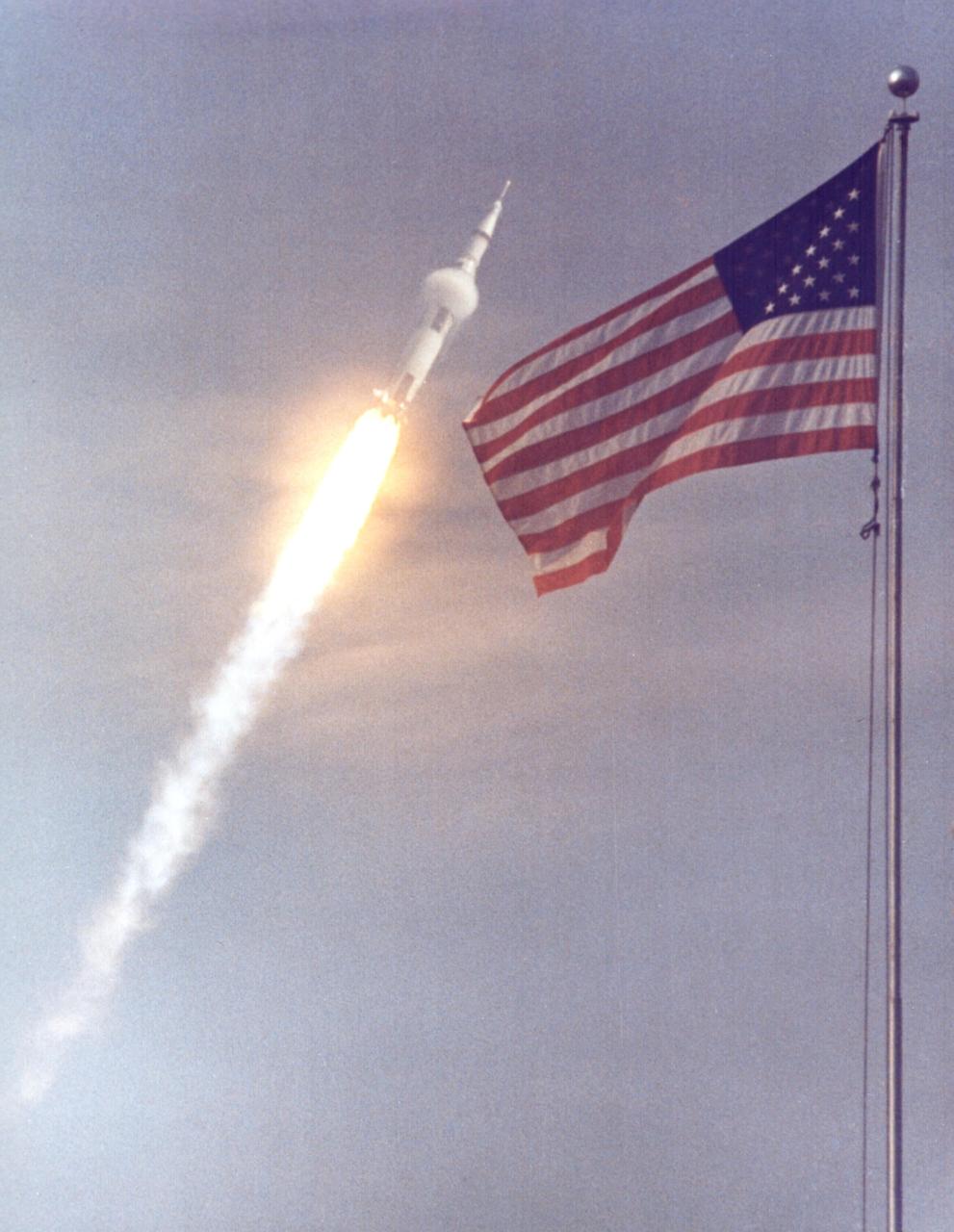
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The American flag heralds the flight of Apollo 11, man's first lunar landing mission. The Apollo 11 Saturn V space vehicle lifted off with astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, Michael Collins and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. at 9:32 a.m. EDT from KSC's Launch Complex 39A. During the planned eight-day mission, Armstrong and Aldrin will descend in a Lunar Module (LM) to the Moon's surface while Collins orbits overhead in the Command Module. The two astronauts are to spend 22 hours on the Moon, including two-and-one-half hours outside the LM. They will gather samples of lunar material and will deploy scientific experiments that will transmit data about the lunar environment. They will rejoin Collins in the Command Module for the return trip to Earth.
