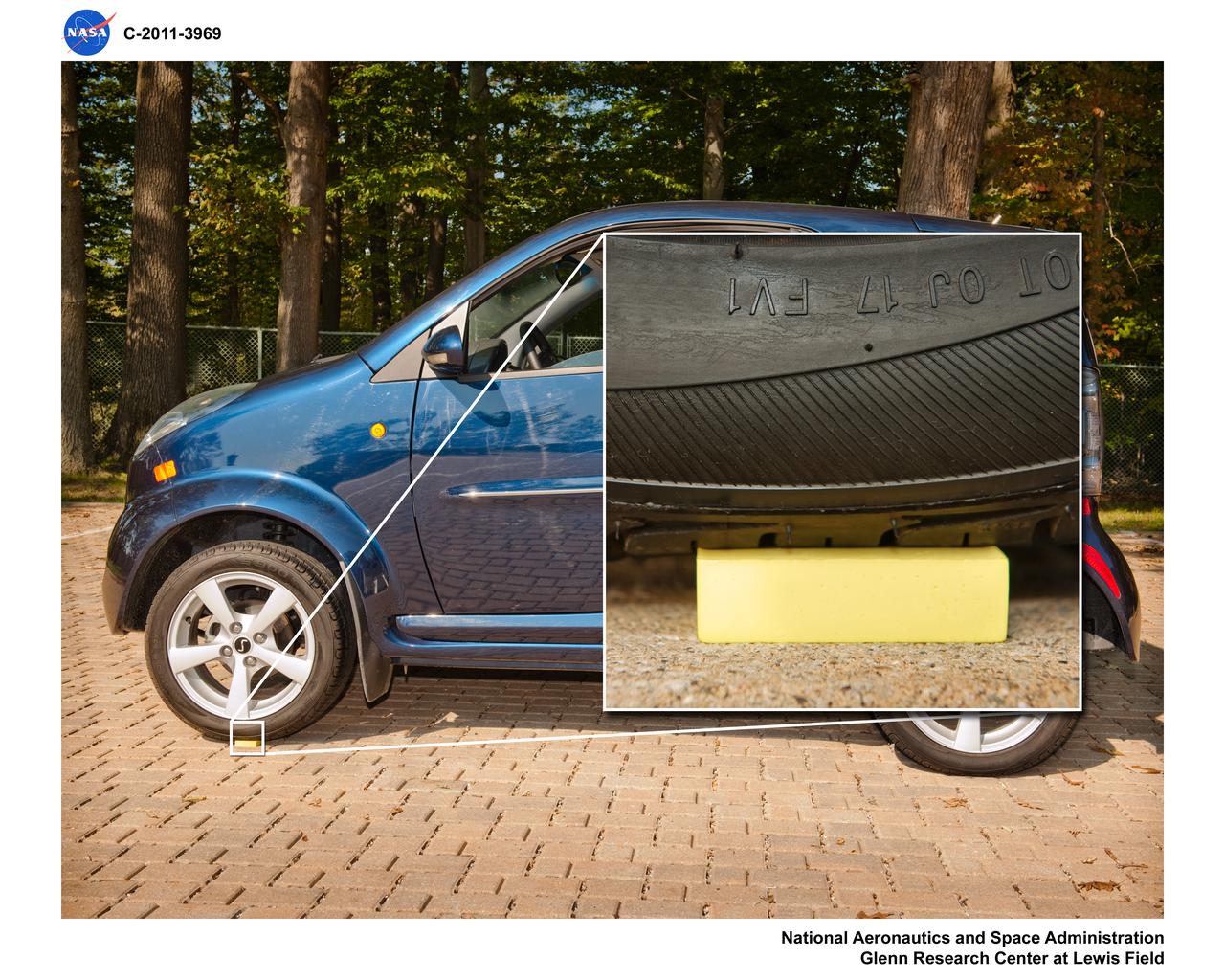

Polyimide Aerogel Material Sample under the weight of an Automobile Tire
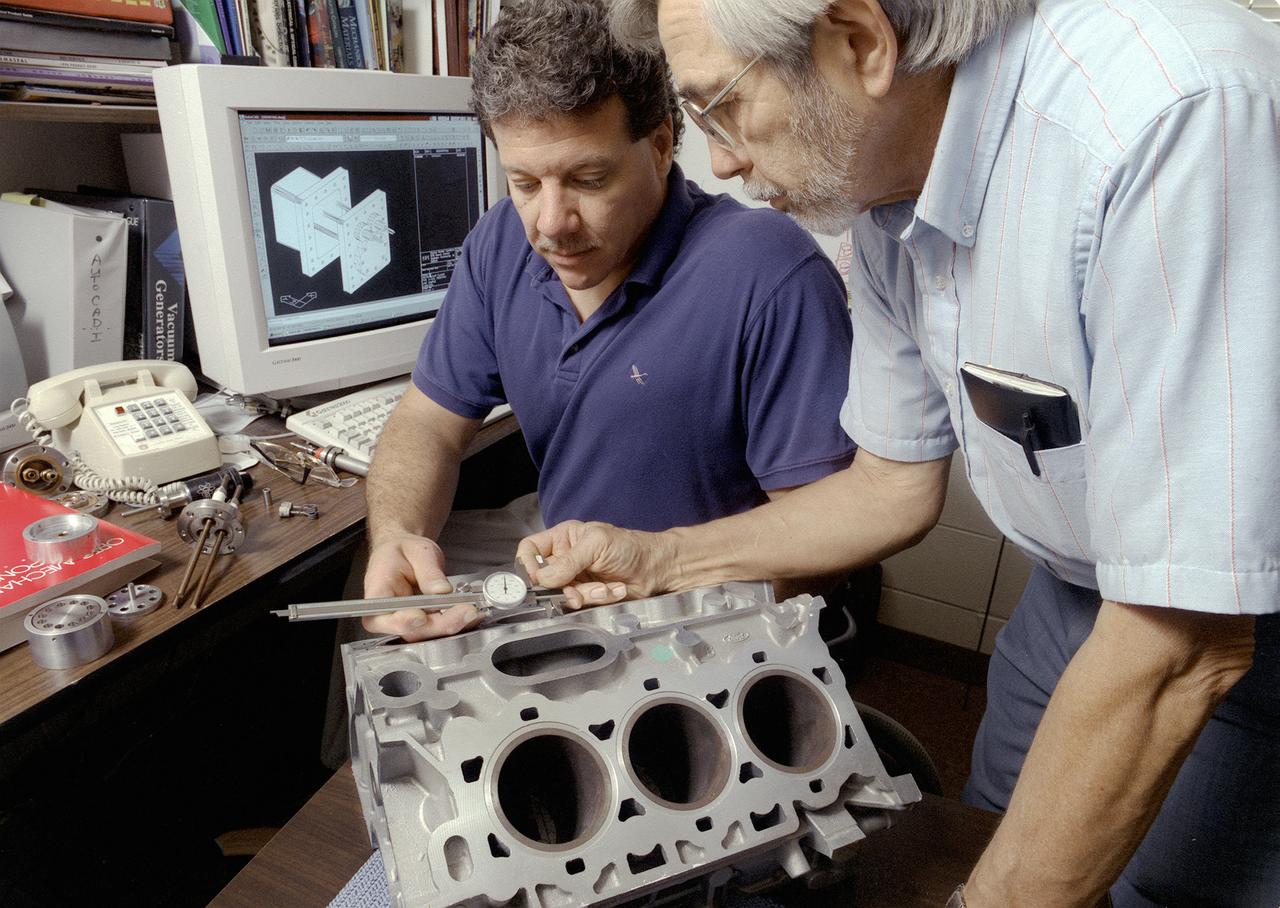
Don Sirois, an Auburn University research associate, and Bruce Strom, a mechanical engineering Co-Op Student, are evaluating the dimensional characteristics of an aluminum automobile engine casting. More accurate metal casting processes may reduce the weight of some cast metal products used in automobiles, such as engines. Research in low gravity has taken an important first step toward making metal products used in homes, automobiles, and aircraft less expensive, safer, and more durable. Auburn University and industry are partnering with NASA to develop one of the first accurate computer model predictions of molten metals and molding materials used in a manufacturing process called casting. Ford Motor Company's casting plant in Cleveland, Ohio is using NASA-sponsored computer modeling information to improve the casting process of automobile and light-truck engine blocks.
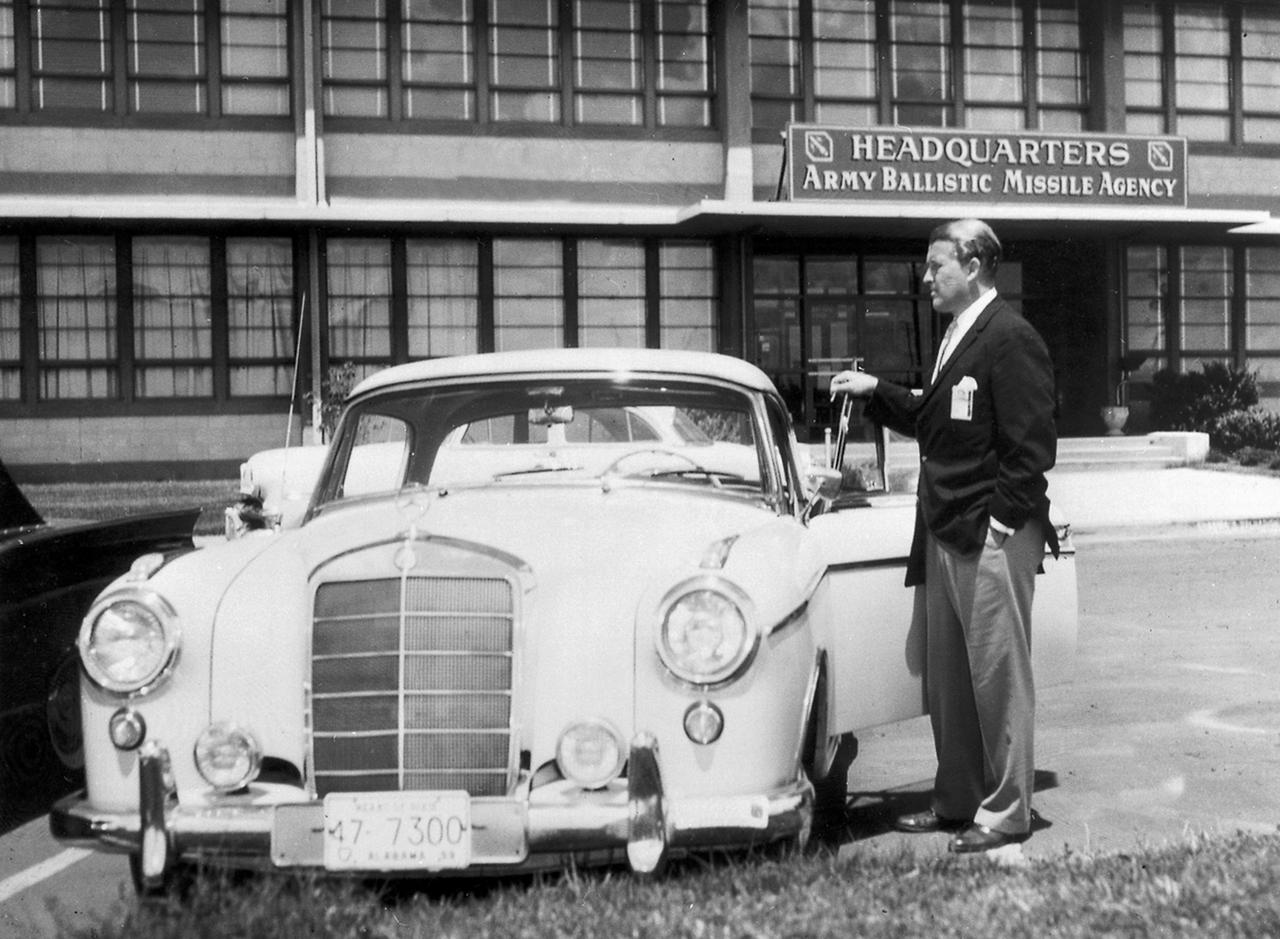

In this picture, Dr. Wernher von Braun, who was serving as Director of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency's (ABMA) Development Operations Division, is shown posed with his Mercedes 220SE automobile in front of Redstone Building 4488, which houses the ABMA.
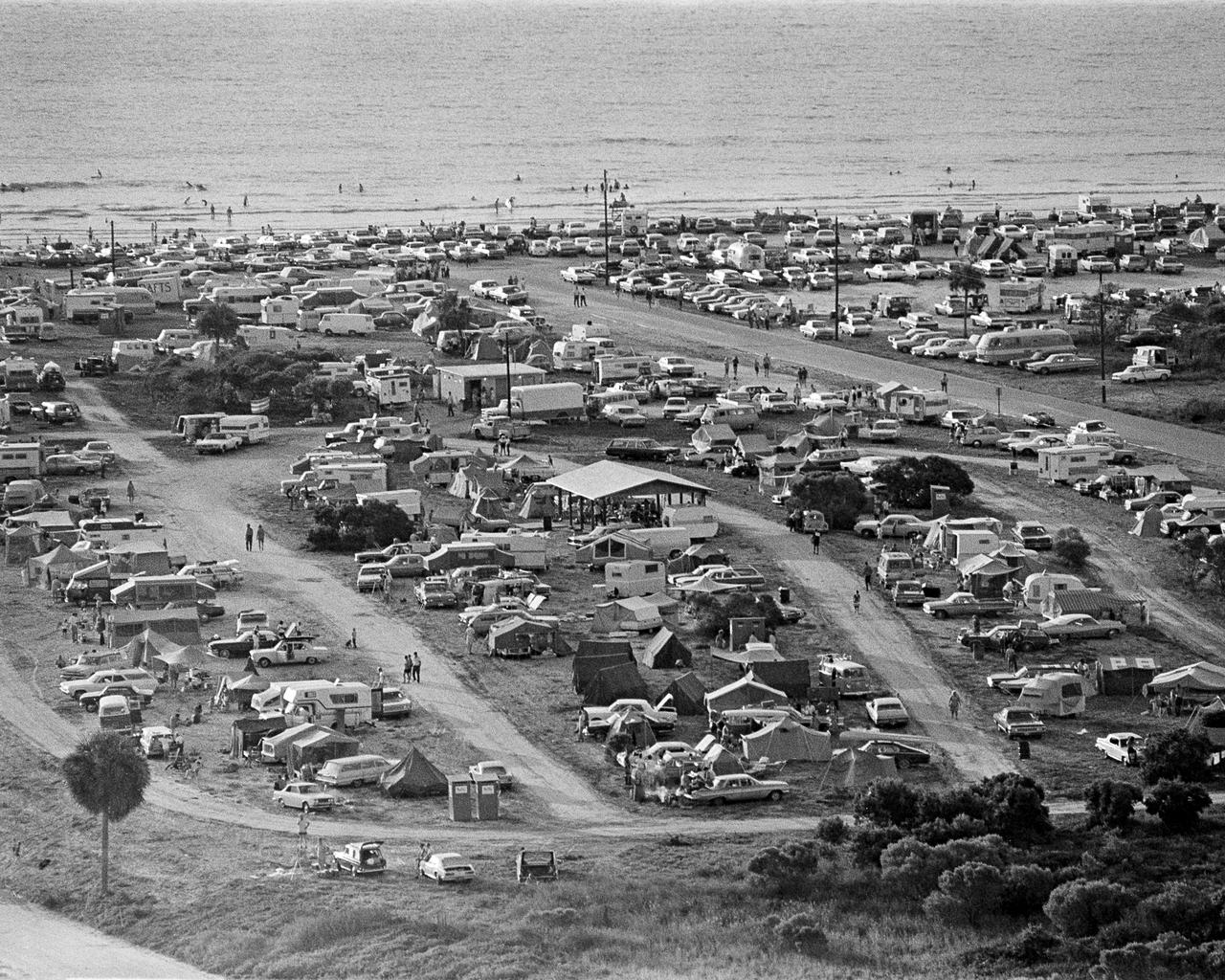

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Thousands of persons spent the night before the Apollo 11 launch in tents, campers, automobiles, and on beaches and roads adjacent to the Kennedy Space Center. In all, an estimated 1,000,000 persons visited the Spaceport area to view the historic launch. Photo credit: NASA

During the Apollo era Marshall Space Flight Center's engineers developed the Magnetomotive Hammer to remove distortions from Saturn V bulkhead gore segments. Using an intense magnetic field, the Hammer removed manufacturing distortions from rejected segments which otherwise would have been discarded at a cost of $30,000 each. Various automobile, ship and aircraft manufacturers adoped the technology for commercial use.
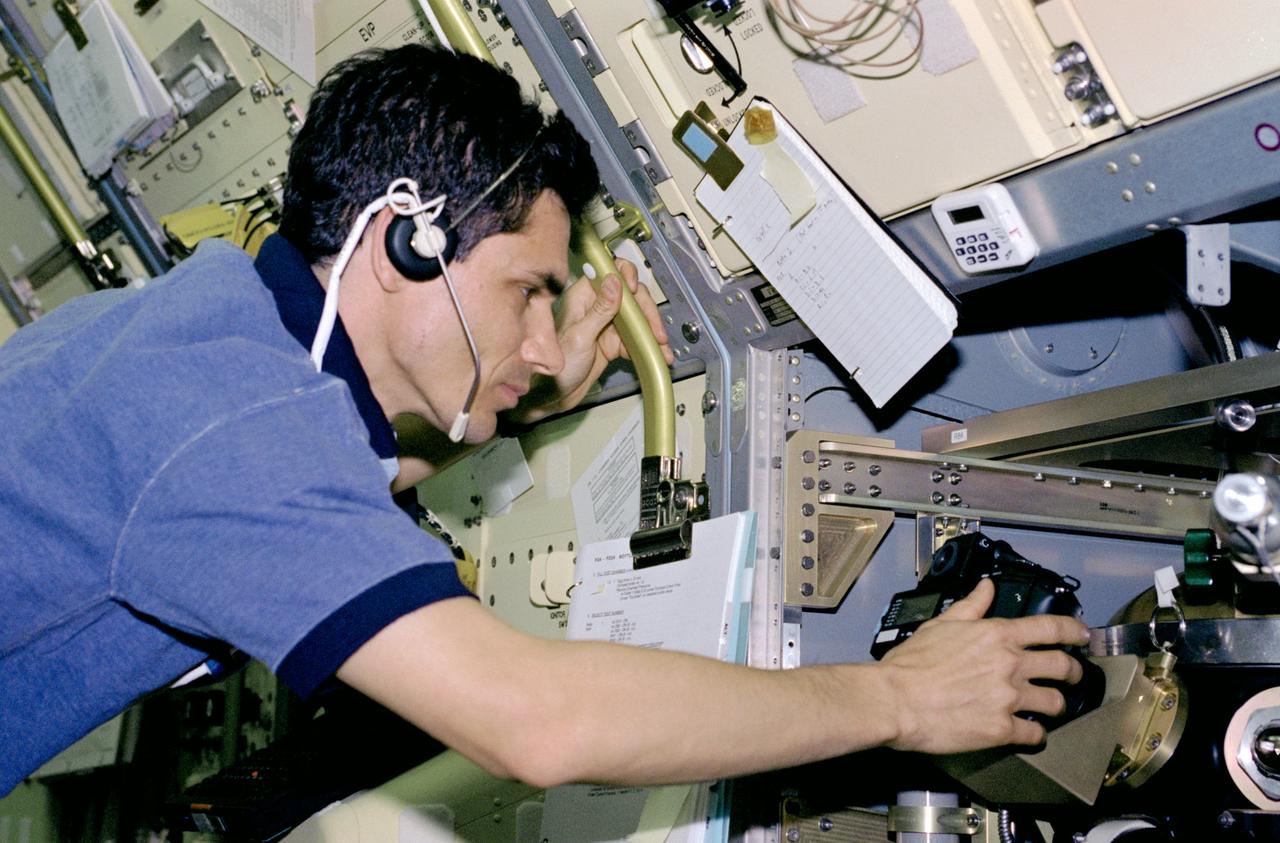

