
New Armed Forces Reserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies and dedication of the United States Armed Forces Center is memorialized in honor of Sgt James Wilkowski.
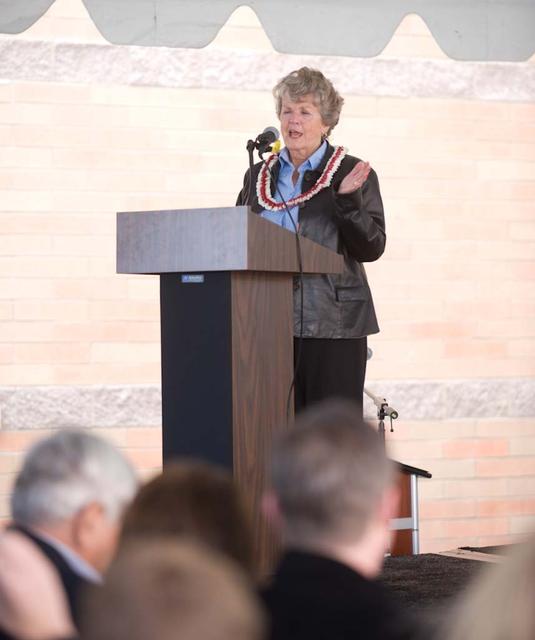

New Armed Forces Reserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies and dedication of the United States Armed Forces Center is memorialized in honor of Sgt James Wilkowski.

New Armed Forces Reserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies and dedication of the United States Armed Forces Center is memorialized in honor of Sgt James Wilkowski.
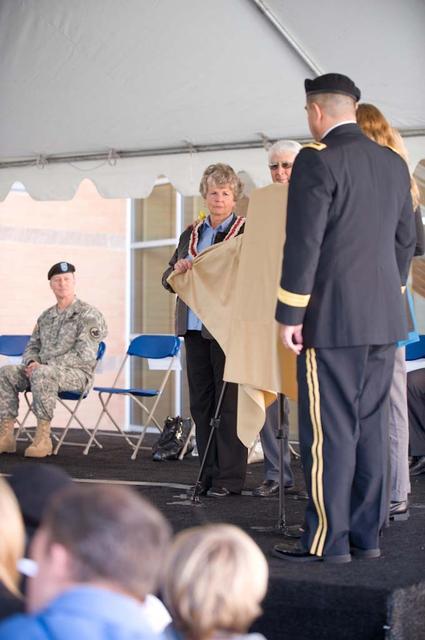

New Armed Forces Reserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies and dedication of the United States Armed Forces Center is memorialized in honor of Sgt James Wilkowski.
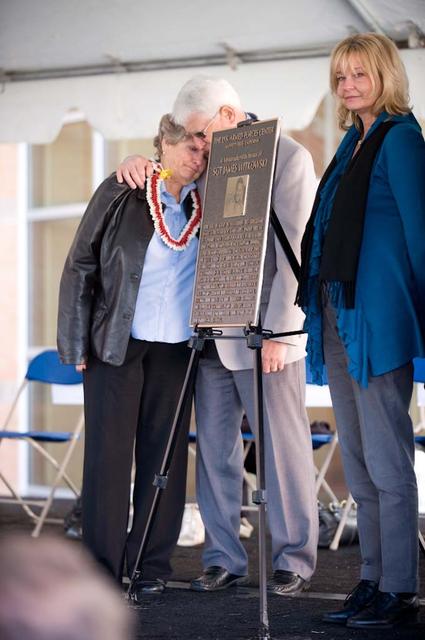

New Armed Forces Reserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies and dedication of the United States Armed Forces Center is memorialized in honor of Sgt James Wilkowski.

New Armed Forces Reserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies and dedication of the United States Armed Forces Center is memorialized in honor of Sgt James Wilkowski.
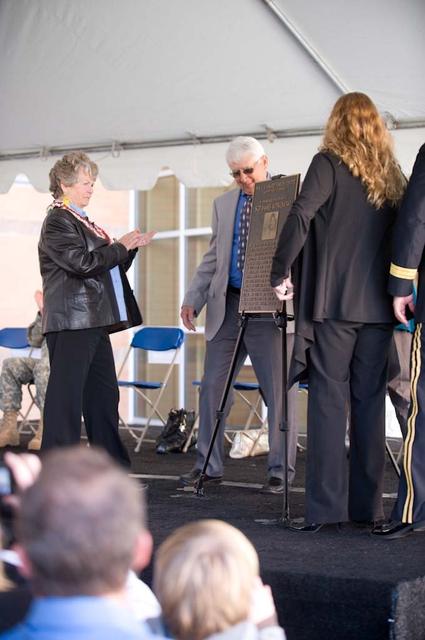

New Armed Forces Reserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies and dedication of the United States Armed Forces Center is memorialized in honor of Sgt James Wilkowski.
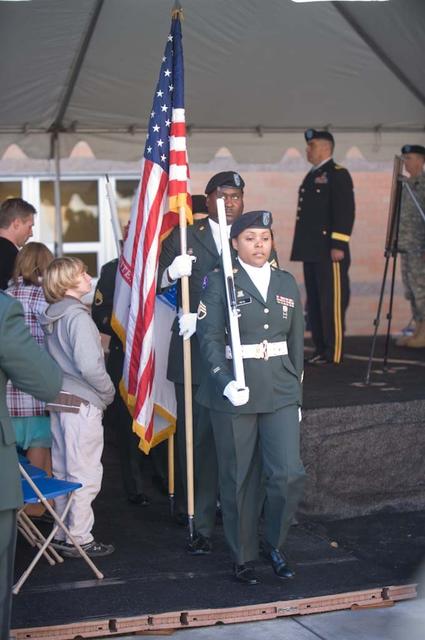

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
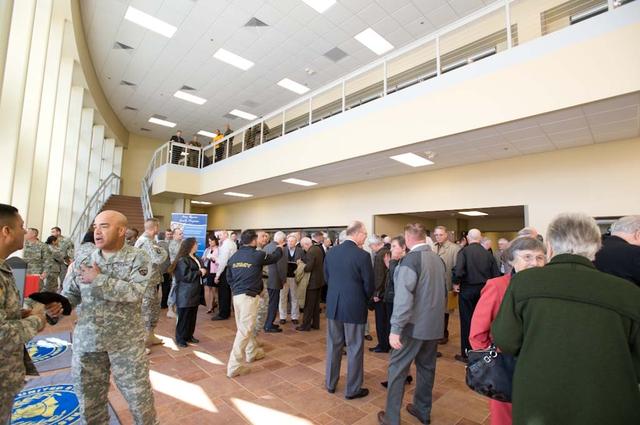

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
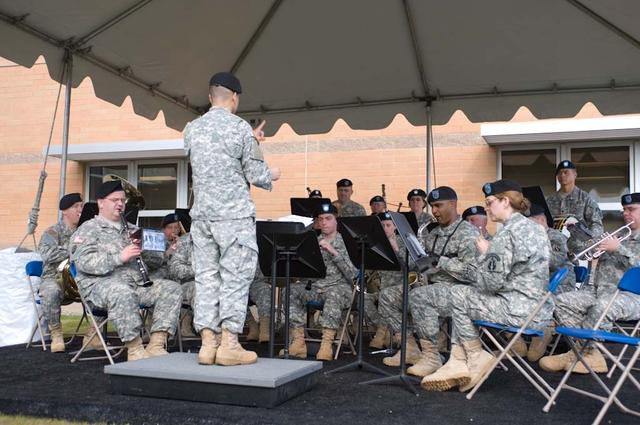

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
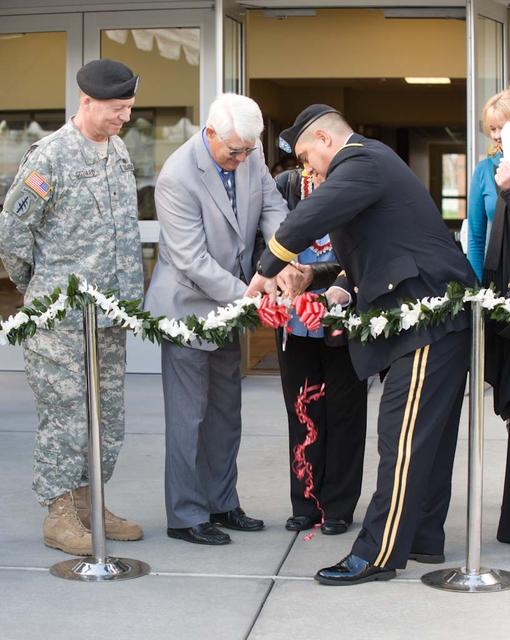

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
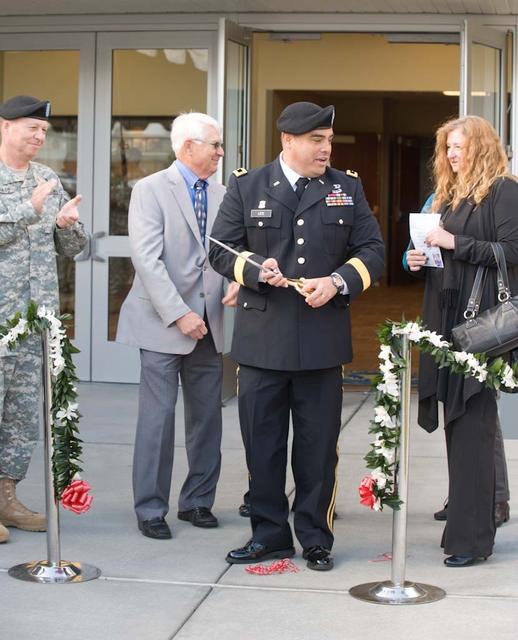

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
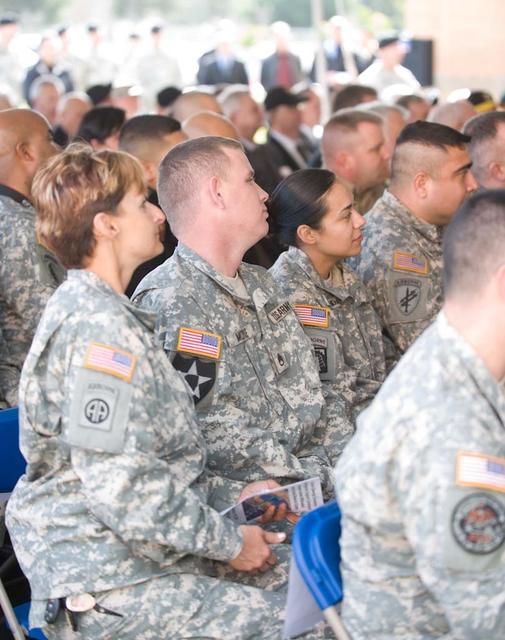

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
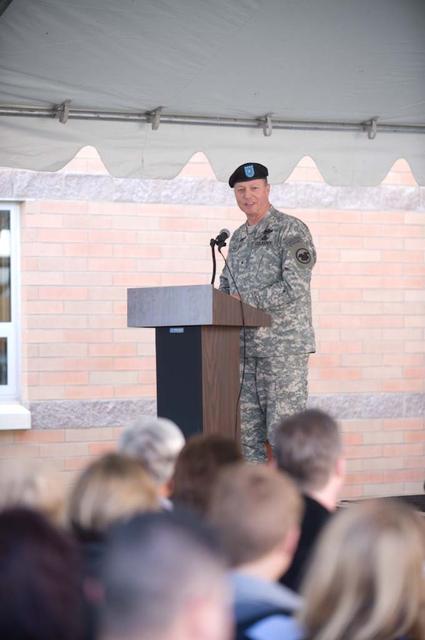

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
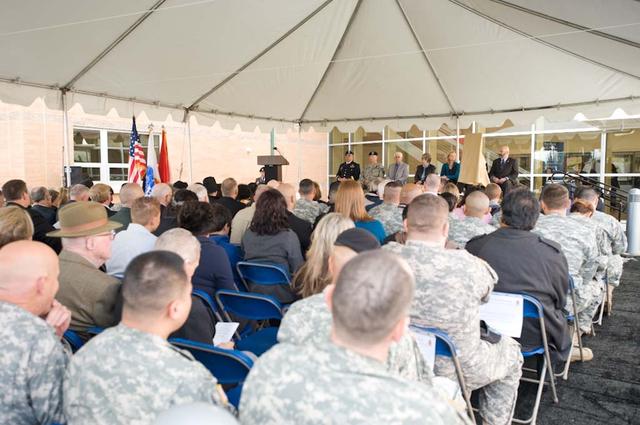

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
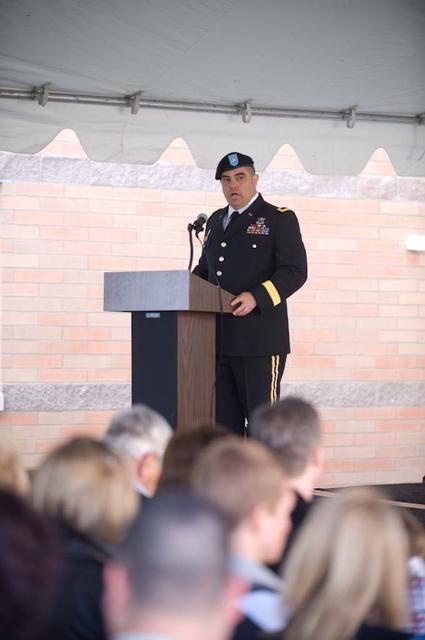

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
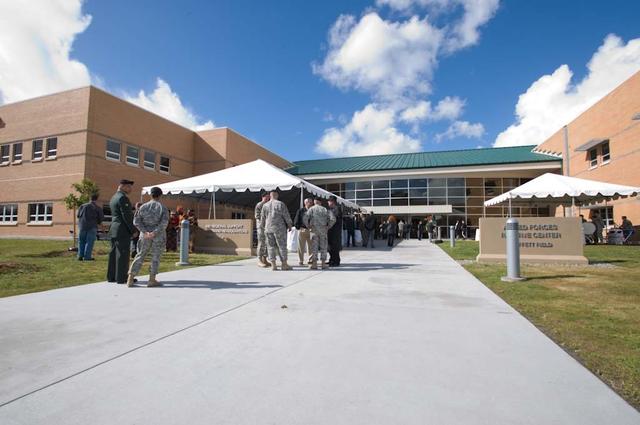

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
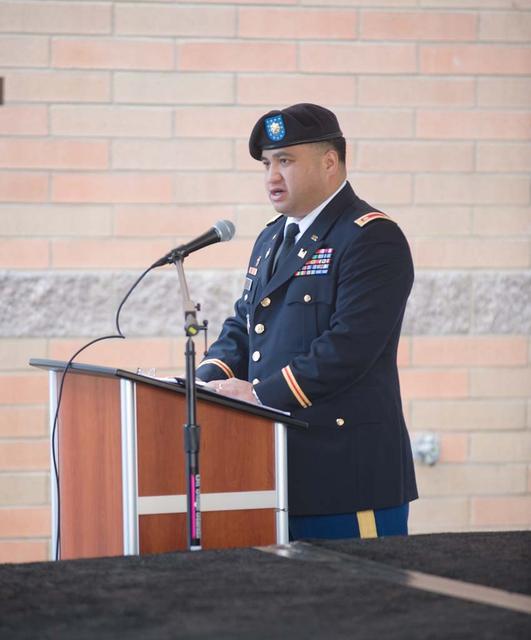

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
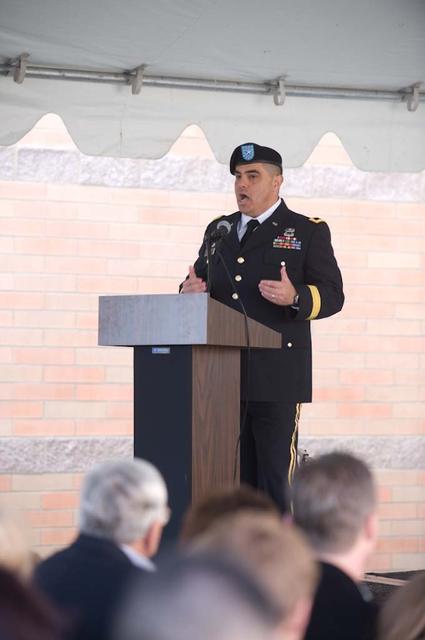

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
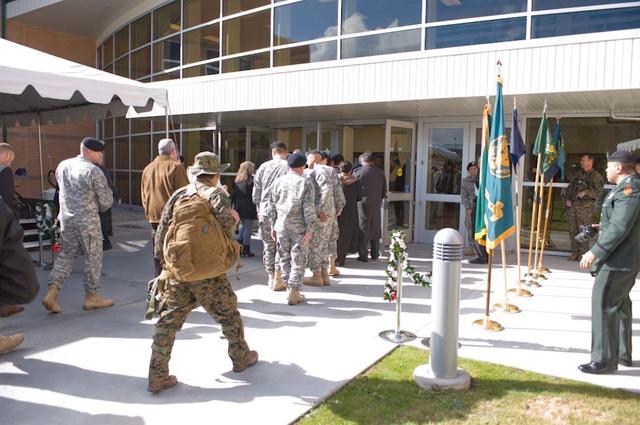

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
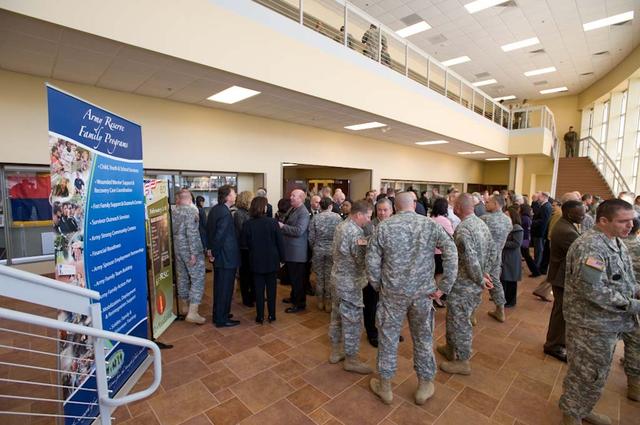

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
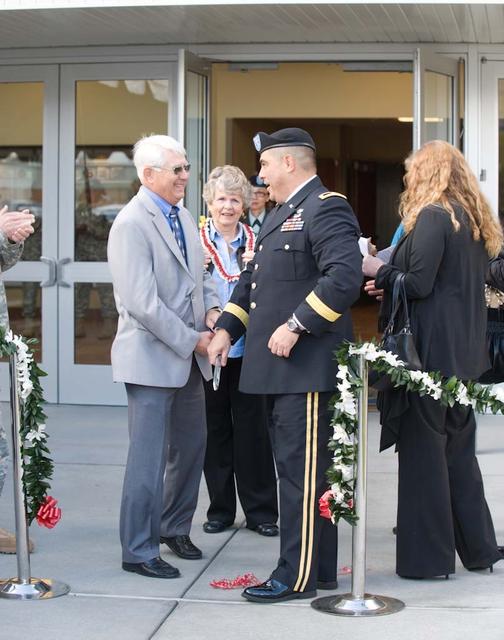

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
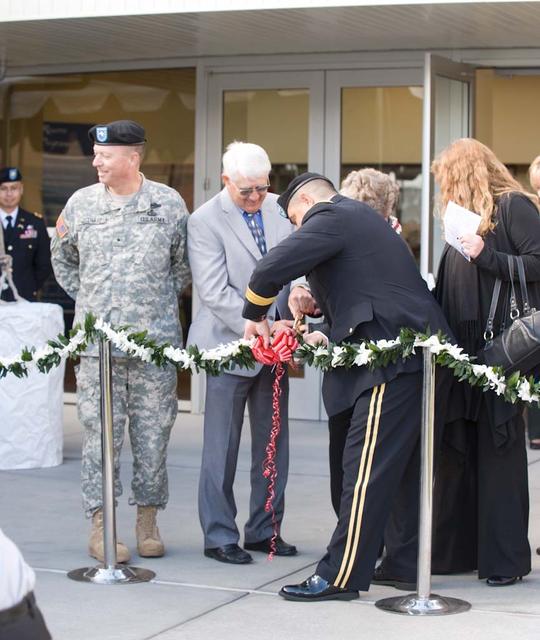

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
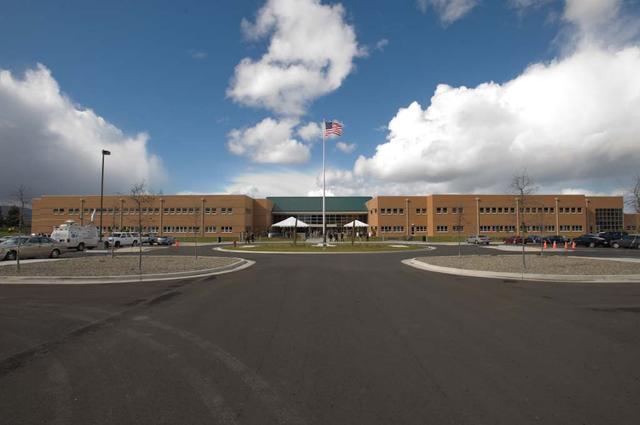

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
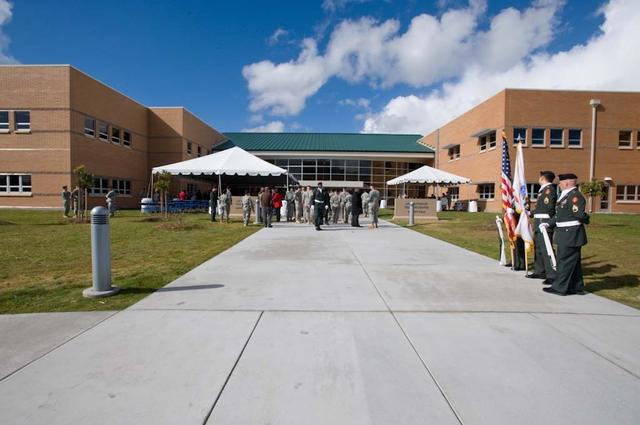

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
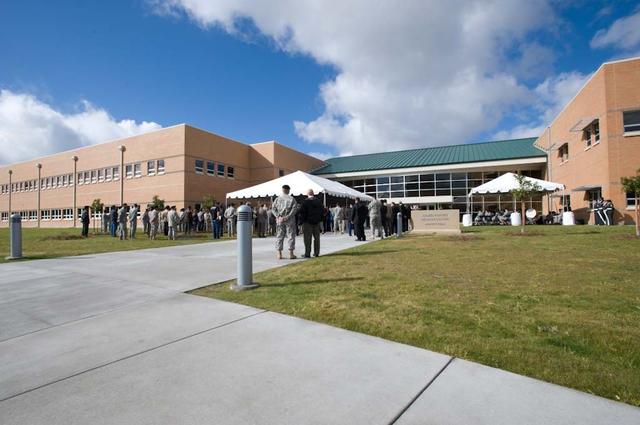

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
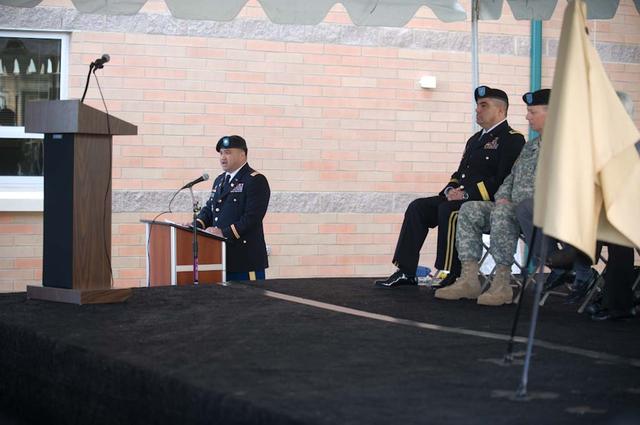

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
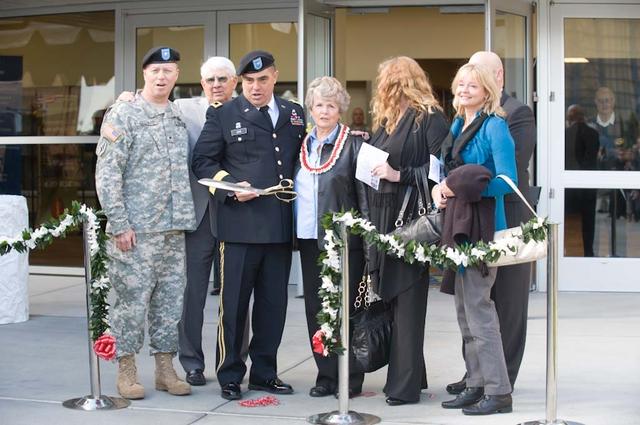

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
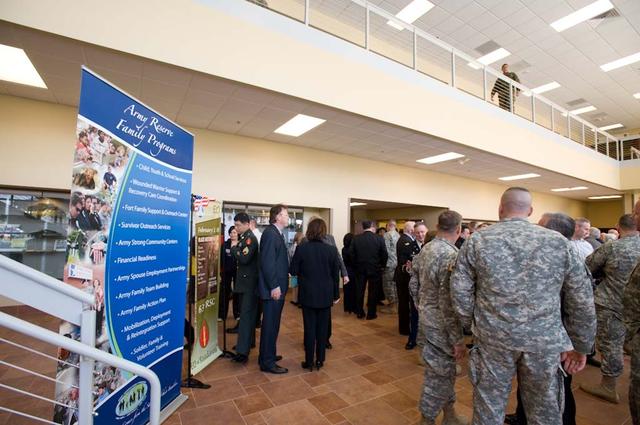

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
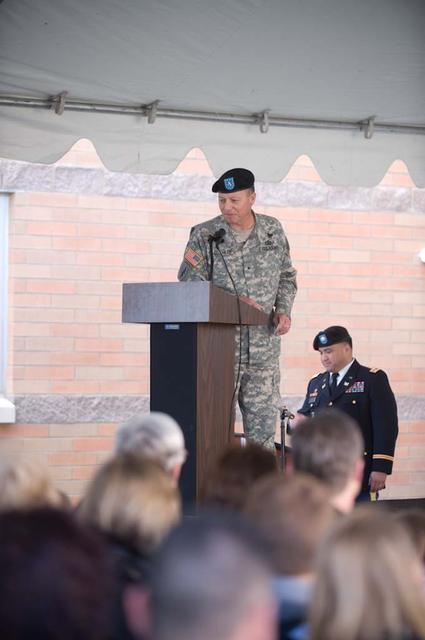

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
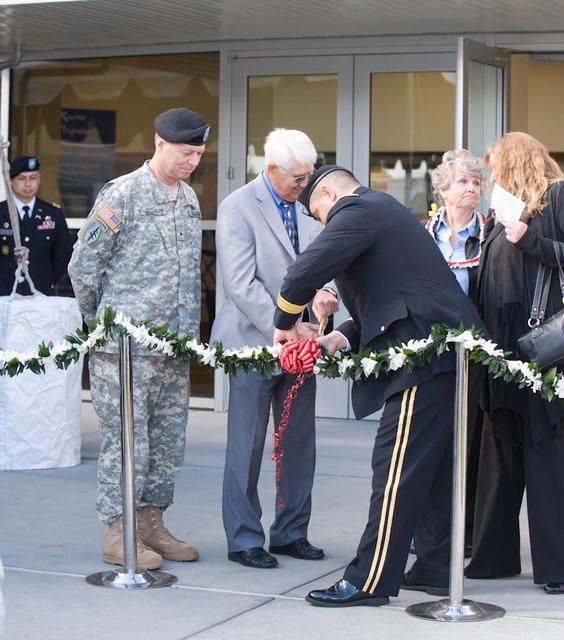

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
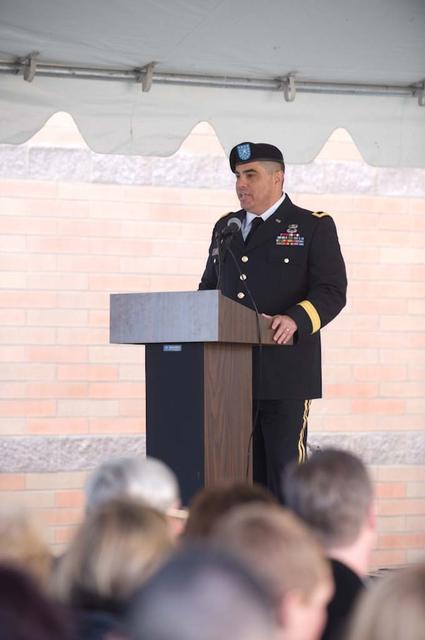

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
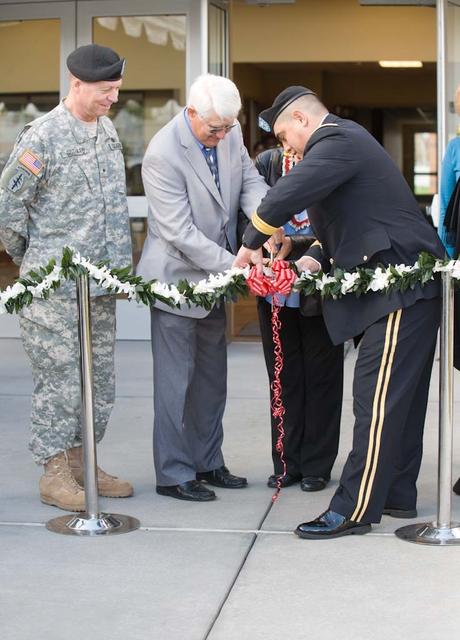

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
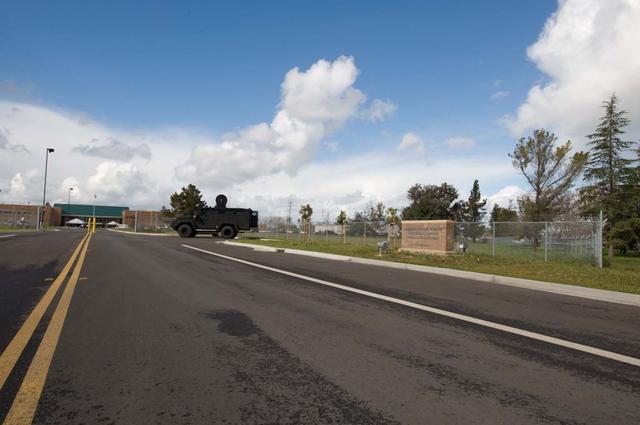

