
Sojourner APXS at Work

Multispectral Slice of APXS
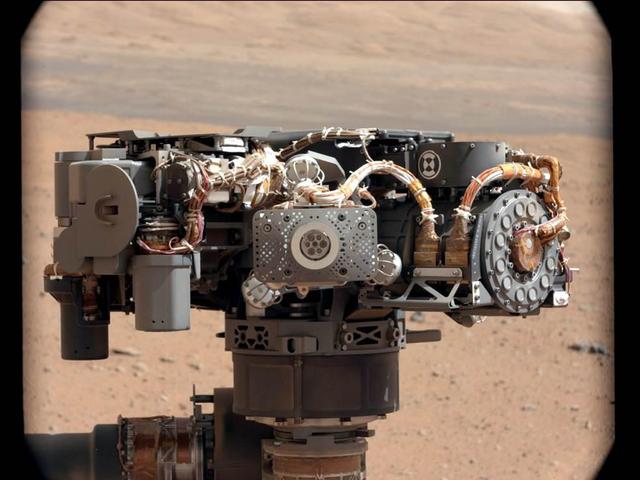

This image shows the Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer APXS on NASA Curiosity rover, with the Martian landscape in the background. This image let researchers know that the APXS instrument had not become caked with dust during Curiosity landing.

APXS on Barnacle

This graph shows the ratio of concentrations of several elements in four different pairs of targets examined by Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) instruments on NASA Mars rovers Curiosity and Spirit. For each pair of targets, one shows evidence of mineral alteration and the other is an unaltered counterpart. The first three pairs (with ratios shown by green, blue and red lines) are targets in Gale Crater analyzed by Curiosity's APXS. The fourth pair (with ratio shown by the black line) is in Gusev Crater and was analyzed by Spirit's APXS. Similar profiles are observed, suggesting the possibility of related formation processes. As with examples of silica enrichment found by Curiosity, the origin of high-silica nodular deposits found by Spirit also remains unresolved: Either acidic weathering or silica addition could be responsible. It is clear, however, that liquid water was involved in either alteration scenario. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20276

Sojourner APXS studies Barnacle

This image of the rock "Wedge" was taken from the Sojourner rover's rear color camera on Sol 37. The position of the rover relative to Wedge is seen in MRPS 83349. The segmented rod visible in the middle of the frame is the deployment arm for the Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer (APXS). The APXS, the bright, cylindrical object at the end of the arm, is positioned against Wedge and is designed to measure the rock's chemical composition. This was done successfully on the night of Sol 37. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00906

