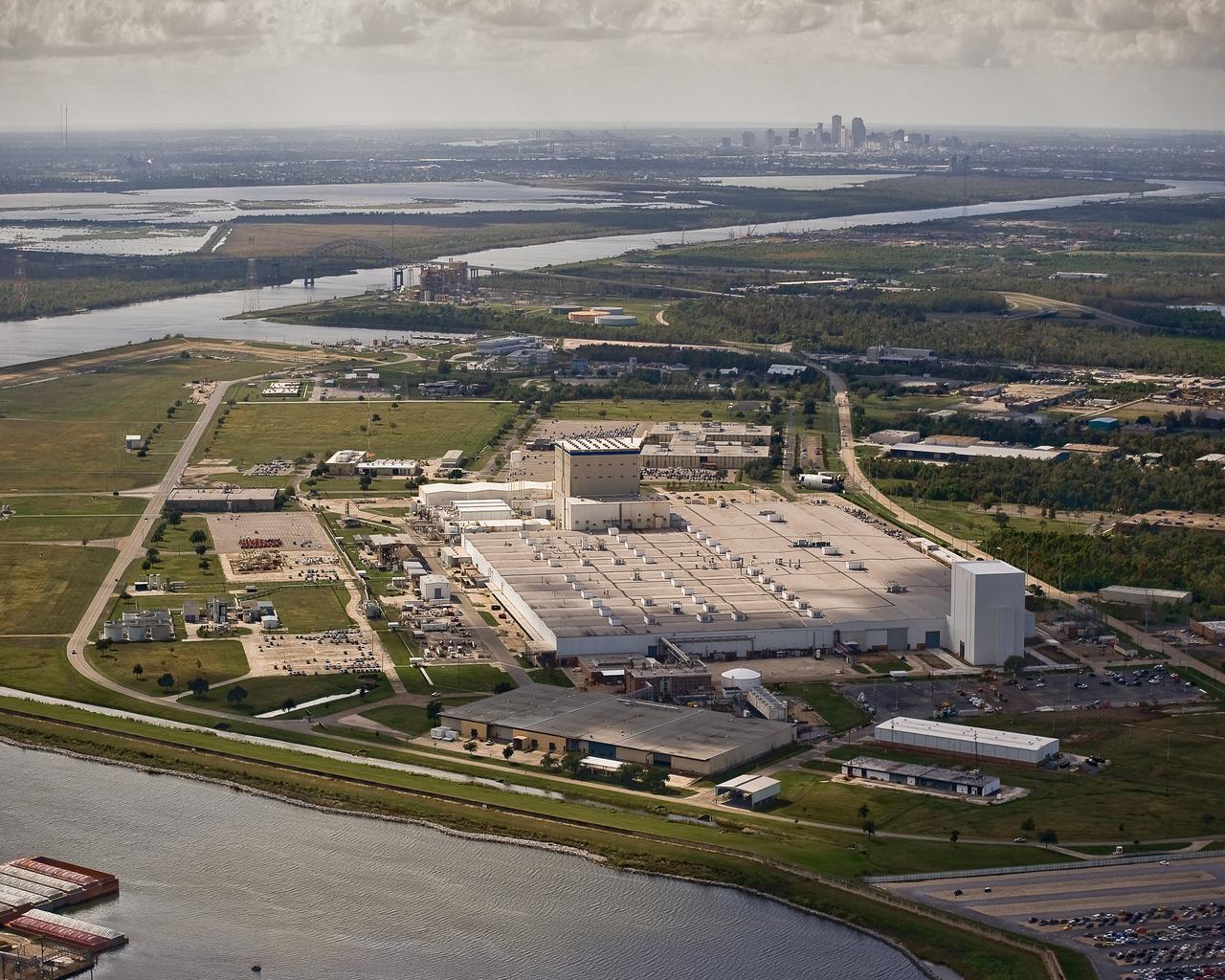

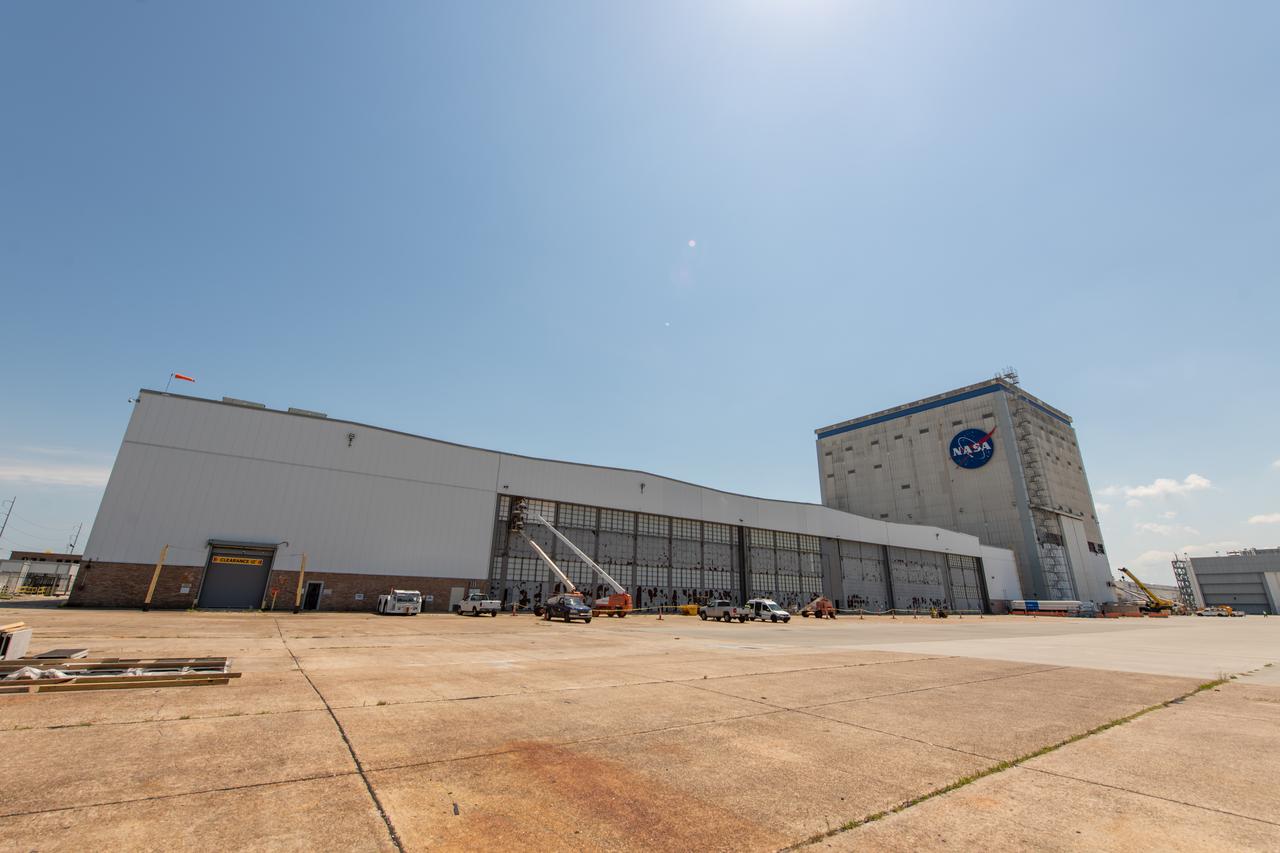
NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility with a view of New Orleans in the background.
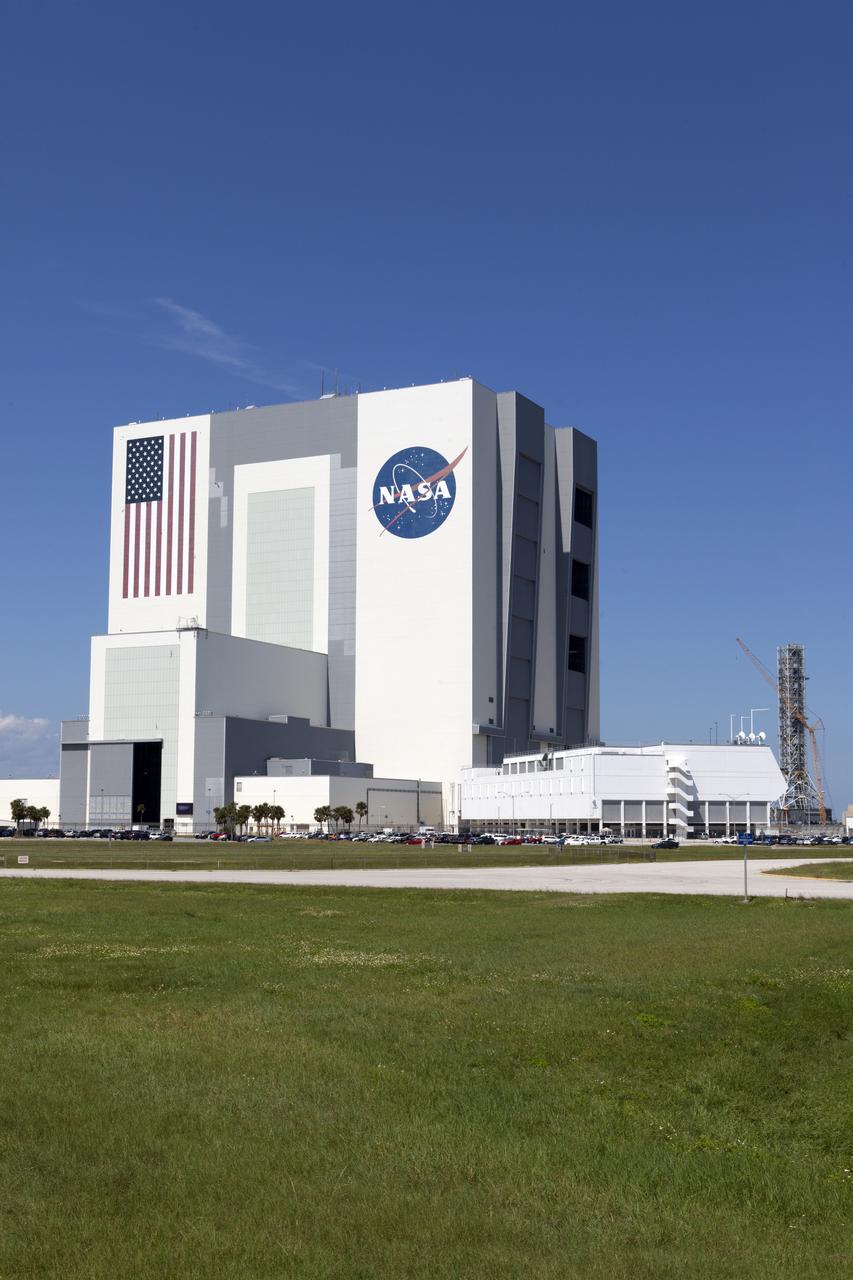

NASA's Vehicle Assembly Building at Kennedy Space Center in Florida was used to assemble and house American-crewed launch vehicles from 1968 to 2011. AT 3,684,883 cubic meters, it is one of the largest buildings in the world by volume. Inside the facility, High Bay 3 is being upgraded and modified to support processing of the agency's Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft.

MAF Director Robert Champion stands in front of the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana – America’s Rocket Factory.
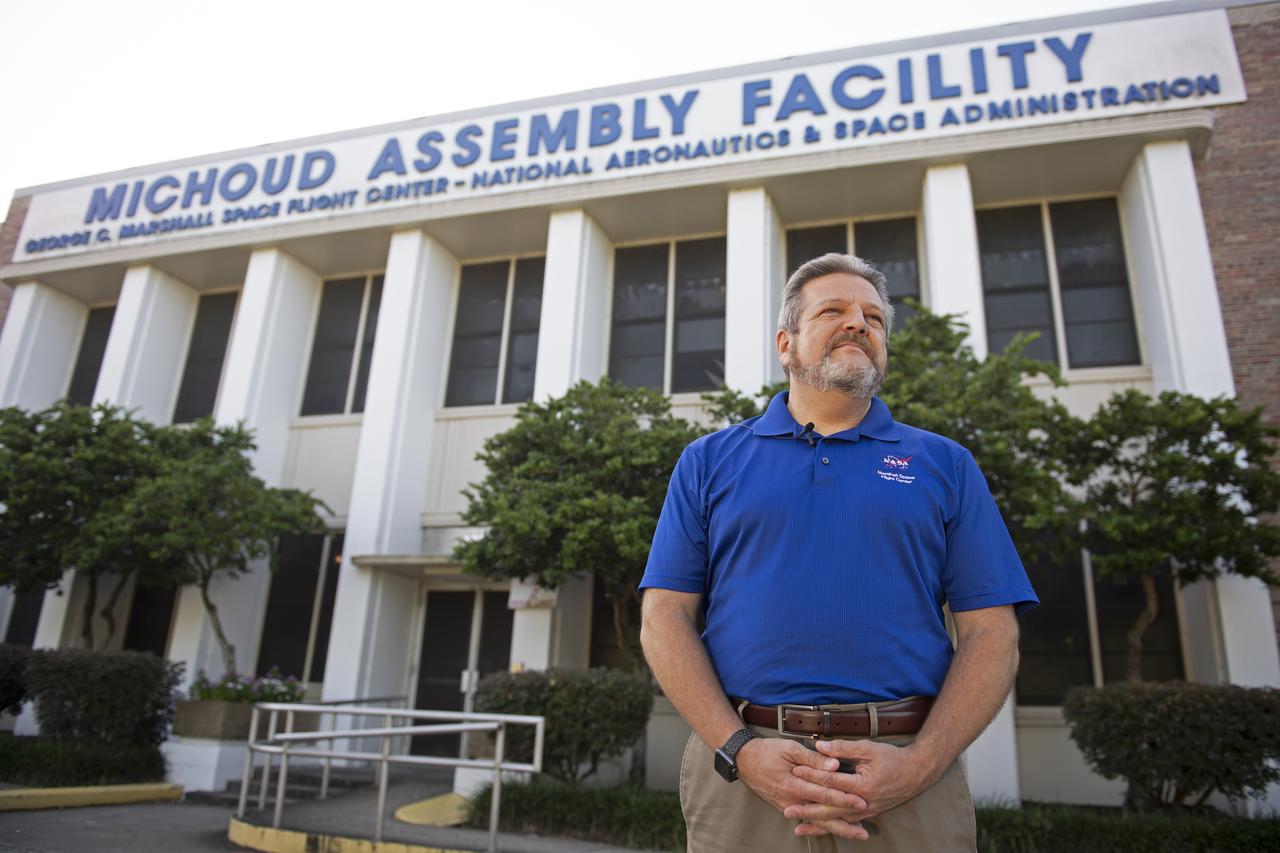

MAF Director Robert Champion stands in front of the Michoud Assembly Facility – America’s Rocket Factory.

MAF Director Robert Champion stands in front of the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana – America’s Rocket Factory.
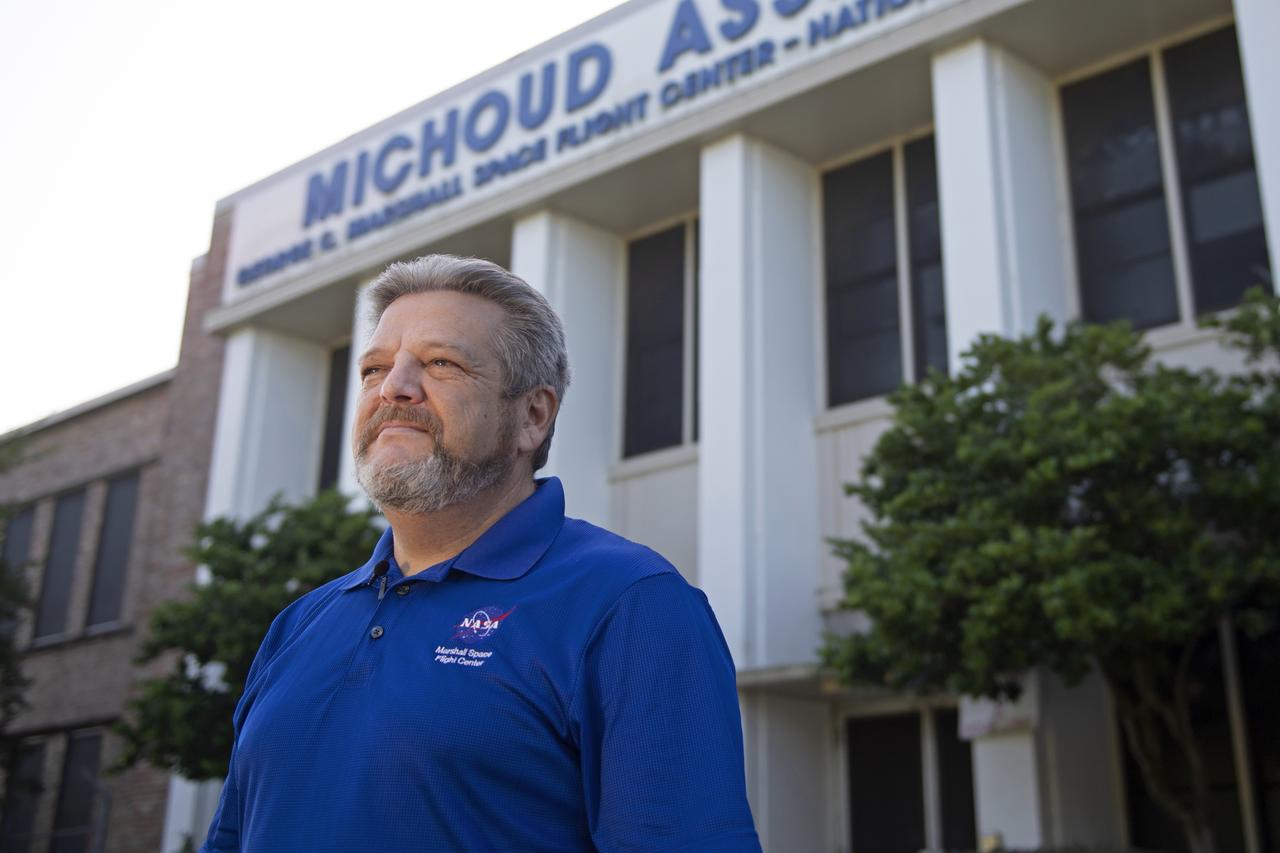

MAF Director Robert Champion stands in front of the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana – America’s Rocket Factory.
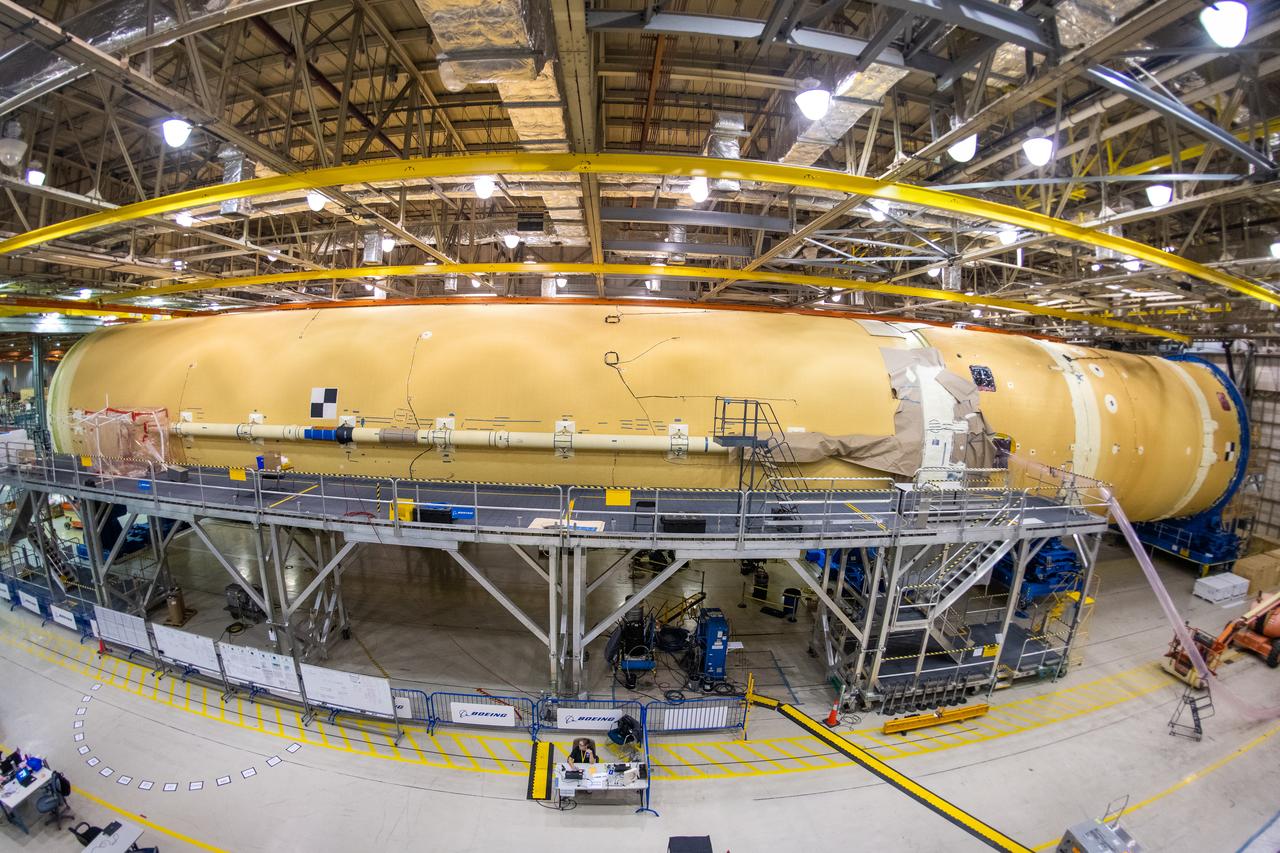

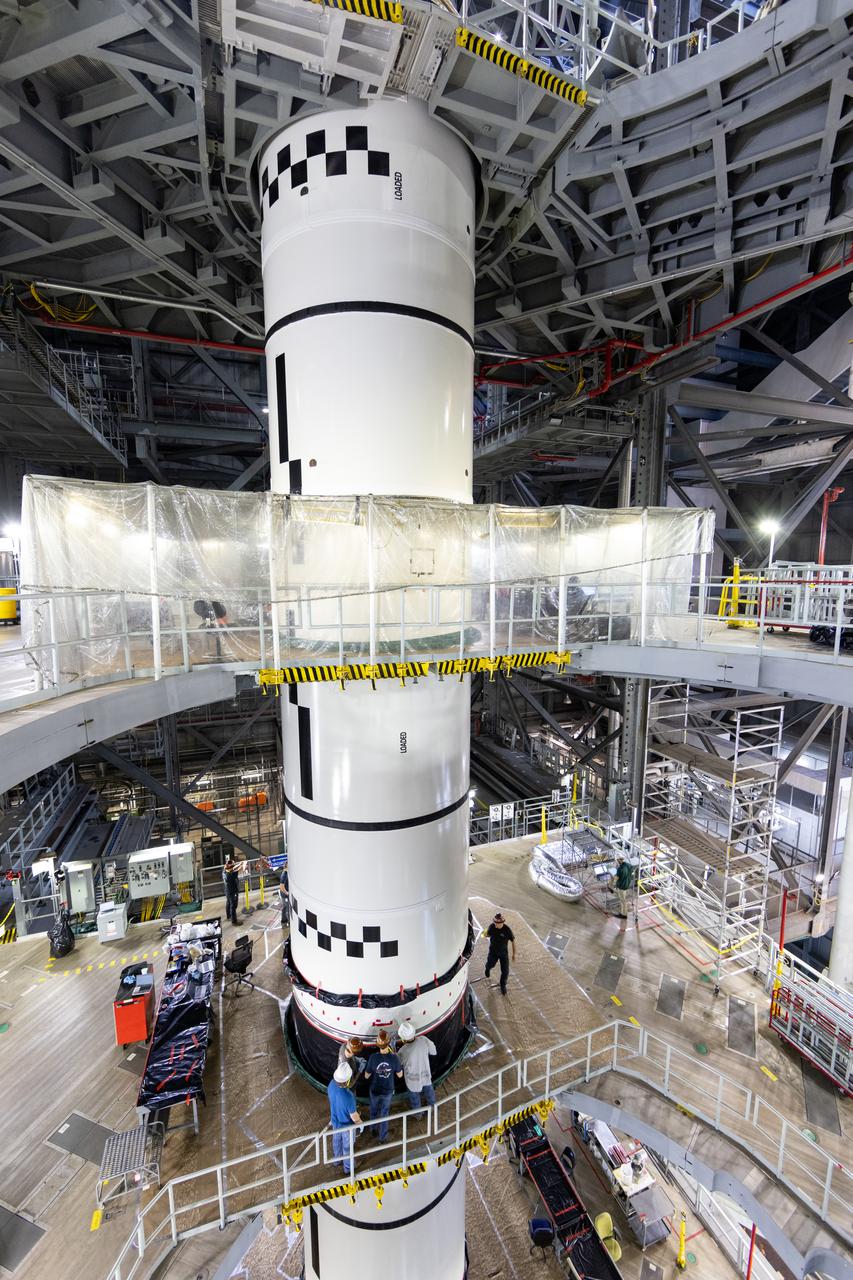
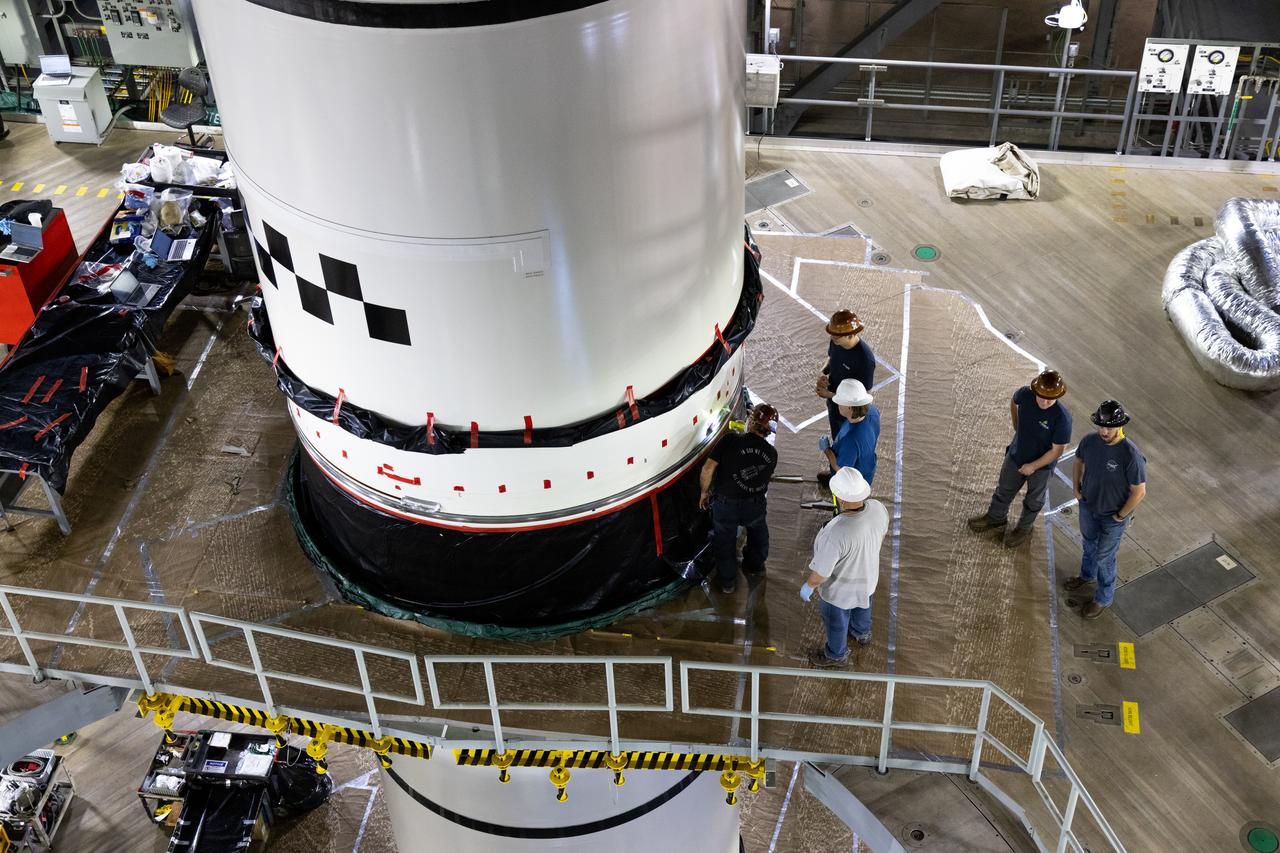
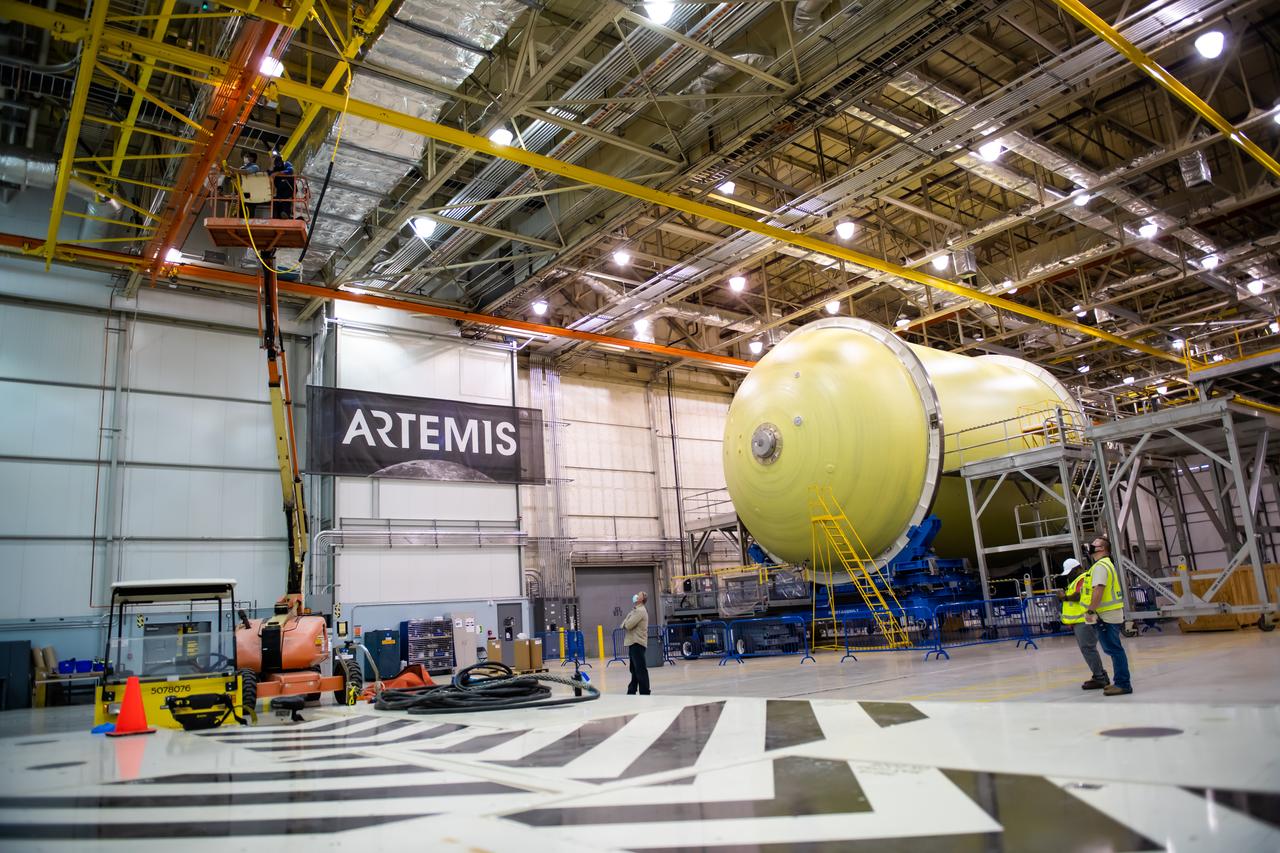
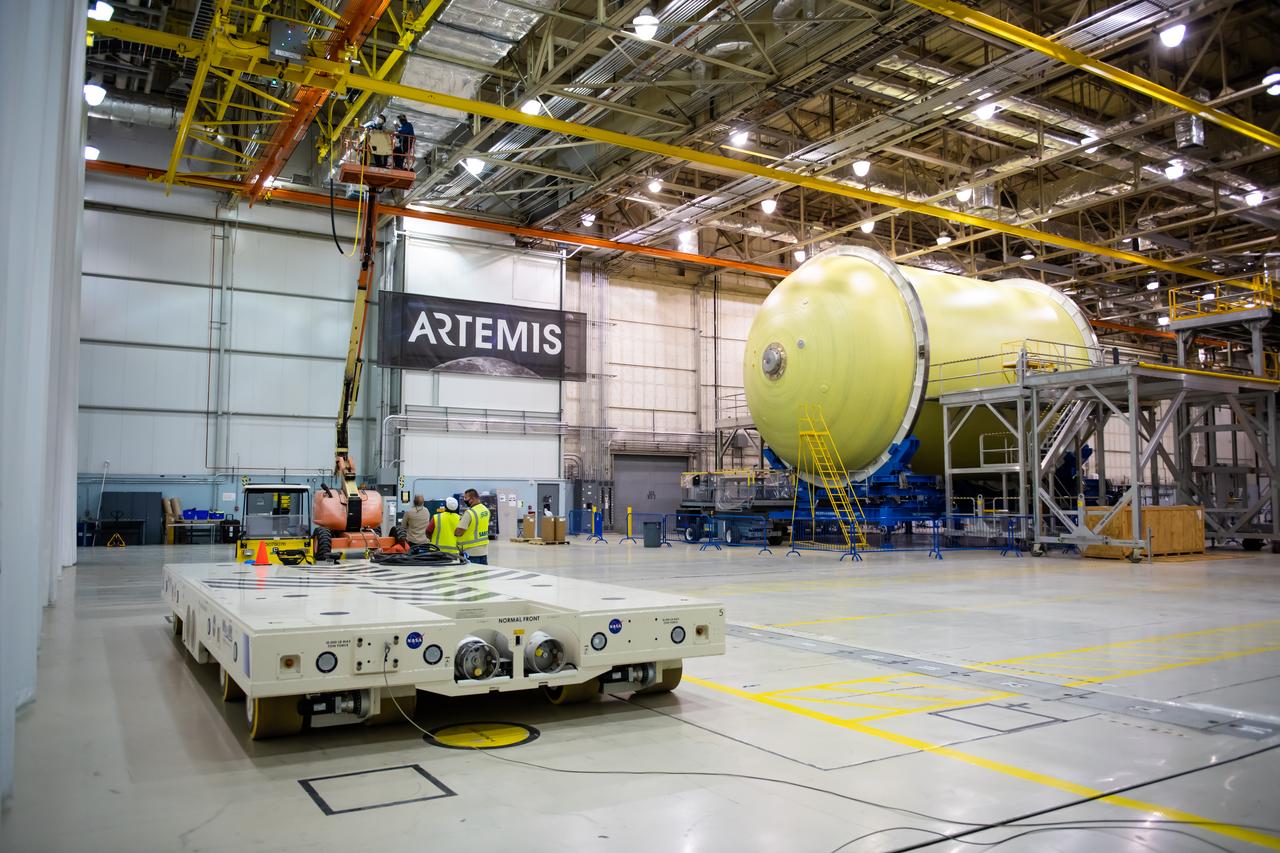
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans completed the “forward join,” which connects structures to form the top part of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage. The first core stage will send Exploration Mission-1, the first integrated flight of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, out beyond the Moon. The forward join mated three structures: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and intertank. This milestone marks the beginning of integration and assembly of the massive, 212-foot-tall SLS core stage, which will include the rocket’s four RS-25 rocket engines, propellant tanks and flight computers. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. These two parts of the core stage will then be assembled to form the largest stage NASA has ever built.
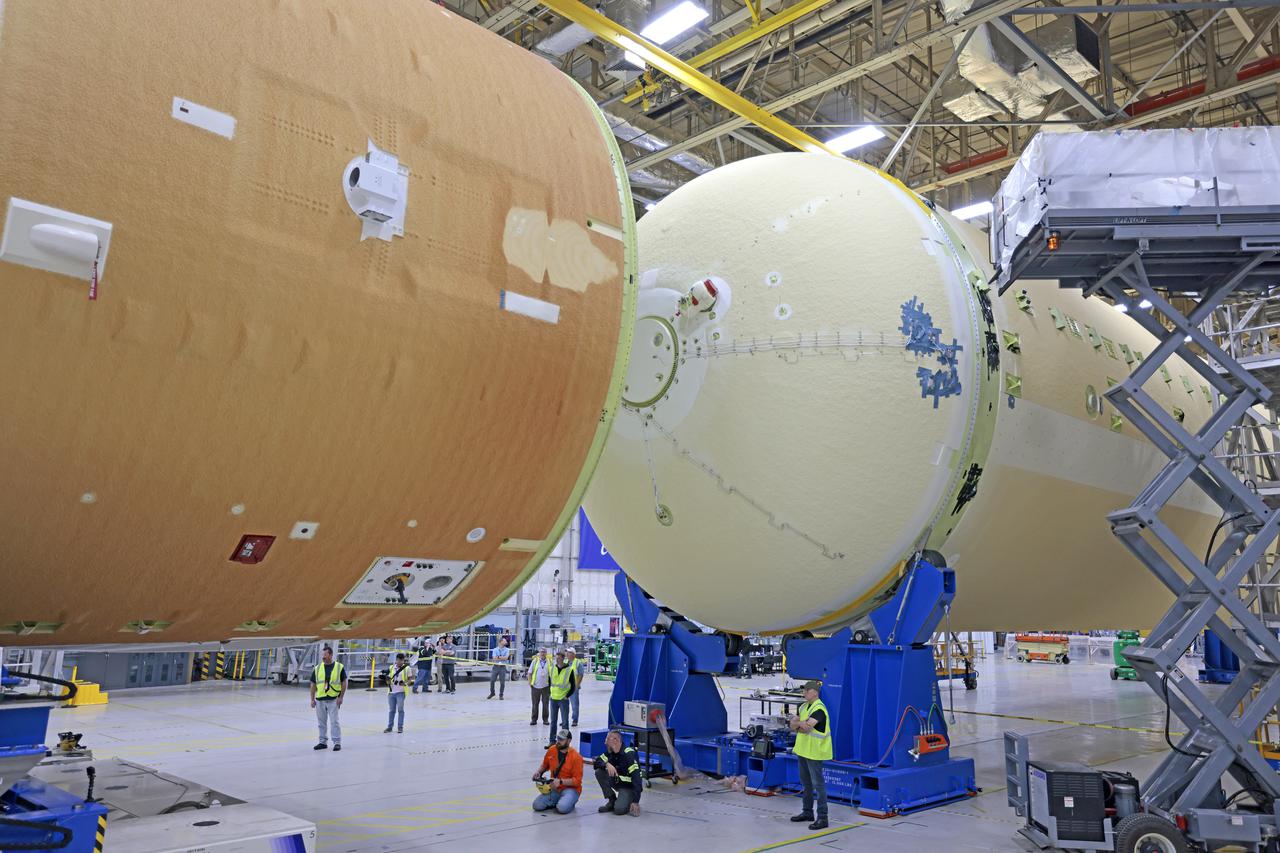