New Armed Forces Seserve Center & 63rd Regional Support Command Headquarters, Moffett Field, CA ribbon cutting ceremonies.
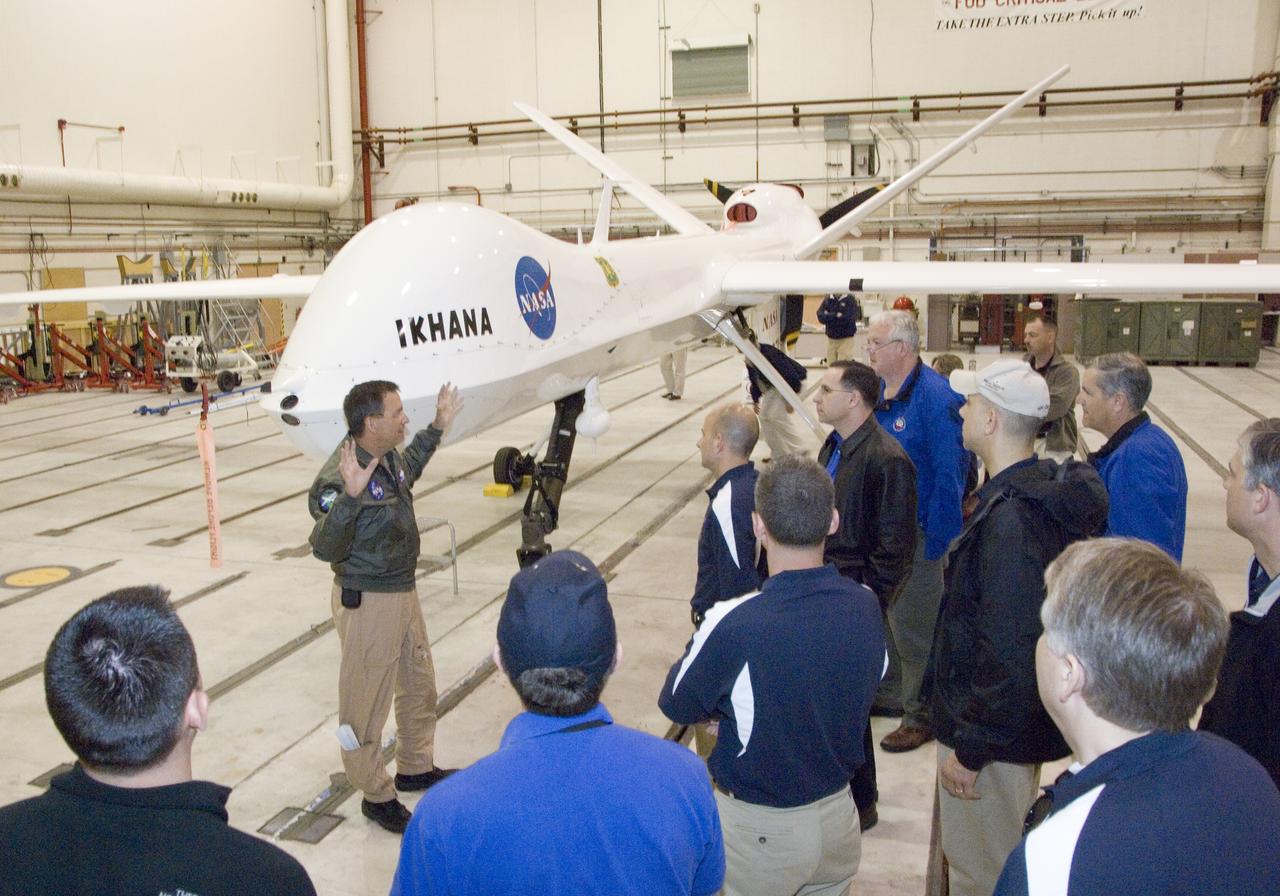

Industrial College of the Armed Forces students on a VIP tour receive a briefing on the Ikhana unmanned air vehicle from NASA Dryden pilot Mark Pestana.
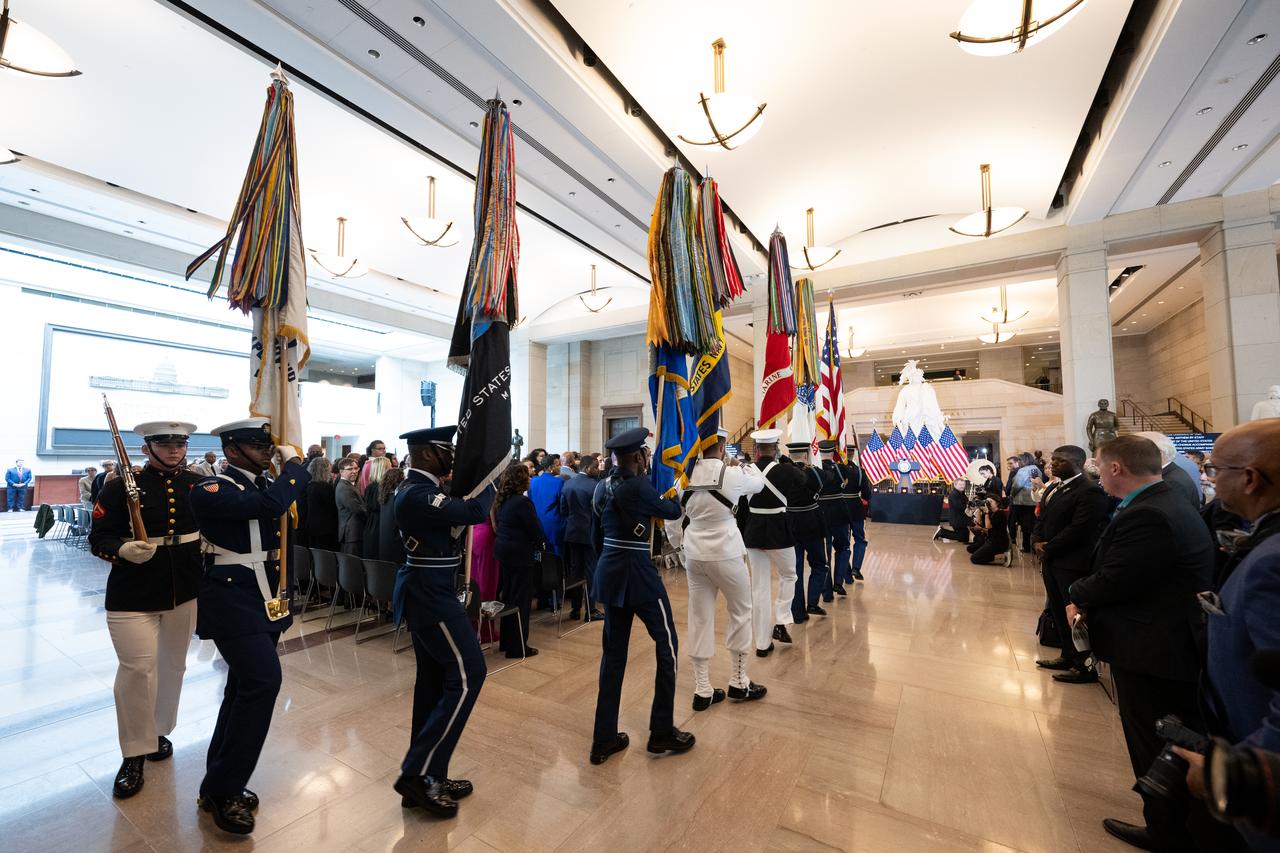

The United States Joint Armed Forces Color Guard presents the colors during a Congressional Gold Medal ceremony recognizing NASA’s Hidden Figures, Wednesday, Sept. 18, 2024, in Emancipation Hall at the U.S. Capitol in Washington. Congressional Gold Medals were awarded to Katherine Johnson, Dr. Christine Darden, Dorothy Vaughan, and Mary W. Jackson in recognition of their service to the United States as well as a Congressional Gold Medal in recognition of all the women who served as computers, mathematicians, and engineers at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics and NASA between the 1930s and 1970s. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
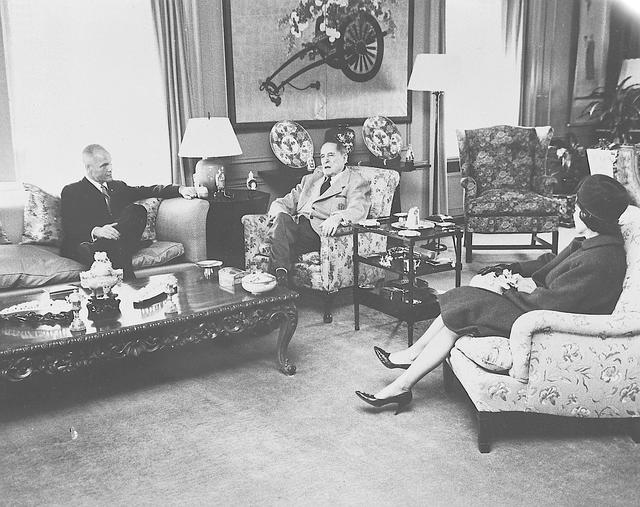

S62-02270 (1962) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. and wife visit with General Douglas McArthur in the Waldorf Astoria hotel. Photo credit: NASA
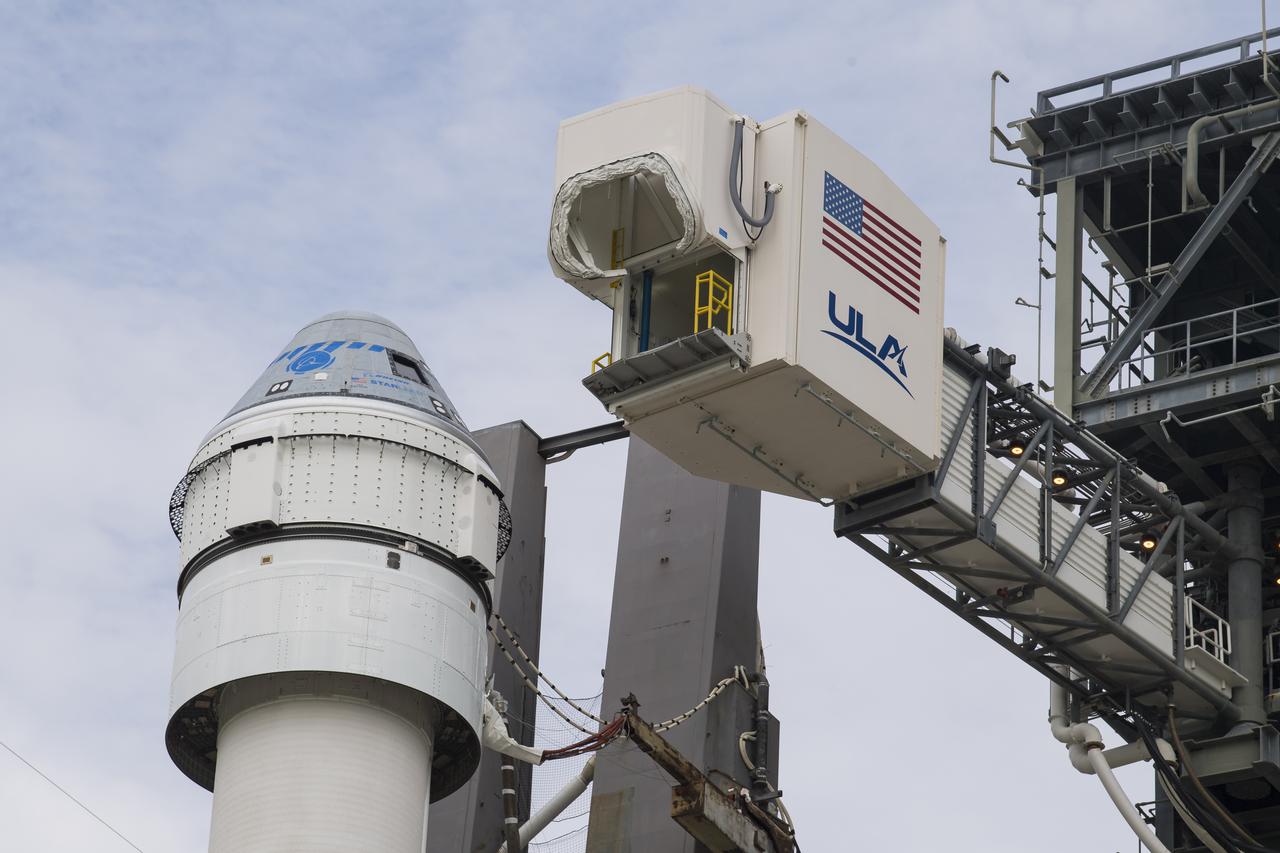

The crew access arm is seen as it swings into position for Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 ahead of the Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) mission, Monday, Aug. 2, 2021 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 will be Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test and will dock to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The mission, currently targeted for launch at 1:20 p.m. EDT Tuesday, Aug. 3, will serve as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
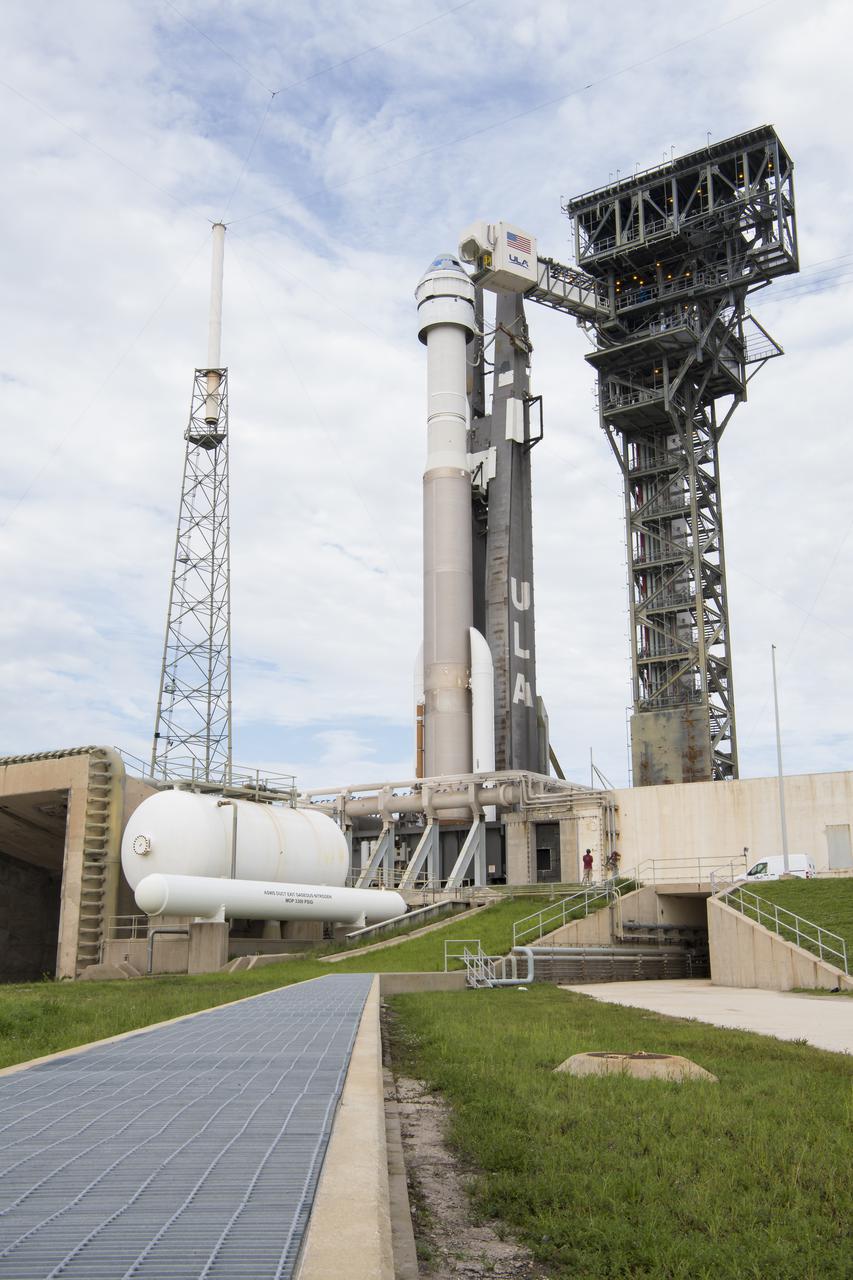

The crew access arm is seen as it swings into position for Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 41 ahead of the Orbital Flight Test-2 (OFT-2) mission, Monday, Aug. 2, 2021 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Boeing’s Orbital Flight Test-2 will be Starliner’s second uncrewed flight test and will dock to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial Crew Program. The mission, currently targeted for launch at 1:20 p.m. EDT Tuesday, Aug. 3, will serve as an end-to-end test of the system's capabilities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
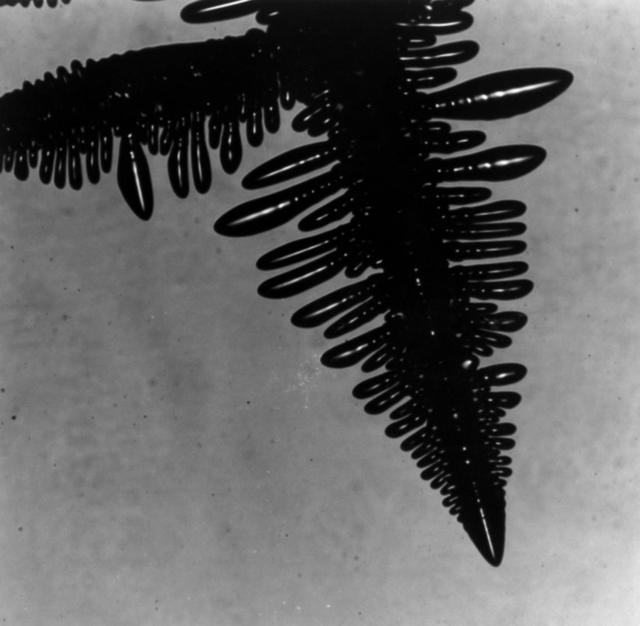

Typical picture of a dendrite: Notice how the branch on the left has no arms coming off the top. This is because of the convective forces (hot liquid rises) that the top of the branch is not solidifying (growing arms) like the bottom, cooler area. The is a gravitational effect. This does not happen in space.
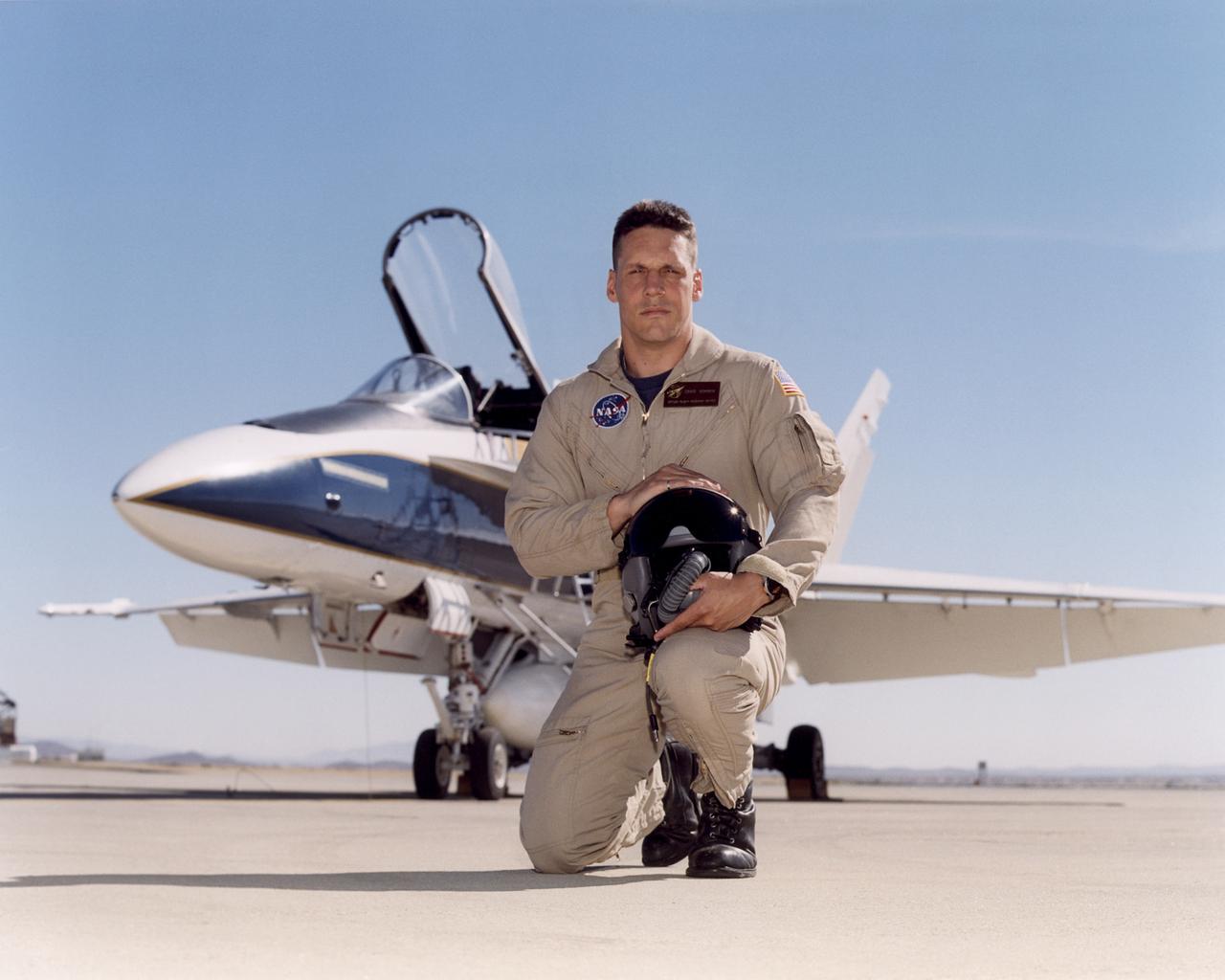

Craig R. Bomben became a pilot in the Flight Crew Branch of NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, Calif., in June 2001. His flying duties include a variety of research and support activities while piloting the F/A-18, DC-8, T-34C and King Air aircraft. He has more than 17 years and 3,800 hours of military and civilian flight experience in over 50 different aircraft types. Bomben came to NASA Dryden from a U.S. Navy assignment to the Personnel Exchange Program, Canada. He served as a test pilot in the Canadian Armed Forces located in Cold Lake, Alberta. He participated in numerous developmental programs to include CT-133 airborne ejection seat testing, F/A-18 weapons flutter testing and F/A-18 night vision goggles integration. Bomben performed U.S. Navy fleet service in 1995 as a strike-fighter department head. He completed two overseas deployments onboard the USS George Washington and USS Stennis. As a combat strike leader, he headed numerous multi-national missions over Iraq in support of Operation Southern Watch. Bomben graduated from the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School in 1992 and was subsequently assigned to the Naval Weapons Test Squadron at Pt. Mugu, Calif. During this tour he developed the F-14D bombsight and worked on various other F-14D and F/A-18 weapon systems developmental programs. Bomben is a 1985 graduate of Washington State University with a bachelor of science degree in electrical engineering. He graduated from naval flight training in 1987 and was recognized as a Commodore List graduate. His first assignment was to Naval Air Station Pensacola, Fla., where he was an instructor in the T-2B Buckeye. When selected to fly the F/A-18 in 1989, he joined a fleet squadron and deployed aboard the USS Forrestal. Bomben is married to the former Aissa Asuncion. They live in Lancaster, Calif., with their 3 children.
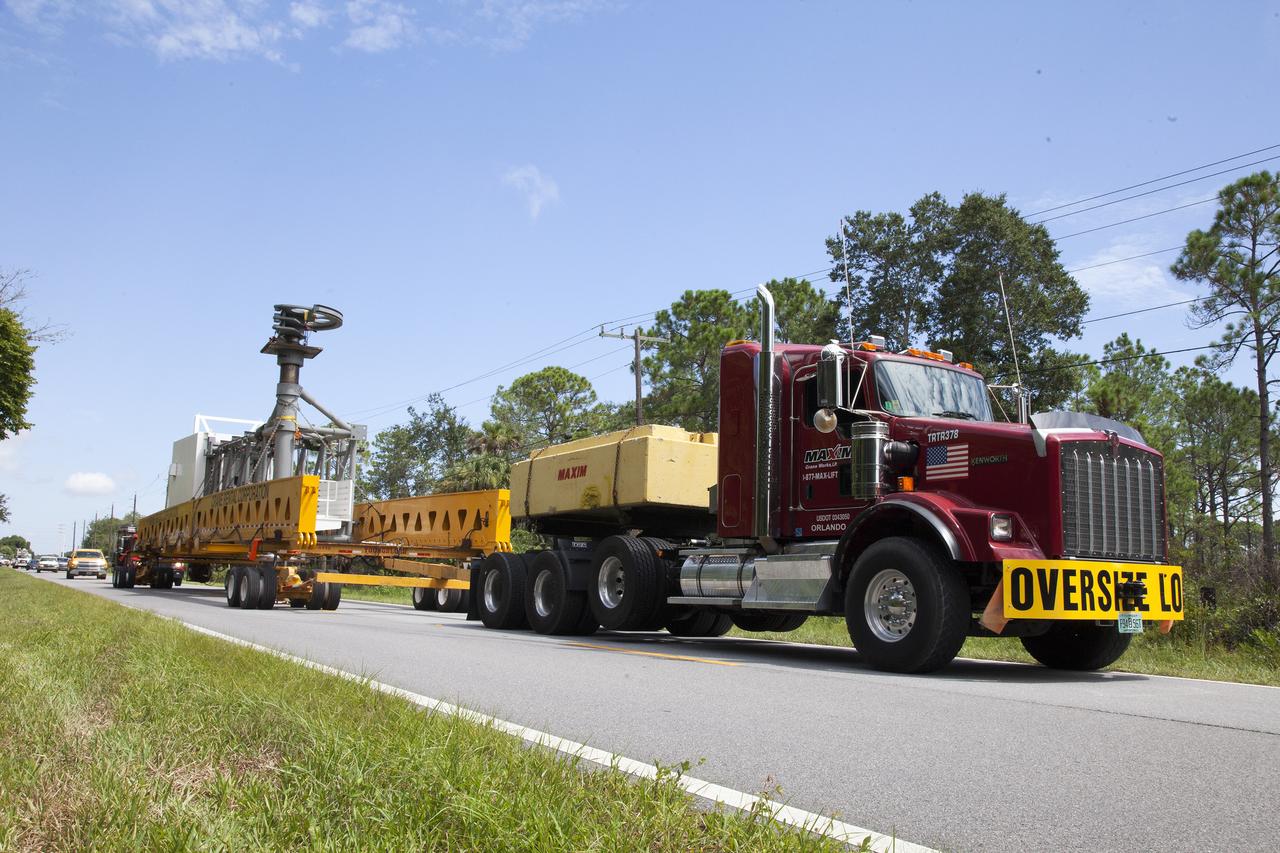

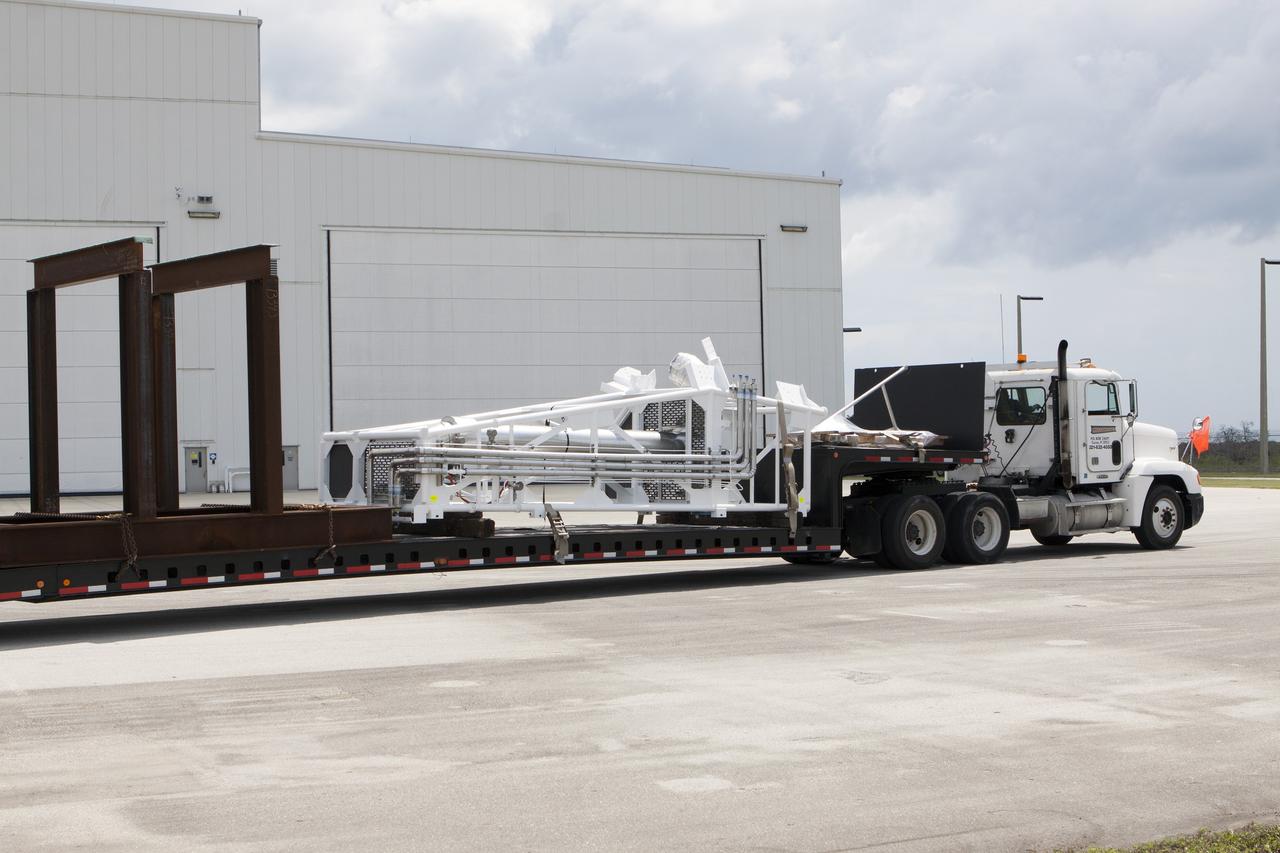
A heavy-lift transport truck, carrying the Crew Access Arm for Space Launch Complex 41, departs from Oak Hill, Florida, and heads to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The arm will be installed on the Complex 41 Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. It will be used as a bridge by astronauts to board Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft as it stands on the launch pad atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
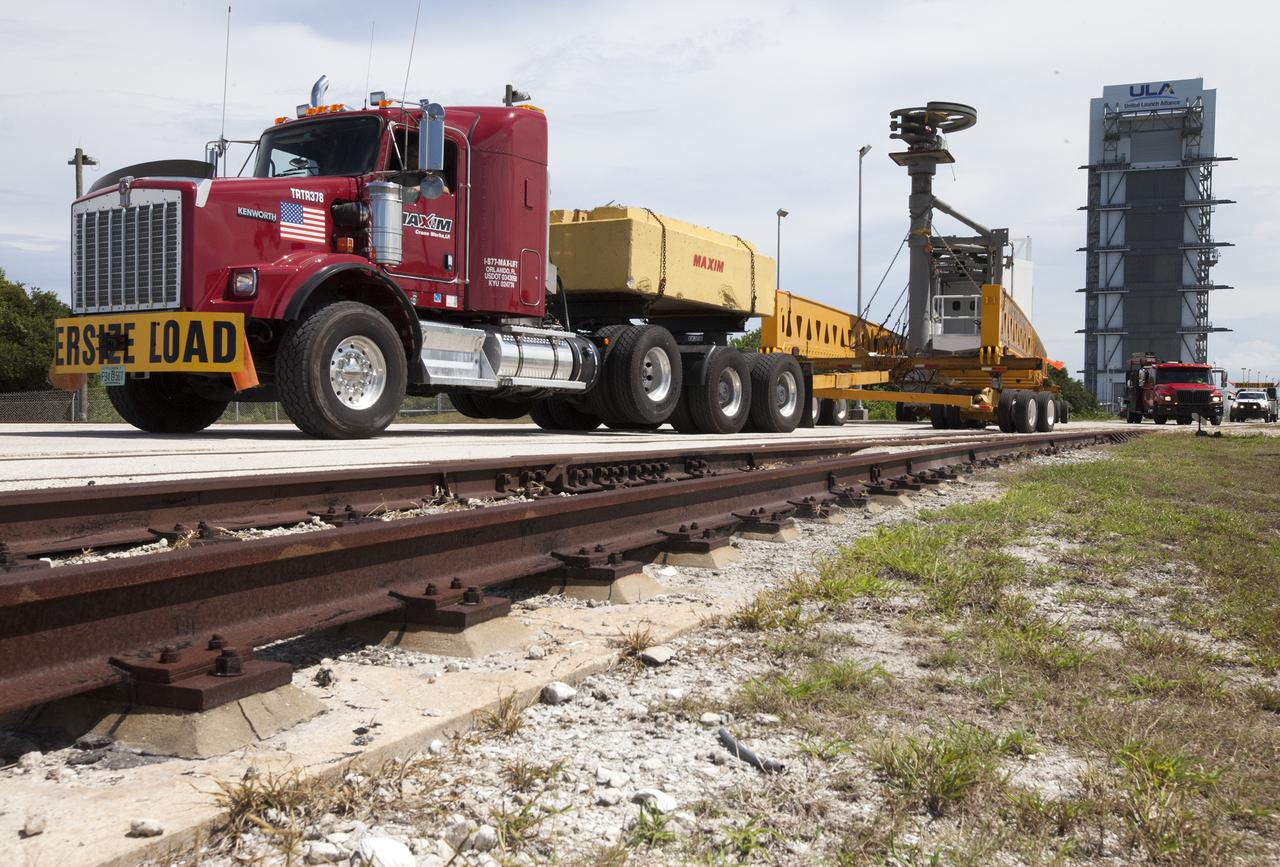