This image shows the Sojourner rover's Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) deployed against the rock "Stimpy" on the afternoon of Sol 68 (September 11). The two rocks behind the rover were previously analyzed by the APXS. Sojourner spent 83 days of a planned seven-day mission exploring the Martian terrain, acquiring images, and taking chemical, atmospheric and other measurements. The final data transmission received from Pathfinder was at 10:23 UTC on September 27, 1997. Although mission managers tried to restore full communications during the following five months, the successful mission was terminated on March 10, 1998. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01563
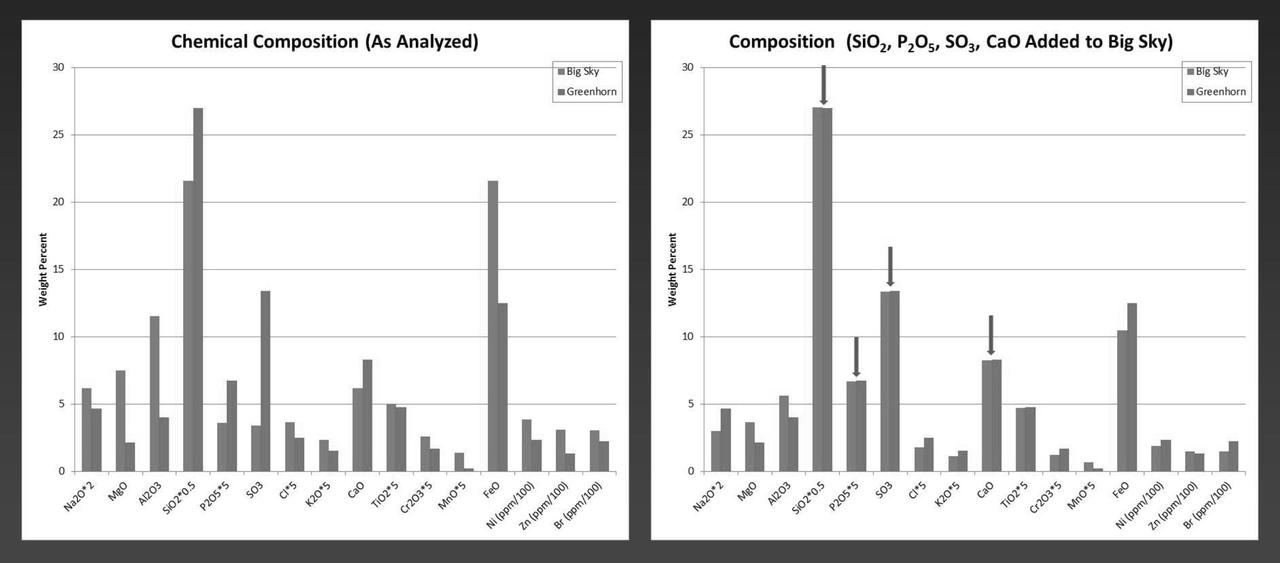
NASA's Curiosity Mars rover examined both the "Greenhorn" and "Big Sky" targets with the rover's Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) instrument. Greenhorn is located within an altered fracture zone and has an elevated concentration of silica (about 60 percent by weight). Big Sky is the unaltered counterpart for comparison. The bar plot on the left shows scaled concentrations as analyzed by Curiosity's APXS. The bar plot on the right shows what the Big Sky composition would look like if silica (SiO2) and calcium-sulfate (both abumdant in Greenhorn) were added. The similarity in the resulting composition suggests that much of the chemistry of Greenhorn could be explained by the addition of silica. Ongoing research aims to distinguish between that possible explanation for silicon enrichment and an alternative of silicon being left behind when some other elements were removed by acid weathering. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20275
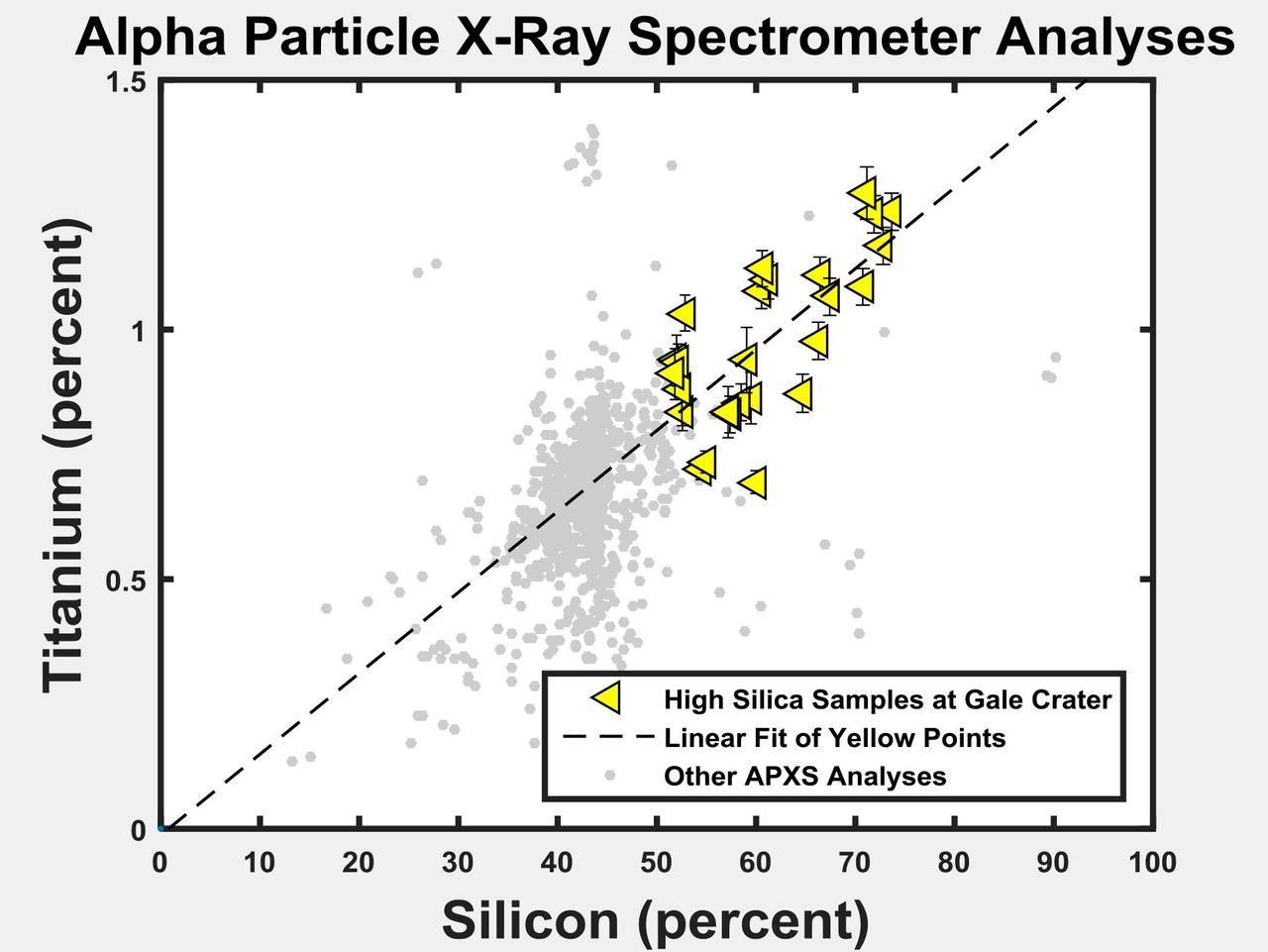
The yellow triangles on this graph indicate concentrations of the elements titanium and silicon in selected rock targets with high silica content analyzed by the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) instrument on NASA's Curiosity rover in Mars' Gale Crater. The pattern shows a correlation between enriched silicon content and enriched titanium content. Titanium is difficult to mobilize in weathering environments, and this correlation suggests that both titanium and silicon remain as the residue of acidic weathering. Ongoing research aims to distinguish between that possible explanation for silicon enrichment and an alternative of mobilized silicon being added to the site (see PIA20275). As a general comparison with these selected high-silica targets in Gale Crater, the gray dots in the graph show the range of titanium and silicon concentrations in all Martian targets analyzed by APXS instruments on three Mars rovers at three different areas of Mars. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20274

The Sojourner rover's Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) is shown deployed against the rock "Moe" on the afternoon of Sol 64 (September 7). The rocks to the left of Moe are "Shark" (left of Sojourner) and "Half Dome" (behind Sojourner). They were previously measured by the APXS. The image was taken by the Imager for Mars Pathfinder (IMP). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00966

This image shows the Sojourner rover's Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) deployed against the rock "Stimpy" on the afternoon of Sol 68 (September 11). The two rocks behind the rover were previously analyzed by the APXS. Sojourner spent 83 days of a planned seven-day mission exploring the Martian terrain, acquiring images, and taking chemical, atmospheric and other measurements. The final data transmission received from Pathfinder was at 10:23 UTC on September 27, 1997. Although mission managers tried to restore full communications during the following five months, the successful mission was terminated on March 10, 1998. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00968

