
S74-17843 (March 1974) --- This is the official emblem of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project chosen by NASA and the Soviet Academy of Sciences. The joint U.S.-USSR space mission is scheduled to be flown in July 1975. Of circular design, the emblem has the words Apollo in English and Soyuz in Russian around a center disc which depicts the two spacecraft docked together in Earth orbit. The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project will be carried out by a Soviet Soyuz spacecraft and a U.S. Apollo spacecraft which will rendezvous and dock in orbit. Soyuz and Apollo will remain docked for as long as two days in which period, the three Apollo astronauts will enter Soyuz and the two Soyuz cosmonauts will visit Apollo via a docking module. The Russian word "soyuz" means "union" in English.

AST-05-263 (17-18 July 1975) --- The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) Commemorative Plaque is assembled in the Soviet Soyuz Orbital Module during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The plaque is written both in English and Russian.
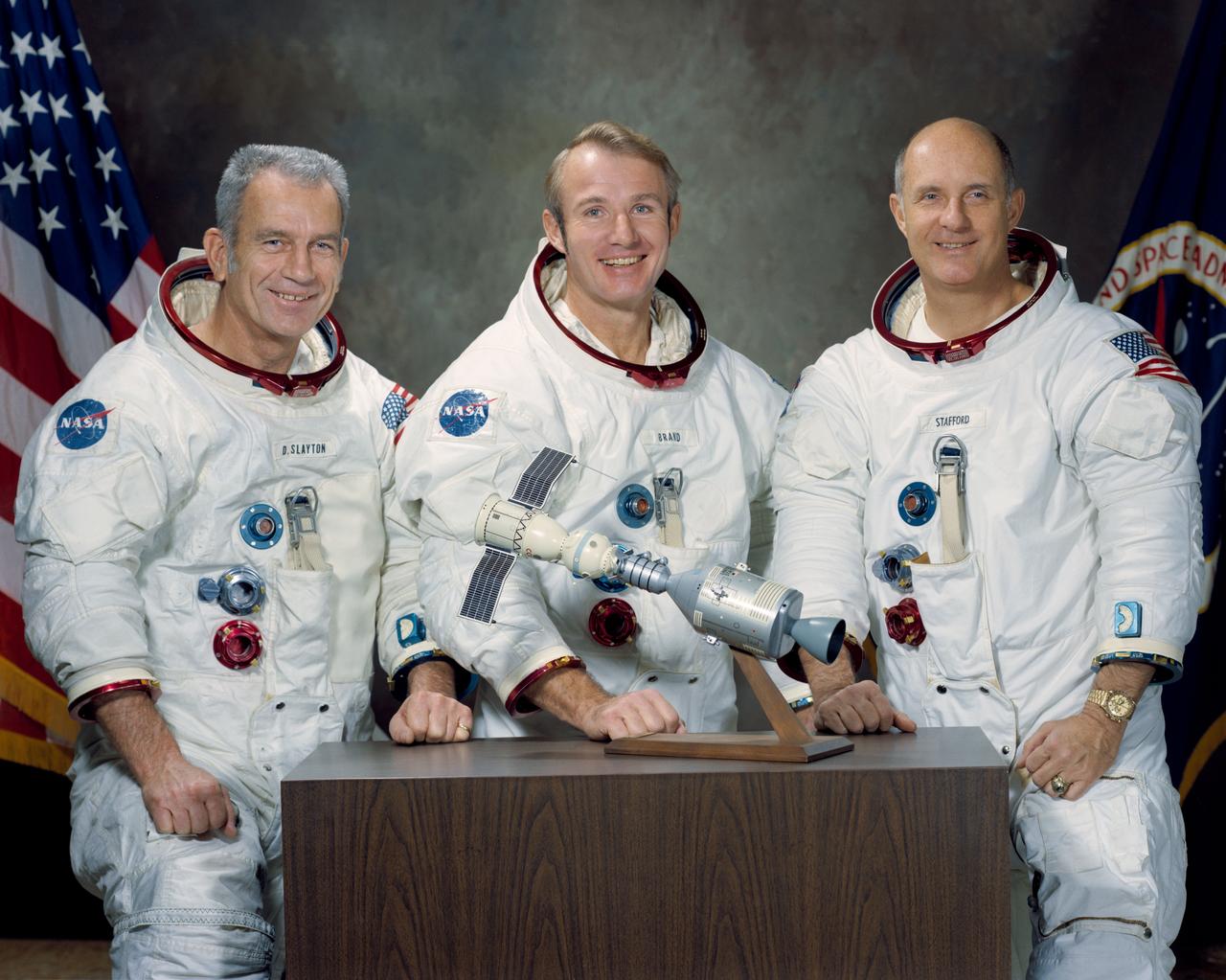

S74-15241 (January 1974) --- These three NASA astronauts are the United States flight crew for the 1975 Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) mission. The prime crew members for the joint United States - Soviet Union spaceflight are, left to right, Donald K. Slayton, docking module pilot; Vance D. Brand, command module pilot; and Thomas P. Stafford, commander. The American and Soviet crews will visit one another?s spacecraft while the Soyuz and Apollo are docked in Earth orbit for a maximum of two days. The ASTP mission is designed to test equipment and techniques that will establish international crew rescue capability in space, as well as permit future cooperative scientific missions.
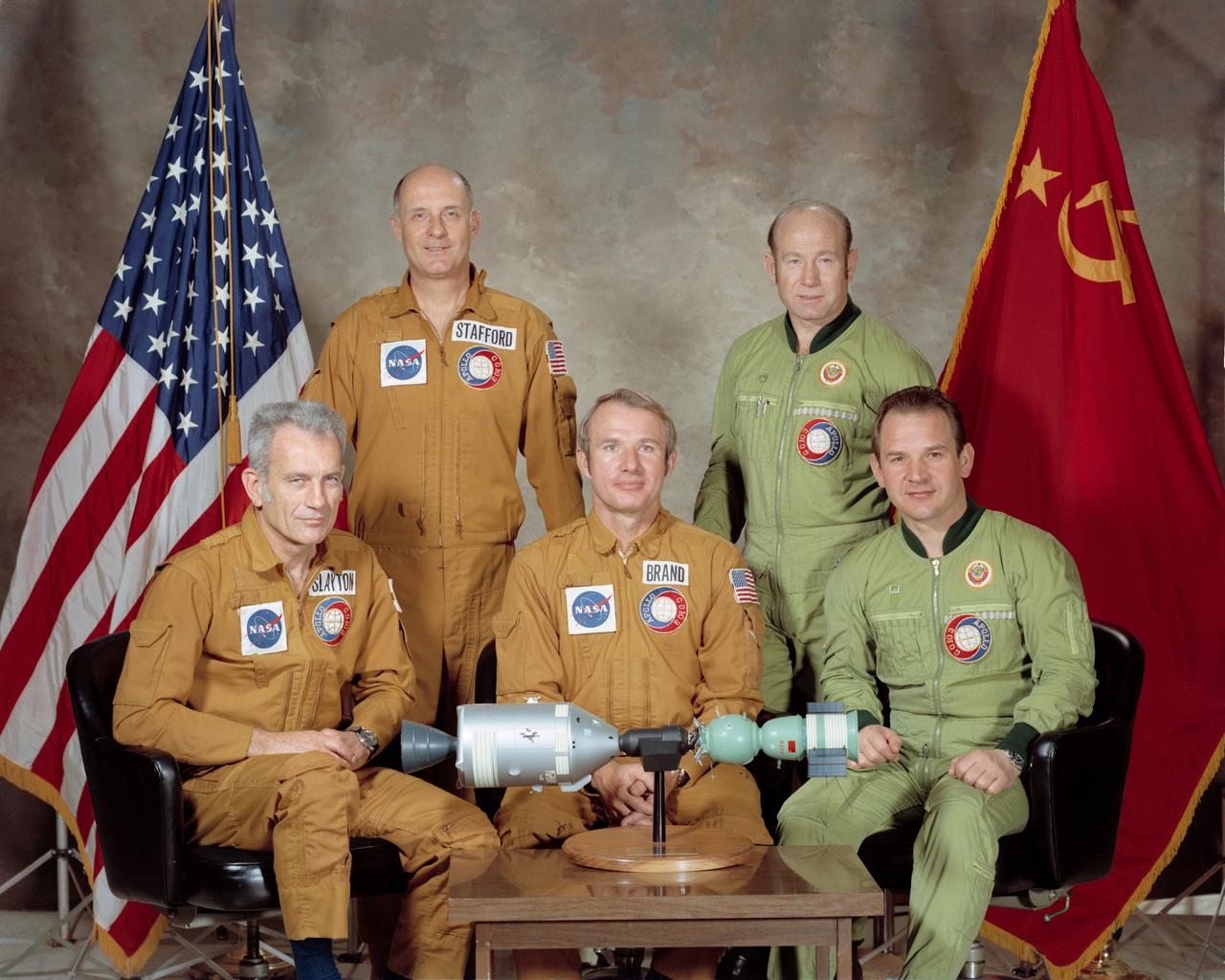

S75-22410 (March 1975) --- These five men compose the two prime crews of the joint United States-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) docking mission in Earth orbit scheduled for July 1975. They are astronaut Thomas P. Stafford (standing on left), commander of the American crew; cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov (standing on right), commander of the Soviet crew; astronaut Donald K. Slayton (seated on left), docking module pilot of the American crew; astronaut Vance D. Brand (seated center), command module pilot of the American crew; and cosmonaut Valeriy N. Kubasov (seated on right), engineer on the Soviet crew.
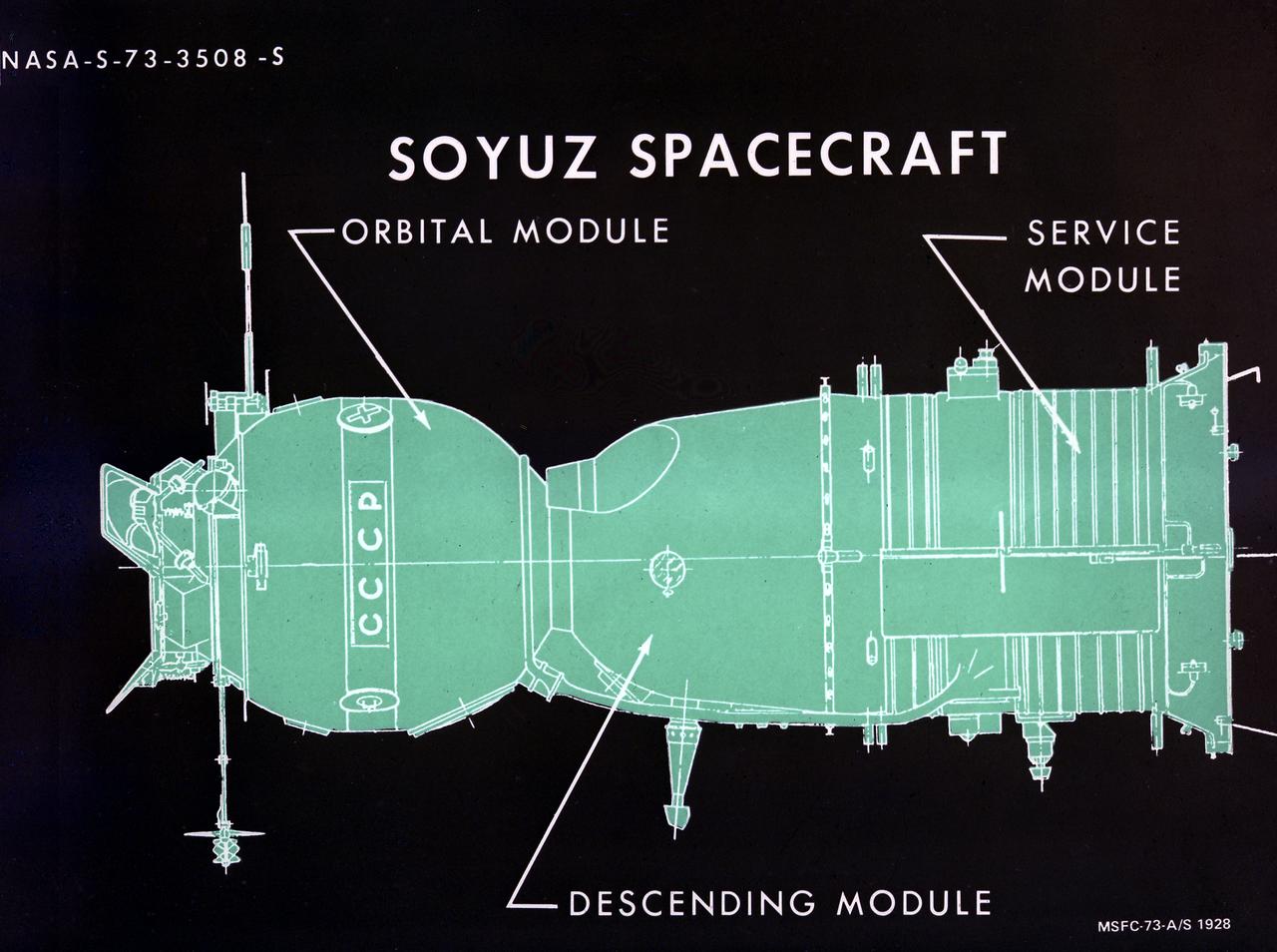
This illustration depicts a configuration of the Soyuz spacecraft for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP). The ASTP was the first international docking of the U.S.'s Apollo spacecraft and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz spacecraft in space. For this project, the Soviets built another in their continuing series of Soyuz space capsules. The U.S. used the Saturn IB Apollo capsule. A joint engineering team from the two countries met to develop a docking system that permitted the two spacecraft to link in space and allowed the crews to travel from one spacecraft to the other.

Project LOLA. Test subject sitting at the controls: Project LOLA or Lunar Orbit and Landing Approach was a simulator built at Langley to study problems related to landing on the lunar surface. It was a complex project that cost nearly 2 million dollars. James Hansen wrote: This simulator was designed to provide a pilot with a detailed visual encounter with the lunar surface the machine consisted primarily of a cockpit, a closed-circuit TV system, and four large murals or scale models representing portions of the lunar surface as seen from various altitudes. The pilot in the cockpit moved along a track past these murals which would accustom him to the visual cues for controlling a spacecraft in the vicinity of the moon. Unfortunately, such a simulation--although great fun and quite aesthetic--was not helpful because flight in lunar orbit posed no special problems other than the rendezvous with the LEM, which the device did not simulate. Not long after the end of Apollo, the expensive machine was dismantled. (p. 379) Ellis J. White wrote in his paper, Discussion of Three Typical Langley Research Center Simulation Programs : A typical mission would start with the first cart positioned on model 1 for the translunar approach and orbit establishment. After starting the descent, the second cart is readied on model 2 and, at the proper time, when superposition occurs, the pilot s scene is switched from model 1 to model 2. then cart 1 is moved to and readied on model 3. The procedure continues until an altitude of 150 feet is obtained. The cabin of the LM vehicle has four windows which represent a 45 degree field of view. The projection screens in front of each window represent 65 degrees which allows limited head motion before the edges of the display can be seen. The lunar scene is presented to the pilot by rear projection on the screens with four Schmidt television projectors. The attitude orientation of the vehicle is represented by changing the lunar scene through the portholes determined by the scan pattern of four orthicons. The stars are front projected onto the upper three screens with a four-axis starfield generation (starball) mounted over the cabin and there is a separate starball for the low window. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 379 Ellis J. White, Discussion of Three Typical Langley Research Center Simulation Programs, Paper presented at the Eastern Simulation Council (EAI s Princeton Computation Center), Princeton, NJ, October 20, 1966.

NASA ENGINEERS DISCUSSING APOLLO PROJECT
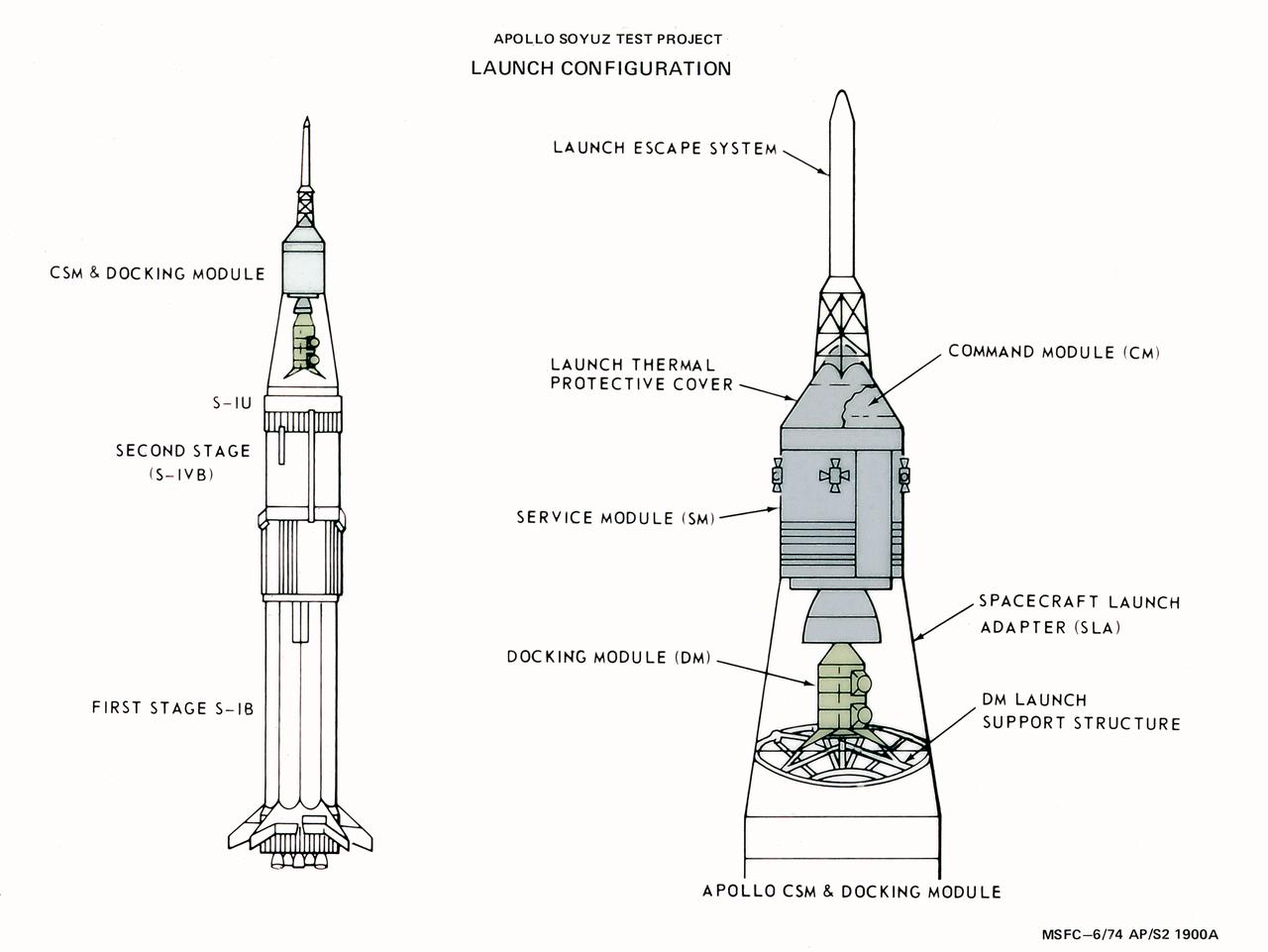
This illustration depicts the launch configuration of the Apollo spacecraft for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP). The ASTP was the first international docking of the U.S.'s Apollo spacecraft and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz spacecraft in space. A joint engineering team from the two countries met to develop a docking system that permitted the two spacecraft to link in space and allowed the two crews to travel from one spacecraft to the other. This system entailed developing a large habitable Docking Module (DM) to be carried on the Apollo spacecraft to facilitate the joining of two dissimilar spacecraft. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development and sustaining engineering of the Saturn IB launch vehicle during the mission.
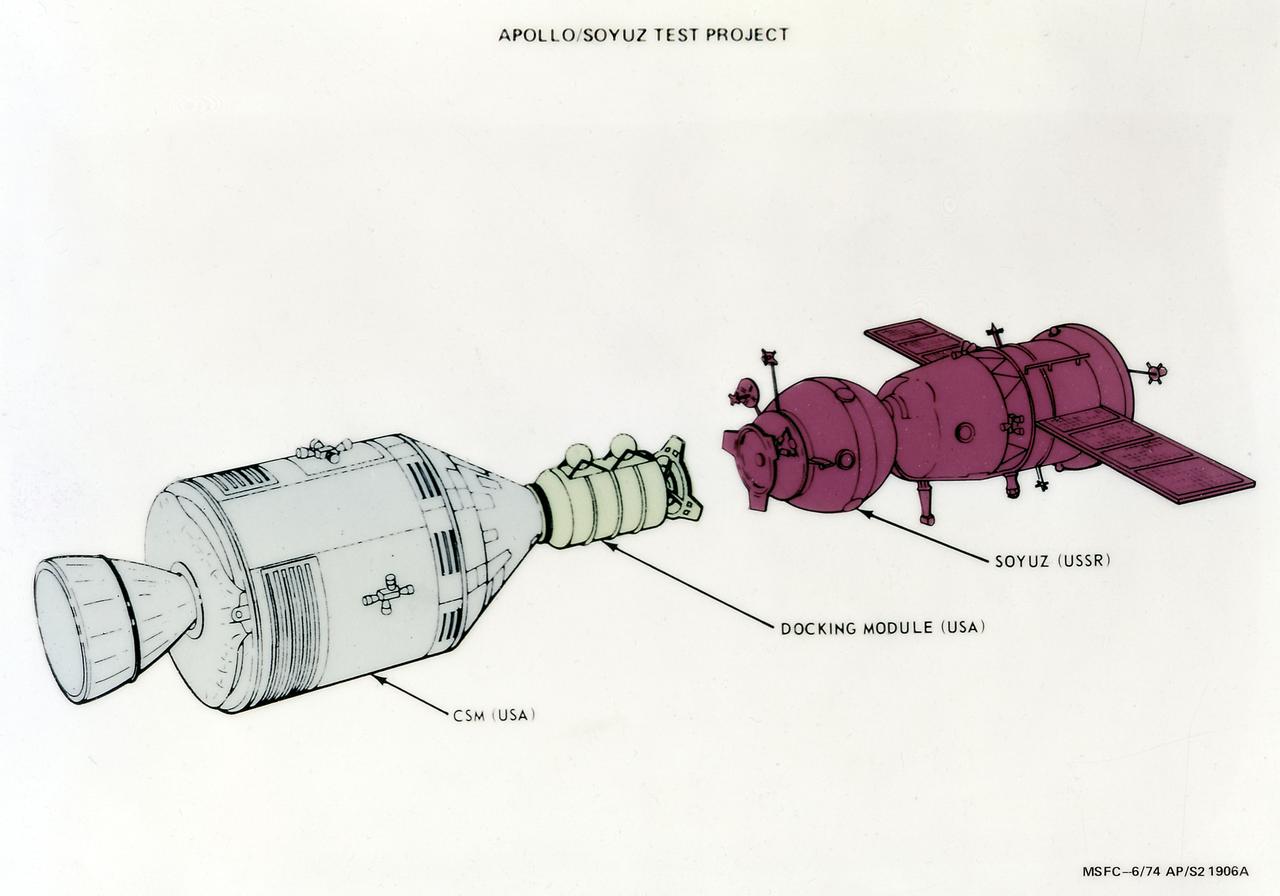
This illustration shows the docking configuration of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP). The ASTP was the first international docking of the U.S.'s Apollo spacecraft and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz spacecraft in space. A joint engineering team from the two countries met to develop a docking system that permitted the two spacecraft to link in space and allowed the two crews to travel from one spacecraft to the other. This system entailed developing a large habitable Docking Module (DM) to be carried on the Apollo spacecraft to facilitate the joining of two dissimilar spacecraft. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development and sustaining engineering of the Saturn IB launch vehicle during the mission. The ASTP marked the last use of the Saturn Launch Vehicle.

Panoramas of Apollo sites were created to familiarize various Constellation projects with the actual nature of the lunar surface. View of the Lunar Surface towards the western Horizon. Image was created using Apollo 14 images - mag 66 frames 9271 thru 9293.
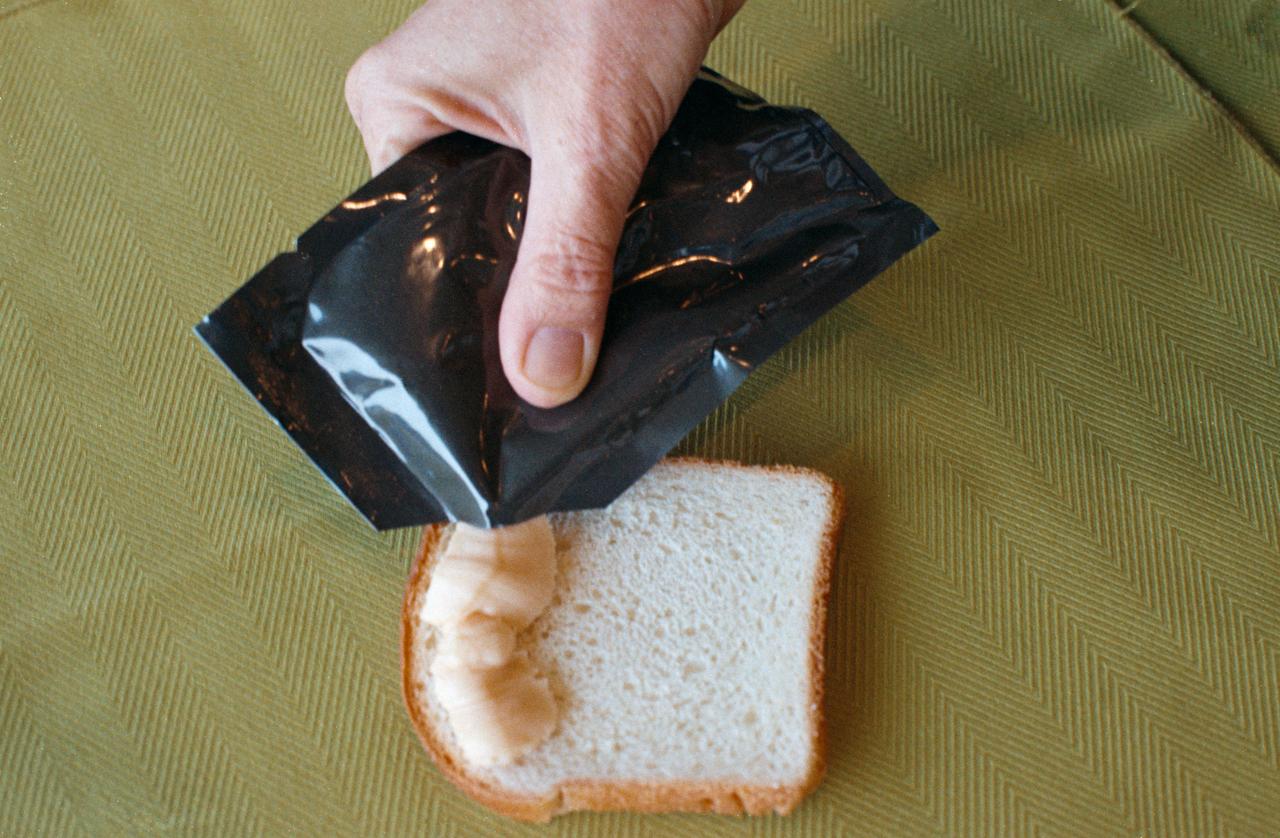

S74-25635 (August 1974) --- A close-up view of cheddar cheese spread, one of the items of food selected for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission scheduled for the summer of 1975. This food item was carried on the Apollo missions also.
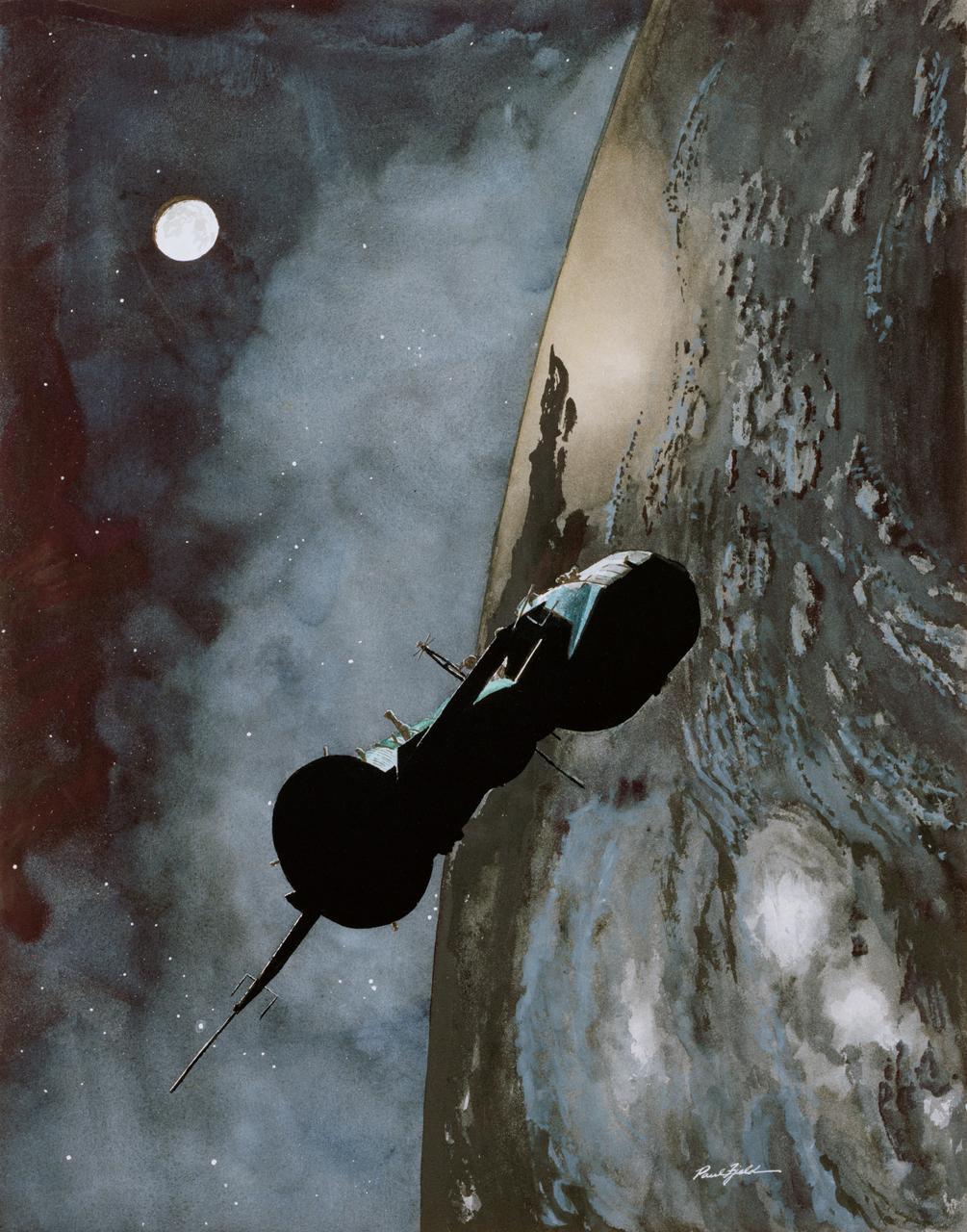

S76-22455 (1976) --- Apollo-Soyuz Test Project artist?s concept by Paul Fjeld.
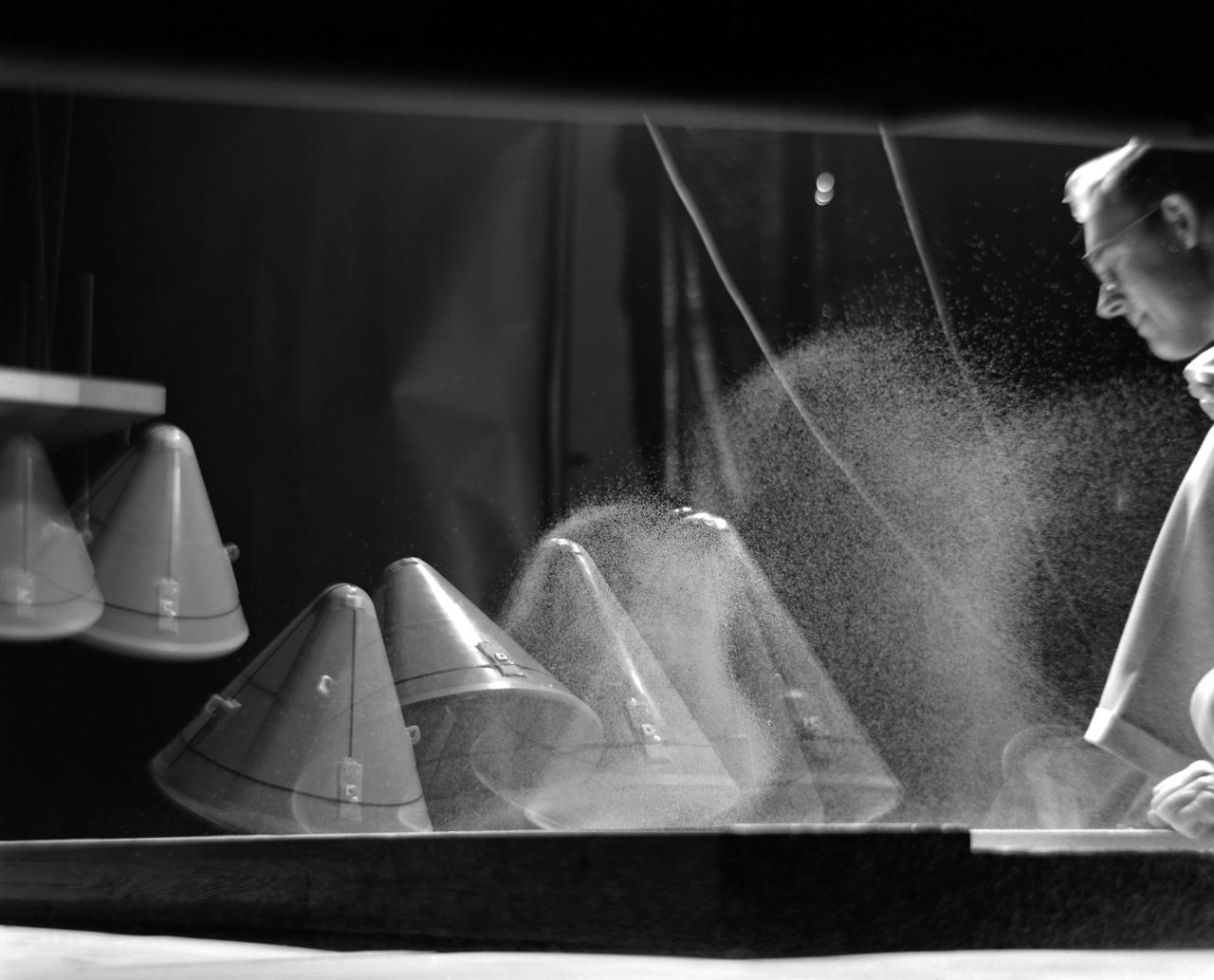

Image L61-8036 is available as an electronic file from the photo lab. See URL. -- Photographed on 12/05/1961. -- Multiple exposure of an impact test of the Apollo command module. In this test the Apollo capsule was tested making a sand landing. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), pp. 361-366.
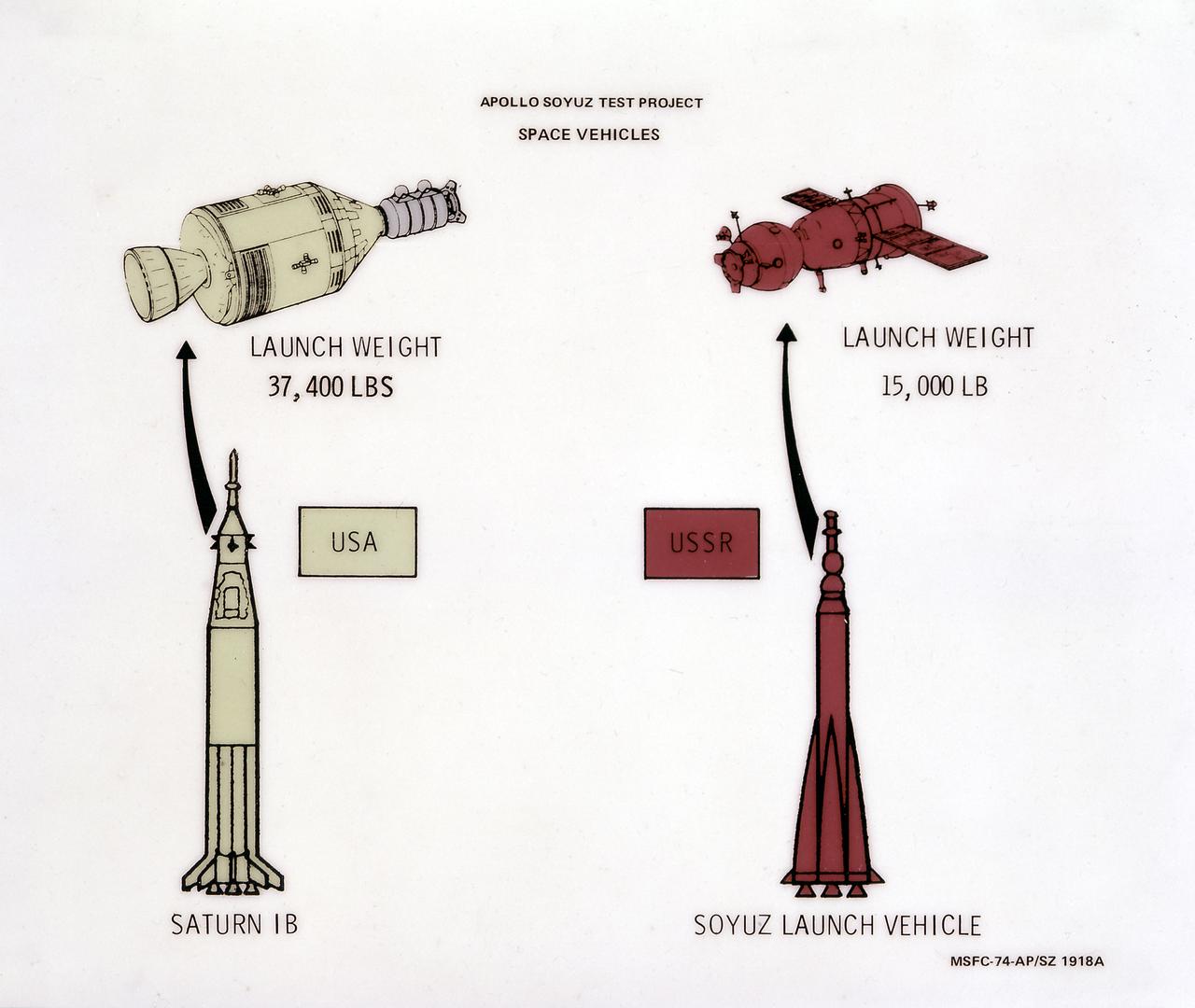
This illustration depicts a comparison of two space vehicles, the U.S.'s Saturn IB launch vehicle and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz launch vehicle, for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The ASTP was the first international docking of the U.S.'s Apollo spacecraft and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz spacecraft in space. A joint engineering team from the two countries met to develop a docking system that permitted the two spacecraft to link in space and allowed the two crews to travel from one spacecraft to the other. This system entailed developing a large habitable Docking Module (DM) to be carried on the Apollo spacecraft to facilitate the joining of two dissimilar spacecraft. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development and sustaining engineering of the Saturn IB launch vehicle during the mission.
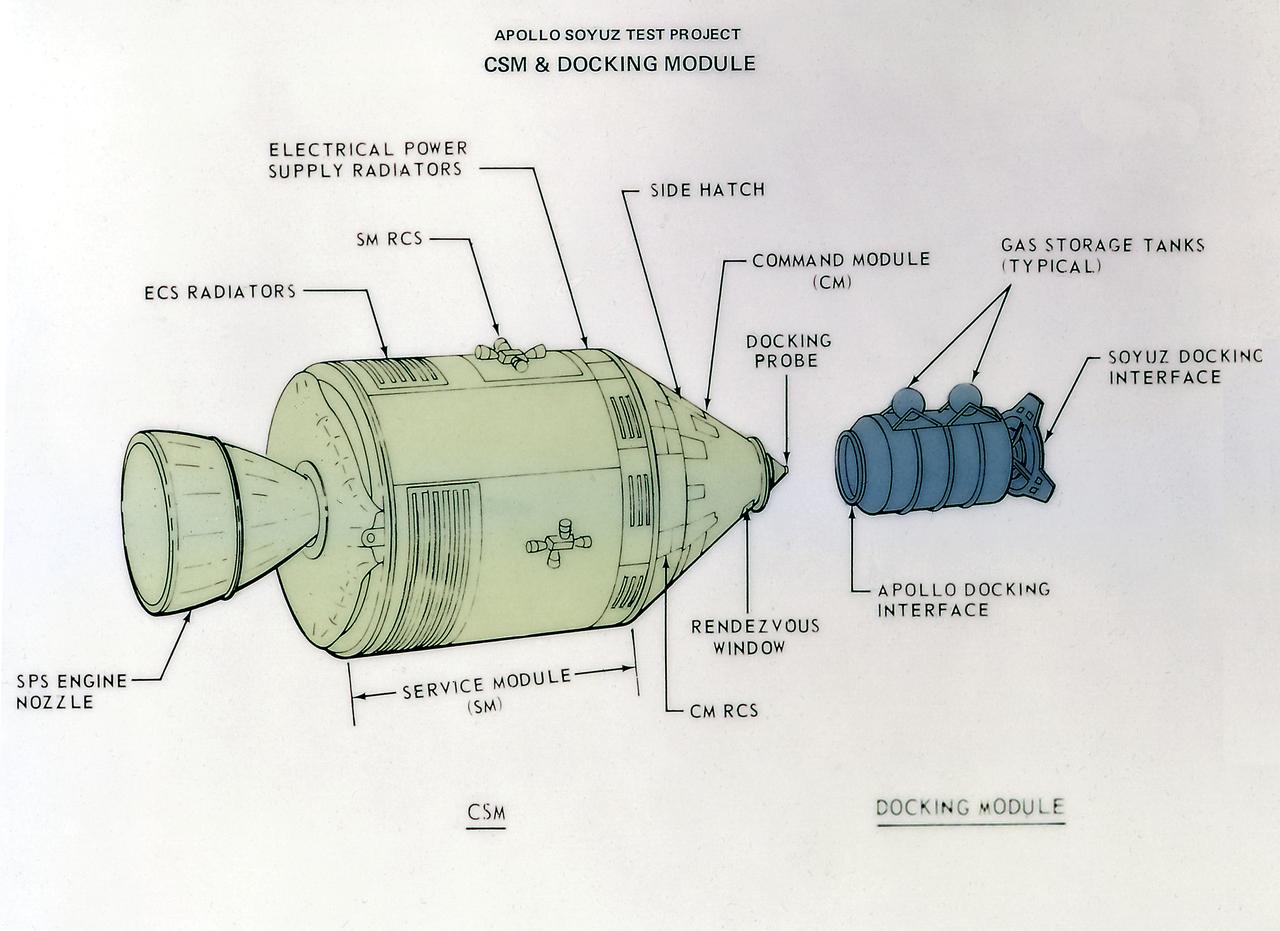
This illustration depicts a configuration of the Command Service Module (CSM) and Docking Module (DM) for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP). The ASTP was the first international docking of the U.S.'s Apollo spacecraft and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz spacecraft in space. A joint engineering team from the two countries met to develop a docking system that permitted the two spacecraft to link in space and allowed the two crews to travel from one spacecraft to the other. This system entailed developing a large habitable Docking Module (DM) to be carried on the Apollo spacecraft to facilitate the joining of two dissimilar spacecraft. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development and sustaining engineering of the Saturn IB launch vehicle during the mission. The ASTP marked the last use of the Saturn Launch Vehicle.