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
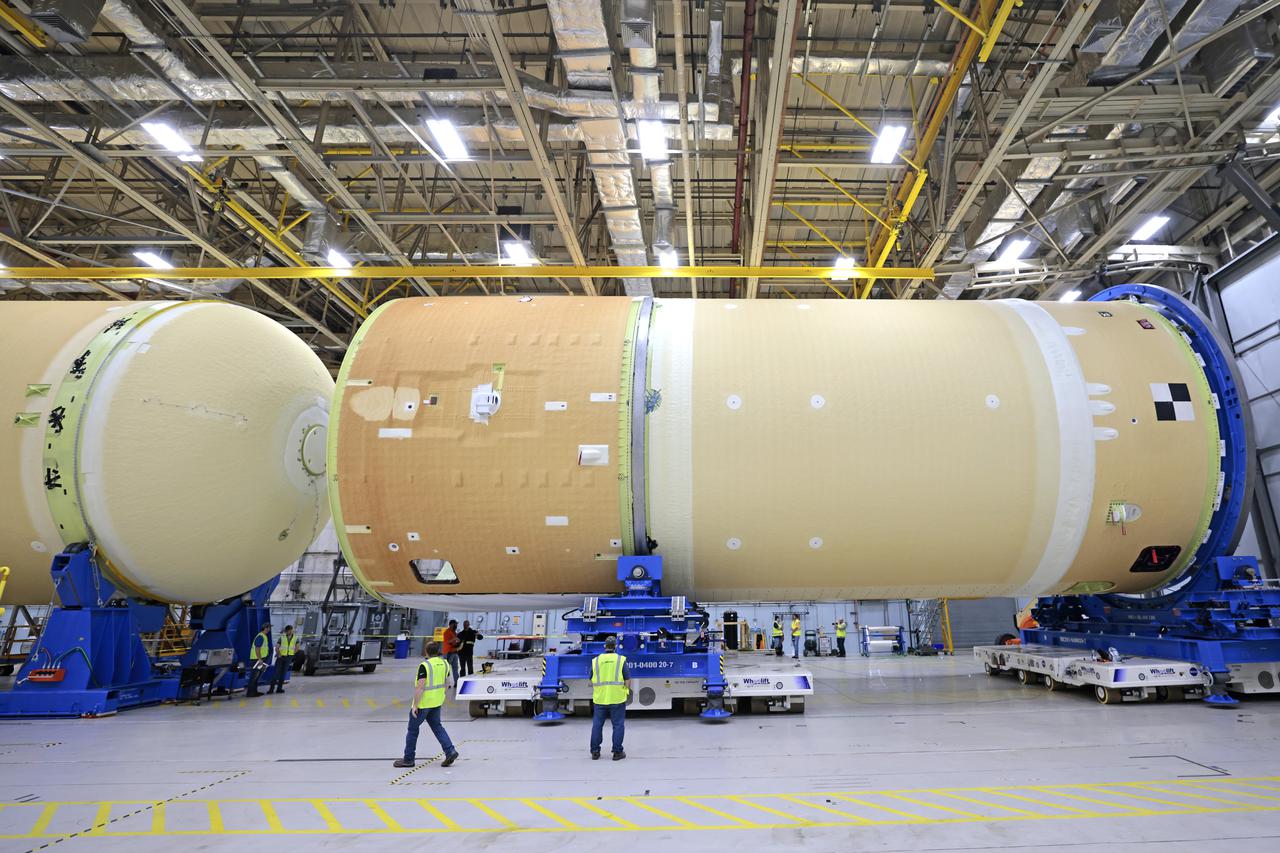

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
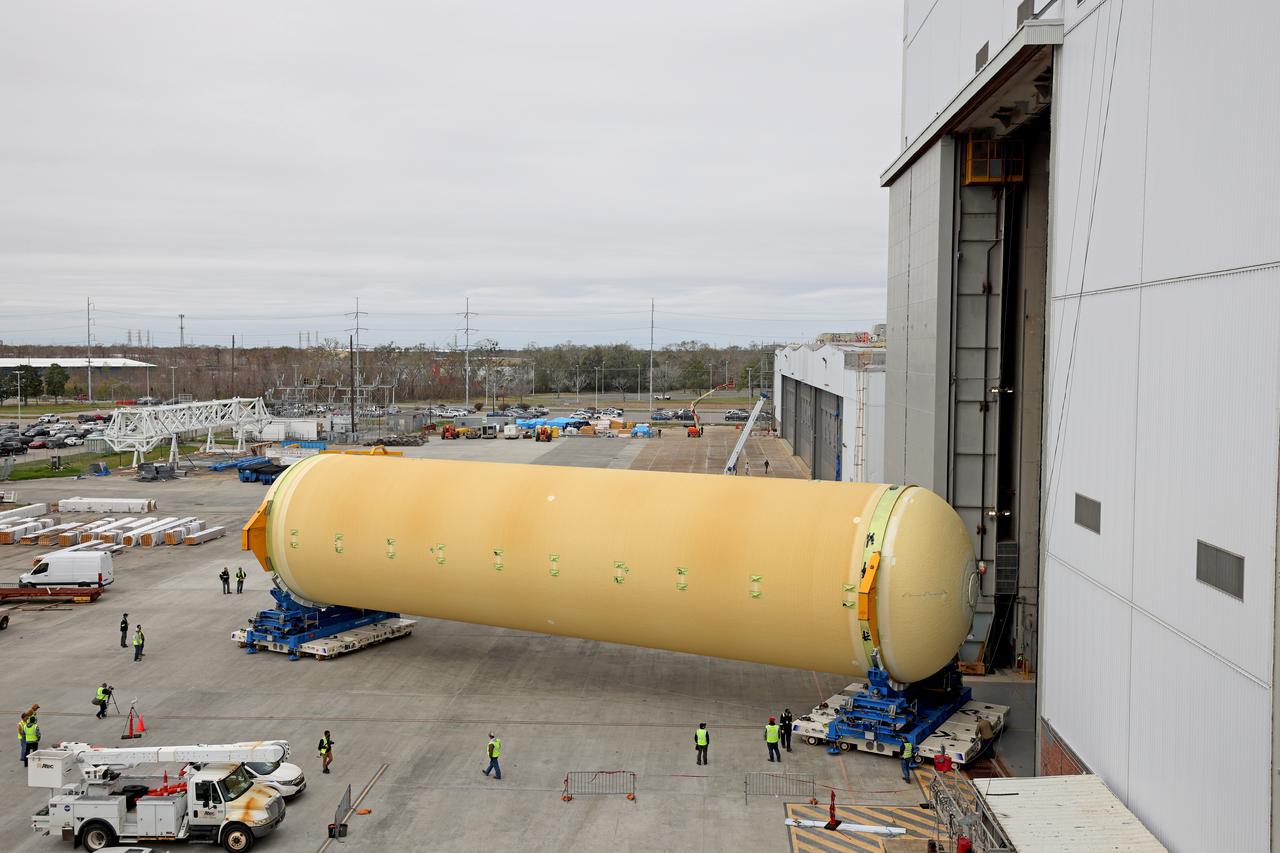

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
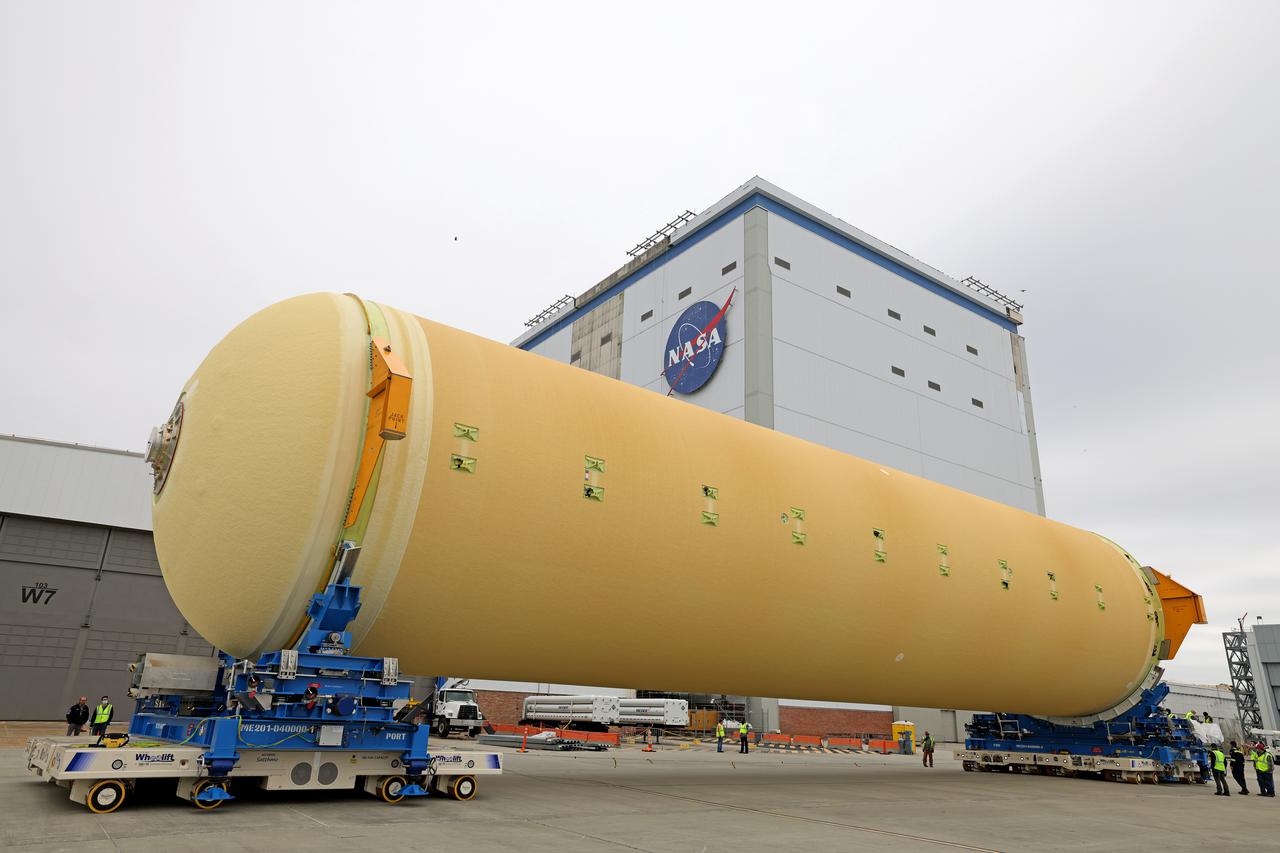

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
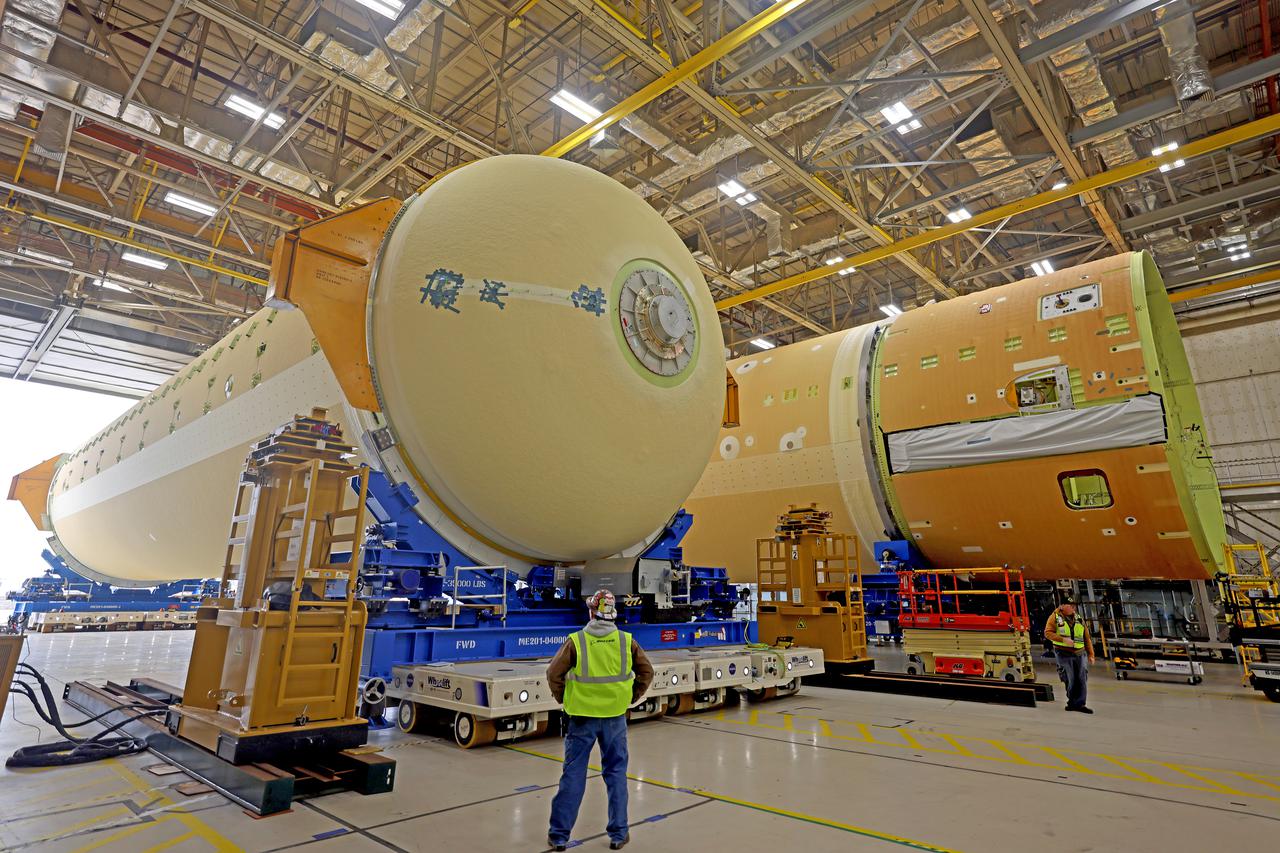

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
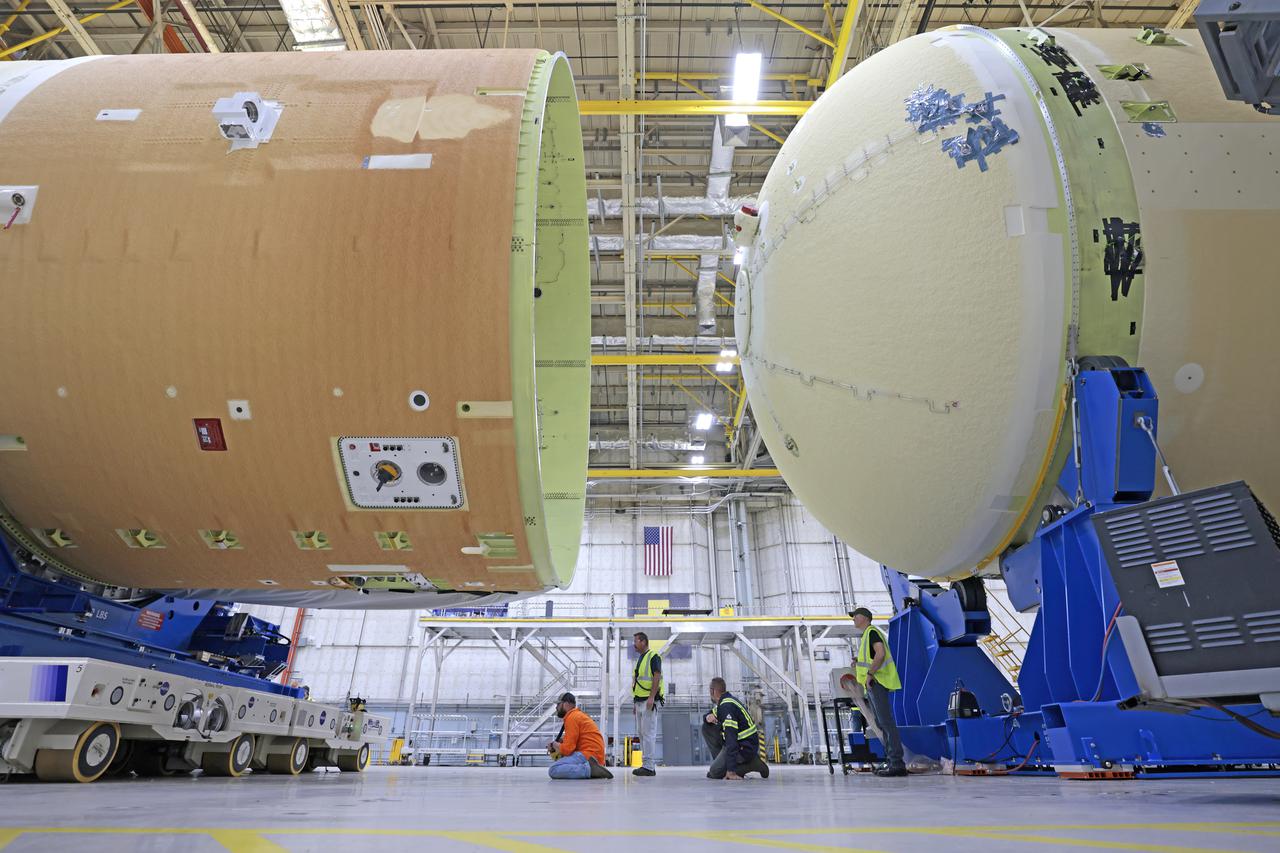

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
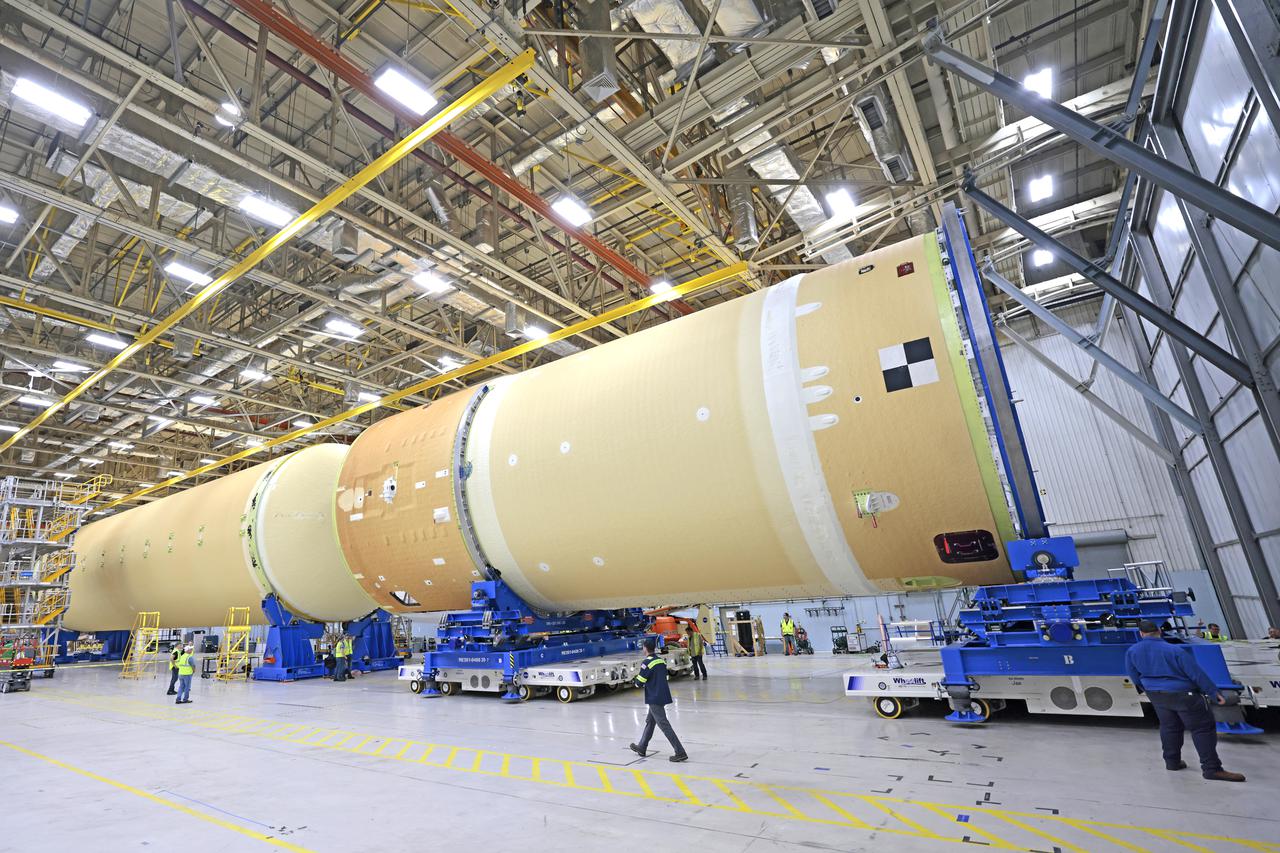

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
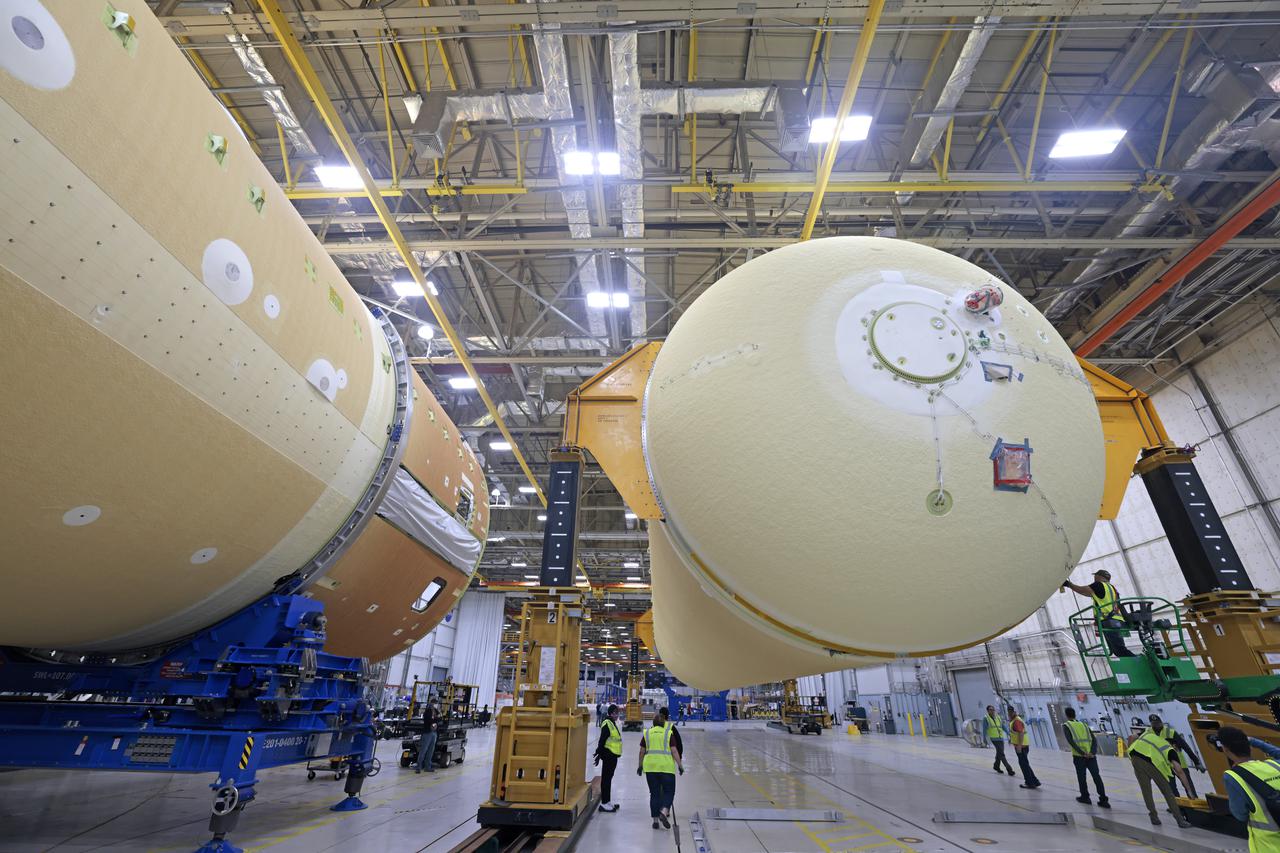

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
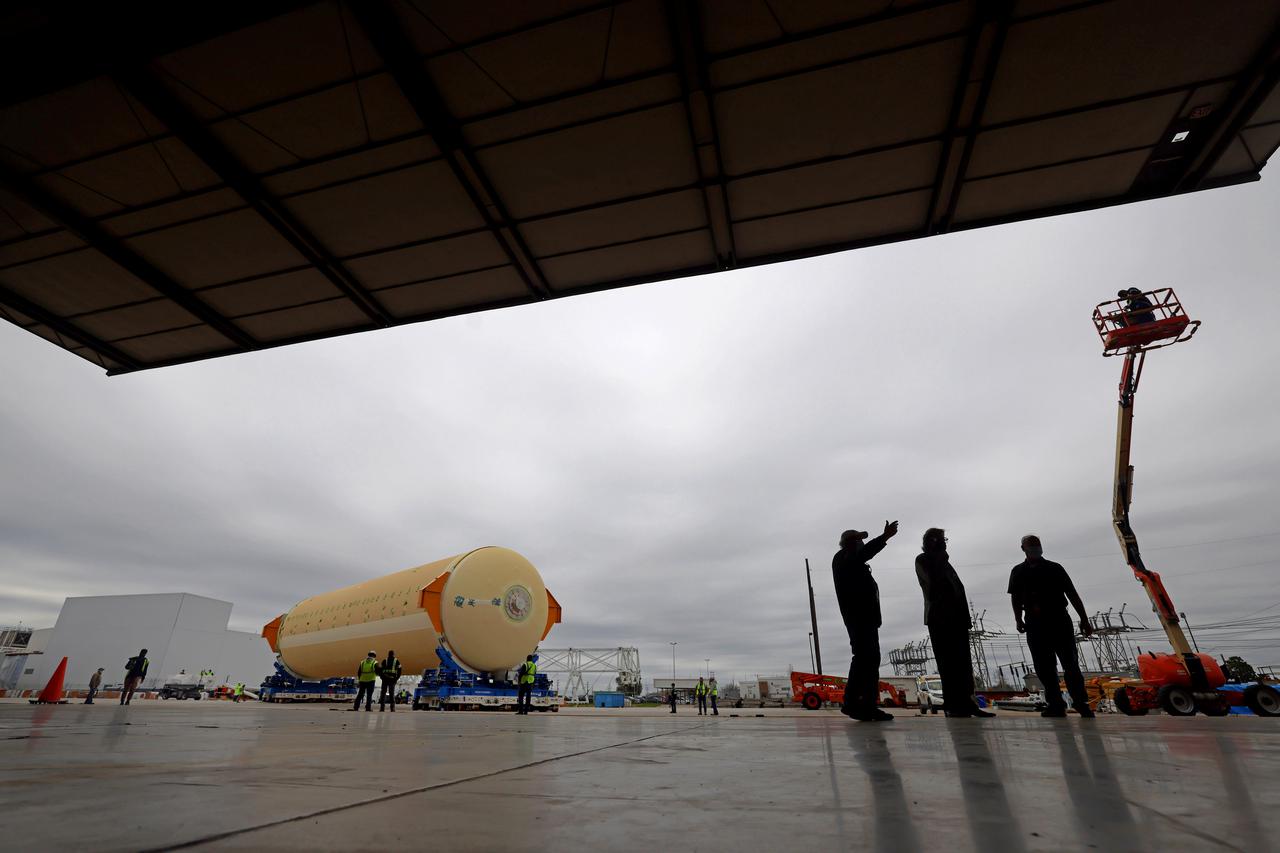

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
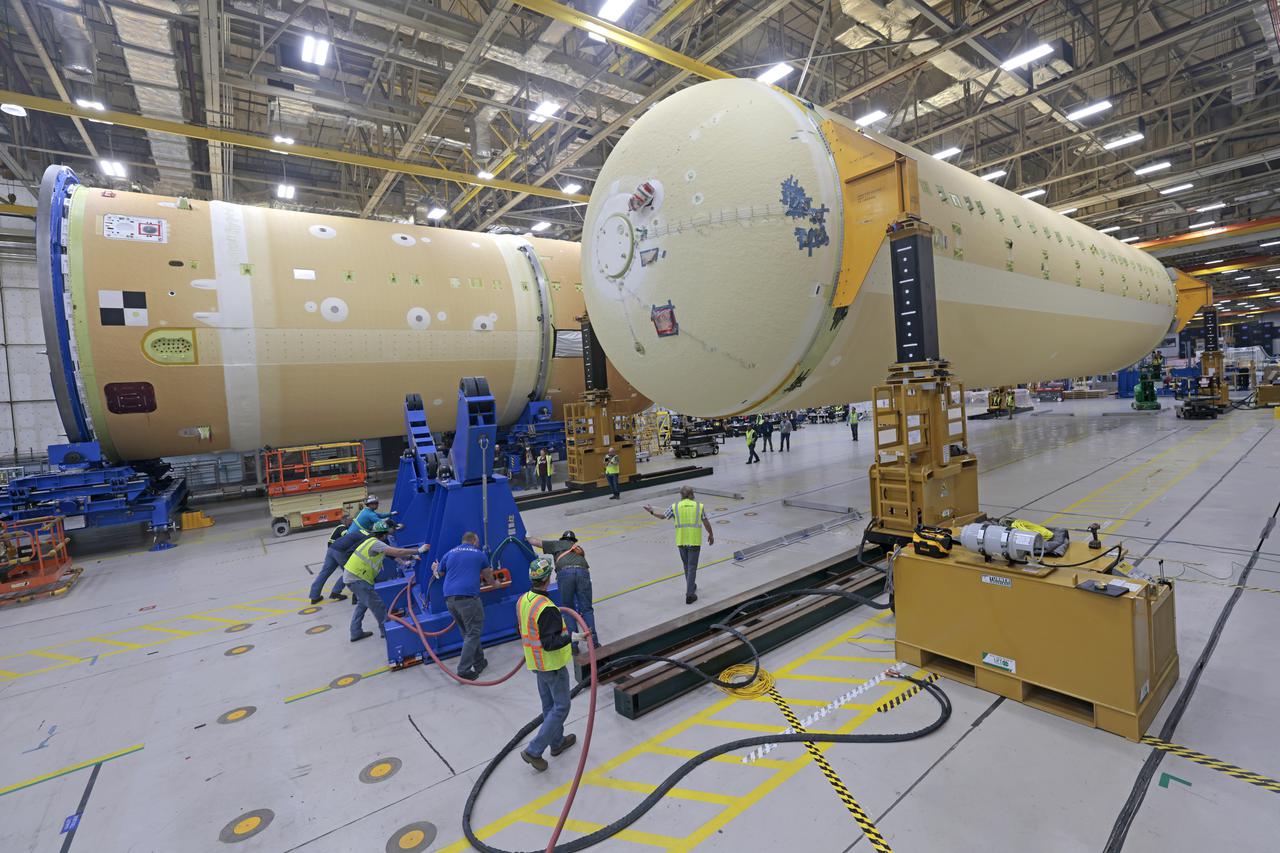