The Sojourner rover's Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) is shown deployed against the rock "Moe" on the afternoon of Sol 64 (September 7). The rocks to the left of Moe are "Shark" (left of Sojourner) and "Half Dome" (behind Sojourner). They were previously measured by the APXS. The image was taken by the Imager for Mars Pathfinder (IMP). Sojourner spent 83 days of a planned seven-day mission exploring the Martian terrain, acquiring images, and taking chemical, atmospheric and other measurements. The final data transmission received from Pathfinder was at 10:23 UTC on September 27, 1997. Although mission managers tried to restore full communications during the following five months, the successful mission was terminated on March 10, 1998. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01560

This image taken on the morning of Sol 80 (September 23) shows the Sojourner rover with its Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) deployed against the rock "Chimp." On the left horizon is the rim of "Big Crater," 2.2 km away. Sojourner spent 83 days of a planned seven-day mission exploring the Martian terrain, acquiring images, and taking chemical, atmospheric and other measurements. The final data transmission received from Pathfinder was at 10:23 UTC on September 27, 1997. Although mission managers tried to restore full communications during the following five months, the successful mission was terminated on March 10, 1998. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00970

This image taken on the morning of Sol 80 (September 23, 1997) shows the Sojourner rover with its Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) deployed against the rock "Chimp." On the left horizon is the rim of "Big Crater," 2.2 km away. Sojourner spent 83 days of a planned seven-day mission exploring the Martian terrain, acquiring images, and taking chemical, atmospheric and other measurements. The final data transmission received from Pathfinder was at 10:23 UTC on September 27, 1997. Although mission managers tried to restore full communications during the following five months, the successful mission was terminated on March 10, 1998. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01585
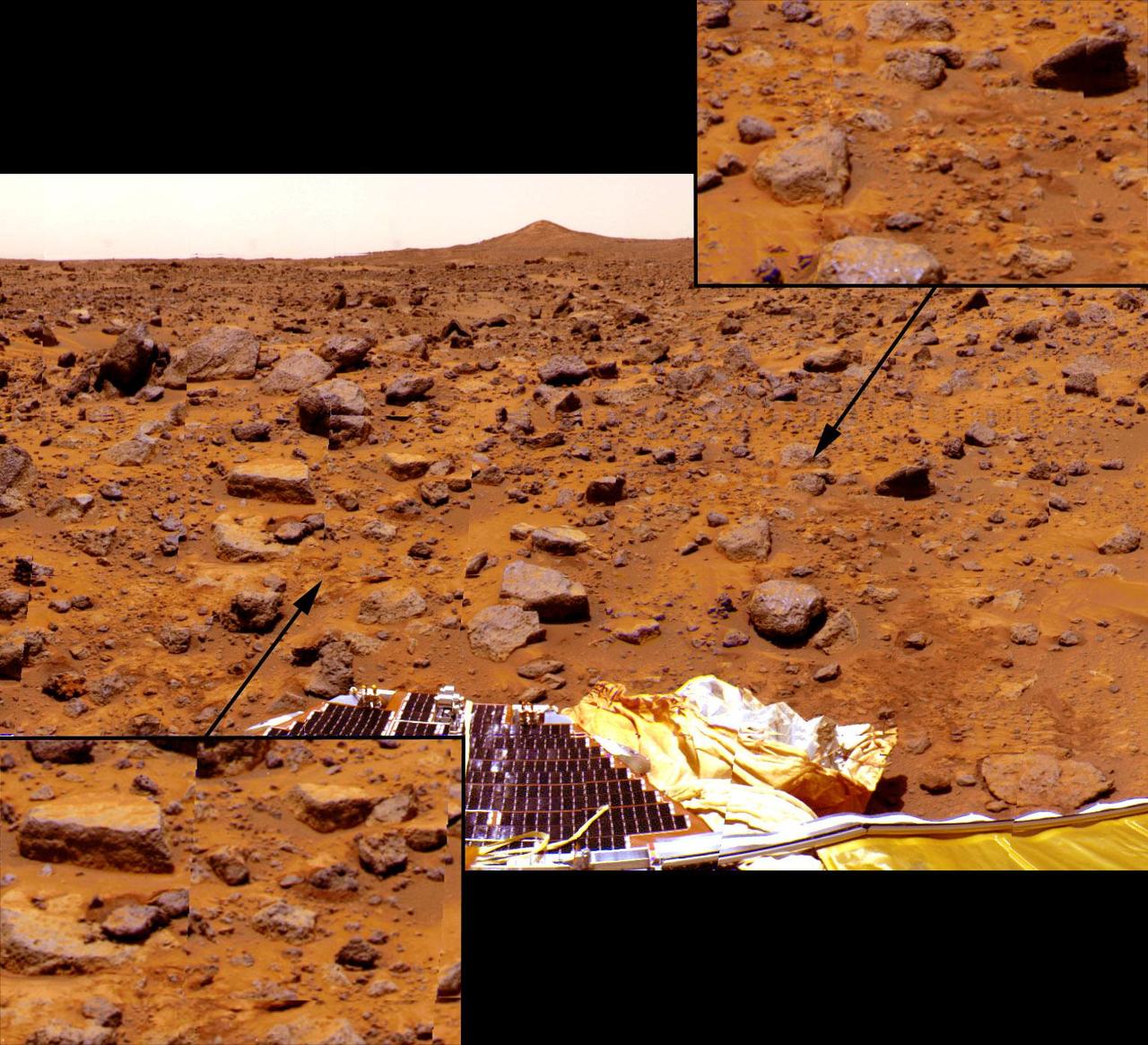
A close up of NASA Sojourner as it placed its Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer APXS upon the surface of the rock Yogi. Distortion in the background is due to parallax.

