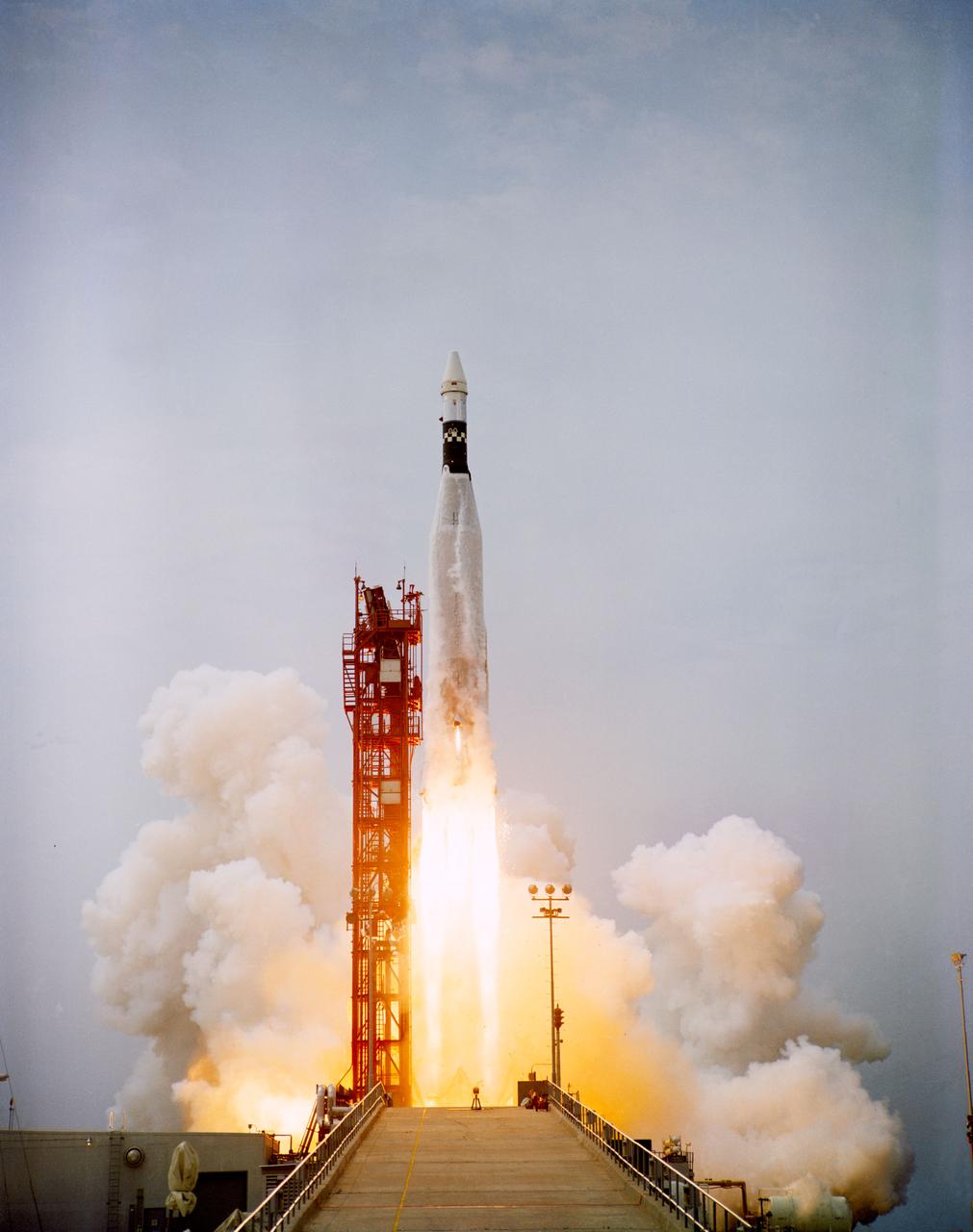

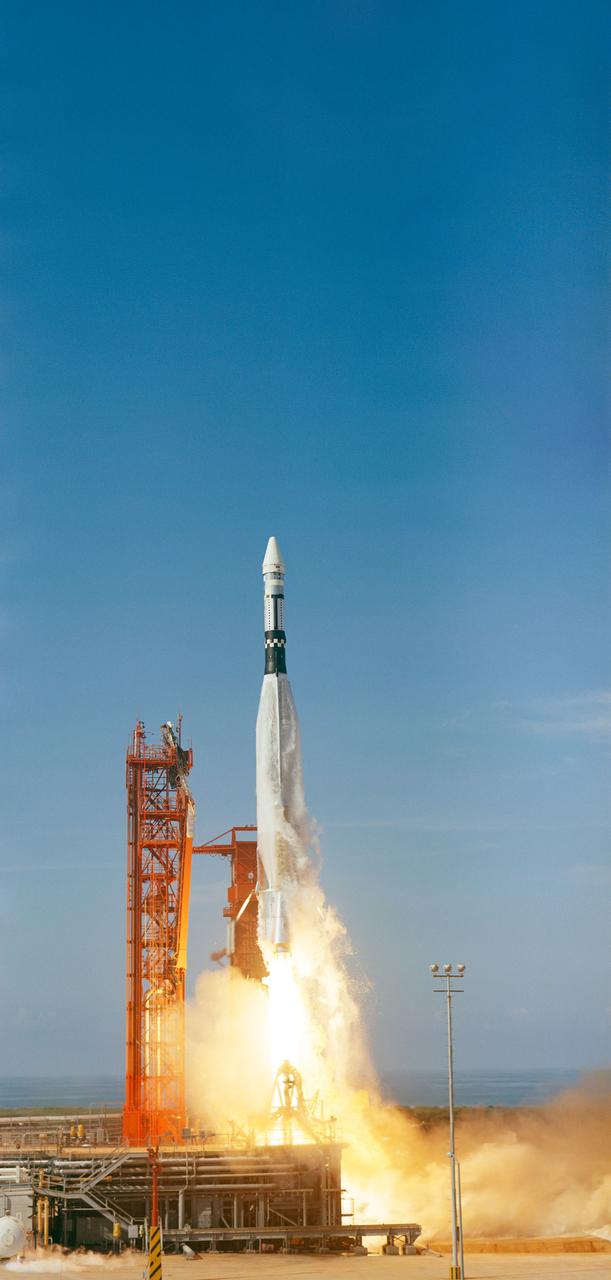
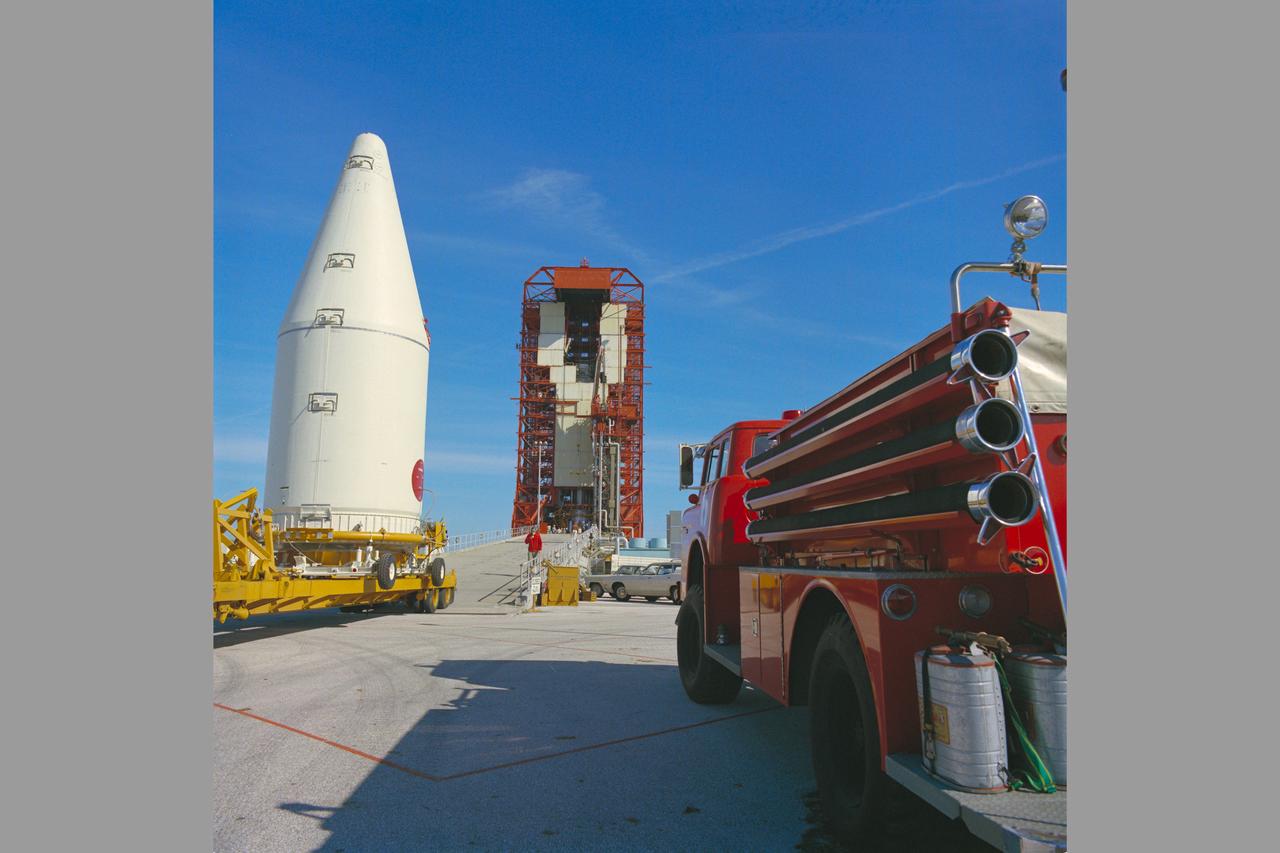
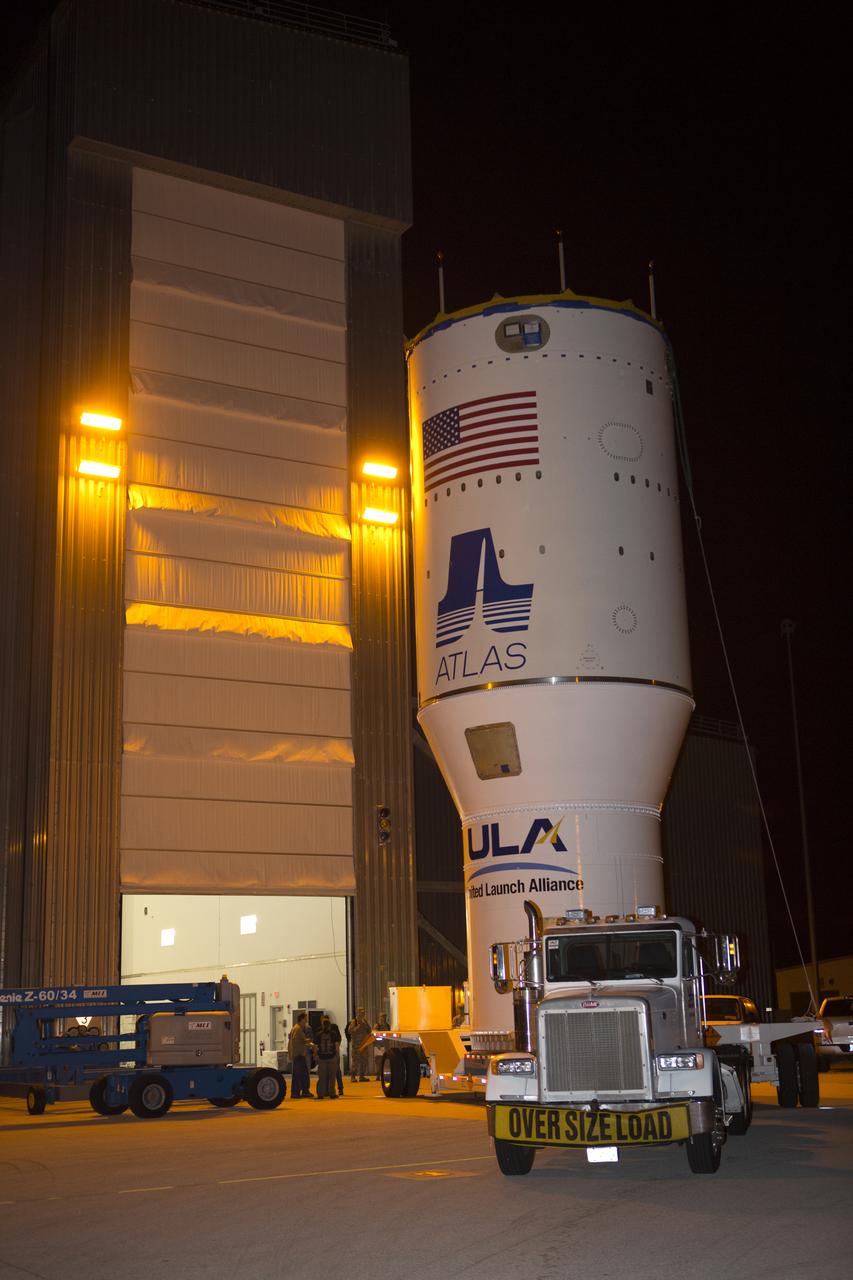
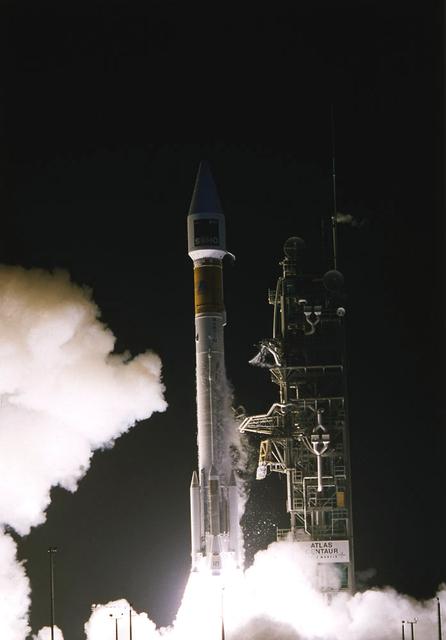
S66-32139 (1 June 1966) --- An Augmented Target Docking Adapter (ATDA) atop an Atlas launch vehicle is launched from Kennedy Space Center's Pad 14 at 10 a.m., June 1, 1966. The ATDA is a rendezvous and docking vehicle for the Gemini-9A space mission. Photo credit: NASA

This artist concept is of the Atlas V541 launch vehicle that will carry NASA Curiosity rover on its way to Mars. The Atlas V 541 vehicle was selected as it has the right liftoff capability for heavy weight requirements of the rover and its spacecraft.

In this artist's concept, a two-stage United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V launch vehicle speeds the Mars 2020 spacecraft toward the Red Planet. The rocket stands at 197 feet (60 meters) tall. This will be the 11th Mars launch on an Atlas rocket and the fifth by the Atlas V following NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter in 2005, Curiosity rover in 2011, MAVEN orbiter in 2013 and InSight lander in 2018. Charged with returning astronauts to the Moon by 2024, NASA will establish a sustained human presence on and around the Moon by 2028 through NASA's Artemis lunar exploration plans. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23922
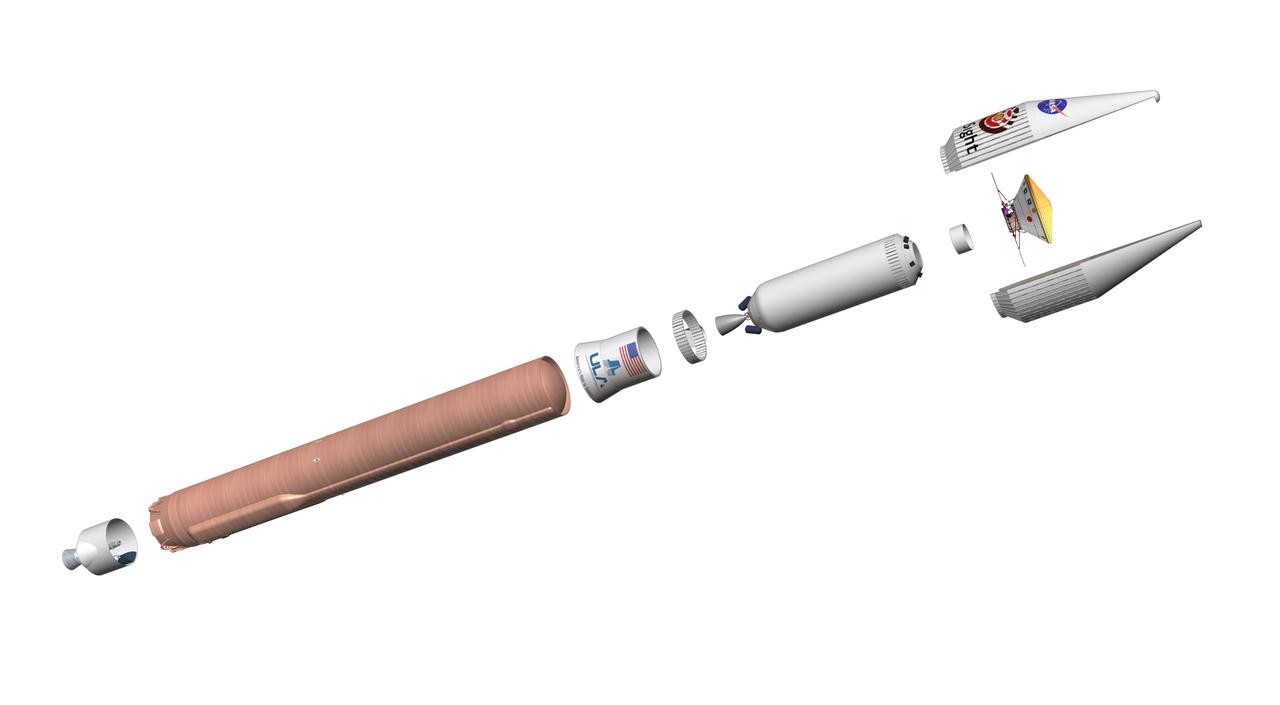
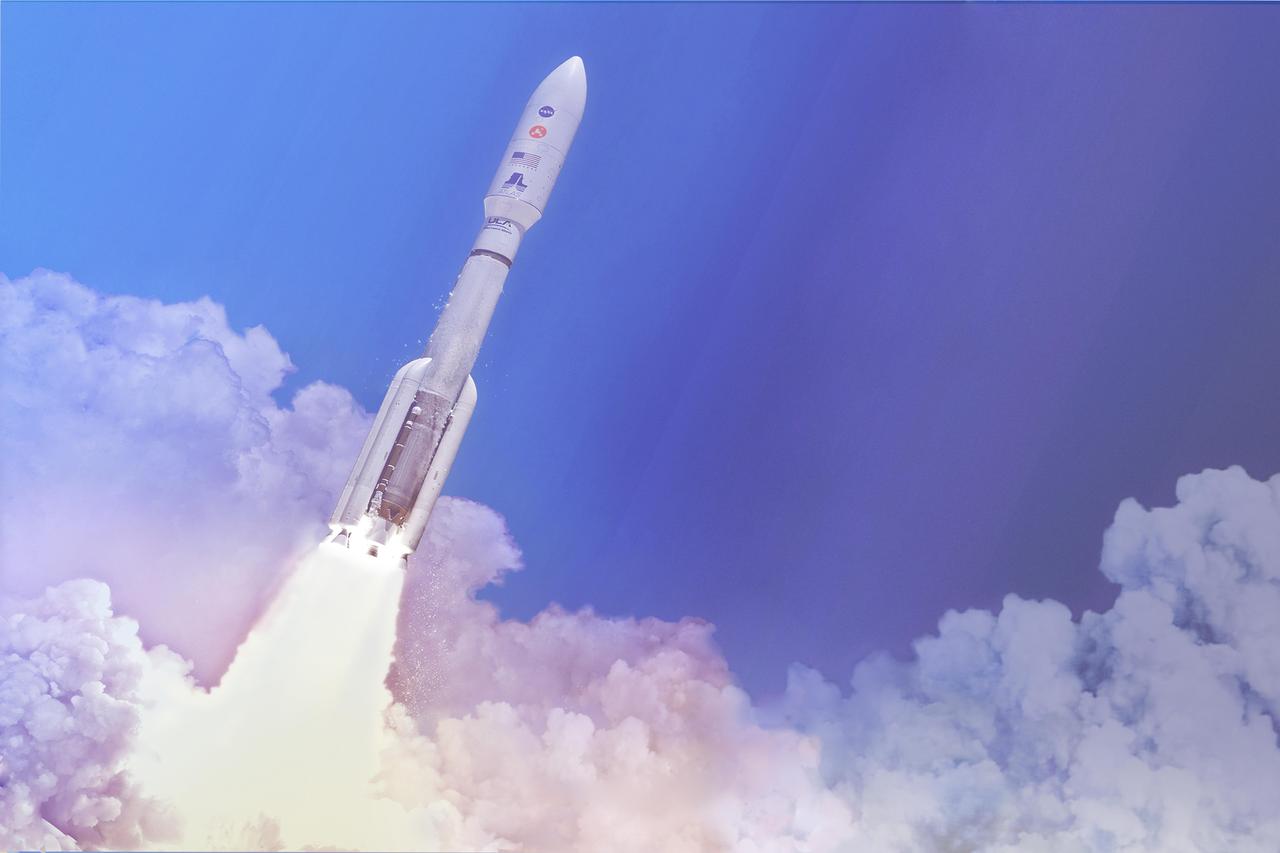
Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, is scheduled to launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base on California's Pacific coast between May 5 and June 8, 2018. The lander will launch to Mars aboard an Atlas V-401 launch vehicle, one of the biggest rockets available for interplanetary flight. It stands 188 feet (57.3 meters) tall, or about as tall as a 19-story building. Fully stacked, with the spacecraft, the Atlas V-401 weighs about 730,000 pounds (333,000 kilograms). That's about 14 big rigs, fully loaded with cargo! The three numbers in the 401 designation signify: 4: a payload fairing -- or nose cone -- that is about 13 feet (4 meters) in diameter 0: solid-rocket boosters supplementing the main booster 1: the upper stage, which has one engine https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22231
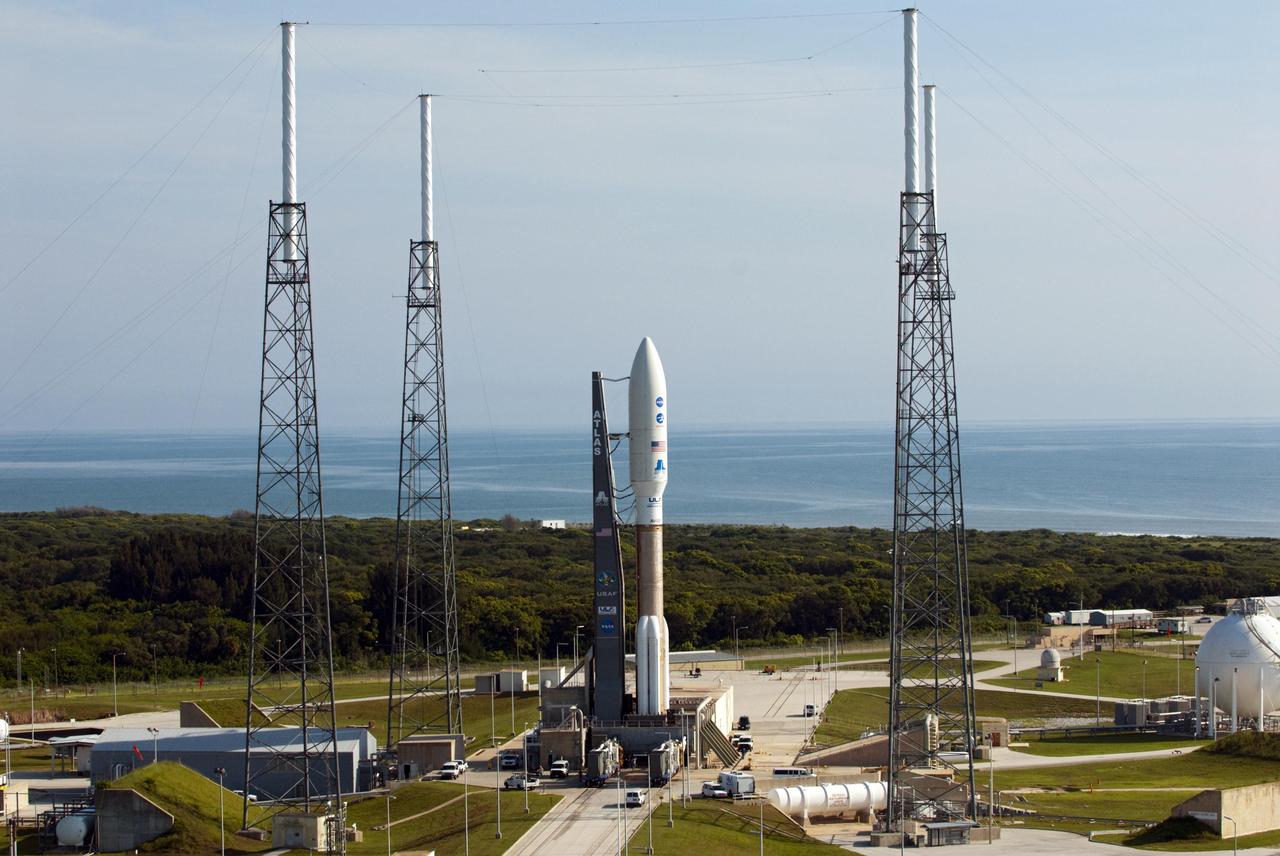

NASA Juno spacecraft awaits launch from inside the payload fairing atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V-551 launch vehicle. Juno and its rocket are at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) mission arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Space Launch Complex 3E in California on Sept. 28, 2022. Once JPSS-2 – enclosed inside its protective payload fairing – arrives at the VIF, it will be secured to the top of the rocket. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series that will be used to capture data and improve weather forecasts, leading scientists to better predict for extreme weather events and climate change. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a technology demonstration of an inflatable heat shield that could one day help land humans on Mars. Liftoff is targeted for 2:25 a.m. Pacific time (5:25 a.m. Eastern time) on Nov. 1, 2022, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 3E.
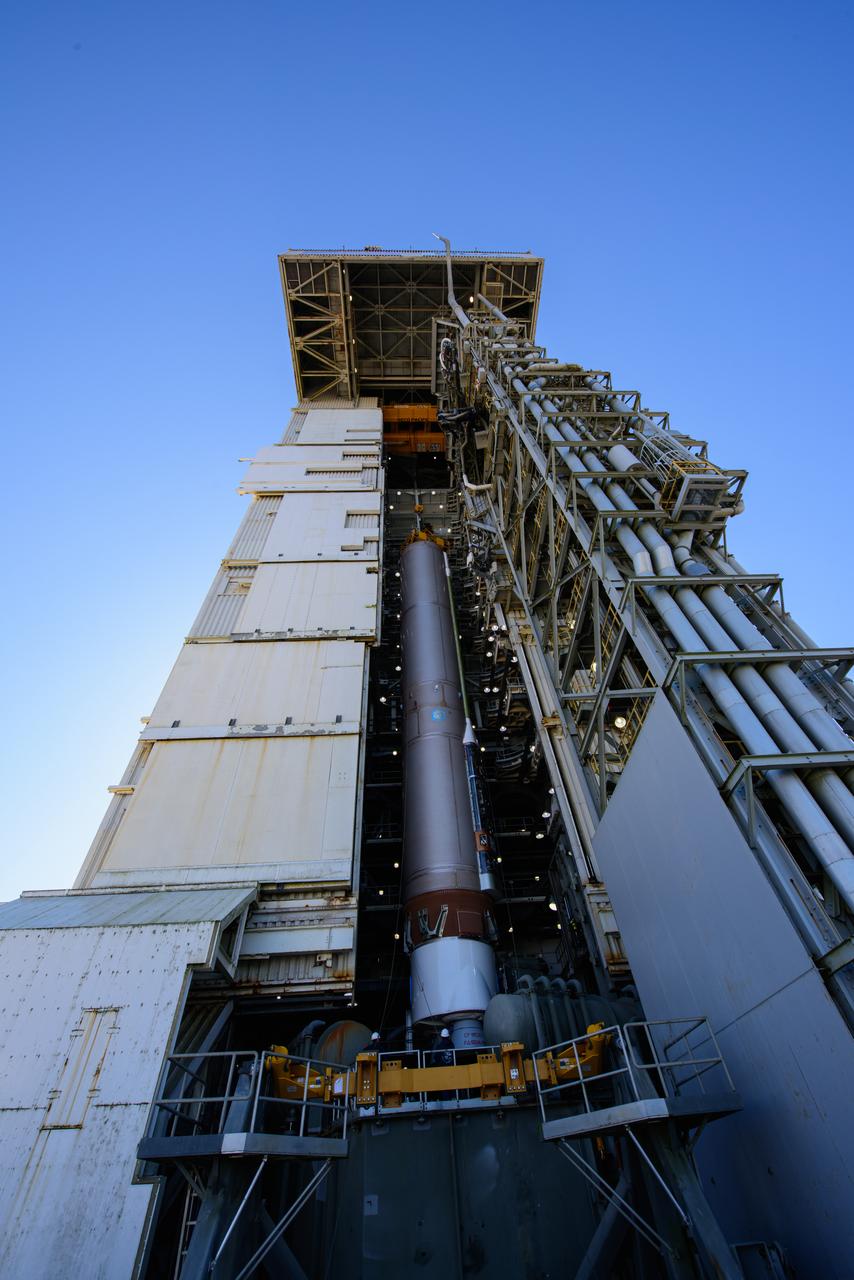

Following its arrival to Space Launch Complex 3E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) mission is moved into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) on Sept. 28, 2022. Once JPSS-2 – enclosed inside its protective payload fairing – arrives at the VIF, it will be secured to the top of the rocket. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series that will be used to capture data and improve weather forecasts, leading scientists to better predict for extreme weather events and climate change. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a technology demonstration of an inflatable heat shield that could one day help land humans on Mars. Liftoff is targeted for 2:25 a.m. Pacific time (5:25 a.m. Eastern time) on Nov. 1, 2022, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 3E.

Following its arrival to Space Launch Complex 3E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) mission is moved into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) on Sept. 28, 2022. Once JPSS-2 – enclosed inside its protective payload fairing – arrives at the VIF, it will be secured to the top of the rocket. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series that will be used to capture data and improve weather forecasts, leading scientists to better predict for extreme weather events and climate change. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a technology demonstration of an inflatable heat shield that could one day help land humans on Mars. Liftoff is targeted for 2:25 a.m. Pacific time (5:25 a.m. Eastern time) on Nov. 1, 2022, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 3E.

Teams prepare to lift the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) mission and rotate it to a vertical position by crane following its arrival to the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sept. 28, 2022. Once JPSS-2 – enclosed inside its protective payload fairing – arrives at the VIF, it will be secured to the top of the rocket. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series that will be used to capture data and improve weather forecasts, leading scientists to better predict for extreme weather events and climate change. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a technology demonstration of an inflatable heat shield that could one day help land humans on Mars. Liftoff is targeted for 2:25 a.m. Pacific time (5:25 a.m. Eastern time) on Nov. 1, 2022, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 3E.
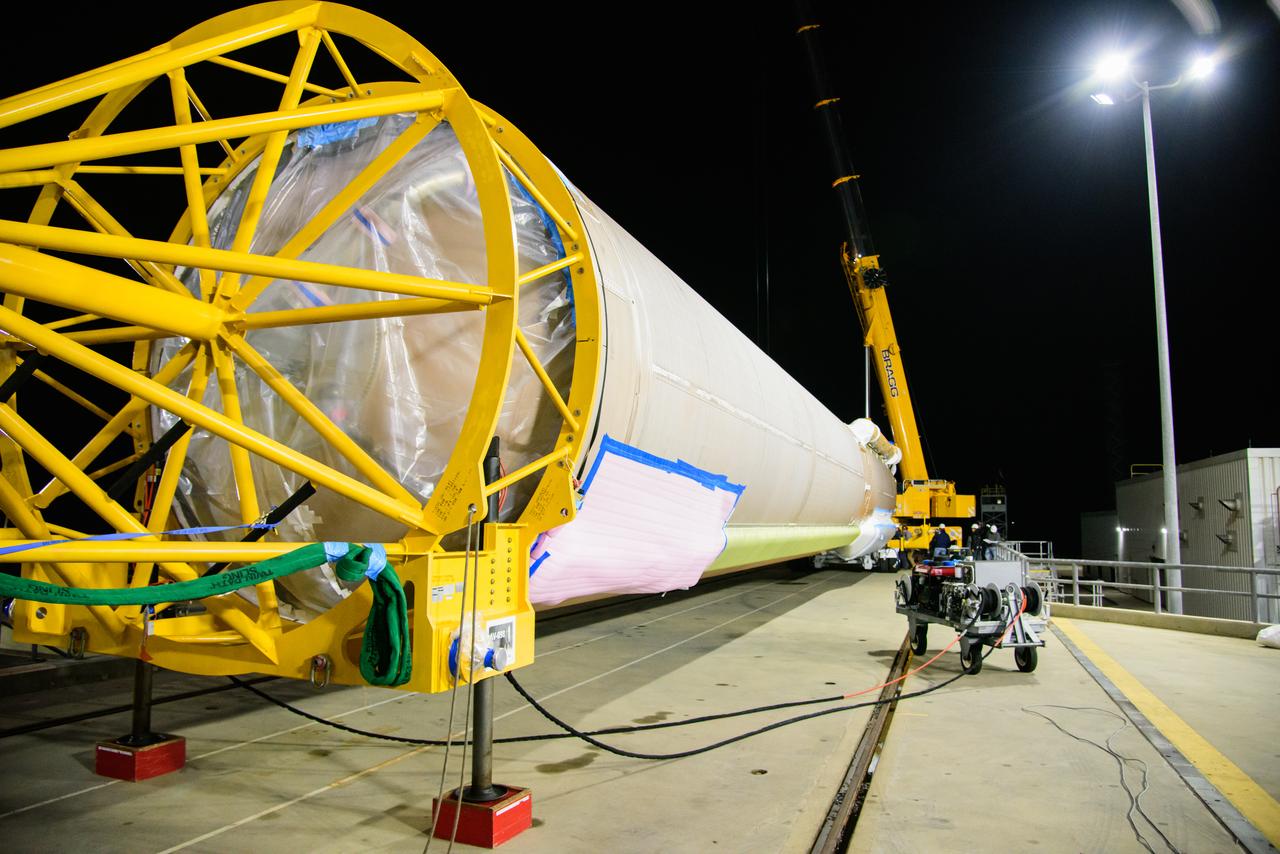

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket that will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) mission arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Vandenberg Space Force Base’s Space Launch Complex 3E in California on Sept. 28, 2022. Once JPSS-2 – enclosed inside its protective payload fairing – arrives at the VIF, it will be secured to the top of the rocket. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series that will be used to capture data and improve weather forecasts, leading scientists to better predict for extreme weather events and climate change. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a technology demonstration of an inflatable heat shield that could one day help land humans on Mars. Liftoff is targeted for 2:25 a.m. Pacific time (5:25 a.m. Eastern time) on Nov. 1, 2022, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 3E.

At Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, teams hoist the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) mission into a vertical position in preparation for a move into the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) on Sept. 28, 2022. Once JPSS-2 – enclosed inside its protective payload fairing – arrives at the VIF, it will be secured to the top of the rocket. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series that will be used to capture data and improve weather forecasts, leading scientists to better predict for extreme weather events and climate change. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a technology demonstration of an inflatable heat shield that could one day help land humans on Mars. Liftoff is targeted for 2:25 a.m. Pacific time (5:25 a.m. Eastern time) on Nov. 1, 2022, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 3E.