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
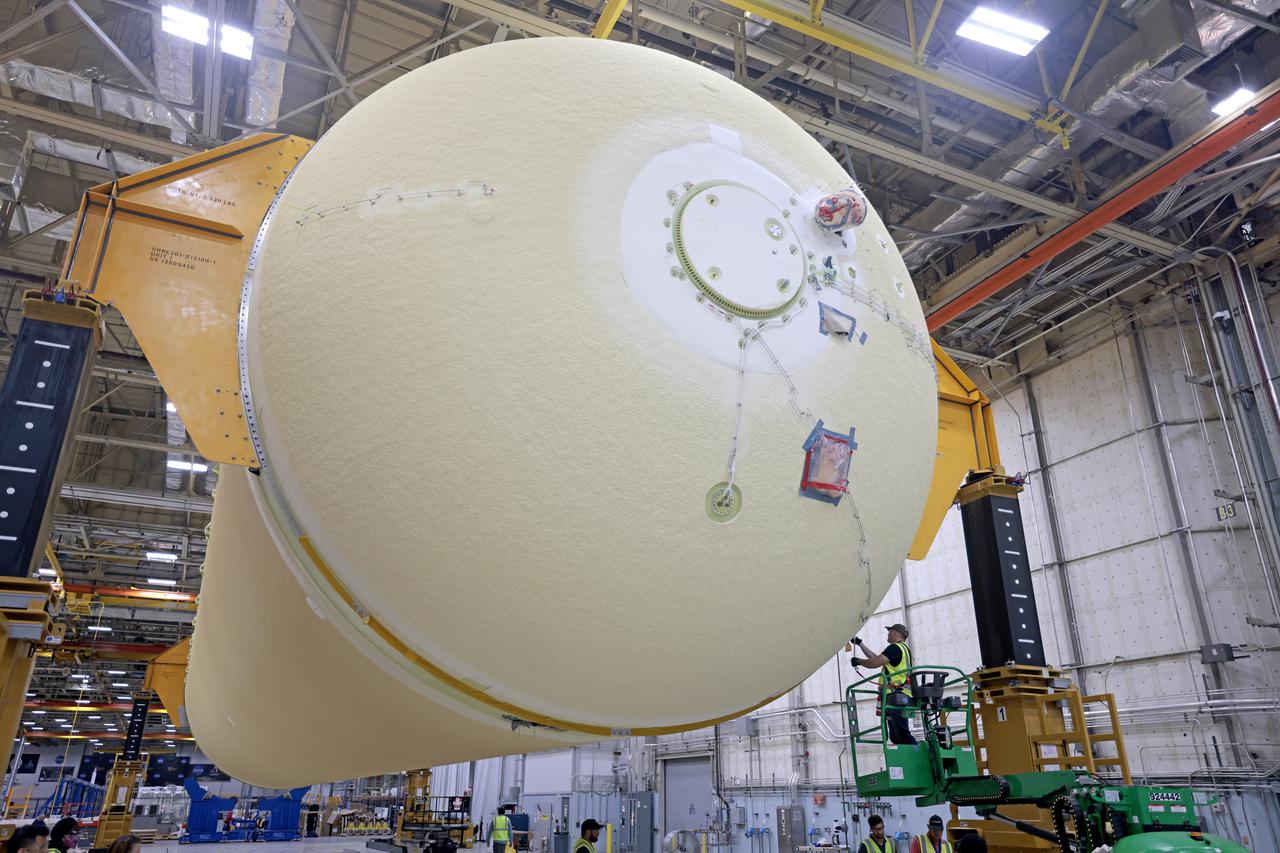

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
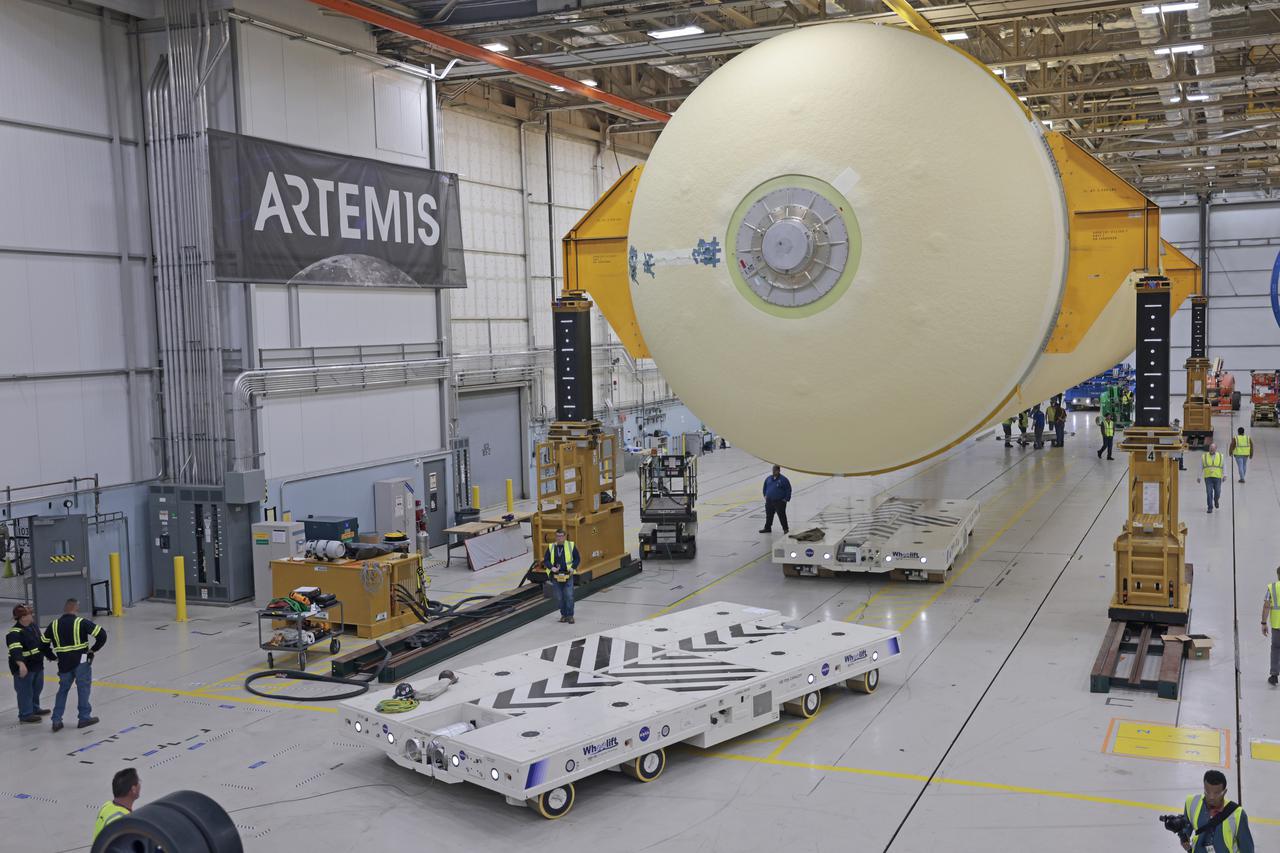

NASA is preparing major pieces of the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage to be joined as part of assembling the core stage for the Artemis II mission that will send crews to lunar orbit. Crews will soon connect the forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank in the final assembly area at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. When this process is completed, four of the five large structures that make up the core stage will be joined. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. This forward assembly will be joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, the largest part of the stage that holds more than 500,000 gallons of cryogenic propellant. To compete the Artemis II core stage, engineers will add the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, Together, with the SLS twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. For more on the core stage: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/multimedia/infographics/corestage101.html Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.

Teams lift a liquid hydrogen tank barrel into the Vertical Assembly Center at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, on July 25, 2025. Inside the center, teams will perform a circumferential weld to connect the barrel to the previously loaded forward dome. The barrel is one of five barrels, which along with the forward and aft domes, make up the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage manufactured at the site. Artemis will pave the way for a long-term human presence on the lunar surface while ushering in the Golden Age of Innovation and Exploration.
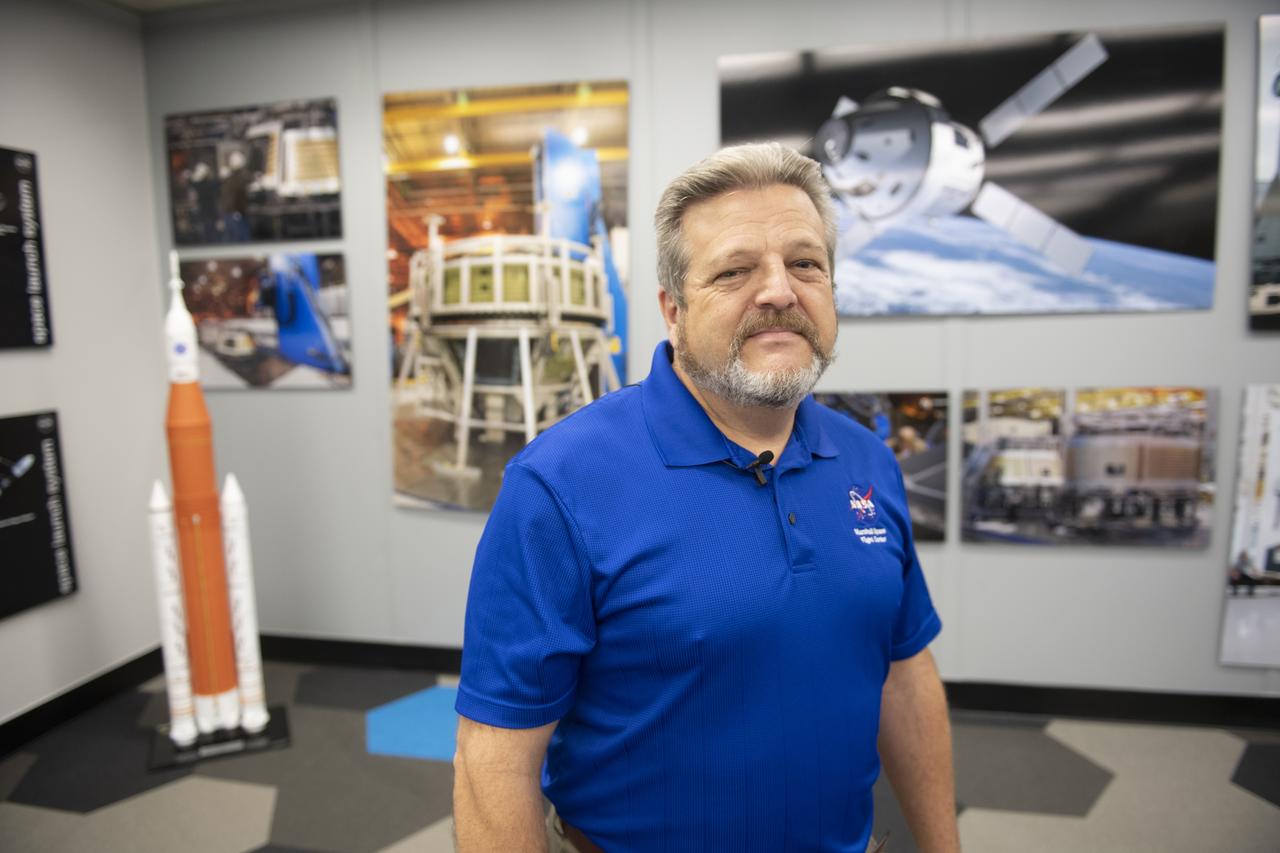

MAF Director Robert Champion stands within the Michoud Assembly Facility model room to showcase the Artemis program, Space Launch System (SLS) hardware, and facility resources of America’s Rocket Factory.

NASA Dawn spacecraft being assembled.

Aerial shots of NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility
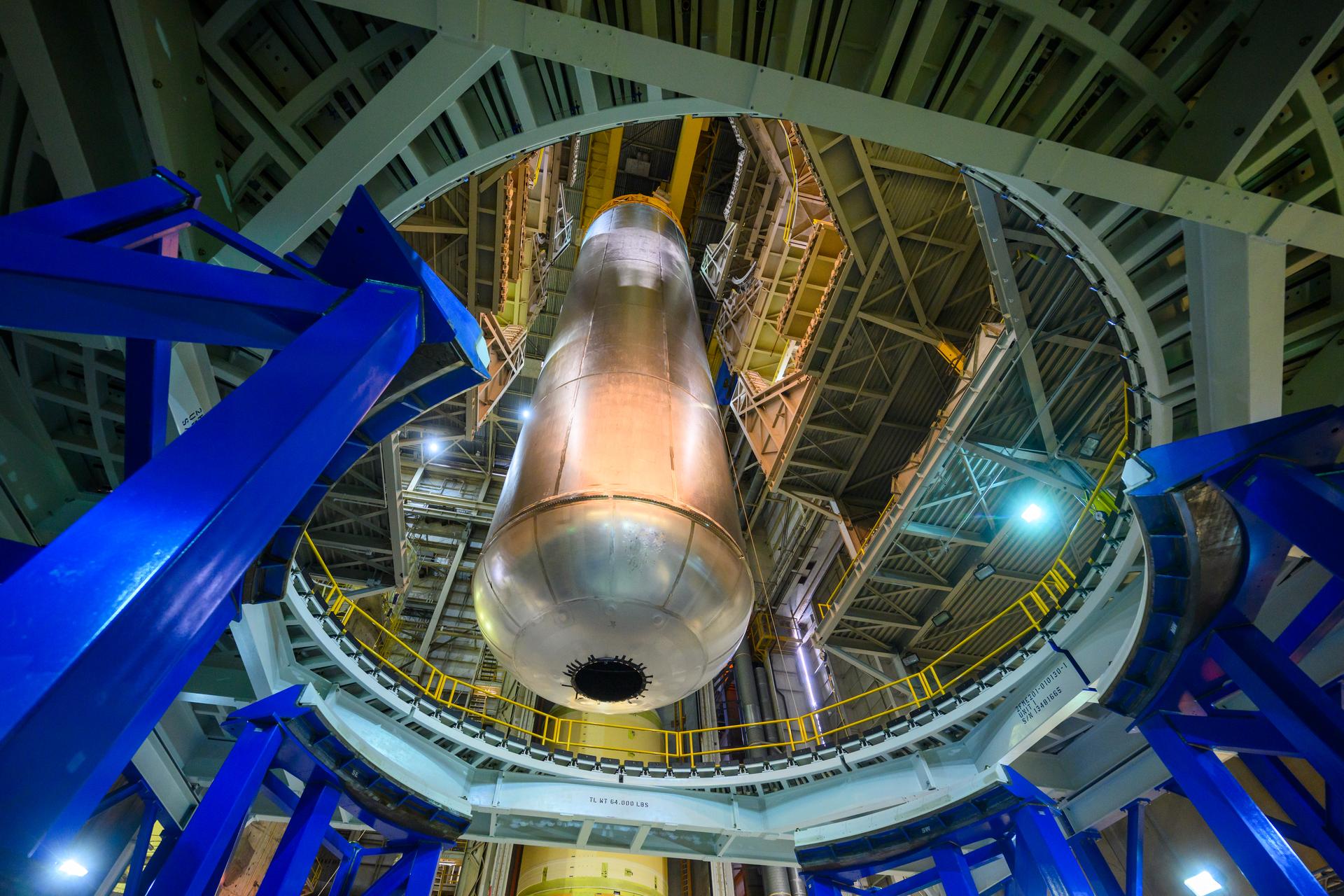

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration.

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the 130-foot-tall liquid hydrogen tank off the vertical assembly center on Nov. 14. This is the fourth liquid hydrogen tank manufactured at the facility for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The completed tank will be loaded into a production cell for technicians to remove the lift tool, perform dimensional scans, and then install brackets, which will allow the move crew to break the tank over from a vertical to a horizontal configuration.

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans reinstalled the iconic NASA meatball logo to the side of the 43-acre factory following a months-long project to replace the corrugated asbestos paneling original to the building’s construction on the outer façade of the facility. The new paneling is an insulated metal sandwich panel, which provides an increased insulation R-value. The new fastening system can withstand significant wind loads, adding greater protection against hurricanes, tornados, and other storm-related events common to the area; and is critical to help protect vital hardware for the Space Launch System rockets and the Orion Spacecrafts manufactured at Michoud for NASA’s Artemis missions, which will land the first woman and first person of color on the moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
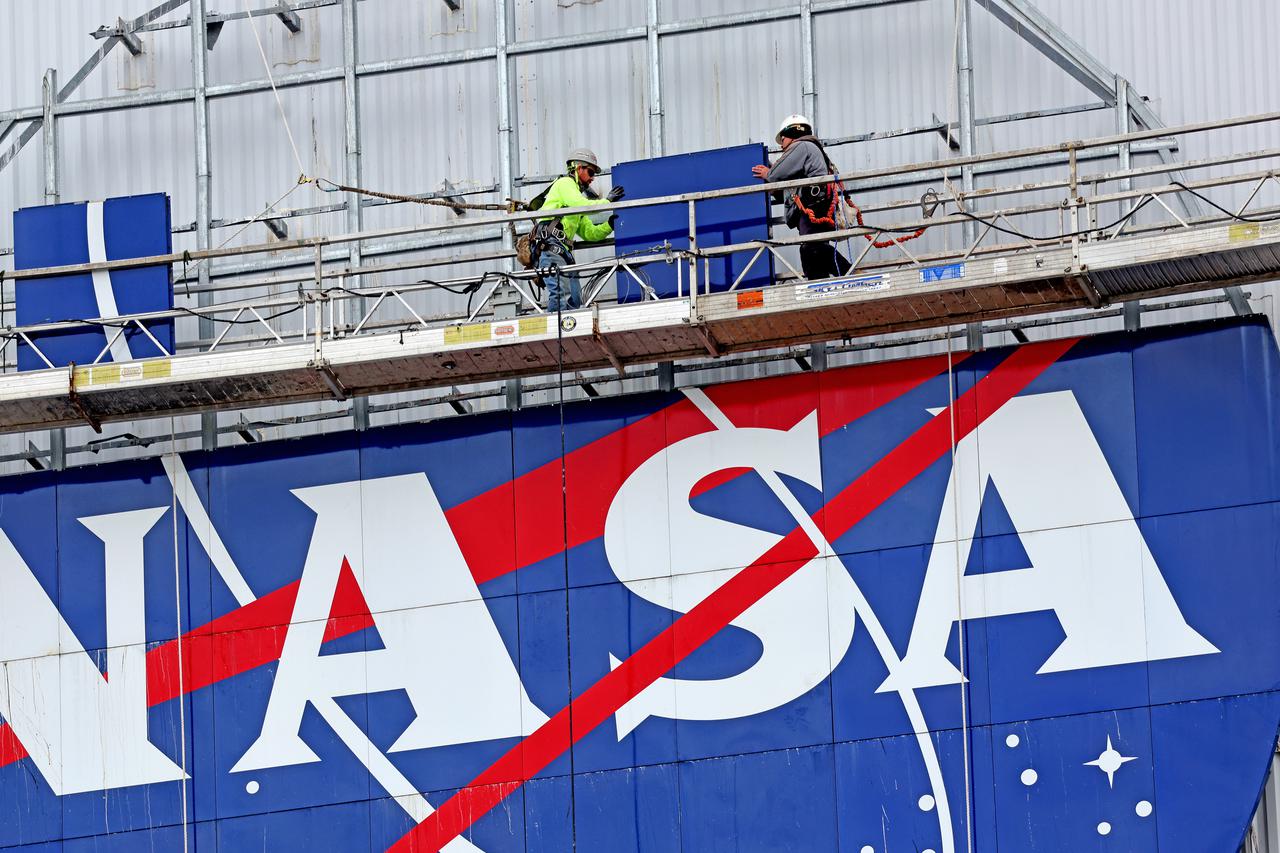

Crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans reinstall the iconic NASA meatball logo to the side of the 43-acre factory following a months-long project to replace the corrugated asbestos paneling original to the building’s construction on the outer façade of the facility. The new paneling is an insulated metal sandwich panel, which provides an increased insulation R-value. The new fastening system can withstand significant wind loads, adding greater protection against hurricanes, tornados, and other storm-related events common to the area; and is critical to help protect vital hardware for the Space Launch System rockets and the Orion Spacecrafts manufactured at Michoud for NASA’s Artemis missions, which will land the first woman and first person of color on the moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

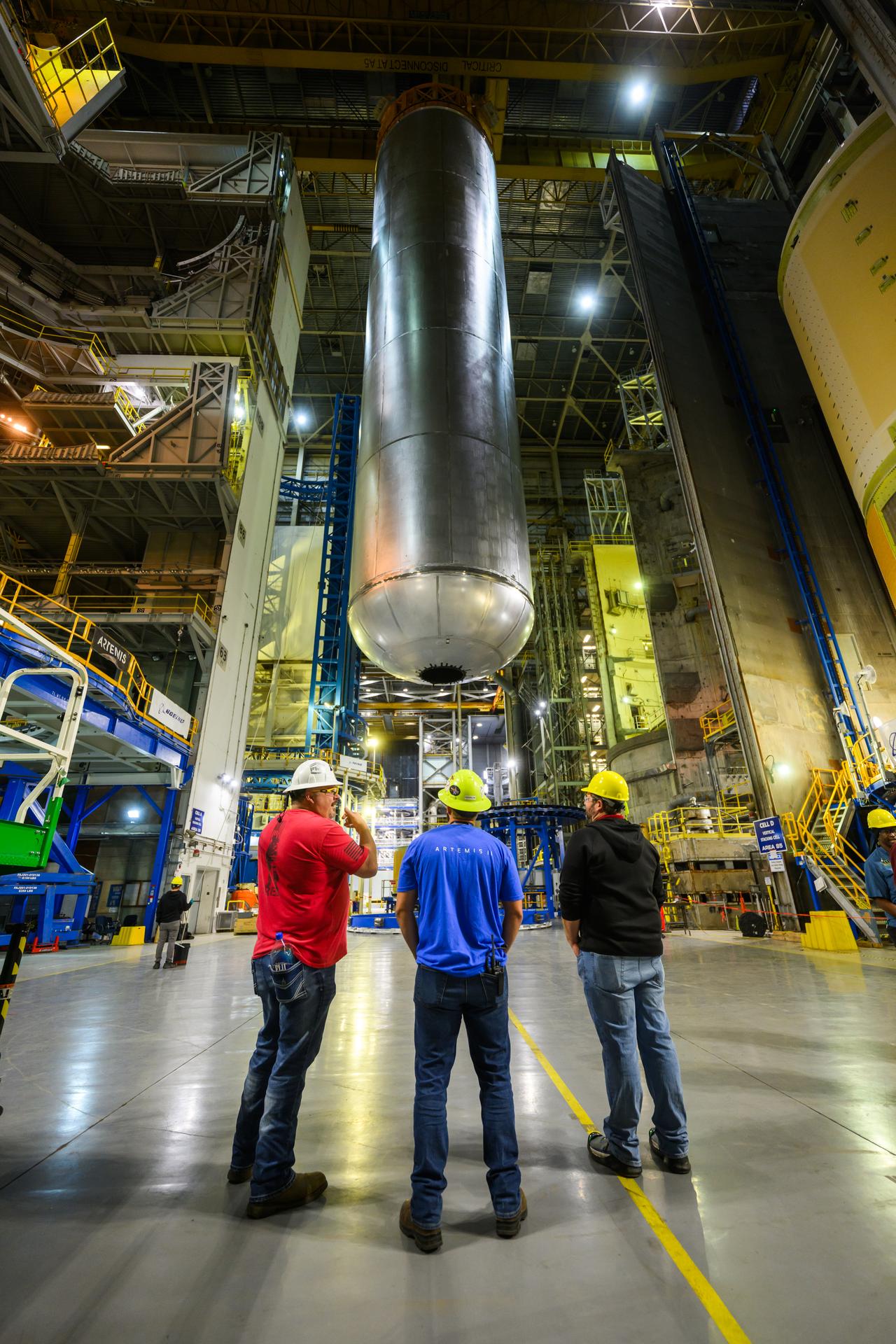
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
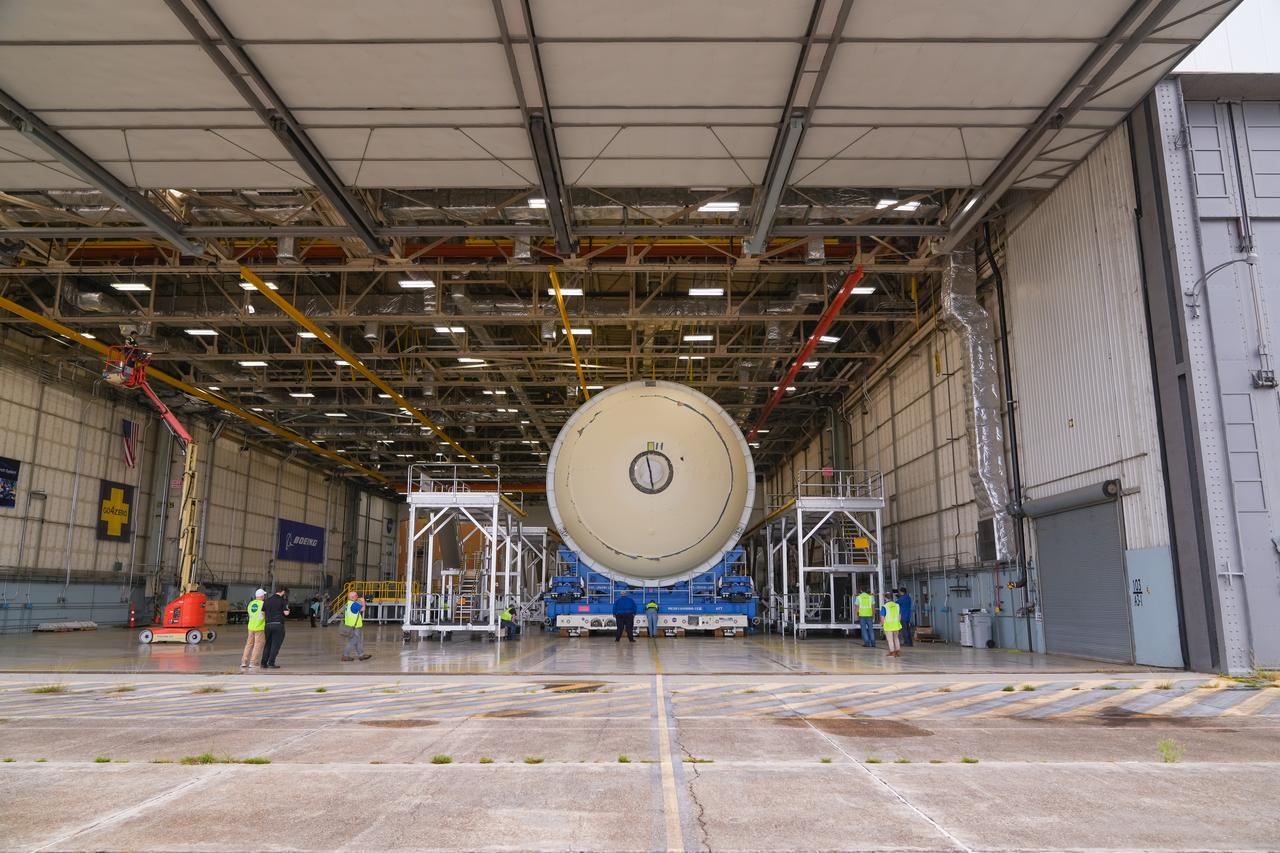

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
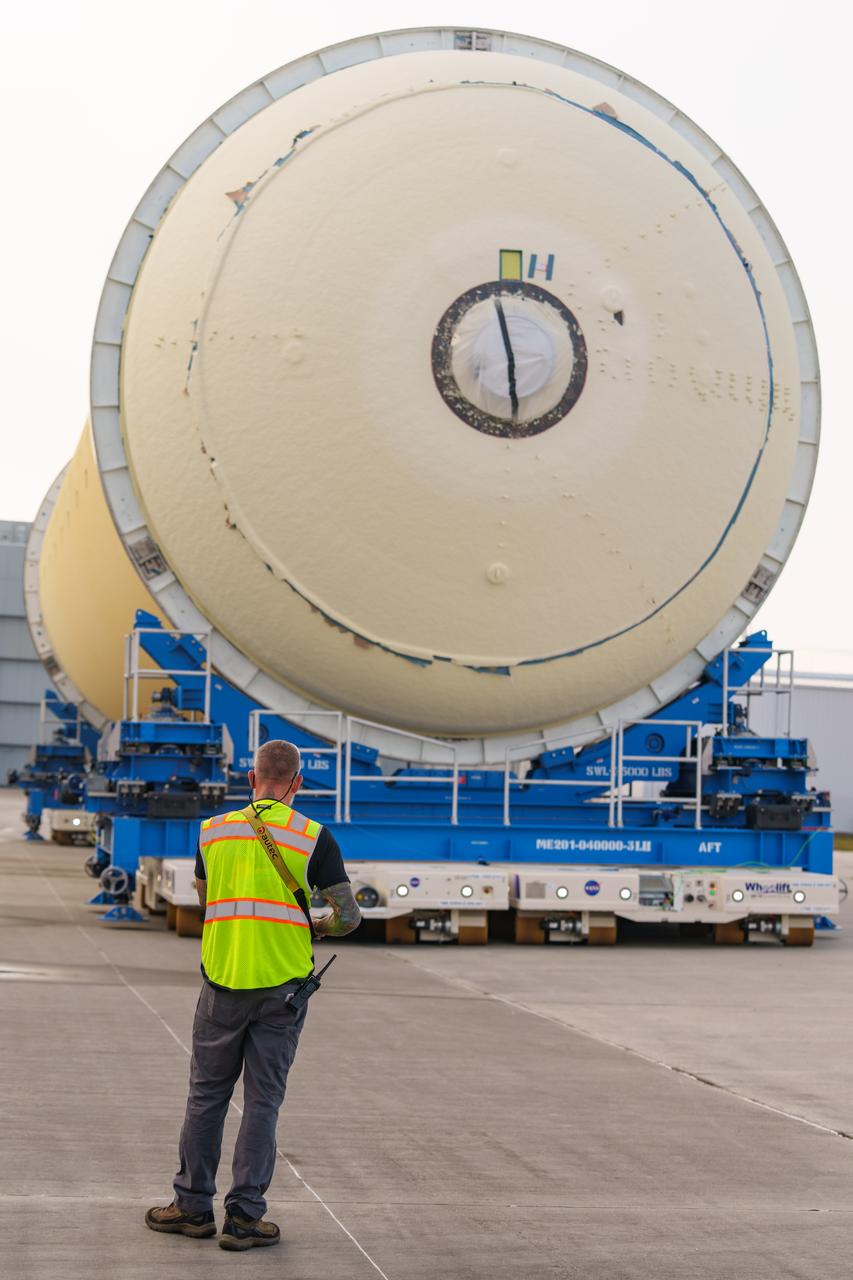

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
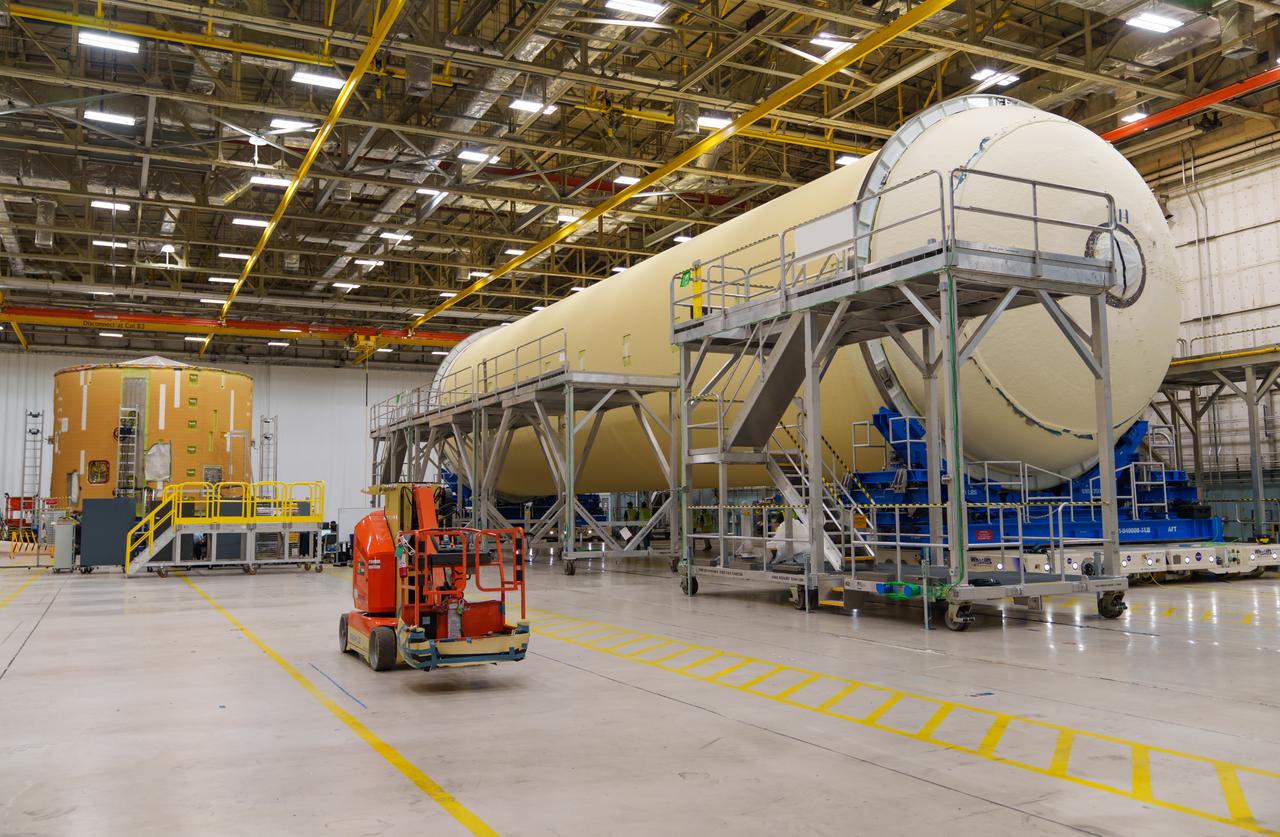