STS083-312-017 (4-8 April 1997) --- Payload specialist Gregory T. Linteris sets up a 35mm camera, one of three photographic/recording systems on the Drop Combustion Experiment (DCE) Apparatus. DCE is an enclosed chamber in which Helium-Oxygen fuel mixtures are injected and burned as single droplets. Combustion of fuel droplets is an important part of many operations, home heating, power production by gas turbines and combustion of gasoline in an automobile engine.
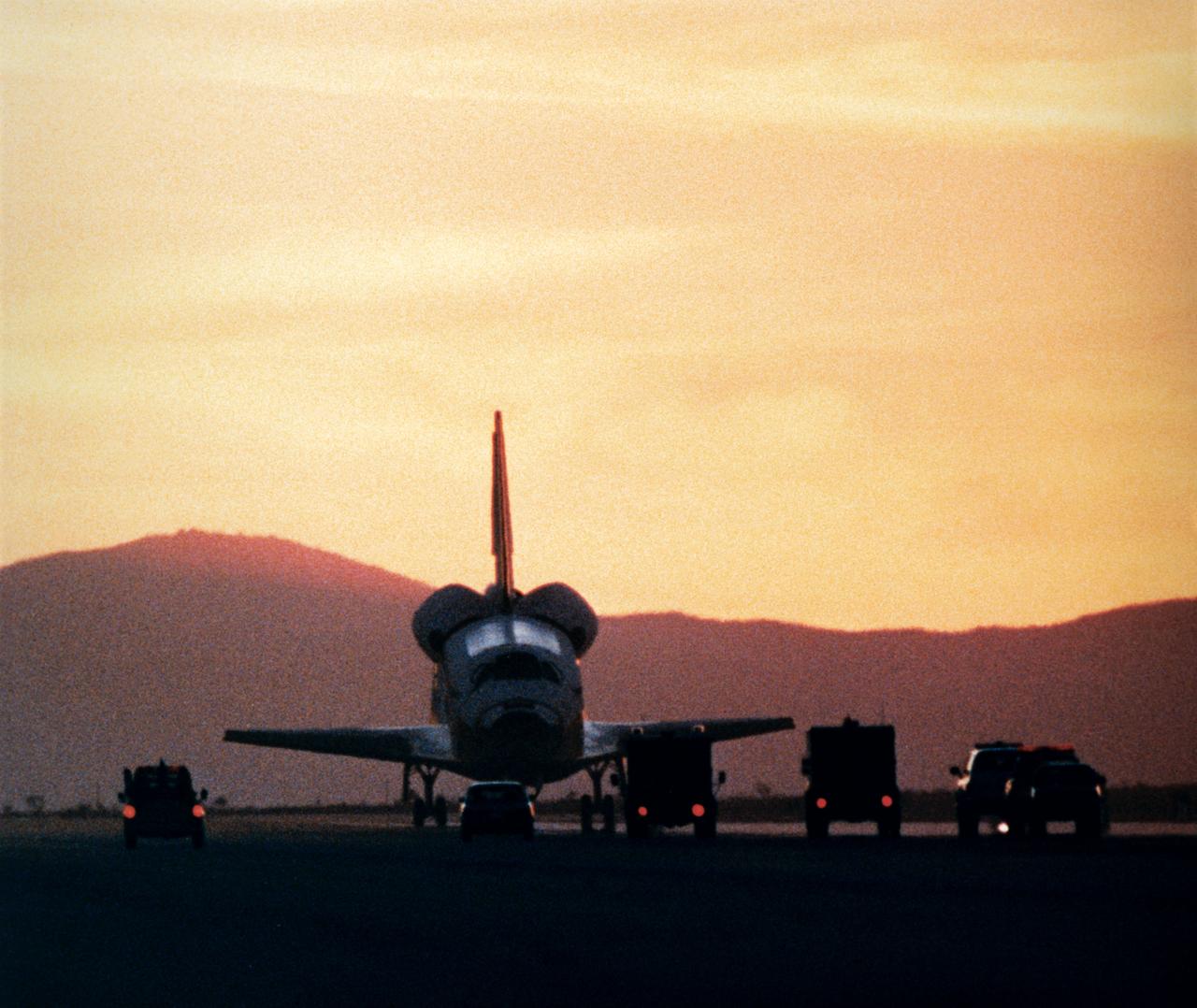

STS033-S-017 (27 Nov 1989) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery is approached by safing vehicles and team members following its late-afternoon landing at Edwards Air Force Base in southern California. A five member crew aboard had just completed the DOD-devoted STS-33 mission. The landing occurred at 16:31:02 p.m. (PST), Nov. 27, 1989. Onboard Discovery for the mission and still aboard the craft when this photo was made were Astronauts Frederick D. Gregory, John E. Blaha, Kathryn C. Thornton, F. Story Musgrave and Manley L. Carter.
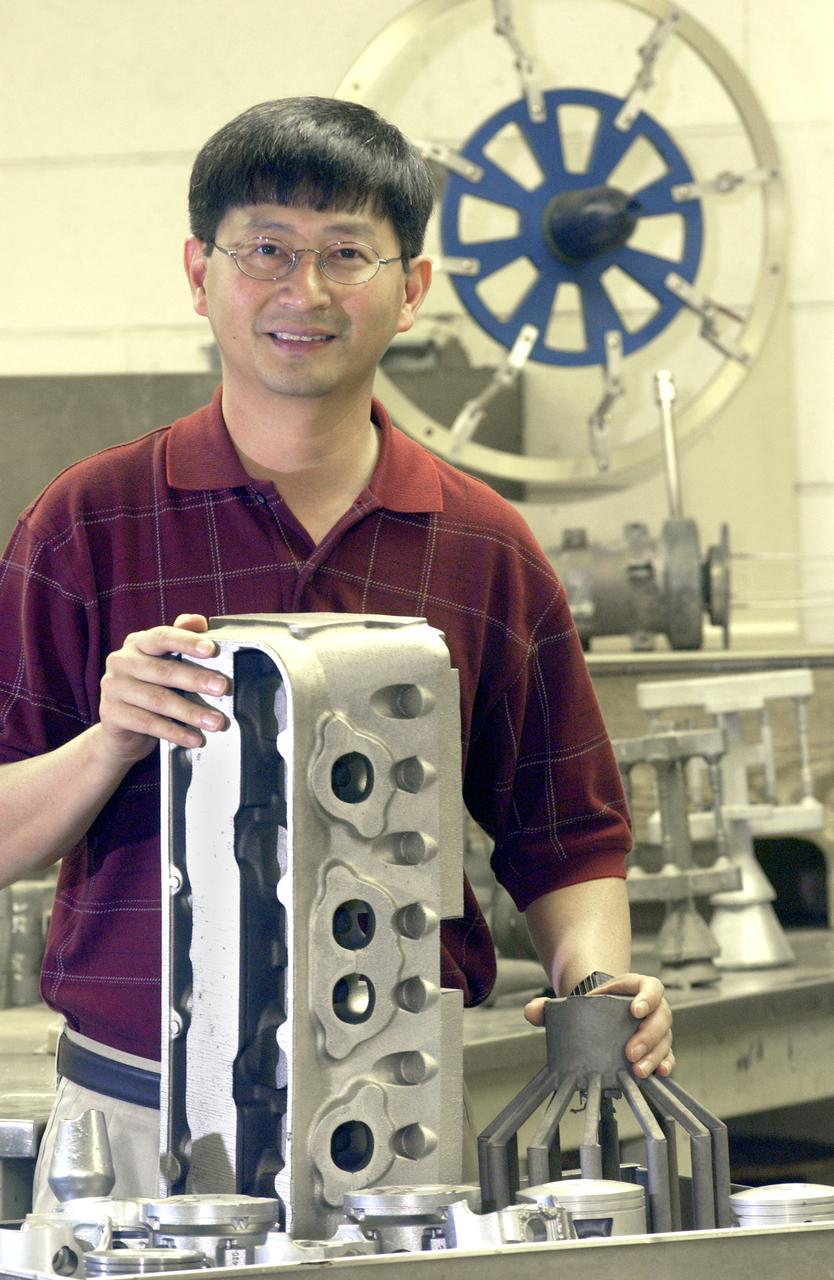
NASA structural materials engineer, Jonathan Lee, displays blocks and pistons as examples of some of the uses for NASA’s patented high-strength aluminum alloy originally developed at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA desired an alloy for aerospace applications with higher strength and wear-resistance at elevated temperatures. The alloy is a solution to reduce costs of aluminum engine pistons and lower engine emissions for the automobile industry. The Boats and Outboard Engines Division at Bombardier Recreational Products of Sturtevant, Wisconsin is using the alloy for pistons in its Evinrude E-Tec outboard engine line.
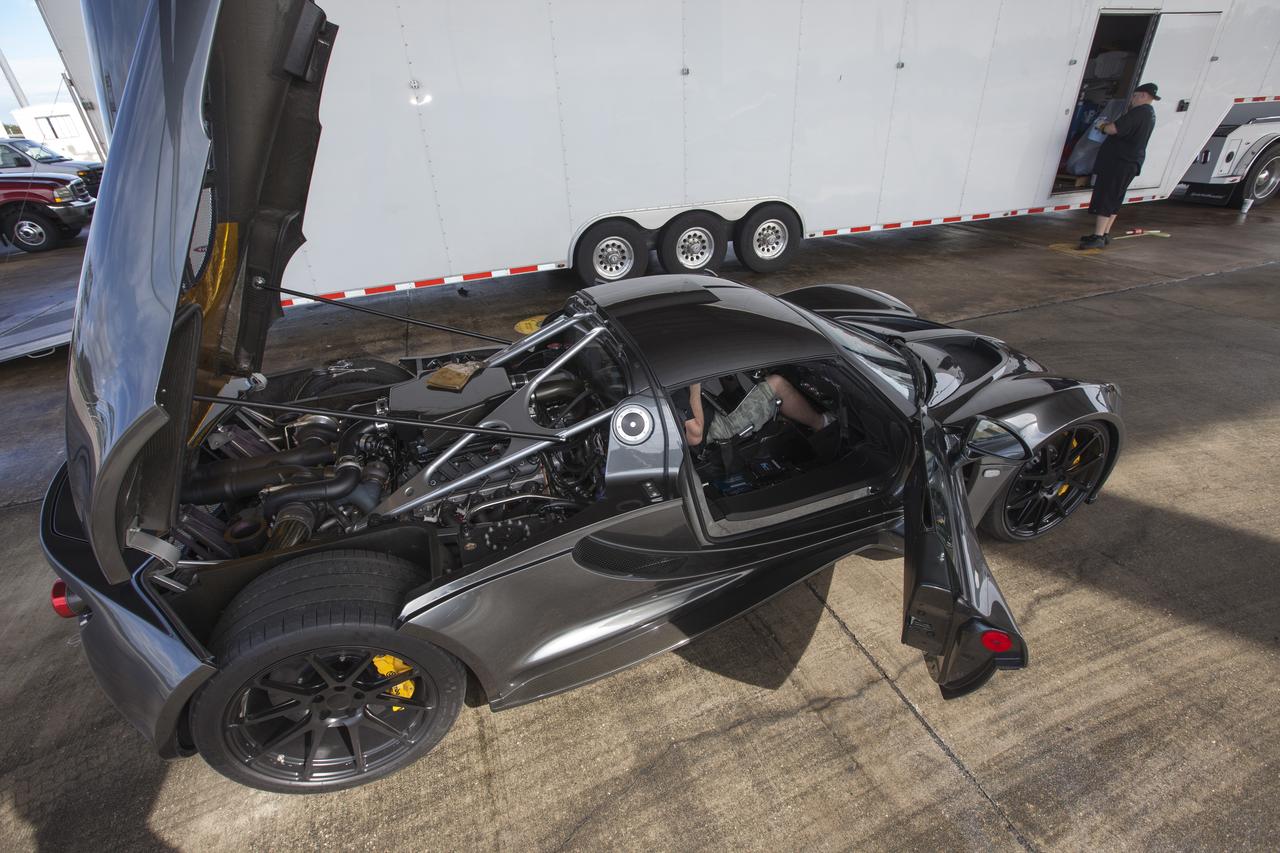

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - An engineer readies a Hennessey Venom GT for test runs on the 3.5-mile long runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The flat concrete runway is one of the few places in the world where high performance automobiles can be tested for aerodynamic and safety designs. Hennessey Performance of Sealy, Texas, worked with Performance Power Racing in West Palm Beach to arrange use of the NASA facility. Performance Power Racing has conducted numerous engineering tests on the runway with a variety of vehicles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
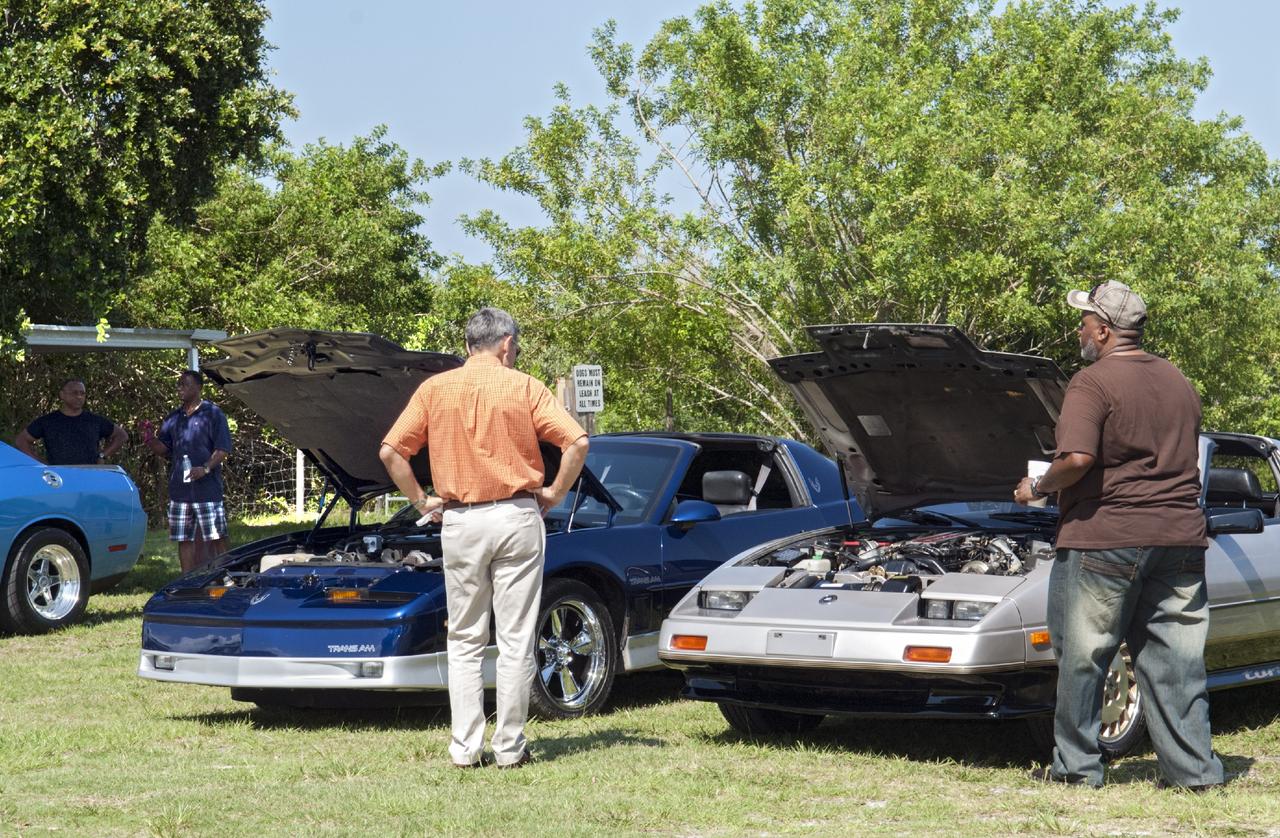