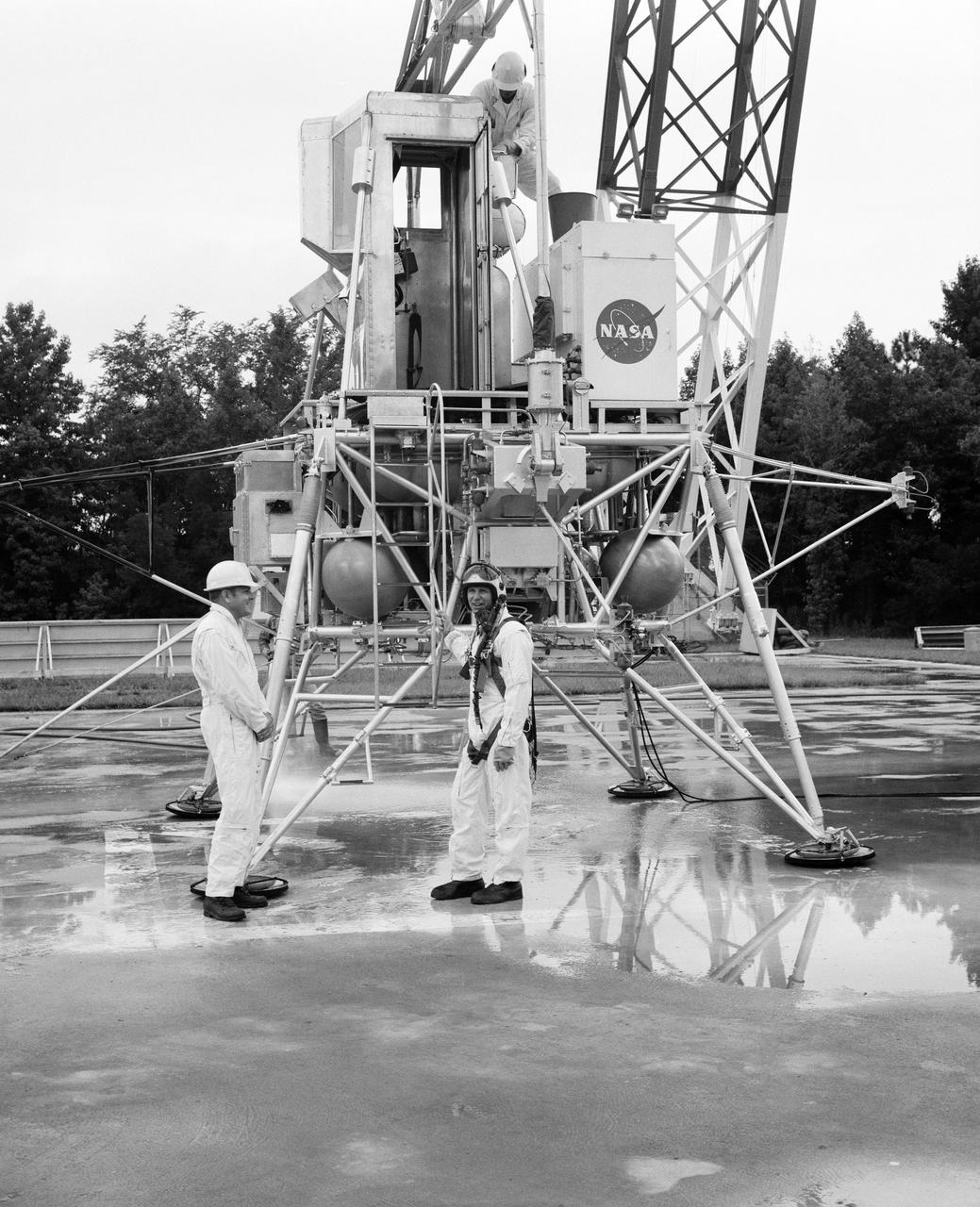

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
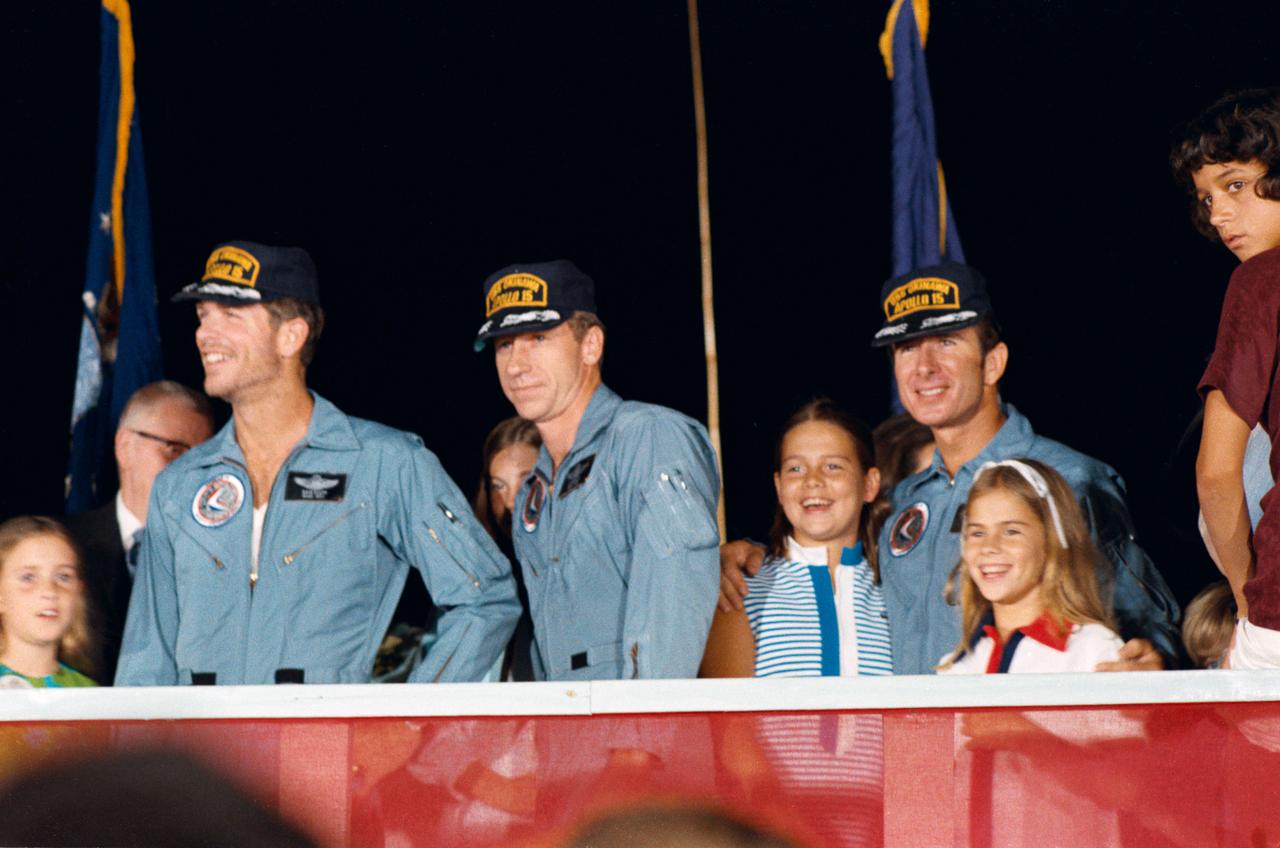

S71-43428 (8 Aug. 1971) --- The three crew men, of the highly successful Apollo 15 lunar landing mission, receive a warm welcome home at Ellington Air Force Base (EAFB), Houston, after an eight hour flight aboard a U.S. Air Force C-141 jet aircraft from Hawaii. Left to right, are astronauts David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. Apollo 15 splashdown in the mid-Pacific at 3:45 p.m. (CDT), Aug. 7, 1971, some 330 miles north of Honolulu. The C-141 landed at EAFB at 9 p.m. (CDT), Sunday, Aug. 8, 1971. Members of the astronauts' families identifiable in the picture are, left to right, Scott's daughter, Tracy; Worden's father, Merrill Worden; Worden's daughter, Merrill; and Irwin's two daughters, Joy and Jill.