S75-21720 (14 Feb. 1975) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean (foreground) and cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov participate in Apollo-Soyuz Test Project joint crew training in Building 35 at NASA's Johnson Space Center. They are in the Apollo Command Module trainer. The training session simulated activities on the first day in Earth orbit. Bean is the commander of the American ASTP backup crew. Leonov is the commander of the Soviet ASTP first (prime) crew.
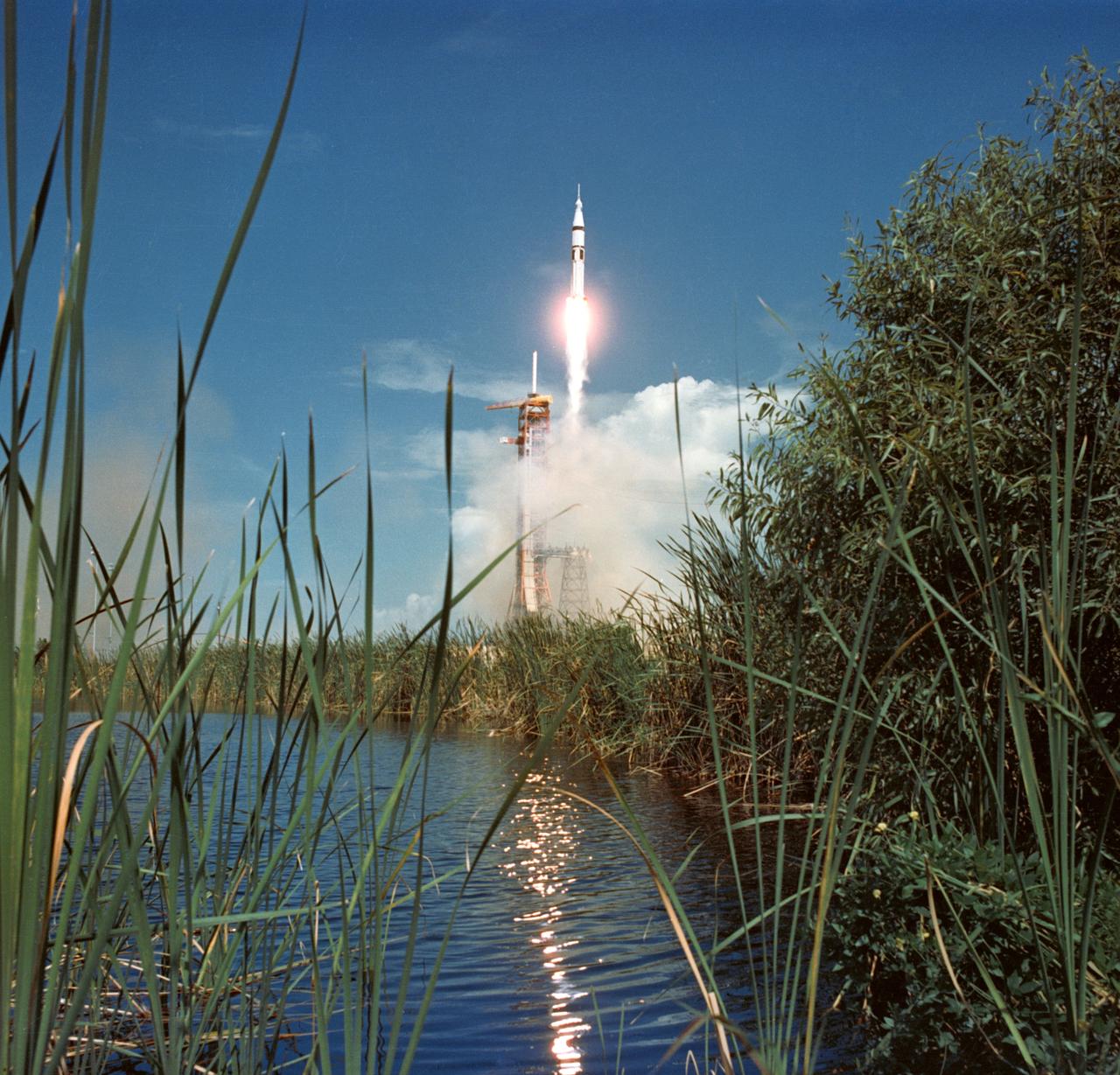

S75-28547 (15 July 1975) --- The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project's (ASTP) NASA Apollo/Saturn 1B space vehicle is launched from Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida, at 3:50 p.m. (EDT), July 15, 1975, to begin Apollo's catch-up journey toward the already Earth-orbiting Soviet Soyuz spacecraft. Aboard the Apollo spacecraft were astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. (Deke) Slayton.
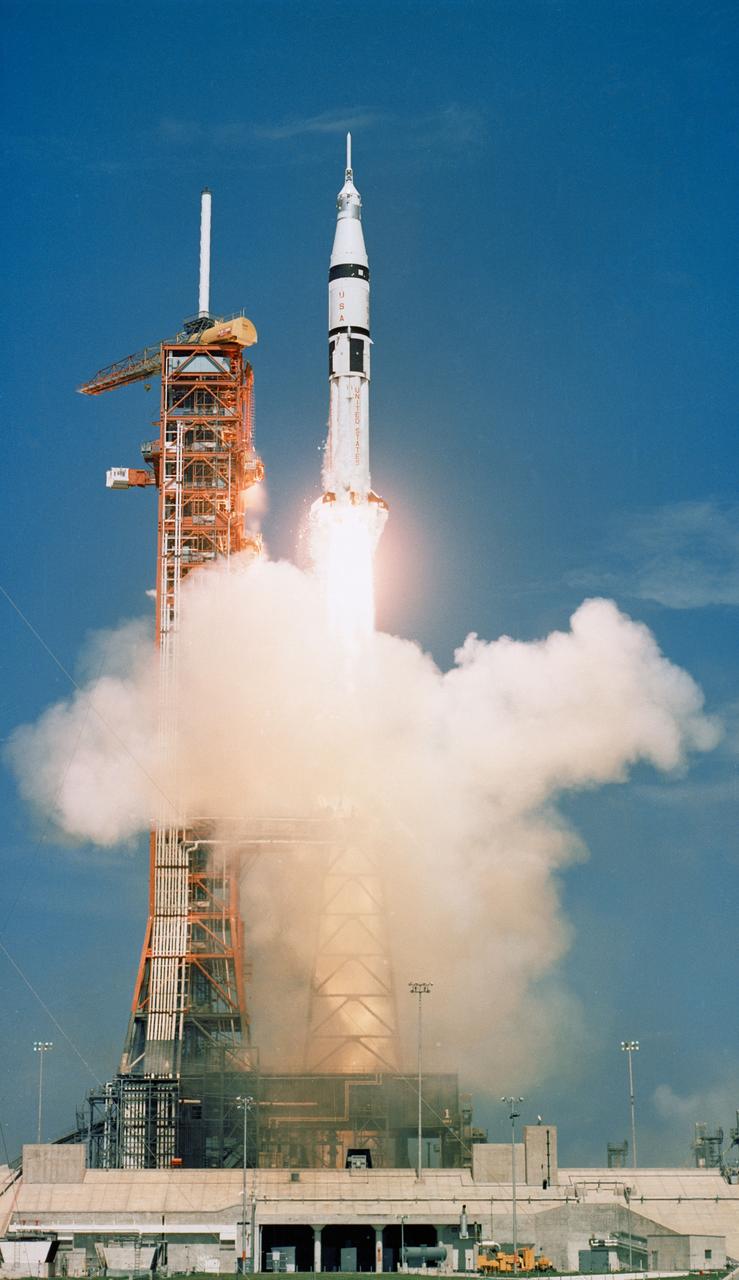

S75-28550 (15 July 1975) --- The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project's (ASTP) NASA Apollo/Saturn 1B space vehicle is launched from Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida, at 3:50 p.m. (EDT), July 15, 1975, to begin Apollo's catch-up journey toward the already Earth-orbiting Soviet Soyuz spacecraft. Aboard the Apollo spacecraft were astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. (Deke) Slayton.
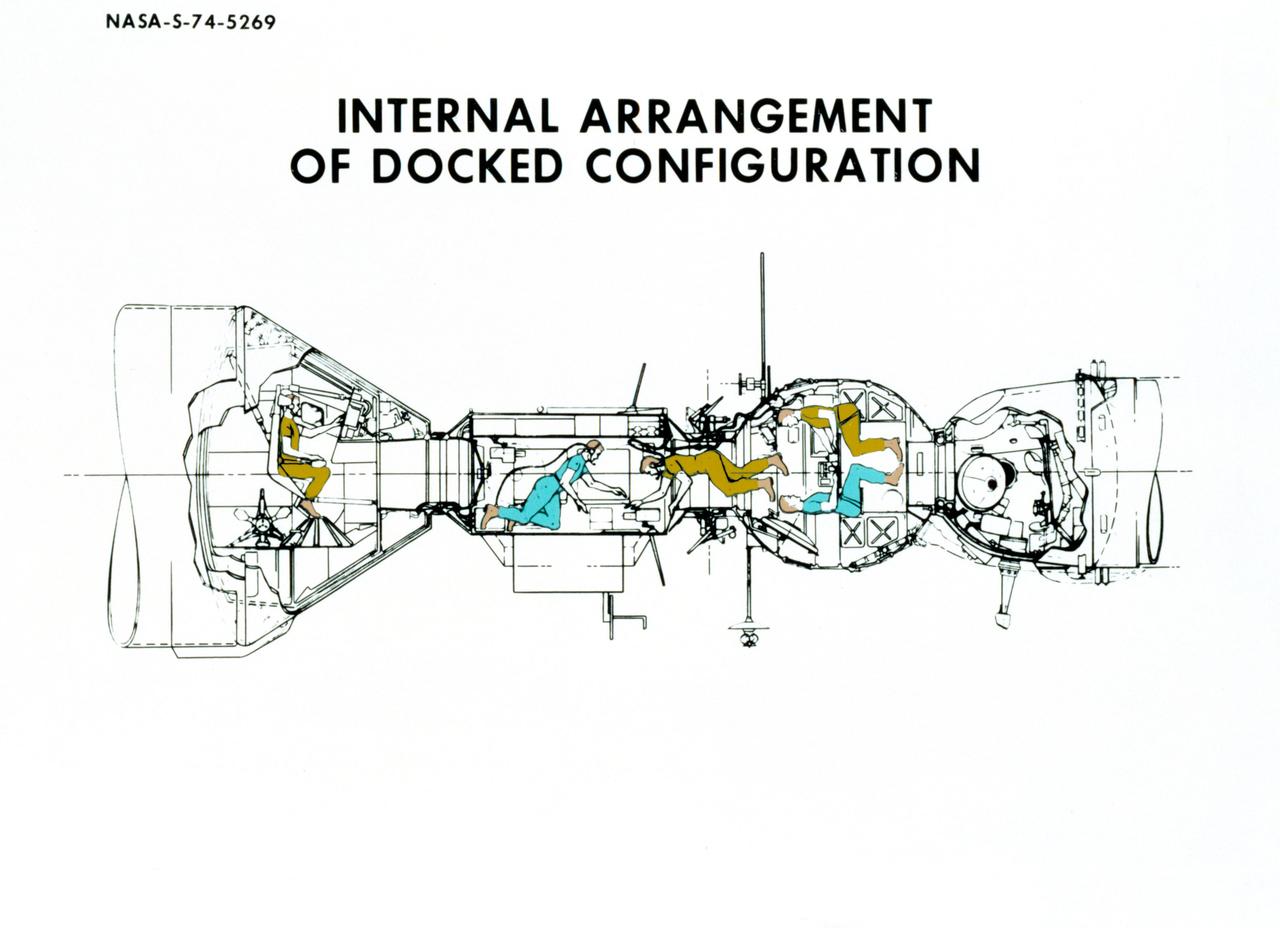
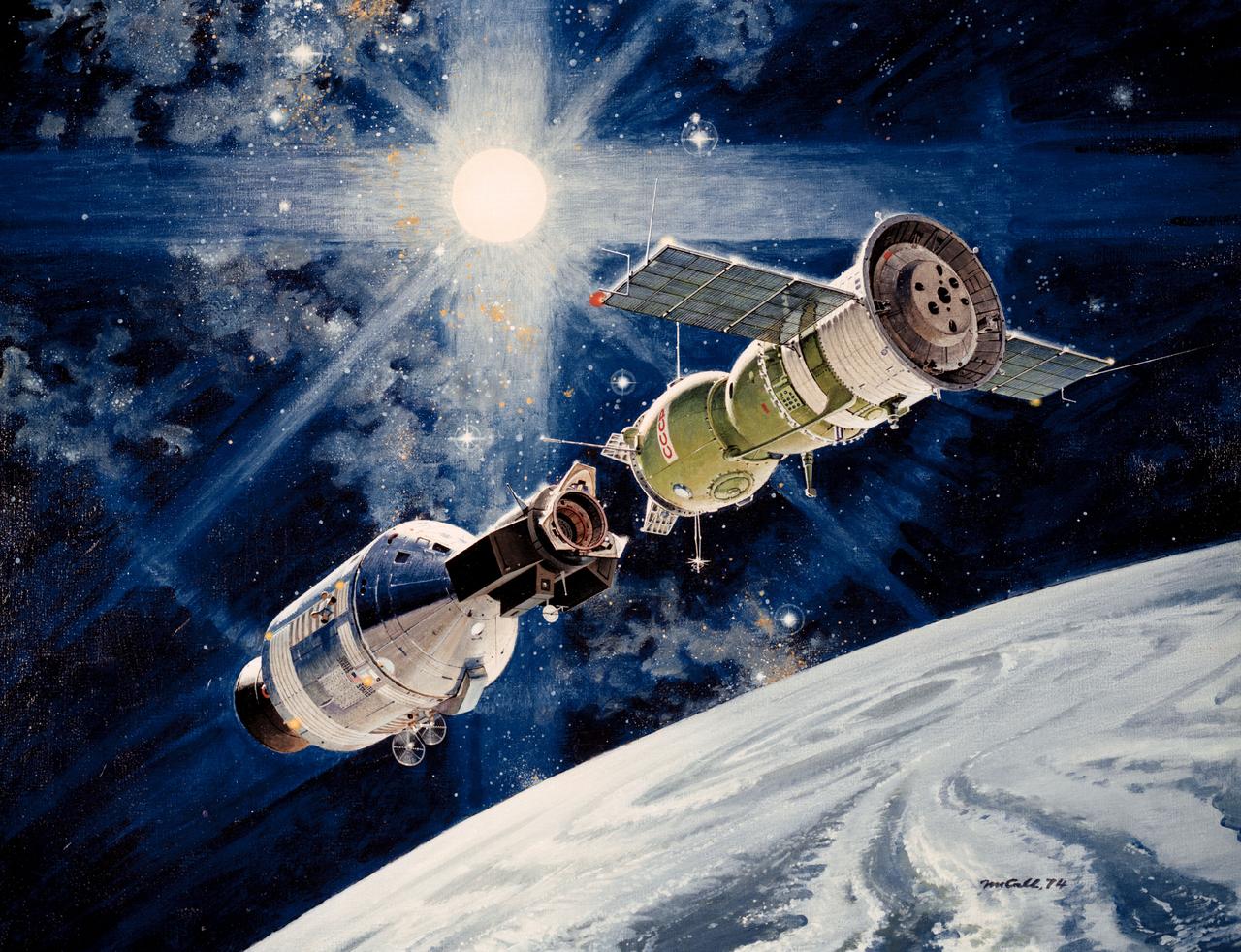
S74-05269 (December 1974) --- An artist?s drawing illustrating the internal arrangement of the Apollo and Soyuz spacecraft in Earth orbit in a docked configuration. The three American Apollo crewmen and the two Soviet Soyuz crewmen will transfer to each other?s spacecraft during the July 1975 ASTP mission. The four Apollo-Soyuz Test Project visible components are, left to right, the Apollo Command Module, the Docking Module, the Soyuz Orbital Module and the Soyuz Descent Vehicle.

S73-02395 (August 1973) --- An artist?s concept illustrating an Apollo-type spacecraft (on left) about to dock with a Soviet Soyuz-type spacecraft. A recent agreement between the United States and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics provides for the docking in space of the Soyuz and Apollo-type spacecraft in Earth orbit in 1975. The joint venture is called the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project.
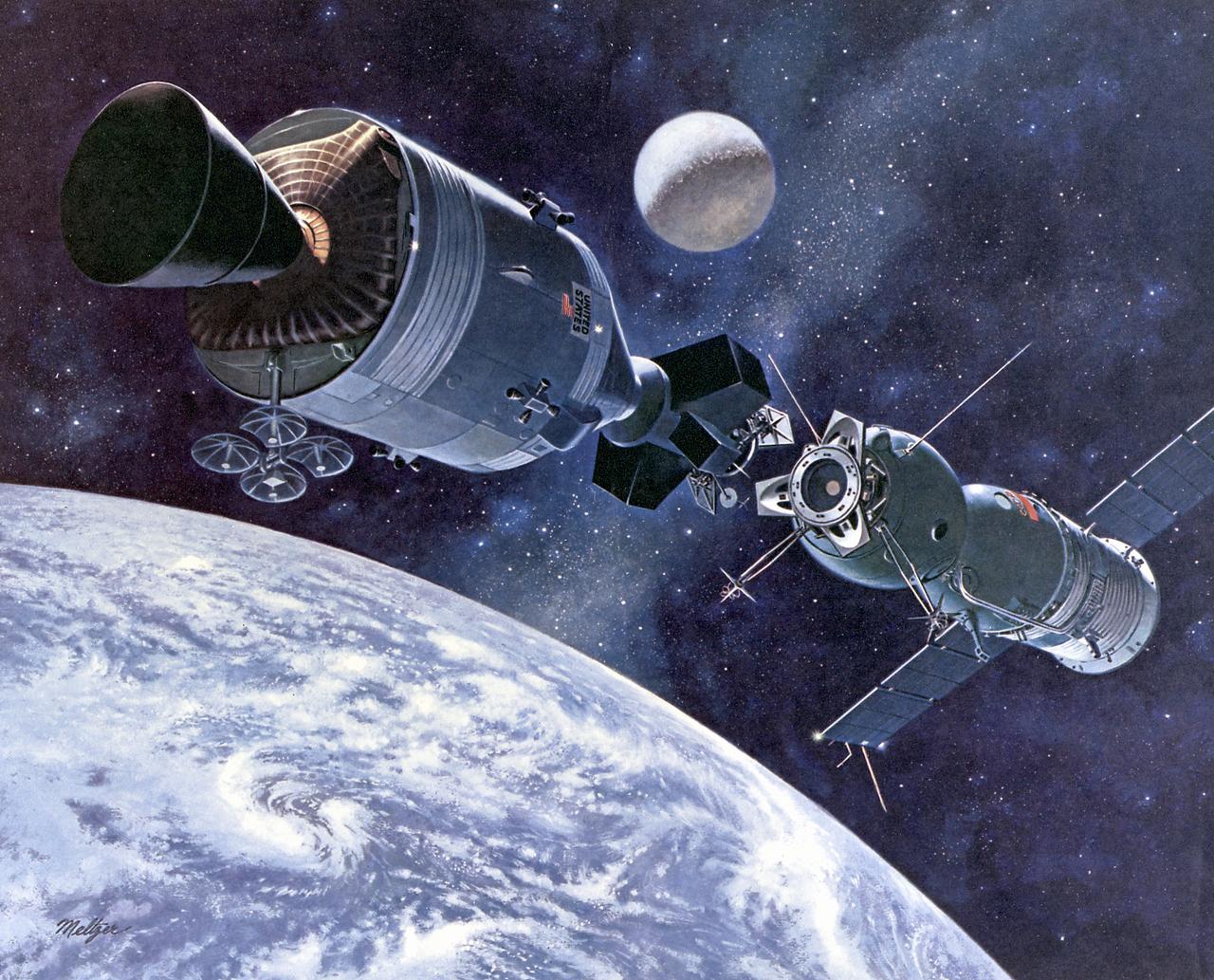

This artist's concept depicts the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP), the first international docking of the U.S.'s Apollo spacecraft and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz spacecraft in space. The objective of the ASTP mission was to provide the basis for a standardized international system for docking of marned spacecraft. The Soyuz spacecraft, with Cosmonauts Alexei Leonov and Valeri Kubasov aboard, was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome near Tyuratam in the Kazakh, Soviet Socialist Republic, at 8:20 a.m. (EDT) on July 15, 1975. The Apollo spacecraft, with Astronauts Thomas Stafford, Vance Brand, and Donald Slayton aboard, was launched from Launch Complex 39B, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 3:50 p.m. (EDT) on July 15, 1975. The Primary objectives of the ASTP were achieved. They performed spacecraft rendezvous, docking and undocking, conducted intervehicular crew transfer, and demonstrated the interaction of U.S. and U.S.S.R. control centers and spacecraft crews. The mission marked the last use of a Saturn launch vehicle. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development and sustaining engineering of the Saturn IB launch vehicle during the mission.
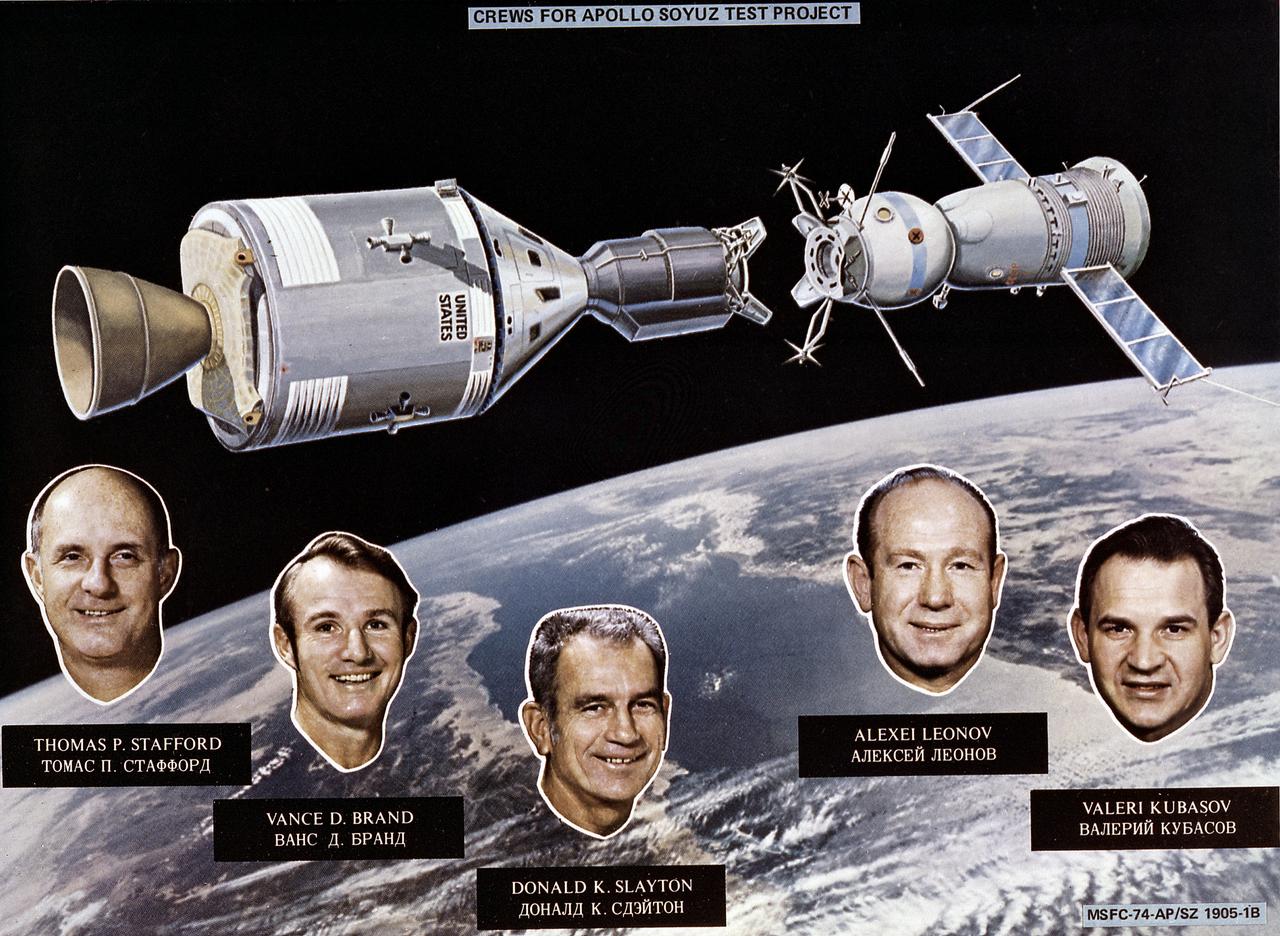
This artist's concept depicts the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) with insets of photographs of three U.S. astronauts (Thomas Stafford, Vance Brand, and Donald Slayton) and two U.S.S.R. cosmonauts (Alexei Leonov and Valeri Kubasov). The objective of the ASTP mission was to accomplish the first docking of a standardized international system, the U.S.'s Apollo spacecraft and the U.S.S.R.'s Soyuz spacecraft, in space. The Soyuz spacecraft was launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome near Tyuratam in the Kazakh, Soviet Socialist Republic, at 8:20 a.m. (EDT) on July 15, 1975. The Apollo spacecraft was launched from Launch Complex 39B, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 3:50 p.m. (EDT) on July 15, 1975. The Primary objectives of the ASTP were achieved. They performed spacecraft rendezvous, docking and undocking, conducted intervehicular crew transfer, and demonstrated the interaction of U.S. and U.S.S.R. control centers and spacecraft crews. The mission marked the last use of a Saturn launch vehicle. The Marshall Space Flight Center was responsible for development and sustaining engineering of the Saturn IB launch vehicle during the mission.
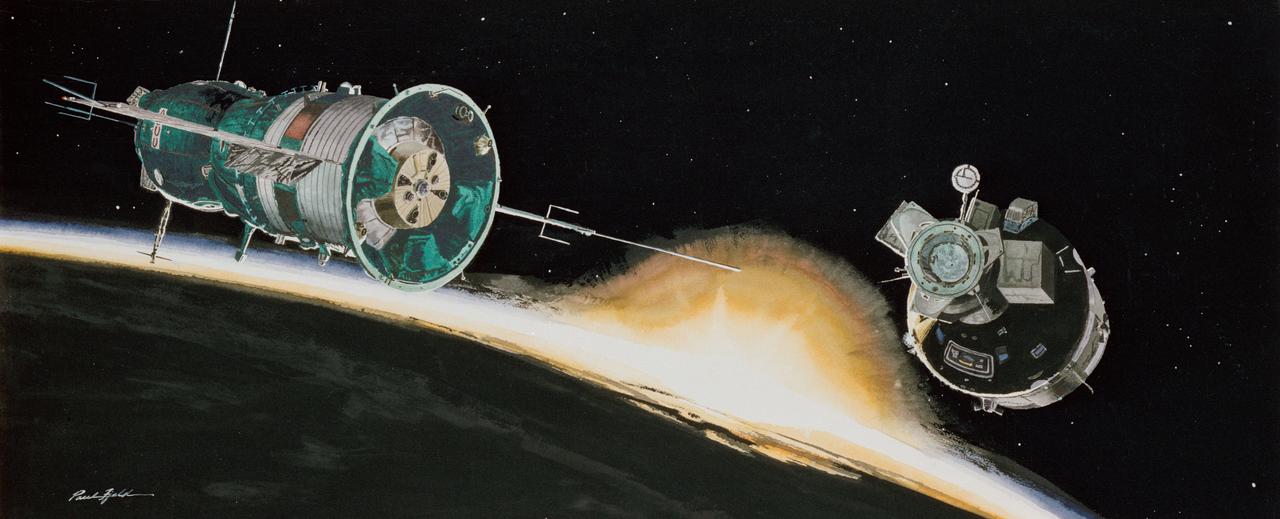
S76-23275 (1976) --- Apollo-Soyuz Test Project artist?s concept by Paul Fjeld.
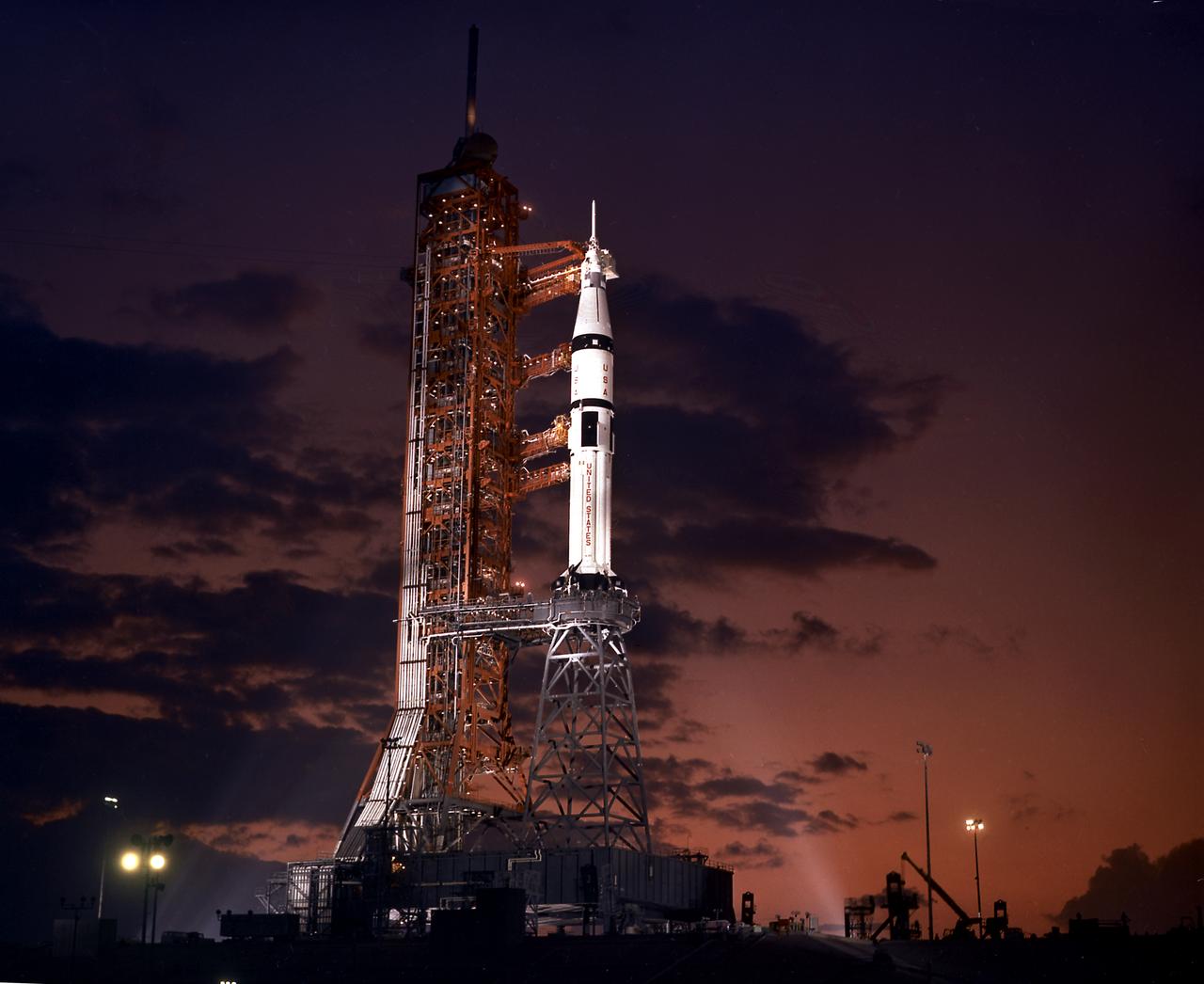

SA-210 Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) awaits the launch scheduled on July 15, 1975 on the launch pad at the Kennedy Space Center, the ASTP mission with astronauts Thomas Stafford, Vance Brand, and Donald "Deke" Slayton. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project .
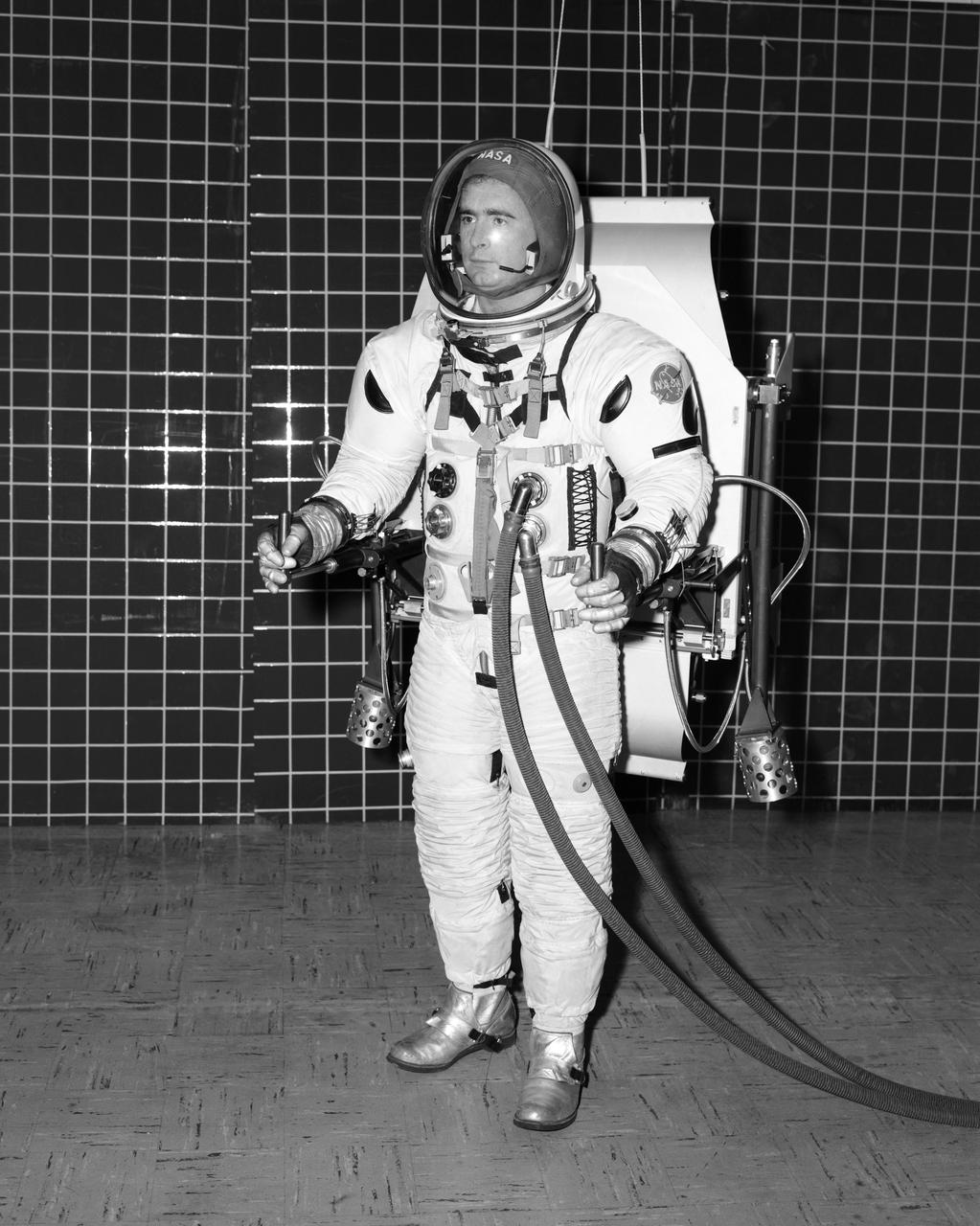

Space Suit: NASA Langley researcher (Kenneth R. Yenni) tries out a proposal for an Apollo space suit.
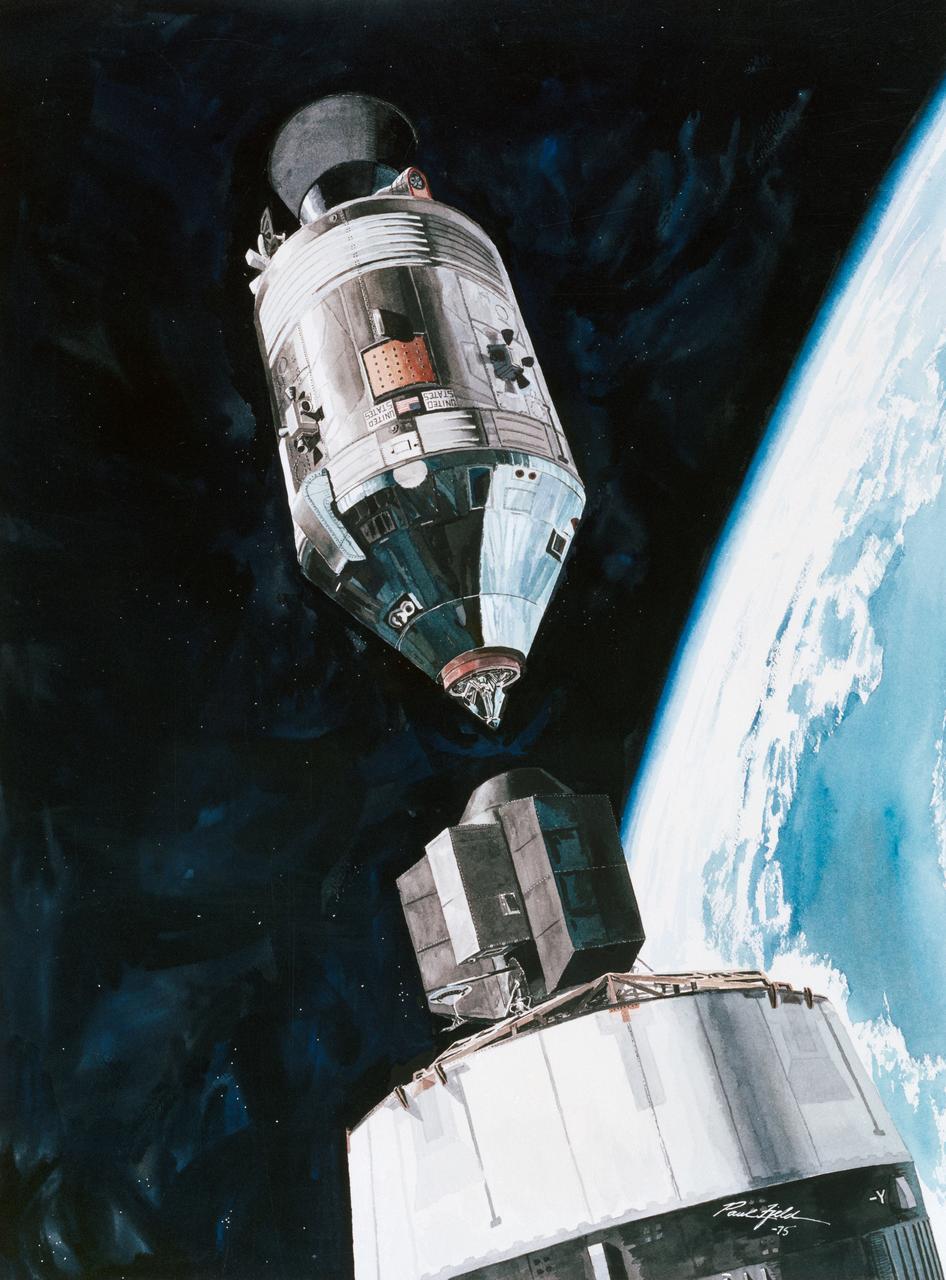