Merritt Island, Fla. – Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana enjoys the automobiles on display in the a noncompetitive car show at 2013 Black Employee Strategy Team BEST BBQ at KARS Park I on Merritt Island. Events also included a spades tournament. BEST hosts the barbecue as a fundraiser for the Evelyn Johnson Scholarship, which is handed out every year to students who exemplify significant achievement both academically and in their community. The scholarship is in honor of Evelyn Johnson, a founding member of BEST and former deputy director of Kennedy’s Diversity and Equal Opportunity Office. Photo credit: NASA/ Charisse Nahser
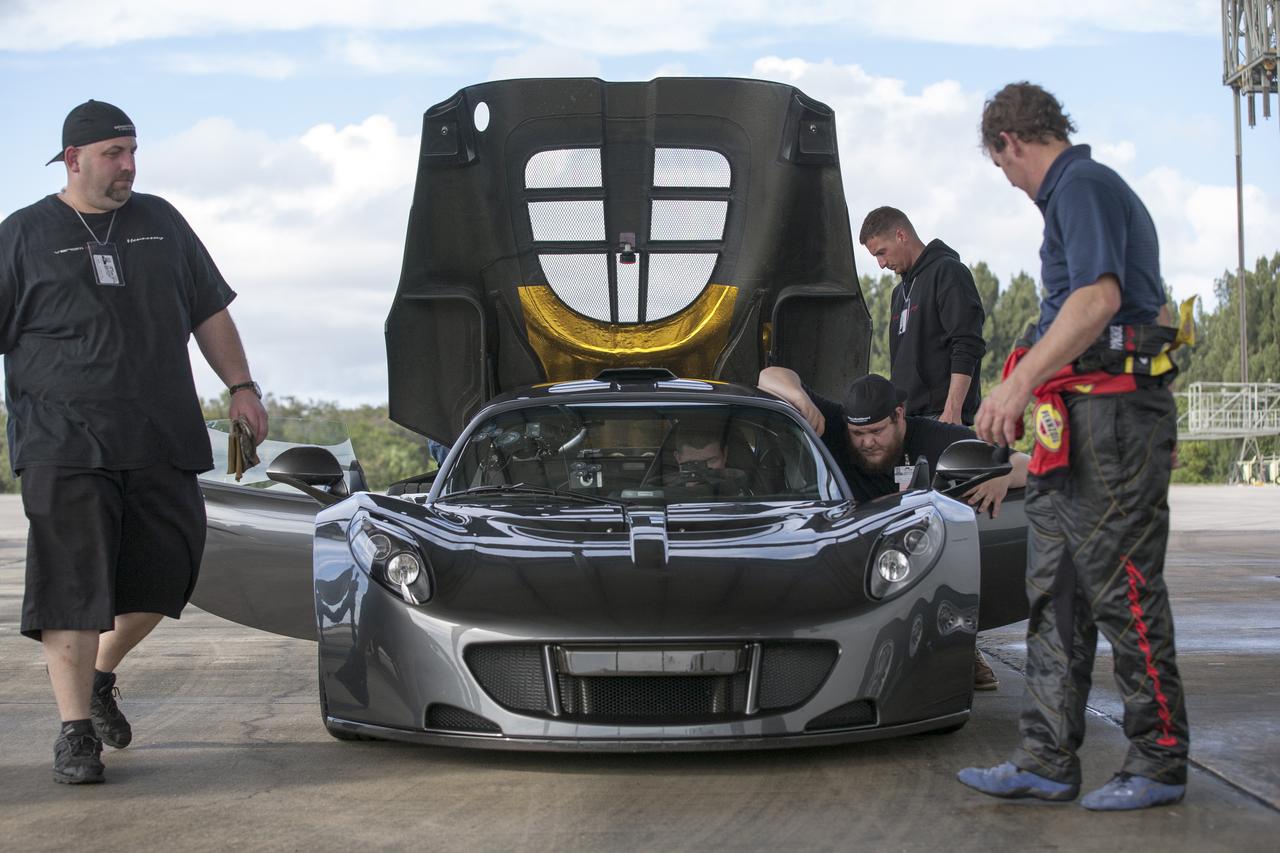

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Mechanics, engineers and Driver Brian Smith, in jumpsuit, ready a Hennessey Venom GT for test runs on the 3.5-mile long runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The flat concrete runway is one of the few places in the world where high performance automobiles can be tested for aerodynamic and safety designs. Hennessey Performance of Sealy, Texas, worked with Performance Power Racing in West Palm Beach to arrange use of the NASA facility. Performance Power Racing has conducted numerous engineering tests on the runway with a variety of vehicles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
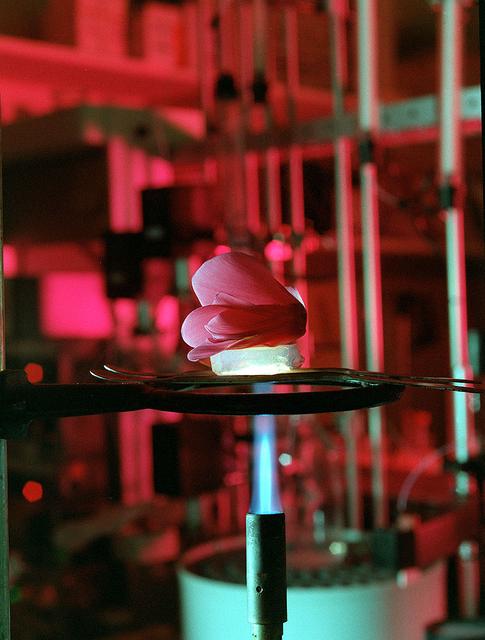

Scientists at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have been studying the properties of Aerogel for several years. Aerogel, the lightest solid known to man, has displayed a high quality for insulation. Because of its smoky countenance, it has yet to be used as an insulation on windows, but has been used in the space program on the rover Sojourner, and has been used as insulation in the walls of houses and in automobile engine compartments. As heat is applied to Aerogel, scientist Dr. David Noever of Space Sciences Laboratory, Principal Investigator of Aerogel, studies for its properties trying to uncover the secret to making Aerogel a clear substance. Once found, Aerogel will be a major component in the future of glass insulation.
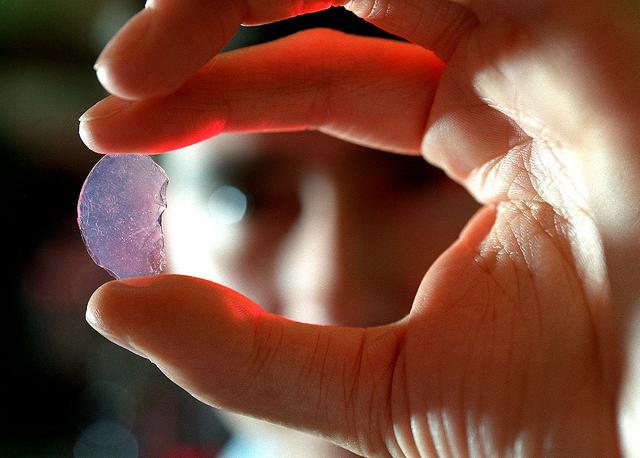

Sceintist at Marshall Space Flight Center have been studying the properties of Aerogel for several years. Aerogel, the lightest solid known to man, has displayed a high quality for insulation. Because of its smoky countenance, it has yet to be used as an insulation on windows, but has been used in the space program on the rover Sojourner, and has been used as insulation in the walls of houses and in automobile engine compartments. MSFC is one of the many research facilities conducting experiments to unlock the smoky properties of Aerogel and make it a clear substance. Recent experimentations in microgravity have resulted in the microstructure of the material. Research on these changes is being continued.
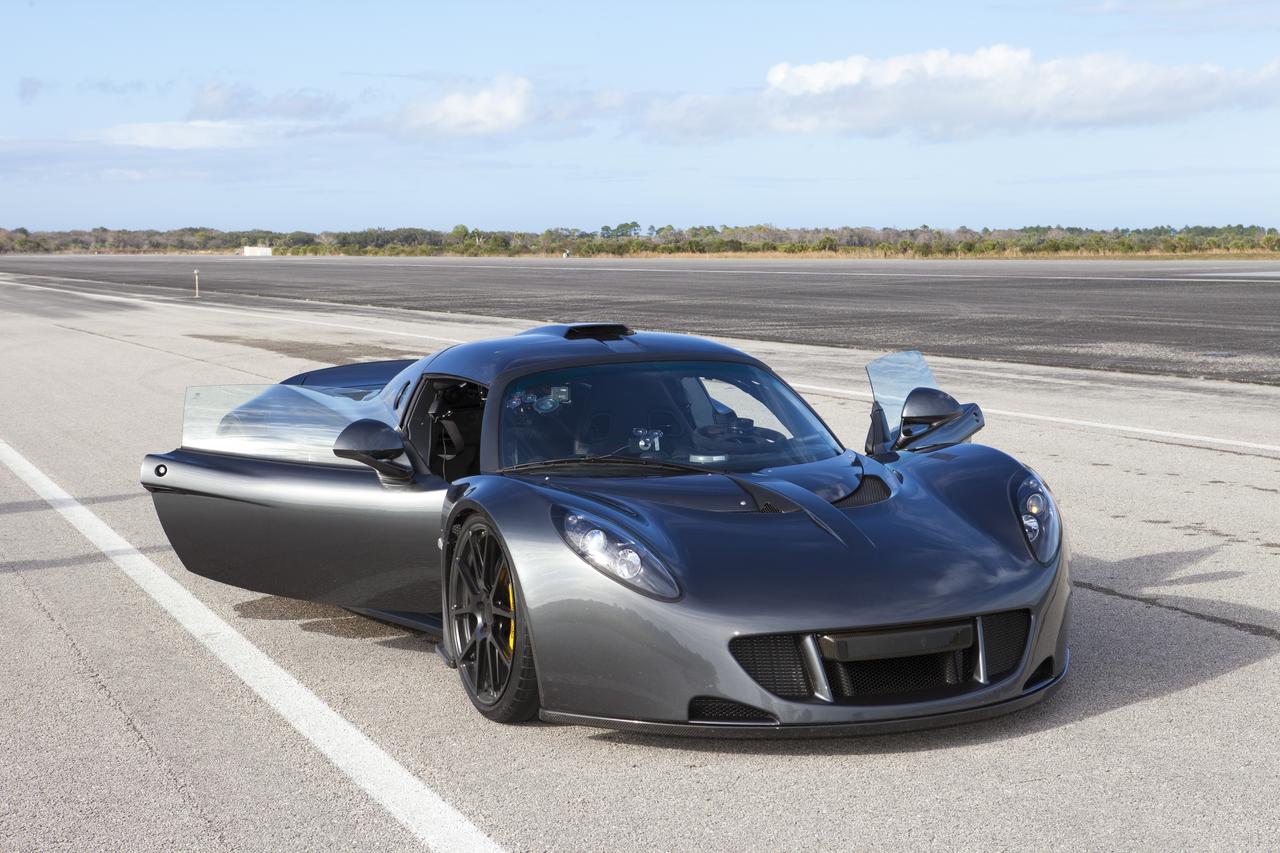

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A Hennessey Venom GT stands on the 3.5-mile long runway between test runs at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The flat concrete runway is one of the few places in the world where high performance automobiles can be tested for aerodynamic and safety designs. Hennessey Performance of Sealy, Texas, worked with Performance Power Racing in West Palm Beach to arrange use of the NASA facility. Performance Power Racing has conducted numerous engineering tests on the runway with a variety of vehicles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
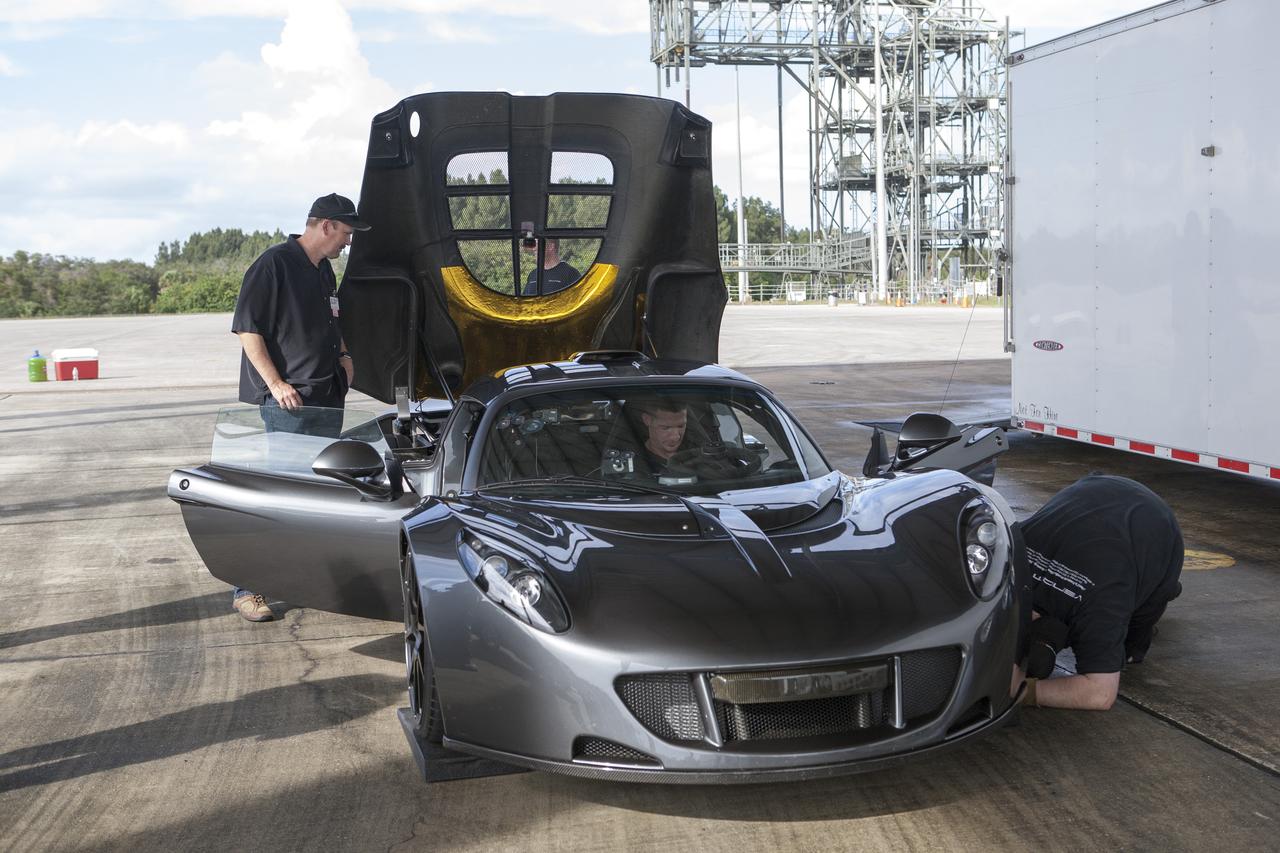

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Mechanics and engineers ready a Hennessey Venom GT for test runs on the 3.5-mile long runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The flat concrete runway is one of the few places in the world where high performance automobiles can be tested for aerodynamic and safety designs. Hennessey Performance of Sealy, Texas, worked with Performance Power Racing in West Palm Beach to arrange use of the NASA facility. Performance Power Racing has conducted numerous engineering tests on the runway with a variety of vehicles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
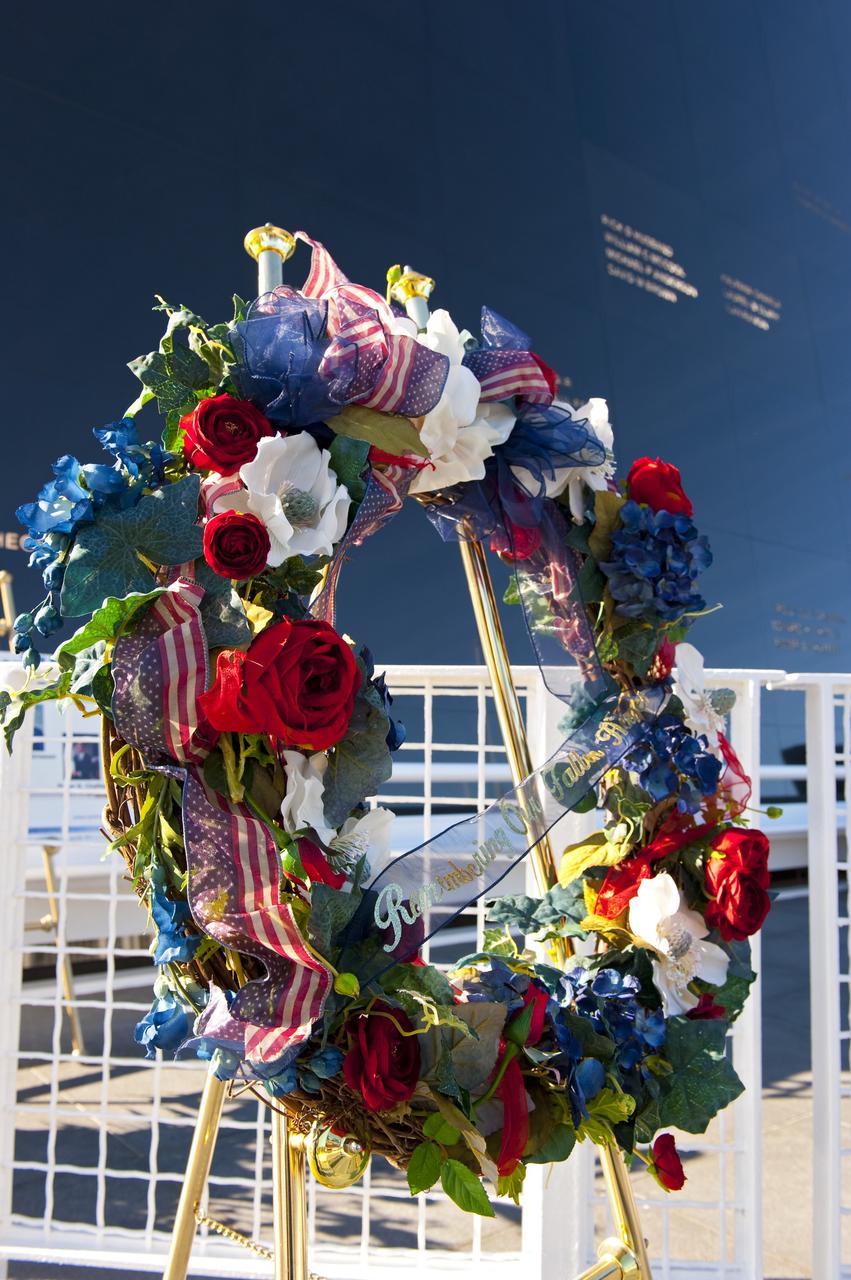