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
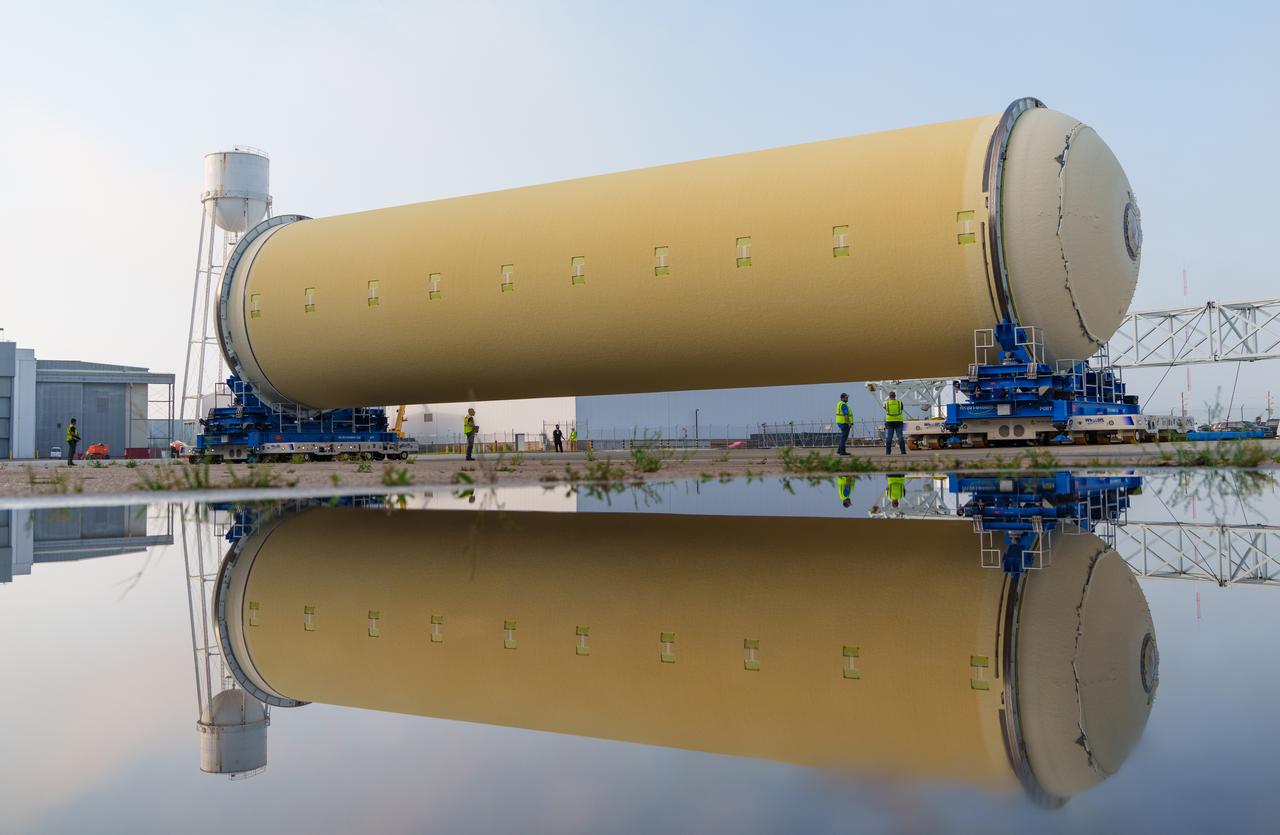

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
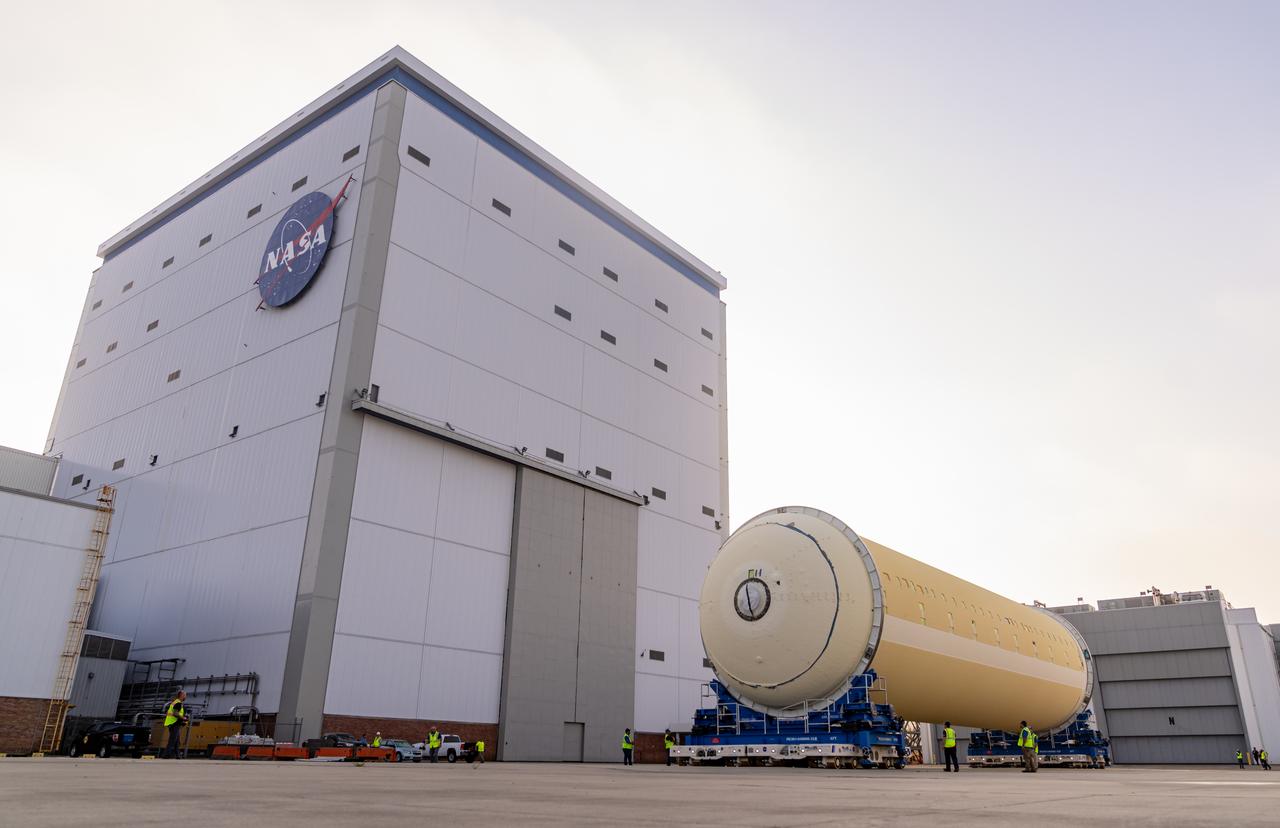

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
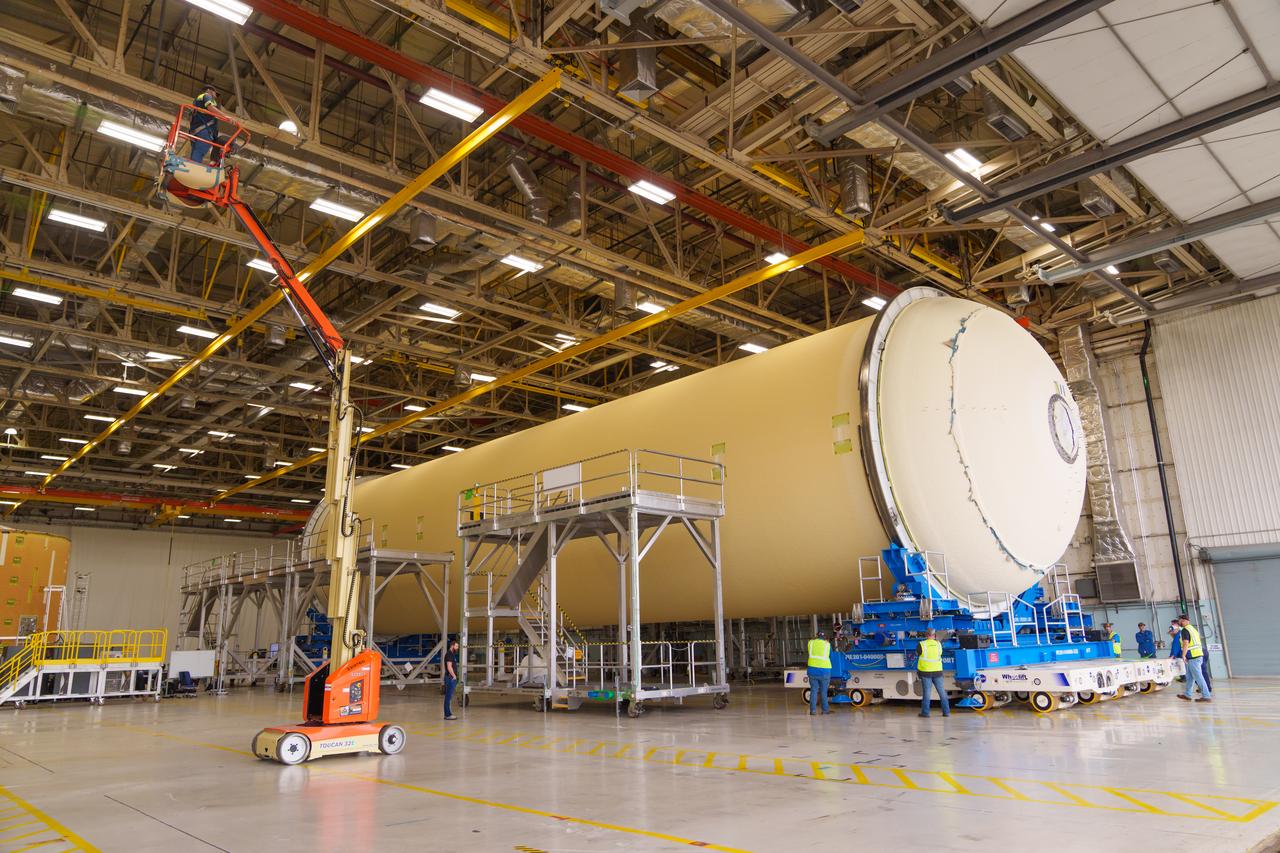

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
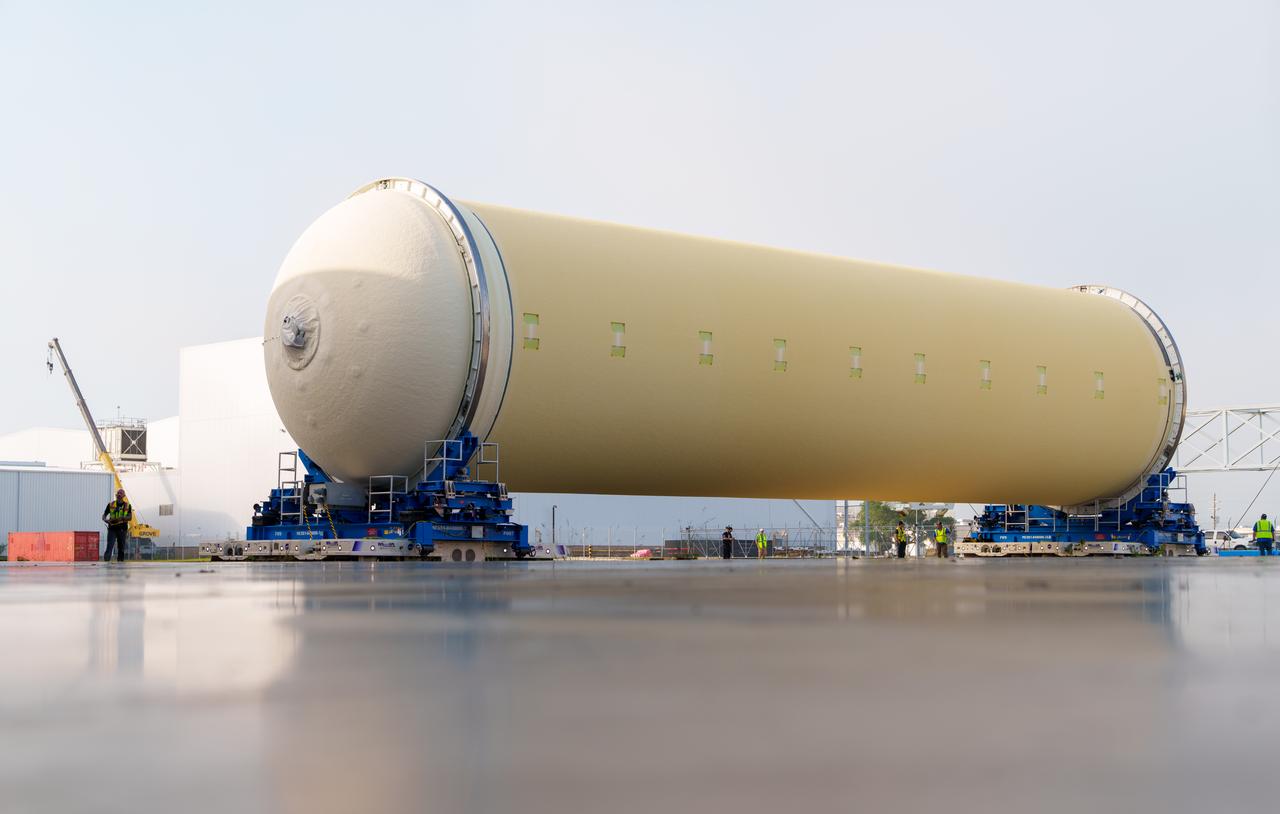

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
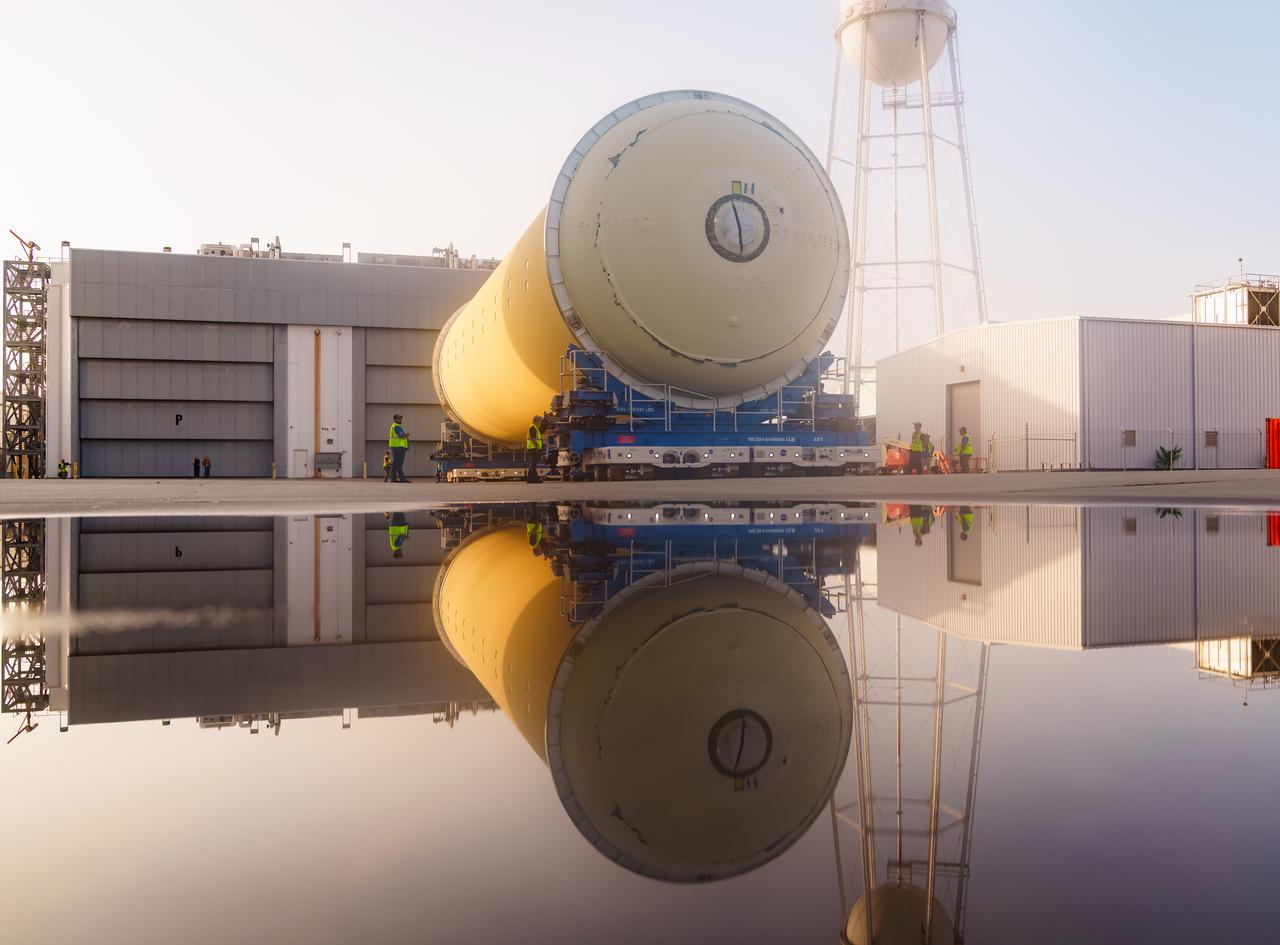

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
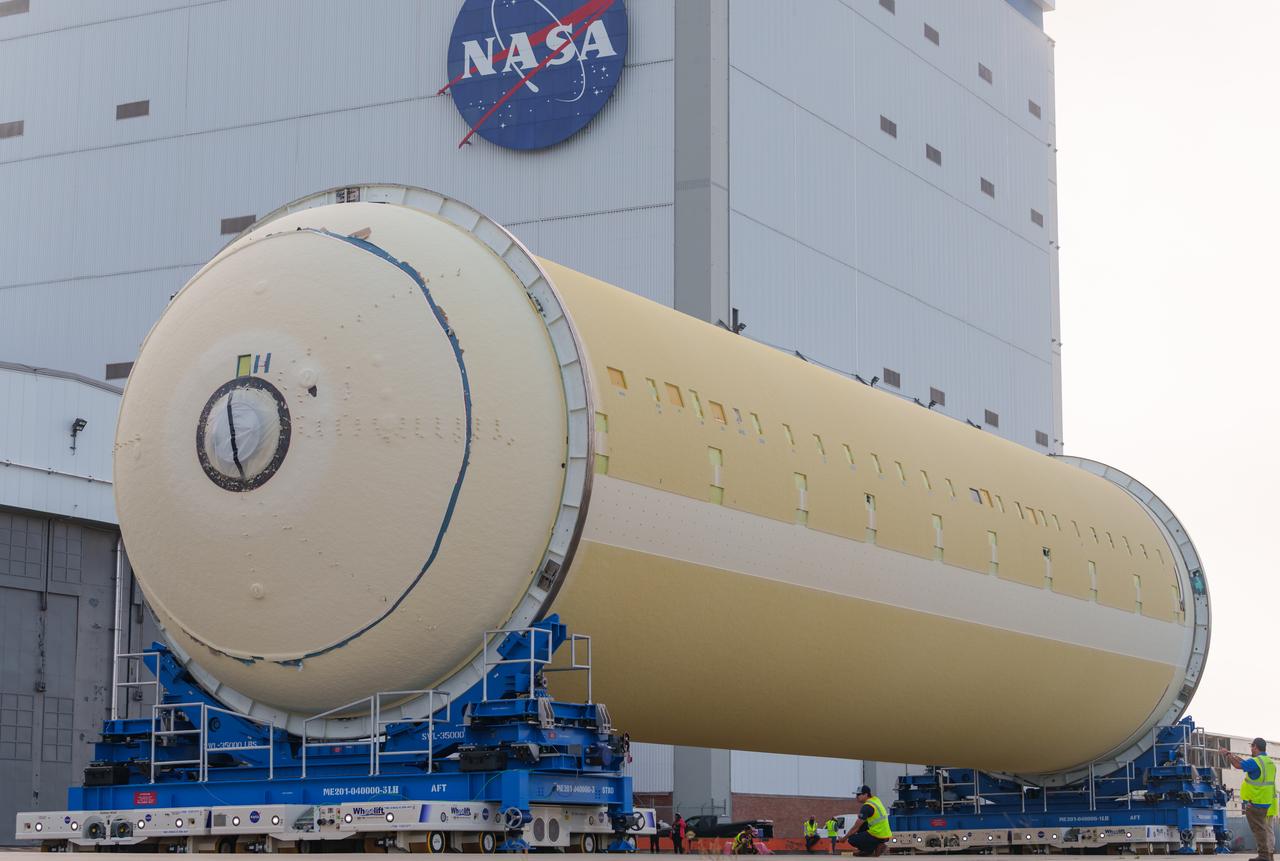

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s final assembly area on April 22. Having recently completed application of the thermal protection system, teams will now continue outfitting the 130-foot-tall tank with critical systems to ready it for its designated Artemis III mission. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
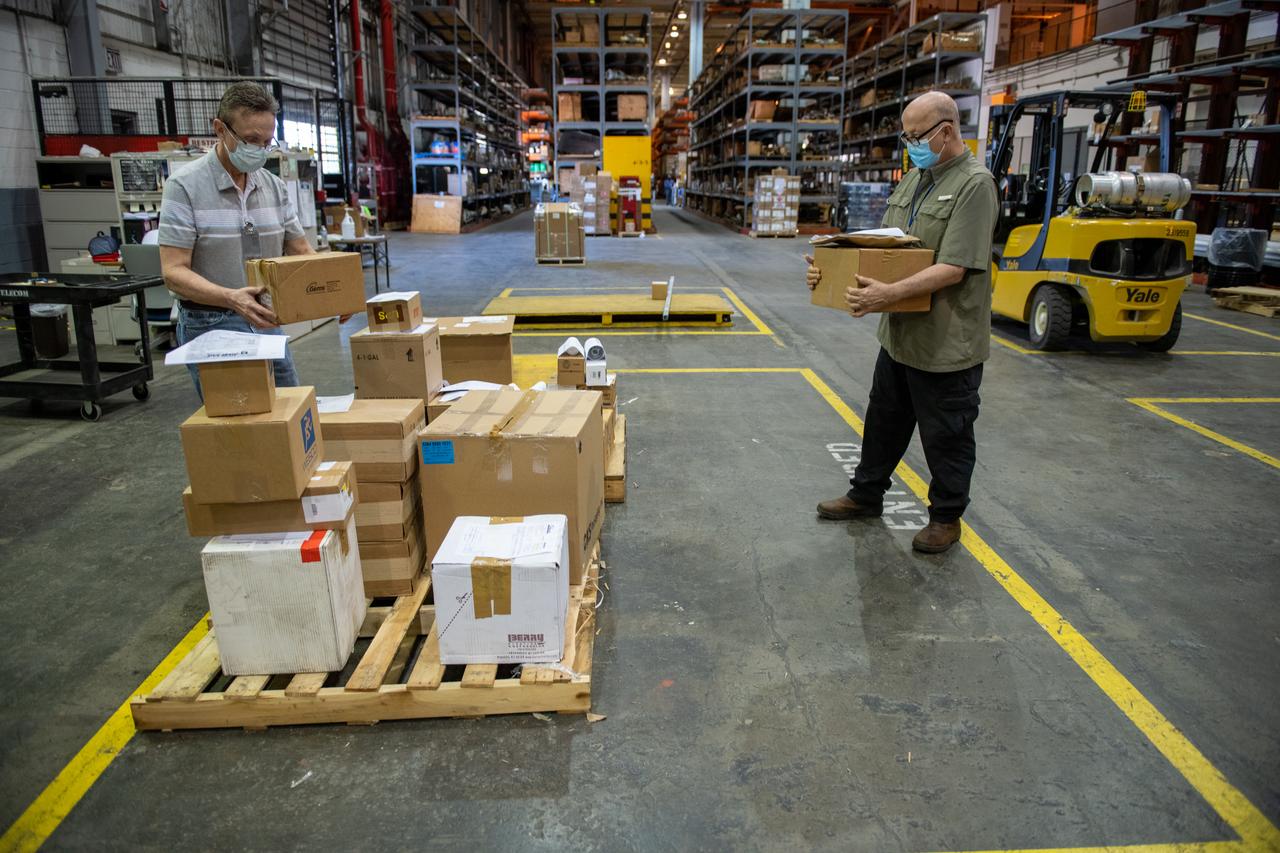

This photo includes two employees wearing personal protective gear in the shipping and receiving area of Michoud Assembly Facility during the Stage 3 transition of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Wearing a facemask is mandatory for common areas where social distancing is difficult to achieve. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Employees at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans will slowly and methodically resume Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion Spacecraft production and assembly activities at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
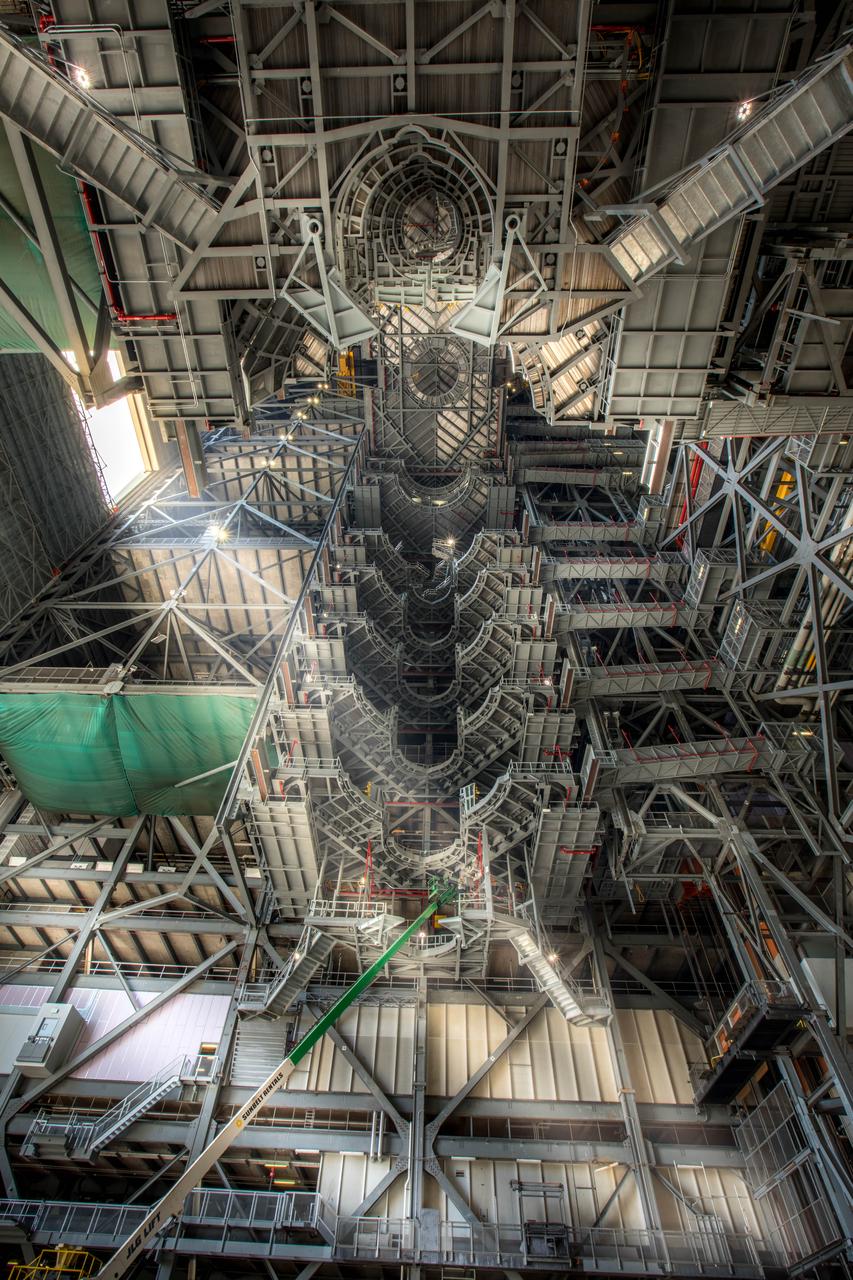

A view looking up at one side of the 10 levels of work platforms in High Bay 3 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The work platforms will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
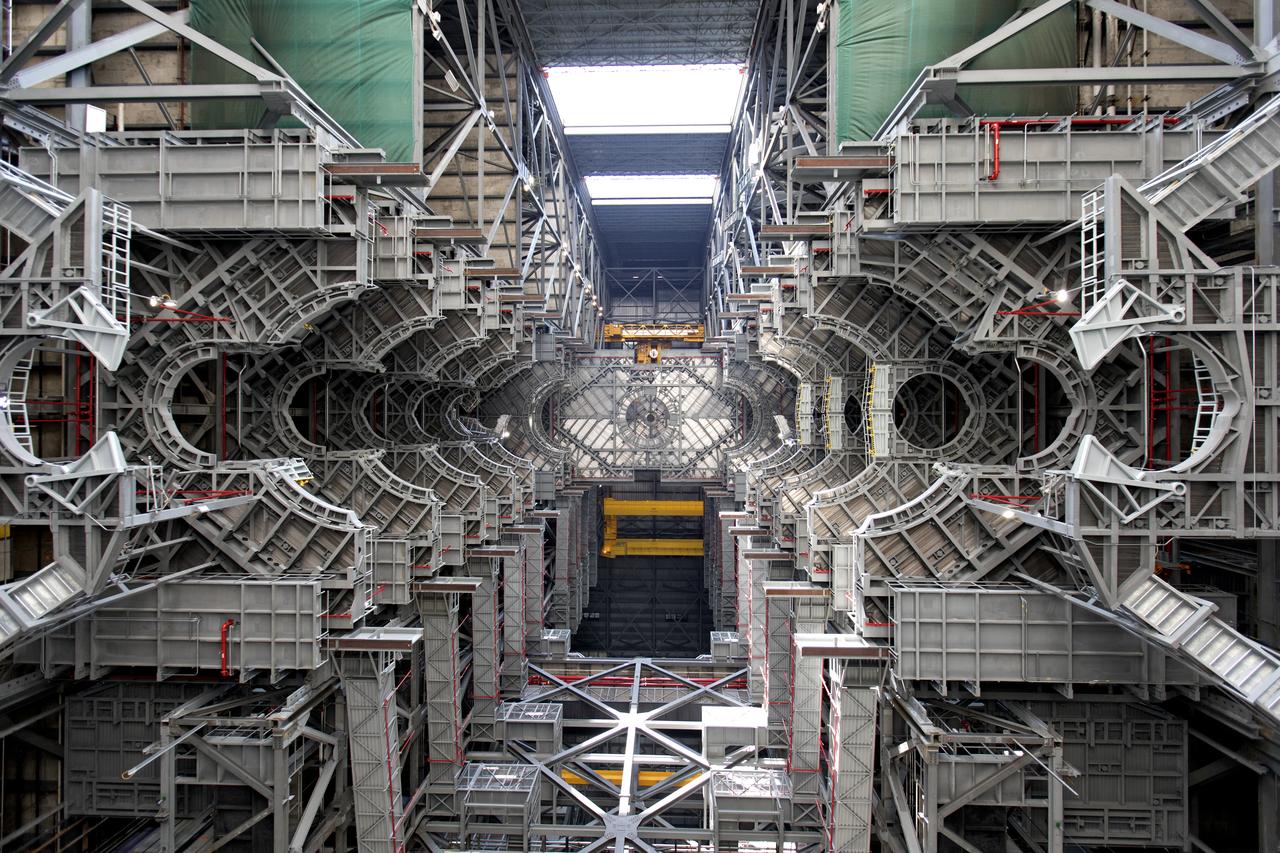

A view looking up at the 10 levels of work platforms in High Bay 3 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The work platforms will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
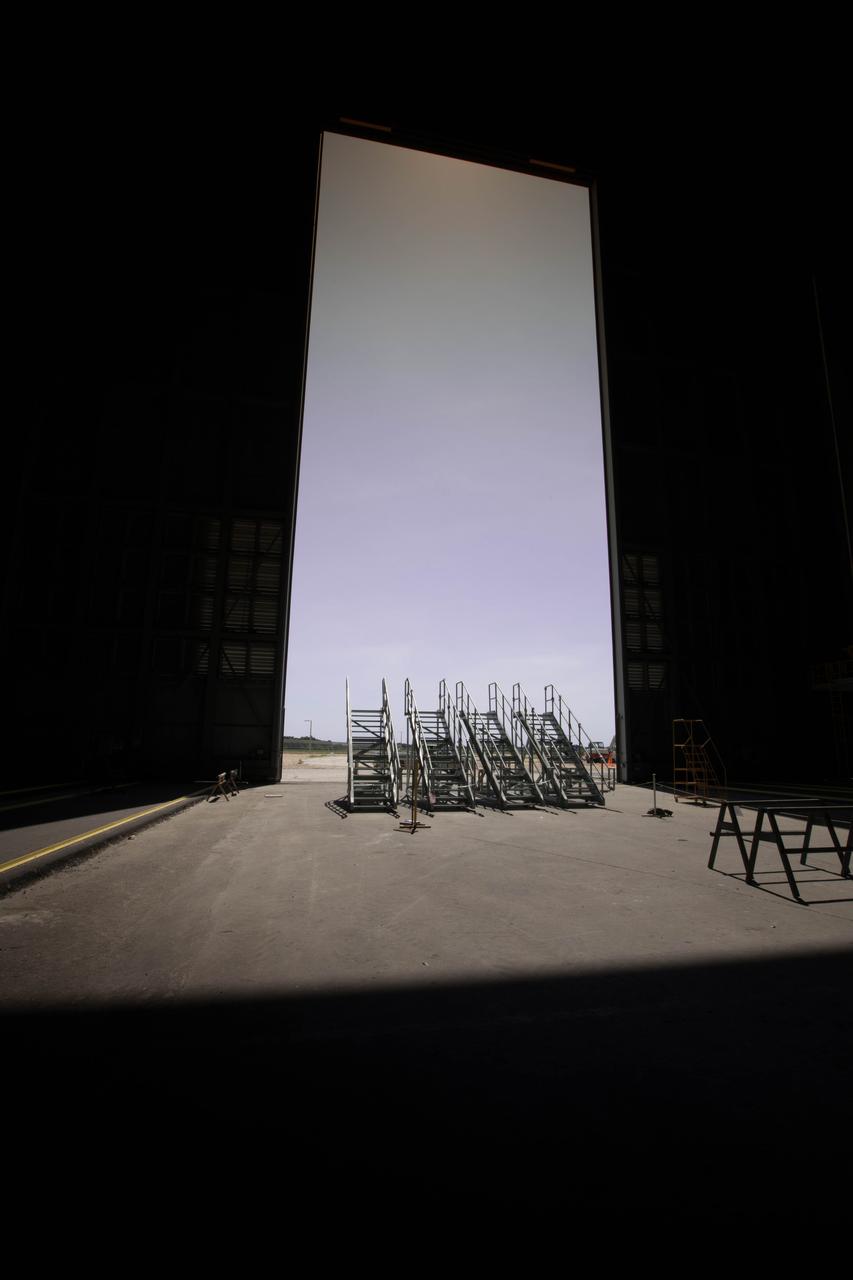

A view looking at High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ten levels of new work platforms have been installed in High Bay 3. They will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.