This image taken by the MAHLI camera shows a sample of basaltic rock from a lava flow in New Mexico serves as a calibration target carried on the front of NASA Mars rover Curiosity for the rover Canadian-made APXS instrument.
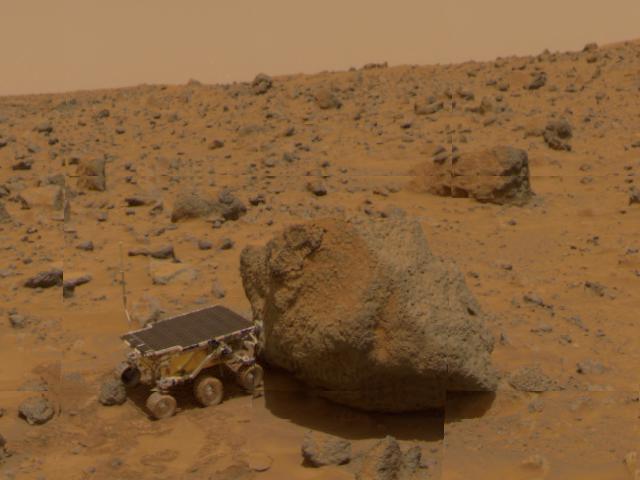

This 1997 image from NASA Mars Pathfinder shows a close up of Sojourner as it placed its Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer APXS upon the surface of the rock Yogi.
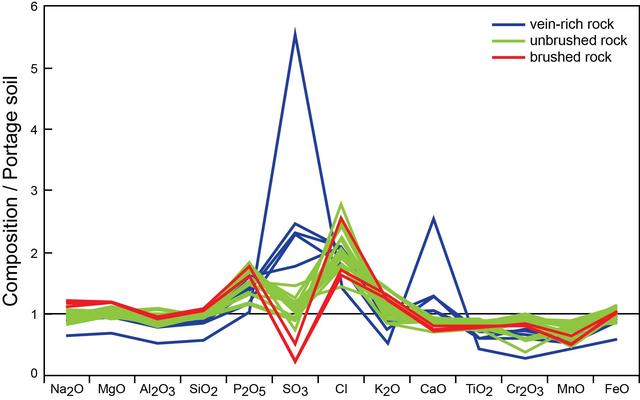
This graphic presents results from APXS onboard NASA rover Curiosity, with the comparisons simplified across diverse elements by dividing the amount of each element measured in the rocks by the amount of the same element in a local soil.

This color image shows the Sojourner rover's Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) deployed against the rock "Moe" on the morning of Sol 65. The rock behind the rover is "Half Dome," which was previously measured by the APXS. Sojourner spent 83 days of a planned seven-day mission exploring the Martian terrain, acquiring images, and taking chemical, atmospheric and other measurements. The final data transmission received from Pathfinder was at 10:23 UTC on September 27, 1997. Although mission managers tried to restore full communications during the following five months, the successful mission was terminated on March 10, 1998. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00967

NASA's Sojourner rover is seen next to the rock "Shark," in this image taken by the Imager for Mars Pathfinder (IMP) near the end of daytime operations on Sol 52. The rover's Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer is deployed against the rock. The rock "Wedge" is in the foreground. The Sojourner rover is seen next to the rock "Shark," in this image taken by the Imager for Mars Pathfinder (IMP) near the end of daytime operations on Sol 52. The rover's Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer is deployed against the rock. The rock "Wedge" is in the foreground.
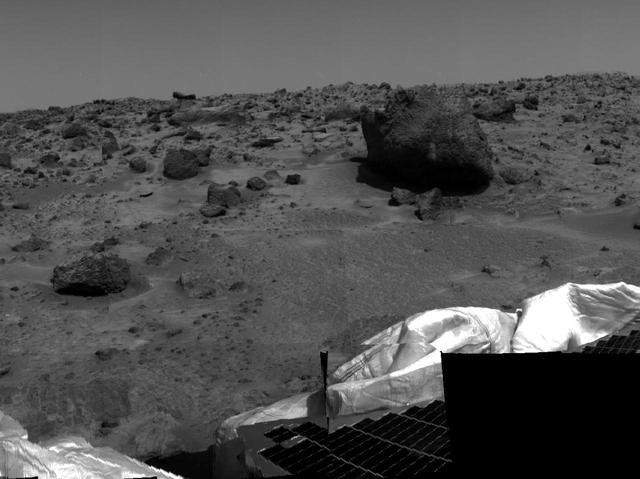

Several possible targets of study for rover Sojourner's Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer (APXS) instrument are seen in this image, taken by the Imager for Mars Pathfinder (IMP) on Sol 2. The smaller rock at left has been dubbed "Barnacle Bill," while the larger rock at right, approximately 3-4 meters from the lander, is now nicknamed "Yogi." Barnacle Bill is scheduled to be the first object of study for the APXS. Portions of a petal and deflated airbag are also visible at lower right. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00629