Teams prepare to lift the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) mission and rotate it to a vertical position by crane following its arrival to the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sept. 28, 2022. Once JPSS-2 – enclosed inside its protective payload fairing – arrives at the VIF, it will be secured to the top of the rocket. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series that will be used to capture data and improve weather forecasts, leading scientists to better predict for extreme weather events and climate change. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a technology demonstration of an inflatable heat shield that could one day help land humans on Mars. Liftoff is targeted for 2:25 a.m. Pacific time (5:25 a.m. Eastern time) on Nov. 1, 2022, from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 3E.
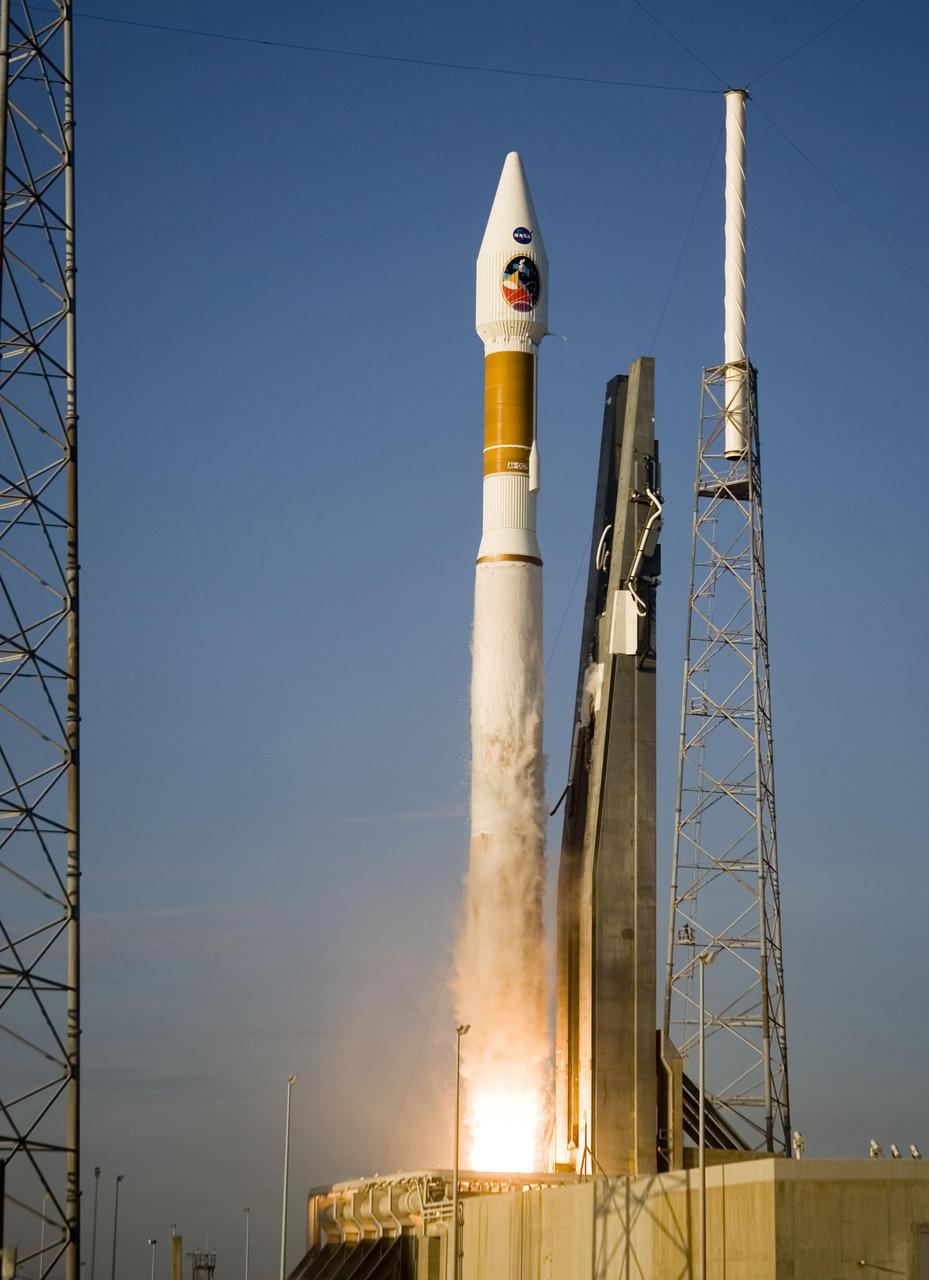

Atlas V launch vehicle, 19 stories tall, with a two-ton NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO on top, lifts off the pad on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Aug. 12, 2005.
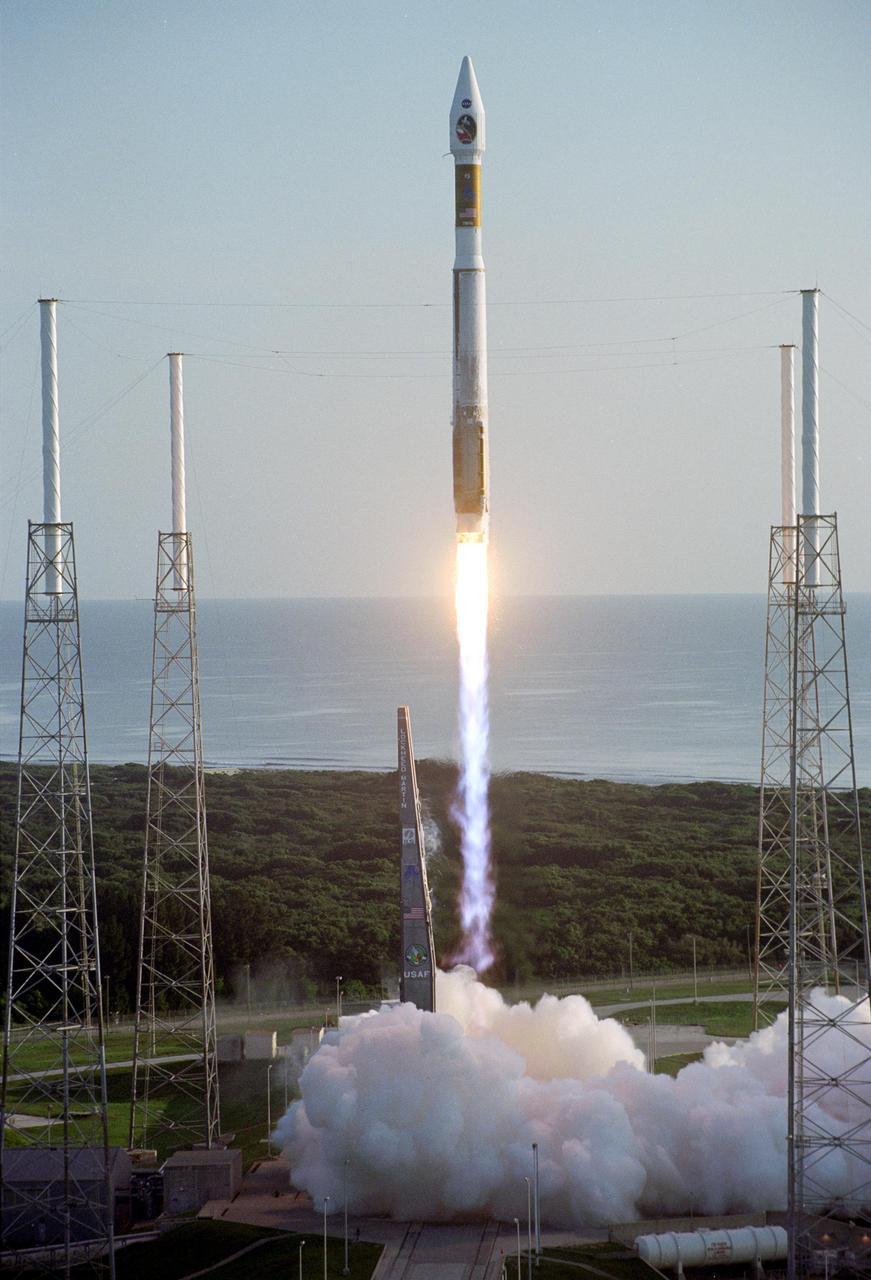

With the Atlantic Ocean as a backdrop, an Atlas V launch vehicle, 19 stories tall, with a two-ton NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO on top, roars away from Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
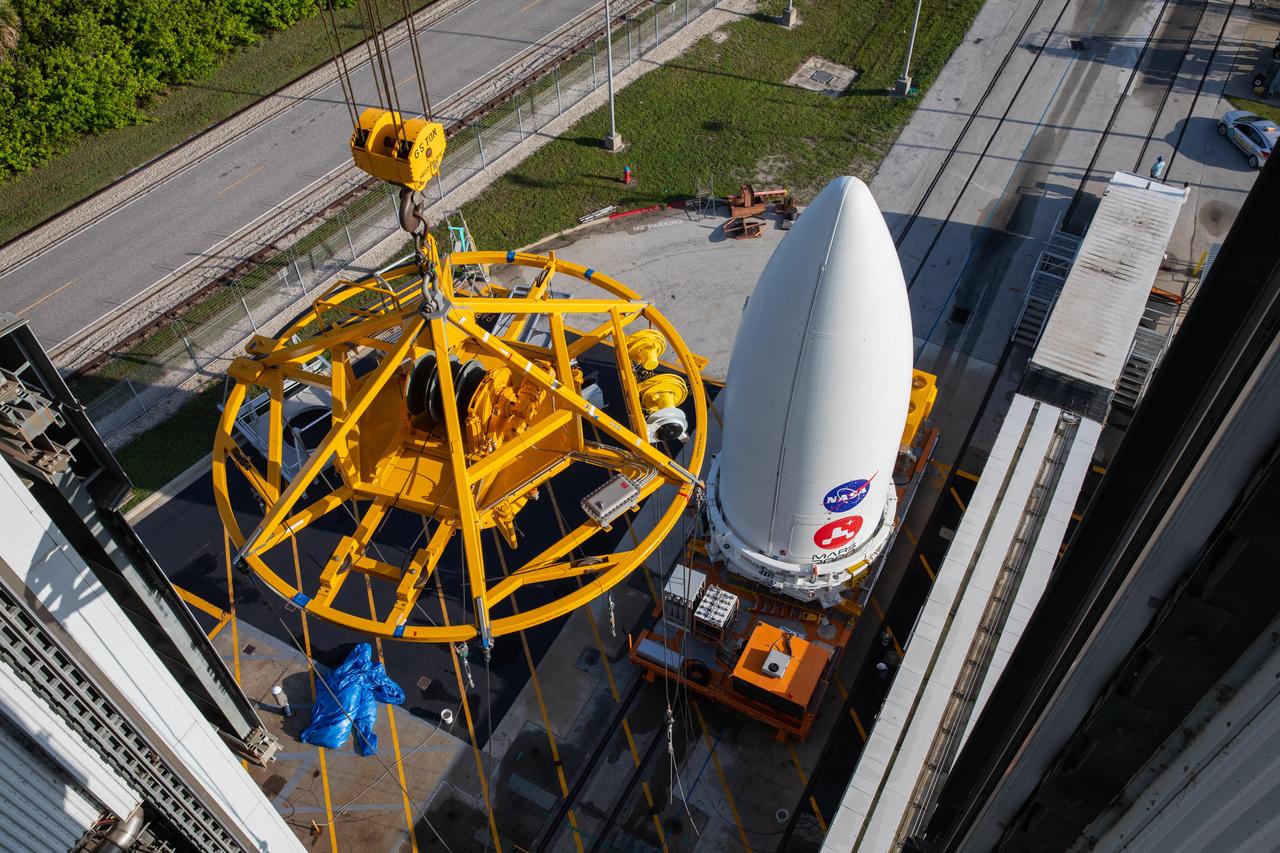

A crane stands at the ready to hoist the payload fairing, or nose cone, containing NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover onto the top of an Atlas V launch vehicle. The image was taken at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on July 7, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23984
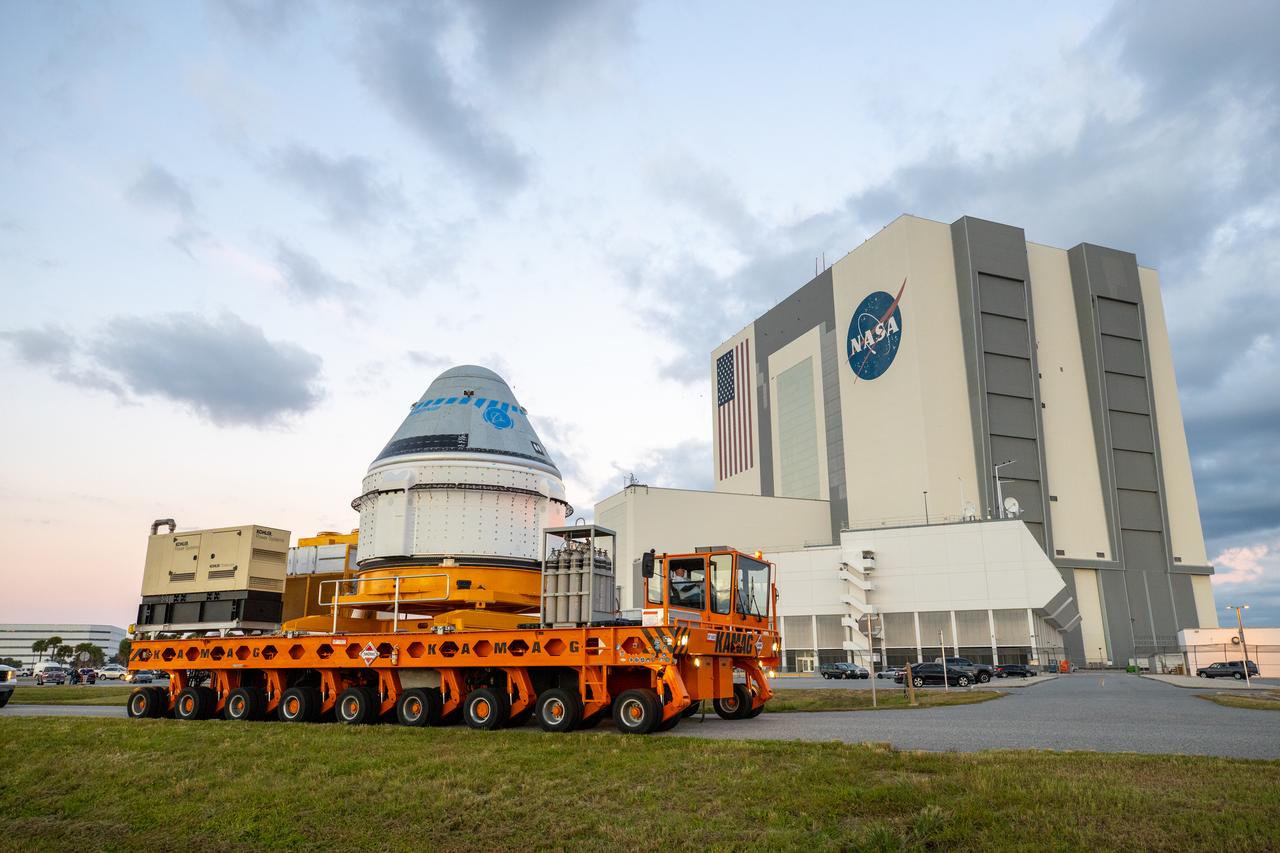

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft passes by the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019, making its way to the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. At the pad, Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in preparation for Boeing’s uncrewed Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
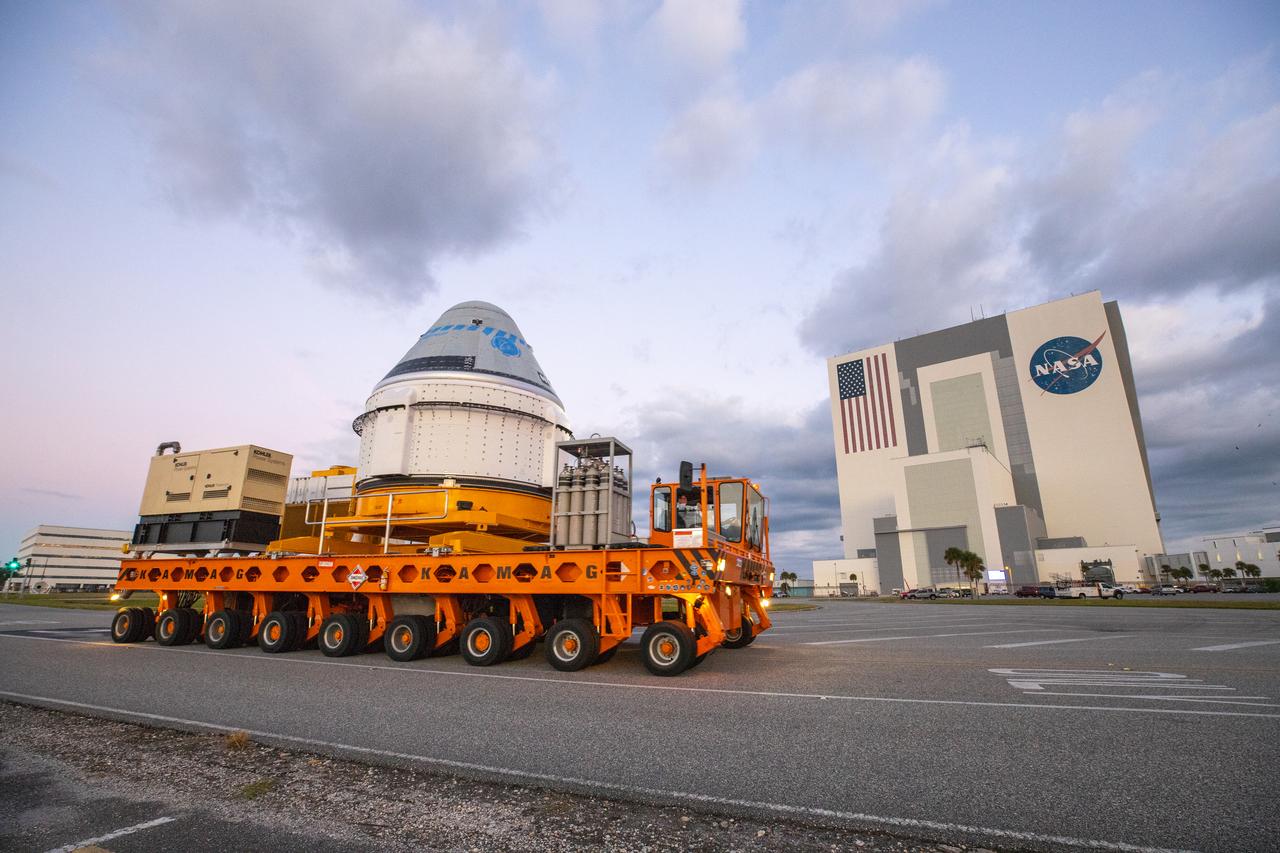

Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft passes by the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019, making its way to the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. At the pad, Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in preparation for Boeing’s uncrewed Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
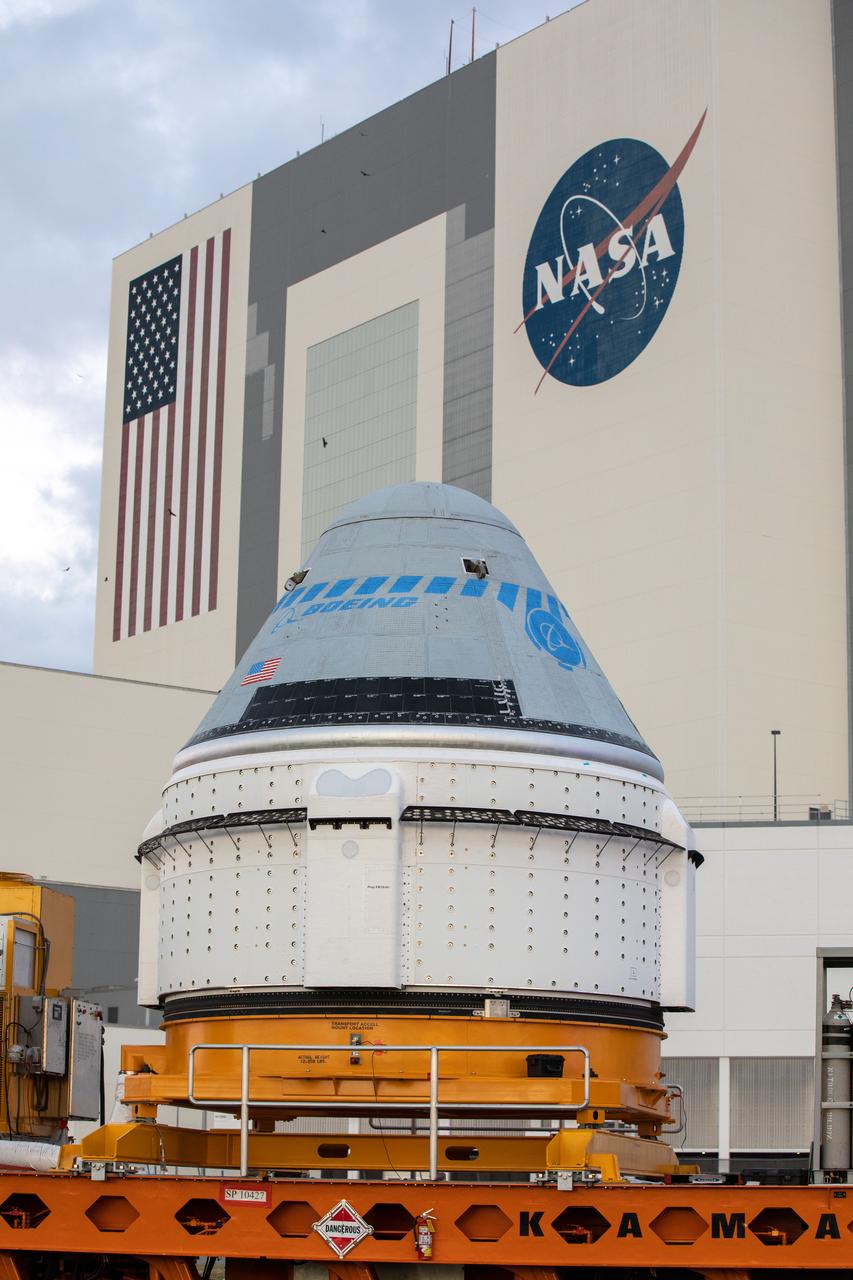
Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner spacecraft passes by the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019, making its way to the Space Launch Complex 41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. At the pad, Starliner will be secured atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in preparation for Boeing’s uncrewed Orbital Flight Test to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
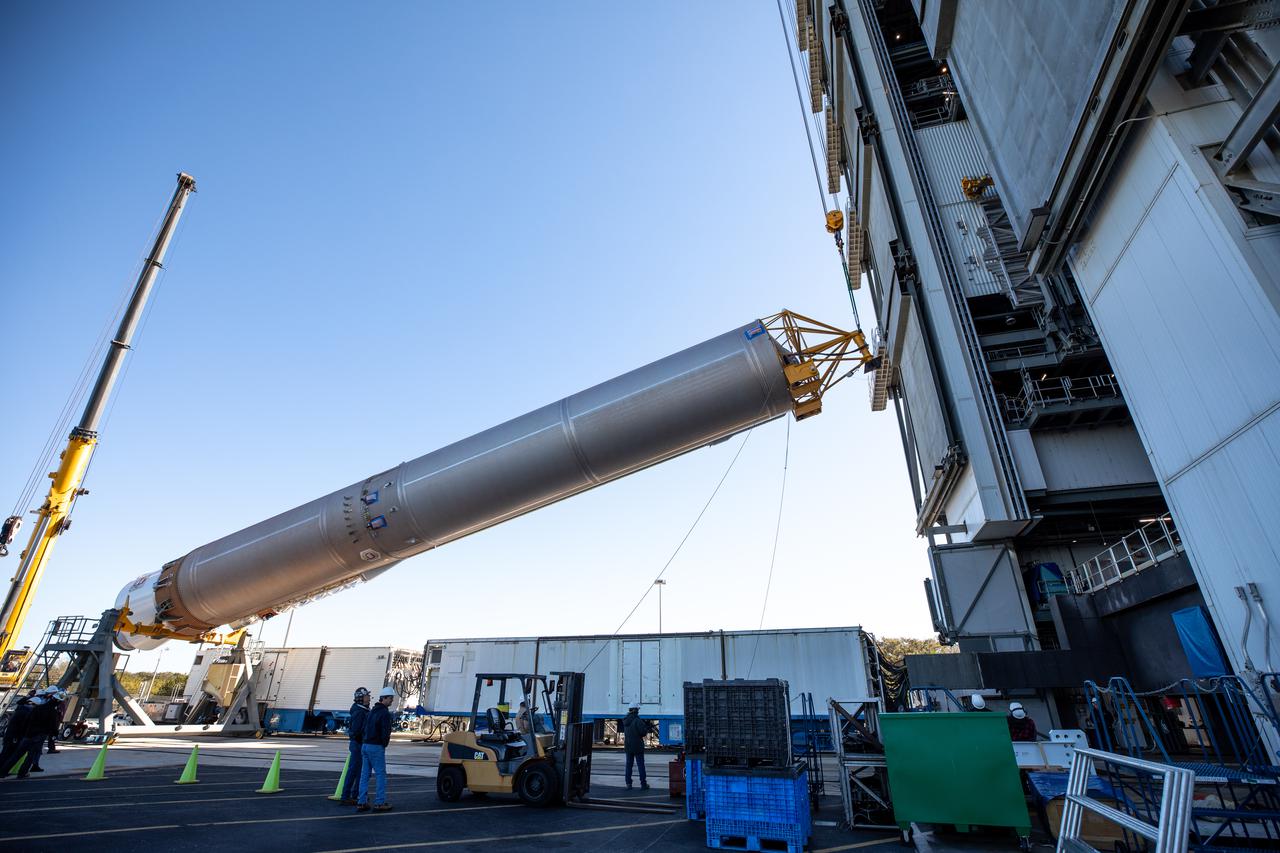

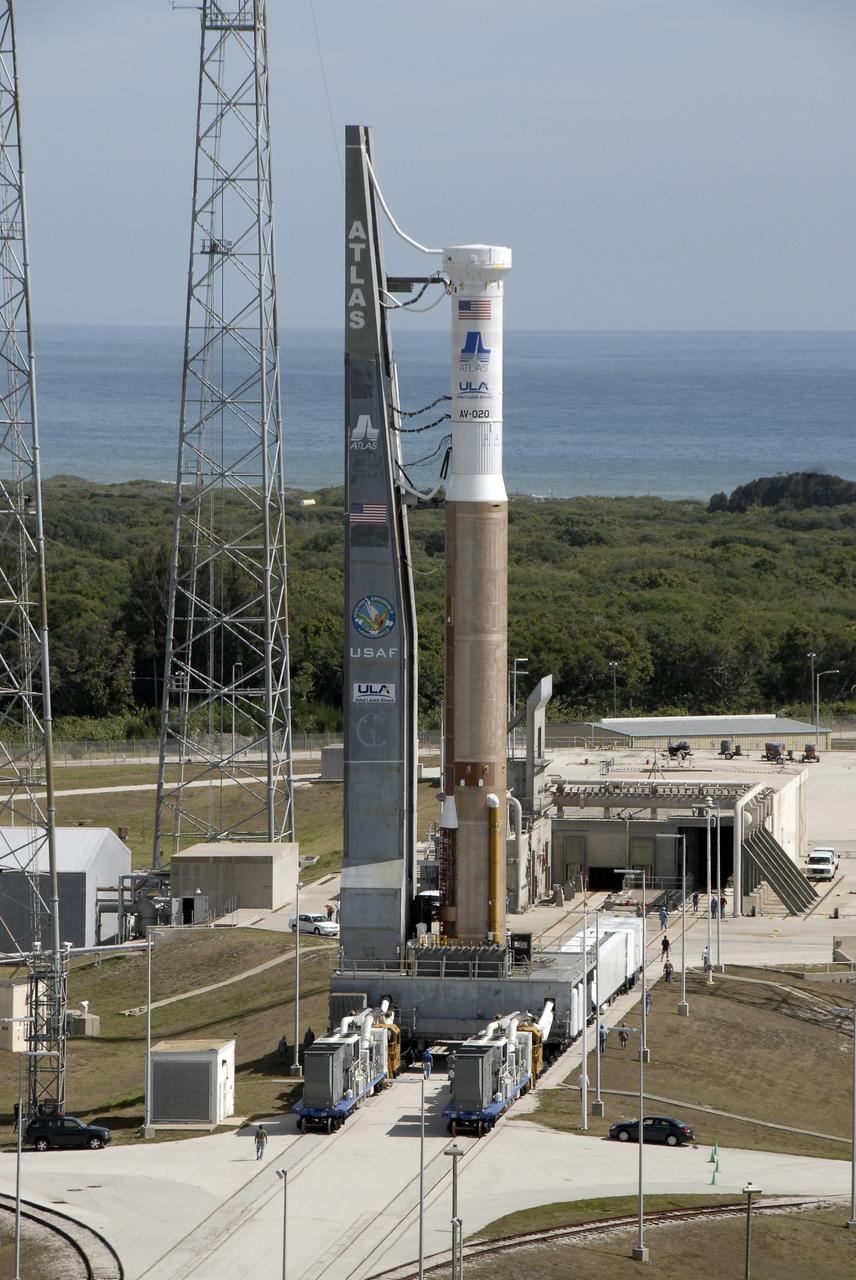
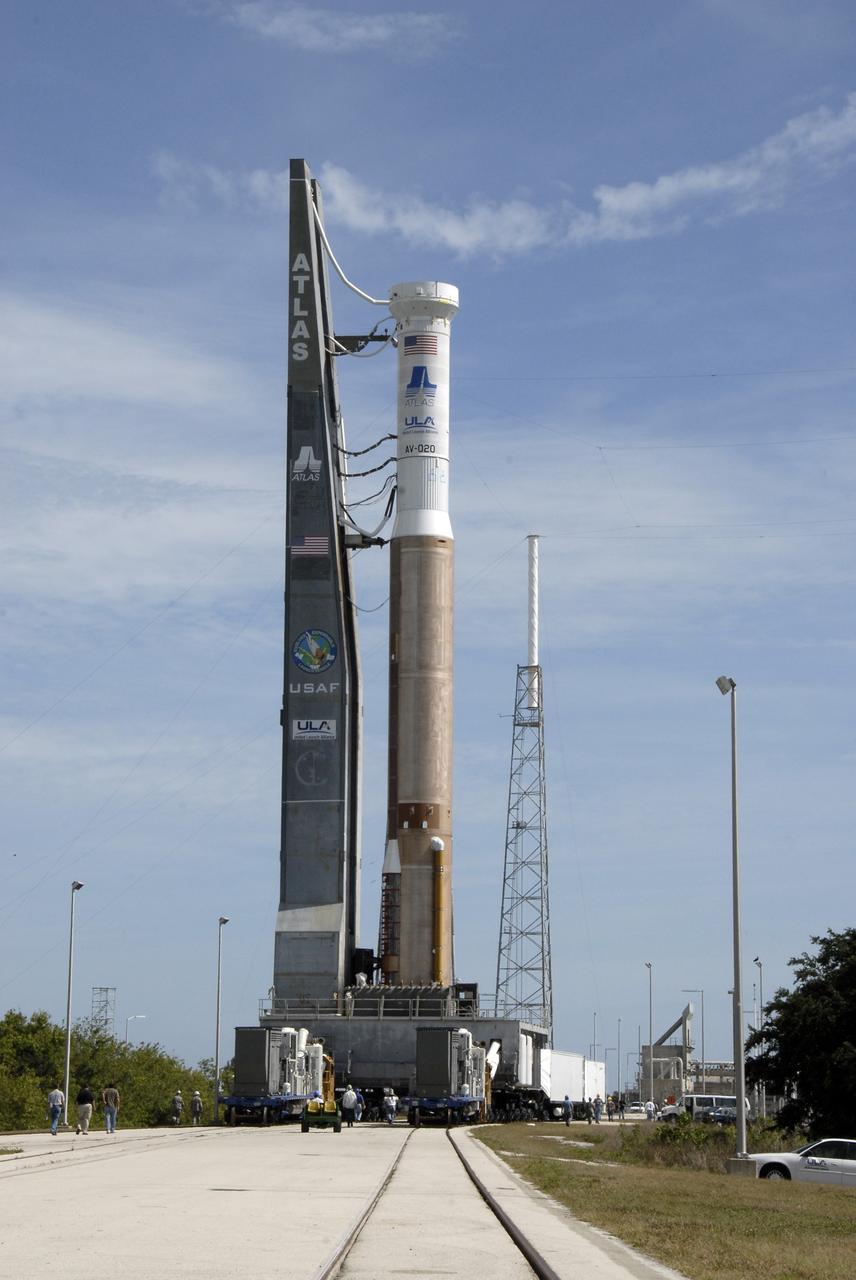
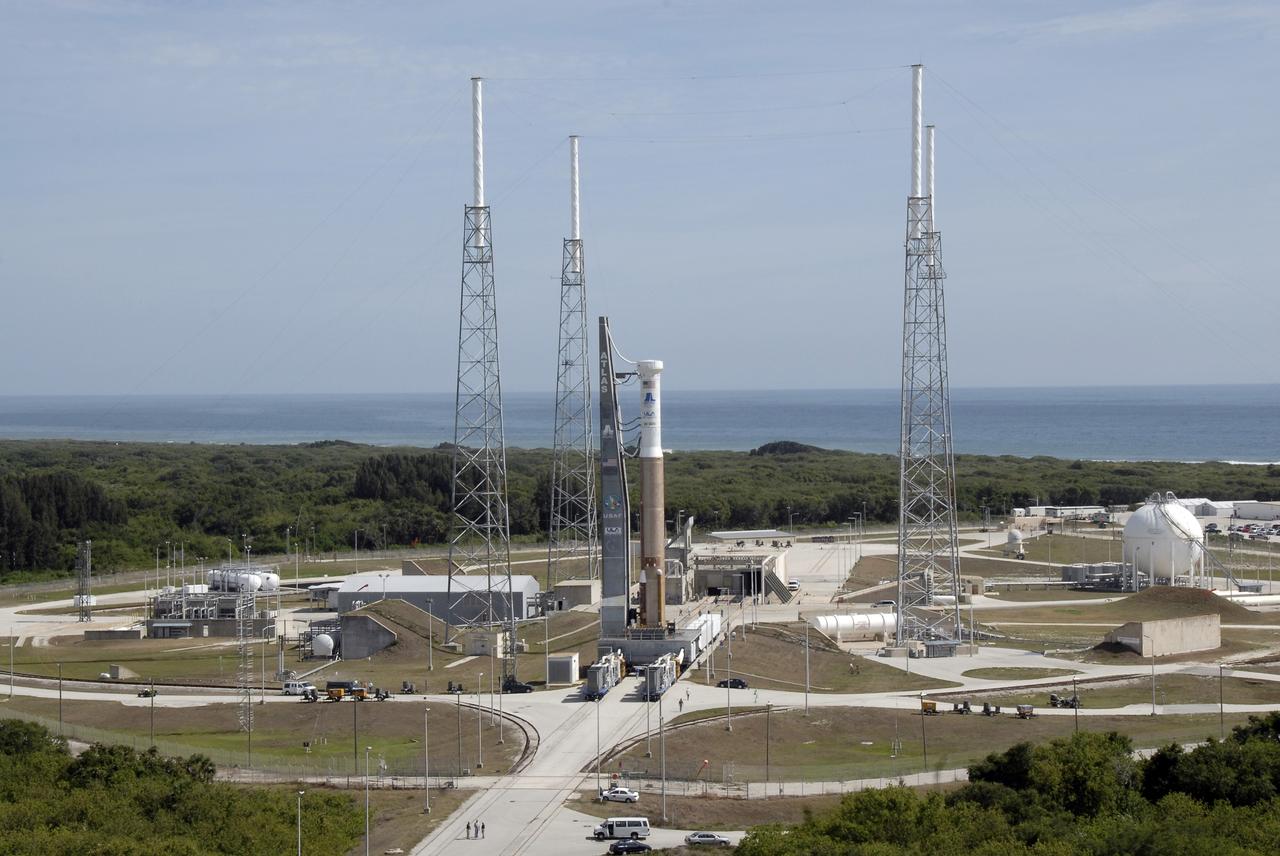
A crane is used to lift the United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket at the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
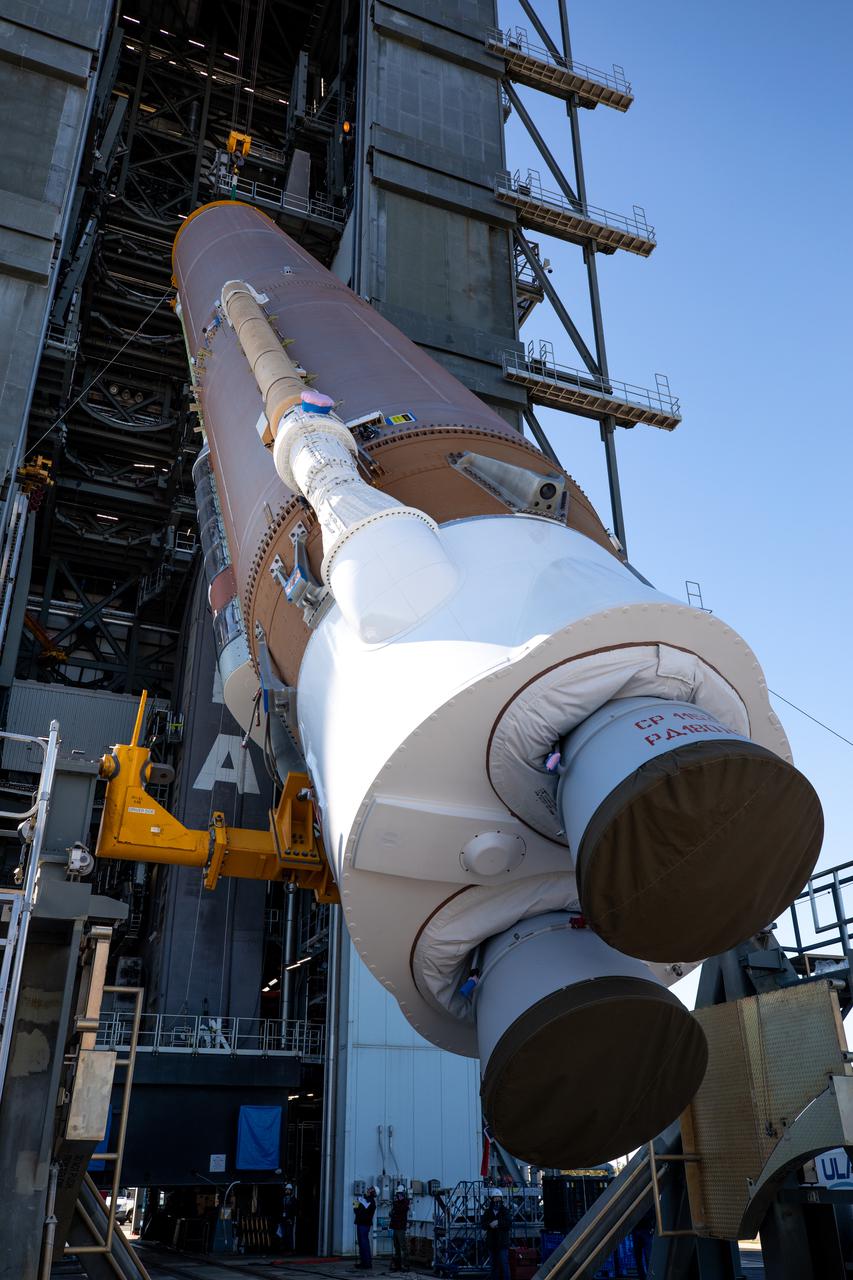

A crane is used to lift the United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket for its move into the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
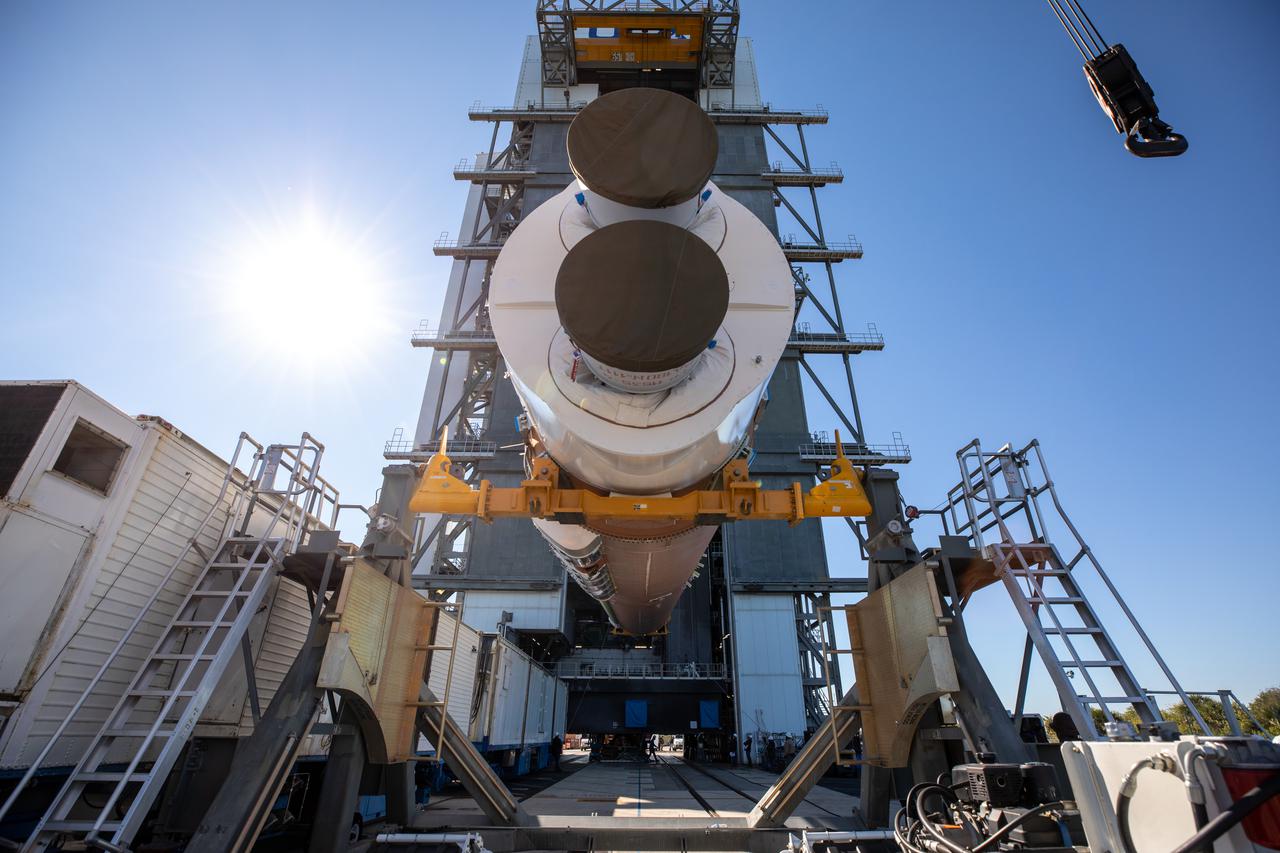

United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket is lifted up at the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.