A view looking up at the 10 levels of work platforms in High Bay 3 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The work platforms will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
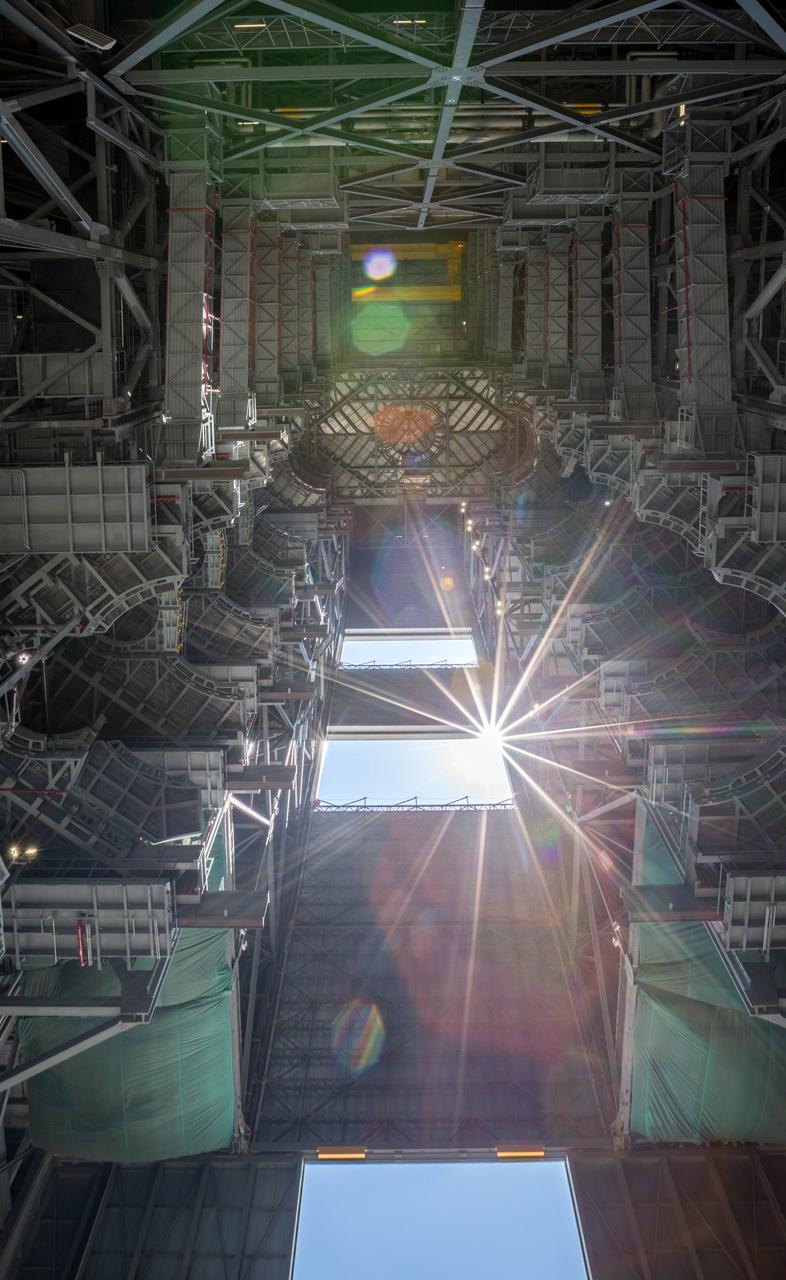

A brilliant sun shines through the doors of High Bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view are ten levels of new work platforms that were installed in the high bay. They will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) and deep space missions.
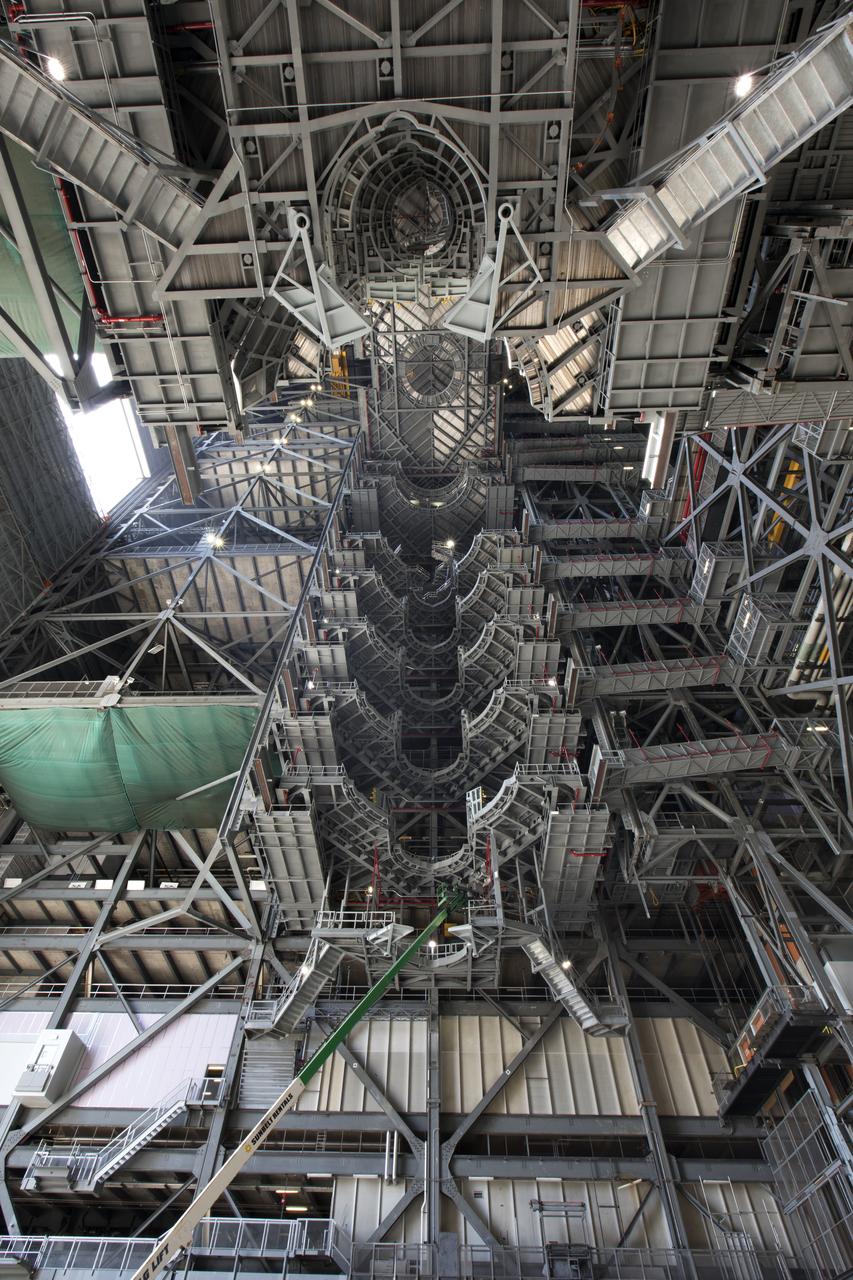

A view looking up at one side of the 10 levels of work platforms in High Bay 3 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The work platforms will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
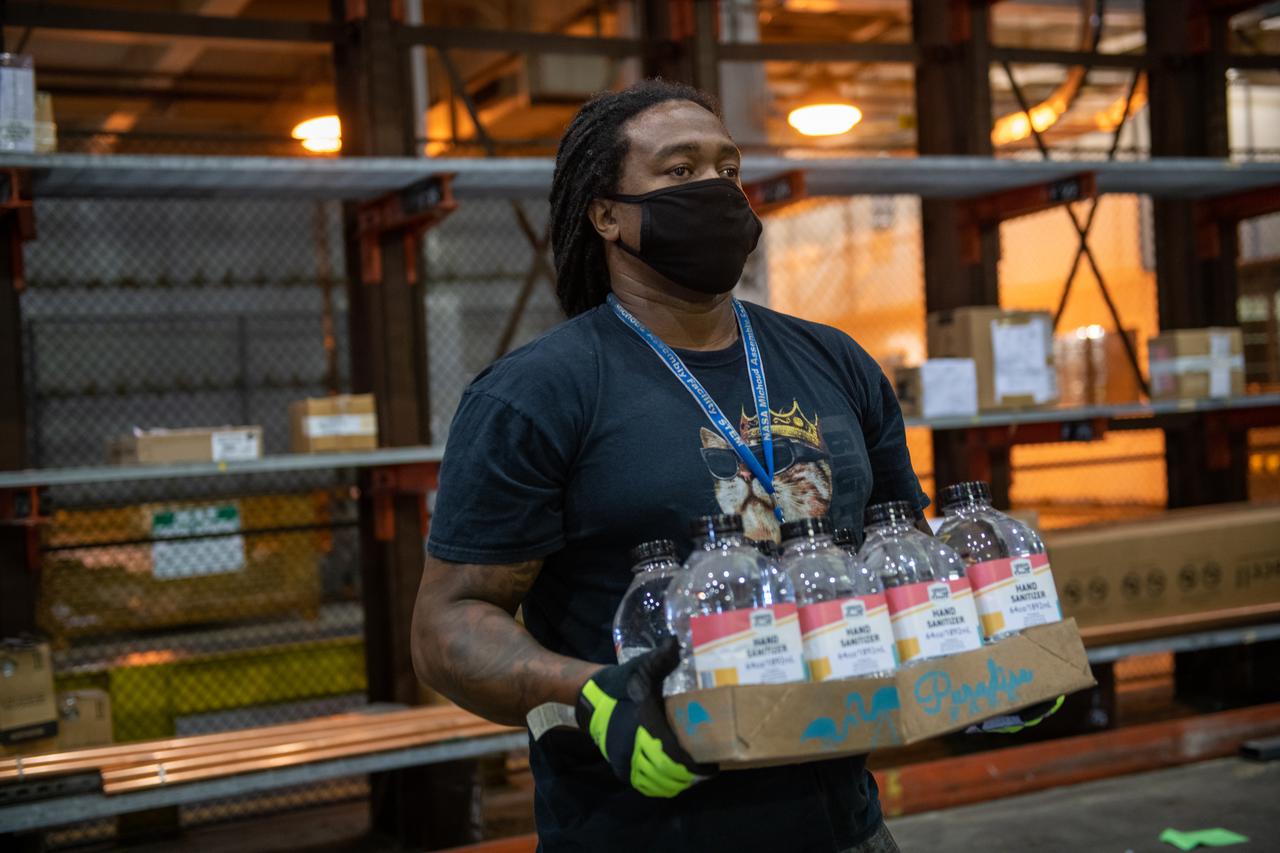

This photo includes two employees wearing personal protective gear in the shipping and receiving area of Michoud Assembly Facility during the Stage 3 transition of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Wearing a facemask is mandatory for common areas where social distancing is difficult to achieve. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Employees at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans will slowly and methodically resume Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion Spacecraft production and assembly activities at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
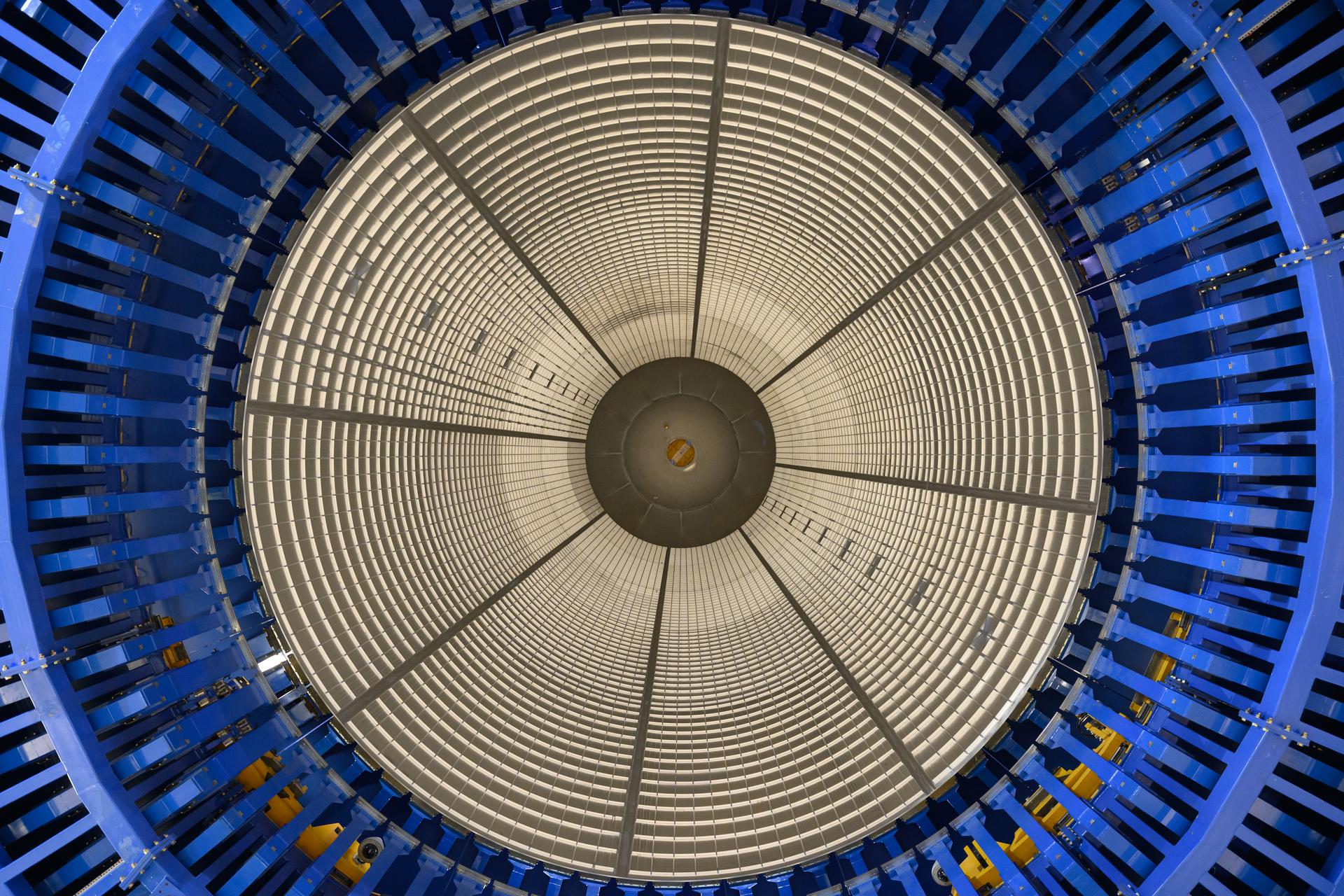

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
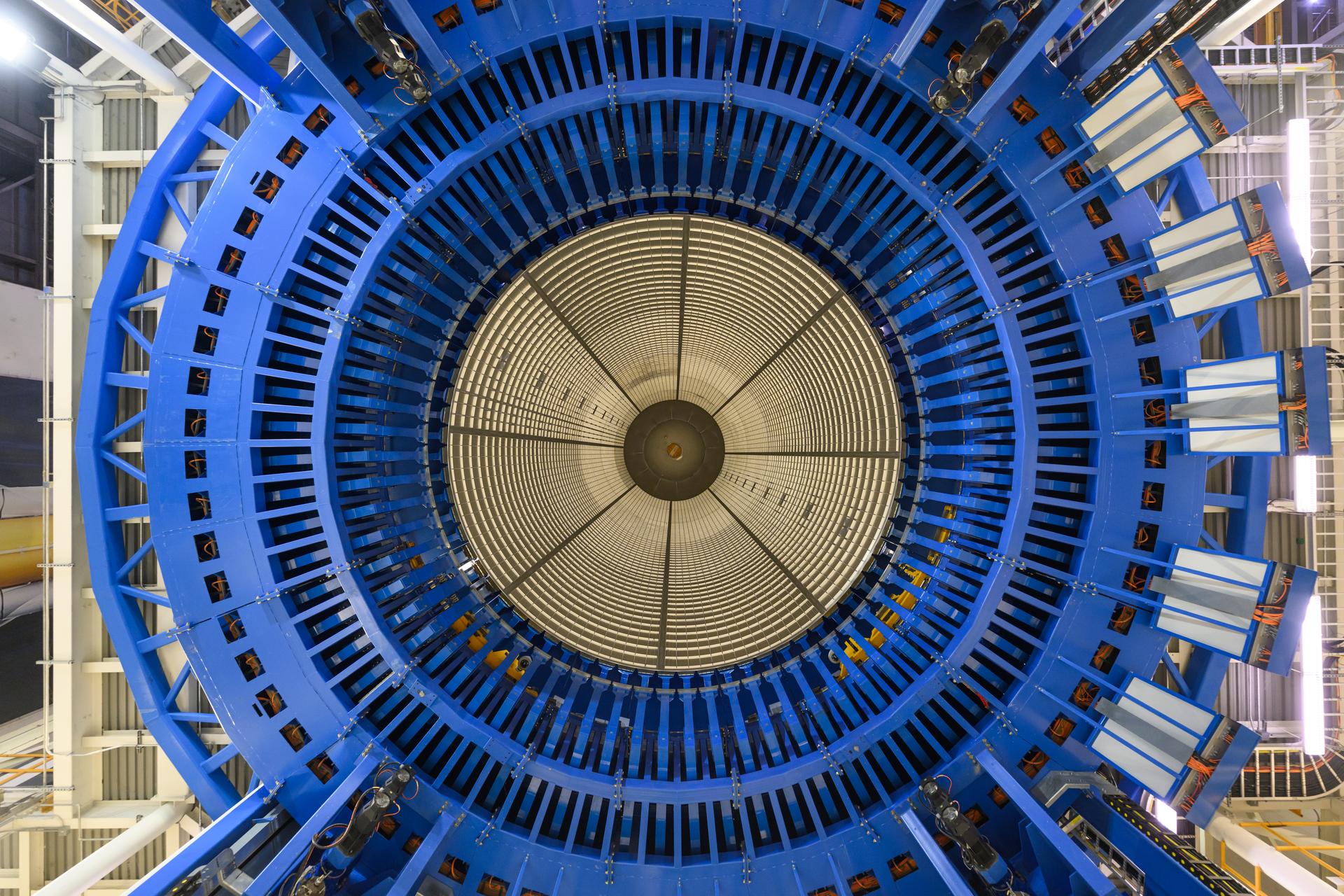
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the aft dome for the liquid hydrogen tank for the fourth core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System), into the in-feeder of the facility’s vertical assembly center. Once loaded into the production tool, teams with SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will circumferentially friction-stir weld the dome to the previously-welded forward dome and five barrels that make up the liquid hydrogen tank. The SLS core stage liquid hydrogen tank holds 537,000 gallons of super-cooled propellant and is one of five unique elements that make up the SLS core stage. Together with the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, and engine section, the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon.
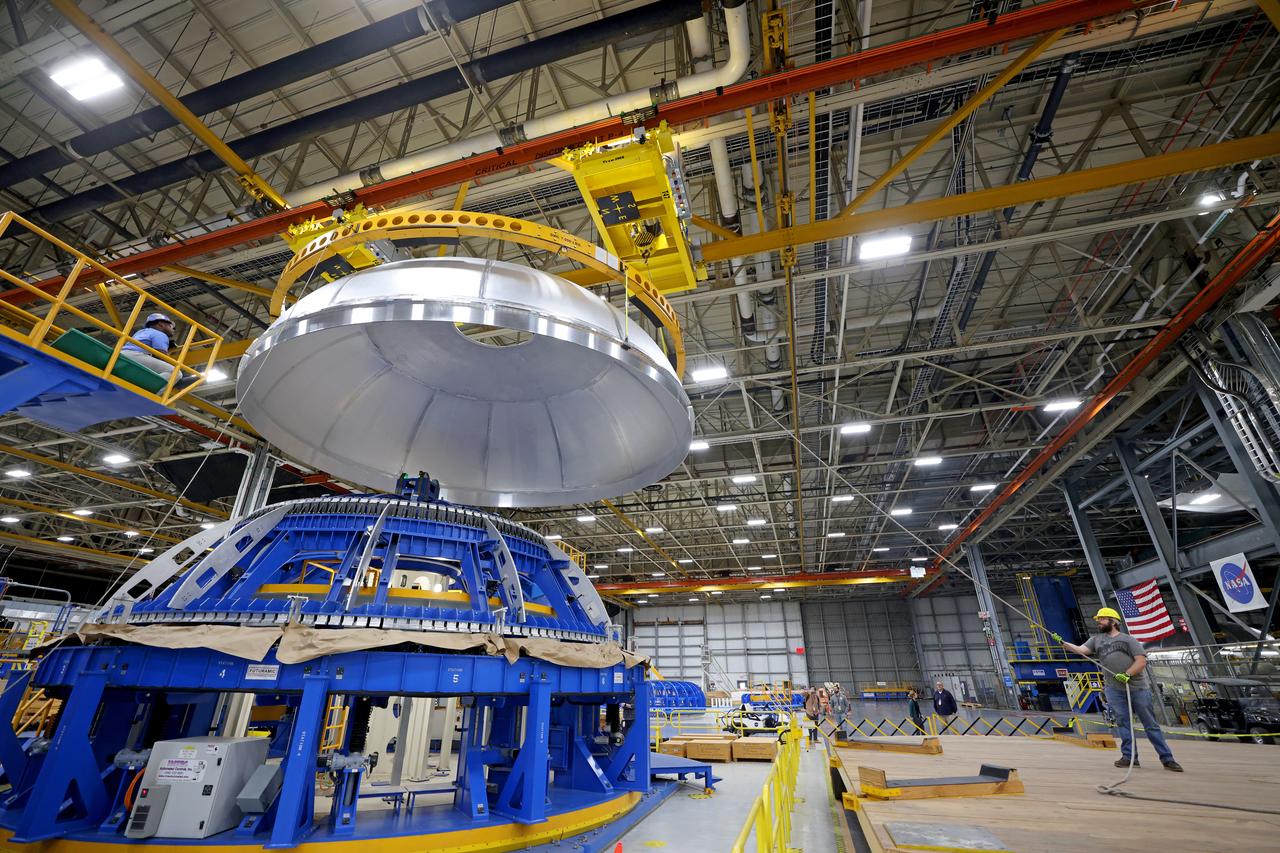

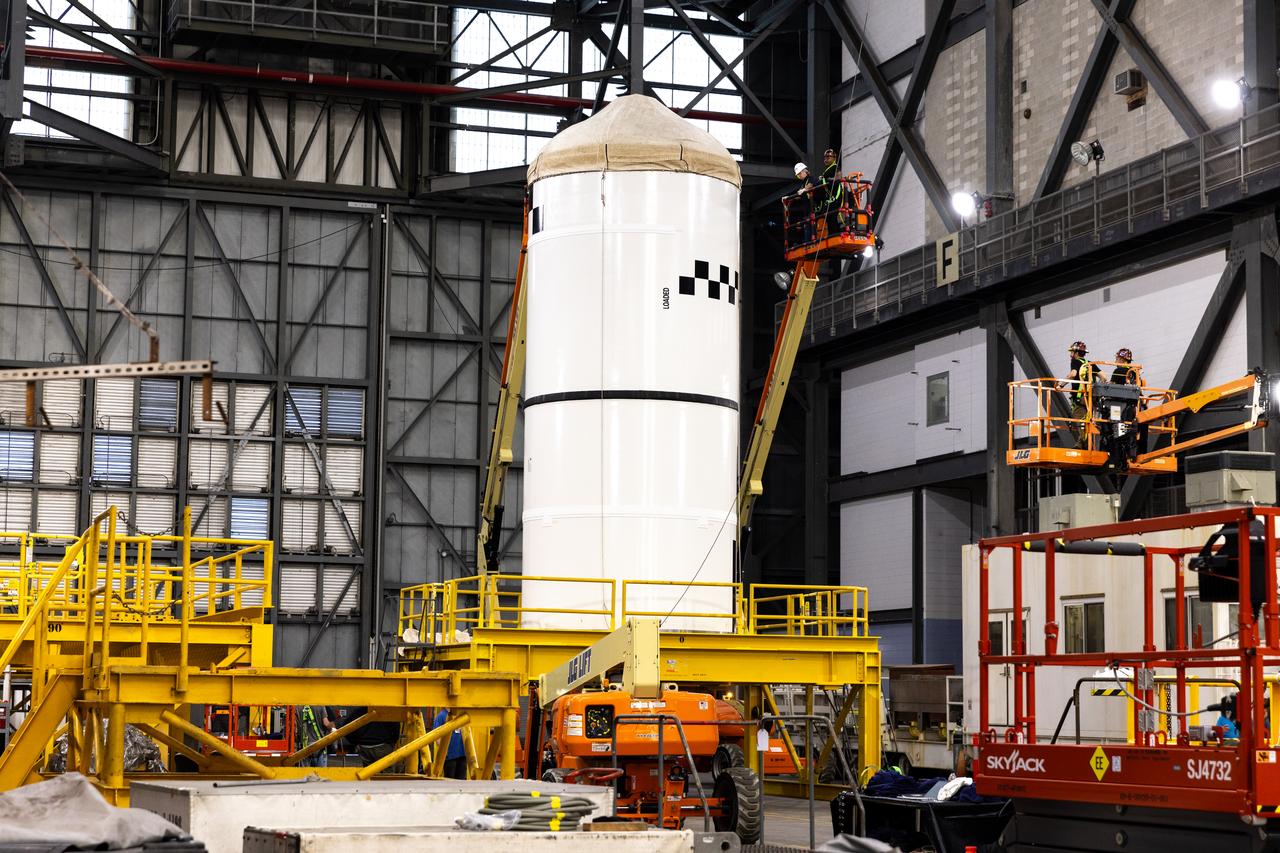
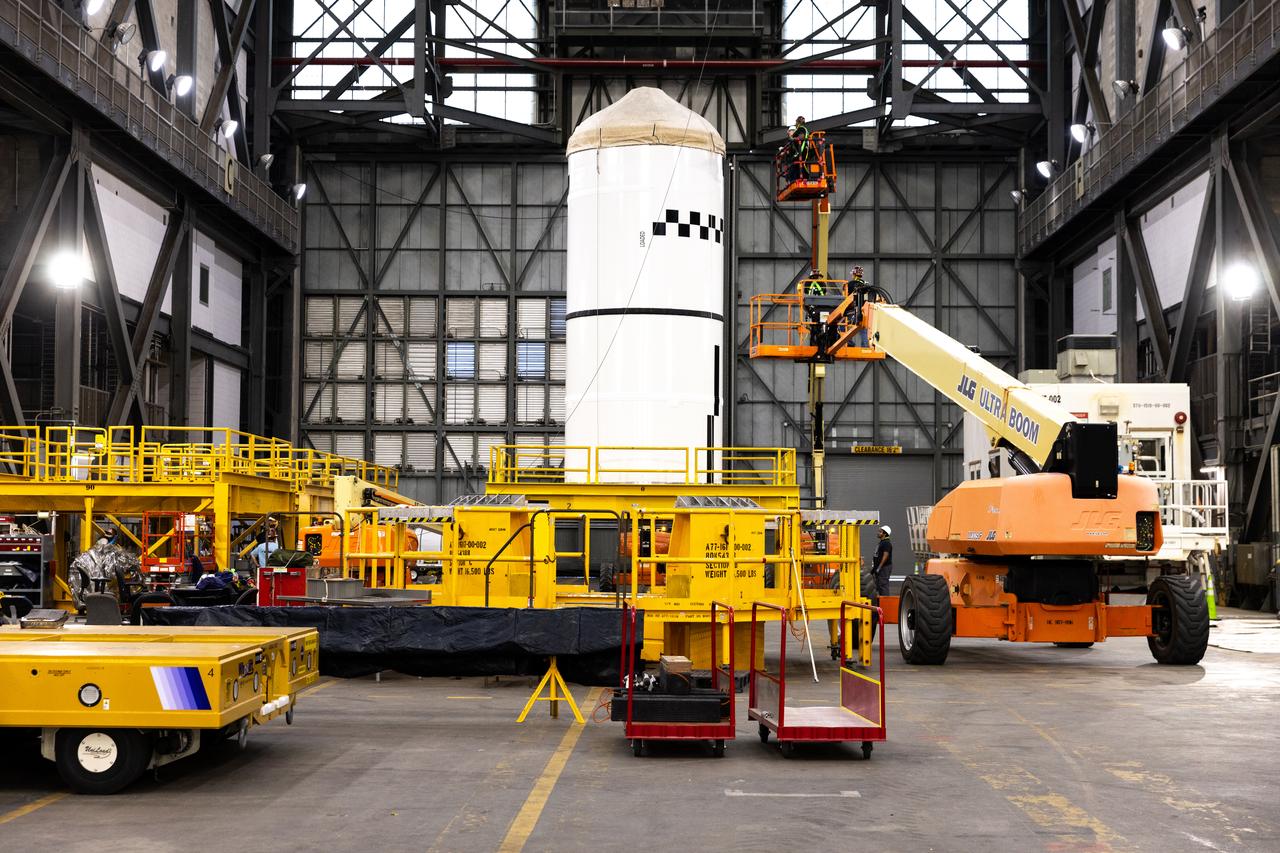
This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.
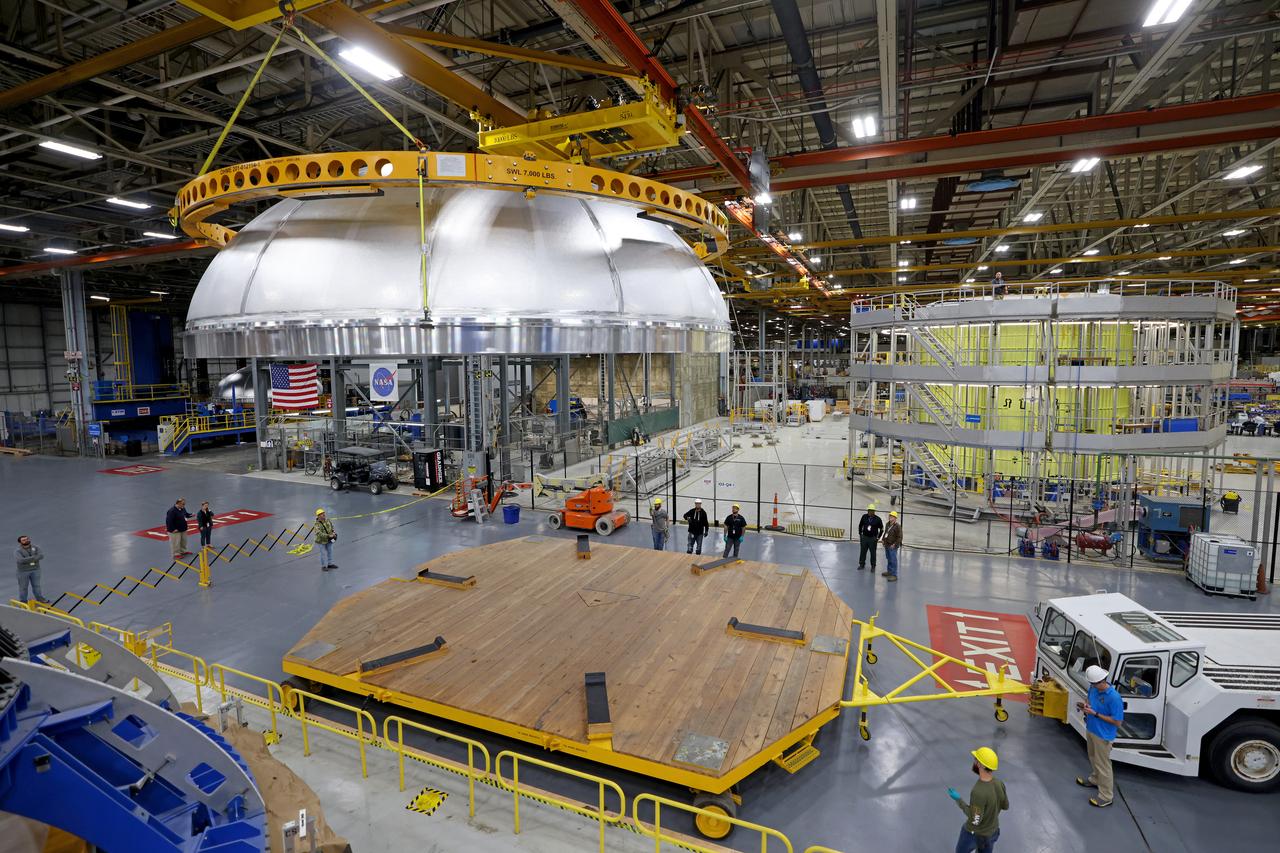