This picture taken by the IMP (Imager for Mars Pathfinder) aboard the Mars Pathfinder spacecraft depicts the rover Sojourner's position after driving onto the Martian surface. Sojourner has become the first autonomous robot ever to traverse the surface of Mars. This image reflects the success of Pathfinder's principle objective -- to place a payload on Mars in a safe, operational configuration. The primary mission of Sojourner, scheduled to last seven days, will be to use its Alpha Proton X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) instrument to determine the elements that make up the rocks and soil on Mars. A full study using the APXS takes approximately ten hours, and can measure all elements except hydrogen at any time of the Martian day or night. The APXS will conduct its studies by bombarding rocks and soil samples with alpha particle radiation -- charged particles equivalent to the nucleus of a helium atom, consisting of two protons and two neutrons. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00623
Yogi is a meter-size rock about 5 meters northwest of NASA Mars Pathfinder lander and was the second rock visited by the Sojourner Rover alpha proton X-ray spectrometer APXS instrument. 3D glasses are necessary to identify surface detail.
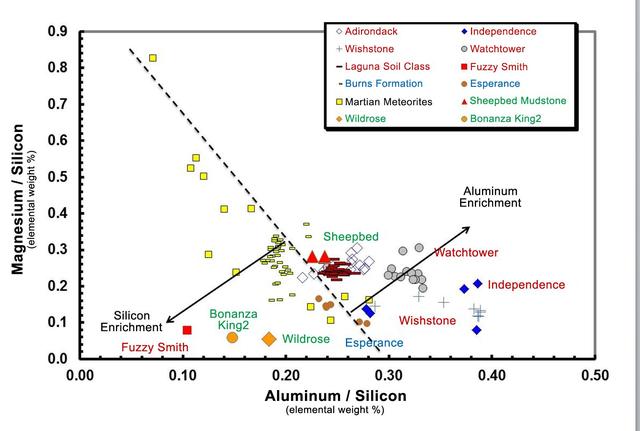
Data from the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer APXS instrument on NASA Mars rover Curiosity show an unusual enrichment of silicon in the rocks dubbed Wildrose and Bonanza King, relative to other rocks studied at Gale Crater on Mars.
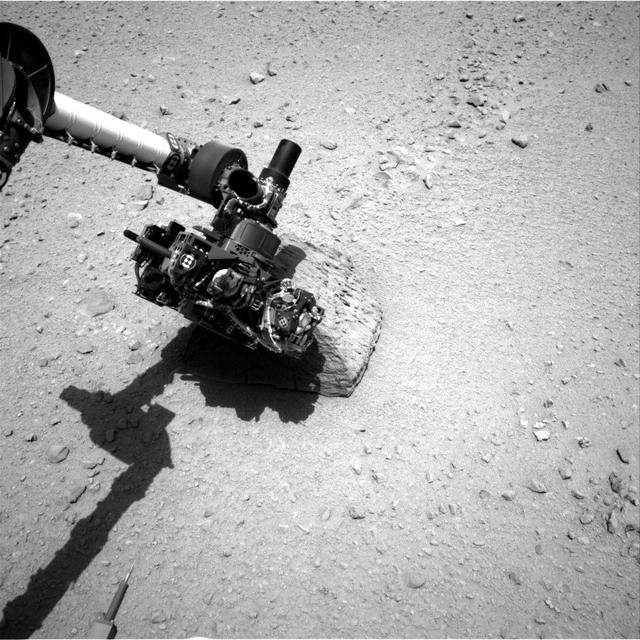

This image shows the robotic arm of NASA Mars rover Curiosity with the first rock touched by an instrument on the arm. The rover placed the APXS instrument onto the rock to assess what chemical elements were present in the rock.
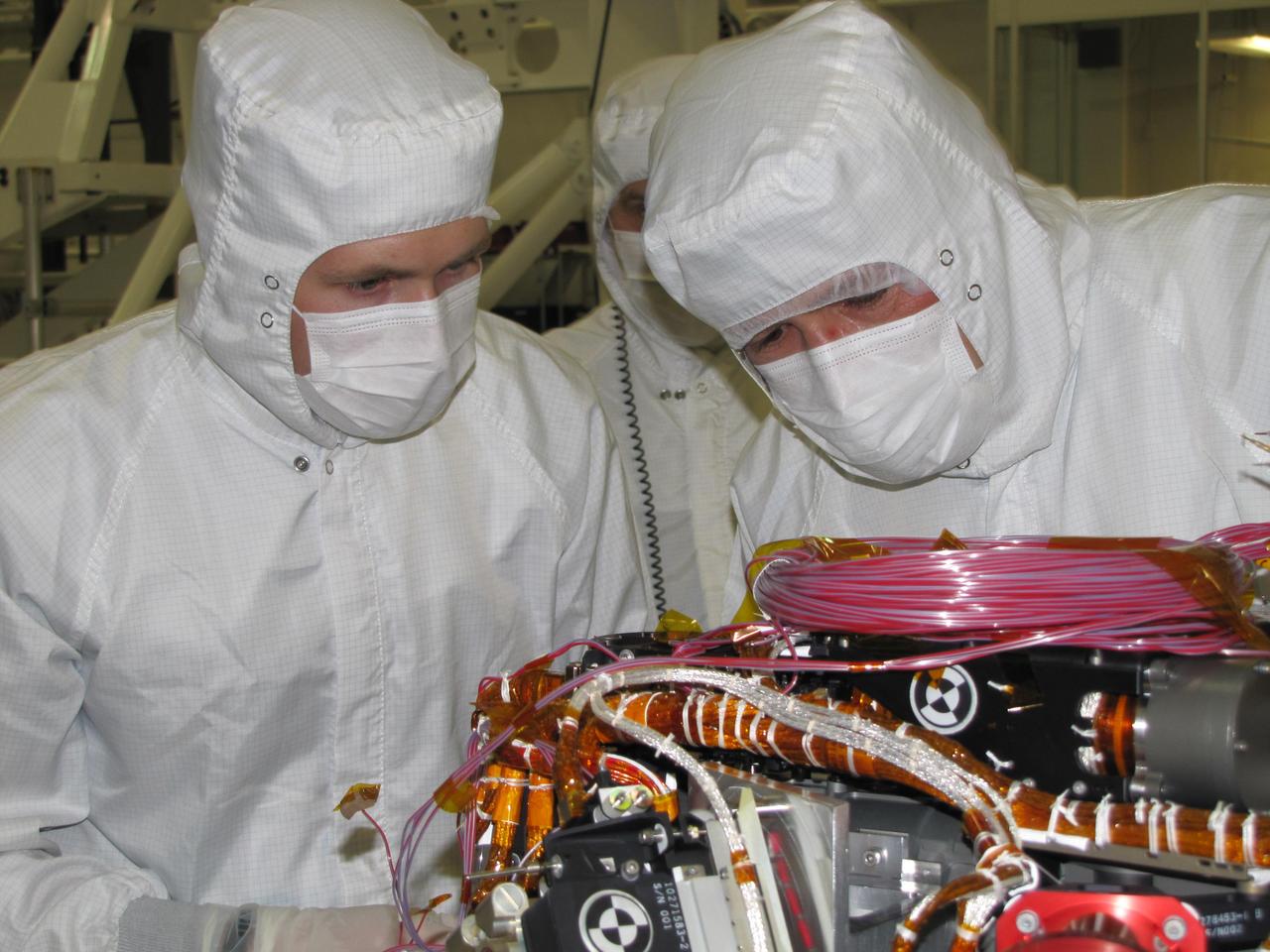