The United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket first stage is secured inside the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
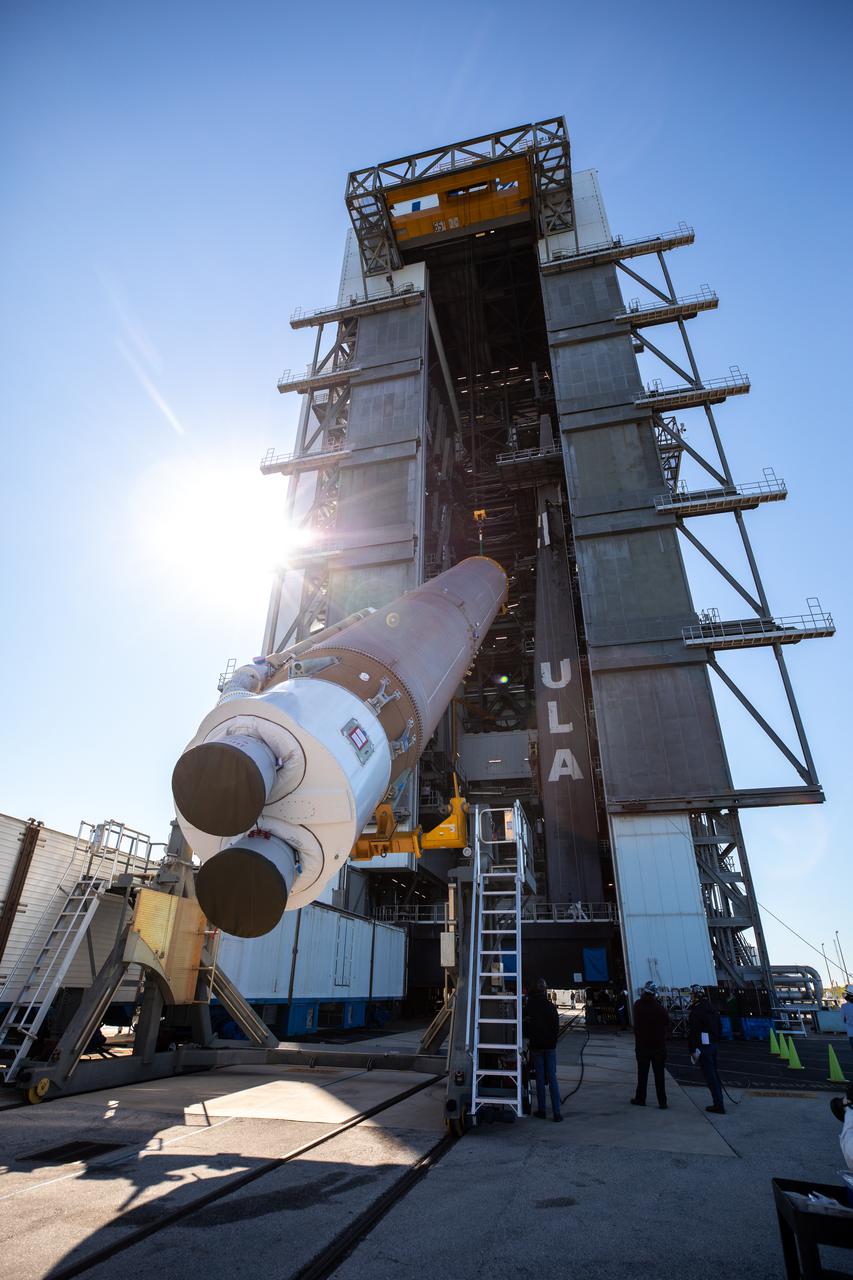

A crane is used to lift the United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket at the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
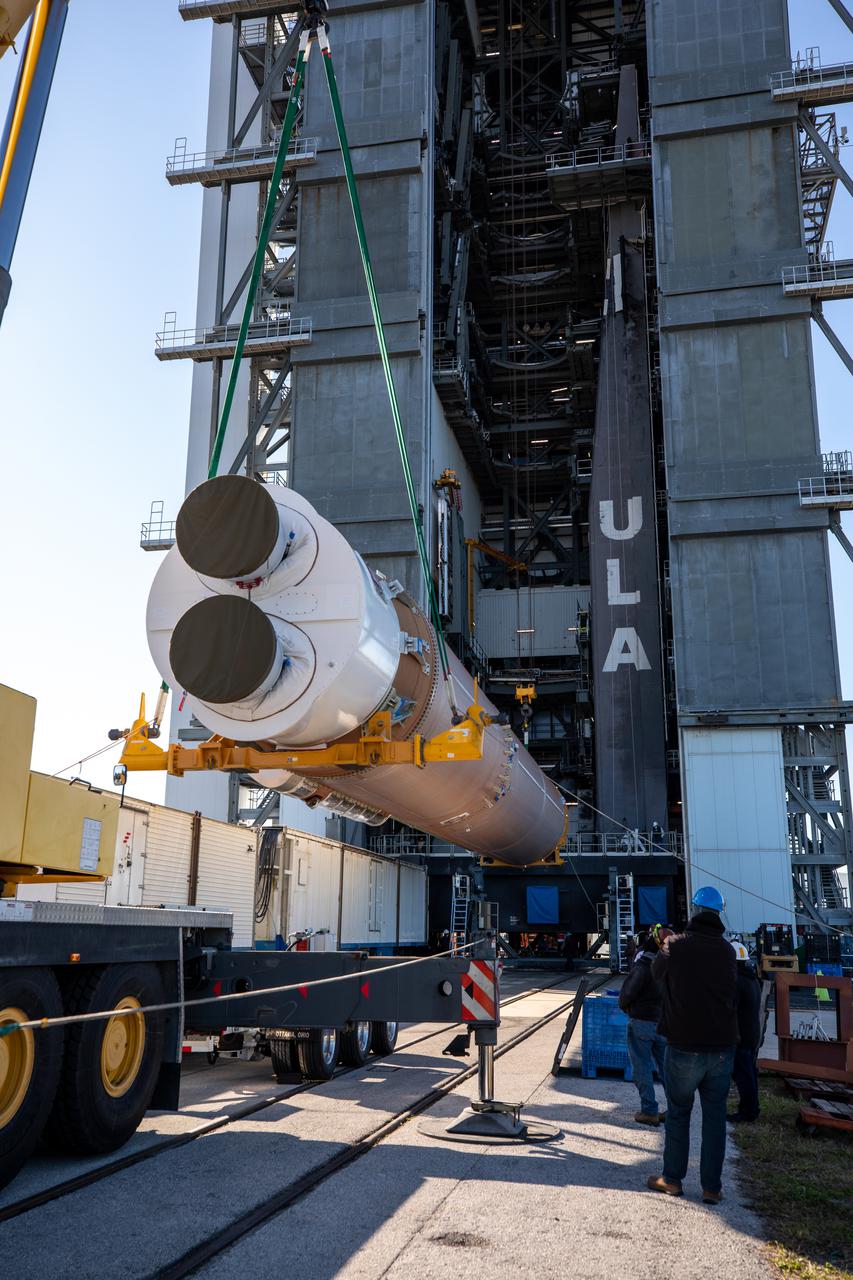

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket first stage is lifted up at the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
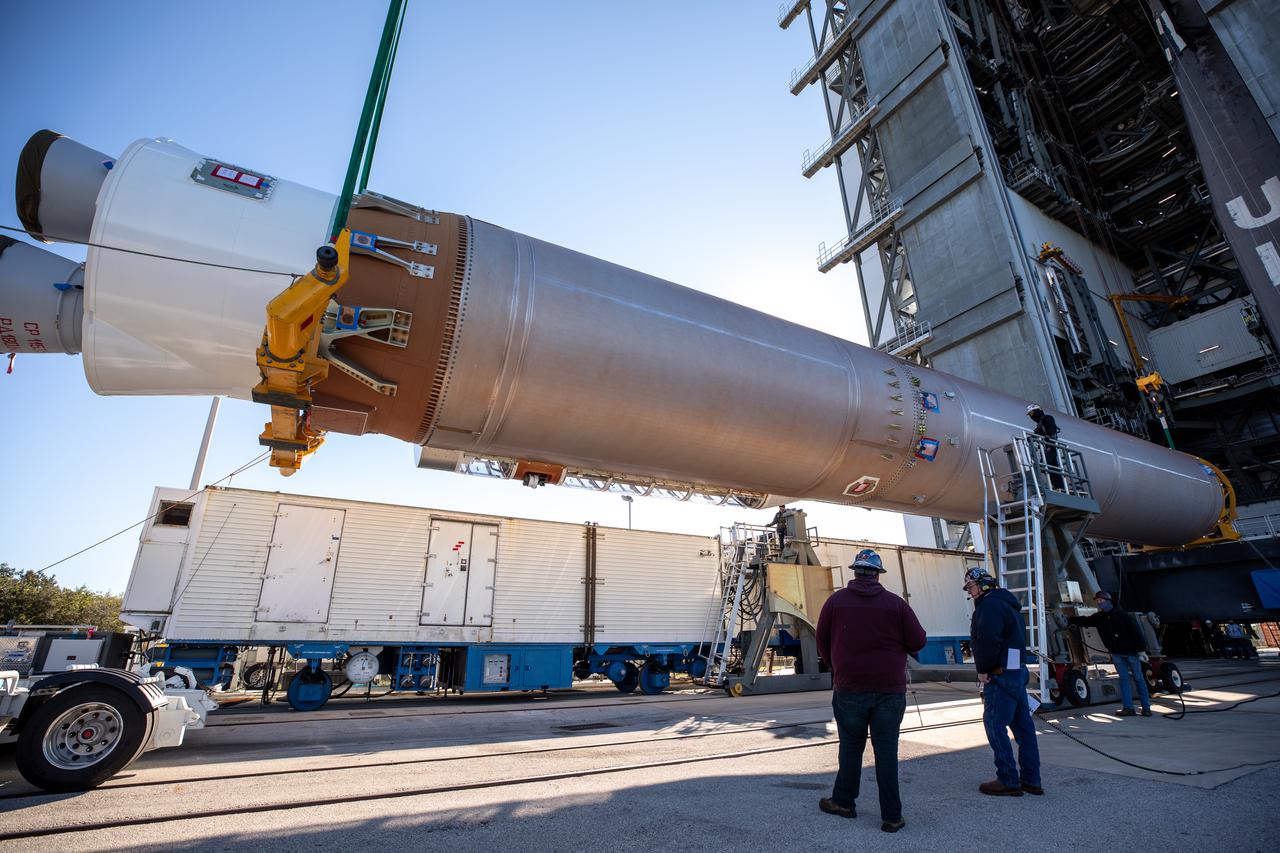

United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket is lifted up at the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
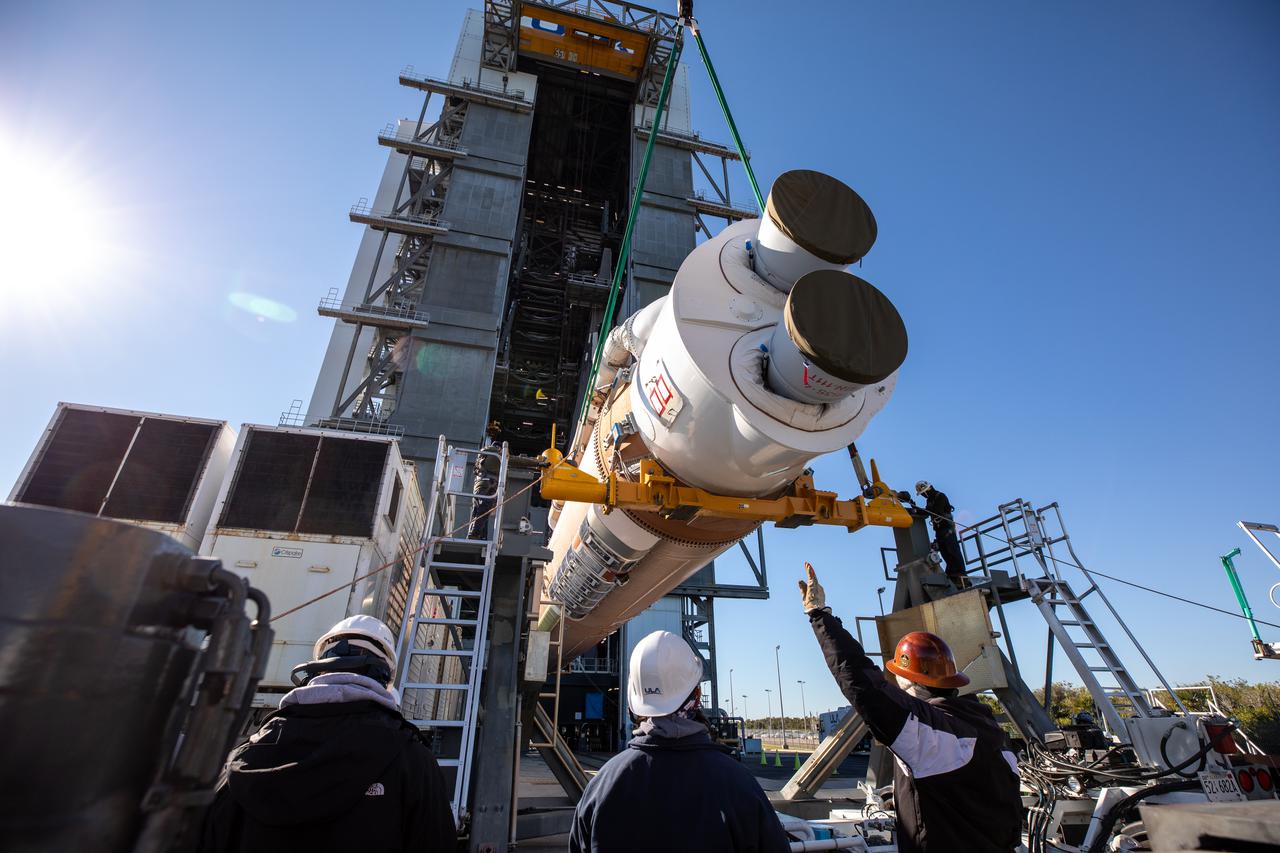

United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket is lifted up at the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
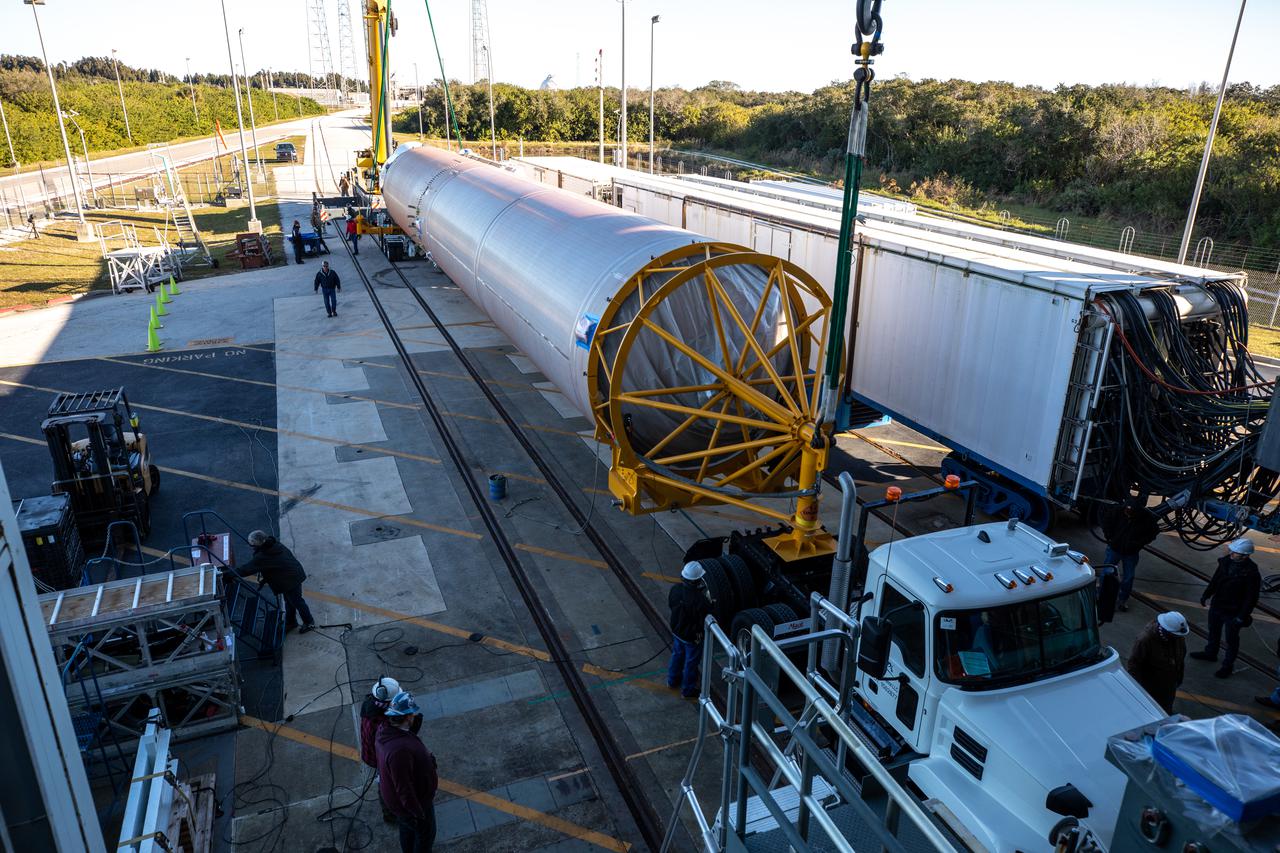

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket first stage arrives at the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
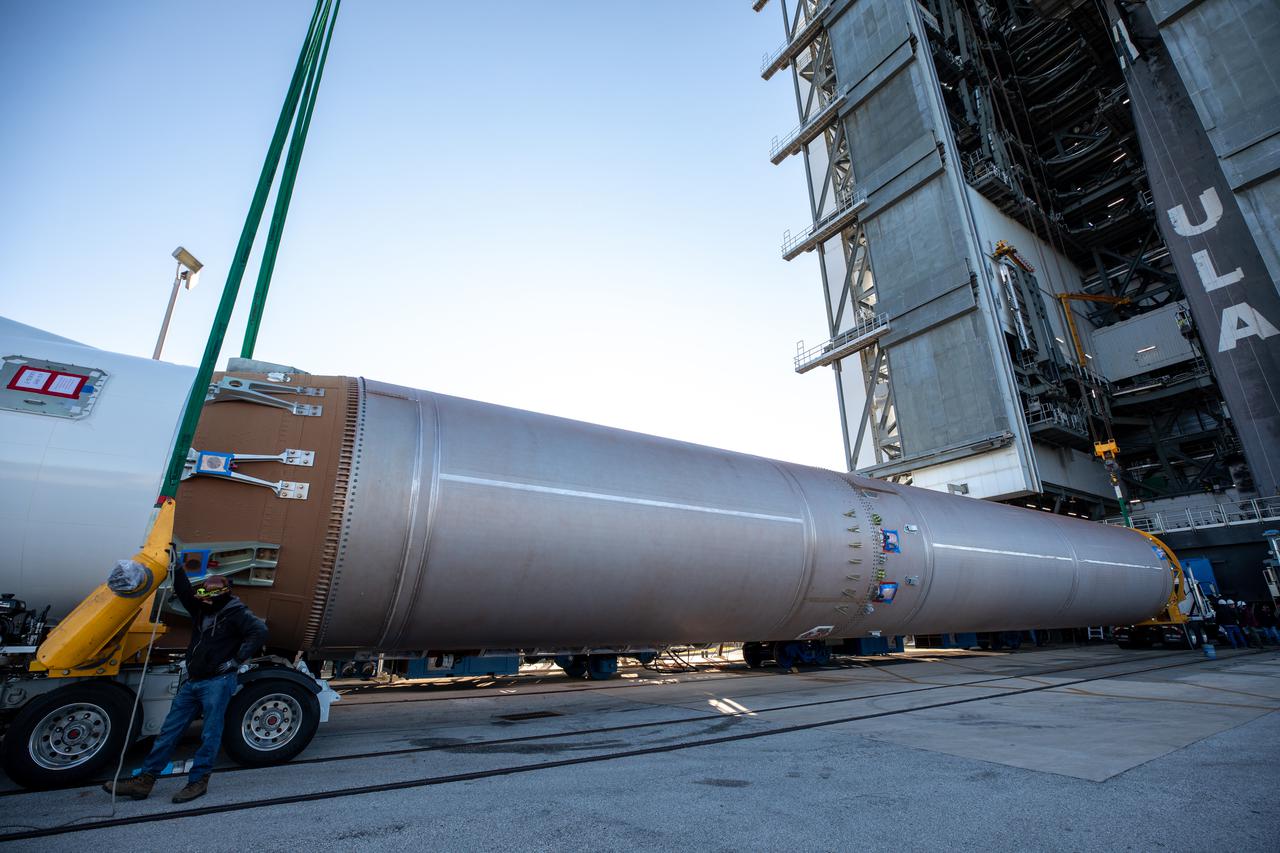

A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket first stage arrives at the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
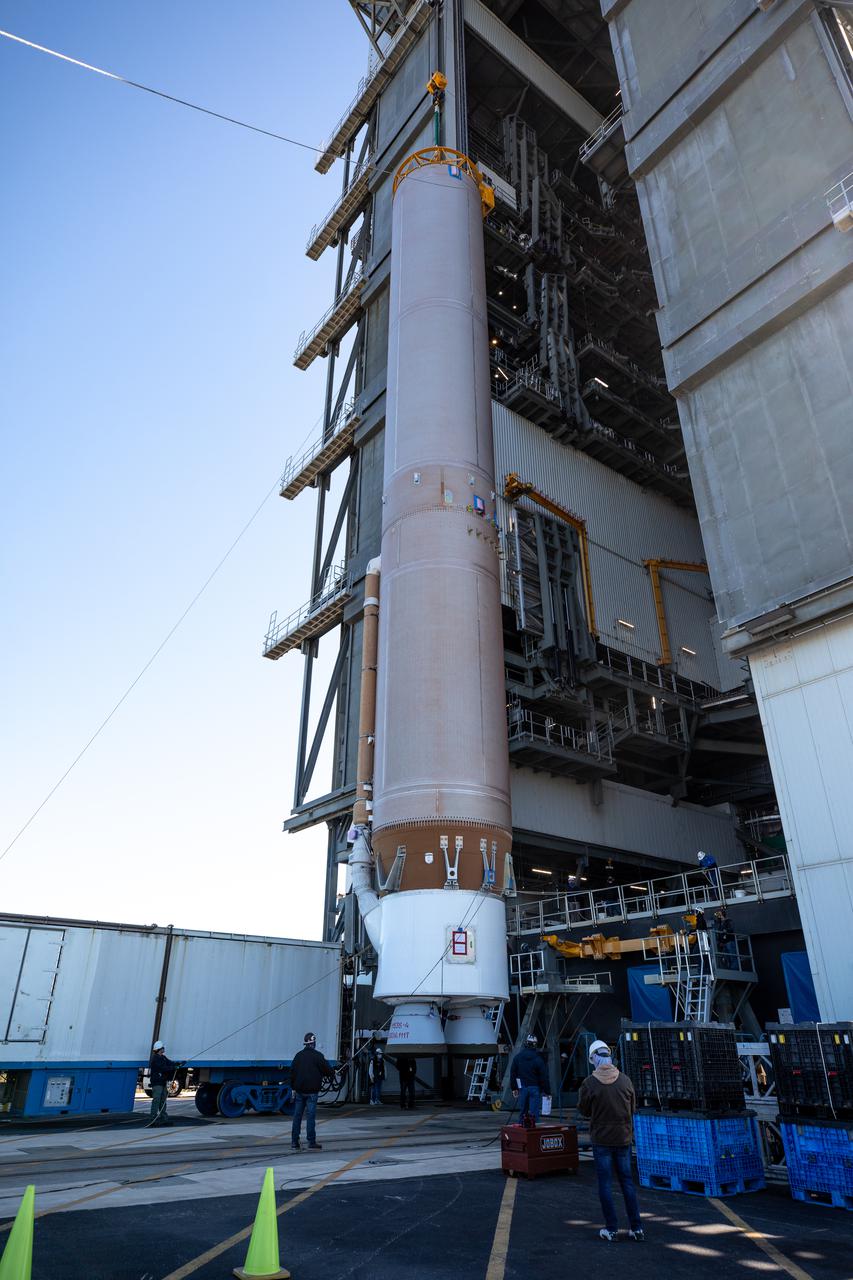

A crane is used to lift the United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) first stage of the Atlas V 541 rocket vertical for its move into the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
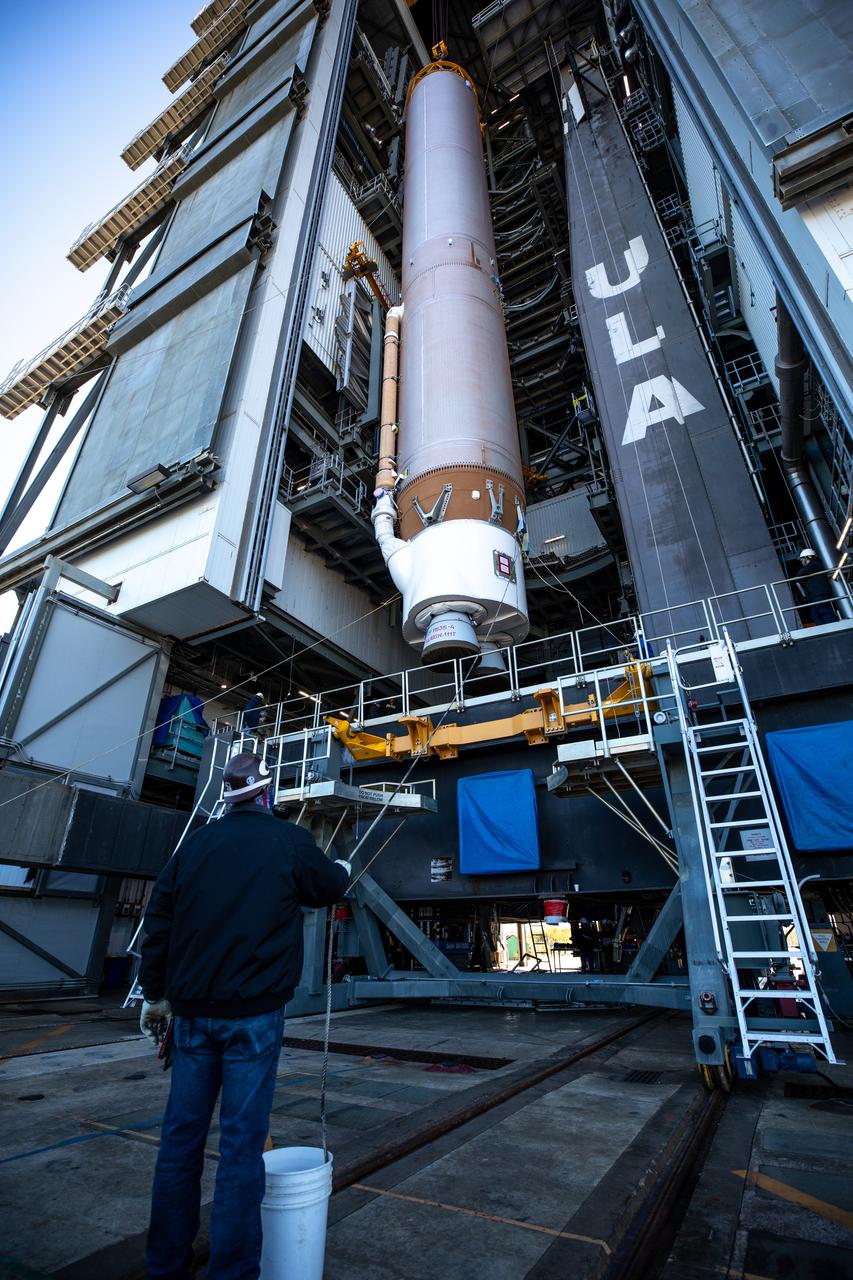

The United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket first stage is lifted vertical for its move into the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
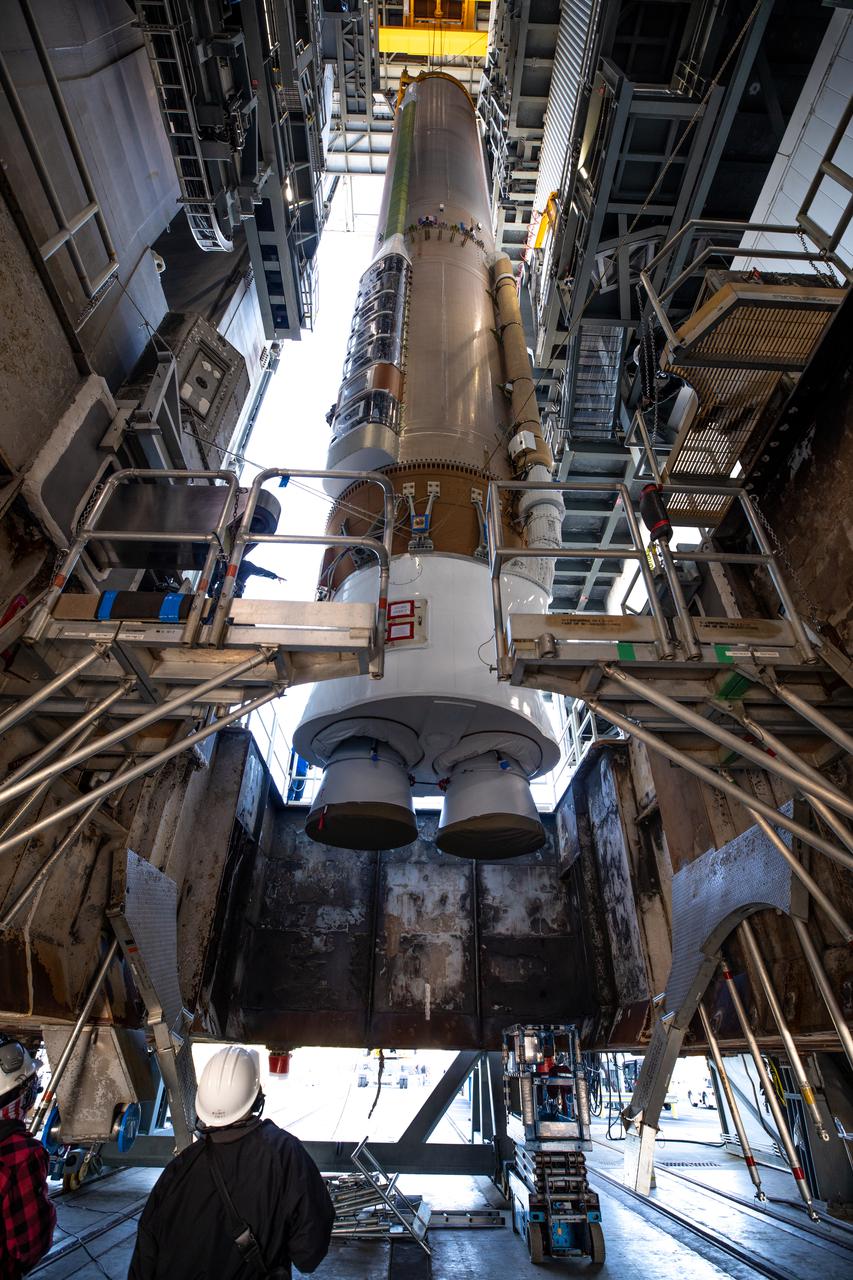

The United Launch Alliance’s (ULA) Atlas V 541 rocket first stage is in the vertical position and moved into the Space Launch Complex-41 Vertical Integration Facility at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Jan. 31, 2022. The Atlas V will launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite T (GOES-T). GOES-T is the third satellite in the GOES-R series that will continue to help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events that affect public safety. GOES-T is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex-41 on March 1, 2022. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multi-user spaceport.
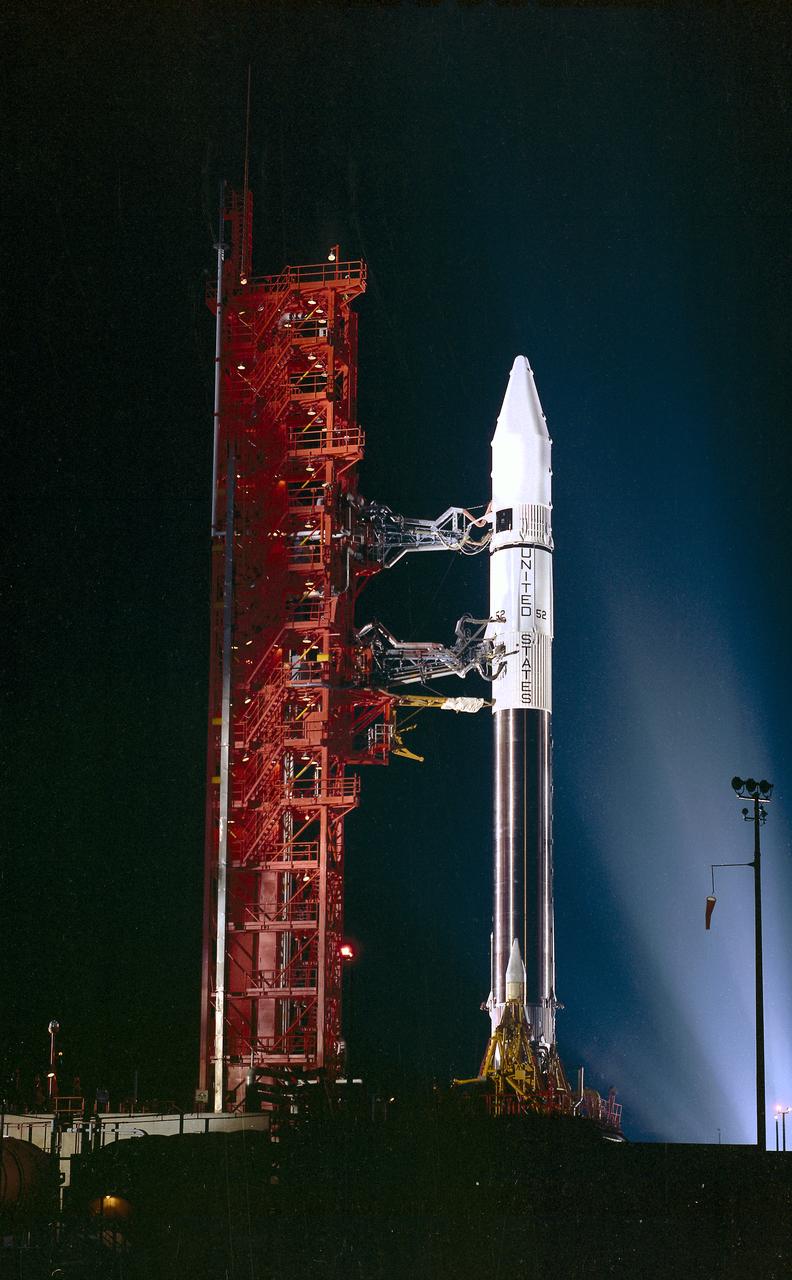
The Atlas-Centaur-52 launch vehicle on the launch pad. The Atlas-Centaur-52 placed the High Energy Astronomy Observatory-2 (HEAO-2) in orbit on November 13, 1978.
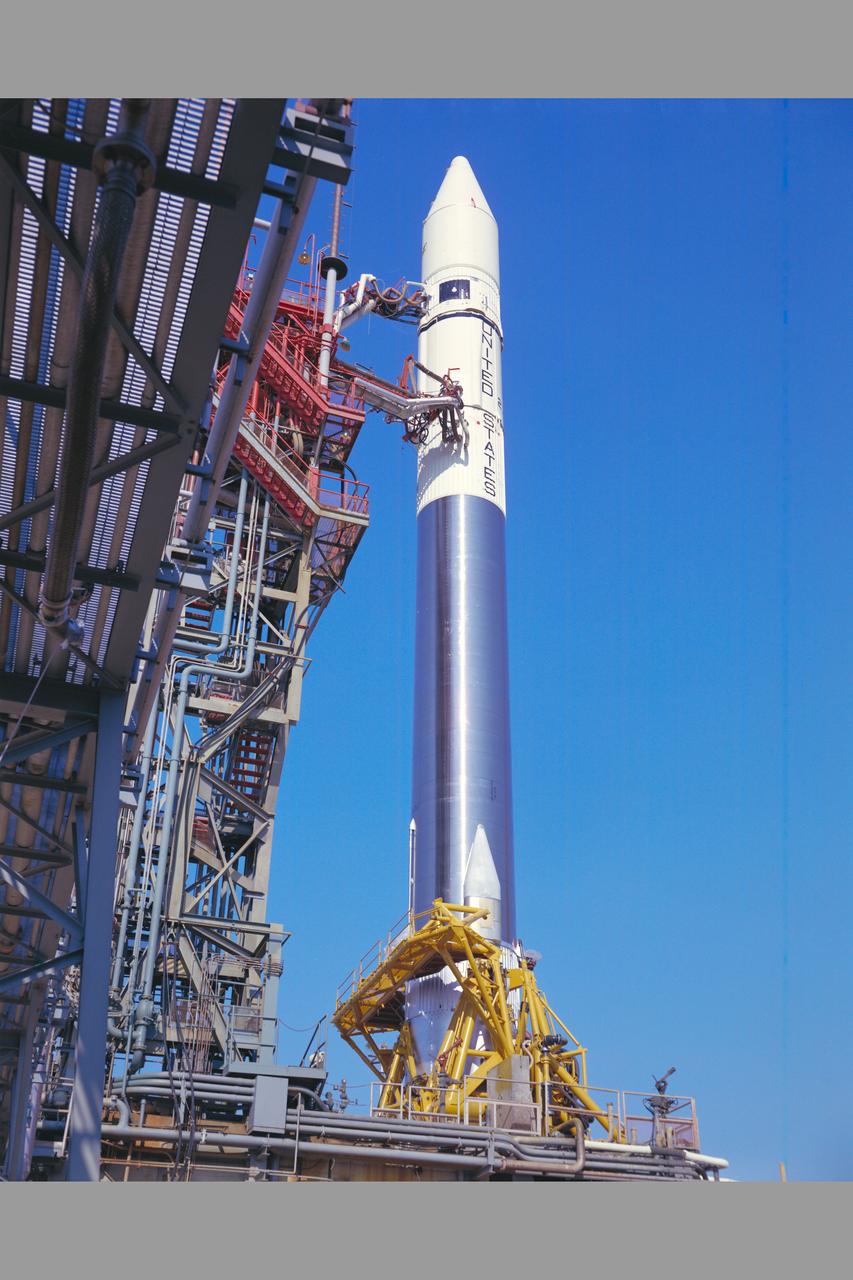