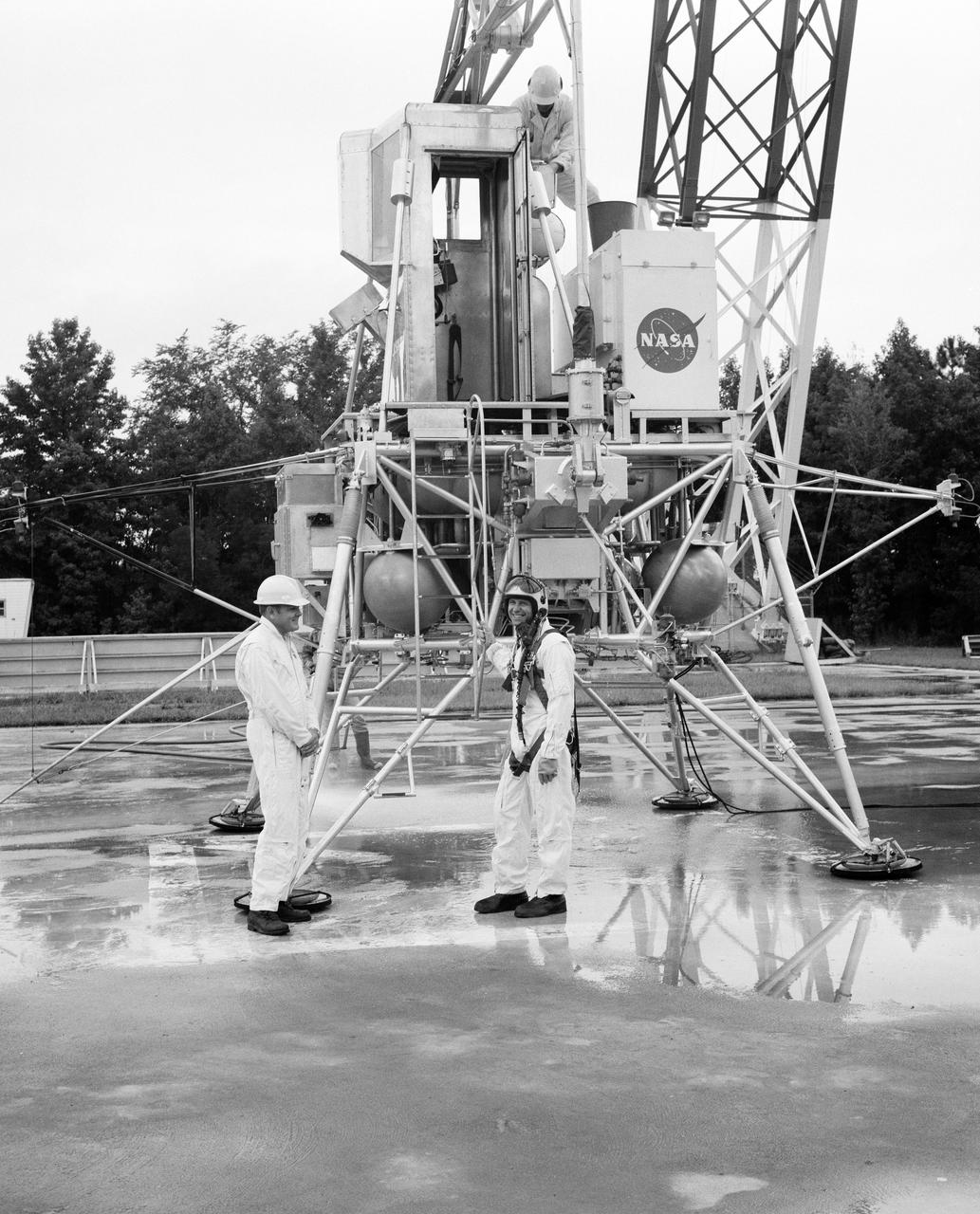
Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
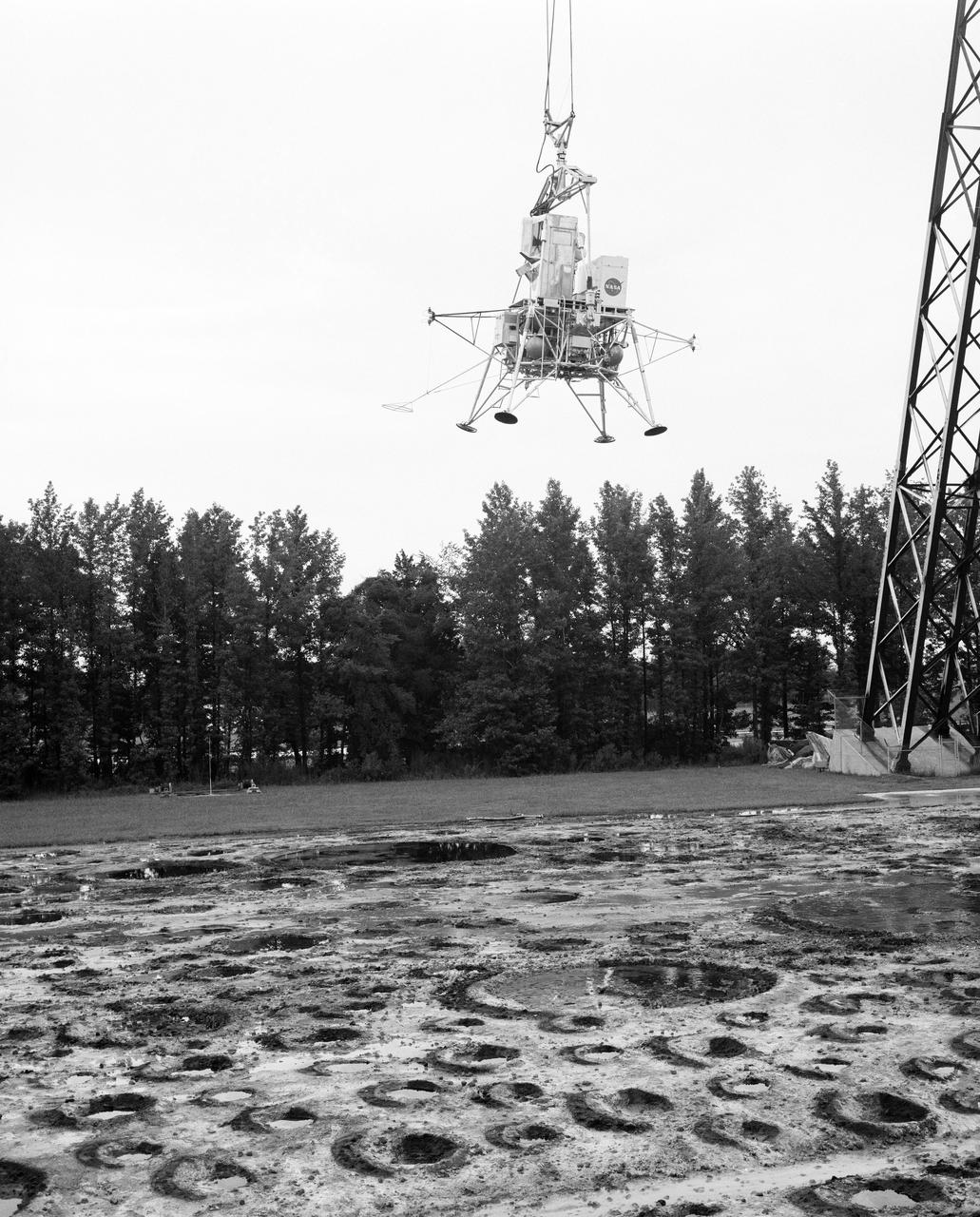

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
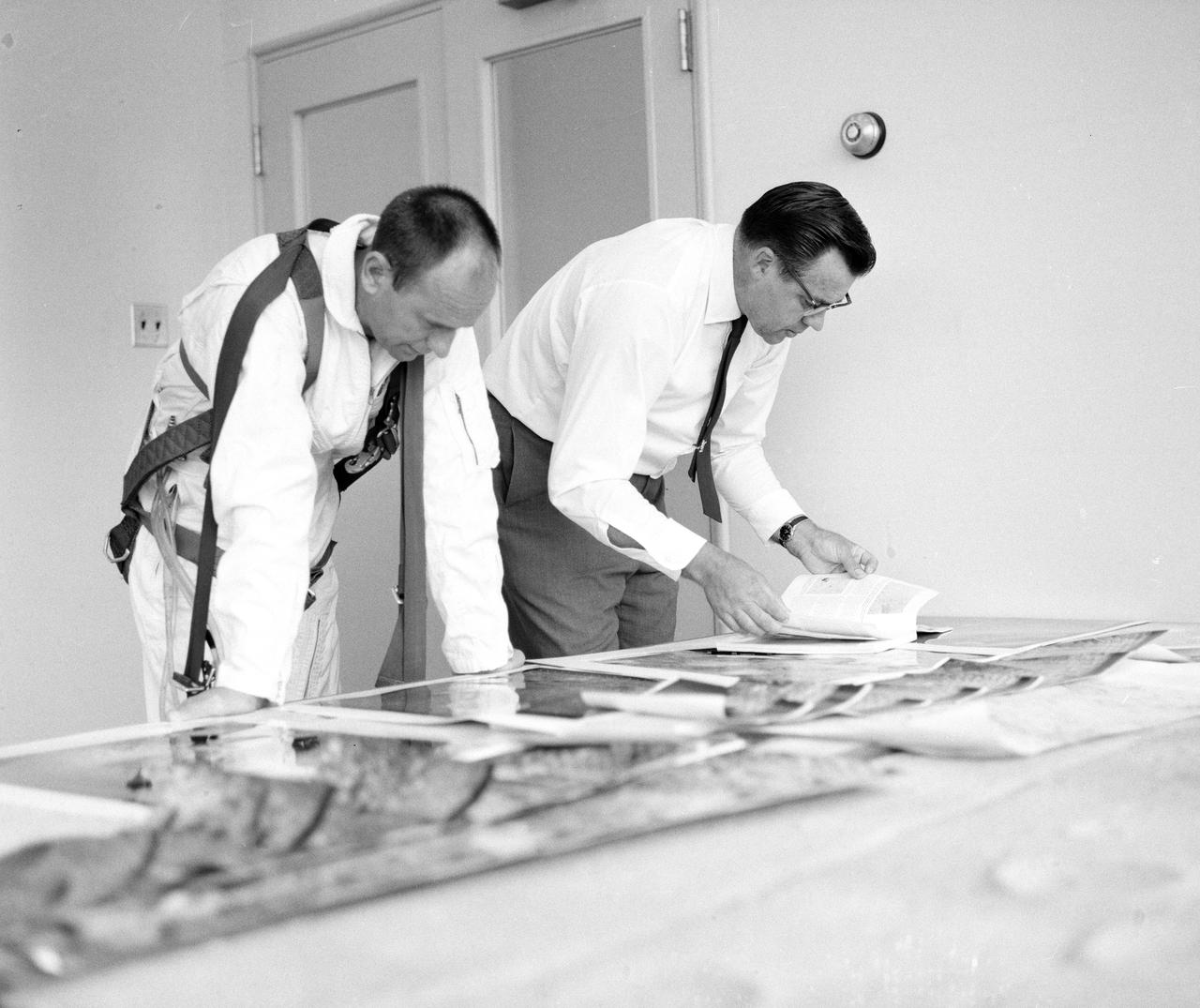

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
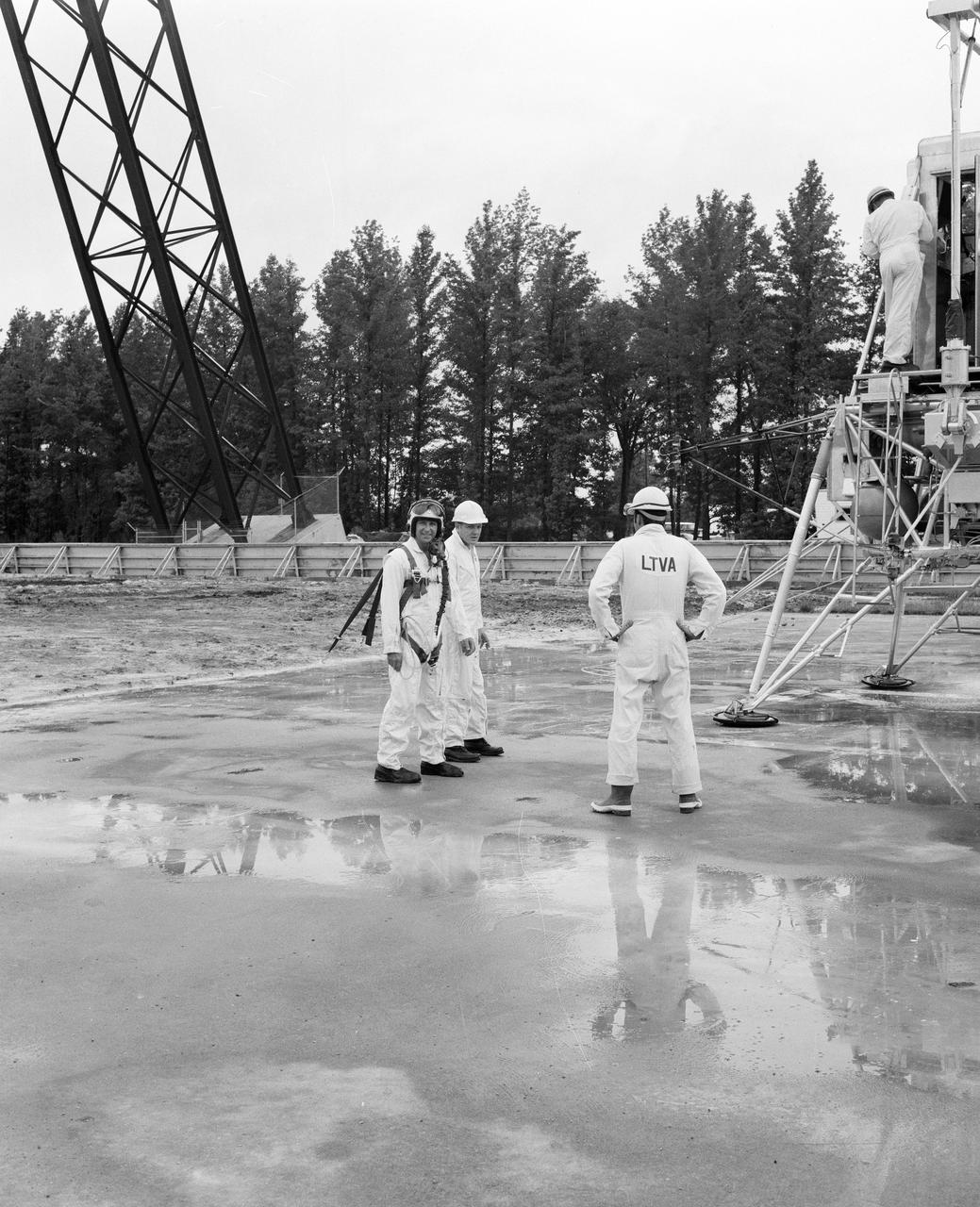

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