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A wreath is displayed at the foot of the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida during a Day of Remembrance ceremony to honor members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The memorial honors 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Pictured near the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida are the members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The memorial honors 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A flag flies at half-staff near the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida during a Day of Remembrance wreath laying ceremony to honor members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The large mirror made of black granite was designated as a national memorial by Congress and President George Bush in 1991. It honors 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
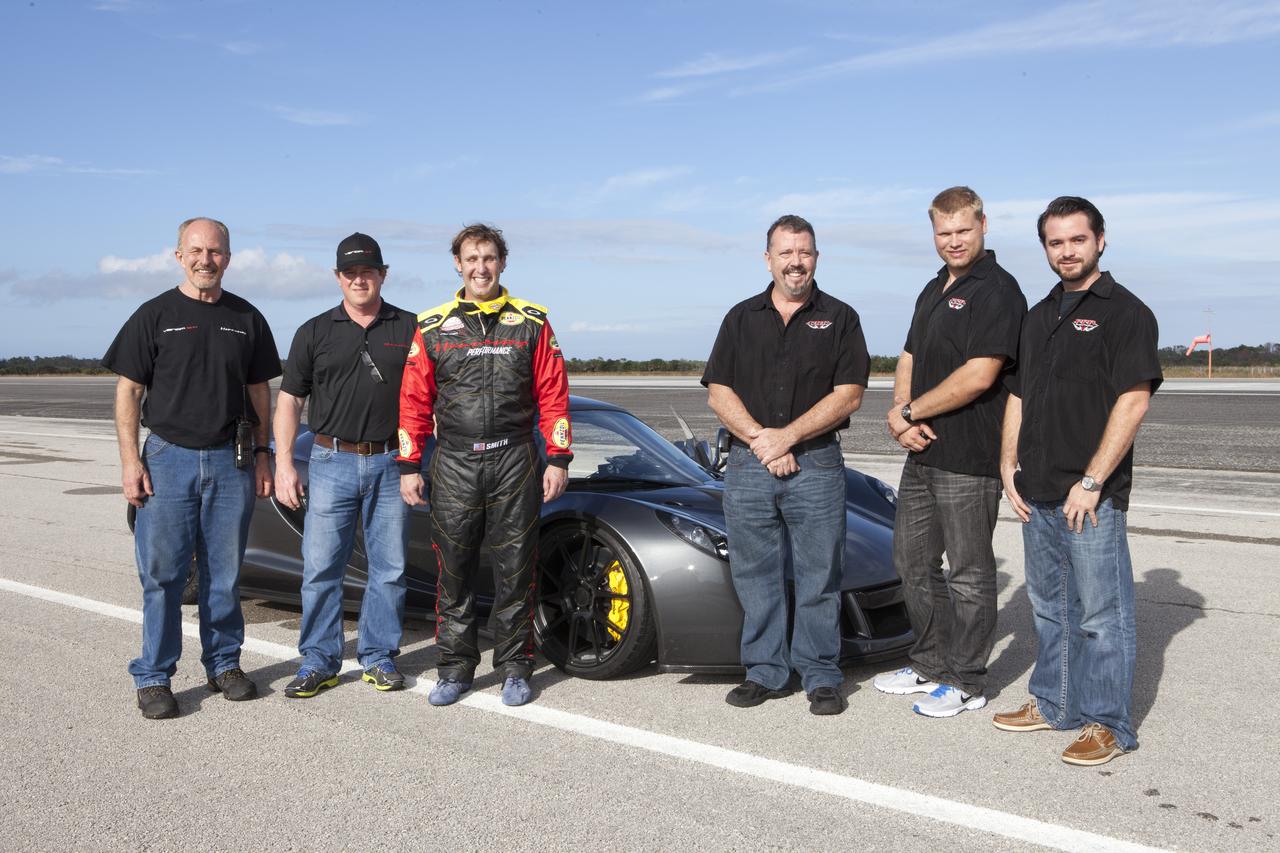

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The Performance Power Racing and Hennessey Performance teams pose with a Hennessey Venom GT at the 3.5-mile long runway at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The teams are, from left, Hennessey's John Heinricy, John Hennessey, Brian Smith, Performance Power Racing's Johnny Bohmer, Matt Lundy and Jeff McEachran. The flat concrete runway is one of the few places in the world where high performance automobiles can be tested for aerodynamic and safety designs. Hennessey Performance of Sealy, Texas, worked with Performance Power Racing in West Palm Beach to arrange use of the NASA facility. Performance Power Racing has conducted numerous engineering tests on the runway with a variety of vehicles.

This is a von Braun 1952 space station concept. In a 1952 series of articles written in Collier's, Dr. Wernher von Braun, then Technical Director of the Army Ordnance Guided Missiles Development Group at Redstone Arsenal, wrote of a large wheel-like space station in a 1,075-mile orbit. This station, made of flexible nylon, would be carried into space by a fully reusable three-stage launch vehicle. Once in space, the station's collapsible nylon body would be inflated much like an automobile tire. The 250-foot-wide wheel would rotate to provide artificial gravity, an important consideration at the time because little was known about the effects of prolonged zero-gravity on humans. Von Braun's wheel was slated for a number of important missions: a way station for space exploration, a meteorological observatory and a navigation aid. This concept was illustrated by artist Chesley Bonestell.
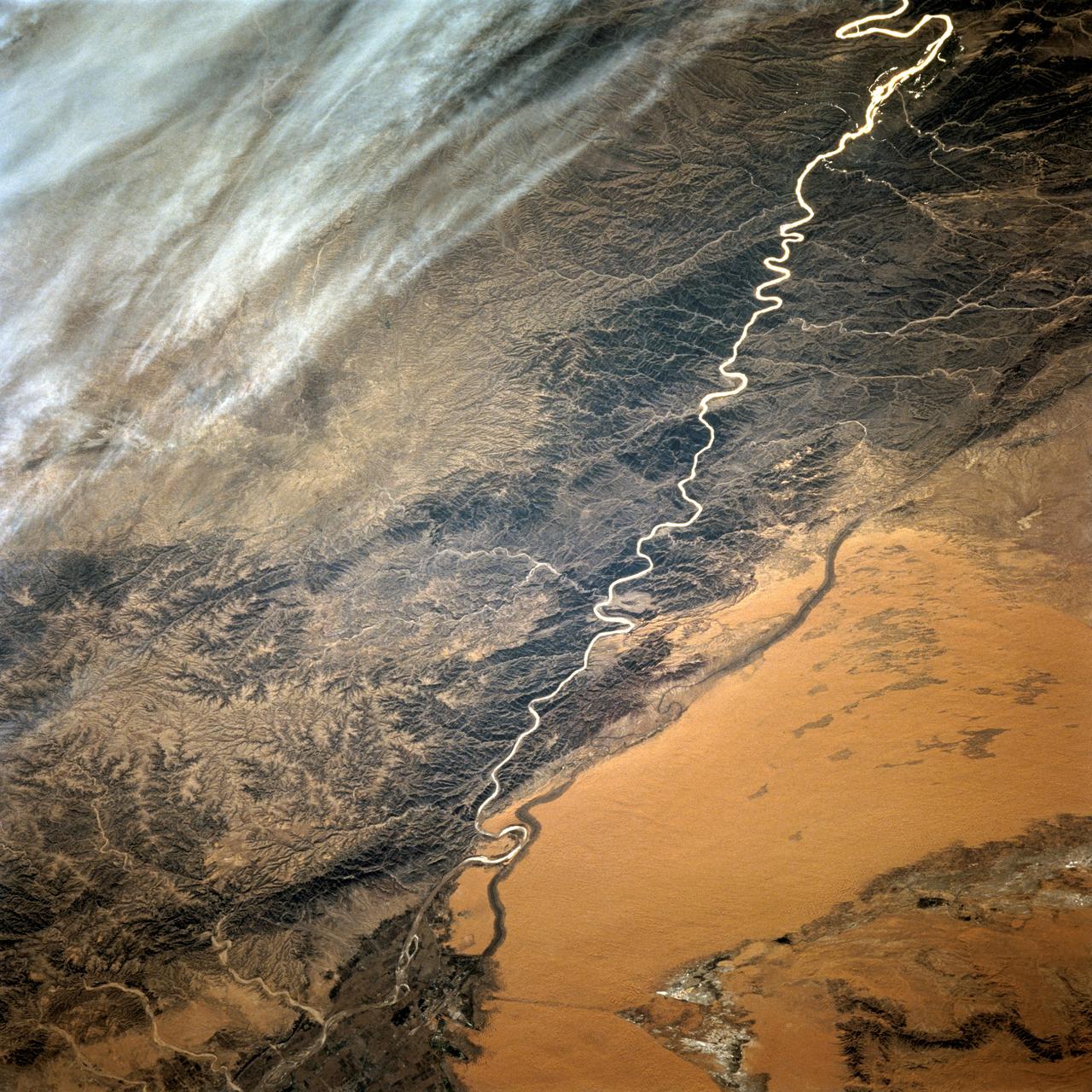

STS068-220-033 (30 September-11 October 1994) --- Photographed through the Space Shuttle Endeavour's flight deck windows, this 70mm frame shows a small section of China's Yellow River (Huang Ho) highlighted by sunglint reflection off the surface of the water. The river flows northeastward toward the village of Tung-lin-tzu. The low dissected mountains that cover more than half of this scene rise some 2,000 feet (on the average) above the valley floor. A major east-west transportation corridor (both railway and automobile) is observed traversing the landscape north of the river. This entire region is considered to be part of the Ordos Desert, actually part of the greater Gobi located just north of this area. Approximate center coordinates of this scene are 37.5 degrees north latitude and 105.0 degrees east longitude.
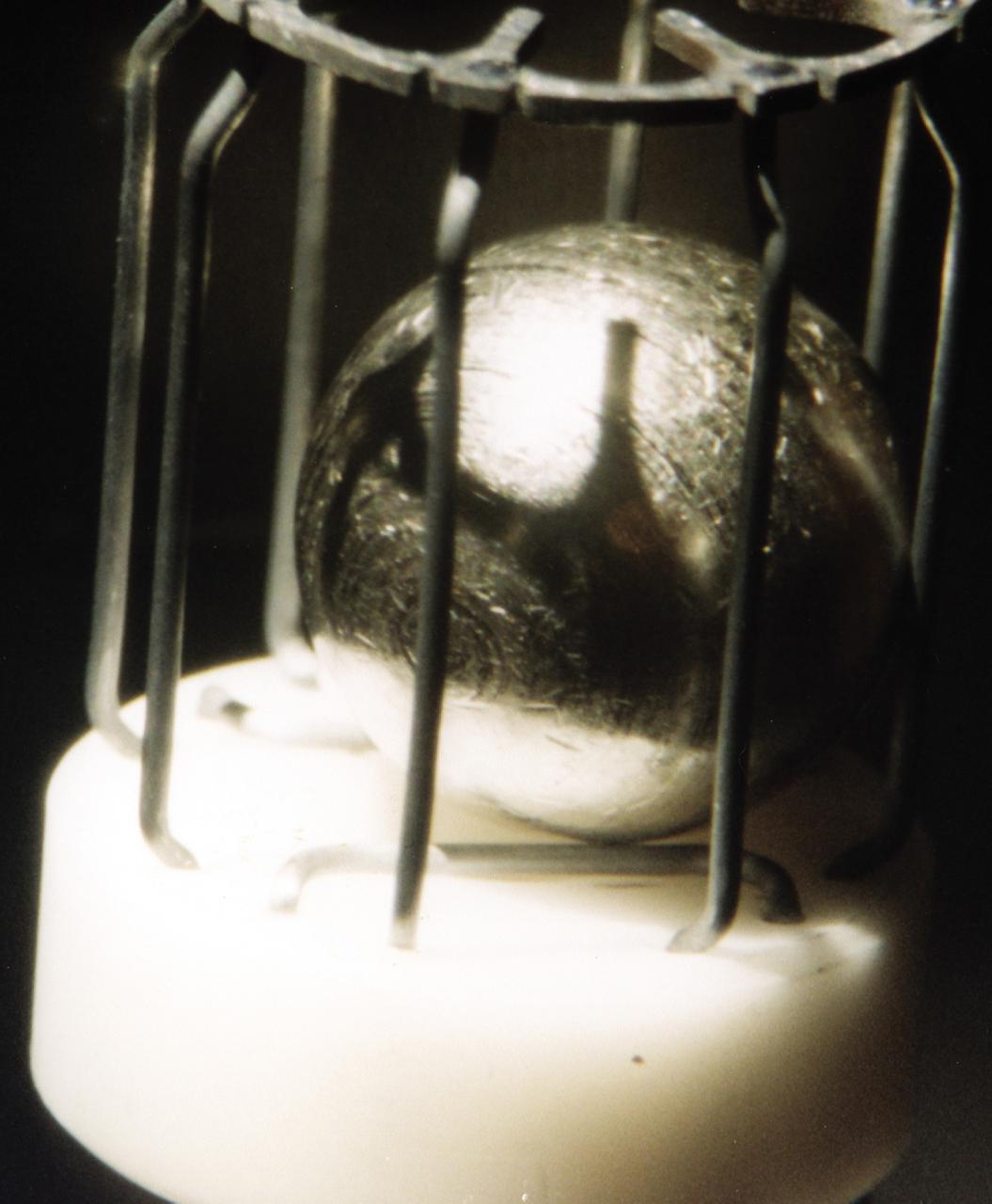
This metal sample, which is approximately 1 cm in diameter, is typical of the metals that were studied using the German designed electromagnetic containerless processing facility. The series of experiments that use this device is known as TEMPUS which is the acronym that stands for the German Tiegelfreies Elektromanetisches Prozessieren Unter Schwerelosigkeit. Most of the TEMPUS experiments focused on various aspects of undercooling liquid metal and alloys. Undercooling is the process of melting a material and then cooling it to a temperature that is below its normal freezing or solidification point. The TEMPUS experiments that used the metal cages as shown in the photograph, often studied bulk metallic glass, a solid material with no crystalline structures. We study metals and alloys not only to build things in space, but to improve things that are made on Earth. Metals and alloys are everywhere around us; in our automobiles, in the engines of aircraft, in our power-plants, and elsewhere. Despite their presence in everyday life, there are many scientific aspects of metals that we do not understand.
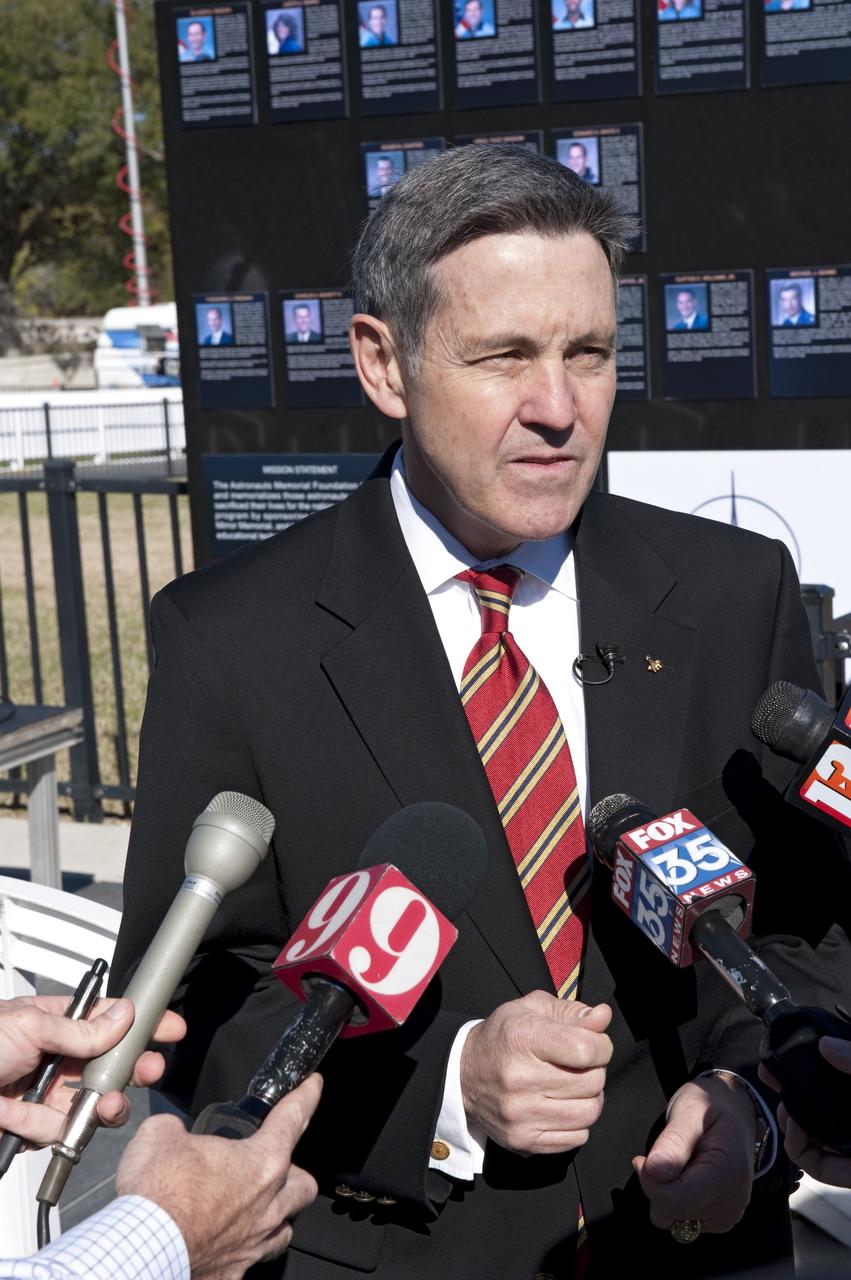