A pre launch view of Pioneer-10 (or F) spacecraft encapsulated and mated with a Atlas-Centaura launch vehicle in preparation for mission to Jupiter
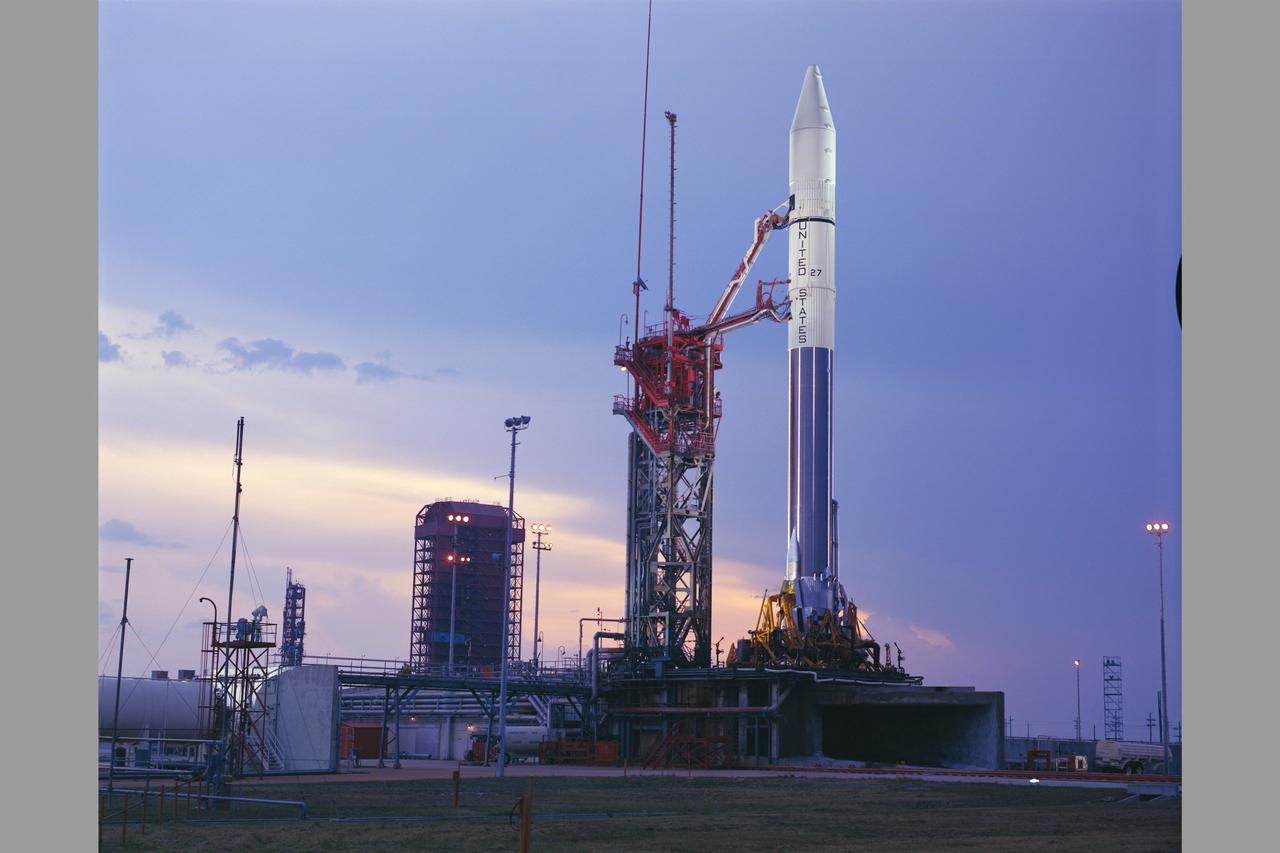

A pre launch view of Pioneer-10 (or F) spacecraft encapsulated and mated with a Atlas-Centaura launch vehicle in preparation for mission to Jupiter
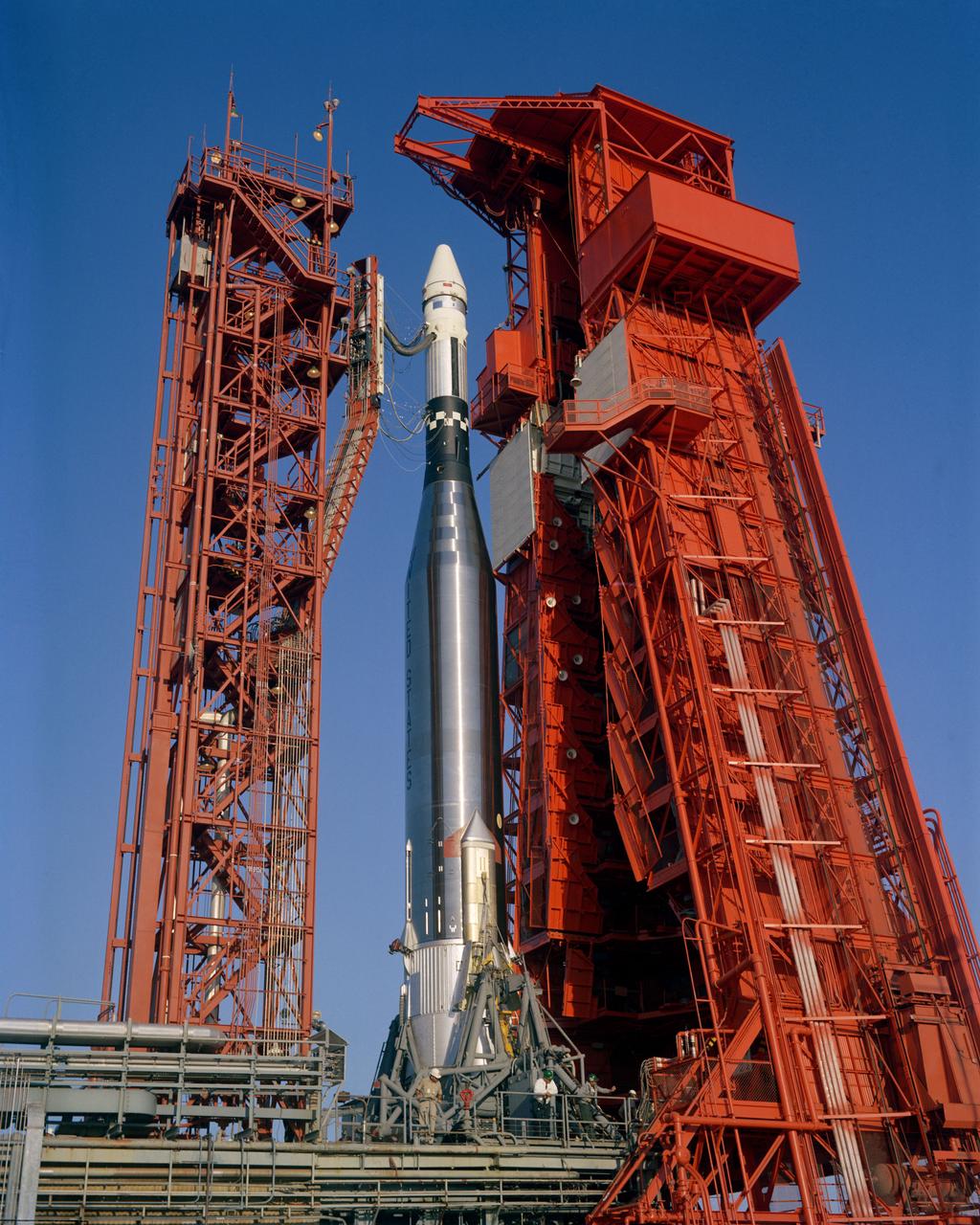

S65-57967 (25 Oct. 1965) --- View at Pad 14 during prelaunch operations for the Atlas/Agena. The Agena is mounted atop its Atlas launch vehicle. The Atlas/Agena liftoff was at 10 a.m. (EST) on Oct. 25, 1965. Intended as a rendezvous target vehicle in the Gemini-6 mission, the Agena failed to achieve orbit, and the Oct. 25 Gemini-6 launch was scrubbed. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
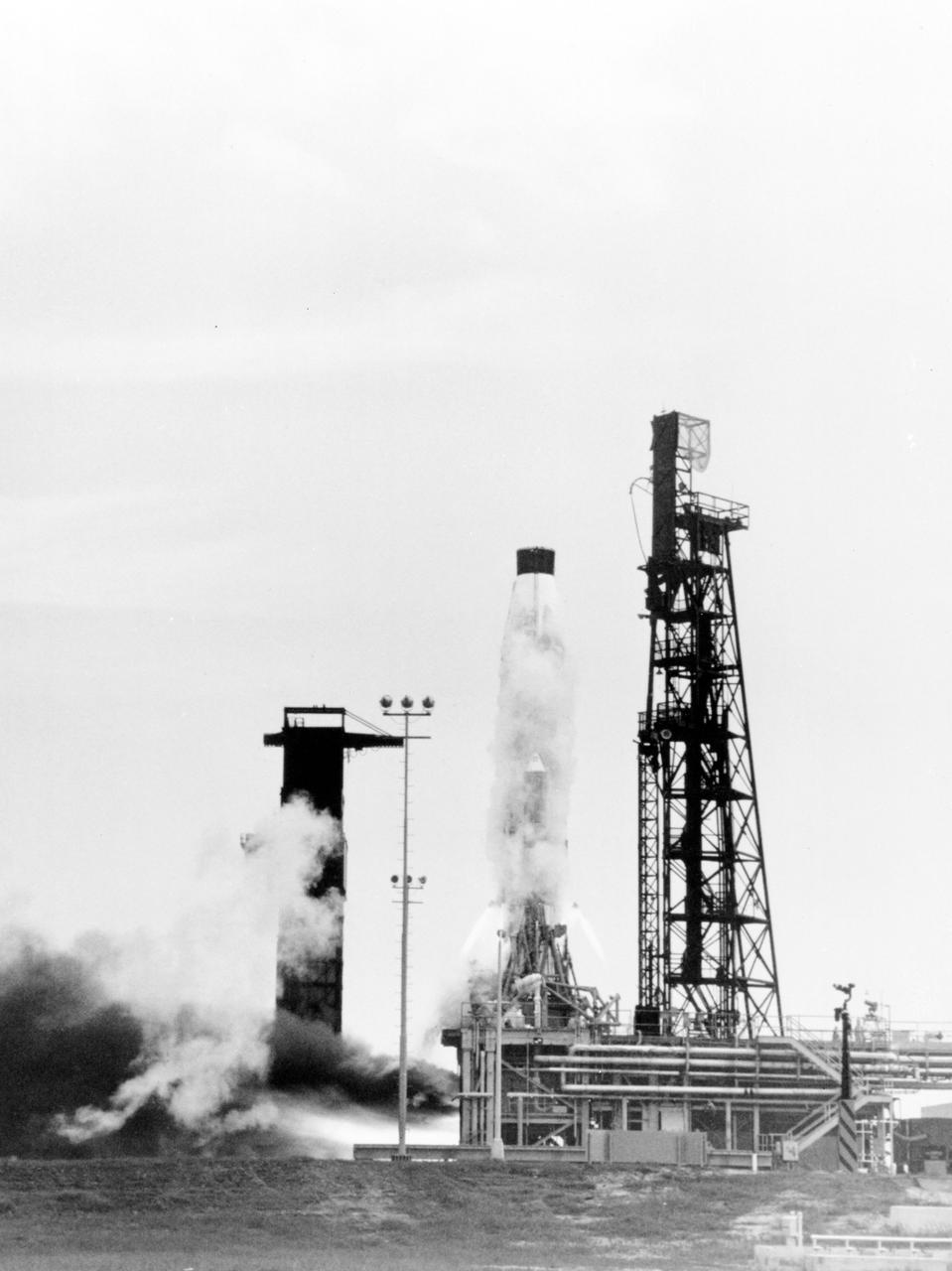

S62-06634 (1962) --- Static test firing of the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) Atlas 113D during preflight verification of launch vehicle systems. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Atlas V/Centaur is undergoing a wet dress rehearsal, or countdown test. The Atlas V is being fully loaded with propellants including liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen and RP-1 fuel. Surrounding the vehicle are four lightning towers. Following the rehearsal, the launch vehicle will be rolled off the pad and returned to the Vertical Integration Facility on May 16. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. They will be mated with the Atlas in late May. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 17. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the Atlas V/Centaur is undergoing a wet dress rehearsal, or countdown test. The Atlas V is being fully loaded with propellants including liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen and RP-1 fuel. Surrounding the vehicle are four lightning towers. Following the rehearsal, the launch vehicle will be rolled off the pad and returned to the Vertical Integration Facility on May 16. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. They will be mated with the Atlas in late May. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 17. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

S66-64544 (11 Nov. 1966) --- An Agena Target Docking Vehicle atop its Atlas launch vehicle was launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 14 at 2:08 p.m. (EST), Nov. 11, 1966. The Agena served as a rendezvous and docking vehicle for the Gemini-12 spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA
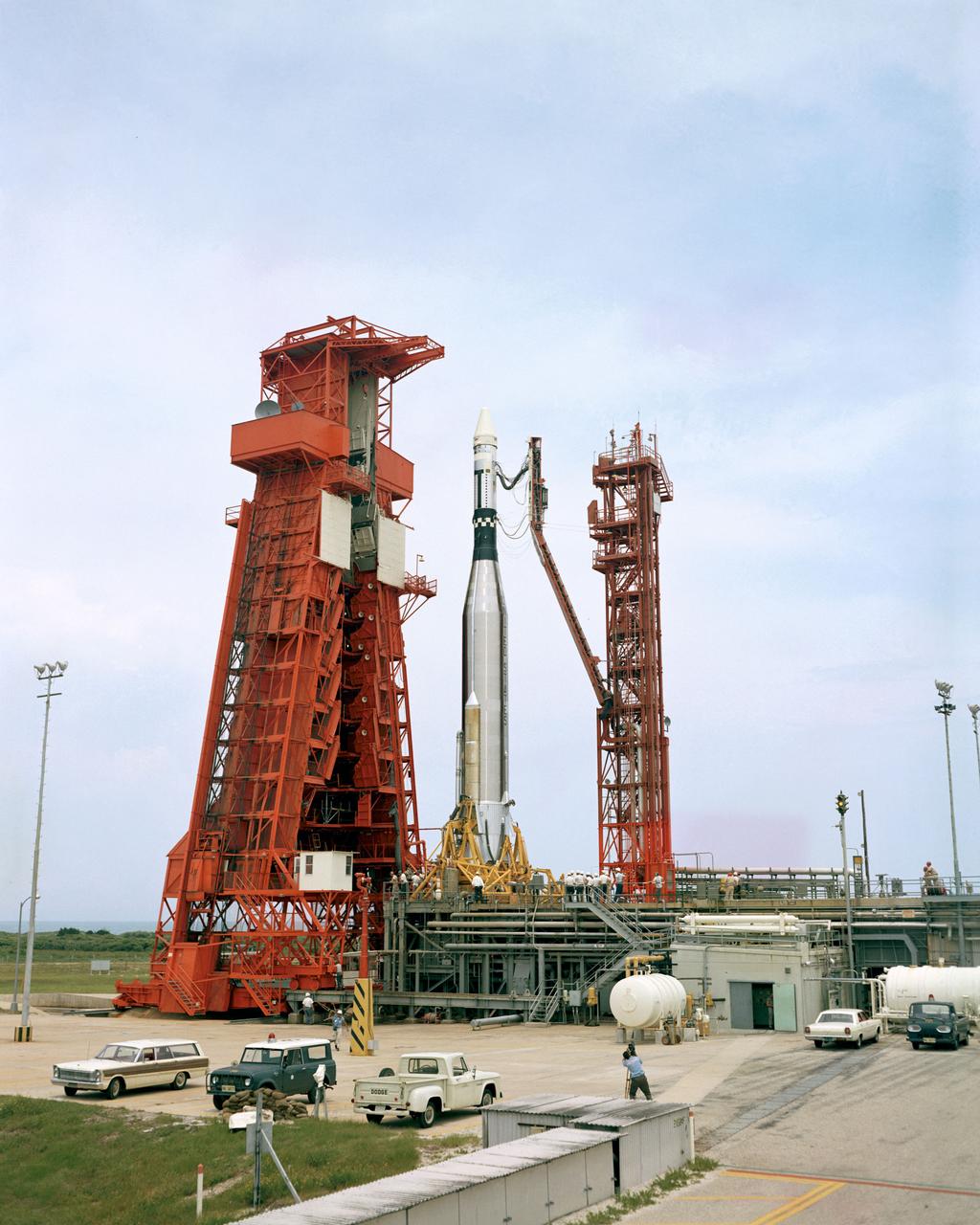

S66-42739 (18 July 1966) --- An Agena Target Docking Vehicle atop its Atlas launch vehicle during prelaunch preparations at Launch Complex 14. The Agena will be a rendezvous and docking vehicle for the Gemini-10 spaceflight. The Agena was launched on July 18, 1966, at 3:39 p.m. (EST). Photo credit: NASA
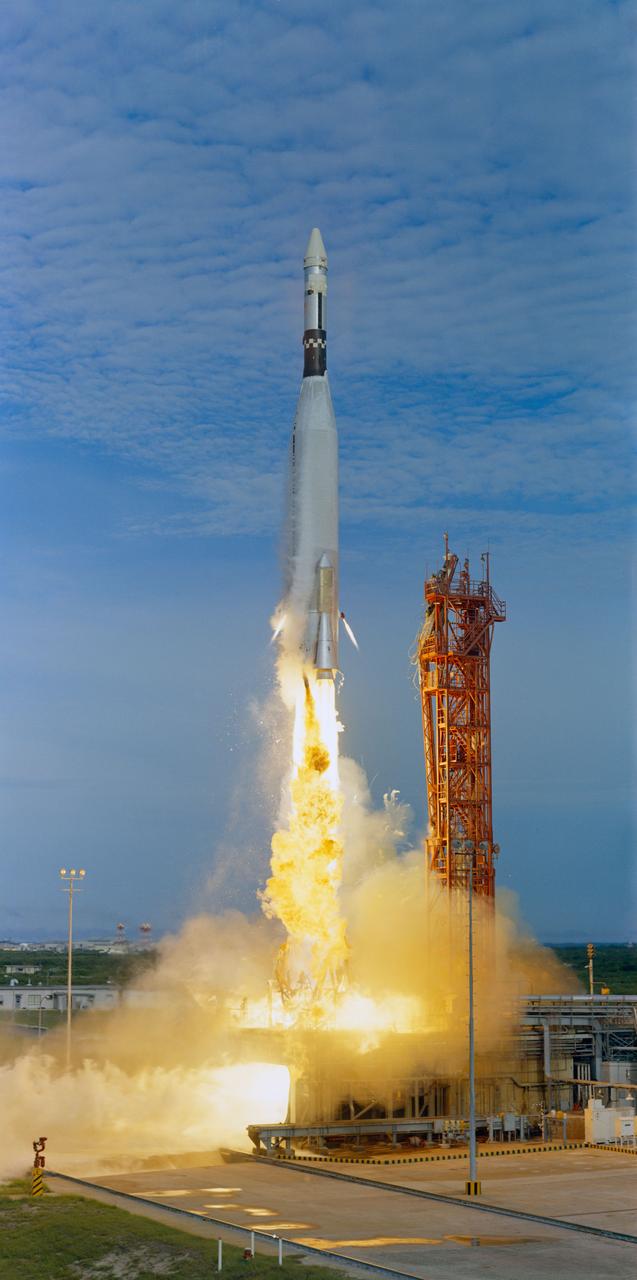

S66-50784 (12 Sept. 1966) --- An Agena Target Docking Vehicle atop its Atlas launch vehicle was launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 14 at 6:05 a.m., Sept. 12, 1966. The Agena served as a rendezvous and docking vehicle for the Gemini-11 spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA
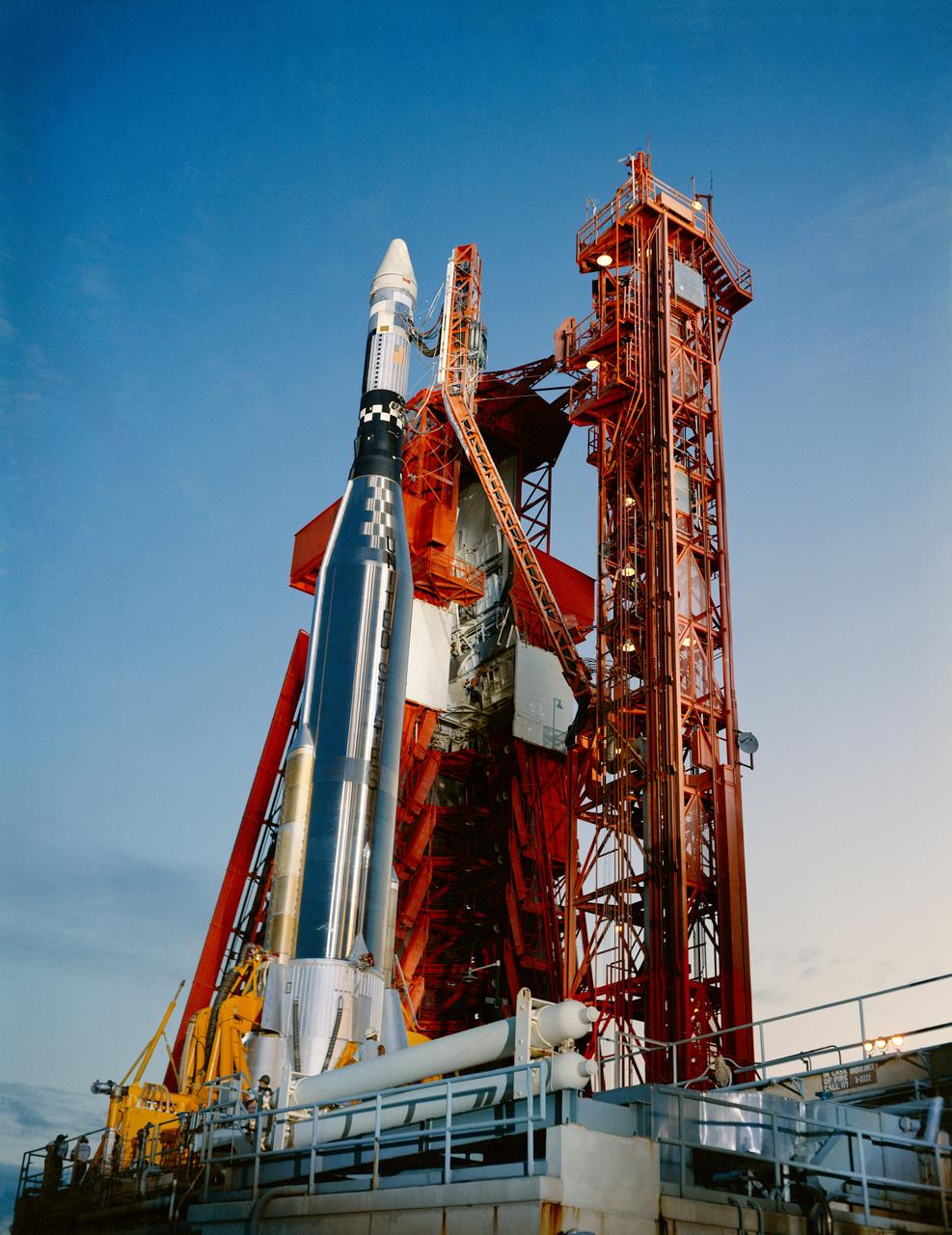

S66-50724 (12 Sept. 1966) --- An Agena Target Docking Vehicle atop its Atlas launch vehicle is ready for launch at Launch Complex 14 at Cape Kennedy, Florida. The Agena served as a rendezvous and docking vehicle for the Gemini-11 spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA
The Atlas/Agena launch vehicle carrying The Mariner-V spacecraft on launch pad on June 14, 1967. The Marina V mission was to explore the planet Venus.
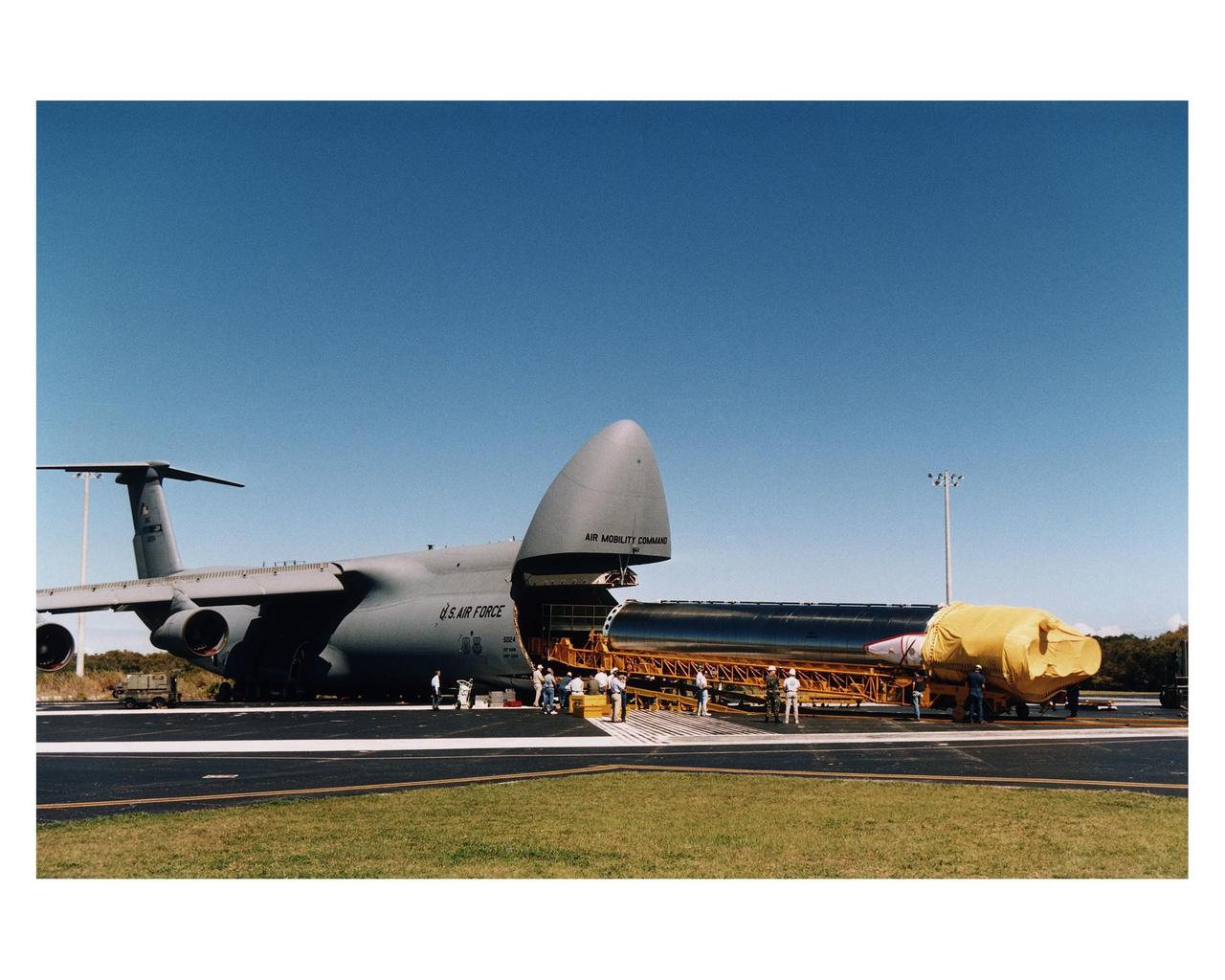

The Atlas 1 rocket which will launch the GOES-K advanced weather satellite is unloaded from an Air Force C-5 air cargo plane after arrival at the Skid Strip, Cape Canaveral Air Station (CCAS). The Lockheed Martin-built rocket and its Centaur upper stage will form the AC-79 vehicle, the final vehicle in the Atlas 1 series which began launches for NASA in 1962. Future launches of geostationary operational environmental satellites (GOES) in the current series will be on Atlas II vehicles. GOES-K will be the third spacecraft to be launched in the new advanced series of geostationary weather satellites built for NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The spacecraft will be designated GOES-10 in orbit. The launch of AC-79/GOES-K is targeted for April 24 from Launch Pad 36B, CCAS

Pioneer-10 (or F) spacecraft encapsulated and moving to pad at Cape Kennedy for matting with a Atlas-Centaura launch vehicle in preparation for mission to Jupiter

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Atlas V/Centaur arrives on Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Atlas was rolled to the launch pad from the Vertical Integration Facility in preparation for the wet dress rehearsal, or countdown test, which means being fully loaded with propellants including liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen and RP-1 fuel. The launch vehicle will be rolled off the pad and returned to the VIF on May 16. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. They will be mated with the Atlas in late May. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 17. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Atlas V/Centaur nears Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Behind it at right is one of the four lightning towers that surround the pad for protection against possible lightning strikes. The Atlas was rolled to the launch pad from the Vertical Integration Facility in preparation for the wet dress rehearsal, or countdown test, which means being fully loaded with propellants including liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen and RP-1 fuel. The launch vehicle will be rolled off the pad and returned to the VIF on May 16. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. They will be mated with the Atlas in late May. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 17. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Atlas V/Centaur arrives on Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Lightning towers surround the pad for protection against possible lightning strikes. The Atlas was rolled to the launch pad from the Vertical Integration Facility in preparation for the wet dress rehearsal, or countdown test, which means being fully loaded with propellants including liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen and RP-1 fuel. The launch vehicle will be rolled off the pad and returned to the VIF on May 16. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. They will be mated with the Atlas in late May. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 17. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
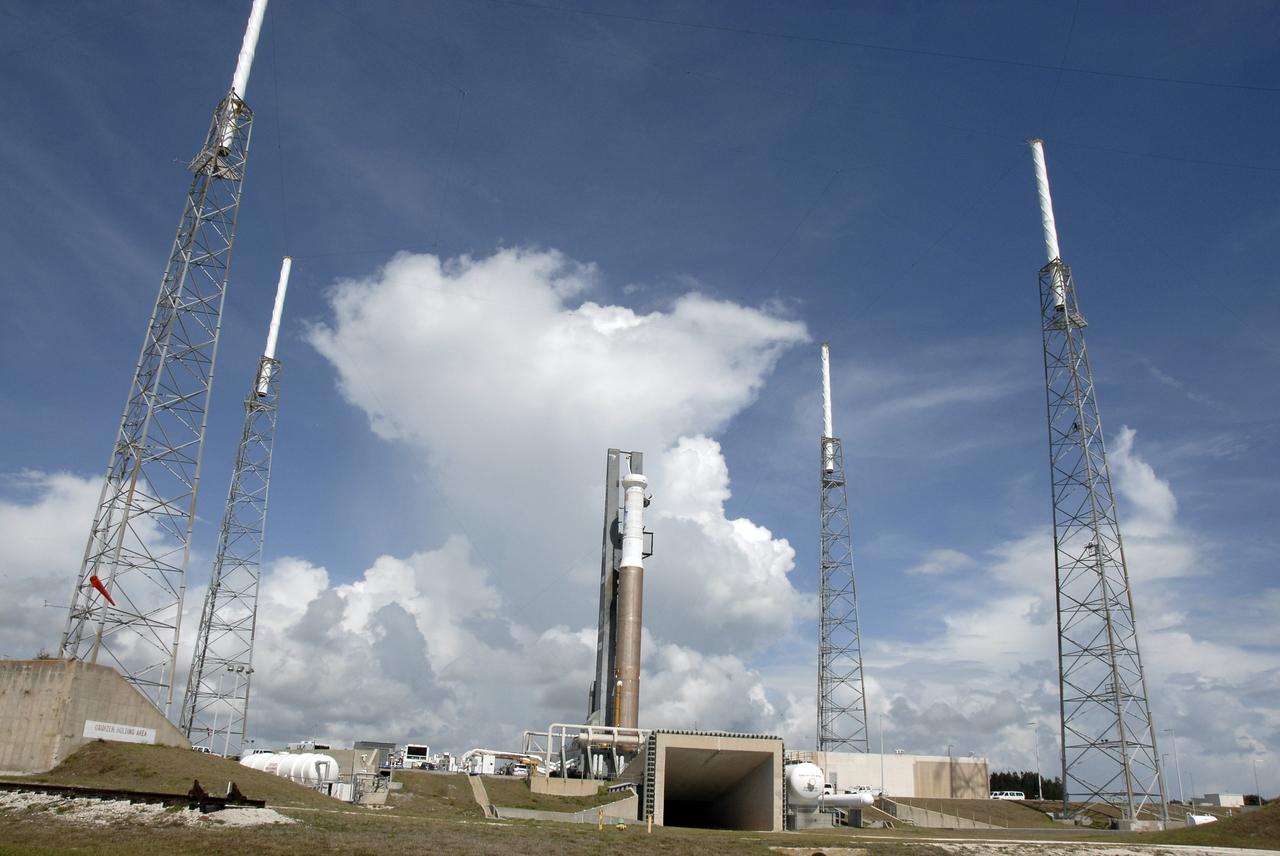

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Atlas V/Centaur arrives on Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Lightning towers surround the pad for protection against possible lightning strikes. The Atlas was rolled to the launch pad from the Vertical Integration Facility in preparation for the wet dress rehearsal, or countdown test, which means being fully loaded with propellants including liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen and RP-1 fuel. The launch vehicle will be rolled off the pad and returned to the VIF on May 16. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. They will be mated with the Atlas in late May. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 17. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
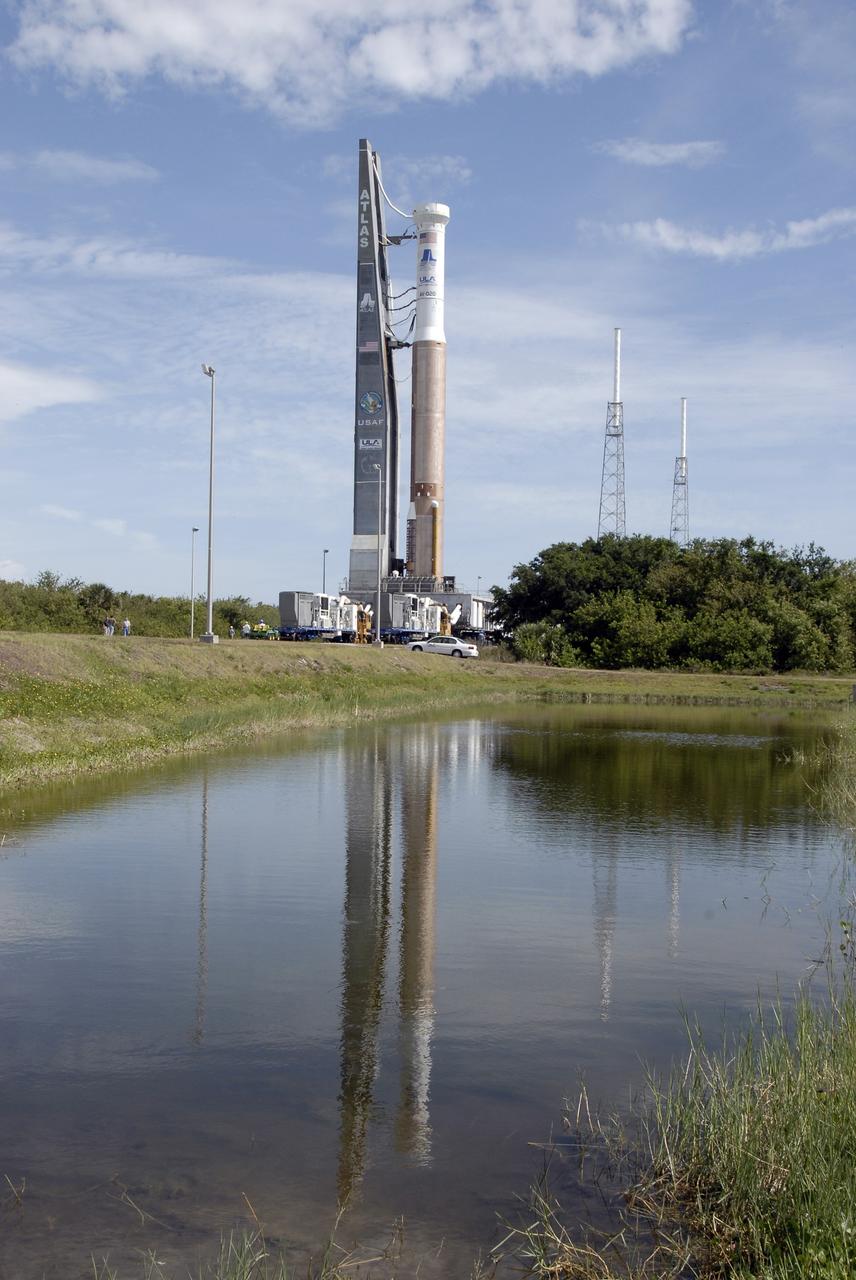