Grad student Nicholas Boyd left and Principal Investigator Ralf Gellert, both of the University of Guelph, Ontario, Canada, prepare for the installation of the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer sensor head during testing at NASA JPL.
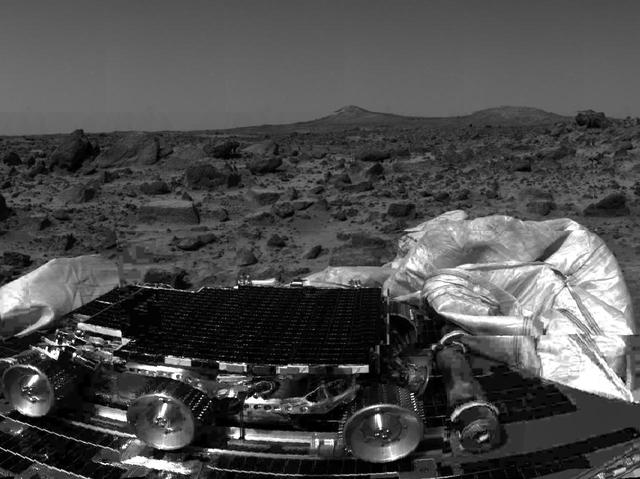

The undeployed Sojourner rover is seen still latched to a lander petal in this image, taken by the Imager for Mars Pathfinder (IMP) on Sol 1, the lander's first day on Mars. Portions of a petal and deflated airbag are in the foreground. The rectangular rock at right has been dubbed "Flat top," and may be a possible object of study for Sojourner's Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer (APXS) instrument. The mismatched portion of image at left is a misregistered section of data. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00631
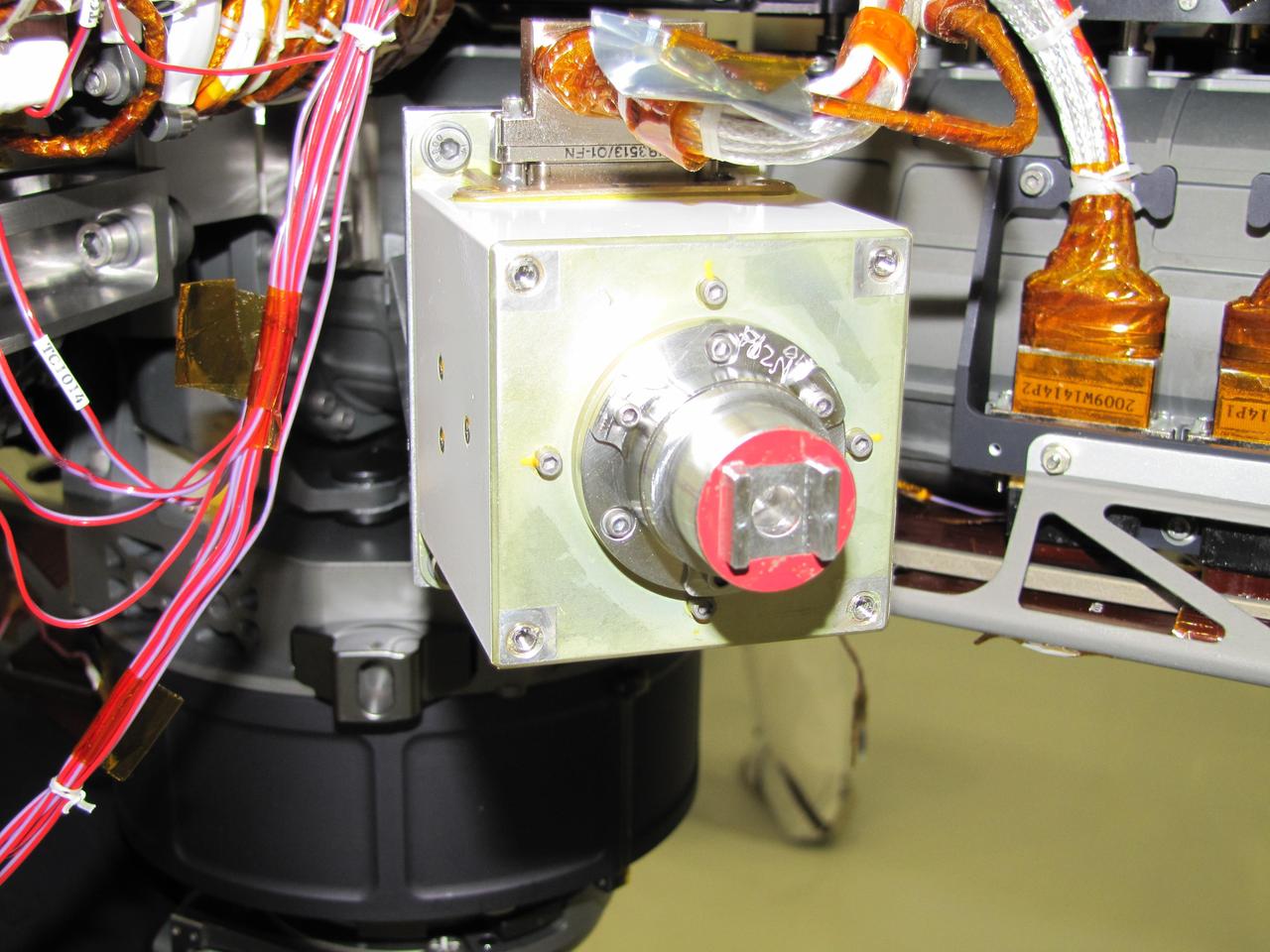