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon.
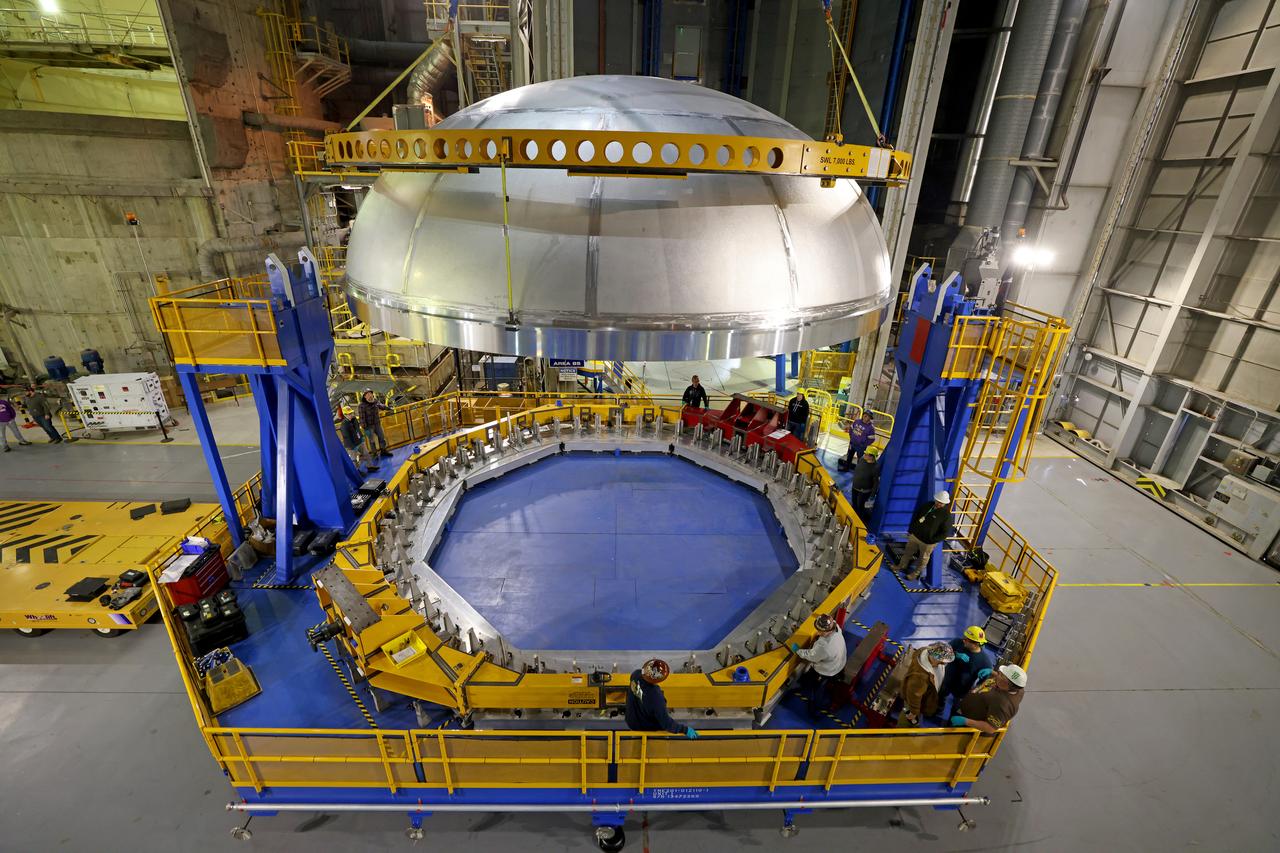

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 6. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
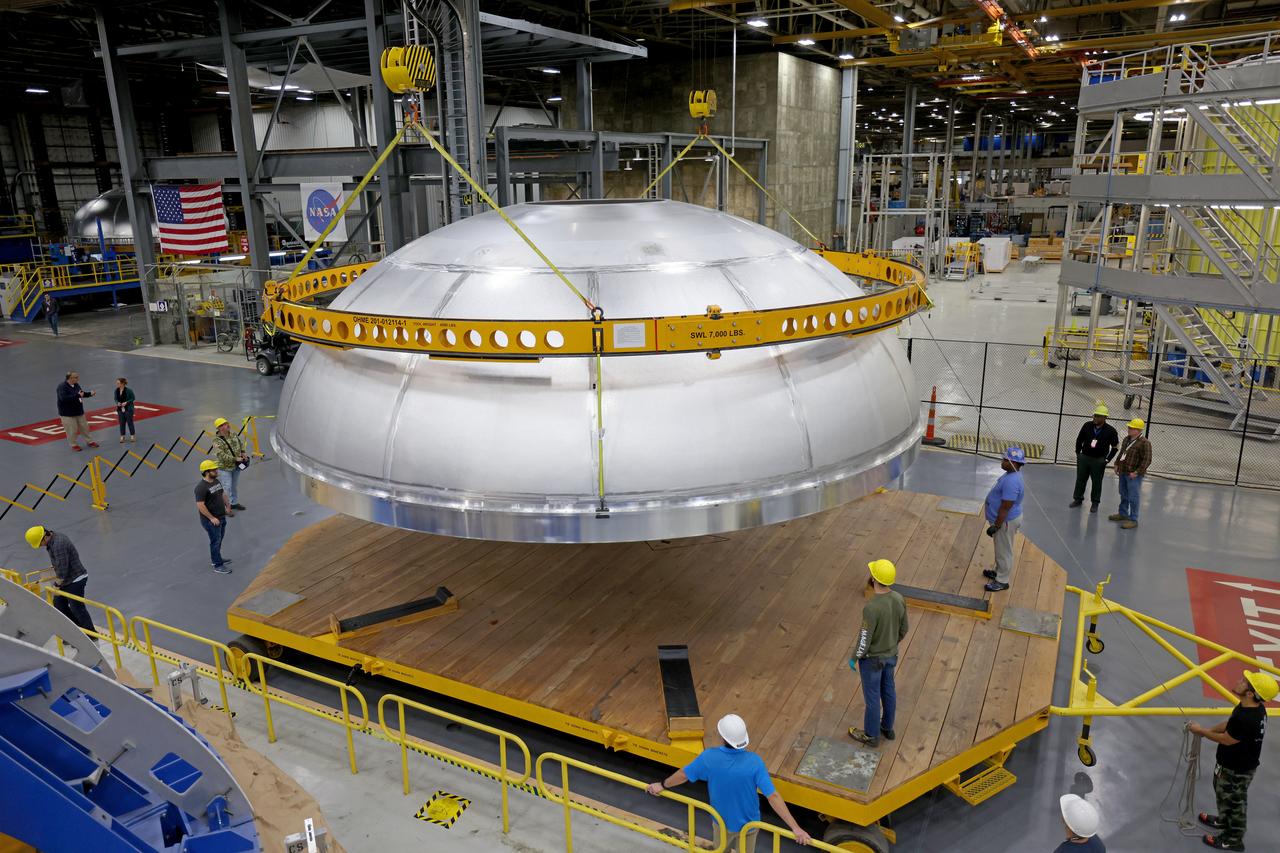

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
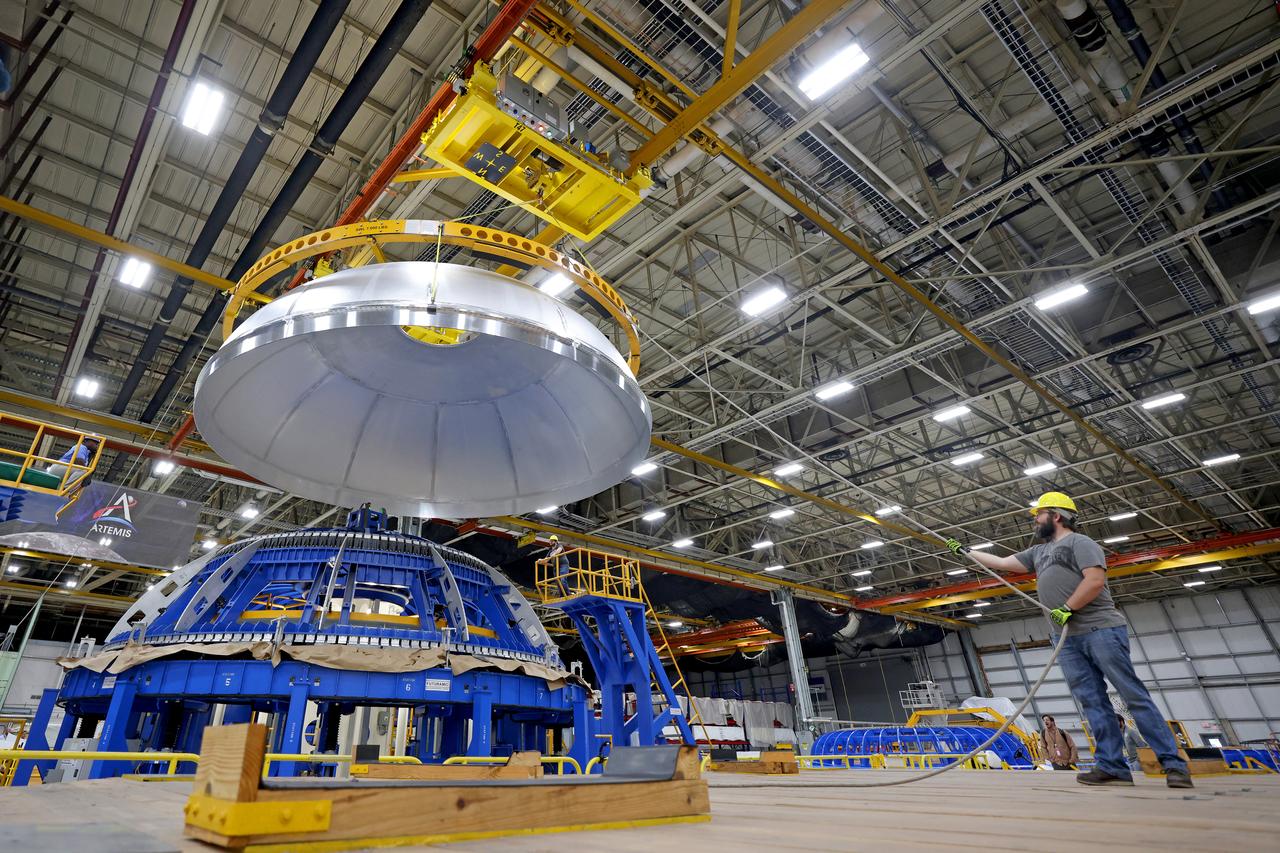

This imagery shows how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility moved the aft dome of the liquid oxygen tank for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the next phase of production inside the Vertical Assembly center Dec. 5. The dome will form part of the core stage that will power NASA’s Artemis III mission. Engineers will soon rotate the dome to attach it to the previously joined forward dome and aft barrel segments using friction-stir welding. The liquid oxygen tank is one of five major components that make up the SLS rocket’s core stage. Together with the forward skirt, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, engine section, along with the four RS-25 engines at its base, the 212-foot core stage will help power NASA’s Artemis missions to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
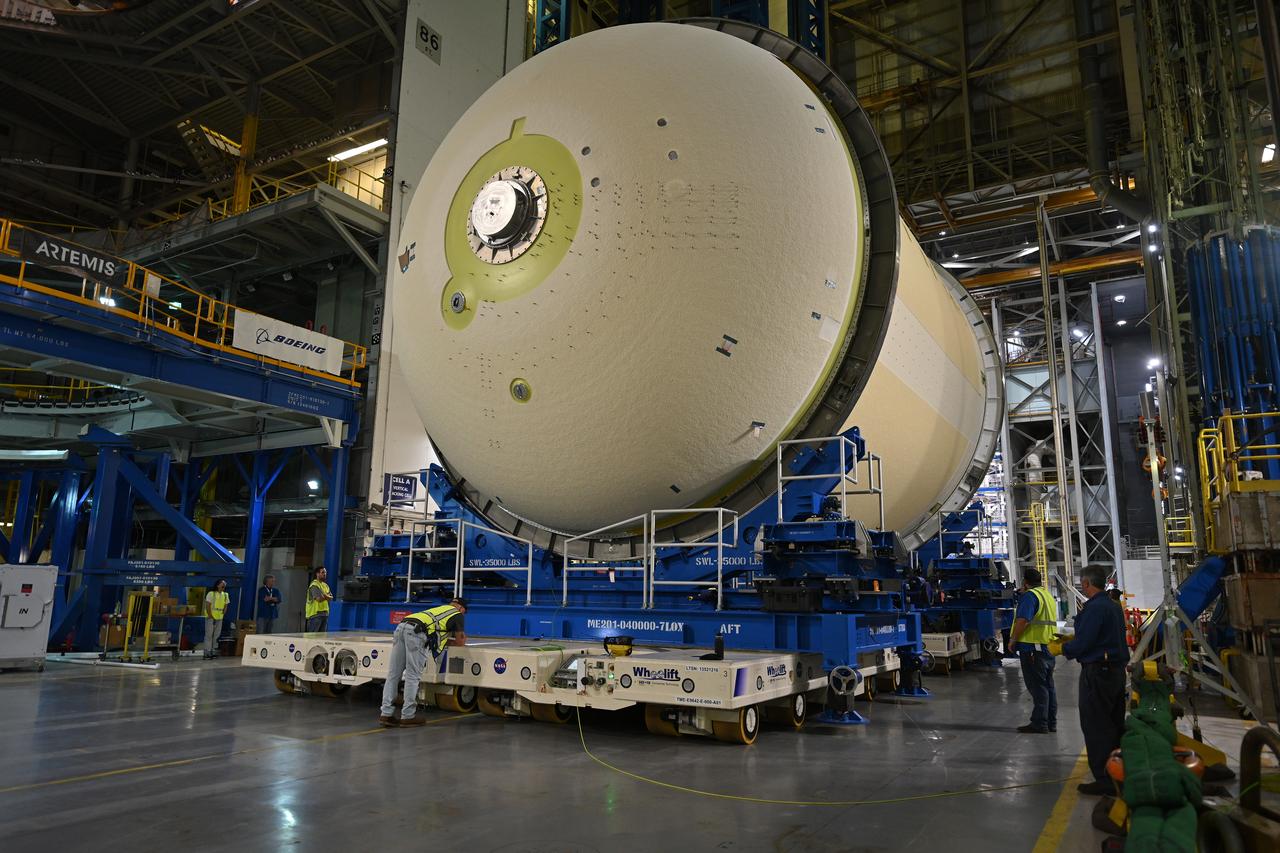

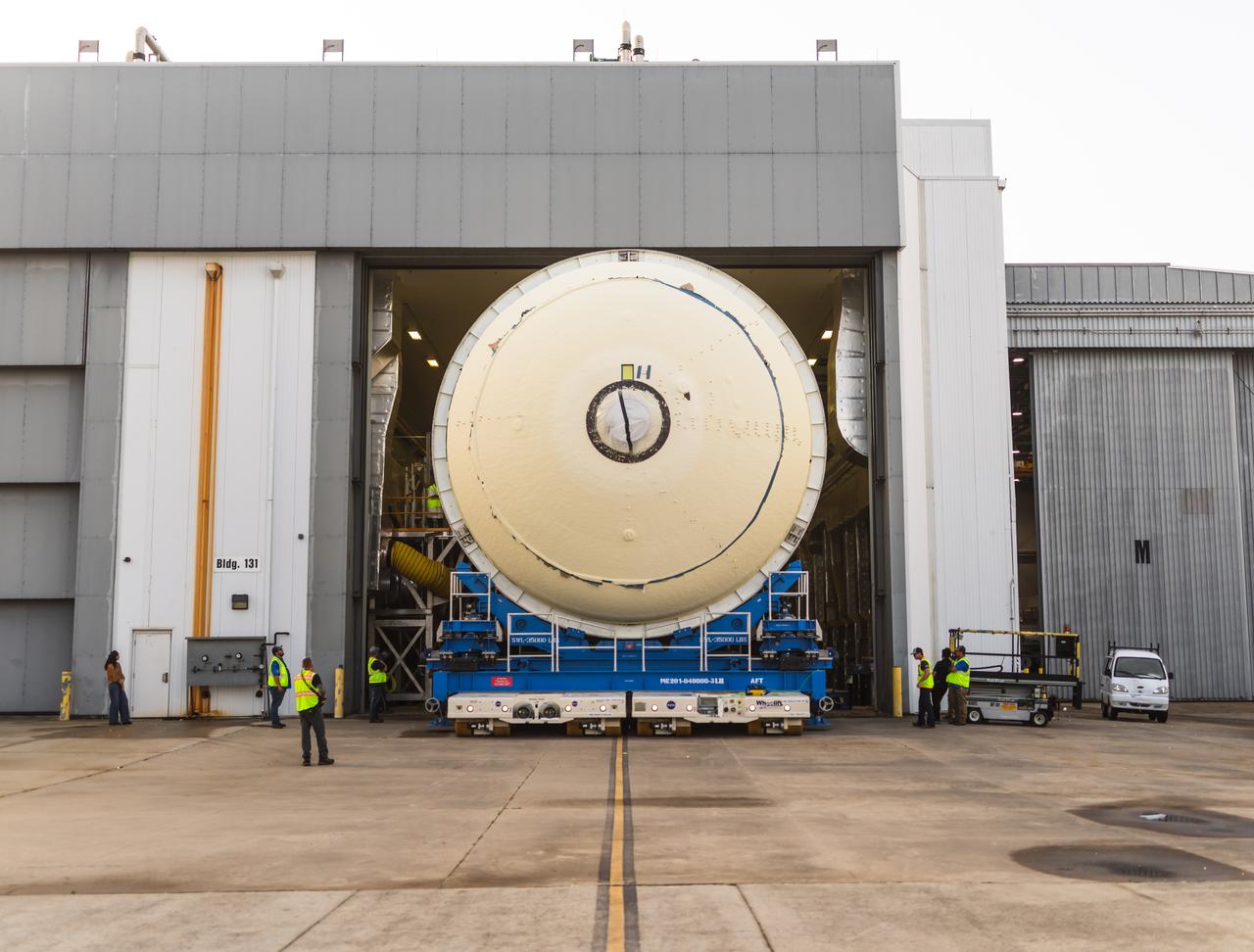
Teams move a liquid oxygen tank – designated for the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission – from the thermal protection system application cell at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the site’s 210-foot-tall Vertical Assembly Building on July 9. Next, NASA’s SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will vertically install the tank’s aft sump subassembly. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
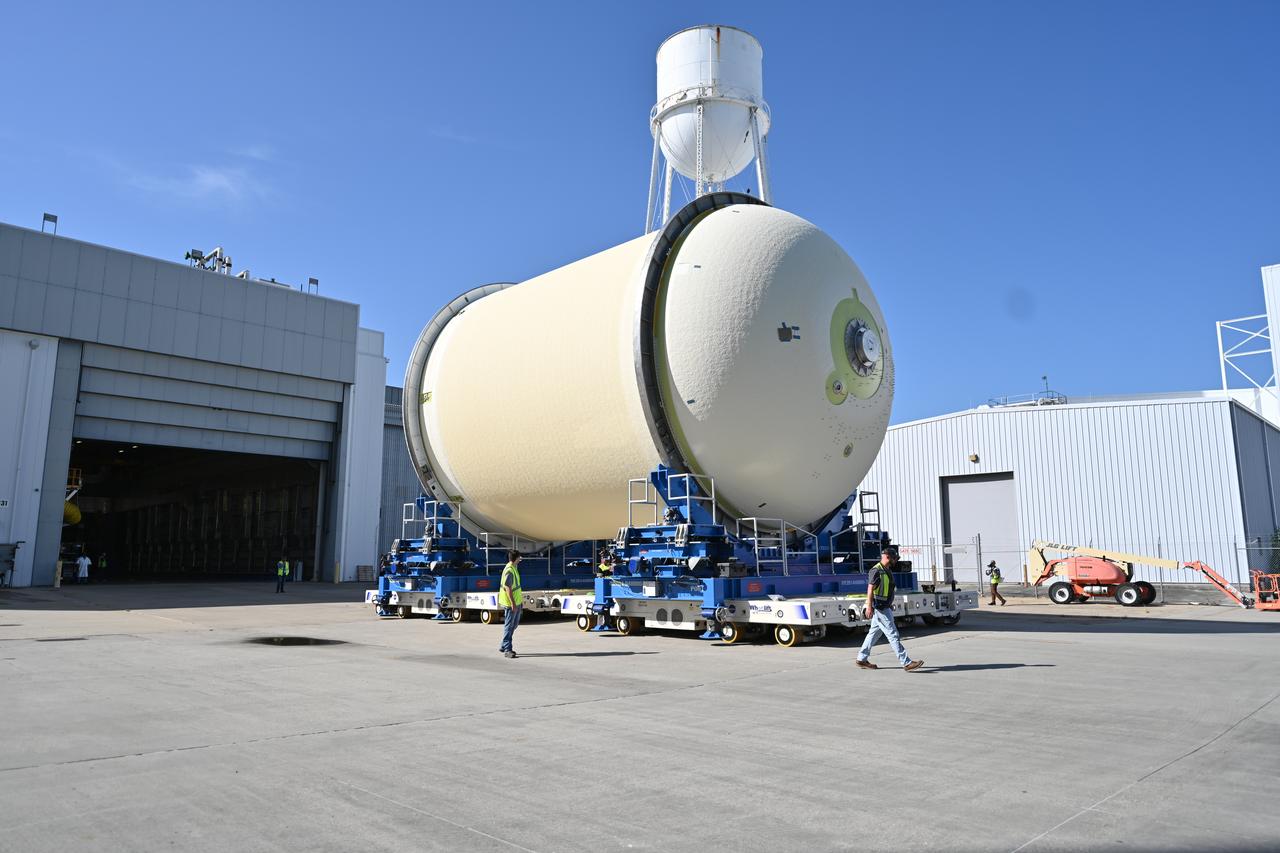

Teams move a liquid oxygen tank – designated for the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission – from the thermal protection system application cell at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the site’s 210-foot-tall Vertical Assembly Building on July 9. Next, NASA’s SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will vertically install the tank’s aft sump subassembly. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Teams move a liquid oxygen tank – designated for the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission – from the thermal protection system application cell at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the site’s 210-foot-tall Vertical Assembly Building on July 9. Next, NASA’s SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will vertically install the tank’s aft sump subassembly. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
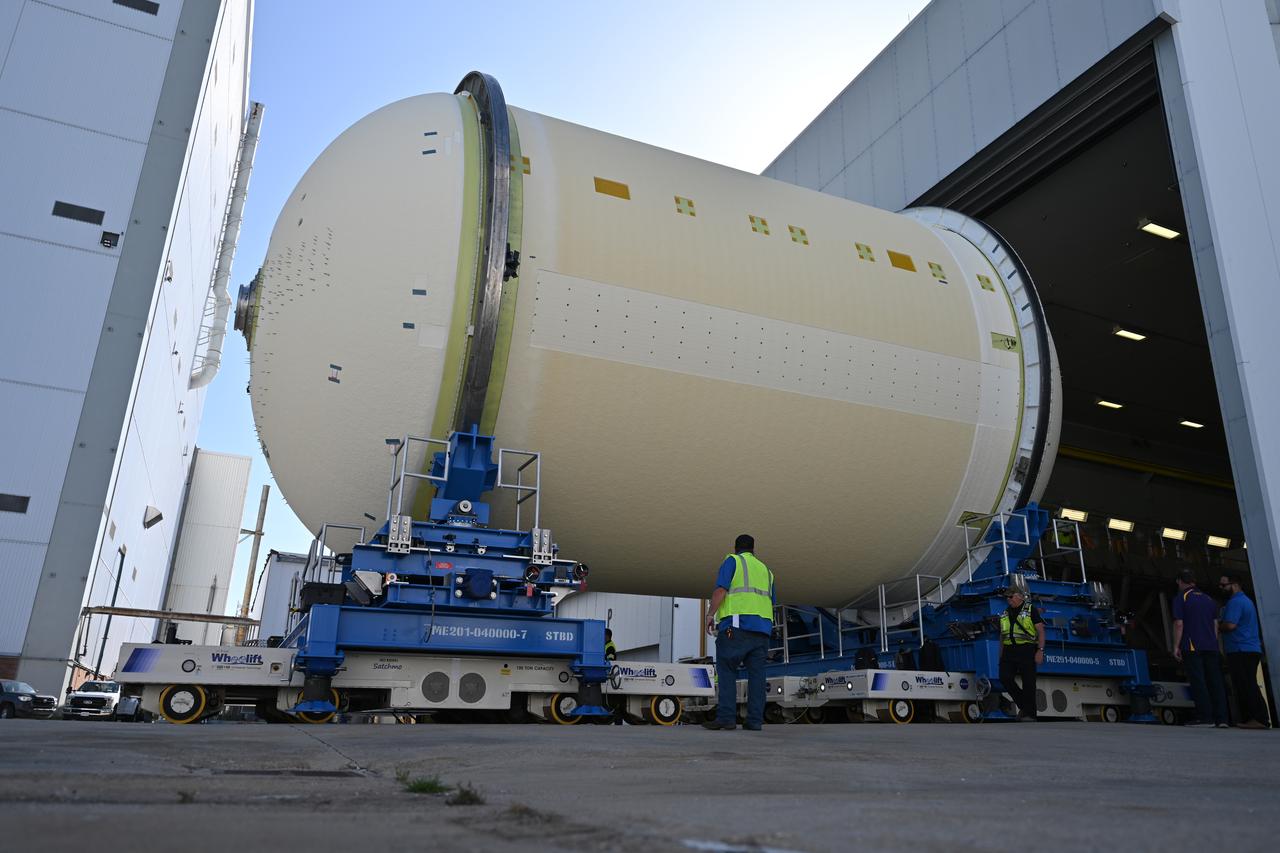

Teams move a liquid oxygen tank – designated for the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission – from the thermal protection system application cell at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the site’s 210-foot-tall Vertical Assembly Building on July 9. Next, NASA’s SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will vertically install the tank’s aft sump subassembly. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
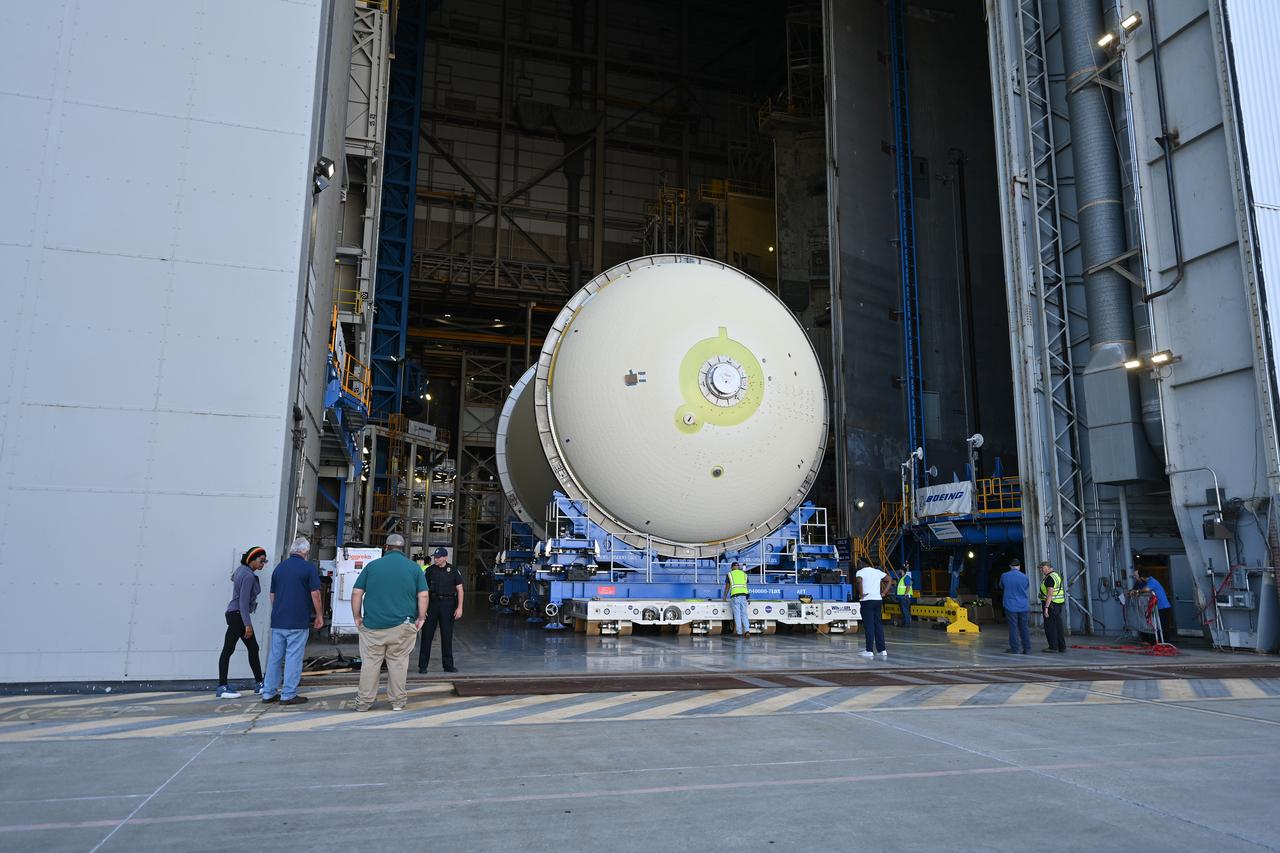

Teams move a liquid oxygen tank – designated for the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission – from the thermal protection system application cell at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the site’s 210-foot-tall Vertical Assembly Building on July 9. Next, NASA’s SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will vertically install the tank’s aft sump subassembly. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

Teams move a liquid oxygen tank – designated for the core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for its Artemis III mission – from the thermal protection system application cell at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the site’s 210-foot-tall Vertical Assembly Building on July 9. Next, NASA’s SLS prime contractor, Boeing, will vertically install the tank’s aft sump subassembly. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

The NASA Vehicle Assembly Building is seen through a rain covered windshield at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, July 10, 2009. NASA is set to launch the space shuttle Endeavour with the crew of STS-127 on Saturday. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
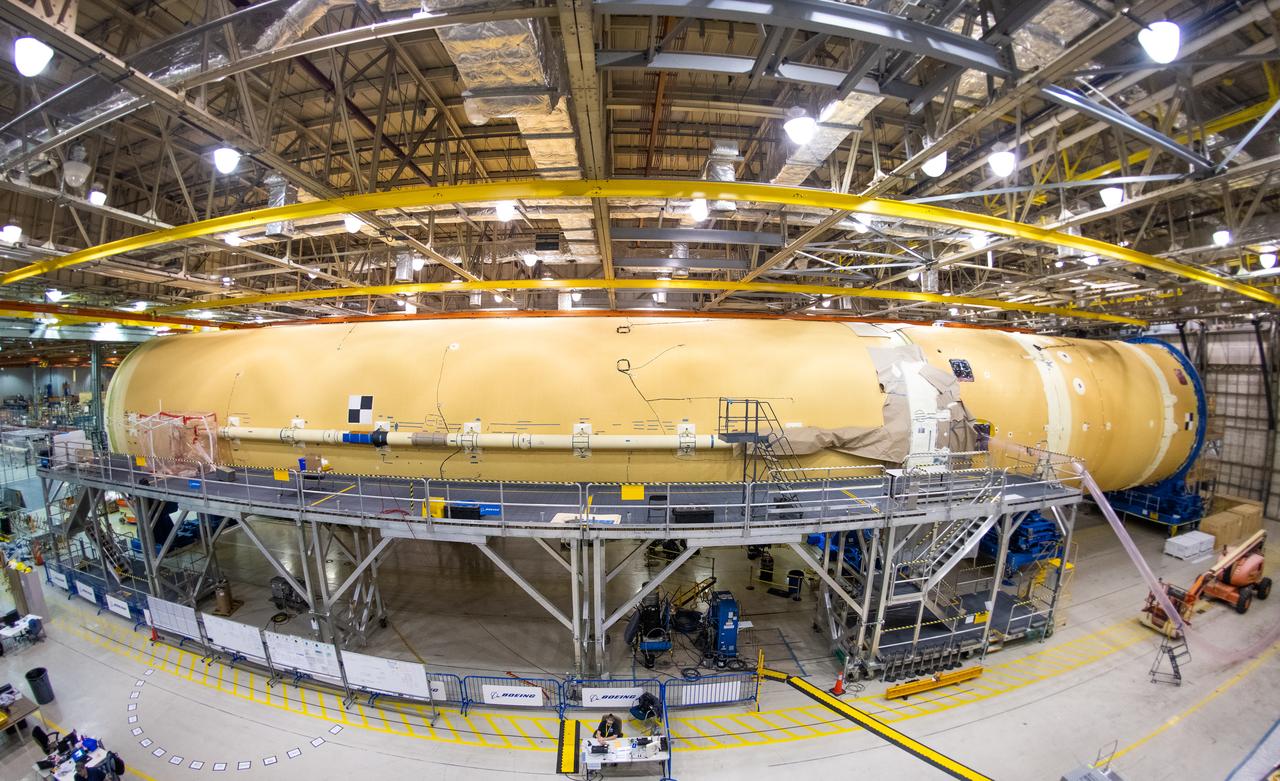

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans completed the “forward join,” which connects structures to form the top part of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s core stage. The first core stage will send Exploration Mission-1, the first integrated flight of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, out beyond the Moon. The forward join mated three structures: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and intertank. This milestone marks the beginning of integration and assembly of the massive, 212-foot-tall SLS core stage, which will include the rocket’s four RS-25 rocket engines, propellant tanks and flight computers. Now, NASA and Boeing, the SLS prime contractor, will continue to integrate various systems inside the forward part of the core stage and prepare for structural joining of the liquid hydrogen tank and engine section to form the bottom of the stage. These two parts of the core stage will then be assembled to form the largest stage NASA has ever built.