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Kennedy Space Center Director and former astronaut Bob Cabana answers media questions during a Day of Remembrance wreath laying ceremony at the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. The ceremony honors members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The memorial displays the names of 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
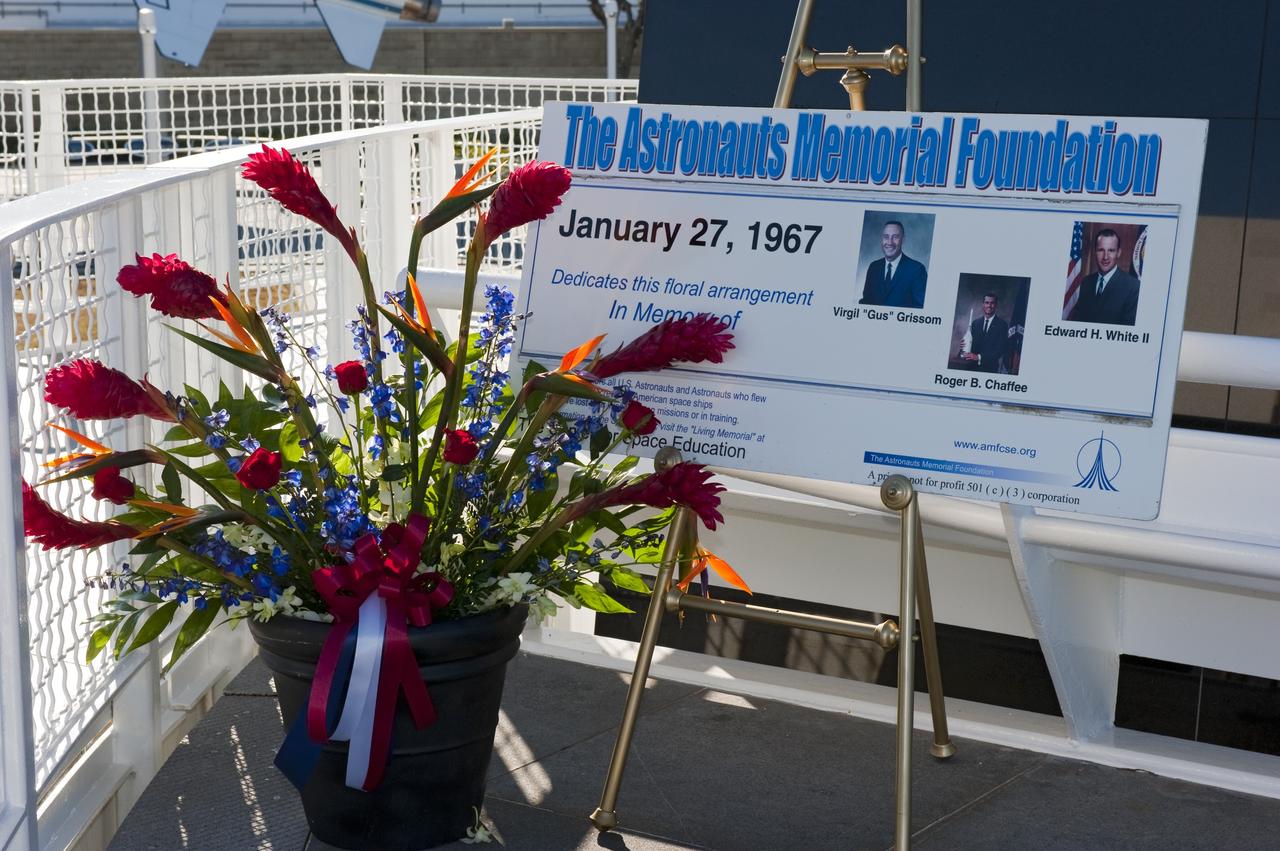

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Flowers lay at the foot of the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida before a Day of Remembrance wreath laying ceremony to honor members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The floral arrangement is dedicated to the Apollo 1 crew members Virgil "Gus" Grissom, Roger B. Chaffee and Edward H. White II. The memorial honors 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Two scientists at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center, atmospheric scientist Paul Meyer (left) and solar physicist Dr. David Hathaway, have developed promising new software, called Video Image Stabilization and Registration (VISAR), that may help law enforcement agencies to catch criminals by improving the quality of video recorded at crime scenes, VISAR stabilizes camera motion in the horizontal and vertical as well as rotation and zoom effects; produces clearer images of moving objects; smoothes jagged edges; enhances still images; and reduces video noise of snow. VISAR could also have applications in medical and meteorological imaging. It could steady images of Ultrasounds which are infamous for their grainy, blurred quality. It would be especially useful for tornadoes, tracking whirling objects and helping to determine the tornado's wind speed. This image shows two scientists reviewing an enhanced video image of a license plate taken from a moving automobile.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Flowers lay at the foot of the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida before a Day of Remembrance wreath laying ceremony to honor members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The memorial honors 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
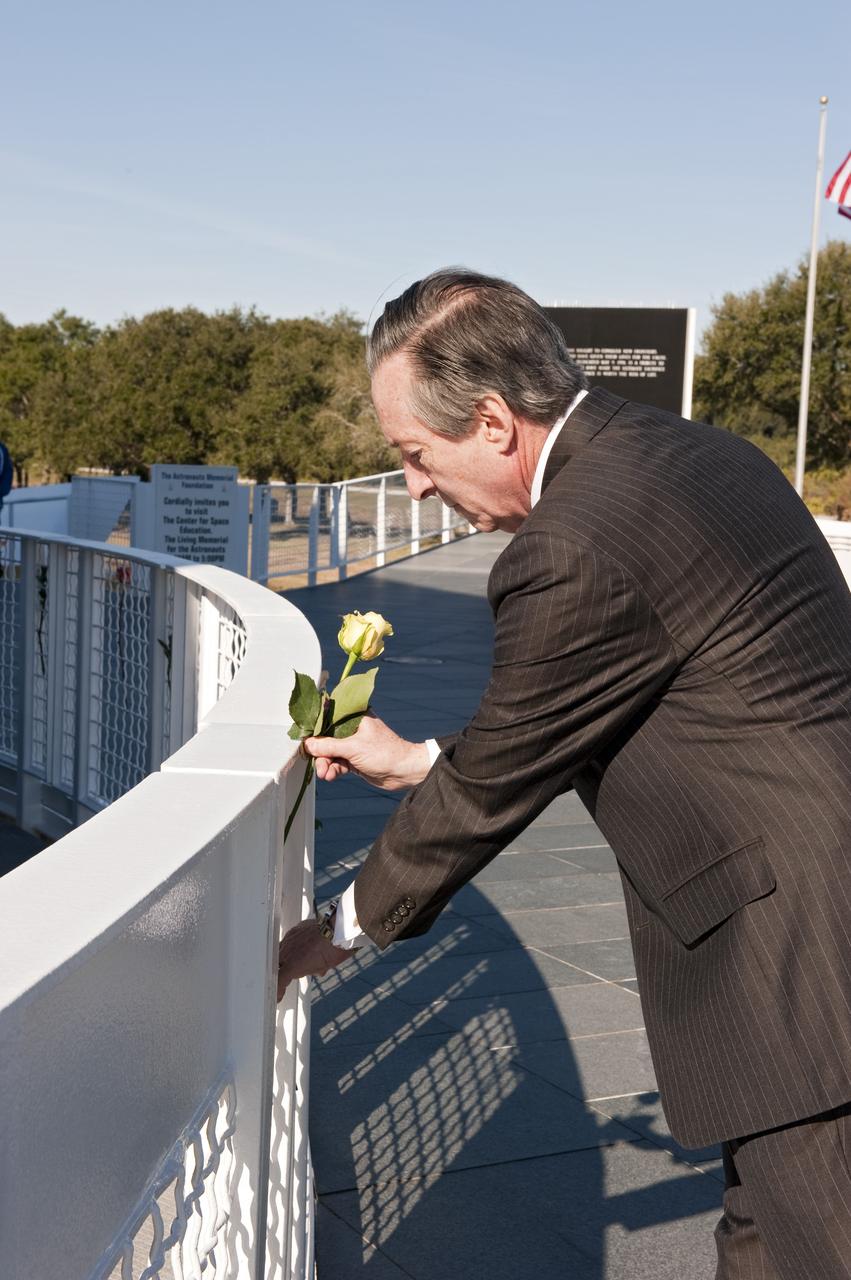

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- President and C.E.O. of The Astronauts Memorial Foundation Stephen Feldman displays a single yellow rose near the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida during a Day of Remembrance ceremony to honor members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The memorial honors 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
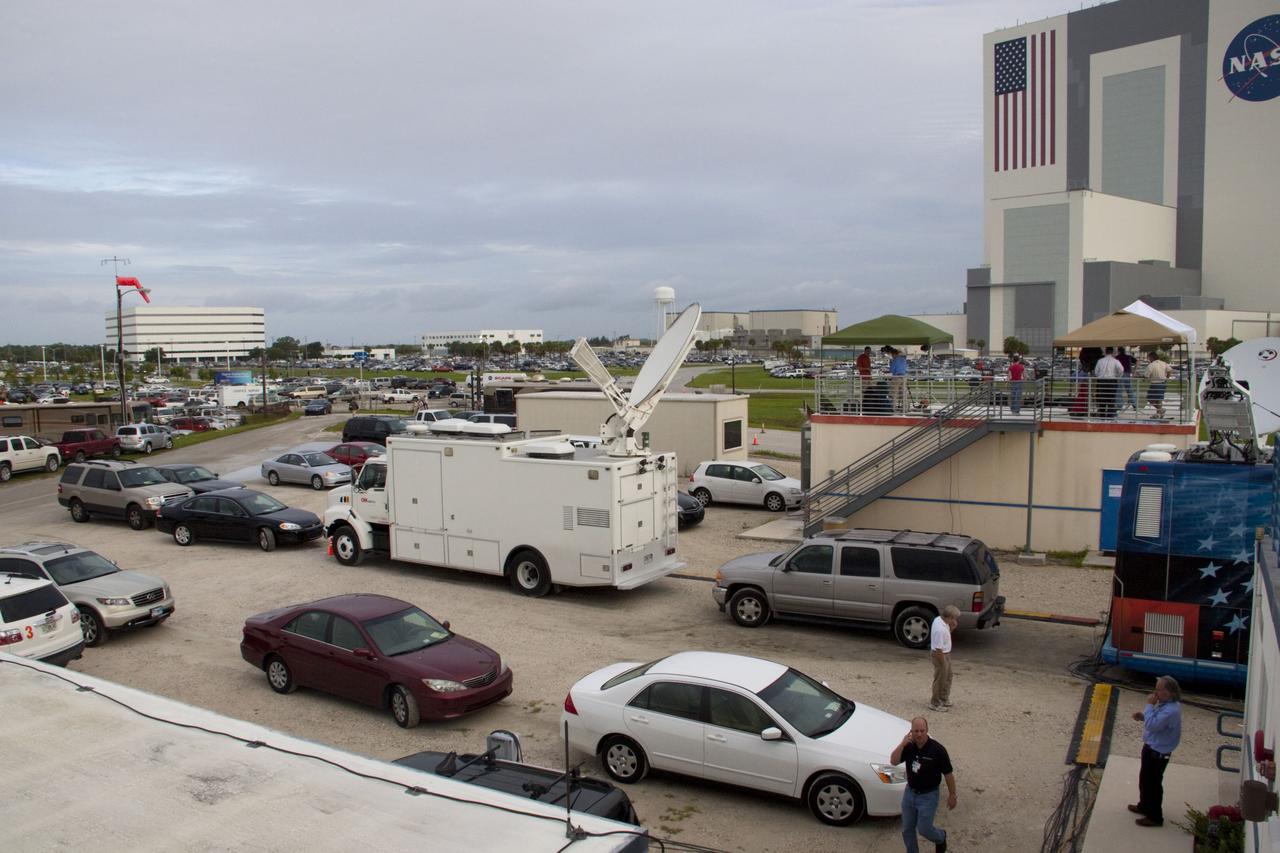

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Seen towering above is the massive Vehicle Assembly Building. Satellite news trucks, trailers and automobiles can be seen in the parking lot with the massive Vehicle Assembly Building towering above. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
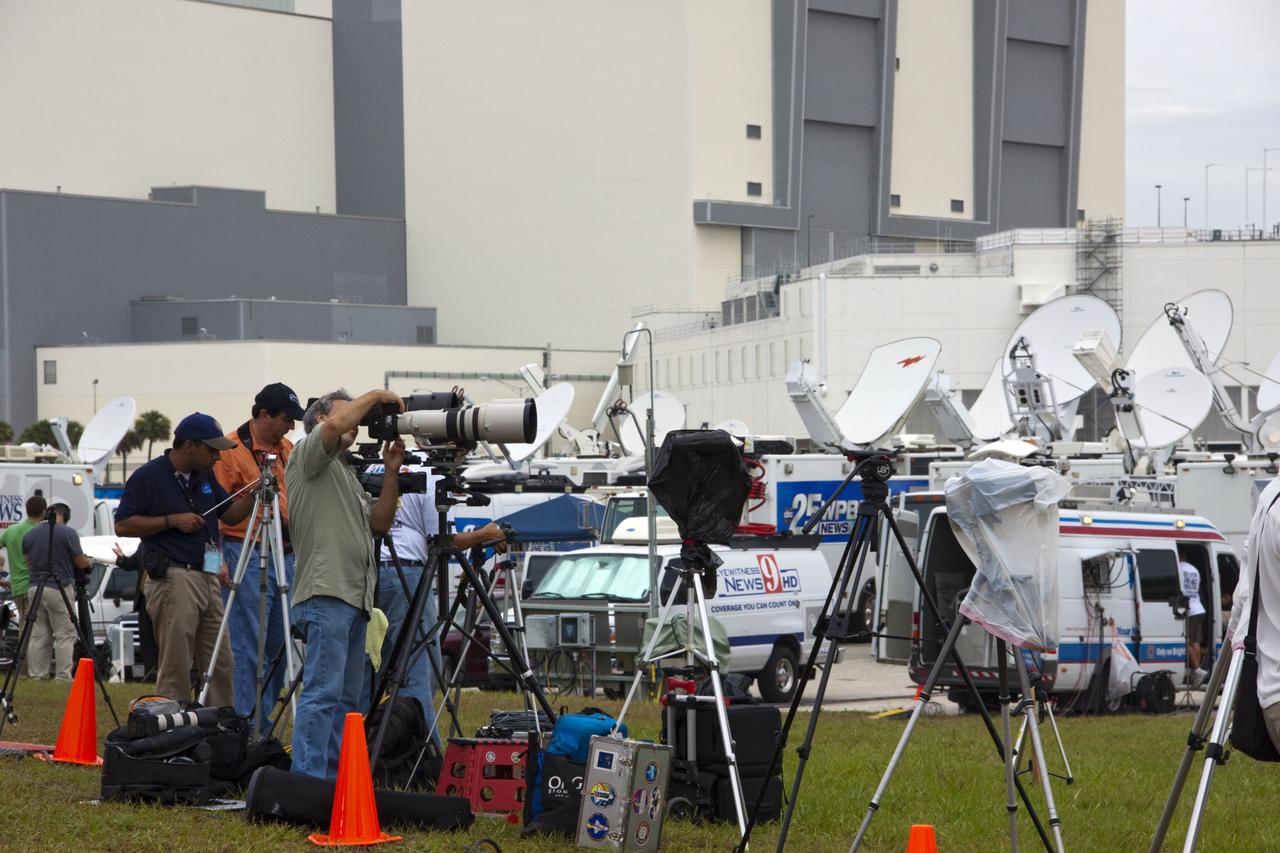

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather at the NASA News Center at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Press Site in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Satellite news trucks, trailers and automobiles can be seen in the parking lot with the massive Vehicle Assembly Building towering above. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
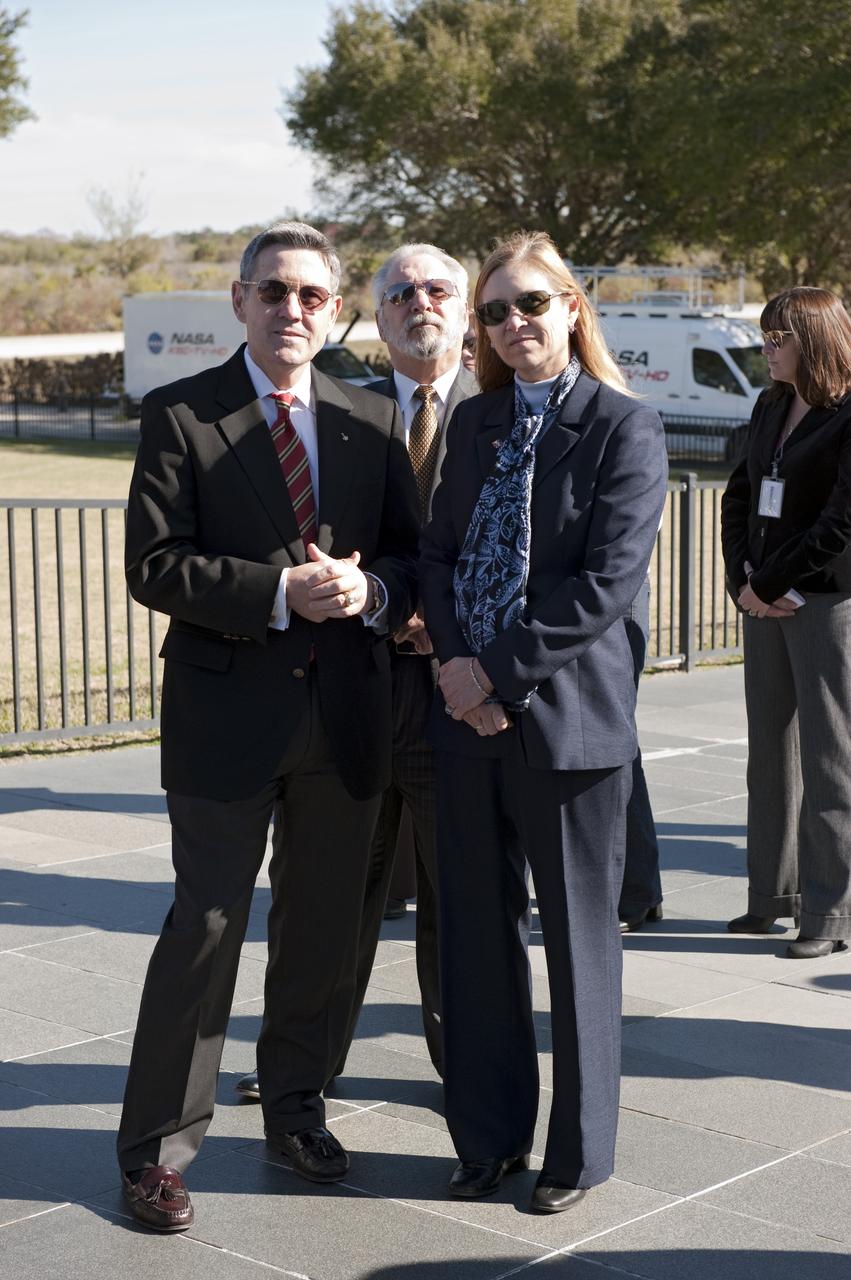