S75-28512 (July 1975) --- An artist?s concept depicting a scene in Earth orbit during the Apollo transposition and docking maneuvers of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Command/Service Module is moving into position to dock with the Docking Module. Following the docking the DM will be extracted from the expended Saturn IVB stage. The Docking Module is designed to link the American Apollo spacecraft with the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft. This scene will take place some one hour and twenty-three minutes after the Apollo-Saturn 1B liftoff from the Kennedy Space Center on July 15, 1975. The Soyuz launch at 7:20 a.m. (CDT) from the Baikonur, Kazakhstan launch pad will precede the Apollo liftoff by seven and one-half hours. The artwork is by Paul Fjeld.
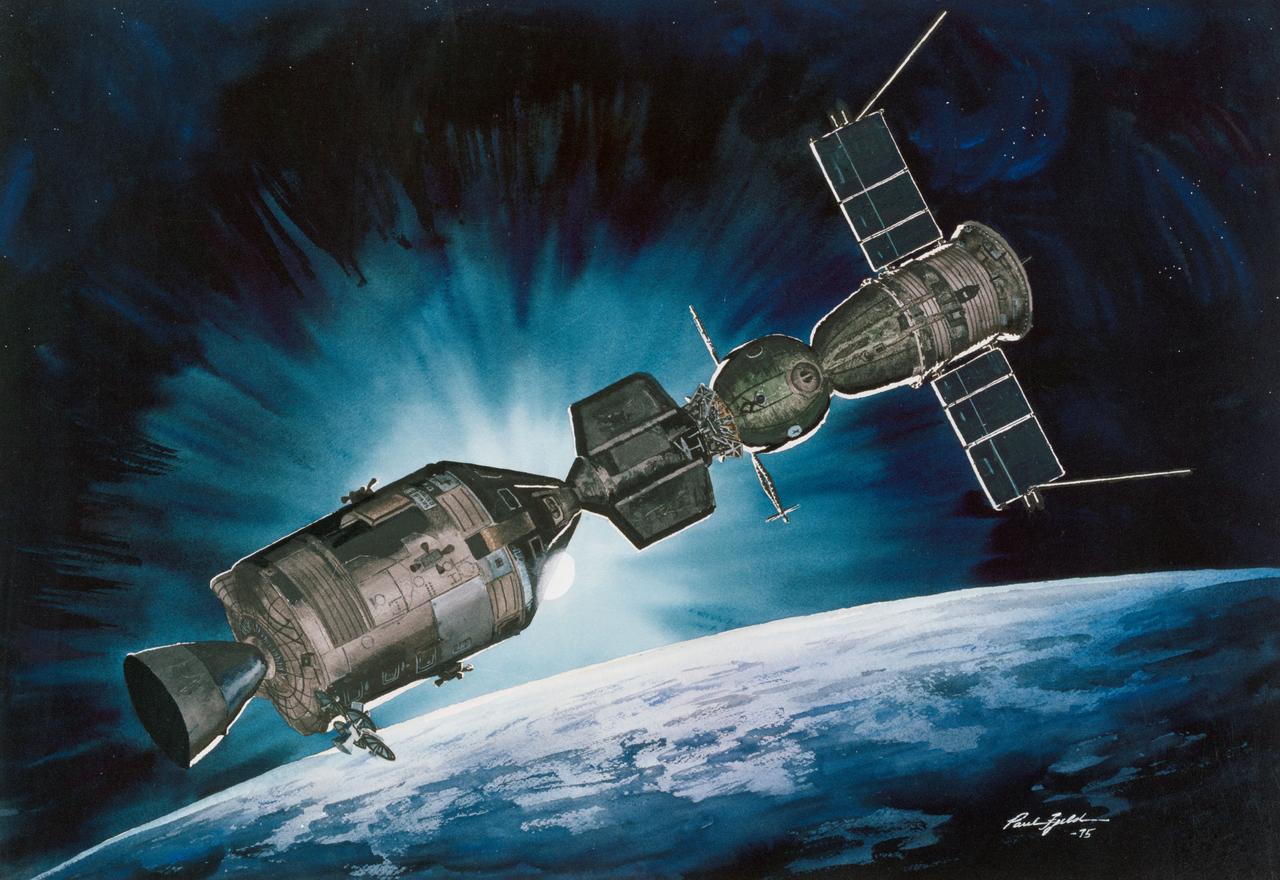
S75-28511 (July 1975) --- An artist?s concept depicting the American and Soviet spacecraft docked in Earth orbit during the July 1975 Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Apollo Command/Service Module is on the left, the Docking Module is in the center, and the Soyuz spacecraft is on the right. The first docking of spacecraft from two different nations was scheduled for July 17, 1975. The American and Soviet ASTP crewmen planned to visit each other?s spacecraft while Apollo and Soyuz are docked for a maximum period of two days. The docking system on the Docking Module and the docking system on the Soyuz Orbital Module are designed to interface with each other. The painting is by artist Paul Fjeld.
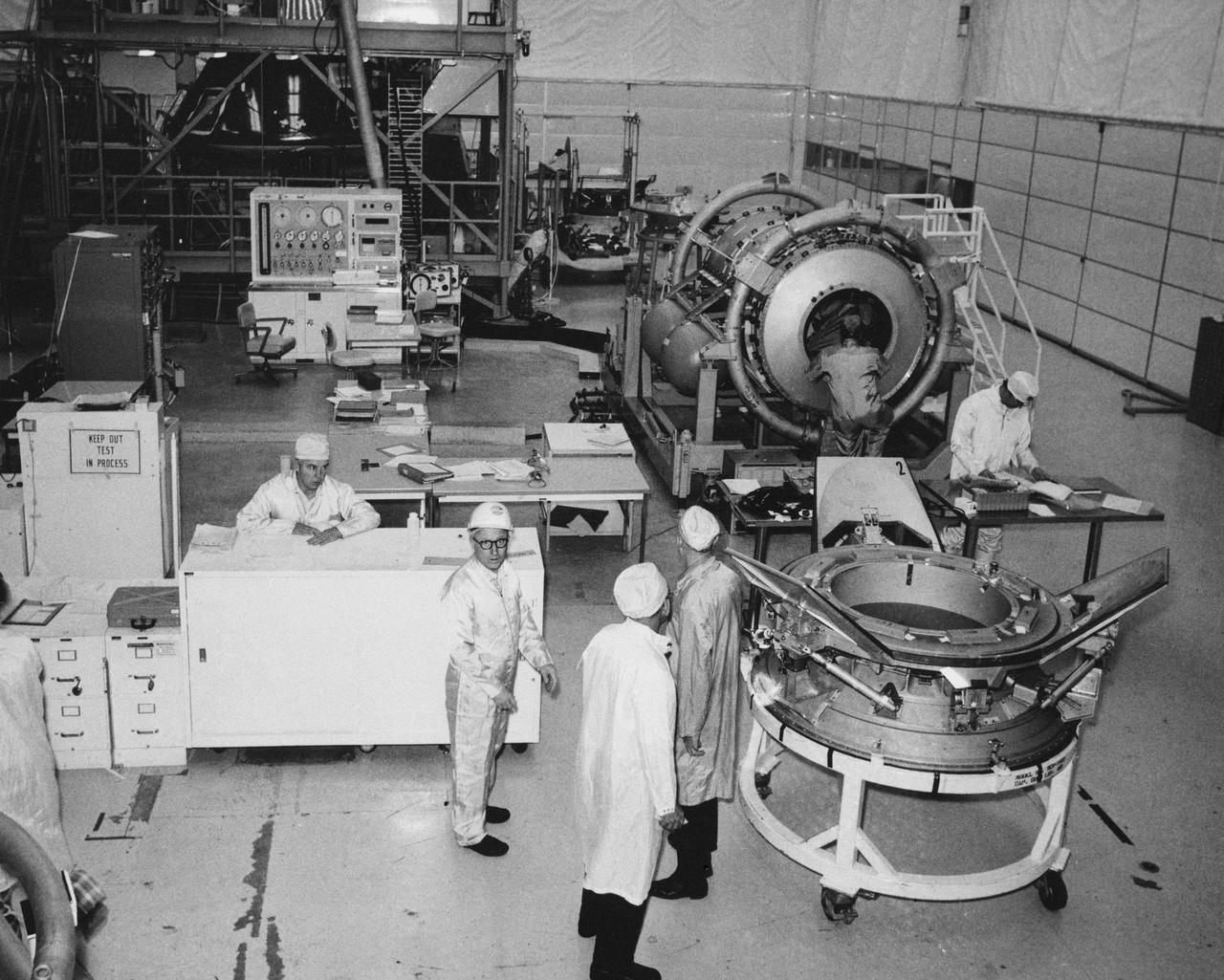
S74-28295 (September 1974) --- American-built hardware for the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission undergoes pre-delivery preparations in the giant clean room at Rockwell International Corporation?s Space Division at Downey, California. The U.S. portion of the ASTP docking system is in the right foreground. In the right background is the cylindrical-shaped docking module, which is designed to link the Apollo and Soyuz spacecraft when they dock in Earth orbit next summer. In the left background is the Apollo Command Module which they will carry the three American astronauts into Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA

Panoramas of Apollo sites were created to familiarize various Constellation projects with the actual nature of the lunar surface. Image is a view taken from northeast of the Lunar module (LM) looking west at panel and Flag, then to southwest at LM and counterclockwise to south and west looking into Surveyor Crater. View was created using Apollo 12 images - mag 47 frames 6982 thru 7006.
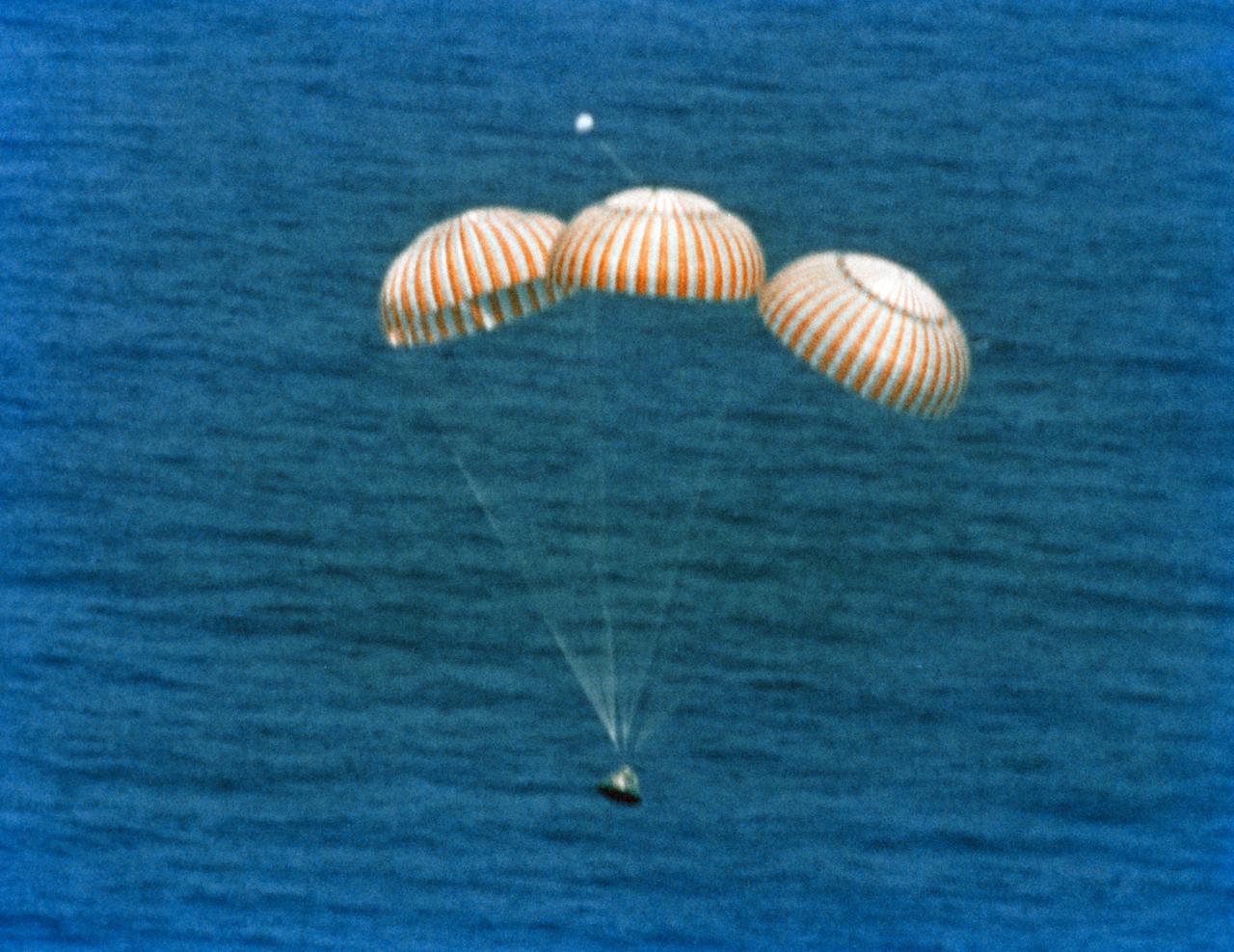

S75-29719 (24 July 1975) --- The ASTP Apollo Command Module, with astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. Slayton aboard, nears a touchdown in the Central Pacific Ocean to conclude the historic joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The spacecraft splashed down in the Hawaiian Islands area at 4:18 p.m. (CDT), July 24, 1975.
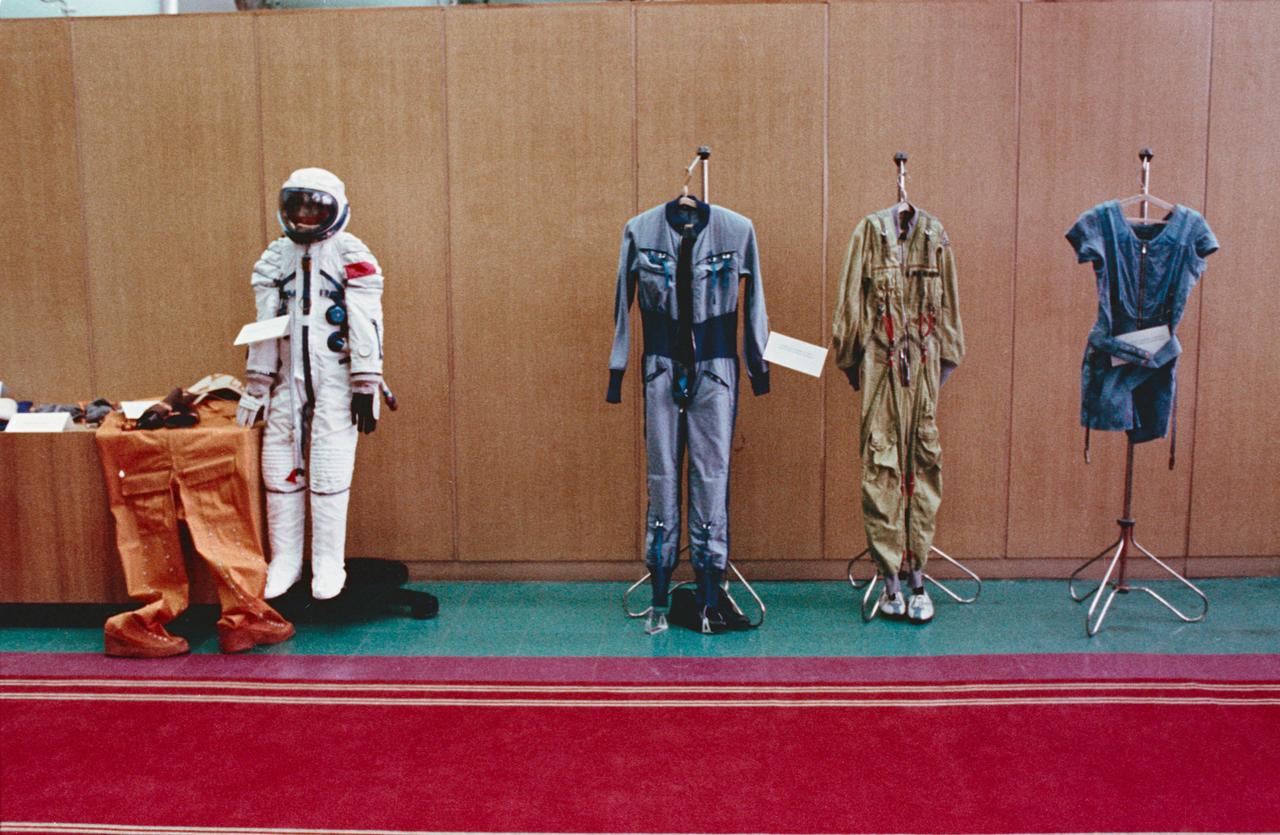

S75-24899 (April 1975) --- An exhibit illustrating the space suits designed for the Soviet cosmonaut crewmen of the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. These were on display in the training building at the Cosmonaut Training Center (Star City) near Moscow.
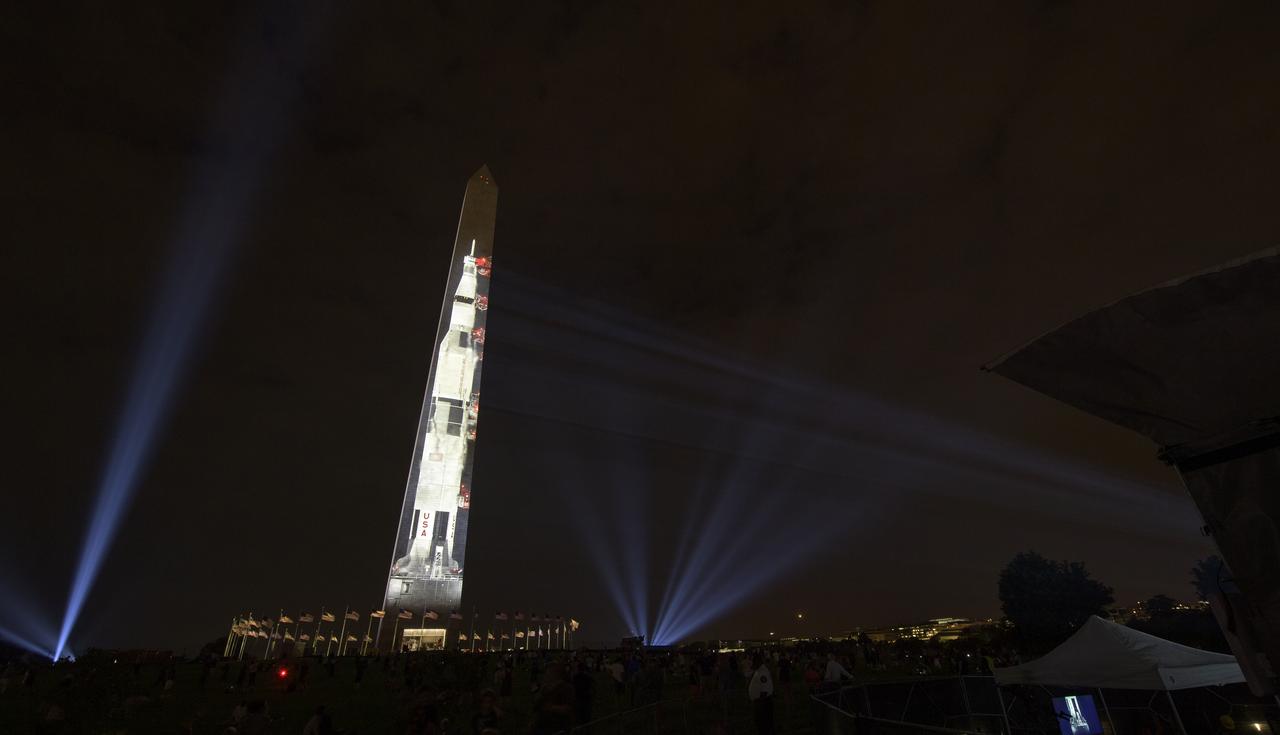

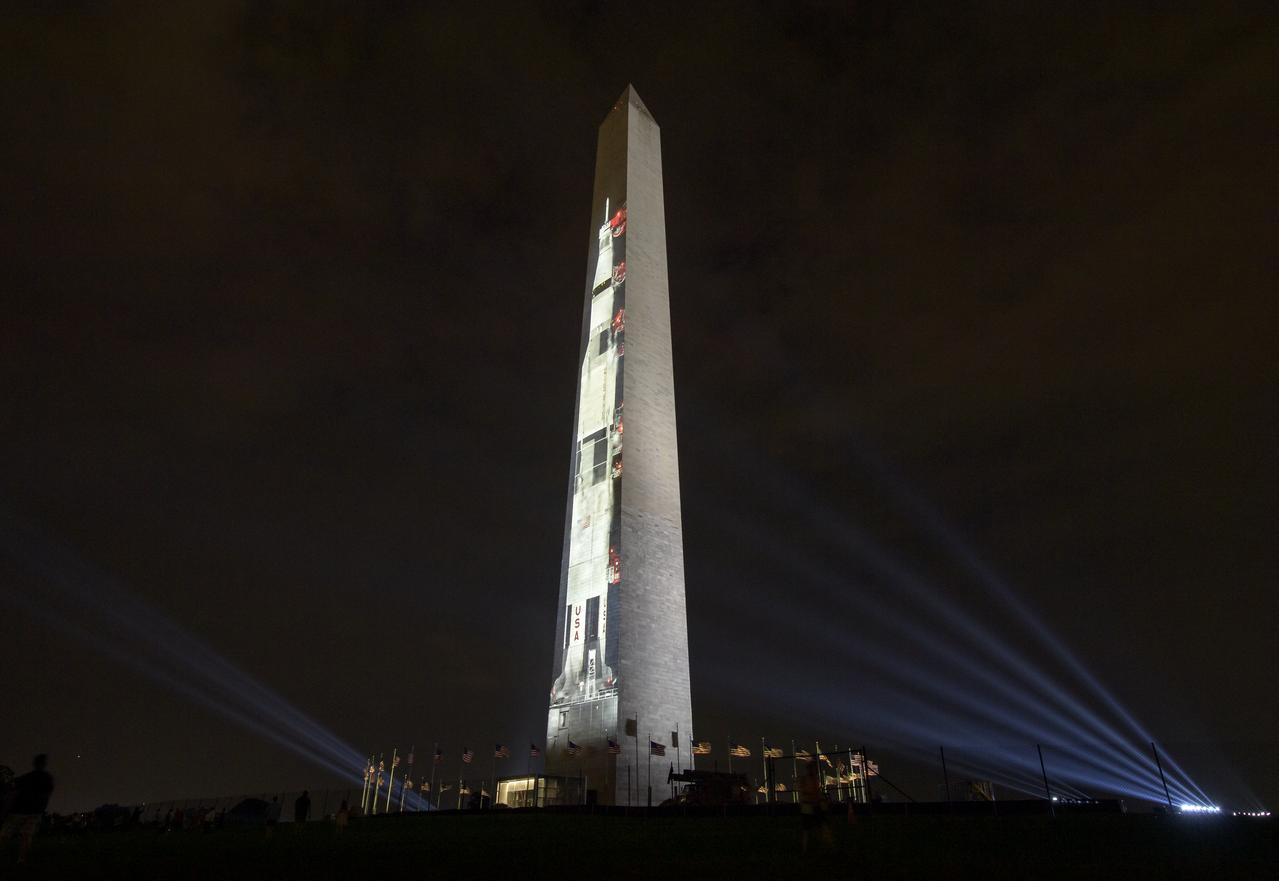
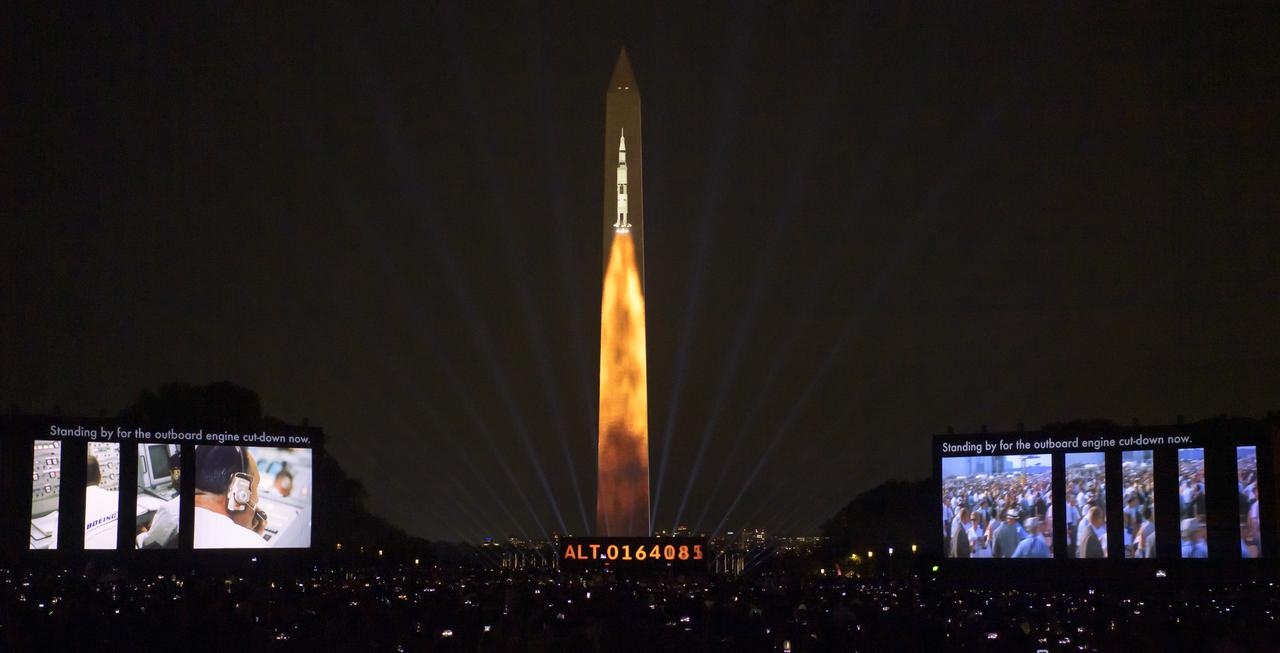
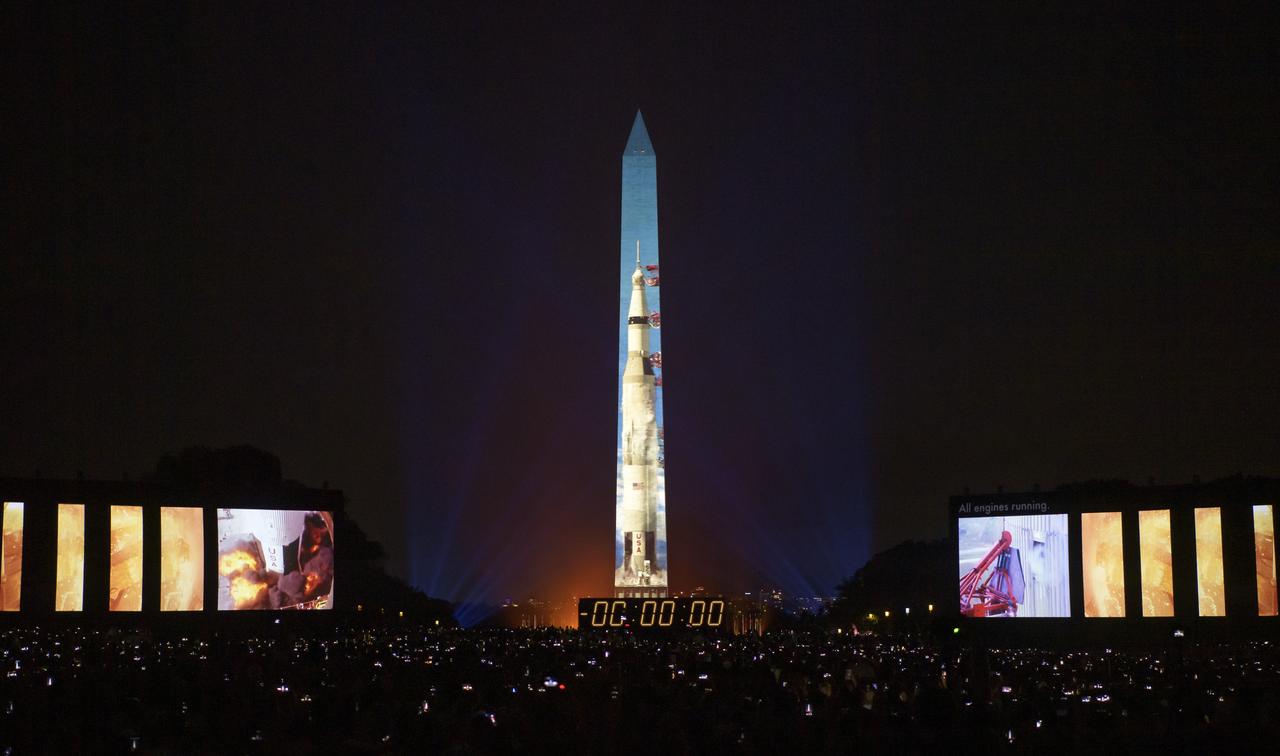
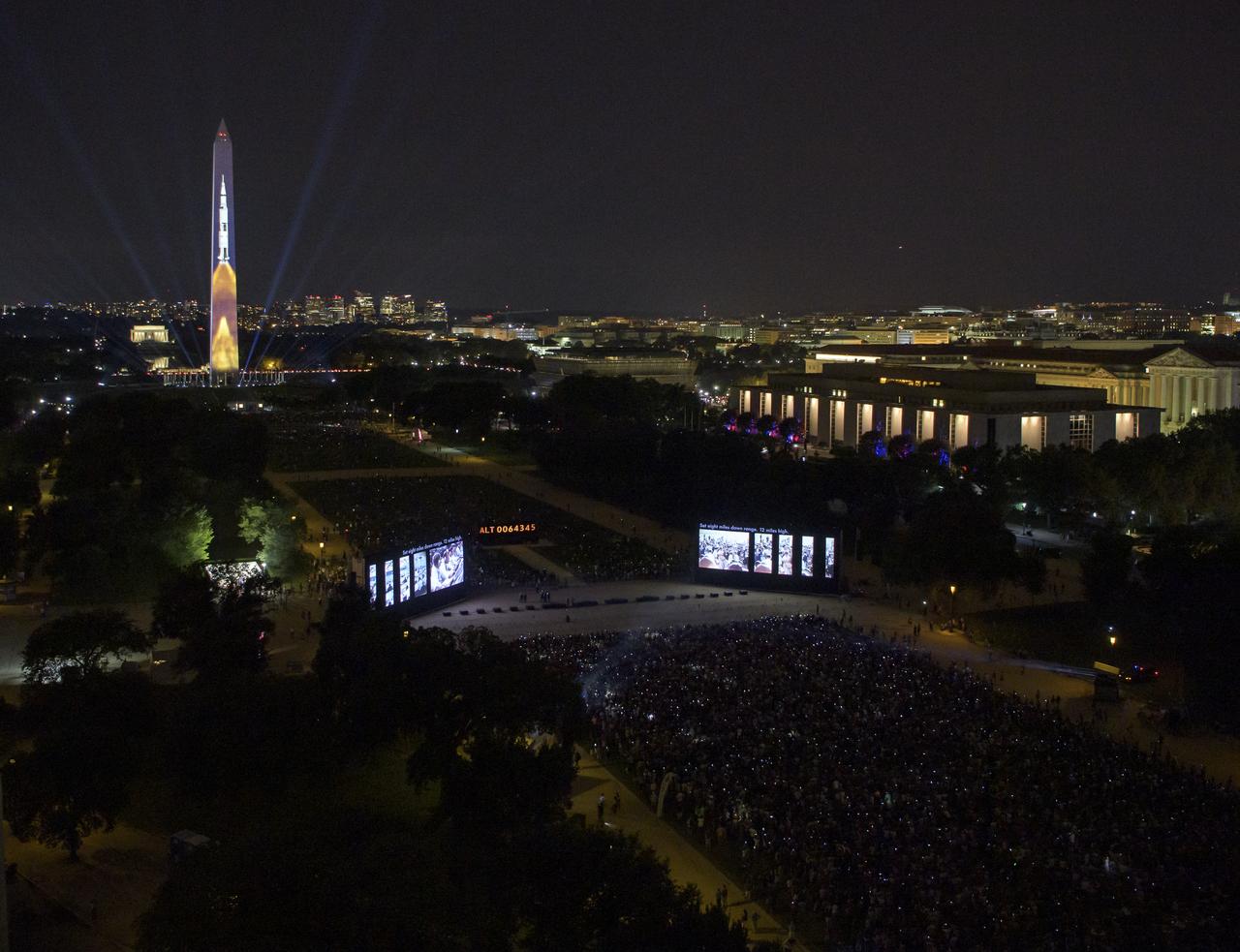
A full-sized, 363-foot Saturn V rocket is projected onto the east face of the Washington Monument 50 years to the day after astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin launched on Apollo 11, the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon, Tuesday, July 16, 2019. On Friday, July 19, and Saturday, July 20, a special 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon” will combine full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
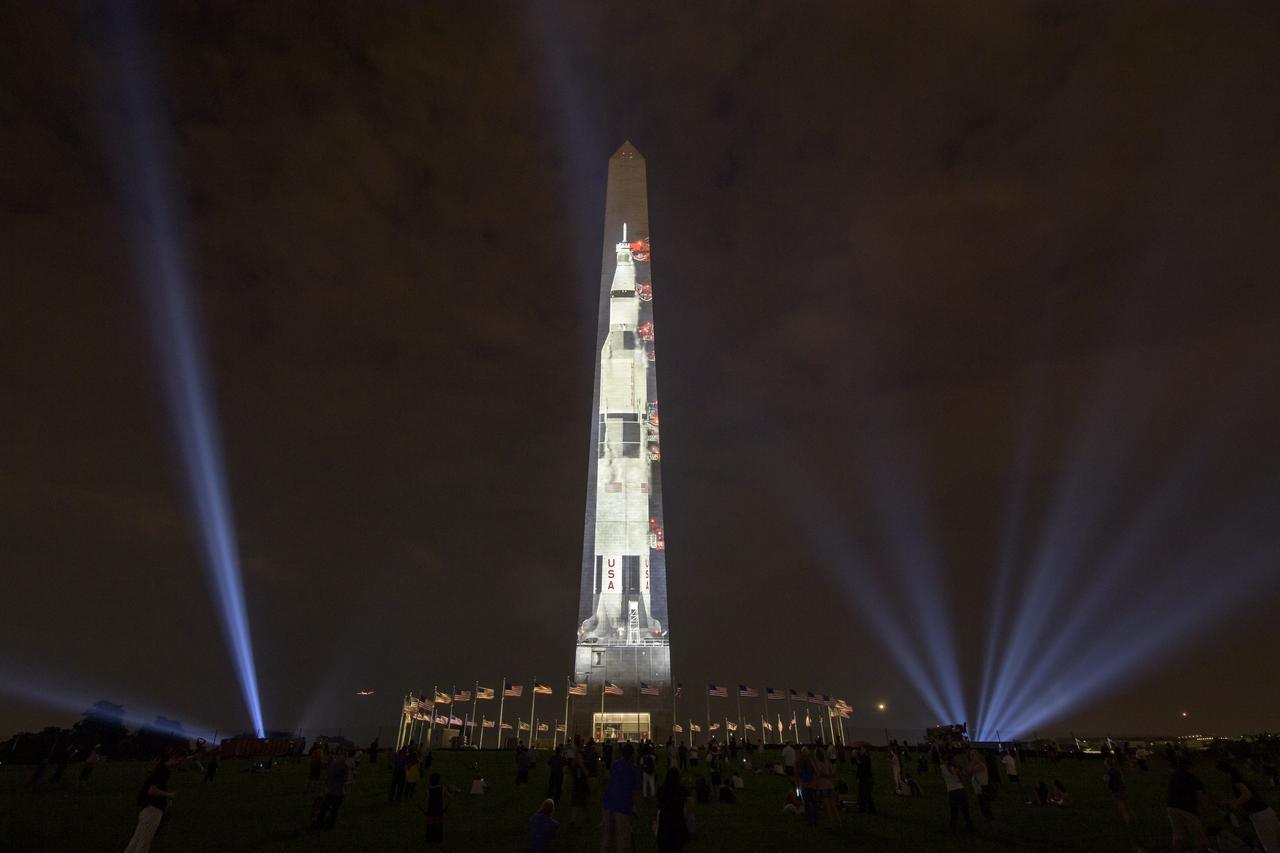

A full-sized, 363-foot Saturn V rocket is projected onto the east face of the Washington Monument 50 years to the day after astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin launched on Apollo 11, the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon, Tuesday, July 16, 2019. On Friday, July 19, and Saturday, July 20, a special 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon” will combine full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
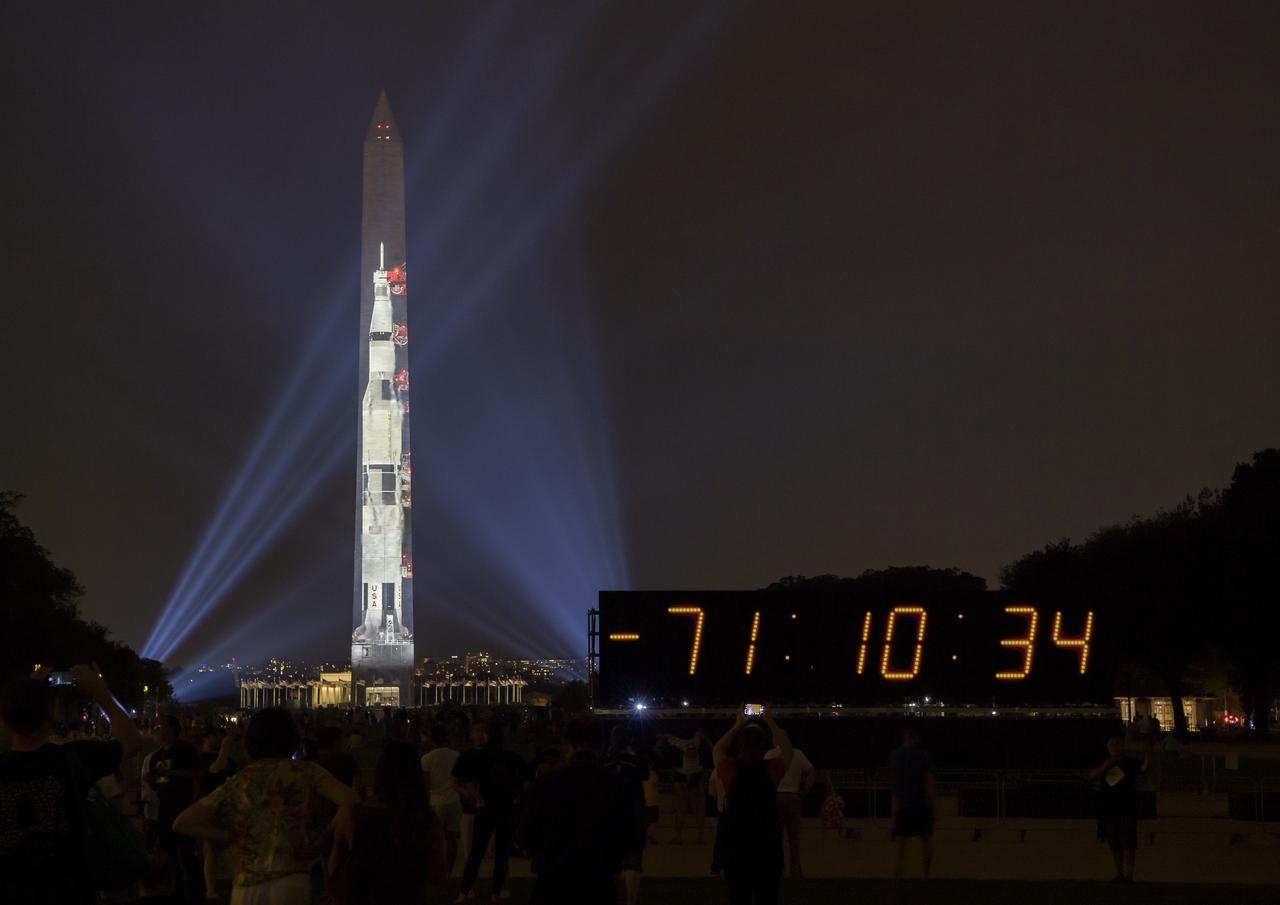

A full-sized, 363-foot Saturn V rocket is projected onto the east face of the Washington Monument 50 years to the day after astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin launched on Apollo 11, the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon, Tuesday, July 16, 2019. On Friday, July 19, and Saturday, July 20, a special 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon” will combine full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
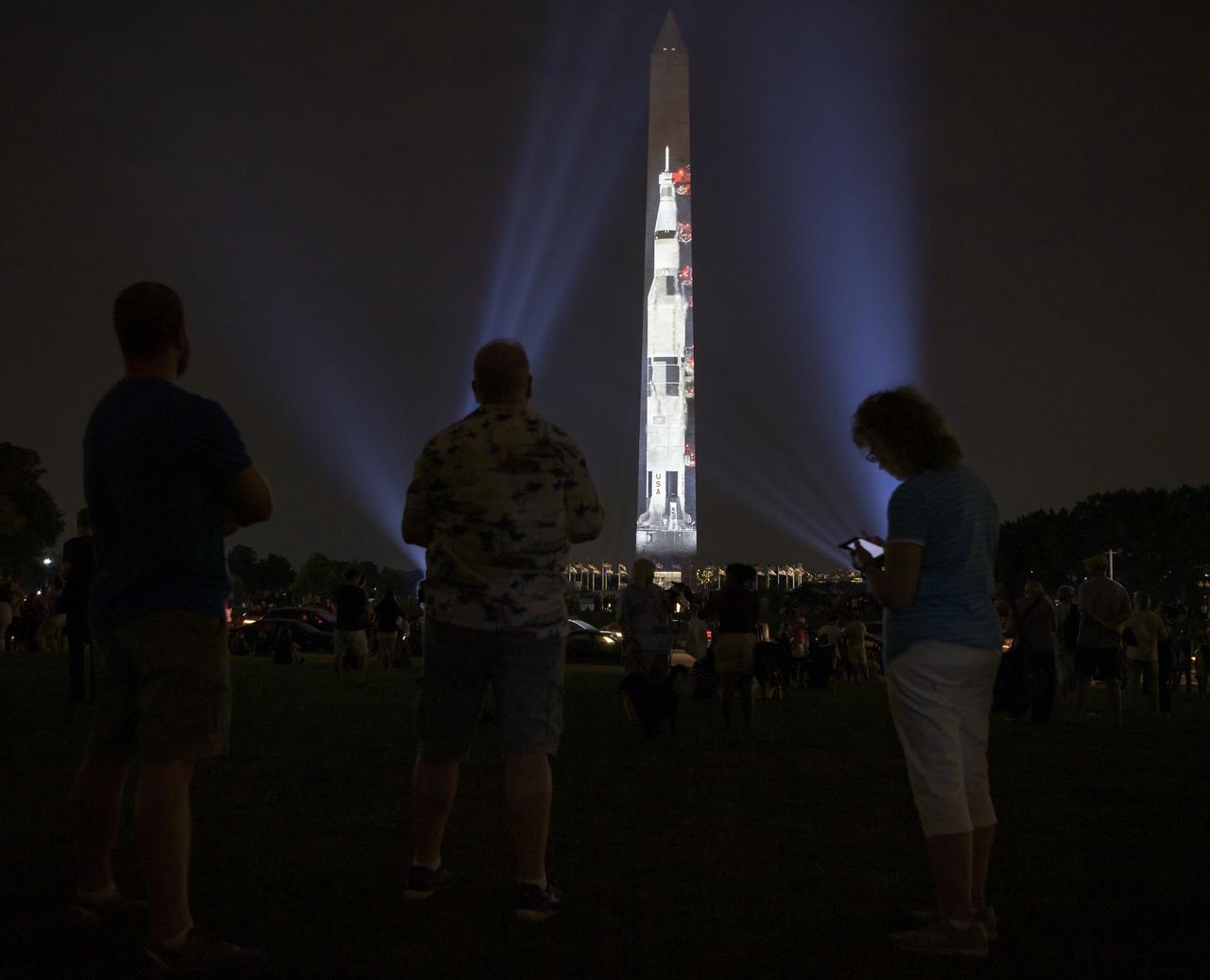

A full-sized, 363-foot Saturn V rocket is projected onto the east face of the Washington Monument 50 years to the day after astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin launched on Apollo 11, the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon, Tuesday, July 16, 2019. On Friday, July 19, and Saturday, July 20, a special 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon” will combine full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A full-sized, 363-foot Saturn V rocket is projected onto the east face of the Washington Monument 50 years to the day after astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin launched on Apollo 11, the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon, Tuesday, July 16, 2019. On Friday, July 19, and Saturday, July 20, a special 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon” will combine full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A full-sized, 363-foot Saturn V rocket is projected onto the east face of the Washington Monument 50 years to the day after astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin launched on Apollo 11, the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon, Tuesday, July 16, 2019. On Friday, July 19, and Saturday, July 20, a special 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon” will combine full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
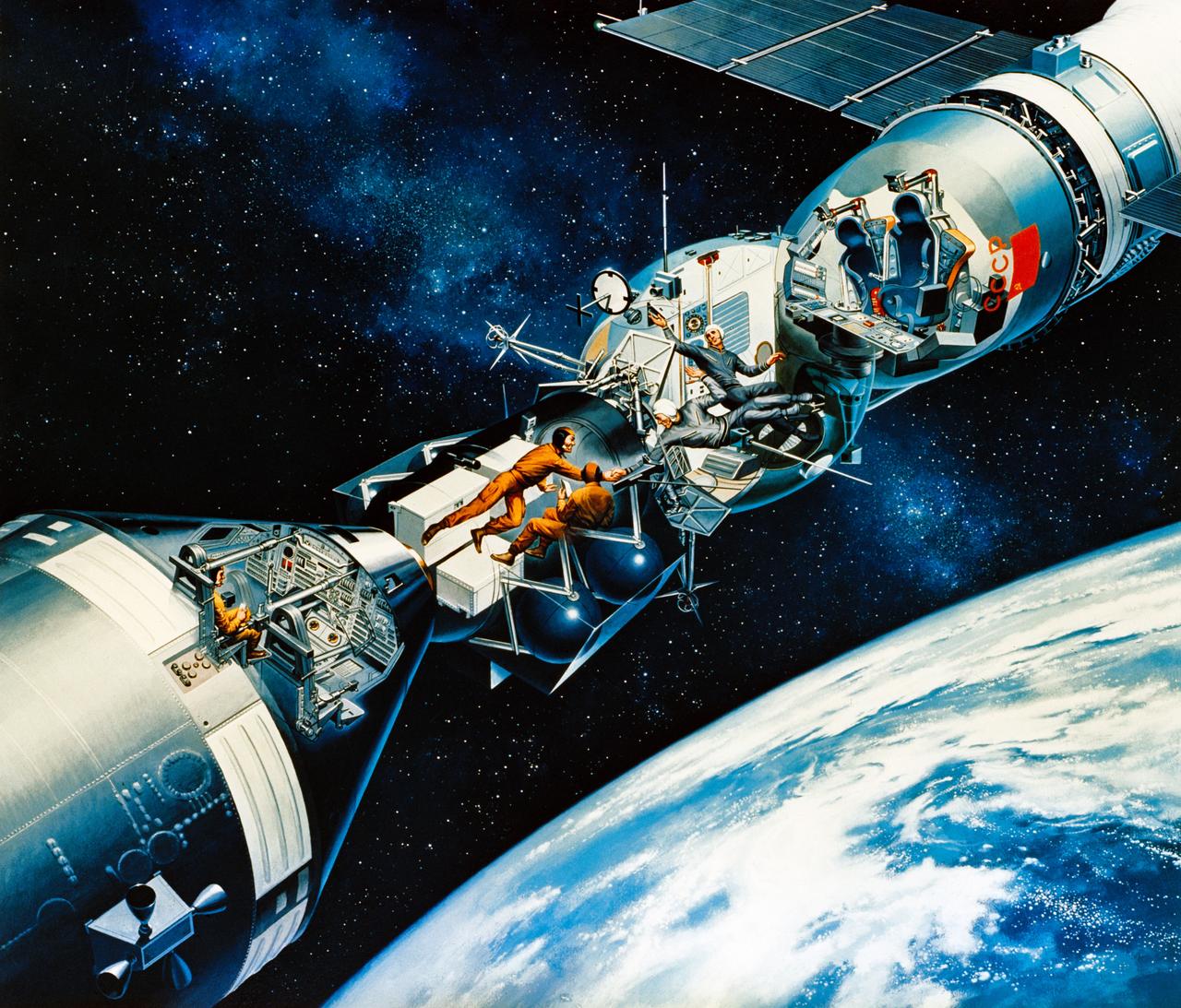