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Atlas V/Centaur nears Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. At right in the background are two of the four lightning towers that surround the pad for protection against possible lightning strikes. The Atlas was rolled to the launch pad from the Vertical Integration Facility in preparation for the wet dress rehearsal, or countdown test, which means being fully loaded with propellants including liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen and RP-1 fuel. The launch vehicle will be rolled off the pad and returned to the VIF on May 16. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. They will be mated with the Atlas in late May. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 17. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
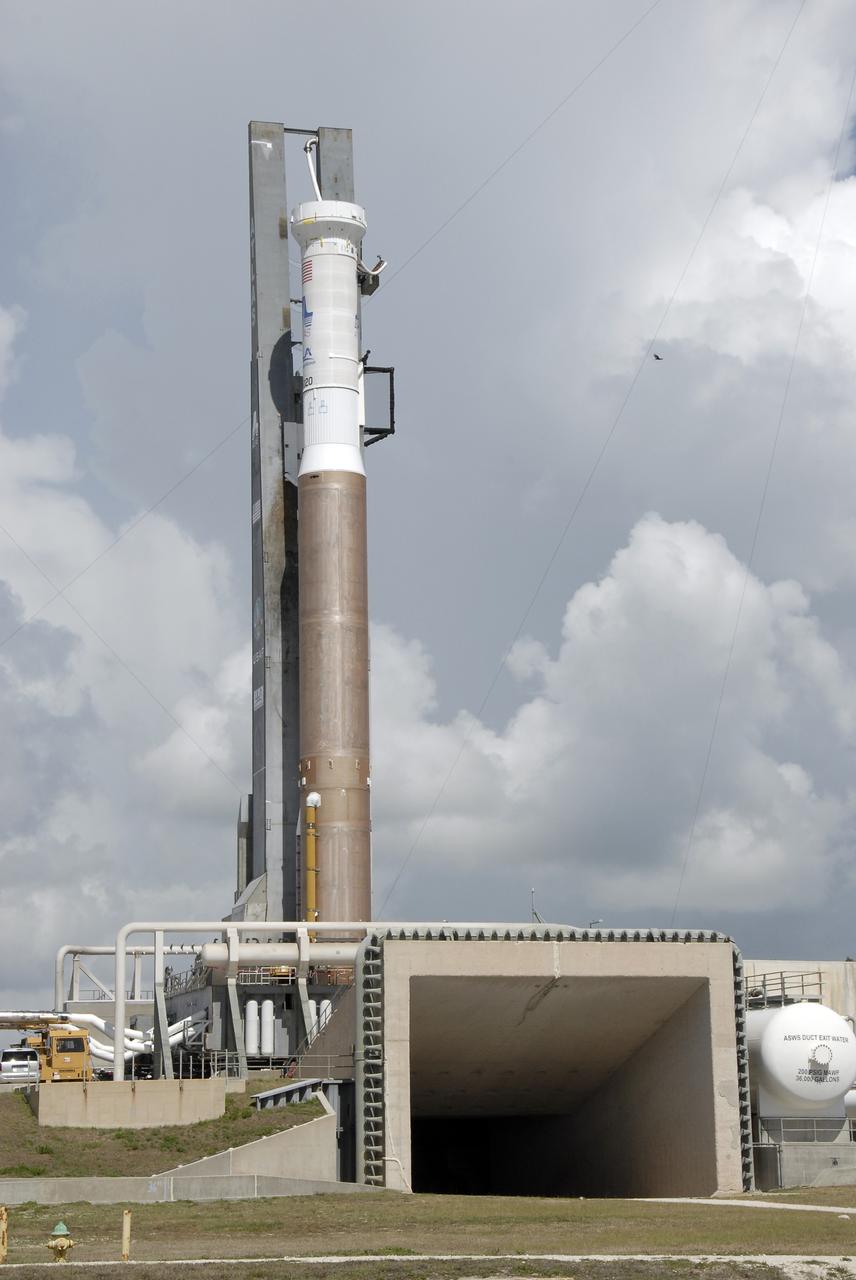

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Atlas V/Centaur arrives on Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Atlas was rolled to the launch pad from the Vertical Integration Facility in preparation for the wet dress rehearsal, or countdown test, which means being fully loaded with propellants including liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen and RP-1 fuel. The launch vehicle will be rolled off the pad and returned to the VIF on May 16. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. They will be mated with the Atlas in late May. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 17. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
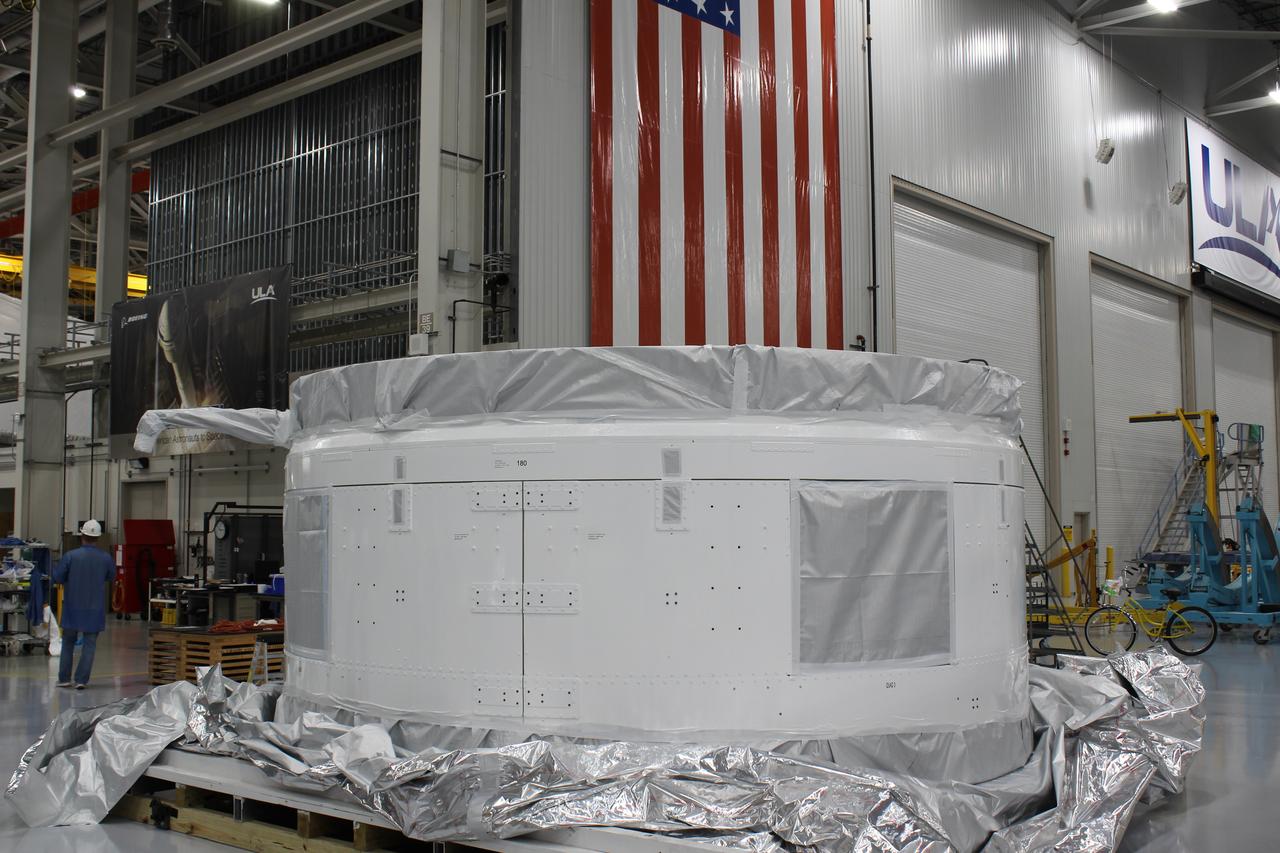

The Launch Vehicle Adapter (LVA) that will attach Boeing’s first Starliner spacecraft to the Atlas V launch vehicle is ready for transport from United Launch Alliance's manufacturing factory in Decatur, Alabama to Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.

The Launch Vehicle Adapter (LVA) that will attach Boeing’s first Starliner spacecraft to the Atlas V launch vehicle arrived at Cape Canaveral in Florida on November 11, 2018. The Mariner cargo vessel brought the LVA and two stages of a Delta IV rocket from United Launch Alliance's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama.
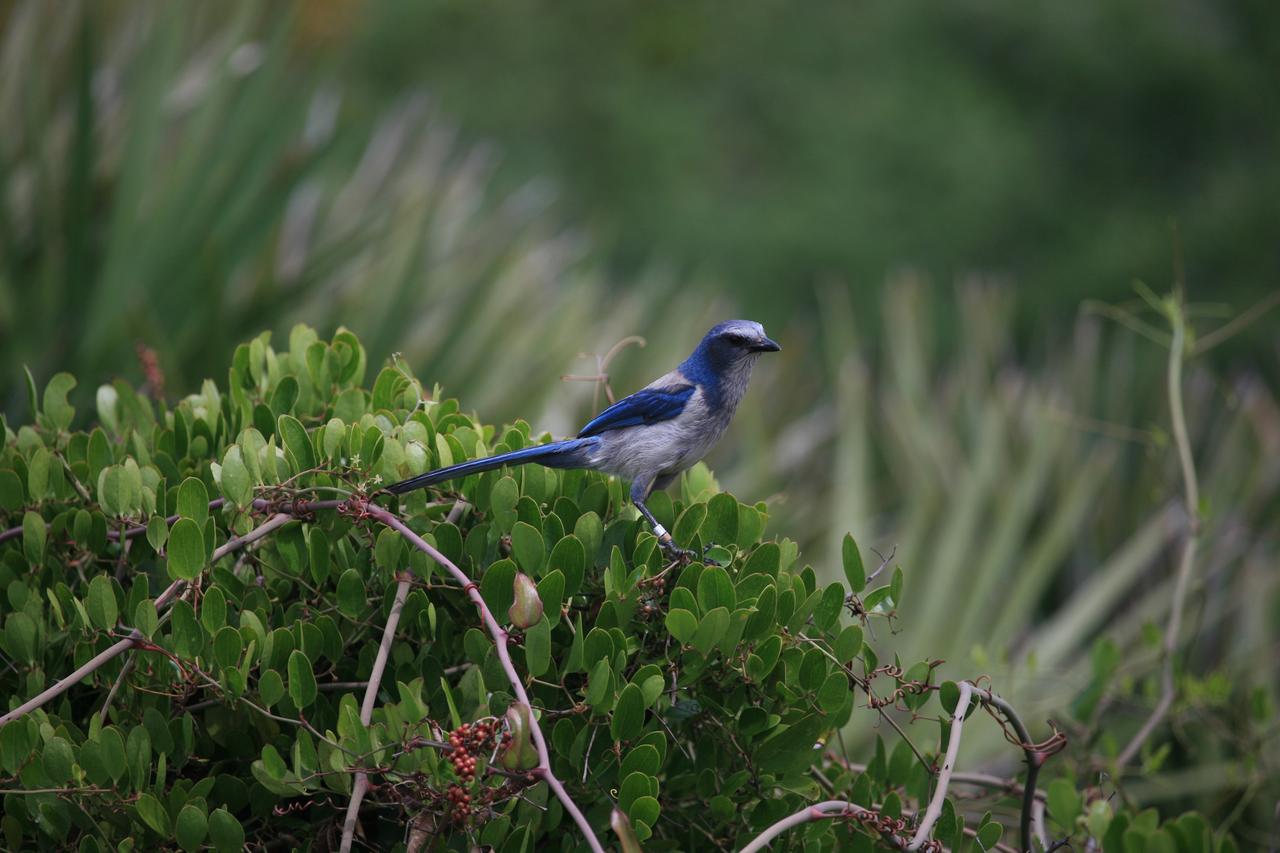

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near Launch Complex-41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a scrub jay keeps watch of activity. On the pad, the Atlas V/Centaur is undergoing a wet dress rehearsal, or countdown test. The Atlas V is being fully loaded with propellants including liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen and RP-1 fuel. Following the rehearsal, the launch vehicle will be rolled off the pad and returned to the Vertical Integration Facility on May 16. The Atlas V/Centaur is the launch vehicle for NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, and NASA's Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, known as LCROSS. They will be mated with the Atlas in late May. LCROSS and LRO are the first missions in NASA's plan to return humans to the moon and begin establishing a lunar outpost by 2020. Launch is scheduled for no earlier than June 17. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket is ready to be lifted to vertical in the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket begins to be lifted to a vertical position at the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
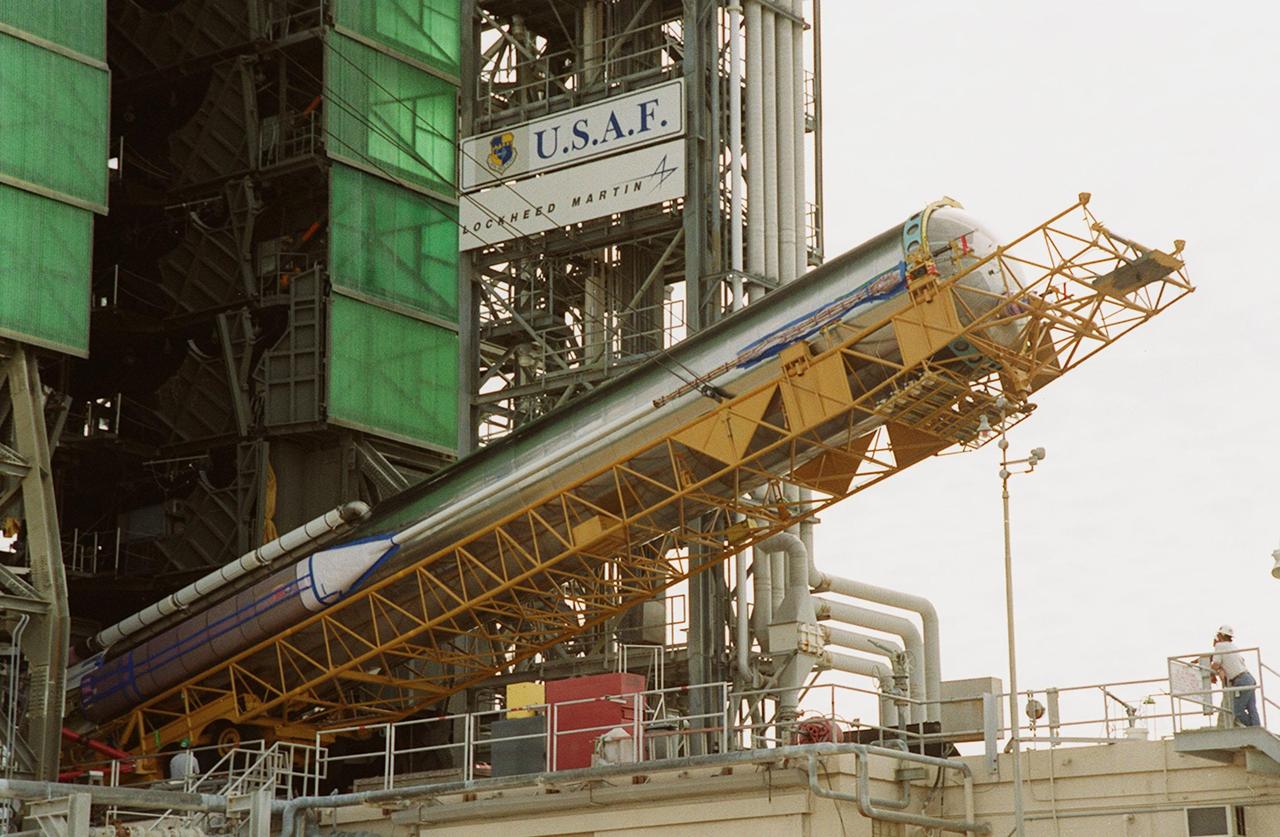

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket begins to be lifted to a vertical position at the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
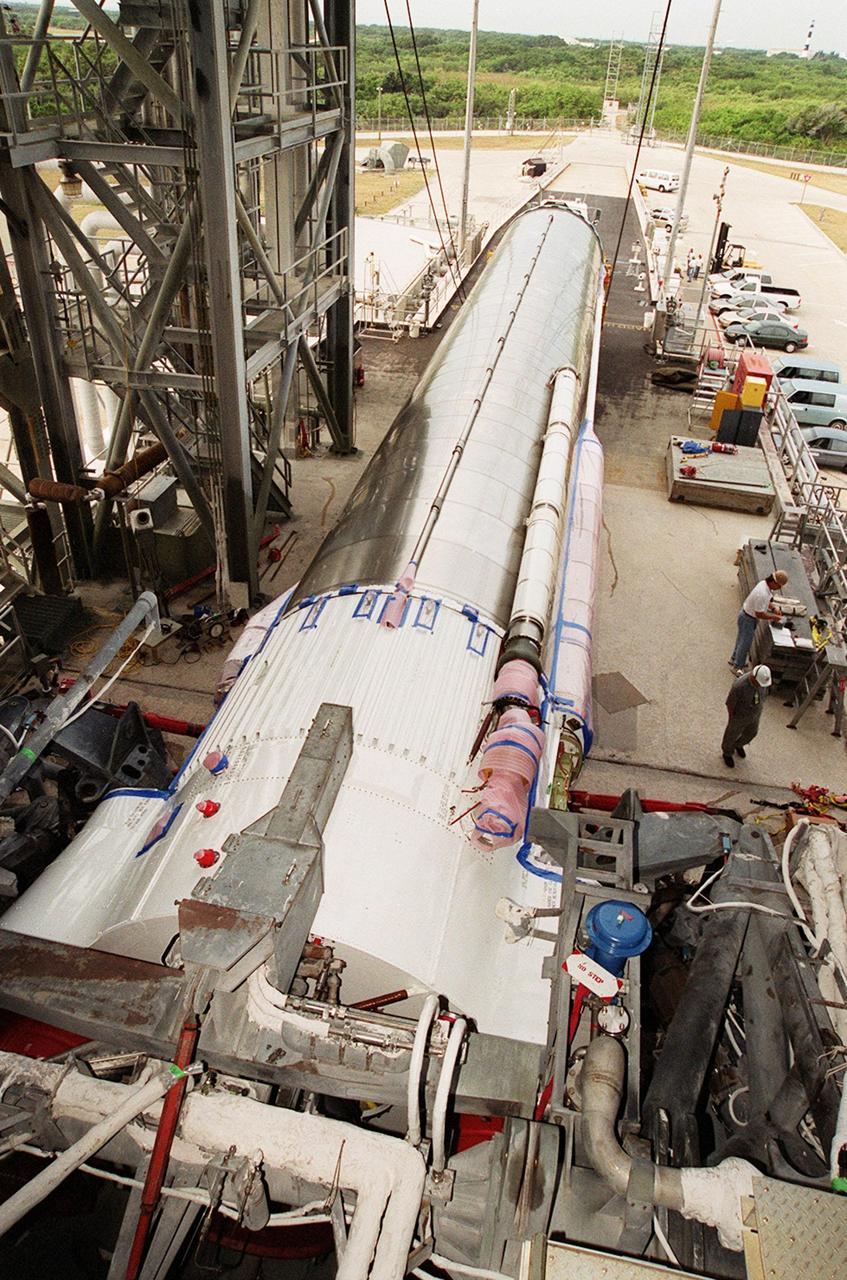

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA rocket is ready to be lifted to vertical in the launch tower. The Atlas rocket, along with the Centaur upper stage, will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
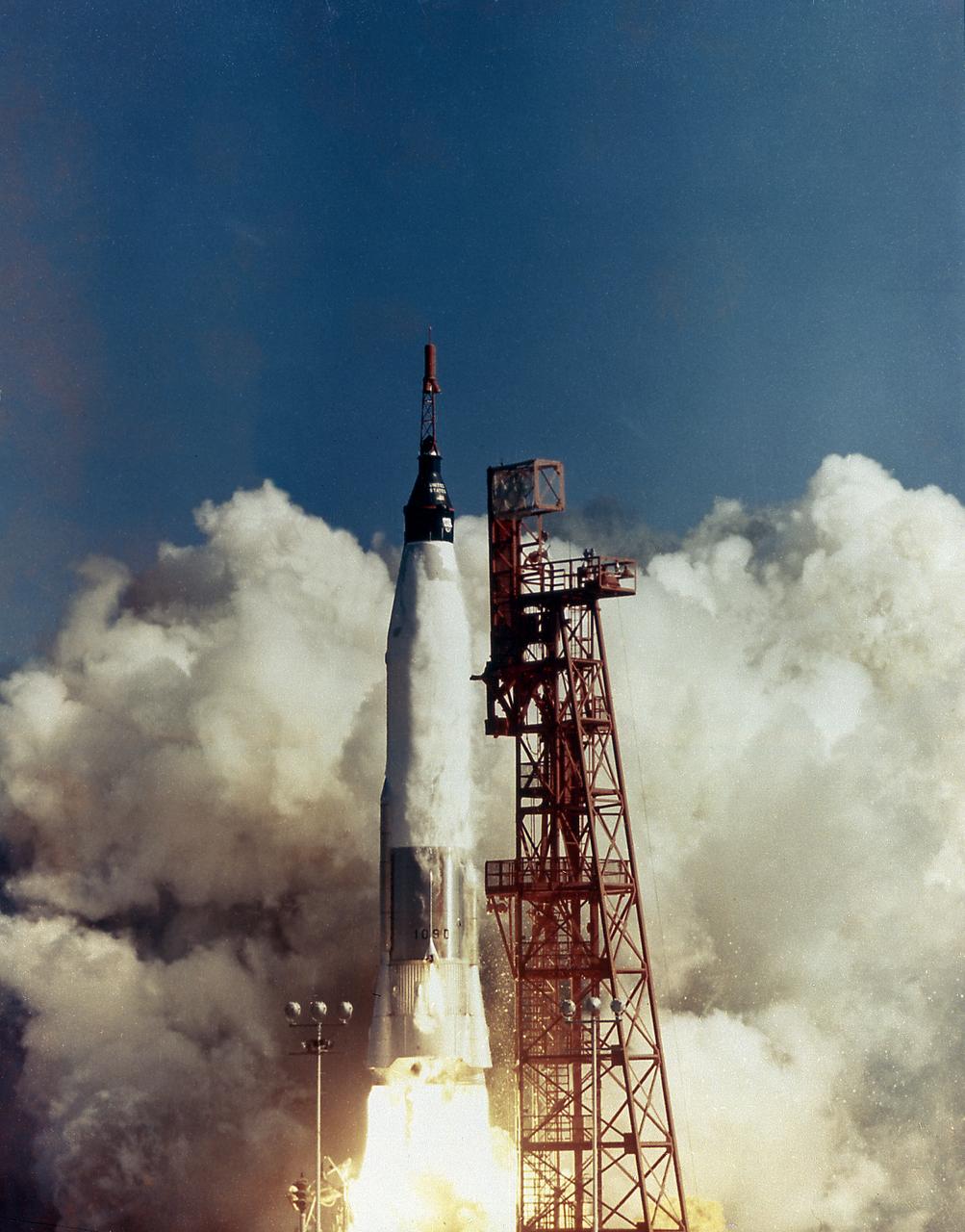

The launch of the MA-6, Friendship 7, on February 20, 1962. Boosted by the Mercury-Atlas vehicle, a modified Atlas Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM), Friendship 7 was the first U.S. marned orbital flight and carried Astronaut John H. Glenn into orbit. Astronaut Glenn became the first American to orbit the Earth.
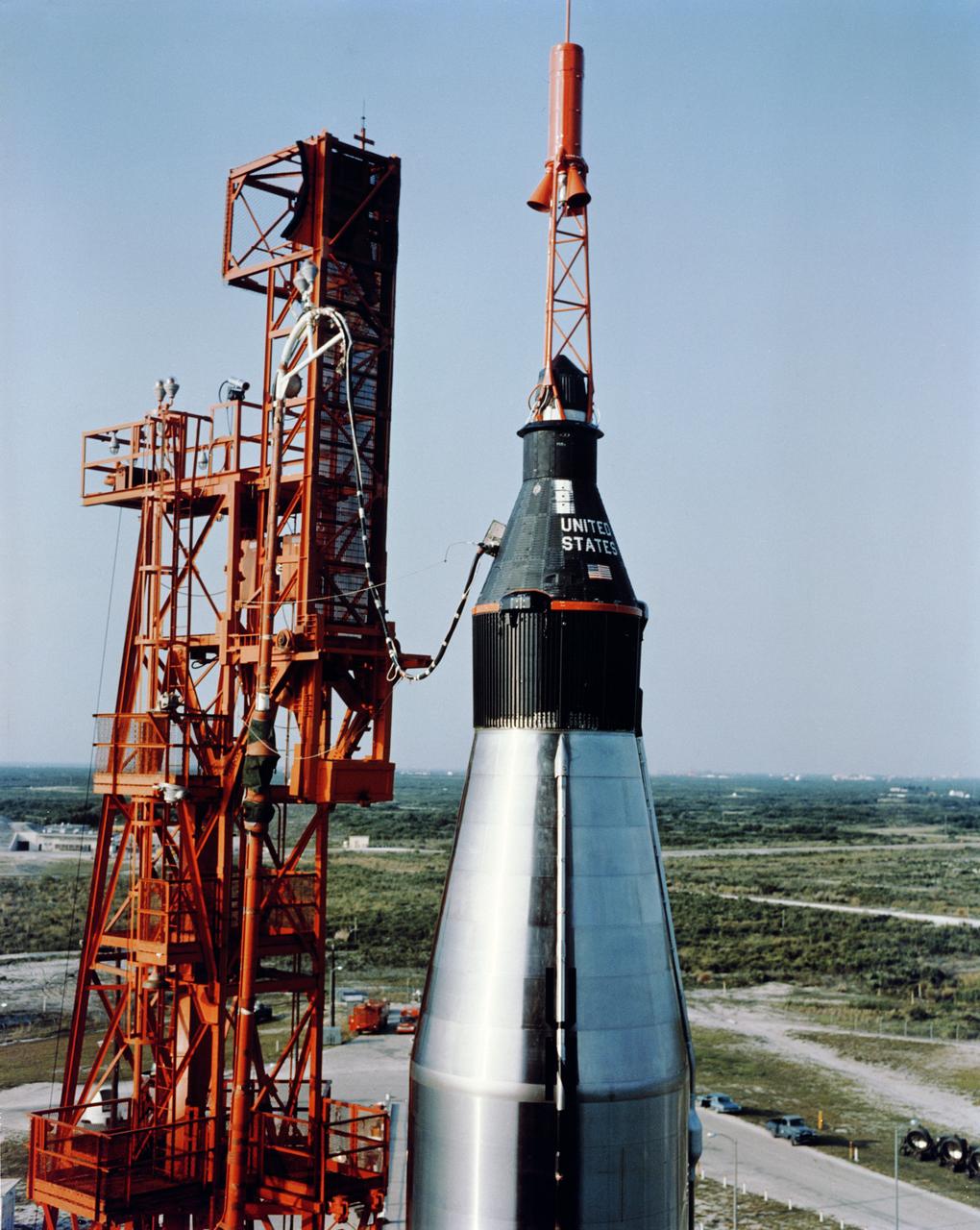

S90-27205 (13 Sept. 1961) --- The unmanned Mercury-Atlas (MA-4) capsule sits atop its Atlas launch vehicle. The successful orbital flight followed the MA-3 mission, which was aborted earlier this year. Photo credit: NASA
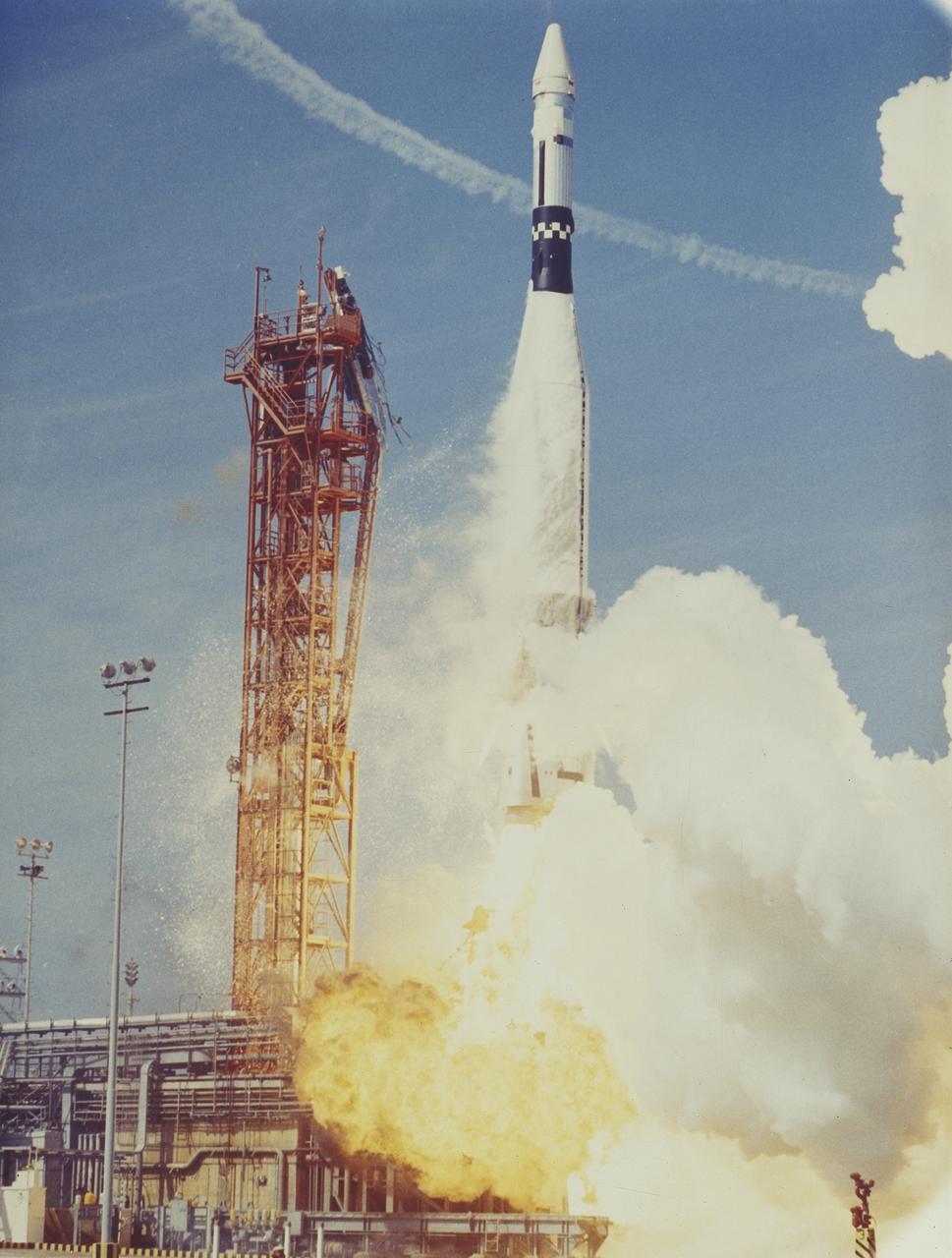

On March 16, 1966, an Atlas booster launched an Agena Target Vehicle for the Gemini 8 mission. The flight crew for the 3 day mission, astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and David R. Scott, achieved the first rendezvous and docking to Atlas/Agena in Earth orbit.
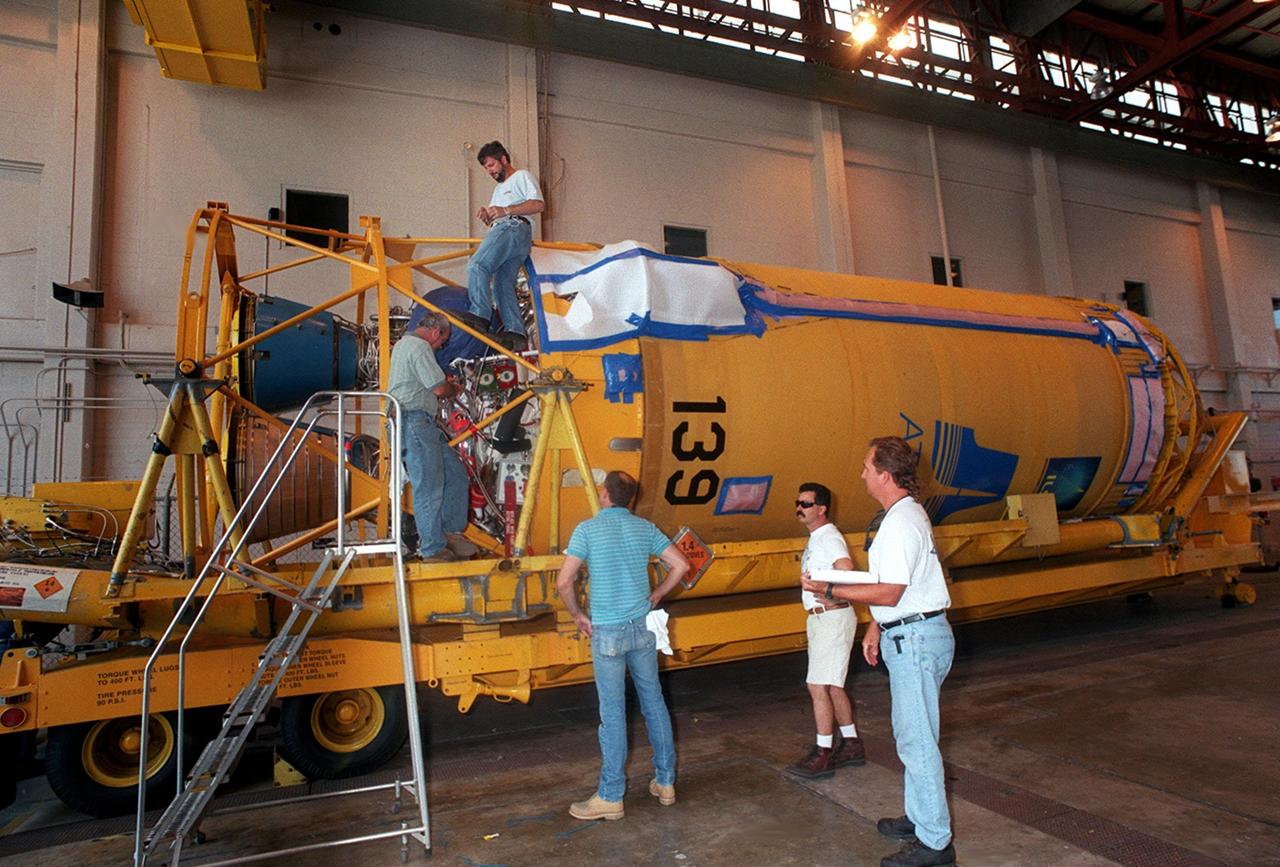

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
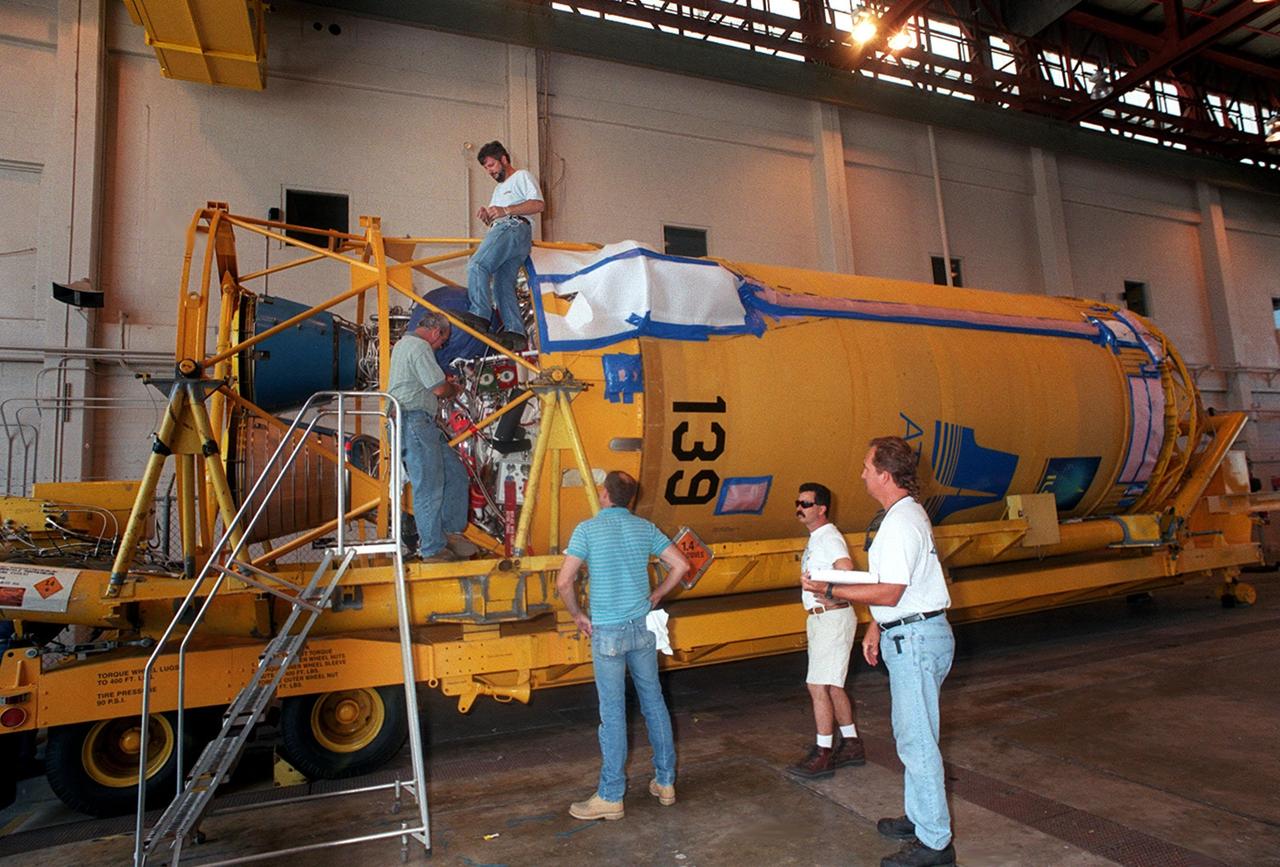