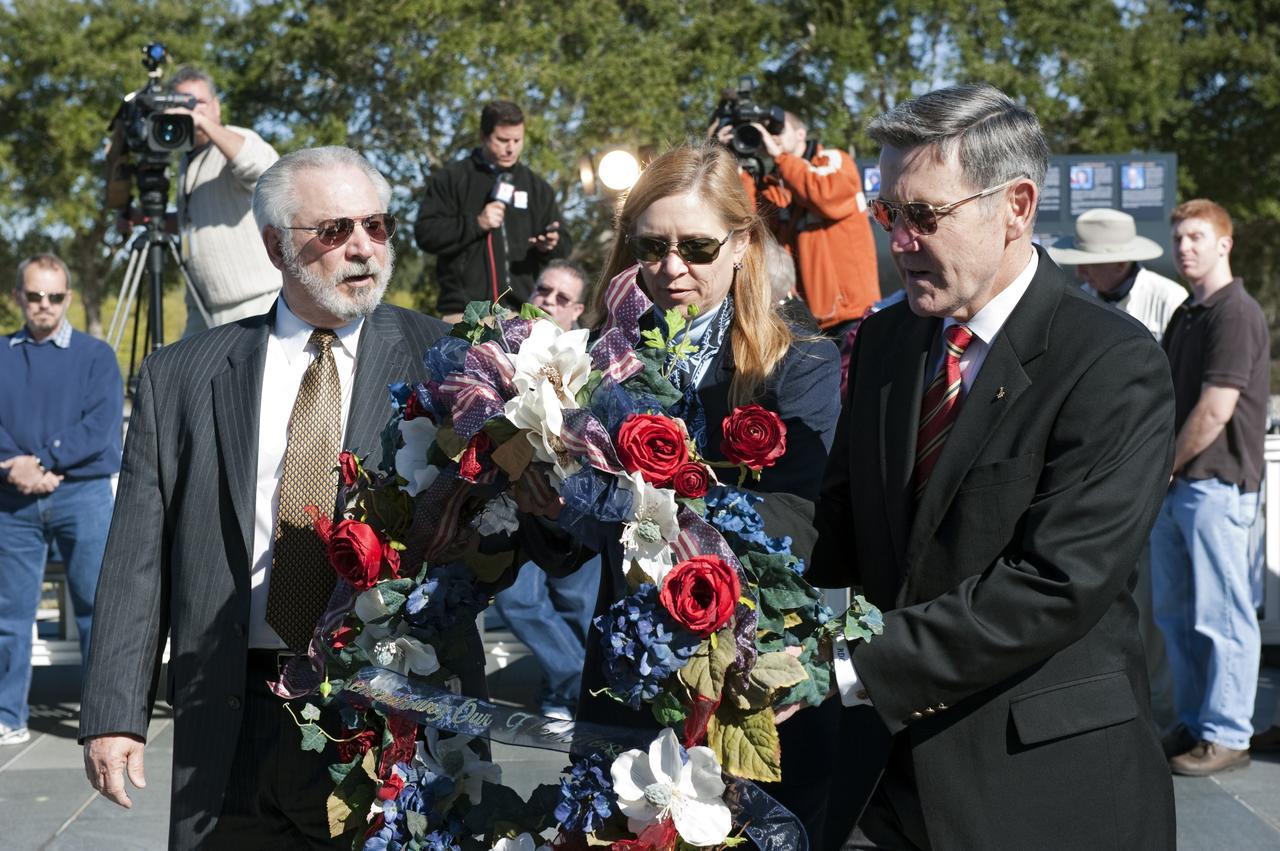
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Kennedy Space Center Director and former astronaut Bob Cabana, left, United Space Alliance's Associate Program Manager for Solid Rocket Boosters Roger Elliott and Center Deputy Director Janet Petro participate in a Day of Remembrance wreath laying ceremony at the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. The ceremony honors members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The memorial displays the names of 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
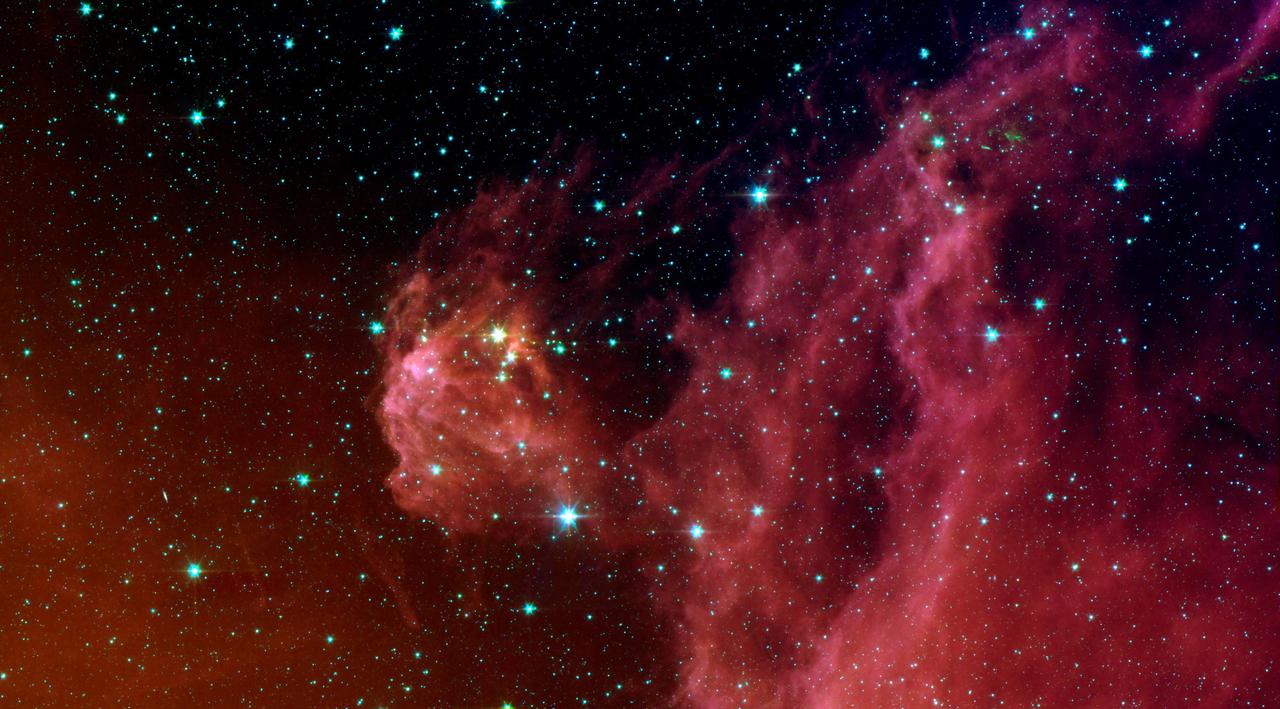

This image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows infant stars "hatching" in the head of the hunter constellation, Orion. Astronomers suspect that shockwaves from a supernova explosion in Orion's head, nearly three million years ago, may have initiated this newfound birth . The region featured in this Spitzer image is called Barnard 30. It is located approximately 1,300 light-years away and sits on the right side of Orion's "head," just north of the massive star Lambda Orionis. Wisps of red in the cloud are organic molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. These molecules are formed anytime carbon-based materials are burned incompletely. On Earth, they can be found in the sooty exhaust from automobile and airplane engines. They also coat the grills where charcoal-broiled meats are cooked. This image shows infrared light captured by Spitzer's infrared array camera. Light with wavelengths of 8 and 5.8 microns (red and orange) comes mainly from dust that has been heated by starlight. Light of 4.5 microns (green) shows hot gas and dust; and light of 3.6 microns (blue) is from starlight. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09412
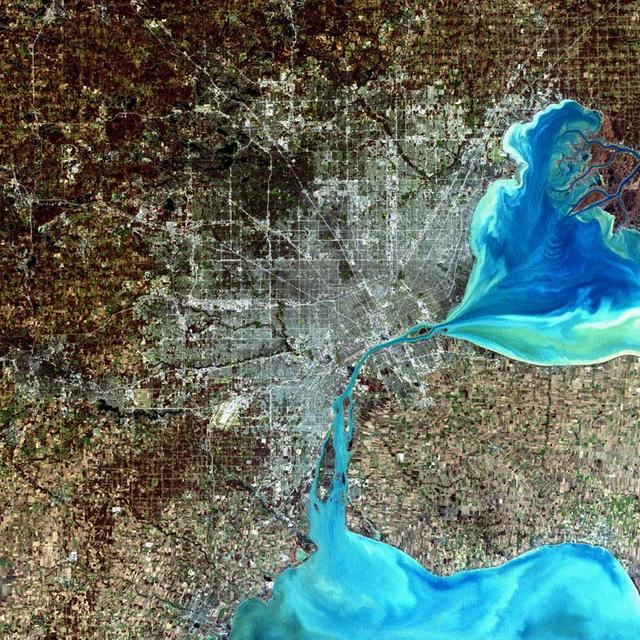
Detroit, Michigan, USA Sensor: L7 ETM+ Acquisition Date: December 11, 2001 Path/Row: 20/30 Lat/Long: 42.330/-83.046 Detroit, Michigan, is commonly referred to as Motor City because of the many automobile manufacturing plants located in the city. It is the largest city in Michigan, with a population approaching one million. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Landsat <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
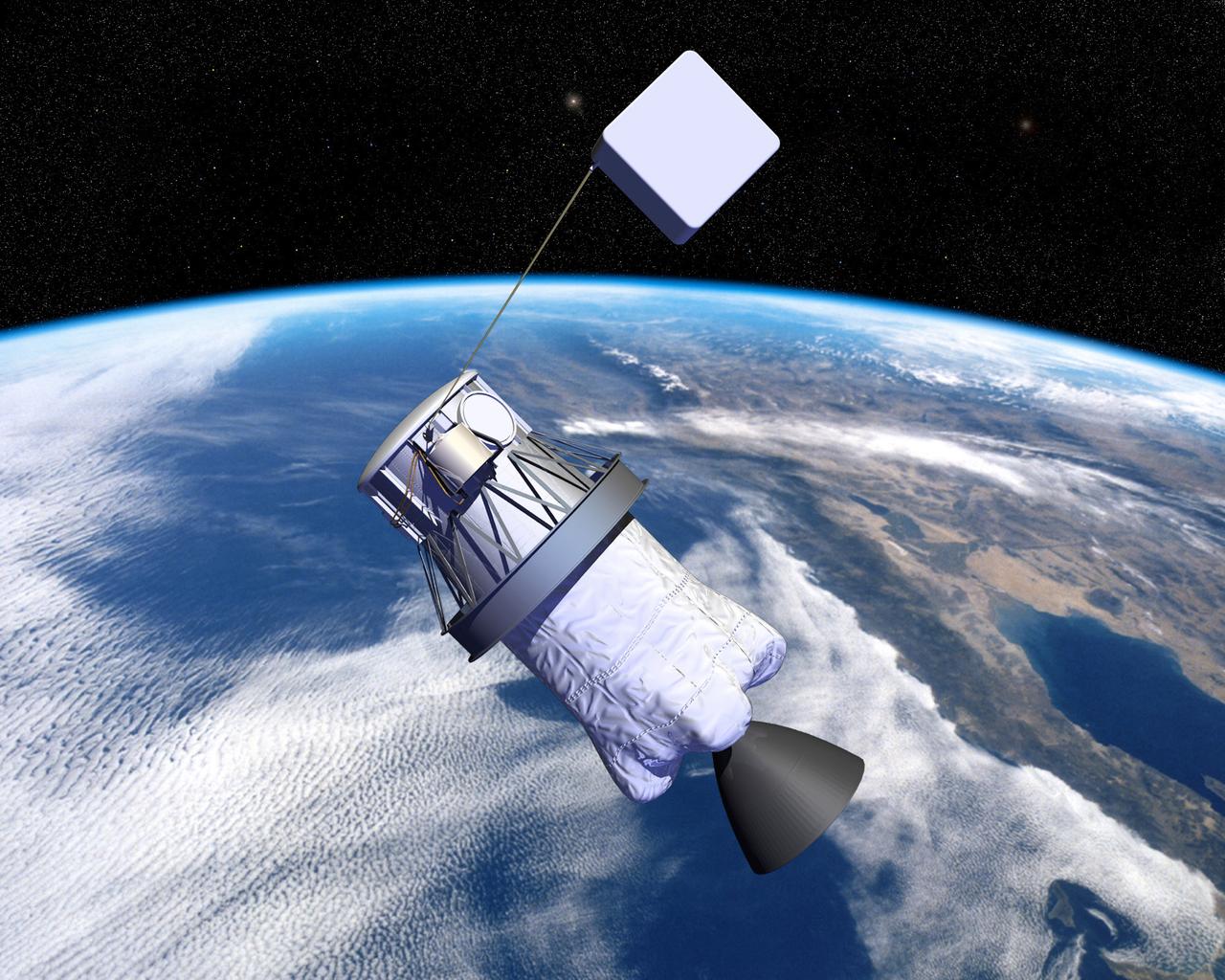

Pictured is an artist's concept of NASA's Propulsive Small Expendable Deployer System experiment (ProSEDS). ProSEDS will demonstrate the use of an electrodynamic tether, basically a long, thin wire, for propulsion. An electrodynamic tether uses the same principles as electric motors in toys, appliances and computer disk drives, and generators in automobiles and power plants. When electrical current is flowing through the tether, a magnetic field is produced that pushes against the magnetic field of the Earth. For ProSEDS, the current in the tether results by virtue of the voltage generated when the tether moves through the Earth's magnetic field at more than 17,000 mph. This approach can produce drag thrust generating useable power. Since electrodynamic tethers require no propellant, they could substantially reduce the weight of the spacecraft and provide a cost-effective method of reboosting spacecraft. The initial flight of ProSEDS is scheduled to fly aboard an Air Force Delta II rocket in summer of 2002. In orbit, ProSEDS will deploy from a Delta II second stage. It will be a 3.1-mile (5 kilometer) long, ultrathin base-wire tether cornected with a 6.2-mile (10 kilometer) long nonconducting tether. The ProSEDS experiment is managed by the Space Transportation Directorate at the Marshall Space Flight Center.

An automobile lies crushed under the third story of this apartment building in the Marina District after the Oct. 17, 1989, Loma Prieta earthquake. The ground levels are no longer visible because of structural failure and sinking due to liquefaction. Sand and soil grains have faces that can cause friction as they roll and slide against each other, or even cause sticking and form small voids between grains. This complex behavior can cause soil to behave like a liquid under certain conditions such as earthquakes or when powders are handled in industrial processes. Mechanics of Granular Materials (MGM) experiments aboard the Space Shuttle use the microgravity of space to simulate this behavior under conditons that carnot be achieved in laboratory tests on Earth. MGM is shedding light on the behavior of fine-grain materials under low effective stresses. Applications include earthquake engineering, granular flow technologies (such as powder feed systems for pharmaceuticals and fertilizers), and terrestrial and planetary geology. Nine MGM specimens have flown on two Space Shuttle flights. Another three are scheduled to fly on STS-107. The principal investigator is Stein Sture of the University of Colorado at Boulder. Credit: J.K. Nakata, U.S. Geological Survey.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Satellite news trucks, trailers and automobiles can be seen in the parking lot. In the background is the Operations and Support Building II where VIPs are able to watch the launch from its upper balcony. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Media from around the globe gather on the grounds of the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to photograph and cover the prelaunch activities and lift off of space shuttle Atlantis on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Satellite news trucks, trailers and automobiles can be seen in the parking lot. Atlantis began its final flight, with Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley and Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim on board, at 11:29 a.m. EDT July 8 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Also in Atlantis' payload bay is the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
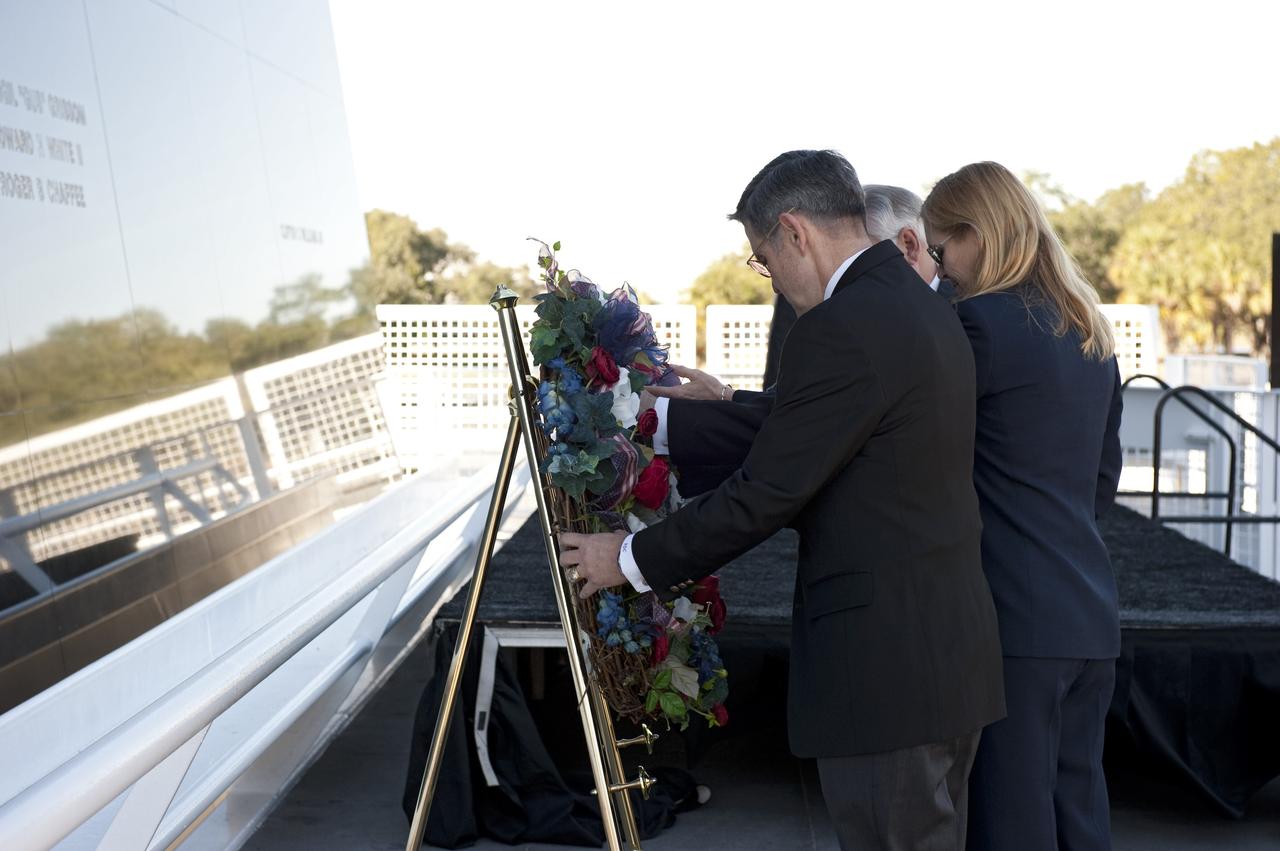