S75-27290 (April 1975) --- An artist?s concept illustrating a cutaway view of the docked Apollo and Soyuz spacecraft in Earth orbit. This scene depicts the moment the two international crews meet in space for the first time. Two of the three American crewmen are in the Docking Module. The two Soviet crewmen are in the Soyuz spacecraft?s Orbital Module. The two crew commanders are shaking hands through the hatchway. The third American crewman is in the Apollo Command Module. During the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission, which is scheduled for July 1975, the American and Soviet crews will visit one another?s spacecraft while the Soyuz and Apollo are docked for a maximum period of two days. The mission is designed to test equipment and techniques that will establish international crew rescue capability in space, as well as permit future cooperative scientific missions. The artwork is by Davis Meltzer.
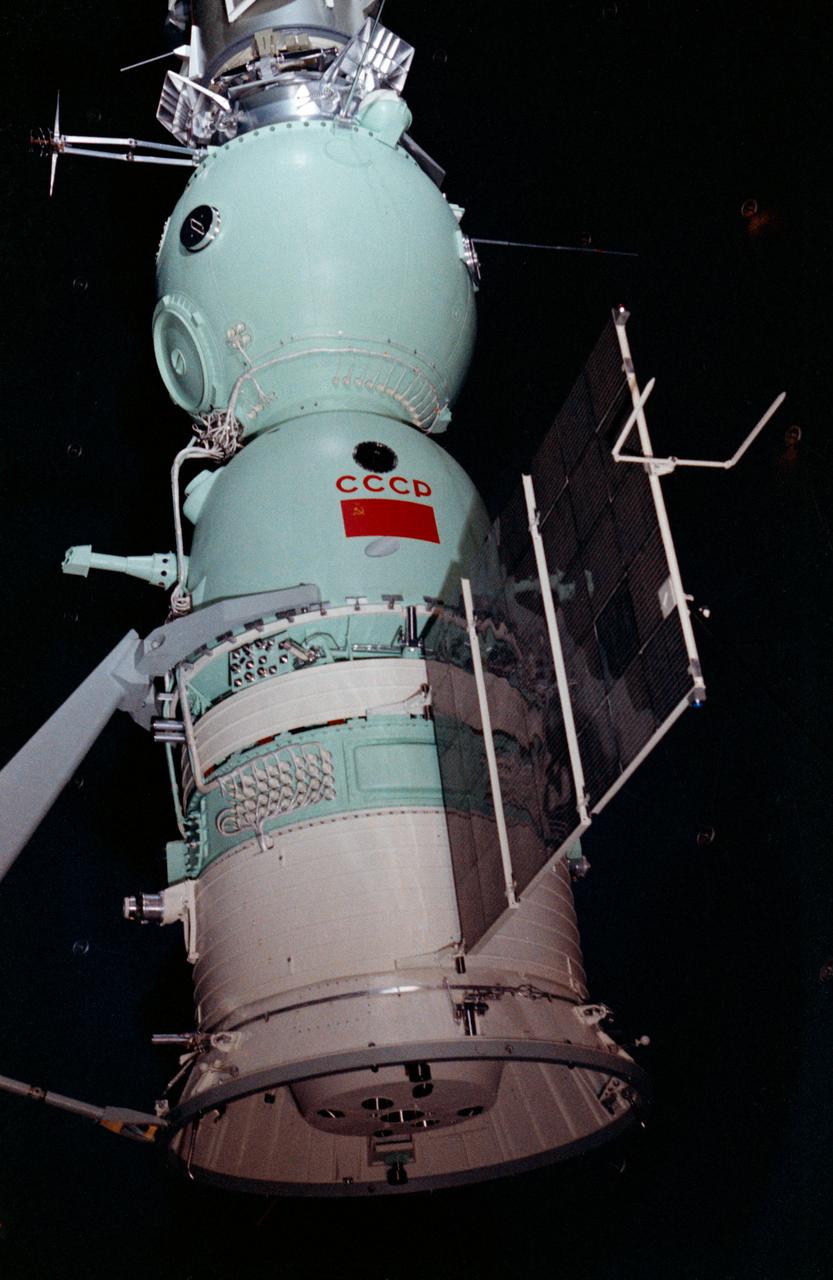
S73-27666 (May-June 1973) --- A close-up view of the Soyuz spacecraft which was part of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project exhibit at the 30th International Aeronautics and Space Exhibition held May 24 ? June 3, 1973 at the Le Bourget Airport in Paris, France. The ASTP exhibit was co-sponsored by the United States and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. An agreement between the U.S. and the USSR provides for the docking in Earth orbit of the Soyuz and Apollo in the summer of 1975. The Apollo spacecraft is out of view to the left. At the far left, a mock-up of a Docking Module connects the Apollo with the Soyuz. The spherical-shaped portion of the Soyuz is called the orbital section. The middle section with the lettering ?CCCP? (USSR) on it is called the cosmonauts? cabin. Two solar panels extend out from the machines and panel section.
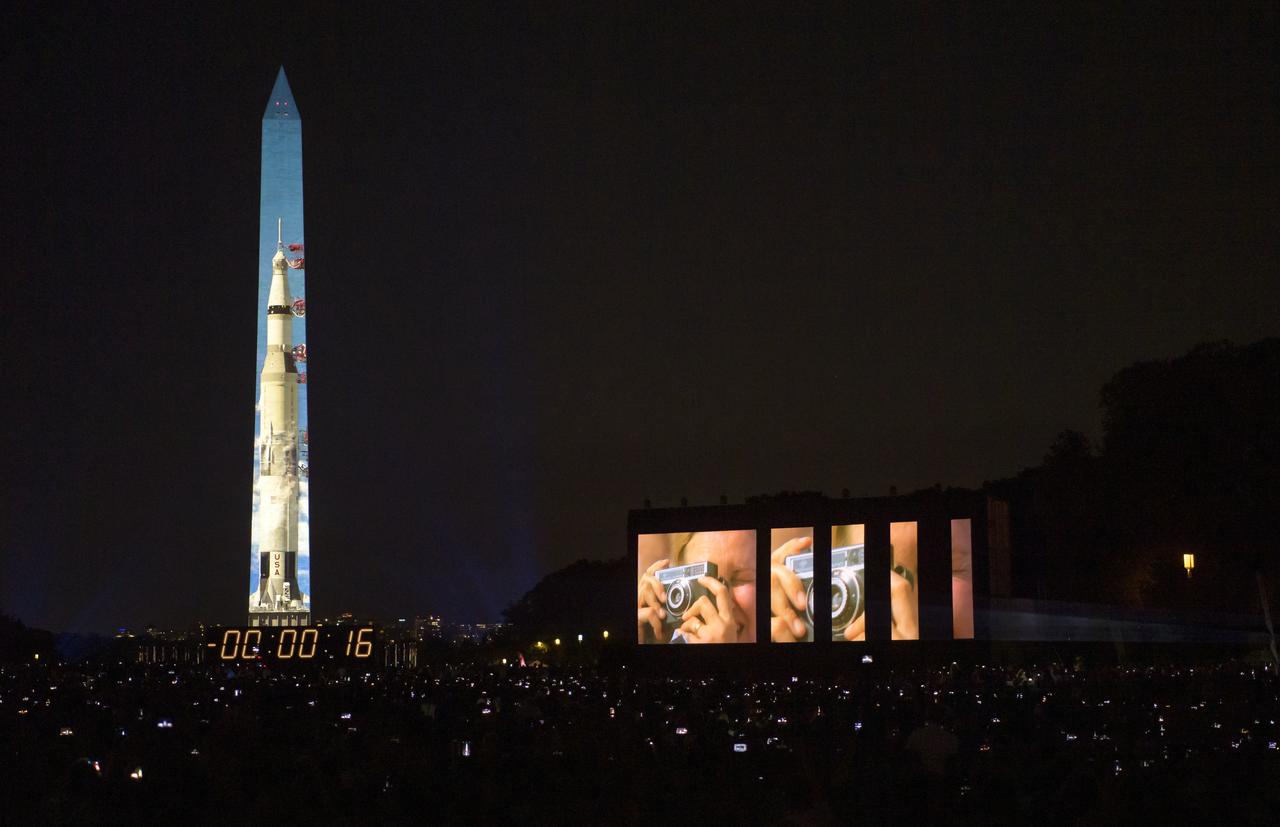

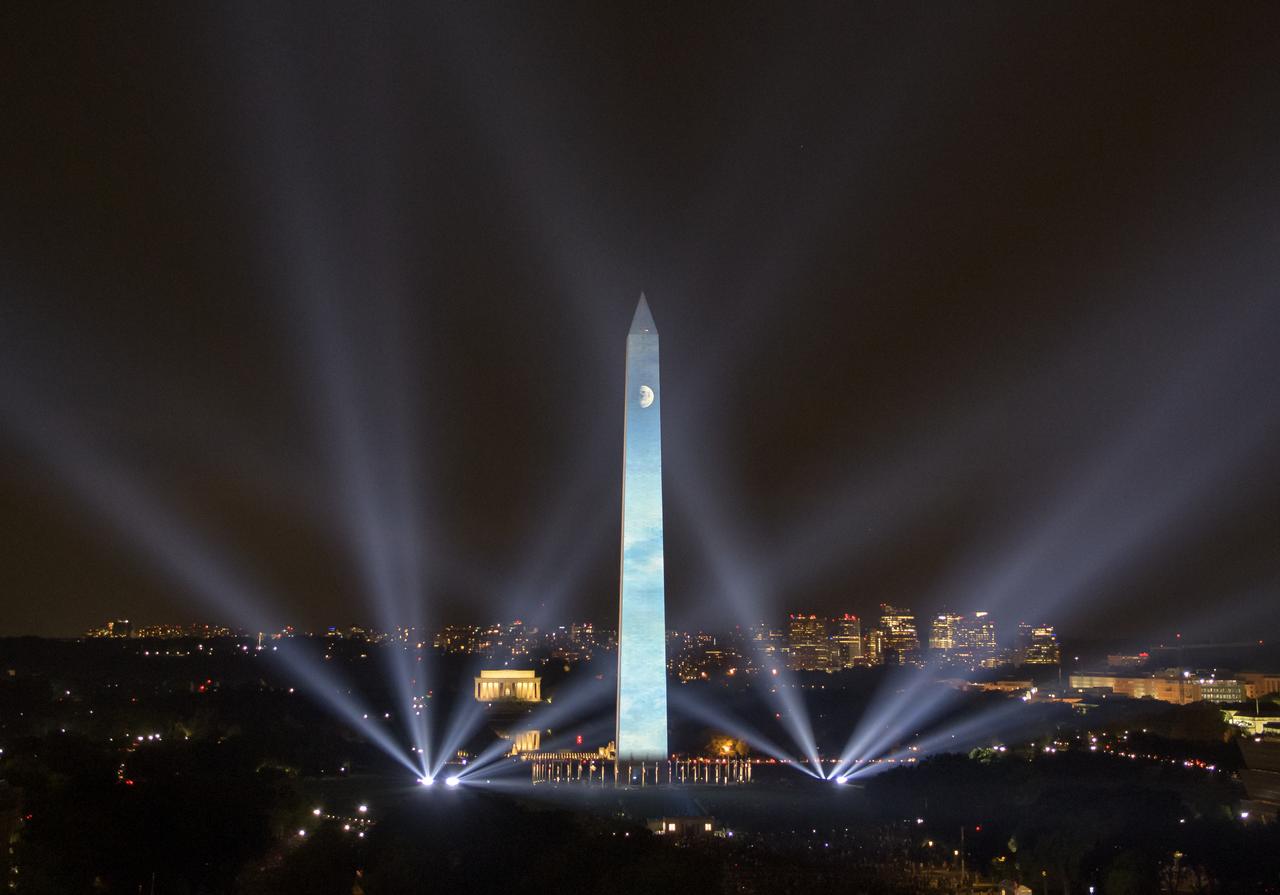
The 50 year anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission with NASA astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin is celebrated in a 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon”, by the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, which combined full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the Washington Monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing, Friday, July 19, 2019 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The 50 year anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission with NASA astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin is celebrated in a 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon”, by the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, which combined full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the Washington Monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing, Friday, July 19, 2019 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
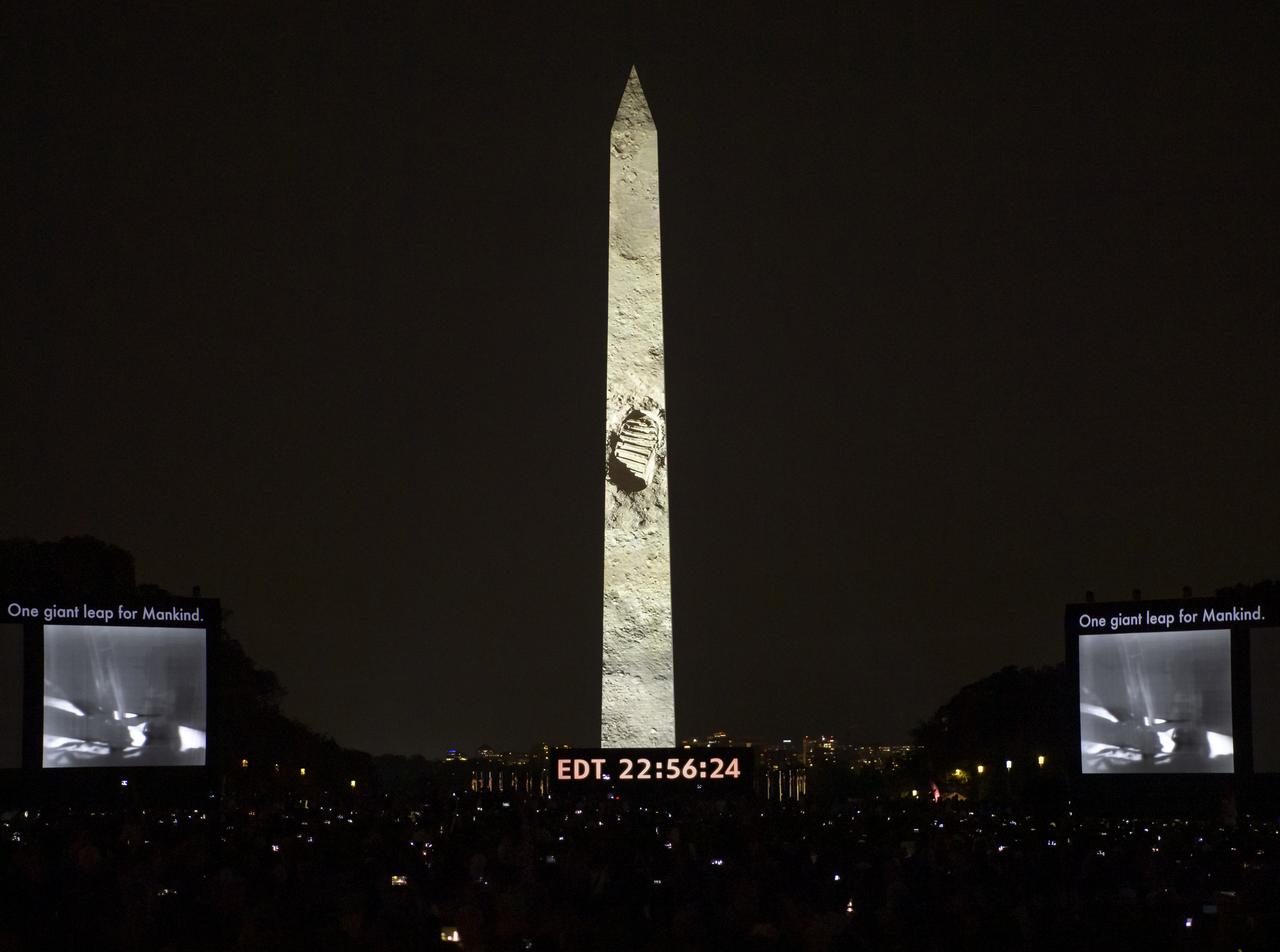

The 50 year anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission with NASA astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin is celebrated in a 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon”, by the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, which combined full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the Washington Monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing, Friday, July 19, 2019 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The 50 year anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission with NASA astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin is celebrated in a 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon”, by the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, which combined full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the Washington Monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing, Friday, July 19, 2019 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The 50 year anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission with NASA astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin is celebrated in a 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon”, by the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, which combined full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the Washington Monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing, Friday, July 19, 2019 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The 50 year anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission with NASA astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin is celebrated in a 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon”, by the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, which combined full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the Washington Monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing, Friday, July 19, 2019 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The 50 year anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission with NASA astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin is celebrated in a 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon”, by the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, which combined full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the Washington Monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing, Friday, July 19, 2019 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

S74-24913 (August 1973) --- An artist's concept illustrating an Apollo-type spacecraft (left) about to dock with a Soviet Soyuz-type spacecraft. A recent agreement between the United States (USA) and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republic (USSR) provides for the docking in space of the Soyuz and Apollo-type spacecraft in Earth orbit in 1975. The joint space venture is called the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP).
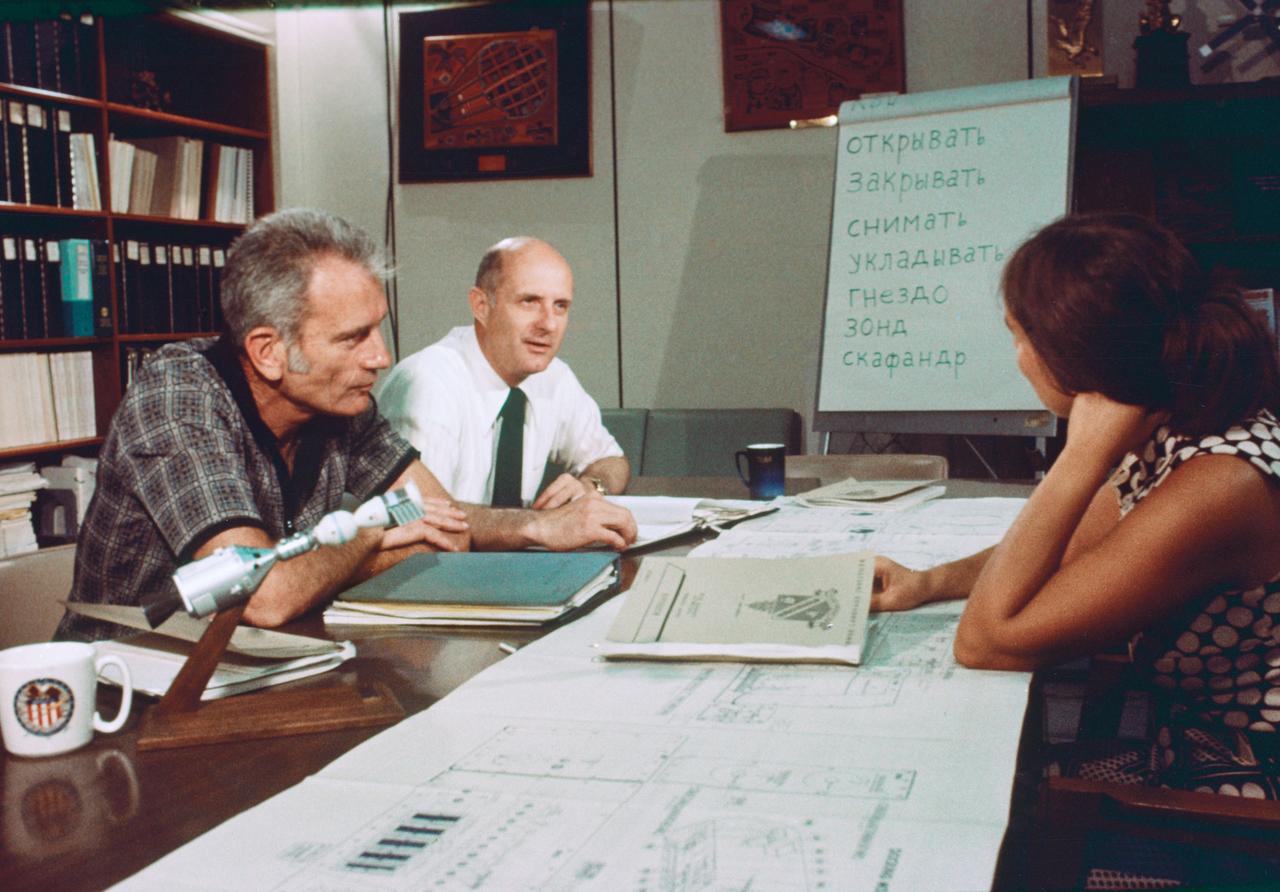

Apollo Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) astronauts Donald K. Slayton, docking module pilot; and Thomas P. Stafford, commander are photographed during ASTP Russian language class.
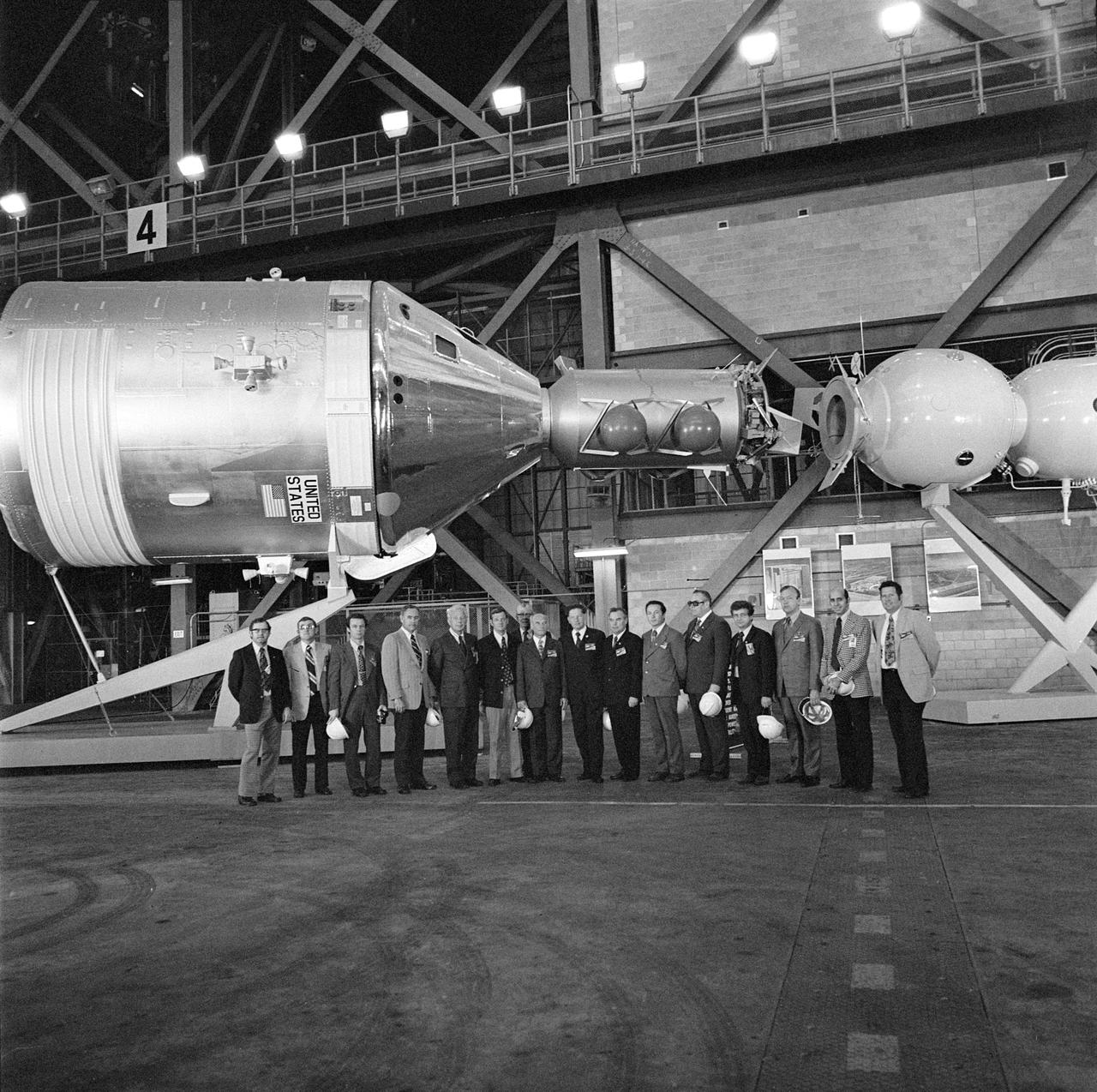

S75-24026 (4 Feb. 1975) --- A group of Soviet and American ASTP officials during a tour of the Kennedy Space Center. They were photographed next to the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking in Earth orbit mock-up at KSC.
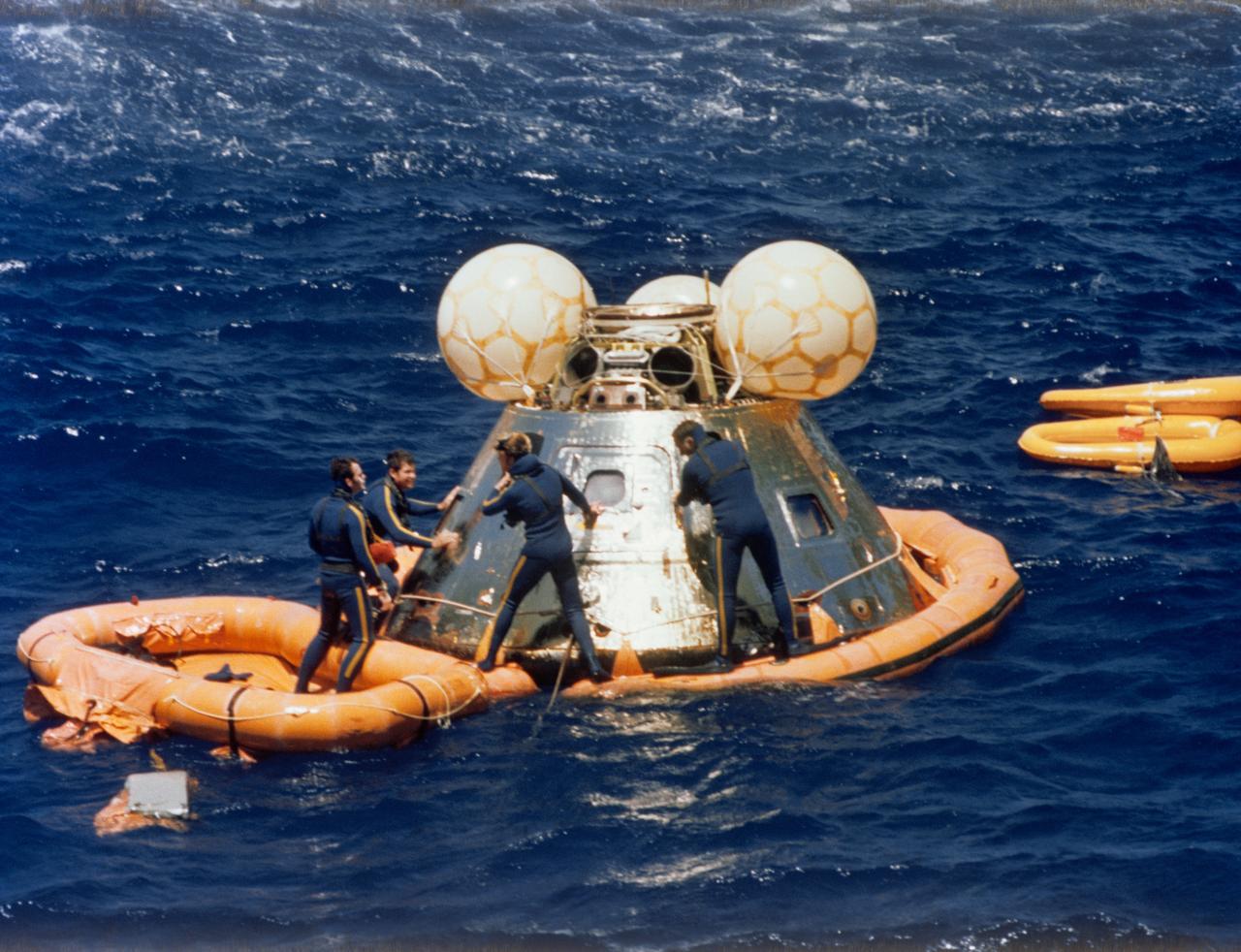

S75-29715 (24 July 1975) --- A team of U.S. Navy swimmers assists with the recovery of the ASTP Apollo Command Module following its splashdown in the Central Pacific Ocean to conclude the historic joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The swimmers have already attached a flotation collar to the spacecraft. The CM touched down in the Hawaiian Islands area at 4:18 p.m. (CDT), July 24, 1975. The crewmen, astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. Slayton, remained in the CM until it was hoisted aboard the prime recovery ship, the USS New Orleans.
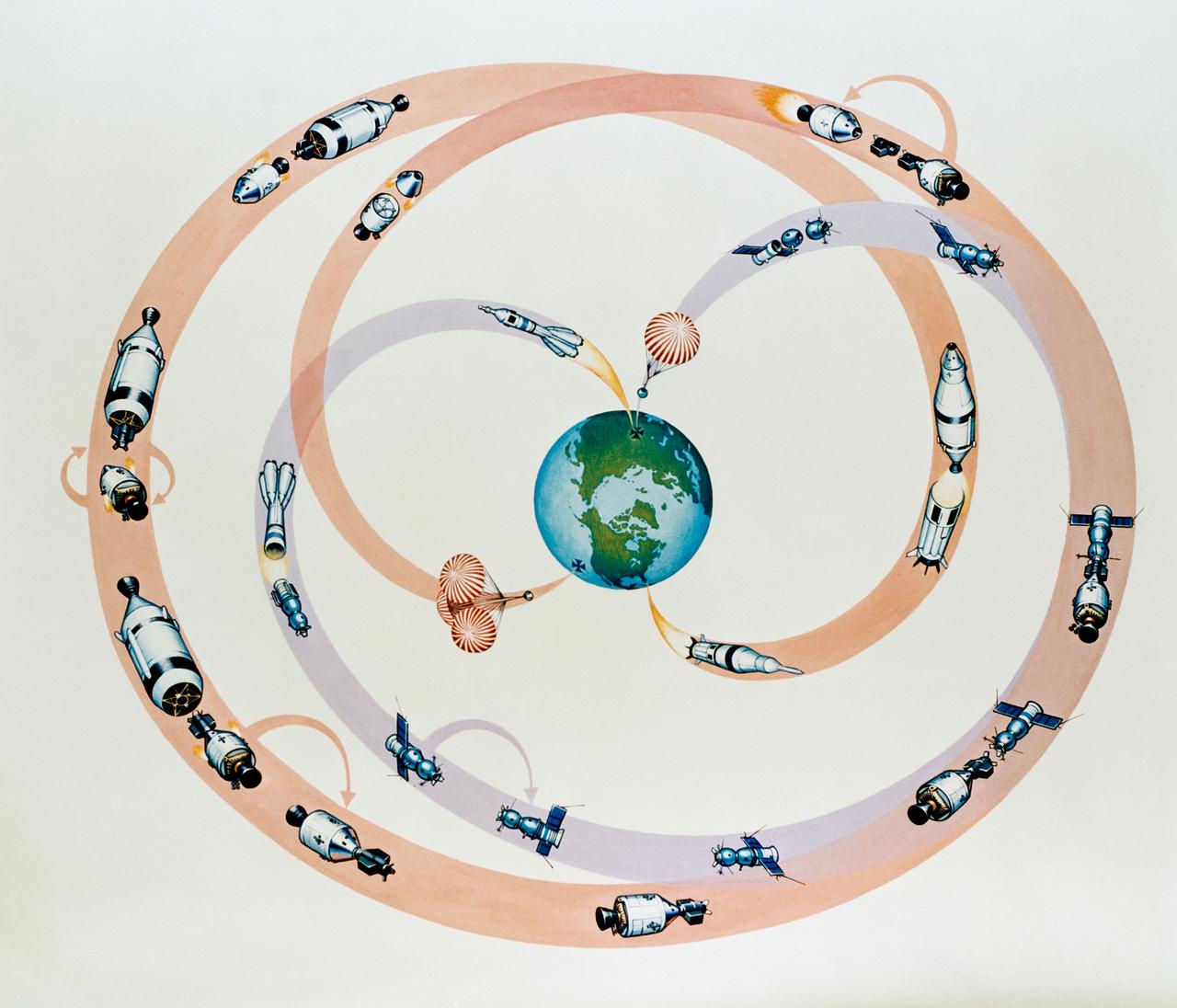

S75-27288 (April 1975) --- An artist?s concept illustrating the mission profile of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. The phases of the mission depicted include launch, rendezvous, docking, separation and splashdown. During the joint U.S.-USSR ASTP flight, scheduled for July 1975, the American and Soviet crews will visit one another?s spacecraft while the Soyuz and Apollo are docked for a maximum period of two days. The mission is designed to test equipment and techniques that will establish international crew rescue capability in space, as well as permit future cooperative scientific missions. This artwork is by Davis Meltzer.

S75-28485 (12 July 1975) --- Astronaut Vance D. Brand, command module pilot of the American ASTP prime crew, practices operating a Docking Module hatch during Apollo-Soyuz Test Project preflight training at NASA's Johnson Space Center. The Docking Module is designed to link the Apollo and Soyuz spacecraft during their docking mission in Earth orbit. Gary L. Doerre of JSC?s Crew Training and Procedures Division is working with Brand. Doerre is wearing a face mask to help prevent possible exposure to Brand of disease prior to the ASTP launch.
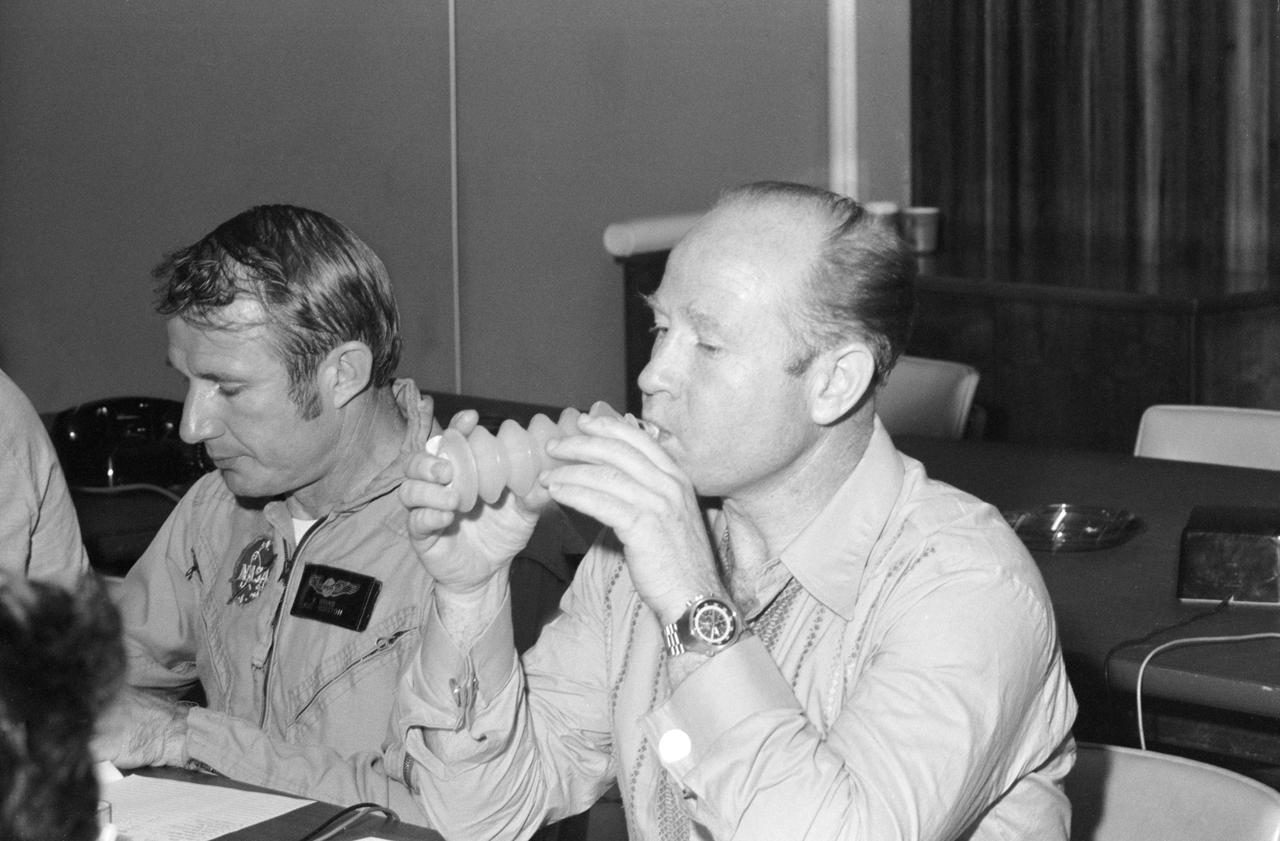