The sensor head on the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer instrument was installed during testing at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The instrument is part of NASA Curiosity rover.
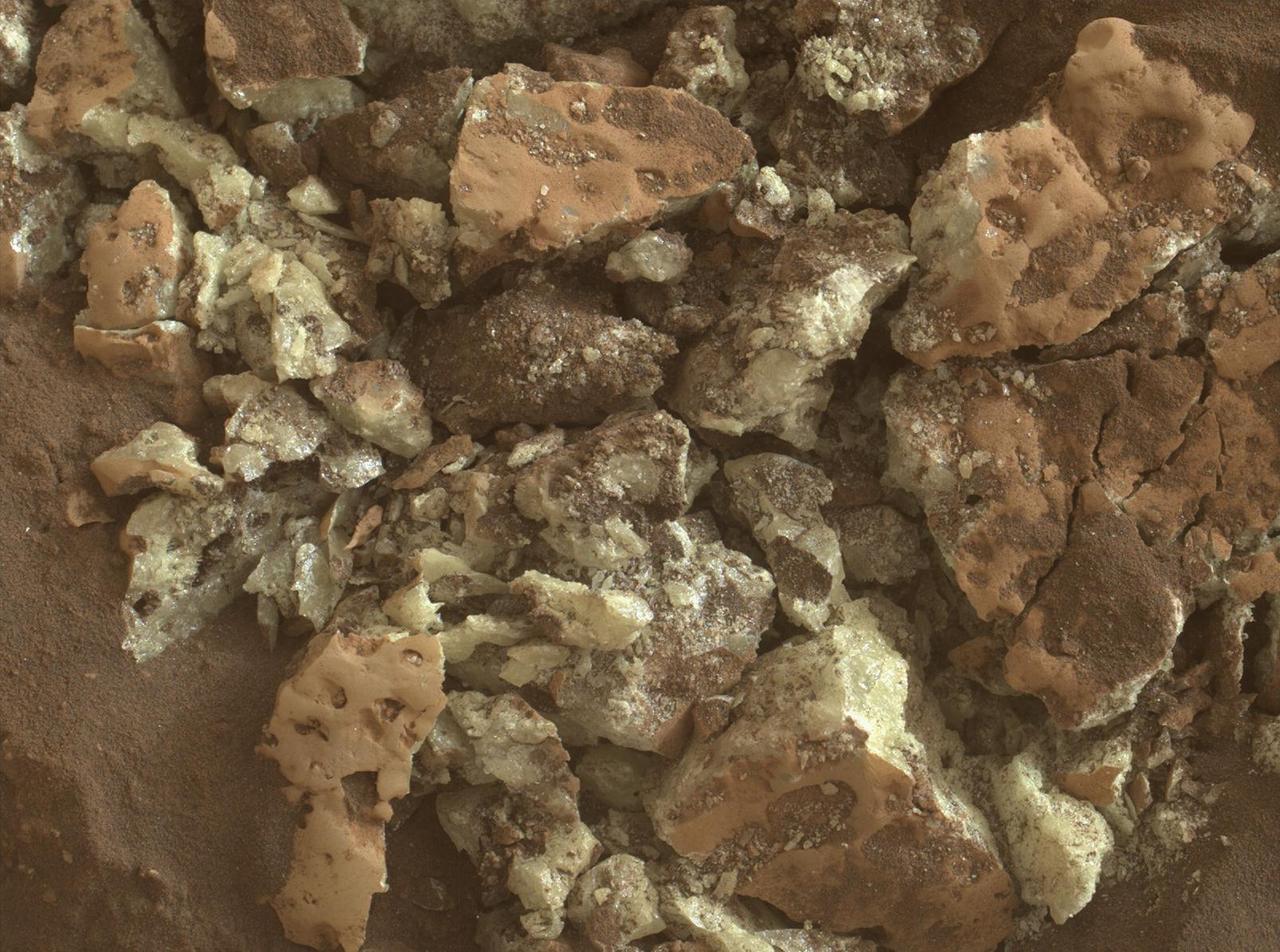