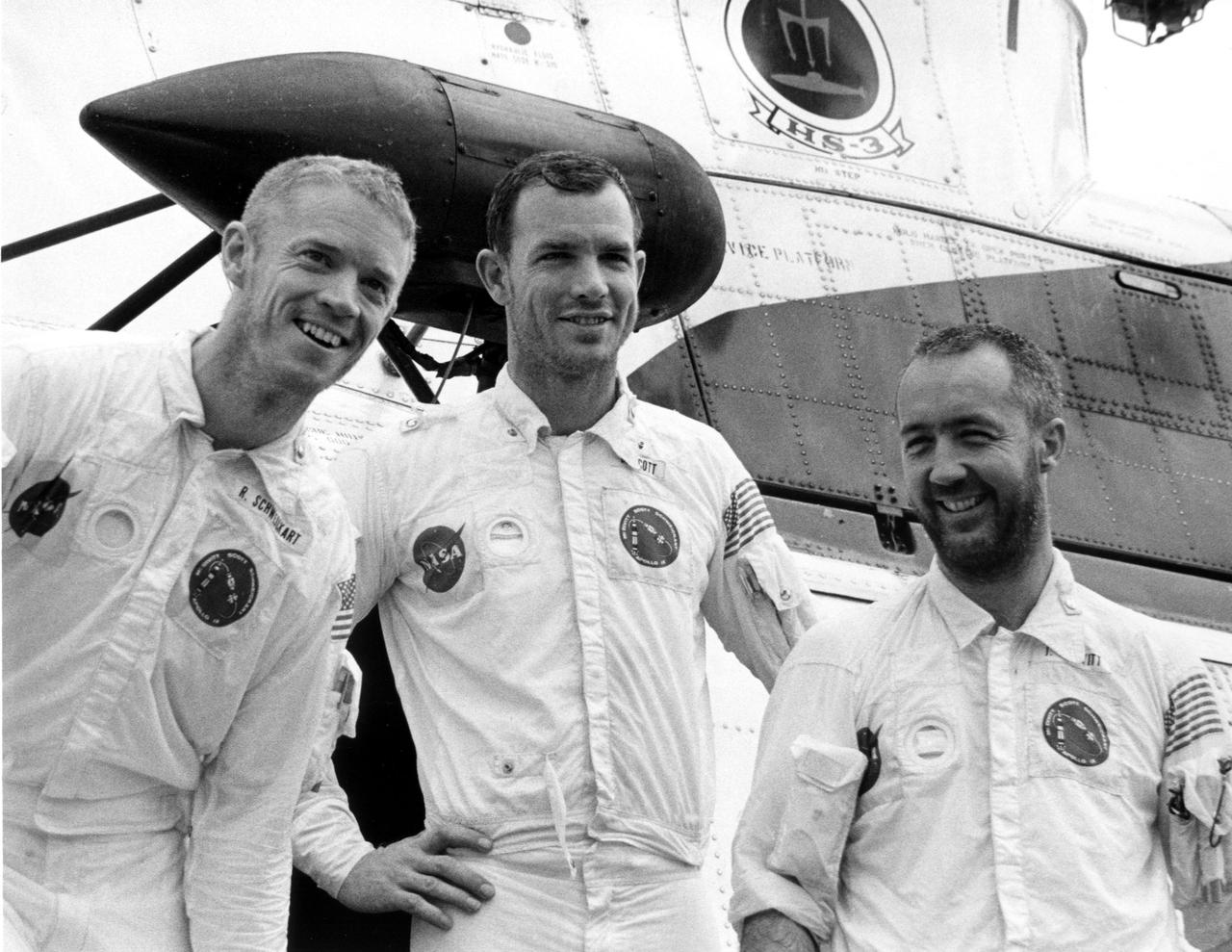

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Bearded and smiling, Apollo 9 astronauts, left to right, Russell L. Schweickart, David R. Scott and James A. McDivitt, pause in front of recovery helicopter, which carried them a short distance from their spacecraft's impact point to the USS Guadalcanal, prime recovery ship. They