S74-20798 (23 April 1974) --- Candidate food items being considered for the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission are sampled by two ASTP crewmen in Building 4 at the Johnson Space Center. They are, left to right, astronaut Vance D. Brand, command module pilot of the American ASTP crew; and cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov, commander of the Soviet ASTP crew. Leonov is drinking orange juice from an accordion-like dispenser. The two Soviet crewmen will have an opportunity to eat with the three American crewmen while the Apollo and Soyuz spacecraft are docked in Earth orbit. Leonov will dine on food being chosen by him now.
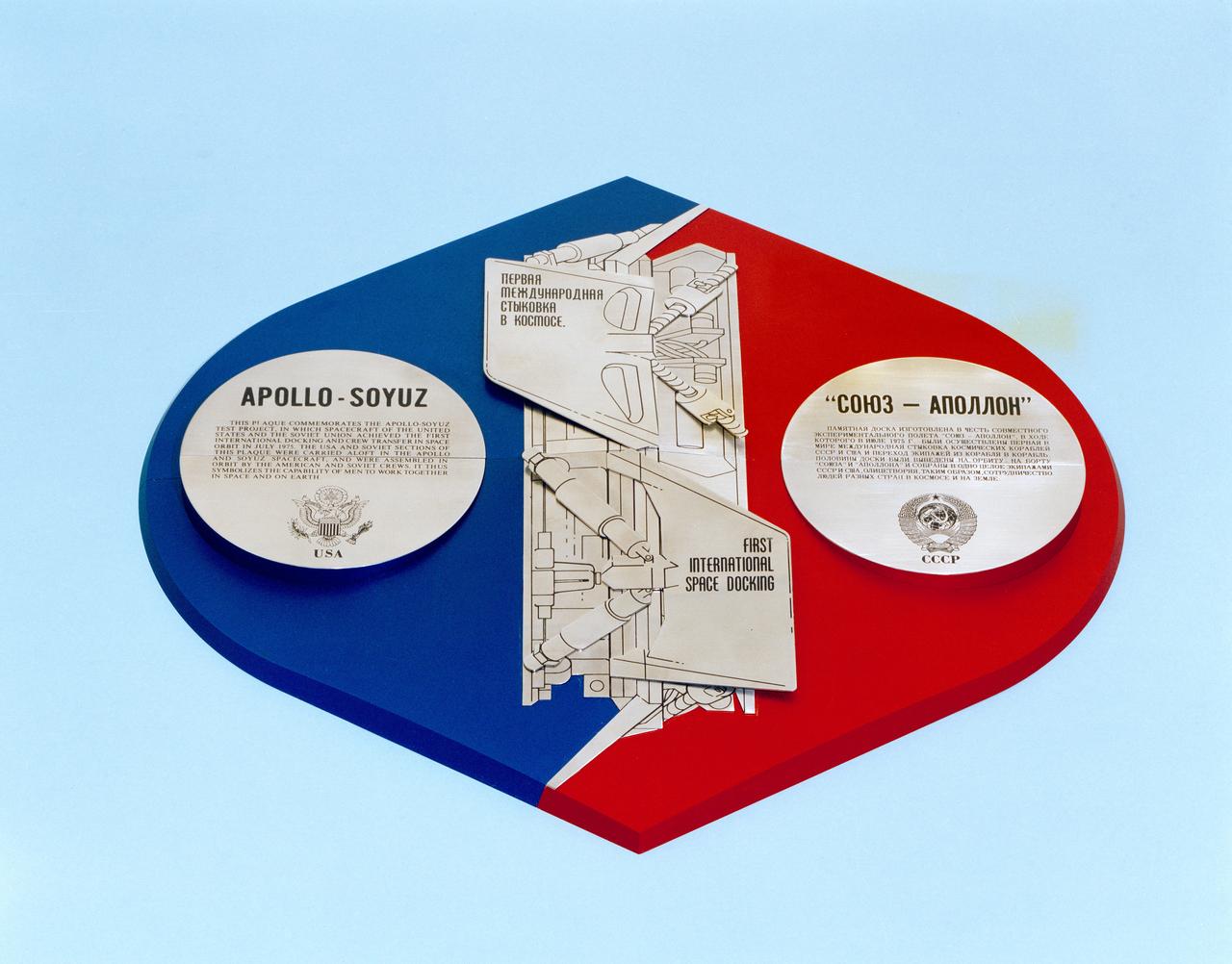
S75-26927 (July 1975) --- A close-up view of the Commemorative Plaque for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. Two plaques divided into four quarters each will be flown on the ASTP mission. A four-part plaque is completely assembled here. The American ASTP crew will carry the four U.S. quarter pieces aboard Apollo; and the Soviet ASTP crew will carry the four USSR quarter sections aboard Soyuz. The eight quarter pieces will be joined together to form two complete commemorative plaques after the two spacecraft rendezvous and dock in Earth orbit. One complete plaque then will be returned to Earth by the astronauts; and the other complete plaque will be brought back by the cosmonauts. The plaque is written in both English and Russian.
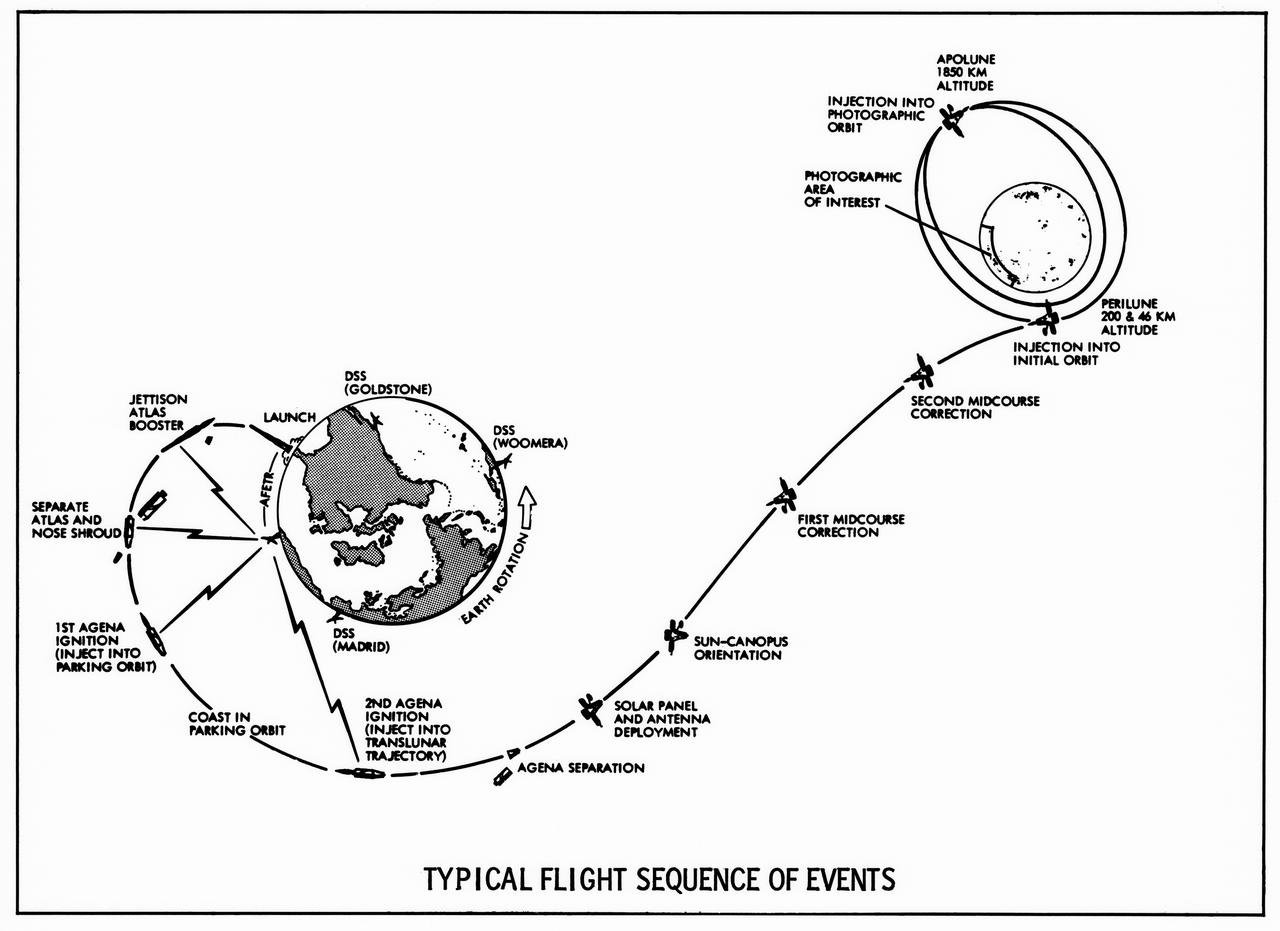
Lunar Orbiter's "Typical Flight sequence of Events" turned out to be quite typical indeed, as all five spacecraft performed exactly as planned. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 340.
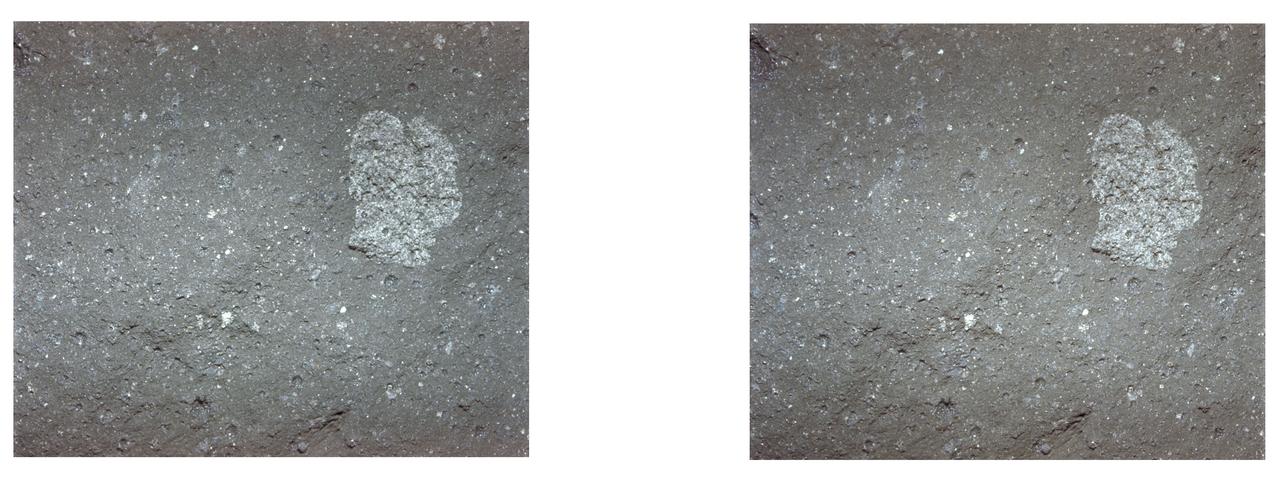
AS11-45-6709 (20 July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 stereo view of the surface of a lunar rock showing an embedded three-fourths inch fragment of a different color. On the surface several small pits are seen; mostly less than one-eighth inch in size, and with a glazed surface. They have a raised rim, characteristic of pits made by high-velocity micro meteorite impacts. The exposure was made by the Apollo 11 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was specially developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. A three-inch square area is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. The pictures are in color and give a stereo view, enabling the fine detail to be seen very clearly. The project is under the direction of Professor T. Gold of Cornell University and Mr. F. Pearce of NASA. The camera was designed and built by Eastman Kodak. Professor E. Purcell of Harvard University and Dr. E. Land of the Polaroid Corporation have contributed to the project. The pictures brought back from the moon by the Apollo 11 crew are of excellent quality and allow fine detail of the undisturbed lunar surface to be seen. Scientists hope to be able to deduce from them some of the processes that have taken place that have shaped and modified the surface.
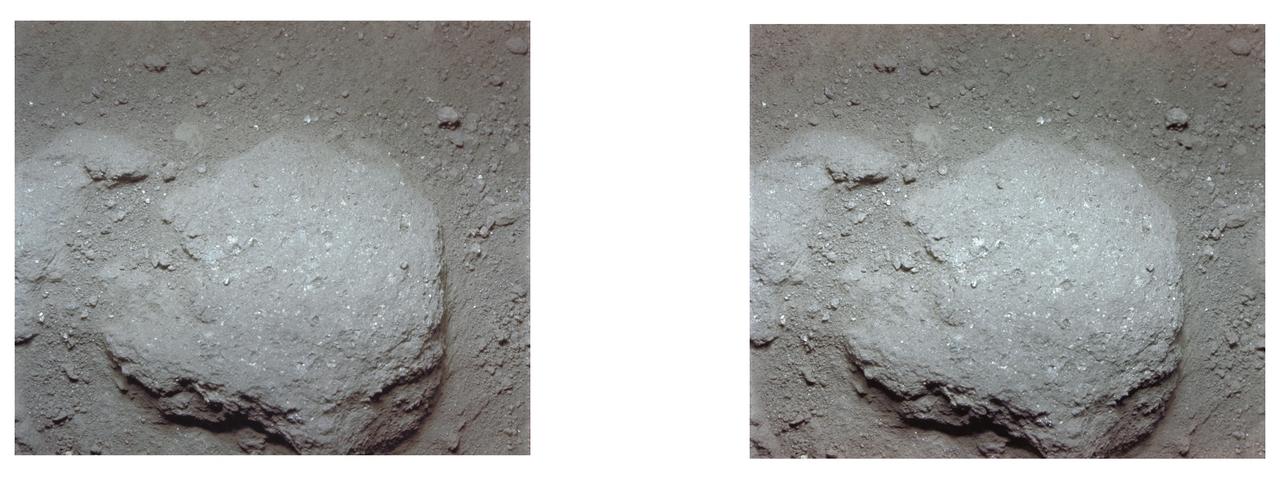

AS11-45-6712 (20 July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 stereo view of a stone, about two and one-half inches long, embedded in the powdery lunar surface material. The little pieces closely around it suggest that it has suffered some erosion. On the surface several small pits are seen, mostly less than one-eighth inch in size, and with a glazed surface. They have a raised rim, characteristic of pits made by the Apollo 11 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was specially developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. A three-inch square area is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. The pictures are in color and give a stereo view, enabling the fine detail to be seen very clearly. The project is under the direction of Professor T. Gold of Cornell University and Mr. F. Pearce of NASA. The camera was designed and built by Eastman Kodak. Professor E. Purcell of Harvard University and Dr. E. Land of the Polaroid Corporation have contributed to the project. The pictures brought back from the moon by the Apollo 11 crew are of excellent quality and allow fine detail of the undisturbed lunar surface to be seen. Scientists hope to be able to deduce from them some of the processes that have taken place that have shaped and modified the surface.
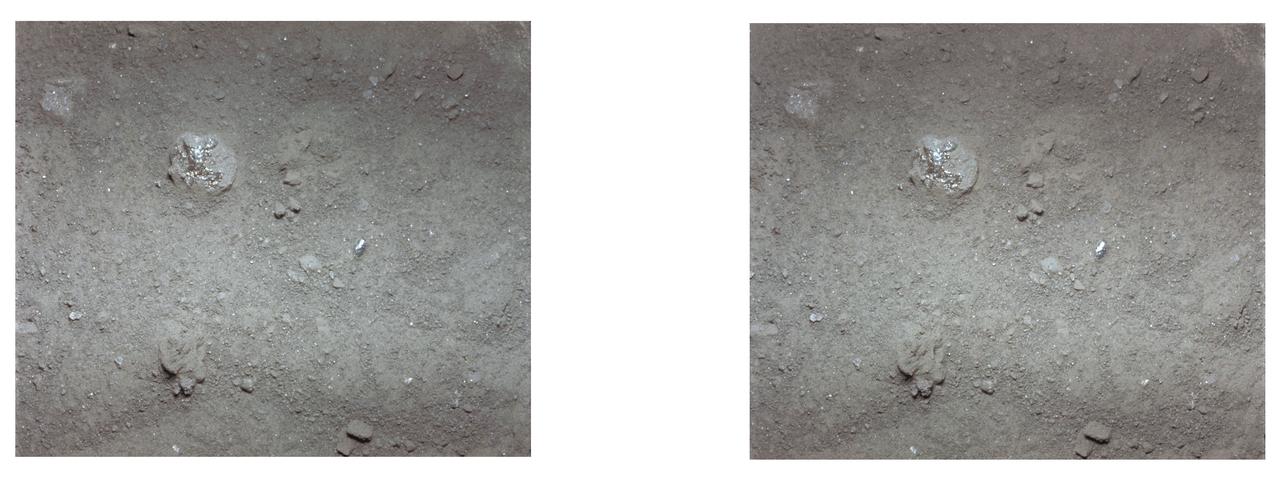
AS11-45-6704 (20 July 1969) --- An Apollo stereo view showing a close-up of a small lump of lunar surface powder about a half inch across, with a splash of a glassy material over it. It seems that a drop of molten material fell on it, splashed and froze. The exposure was made by the Apollo 11 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was specially developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. A three-inch square area is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. The pictures are in color and give a stereo view, enabling the fine detail to be seen very clearly. The project is under the direction of Professor T. Gold of Cornell University and Dr. F. Pearce of NASA. The camera was designed and built by Eastman Kodak. Professor E. Purcell of Harvard University and Dr. E. Land of the Polaroid Corporation have contributed to the project. The pictures brought back from the moon by the Apollo 11 crew are of excellent quality and allow fine detail of the undisturbed lunar surface to be seen. Scientists hope to be able to deduce from them some of the processes that have taken place that have shaped and modified the surface.
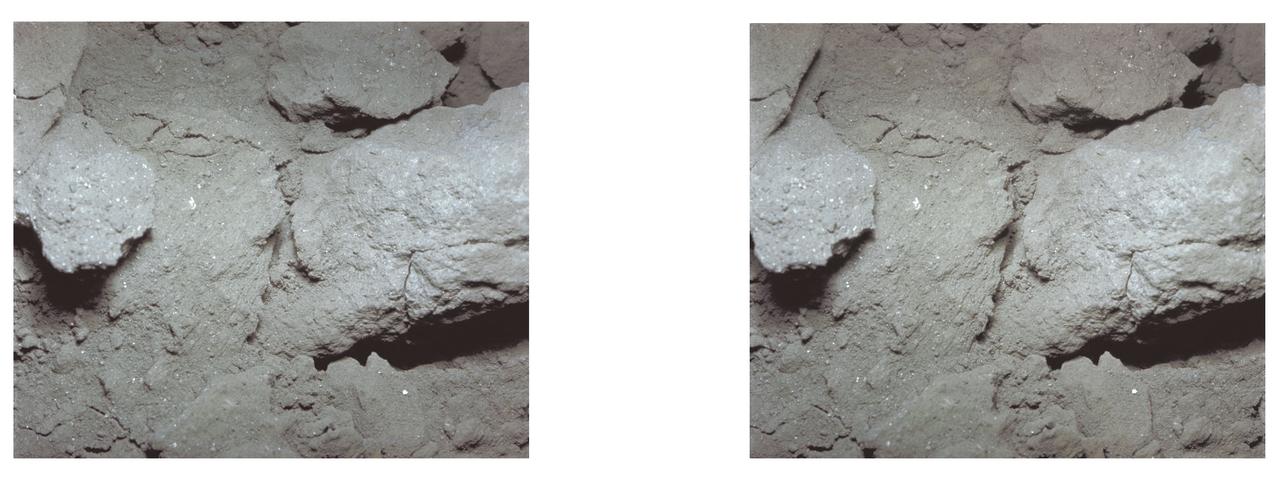

AS11-45-6706 (20 July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 stereo view showing a clump of lunar surface powder, with various small pieces of different color. Many small, shiny spherical particles can be seen. The picture is three inches across. The exposure was made by the Apollo 11 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was specially developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. A three-inch square area is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. The pictures are in color and give a stereo view, enabling the fine detail to be seen very clearly. The project is under the direction of Professor T. Gold of Cornell University and Mr. F. Pearce of NASA. The camera was designed and built by Eastman Kodak. Professor E. Purcell of Harvard University and Dr. E. Land of the Polaroid Corporation have contributed to the project. The pictures brought back from the moon by the Apollo 11 crew are of excellent quality and allow fine detail of the undisturbed lunar surface to be seen. Scientists hope to be able to deduce from them some of the processes that have taken place that have shaped and modified the surface.
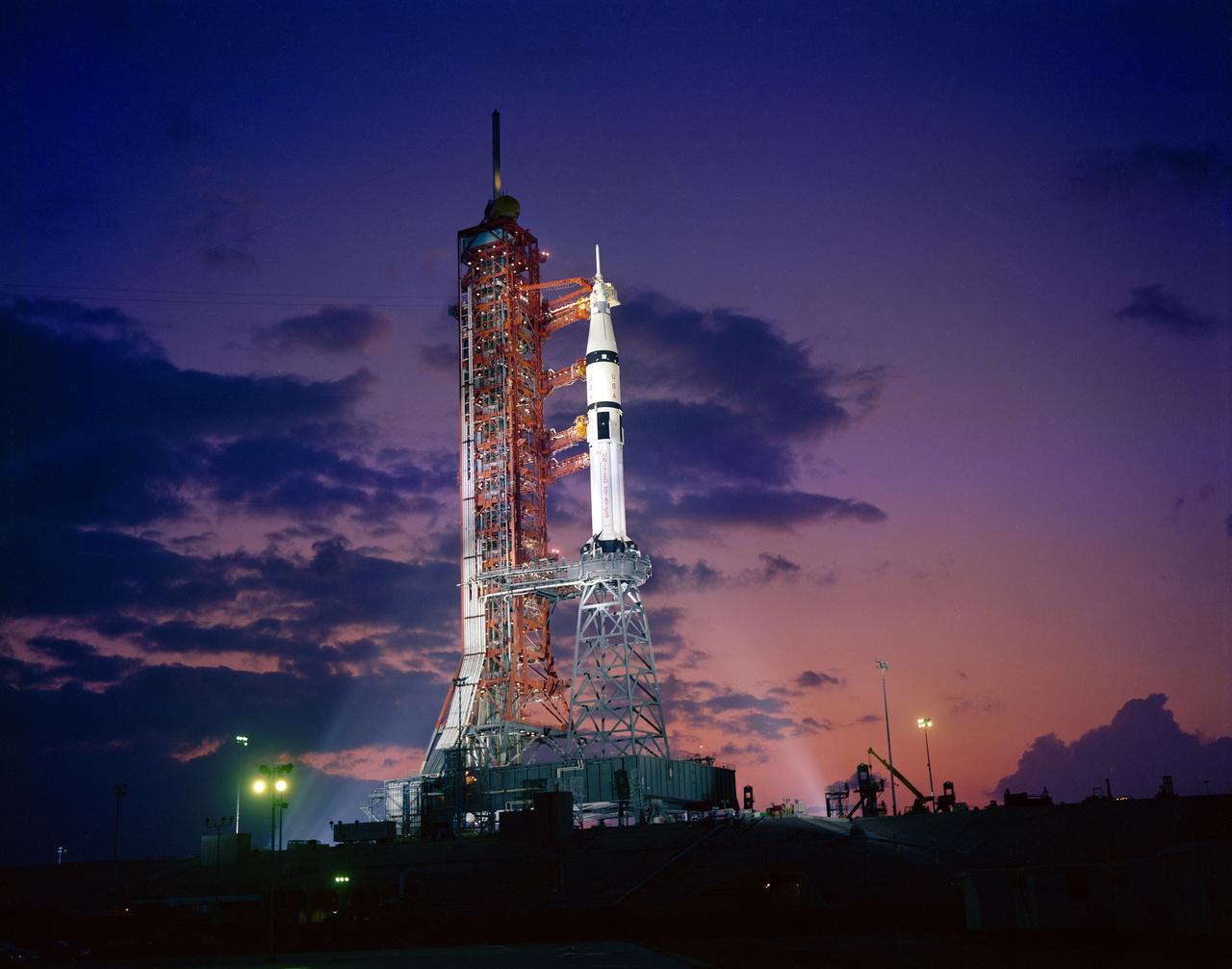

S75-28386 (2 July 1975) --- An early morning view of Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, showing the ASTP Apollo/Saturn 1B space vehicle on the pad during Apollo-Soyuz Test Project prelaunch preparations. An ASTP countdown demonstration "wet" test (CDDT) was being conducted at KSC when this photograph was taken. The liftoff was on July 15, 1975.

Panoramas of Apollo sites are required to familiarize various Constellation projects with the actual nature of the lunar surface. This image is the first of a multi-framed panorama photographed from a point some 30 or 40 feet west of the plus-Z (west) footpad of the Lunar Module "Eagle." The view is looking toward the southwest showing part of the horizon crater rim that was pointed out as being visible from the Eagle's window. Image taken at Tranquility Base. View was created using Apollo 11 images - mag 40 frames 5881 thru 5891.
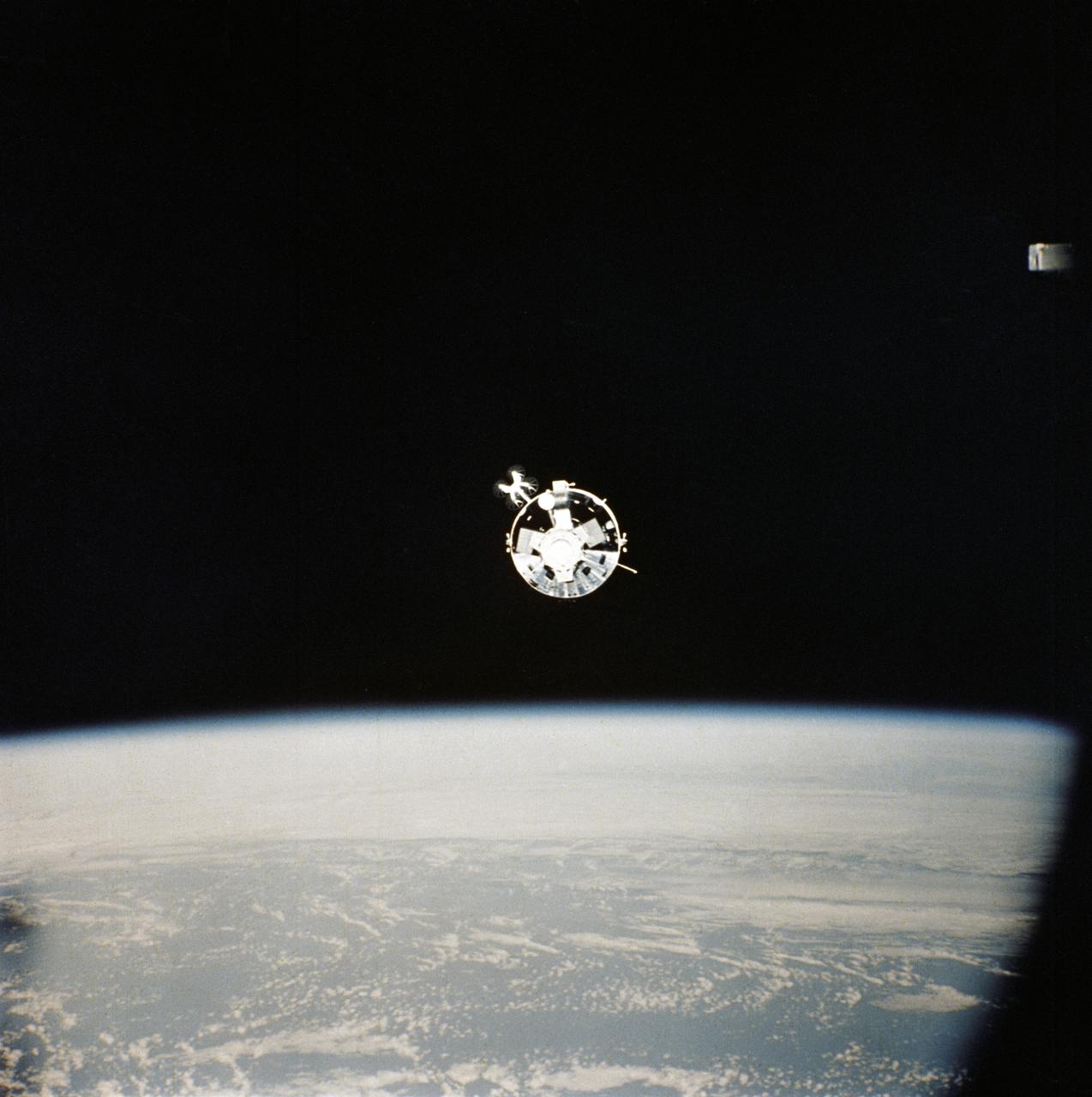

AST-32-2675 (17-19 July 1975) --- The American Apollo spacecraft as seen in Earth orbit from the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Command/Service Module and Docking Module are contrasted against a black-sky background. This is a "head on" view of the Apollo. The horizon of Earth is below. This picture was furnished by the USSR in an exchange of photography taken during the ASTP flight. The American and Soviet spacecraft were joined together in space for approximately 47 hours on July 17-18-19, 1975. Note the docking mechanism on the Docking Module. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
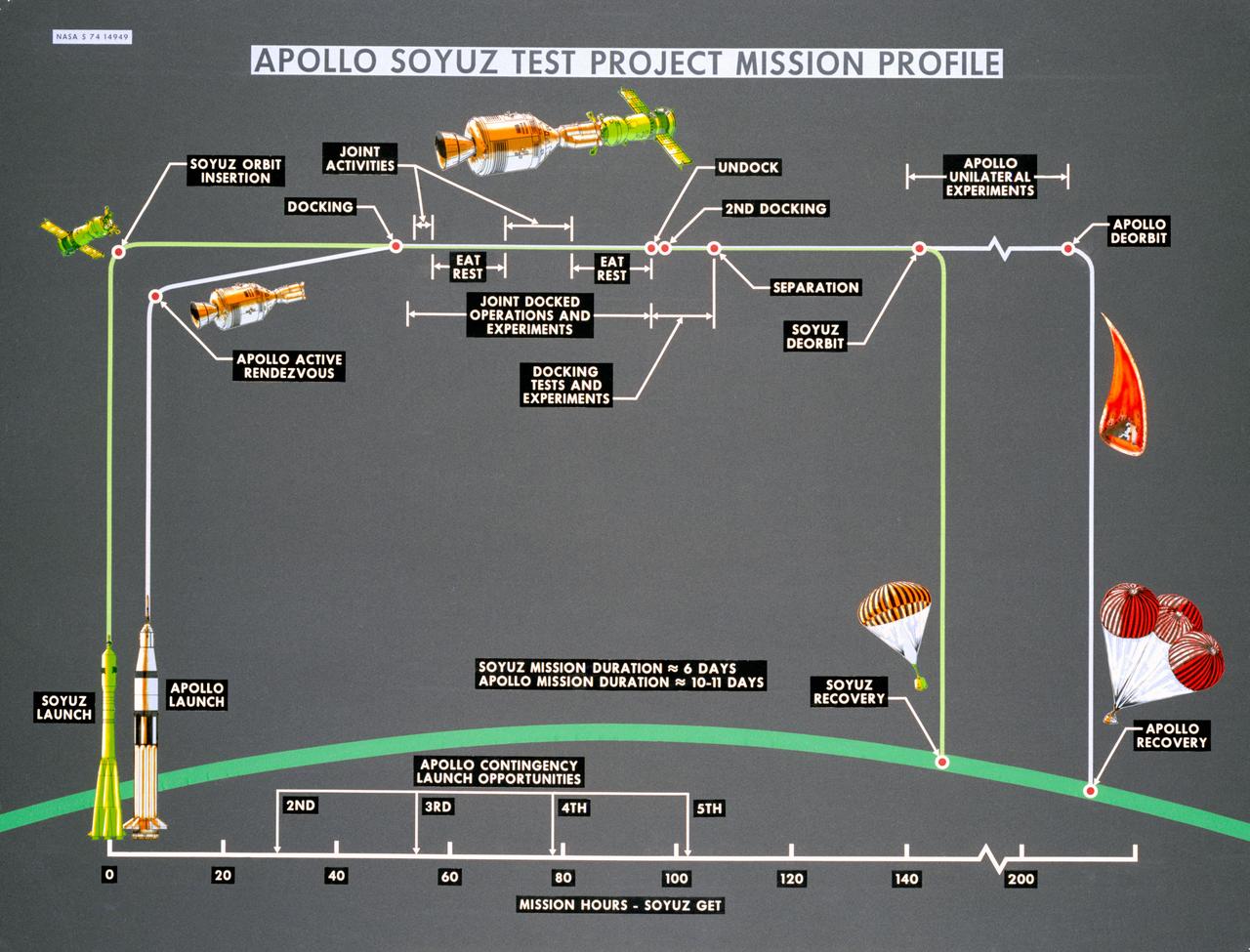
S74-14949 (October 1974) --- Artist?s drawings and call-outs depict phases of the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, an Earth-orbital mission which will feature rendezvous and docking of the respective spacecraft of the two nations. ASTP crewmen for the USSR include Aleksey A. Leonov and Valeriy N. Kubasov. The astronaut team includes astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. Slayton. The mission is scheduled to take place in summer 1975.
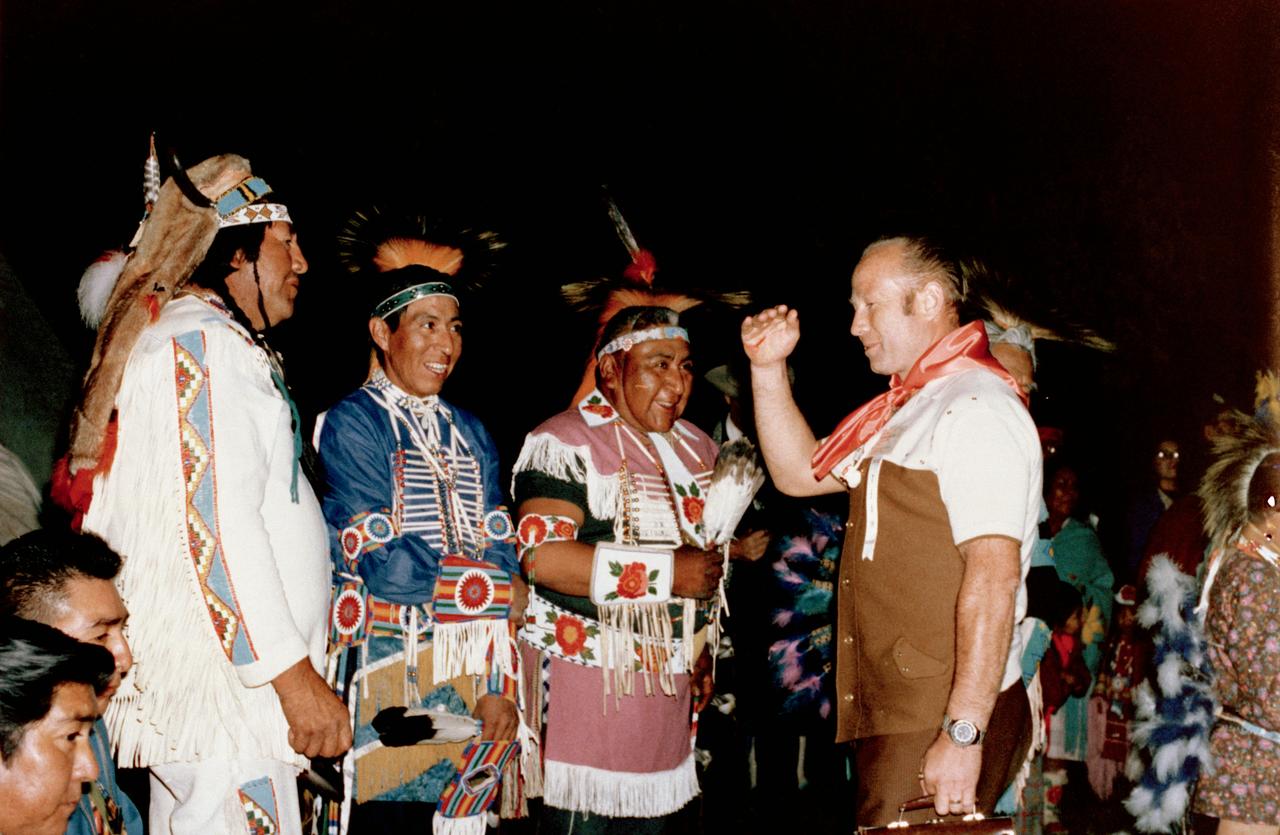

S75-20108 (September 1974) --- Cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov (right), commander of the first (prime) crew of Soviet cosmonauts on the planned Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP), enjoys a tribal welcome from Shoshone Indians during a hunting trip in the Lander, Wyoming area. Leonov was in the United States to take part in joint crew training at the Johnson Space Center.
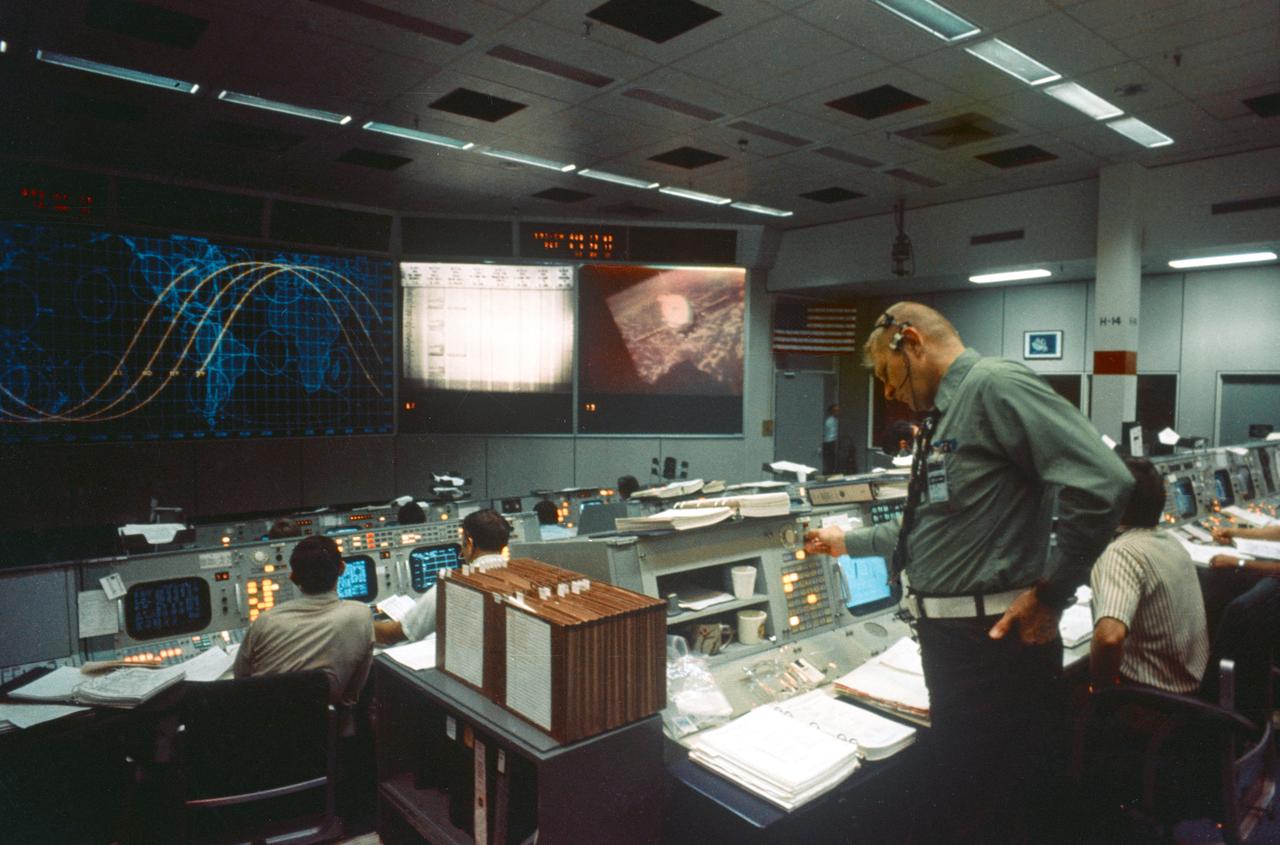

S75-28682 (17 July 1975) --- An overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. The large television monitor shows a view of the Soyuz spacecraft as seen from the Apollo spacecraft during rendezvous and docking maneuvers. Eugene F. Kranz, JSC Deputy Director of Flight Operations, is standing in the foreground. M.P. Frank, the American senior ASTP flight director, is partially obscured on the right.
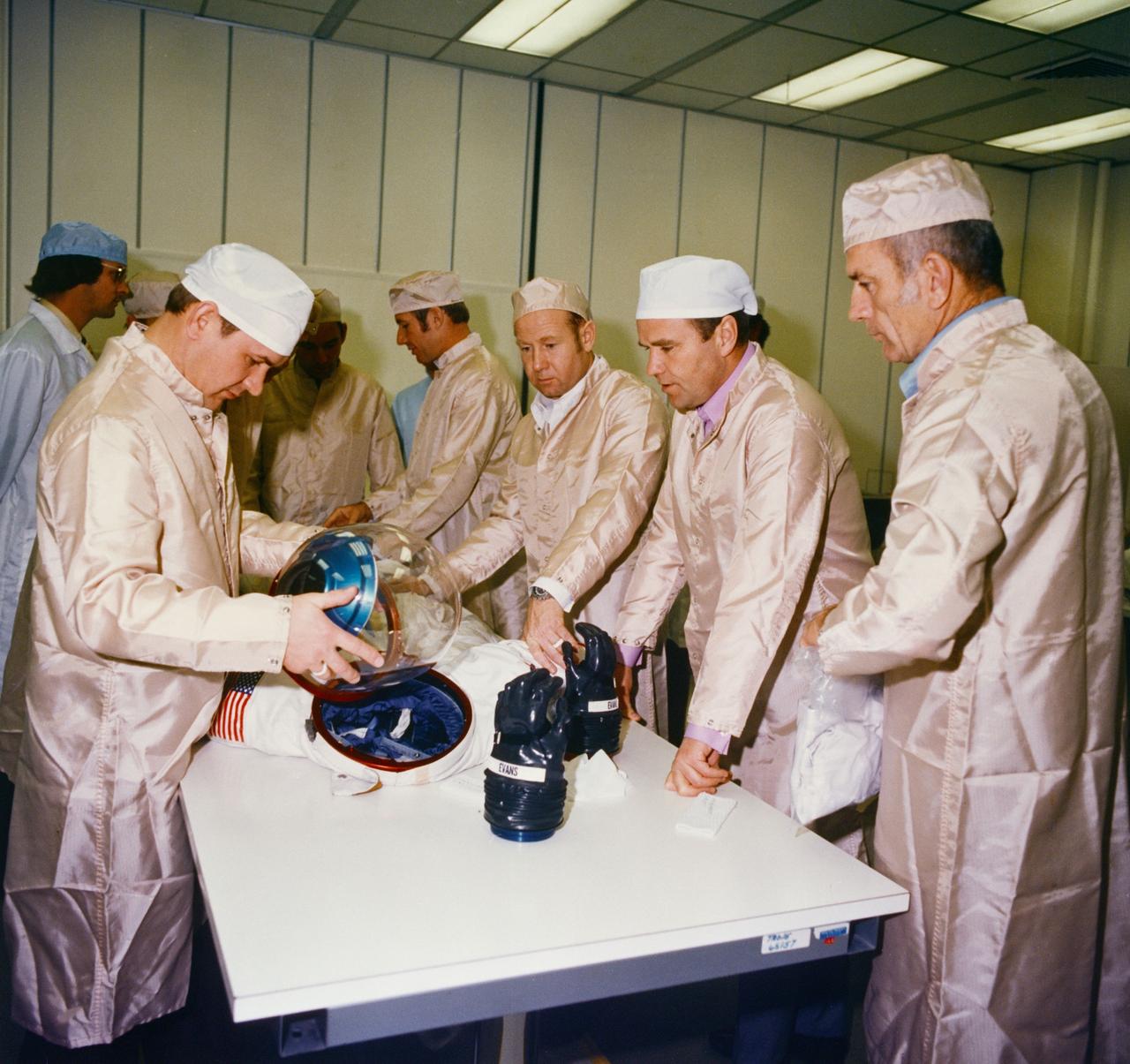

S75-24108 (8-10 Feb. 1975) --- A group of Apollo-Soyuz Test Project crewmen inspects an Apollo spacesuit during a three-day tour of NASA's Kennedy Space Center. They were at KSC to look over ASTP launch facilities and flight hardware. The six men wearing white caps are, left to right, cosmonaut Valeriy N. Kubasov, interpreter K.S. Samofal (far end of table), astronaut Vance D. Brand, cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov, cosmonaut Vladimir A. Shatalov and astronaut Donald K. Slayton.
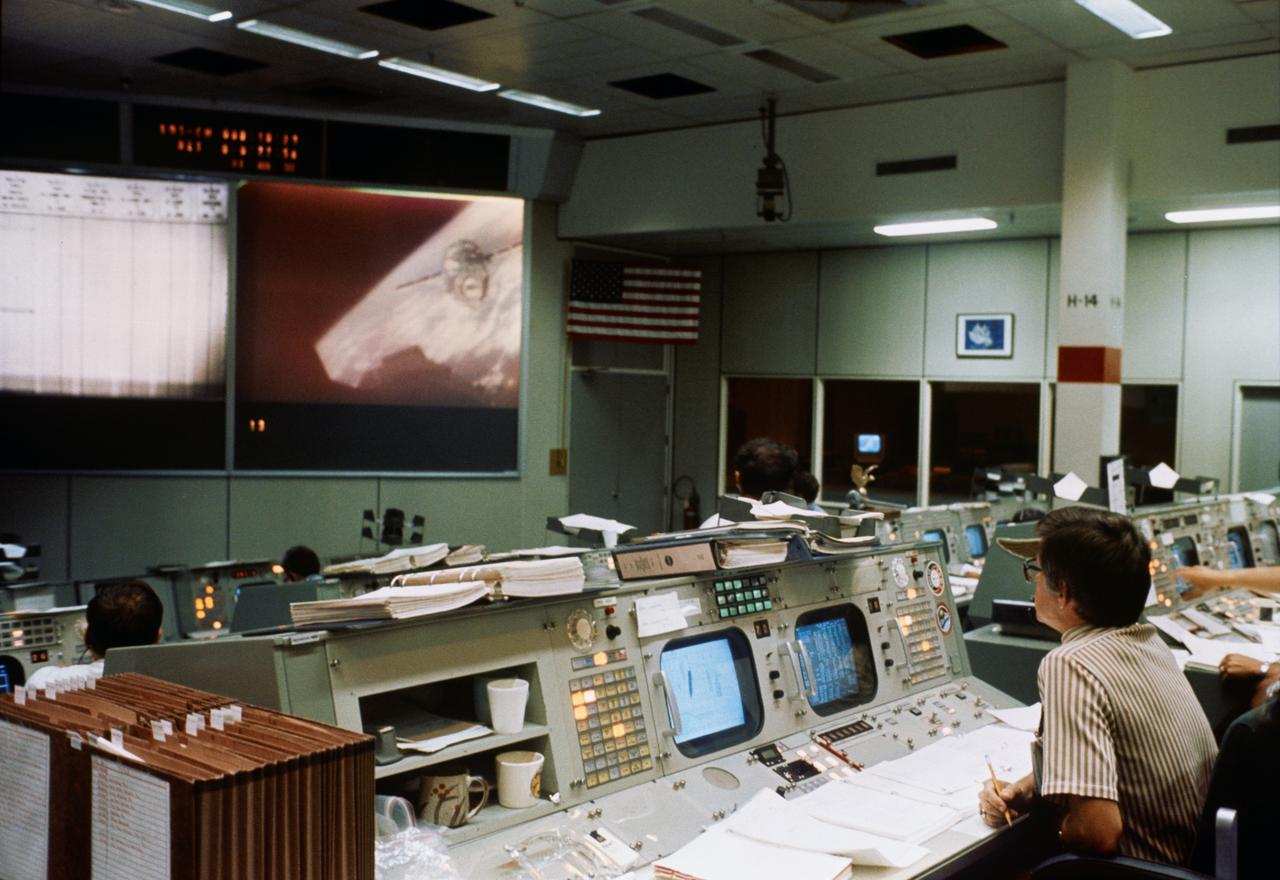