A heavy-lift transport truck, carrying the Crew Access Arm for Space Launch Complex 41, backs up toward Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The arm will be installed on the Complex 41 Crew Access Tower. It will be used as a bridge by astronauts to board Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft as it stands on the launch pad atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
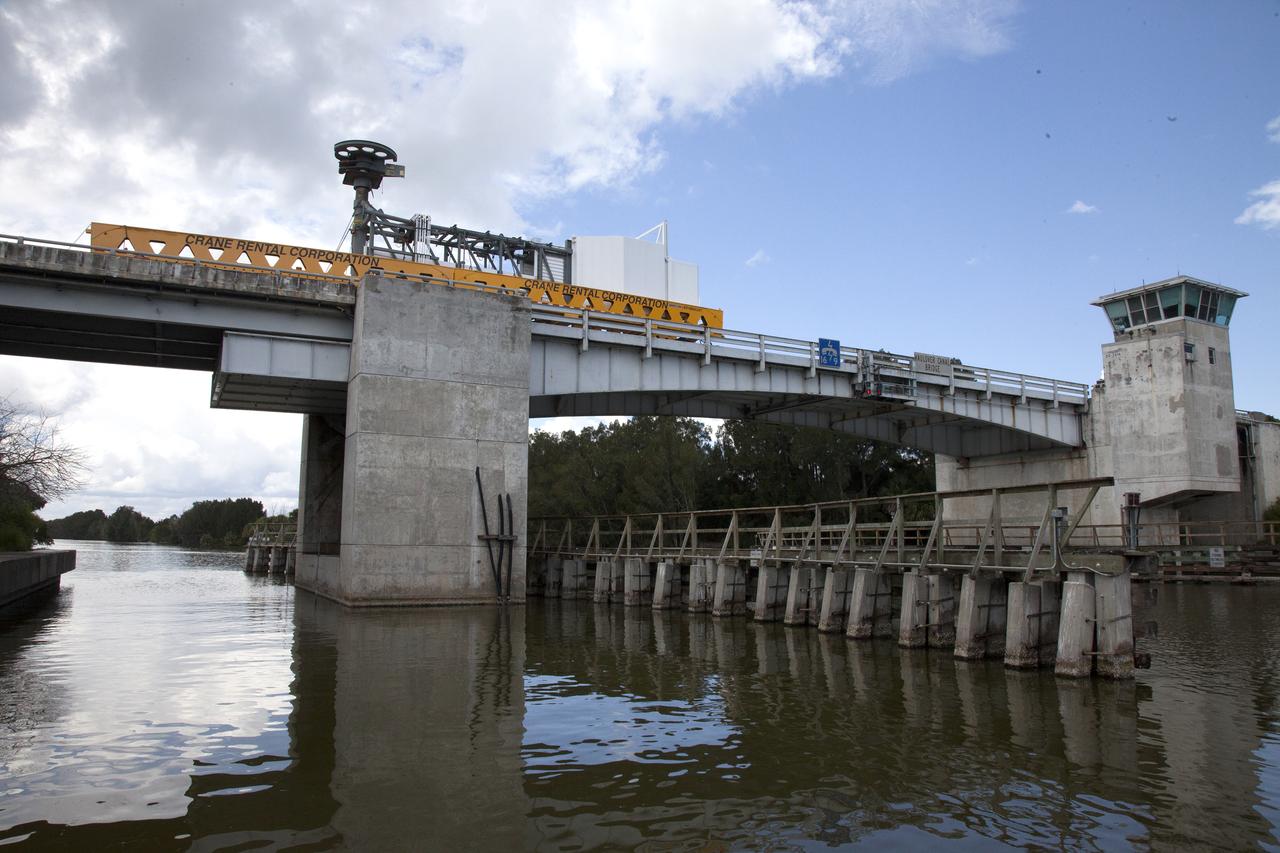

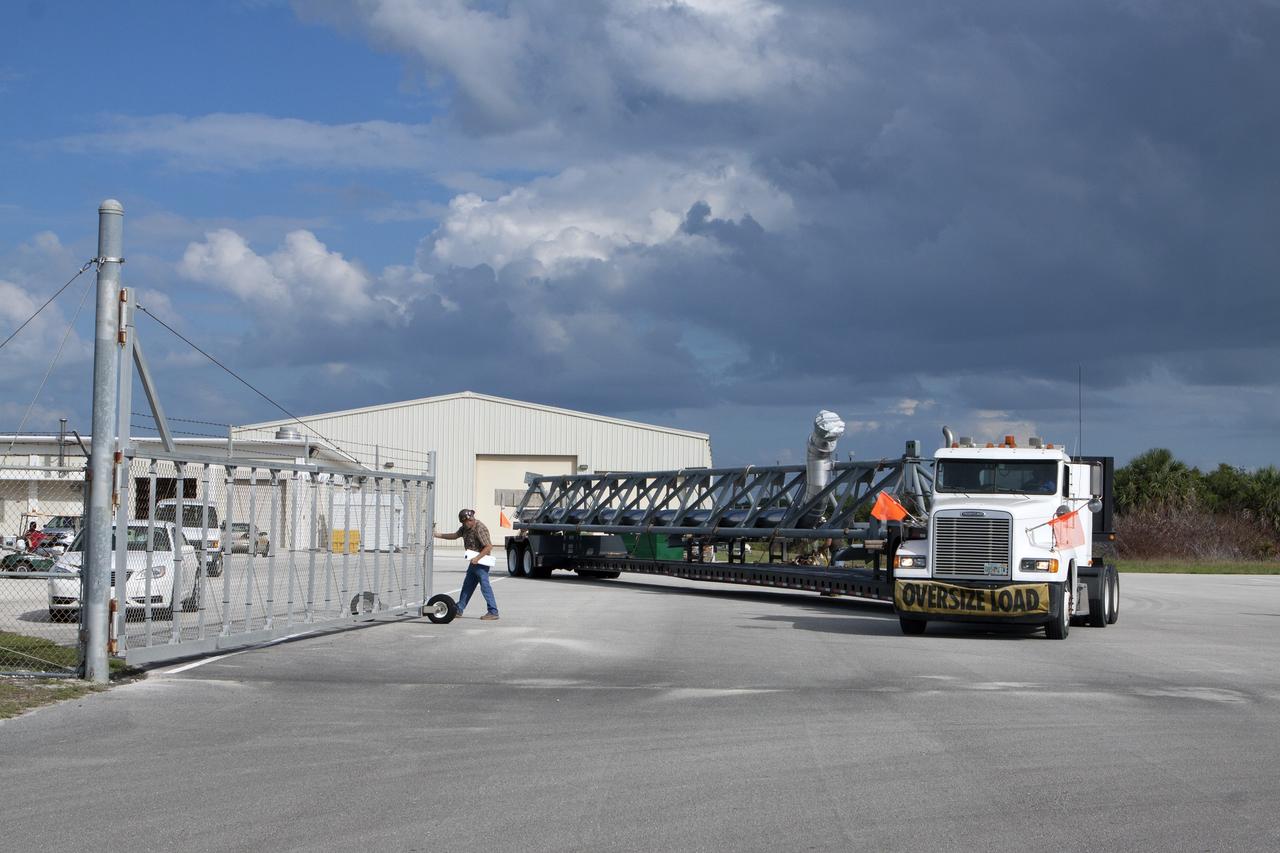
A heavy-lift transport truck, carrying the Crew Access Arm for Space Launch Complex 41, crosses the Haulover Canal Bridge on its way to the entrance of NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The arm will be installed on the Complex 41 Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. It will be used as a bridge by astronauts to board Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft as it stands on the launch pad atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.

A heavy-lift transport truck, carrying the Crew Access Arm for Space Launch Complex 41, backs up toward Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The arm will be installed on the Complex 41 Crew Access Tower. It will be used as a bridge by astronauts to board Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft as it stands on the launch pad atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
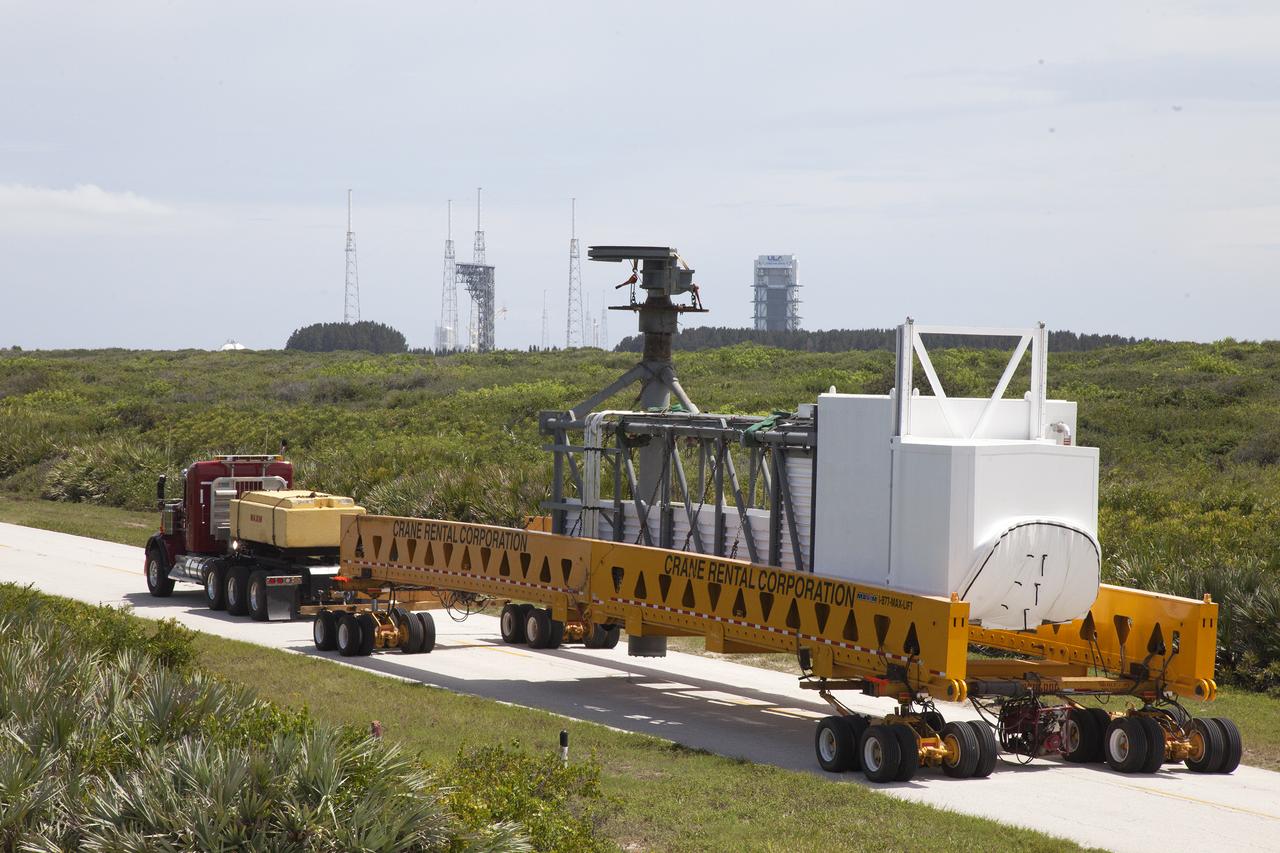

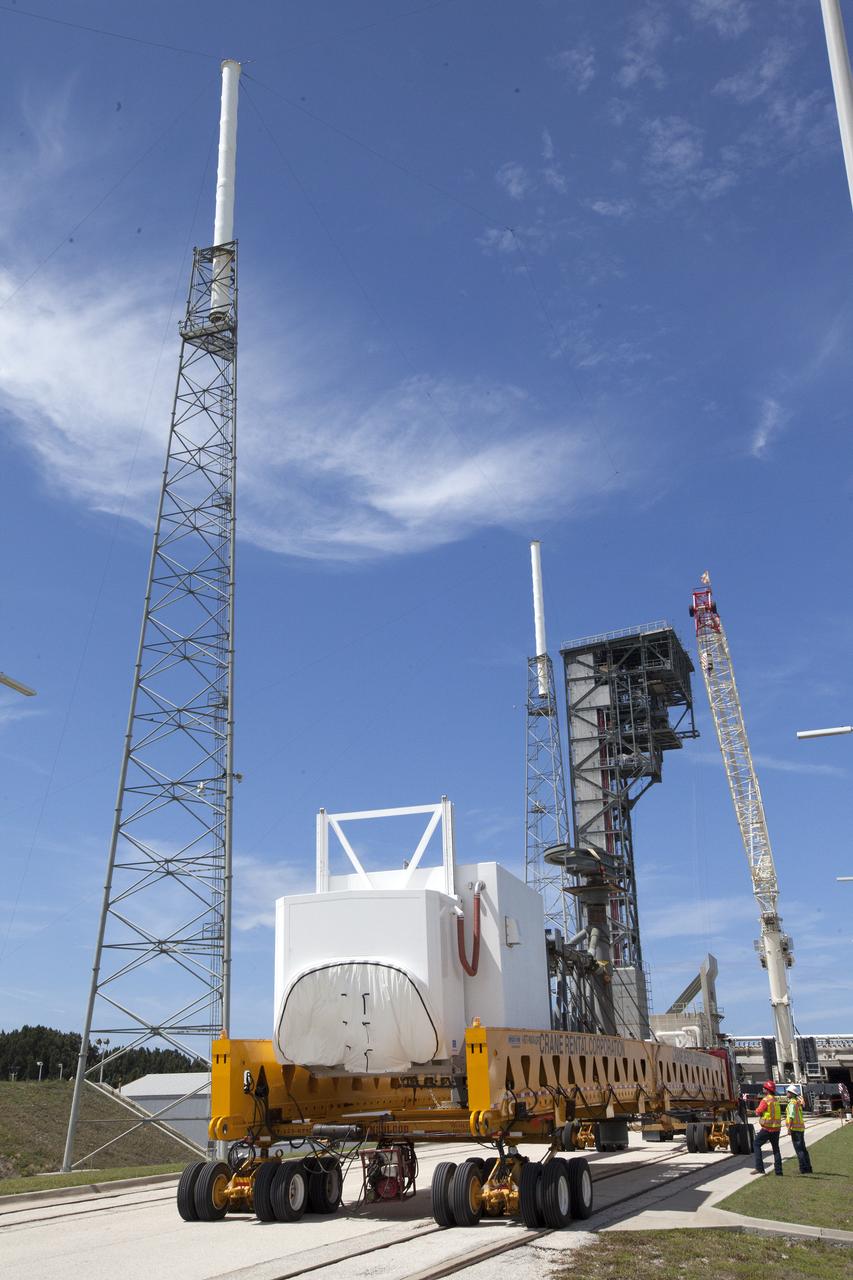
A heavy-lift transport truck, carrying the Crew Access Arm for Space Launch Complex 41, travels along the road toward Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The arm will be installed on the Complex 41 Crew Access Tower. It will be used as a bridge by astronauts to board Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft as it stands on the launch pad atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
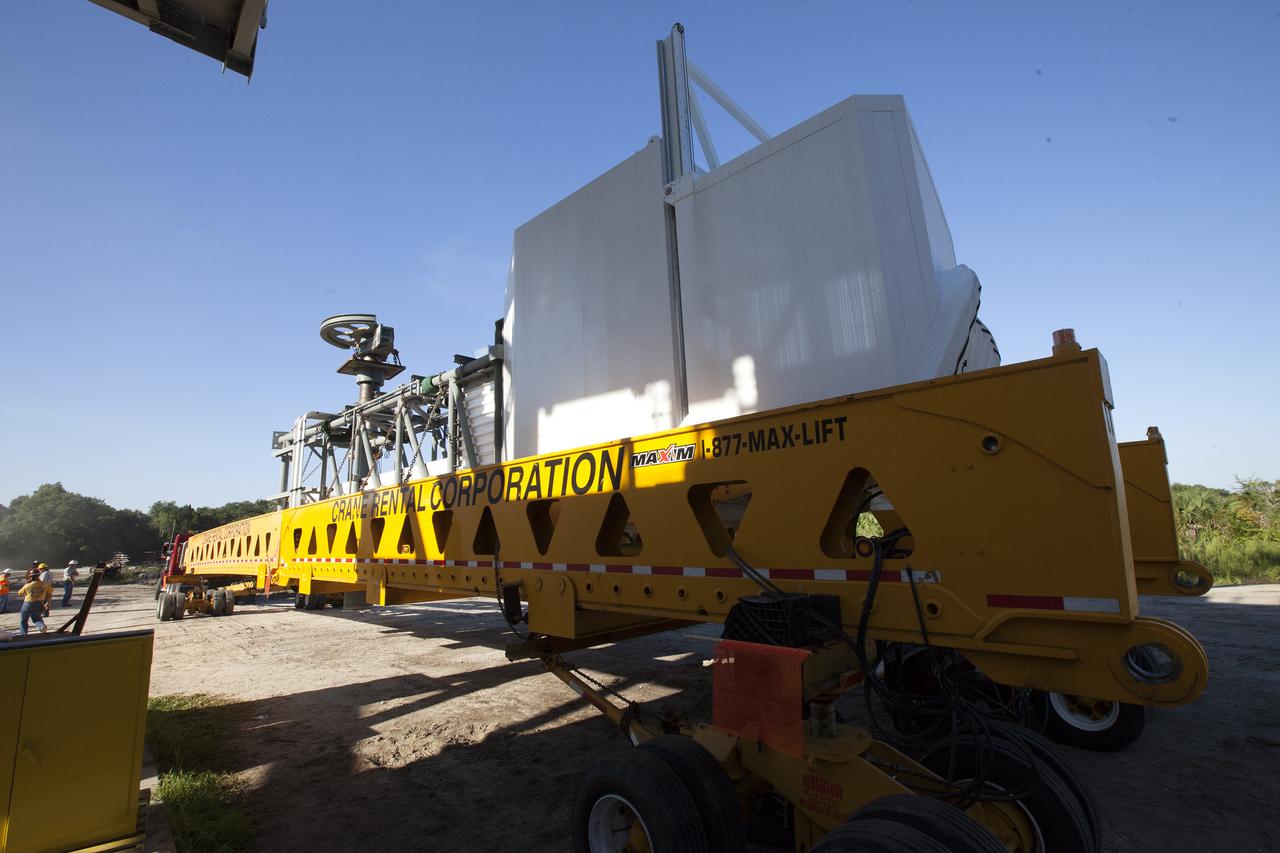

A heavy-lift transport truck, carrying the Crew Access Arm for Space Launch Complex 41, departs from Oak Hill, Florida, and heads to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The arm will be installed on the Complex 41 Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. It will be used as a bridge by astronauts to board Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft as it stands on the launch pad atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
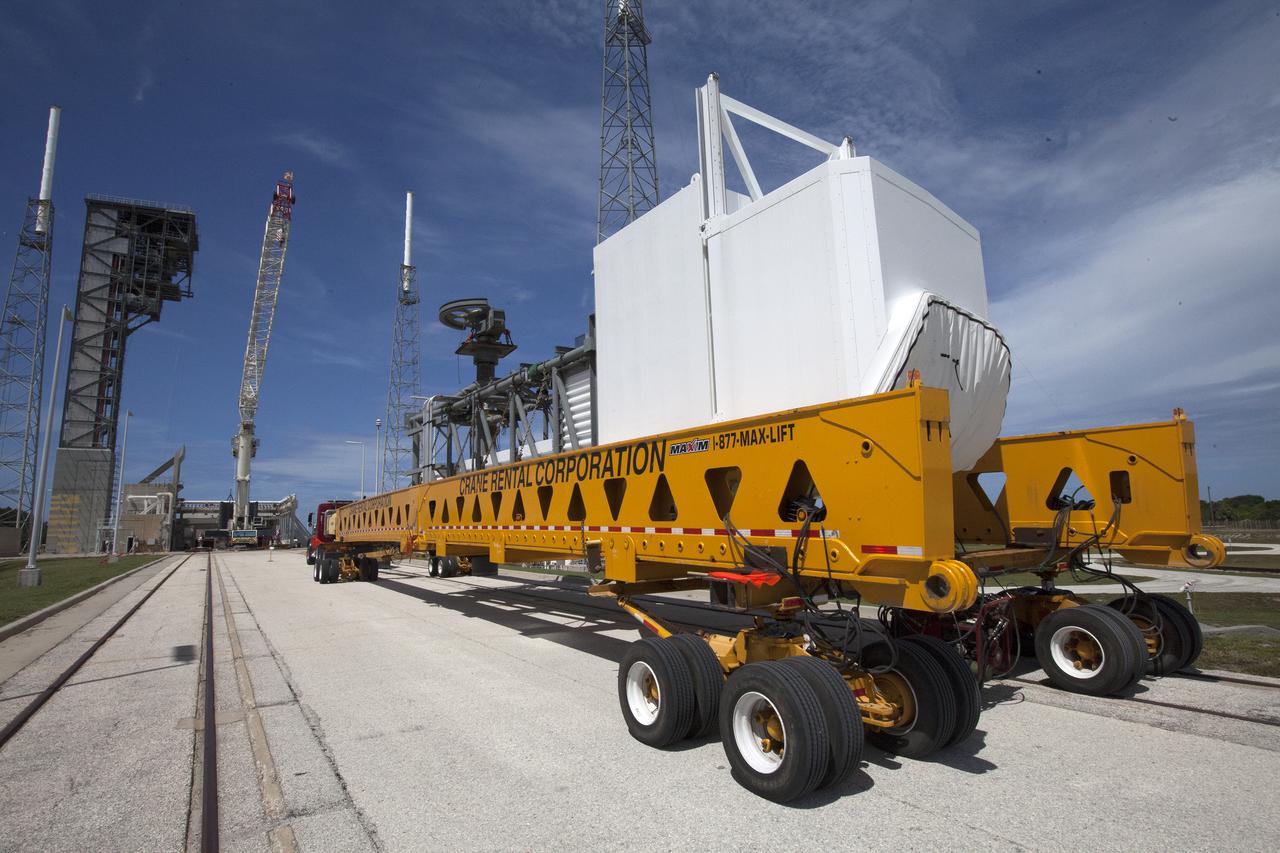

A heavy-lift transport truck, carrying the Crew Access Arm for Space Launch Complex 41, arrives at Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The arm will be installed on the Complex 41 Crew Access Tower. It will be used as a bridge by astronauts to board Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft as it stands on the launch pad atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
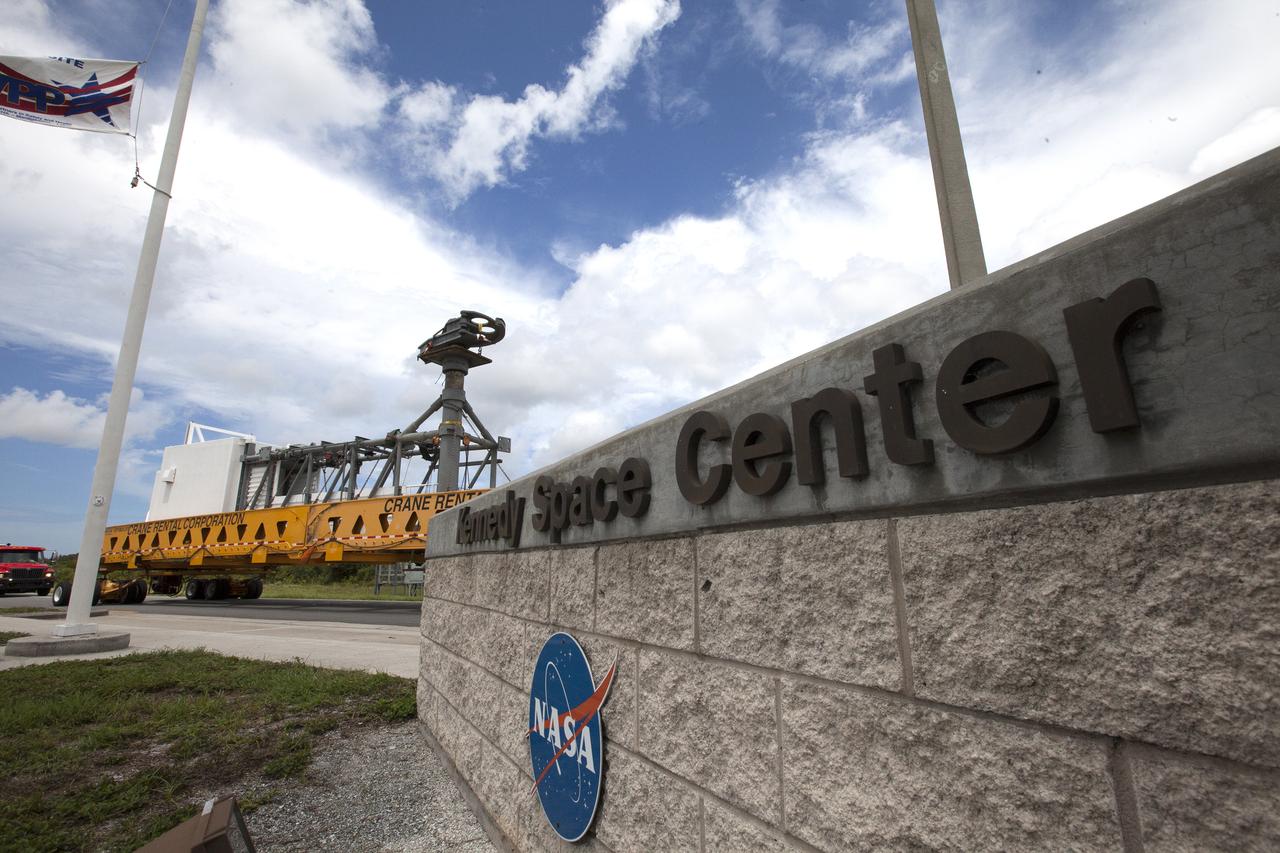

A heavy-lift transport truck, carrying the Crew Access Arm for Space Launch Complex 41, passes through the entrance to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The arm will be installed on the Complex 41 Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. It will be used as a bridge by astronauts to board Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft as it stands on the launch pad atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
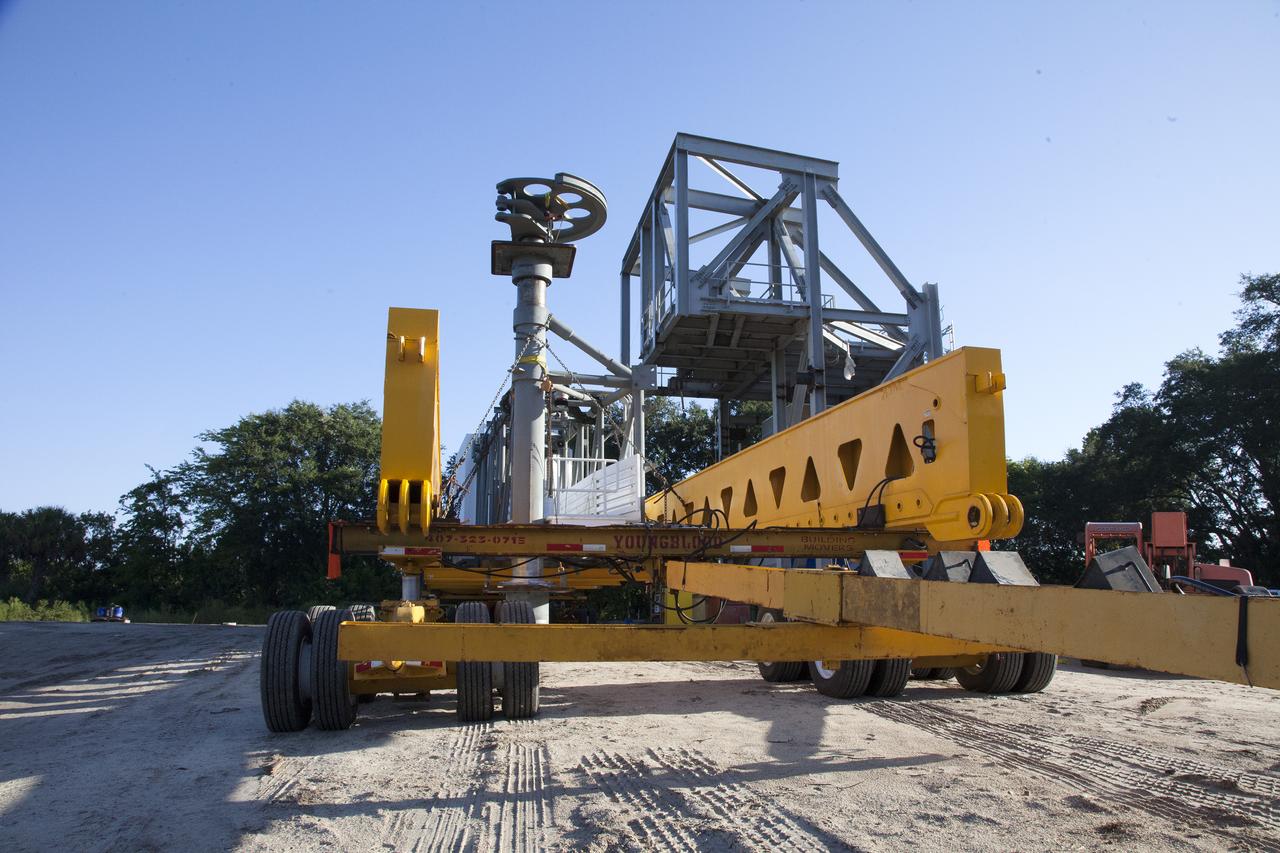

A heavy-lift transport truck, carrying the Crew Access Arm for Space Launch Complex 41, departs from Oak Hill, Florida, and heads to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The arm will be installed on the Complex 41 Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. It will be used as a bridge by astronauts to board Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft as it stands on the launch pad atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.