This overhead view of the X-59 shows the aircraft’s current state of assembly at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. Throughout the manufacturing process, the team often removes components to effectively and safely assemble other sections of the aircraft. The X-59’s horizontal tails and lower empennage were recently removed from the aircraft and can be seen behind it as the team prepares for the installation of the engine. The X-59 is the centerpiece of the Quesst mission which plans to help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
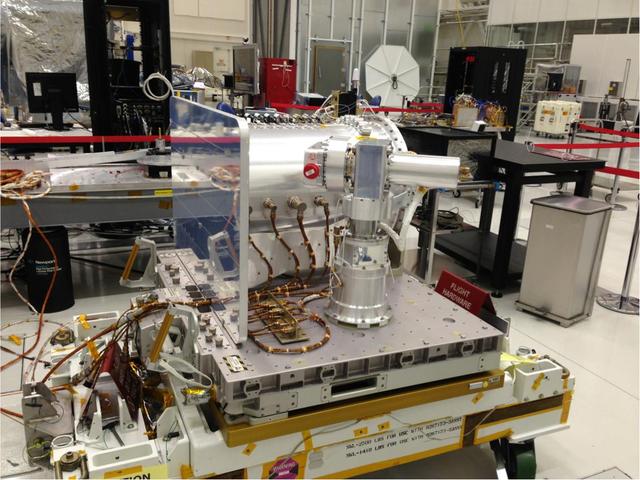
NASA Optical PAyload for Lasercomm Science OPALS is pictured in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory prior to shipment.
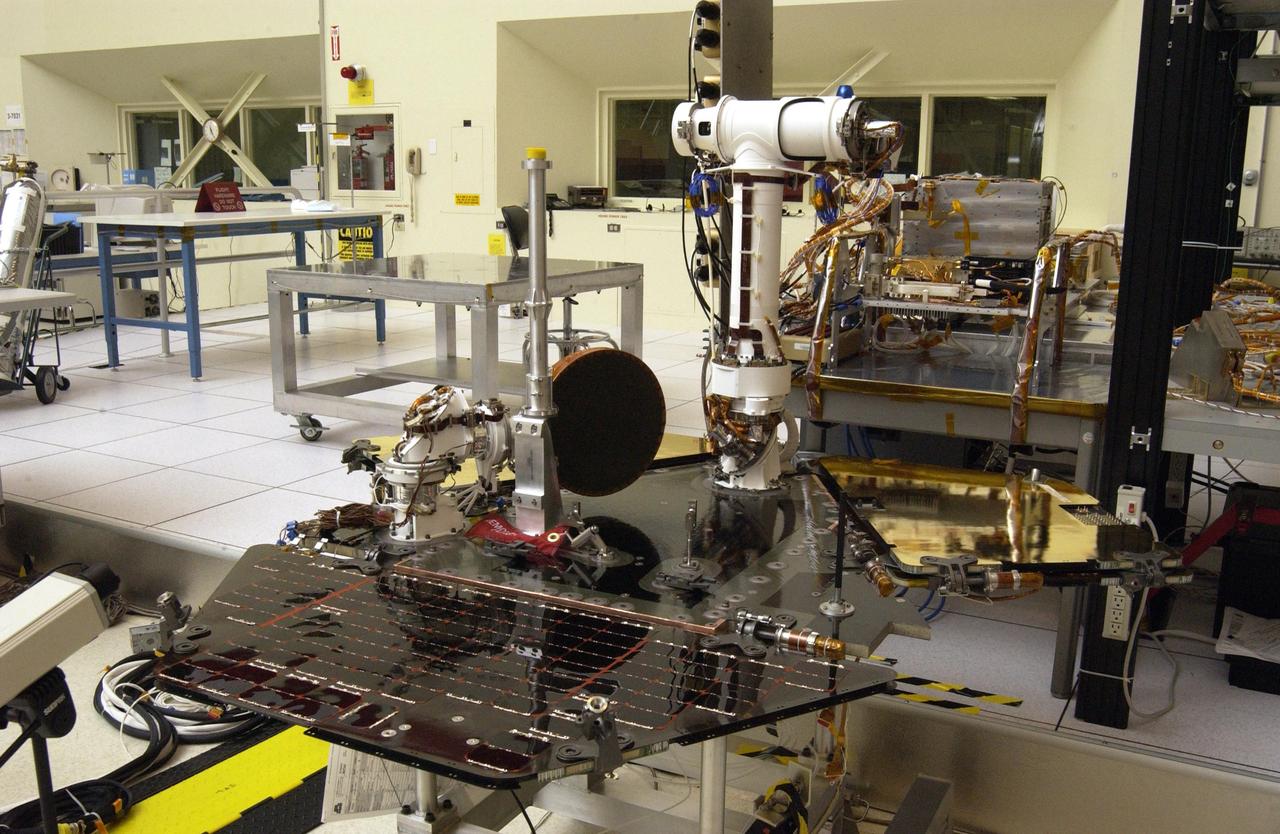
NASA Rover 2 equipment deck, with solar arrays partially deployed, in NASA JPL Spacecraft Assembly Facility cleanroom.

Technicians transport the right forward segment for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket boosters from the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility to NASA’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Monday, Feb. 15, 2025. The right forward segment will be transferred into High Bay 3 where it will be attached to the center forward segment on mobile launcher 1. The twin solid boosters, five segments on each side, will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.

Technicians transport the right forward segment for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket boosters from the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility to NASA’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Monday, Feb. 15, 2025. The right forward segment will be transferred into High Bay 3 where it will be attached to the center forward segment on mobile launcher 1. The twin solid boosters, five segments on each side, will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems complete the integration of the left forward segment to the center forward segment on mobile launcher 1 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 7, 2025. The twin solid boosters, five segments on each side, will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems complete the integration of the left forward segment to the center forward segment on mobile launcher 1 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 7, 2025. The twin solid boosters, five segments on each side, will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.
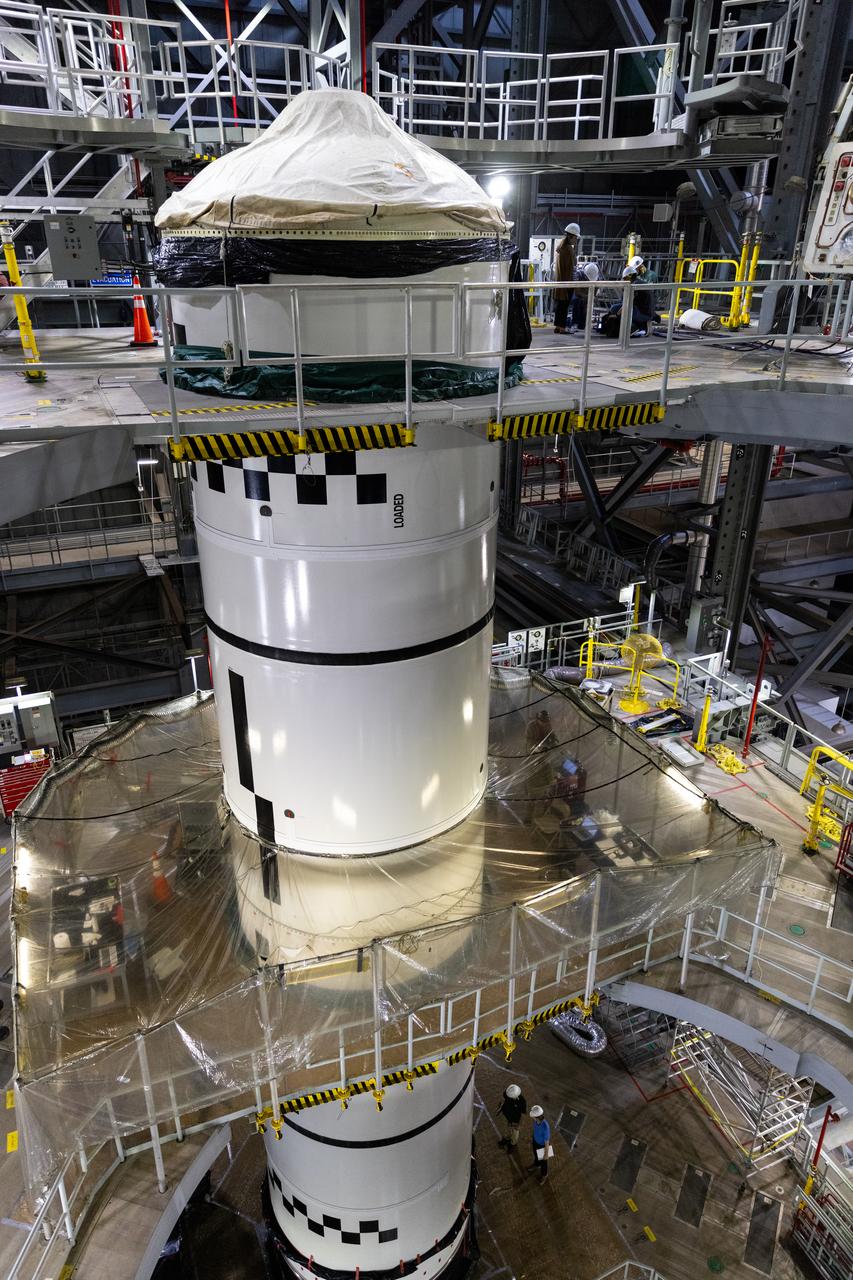

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems complete the integration of the left forward segment to the center forward segment on mobile launcher 1 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 7, 2025. The twin solid boosters, five segments on each side, will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.

Technicians transport the right forward segment for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) Moon rocket boosters from the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility to NASA’s Vehicle Assembly Building in Florida on Monday, Feb. 15, 2025. The right forward segment will be transferred into High Bay 3 where it will be attached to the center forward segment on mobile launcher 1. The twin solid boosters, five segments on each side, will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems complete the integration of the left forward segment to the center forward segment on mobile launcher 1 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 7, 2025. The twin solid boosters, five segments on each side, will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.
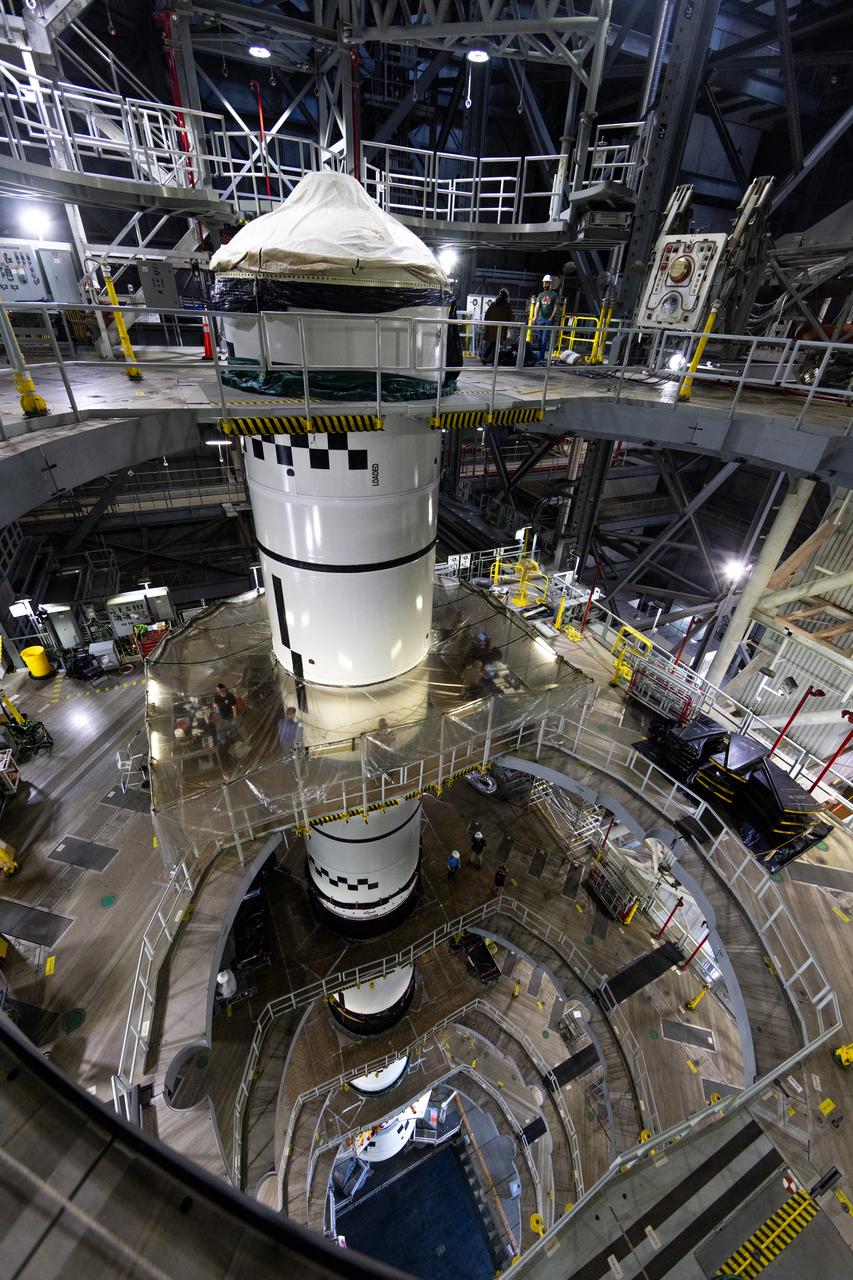

Technicians with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems complete the integration of the left forward segment to the center forward segment on mobile launcher 1 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 7, 2025. The twin solid boosters, five segments on each side, will help support the remaining rocket components and the Orion spacecraft during final assembly of the Artemis II Moon rocket and provide more than 75 percent of the total SLS thrust during liftoff from NASA Kennedy’s Launch Pad 39B.
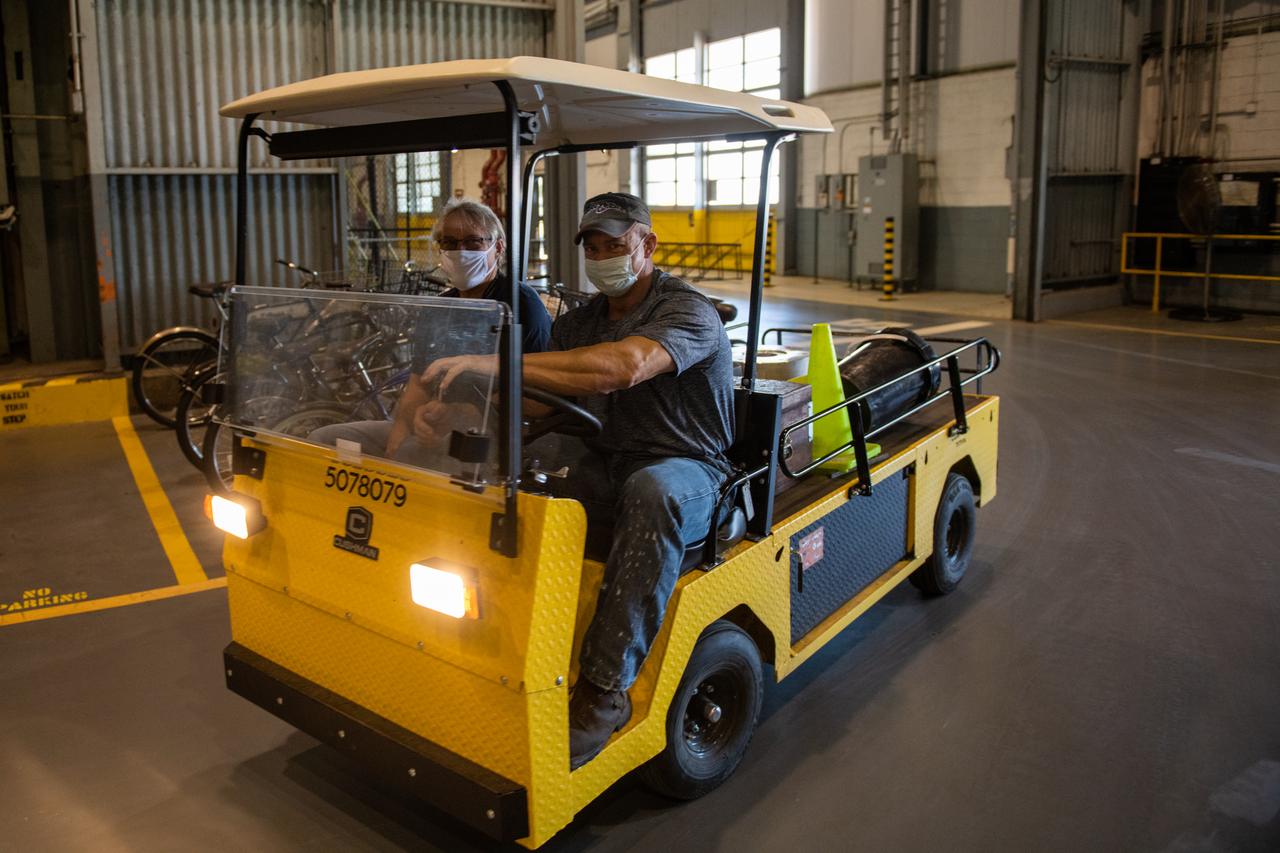

This photo includes two employees wearing personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Every team member who goes on-site brings their own cloth face covering and wears it when social distancing is not possible, such as in a shared vehicle when working inside the large factory. Michoud Assembly Facility is made up of multiple buildings, the largest of which is more than 38 acres under one roof. Wearing a facemask is mandatory for common areas where social distancing is difficult to achieve. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
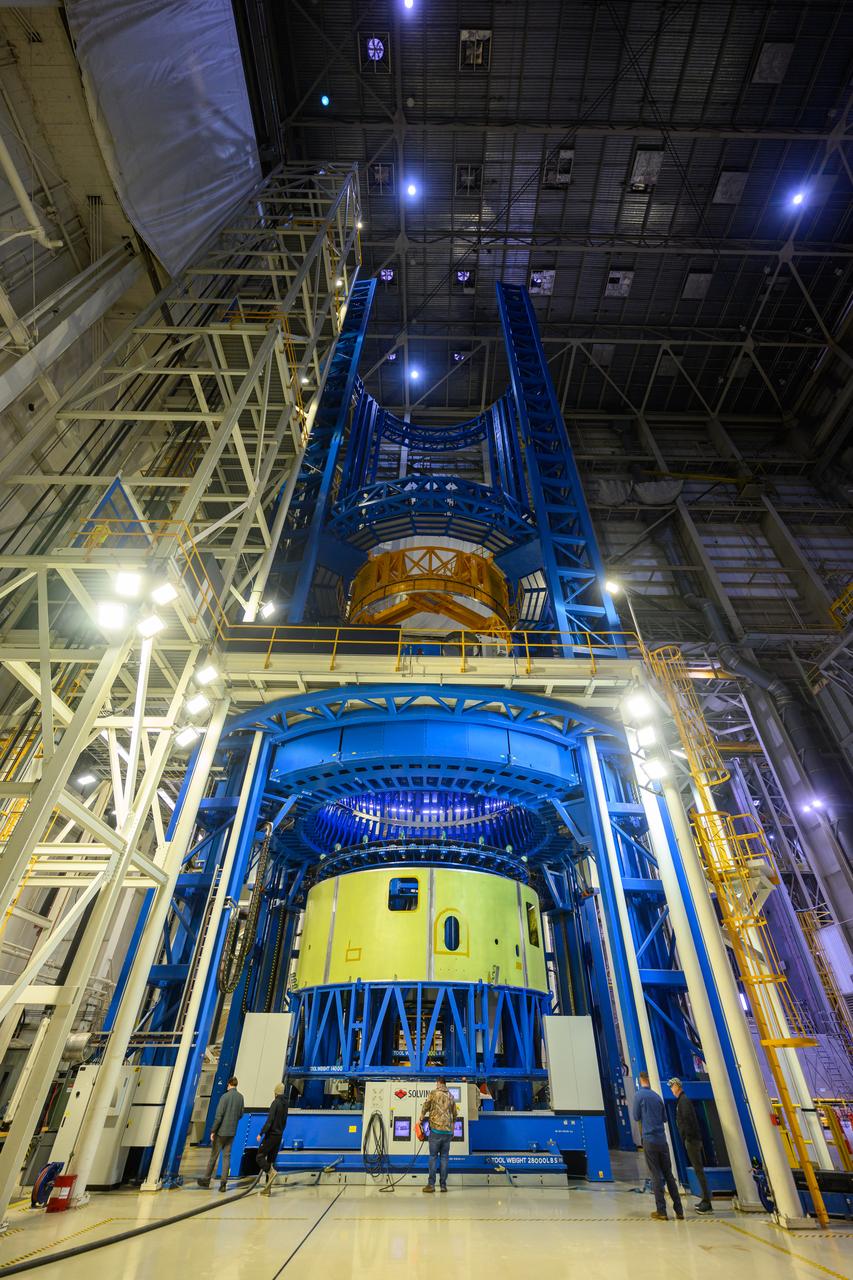
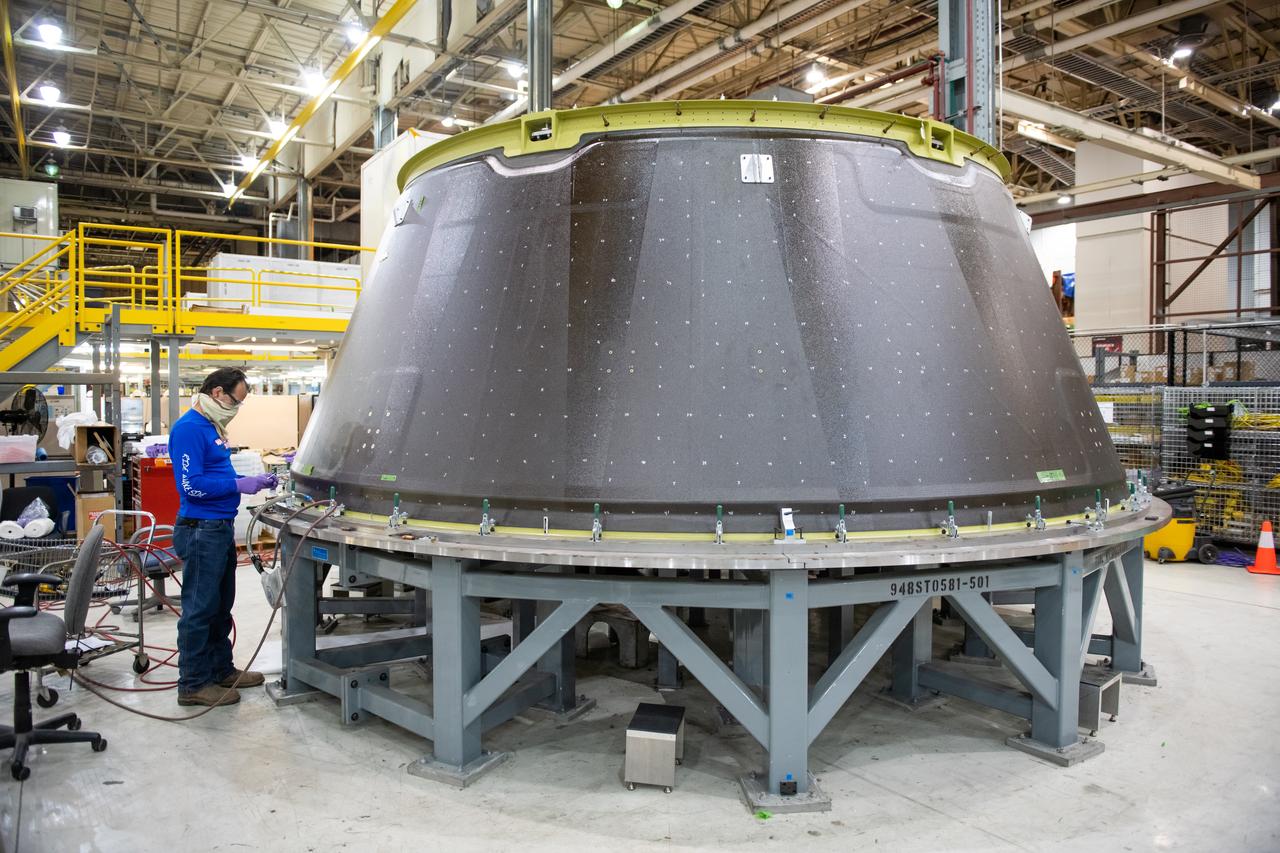
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt, which will be used on the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s core stage for the agency’s Artemis IV mission, into the vertical assembly center on Dec. 2. Inside the tooling, the forward skirt receives its forward and aft rings through a circumferential friction-stir welding process. Seven rings are used in the production of the core stage. They provide stiffening for the dome structures on the propellant tanks and, as on the forward skirt, serve as attachment points for the major components to form the SLS core stage. The forward skirt is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
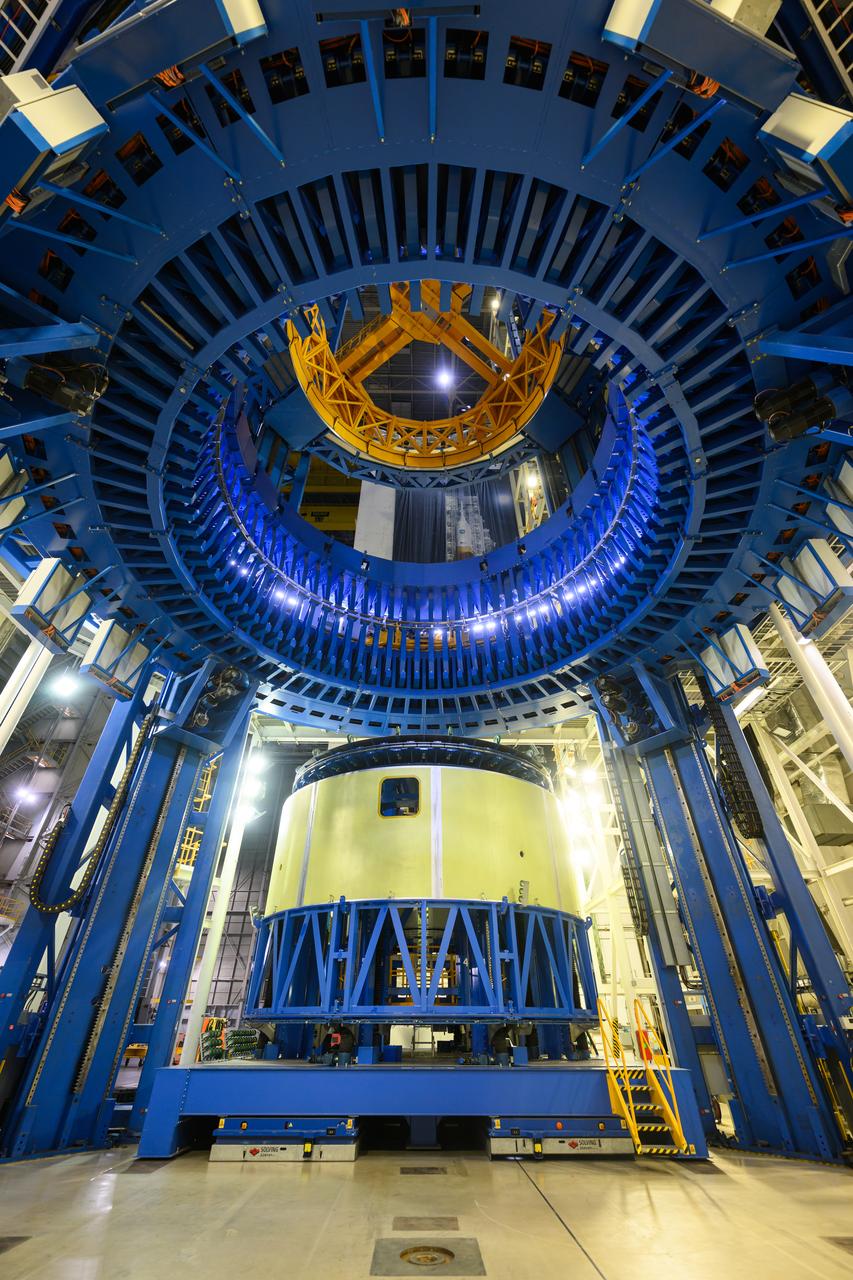
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt, which will be used on the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s core stage for the agency’s Artemis IV mission, into the vertical assembly center on Dec. 2. Inside the tooling, the forward skirt receives its forward and aft rings through a circumferential friction-stir welding process. Seven rings are used in the production of the core stage. They provide stiffening for the dome structures on the propellant tanks and, as on the forward skirt, serve as attachment points for the major components to form the SLS core stage. The forward skirt is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
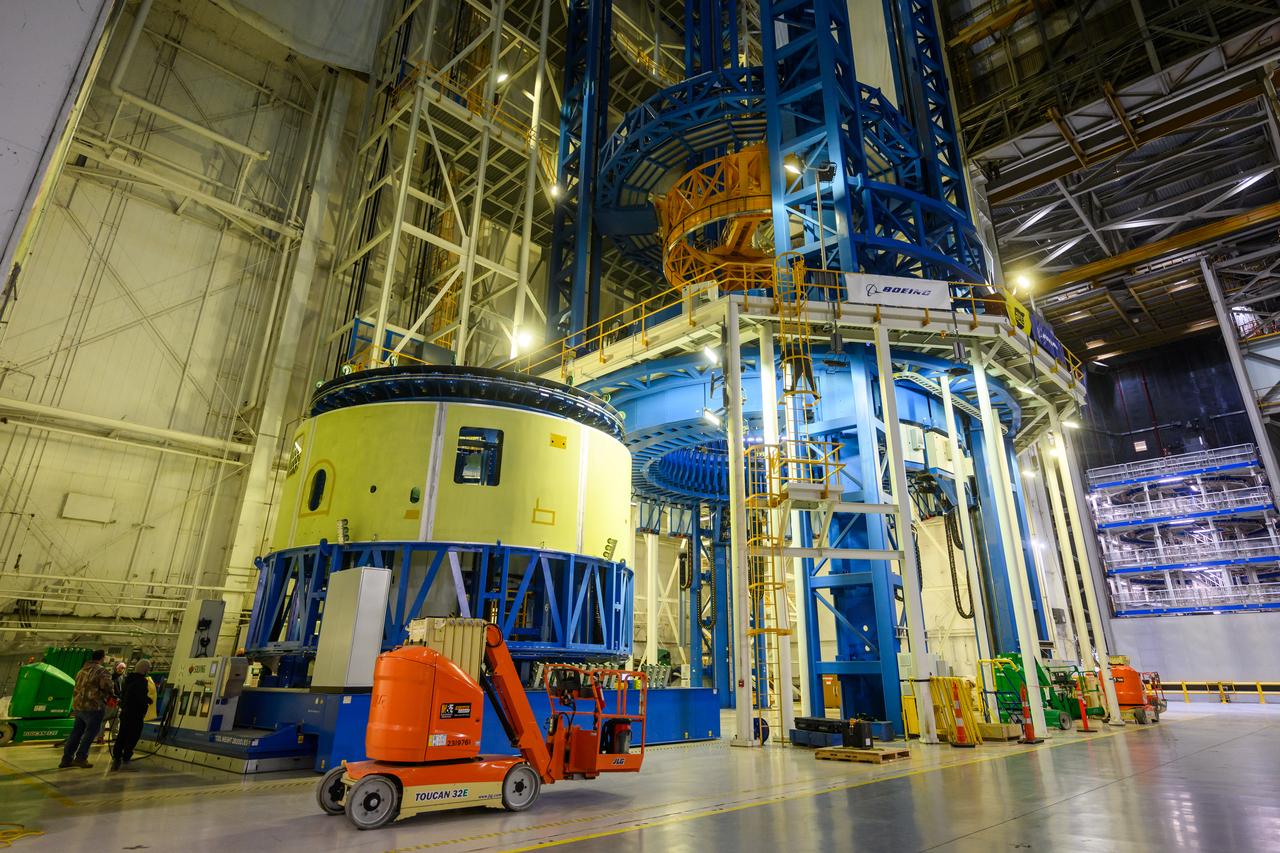

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt, which will be used on the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s core stage for the agency’s Artemis IV mission, into the vertical assembly center on Dec. 2. Inside the tooling, the forward skirt receives its forward and aft rings through a circumferential friction-stir welding process. Seven rings are used in the production of the core stage. They provide stiffening for the dome structures on the propellant tanks and, as on the forward skirt, serve as attachment points for the major components to form the SLS core stage. The forward skirt is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
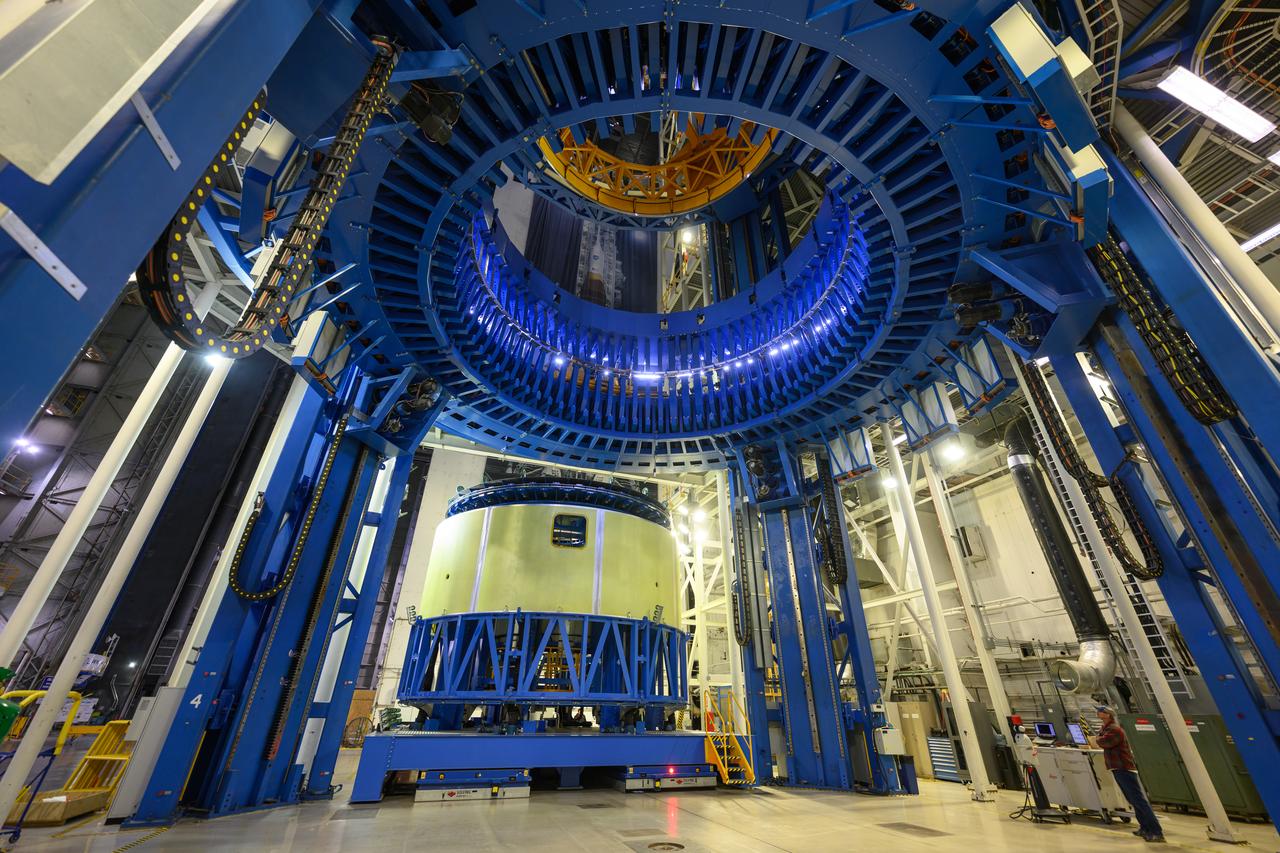