S75-28683 (17 July 1975) --- An overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. M.P. Frank, the American senior ASTP flight director, is seated at his console in the right foreground. He is watching the large television monitor which shows a view of the Soyuz spacecraft as seen from the Apollo spacecraft during rendezvous and docking maneuvers.
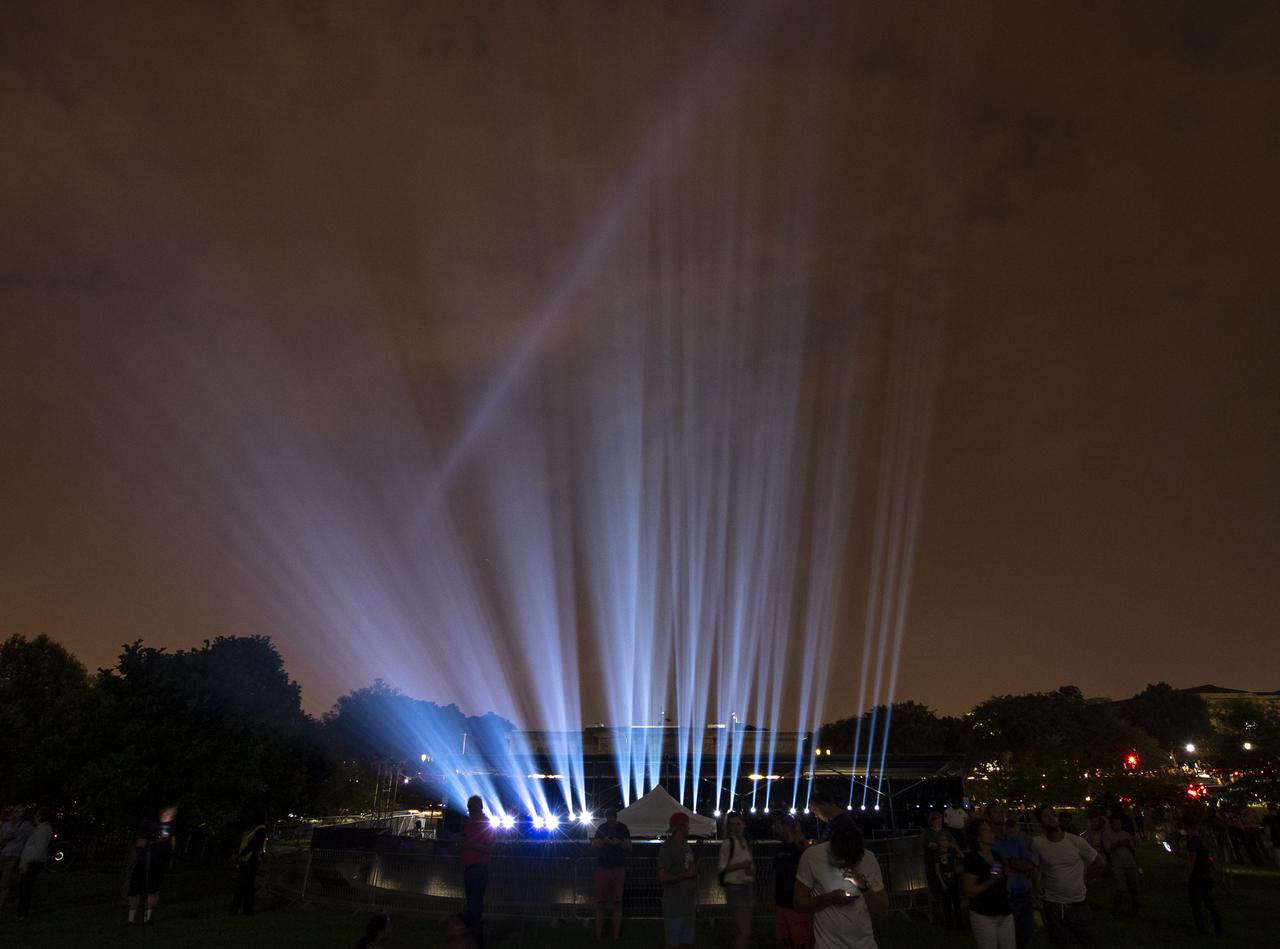

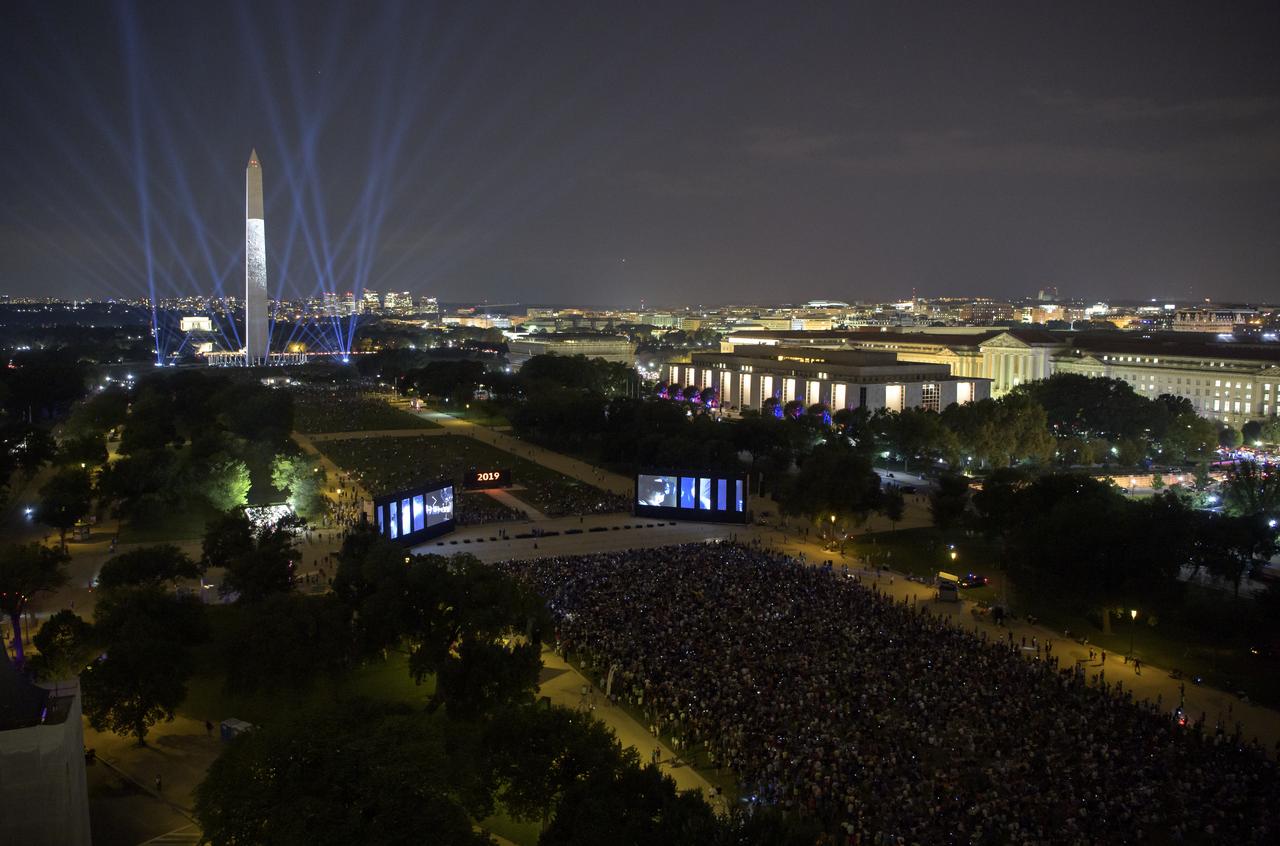
Projectors used to display a full-sized, 363-foot Saturn V rocket at the Washington Monument are seen 50 years to the day after astronauts Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Buzz Aldrin launched on Apollo 11, the first mission to land astronauts on the Moon, Tuesday, July 16, 2019. On Friday, July 19, and Saturday, July 20, a special 17-minute show, “Apollo 50: Go for the Moon” will combine full-motion projection-mapping artwork on the monument and archival footage to recreate the launch of Apollo 11 and tell the story of the first moon landing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
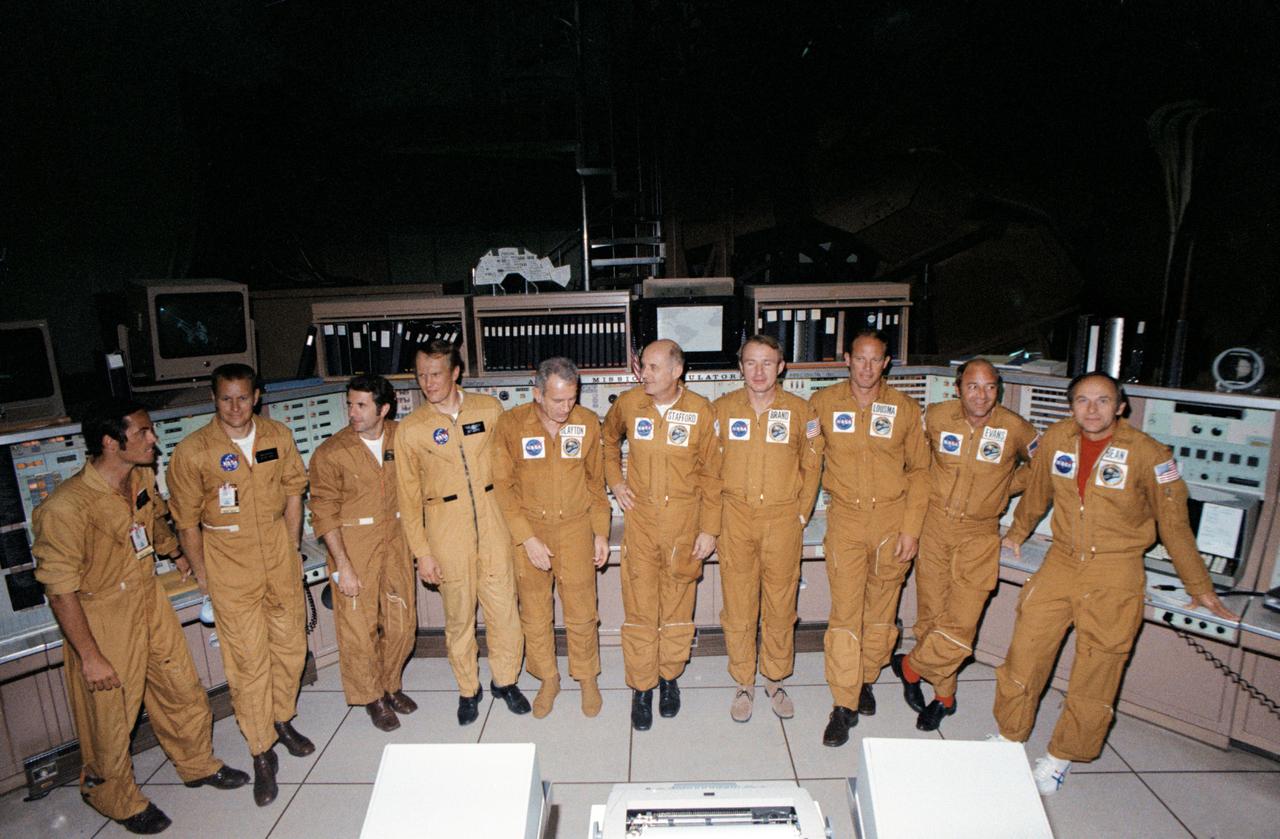

S75-28361 (9 July 1975) --- These ten American astronauts compose the U.S. prime crew, the backup crew and the crew support team for the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. They are, left to right, Robert L. Crippen, support team; Robert F. Overmyer, support team; Richard H. Truly, support team; Karol J. Bobko, support team; Donald K. Slayton, prime crew docking module pilot; Thomas P. Stafford, prime crew commander; Vance D. Brand, prime crew command module pilot; Jack R. Lousma, backup crew docking module pilot; Ronald E. Evans, backup crew command module pilot; and Alan L. Bean, backup crew commander. They are photographed by the Apollo Mission Simulator console in Building 5 at NASA's Johnson Space Center.
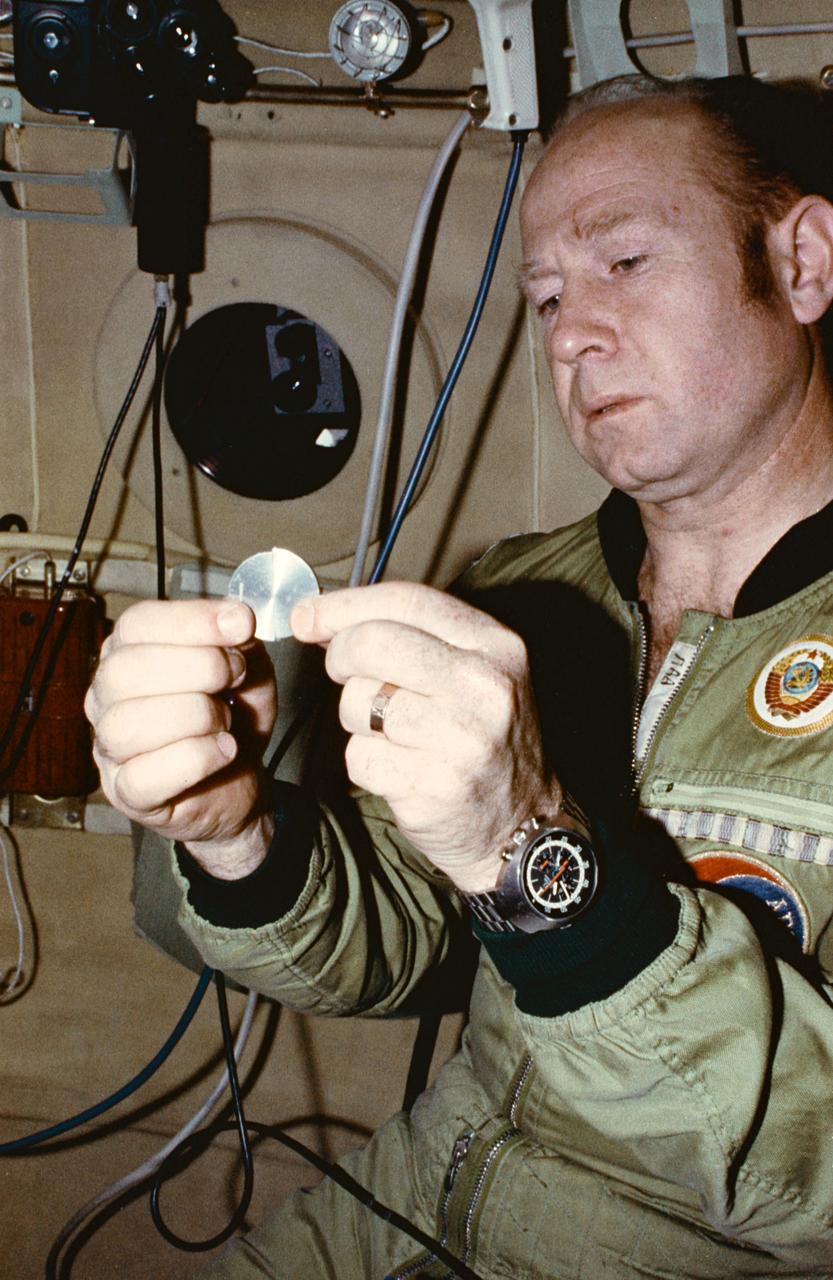

S75-24926 (April 1975) --- Cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov, commander of the Soviet ASTP prime crew, practices with a training mock-up of the ASTP commemorative medal during Apollo-Soyuz Test Project activity at the Cosmonaut Training Center (Star City) near Moscow. Leonov is in the Soyuz orbital module trainer. Two medals divided into two halves each will be flown on the mission. The American ASTP crew will carry two halves aboard Apollo; and the Soviet ASTP crew will carry the other two halves aboard Soyuz. The four halves will be joined together to make two complete medals after the two spacecraft rendezvous and dock in Earth orbit. Grooved slots in the halves will allow the medals to be fitted together. One medal then will be returned to Earth by the astronauts; and the second medal will be brought back by the cosmonauts.
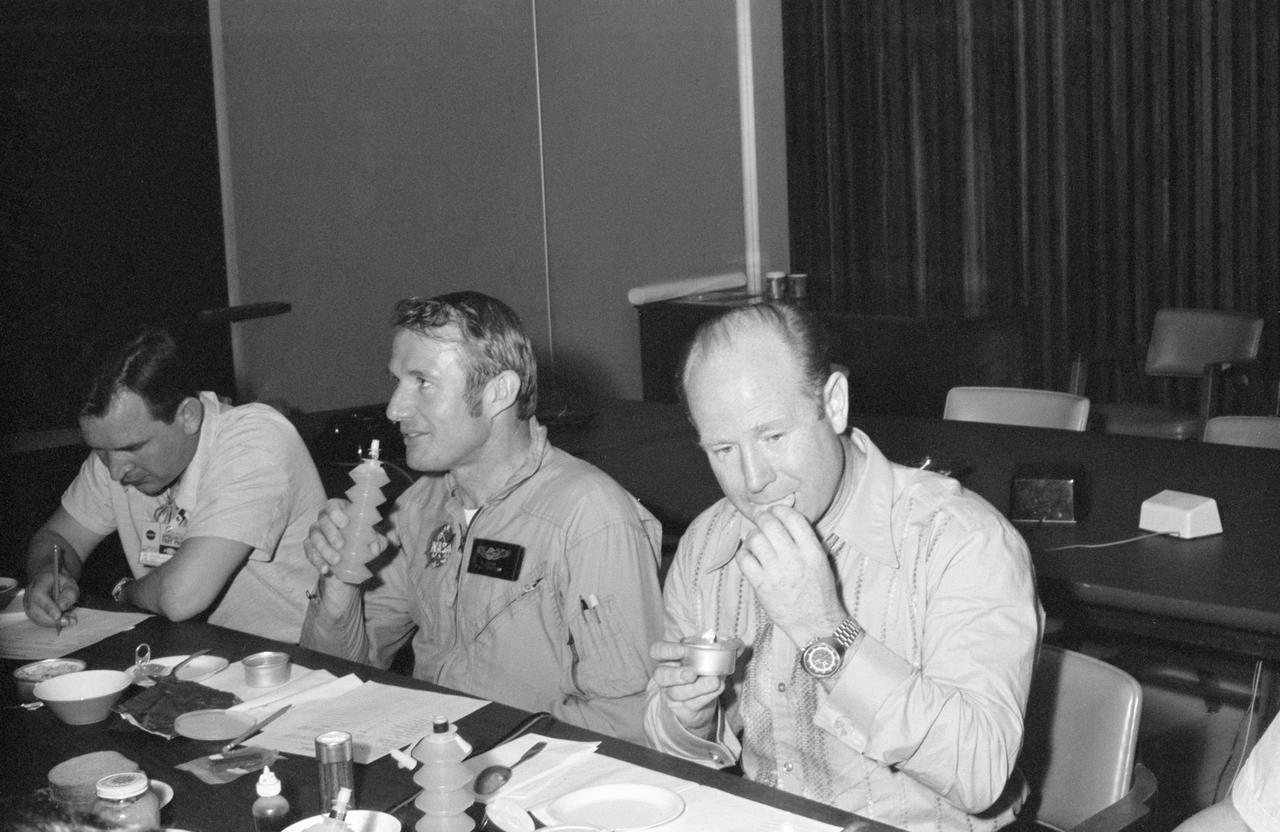

S74-20797 (23 April 1974) --- Candidate food items being considered for the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission are sampled by three ASTP crewmen in Building 4 at the Johnson Space Center. They are, left to right, cosmonaut Valeriy N. Kubasov, engineer on the Soviet ASTP crew; astronaut Vance D. Brand, command module pilot of the American ASTP crew; and cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov, commander of the Soviet ASTP crew. Kubasov is marking a food rating chart on which the crewmen mark their choices, likes and dislikes of the food being sampled. Brand is drinking orange juice from an accordion-like dispenser. Leonov is eating butter cookies. The two Soviet crewmen will have an opportunity to eat with the three American crewmen while the Apollo and Soyuz spacecraft are docked in Earth orbit. Leonov and Kubasov will dine on food being chosen individually by them now.
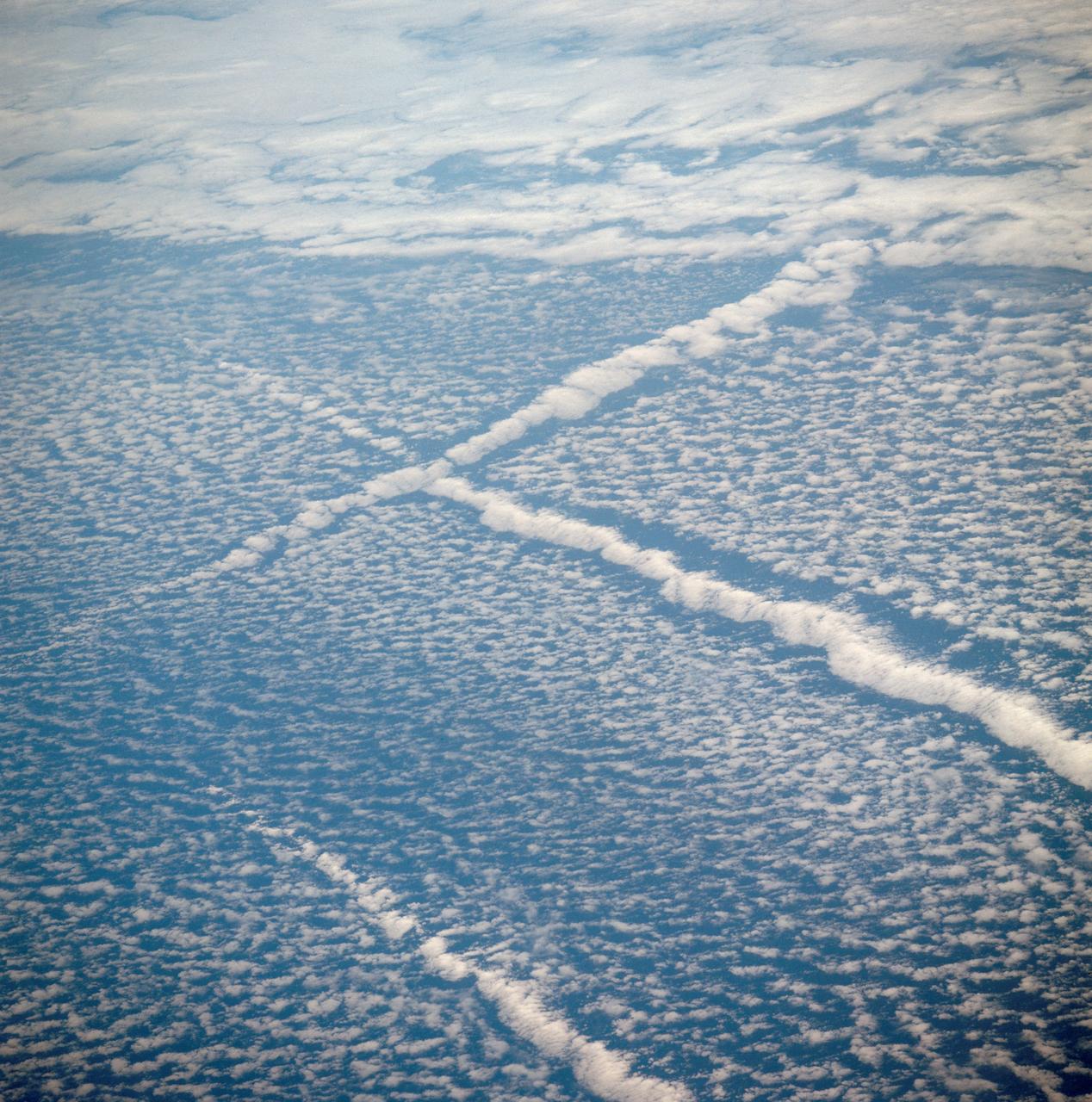

AST-01-042 (16 July 1975) --- An oblique view of unique cloud patterns over the Pacific Ocean caused by aircraft contrail shadows altering cumulus clouds and forming straight line clouds, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. This area is southwest of Los Angeles, California. This photograph was taken at an altitude of 177 kilometers (110 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film.
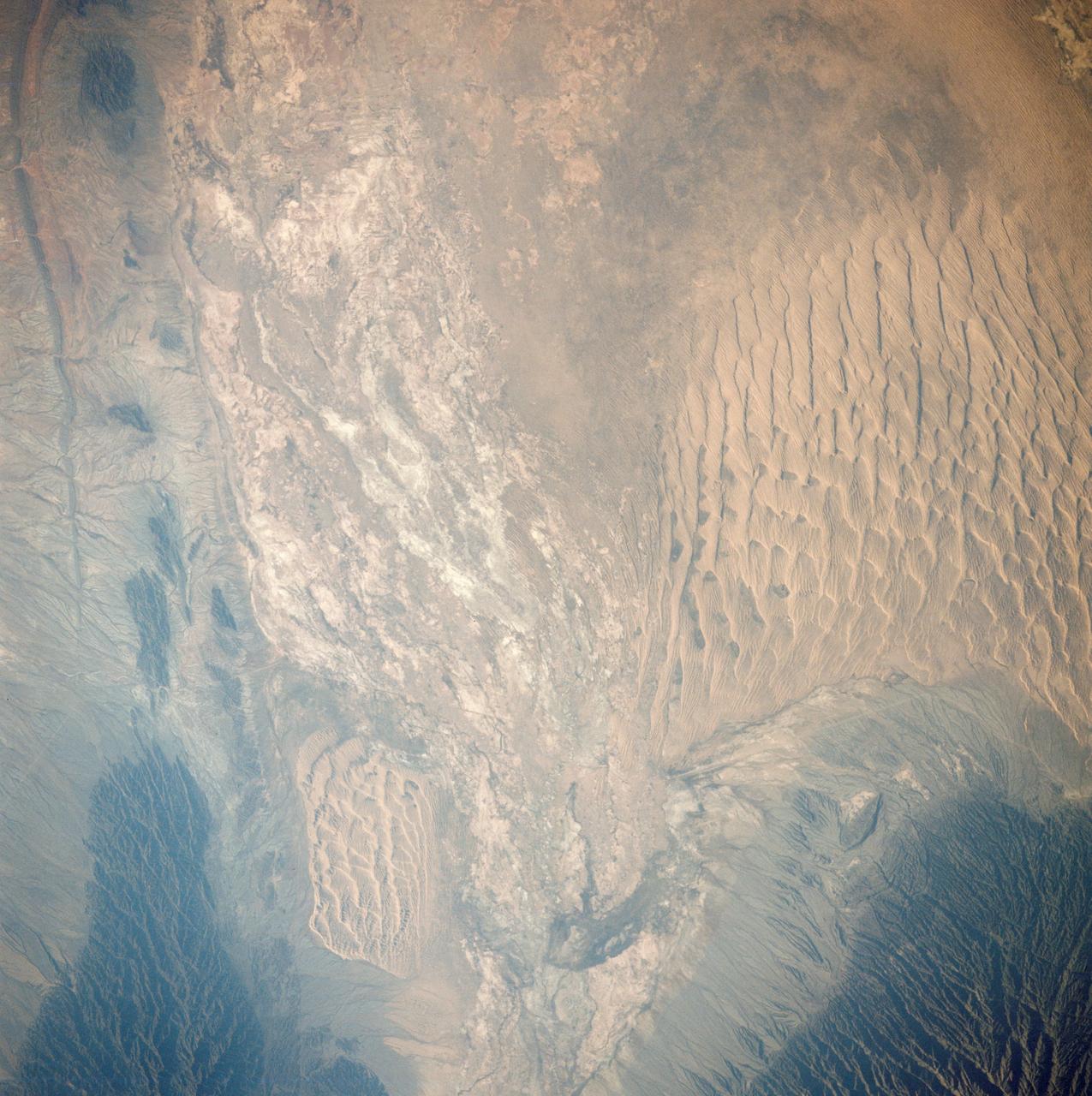

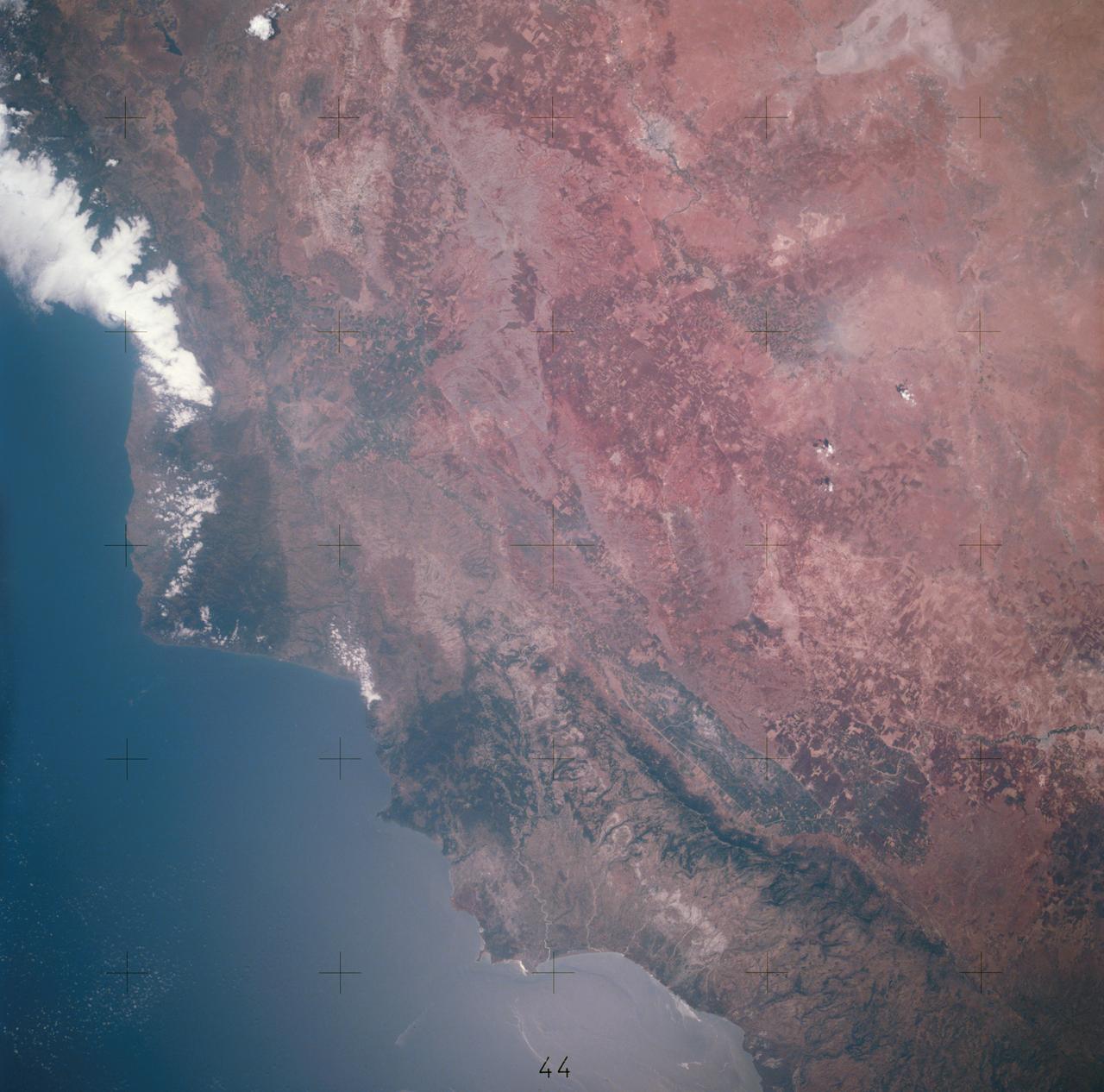
AST-27-2341 (20 July 1975) --- A near vertical view of sand dunes in the San Juan Province of Western Argentina, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The picture was taken at an altitude of 220 kilometers (136 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film.
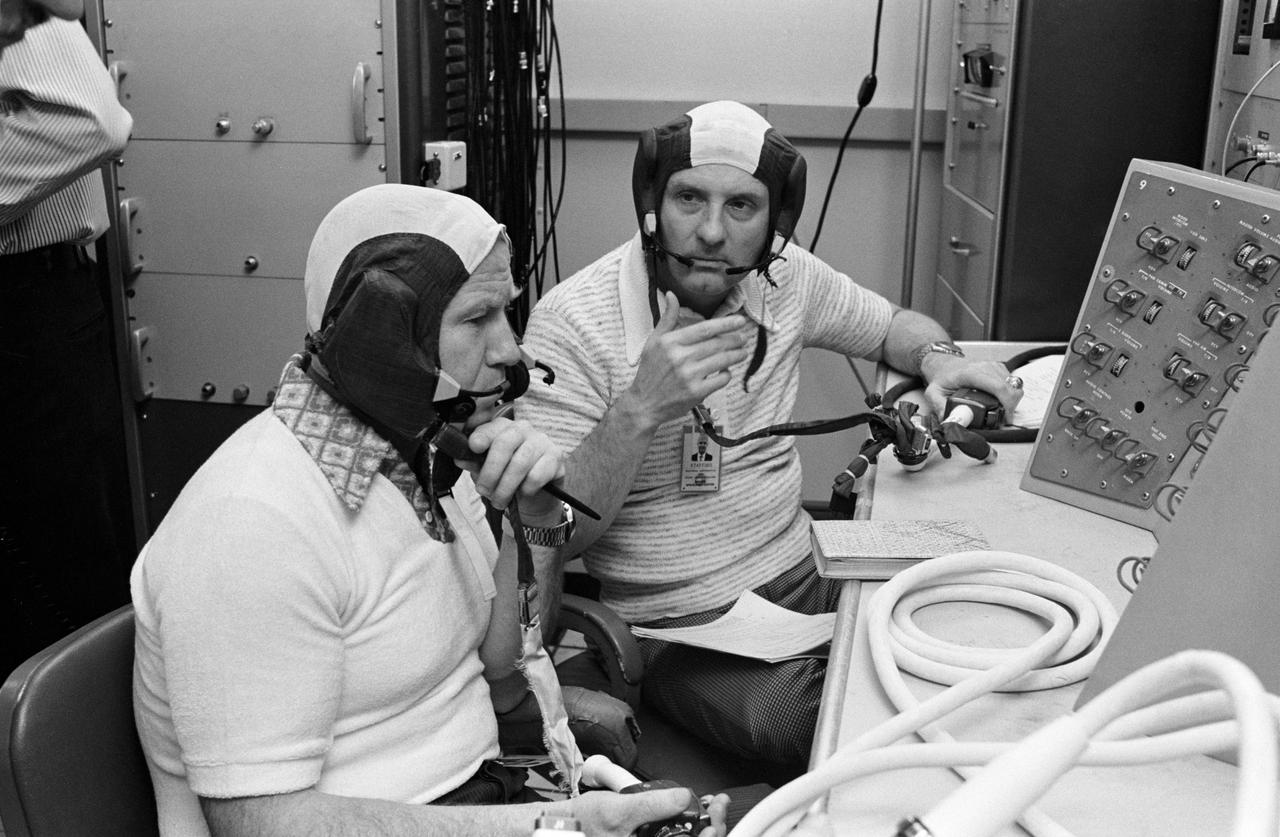

S74-20807 (23 April 1974) --- Cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov (foreground) is briefed on the Apollo communications test system console in the Building 440 laboratory during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project training activity at the Johnson Space Center. Leonov is the commander of the Soviet ASTP crew. Leonov is being briefed by astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, commander of the American ASTP crew.
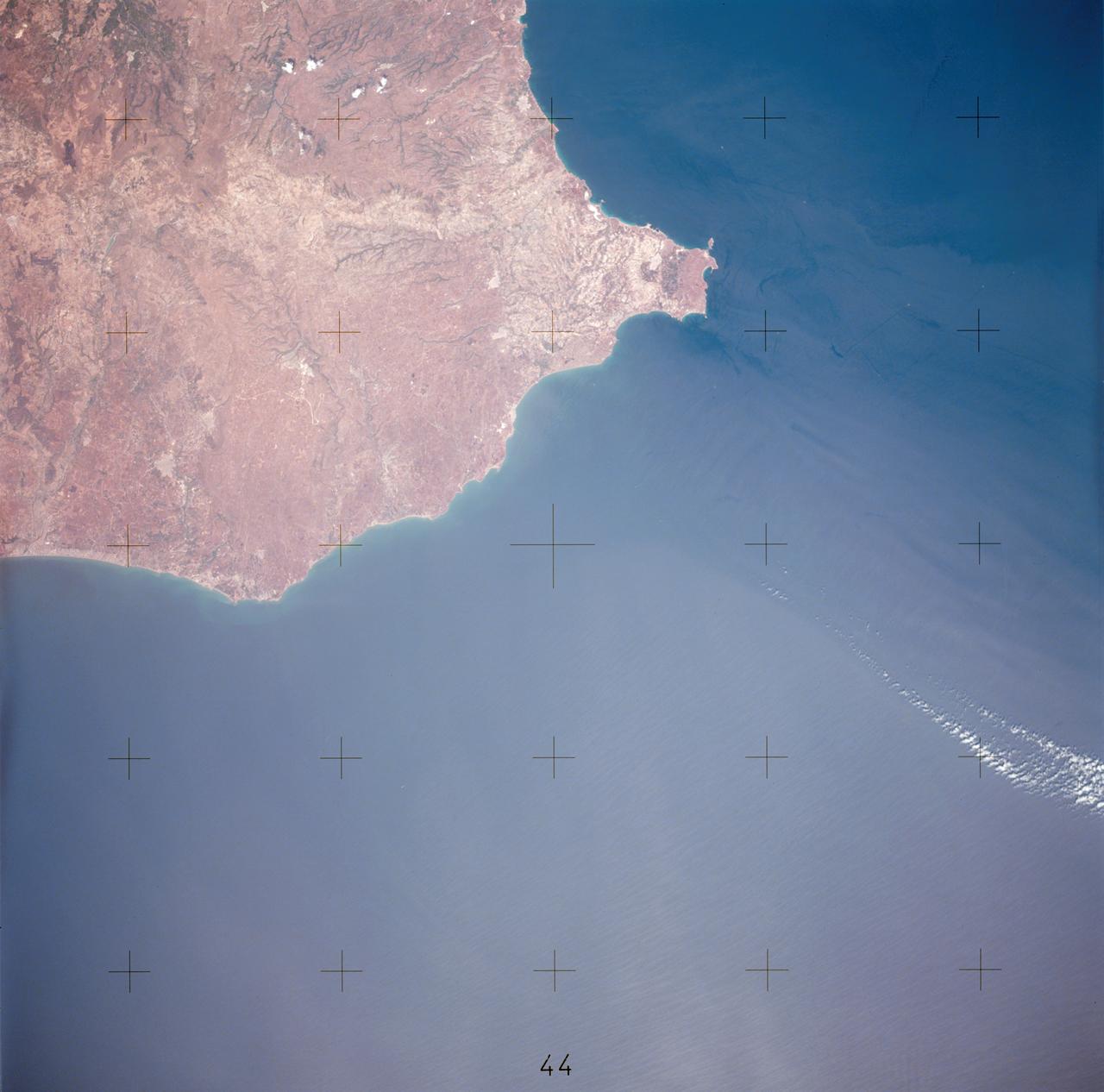

AST-17-1378 (20 July 1975) --- A near vertical view of the most southerly portion of the Island of Sicily in the Mediterranean Sea, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. This view includes the towns of Gala, Pachino, Avela and Pozzalo. The photograph was taken at an altitude of 228 kilometers (141 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using high-definition aerial Ektachrome SO-242 type film.