A heavy-lift transport truck, carrying the Crew Access Arm for Space Launch Complex 41, travels along the road toward Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The arm will be installed on the Complex 41 Crew Access Tower. It will be used as a bridge by astronauts to board Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft as it stands on the launch pad atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
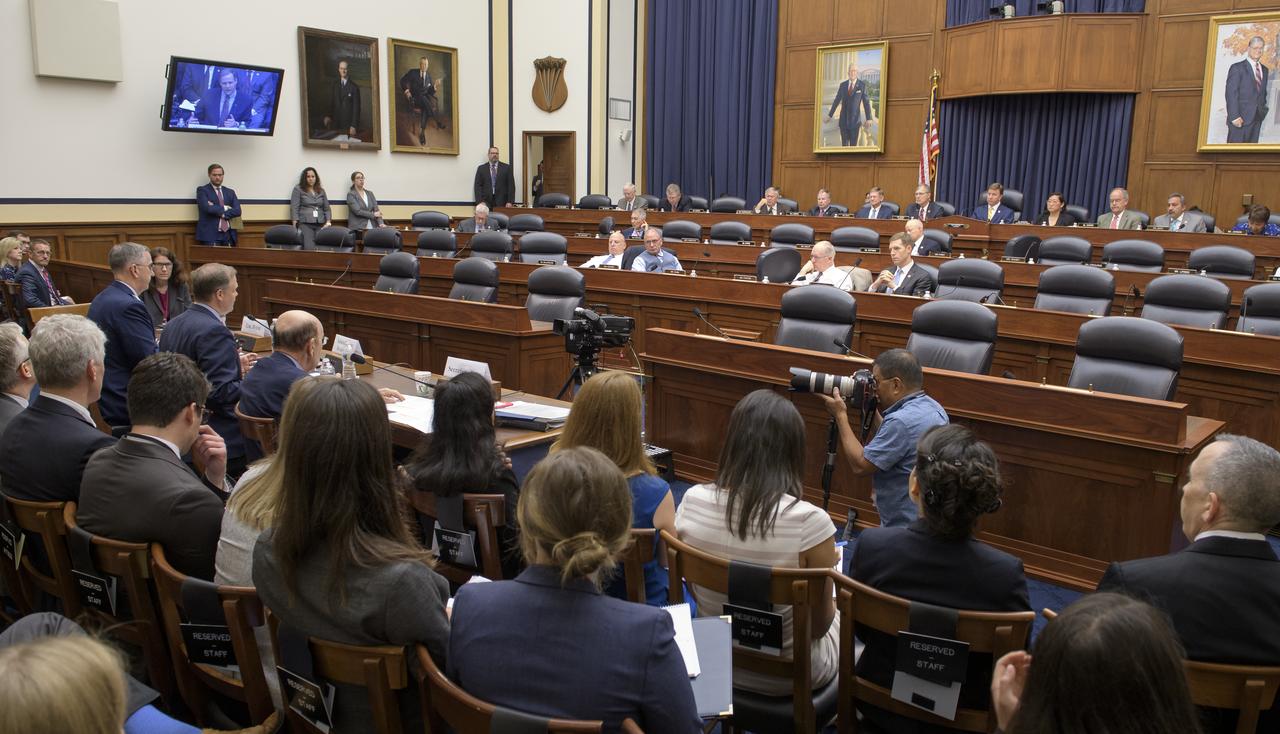

House Subcommittee on Strategic Forces holds a hearing on Space Situational Awareness: Whole of Government Perspectives on Roles and Responsibilities, Friday, June 22, 2018 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Witnesses: NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine; Commander, U.S. Strategic Command, General John Hyten; and Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

House Subcommittee on Strategic Forces holds a hearing on Space Situational Awareness: Whole of Government Perspectives on Roles and Responsibilities, Friday, June 22, 2018 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Witnesses: NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine; Commander, U.S. Strategic Command, General John Hyten; and Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
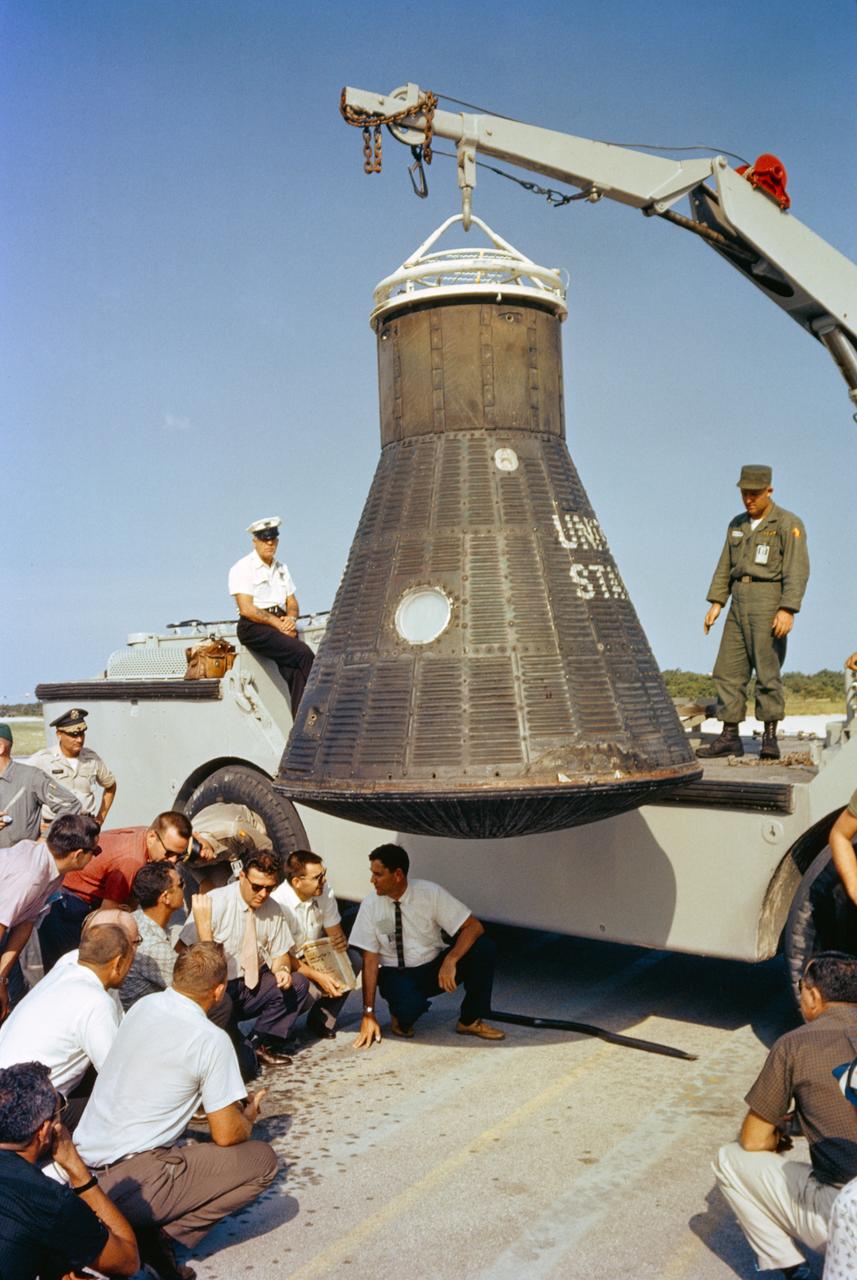

S64-14861 (1962) --- Department of Defense (DOD) recovery personnel and spacecraft technicians from NASA and McDonnell Aircraft Corp., inspect astronaut John Glenn's Mercury spacecraft, Friendship 7, following its return to Cape Canaveral after recovery in the Atlantic Ocean. Photo credit: NASA
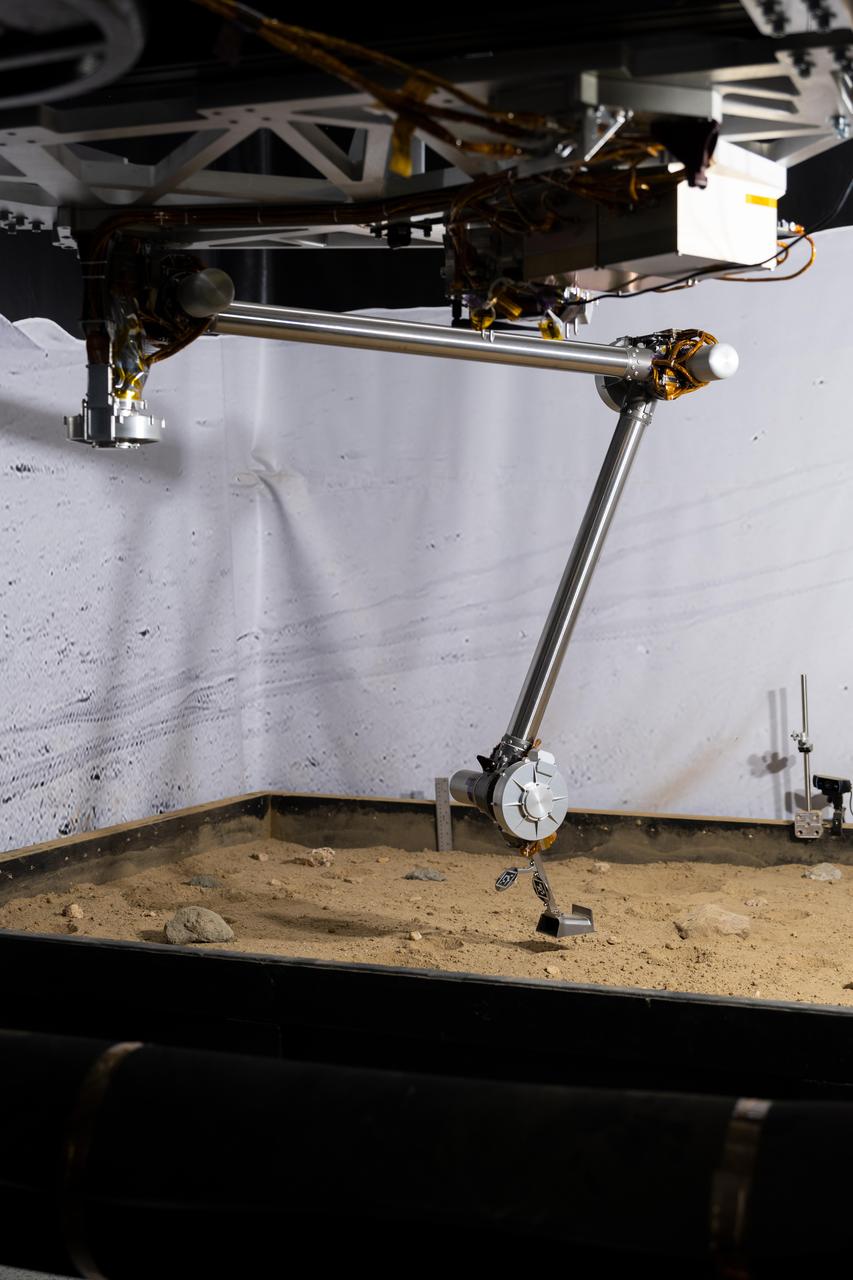
The 3D-printed titanium scoop of the Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) robotic arm system is poised above a test bed filled with material to simulate lunar regolith (broken rocks and dust) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. COLDArm can function in temperatures as cold as minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). COLDArm is designed to go on a Moon lander and operate during lunar night, a period that lasts about 14 Earth days. Frigid temperatures during lunar night would stymie current spacecraft, which must rely on energy-consuming heaters to stay warm. To operate in the cold, the 6-foot-6-inch (2-meter) arm combines several key new technologies: gears made of bulk metallic glass that require no lubrication or heating, cold motor controllers that don't need to be kept warm in an electronics box near the core of the spacecraft, and a cryogenic six-axis force torque sensor that lets the arm "feel" what it's doing and make adjustments. A variety of attachments and small instruments could go on the end of the arm, including the scoop, which could be used for collecting samples from a planet's surface. Like the arm on NASA's InSight Mars lander, COLDArm could deploy science instruments to the surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25317

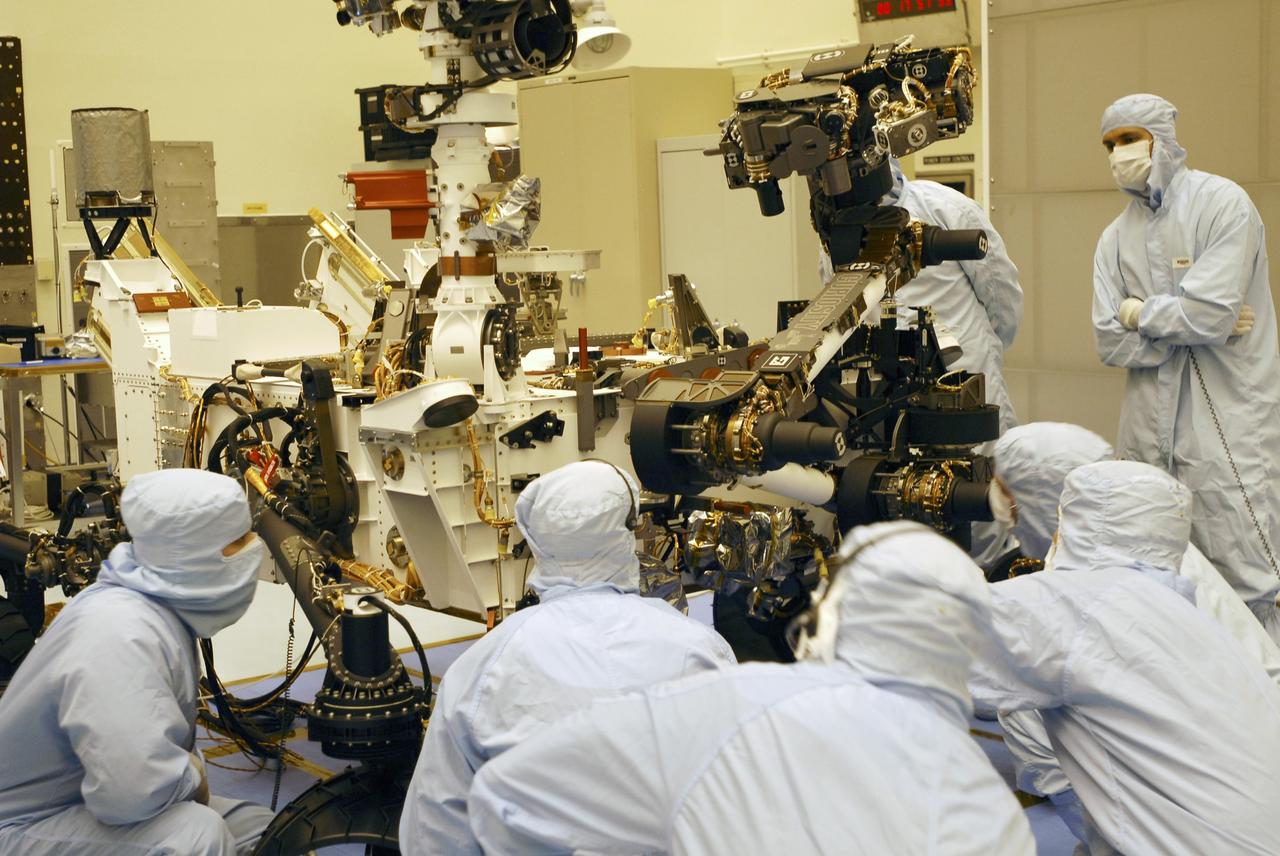
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Under the watchful eyes of the spacecraft technicians in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the robotic arm of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover, Curiosity, moves into place against the body of the spacecraft. The arm will hold and maneuver instruments that will help scientists analyze Martian rocks and soil. Much like a human arm, the robotic arm has flexibility through shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints that permit the arm to extend, bend, and angle precisely against rocks and soil to grind away layers, take microscopic images and analyze their elemental composition. At the end of the arm is a hand-like structure, the turret, for holding various tools that can spin through a 350-degree turning range. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

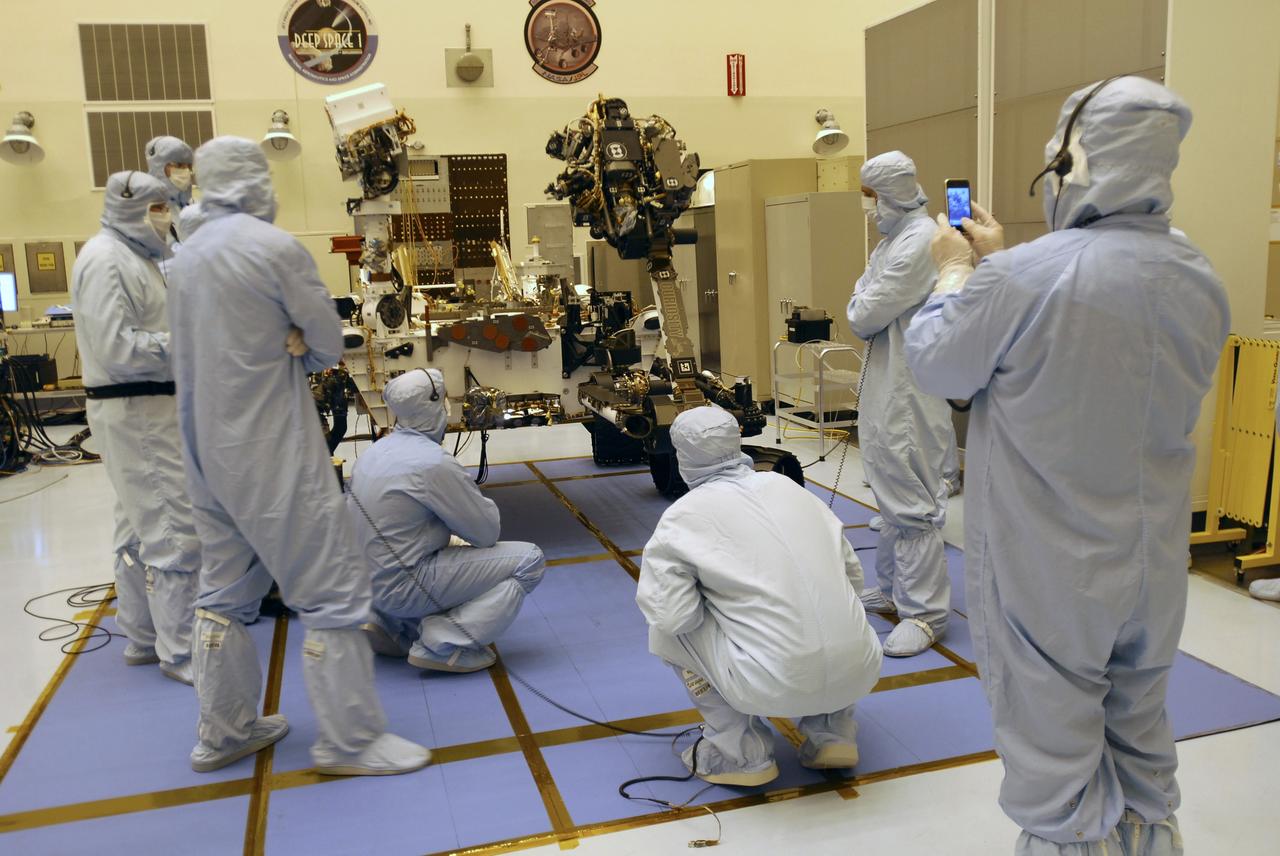
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians monitor the movement of the robotic arm of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover, Curiosity, as it is stowed against the body of the spacecraft. The arm will hold and maneuver instruments that will help scientists analyze Martian rocks and soil. Much like a human arm, the robotic arm has flexibility through shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints that permit the arm to extend, bend, and angle precisely against rocks and soil to grind away layers, take microscopic images and analyze their elemental composition. At the end of the arm is a hand-like structure, the turret, for holding various tools that can spin through a 350-degree turning range. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are under way to stow the robotic arm on the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover, Curiosity. The arm will hold and maneuver instruments that will help scientists analyze Martian rocks and soil. Much like a human arm, the robotic arm has flexibility through shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints that permit the arm to extend, bend, and angle precisely against rocks and soil to grind away layers, take microscopic images and analyze their elemental composition. At the end of the arm is a hand-like structure, the turret, for holding various tools that can spin through a 350-degree turning range. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
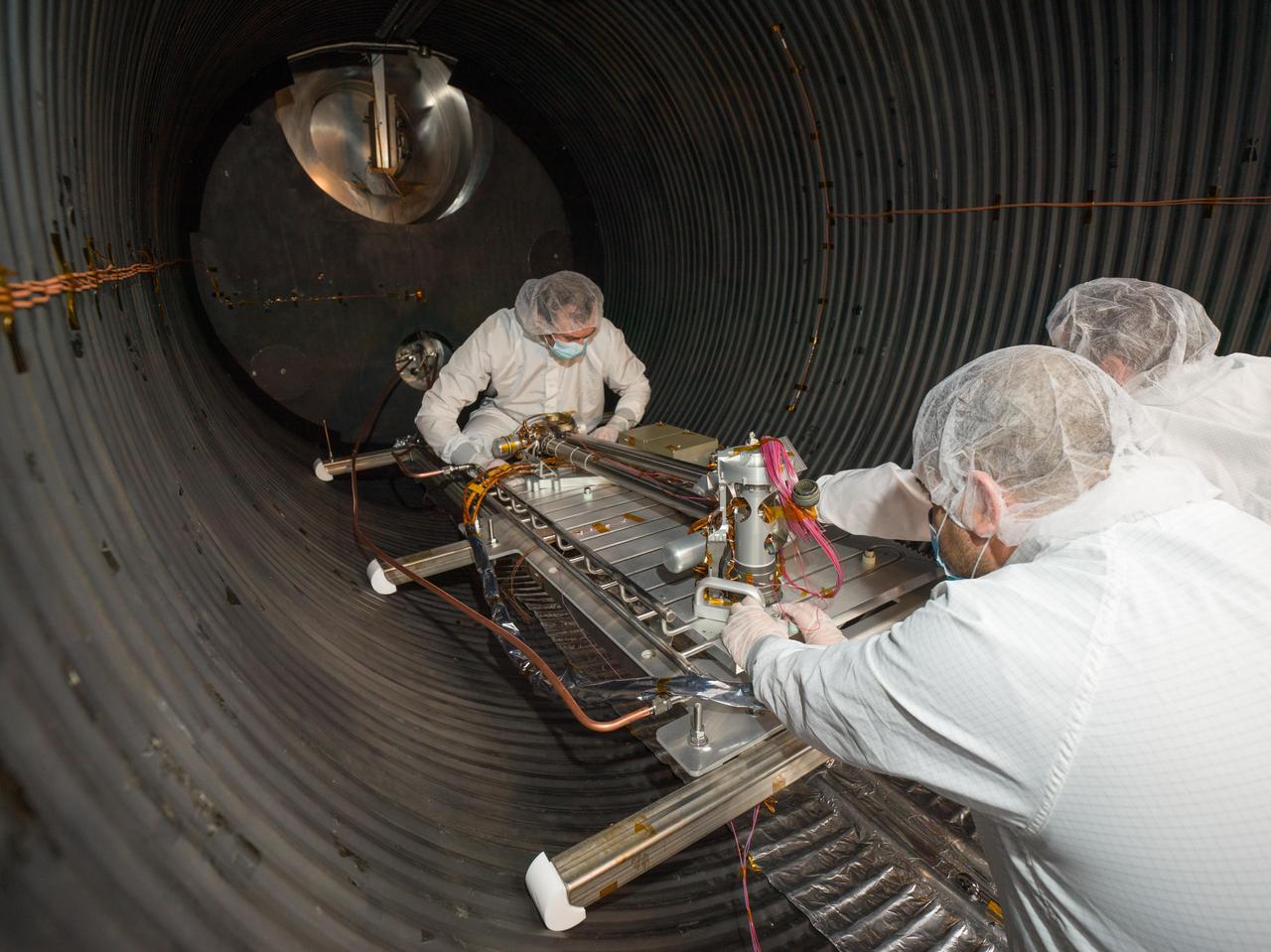

Engineers and technicians prepare NASA's Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) robotic arm system for testing in a thermal vacuum chamber at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in November 2023. Successful testing in this chamber, which was reduced to minus 292 F (minus 180 C), demonstrates the arm can withstand the conditions it would face on the surface of the Moon. To operate in the cold, COLDArm combines several key new technologies: gears made of bulk metallic glass, which require no wet lubrication or heating; cold motor controllers that don't need to be kept warm in an electronics box near the core of the spacecraft, and a cryogenic six-axis force torque sensor that lets the arm "feel" what it's doing and make adjustments. A variety of attachments and small instruments could go on the end of the arm, including a 3D-printed titanium scoop that could be used for collecting samples from a celestial body's surface. Like the arm on NASA's InSight Mars lander, COLDArm could deploy science instruments to the surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26162
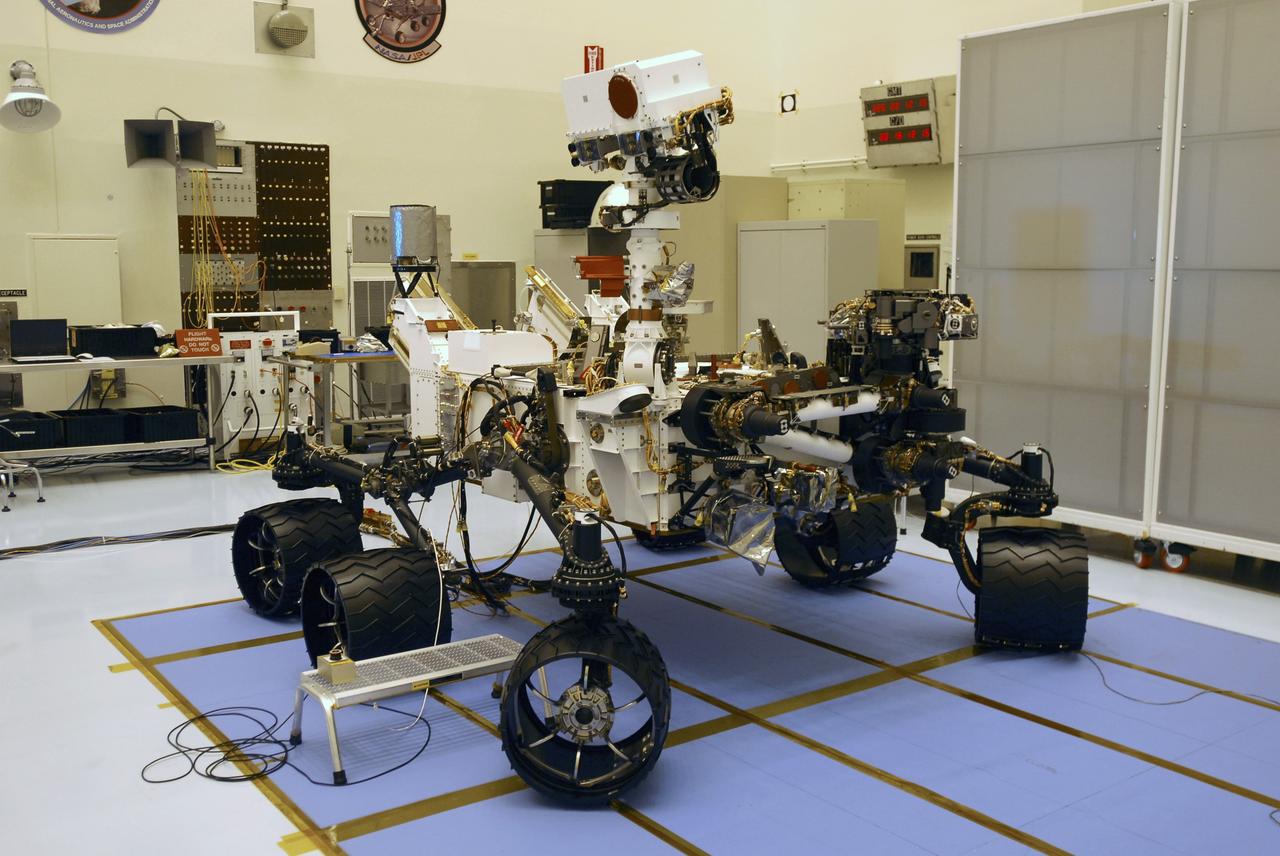