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move the forward skirt, which will be used on the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s core stage for the agency’s Artemis IV mission, into the vertical assembly center on Dec. 2. Inside the tooling, the forward skirt receives its forward and aft rings through a circumferential friction-stir welding process. Seven rings are used in the production of the core stage. They provide stiffening for the dome structures on the propellant tanks and, as on the forward skirt, serve as attachment points for the major components to form the SLS core stage. The forward skirt is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
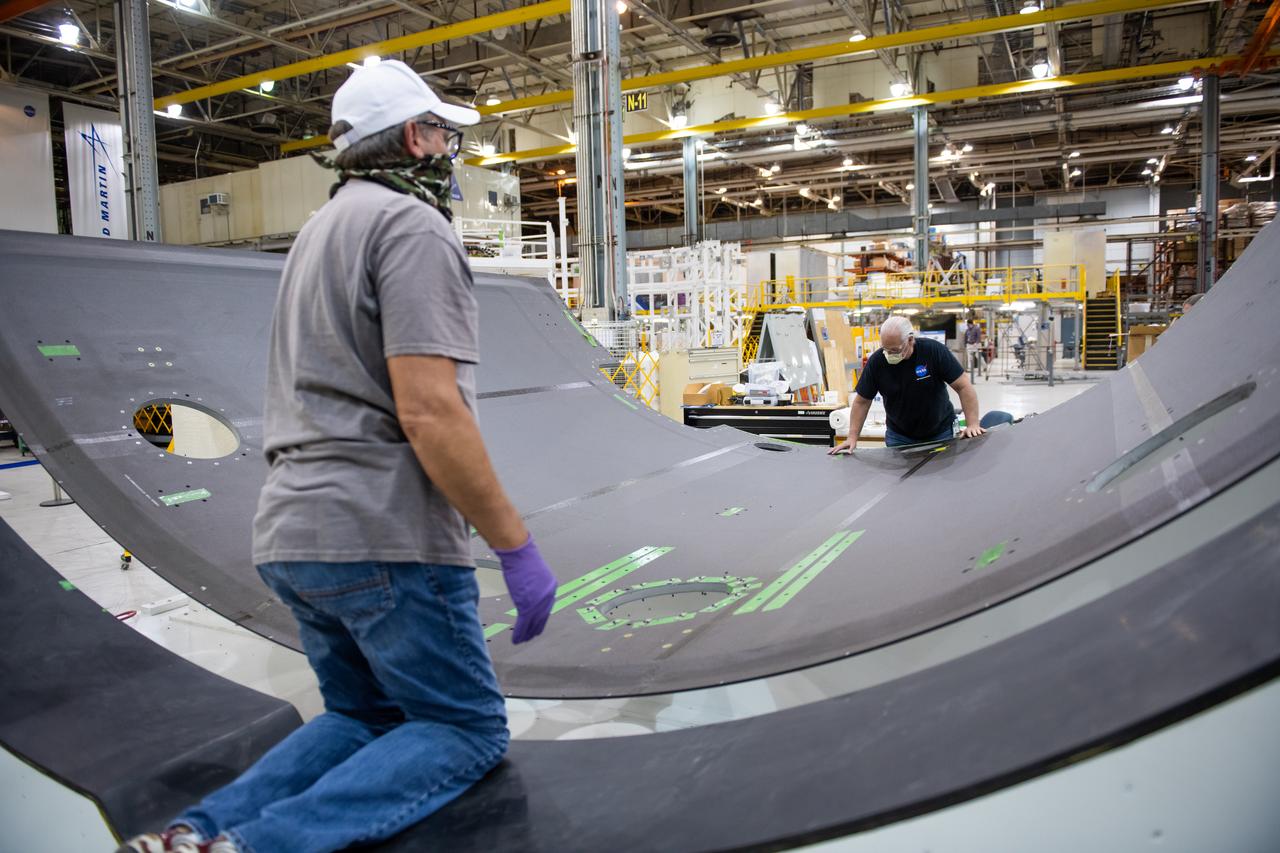

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
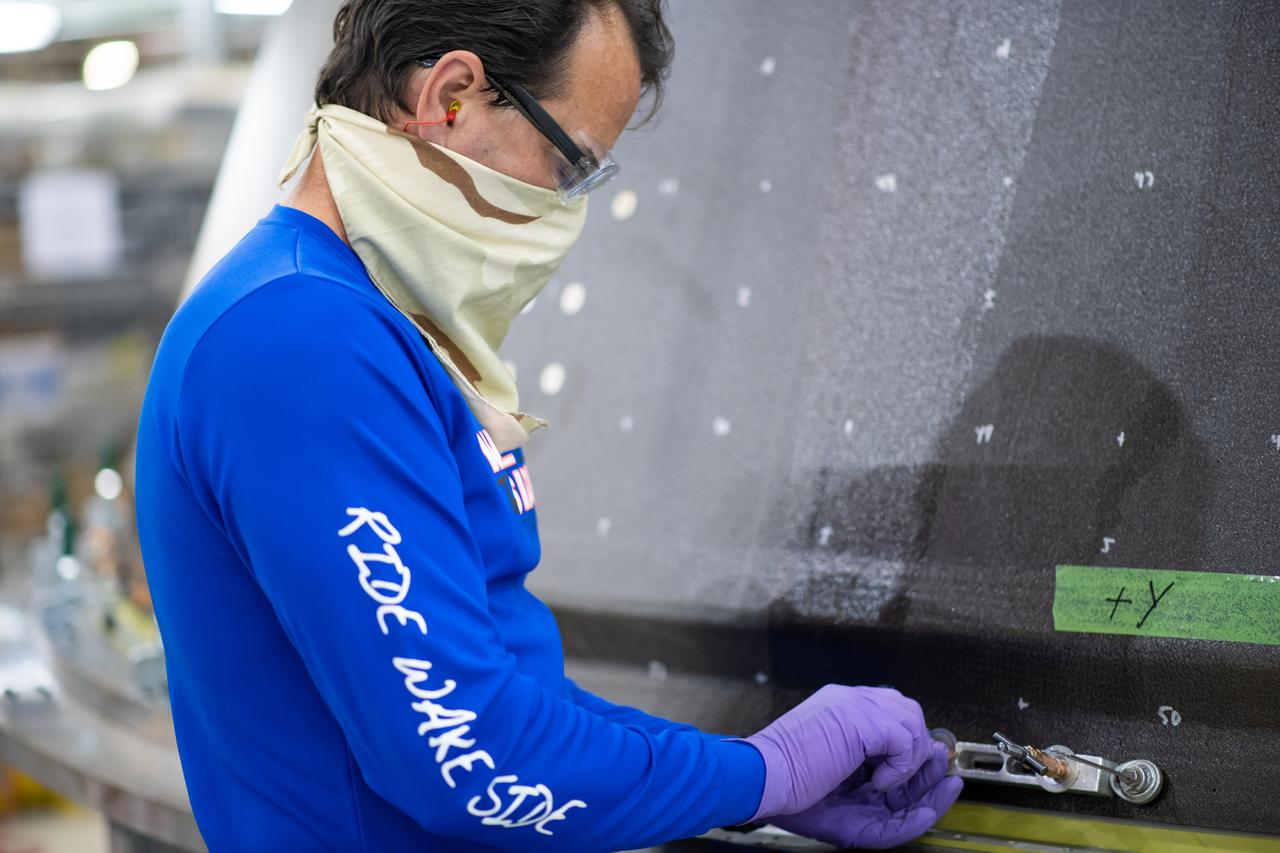

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
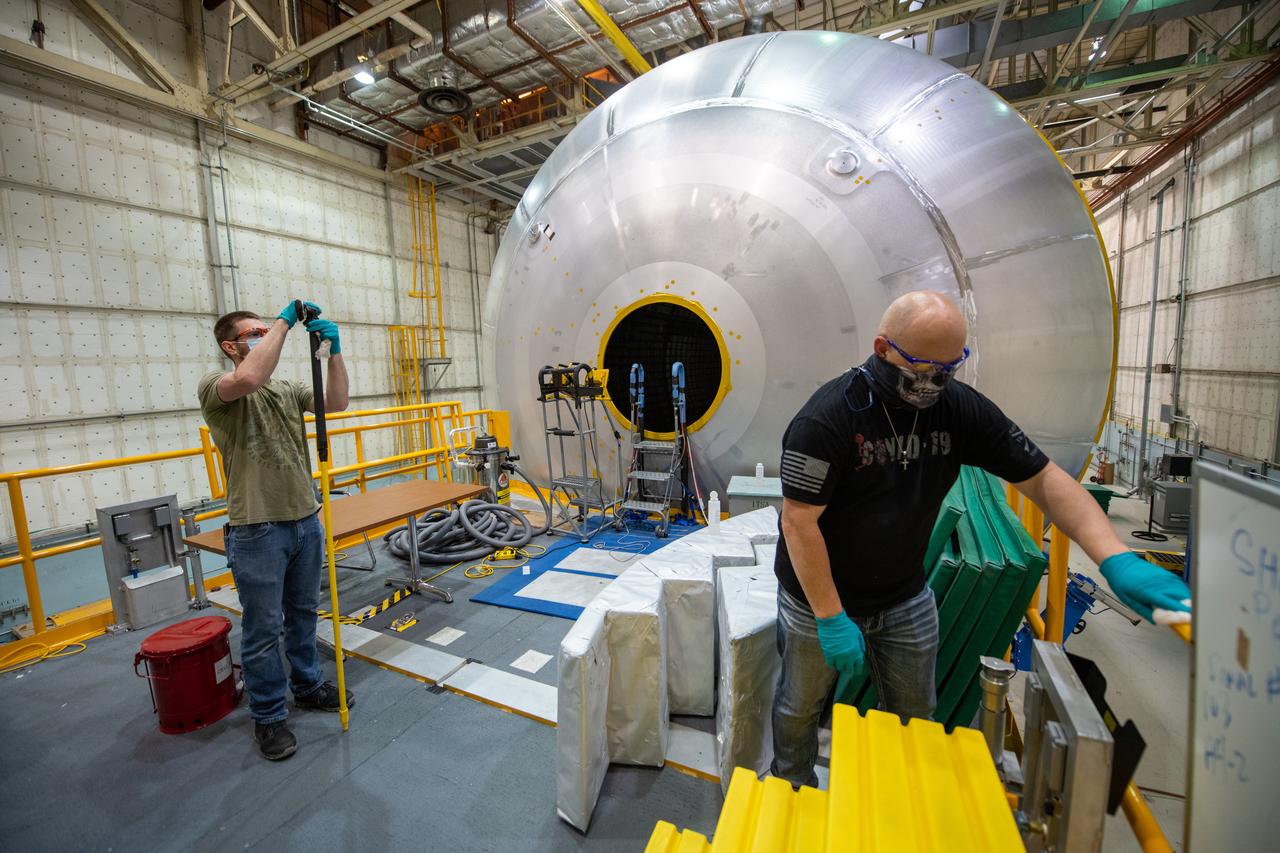

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
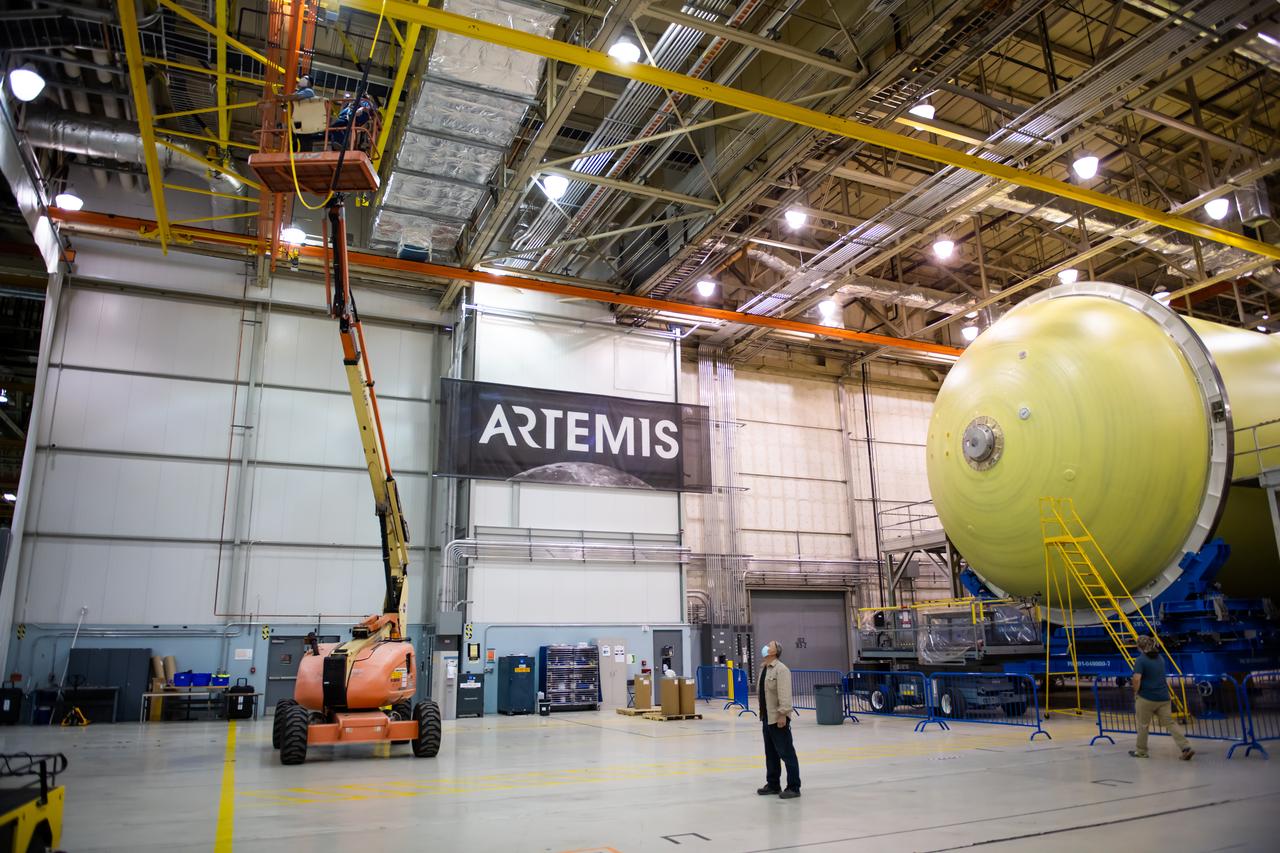

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
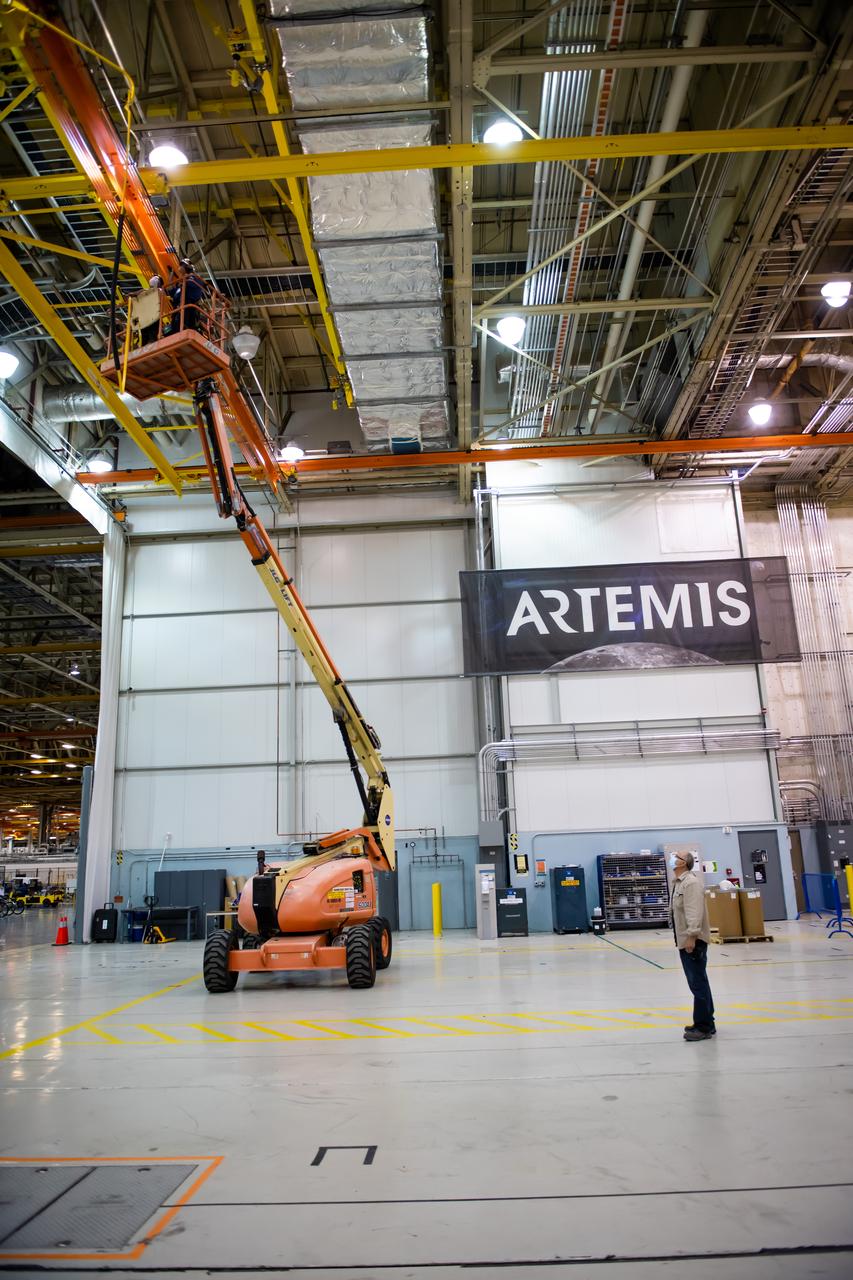

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
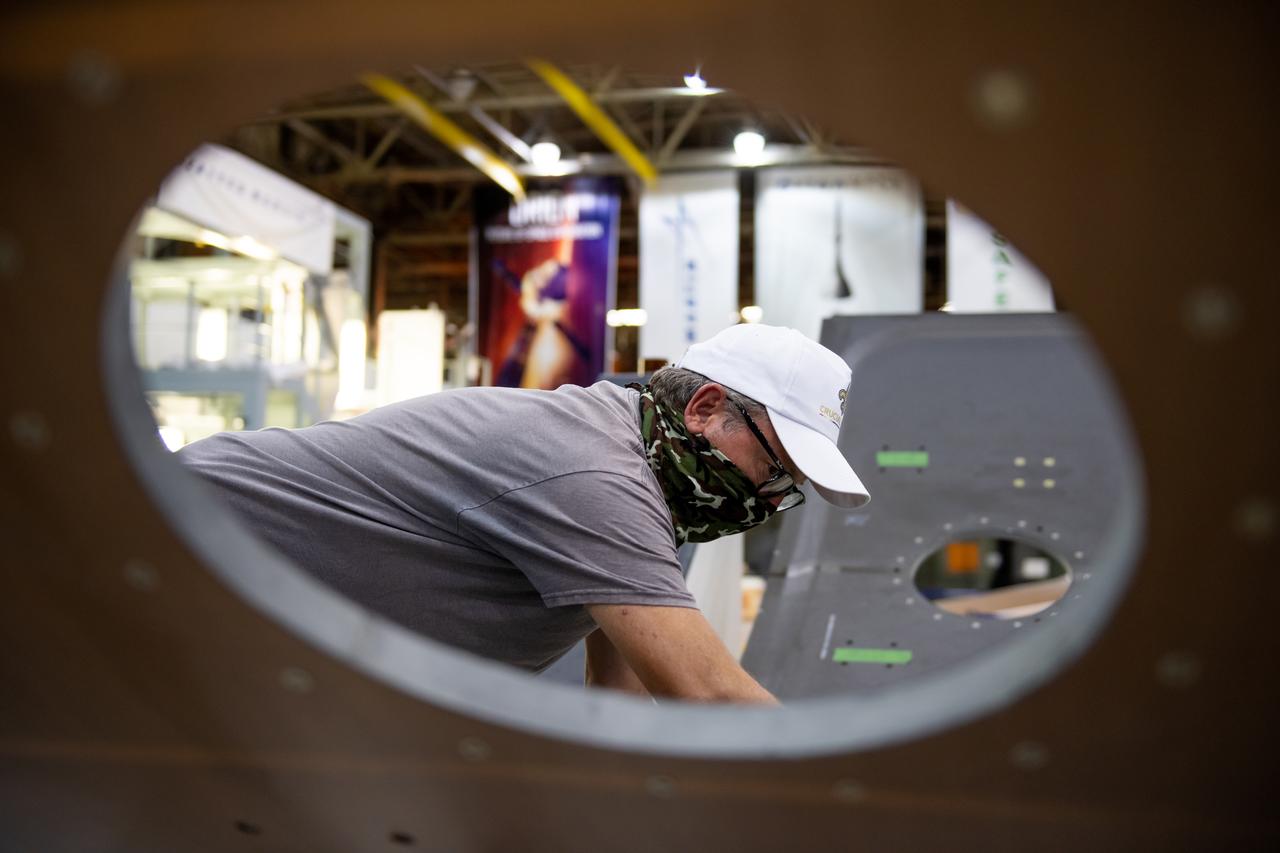

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
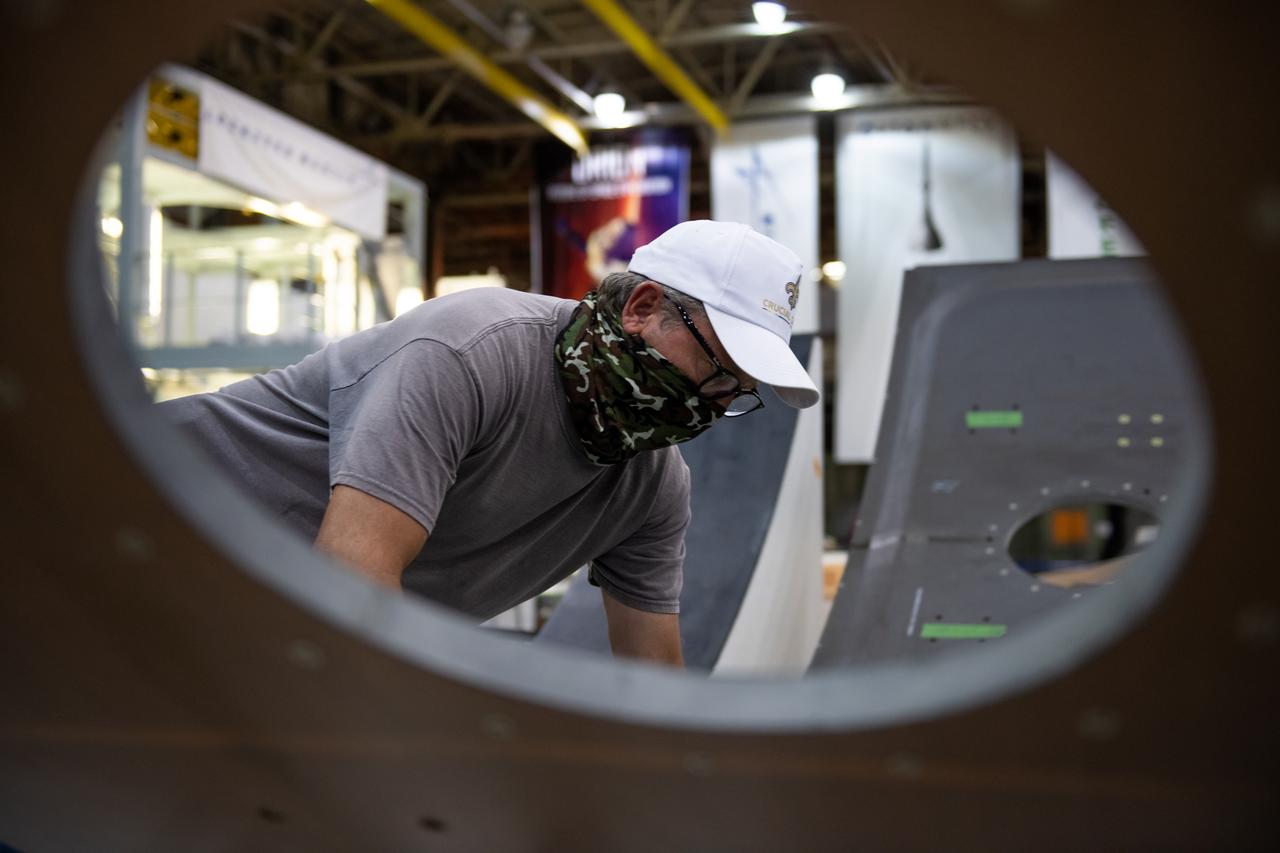

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
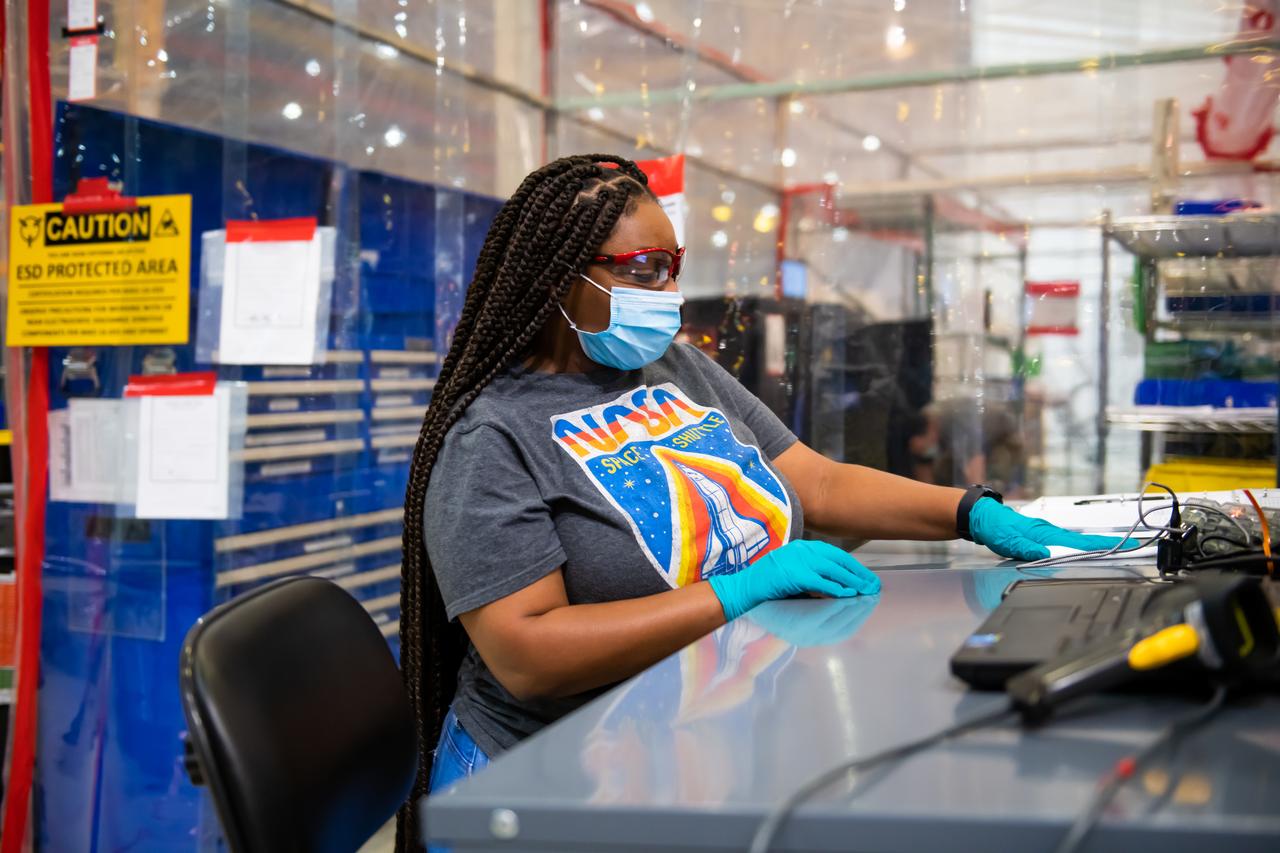

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
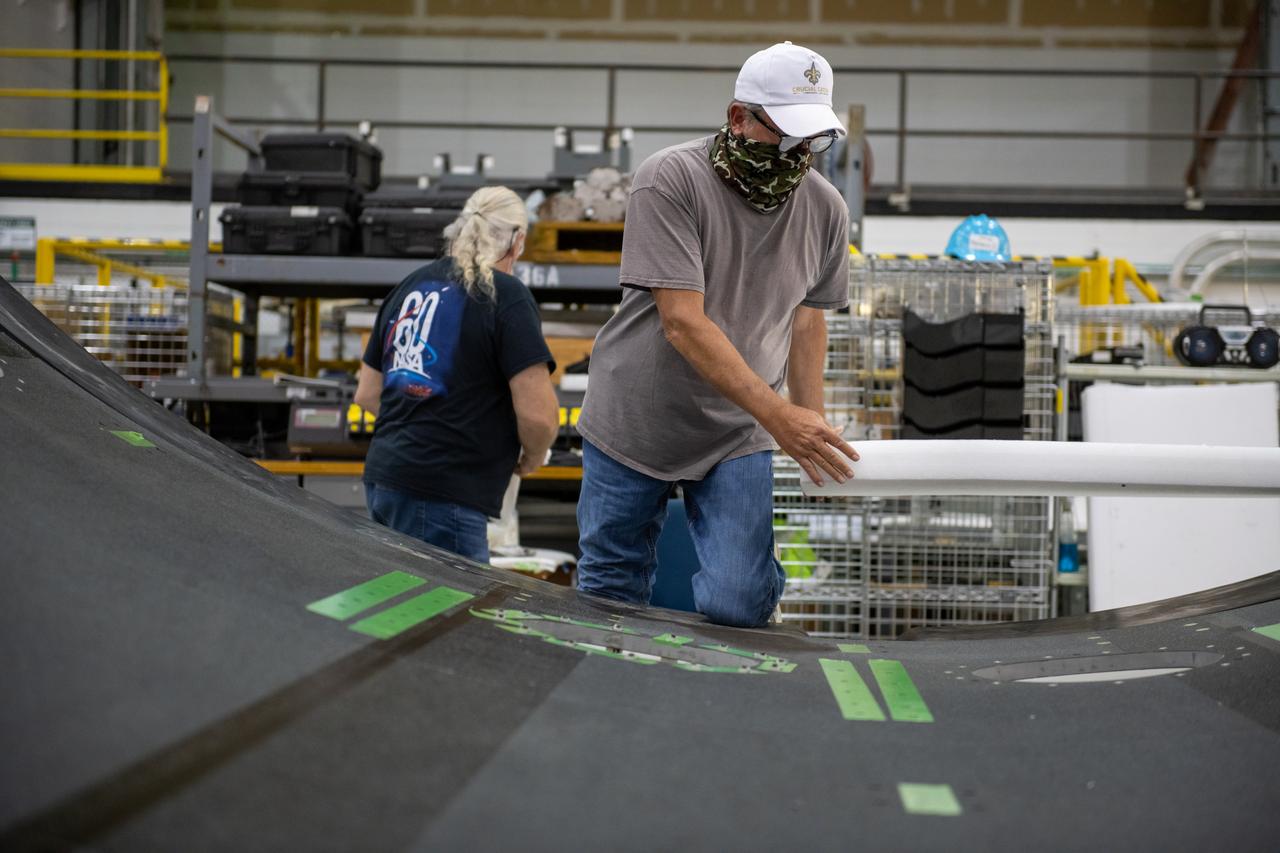

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.
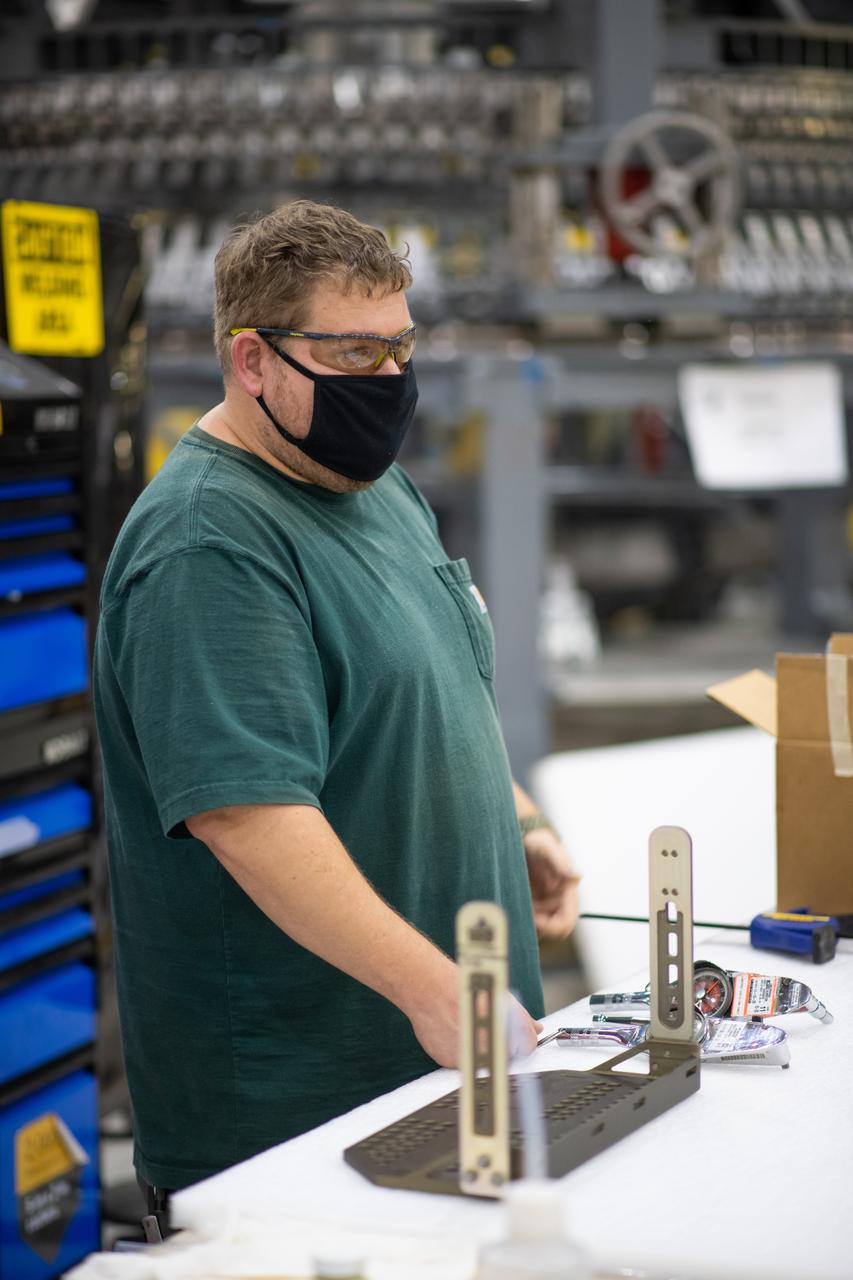

Employees wear personal protective gear at Michoud Assembly Facility as the facility transitioned to Stage 3 of NASA’s Framework for Return To On-Site Work. Employees wear the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or cloth face coverings as required for assigned tasks. Access to the facility is limited to authorized personnel working on mission-critical tasks that must be conducted onsite. Mission-critical tasks include slowly and methodically resuming Space Launch System (SLS) Core Stage and Orion production activities, particularly critical path deliverables to support the Artemis Program, at a pace that limits personnel and follows federal guidelines for social distancing and use of personal protective equipment such as face masks. For more information about SLS, visit nasa.gov/sls.