AST-02-130 (20 July 1975) --- An oblique view of a portion of Libya and the Arab Republic of Egypt, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The geological features are the Jebel Uweinat and Jebel Arkenu basaltic mountains in the Libyan sand sea. This picture was taken with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film. The spacecraft was at an altitude of 219 kilometers (136 statute miles).
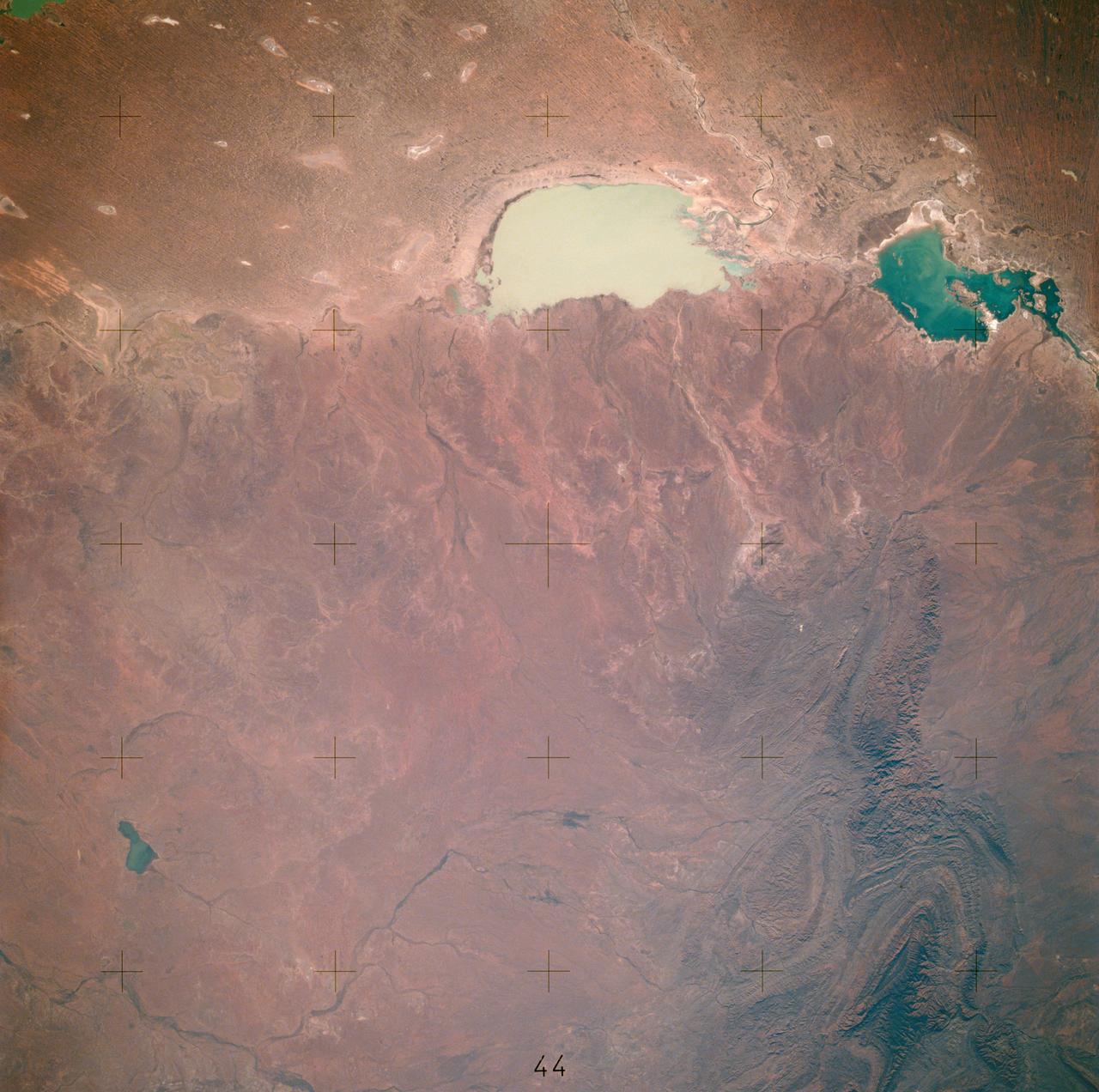

AST-16-1132 (20 July 1975) --- A vertical view of the eastern portion of the state of South Australia in Australia, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The highlands area is the Flinders Range. The light-colored body of water is Lake Blanche. The lake to the south is Callabonna. This picture was taken at an altitude of 224 kilometers (139 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using high-definition aerial Ektachrome SO-242 type film.
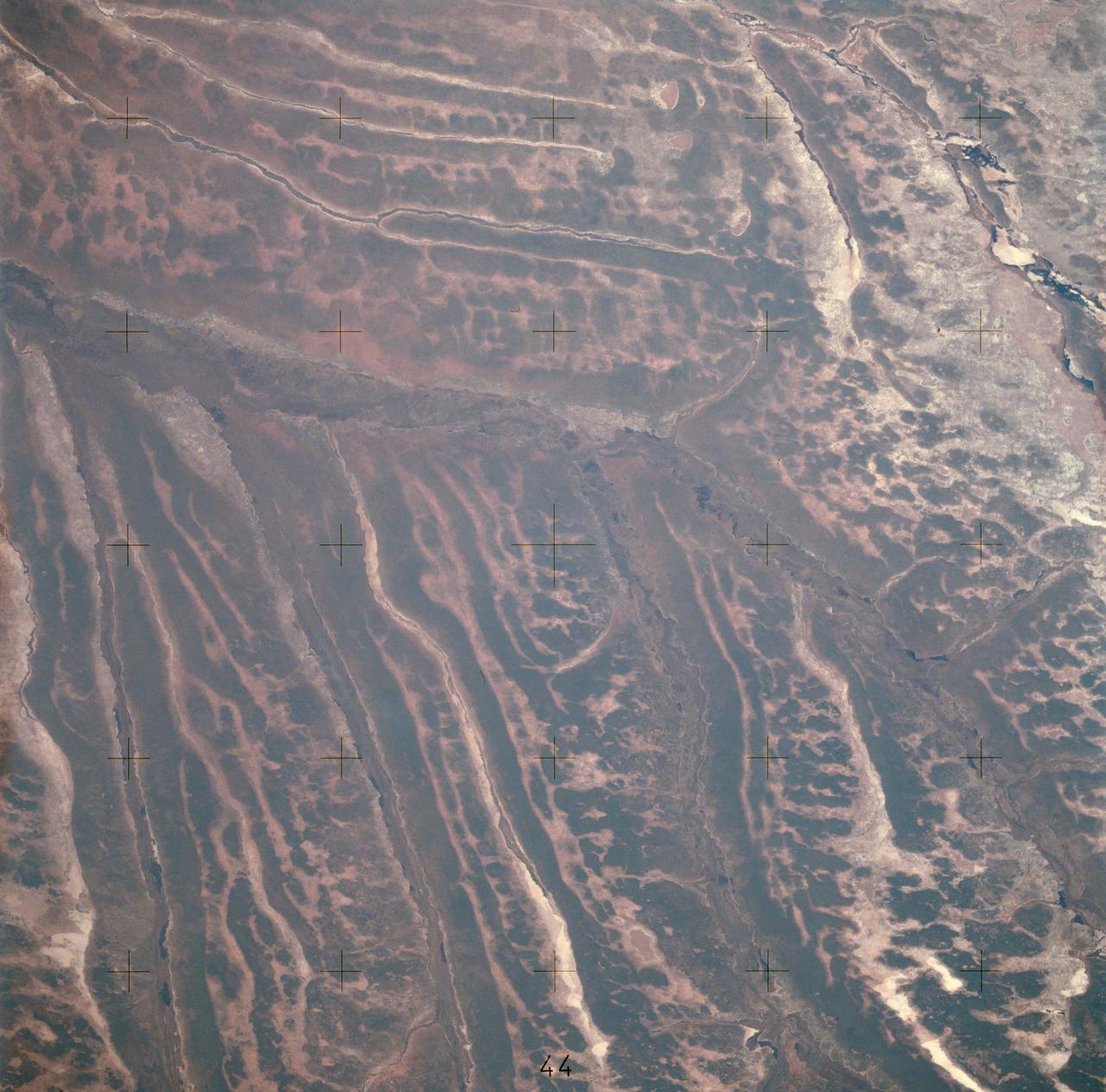

AST-14-890 (18 July 1975) --- An oblique view of unique drainage patterns in southwestern Africa in the Rio Cuando area of Angola and South-West Africa, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The picture was taken at an altitude of 223 kilometers (138 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using high-definition Ektachrome aerial SO-242 type film.
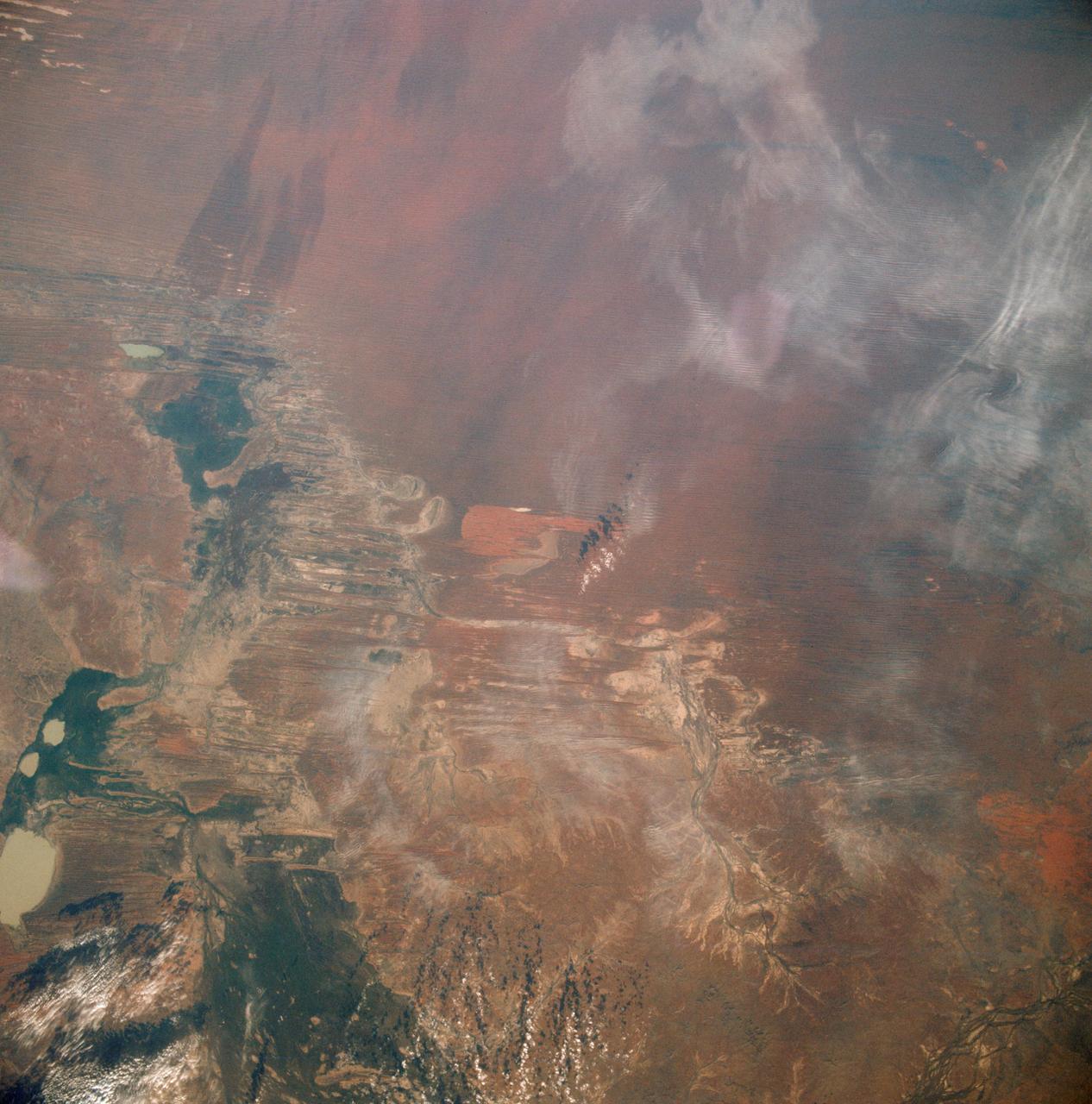

AST-19-1550 (24 July 1975) --- A vertical view of the Lake Eyre Basin area in the state of South Australia in Australia, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The picture was taken at an altitude of 241 kilometers (150 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film.
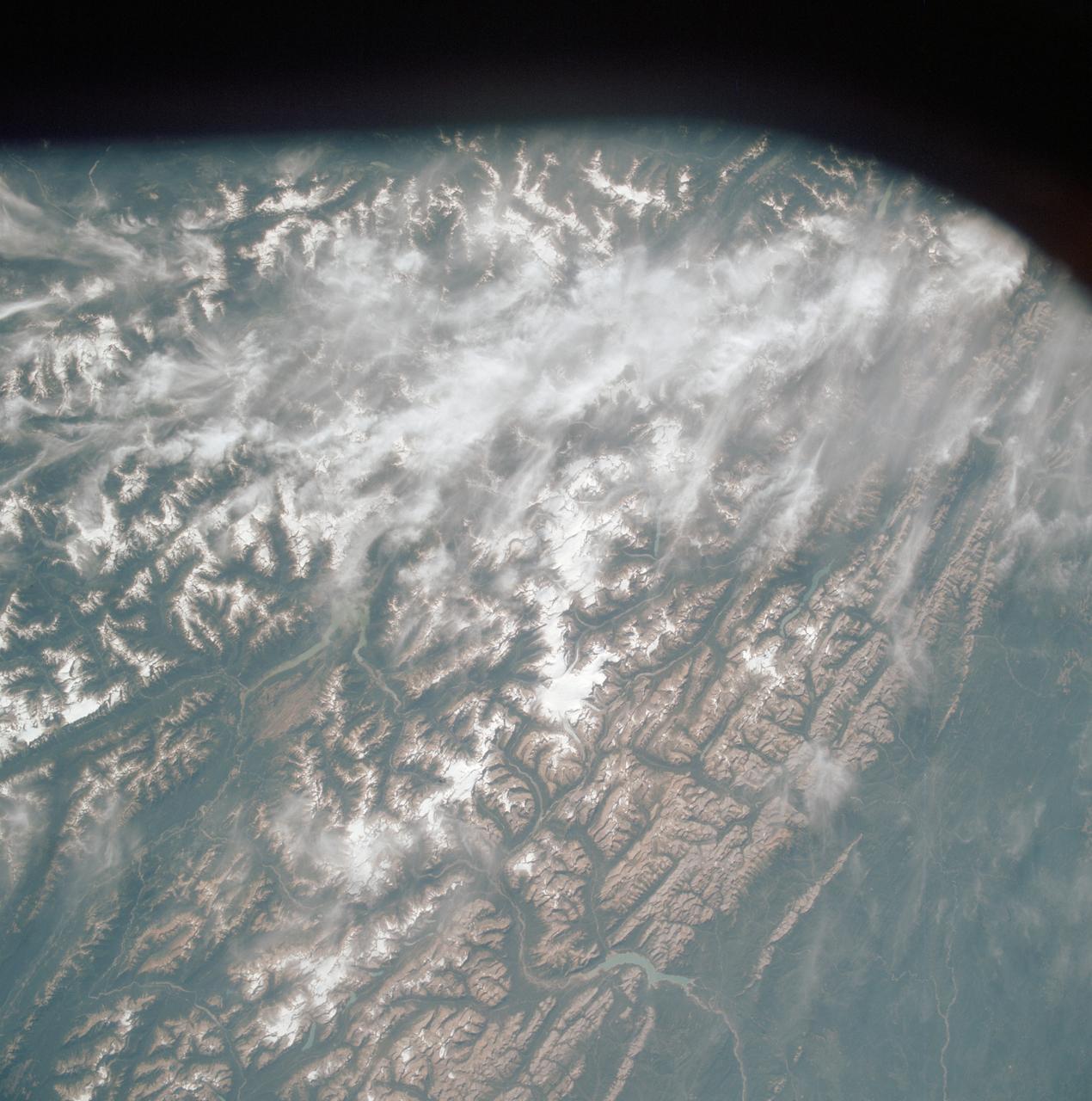

AST-19-1570 (24 July 1975) --- An oblique view of the Rocky Mountains area of British Columbia and Alberta in Canada, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. This picture was taken at an altitude of 222 kilometers (138 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film.
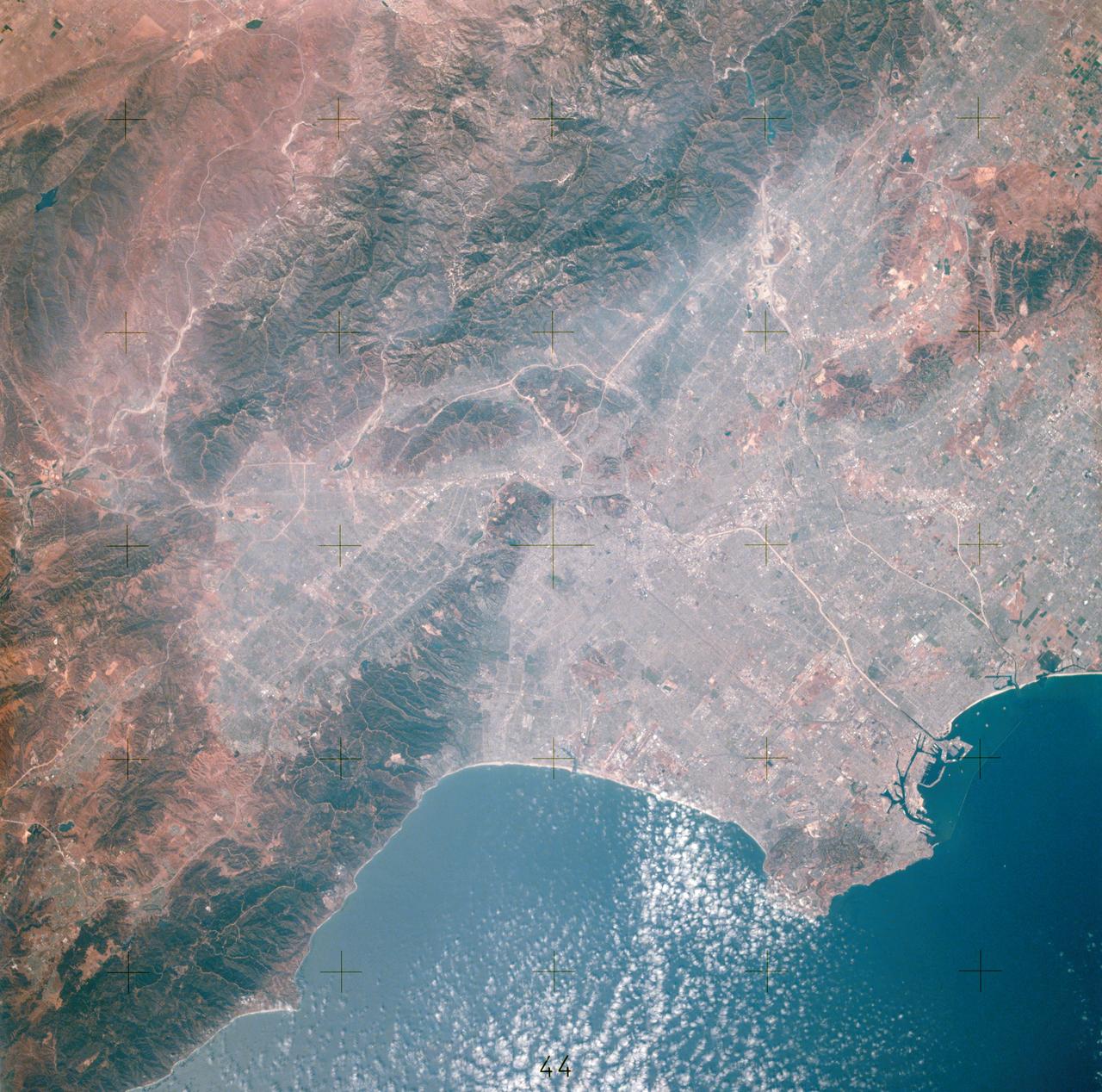

AST-14-881 (16 July 1975) --- An excellent view of Los Angeles, California, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) mission. Downtown Los Angeles is near the center of the picture. The photograph was taken at an altitude of 193 kilometers (120 statute miles), with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using SO-242 high-definition Ektachrome film.
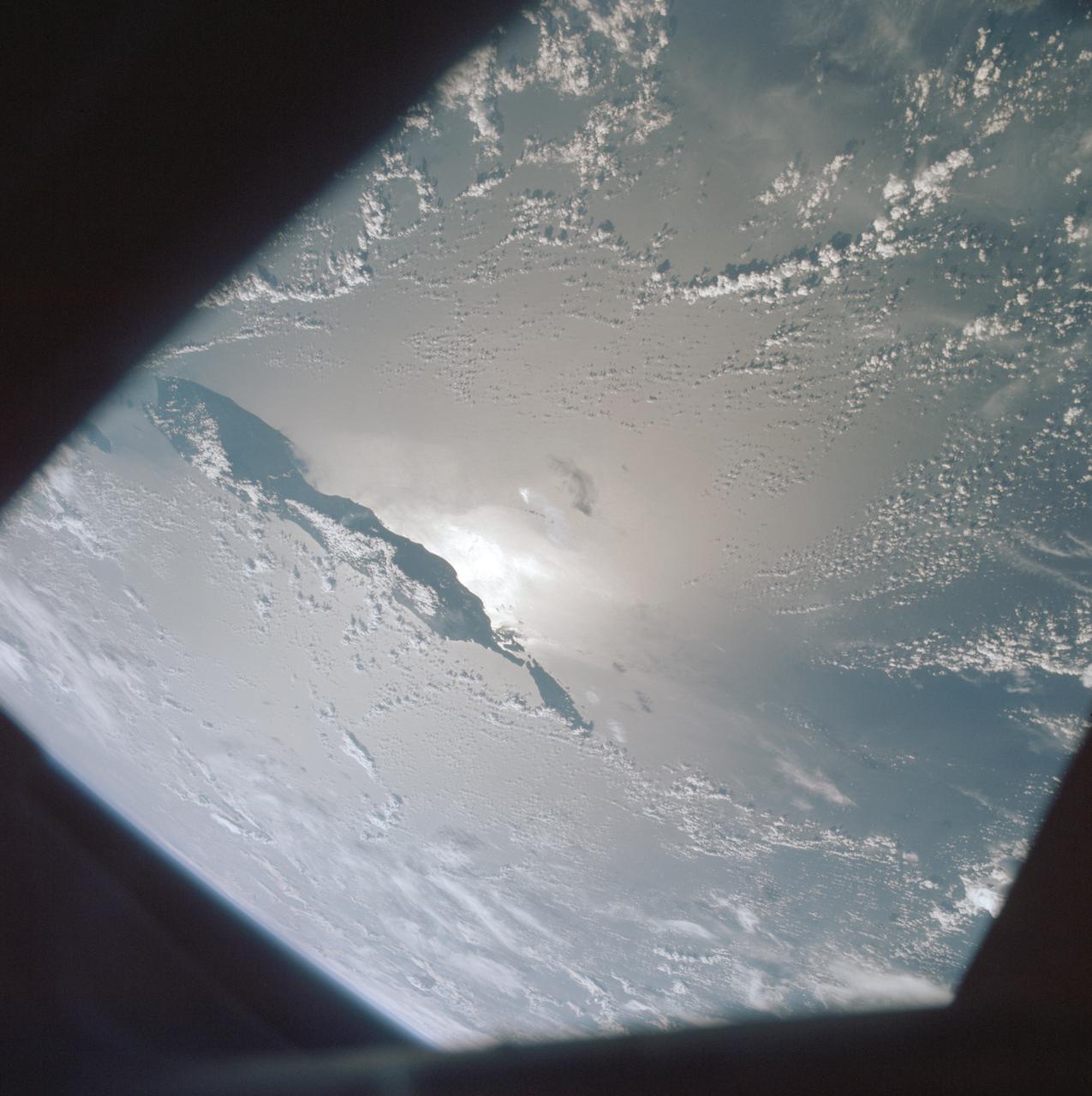

AST-19-1555 (24 July 1975) --- A sunglint in the South Western Pacific Ocean, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The island is Bougainville of the Solomon Islands group. The horizon of Earth is in the background. The picture was taken at an altitude of 231 kilometers (143 statute miles), with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film.
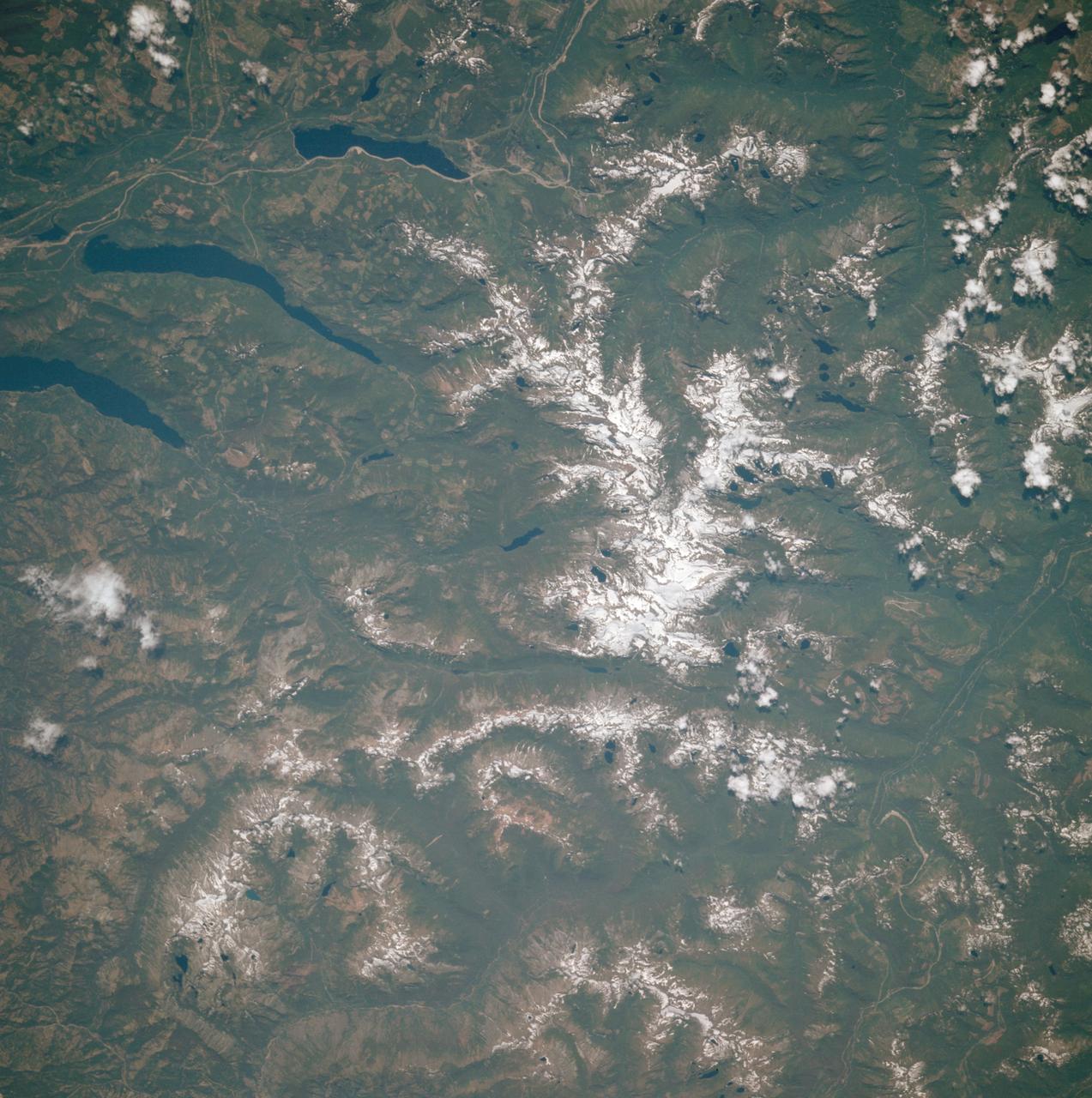

AST-30-2601 (20 July 1975) --- An area of the Cascade Mountains southeast of Seattle in the State of Washington, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The view includes Snoqualmie Pass, Cle Elum Lake, Kachess Lake and Keechelus Lake. The picture was taken at an altitude of 228 kilometers (141 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film.
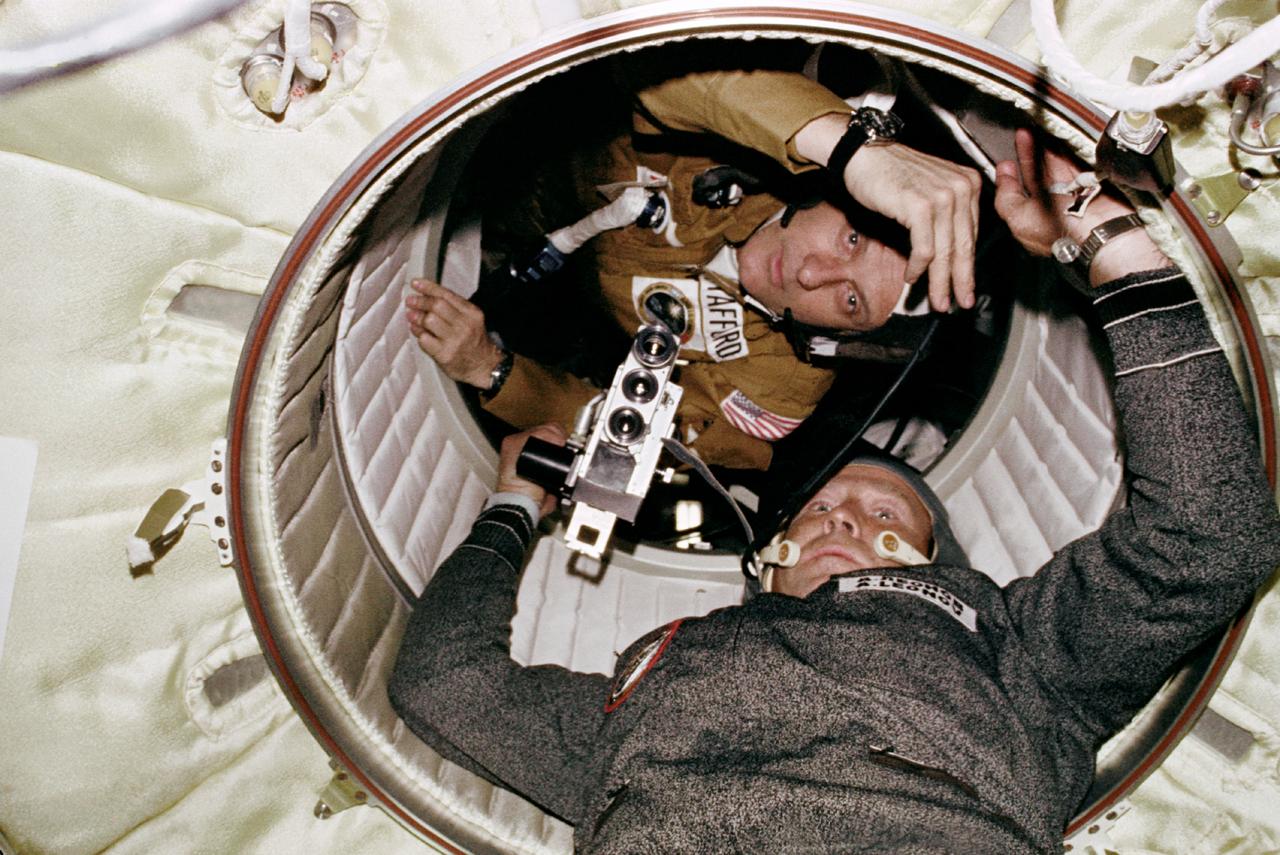

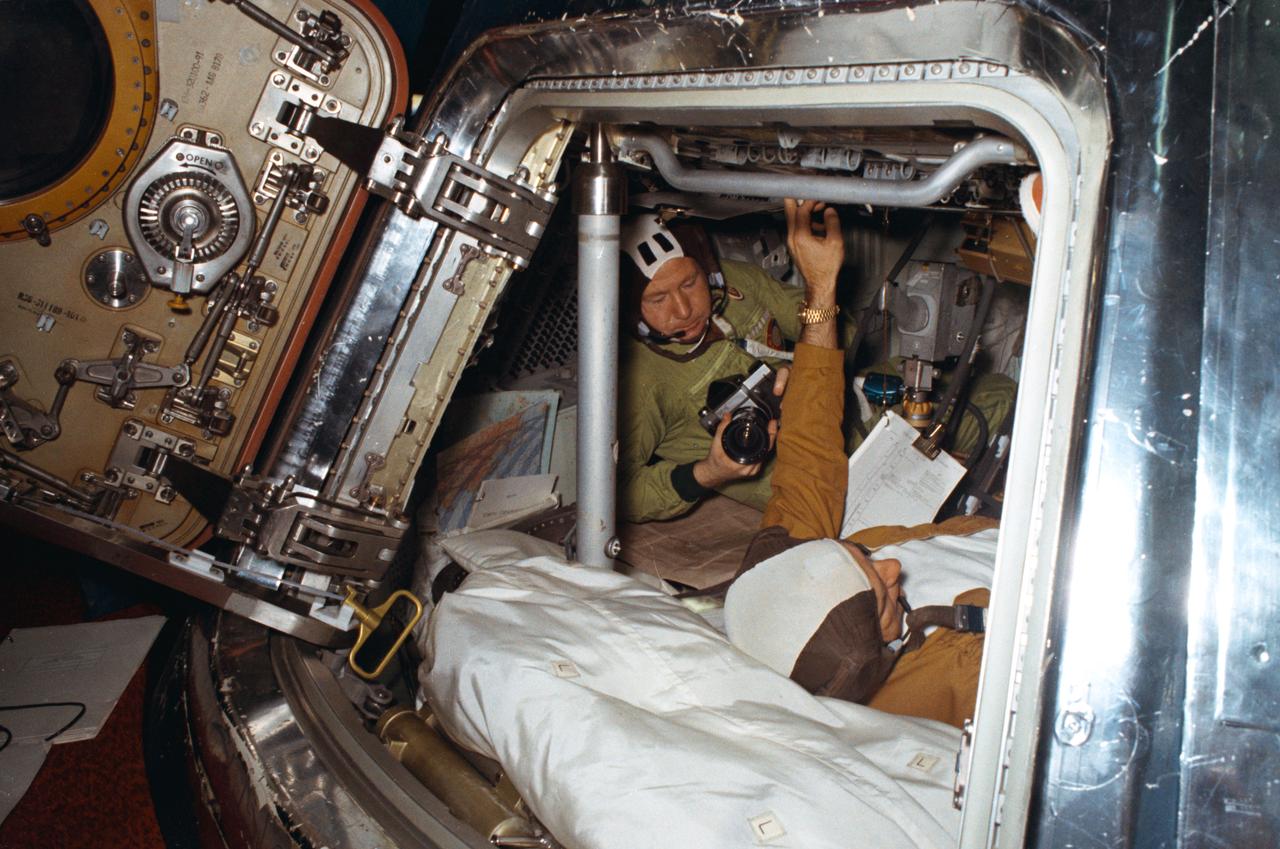
AST-03-191 (17-19 July 1975) --- Astronaut Thomas P. Stafford and cosmonaut Aleksei A. Leonov are seen at the hatchway leading from the Apollo Docking Module (DM) to the Soyuz Orbital Module (OM) during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) docking mission in Earth orbit. Cosmonaut Leonov is in the OM and astronaut Stafford is in the DM. Leonov holds a camera. The Apollo crew consisted of astronauts Stafford, commander; Donald K. "Deke" Slayton, docking module pilot; Vance D. Brand, command module pilot. The Soyuz 19 crew consisted of cosmonauts Leonov, command pilot; and Valeri N. Kubasov, flight engineer.
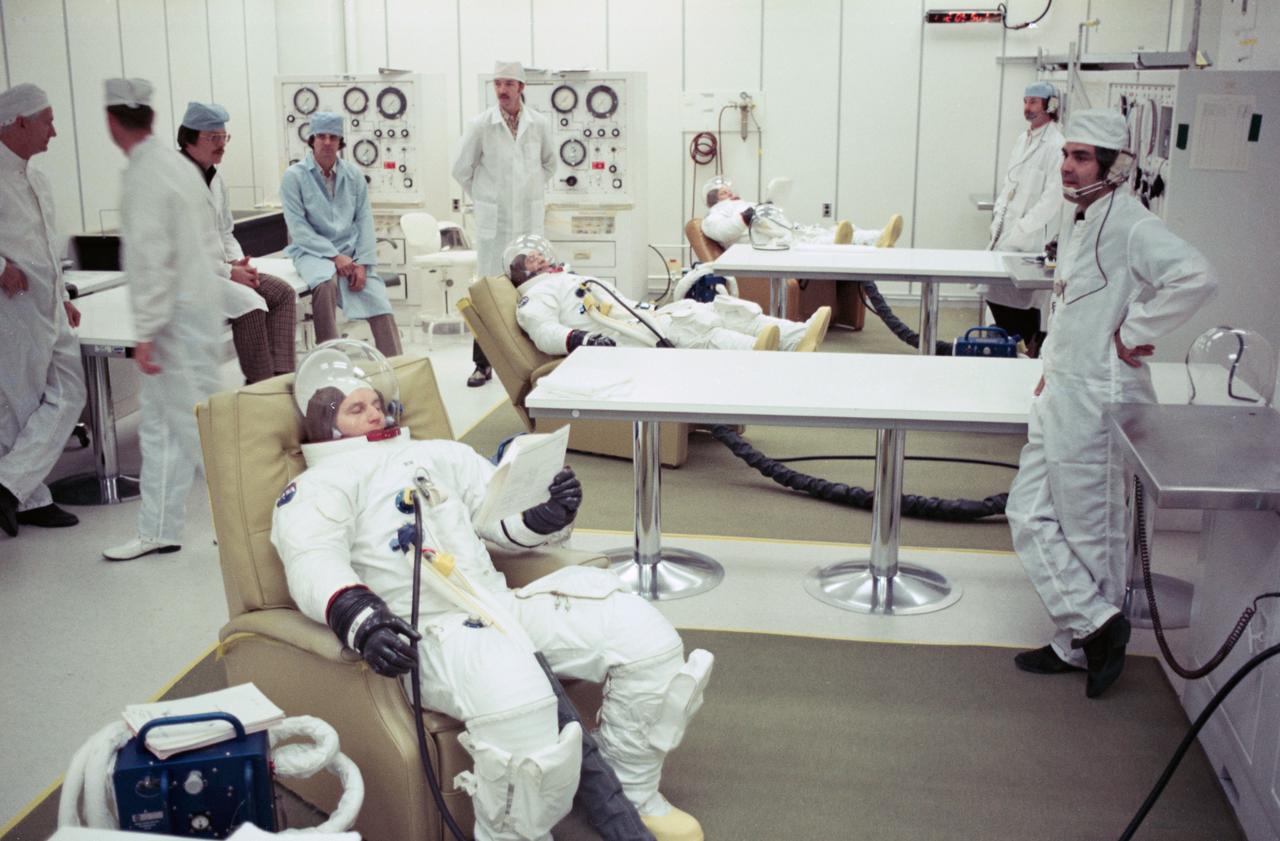

S75-21063 (January 1975) --- The three members of the American ASTP backup crew are suited up for the testing of the Apollo spacecraft at the Kennedy Space Center. They are (from foreground) astronauts Alan L. Bean, commander; Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot; and Jack R. Lousma, docking module pilot. Later, they entered the Apollo Command Module in an altitude chamber for tests of spacecraft systems. The testing was in preparation for the joint U.S.?USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit scheduled for July 1975.
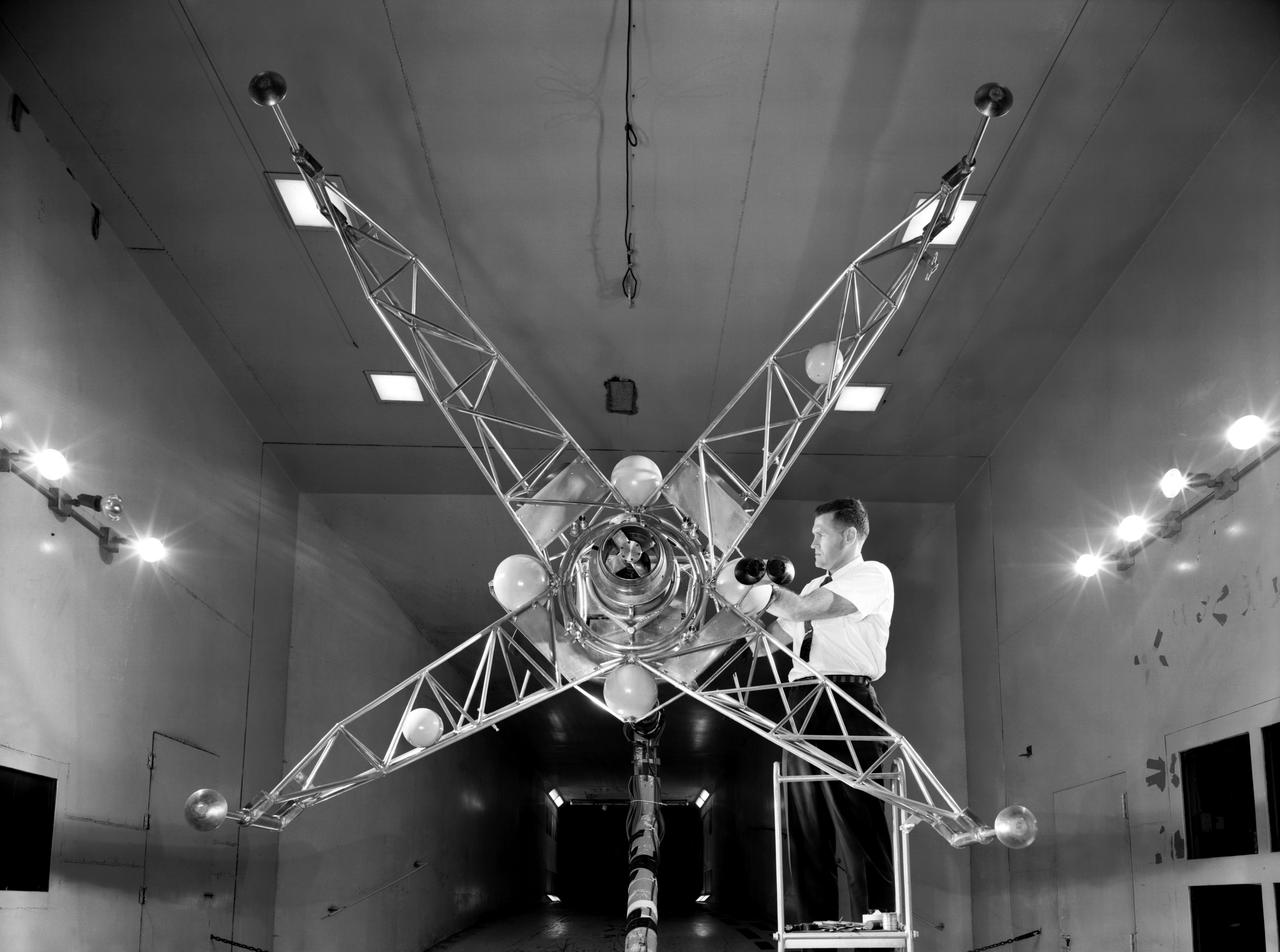

Lunar Landing Research Model. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 356.
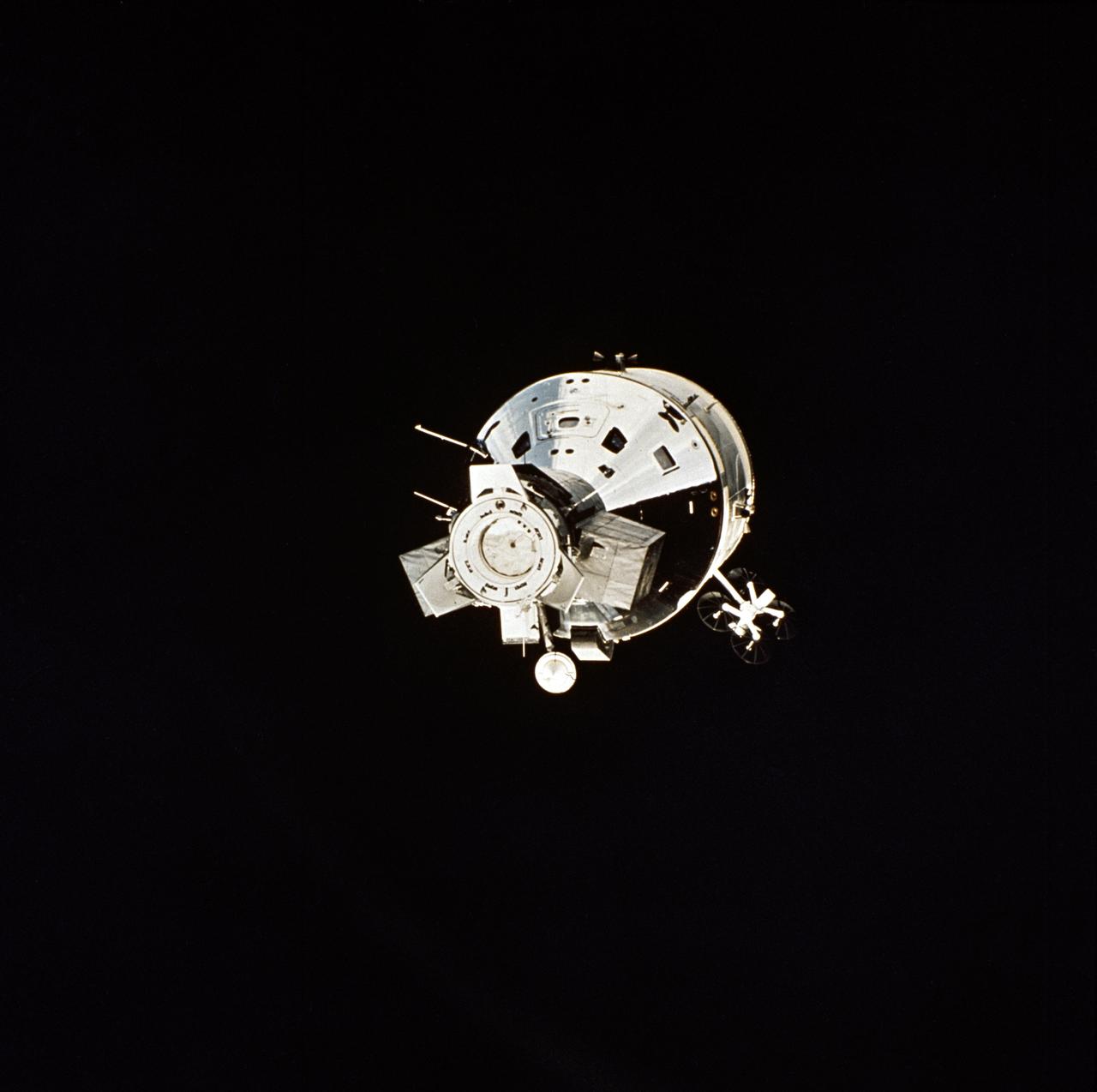

AST-32-2691 (17-19 July 1975) --- The American Apollo spacecraft as seen in Earth orbit from the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Command/Service Module and Docking Module are contrasted against a black-sky background. This is a near "head on" view of the Apollo. This picture was furnished by the USSR in an exchange of photography taken during the ASTP flight. Note the docking mechanism and docking target on the Docking Module. The four dish-like reflectors of the unified S-band high-gain antenna protrude from the side of the Service Module. The American and Soviet spacecraft were joined together in space for approximately 47 hours on July 17-18-19, 1975. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
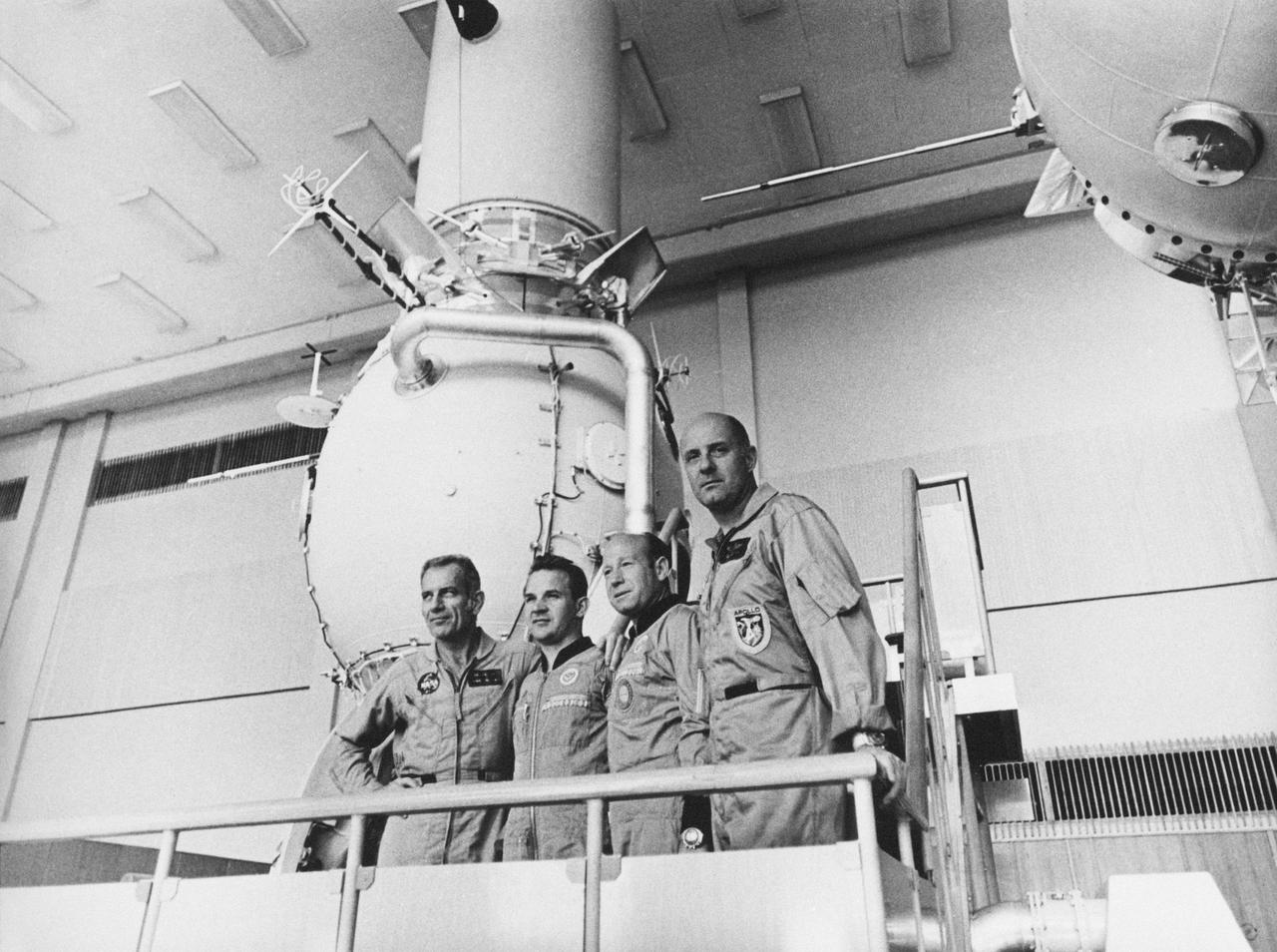