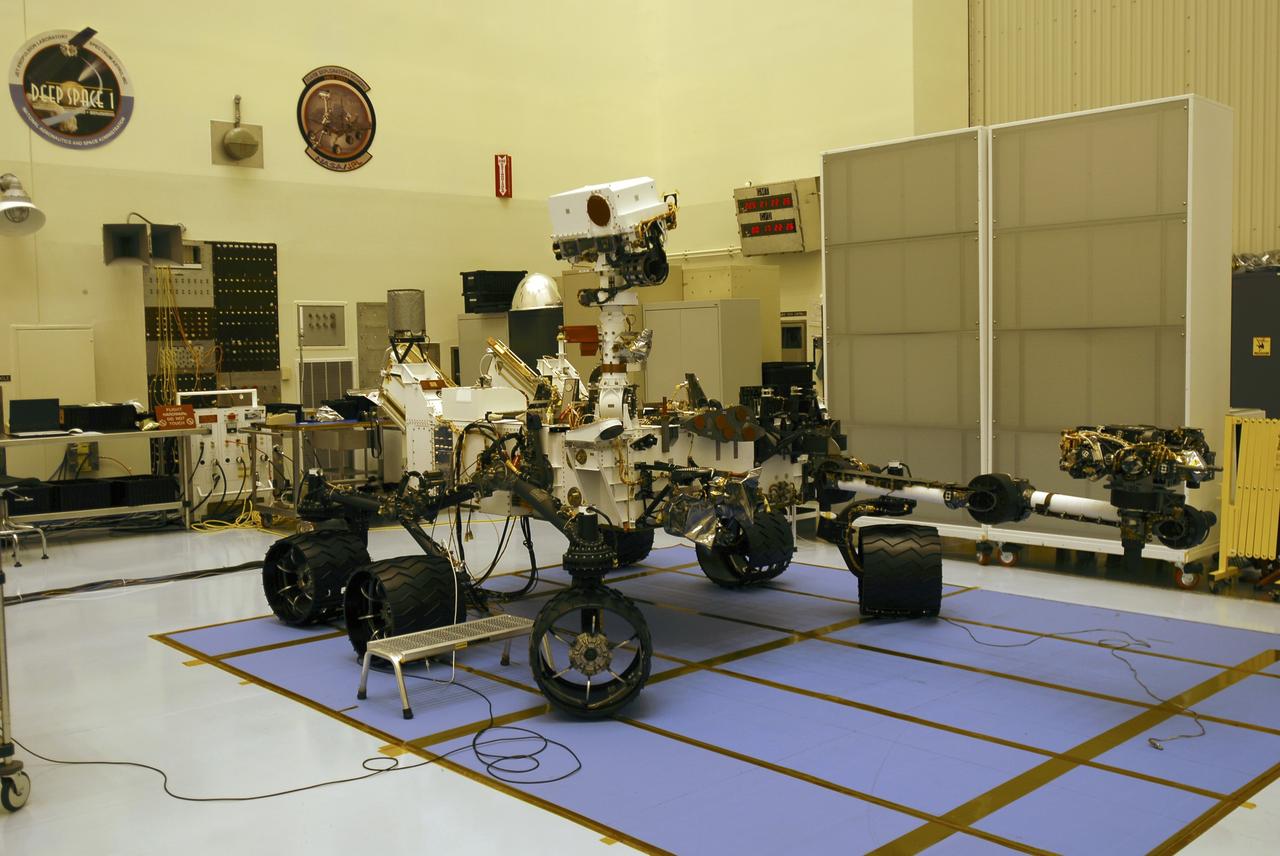
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the robotic arm of the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover, Curiosity, has been stowed against the body of the spacecraft. The arm will hold and maneuver instruments that will help scientists analyze Martian rocks and soil. Much like a human arm, the robotic arm has flexibility through shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints that permit the arm to extend, bend, and angle precisely against rocks and soil to grind away layers, take microscopic images and analyze their elemental composition. At the end of the arm is a hand-like structure, the turret, for holding various tools that can spin through a 350-degree turning range. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
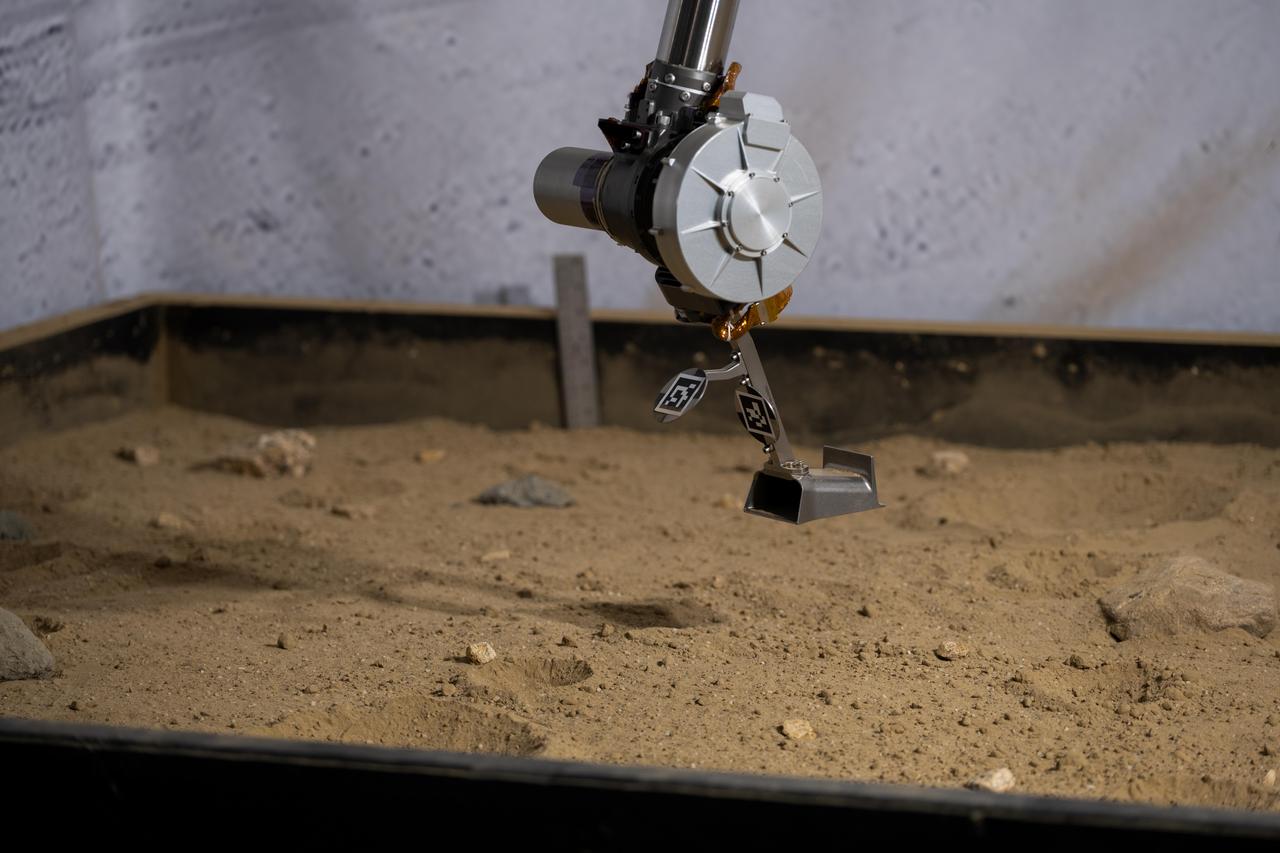

The 3D-printed titanium scoop of the Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) robotic arm system is poised above a test bed filled with material to simulate lunar regolith (broken rocks and dust) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. COLDArm can function in temperatures as cold as minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). COLDArm is designed to go on a Moon lander and operate during lunar night, a period that lasts about 14 Earth days. Frigid temperatures during lunar night would stymie current spacecraft, which must rely on energy-consuming heaters to stay warm. To operate in the cold, the 6-foot-6-inch (2-meter) arm combines several key new technologies: gears made of bulk metallic glass that require no lubrication or heating, cold motor controllers that don't need to be kept warm in an electronics box near the core of the spacecraft, and a cryogenic six-axis force torque sensor that lets the arm "feel" what it's doing and make adjustments. A variety of attachments and small instruments could go on the end of the arm, including the scoop, which could be used for collecting samples from a planet's surface. Like the arm on NASA's InSight Mars lander, COLDArm could deploy science instruments to the surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25318
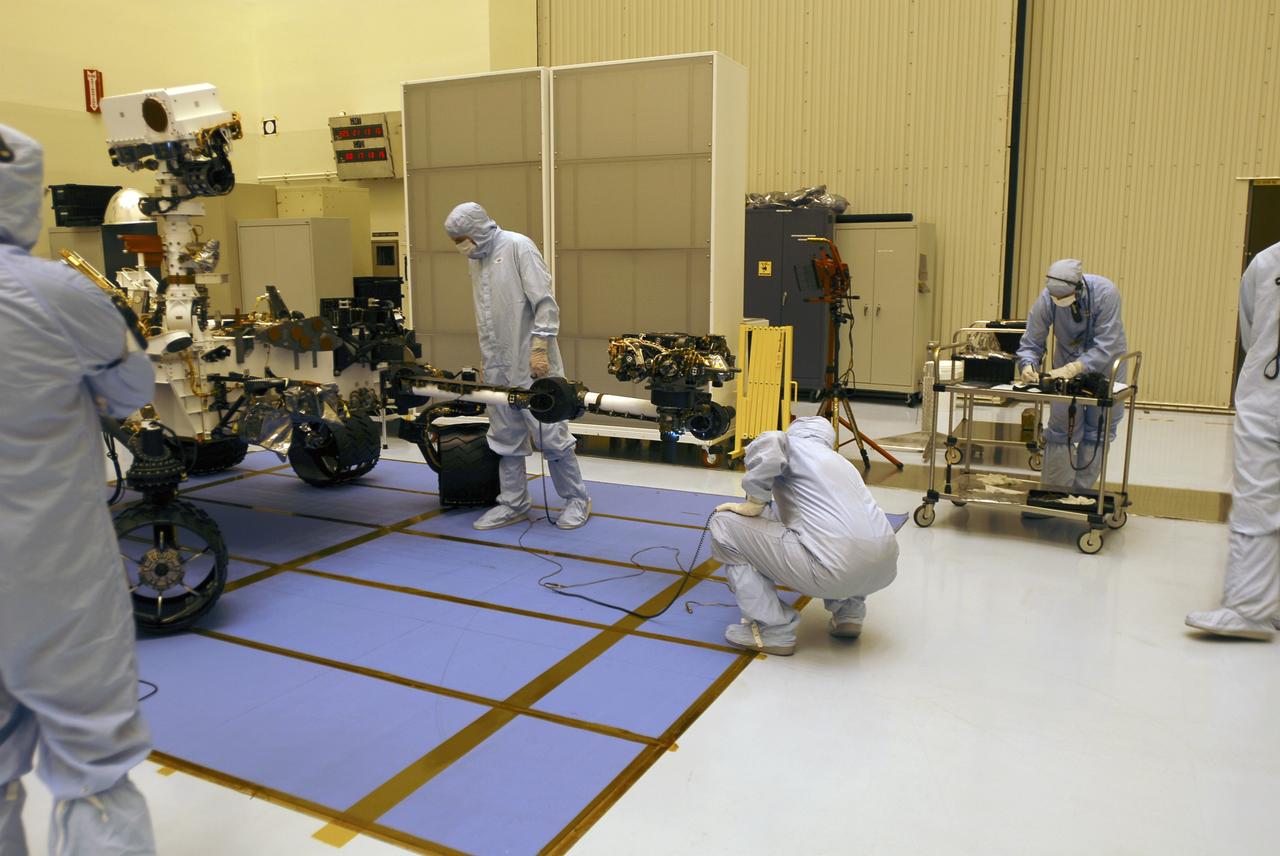

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians prepare to stow the robotic arm on the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover, Curiosity. The arm will hold and maneuver instruments that will help scientists analyze Martian rocks and soil. Much like a human arm, the robotic arm has flexibility through shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints that permit the arm to extend, bend, and angle precisely against rocks and soil to grind away layers, take microscopic images and analyze their elemental composition. At the end of the arm is a hand-like structure, the turret, for holding various tools that can spin through a 350-degree turning range. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, spacecraft technicians discuss their readiness to stow the robotic arm on the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover, Curiosity. The arm will hold and maneuver instruments that will help scientists analyze Martian rocks and soil. Much like a human arm, the robotic arm has flexibility through shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints that permit the arm to extend, bend, and angle precisely against rocks and soil to grind away layers, take microscopic images and analyze their elemental composition. At the end of the arm is a hand-like structure, the turret, for holding various tools that can spin through a 350-degree turning range. A United Launch Alliance Atlas V-541 configuration will be used to loft MSL into space. Curiosity’s 10 science instruments are designed to search for evidence on whether Mars has had environments favorable to microbial life, including chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release its gasses so that the rover’s spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth. MSL is scheduled to launch Nov. 25 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
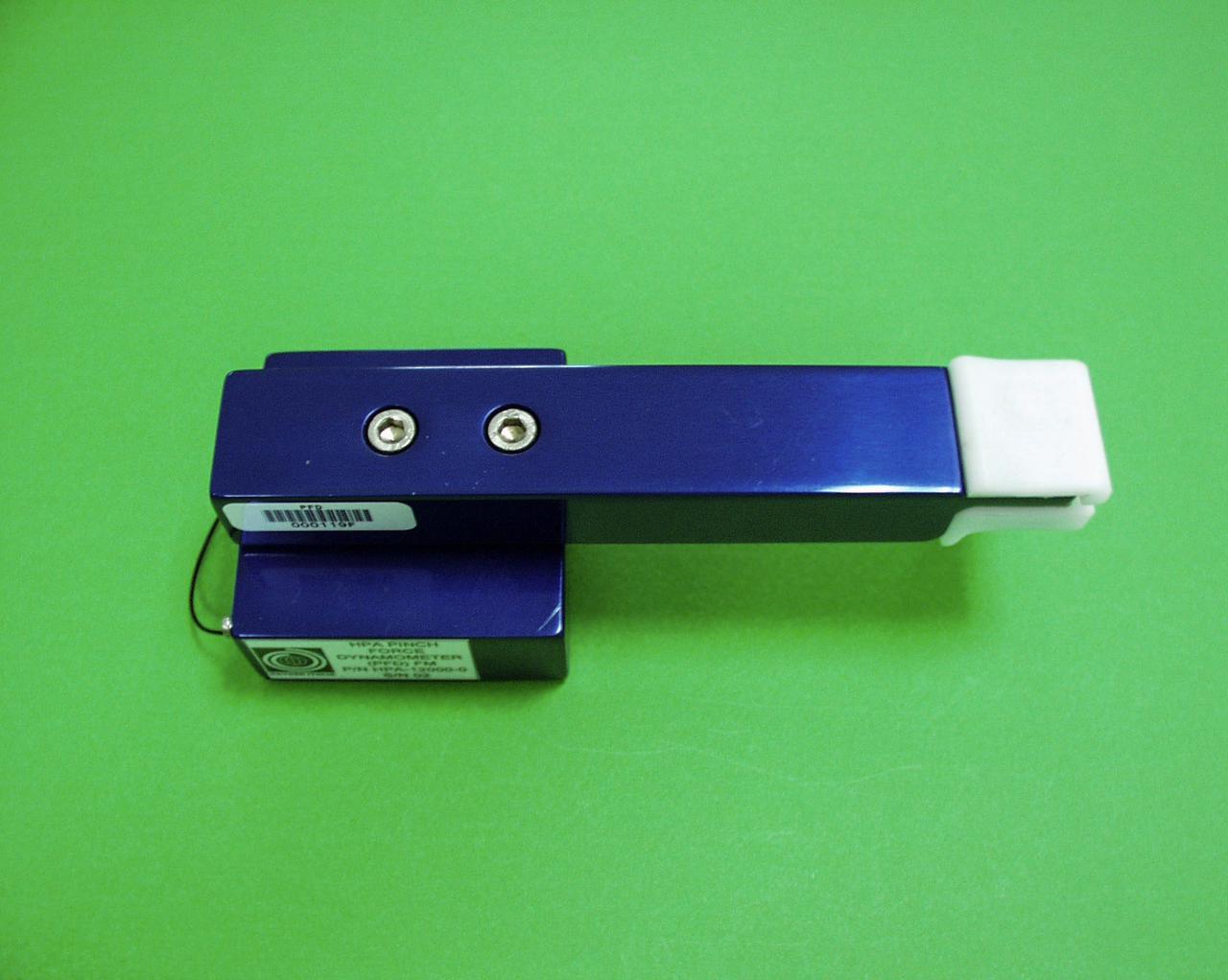

jsc2021e009417 (8/12/2002) --- A preflight view of the Hand Posture Analyzer (HPA) Pinch Force Dynamometer (PFD). The Hand Posture Analyzer (HPA) facility helps to examine the way hand and arm muscles are used differently aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Image courtesy of the Italian Space Agency (ASI).
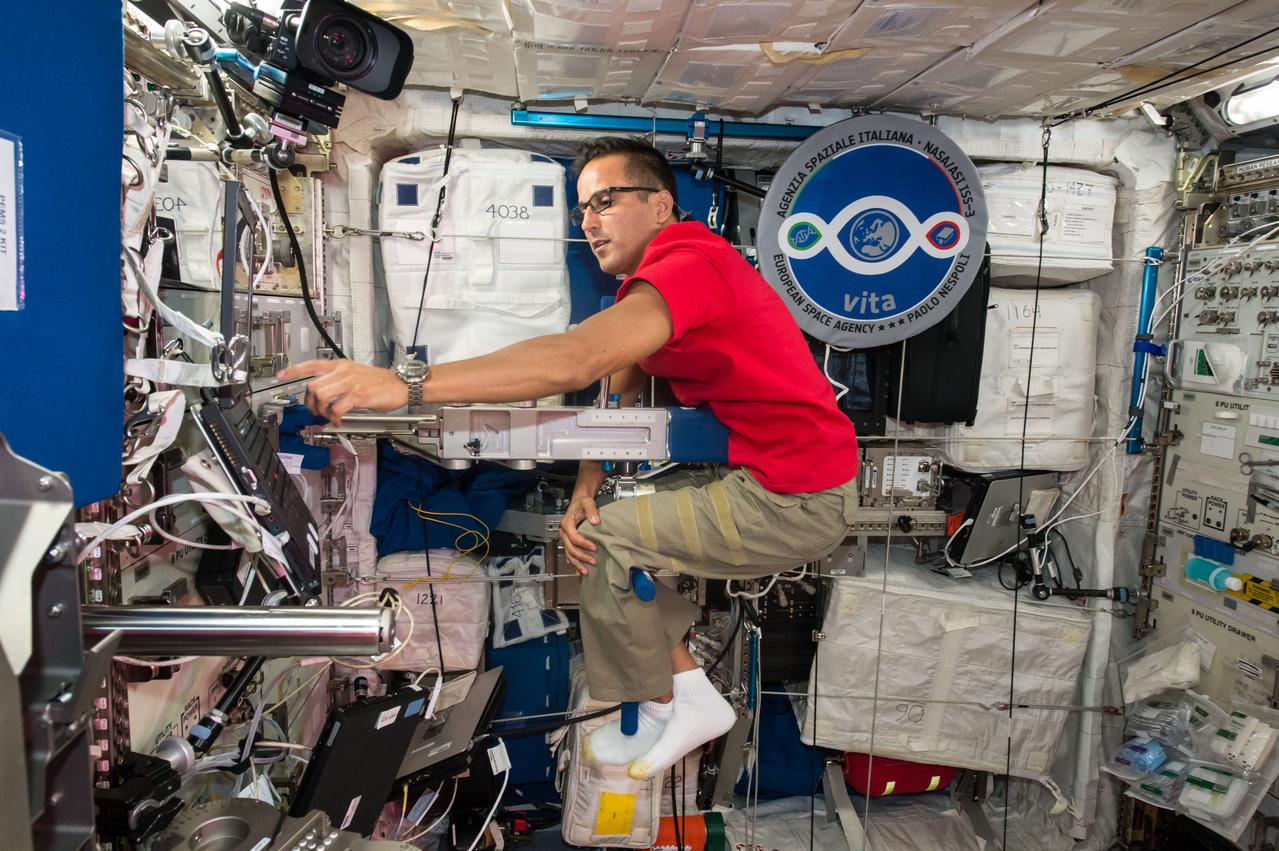

iss053e059889 (Sept. 28, 2017) --- Astronaut Joe Acaba calculates his mass inside the Columbus laboratory module using the Space Linear Acceleration Mass Measurement Device (SLAMMD). The device generates a known force against a crew member mounted on an extension arm with the resulting acceleration used to calculate the subject’s mass.
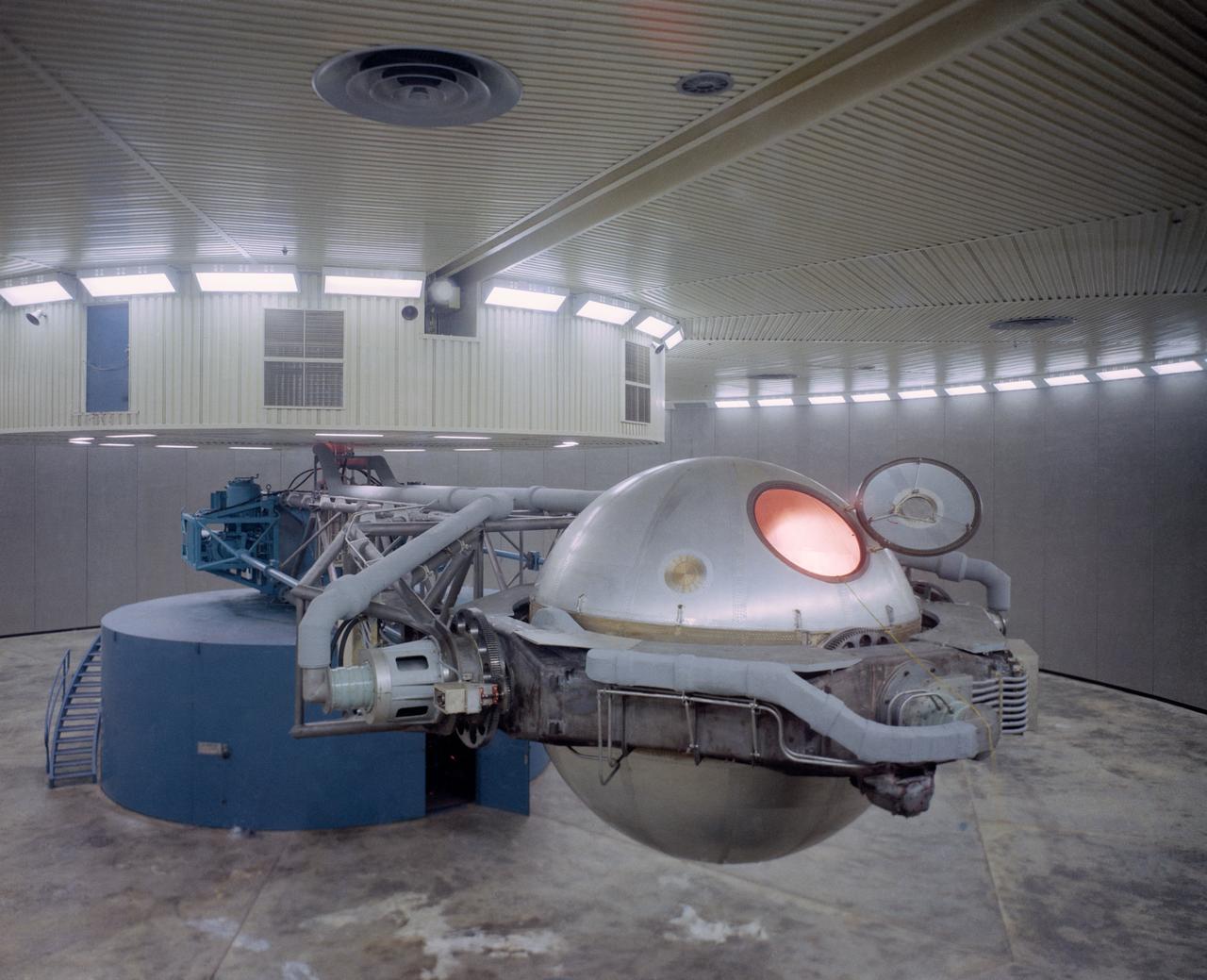

The new centrifuge at MSC, located in the Flight Acceleration Facility (FAF), Bldg. 29. The 50-ft. arm can swing the 3-man gondola to create G-Forces Astronauts will experience during liftoffs and re-entry conditions. MSC, HOUSTON, TX CN
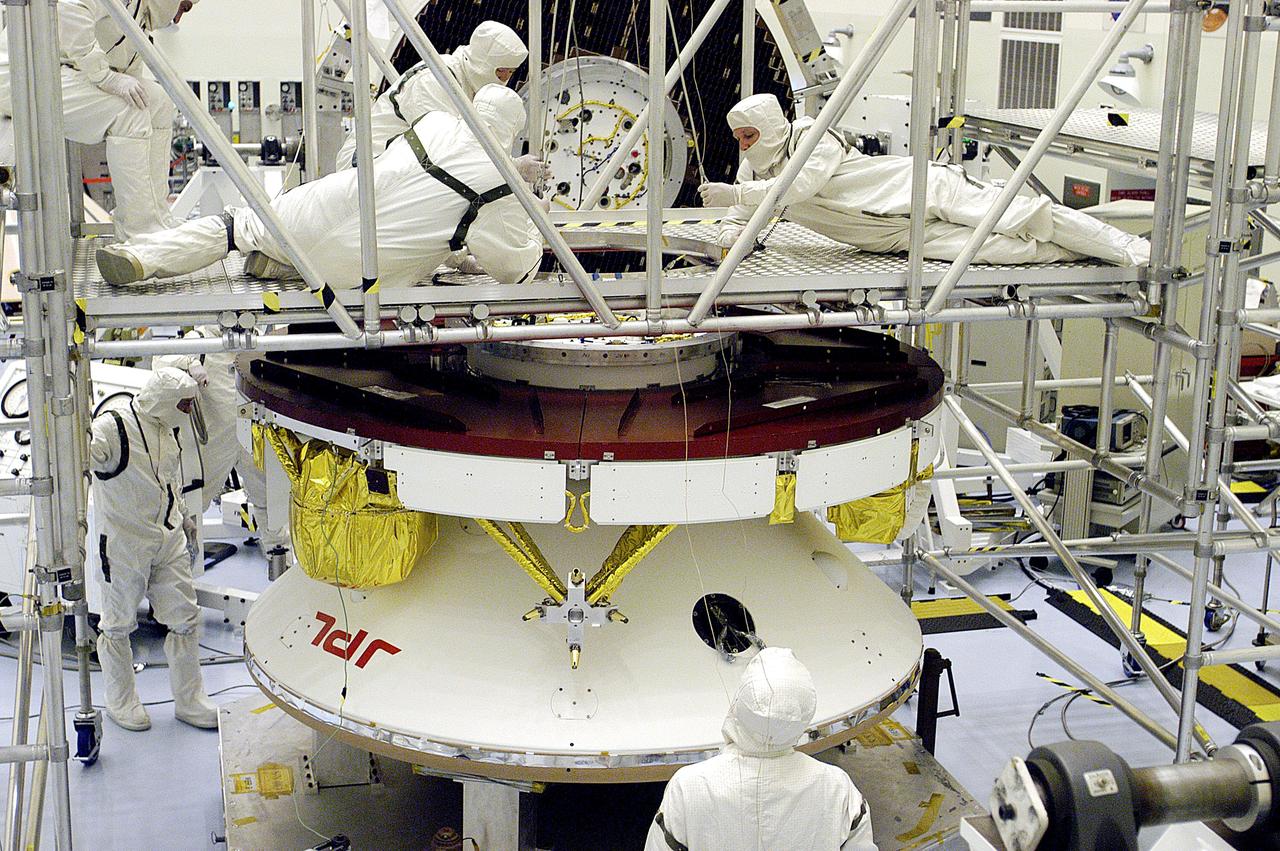

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility prepare the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) for a weight and center of gravity determination. NASA's twin Mars Exploration Rovers are designed to study the history of water on Mars. These robotic geologists are equipped with a robotic arm, a drilling tool, three spectrometers, and four pairs of cameras that allow them to have a human-like, 3D view of the terrain. Each rover could travel as far as 100 meters in one day to act as Mars scientists' eyes and hands, exploring an environment where humans can't yet go. Launch of MER-2 is scheduled for June 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
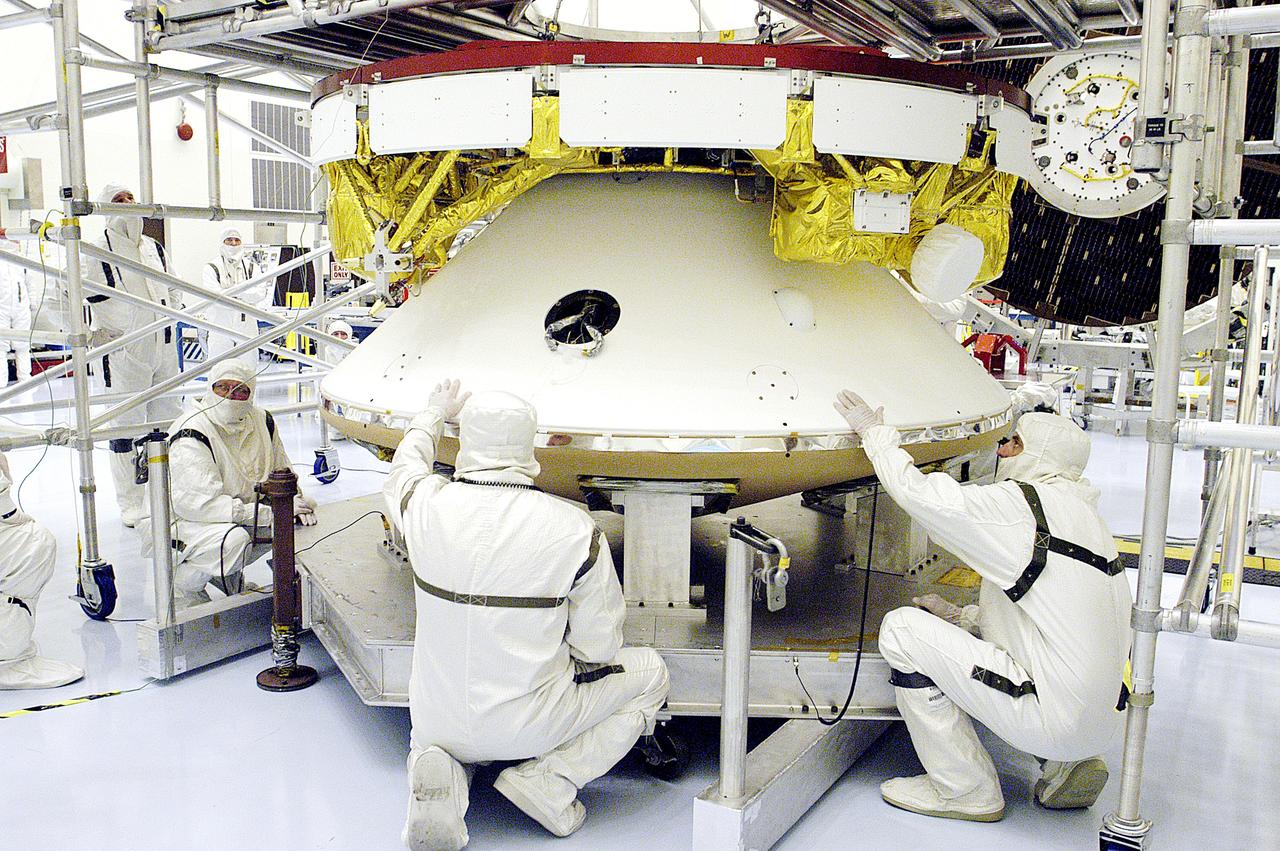

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) undergoes a weight and center of gravity determination in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. NASA's twin Mars Exploration Rovers are designed to study the history of water on Mars. These robotic geologists are equipped with a robotic arm, a drilling tool, three spectrometers, and four pairs of cameras that allow them to have a human-like, 3D view of the terrain. Each rover could travel as far as 100 meters in one day to act as Mars scientists' eyes and hands, exploring an environment where humans can't yet go. Launch of MER-2 is scheduled for June 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
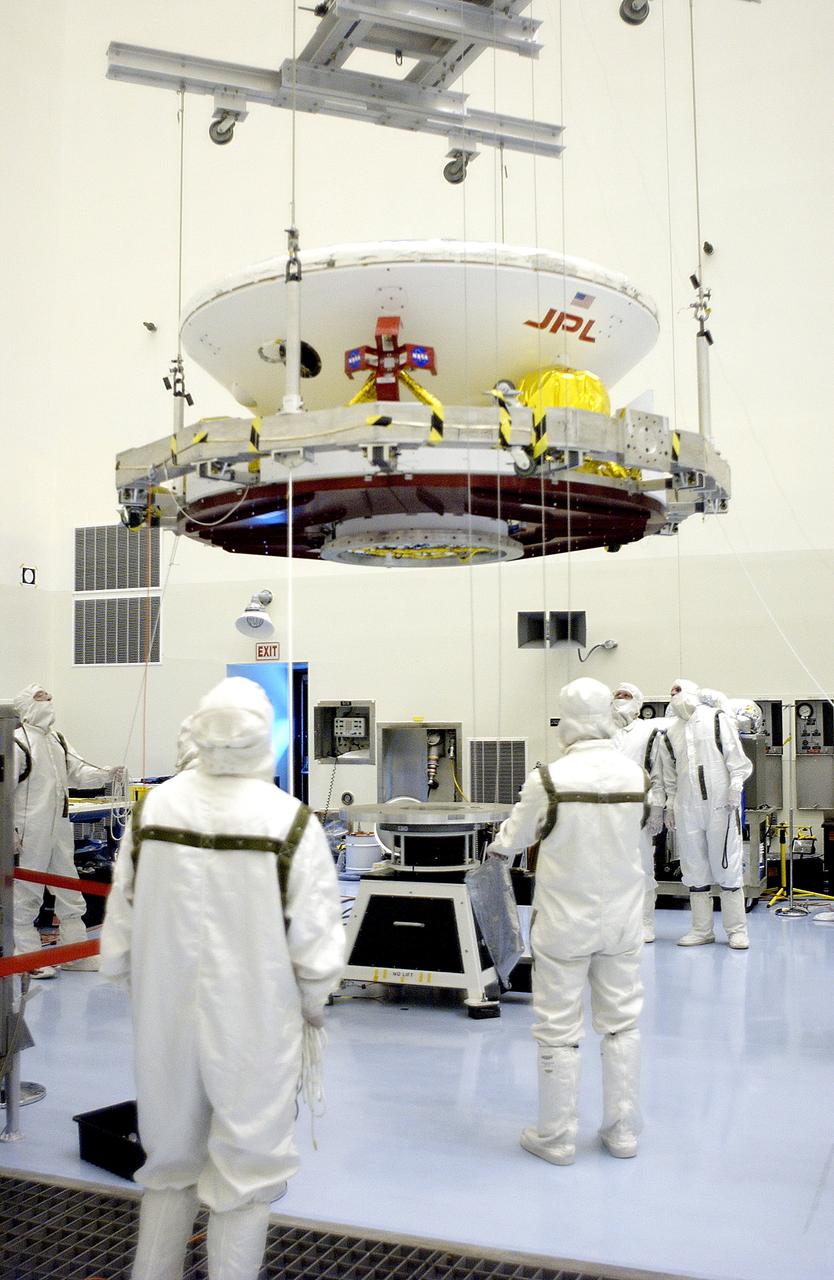