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
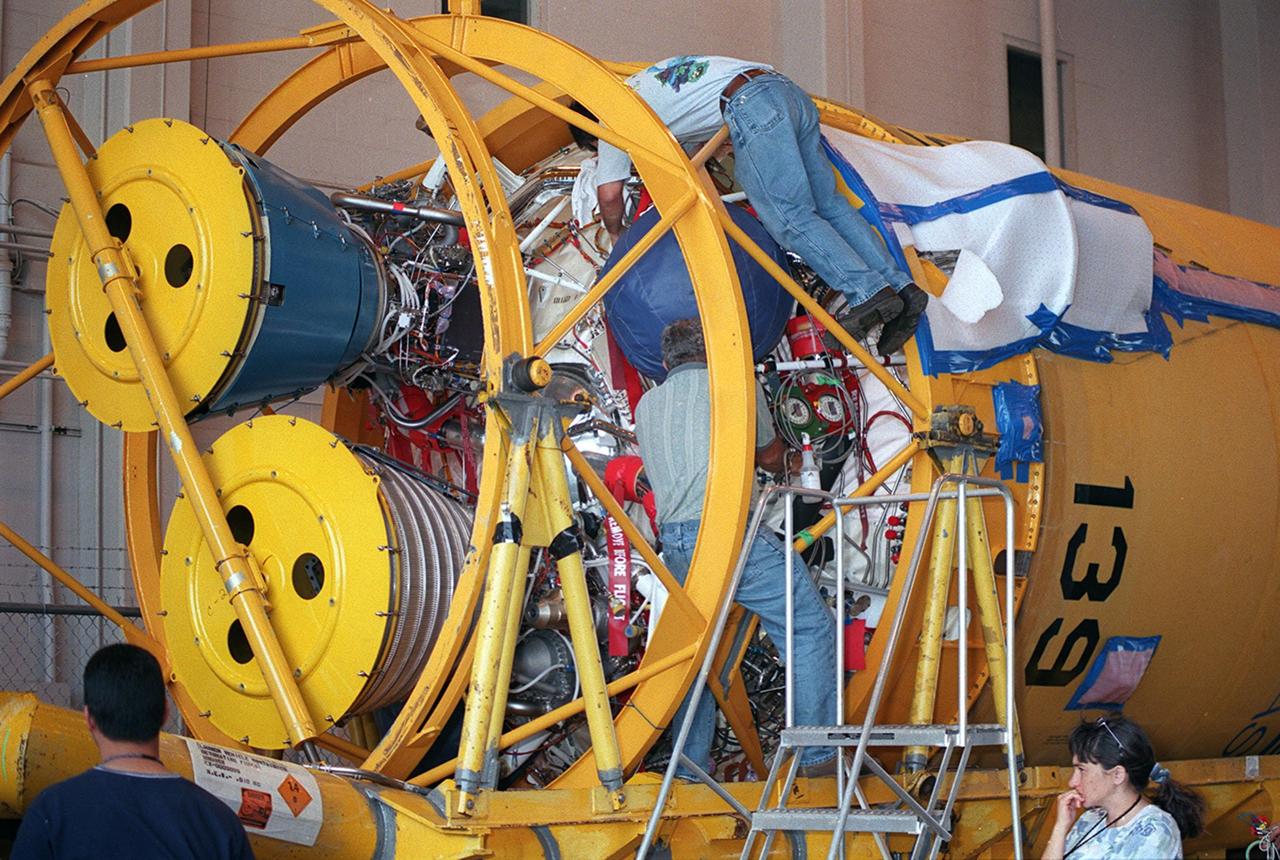

At Hangar J, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), work is begun on the Centaur upper stage that will be used with an Atlas IIA rocket to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems to geosynchronous transfer orbit
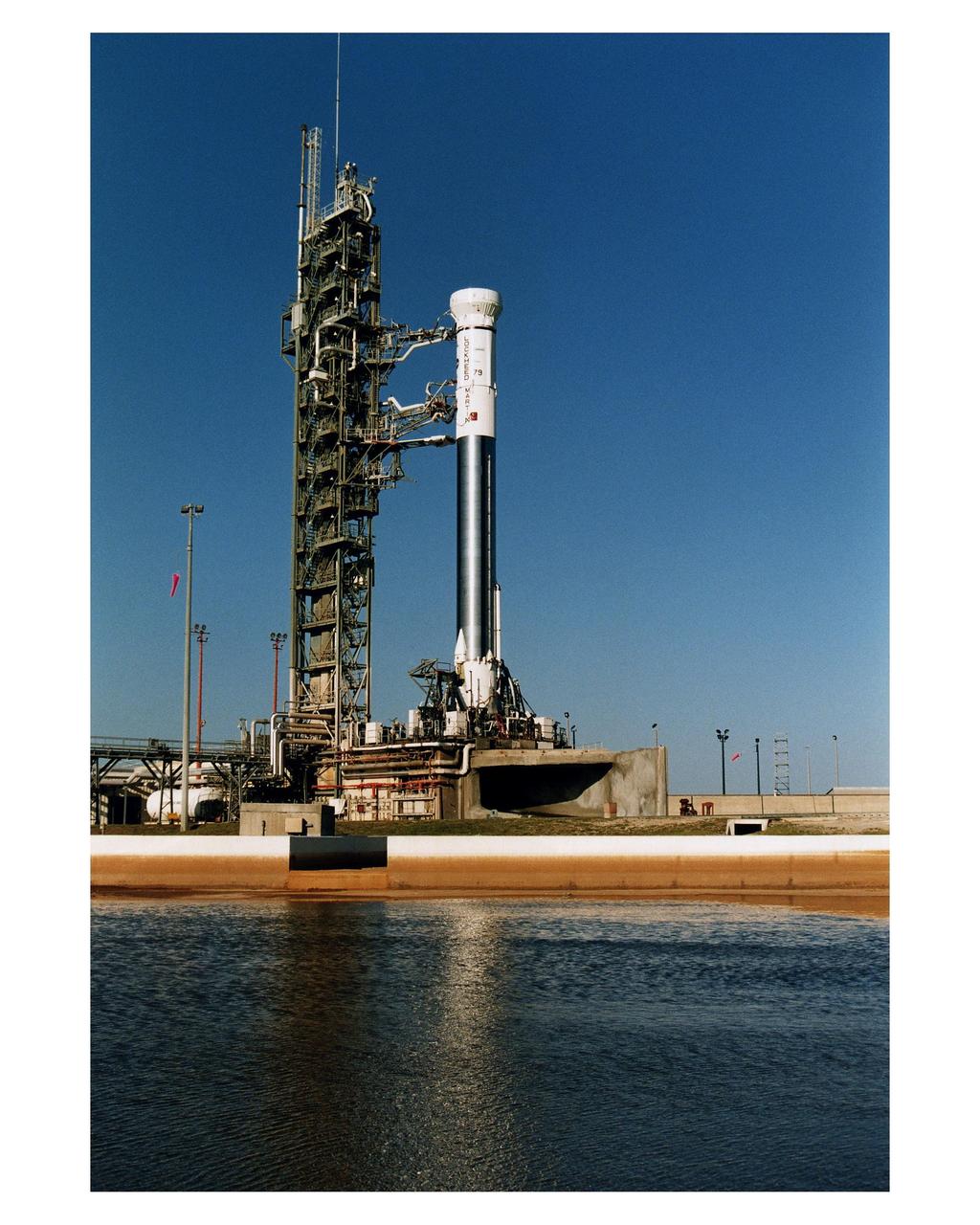

The Lockheed Martin Atlas 1 expendable launch vehicle (AC-79) which will carry the GOES-K advanced weather satellite undergoes a critical prelaunch test with its mobile service tower pulled back. The Wet Dress Rehearsal is a major prelaunch test designed to demonstrate, in part, the launch readiness of the vehicle and launch support equipment. AC-79 will be the final launch of an Atlas 1 rocket, a derivative of the original Atlas Centaur which had its first successful launch for NASA in 1963. Future launches of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) in the current series will be on Atlas II vehicles. The GOES satellites are owned and operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA); NASA manages the design, development and launch of the spacecraft. The launch of AC-79 with the GOES-K is targeted for <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/63-97.htm">April 24</a> during a launch window which extends from 1:50-3:09 a.m. EDT
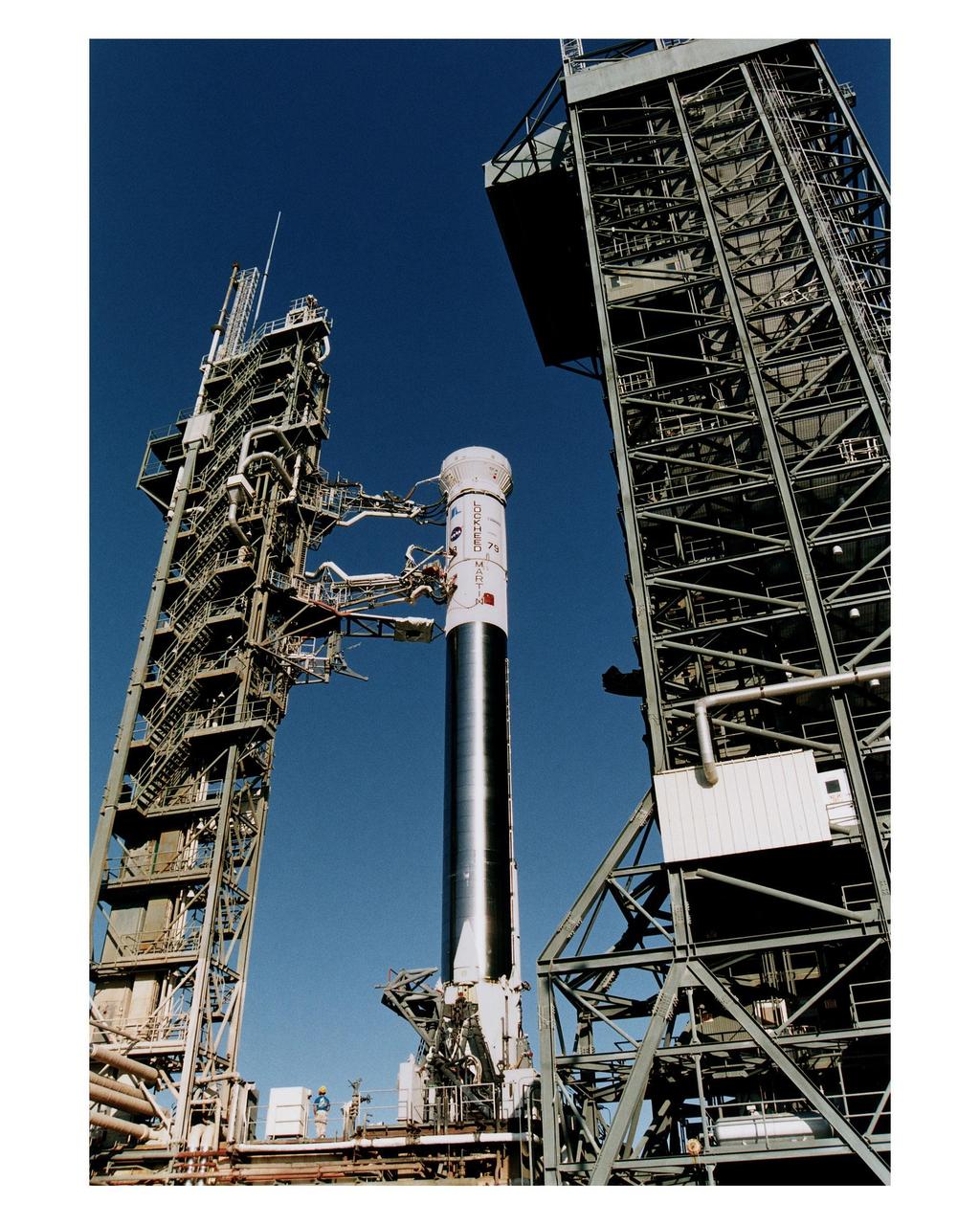

The Lockheed Martin Atlas 1 expendable launch vehicle (AC-79) which will carry the GOES-K advanced weather satellite undergoes a critical prelaunch test with its mobile service tower pulled back. The Wet Dress Rehearsal is a major prelaunch test designed to demonstrate, in part, the launch readiness of the vehicle and launch support equipment. AC-79 will be the final launch of an Atlas 1 rocket, a derivative of the original Atlas Centaur which had its first successful launch for NASA in 1963. Future launches of Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) in the current series will be on Atlas II vehicles. The GOES satellites are owned and operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA); NASA manages the design, development and launch of the spacecraft. The launch of AC-79 with the GOES-K is targeted for <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/63-97.htm">April 24</a> during a launch window which extends from 1:50-3:09 a.m. EDT
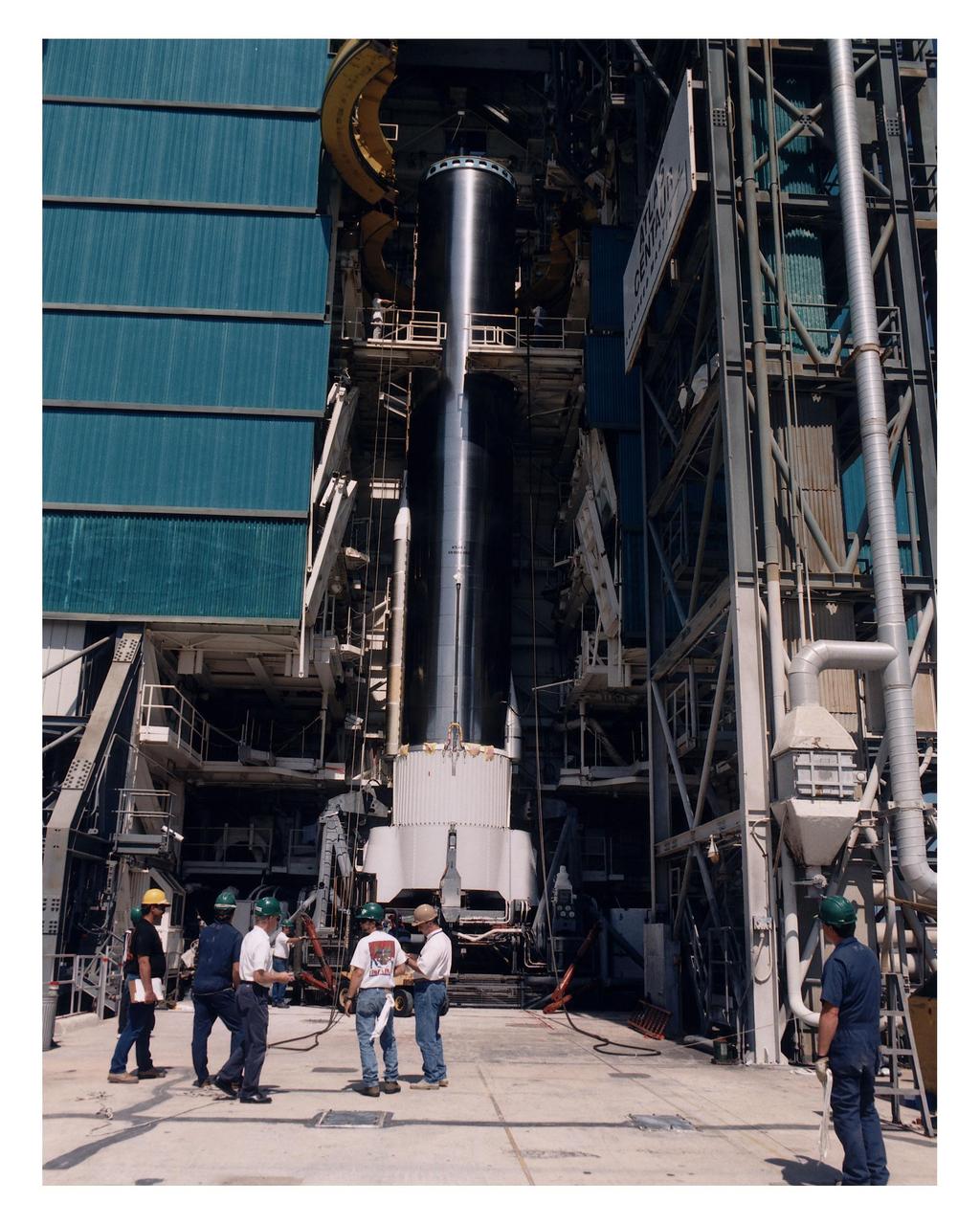

The Atlas 1 rocket which will carry the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-K (GOES-K) into space is erected at Launch Complex 36, Pad B, Cape Canaveral Air Station. The Lockheed Martin-built rocket and its Centaur upper stage will form the AC-79 vehicle, the final vehicle in the Atlas 1 series which began launches for NASA in 1962. GOES-K will be the third spacecraft to be launched in the advanced series of geostationary weather satellites built for NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The spacecraft will be designated GOES-10 in orbit. Launch is targeted for April 24
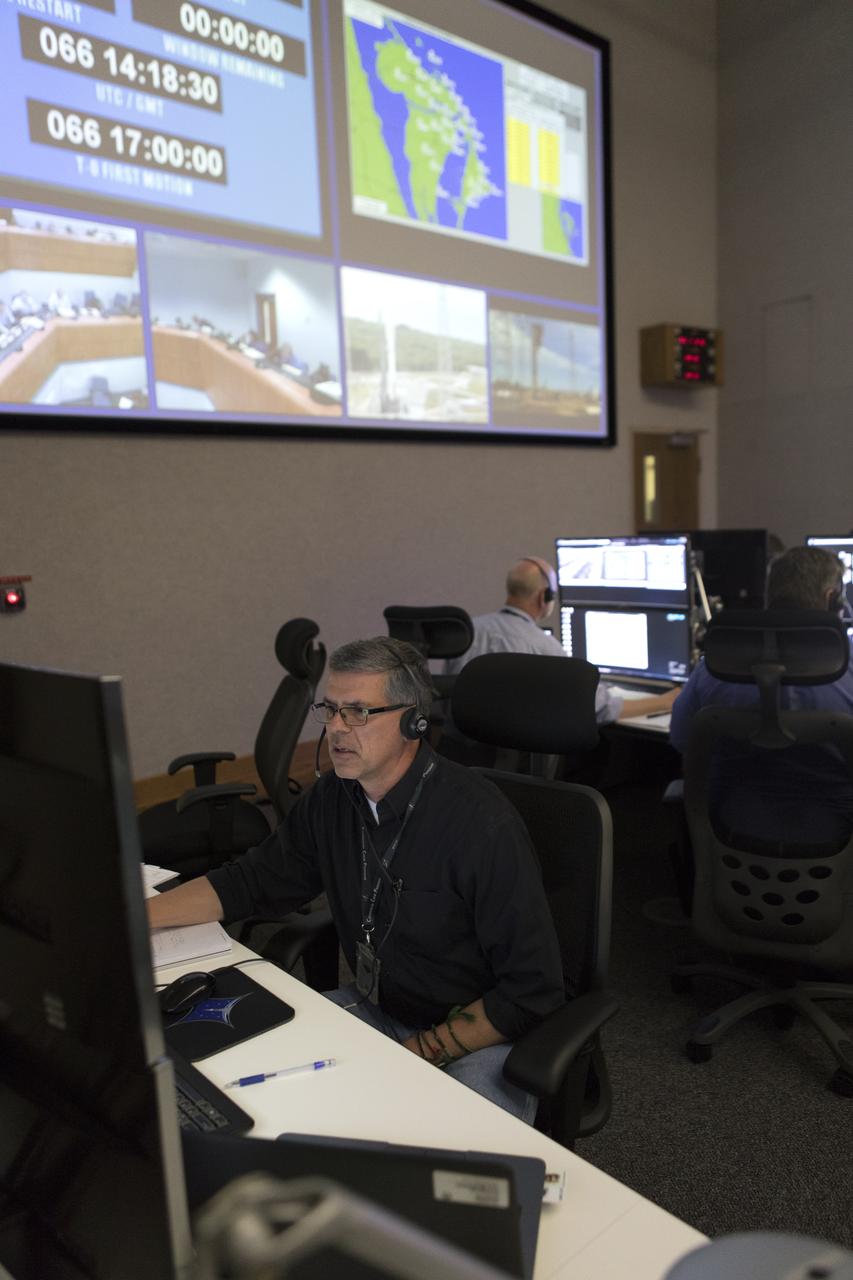

NASA, Boeing and United Launch Alliance (ULA) conduct a simulation of launch procedures for Boeing’s Orbital Test Flight, the first uncrewed test of the company’s CST-100 Starliner and a ULA Atlas V rocket. Launch teams participated in the simulation across the country, including inside the Launch Vehicle Data Center at Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Starliner will launch on an Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
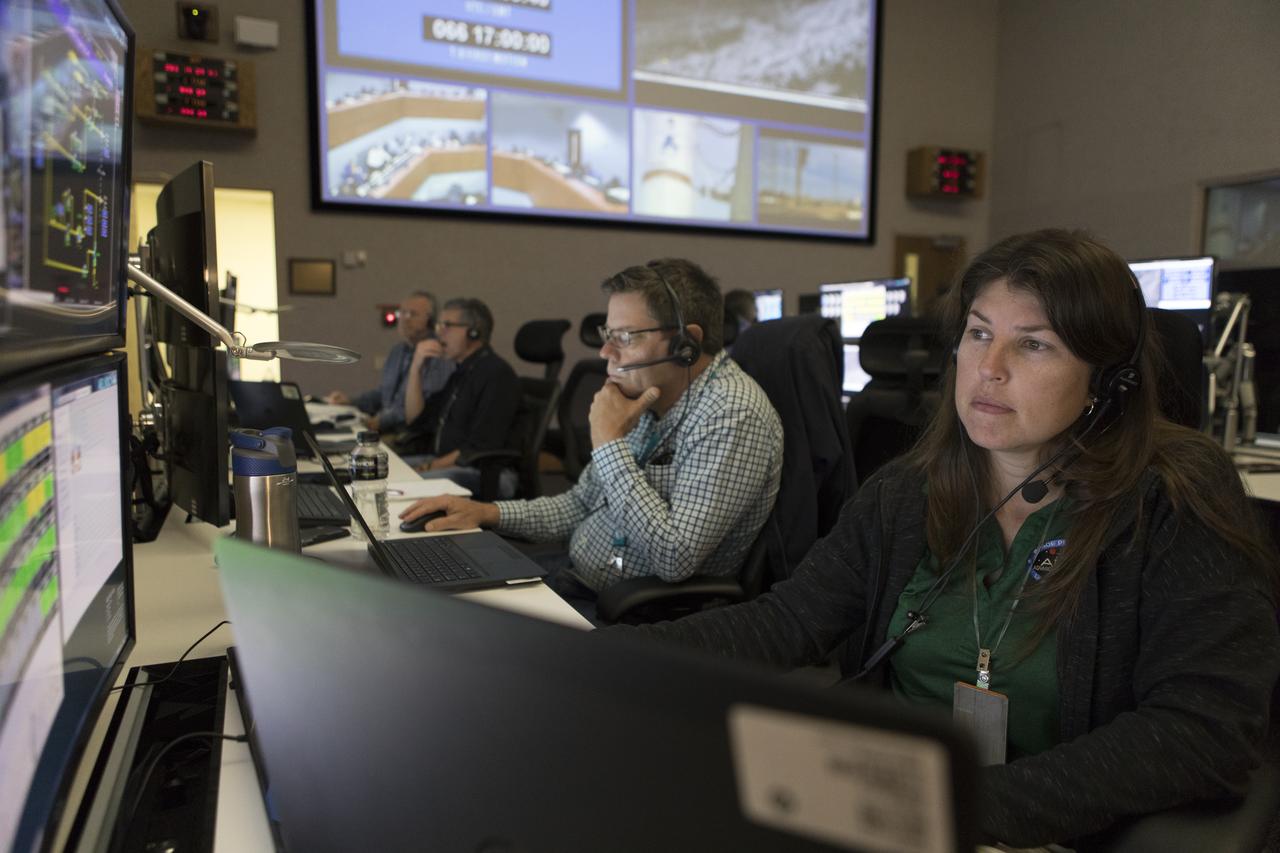

NASA, Boeing and United Launch Alliance (ULA) conduct a simulation of launch procedures for Boeing’s Orbital Test Flight, the first uncrewed test of the company’s CST-100 Starliner and a ULA Atlas V rocket. Launch teams participated in the simulation across the country, including inside the Launch Vehicle Data Center at Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Starliner will launch on an Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
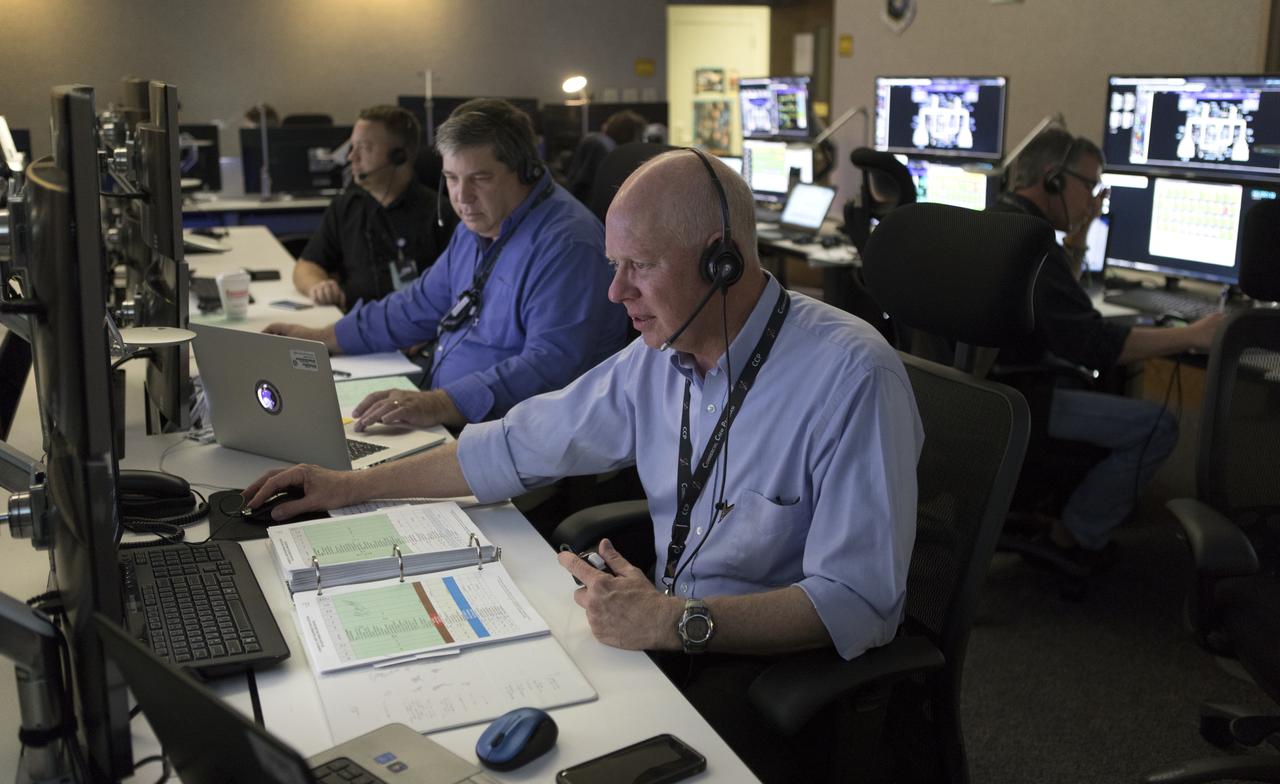

NASA, Boeing and United Launch Alliance (ULA) conduct a simulation of launch procedures for Boeing’s Orbital Test Flight, the first uncrewed test of the company’s CST-100 Starliner and a ULA Atlas V rocket. Launch teams participated in the simulation across the country, including inside the Launch Vehicle Data Center at Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Starliner will launch on an Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
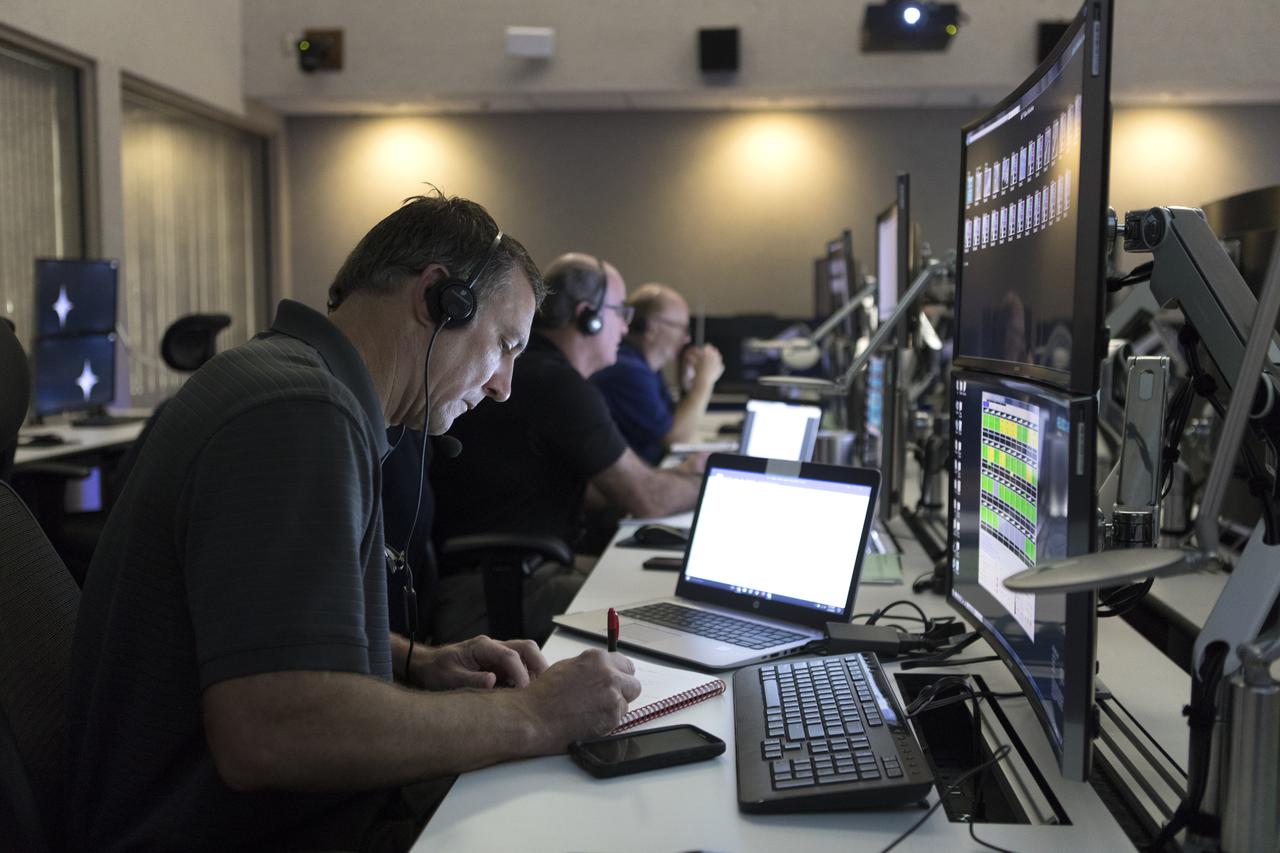

NASA, Boeing and United Launch Alliance (ULA) conduct a simulation of launch procedures for Boeing’s Orbital Test Flight, the first uncrewed test of the company’s CST-100 Starliner and a ULA Atlas V rocket. Launch teams participated in the simulation across the country, including inside the Launch Vehicle Data Center at Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Starliner will launch on an Atlas V rocket to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage departs the Launch Vehicle Integration Facility aboard a transport trailer for delivery to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

The Solar Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) is launched atop an ATLAS-IIAS expendable launch vehicle. Liftoff from launch complex 36B at Cape Canaveral Air Station marked the 10th Atlas launch from the Eastern range for 1995. SOHO is a cooperative effort involving NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) within the framework of the International Solar-Terrestrial Physics Program. During its 2-year mission, the SOHO spacecraft gathered data on the internal structure of the Sun, its extensive outer atmosphere and the origin of the solar wind.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage emerges from the Launch Vehicle Integration Facility aboard a transport trailer for delivery to the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) will launch aboard the Atlas V rocket in November. GOES-R is the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites.

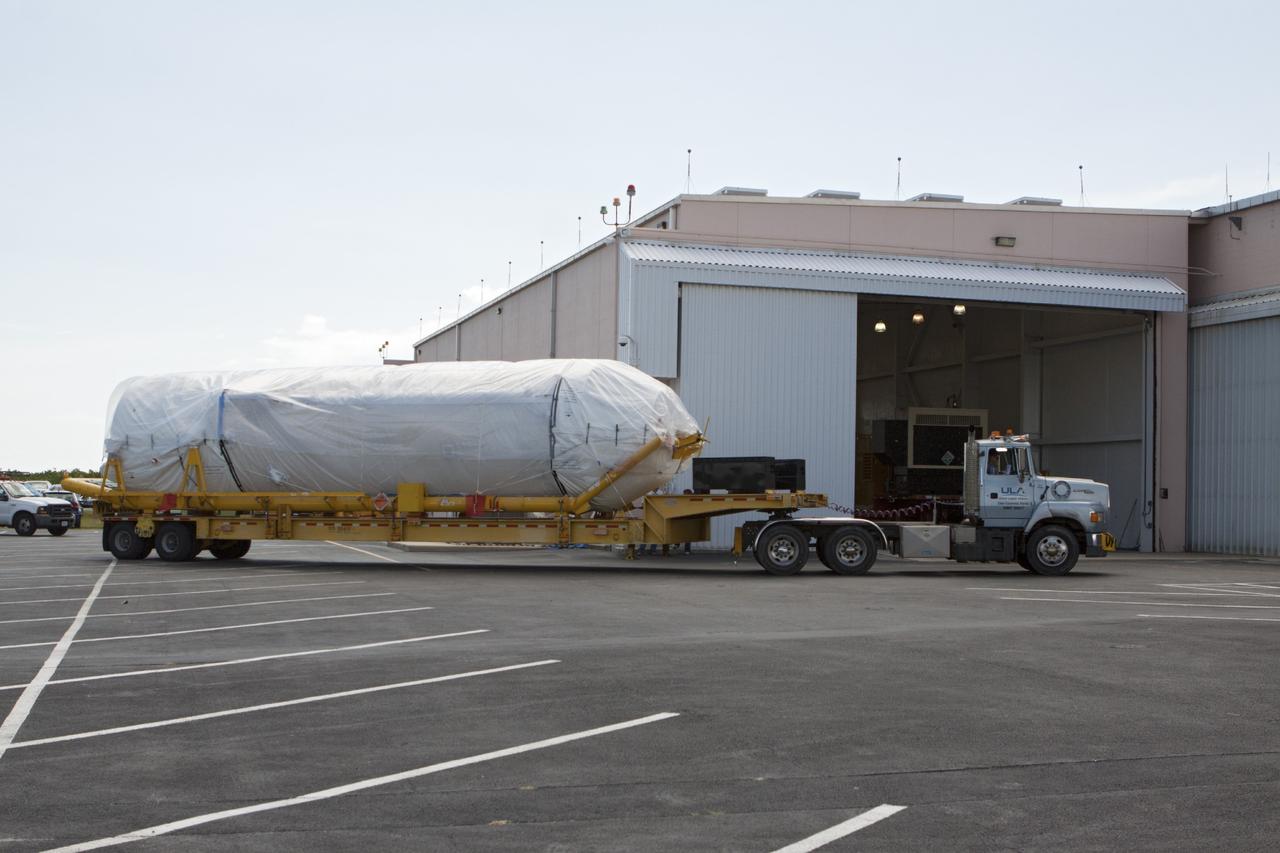
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first and second stages arrive at to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the launch vehicle will begin processing for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft to the Red Planet. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch in November from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first and second stages arrive at to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the launch vehicle will begin processing for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft to the Red Planet. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch in November from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
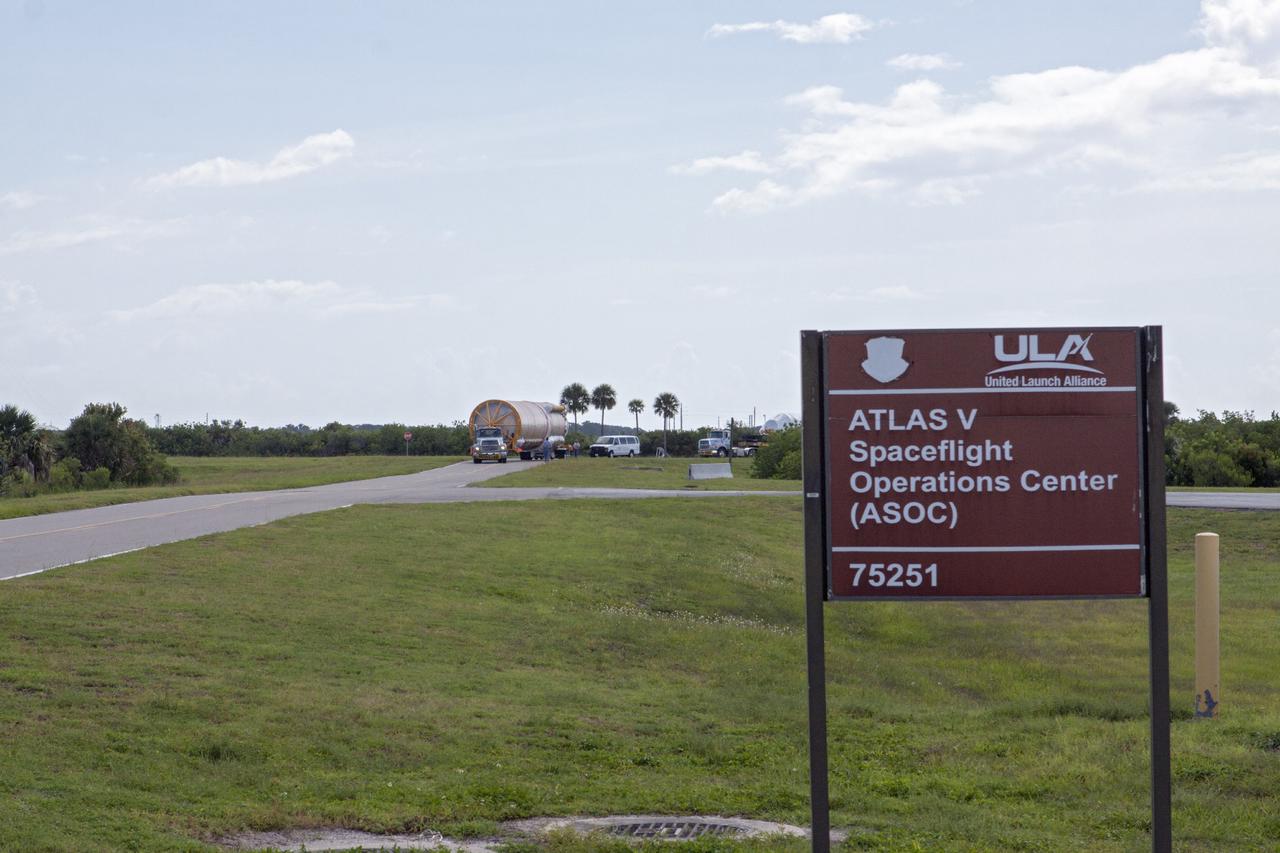