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- United Space Alliance's Associate Program Manager for Solid Rocket Boosters Roger Elliott, back, Kennedy Space Center Deputy Director Janet Petro, and Center Director and former astronaut Bob Cabana, participate in a Day of Remembrance wreath laying ceremony at the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. The ceremony honors members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The memorial displays the names of 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- United Space Alliance's Associate Program Manager for Solid Rocket Boosters Roger Elliott, left, Kennedy Space Center Deputy Director Janet Petro, and Center Director and former astronaut Bob Cabana, participate in a Day of Remembrance wreath laying ceremony at the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. The ceremony honors members of the NASA family who lost their lives while furthering the cause of exploration and discovery. The memorial displays the names of 24 United States astronauts, including the crew members of space shuttles Columbia and Challenger, Apollo 1, and those who died in training and commercial airplane accidents. The memorial is a project of the Astronauts Memorial Foundation and was paid for by Florida residents who purchased special Challenger mission automobile license plates. 2011 marks the 25th anniversary of the loss of Challenger, which broke apart over the Atlantic Ocean 73 seconds into flight on Jan. 28, 1986. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
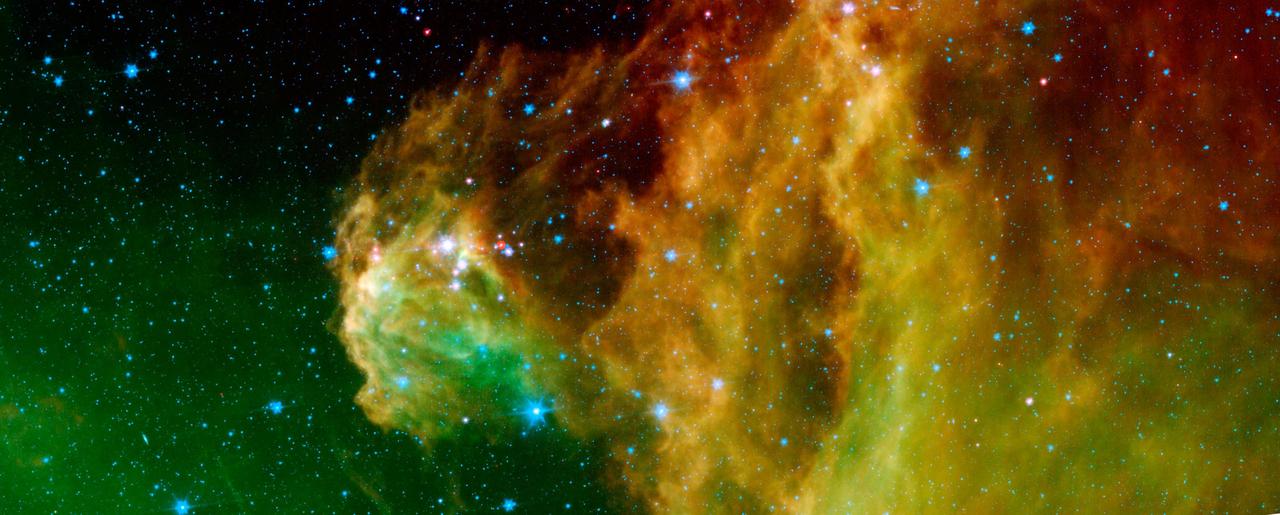

This image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows infant stars "hatching" in the head of the hunter constellation, Orion. Astronomers suspect that shockwaves from a supernova explosion in Orion's head, nearly three million years ago, may have initiated this newfound birth. The region featured in this Spitzer image is called Barnard 30. It is located approximately 1,300 light-years away and sits on the right side of Orion's "head," just north of the massive star Lambda Orionis. Wisps of green in the cloud are organic molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. These molecules are formed anytime carbon-based materials are burned incompletely. On Earth, they can be found in the sooty exhaust from automobile and airplane engines. They also coat the grills where charcoal-broiled meats are cooked. Tints of orange-red in the cloud are dust particles warmed by the newly forming stars. The reddish-pink dots at the top of the cloud are very young stars embedded in a cocoon of cosmic gas and dust. Blue spots throughout the image are background Milky Way along this line of sight. This composite includes data from Spitzer's infrared array camera instrument, and multiband imaging photometer instrument. Light at 4.5 microns is shown as blue, 8.0 microns is green, and 24 microns is red. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09411
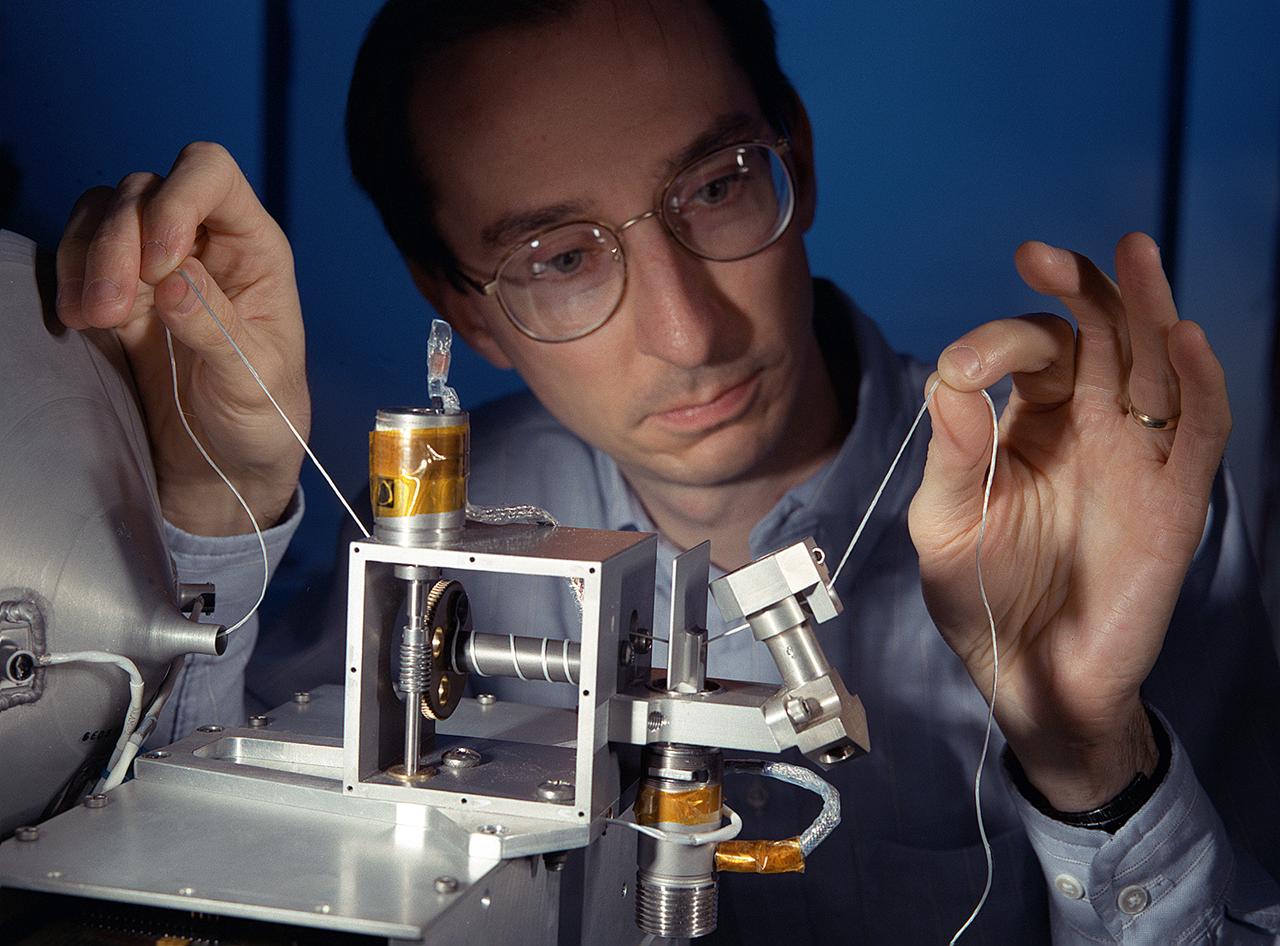

NASA's Propulsive Small Expendable Deployer System experiment (ProSEDS) will demonstrate the use of an electrodynamic tether, basically a long, thin wire, for propulsion. An electrodynamic tether uses the same principles as electric motors in toys, appliances and computer disk drives, and generators in automobiles and power plants. When electrical current is flowing through the tether, a magnetic field is produced that pushes against the magnetic field of the Earth. For ProSEDS, the current in the tether results by virtue of the voltage generated when the tether moves through the Earth's magnetic field at more than 17,000 mph. This approach can produce drag thrust generating useable power. Since electrodynamic tethers require no propellant, they could substantially reduce the weight of the spacecraft and provide a cost-effective method of reboosting spacecraft. The initial flight of ProSEDS is scheduled to fly aboard an Air Force Delta II rocket in the summer of 2002. In orbit, ProSEDS will deploy from a Delta II second stage. It will be a 3.1-mile (5 kilometer) long, ultrathin base-wire cornected with a 6.2-mile (10 kilometer) long nonconducting tether. This photograph shows Less Johnson, a scientist at MSFC inspecting the nonconducting part of a tether as it exits a deployer similar to the one to be used in the ProSEDS experiment. The ProSEDS experiment is managed by the Space Transportation Directorate at MSFC.
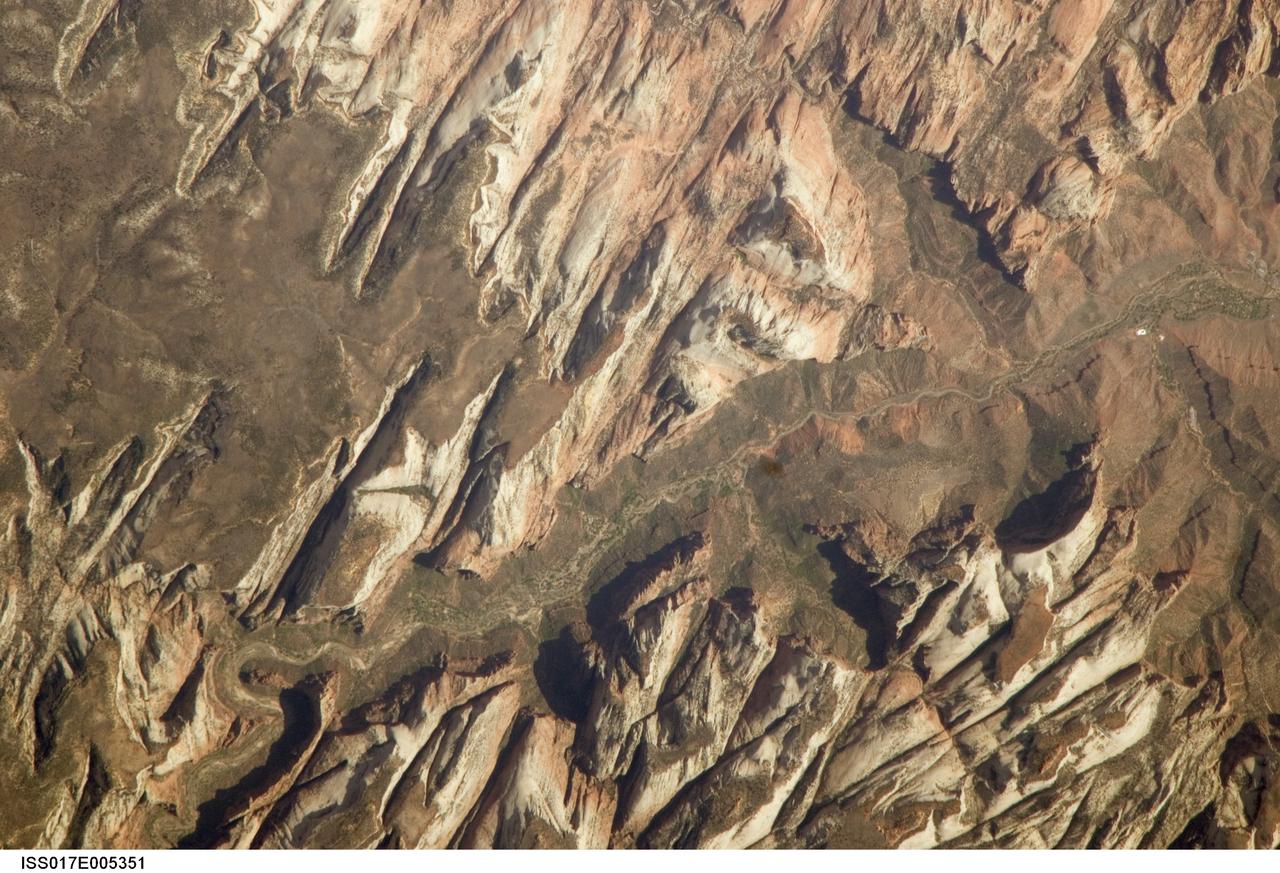

ISS017-E-005351 (26 April 2008) --- Zion National Park, Utah is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 17 crewmember on the International Space Station. Zion National Park is located in southwestern Utah, along the western margin of the Colorado Plateau. The park was established in 1919, after roadway improvements in southwestern Utah allowed access to the preceding Mukuntuweap National Monument (1909) located in Zion Canyon. The towering cliffs bounding the North Fork of the Virgin River are formed mainly of tan to light pink Navajo Sandstone, the lithified remnants of an extensive sand dune sea that covered the area during the early Mesozoic Era, nearly 200 million years ago, according to scientists. The Zion region would have looked much like the present-day Sahara desert at this time in its geologic history. Brown rock capping the Navajo Sandstone (right) is comprised of younger beds that record changing environmental conditions that fluctuated between shallow seas and deserts. This high resolution image illustrates the incised nature of the bedrock forming the park. The long linear features are joints -- fractures in the rock mass -- formed in response to tectonic stresses that affected the region during its geologic history. The mainly north-northwest trending joints serve to channelize water runoff and are thought to be the main factor that determined the present canyon network. While the park is perhaps best experienced by hiking, backpacking, or biking, Utah State Route 9 provides automobile access up the side of Zion Canyon. The road is visible in this view as a thin brown line climbing the south wall of the canyon (lower left). Access to the rest of the park is provided by a shuttle bus system instituted in 2000 to reduce vehicle noise, improve air quality, and improve wildlife habitat.
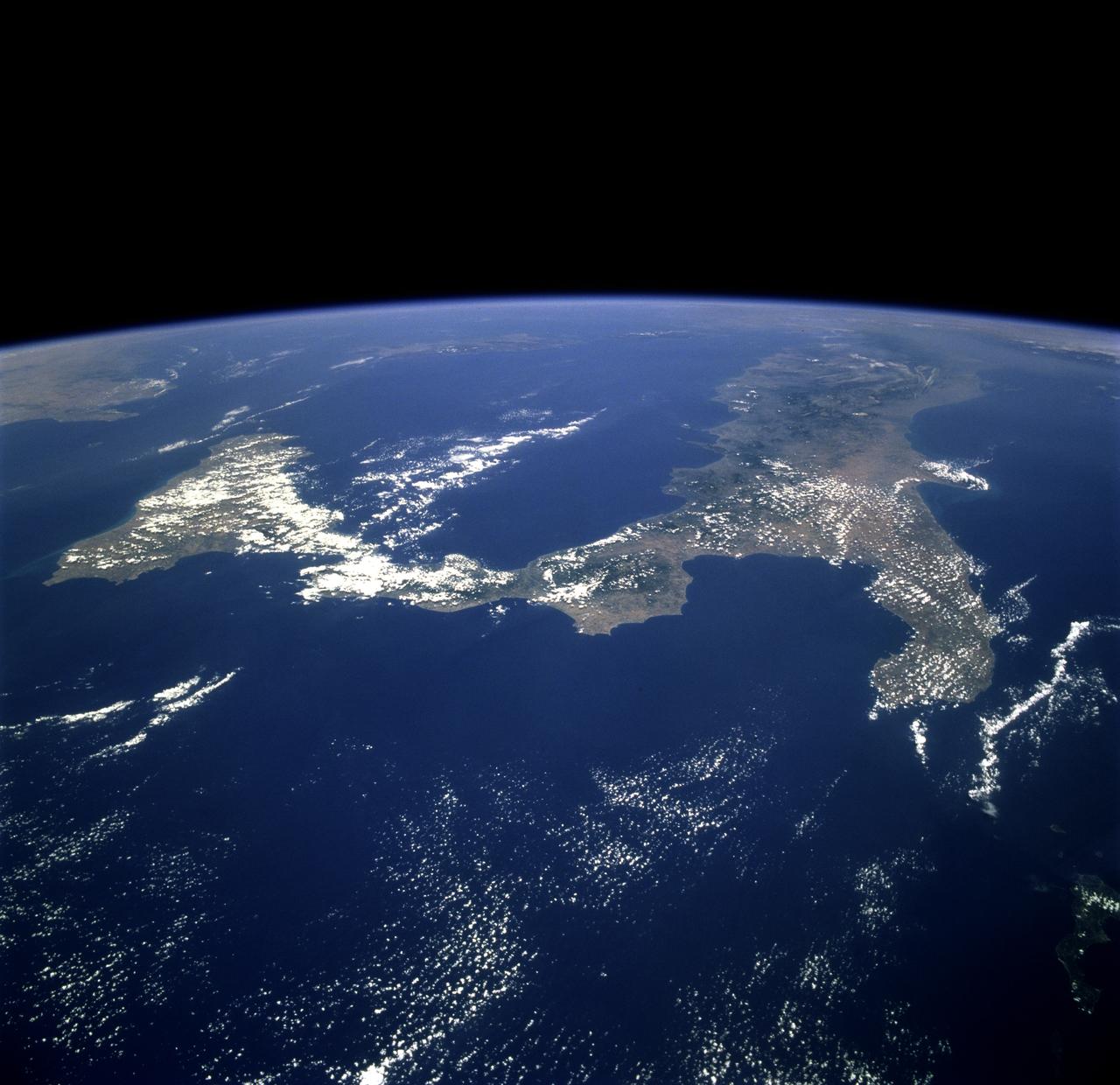

STS078-751-012 (20 June-7 July 1996) --- The international crew of the Life and Microgravity Spacelab (LMS-1) mission onboard the Space Shuttle Columbia photographed this oblique view of the "toe" of Italy and the island of Sicily. Southern Italy is known as the Mezzogiorno because of the intensity of sunshine there at midday (Mezzogiorno is the Italian term for "midday" or "noon"). Mezzogiorno is a mainland subregion consisting of the modern southern Italian regions of Abruzzi, Molise, Campania, Puglia, Basilicata, and Calabria and an insular subregion composed of Sicily and Sardinia. Southern Italy is dominated by the Apennine Range, seen in the photo on the west side, and up to one-half of the land is too steep for any form of cultivation. Coastal plains are generally narrow and poorly drained and are limited to the environs of the cities of Naples and Salerno, Foggia, and Taranto. Chief crops in this region include wheat, olives, grapes, peaches, apricots, pears, and various vegetables. Iron, steel, machine tools, agricultural machinery, and petrochemicals are produced in the industrial triangle of Bari, Brindisi, and Taranto; industries around Naples are more diversified and produce textiles and various consumer goods, iron, steel, Olivetti office machinery, Pirelli cables, Alfa Romeo automobiles, and ships. The Adriatic Sea on the east separates it from the Balkans, and the Mediterranean Sea on the south separates it from North Africa. Three major tectonic plates, converging from the south, the west, and the northeast, create geologically unstable conditions throughout southern Italy and Sicily. The most famous of southern Italy's four active volcanoes is Mount Vesuvius, whose eruption in AD 79 destroyed Pompeii. Sicily's Mount Etna and Stromboli, on an island north of Sicily, were active during this Space Shuttle mission.