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) is moved to a spin table. NASA’s twin Mars Exploration Rovers are designed to study the history of water on Mars. These robotic geologists are equipped with a robotic arm, a drilling tool, three spectrometers, and four pairs of cameras that allow them to have a human-like, 3D view of the terrain. Each rover could travel as far as 100 meters in one day to act as Mars scientists' eyes and hands, exploring an environment where humans can’t yet go. The MER-2 is scheduled to launch June 5 from Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
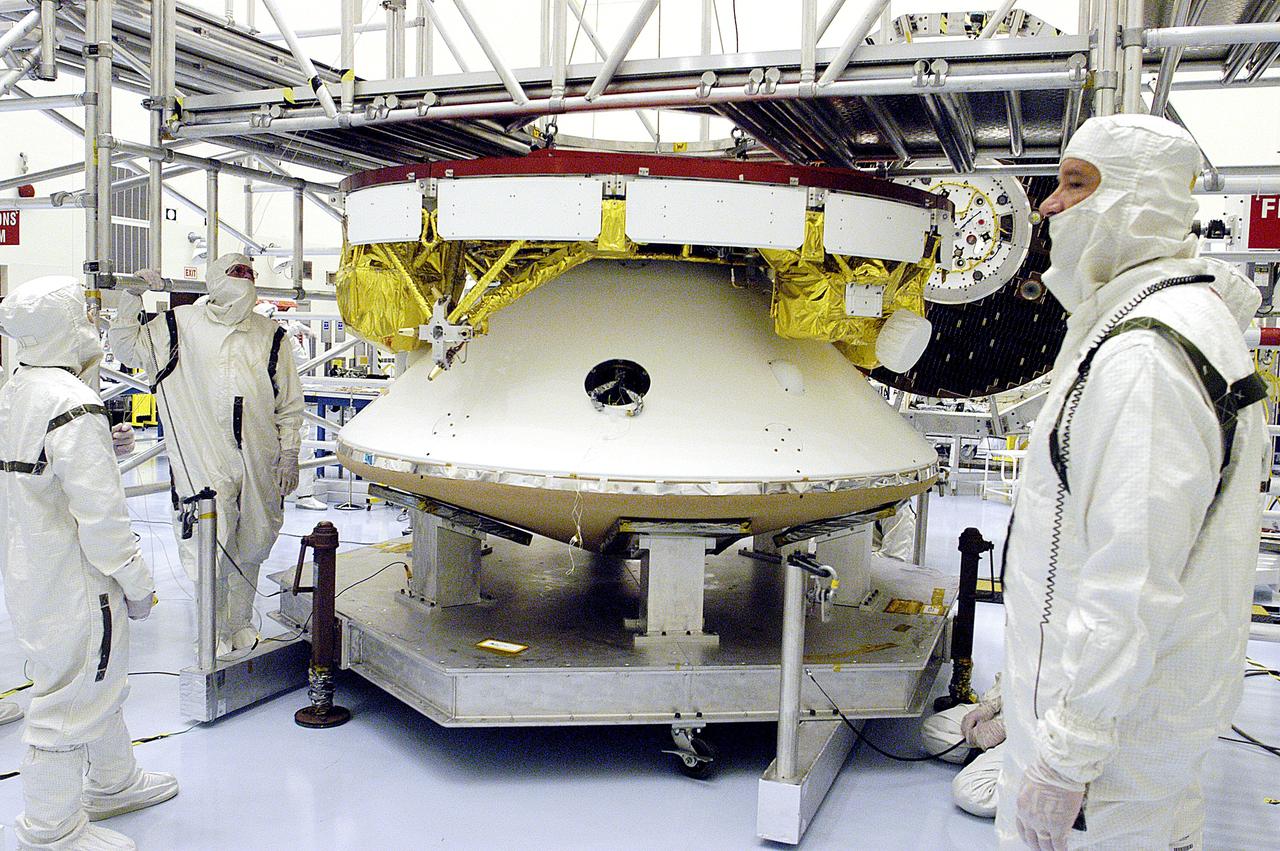

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) undergoes a weight and center of gravity determination in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. NASA's twin Mars Exploration Rovers are designed to study the history of water on Mars. These robotic geologists are equipped with a robotic arm, a drilling tool, three spectrometers, and four pairs of cameras that allow them to have a human-like, 3D view of the terrain. Each rover could travel as far as 100 meters in one day to act as Mars scientists' eyes and hands, exploring an environment where humans can't yet go. Launch of MER-2 is scheduled for June 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
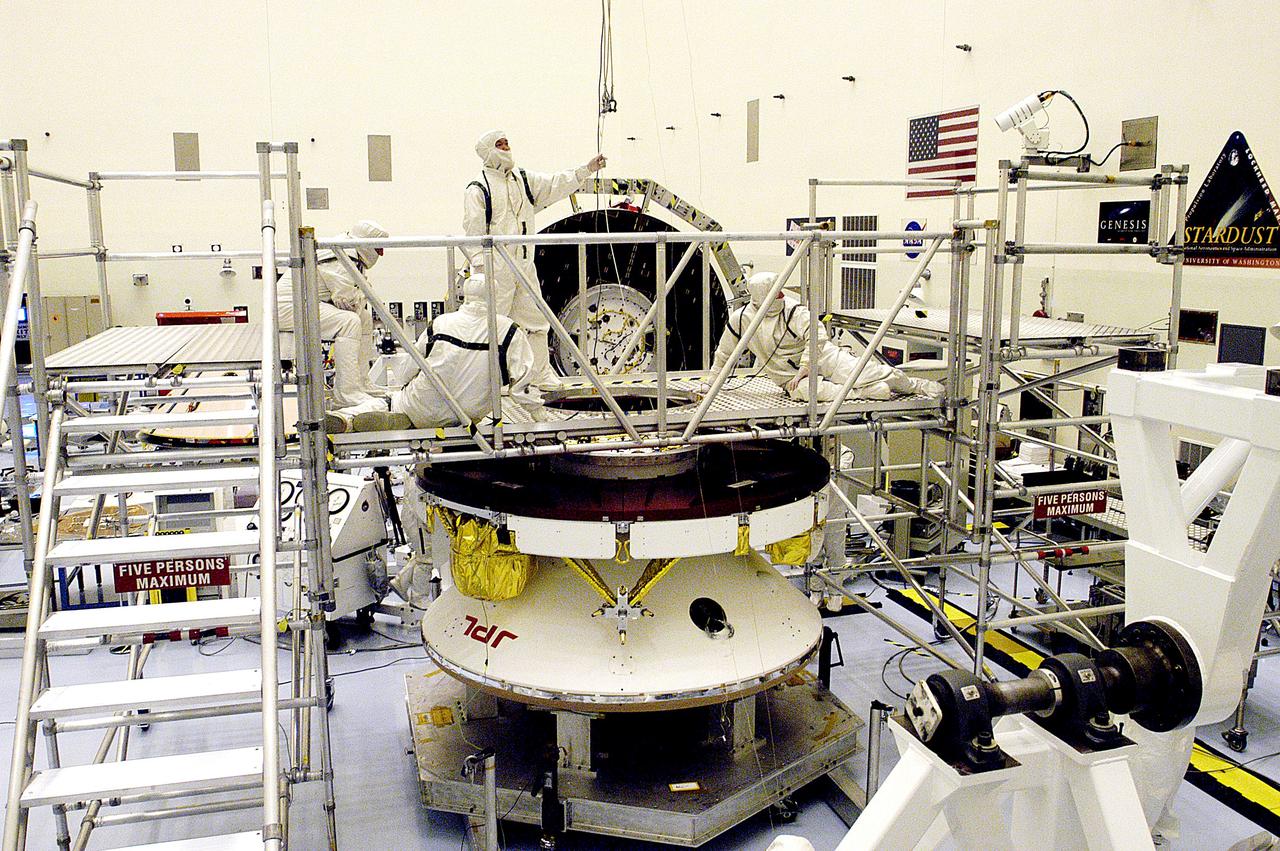
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility prepare the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2) for a weight and center of gravity determination. NASA's twin Mars Exploration Rovers are designed to study the history of water on Mars. These robotic geologists are equipped with a robotic arm, a drilling tool, three spectrometers, and four pairs of cameras that allow them to have a human-like, 3D view of the terrain. Each rover could travel as far as 100 meters in one day to act as Mars scientists' eyes and hands, exploring an environment where humans can't yet go. Launch of MER-2 is scheduled for June 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
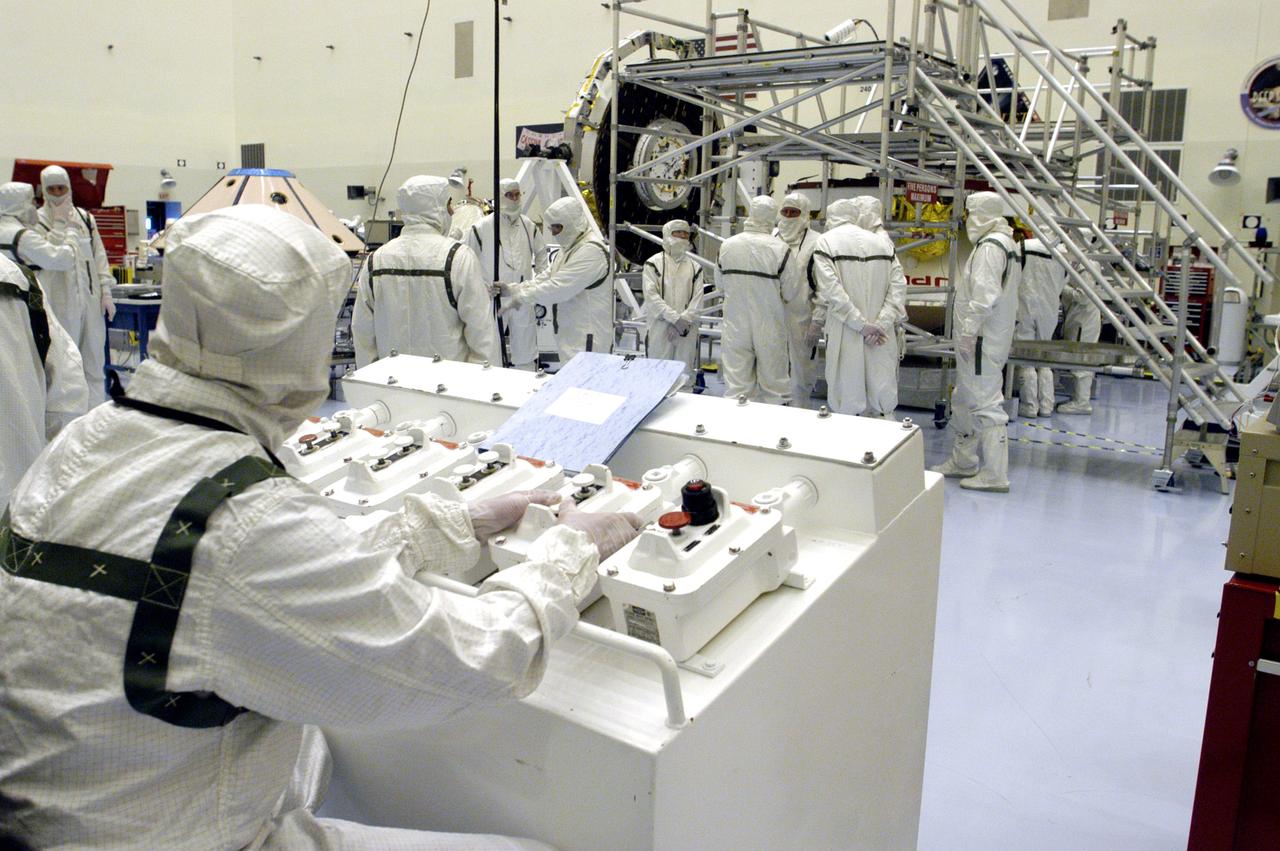

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility are preparing to determine weight and center of gravity for the Mars Exploration Rover 2 (MER-2). NASA's twin Mars Exploration Rovers are designed to study the history of water on Mars. These robotic geologists are equipped with a robotic arm, a drilling tool, three spectrometers, and four pairs of cameras that allow them to have a human-like, 3D view of the terrain. Each rover could travel as far as 100 meters in one day to act as Mars scientists' eyes and hands, exploring an environment where humans can't yet go. Launch of MER-2 is scheduled for June 5 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
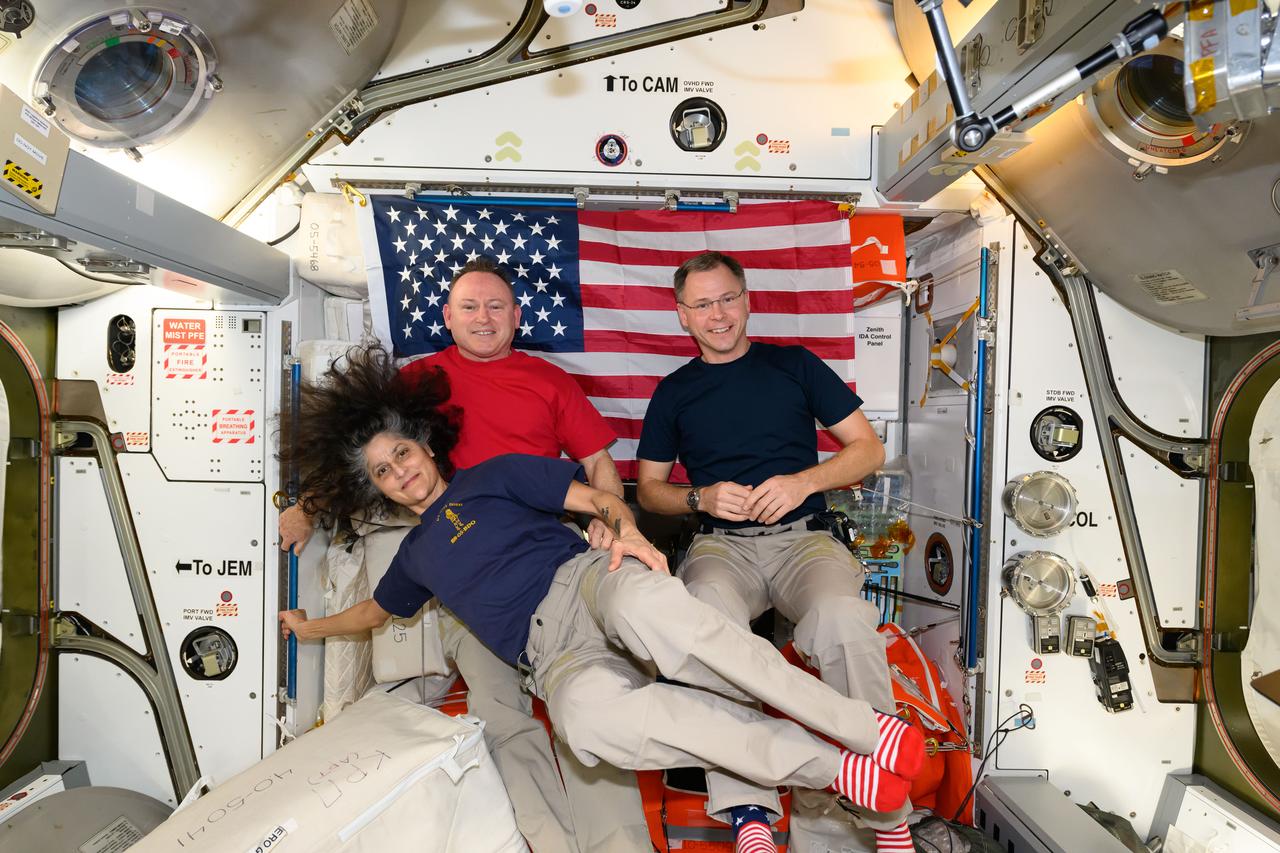

iss072e147414 (Nov. 15, 2024) --- Expedition 72 Commander Suni Williams and Flight Engineers Butch Wilmore and Nick Hague, all three NASA astronauts, pose for a portrait together with the U.S. flag behind them aboard the International Space Station's Harmony module. The trio was honoring veteran members of the U.S. Armed Forces during Veteran's Day. Williams is a retired U.S. Navy captain, Wilmore is a U.S. Navy test pilot, and Hague is U.S. Space Force colonel.
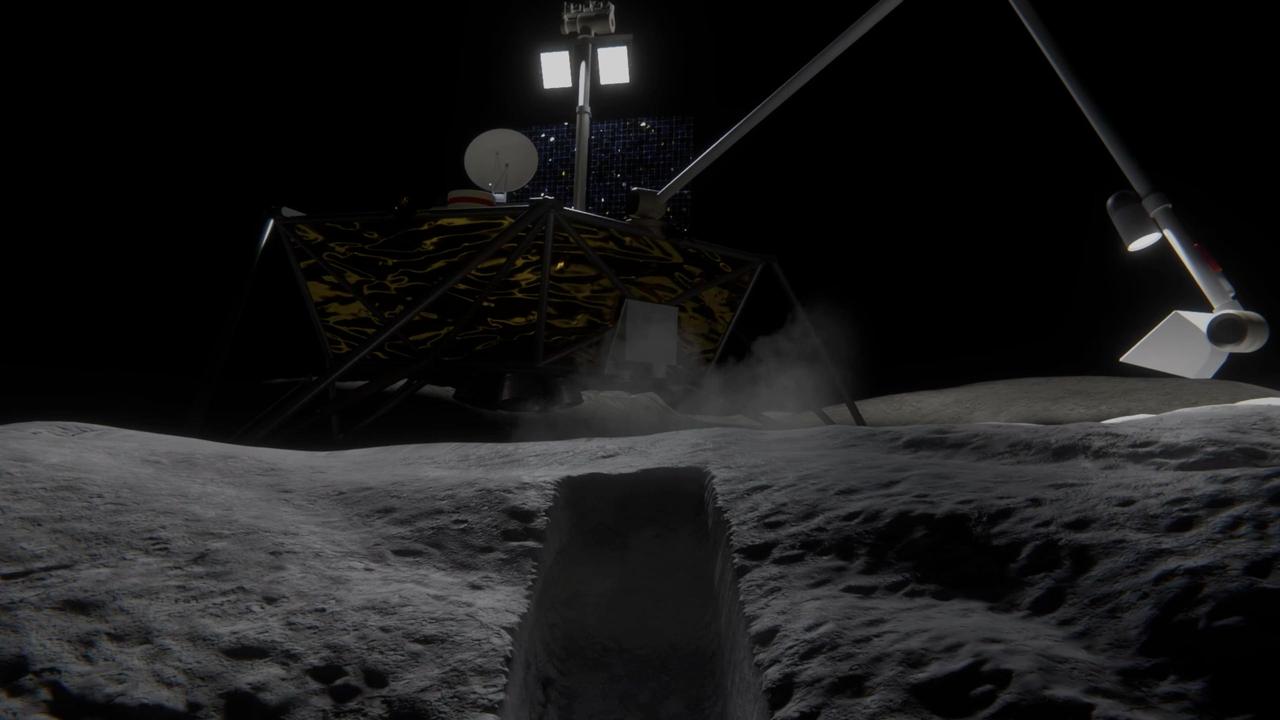

NASA's Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) robotic arm system reaches out from a lander on the Moon and scoops up regolith (broken rock and dust). Managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, COLDArm is designed to operate during lunar night, a period that lasts about 14 Earth days. It can function in temperatures as cold as minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). Frigid temperatures during lunar night would stymie the arms on current spacecraft, which must rely on energy-consuming heaters to stay warm. To operate in the cold, the 6-foot-6-inch (2-meter) arm combines several key new technologies: gears made of bulk metallic glass that require no wet lubrication or heating, cold motor controllers that don't need to be kept warm in an electronics box near the core of the spacecraft, and a cryogenic six-axis force torque sensor that lets the arm "feel" what it's doing and make adjustments. A variety of attachments and small instruments could go on the end of the arm, such as a 3D-printed titanium scoop that could collect samples from a planet's surface, similar to what's depicted here. Like the arm on NASA's now-retired InSight Mars lander, COLDArm is also capable of deploying science instruments to the surface. The arm system could be attached to a stationary lander or to a rover. Motiv Space Systems, a partner on COLDArm, developed the cold motor controllers, and also built sections of the arm and assembled it from JPL-supplied parts at the company's Pasadena, California, facility. The COLDArm project is funded through the Lunar Surface Innovation Initiative and managed by the Game Changing Development program in NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26347
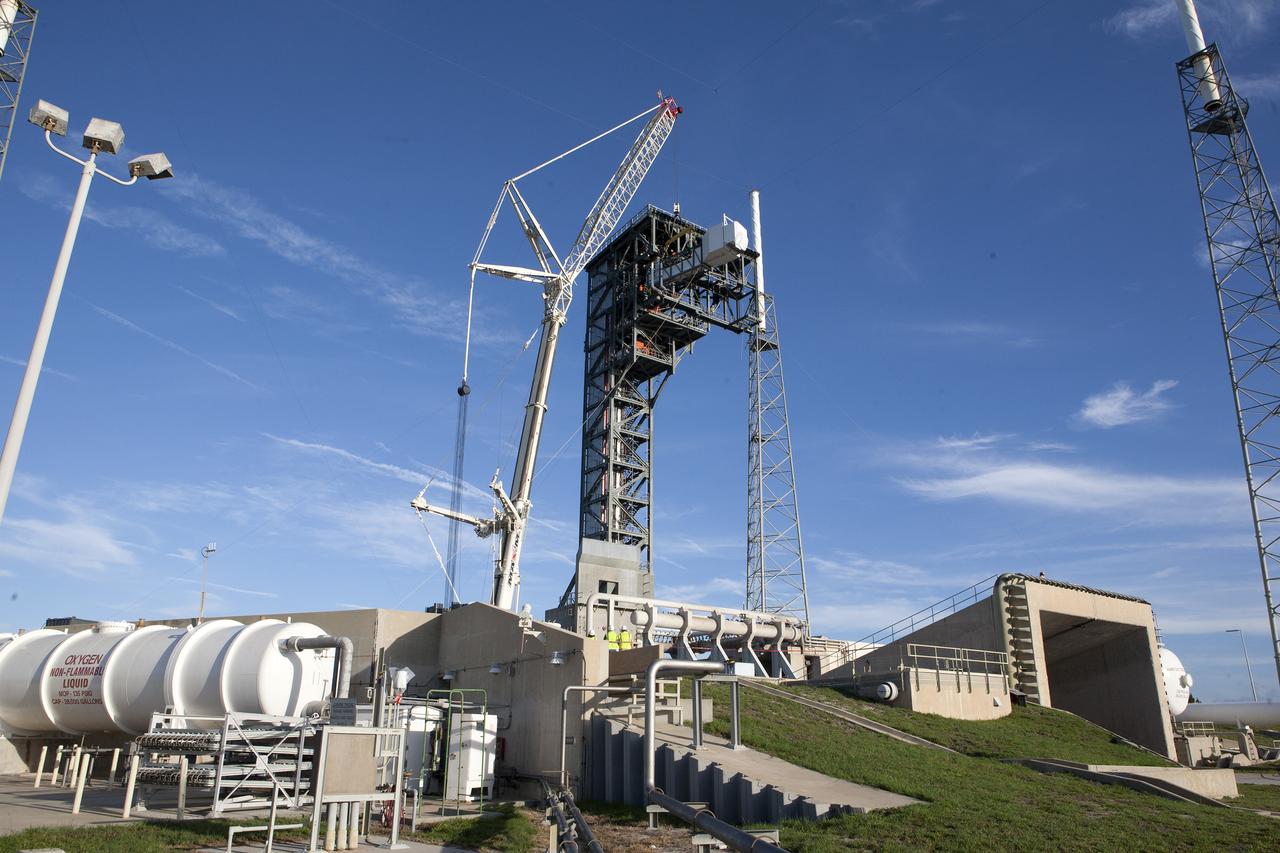

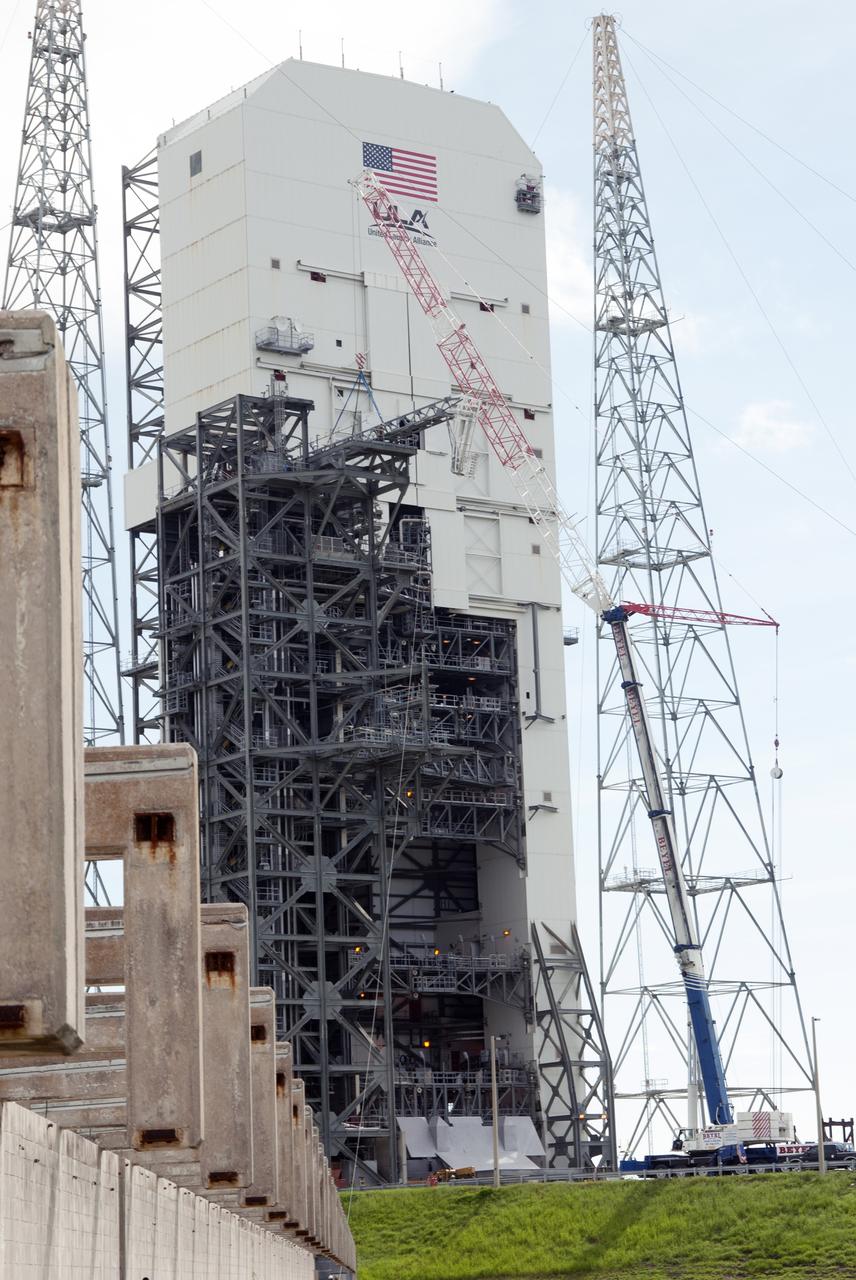
The Crew Access Arm and White Room for Boeing's CST-100 Starliner are attached to the Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41. The arm will serve as the connection that astronauts will walk through prior to boarding the Starliner spacecraft when stacked atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. This installation completes the major construction of the first new Crew Access Tower to be built at the Cape since the Apollo era. Under a Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) contract with NASA, Boeing’s Starliner system will be certified by NASA's Commercial Crew Program to fly crews to and from the International Space Station.
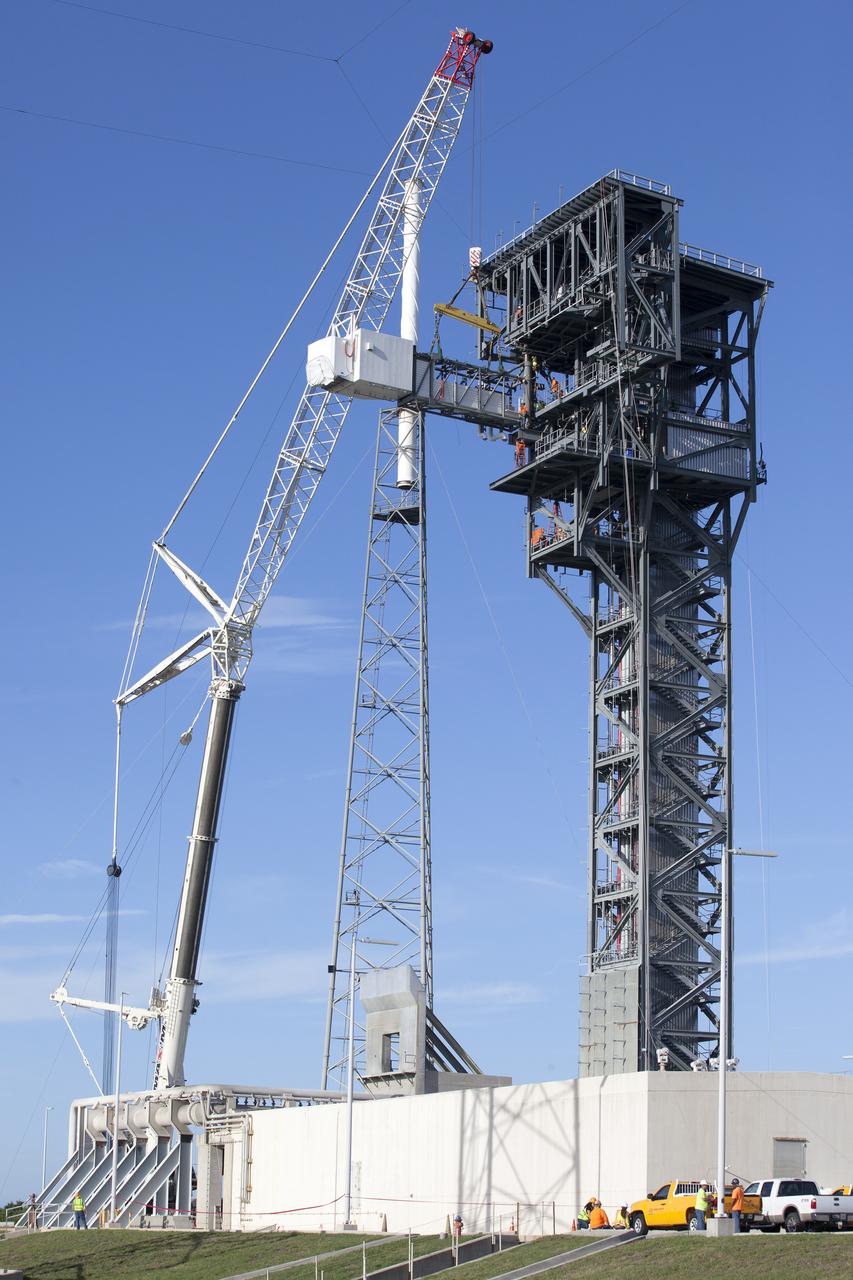