S74-25259 (June 1974) --- Four crewmen of the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission are photographed beside a Soyuz spacecraft trainer during ASTP crew training activity at the Cosmonaut Training Center (Star City) near Moscow. They are, left to right, astronaut Donald K. Slayton, docking module pilot of the American ASTP prime crew; cosmonaut Valeriy N. Kubasov, engineer of the Soviet ASTP first (prime) crew; cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov, commander of the Soviet ASTP first (prime) crew; and astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, commander of the American ASTP prime crew.
S74-20794 (23 April 1974) --- Cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov (center), commander of the Soviet crew of the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission, goes through familiarization training with a television camera during ASTP activity at the Johnson Space Center. Cosmonaut Valeriy N. Kubasov (right), engineer on Leonov?s crew, is looking on. An ASTP docking module mock-up is on the left. Interpreter K.S. Samofal is behind Kubasov. David Brooks, with JSC?s Crew Procedures Division, is in the left background. This phase of the ASTP communications training was conducted in JSC?s Building 35. The equipment being used in the picture is an early design of the Westinghouse TV camera.
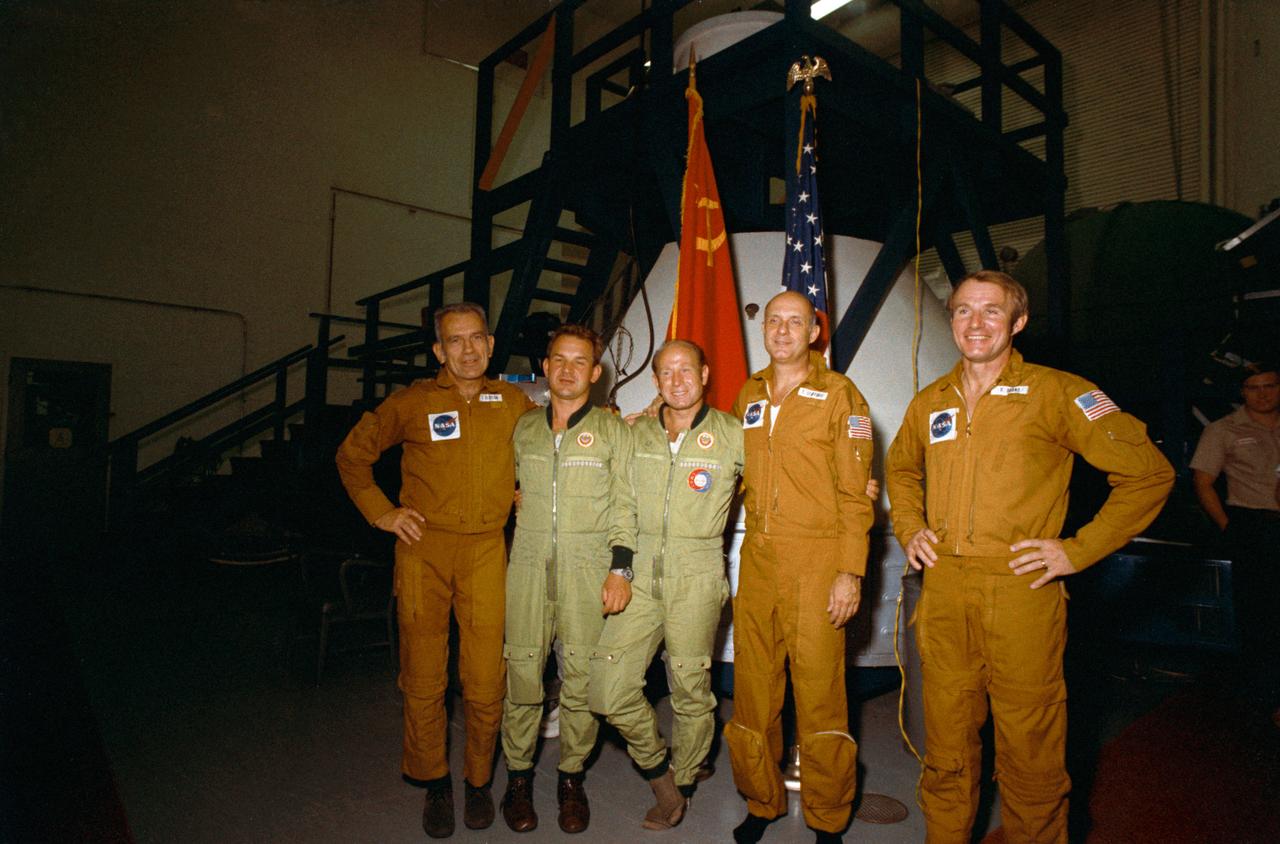

S74-28811 (23 Sept. 1974) --- The five prime crewmen of the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission are photographed in the Flight Crew Training Facility, Building 35, at the Johnson Space Center during ASTP crew training activity. They are, left to right, astronaut Donald K. Slayton, docking module pilot of the American crew; cosmonaut Valeriy N. Kubasov, engineer on the Soviet crew; cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov, commander of the Soviet crew; astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, commander of the American crew; and astronaut Vance D. Brand, command module pilot of the American crew.
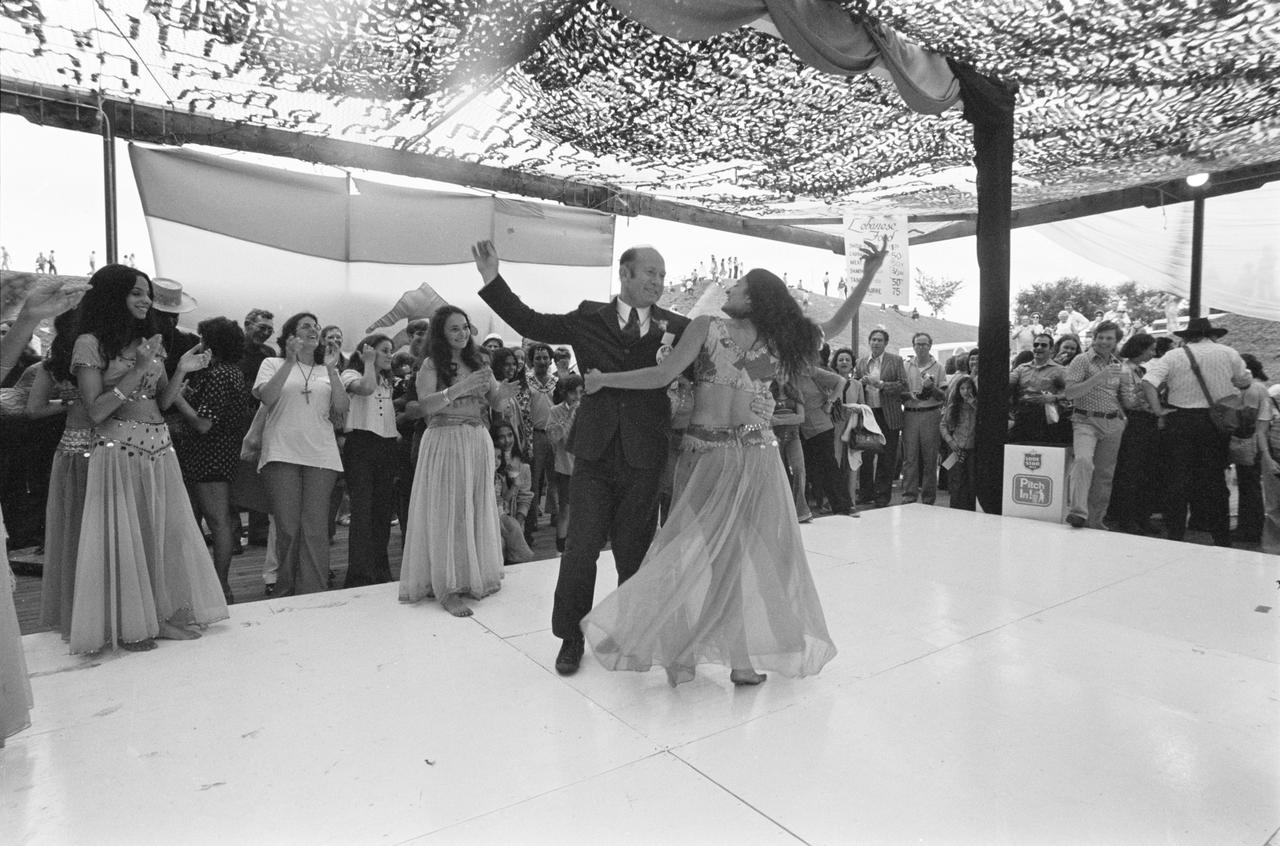

S74-28666 (14 Sept. 1974) --- Cosmonaut Aleksey A. Leonov, in one of the lighter moments of activity involving Soviet cosmonauts and American astronauts, joins a belly dancer on stage as several visitors to weekend activity at the site of San Antonio?s HemisFair look on. Leonov is commander of the Soviet Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) crew. A group of cosmonauts is in this country training with American astronauts for the joint U.S.-USSR ASTP rendezvous and docking mission scheduled for the summer of 1975. The Lebanese dancing was just one feature among many during the Texas Folklife Festival, in which members of 26 ethnic groups participated.
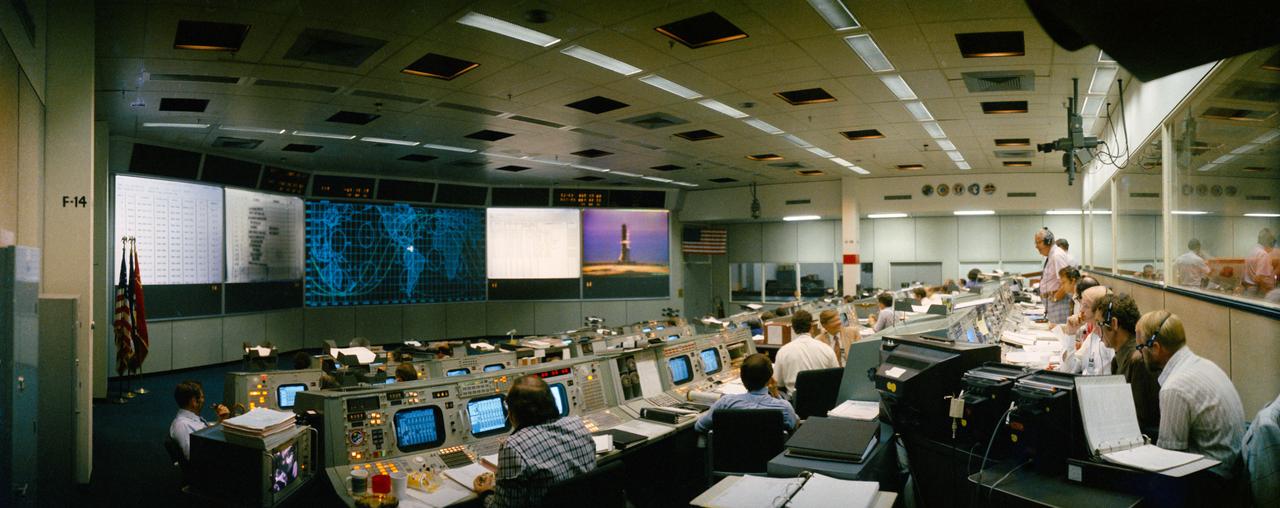

S75-28519 (15 July 1975) --- An overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center, Building 30, Johnson Space Center, on the first day of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project docking mission in Earth orbit. This photograph was taken shortly before the American ASTP launch from the Kennedy Space Center. The television monitor in the center background shows the ASTP Apollo-Saturn 1B space vehicle on Pad B at KSC?s Launch Complex 39. The American ASTP liftoff followed the Soviet ASTP launch of the Soyuz space vehicle from Baikonur, Kazakhstan by seven and one-half hours.
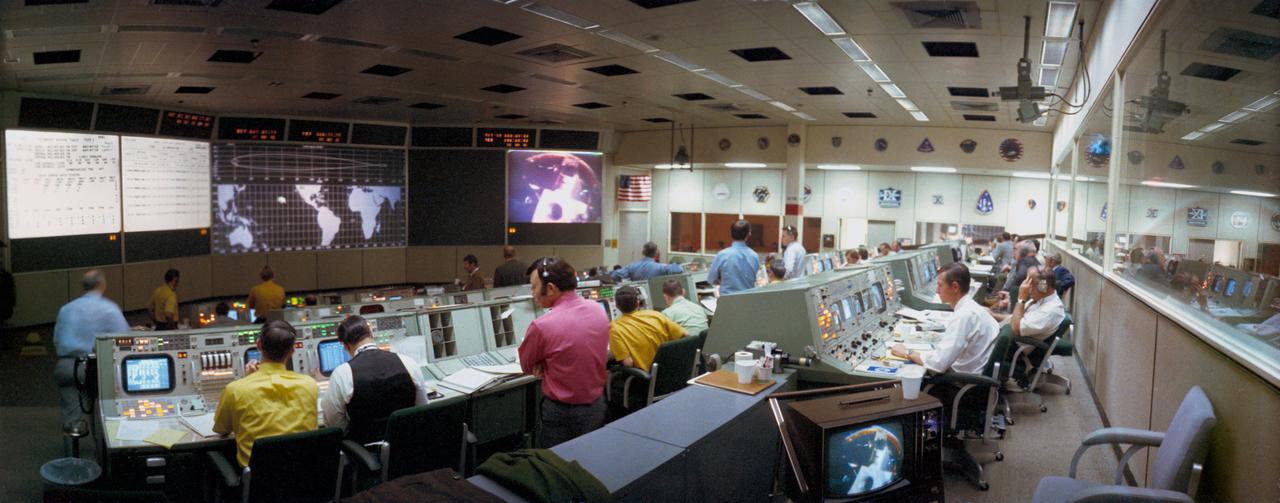

S71-17122 (31 Jan. 1971) --- A wide angle overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center at the Manned spacecraft Center. This view was photographed during the first color television transmission from the Apollo 14 Command Module. Projected on the large screen at the right front of the MOCR is a view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module, still attached to the Saturn IVB stage. The Command and Service Modules were approaching the LM/S-IVB during transposition and docking maneuvers.

AST-16-1268 (20 July 1975) --- A near vertical view of a portion of the Mediterranean coast of Turkey and Syria, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. This view covers the Levant Coast north of Beirut, showing the cities of Aleppo, Hamah, Homs and Latakia. The Levantine rift bends to the northeast. This picture was taken with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using high-definition aerial Ektachrome SO-242 type film. The altitude of the spacecraft was 225 kilometers (140 statute miles) when this photograph was taken.
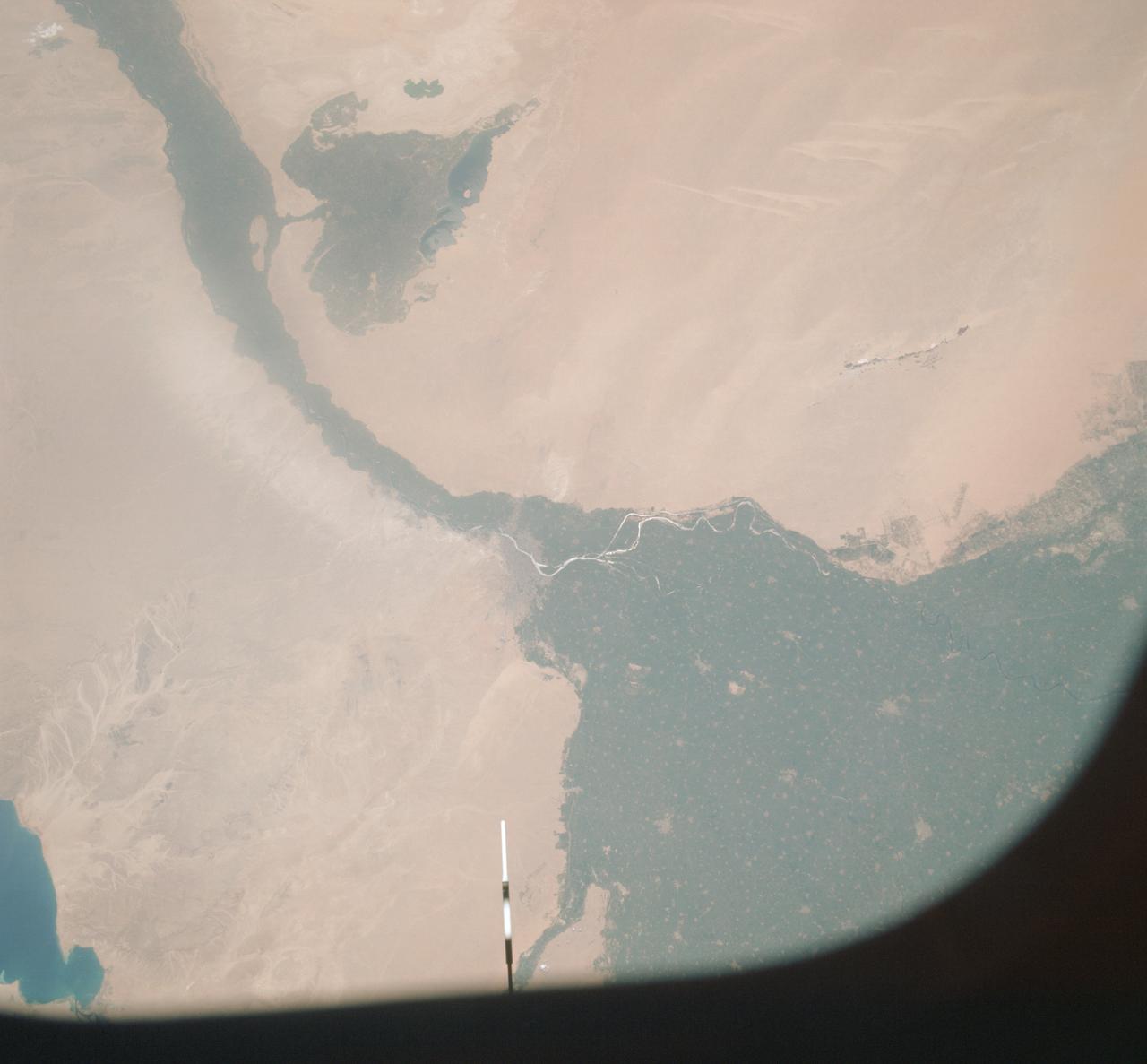

AST-09-555 (19 July 1975) --- A vertical view of a portion of the Arab Republic of Egypt, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Nile Delta is in the most northerly corner of the picture. The City of Cairo on the Nile River is in the center of the photograph. The Gulf of Suez is in the most easterly corner of the picture. El Faiyum is south-southwest of Cairo. This picture was taken at an altitude of 223 kilometers (138 statute miles), with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film.
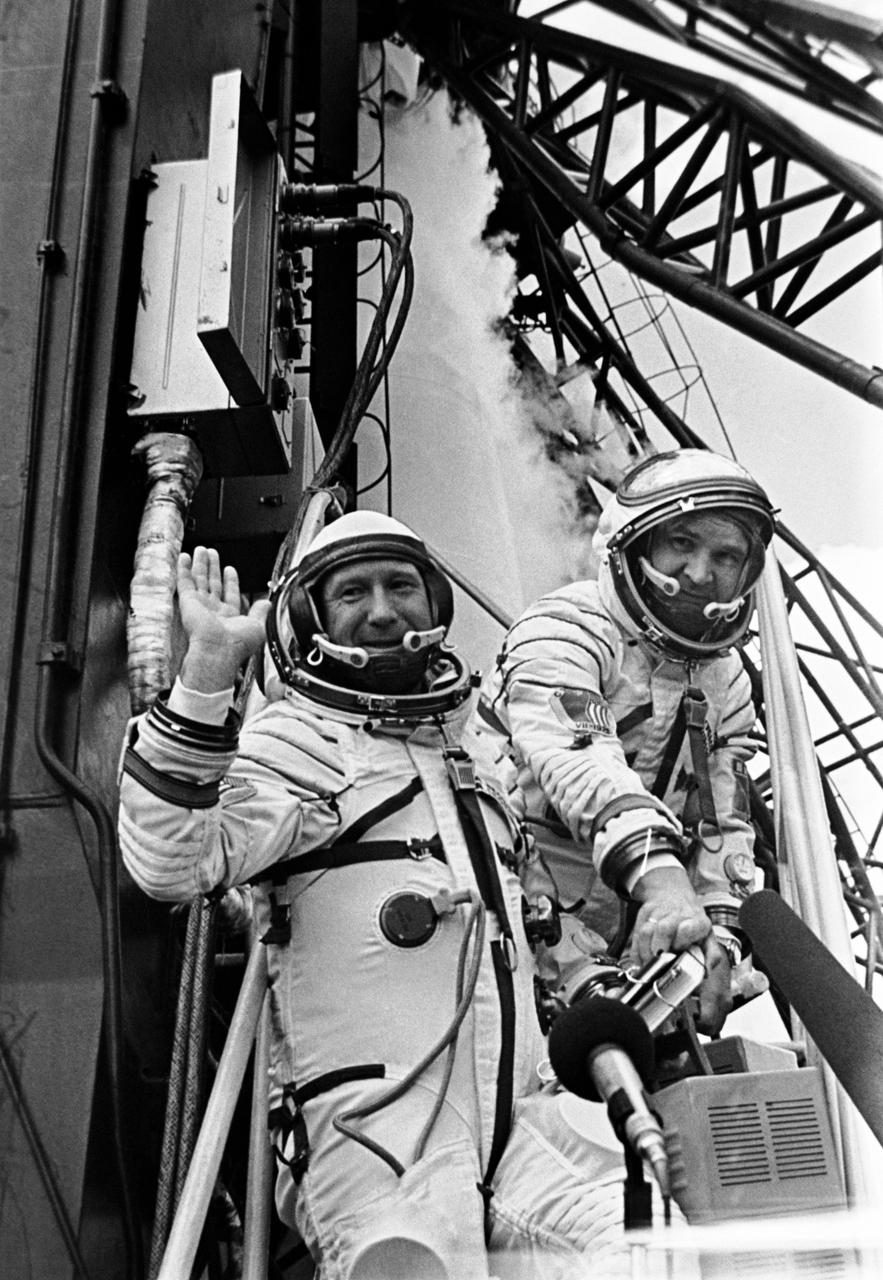

S75-32343 (15 July 1975) --- The two Soviet crewmen for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission are photographed at the launch pad at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on the morning of the Soviet ASTP liftoff on July 15, 1975. They are cosmonauts Aleksey A. Leonov (left), commander; and Valeriy N. Kubasov, flight engineer. Leonov is waving to well-wishers at the launch pad. The Soviet ASTP launch preceded the American ASTP Apollo liftoff by seven and one-half hours. The American and Soviet spacecraft were docked in Earth orbit for a total of about 47 hours on July 17-19, 1975. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
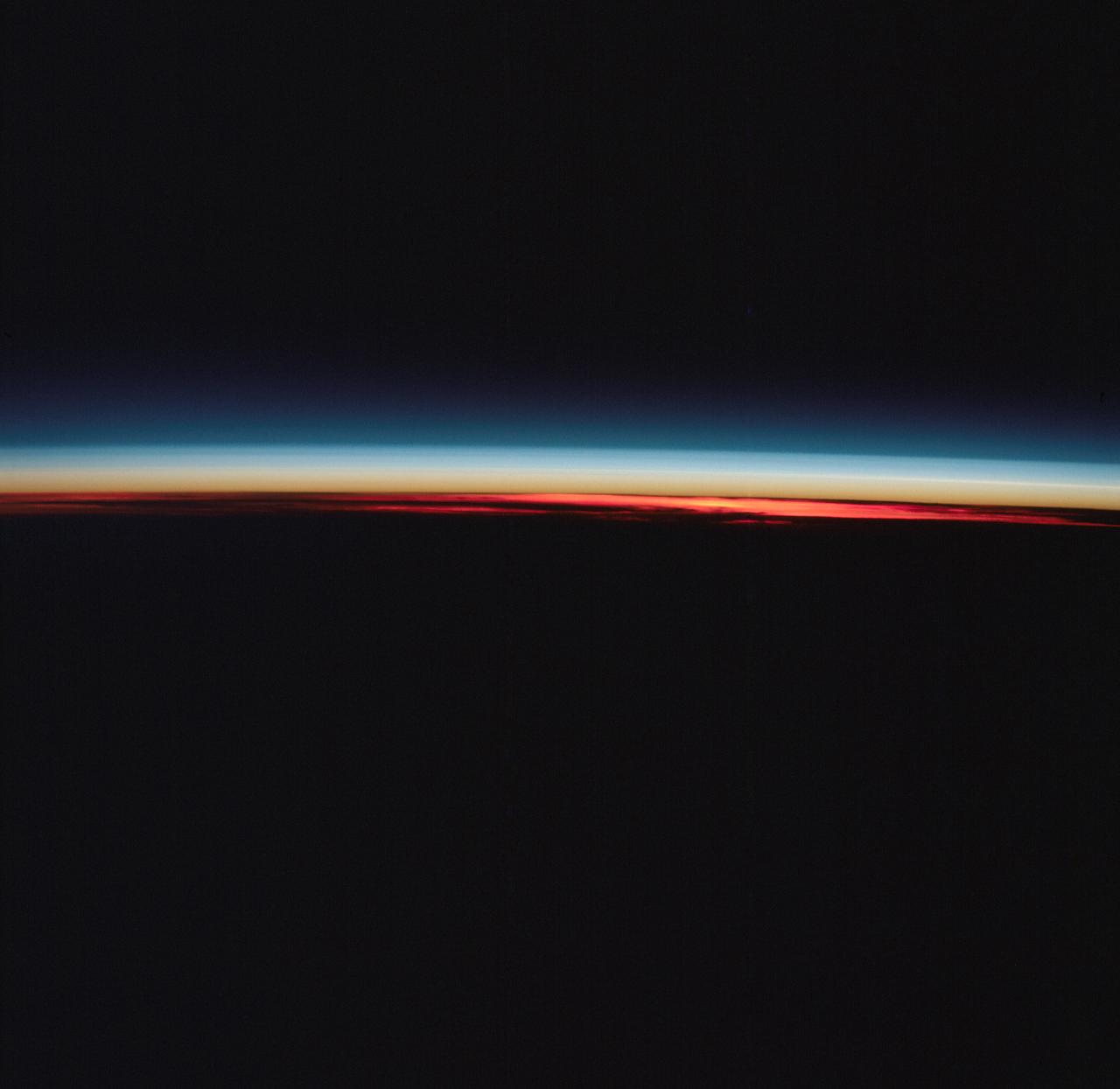

AST-27-2339 (20 July 1975) --- The Earth’s limb at sunrise and cloud silhouettes in the Southern Hemisphere, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The photograph was taken at an altitude of 230 kilometers (143 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using medium-speed Ektachrome QX-807 type film.
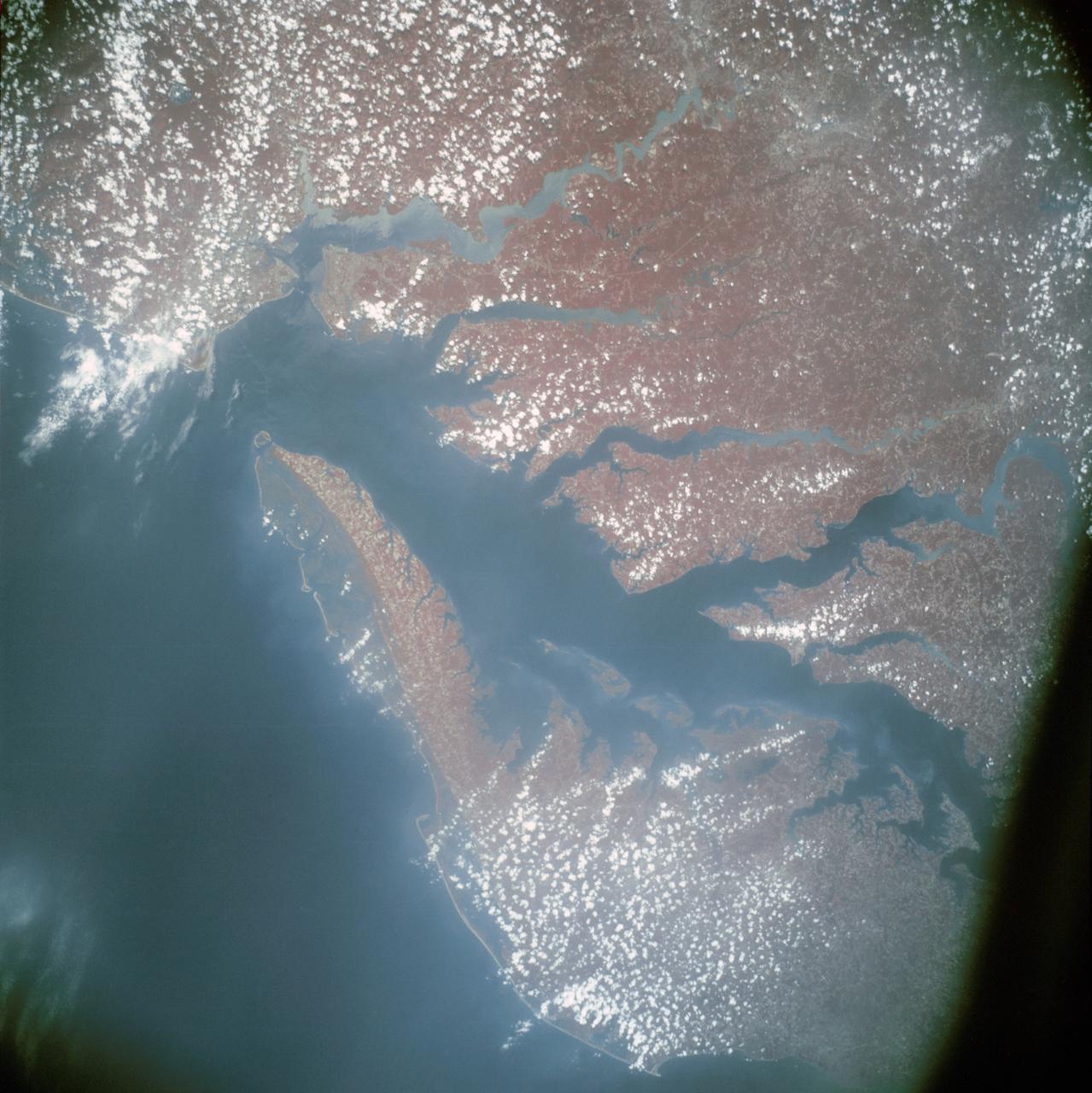

AST-13-797 (24 July 1975) --- An infrared, near vertical view of the Chesapeake Bay area showing portions of Virginia, Maryland and Delaware, as photographed from the Apollo spacecraft in Earth orbit during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. Richmond and Norfolk can be seen in this picture. Tidewater Virginia covers much of this view. The photograph was taken at an altitude of 217 kilometers (135 statute miles) with a 70mm Hasselblad camera using infrared Aerochrome type 2443 Ektachrome film.
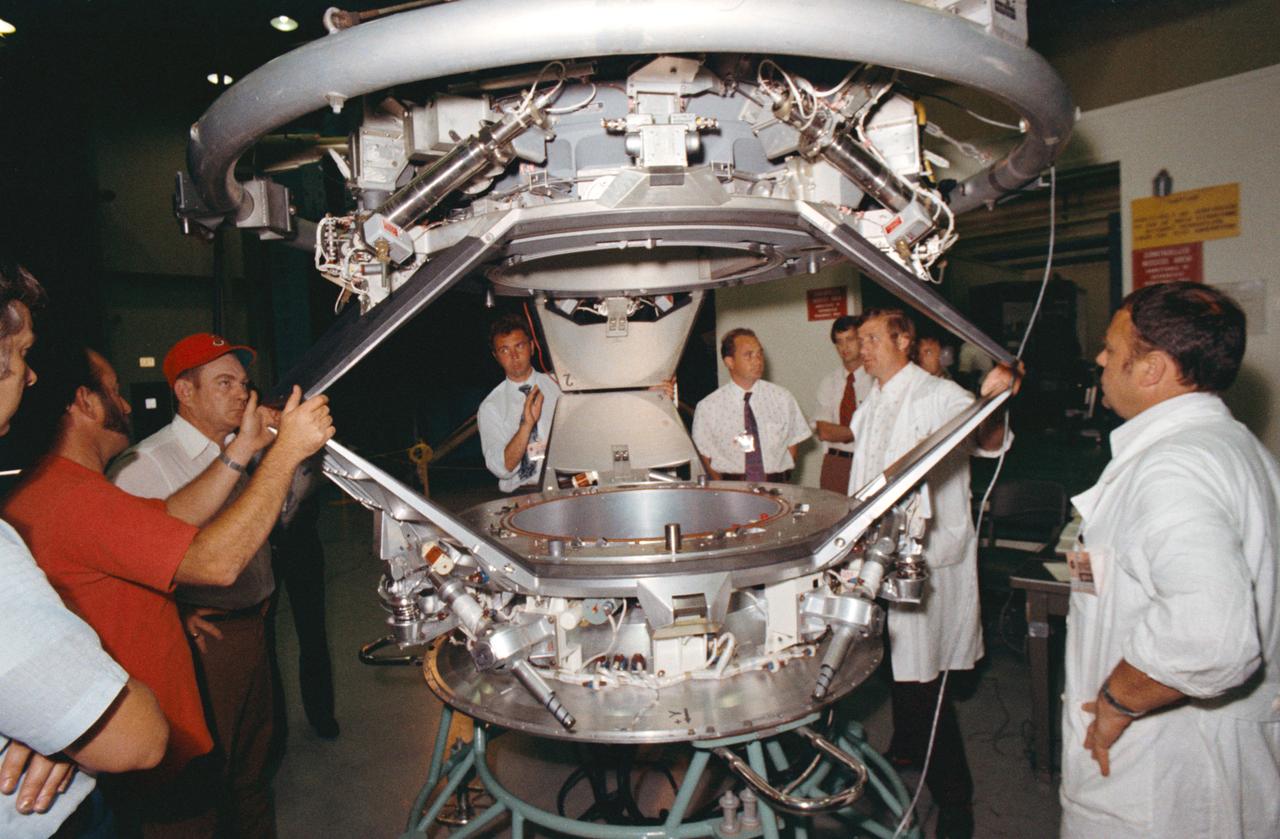

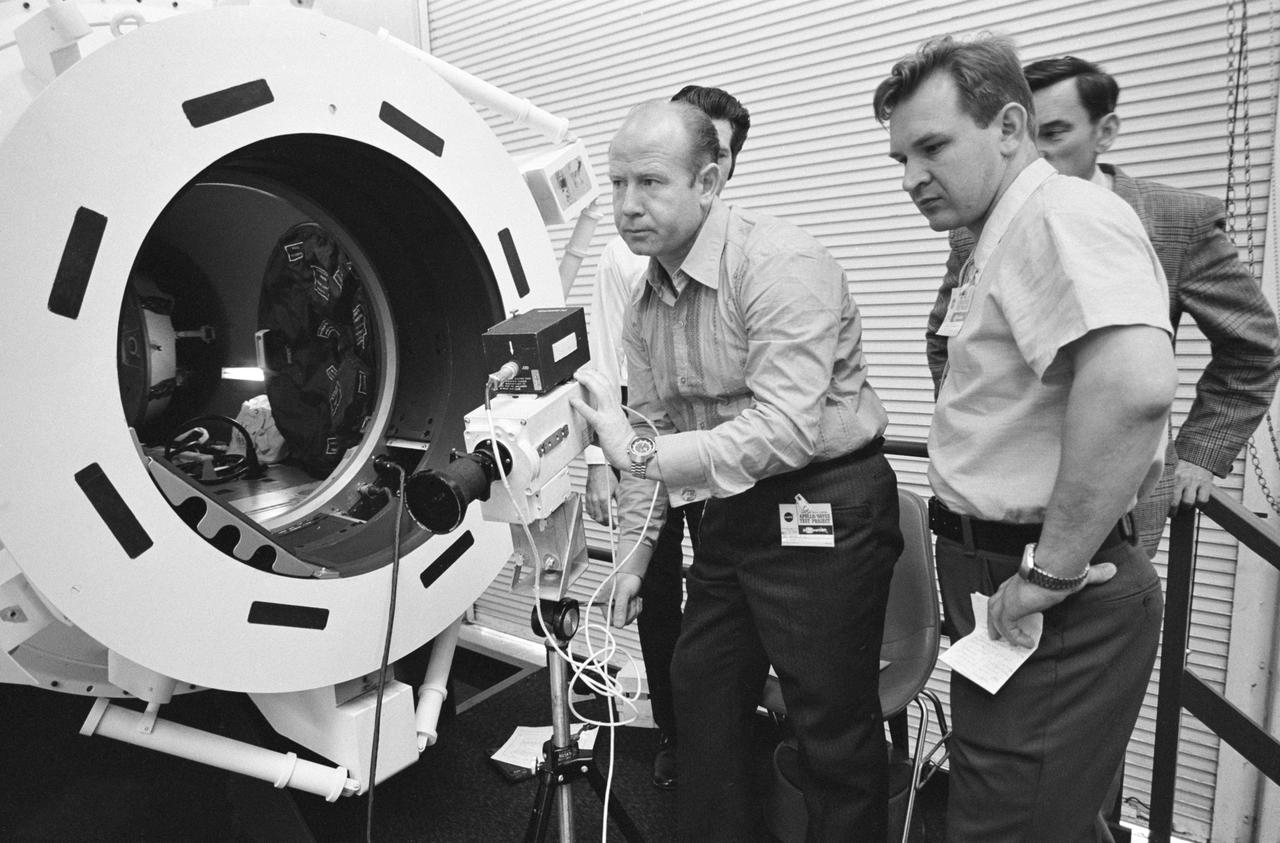
S74-25394 (10 July 1974) --- A group of American and Soviet engineers of the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project working group three examines an ASTP docking set-up following a docking mechanism fitness test conducted in Building 13 at the Johnson Space Center. Working Group No. 3 is concerned with ASTP docking problems and techniques. The joint U.S.-USSR ASTP docking mission in Earth orbit is scheduled for the summer of 1975. The Apollo docking mechanism is atop the Soyuz docking mechanism.
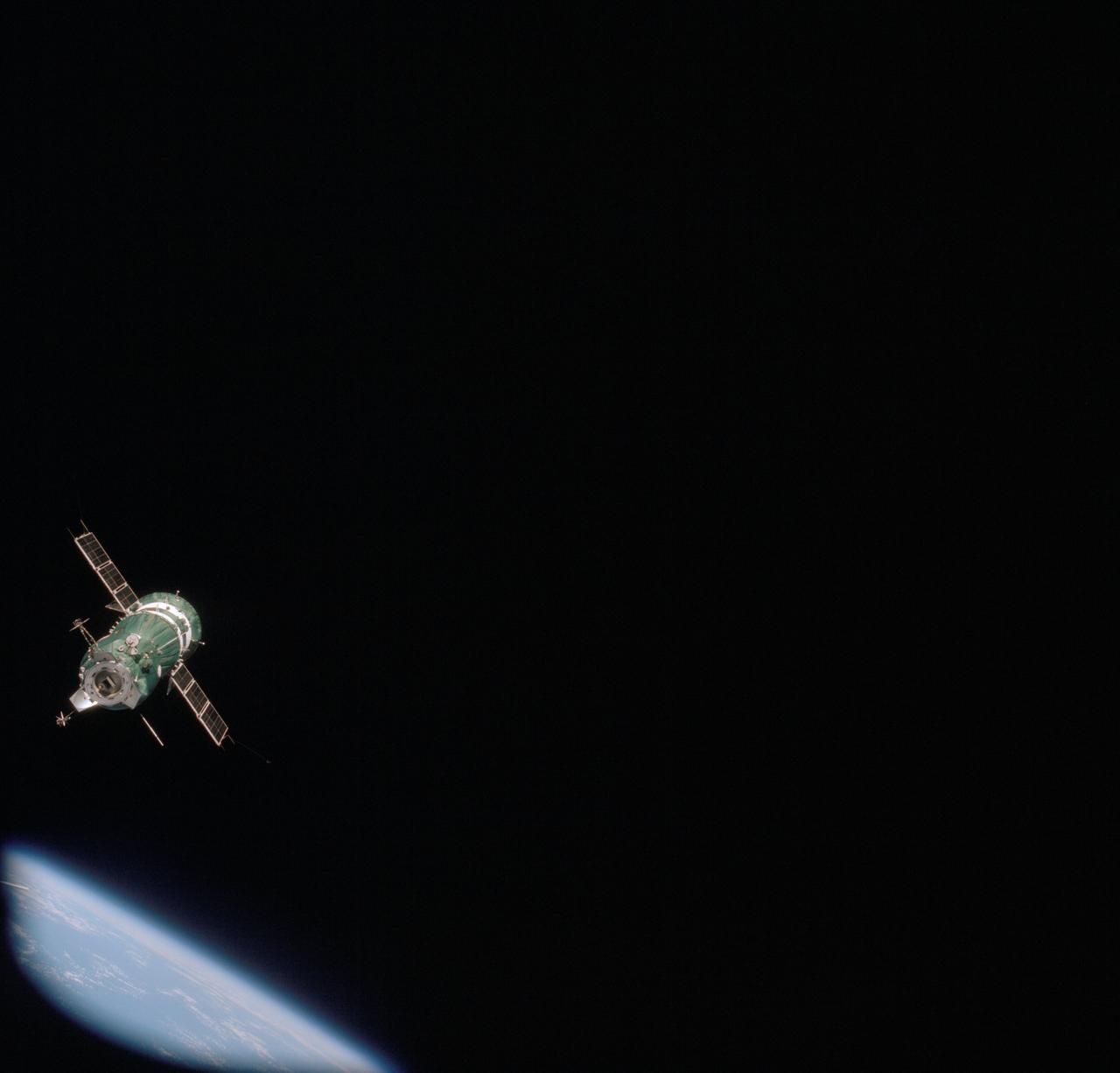

AST-09-572 (17-18 July 1975) --- The Soviet Soyuz 19 spacecraft is photographed from the American Apollo spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) docking mission in Earth orbit. Earth is visible in the lower left corner. This picture was taken with a 70mm camera. The Apollo crew consisted of astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; Donald K. "Deke" Slayton, docking module pilot; and Vance D. Brand, command module pilot. The Soyuz 19 crew consisted of cosmonauts Aleksei A. Leonov, command pilot; and Valeri N. Kubasov, flight engineer.