splashed down today less than five miles from the Guadalcanal, 780 nautical miles southeast of Cape Kennedy. The astronauts reentered at the beginning of their 152nd Earth orbit following a textbook flight that verified a lunar module spacecraft. It was similar to the one that is to land Americans on the Moon later this year. They were launched March 3, 1969, from the Kennedy Space Center aboard an Apollo_Saturn V space vehicle. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration directs the Apollo program.
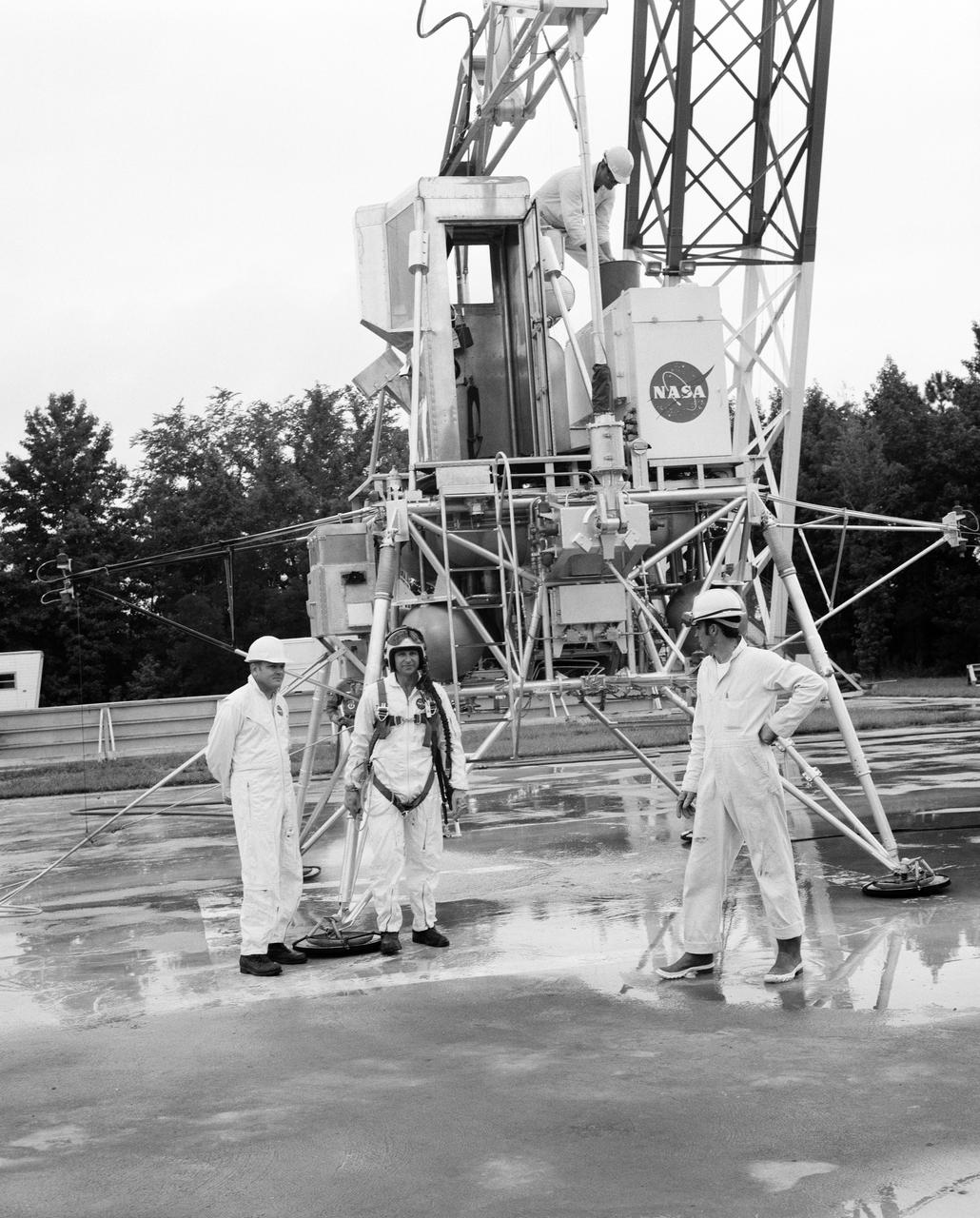

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
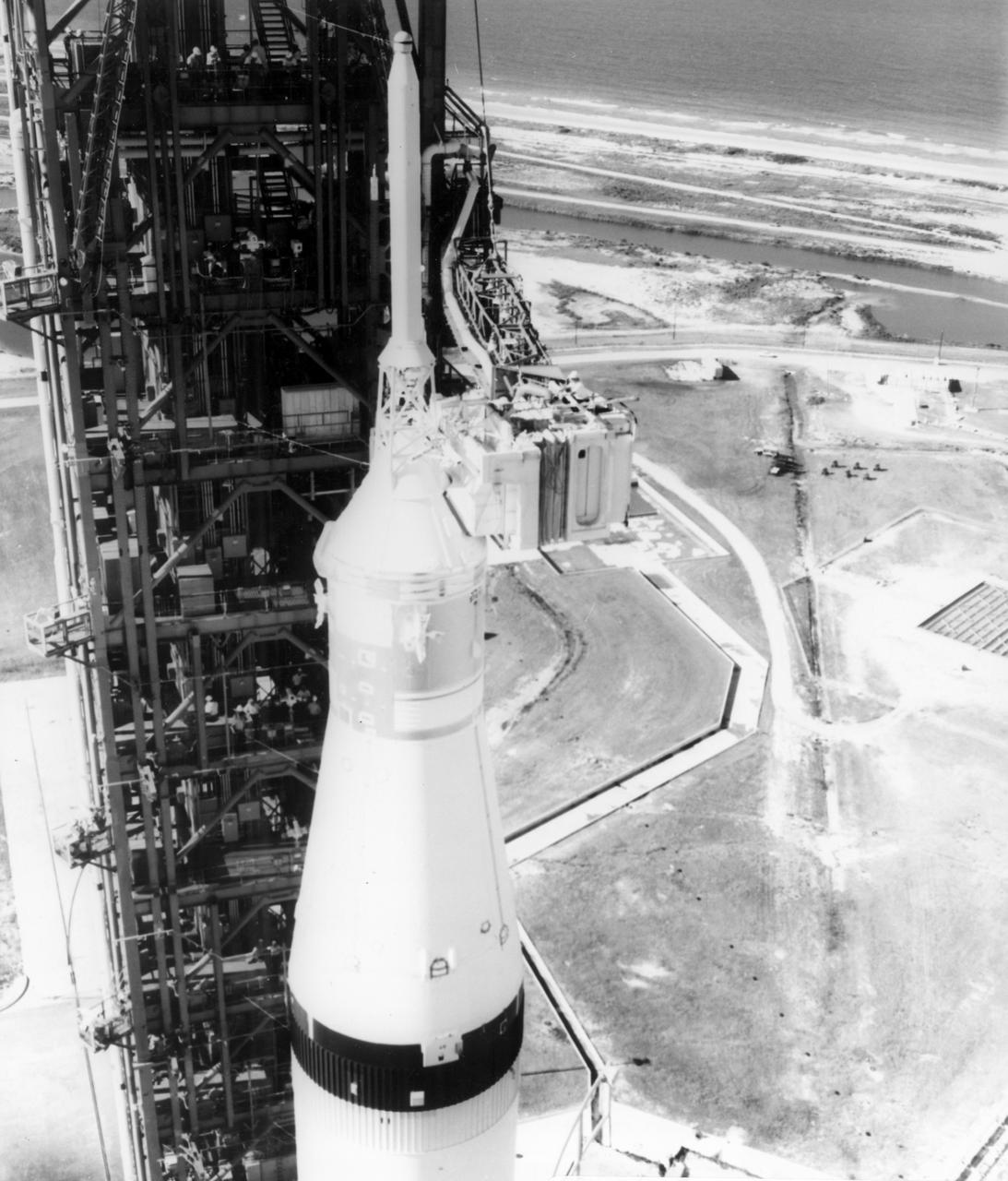

A technician is barely visible performing a last minute task atop the white room next to the