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first and second stages arrive at to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the launch vehicle will begin processing for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft to the Red Planet. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch in November from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
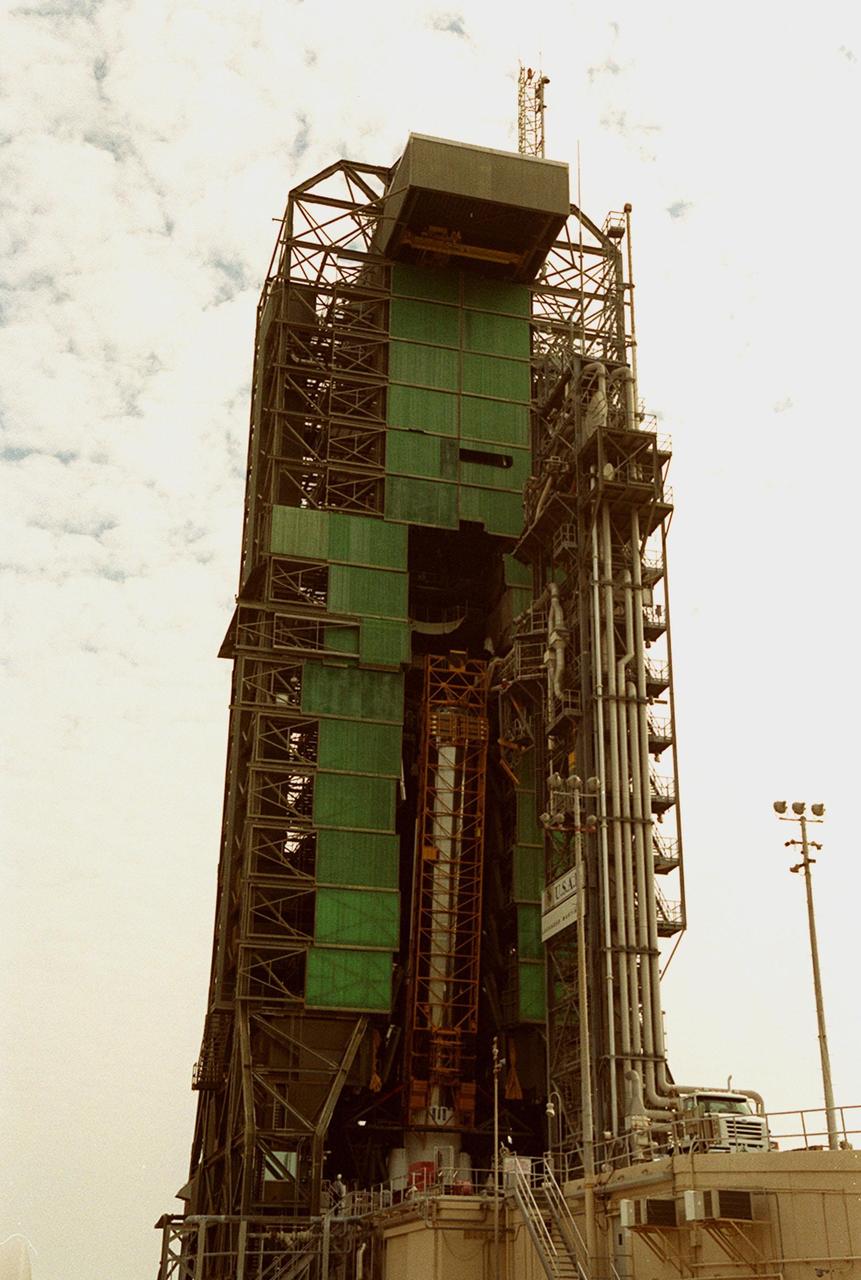

The Atlas IIA rocket is close to its vertical position in the launch tower at Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). It will be mated with a Centaur upper stage to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first and second stages arrive at to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the launch vehicle will begin processing for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft to the Red Planet. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch in November from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first and second stages arrive at to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the launch vehicle will begin processing for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft to the Red Planet. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch in November from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
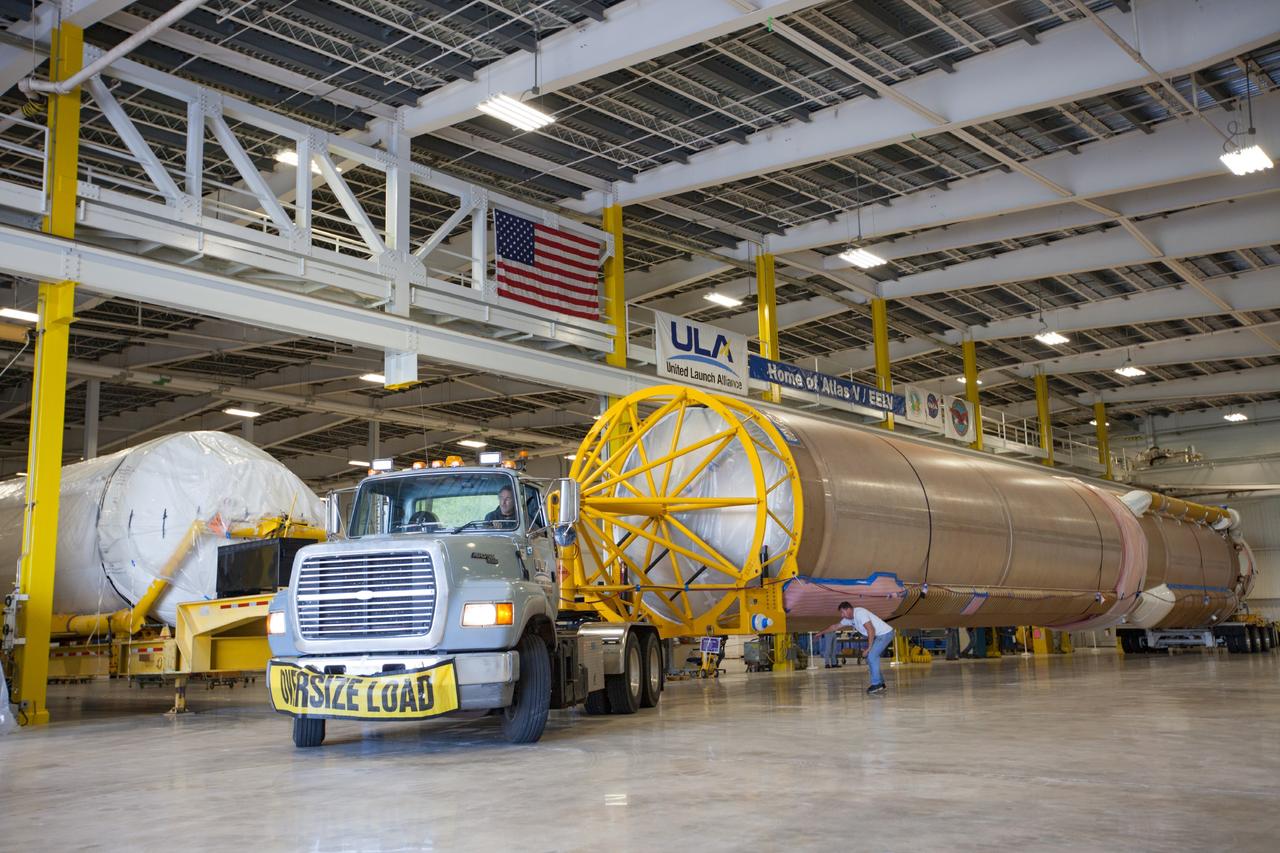

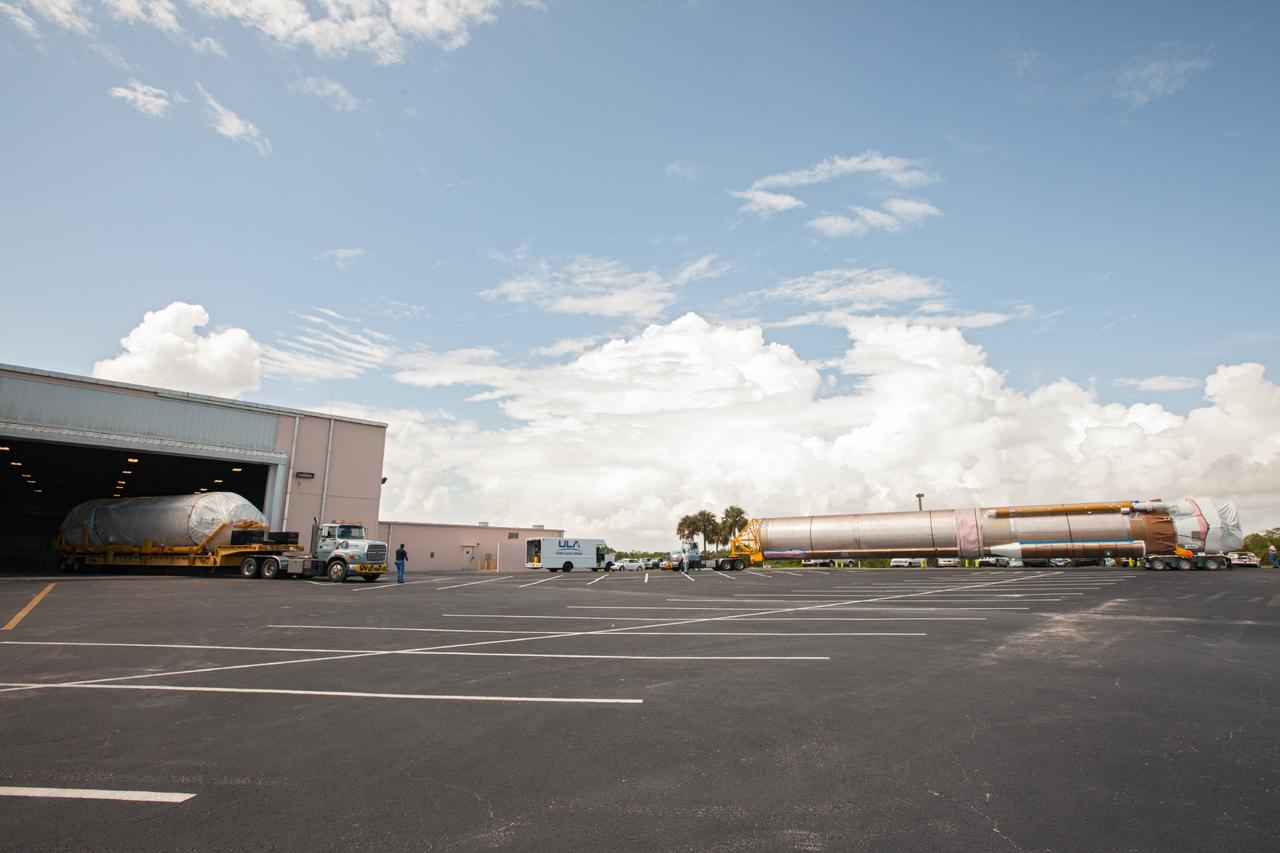
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first and second stages arrive at to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the launch vehicle will begin processing for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft to the Red Planet. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch in November from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
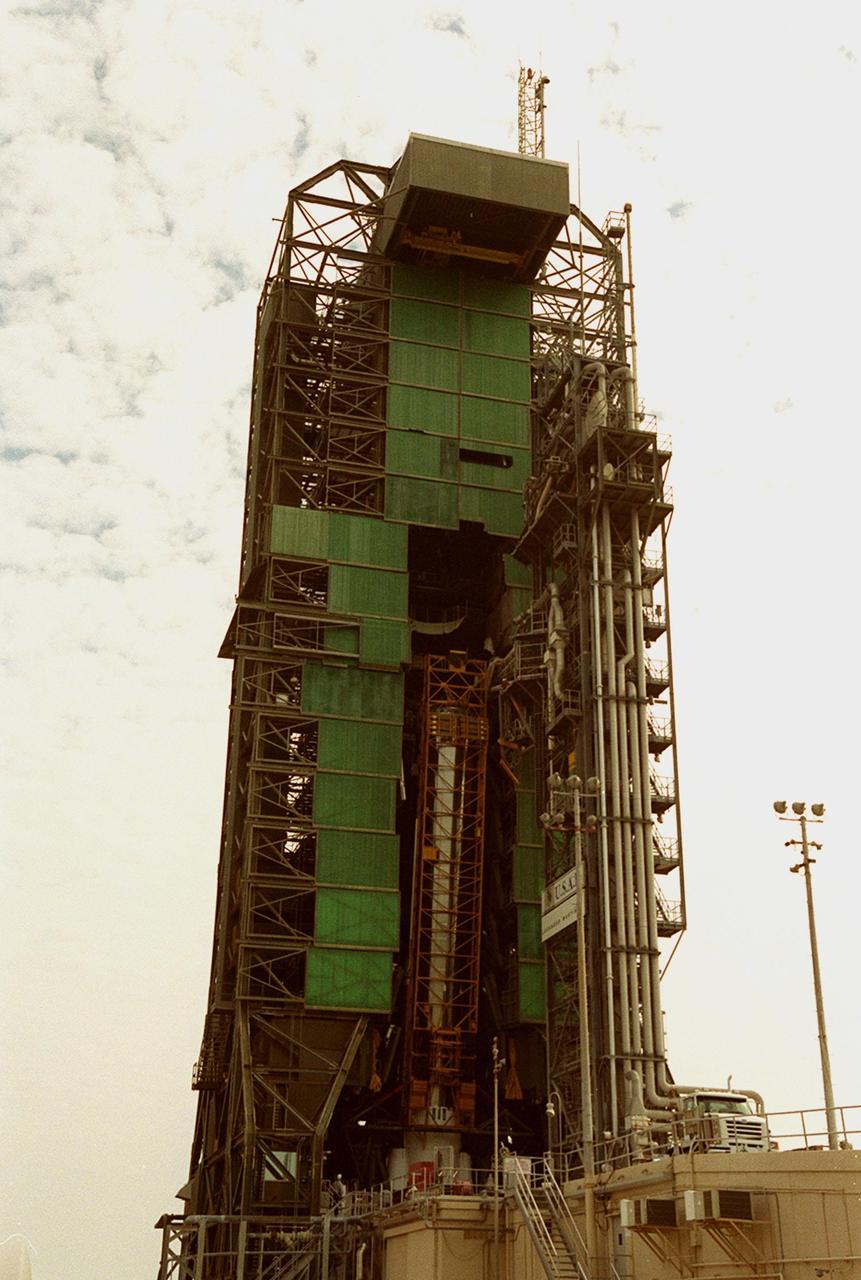

The Atlas IIA rocket is close to its vertical position in the launch tower at Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS). It will be mated with a Centaur upper stage to launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is manufactured and operated by Lockheed Martin. Atlas IIA is capable of lifting payload systems weights in the 2,850 kg (6,300 lb) to 3,070 kg (6,760 lb) class to geosynchronous transfer orbit. It is 25 m (82 ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Centaur is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter
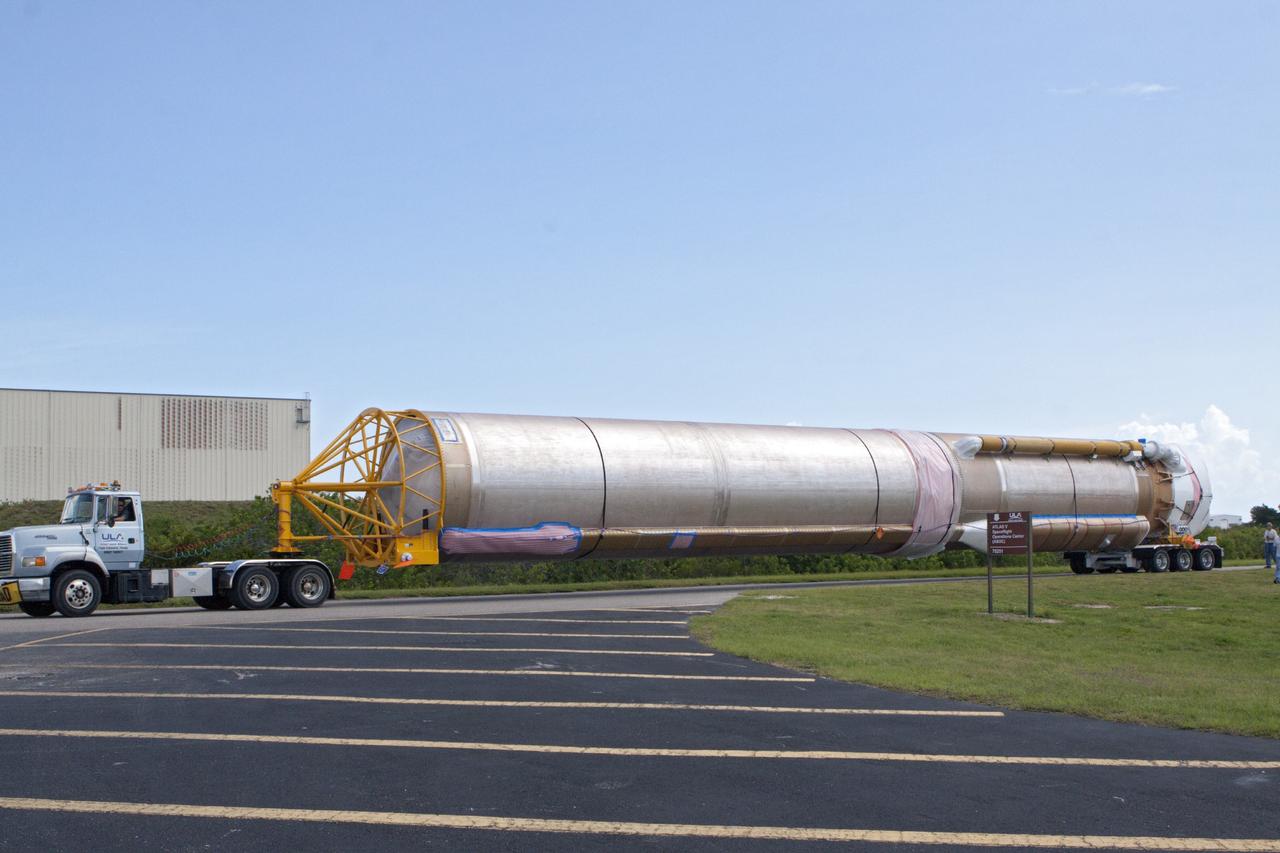

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first and second stages arrive at to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the launch vehicle will begin processing for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft to the Red Planet. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch in November from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
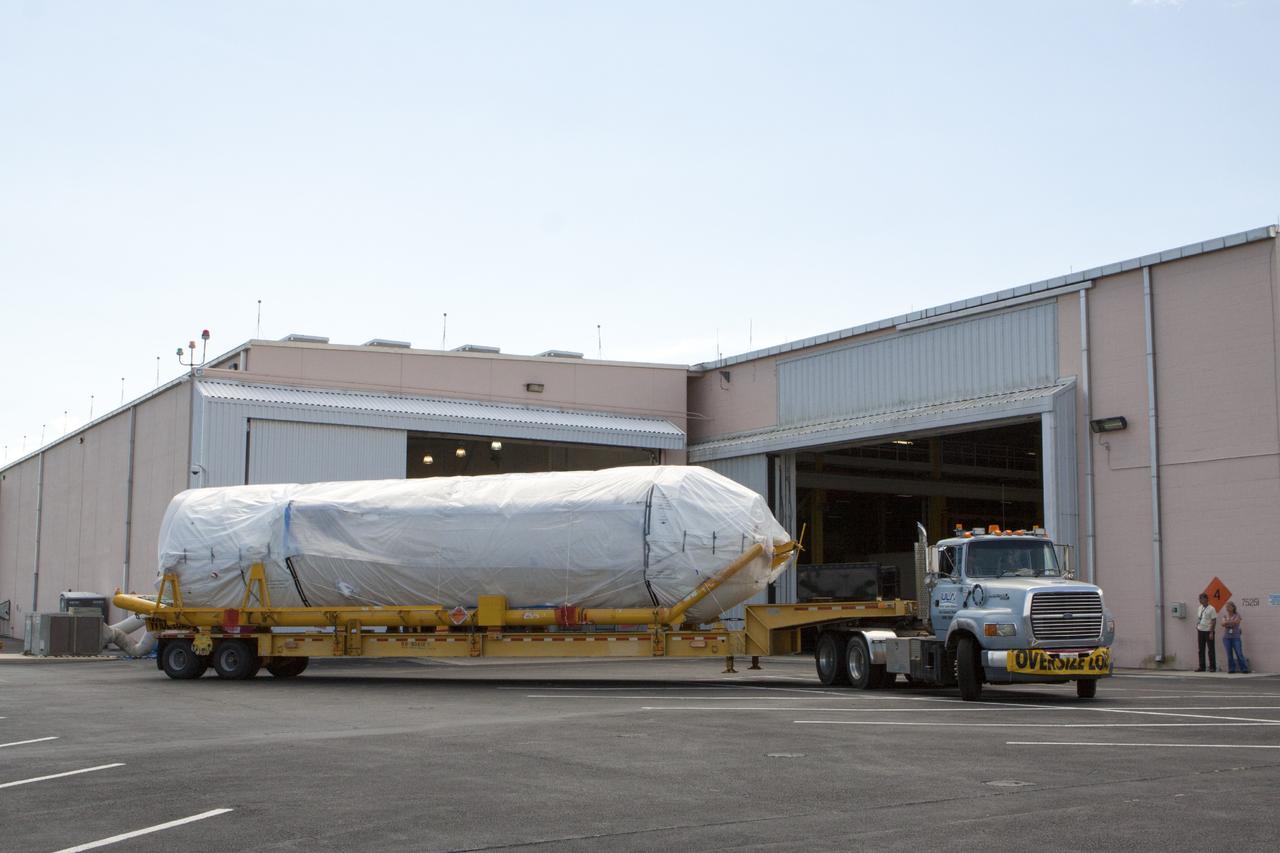

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first and second stages arrive at to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the launch vehicle will begin processing for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft to the Red Planet. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch in November from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
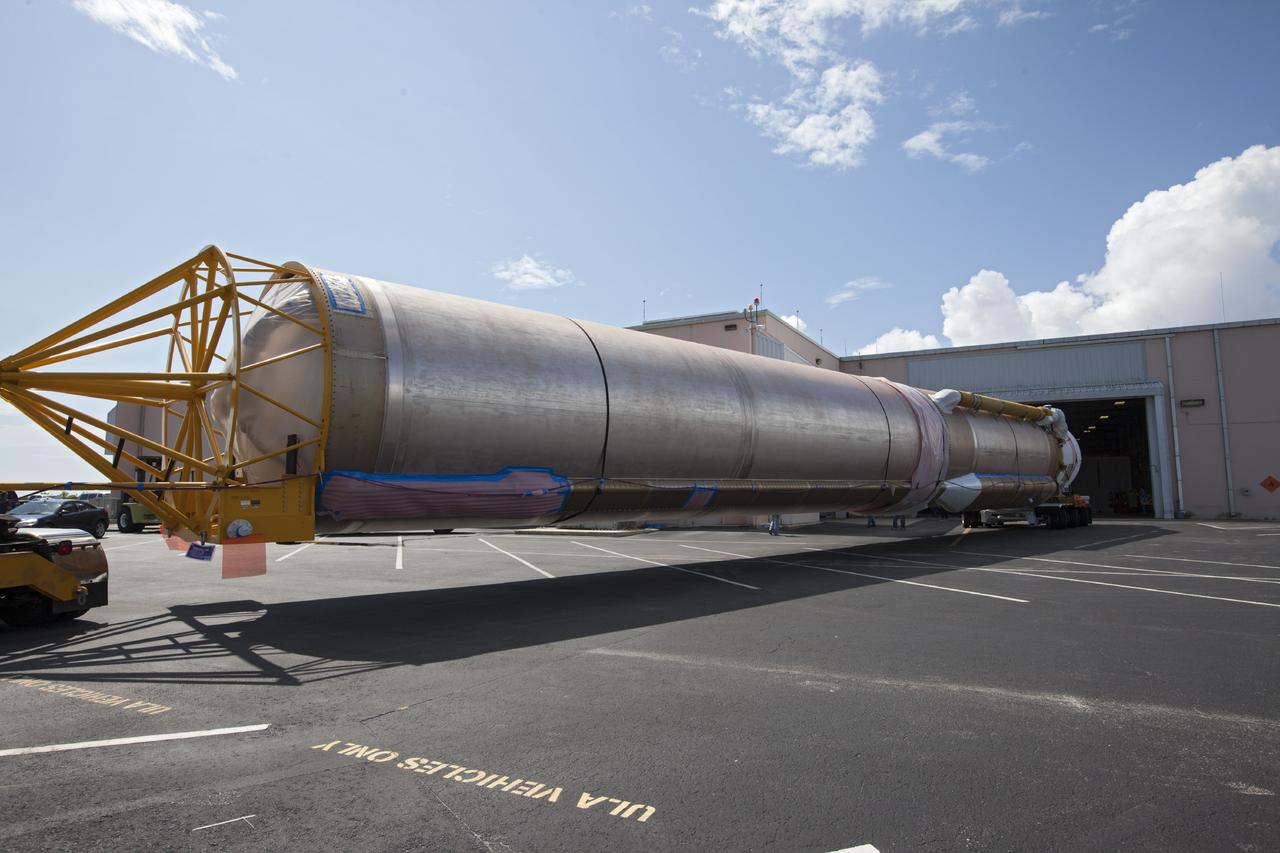

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first and second stages arrive at to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the launch vehicle will begin processing for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft to the Red Planet. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch in November from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
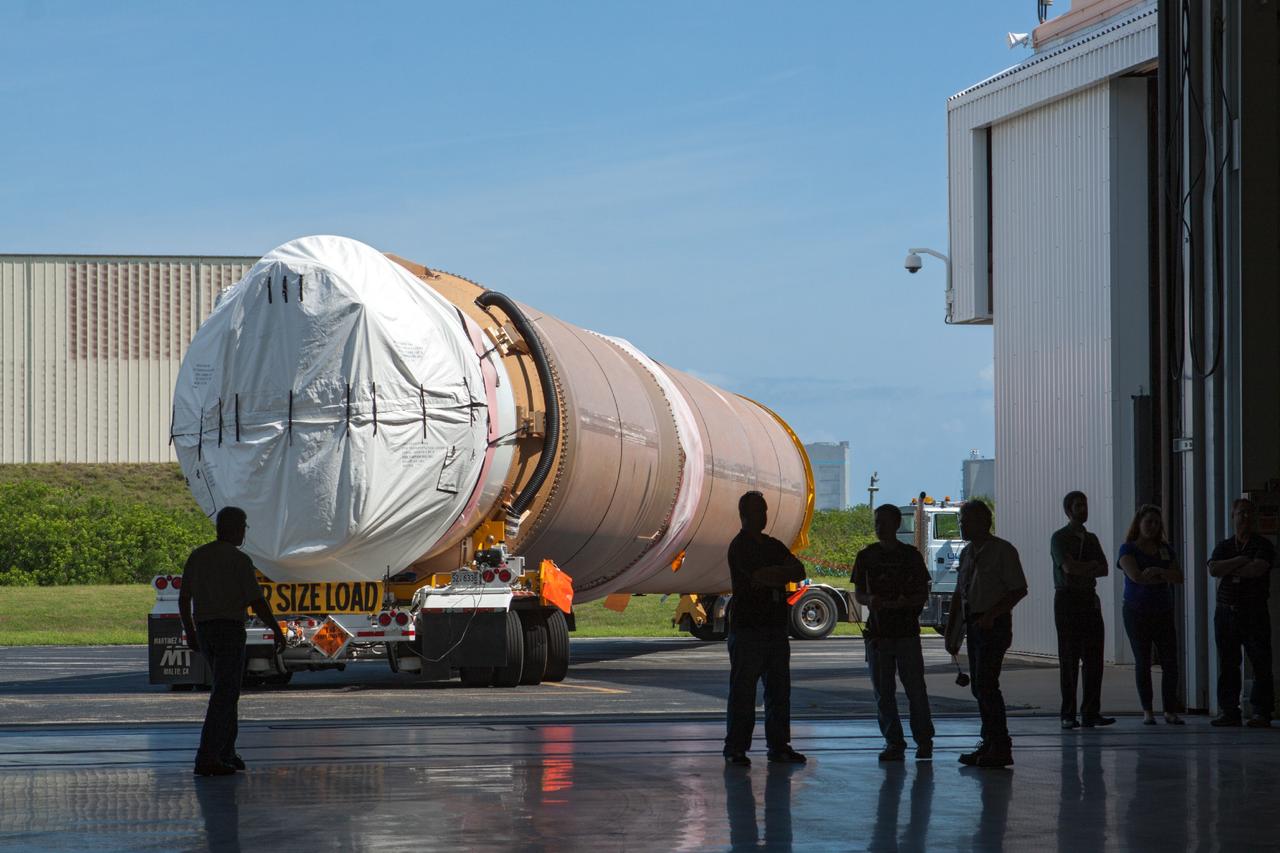

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket first and second stages arrive at to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center, or ASOC, at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. There, the launch vehicle will begin processing for the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, spacecraft to the Red Planet. MAVEN is being prepared for its scheduled launch in November from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. Positioned in an orbit above the Red Planet, MAVEN will study the upper atmosphere of Mars in unprecedented detail. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/maven/main/index.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
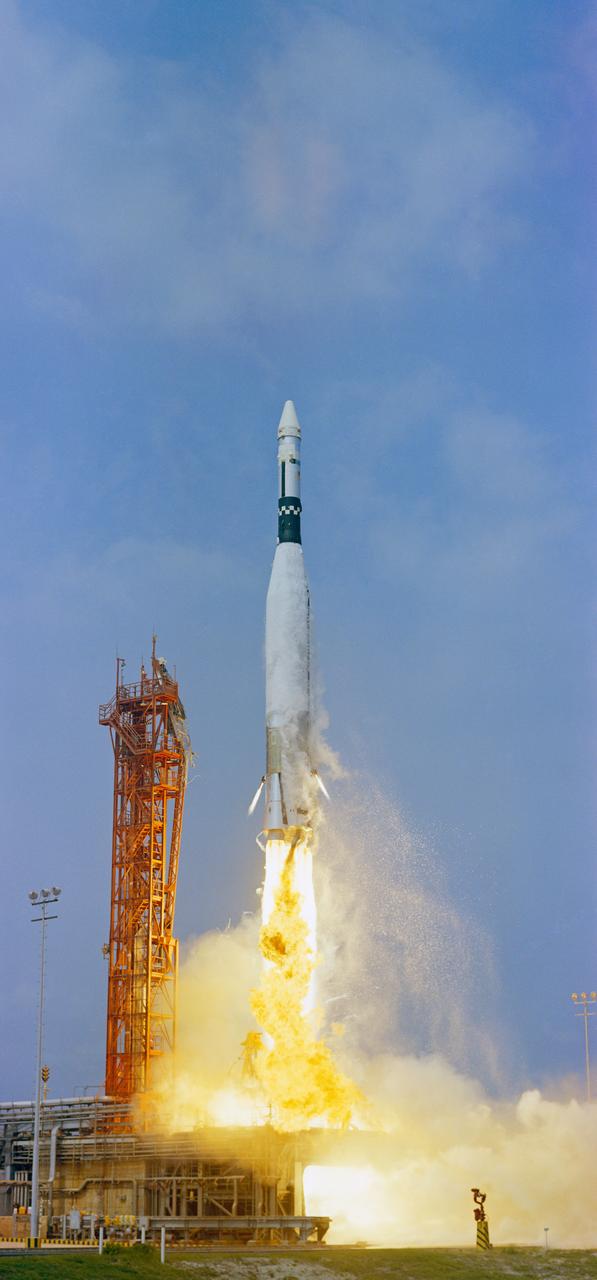

S66-34610 (17 May 1966) --- An Agena Target Vehicle atop its Atlas Launch vehicle is launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex 14 at 10:15 am., May 17, 1966. The Agena was intended as a rendezvous and docking vehicle for the Gemini-9 spacecraft. However, since the Agena failed to achieve orbit, the Gemini-9 mission was postponed. Photo credit: NASA

S66-42751 (18 July 1966) --- An Agena Target Docking Vehicle atop its Atlas launch vehicle was launched from the Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 14 at 3:39 p.m. (EST), July 18, 1966. The Gemini-10 liftoff followed the Agena liftoff by 101 minutes. The Agena served as a rendezvous and docking vehicle for the Gemini-10 spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA
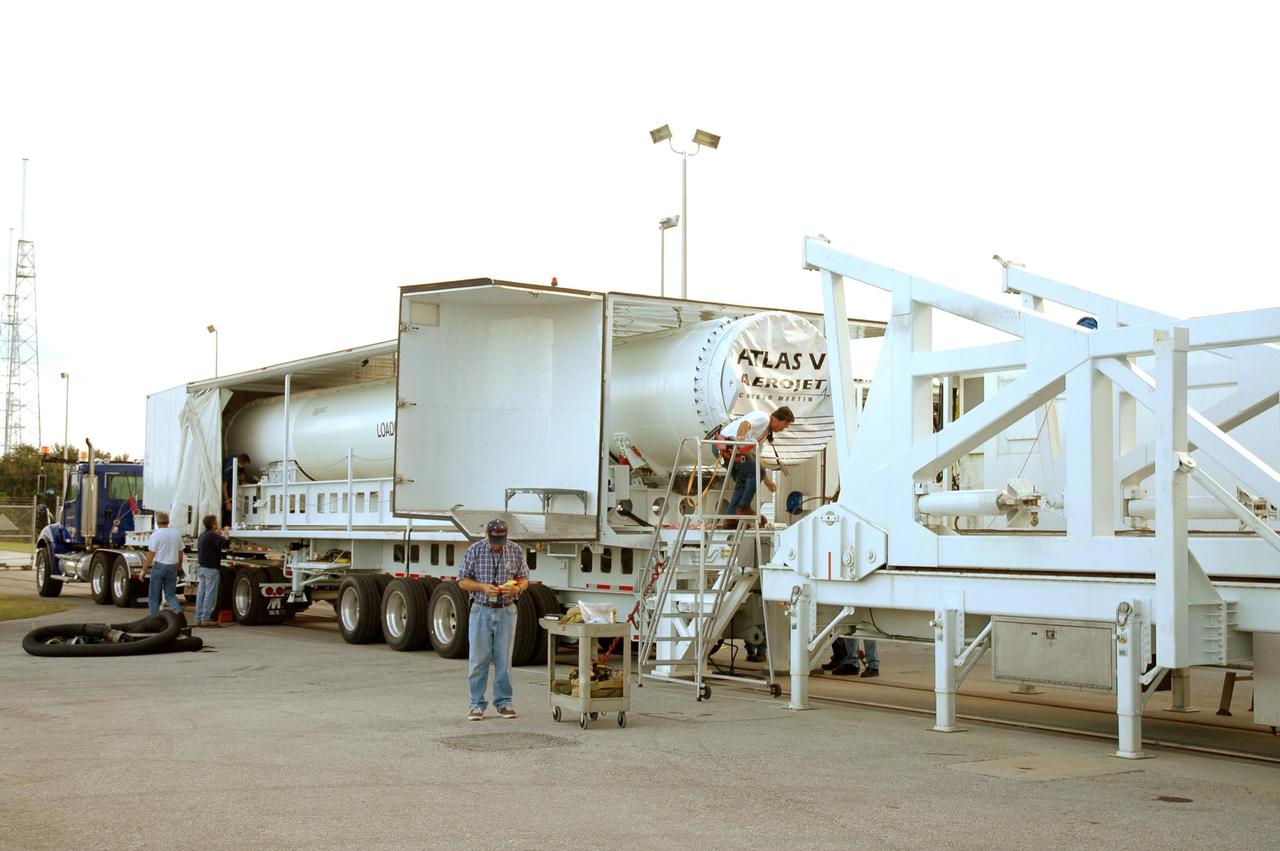