ISS027-E-016922 (25 April 2011) --- River deltas and Lake Ayakum in China (Tibet) are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 27 crew member on the International Space Station. The Tibetan Plateau contains numerous lakes that dot an otherwise arid landscape. Lake Ayakum is located near the northern boundary of the Plateau to the southeast of the Kunlun Mountains. While many of the small glacier- and snowmelt-fed streams that cross the Tibetan Plateau eventually give rise to major Southeast Asian rivers including the Mekong and Yangtze, some empty into saline lakes such as Lake Ayakum. This detailed photograph highlights two river deltas (upper left and lower right) formed along the southwestern shoreline of the lake. When sediments build up to the point that a river can no longer flow over them, it will jump to a new channel position and begin the process anew. Scientists have noted that, over geologic time, the channels tend to sweep back and forth ? similar to the motion of an automobile windshield wiper ? to form the typical semi-circular or fan shape of the delta. Gray to tan surfaces of both deltas indicate prior positions of their respective river channels; the uniform coloration and smooth texture suggest that they are relatively old and are now inactive. In contrast, the younger and currently active delta surfaces can be recognized by reddish-brown sediment and clearly visible river channels. Lateral channel migration is particularly evident in the approximately eight-kilometer-wide active delta area at upper left. The reddish coloration of the actively depositing sediment may indicate a change from the sources that formed the older parts of the deltas (or indicate weathering and soil formation on the older deposits), or an episodic input of dust or other material to the river catchments.

ISS031-E-006398 (30 April 2012) --- Lake Powell and the Rincon in Utah are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 31 crew member on the International Space Station. This photograph highlights part of Lake Powell; the lake extends across southeastern Utah and northeastern Arizona. Lake Powell started filling in 1963 when the Glen Canyon Dam on the Colorado River in Arizona was completed, and Glen Canyon flooded. The serpentine water surface of the reservoir-highlighted by gray regions of sunglint-follows the incised course of the canyon. Today Lake Powell is part of the Glen Canyon National Recreation Area which extends for more than 186 miles along the shoreline and side canyons. The primary intended use of Lake Powell?s water is support of agricultural production, with a small portion allocated to urban use in Arizona, Nevada, and California. The reservoir did not reach its maximum capacity of 27 million acre-feet until 1980. More recently, extended drought conditions in the southwestern United States over the past decade have resulted in a significant lowering of the Lake water level and emergence of parts of Glen Canyon. Should average precipitation in the Colorado River watershed lessen (as predicted by regional climate change models), that could result in further lowering of the Lake Powell water level and changes to the current water management plans. Fluctuations in water levels and change of river courses are a common occurrence seen in the geologic record of rivers. Looking somewhat like a donut or automobile tire from the vantage point of the space station, the Rincon (center) is an entrenched and abandoned meander, or loop, of the Colorado River, thought to have formed several thousand years ago when the river cut straight across the ends of the loop and shortened its course by six miles. The resulting canyon and 600 ? 750 feet-high central mesa indicate where the river used to flow. The term ?Rincon? also is used by geomorphologists to describe similar ancient river features observed elsewhere. The Goosenecks of the San Juan River are an example of an active entrenched meander.
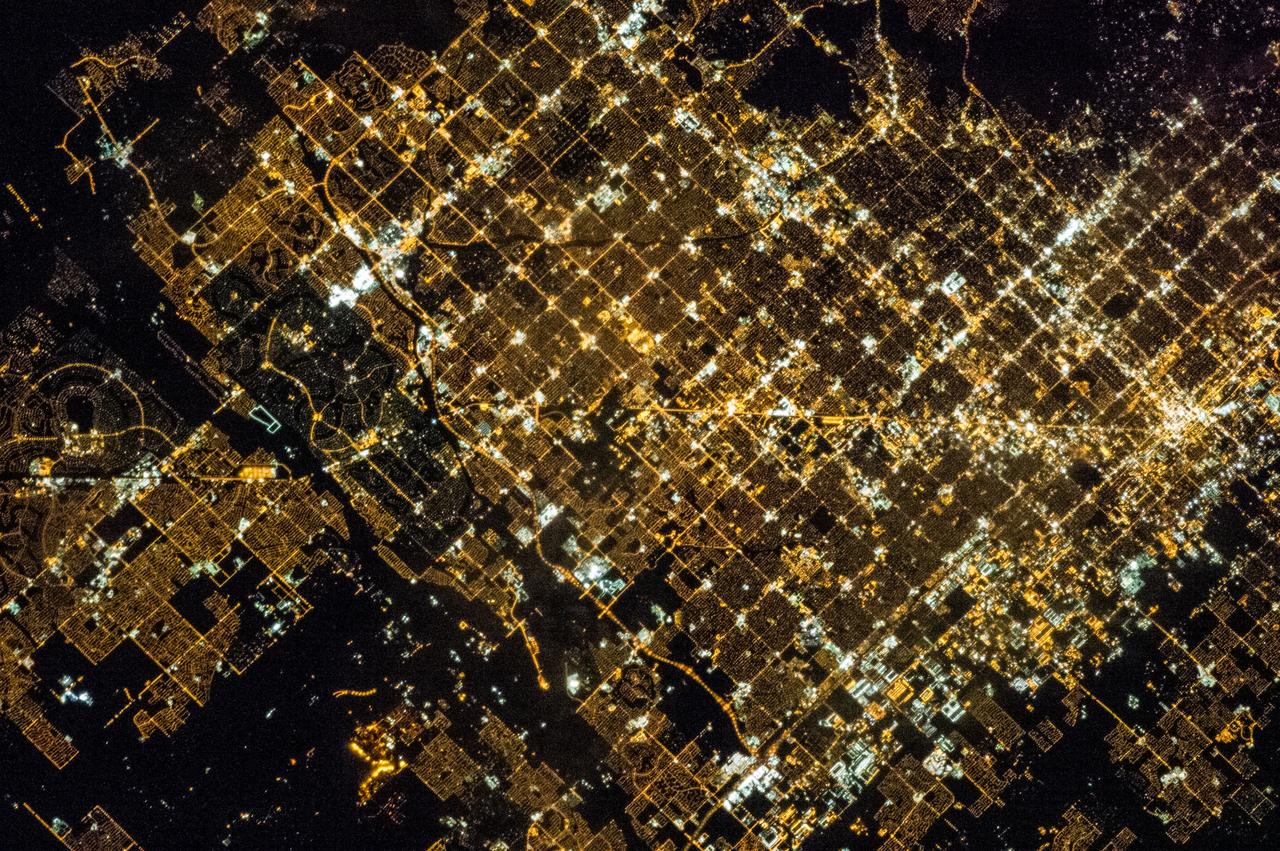

ISS035-E-005438 (16 March 2013) --- One of the Expedition 35 crew members on the International Space Station used a still camera with a 400 millimeter lens to record this nocturnal image of the Phoenix, Arizona area. Like many large urban areas of the central and western United States, the Phoenix metropolitan area is laid out along a regular grid of city blocks and streets. While visible during the day, this grid is most evident at night, when the pattern of street lighting is clearly visible from above – in the case of this photograph, from the low Earth orbit vantage point of the International Space Station. The urban grid form encourages growth of a city outwards along its borders, by providing optimal access to new real estate. Fueled by the adoption of widespread personal automobile use during the 20th century, the Phoenix metropolitan area today includes 25 other municipalities (many of them largely suburban and residential in character) linked by a network of surface streets and freeways. The image area includes parts of several cities in the metropolitan area including Phoenix proper (right), Glendale (center), and Peoria (left). While the major street grid is oriented north-south, the northwest-southeast oriented Grand Avenue cuts across it at image center. Grand Avenue is a major transportation corridor through the western metropolitan area; the lighting patterns of large industrial and commercial properties are visible along its length. Other brightly lit properties include large shopping centers, strip centers, and gas stations which tend to be located at the intersections of north-south and east-west trending streets. While much of the land area highlighted in this image is urbanized, there are several noticeably dark areas. The Phoenix Mountains at upper right are largely public park and recreational land. To the west (image lower left), agricultural fields provide a sharp contrast to the lit streets of neighboring residential developments. The Salt River channel appears as a dark ribbon within the urban grid at lower right.
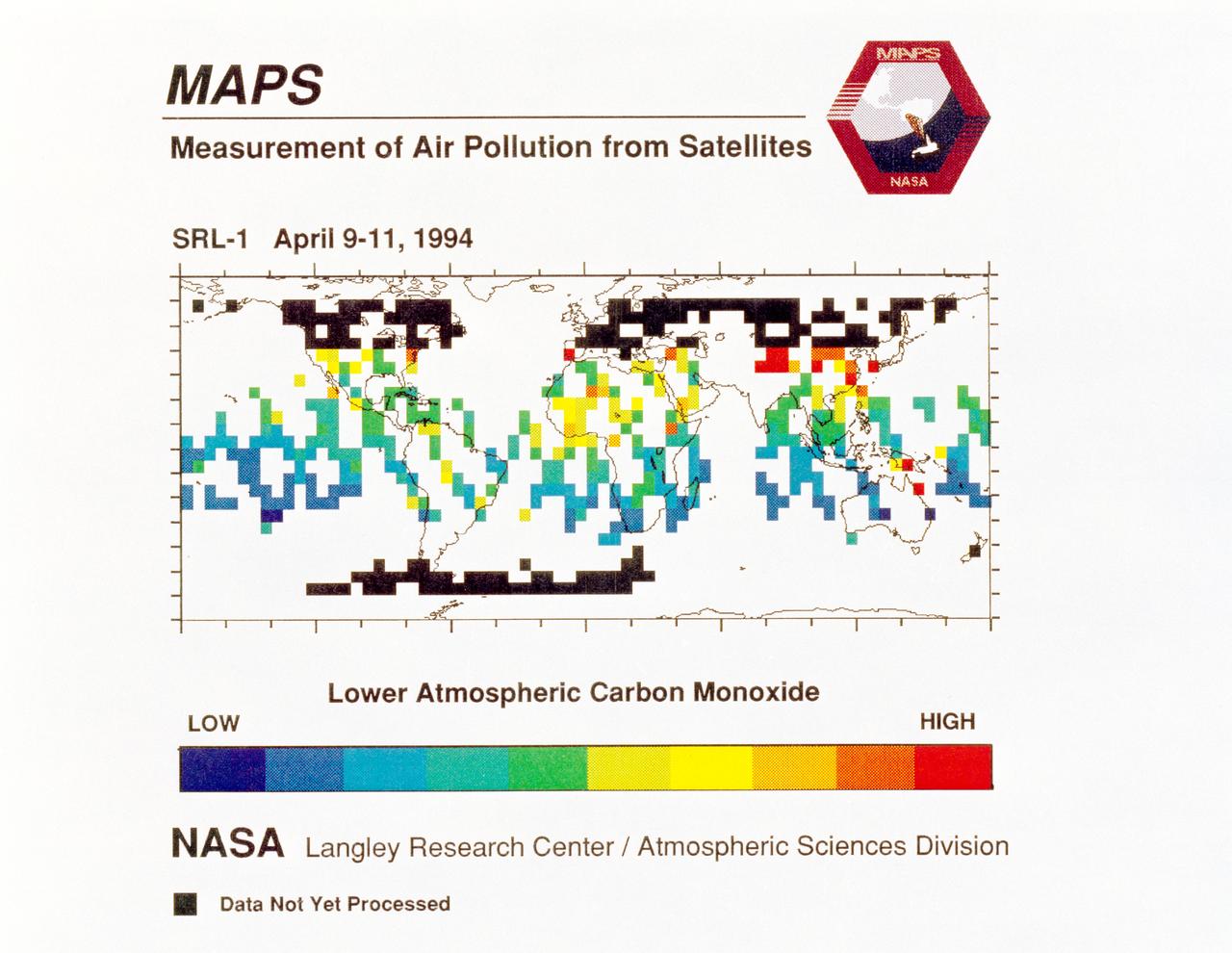
STS059-S-040 (12 April 1994) --- STS-59's MAPS (Measurement of Air Pollution from Satellites) experiment is sending real-time data that provides the most comprehensive view of carbon monoxide concentrations on Earth ever recorded. This computer image shows a summary of "quick look" data obtained by the MAPS instrument during its first days of operations as part of the Space Shuttle Endeavour's SRL-1 payload. This data will be processed using more sophisticated techniques following the flight. The color red indicates areas with the highest levels of carbon monoxide. These Northern Hemisphere springtime carbon monoxide values are generally significantly higher than the values found in the Southern Hemisphere. This is in direct contrast to the data obtained by the MAPS experiment during November 1981 and October 1984, i.e. during Northern Hemisphere fall. The astronauts aboard Endeavour have seen fires in most of the areas showing higher carbon monoxide values (China, Eastern Australia, and equatorial Africa). The relationship between the observed fires and the higher carbon monoxide values will be investigated following SRL-1 by combining the MAPS data with meteorological data, surface imagery, and Space Shuttle hand-held photographs. By the end of SRL-1, MAPS will have acquired data over most of the globe between 57 degrees north and 57 degrees south latitudes. The entire data set will be carefully analyzed using sophisticated post-flight data processing techniques. The data will then be applied in a variety of scientific studies concerning chemistry and transport processes in the atmosphere. The MAPS experiment measures the carbon monoxide in the lower atmosphere. This gas is produced both as a result of natural processes and as a result of human activities. The primary human resources of carbon monoxide are automobiles and industry and the burning of plant materials. The primary natural source is the interaction of sunlight with naturally occurring ozone and water vapor. The strength of all of these sources changes seasonally.
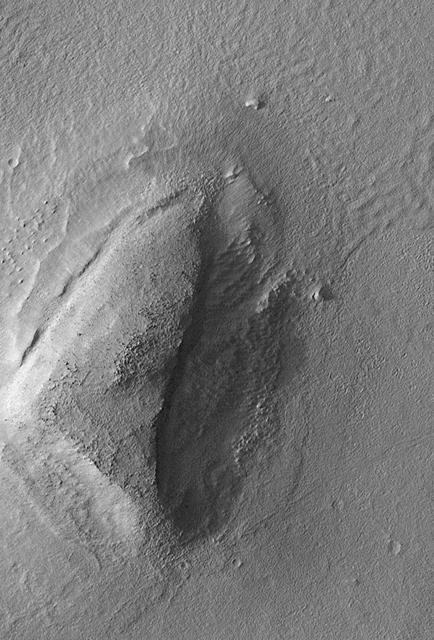

The Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) was designed specifically to provide images of Mars that have a resolution comparable to the aerial photographs commonly used by Earth scientists to study geological processes and map landforms on our home planet. When MGS reaches its Mapping Orbit in March 1999, MOC will be able to obtain pictures with spatial resolutions of 1.5 meters (5 feet) per pixel--this good enough to easily see objects the size of an automobile. Boulders are one of the keys to determining which processes have eroded, transported, and deposited material on Mars (e.g.,landslides, mud flows, flood debris). During the first year in orbit,MGS MOC obtained pictures with resolutions between 2 and 30 meters (7to 98 feet) per pixel. It was found that boulders are difficult to identify on Mars in images with resolutions worse than about 2-3 meters per pixel. Although not known when the MOC was designed,"thresholds" like this are found on Earth, too. The MOC's 1.5 m/pixel resolution was a compromise between (1) the anticipation of such resolution-dependent sensitivity based on our experience with Earth and (2)the cost in terms of mass if we had built a larger telescope to get a higher resolution. Some rather larger boulders (i.e., larger than about 10 meters--or yards--in size) have already been seen on Mars by the orbiting camera. This is a feat similar to that which can be obtained by "spy" satellites on Earth. The MOC image 53104 subframe shown above features a low, rounded hill in southeastern Utopia Planitia. Each of the small, lumpy features on the top of this hill is a boulder. In this picture, boulders are not seen on the surrounding plain. These boulders are interpreted to be the remnants of a layer of harder rock that once covered the top of the hill, but was subsequently eroded and broken up by weathering and wind processes. MOC image 53104 was taken on September 2, 1998. The subframe shows an area 2.2 km by 3.3 km (1.4 miles by 2.7 miles). The image has a resolution of about 3.25 meters (10.7 feet) per pixel. The subframe is centered at 41.0°N latitude and 207.3°W longitude. North is approximately up, illumination is from the left. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01500