Apollo 11 spacecraft a few hours before launch at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) launch complex 39. The spacecraft is perched atop the massive Saturn V rocket, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Wernher von Braun. Liftoff occurred at 9:32 am on July 16, 1969, carrying man to the Moon for a first successful lunar landing. Aboard the spacecraft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The crew safely splashed down into the Pacific Ocean on July 24, 1969. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
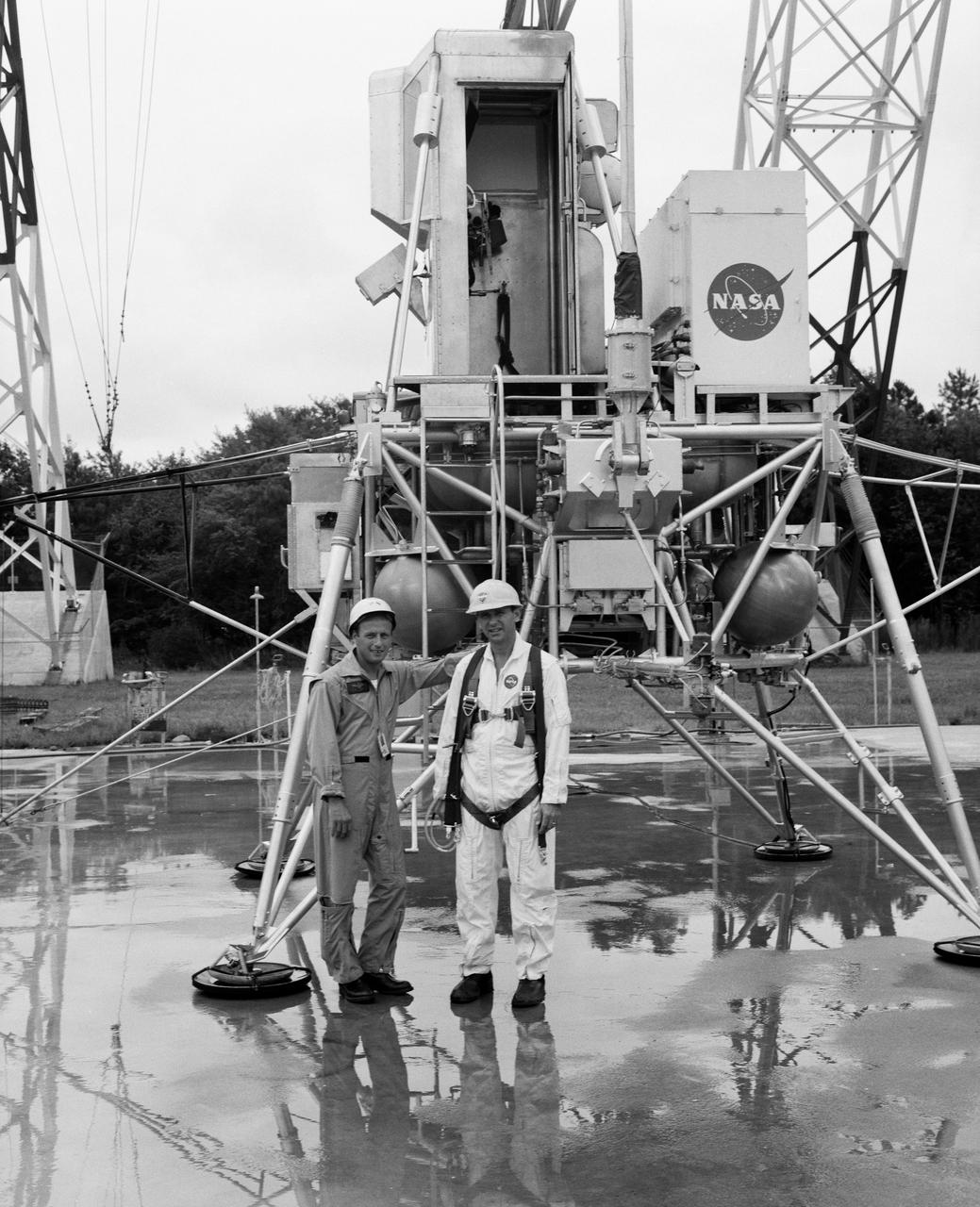

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
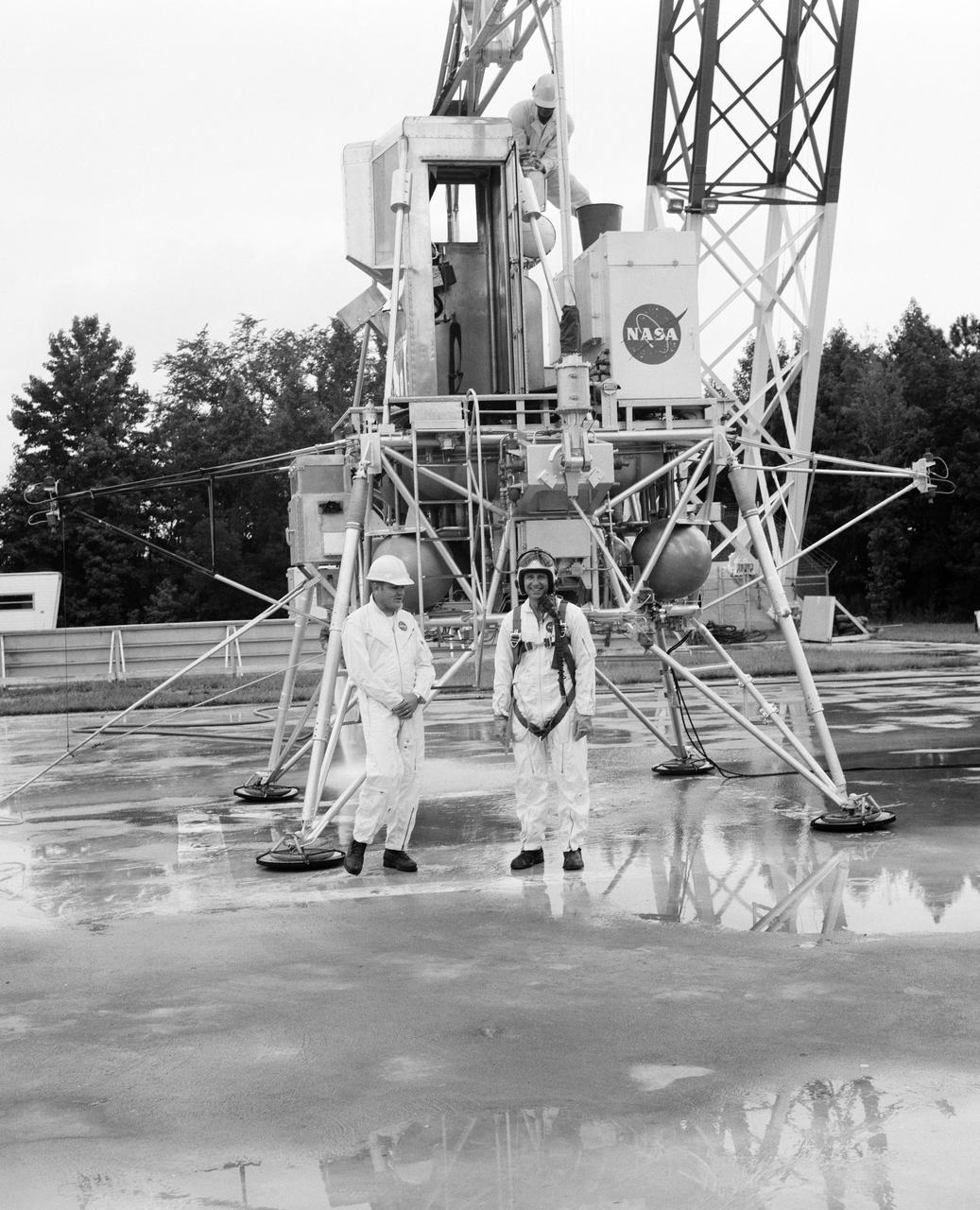

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.