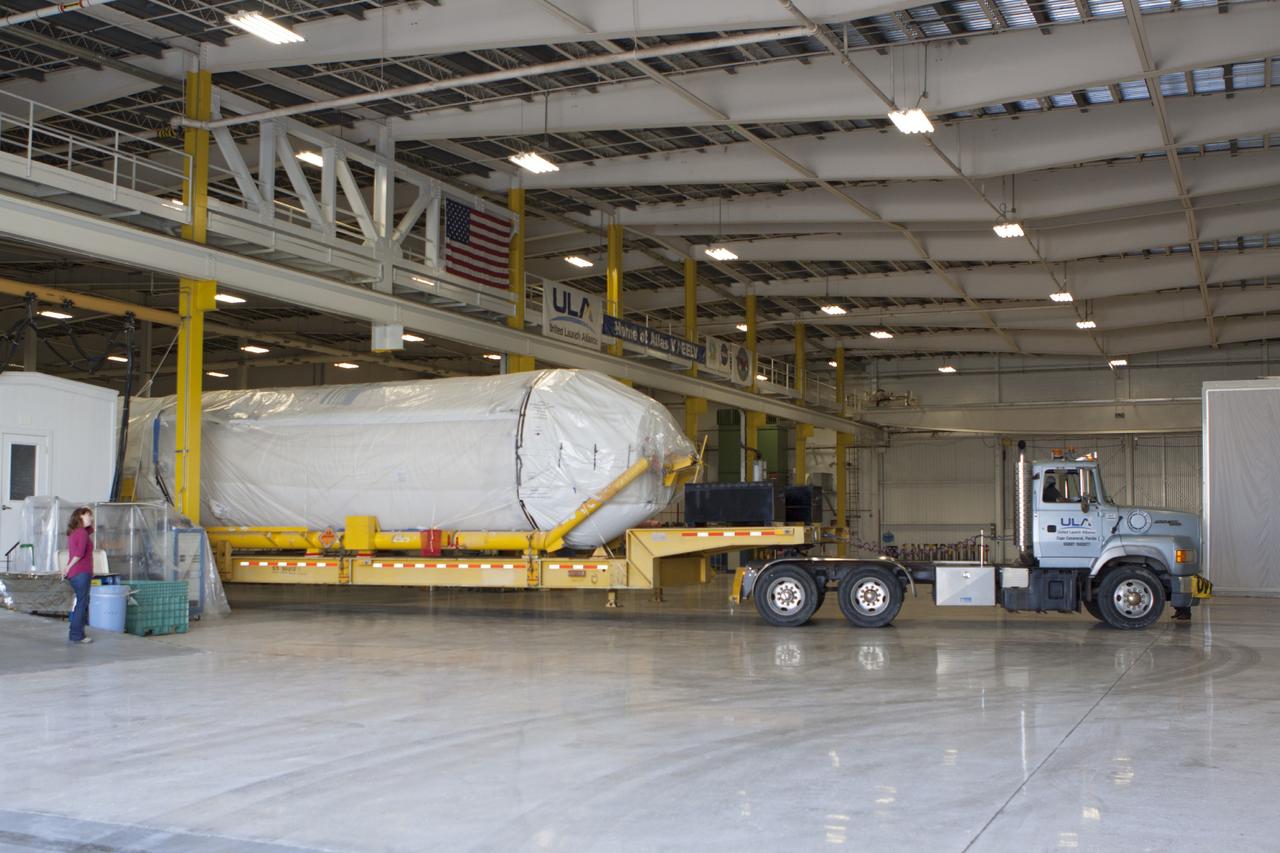
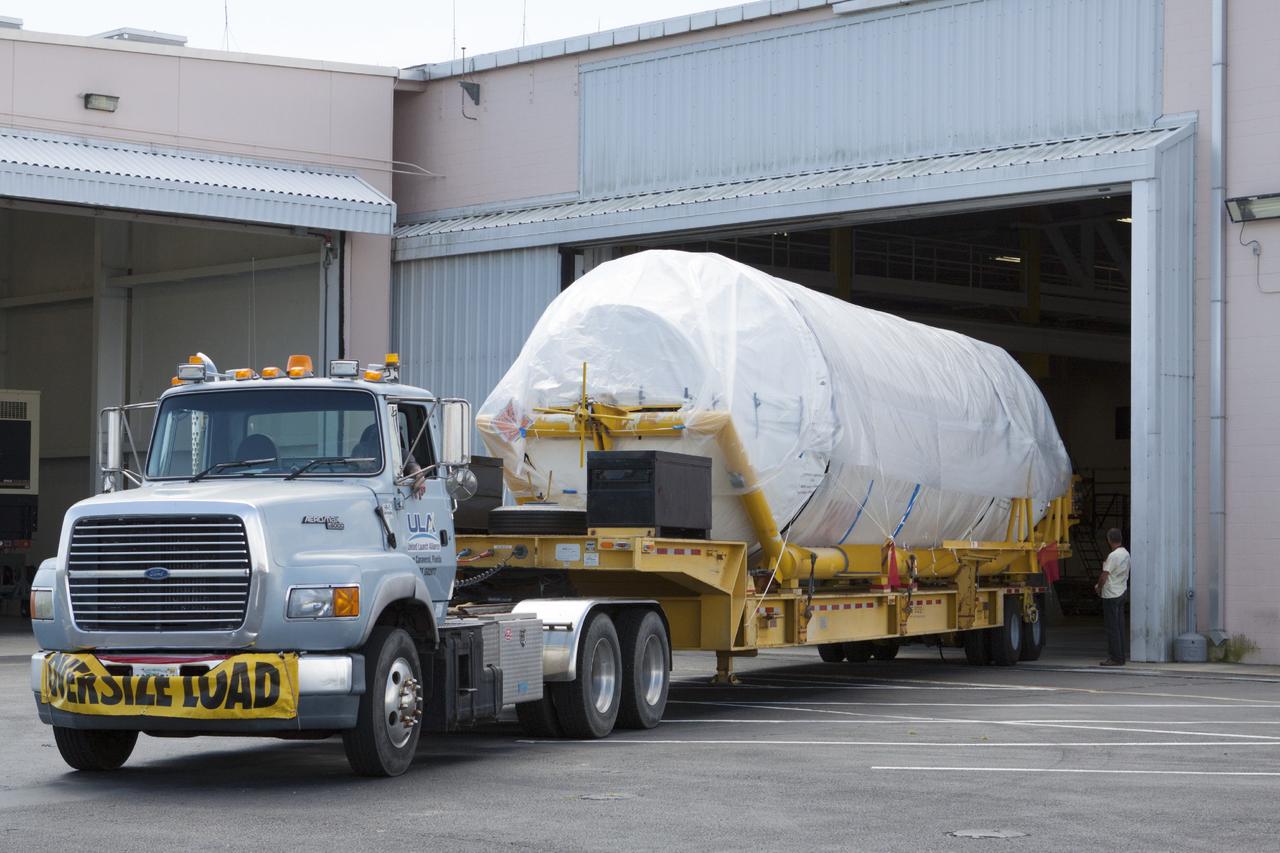
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A transport trailer carrying a solid rocket booster is opened up after arriving at the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The booster rocket will be mated, along with others, to the Atlas V already in the VIF. The Atlas V is the launch vehicle for NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, scheduled to launch in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon.
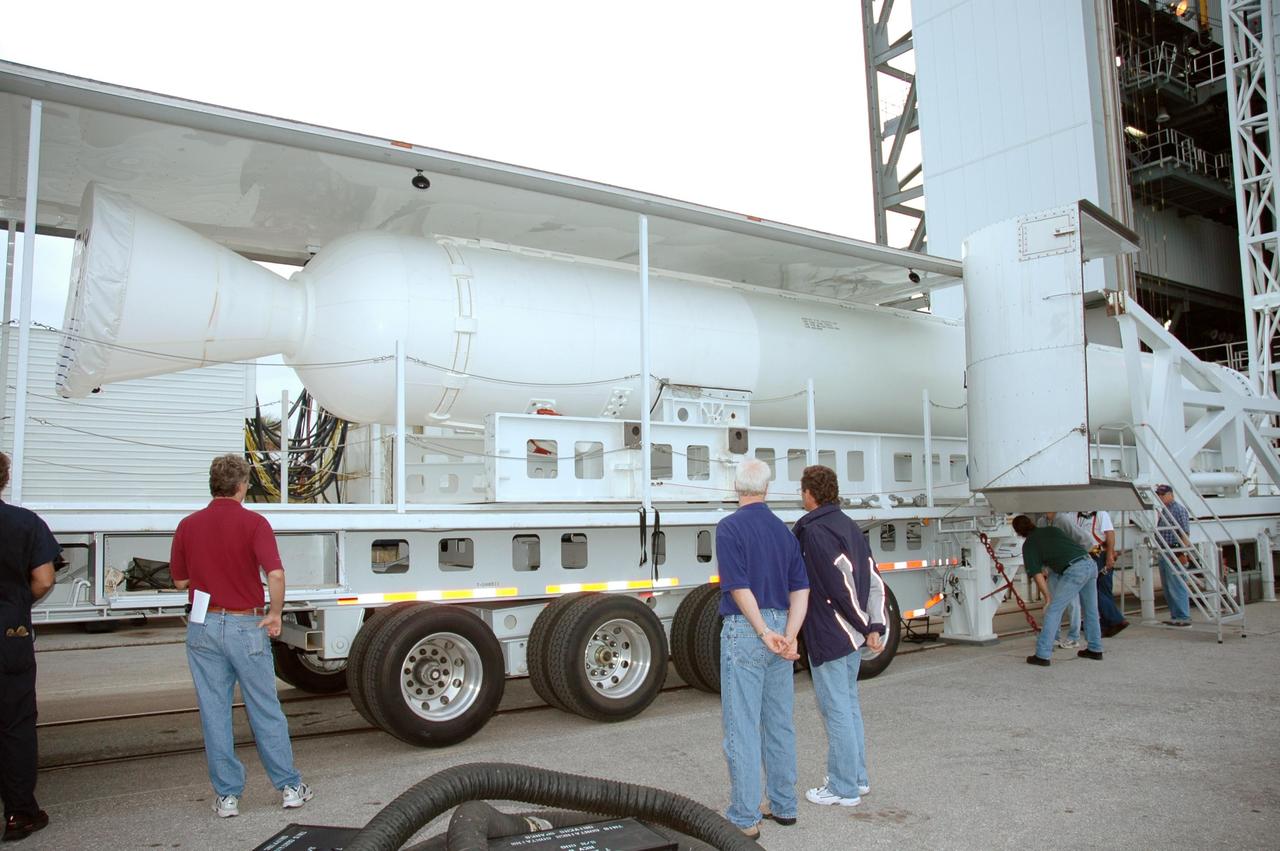

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida stand by as the solid rocket booster in front of them is prepared to be raised to vertical. The booster rocket will be mated, along with others, to the Atlas V already in the Vertical Integration Facility, at right. The Atlas V is the launch vehicle for NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, scheduled to launch in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon.

The launch of an Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle is shown in this photograph. The Atlas/Centaur, launched on November 13, 1978, carried the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-2 into the required orbit. The second observatory, the HEAO-2 (nicknamed the Einstein Observatory in honor of the centernial of the birth of Albert Einstein) carried the first telescope capable of producing actual photographs of x-ray objects.
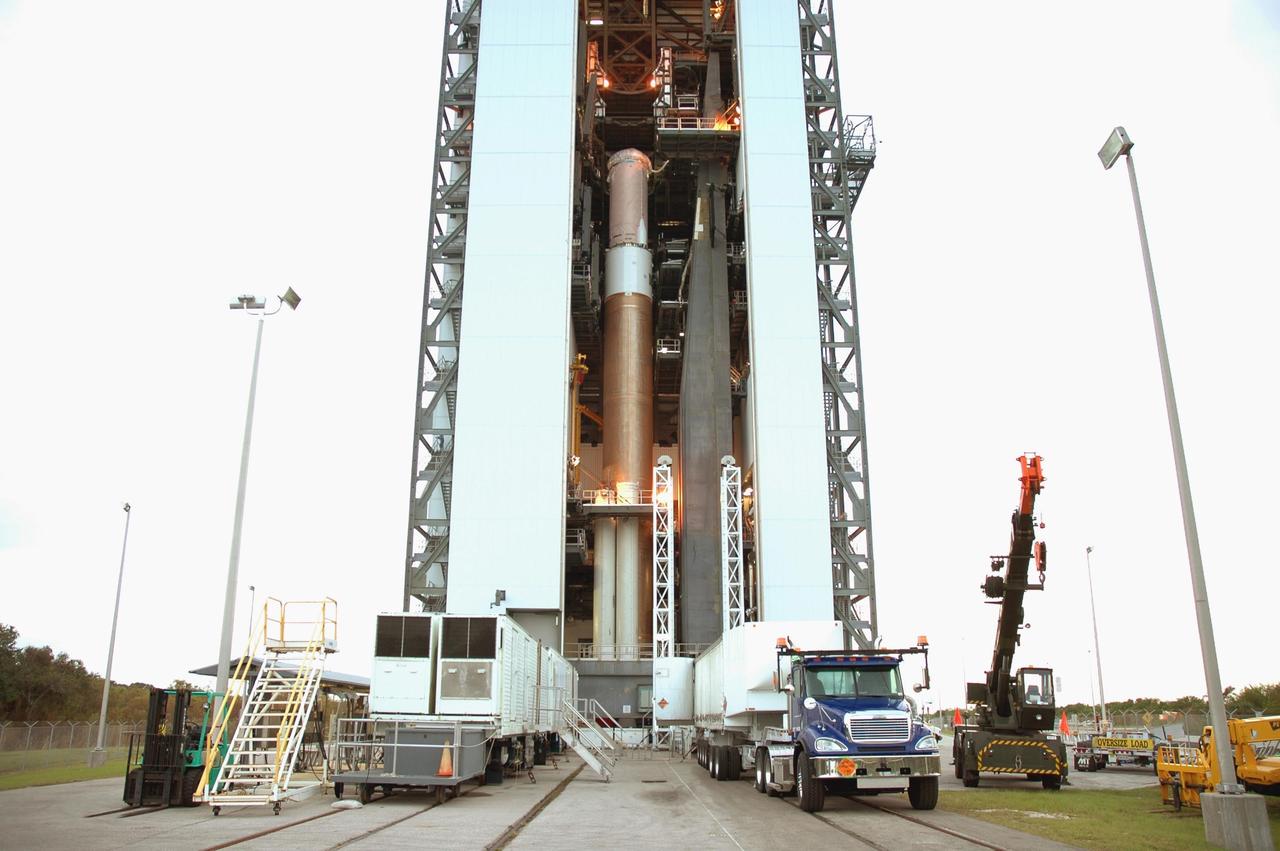

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A transport trailer carrying a solid rocket booster arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The booster rocket will be mated, along with others, to the Atlas V already in the VIF. The Atlas V is the launch vehicle for NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, scheduled to launch in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon.
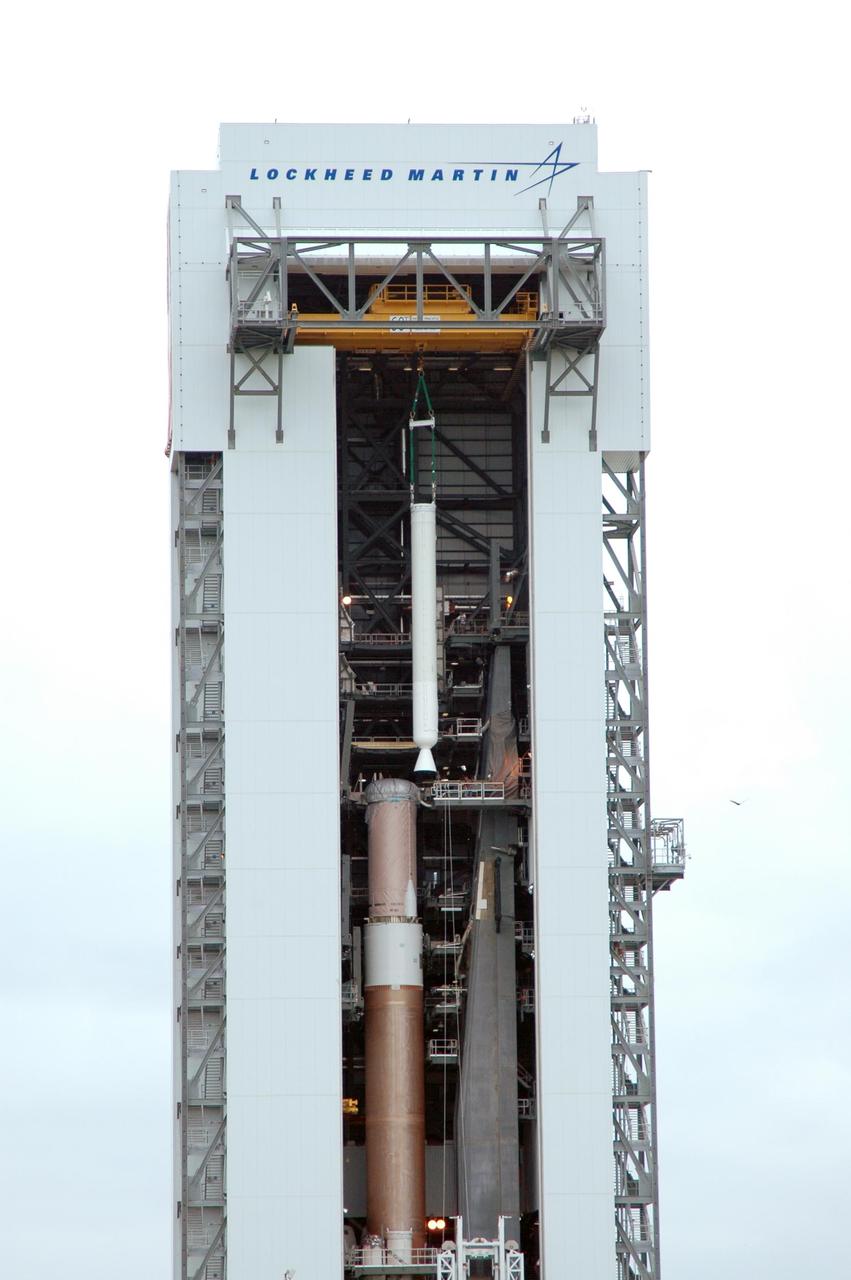

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a solid rocket booster is being lowered into position on the Atlas V rocket at left. The Atlas V is the launch vehicle for NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, scheduled to launch in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon.
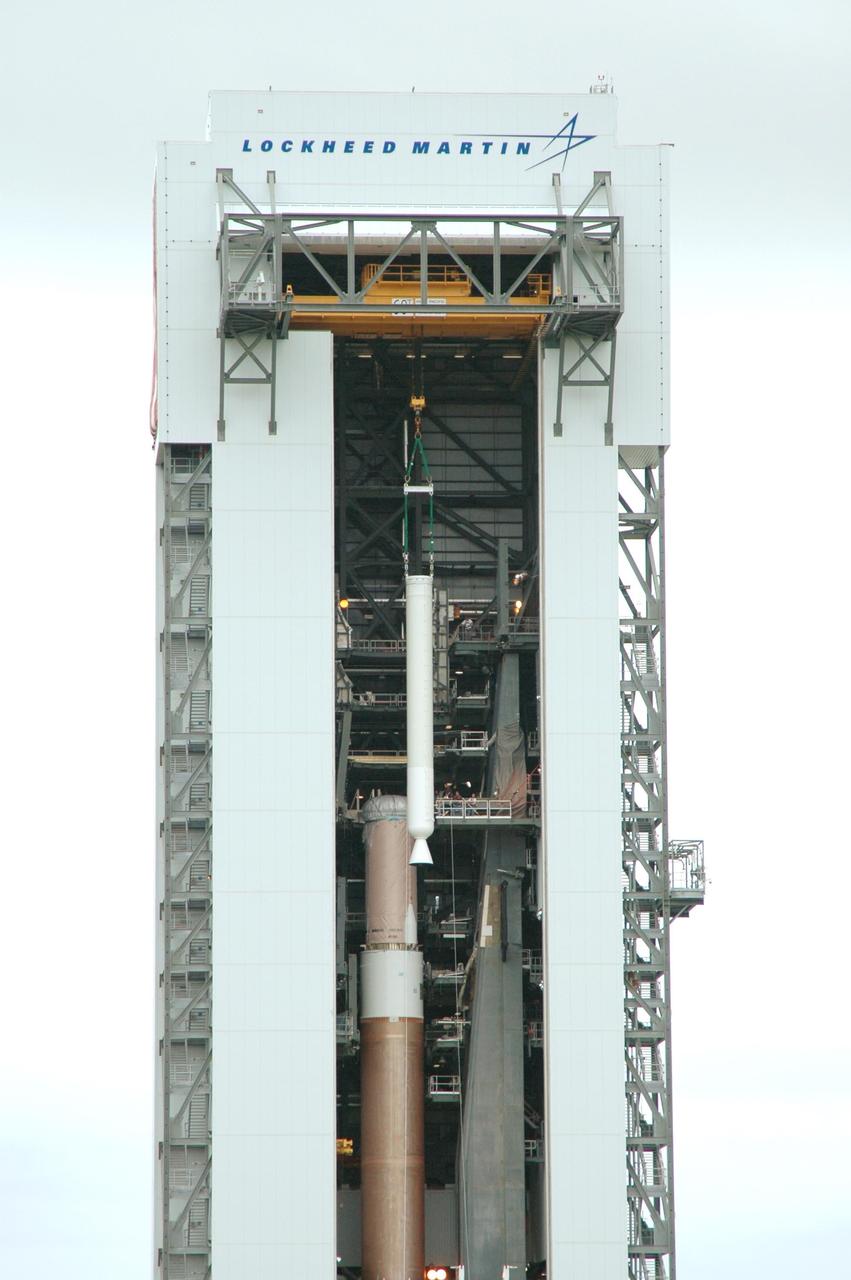

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a solid rocket booster is being lowered into position on the Atlas V rocket at left. The Atlas V is the launch vehicle for NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, scheduled to launch in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon.
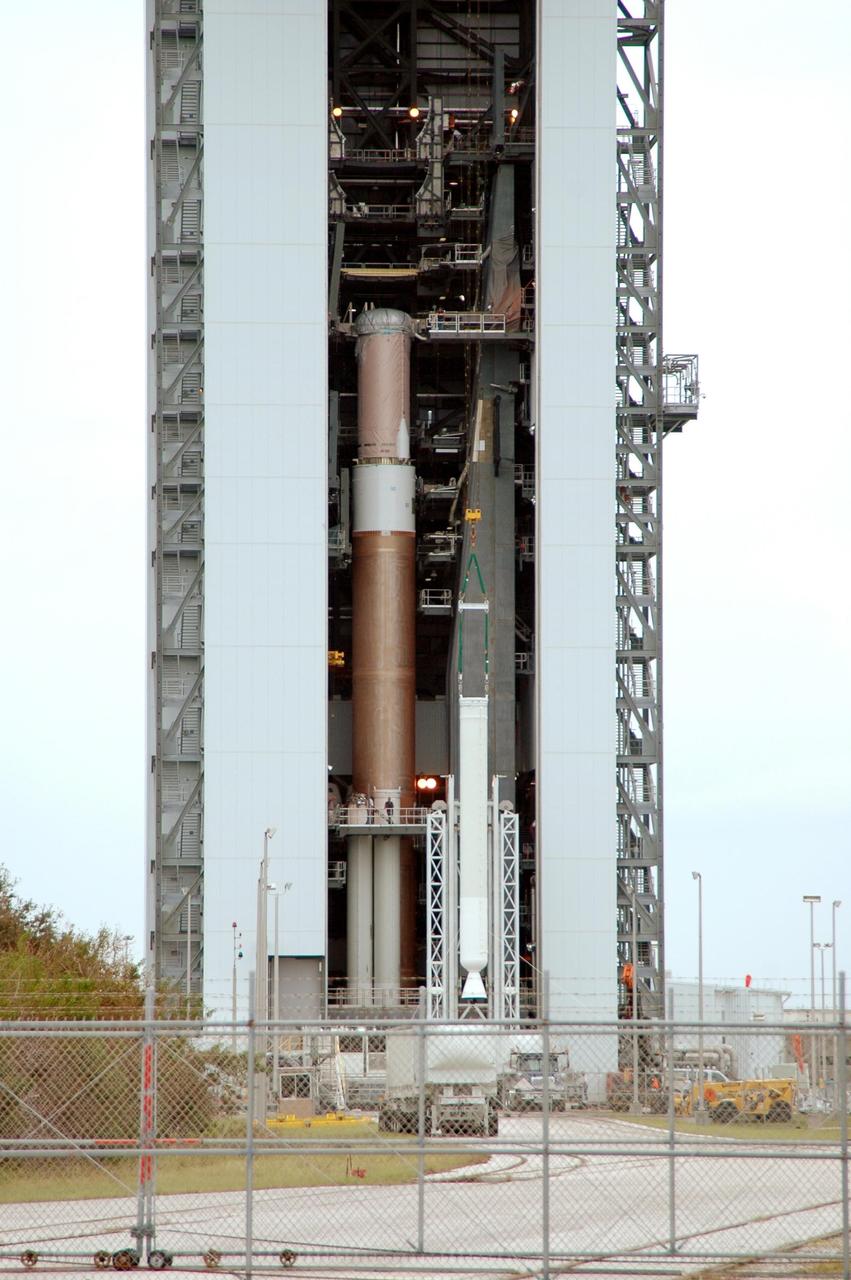

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A solid rocket booster, on the right, is lifted up into the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The booster rocket will be mated, along with others, to the Atlas V, at left. The Atlas V is the launch vehicle for NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, scheduled to launch in January 2006 on a journey to Pluto and its moon, Charon.

Launch Vehicles: Launch vehicles are the rocket-powered systems that provide transportation from the Earth’s surface into the environment of space. Kennedy Space Center’s heritage includes launching robotic and satellite missions into space primarily using Atlas, Delta and Titan launch vehicles. Other launch vehicles include the Pegasus and Athena. The Launch Services Program continues this mission today directing launches from the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. Kodiak, Alaska and Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
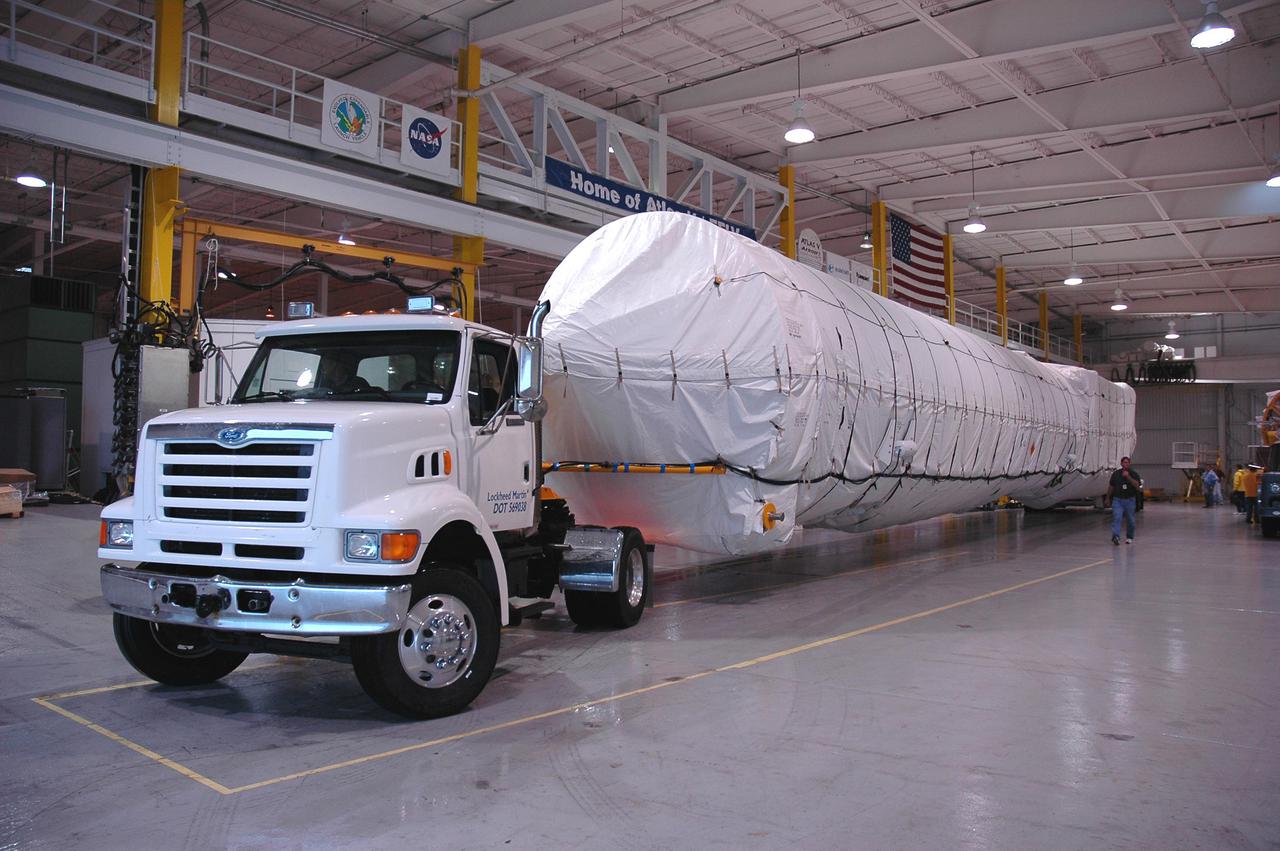

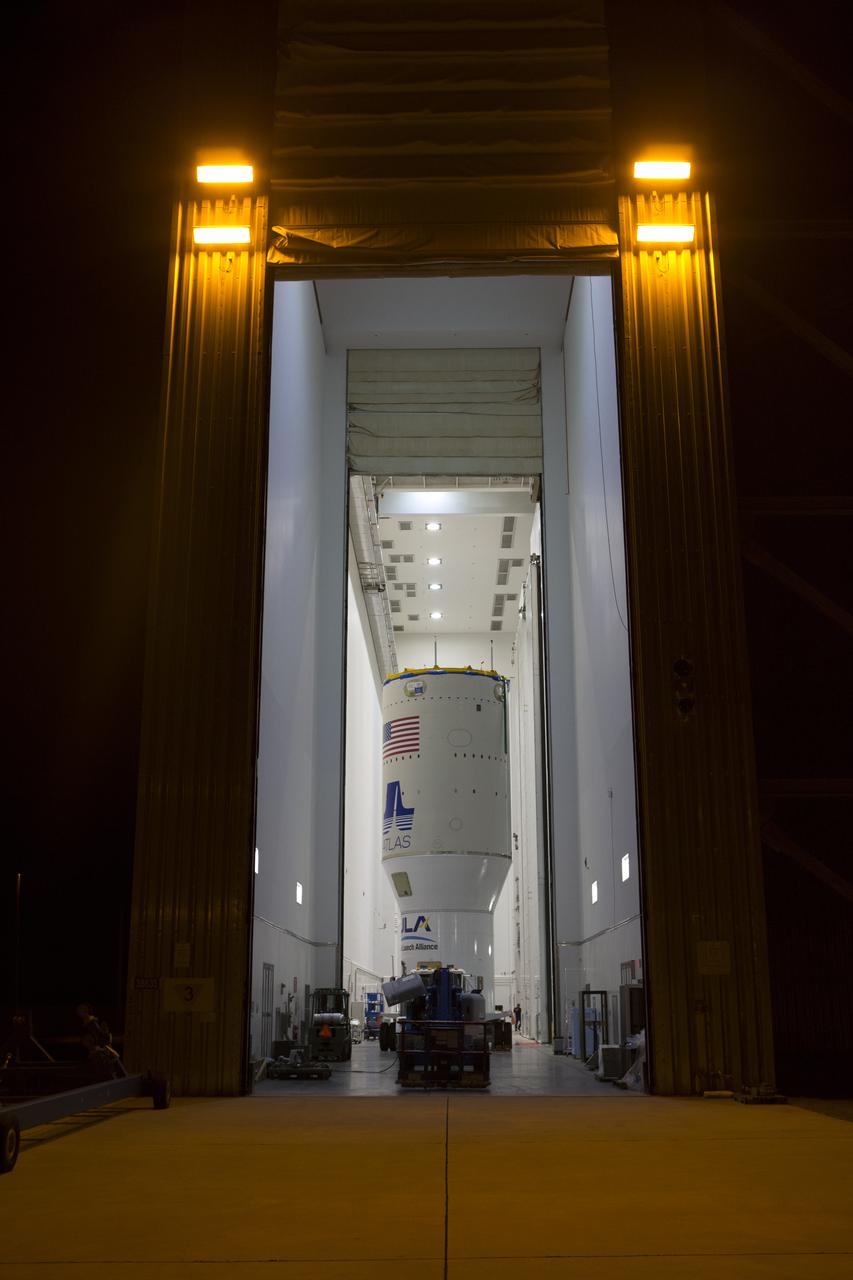
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — A truck delivers the Atlas V rocket to the Atlas Space Operations Center. The Atlas V is the launch vehicle for the New Horizons spacecraft. New Horizons is designed to help us understand worlds at the edge of our solar system by making the first reconnaissance of Pluto and Charon - a 'double planet' and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and its moon, Charon, in July 2015.
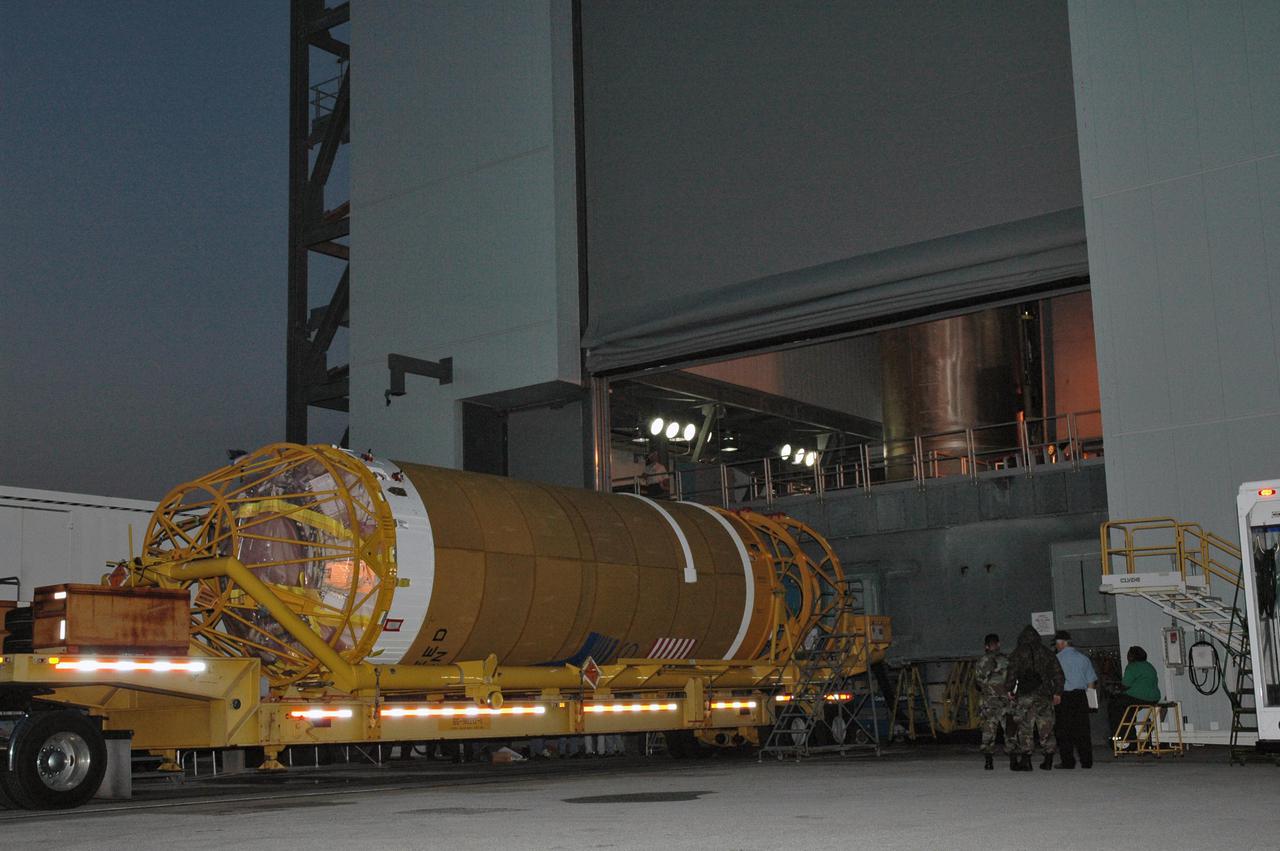

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Lockheed Martin Atlas V_Centaur second stage arrives at the Vertical Integration Facility on Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. It will be mated with the Atlas V already placed in the tower. The Atlas V_Centaur is the launch vehicle for the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). The MRO is designed for a series of global mapping, regional survey and targeted observations from a near-polar, low-altitude Mars orbit. These observations will be unprecedented in terms of the spatial resolution and coverage achieved by the orbiter’s instruments as they observe the atmosphere and surface of Mars while probing its shallow subsurface as part of a “follow the water” strategy. The launch window for the MRO begins Aug. 10.
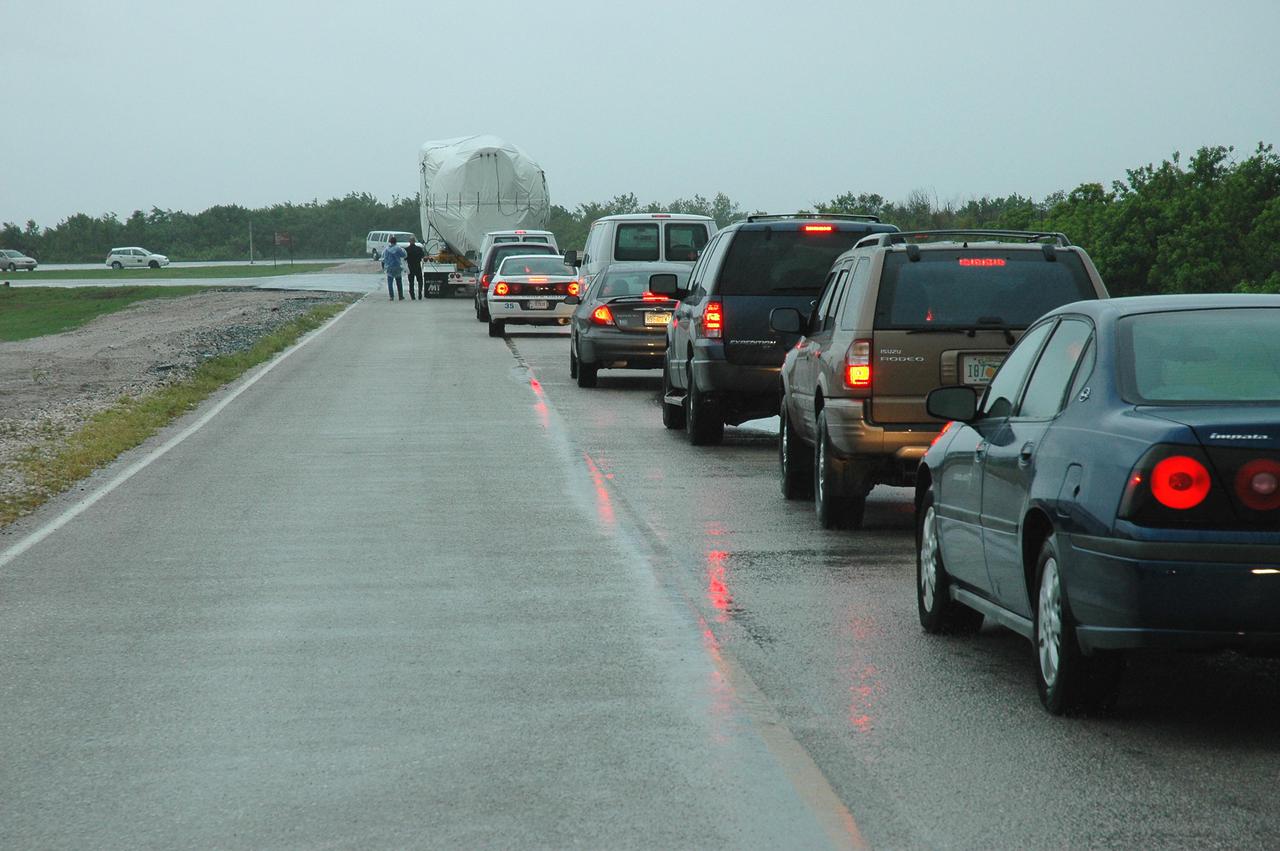

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — A convoy of vehicles follows behind a truck carrying an Atlas V rocket. The rocket is being transferred to the Atlas Space Operations Center. The Atlas V is the launch vehicle for the New Horizons spacecraft. New Horizons is designed to help us understand worlds at the edge of our solar system by making the first reconnaissance of Pluto and Charon - a 'double planet' and the last planet in our solar system to be visited by spacecraft. The mission will then visit one or more objects in the Kuiper Belt region beyond Neptune. New Horizons is scheduled to launch from Launch Complex 41 at CCAFS in January 2006, swing past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February or March 2007, and reach Pluto and its moon, Charon, in July 2015.