The Crew Access Arm and White Room for Boeing's CST-100 Starliner are attached to the Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41. The arm will serve as the connection that astronauts will walk through prior to boarding the spacecraft when stacked atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The installation completes the major construction of the first new Crew Access Tower to be built at the Cape since the Apollo era. Under a Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) contract with NASA, Boeing’s Starliner system will be certified by NASA's Commercial Crew Program to fly crews to and from the International Space Station.
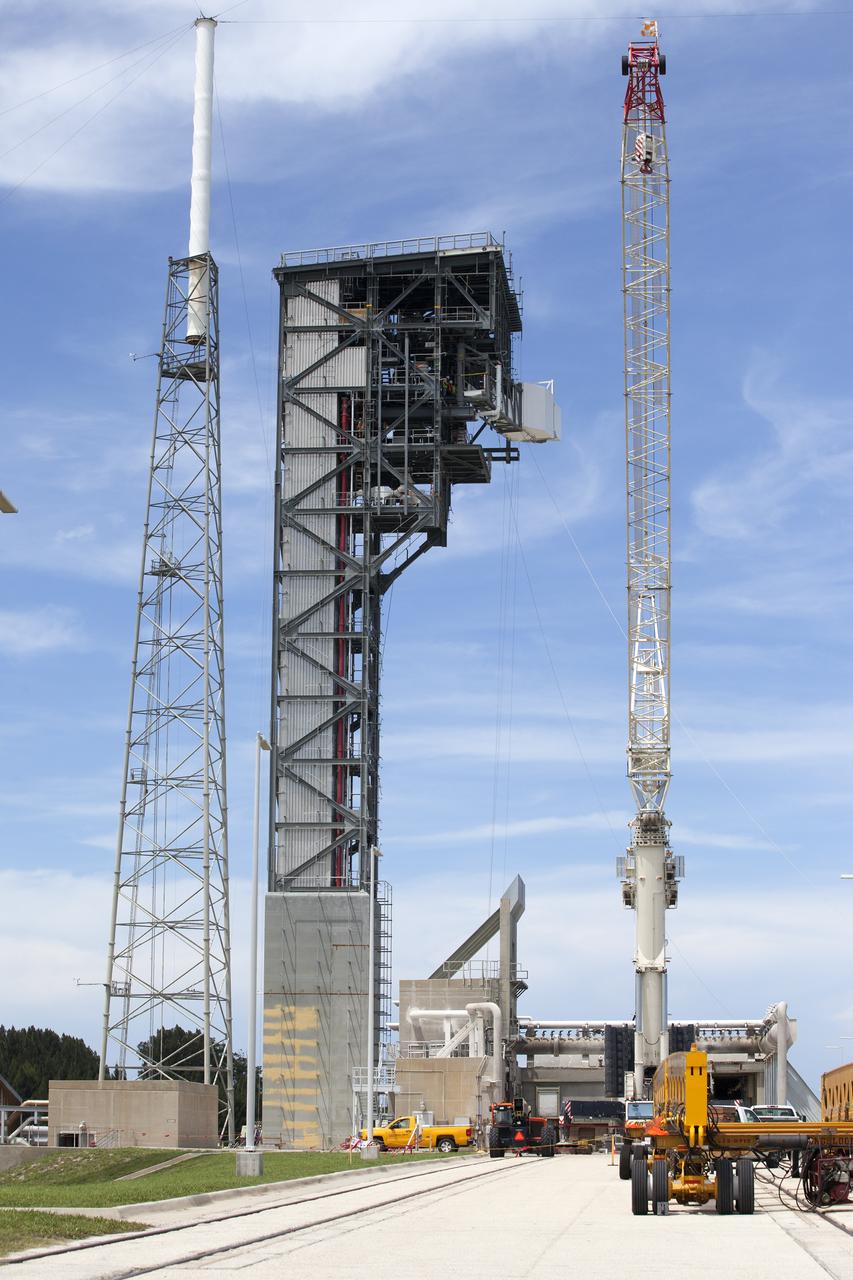

The Crew Access Arm and White Room for Boeing's CST-100 Starliner are attached to the Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41. The arm will serve as the connection that astronauts will walk through prior to boarding the Starliner spacecraft when stacked atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. This installation completes the major construction of the first new Crew Access Tower to be built at the Cape since the Apollo era. Under a Commercial Crew Transportation Capability contract with NASA, Boeing’s Starliner system will be certified by NASA's Commercial Crew Program to fly crews to and from the International Space Station.
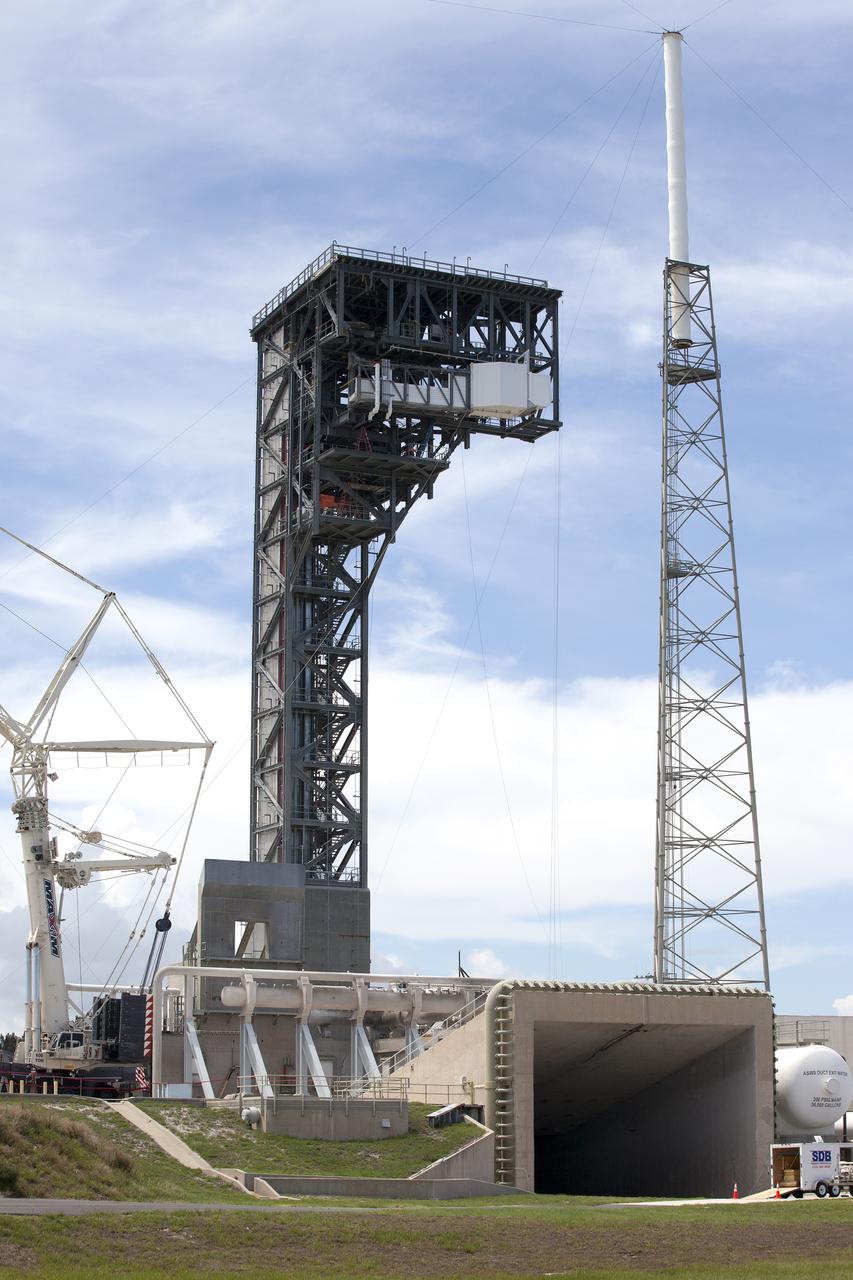

The Crew Access Arm and White Room for Boeing's CST-100 Starliner are attached to the Crew Access Tower at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41. The arm will serve as the connection that astronauts will walk through prior to boarding the Starliner spacecraft when stacked atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. This installation completes the major construction of the first new Crew Access Tower to be built at the Cape since the Apollo era. Under a Commercial Crew Transportation Capability contract with NASA, Boeing’s Starliner system will be certified by NASA's Commercial Crew Program to fly crews to and from the International Space Station.
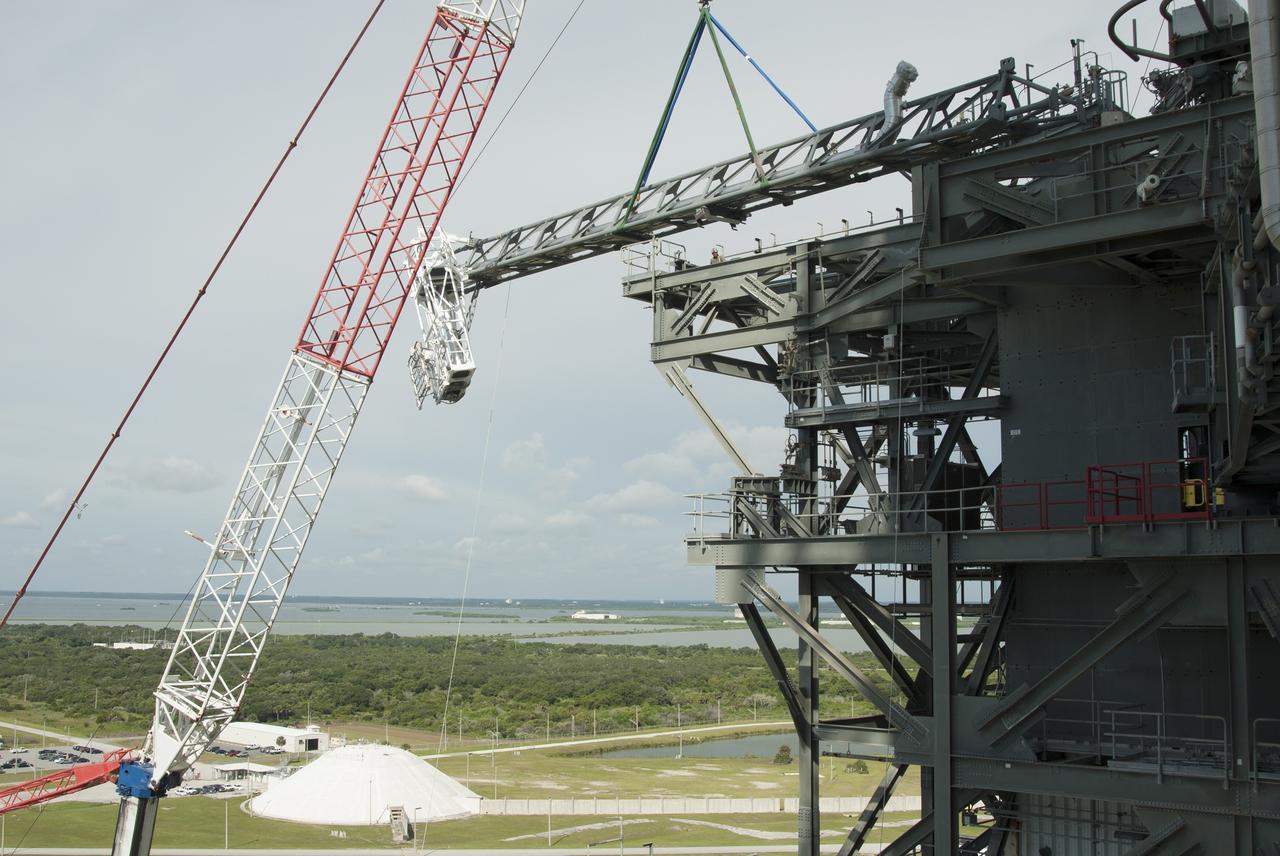

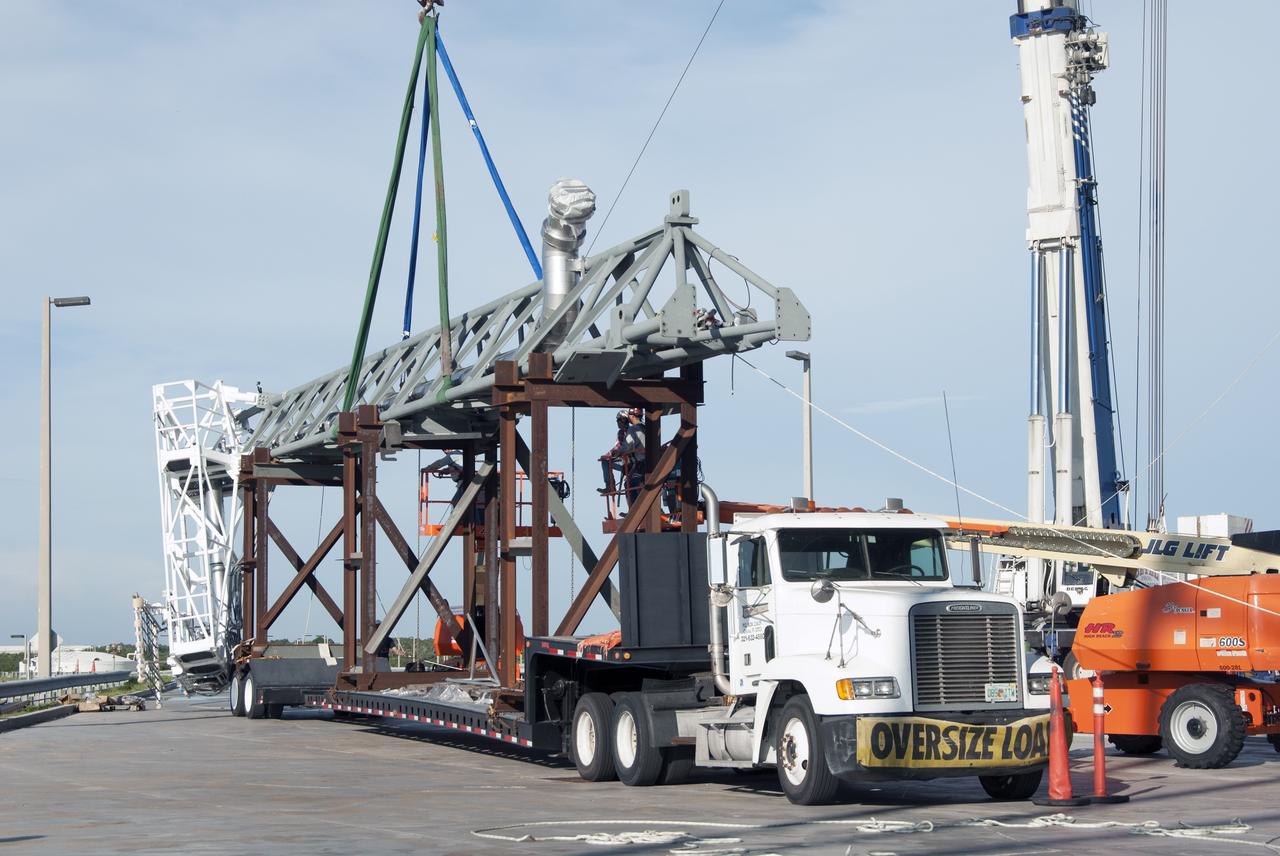
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A crane brings the umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, closer for installation on the fixed umbilical tower at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
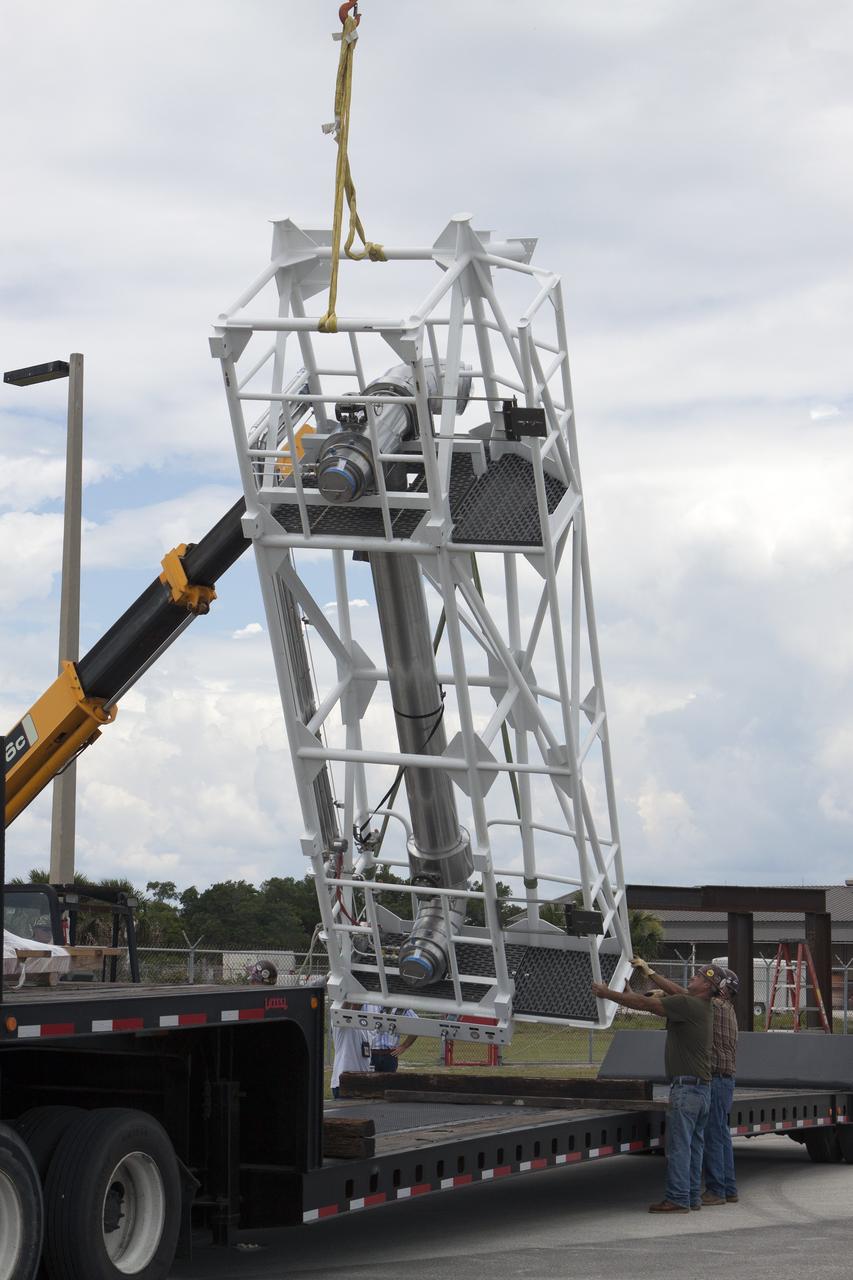

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Part of the umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida and is being lifted by crane from its transporter. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower on the launch pad. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
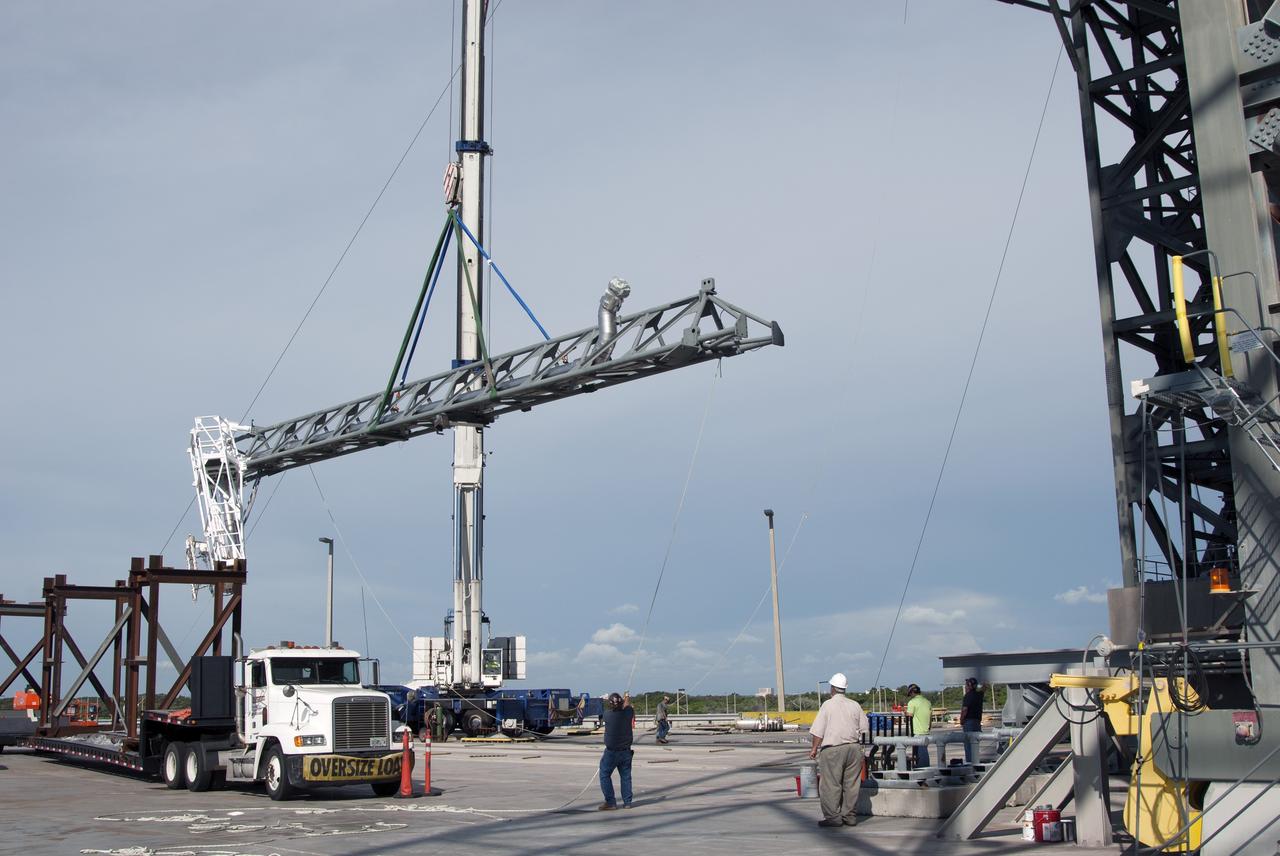

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, is lifted by crane for installation on the fixed umbilical tower at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

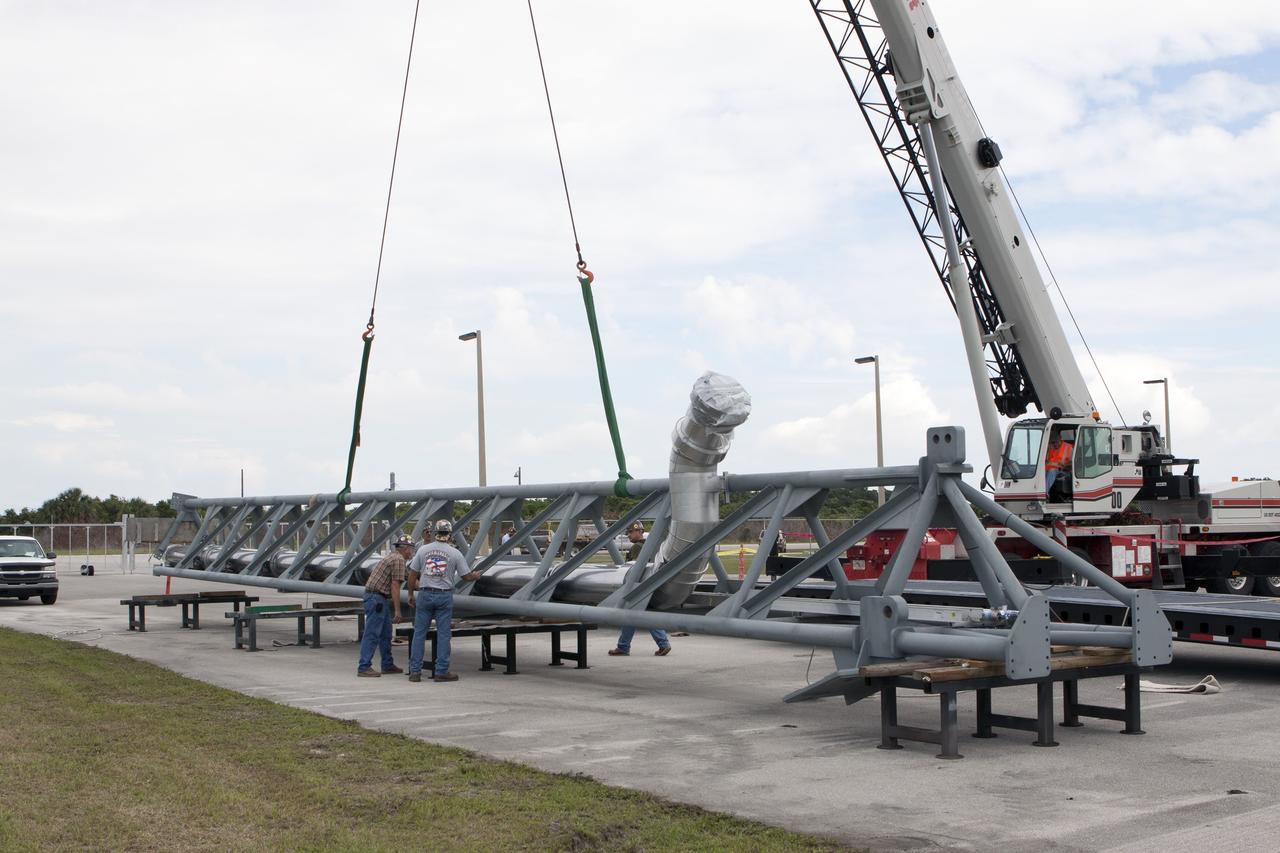
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Both parts of the umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, have arrived at the Horizontal Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. They have been removed from the transporter and placed on stands. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower on the launch pad. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida and has been lifted by crane from its transporter. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower on the launch pad. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
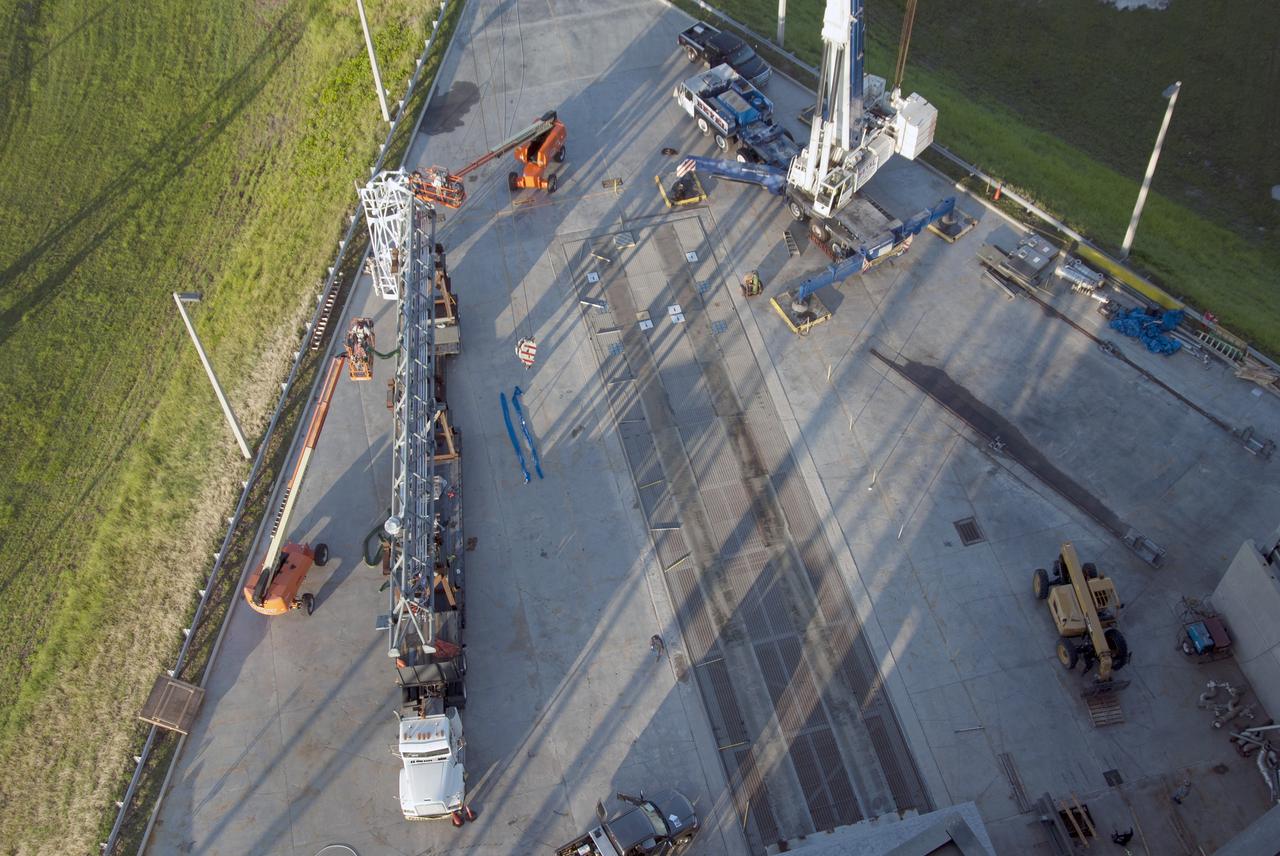