These sulfur crystals were found inside a rock after NASA's Curiosity Mars rover happened to drive over it and crush it on May 30, 2024, the 4,200th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This image was captured by Curiosity's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI), a camera on the end of its robotic arm, on June 4, 2024, the 4,205th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This rock was nicknamed "Convict Lake" after a location in California's Sierra Nevada. Curiosity's Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer (APXS) found that the crystalline material is elemental sulfur. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26307
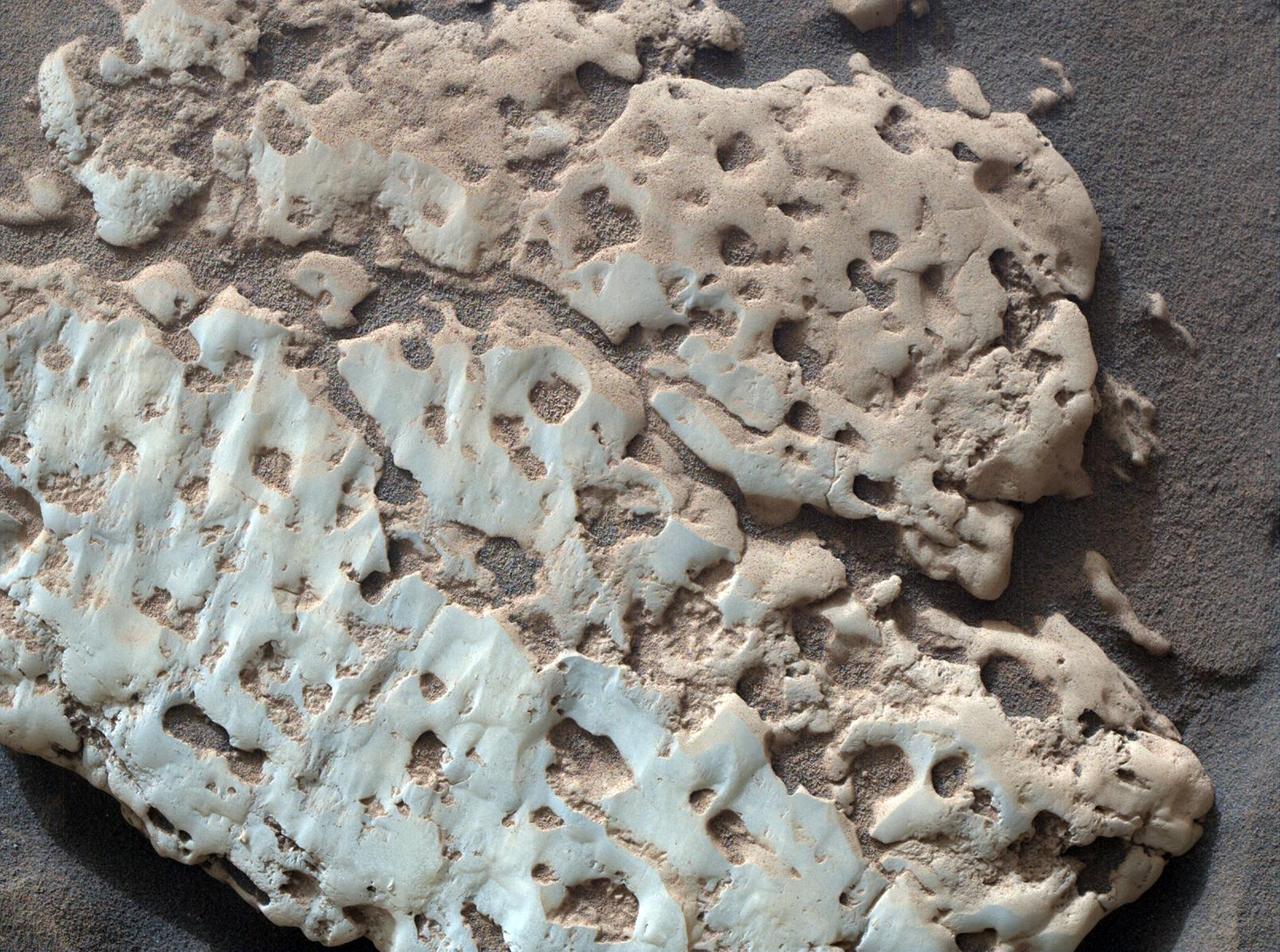

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover captured this close-up image of a rock nicknamed "Snow Lake" on June 8, 2024, the 4,209th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The image was captured by Curiosity's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI), a camera on the end of the rover's robotic arm. Nine days before this image was captured, Curiosity crushed a similar-looking rock and revealed crystalline textures inside. Curiosity's Alpha Particle X-Ray Spectrometer (APXS) found that the rock was made of elemental sulfur. An entire field of similar-looking rocks were found in this area; all are expected to have sulfur inside them. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26308

"Barnacle Bill" is a small rock immediately west-northwest of the Mars Pathfinder lander and was the first rock visited by the Sojourner Rover's alpha proton X-ray spectrometer (APXS) instrument. This image shows super resolution techniques applied to the first APXS target rock, which was never imaged with the rover's forward cameras. Super resolution was applied to help to address questions about the texture of this rock and what it might tell us about its mode of origin. This view of Barnacle Bill was produced by combining the "Super Panorama" frames from the IMP camera. Super resolution was applied to help to address questions about the texture of these rocks and what it might tell us about their mode of origin. The composite color frames that make up this anaglyph were produced for both the right and left eye of the IMP. The composites consist of 7 frames in the right eye and 8 frames in the left eye, taken with different color filters that were enlarged by 500% and then co-added using Adobe Photoshop to produce, in effect, a super-resolution panchromatic frame that is sharper than an individual frame would be. These panchromatic frames were then colorized with the red, green, and blue filtered images from the same sequence. The color balance was adjusted to approximate the true color of Mars. The anaglyph view was produced by combining the left with the right eye color composite frames by assigning the left eye composite view to the red color plane and the right eye composite view to the green and blue color planes (cyan), to produce a stereo anaglyph mosaic. This mosaic can be viewed in 3-D on your computer monitor or in color print form by wearing red-blue 3-D glasses. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01409
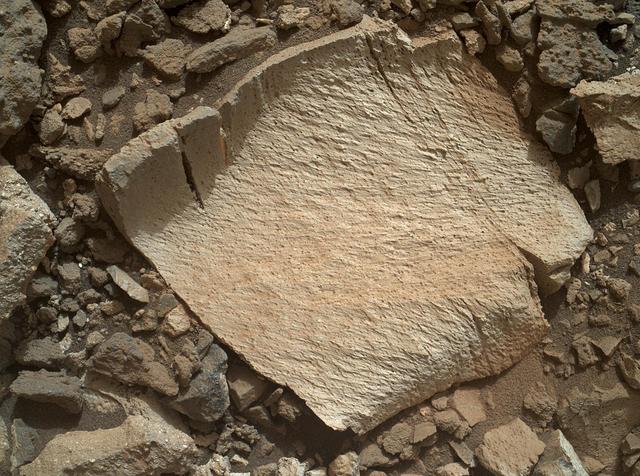

A rock fragment dubbed "Lamoose" is shown in this picture taken by the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on NASA's Curiosity rover. Like other nearby rocks in a portion of the "Marias Pass" area of Mt. Sharp, Mars, it has unusually high concentrations of silica. The high silica was first detected in the area by the Chemistry & Camera (ChemCam) laser spectrometer. This rock was targeted for follow-up study by the MAHLI and the arm-mounted Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS). Silica is a rock-forming compound containing silicon and oxygen, commonly found on Earth as quartz. High levels of silica could indicate ideal conditions for preserving ancient organic material, if present, so the science team wants to take a closer look. The rock is about 4 inches (10 centimeters) across. It is fine-grained, perhaps finely layered, and etched by the wind. The image was taken on the 1,041st Martian day, or sol, of the mission (July 11, 2015). MAHLI was built by Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington. JPL designed and built the project's Curiosity rover. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19828