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In this view from above at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, is being prepared to be lifted by crane and attached to the fixed umbilical tower on the launch pad. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
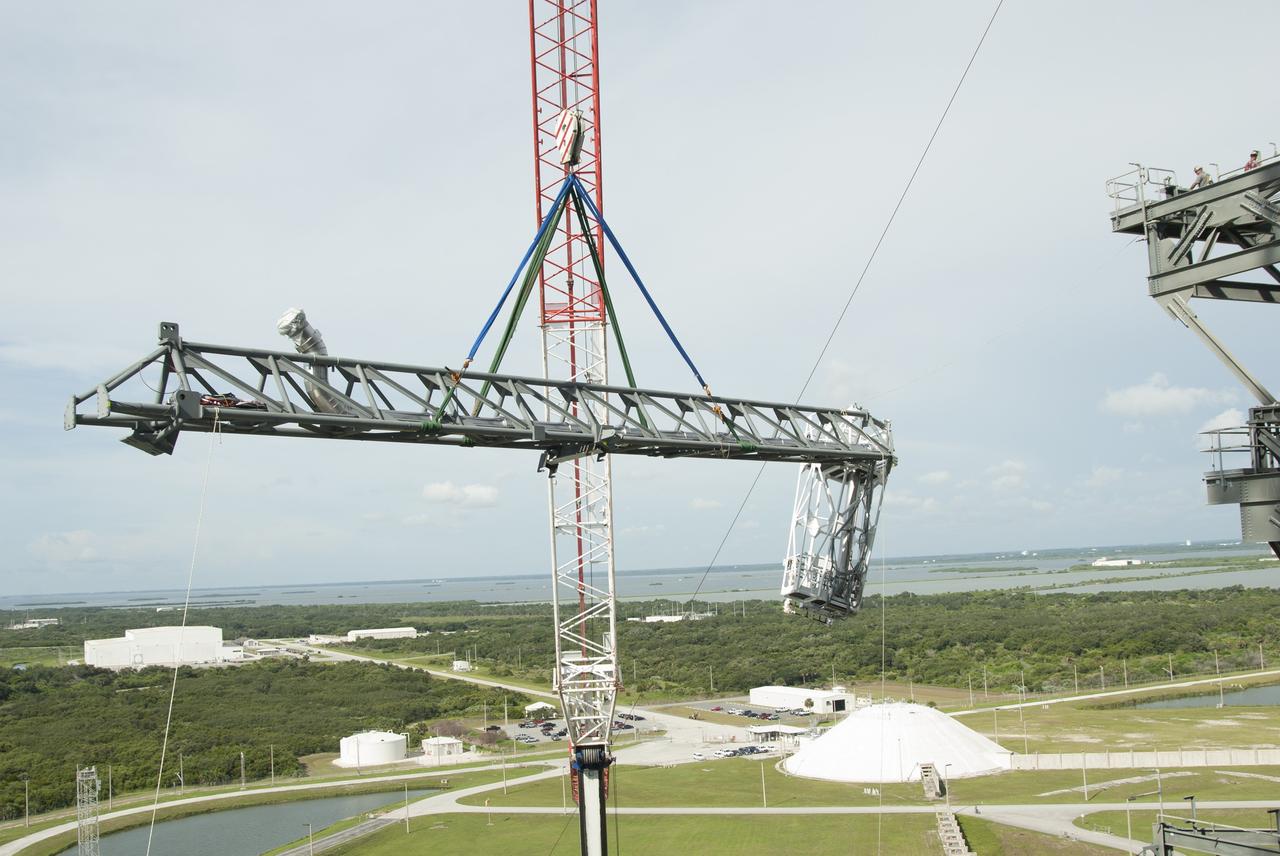

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, is lifted high by crane for installation on the fixed umbilical tower at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
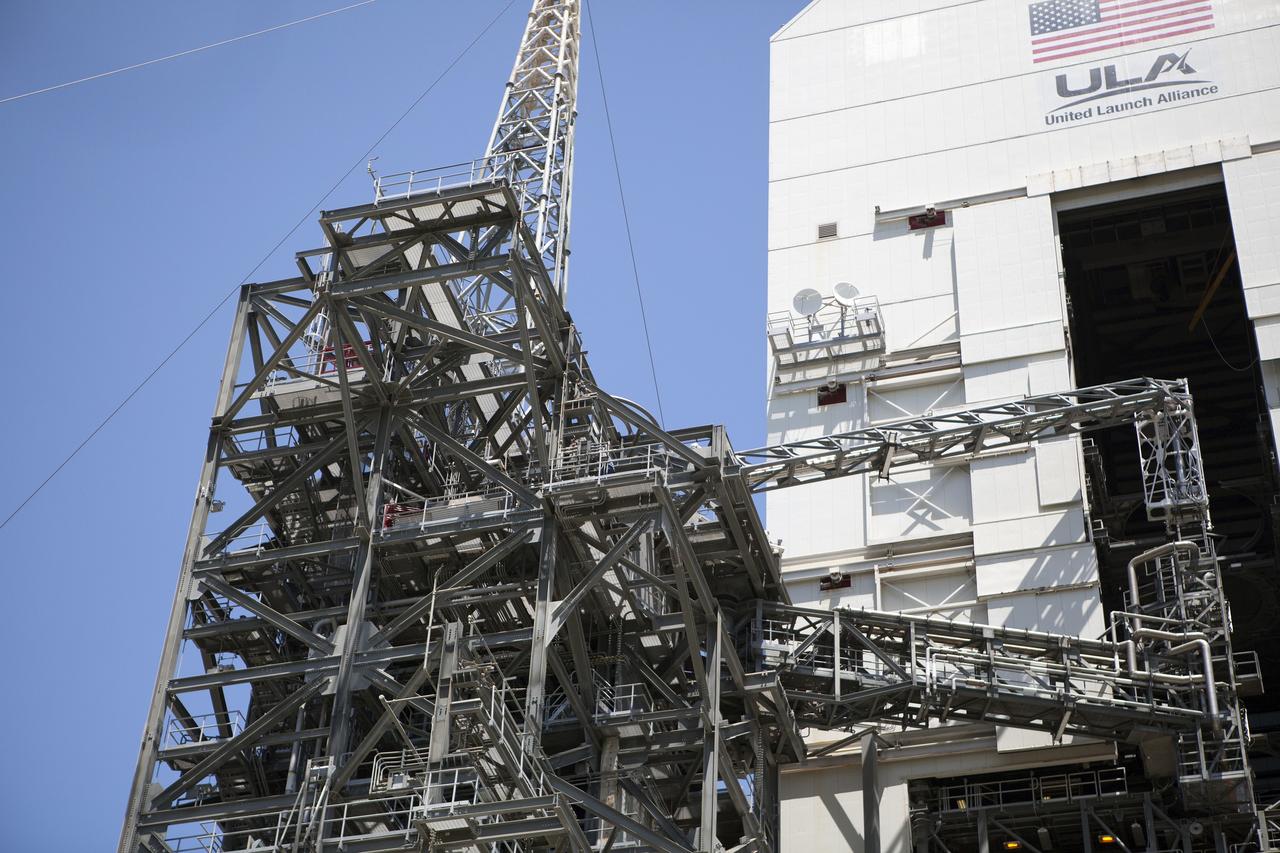

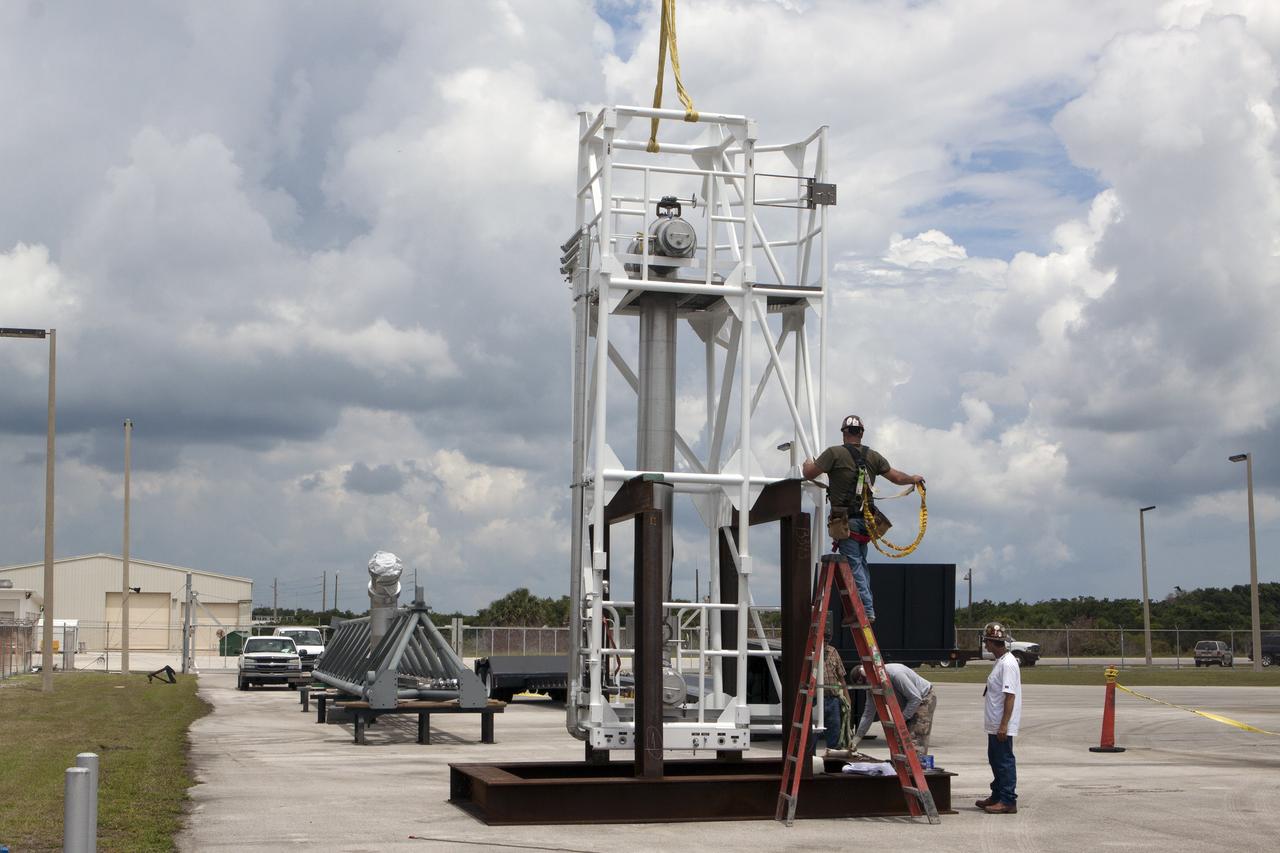
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The umbilical swing arm for Orion's Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, has been attached to the uppermost location on the fixed umbilical tower at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is undergoing a test to confirm that it is operating correcting. During the test, the arm was swung out and closer to the Vertical Integration Facility at the pad. The uppermost swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, all three umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A crane brings the umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, closer for installation on the fixed umbilical tower at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
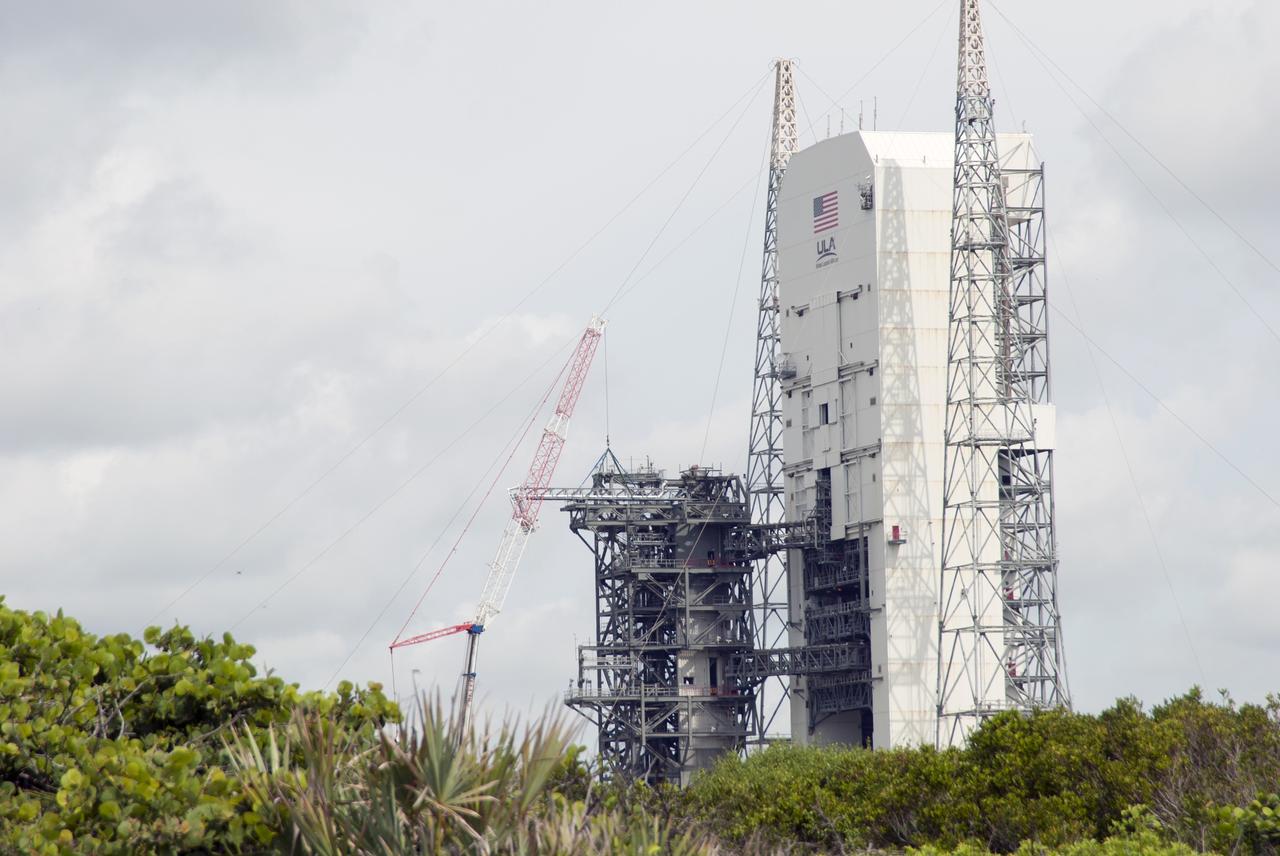

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A crane brings the umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, closer for installation on the fixed umbilical tower at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
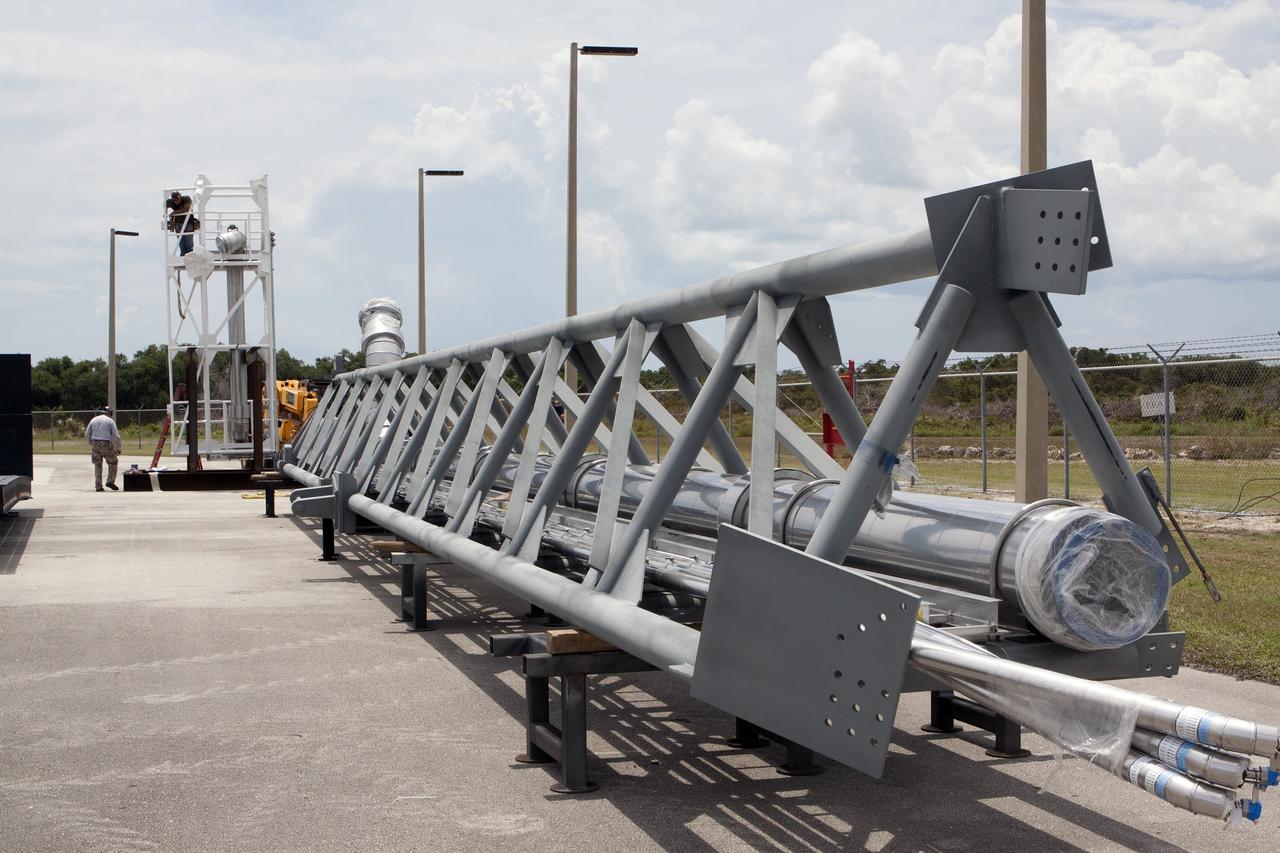

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Both parts of the umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, have arrived at the Horizontal Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. They have been removed from the transporter and placed on stands. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower on the launch pad. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Part of the umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower on the launch pad. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A crane brings the umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, closer for installation on the fixed umbilical tower at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower on the launch pad. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, is being prepared to be lifted by crane and attached to the fixed umbilical tower at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
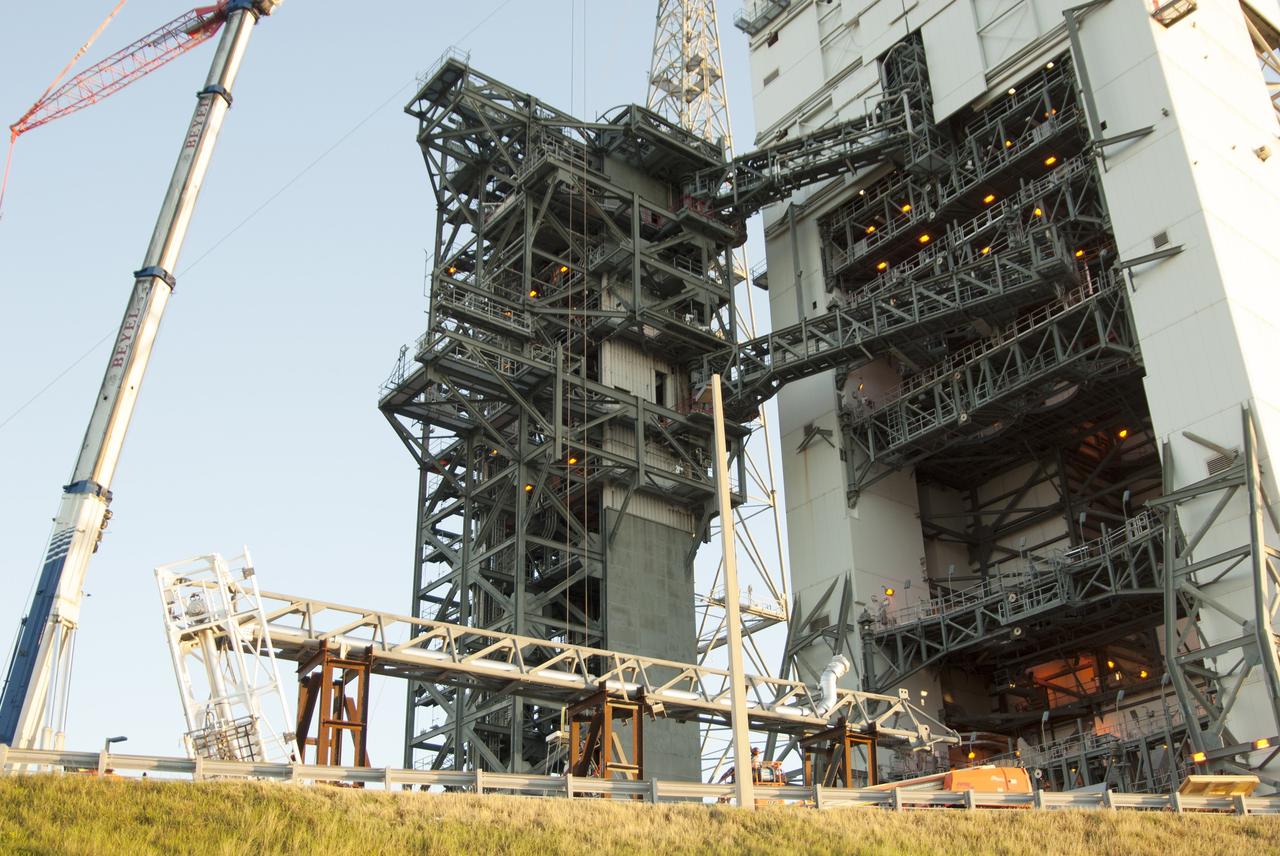

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, arrives at the launch pad at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower on the launch pad. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
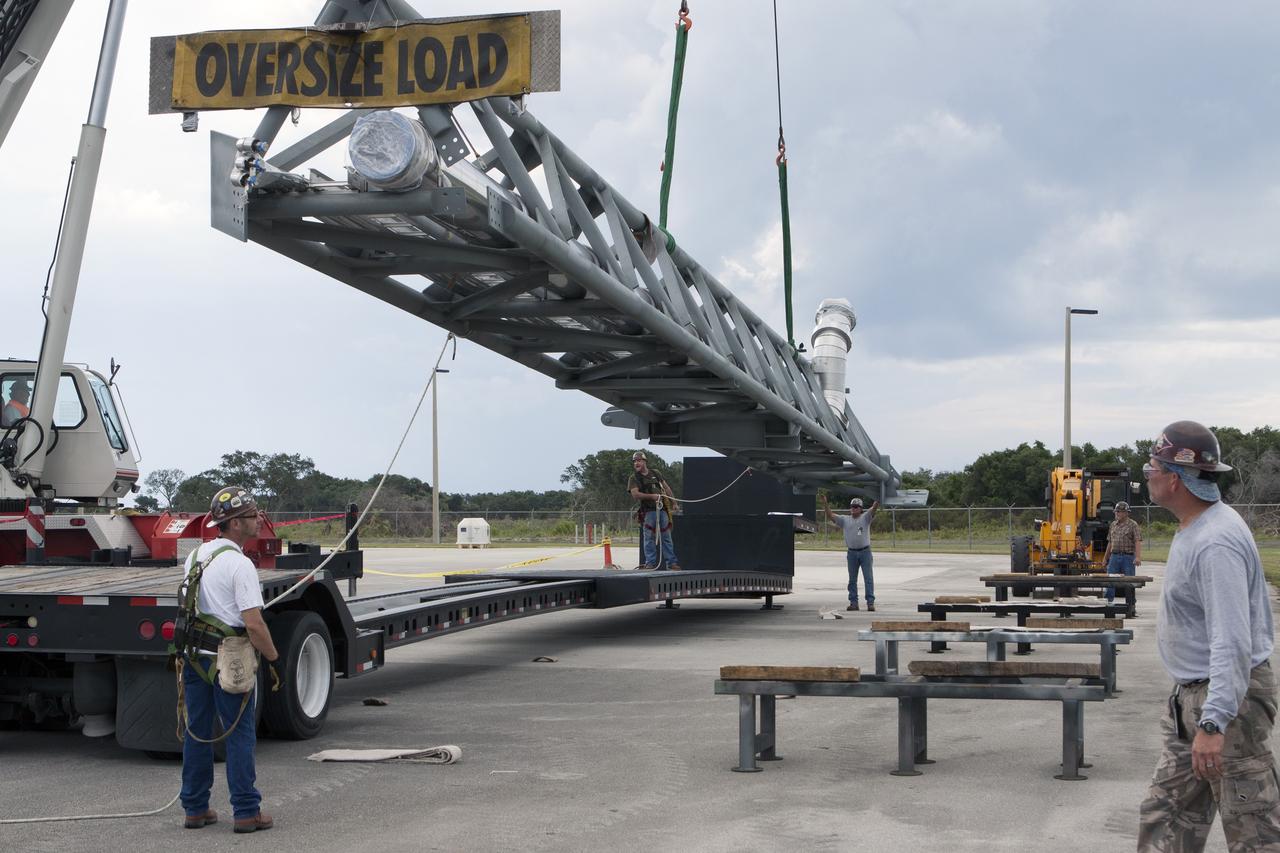

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, arrives at the Horizontal Integration Facility near Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida and is being lifted by crane from its transporter. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower on the launch pad. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
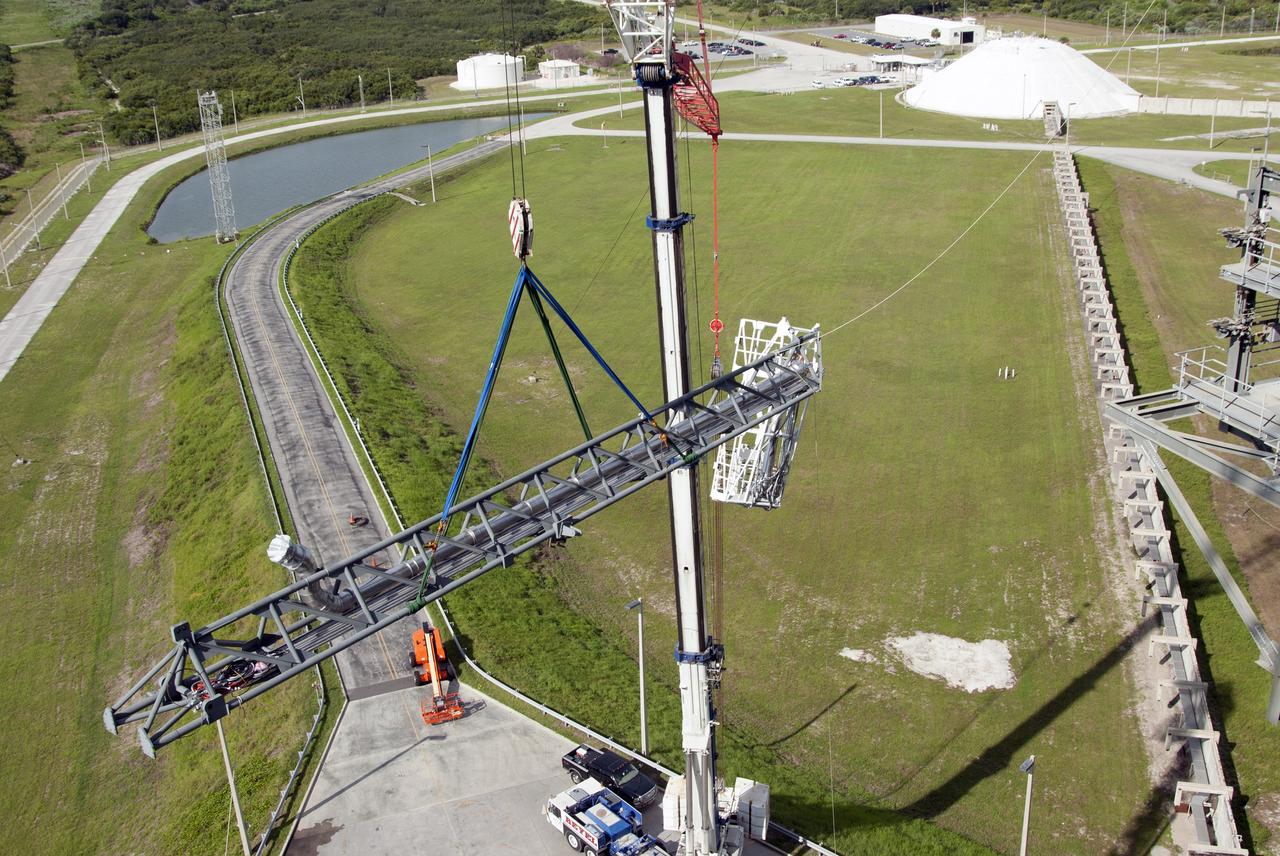

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, is lifted by crane for installation on the fixed umbilical tower at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
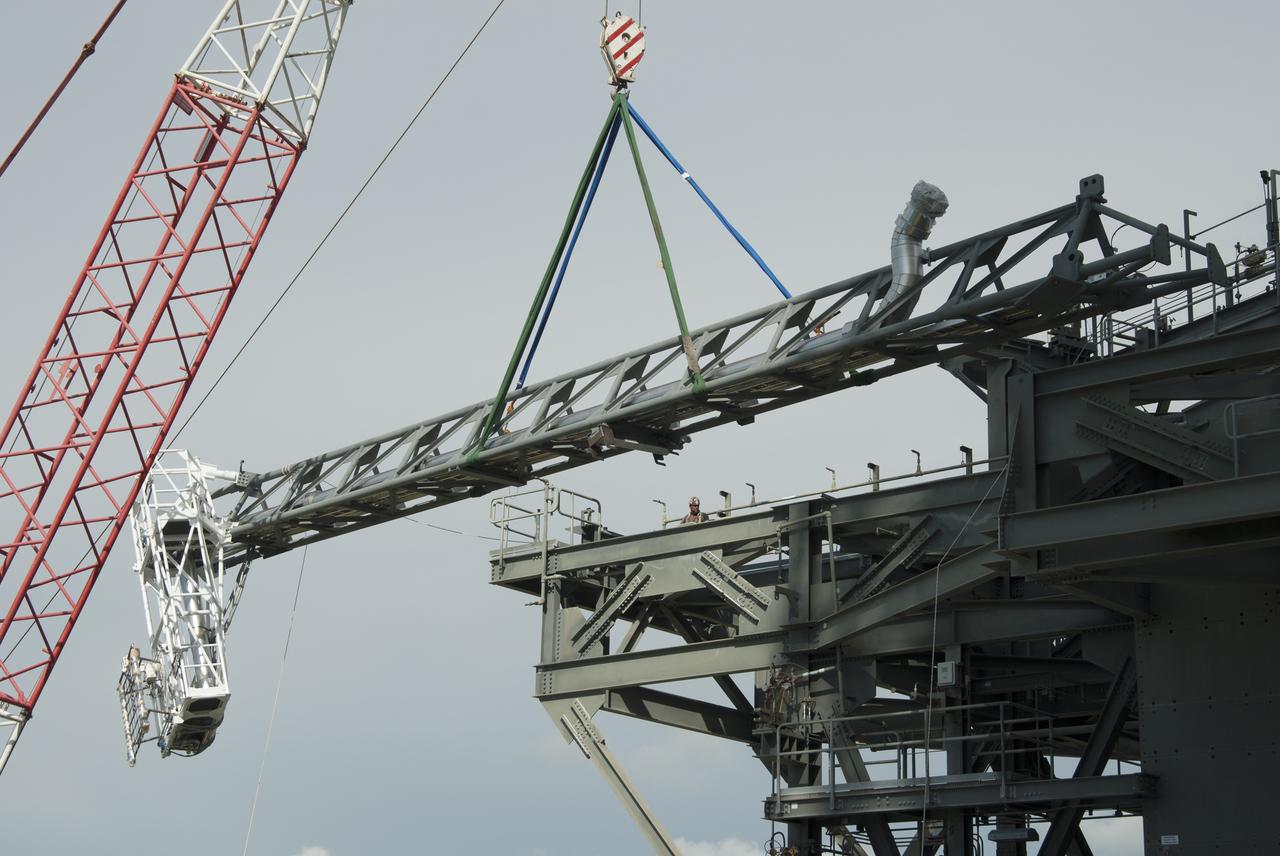

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A crane brings the umbilical swing arm for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, closer for installation on the fixed umbilical tower at Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The swing arm is the uppermost of three swing arms that will be attached to the fixed umbilical tower. The swing arm will carry umbilicals that will be mated to Orion's launch abort system and environmental control system. During launch, the umbilicals will pull away from Orion and the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket at T-0. During the EFT-1 mission, Orion will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The data gathered during the flight will influence design decisions, validate existing computer models and innovative new approaches to space systems development, as well as reduce overall mission risks and costs for later Orion flights. Liftoff of Orion on its first flight test is planned for fall 2014. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann